Patents
Literature
1251results about "Cross-talk reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
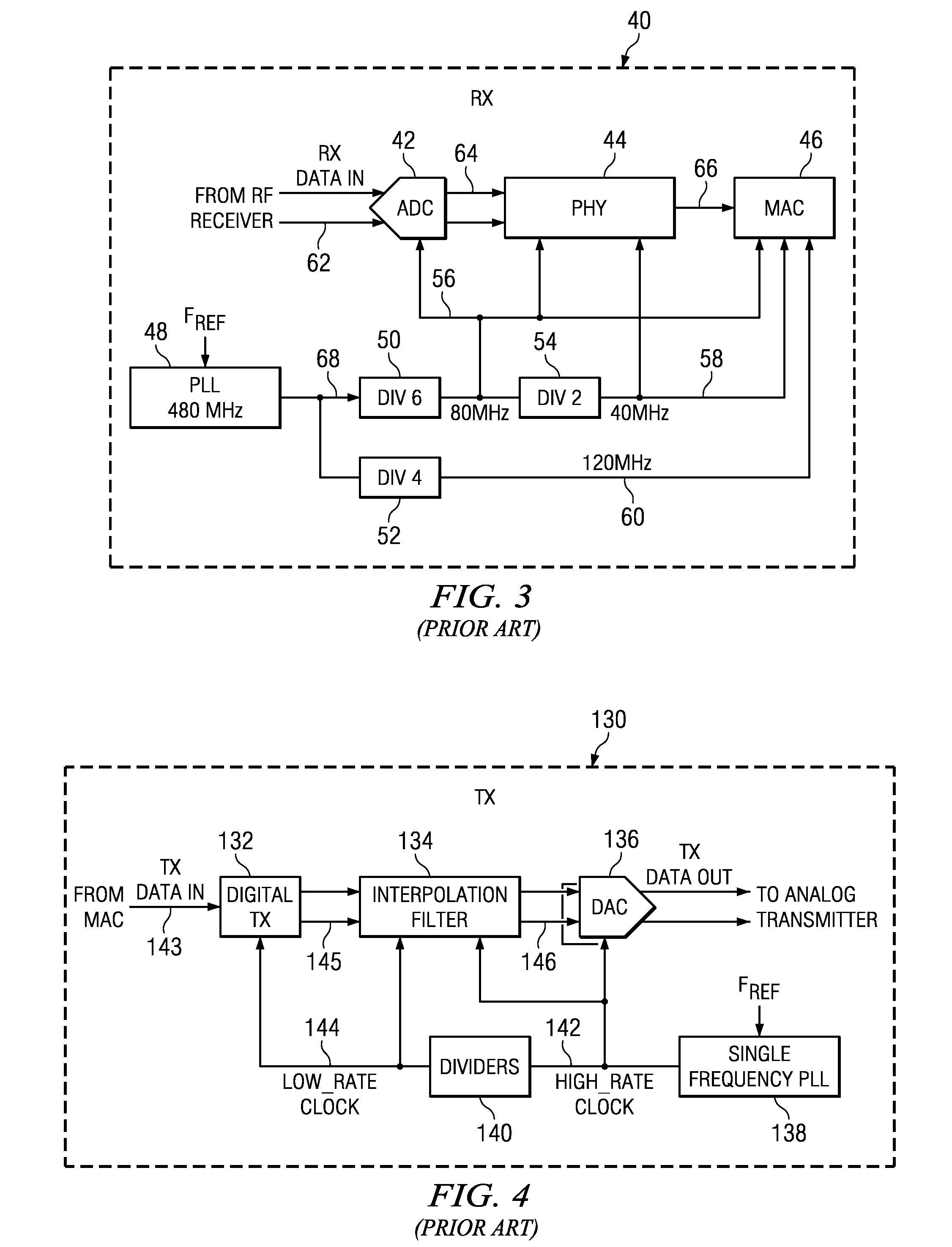
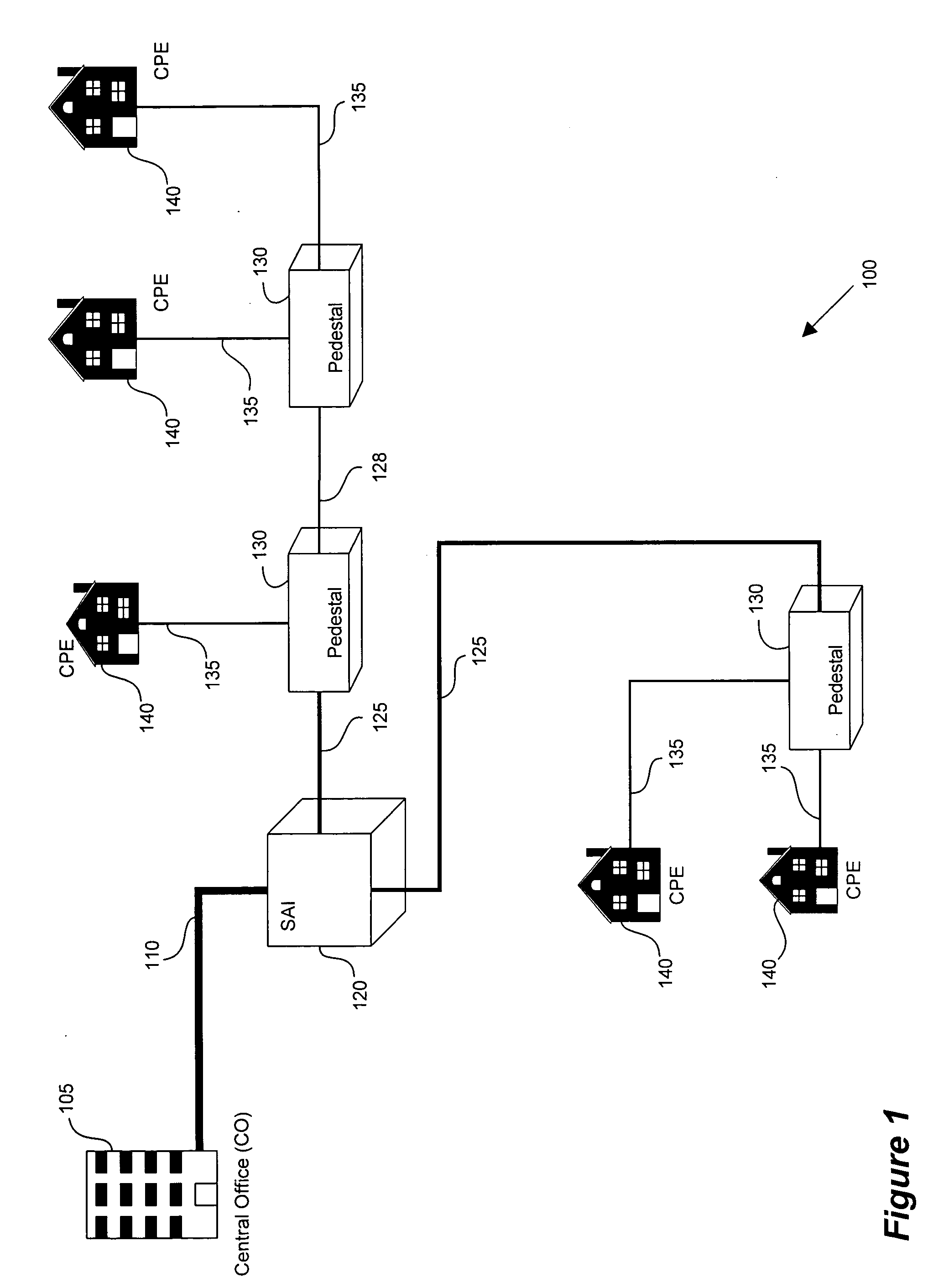
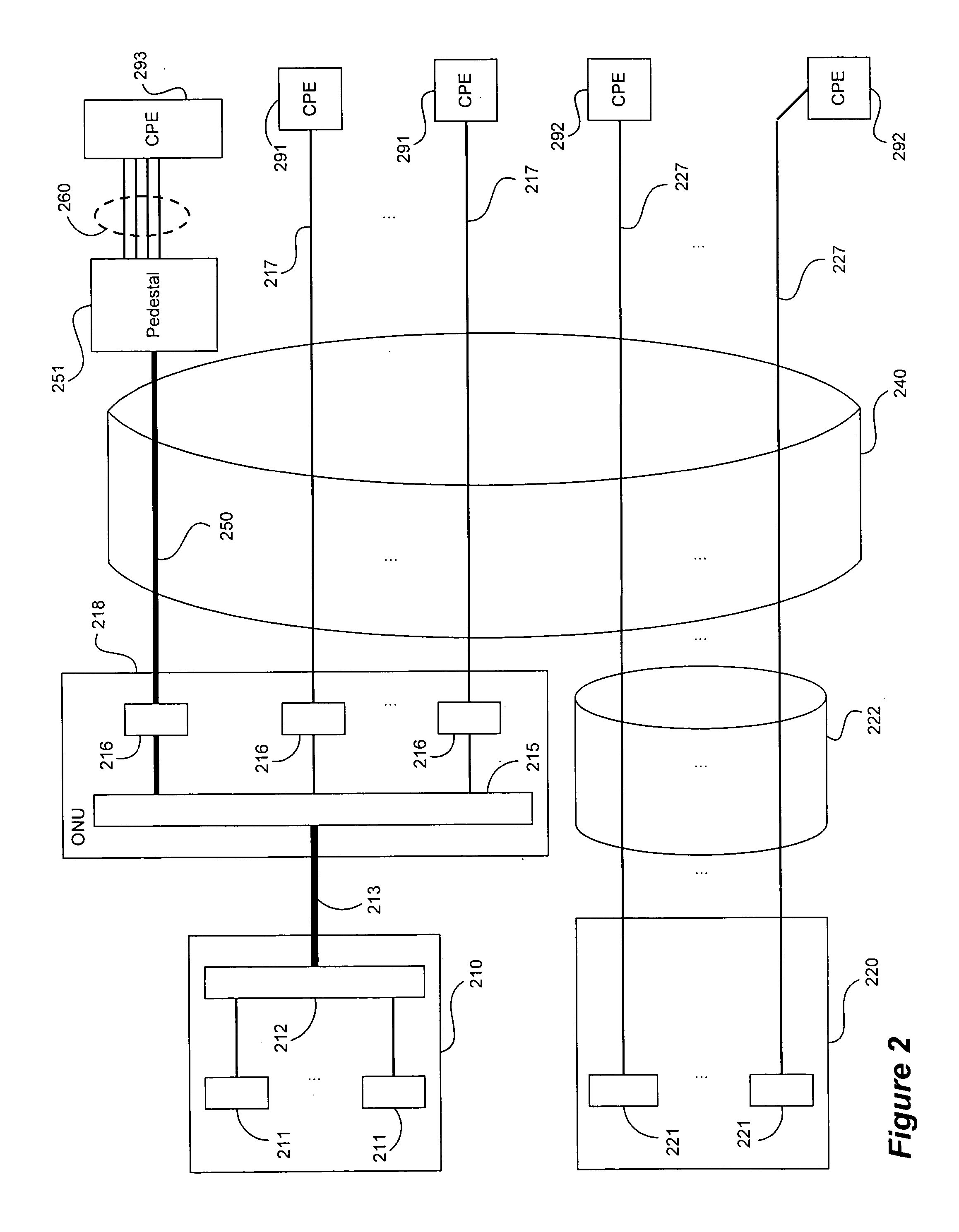
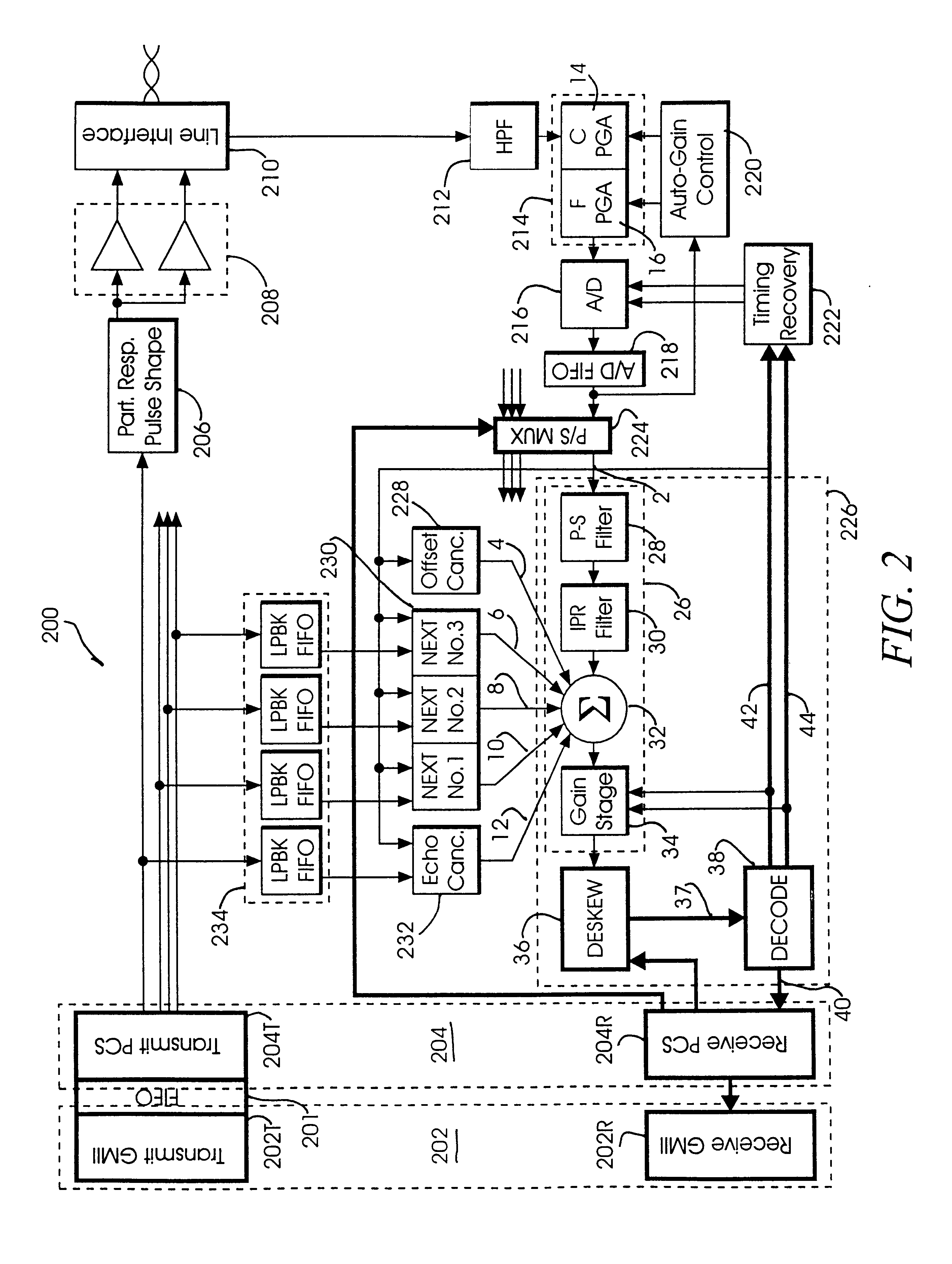
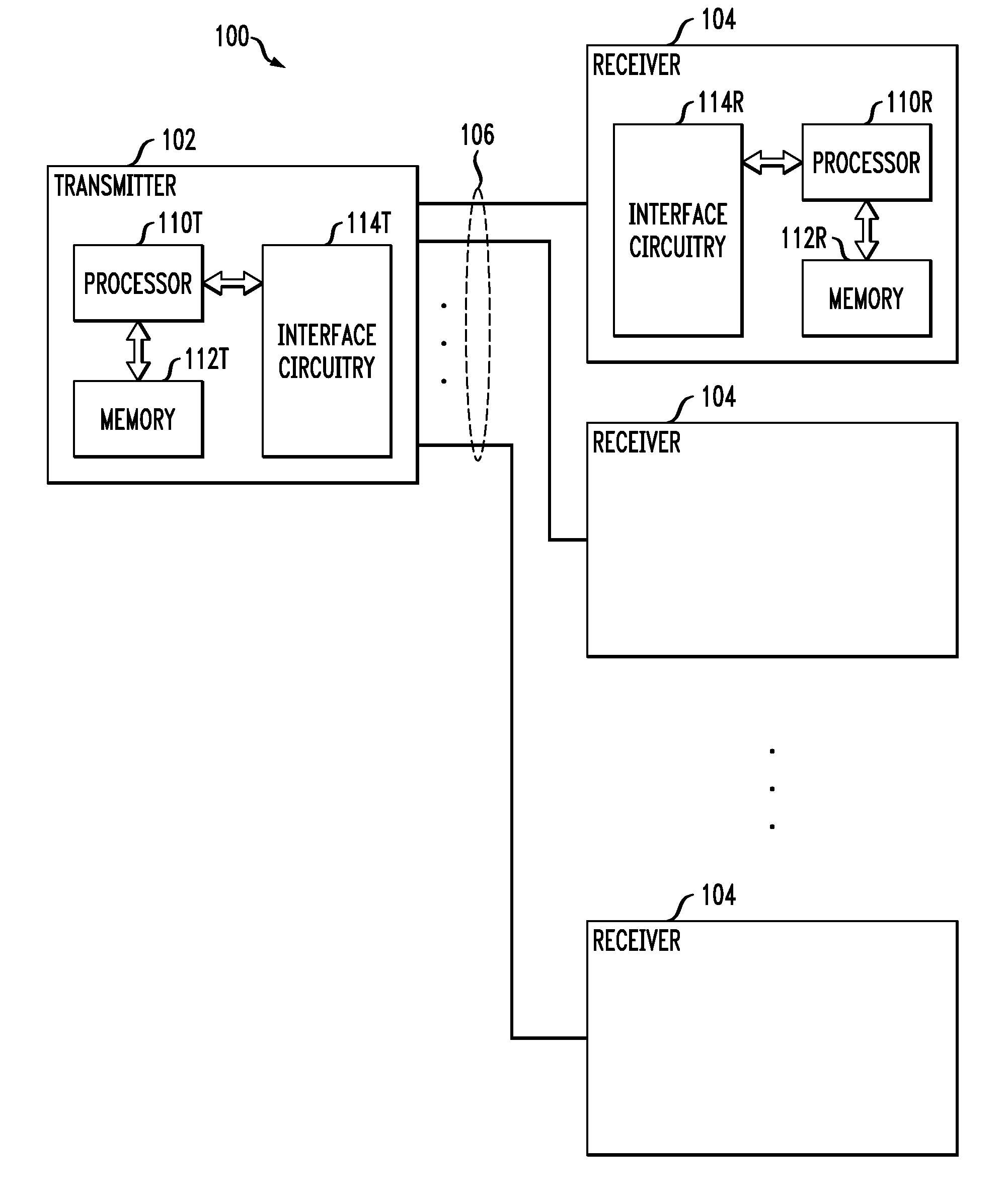
Channel equalization system and method
InactiveUS6904110B2Increase high performance and data rate capacityLow costMultiple-port networksChannel dividing arrangementsFiberEngineering
A system and method for delivering increases speed, security, and intelligence to wireline and wireless systems. The present invention increases channel capacity by using a parallel or multi-channel structure in such wireless and wireline at the edge or the core of. This new architecture of the present invention uses parallel bitstreams in a flexible way and distributed switching / routing technique, is not only to avoid the potential bottlenet of centralized switches, but also to increase speed with intelligence that is seamlessly integrating into the Fiber Optic Backbone such as WDM and SONET of the MAN / WAN network with a Real-time guarantees, different types of traffic (such as Stringent synchronous, isochronous, and asynchronous data messages) with different demands, and privacy & security of multi access and integrated services environment.
Owner:B C LEOW
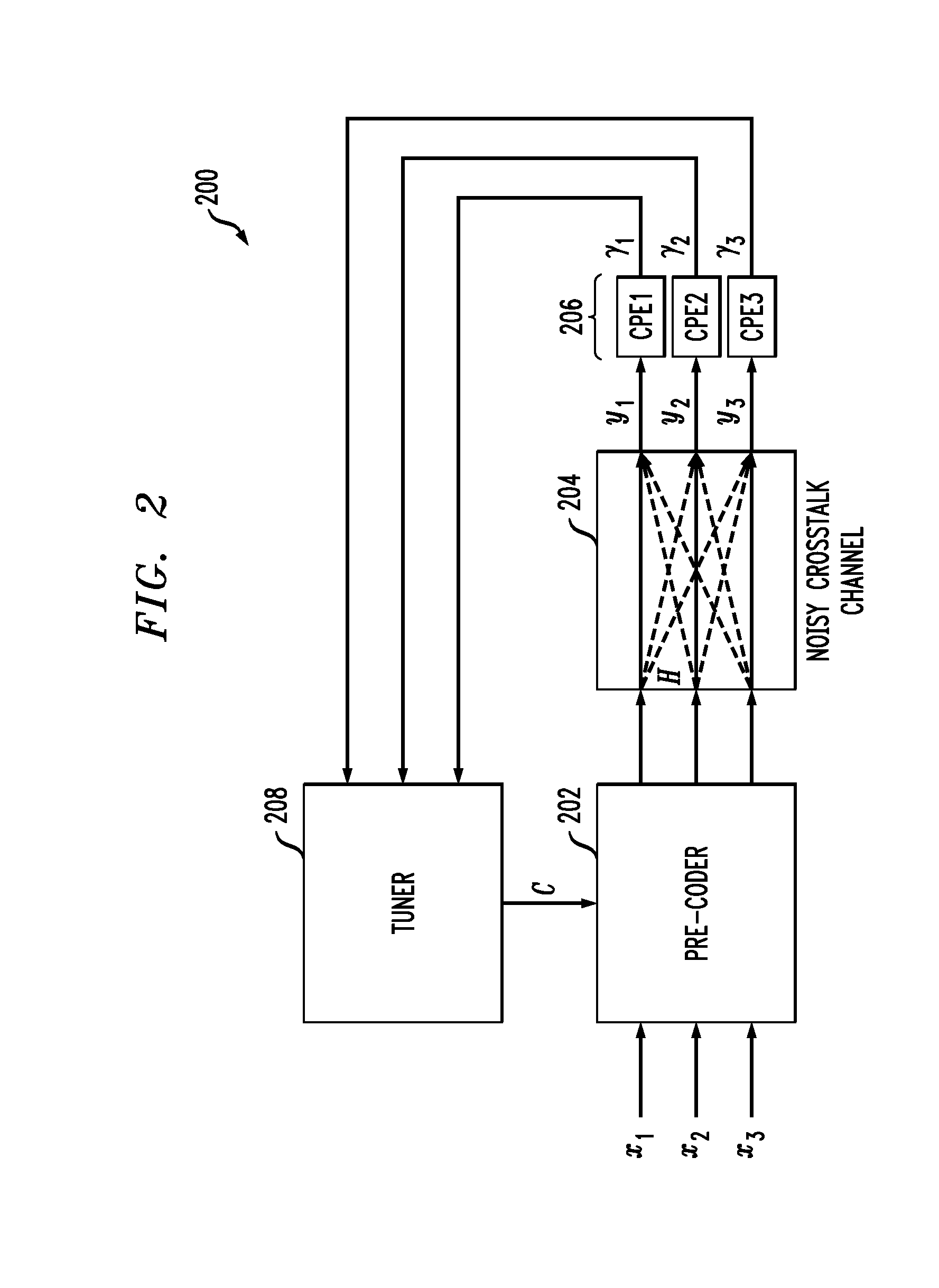
Channel adaptive equalization precoding system and method
InactiveUS20030086515A1Increase high performance and data rate capacityLow costChannel dividing arrangementsError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorPrecodingOperational system
A system and method for delivering increased speed, security, and intelligence to wireline and wireless systems. The present invention includes a new generation Fast Circuit Switch (packet / circuit) Communication processors and platform which enables a new Internet Exchange Networking Processor Architecture at the edge and core of every communication system, for next generation Web Operating System or Environment (WOE) to operate on with emphasis of a non-local processor or networking processor with remote web computing capabilities.
Owner:TRANS FRANCOIS +1
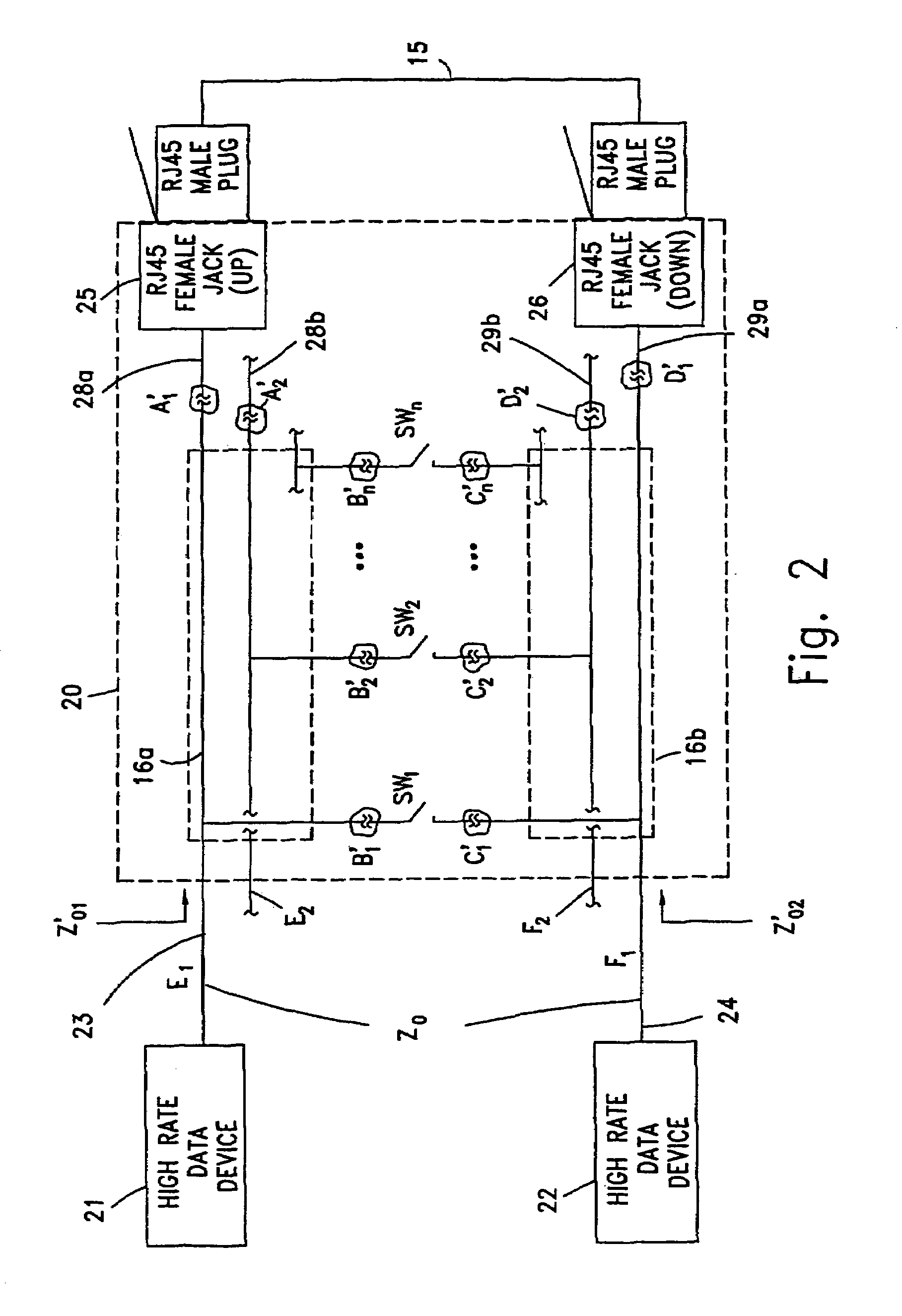
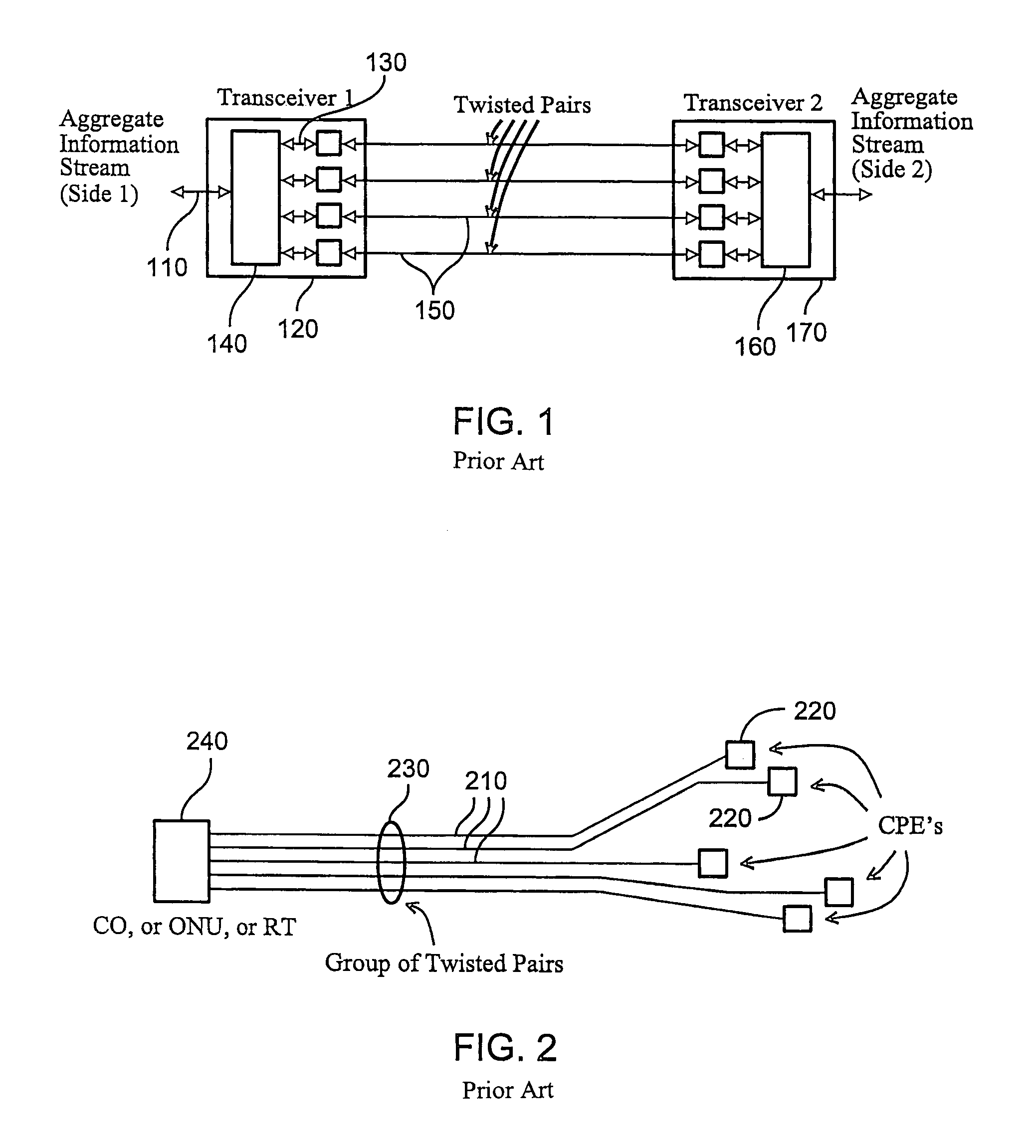
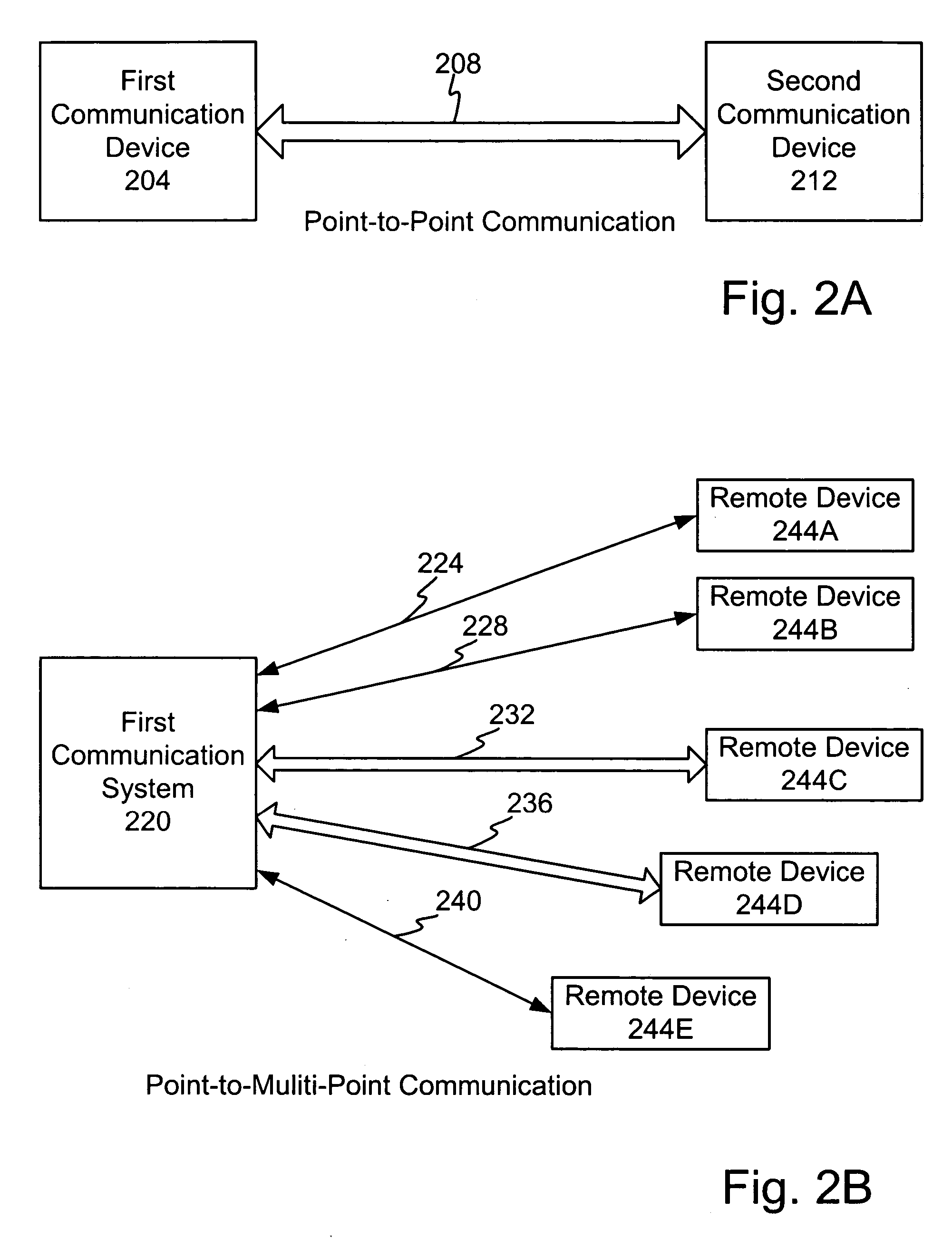
High data rate interconnecting device
InactiveUS7315224B2Minimize impedance mismatchConsiderable immunity to external interferenceCoupling for high frequencyPrinted circuit detailsData signalEngineering
An interconnect apparatus for providing a communication path for data signals in a predetermined frequency band, that includes a first and a second sections of a transmission line, connected at one end to first and second data transceiving devices, respectively. A switch, such as a mechanical, electro-mechanical, electronic, electro-magnetic and electro-optical switch, having conductive / non-conductive states, is provided for connecting / disconnecting between the other ends of the first and the second sections, for providing a data communication path between the data transceiving devices while being in its conductive state a third and a fourth sections of a transmission line, each of which connected at one end to a contact of the switch and at the other end to a first and a second connector, respectively. A compensation circuitry is provided for compensating, within the frequency band, parasitic effects caused by the switch and / or cord, while the switch is in its conductive state or, while the switch is in its non-conductive state and while a connection between the first and the second connectors is provided by a cord having predetermined characteristics, such that the compensation circuitry compensates the influence of parasitic effects introduced along the communication path by the switch while being in its non-conductive state and while the cord is a part of the communication path or, by the combination of the third and a fourth sections and the connectors while the switch is in its conductive state.
