Patents
Literature
5939 results about "DC motor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
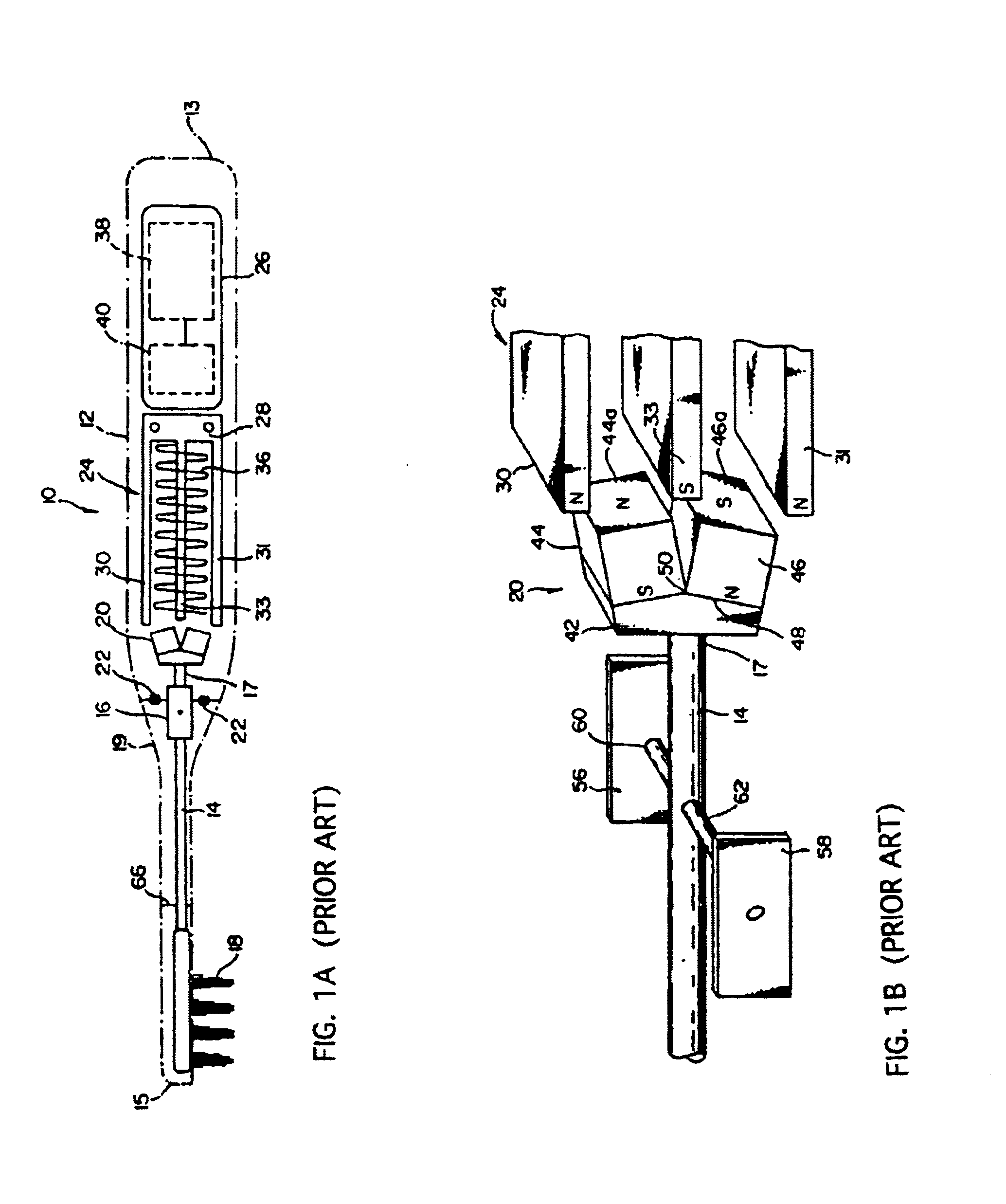
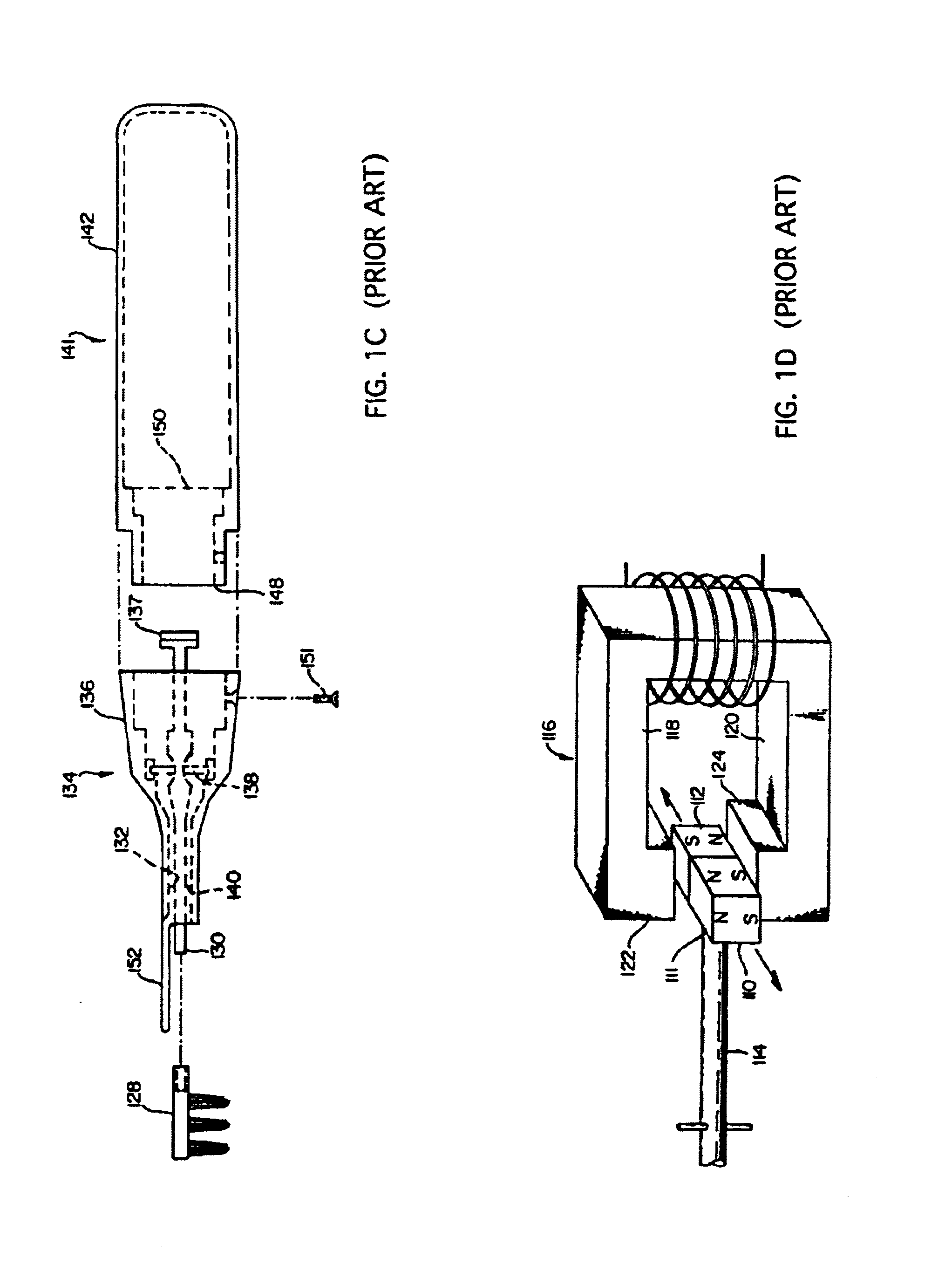
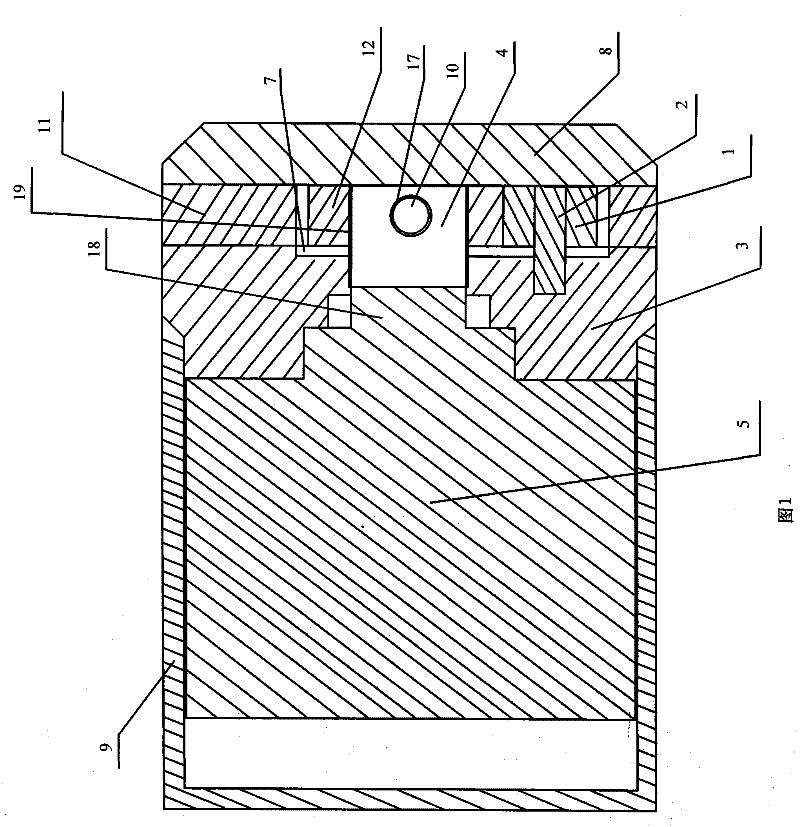
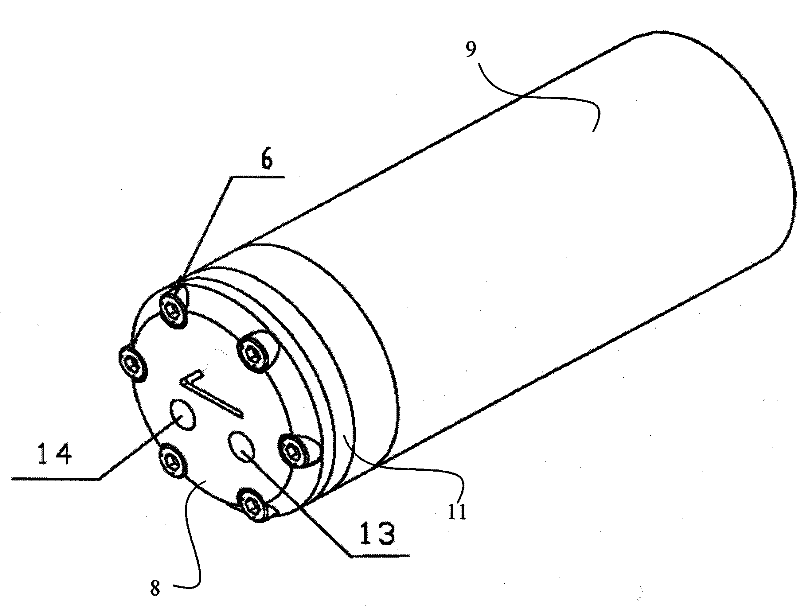
A DC motor is any of a class of rotary electrical machines that converts direct current electrical energy into mechanical energy. The most common types rely on the forces produced by magnetic fields. Nearly all types of DC motors have some internal mechanism, either electromechanical or electronic, to periodically change the direction of current flow in part of the motor.
Method and arrangement for control of direct current motor
InactiveUS7567045B2Efficient coordinationLow costVehicle seatsMultiple motor speed/torque controlTelecommunications linkControl signal
Owner:KONGSBERG AUTOMOTIVE AB (SE)
Method of driving DC motor and related circuit for avoiding reverse current
ActiveUS8183807B2Avoid it happening againMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlDriver circuitPower flow
Owner:ANPEC ELECTRONICS CORPORATION
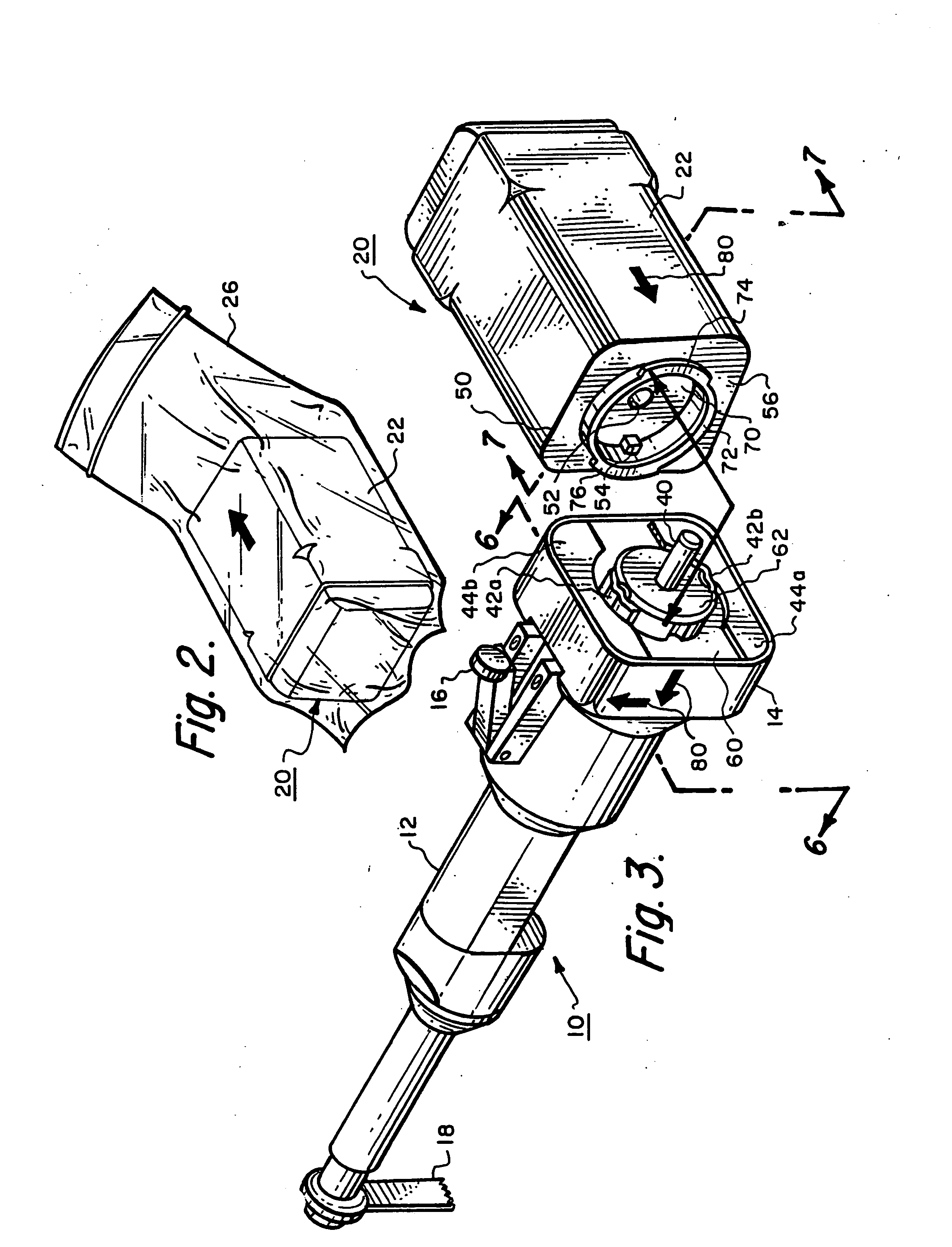
Powered Hand Tool
The invention relates to a hand tool for use with attachments. The hand tools of the invention may be used with attachments with various speed and torque requirements. Preferred hand tools comprise a body with a brushless DC motor and means. which control the energisation of the motor. In use the brushless DC motor of the preferred hand tool is electrically supplied to drive a power output means connected to said motor. Another preferred hand tool comprises a body with a motor contained therein, a void space between an internal surface of the body and at least a part of the motor, a fluid inlet port provided and a fluid outlet port provided in or on the body, and ducting means which provides a channel for fluid supplied via the fluid inlet port to and from the void space and then on to the fluid outlet port.
Owner:IBEX INDS
Brushless DC motor with bearings
A brushless DC motor including a rotor, a magnet provided to the rotor, a pair of bearings to rotatably support the rotor, a stator assembly that at least partly surrounds the rotor and magnet thereof and adapted to control movement of the rotor, and a bearing tube having an exterior surface and an interior surface that defines a tube interior. The stator assembly is provided along the exterior surface of the tube and the bearings are provided along the interior surface of the tube to support the rotor and magnet within the tube interior. The motor has sample application for use in PAP devices for delivery of positive airway pressure therapy for users or patients.
Owner:RESMED MOTOR TECH
Cordless surgical handpiece with disposable battery; and method
A surgical procedure is disclosed utilizing a cordless surgical handpiece powered from a sterile battery pack that contains a battery in condition for immediate use without further charging or sterilization. The battery chemistry is based upon lithium / manganese dioxide, and the battery after a single use may be disposed of into non-hazardous waste. The compact surgical handpiece has a brushless DC motor and a manually operated external trigger for activating and controlling the motor operations. Interengaging sets of contacts on the handpiece and battery are adapted to become lockingly and conductively interengaged upon rotation of the battery pack relative to the handpiece, in a manner that rapidly achieves correct alignment of the parts and also ensures stable mechanical attachment and support during the surgical procedure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
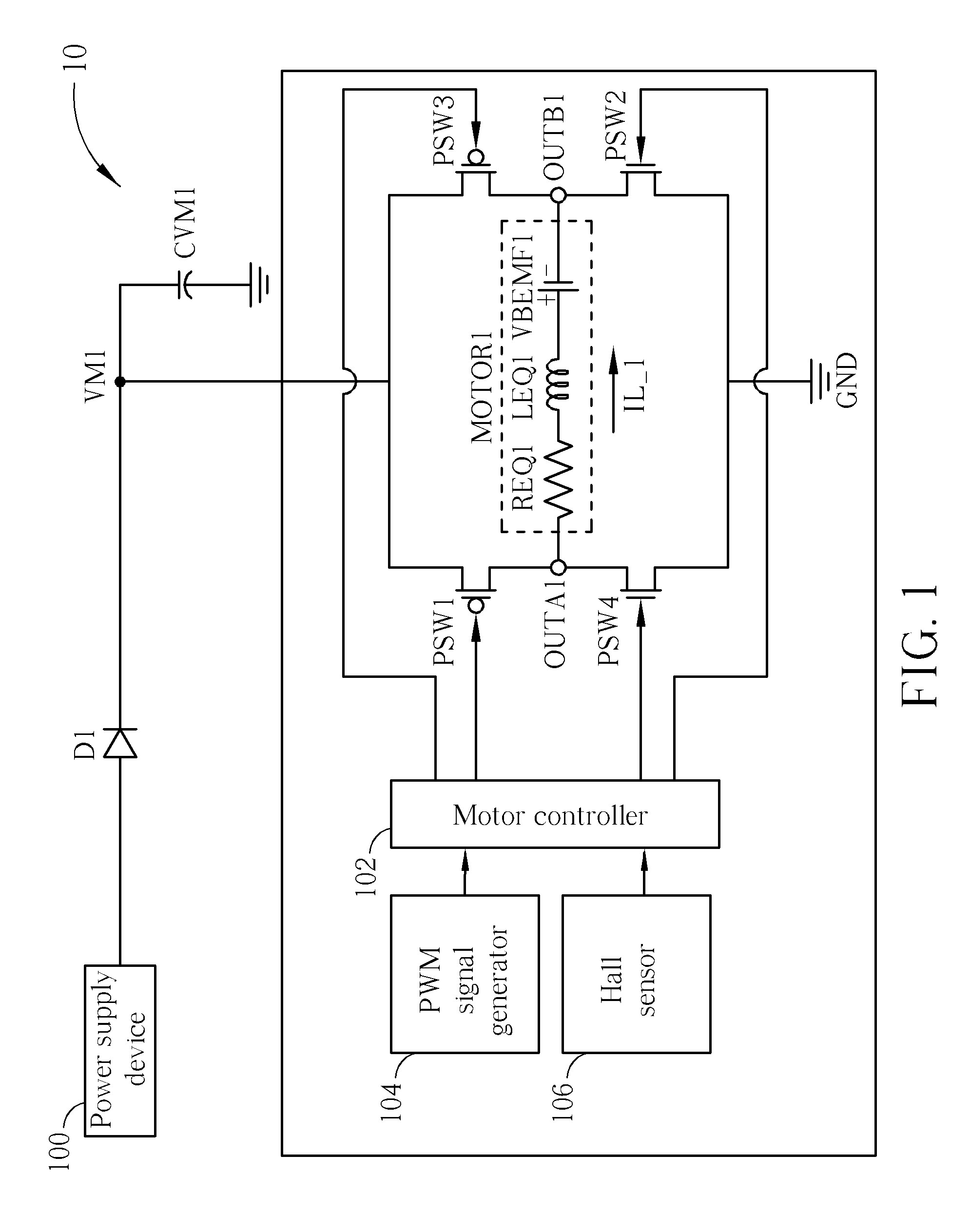
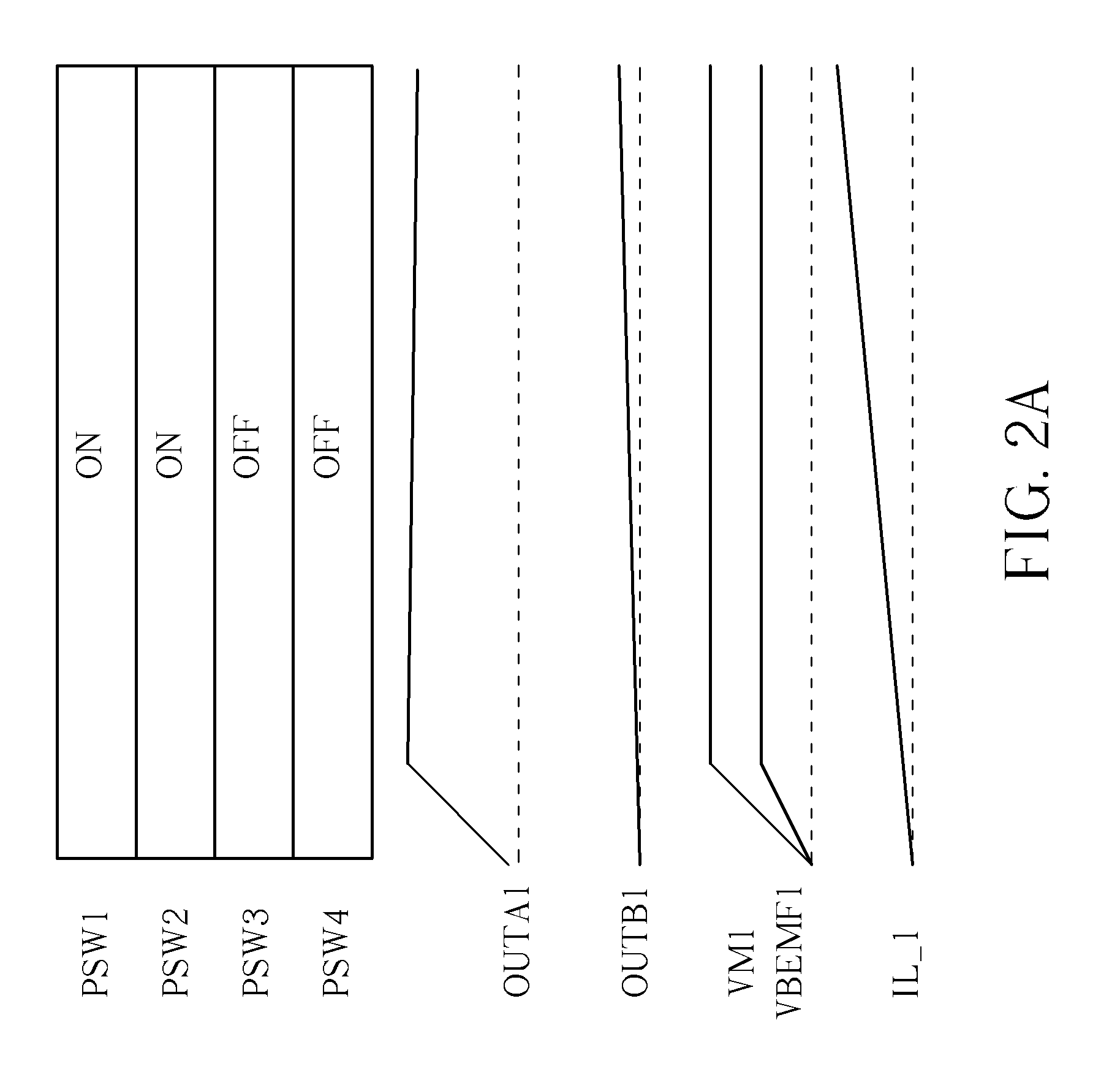
Control circuit for a DC motor
ActiveUS9385640B2Inhibit currentSingle motor speed/torque controlField or armature current controlControl circuitDC motor
A control circuit for a DC motor, has: a first and second input ports for connection to a DC source; a H-bridge driving circuit, having first and second switches connected in series between the input ports, and third and fourth switches connected in series between the input ports, a first output port between the first and second switches and a second output port between the third and fourth switches, and a shunt circuit and / or a blocking circuit. The motor is connected between the first and second output ports. The shunt circuit is connected between the first second output ports and has a resistance that will decrease in response to BEMF generated by the motor. The blocking circuit is connected in series with the motor between the output ports and has a resistance that increases in response to BEMF generated by the motor.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC SA
Portable Arm Exoskeleton for Shoulder Rehabilitation
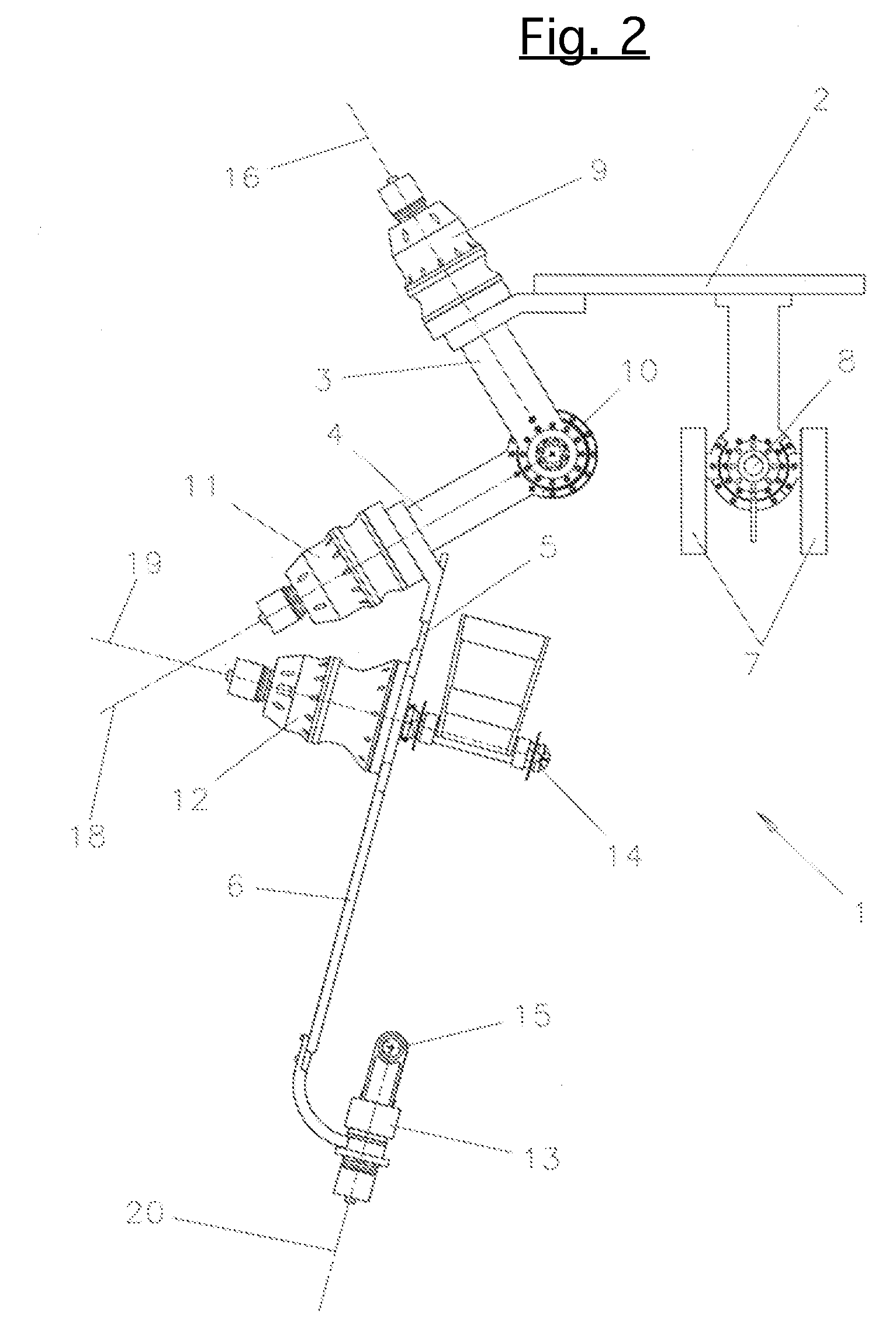
The present invention relates to an exoskeleton interface apparatus that parallels human arm motion and is comprised of a serial assemblage of five powered linkages and joints based at a rigid support structure worn on the torso of the human subject. Such apparatus generates shoulder rotation using three orthogonal revolute joints mounted on serial linkages encompassing and intersecting at the anatomical glenohumeral joint. Elevation of the shoulder joint is articulated using a link member driven by a single revolute joint mounted in the torso structure. Passive adjustable linkages are used to match variation in anatomical forearm length, upper arm length, and scapula-to-glenohumeral radius. A plurality of integrated dc motor / harmonic drive transmission modules is co-located on adjoining linkages to power the joints. Force is exchanged with the human at the handgrip and elbow brace, and reacted to the torso structure via the base attachment. The present invention is applicable in particular to rehabilitation of the shoulder.
