Patents
Literature
1618 results about "White noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In signal processing, white noise is a random signal having equal intensity at different frequencies, giving it a constant power spectral density. The term is used, with this or similar meanings, in many scientific and technical disciplines, including physics, acoustical engineering, telecommunications, and statistical forecasting. White noise refers to a statistical model for signals and signal sources, rather than to any specific signal. White noise draws its name from white light, although light that appears white generally does not have a flat power spectral density over the visible band.
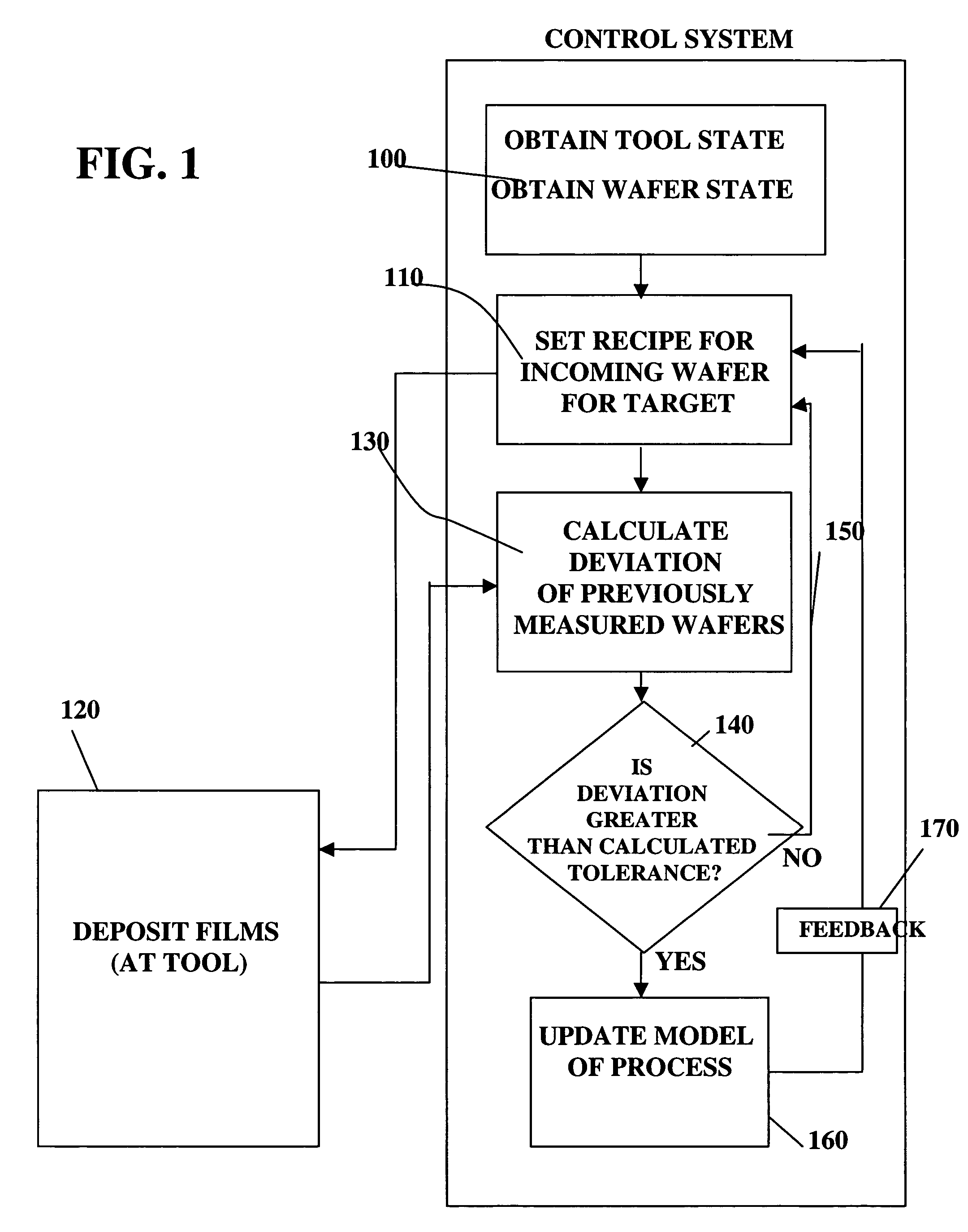
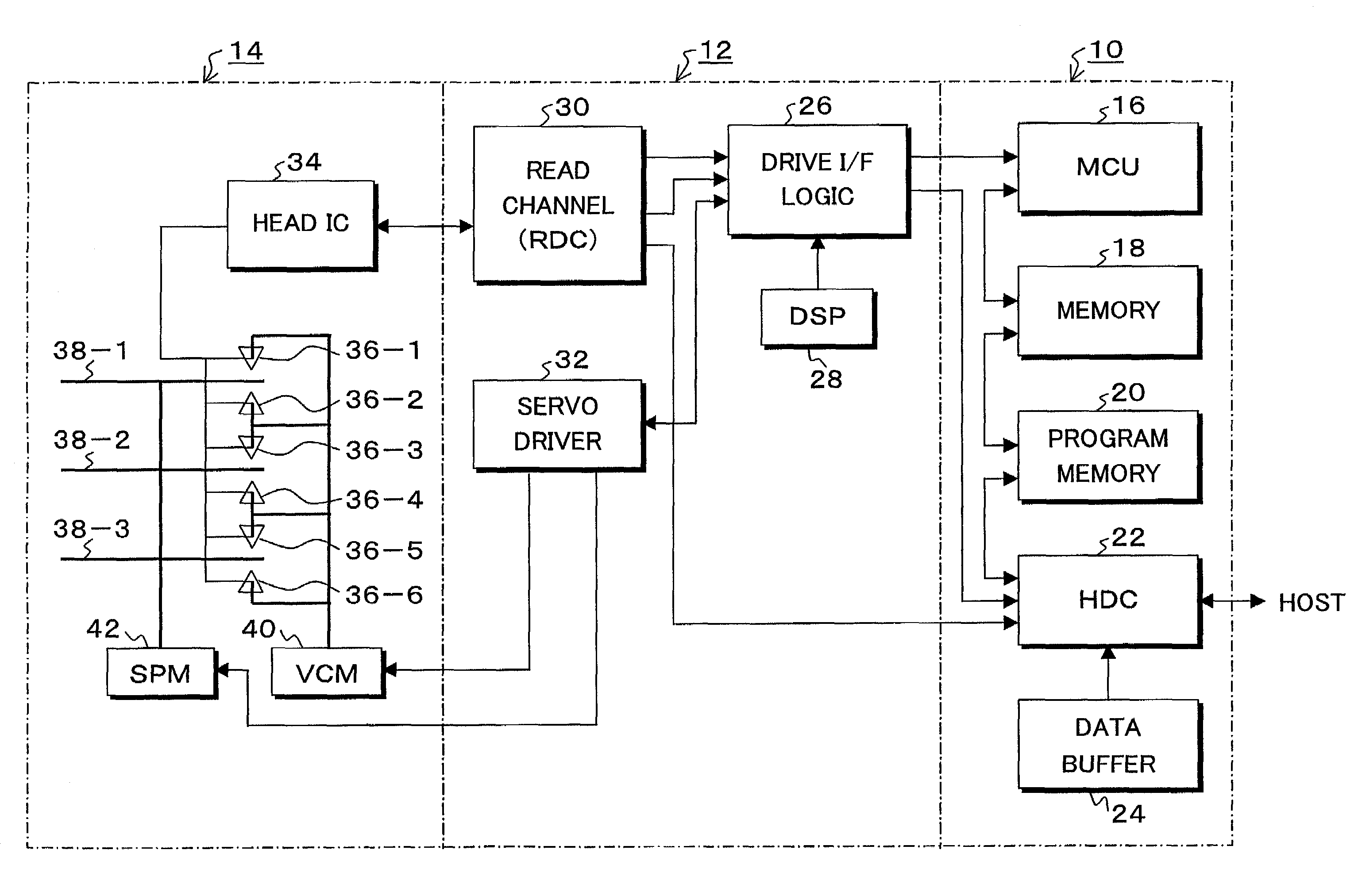
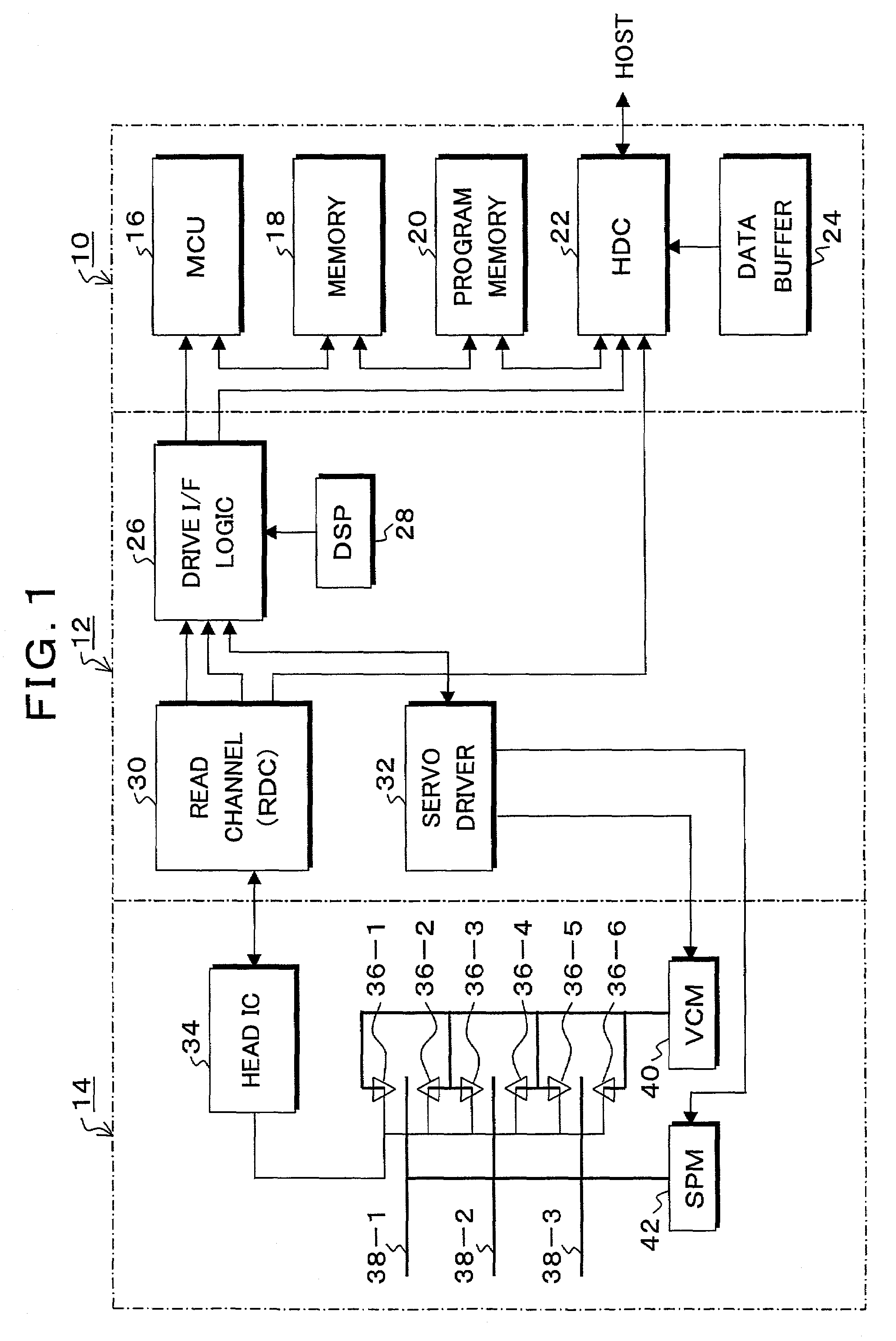
Open Web Services-Based Indoor Climate Control System
InactiveUS20080281472A1Improve productivityCost of sameProgramme controlSampled-variable control systemsReal-time Control SystemWeb service
The present invention relates generally to a building automation system, and, more particularly, to an Internet-centric, open, extensible software and hardware framework supporting all aspects of control and monitoring of a smart building ecosphere. The present invention further relates to an “intelligent,” real-time control system capable of both autonomous process control and interaction with system users and system administrators, which is configured to accommodate functional extensions and a broad array of sensors and control devices. The system allows individuals to communicate, monitor and adjust their personal environmental preferences (temperature, light, humidity, white noise, etc.) much like they would in an automobile, via the Internet. The system is equipped with an occupancy sensor that recognizes the presence and identity of the individual. A built-in expert system can make decisions based on data from multiple sources so that the system can alter its activity to conserve energy while maintaining users' comfort.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
Open web services-based indoor climate control system
InactiveUS7904209B2Improve productivityCost of sameProgramme controlSampled-variable control systemsReal-time Control SystemWeb service
The present invention relates generally to a building automation system, and, more particularly, to an Internet-centric, open, extensible software and hardware framework supporting all aspects of control and monitoring of a smart building ecosphere. The present invention further relates to an “intelligent,” real-time control system capable of both autonomous process control and interaction with system users and system administrators, which is configured to accommodate functional extensions and a broad array of sensors and control devices. The system allows individuals to communicate, monitor and adjust their personal environmental preferences (temperature, light, humidity, white noise, etc.) much like they would in an automobile, via the Internet. The system is equipped with an occupancy sensor that recognizes the presence and identity of the individual. A built-in expert system can make decisions based on data from multiple sources so that the system can alter its activity to conserve energy while maintaining users' comfort.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
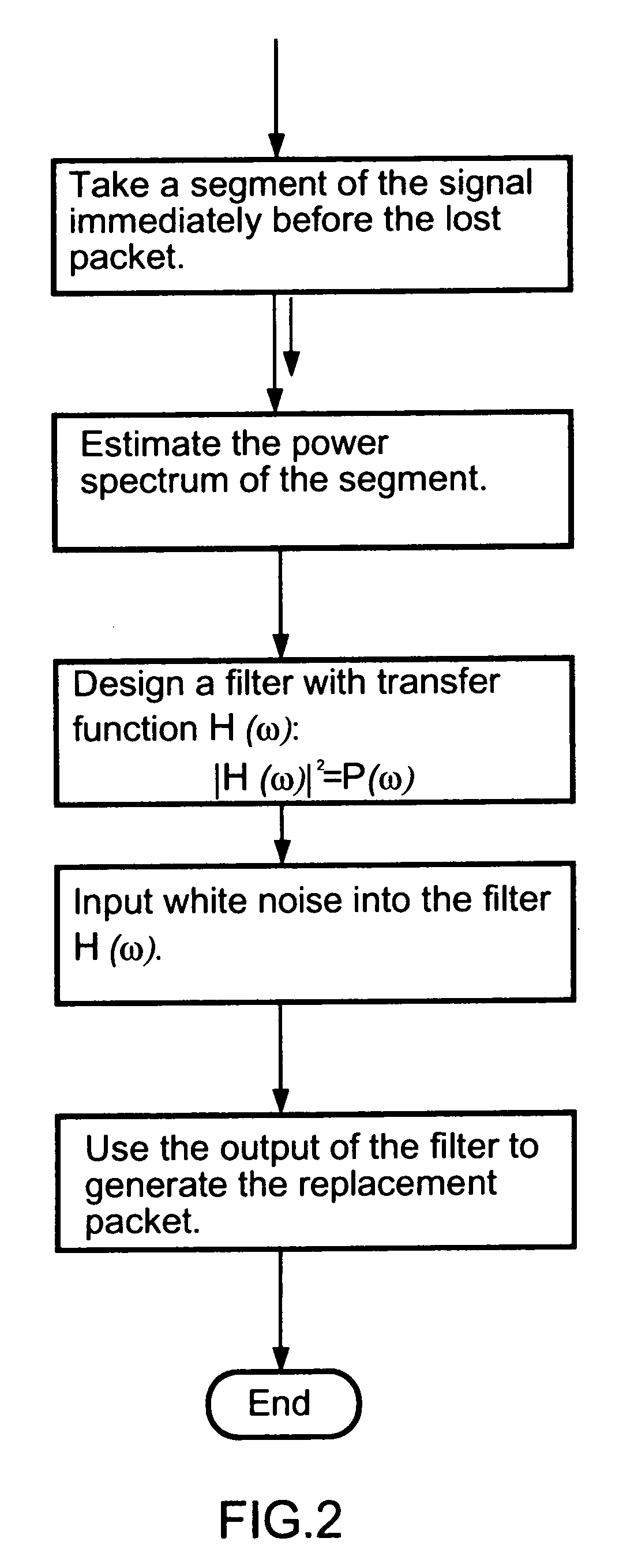
Packet loss compensation method using injection of spectrally shaped noise
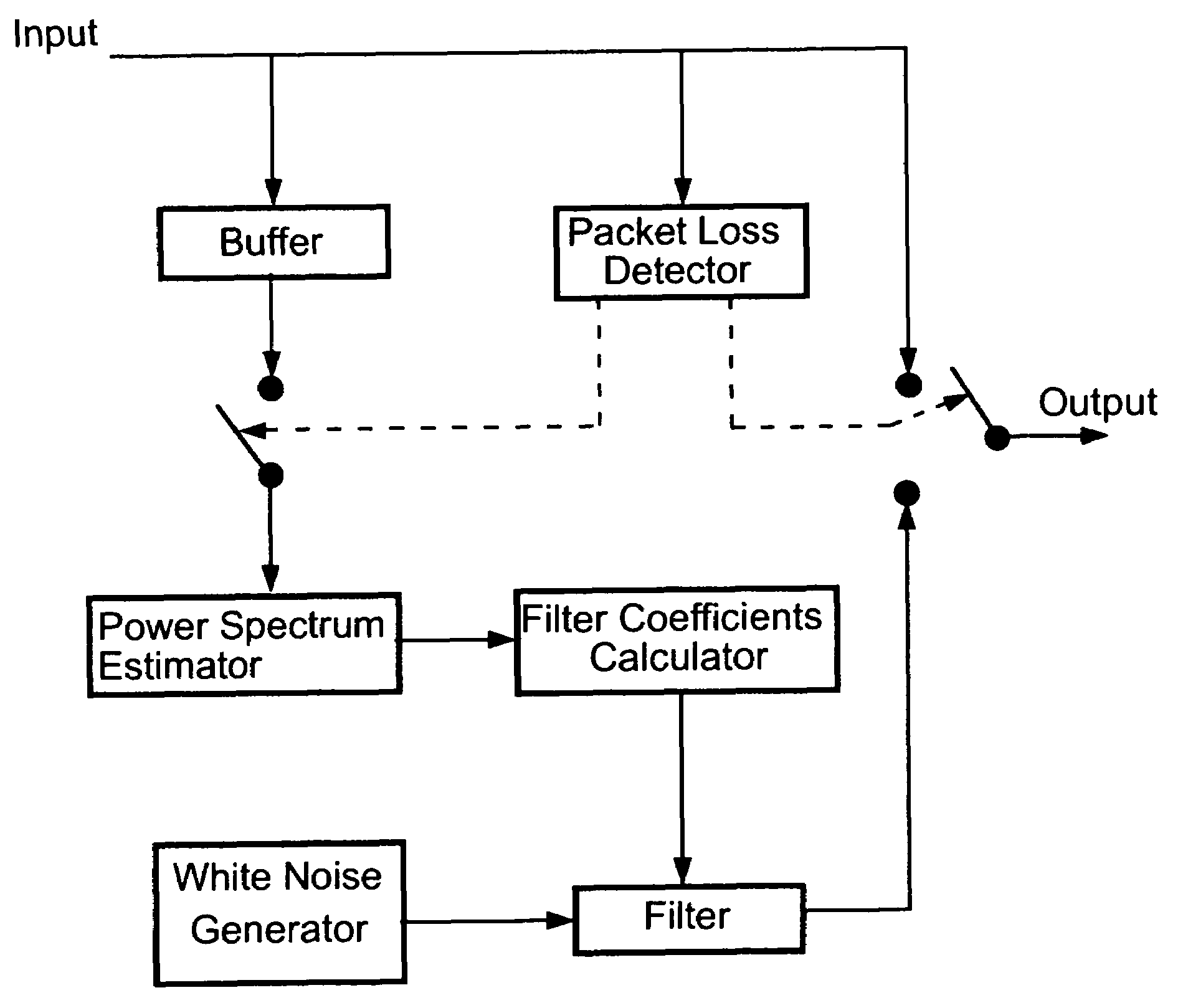
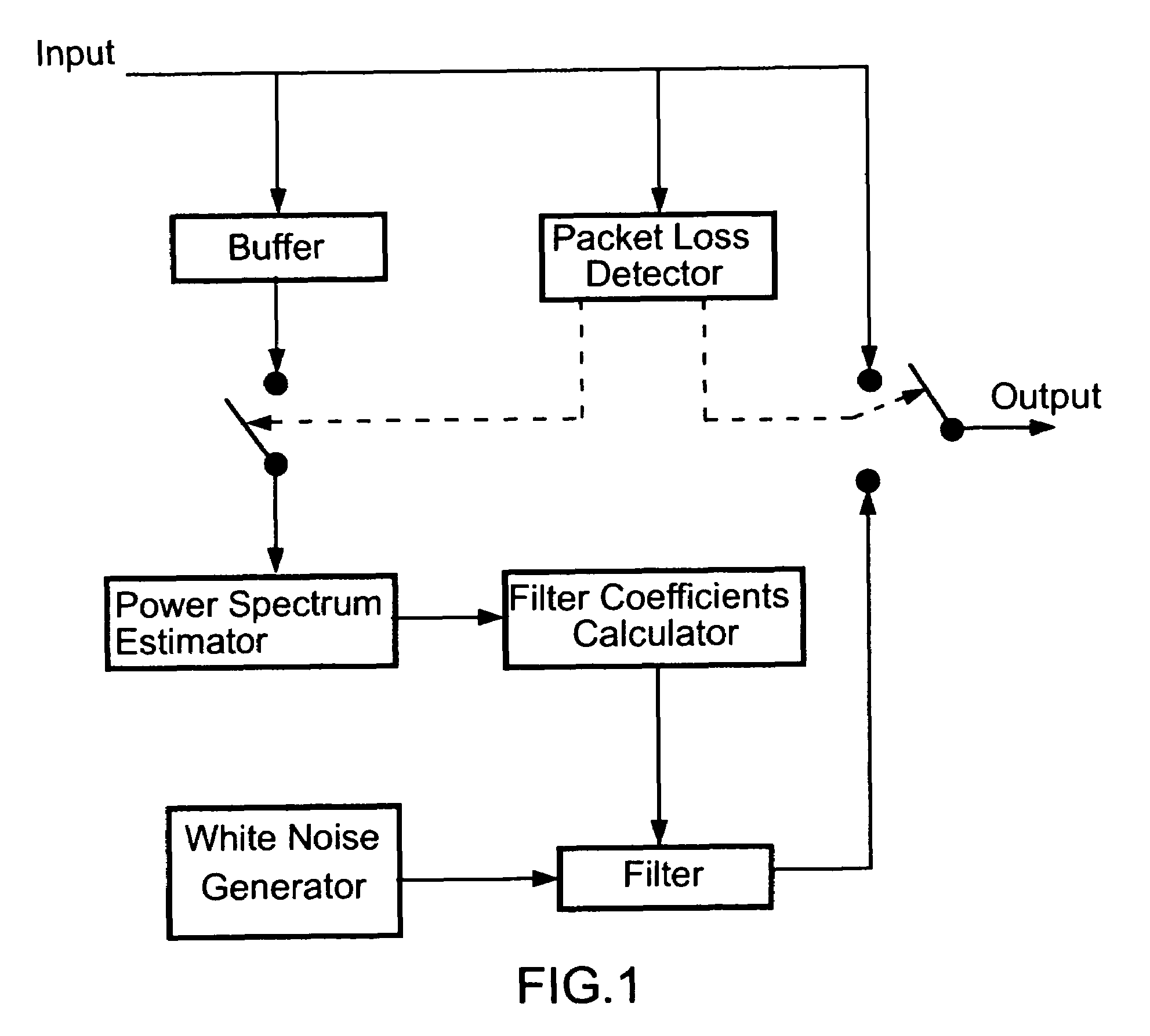
An insertion-based error concealment method and apparatus are provided whereby, instead of directly inserting white noise, a filter is created to shape the white noise. The filtered white noise is then used to replace lost data. The method of the present invention is implemented by first estimating the power spectrum of the previous frame; then designing a filter with transfer function H(f), where |H(f)|2=the estimated power spectrum; and finally generating the replacement packet using noise which has been spectrally modified by the filter. The resulting filtered noise has the same power spectrum as the previous packet but is not highly correlated with it.
