Patents
Literature
8205results about "Static/dynamic balance measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
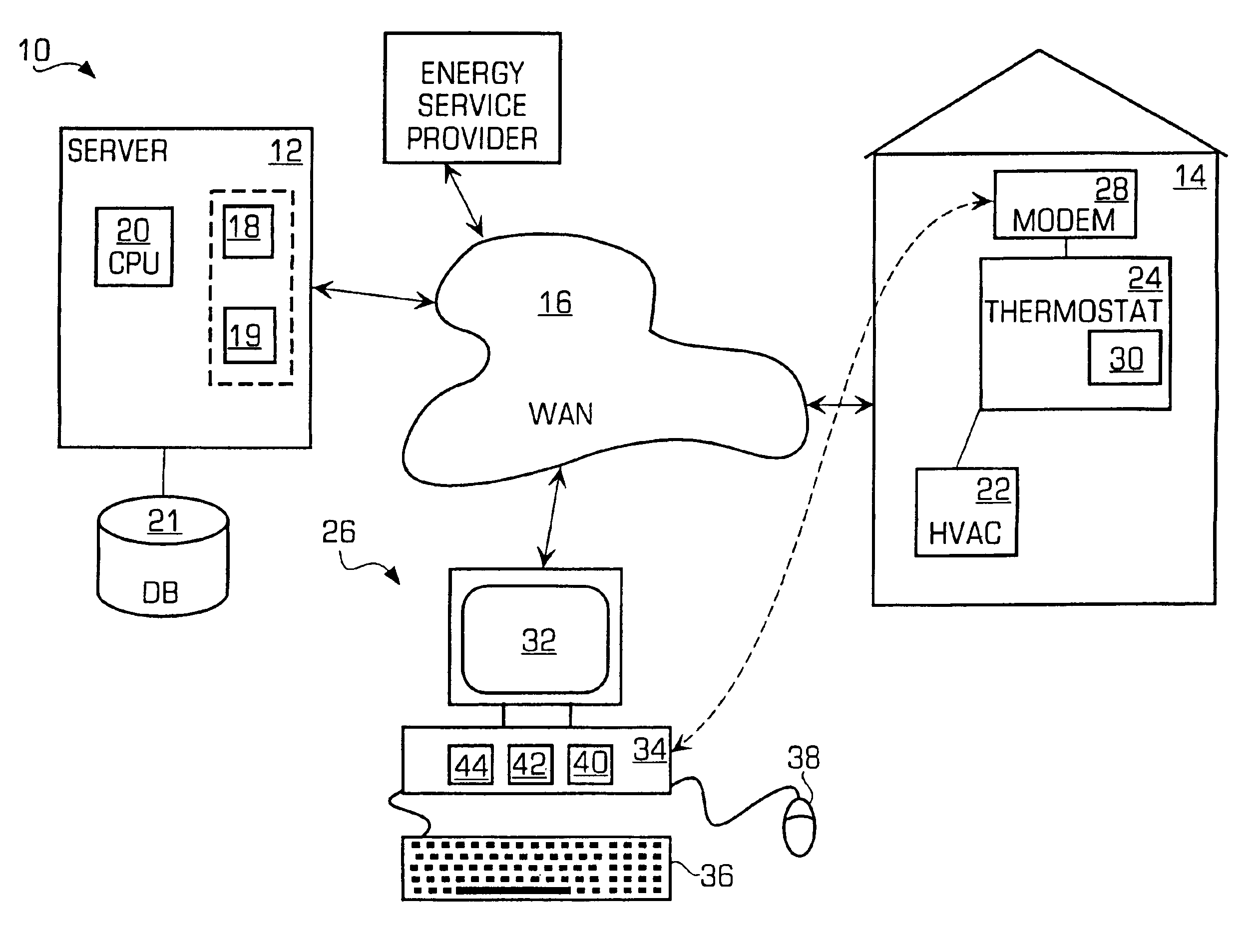
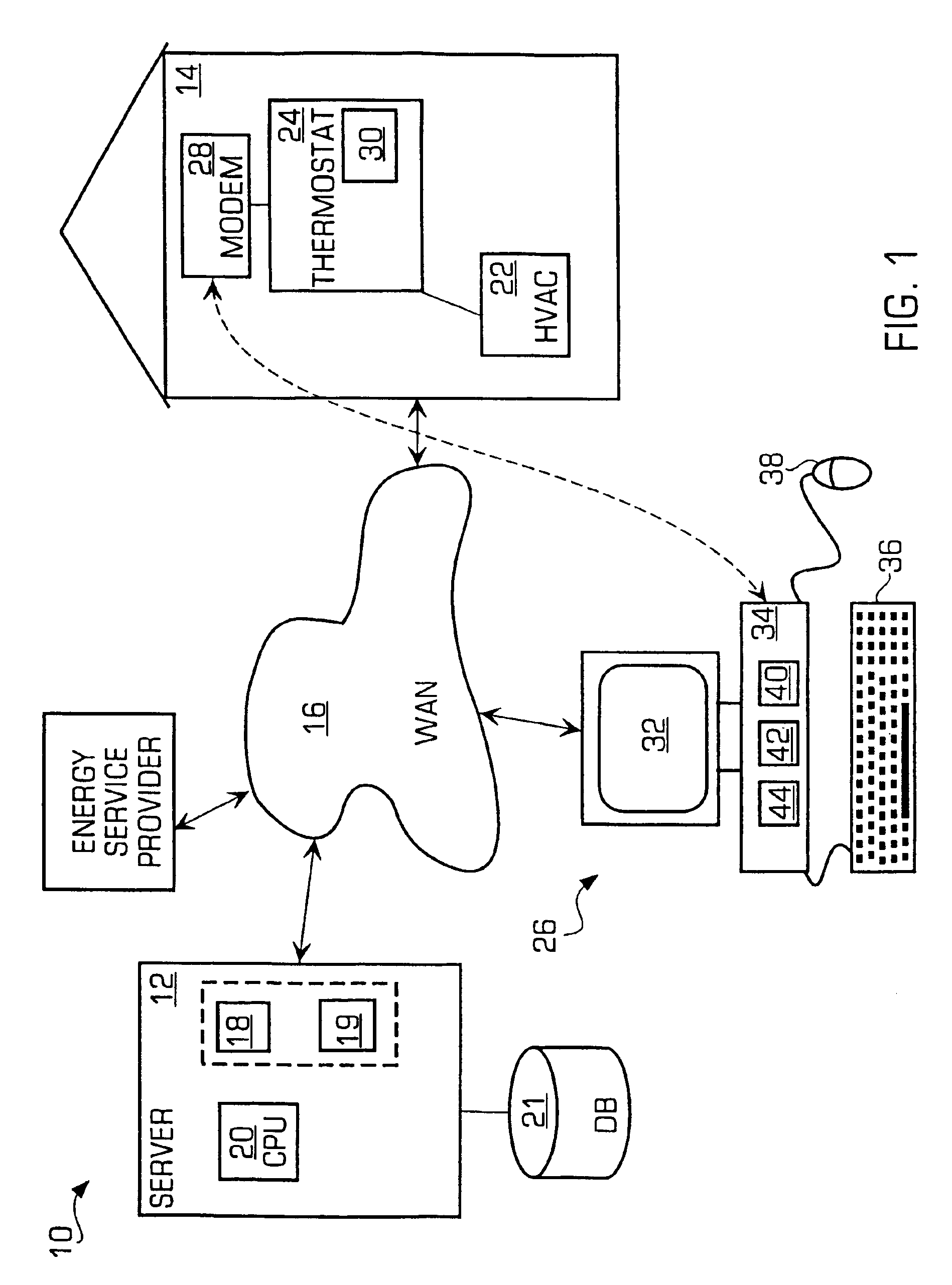
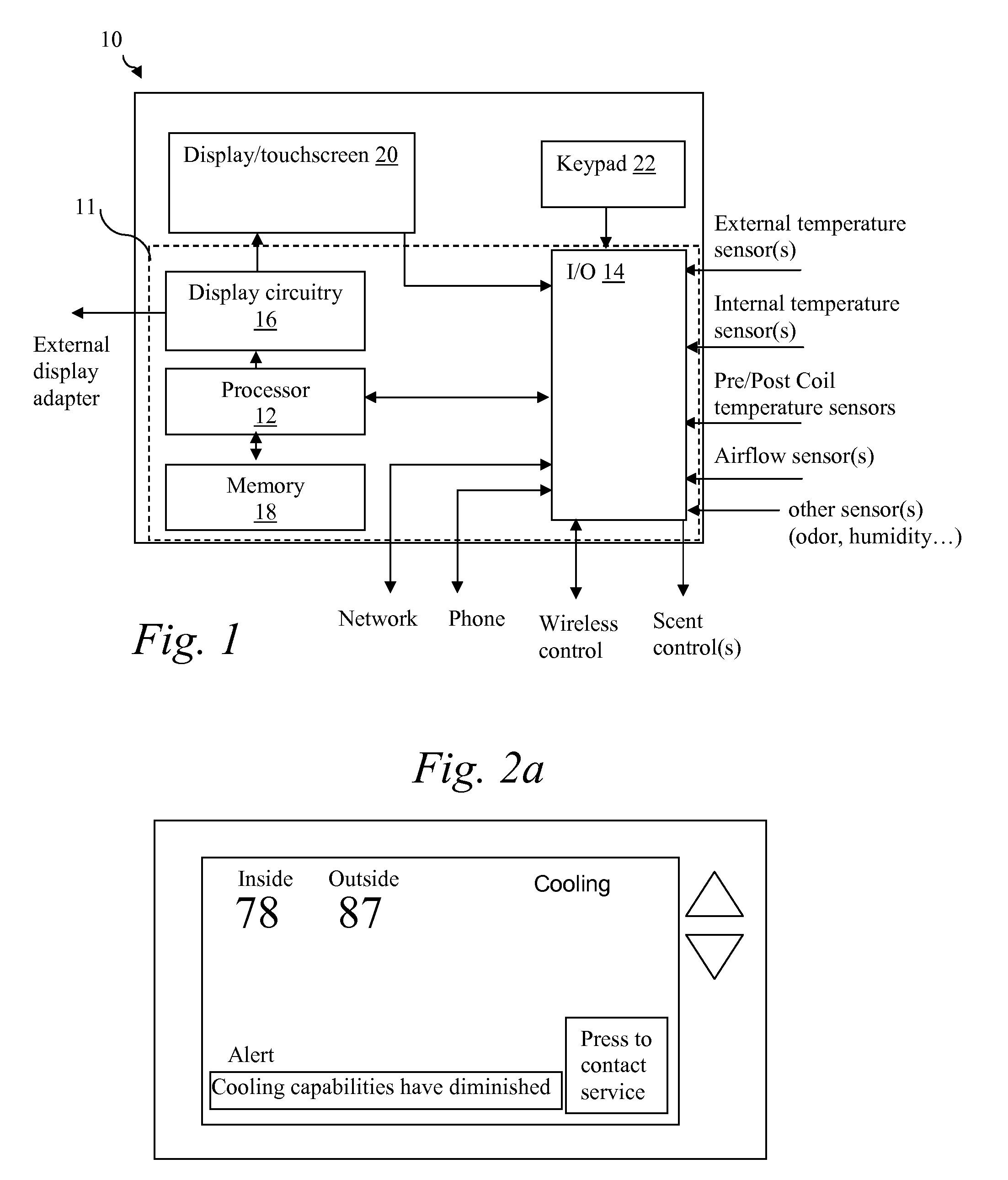
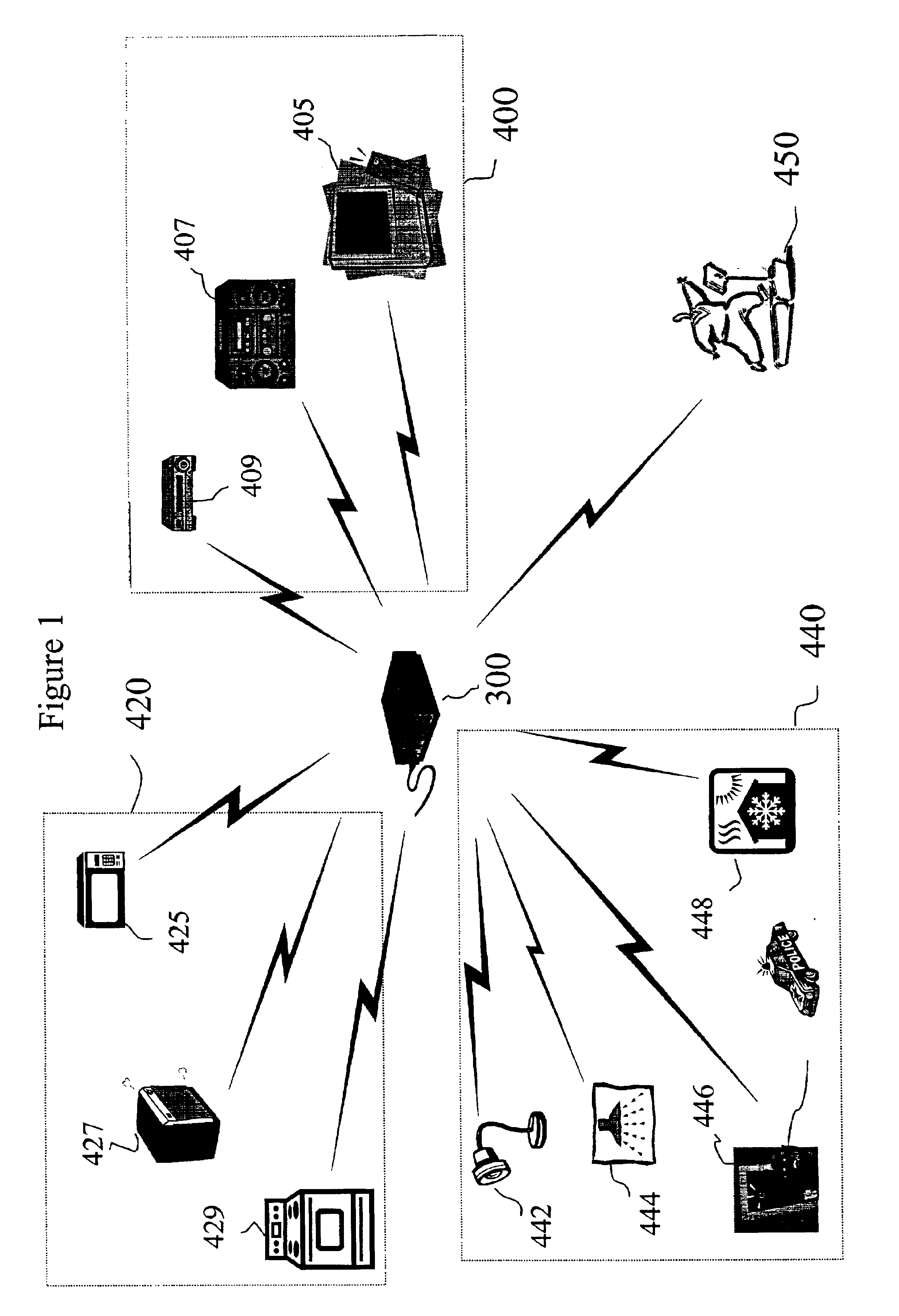
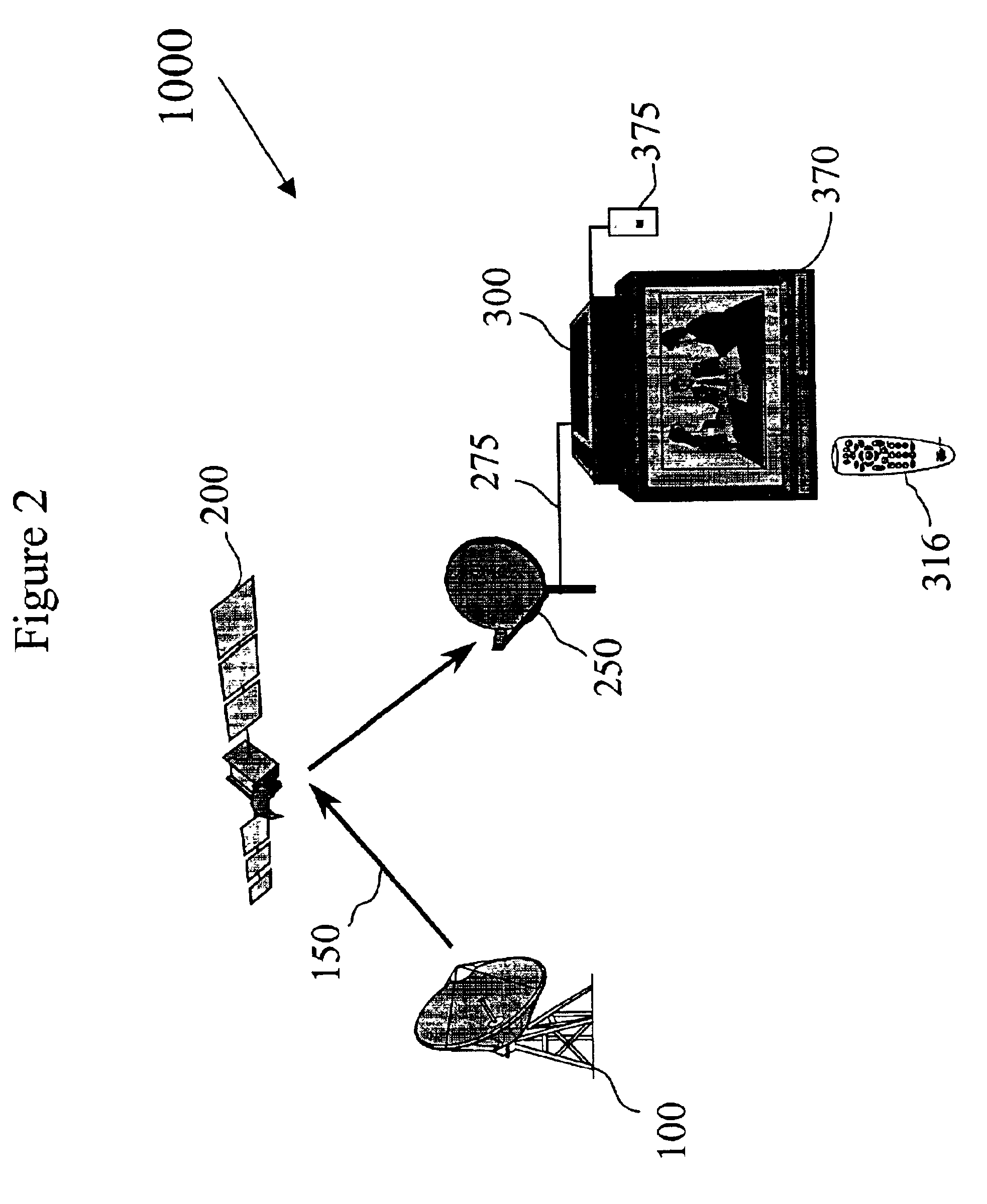
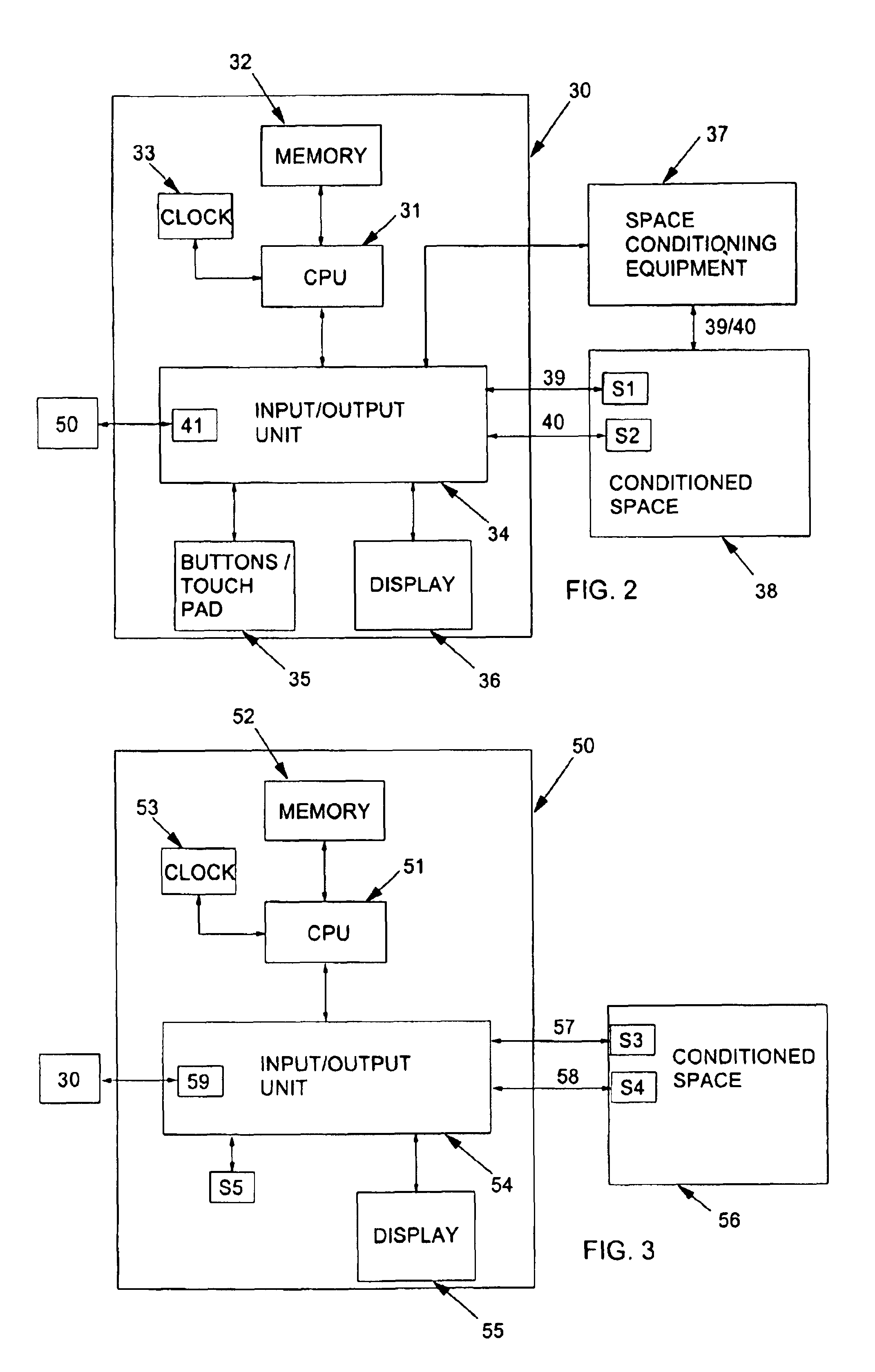
System and method of controlling an HVAC system
InactiveUS20070043478A1Sampled-variable control systemsMechanical apparatusControl systemEnergy control
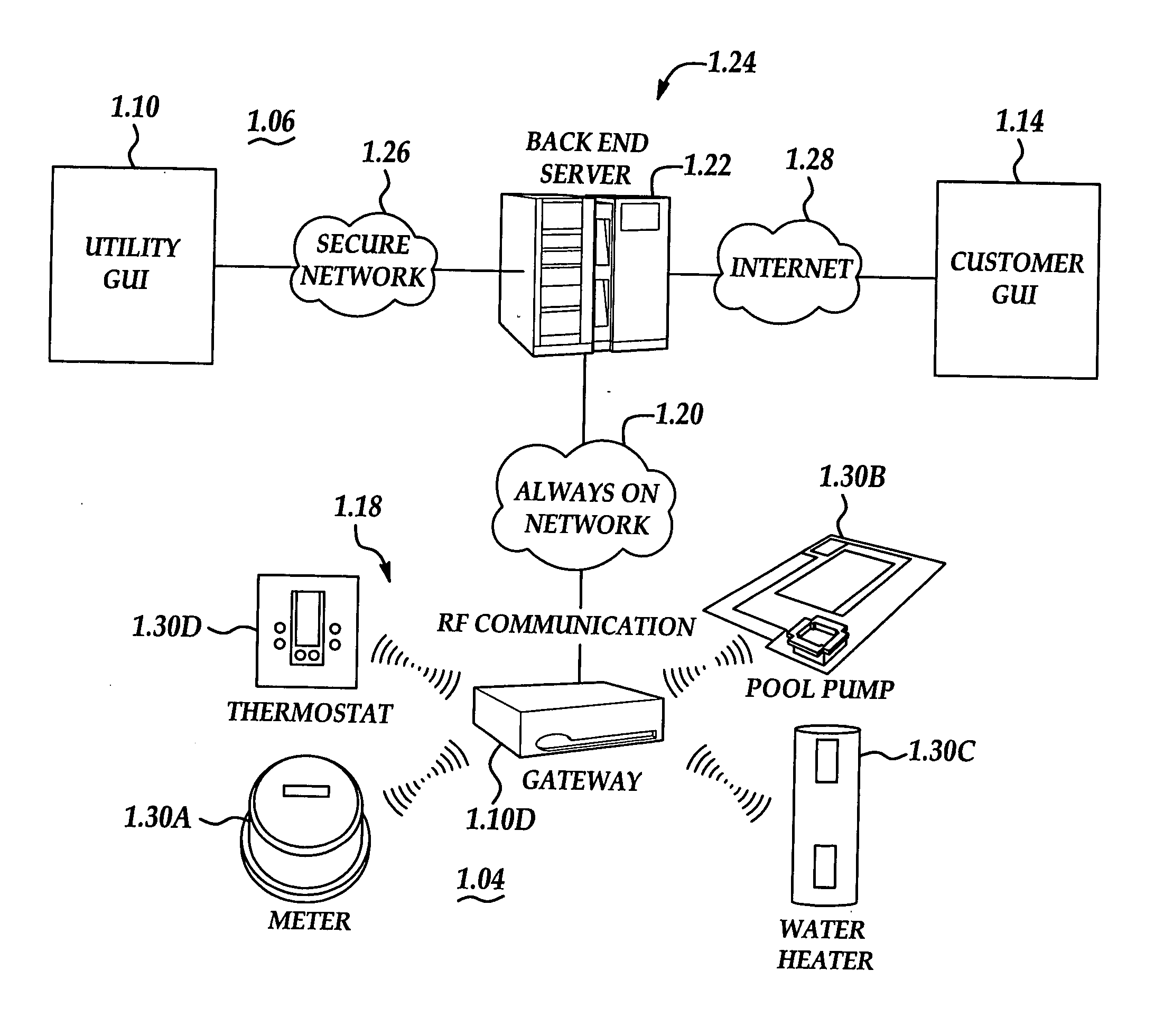
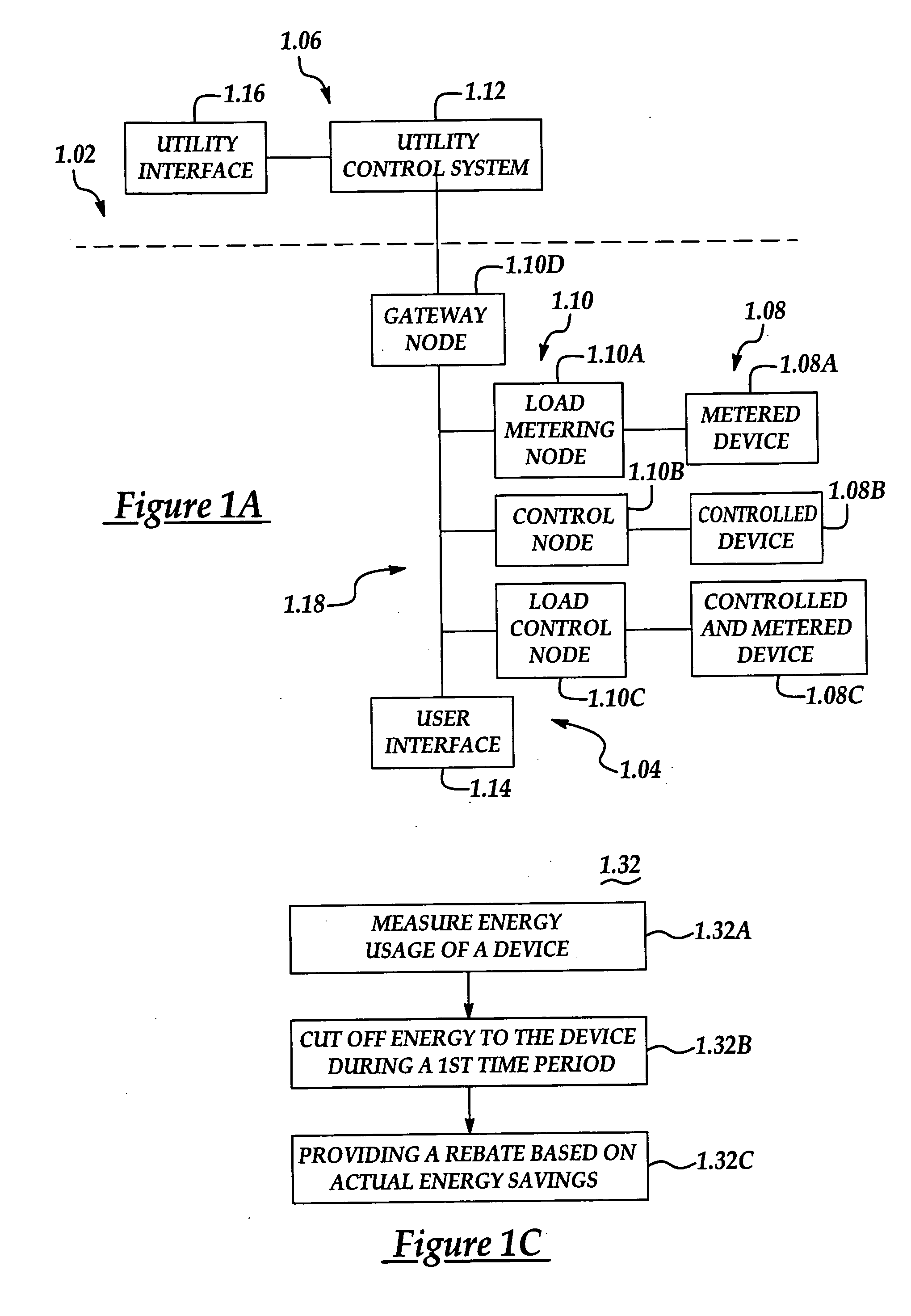
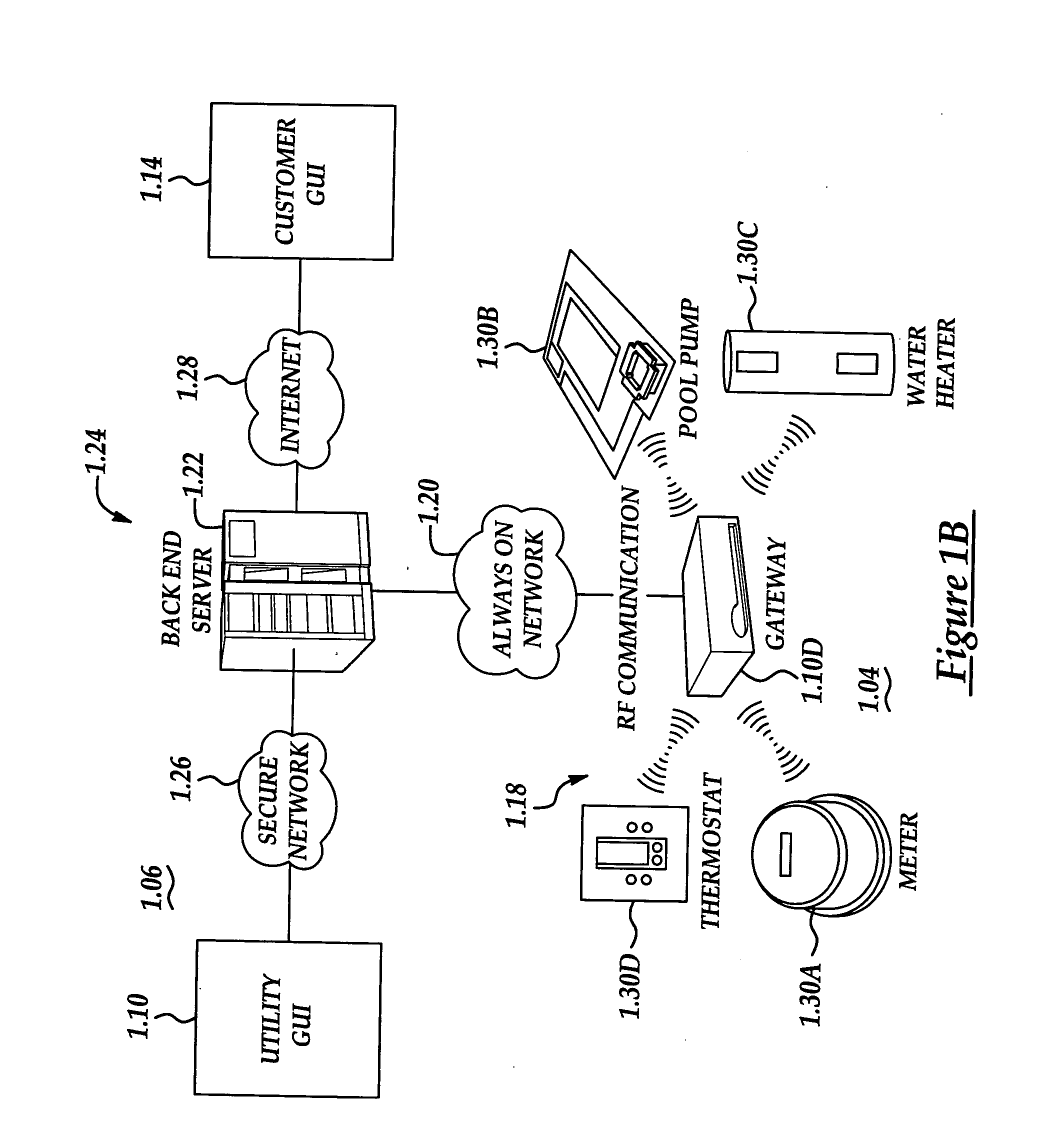
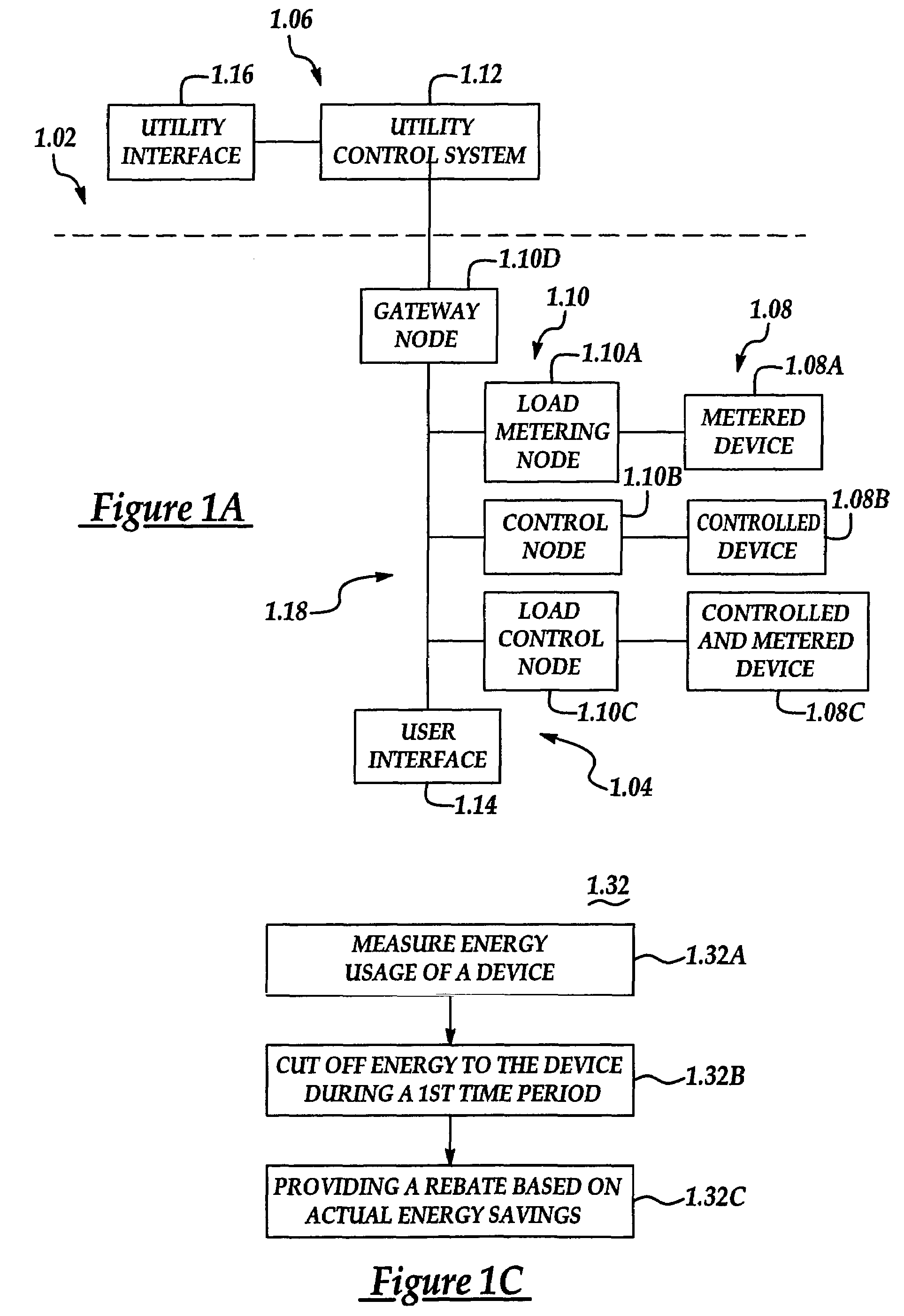
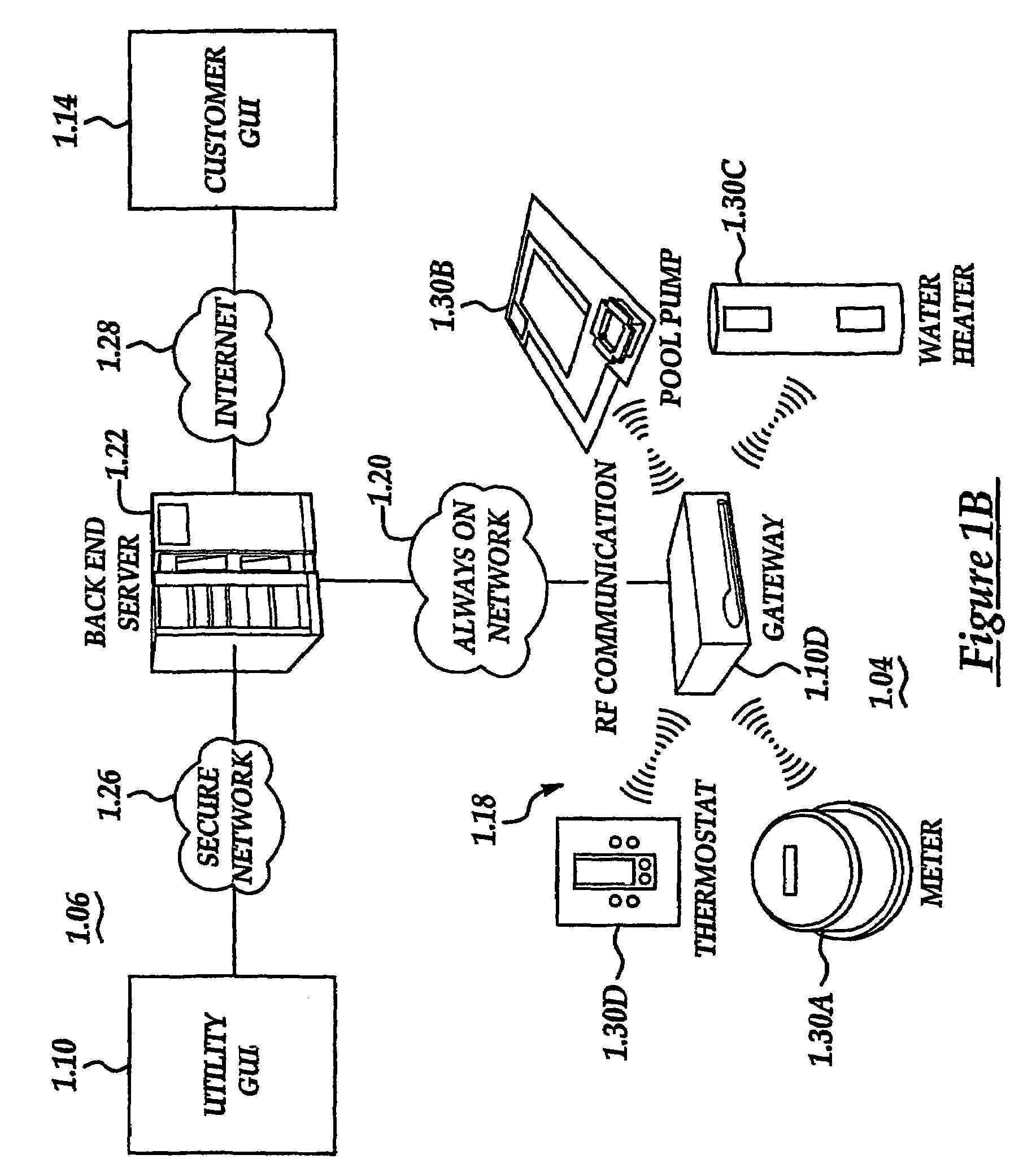
A system and method manage delivery of energy from a distribution network to one or more sites. Each site has at least one device coupled to the distribution network. The at least one device controllably consumes energy. The system includes a node and a control system. The node is coupled to the at least one device for sensing and controlling energy delivered to the device. A control system is coupled to the node and distribution network for delivering to the node at least one characteristic of the distribution network. The node for controls the supply of energy to the device as a function of the at least one characteristic.
