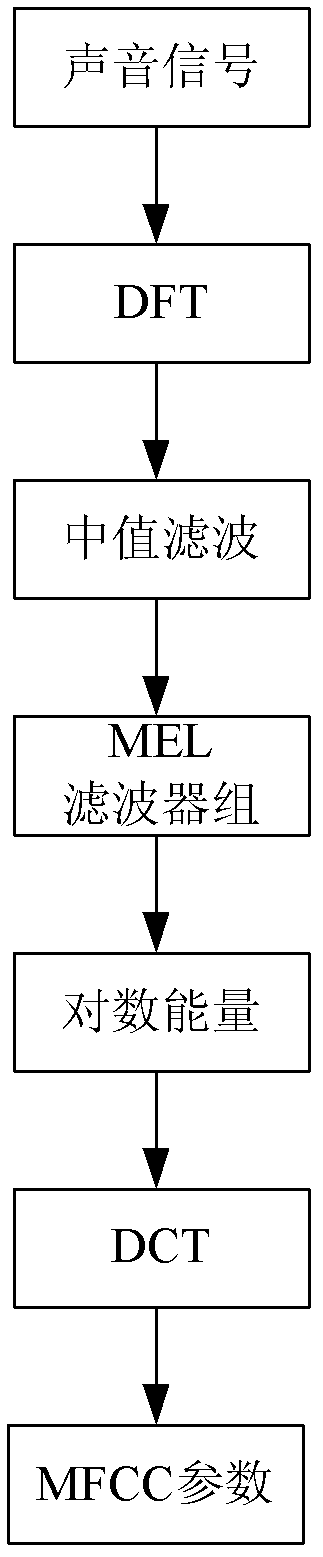
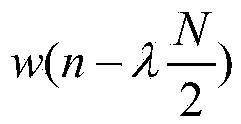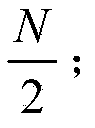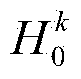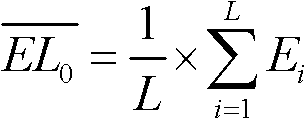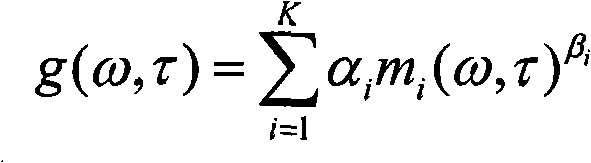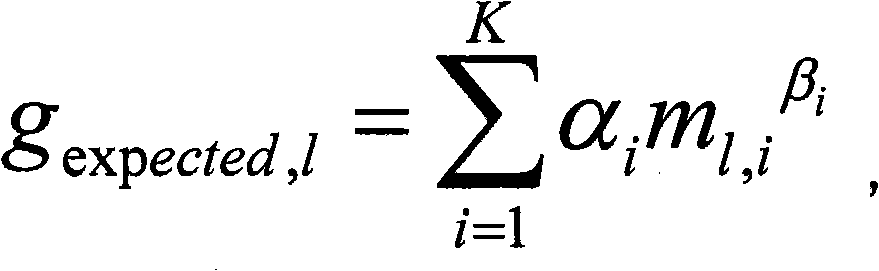Patents
Literature
1705 results about "Time frequency domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Time domain is the domain for analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to time. Frequency domain is the domain for analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency. The time domain systems tend to use photon counting detectors which are slow but highly sensitive.
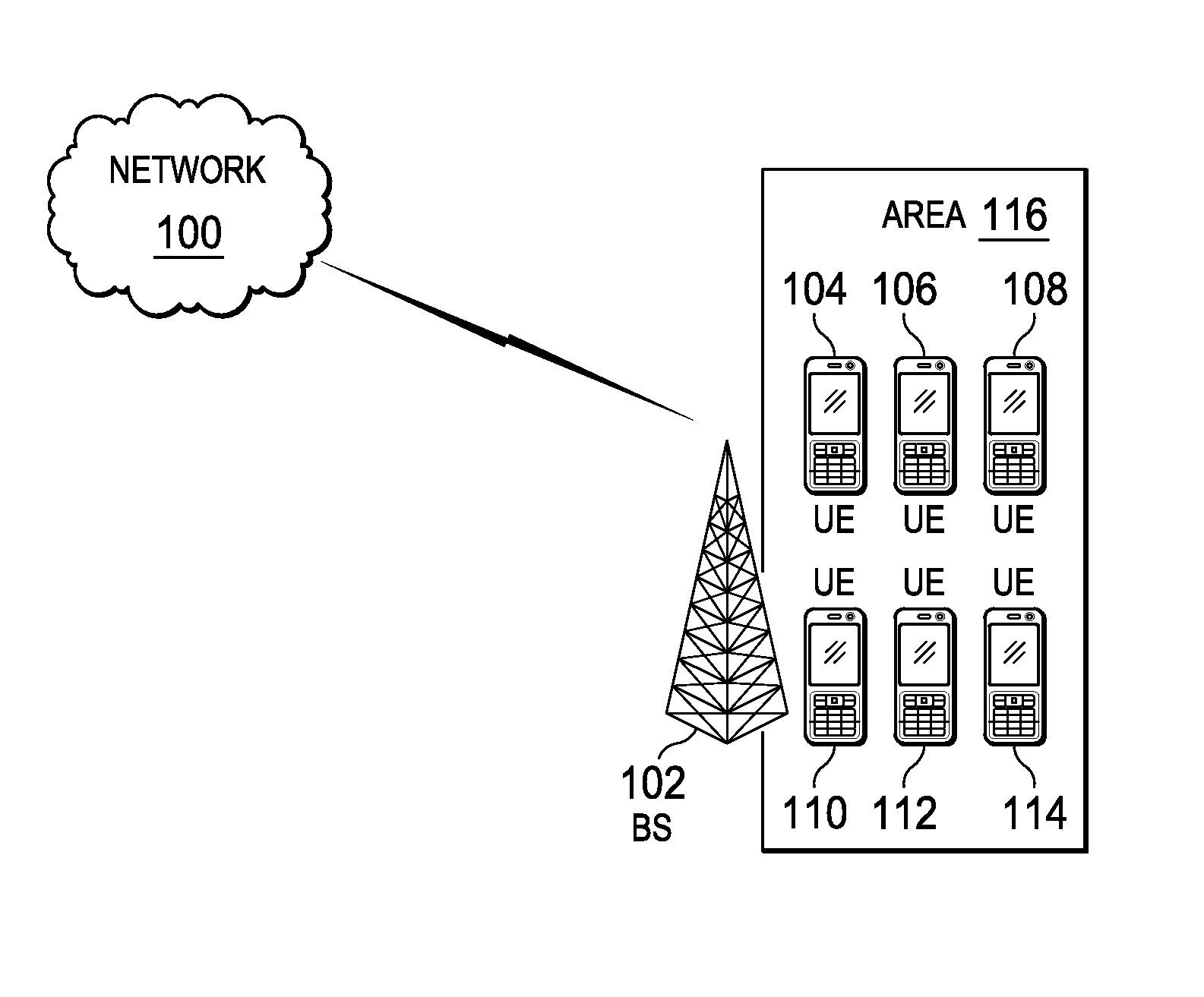
System and Method for Uplink Grant-Free Transmission Scheme
ActiveUS20140254544A1Transmission path divisionReceiver specific arrangementsTime frequency domainUser equipment
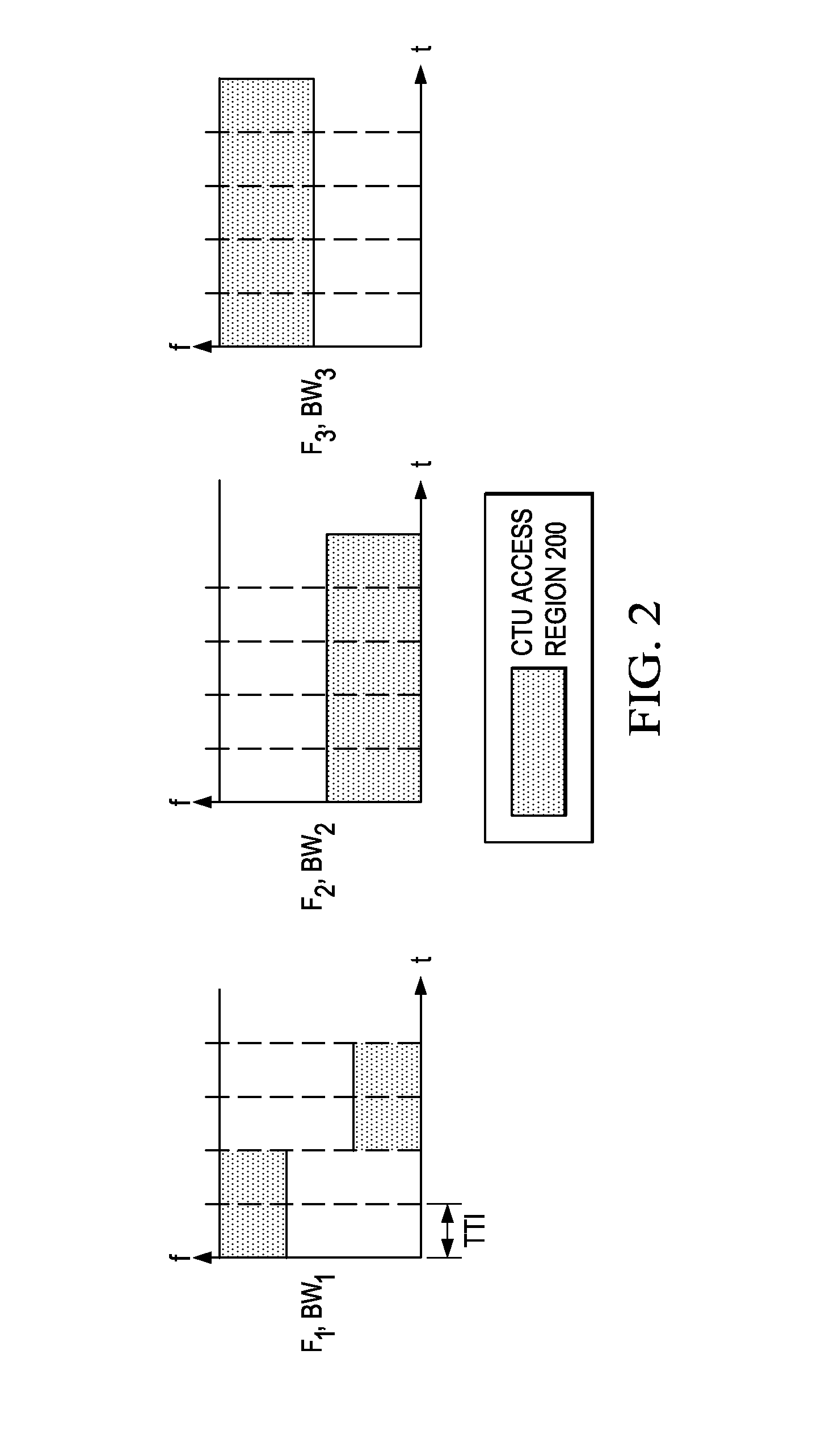
A method embodiment includes implementing, by a base station (BS), a grant-free uplink transmission scheme. The grant-free uplink transmission scheme defines a first contention transmission unit (CTU) access region in a time-frequency domain, defines a plurality of CTUs, defines a default CTU mapping scheme by mapping at least some of the plurality of CTUs to the first CTU access region, and defines a default user equipment (UE) mapping scheme by defining rules for mapping a plurality of UEs to the plurality of CTUs.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
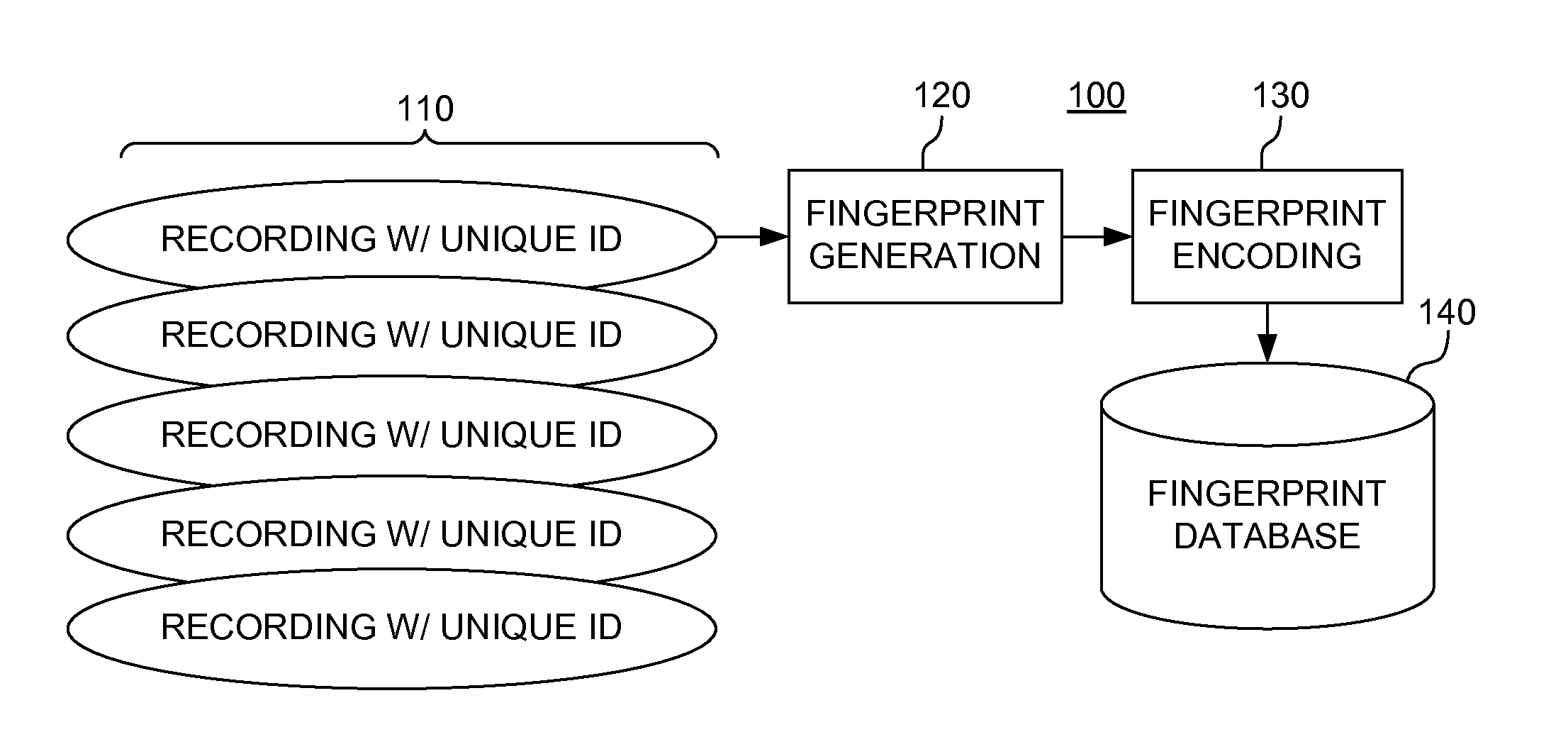
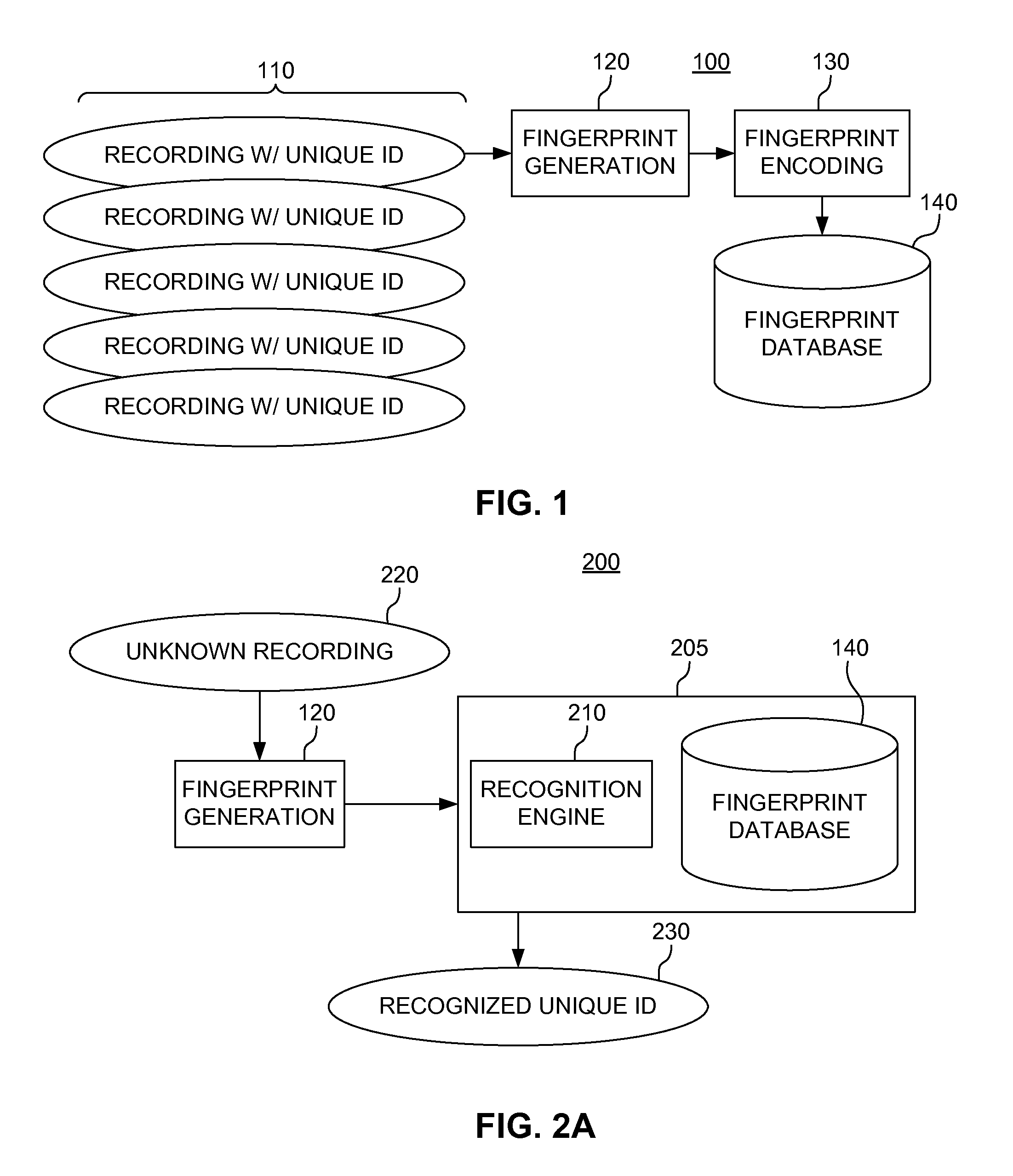
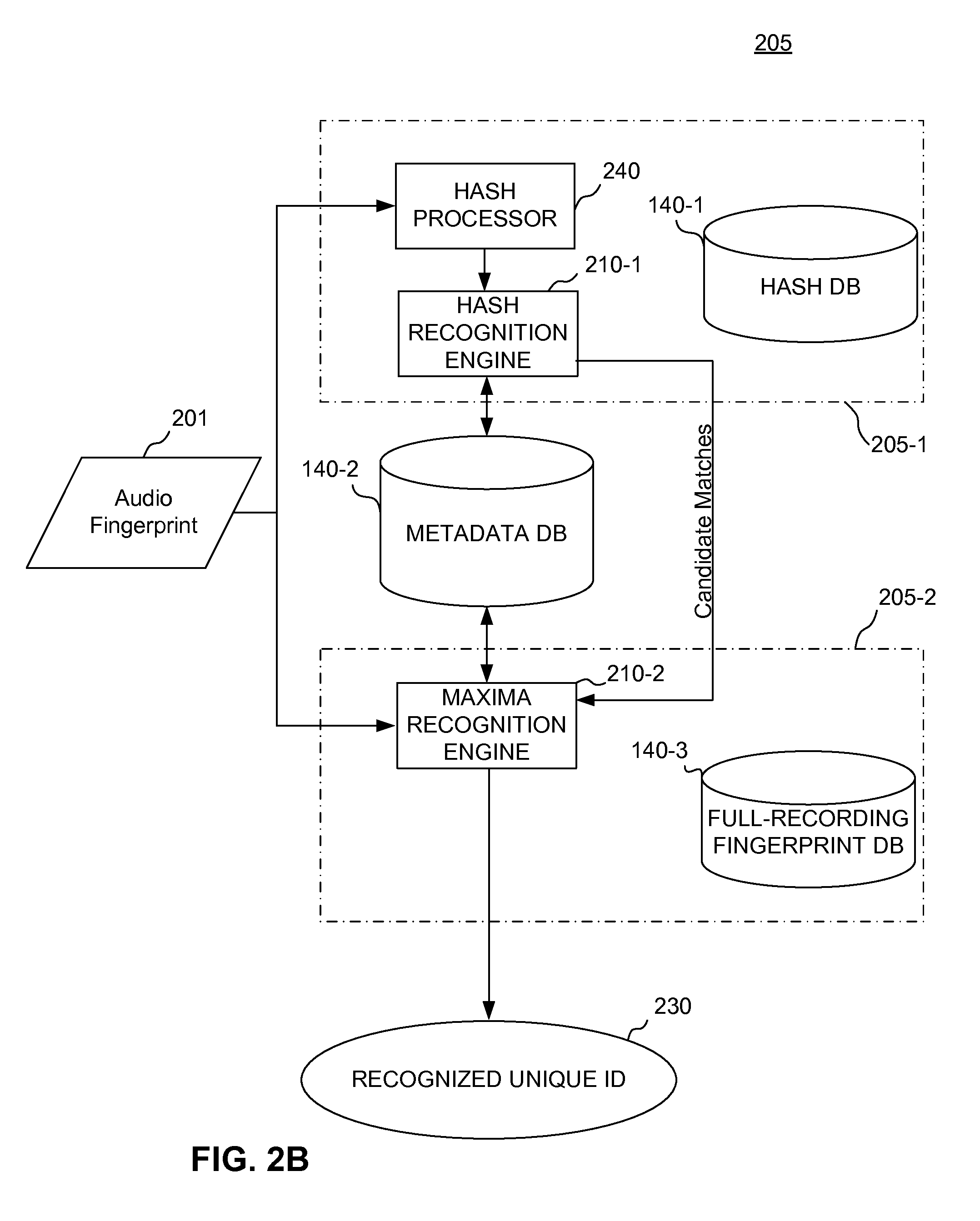
Rolling audio recognition
ActiveUS20110173208A1Fast constructionDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwareAudio recognition
An audio fingerprint is generated by transforming an audio sample of a recording to a time-frequency domain and storing each time-frequency pair in a matrix array, detecting a plurality of local maxima for a predetermined number of time slices, selecting a predetermined number of largest-magnitude maxima from the plurality of local maxima detected by said detecting, and generating one or more hash values corresponding to the predetermined number of largest-magnitude maxima.