Owner:RIT TECHNOLOGIES
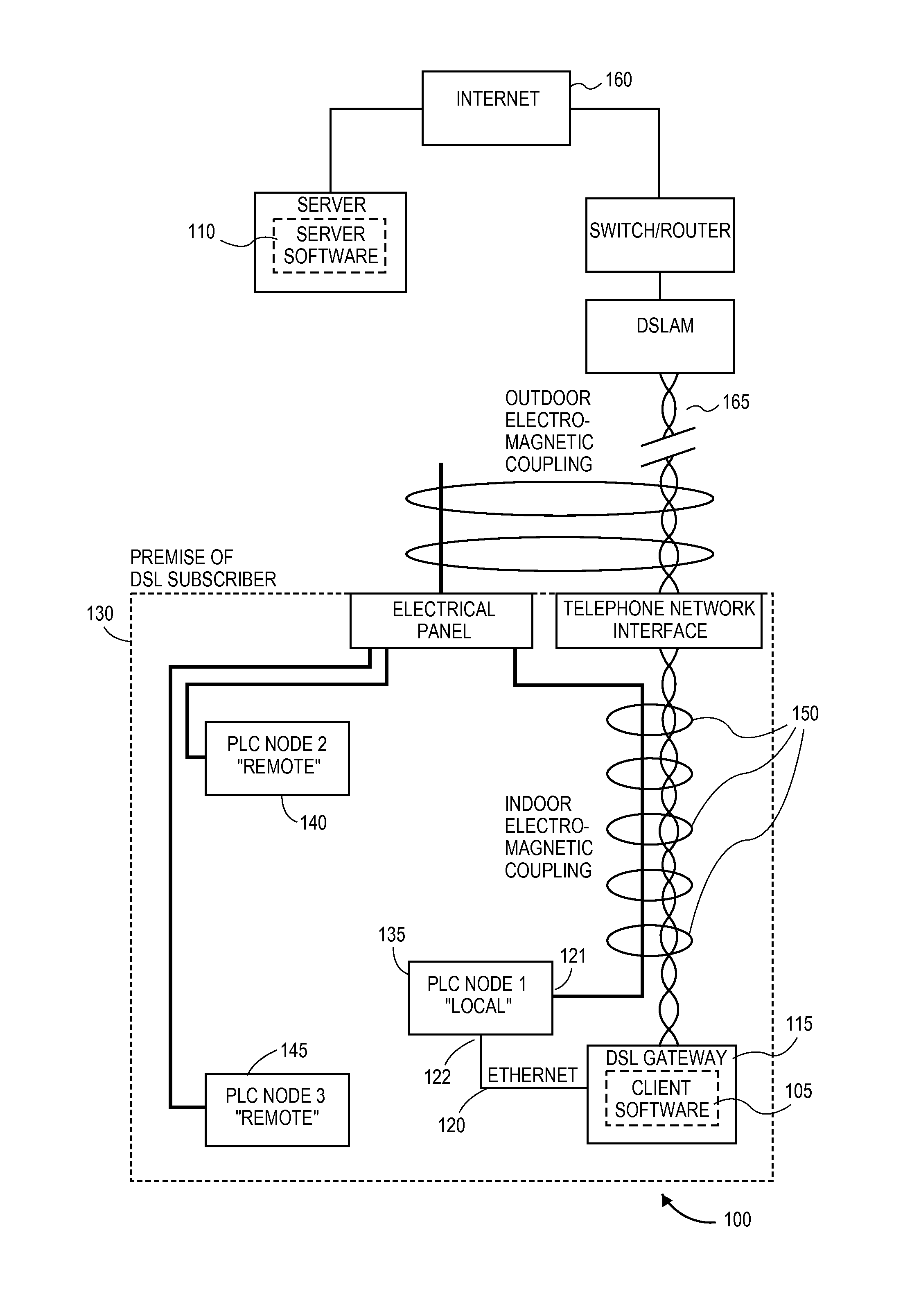
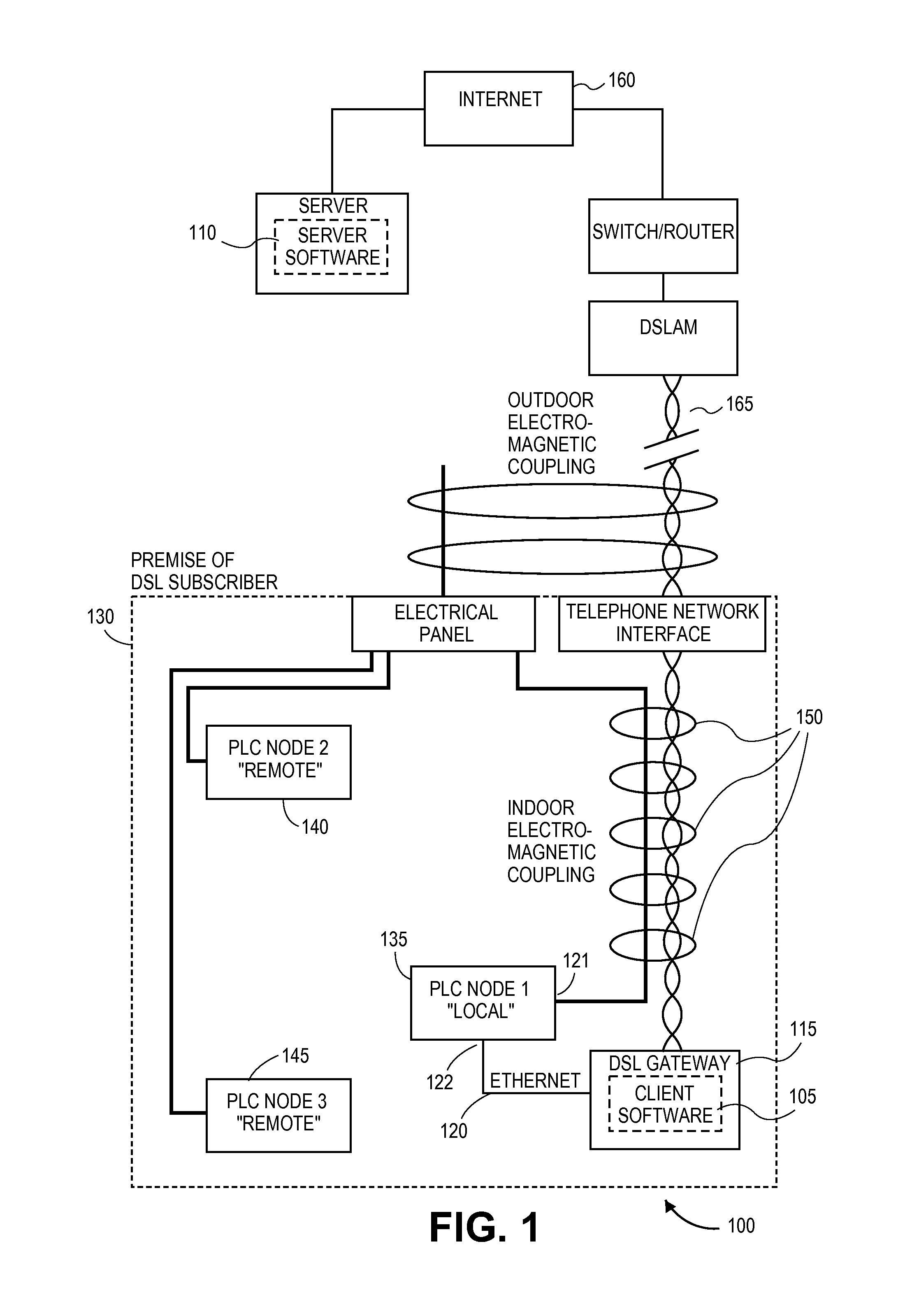
Method and apparatus for reducing the power of a signal electromagnetically coupled from a PLC medium to a DSL medium
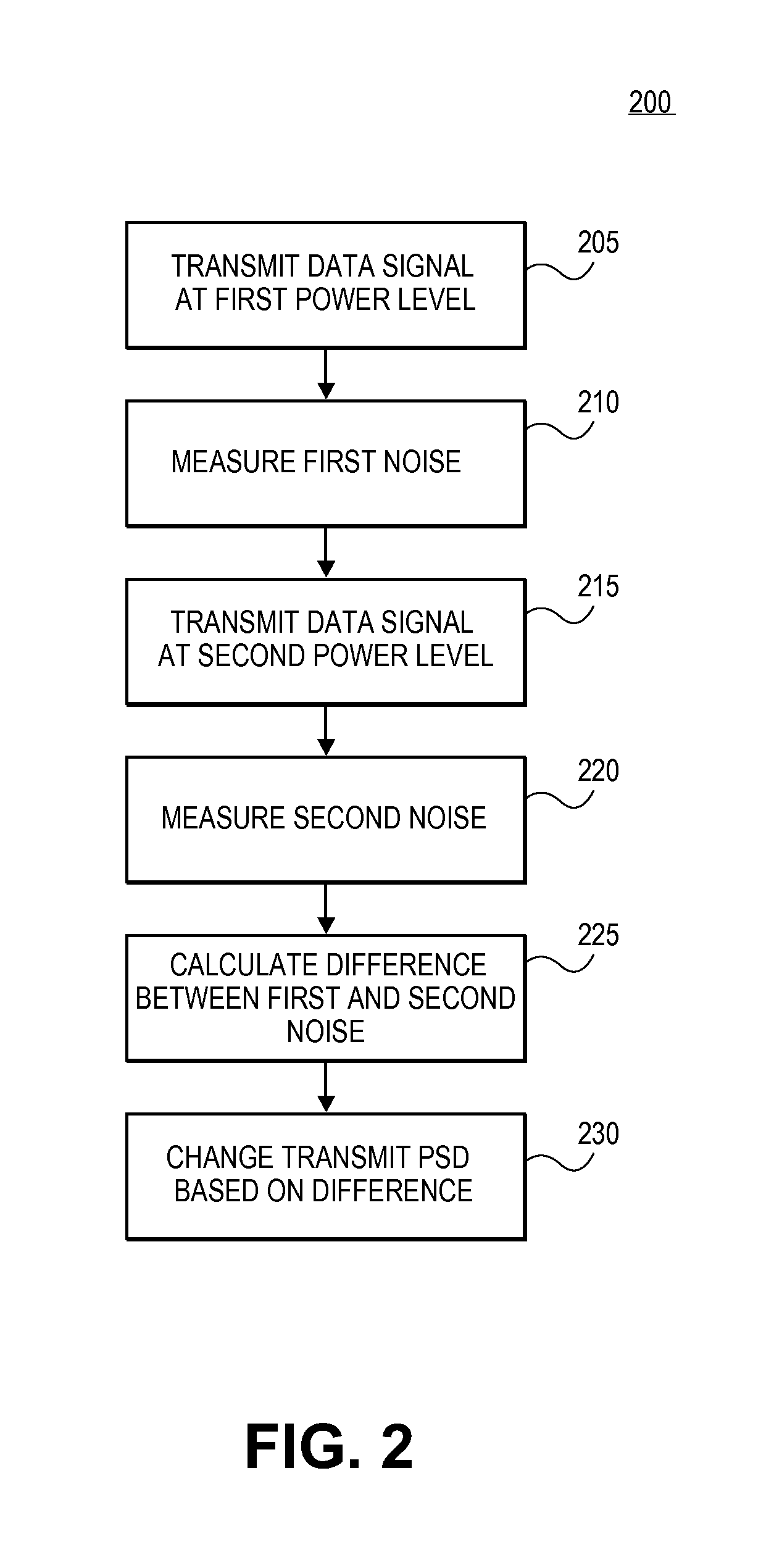
ActiveUS20140369430A1Reduce impactDecrease phenomenonPower managementSystems with measurements/testing channelsDigital subscriber lineTransmitted power
Reducing a power of a signal electromagnetically coupled from a PLC medium to a digital subscriber line (DSL) medium. The method involves transmitting a data signal over the PLC medium at a first average power level from one of a plurality of PLC transmitters coupled to the PLC medium, then measuring first noise associated with a first signal received at a DSL receiver coupled to the DSL communication medium caused at least in part by the data signal transmitted over the PLC medium at a second average power level from the one PLC transmitter, the second average power level different than the first average power level, followed by measuring second noise associated with a second signal received at the DSL receiver coupled to the DSL communication medium caused at least in part by the data signal transmission over the PLC medium at the second average power level. A transmit power spectral density (PSD) for the data signal transmitted by the one PLC transmitter over the PLC medium is then changed, based on a difference between the first noise and the second noise, such that the changed transmit PSD for the data signal transmitted by the one PLC transmitter over the PLC medium reduces the power of the signal electromagnetically coupled from the PLC medium to the DSL medium caused by the data signal transmission from the one PLC transmitter over the PLC medium.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
Method and device for transmission without crosstalk
ActiveUS7408426B2Simplifying the transmitting circuits and/or the receiving circuitsSimplification of the transmitting circuits and/or the receiving circuitsReliability increasing modificationsDc network circuit arrangementsElectrical conductorInterconnection
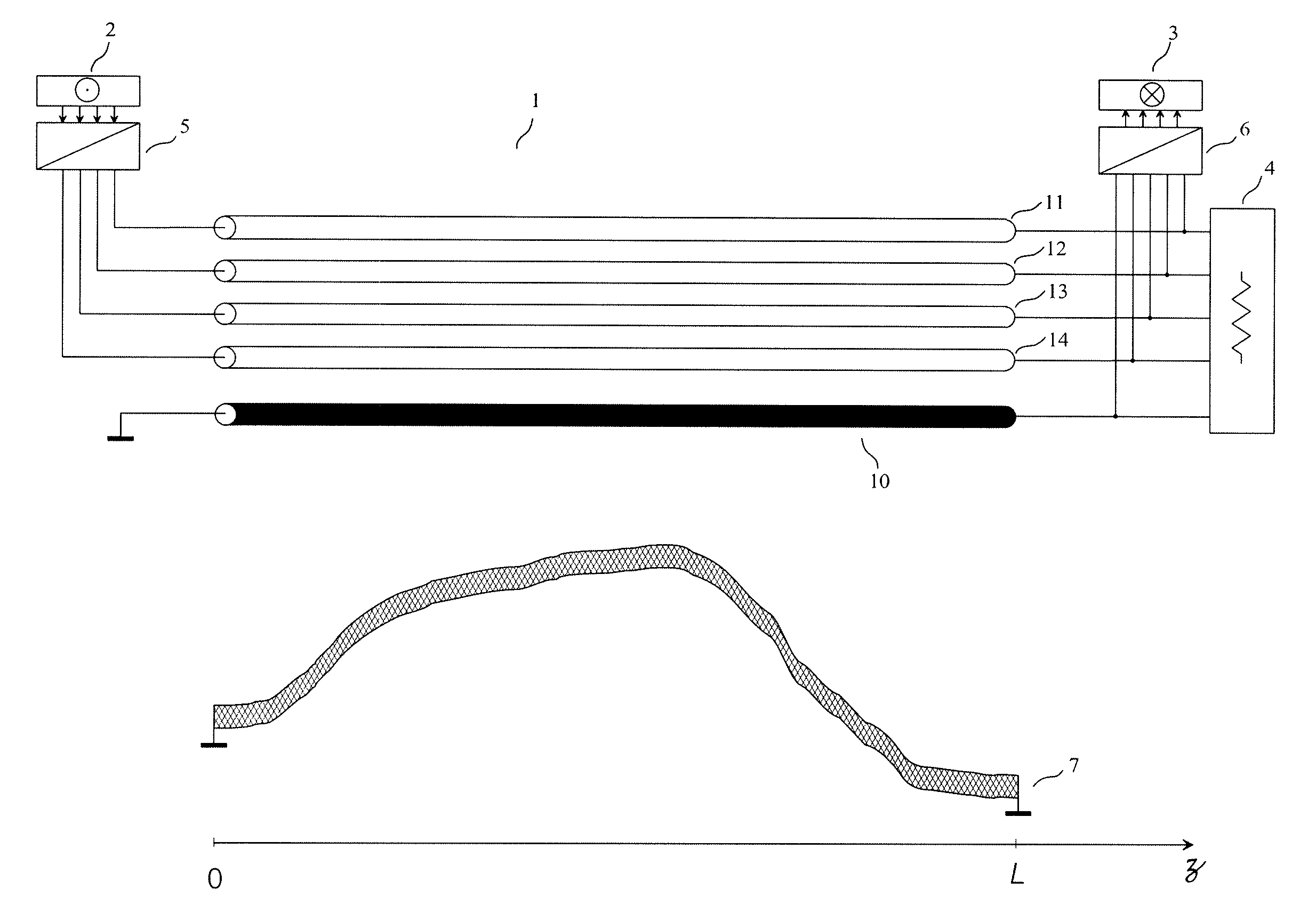
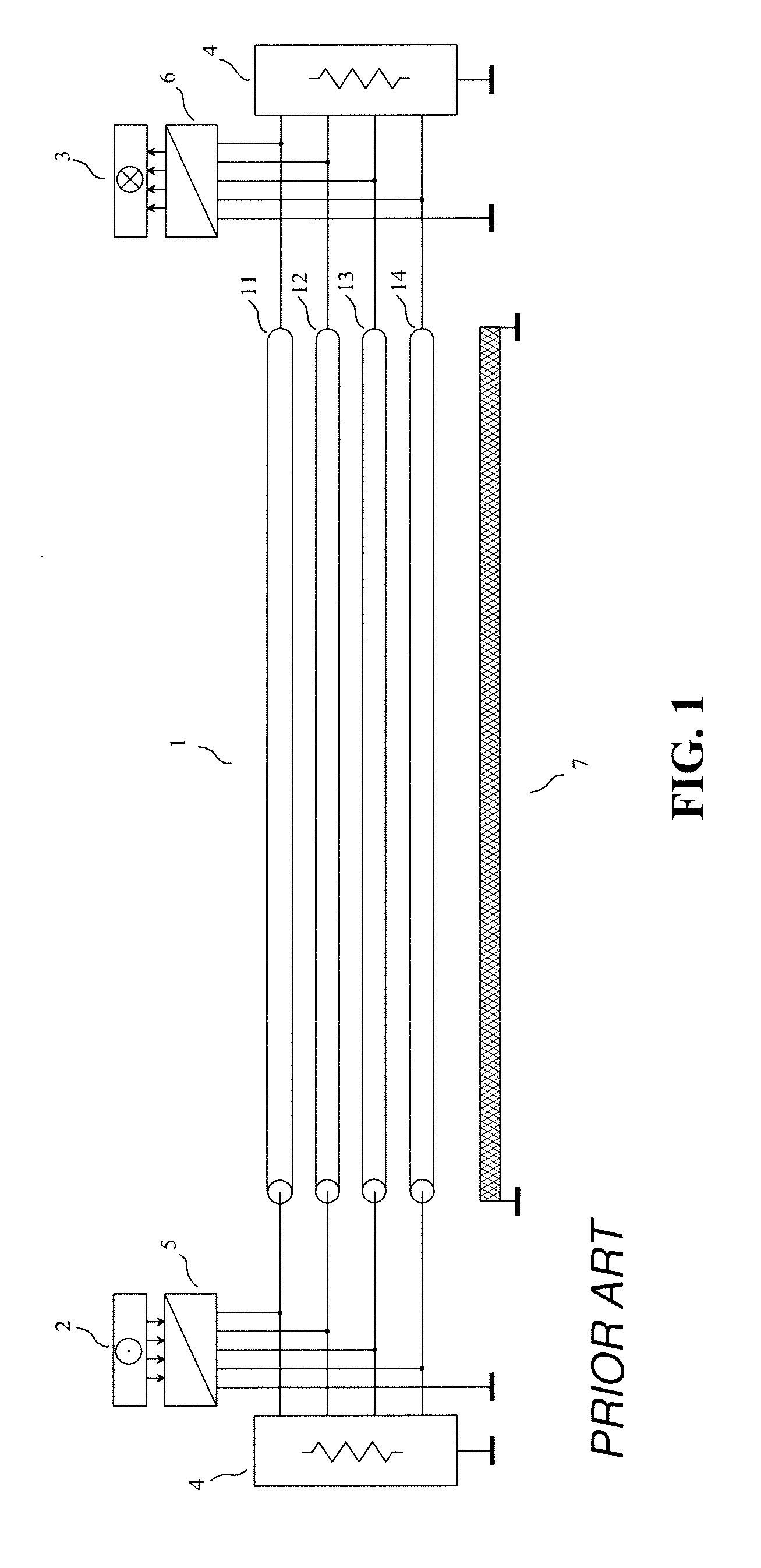
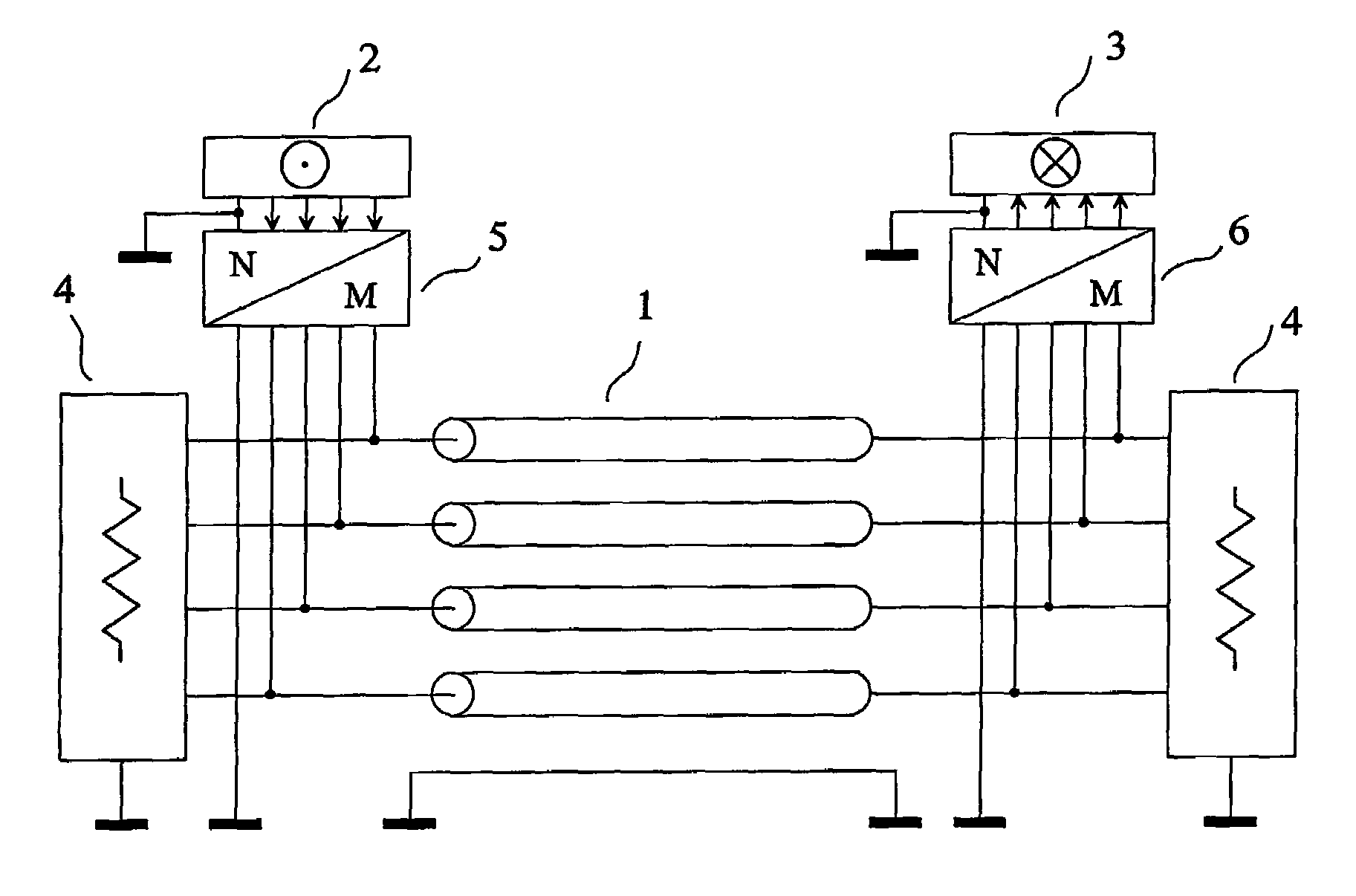
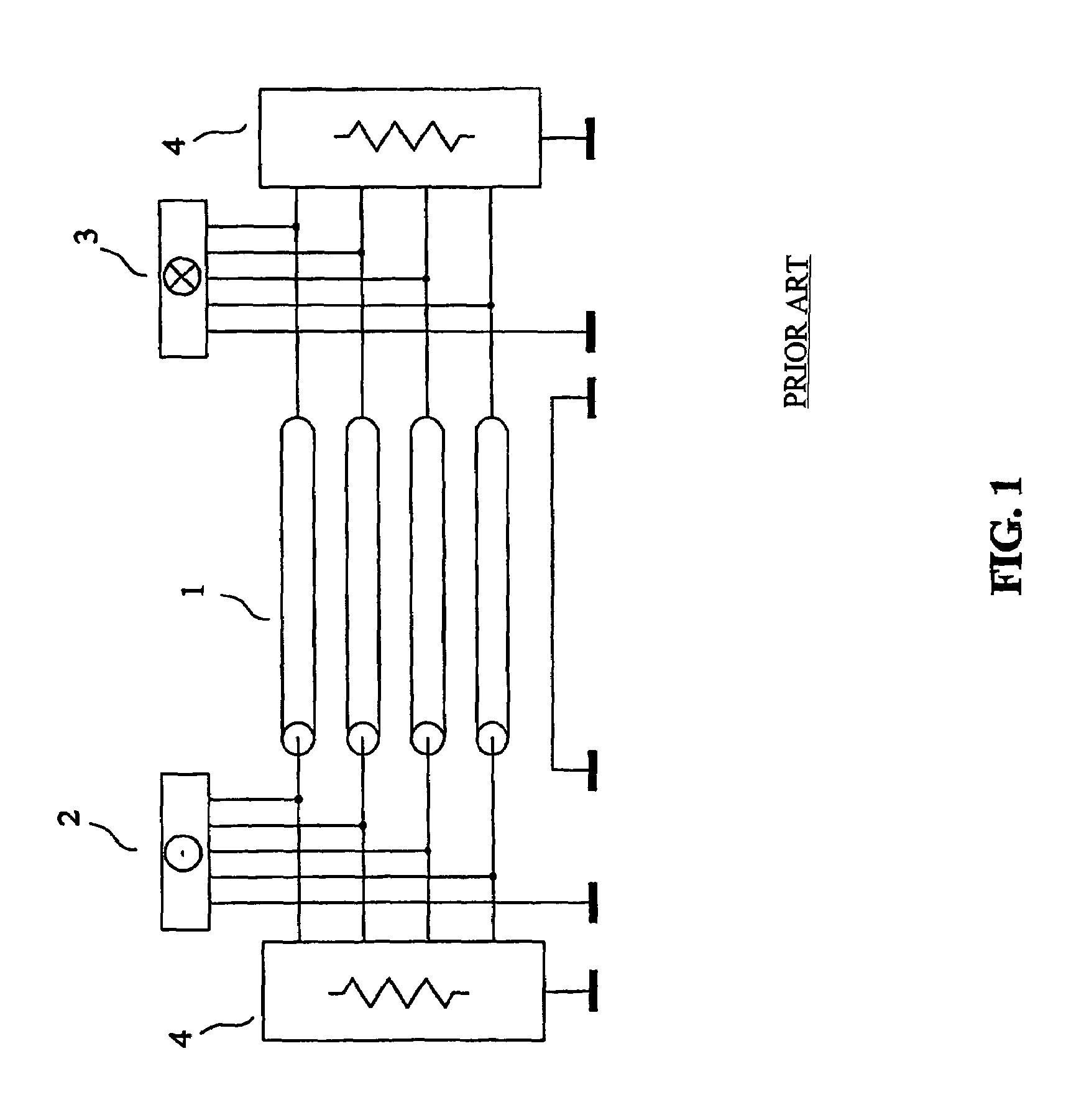
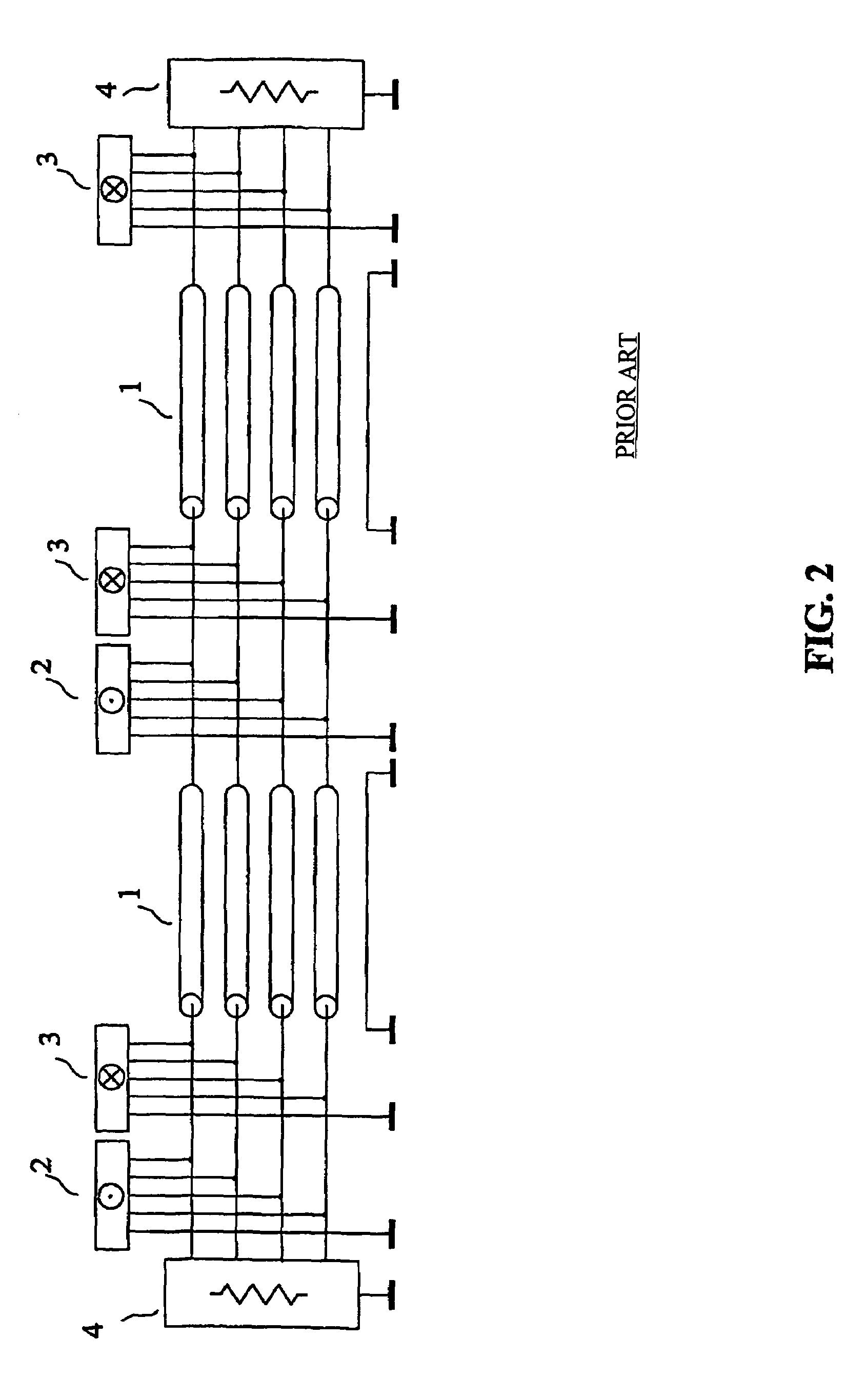
The invention relates to a method and a device for transmission without crosstalk in interconnections used for sending a plurality of signals, such as the interconnections made with flat multiconductor cables, or with the tracks of a printed circuit board, or inside an integrated circuit. An interconnection with four parallel transmission conductors plus a reference conductor has each of its ends connected to a termination circuit. The transmitting circuit receives at its input the signals of the four channels of the source and its output terminals are connected to the conductors of the interconnection. The receiving circuit(s) input terminals are connected to the conductors of the interconnection, and its four output channels are connected to the destination. The signals of the four channels of an active source are sent to the four channels of the destination, without noticeable crosstalk.
