Patents
Literature
1721 results about "Radial position" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The radial positioning area is the wedge-shaped area about 45° on each side of your center-line. The object is to keep your opponent inside your radial positioning area while staying outside of his/her radial positioning area.
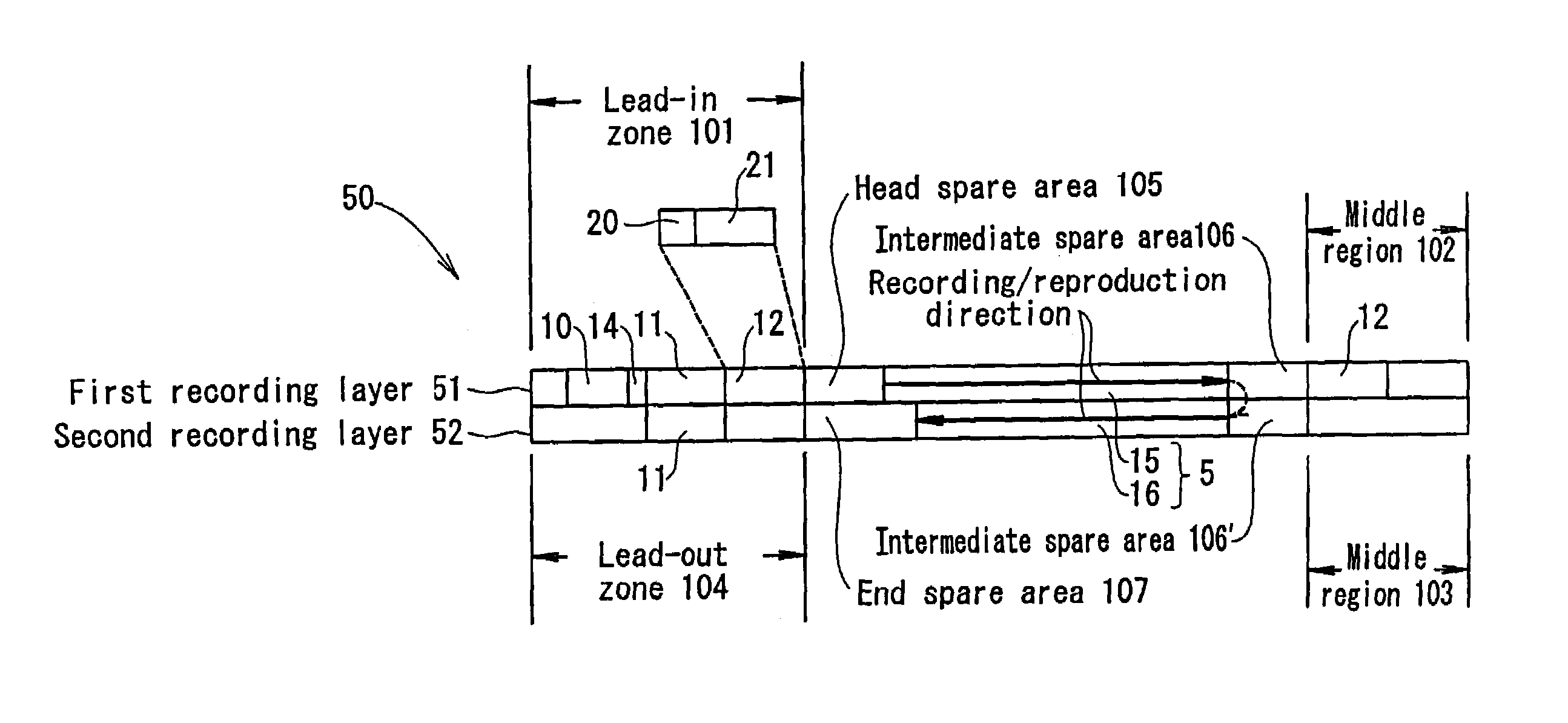
Multi-layered information recording medium, recording apparatus, and recording method
ActiveUS7184377B2Effective areaEasy accessFilamentary/web record carriersOptical beam sourcesComputer hardwareRadial position
A multi-layered information recording medium including a plurality of recording layers, the multi-layered information recording medium comprising: a user data area for recording user data; and a plurality of spare areas including at least one replacement region, wherein when the user data area includes at least one defect region, the at least one replacement region may be used in place of the at least one defect region, wherein a first spare area of the plurality of spare areas is positioned so as to be contiguous to a first user data area of a first recording layer, a second spare area of the plurality of spare areas is positioned so as to be contiguous to a second user data area of a second recording layer, and the first spare area and the second spare area are positioned approximately at the same radial position on the multi-layered information recording medium.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
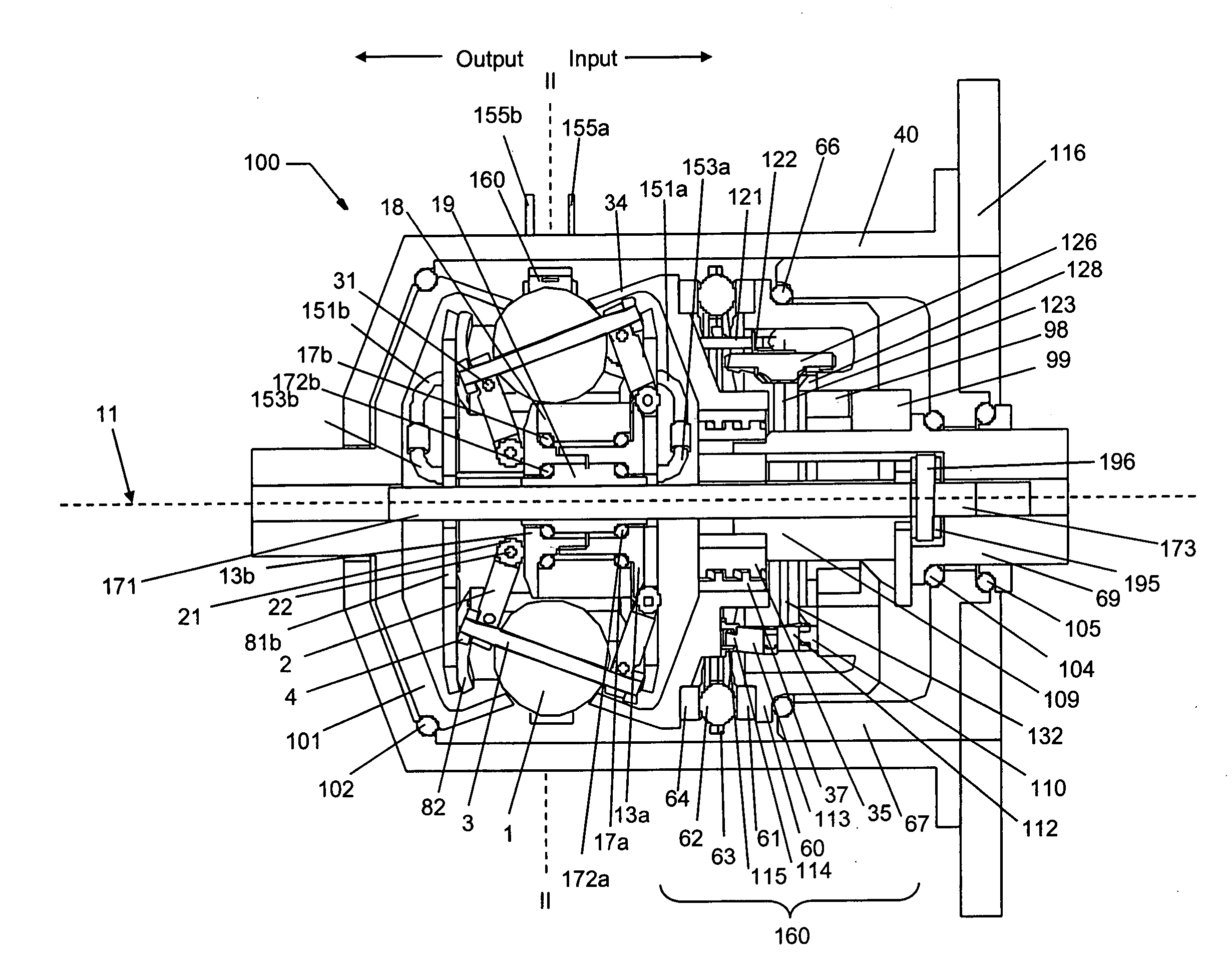
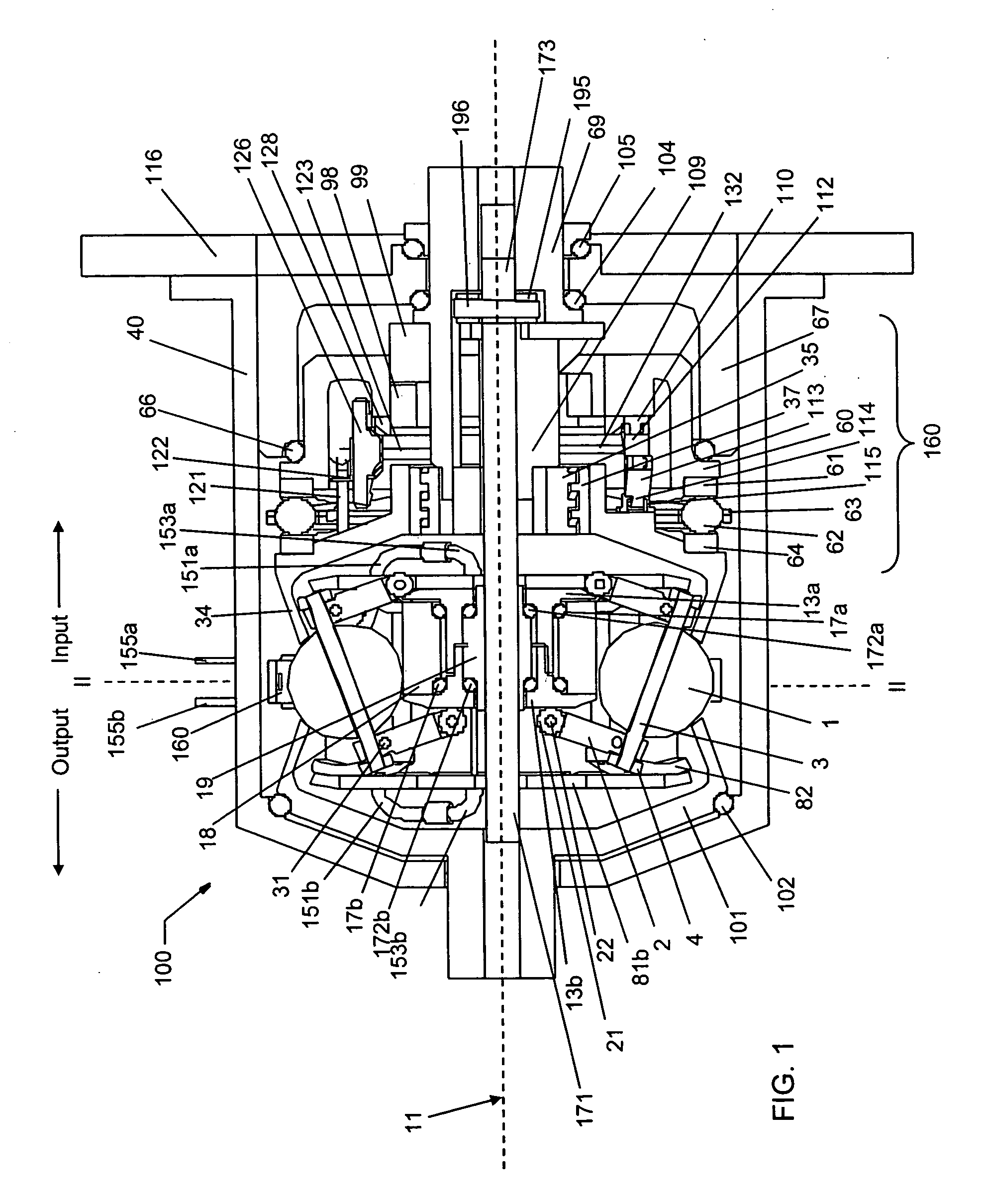
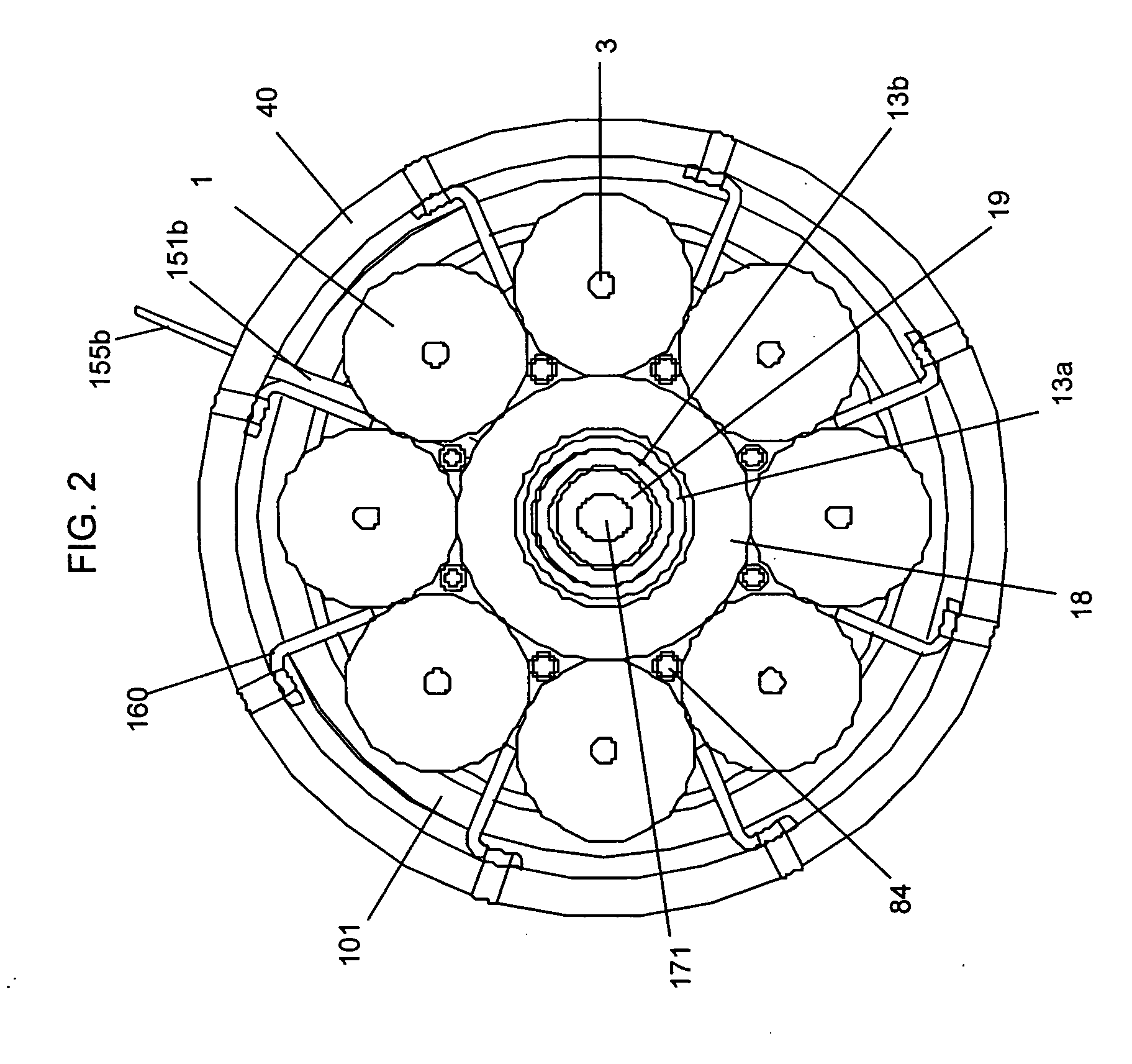
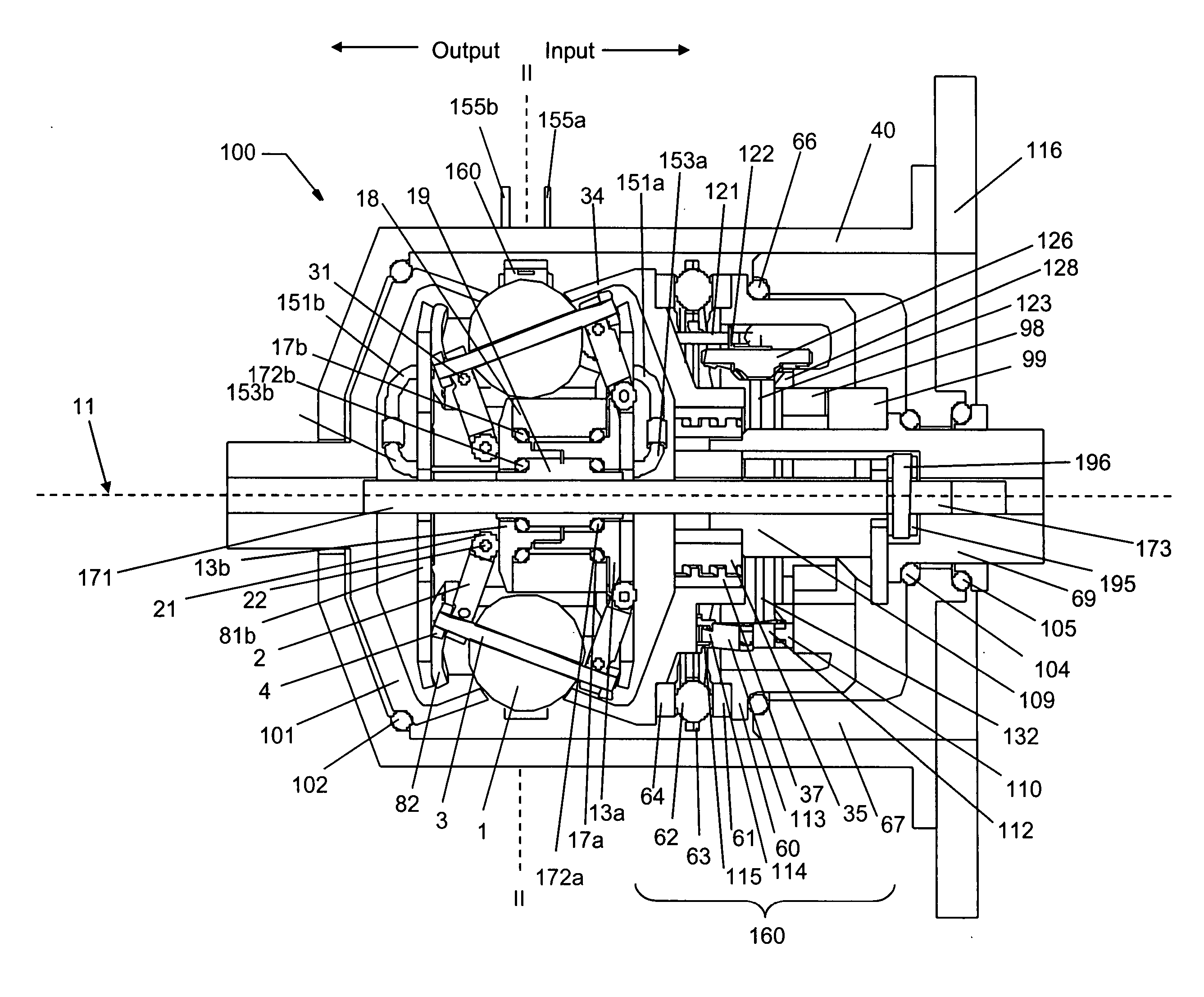
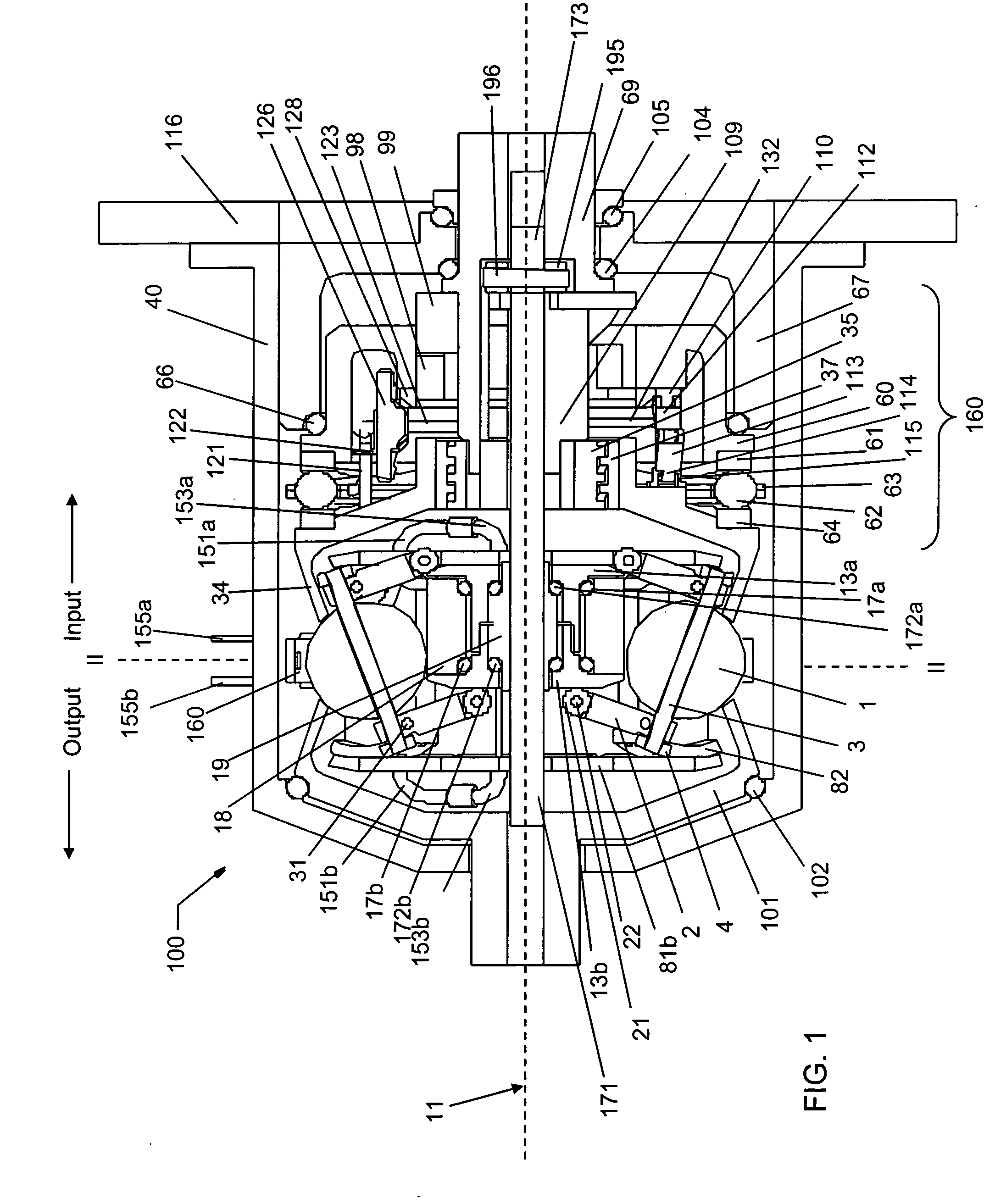
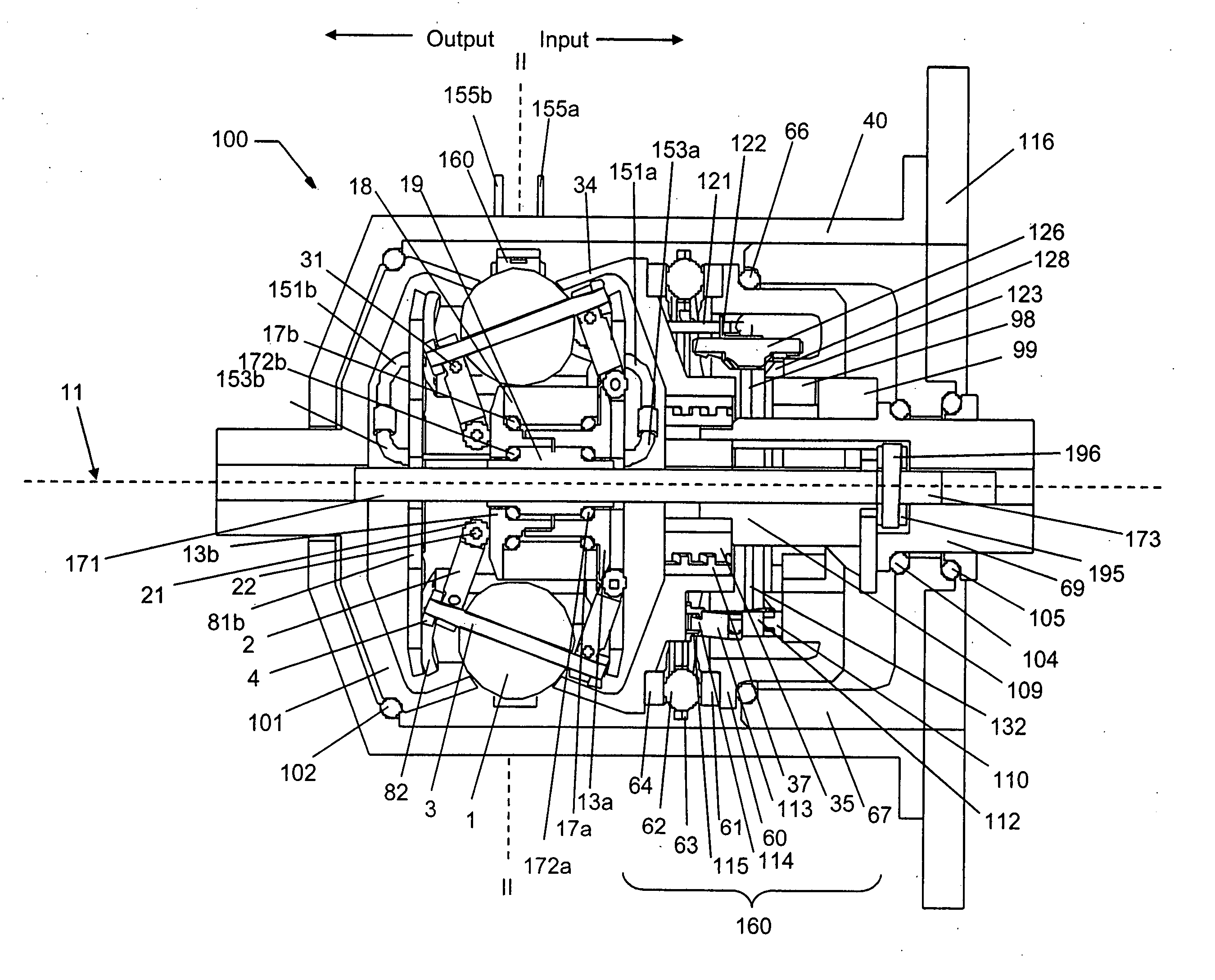
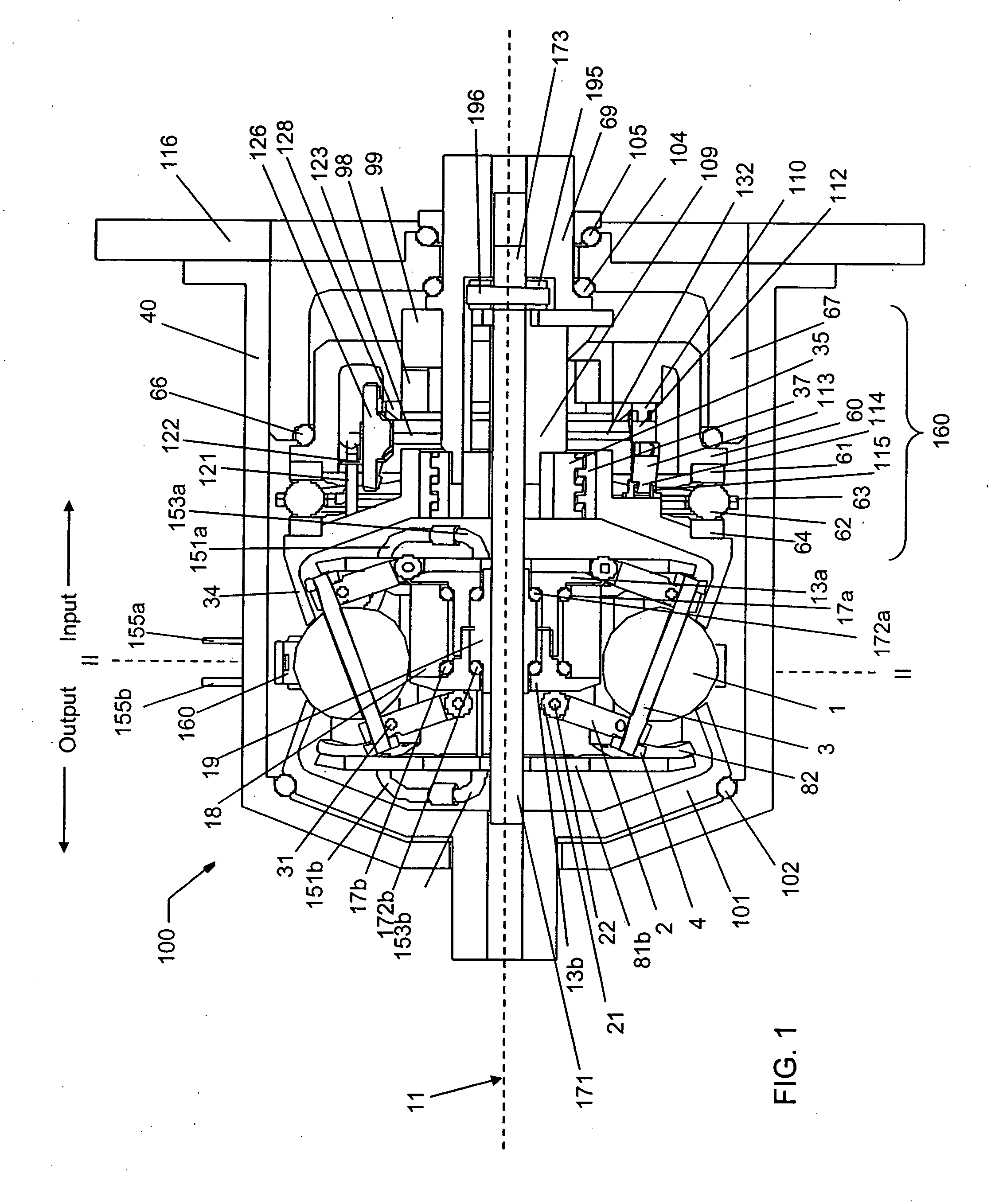
Continuously variable planetary gear set
A continuously variable planetary gear set is described having a generally tubular idler, a plurality of balls distributed radially about the idler, each ball having a tiltable axis about which it rotates, a rotatable input disc positioned adjacent to the balls and in contact with each of the balls, a rotatable output disc positioned adjacent to the balls opposite the input disc and in contact with each of the balls such that each of the balls makes three-point contact with the input disc, the output disc and the idler, and a rotatable cage adapted to maintain the axial and radial position of each of the balls, wherein the axes of the balls are oriented by the axial position of the idler.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Tissue scaffold having aligned fibrils, apparatus and method for producing the same, and artificial tissue and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20050009178A1Improve structural strengthMinimal immunological responsePeptide/protein ingredientsHollow filament manufactureFiberRadial position
