Patents
Literature
755 results about "Common-mode signal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
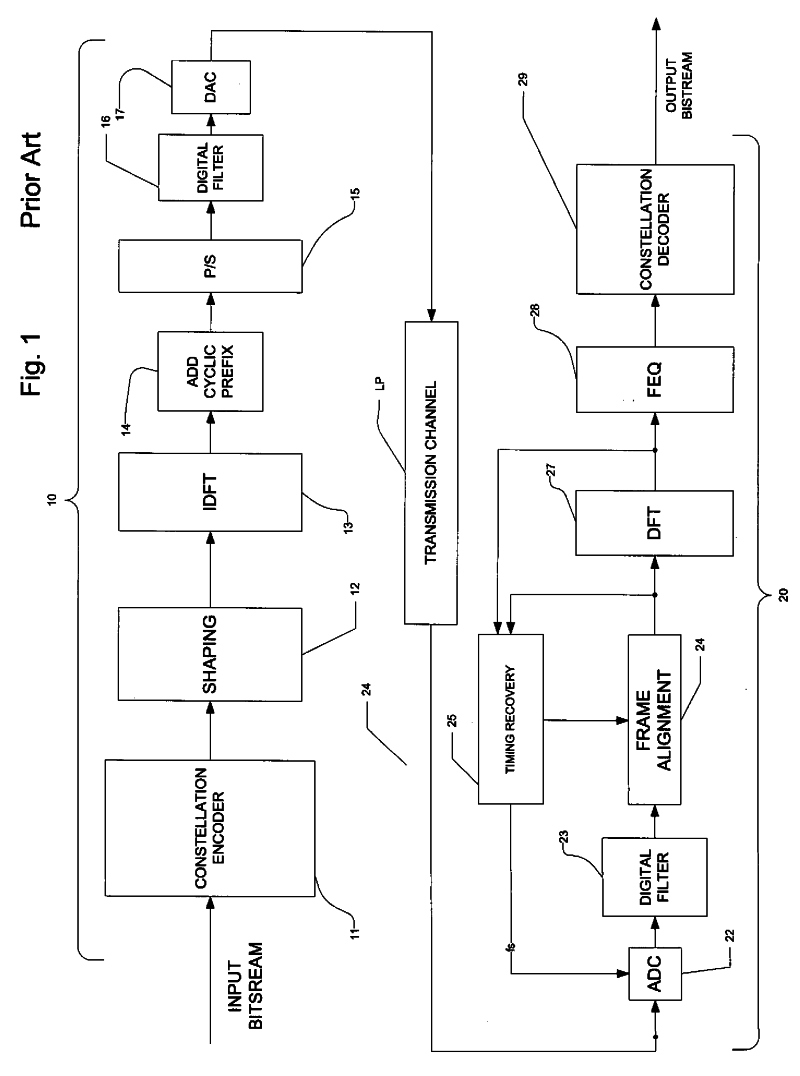
Common-mode signal is the component of an analog signal which is present with one sign on all considered conductors. In telecommunication, common-mode signal on a transmission line is known as longitudinal voltage. In electronics where the signal is transferred by differential voltage, the common-mode signal is a half-sum of voltages Ucₘ=(U₁+U₂)/2 When referenced to the local common or ground, a common-mode signal appears on both lines of a two-wire cable, in-phase and with equal amplitudes.
Balance feed differential slot antenna for restraining common-mode noise
ActiveCN104092028ASuppress emissionSuppress receptionAntenna couplingsSlot antennasPlanar substrateWaveguide
The invention discloses a balance feed differential slot antenna for restraining common-mode noise. Based on a planar substrate integrated waveguide structure, the slot antenna is adopted as a radiating unit; due to different electric field distributions in the substrate integrated waveguide under different stimulation modes, energy can be effectively radiated under the different-mode signal stimulation, and most of energy is reflected under the common-mode signal stimulation. Due to the adoption of the antenna of the structure, different-mode signals can be effectively transmitted and received, meanwhile, common-mode signals are restrained from being transmitted and received, and therefore the function of restraining common-mode noise is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
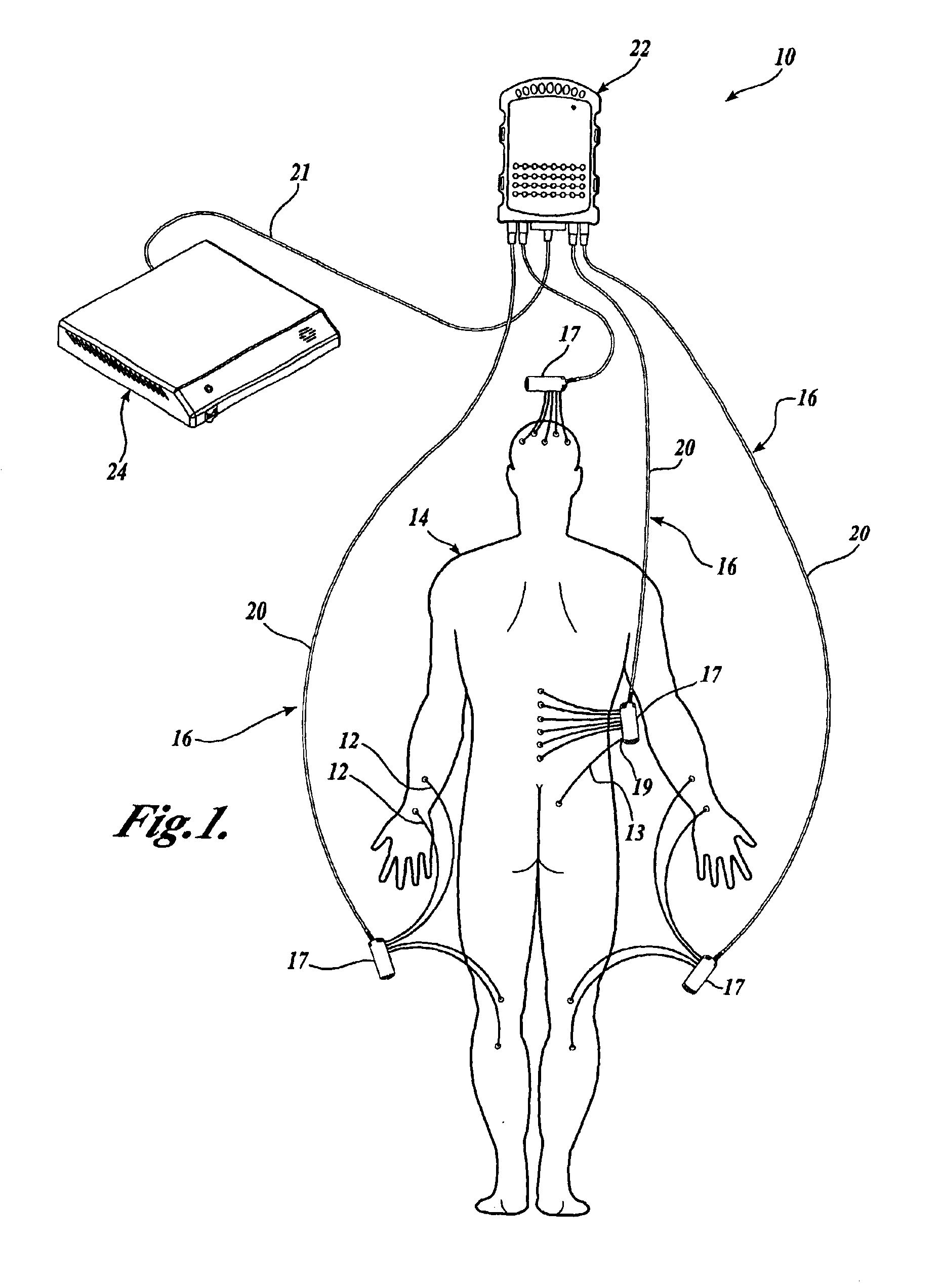
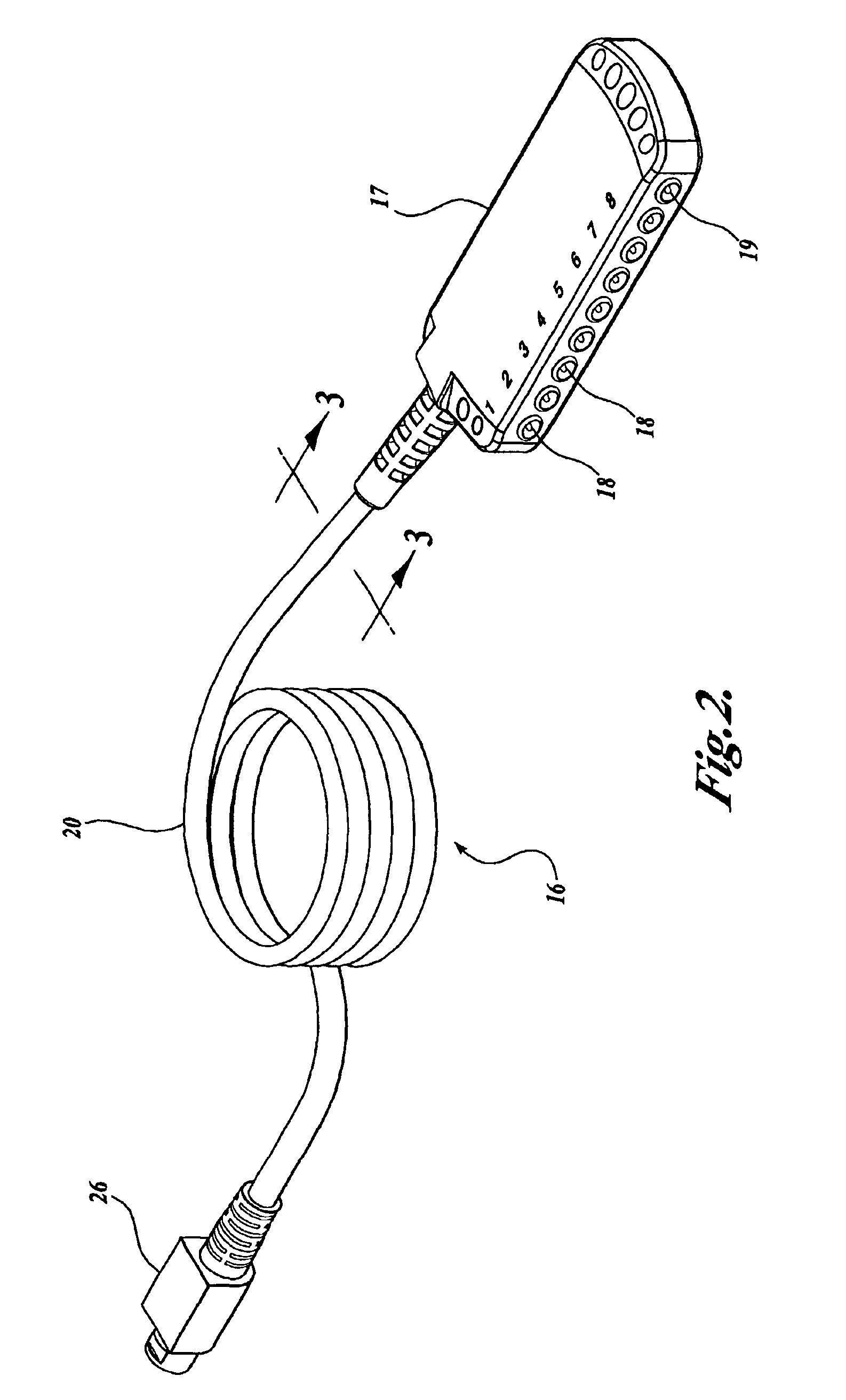
Signal Common Mode Cancellation For Handheld Low Voltage Testing Device
InactiveUS20080243021A1Reduce interferenceReduce signal noiseElectroencephalographySensorsAudio power amplifierLow voltage
An apparatus for monitoring bioelectric signals of a patient which includes a processing system and an interface for receiving external electrical signals representative of a condition of the patient. The interface is configured to convey a representation of the received external signals to the processing system, and includes a common mode cancellation amplifier circuit which is adapted to reduce common mode signal noise present in the external signals.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Controlled mode conversion connector for reduced alien crosstalk
ActiveUS7201618B2Reduce alien crosstalkCoupling device detailsTwo-part coupling devicesElectrical conductorElectrical polarity
A telecommunications connector includes first and second pairs of electrical conductors. The first and second pairs of conductors are arranged in one region of the connector such that one conductor of the first pair is selectively positioned to be closer to both of the conductors of the second pair than is the other conductor of the first pair, and such that the one conductor of the first pair couples a common mode signal of a first polarity onto the conductors of the second pair. In another region of the connector the other conductor of the first pair is selectively positioned to be closer to both of the conductors of the second pair to asymmetrically couple a common mode signal of a second polarity onto the conductors of the second pair.
Owner:COMMSCOPE INC
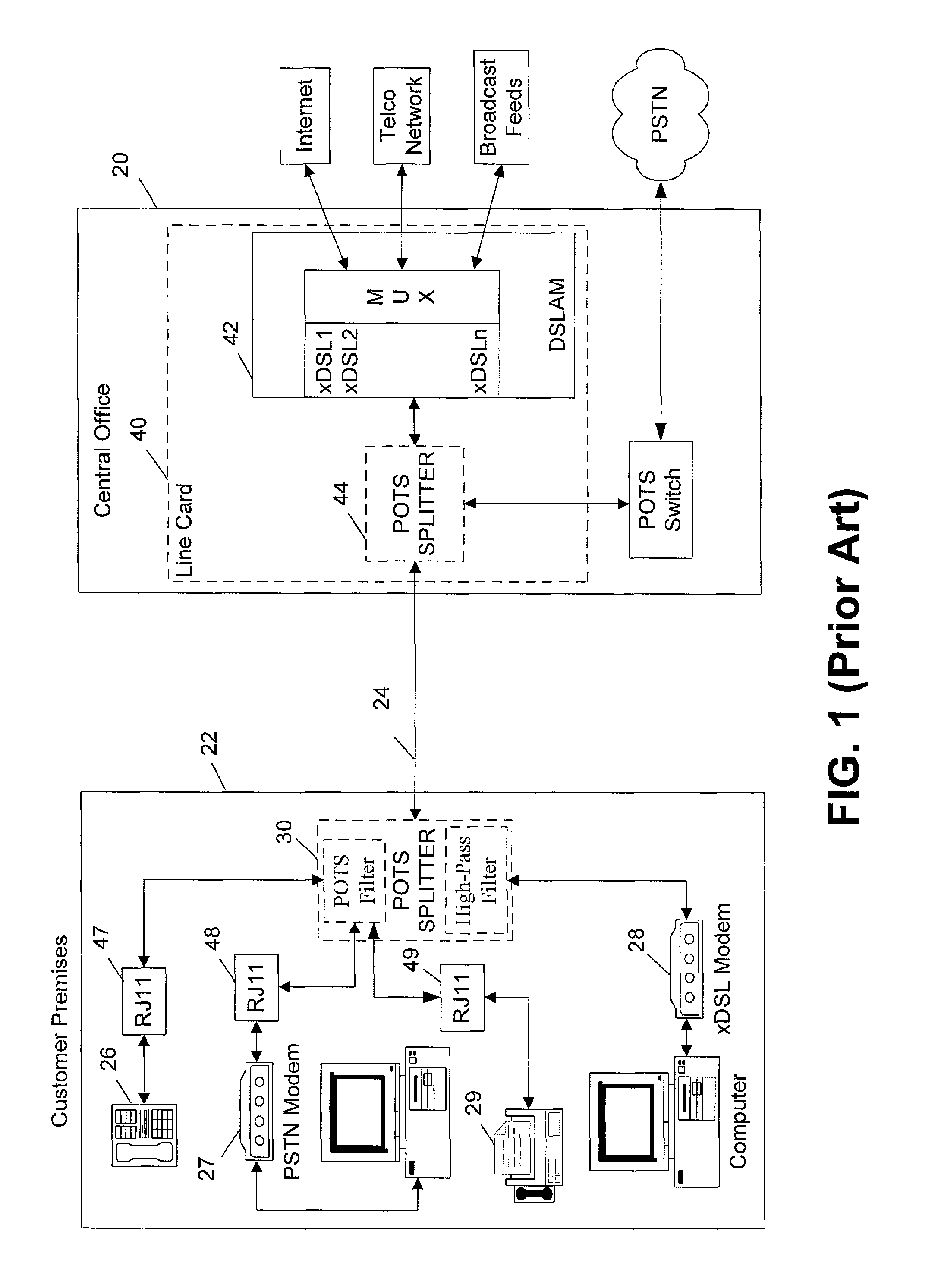
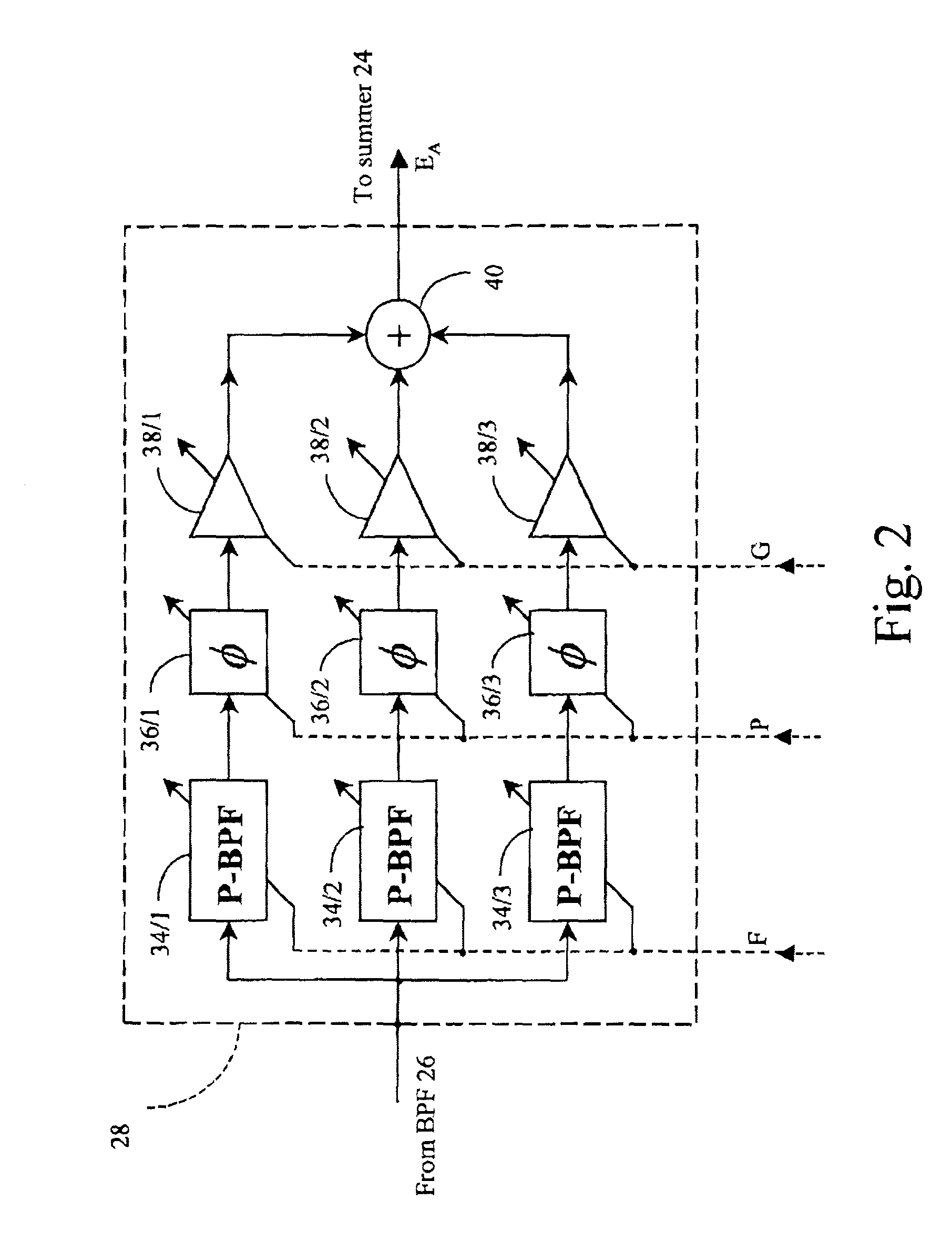
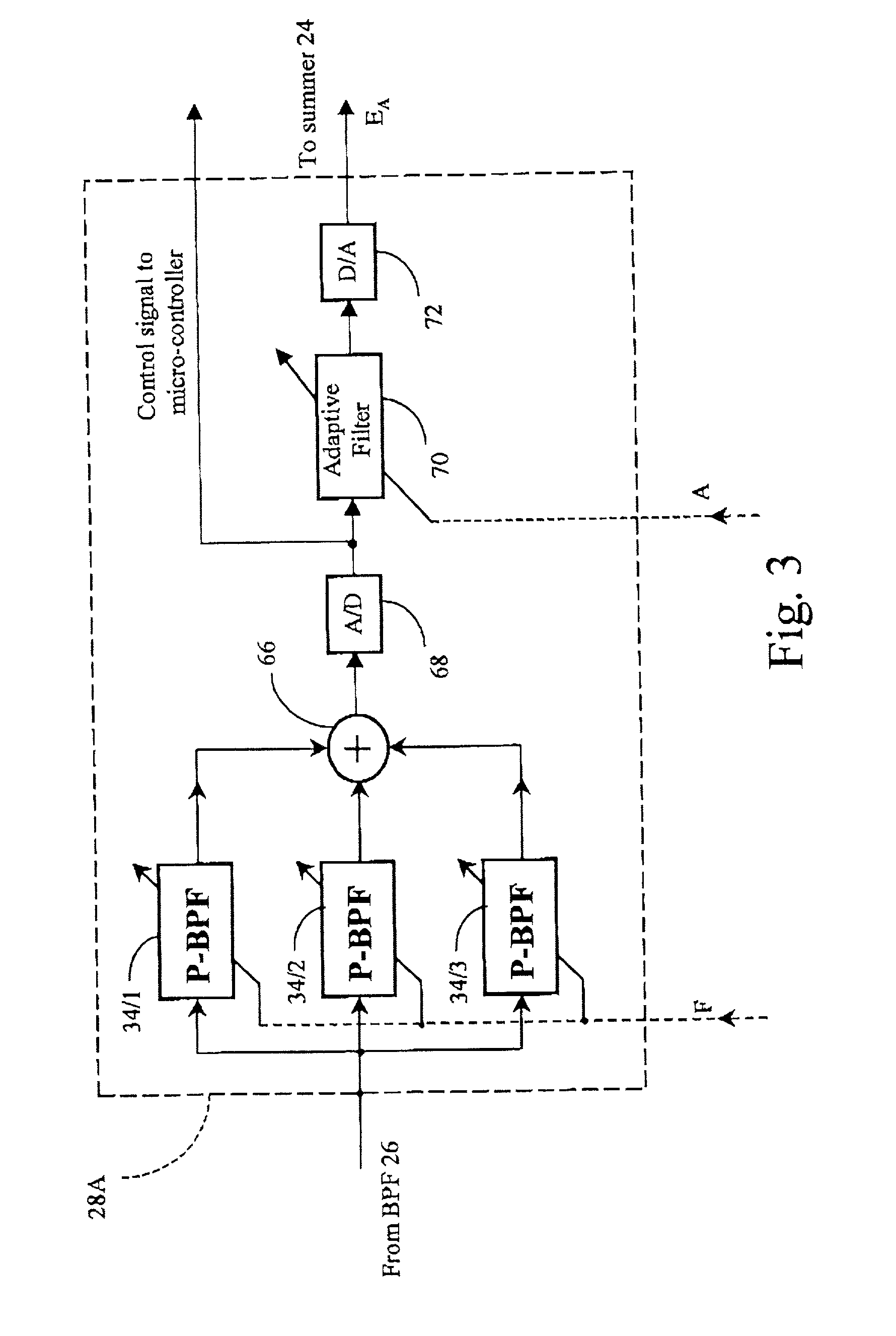
Method and apparatus for cancelling common mode noise occurring in communications channels
InactiveUS6940973B1Substations coupling interface circuitsInterconnection arrangementsCapacitanceAdaptive filter
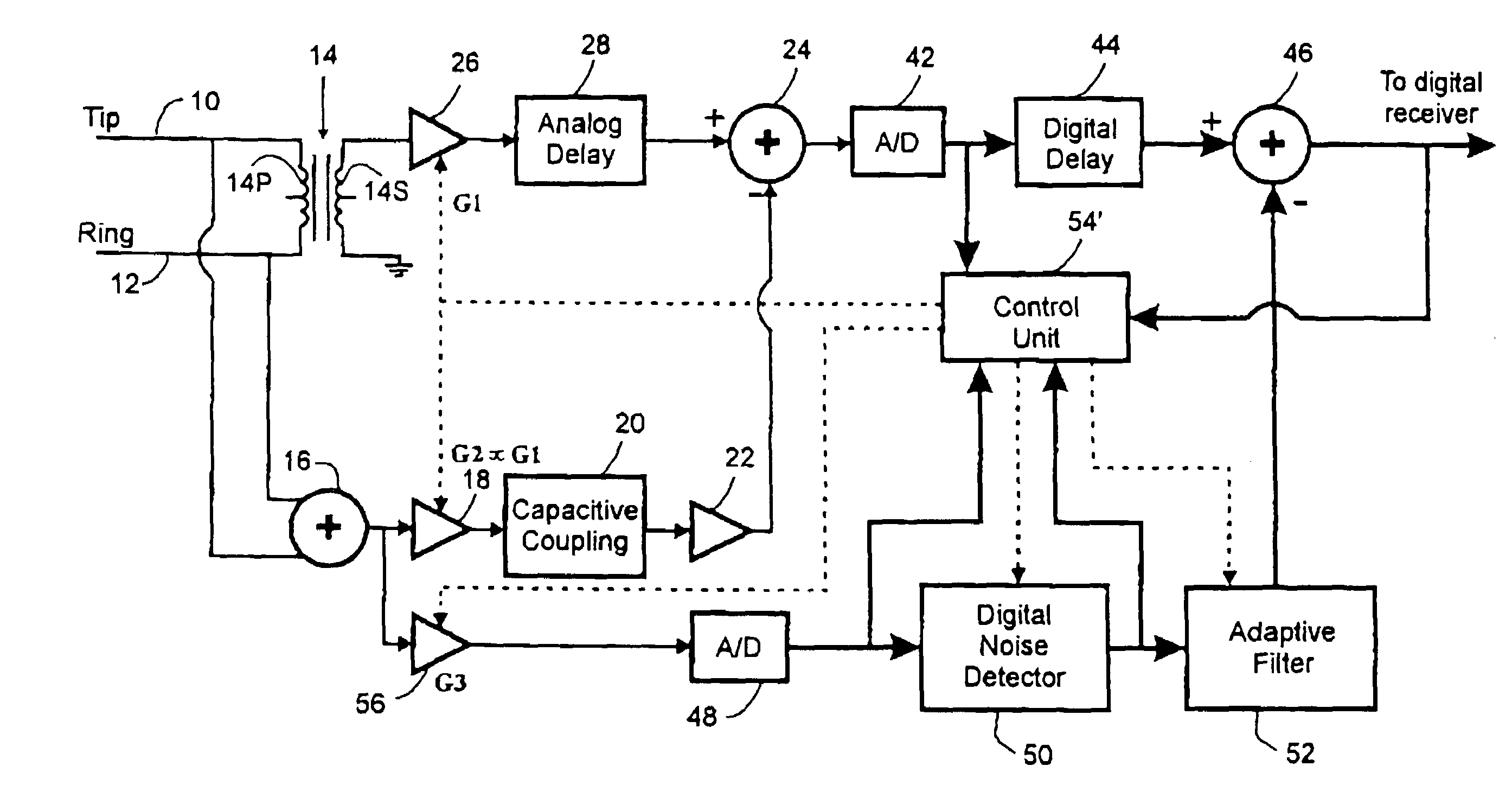
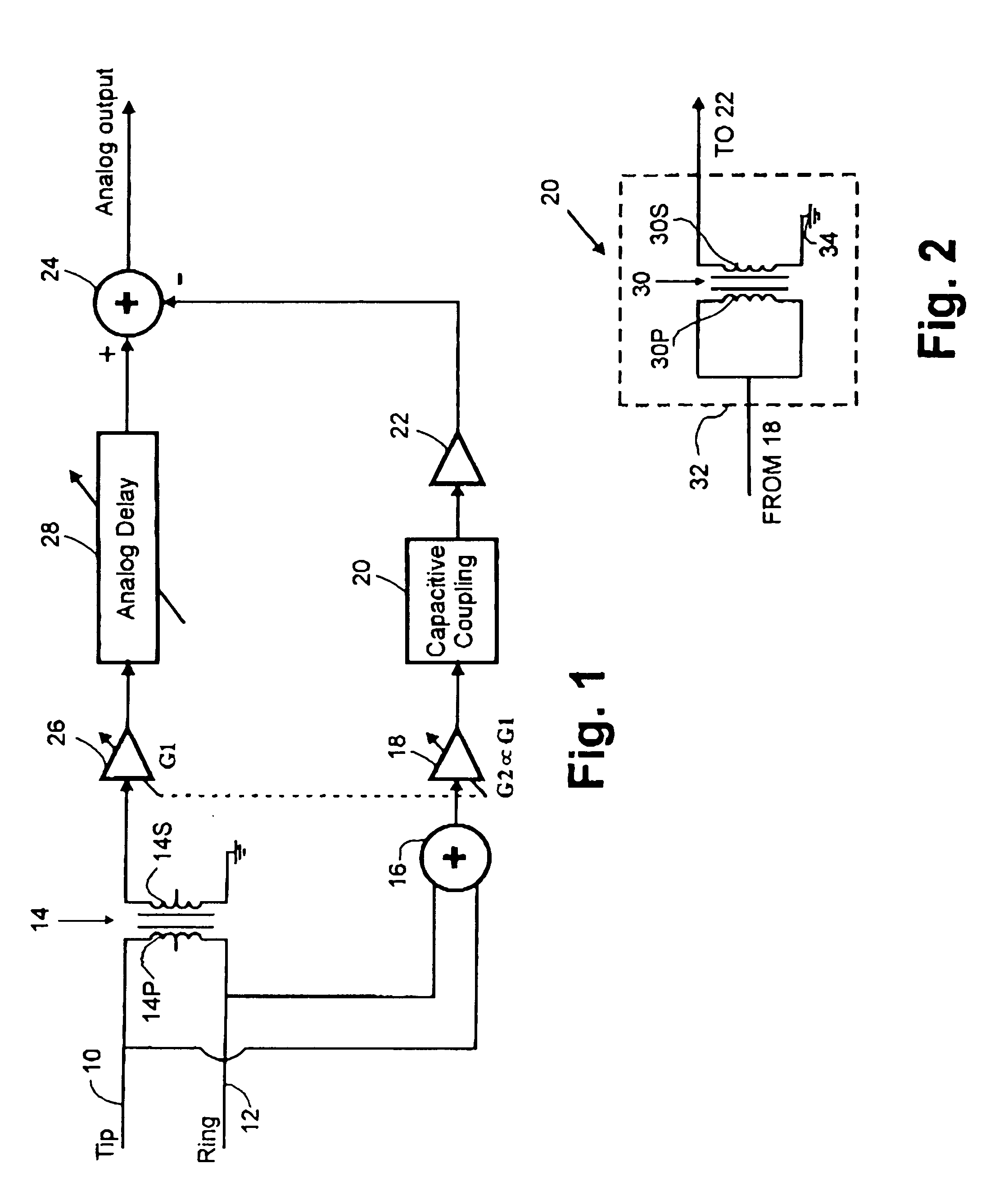
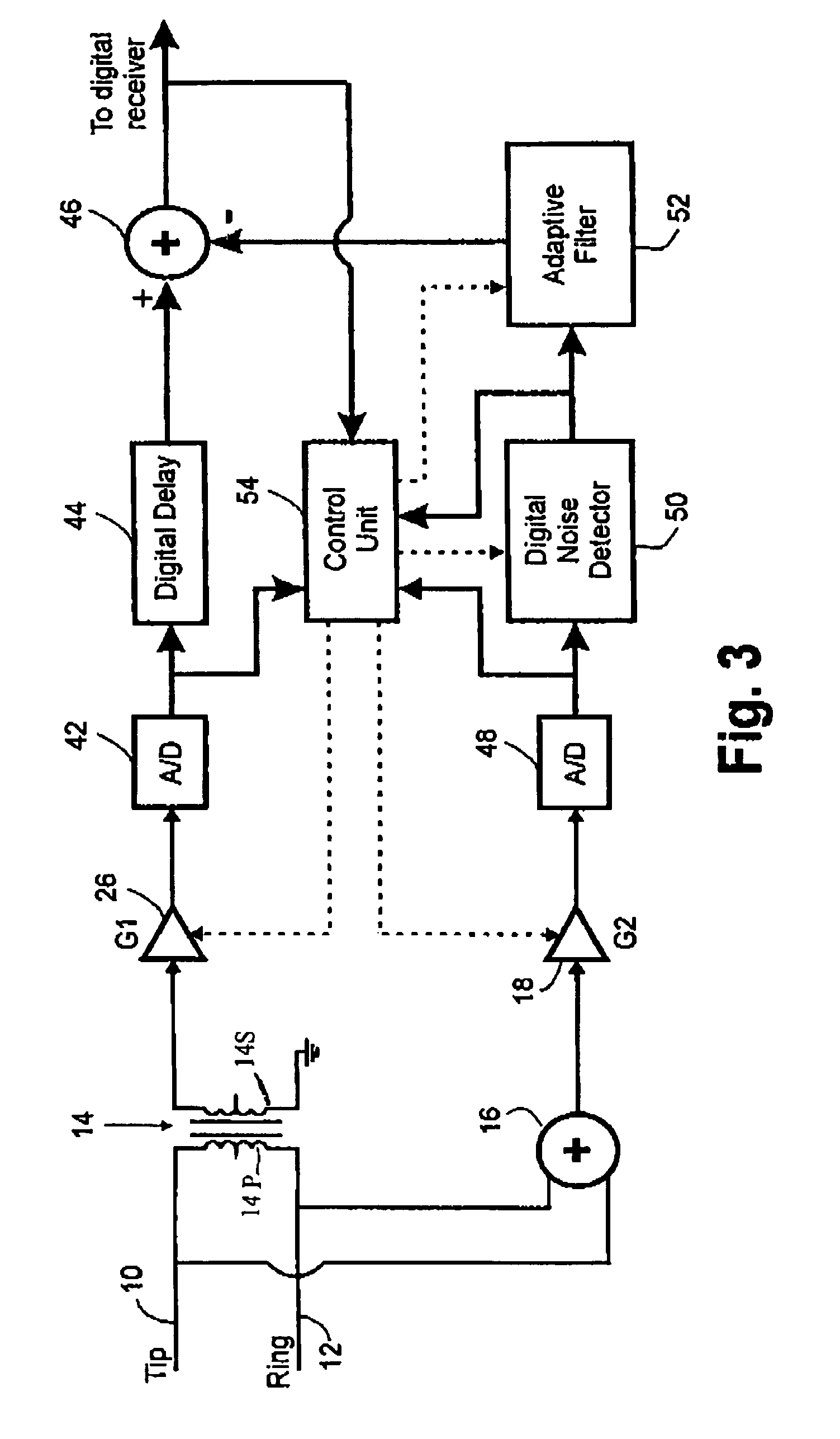
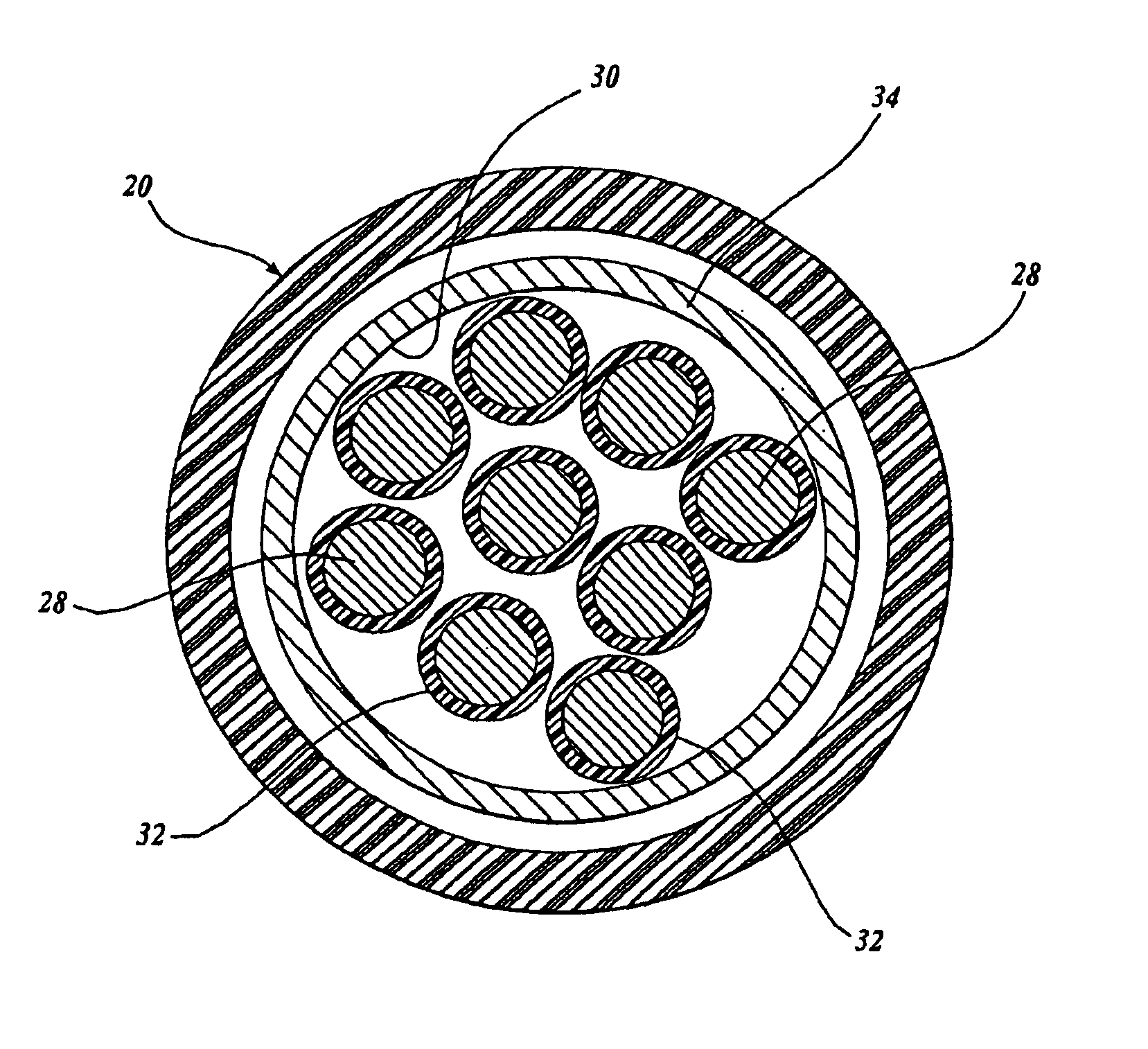