Owner:CARIGNAN CRAIG R +1
Chronic performance control system for rotodynamic blood pumps
InactiveUS7645225B2Simple control circuitIncrease control flexibilityDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlMicrocontrollerMotor speed
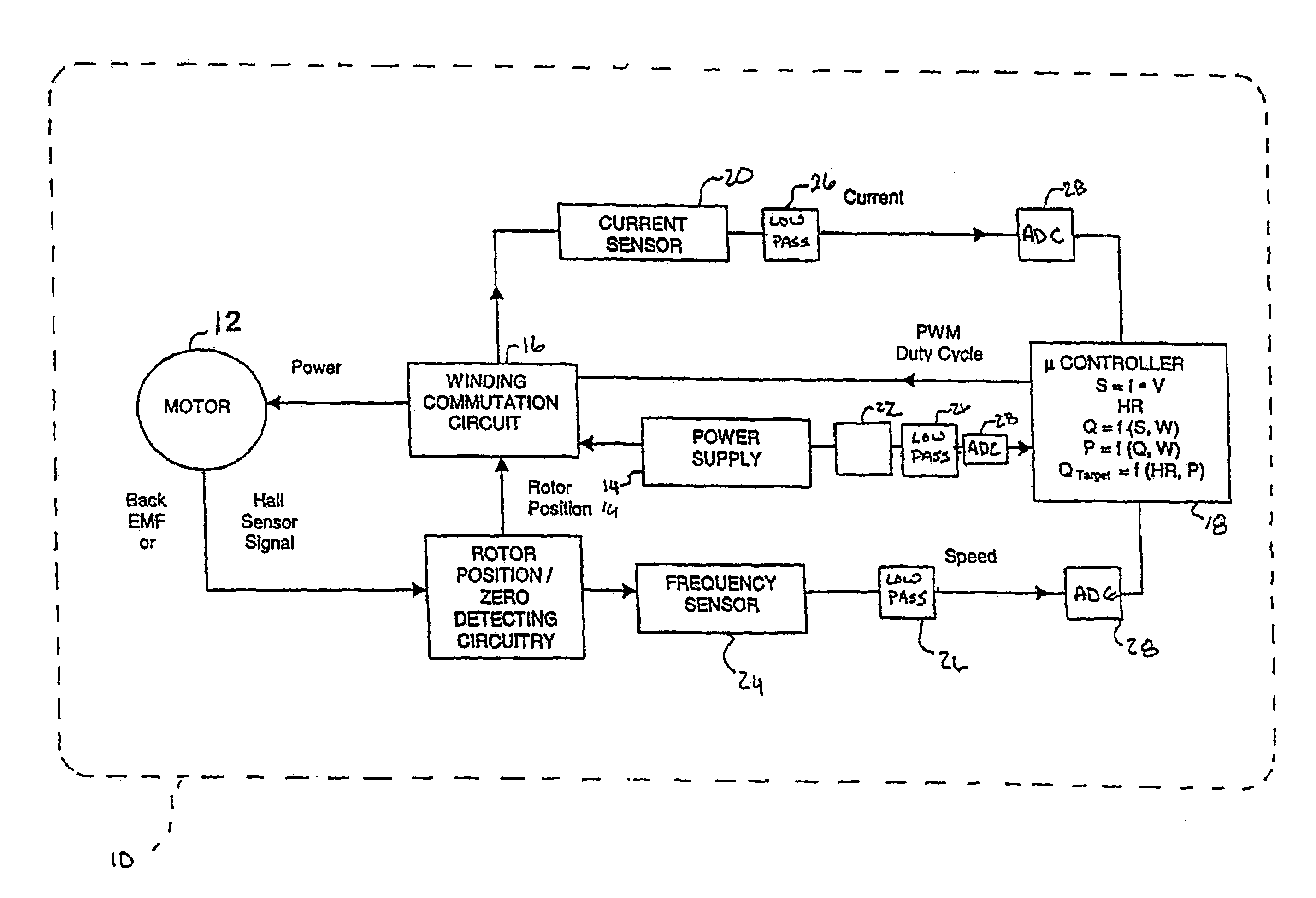
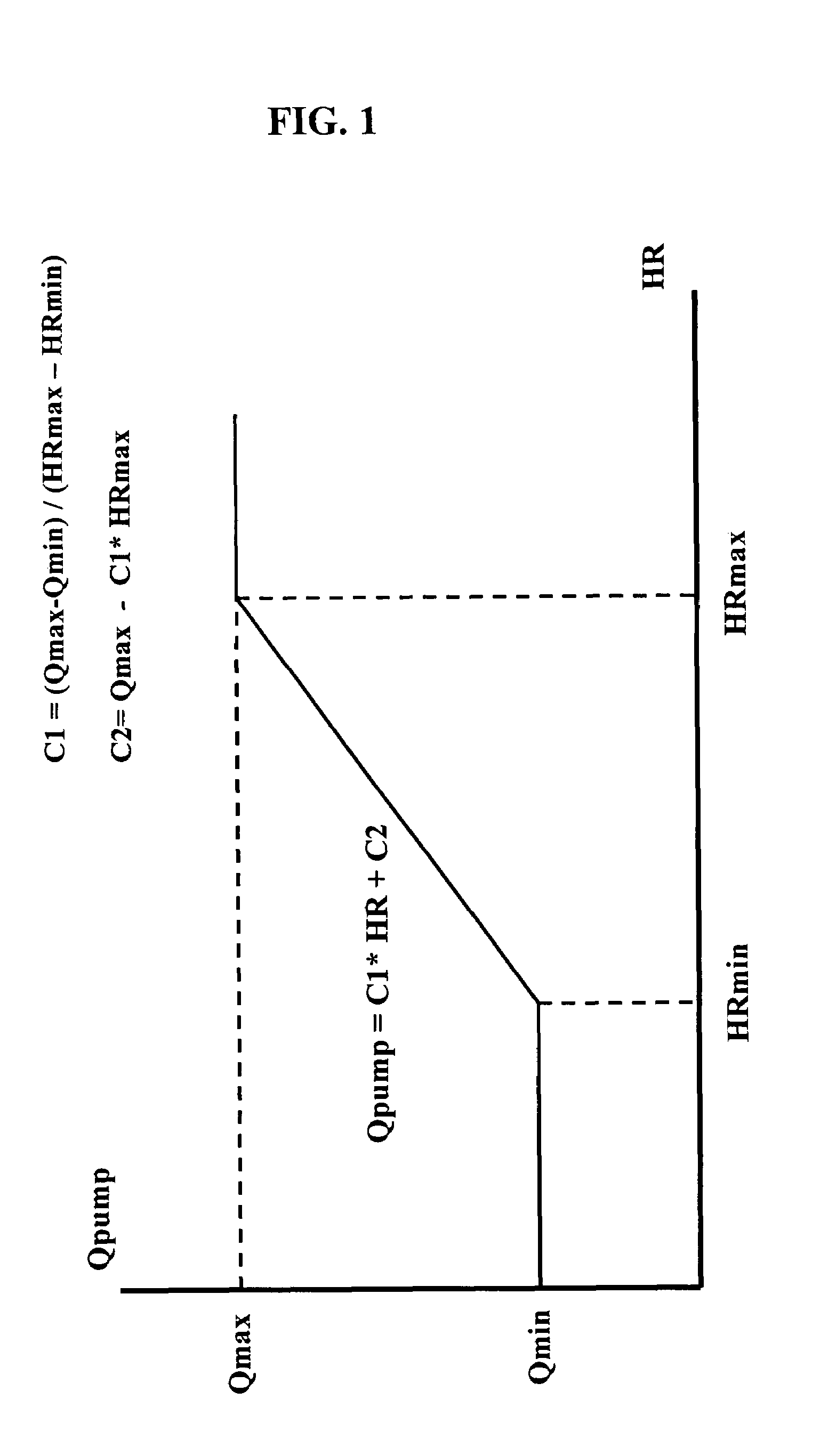
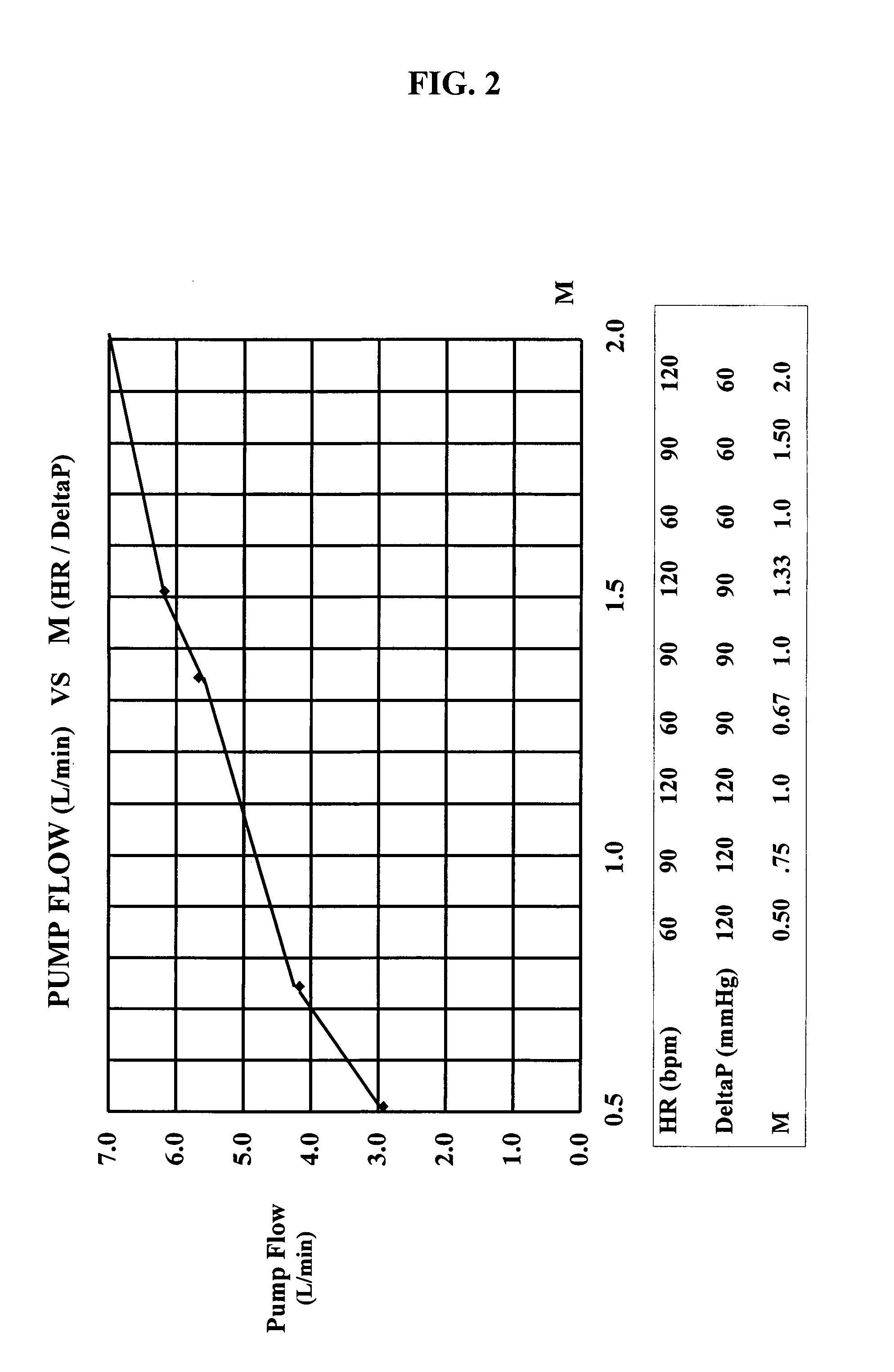
In a left ventricular assist device (LVAD) a rotodynamic blood pump (10) is powered by a brushless DC motor (12). A power supply (14) supplies power to the motor (12). Three feedback channels, one for each of voltage, current, and motor speed lead to a microcontroller or microprocessor (18). The three feedback waveforms are analyzed, and from these waveforms, motor input power, patient heart rate, current pump flow rate, and systemic pressure are determined. The microprocessor (18) then calculates a desired flow rate proportional to the patient heart rate. The microprocessor communicates a new power output to a commutation circuit (16), which regulates power to the motor (12). The pump (10) also includes safety checks that are prioritized over desired pump flow. These include prevention of ventricular suction, low pulsatility, minimum and maximum pump speed, minimum speed-relative pump flow, minimum absolute pump flow, minimum and maximum motor input power.
Owner:MEDVEDEV ALEXANDER +2
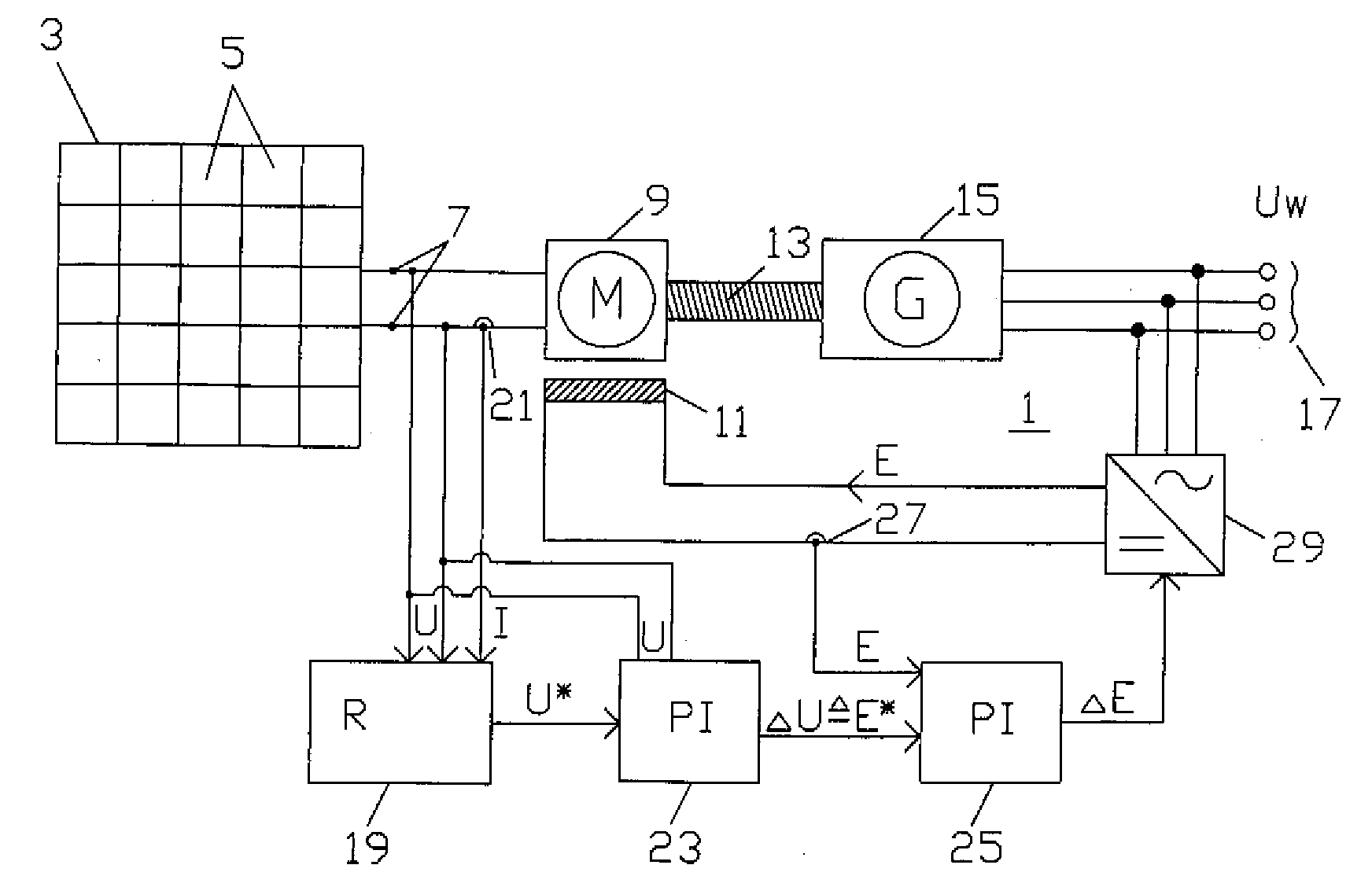
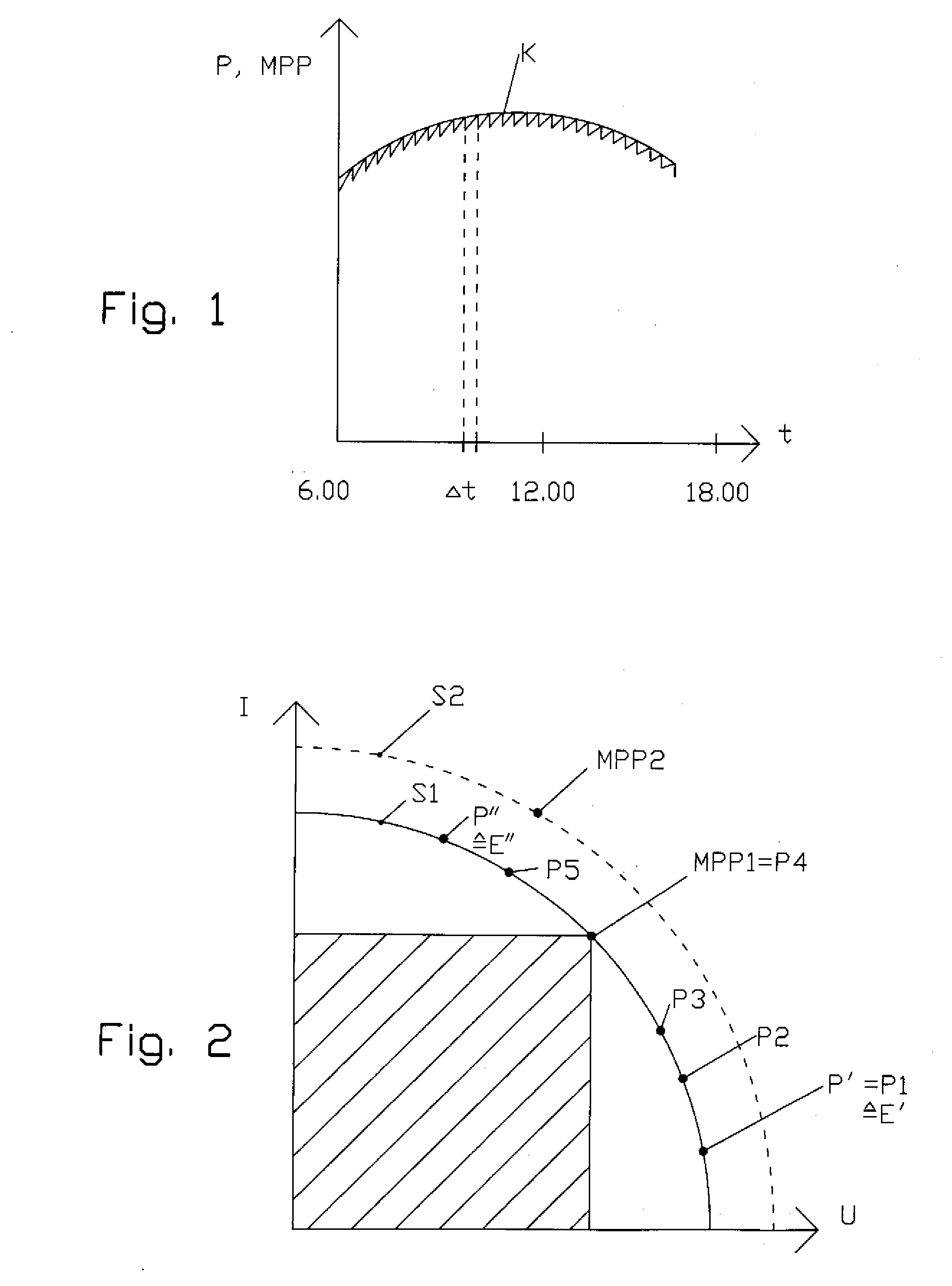
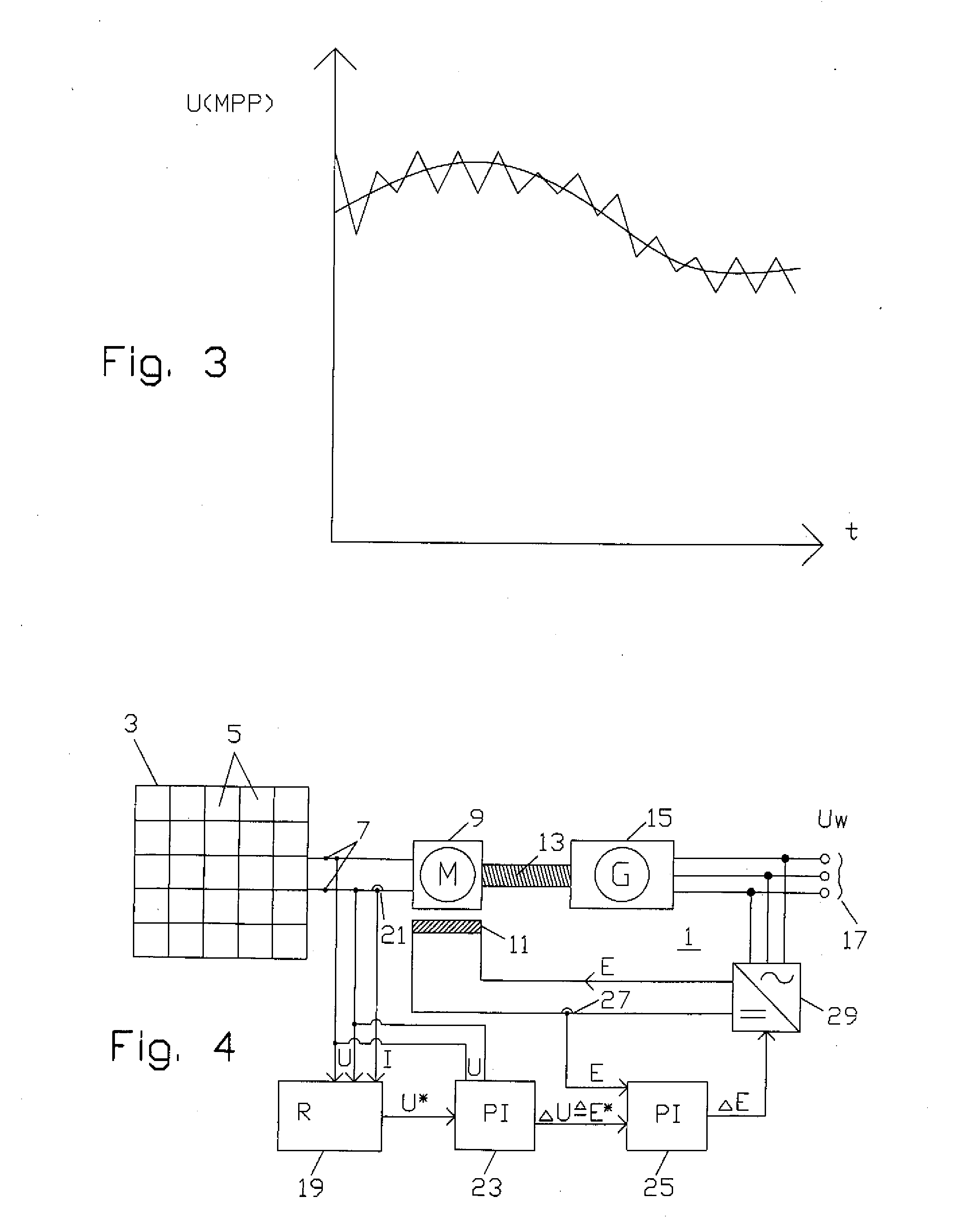
Photovoltaic system and method for operating a photovoltaic system
InactiveUS20070290636A1Easy to useReduce maintenance costsBatteries circuit arrangementsMultiple dynamo-motor startersExcitation currentEngineering
A photovoltaic system includes a plurality of photovoltaic modules and a DC motor connected to a three-phase generator driven by a shaft. The three-phase generator is connected to a power mains. The electric power supplied to the DC motor by the plurality of photovoltaic modules is repeatedly measured and adjusted, by changing an external excitation current of the DC motor, to the peak power attainable at the current ambient temperature and the current incident solar radiation intensity. The peak power is preferably determined by incrementally changing the excitation current in predetermined time intervals, until the supplied electric power produces a power level which can be regarded as the peak power.