Owner:S AQUA SEMICONDUCTOR LLC
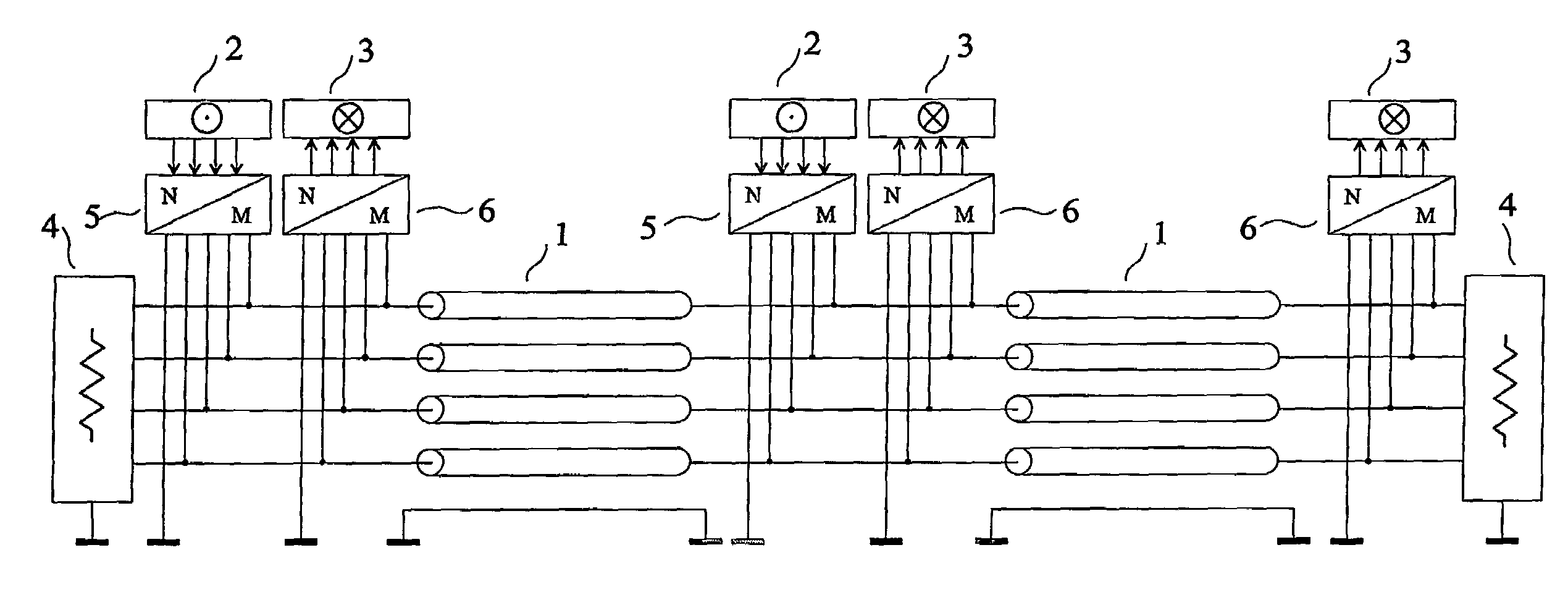
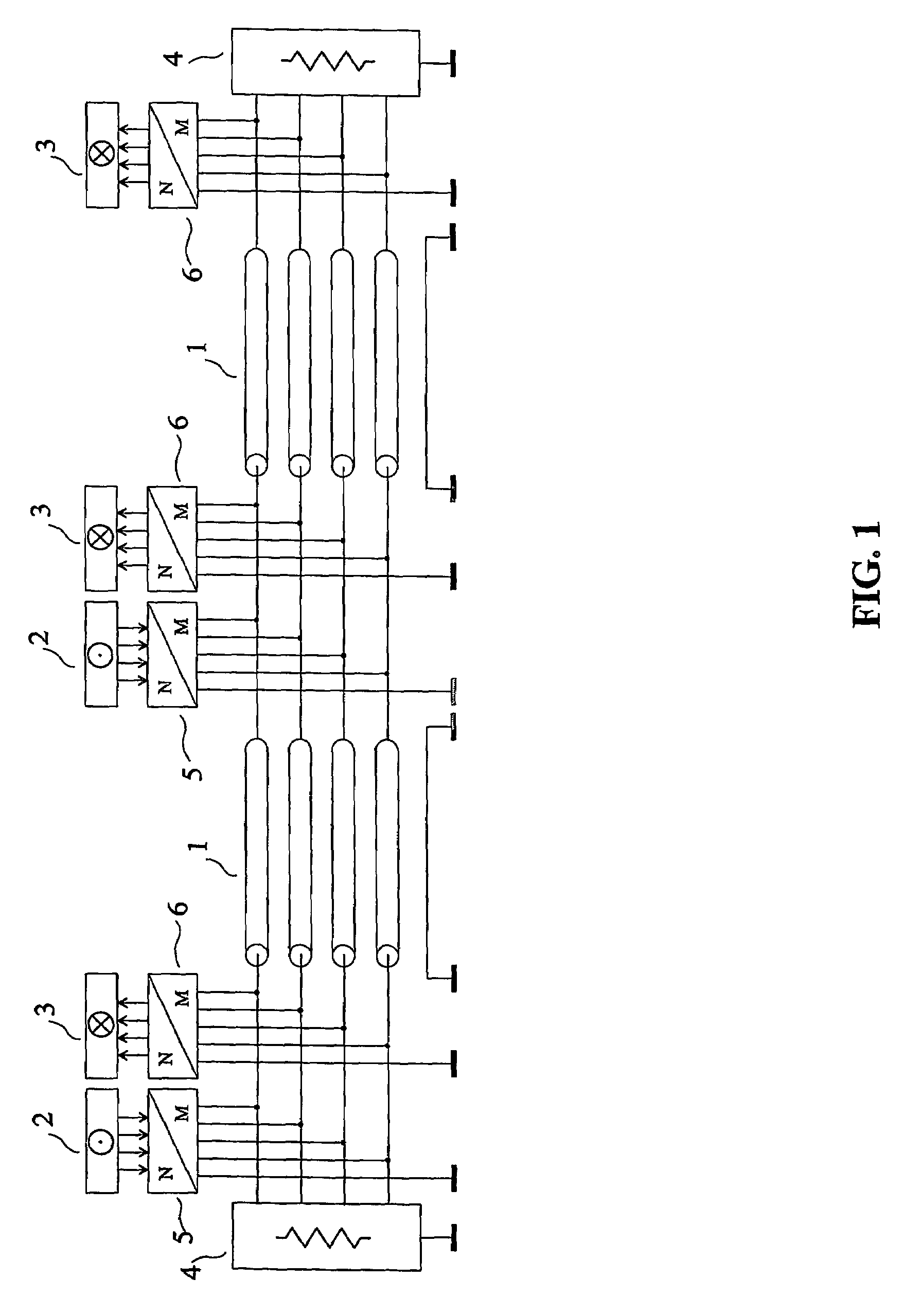
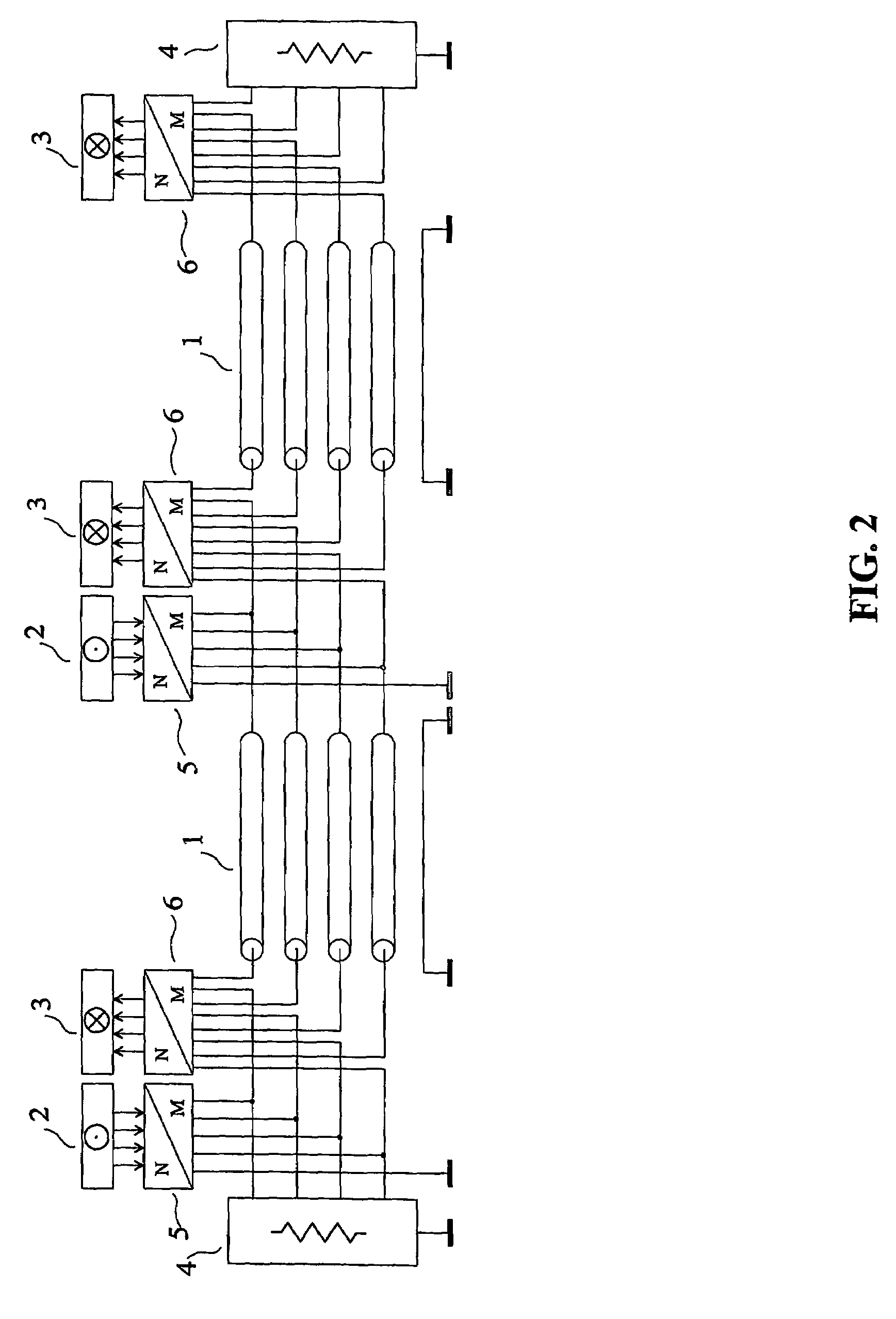
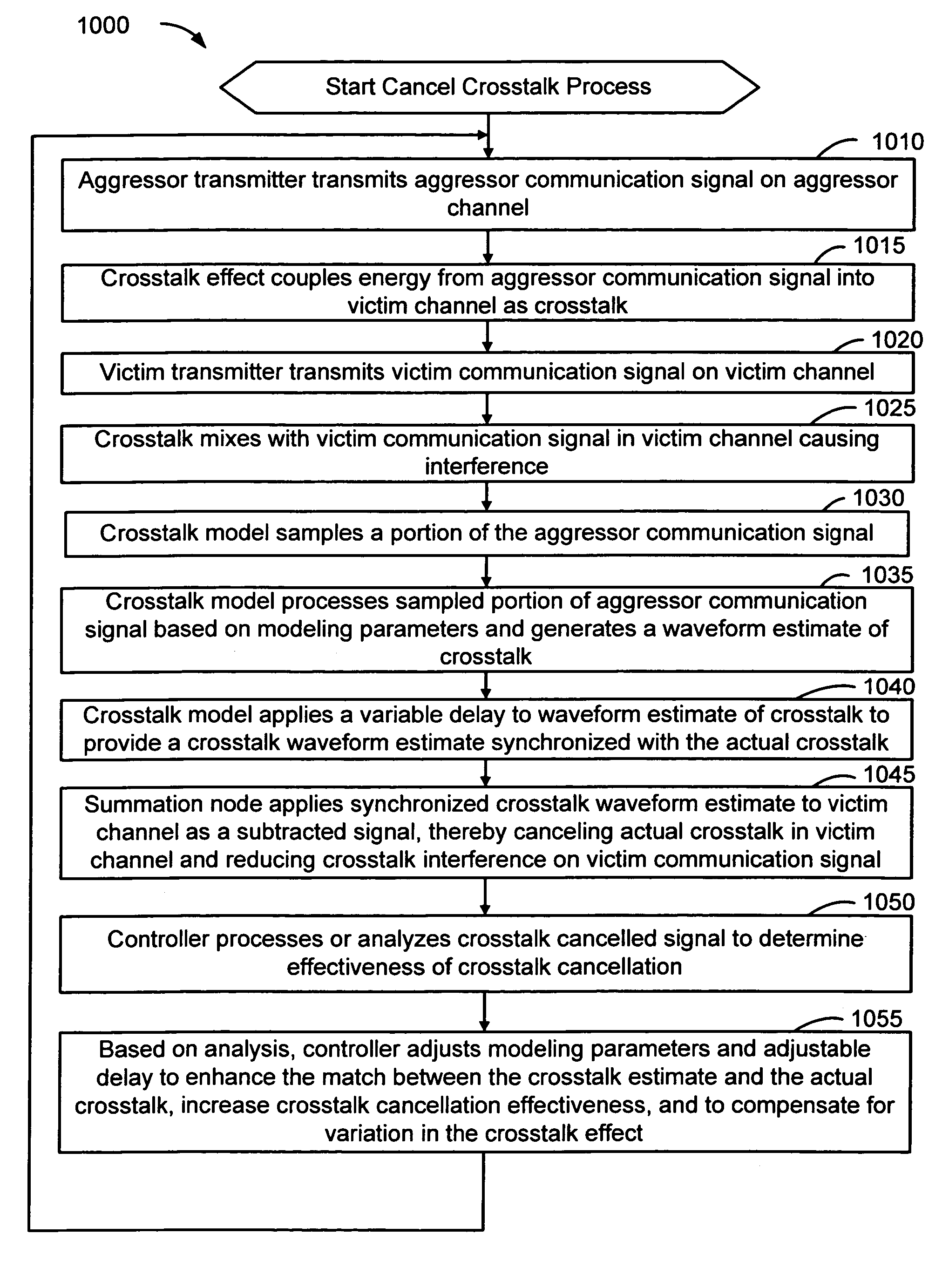
Method and system for crosstalk cancellation
ActiveUS7050388B2Improve signal qualityHigh bandwidthFrequency-division multiplex detailsCross-talk reductionCrosstalk cancellationElectrical and Electronics engineering
Signals propagating in one communication channel can generate crosstalk interference in another communication channel. A crosstalk cancellation device can process the signals causing the crosstalk interference and generate a crosstalk cancellation signal that can compensate for the crosstalk when applied to the channel receiving crosstalk interference. The crosstalk cancellation device can include a model of the crosstalk effect that generates a signal emulating the actual crosstalk both in form an in timing. The crosstalk cancellation device can include a controller that monitors crosstalk-compensated communication signals and adjusts the model to enhance crosstalk cancellation performance. The crosstalk cancellation device can have a mode of self configuration or calibration in which defined test signals can be transmitted on the crosstalk-generating channel and the crosstalk-receiving channel.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Method for pseudo-differential transmission using modal electrical variables
InactiveUS8049576B2Reduce reflectivityReduce reflectionMultiple-port networksCross-talk reductionElectrical conductorDifferential transmission
The invention relates to a method and a device for pseudo-differential transmission in interconnections used for sending a plurality of electrical signals.The ends of an interconnection having 4 transmission conductors and a return conductor distinct from the reference conductor are each connected to a termination circuit. Three damping circuits are connected between the return conductor and the reference conductor. The transmitting circuits receive at their inputs the signals from the 4 channels of the two sources, and are connected to the conductors of the interconnection. A transmitting circuit in the activated state produces modal electrical variables, each modal electrical variable being allocated to one and only one channel. The receiving circuits are connected to the conductors of the interconnection, each receiving circuit being such that the 4 channels of a source connected to a transmitting circuit in the activated state are sent to the four channels of the destinations, without noticeable echo, internal crosstalk and external crosstalk.
Owner:ZXNOISE LLC
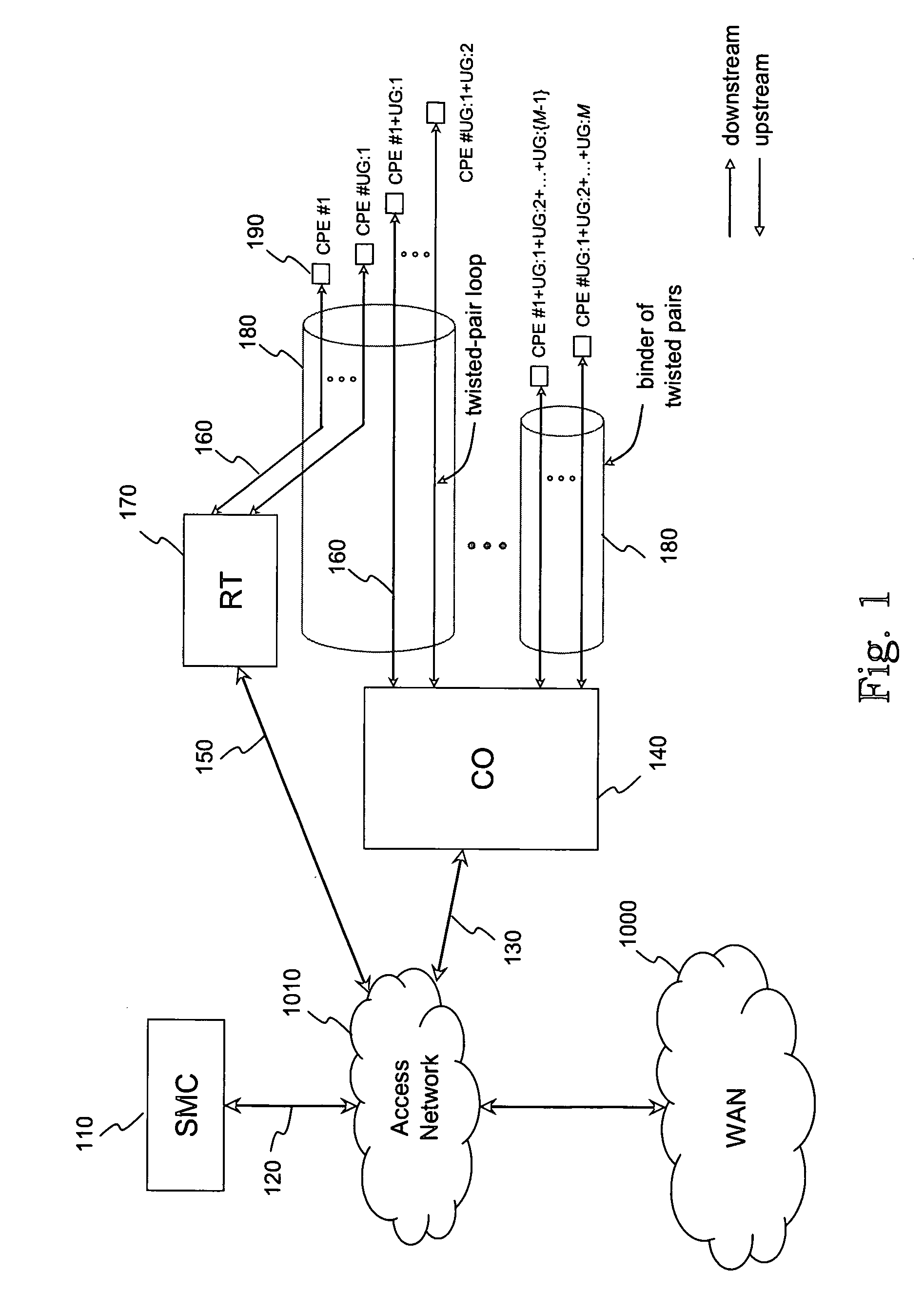
DSL system estimation and parameter recommendation
ActiveUS20050123027A1Improve performanceError preventionModulated-carrier systemsCarrier signalEngineering
Estimates of a communication system configuration, such as a DSL system, are based on operational data collected from a network element management system, protocol, users and / or the like. The operational data collected from the system can include performance-characterizing operational data that typically is available in an ADSL system via element-management-system protocols. Generated estimates and / or approximations can be used in evaluating system performance and directly or indirectly dictating / requiring changes or recommending improvements in operation by transmitters and / or other parts of the communication system. Data and / or other information may be collected using “internal” means or may be obtained from system elements and components via email and / or other “external” means. The likelihood of a model's accuracy can be based on various data, information and / or indicators of system performance, such as observed normal operational data, test data and / or prompted operational data that shows operating performance based on stimulation signals. One example of such prompted data uses frequency carrier masks to approximate the Hlog of a given channel, including information regarding bridged taps, attenuation, etc.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
Enhanced communication connector assembly with crosstalk compensation
InactiveUS6186834B1Substations coupling interface circuitsCoupling for high frequencyMating connectionCapacitance
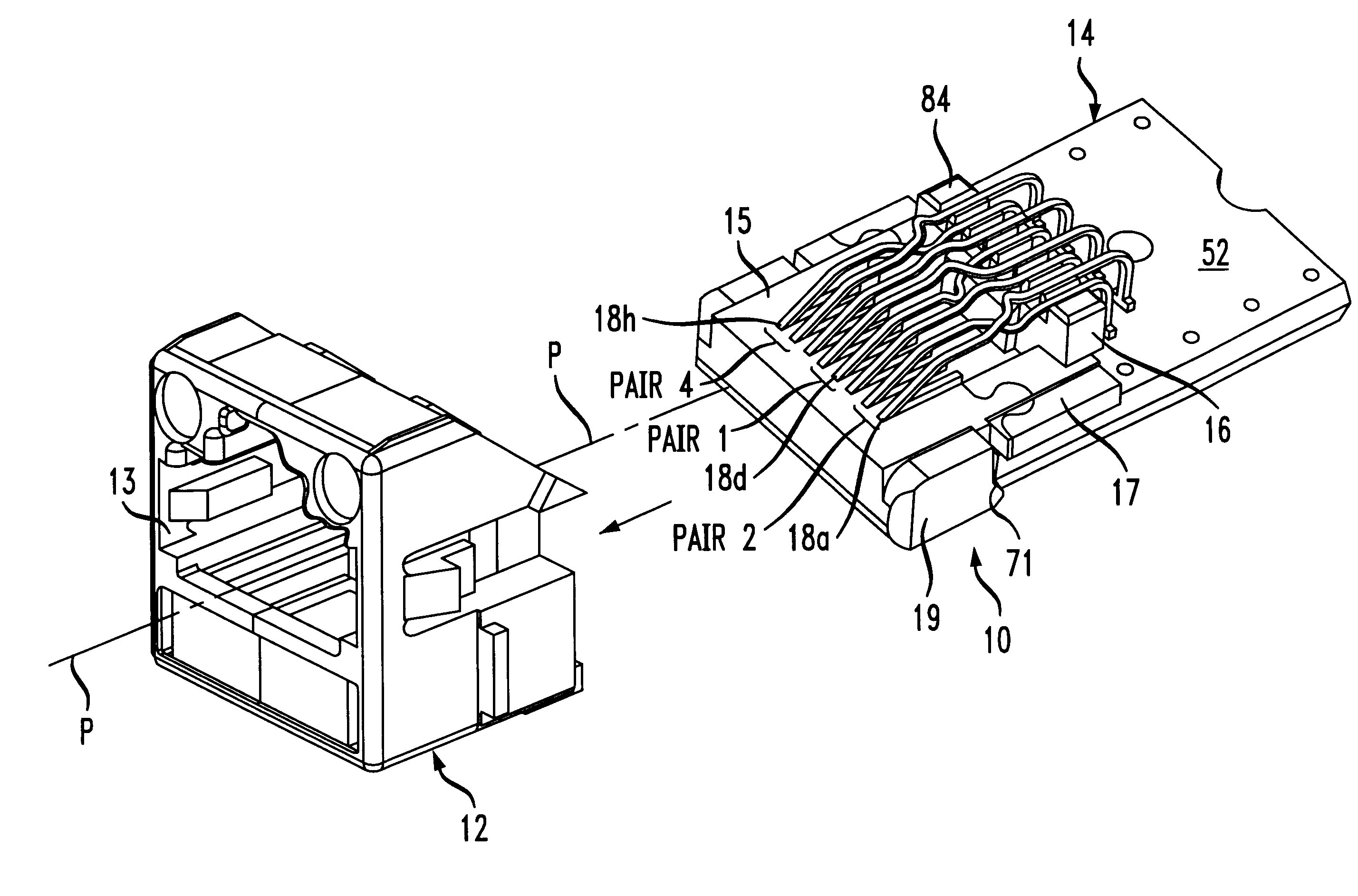
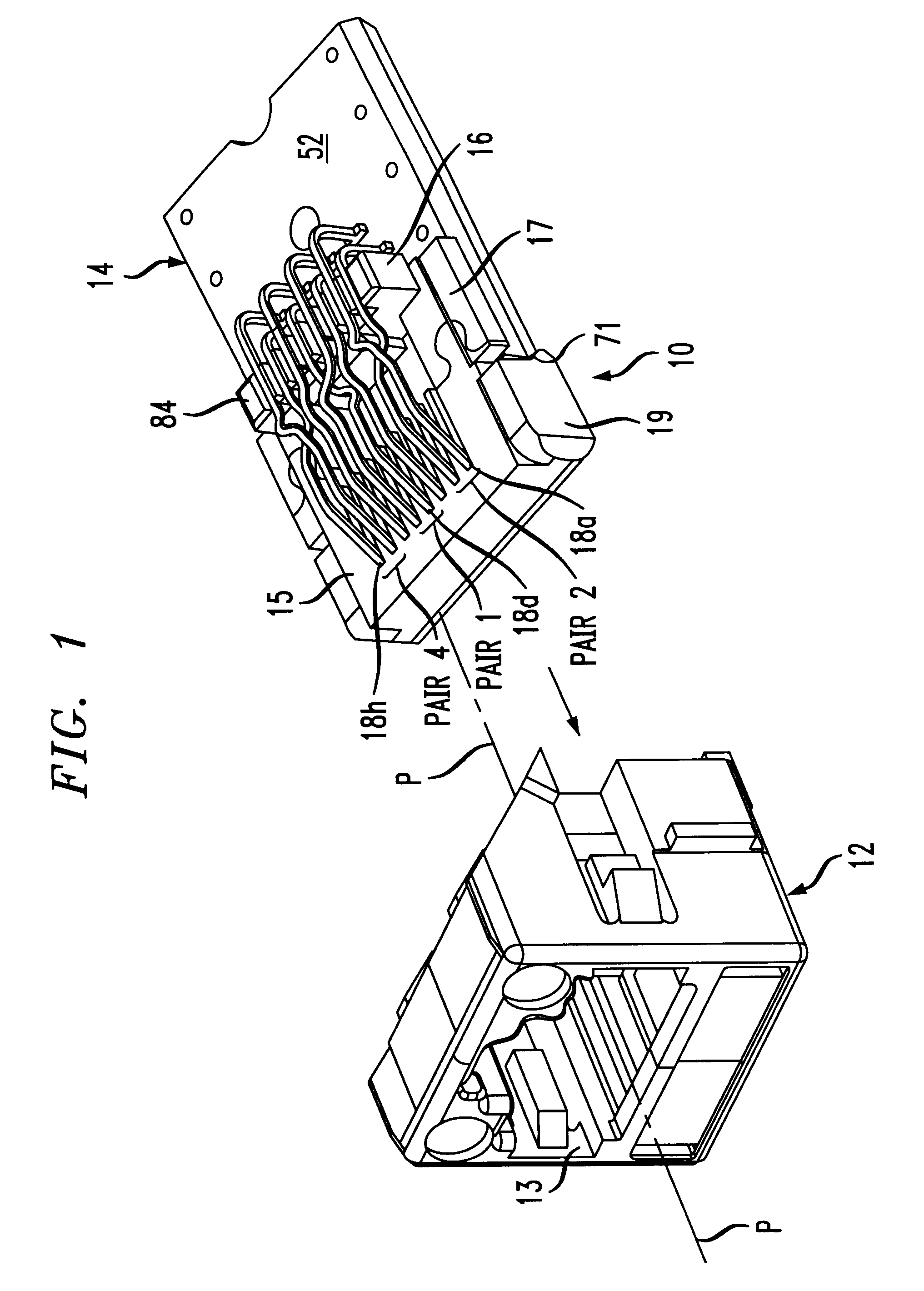
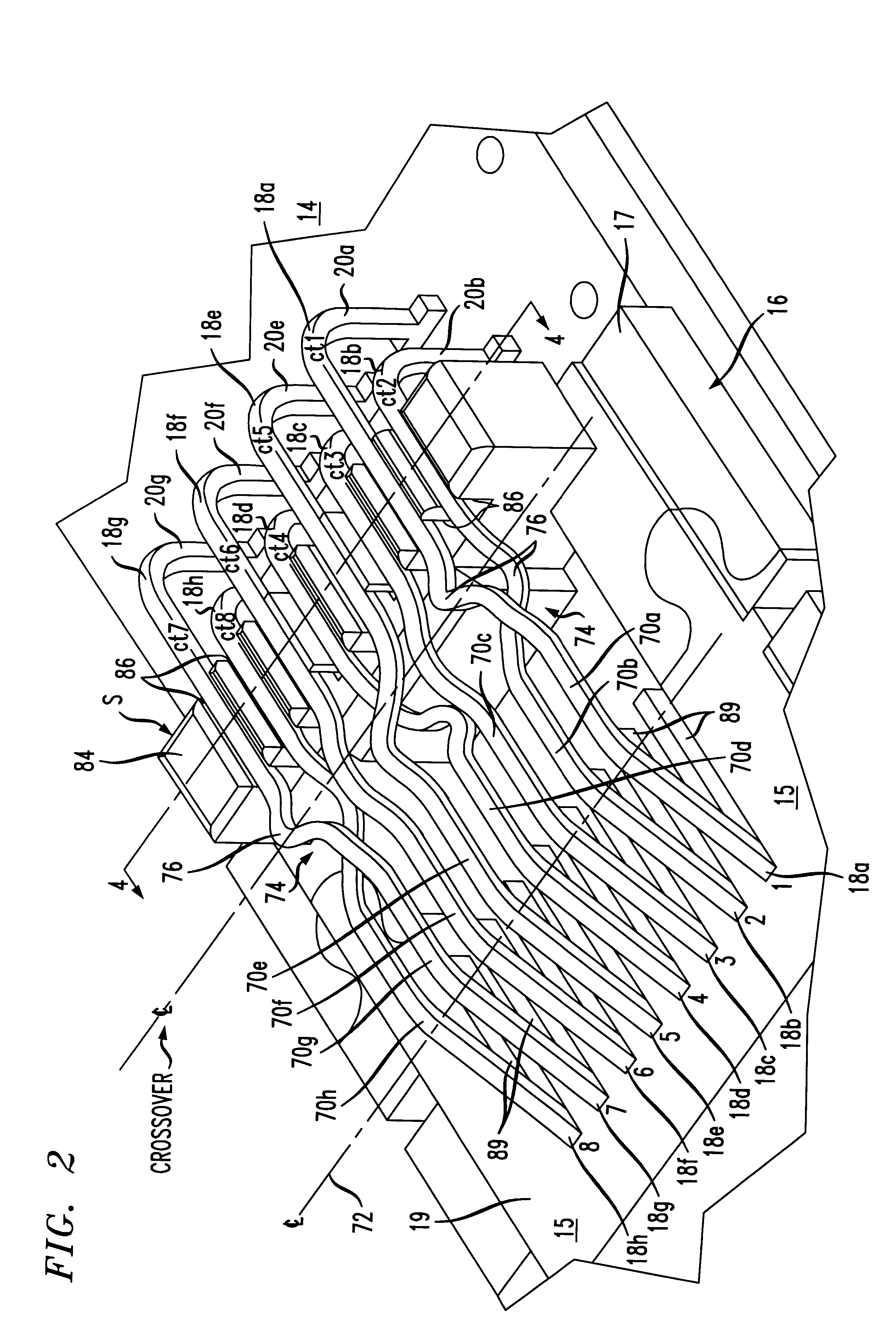
An enhanced communication connector assembly capable of meeting Category 6 performance levels with respect to near end crosstalk (NEXT), when the assembly is connected to a mating connector. The assembly includes a wire board, and a number of elongated terminal contact wires with base portions that are supported on the board. The contact wires have free end portions opposite the base portions for making electrical contact with a mating connector. A crosstalk compensating device on the wire board is constructed and arranged to cooperate with sections of selected terminal contact wires to provide capacitive compensation coupling between the selected terminal contact wires, when the contact wires are engaged by the mating connector.