In order to overcome problems when using an adaptive filter for cancellation of common-mode noise in digital subscriber loops, caused by a portion of the differential signal being converted to common mode, which degrades the performance of the filter, a noise cancellation technique is proposed which compensates for this cross-coupled signal energy. In particular, a digital noise detector is used to detect one or more noisy frequency bands of the common mode signal and pass only the digitized common mode signal in those detected frequency bands through the adaptive filter to produce a digital common mode noise estimate signal. A control unit adjusts coefficients of the adaptive filter to reduce correlation between the differential signal and common mode signal. It is also proposed to compensate for the effects of stray capacitive coupling across the usual hybrid device by including an equivalent capacitive component in a common mode noise estimation circuit.
Owner:BELL CANADA
System and device for reducing signal interference in patient monitoring systems
InactiveUS6870109B1Reduce signal interferenceBioelectric signal measurementPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsShielded cableMonitoring system
A system and device for mitigating interference in patient physiological monitoring is provided, particularly in surgical environments. One or more sets of electrodes are placed on a patient's body and connected to corresponding terminals of an input extender. The terminals of the input extender are connected to a set of signal wires encased by a ferrous shielded cable. The ferrous shielded cable connects to a signal processing unit, which includes a differential amplifier and an active drive topology to drive the shield with a common mode signal. The signal processing unit connects to physiological monitoring equipment.
Owner:CADWELL INDS
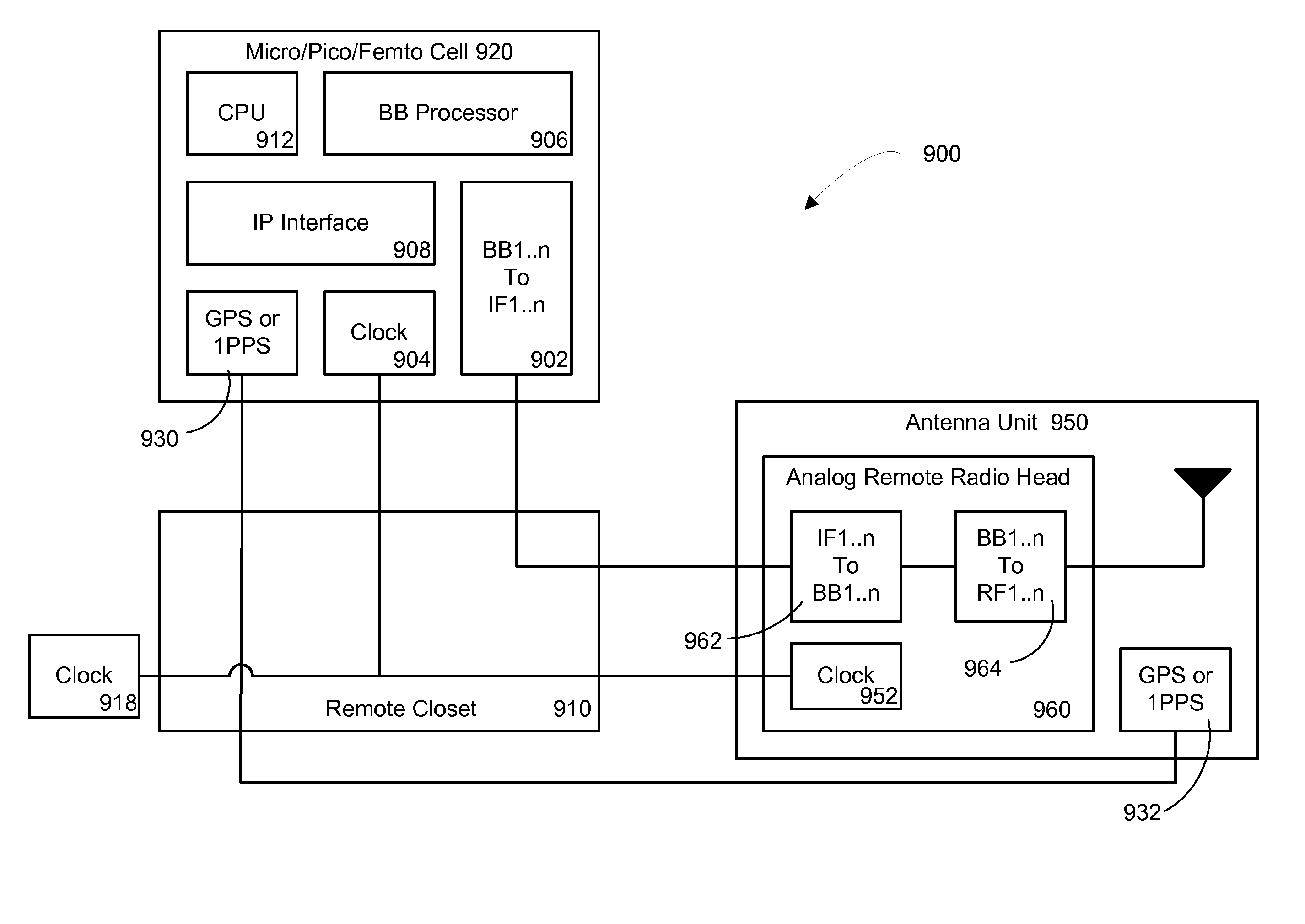
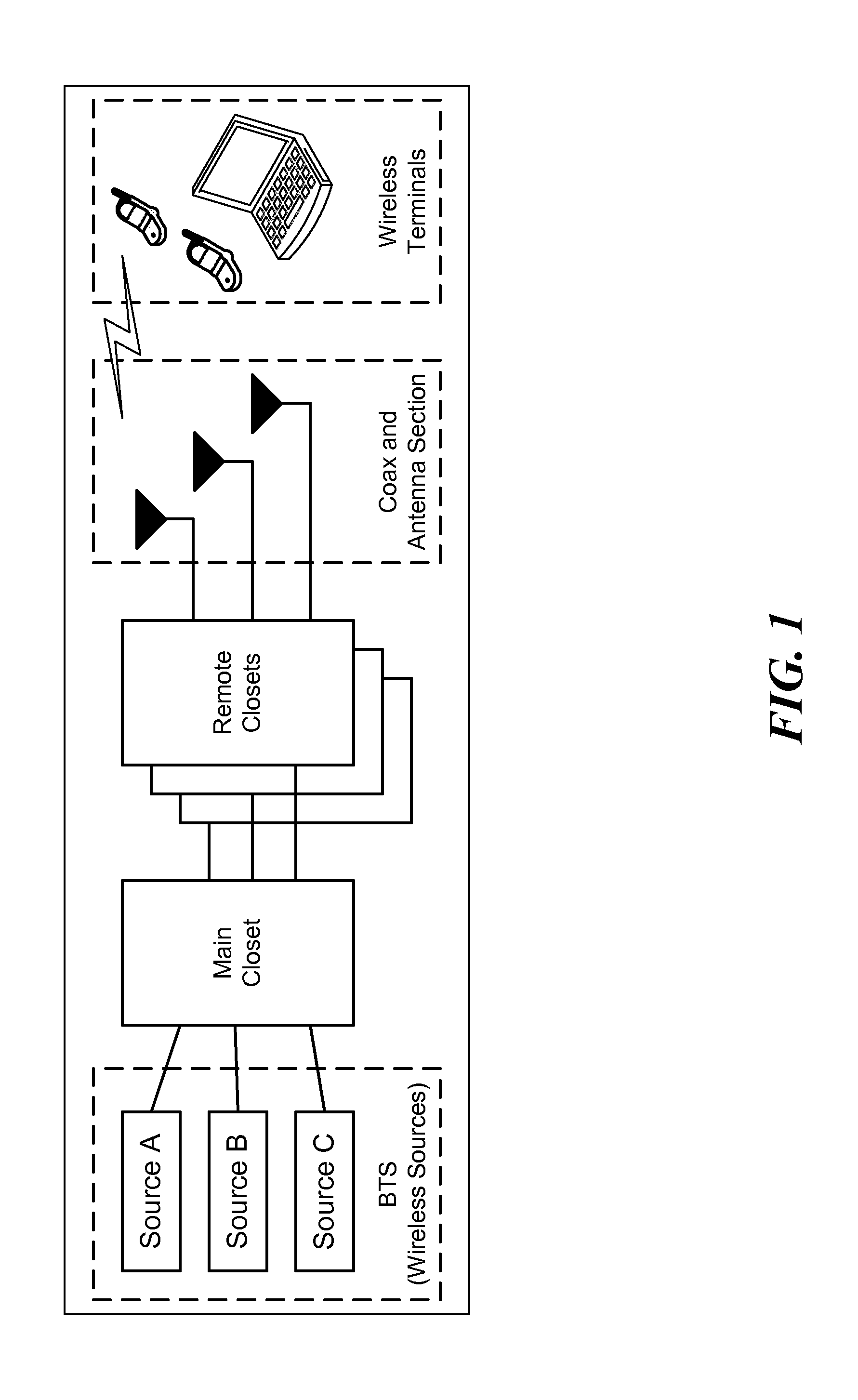
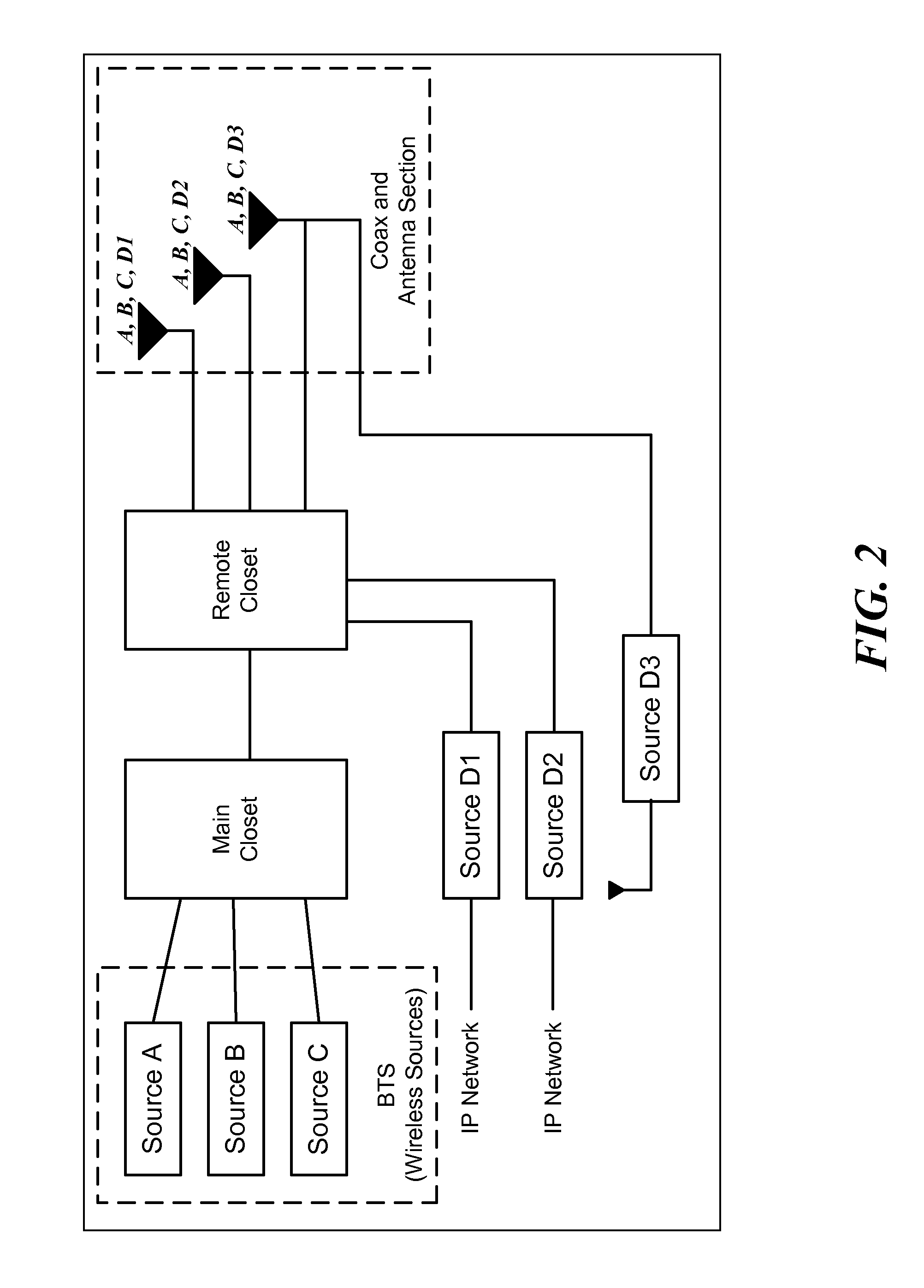
Multiple Data Services Over a Distributed Antenna System
InactiveUS20100093391A1Avoid spendingReduce energy costsSite diversityNetwork traffic/resource managementDistributed antenna systemGps receiver
The invention is directed to a method and system for supporting multiple time division duplexed (TDD) based wireless services or frequency division duplexed (FDD) wireless services on a Distributed Antenna System (DAS). A DAS can support a many wireless services, including voice and data services using the same physical equipment. TDD based services use a common clock signal to synchronize the components of the DAS for transmission and reception of TDD signals. In accordance with the invention, the DAS can include a GPS receiver which can extract a timing signal (such as a 1 pps signal) from a GPS signal and distribute the timing signal to any and all components of the DAS to enable synchronization of the components for transmitting and receiving TDD signals. The GPS receiver can be part of the interface that connects a TDD based service to the DAS or separate component of the DAS. In accordance with the invention, the DAS can distribute a reference clock signal to all of the components of the DAS in order to maintain zero frequency shift while manipulating with the carrier frequencies of the various wireless services carried by the DAS. In addition, and in accordance with the invention, two analog architectures for better integration between the services sources (BTS) and the DAS are disclosed.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM WIRELESS
System and method for canceling crosstalk
ActiveUS6999504B1Improved crosstalk cancellation circuitryReduce crosstalkFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexCrosstalk cancellationModem device
A method and apparatus are disclosed for reducing crosstalk in a telecommunication system. Broadly, the present invention utilizes a common mode signal to obtain additional information that can be used to better approximate the transmitted signal (by approximating and canceling crosstalk or otherwise). In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, a modem is provided having improved crosstalk cancellation circuitry for canceling crosstalk received on a local loop (or otherwise estimating the remotely transmitted signal) carrying modem communications. The modem includes a first input for receiving a signal carried on the local loop and a second input for receiving a signal obtained from the common mode. The modem further includes processing circuitry configured to either reduce crosstalk present in the signal carried on the local loop, or to otherwise closely approximate the remotely transmitted signal. Using both the first and second signals allows the processing circuitry of the modem to obtain more accurate results.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