Owner:ADENSIS
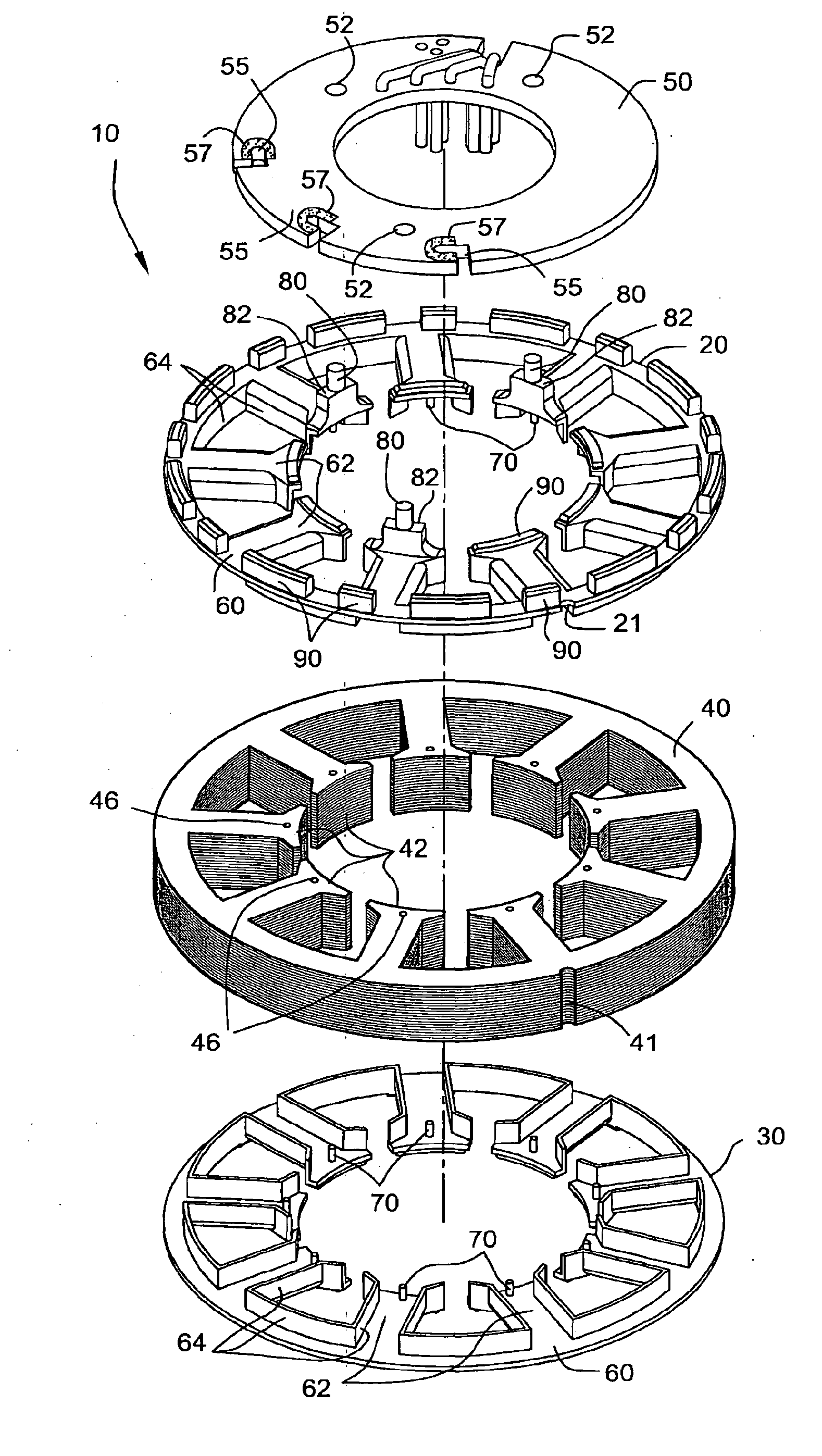
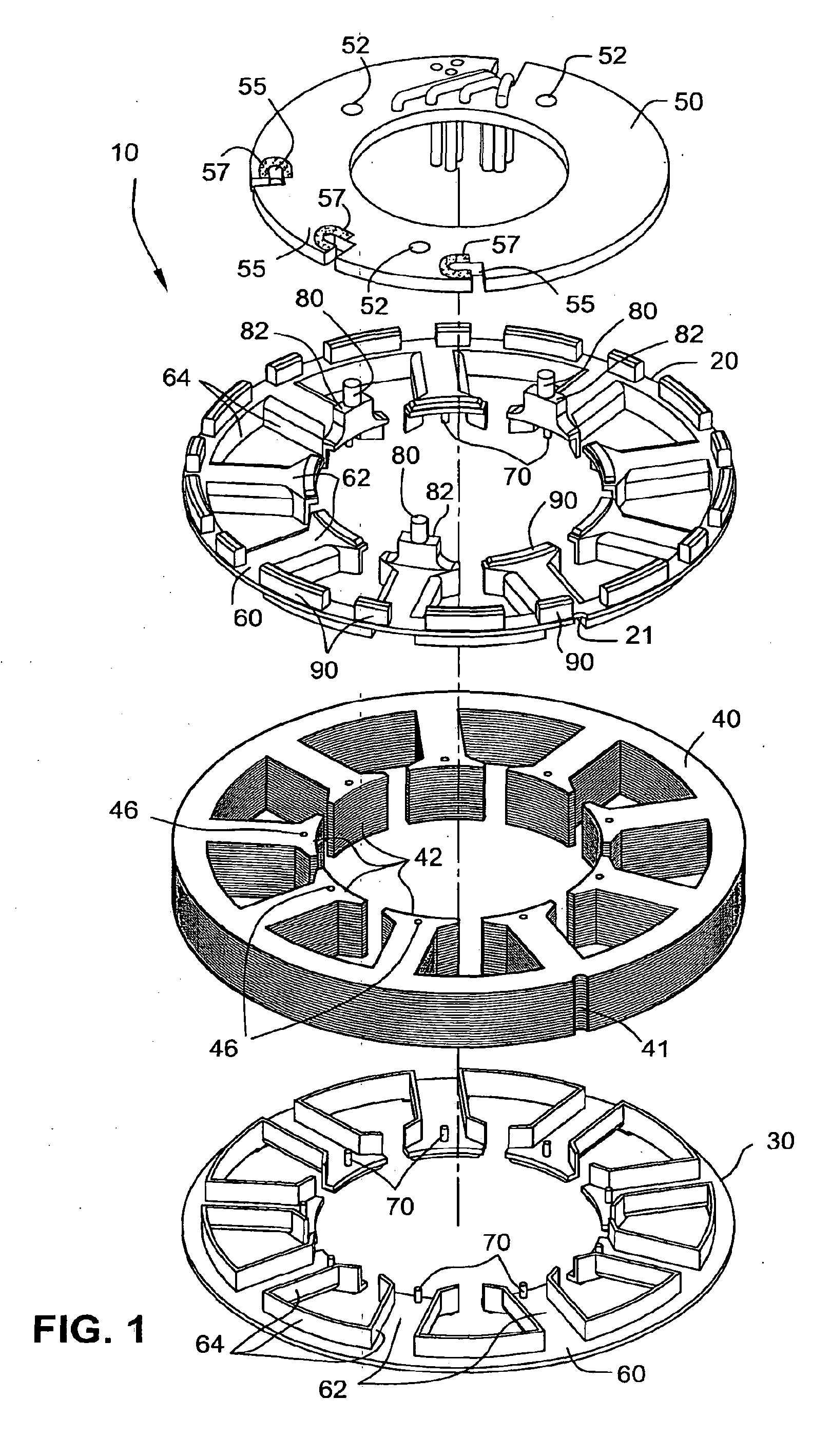
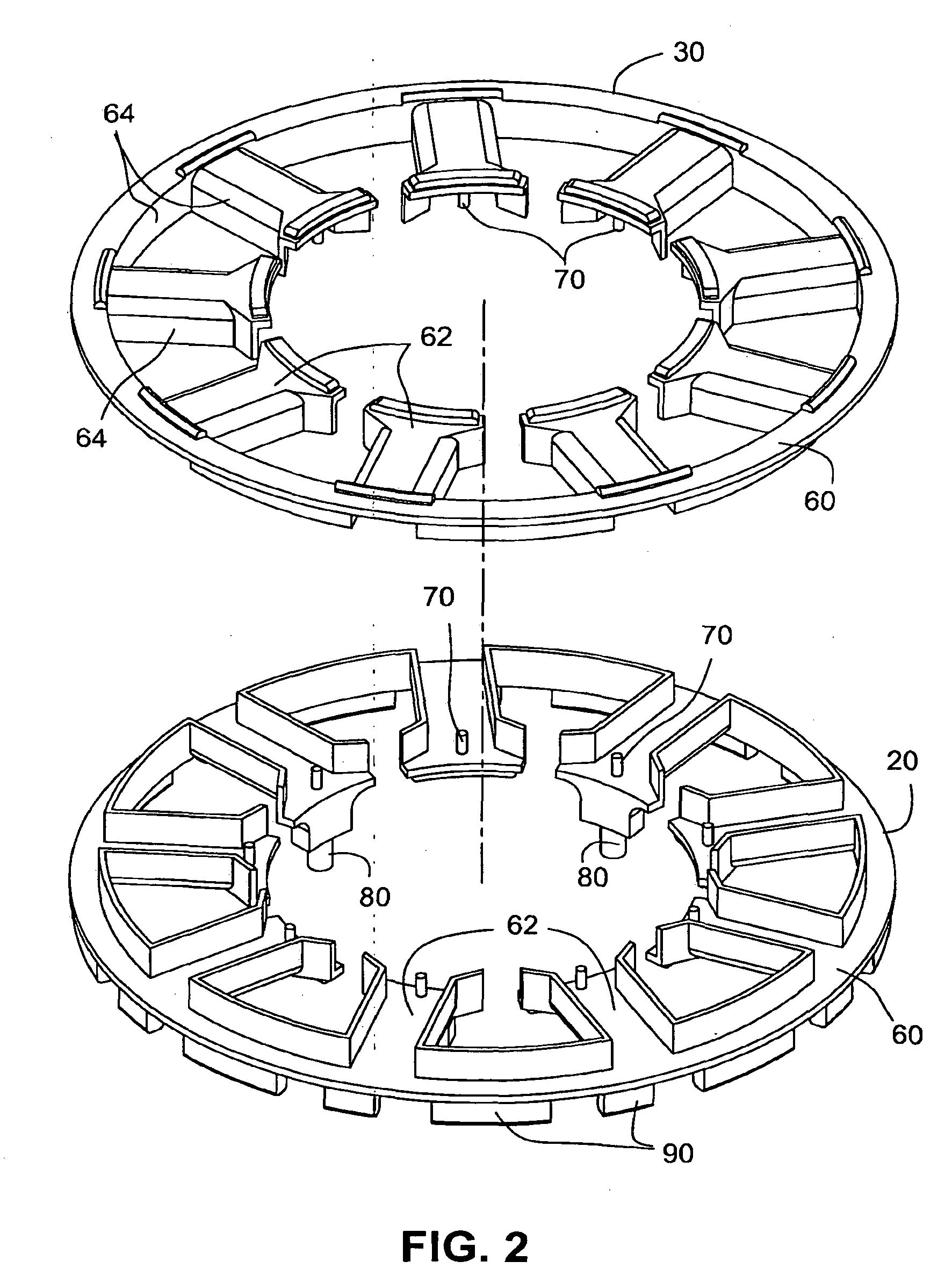
Insulator for stator assembly of brushless DC motor
ActiveUS20090324435A1Precise positioningSynchronous generatorsWindings insulation shape/form/constructionEngineeringDC motor
An insulator for a stator assembly includes at least a first insulator adapted to be mounted to the stator core and structured to insulate the stator core from the coils. The at least one insulator includes structure to perform at least one additional function. For example, the structure may include a support member to support and / or locate the PCBA on the stator core, a wire guide to guide cross-over wires that form a connection between coils, and / or positioning structure to precisely position the PCBA with respect to the coils.
Owner:RESMED MOTOR TECH
Controller and power source for implantable blood pump
Methods and apparatus for controlling the operation of, and providing power for and to, implantable ventricular assist devices which includes a pump employing a brushless DC motor-driven blood pump, are disclosed. In one embodiment, a control system for driving an implantable blood pump is provided. The digital processor is responsive to data associated with the operation of the pump received at the data transfer pump, and from program data stored in the memory, (i) to determine therefrom, the identity of the pump, (ii) to determine therefrom, electrical characteristics and features of the identified pump, and (iii) to adaptively generate and apply to the data port, control signals for driving the identified pump.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Environmental control and power system
InactiveUS20080161974A1Decrease external thermal signatureHeat dissipationStatic/dynamic balance measurementSpeed sensing governorsControl mannerElectric power system
A self-contained environmental control and power system (ECAPS) unit including an HVAC system with at least one variable-speed compressor driven by a DC motor, wherein the HVAC system is adapted to condition air and output the conditioned air and a variable-speed diesel engine connected to a generator. The generator is configured to vary in speed so as to output AC power at a variable frequency. The unit includes a rectification assembly which transforms the AC power from the generator and / or external AC power to DC power, and an inverter assembly which transforms the DC power to an export AC power. The ECAPS unit directs the DC power to the DC motor to drive the variable speed compressor and varies, in a controlled manner, at least one parameter of the outputted conditioned air from the HVAC system.
Owner:GLACIER BAY
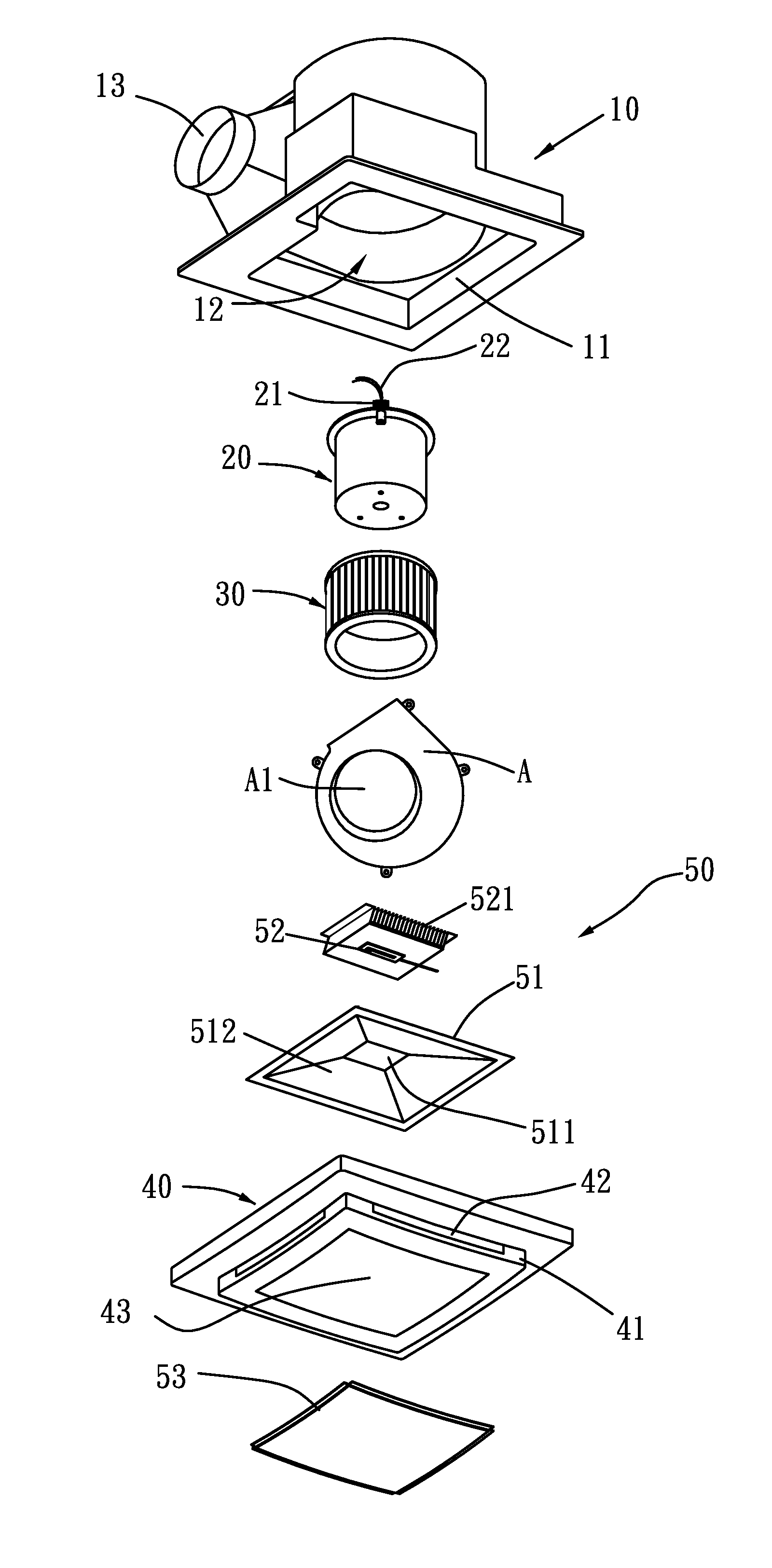
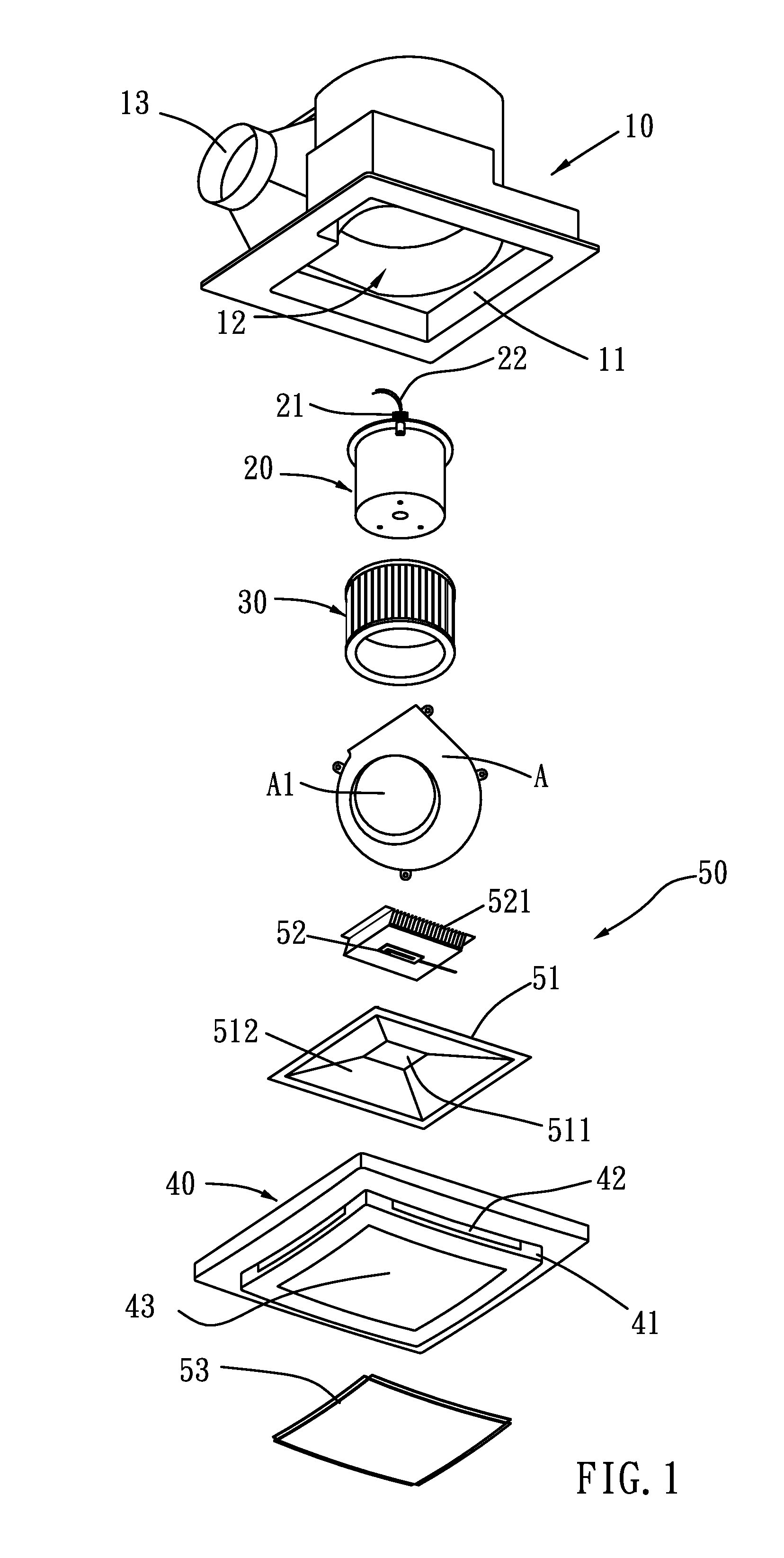
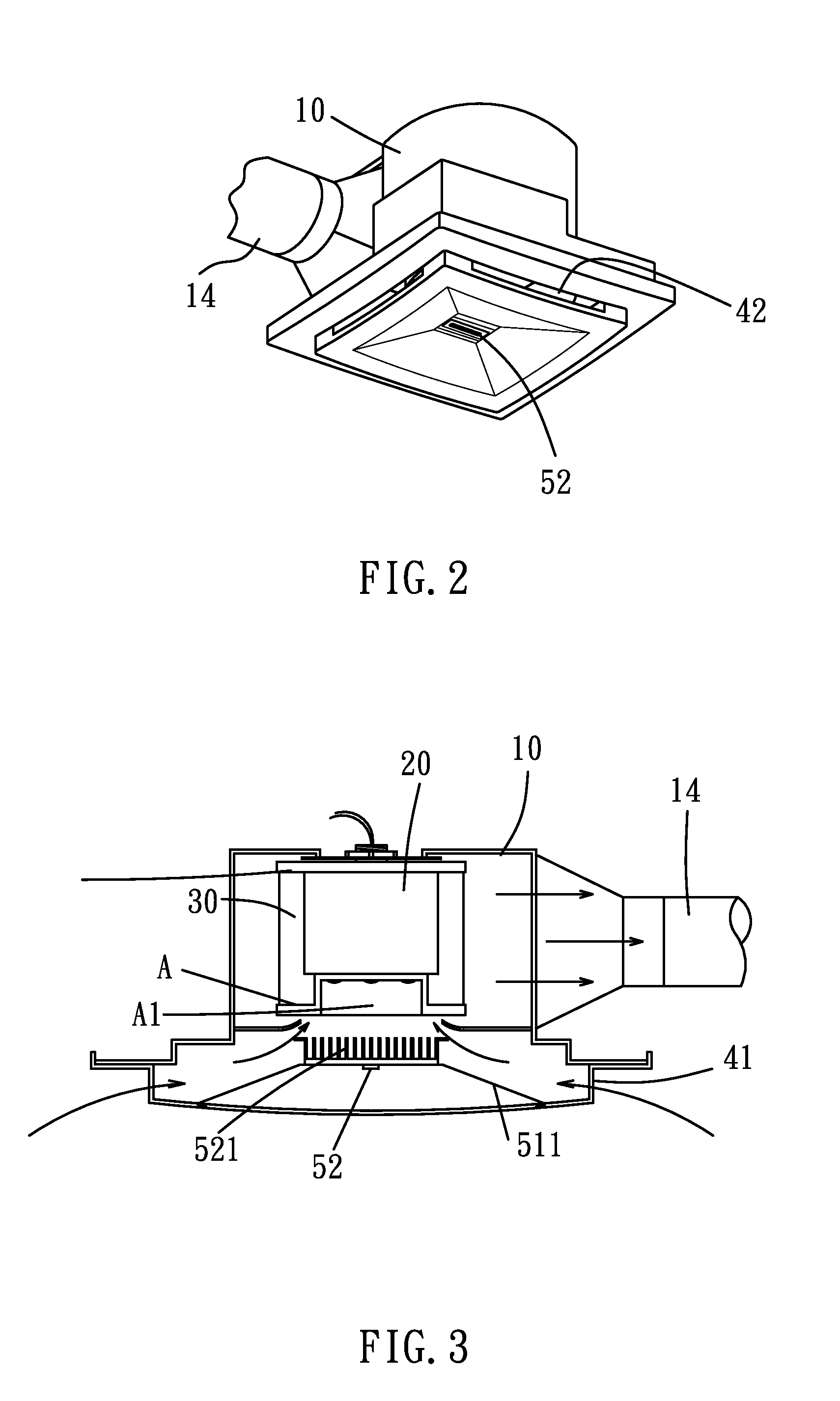
External rotor brushless DC motor driven exhaust fan
An external rotor brushless DC motor driven exhaust fan is provided with an external rotor brushless DC motor and a LED illumination device in its inner space. The uses of the external rotor brushless DC motor and the low voltage driven LED illumination device enable the exhaust fan to have the functions of air exhausting and illumination, and to reduce the power consumption and noise. On top of that, the reduction in power consumption of the external rotor brushless DC motor can lower the carbon emission of the exhaust fan, so the exhaust fan is not only environmentally friendly but also energy saving.