A tubular tissue scaffold is described which comprises a tube having a wall, wherein the wall includes biopolymer fibrils that are aligned in a helical pattern around the longitudinal axis of the tube where the pitch of the helical pattern changes with the radial position in the tube wall. The scaffold is capable of directing the morphological pattern of attached and growing cells to form a helical pattern around the tube walls. Additionally, an apparatus for producing such a tubular tissue scaffold is disclosed, the apparatus comprising a biopolymer gel dispersion feed pump that is operably connected to a tube-forming device having an exit port, where the tube-forming device is capable of producing a tube from the gel dispersion while providing an angular shear force across the wall of the tube, and a liquid bath located to receive the tubular tissue scaffold from the tube-forming device. A method for producing the tubular tissue scaffolds is also disclosed. Also, artificial tissue comprising living cells attached to a tubular tissue scaffold as described herein is disclosed. Methods for using the artificial tissue are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
Continuously variable planetary gear set
A continuously variable planetary gear set is described having a generally tubular idler, a plurality of balls distributed radially about the idler, each ball having a tiltable axis about which it rotates, a rotatable input disc positioned adjacent to the balls and in contact with each of the balls, a rotatable output disc positioned adjacent to the balls opposite the input disc and in contact with each of the balls such that each of the balls makes three-point contact with the input disc, the output disc and the idler, and a rotatable cage adapted to maintain the axial and radial position of each of the balls, wherein the axes of the balls are oriented by the axial position of the idler.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
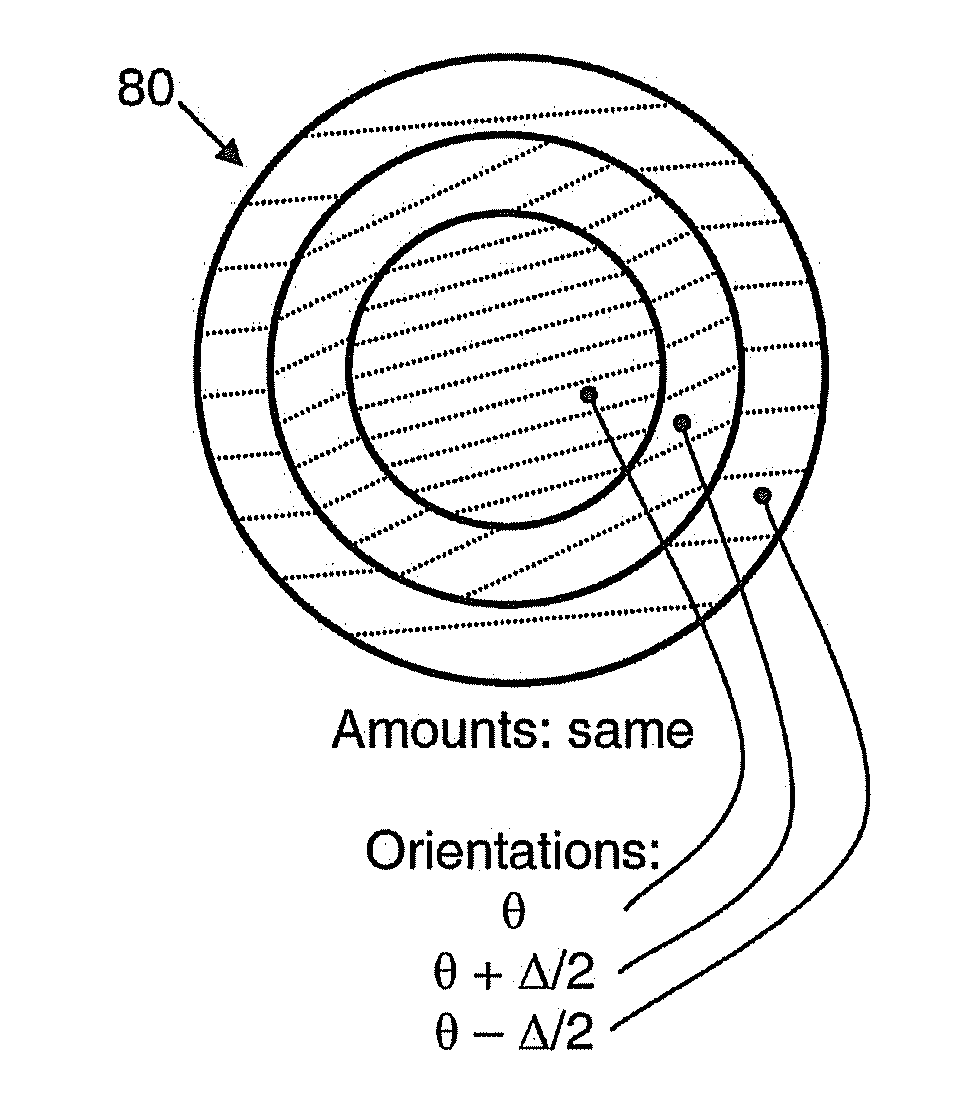
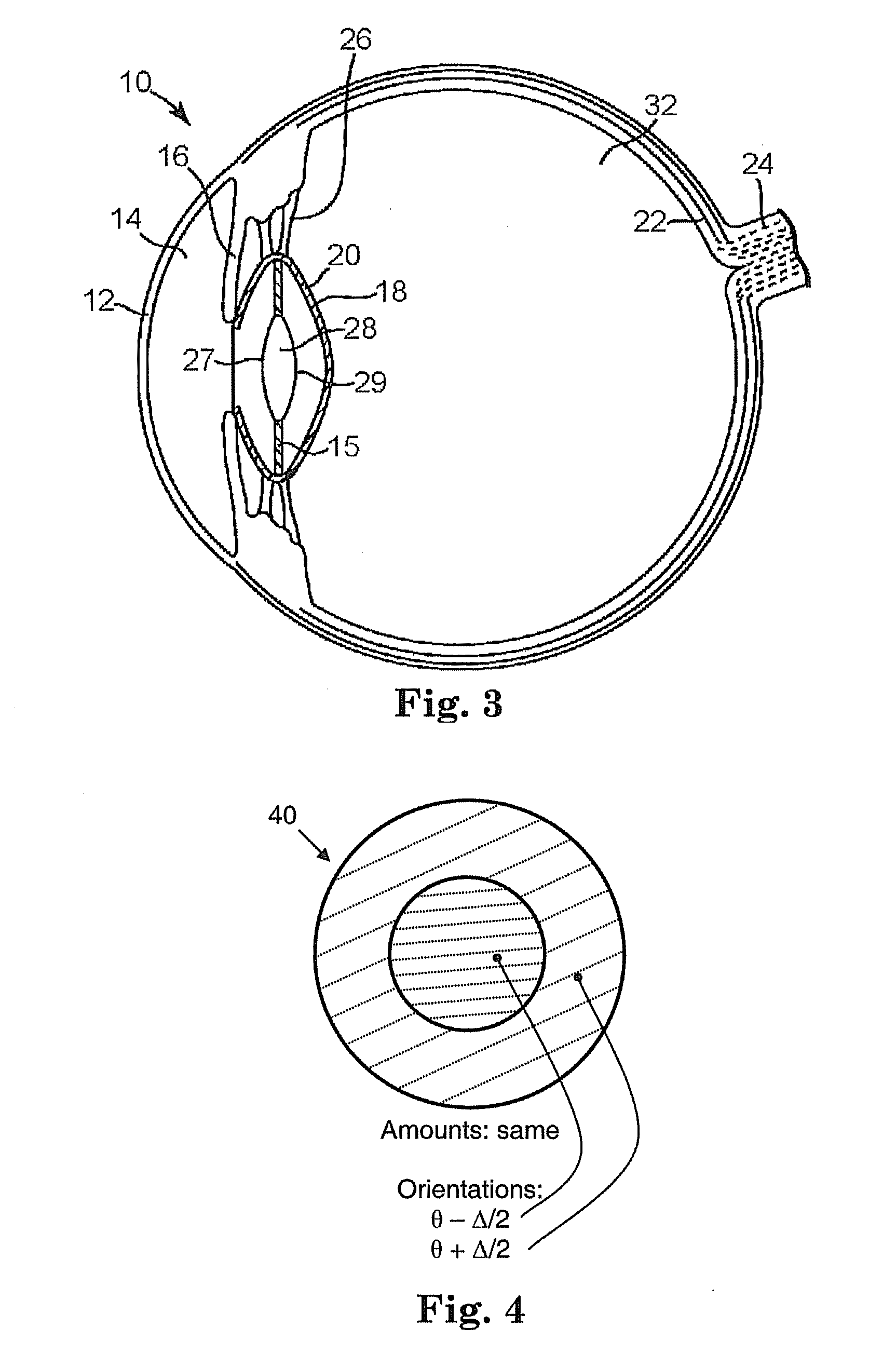
Toric intraocular lens with modified power characteristics
An intraocular lens for correcting or reducing the astigmatism of a cornea includes an optical element that has optical properties and characteristics that make it tolerant of rotational misalignment, when compared to a comparable lens having a uniform astigmatism orientation across its entire optical element, leading to more relaxed tolerances for a surgeon that implants the lens. The optical element of the toric ophthalmic lens has meridians associated therewith, including a high power meridian and a low power meridian orthogonal to the high power meridian. The optical element has at least one radially modulated meridian along which power monotonically varies with increasing radial position.
