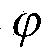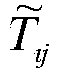Patents
Literature
296 results about "Broadband noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
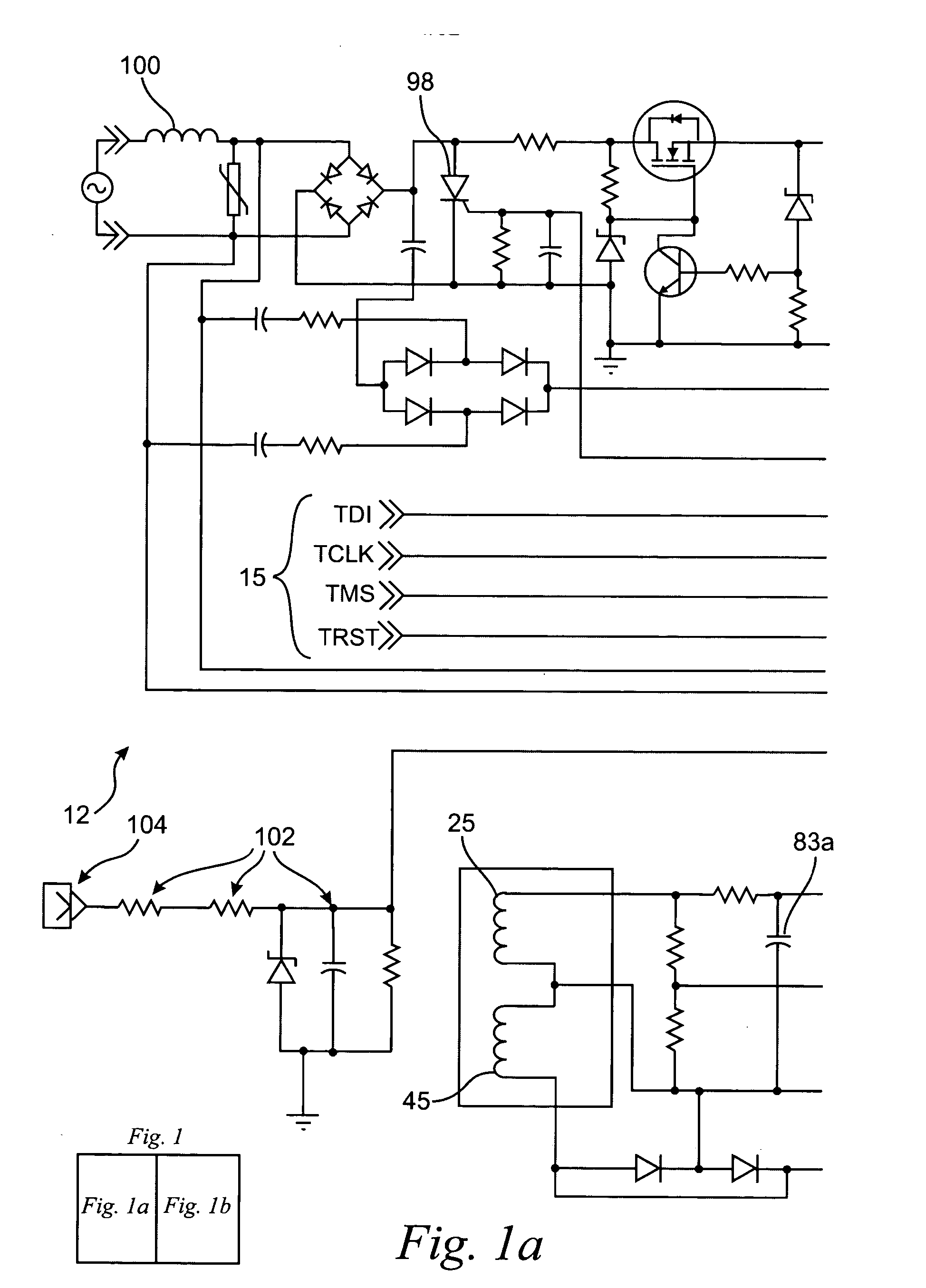
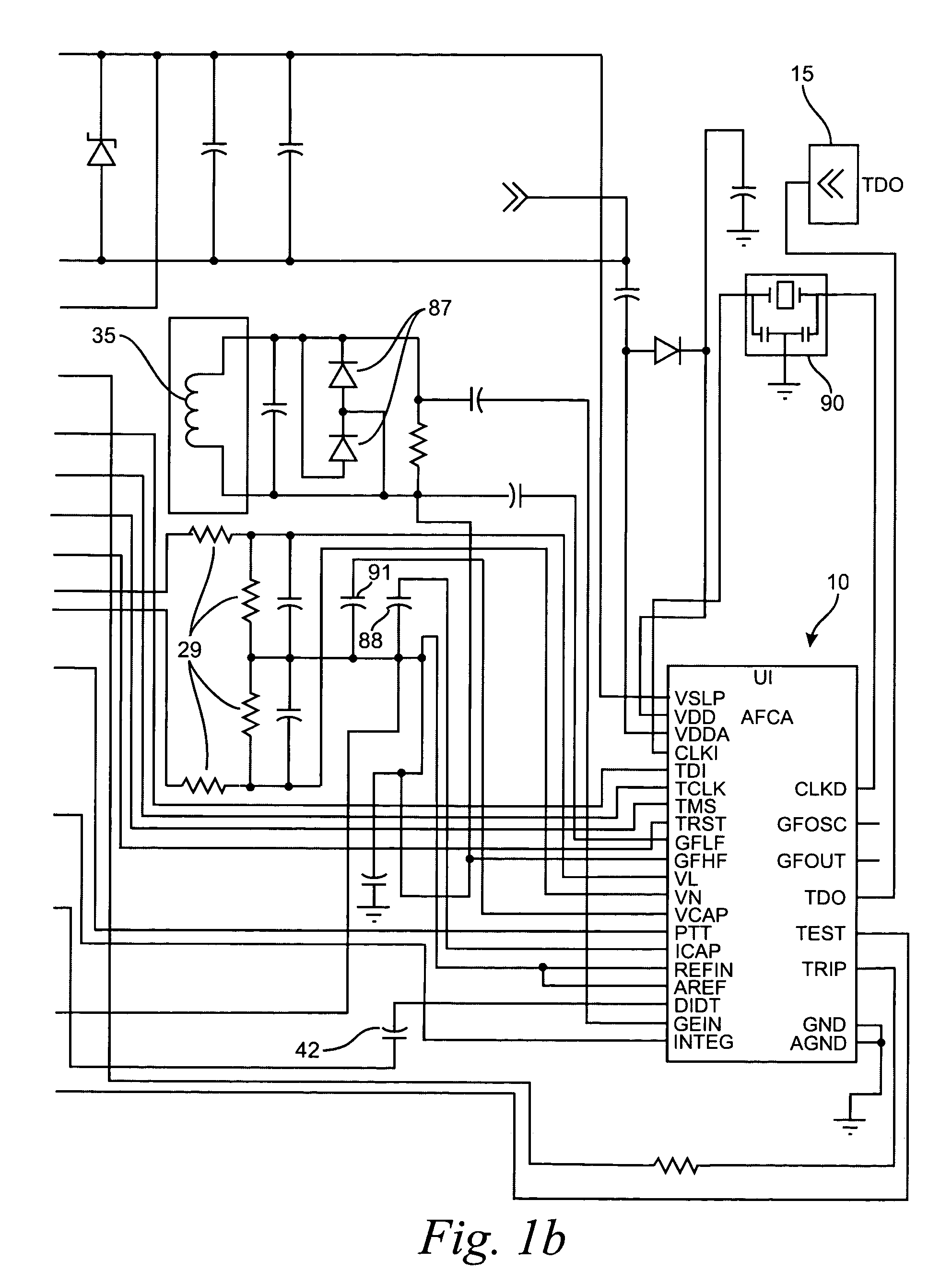
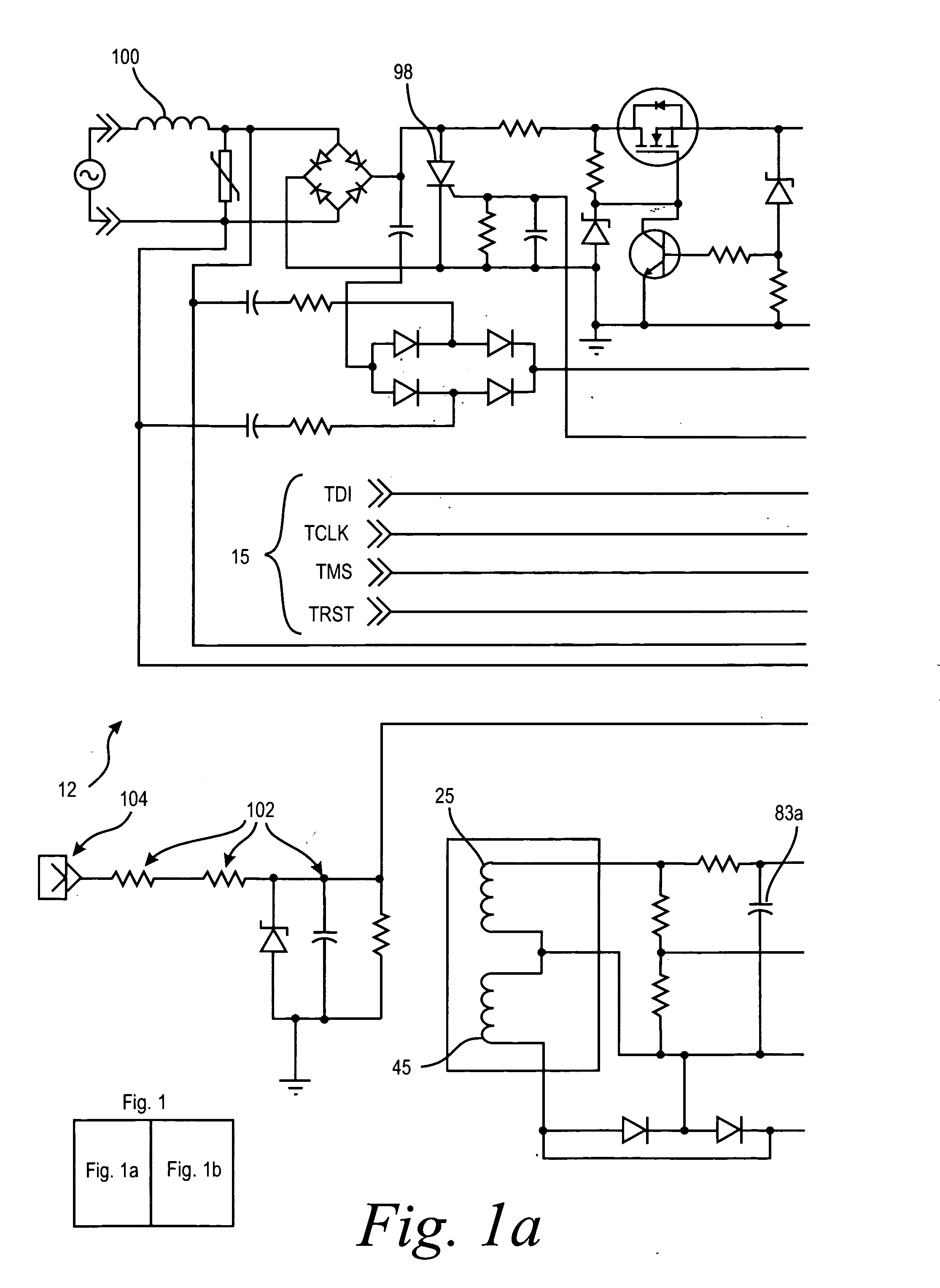
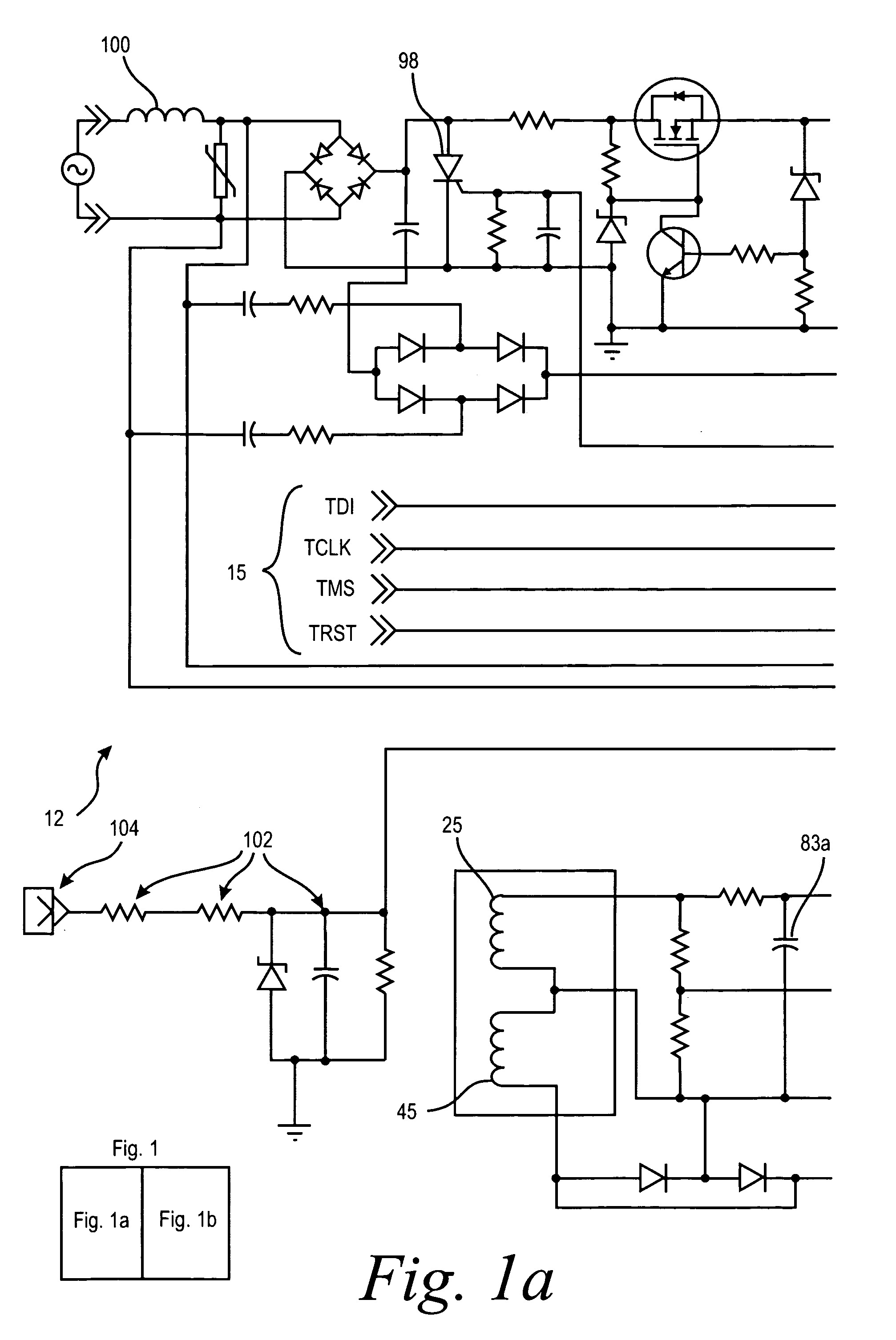
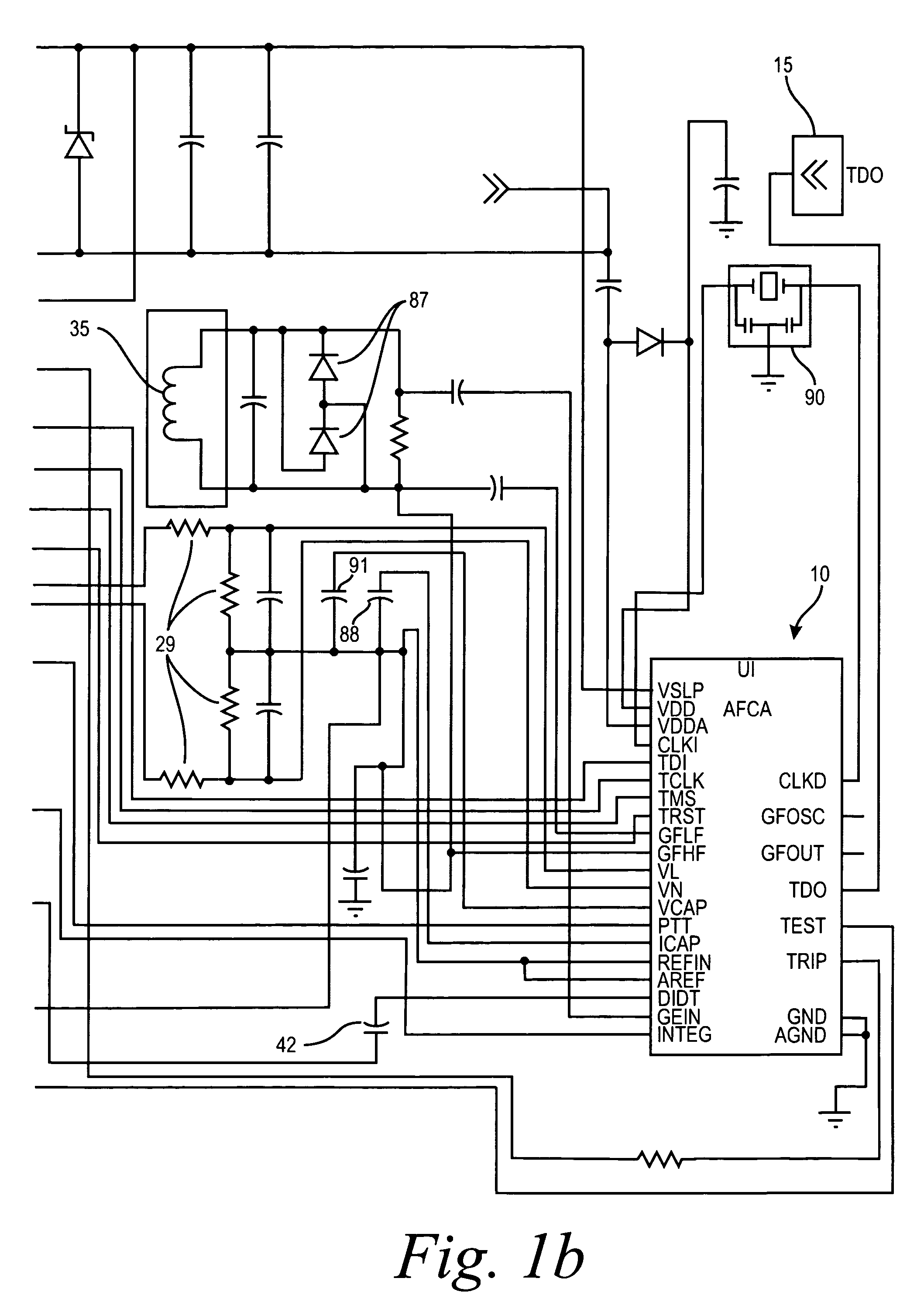
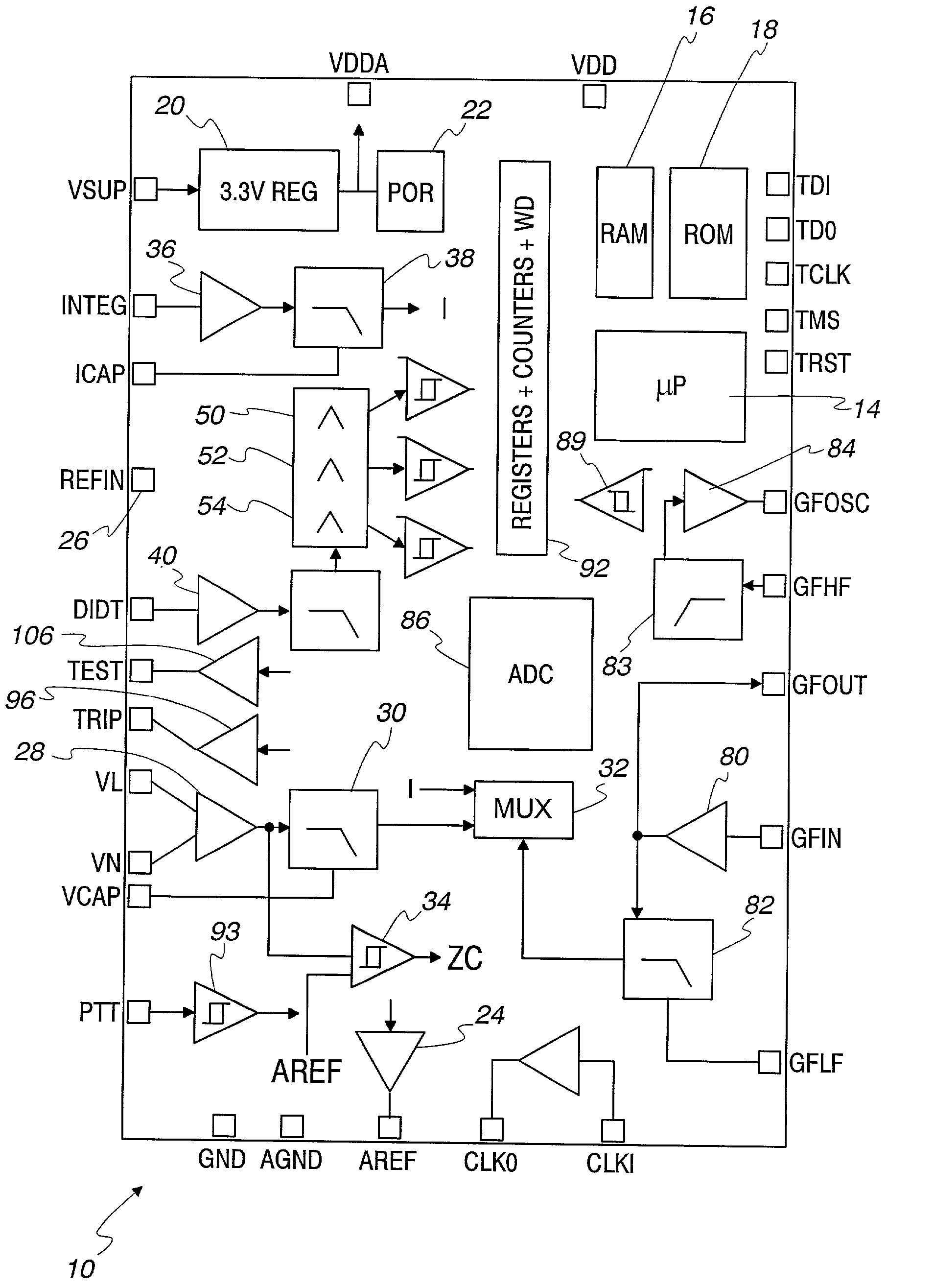
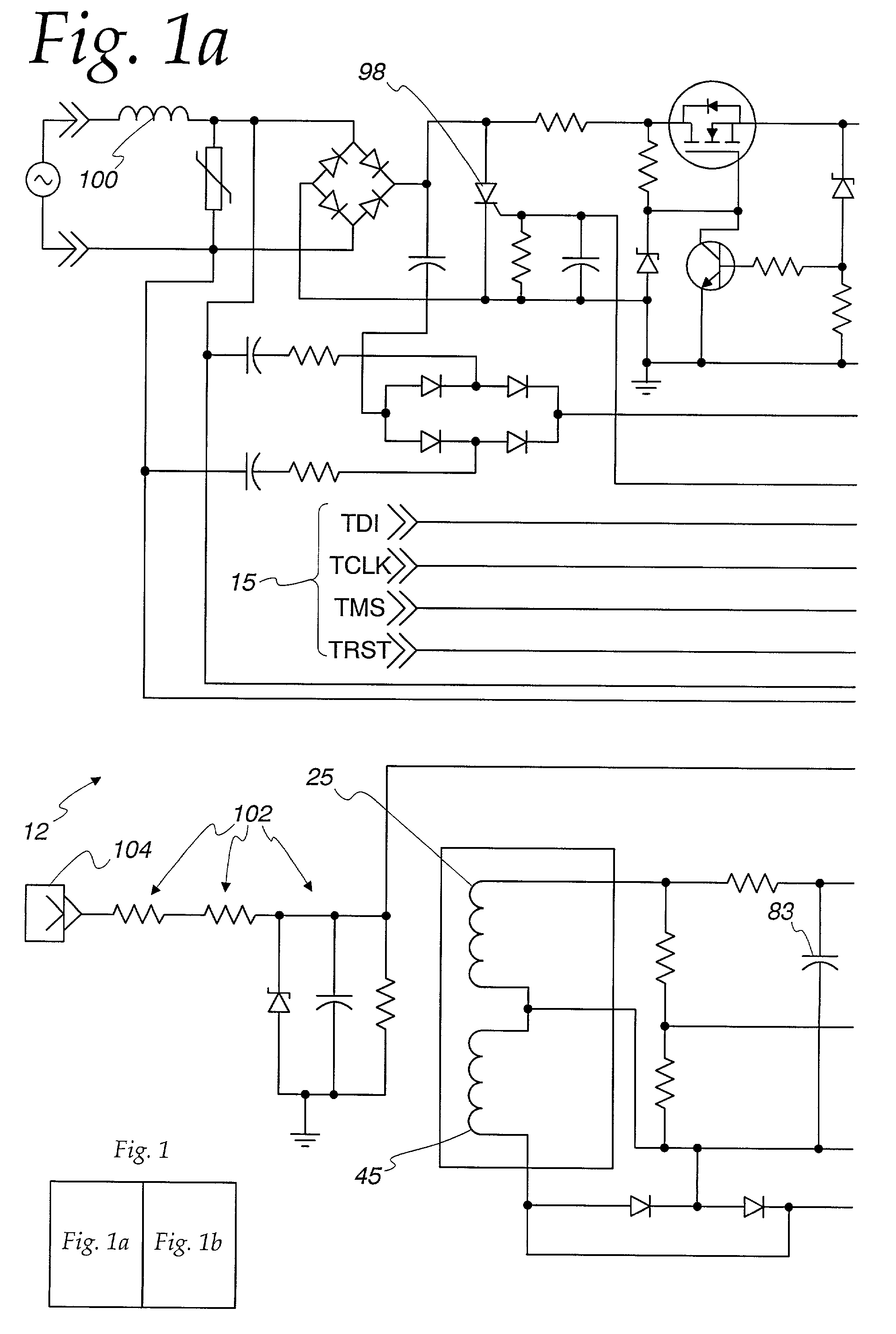
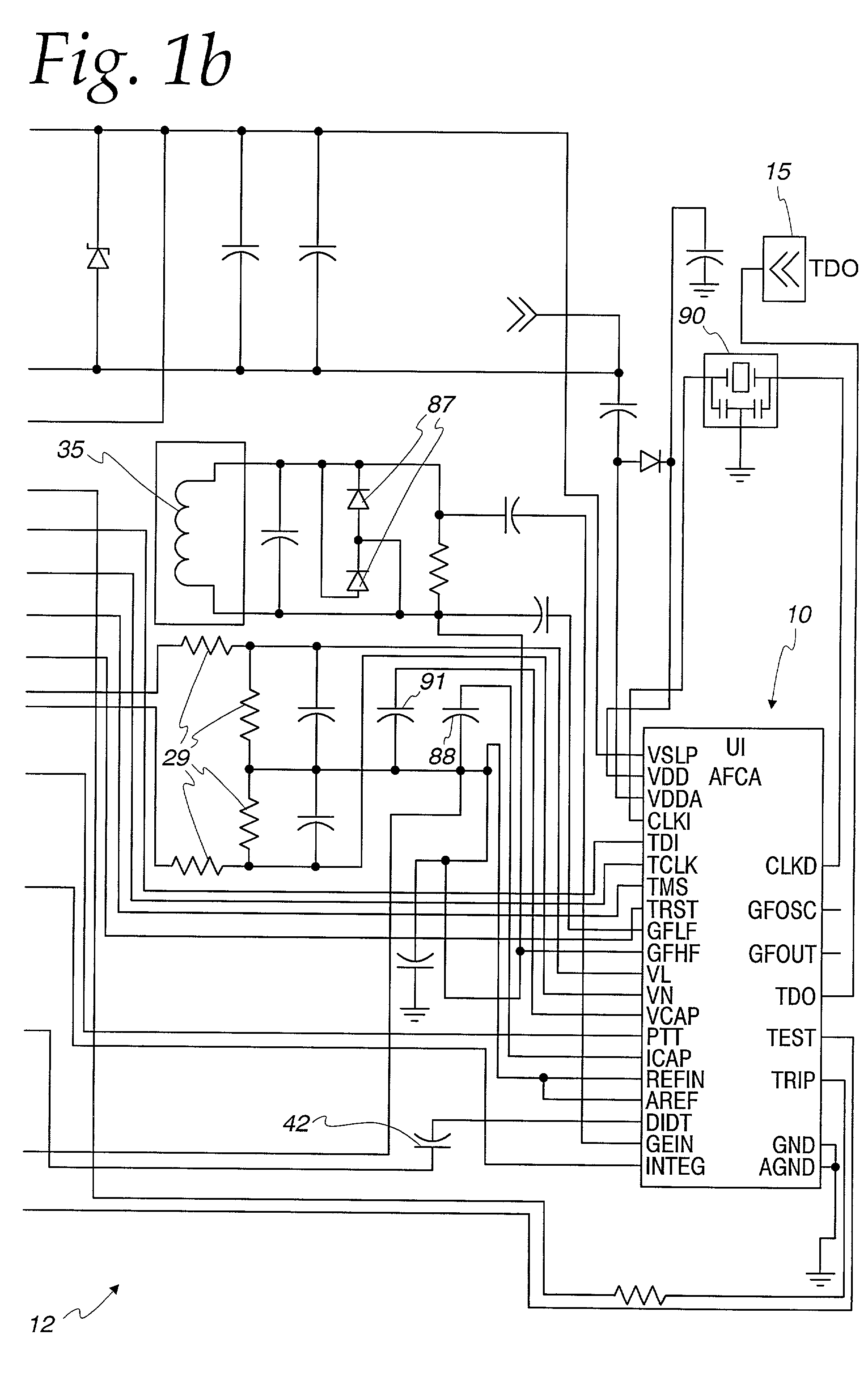
Arc fault detection system
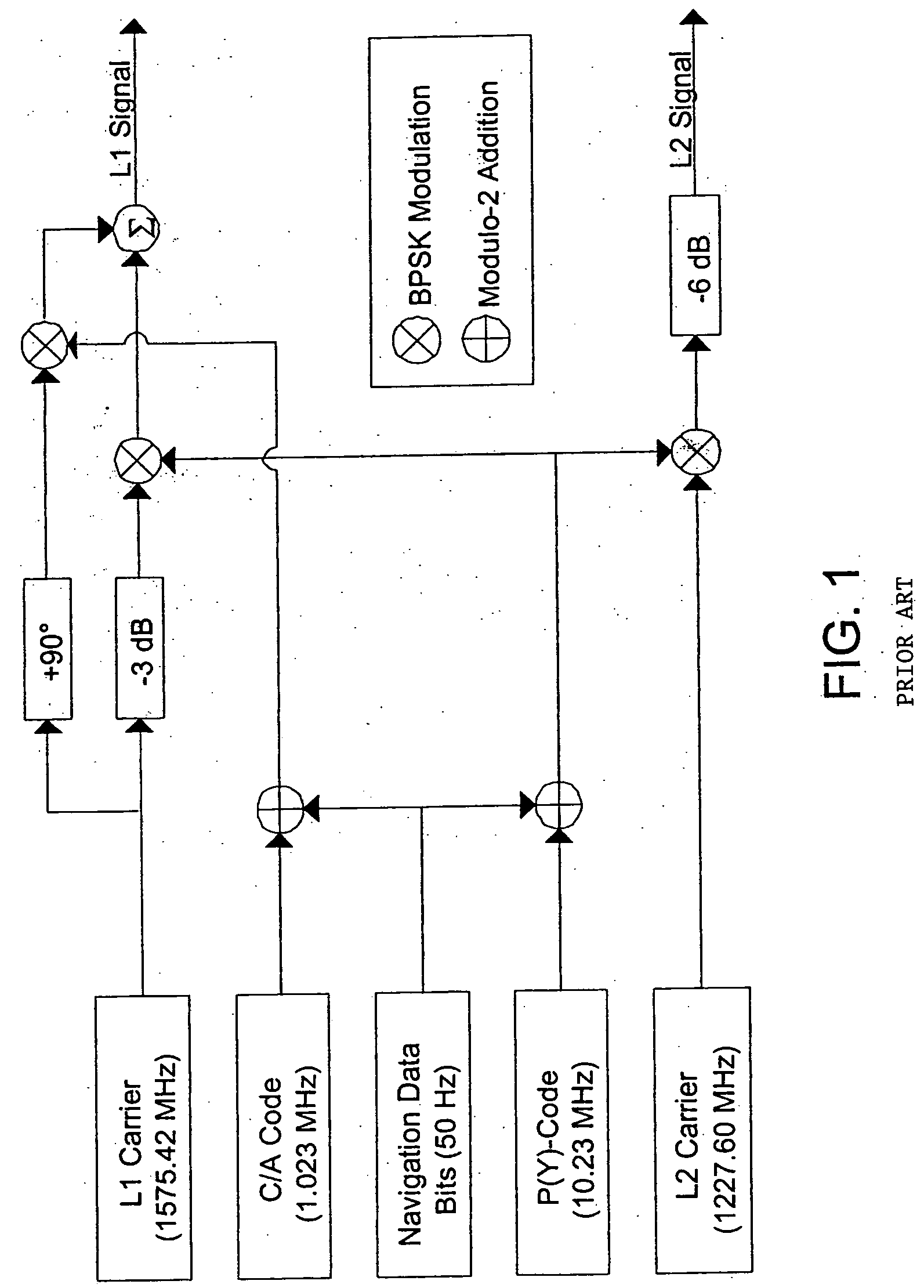
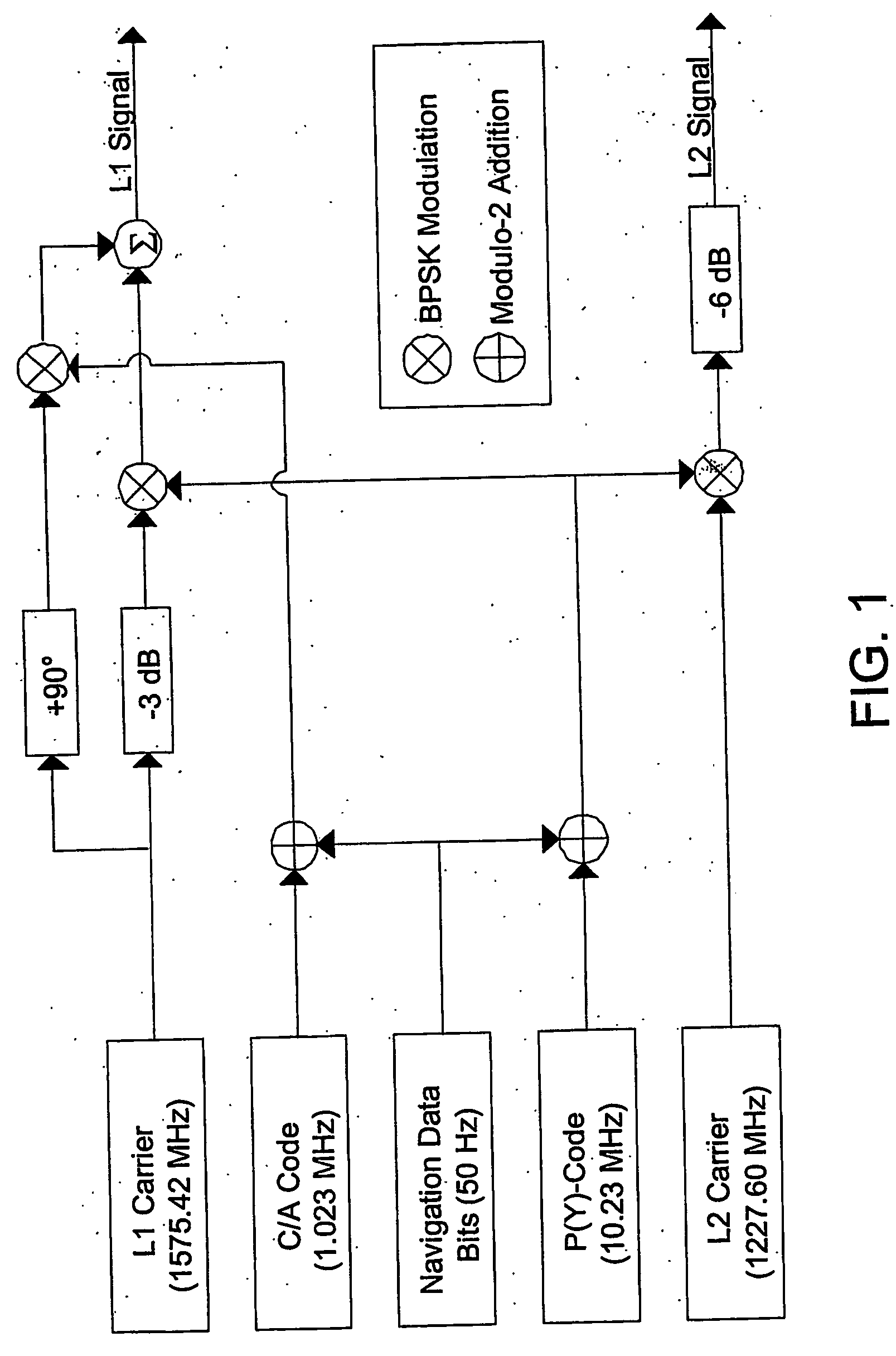
InactiveUS6259996B1Reliably detectsGuaranteed uptimeLevel controlNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementBroadband noiseSystems analysis
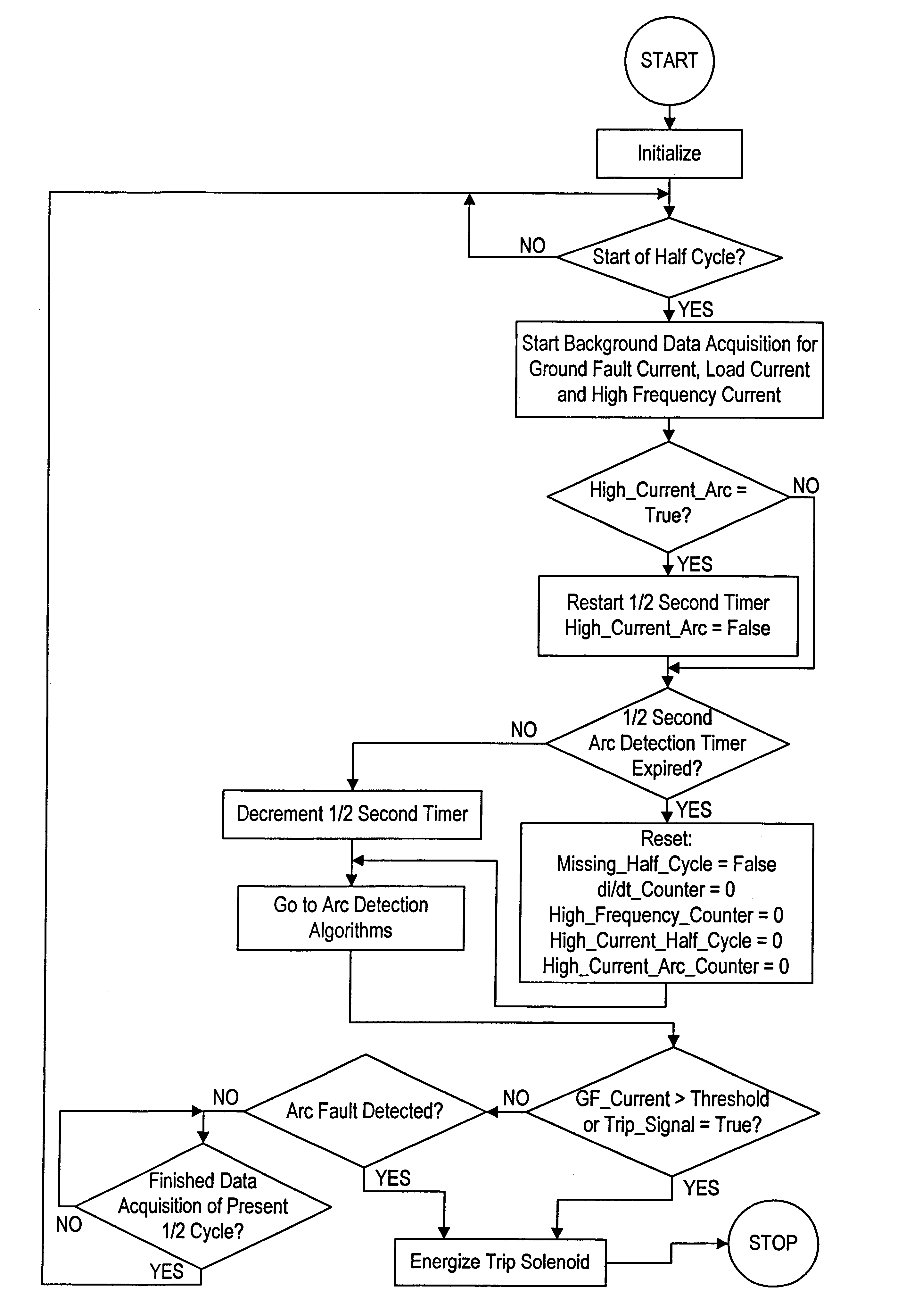
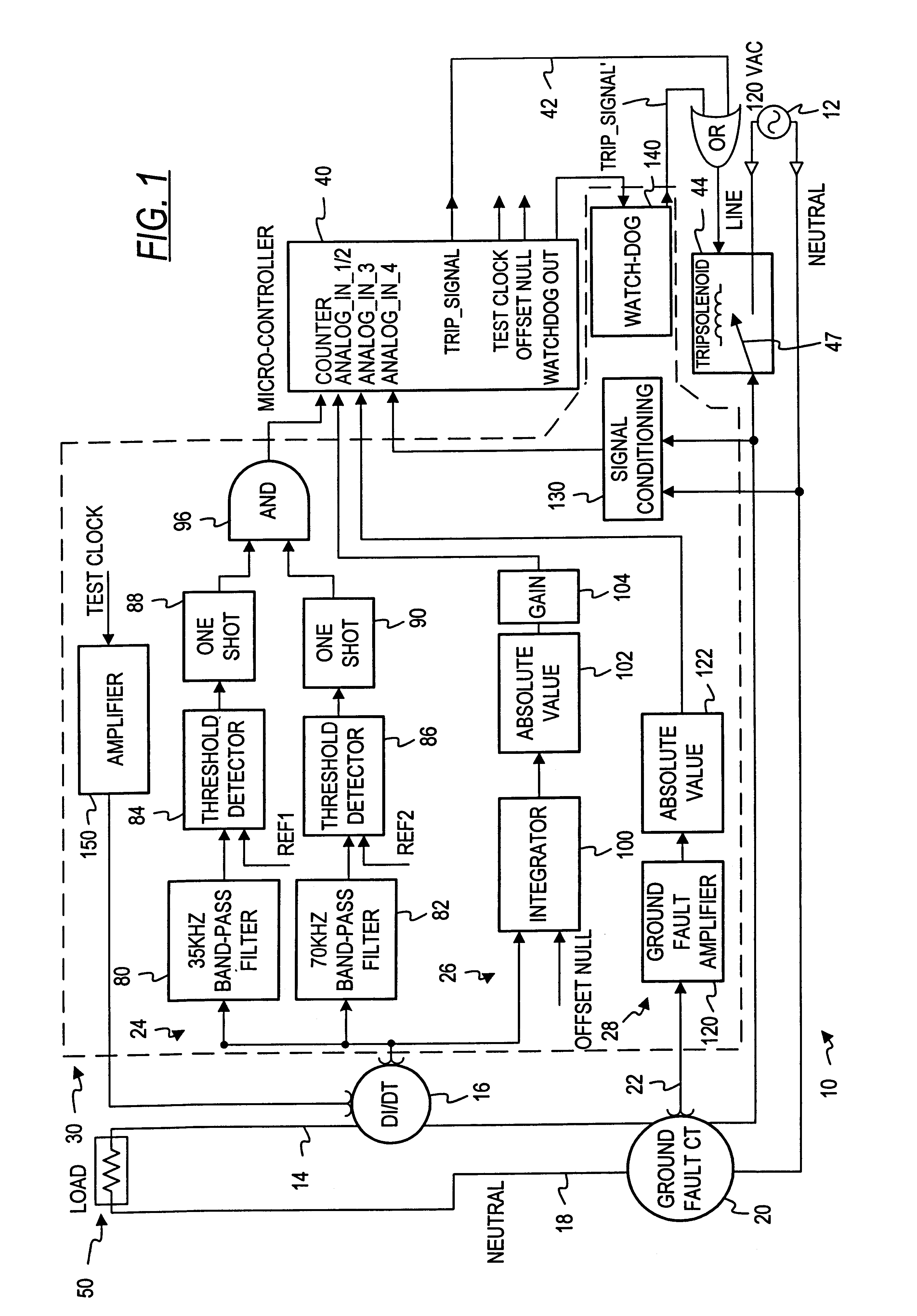
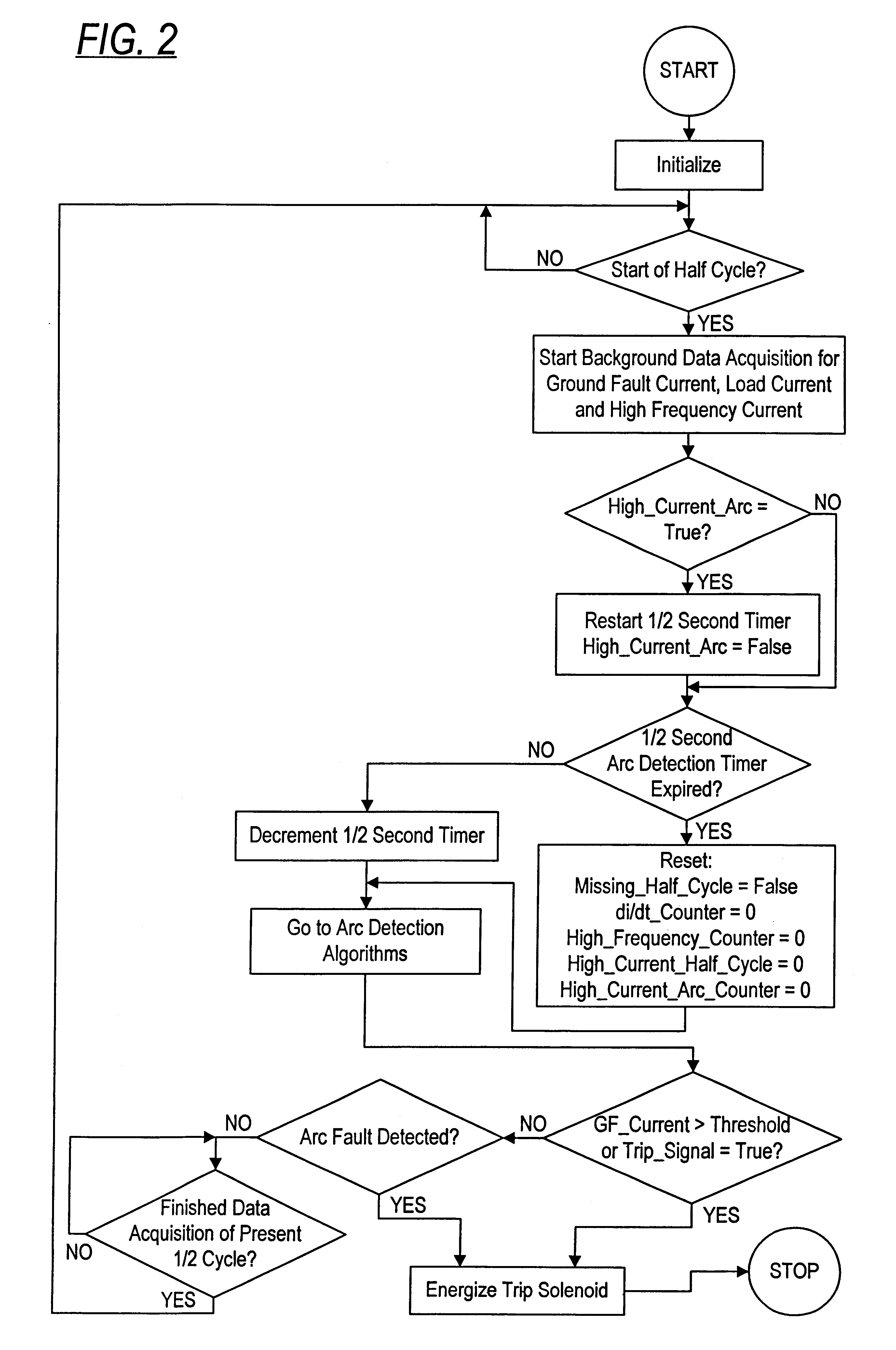
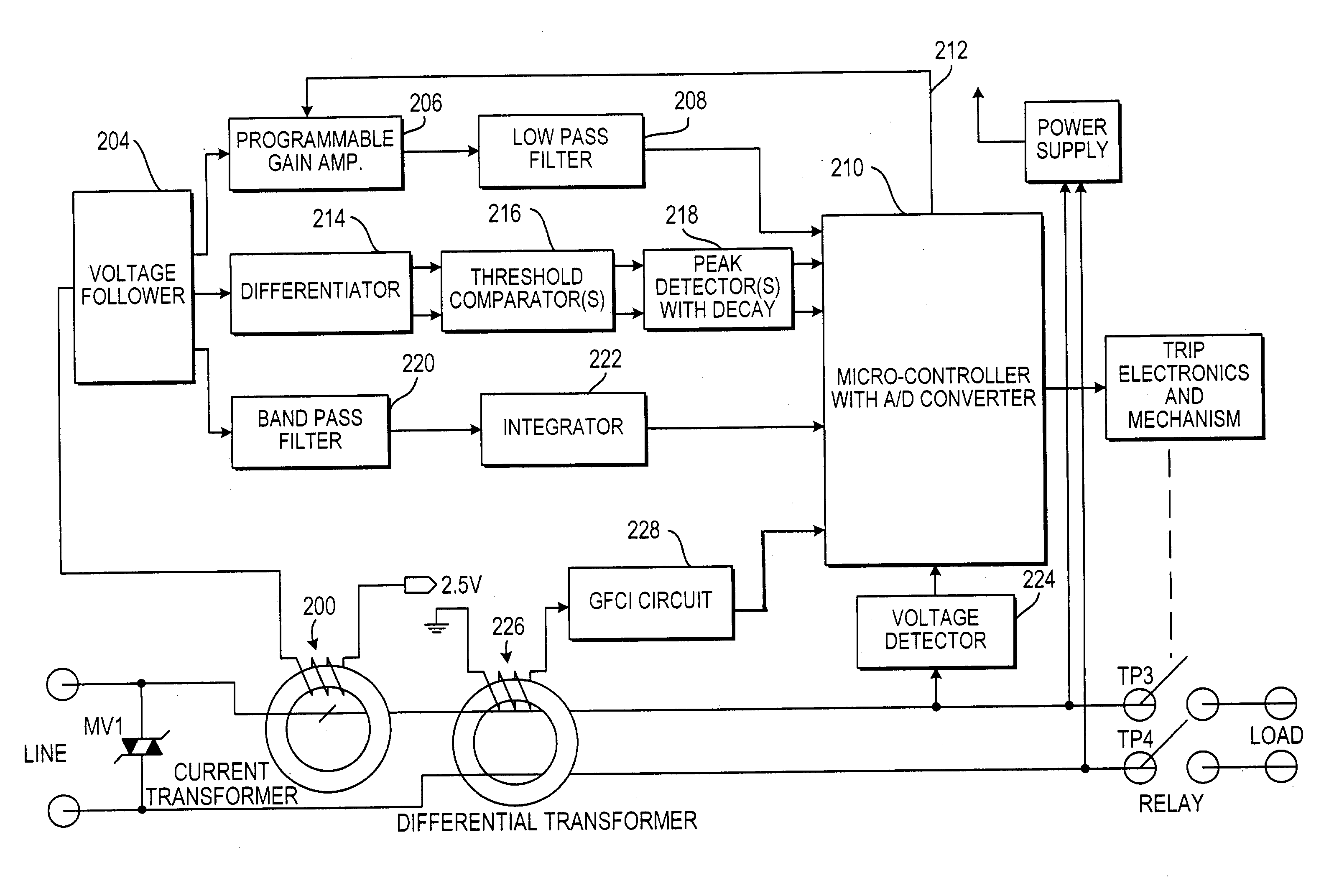
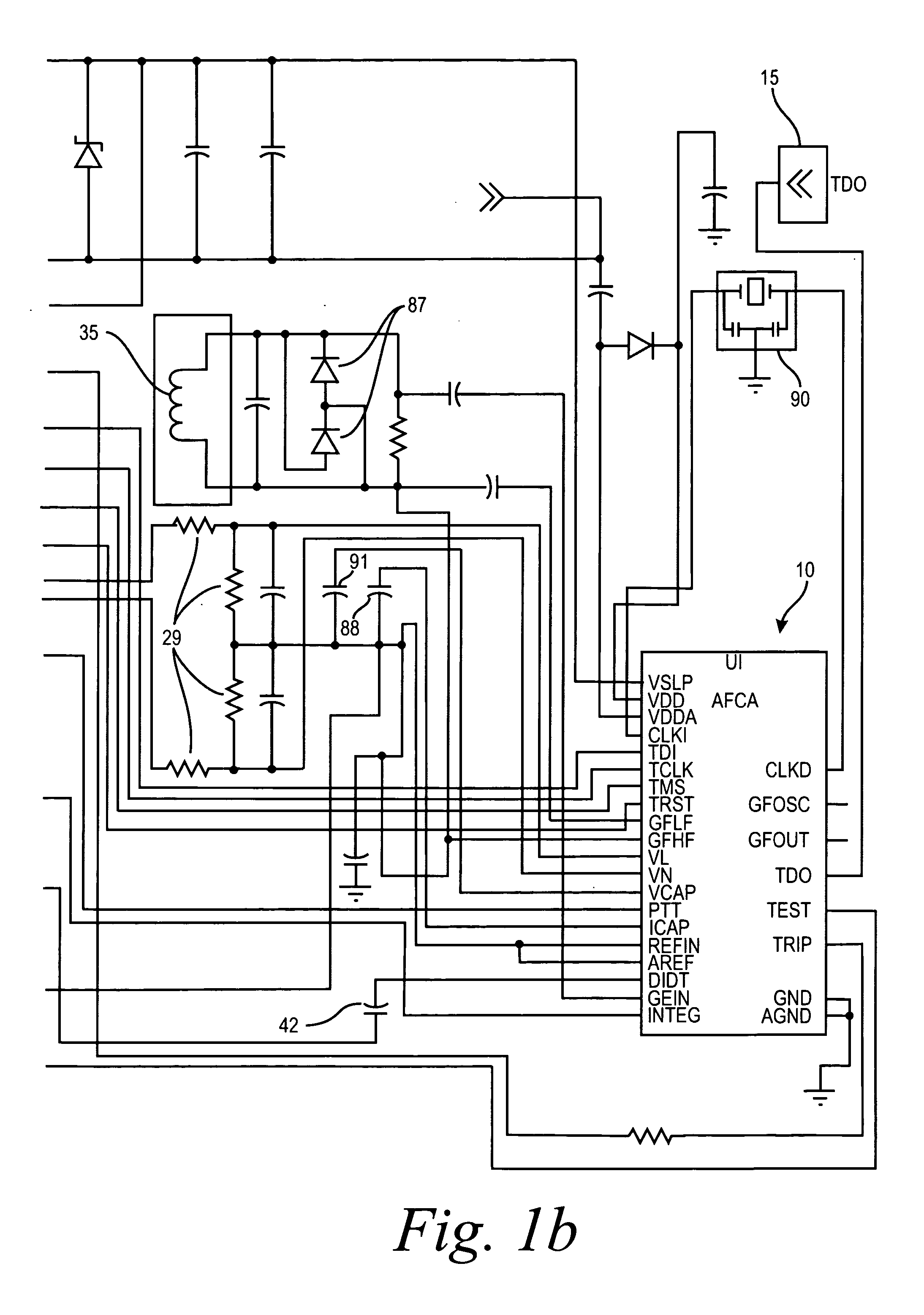
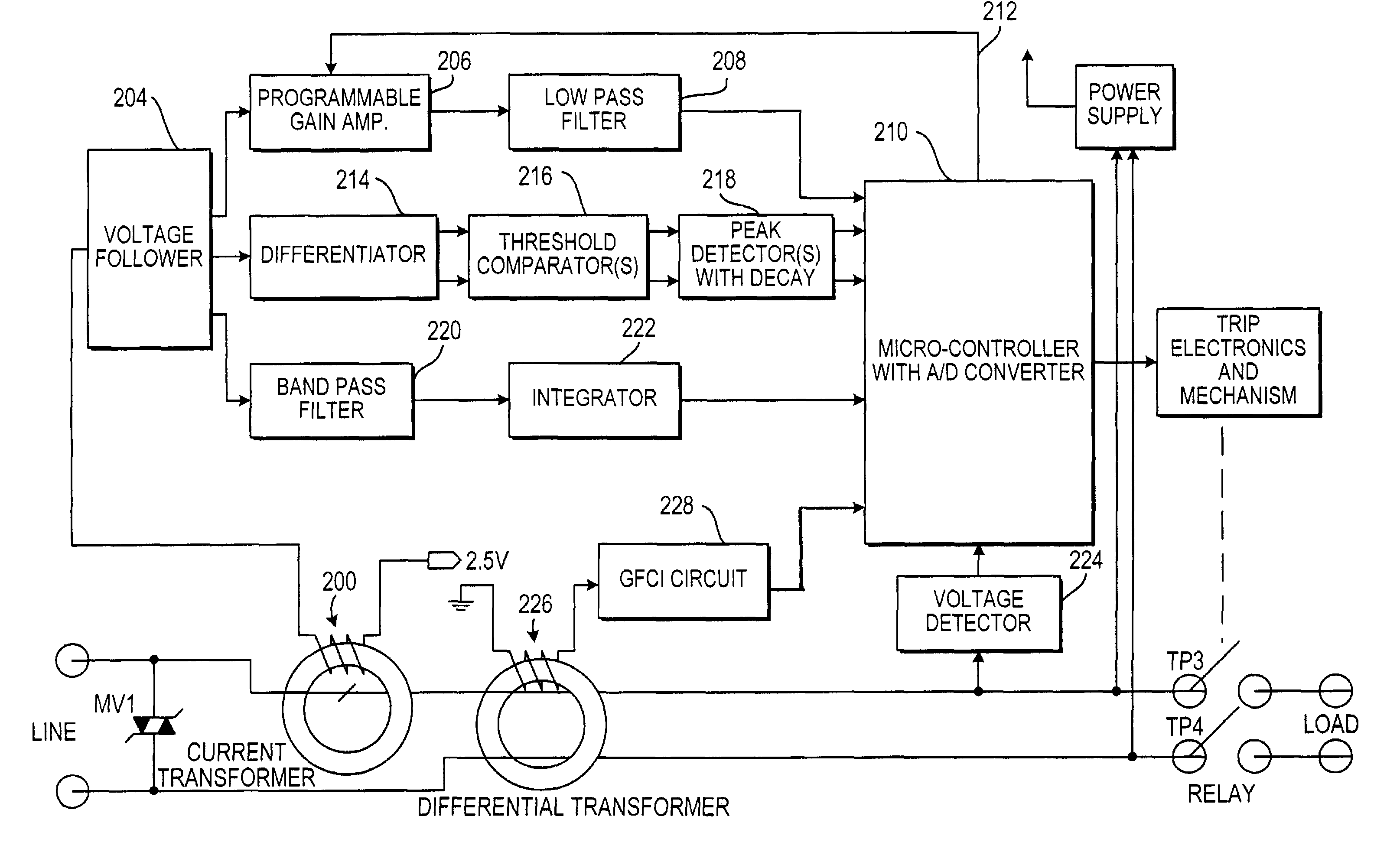
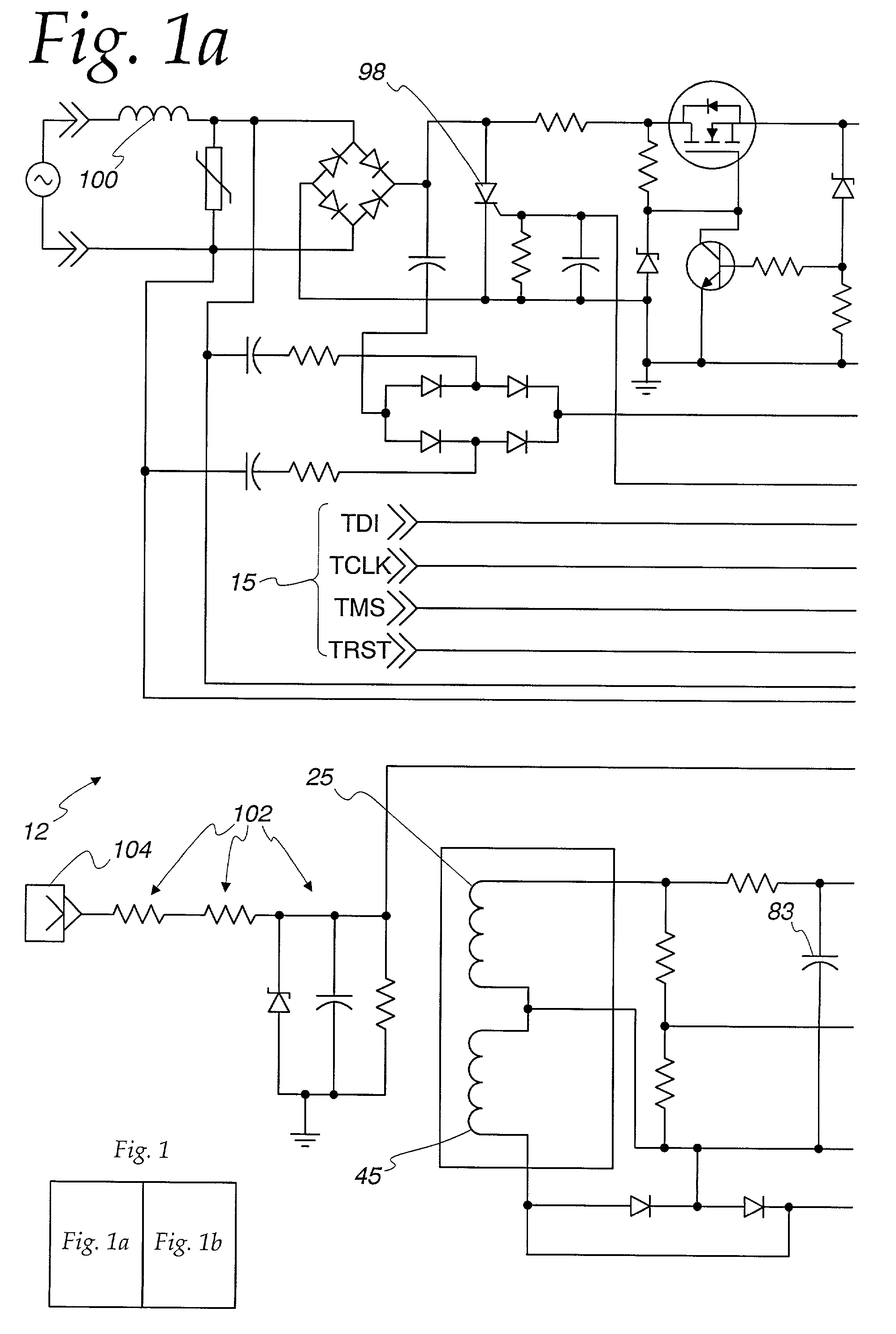
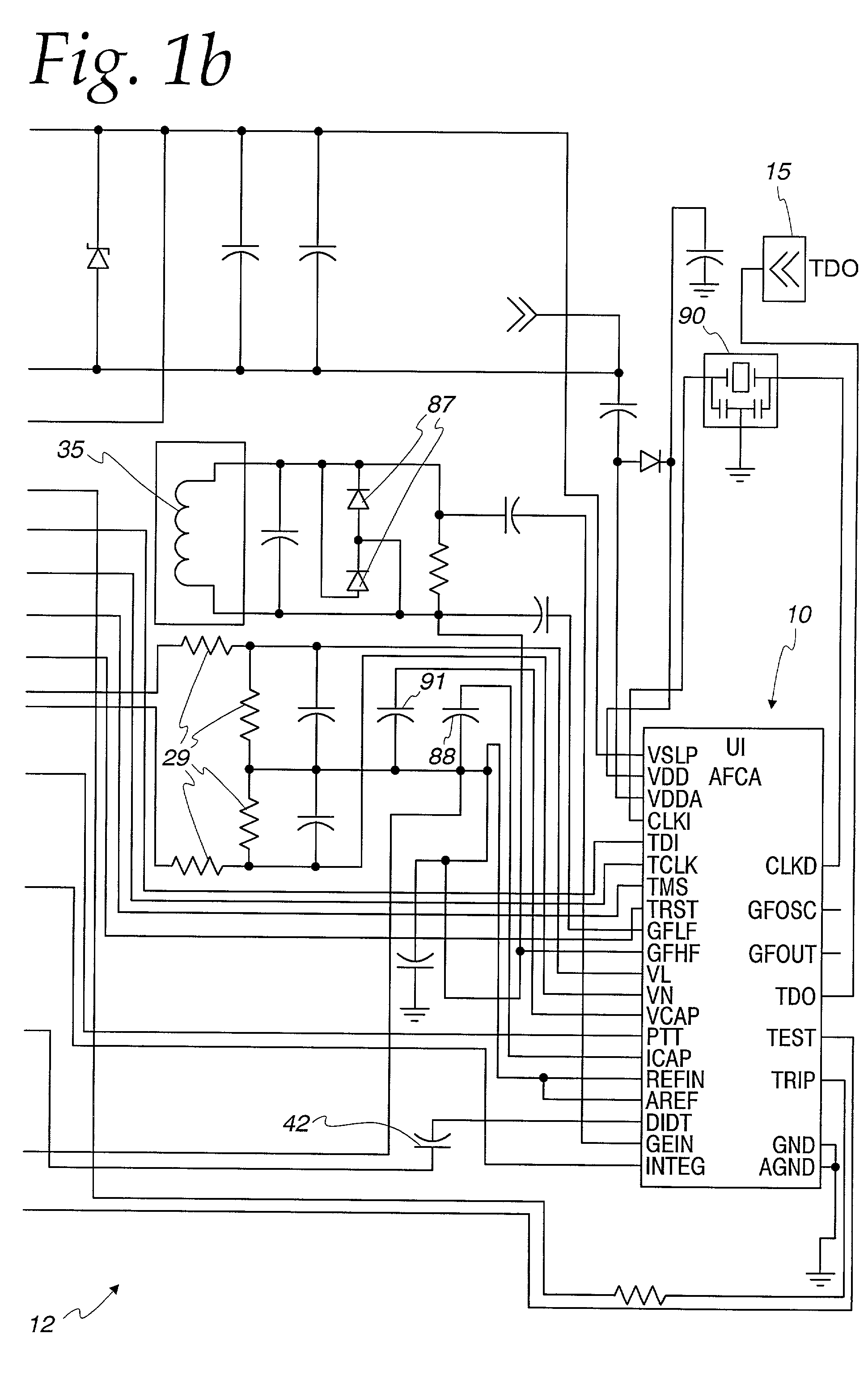
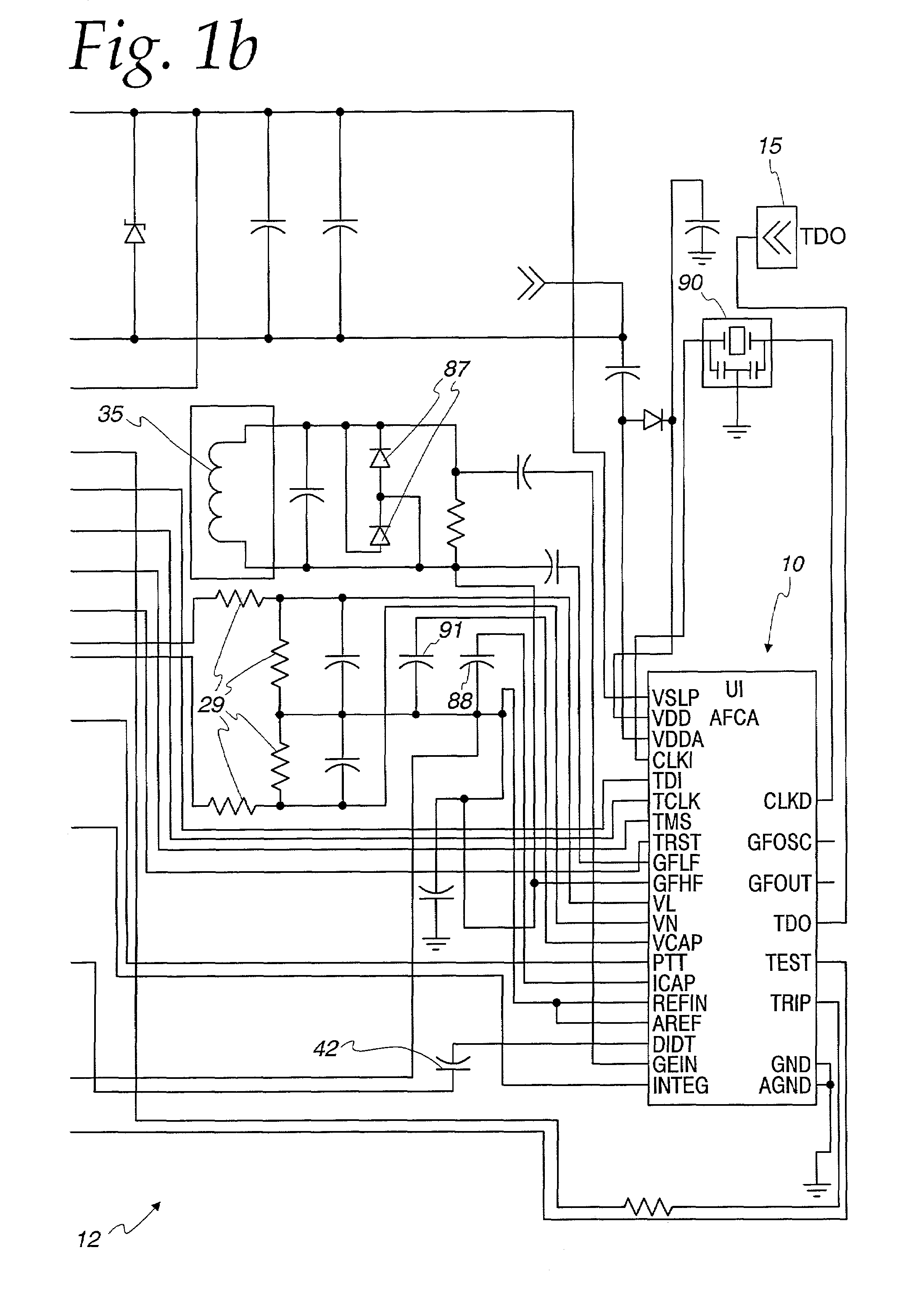