Owner:ROVI TECH CORP
Brain wave analysis method
InactiveCN101690659AReal-time evaluationTargetedSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringSupport vector machineFeature extraction
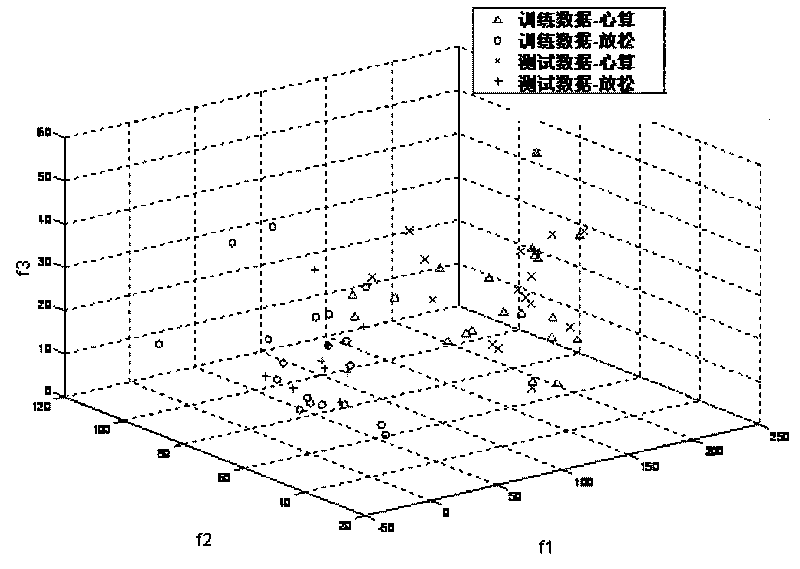
The invention provides a brain wave analysis method. The method uses classical time-frequency domain analysis and principal component analysis methods to solve the problem of electroencephalographic feature extraction, successfully extracts time-frequency domain parameters closely related to the tension, fatigue and relaxation of human bodies, maps the time-frequency domain parameters into principal component space, and uses a support vector machine to efficiently analyze non-linear relation in the principal component space so as to improve the accuracy and validity of interpretation.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Ack/nack transmission on pucch in lte-atdd with nxpdcch structure
InactiveUS20110141878A1Maximum transmissionImprove reliabilityFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsBundle methodTime domain
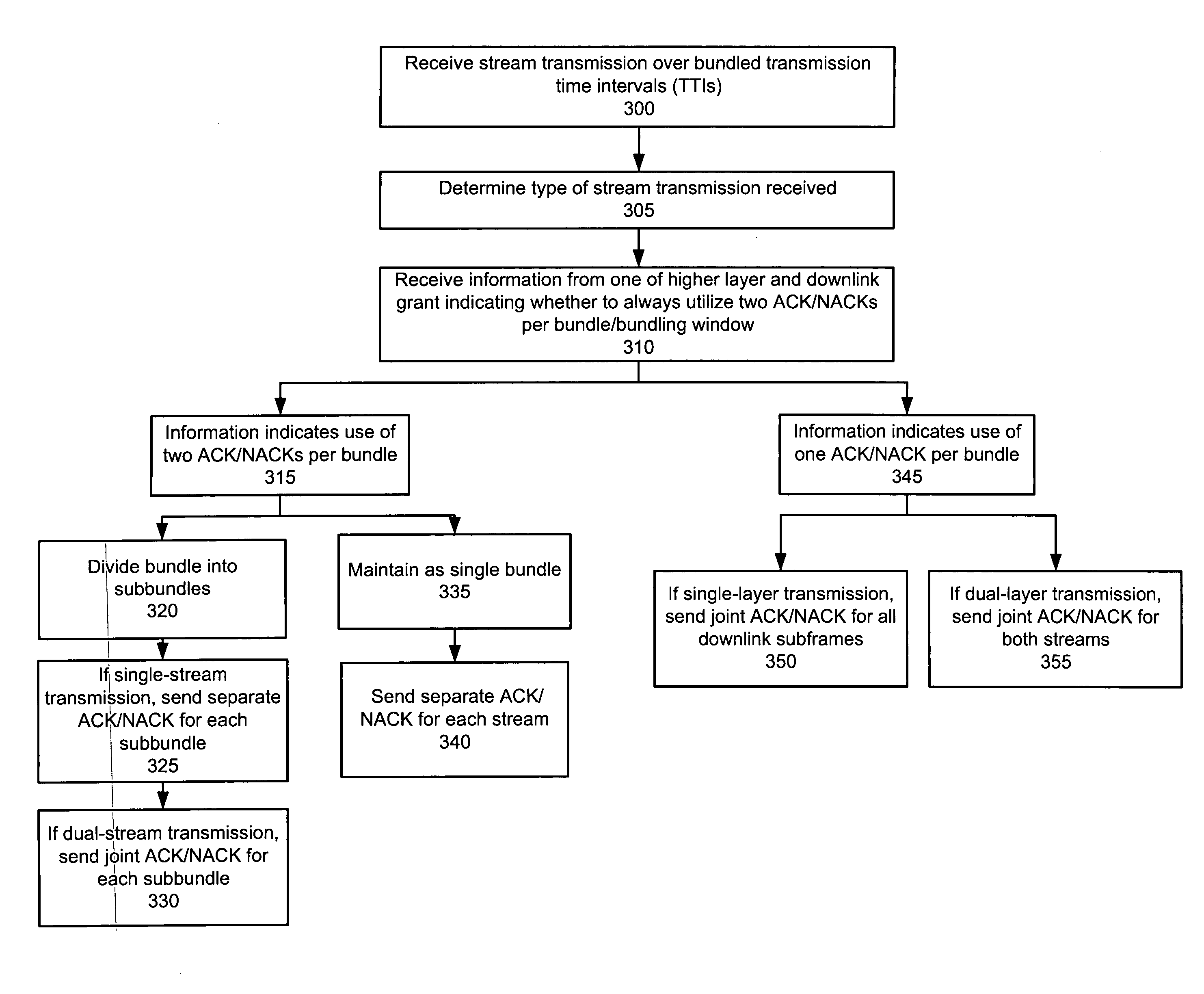
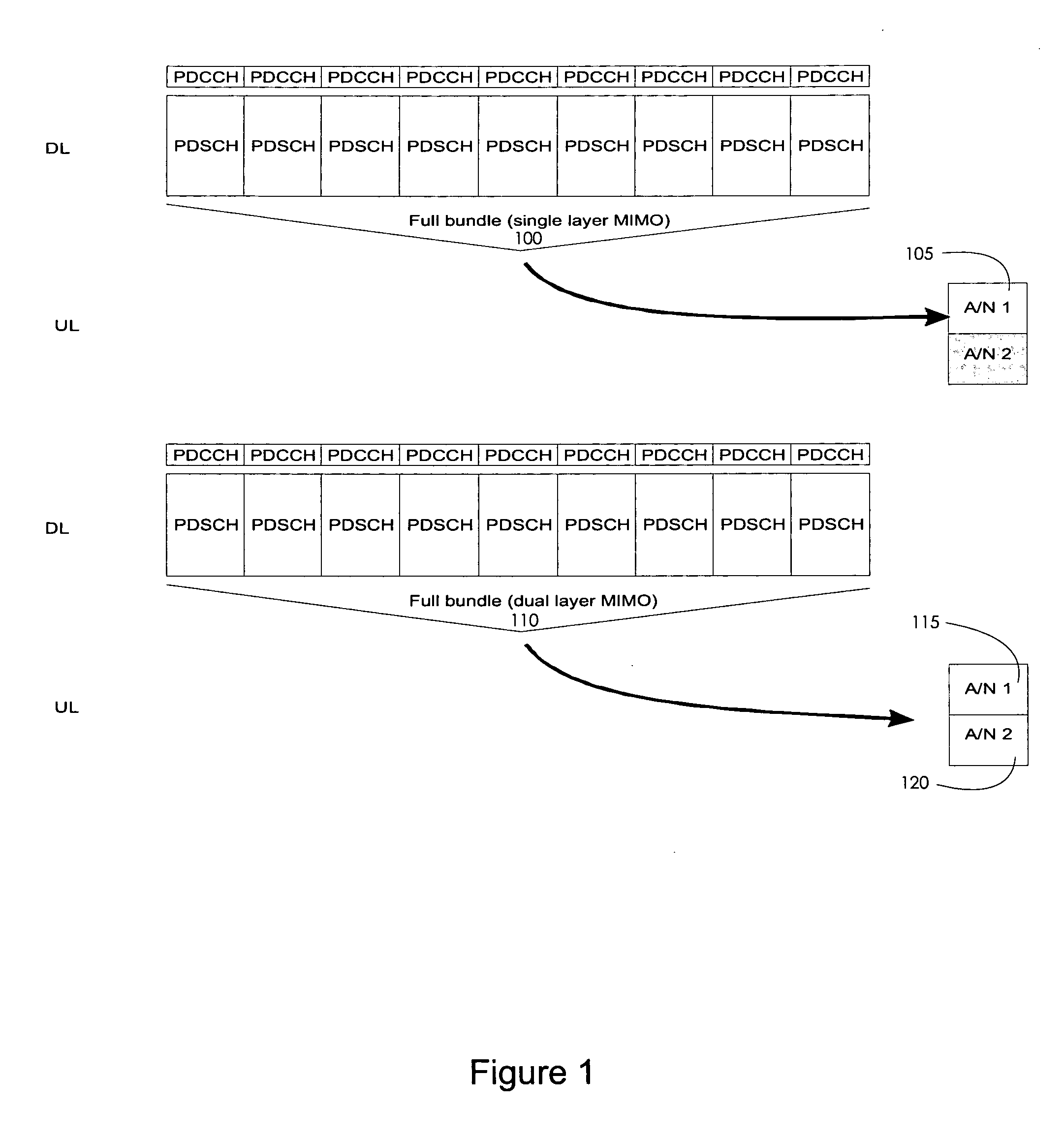
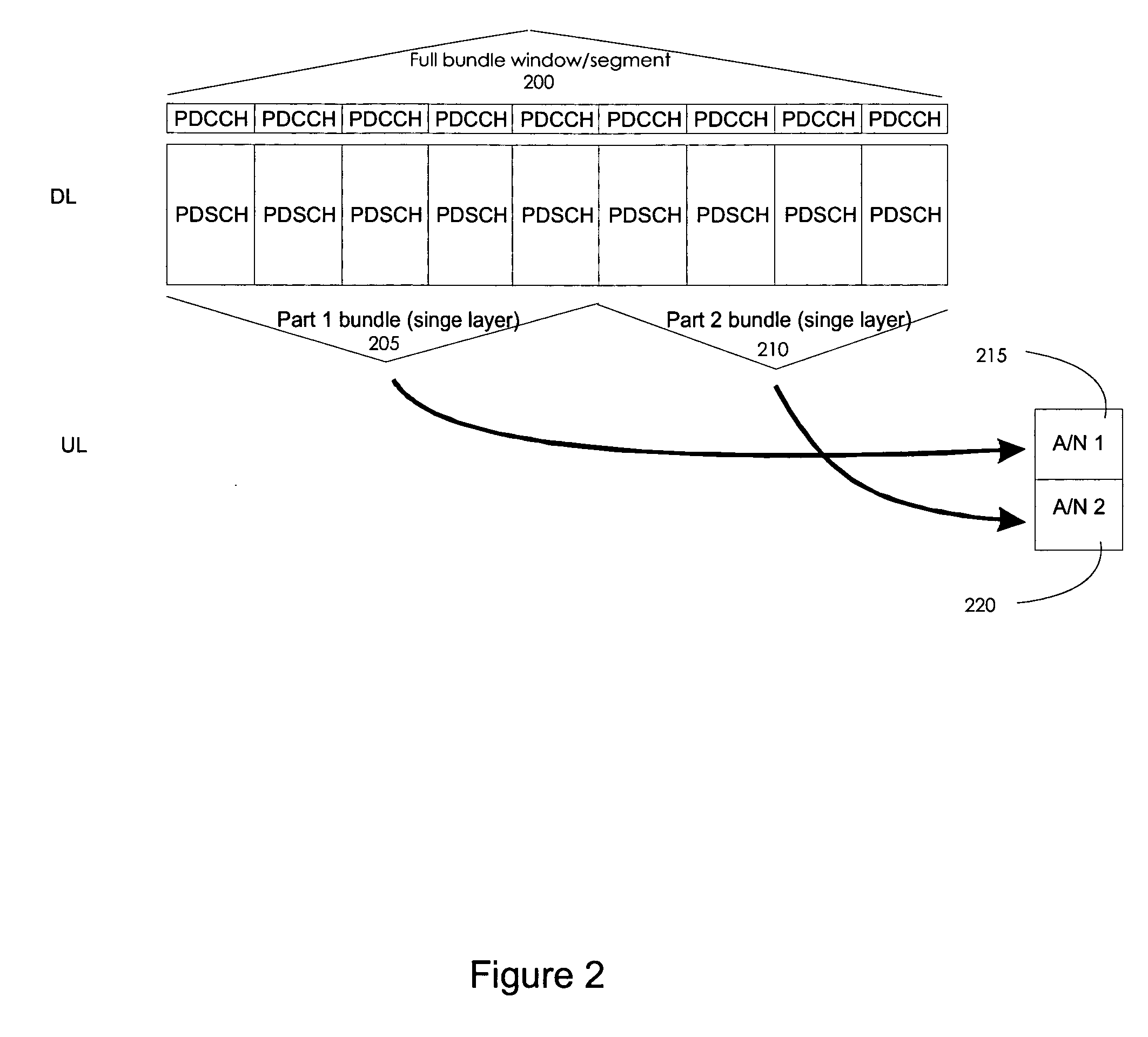
Systems and methods are provided for enabling different “bundling” methods for downlink transmissions and provide different interpretations of the acknowledgement / negative-acknowledgement bit. A user equipment is configured so that it commonly acknowledges all downlink transmission time intervals within a bundle so that if one packet is determined to be erroneous, all packets in that bundle will be retransmitted. Additionally, the systems and methods are implemented by allowing an interpretation to be applied to the uplink acknowledgement / negative-acknowledgement field such that the user equipment is able to divide bundled downlink packets into smaller windows in Long Term Evolution (LTE) Release 8 time division duplex (TDD) mode. In LTE Advanced (LTE-A) TDD mode, various embodiments provide bundling within the time domain, within the frequency domain, and within a hybrid time-frequency domain. Furthermore, enhanced channel selection methods are also provided in support of the above-mentioned bundling methods in accordance with various embodiments.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
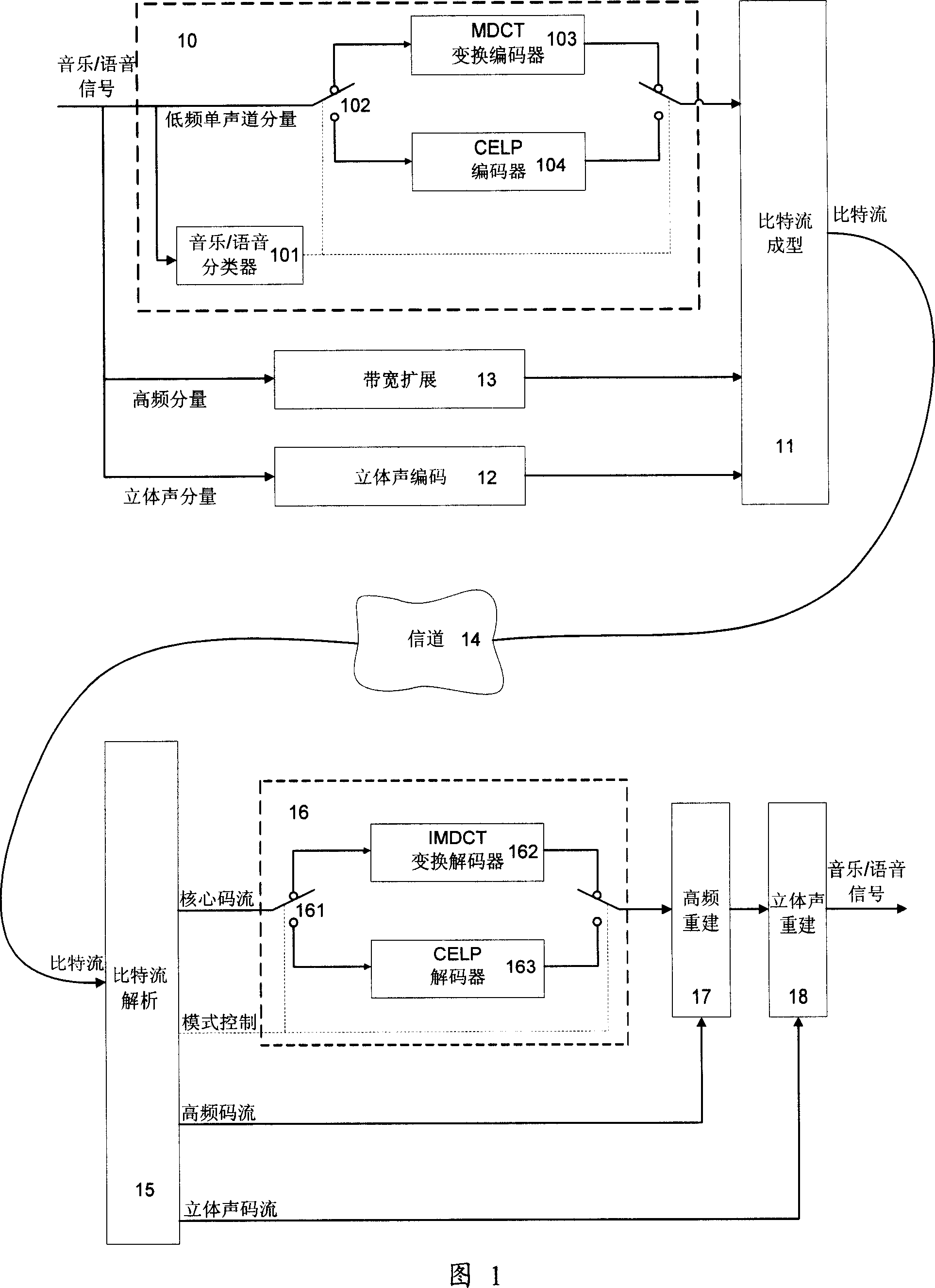
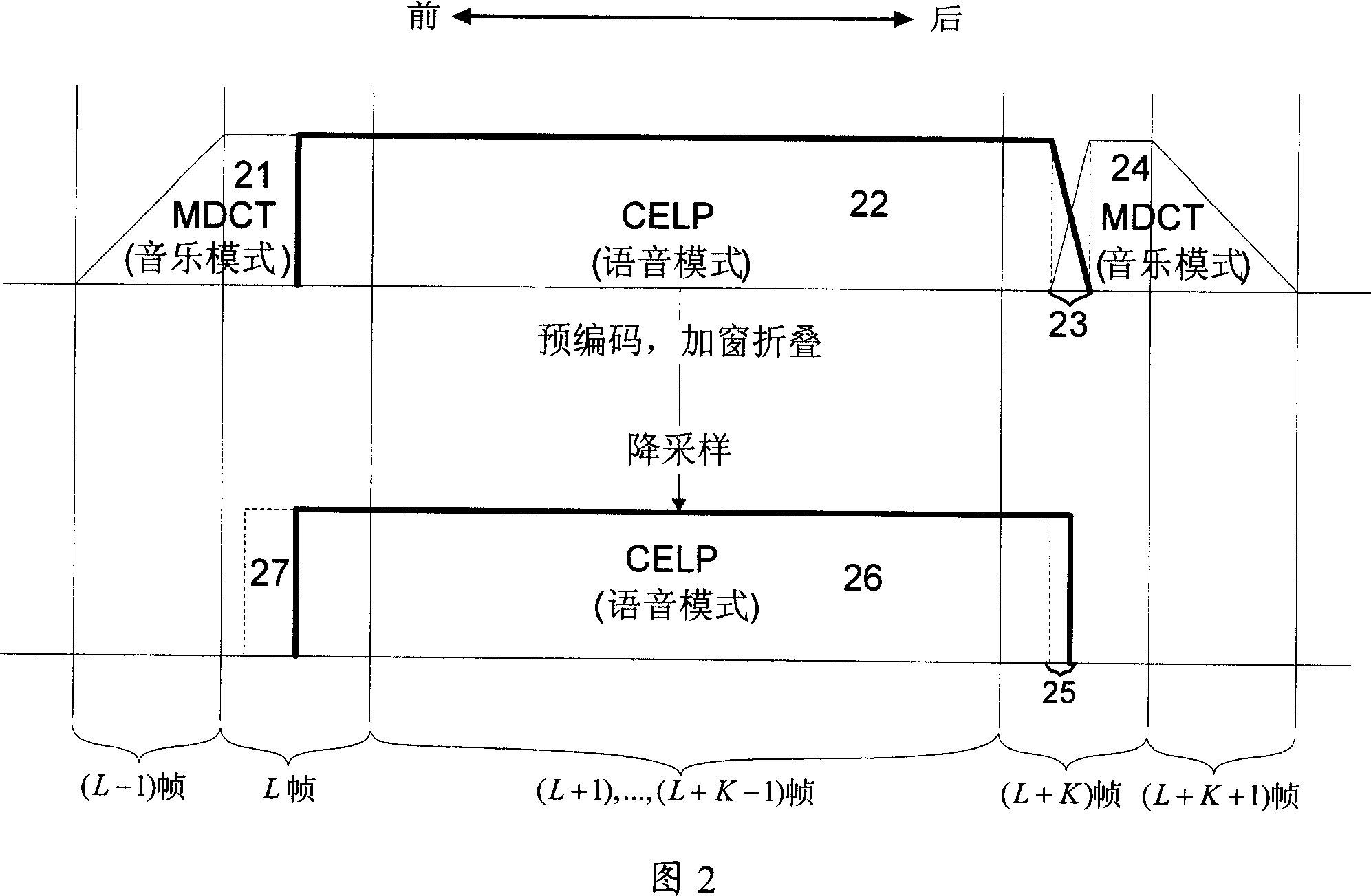
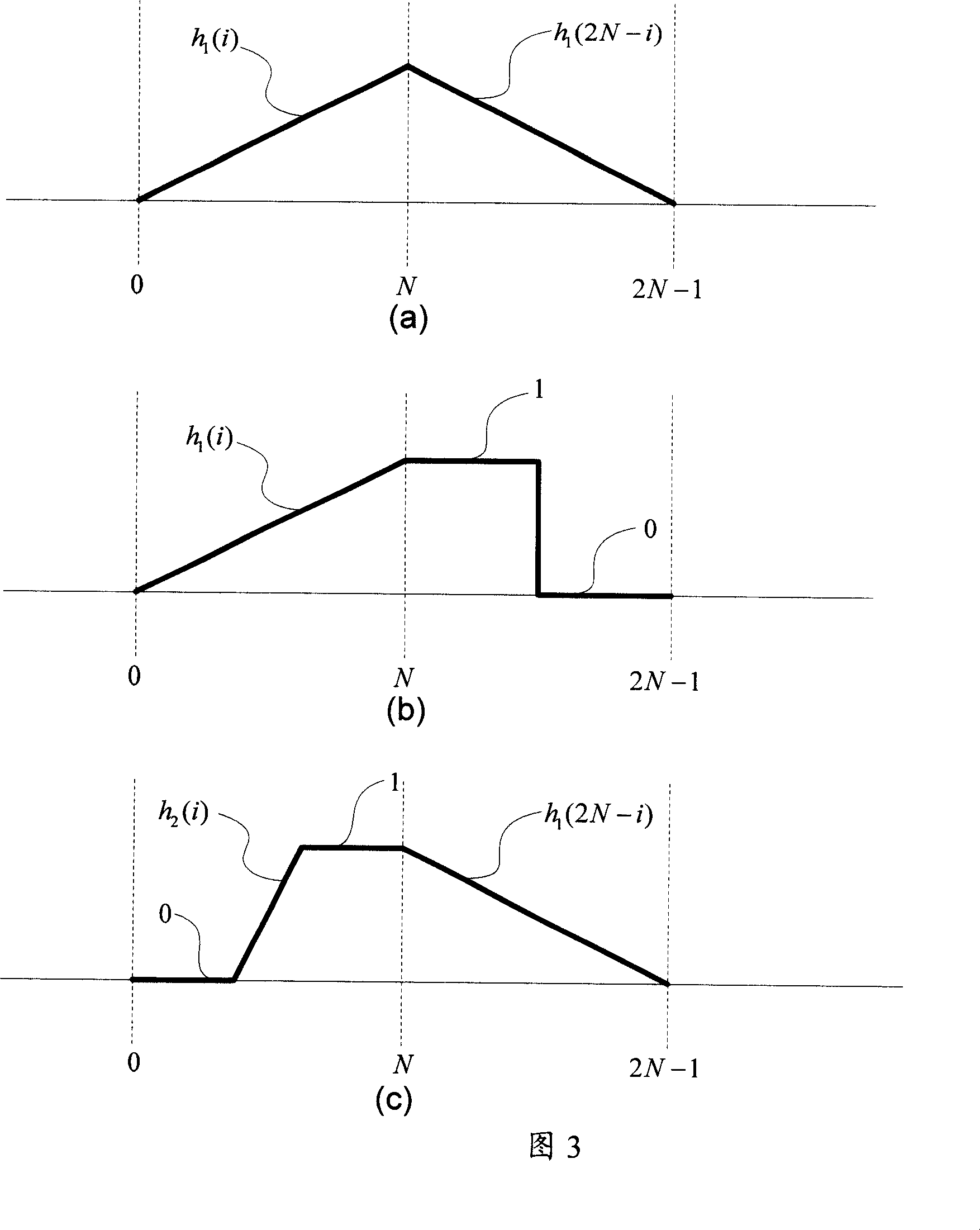
Voice/music dual-mode coding-decoding seamless switching method