Owner:ABBOTT MEDICAL OPTICS INC
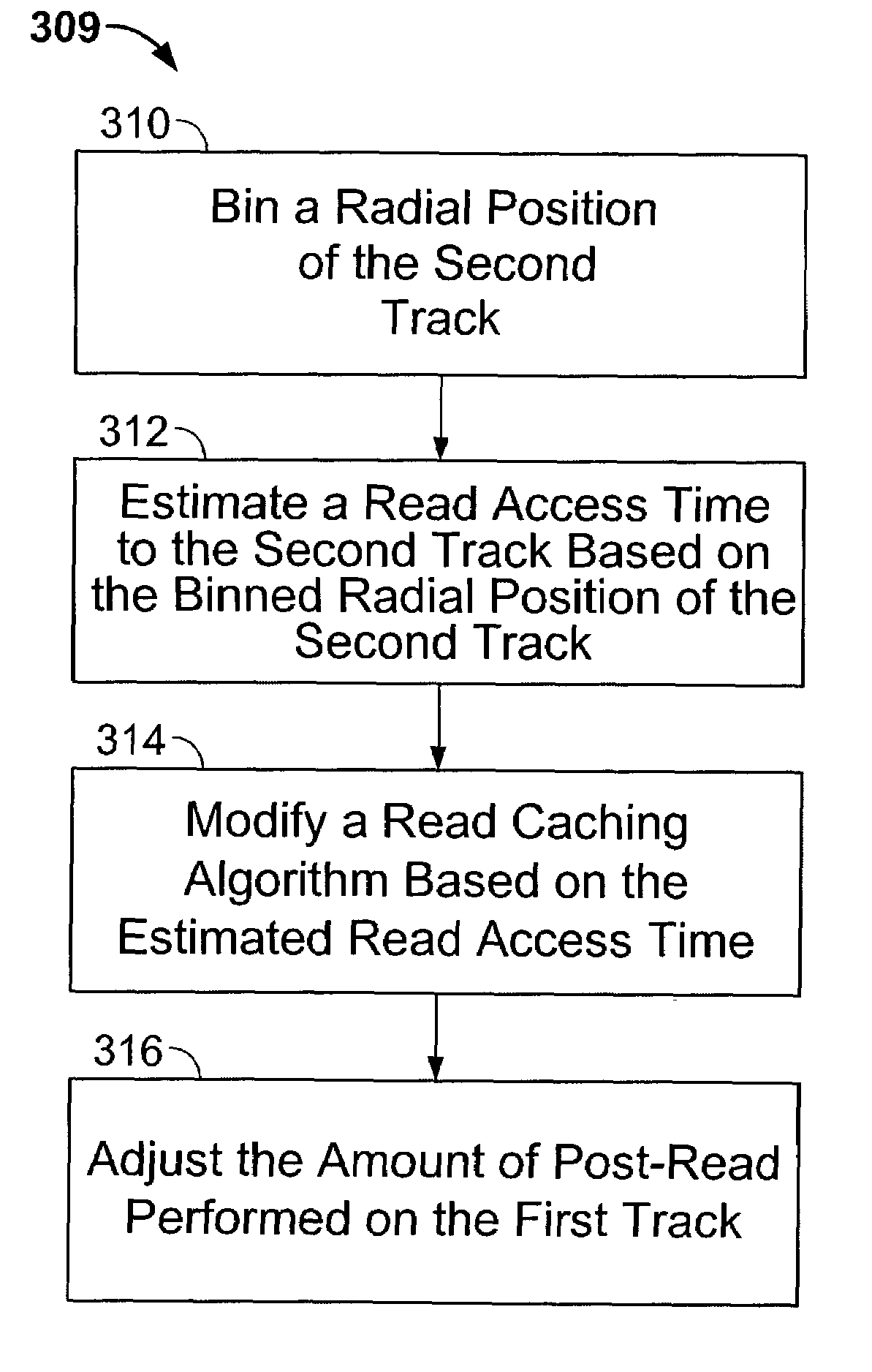
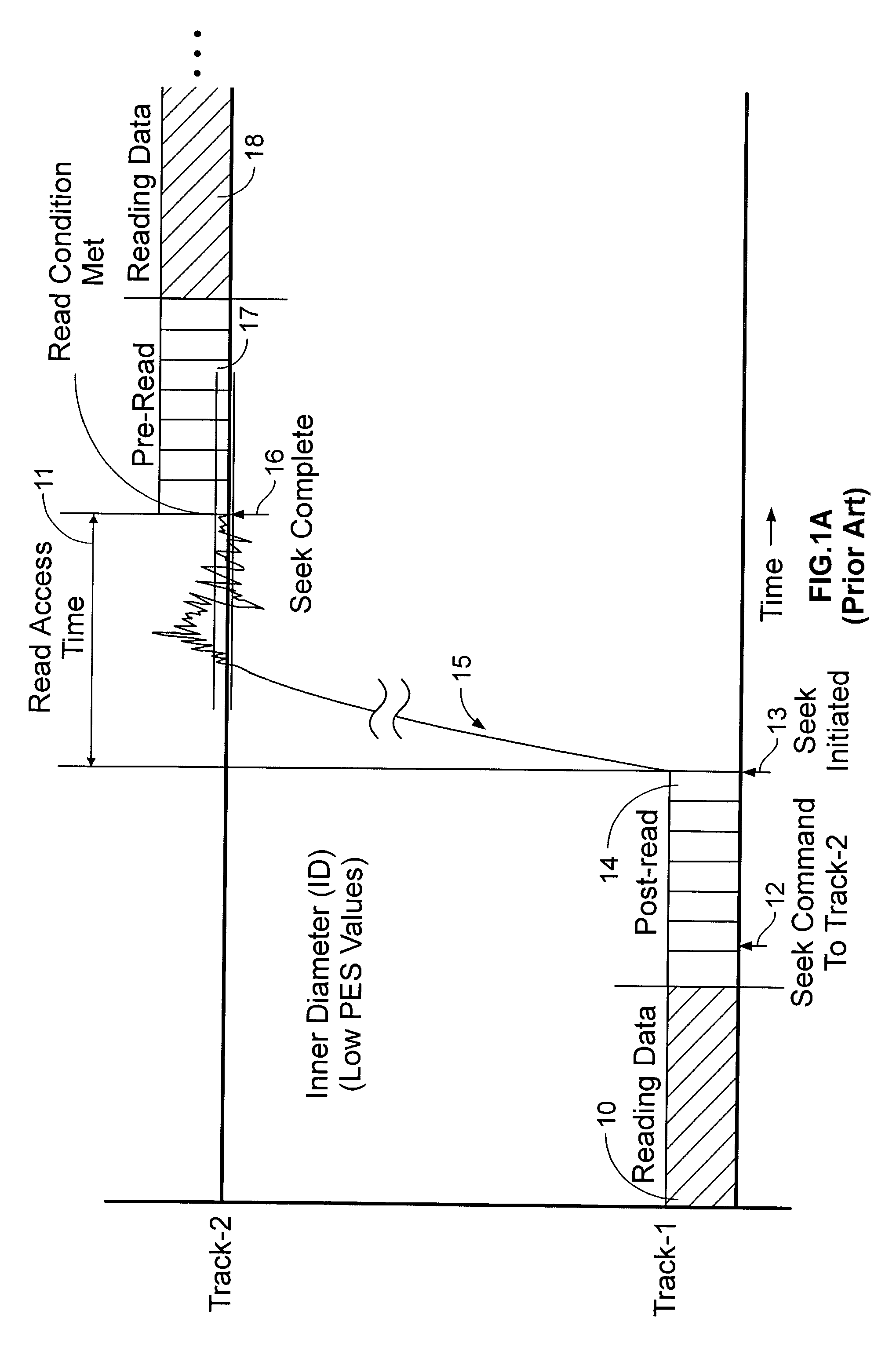
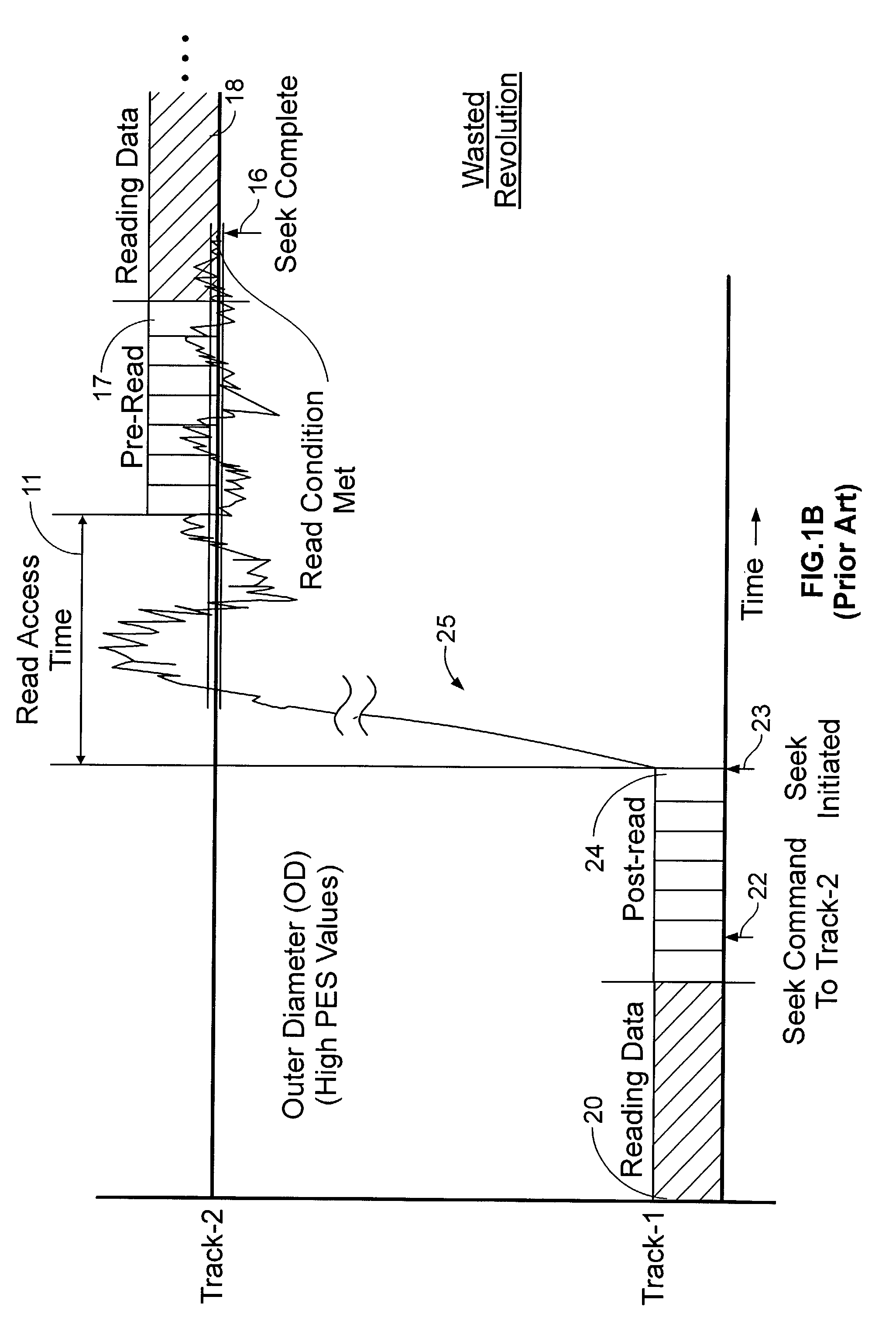
Adaptively estimating a read access time to a second track based upon the binned radial position of the second track within a rotating media storage device
InactiveUS7088538B1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease volumeFilamentary/web record carriersRecord information storageRadial positionAccess time
A rotating media storage device (RMSD) to adaptively estimate a read access time to a second track based on the radial position of the second track is disclosed. The RMSD includes a disk having at least a first track and a second track and a microprocessor for controlling operations in the RMSD including seek operations. During a seek operation, the microprocessor bins a radial position of the second track and estimates a read access time to the second track based on the binned radial position of the second track.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
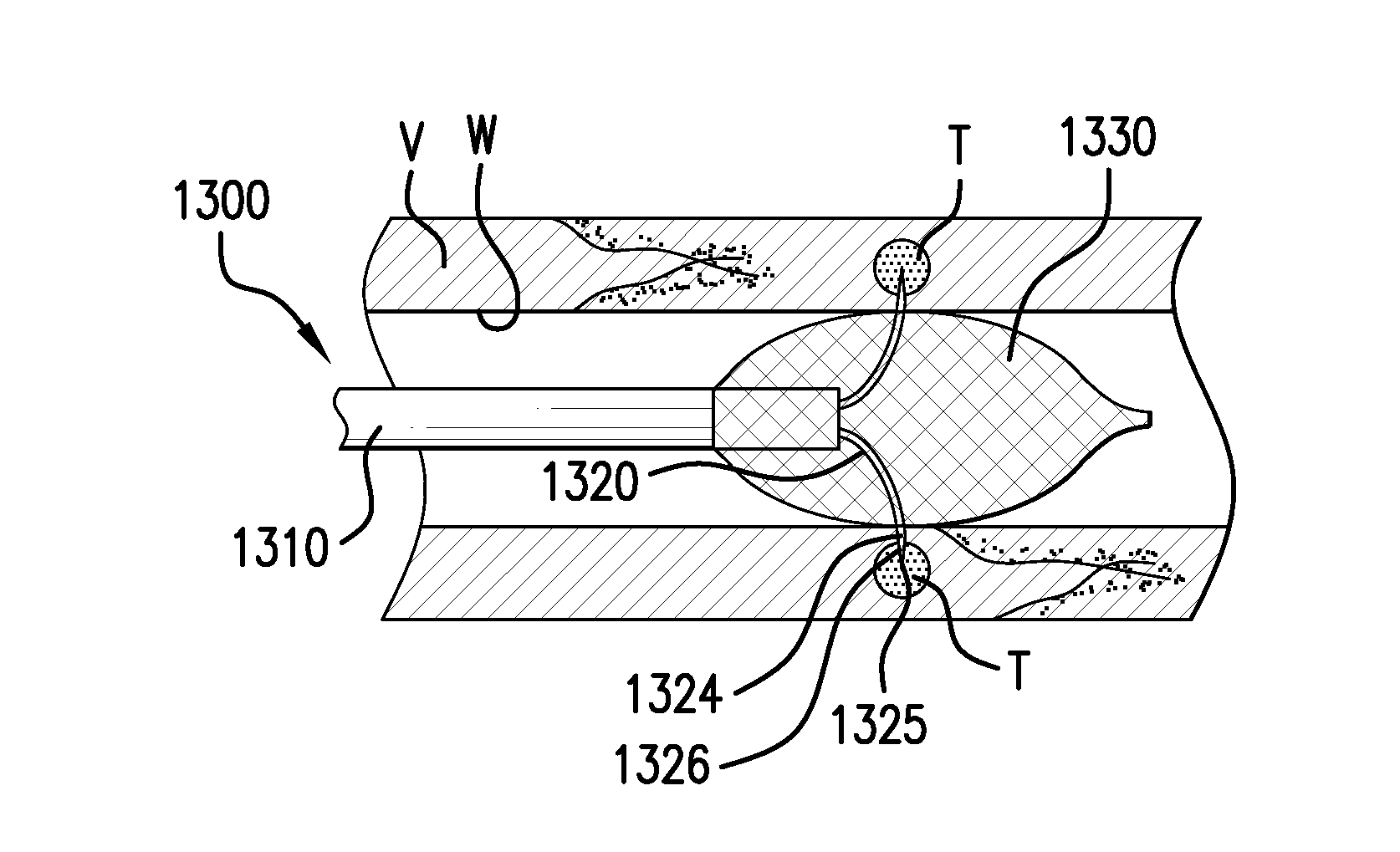
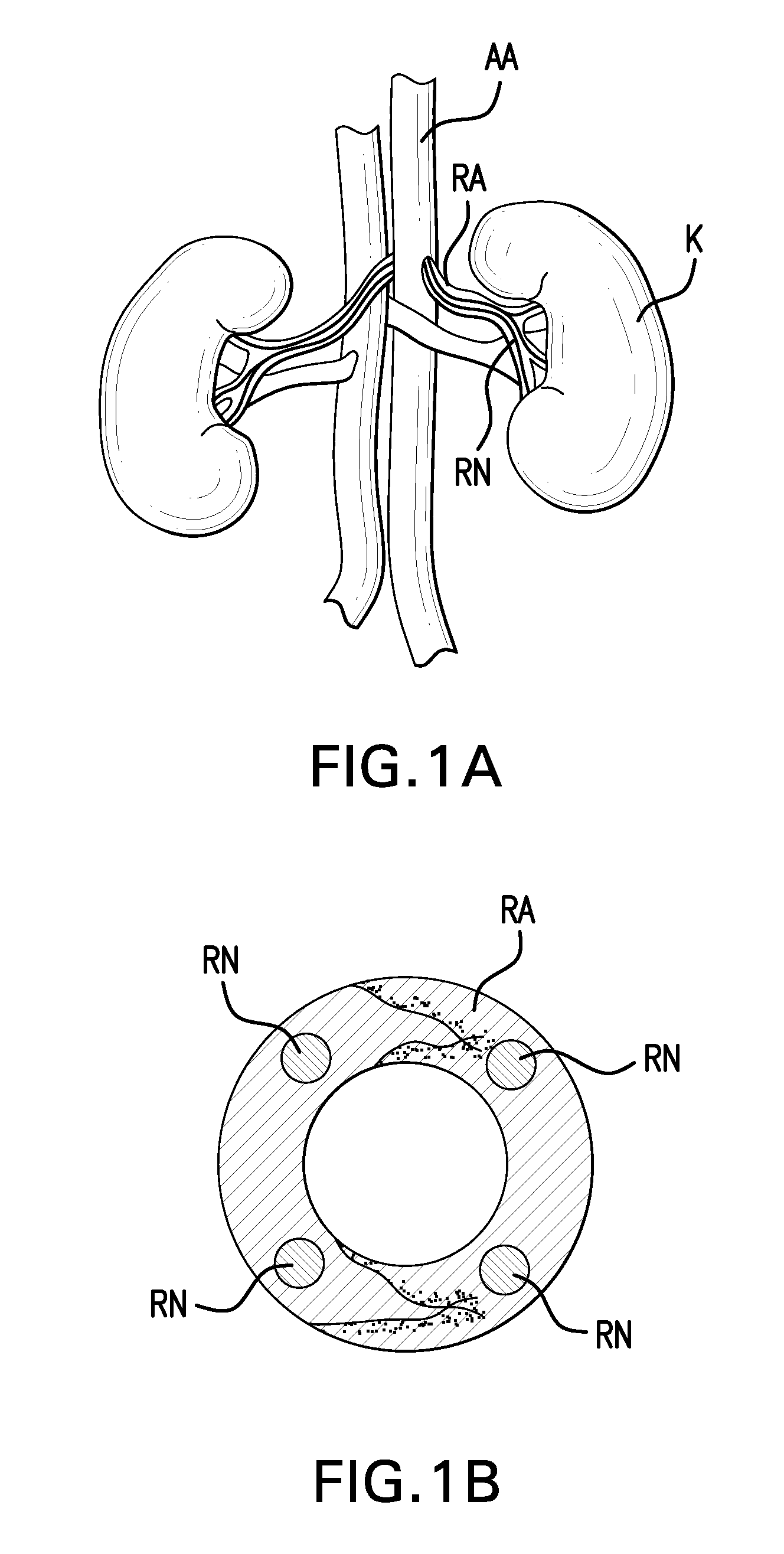
Methods and devices for denervation
Various delivery devices are described to deliver an agent locally to the renal nerves. The delivery devices are positioned in the renal artery and penetrate into the wall of the renal artery to deliver the agent to the renal nerves. The delivery devices may be used to deliver the agent according to longitudinal position, radial position, and depth of the renal nerves relative to the renal artery. In addition, various methods are described to denervate, modulate, or otherwise affect the renal nerves and other neural tissue. Also, various agents are described to denerve, modulate, or otherwise affect the renal nerves and other neural tissue.