Owner:HSIEH TE HSUAN
Method and apparatus for controlling brushless DC motors in implantable medical devices
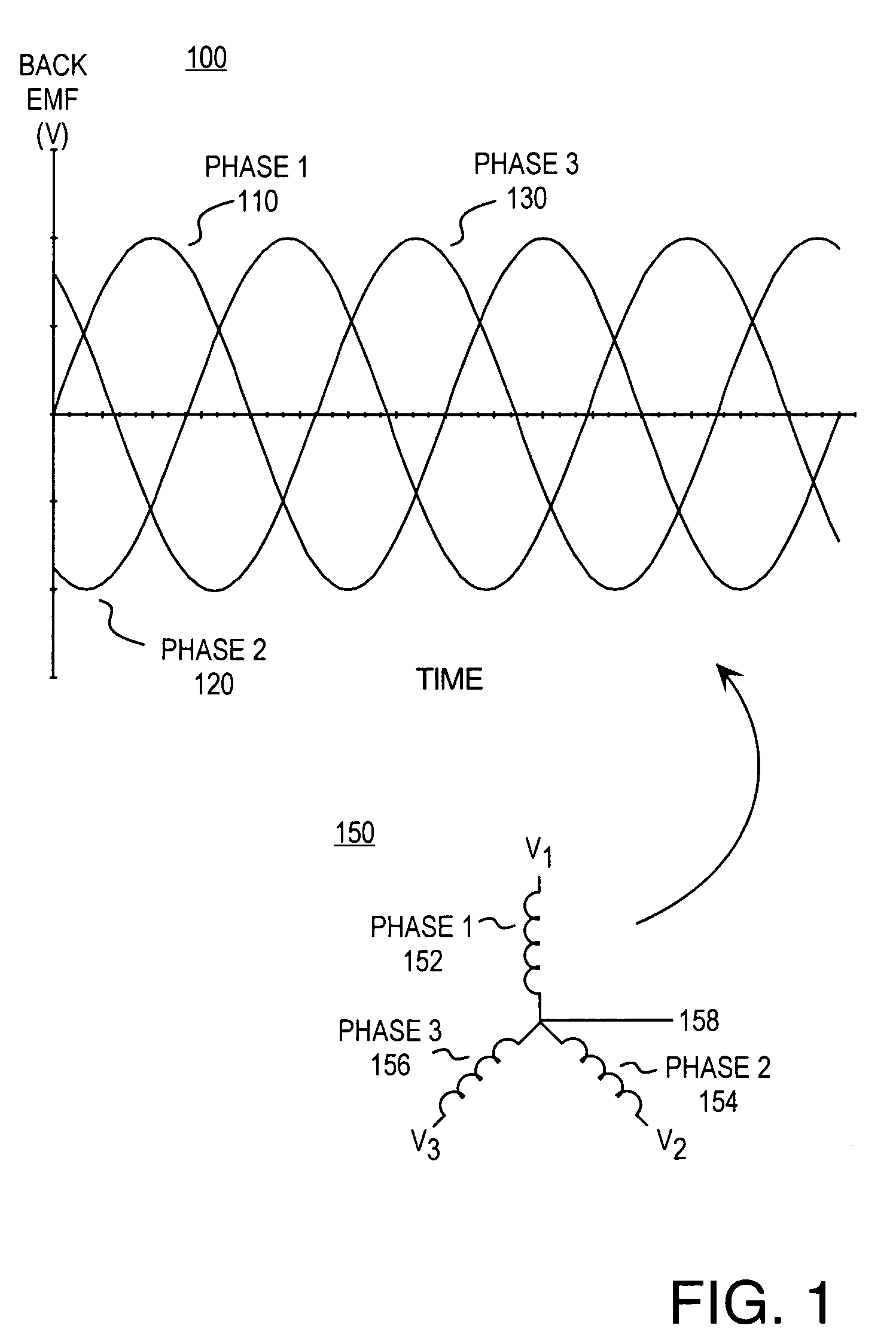
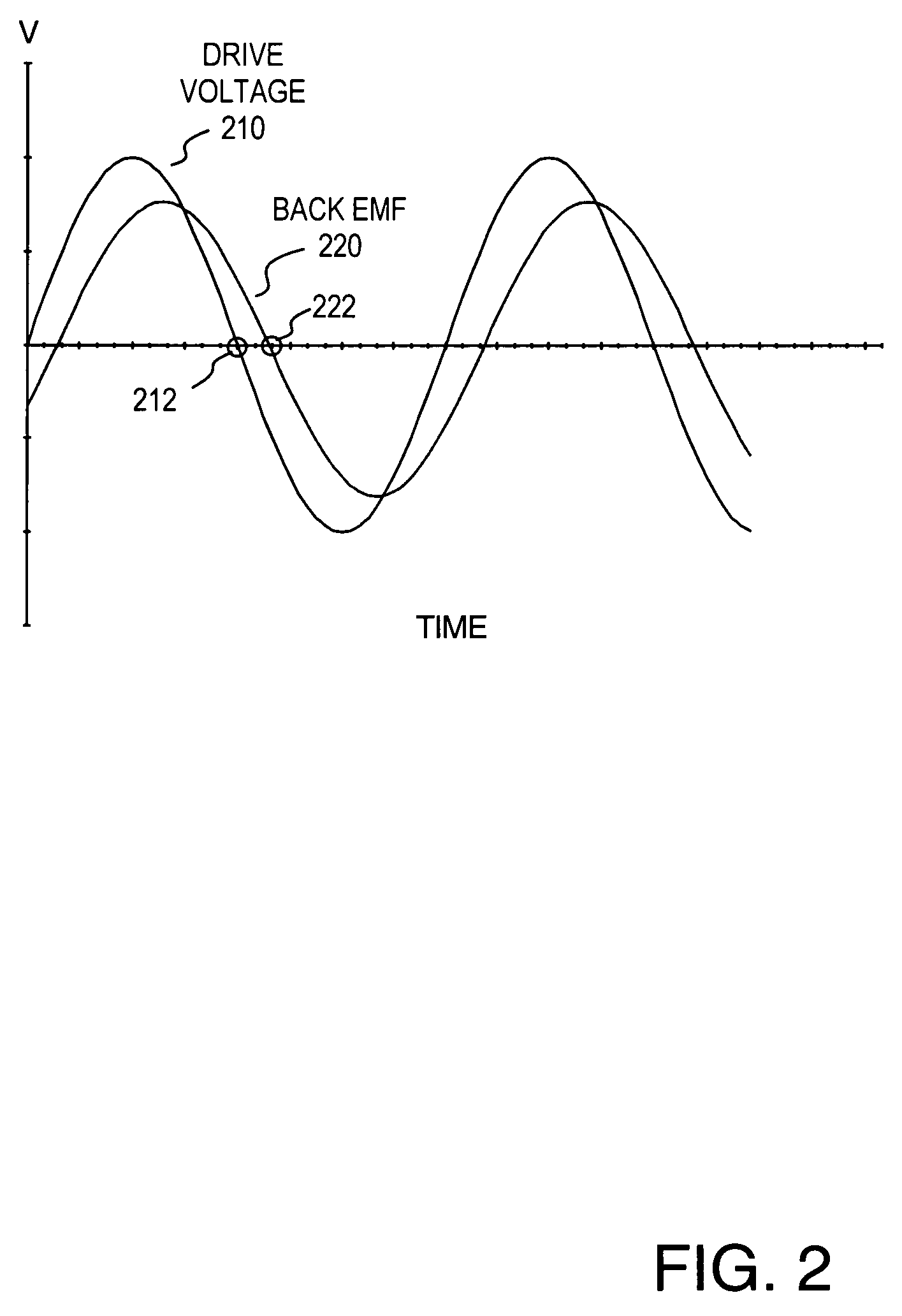
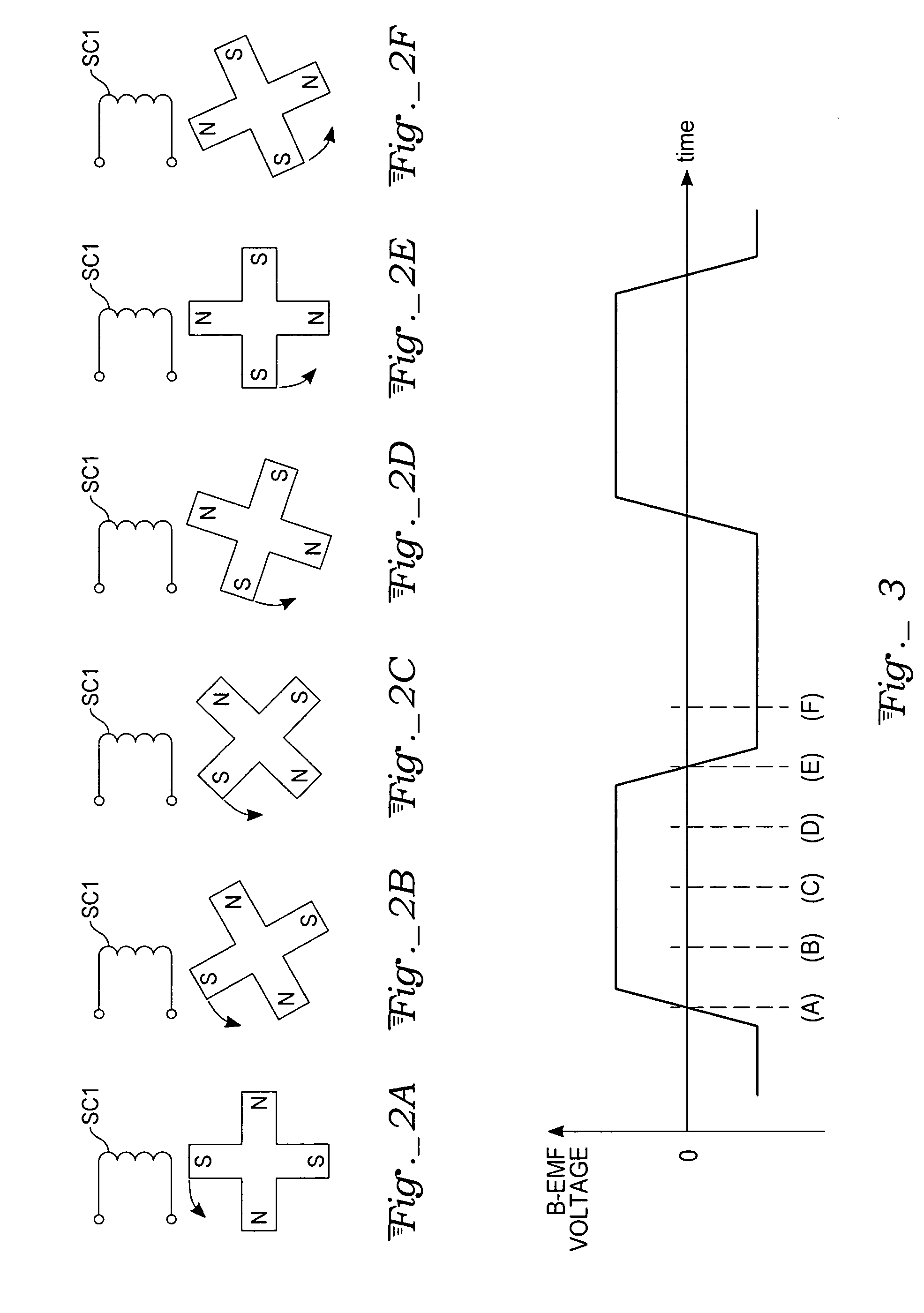
Methods and apparatus for controlling a polyphase motor in implantable medical device applications are provided. In one embodiment, the polyphase motor is a brushless DC motor. The back emf of a selected phase of the motor is sampled while a drive voltage of the selected phase is substantially zero. Various embodiments utilize sinusoidal or trapezoidal drive voltages. The sampled back emf provides an error signal indicative of the positional error of the rotor. In one embodiment, the sampled back emf is normalized with respect to a commanded angular velocity of the rotor to provide an error signal proportional only to the positional error of the motor rotor. The error signal is provided as feedback to control a frequency of the drive voltage. A speed control generates a speed control signal corresponding to a difference between a commanded angular velocity and an angular velocity inferred from the frequency of the drive voltage. The speed control signal is provided as feedback to control an amplitude of the drive voltage. In one embodiment, an apparatus includes a brushless DC motor and a commutation control. The commutation control provides a commutation control signal for a selected phase of the motor in accordance with a sampled back electromotive force (emf) of that phase. The back emf of the phase is sampled only while the corresponding drive voltage for the selected phase is substantially zero, wherein a frequency of a drive voltage of the motor is varied in accordance with the commutation control signal.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
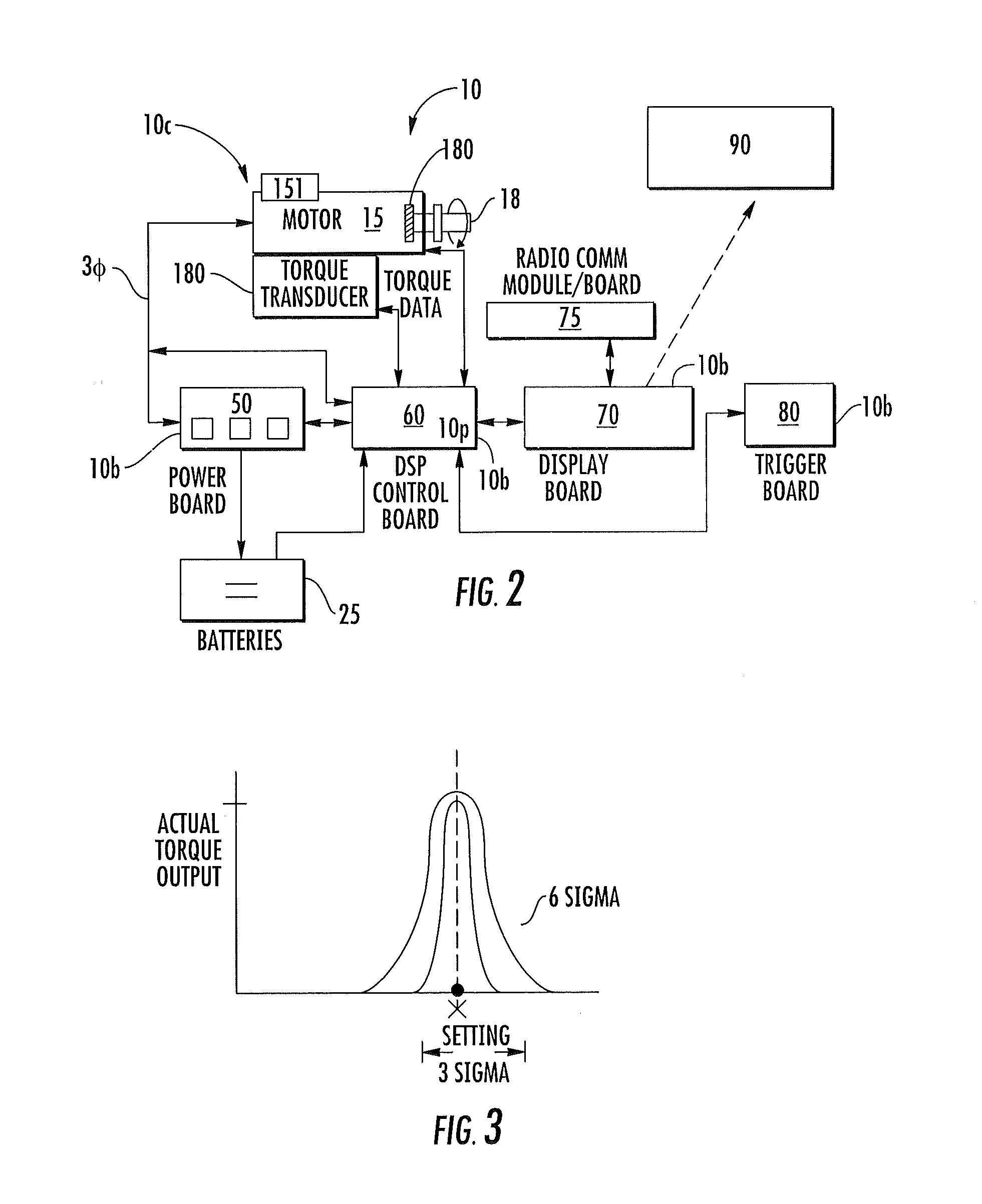
Precision-fastening handheld cordless power tools
ActiveUS20130193891A1Total current dropMotor/generator/converter stoppersSingle motor speed/torque controlMotor speedOn board
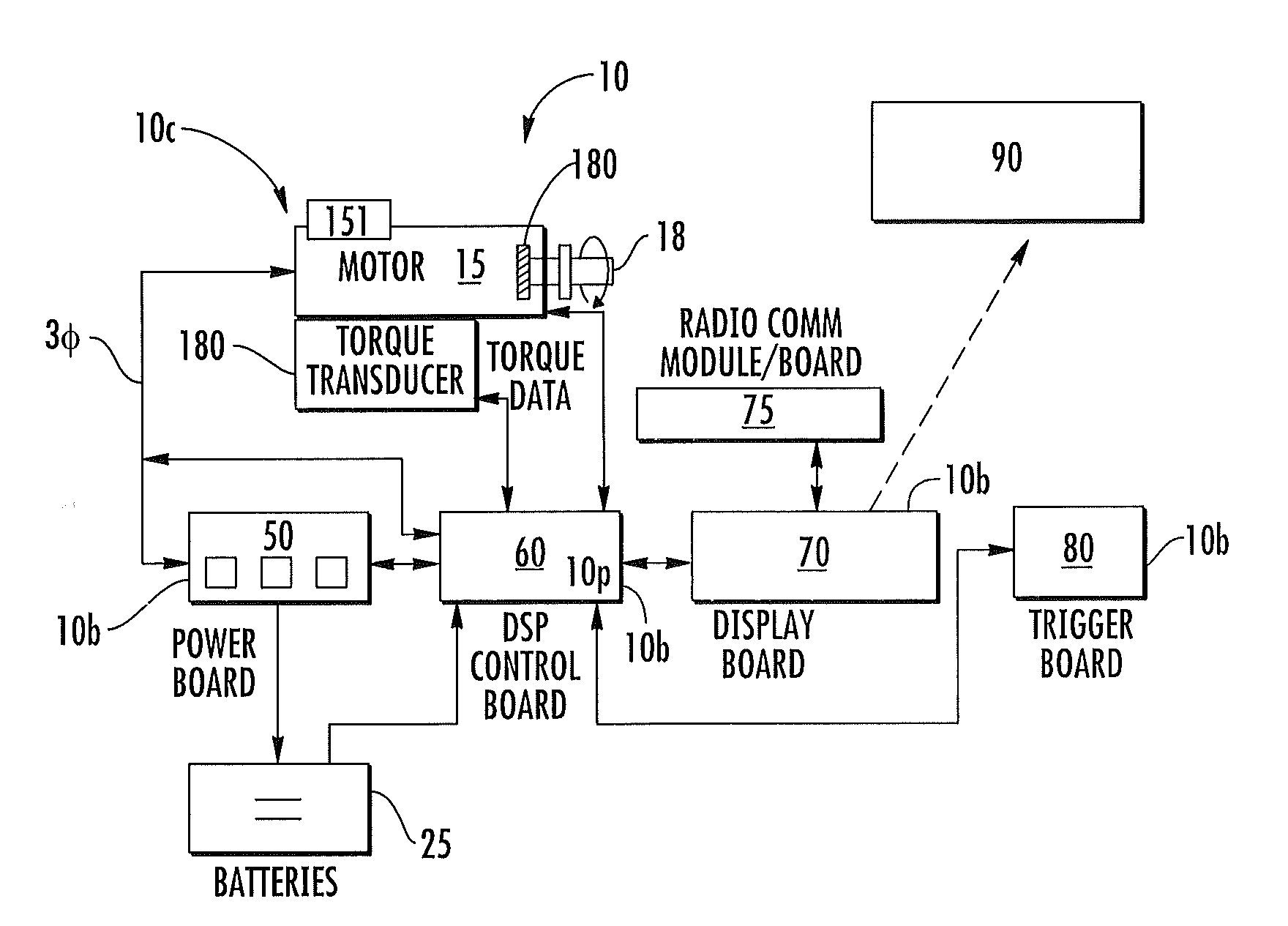
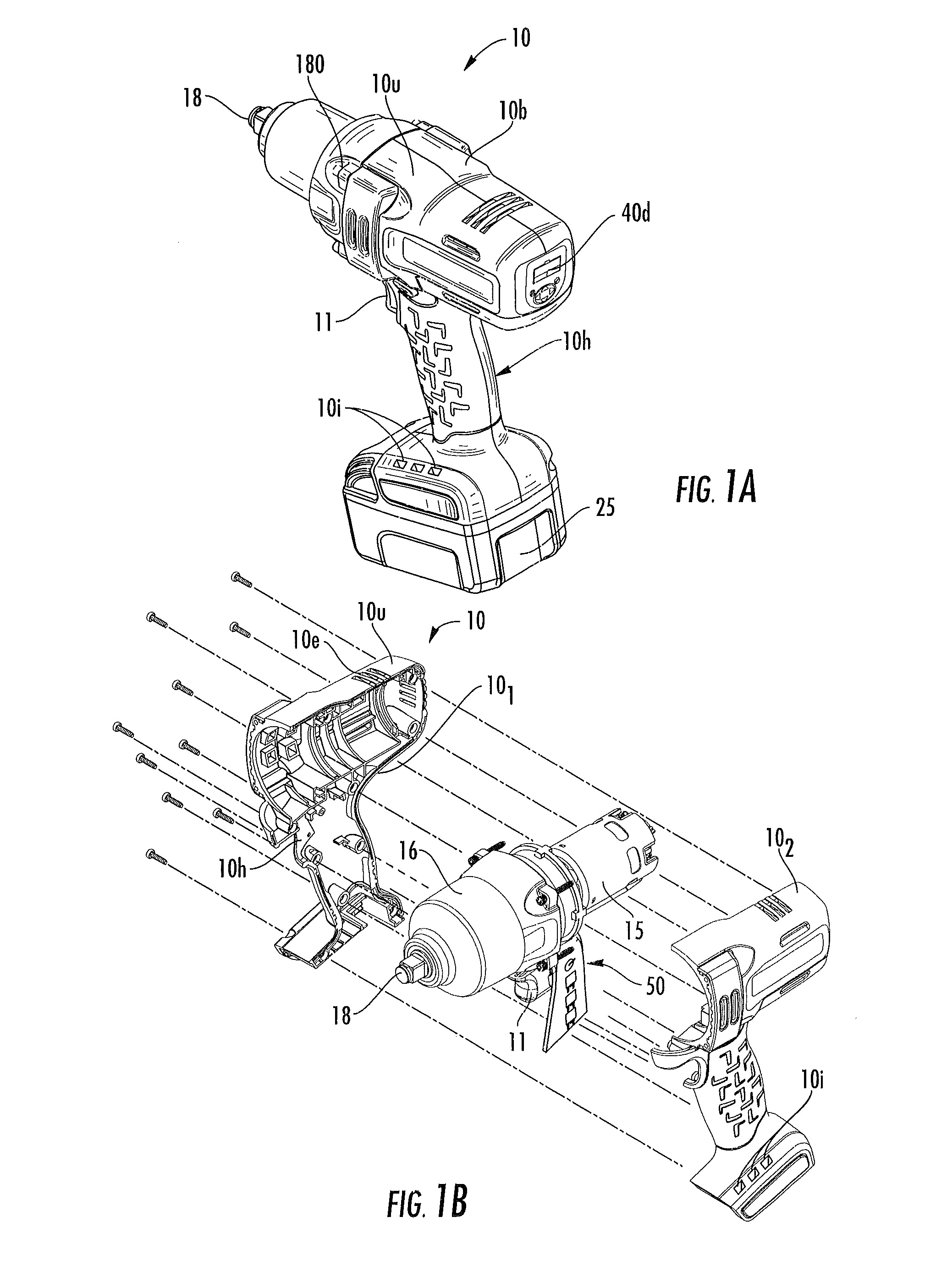
Cordless power tools include a pistol housing having an upper portion that merges into a downwardly extending handle, a DC motor residing in the upper portion of the housing, the DC motor having a rotor that drives an output shaft; a torque transducer on board the tool in communication with the output shaft; and a dynamic motor control circuit residing in the housing in communication with the motor and torque transducer. The dynamic motor control circuit includes a Kelvin resistor in communication with the motor for measuring motor current and digital hall switches in communication with the motor for measuring motor speed. The motor current can vary by at least 100 A during operation.