Owner:ZARLINK SEMICON LTD
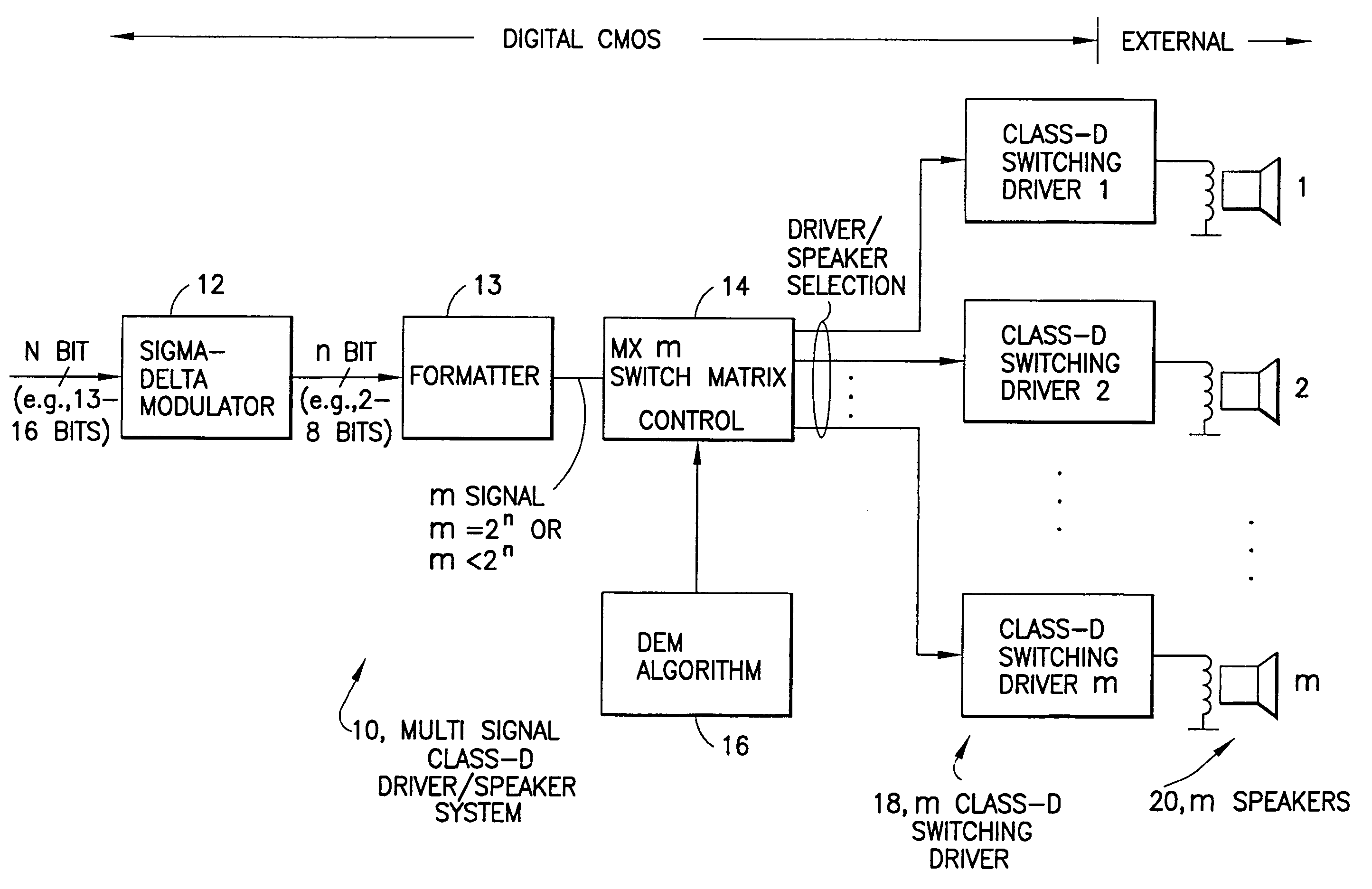
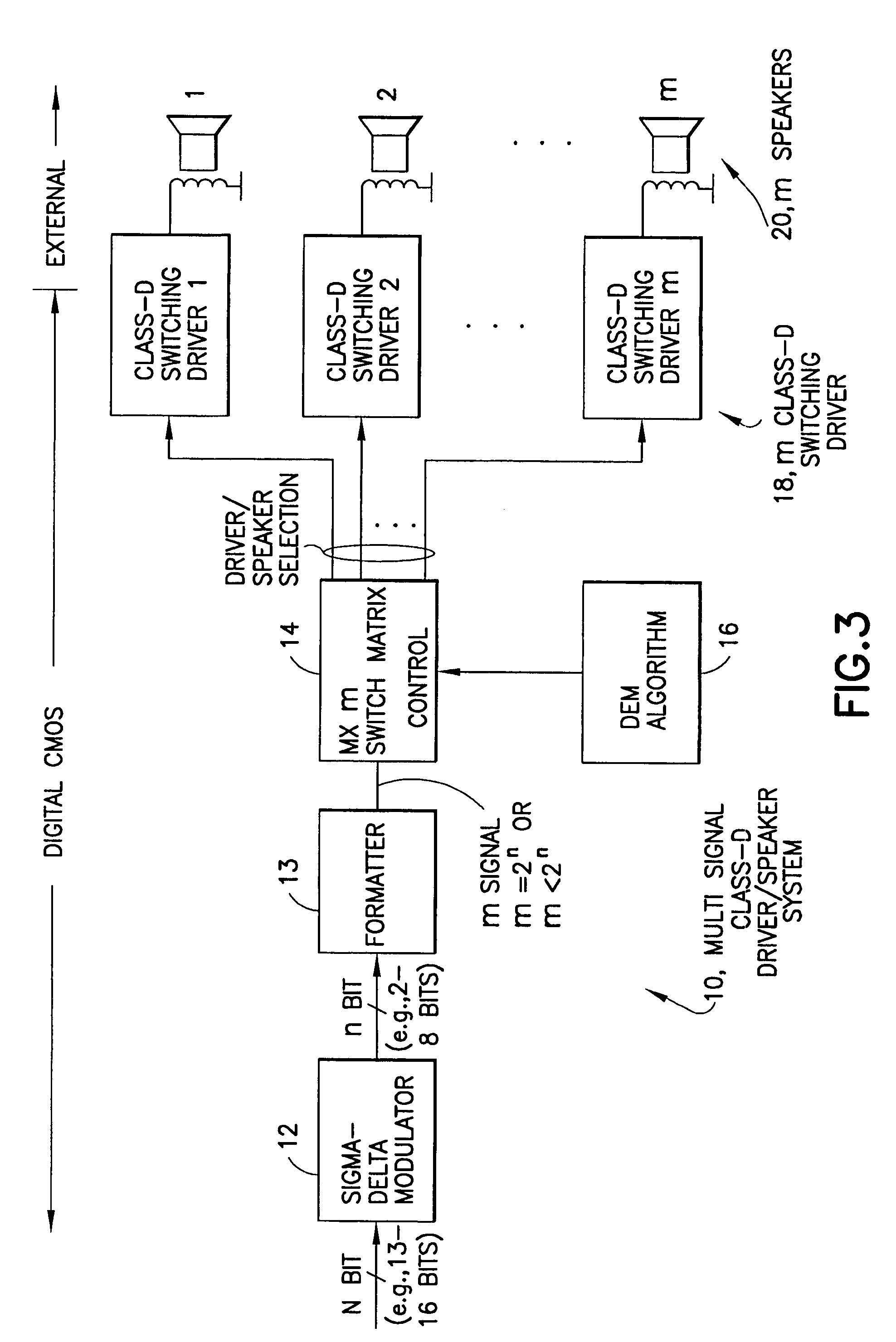
Method and apparatus for implementing a class D driver and speaker system
InactiveUS7058463B1Spread distortionDigitally weighted transducing elementsAnalogue conversionImage resolutionWide band
An audio path is constructed to include a multi-bit sigma-delta converter for converting an N-bit digital input to an n-bit output representing an over-sampled, lower resolution n-bit version of the N-bit digital input; a formatter for converting the n-bit output to an m signal output (e.g., as a thermometer code, a SDM format or a PWM format); an m-by-m switching matric for receiving the m output signals and for reordering the m output signals, m class-D drivers individual ones of which are driven by one of the reordered m output signals for driving one of m speakers; and a dynamic element matching (DEM) block coupled to the switching matric for controlling the reordering of the m output signals driving the m class-D drivers for spreading the distortion due at least to driver-speaker pair mismatch to wide band noise. The DEM may operate to generate white noise, or it may generate shaped (colored) noise.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Hearing compensation system incorporating signal processing techniques
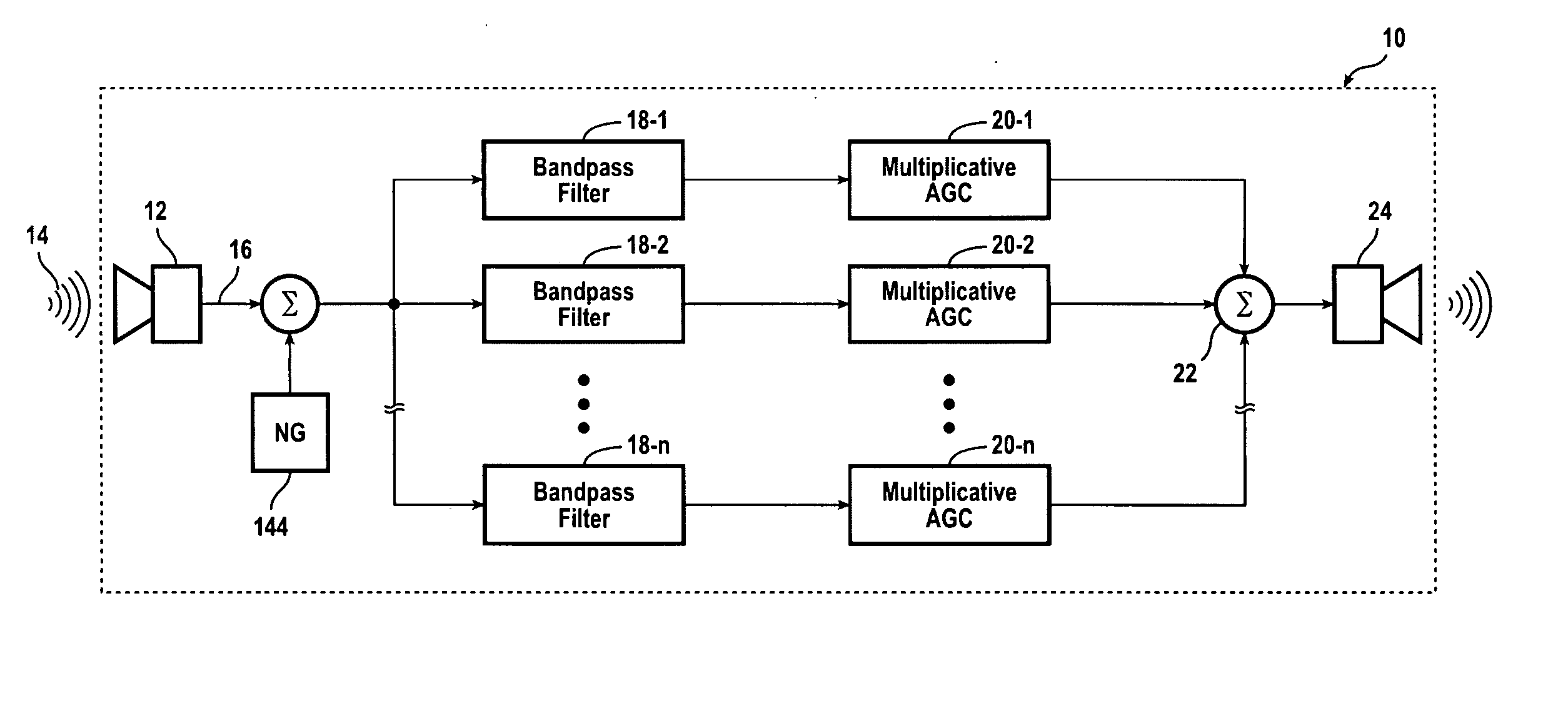
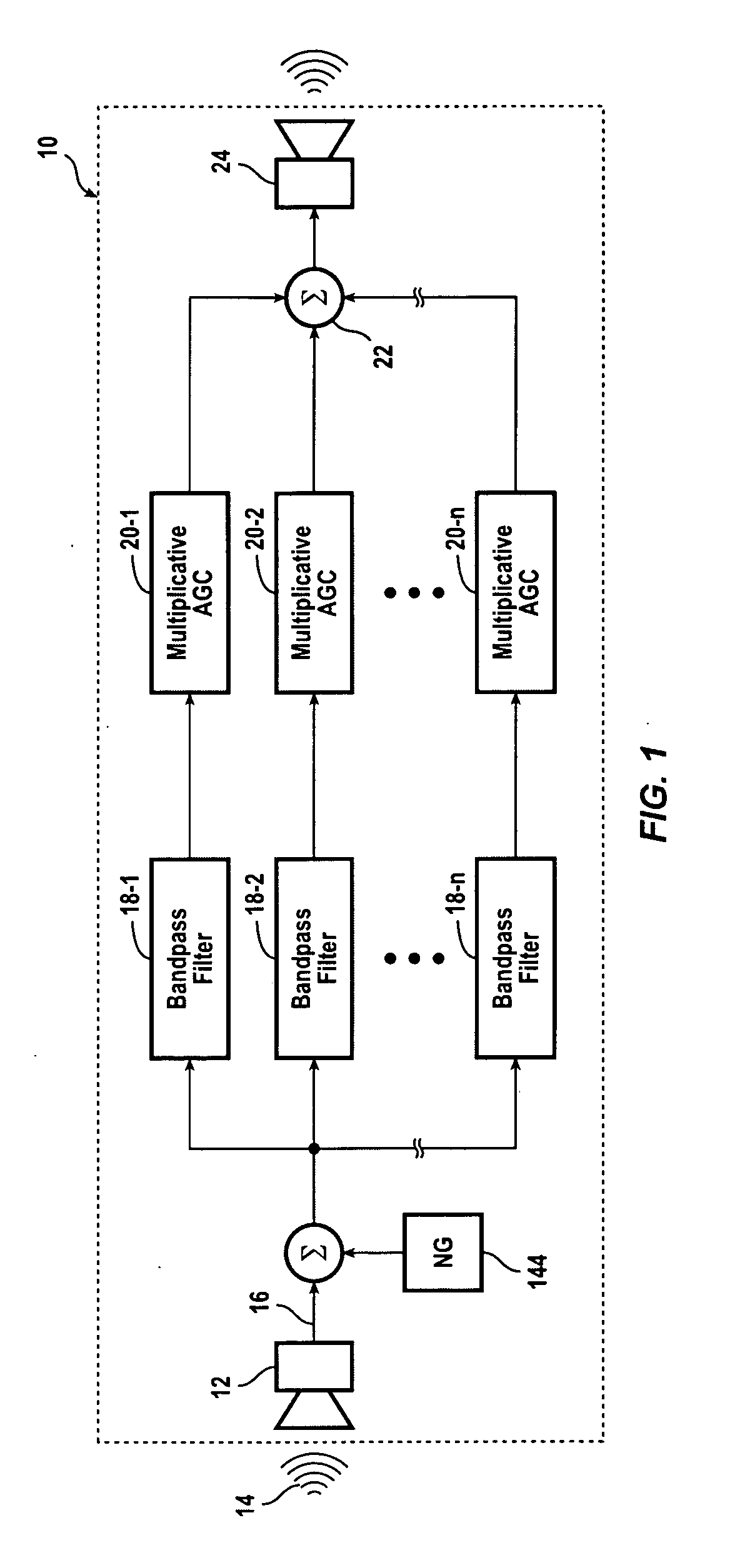
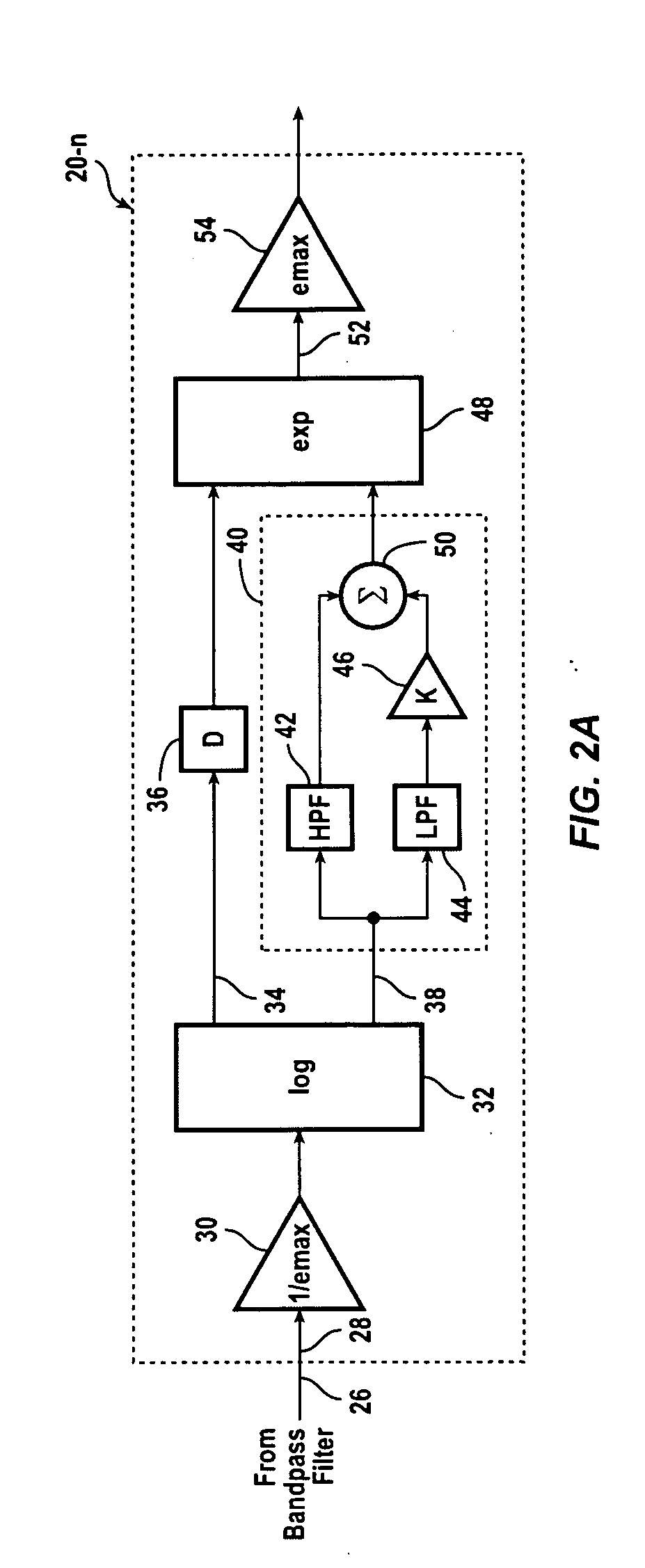
InactiveUS20050111683A1Signal processingCombination control in untuned amplifierBandpass filteringEngineering
A hearing compensation system comprises a plurality of bandpass filters having an input connected to an input transducer and each bandpass filter having an output connected to the input of one of a plurality of multiplicative automatic gain control (MAGC) circuits whose outputs are summed together and connected to the input of an output transducer. The MAGC circuits attenuate acoustic signals having a constant background level without the loss of speech intelligibility. The identification of the background noise portion of the acoustic signal is made by the constancy of the envelope of the input signal in each of the several frequency bands. The background noise that will be suppressed includes multi-talker speech babble, fan noise, feedback whistle, florescent light hum, and white noise. For use in the consumer electronics field background acoustic noise may be sensed and used to adjust gain in the various MAGC circuits so as to improve a user's listening experience, whether the user is hearing impaired or not.
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
Apparatus and method of in-service audio/video synchronization testing
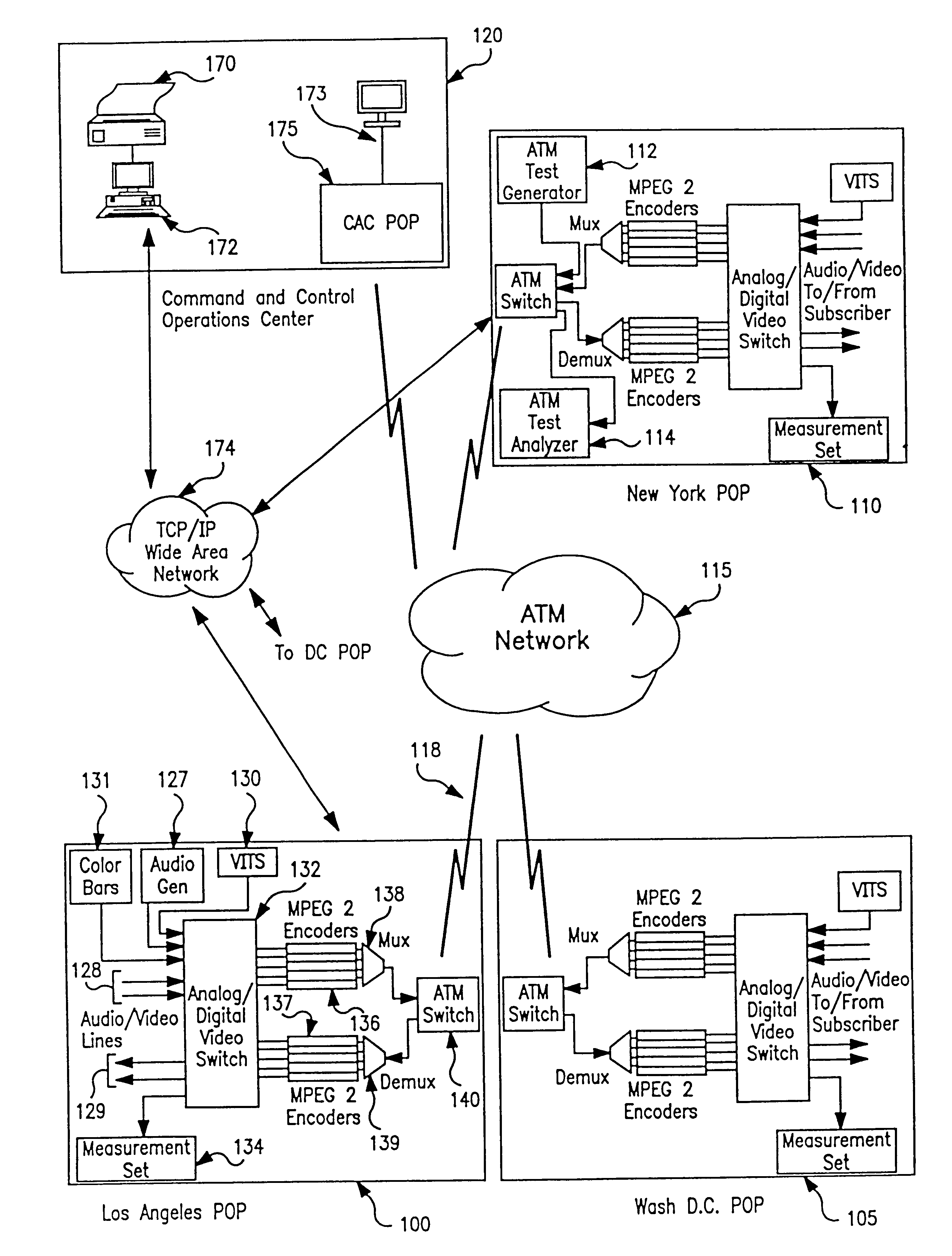
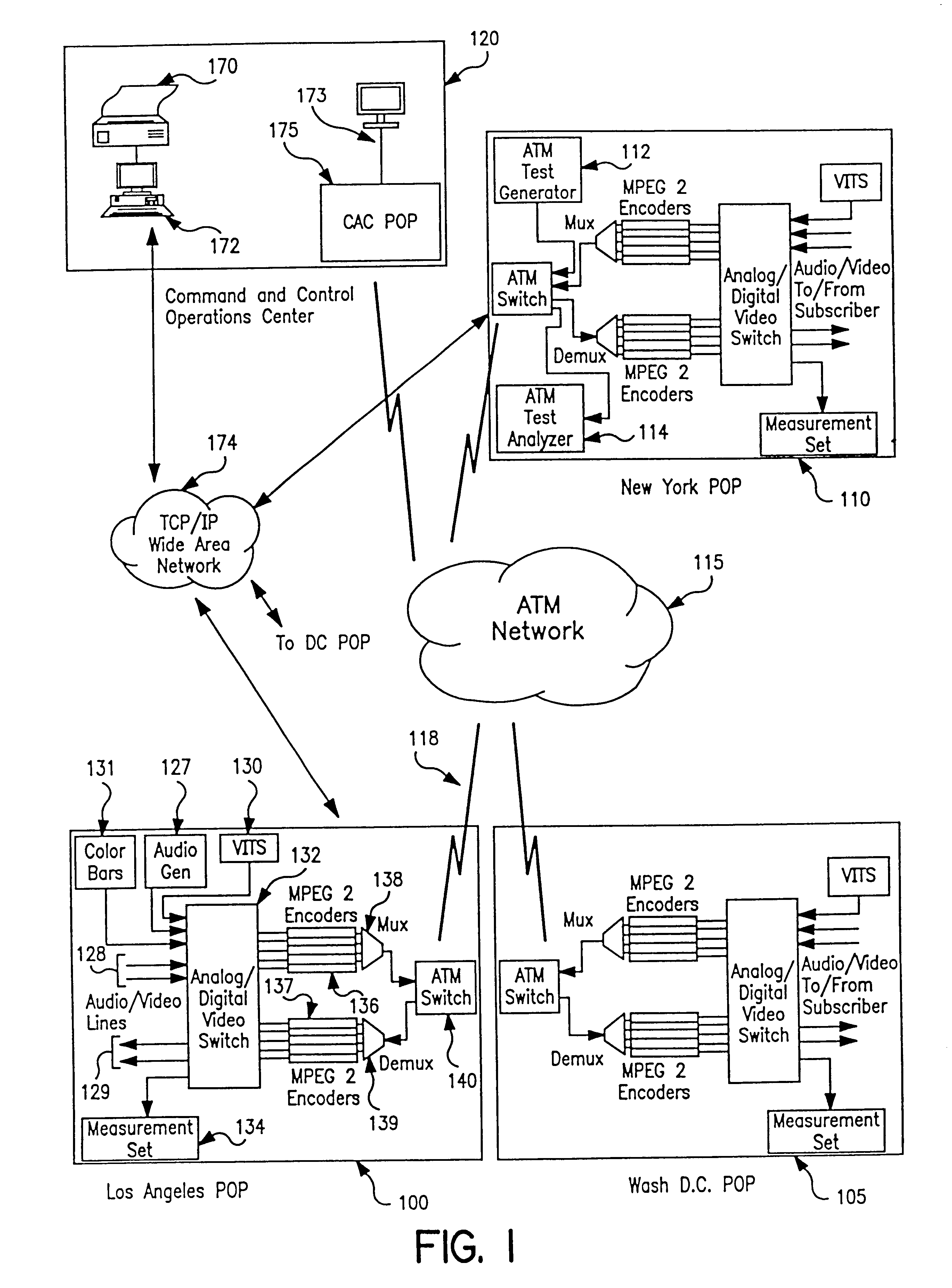
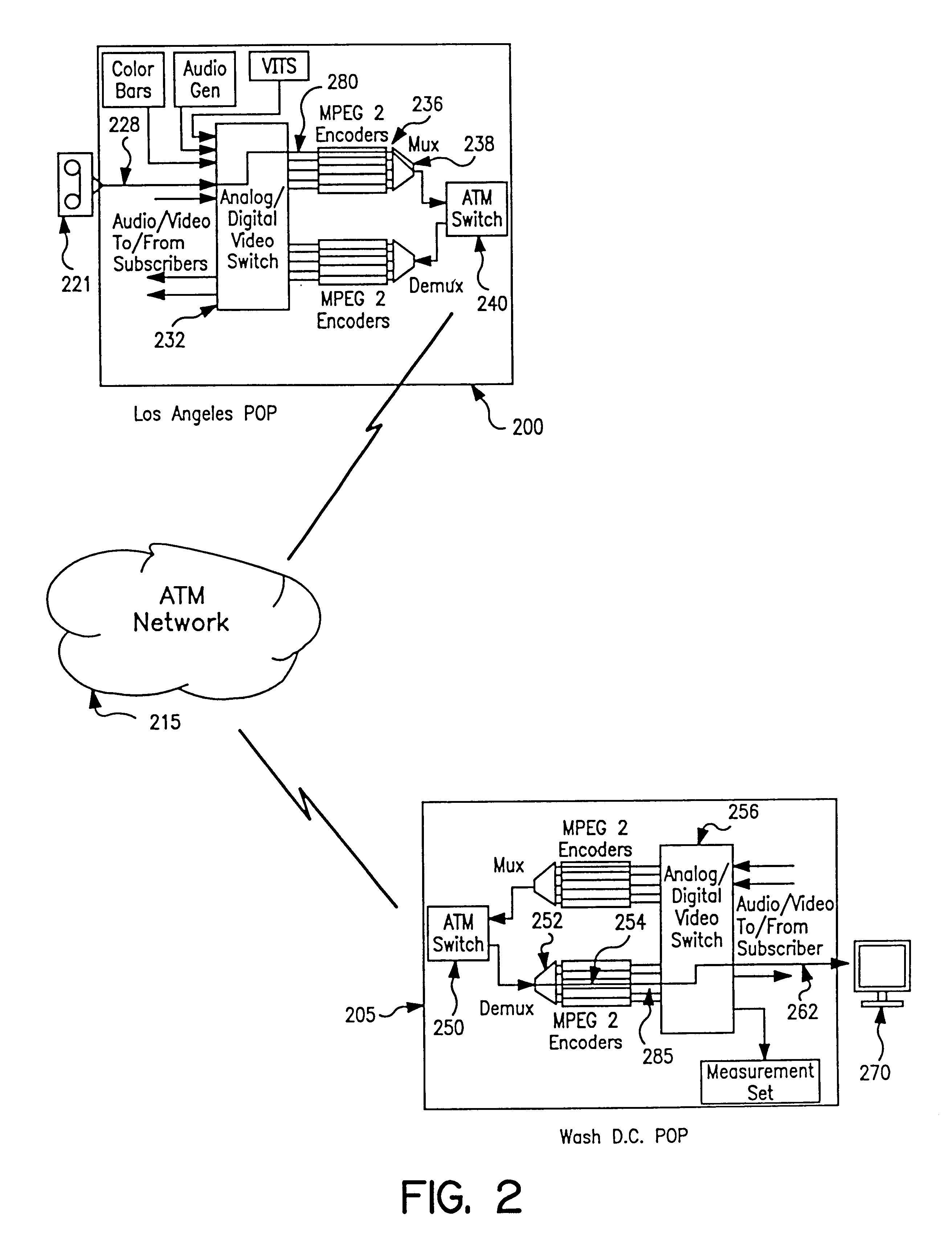
InactiveUS6414960B1Easy to testTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationVideo-signal generatorNoise level
An apparatus and method provide non-intrusive in-service testing of audio / video synchronization testing without using traditional audio marker tones. The network includes an A / V synchronous test signal generator which injects video and audio markers into the video and audio non-intrusively and routes the two signals into a switch where they are switched into a channel for encoding and transmission via the ATM network. At the distant end the signal is decoded and routed by a switch into the A / V test generator and measurement set where the markers are detected and the A / V skew calculated, after which the audio and video are routed to the subscriber. The A / V test set signal generator includes a Video Blanking Interval (VBI) test signal generator and a white noise generator, the former injecting a marker into the video signal and the later injecting an audio marker into the audio signal. The video marker is injected into the VBI and broadband, background audio noise to measure the delay between the audio and video components of a broadcast. The marking of the audio is accomplished by gradually injecting white noise into the audio channel until the noise level is 6 dB above the noise floor of the audio receiver. As a precursor A / V sync signal, a small spectrum of the white noise is notched or removed. This signature precludes inadvertent recognition of program audio noise as the audio marker.