Owner:COMMSCOPE INC
Active resistive summer for a transformer hybrid
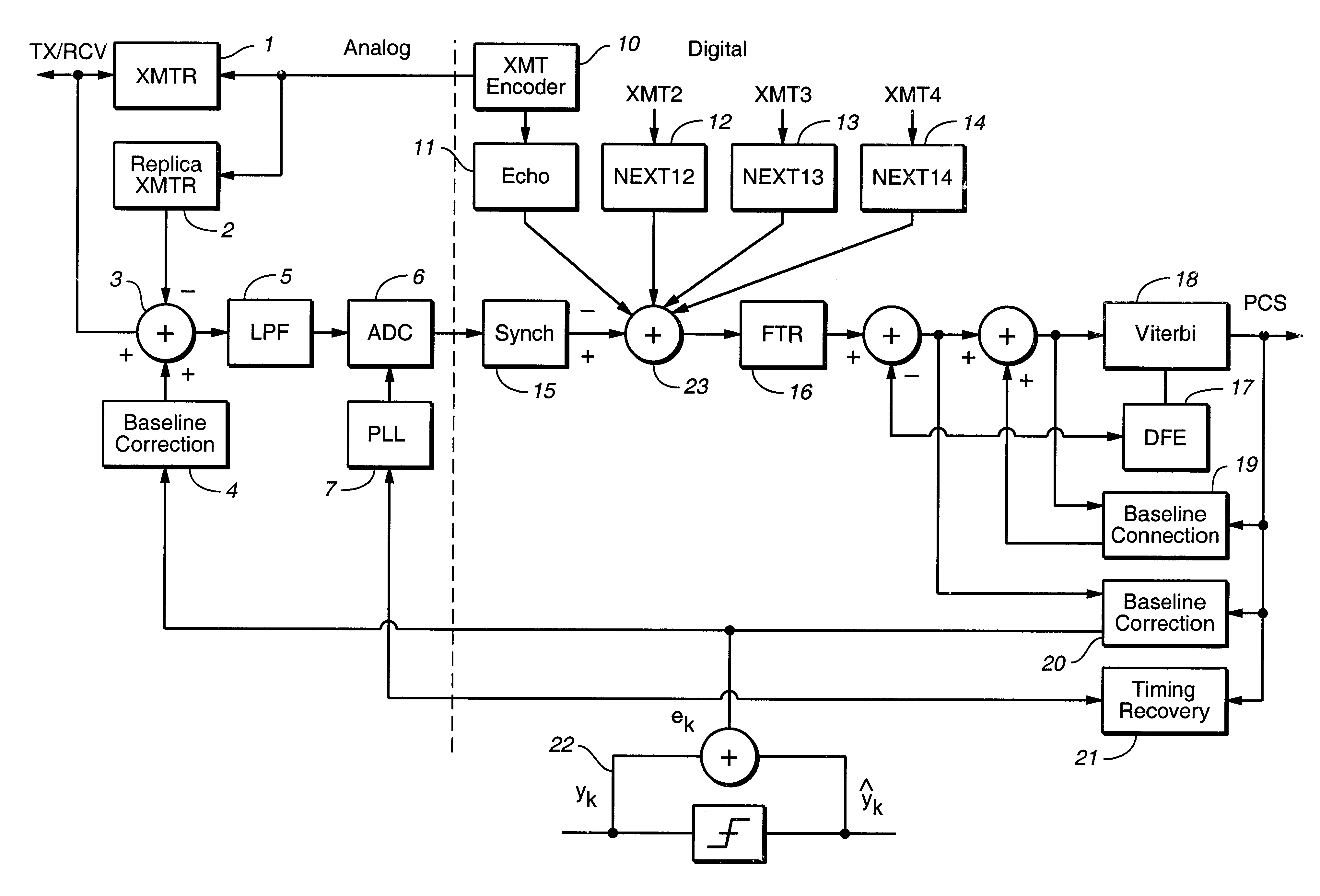
An electrical circuit in a communications channel is provided. The electrical circuit includes an active resistive summer. The active resistive summer has a composite signal as an input. The composite signal includes a transmission signal component and a receive signal component. A replica transmission signal is also an input to the active resistive summer. The active resistive summer includes the receive signal component as an output.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Distributed coexistence system for interference mitigation in a single chip radio or multi-radio communication device
ActiveUS20100137025A1Reduce distractionsAvoid interferenceCross-talk reductionSubstation equipmentTransceiverRadio reception
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of distributed coexistence for mitigating interference in a single chip radio and / or a multi-radio (i.e. multi-transceiver) communications device. The invention enables coexistence ‘friendly’ radio IPs having frequency agility in that they are capable of shifting their clock frequencies thereby avoiding frequency bands of potential victim radios. Frequency agility on the aggressor radio side (rather than by mitigating the effect of interference on the victim radio side) prevents harmonics from the aggressor's clock scheme from falling in the operating frequency band of the victim radio, and in turn causing degradation to its performance. Each aggressor radio, based on information received from other radios, configures the root clock frequency of its RX and / or TX chain clock generation circuits.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
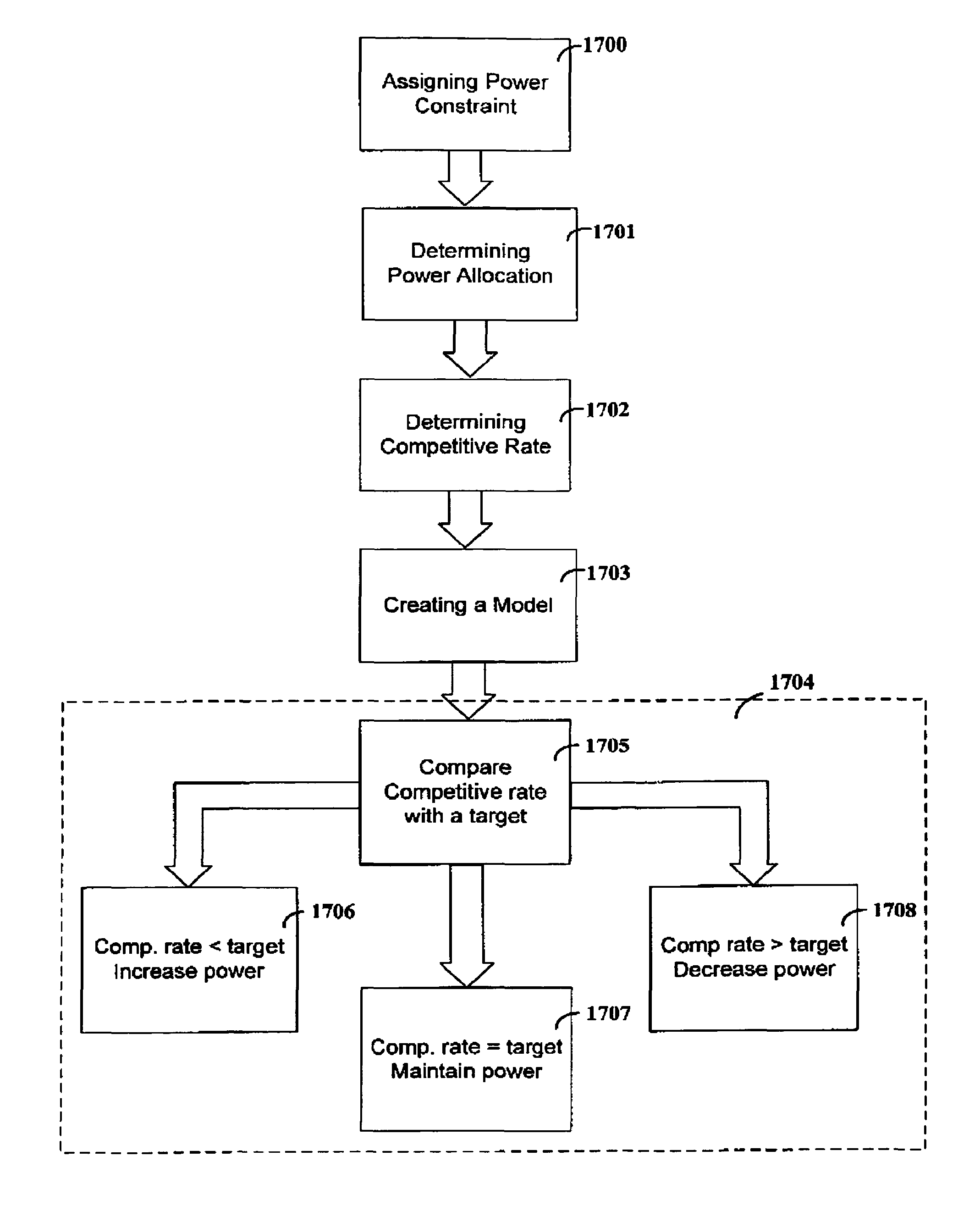
Dynamic digital communication system control
InactiveUS7158563B2Improve performanceMinimize impactError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemControl system
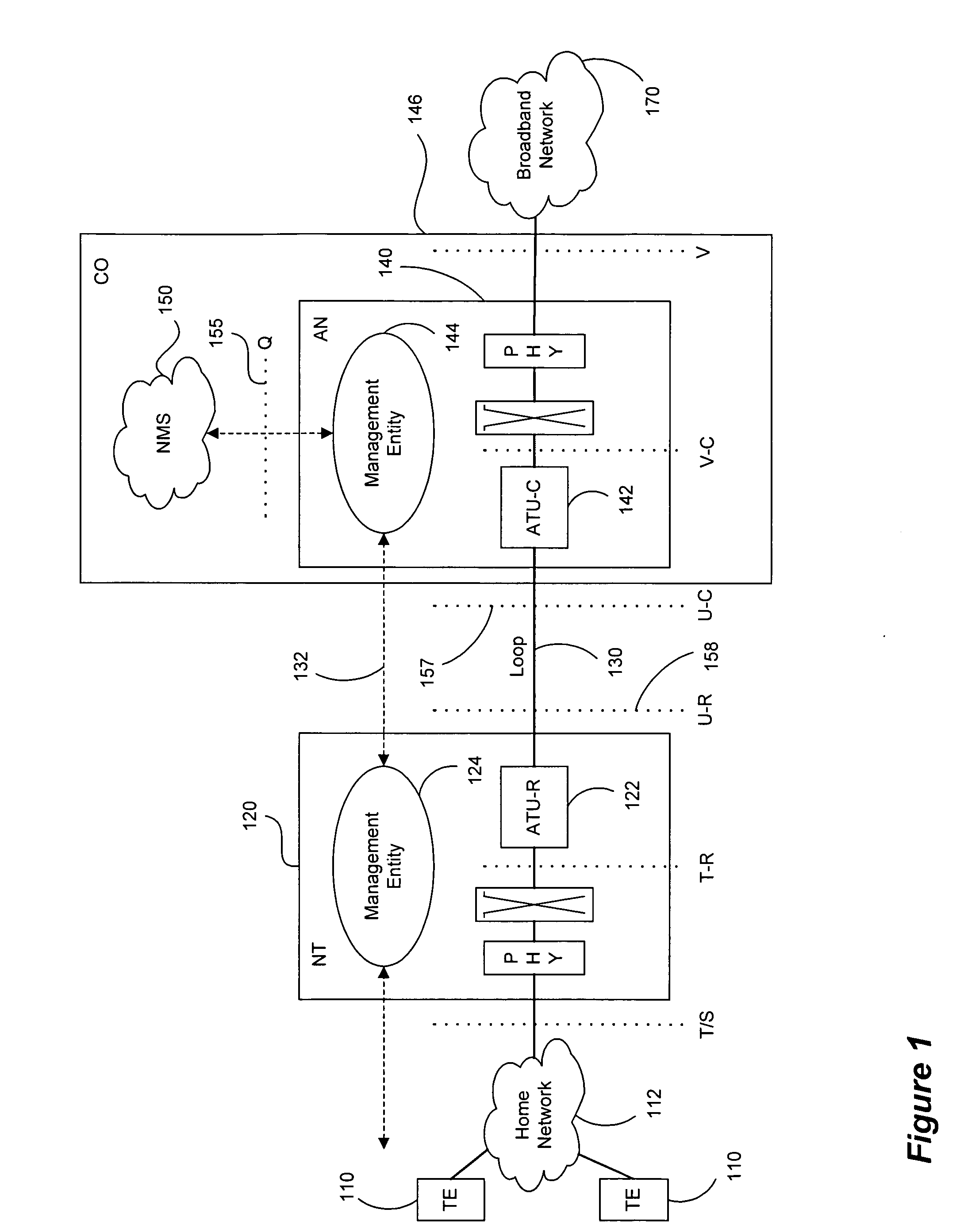
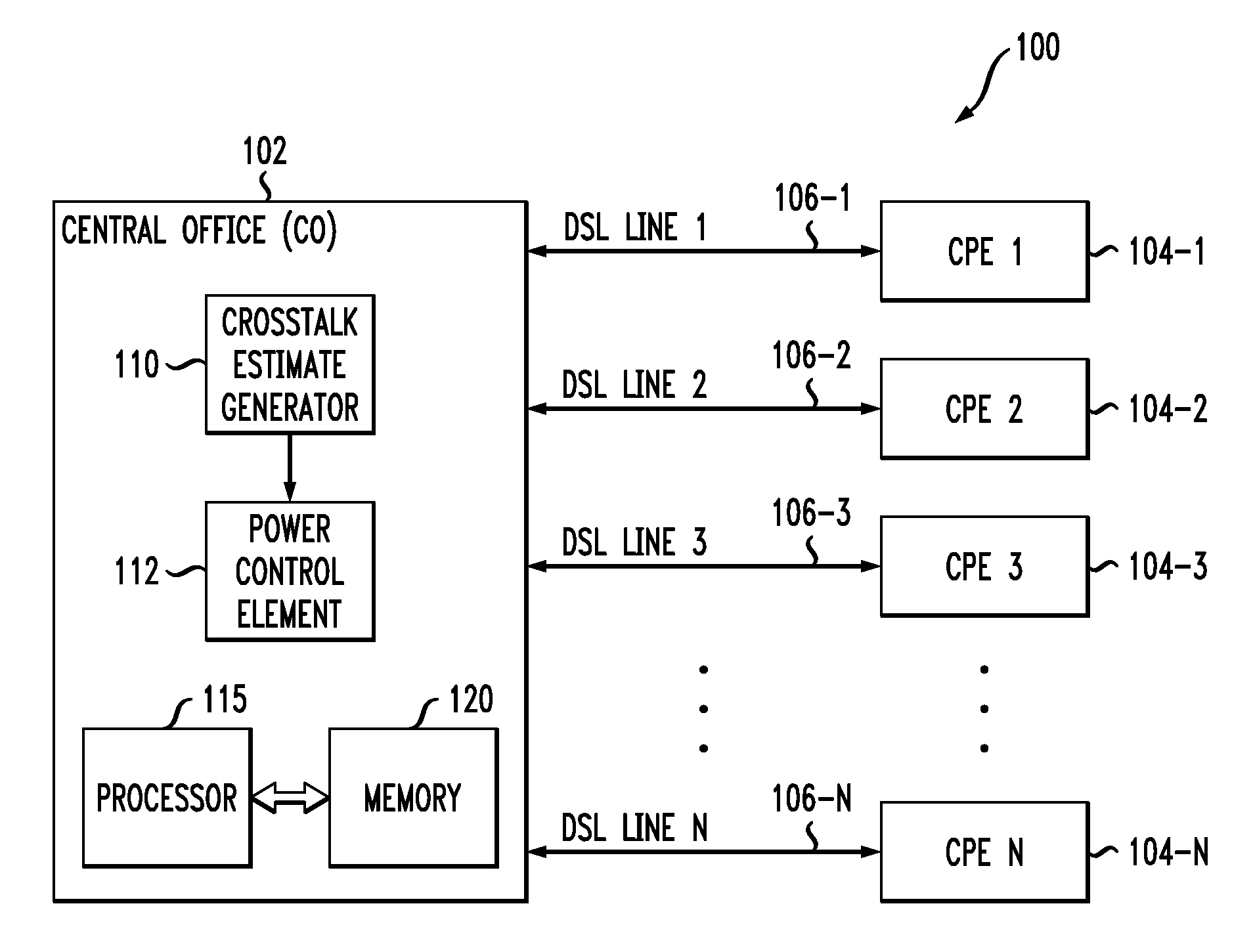
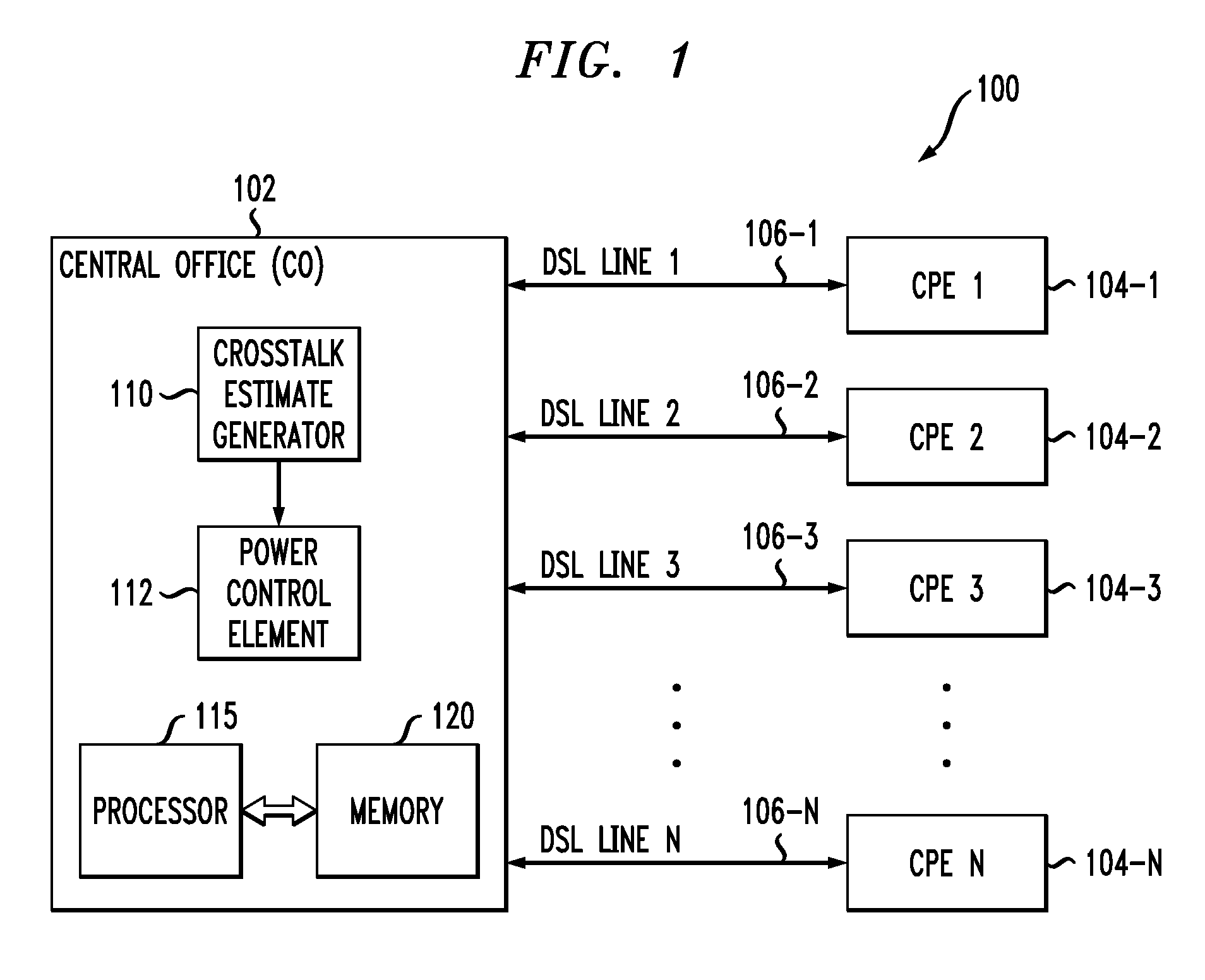
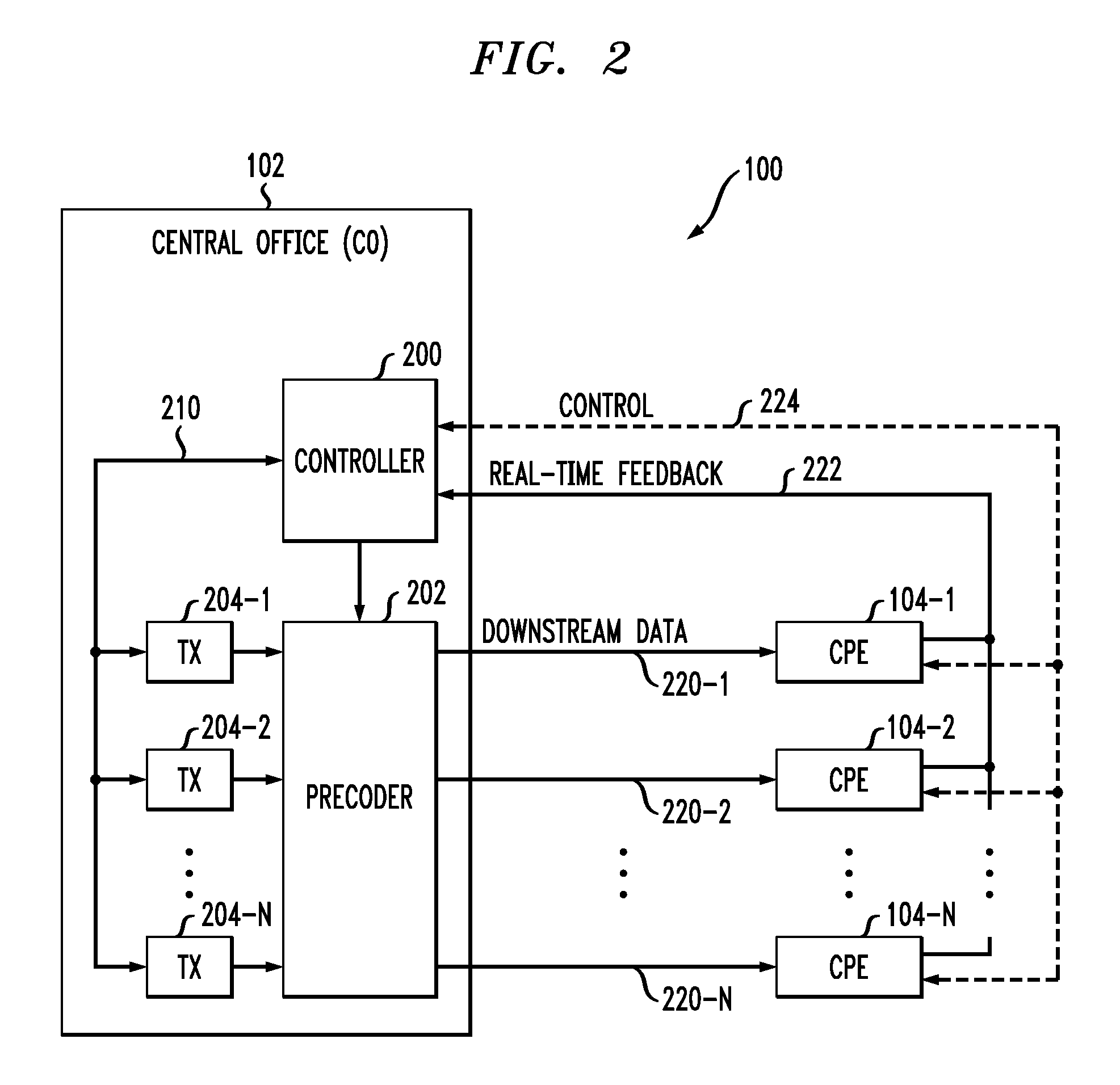
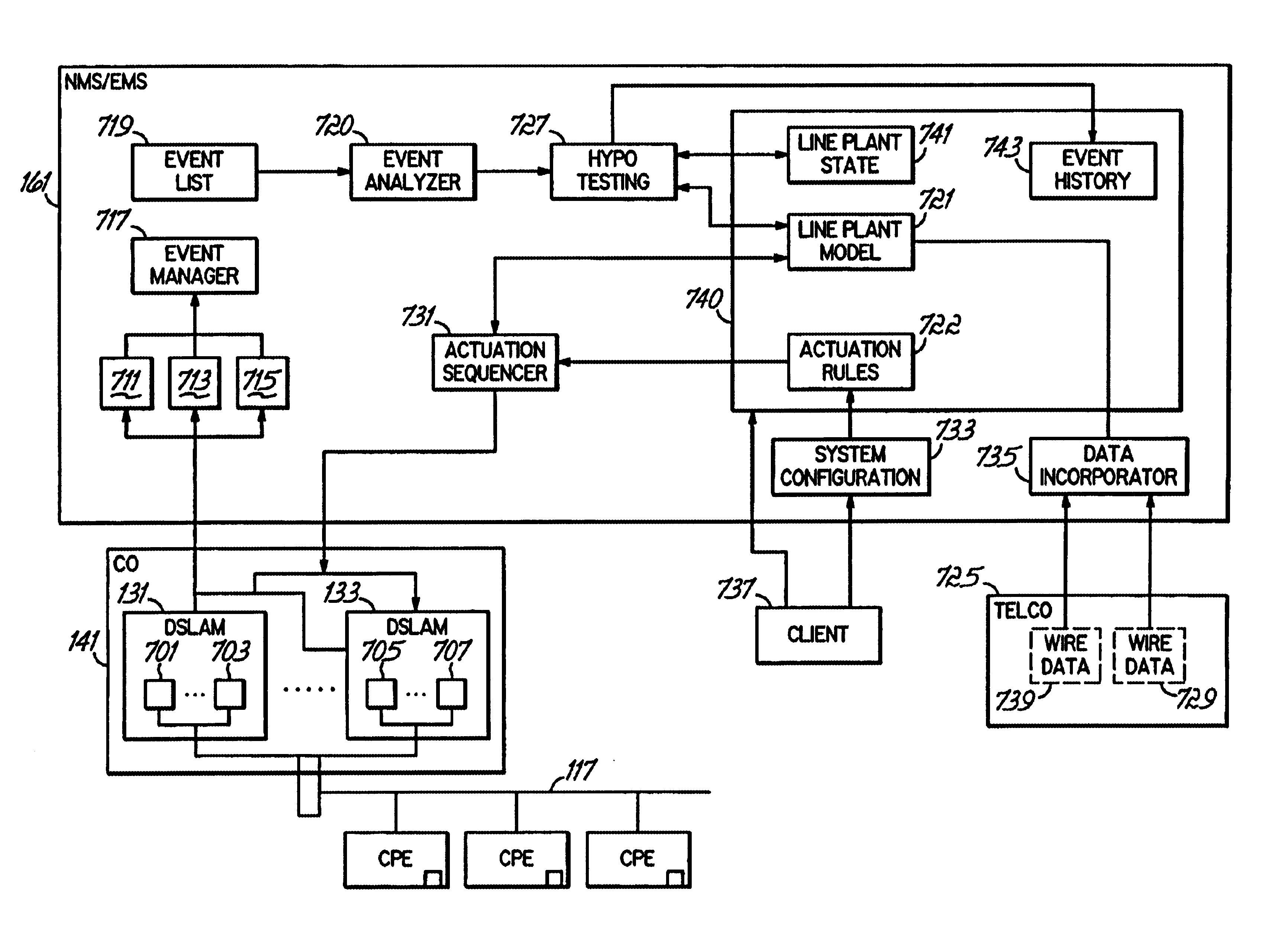
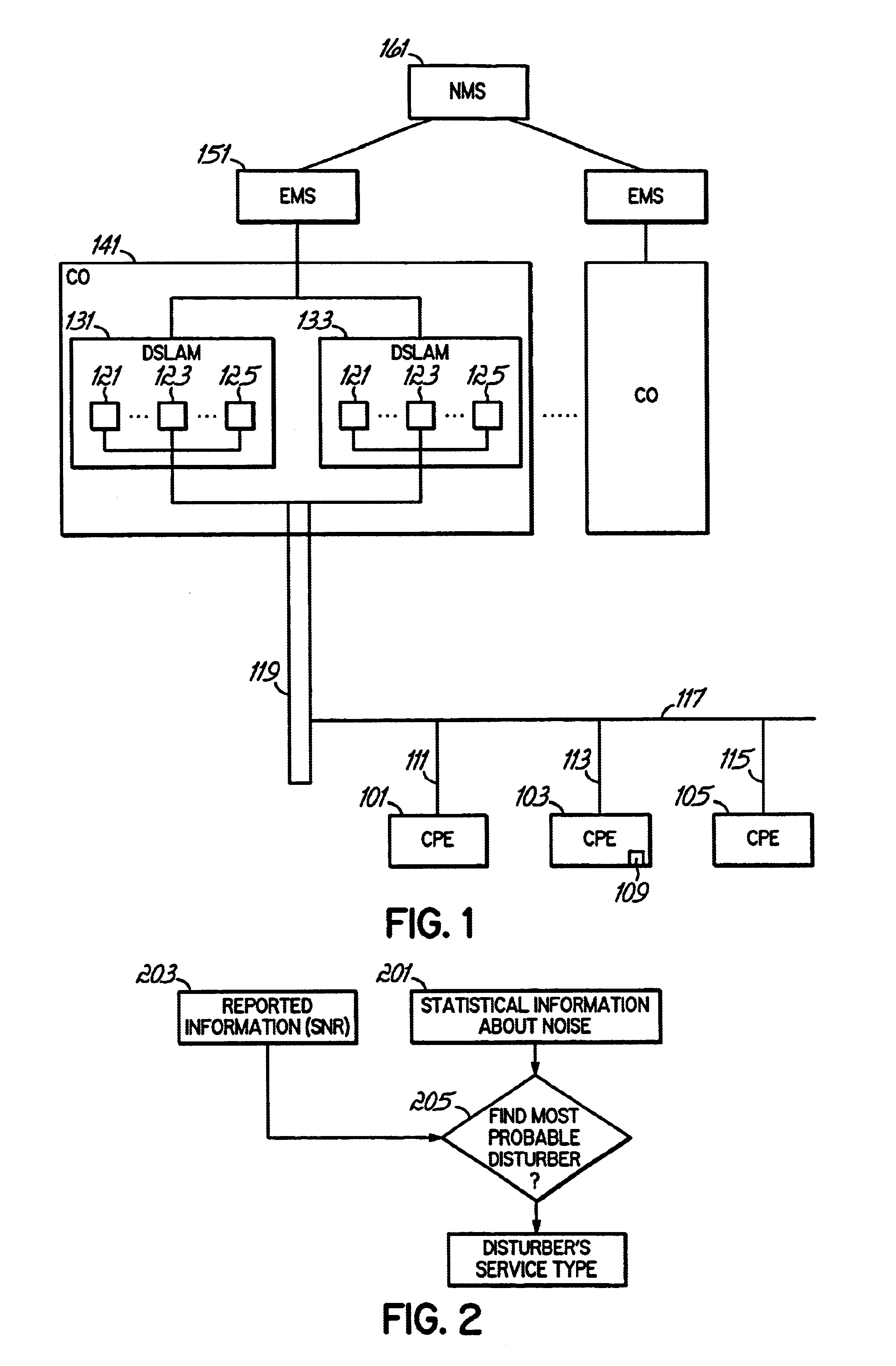
Methods, apparatus and systems for dynamically controlling a digital communication system, such as a DSL system, collect information about digital communication lines in the system and adaptively and / or dynamically determine line and signal characteristics of the digital communication lines, including interference effects. Based on the determined characteristics and the desired performance parameters, operation of the digital communication lines is adjusted to improve or otherwise control the performance of the system. The collection and processing of information may be performed by a party that is not a user in the system. This independent party also may control operational characteristics and parameters of the system. The invention can be used to eliminate or reduce signal interference such as crosstalk that can be induced on communication lines in systems such as DSL systems. Specific iterative power allocation and vectored transmission techniques and apparatus are disclosed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
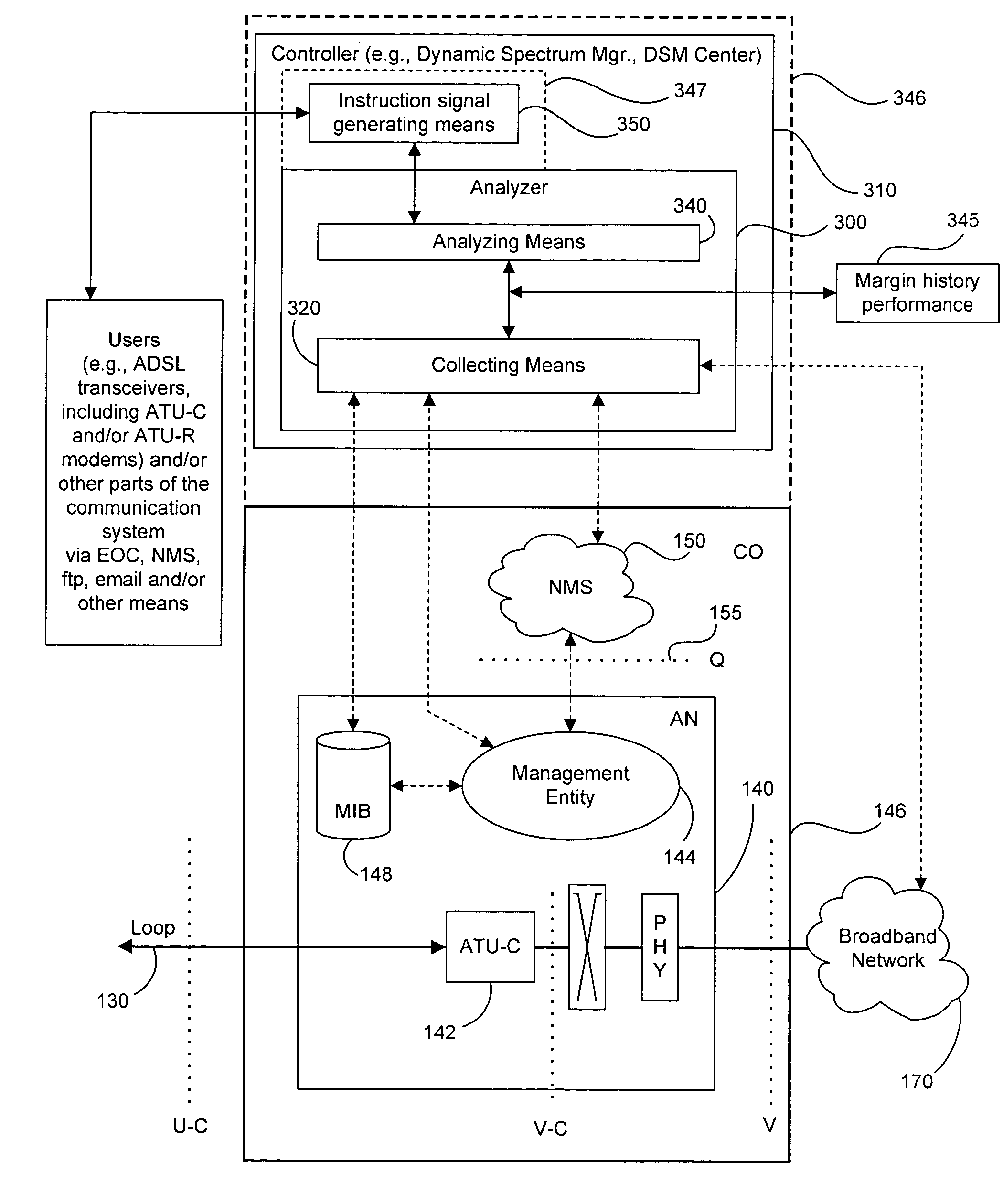
Adaptive margin and band control
ActiveUS20050123028A1Reduce the required powerImprove abilitiesSubstation equipmentPayload allocationFrequency spectrumModem device
Controlling margins in a DSL modem pair is based on collected operational data. The operational data is analyzed and at least one of the modems in the modem pair is instructed to use a margin-related parameter value to assist the modem pair in meeting a margin target, such as a margin limit imposed by a DSL standard or the like. A controller, such as a DSM Center, a “smart” modem unit and / or a computer system can collect and analyze the operational data and generate one or more margin-related parameter values. The margin-related parameter value may be a PSD-related value, such as the MAXNOMPSD, MAXNOMATP or PSDMASK parameter used by various ADSL systems, and may be a shaped spectral mask and / or caps or limits on bit loading for use in transmissions between the modems. In some cases, preference bands can be imposed to direct modems to favor and / or avoid certain frequencies in the modem's usable band(s). The operational data may include historical data relating to prior performance of the modem pair and prior margin compliance. A distribution of margins also may be based on operational data and may be estimated as a function of data rate. Using the estimated margin distribution, a distribution of performance parameters also is calculated, including the probabilities of line outages and probabilities of one or more error parameters exceeding minimum levels. Data rates and / or performance-related parameters may be set on the basis of the estimated performance of the system using various margin settings and levels.