InactiveCN101025918ASmooth transitionEfficient switchingSpeech analysisRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTime domainTelecommunications
The invention relates to a seamless switching method for voice / music dual-mode en-decoding. When a dual-mode en-decoder switches from CELP voice mode to MDCT music mode, the audio signal-rear of the final CELP frame in the time domain before switching adopts window-adding and folding process, and the overlapping nature of MDCT transforming ensures the continuity of switching. When a dual-mode en-decoder switches from MDCT music mode to CELP voice mode, the final MDCT frame before switching adopts a new window type in order to ensure there is no overlapping time domain with the first CELP frame, and the pre-coding technology ensures the continuity of switching.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
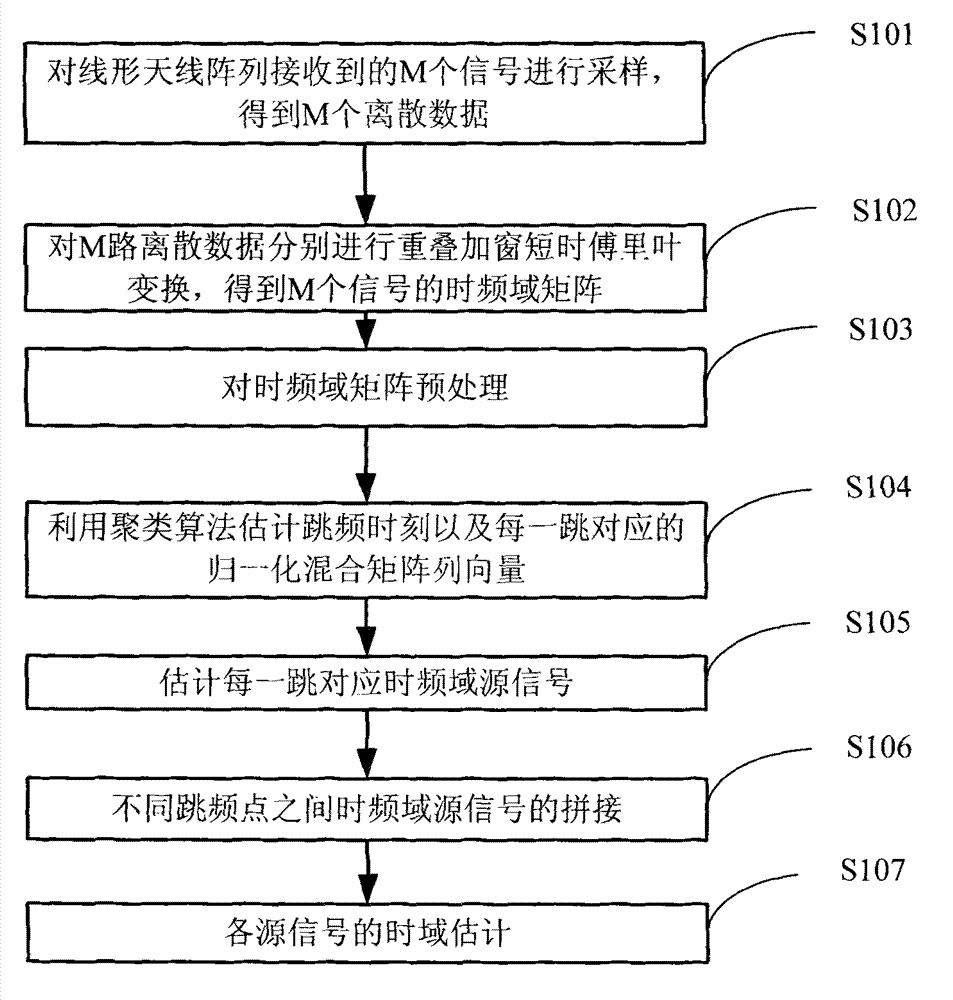
Clustering-based blind source separation method for synchronous orthogonal frequency hopping signals
InactiveCN103051367ASmall amount of calculationEasy to implementSpatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainDiscrete time domain
The invention discloses a clustering-based blind source separation method for synchronous orthogonal frequency hopping signals. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring M sampled paths of discrete time-domain mixed signals; obtaining M time-frequency domain matrixes of the mixed signals; preprocessing the time-frequency domain matrixes of the frequency hopping mixed signals; estimating frequency hopping moments, normalized mixed matrix column vectors and frequency hopping frequency; estimating time-frequency domain frequency hopping source signals by utilizing the estimated normalized mixed matrix column vectors; splicing the time-frequency domain frequency hopping source signals between different frequency hopping points; and recovering time-domain source signals according to time-frequency domain estimate values of the source signals. According to the method, the frequency hopping source signals are estimated only according to the received mixed signals of a plurality of frequency hopping signals under the condition of unknown channel information, and the frequency hopping signals can be subjected to blind estimation under the condition that the number of receiving antennae is smaller than that of the source signals; short-time Fourier transform is utilized, so that the method is low in computation amount; and the frequency hopping signals are subjected to blind separation, and meanwhile, a part of parameters can also be estimated, so that the method is high in practicability.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