RF isolator with differential input/output
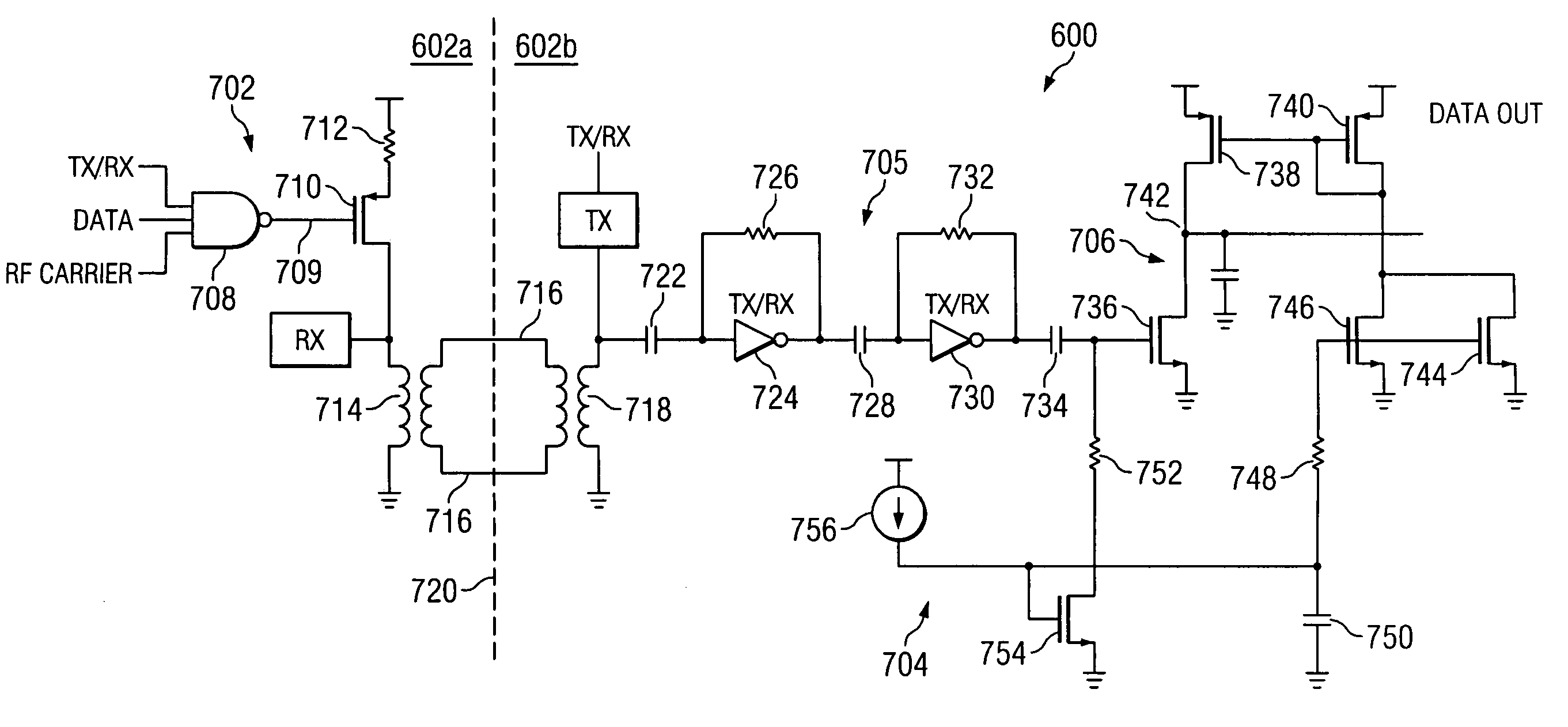
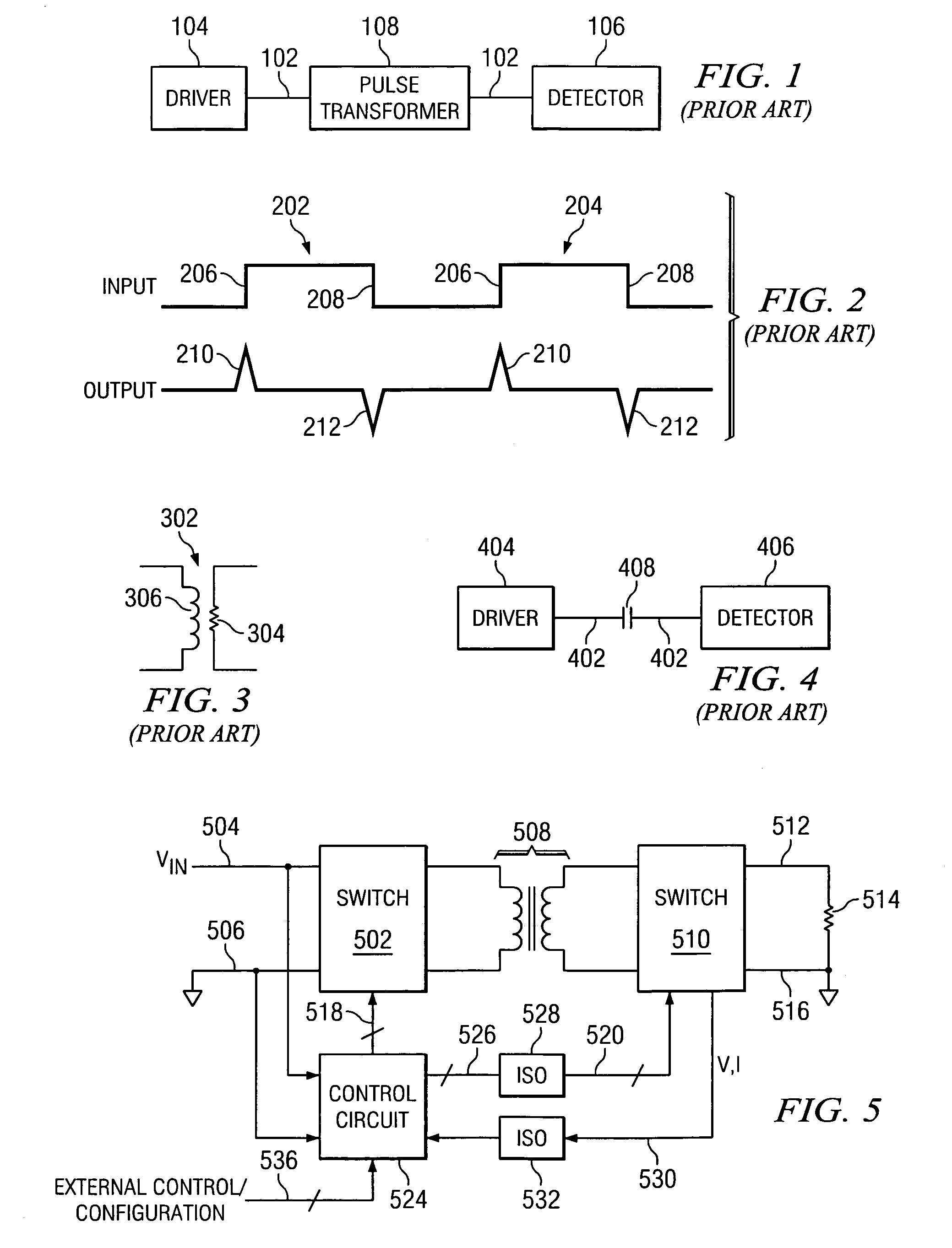
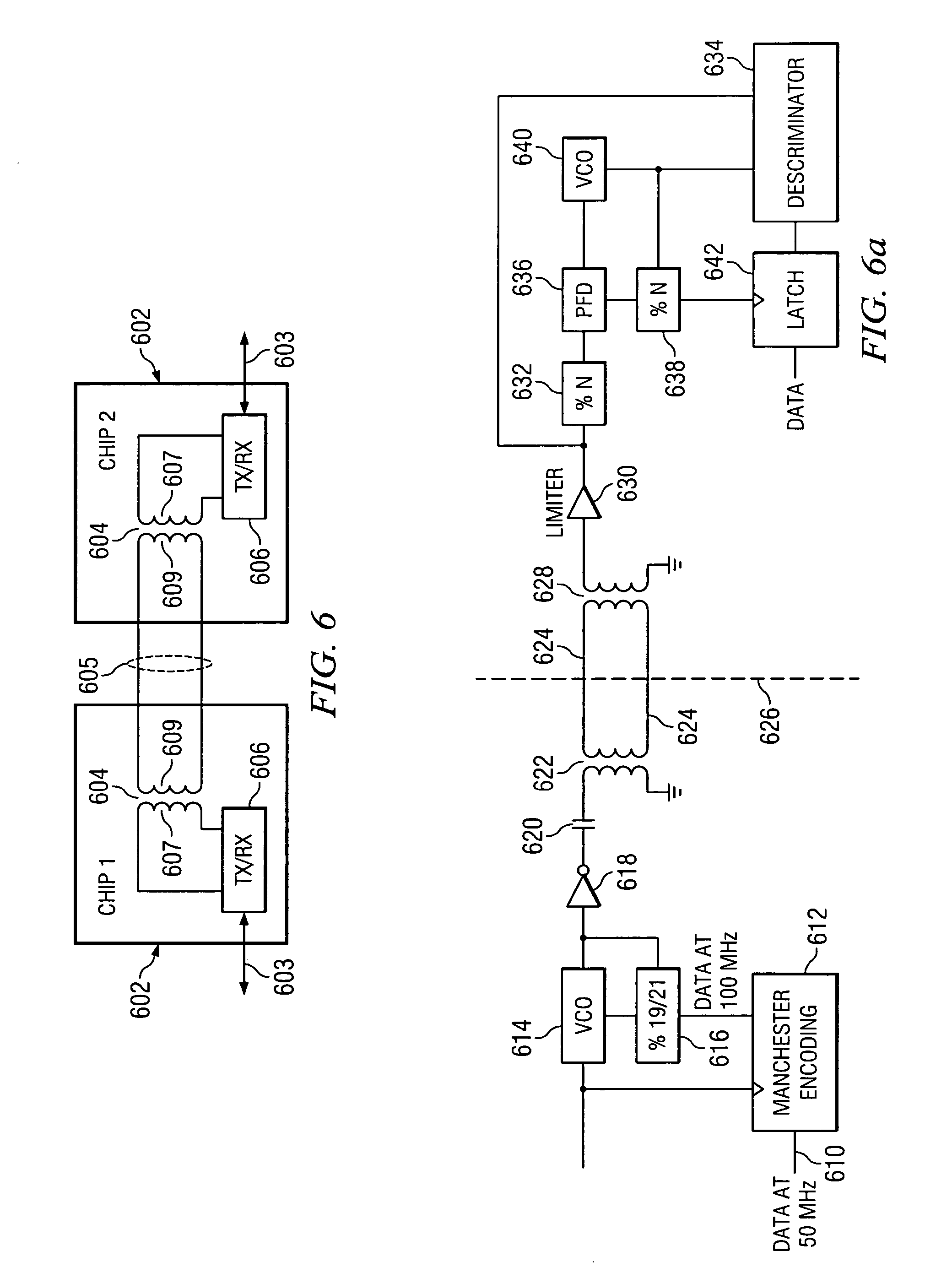
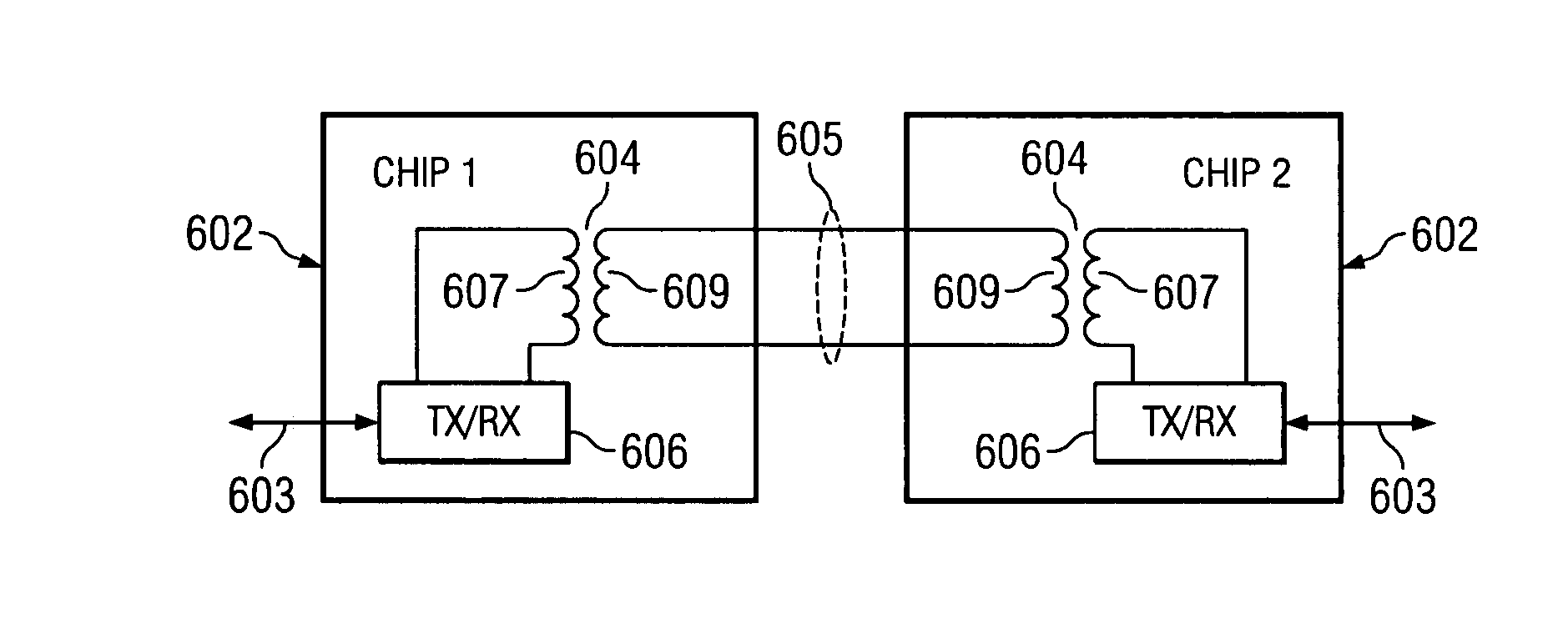
ActiveUS7376212B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
RF isolator with differential input/output
ActiveUS20050271148A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInput/outputCommon-mode signal
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
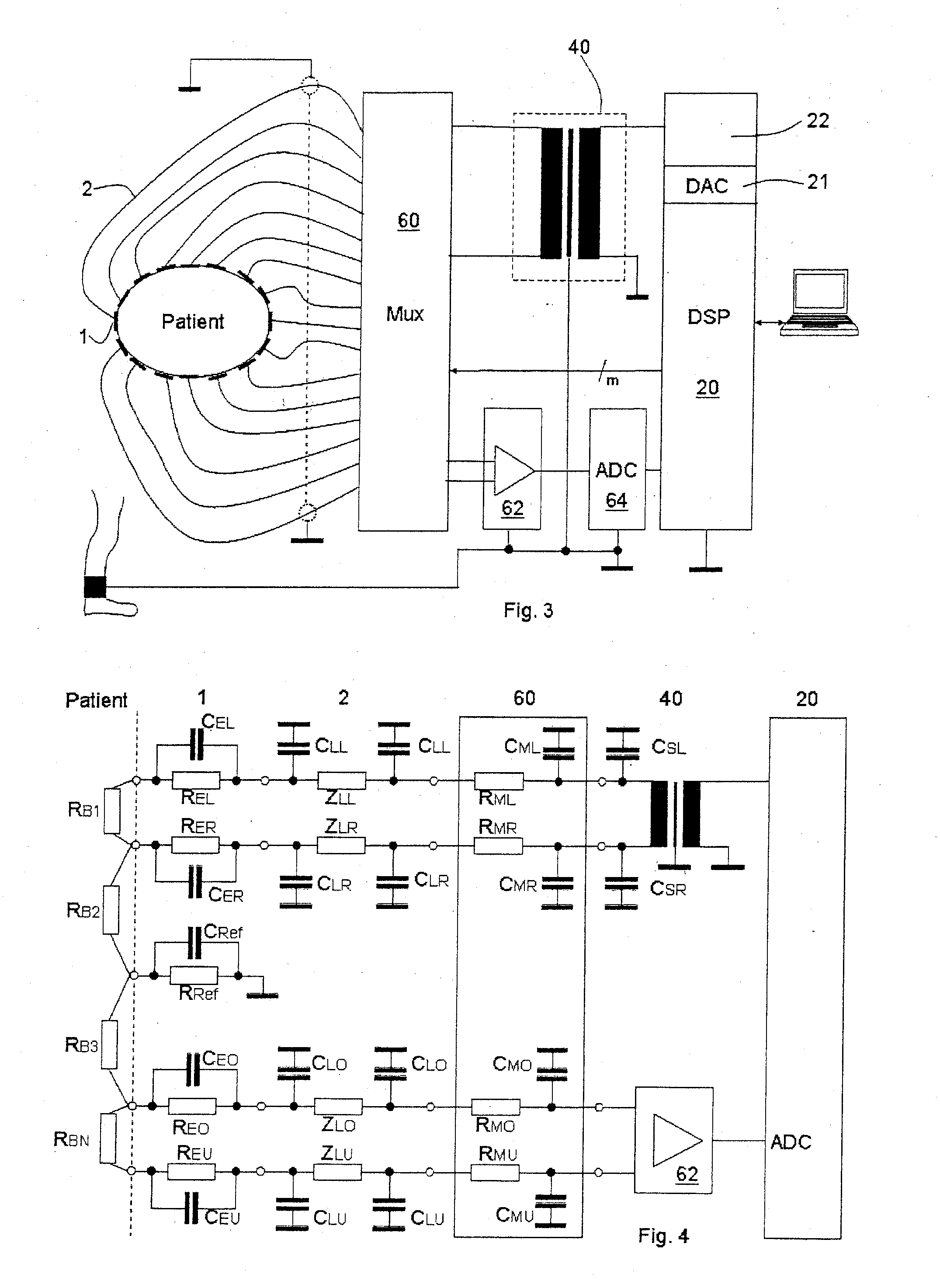
Electroimpedance tomograph with common-mode signal suppression
ActiveUS20070010758A1Suppress interferenceReduce signalingResistance/reactance/impedenceAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesElectrical resistance and conductanceImpedance distribution
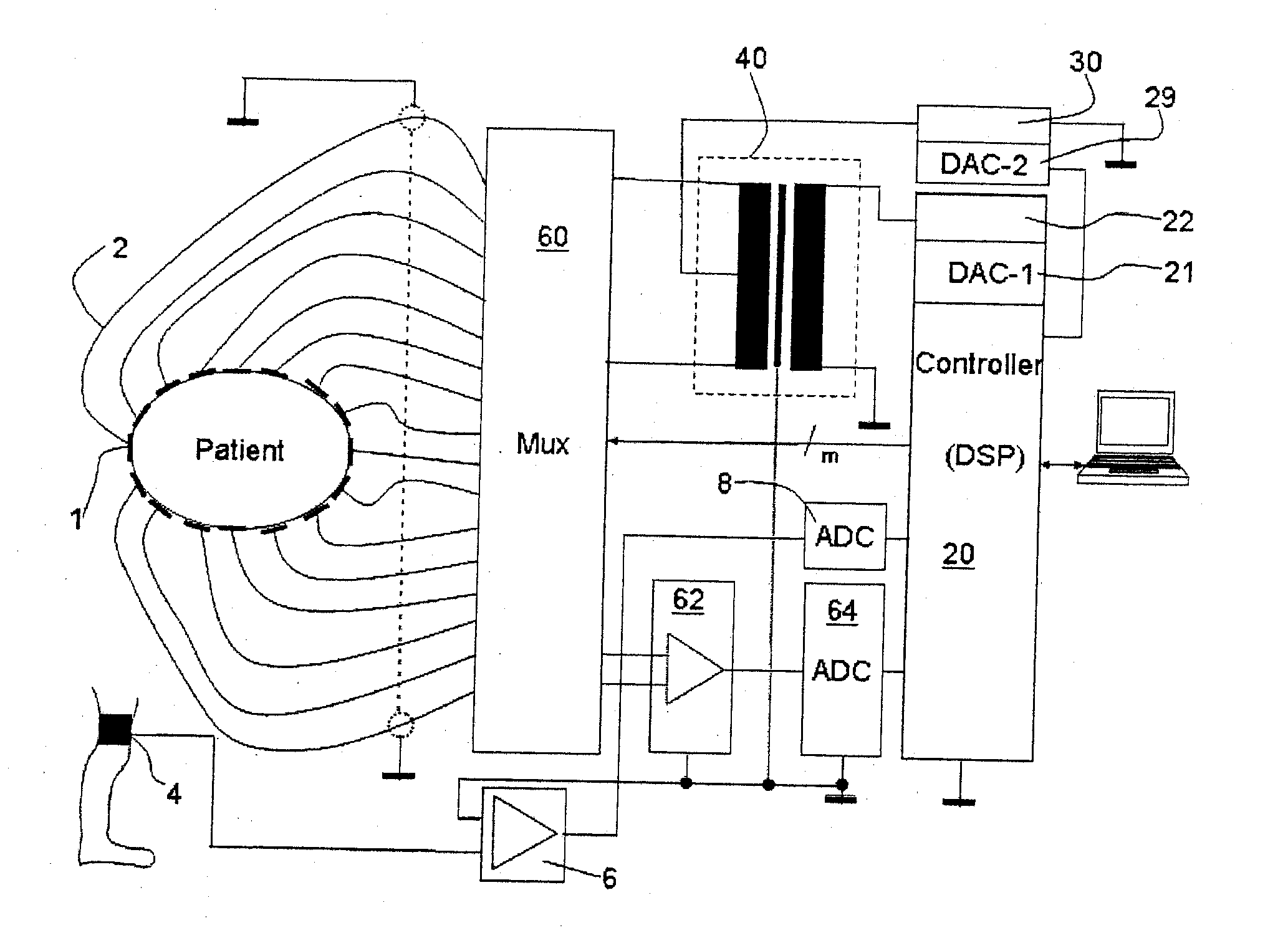
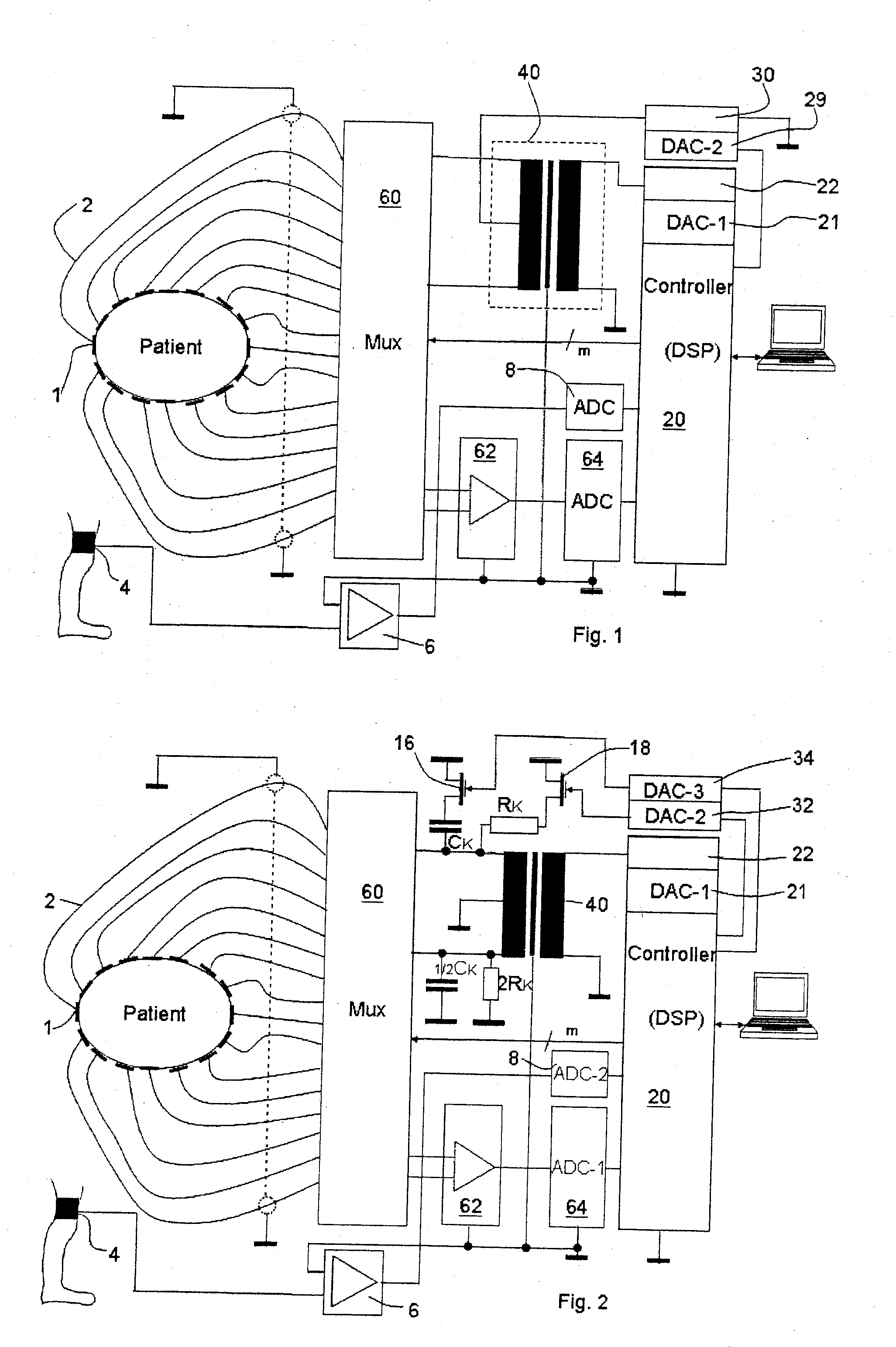
An electroimpedance tomograph with a plurality of electrodes (1) is provided, which can be placed on the body of a patient and are connected via a selector switch (60) with a control and evaluating unit (20). The control and evaluating unit (20) cooperates with the selector switch (60) such that two electrodes each are supplied with an alternating current from an AC power source (22) and the detected analog voltage signals of the other electrodes are processed in order to reconstruct therefrom the impedance distribution of the body in the plane of the electrodes, wherein a symmetrical AC power source is used to reduce common-mode signals. To further suppress interferences due to common-mode signals, provisions are made for the control and evaluating unit (20) to be set up, furthermore, for detuning the common-mode signal of the alternating current on the body against the ground by means of a common-mode signal measuring electrode (4) and, based on this, the symmetry of the symmetrical AC power source such that the common-mode signal on the body is minimized, and the corresponding detuning parameters are stored for each electrode pair.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
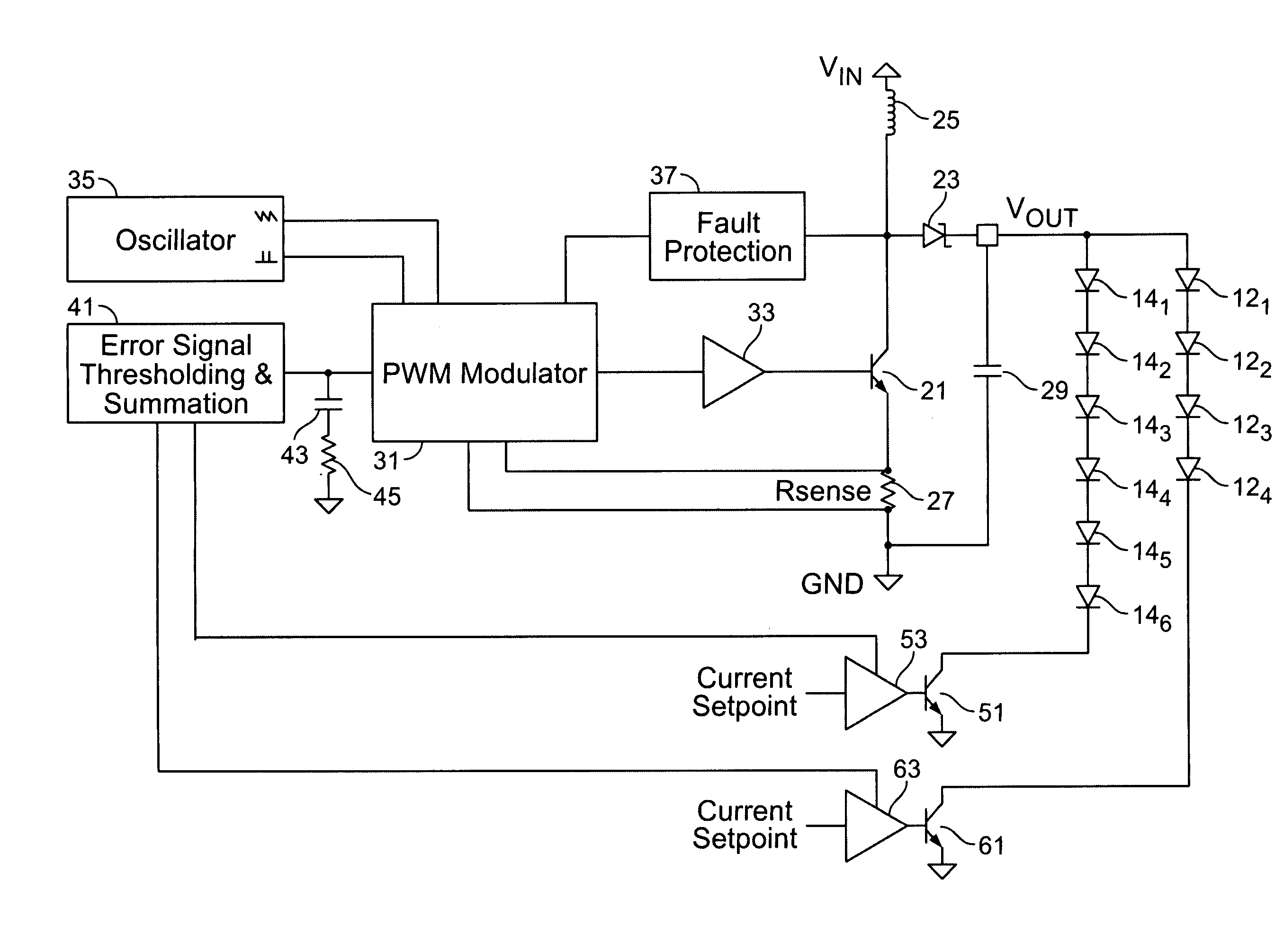
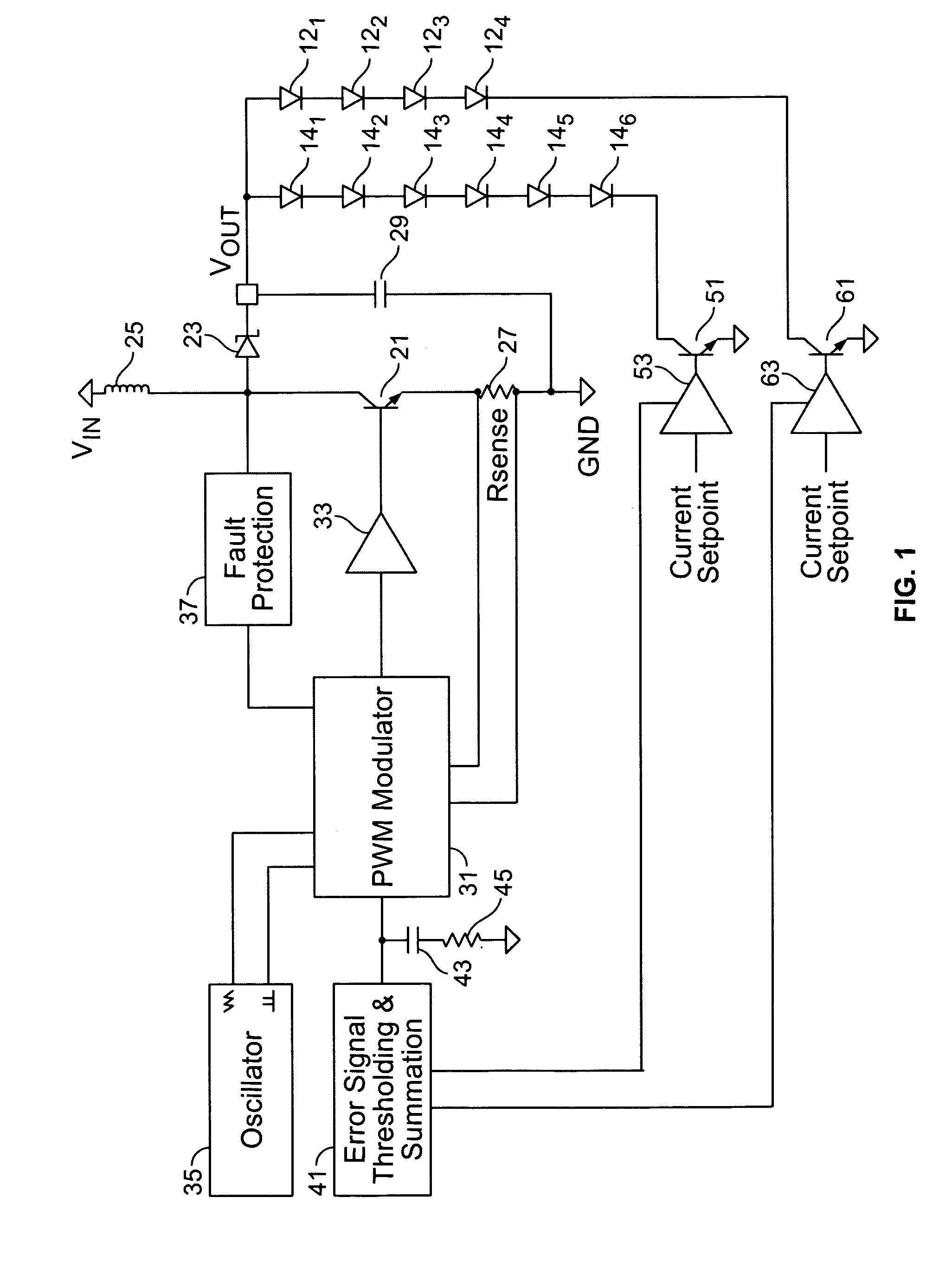
High efficiency power supply for LED lighting applications
InactiveUS7265504B2Accurate currentEffective pointingElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesEffect lightVoltage regulation
A power supply for plural loads coupled in parallel comprises a voltage regulator, a plurality of current regulators, and an error control circuit. The voltage regulator provides a common output voltage to the plural loads. The voltage regulator comprises a sensor circuit providing a voltage sense signal corresponding to the output voltage, which provides feedback to regulate the output voltage at a selected level. The plurality of current regulators are coupled to respective ones of the plural loads. Each of the plurality of current regulators regulates current drawn by respective ones of the plural loads to within a desired regulation range. The plurality of current regulators each further provide a respective error signal corresponding to an ability to remain within the desired regulation range. The error control circuit is operatively coupled to the voltage regulator and to the plurality of current regulators. The error control circuit receives the error signals from the plurality of current regulators and provides a common error signal to the voltage regulator. The voltage regulator thereby changes the selected level of the output voltage in response to the common error signal. Accordingly, the selected level of the output voltage remains at a minimum voltage necessary to keep the plural loads in the desired regulation range.