Owner:EHLERS GREGORY A +1
System and method of controlling an HVAC system
A system and method manage delivery of energy from a distribution network to one or more sites. Each site has at least one device coupled to the distribution network. The at least one device controllably consumes energy. The system includes a node and a control system. The node is coupled to the at least one device for sensing and controlling energy delivered to the device. A control system is coupled to the node and distribution network for delivery to the node at least one characteristic of the distribution network. The node controls the supply of energy to the device as a function of the at least one characteristic.
Owner:INVENSYS SYST INC
Configurable vibration sensor
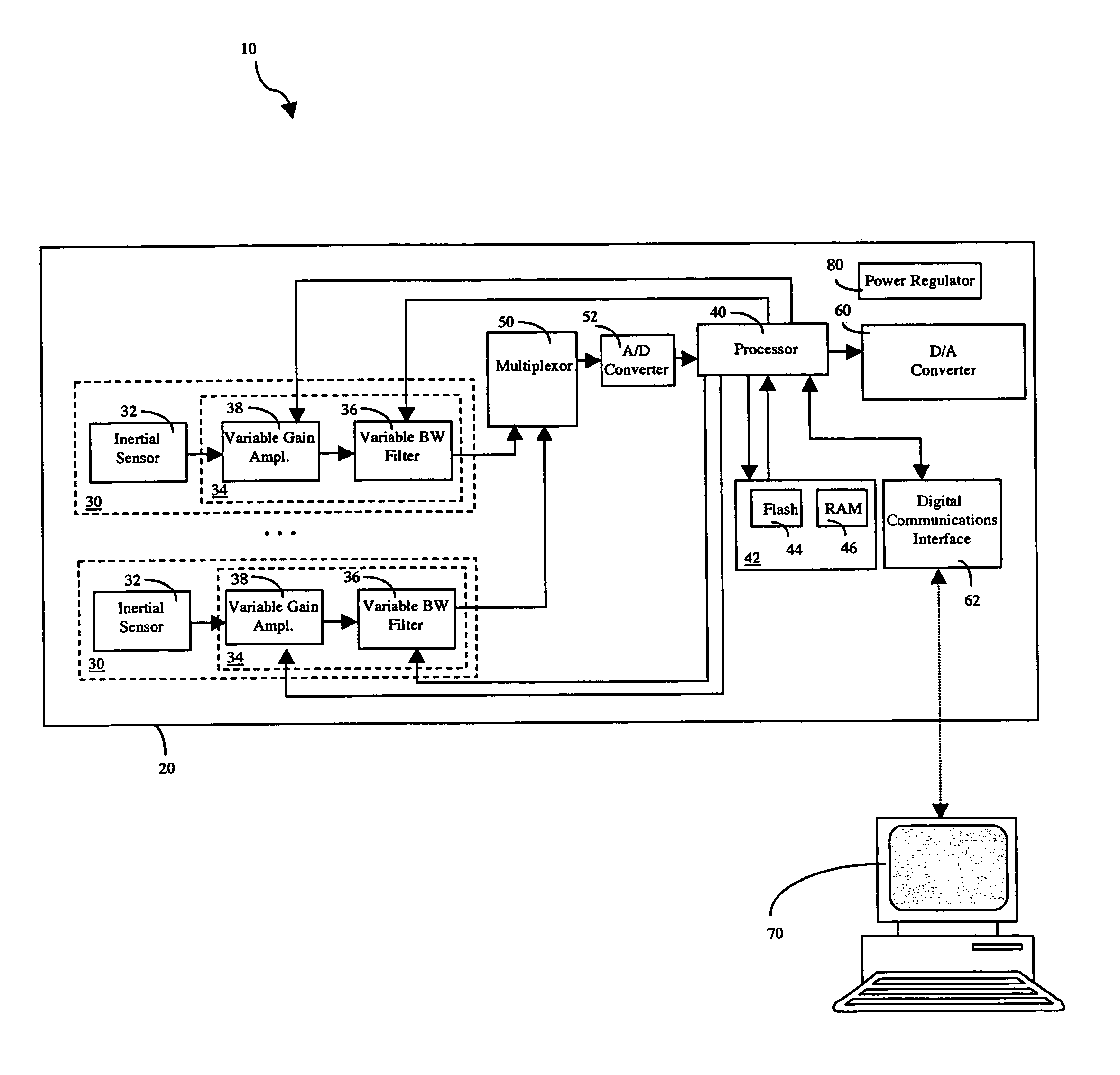
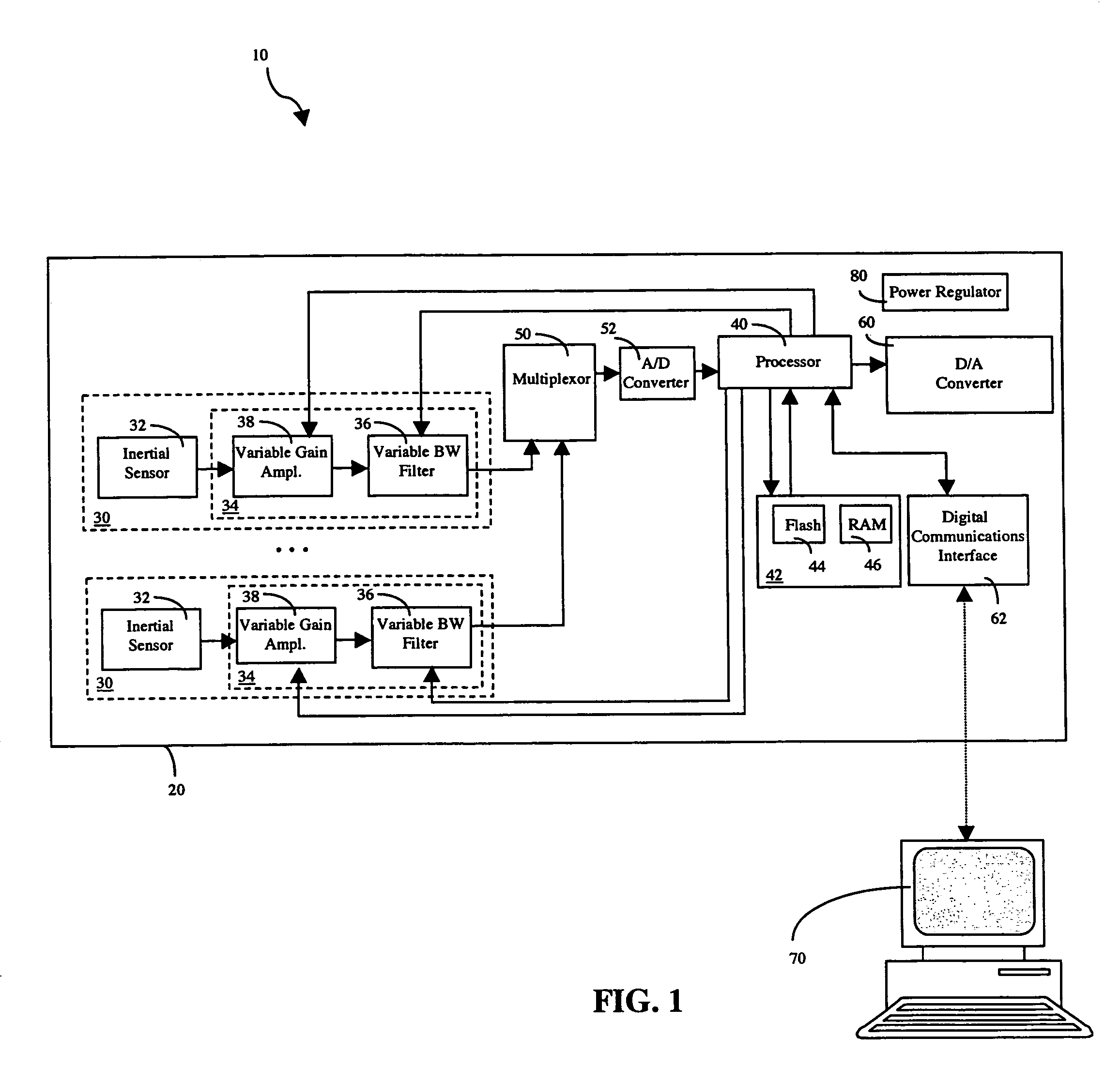
InactiveUS7093492B2Vibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingVibration measurementVariable-gain amplifier
A configurable vibration sensor having a sensor circuit, an analog-to-digital converter and a processor is provided. The sensor circuit employs a vibration sensing element and a variable bandwidth filter controllable by the processor. In addition to the variable bandwidth filter, other configurable elements may also be employed in the sensor circuit, including a variable gain amplifier. These configurable elements allow the configurable vibration sensor to be configured for different vibration measurement applications when measuring vibrations from vibrating structures such as machinery and the like.
Owner:MECHWORKS SYST
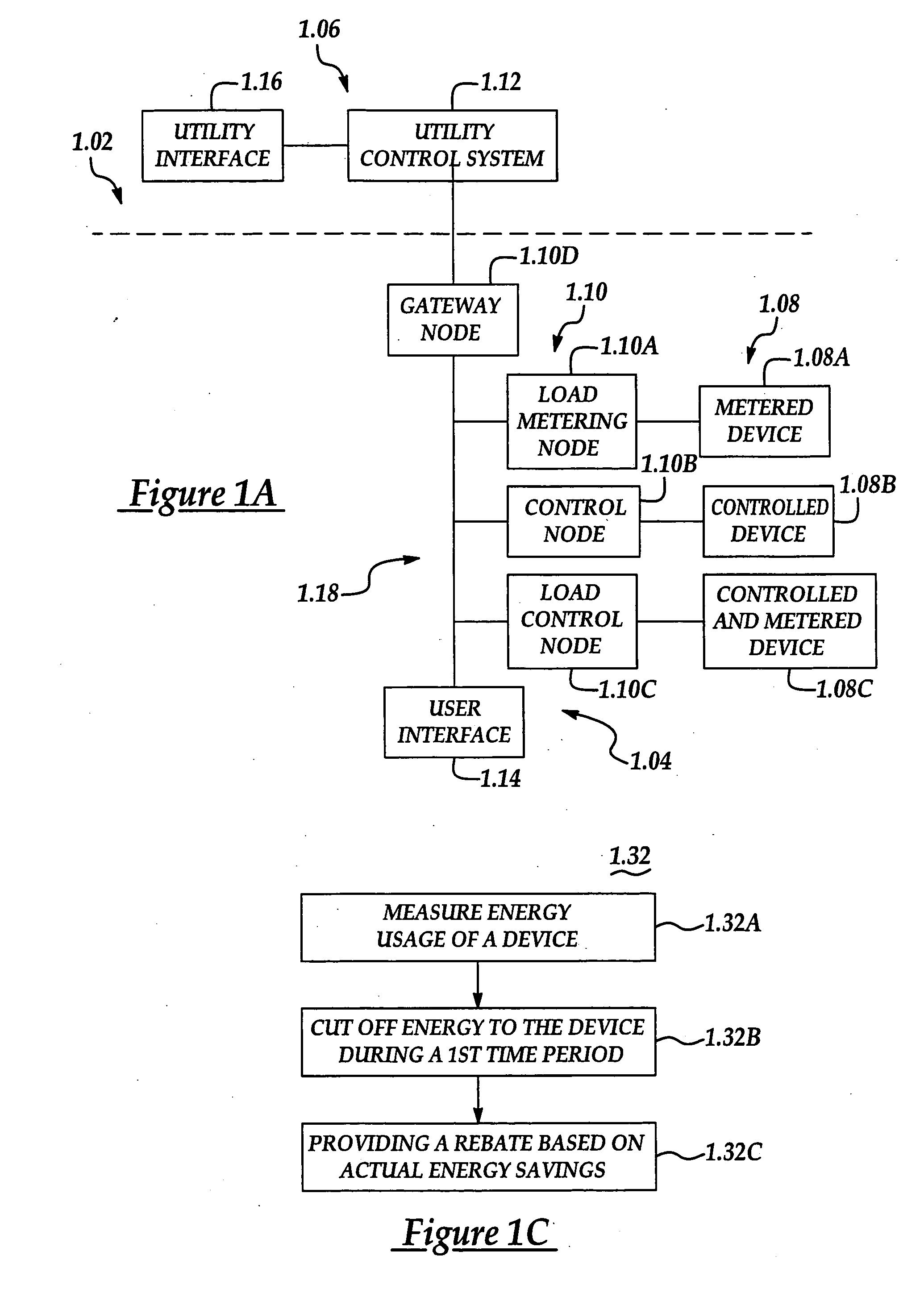
Home automation system and method
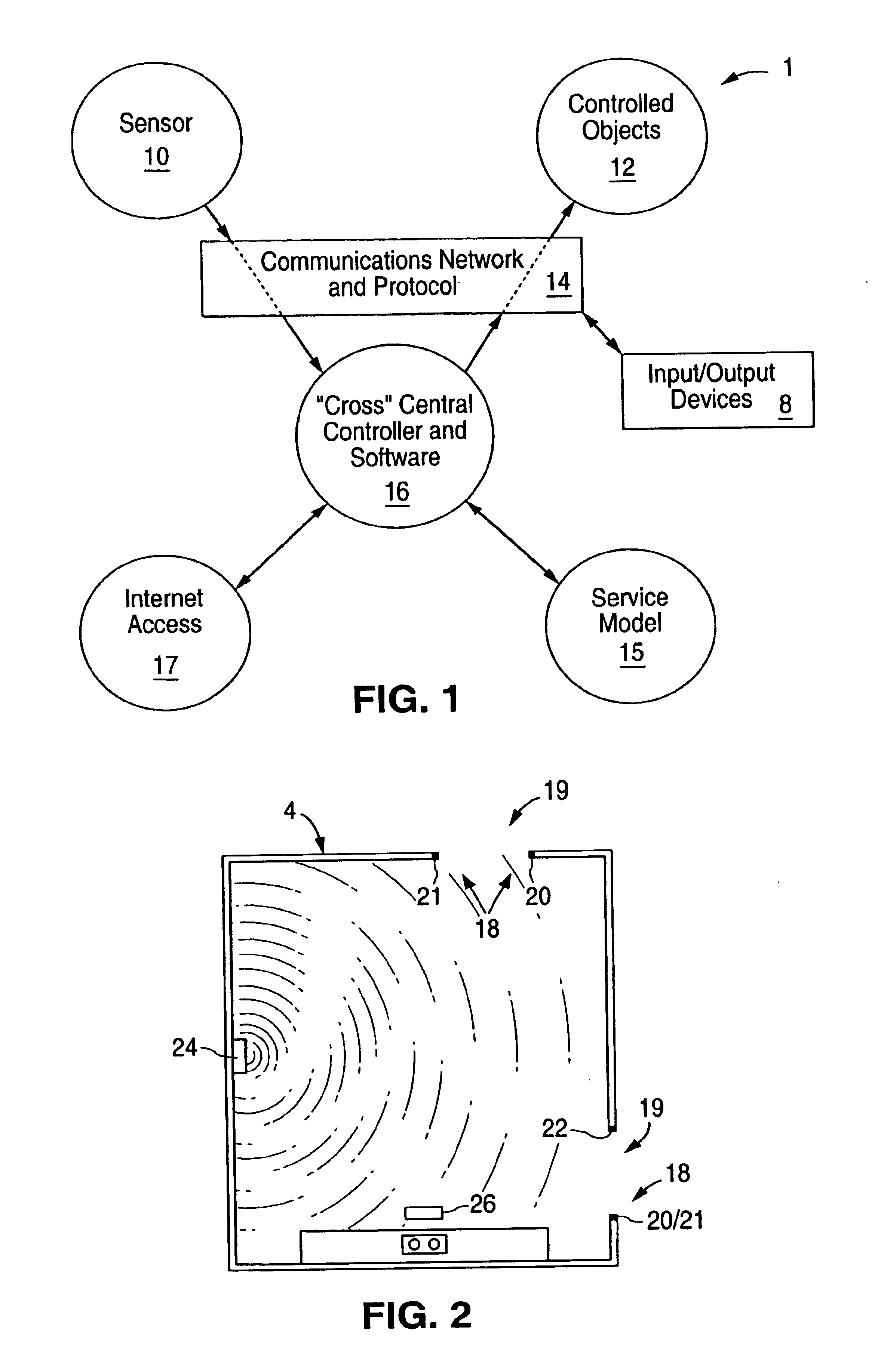
InactiveUS6912429B1Matches need and abilityImprove automationSpace heating and ventilationTemperatue controlAutomatic controlEngineering
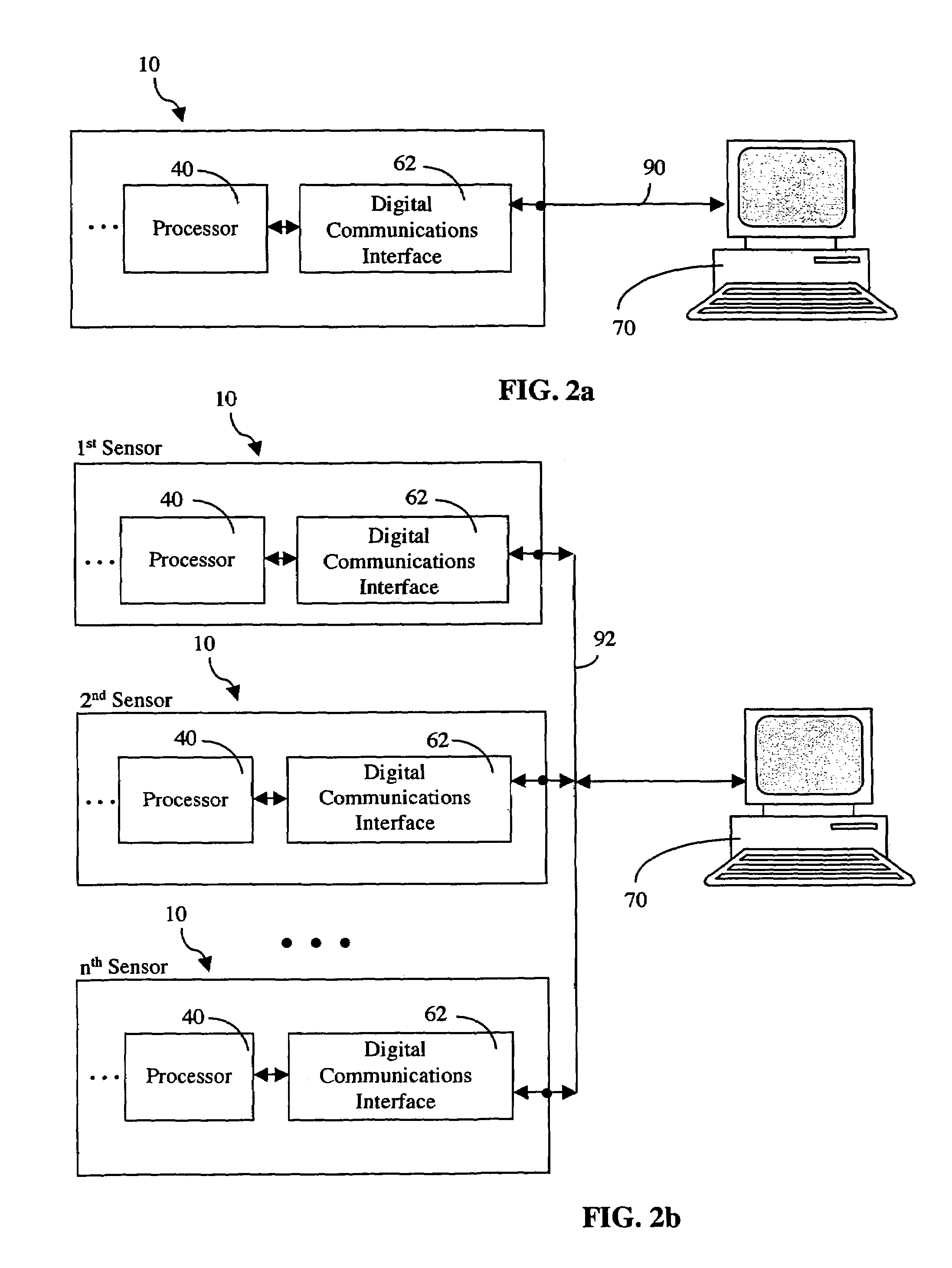
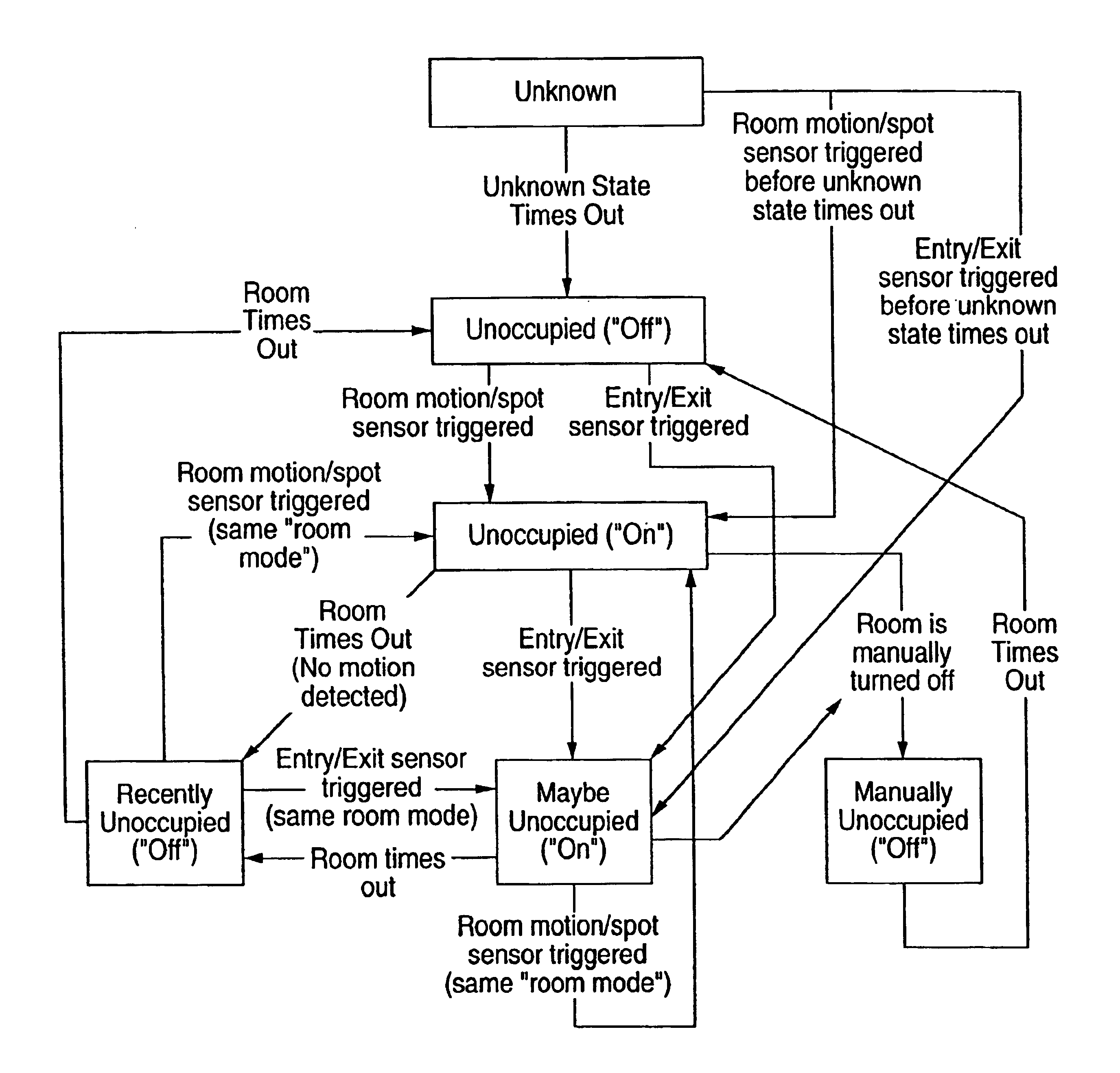
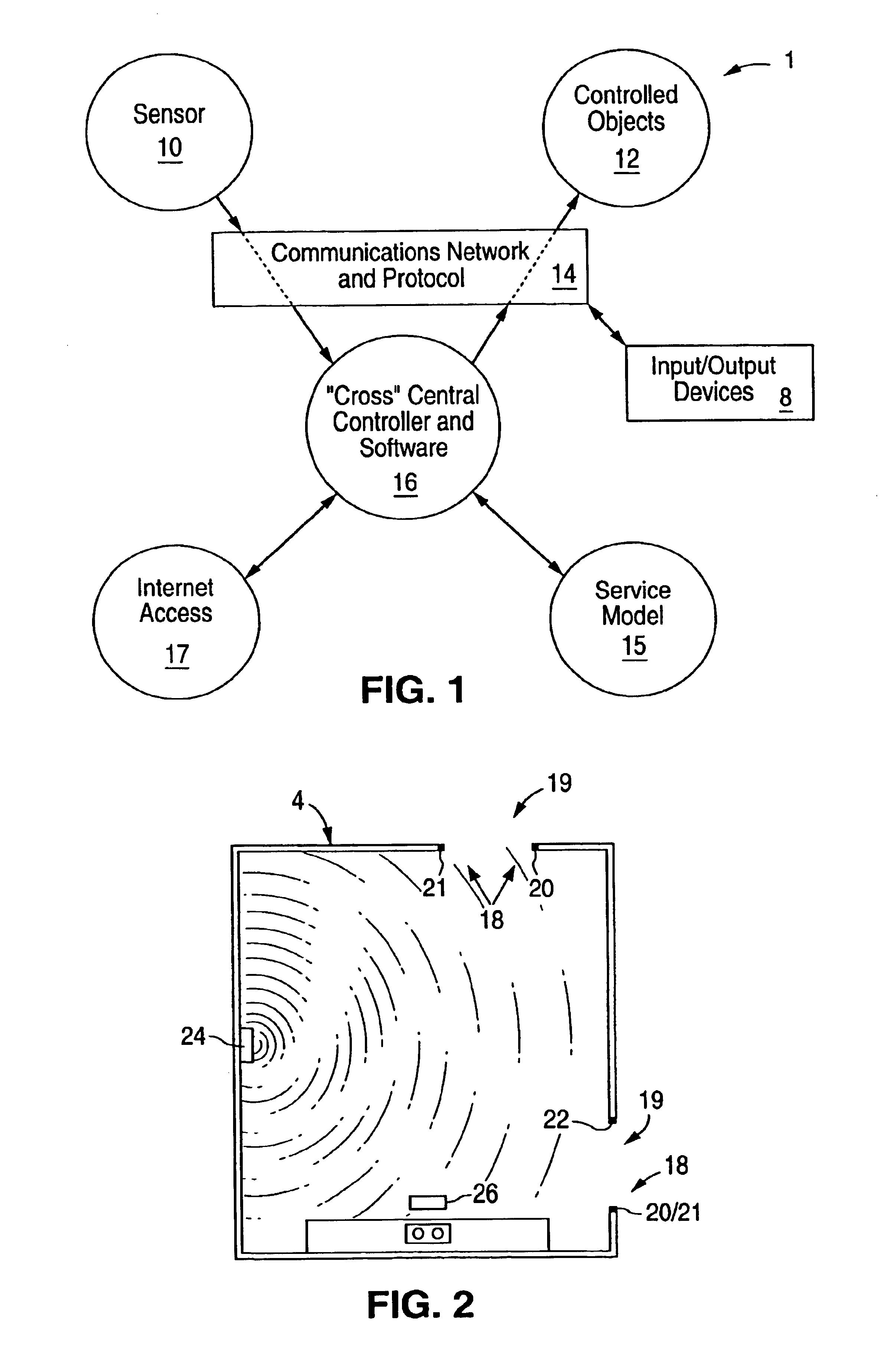
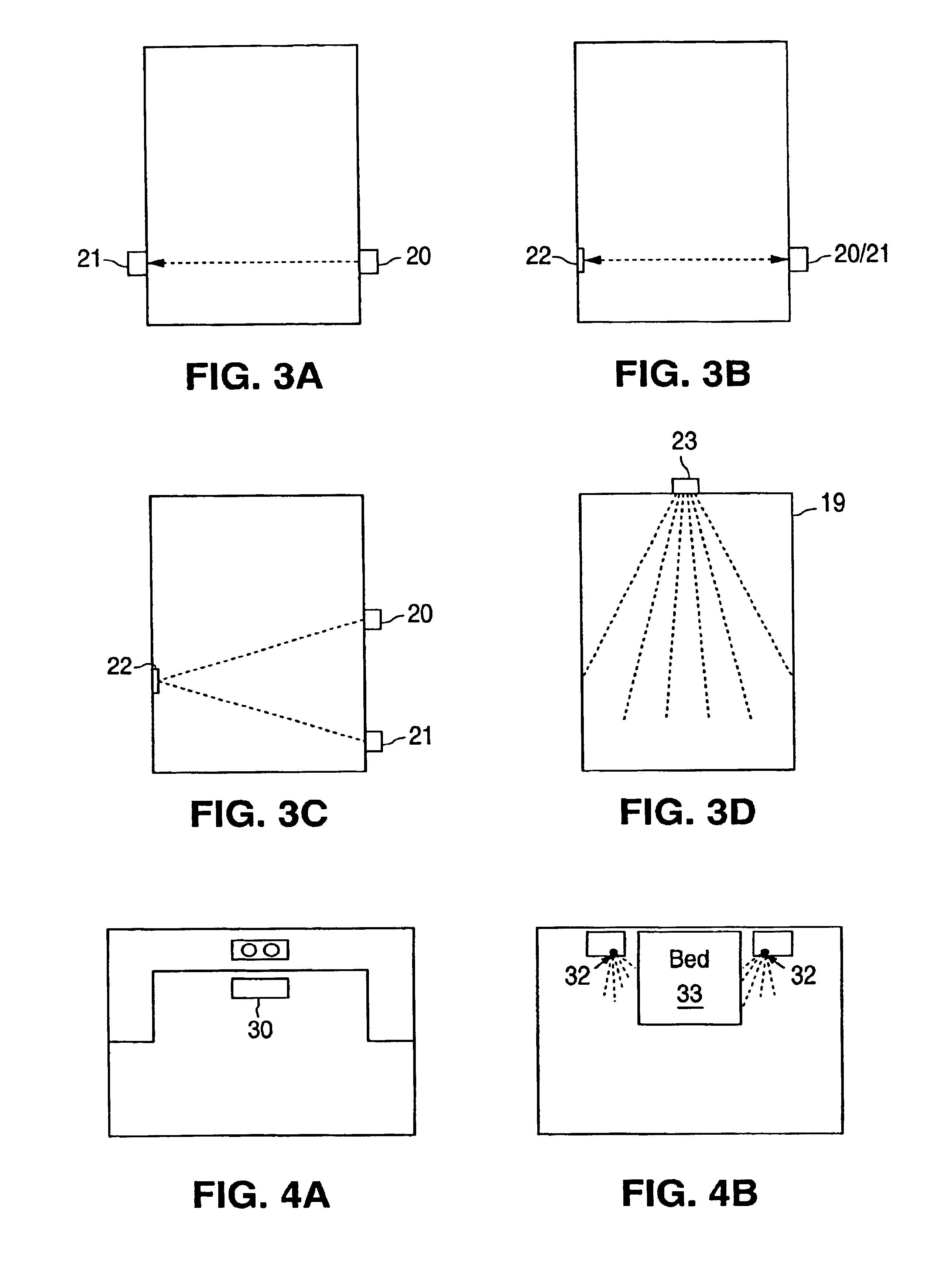
A home automation system and method for automatic control of controlled devices throughout a home. A unique architecture of occupancy sensors includes entry / exit sensors for detecting movement through doorways that separate rooms in the home, room motion sensors for detecting room occupancy, spot sensors to detect occupancy of specific locations within the rooms, and house status sensors to detect the status of certain parameters of the home. A central controller communicates with the sensors and controlled objects over a communications network, where the sensors and controlled objects can be added to the system in a ‘plug and play’ manner. The central controller controls the controlled objects in response to the entry / exit sensors, room motion sensors, spot sensors and the house status sensors. This control is accomplished by assigning each room to one of a plurality of room occupancy states, and to one of a plurality of room modes for creating desired room atmospheres using the controlled objects, which both dictate how the controlled objects are controlled by the central controller. The room modes travel from room to room as the occupant moves throughout the home, and multiple occupants can be using different room modes as they move about the home. The controlled objects also have controlled object states, which are used by the central controller to control the controlled objects.