Owner:INGERSOLL RAND IND U S INC
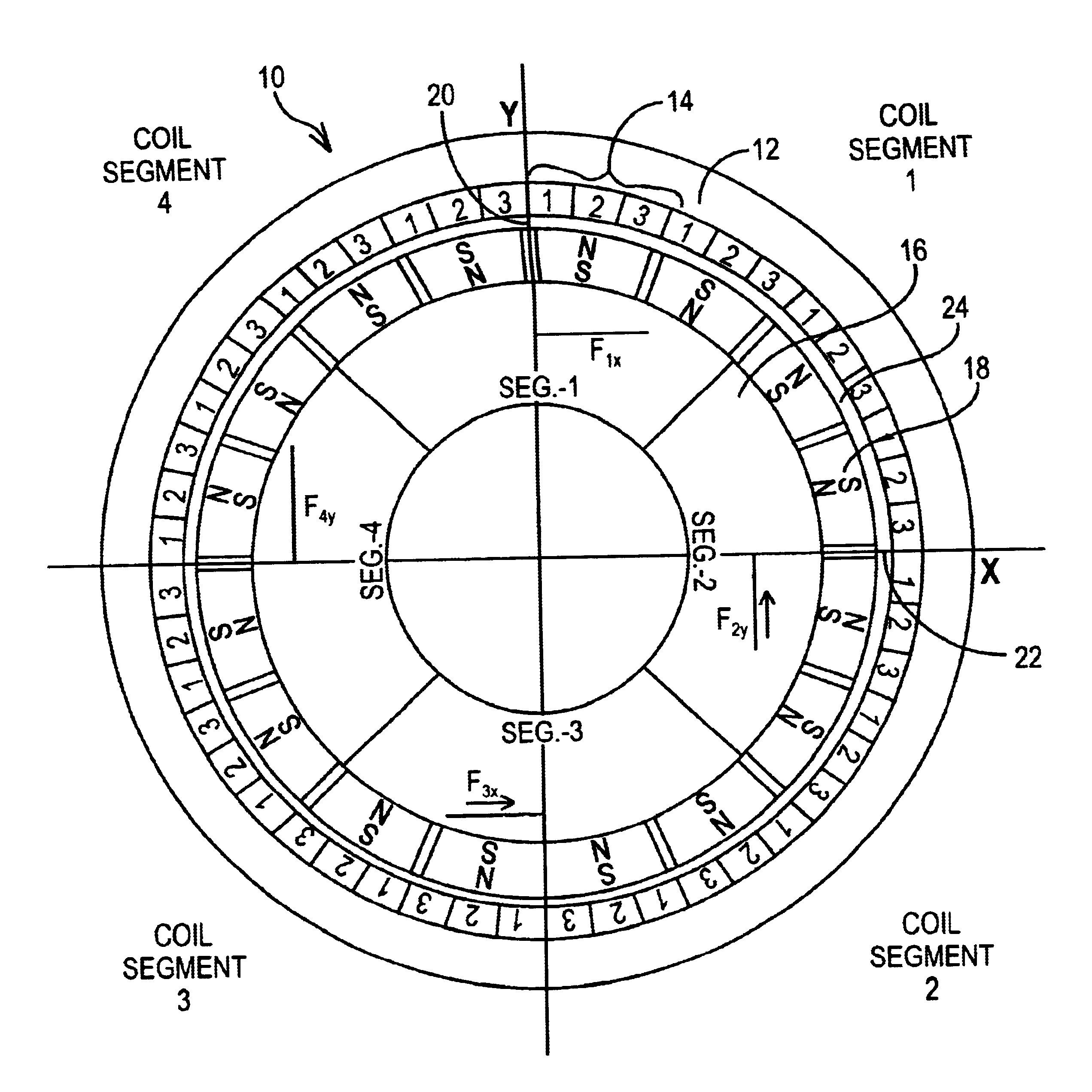
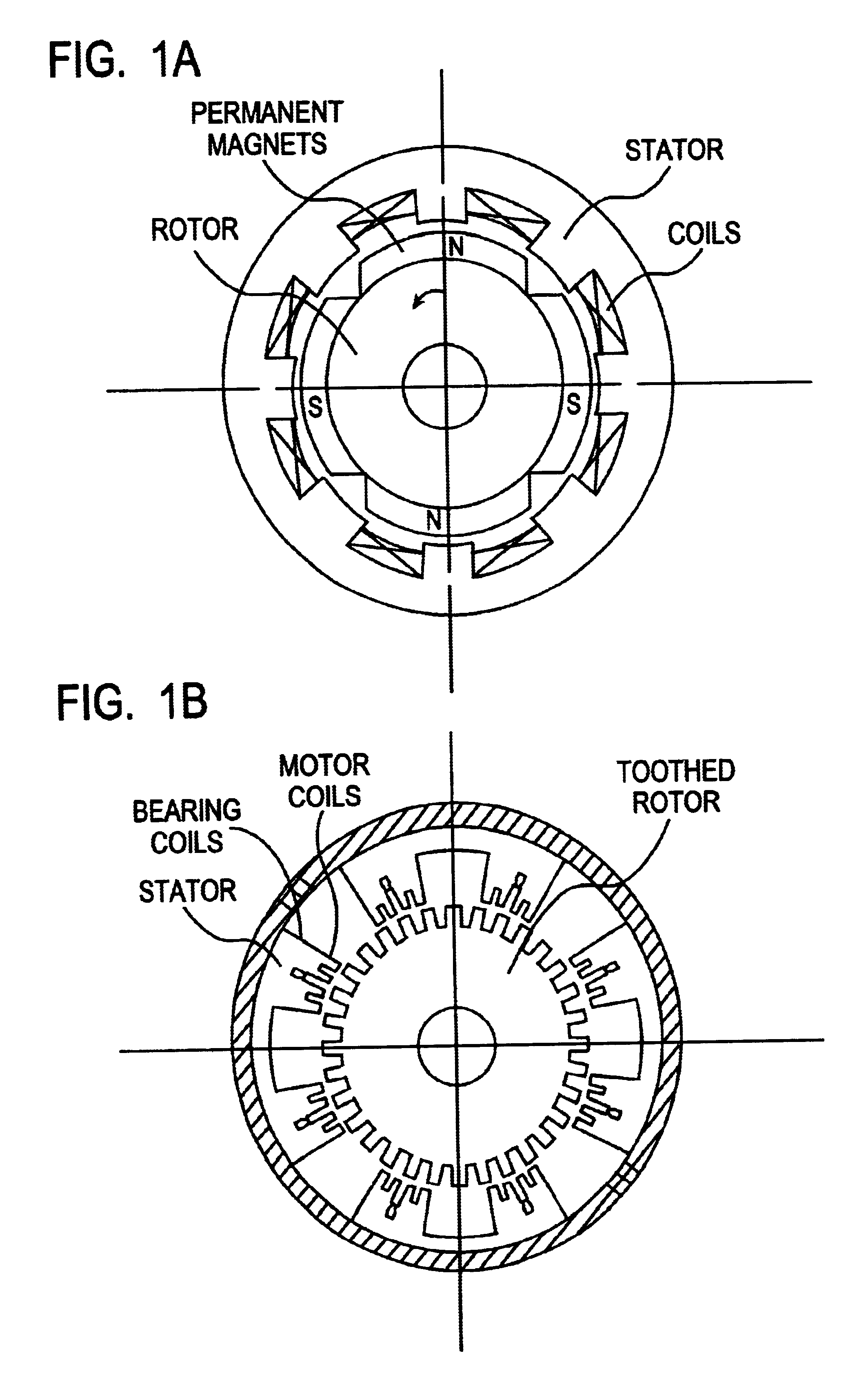
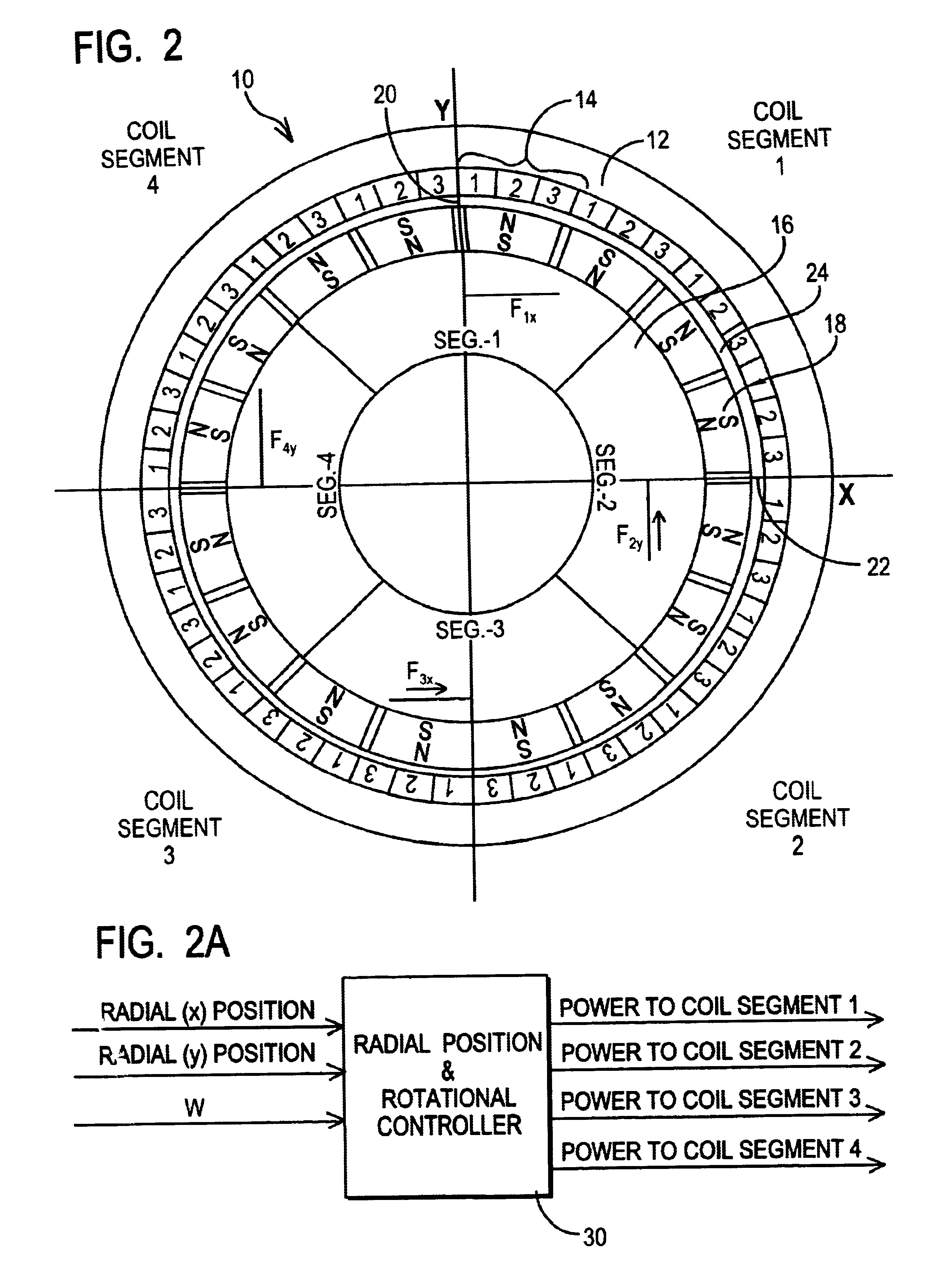
Integrated magnetic bearing
The present invention provides a rotational magnetic gimbal with an integral magnetic bearing. Brushless DC motor technology provides electromagnetic suspension, using a single electromagnetic actuator to perform both the radial bearing and rotary torque (motoring) functions. An integrated motor and magnetic bearing consistent with the invention comprises a rotor comprising a plurality of permanent magnets and a stator comprising a plurality of independently controlled coil segments magnetically coupled to the permanent magnets. Embodiments may further comprise first and second radial position sensors, the first radial position sensor disposed in or adjacent to a clearance gap between the rotor and the stator for sensing the position of the rotor with respect to the stator along a first axis, and a second radial position sensor disposed in or adjacent to the clearance gap between the rotor and the stator for sensing the position of the rotor with respect to the stator along a second axis. In method form, a method for providing integral electromagnetic motor and bearing functions comprises sensing a first radial position of a rotor, the rotor comprising a plurality of permanent magnets, with respect to a stator along a first axis, the stator comprising a plurality of independently controlled coil segments magnetically coupled to the permanent magnets; and sensing a second radial position of the rotor with respect to the stator along a second axis; and delivering current to at least one coil segment, the amount of current based on at least one sensed position.
Owner:AIREX CORP
Programmable power tool with brushless DC motor
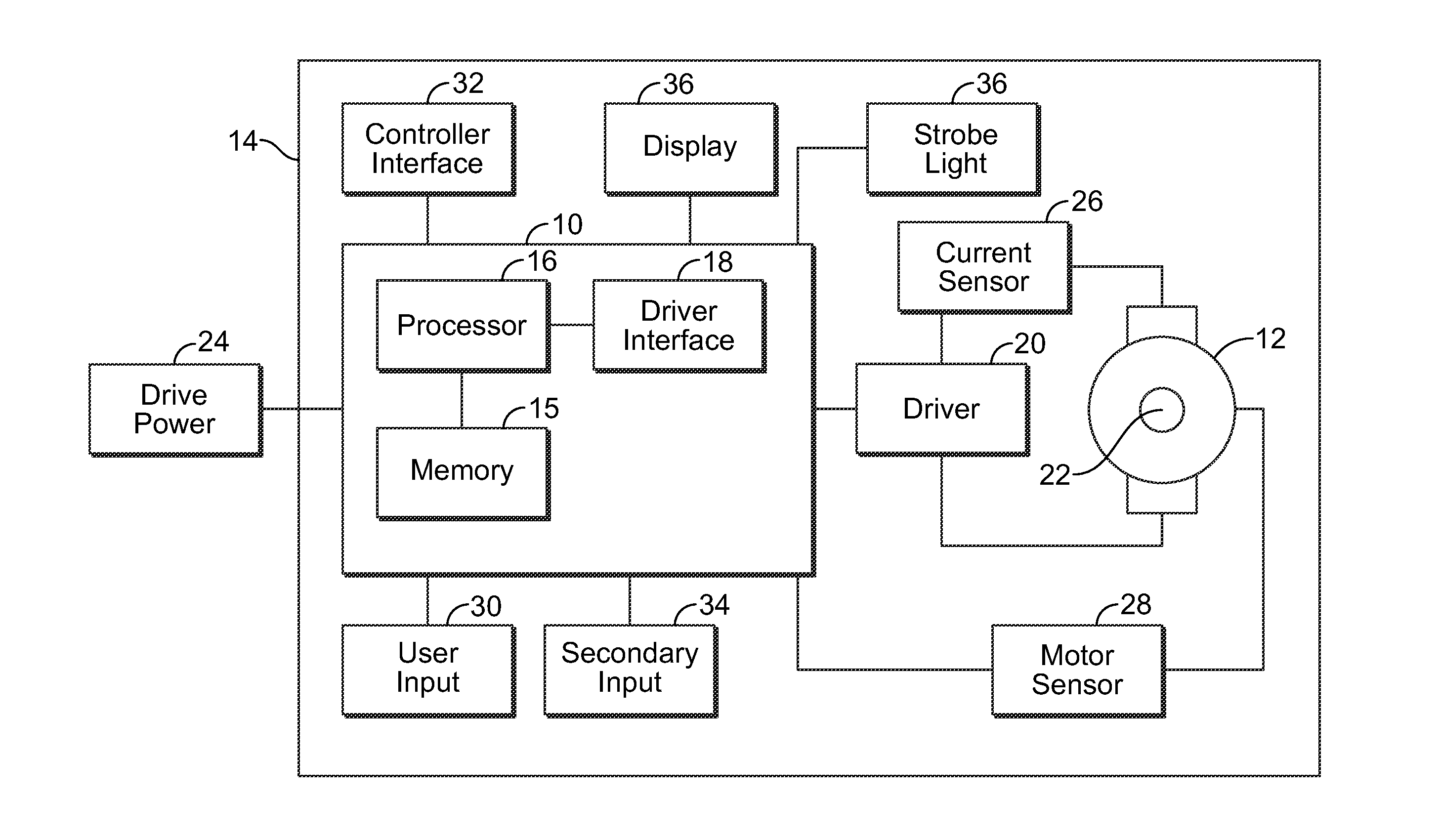
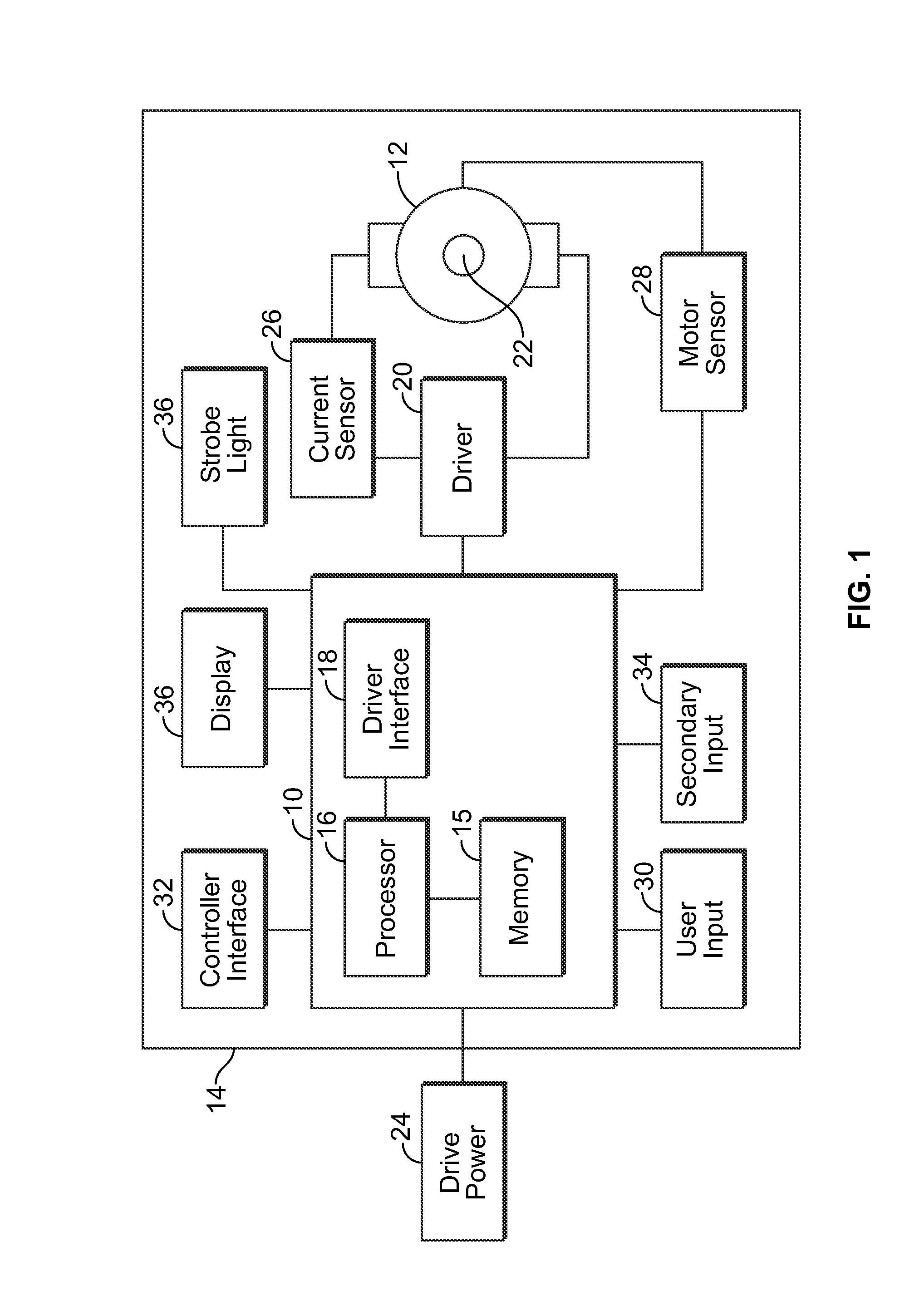
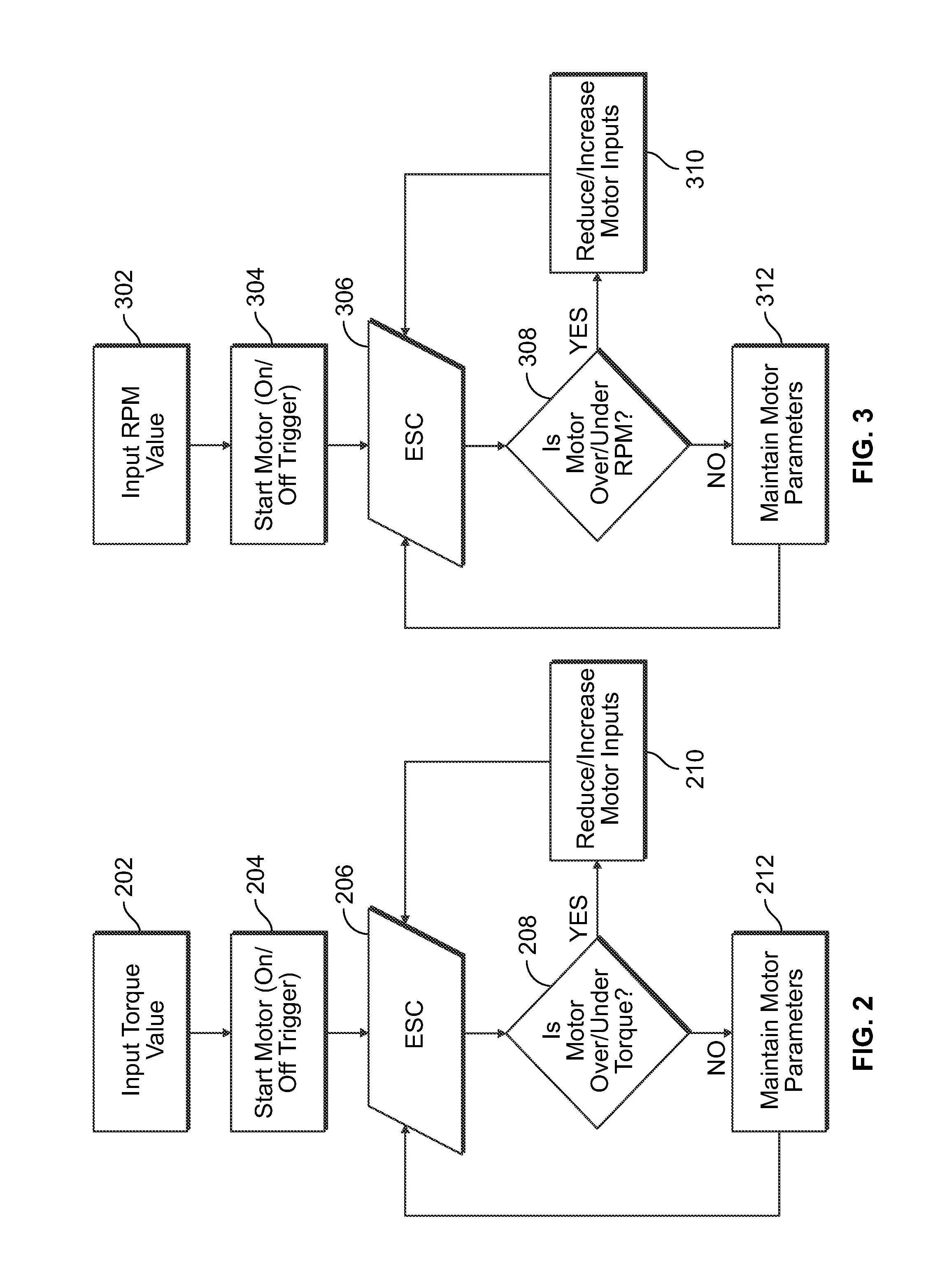
ActiveUS20130187587A1High performance featuresAccurate stopMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersEngineeringPower tool
A power tool that includes a brushless DC motor, one or more motor sensors, and a controller, such as, for example, an electronic speed control (ESC) circuit. The controller is adapted to provide instructions to control the operation of one or more parameters of the brushless DC motor. The controller is also adapted to receive feedback from one or more motor sensors that reflect whether the motor is attaining the one or more parameters. The controller may also be adapted to have a learning mode, in which feedback provided during use of the power tool is stored by the controller as a program so that the same operating parameters may be subsequently replicated by using the program to operate the tool. The controller may also use the feedback to adjust the operation of the motor so that the motor maintains one or more selected or programed operating parameters.