An arc fault detector system detects arcing faults in an electrical distribution system by monitoring one or more conductors and producing an input signal representing one or more electrical signal conditions in the circuit to be monitored. This input signal is processed to develop signals representing the electrical current flow through the monitored circuit and broadband noise signal components. The system analyzes these signals to determine whether an arcing fault is present, and if so, outputs a trip signal which may be used directly or indirectly to trip a circuit breaker or other circuit interruption device.
Owner:SQUARE D CO
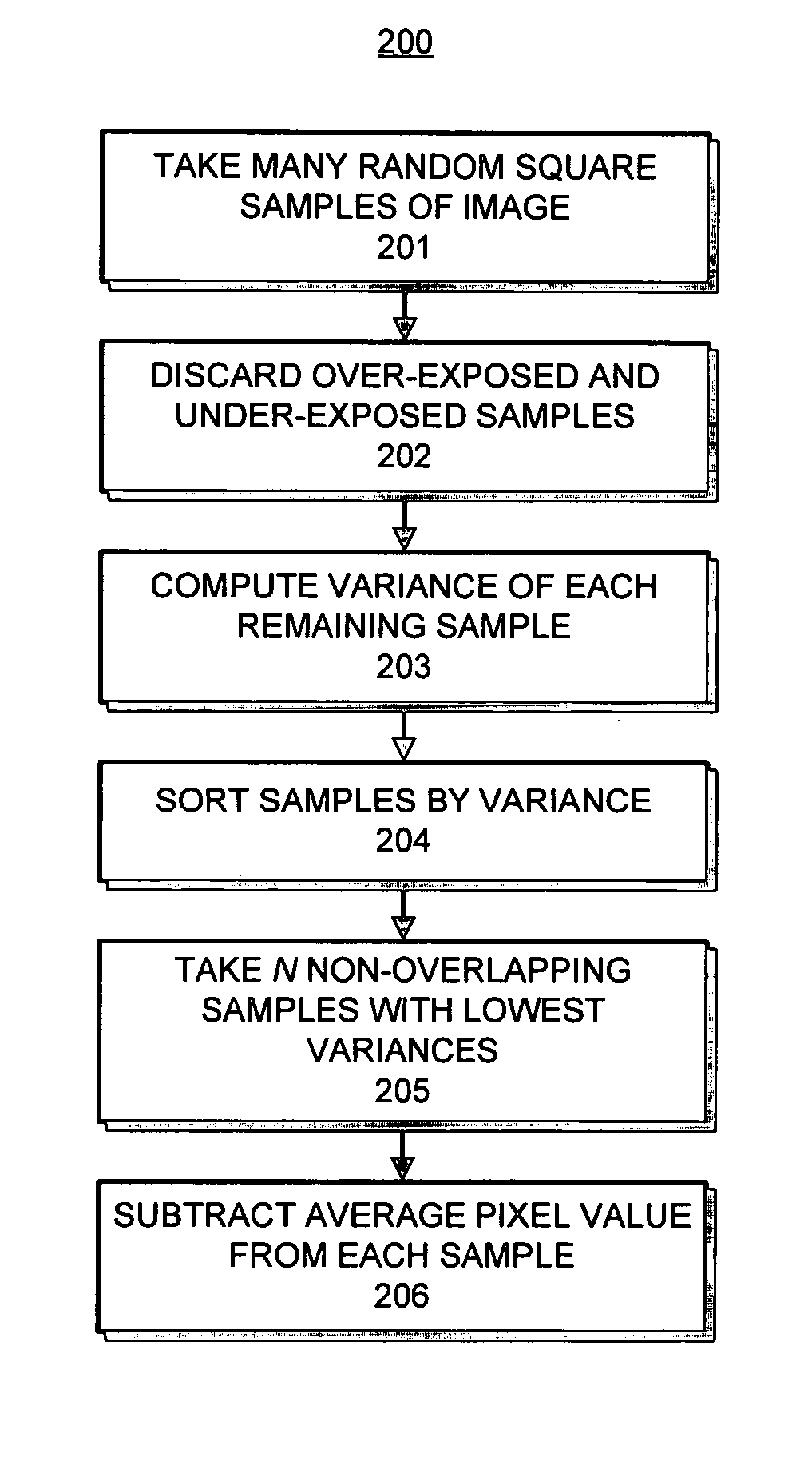
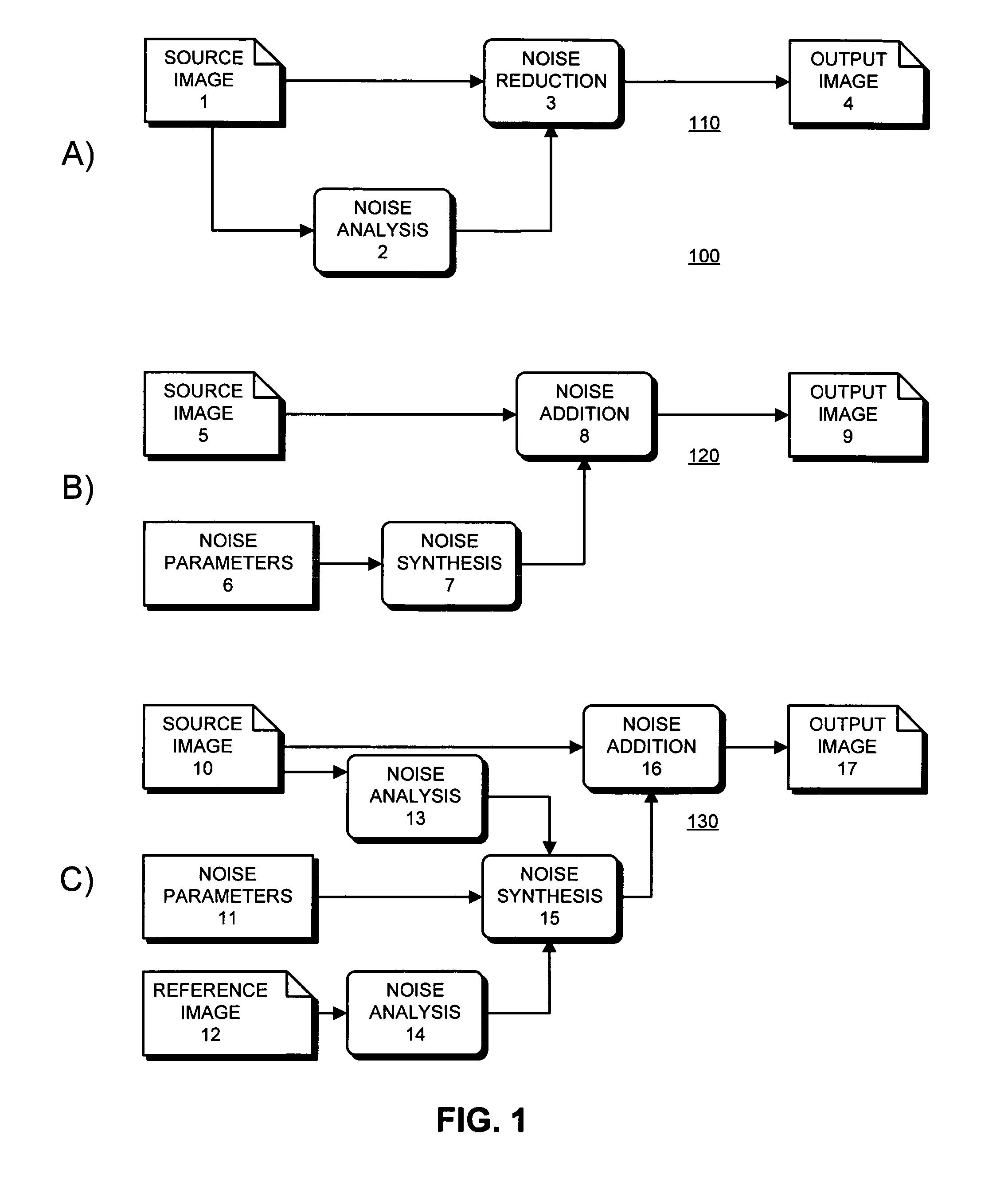
System for manipulating noise in digital images
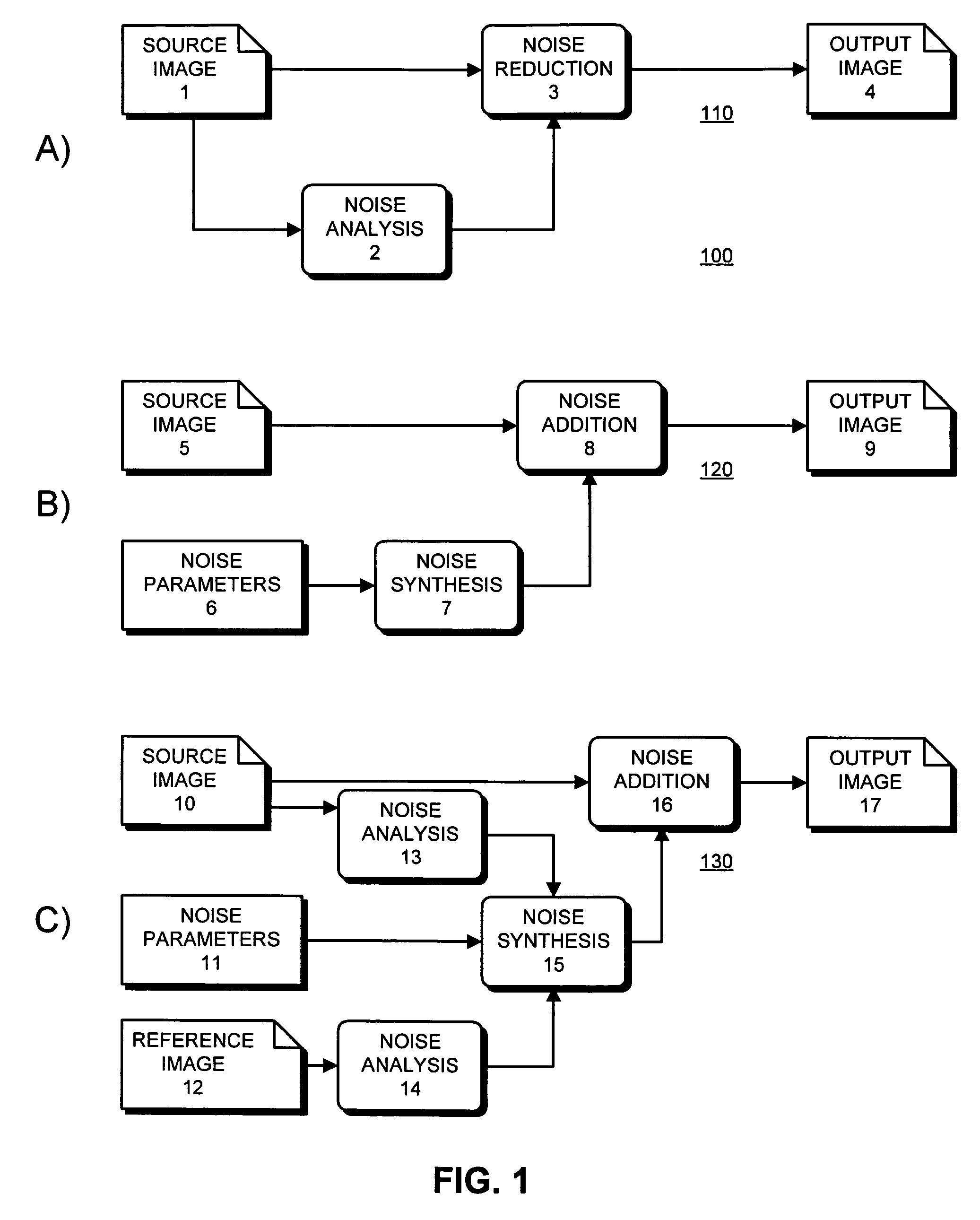
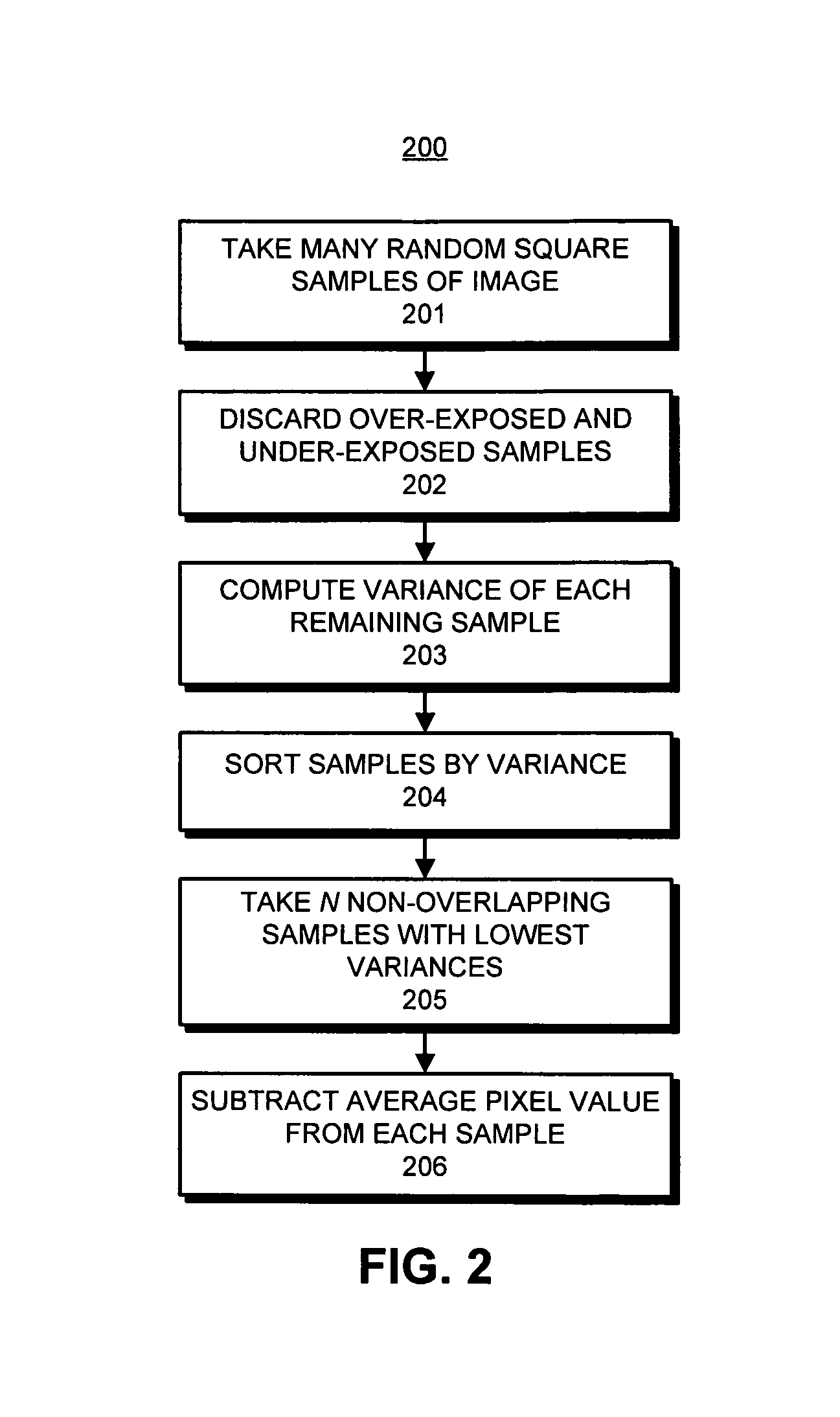
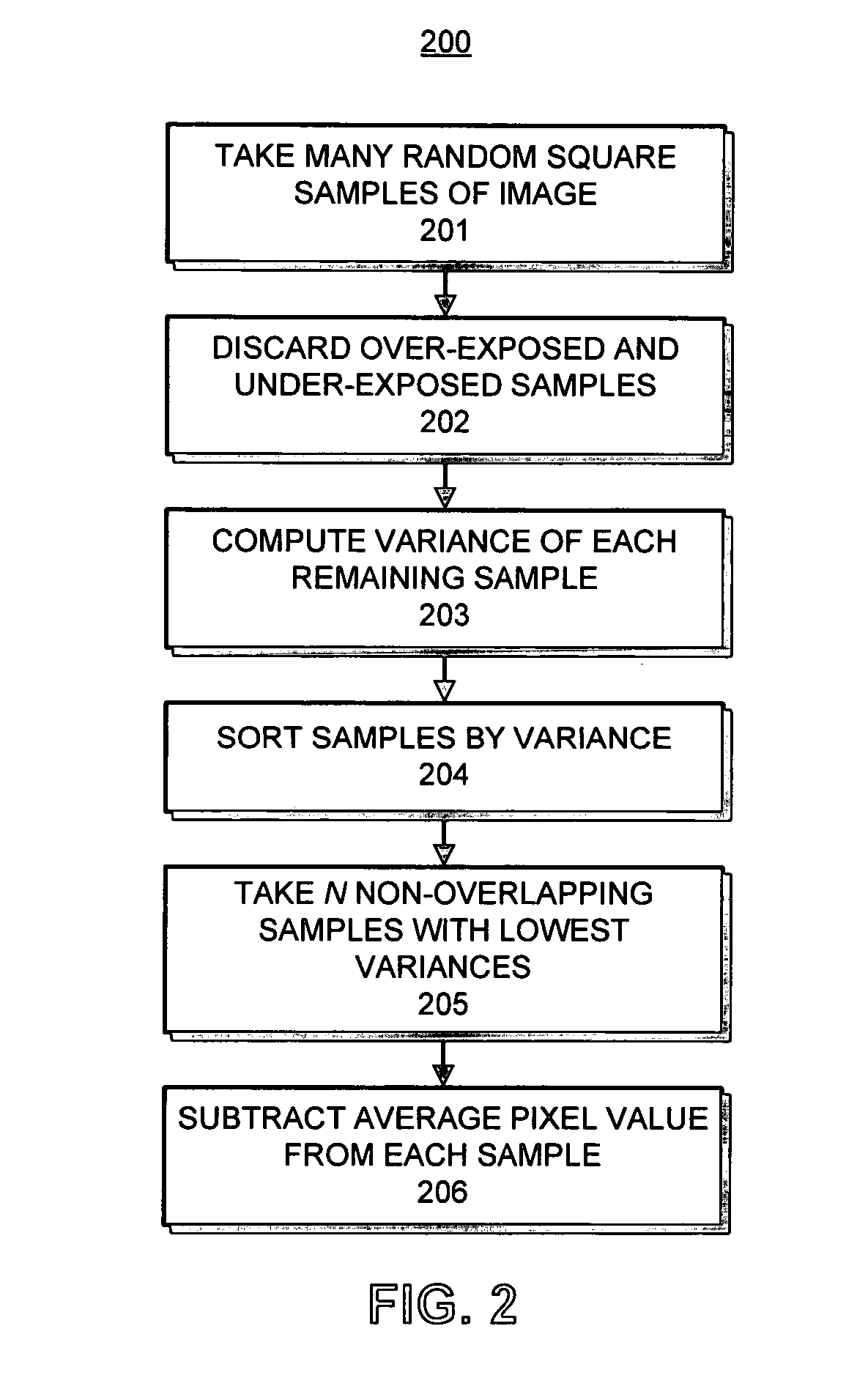
An apparatus for analyzing the broadband noise content of a digital image comprising the following: a means of automatically identifying regions of originally constant color in the image by analysis of the variance of pixel values of regions of the image; a means of automatically detecting and discarding regions deemed to be unrepresentative of the true noise content of an image, including under- and over-exposed regions; a means of allowing the user to manually select some or all required constant color regions if desired; and, a means of analyzing such constant color regions to generate a parametric or non-parametric model of the noise in the image, including frequency characteristic within and between channels and other characteristics such as phase which might describe structured noise.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Arc detection using load recognition, harmonic content and broadband noise
InactiveUS20030072113A1Reliably detectsGuaranteed uptimeEmergency protective arrangement detailsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionBroadband noiseHarmonic
A method of determining whether arcing is present in an electrical circuit includes sensing a change in current in the circuit and developing a corresponding input signal, analyzing the input signal to determine the presence of broadband noise in a predetermined range of frequencies, and producing a corresponding output signal, and processing the input signal and the output signal in a predetermined fashion to determine whether an arcing fault is present in the circuit. The processing includes determining a type of load connected to the electrical circuit, based at least in part upon the input signal and the output signal.