Owner:NORTHWIND MEDICAL
Integrated magnetic bearing
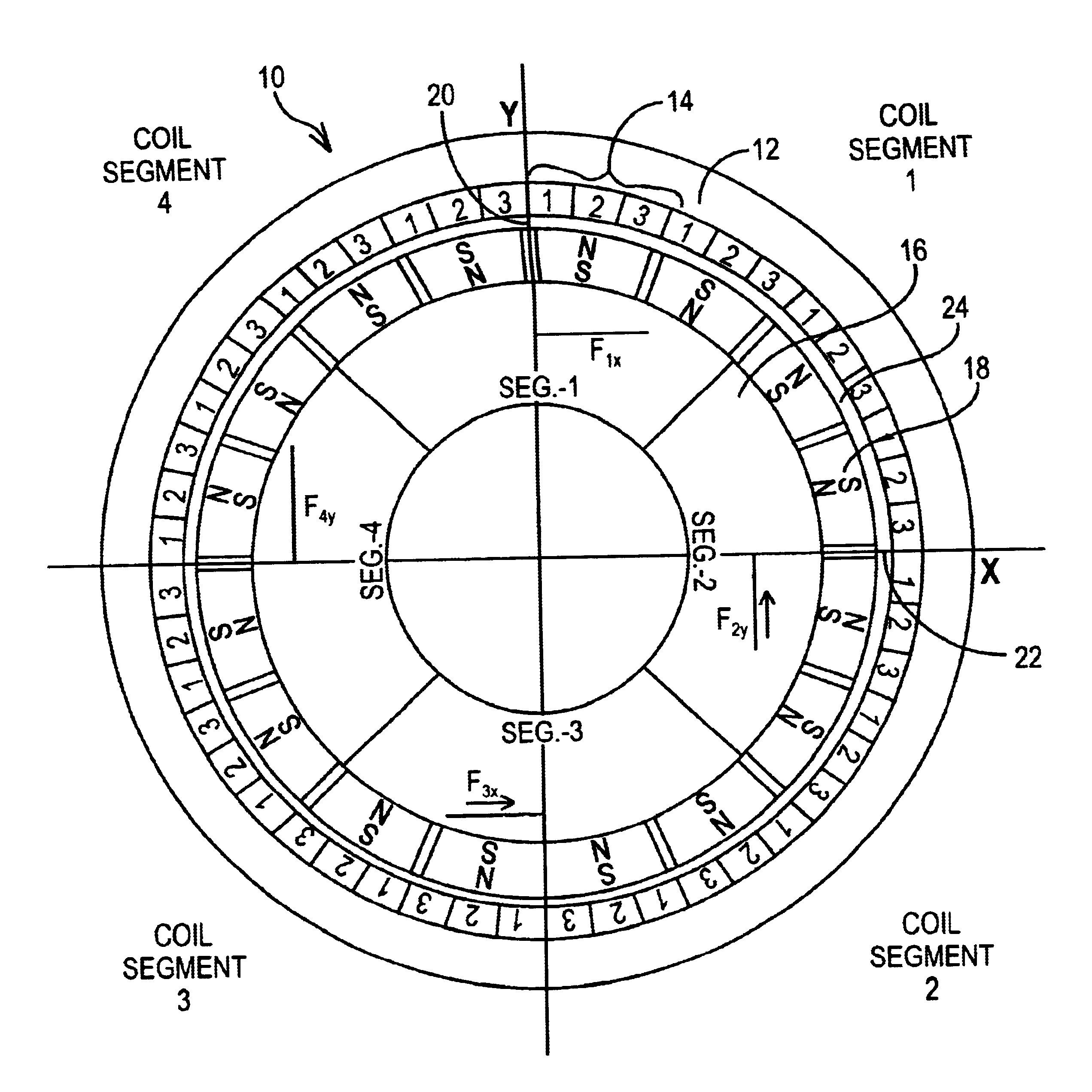
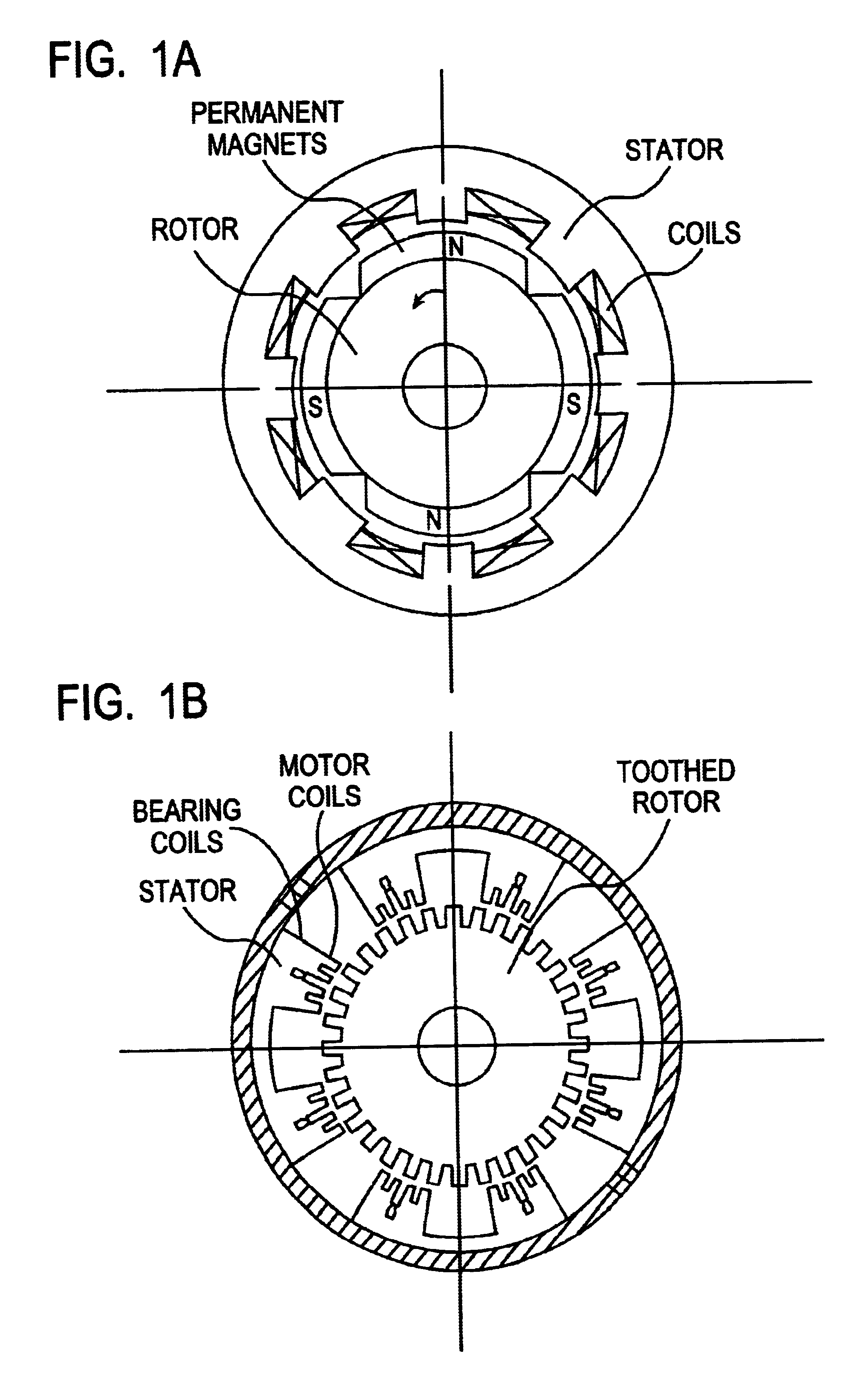
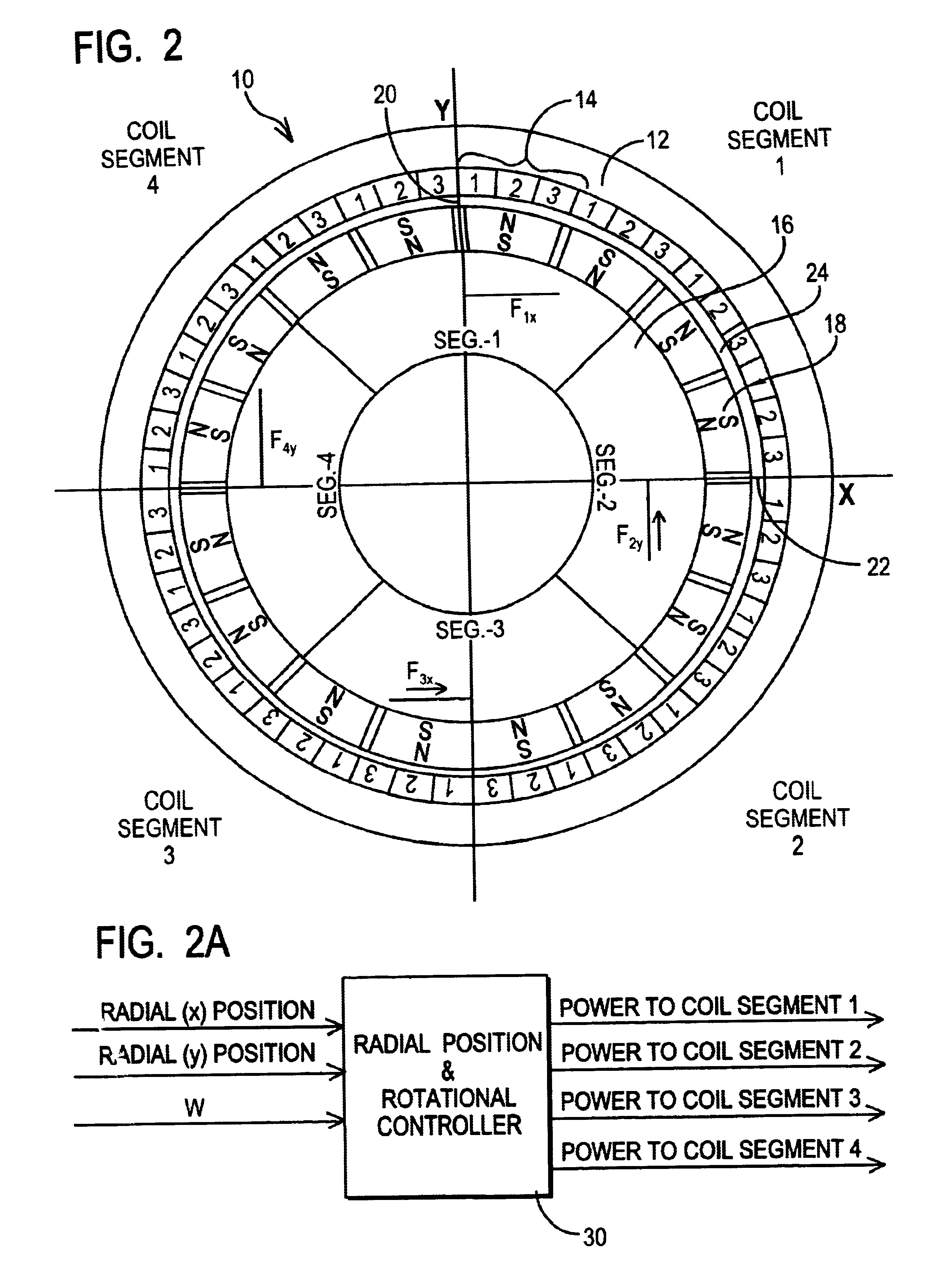
The present invention provides a rotational magnetic gimbal with an integral magnetic bearing. Brushless DC motor technology provides electromagnetic suspension, using a single electromagnetic actuator to perform both the radial bearing and rotary torque (motoring) functions. An integrated motor and magnetic bearing consistent with the invention comprises a rotor comprising a plurality of permanent magnets and a stator comprising a plurality of independently controlled coil segments magnetically coupled to the permanent magnets. Embodiments may further comprise first and second radial position sensors, the first radial position sensor disposed in or adjacent to a clearance gap between the rotor and the stator for sensing the position of the rotor with respect to the stator along a first axis, and a second radial position sensor disposed in or adjacent to the clearance gap between the rotor and the stator for sensing the position of the rotor with respect to the stator along a second axis. In method form, a method for providing integral electromagnetic motor and bearing functions comprises sensing a first radial position of a rotor, the rotor comprising a plurality of permanent magnets, with respect to a stator along a first axis, the stator comprising a plurality of independently controlled coil segments magnetically coupled to the permanent magnets; and sensing a second radial position of the rotor with respect to the stator along a second axis; and delivering current to at least one coil segment, the amount of current based on at least one sensed position.
Owner:AIREX CORP
Apparatus and Method for Providing an Alternate Flow Path in Isolation Devices
ActiveUS20100155064A1Easy to operateReduce stepsFluid removalSealing/packingRadial positionEngineering
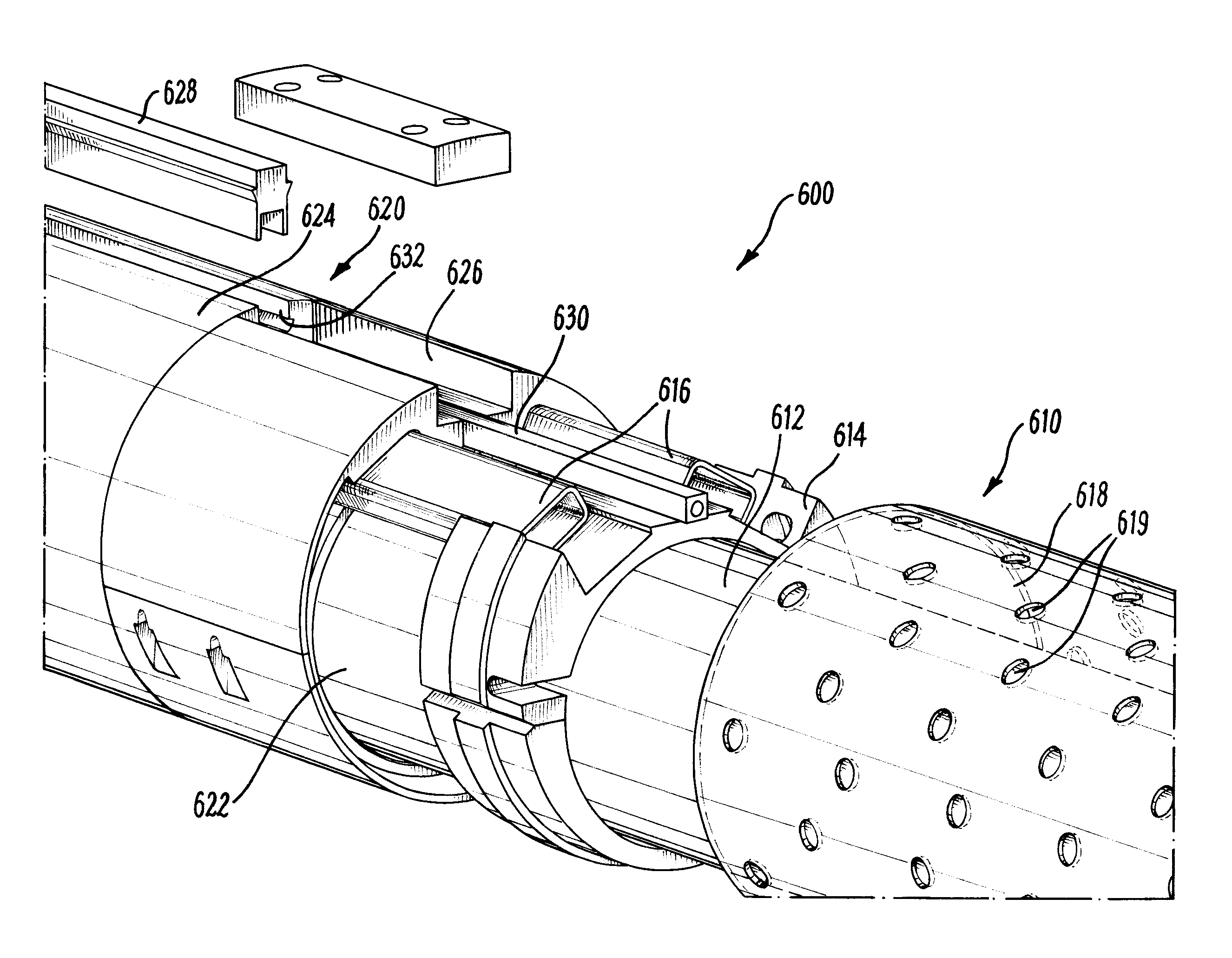
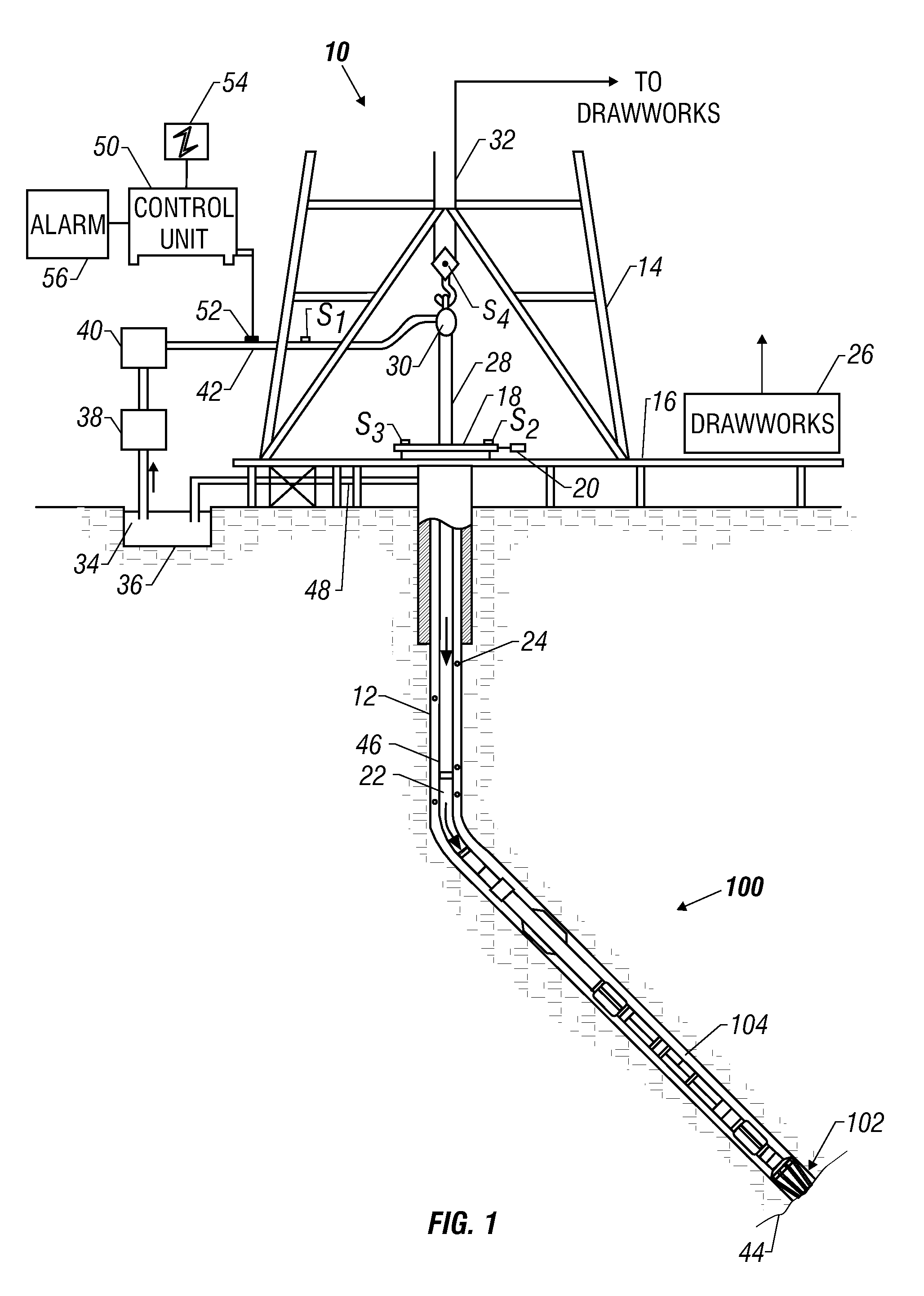
An apparatus for use in a wellbore is described, the apparatus having a tubular body and a throughbore which defines a primary fluid path through the apparatus. An expanding element is disposed around the tubular body and is configured to provide an annular barrier in a space between the tubular body and a surrounding wall. A conduit defining a secondary flow path through the apparatus is provided, and is configured to be in fluid communication with at least one alternate path, such as a shunt tube. The conduit is arranged to vary the secondary flow path along a longitudinal direction of the apparatus, for example to redirect the flow path to a radial position closer to the tool body. The conduit is configured to have a reduced effect on the operation of the expanding element, while still allowing the conduit to be coupled to alternate flow paths of adjacent apparatus.