Owner:IBM CORP
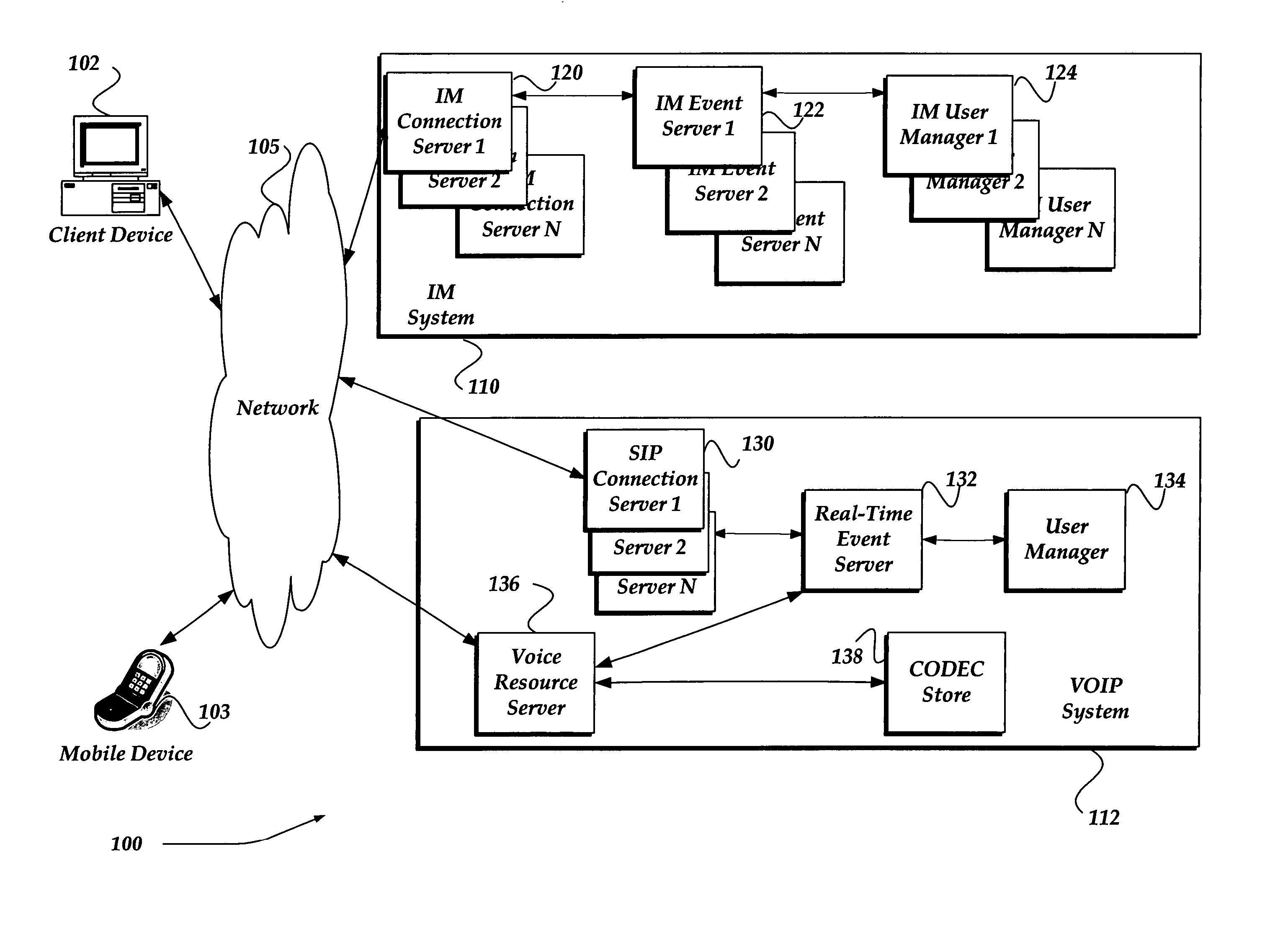
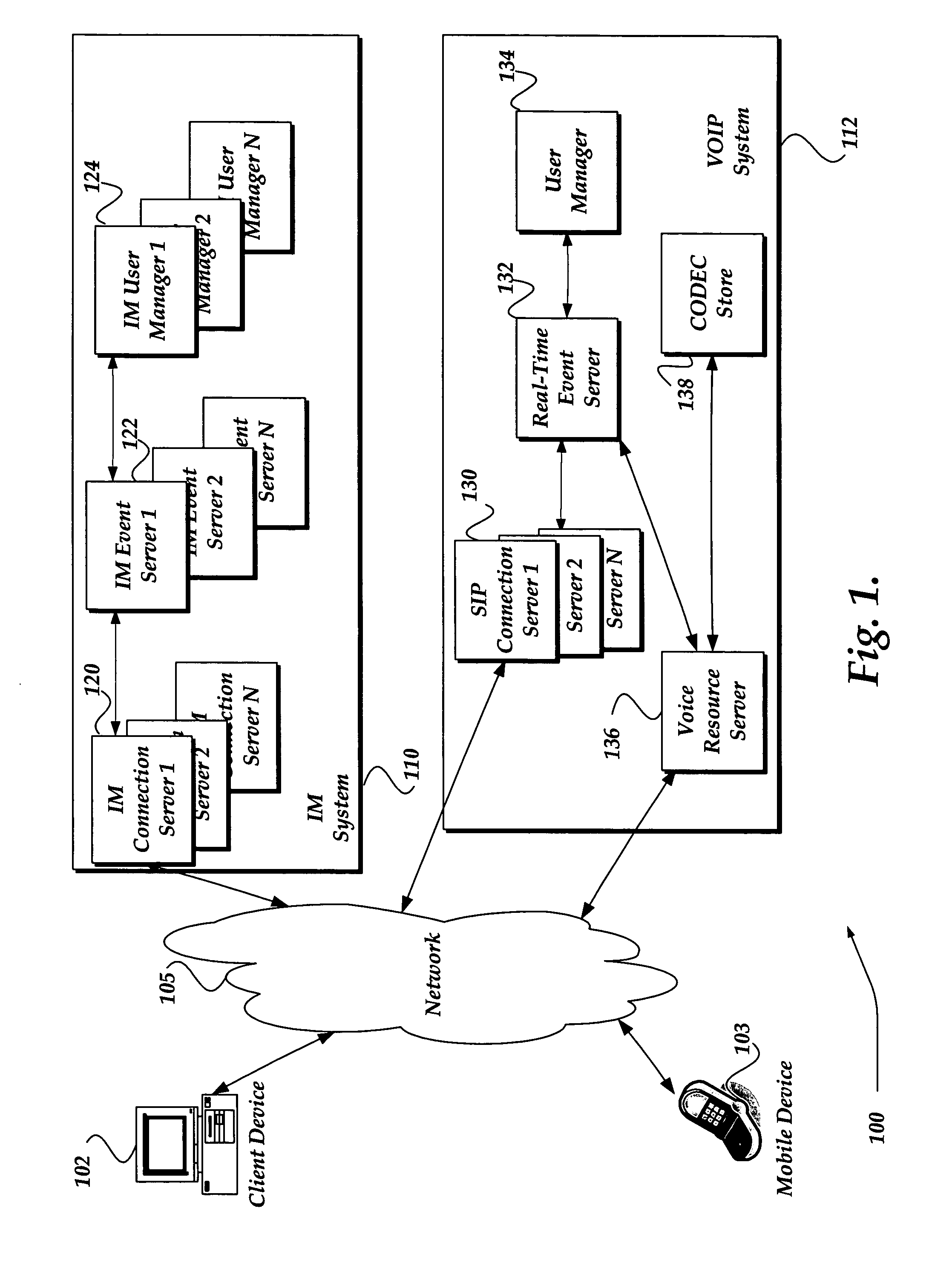
Dynamically selecting CODECS for managing an audio message
A system, method, and apparatus are directed towards a system, method, and apparatus for managing a communication session by dynamically selecting a CODEC. A client device requests a communication session with a receiver device. If available, historical information may be used to establish an initial CODEC and its associated sampling frequency for the communication session. Signals, such as a white noise signal, and / or a ring tone may be sent between the client device and the receiver to determine a metric for the communication session. The metric may be used to adjust the CODEC and / or its sampling frequency for the communication session. In one embodiment, if it is determined that the sampling frequency is less than a minimum determined value, a message may be sent to the client device advising that the current communication session be terminated.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
High frequency and low frequency audio signal encoding and decoding system
InactiveUS6772114B1Low computing performanceCode conversionTransmissionFrequency spectrumTransmitter
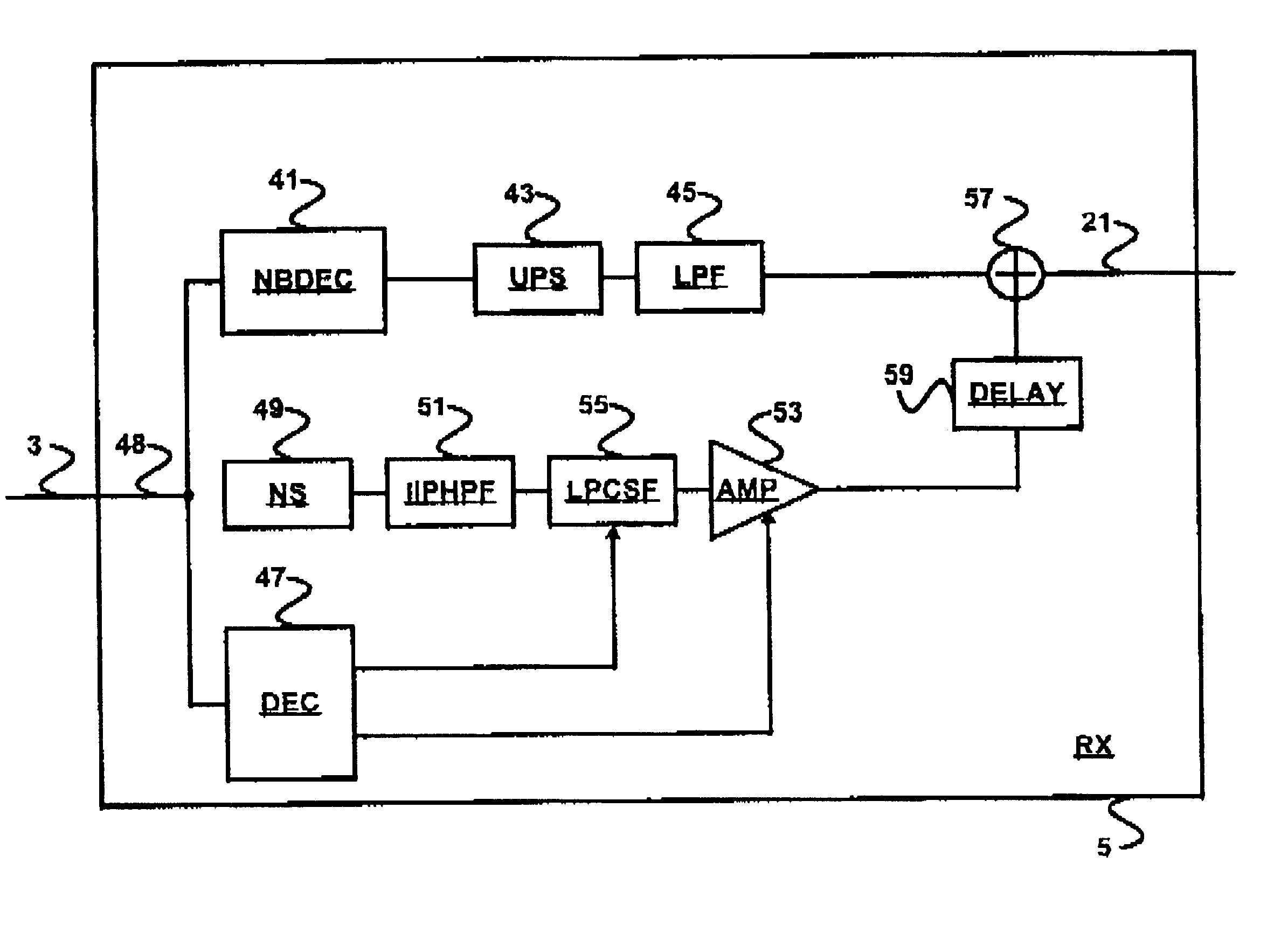
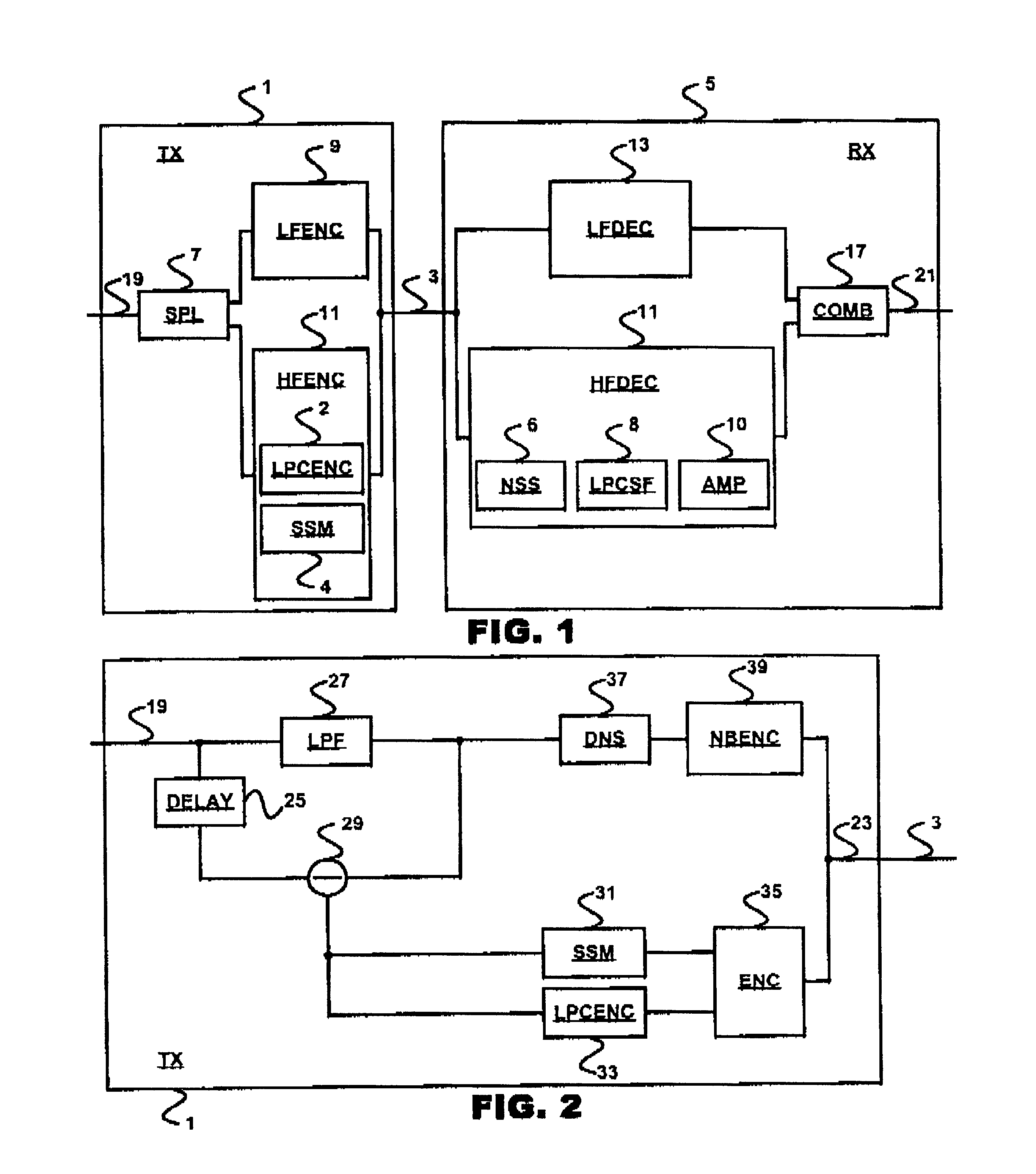
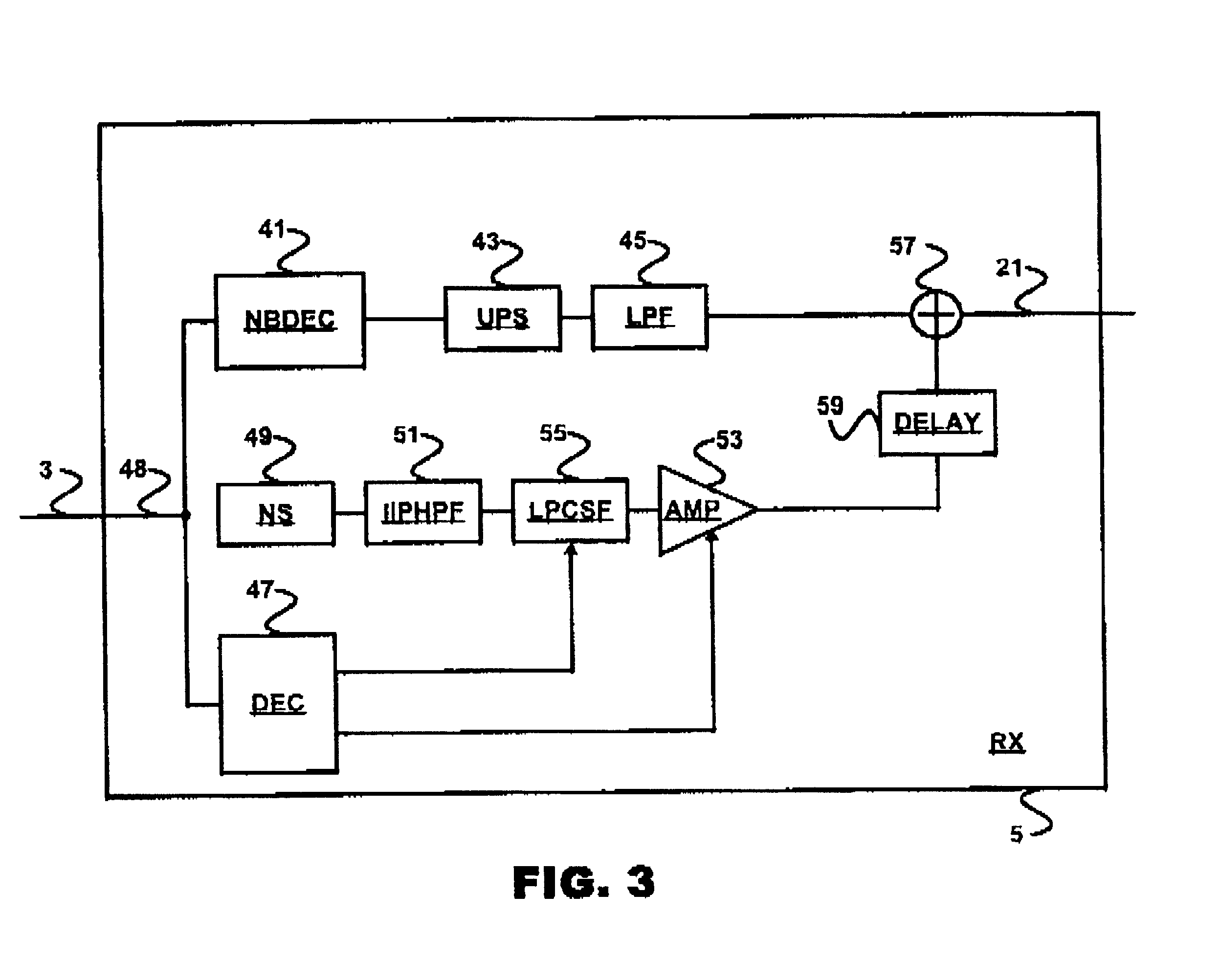
In an audio transmission system, an input signal is split up into two spectral portions in a transmitter. These spectral portions are coded by their own respective coder. The low-frequency signal portion is coded by a regular narrow-band coder and the high frequency portion is coded using a coder that outputs LPC codes and signal amplitude codes. In the receiver, the low frequency signal portion is reconstructed by a narrow-band decoder and the high frequency portion is reconstructed by applying a high pass filter to a white noise signal and applying an LPC filter that is controlled by the LPC codes to this filtered white noise signal and adjusting the signal amplitude with an amplifier that is controlled using the amplitude codes of the transmitter. The reconstructed low frequency signal and the reconstructed high frequency signal are then combined to yield a reconstructed output signal containing both frequency ranges.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Digital entroping for digital audio reproductions
ActiveUS7177430B2Increase randomnessIncrease entropyRecord information storageCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital audio broadcastingDigital audio signals
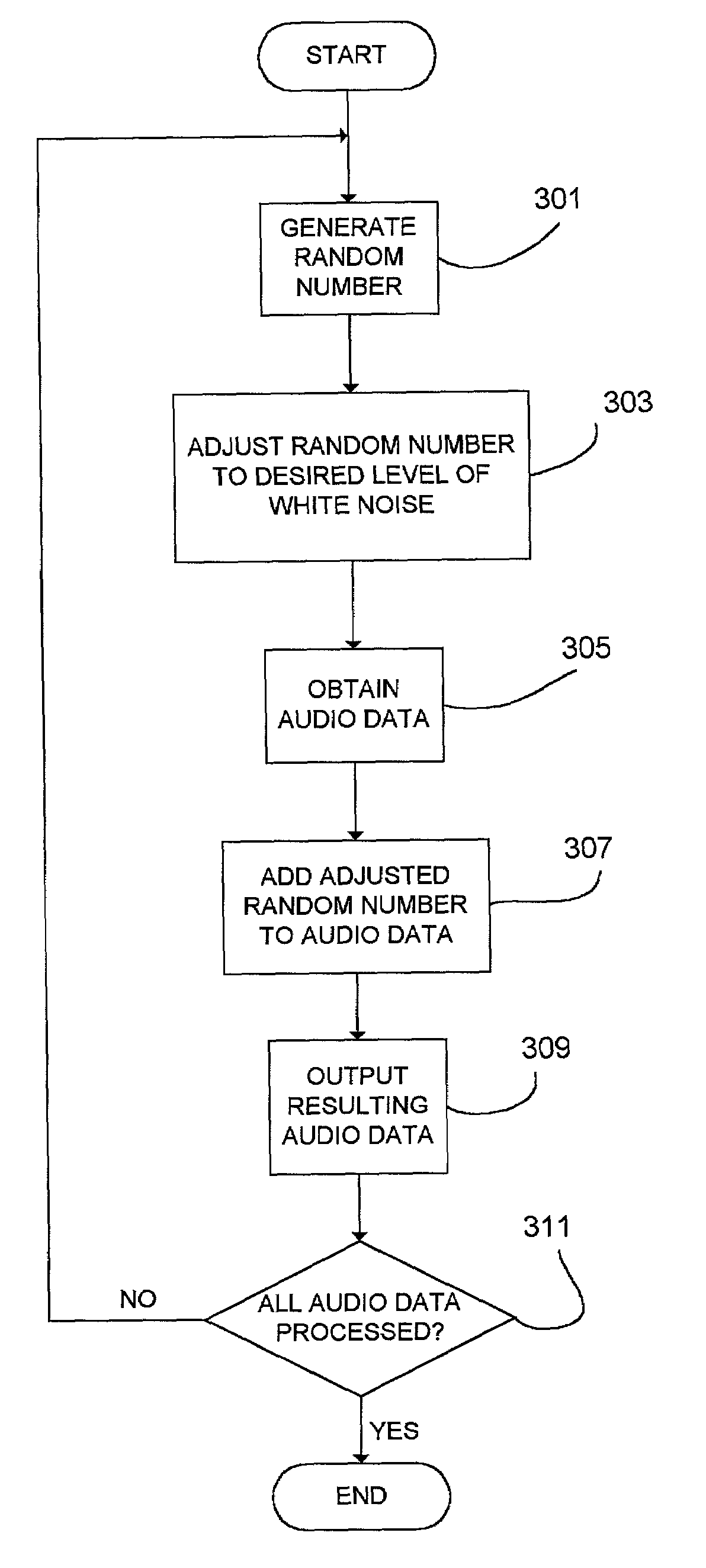
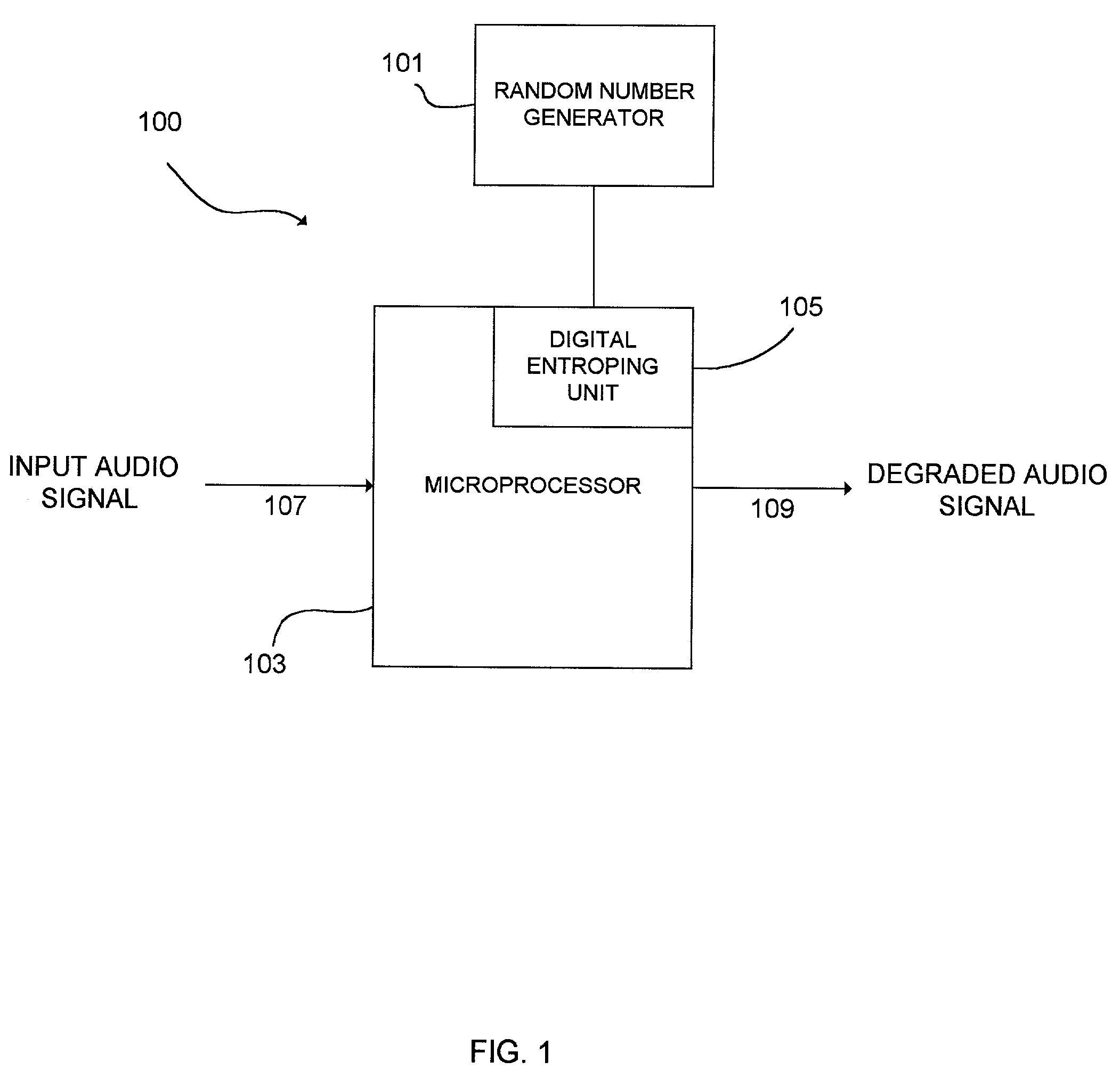
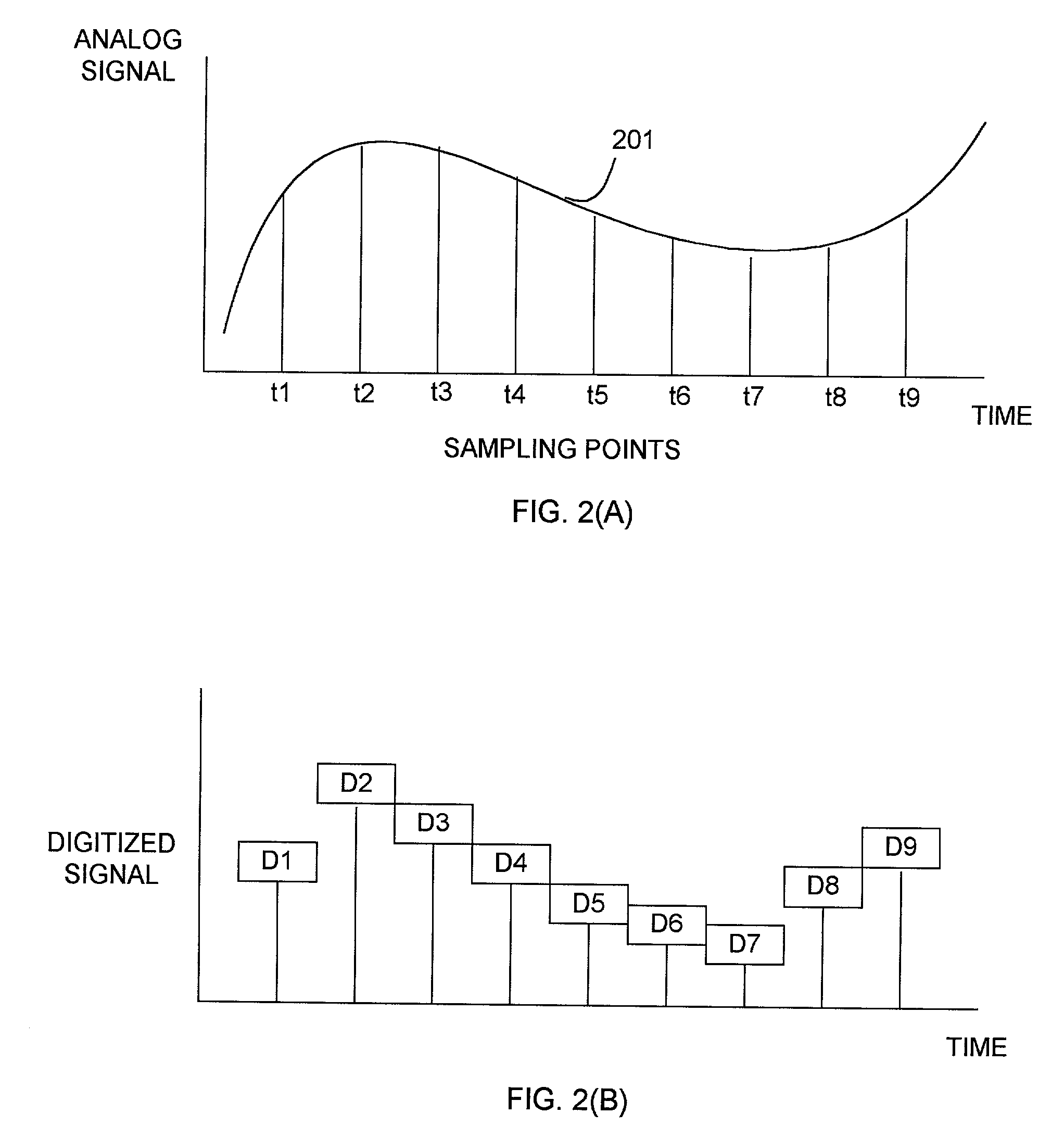
The present invention provides a system and method for introducing white noises into a digital audio signal so that there is progressive and cumulative degradation in audio quality after each successive reproduction of the audio sound signal in a fashion analogous to analog audio reproduction. The invention provides a white noise generator, and a digital entroping unit. In a preferred embodiment, the white noise generator is implemented by a hardware random number generator. The digital entroping unit controls the magnitude of white noise desired based on a random number generated by the random number generator, and adds the white noise to the input audio sound signal to produce a degraded audio sound signal. The magnitude of white noise can be controlled by using various masking and formatting of random number data.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
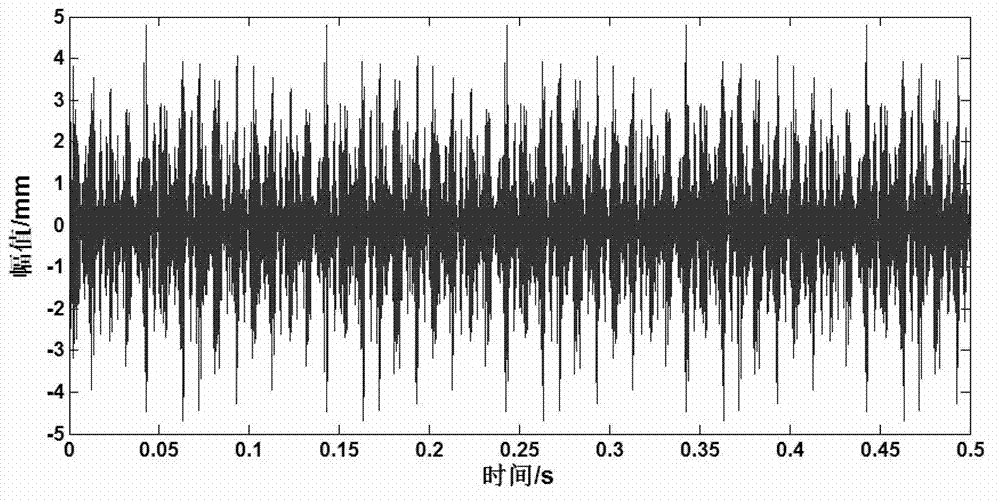
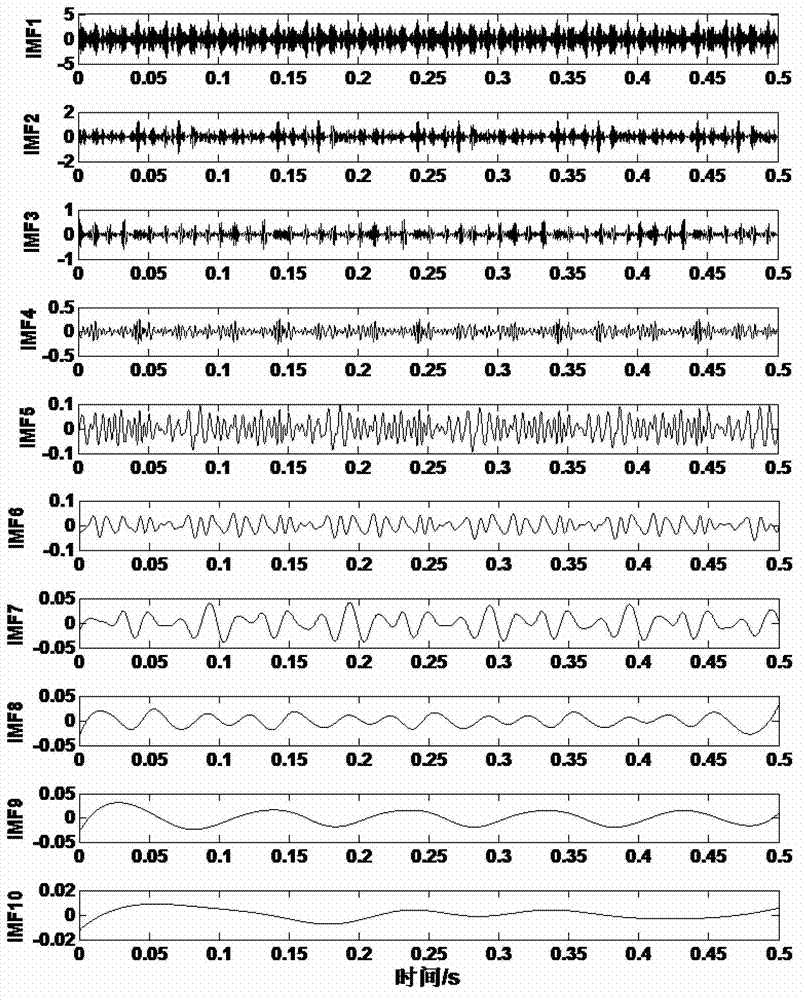
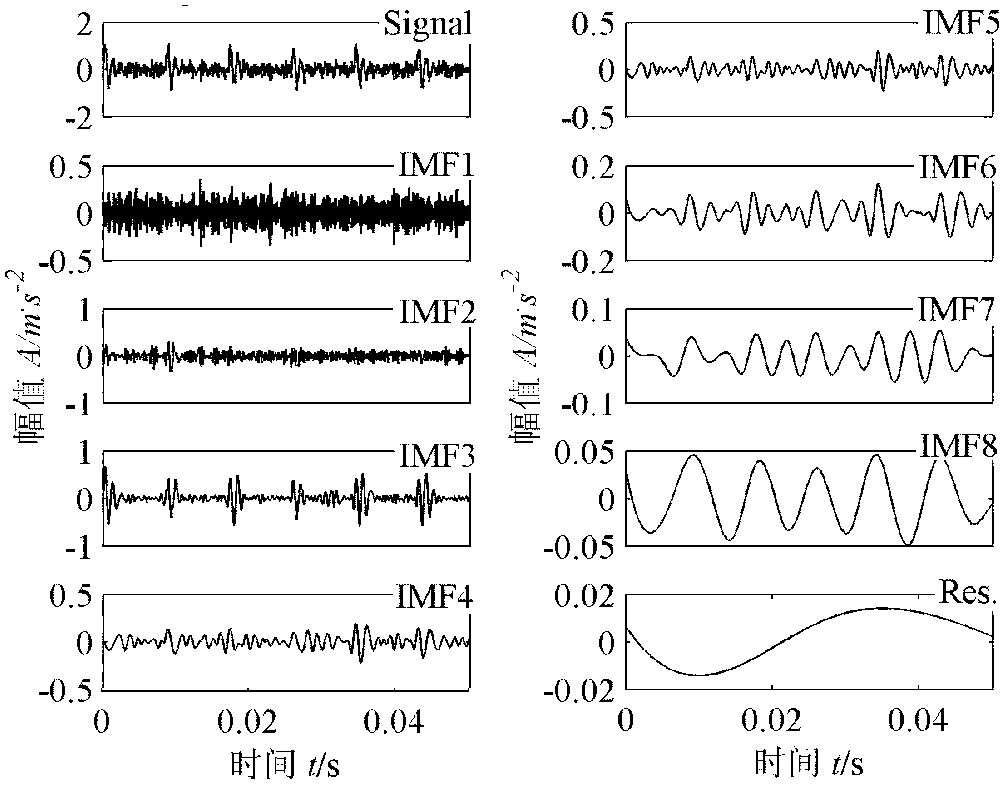
Extraction method for early failure sensitive characteristics based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) and wavelet packet transform
InactiveCN103091096AGuaranteed Adaptive Accurate PartitioningAdaptive Precise Partition PreciseMachine gearing/transmission testingMachine bearings testingNODALDecomposition
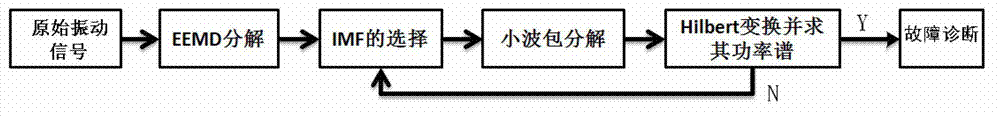
The invention relates to an extraction method for early failure sensitive characteristics based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) and wavelet packet transform. The extraction method for the early failure sensitive characteristics based on the EEMD and the wavelet packet transform includes the following steps: (1), collected original vibration signals of mechanical and electrical equipment are decomposed according to the EEMD, white noise is added, and intrinsic mode function (IMF) components are obtained through decomposition; (2), the sensitive IMF components closely related to failure are chosen, and other irrelative IMF components are ignored; (3), the sensitive IMF components chosen through step (2) are decomposed in an orthogonal wavelet packet mode, and a wavelet coefficient of each node is obtained; and (4), envelopes are extracted from the obtained wavelet packet coefficients by adoption of the Hilbert transform and the Fourier transform, power spectrums are calculated, the power spectrum corresponding to each wavelet packet coefficient is obtained and serves as the early failure sensitive characteristic , and the sensitive characteristics are automatically obtained. Self-adapting signals can be decomposed, the sensitive characteristics can be convenient to obtain automatically, diagnosis precision and speed are improved, and a mechanical and electrical system can be diagnosed quickly, accurately and stably. The extraction method for the early failure sensitive characteristics based on the EEMD and the wavelet packet transform can be applied to the field of mechanical and electrical equipment failure diagnosis.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
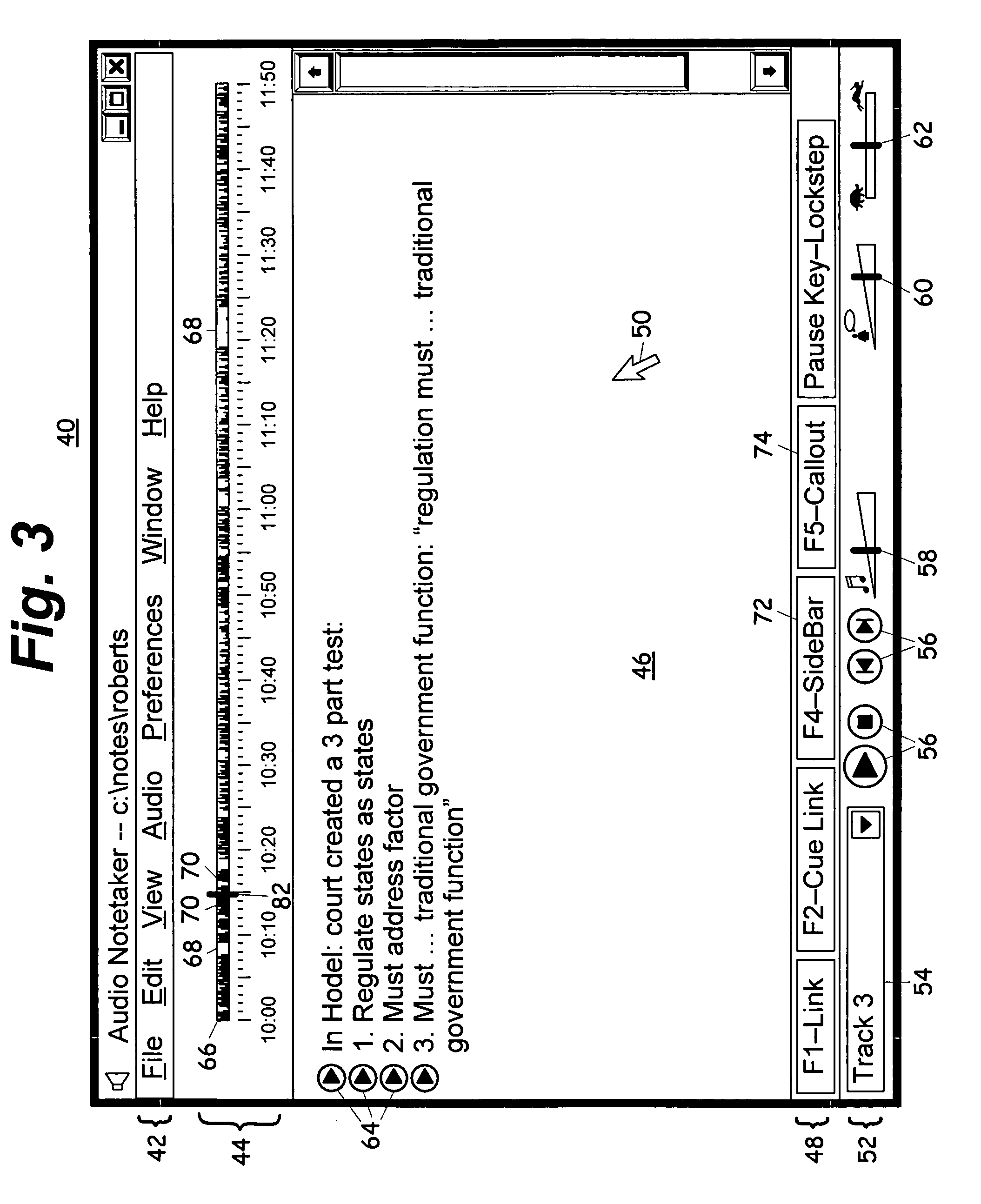
Computerized notetaking system and method
InactiveUS20060075347A1Improve experienceImprove user experienceSound input/outputSpeech recognitionTimestampProbable Case
A computerized notetaking system that records audio and links notes to the audio and has enhancements such as: Always-on audio recording and external timestamp button that work even when the system is turned off. A “next-topic” command that prepares and timestamps a new paragraph while allowing the user to complete the current paragraph. Commands for creating callouts and sidebar boxes in the user notes. A choice of audio filters. Speech recognition for searching through and navigating an audio recording. Speech recognition accuracy enhancement based upon typed notes. Playback, including lockstep playback, that prefers starting and stopping at word boundaries without overlap when possible. A self-adjusting preplay parameter. A “repeat slower” command that replays a few seconds of audio and then resumes at normal speed. Integrated background audio that plays music or white noise when notes-related audio is not being played. Several other enhancements are disclosed.