Owner:HOME DIRECTOR
Method and apparatus for improved building automation
InactiveUS20020016639A1Large modularityCommunicationSampled-variable control systemsComputer controlModularityEngineering
The improved building automation system of the present invention is modular in the extreme. This diminishes the amount of custom programming required in order to affect control of a particular building. It allows for a relatively open architecture which can accommodate a variety of unique control applications which are scripted for a particular building. By modularizing many of the common processes utilized in the automation system, the custom programming required to control any particular building is minimized. This modularity in design allows for uniform and coordinated control over a plurality of automation subsystems which may be incompatible with one another at the device or machine level, but which can be controlled utilizing a relatively small and uniform set of "interprocess control commands" which define an interprocess control protocol which is utilized in relatively high level scripts and control applications which may be written for a particular building.
Owner:UNIDEN AMERICA
Programmable and expandable building automation and control system
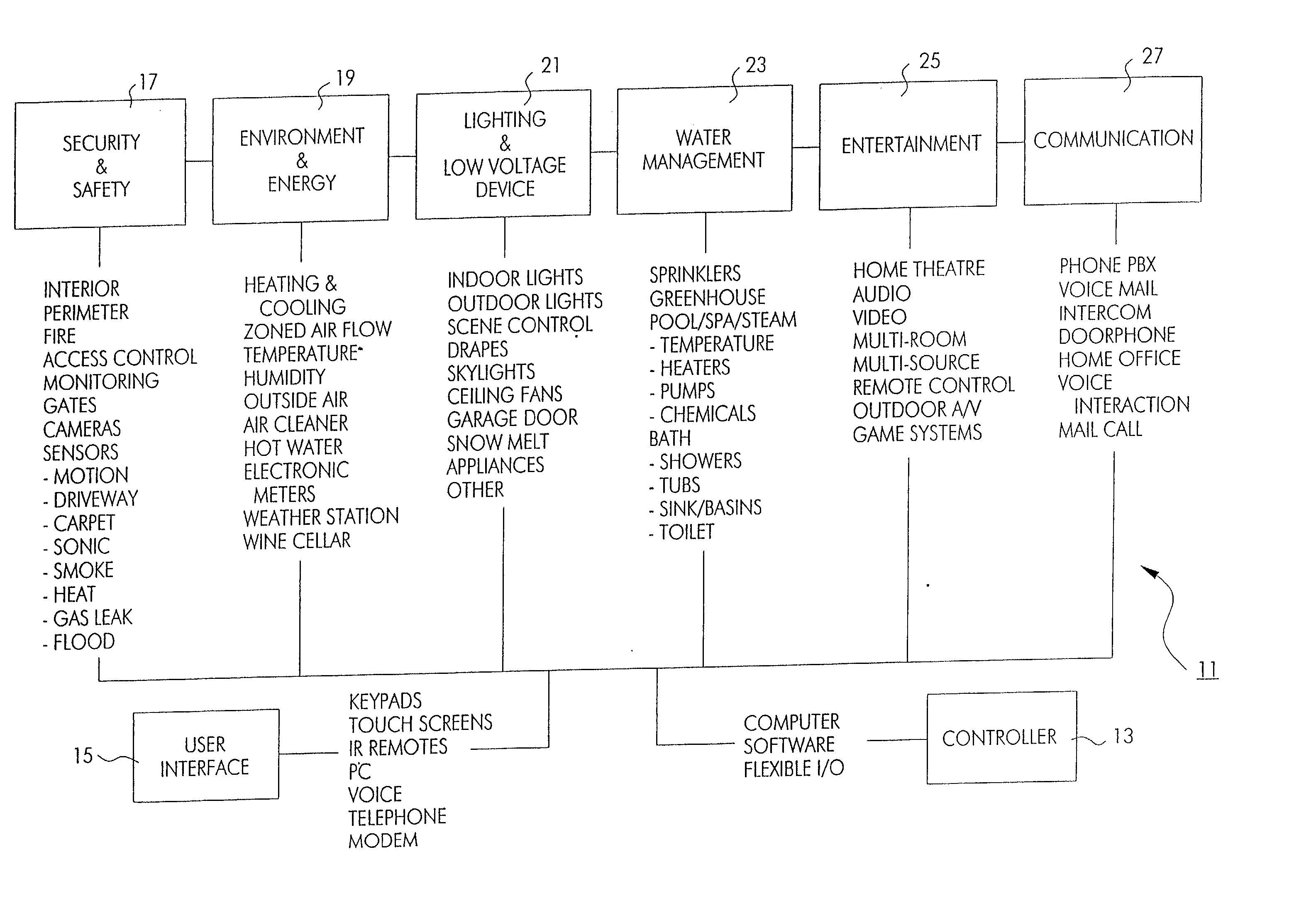
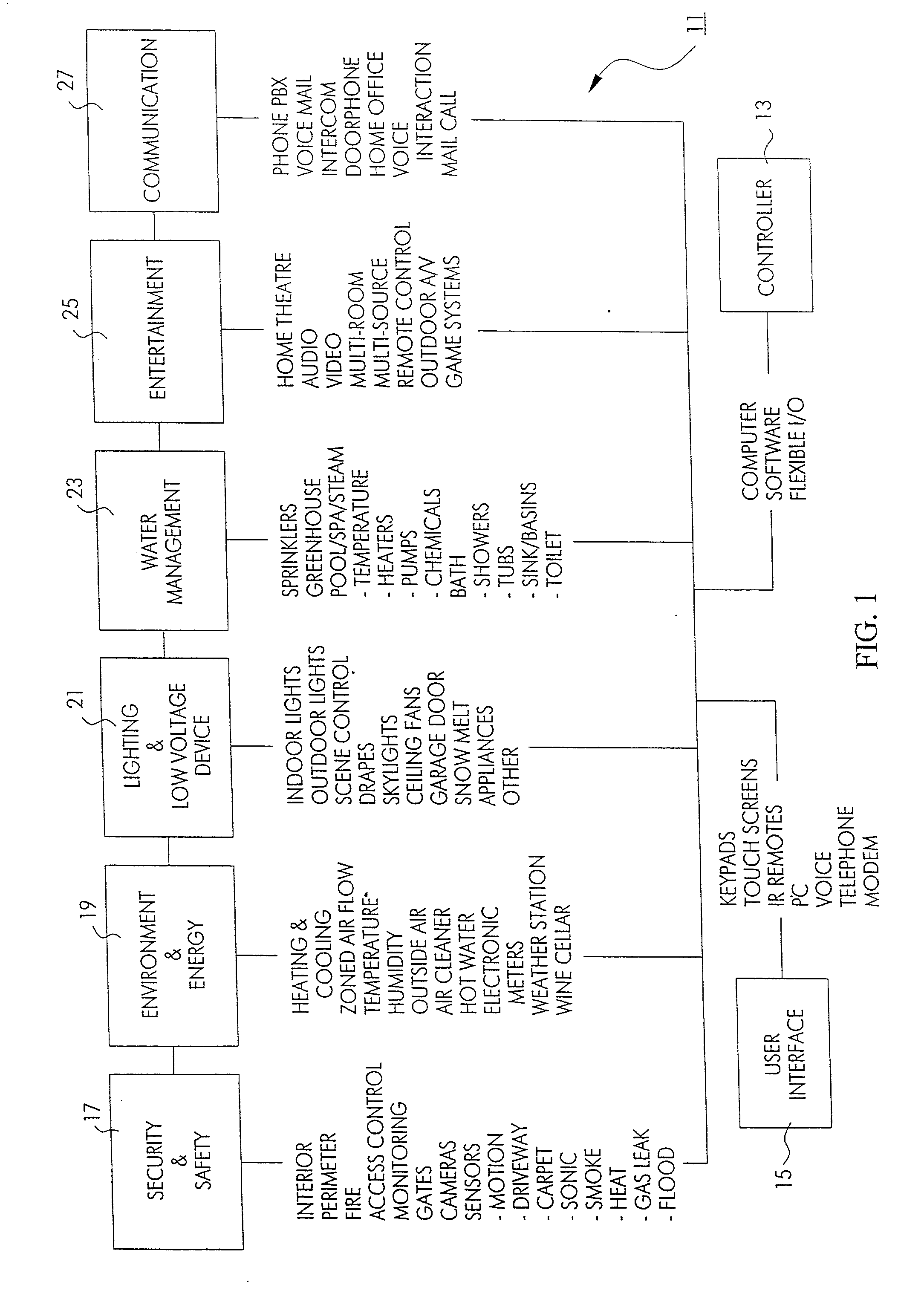
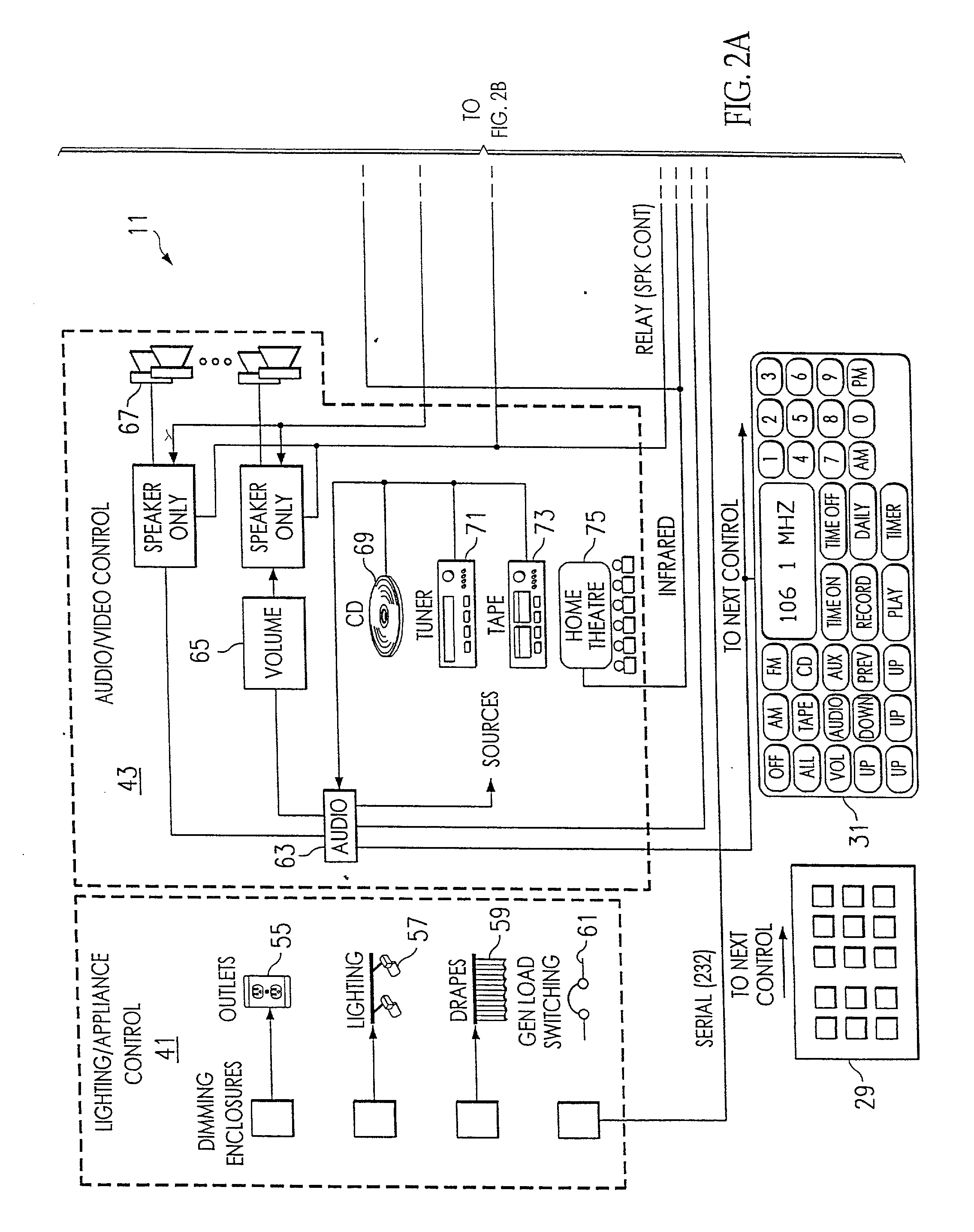
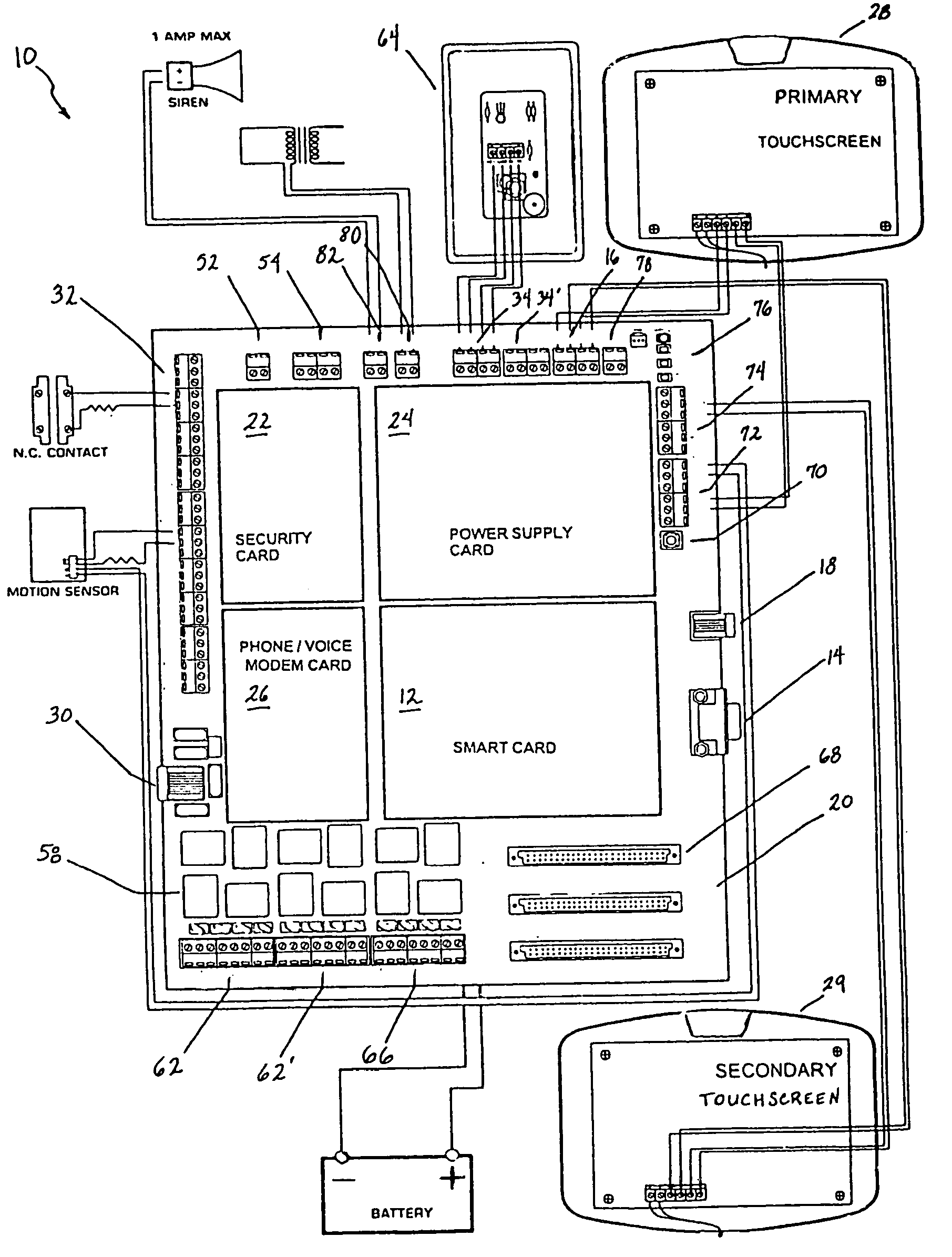
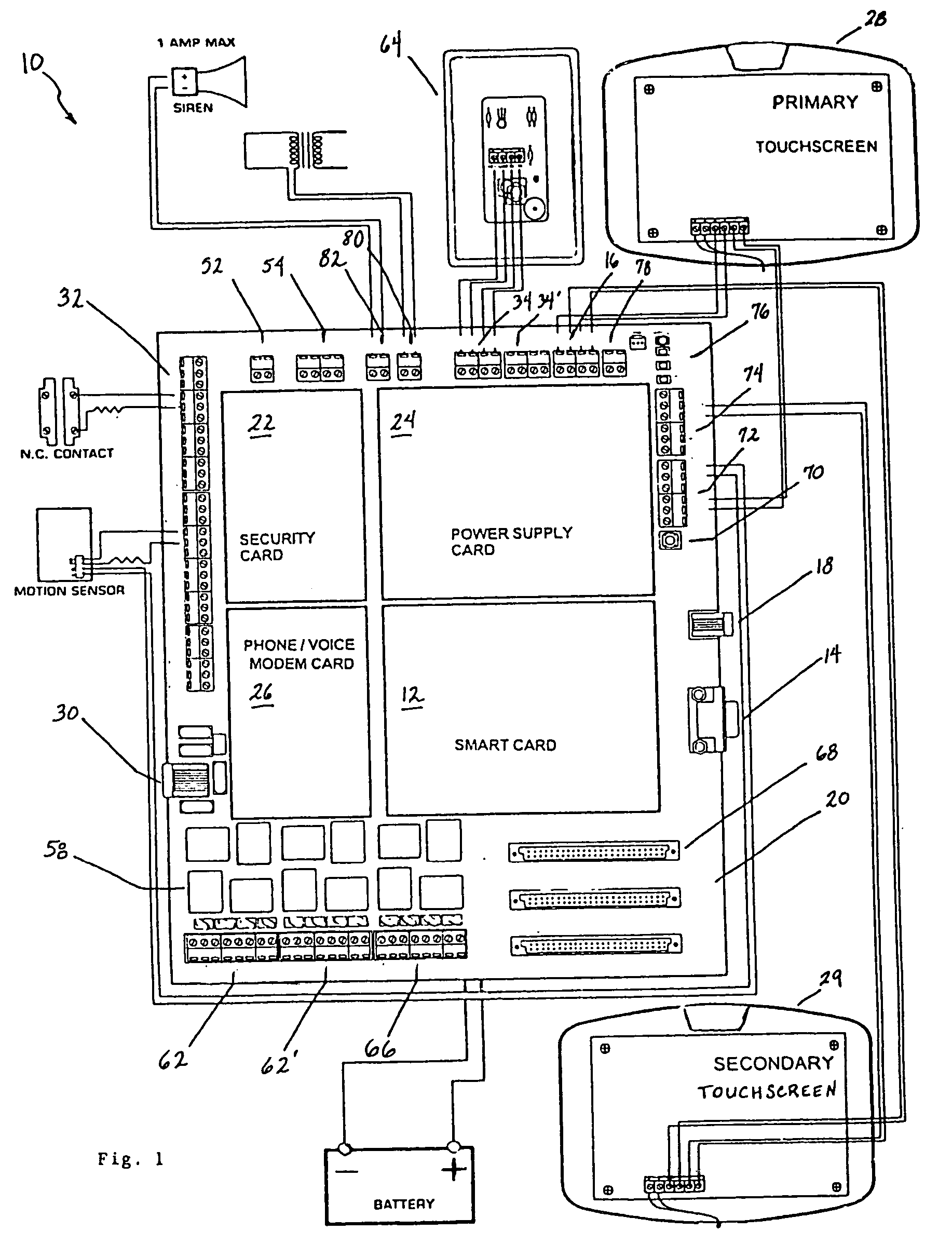
InactiveUS20050090915A1Readily modified and expanded and repairedReduces warranty and support costProgramme controlSampled-variable control systemsModem deviceSmart card
A programmable and expandable building automation and control system 10. A system platform supports interchangeable smart card 12, security card 22, power supply card 24, telephone / voice / modem card 26, HVAC relay control 62, auxiliary relay control 66, power 80, telephone interface 30, sensor analog inputs 32, smoke detector interface 54, siren / strobe output 82, tamper loop 52, protected peripheral power supply 72, switched peripheral power supply 74, PLC communication protocol interface 18, RS 232 communication interface 14, RS 485 communication interface 16, touchscreen user interface 28, and “smart” key interface 34 via “smart” key 104. In addition to touchscreen and smart key interface, user-interface with system 10 is accommodated via telephone, personal computer or personal digital assistant, or through infrared or radio frequency transmission.
Owner:SMART SYST TECH
Occupancy sensor and method for home automation system
InactiveUS6909921B1Good roomTemperatue controlStatic/dynamic balance measurementAuto regulationAutomatic control
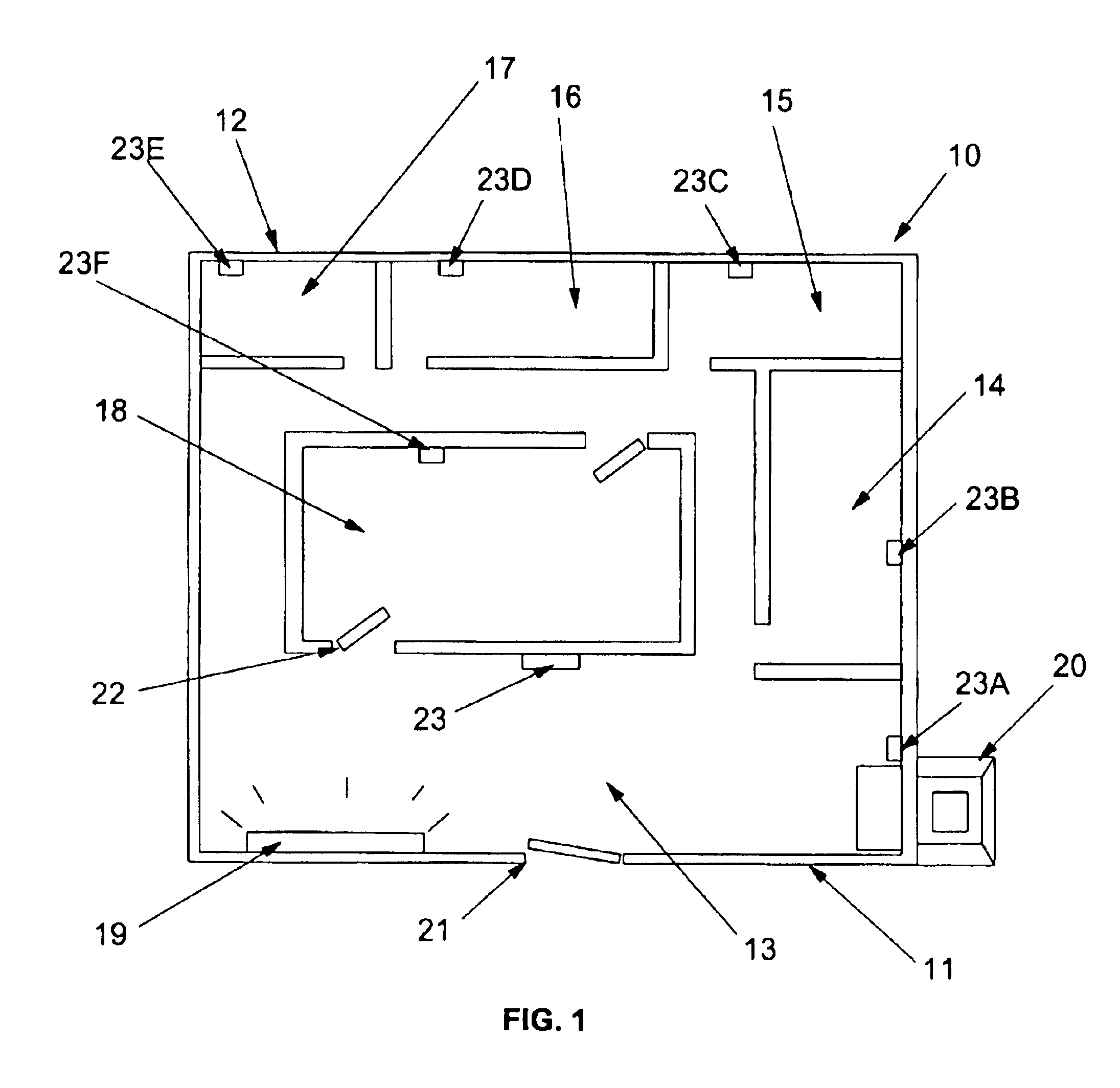
A room occupancy sensor, a home automation system and a method for automatic control of controlled devices throughout a home. A unique architecture of occupancy sensors includes entry / exit sensors for detecting movement through doorways that separate rooms in the home, room motion sensors for detecting room occupancy, spot sensors to detect occupancy of specific locations within the rooms, and house status sensors to detect the status of certain parameters of the home. A central controller communicates with the sensors and controlled objects over a communications network, where the sensors and controlled objects can be added to the system in a ‘plug and play’ manner. The central controller controls the controlled objects in response to the entry / exit sensors, room motion sensors, spot sensors and the house status sensors. This control is accomplished by assigning each room to one of a plurality of room states, which dictate how the controlled objects are controlled by the central controller. The controlled objects also have controlled object states, which are used by the central controller to control the controlled objects. The room occupancy sensors have a sensitivity that is automatically adjusted based upon temperature measurements, and the number and timing of occupancy detections.