Owner:WEATHERFORD UK LIMITED
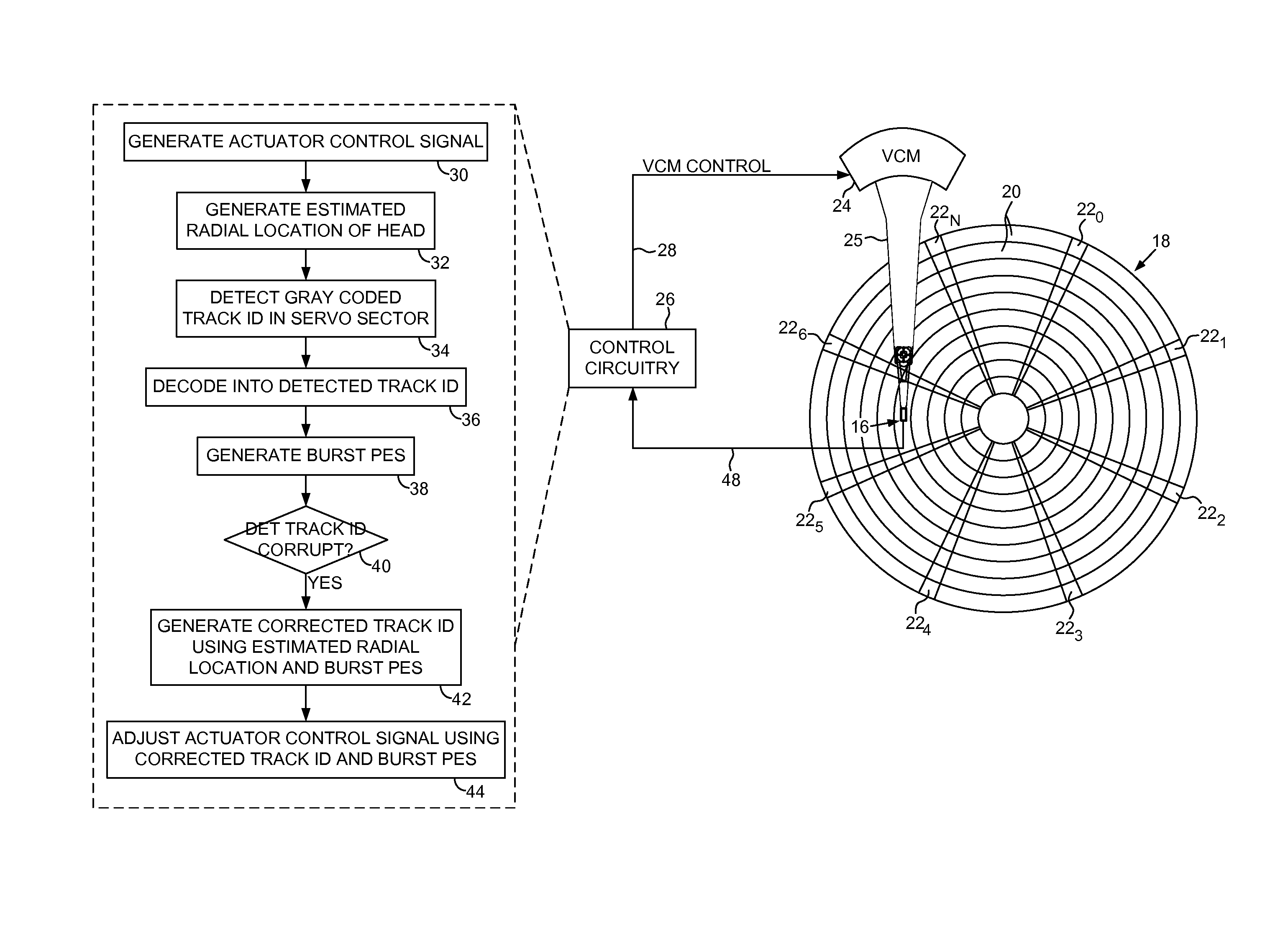
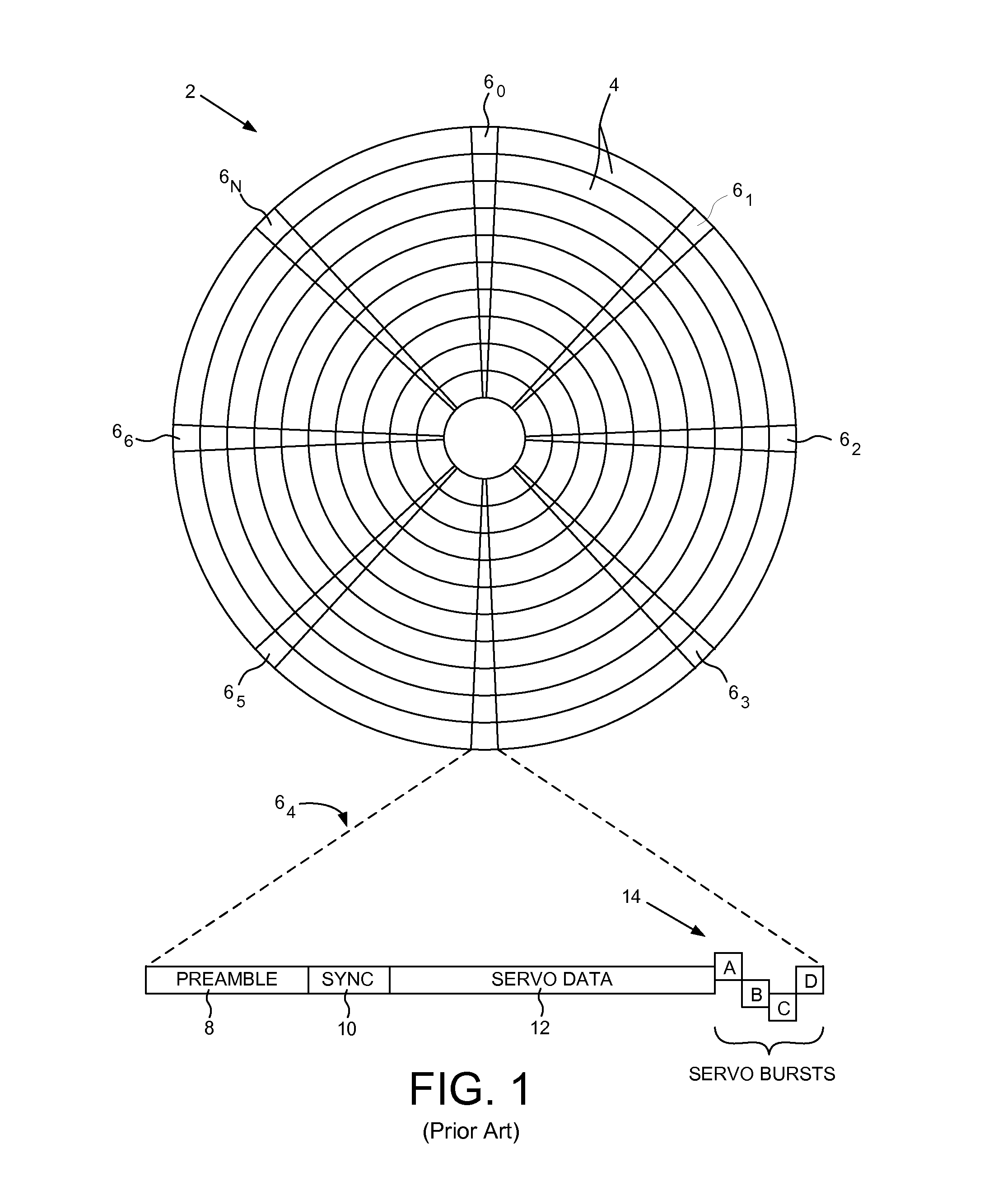
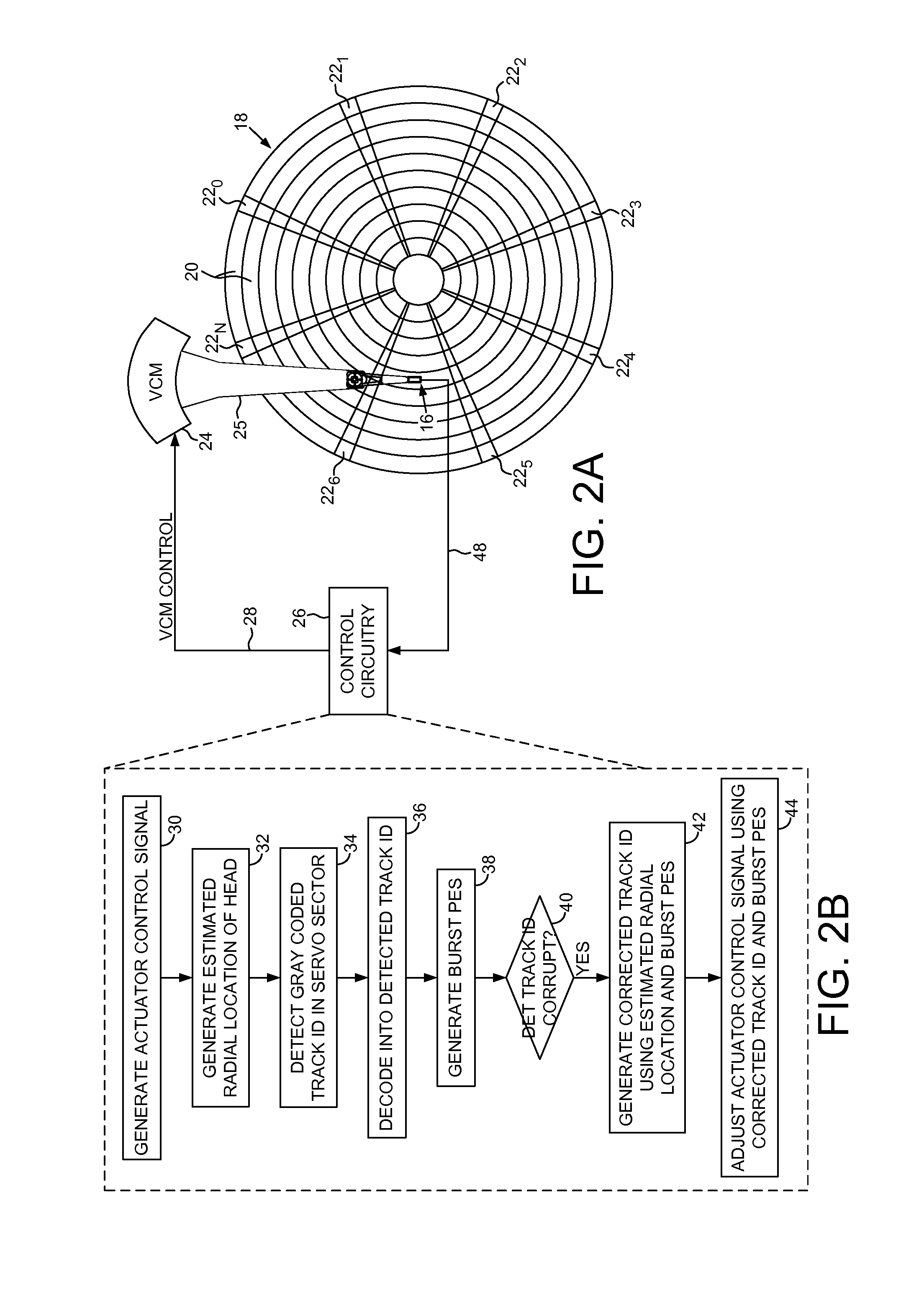
Disk drive correcting track ID in response to an estimated radial location and a burst PES
InactiveUS8553351B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageControl signalRadial position
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a head actuated over a disk, the disk comprising a plurality of servo tracks defined by a plurality of servo sectors. An estimated radial location of the head is generated in response to an actuator control signal. A Gray coded track ID is detected from reading a servo sector, and decoded into a detected track ID. A burst position error signal (PES) is generated from reading servo bursts in the servo sector, wherein the burst PES represents a detected fractional servo track offset of the head. When the detected track ID is corrupt, a corrected track ID is generated using the estimated radial location and the burst PES, and the actuator control signal is adjusted in response to the corrected track ID and the burst PES.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Continuously variable planetary gear set
ActiveUS20040224808A1Reduce amountEasy to removeHybrid vehiclesChain/belt transmissionRadial positionEngineering
A continuously variable planetary gear set is described having a generally tubular idler, a plurality of balls distributed radially about the idler, each ball having a tiltable axis about which it rotates, a rotatable input disc positioned adjacent to the balls and in contact with each of the balls, a rotatable output disc positioned adjacent to the balls opposite the input disc and in contact with each of the balls such that each of the balls makes three-point contact with the input disc, the output disc and the idler, and a rotatable cage adapted to maintain the axial and radial position of each of the balls, wherein the axes of the balls are oriented by the axial position of the idler.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Apparatus and method for establishing branch wells from a parent well
InactiveUS6283216B1Optimized areaFluid communicationFluid removalDirectional drillingRadial positionCasing string
A method and apparatus for multilateral completion comprises providing a casing string having a casing, a branching sub connected to the casing, and a locating profile. An expanding tool positionable in the branching sub is adapted to mate with the locating profile to fix a position of the expanding tool, such as to rotationally orient the expanding tool, fix a radial position of the expanding tool, and / or fix an axial position of the expanding tool. The branching sub has a non-expanded state, and the expanding tool is adapted to expand the branching sub.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Passive clearance control
ActiveUS6877952B2Easy to processEasy to assemblePump componentsBlade accessoriesRadial positionEngineering
The clearance between the tips of the rotor blades and the segmented shroud of a gas turbine engine is controlled by a passive clearance control that includes a support ring made from a low thermal expansion material supporting a retainer for the blade outer air seal that is slidable relative thereto so that the segments expand circumferentially and move radially to match the rate of change slope of the rotor during expansion and contraction for all engine operations. A leaf spring between the support ring and outer air seal biases the outer air seal in the radial direction and maintains the desired radial position during steady state operation of the gas turbine engine.
Owner:FLORIDA TURBINE TECH
Windturbine with slender blade
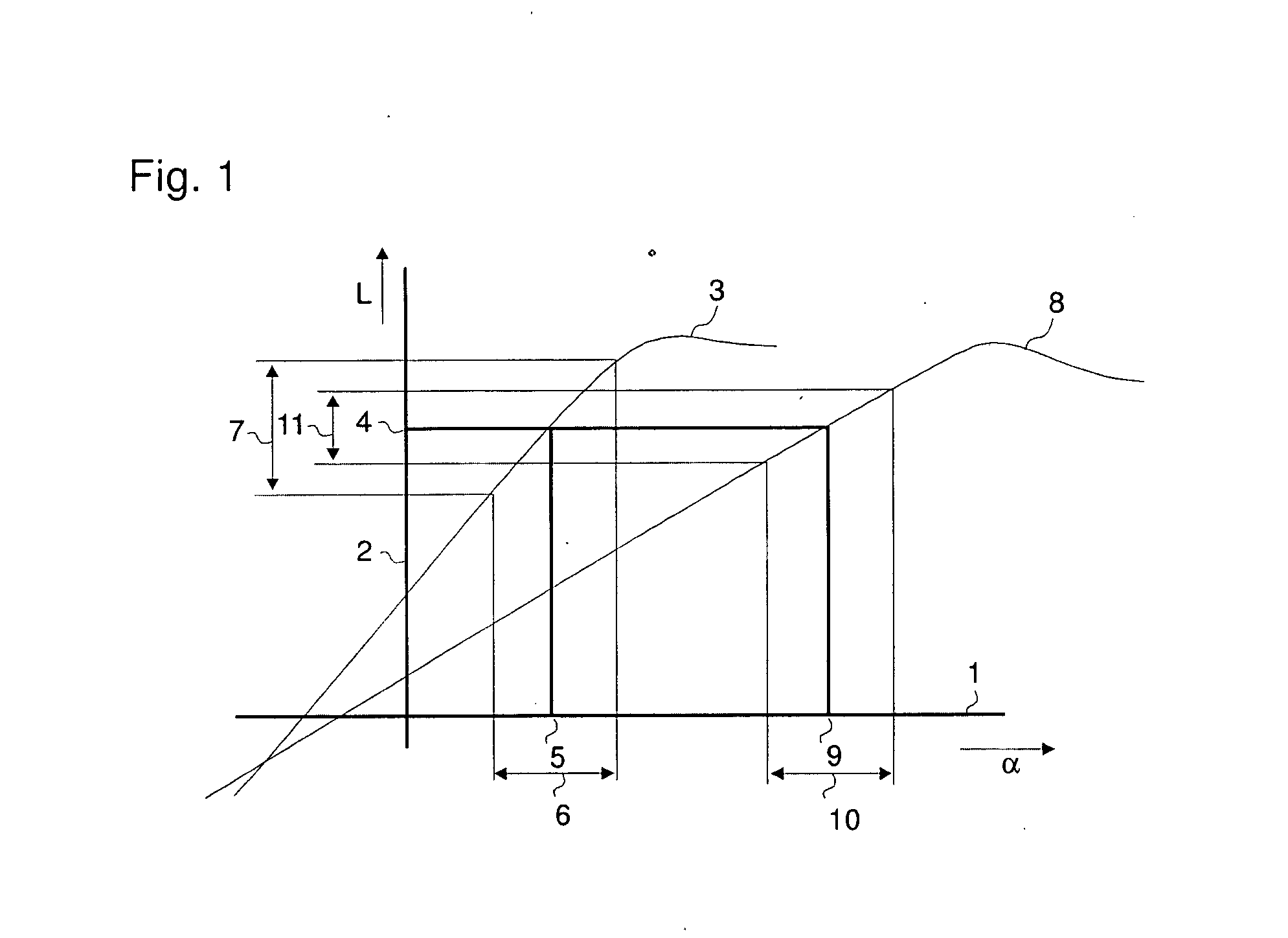
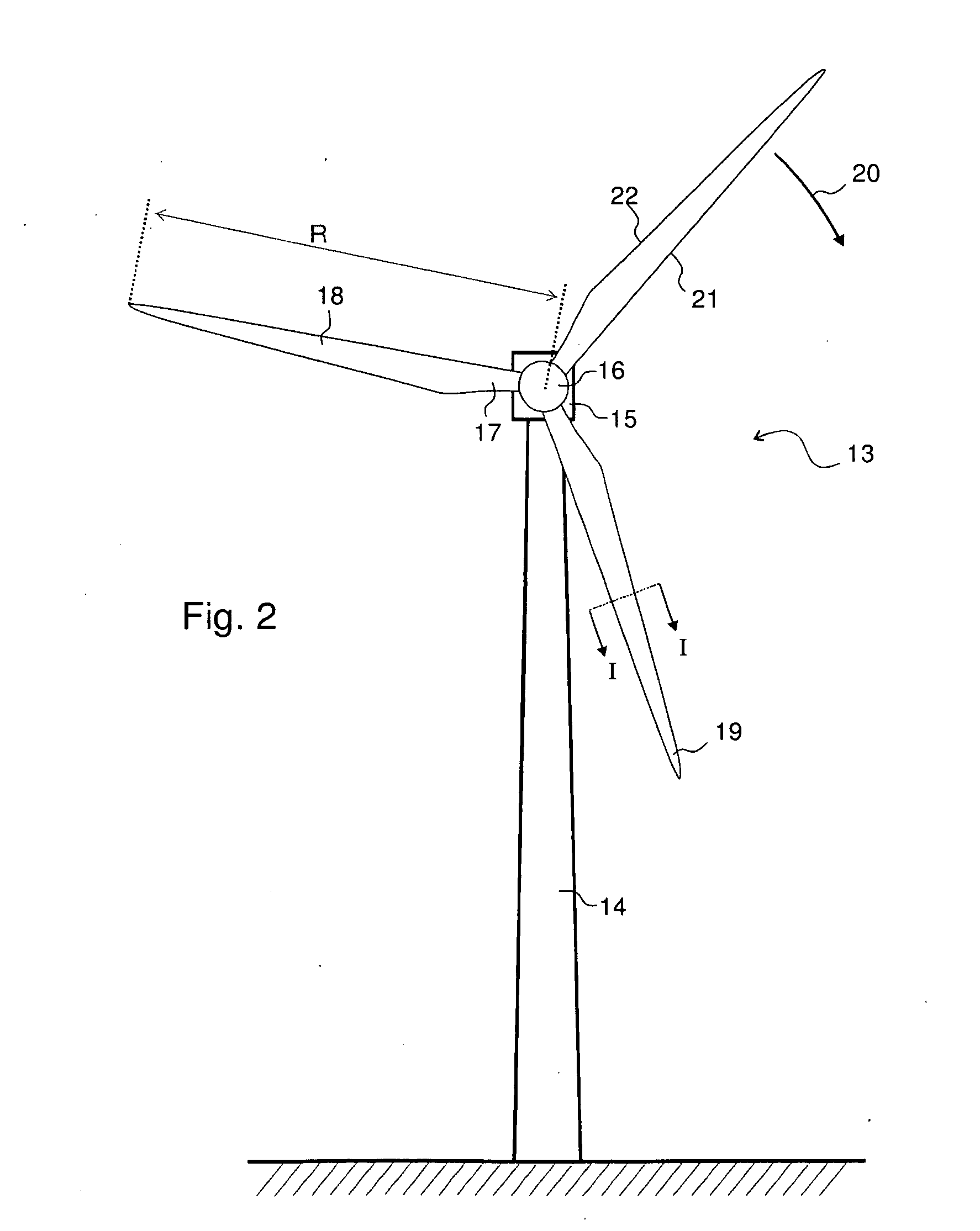