Owner:REHM PETER H
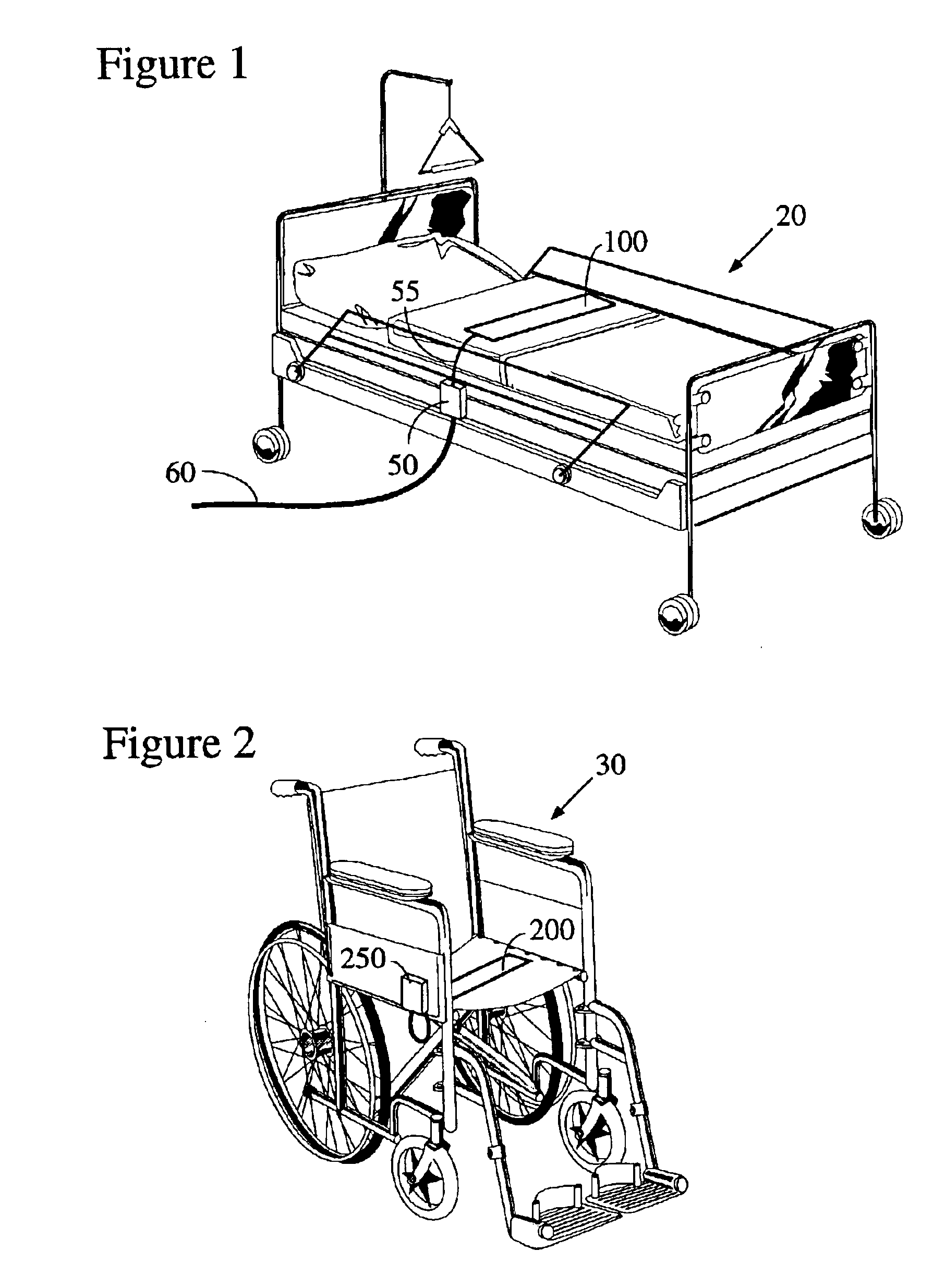
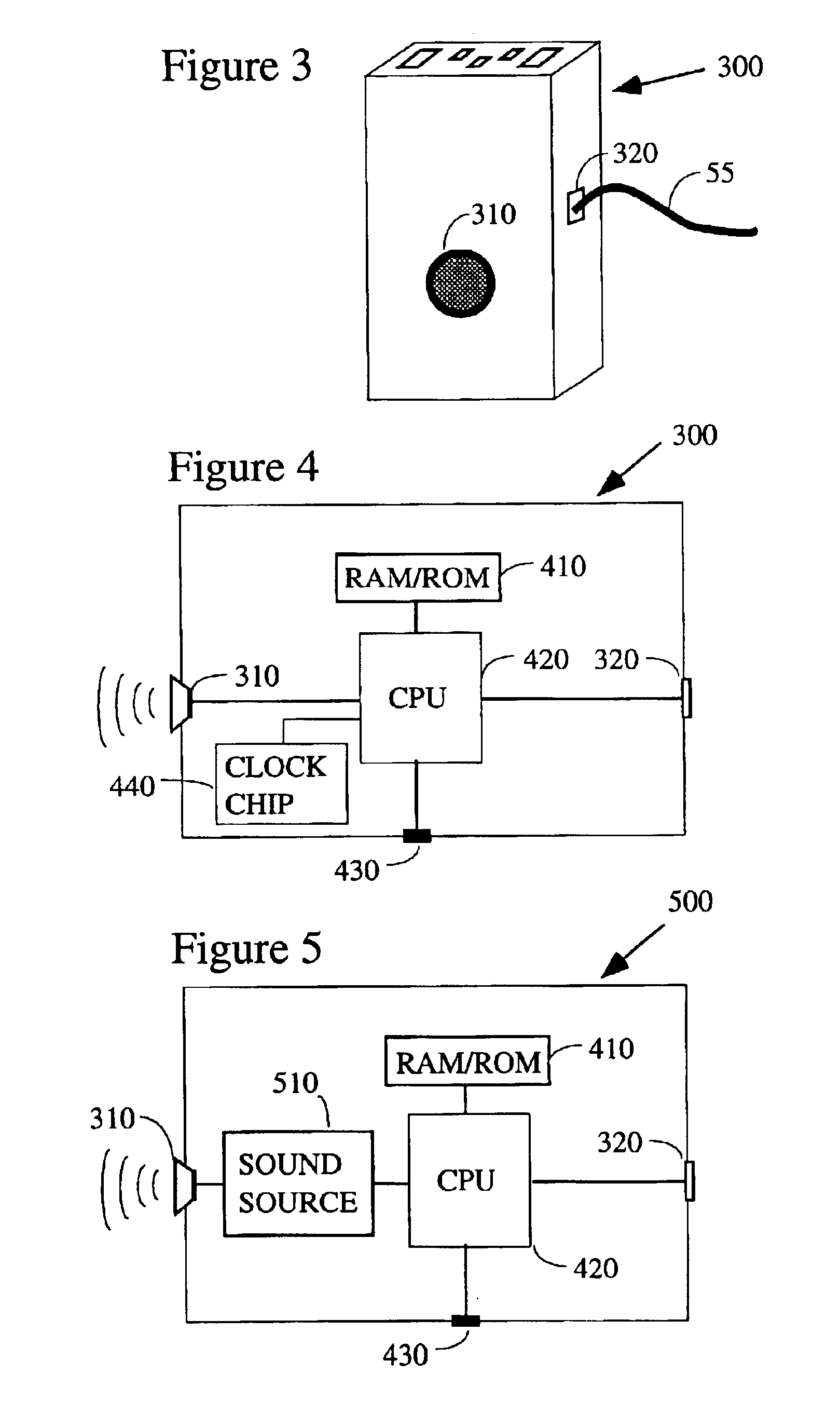
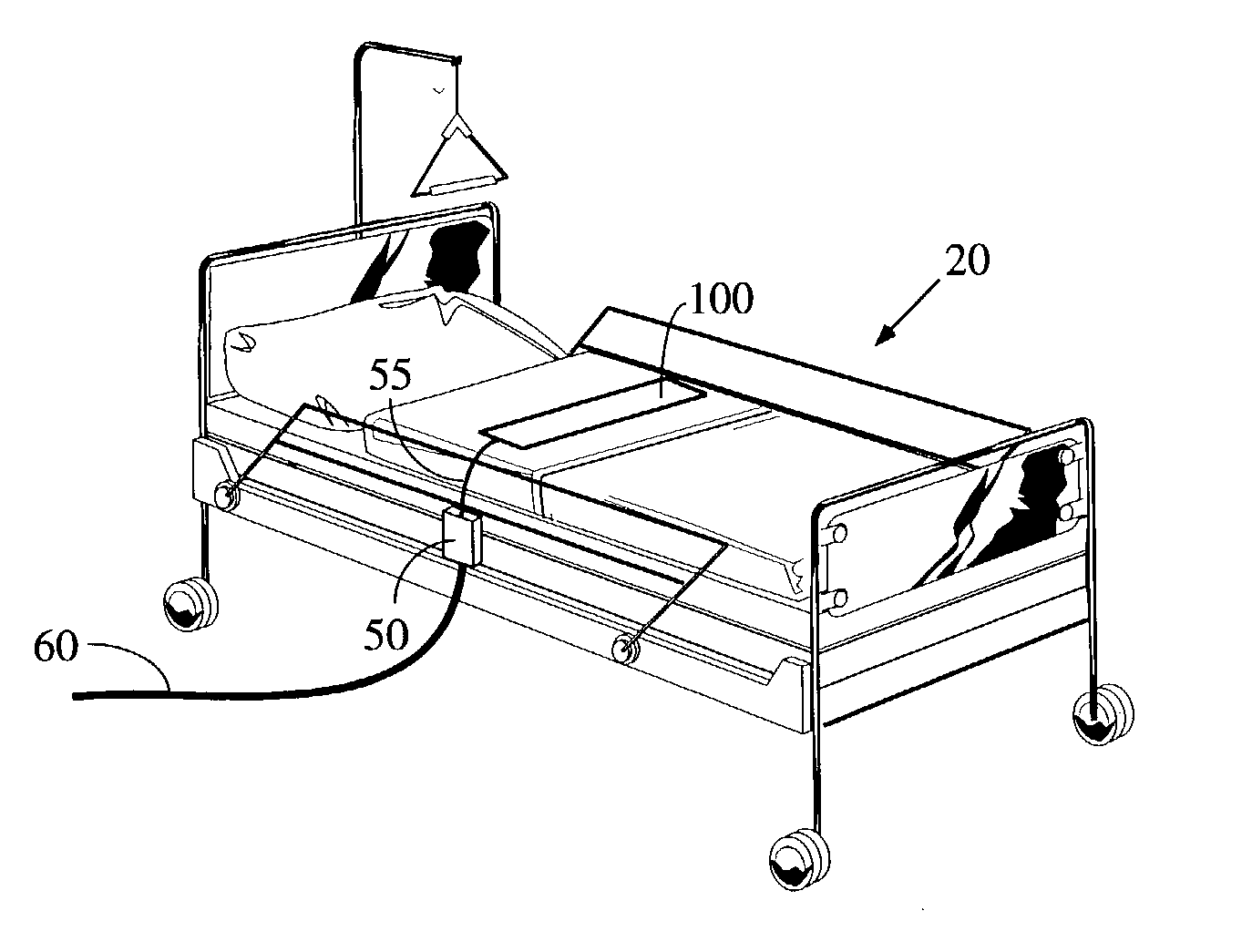
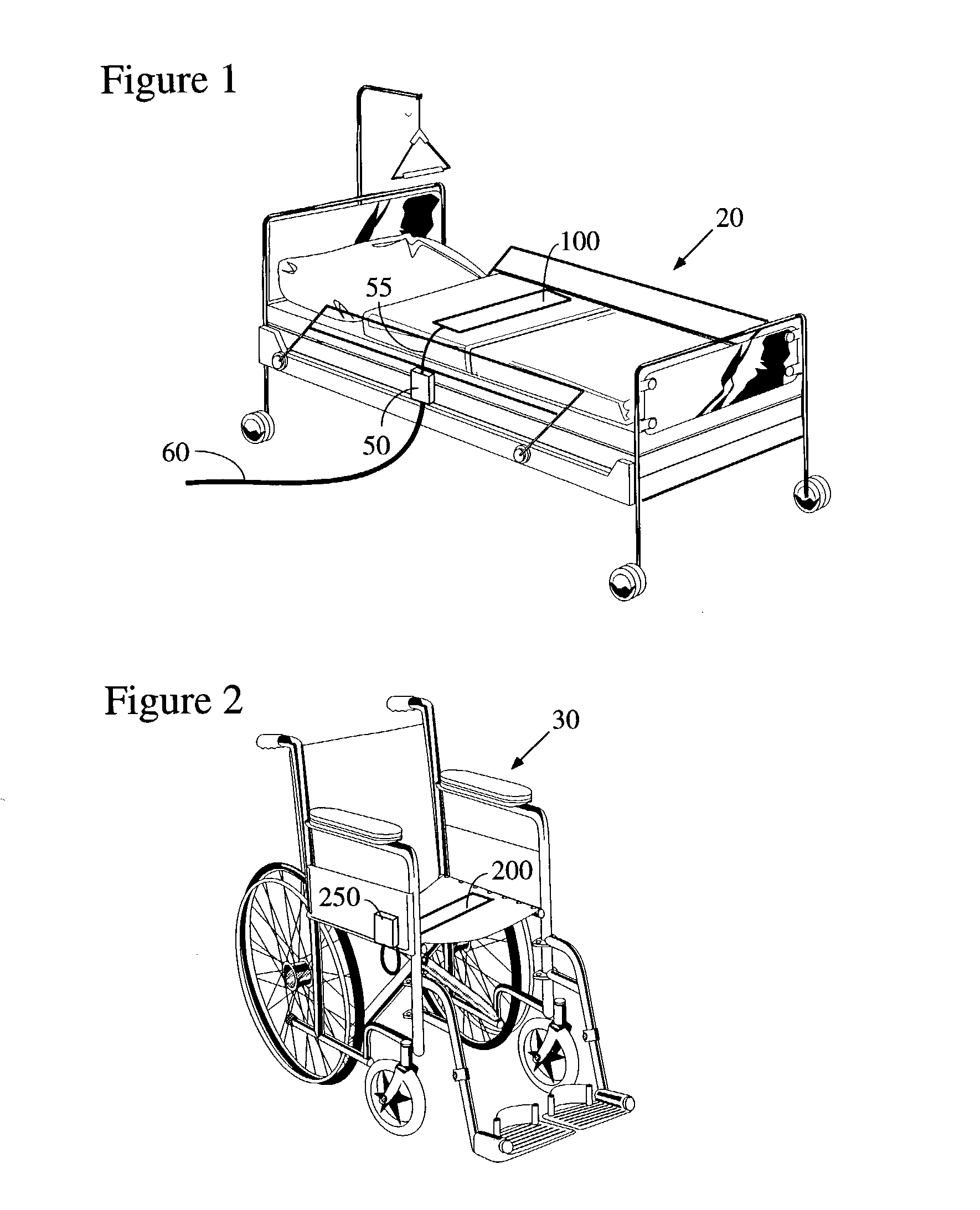
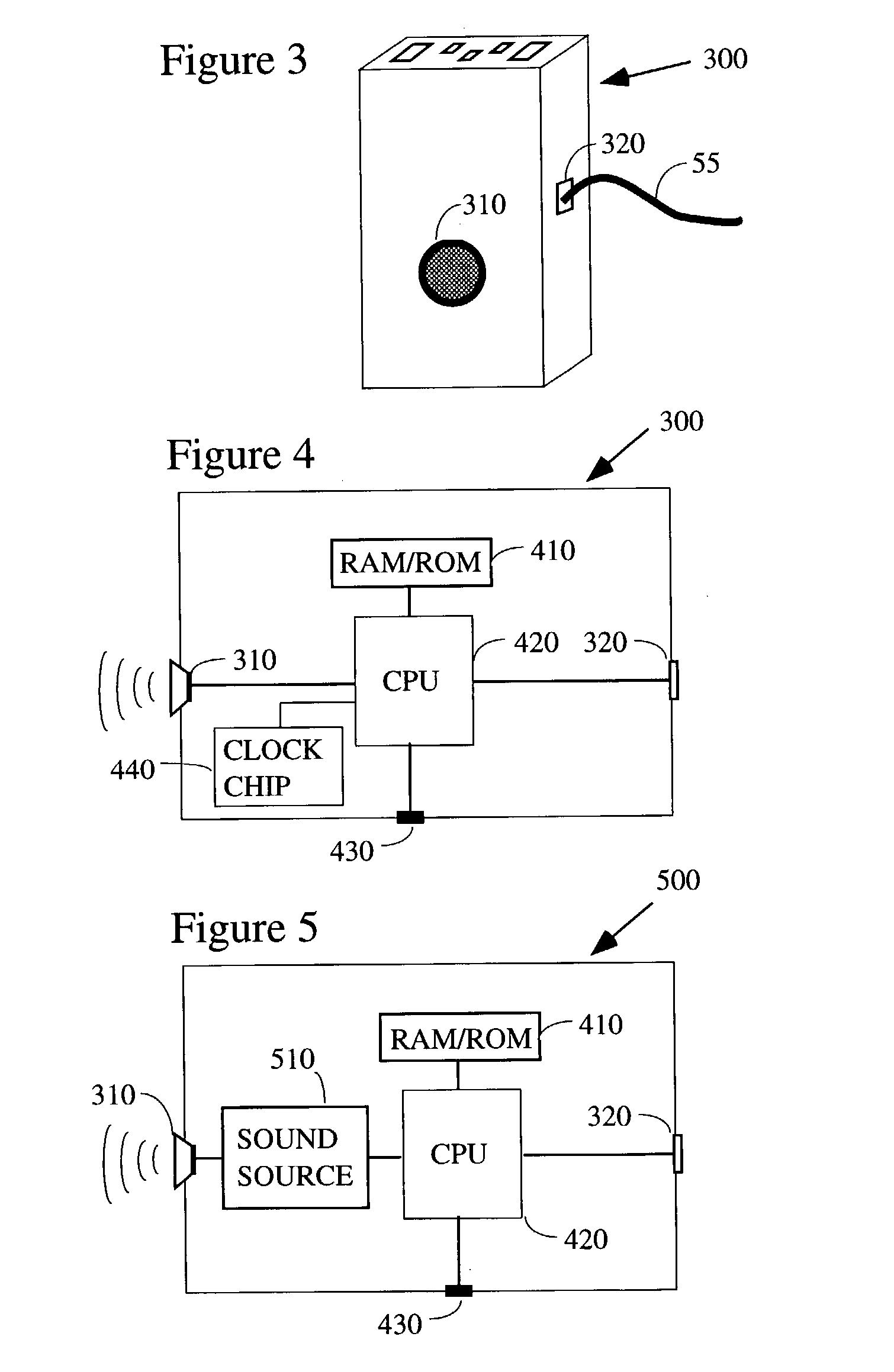
Electronic patient monitor and white noise source
InactiveUS6897781B2Easy for to fall asleepReduce environmental noiseEar treatmentDiagnostic recording/measuringPatient needCare personnel
According to a preferred embodiment, there is provided an electronic patient monitor for use in reducing the risk of decubitus ulcers. The monitor utilizes a separate sensor which senses the position of the patient in the bed or chair for purposes of determining when the patient moves. Additionally, the monitor broadcasts masking noise through its own, or through a remote, speaker, thereby enabling the patient to rest more comfortably in a noisy institutional environment. If the patient does not move on his or her own accord within a predetermined turn interval, the masking sound broadcast will be terminated which will gently encourage the patient to move. An alarm may additionally be sounded to notify the caregiver that the patient needs to be manually turned to reduce the risk of decubitus ulcers.
Owner:BED CHECK CORP
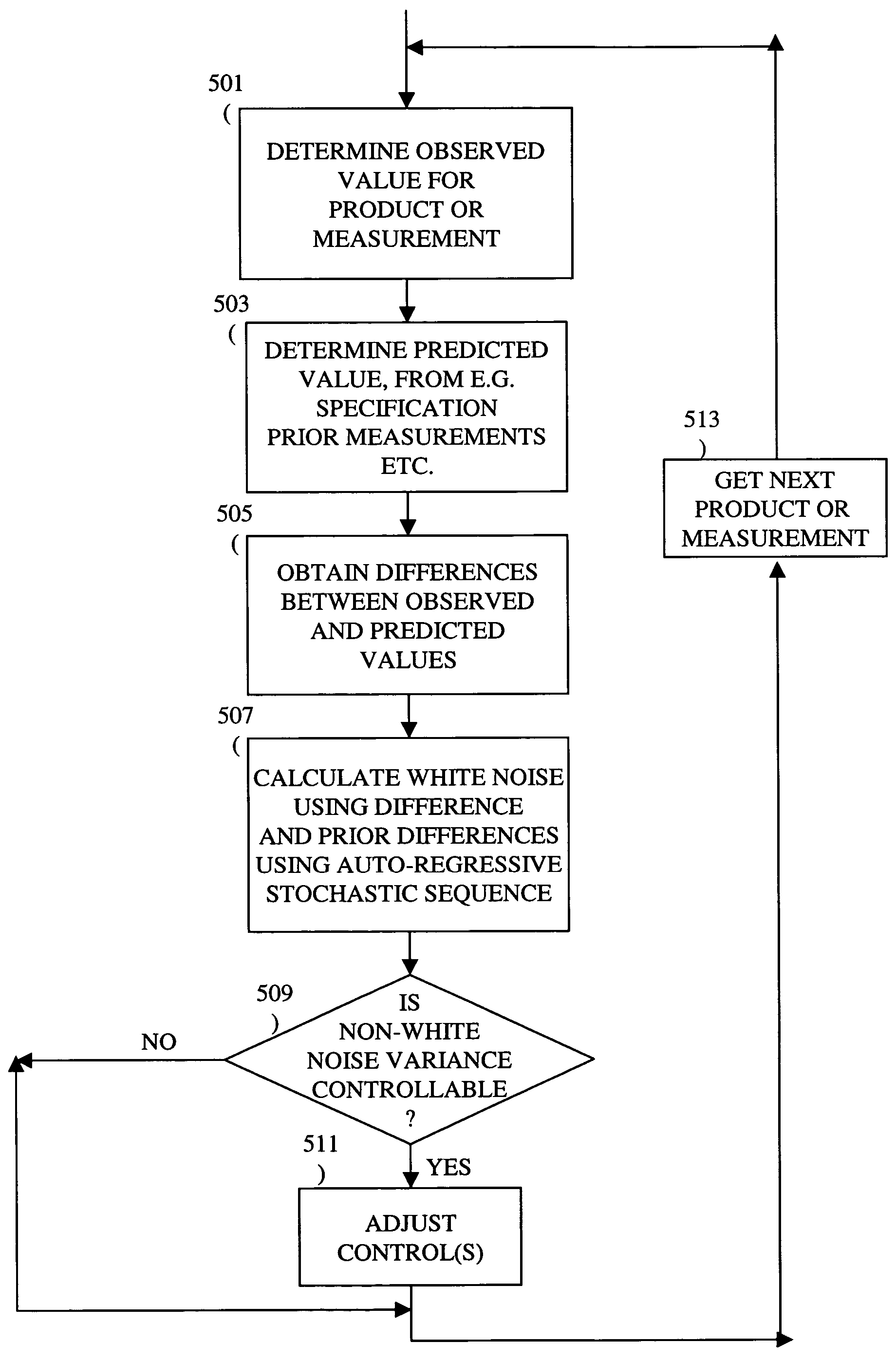
Dynamic offset and feedback threshold
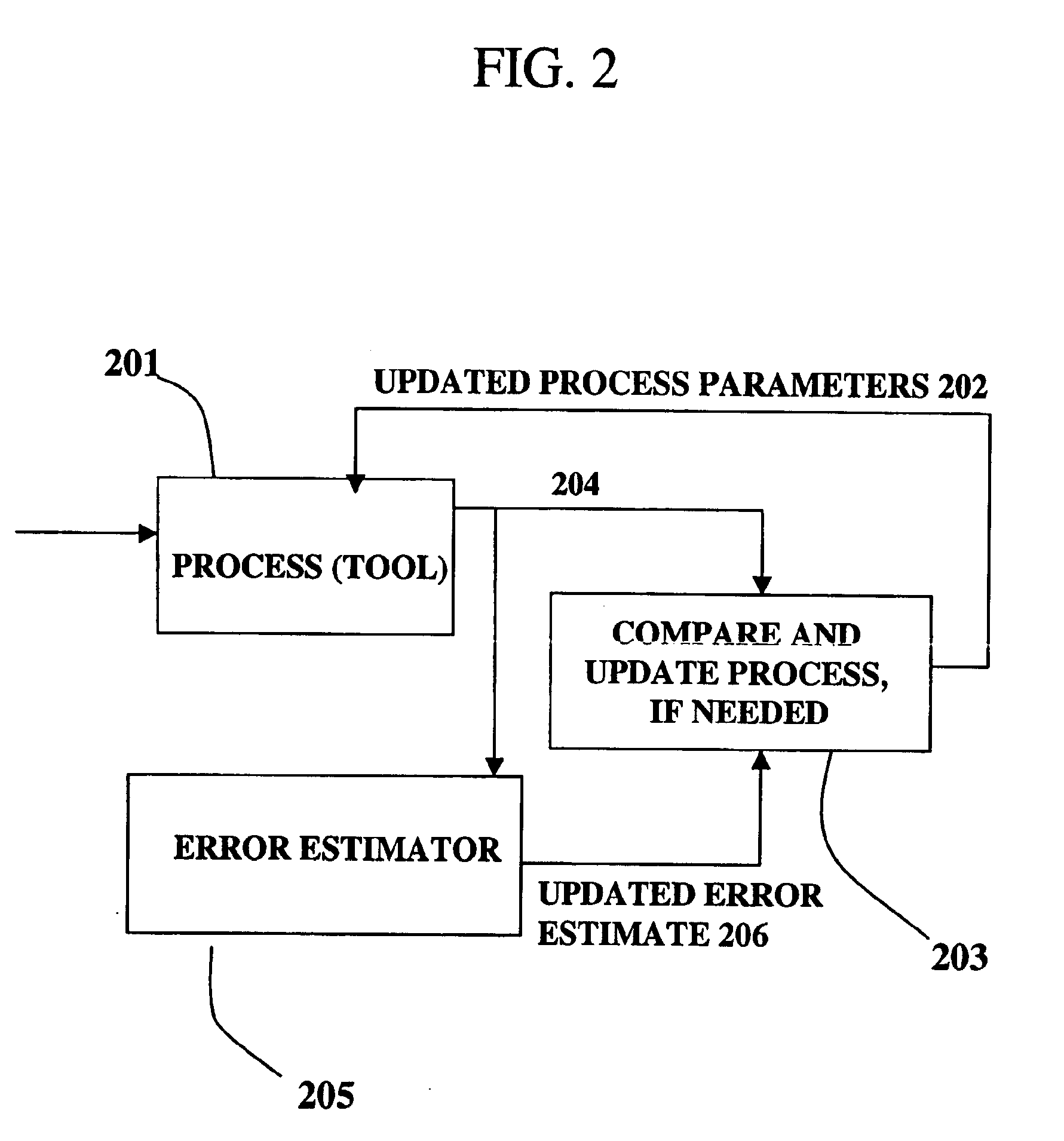
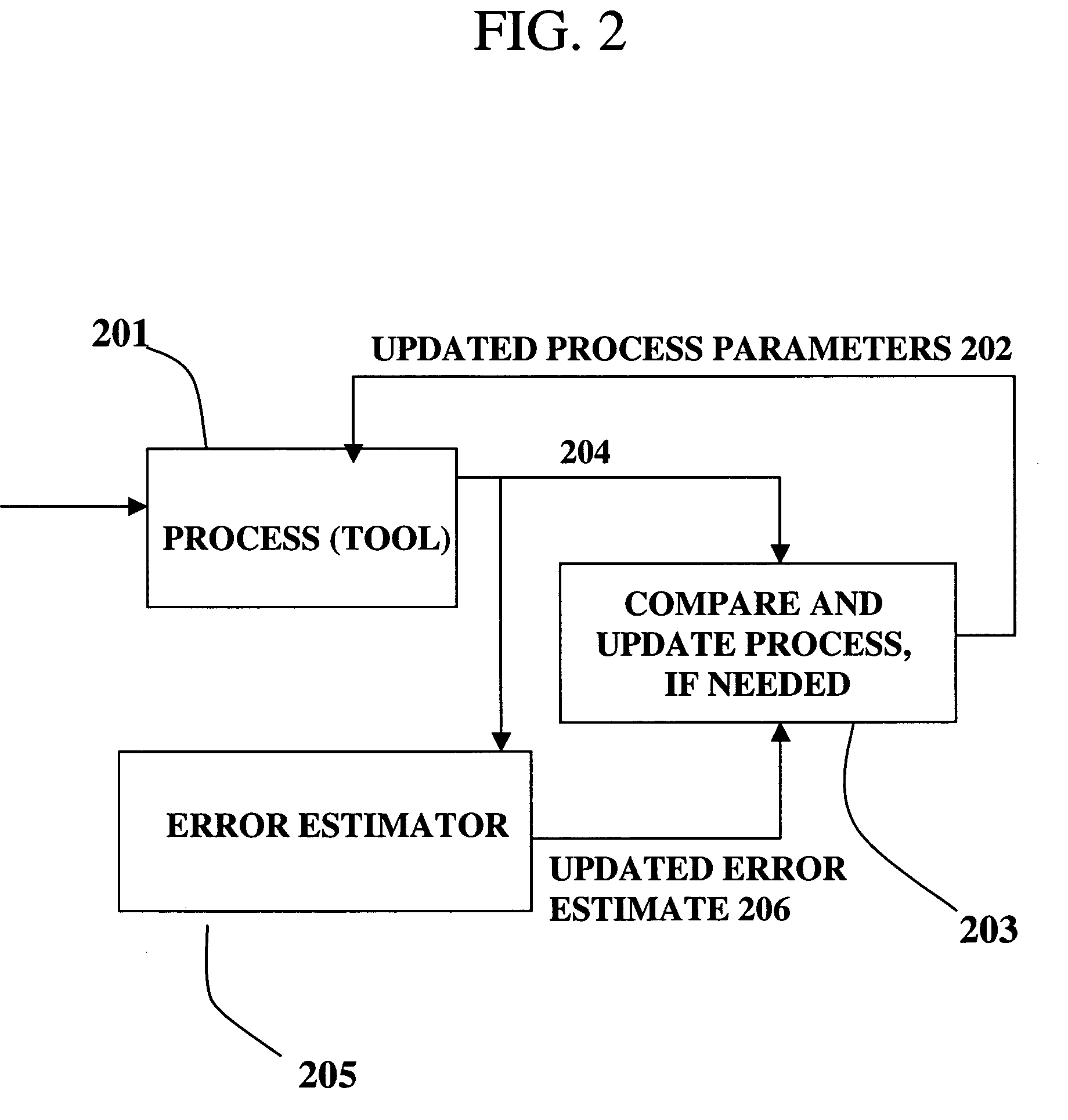
InactiveUS6961626B1Strict controlNon-controllableTotal factory controlSpecial data processing applicationsProcess varianceSemiconductor chip
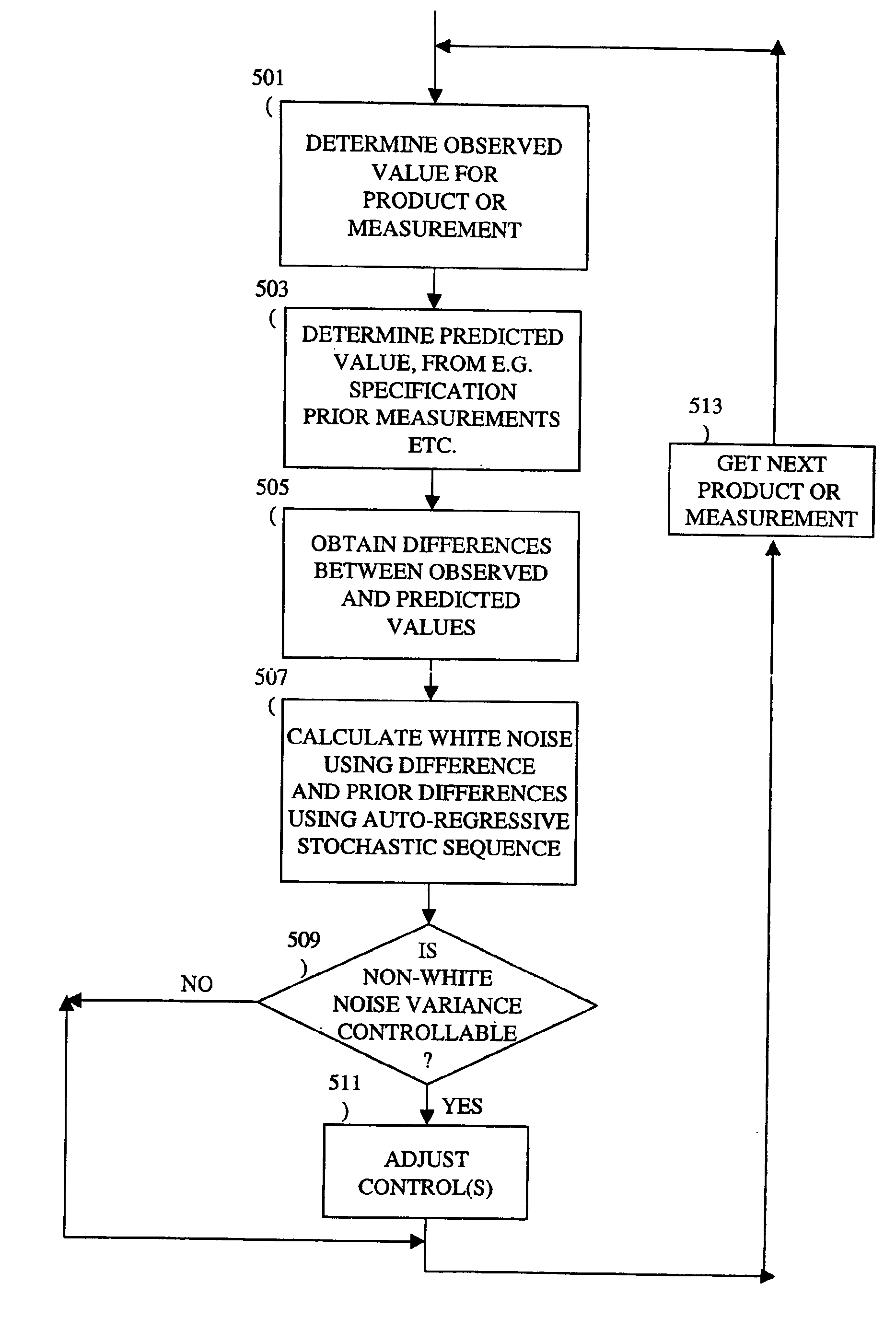
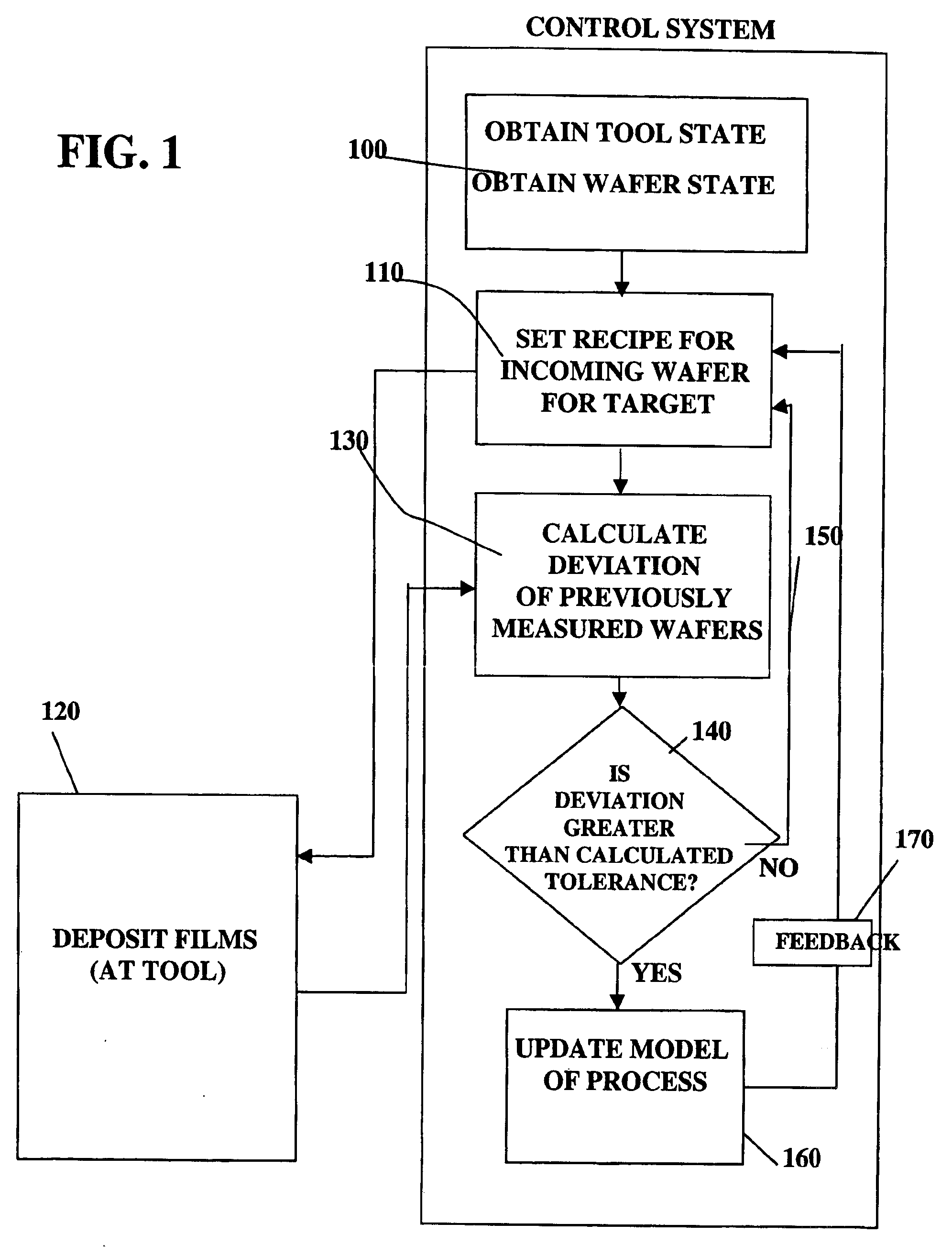
A method, system and medium are provided for enabling improved feedback and feedforward control. An error, or deviation from target result, is observed during manufacture of semi conductor chips. The error within standard deviation is caused by two components: a white noise component and a signal component (such as systematic errors). The white noise component is random noise and therefore is relatively non-controllable. The systematic error, in contrast, may be controlled by changing the control parameters. A ratio between the two components is calculated autoregressively. Based on the ratio and using the observed or measured error, the actual value of the error caused by the signal component is calculated utilizing an autoregressive stochastic sequence. The actual value of the error is then used in determining when and how to change the control parameters. The autoregressive stochastic sequence addresses the issue of real-time control of the effects of run-to-run deviations, and provides a mechanism that can extract white noise from the statistical process variance in real time. This results in an ability to provide tighter control of feedback and feedforward variations.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Electronic patient monitor and white noise source
According to a preferred embodiment, there is provided an electronic patient monitor for use in reducing the risk of decubitus ulcers. The monitor utilizes a separate sensor which senses the position of the patient in the bed or chair for purposes of determining when the patient moves. Additionally, the monitor broadcasts masking noise through its own, or through a remote, speaker, thereby enabling the patient to rest more comfortably in a noisy institutional environment. If the patient does not move on his or her own accord within a predetermined turn interval, the masking sound broadcast will be terminated which will gently encourage the patient to move. An alarm may additionally be sounded to notify the caregiver that the patient needs to be manually turned to reduce the risk of decubitus ulcers.
Owner:BED CHECK
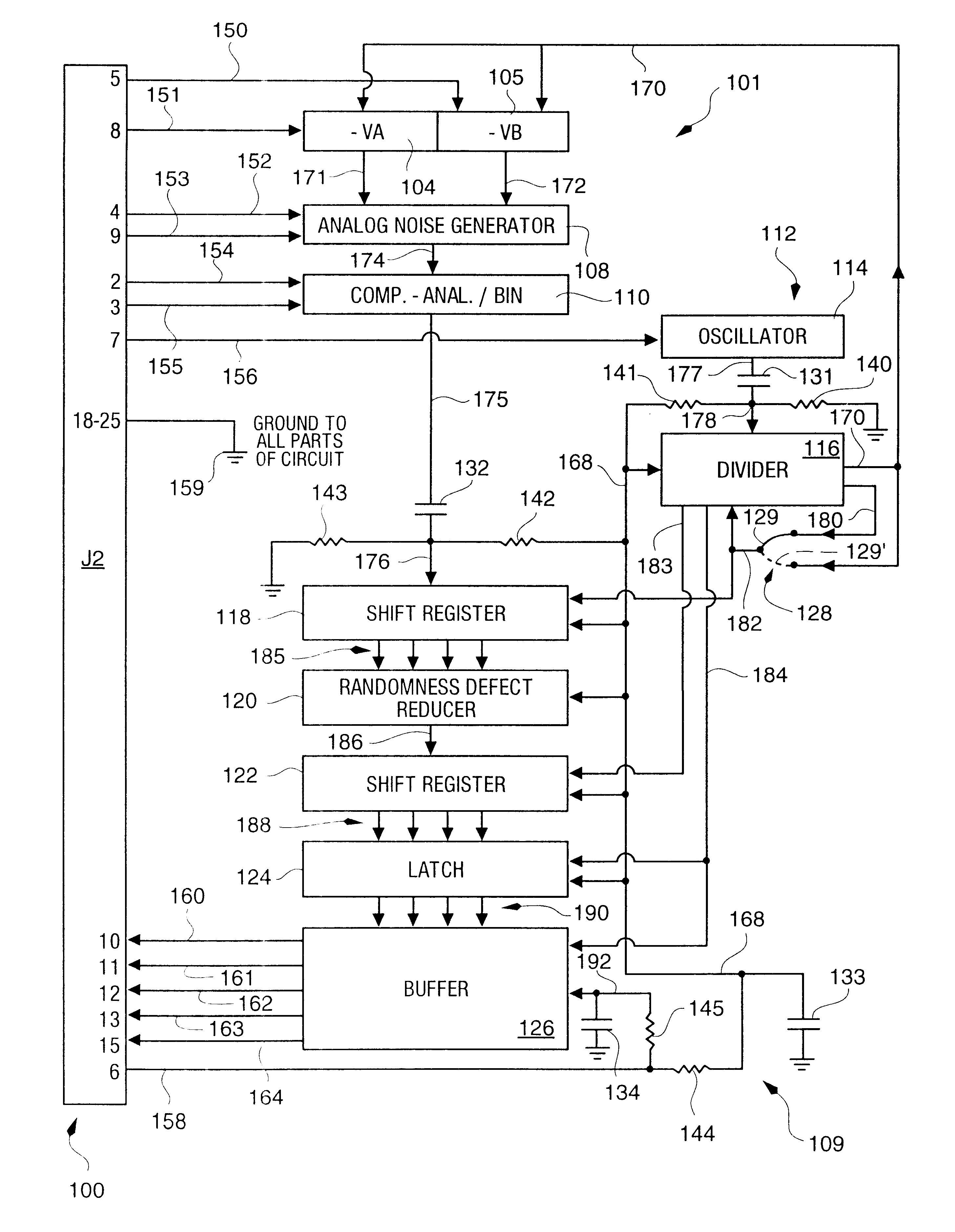