Owner:HOME DIRECTOR
HVAC remote monitoring system
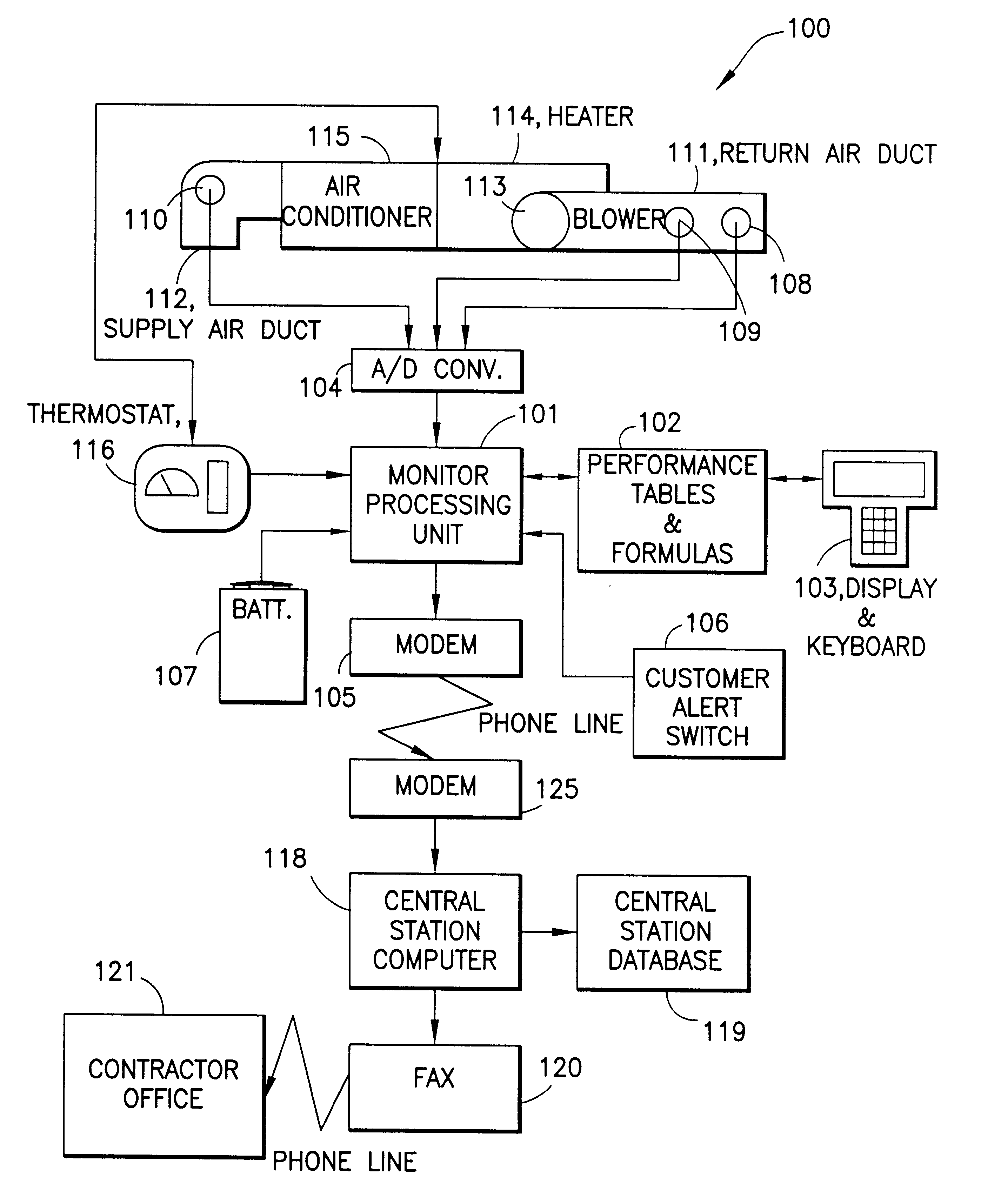
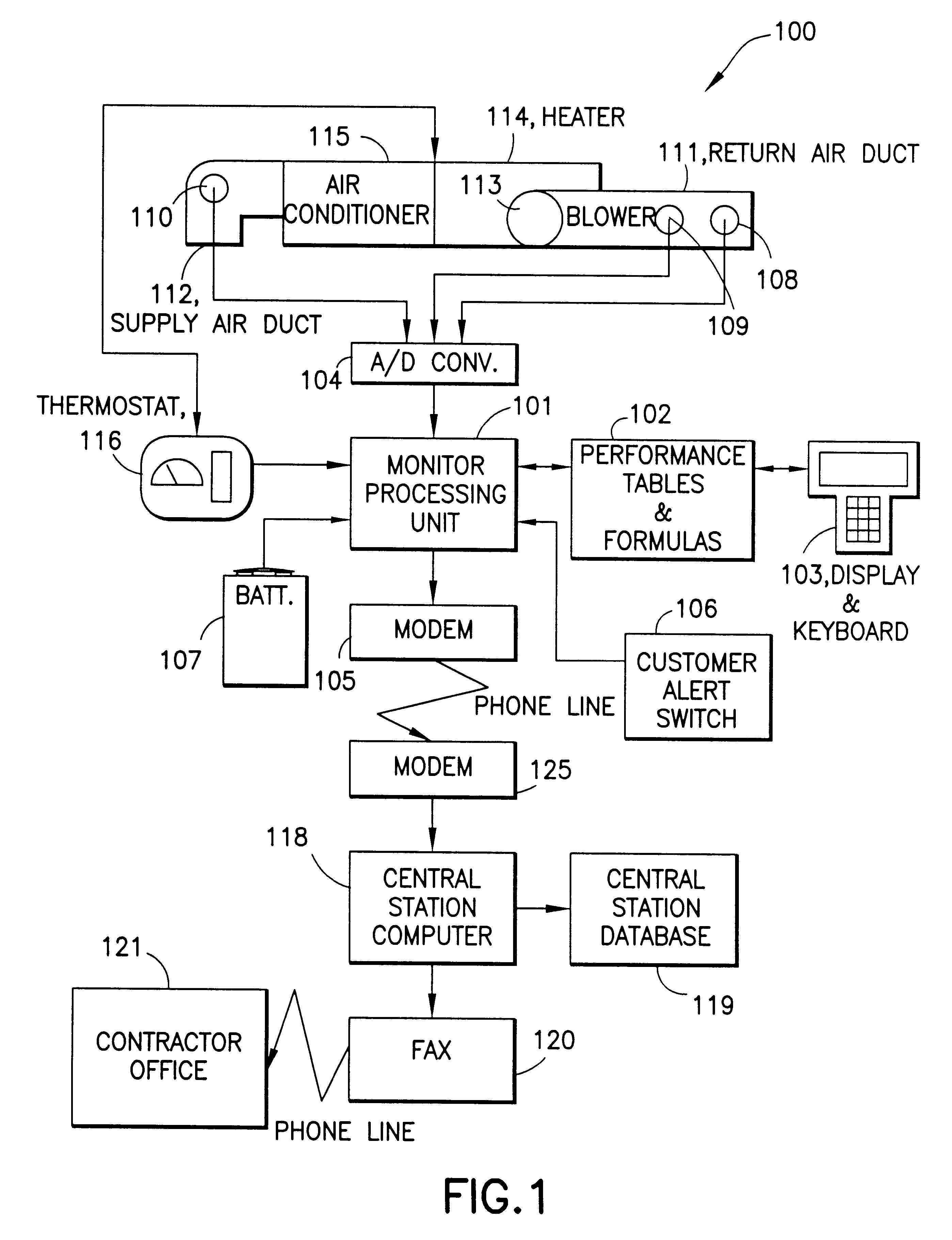
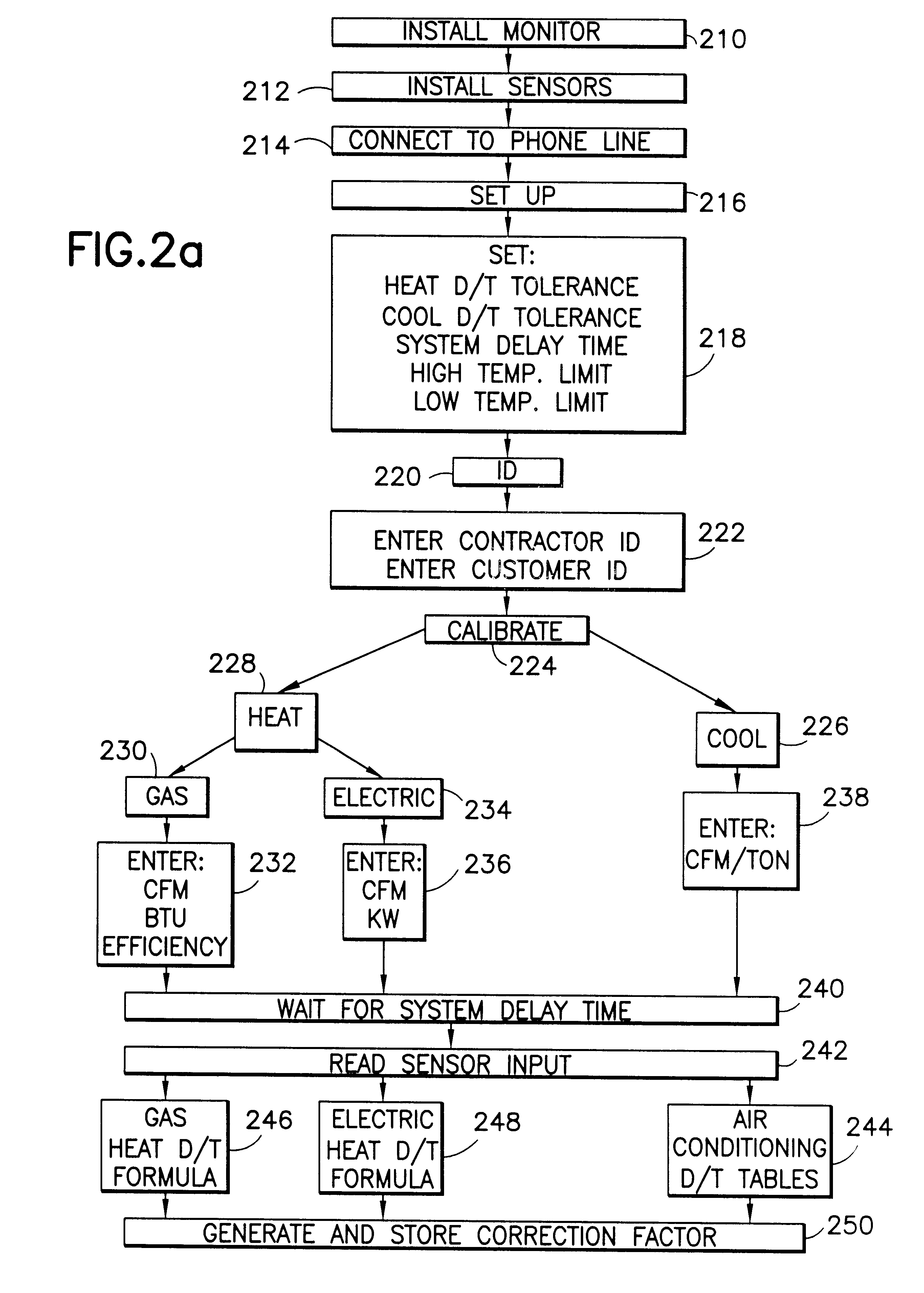
InactiveUS6385510B1Save moneyOvercome problemsSampled-variable control systemsMechanical apparatusModem deviceMonitoring system
An electronic HVAC monitoring computer continuously monitors the general condition and efficiency of an HVAC system and notifies a central station computer via modem link or other signal transmission means, when the general condition or efficiency of the HVAC system falls below certain industry standard values by a pre-set amount.
Owner:HOOG KLAUS D +1
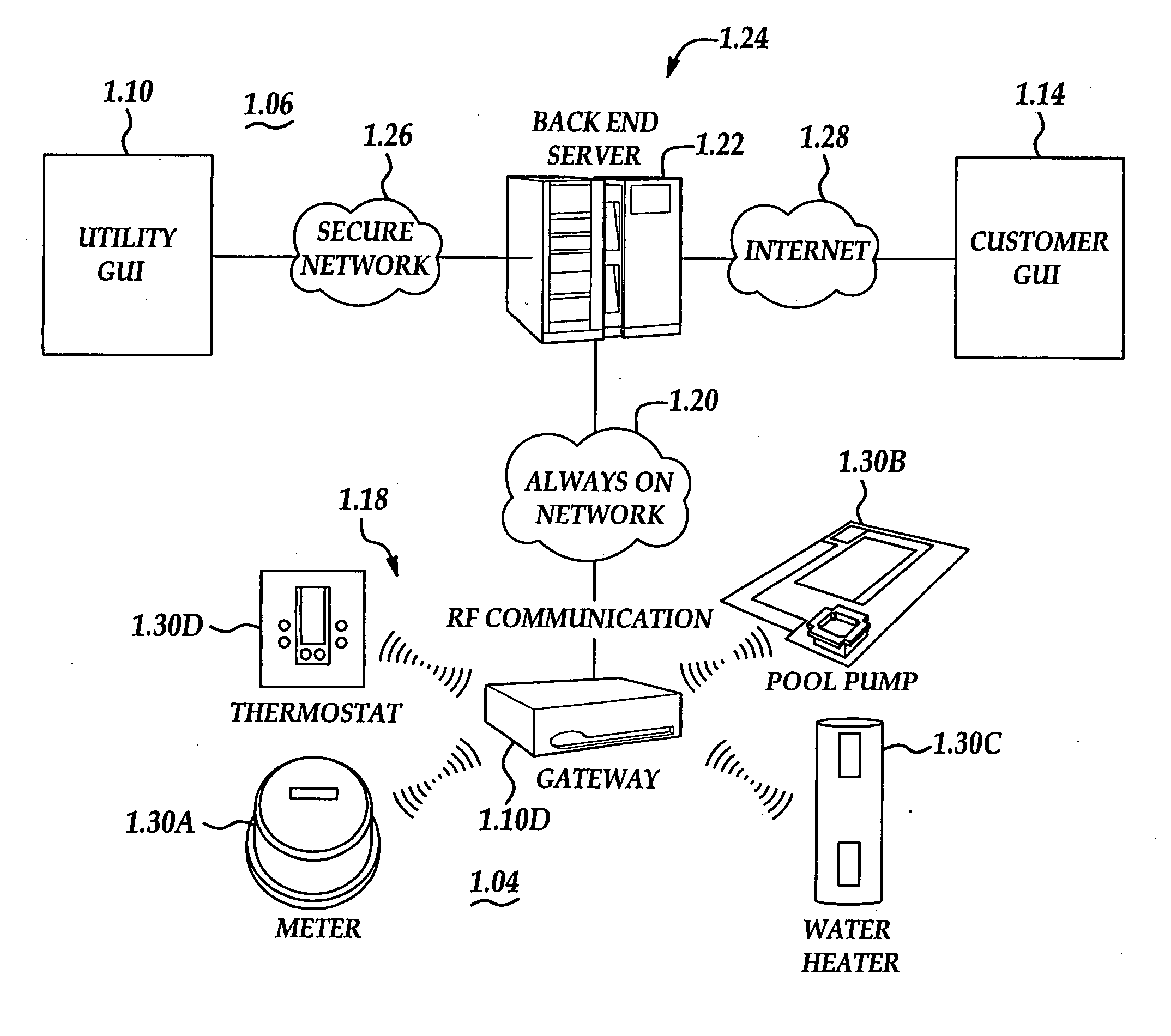
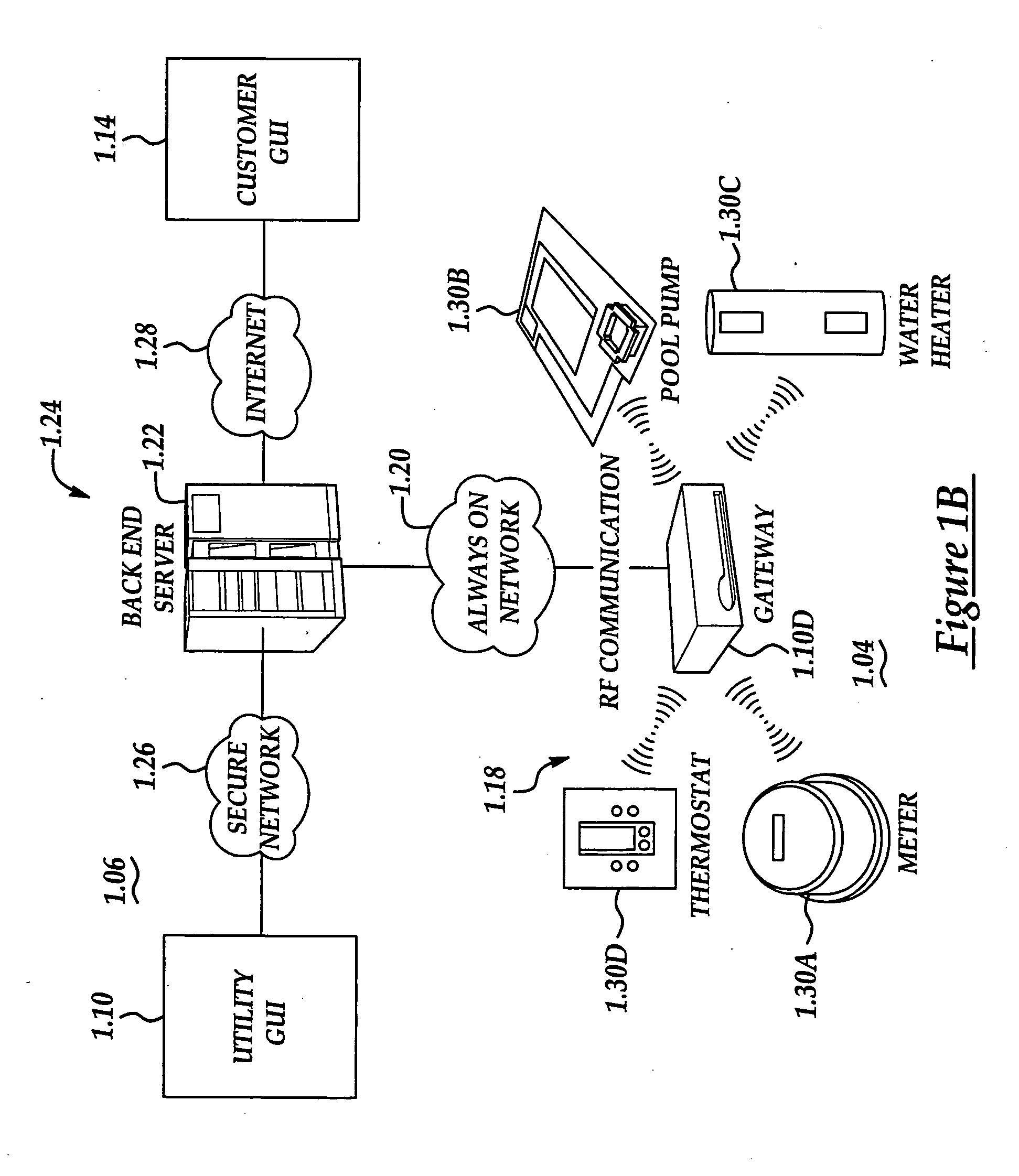
System and method for energy usage curtailment
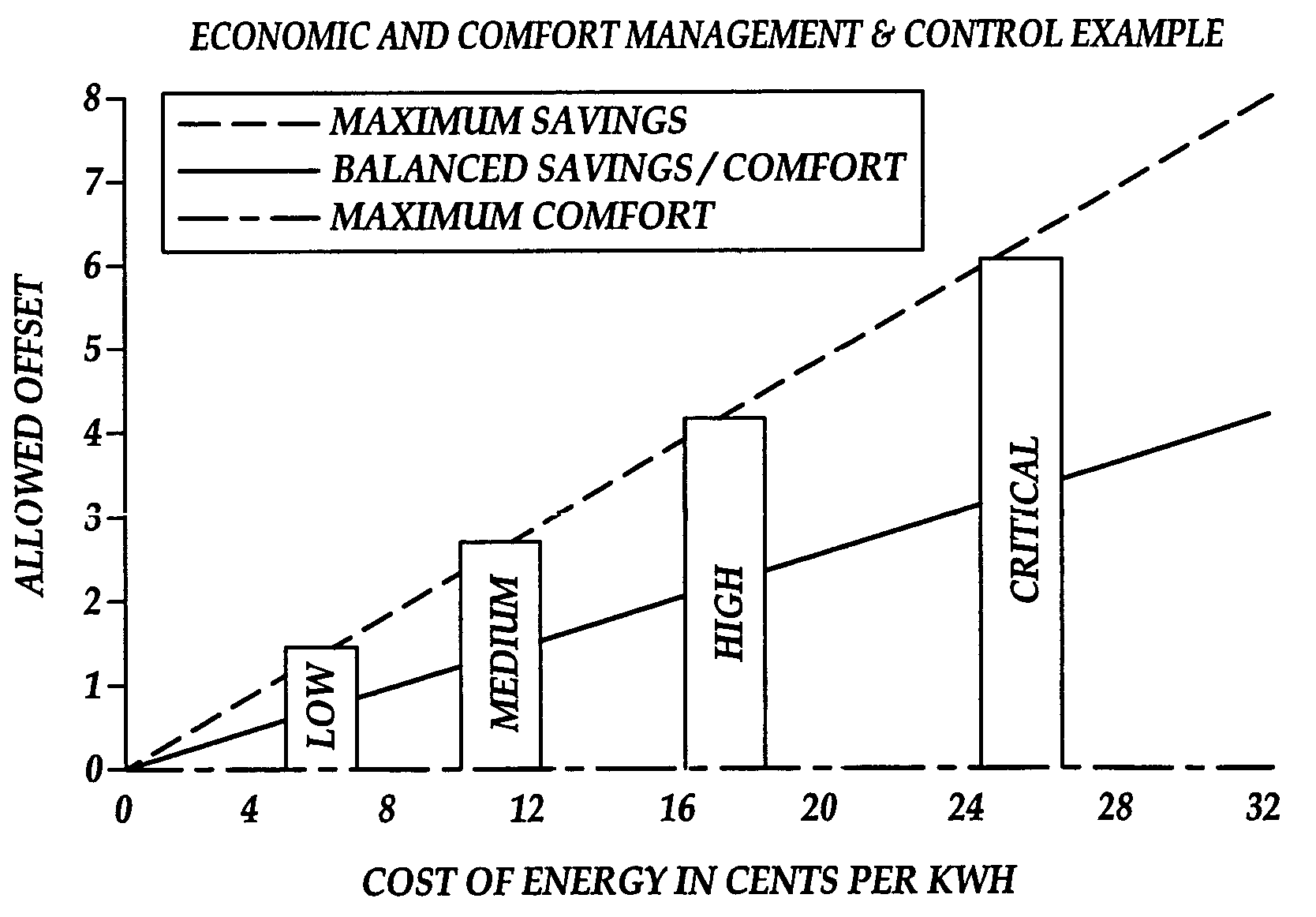
A system and method are disclosed for performing energy usage management within a network. The system may include an energy management system, such as a thermostat device, that may be associated with an energy consuming entity, such as a residence. A server may be remotely located from the energy consuming entity and may perform one or more energy curtailment management operations within the network. The server may be in communication with the energy management system over the network. One or more software applications may be stored thereon for remotely controlling the energy management system in accordance with a particular energy curtailment management operation. Additionally, a database may be associated with the server for storing curtailment event information relating to the network. A signal may be transmitted by the server to the thermostat device to alter an offset temperature setting of the thermostat device thereby remotely controlling the operation of the thermostat device. The thermostat device may also include a networking software application for enabling the remote monitoring and controlling of the thermostat device.
Owner:ITRON
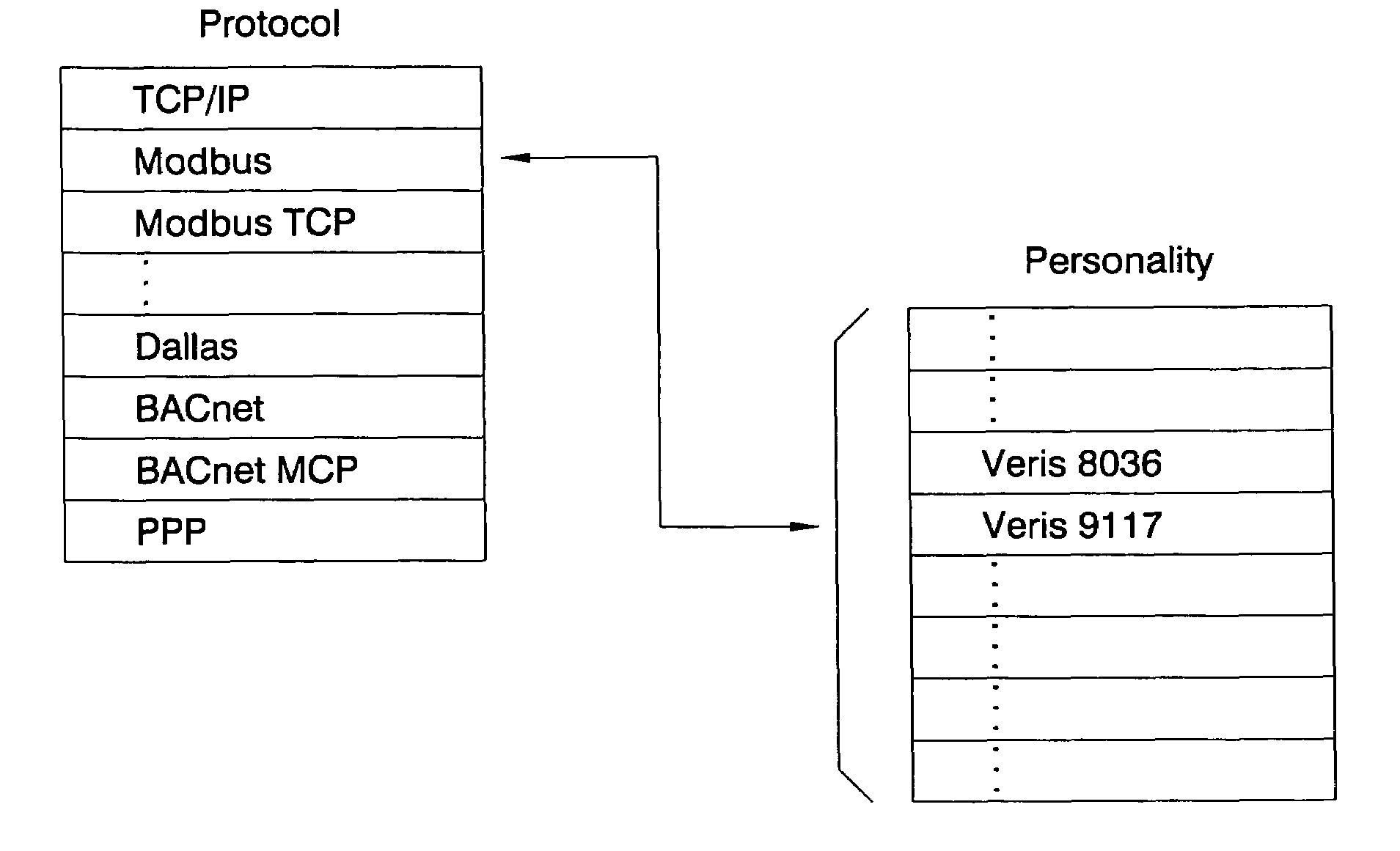
System and method for distributed facility management and operational control
ActiveUS7349761B1Programme controlSampled-variable control systemsControl systemEnvironmental control system
An environmental control system controls monitoring and operation of a multiplicity of disparate environmental control devices by determining an appropriate configuration for each control device and communicates corresponding monitoring and control commands to each device in accordance with its corresponding communication protocol over a selected I / O port. An operational instruction set includes a structural definition of an enterprise facility in which devices are defined by personality modules and communicate with a system host in accordance with a protocol defined in a protocol module. Facility implementation is defined by a node tree structure which collects suitable protocol nodes under a corresponding I / O interface port node. Device (personality) nodes are collected under corresponding protocol nodes, and data point nodes depend from their corresponding device nodes. Data points nodes are individually accessible by merely traversing the node tree using a URL-like notational structure, allowing off-site users to control and monitor environmental devices by issuing commands in the form of a URL.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC +1
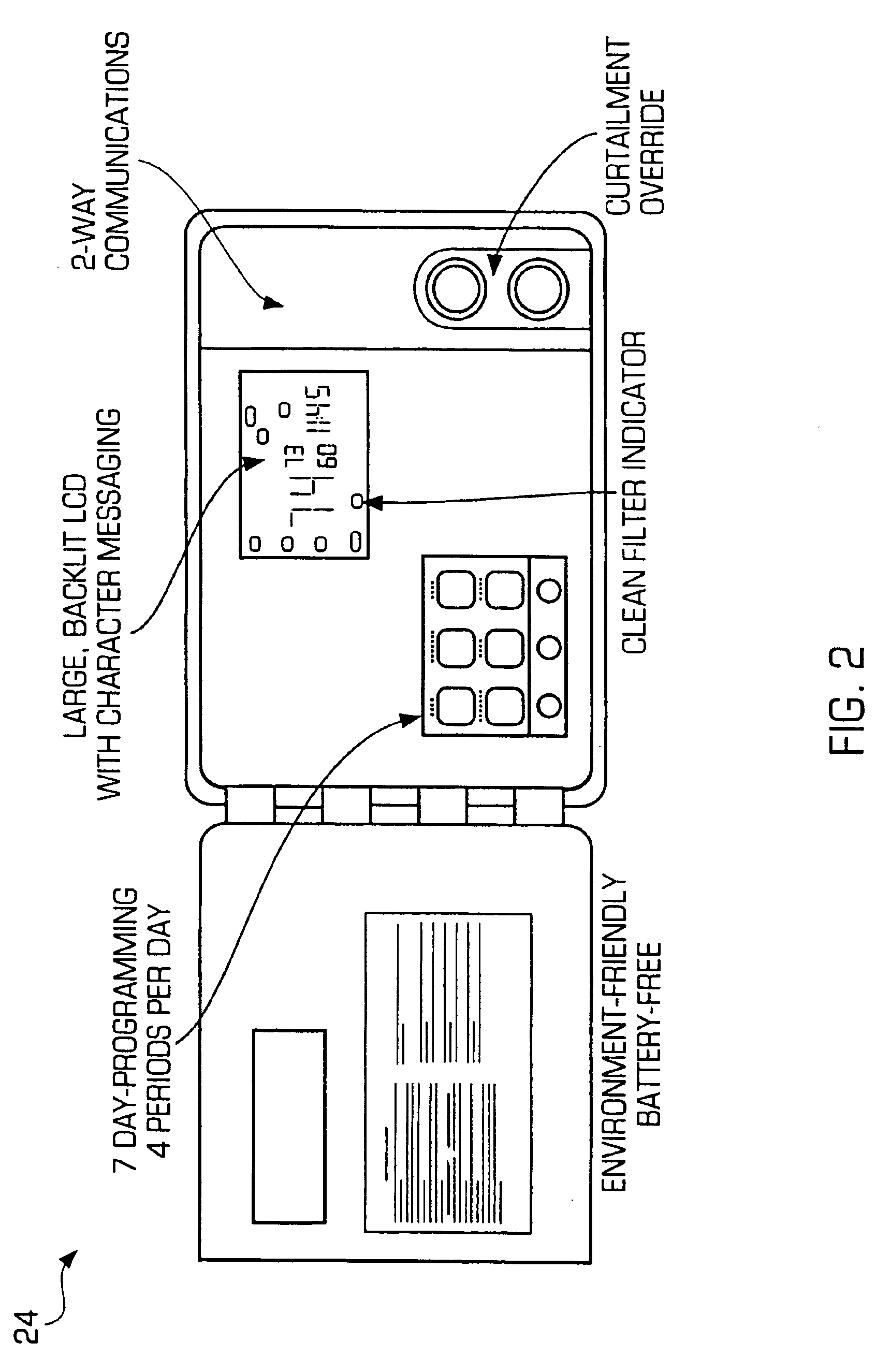
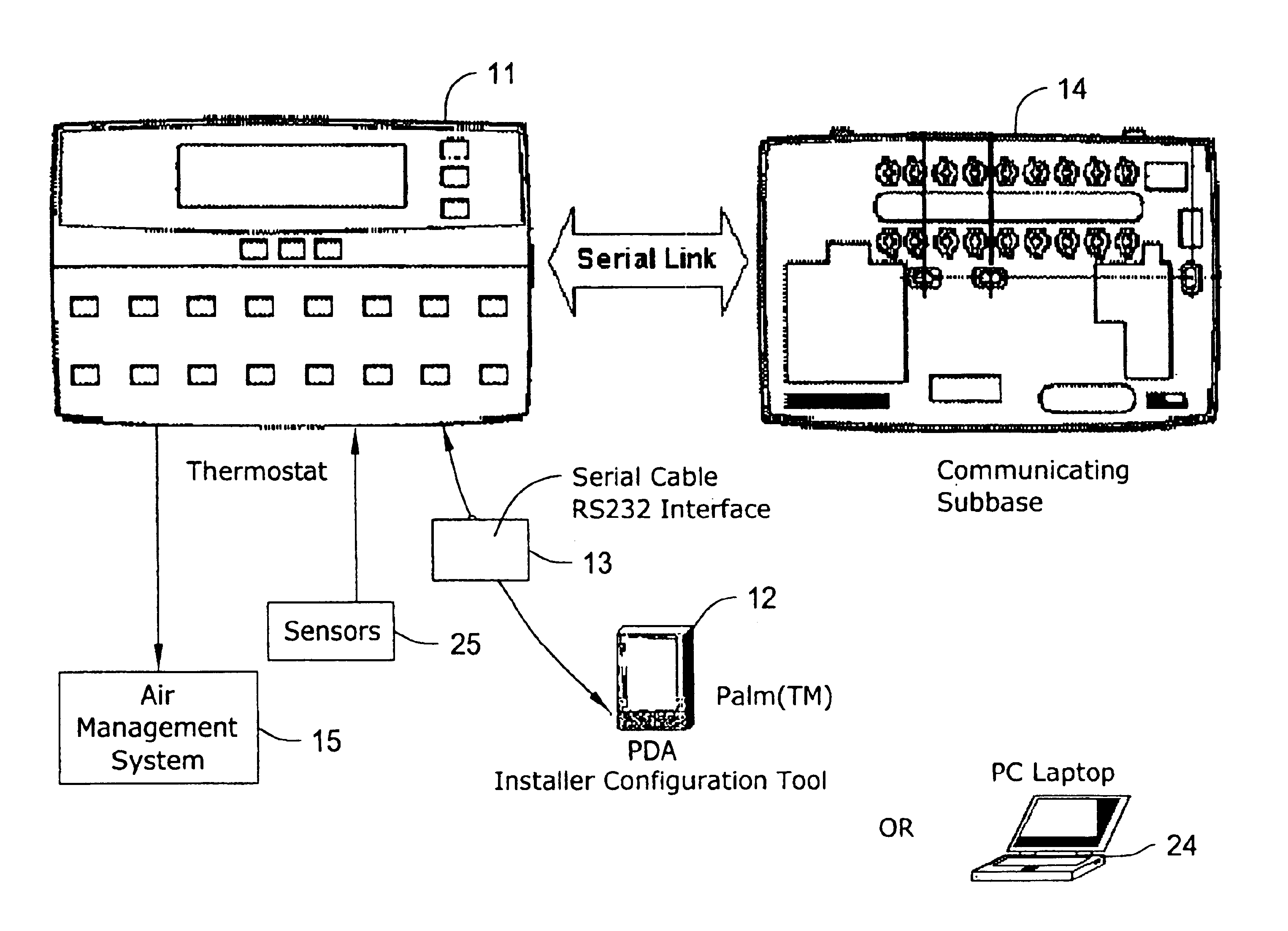
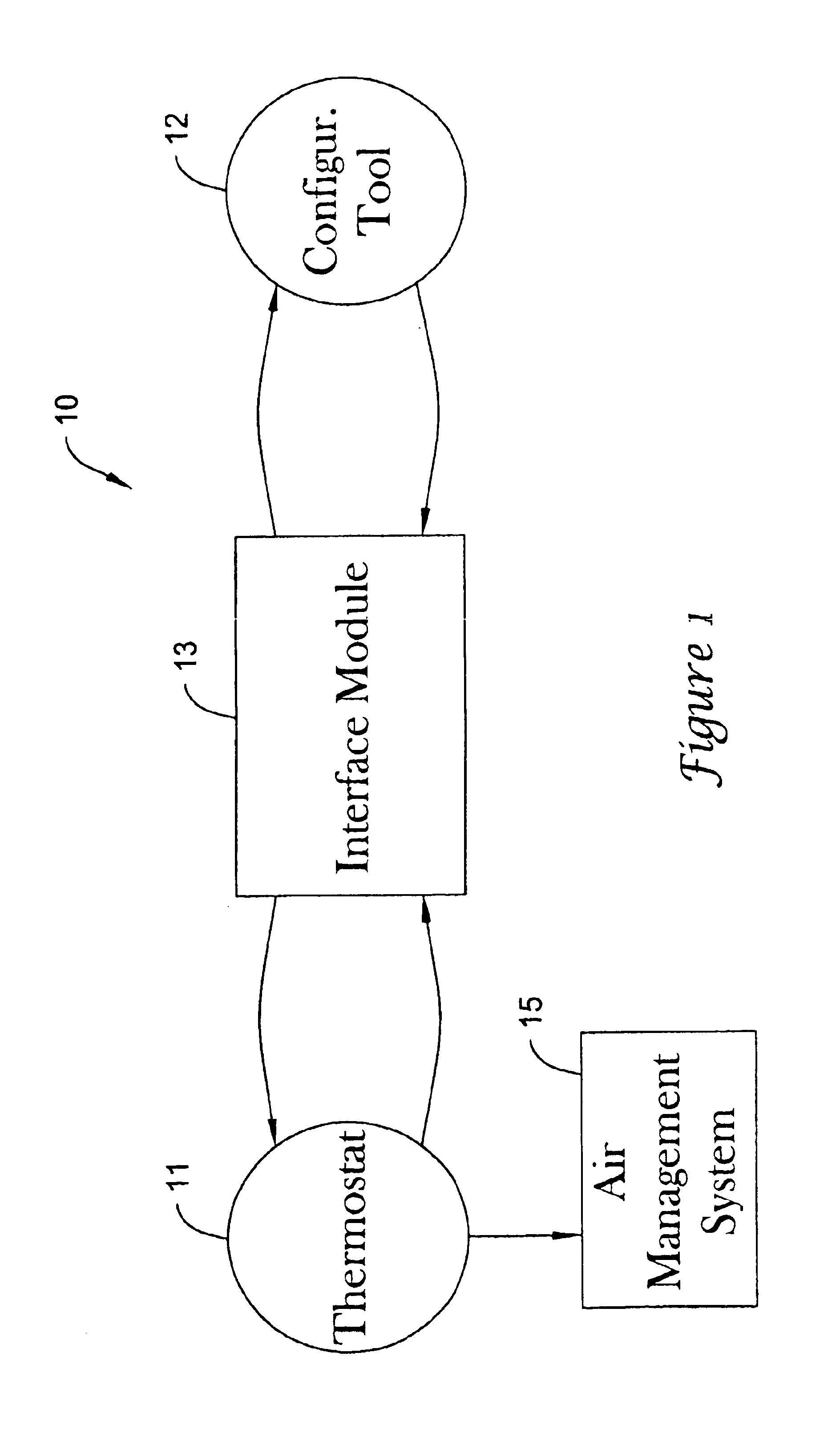
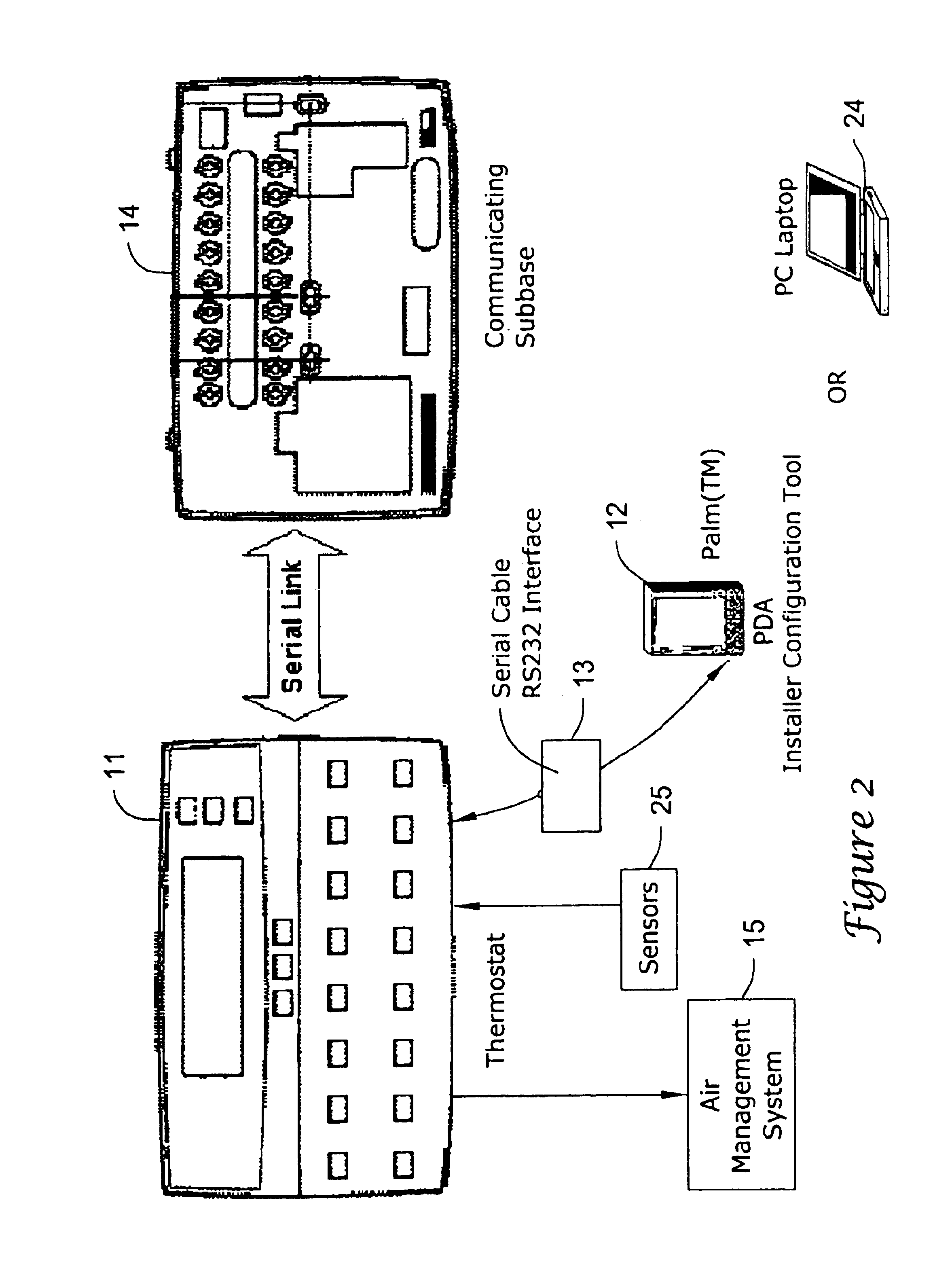
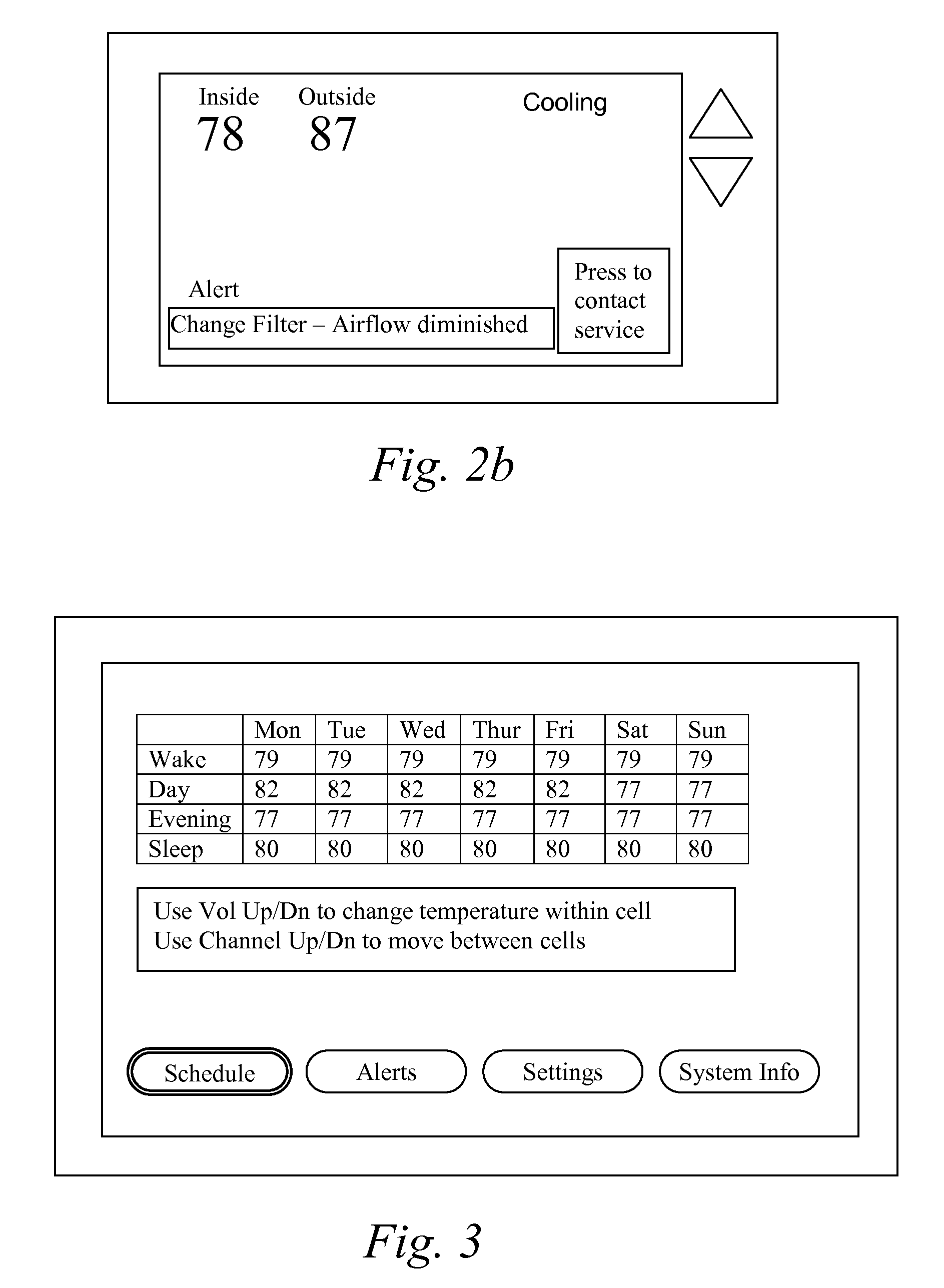
PDA diagnosis of thermostats
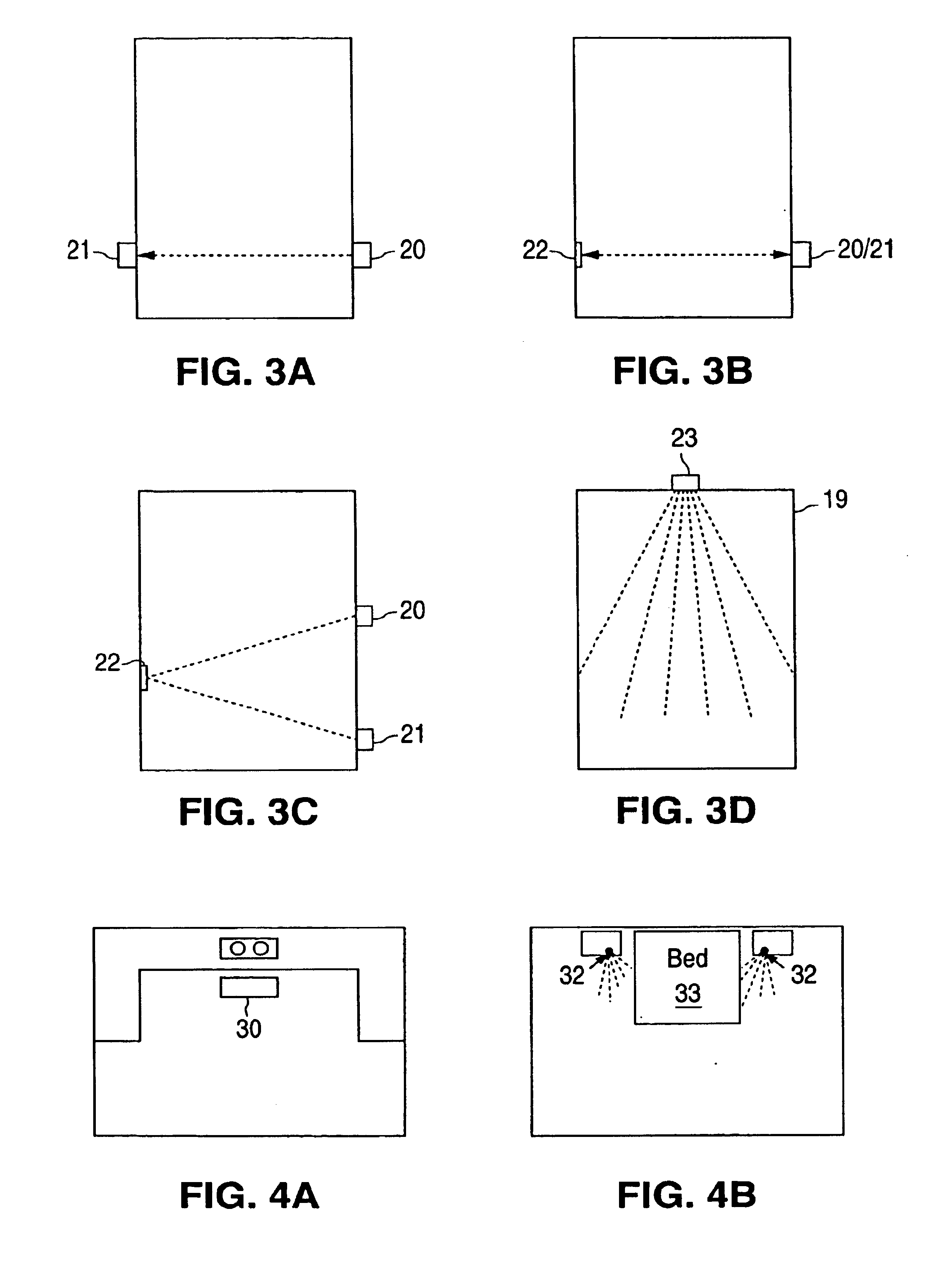
InactiveUS6851621B1Less expertiseActivity can be delayedMechanical apparatusStatic/dynamic balance measurementThermostatSet point