Owner:SQUARE D CO
Arc fault detector with circuit interrupter
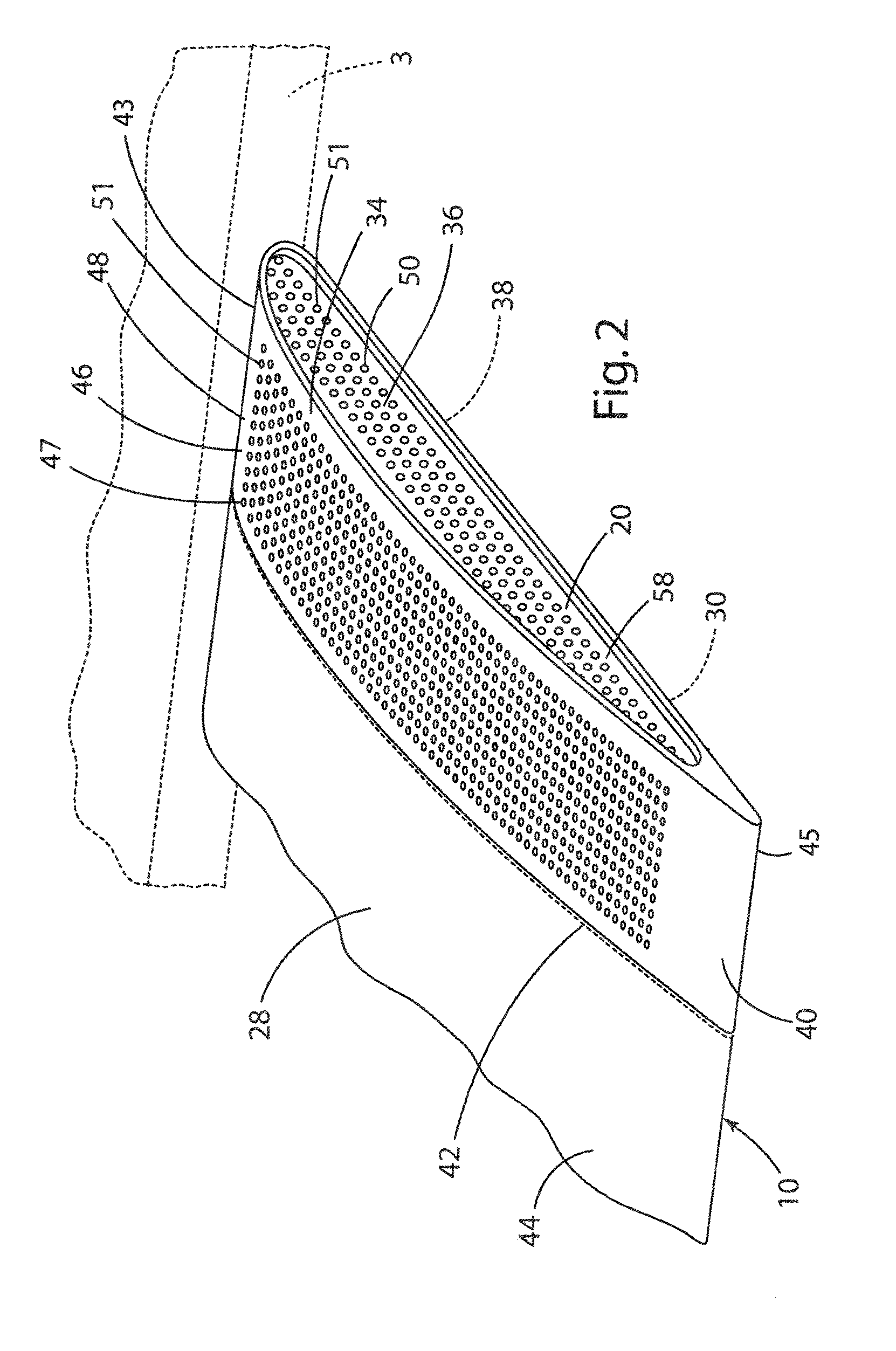
InactiveUS20040066593A1Testing dielectric strengthEmergency protective arrangement detailsBroadband noiseElectrical conductor
There is here disclosed a method and apparatus for detecting the occurrence of arcing of a conductor by monitoring the current on an AC power line. The signal detected is split and directed along four separate paths to generate four signals having separate characteristics which represent the current in the line. A first path is for a signal representative of the current flowing in the line. A second path is for a signal having a pulse for each occurrence of a positive step change in current that is significant and has a di / dt value above a predetermined value. A third path is for a signal having a pulse for each occurrence of a negative step change in current that is significant and has a di / dt value above a predetermined value. A fourth path is for a signal having a voltage level representative of the broadband noise signal on the line. Using at least one of five different methods in combination with one of three input signals, a reference signal designated as "SINE" is generated. The SINE signal generated in combination with a CURRENT input is used to produce a control waveform "DELTA". DELTA can be represented as a relative value or as an absolute difference between the SINE and the CURRENT. Each occurring half cycle of the DELTA signal is analyzed by, for example, a micro-controller for specific identifiable characteristics found to indicate the presence of arcing. Upon the detection of arcing, an output signal can be generated to activate a circuit interrupting mechanism, sound an audio alarm and / or alert a central monitoring station.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
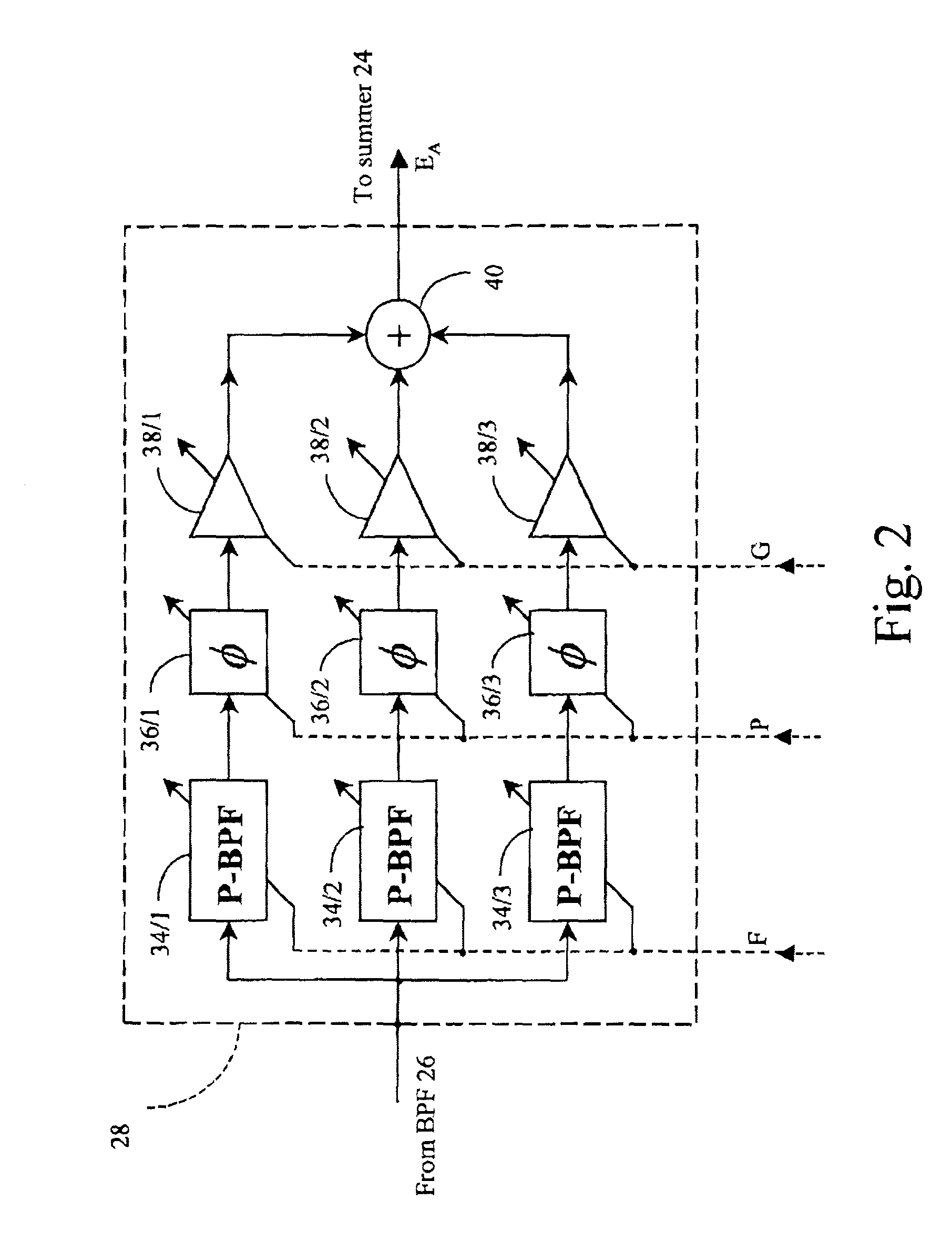
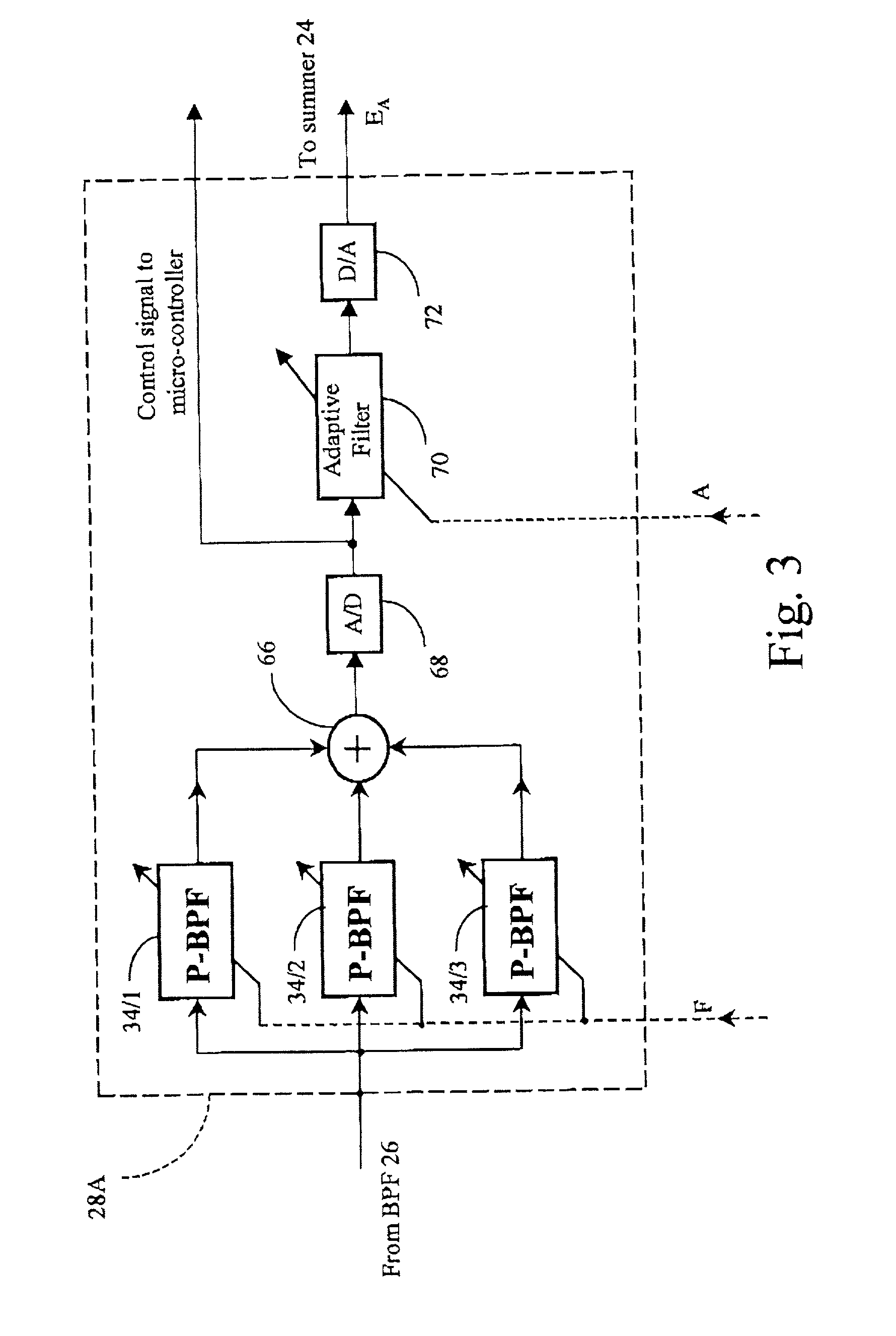
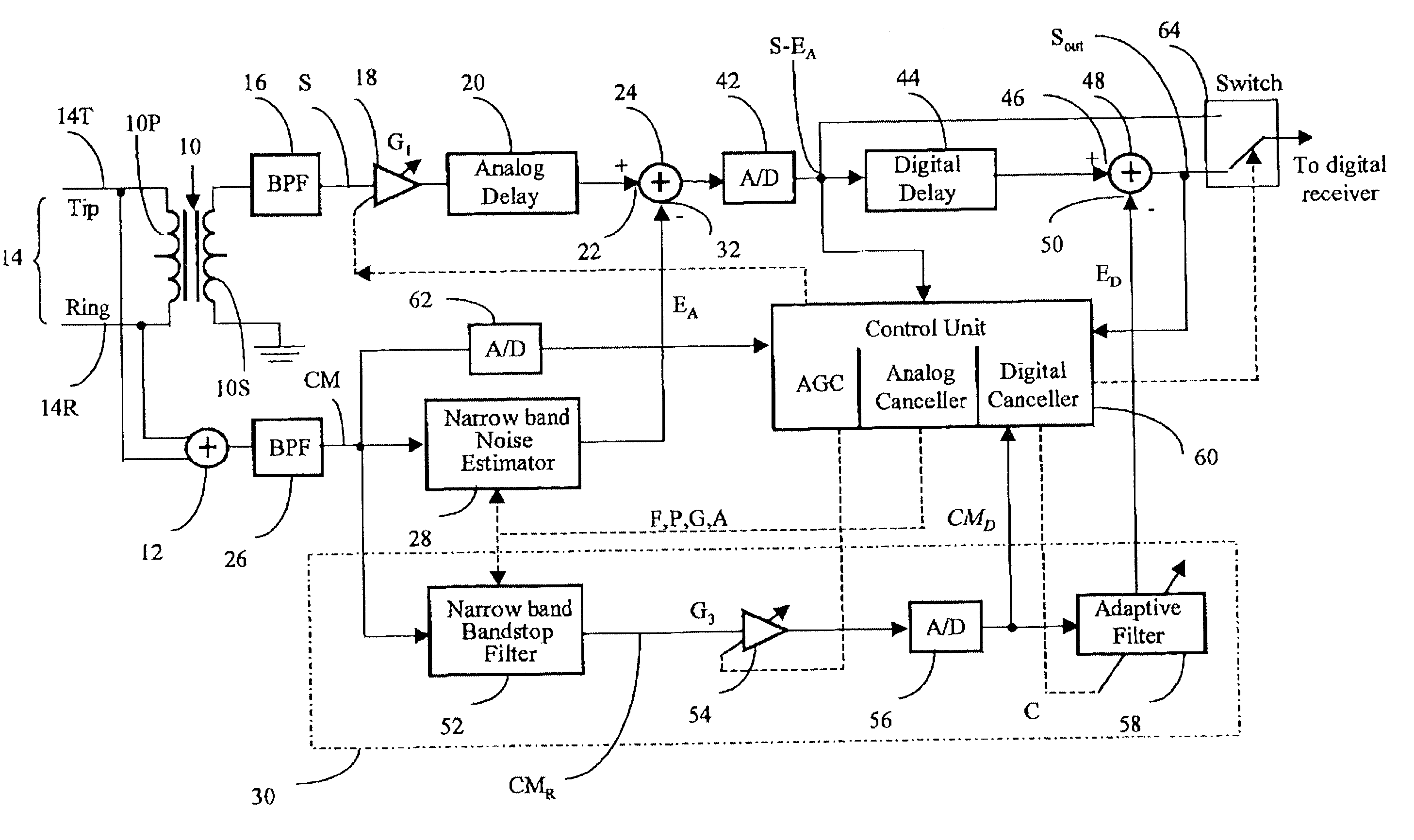
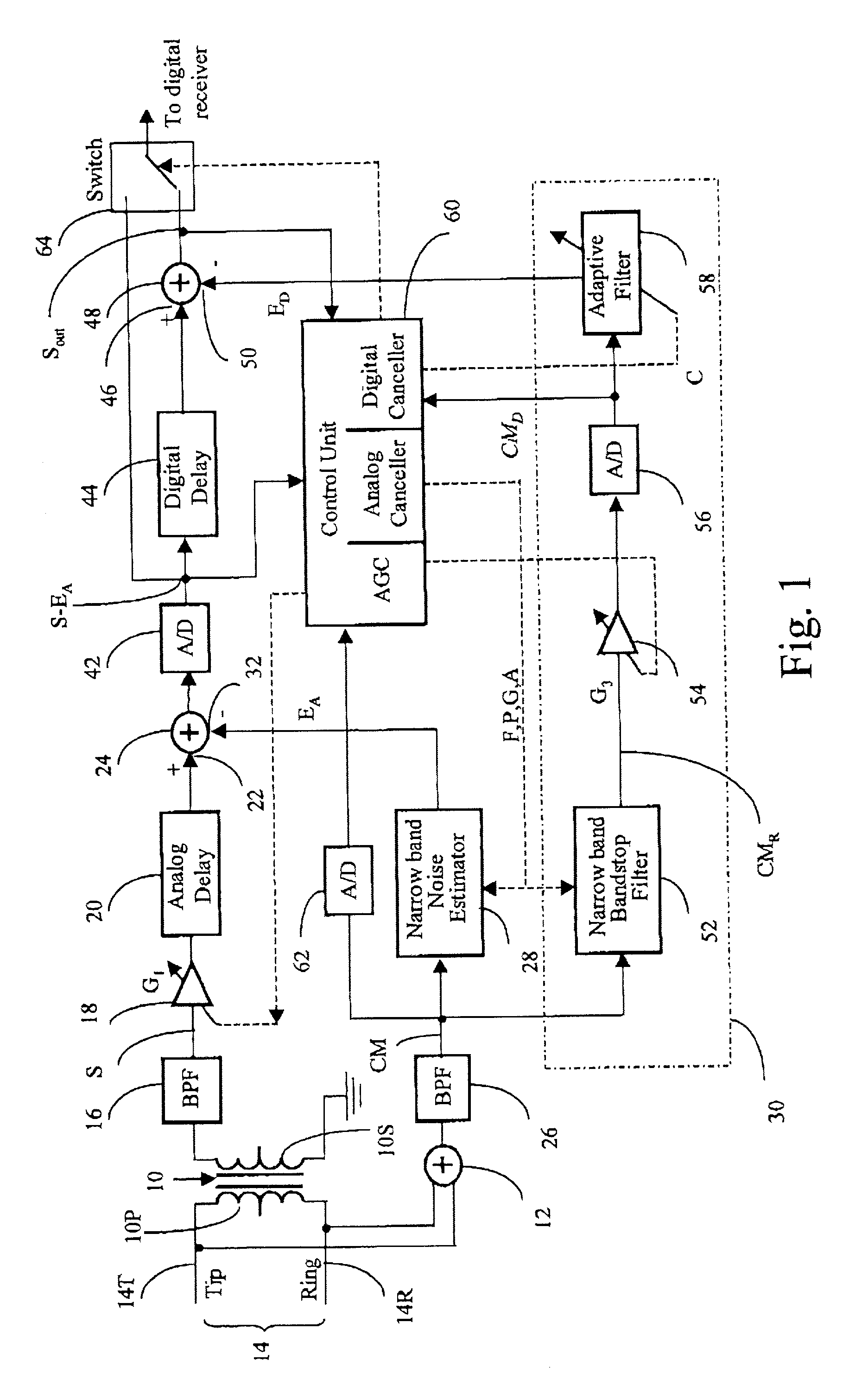
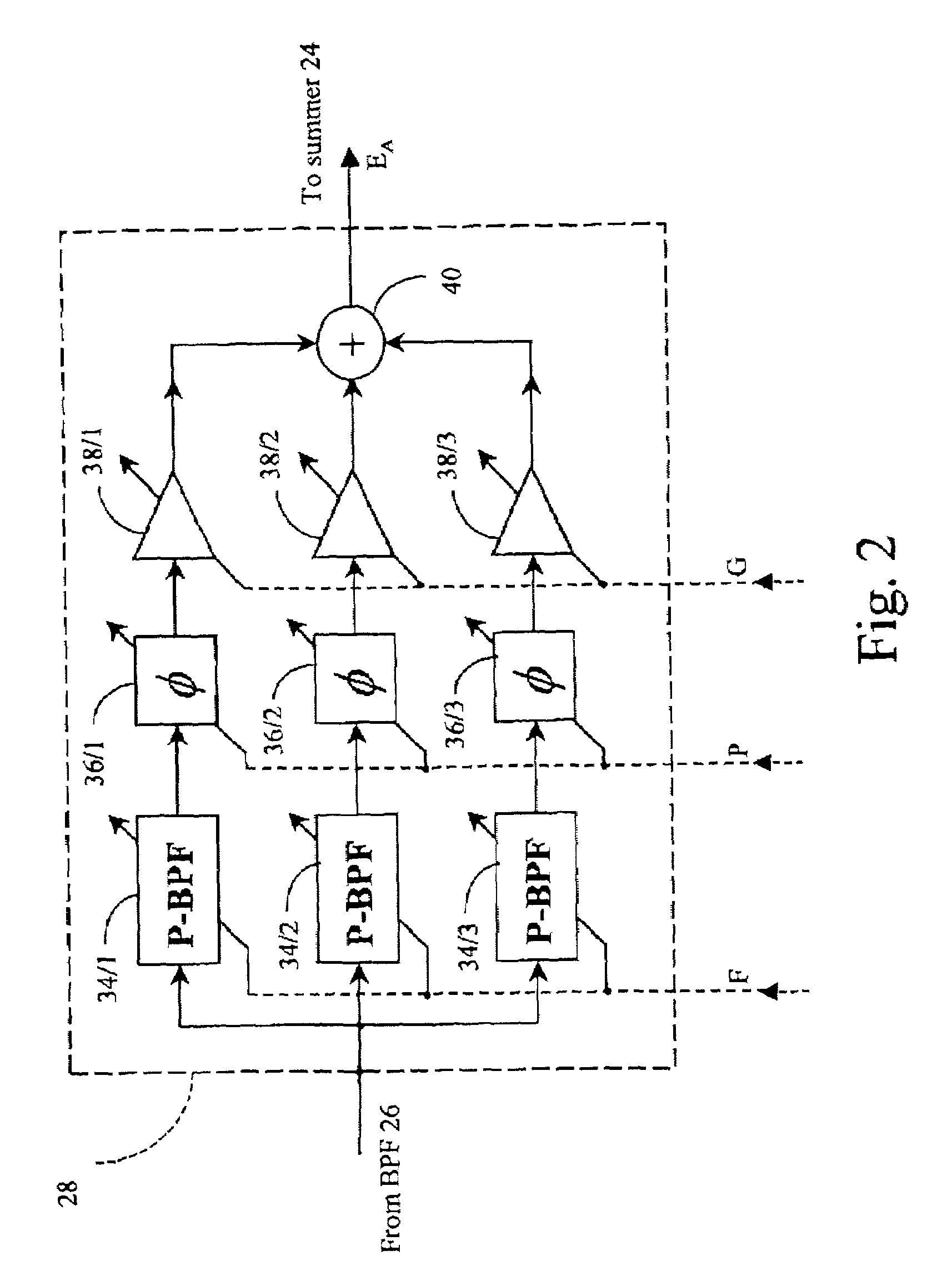
RFI canceller using narrowband and wideband noise estimators
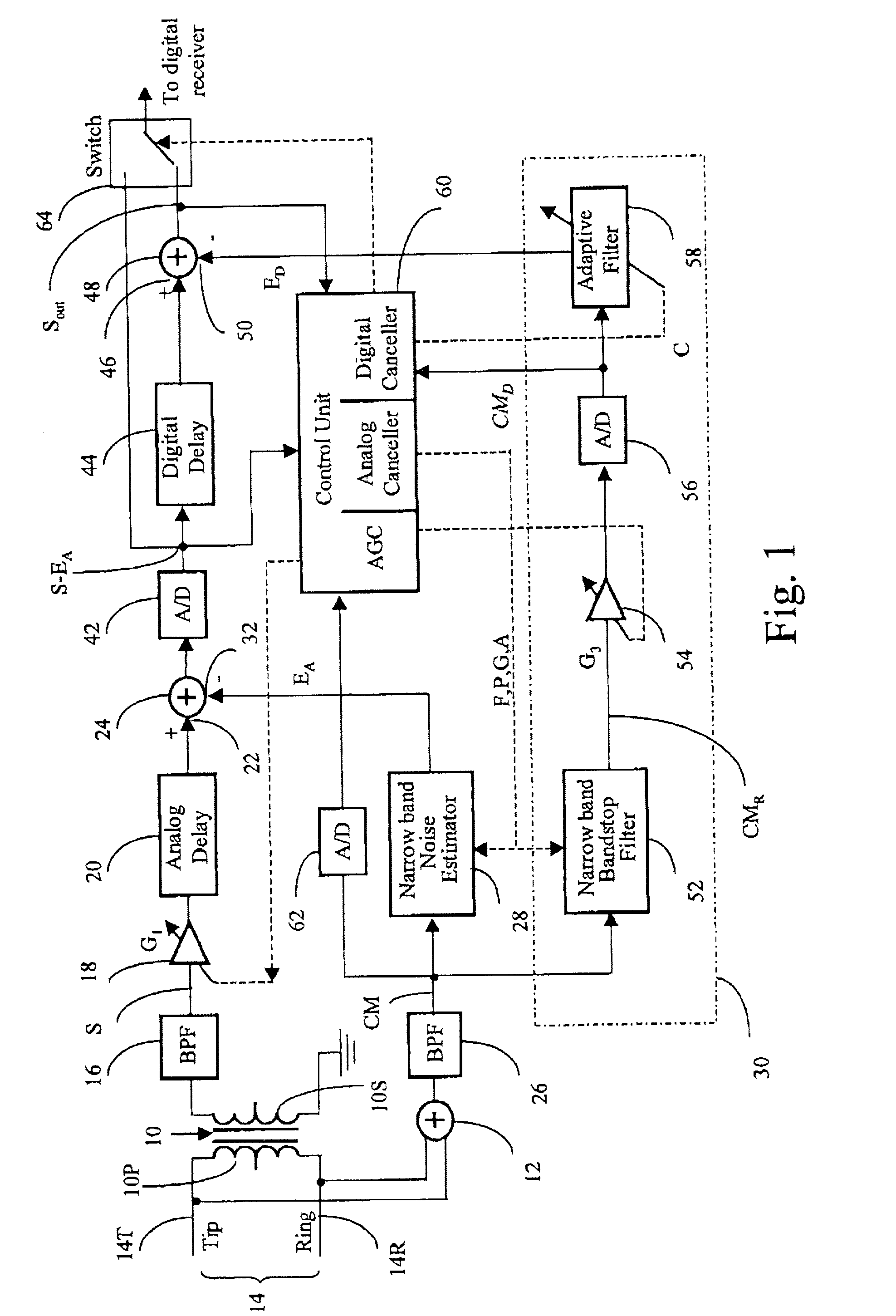
InactiveUS20010050987A1Remove restrictionsInterconnection arrangementsError preventionBroadband noiseAdaptive filter
In an adaptive filter for cancelling common-mode noise in digital subscriber loops, a narrowband noise estimator is used to detect one or more noisy frequency bands of the common mode signal and derive therefrom a first noise estimation signal. A wideband noise estimator derives from the remainder of the common mode signal a second noise estimation signal. The first and second noise estimation signals are subtracted from the differential signal, The wideband noise estimator comprises a bandstop filter for removing the frequencies detected by the narrowband noise estimator, an analog-to-digital converter for digitizing the bandstopped signal, and an adaptive filter for deriving the second noise estimation signal from the digitized bandstopped signal and, in the process, compensating for phase and gain differences, especially attributable to the interference being injected at different points along the length of the channel.