Random number generator and generation method
InactiveUS6324558B1Improve its ability to generateReduce defectsRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsCmos comparatorShift register
An RNG circuit is connected to the parallel port of a computer. The circuit includes a flat source of white noise and a CMOS amplifier circuit compensated in the high frequency range. A low-frequency cut-off is selected to maintain high band-width yet eliminate the 1 / f amplifier noise tail. A CMOS comparator with a 10 nanosecond rise time converts the analog signal to a binary one. A shift register converts the serial signal to a 4-bit parallel one at a sample rate selected at the knee of the serial dependence curve. Two levels of XOR defect correction produce a BRS at 20 kHZ, which is converted to a 4-bit parallel word, latched and buffered. The entire circuit is powered from the data pins of the parallel port. A device driver interface in the computer operates the RNG. The randomness defects with various levels of correction and sample rates are calculated and the RNG is optimized before manufacture.
Owner:QUANTUM WORLD
Adjusting manufacturing process control parameter using updated process threshold derived from uncontrollable error
InactiveUS7349753B2Strict controlNon-controllableTotal factory controlSpecial data processing applicationsSemiconductor chipRandom noise
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
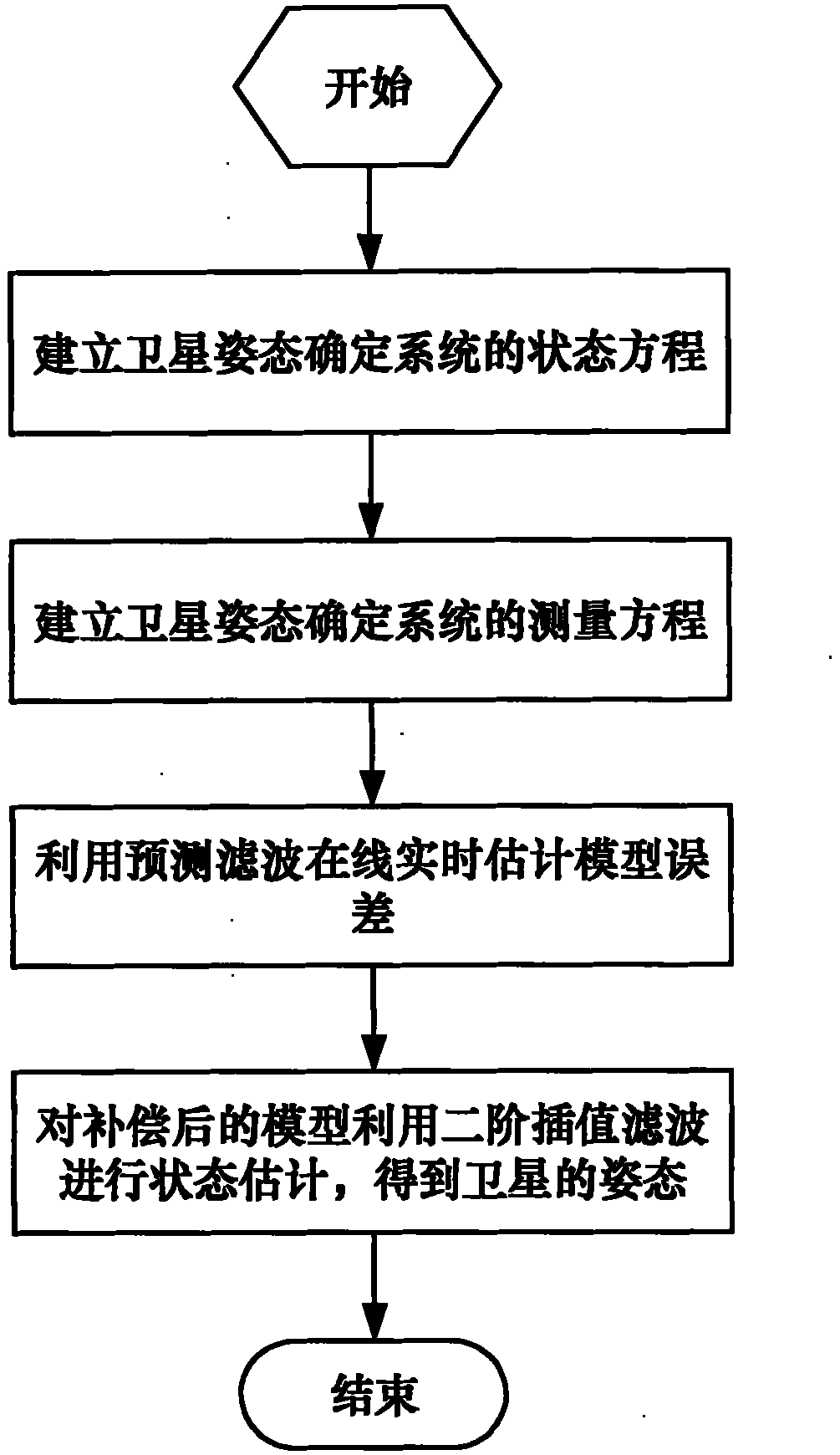
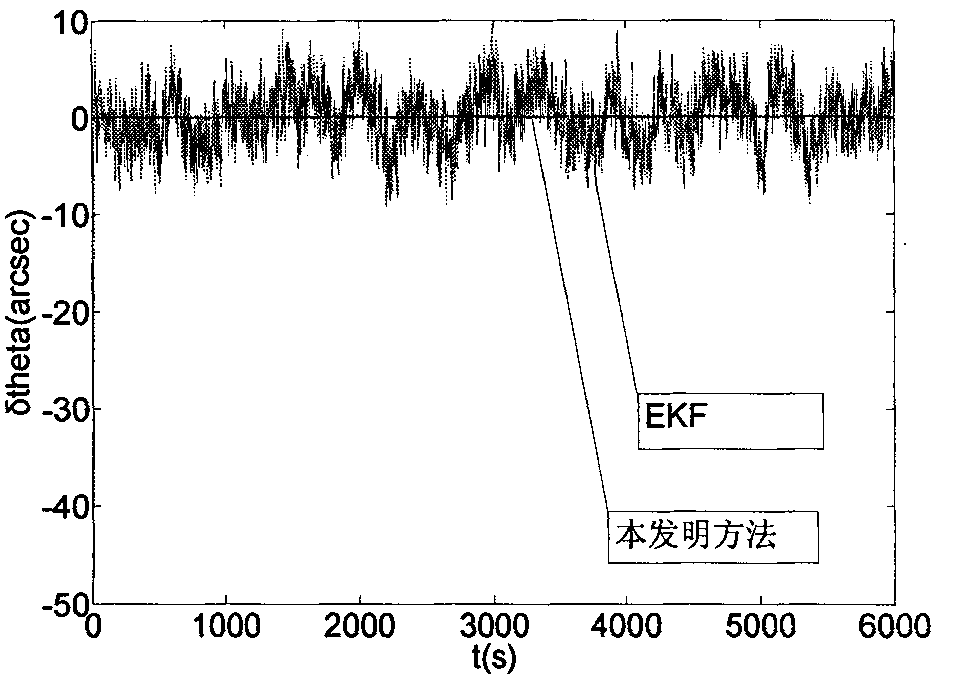
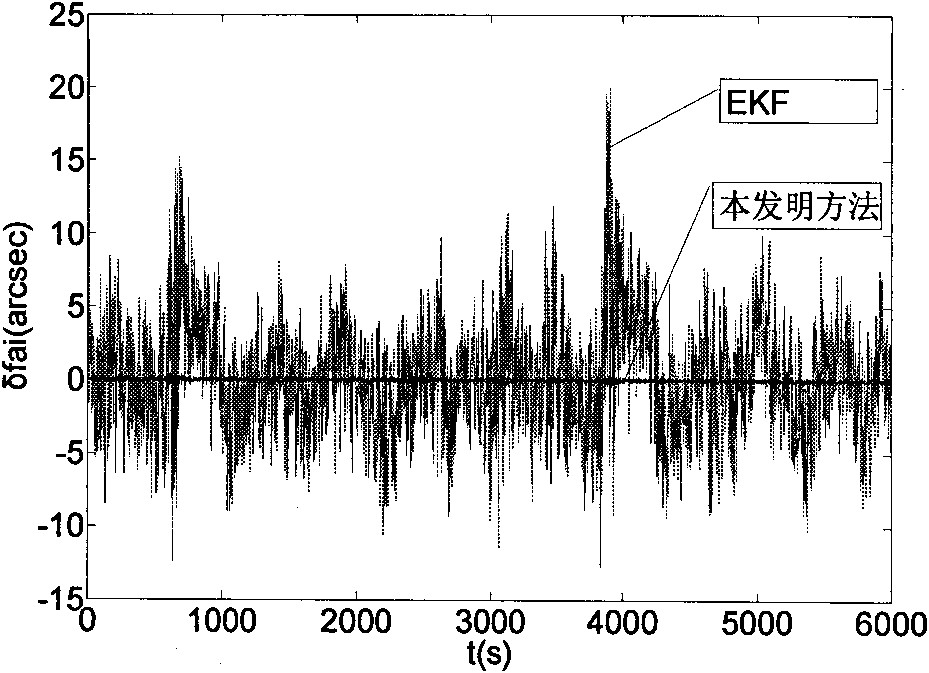
High-precision satellite attitude determination method based on star sensor and gyroscope
InactiveCN101846510AOvercome the disadvantage of error processing as zero-mean white noiseHigh precisionAngle measurementNavigation instrumentsGyroscopeZero mean
The present invention discloses a high-precision satellite attitude determination method based on star sensor and gyroscope, which comprises the following steps: step 1. establishing a status equation of a satellite attitude determination system; step 2. establishing a measurement equation of the satellite attitude determination system; step 3. performing an online real-time model error estimation through predictive filtering; and step 4. performing a status estimation on a compensated model through 2-order interpolation filtering to obtain the attitude of a satellite. By applying predictive filtering to performing an online real-time model error estimation and correcting the system model, the invention overcomes the shortcoming existing in the conventional estimation process that error is processed into zero-mean white noise; and in addition, the invention can process any nonlinear system and noise conditions to obtain an estimation result of higher precision and is applicable to thefield of high-precision attitude determination.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
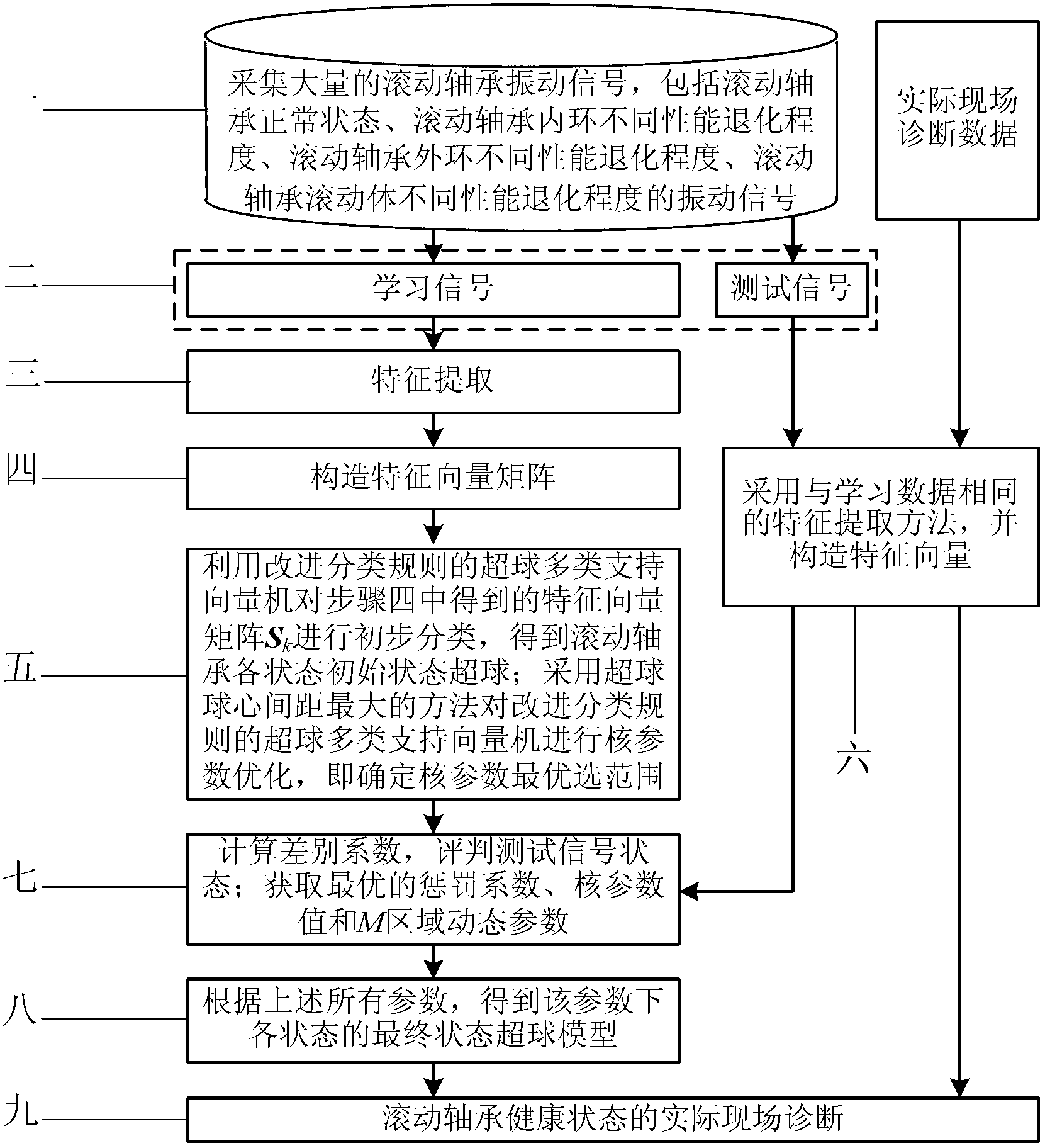
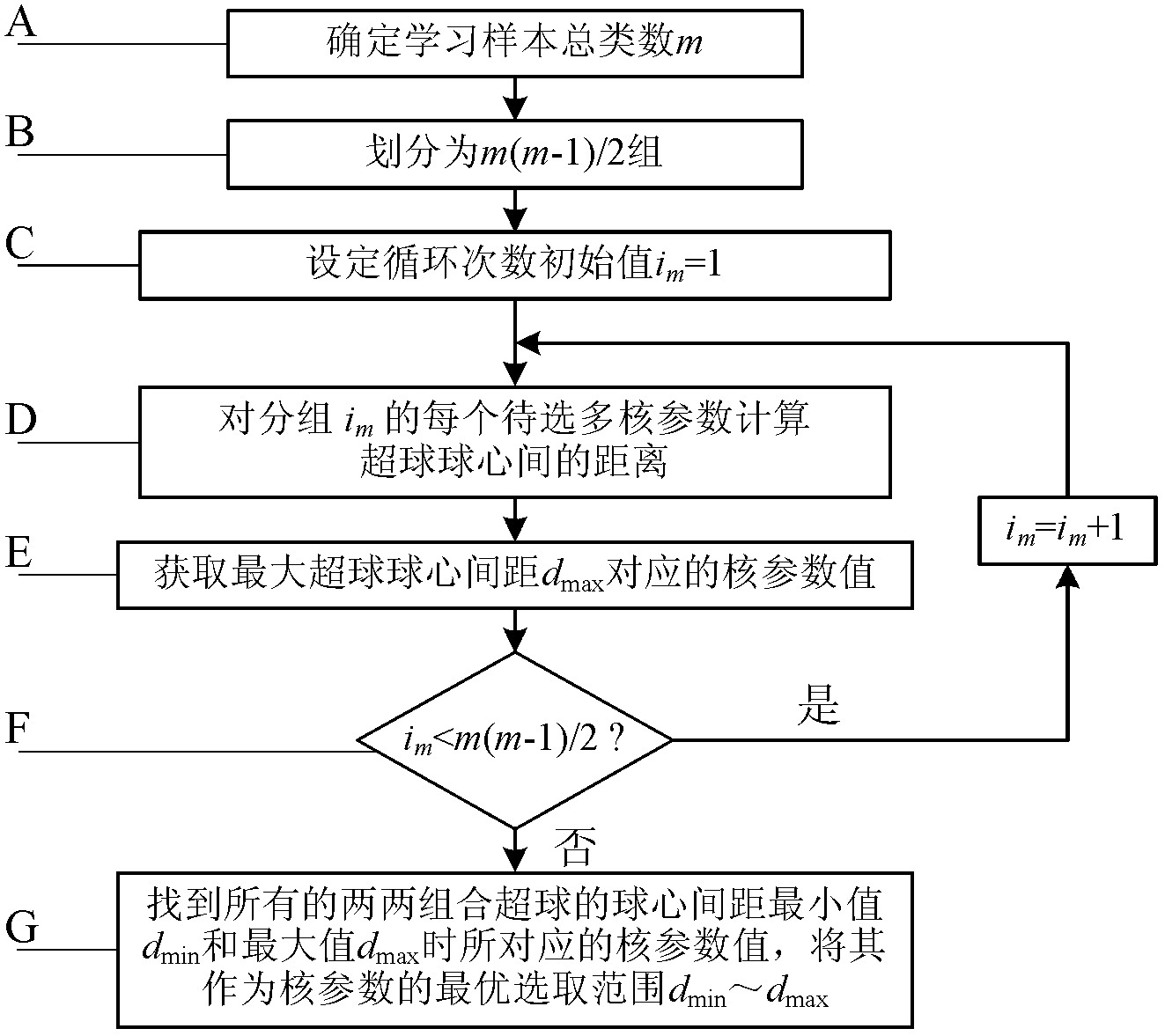
Diagnosis method for fault position and performance degradation degree of rolling bearing
InactiveCN102854015AOptimization determination methodReduce consumptionMachine bearings testingSingular value decompositionSupport vector machine