Owner:TRANSFORM SR BRANDS LLC
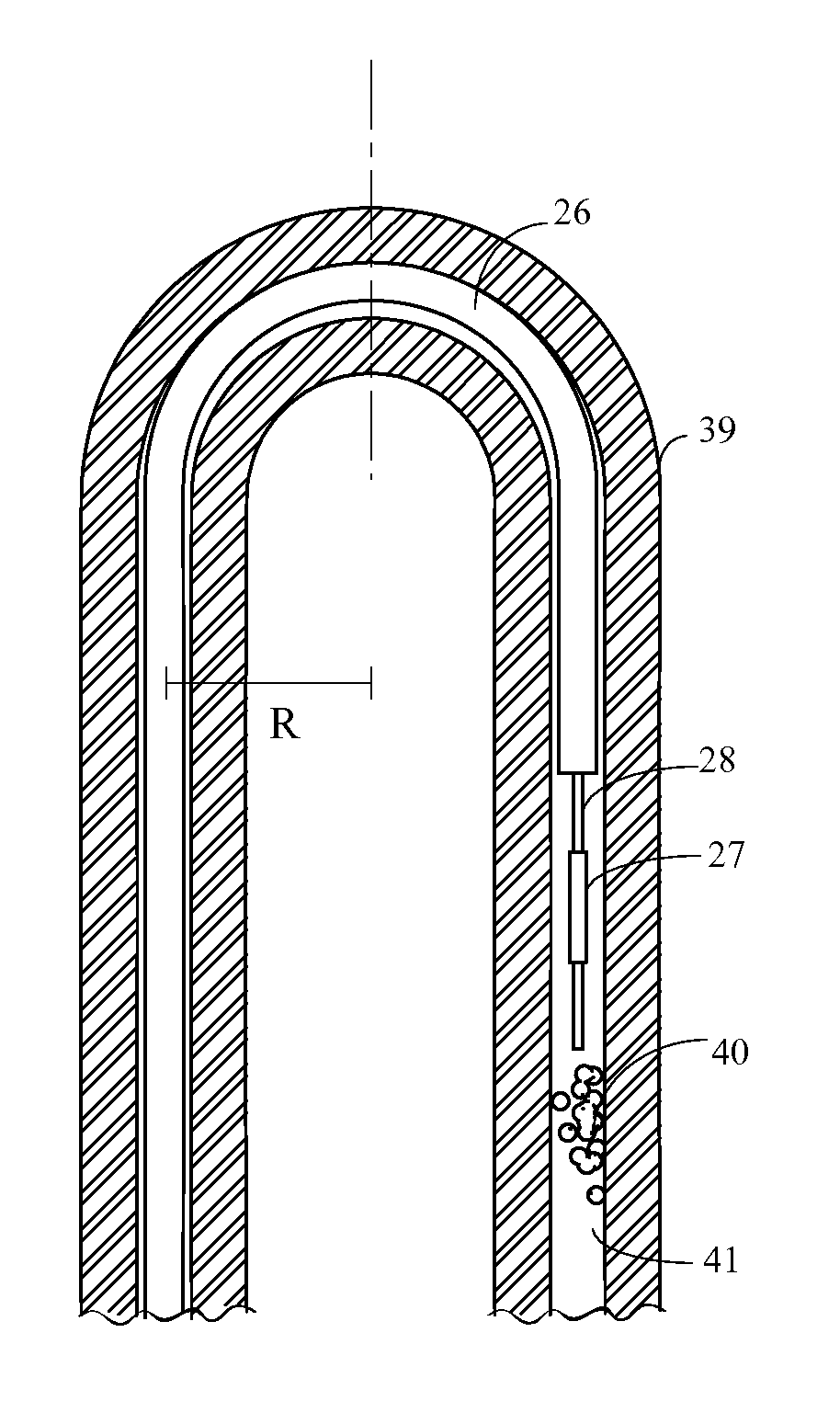
Image-guided therapy delivery and diagnostic needle system
ActiveUS20100036245A1Loading and unloadingSimple structureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryAdemetionineBending force
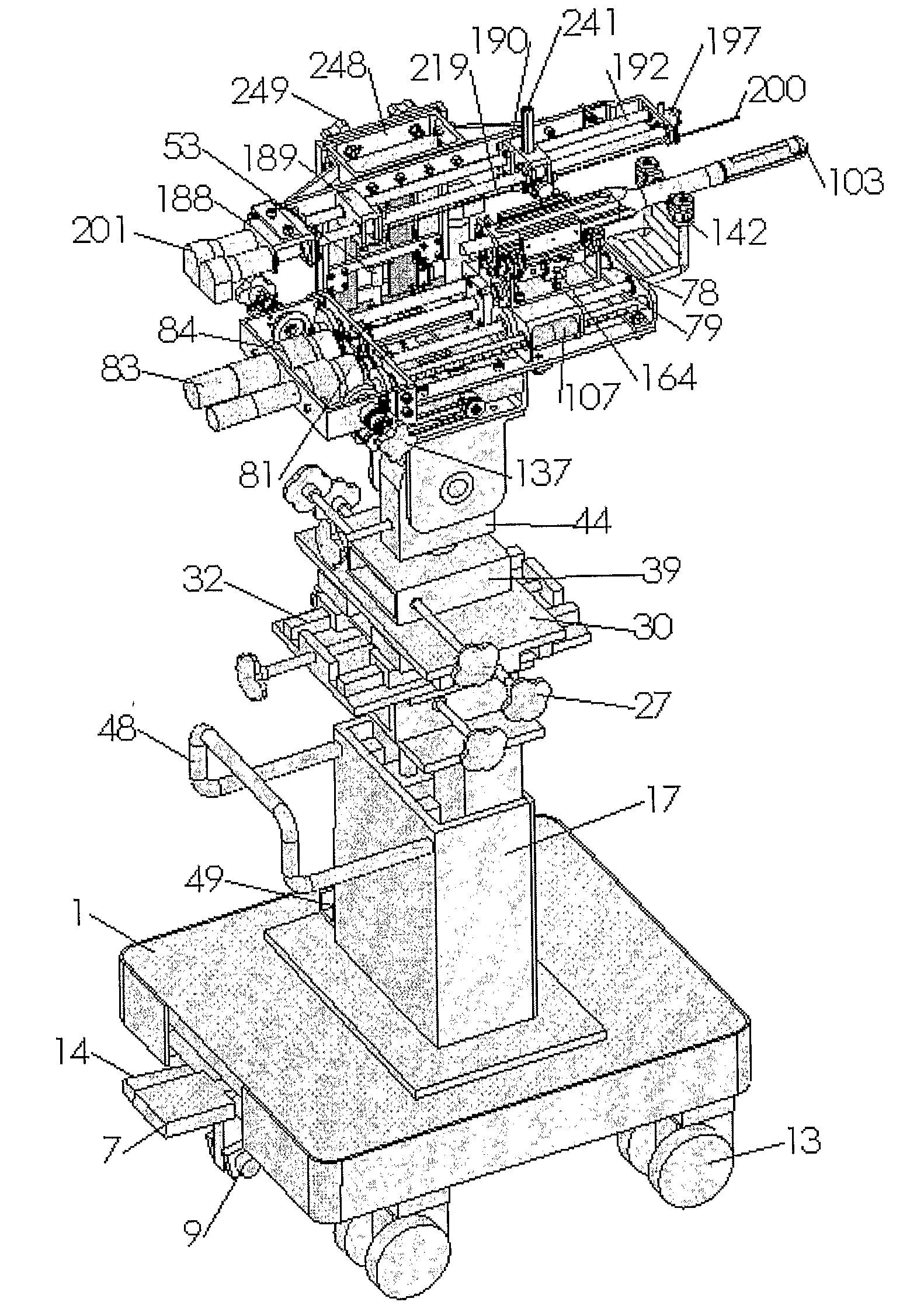
An automated system for delivery of seeds or other therapeutic or diagnostic capsules to internal organs of the patient's body for radiation brachytherapy includes a needling mechanism, a 2DOF robot, an ultrasound probe driver, a 5DOF passive platform, and an easy lock cart. The needling mechanism implants radioisotope seeds by its cannula and stylet driven by two moving stages pushed by DC motors with ball screw transmission. Force sensors are included for detecting insertion forces and bending force. In another embodiment, the needle is rotated for insertion into the patient and can also be used for tissue removal for biopsy. The two embodiments are usable together or separately.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Disposable battery pack for a surgical drill; and method
A surgical procedure is disclosed utilizing a cordless surgical handpiece powered from a sterile battery pack that contains a battery in condition for immediate use without further charging or sterilization. The battery chemistry is based upon lithium / manganese dioxide, and the battery after a single use may be disposed of into non-hazardous waste. The compact surgical handpiece has a brushless DC motor and a manually operated external trigger for activating and controlling the motor operations. Interengaging sets of contacts on the handpiece and battery are adapted to become lockingly and conductively interengaged upon rotation of the battery pack relative to the handpiece, in a manner that rapidly achieves correct alignment of the parts and also ensures stable mechanical attachment and support during the surgical procedure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Devices for clearing blockages in in-situ artificial lumens
Devices and methods for the effective clearing of artificial tubes, especially in-situ clearing of artificial tubes in a living being are covered in this disclosure. The devices and methods provide an elongated clearing member having a first end that is coupled to a driving mechanism and having a second working end that is subjected to repetitive motion for clearing blockages within the artificial tube. The elongated clearing member includes either a fixed or an adjustable element that selectively defines the portion of the elongated clearing member that is insertable within the artificial tube. The proximal end of the clearing member is releasably secured to the driving mechanism and the driving mechanisms may comprise a wide variety of repetitive motion drivers such as voice coil motors, piezoelectric actuators, pneumatic actuators, DC motors, etc. These devices / methods may comprise a free-standing console for hands-free operation or may comprise hand-held versions. The distal working end of the clearing member may comprise tips of differing functions, including an irrigation / aspiration feature.
Owner:ACTUATED MEDICAL
Motion control system for barrier drive
ActiveUS20060197481A1Facilitate fasterPrecise positioningDC motor speed/torque controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsLinear motionAudio power amplifier
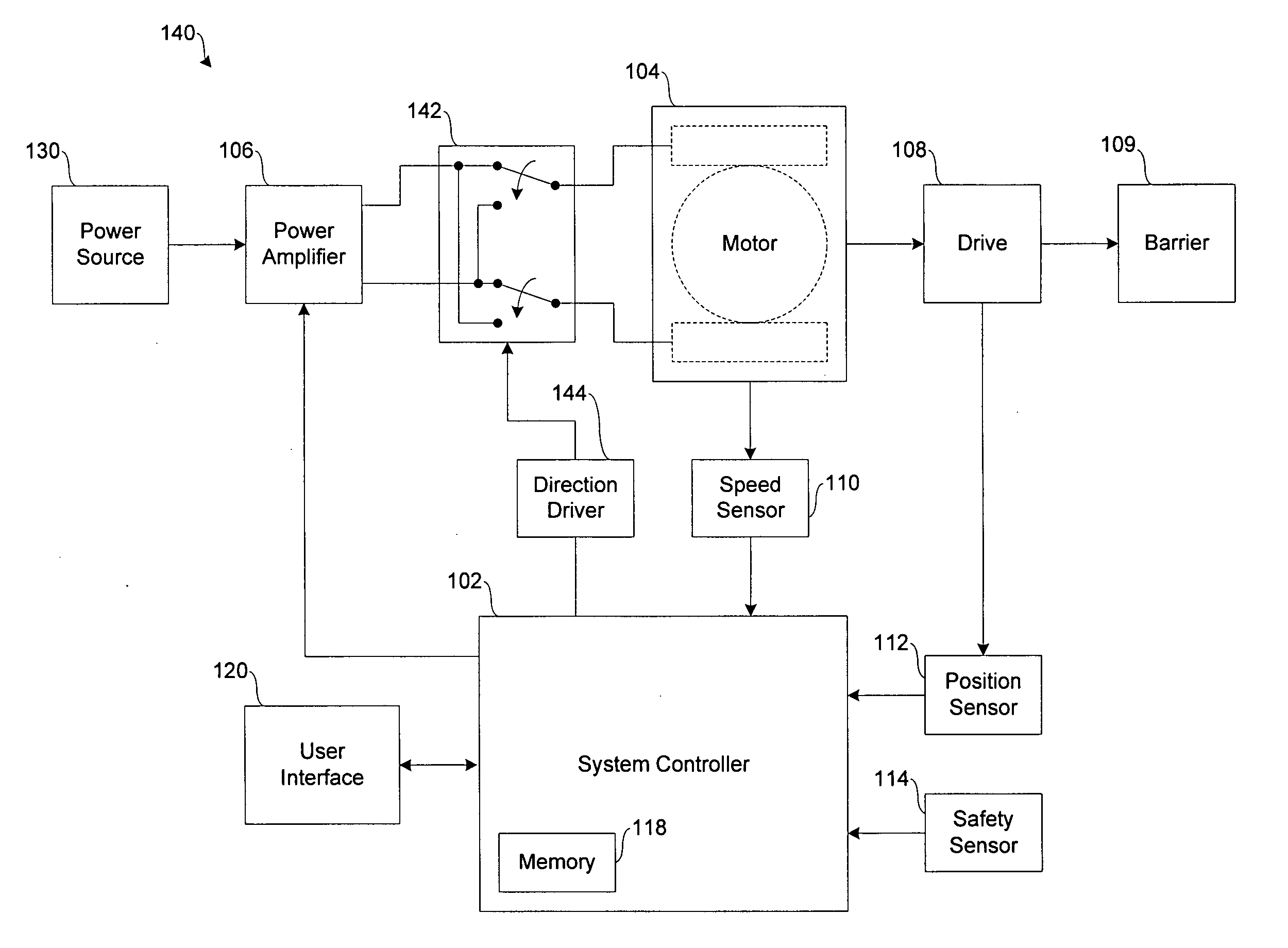
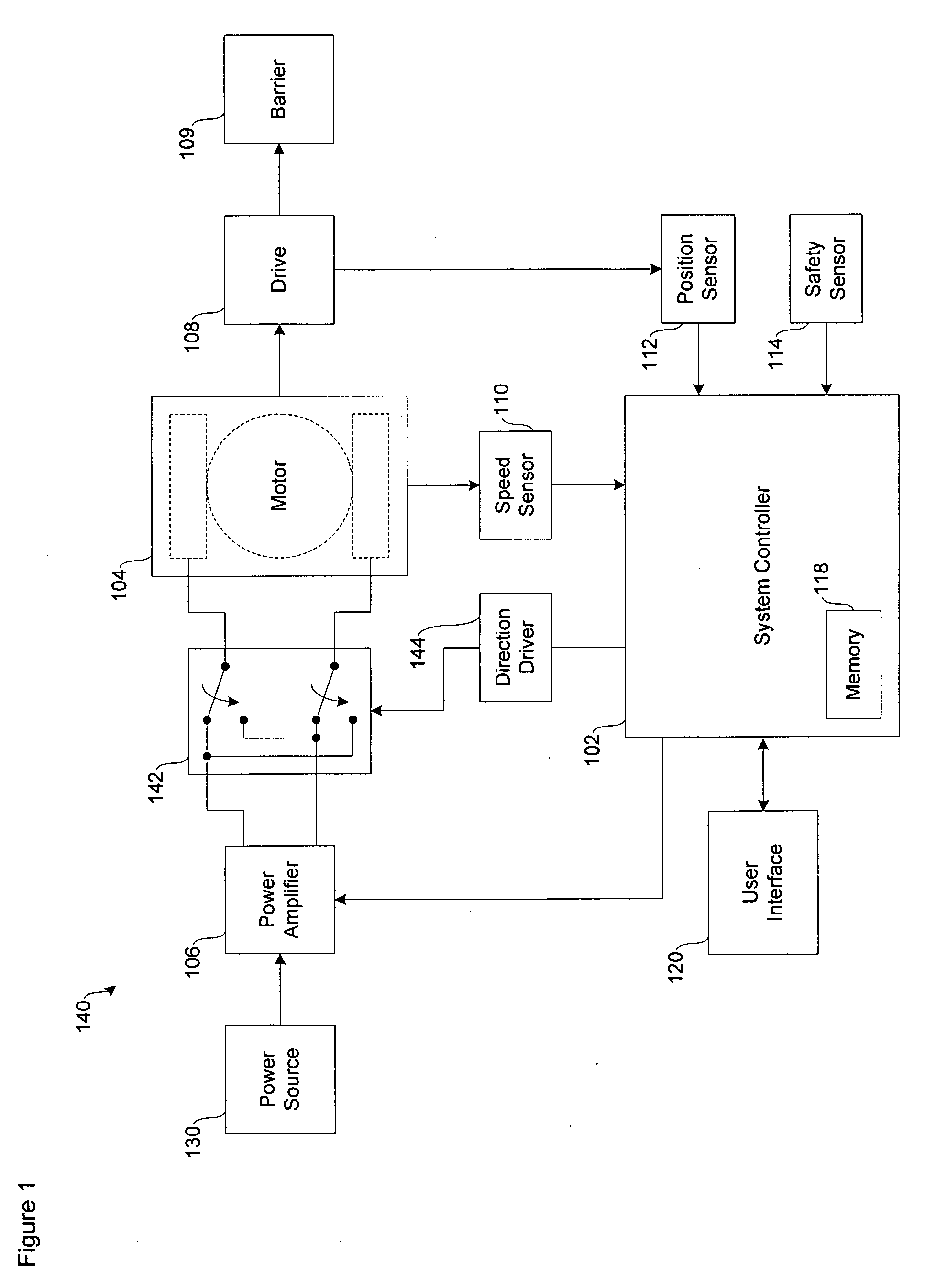
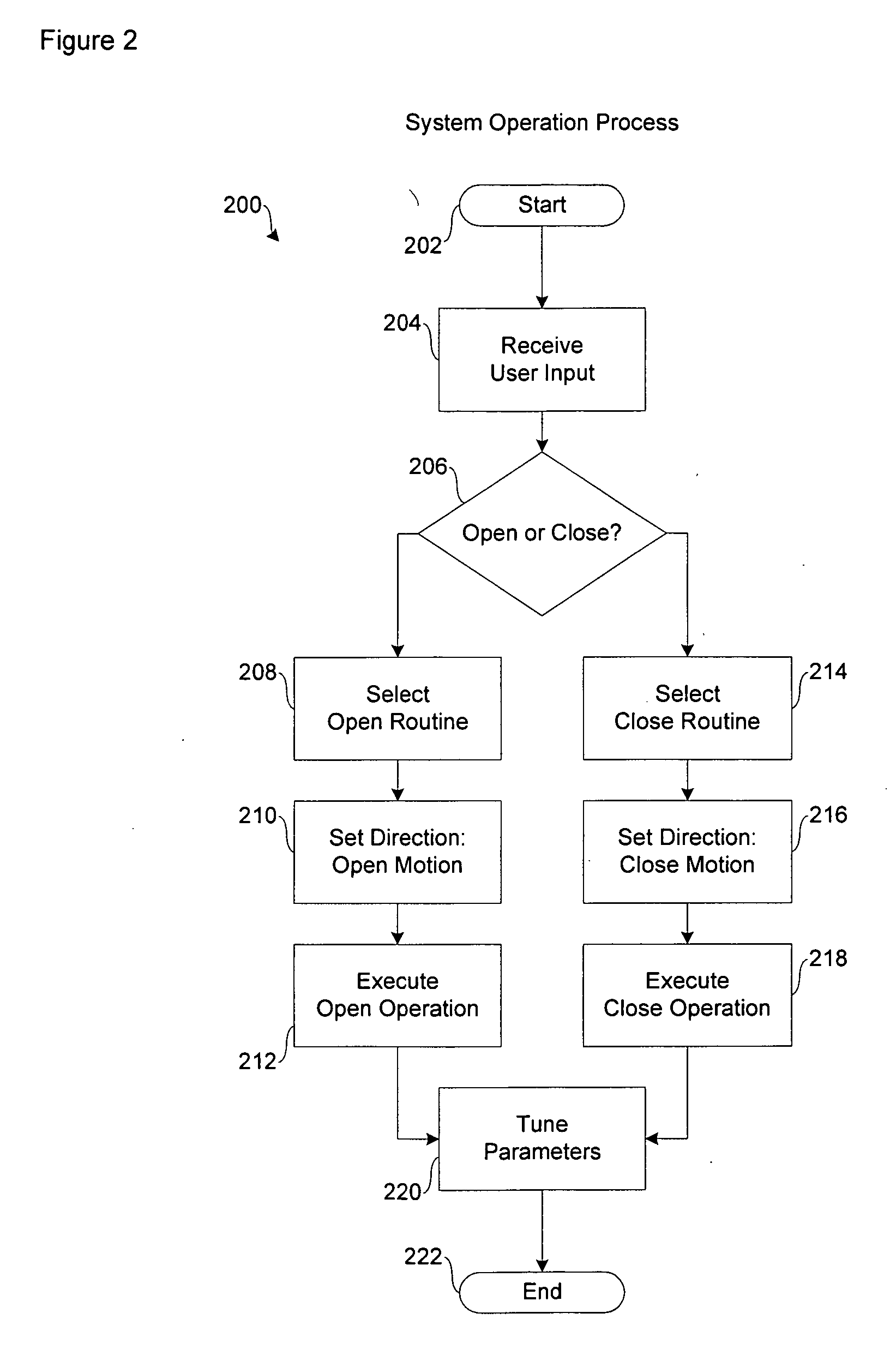
A system for operating a barrier system such as a garage door, gate or fence. A DC motor is connected to and operates a barrier drive. A power amplifier is configured to receive power signals from a power supply and to output modulated DC signals to the DC motor. A controller implements an intelligent closed-loop motion control algorithm to control the power amplifier according to a non-linear motion profile. A feedback sensor provides status signals to the controller to determine position or speed of the barrier.
Owner:NORTEK SECURITY & CONTROL LLC
Automatic power-driven toothbrushes
InactiveUS6845537B2Improve charging capacityDirect and efficient utilizationBowling gamesCarpet cleanersBristleEngineering
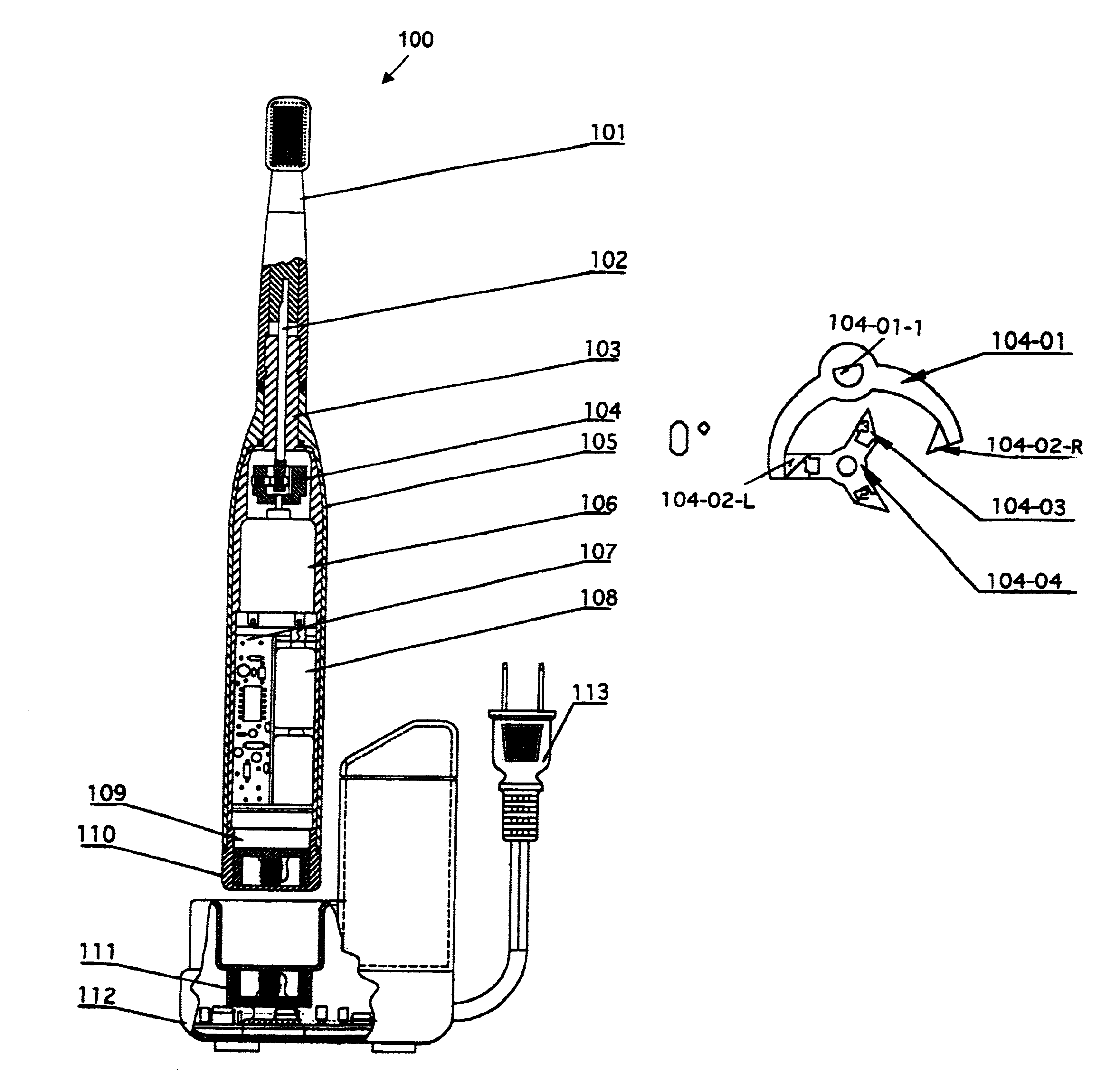
The present invention discloses the present invention discloses a power toothbrush that includes a body portion 105. An elongated level arm 102 extends from one end of the body portion to a toothbrush head 101 disposed at a distal end of the toothbrush. The toothbrush head includes a plurality of brush bristles. The elongated lever arm 102 is mounted on a vibrating pivot 104 driven by rotational DC motor engaging and pushing a set of permanent magnets attached to a two-arm fork rotating along the lever arm 102. In a preferred embodiment, the DC motor drives a three-leg permanent magnets each disposed at a 120-degree phase from each other for driving the two-arm fork for generating a vibration that three-times the frequency of the DC motor's rotational frequency.
Owner:WONG MAN KWAN
Gear pump for micro-miniature turbojet engine
ActiveCN101403382BReduce weightReduce leakageRotary piston pumpsRotary piston liquid enginesMicrocontrollerJet engine
The invention discloses a gear pump used for a microminiature turbo-jet engine, comprising a direct current motor, a pump body, an upper pump cover, a lower pump cover, a shell, a pair of driving and driven gears which are meshed and a driving shaft and a driven shaft. The driving gear is arranged on the driving shaft; the driven gear is arranged on the driven shaft and is aligned and meshed withthe driving gear; the lower pump cover is fixed on the direct current motor, the upper pump cover is connected to the lower pump cover and the plane of the pump body is pressed tightly and sealed so as to lead the structure to be simple; the shell is sleeved at the outside of the lower pump cover; the driving gear and the driving shaft adopt a method of combining clearance fit and a transmission pin to eliminate the installation error of an output shaft of the direct current motor; and an antifriction material is embedded at the positions on the lower pump cover and the upper pump cover corresponding to the driving gear and the driven gear so as to increase the reliability and durability of the gear pump. Most parts of the gear pump adopt aluminium alloy so as to reduce the weight furthest. The gear pump can control the rotating speed of the direct current motor by pulse-width modulation of a single-chip microcontroller and control the flow rate of the gear pump precisely.