Owner:ADAPTIVE SPECTRUM & SIGNAL
High speed multiple loop DSL system
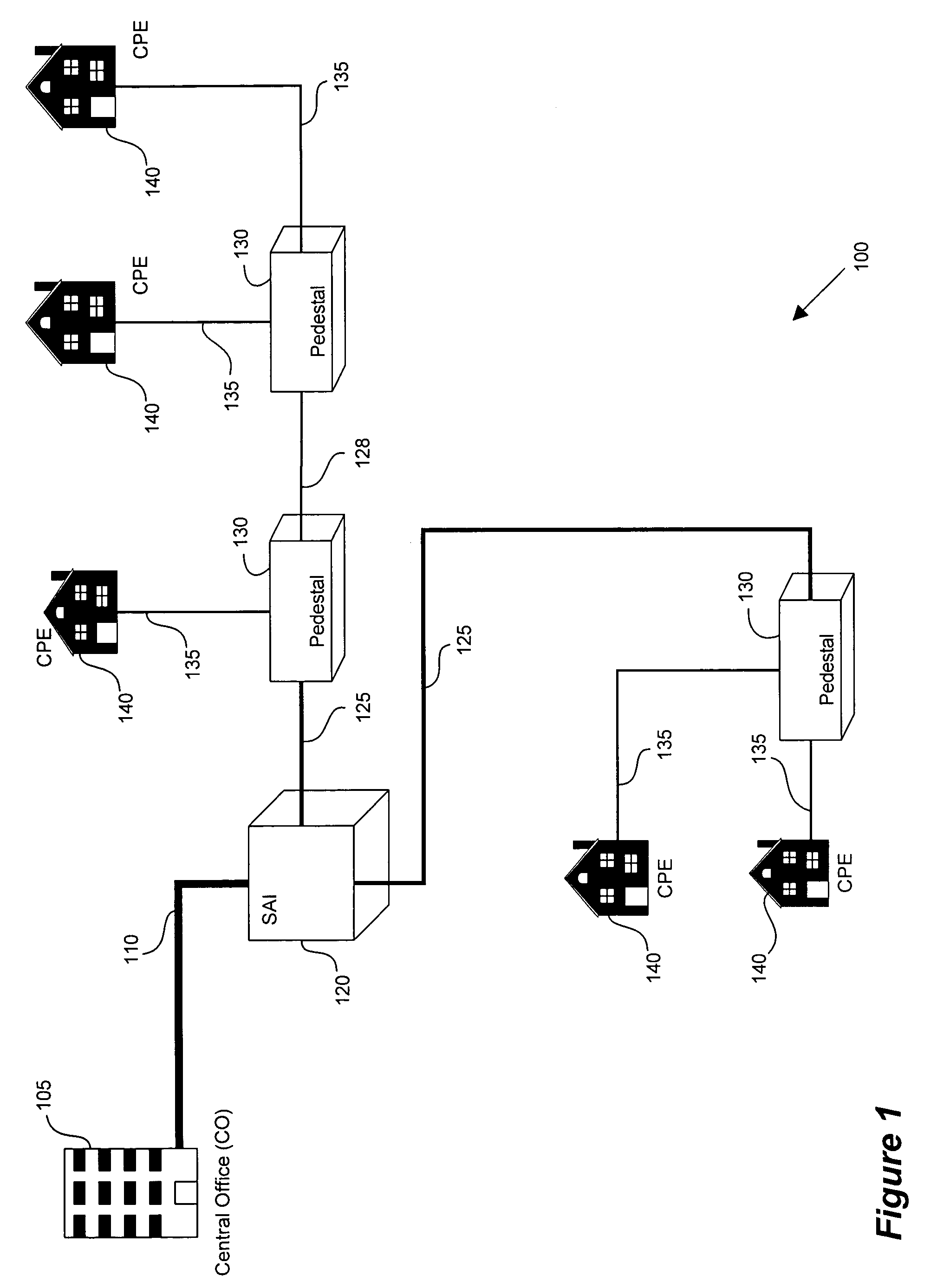
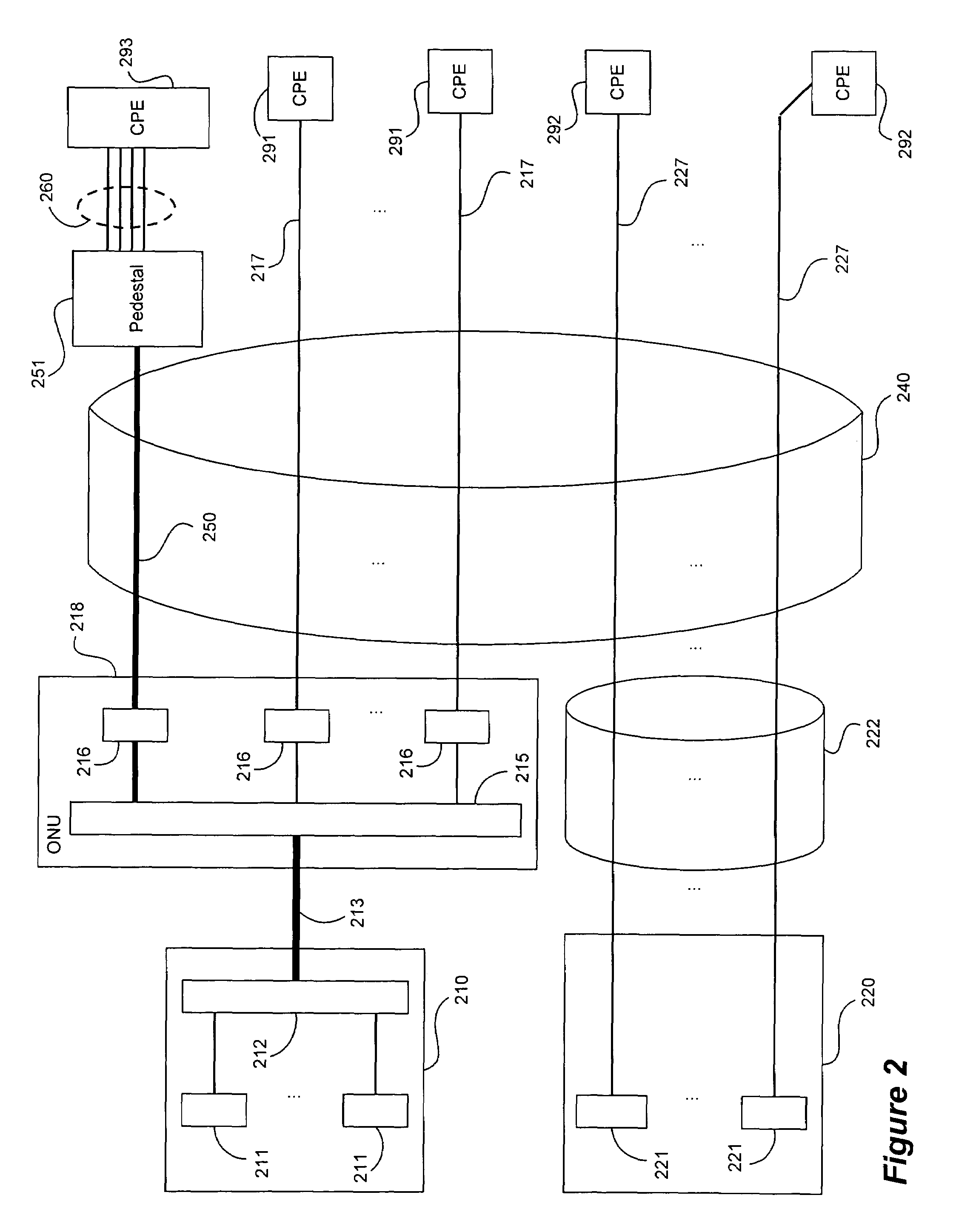
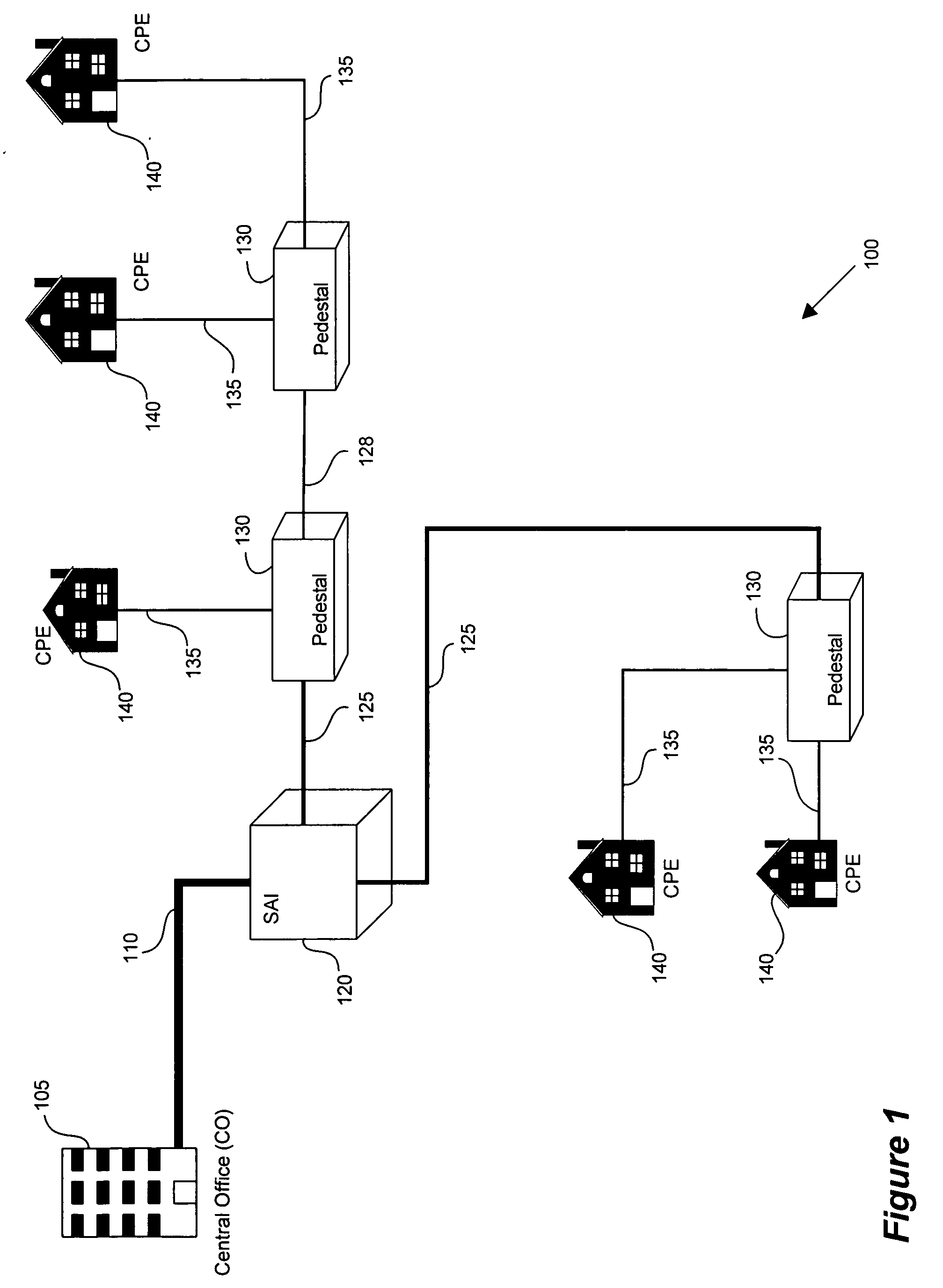
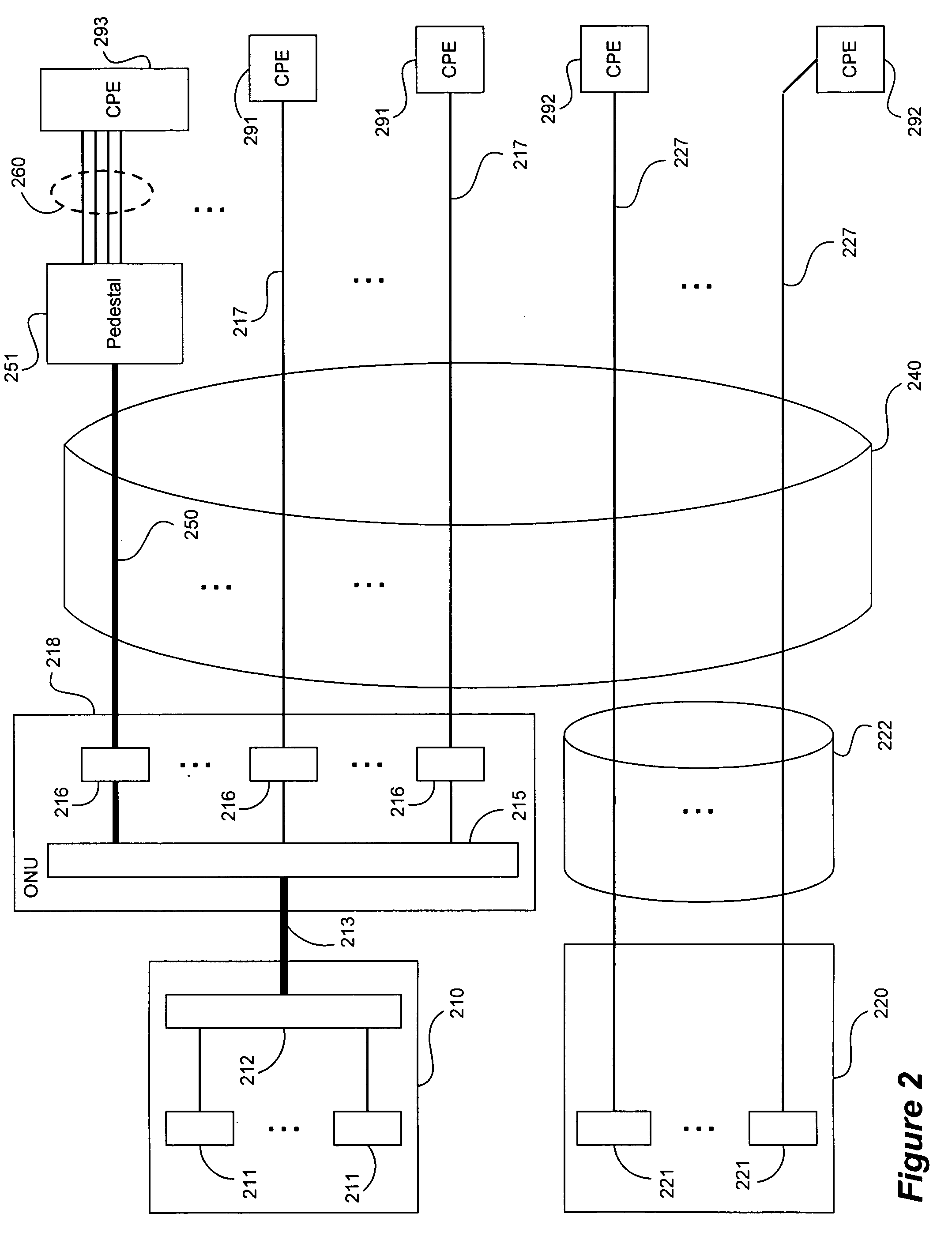
ActiveUS20050152385A1Increase speedIncrease data carrying capabilityTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsFrequency spectrumDynamic spectrum management
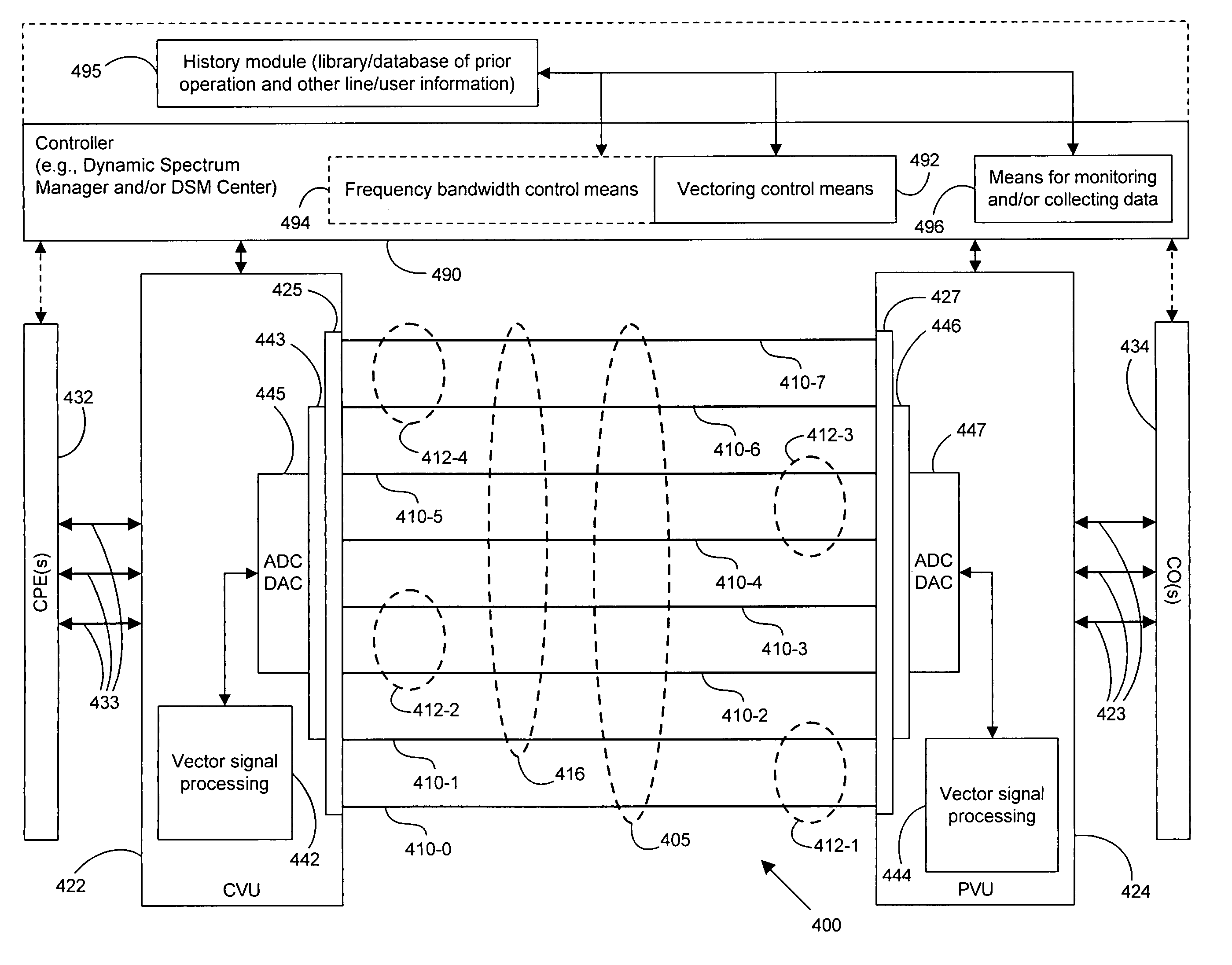
A DSL system includes a multiple loop segment where K loops are bonded to provide a multiple loop segment having up to (2K−1) communication channels on which transmissions are vectored. The segment may be a drop to a customer premises, an inter-pedestal link, or any other suitable part of a larger DSL system. Generally the bonded loops are relatively short, being 300 meters or less. Signal vectoring is used to increase the speed and data carrying capability of the channels. In some embodiments, an expanded frequency spectrum also can be used to increase the data carrying capability of one or more of the channels. An impedance matching circuit may be coupled to each end of the segment to provided efficient transmission of data across the segment. A controller may provide control signals used to operate the segment as a vectored system and, if desired, frequency bandwidth control signals. The controller may monitor and / or collect data and information from the DSL system to assist in generating control signals. The controller can be a dynamic spectrum manager or DSM Center that includes a computer system and / or other hardware to assist in performing the required functions.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
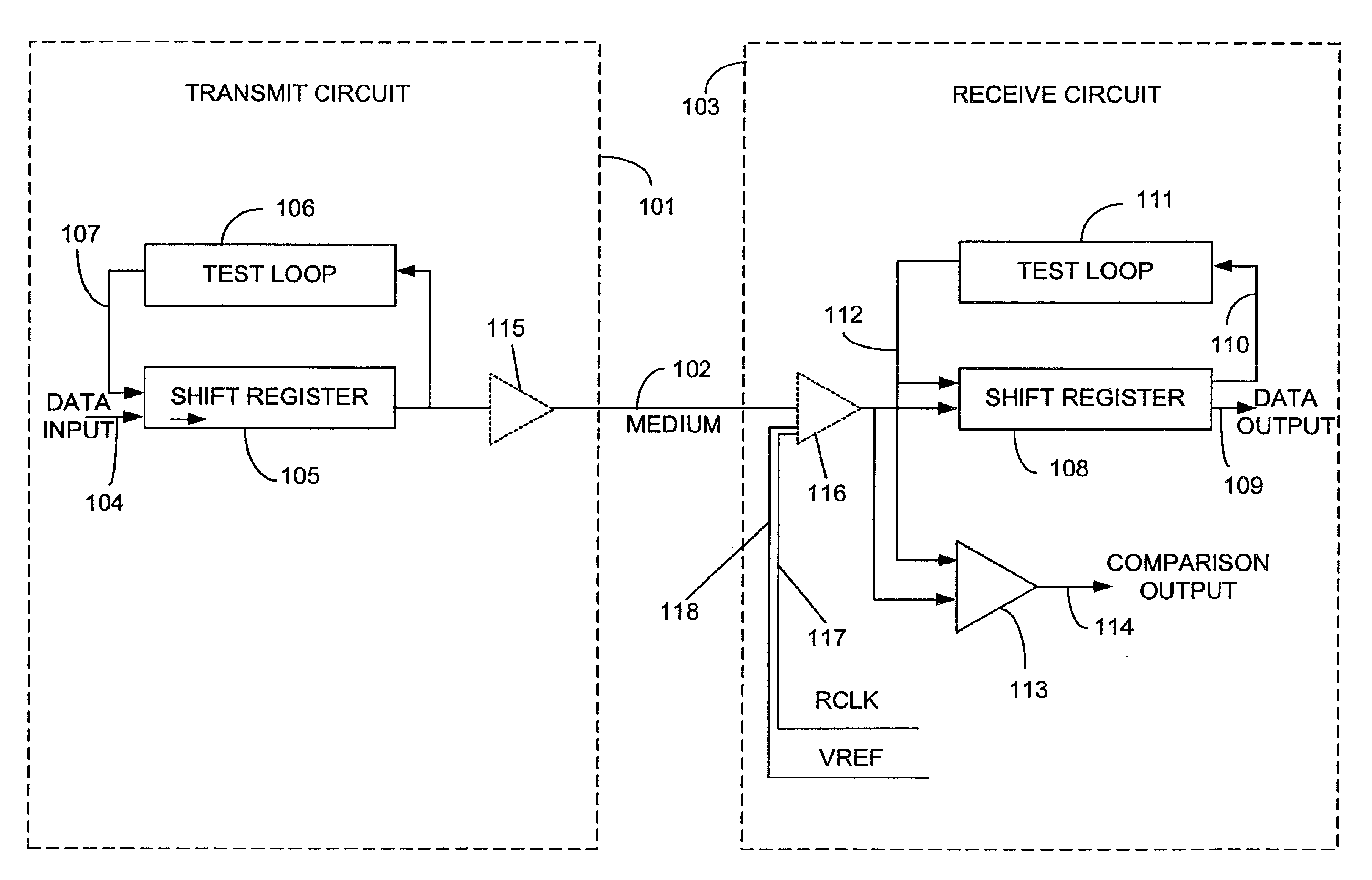
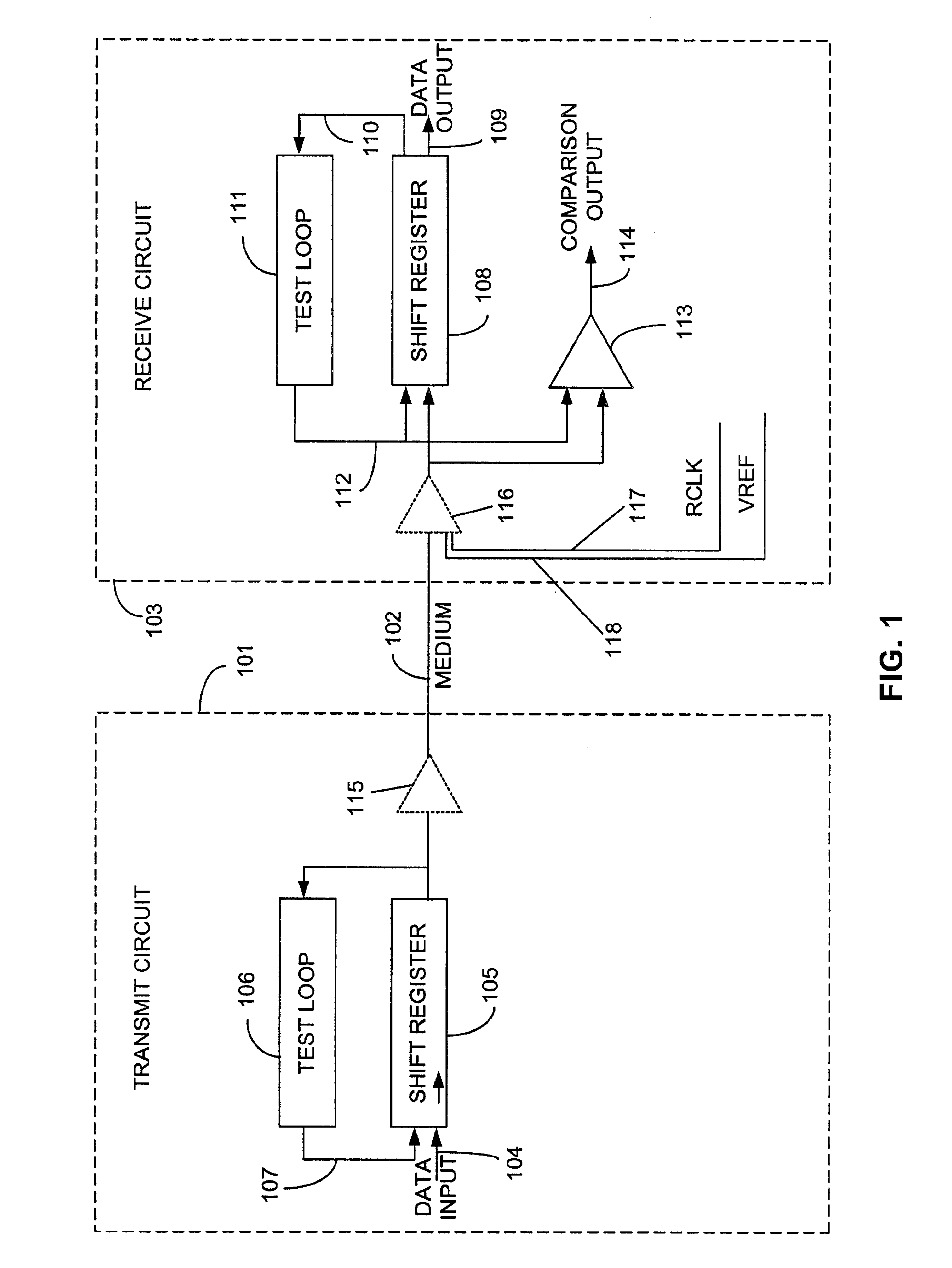
Method and apparatus for evaluating and calibrating a signaling system
InactiveUS6873939B1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceElectronic circuit testingCrosstalk cancellationElectrical conductor
A method and apparatus for evaluating and calibrating a signaling system is described. Evaluation is accomplished using the same circuits actually involved in normal operation of the signaling system. Capability for in-situ testing of a signaling system is provided, and information may be obtained from the actual perspective of a receive circuit in the system. A pattern of test information is generated in a transmit circuit of the system and is transmitted to a receive circuit. A similar pattern of information is generated in the receive circuit and used as a reference. The receive circuit compares the patterns. Any differences between the patterns are observable. Preferably, the patterns are repeating patterns that allow many iterations of testing to be performed. In one embodiment, a linear feedback shift register (LFSR) is implemented to produce patterns. Information obtained from testing may be used to assess the effects of various system parameters, including but not limited to output current, crosstalk cancellation coefficients, and self-equalization coefficients, and system parameters may be adjusted to optimize system performance. An embodiment of the invention may be practiced with various types of signaling systems, including those with single-ended signals and those with differential signals. An embodiment of the invention may be applied to systems communicating a single bit of information on a single conductor at a given time and to systems communicating multiple bits of information on a single conductor simultaneously.