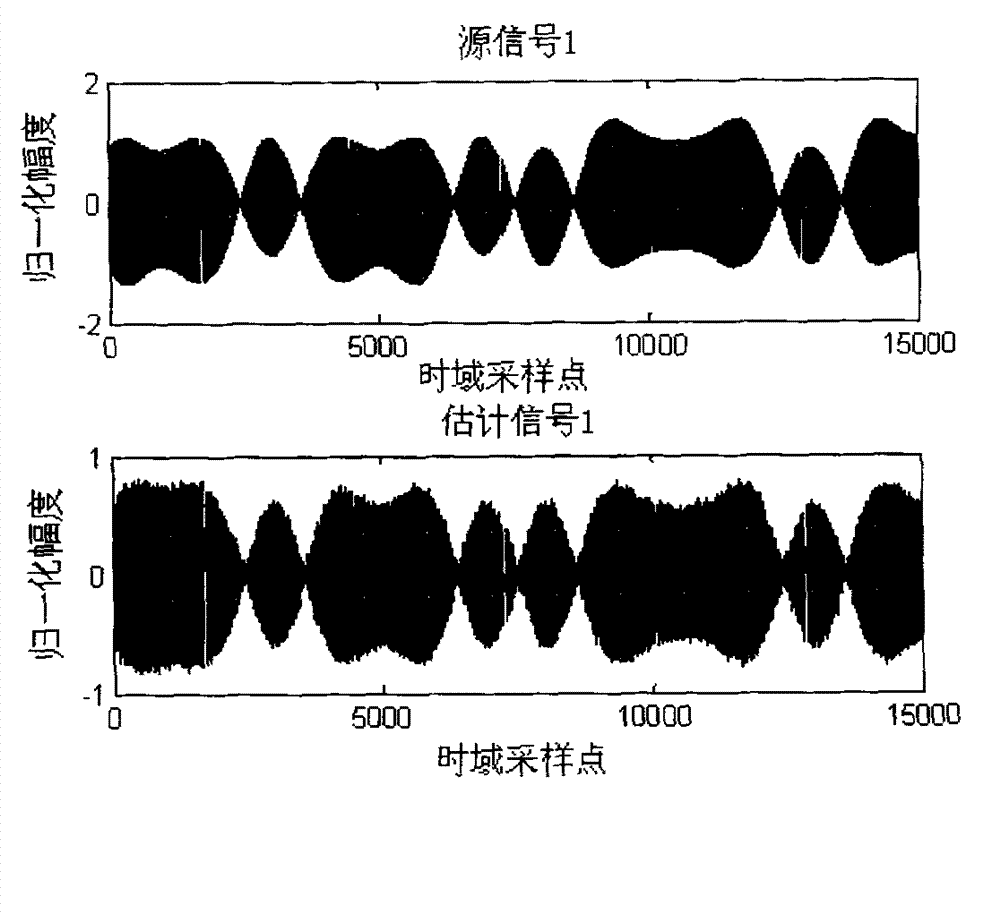
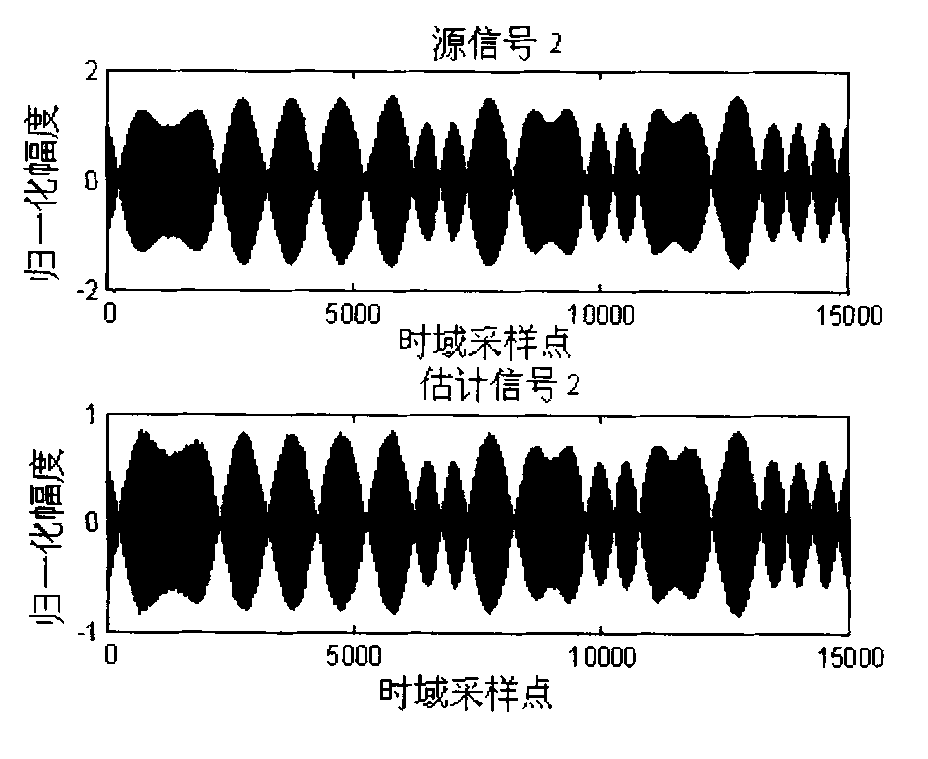
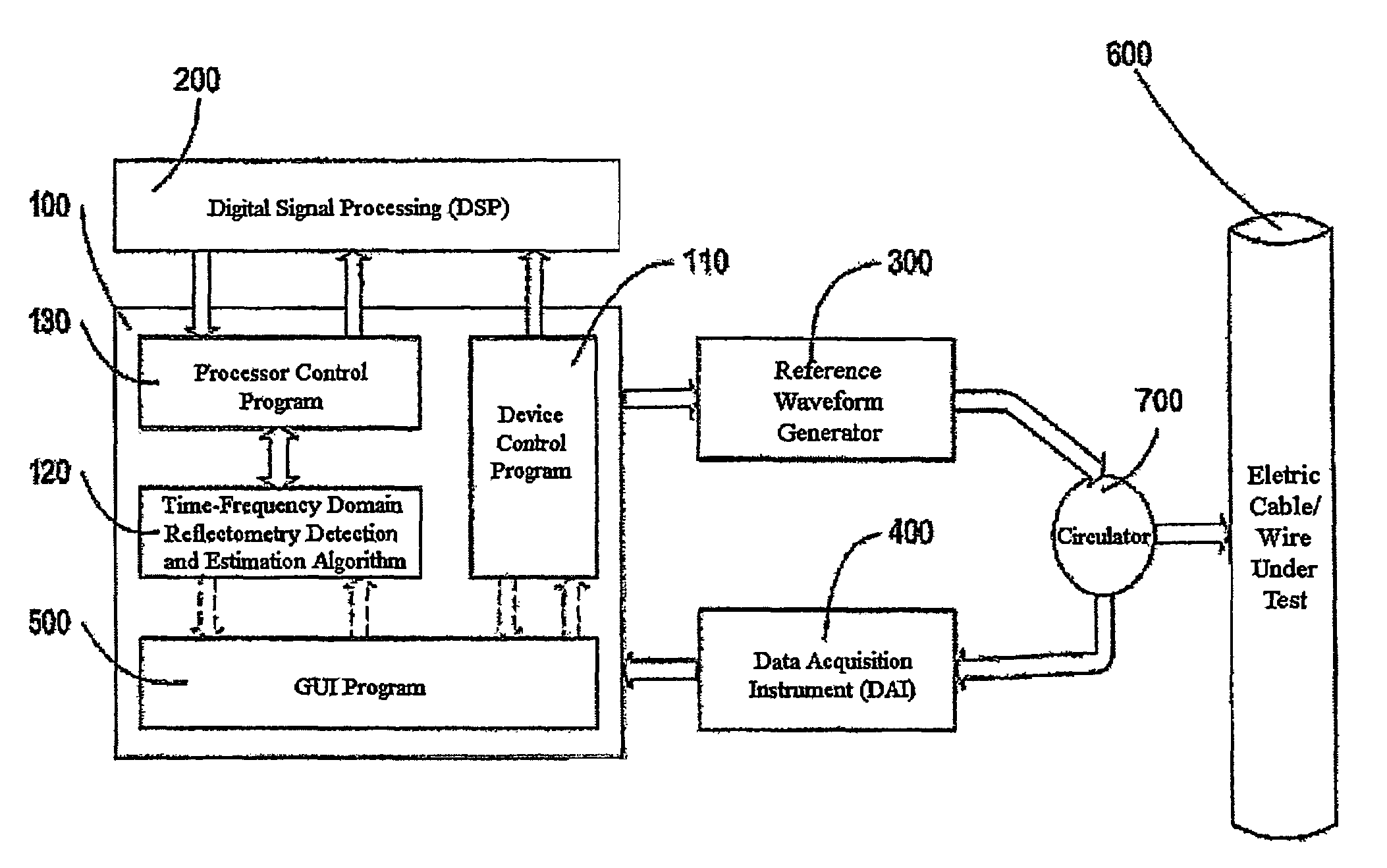
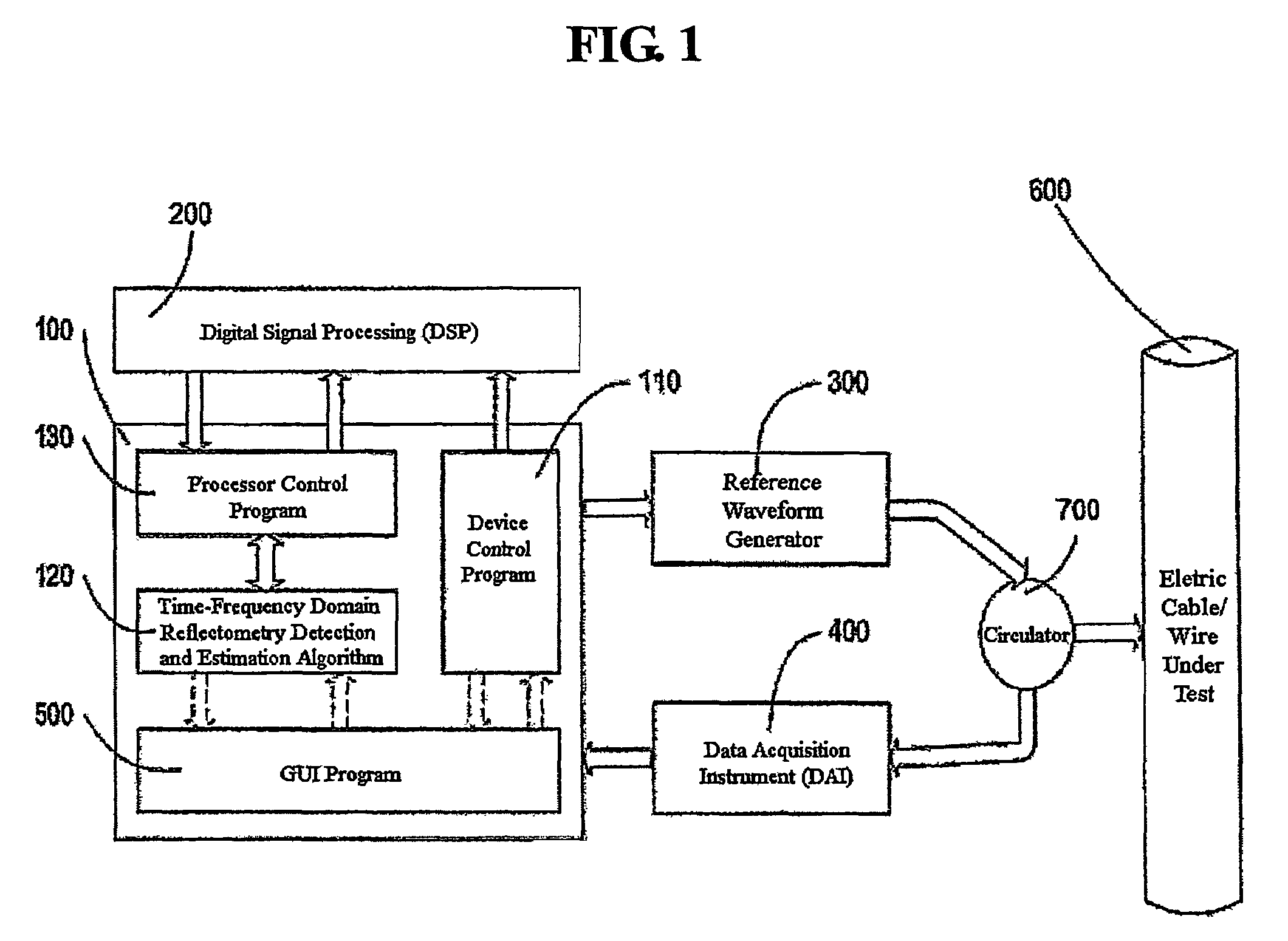
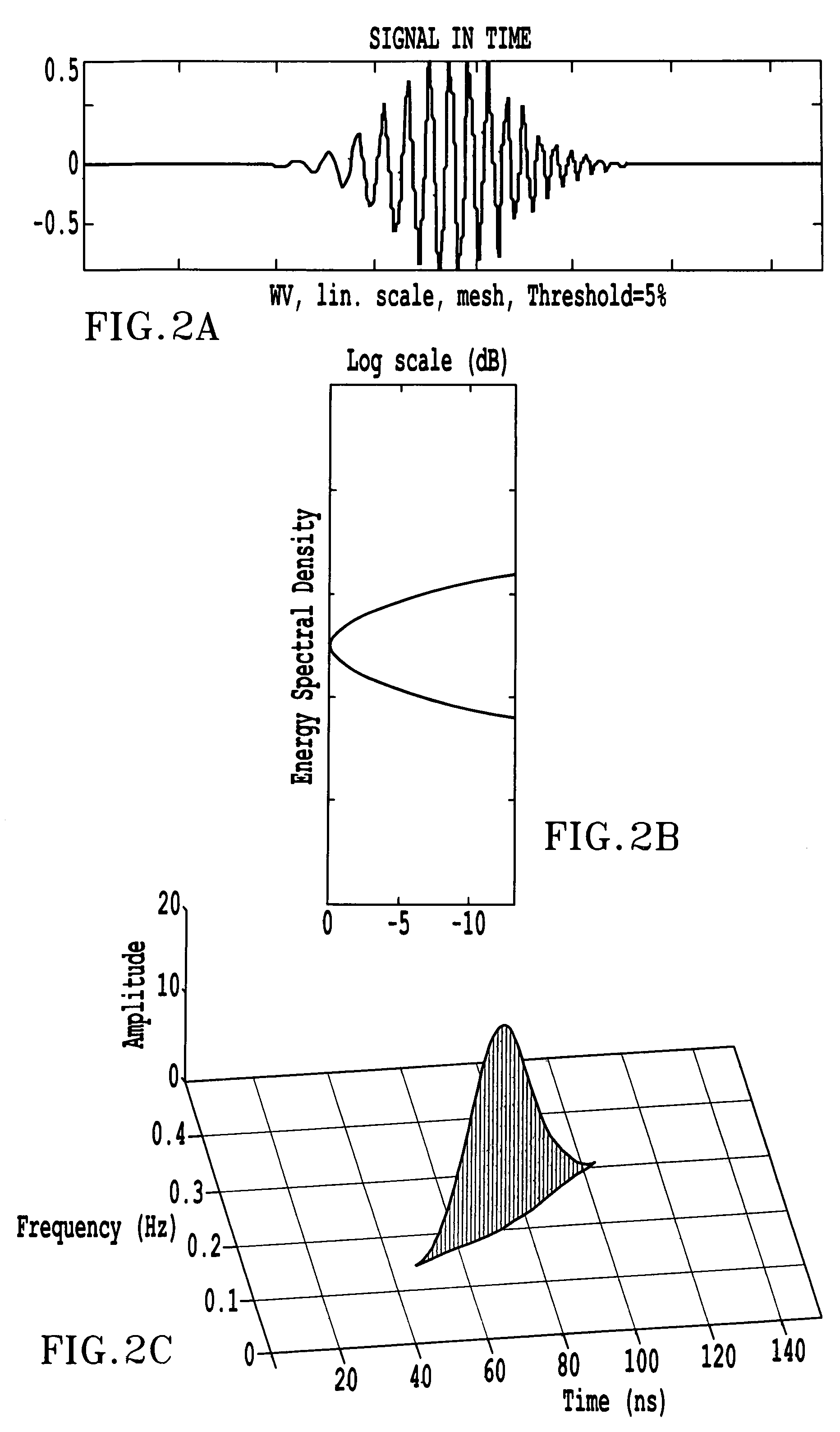
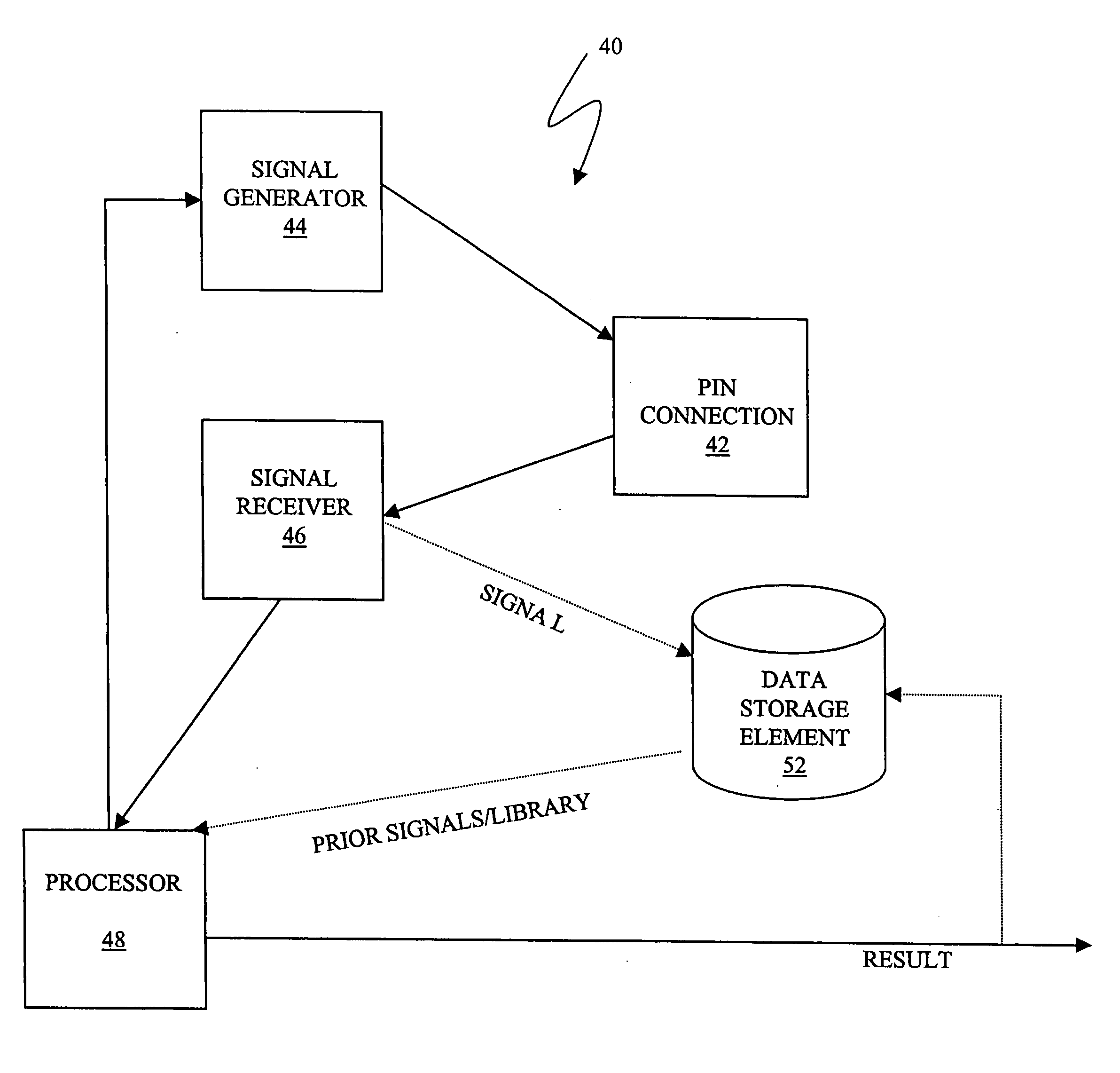
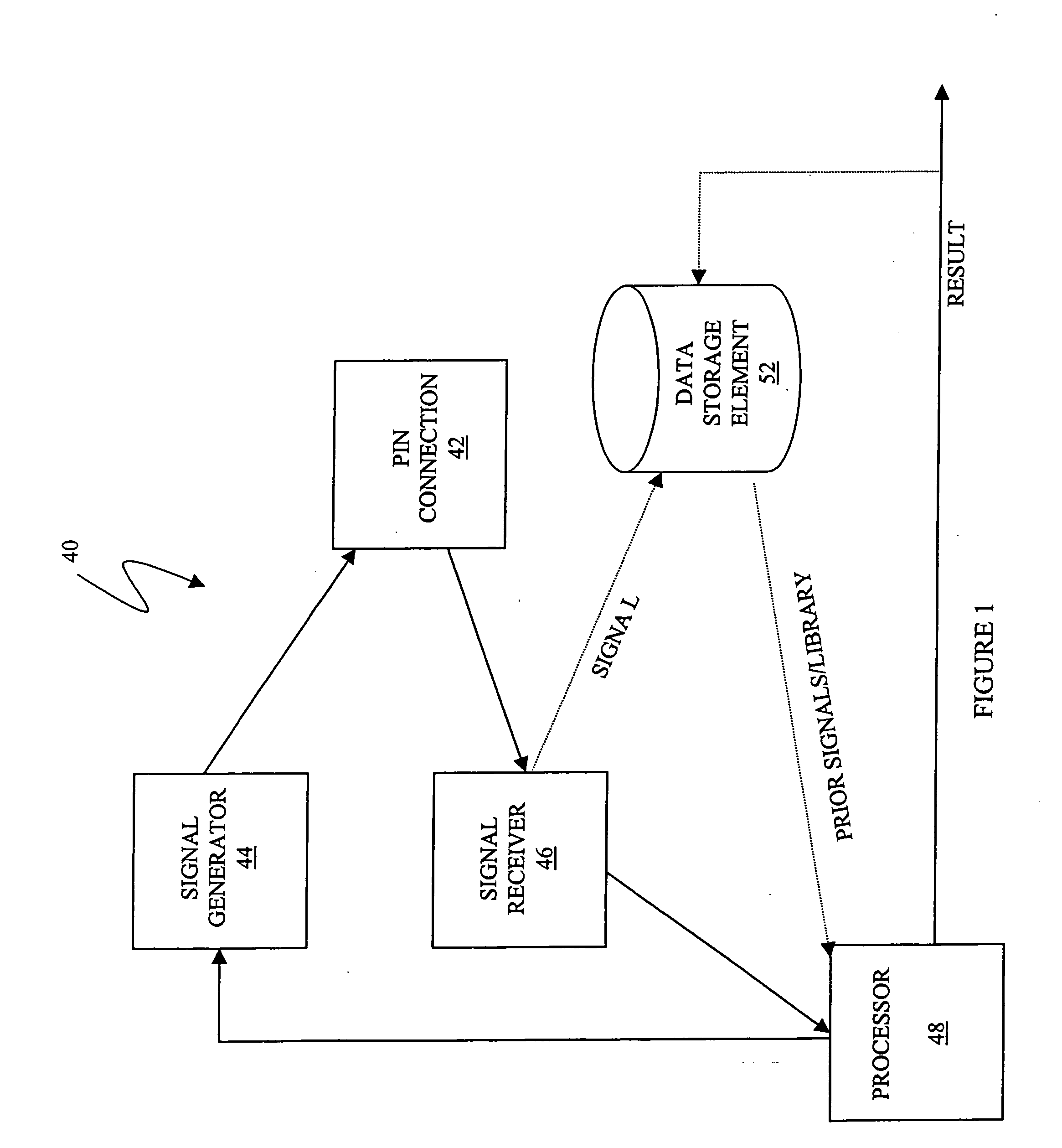
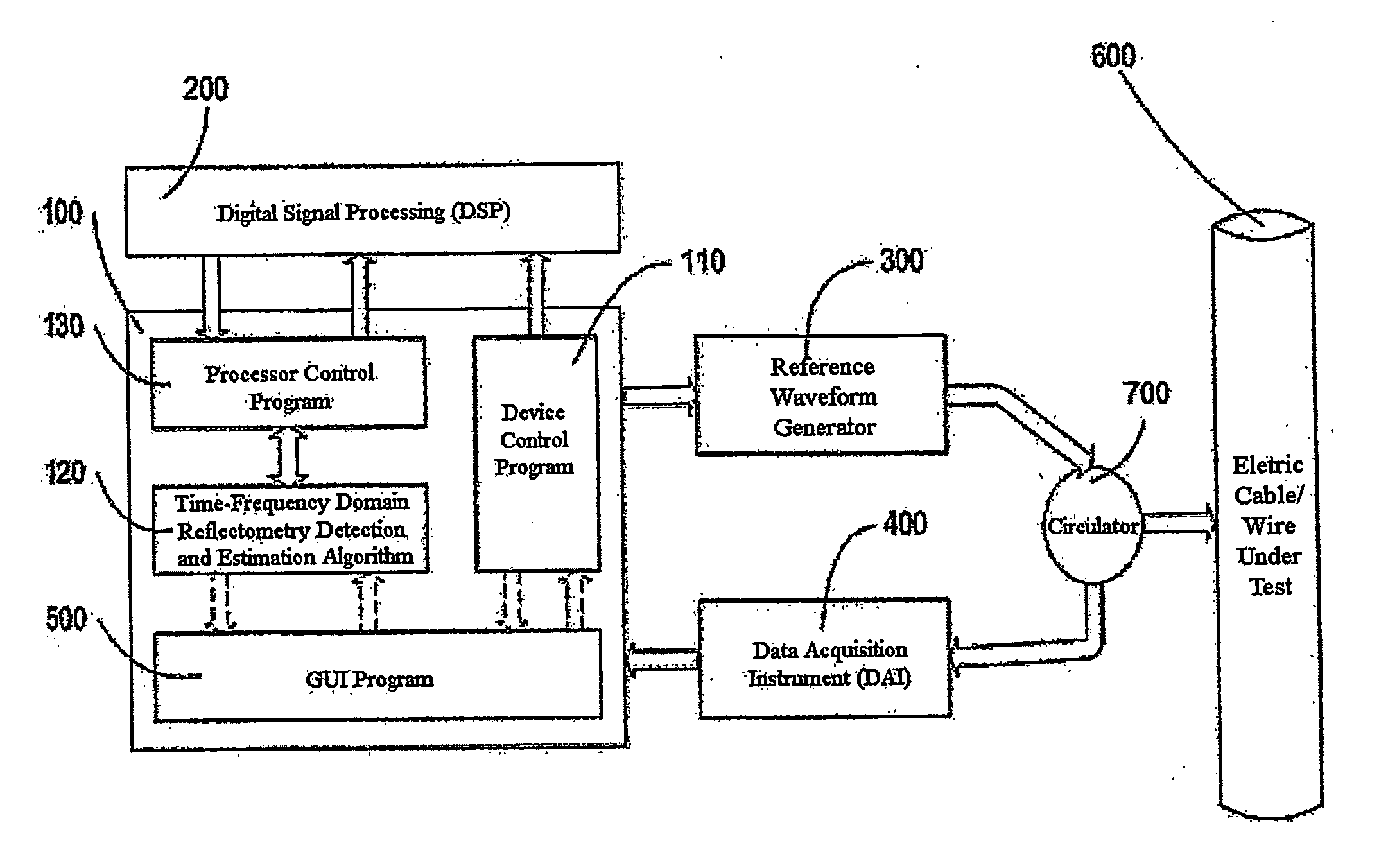
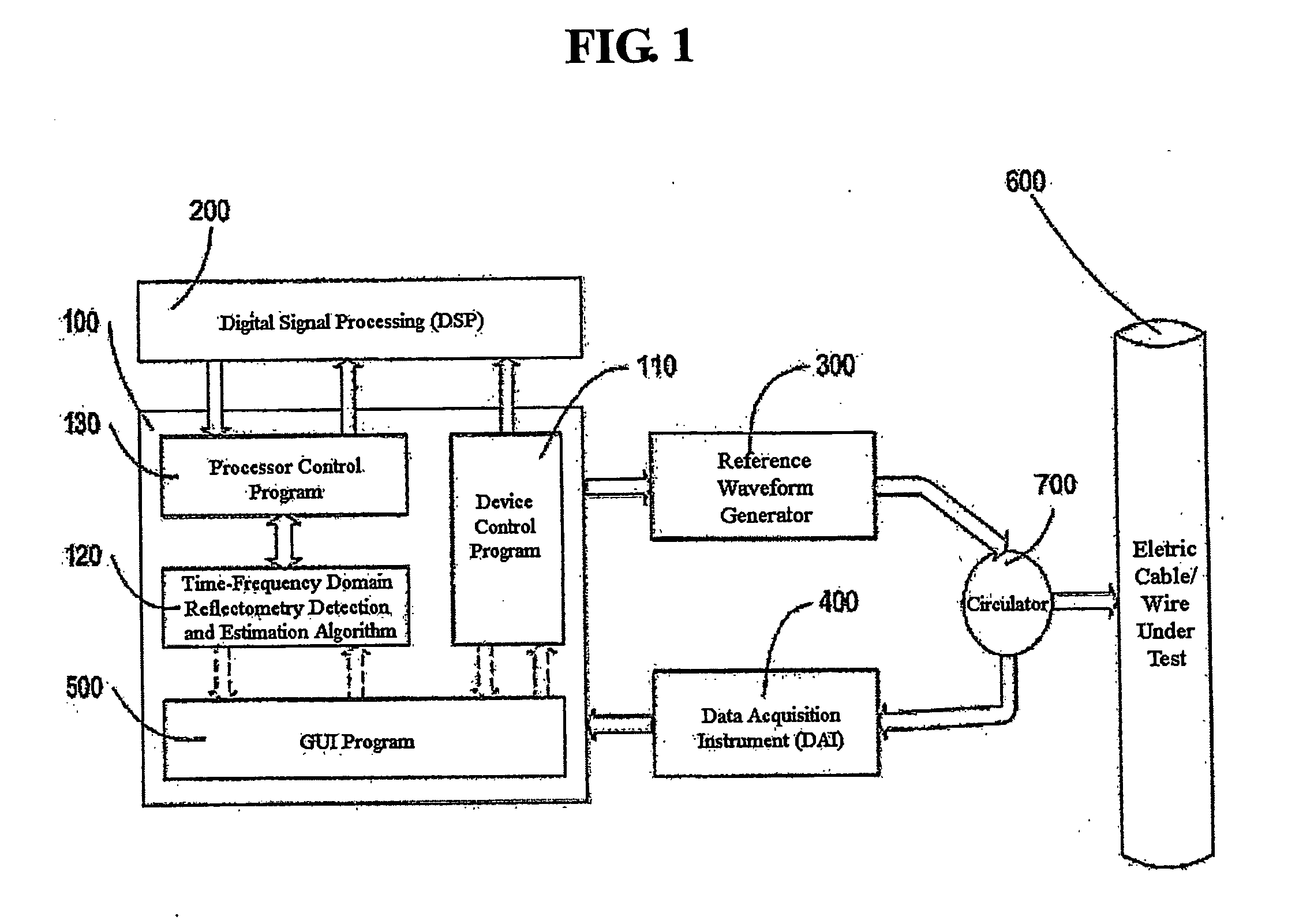
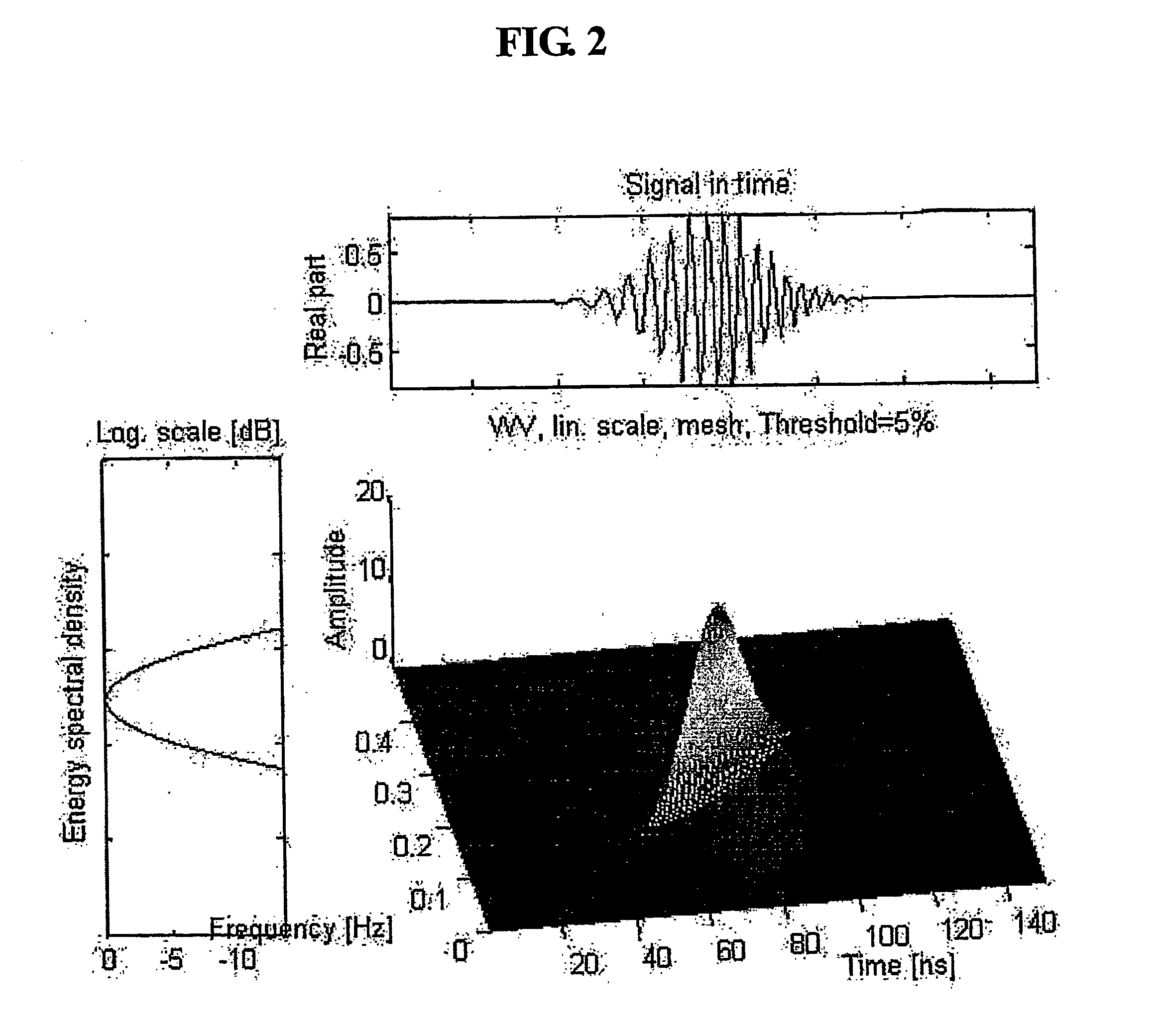
Time-frequency domain reflectometry apparatus and method
InactiveUS7337079B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceFault location by pulse reflection methodsMeasurement deviceTime delays
An apparatus and method for high-resolution reflectometry that operates simultaneously in both the time and frequency domains, utilizing time-frequency signal analysis and a chirp signal multiplied by a Gaussian time envelope. The Gaussian envelope provides time localization, while the chirp allows one to excite the system under test with a swept sinewave covering a frequency band of interest. High resolution in detection of the reflected signal is provided by a time-frequency cross correlation function. The high-accuracy localization of faults in a wire / cable can be achieved by measurement of time delay offset obtained from the frequency offset of the reflected signal. The apparatus enables one to execute an automated diagnostic procedure of a wire / cable under test by control of peripheral devices.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
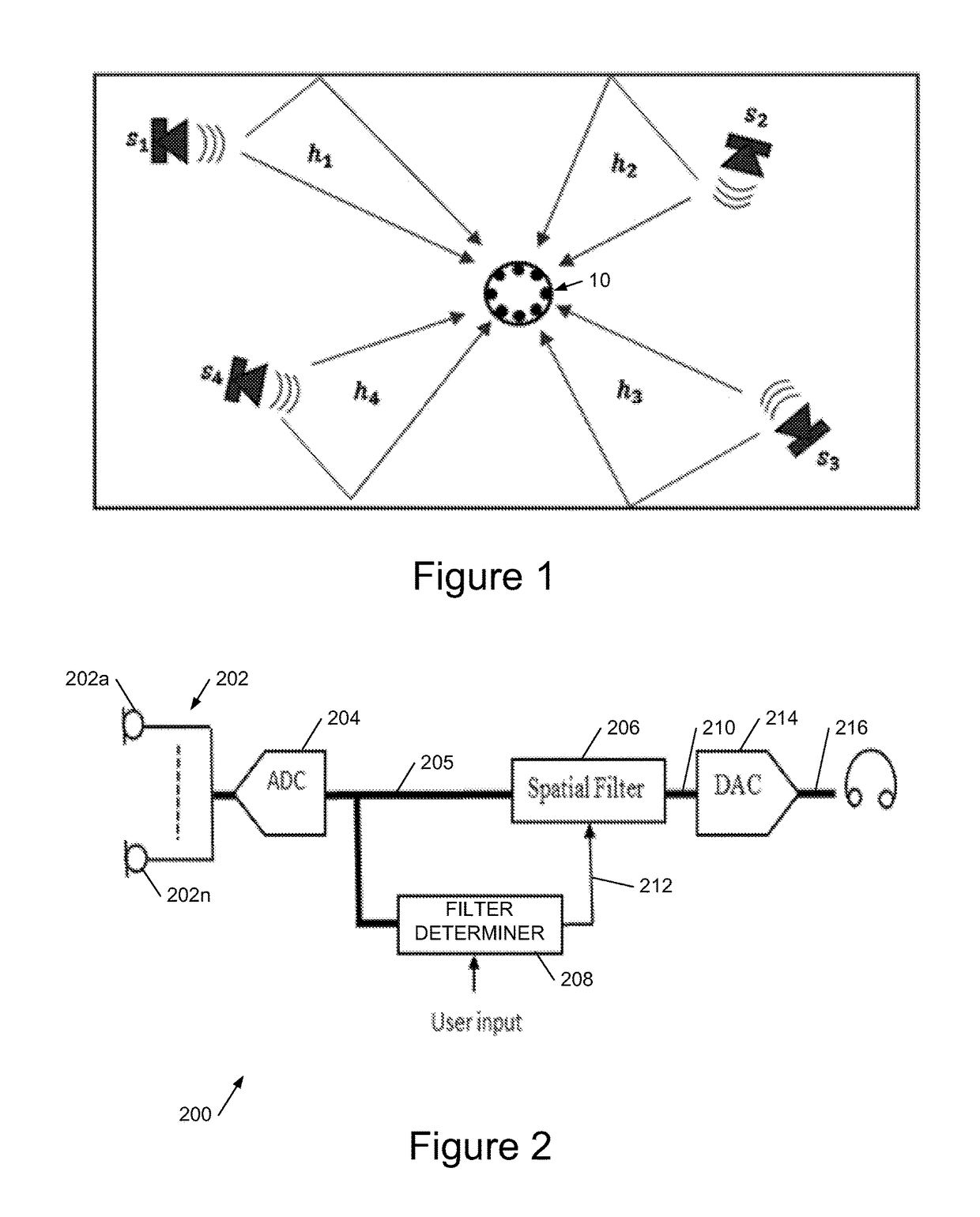
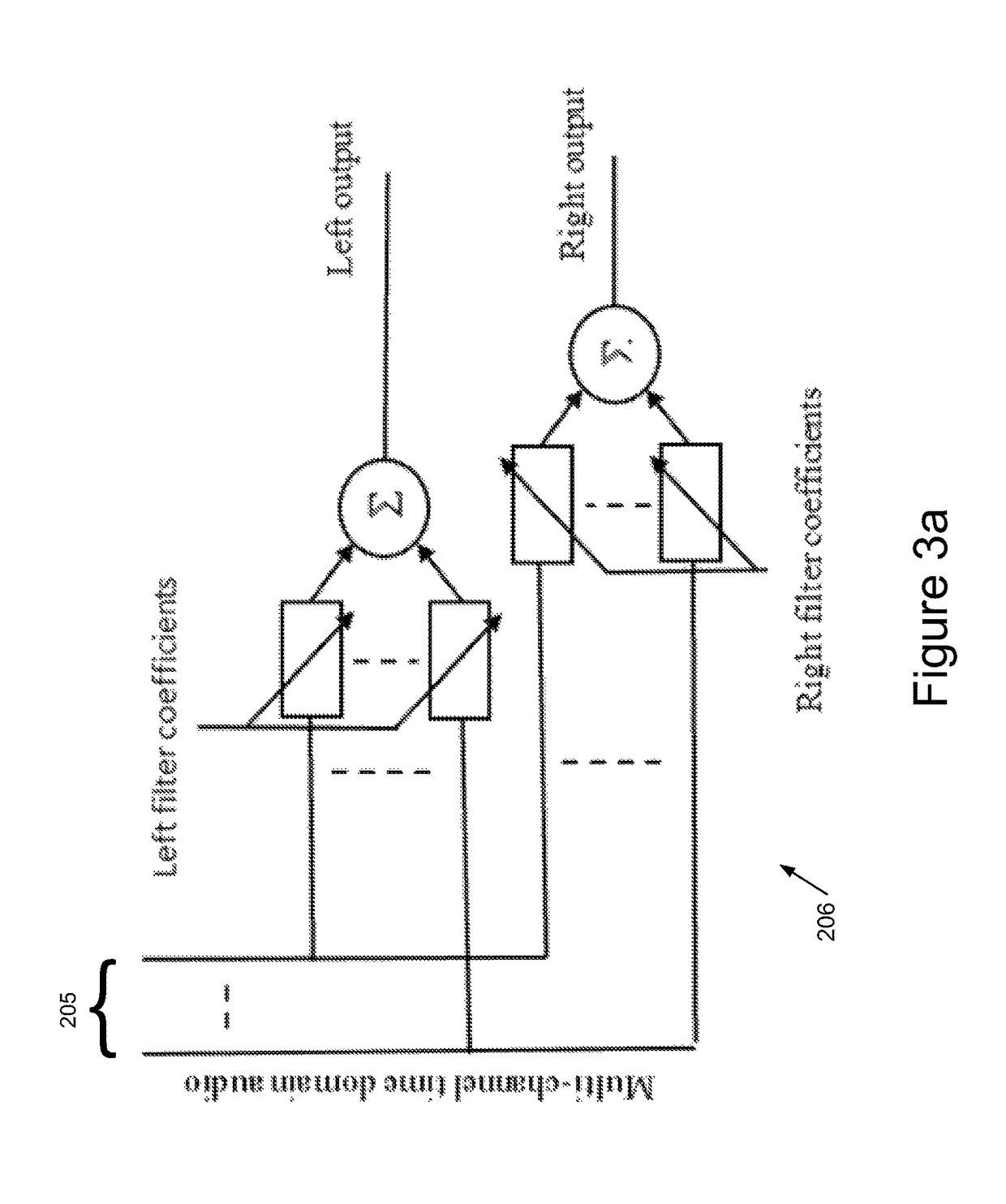
Blind source separation systems
ActiveUS9668066B1Cost for rotationSave spaceSignal processingSets with desired directivityFrequency spectrumHearing aid
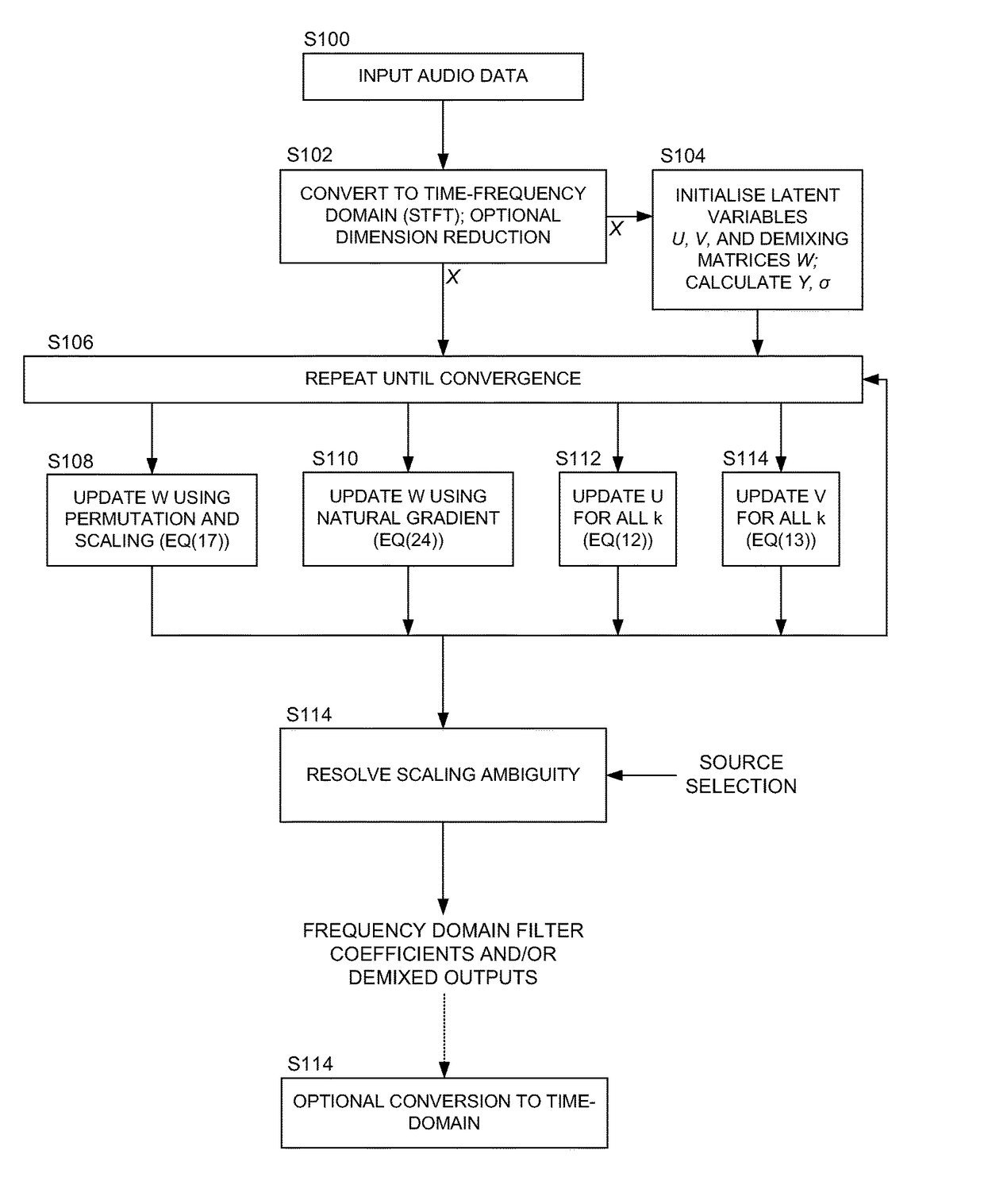
We describe a method of blind source separation for use, for example, in a listening or hearing aid. The method processes input data from multiple microphones each receiving a mixed signal from multiple audio sources, performing independent component analysis (ICA) on the data in the time-frequency domain based on an estimation of a spectrogram of each acoustic source. The spectrograms of the sources are determined from non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) models of each source, the NMF model representing time-frequency variations in the output of an acoustic source in the time-frequency domain. The NMF and ICA models are jointly optimized, thus automatically resolving an inter-frequency permutation ambiguity.