Owner:SEMTECH CORP
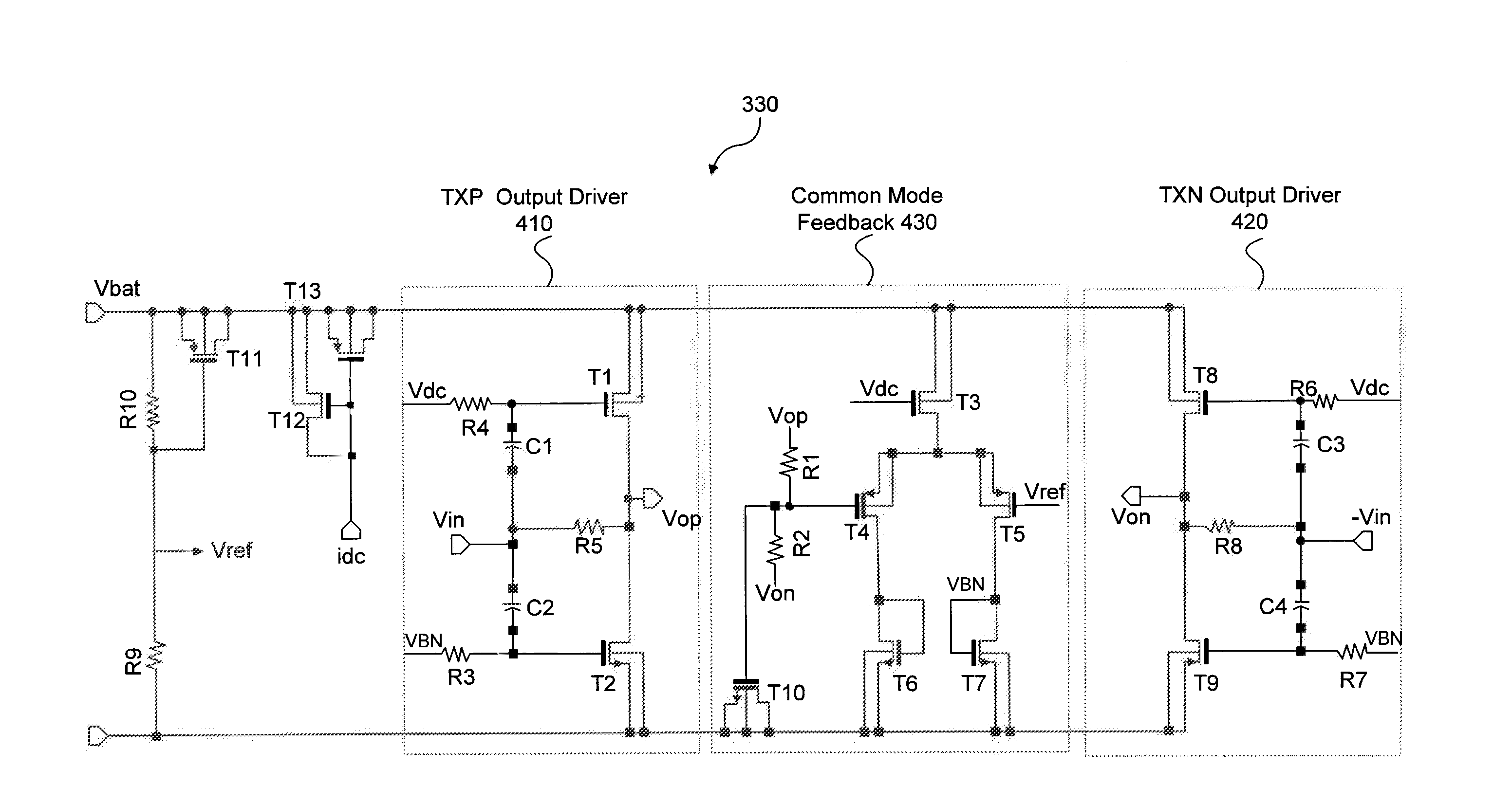
Antenna Driver Circuit for NFC Reader Applications
ActiveUS20130084799A1Near-field transmissionDifferential amplifiersDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
A power amplifier, supplied by a supply voltage, to drive an antenna to output a magnetic field, comprising a differential stage configured to output an output signal to drive the antenna, and a feedback stage configured to receive a common mode output voltage from the differential stage and to output a feedback voltage to regulate the output common mode signal to be proportional to the supply
Owner:NXP USA INC
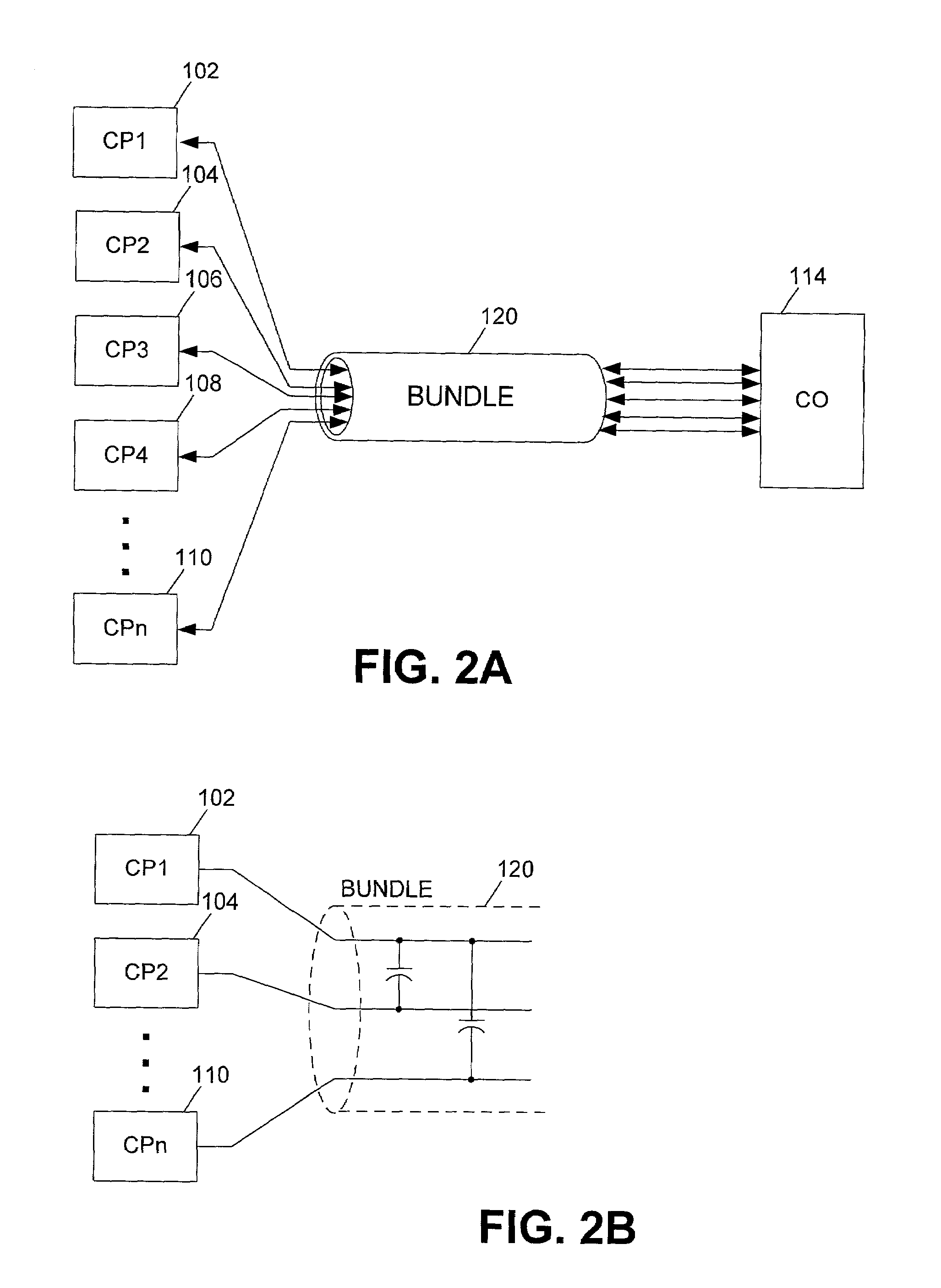
RFI canceller using narrowband and wideband noise estimators
InactiveUS20010050987A1Remove restrictionsInterconnection arrangementsError preventionBroadband noiseAdaptive filter
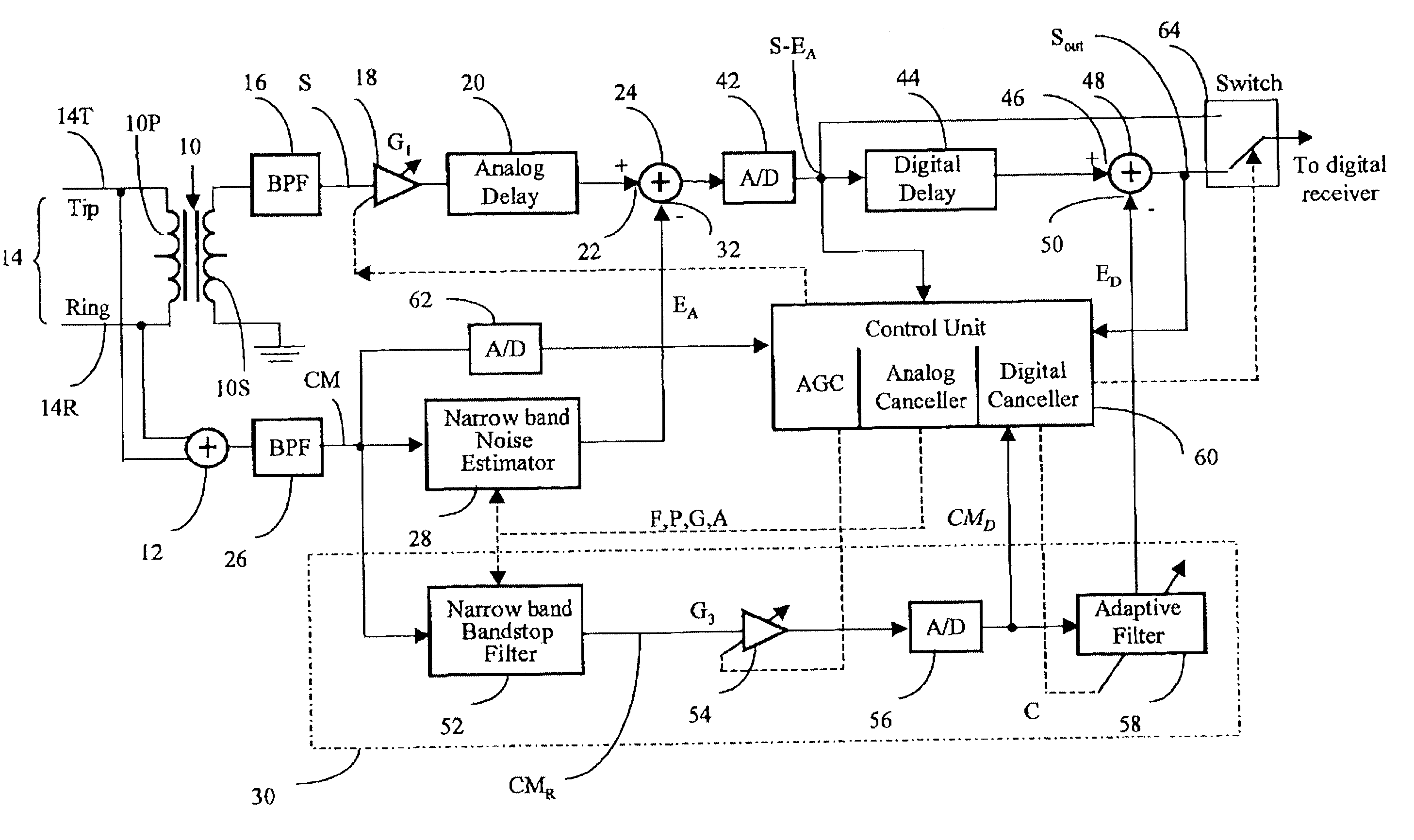
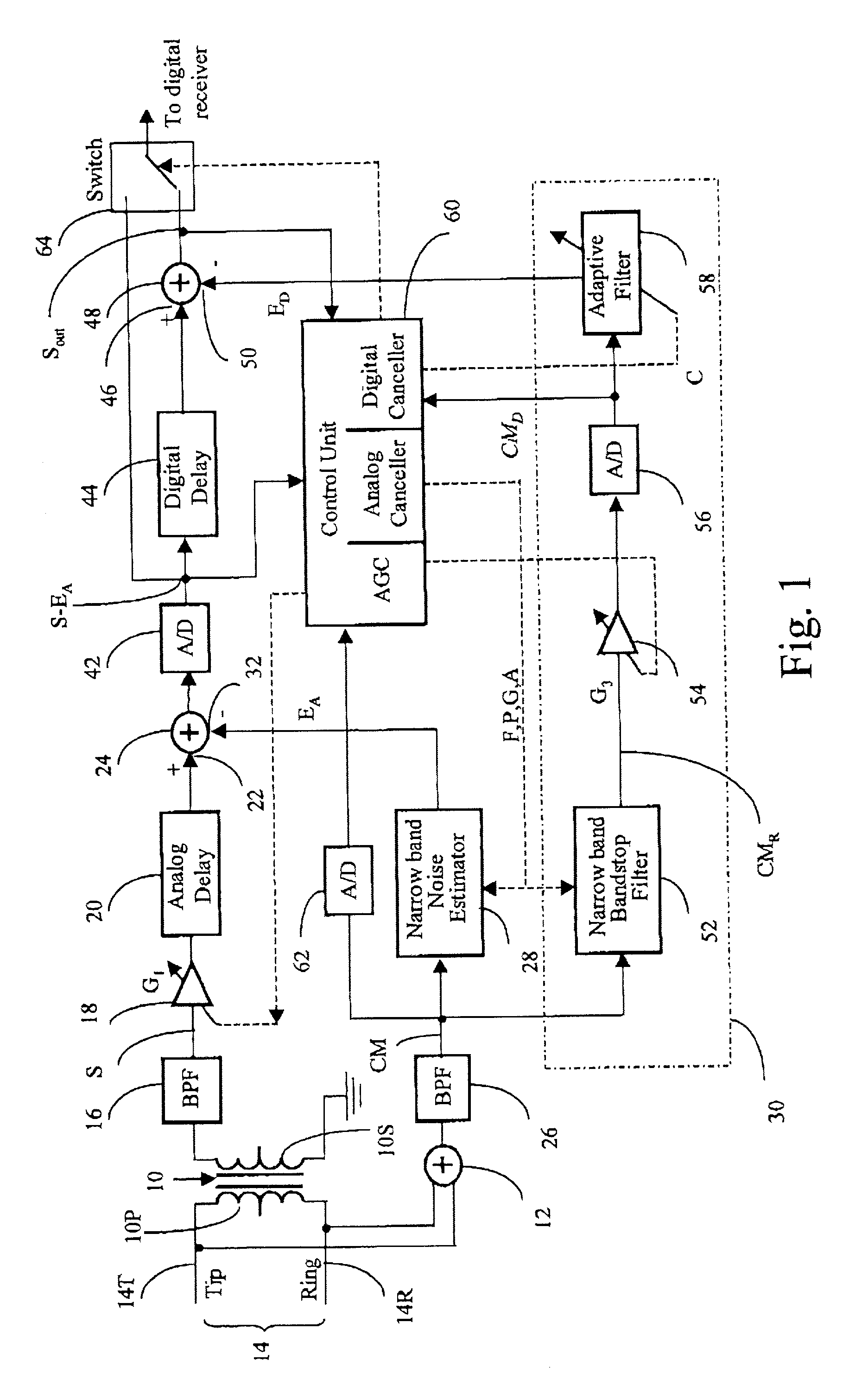
In an adaptive filter for cancelling common-mode noise in digital subscriber loops, a narrowband noise estimator is used to detect one or more noisy frequency bands of the common mode signal and derive therefrom a first noise estimation signal. A wideband noise estimator derives from the remainder of the common mode signal a second noise estimation signal. The first and second noise estimation signals are subtracted from the differential signal, The wideband noise estimator comprises a bandstop filter for removing the frequencies detected by the narrowband noise estimator, an analog-to-digital converter for digitizing the bandstopped signal, and an adaptive filter for deriving the second noise estimation signal from the digitized bandstopped signal and, in the process, compensating for phase and gain differences, especially attributable to the interference being injected at different points along the length of the channel.
Owner:BELL CANADA
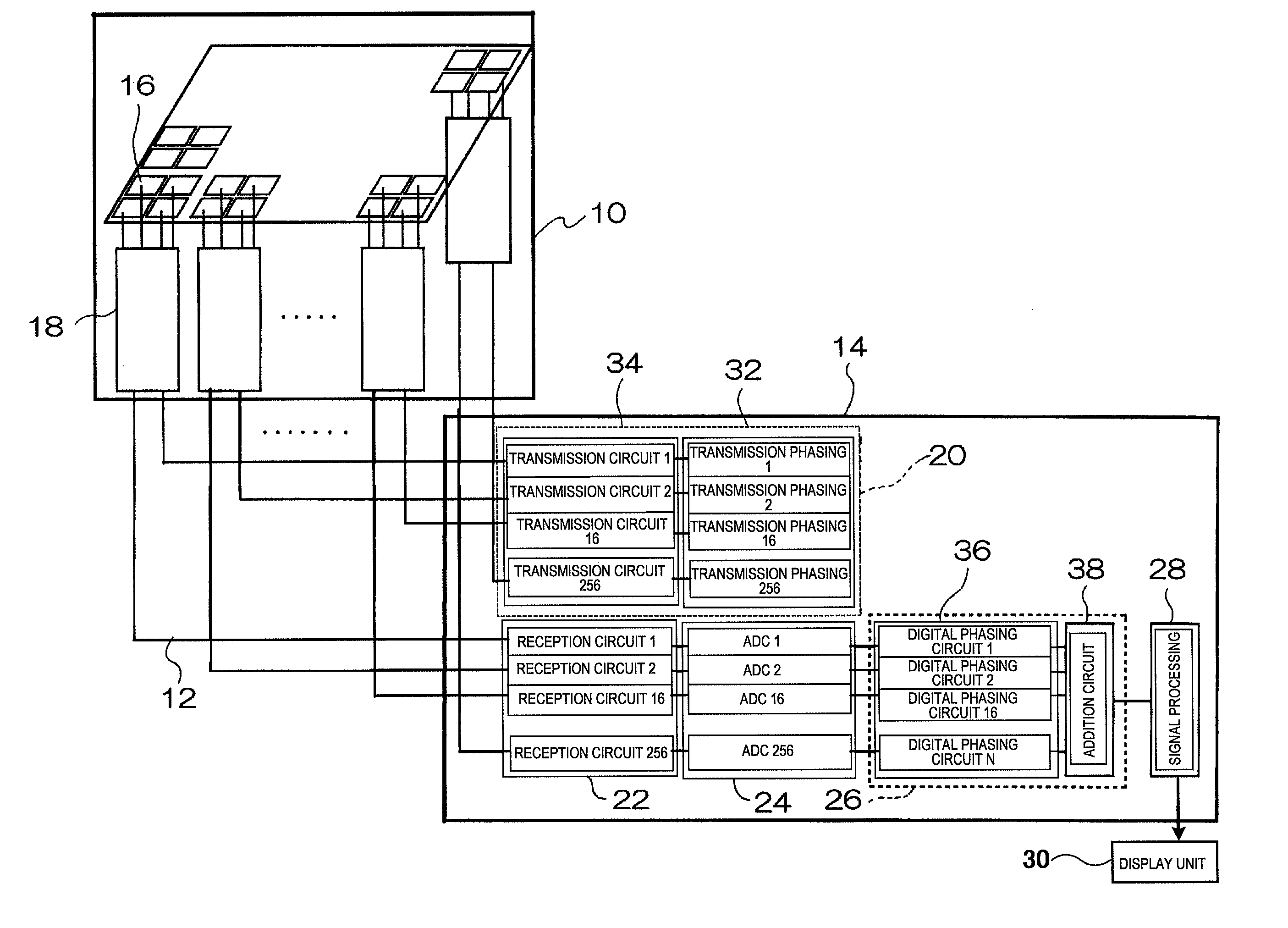
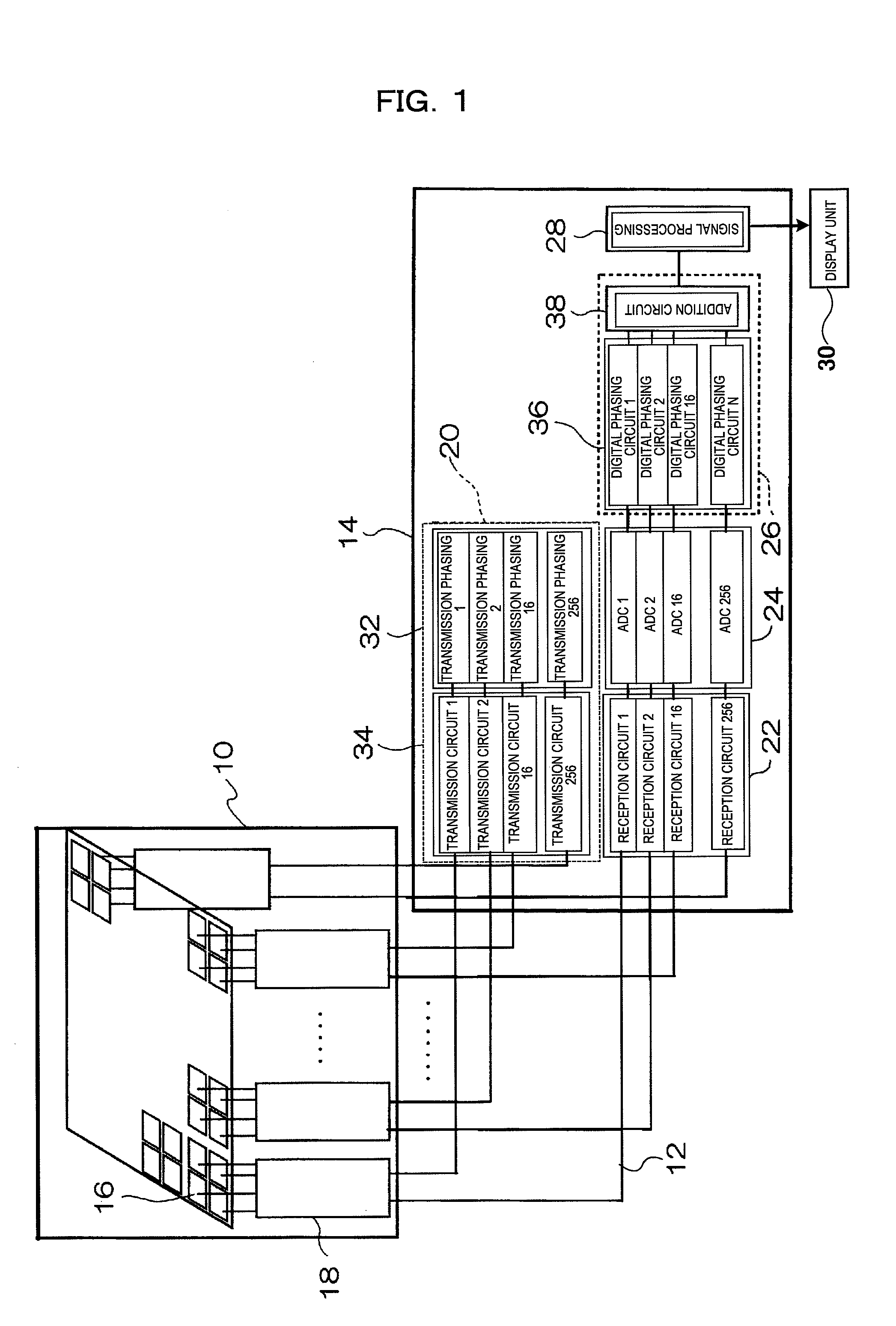
Ultrasonic Imaging Apparatus
InactiveUS20080294050A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingImaging processing
It is possible to realize an ultrasonic imaging apparatus capable of eliminating deterioration of the S / N of the ultrasonic image while suppressing enlargement of the circuit size. The ultrasonic imaging apparatus includes: an ultrasonic probe having a plurality of transducers arranged for transmitting and receiving ultrasonic waves to / from an object to be examined; transmission means for supplying a drive signal to each of the transducers; reception means for phasing / adding and receiving a reflected echo signal received by each transducer; and an image processing unit for reconfiguring an ultrasonic image based on the reflected echo signal received. The transmission means divides the plurality of transducers into a plurality of groups, supplies a common drive signal to the transducers belonging to the same group, and performs focus control by group units.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
RFI canceller using narrowband and wideband noise estimators
In an adaptive filter for cancelling common-mode noise in digital subscriber loops, a narrowband noise estimator is used to detect one or more noisy frequency bands of the common mode signal and derive therefrom a first noise estimation signal. A wideband noise estimator derives from the remainder of the common mode signal a second noise estimation signal. The first and second noise estimation signals are subtracted from the differential signal, The wideband noise estimator comprises a bandstop filter for removing the frequencies detected by the narrowband noise estimator, an analog-to-digital converter for digitizing the bandstopped signal, and an adaptive filter for deriving the second noise estimation signal from the digitized bandstopped signal and, in the process, compensating for phase and gain differences, especially attributable to the interference being injected at different points along the length of the channel.