Owner:BELL CANADA
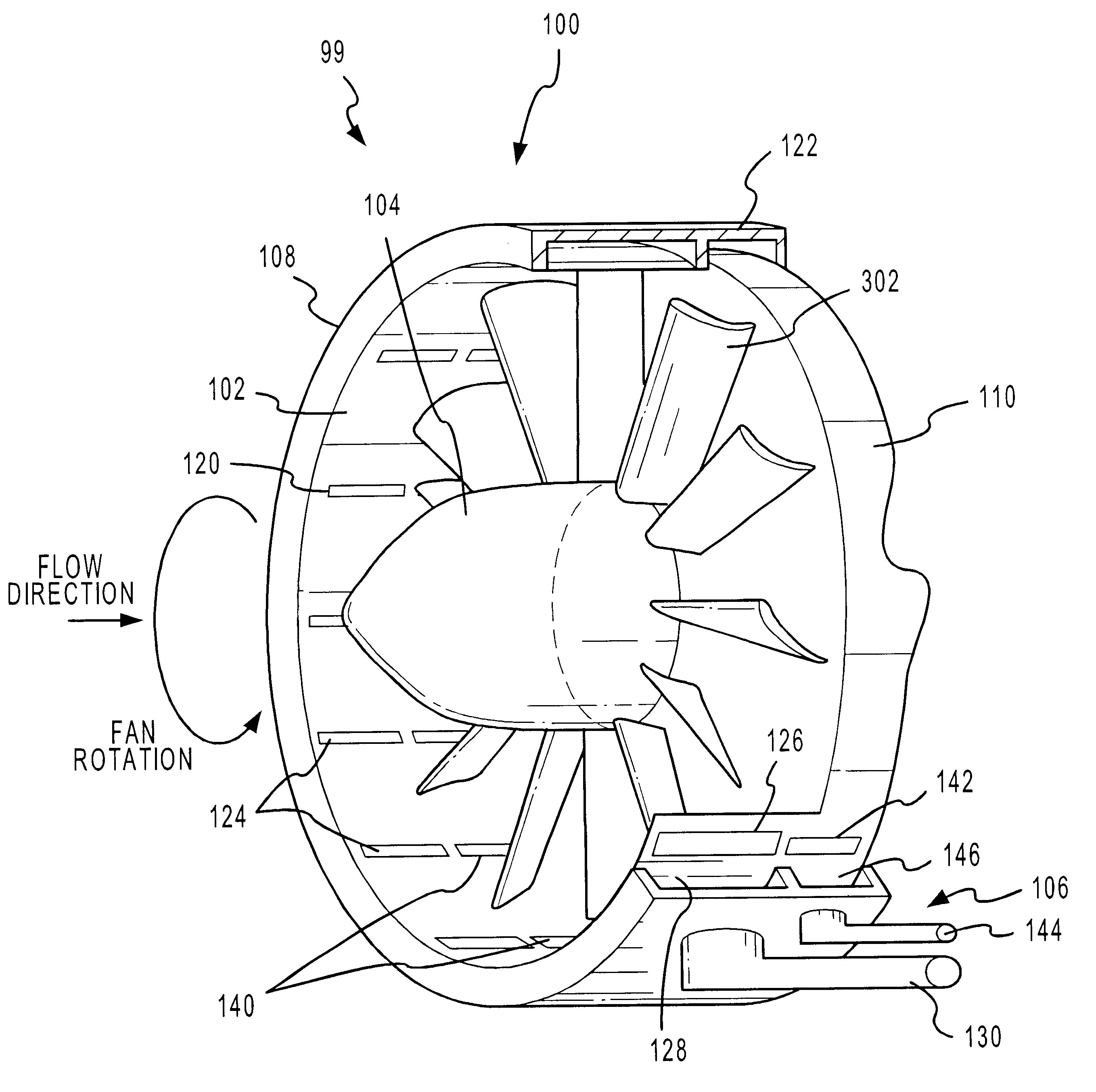
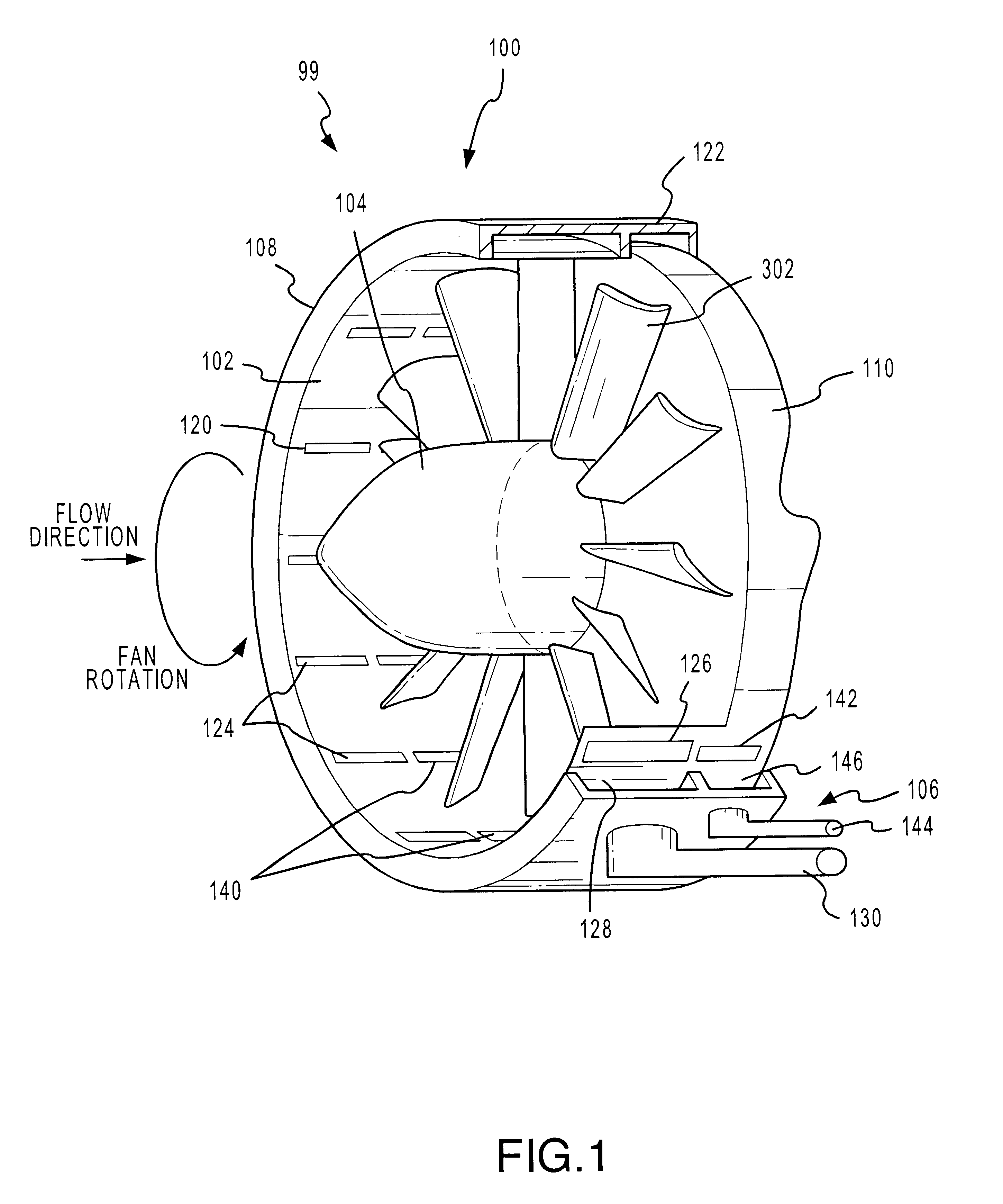
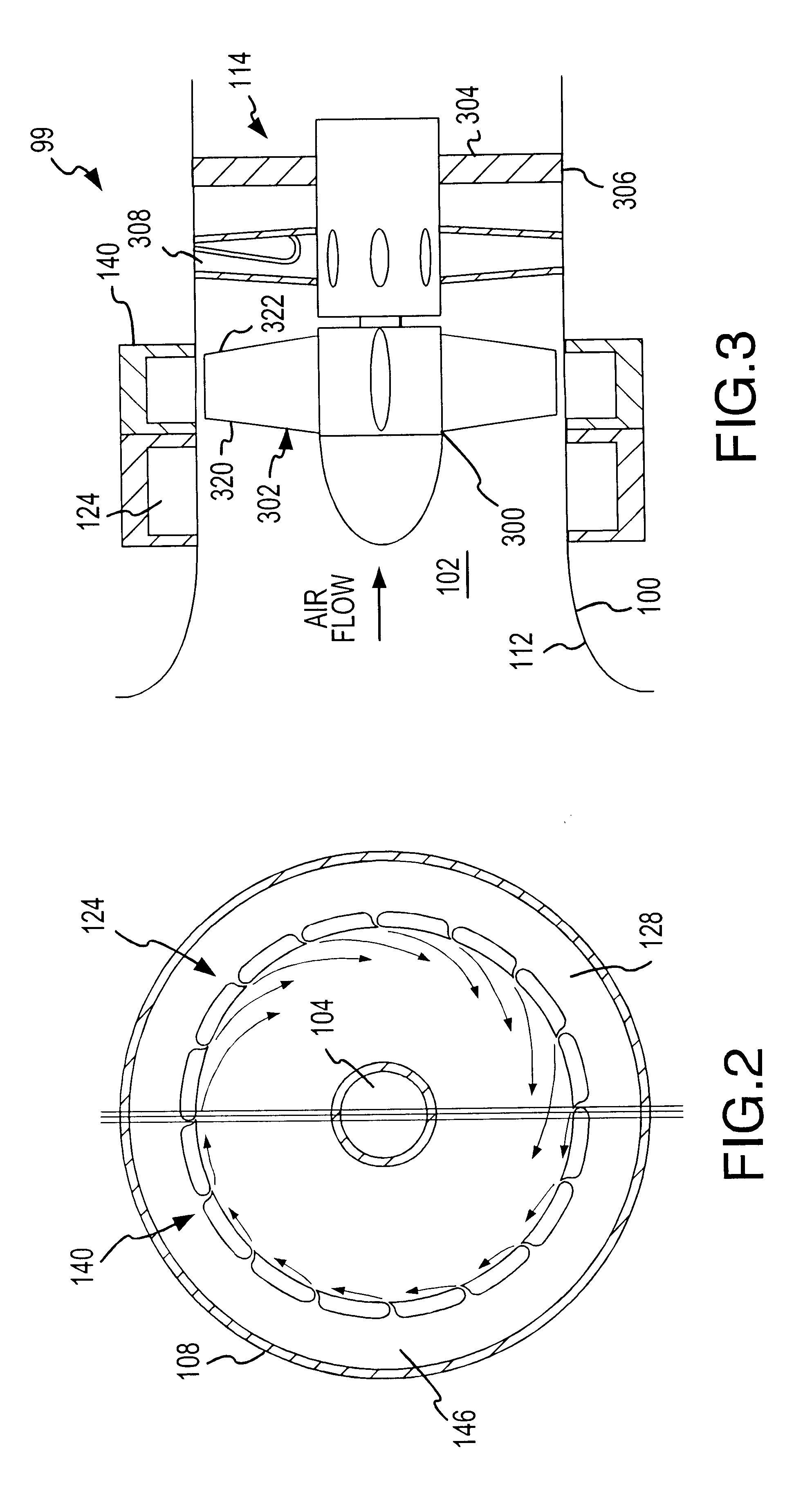
Method and apparatus for a fan noise controller
A fan system, such as a turbofan, marine propeller, or a cooling fan, includes a fan noise control system for reducing noise generated by the fan system. The noise control system may be configured to reduce either broadband noise, blade-passage noise, or both. In particular, the fan noise control system suitably includes a pre-swirl generator configured to provide a layer of fluid upstream from the fan blades. The layer swirls in the direction of the fan's rotation, reducing the angular velocity differential between the fan blades and the incident fluid. In addition, the fan noise control system may also include a fluid seal generator configured to create a fluid barrier between the fan blade tips and the interior surface of the fluid flow channel. The fluid seal inhibits leakage flow between the fan blade tips and the interior surface as well as the formation of blade vortices. By minimizing the blade wake and the blade tip vortices without adding solid surfaces, noise tends to diminish.
Owner:MCDONNELL DOUGLAS
RFI canceller using narrowband and wideband noise estimators
In an adaptive filter for cancelling common-mode noise in digital subscriber loops, a narrowband noise estimator is used to detect one or more noisy frequency bands of the common mode signal and derive therefrom a first noise estimation signal. A wideband noise estimator derives from the remainder of the common mode signal a second noise estimation signal. The first and second noise estimation signals are subtracted from the differential signal, The wideband noise estimator comprises a bandstop filter for removing the frequencies detected by the narrowband noise estimator, an analog-to-digital converter for digitizing the bandstopped signal, and an adaptive filter for deriving the second noise estimation signal from the digitized bandstopped signal and, in the process, compensating for phase and gain differences, especially attributable to the interference being injected at different points along the length of the channel.
Owner:BELL CANADA
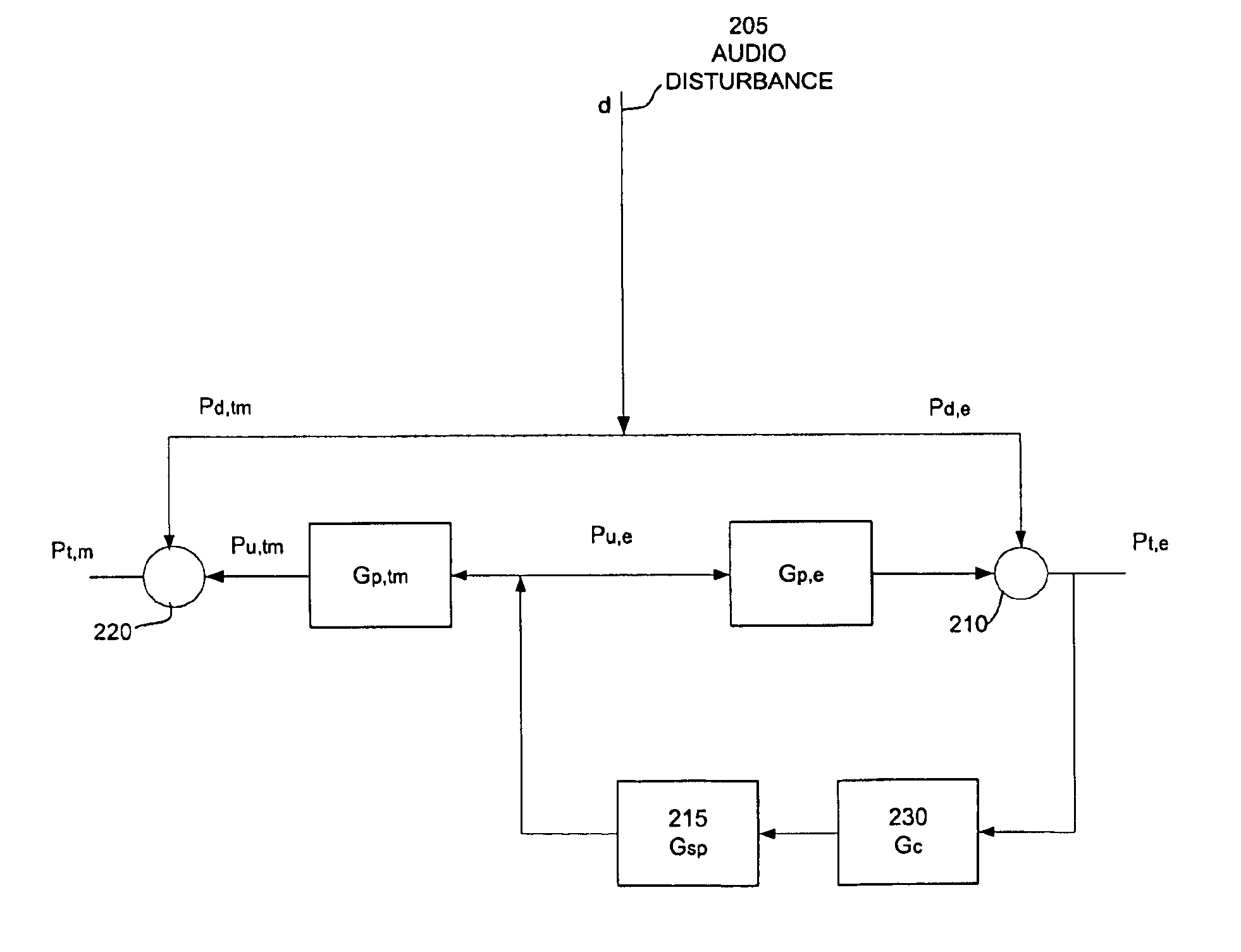
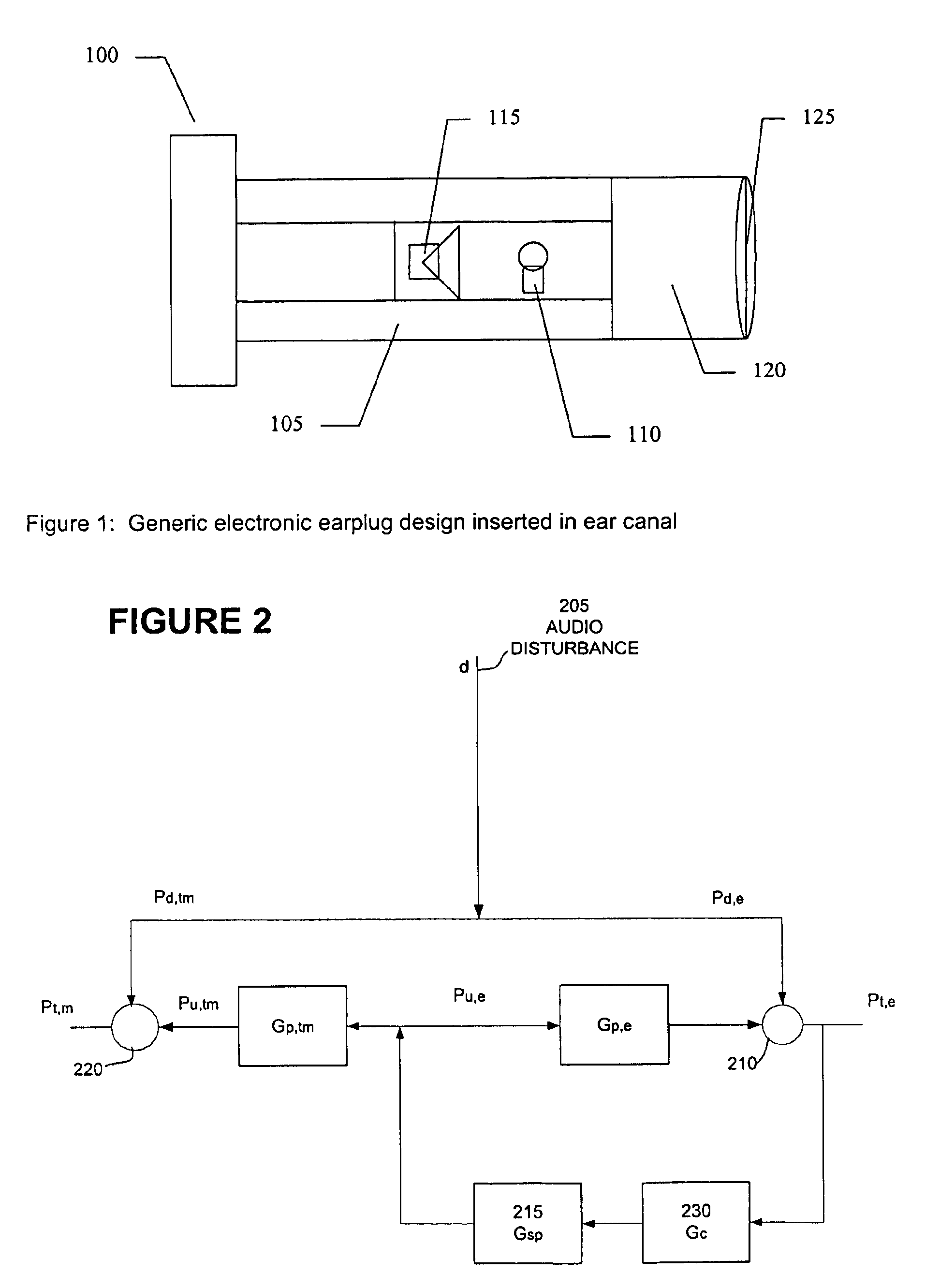
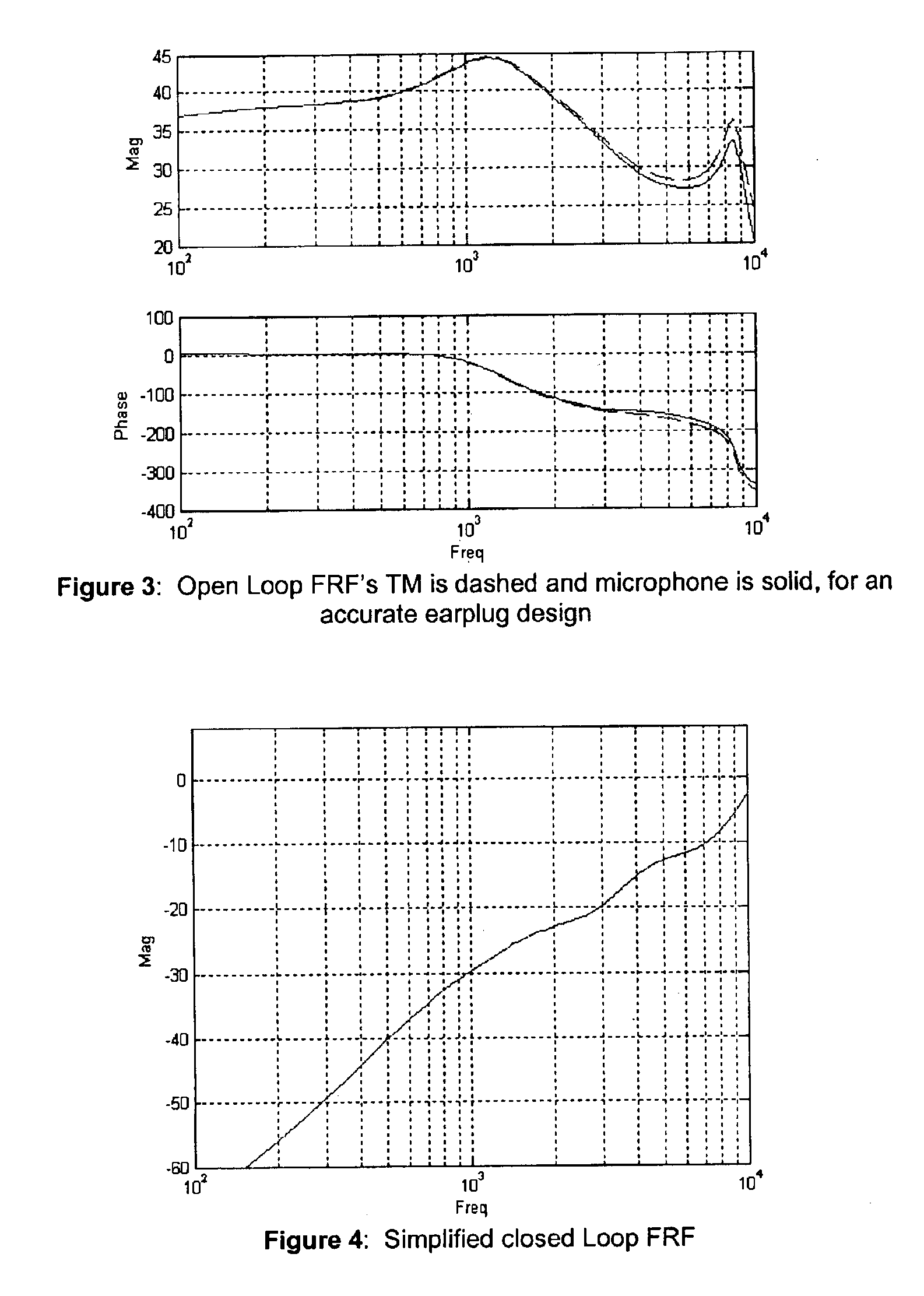
Electronic earplug for monitoring and reducing wideband noise at the tympanic membrane
ActiveUS7024010B2Accurate monitoringHigh degreeEarplugsNoise generationBroadband noiseEnvironmental noise
An electronic earplug for wideband control of pressures at, the tympanic membrane is presented. A unique methodology of determining effective component placement inside an earplug that provides acoustic isolation between the ambient noise and tympanic membrane is explained. Methods for providing accurate dosimetry and improved active control result from the unique earplug design process, leading to very wideband active noise reduction at the tympanic membrane.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
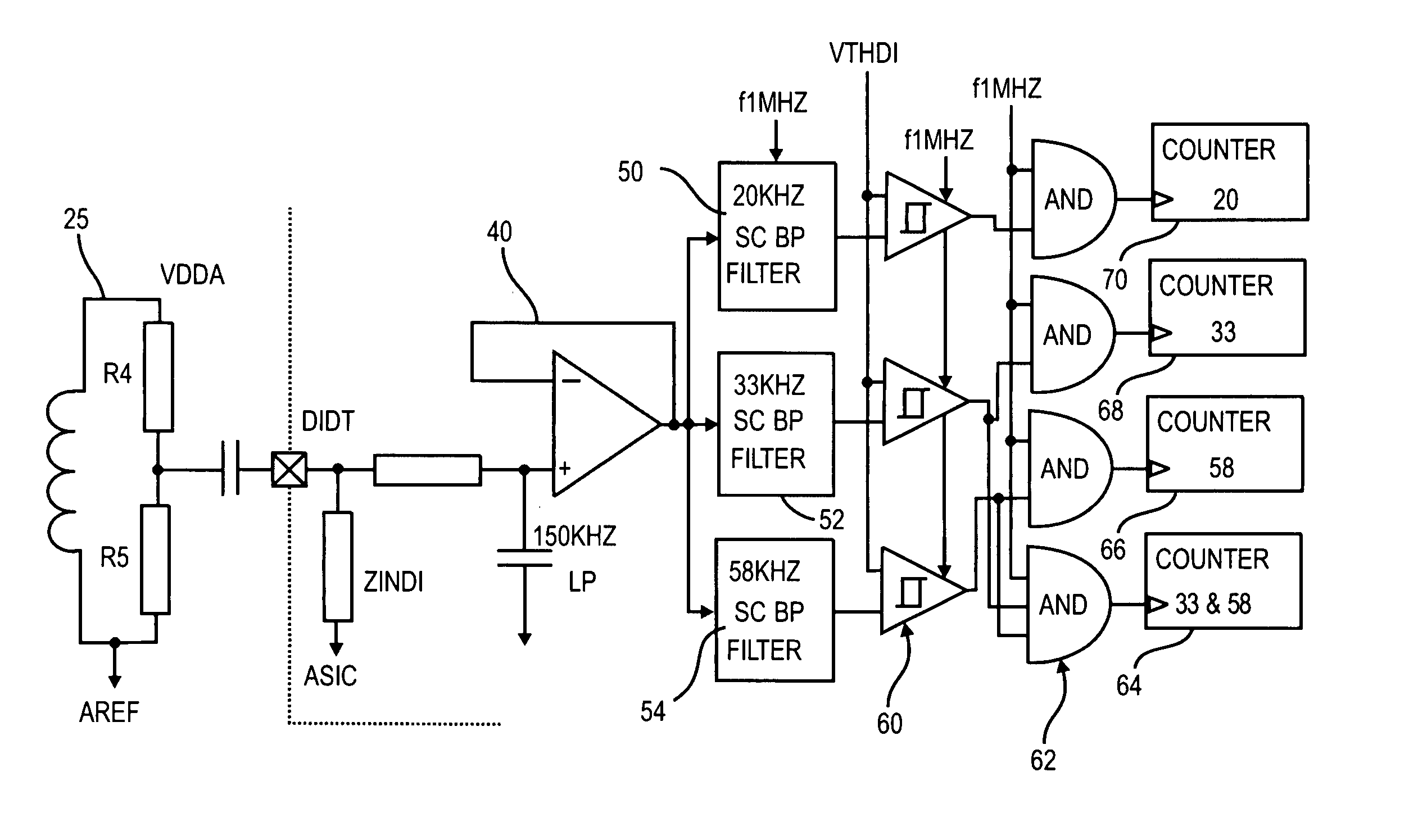
Load recognition and series arc detection using bandpass filter signatures
InactiveUS20040042137A1Reliably detectsGuaranteed uptimeEmergency protective arrangement detailsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionBroadband noiseBandpass filtering
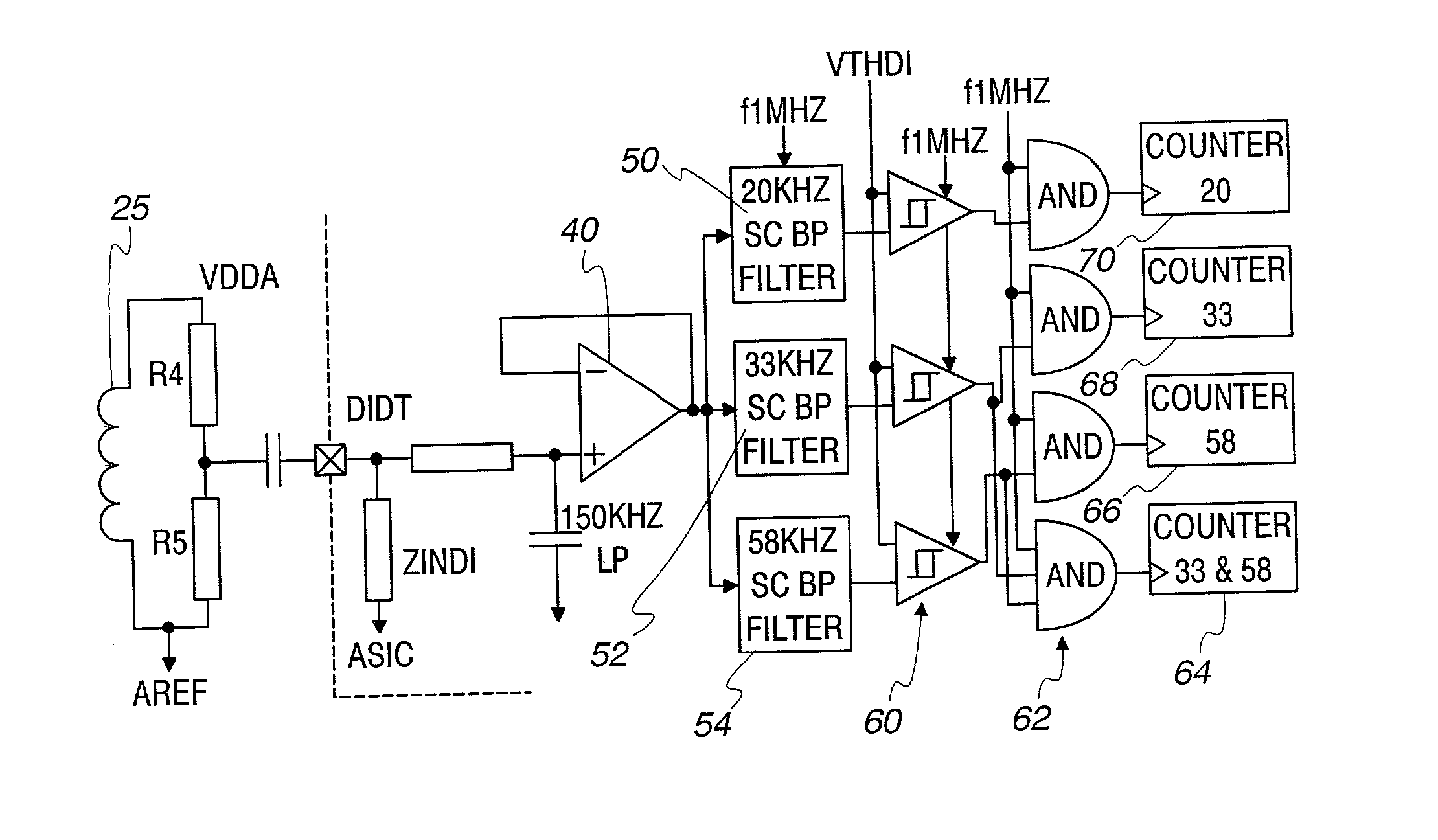
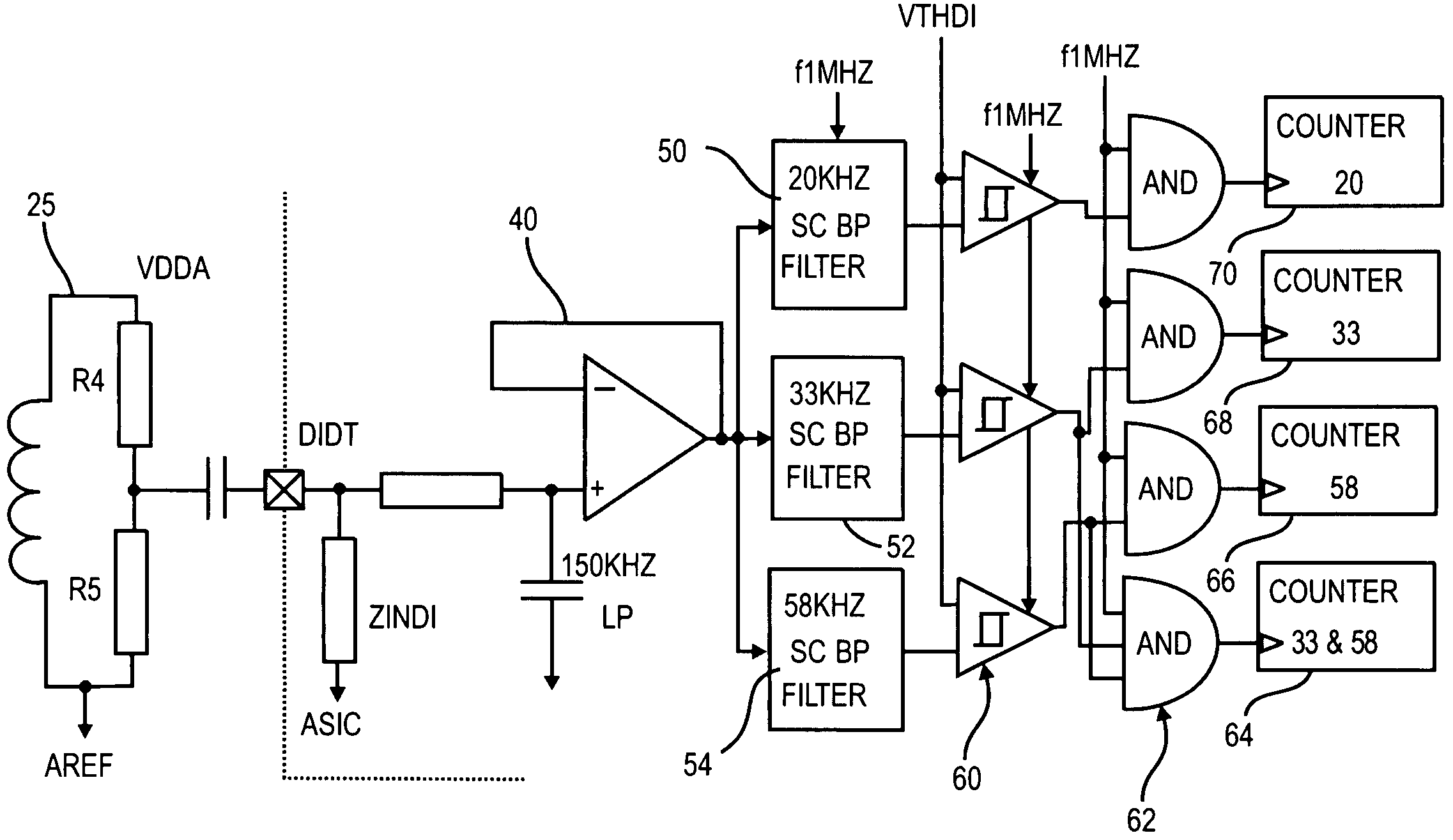
A method and system for determining whether arcing is present in an electrical circuit includes sensing a change in an alternating current in the circuit and developing a corresponding input signal, analyzing the input signal to determine the presence of broadband noise in a predetermined range of frequencies, and producing a corresponding output signal, and processing the input signal and the output signal in a predetermined fashion to determine whether an arcing fault is present in the circuit. The processing includes determining a type of load connected to the electrical circuit, based at least in part upon the input signal and the output signal, and monitoring high frequency noise in a 20 KHz band for each 1 / 8 cycle of the alternating current.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC USA INC
Load recognition and series arc detection using load current/line voltage normalization algorithms
InactiveUS20060114627A1High-frequency noiseEmergency protective arrangement detailsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionBroadband noiseEngineering
A method and system for determining whether arcing is present in an electrical circuit. The methods includes sensing a change in an alternating current in the circuit and developing a corresponding input signal, analyzing the input signal to determine the presence of broadband noise in a predetermined range of frequencies, and producing a corresponding output signal. The method further includes determining a type of load connected to the electrical circuit, based at least in part upon the input signal and the output signal, incrementing one or more of a plurality of counters in a predetermined fashion in accordance with the input signal and the output signal and determining whether an arcing fault is present based at least in part on the states of one or more of a plurality of counters. The method also includes decrementing one or more of the plurality of counters based upon a secondary analysis.