Owner:AUDIOTELLIGENCE LTD
Wire fault detection
InactiveUS20040230385A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsUltrasound attenuationEngineering
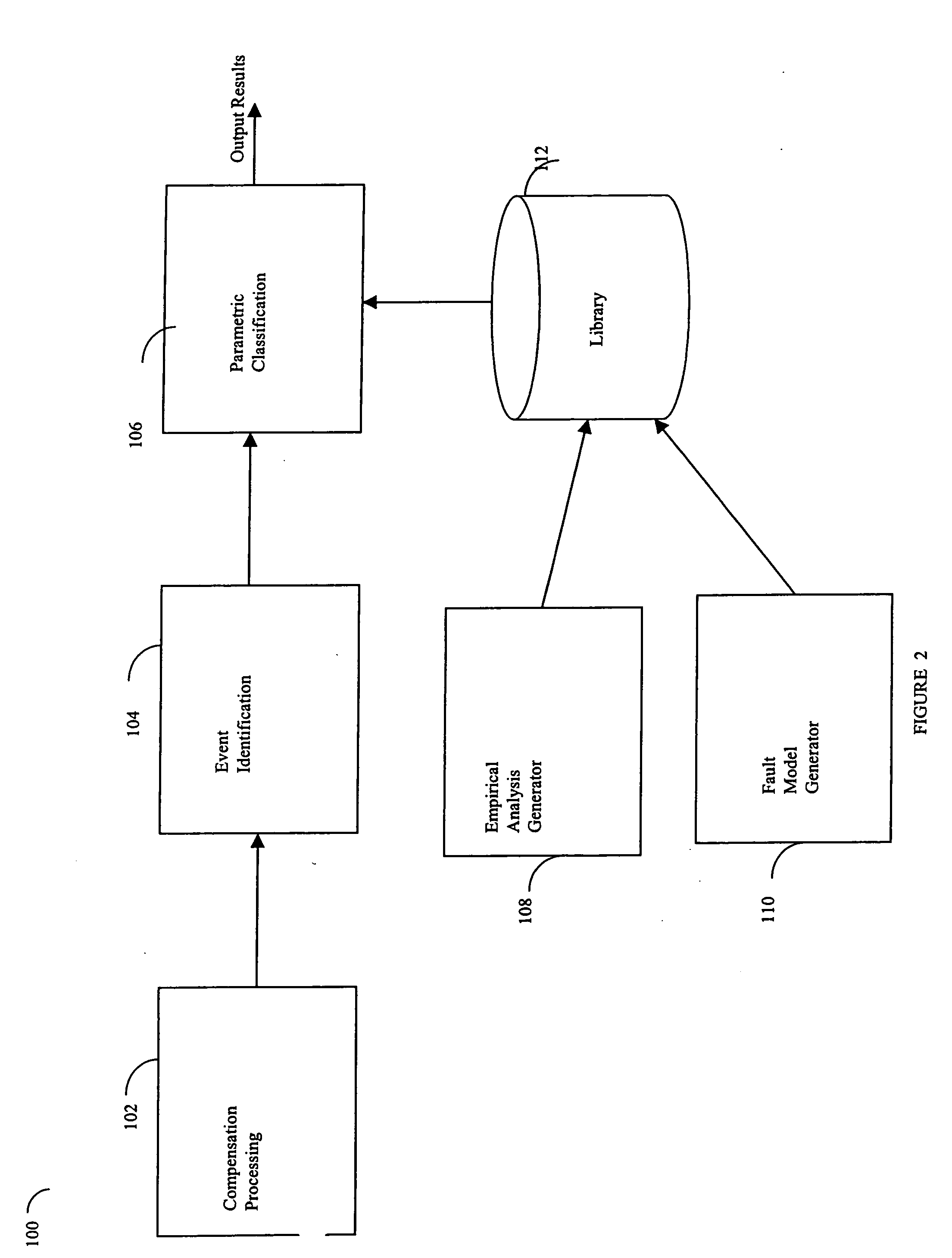
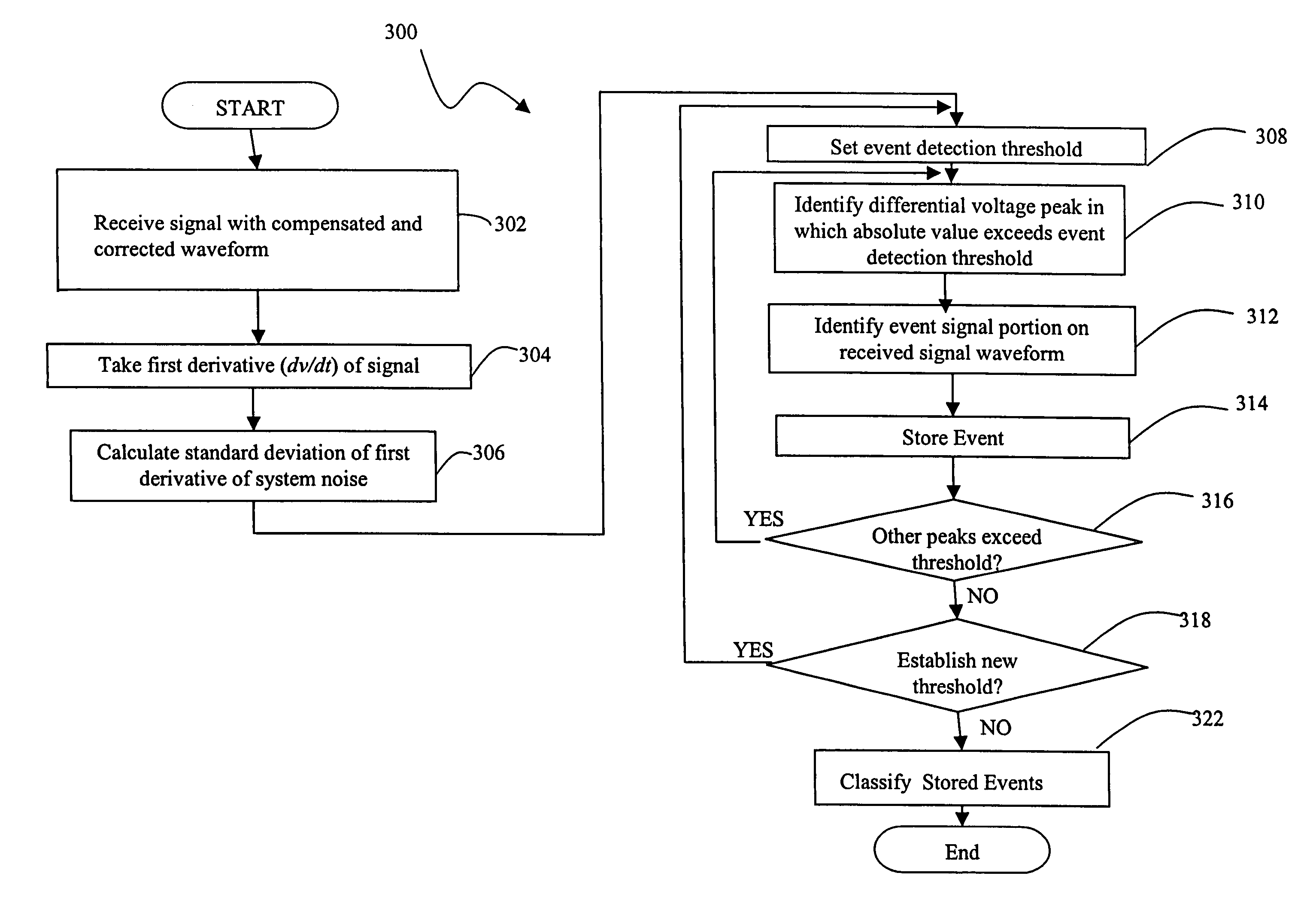
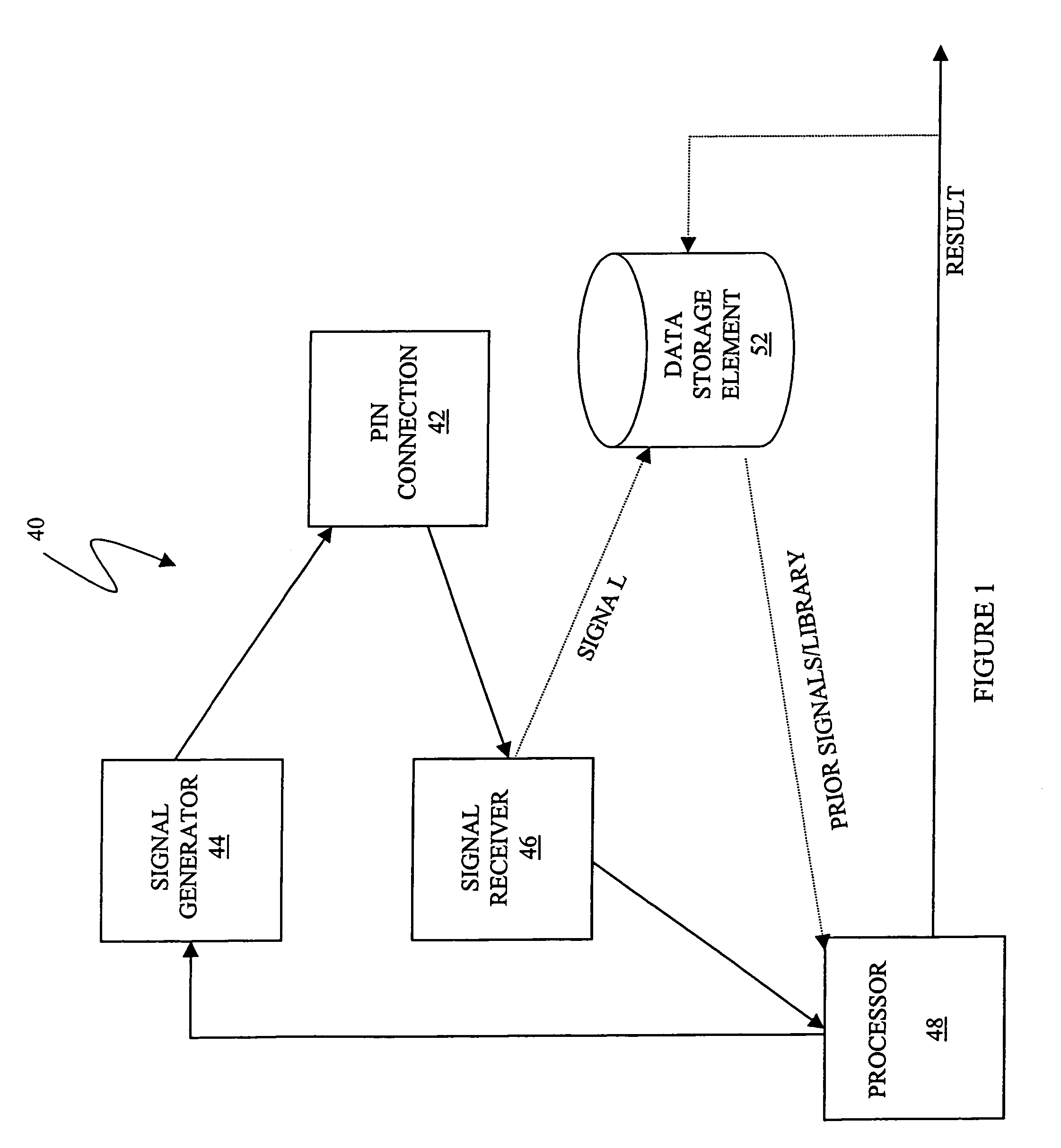
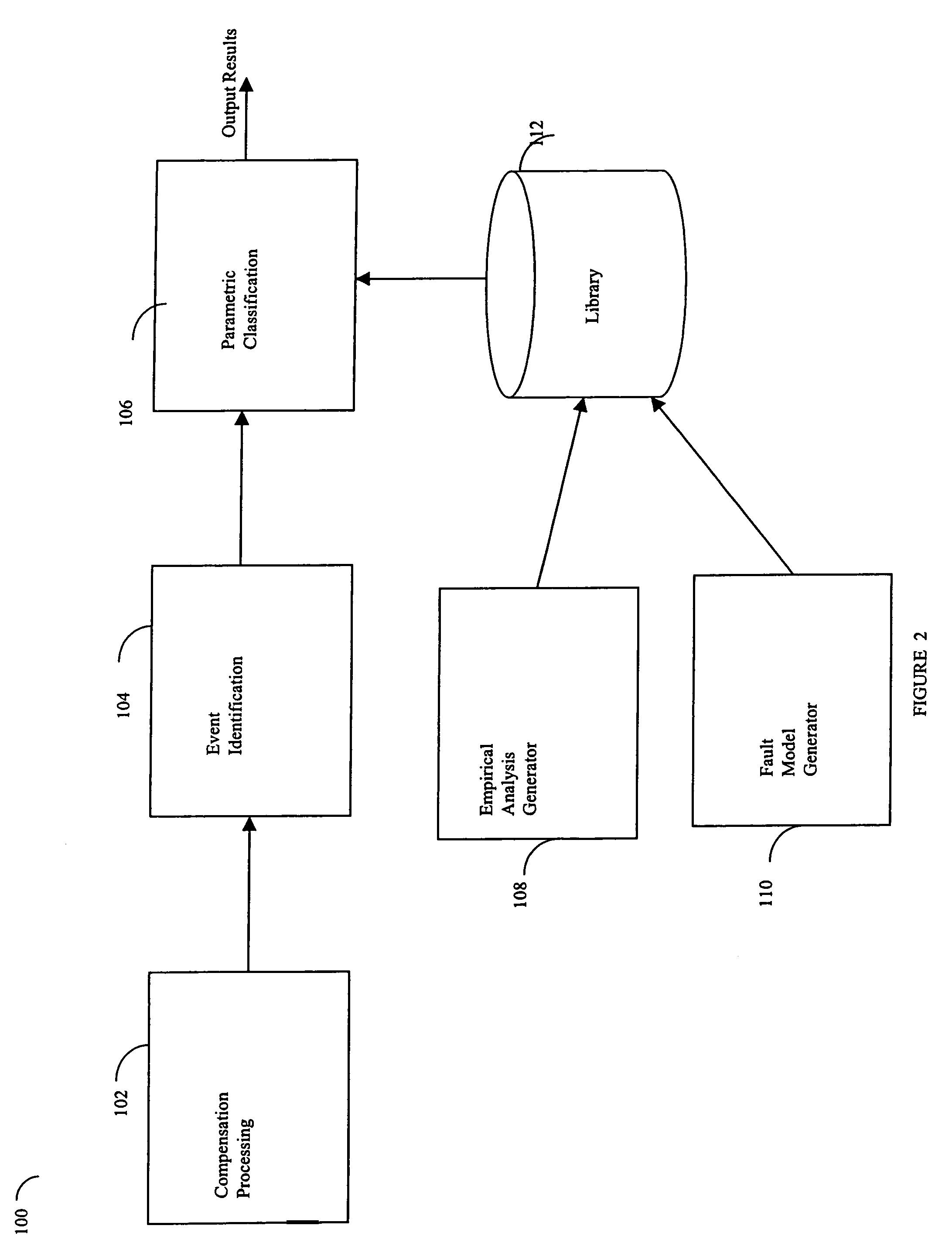
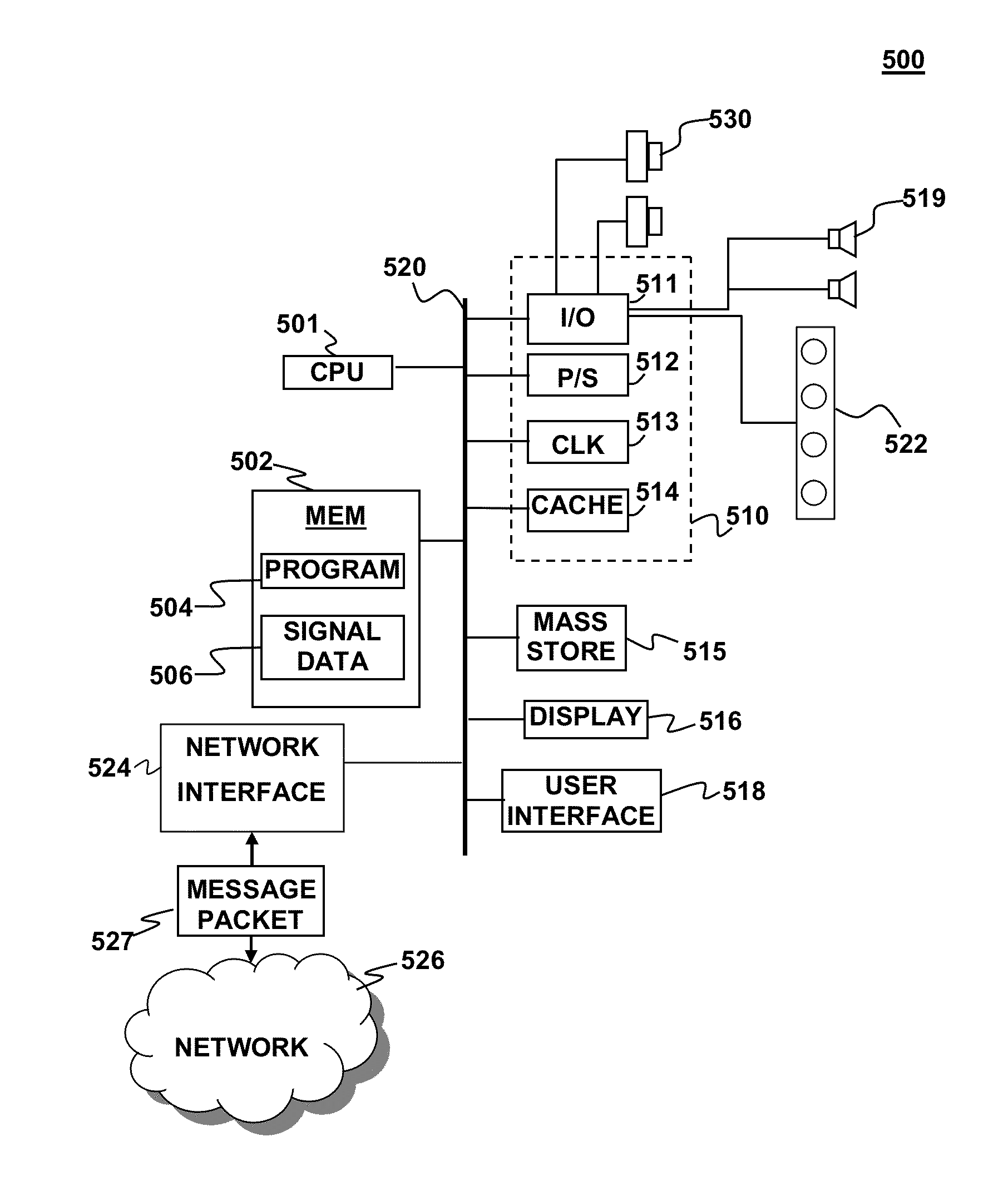
Described are techniques used in a wire diagnostics system to detect events, such as defects, that may occur within a wire or cable under test. An incident voltage signal is sent out on the wire and a measured voltage signal is obtained which includes the incident voltage and the reflected voltage. Compensation processing is performed on the measured waveform to remove unwanted reflective components. Additionally, the waveform is then subject to attenuation processing and event detection processing. Detected events, such as defects, are classified and output as results. Events are classified by parametric classification using a library of known events or faults. The library of known events or faults is previously generated using empirical analysis and modeling techniques. Additionally, joint time-frequency domain reflectometry (TFDR) techniques are described for event identification and classification for a wire under test.