Owner:BELL CANADA
Touch control display panel, touch control display device and production method
ActiveCN104850268AOffset Potential InterferenceSimple structureInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceComputer science
The invention provides a touch control display panel, a touch control display device and a production method and belongs to the touch control display field. The touch control display panel comprises a first base plate and a second base plate; the first substrate comprises a substrate as well as an anode, an organic light-emitting layer and a cathode formed on the substrate, wherein the cathode is composed of a plurality of first sub electrodes, wherein each first sub electrode is adopted as a touch control electrode to upload touch control scanning signals in a touch control scanning stage, and is adopted a common electrode to upload common electrode signals at a display stage; and the first base plate further comprises a driving electrode layer arranged between the anode and the substrate, wherein the driving electrode layer uploads touch control scanning signals in a touch control scanning stage. With the above technical schemes of the invention adopted, the cathode in the touch control display panel can be multiplexed as a touch control electrode in the touch control scanning stage, and at the same time, influences of the anode on the electric potential of the cathode in the touch control scanning stage can be offset.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
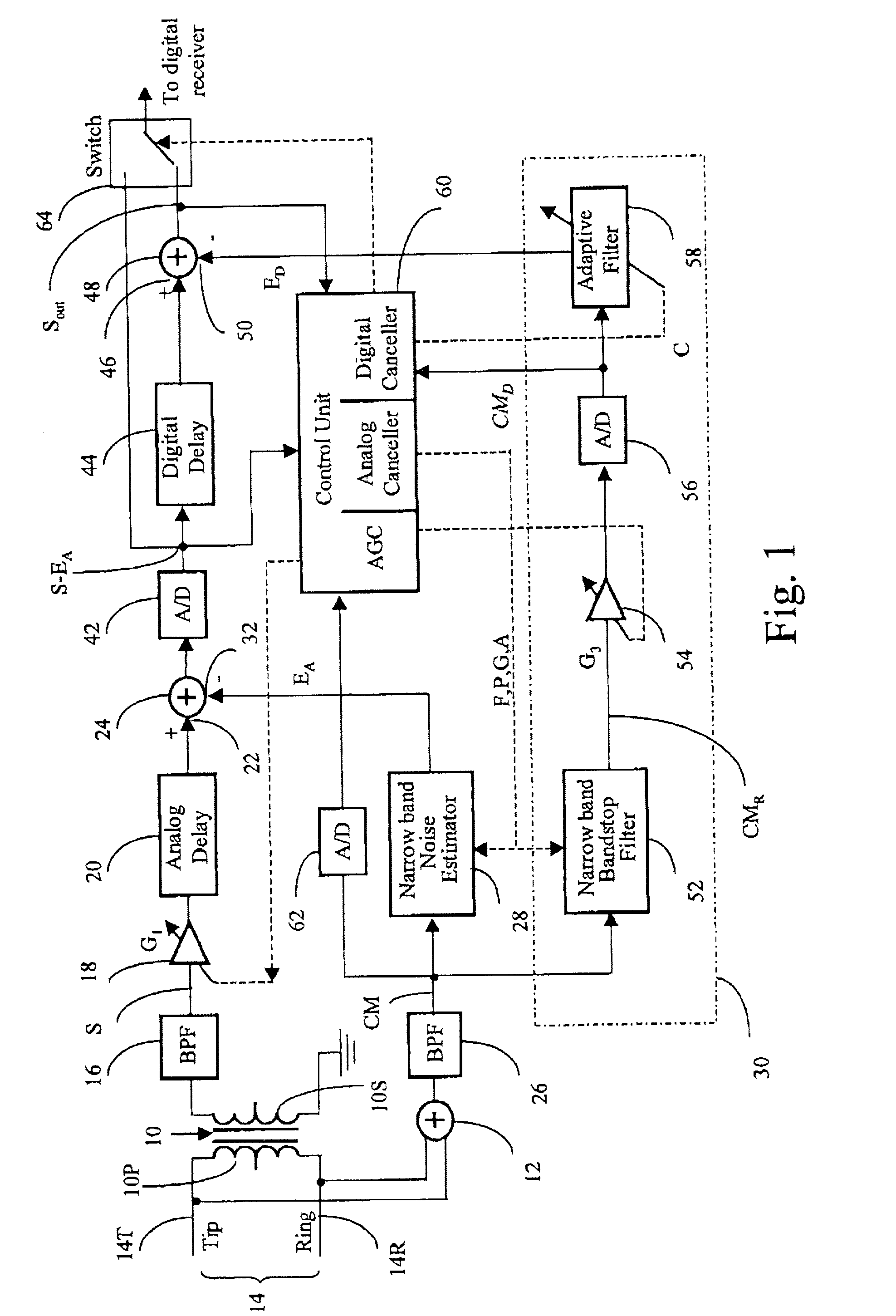
Suppression of radio frequency interference and impulse noise in communications channels
InactiveUS6546057B1Error preventionUnbalanced current interference reductionDifferential signalingEngineering
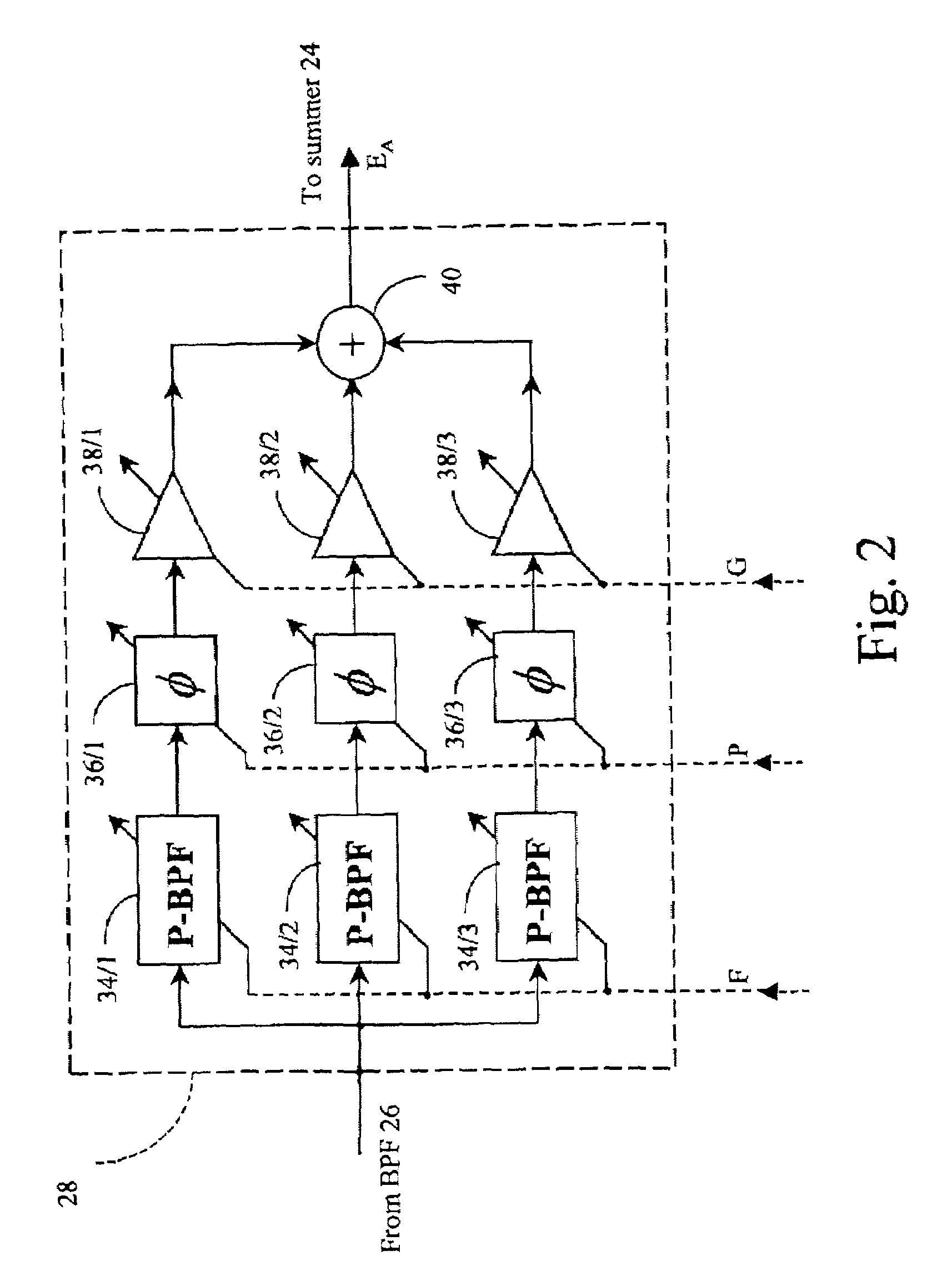
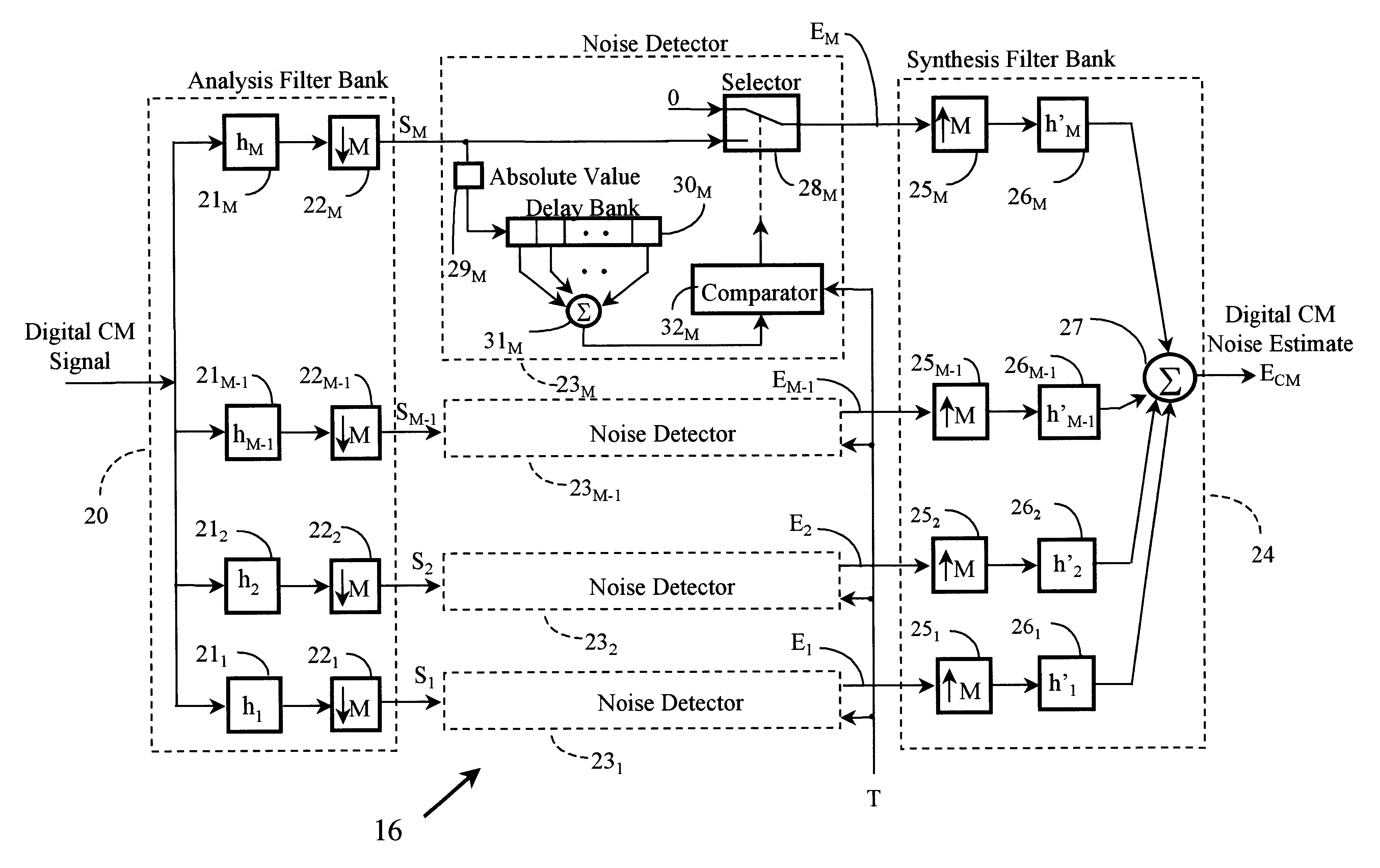
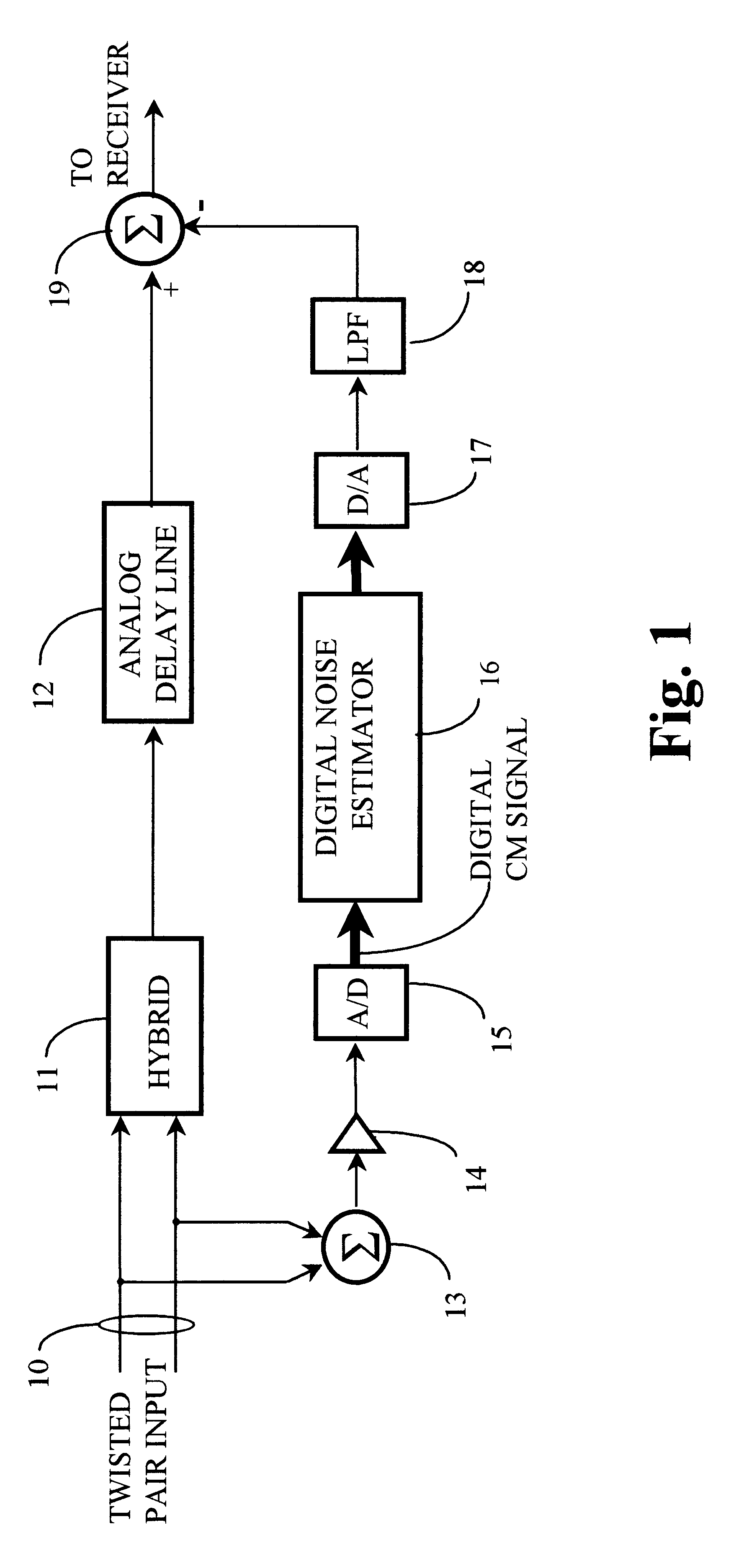
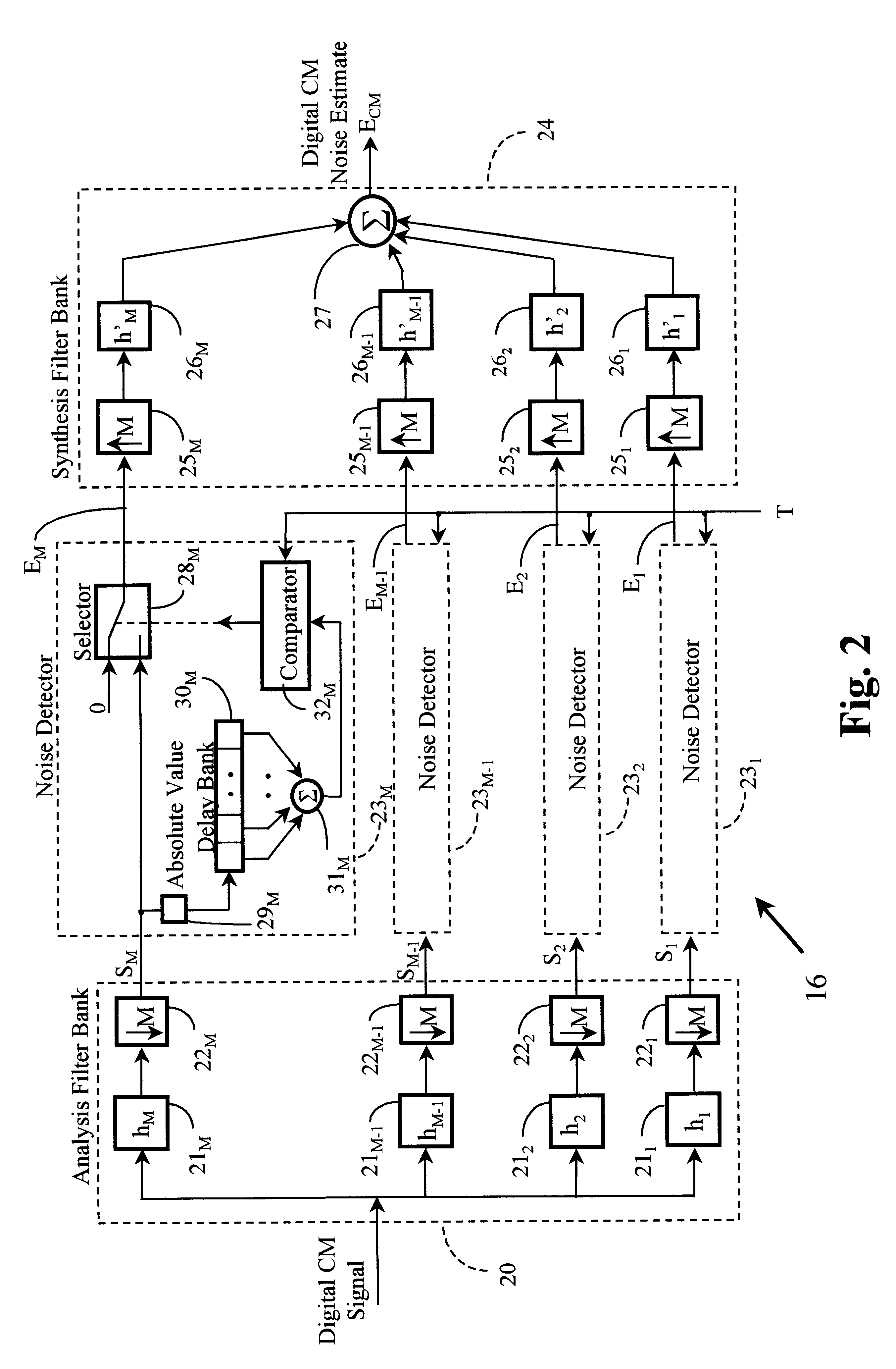
A noise suppression circuit for a communications channel (10) comprises a hybrid device (11) coupled to the channel for providing a differential output signal corresponding to a received signal. A delay unit (12) delays the differential signal by a suitable amount to allow for the generation and subtraction of a noise estimate. A summing device (13) extracts a digital common mode signal from the channel, and a noise estimation unit (16) provides a common mode noise estimate signal in dependence upon a history of the common mode signal over a predetermined period of time and over a plurality of frequency bands. The common mode noise estimate signal is combined subtractively (19) with the delayed differential signal to cancel common mode noise elements of the delayed differential signal. The noise estimation unit may comprise an analysis filter bank (20) for producing a plurality of subband signals (S1-SM), each at a different one of a plurality of different frequencies, a plurality of noise detection circuits (231-23M), each for processing a respective one of the plurality of subband signals to provide a component of the common mode noise estimate signal, and a synthesis filter bank (24) for processing the common mode noise signal components to provide the noise estimate signal.
Owner:BELL CANADA
System for phase inversion ultrasonic imaging
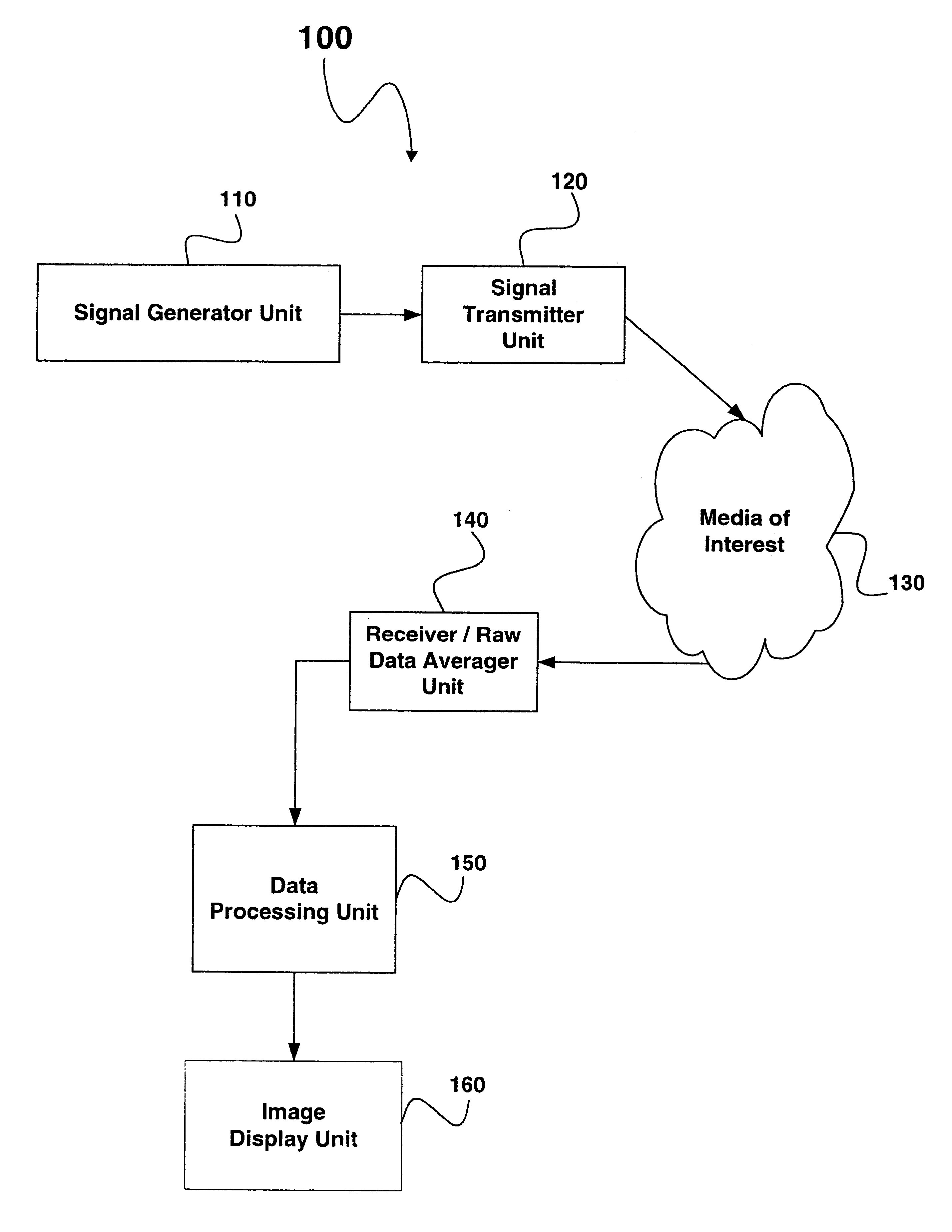
A system and method for ultrasonic imaging utilizing multiple sets of transmit pulses differing in amplitude, frequency, phase, and / or pulse width. One embodiment has phase differences between the k transmit signal as 360kdegrees providing for constructive interference of the kth order harmonic pulse, while an amplitude modulation of each transmit profile is constant between sets. These sets of pulses are transmitted into media of interest and received echoes from these pulses are combined to form an averaged signal. The averaged pulses represent the net common mode signal received from each of the transmit sets. This combined signal set is used to reconstruct an ultrasound image based on broad beam reconstruction methodology.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Filter Circuit, Differential Transmission System Having Same, and Power Supply
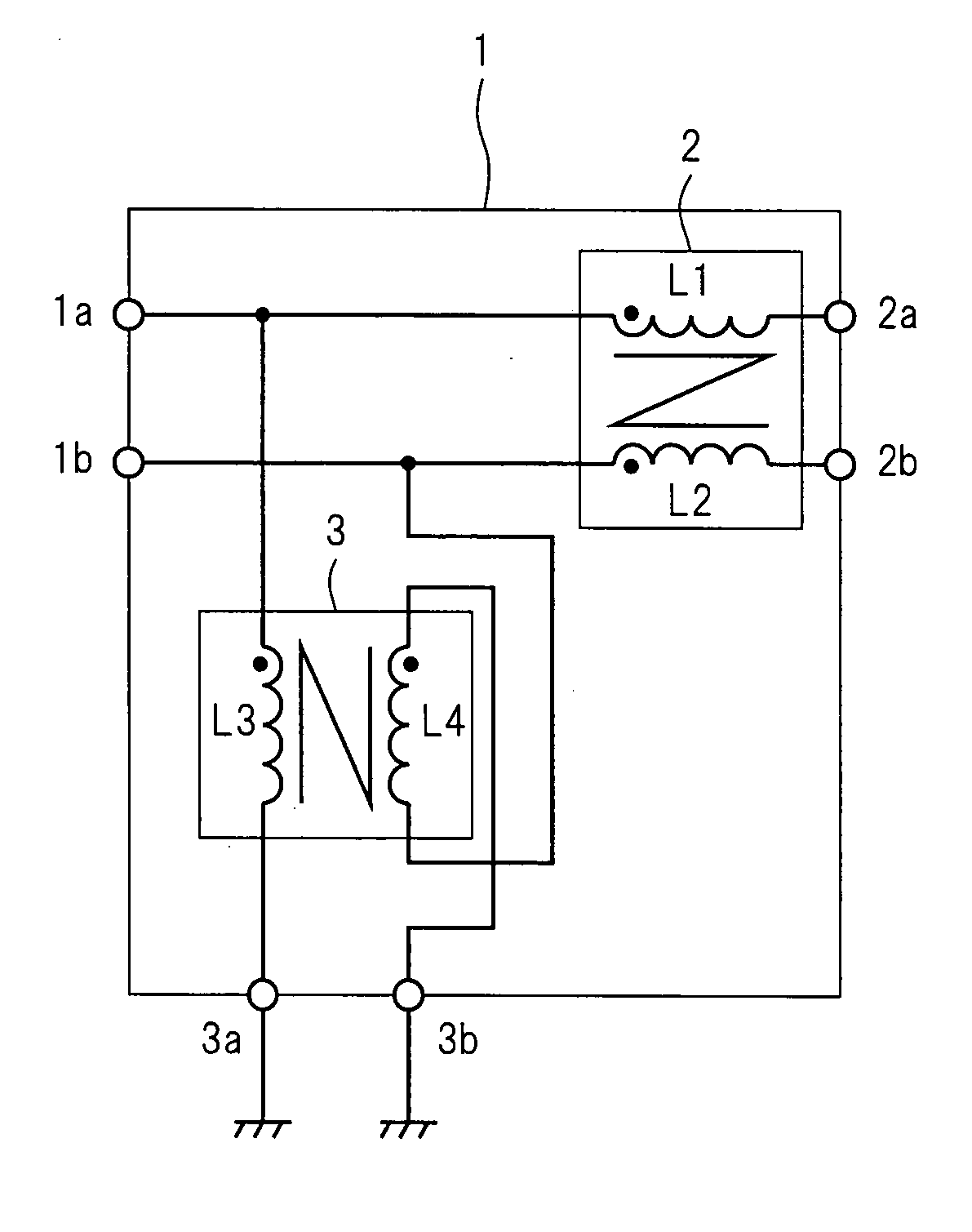
InactiveUS20070252659A1Quality improvementEnhanced inhibitory effectMultiple-port networksUnbalanced current interference reductionTransfer systemNormal mode
In a filter circuit (1), a common mode choke (2) and a normal mode choke (3) have extremely high and low impedances, respectively, for common mode signals received through two input terminals (1a and 1b). The chokes have the opposite impedance characteristics for differential signals. In particular, the difference in impedance is large. Furthermore, the normal mode choke (3) is installed as a previous stage of the common mode choke (2). Accordingly, common mode noises which enter the two input terminals (1a and 1b) penetrate the normal mode choke (3), but neither penetrate the common mode choke (2) nor are reflected from the common mode choke (2). In particular, common mode currents flow through the normal mode choke (3) but do not flow through the common mode choke (2).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Resolving user-specific narrow beam signals using a known sequence in a wireless communications system with a common pilot channel
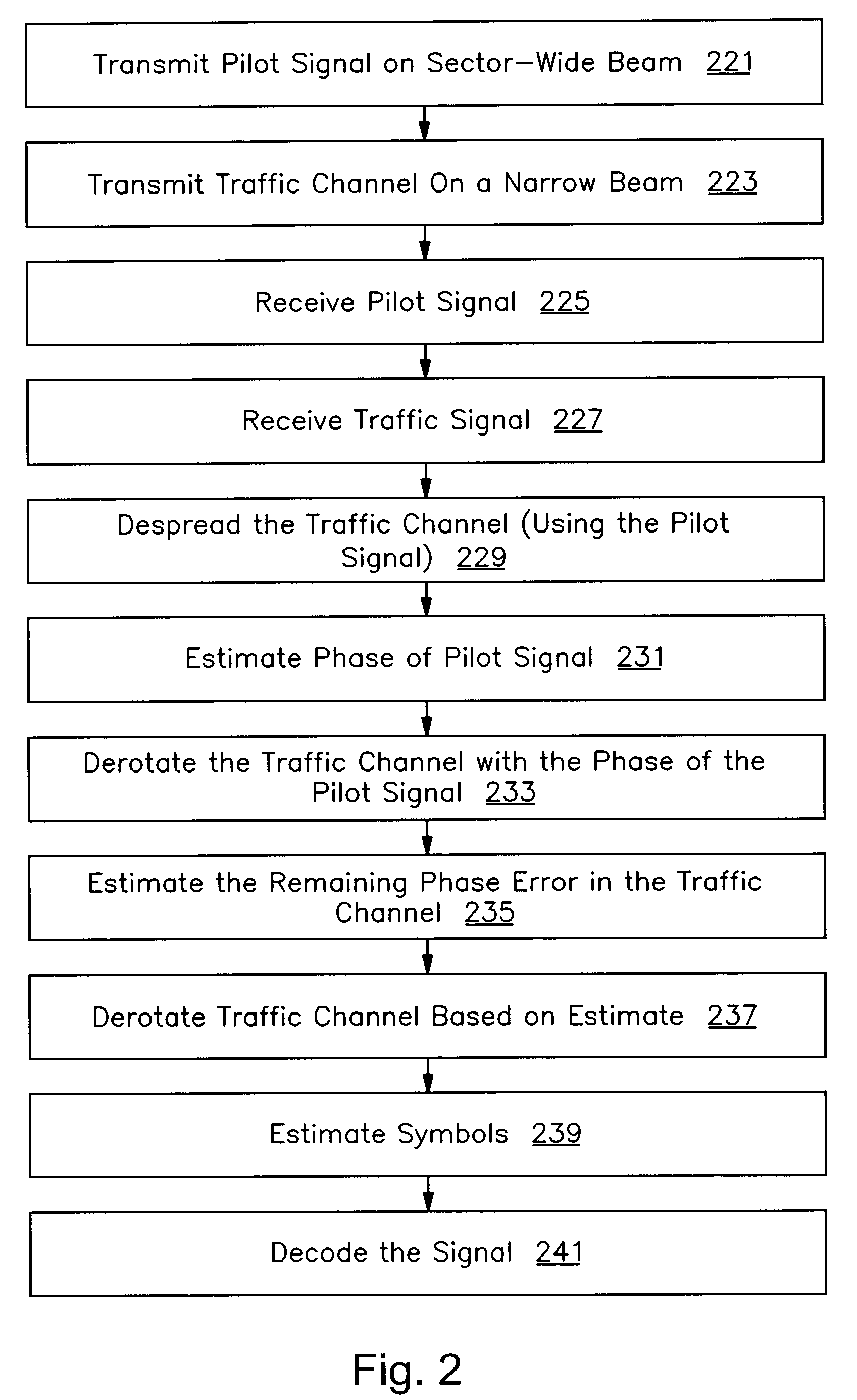
A method and apparatus are provided that corrects for differences in reception between a user-specific signal and a common signal. In one embodiment, the invention includes receiving a common pilot signal transmitted on a wide beam at a remote terminal, receiving a user-specific signal transmitted on a directed narrow beam at the remote terminal, demodulating the user-specific signal using the common pilot signal for channel estimation, estimating a phase error in the demodulated user-specific signal using known symbols in the user-specific signal, and correcting for the phase error in the demodulated user-specific signal using the phase error estimates.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Inductive Component and Method for Producing an Inductive Component
ActiveUS20170025212A1Compact designTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsFixed transformers or mutual inductancesCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
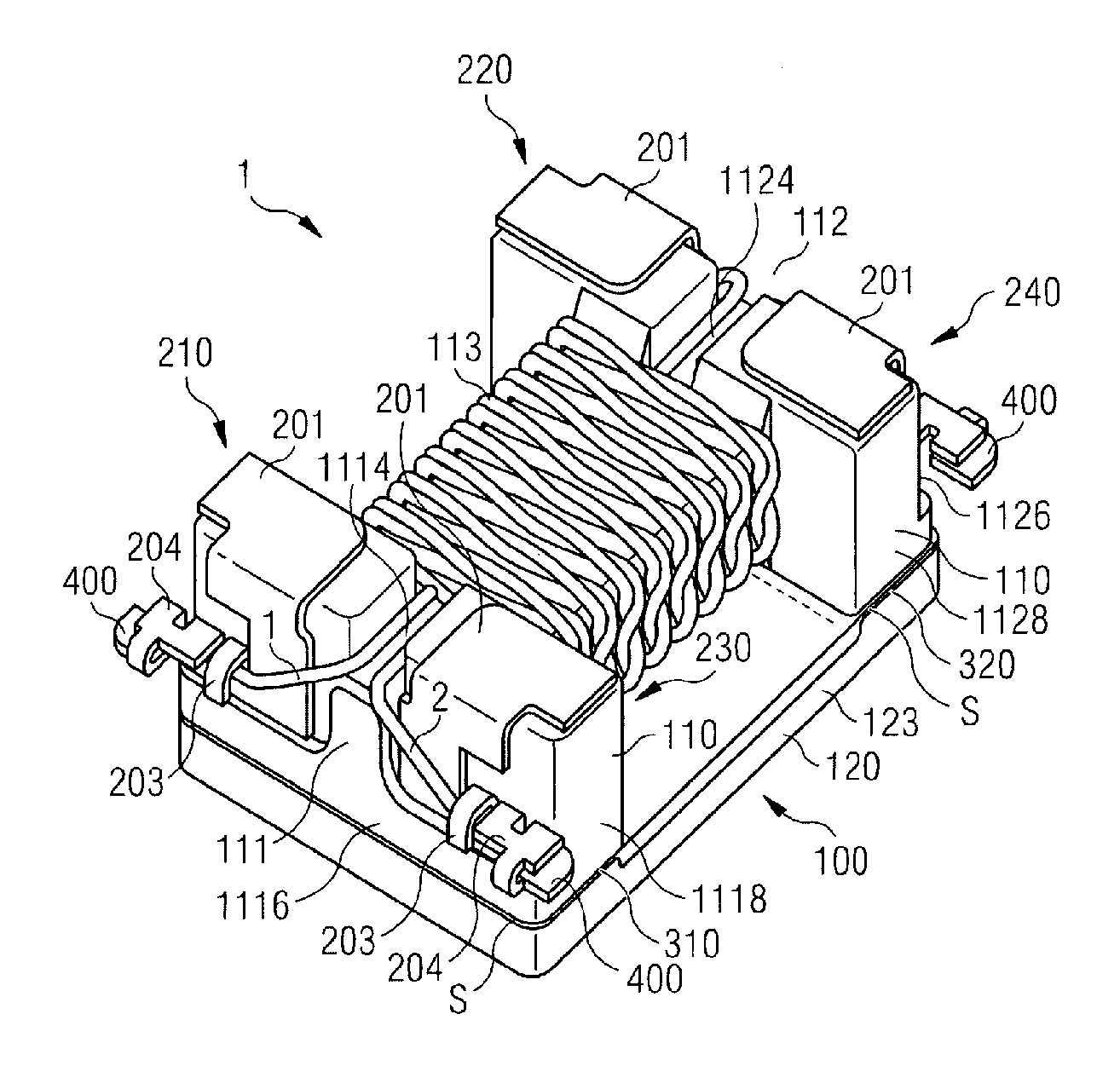
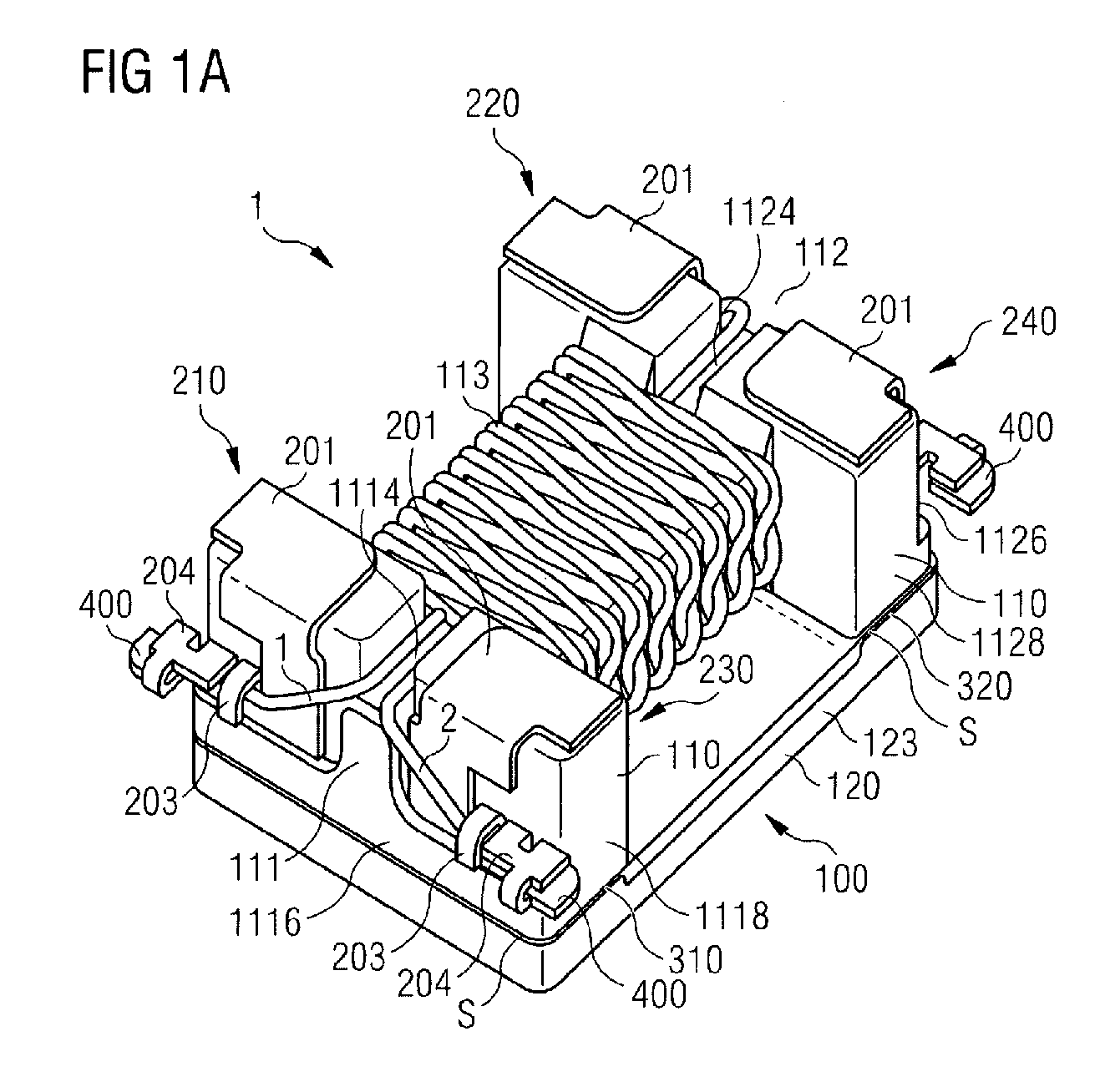
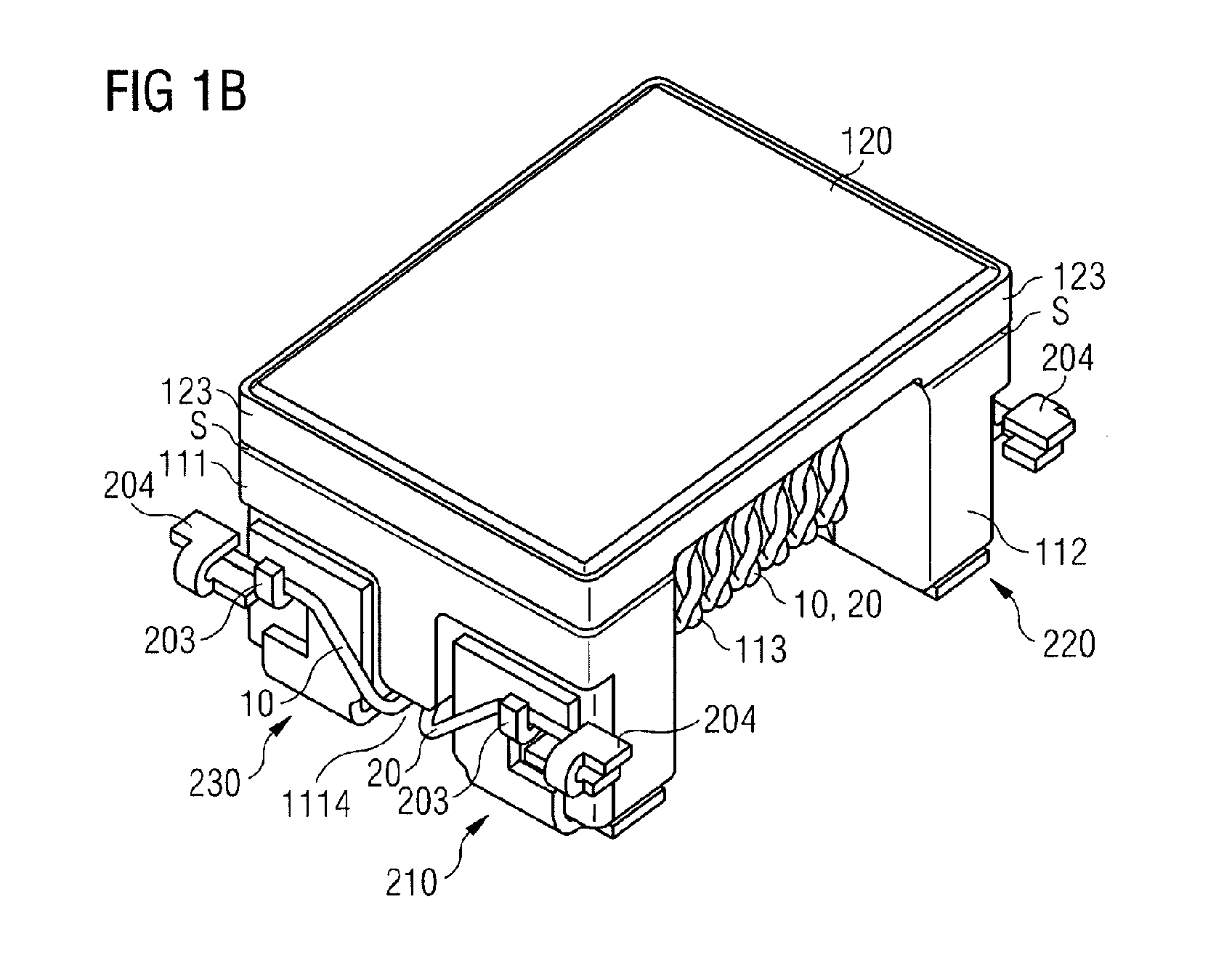
An inductive component and a method for producing an inductive component are disclosed. In an embodiment, the inductive component includes a first core part having wound first and second wires and a second core part arranged on the first core part. In various embodiments the inductive component has a low mode conversion, a low inductance in differential-mode operation, a high inductance for common-mode signals, a constant characteristic impedance, a low capacitive coupling of the wires, and / or a low leakage inductance.