A system PDA-based on line diagnostics for automatically discovering a thermostat configuration, turning off normal controller delays, temporary overriding sensor inputs and set points, and verifying proper output action including the monitoring the discharge air temperature for the resulting temperature behavior based on the equipment stages activated. The diagnosis may include the testing of sensors, set points, the fan, cooling equipment, heating equipment and the wiring connecting the controls with the fan, and the cooling and heating equipment. Problems discovered may be reported, automatically recorded and the original operating parameters may be restored.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Open Web Services-Based Indoor Climate Control System
InactiveUS20080281472A1Improve productivityCost of sameProgramme controlSampled-variable control systemsReal-time Control SystemWeb service
The present invention relates generally to a building automation system, and, more particularly, to an Internet-centric, open, extensible software and hardware framework supporting all aspects of control and monitoring of a smart building ecosphere. The present invention further relates to an “intelligent,” real-time control system capable of both autonomous process control and interaction with system users and system administrators, which is configured to accommodate functional extensions and a broad array of sensors and control devices. The system allows individuals to communicate, monitor and adjust their personal environmental preferences (temperature, light, humidity, white noise, etc.) much like they would in an automobile, via the Internet. The system is equipped with an occupancy sensor that recognizes the presence and identity of the individual. A built-in expert system can make decisions based on data from multiple sources so that the system can alter its activity to conserve energy while maintaining users' comfort.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
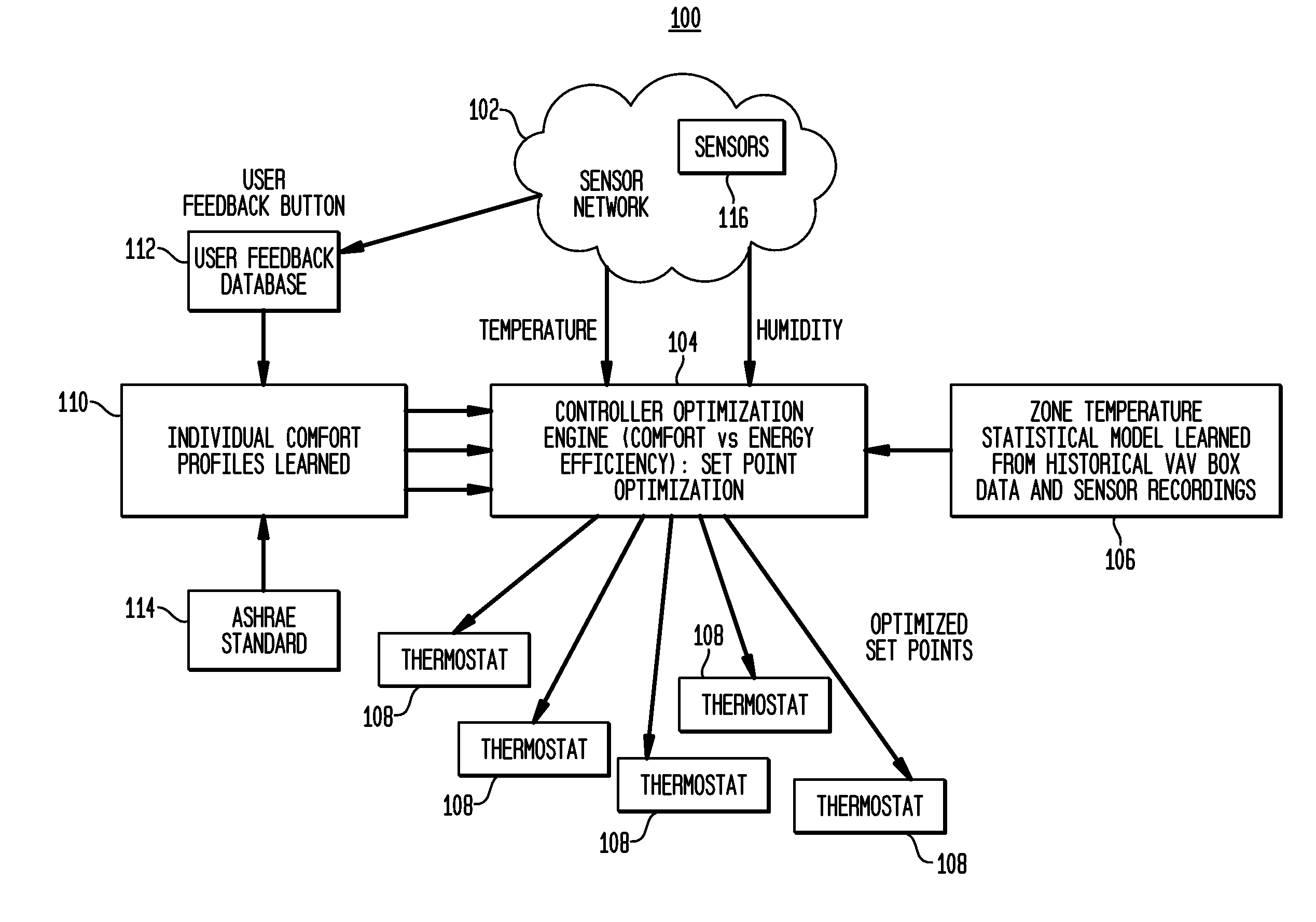
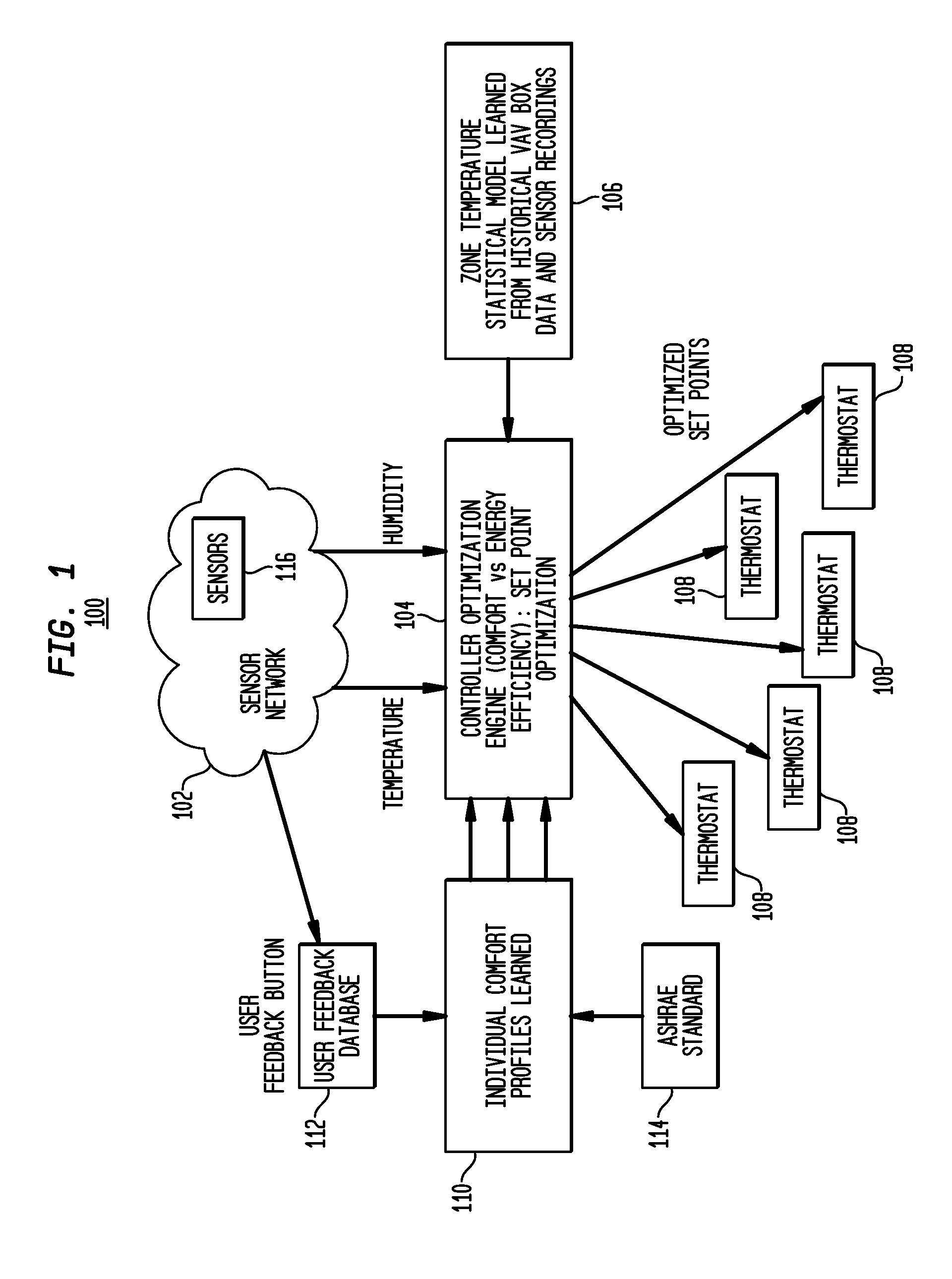
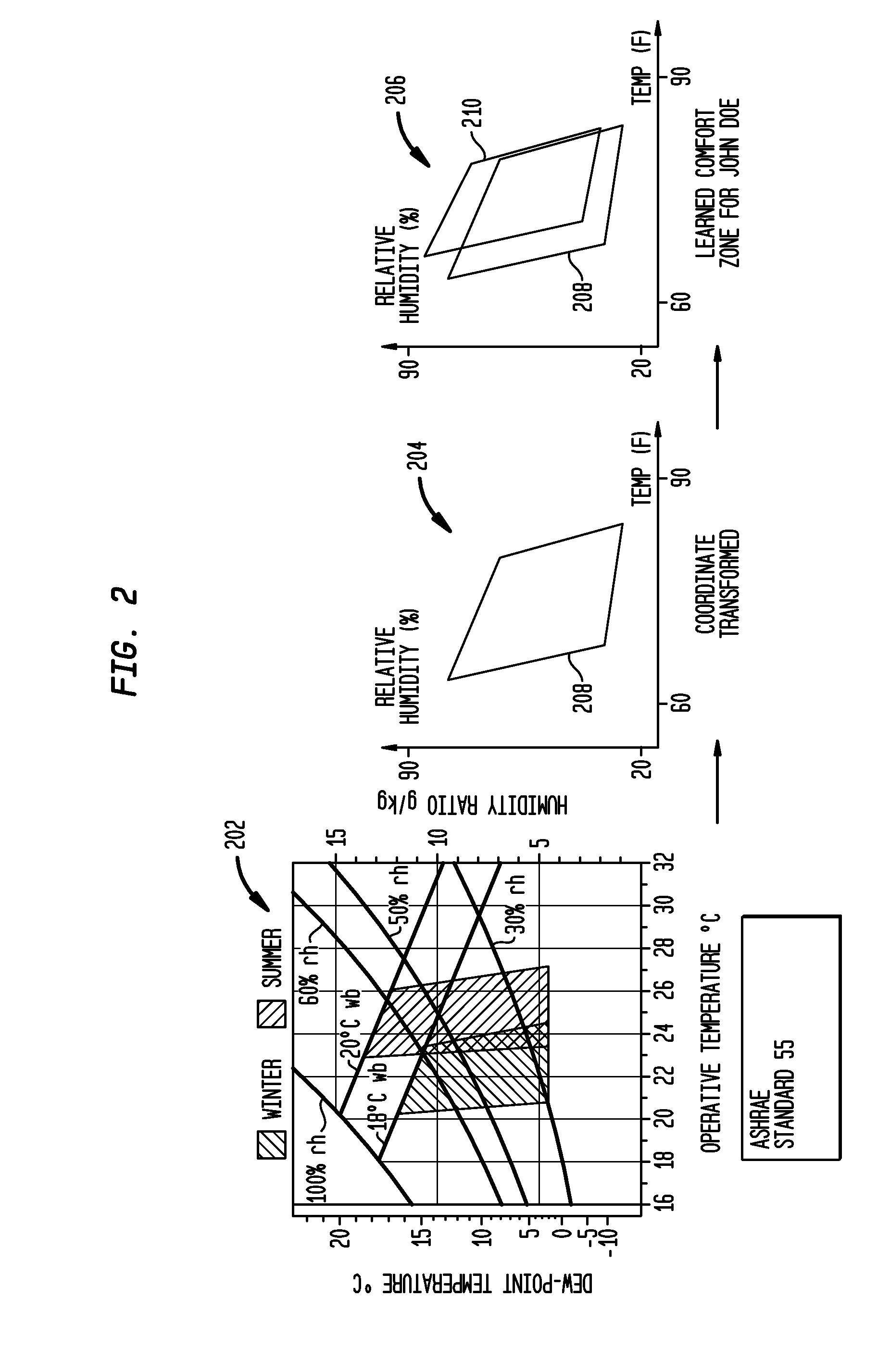
System and Method for Climate Control Set-Point Optimization Based On Individual Comfort
A system and method for calibrating a set-point for climate control includes a sensor network having a plurality of sensors configured to report a climate condition. A database is configured to receive reports from the sensors and generate one or more profiles reflecting at least one of historic climate control information and occupant preferences. A controller is configured to receive information from the profiles to generate a set-point based upon an optimization program. The optimization program is implemented to balance competing goals to generate the set-point for controlling climate control equipment in accordance with the set-point.
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
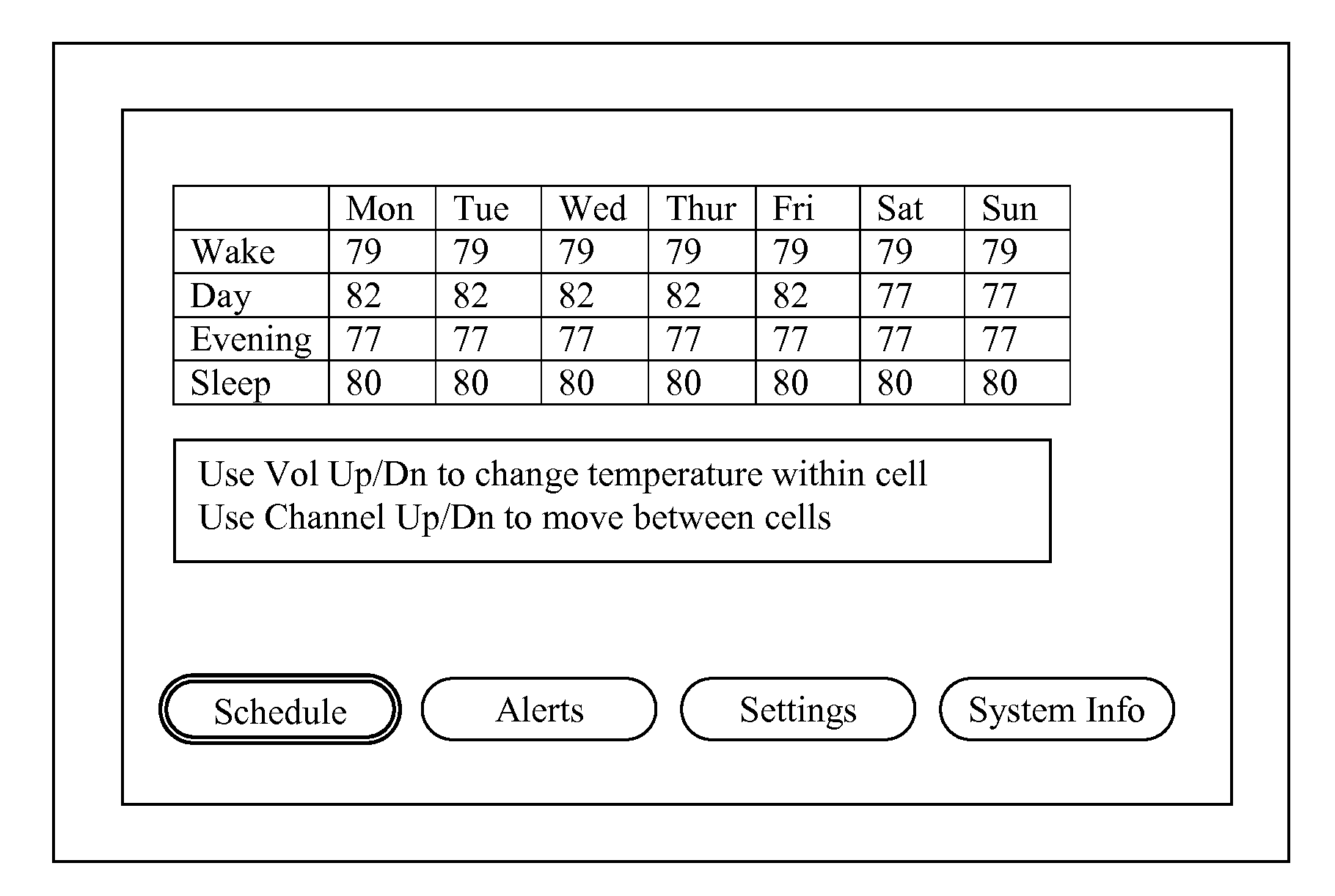
Thermostat
InactiveUS20100084482A1Energy efficient ICTSampled-variable control systemsTelecommunications linkRemote control
A thermostat includes an improved user interface, including automatic scheduling, remote control, system failure warning messages, and Energy Star compliance messages. Diagnostics can be provided without additional communication links to the thermostat. A sub-base accepts multiple thermostats and uses color coded terminals to ease installation. Glow-in-the dark features reduce power needs. In one embodiment, thermostats are coupled to AC power sources and communicate using wireless communications to control an HVAC system. A dampered system can be effected through a thermostat that communicates directly with zoned dampers.