Owner:SIMMONDS PRECISION PRODS
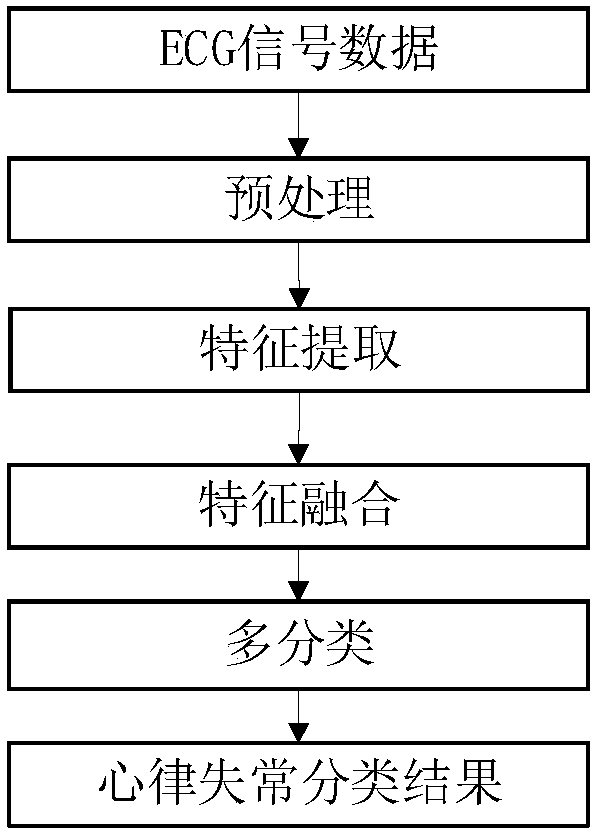
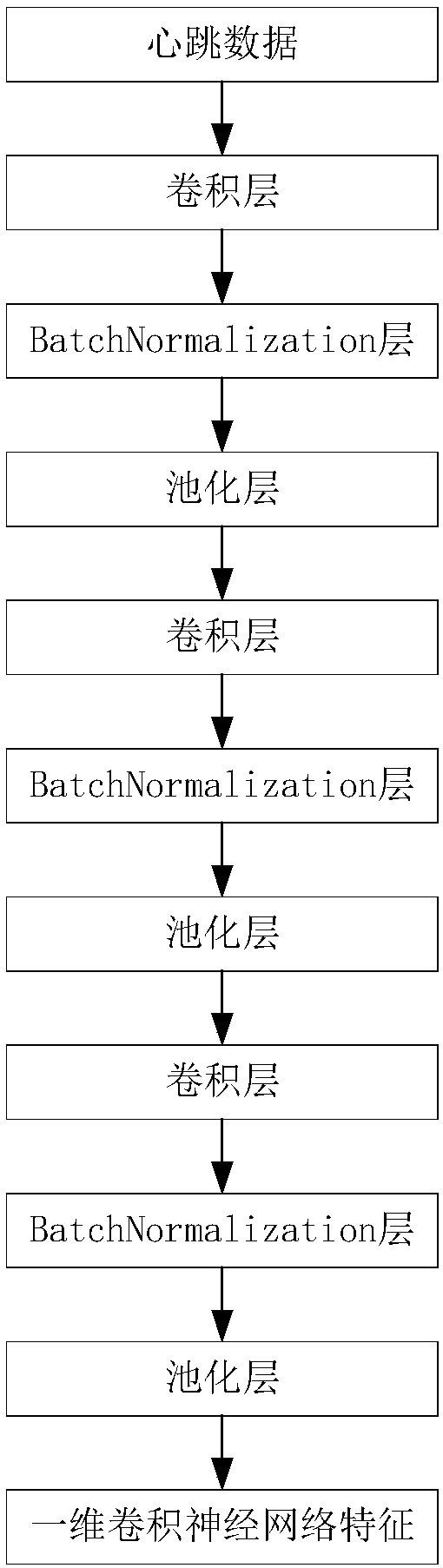
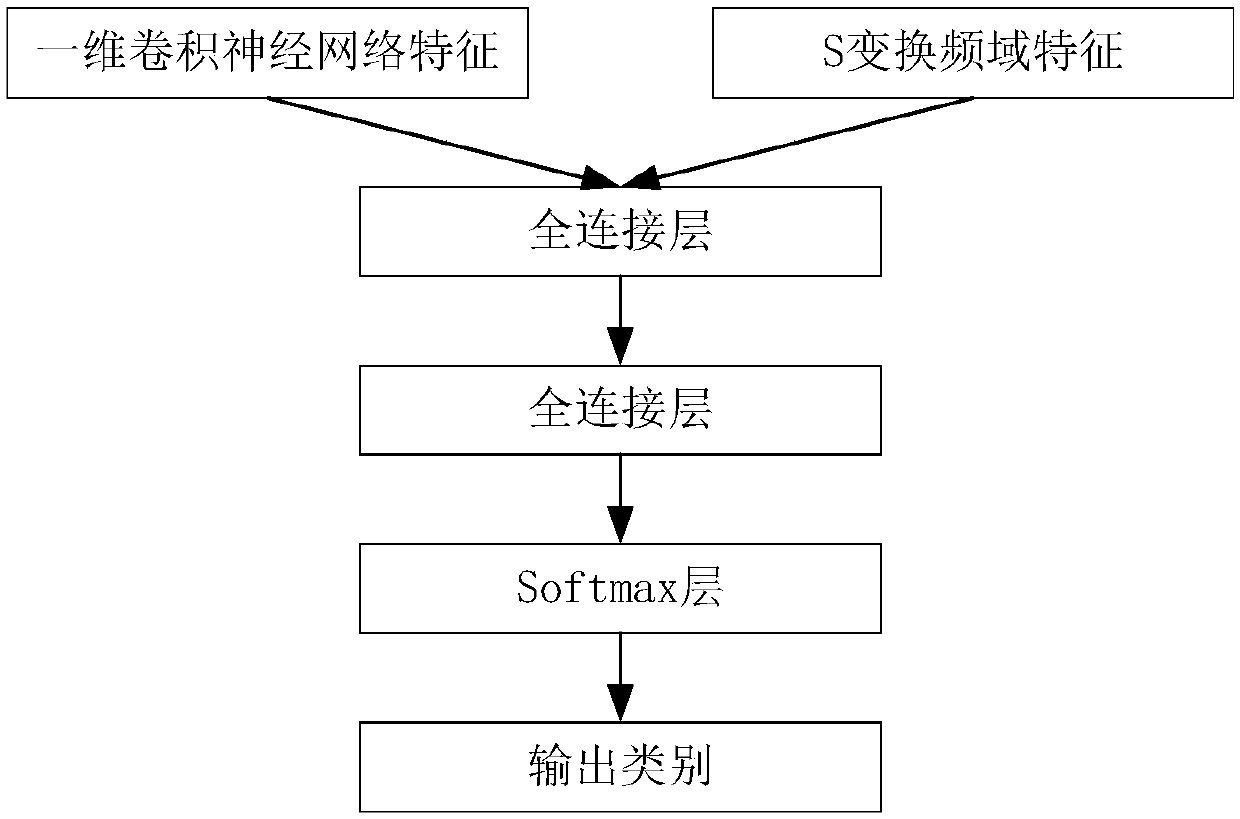
Classification method for arrhythmia based on one-dimension convolution neural-network and S transformation
InactiveCN107811626AImprove accuracyFast convergenceSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateEcg signalFeature extraction
Provided is a classification method for arrhythmia based on a one-dimension convolution neural-network and S transformation. The method includes the steps of pre-possessing electrocardiosignal; extracting the deep nonlinear characteristic of the electrocardiosignal by using the one-dimension convolution neural-network; extracting the time-frequency domain characteristic of the electrocardiosignalby using the S transformation; combining the deep nonlinear characteristic of the electrocardiosignal with the time-frequency domain characteristic of the electrocardiosignal, continuing to conduct characteristic learning after passing through a whole-connection layer, and obtaining the output characteristic of the whole-connection layer; conducting classification after the output characteristic of the whole-connection layer is connected to the softmax layer of the one-dimension convolution neural-network; outputting a classification result. According to the method, it is not necessary to conduct compression and bilinear interpolation on the electrocardiosignal to obtain the picture form of fixed pixel points to extract the characteristics. According to the method, in the aspect of characteristic extraction, the advantages of a deep learning characteristic and the time-frequency domain characteristic are combined to be composed into more complete characteristics, convergence can be quickened, over-fitting is controlled, and the insensitivity of the interwork to initialization weight is lowered. The accuracy rate of multiple kinds of arrhythmia identification is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
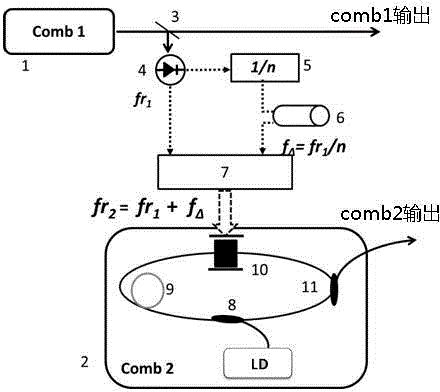
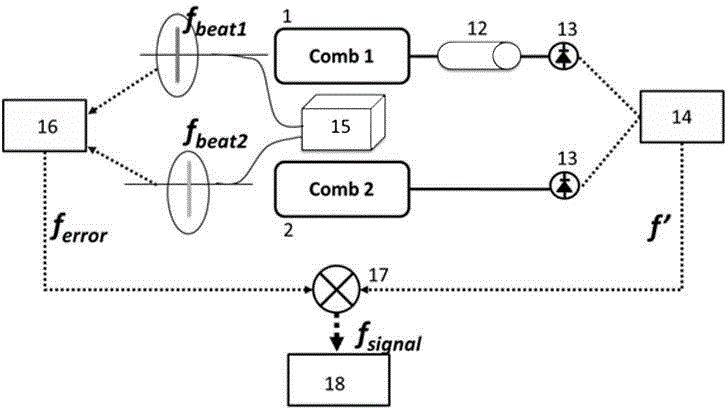
Spectral measurement method based on optical frequency combs
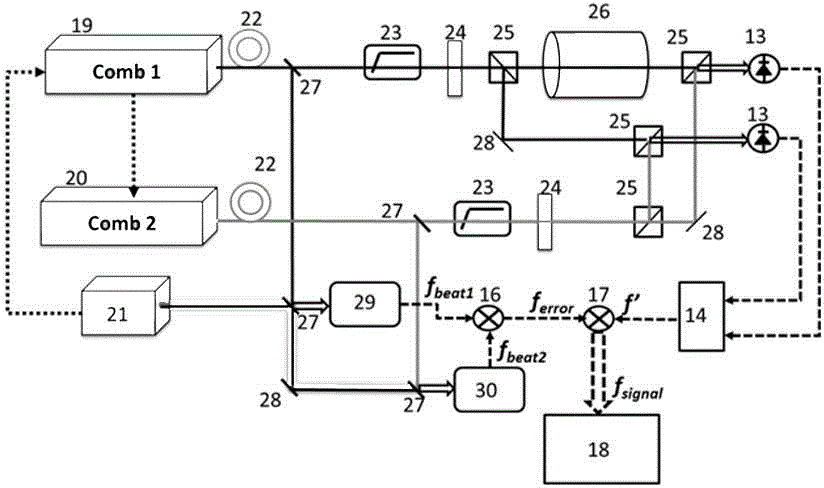
ActiveCN104316186AReduce volumeReduce maintenance difficultyAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsFourier analysisVIT signals
The invention discloses a spectral measurement method based on optical frequency combs. The measurement method is characterized in that firstly, an annular laser resonant cavity based on a phase modulator is actively modulated by use of a first optical frequency comb controllable in time domain and frequency domain so that the annular laser resonant cavity is converted into a second optical frequency comb having tiny difference in repetition frequency with the first optical frequency comb, and spectrum detection is performed on the two optical frequency combs to obtain an interference signal carrying the information of a sample to be tested, and meanwhile, frequency beating is performed on the two optical frequency combs and continuous frequency stabilized laser, respectively, the difference frequency signal of two obtained beat frequency signals is mixed with the interference signal, and a signal obtained by virtue of detection mixing is taken as a spectral signal for Fourier analysis so as to reduce the optical information of the sample to be tested. The spectral measurement method has the advantages that the error of the spectral detection due to own phase drift of a dual-optical comb system can be eliminated, and therefore, the resolution and the detection accuracy of the spectral measurement can be improved.
Owner:CHONGQING HUAPU INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
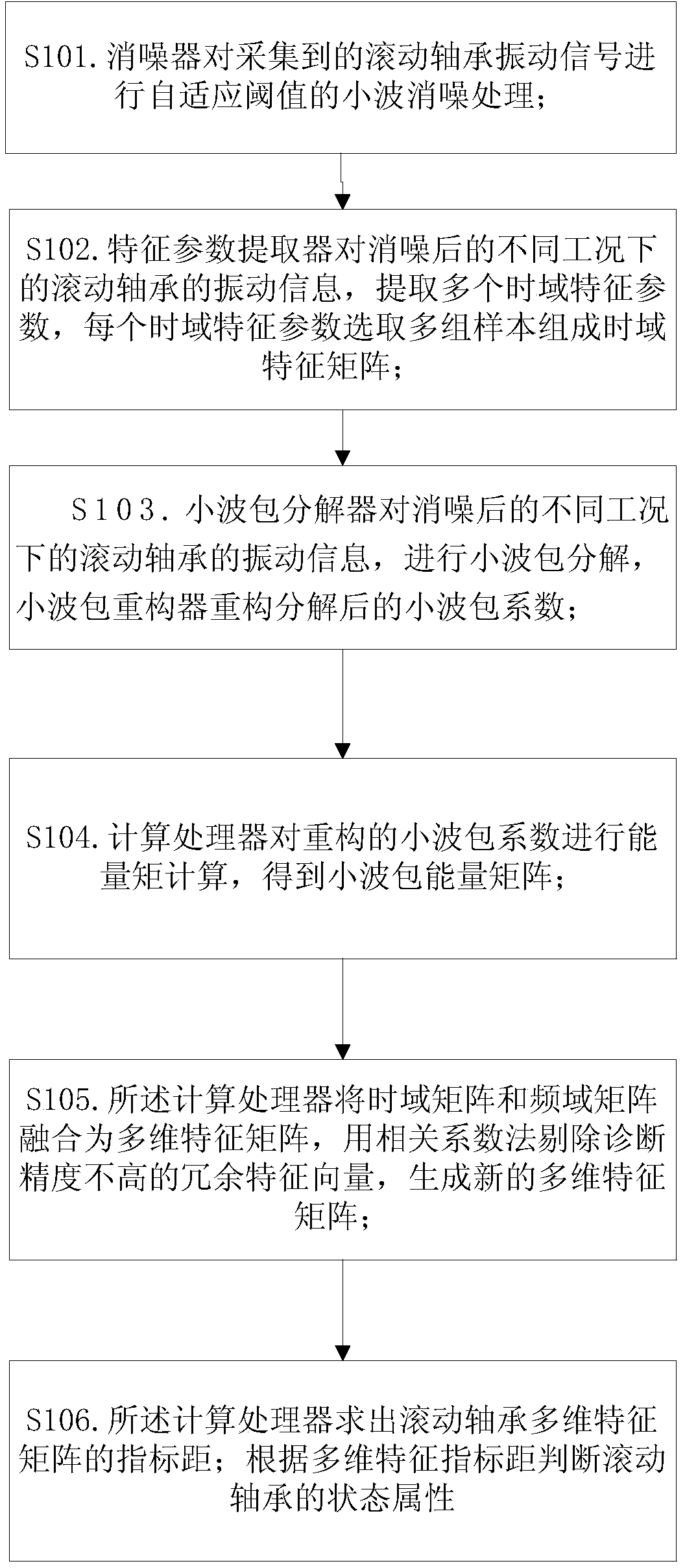
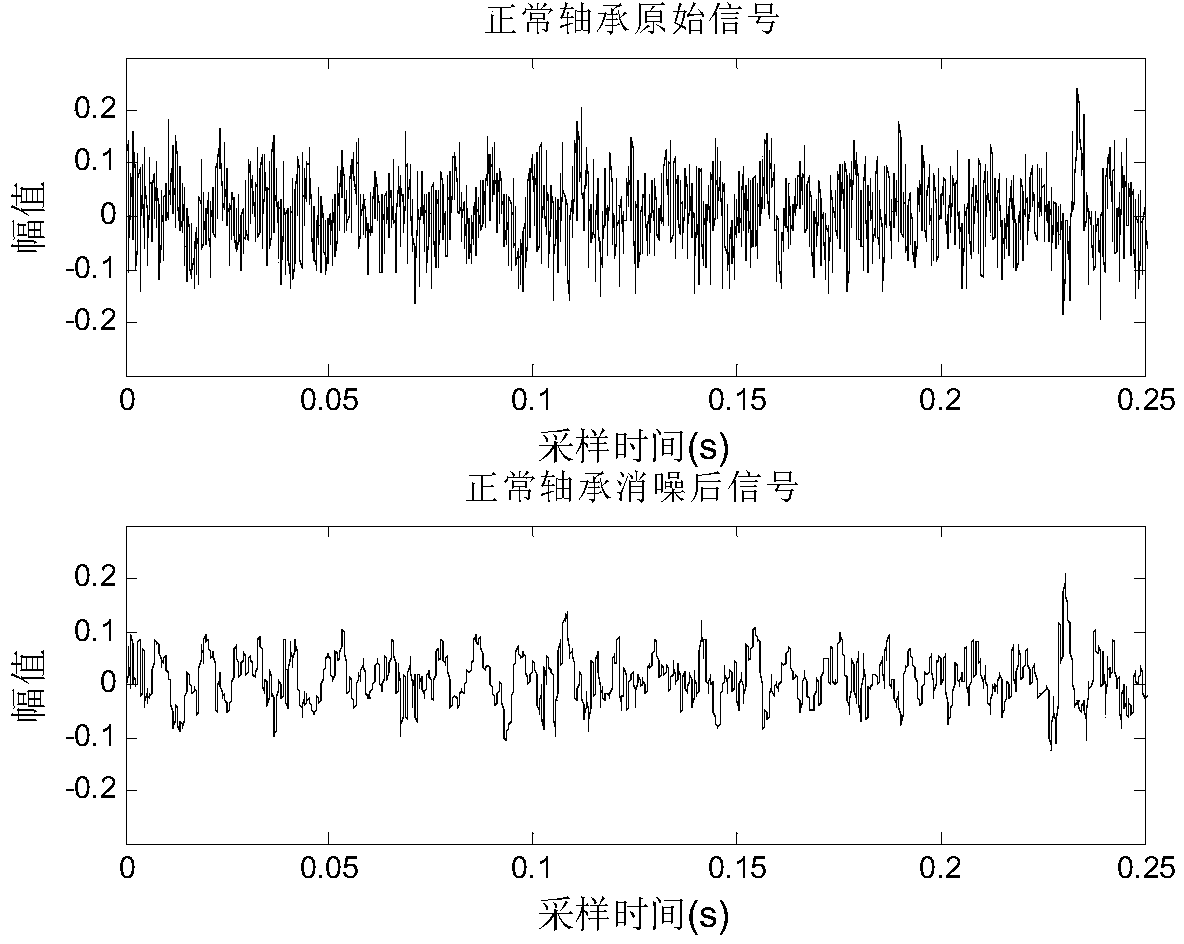
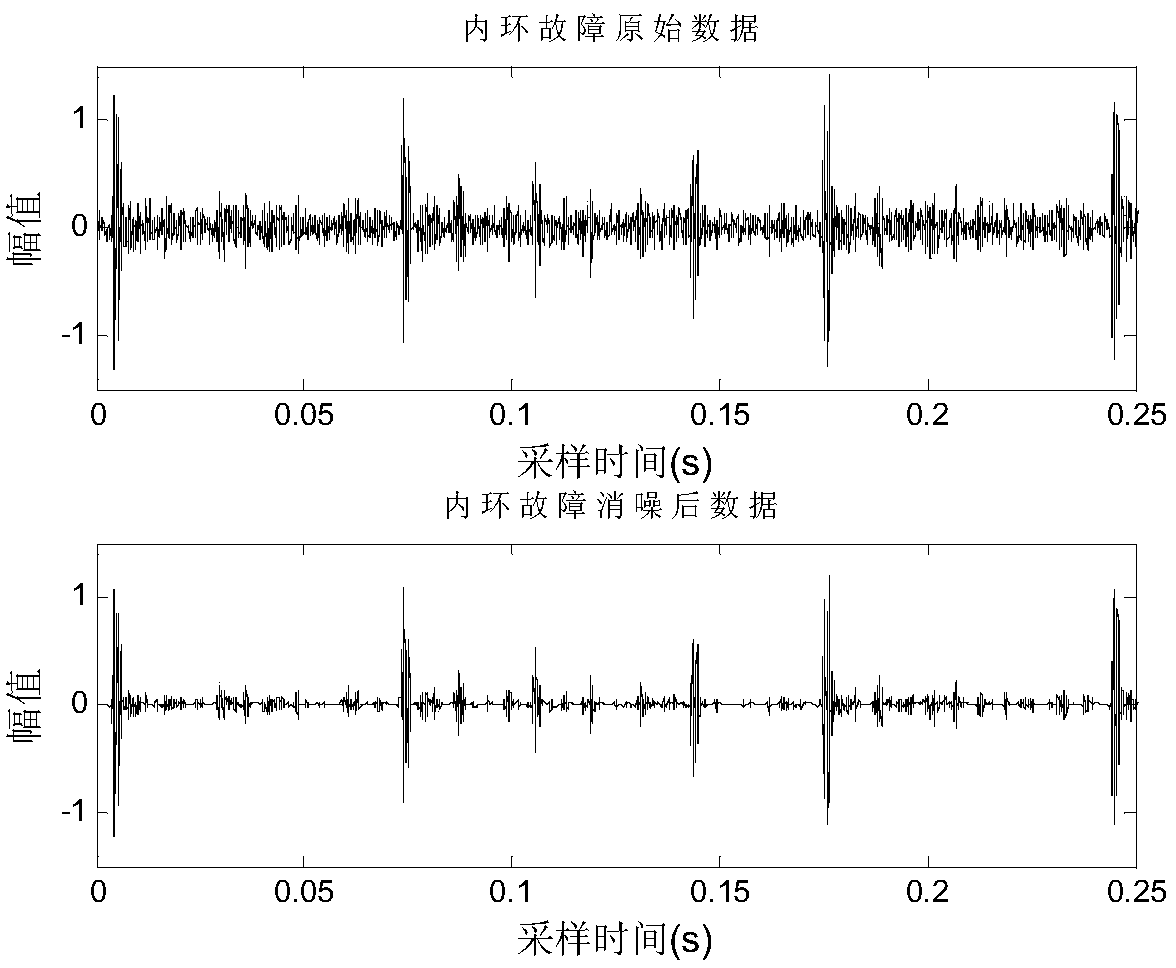
Rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on time-frequency domain multidimensional vibration feature fusion
ActiveCN104655423AIncrease computational time complexityImprove diagnostic accuracyMachine bearings testingEngineeringEuclidean vector
The invention provides a rolling bearing fault diagnosis algorithm based on time-frequency domain multidimensional fault feature fusion. Aiming at the respective features of vibration signals of a rolling bearing in a normal state, a roller fault state, an inner ring fault state and an outer ring fault state in a time-frequency domain, through extraction of time domain and frequency domain features, redundancy removal and re-fusion, fault features are described in an optimal way to obtain an intelligent judgment result. First, wavelet de-noising is performed on extracted original rolling bearing vibration data; then, time domain feature vectors are extracted to form a time domain feature matrix, and coefficient energy moments after wavelet packet decomposition and reconstruction are extracted to form a frequency domain feature matrix; and the time and frequency domain matrixes are further fused to obtain a time-frequency domain multidimensional fault feature matrix. Redundancy of the multidimensional feature matrix is eliminated to obtain a new multidimensional feature matrix. Then, information of multidimensional features is fused with a weighted feature index distance, and a state judgment result of the rolling bearing is obtained through the feature index distance obtained through fusion.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV +1