Owner:北京领动国创科技有限公司
Vacuum generating apparatus with multiple rotors
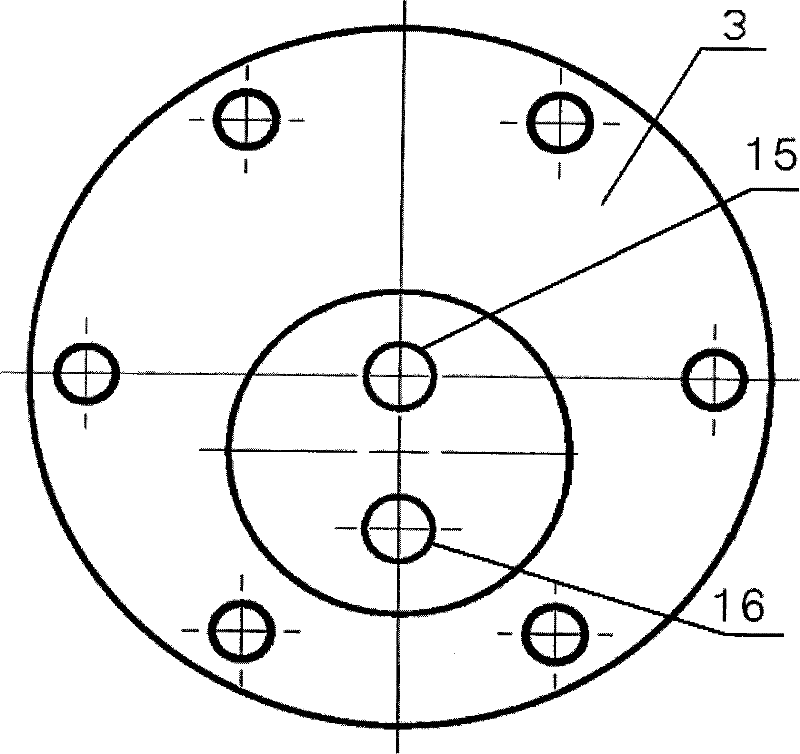
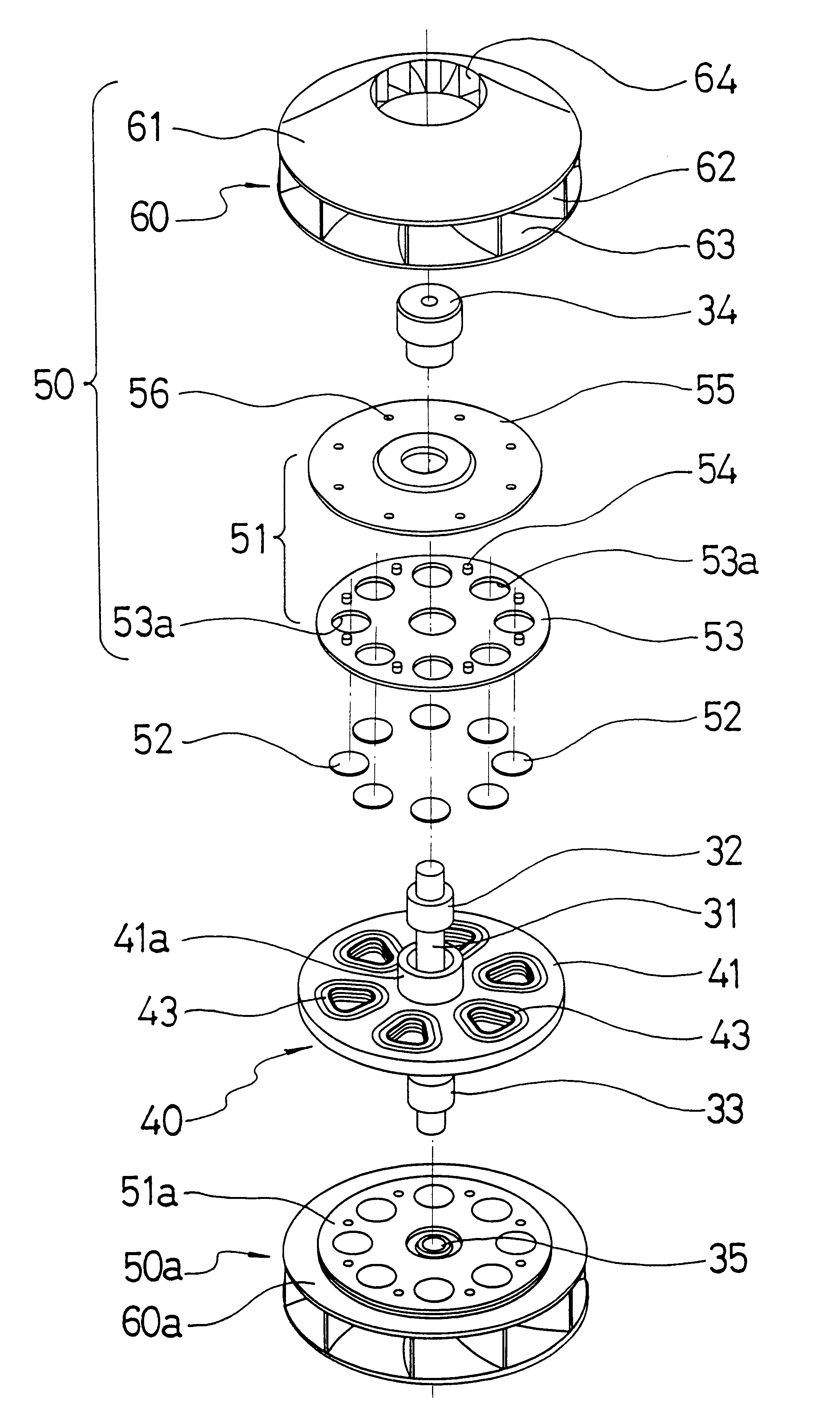
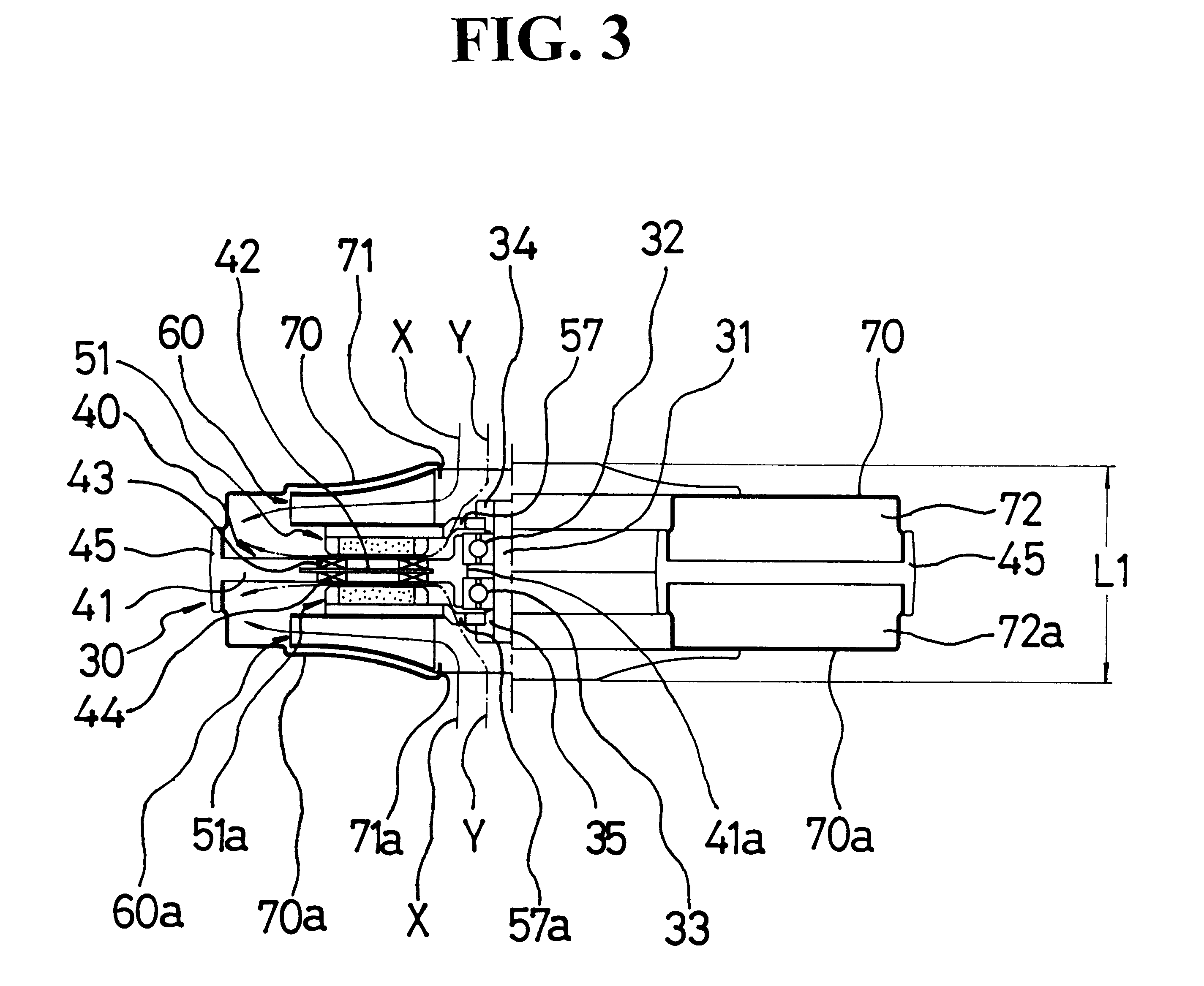
A vacuum generating apparatus for a vacuum cleaner is provided, in which an axial type coreless brushless direct-current (DC) motor is implemented in the form of a rotor-impeller integration structure. The vacuum generating apparatus includes an axial type brushless DC motor in which disc-shaped upper and lower rotors are symmetrically disposed facing the upper and lower portions of a disc-shaped stator at either end of a rotating shaft rotatably supported in the inner circumferential portion of the stator, upper and lower impellers integrally fixed in the upper and lower rotors, respectively, and upper and lower housings whose outer circumferential portions are combined with the outer circumferential portions of the respective disc-shaped stator such that air sucked via sucking inlets formed at the center of the housings is guided to a discharging outlet together with the stator. A single rotor structure can also be adopted.
Owner:AMOTECH
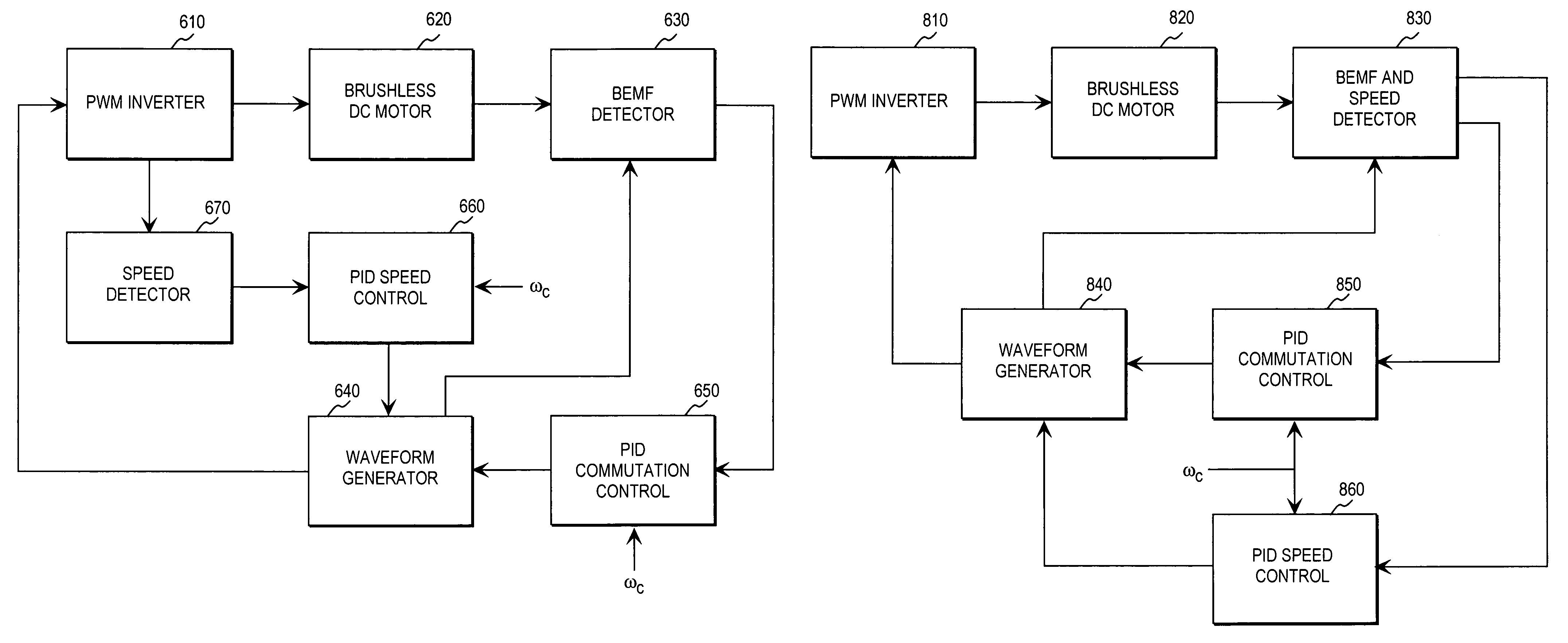
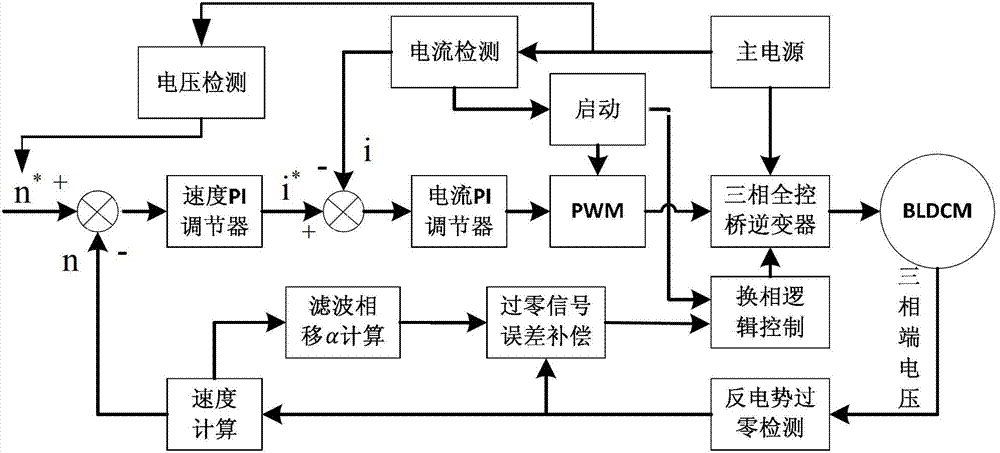
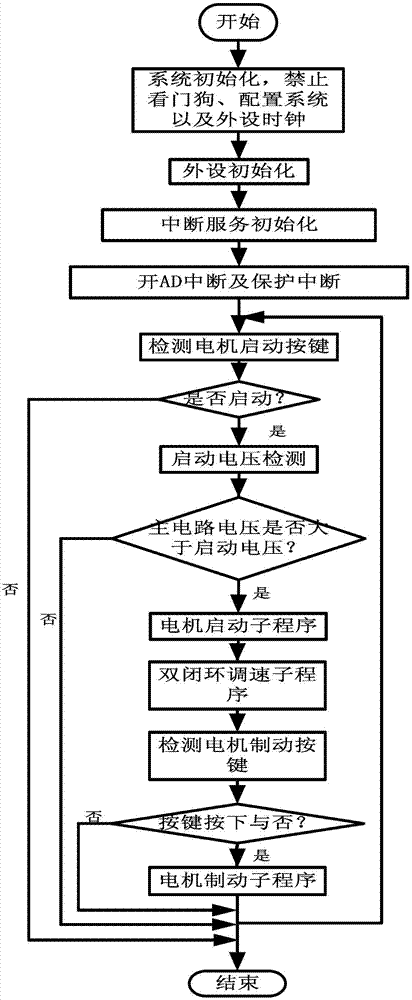
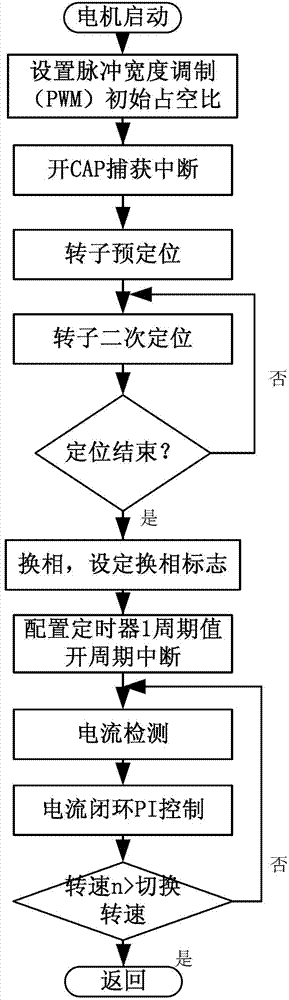
Position sensor-free double closed-loop speed regulation control method for brushless DC motor
InactiveCN103248294AAccurate control of different speedsSolve the problems of large volume and low speed accuracyTorque ripple controlSingle motor speed/torque controlClosed loopEngineering
A position sensor-free double closed-loop speed regulation control method for a brushless DC motor comprises the following steps: (1) initializing functional modules and peripherals; (2) opening AD (Analog-Digital) interruption and protection interruption; (3) detecting the start key of the motor, judging whether to start the motor, if yes, executing the next step, and if not, continuing to execute the step; (4) starting voltage detection, judging whether the voltage of a main circuit is larger than starting voltage, if yes, executing the next step, and if not, returning to the step (3); (5) entering a motor starting subprogram and beginning operating the motor; (6) entering a double closed-loop speed regulation subprogram, and regulating the rotational speed and the current of the motor according to voltage value; and (7) detecting a motor brake key, judging whether to press the key, if yes, entering a motor brake subprogram, and if not, returning to the step (3). The method provided by the invention overcomes the defects of larger size, low rotational speed accuracy and the like of the conventional motor controller, can accurately control different rotational speeds of the motor, and can simultaneously realize counter electromotive force zero-cross comparison position sensor-free reversing and Hall position signal reversing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
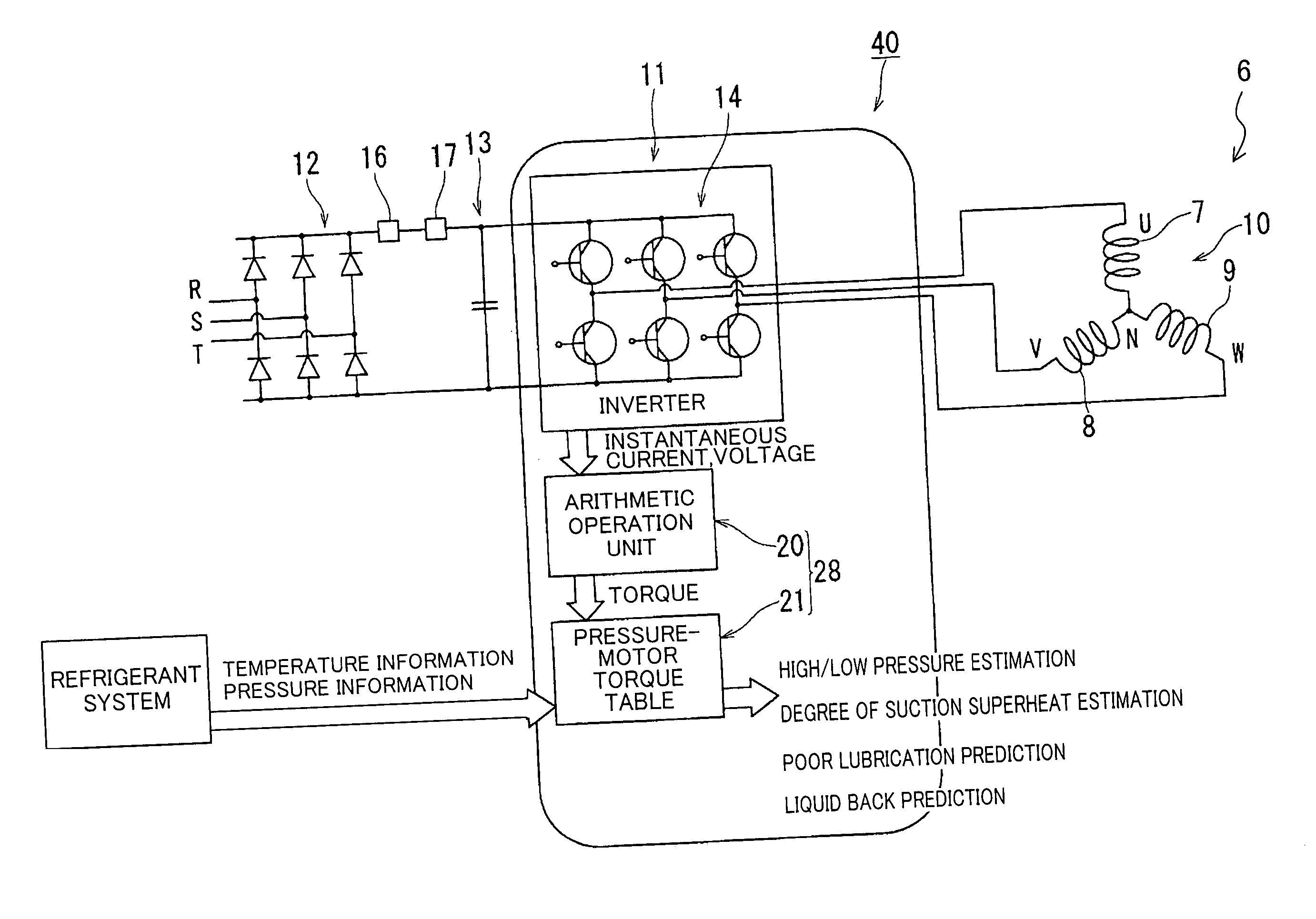
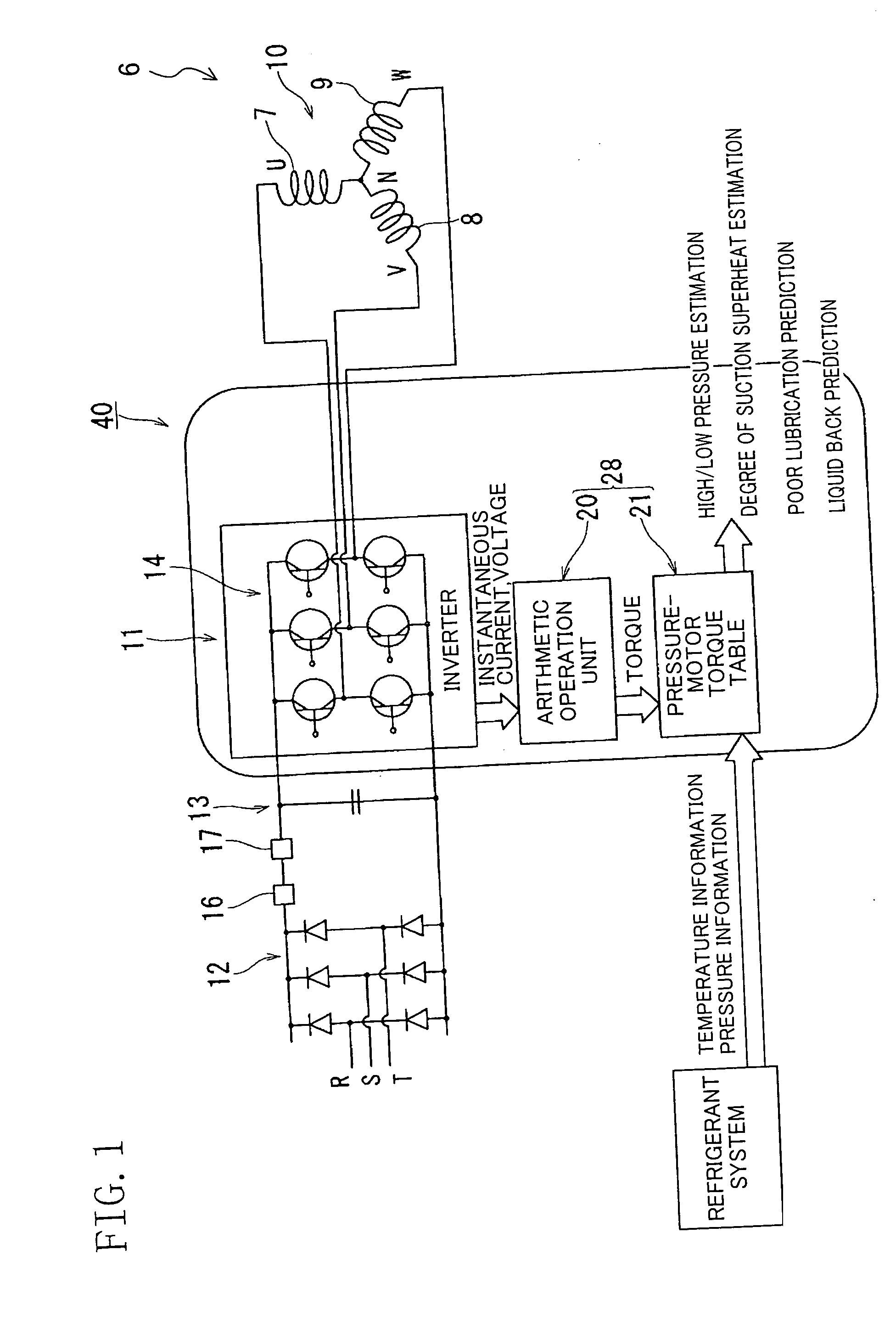
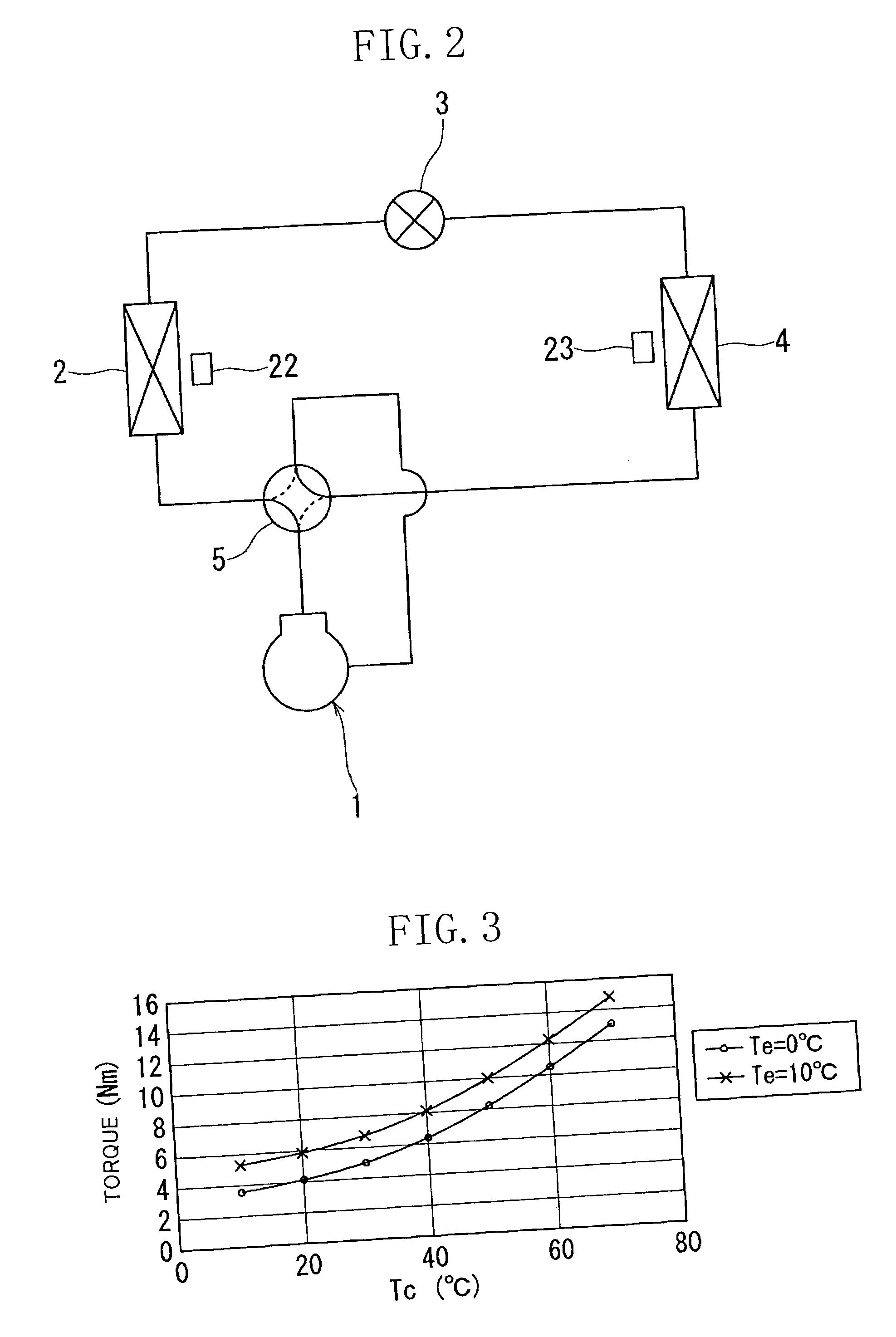
Driver of compressor and refrigerator
ActiveUS20050247073A1Easy to operateOperating frequency of the compressor <b>1Commutation monitoringSpace heating and ventilationPower flowMotor drive
An instantaneous current and instantaneous voltage of a three-phase coil of a brushless DC motor are detected, and the internal condition of a compressor is predicted from these detection values. The prediction about the internal condition of the compressor is made in such a way that motor driving torque which is a parameter of a motor model is identified and poor lubrication, liquid compression or the like is predicted from this identified motor driving torque. This enables it to make, in real time, a failure forecast, failure diagnosis etc. on the compressor.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
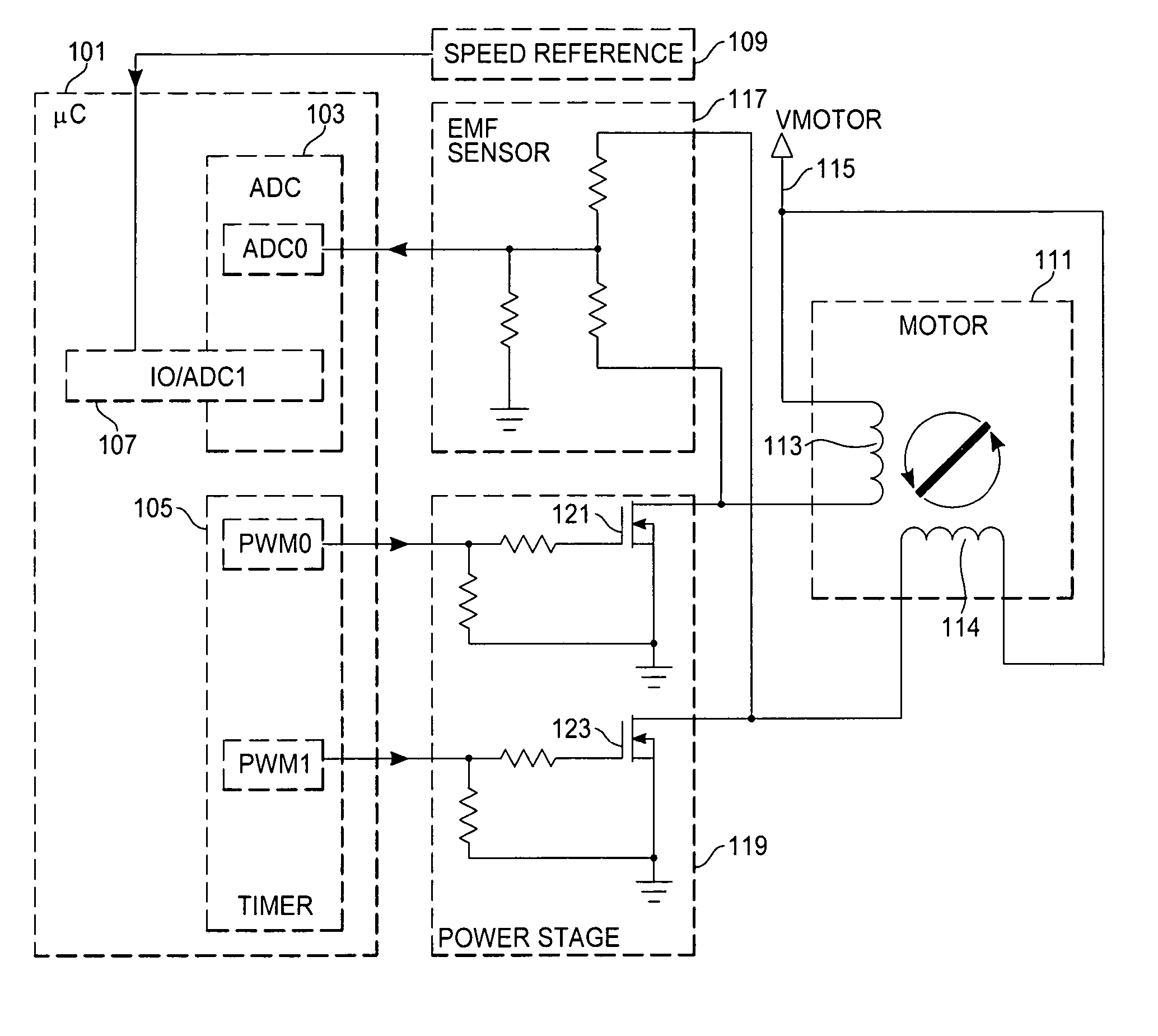
Sensorless control of two-phase brushless DC motor