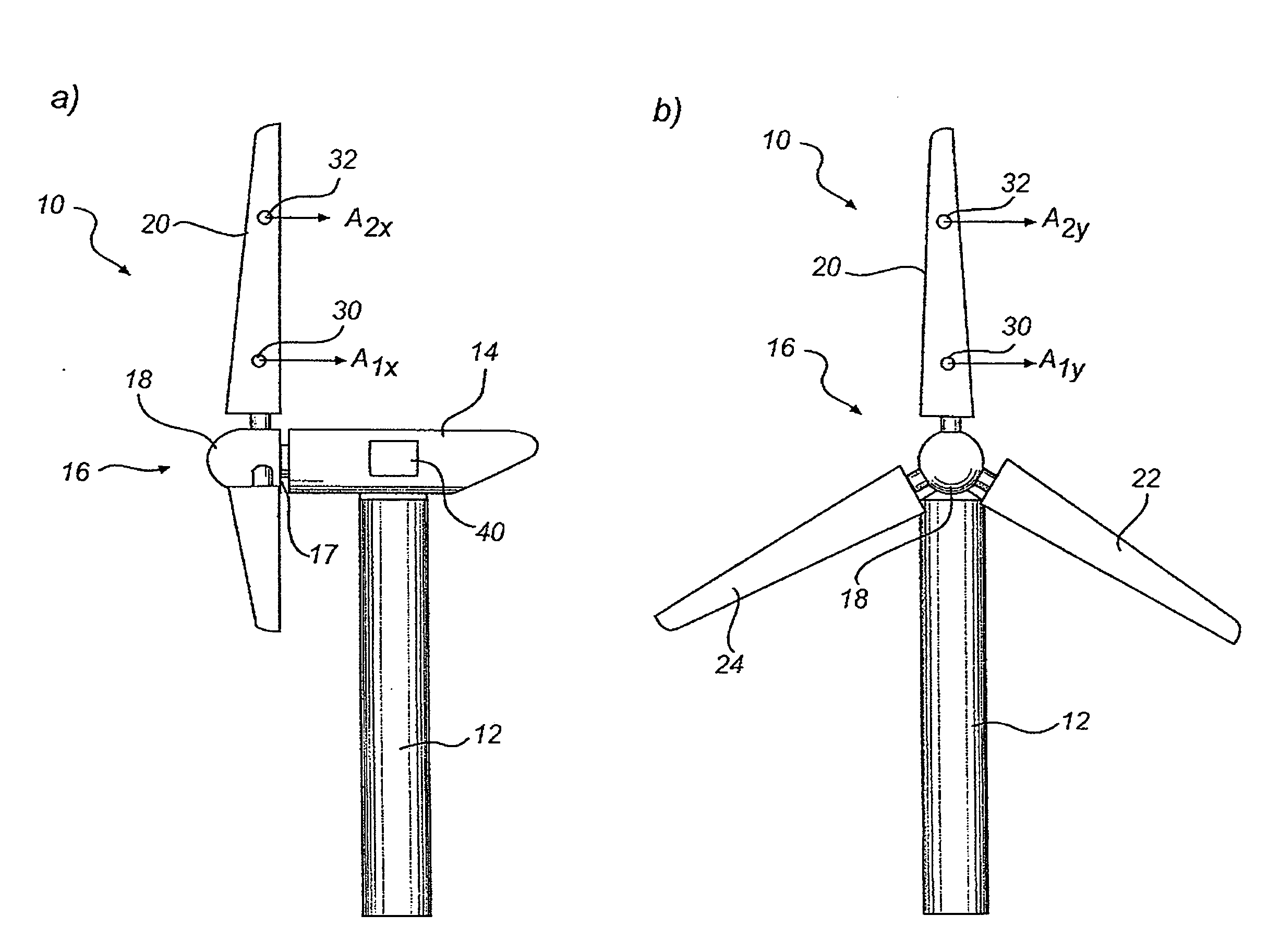
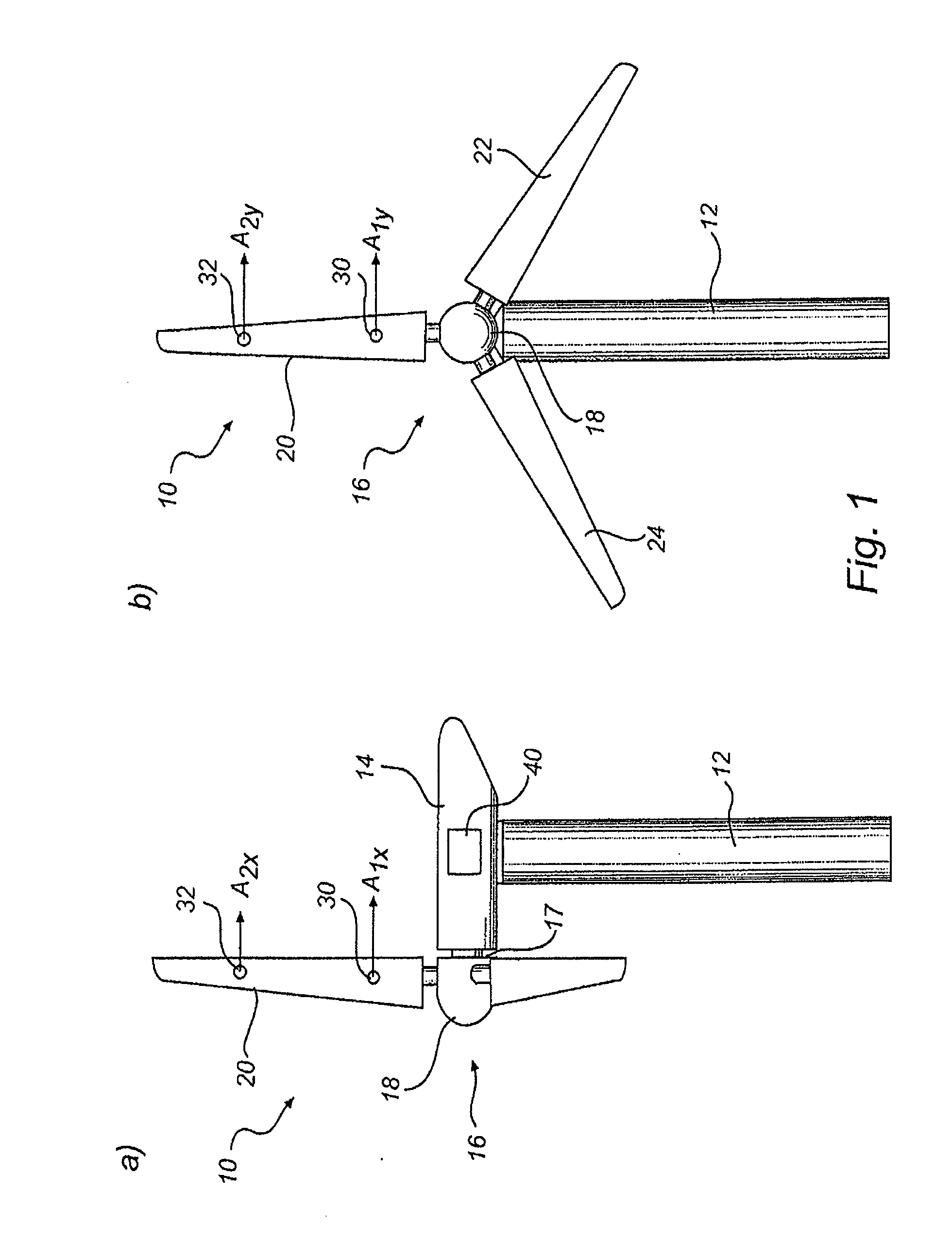
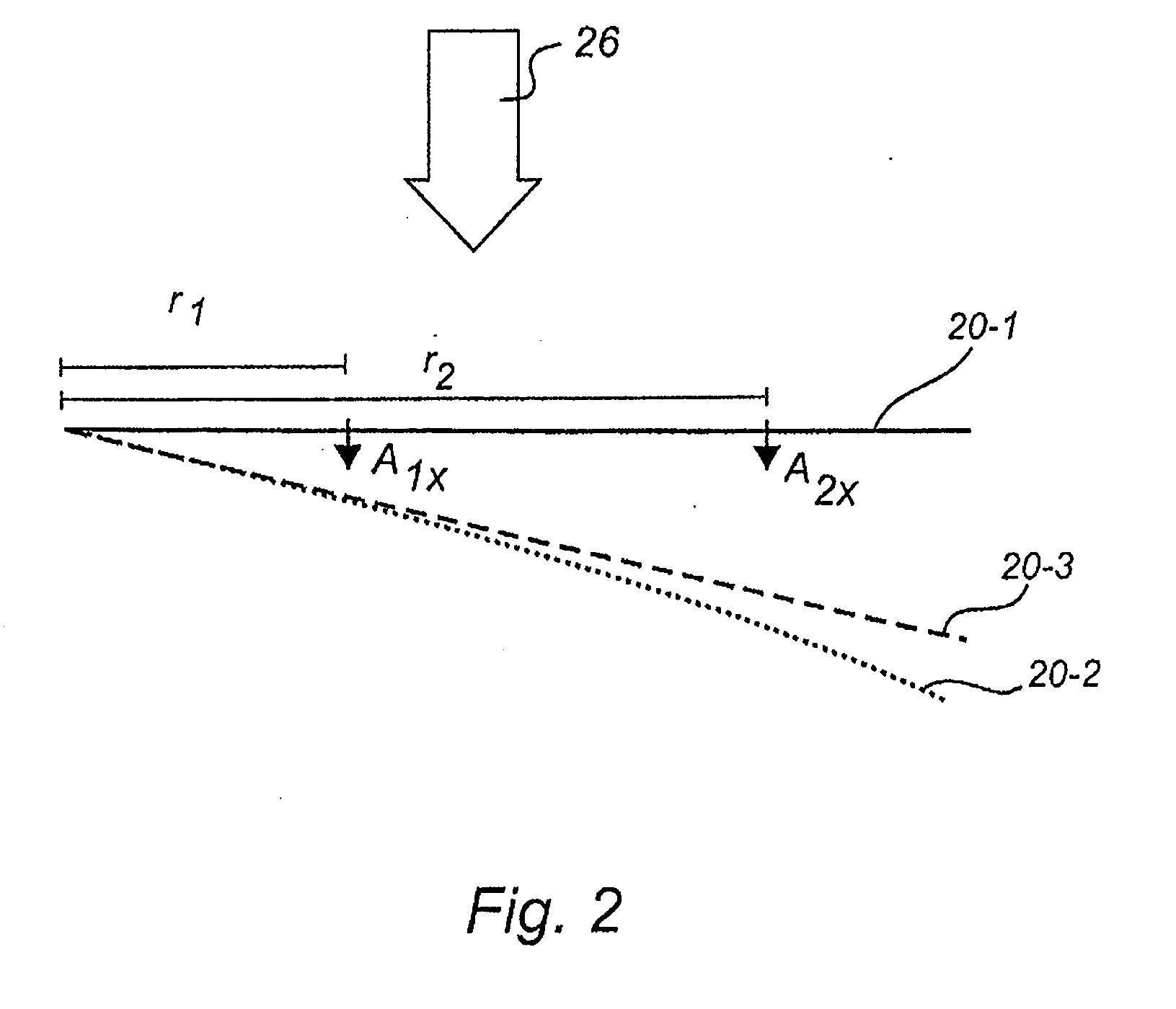
ActiveUS20090068018A1Reduce spacingIncrease the angleWind motor controlBlade accessoriesRadial positionTip-speed ratio
Wind turbine with a rotor blade relatively insensitive to turbulence because it is more slender than prior blades and is nevertheless able to generate sufficient lift by virtue of the fact that flow enhancing elements such as vortex generators combat flow separation. The slenderness is defined by the chord numbers C and D of which C is defined as C=Ncrclrλ2 / R2, in which N is the number of blades, cr is the local chord, cl the lift coefficient, r the radial position, λ the tip speed ratio and R the rotor radius. Subsequently, the chord should be less than what follows from the equation C=M in which M=−1.19+9.74Cp−21.01Cp2+17.50Cp3 and Cp is the power coefficient. This wind turbine is subject to about 2-12% less operational loads and to about 5-40% reduced survival wind speed loads compared to classical designs.
Owner:WOBBEN PROPERTIES GMBH
Magnetic detent for rotatable knob
A roller pump including a stator and a rotor assembly disposed within the stator. The rotor assembly includes a rotor hub, a first roller slide and a second roller slide slidingly disposed within the rotor hub. Each of the roller slides rotatably supports a roller. An occlusion adjustment knob for adjusting a radial position of the first and second roller slides and a magnetic detent assembly for providing an audible indicator as the occlusion adjustment knob is rotated.
Owner:TERUMO CARDIOVASCULAR SYST CORP
Magnetic bearing
There is disclosed a magnetic bearing which is an improvement over conventional radial magnetic bearings, and has a very small bearing loss. At least three U-shaped laminates 10 of electromagnetic steel sheets are circumferentially arranged around a rotation shaft 1, and are fixedly mounted on a housing 100. Exciting coils 31 and 32 are wound on each electromagnetic steel sheet laminate 10, and permanent magnets 20 and 21 are provided in the laminate 10. Rotor cores 2, each comprising a laminate of I-shaped electromagnetic steel sheets stacked together in the circumferential direction, are mounted on the rotation shaft 1 in such a manner that each rotor core 2 is opposed to magnetic pole surfaces of the electromagnetic steel sheet laminates 10. In accordance with a signal from position sensors 5 which detect the radial position of the rotation shaft 1, control current is caused to flow through the exciting coils 31 and 32 to thereby control the position of the rotation shaft 1. Thus, merely by causing the control current to flow through the exciting coils 31 and 32 when this is required, the control of the rotation shaft 1 can be achieved, and with this method, the energy consumption can be much reduced.
Owner:NSK LTD
Electromagnetic method for non-destructive testing of prestressed concrete pipes for broken prestressing wires
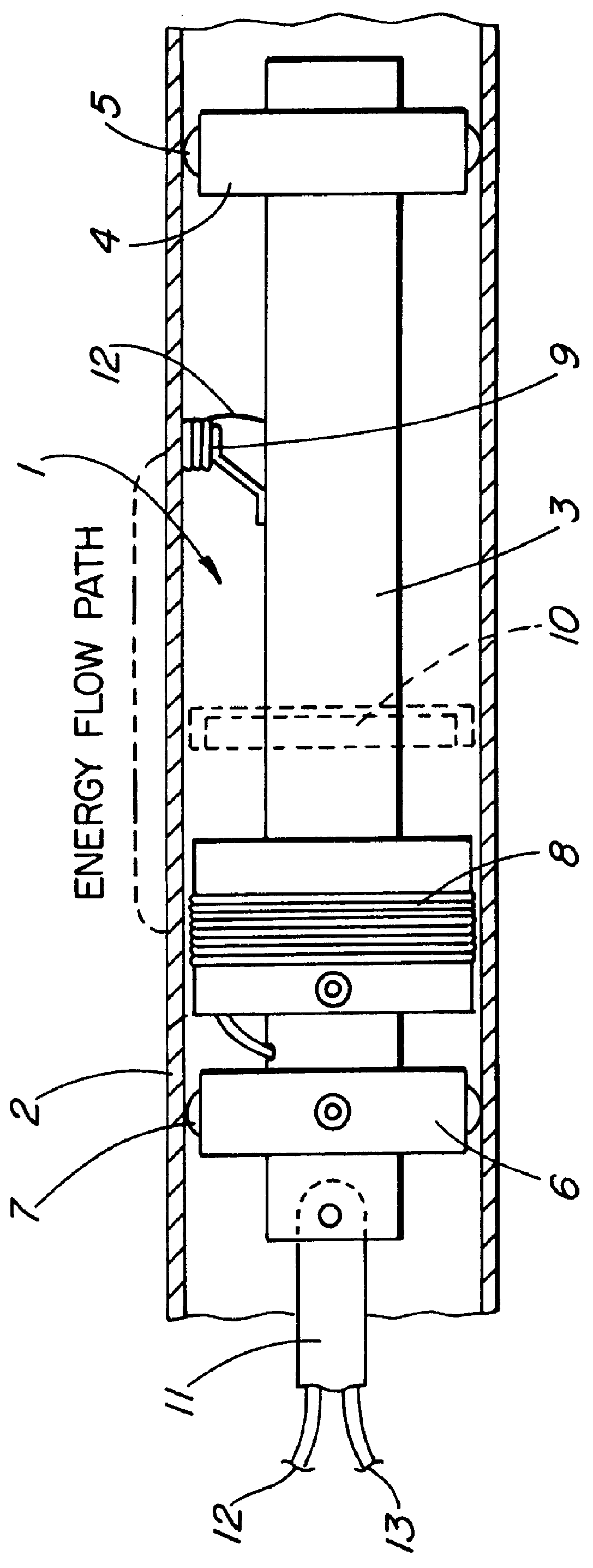
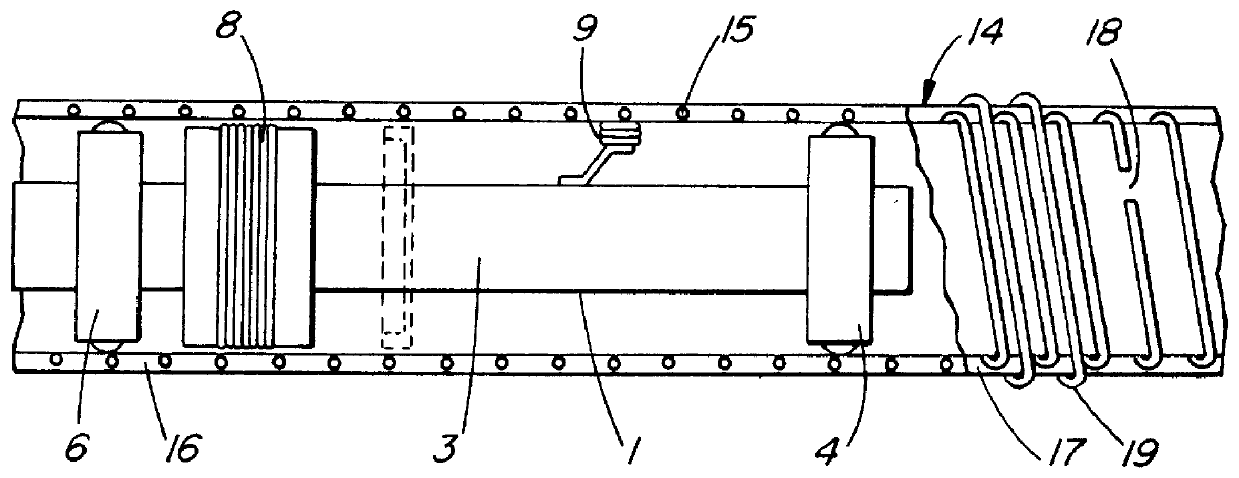
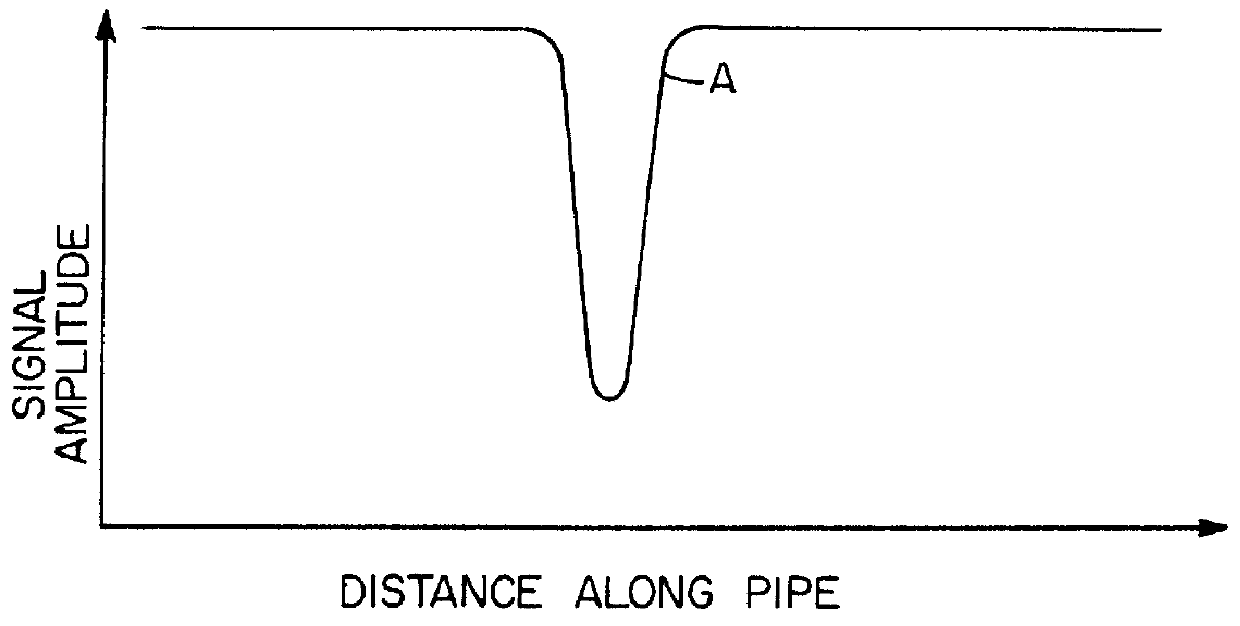
InactiveUS6127823AImprove energy transferMagnetic property measurementsMaterial magnetic variablesNon destructivePre stress
A method for detecting breaks in a prestressed wire, rod or bar embedded in concrete surrounding a metal pipe is described. A remote field eddy current probe is traversed axially internally through the pipe so as to create an energy flow path externally of the pipe and a transformer coupling through the pipe, and generate a signal in a detector coil axially spaced from an exciter coil. As the exciter coil traverses the wire, rod or bar containing the break a signal change is generated, regardless of the radial position of the detector coil relative to the break.