Owner:SQUARE D CO
Noise canceling microphone system and method for designing the same
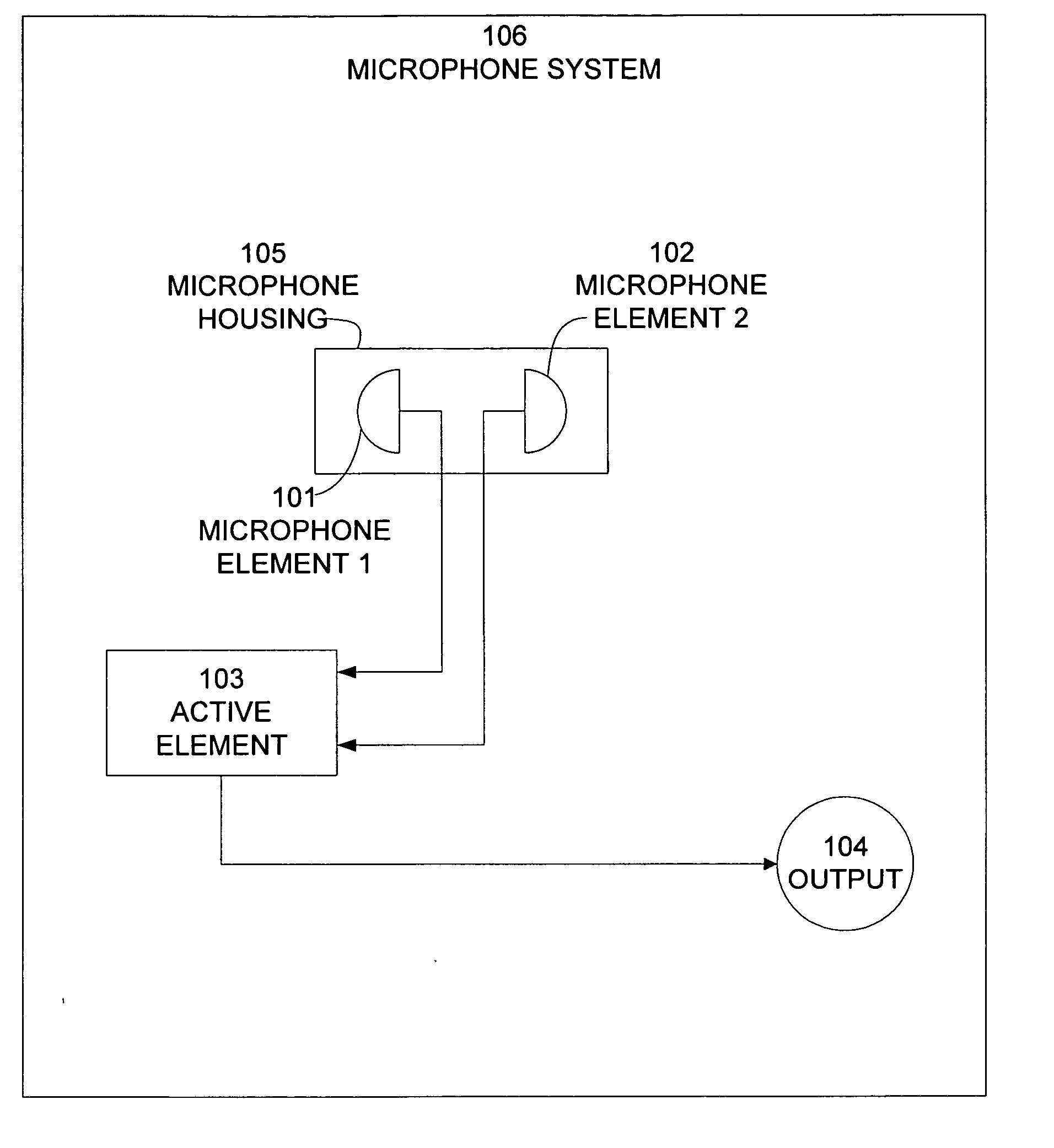
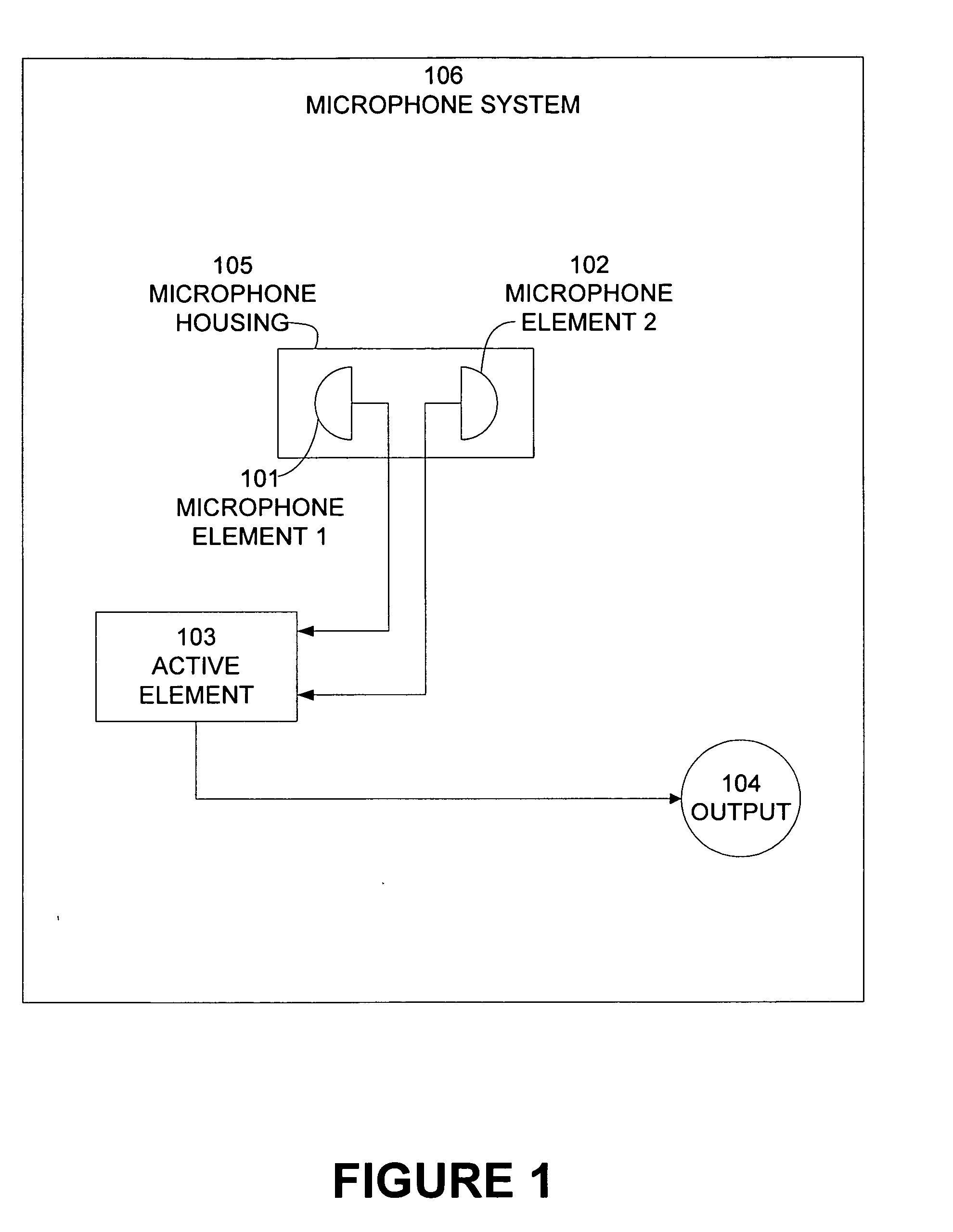
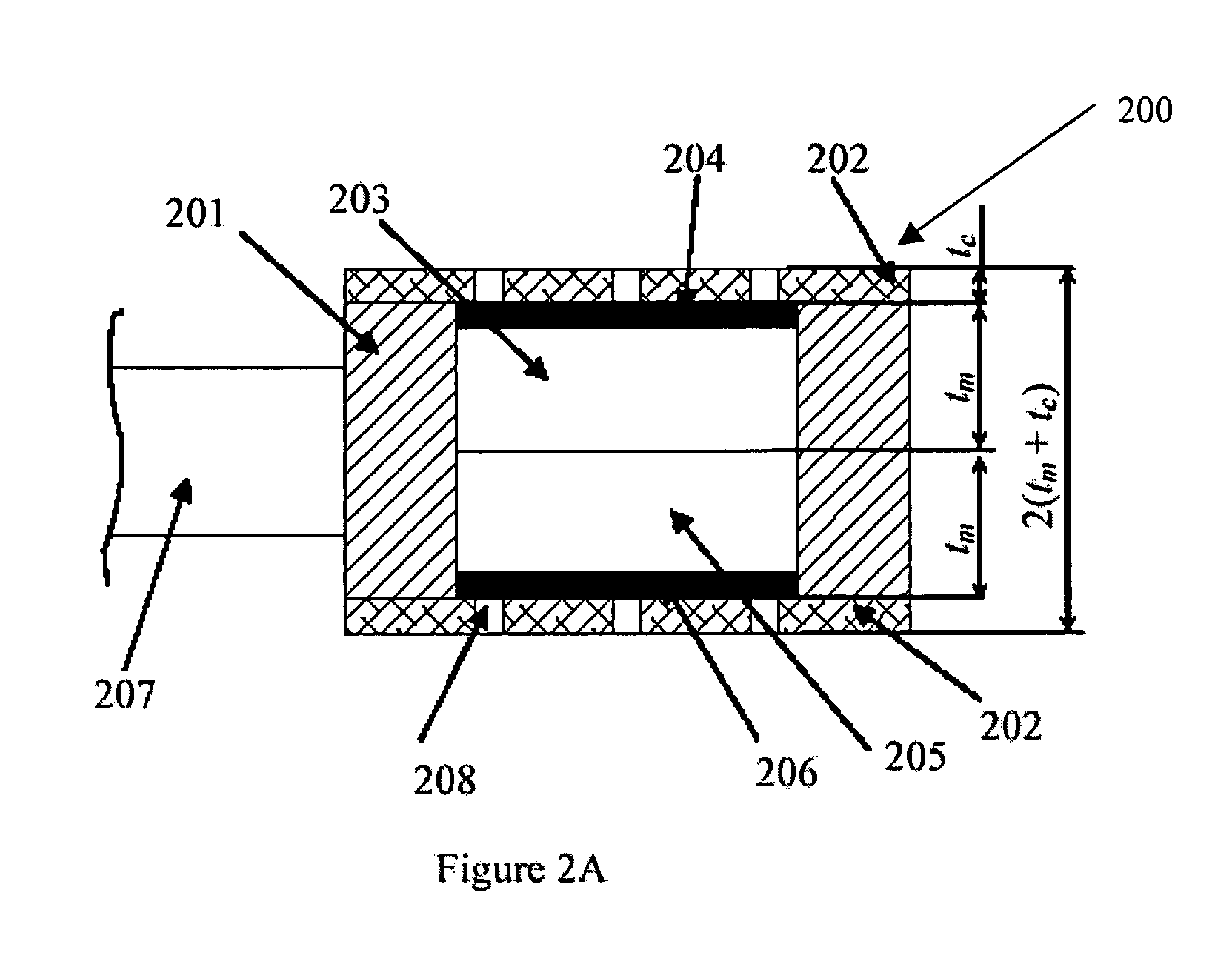
InactiveUS20050031136A1Improves broadband noise canceling performanceSpread the wordPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesMicrophonesBroadband noiseEngineering
A microphone housing improves the broadband noise canceling performance of an active noise canceling microphone system while also ensuring improved speech transmission through the system. First and second microphone elements are selected each having a diameter “d” and a thickness “t”. The two microphone elements are aligned axially with the back surfaces in contact and secured in an axially aligned cylindrical cavity within a cylindrically shaped housing. The cylindrically shaped housing has an outside diameter “D,” an interior cavity of diameter of “d,” and a height “2t”. The housing is exposed to an environment comprising both speech and noise. The first microphone element is adapted to receive a signal having both voice and noise components, while the second microphone element is adapted to receive a signal that is predominantly noise. A controller processes signals from the first microphone element and the second microphone element. The values of D and d are selected so to obtain a ratio of D over d between 1 and about 2.4 or a near field power difference of the first microphone signal and the second microphone signal between 8 dB and 11 dB. In the event the near field power difference is more than 11 dB, the outside diameter of the microphone housing “D” is reduced. In the event the near field power difference is less than 8 dB, the outside diameter of the microphone housing “D” is increased.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Arc fault detector with circuit interrupter
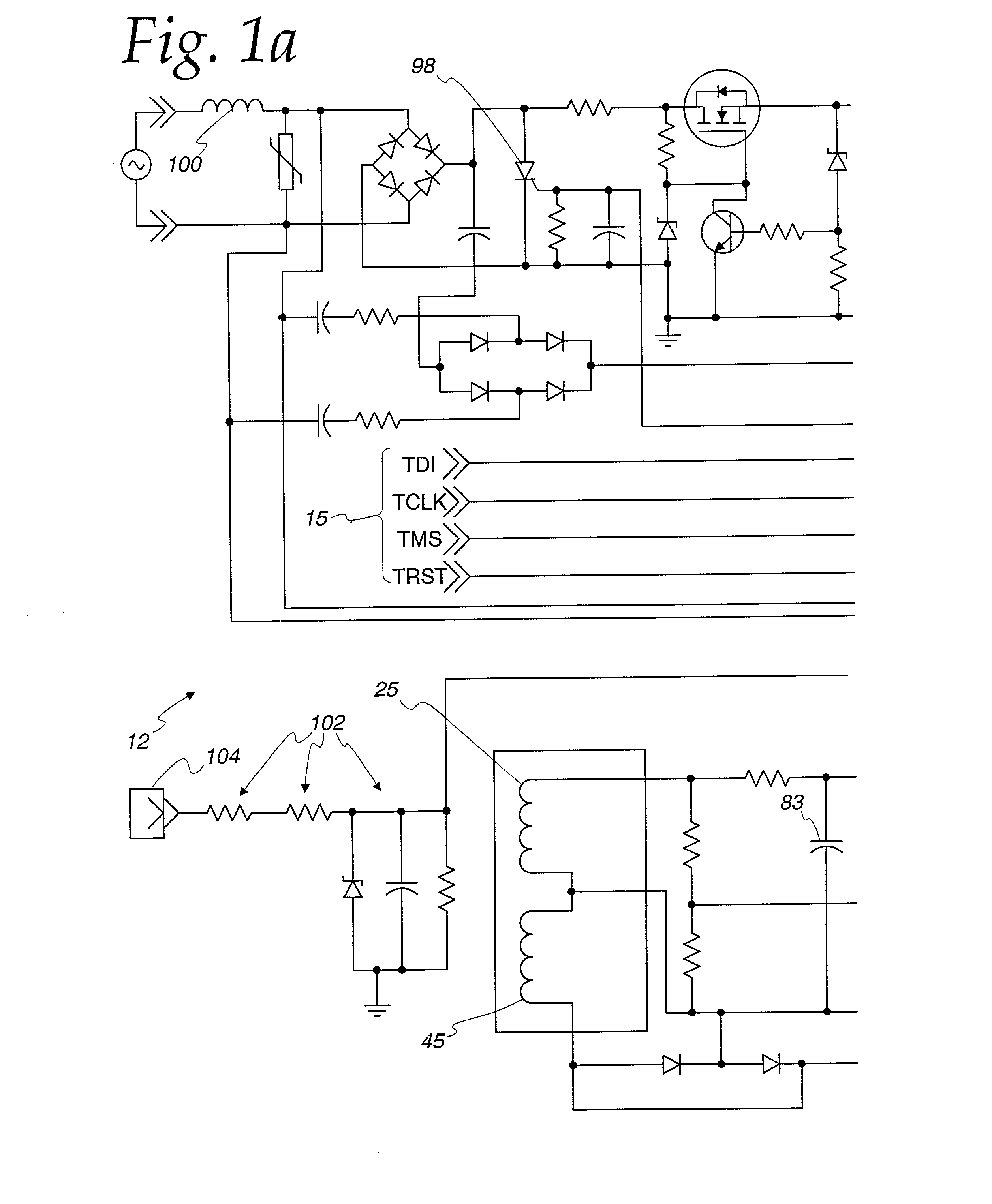
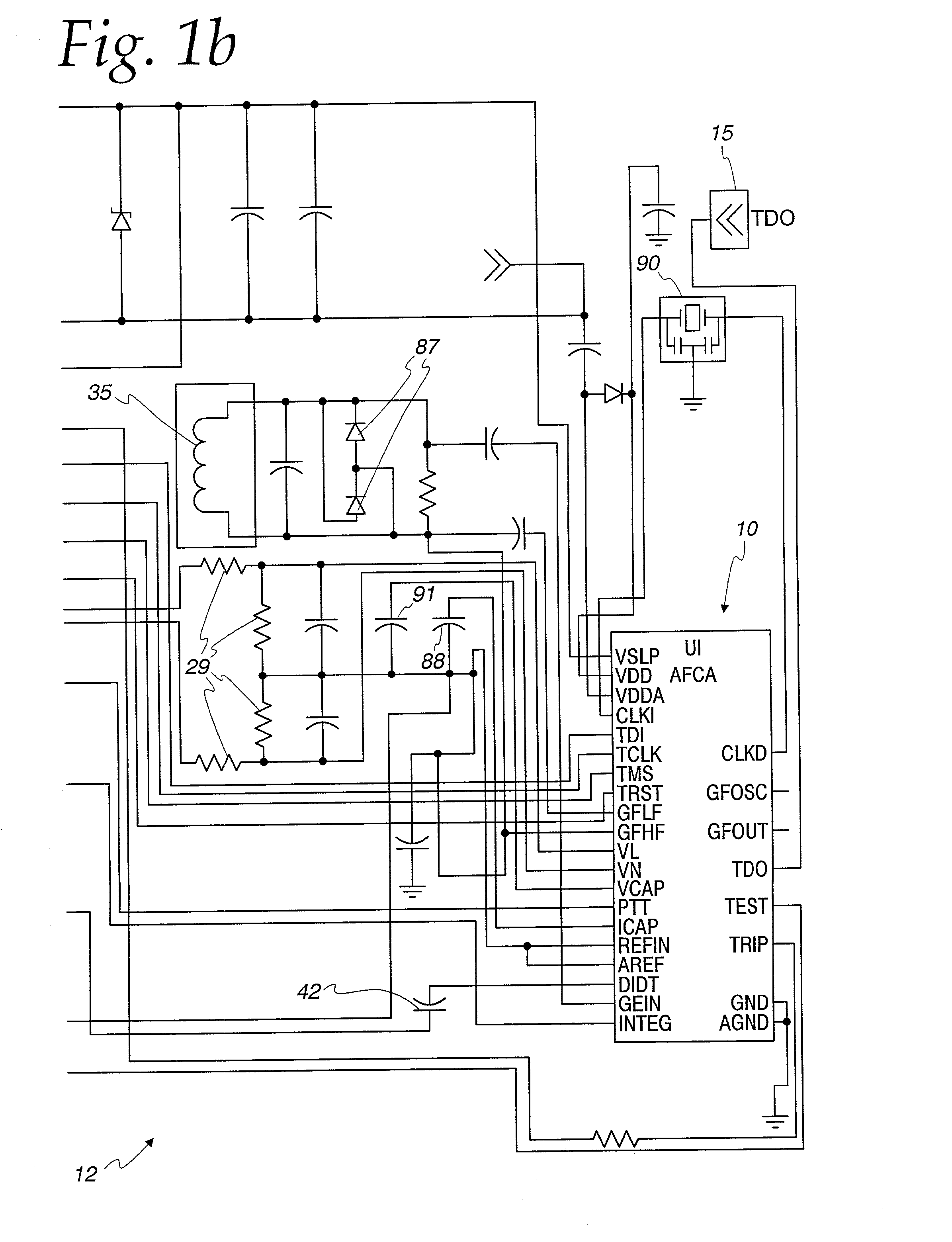
InactiveUS7003435B2Reduce manufacturing costEnhance GFCITesting dielectric strengthEmergency protective arrangement detailsBroadband noiseFirst pathway
There is here disclosed a method and apparatus for detecting the occurrence of arcing of a conductor by monitoring the current on an AC power line. The signal detected is split and directed along four separate paths to generate four signals having separate characteristics which represent the current in the line. A first path is for a signal representative of the current flowing in the line. A second path is for a signal having a pulse for each occurrence of a positive step change in current that is significant and has a di / dt value above a predetermined value. A third path is for a signal having a pulse for each occurrence of a negative step change in current that is significant and has a di / dt value above a predetermined value. A fourth path is for a signal having a voltage level representative of the broadband noise signal on the line. Using at least one of five different methods in combination with one of three input signals, a reference signal designated as “SINE” is generated. The SINE signal generated in combination with a CURRENT input is used to produce a control waveform “DELTA”. DELTA can be represented as a relative value or as an absolute difference between the SINE and the CURRENT. Each occurring half cycle of the DELTA signal is analyzed by, for example, a micro-controller for specific identifiable characteristics found to indicate the presence of arcing. Upon the detection of arcing, an output signal can be generated to activate a circuit interrupting mechanism, sound an audio alarm and / or alert a central monitoring station.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
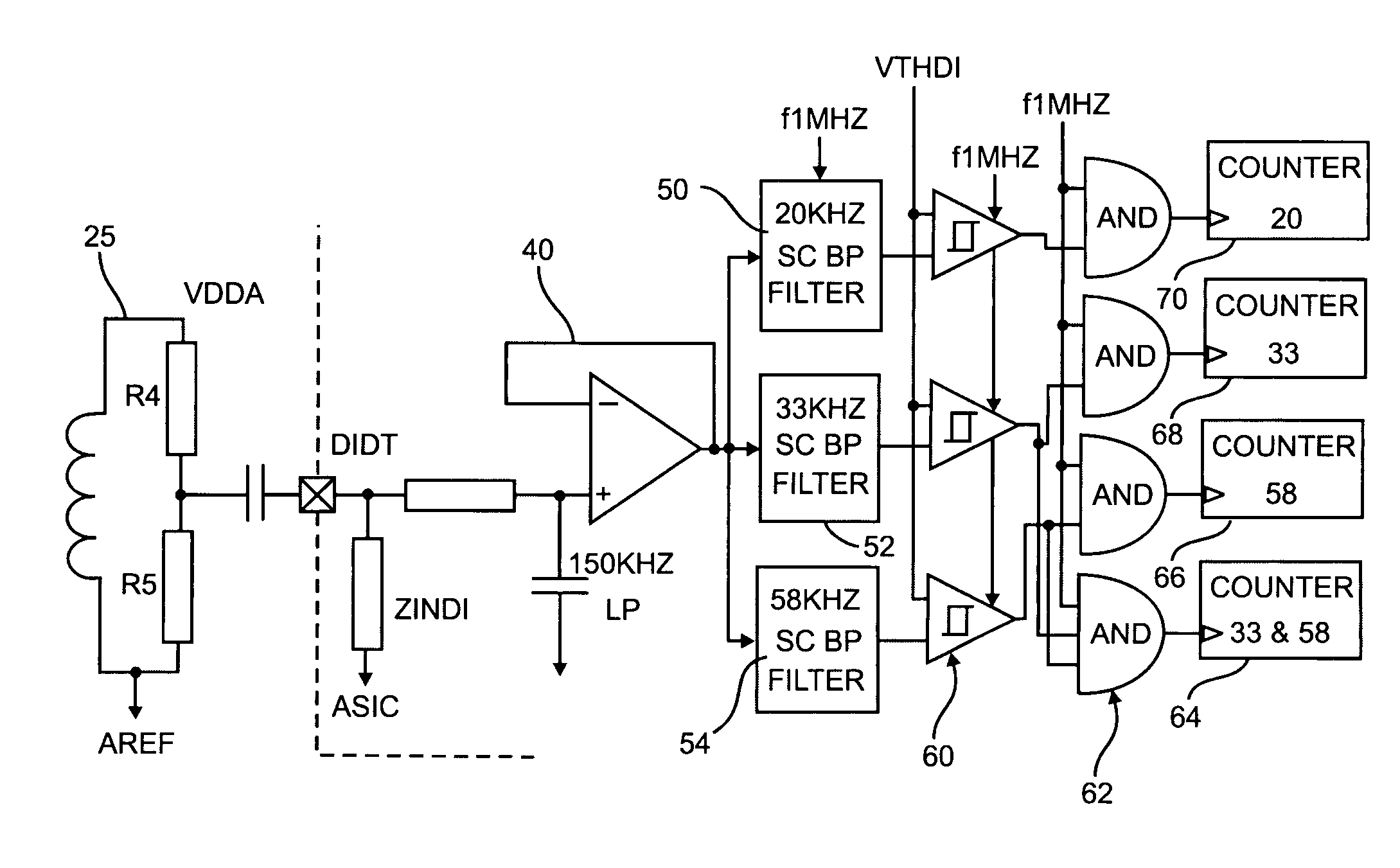
Arc fault circuit interrupter system
InactiveUS7151656B2Reliably detectsGuaranteed uptimeMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlBroadband noisePeak value
A system for determining whether arcing is present in an electrical circuit in response to a sensor signal corresponding to current in the circuit includes a circuit for analyzing the sensor signal to determine the presence of broadband noise in a predetermined range of frequencies, and producing a corresponding output signal. A controller processes the sensor signal and the output signal to determine current peaks and rise times and to determine, using the current peaks and rise times and the presence of broadband noise, whether an arcing fault is present in the circuit, by comparing data corresponding to the current peaks and rise times and broadband noise with preselected data indicative of an arcing fault. The circuit for analyzing and the controller are integrated onto a single application specific integrated circuit chip.