Owner:PRO1 IAQ
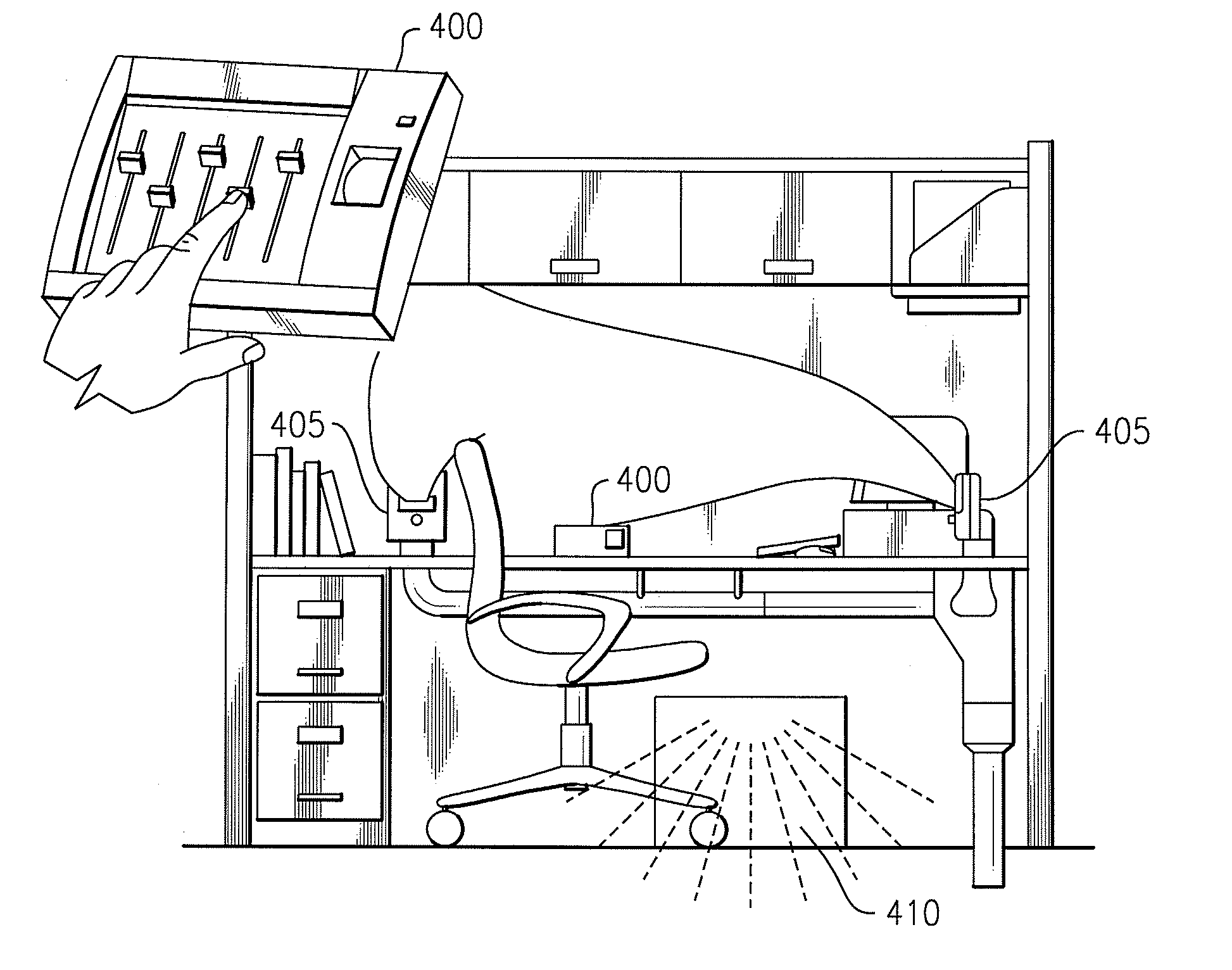
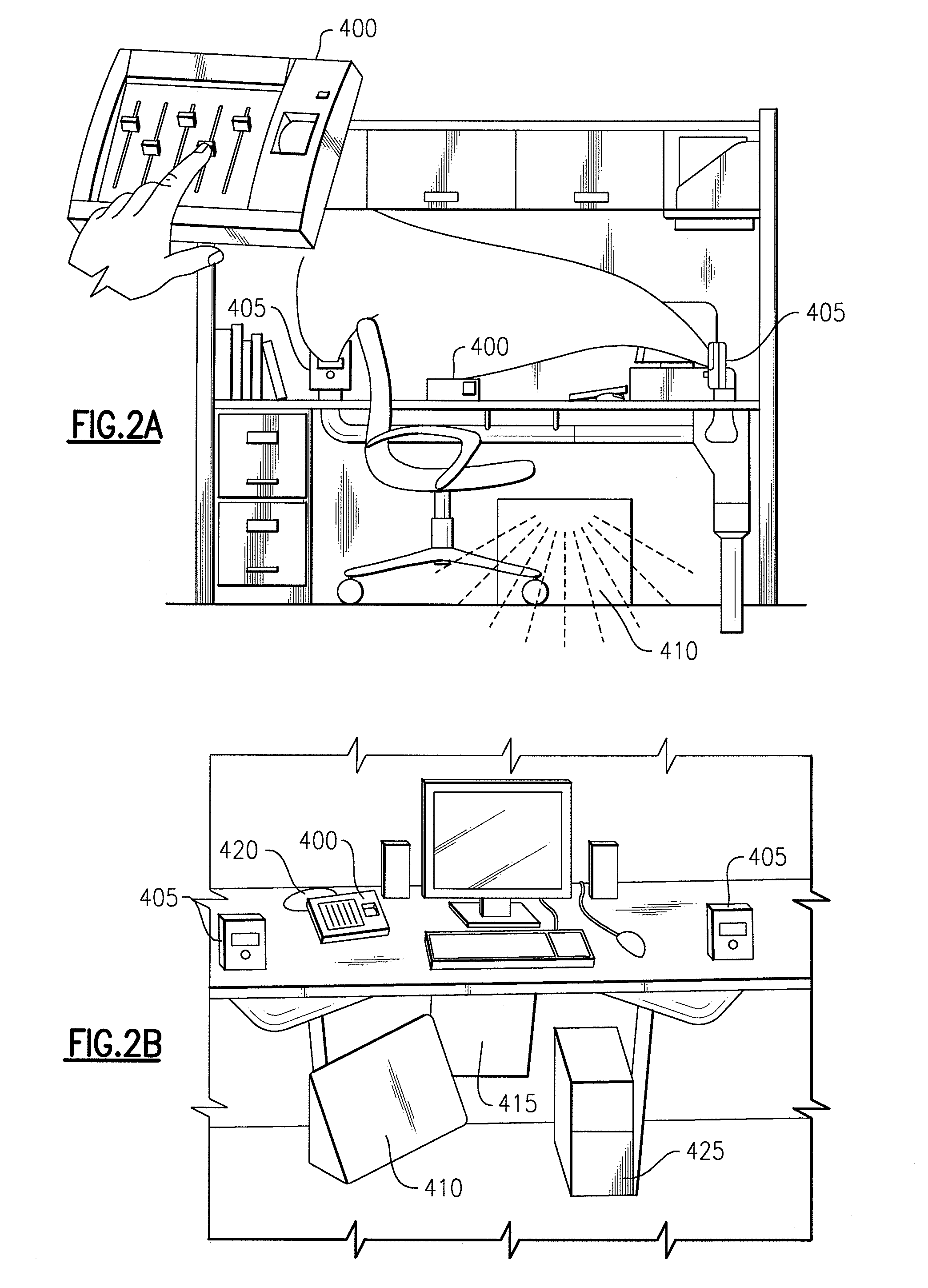
Integrated building environment data system
ActiveUS20050154494A1Shorten the timeEfficient constructionTravelling carriersHoldersComputer moduleData system
A system for gathering date in a space includes a data server, a first wireless module operably connected to the data server, a first plurality of wireless sensor modules, and at least one other wireless sensor module. The first plurality of wireless sensors module are operable to generate sensor data relating to the control and operation of an HVAC system. The first plurality of wireless sensor modules are also operable to communicate the first sensor data to the first wireless module. The at least one other wireless sensor module is operable to generate second sensor data relating to at least one of the group consisting of light fixtures, architectural fixtures and plumbing fixtures, office equipment, and vending machines and furniture. The at least one other wireless sensor module is also operable to communicate the second sensor data to the first wireless module.
Owner:OLLNOVA TECH LTD
System and method for optimizing use of plug-in air conditioners and portable heaters
InactiveUS8090477B1Improve cooling effectImprove the heating effectMechanical apparatusLevel controlEngineeringEnergy management system
Thermostatic HVAC and other energy management controls that are connected to a computer network. For instance, remotely managed load switches incorporating thermostatic controllers inform an energy management system, to provide enhanced efficiency, and to verify demand response with plug-in air conditioners and heaters. At least one load control device at a first location comprises a temperature sensor and a microprocessor. The load control device is configured to connect or disconnect electrical power to the an attached air conditioner or heater, and the microprocessor is configured to communicate over a network. In addition, the load control device is physically separate from an air conditioner or heater but located inside the space conditioned by the air conditioner or heater.
Owner:ECOFACTOR
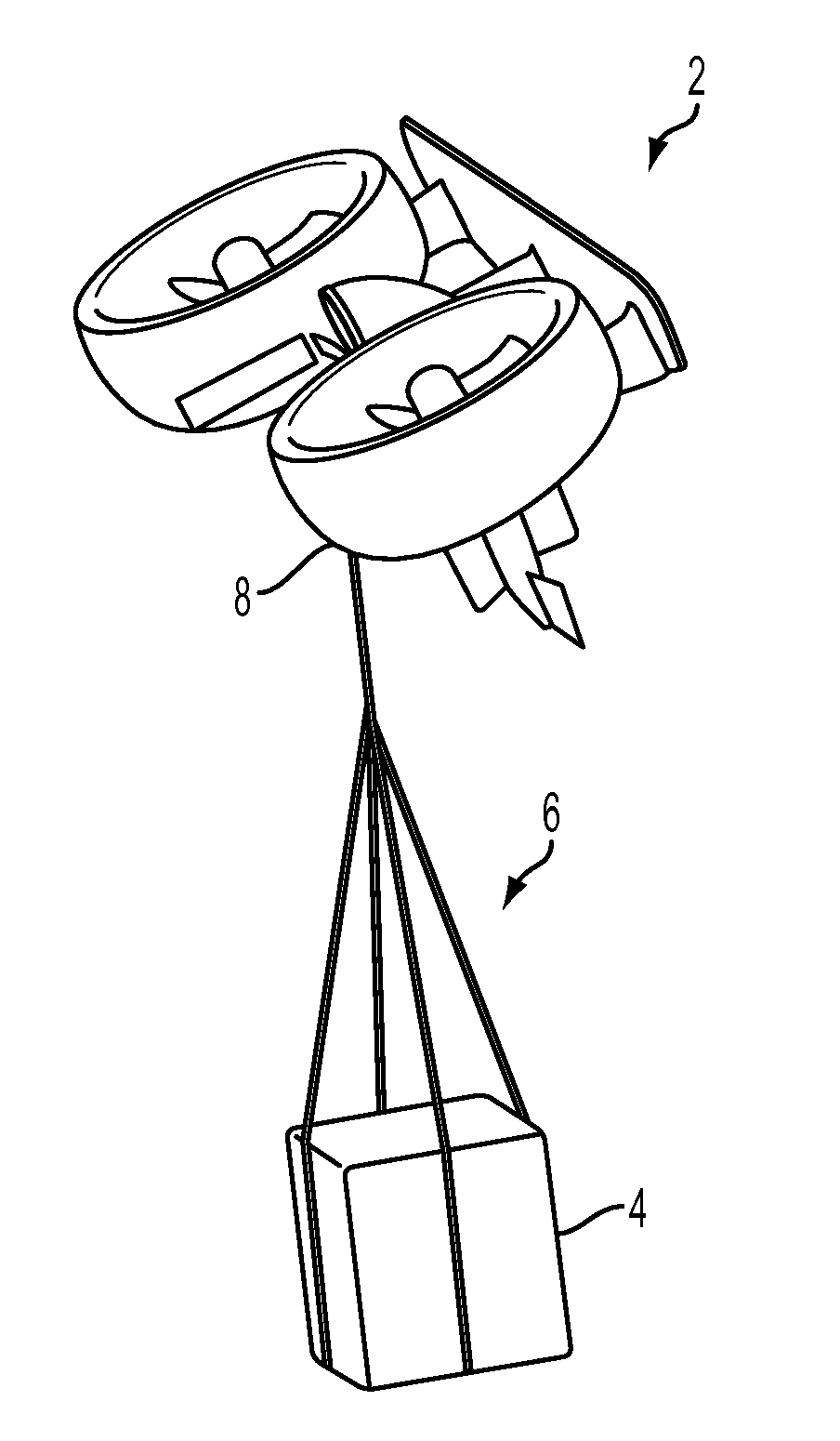
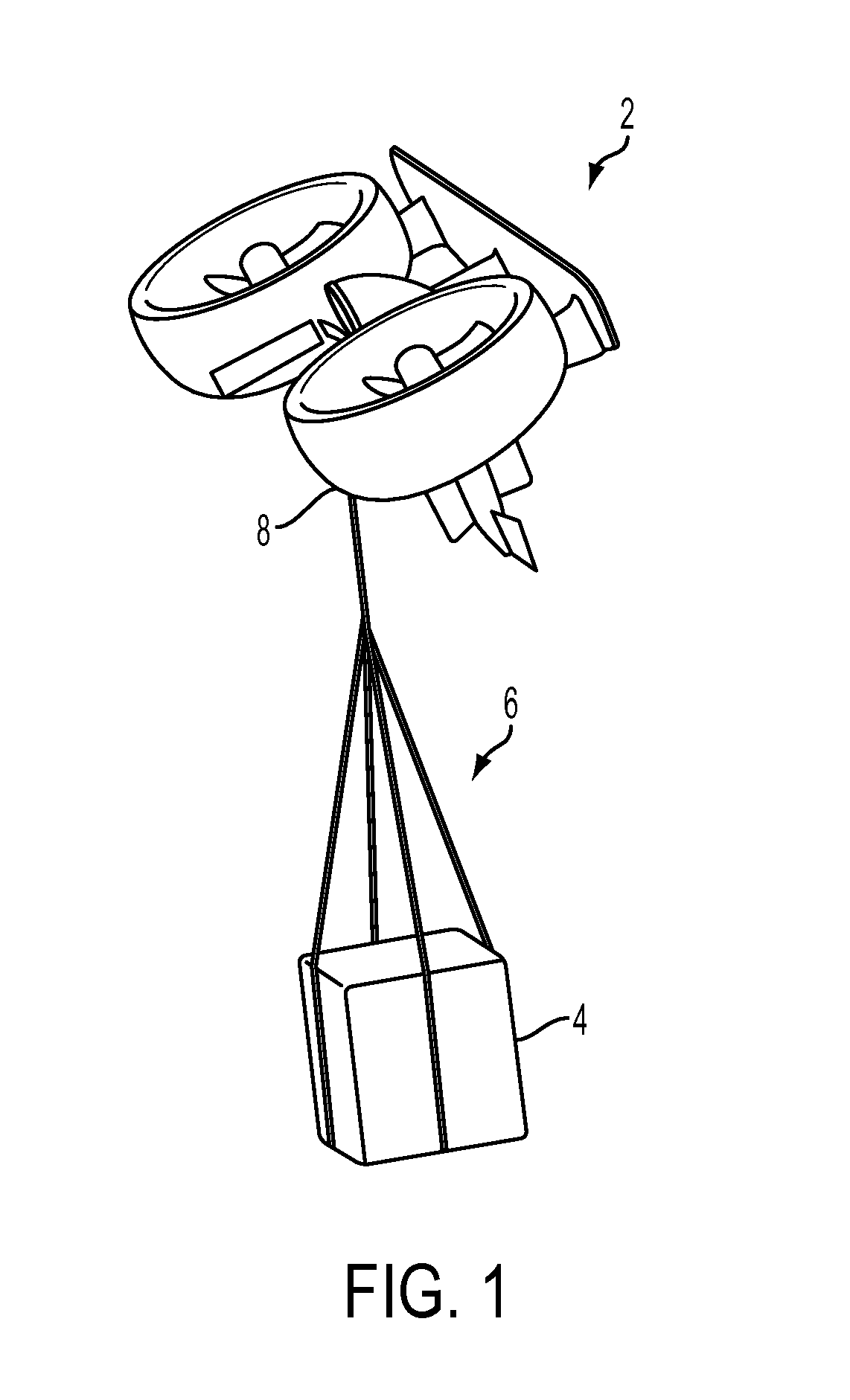
Autonomous Payload Parsing Management System and Structure for an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
InactiveUS20110084162A1Improve versatilityIncrease in sizeStatic/dynamic balance measurementRemote controlled aircraftManagement systemControl logic
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) for making partial deliveries of cargo provisions includes a UAV having one or more ducted fans and a structural interconnect connecting the one or more fans to a cargo pod. The cargo pod has an outer aerodynamic shell and one or more internal drive systems for modifying a relative position of one or more cargo provisions contained within the cargo pod. Control logic is configured to, after delivery of a partial portion of the cargo provisions contained within the cargo pod, vary a position of at least a portion of the remaining cargo provisions to maintain a substantially same center of gravity of the UAV relative to a center of gravity prior to delivery of the partial portion. Other center of gravity compensation mechanisms may also be controlled by the control logic to aid in maintaining the center of gravity of the UAV.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
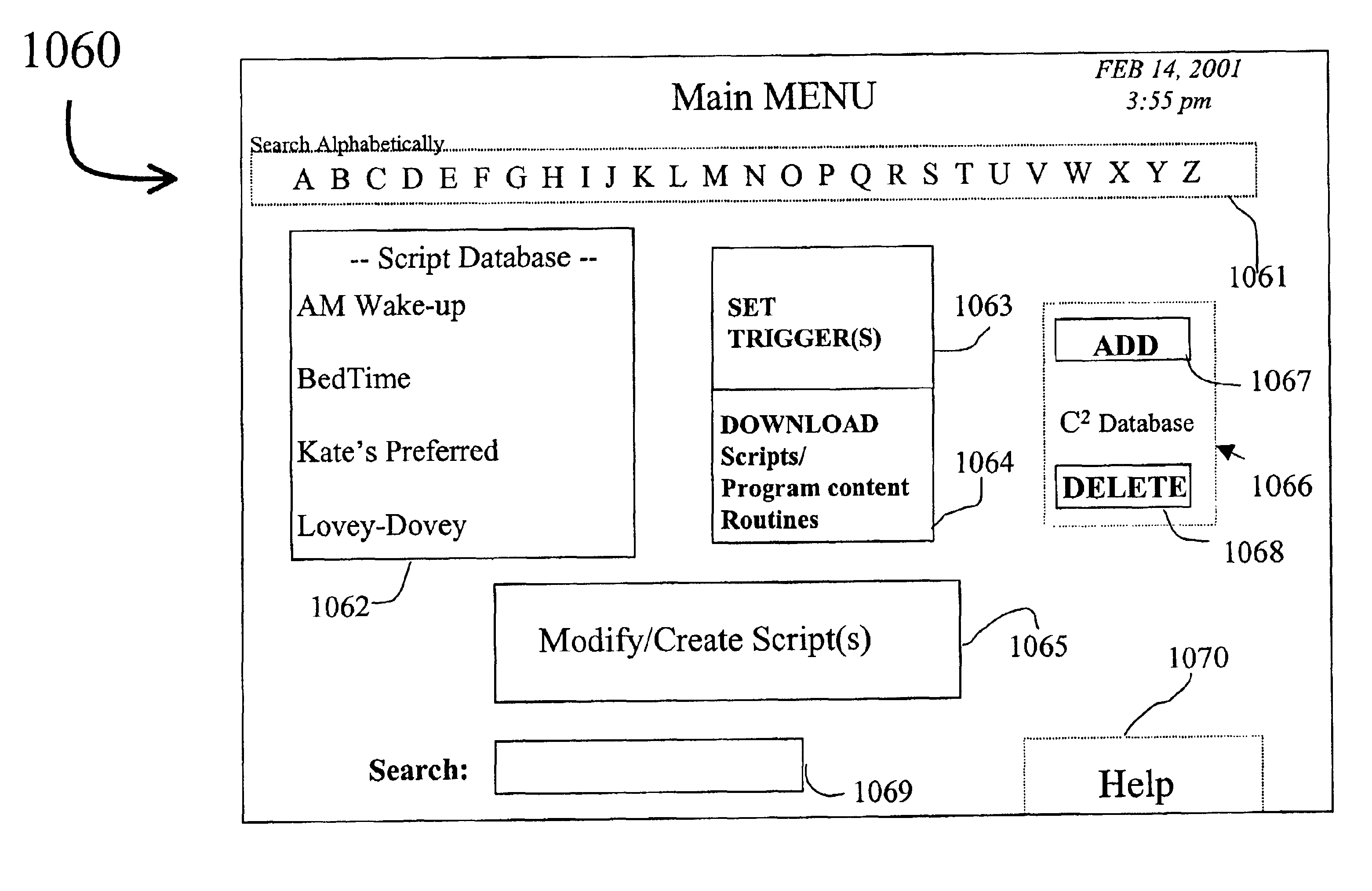
Device control via digitally stored program content
InactiveUS6868292B2Avoid less flexibilityMore functionalityTemperatue controlElectric testing/monitoringHome environmentDigital storage
A method and system of controlling devices with digitally stored content. Devices such as home electronic appliances, lighting systems, heating, ventilating and air conditioning (HVAC) equipment, home security systems and home entertainment systems are controlled from a single, centralized device. A set top box (STB) stores scripts that include program content for controlling the operation of a plurality of these devices from the STB. A user of the STB selects the desired scripts, and the STB accesses the selected scripts from storage based on a triggering mechanism such as time, content, event, etc. The STB selectively controls operation of certain devices designated in the script. The method provides ease of control over multiple and diverse devices, applications and media within a user's own home environment, with more functionality and flexibility than currently available.
Owner:DIRECTV LLC
Heating and cooling control methods and systems
InactiveUS20100211224A1Improve energy efficiencySampled-variable control systemsMechanical apparatusCarbon footprintOperating energy
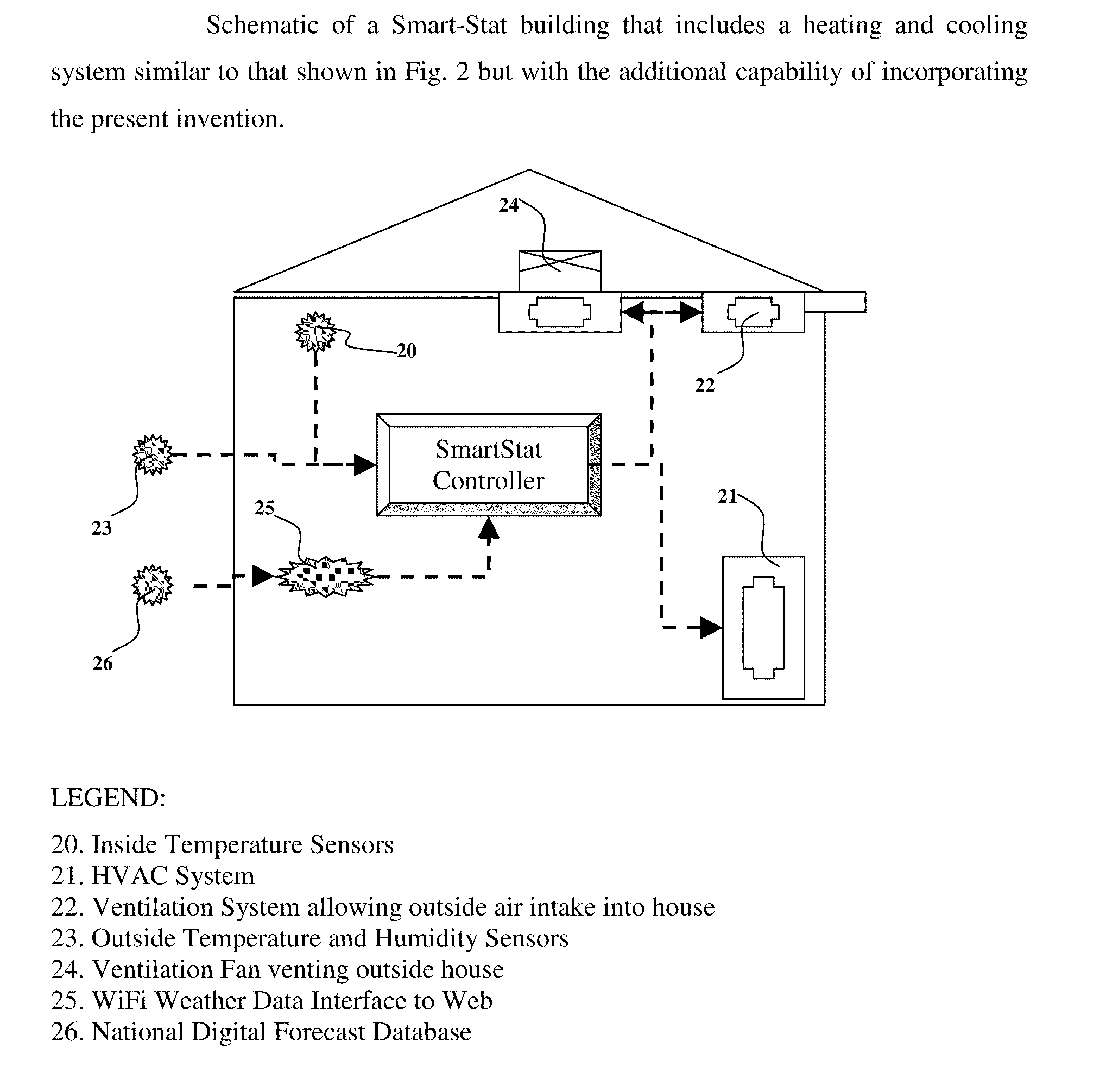
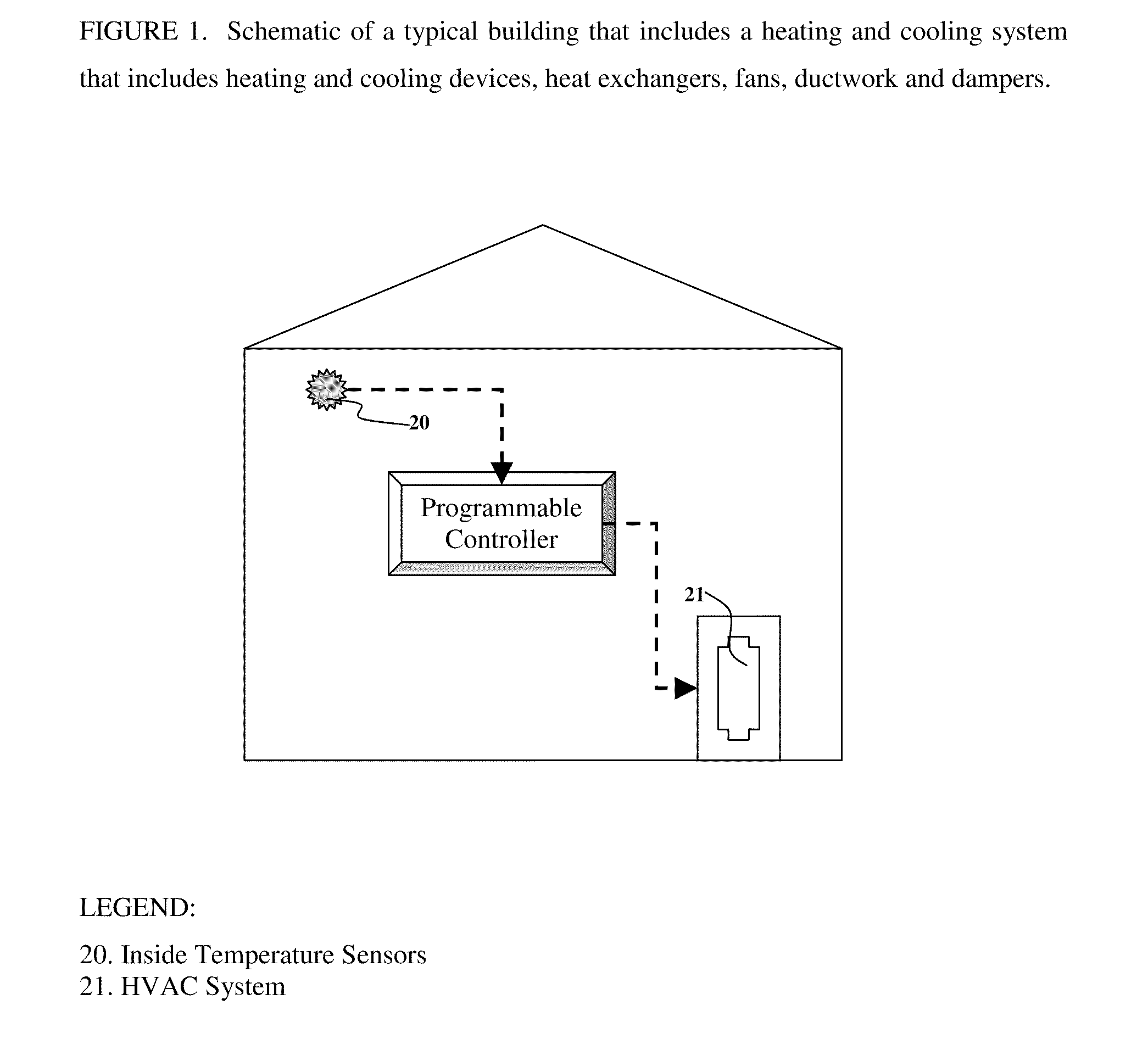
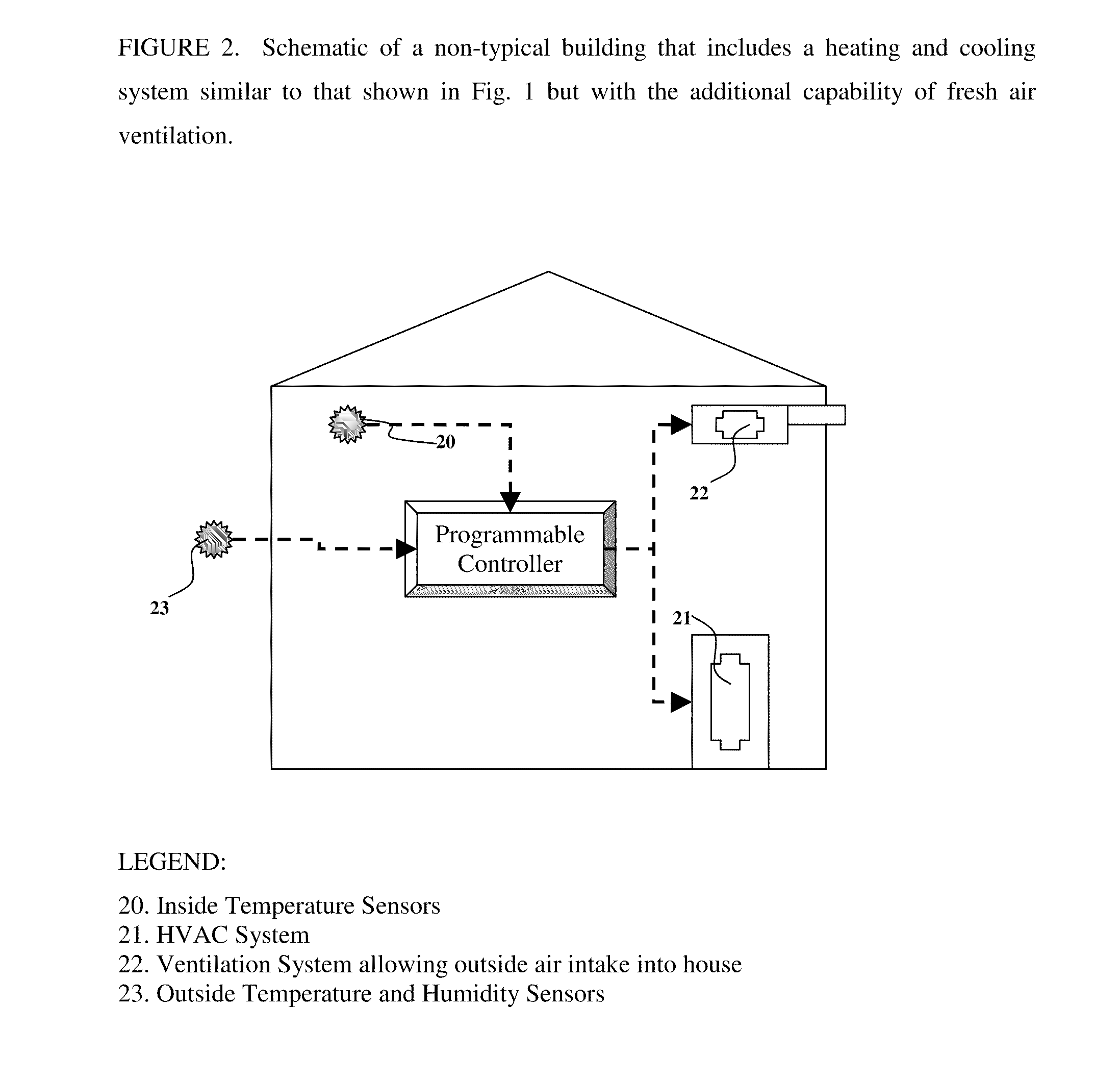
The present invention is related to the field of heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC). More particularly, the present invention is related to methods and systems for controlled heating and cooling in order to reduce costs and the carbon footprint of said heating and cooling by optimizing the use of fresh air ventilation. The present invention is directed to mathematical algorithms incorporated into a controller and a method of determining control signals that are dependent on said mathematical algorithms and user programming that integrates information from multiple sensors, thermostats as well as weather information. Used in any home or building, the controller controls heating, cooling and ventilation systems in order to reduce costs and the carbon footprint of said heating and cooling by optimizing the use of fresh air ventilation. The controller works with typical HVAC systems generally in buildings and homes. The Smart-Stat algorithms are programmed into the controller and enable the controller to identify user-determined set-points alongside data from one or multiple internal temperature sensors. The user-determined set-points are also linked to time of day and day of week in a manner typical for typical thermostat devices available today. In such typical thermostat devices the controller will call for cooling or heating depending on the set points and conditions determined by the sensors in the building. The present invention is capable of interrupting the call for cooling or heating depending on whether the mathematical algorithms identify suitable outside weather conditions that permit the use of outside air cooling or outside air heating. Thus the call for heating or cooling can be redirected to call for ventilation instead of heating or cooling.