The invention discloses a diagnosis method for the fault position and the performance degradation degree of a rolling bearing, belonging to the technical field of fault diagnosis for bearings, and solving the problems of low accuracy of diagnosis for fault position and performance degradation degree, and high time consumption of training existing in an intelligent diagnosis method for a rolling bearing in the prior art. A white noise criterion is added in the disclosed integrated empirical mode decomposition method, so that artificial determination for decomposition parameters can be avoided, and the decomposition efficiency can be increased; and via the disclosed nuclear parameter optimization method based on a hypersphere centre distance, the small and effective search region of nuclear parameters in a multi-classification condition can be determined, so that training time is reduced, and the final state hypersphere model of a classifier is given. The intelligent diagnosis method based on parameter-optimized integrated empirical mode decomposition and singular value decomposition, and combined with a nuclear parameter-optimized hypersphere multi-class support vector machine based on the hypersphere centre distance is higher in identification rate compared with the existing diagnosis method. The diagnosis method disclosed by the invention is mainly applied to intelligent diagnosis on the fault position and the performance degradation degree of the rolling bearing.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System and method for simultaneously controlling spectrum and kurtosis of a random vibration
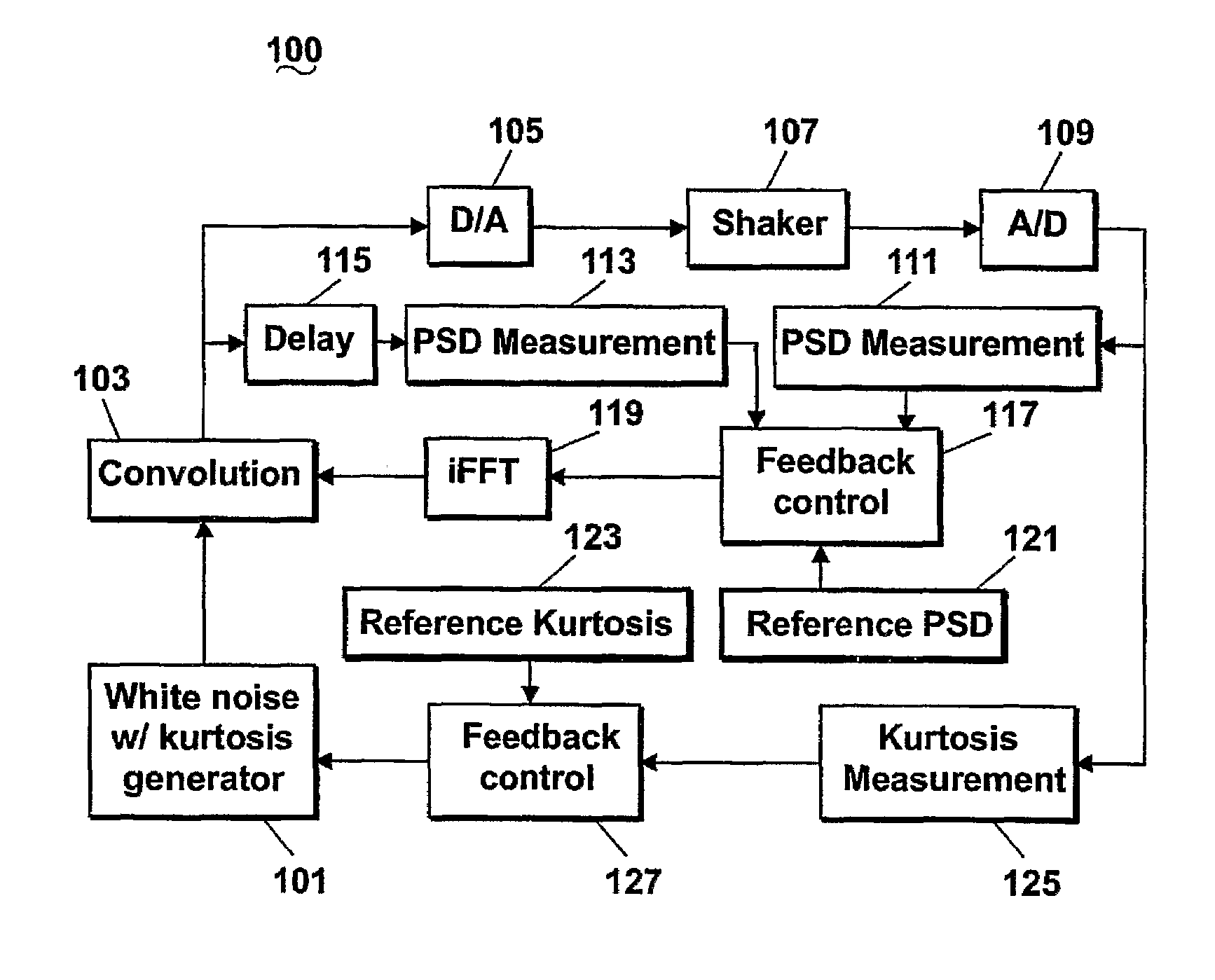
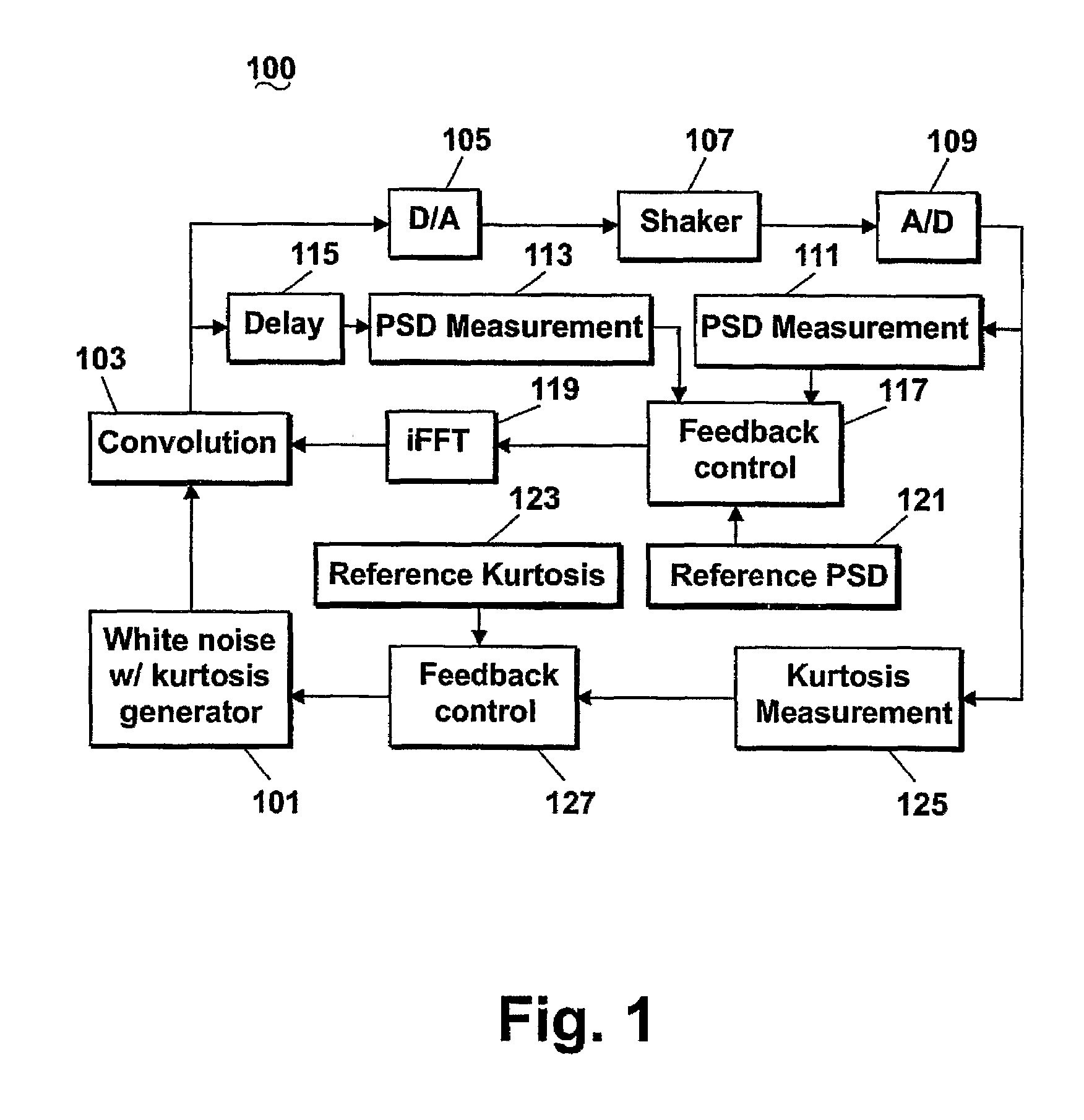
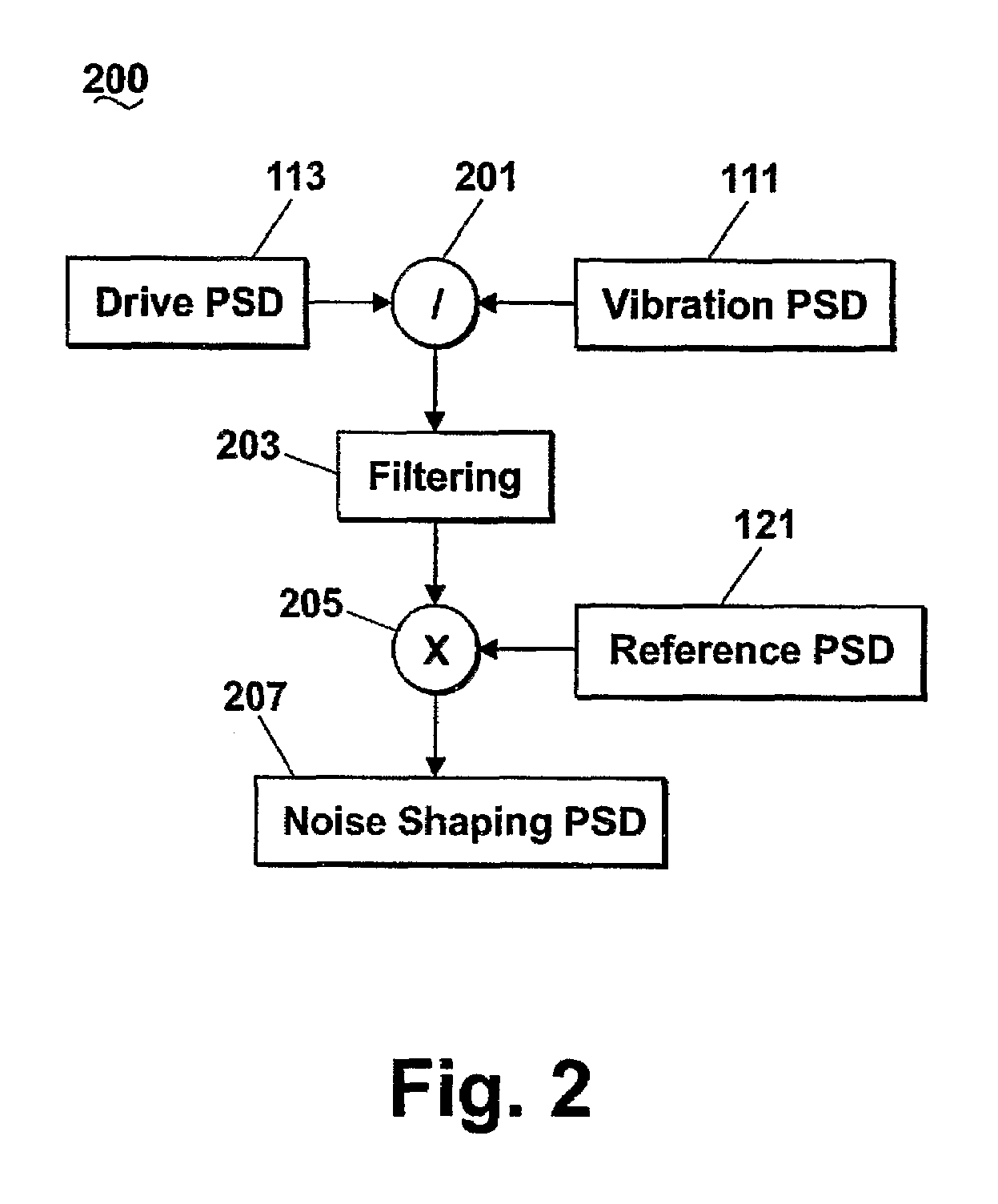
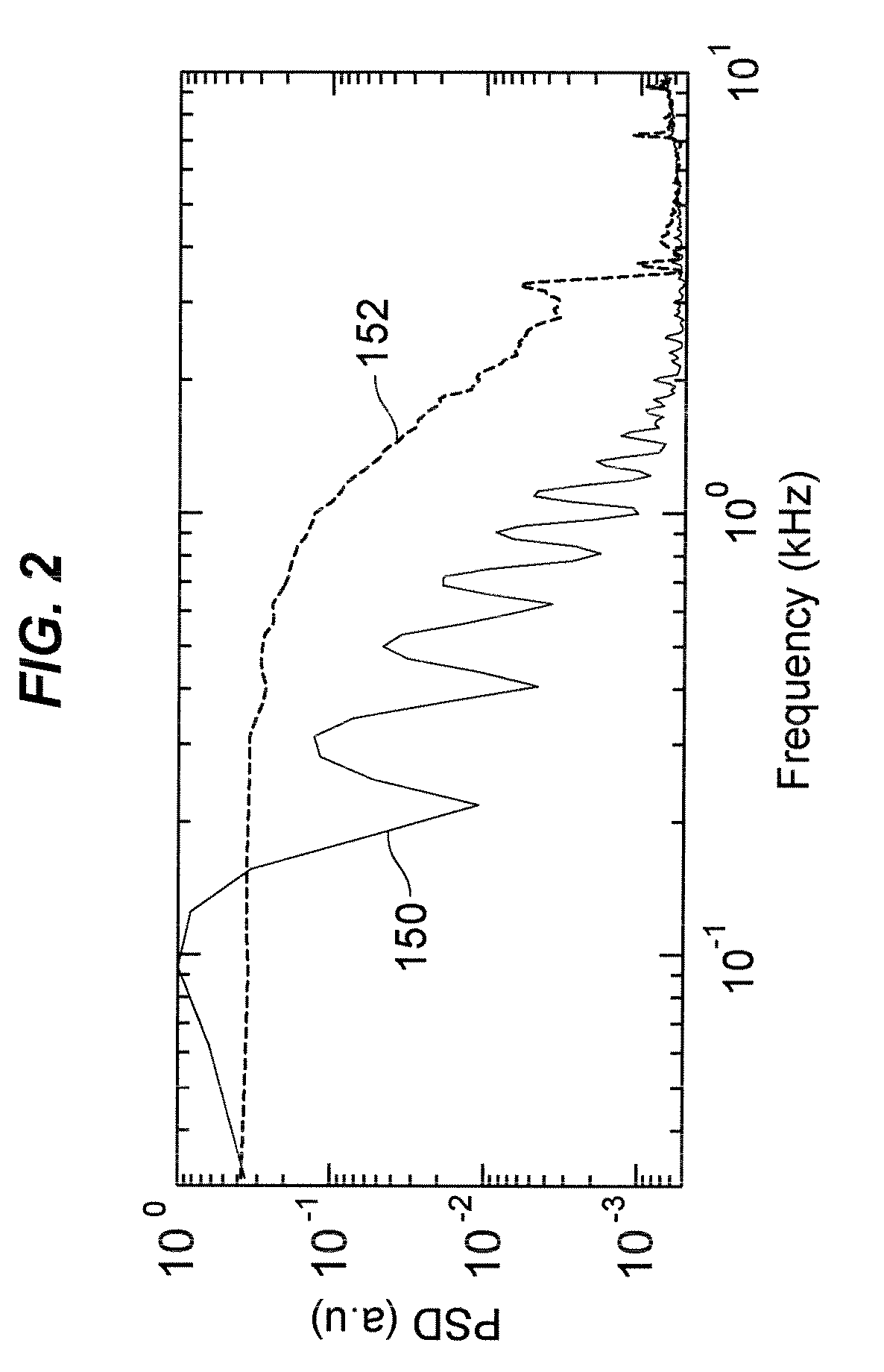
ActiveUS7426426B2Sampled-variable control systemsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceFast Fourier transformAdaptive filter
A system and method for producing and controlling a random signal with simultaneous control of both the power spectral density (PSD) and kurtosis (100) where a controlled signal is measured from a transducer, and converted to a PSD (111) using a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). The measured PSD is compared (117) with a reference PSD (121) where an adaptive filter (119) is updated to compensate for the error. Simultaneously the kurtosis of the measured data is computed (125) and compared to a reference kurtosis (123). A feedback control loop (127) is employed to adjust the kurtosis of a white noise random generator with variable kurtosis (101). This white noise is then filtered by the adaptive filter (119) to provide the output signal used to drive the control process.
Owner:VIBRATION RES CORP
A dynamic identification method and its device for normal fluctuation range of performance normal value
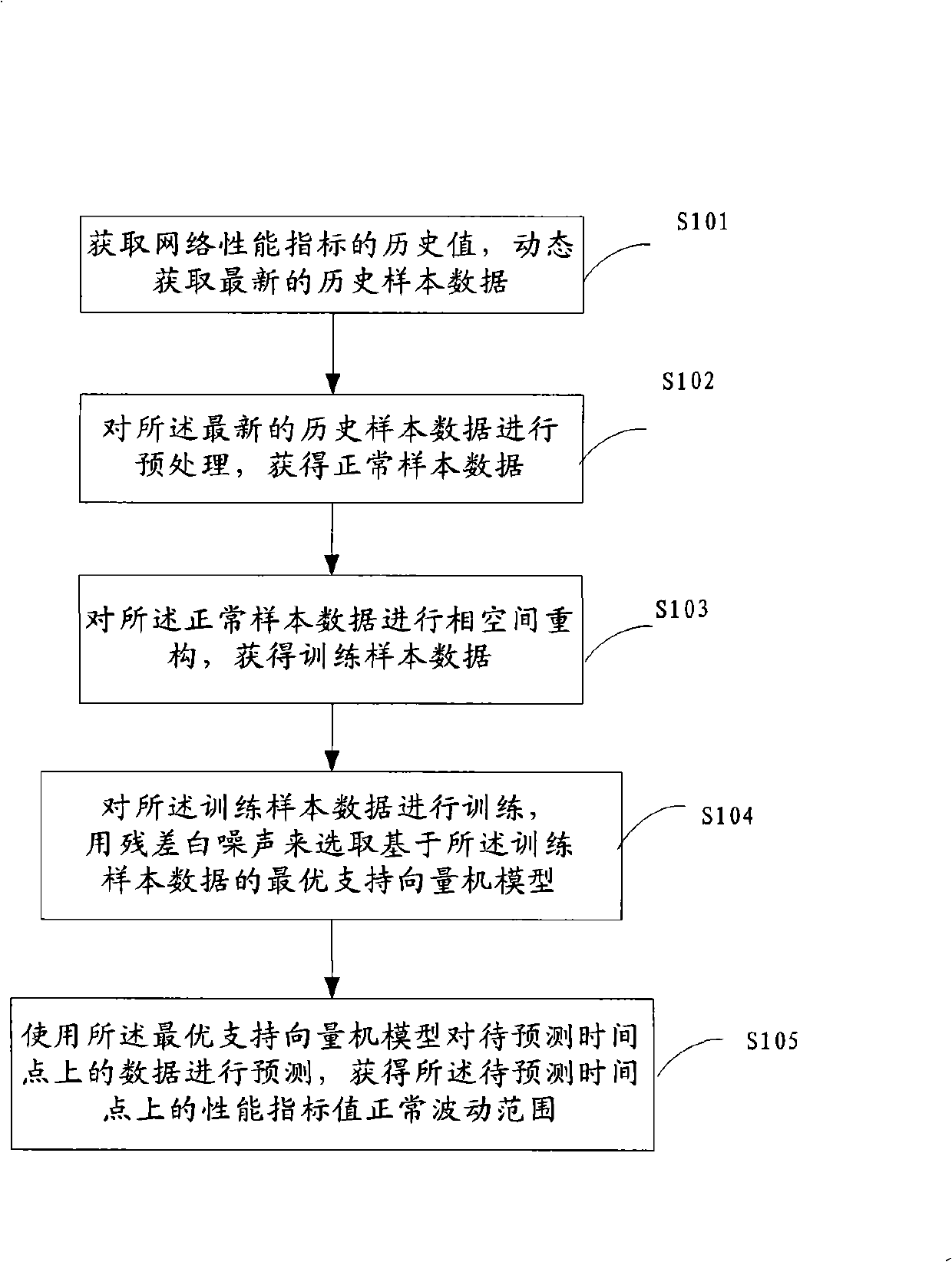
ActiveCN101267362AImprove accuracyReduce false positivesPhysical realisationData switching networksSupport vector machineAlgorithm
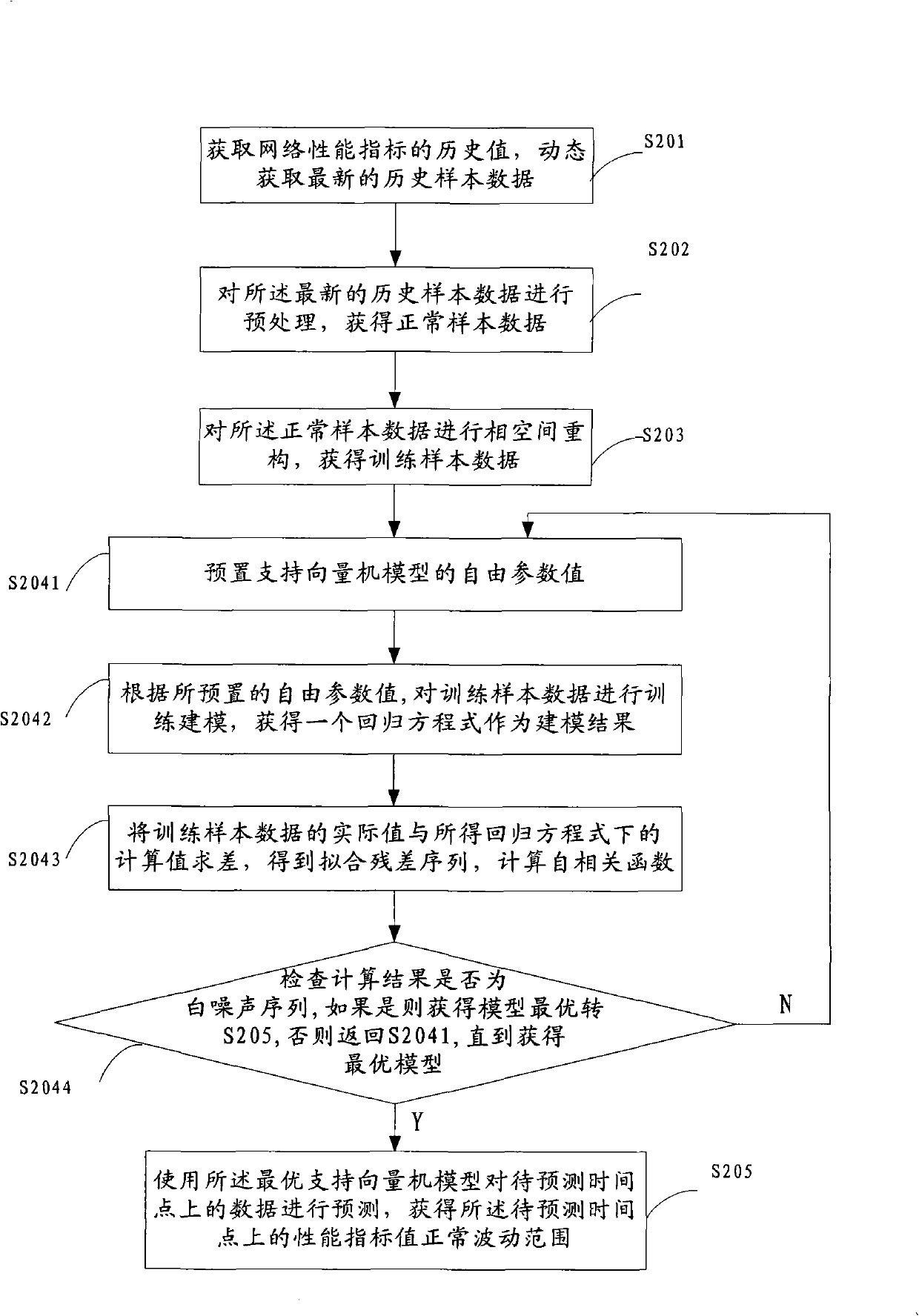
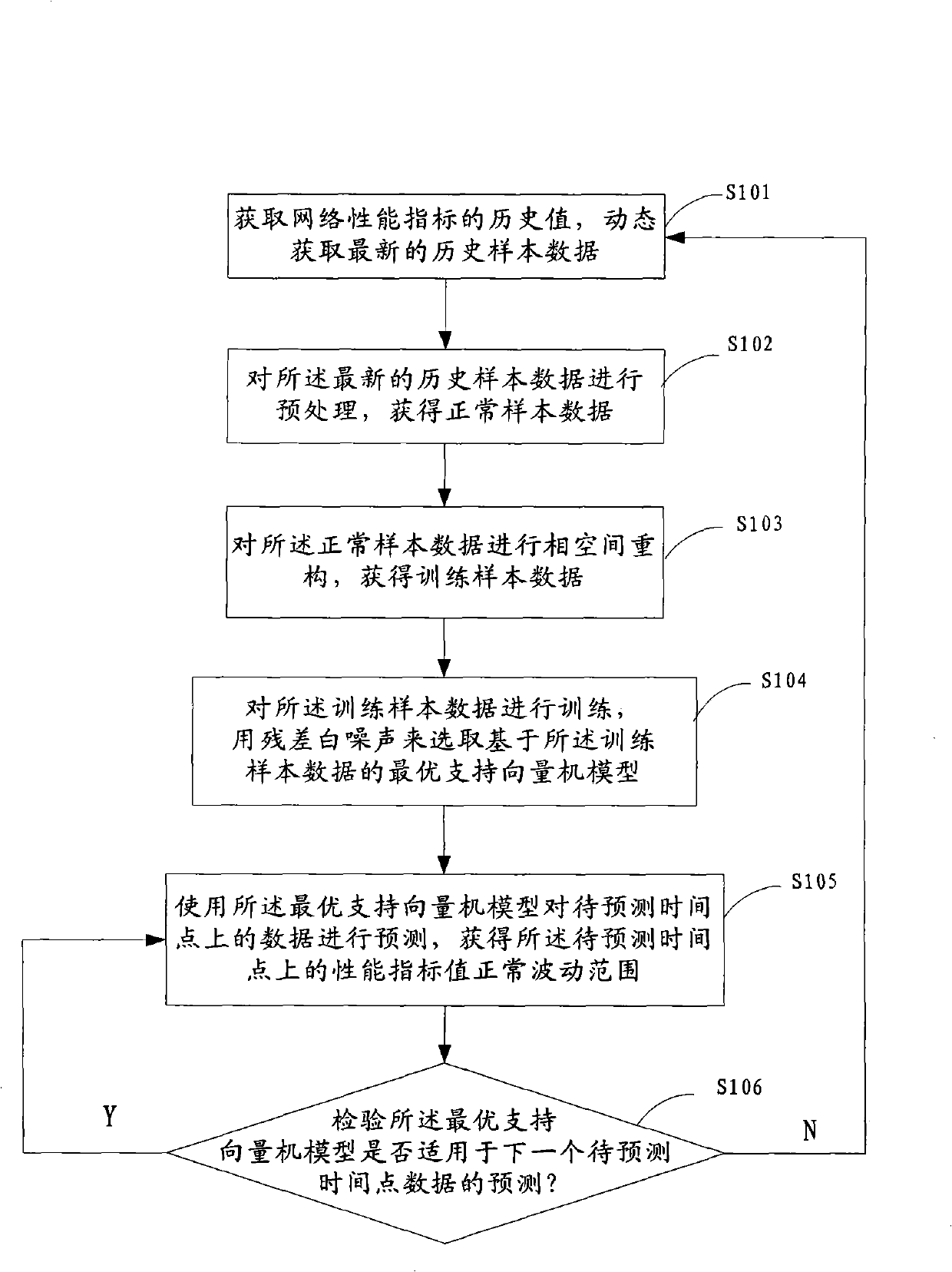
The invention discloses a dynamic confirming method for performance index value normal fluctuating range, comprising following steps: obtaining a historical value of the network performance index, and dynamically obtaining the latest historical sample data; processing pre-treatment to obtain a normal sample data; processing phase space re-construction to obtain a training sample data; processing training modeling to take residual error white noise as condition of selecting the optimal supporting vector machine model; using the optimal supporting vector machine model to predict the data on the to-be predicted time point, and calculating the confidence interval of the predicted value to obtain the performance index value normal fluctuating range; detecting whether the optimal supporting vector machine model is suitable for the next prediction of the to-be predicted time point; if the model is not suitable, processing re-training. The invention also discloses a device for the dynamic confirmation performance index value normal fluctuating range. The invention significantly enhances the precision of the performance dynamic early warning, and reduces wrong report and missing report of the performance warning.