Owner:SQUARE D CO
Flap side edge liners for airframe noise reduction
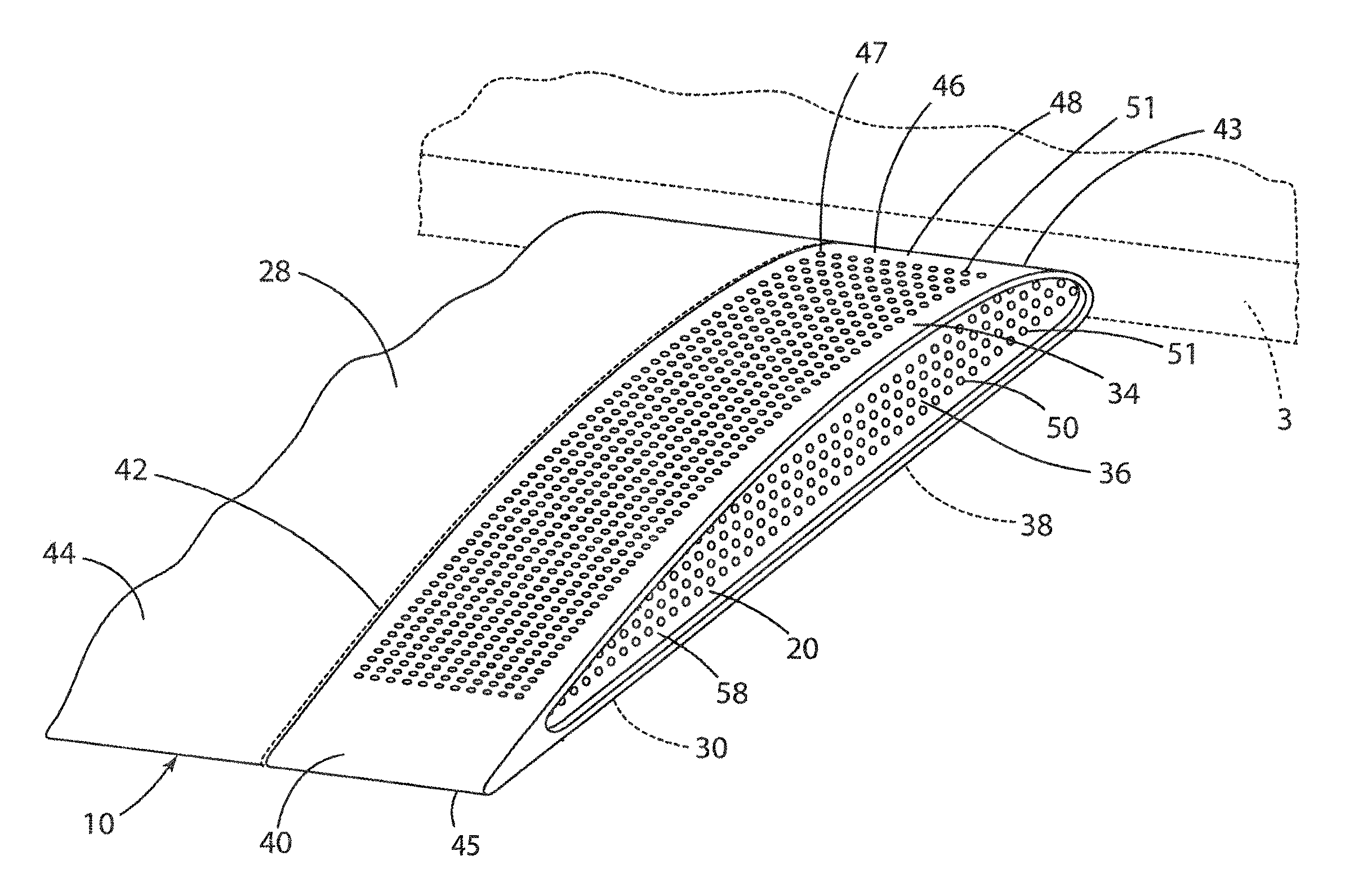
InactiveUS8695915B1Reduce the amount requiredReduce volatilityBoundary layer controlsWingsBroadband noiseAbsorbed energy
One or more acoustic liners comprising internal chambers or passageways that absorb energy from a noise source on the aircraft are disclosed. The acoustic liners may be positioned at the ends of flaps of an aircraft wing to provide broadband noise absorption and / or dampen the noise producing unsteady flow features, and to reduce the amount of noise generated due to unsteady flow at the inboard and / or outboard end edges of a flap.
Owner:NASA
Load recognition and series arc detection using bandpass filter signatures
InactiveUS7136265B2Reliably detectsGuaranteed uptimeEmergency protective arrangement detailsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionBroadband noiseBandpass filtering
A method and system for determining whether arcing is present in an electrical circuit includes sensing a change in an alternating current in the circuit and developing a corresponding input signal, analyzing the input signal to determine the presence of broadband noise in a predetermined range of frequencies, and producing a corresponding output signal, and processing the input signal and the output signal in a predetermined fashion to determine whether an arcing fault is present in the circuit. The processing includes determining a type of load connected to the electrical circuit, based at least in part upon the input signal and the output signal, and monitoring high frequency noise in a 20 KHz band for each ⅛ cycle of the alternating current.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC USA INC
Active noise control method for eliminating and reducing noise
InactiveCN101833949AFast convergenceAdjust runtimeSound producing devicesNoise controlBroadband noise
The invention discloses an active noise control method for eliminating and reducing noise. An active noise control device is subjected to the operation in the following steps of: (1) identifying a transfer function between a secondary source and an error sensor by using a common LMS (Least Mean Square) algorithm to obtain a transfer function estimating value of a signal transmitting channel; (2) obtaining an output signal y1(n) of an FXLMS (Filtered-x Least Mean Square) algorithm self-adapting filter W(n) according to a primary noise source signal x(n); (3) obtaining an output signal y2(n) of a DFT-FSF (Discrete Forurier Transform-Fast Forurier Transform) algorithm self-adapting filter according to a filtering reference signal of the signal transmitting channel; (4) adding y1(n) and y2(n) to obtain y(n) and respectively obtaining an expected signal d(n) and an error signal e(n) at the error sensor position and an estimating value of d(n); and (5) updating the DFT-FSF algorithm self-adapting filter V(n) and adjusting the FXLMS self-adapting filter W(n); and repeating the steps (2) to (5) and gradually reducing e(n) to achieve the aim of noise reduction at the error sensor position. The invention has the advantage of combining and utilizing the favorable benefits that an FXLMS algorithm is suitable for narrowband noise reduction and a DFT-FSF algorithm is suitable for broadband noise reduction and greatly reduces computation burden.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANLI UNIV
Load recognition and series arc detection using load current/line voltage normalization algorithms
InactiveUS7345860B2High-frequency noiseEmergency protective arrangement detailsEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentBroadband noiseEngineering
A method and system for determining whether arcing is present in an electrical circuit. The methods includes sensing a change in an alternating current in the circuit and developing a corresponding input signal, analyzing the input signal to determine the presence of broadband noise in a predetermined range of frequencies, and producing a corresponding output signal. The method further includes determining a type of load connected to the electrical circuit, based at least in part upon the input signal and the output signal, incrementing one or more of a plurality of counters in a predetermined fashion in accordance with the input signal and the output signal and determining whether an arcing fault is present based at least in part on the states of one or more of a plurality of counters. The method also includes decrementing one or more of the plurality of counters based upon a secondary analysis.
Owner:SQUARE D CO
System for manipulating noise in digital images
ActiveUS20050276515A1Preserving fine image detailPreserving sharpnessImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionBroadband noise
An apparatus for analyzing the broadband noise content of a digital image comprising the following: a means of automatically identifying regions of originally constant color in the image by analysis of the variance of pixel values of regions of the image; a means of automatically detecting and discarding regions deemed to be unrepresentative of the true noise content of an image, including under- and over- exposed regions; a means of allowing the user to manually select some or all required constant color regions if desired; and, a means of analyzing such constant color regions to generate a parametric or non-parametric model of the noise in the image, including frequency characteristic within and between channels and other characteristics such as phase which might describe structured noise.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Arc fault circuit interrupter and method providing improved nuisance trip rejection
ActiveUS20100157486A1Improve abilitiesEmergency protection data processing meansEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionBroadband noiseCurrent sensor
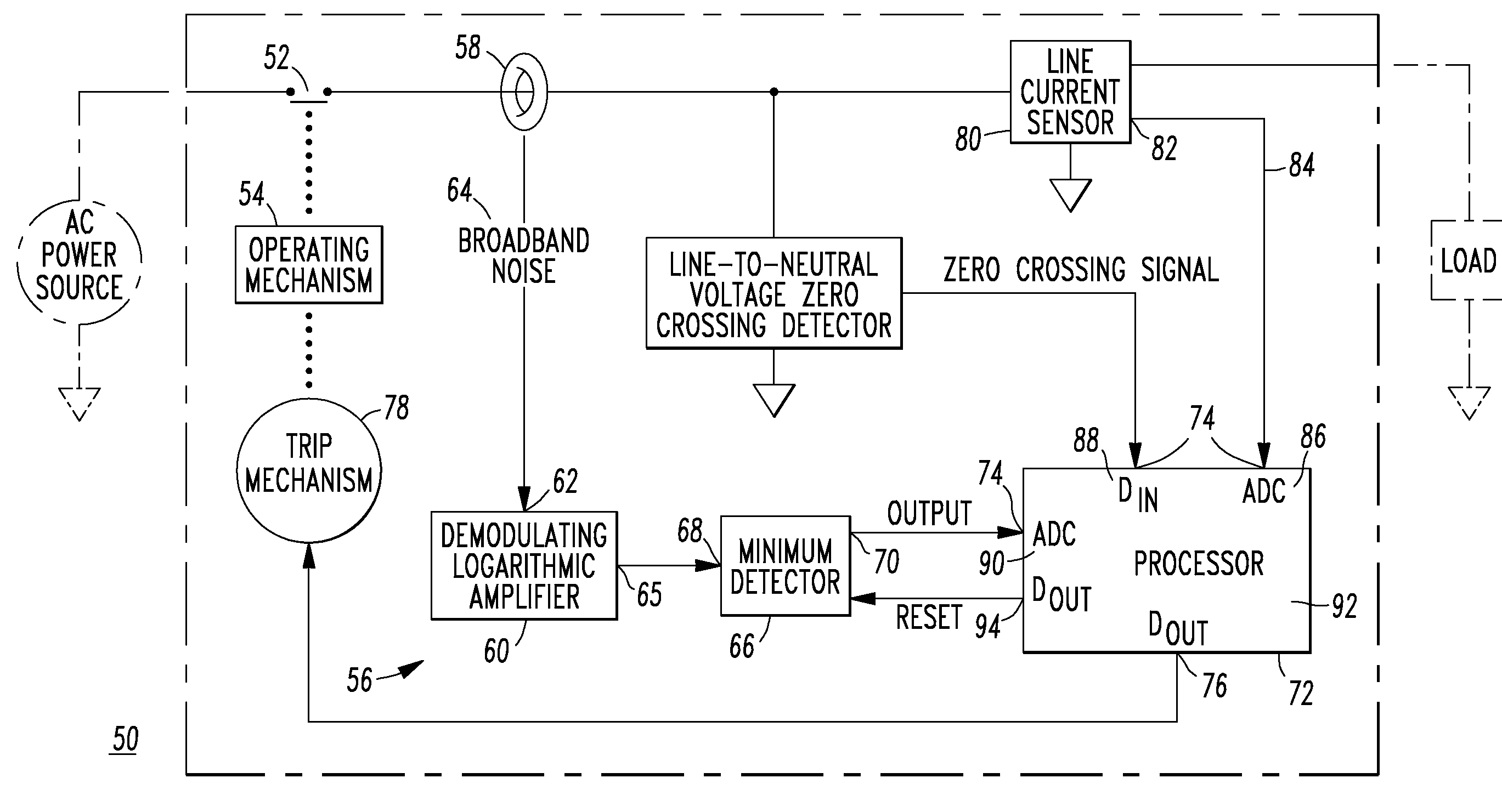
An arc fault circuit interrupter includes separable contacts, an operating mechanism and an arc fault detector structured to detect an arc fault condition operatively associated with the contacts. The arc fault detector includes a tuned current sensor structured to sense broadband noise of a current flowing through the contacts, a compression circuit including an input of the sensed broadband noise and an output. The compression circuit compresses the dynamic range of the sensed broadband noise. A minimum detector includes an input of the compression circuit output and an output of the minimum value of the minimum detector input. A processor includes a number of inputs and an output. One of the inputs is the output of the minimum value of the minimum detector. A trip mechanism cooperates with the output of the processor and the operating mechanism to trip open the contacts responsive to the detected arc fault condition.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Arc fault circuit interrupter system
InactiveUS20030074148A1Reliably detectsGuaranteed uptimeMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlBroadband noiseHemt circuits
A system for determining whether arcing is present in an electrical circuit in response to a sensor signal corresponding to current in the circuit includes a circuit for analyzing the sensor signal to determine the presence of broadband noise in a predetermined range of frequencies, and producing a corresponding output signal. A controller processes the sensor signal and the output signal to determine current peaks and rise times and to determine, using the current peaks and rise times and the presence of broadband noise, whether an arcing fault is present in the circuit, by comparing data corresponding to the current peaks and rise times and broadband noise with preselected data indicative of an arcing fault. The circuit for analyzing and the controller are integrated onto a single application specific integrated circuit chip.
Owner:SQUARE D CO
Real-time extracting device and detection method for focused ultrasonic cavitation and microbubbles thereof
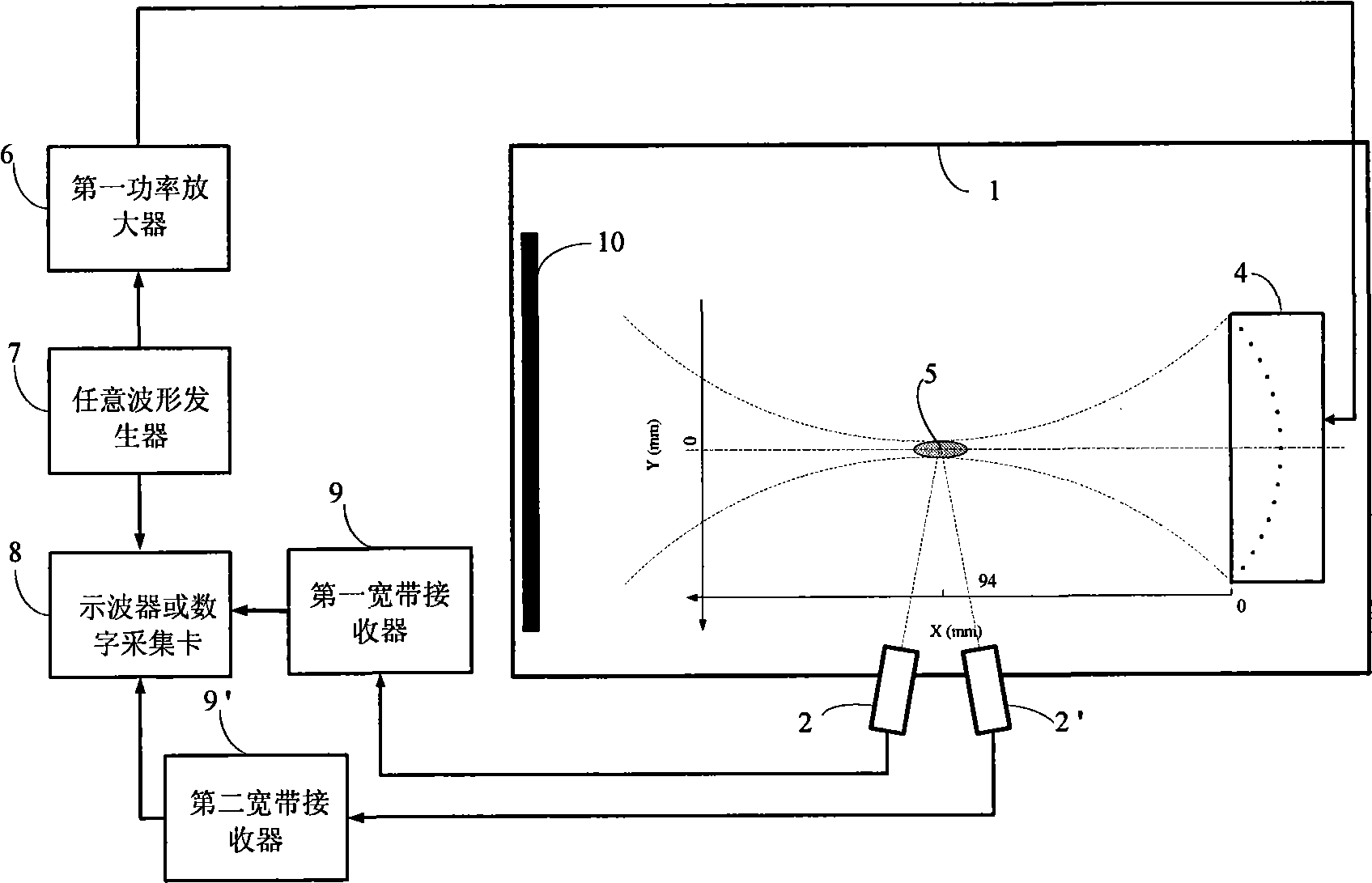
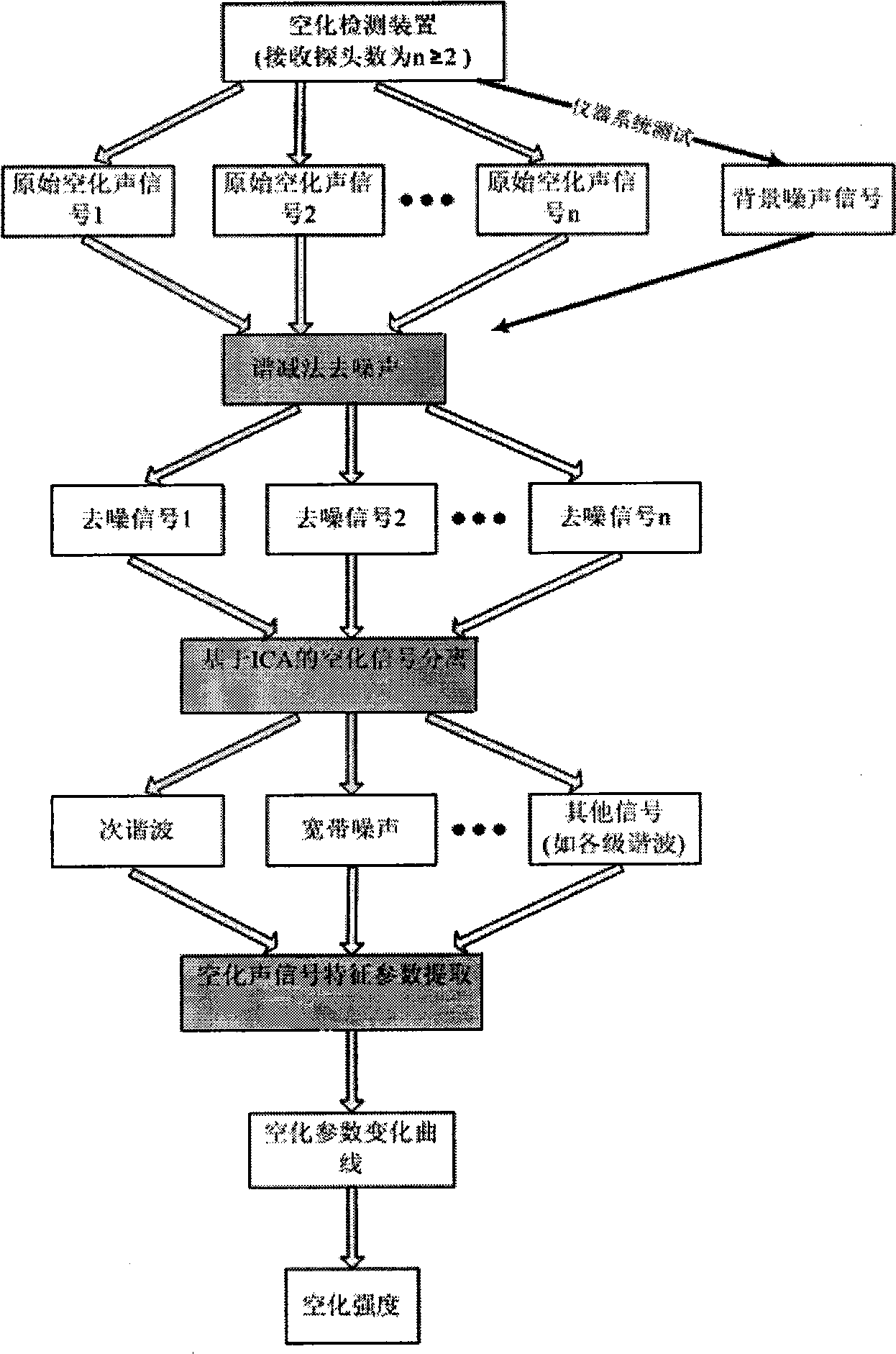
InactiveCN101530320AAchieving real-time identification detectionHas inhibitory effectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBroadband noiseUltrasonic cavitation
The invention belongs to the technical field of ultrasonic cavitation detection and signal analysis, and relates to a method and a device for separating and detecting focused ultrasonic cavitation signals. An ultrasonic transducer of a device emits cavitation detecting signals in a pulse-inversion mode, and another ultrasonic transducer receives acoustic signals diffused by ultrasonic cavitation and movement of microbubbles; a transducer of another device generates cavitation signals in the pulse-inversion mode; for each cavitation detecting experiment, the detection method extracts background signals when the cavitation does not happen, respectively calculates power spectrums of the acquired cavitation acoustic signals and the background signals, calculates the subtracted power spectrum estimation and phase position estimation, and converts the power spectrum estimation and the phase position estimation into time domain signals to filter noise of a system; and an ICA method separates target signals such as broadband noise component, subharmonic and the like in cavitation acoustic signals from other signal components and extracts characteristic parameters of the cavitation acoustic signals. The detection method has high sensitivity and can perform quantitative analysis.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Arc detection using load recognition, harmonic content and broadband noise
InactiveUS7068480B2Reliably detectsGuaranteed uptimeEmergency protective arrangement detailsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionBroadband noiseHarmonic
A method of determining whether arcing is present in an electrical circuit includes sensing a change in current in the circuit and developing a corresponding input signal, analyzing the input signal to determine the presence of broadband noise in a predetermined range of frequencies, and producing a corresponding output signal, and processing the input signal and the output signal in a predetermined fashion to determine whether an arcing fault is present in the circuit. The processing includes determining a type of load connected to the electrical circuit, based at least in part upon the input signal and the output signal.