Owner:KEELING OLIVER JOE +1
Open web services-based indoor climate control system
InactiveUS7904209B2Improve productivityCost of sameProgramme controlSampled-variable control systemsReal-time Control SystemWeb service
The present invention relates generally to a building automation system, and, more particularly, to an Internet-centric, open, extensible software and hardware framework supporting all aspects of control and monitoring of a smart building ecosphere. The present invention further relates to an “intelligent,” real-time control system capable of both autonomous process control and interaction with system users and system administrators, which is configured to accommodate functional extensions and a broad array of sensors and control devices. The system allows individuals to communicate, monitor and adjust their personal environmental preferences (temperature, light, humidity, white noise, etc.) much like they would in an automobile, via the Internet. The system is equipped with an occupancy sensor that recognizes the presence and identity of the individual. A built-in expert system can make decisions based on data from multiple sources so that the system can alter its activity to conserve energy while maintaining users' comfort.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
Medical robotic system with coupled control modes
In a coupled control mode, the surgeon directly controls movement of an associated slave manipulator with an input device while indirectly controlling movement of one or more non-associated slave manipulators, in response to commanded motion of the directly controlled slave manipulator, to achieve a secondary objective. By automatically performing secondary tasks through coupled control modes, the system's usability is enhanced by reducing the surgeon's need to switch to another direct mode to manually achieve the desired secondary objective. Thus, coupled control modes allow the surgeon to better focus on performing medical procedures and to pay less attention to managing the system.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Method and apparatus for assessing performance of an environmental control system
A method and apparatus is disclosed for assessing performance of control applications in an environmental control network and for diagnosing performance problems. The apparatus includes a performance assessment and diagnostic display comprising a facility navigation tree, a system navigation tree and a performance / diagnostics window. The facility navigation tree and system navigation tree may be used to select the facilities and systems that are to have their associated control applications assessed and / or diagnosed. The performance / diagnostics window includes graphs of performance indictors that are indicative of performance levels for the included control applications. The system tree may be used to delve to more detailed views of the performance indicators to obtain additional information that may help to diagnose problems noted in performance of the selected control applications.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TECH CO
Thermostat system with remote data averaging
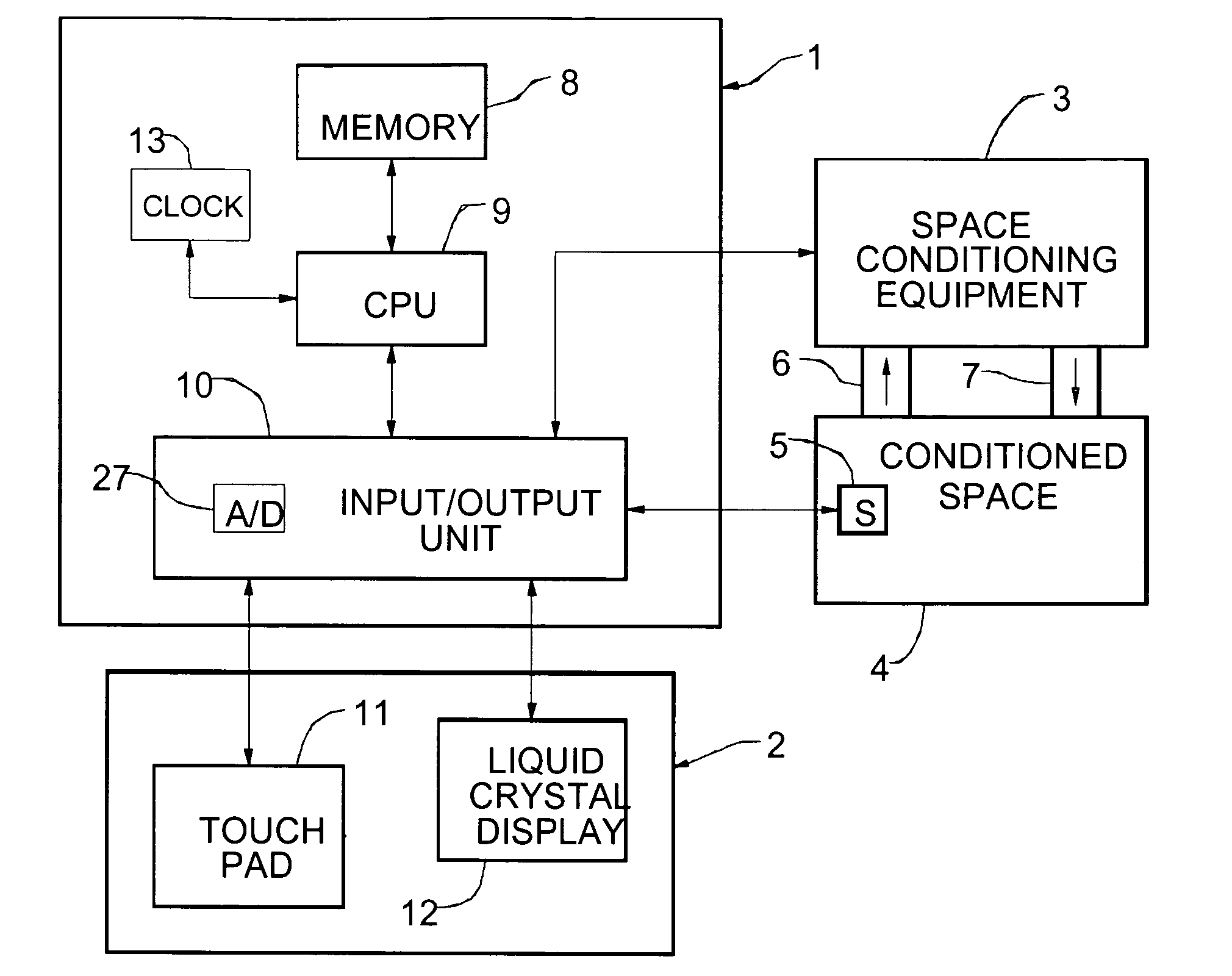
ActiveUSRE40437E1Sampled-variable control systemsTemperature control without auxillary powerData averagingData information
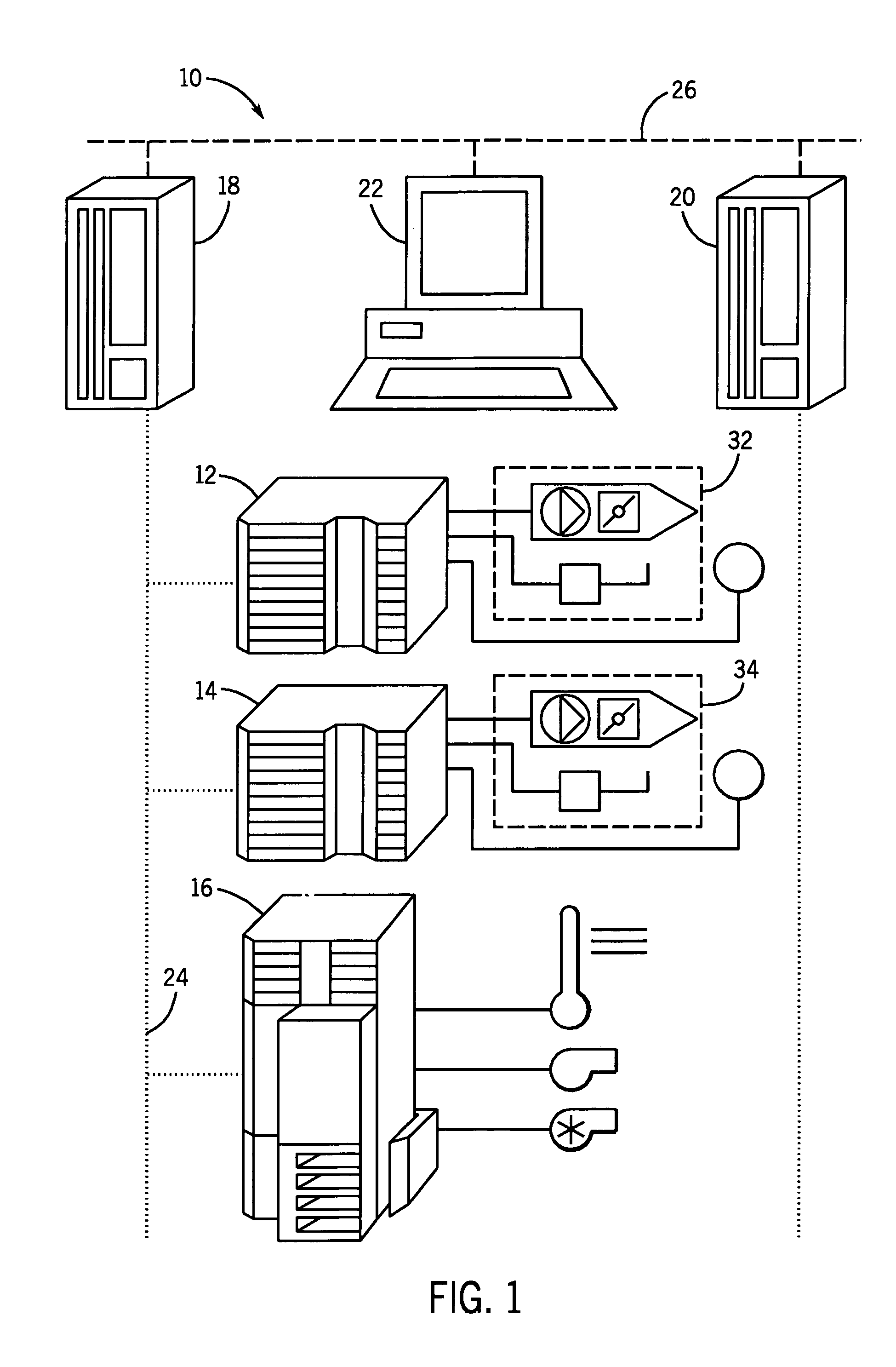
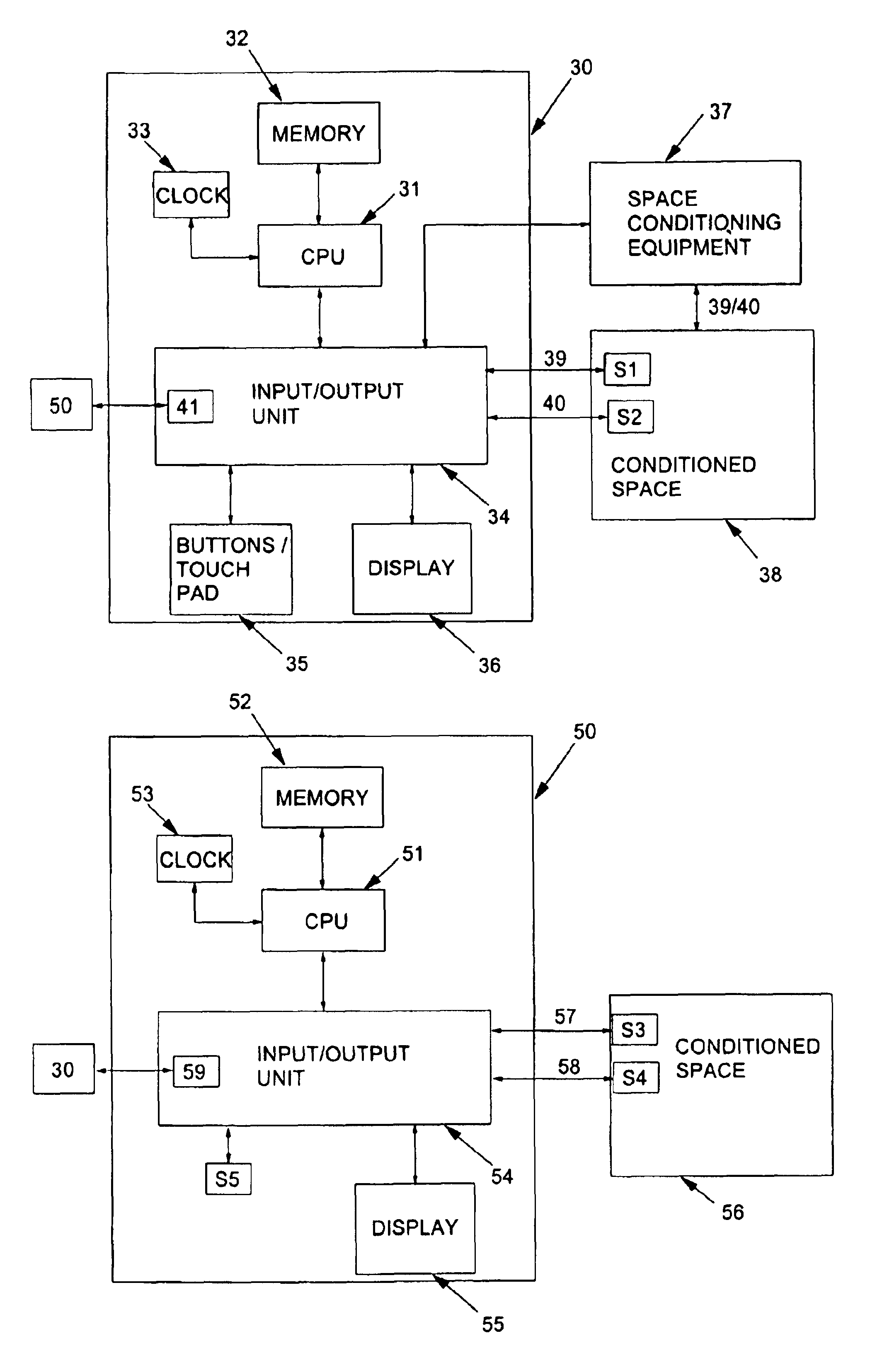
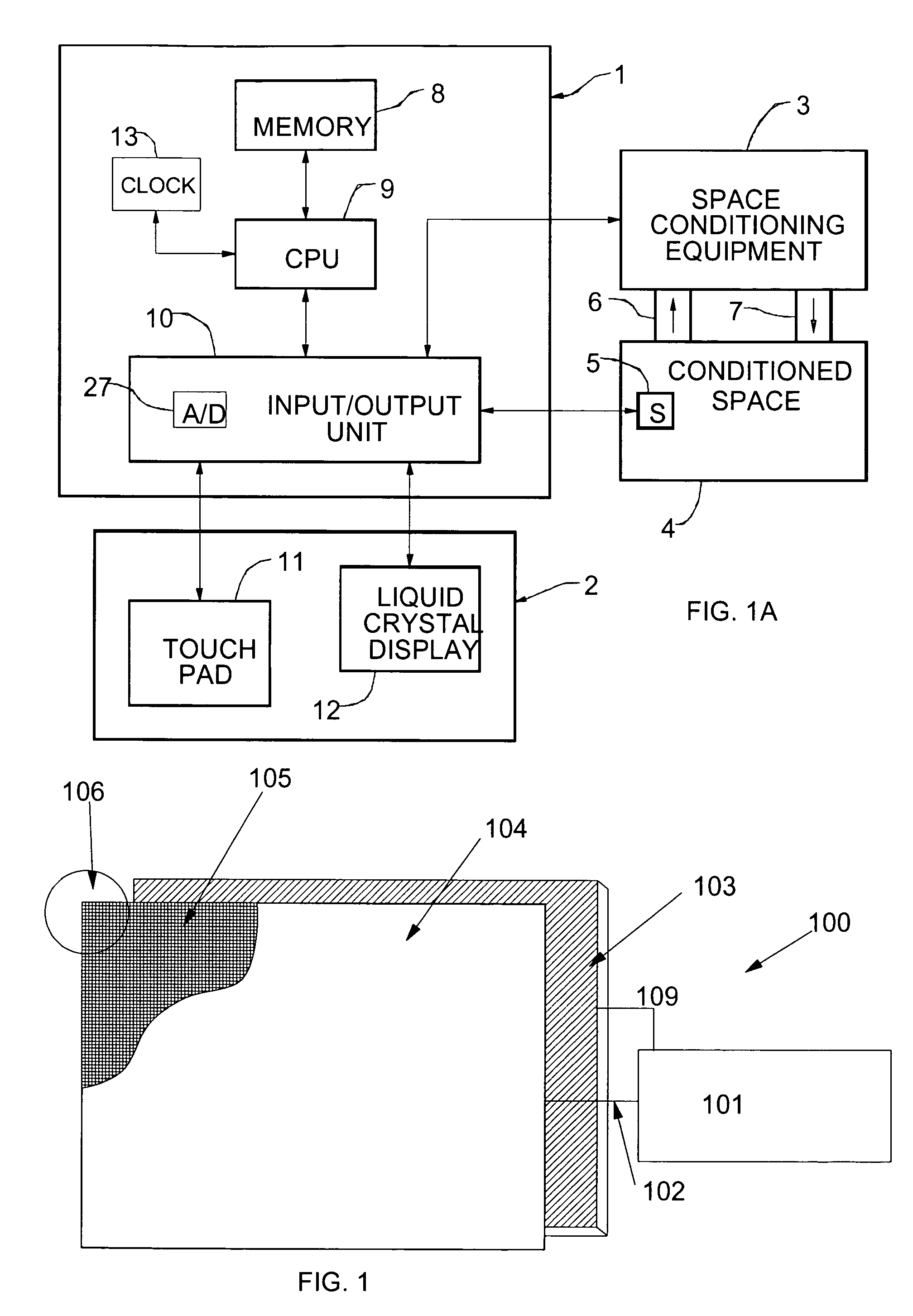
A thermostat system according to the invention includes: a central control device (typically a programmable thermostat with a processor having: a CPU, real time clock and a memory for storing a control program and data information), multiple rooms comprising a conditioned space, environmental control equipment, and multiple environmental sensors capable of sensing an environmental condition (such as temperature, humidity, or other condition). The sensors are associated with transmission means, which control transmission of sensor signals, and occupancy sensors. Each sensor measures a local environmental condition. Occupancy sensors comprise infrared or other motion sensors, light detection sensors, door opening sensors, and other such sensors that detect the presence of humans in a room of the conditioned space where its associated sensor is located. Space conditioning equipment is activated by comparison of a setpoint to a control value averaged from values of environmental conditions in occupied rooms.
Owner:ROSEN TECH LLC
System and method of controlling an HVAC system
A system and method manage delivery of energy from a distribution network to one or more sites. Each site has at least one device coupled to the distribution network. The at least one device controllably consumes energy. The system includes a node and a control system. The node is coupled to the at least one device for sensing and controlling energy delivered to the device. A control system is coupled to the node and distribution network for delivery to the node at least one characteristic of the distribution network. The node for controls the supply of energy to the device as a function of the at least one characteristic.
Owner:INVENSYS SYST INC
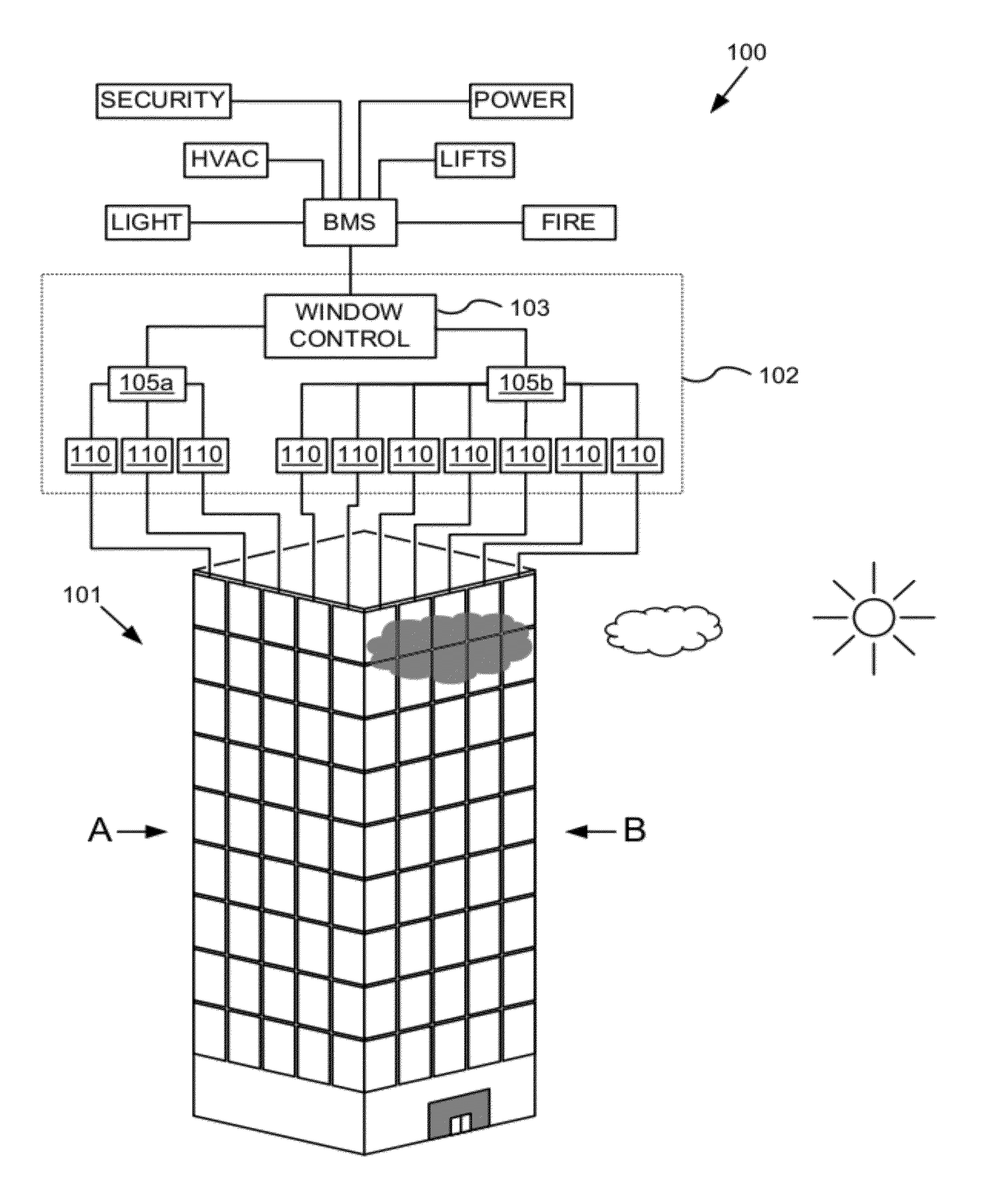
Multipurpose controller for multistate windows
ActiveUS20120239209A1Improve the environmentSampled-variable control systemsComputer controlTransmittanceLocal environment
“Smart” controllers for windows having controllable optical transitions are described. Controllers with multiple features can sense and adapt to local environmental conditions. Controllers described herein can be integrated with a building management system (BMS) to greatly enhance the BMS's effectiveness at managing local environments in a building. The controllers may have one, two, three or more functions such as powering a smart window, determining the percent transmittance, size, and / or temperature of a smart window, providing wireless communication between the controller and a separate communication node, etc.