Owner:BOCO INTER TELECOM +1
Wind turbine generator bearing fault diagnosis method under variable speed
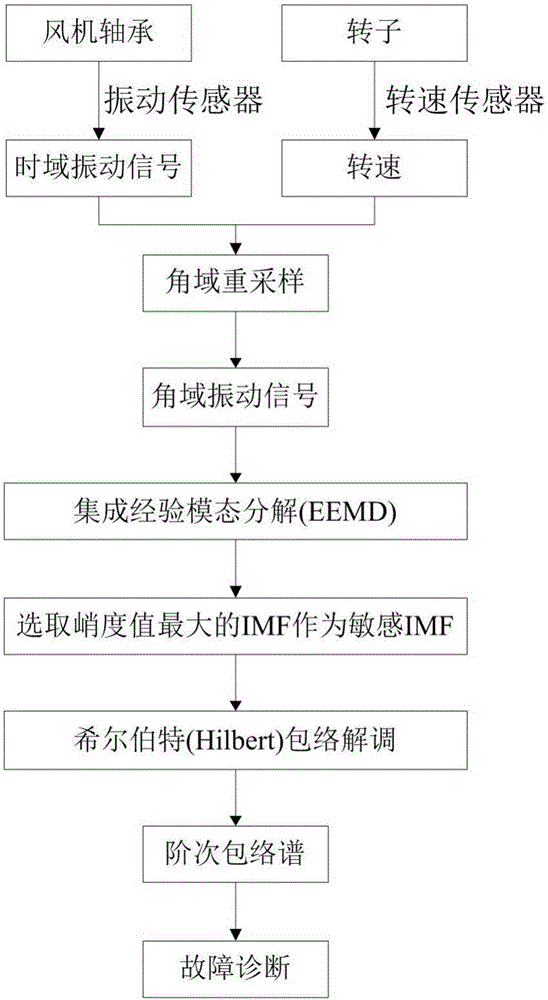
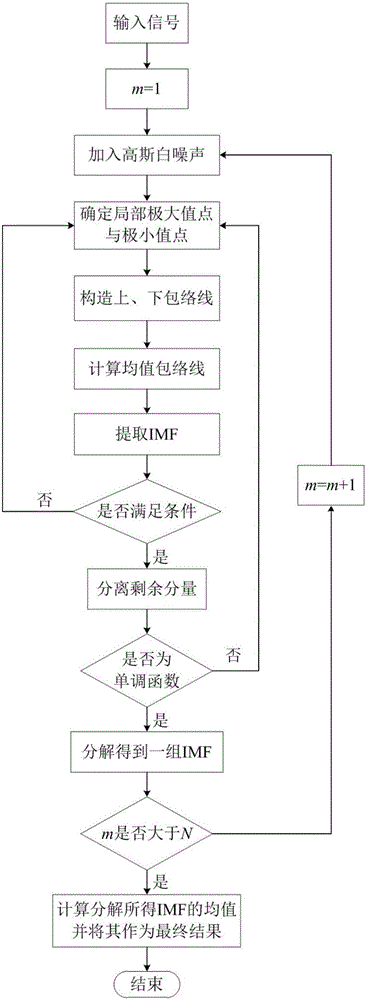
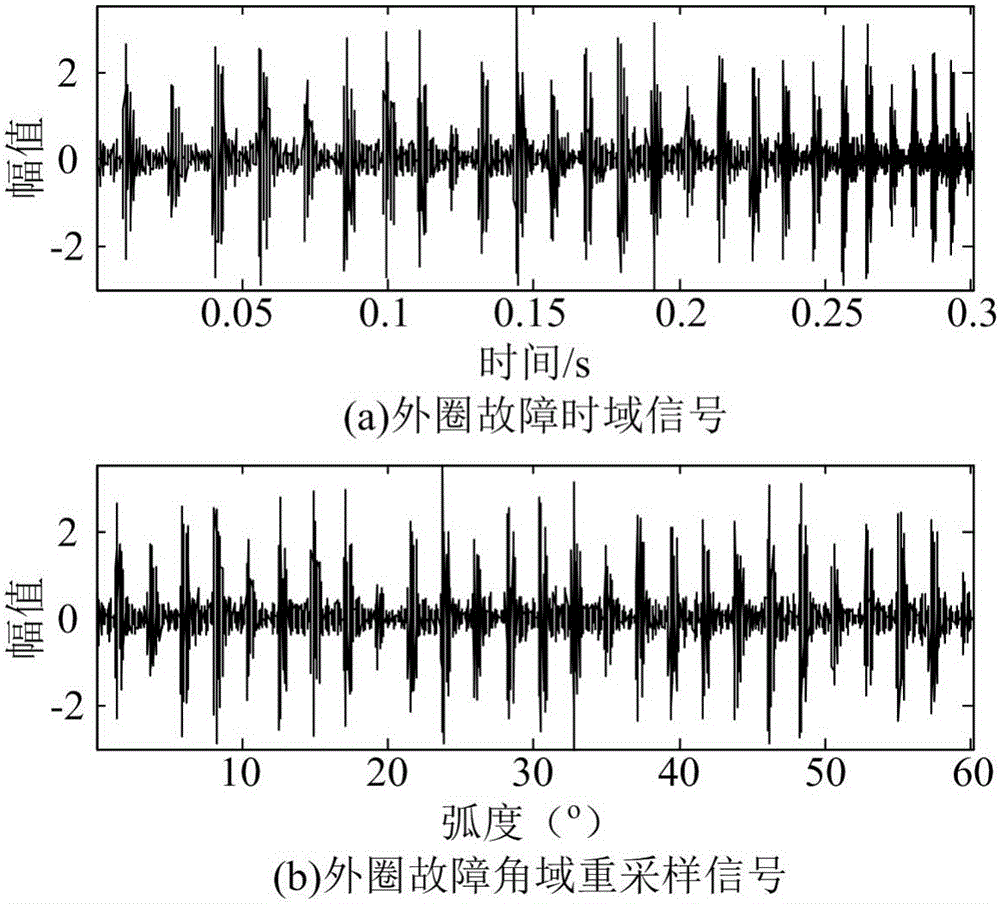
InactiveCN105784366AEliminate the effects of analysisImprove accuracyMachine bearings testingElectricityBearing vibration
The invention discloses a wind turbine generator bearing fault diagnosis method under the variable speed. According to the method, a rotation angle change curve is drafted according to the bearing rotation speed; equal angle division for the rotation angle change curve is carried out, and an equal angle re-sampling time sequence is determined; interpolation for a bearing vibration signal is carried out according to the time sequence, a random Gauss white noise sequence is added to an angle domain vibration signal, and the signal added with the white noise is processed by utilizing an empirical mode decomposition (EMD) algorithm to acquire multiple sets of IMF; a kurtosis value of each IMF component is calculated; the IMF with the largest kurtosis value is selected and taken as a sensitive IMF; Hilbert envelope demodulation for the sensitive IMF is carried out to obtain an envelope signal, the envelope signal is processed by utilizing Fourier transform to obtain order envelope spectrum of the sensitive IMF, the fault characteristic frequency is extracted, and fault diagnosis on the wind turbine generator bearing is realized. The method is advantaged in that influence of rotation speed change on vibration signal analysis can be eliminated, and accuracy and validity of fault diagnosis can be improved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
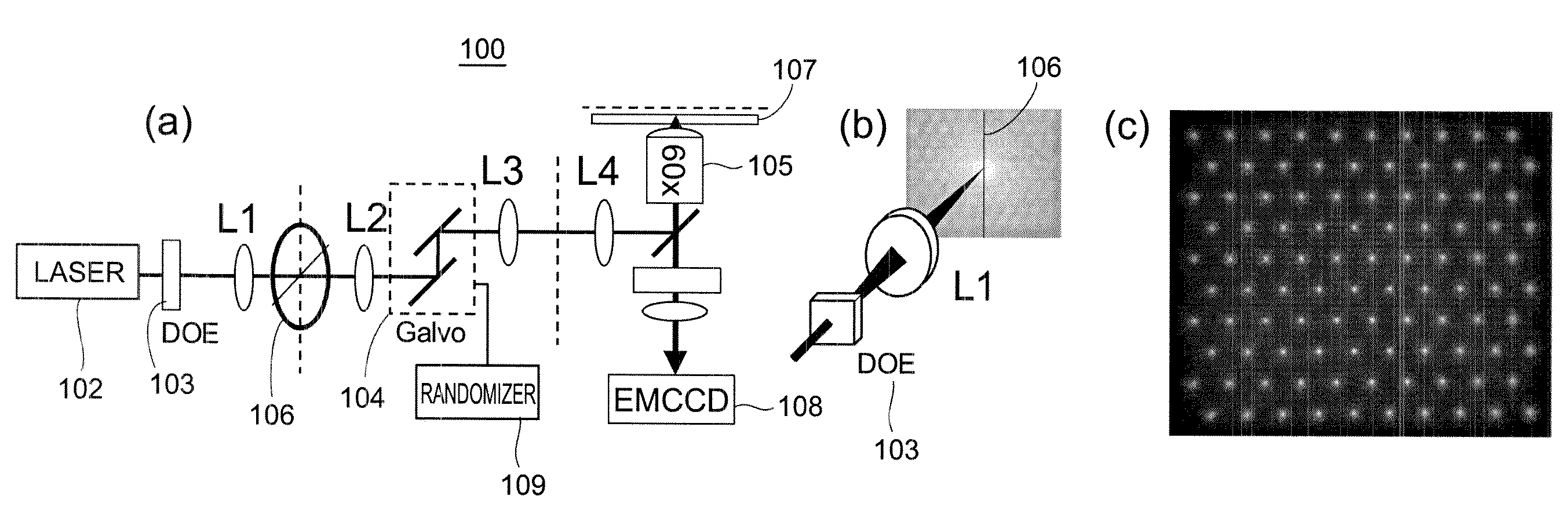
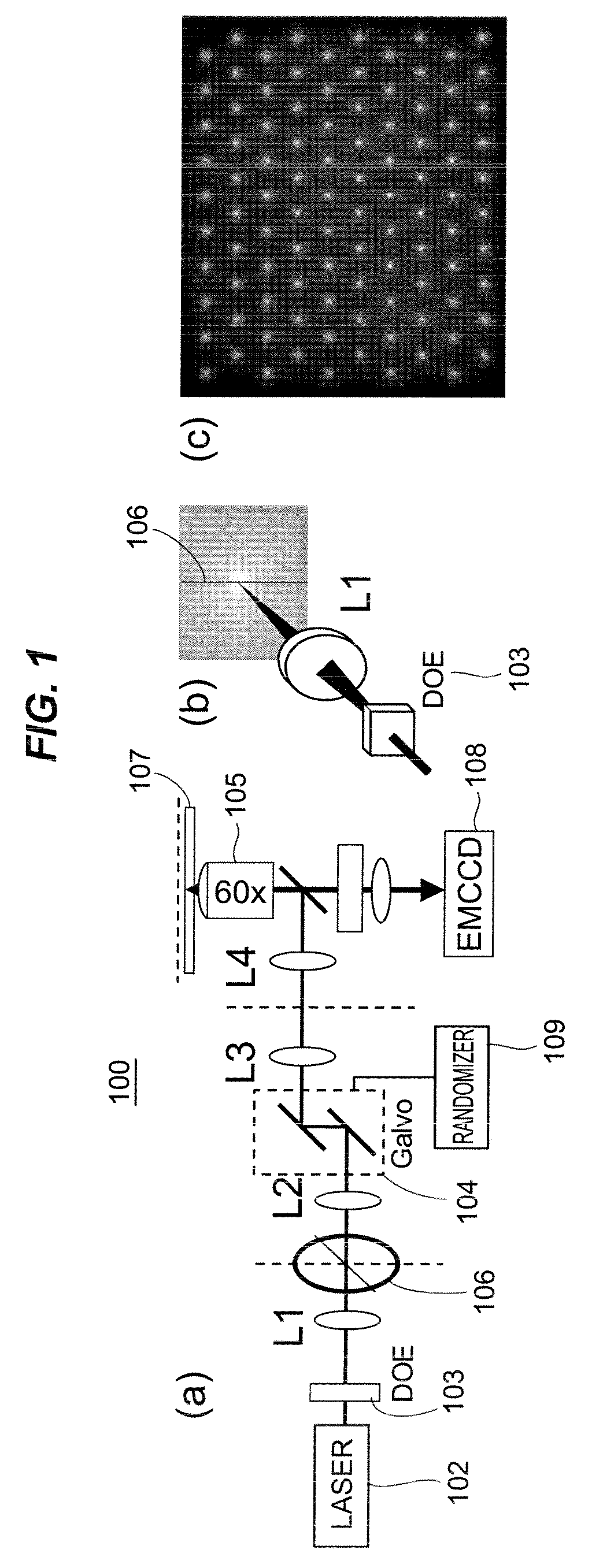
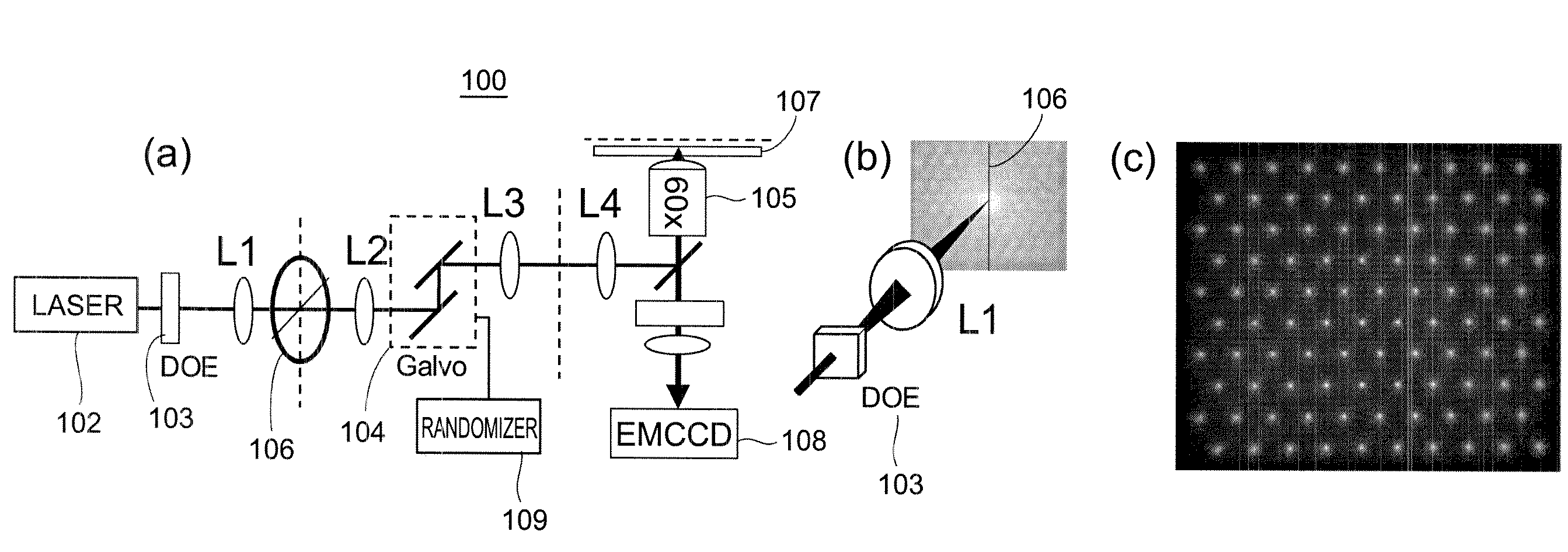
Stochastic scanning apparatus using multiphoton multifocal source
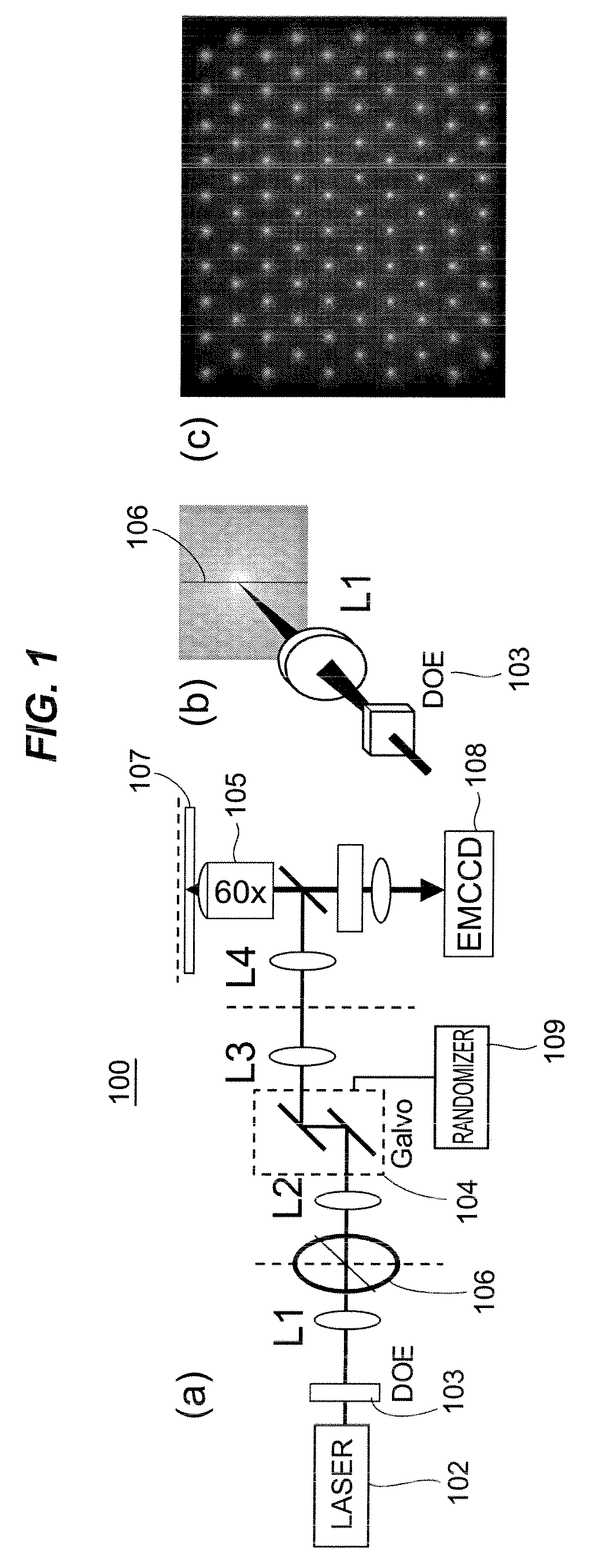
A rapid-sampling stochastic scanning multiphoton multifocal microscopy (SS-MMM) fluorescence imaging technique enables multiparticle tracking at rates upwards of 1,000 times greater than conventional single point raster scanning. Stochastic scanning of a diffractive optical element may generate a 10×10 hexagonal array of foci with a white noise driven galvanometer to yield a scan pattern that is random yet space-filling. SS-MMM may create a more uniformly sampled image with fewer spatio-temporal artifacts than obtained by conventional or multibeam raster scanning.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
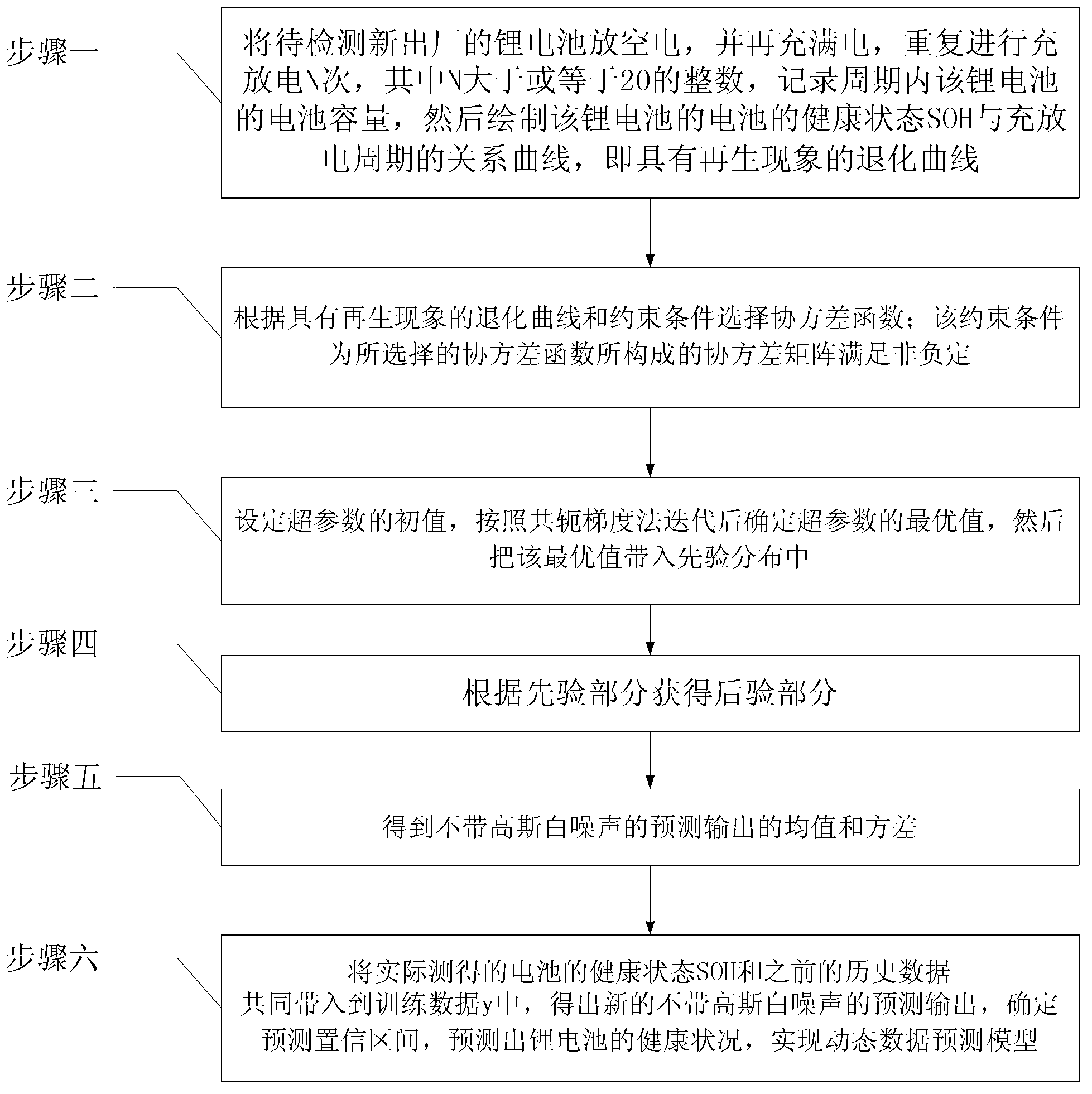
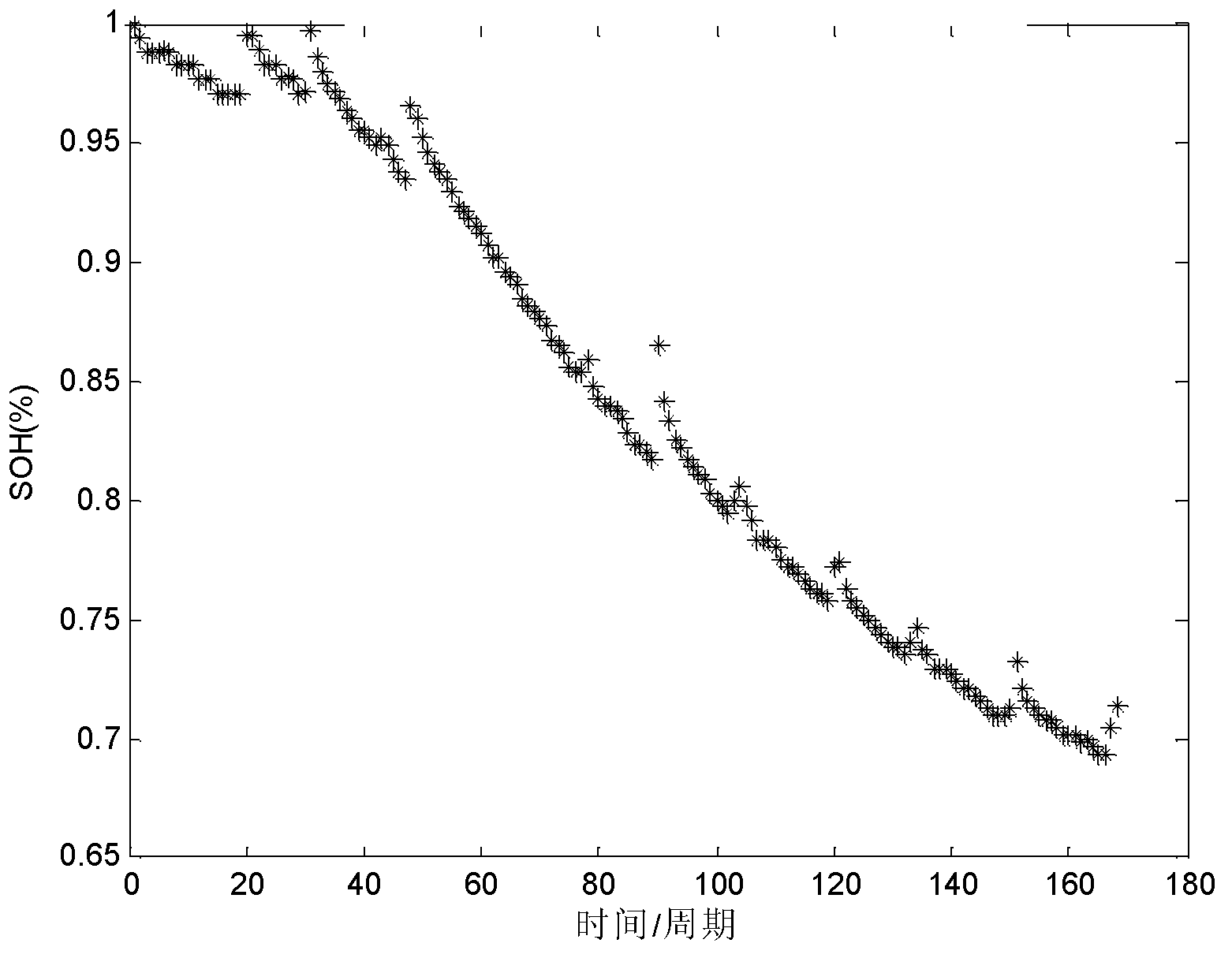
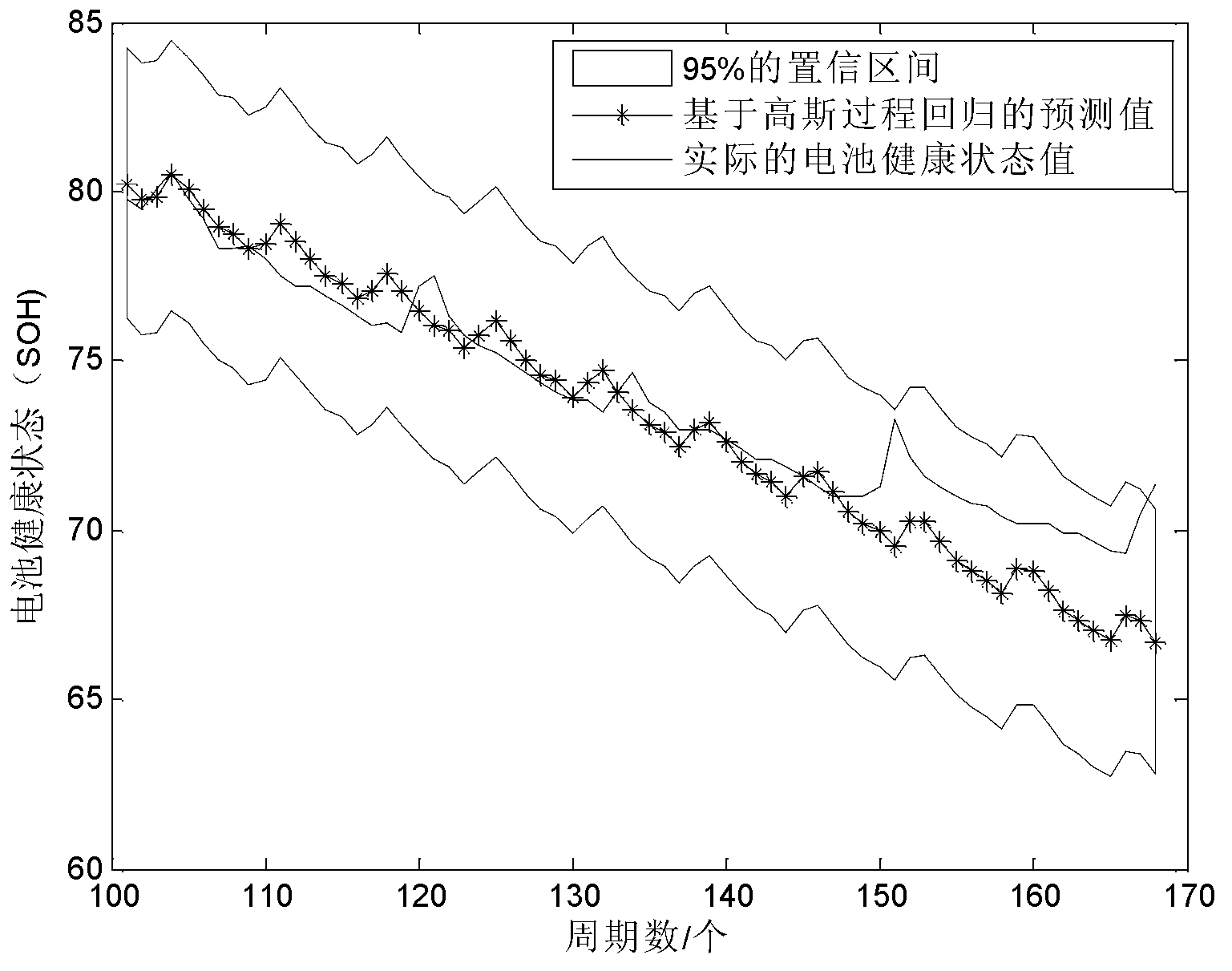
Gaussian process regression-based method for predicting state of health (SOH) of lithium batteries
InactiveCN102798823AImprove adaptabilityImprove effectivenessElectrical testingConfidence intervalCharge discharge
The invention discloses a Gaussian process regression-based method for predicting state of health (SOH) of lithium batteries, relates to a method for predicting the SOH of the lithium batteries, belongs to the fields of electrochemistry and analytic chemistry and aims at the problem that the traditional lithium batteries are bad in health condition prediction adaptability. The method provided by the invention is realized according to the following steps of: I. drawing a relation curve of the SOH of a lithium battery and a charge-discharge period; II, selecting a covariance function according to a degenerated curve with a regeneration phenomenon and a constraint condition; III, carrying out iteration according to a conjugate gradient method, then determining the optimal value of a hyper-parameter and bringing initial value thereof into prior distribution; IV, obtaining posterior distribution according to the prior part; V, obtaining the mean value and variance of predicted output f' without Gaussian white noise; and VI, together bringing the practically predicted SOH of the battery and the predicted SOH obtained in the step V into training data y to obtain the f', then determining the prediction confidence interval and predicting the SOH of the lithium battery. The method provided by the invention is used for detecting lithium batteries.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Stochastic Scanning Apparatus Using Multiphoton Multifocal Source
A rapid-sampling stochastic scanning multiphoton multifocal microscopy (SS-MMM) fluorescence imaging technique enables multiparticle tracking at rates upwards of 1,000 times greater than conventional single point raster scanning. Stochastic scanning of a diffractive optical element may generate a 10×10 hexagonal array of foci with a white noise driven galvanometer to yield a scan pattern that is random yet space-filling. SS-MMM may create a more uniformly sampled image with fewer spatio-temporal artifacts than obtained by conventional or multibeam raster scanning.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Anti-islanding device and method for grid connected inverters using random noise injection
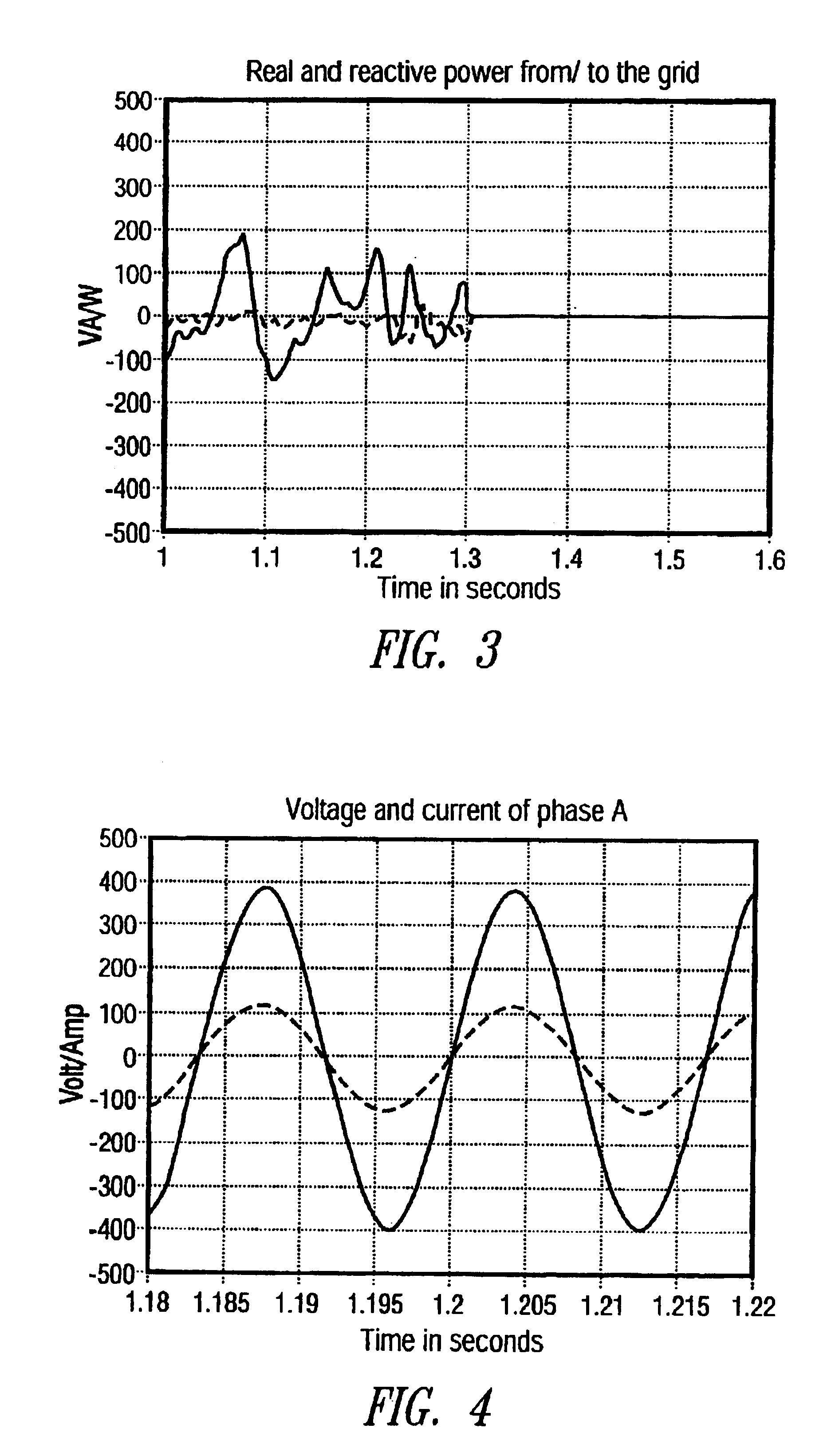
InactiveUS6853940B2Improves harmonic contentImproves direct current (dc) offset of currentSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectrical measurementsIslandingGrid-tie inverter
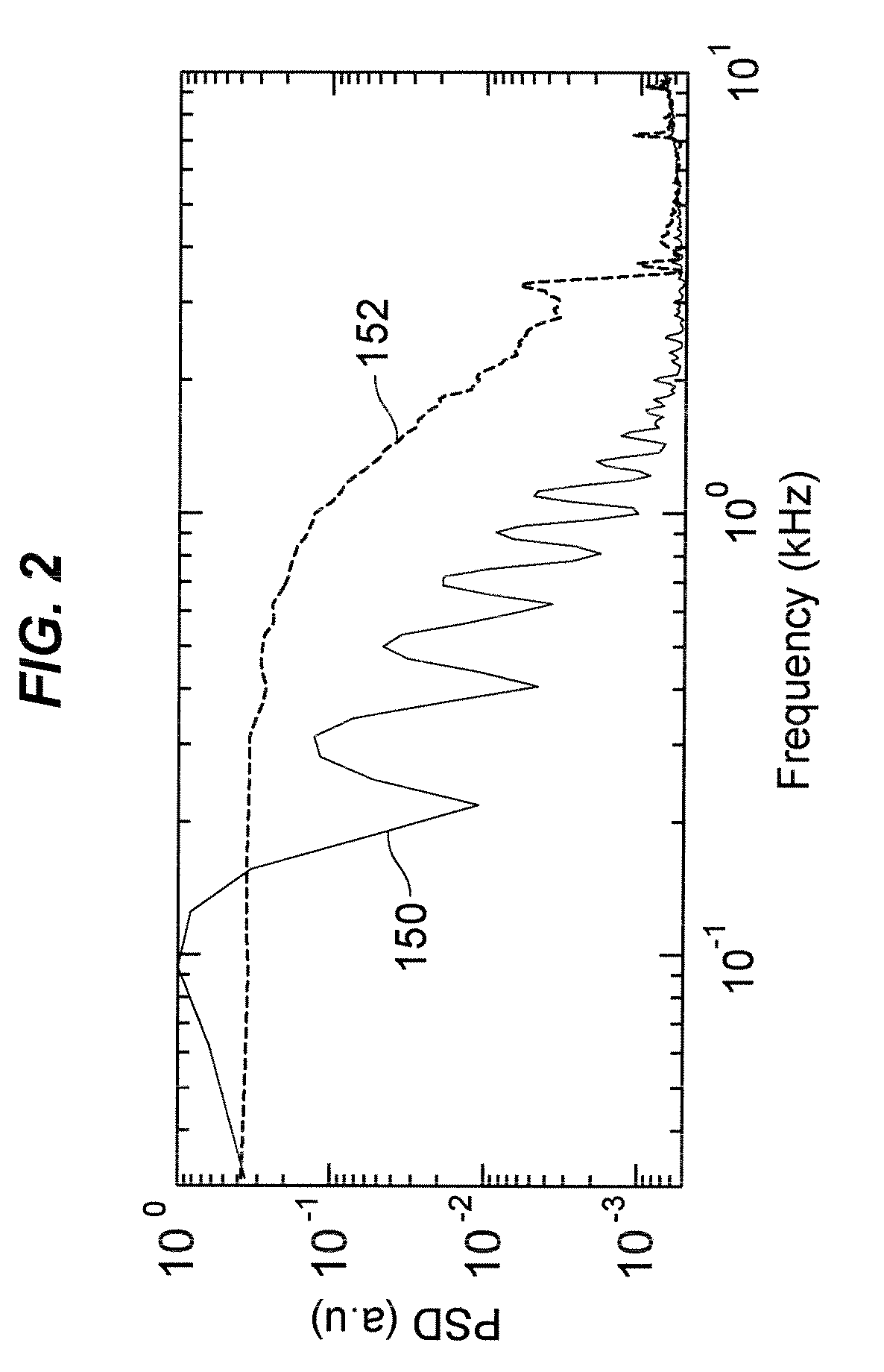
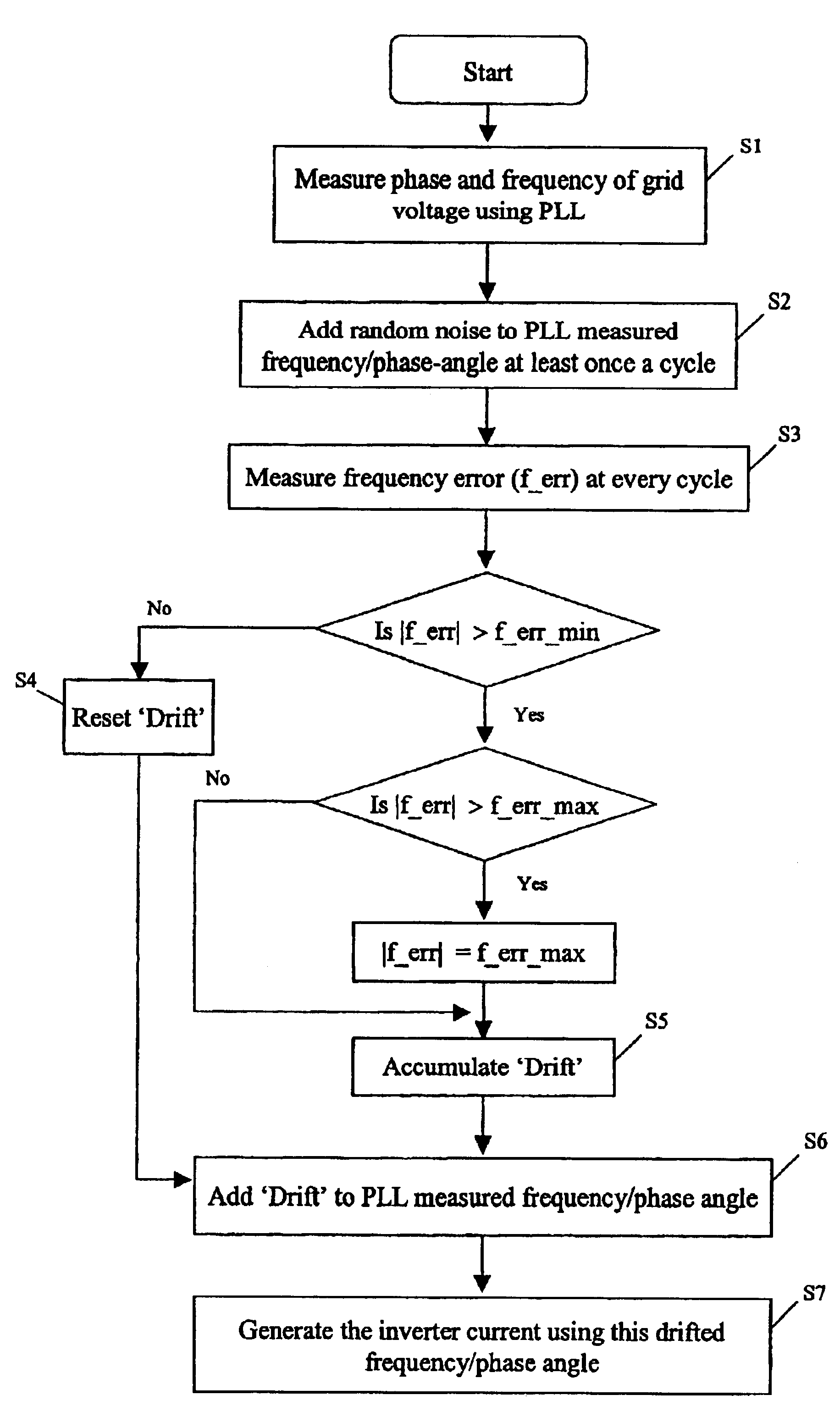
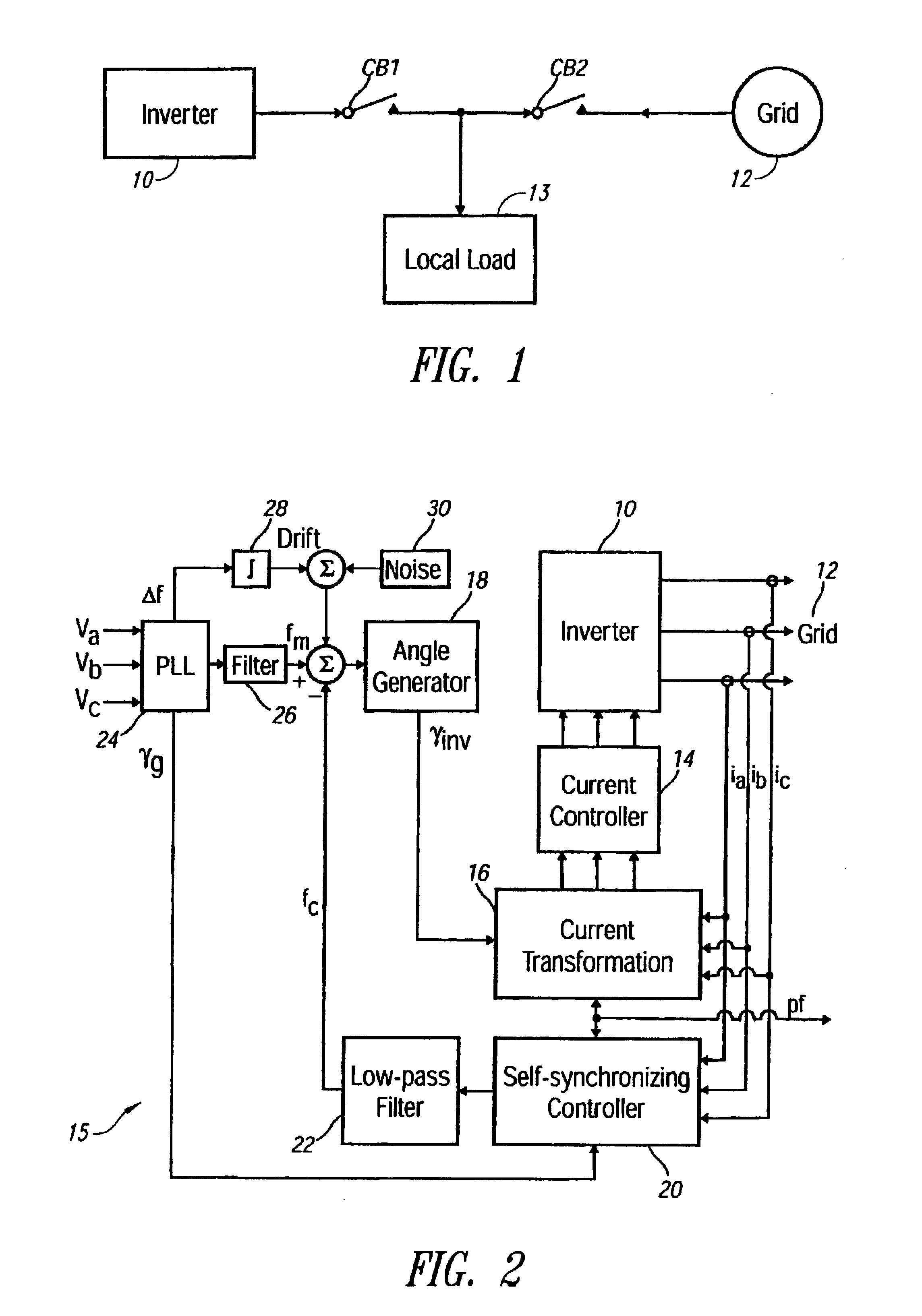
A device and method for detecting islanding of a grid connected inverter makes use of an injected white noise as a perturbing force on the output voltage of the inverter. The white noise is injected at least once in every cycle and can be generated at different rates in implementation. On loss of the grid, a frequency drift of the output voltage is detected and a positive feedback is activated that accelerates the drift.
Owner:RHOMBUS ENERGY SOLUTIONS
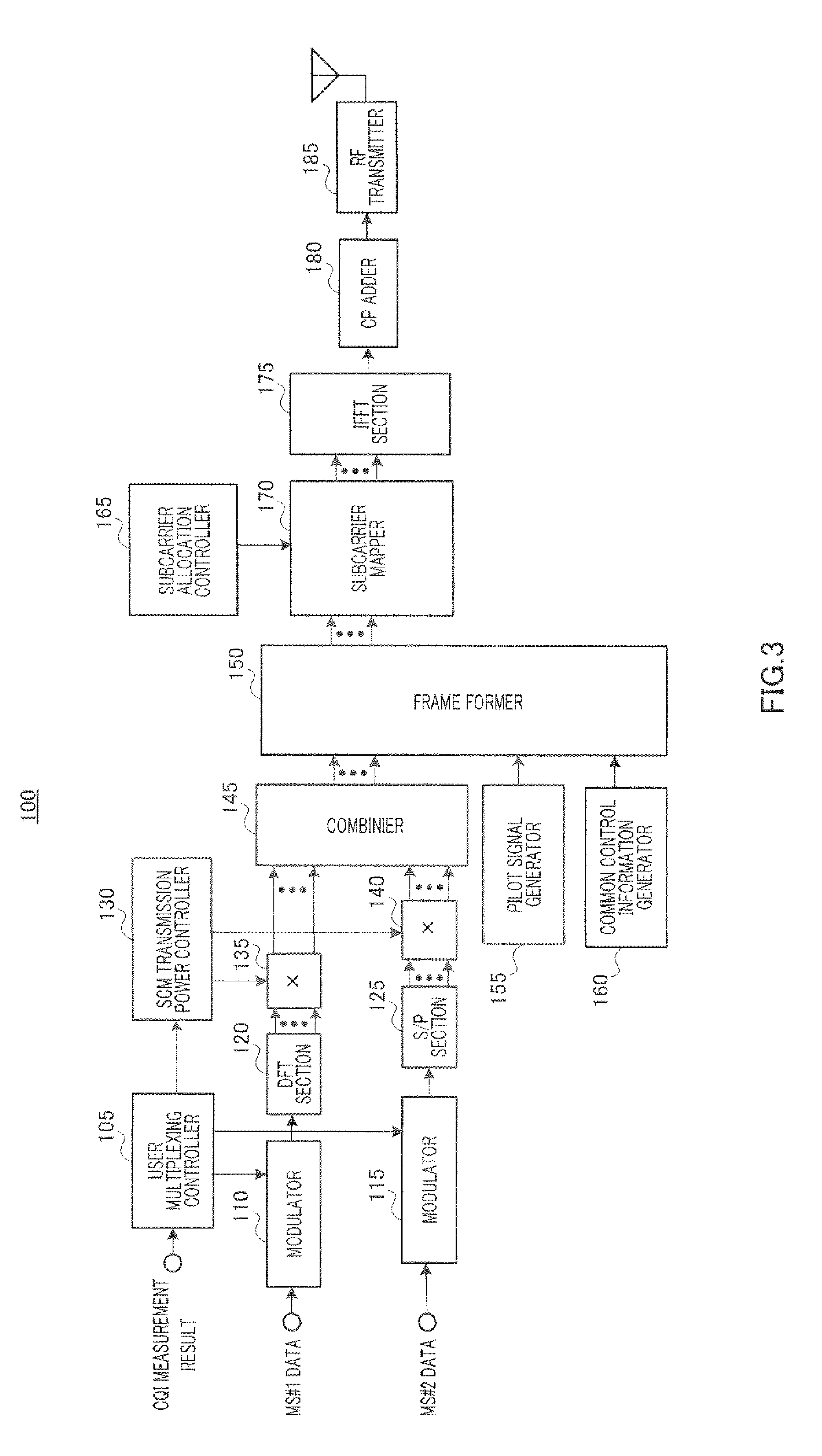
Multicarrier transmitter and multicarrier receiver
InactiveUS20100246711A1Improve reception performancePower managementModulated-carrier systemsMultiplexingMulti carrier