Owner:RAMPART ASSET MANAGEMENT LLC
Method and device for transmission with reduced crosstalk
InactiveUS7167019B2Accurately determinedOptimize locationReliability increasing modificationsElectrically conductive connectionsElectrical conductorInterconnection
The invention relates to a method and a device for transmission with reduced crosstalk in interconnections used for sending a plurality of signals, such as the interconnections made with flat multiconductor cables, or with the tracks of a printed circuit board, or inside an integrated circuit. An interconnection with four parallel transmission conductors plus a reference conductor has each of its ends connected to a termination circuit. The transmitting circuit receives at its input the signals of the four channels of the source and its output terminals are connected to the conductors of the interconnection. The receiving circuit's input terminals are connected to the conductors of the interconnection, and its four output channels are connected to the destination. The signals of the four channels of the source are sent to the four channels of the destination, without noticeable crosstalk.
Owner:RAMBUS INC +1
Channel Estimation in a Multi-Channel Communication System Using Pilot Signals Having Quasi-Orthogonal Subpilots
ActiveUS20100303136A1High speedLess timeCross-talk reductionSecret communicationCommunications systemData signal
An access node of a communication system comprises a plurality of transmitters adapted for communication with at least one receiver. The access node is operative to transmit pilot signals from respective associated ones of the transmitters, to estimate channel coefficients between the transmitters and the receiver, and to utilize the estimated channel coefficients to control at least one data signal sent by at least one of the transmitters. The pilot signals are partitioned into a plurality of sets of pilot signals such that pilot signals from the same set have respective subpilots that are orthogonal to one another and pilot signals from different sets have respective subpilots that are not orthogonal to one another but are instead quasi-orthogonal to one another. The pilot signals are associated with the respective transmitters based on the partitioning of the pilot signals into sets.
Owner:RPX CORP
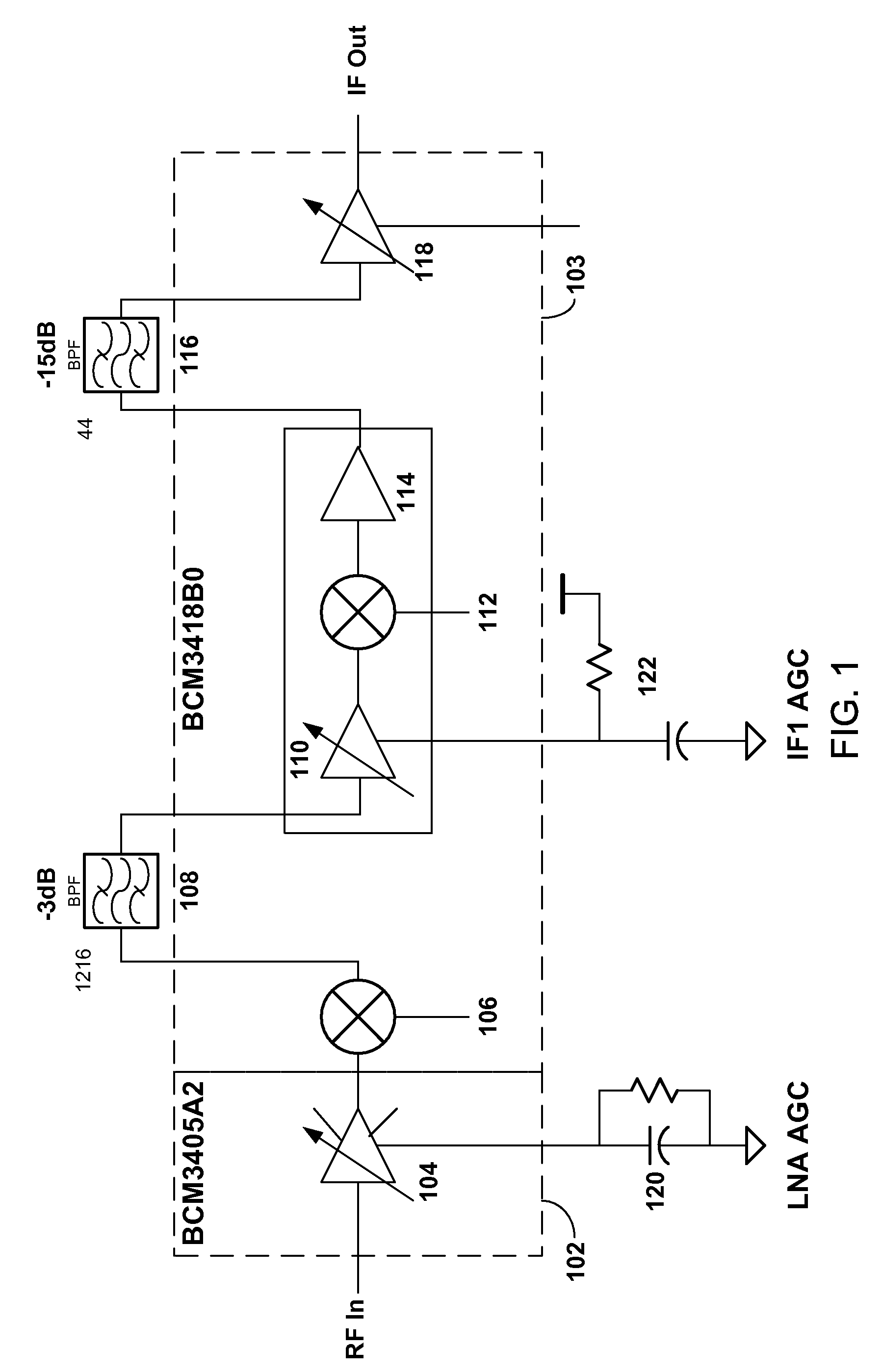
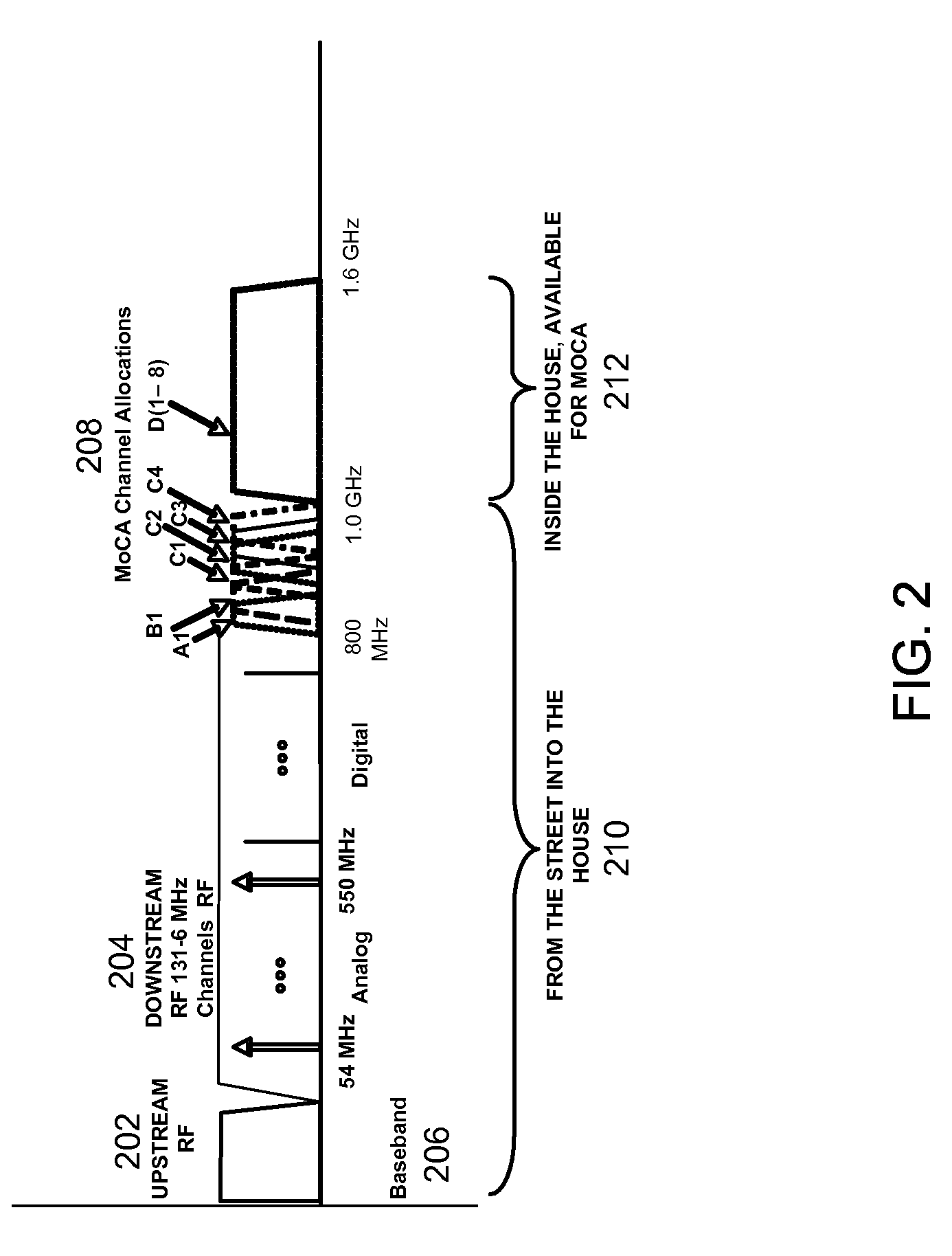
SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR PROVIDING A MoCA COMPATABILITY STRATEGY
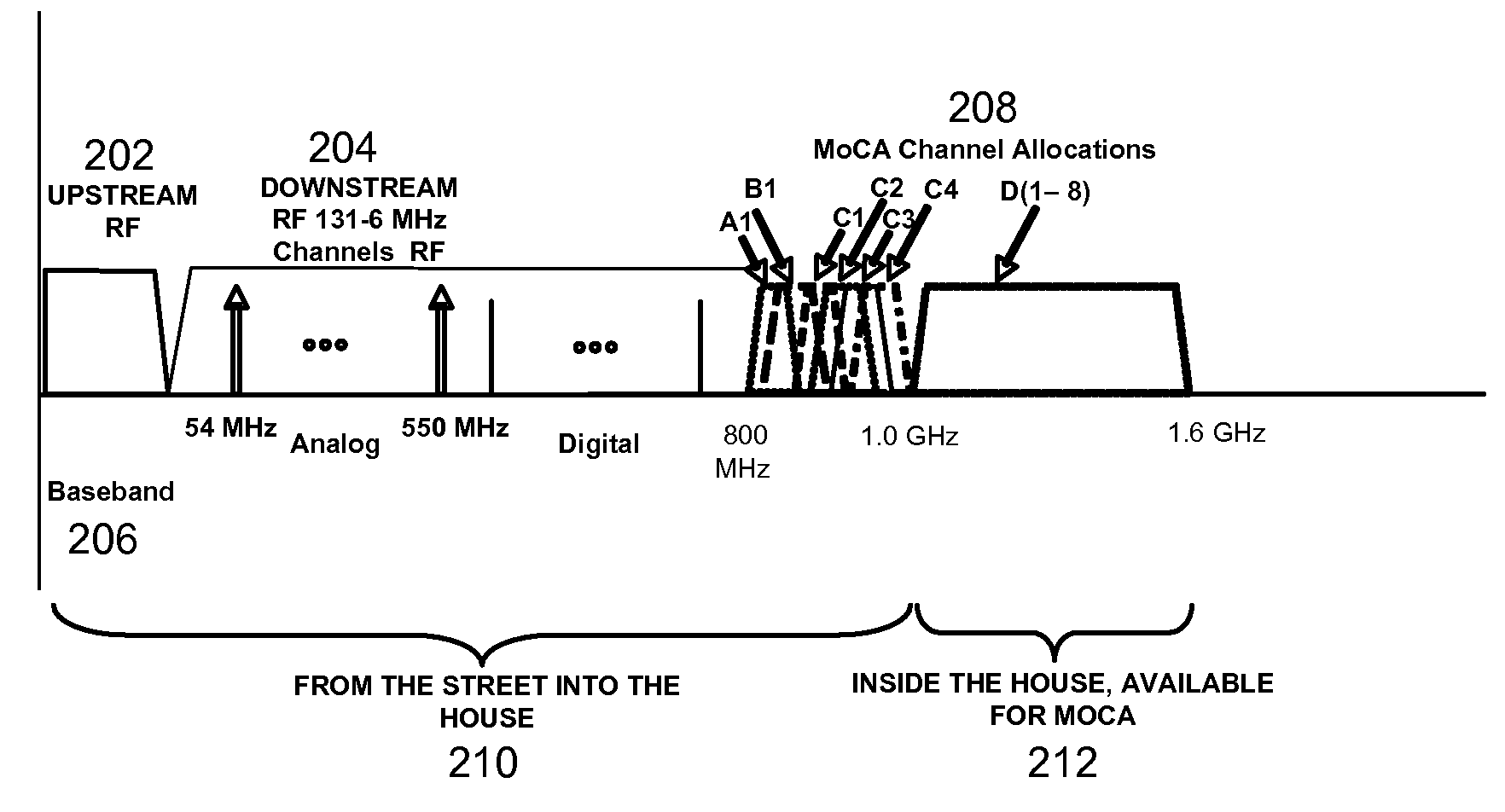
InactiveUS20090165070A1Reduce performance degradationBroadcast transmission systemsCross-talk reductionCoaxial cableIntermediate frequency
Systems and methods for perform a method for reducing interference from Multimedia over Coax Alliance (MOCA) signals in a cable television double conversion tuner are provided. The method may include receiving an indication of the channel in which MoCA signals are operating. When the channel in which the MoCA signals are operating is in the same frequency band as an intermediate frequency of the tuner, the method may require shifting an intermediate frequency of the tuner out of the frequency band occupied by the channel in which the MoCA signals are operating.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
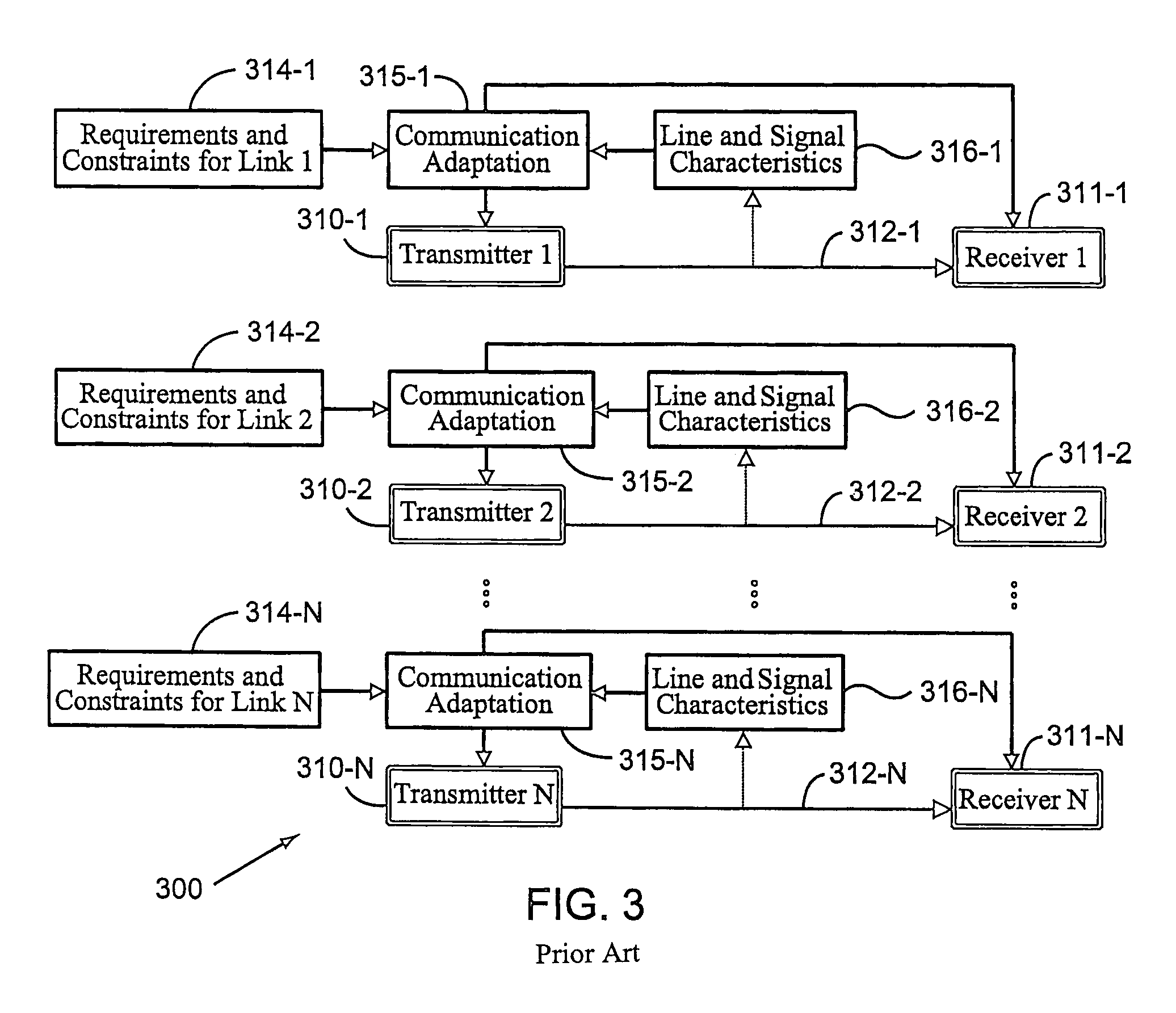
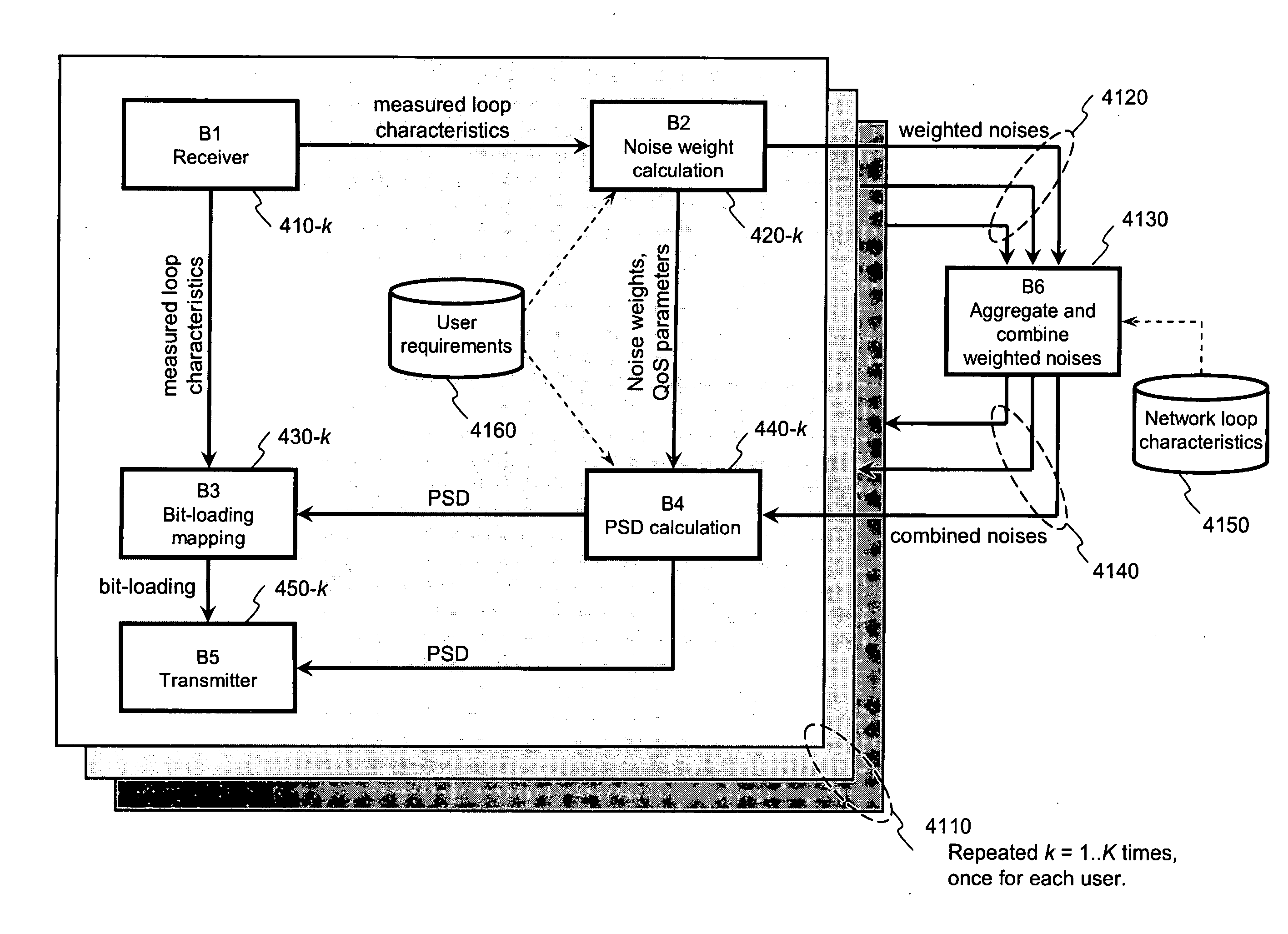
Method for distributed spectrum management of digital communications systems
ActiveUS20070274404A1Lower Level RequirementsManagement overheadFrequency-division multiplex detailsAnalogue computers for nuclear physicsFrequency spectrumCommunications system
A method for distributed spectrum management of digital communication systems having a plurality of communication lines on which signals are transmitted and received by respective users, the method comprising the steps of: collecting information about line, signal and interference characteristics of a plurality of the communication lines from a plurality of sources; determining the line, signal and interference characteristics of a plurality of the communication lines; varying power allocation of particular plurality of the communication lines between respective transmitter and receiver taking into consideration the determined line, signal and interference characteristics of a plurality of the communication lines and consideration of a noise weight of a plurality of the communication lines to enable a minimum power on a plurality of the communication lines and to allow required effective data-rates for each of said respective users to be satisfied.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
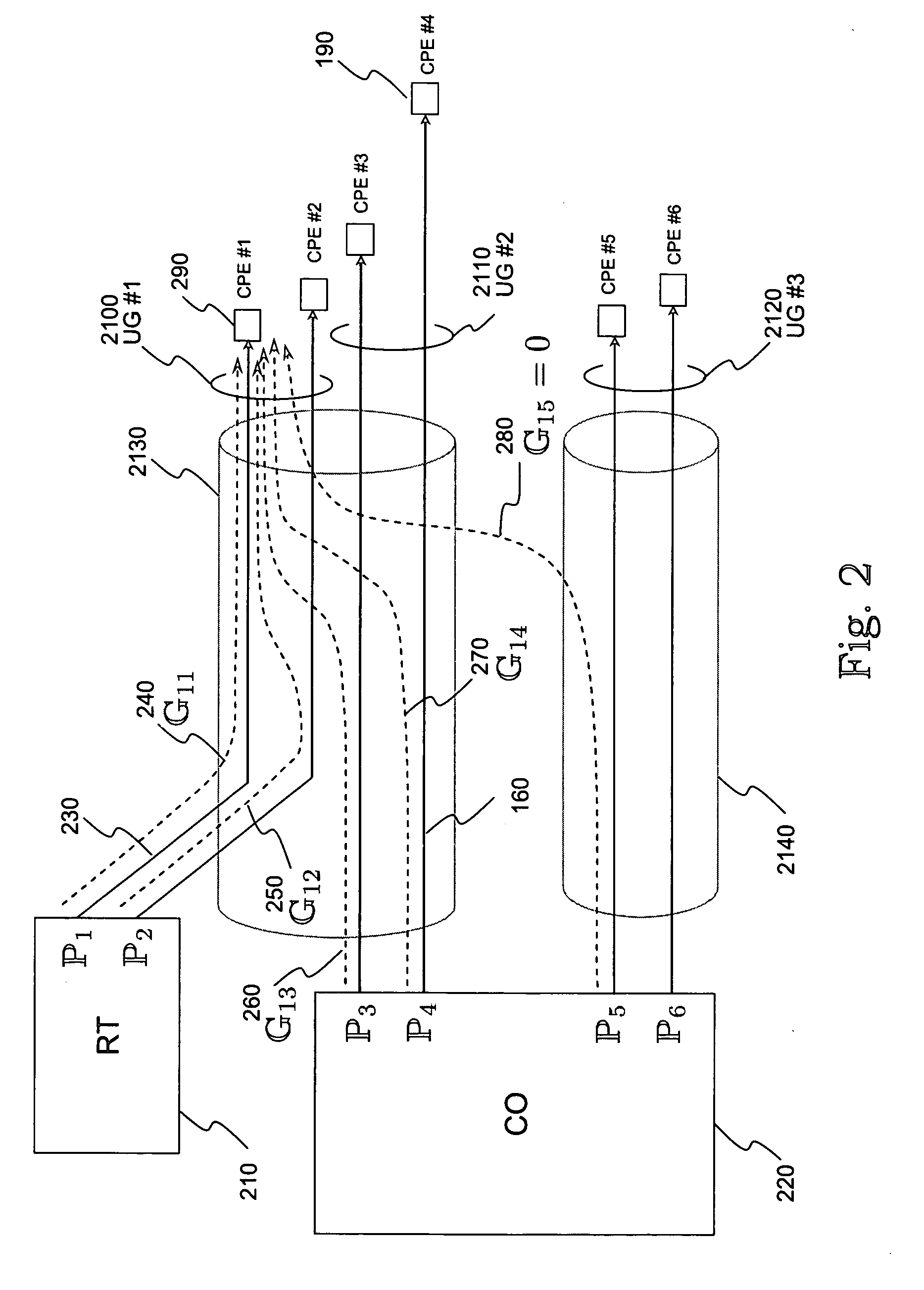
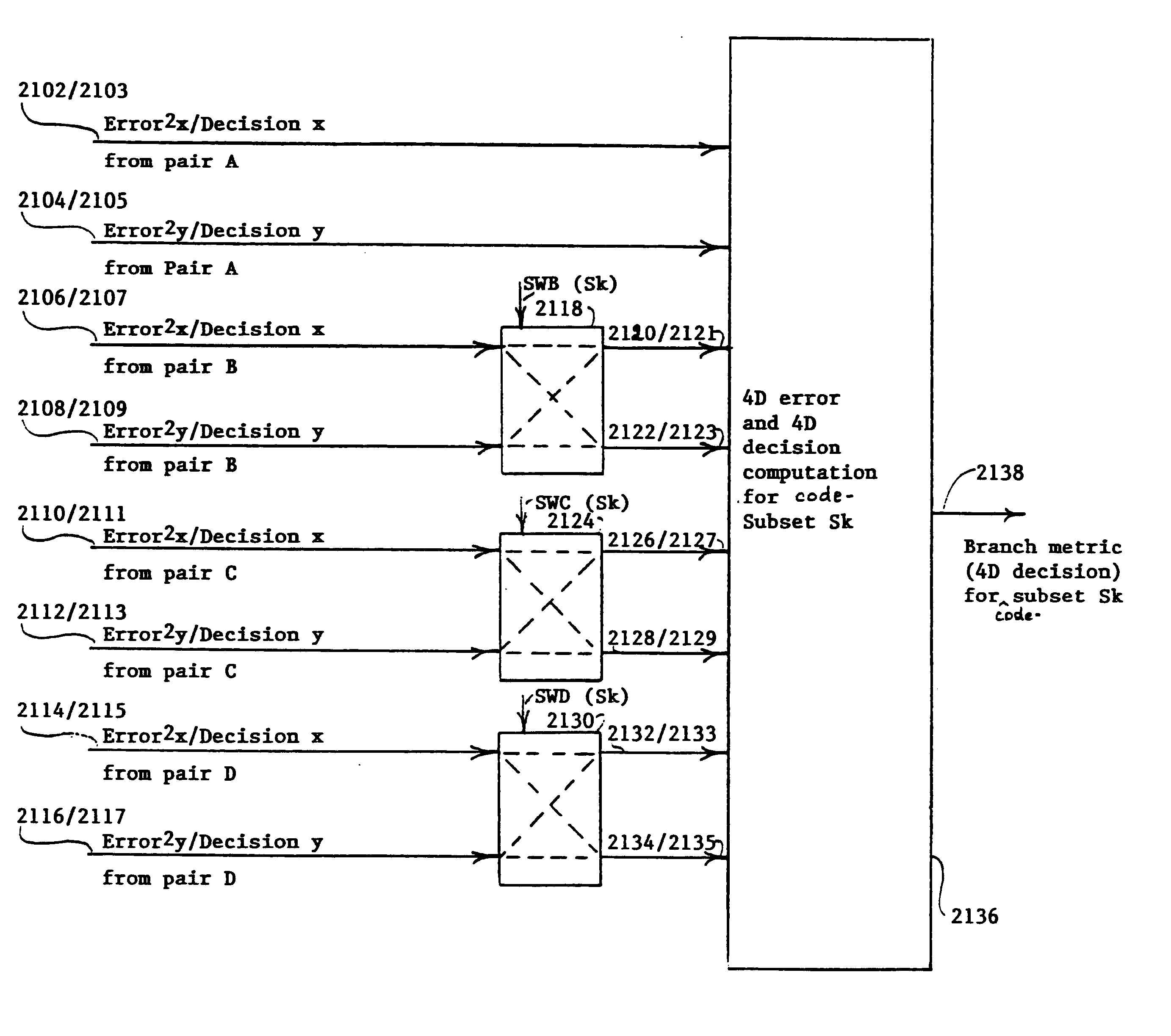
Pair-swap independent trellis decoder for a multi-pair gigabit transceiver
InactiveUS6865234B1Channel dividing arrangementsDigital circuit testingGigabitMulti-gigabit transceiver
A method and a system for compensating for a permutation of L pairs of cable such that the compensation is localized in a trellis decoder of a receiver. The L pairs of cable correspond to L dimensions of a trellis code associated with the trellis decoder. The trellis code includes a plurality of code-subsets. The permutation of the L pairs of cable is determined. A plurality of sets of swap indicators based on the permutation of the L pairs of cable is generated. Each of the sets of swap indicators corresponds to one of the code-subsets. The code-subsets are remapped based on the corresponding sets of swap indicators.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and method for crosstalk cancellation