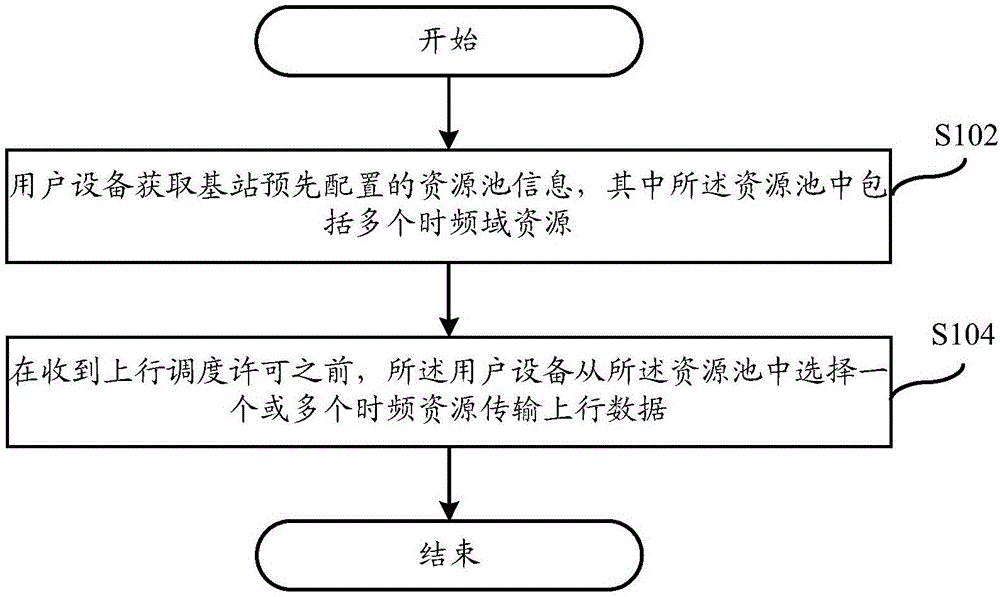
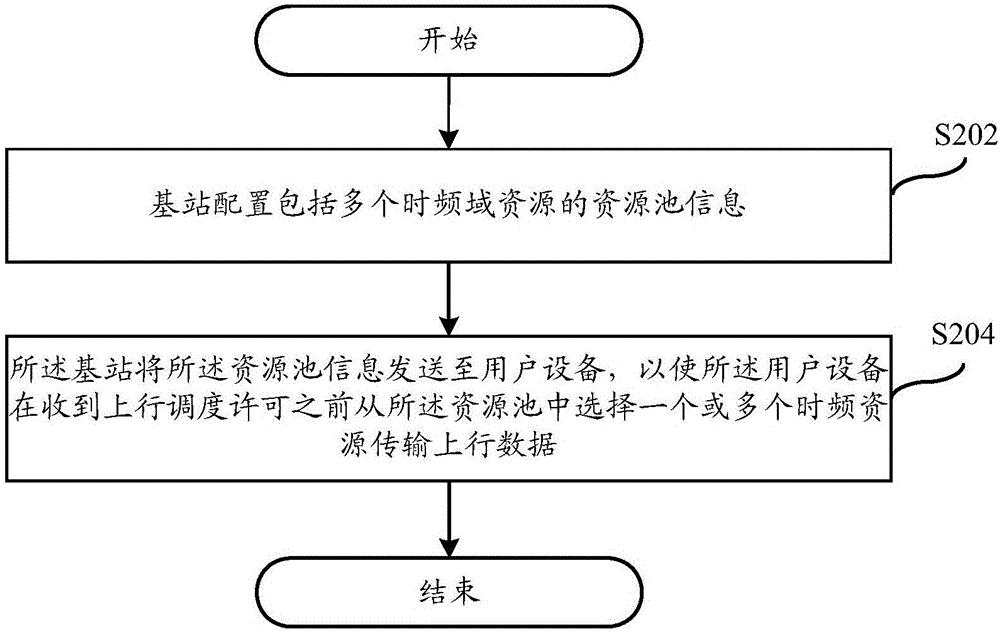
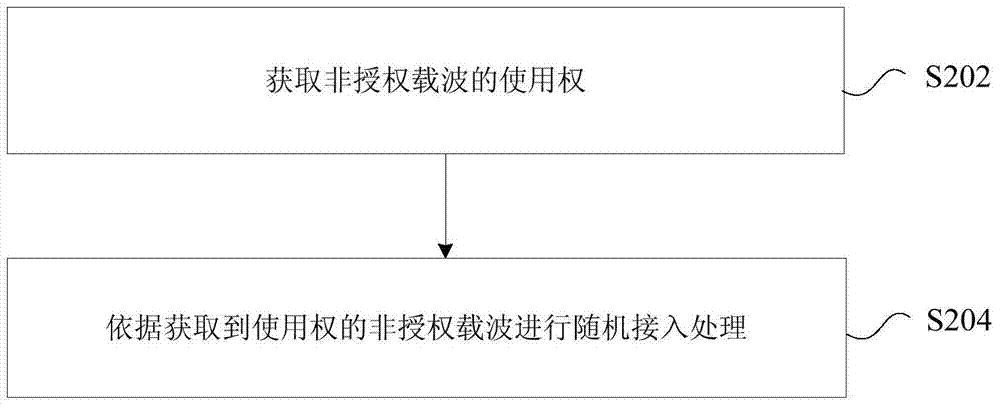
Uplink-grant-free resource allocation method, user equipment and base station
ActiveCN106788943AReduce latencyImprove transmission efficiencyInter user/terminal allocationPayload allocationResource poolUplink scheduling
The invention discloses an uplink-grant-free resource allocation method, user equipment and a base station. The resource allocation method in an embodiment includes: the user equipment acquires resource pool information pre-allocated by the base station, wherein the resource pool includes a plurality of time-frequency domain resources; before uplink grant is received, the user equipment selects one or more time-frequency resources from the resource pool to realize uplink data transmission. Time delay can be effectively reduced while data transmission efficiency is improved.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Time-frequency domain reflectometry apparatus and method
ActiveUS20060097730A1Wide applicationResistance/reactance/impedenceFault location by pulse reflection methodsMeasurement deviceTime delays
An apparatus and method for high-resolution reflectometry that operates simultaneously in both the time and frequency domains, utilizing time-frequency signal analysis and a chirp signal multiplied by a Gaussian time envelope. The Gaussian envelope provides time localization, while the chirp allows one to excite the system under test with a swept sinewave covering a frequency band of interest. High resolution in detection of the reflected signal is provided by a time-frequency cross correlation function. The high-accuracy localization of faults in a wire / cable can be achieved by measurement of time delay offset obtained from the frequency offset of the reflected signal. The apparatus enables one to execute an automated diagnostic procedure of a wire / cable under test by control of peripheral devices.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
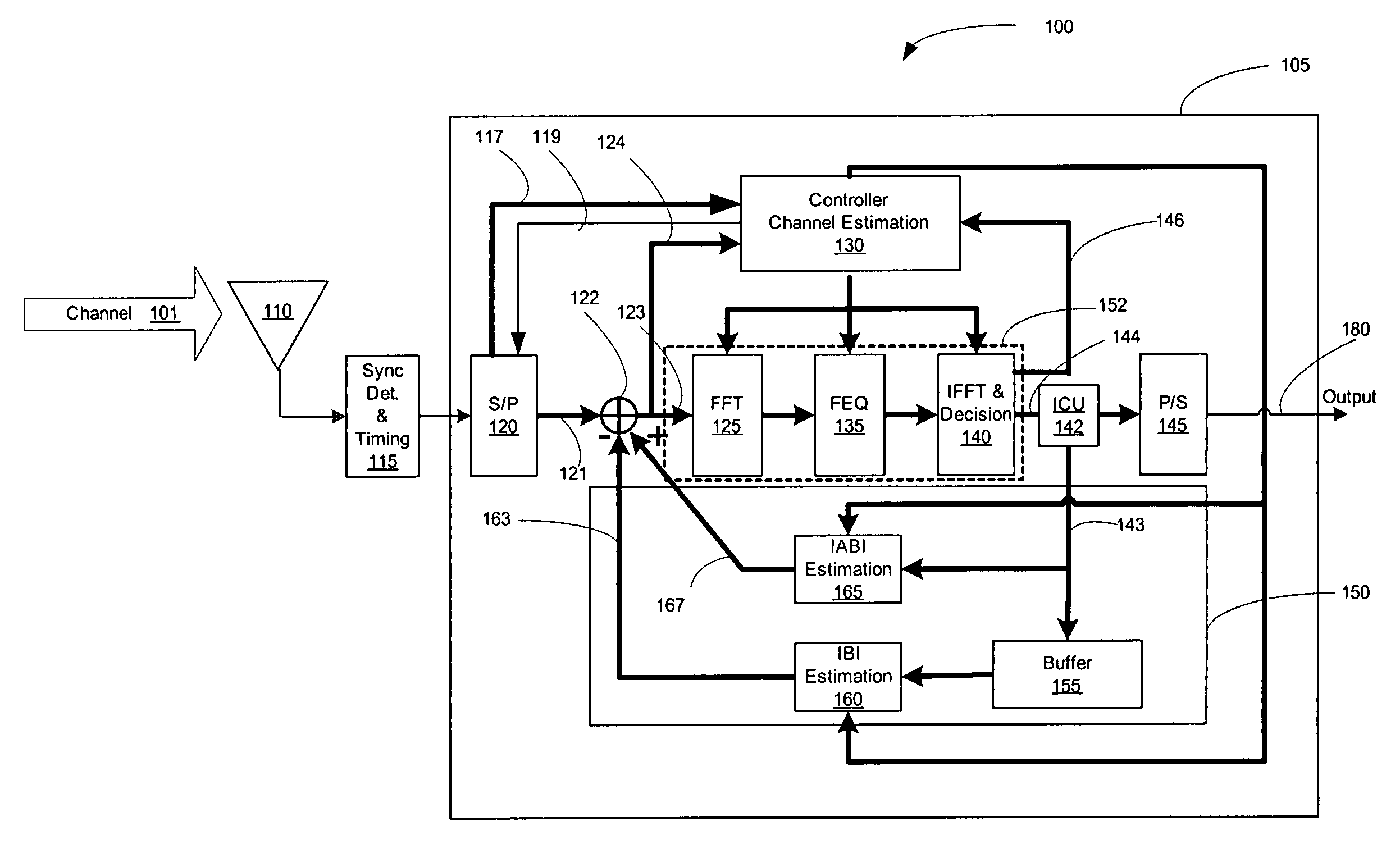
Hybrid domain block equalizer
The invention provides a method and device for iterative hybrid time-frequency domain block equalization of signals received via a communication channel subject to multipath interference. The equalization method includes frequency-domain equalization of blocks of received signals in a forward path, and time-domain inter-block echo correction and intra-block cyclic echo addition in the feedback path. The invention can be used for equalizing signals transmitted without cyclic prefix and subjected to multi-path interference with long delay spread.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
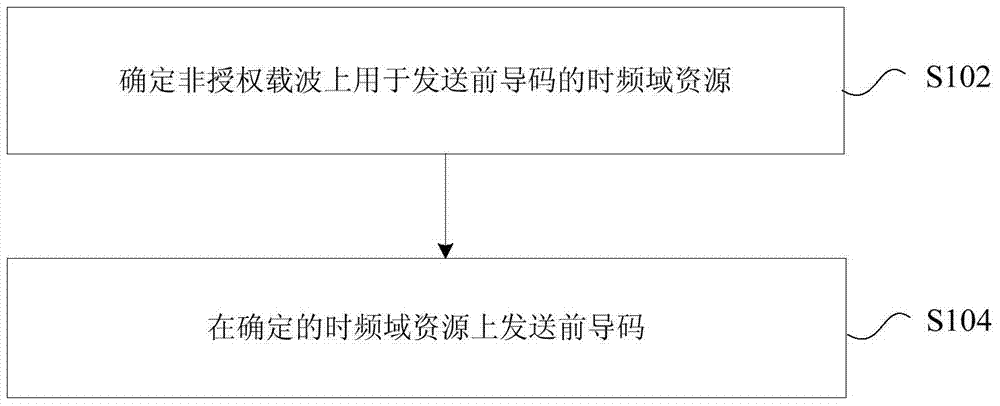
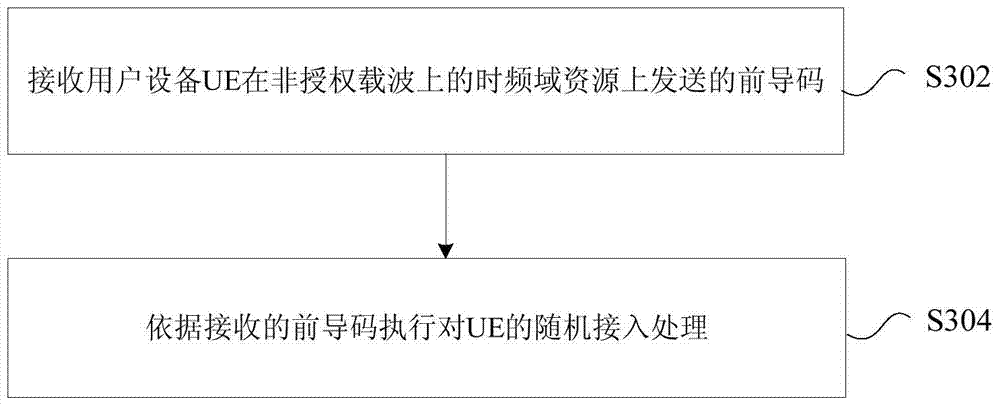
Preamble transmission and receiving methods and devices, user equipment and base station
The invention provides preamble transmission and receiving methods and devices, user equipment and a base station. The preamble transmission method comprises the following steps: determining time-frequency domain resources for transmitting preambles on an unlicensed carrier; and transmitting the preambles on the determined time-frequency domain resources. Through adoption of the preamble transmission and receiving methods and devices, the user equipment and the base station, the problem that a random access process cannot be implemented on the unlicensed carrier in the prior art is solved, and the effect of successfully performing random access on the unlicensed carrier is achieved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
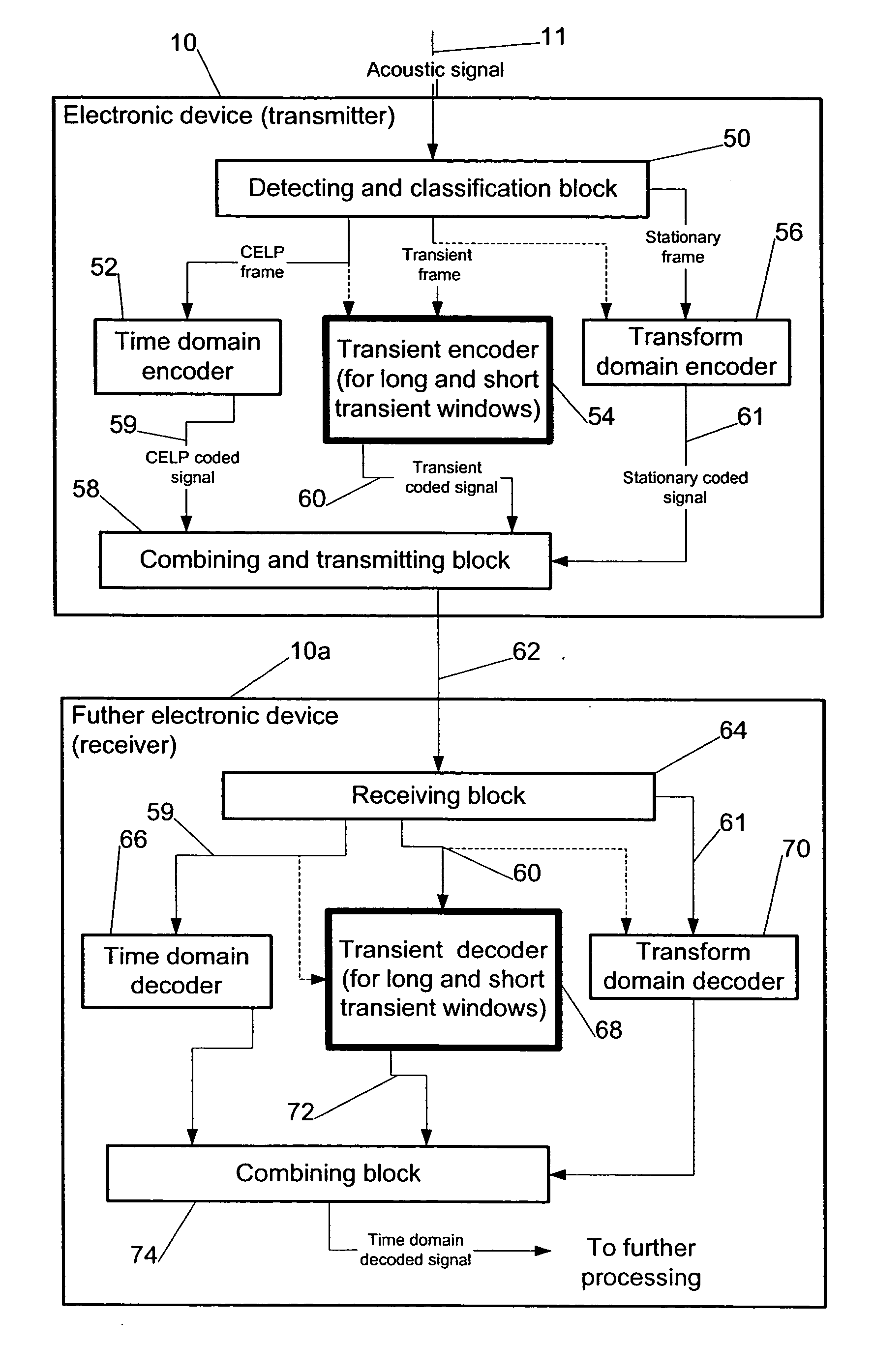
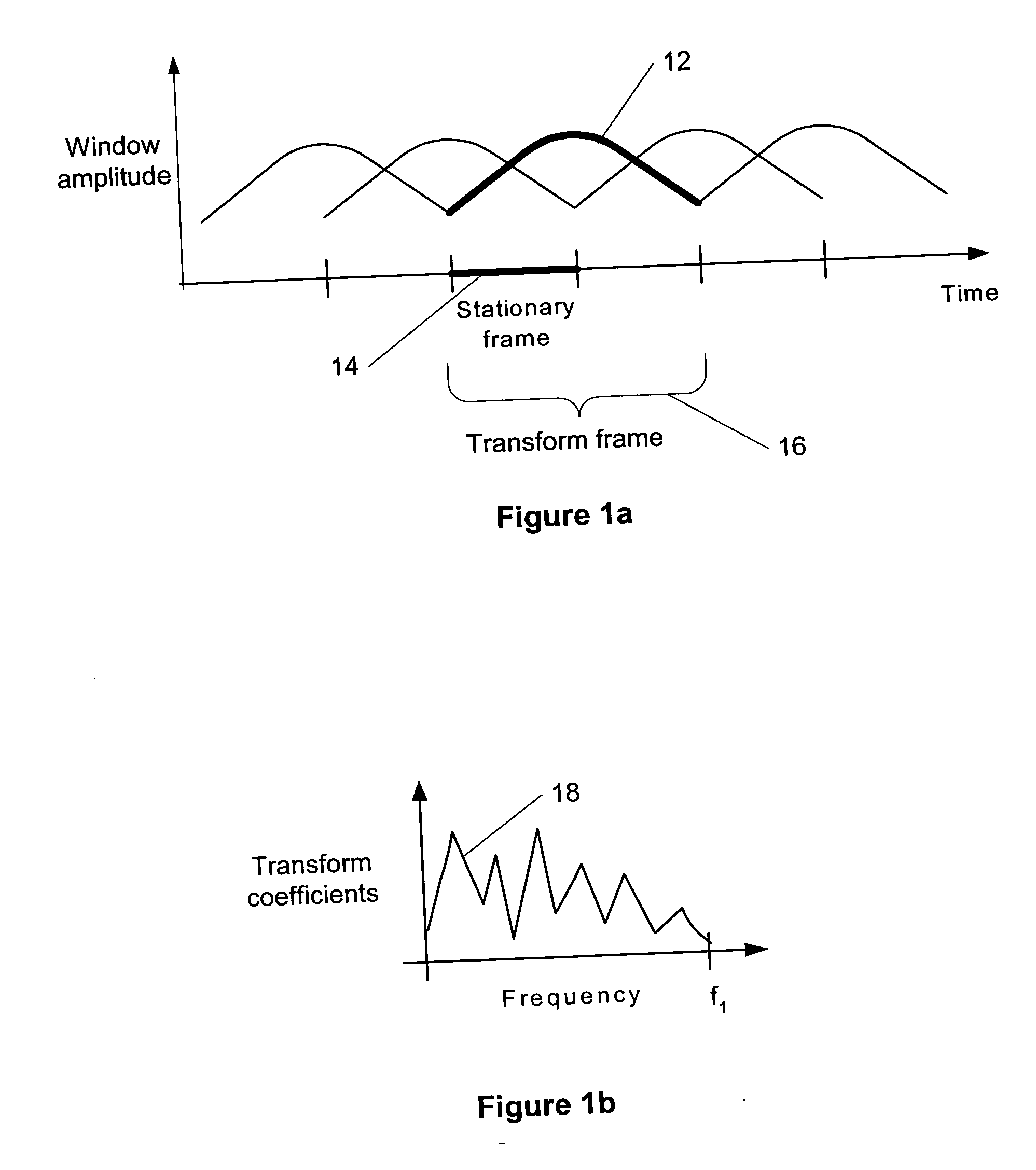
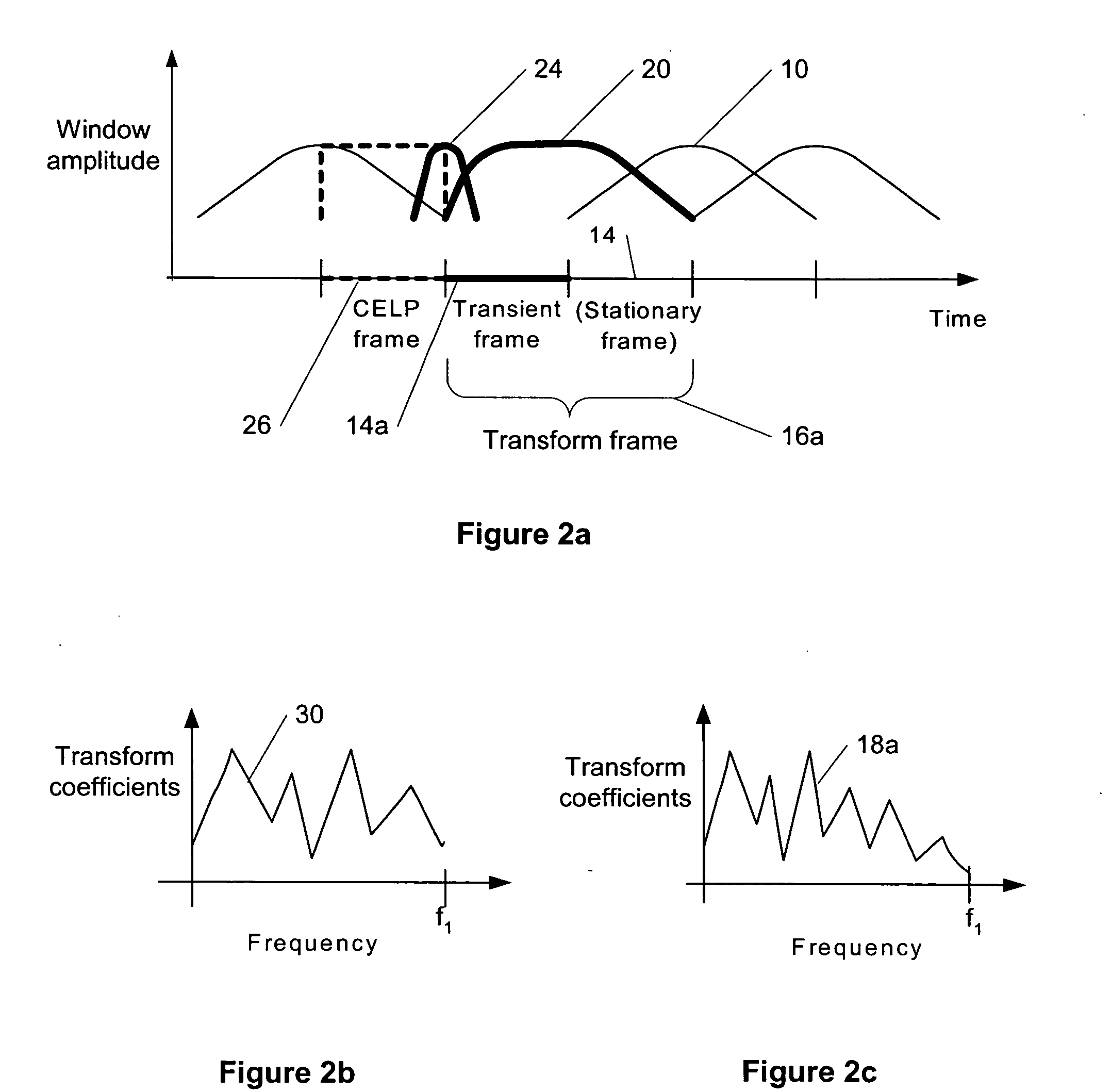
Compensation of transient effects in transform coding
The present invention provides a method for compensating transient effects in transform coding and decoding of a combined speech and audio in electronic devices by using a transform based time-frequency domain codec. The method can combine, e.g., a CELP (code excited linear prediction) type speech codec and a transform type audio codec. The invention describes a compensation method to handle the transient (e.g., from the CELP coding to the transform coding) in transform coding when the number of quantized transform coding coefficients is lower than in the output of the transform.