A multicarrier transmitter and a multicarrier receiver both enabling improvement of the reception characteristic of hierarchical modulation multiplex communication. A base station (100) transmits a multicarrier signal which is a superposition of a modulated signal addressed to a far user and a modulated signal addressed to a near user and modulated with a modulation multivalued number different from that of the modulated signal addressed to the far user. The base station (100) comprises a DFT section (120), an S / P section (125), and a combining section (145). The DFT section (120) separates the modulated signal addressed to the far user into signals in frequency ranges for each symbol. The S / P section (125) serial / parallel-transforms the modulated signal addressed to the near user to generate N1 parallel signals. The combining section (145) combines the N1 frequency components generated by the DFT section (120) and the N1 parallel signals. Since the far user receiver can change the modulated signal addressed to the near user into white noise by IDFT, the far user receiver can demodulate the modulated signal addressed to the far user with high accuracy. The near user receiver can acquire the signal addressed thereto with high accuracy by subtracting the modulated signal addressed to the far user, which is an interference signal, from the received signal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
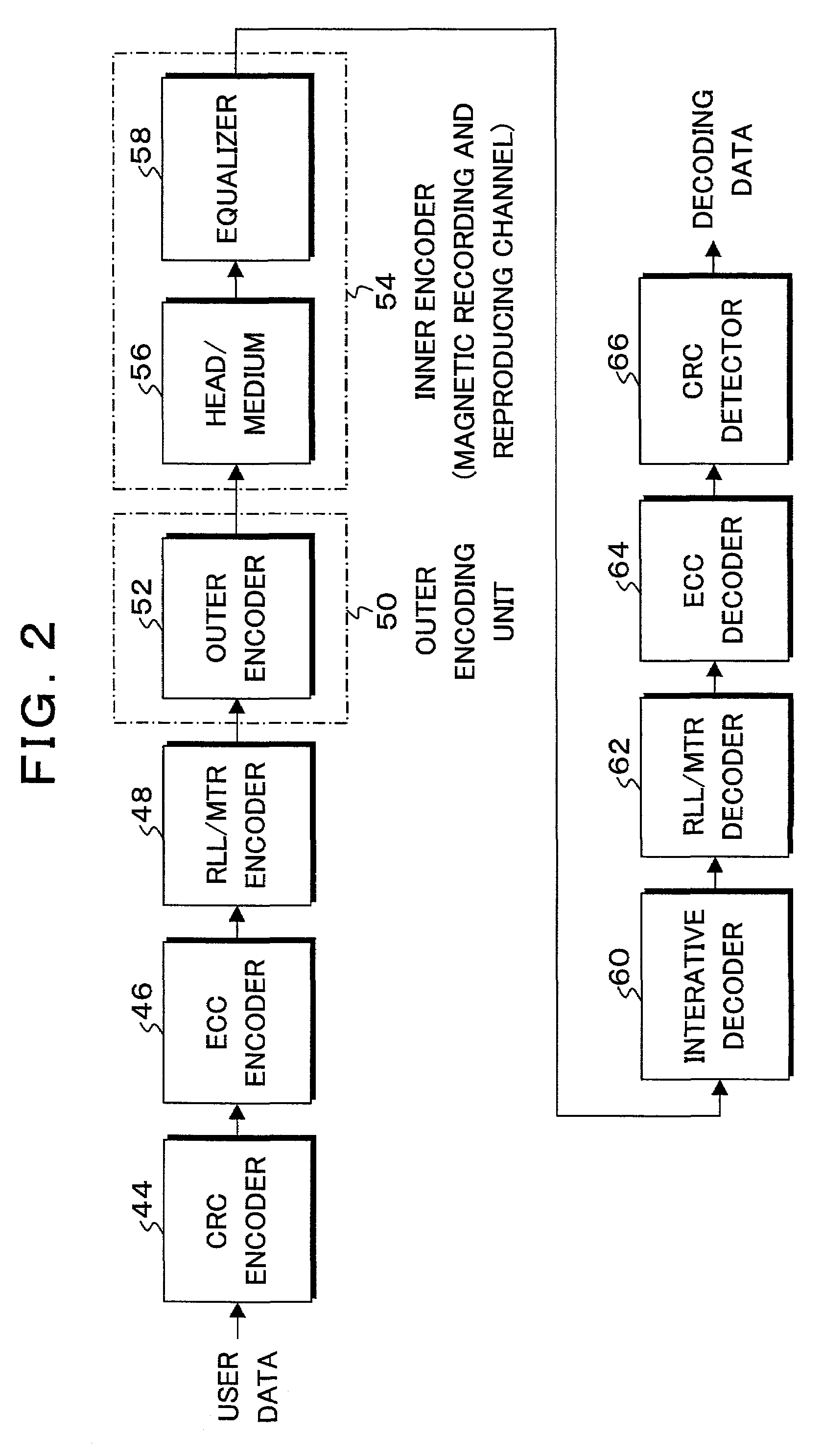
Information recording and reproducing apparatus and method and signal decoding circuit having improved noise processing characteristics
InactiveUS7031090B2Effective applicationImprove decoding performanceModification of read/write signalsOther decoding techniquesMaximum a posteriori estimationComputer science
In a Maximum A posteriori Probability decoding (MAP decoding), a correlation and a deviation of noises for past and future states which depend on input signal patterns in past N bits and future Q bits are calculated by training by a noise correlation arithmetic operating unit 84 and they are stored. Upon reproduction, in a white noise arithmetic operating unit 91, white noise values for the past and future states in which colored noises are converted into white noises are obtained by using the stored correlation and deviation of the noises. In an input signal arithmetic operating unit 92, an input signal (channel information) Λc(yk|Smk) of the MAP decoding is calculated from the white noise values and the deviation for the past and future states. A likelihood in the MAP decoding is obtained from the input signal.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
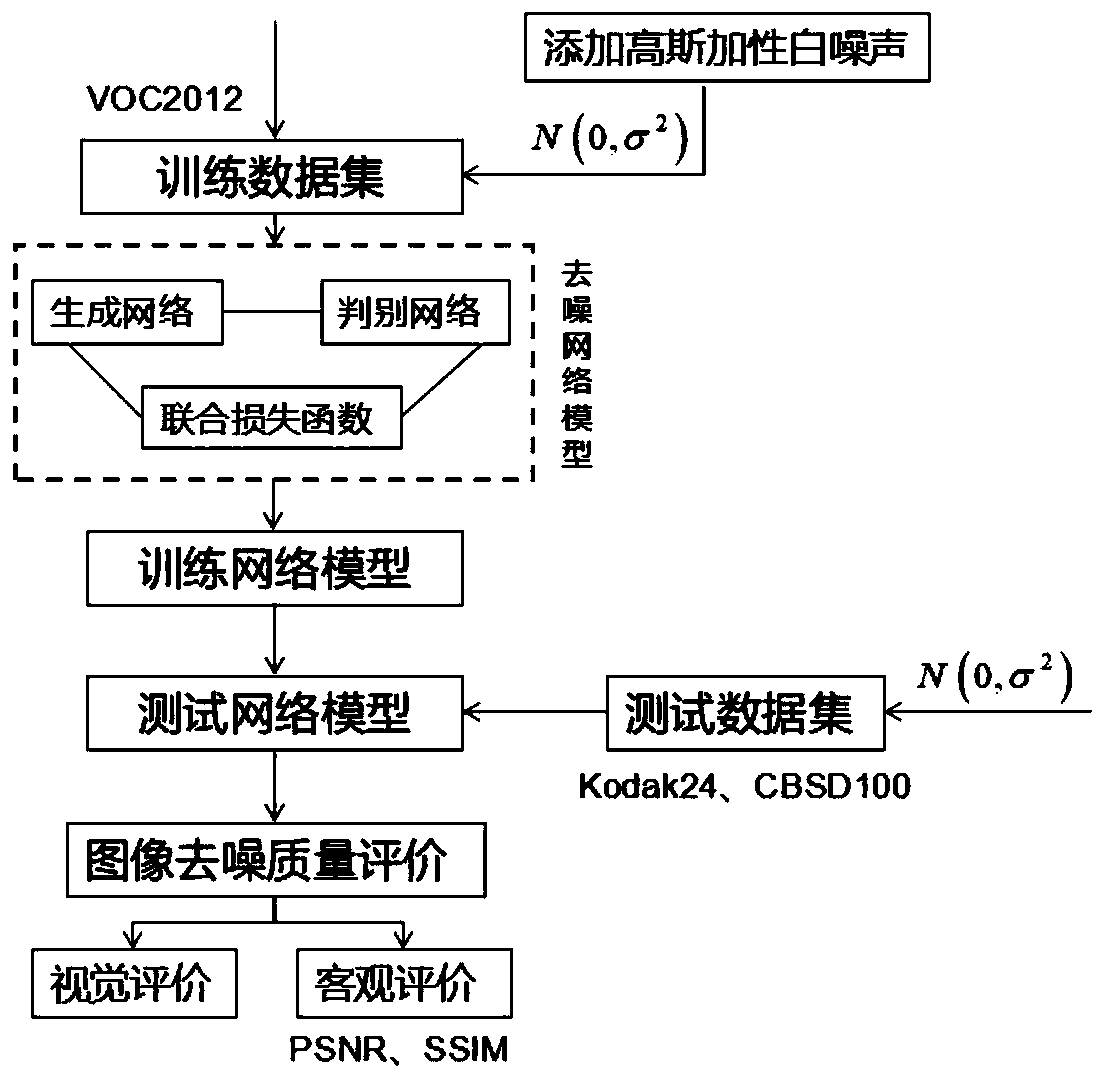
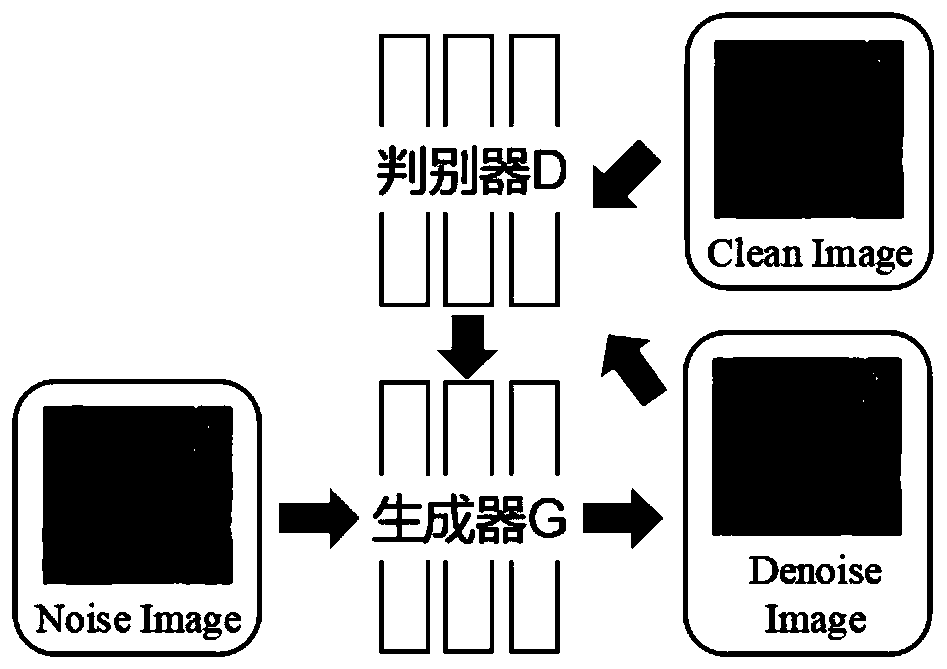
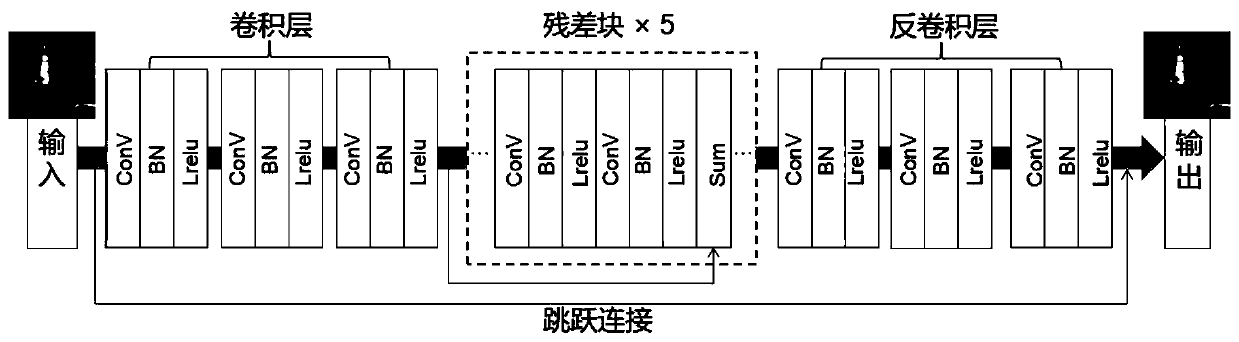
Image denoising method based on generative adversarial network
ActiveCN110473154AReduce the "checkerboard effect"Reduce "chessboard effect"Image enhancementImage analysisImage denoisingPattern recognition
The invention discloses an image denoising method based on a generative adversarial network, and the method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1, selecting an experiment data set; 2,selecting Gaussian additive white noise as a noise model; 3, building a generative network model, and training a generator network G for denoising; 4, establishing a discrimination network model, wherein a discriminator D is used for carrying out authenticity classification on the input image; 5, constructing a joint loss function model; 6, training a generative adversarial network; and step 7, carrying out image denoising quality evaluation. According to the image denoising method based on the generative adversarial network, the denoising effect of reserving more texture details and edge features can be achieved.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
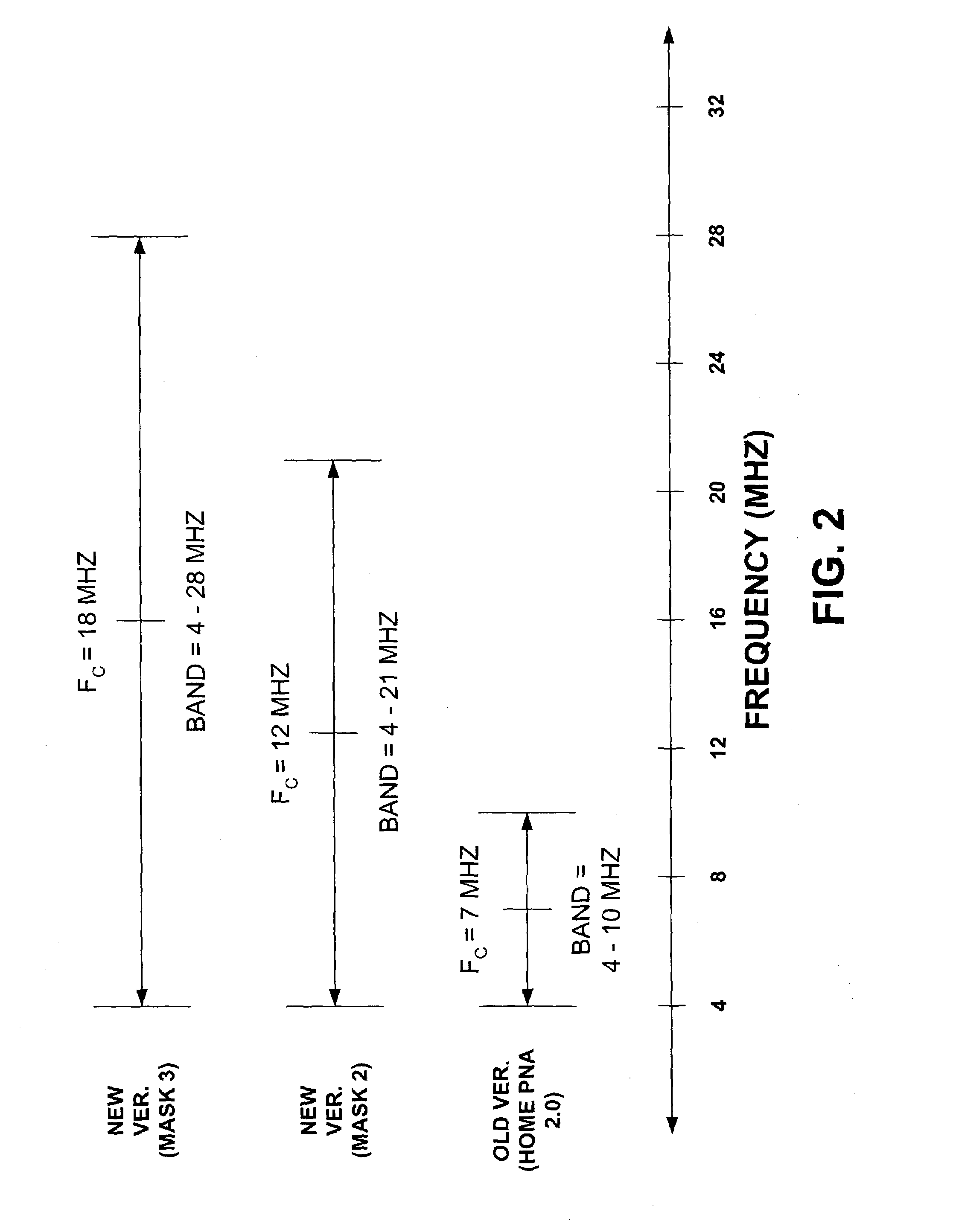
Home phone line networking next generation enhancements
ActiveUS7327765B1Good carrier senseHigh operating requirementsModulated-carrier systemsCross-talk reductionFrequency spectrumConstant power
New version devices of a home phone line network may operate on a first carrier frequency (within the new version frequency band) while old version devices may operate at a second carrier frequency (within the old version frequency band). Preamble, header, and trailer portions of a new version signal include a plurality of spectral copies of a baseband modulated signal. One or more of these spectral copies of the baseband modulated signal is / are indistinguishable from corresponding components of an old version signal. The new version signal is transmit filtered to have a negatively sloping power spectral density in order to maintain a constant power level in relation to old version signals and to have slope that is opposite of binder crosstalk so as to form, with the average crosstalk, a constant level white noise floor.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Laser radar 3D point cloud data combined camera self-calibrating method
The invention discloses a laser radar 3D point cloud data combined camera self-calibrating method, and relates to the technical fields of photography measurement and 3D reconstruction. 3D scanning iscarried out on a measured object, images of the same scene are collected in different viewpoints, features are extracted from the multiple collected images to obtain characteristic points, characteristic points in an overlapped area of any two images are searched for a corresponding nearest point, and a matching point pair is obtained by combining a random consistency algorithm; the matching pointpair is used to solve a fundamental matrix F so that the fundamental matrix F is not sensitive to Gaussian white noise; an objective function related to internal reference of a camera is establishedaccording to relation between the fundamental matrix and internal reference of the camera, and an optimization algorithm is used to solve the internal reference of the camera; and the internal reference, of the camera, needed by the optimization algorithm is set on the basis of laser radar 3D point cloud data, a pinhole imaging principle, a pixel size of a CCD camera and an image central position.Thus, the internal reference of the camera is calibrated accurately.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com