Owner:EPCOS AG
Robust Self Testing of a Motion Sensor System
ActiveUS20100251800A1Acceleration measurementTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesAccelerometerTime signal
A method for self-testing a dual-mass linear accelerometer in which a self-test voltage is applied to urge the two masses to move in opposite directions. Self-test signals are then applied to obtain a differential mode signal to detect masses repositioned in opposing directions. During testing, common disturbances to the two masses are rejected as common mode signals.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
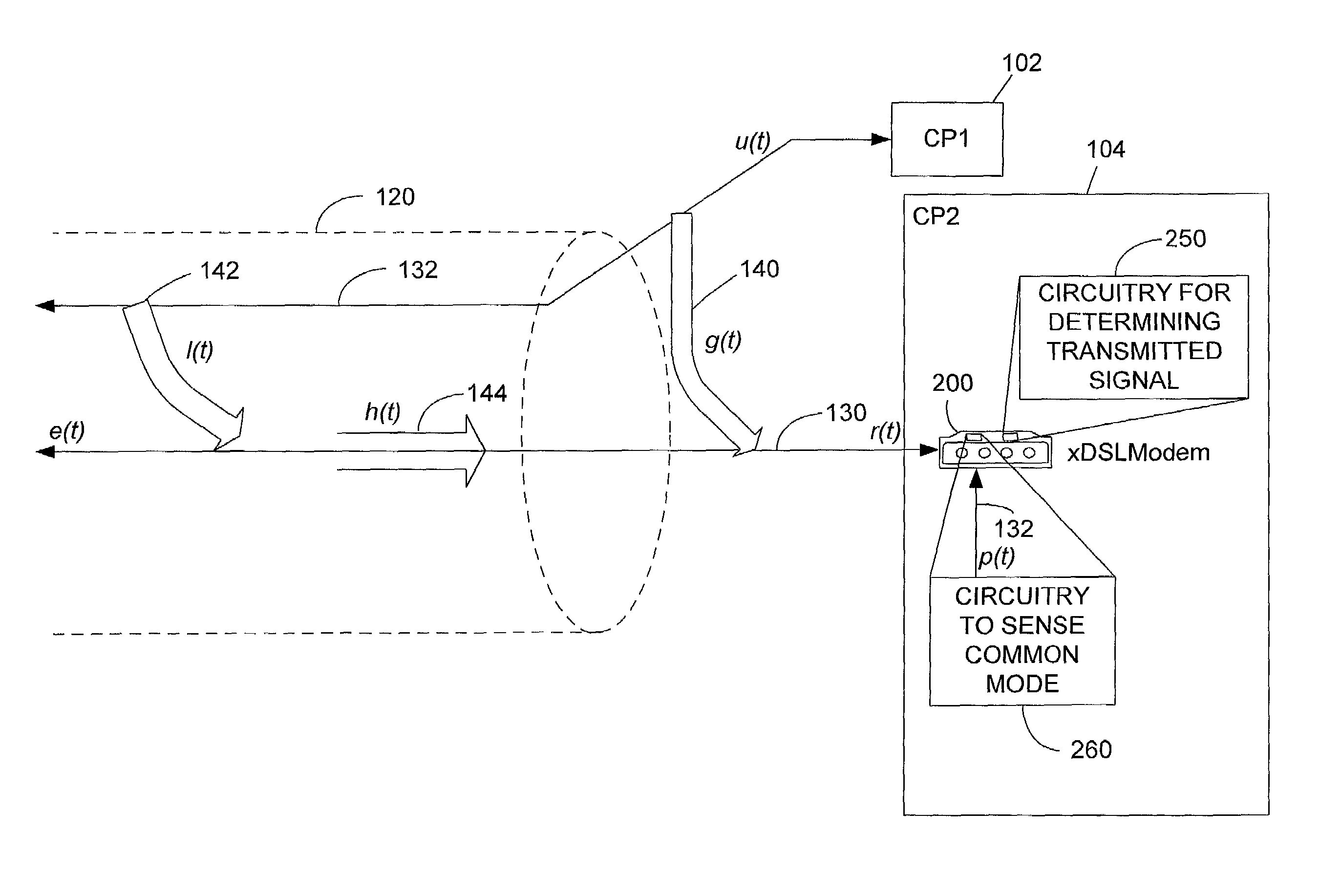
Crosstalk Cancellation in Digital Subscriber Line Communications
ActiveUS20090034592A1Easy to implementLow additional costCross-talk reductionSecret communicationDigital subscriber lineCrosstalk cancellation
A digital subscriber line (DSL) modem that has a canceller digital filter for cancelling crosstalk and RF interference in a received DSL signal is disclosed. The modem includes common-mode sense circuitry and also differential-mode sense circuitry. Samples of the common-mode signal are acquired during a “quiet” period of initialization of the DSL modem, and samples of the differential-mode signal are acquired during live transmission of a DSL signal. An estimate of an autocorrelation function is obtained from the common-mode samples, and a cross-correlation of the common-mode samples and differential-mode samples is also estimated. Digital filter coefficients are derived from these estimates, based on the assumption that the common-mode samples acquired during the “quiet” phase represent crosstalk and RF interference present during differential-mode communications. The digital filter coefficients can also be updated during showtime of the DSL link, using an expanded number of samples of the common-mode and differential-mode signals.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Magnetic positioning method and device in high background magnetic field
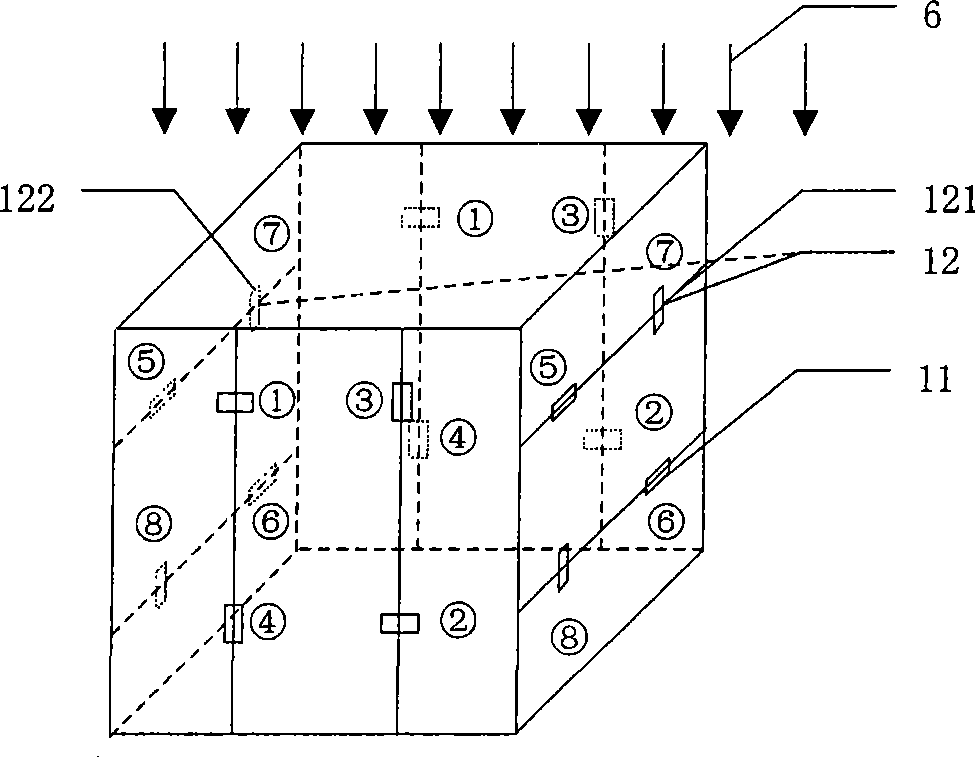
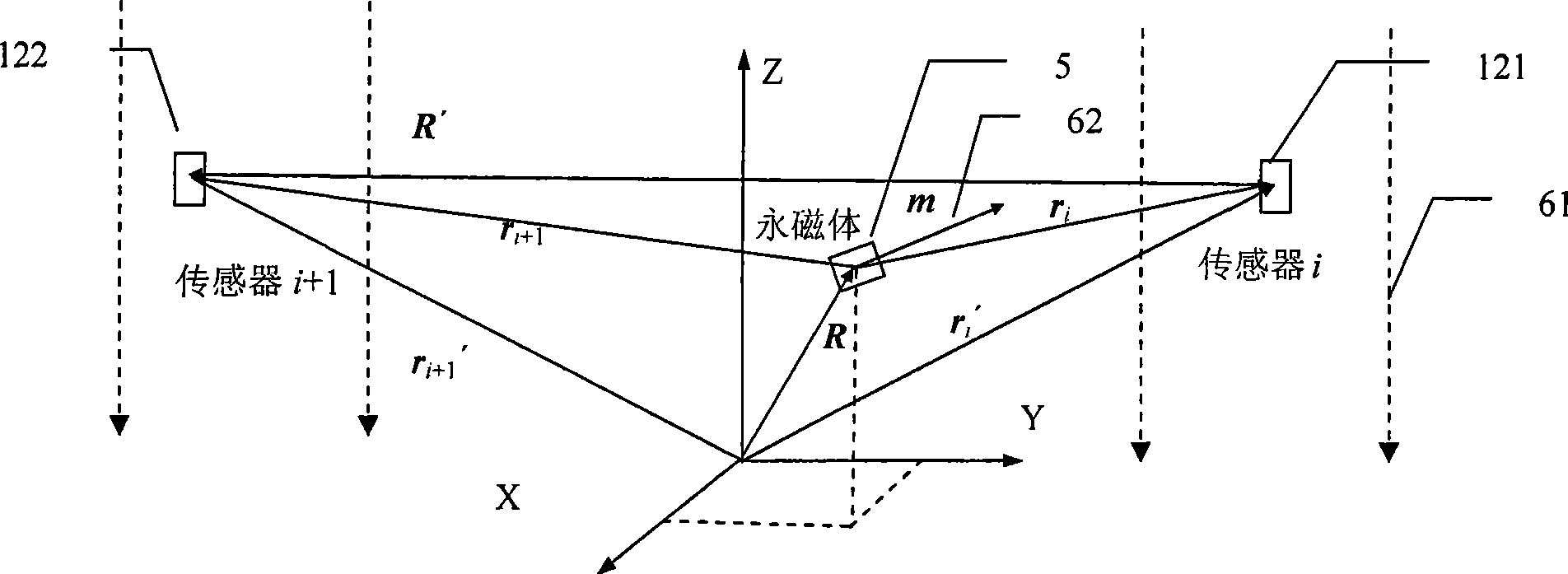
InactiveCN101476860AReal-time display of motion trajectoryDisplay direction information in real timeUsing electrical meansSensor arrayObject function
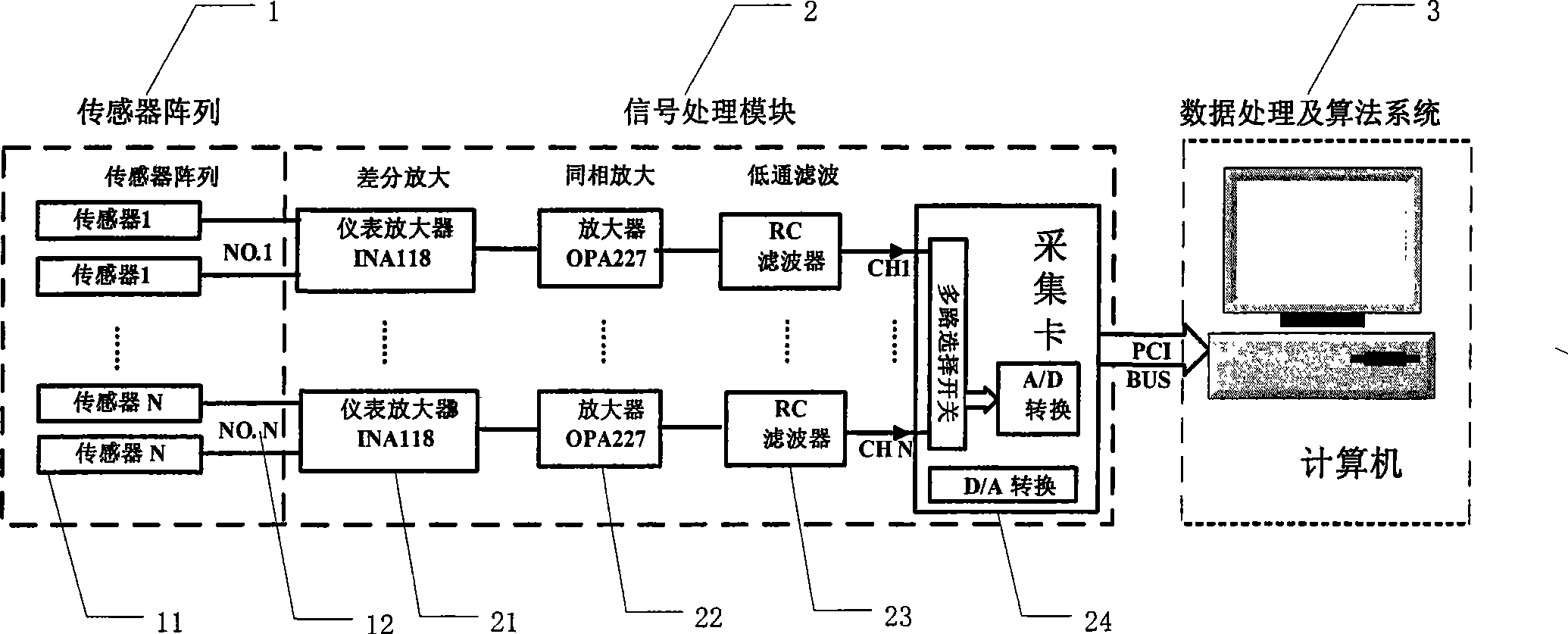
The invention relates to a magnetic positioning method in high background magnetic fields, which comprises: using a sensor group which is arranged on two spatially symmetrical position points to detect background magnetic fields and magnetic fields of a permanent magnetic block of a target object, adopting a differential amplifier circuit to take equal magnetic induction intensity of the background fields detected by the sensor group as common-mode signals for subtraction, eliminating the high background magnetic fields, and obtaining a magnetic induction intensity difference value of the permanent magnetic block of the target object on the two sensor position points in the sensor group; using N (N is more than or equal to 5) groups of sensor groups for measurement, and obtaining a magnetic induction intensity difference value vector which comprises N (N is more than or equal to 5) magnetic induction intensity difference values; adopting a differential magnetic positioning algorithm to obtain a differential magnetic positioning equation system; establishing an objective function by the differential magnetic positioning equation system and the magnetic induction intensity difference value vector which is obtained by actual measurement; and solving the objective function, and obtaining the three-dimensional position and the two-dimensional attitude of the permanent magnetic block of the target object. A device applying the positioning method comprises a sensor array (1), a signal processing module (2) and a data processing and algorithm system (3).
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-performance direct current amplification device for acquiring biological electric signals
ActiveCN101889863AImprove performanceHigh Common Mode Rejection RatioDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsLow-pass filterVery High Level
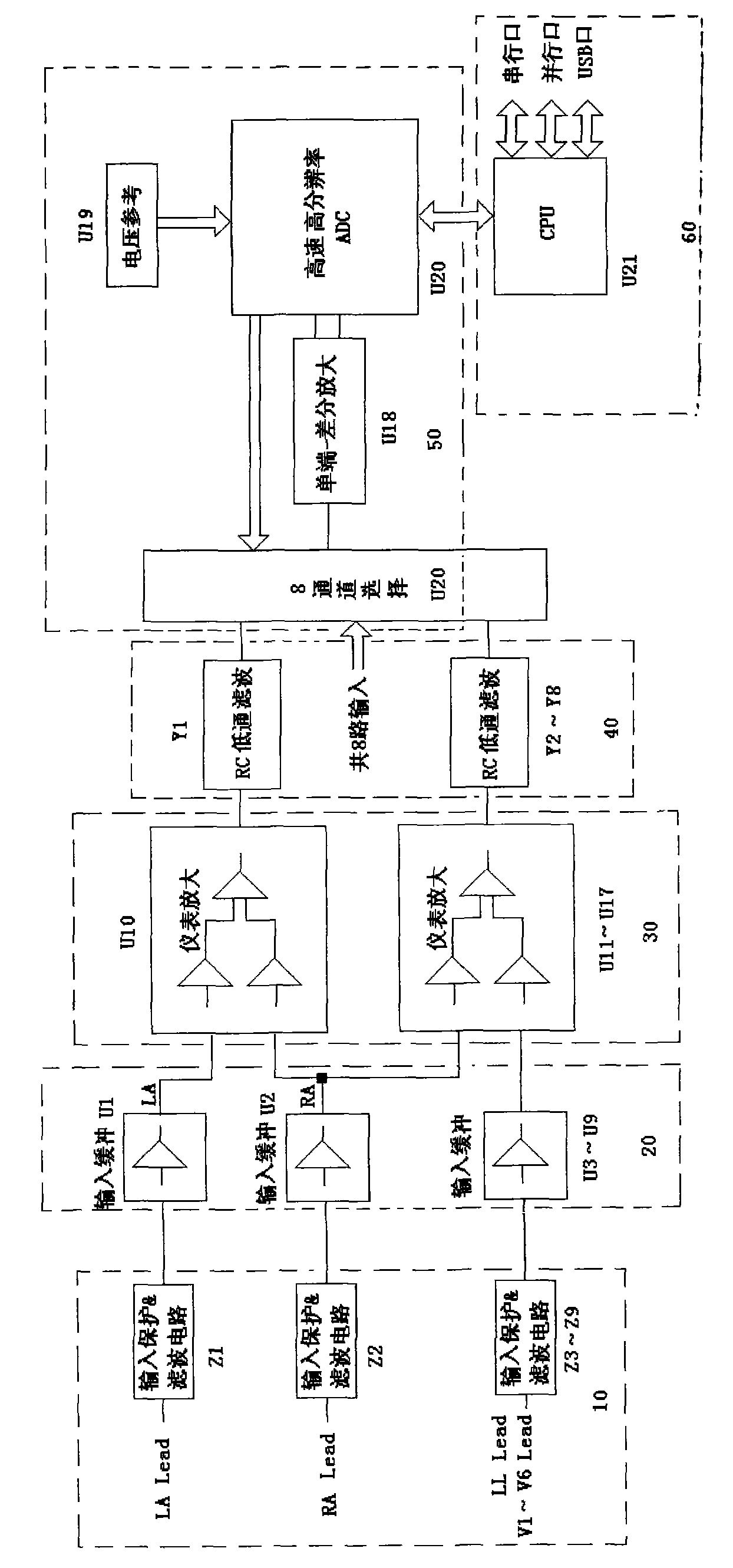
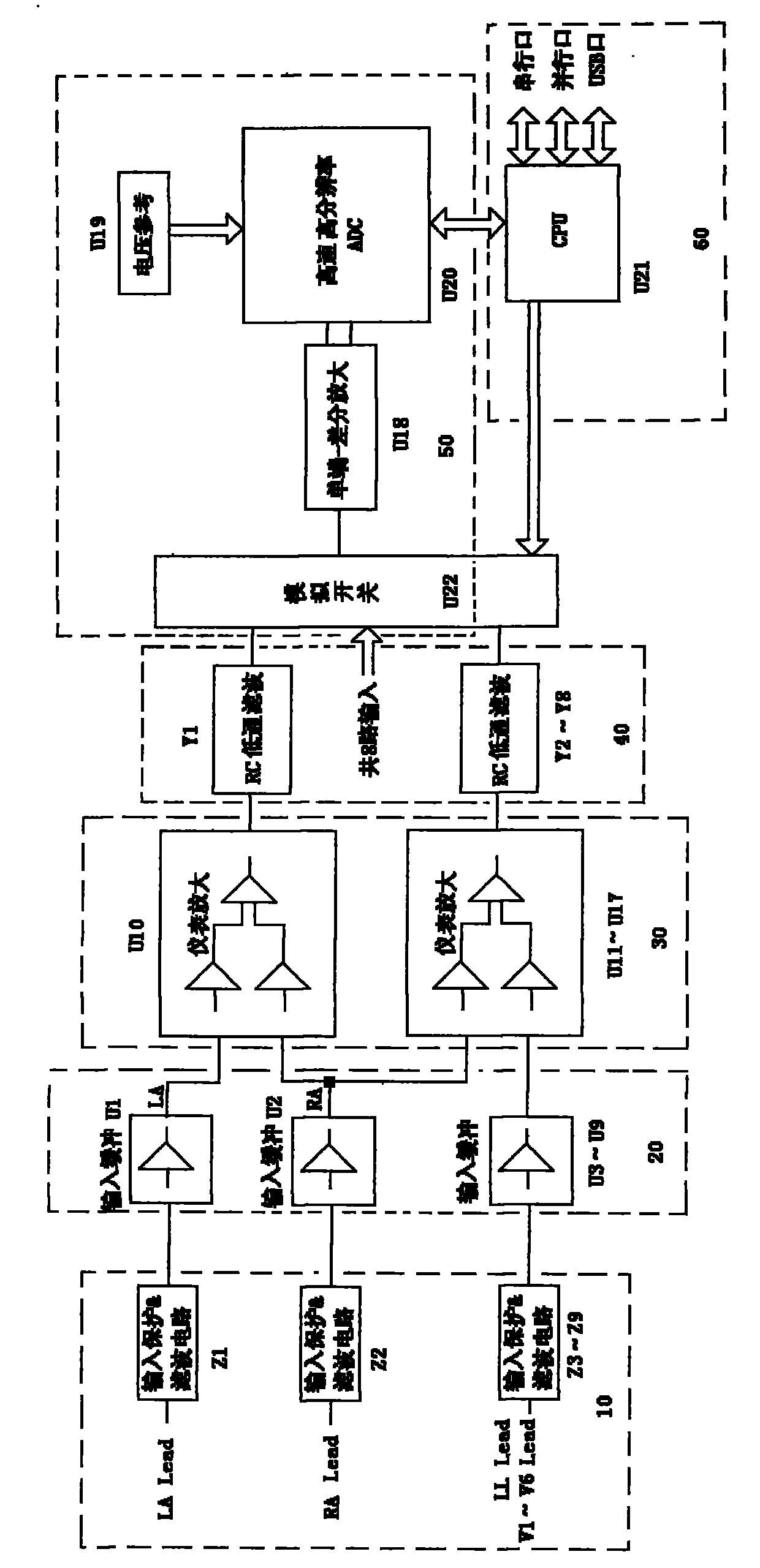
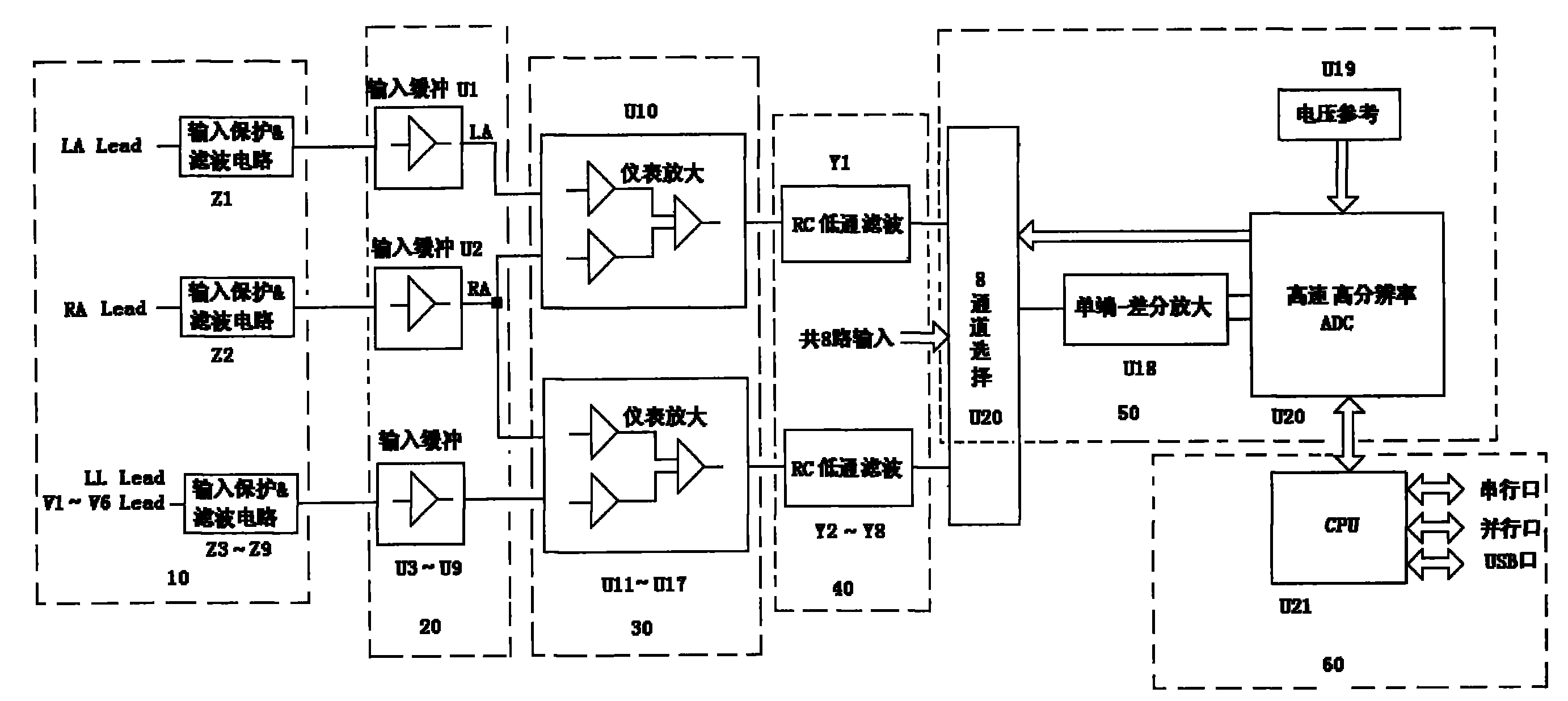
The invention discloses a high-performance direct current amplification device for acquiring biological electric signals, which comprises an input protection / filter circuit, an input buffer circuit, an instrument amplifying circuit, an RC low-pass filter circuit, an analog-digital conversion and peripheral circuit and a CPU connected in sequence, wherein the input protection / filter circuit acquires the biological electric signals and inputs the biological electric signals into the input buffer circuit, and then the biological electric signals pass through the instrument amplifying circuit, the RC low-pass filter circuit and the analog-digital conversion and peripheral circuit in turn; and the CPU controls the analog-digital conversion and peripheral circuit to work. The high-performance direct current amplification device performs impedance conversion on the biological electric signals first, then amplifies the signals, inhibits common-mode signals, and filters high-frequency noise, and a single-end transfer differential amplifier performs secondary amplification on the biological electric signals, so the indexes such as the noise, the common-mode rejection ratio and the like of the signals after analog-digital conversion reach a very high level; besides, a base line is very stable, the signal input dynamic range is large and is difficult to saturate, and simultaneously required devices are fewer, and the reliability of the high-performance direct current amplification device is improved.