A motor control system for a two-phase brushless DC motor uses measured EMF voltage from the passive set of stator coils to control commutation. A microcontroller receives the EMF voltage measurement and compares it to a threshold voltage value, which may be speed-dependent for advance commutation at high motor speeds. A match of the EMF voltage measurement with the threshold value triggers commutation of the drive to the opposite set of stator coils. The microcontroller also has an up-down counter timer whose count value is compared to an external speed reference. Each match of the count value triggers a transition in a pulse-width modulated (PWM) drive signal. The duty cycle of the PWM signal establishes an average drive voltage that controls motor speed.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
High-power low-RPM DC motor
InactiveUS6194799B1Increase profitIncreasing motor torqueAsynchronous induction motorsPropulsion by batteries/cellsEngineeringConductor Coil
A high power low RPM direct current electric motor is disclosed whereby the high power output is achieved in one of two ways or both. In the first case, the need for cooling is reduced simultaneously along with an increase in the utilization of the magnetic field present in the motor permanent magnets. This is achieved by wrapping the electromagnet core with windings that are capable of demagnetizing the rotor permanent magnets under stall conditions. Interlocking motor circuitry is provided which prevents the full activation of these motor windings until motor RPM values reach a safe level. This increases motor power while decreasing resistive losses in electromagnet windings. In the second case, the rotary portion consists of a large diameter relatively flat rotor containing permanent magnets and having built in vanes for moving air over the electromagnet stator windings providing forced air cooling.
Owner:MAGNETIC MOTORS
Washing machines
ActiveUS20070113595A1Increase water flowReduce stressOther washing machinesControl devices for washing apparatusWastewaterEngineering
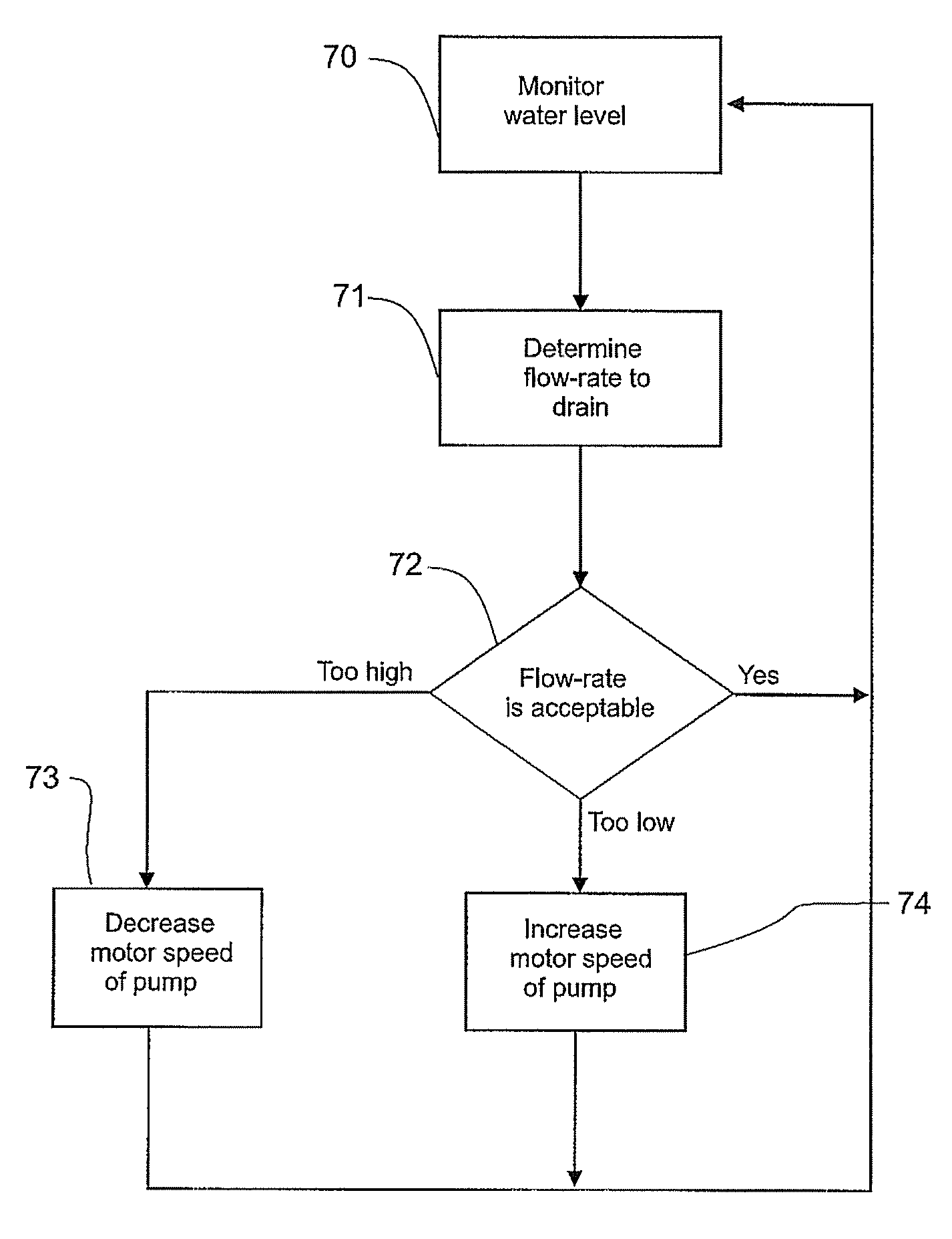
The present invention relates to a washing machine (7) and pump (8) for a washing machine (7). The pump is driven by a brushless DC motor (38). The pump can be controlled to improve the operation of the washing machine. In one aspect the invention comprises a washing machine (7) with a variable speed pump (8) for pumping out wastewater, a controller (50) for controlling the speed of the pump and a sensor (10) for determining the flow-rate of water being pumped from the washing machine, wherein the controller (50) controls the speed of the pump to maintain the flow-rate at a desirable level.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL APPLIANCES LTD
Constant detecting apparatus for brushless DC motor, control apparatus for brushless DC motor, and program for detecting constant of brushless DC motor
InactiveUS20020113615A1Easy to calculateImprove errorAnalogue computers for vehiclesSynchronous motors startersPhase currentsConductor Coil
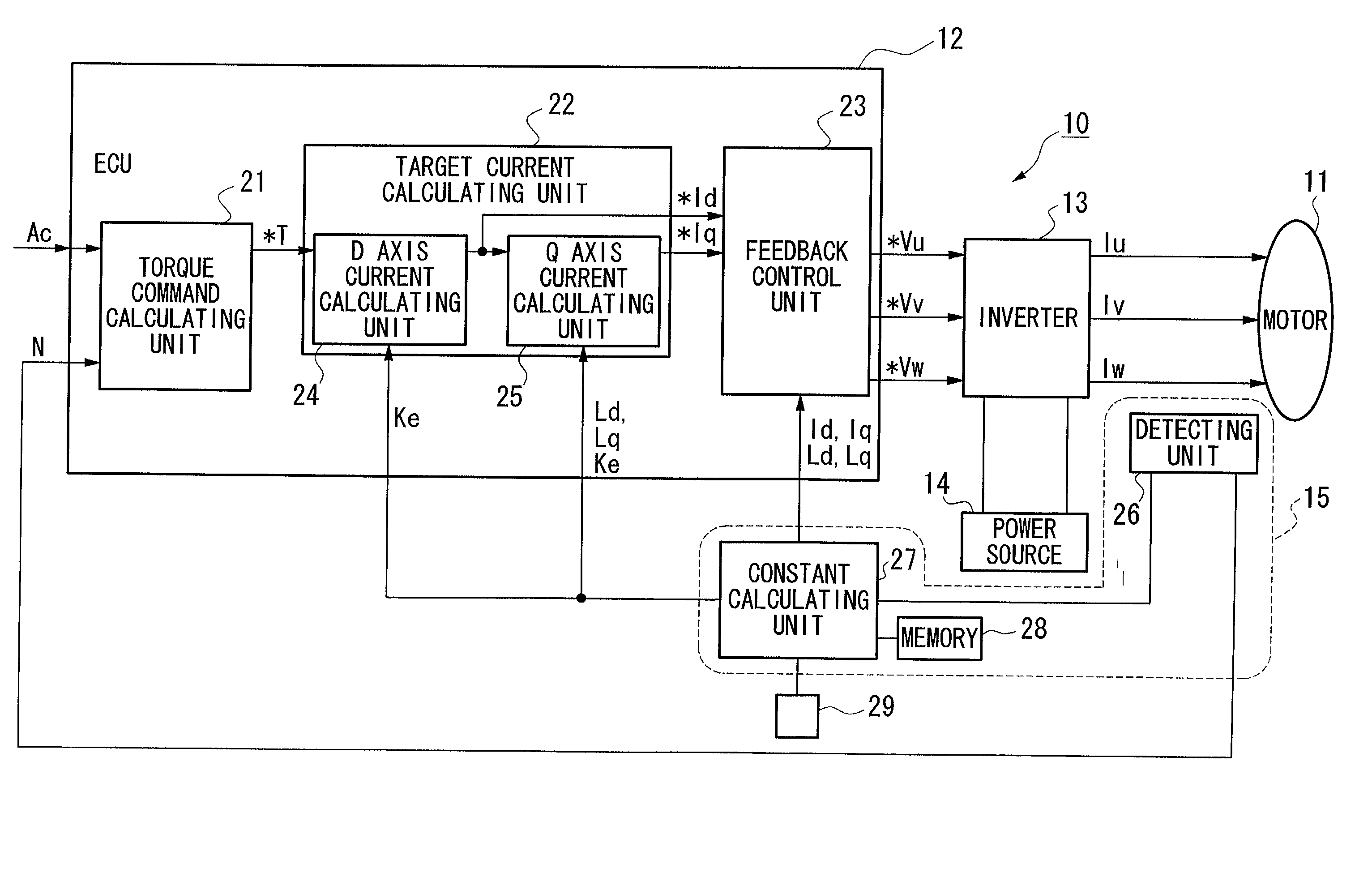
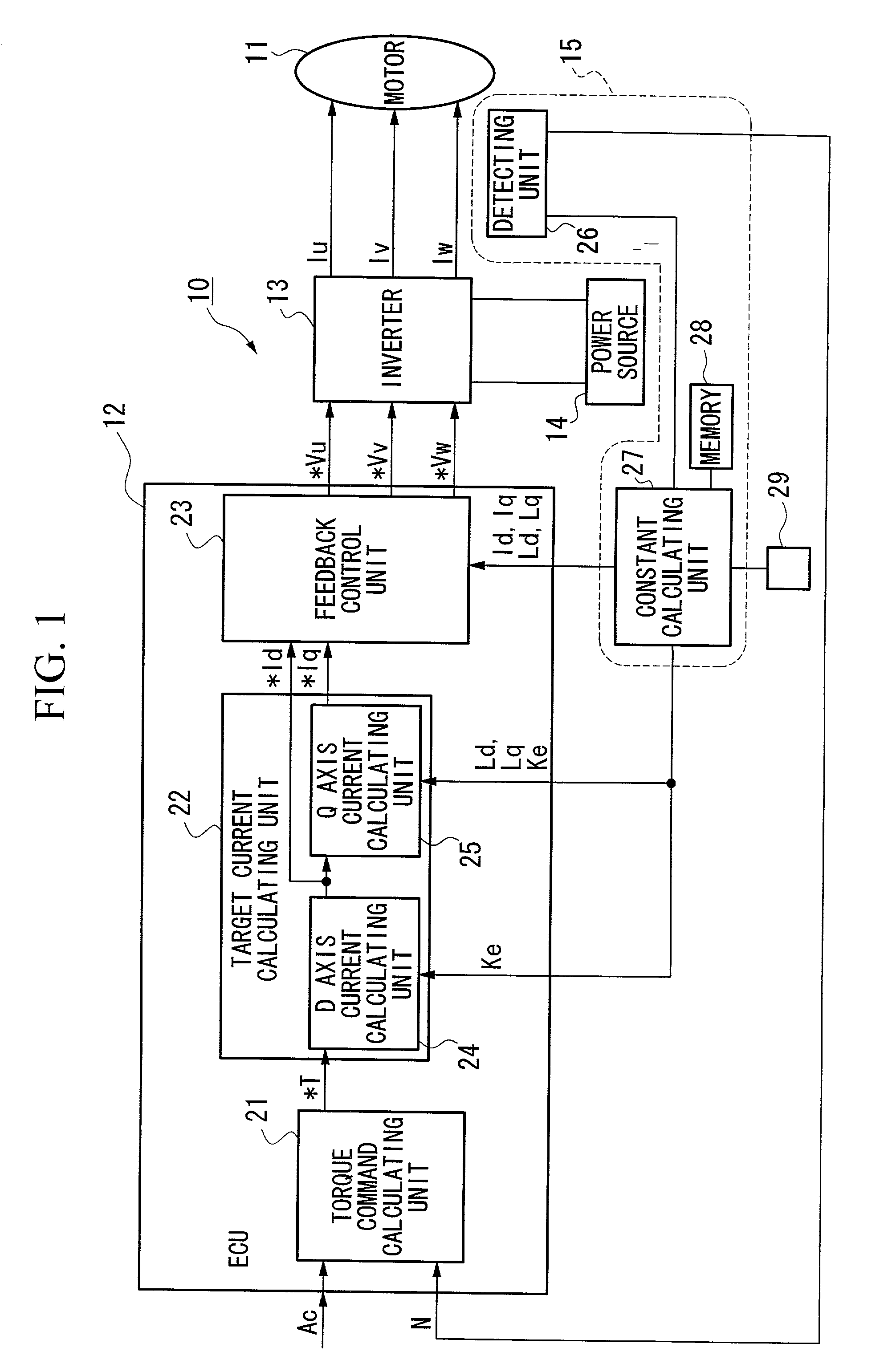
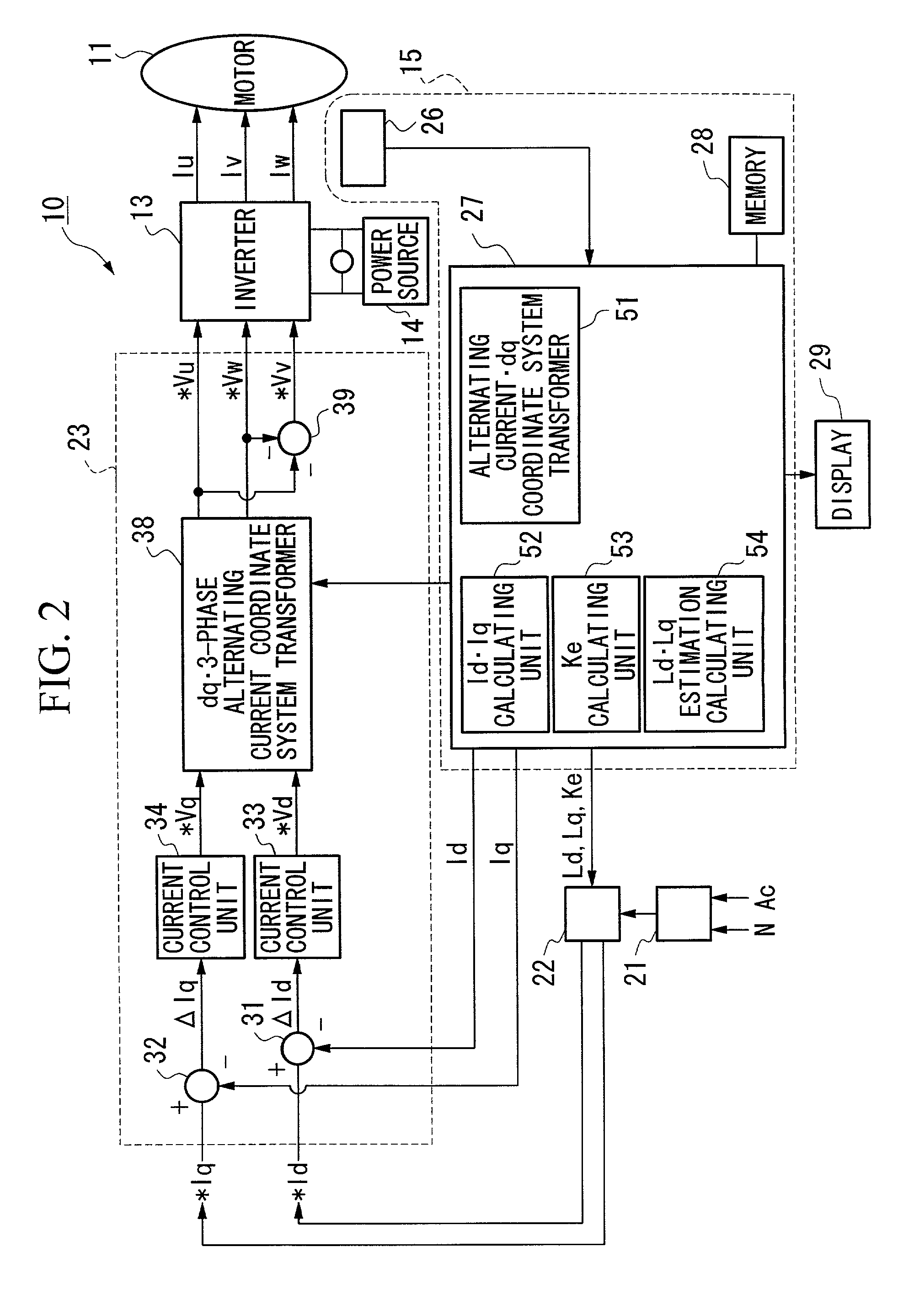
A constant detecting apparatus 15 comprising a detecting unit 26 and a calculating unit 27. The detecting unit 26 is structured comprising a rotation sensor 41, a torque sensor 42, a position sensor 43, a rotor temperature sensor 44, a winding temperature sensor 45, a phase voltage detector 46, and phase current detectors 47 and 47. The calculating unit 27 calculates the induced voltage constant Ke that changes depending on the motor temperature Tmag while the motor 11 is being driven based on each of the detected signals from the detecting unit 26, and at the same time, the d axis current Id and the q axis current Iq are calculated after elimination of the iron loss, and the d axis inductance Ld and the q axis inductance Lq in the actual operating state of the motor 11 are calculated.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com