InactiveUS20080159448A1Small amount requiredHigh acceptanceMultiple-port networksError preventionDigital dataCrosstalk cancellation
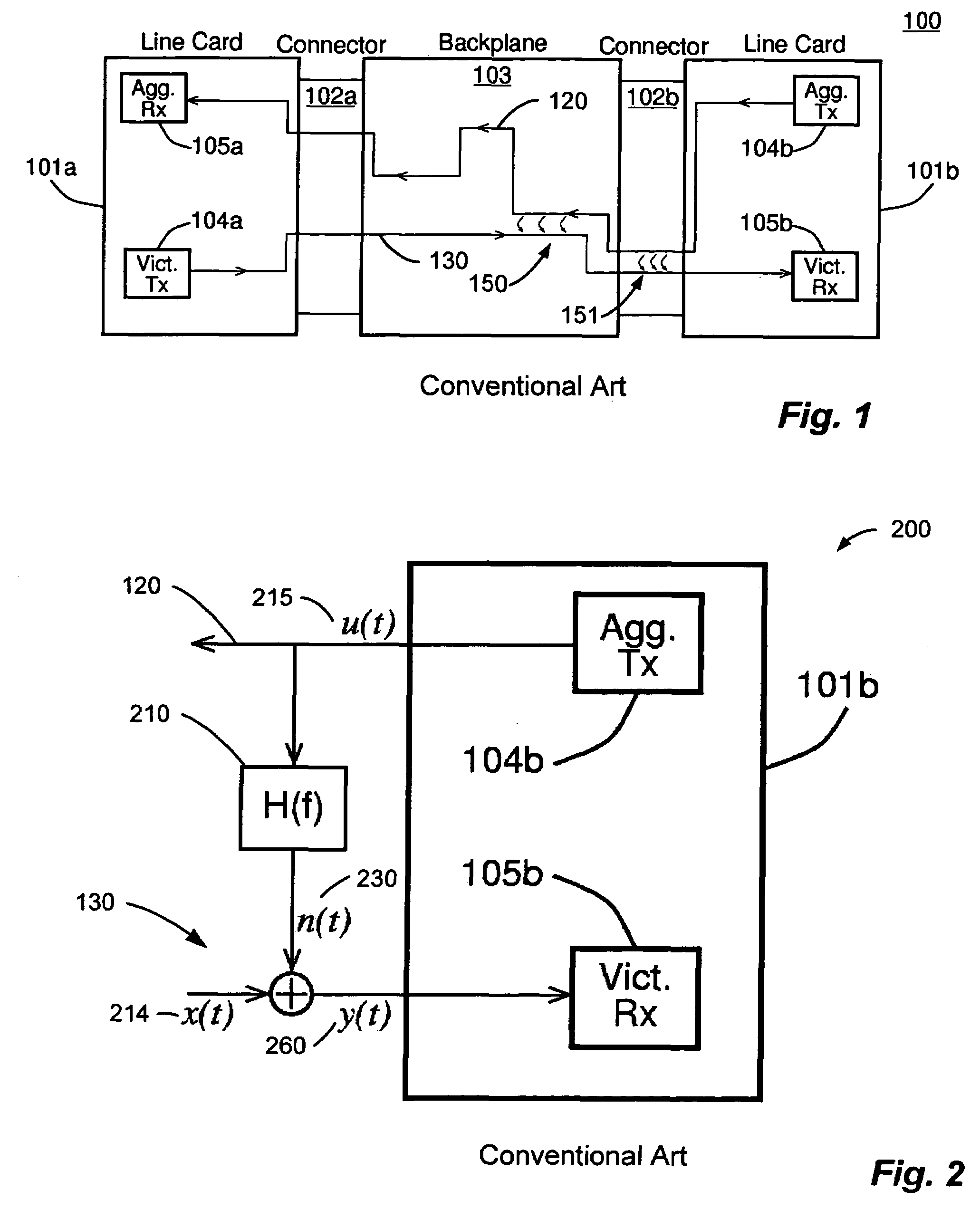
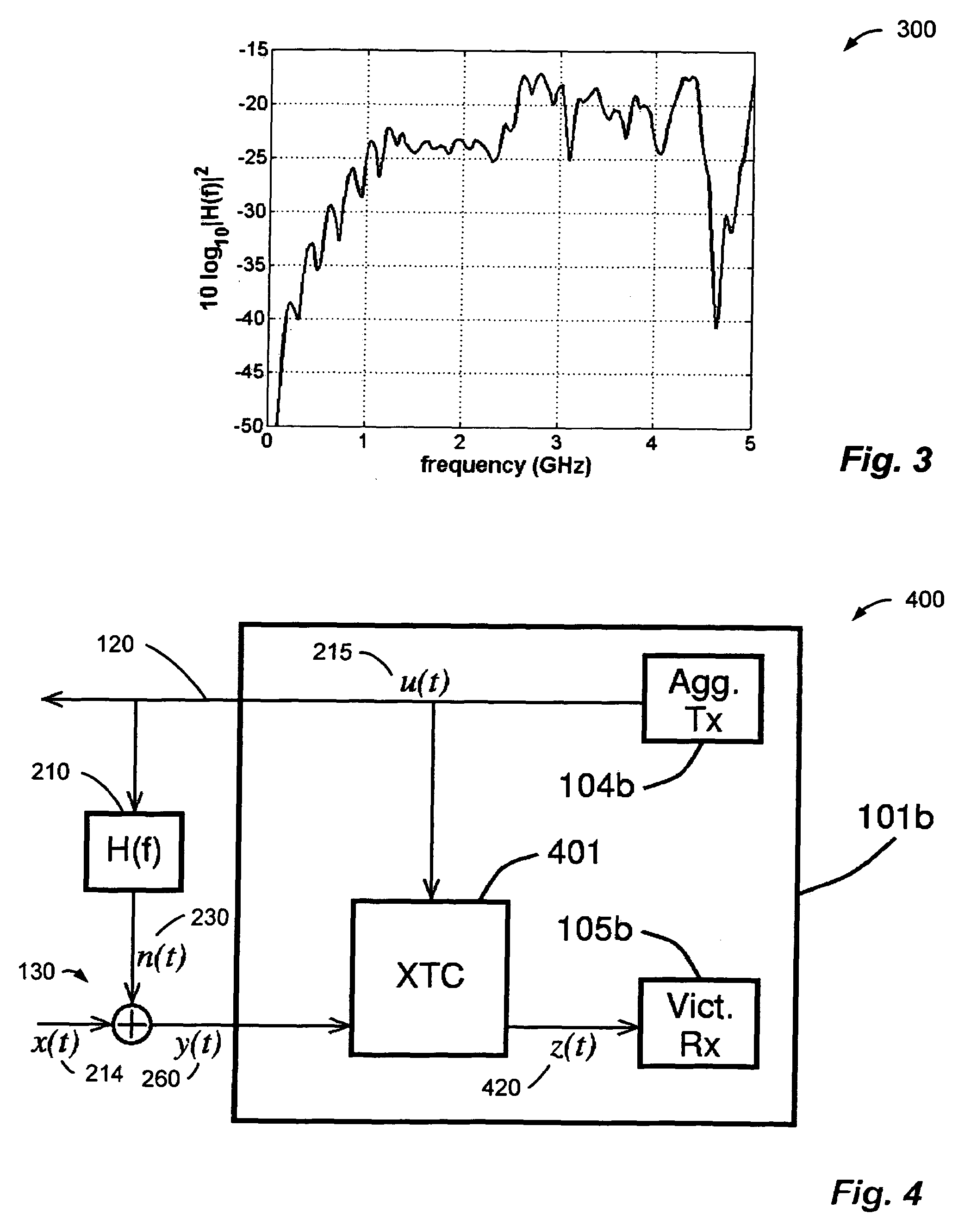
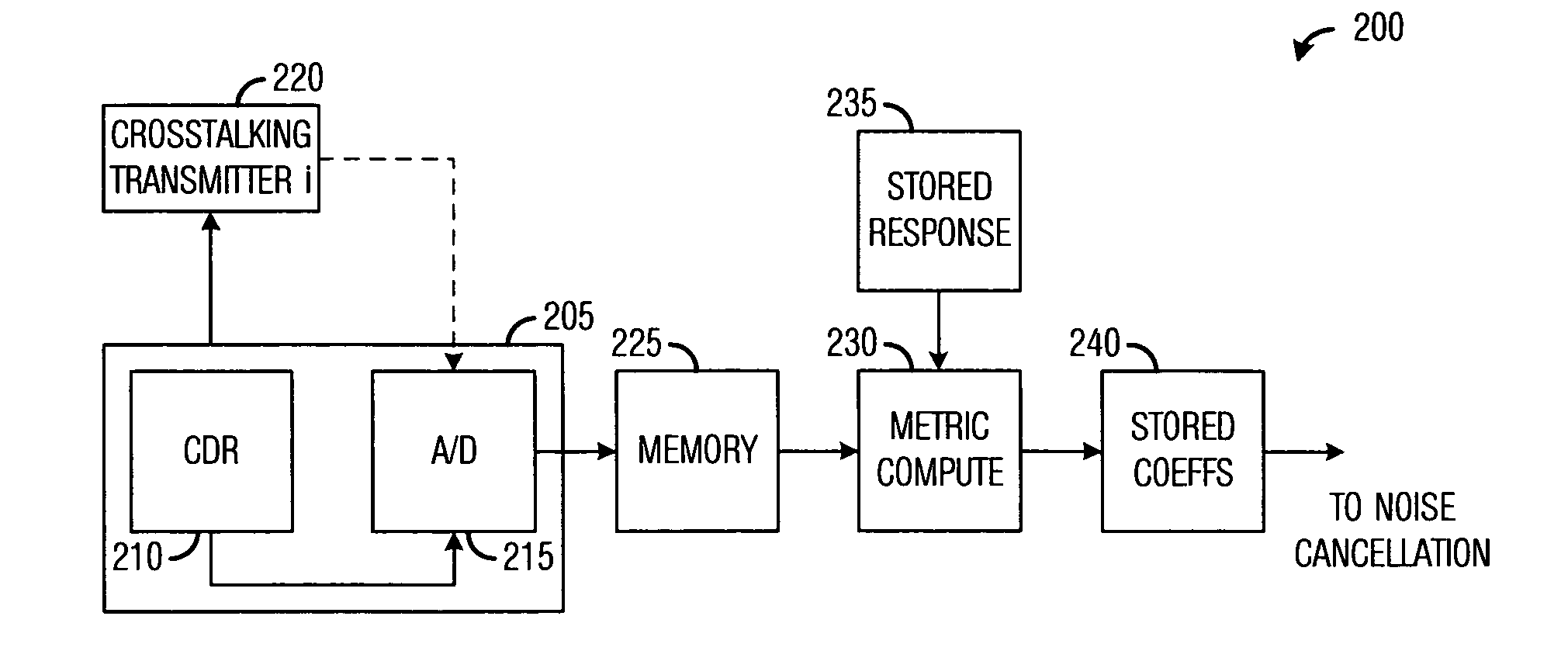
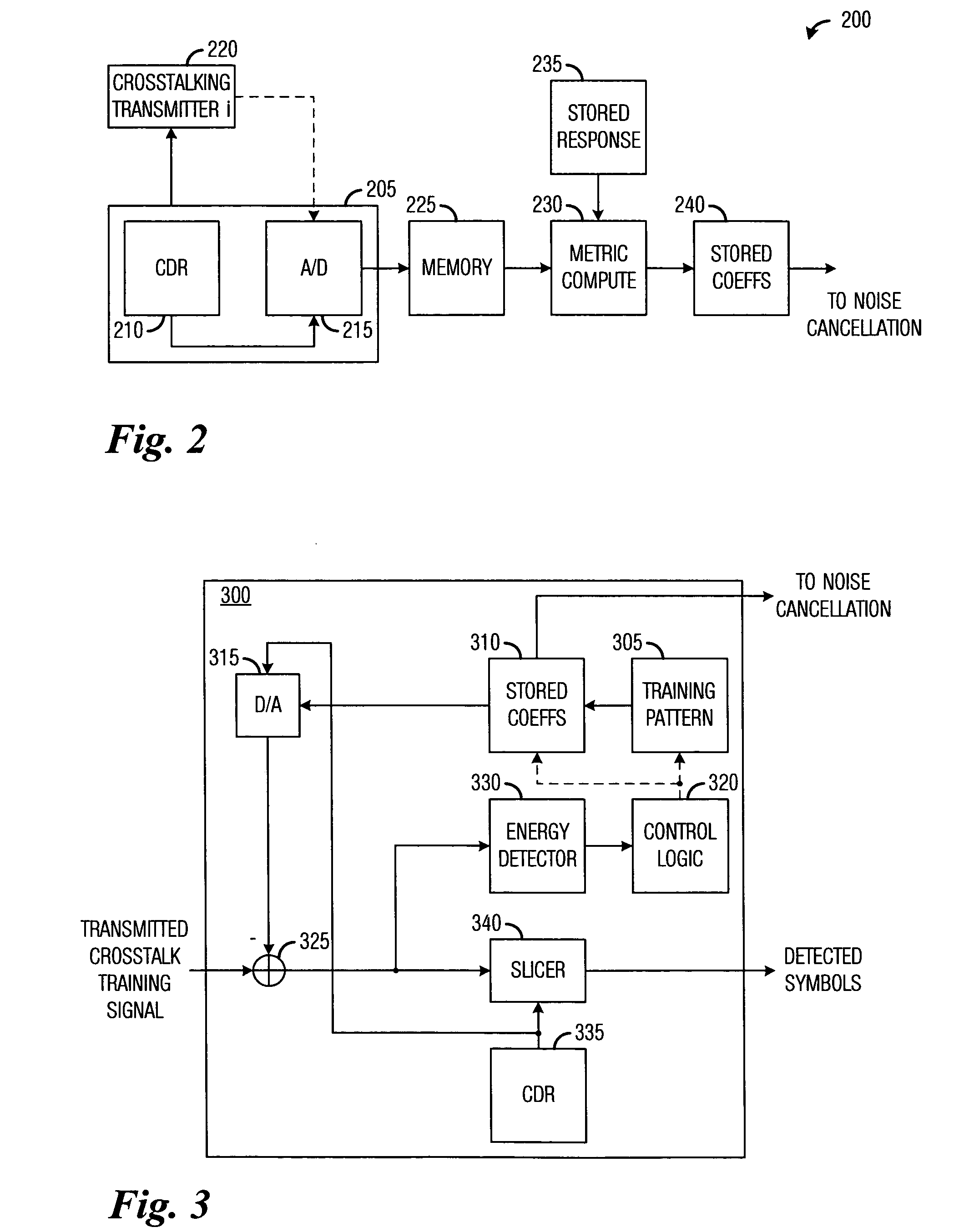
System and method for canceling crosstalk in high-speed communications systems. An embodiment comprises precomputing channel pulse responses for a set of communications channels in a communications backplane, precomputing channel signal responses for the set of communications channels in the backplane with a training sequence, estimating noise coefficients using receiver training and the training sequence, storing noise coefficients for each communications channel in the set of communications channels, and canceling noise in a received transmission of a data sequence using the stored noise coefficients. The regularity of the communications backplane enables the precomputing of various values, which reduces computational requirements. Furthermore, it is often the case that a victim receiver has access to the digital data that is being transmitted by its dominant crosstalking transmitters, thereby simplifying noise cancellation.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
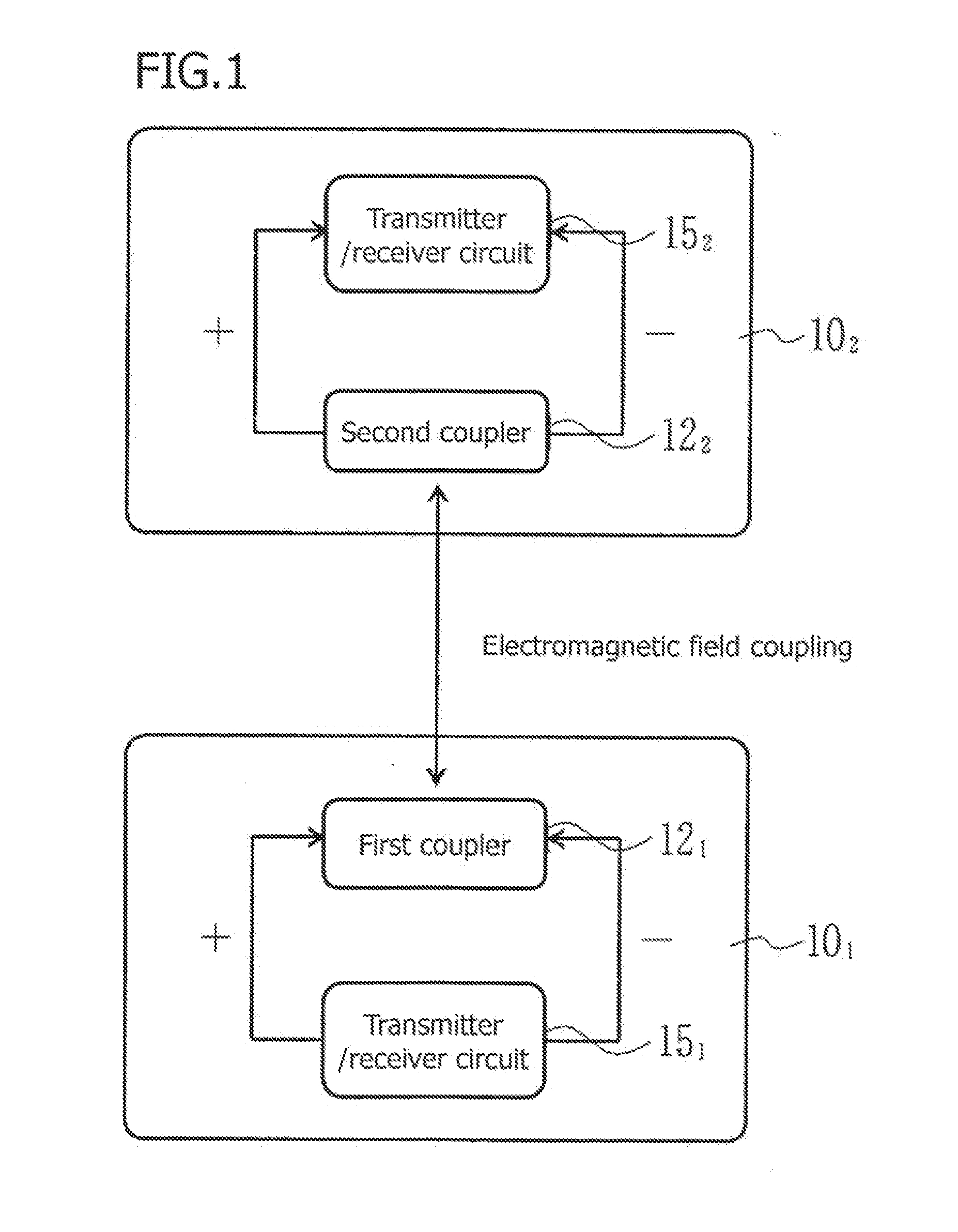
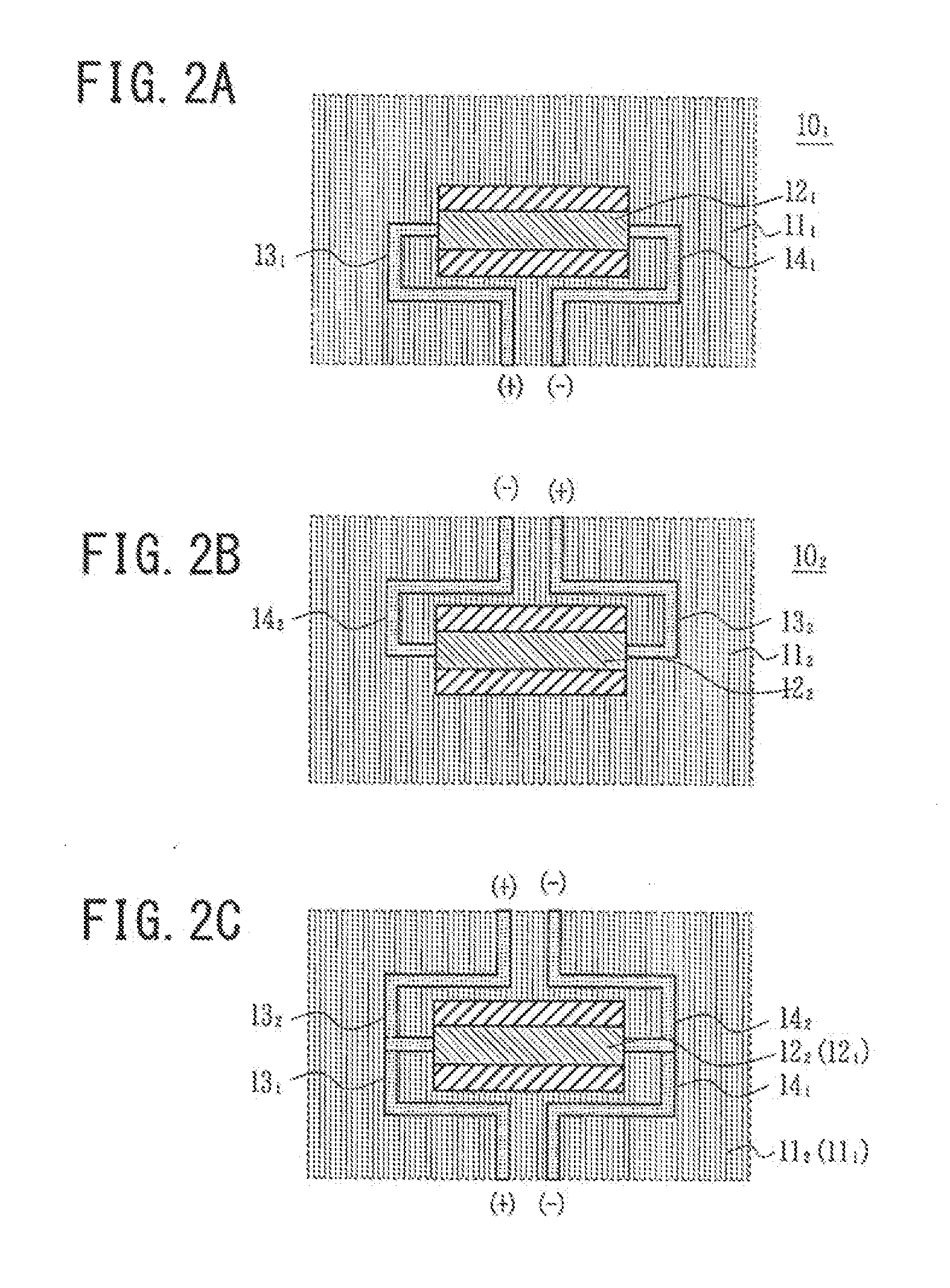
Directional coupling communication apparatus
ActiveUS20150207541A1Reduce reflectionImprove communication reliabilityHigh frequency circuit adaptationsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
The invention relates to a directional coupling communication apparatus where the coupling impedance can be easily matched to reduce reflections, and thus, the speed of communication channels is increased as compared to that with inductive coupling, and at the same time, the reliability of communication is improved by increasing the signal intensity. Modules having a coupler where an input / output connection line is connected to a first end, and either a ground line or an input / output connection line to which an inverse signal of a signal to be inputted into the input / output connection line connected to the above-described first end is inputted is connected are layered on top of each other so that the couplers are couplers to each other using capacitive coupling and inductive coupling.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
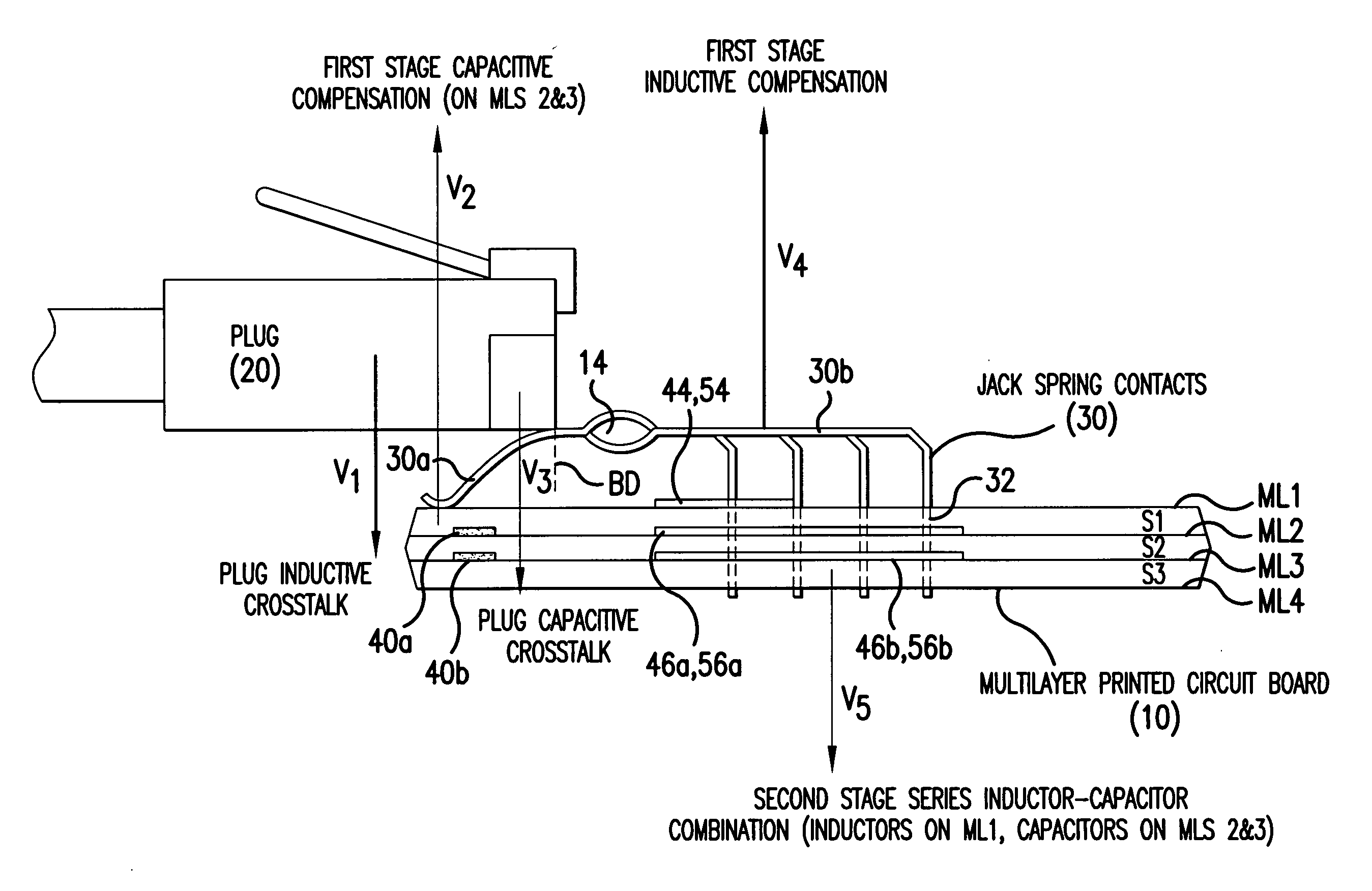
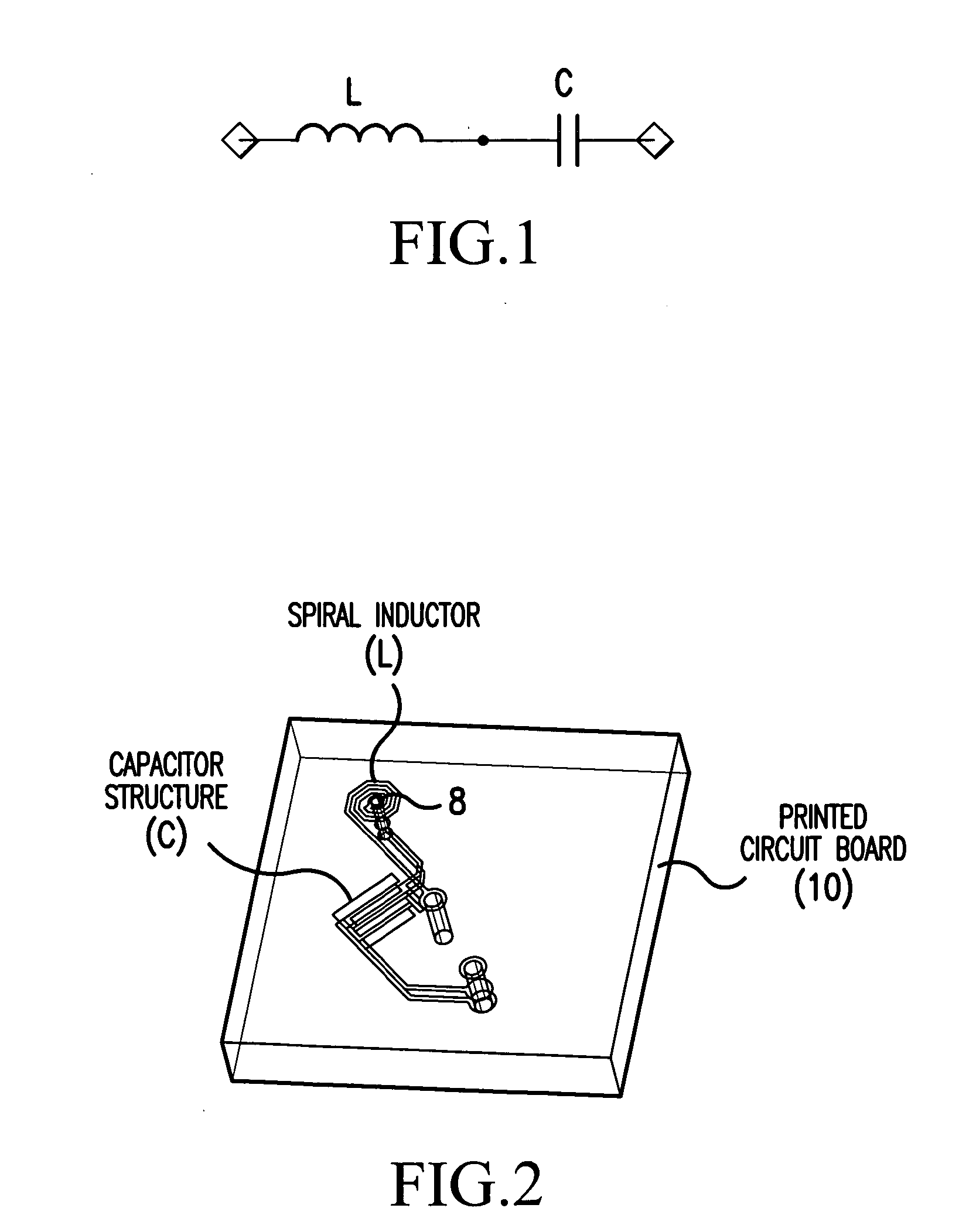
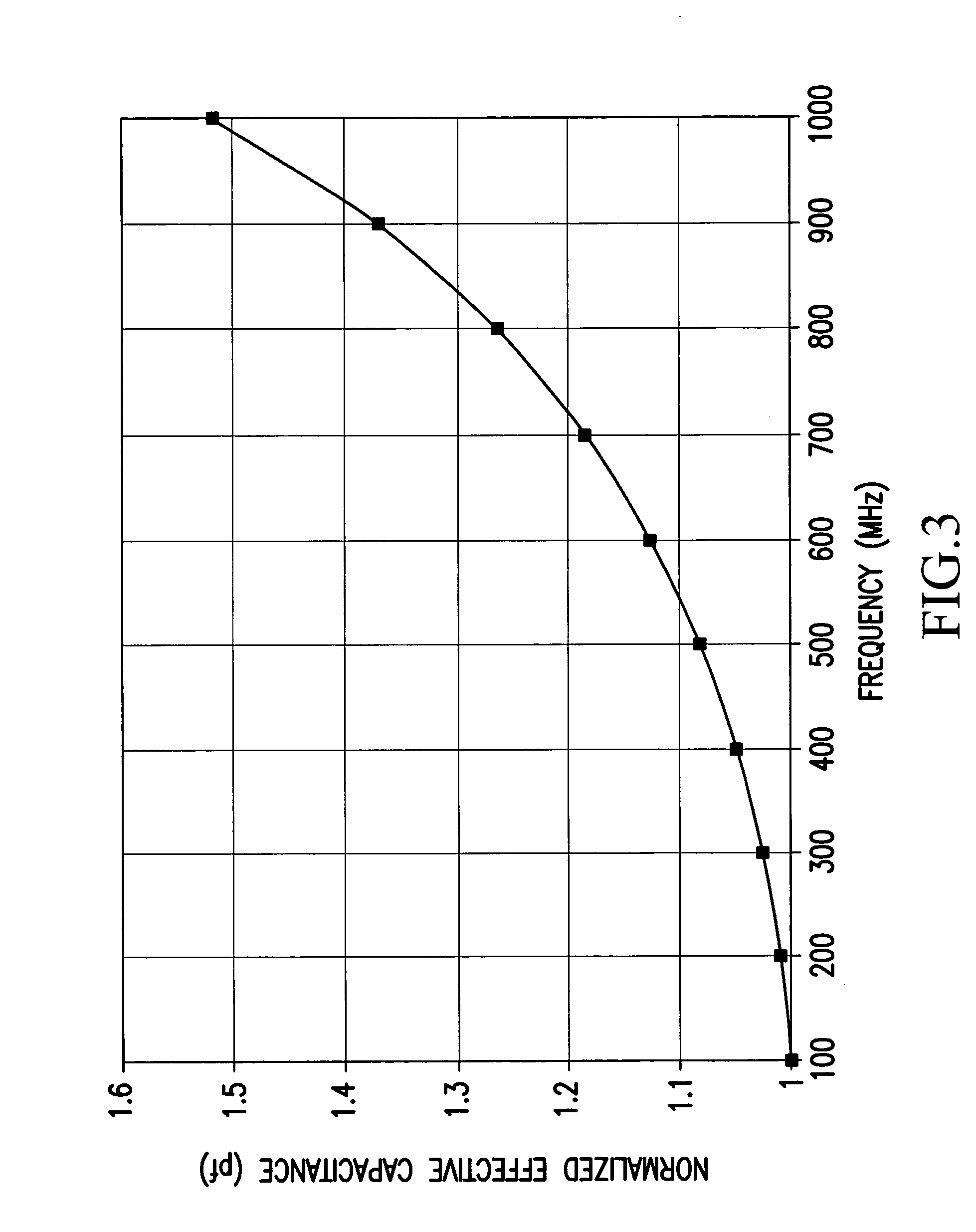
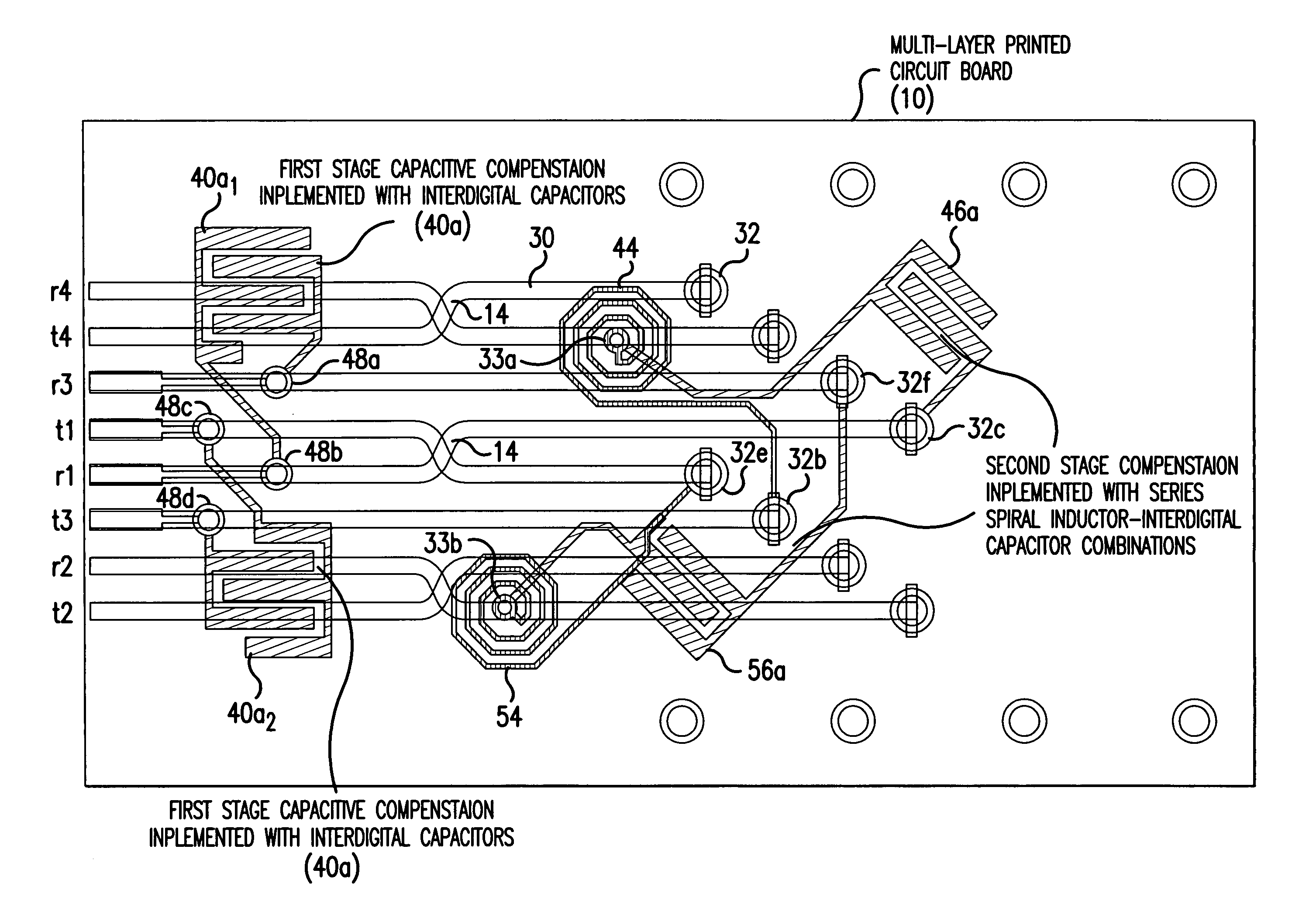
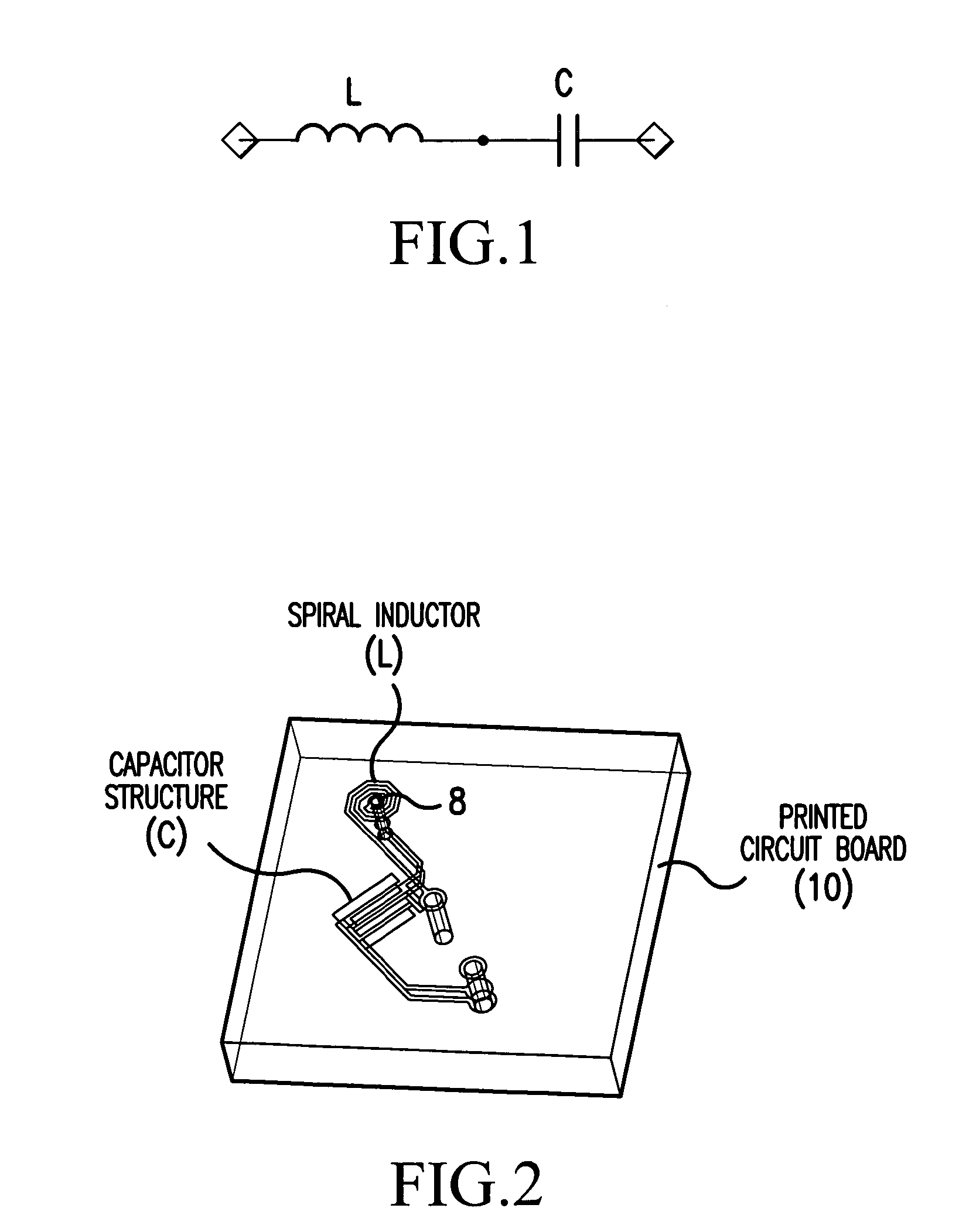
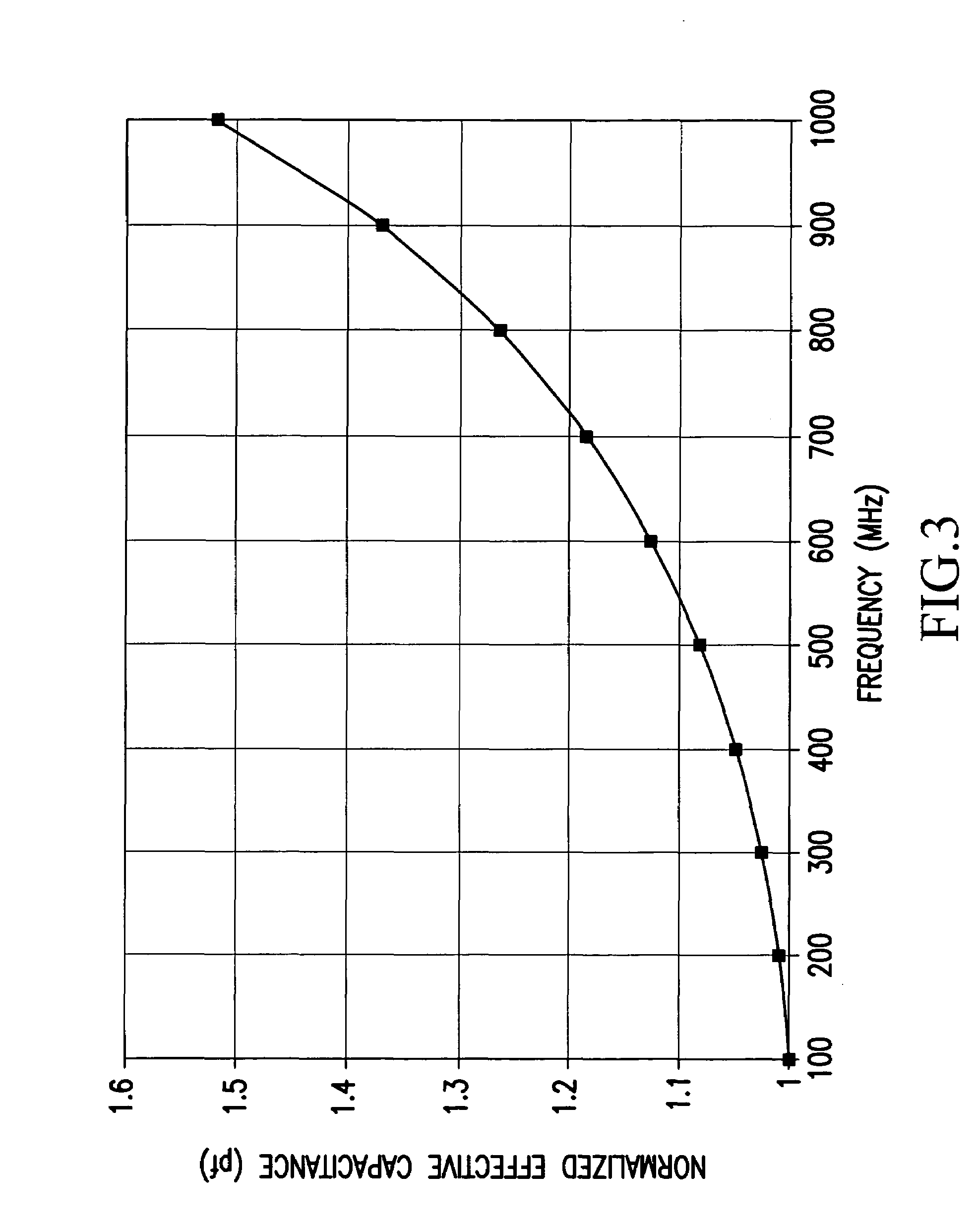
Next high frequency improvement by using frequency dependent effective capacitance
ActiveUS20050254223A1Improve performanceFlat effective capacitance responseOne-port networksPrinted circuit aspectsCapacitanceEffective capacitance
A connector is provided for simultaneously improving both the NEXT high frequency performance when low crosstalk plugs are used and the NEXT low frequency performance when high crosstalk plugs are used. The connector includes a first compensation structure provided on an inner metalized layer of the PCB at a first stage area of the PCB, and a second compensation structure, provided at a second stage area of the PCB, for increasing compensation capacitance with increasing frequency.
Owner:COMMSCOPE INC
Method and apparatus for training using variable transmit signal power levels
InactiveUS20060029147A1Increase power levelOvercomes drawbackPower managementTransmission control/equlisationPrecodingSignal on
A method and apparatus for a multiple channel communication device training, and processing utilizing a transmit signal power control operation. Multiple channel communication devices utilize inter-channel crosstalk mitigation techniques, such as MIMO processing modules or MIMO precoding systems, to cancel unwanted crosstalk coupling across active and provisioned channels. Upon provisioning and activation of a new channel that connects to the multiple channel communication device the signal on the new channel couples into other channels and the existing MIMO filtering or processing structure is untrained to mitigate the crosstalk from the new channel. A power control training operation prevents crosstalk from hindering operation on other channels during the training operation. During one example training operation, the power level of a transmit signal is incrementally increased as the crosstalk cancellation filter(s) are trained.
Owner:POSITRON ACCESS SOLUTIONS
Design and architecture of an impairment diagnosis system for use in communications systems
InactiveUS6870901B1Substations coupling interface circuitsInterconnection arrangementsCommunications systemAlgorithm
A method and apparatus are disclosed. The method includes one or more of the following: compiling statistical models of physical layers of a communications system; creating a priori distributions of cross-talk transfer functions; storing the models and the a priori distribution in a storage medium; and using the models and the a priori distributions to diagnose probable causes of events detected in said communications system.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
High speed multiple loop DSL system