Owner:VIEW INC
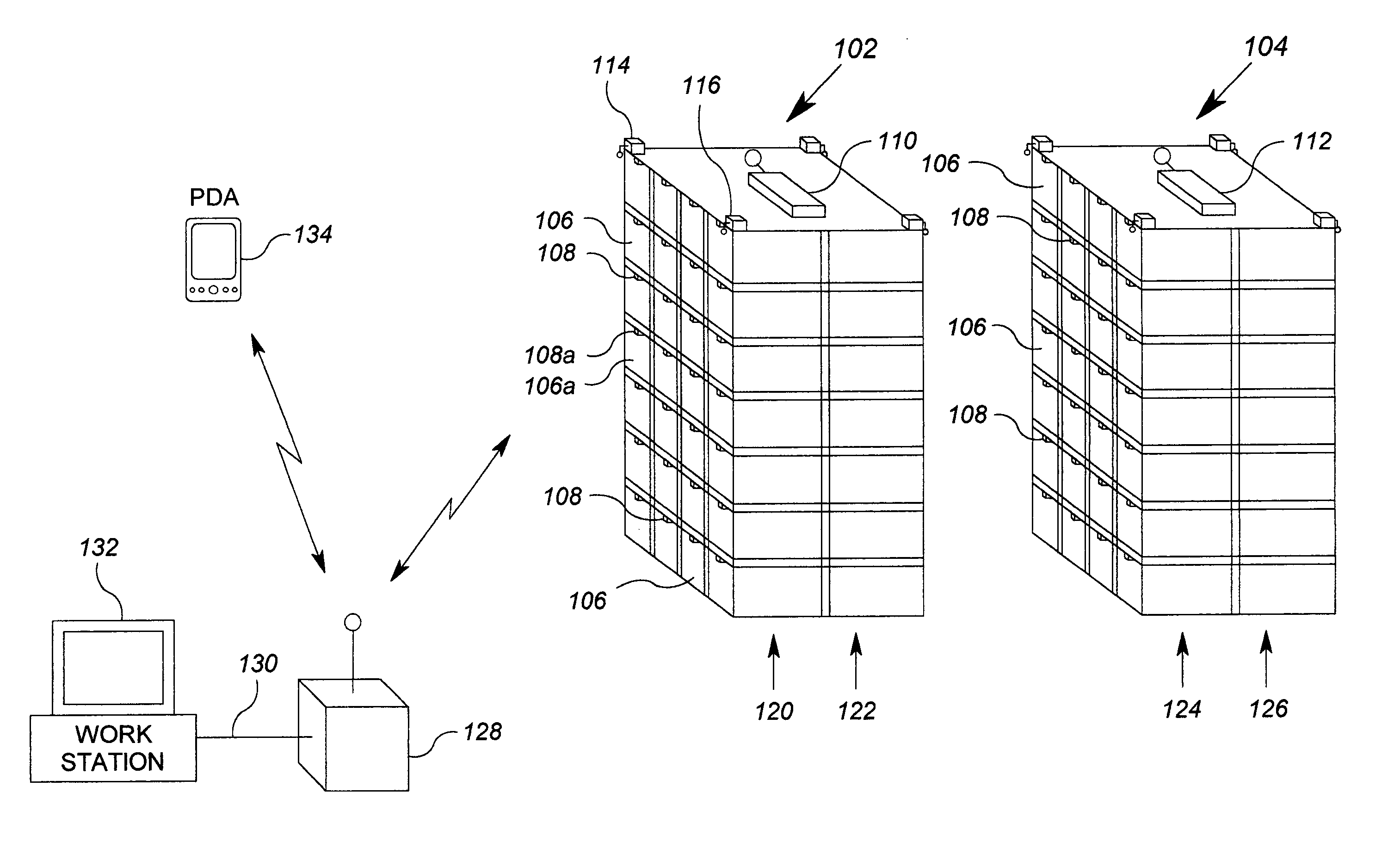
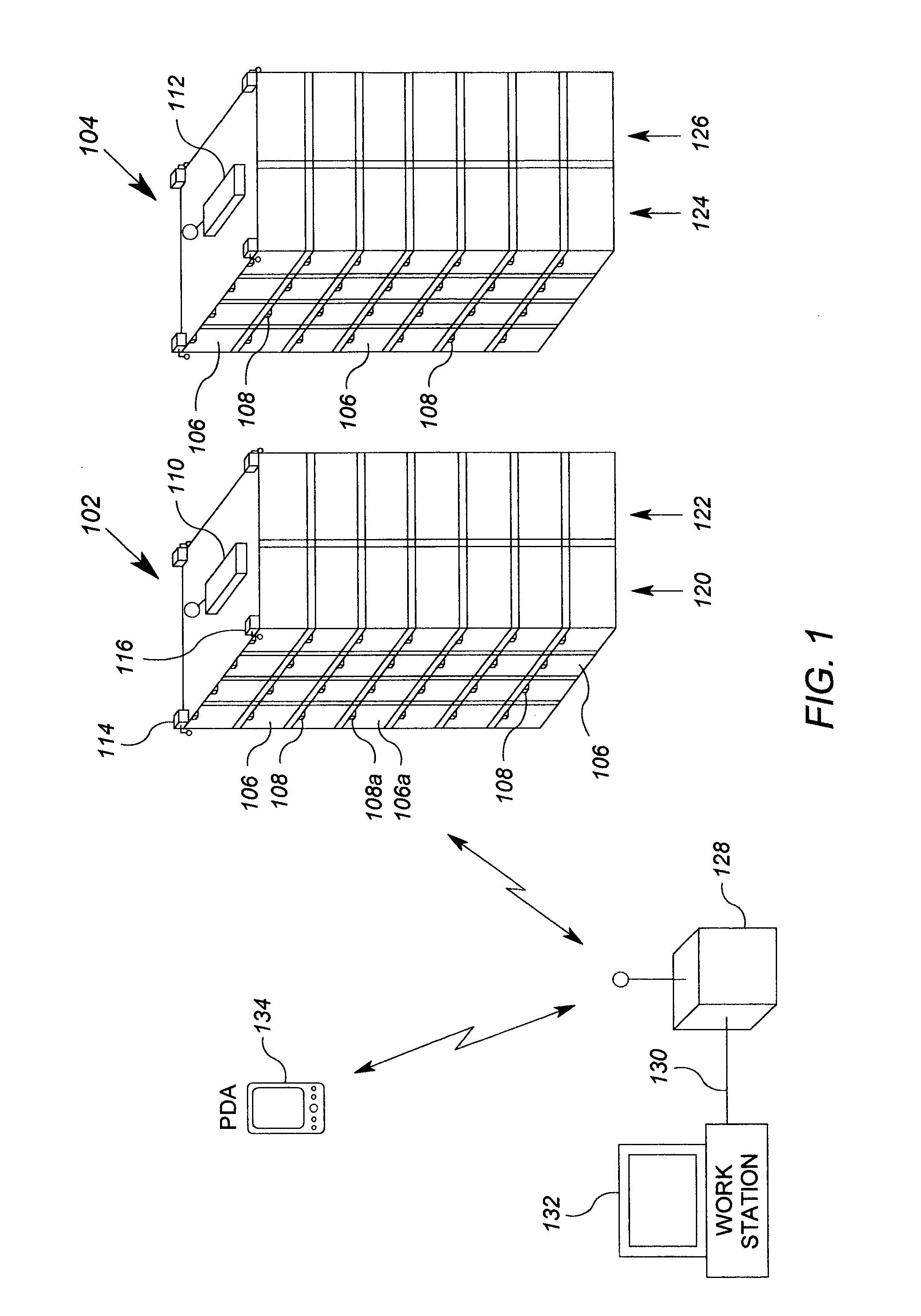
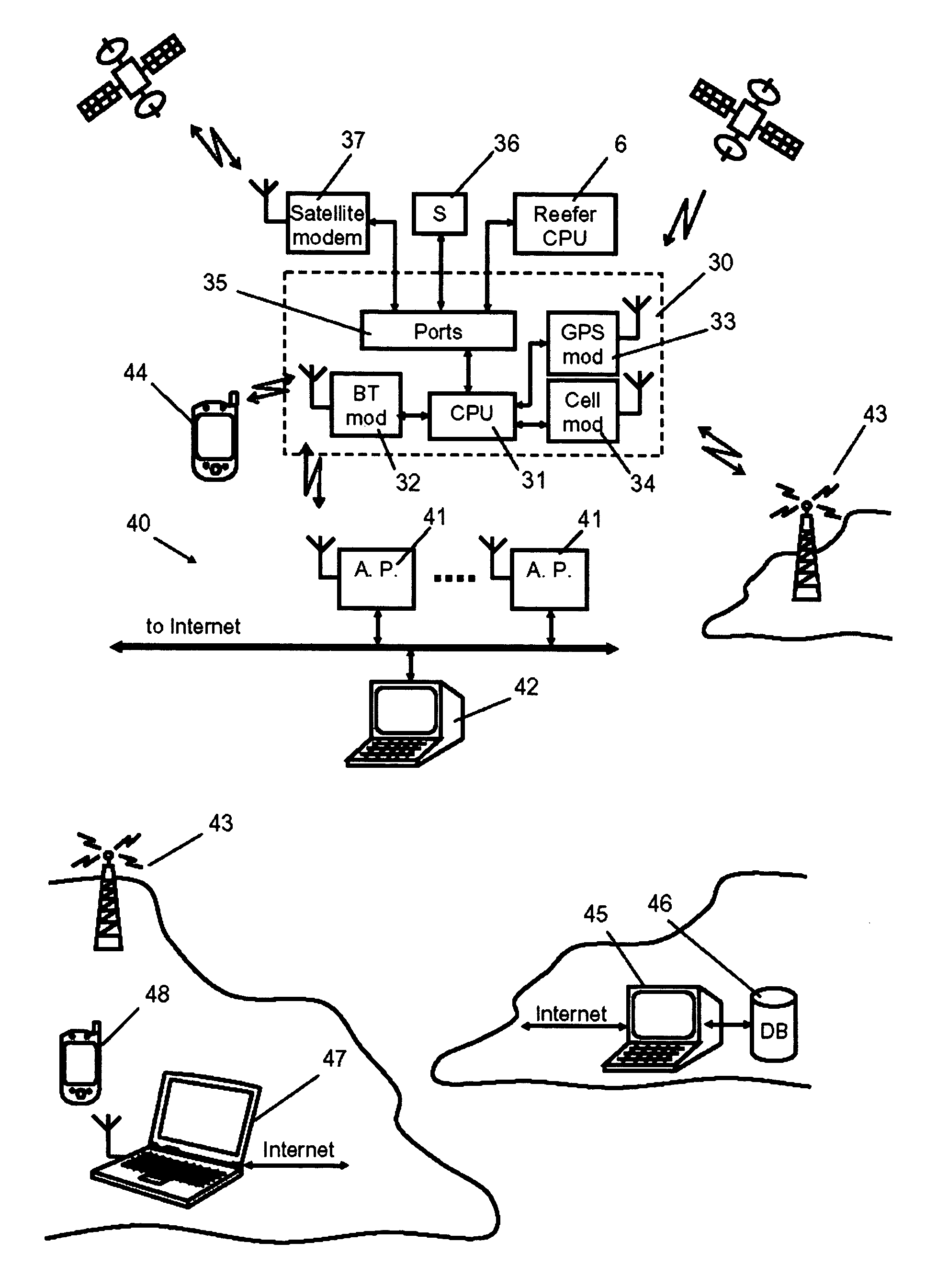
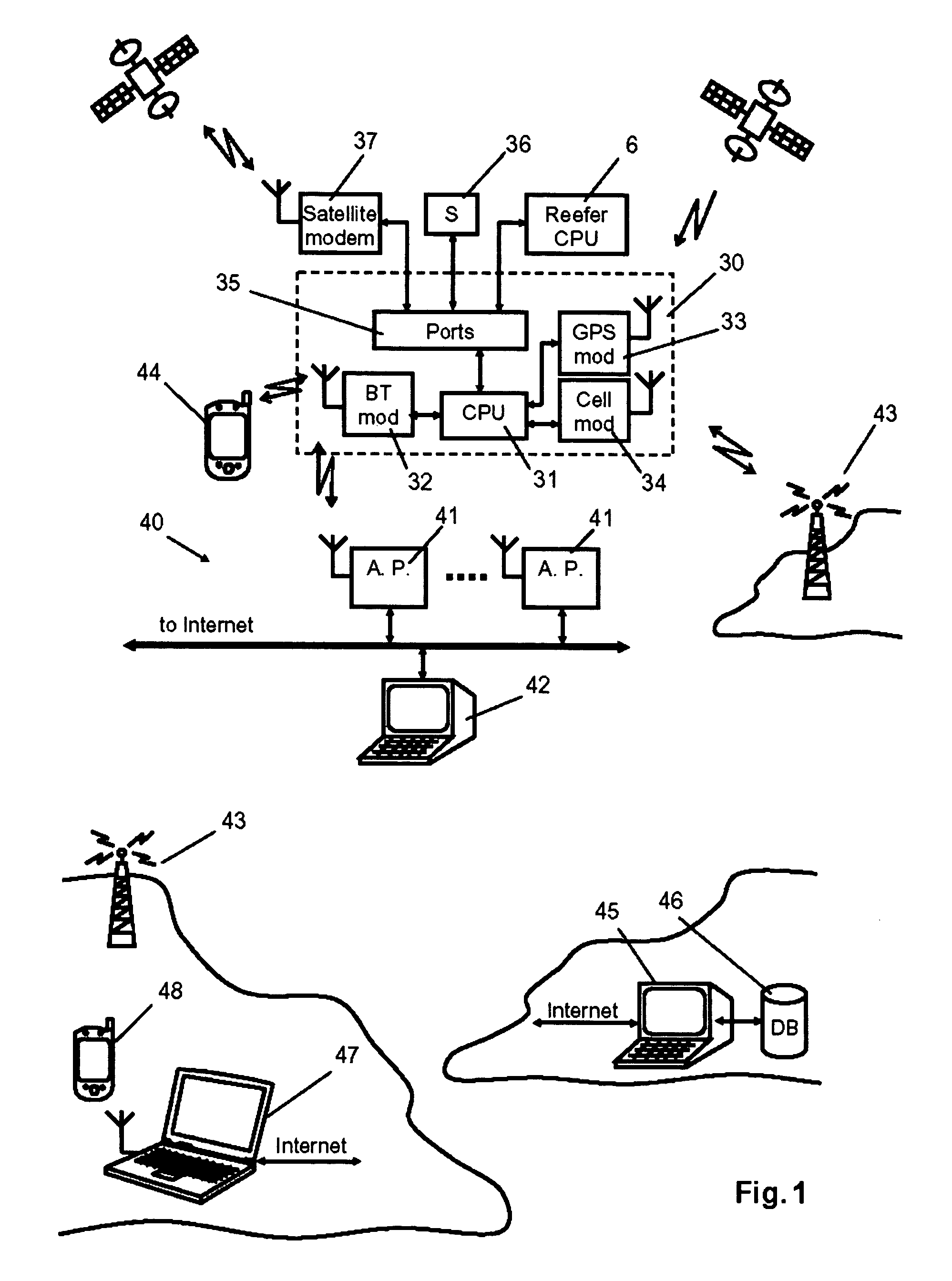
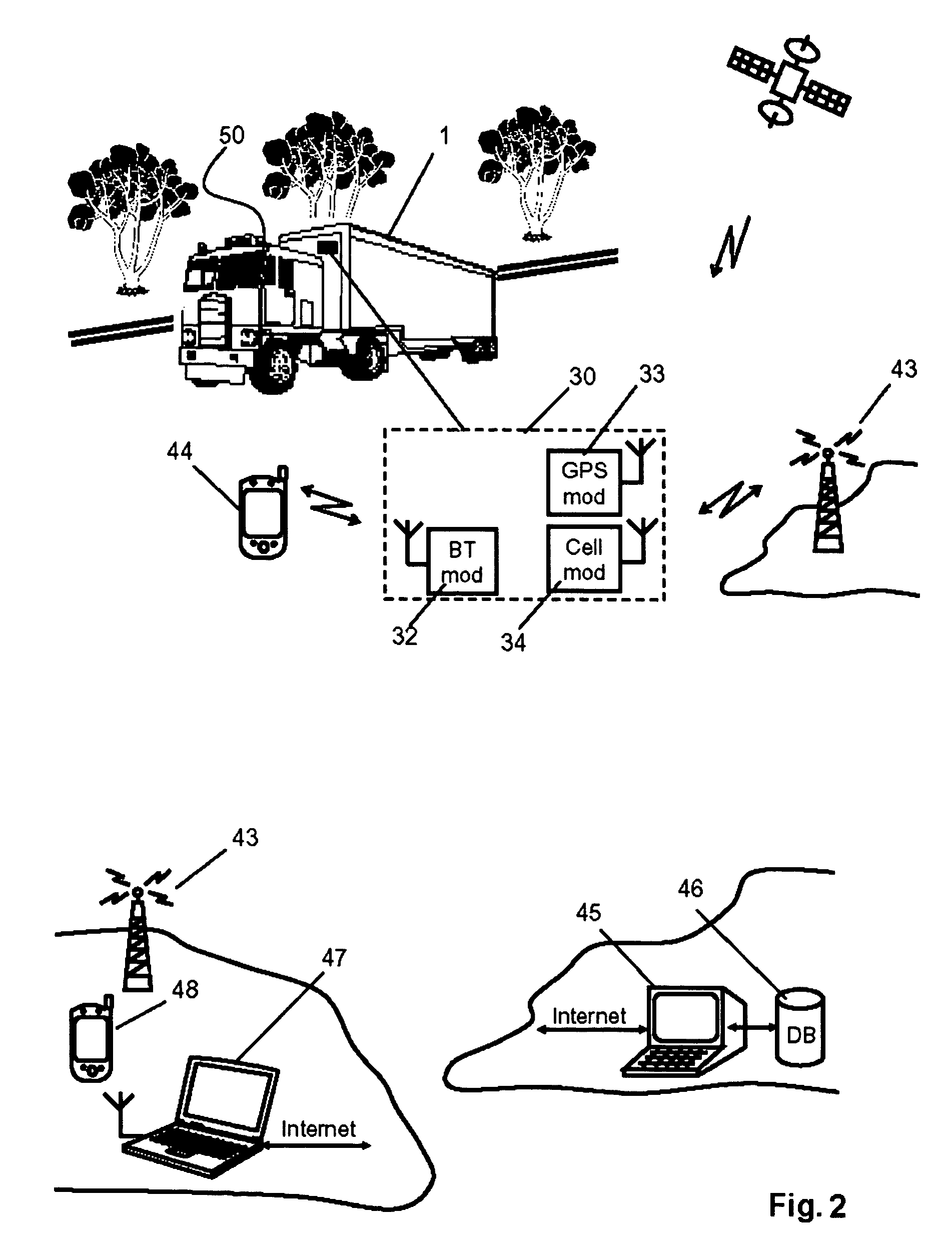
System for monitoring and control of transport containers
The invention comprises a unit and system for remote monitoring and controlling of various conditions in a container during cargo. The system includes a local wireless or cable (wired) network with a local station and access points positioned in the vicinity of location of containers, a remote central station connected with the Internet and a container-mounted means for monitoring and control of reefer equipment, each of which includes a processor (CPU) and a transceiver of wireless local communication, a GPS-receiver and a transceiver of cellular communication (with all of them being connected to the said processor). In addition the processor (CPU) of the device is connected to the controller of reefer equipment, while the transceiver of wireless local communication is made so that the creation of Personal Area Network (PAN) with mobile electronic devices (e.g., Notebook, Pocket PC, PDA) is possible, and establishment of wireless communication with a communication gateway of the said local network is also possible.
Owner:WIRELESS DATA SOLUTIONS
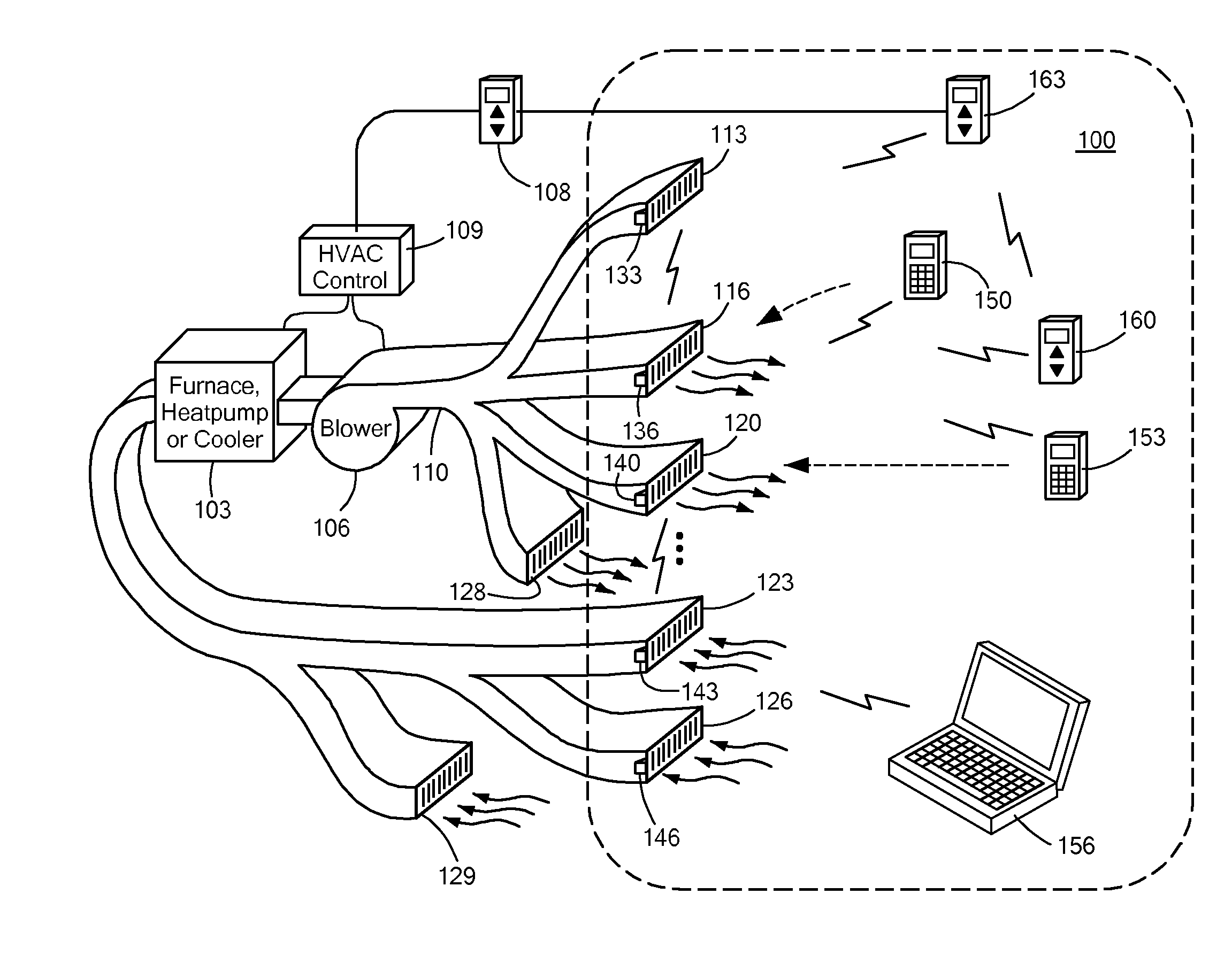
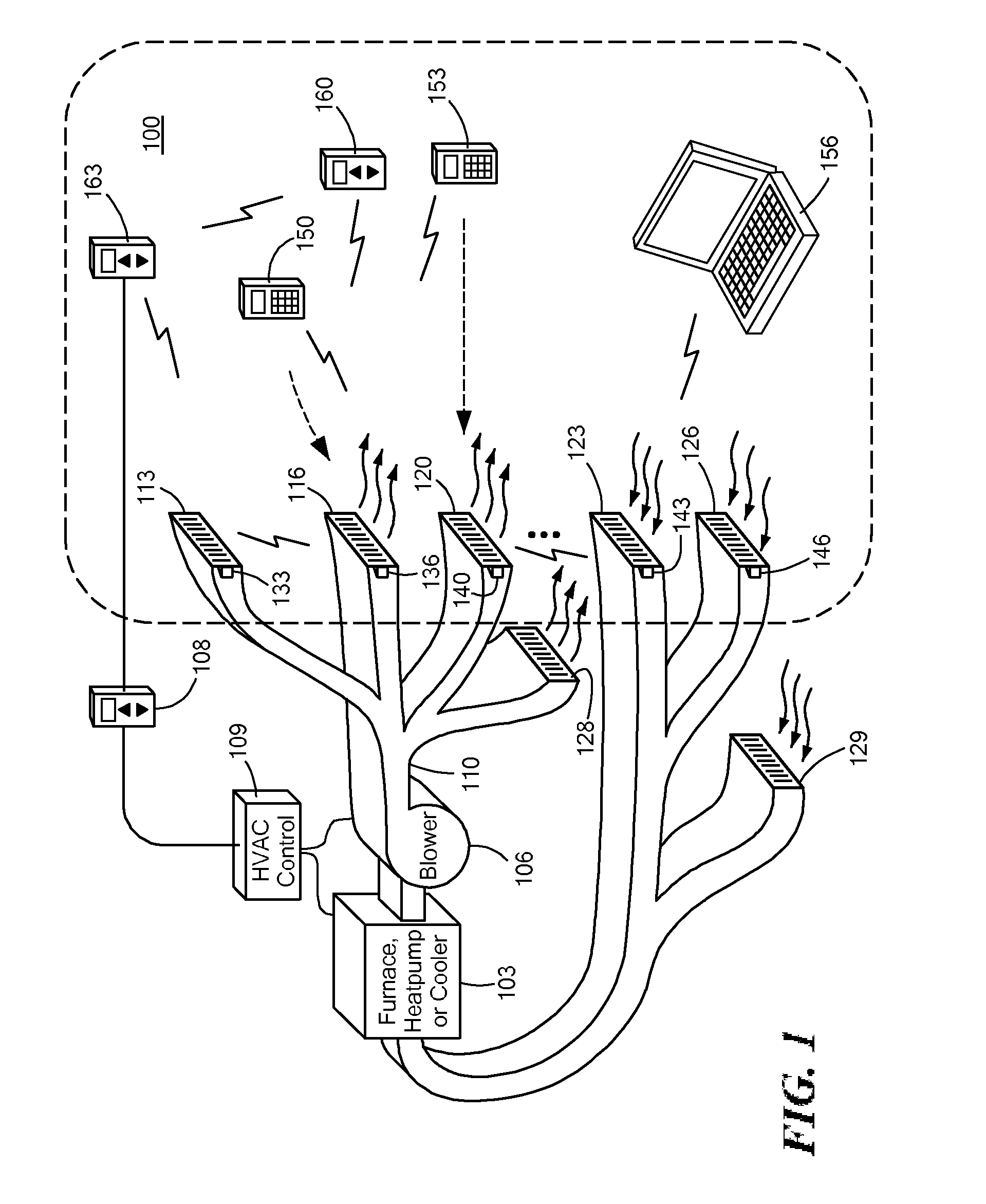
Automatically Balancing Register for HVAC Systems
Distributed nodes, such as intelligent register controllers, of a heating, ventilating and / or air conditioning (HVAC) system wirelessly communicate with each other on a peer-to-peer basis, forming a network, and collectively control the HVAC system, without a central controller. The intelligent register controllers collectively control the amount of conditioned air introduced into each region. Each node may base its operation at least in part on information about one or more (ideally all) of the other nodes. Each intelligent register controller automatically determines how much conditioned air to allow into its region, or how much return air to allow to be withdrawn from its region, based on information collected by the register controller, such as: current temperature of the region; desired temperature of the region; calculated amount of conditioned air required to change the region's temperature to the desired temperature; temperature of conditioned air begin supplied by a duct to the register; current time, day of week, vacation or other schedule data; temperatures of other regions and their respective desired temperatures; calculated amounts of air required to be supplied or withdrawn by the other controlled registers to change their respective regions' temperatures to their desired temperatures; or combinations thereof. Each register controller automatically determines when and to what extent to operate its respective controllable damper.
Owner:ZONER
System and method for evaluating changes in the efficiency of an HVAC system
ActiveUS8019567B2Improve comfortReduce energy useTime indicationSpace heating and ventilationControl systemEngineering
The invention comprises systems and methods for evaluating changes in the operational efficiency of an HVAC system over time. The climate control system obtains temperature measurements from at least a first location conditioned by the climate system, and status of said HVAC system. One or more processors receives measurements of outside temperatures from at least one source other than said HVAC system and compares said temperature measurements from said first location with expected temperature measurements. The expected temperature measurements are based at least in part upon past temperature measurements.
Owner:ECOFACTOR
User friendly interface for control unit
ActiveUS20120203379A1Sampled-variable control systemsMechanical apparatusGraphicsDiagnostic Radiology Modality
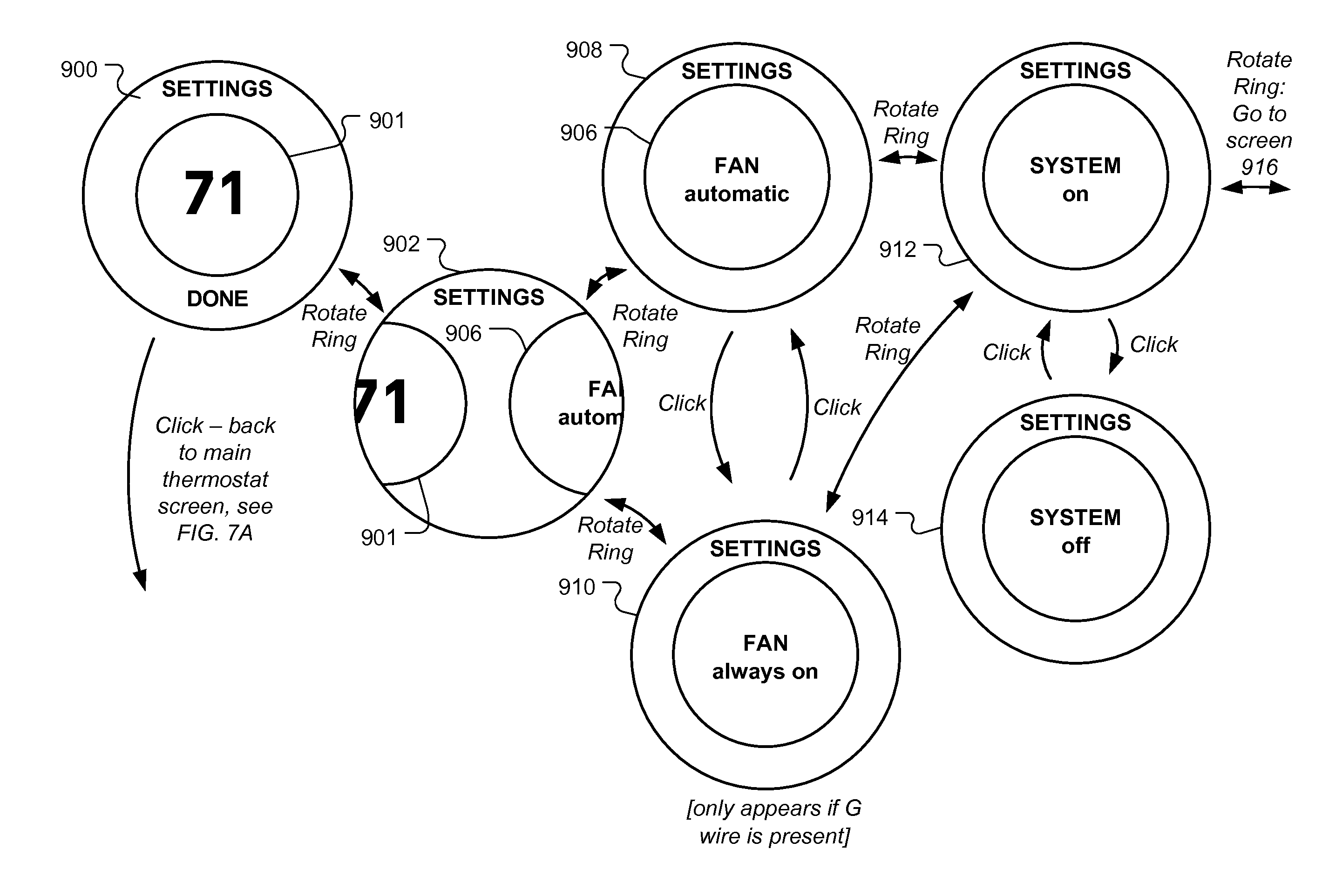
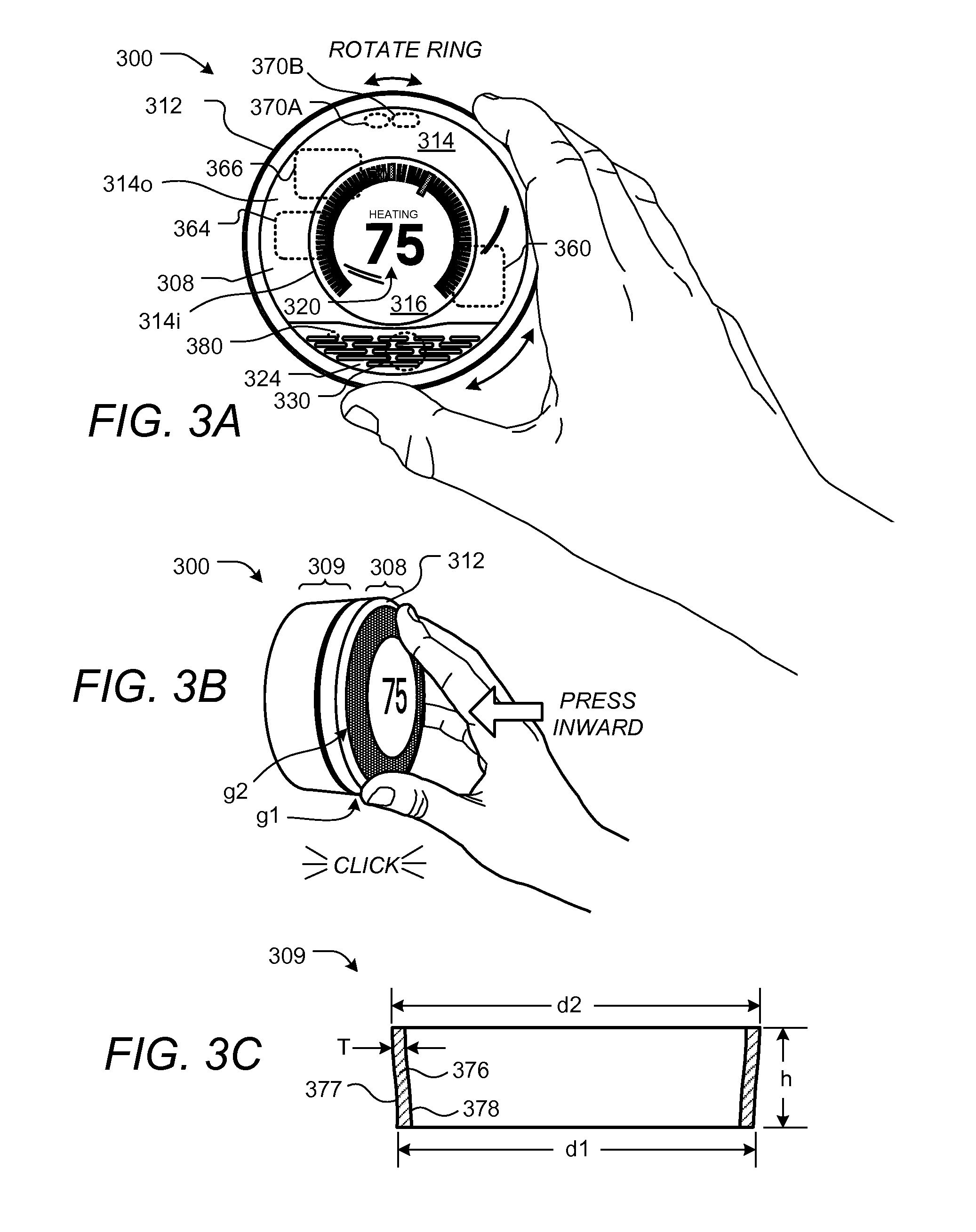
A user-friendly programmable thermostat is described that includes a central electronic display surrounded by a ring that can be rotated and pressed inwardly to provide user input in a simple and elegant fashion. The current temperature and setpoint are graphically displayed as prominent tick marks. Different colors and intensities can be displayed to indicate currently active HVAC functions and an amount of heating or cooling required to reach a target temperature. The setpoint can be altered by user rotation of the ring. The schedule can be displayed and altered by virtue of rotations and inward pressings of the ring. Initial device set up and installation, the viewing of device operation, the editing of various settings, and the viewing of historical energy usage information are made simple and elegant by virtue of the described form factor, display modalities, and user input modalities of the device.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
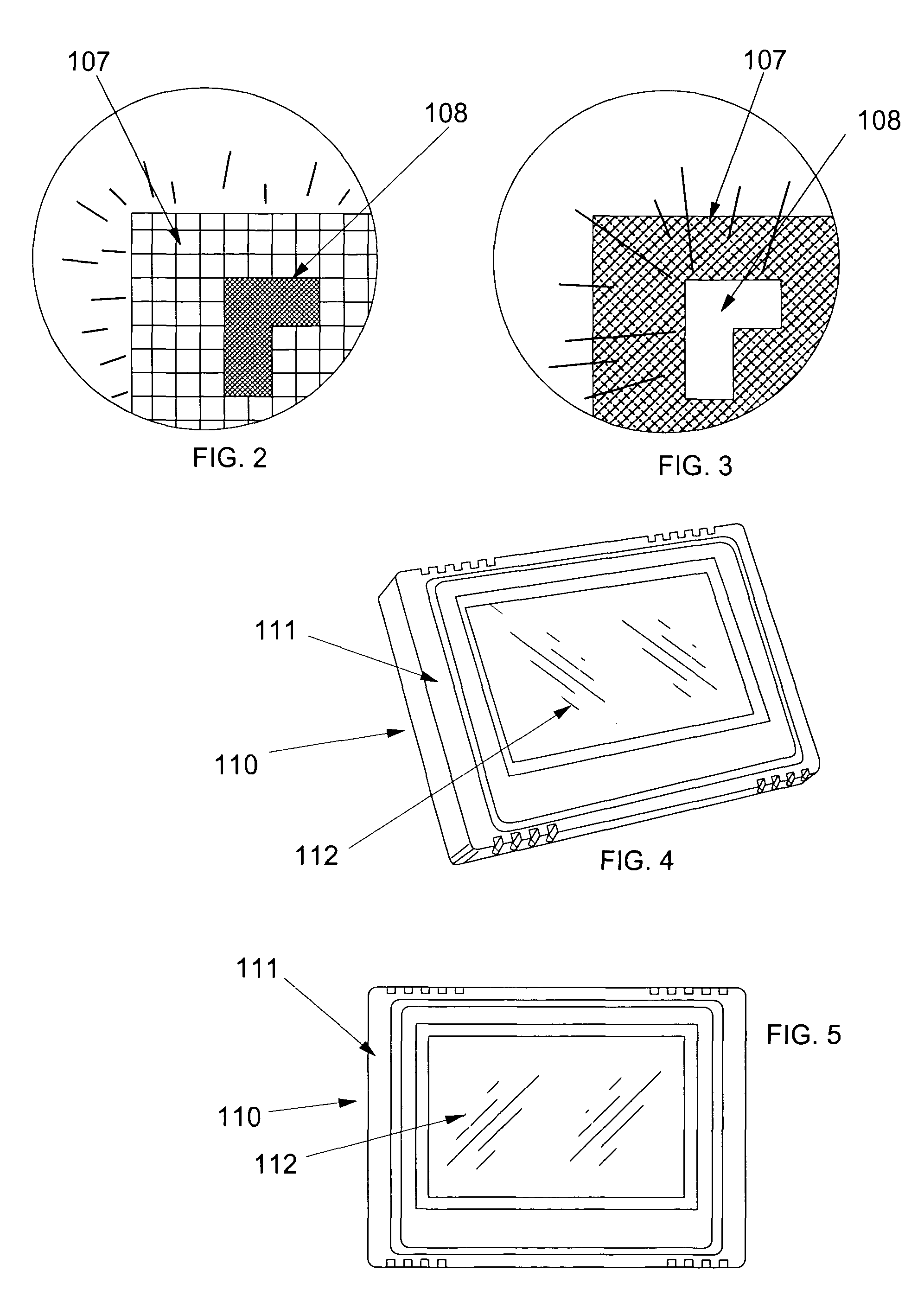
Programmable thermostat incorporating a liquid crystal display selectively presenting adaptable system menus including changeable interactive virtual buttons
ActiveUS7156318B1Easy for a user to programFacilitate intuitive programmingSampled-variable control systemsAir-treating devicesLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
A programmable thermostat, with a touch screen liquid crystal display having the capability to add to or remove virtual buttons to the display depending on the items of space conditioning equipment connected with and controlled by the thermostat.
Owner:ROSEN TECH LLC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com