Owner:EDAN INSTR
Apparatus and method for improved chopping mixer
InactiveUS6933766B2Modulation transference balanced arrangementsComputations using contact-making devicesClock rateEngineering
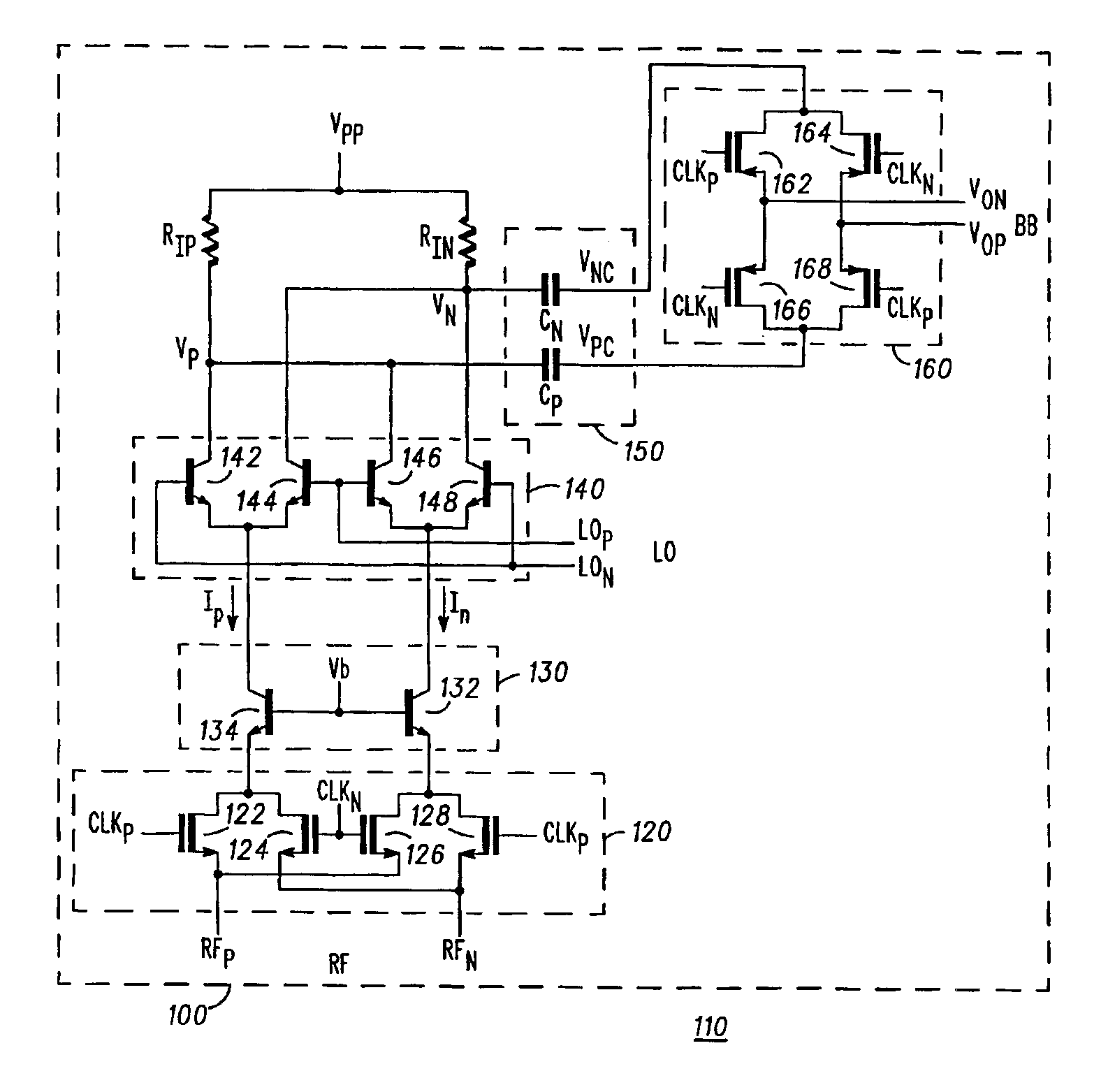
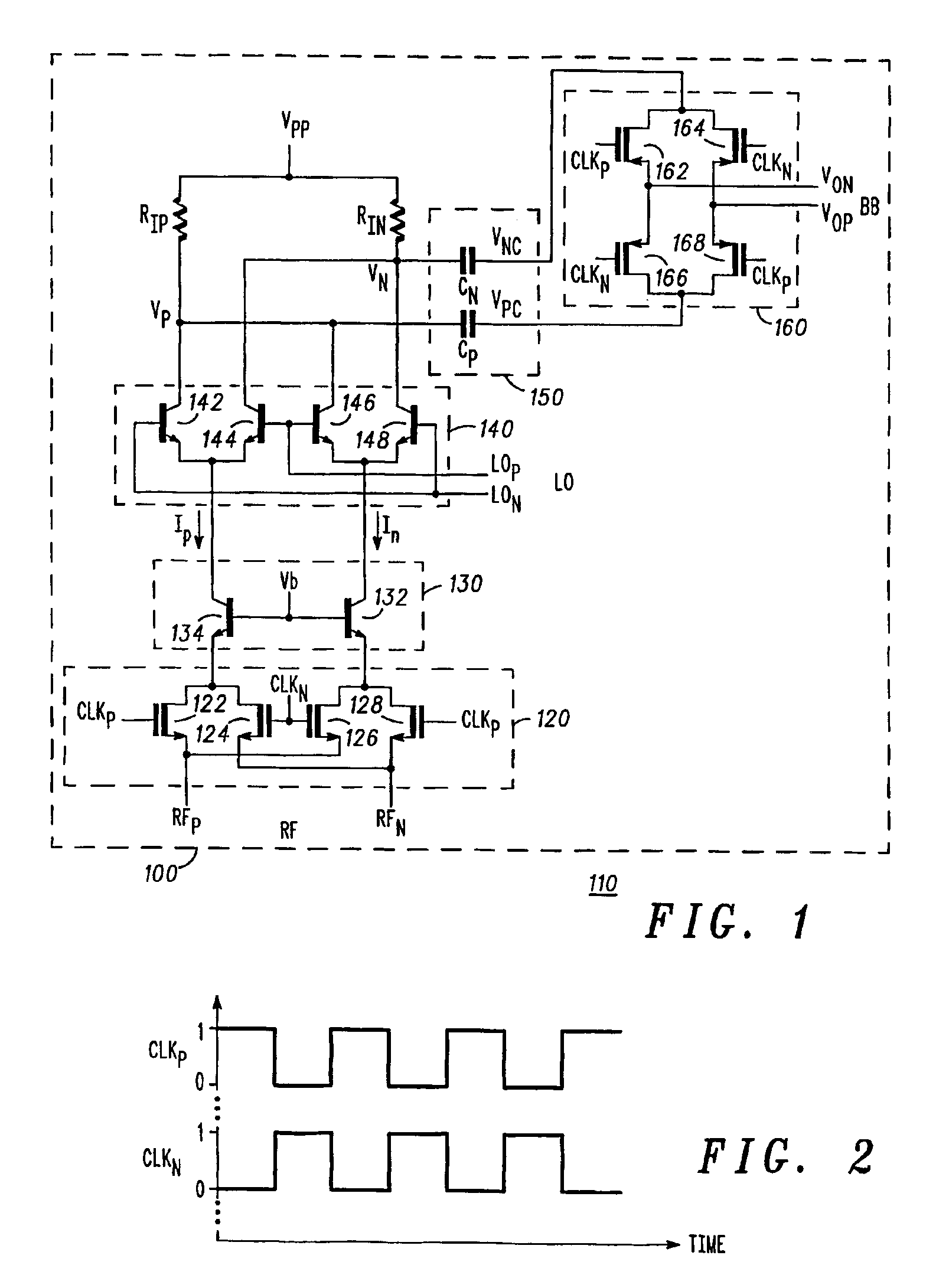
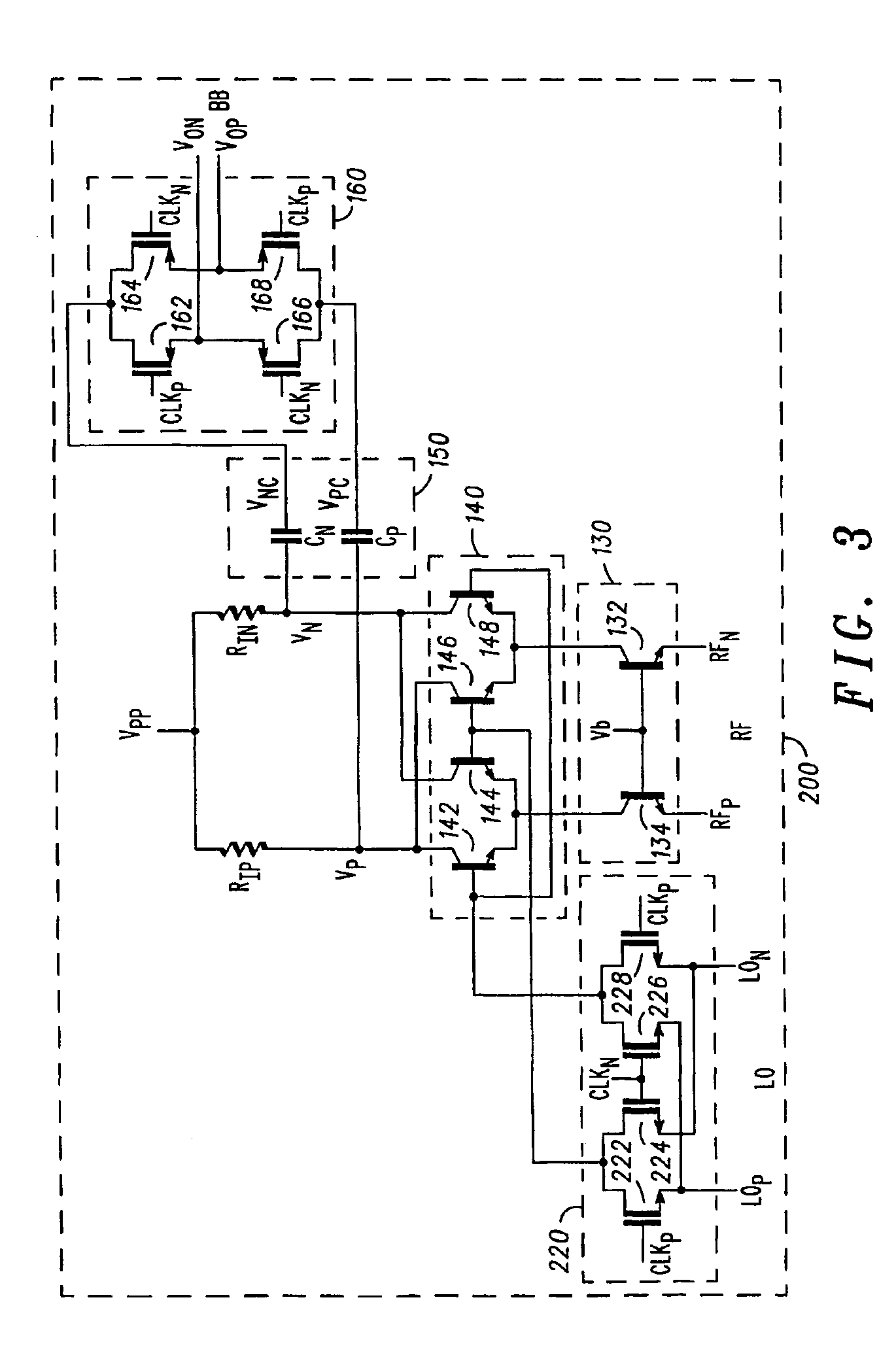
An apparatus and method for an improved chopping mixer (100) having a bipolar mixer stage (140) for mixing signals (lp, In, LOp, LOn) received thereby; an output chopping stage (160); and an AC coupling stage (150) for coupling the mixed signal to the output chopping stage. The signal prior to the chopping output stage is centered at the chopping clock frequency rather than DC. AC coupling allows removal of common mode signal in a desired frequency range. Also, the second order component present on each single ended output will also be DC blocked by the AC coupling capacitors, resulting in improved second order IP2 performance.
Owner:APPLE INC
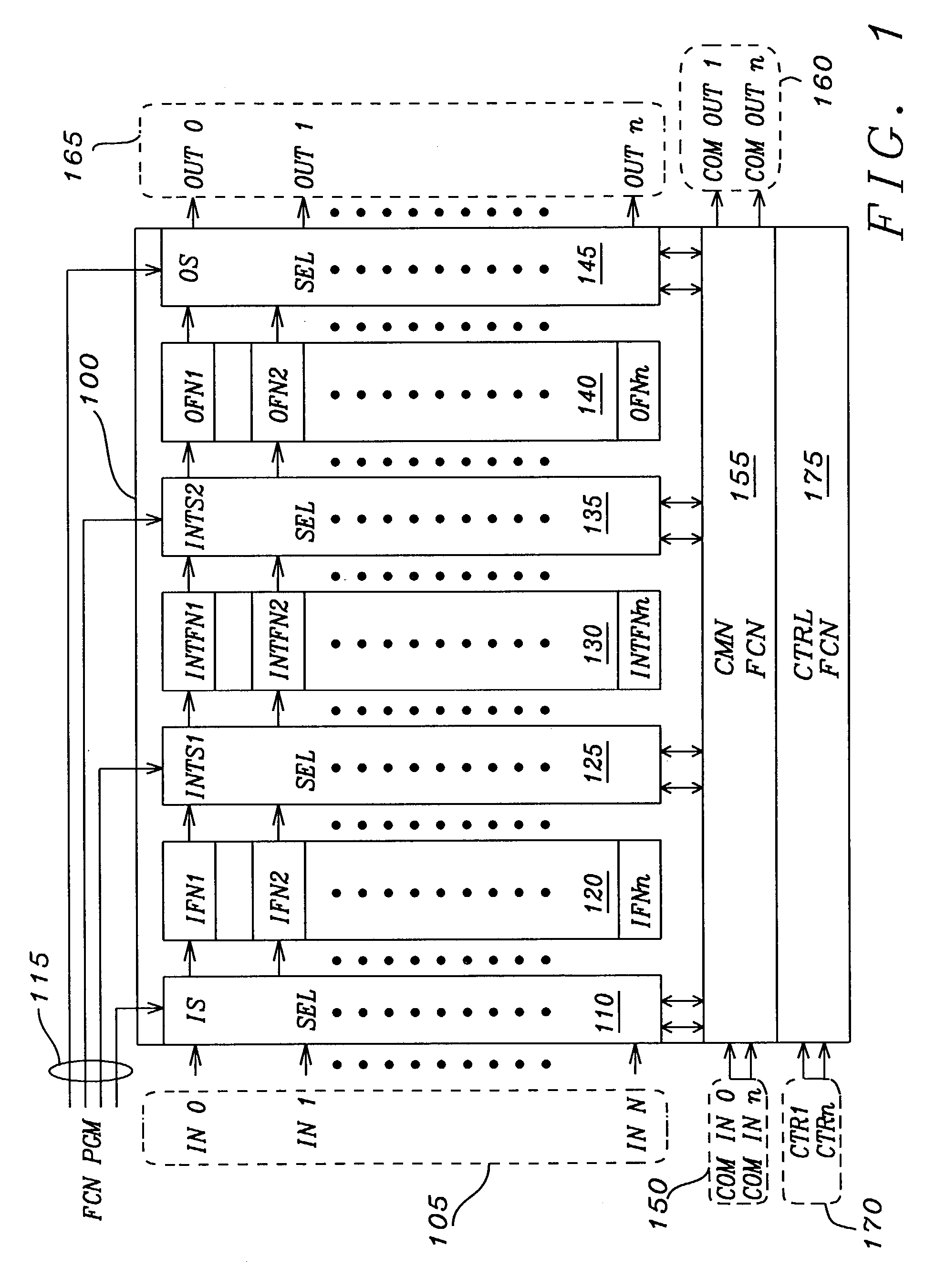
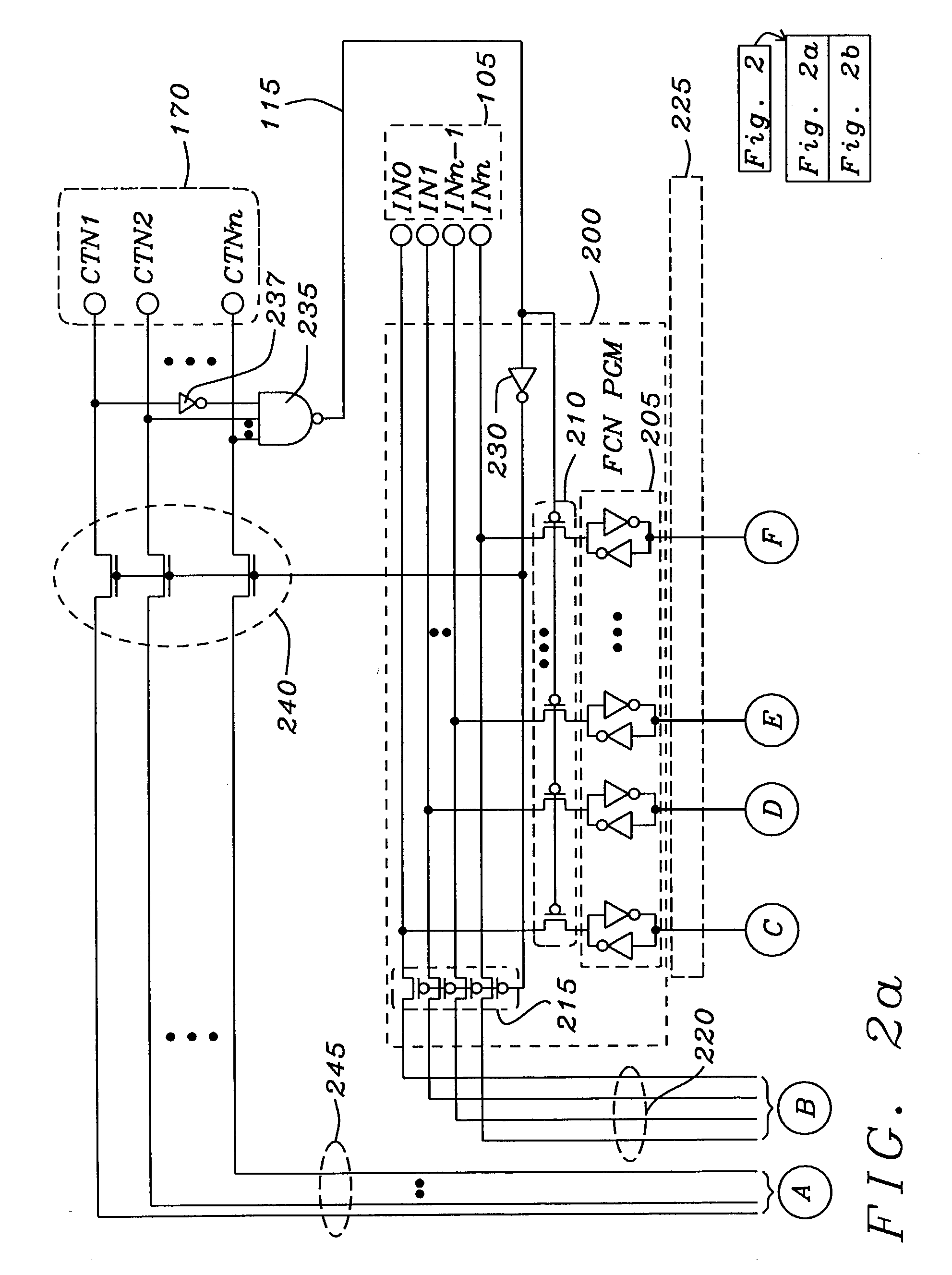
Software programmable multiple function integrated circuit module
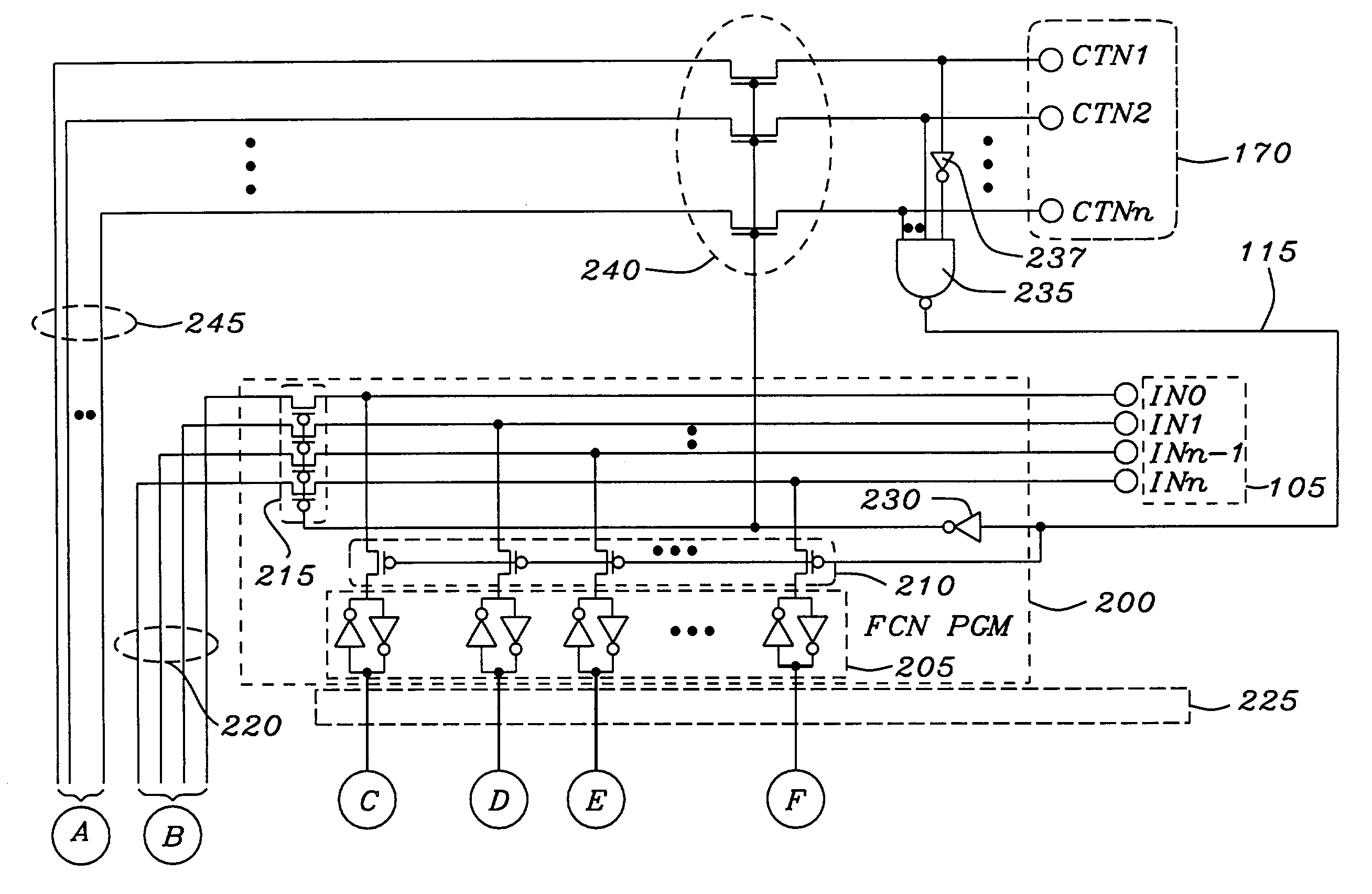
InactiveUS7360005B2Slow to programSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementCurrent/voltage measurementFunctional connectivityElectricity
An electrically programmable multiple selectable function integrated circuit module has a plurality of optionally selectable function circuits, which receive and manipulate a plurality of input data signals. The outputs of the plurality of optionally selectable function circuits are either interconnected to each other or connected to a plurality of output connectors to transmit manipulated output data signals to external circuitry. The electrically programmable multiple selectable function integrated circuit module has at least one configuration connector, which may be multiplexed with input control and timing signals, connected to a function configuration circuit to receive electrical configuration signals indicating the activation of a program mode and which of the optionally selectable function circuits are to be elected to manipulate the input data signals. The function configuration circuit is connected to the optionally selectable function circuits to selectively elect, which of the optionally selectable function circuits are to is manipulate the input data signals. The electrically programmable multiple selectable function integrated circuit module optionally has common function circuit connected to common function connectors and the plurality of optionally selectable function circuits to manipulate common data signals, and transmit common output data signals to the selectable function circuits.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