Owner:THE PRESSURE PIPE INSPECTION COMPANY
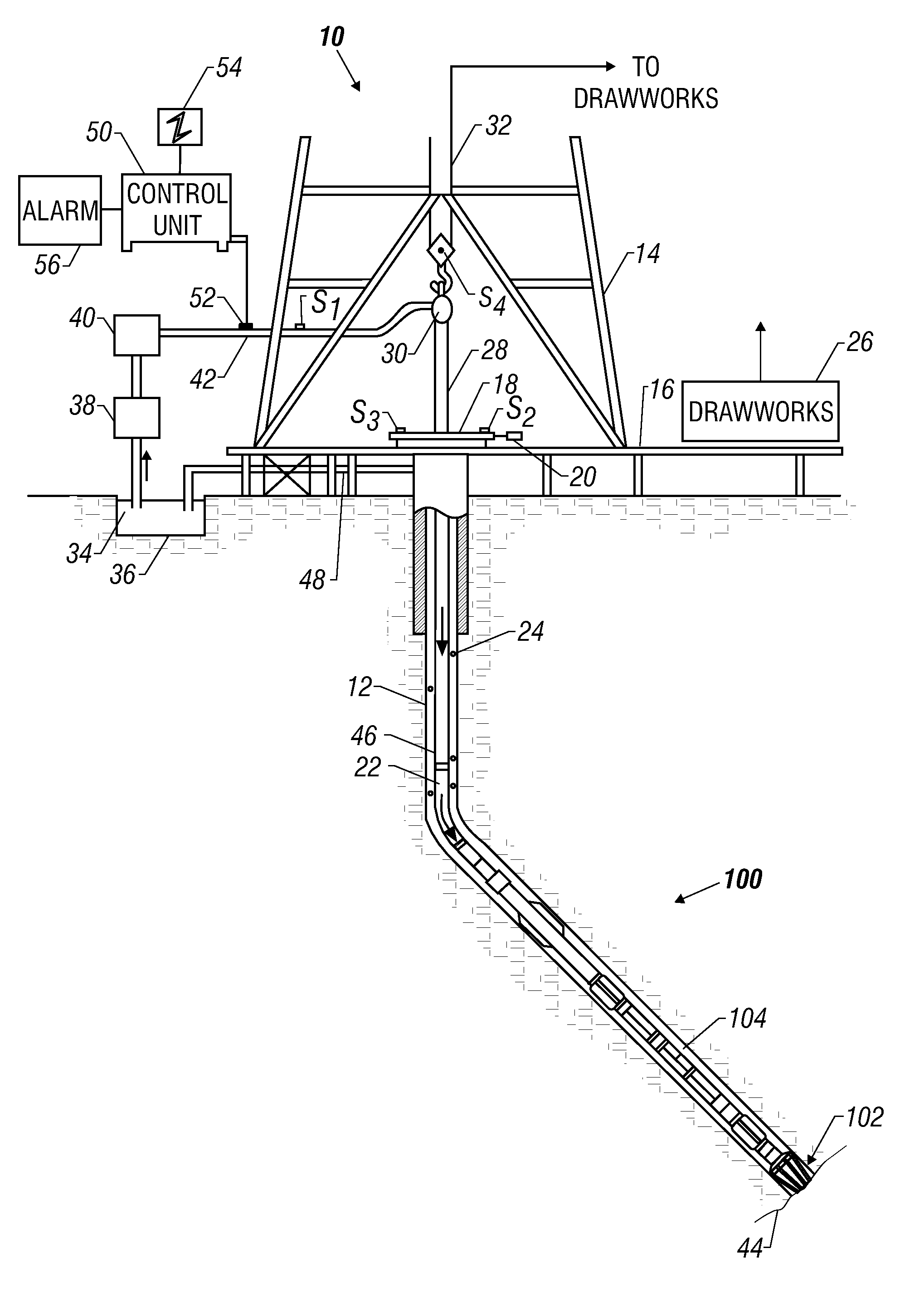
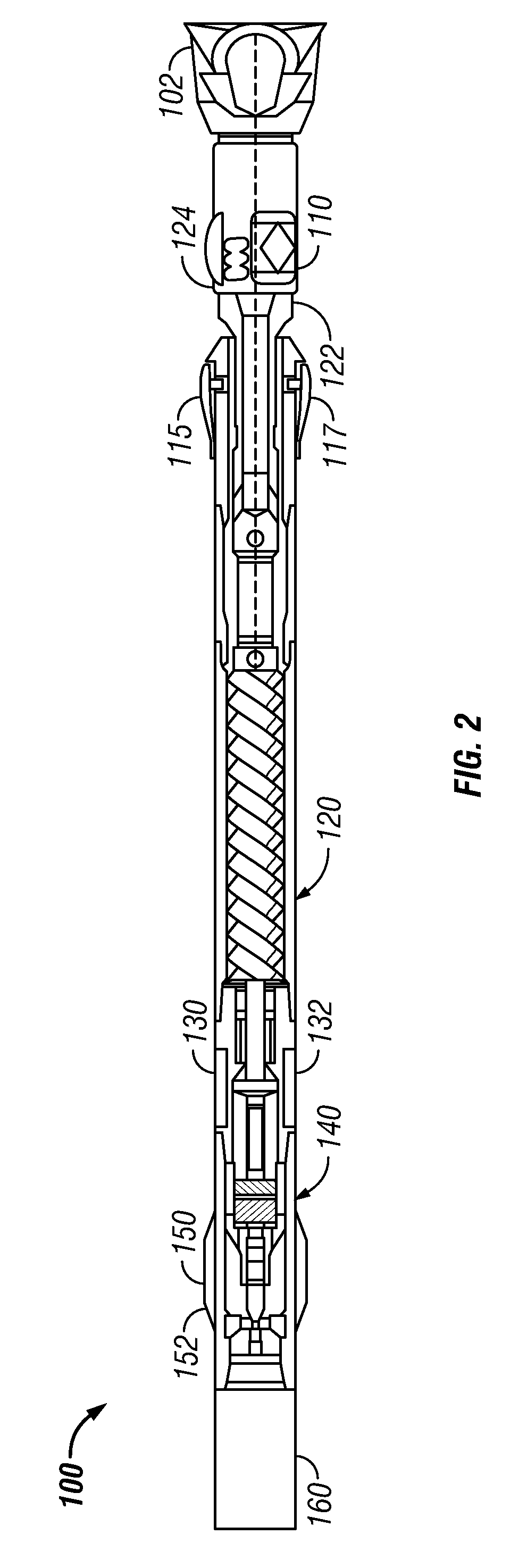
Automated steerable hole enlargement drilling device and methods
A bottomhole assembly (BHA) coupled to a drill string includes a steering device, one or more controllers, and a hole enlargement device that selectively enlarges the diameter of the wellbore formed by the drill bit. In an automated drilling mode, the controller controls drilling directing by issuing instructions to the steering device. In one arrangement, the hole enlargement device is integrated into a shaft of a drilling motor that rotates the drill bit. The hole enlargement device includes an actuation unit and an electronics package that cooperate to translate extendable cutting elements between a radially extended position and a radially retracted position. The electronics package may be responsive to a signal that is transmitted from a downhole and / or a surface location. The hole enlargement device may also include one or more position sensors that transmit a position signal indicative of a radial position of the cutting elements.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Continuously variable planetary gear set
A continuously variable planetary gear set is described having a generally tubular idler, a plurality of balls distributed radially about the idler, each ball having a tiltable axis about which it rotates, a rotatable input disc positioned adjacent to the balls and in contact with each of the balls, a rotatable output disc positioned adjacent to the balls opposite the input disc and in contact with each of the balls such that each of the balls makes three-point contact with the input disc, the output disc and the idler, and a rotatable cage adapted to maintain the axial and radial position of each of the balls, wherein the axes of the balls are oriented by the axial position of the idler.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Advanced elevated feed distribution system for very large diameter RCC reactor risers
InactiveUS20080081006A1Good dispersionImprove conversion efficiencyCatalytic crackingChemical/physical/physico-chemical nozzle-type rreactorsRadial positionDistribution system
An FCC process and apparatus may include injecting hydrocarbon feedstock at different radial positions inside a riser. Multiple distributors may be used to position the openings for injecting feedstock at multiple radial positions. In addition, the openings may be away from riser peripheral wall and at different elevations along the riser wall or extending up from the riser bottom. The different opening positions introduce the feedstock across a larger area of the cross-section of the riser, which may improve the feedstock dispersion and mixing with catalyst. Improved mixing may increase conversion of the feedstock. Larger FCC units generally have greater riser diameters that may cause problems for feedstock dispersion and decrease the ability for the feedstock to mix with catalyst. Injecting the feedstock at multiple radial positions may improve feedstock dispersion in larger FCC units and increase mixing.
Owner:UOP LLC
Evaluation method of magnetic disk, manufacturing method of magnetic disk, and magnetic disk
InactiveUS20120077060A1Easily evaluate propertyAccurately evaluate propertyMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageCarbon filmRadial position
An evaluation method that can easily evaluate properties of a carbon protective film and a lubricant on a magnetic-disk surface or particularly, an evaluation method of a magnetic disk in which the properties of the magnetic-disk surface can be evaluated accurately so that a strict demand for interactions between the magnetic-disk surface and a head can be met is provided. In a state in which an element portion of the magnetic head provided with the head element portion that projects by thermal expansion is projected, after being brought into contact with a predetermined radial position on the surface of the rotating magnetic disk, the head is further made to perform seeking in a state in which the element portion is projected by a specified amount, whereby the properties of the carbon film or the lubricant formed on the magnetic-disk surface is evaluated.
Owner:WD MEDIA SINGAPORE PTE
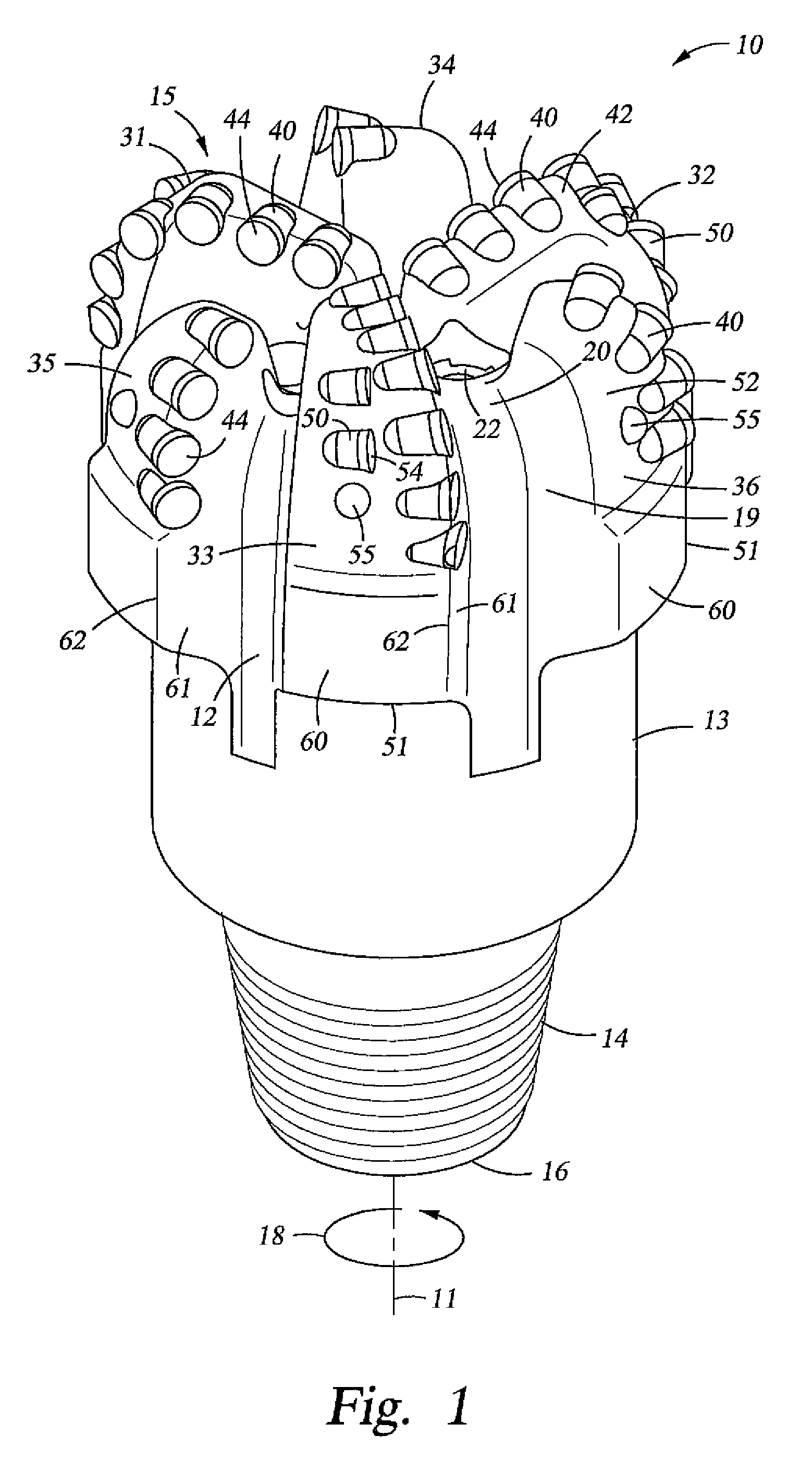
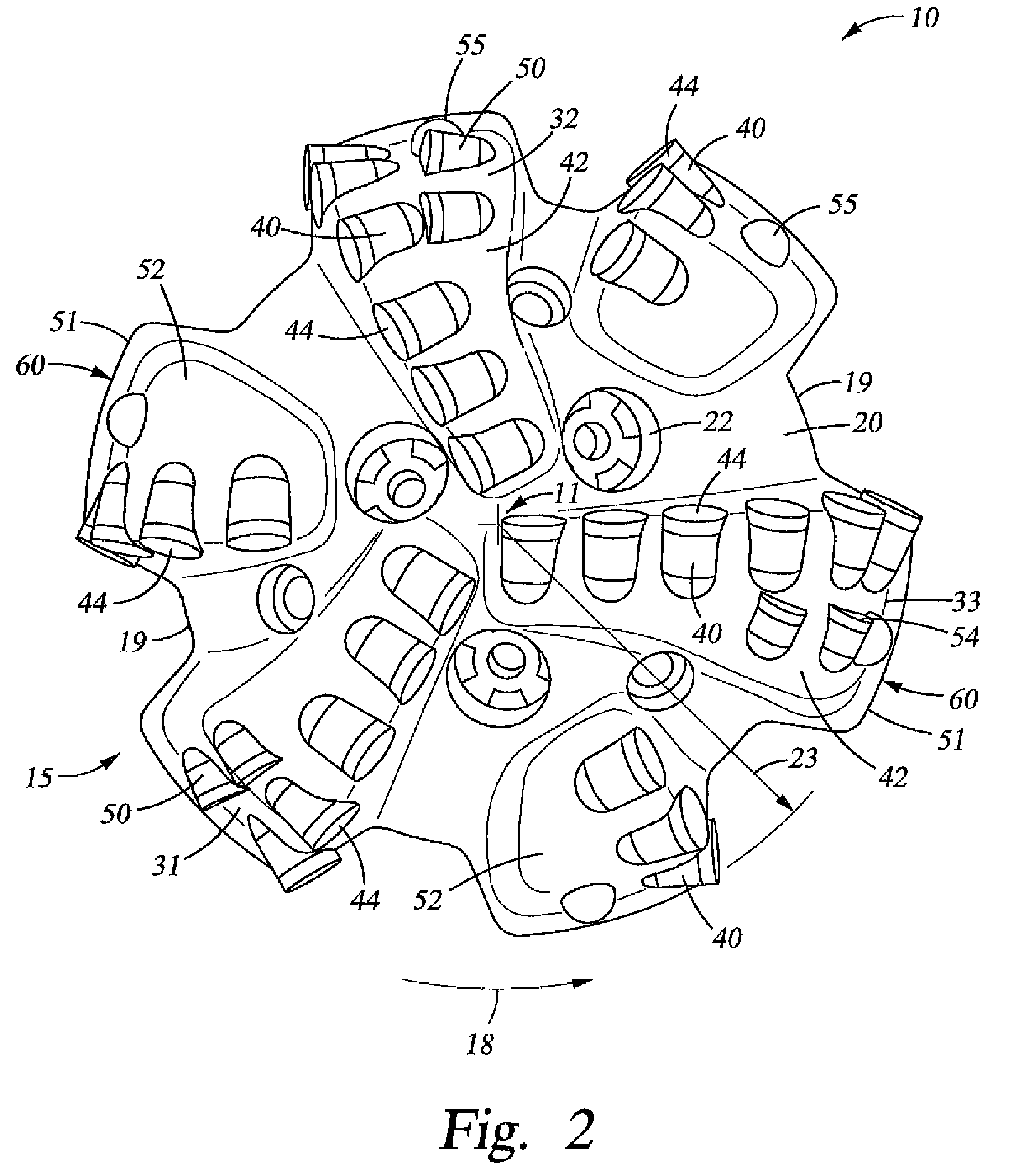
Kerfing hybrid drill bit and other downhole cutting tools
A drill bit for drilling a borehole in earth formations may include a bit body having a bit axis and a bit face; a plurality of blades extending radially along the bit face; and a plurality of cutting elements disposed on the plurality of blades, the plurality of cutting elements comprising: at least one cutter comprising a substrate and a diamond table having a substantially planar cutting face; and at least two conical cutting elements comprising a substrate and a diamond layer having a conical cutting end, wherein in a rotated view of the plurality of cutting elements into a single plane, the at least one cutter is located a radial position from the bit axis that is intermediate the radial positions of the at least two conical cutting elements.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
Method of and apparatus for handling thin and flat workpieces and the like
InactiveUS6174011B1Low costGripping headsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCircular discRadial position
A novel technique and apparatus for receiving, holding and / or transporting thin planar workpieces and the like that involves radially supporting circumferentially spaced thin and flexible annular ring sectors about a fixed planar central circular disc upon which the workpiece is to be received, and by limitedly rotationally bending the ring sectors about the disc, causing circumferential leaf springs bridging the successive ring sectors and carrying workpiece holding fingers to deform and thereby expand (or retract) the radial position of the fingers to accommodate the edges of the workpiece.