ActiveUS7639596B2Increase speed and data carrying capabilityImprove rendering capabilitiesTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsFrequency spectrumDynamic spectrum management
A DSL system includes a multiple loop segment where K loops are bonded to provide a multiple loop segment having up to (2K−1) communication channels on which transmissions are vectored. The segment may be a drop to a customer premises, an inter-pedestal link, or any other suitable part of a larger DSL system. Generally the bonded loops are relatively short, being 300 meters or less. Signal vectoring is used to increase the speed and data carrying capability of the channels. In some embodiments, an expanded frequency spectrum also can be used to increase the data carrying capability of one or more of the channels. An impedance matching circuit may be coupled to each end of the segment to provided efficient transmission of data across the segment. A controller may provide control signals used to operate the segment as a vectored system and, if desired, frequency bandwidth control signals. The controller may monitor and / or collect data and information from the DSL system to assist in generating control signals. The controller can be a dynamic spectrum manager or DSM Center that includes a computer system and / or other hardware to assist in performing the required functions.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
Common mode noise cancellation
InactiveUS7315592B2Avoid complex processTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSubstations coupling interface circuitsCommunications systemDifferential signaling
A noise cancellation system configured to isolate and process a common mode noise signal to generate a cancellation signal. The cancellation signal is combined with a differential signal to cancel unwanted differential mode noise that coupled onto the differential signal. In one embodiment a multi-channel communication system utilizes two or more channels that are in close proximity to other alien channels. A common mode signal isolation unit is configured to isolate common mode noise. The common mode noise signal is processed with a filter or other means to generate a cancellation signal. The cancellation signal is combined with the differential signal to thereby cancel noise that coupled onto the differential signal. The processed common mode noise signal may be made to approximate the differential mode noise signal. The common mode signal may be obtained from a center tap of a transformer, or a sensing winding of a three winding transformer.
Owner:POSITRON ACCESS SOLUTIONS
Next high frequency improvement by using frequency dependent effective capacitance
ActiveUS7190594B2Improve performanceFlat responseOne-port networksPrinted circuit aspectsCapacitanceEngineering
Owner:COMMSCOPE INC
Optimizing precoder settings using average sinr reports for groups of tones
InactiveUS20090060013A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCross-talk reductionPrecodingCrosstalk measurement
Techniques are disclosed for compensating for crosstalk using adaptation of data signals transmitted over respective channels of a communication network. In one example, a method comprises the following steps. Data is transmitted to a communication network device via a communication line during a sequence of periods. For each period of the sequence of periods, a separate value of a measure of crosstalk that was measured at the communication network device is received, each value being an average of measurements at the device of measures of crosstalk for a plurality of communication network signal subcarriers. For each individual signal subcarrier of the plurality, a matrix is updated based on the received values, the matrix being configured to precode data transmissions to the communication network device over the individual signal subcarrier. The communication network may be a DSL system, the signal subcarriers may be DSL tones, and the measure of crosstalk may be a SINR value.
Owner:RPX CORP
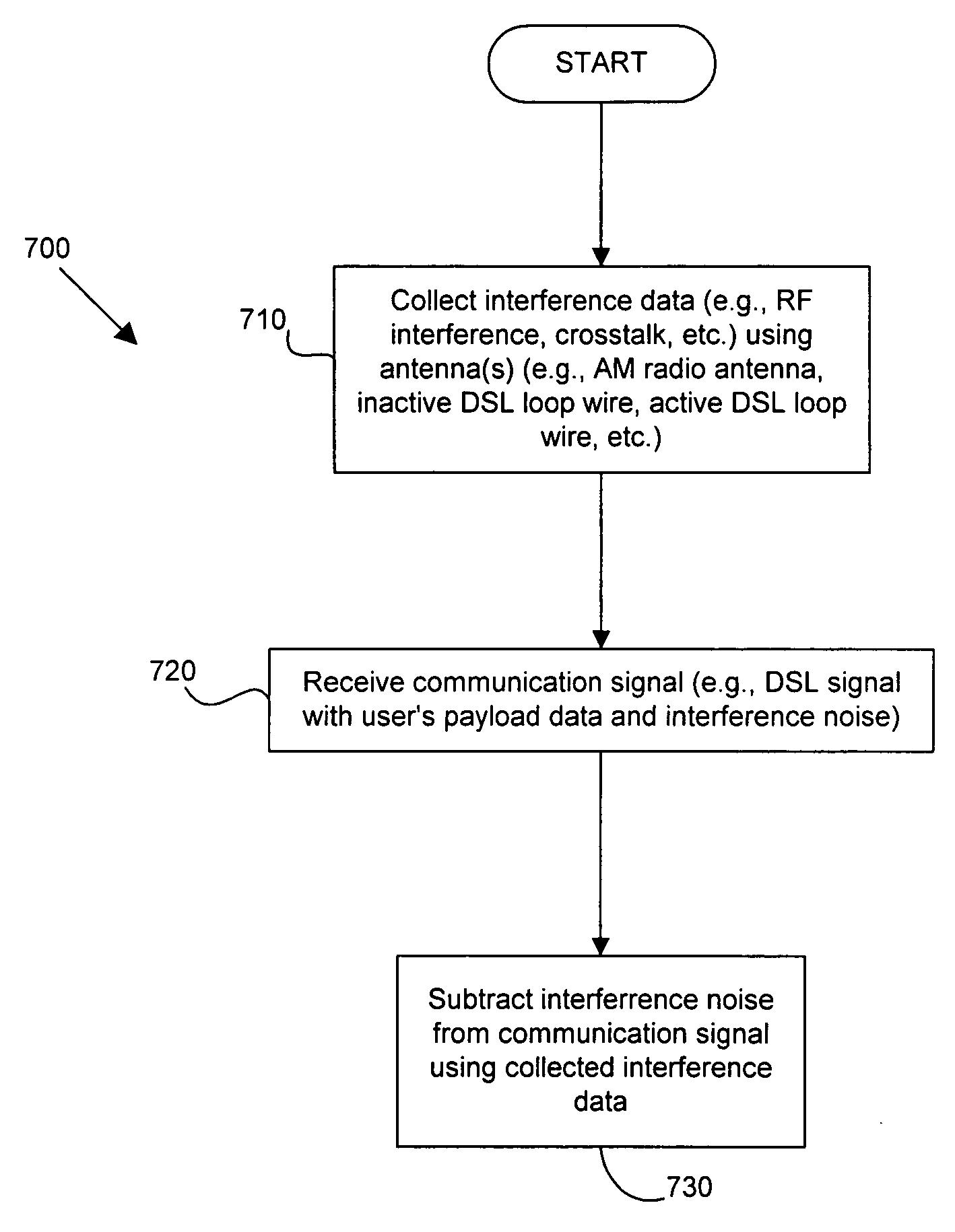
Interference cancellation system
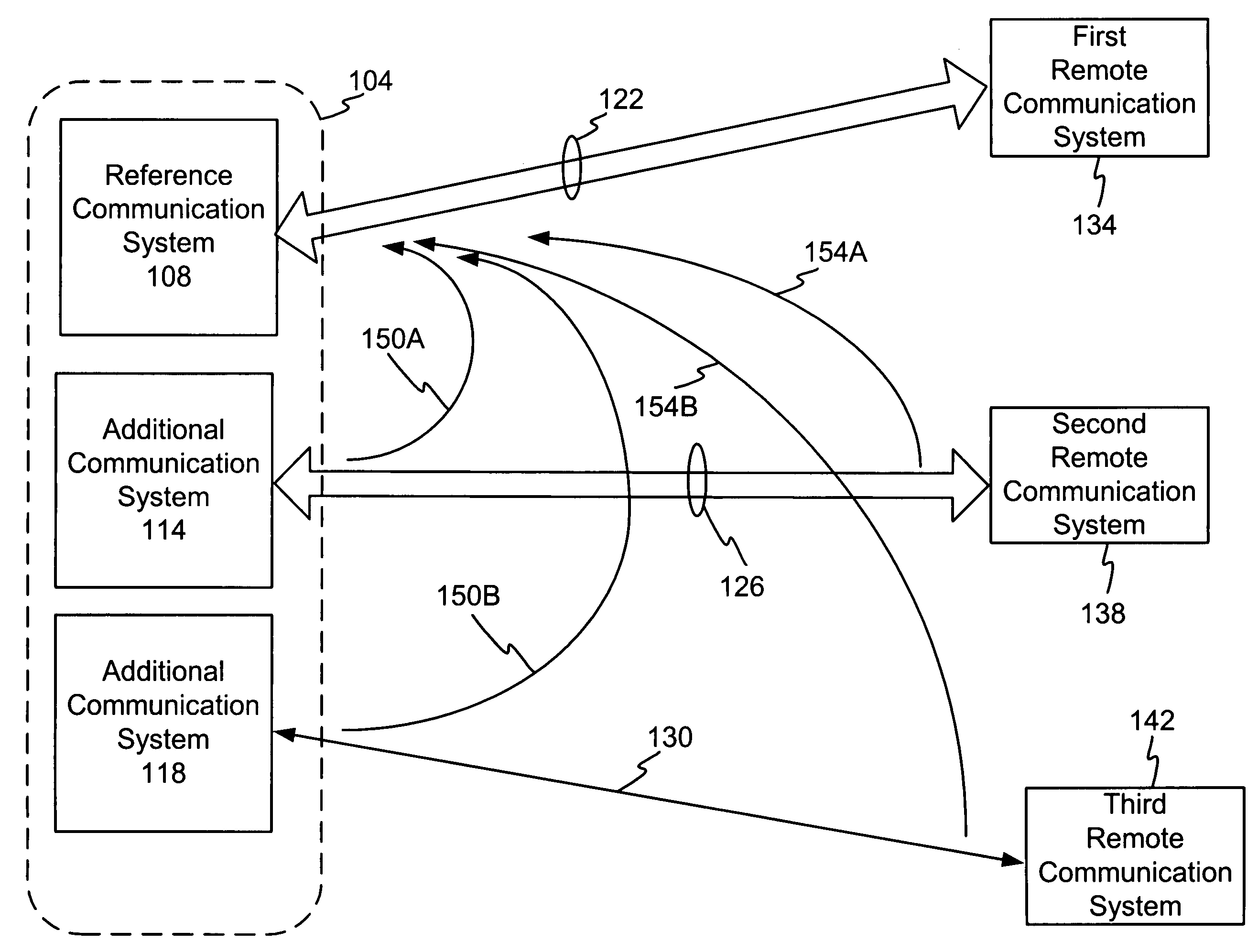
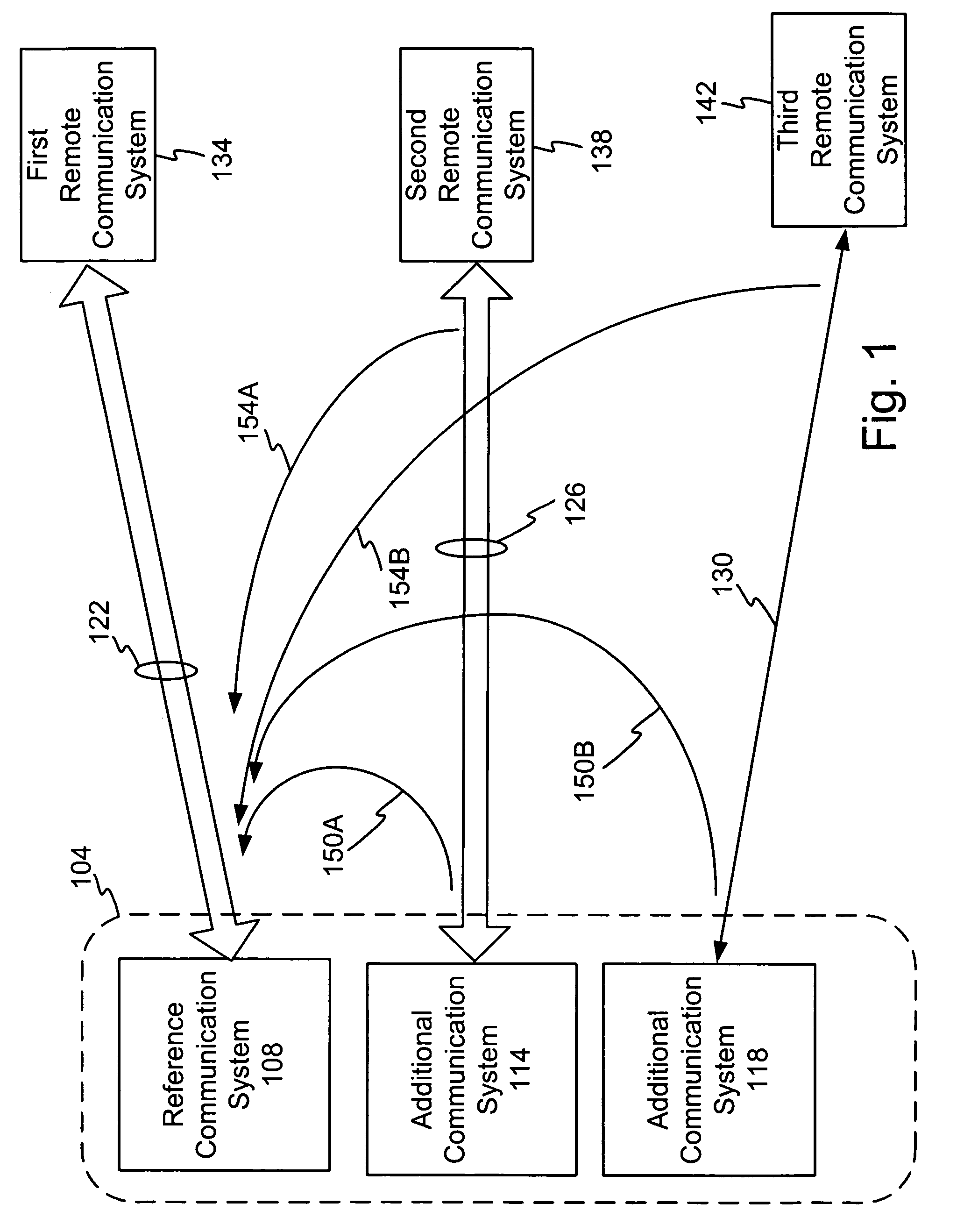
ActiveUS20060039454A1Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsError preventionInterference cancelationInterference canceller
A DSL or other communication system includes a modem or other communication device having at least one antenna that is configured to collect interference data relating to interference noise affecting communication signals being received by the communication device. The interference may include RF interference, such as AM radio interference, crosstalk and other types of interference from various sources. The interference data collected by the antenna is used by an interference canceller to remove and / or cancel some or all of the interference affecting received signals. In some embodiments of the present invention, more than one antenna may be used, wherein each antenna can collect interference data pertaining to a single source of interference noise. Where a modem or other communication device is coupled to multiple telephone lines, only one of which is being used as the active DSL line, wires in the remaining telephone lines or loops can be used as antennas. Moreover, the antenna may be an antenna, per se, such as a compact AM radio antenna or any other suitable structure or device for collecting the type(s) of interference affecting signals received by the communication device.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com