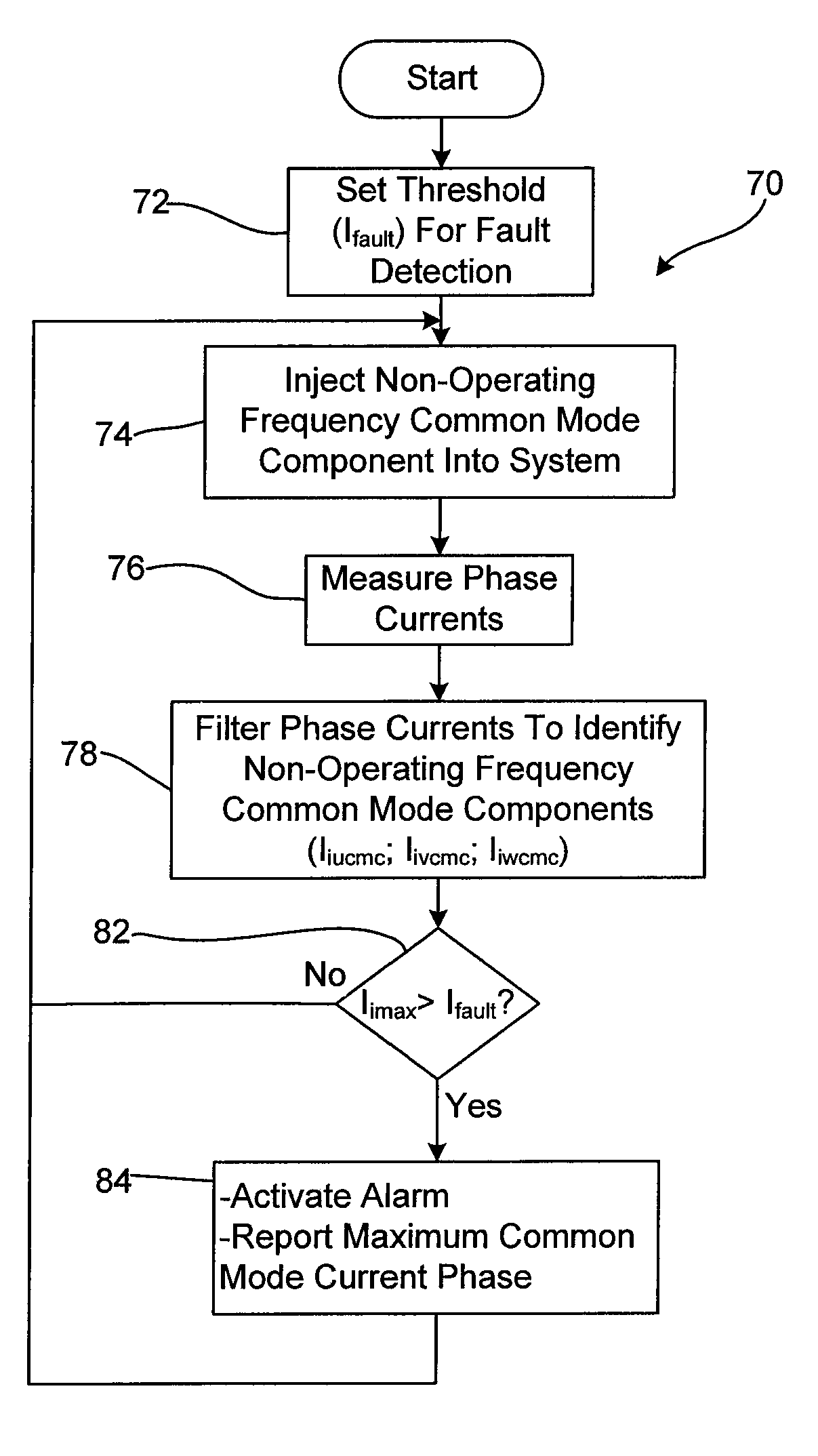
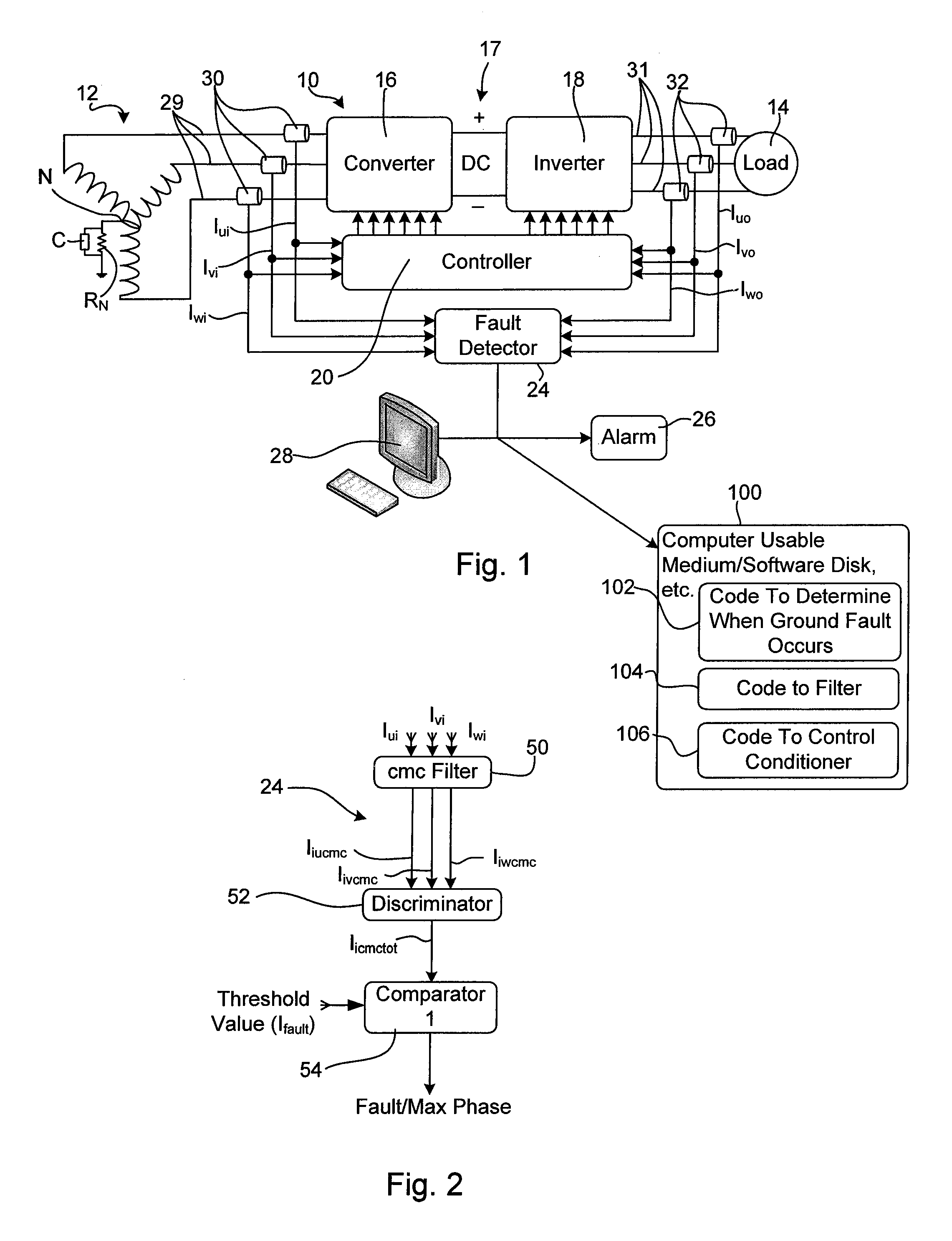
High Resistance Ground Protection Employing AC Drive Characteristics
ActiveUS20090296289A1Improve accuracyLower the thresholdEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentHigh resistanceMotor drive
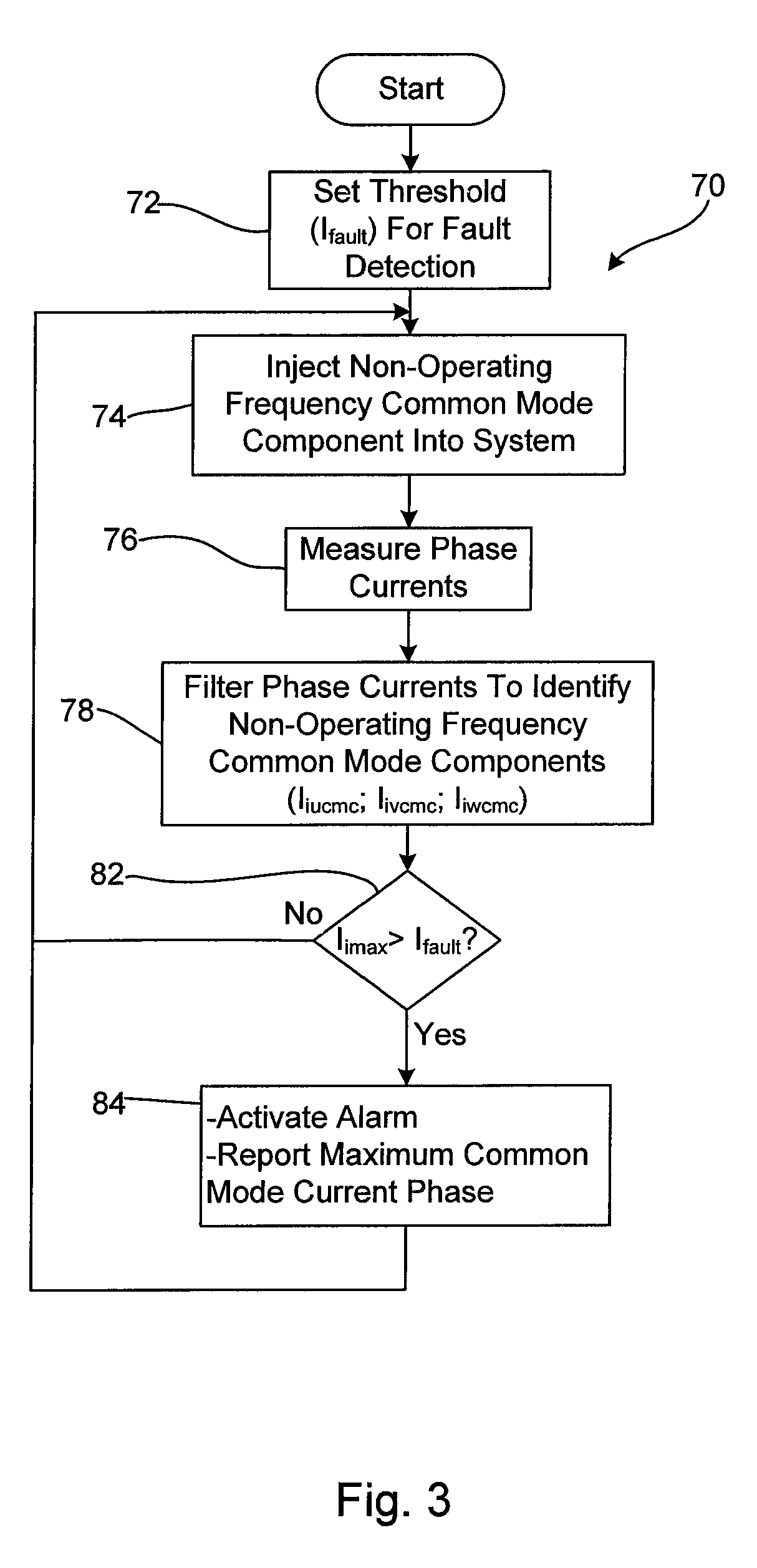
A method and apparatus for identifying a ground fault in a motor drive system that includes at least one three phase power conditioner that is linked to three phase supply lines and to positive and negative DC buses, the method comprising the steps of controlling the power conditioner at an operating frequency to convert power, while controlling the power conditioner to convert power, controlling the power conditioner to apply a common mode signal on each of the three phase supply lines where the common mode signal has a frequency that is different than the operating frequency, sensing the common mode signal on at least one of the three phase supply lines and when the common mode signal on the at least one of the three phase supply lines is greater than a threshold level, indicating that a ground fault has occurred.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Reducing Electromagnetic Interference in a Received Signal
ActiveUS20110296267A1Reduce electromagnetic interferenceError preventionTransmission systemsElectrical conductorElectromagnetic interference
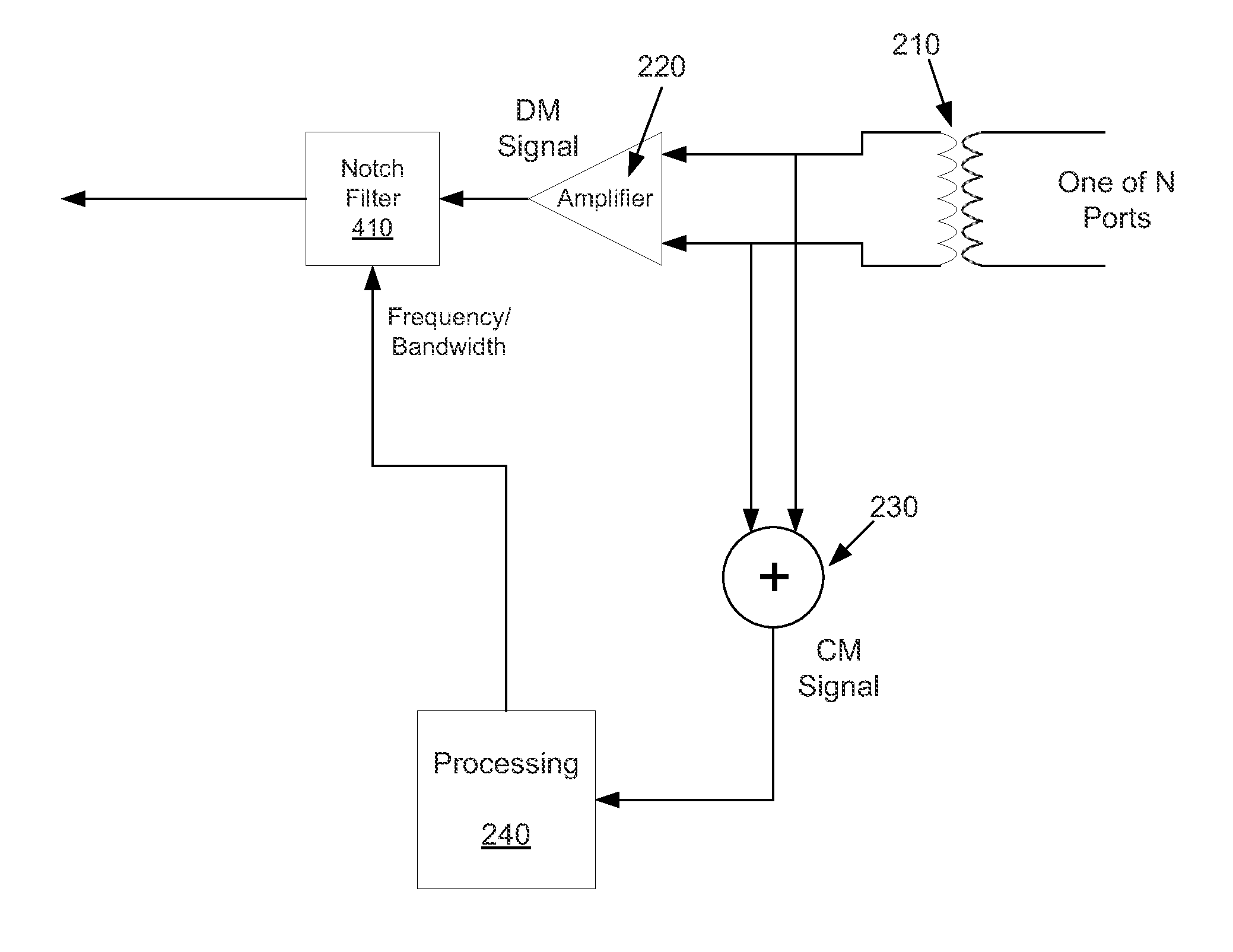
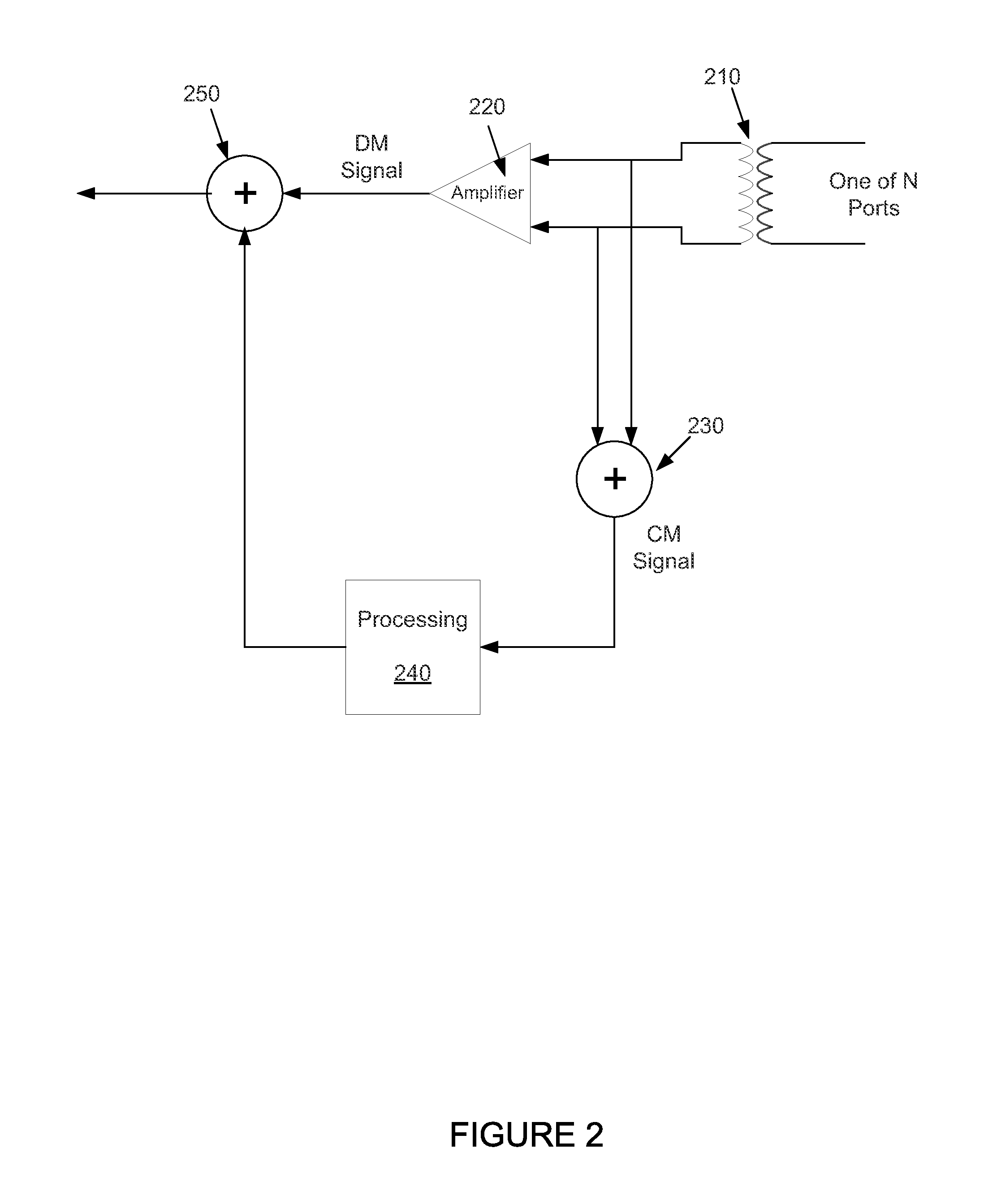
Embodiments of methods and apparatus for reducing electromagnetic interference of a received signal are disclosed. One method includes receiving a signal over at least two conductors, extracting a common-mode signal from the at least two conductors, processing the common-mode signal, and reducing electromagnetic interference of the received signal by summing the processed common-mode signal with the received signal.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
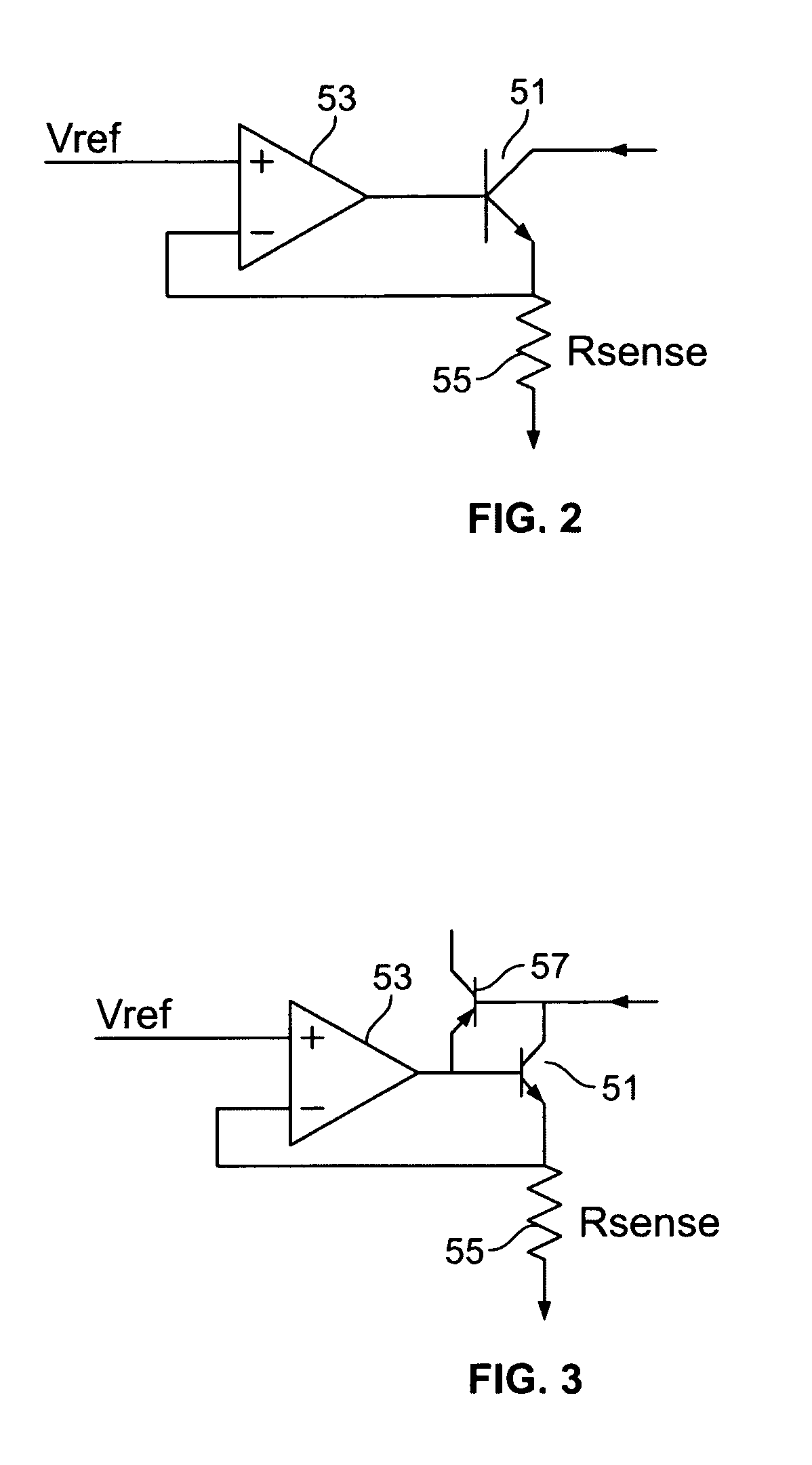
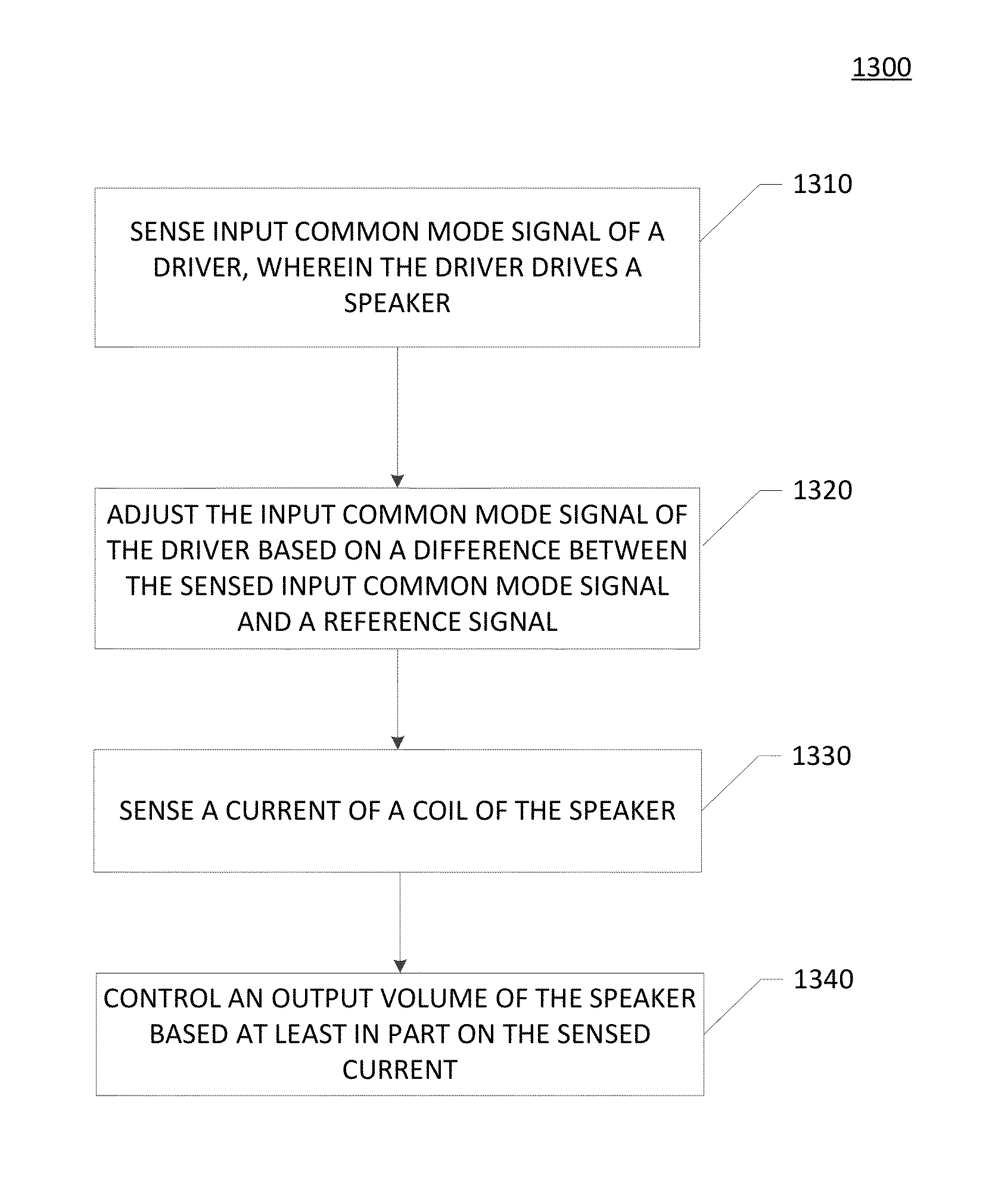
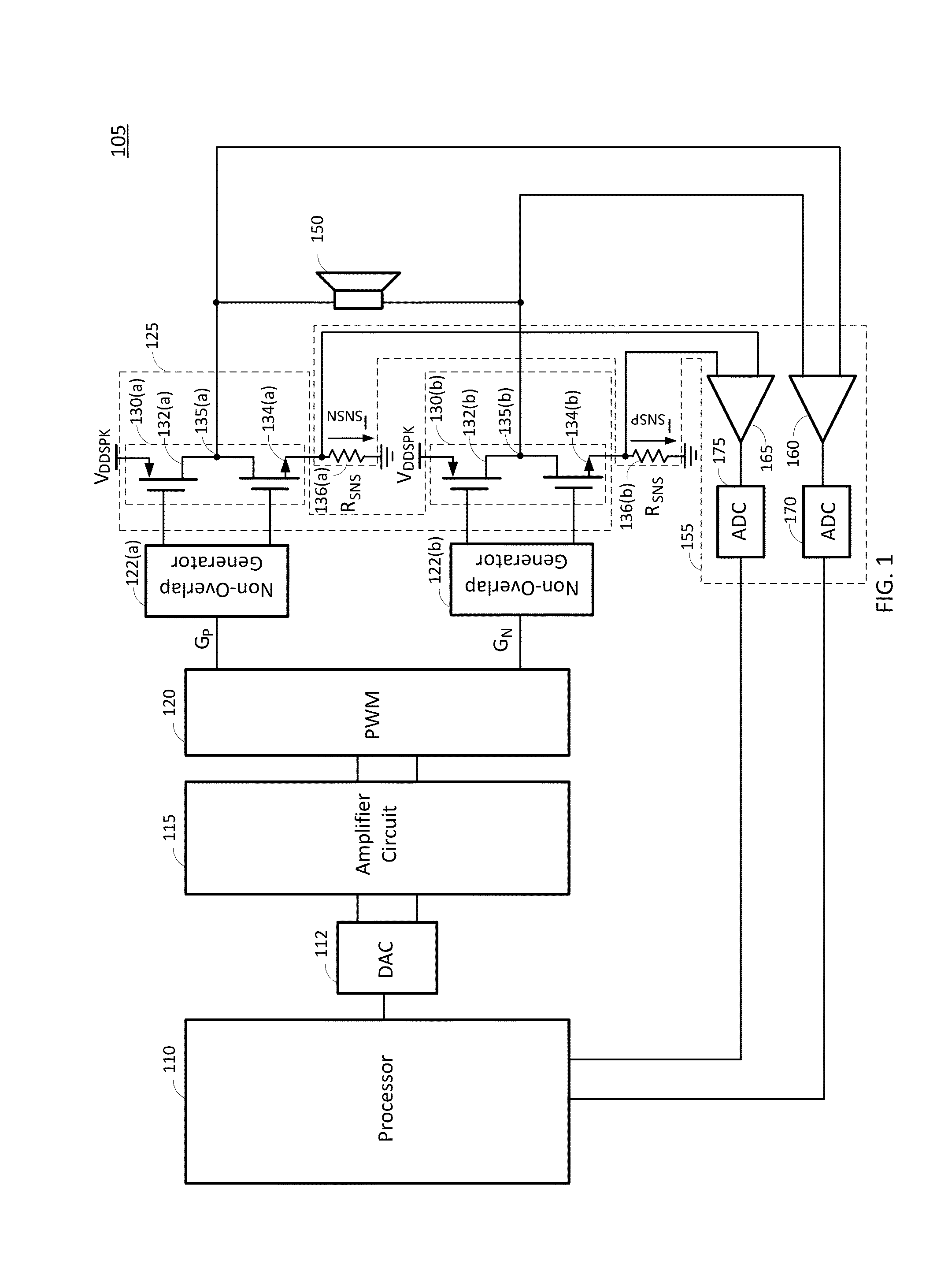
Speaker protection circuit with improved accuracy
In one embodiment, a method for speaker operation comprises sensing an input common mode signal of a driver, wherein the driver drives a speaker, and adjusting the input common mode signal of the driver based on a difference between the sensed input common mode signal and a reference signal. The method also comprises sensing a current of a coil of the speaker, and control an output volume of the speaker based at least in part on the sensed current.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com