Owner:HERCULES TECH GROWTH CAPITAL
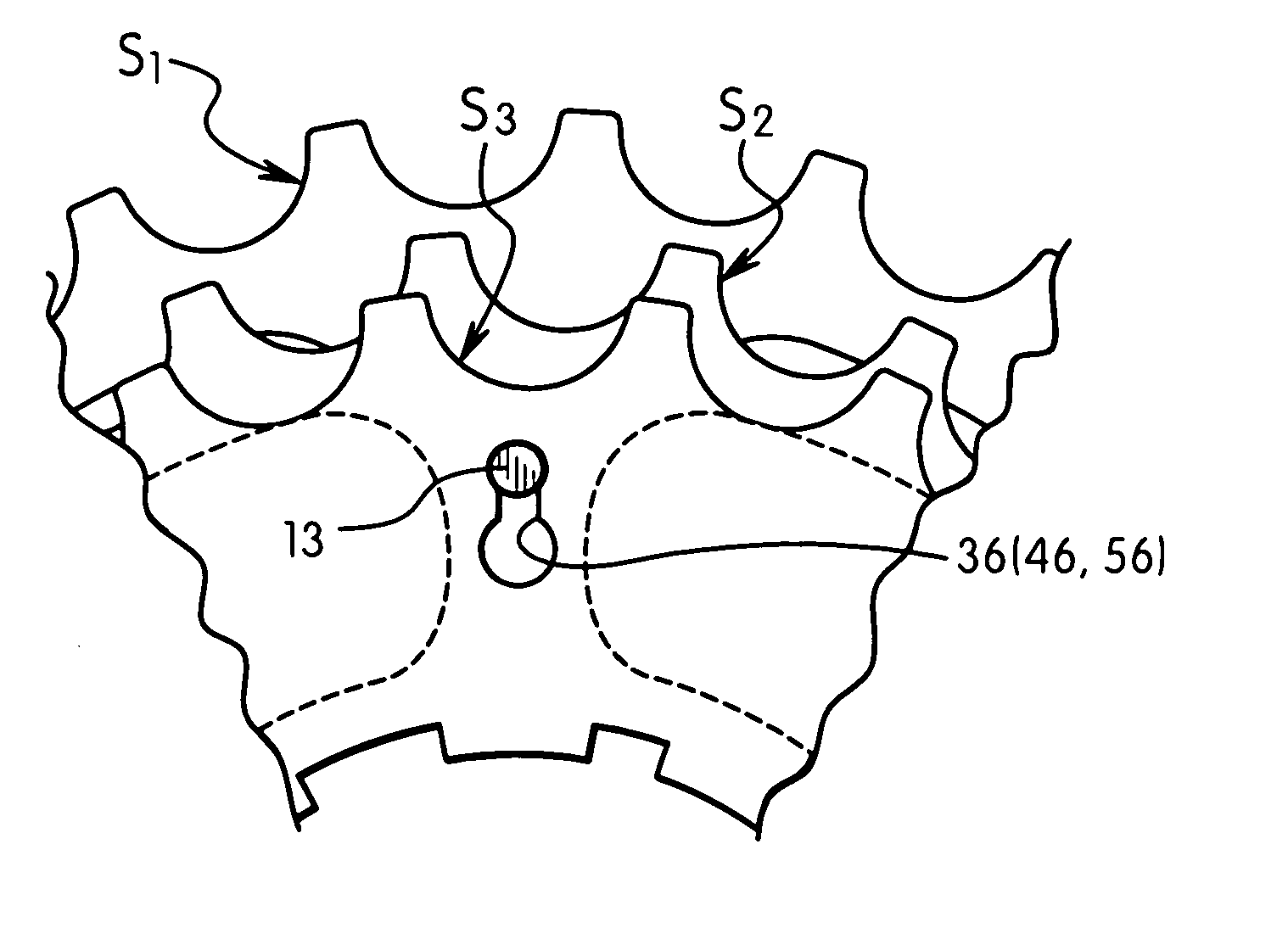
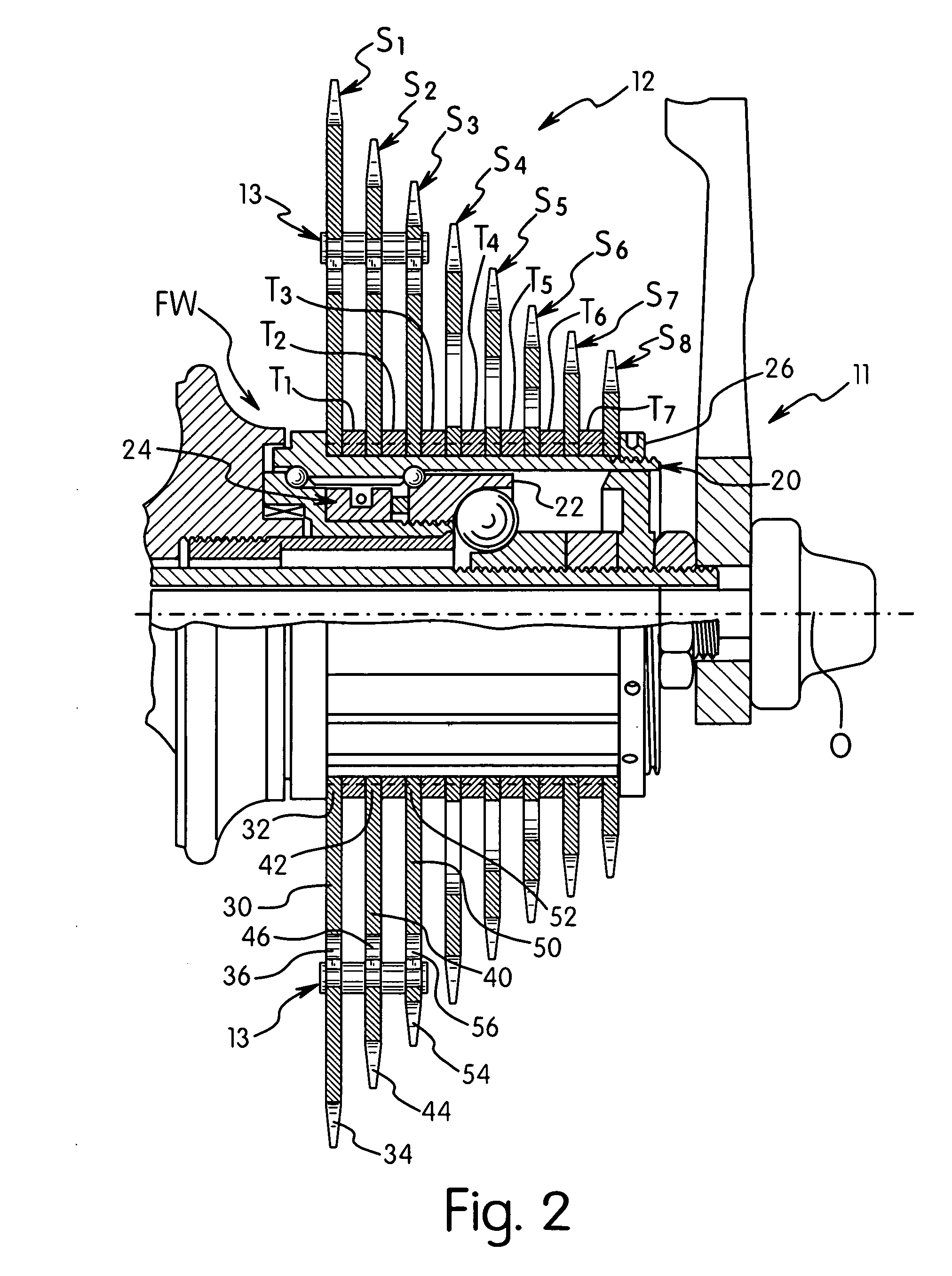
Bicycle sprocket assembly
InactiveUS20080058144A1Facilitates smooth shifting of a chainChain/belt transmissionPortable liftingRadial positionSprocket
A bicycle sprocket assembly includes a first sprocket, a second sprocket and at least one reinforcement member. The first sprocket includes a first main body and a first chain engagement portion. The second sprocket includes a second main body and a second chain engagement portion. The reinforcement member is coupled between the sprockets. Preferably, the reinforcement member is disposed in first and second apertures of the first and second sprockets at a radial location spaced radially outwardly of first and second inner end portions of the first and second sprockets. Preferably, a spacer is disposed between the first and second sprockets radially inwardly of the reinforcement member. The reinforcement member is preferably installable in the first and second apertures by a sliding movement generally perpendicular to a rotation axis of the first and second sprockets.
Owner:SHIMANO INC
Electroplating apparatus for tailored uniformity profile
ActiveUS20120258408A1Maximizing randomization of flow patternSimple processCellsMachining electric circuitsRadial positionEngineering
Methods of electroplating metal on a substrate while controlling azimuthal uniformity, include, in one aspect, providing the substrate to the electroplating apparatus configured for rotating the substrate during electroplating, and electroplating the metal on the substrate while rotating the substrate relative to a shield such that a selected portion of the substrate at a selected azimuthal position dwells in a shielded area for a different amount of time than a second portion of the substrate having the same average arc length and the same average radial position and residing at a different angular (azimuthal) position. For example, a semiconductor wafer substrate can be rotated during electroplating slower or faster, when the selected portion of the substrate passes through the shielded area.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method and apparatus for absolute track spacing determination for self-servowriting
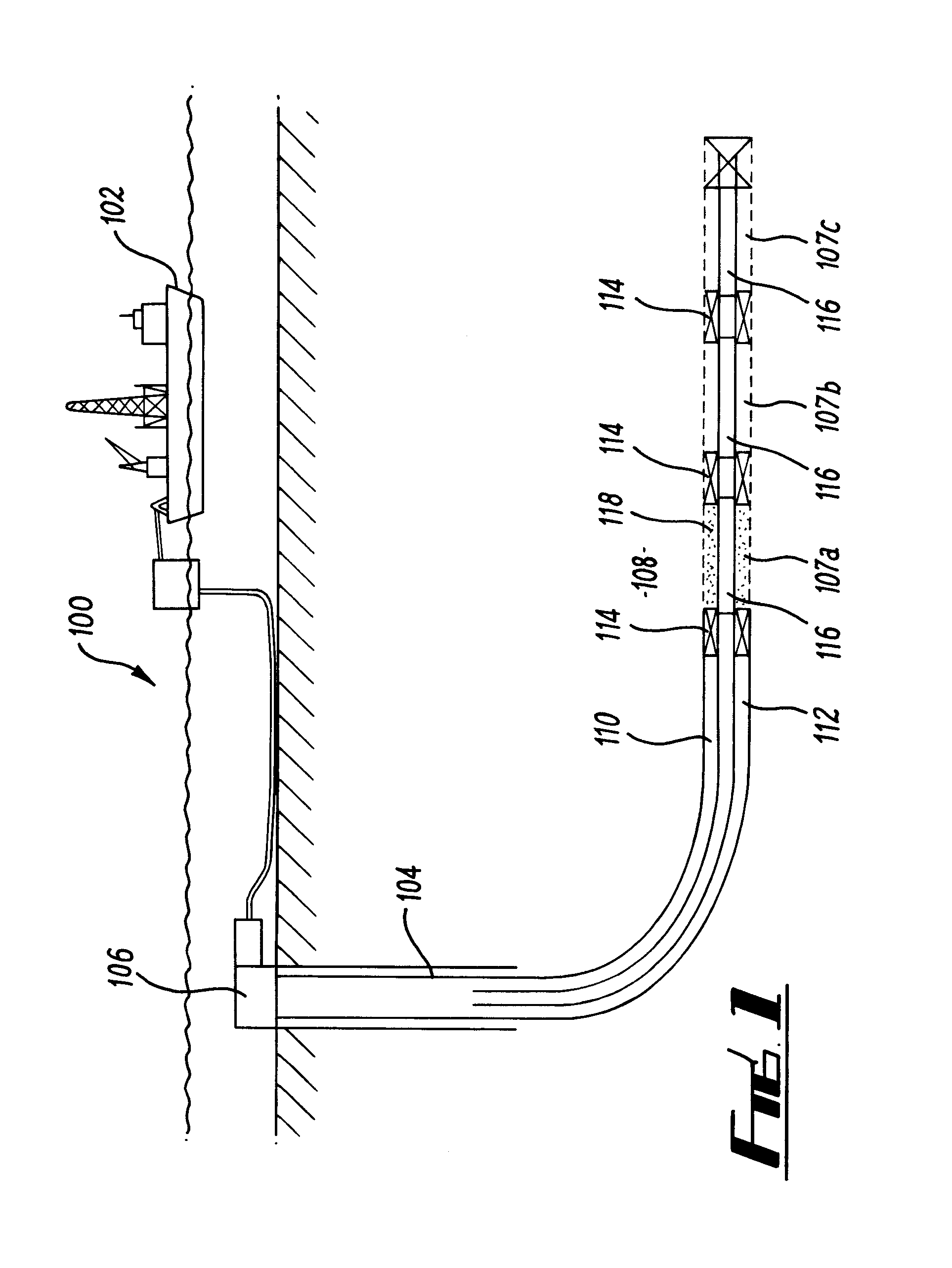
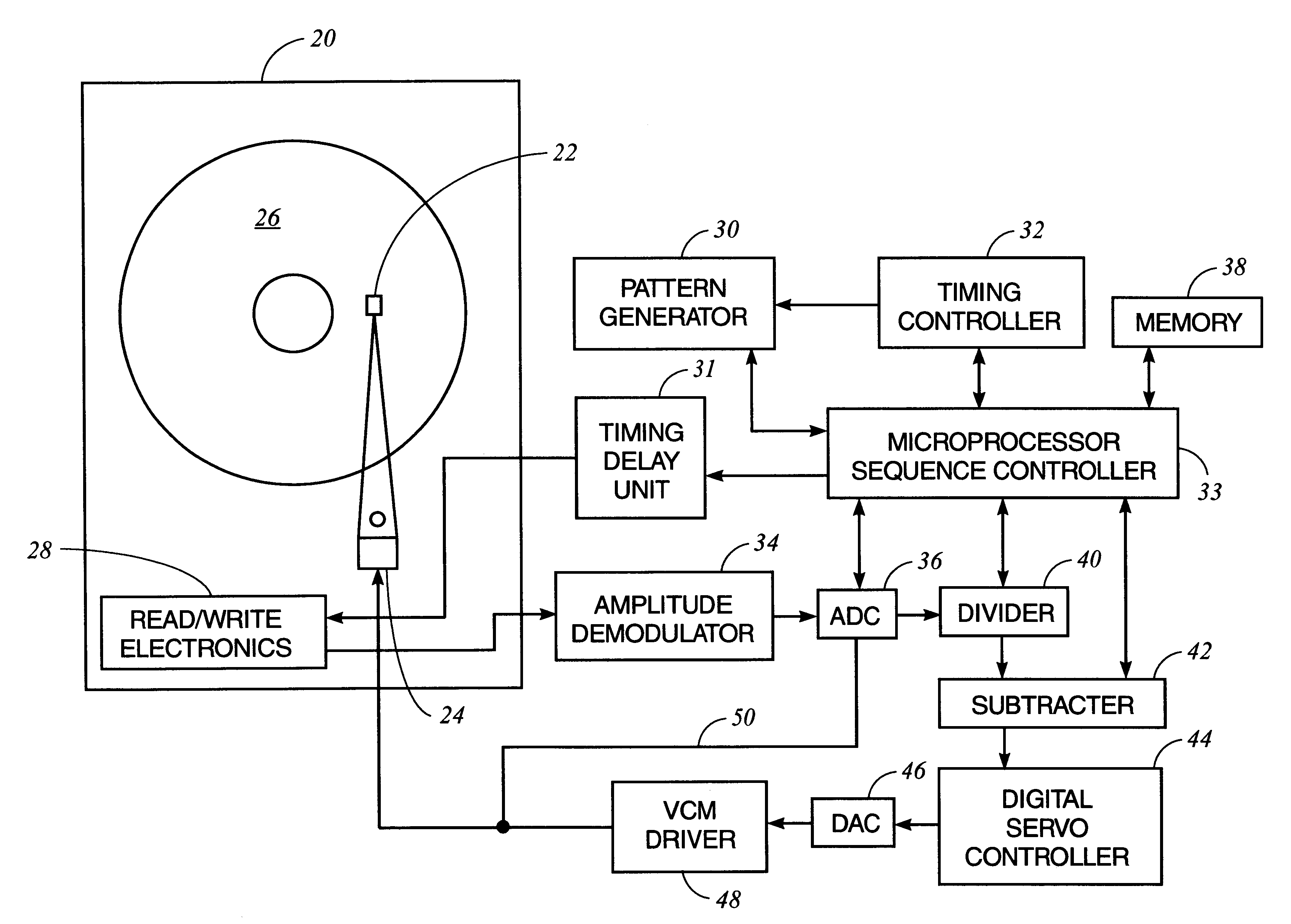
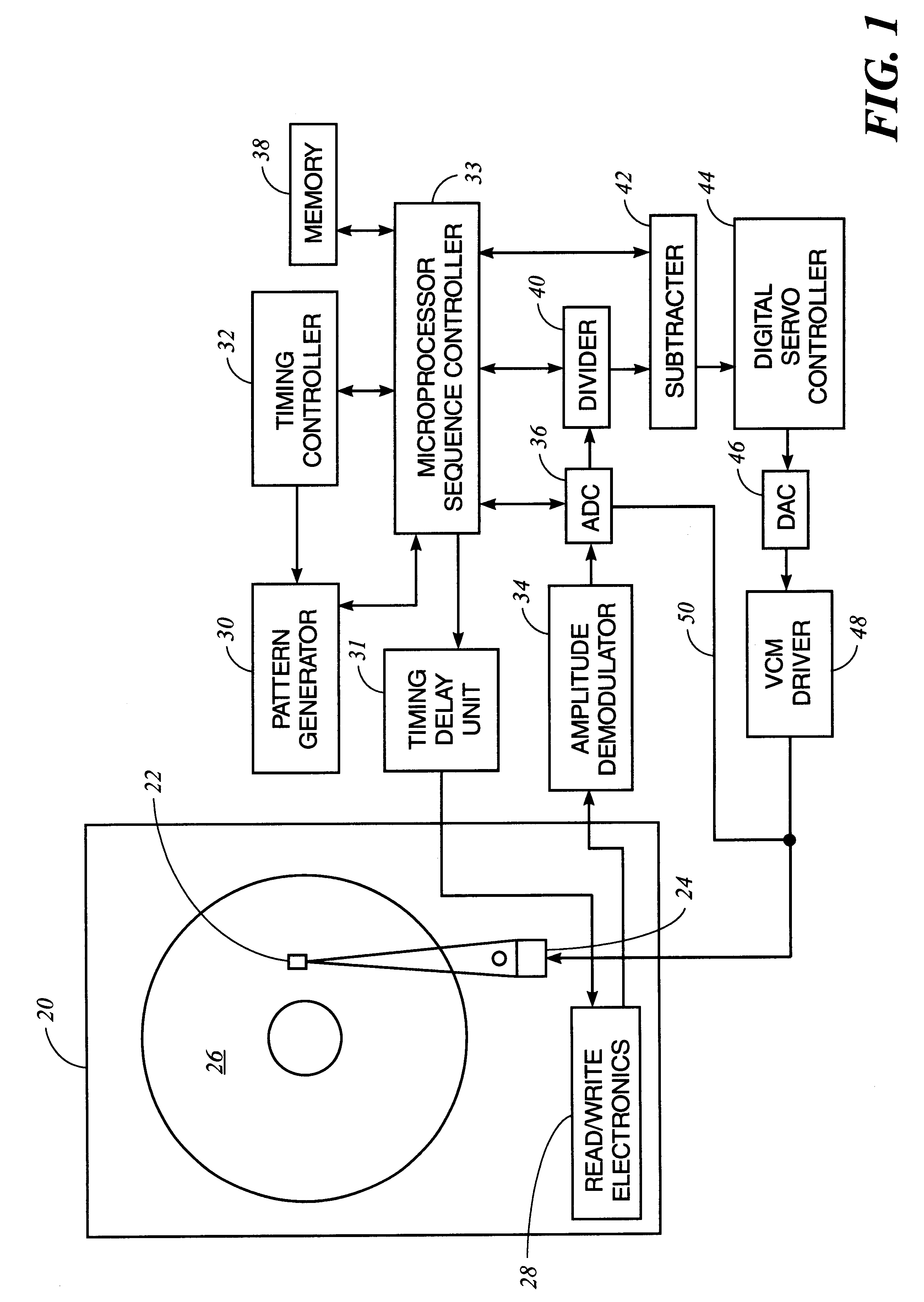
A method and apparatus to determine and correct track spacing during self-servowriting on a rotating recording medium. The recording medium comprising a plurality of tracks, wherein each track comprises a plurality of sectors, and a transducer mounted on an actuator arm pivotally coupled to a voice coil motor (VCM). The actuator arm is positioned by a servo. The method comprising the steps of: servowriting the at least one of the plurality of sectors with a servo pattern consisting of recorded transitions. The servowriting is performed on one more tracks within the sectors where the number of tracks being servowritten is less than total number of tracks that fills the rotating medium. The transducer is positioned relative to the rotating recording medium to a preselected radial position over a previously servowritten area of the rotating recording medium that has one or more previously recorded transitions. Next, an angular acceleration is imposed on the actuator arm by applying a predetermined amount of current to the VCM. The measurement and correction of a spacing of the tracks in the previously servowritten area is performed by measuring the amplitudes of the previously recorded transitions at least one time during the passage of the sectors beneath the transducer, and if the calibratng of the spacing is outside a predetermined tolerance, then continuing servowriting new recorded transitions using said adjustment factor on tracks following said previously servowritten area. In one embodiment, the method includes measuring a VCM torque constant (K) by applying a current impulse for a predetermined time (t) and measuring the back Electromotive Force (EMF) generated from the VCM to determine the torque per unit for the current impulse for the predetermined time (t) and to determine the back Electronic Force (EMF) per unit of angular velocity of the actuator arm. After the torque constant is determined, an adjustment factor is computed based on the values of the torque constant (K), the current impulse for the period of time (t), and the back Electromotive Force (EMF)per unit of angular velocity of the actuator arm. This adjustment factor is used while servowriting now recorded transitions tacks following the previously servowritten area.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Hypersonic aerocraft and air inlet internal and external waverider integrated design method
ActiveCN103662087ARealize seamless dockingRealize integrated designTurbine/propulsion air intakesGround installationsShock waveRadial position
The invention discloses a hypersonic aerocraft and air inlet internal and external waverider integrated design method, and relates to a near space aerocraft. An aerodynamics characteristic is firstly appointed, and then a design scheme meeting the characteristic is inferred backwards; a three-dimensional shock wave curved surface in a complex shape is appointed, the change rule of the transverse curvature center is obtained, and a series of basic flow fields meeting the needs of the waverider design are inferred backwards according to the change rule; flow lines of different curvature centers and different radial positions are traced in every basic flow field in the circumferential direction; a waverider device capable of producing the appointed complex three-dimensional shock wave curved surface is obtained finally, namely the integrated design scheme is obtained. The advantages of a waveriders and an internal waverider air inlet are kept, the integrated design of the two high-performance devices is achieved, the waverider model with high lift-drag ratio and the scheme of the air inlet with full-flow capture can be obtained at the same time, and accordingly the overall performance of the aerocraft is improved.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
wind turbine and a method for monitoring a wind turbine
ActiveUS20110285129A1Reliable and tolerant blade monitoringPrevent large blade bending and of bladeWind motor controlEngine fuctionsAccelerometerRadial position
According to the inventive concept, there is provided a wind turbine with at least one blade. The wind turbine comprises a first accelerometer mounted at a first radial position of the blade and being adapted to determine a first acceleration value, and a second accelerometer mounted at a second radial position of the blade different from the first radial position, and the accelerometer being adapted to determine a second acceleration value. The wind turbine further comprises a controller adapted to generate a signal based on said first and second acceleration values. There is also provided a method for monitoring a blade of a wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Fixed cutter bit with backup cutter elements on primary blades
A drill bit for drilling a borehole comprises a bit body having a bit face. In addition, the drill bit comprises a plurality of primary blades. Further, the drill bit comprises a plurality of primary cutter elements mounted to each primary blade and at least one backup cutter element mounted to each primary blade. Still further, the drill bit comprises a plurality of secondary blades. Moreover, the drill bit comprises a plurality of primary cutter elements mounted to each secondary blade. The ratio of the total number of backup cutter elements mounted to the plurality of primary blades to the total number of backup cutter elements mounted to the plurality of secondary blades is greater than 2.0. Each backup cutter element on each primary blade has substantially the same radial position as one of the primary cutter elements on the same primary blade.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
Tissue scaffold having aligned fibrils and artificial tissue comprising the same
ActiveUS7338517B2Sufficient structural strength to withstand pressureMinimal immunological responsePeptide/protein ingredientsDough-sheeters/rolling-machines/rolling-pinsFiberFibril
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com