Owner:SQUARE D CO
Carrier-borne full-coherent phased-array radar calibrator
ActiveCN102608582ATest target detection capabilitiesWave based measurement systemsBroadband noiseIntermediate frequency
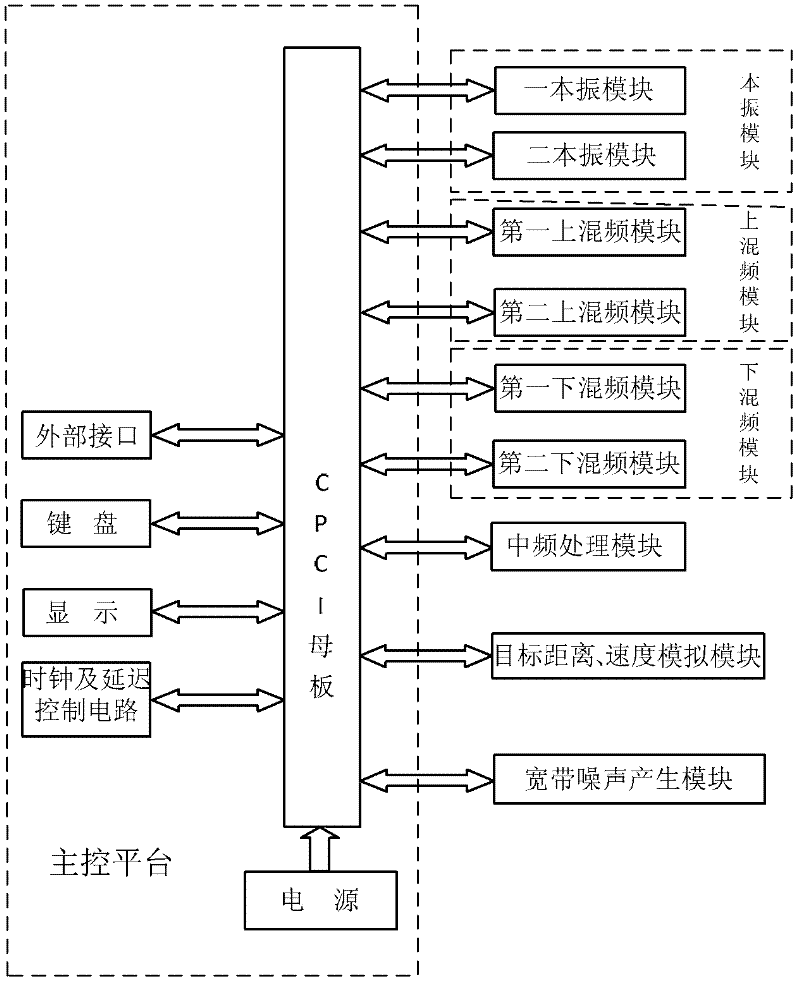
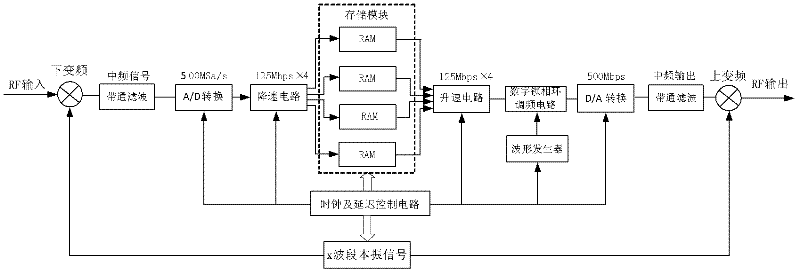
The invention relates to a carrier-borne full-coherent phased-array radar calibrator which comprises a local oscillator module, upper and lower frequency mixing modules, an intermediate frequency processing module, a target distance, a speed simulation module, a broadband noise generating module, a master control platform and the like, wherein the local oscillator module is divided into first and second local oscillator modules; the upper frequency mixing module is divided into first and second upper frequency mixing modules; the lower frequency mixing module is divided into first and second lower frequency mixing modules; the master control platform comprises a CPCI (Compact Peripheral Component Interconnect) motherboard, a power supply, a keyboard, a display, an external interface and a clock and delay control circuit; and each module and each component of the master control platform are supplied with power and carry out data exchange by the CPCI motherboard. According to the invention, a radar echo signal synthesized by overlaying a target and a broadband noise power can be vividly simulated and the detection capacity of the target under the noise interference of a carrier-borne full-coherent phased-array radar can be tested. The carrier-borne full-coherent phased-array radar calibrator has good application prospect in the technical field of calibration and checking of the phased-array radar.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Performance of a receiver in interfering conditions
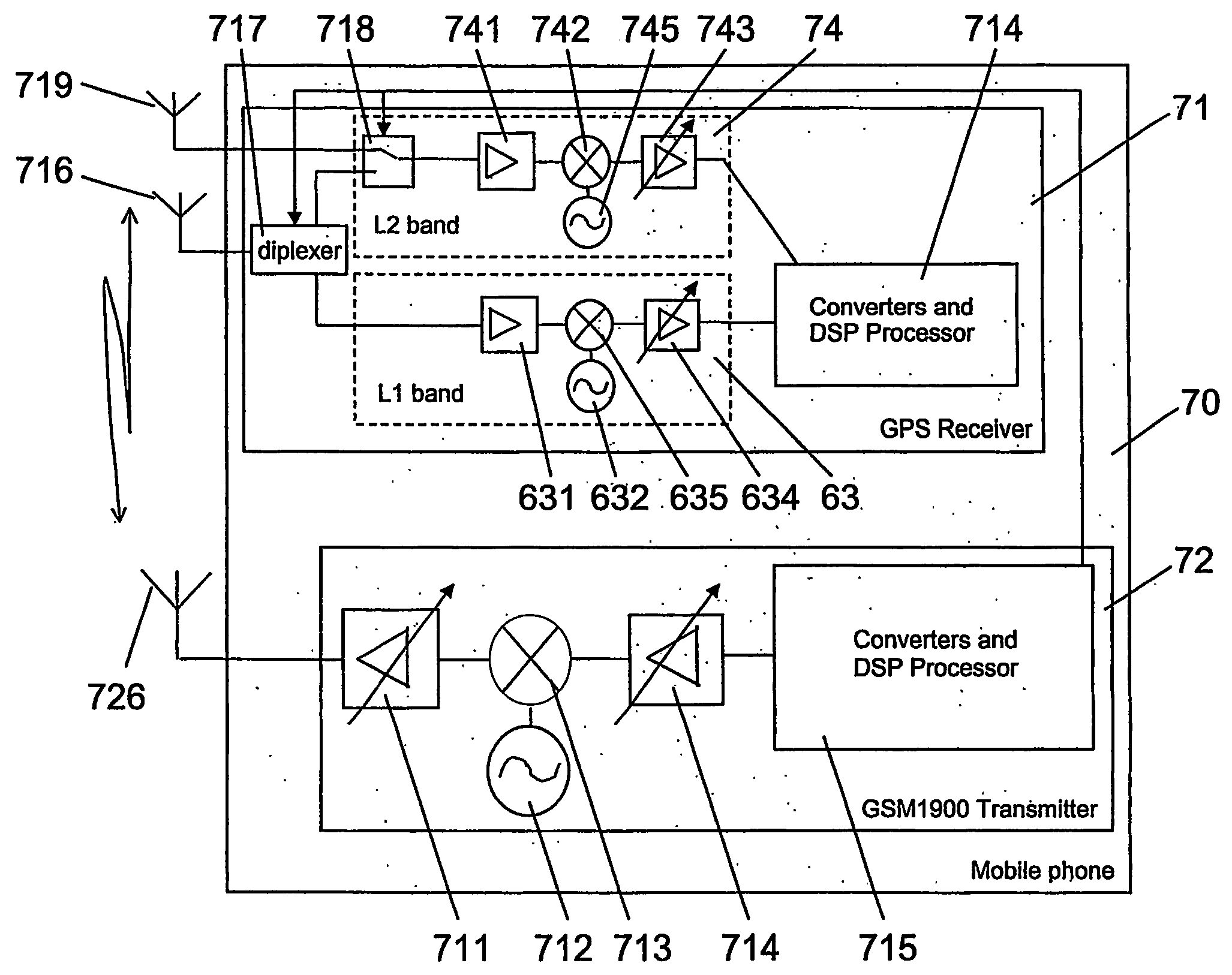
InactiveUS20060152408A1Attenuating wideband noiseReduce noisePosition fixationSubstation equipmentEngineeringWideband
A device 20 includes a receiver 21 for receiving and processing signals at least in a first frequency band and an antenna 216 which is connected to the receiver 21. In order to improve the performance of such a receiver, the device 20 in addition includes a tuning component 217 for shifting a frequency response of the antenna 216 from the first frequency band to a second frequency band. Further, the device 20 includes a controlling portion 221 causing the tuning component 217 to shift the frequency response of the antenna 216 from the first frequency band to the second frequency band, in case a wideband noise is expected in the first frequency band. A corresponding method is shown as well.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Real-time frequency domain super-resolution direction estimation method and device
InactiveCN101644773AEasy to implementCalculation speedAcoustic wave reradiationBroadband noiseEstimation methods
The invention provides a real-time frequency domain super-resolution direction estimation method and a device, and the method comprises the following steps: 1) dividing a linear array for obtaining M1sub-arrays; 2) respectively carrying out beamforming on a time-space two-dimensional signal of each sub-array for obtaining an output beam of each sub-array on the scanning direction; 3) carrying outsynthesis treatment on the output beams of various sub-arrays on the scanning direction for obtaining a multi-sub-array synthetic beam; and 4) and obtaining the target direction according to the multi-sub-array synthetic beam obtained by the step 3). The invention provides the real-time frequency domain super-resolution direction estimation device. The method and the device have the following technical effects: (1) the calculation is highly efficient, the speed is fast, the DSP engineering is convenient to realize, and the real-time treatment can be realized; (2) the method and the device areapplicable to broadband noise target direction finding; (3) the high-resolution beam can be obtained; and (4) compared with the frequency domain beamforming algorithm in the prior art, the method andthe device can obtain beam output with even narrow main lobe and even weak strength of a side lobe, thereby obtaining the target direction estimation with higher resolution.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Secure and high-speed key distribution system and method
ActiveCN105262585AImprove securityIncreased complexityKey distribution for secure communicationBroadband noiseEngineering
The invention relates to the key distribution technology in the secure communication field and particularly provides a secure and high-speed key distribution system and method. The According to the technical scheme of the invention, the problems in the prior art that the conventional key distribution technology is poor in security and slow in key distribute on speed can be solved. The secure and high-speed key distribution system comprises a broadband noise-like drive source, a 1*2 main optical fiber coupler, a 1*2 left optical fiber coupler, a 1*2 right optical fiber coupler, two left filtering frequency selectors, two right filtering frequency selectors, two left optical feedback chaotic semiconductor lasers, two right optical feedback chaotic semiconductor lasers, a left electro-optical modulation system, a right electro-optical modulation system, a left storage channel, a right storage channel, a 2*1 left optical fiber coupler, a 2*1 right optical fiber coupler, a left photoelectric detector, a right photoelectric detector, a left analog-to-digital converter, a right analog-to-digital converter, a left memory, a right memory and a common channel. The above system and method can be applied to the filed of secure communication.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Systems and methods for optical dark section conditioning
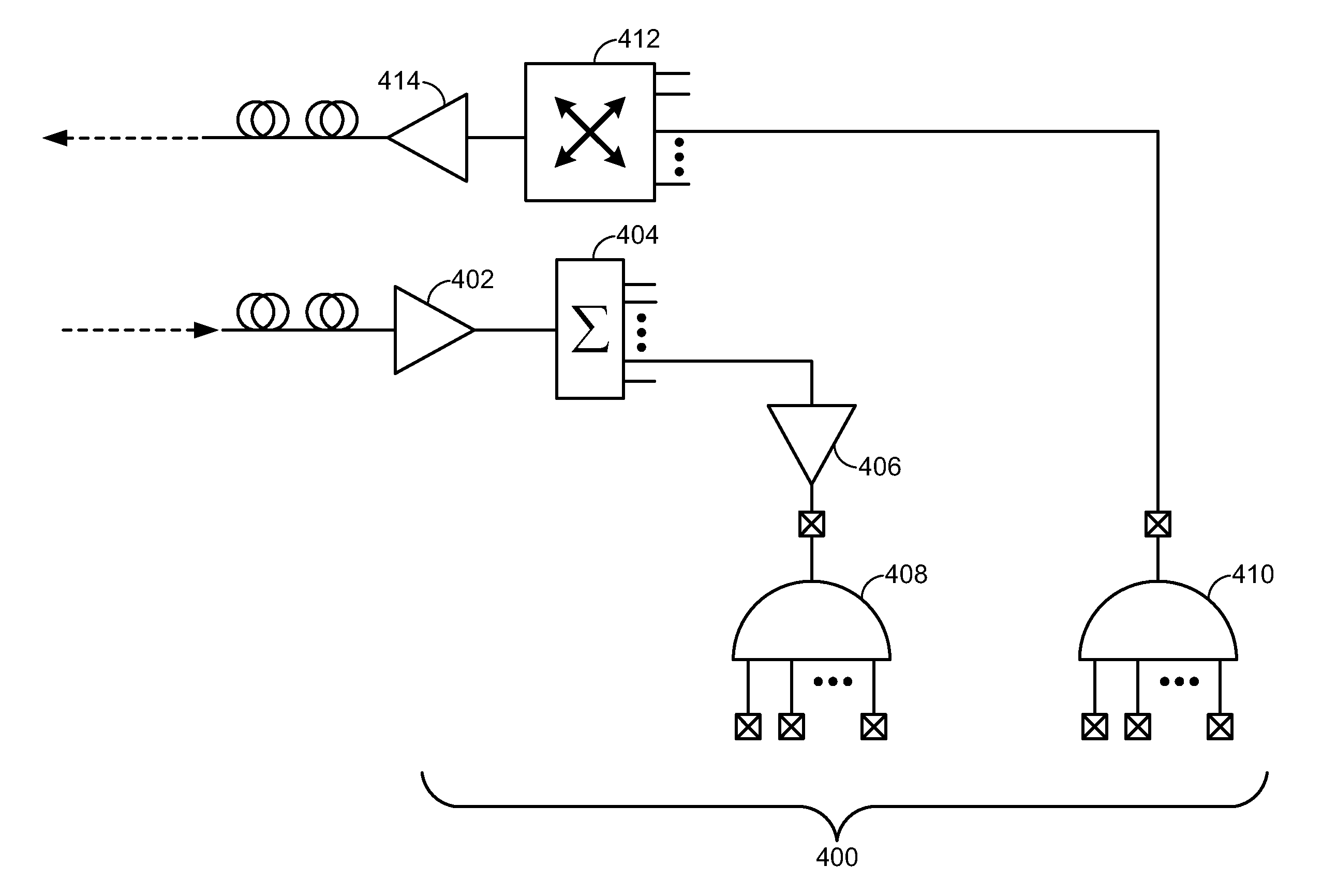
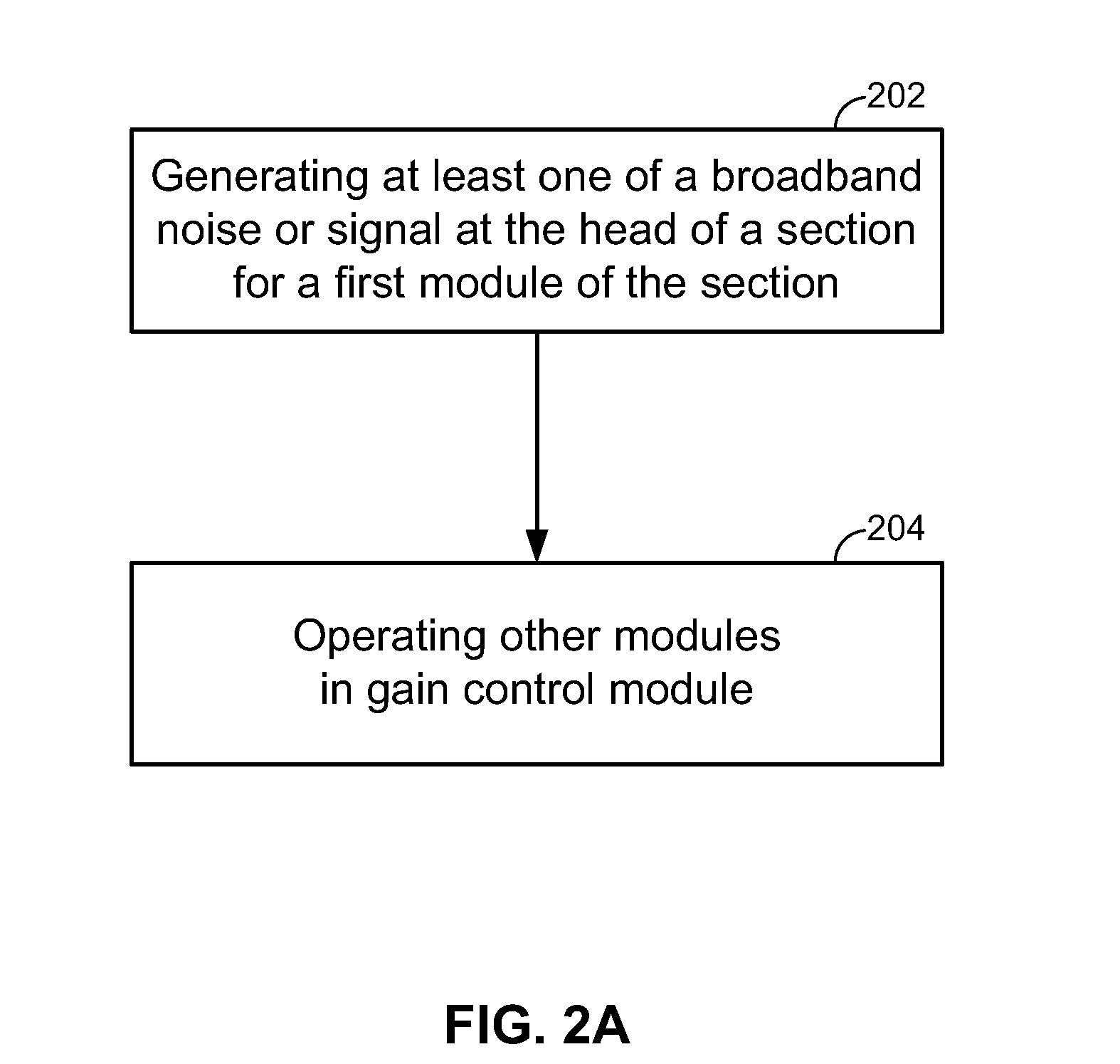
ActiveUS20140328583A1Reduce output powerNot to damageLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsBroadband noiseEngineering
Embodiments of the disclosure are directed to optical dark section conditioning. An embodiment generates at least one of a broadband noise or signal at the head end of a section for a first module of the section; and operates all other modules of the section in gain control mode.
Owner:CIENA
Adaptive frequency hopping strategy
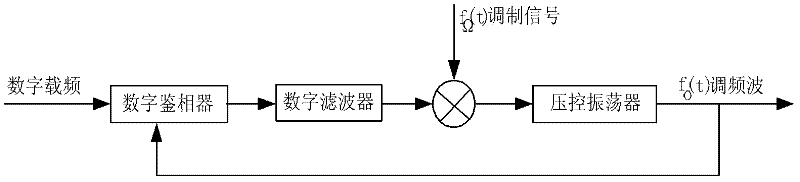
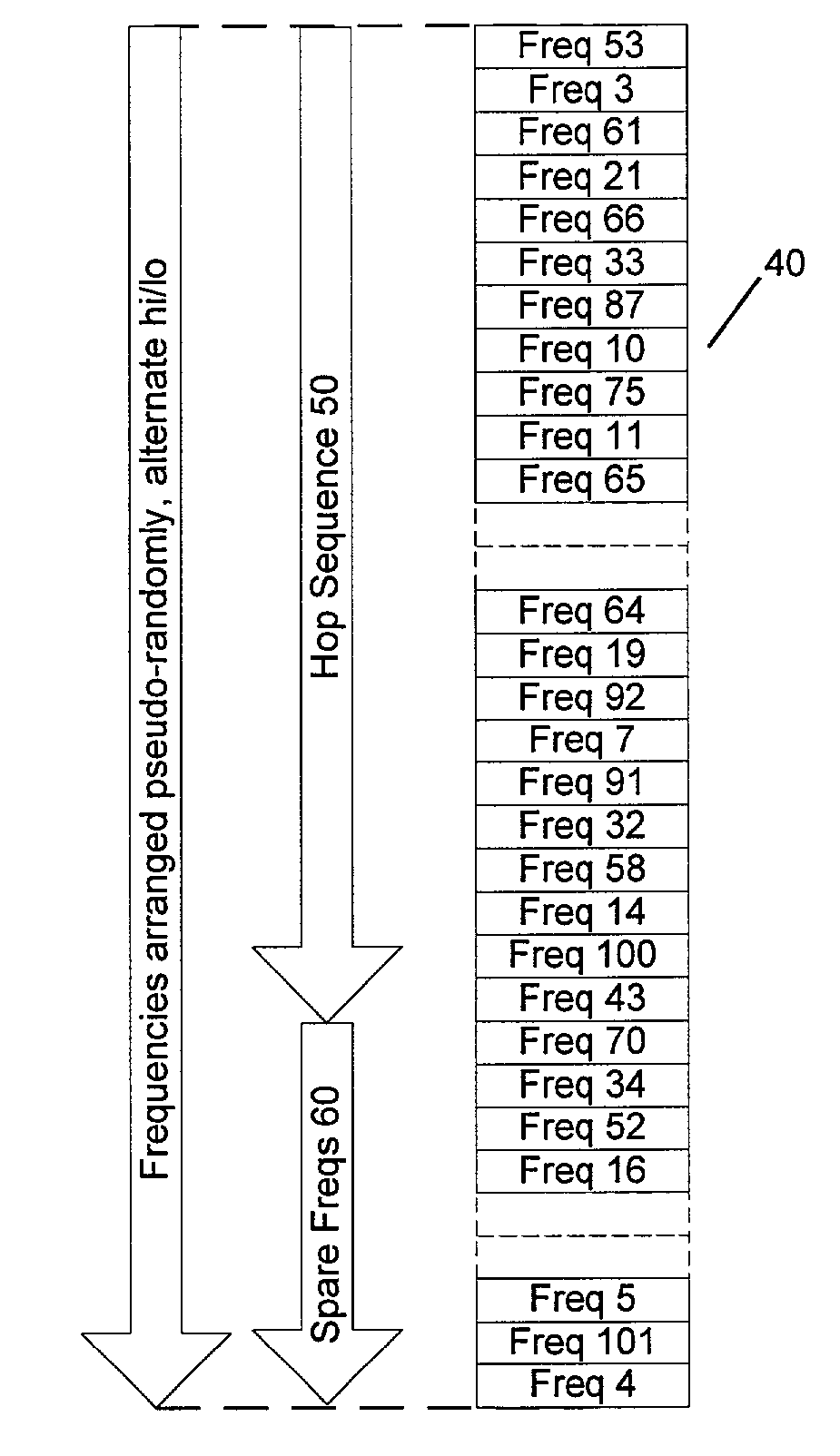
A technique for controlling the frequency allocation in the hop sequence of a frequency hopping digital communications system is presented. The hop sequence is initially formed such that consecutive channels are likely to differ substantially in frequency. Therefore, channel substitution commands can be transmitted twice on consecutive hops without acknowledgement, inasmuch as the likelihood of a broadband noise source blocking consecutive channels is reduced. The number of channels identified as requiring substitution in the hop sequence is monitored, such that a hop sequence repair operation or communications link termination can be implemented if channel substitution data traffic becomes too great.
Owner:VTECH COMM
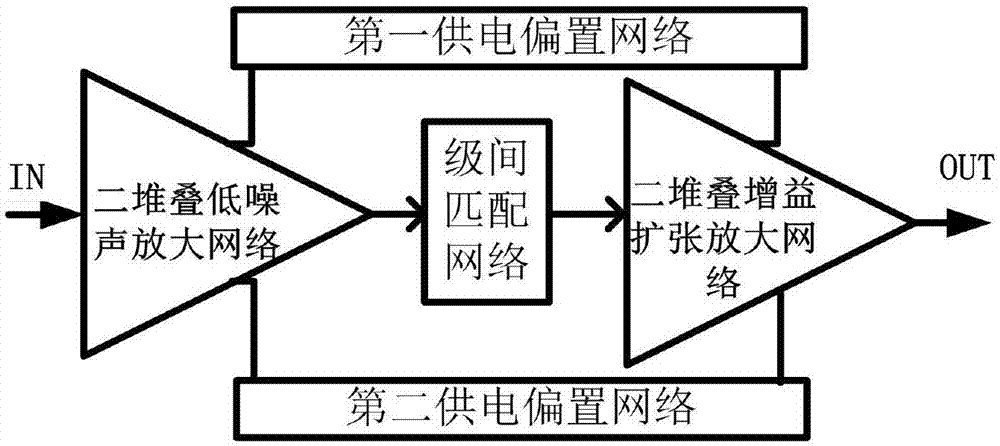
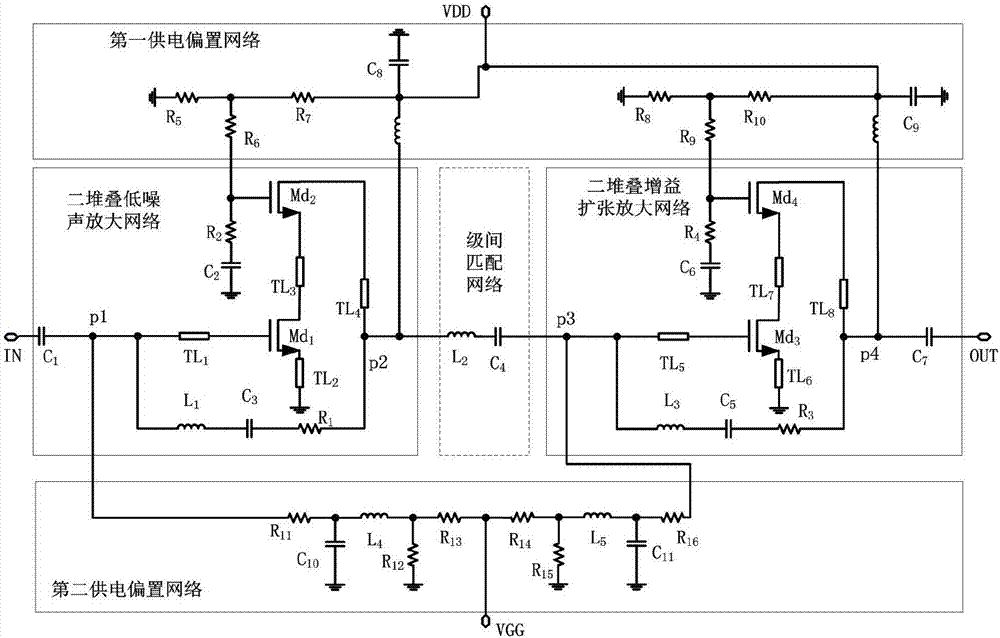
High-linearity broadband stacking low noise amplifier based on gain compensation technology
ActiveCN107332517AImprove linearity metrics1dB higher compression pointAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceUltra-widebandLow noise
The invention discloses a high-linearity broadband stacking low noise amplifier based on a gain compensation technology. The high-linearity broadband stacking low noise amplifier comprises a two-stacking low noise amplification network, an interstage matching network and a two-stacking gain expansion amplification network which are connected in sequence; and a first power supply bias network and a second power supply bias network which are connected with the two-stacking low noise amplification network and the two-stacking gain expansion amplification network. According to the high-linearity broadband stacking low noise amplifier, a serial stacking structure is realized through adoption of two transistors with different sizes and ultra wide band noise and impedance matching are realized through combination of an RLC feedback network; through utilization of the gain compression compensation technology, the gain compression property of the two-stacking low noise amplification network is cancelled within a certain bias range through the two-stacking gain expansion amplification network and a linearity index of the amplifier is improved, so the whole low noise amplifier has good broadband, linearity, low power consumption and low noise amplification capability; and moreover, the low breakdown voltage property of an integrated circuit technology is avoided and the stability and reliability of a circuit are improved.
Owner:CHENGDU GANIDE TECH
Centrifugal pump flow induction noise numerical prediction method
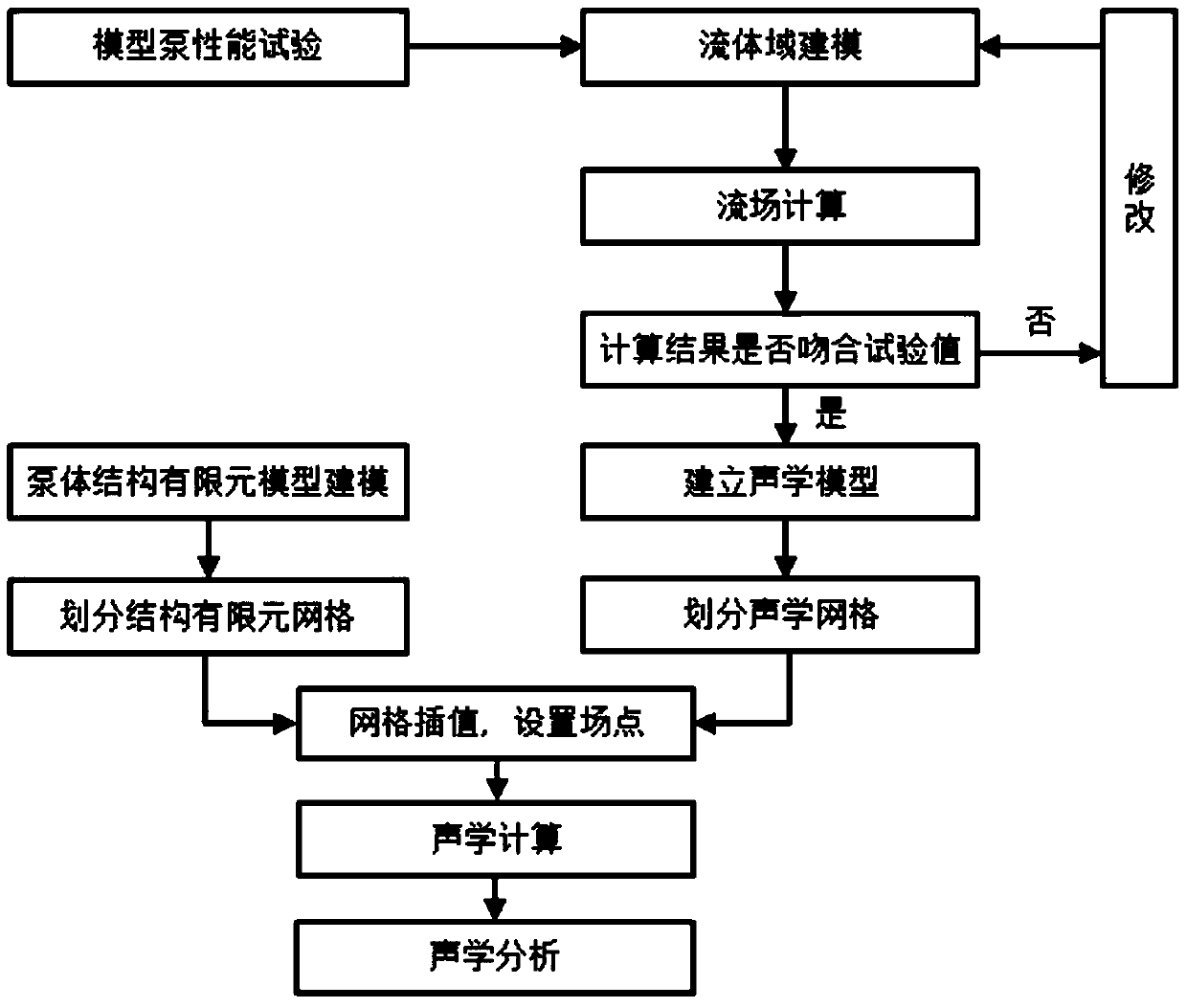
ActiveCN103631989AImprove design qualityOptimize early designSpecial data processing applicationsLow noiseBroadband noise
The invention discloses a centrifugal pump flow induction noise numerical prediction method which is used for computing the sound source feature of flow noise on the basis of the test results of a centrifugal pump performance test. The method can well overcome the shortcomings that in a traditional computing method, the influence from a pump body structure on acoustic propagation is not considered, and eddy broadband noise is ignored. Centrifugal pump inner flow analysis and far-field noise value computing results are used in centrifugal pump low-noise waterpower design, test frequency can be reduced, the development cycle can be shortened, development cost can be saved, the design quality of a centrifugal pump can be effectively improved, an interpolation method is used between a fluid mesh and an acoustics mesh, sound source information of flow field calculation can be reserved to the maximum degree, GREEN analysis is used, the contribution degree on noise from different parts of a shell body can be obtained, such study is carried out, and early design or later modifying of the shell body can be optimized.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com