Owner:CONVERSANT WIRELESS LICENSING LTD
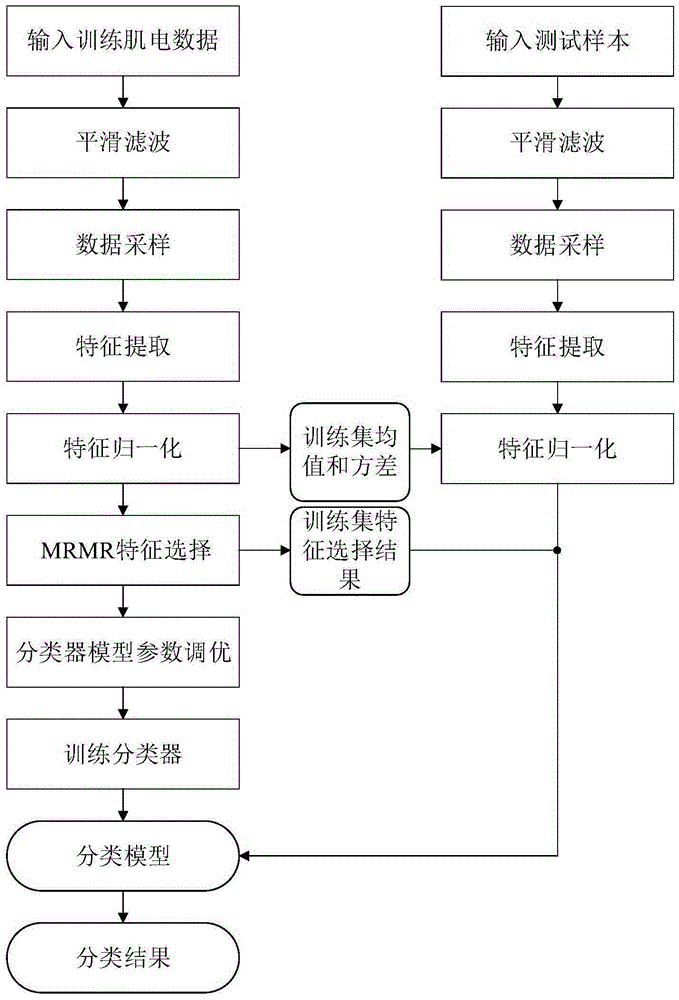
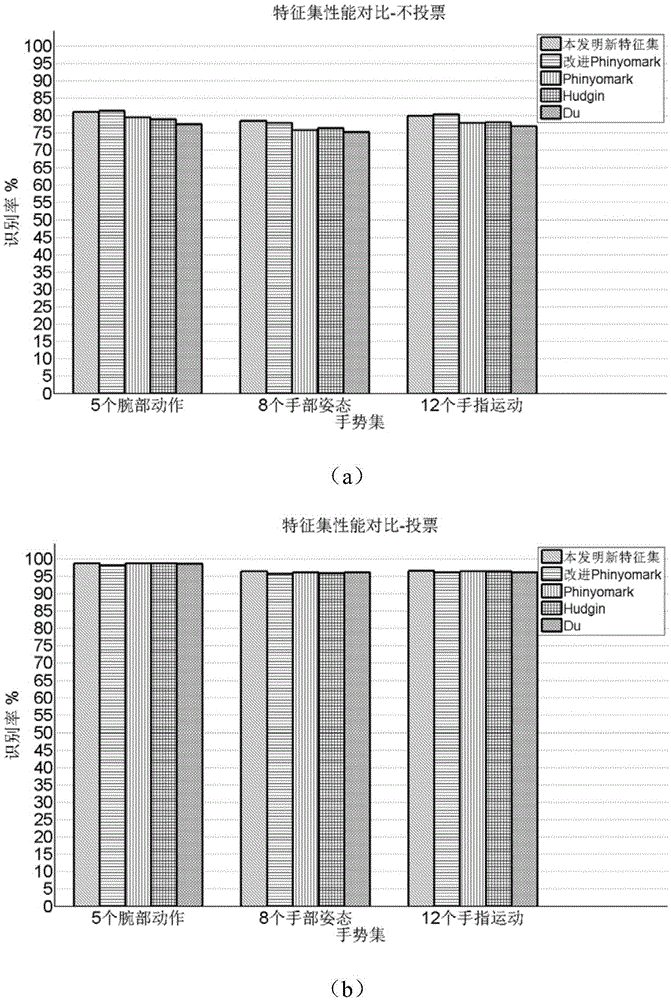
Support vector machine based surface electromyogram signal multi-hand action identification method
InactiveCN105426842AImprove classification performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionTime domainFeature vector
The invention discloses a support vector machine based surface electromyogram signal multi-hand action identification method. The method comprises the following main steps: 1) obtaining electromyogram data, performing smooth filtering on a signal, and generating data samples through sampling windows of different scales; 2) by taking the data samples as units, extracting a novel multi-feature set containing 19 time domain, frequency domain and time-frequency domain features from each data sample, and performing normalization and minimum redundancy maximum correlation criterion based feature selection on eigenvectors; 3) designing a Pearson VII generalized kernel based support vector machine classifier and optimizing parameters of a support vector machine by using a cross validation based coarse grid search optimization algorithm; and 4) training a classification model by using data samples in a training set and optical classifier parameters obtained in the parameter optimization process of the step 3) and inputting data samples in a test set into the classification model to perform classification testing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Speech enhancing and frequency response compensation fusion method in digital hearing-aid
ActiveCN103778920AEasy to implementImprove intelligibilitySpeech analysisHearing disorderTime frequency domain
The invention provides a speech enhancing and frequency response compensation fusion method in a digital hearing-aid. The speech enhancing and frequency response compensation fusion method includes the steps of (1) obtaining estimated noise and initial enhanced speech with an MCRA method, respectively carrying out filtering processing on the estimated noise and the initial enhanced speech through a gammatone filter, dividing a signal into M frequency bands through the perception mechanism of the cochleas to the signal, and meanwhile obtaining a time frequency expression mode of the signal, (2) computing masking threshold values of the frequency bands through factors such as the audio masking characteristic of the human ears and the frequency band signal to noise ratios, (3) dynamically computing masking values of noise-contained speech in a time frequency domain through a hearing curve of a hearing disorder patient, and processing speech enhancing and frequency response compensation at the same time, and (4) synthesizing output speech of the heating-aid through the masking values. According to the speech enhancing and frequency response compensation fusion method, the working mechanism of the human ears is sufficiently used, the speech characteristics are kept, music noise introduced through a spectral subtraction method is eliminated, the speech intelligibility of output signals of the hearing-aid is greatly improved, and the low complexity and the low power consumption are achieved.
Owner:湖南汨罗循环经济产业园区科技创新服务中心
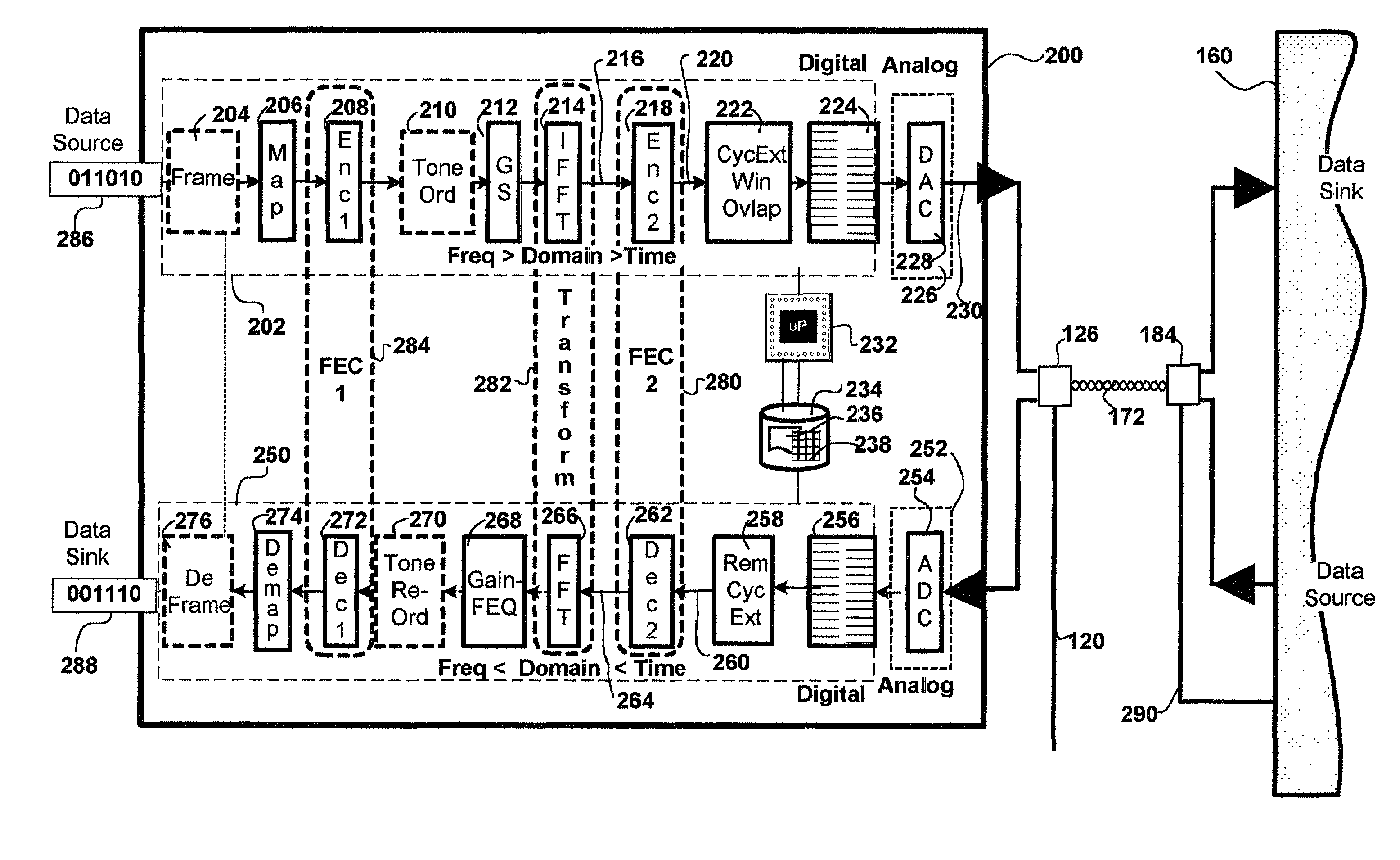
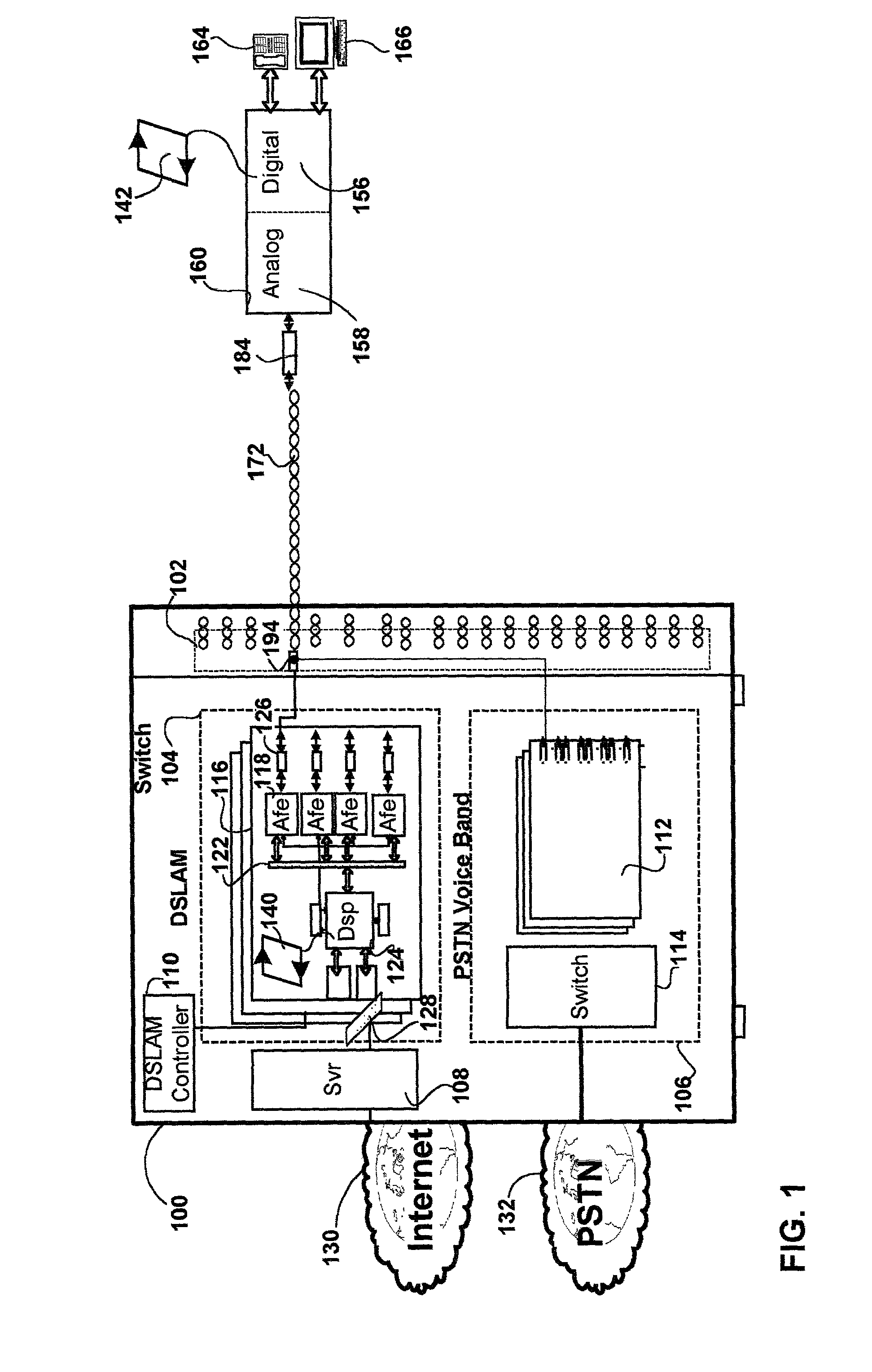
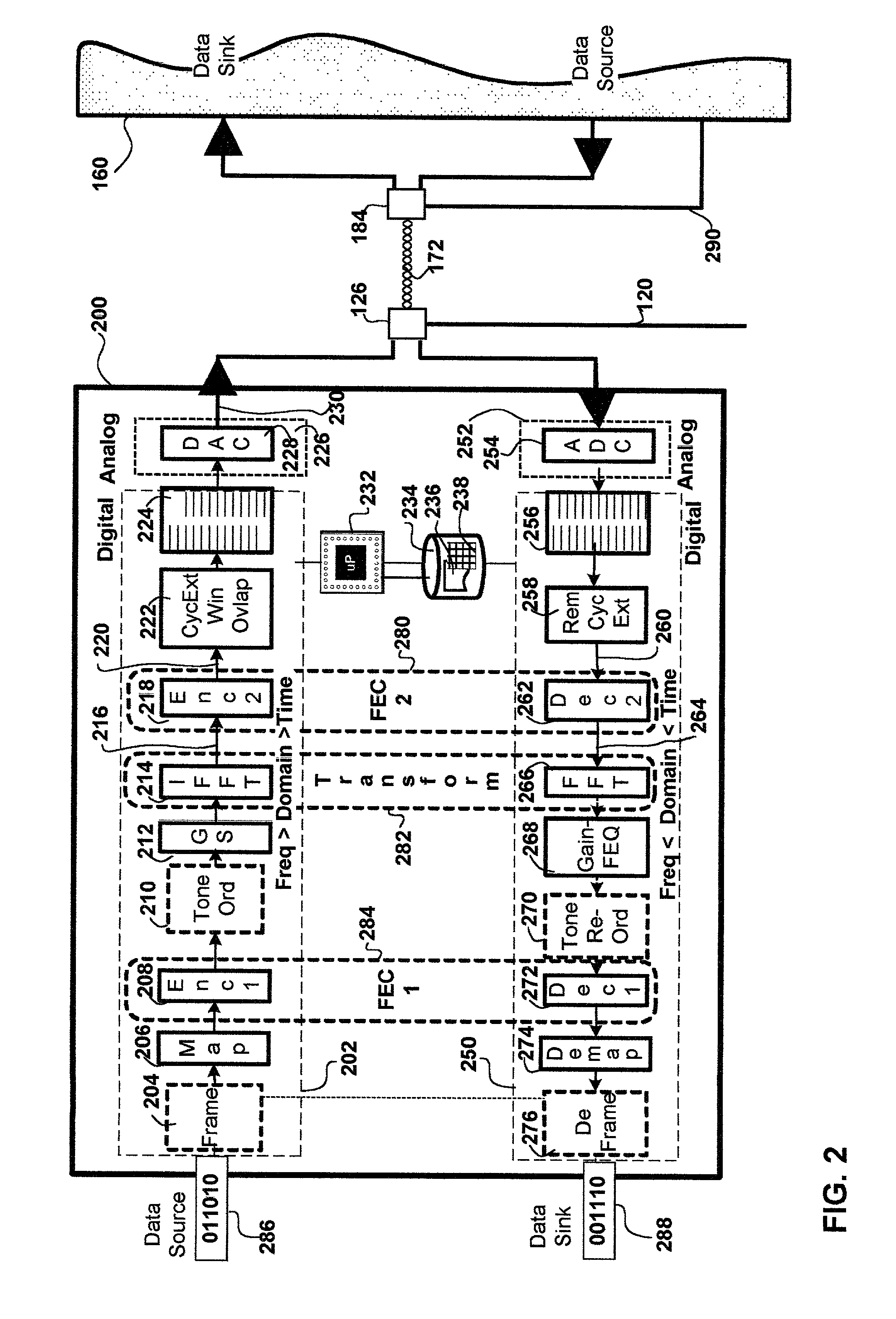
Method and apparatus for time-frequency domain forward error correction for digital communication systems
InactiveUS6976202B1Reduce overheadData representation error detection/correctionTransmission path divisionTime domainModem device
A method and apparatus for time and frequency domain forward error correction (FEC) in a modem which communicates data using multiple discrete sub-channels is provided. The invention may be implemented in hardware, software or firmware. In an embodiment of the invention a modem with a plurality of components forming a transmit path and a receive path is disclosed. The modem communicates data across a wired or wireless communication medium using a multiplicity of discrete sub-channels. The modem includes a transform component and a time domain FEC component. The transform component transforms the multiplicity of discrete sub-channels of a communication between a time domain and a frequency domain on the receive path and vice-versa on the transmit path. The time domain FEC component couples to the transform component. The time domain FEC component has a complementary encoder and decoder portion on the transmit and receive paths respectively. The encoder and decoder portions encode and decode respectively the multiplicity of discrete sub-channels in the time domain.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
Wire fault detection
InactiveUS7120563B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsUltrasound attenuationReflectometry
Described are techniques used in a wire diagnostics system to detect events, such as defects, that may occur within a wire or cable under test. An incident voltage signal is sent out on the wire and a measured voltage signal is obtained which includes the incident voltage and the reflected voltage. Compensation processing is performed on the measured waveform to remove unwanted reflective components. Additionally, the waveform is then subject to attenuation processing and event detection processing. Detected events, such as defects, are classified and output as results. Events are classified by parametric classification using a library of known events or faults. The library of known events or faults is previously generated using empirical analysis and modeling techniques. Additionally, joint time-frequency domain reflectometry (TFDR) techniques are described for event identification and classification for a wire under test.
Owner:SIMMONDS PRECISION PRODS
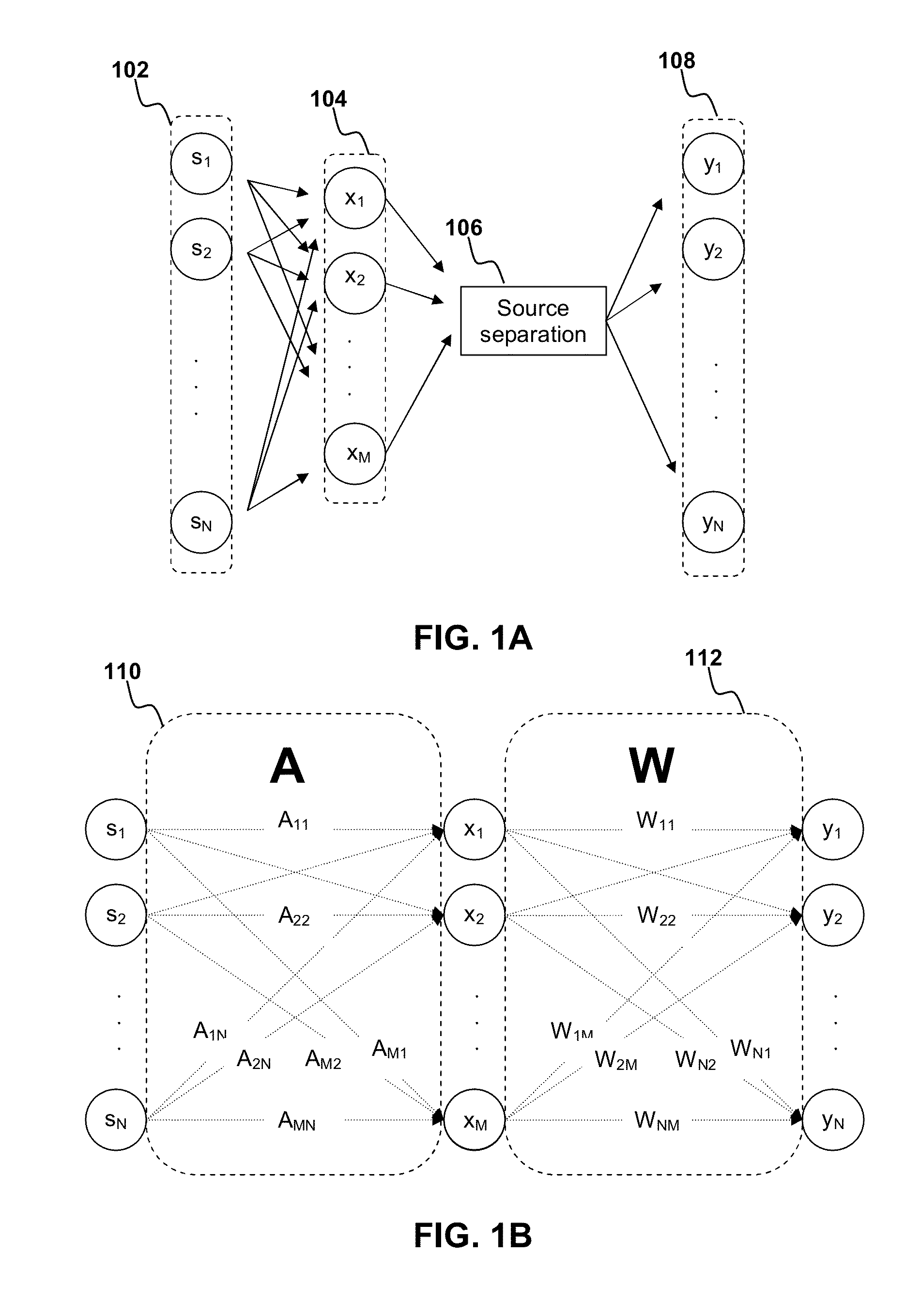
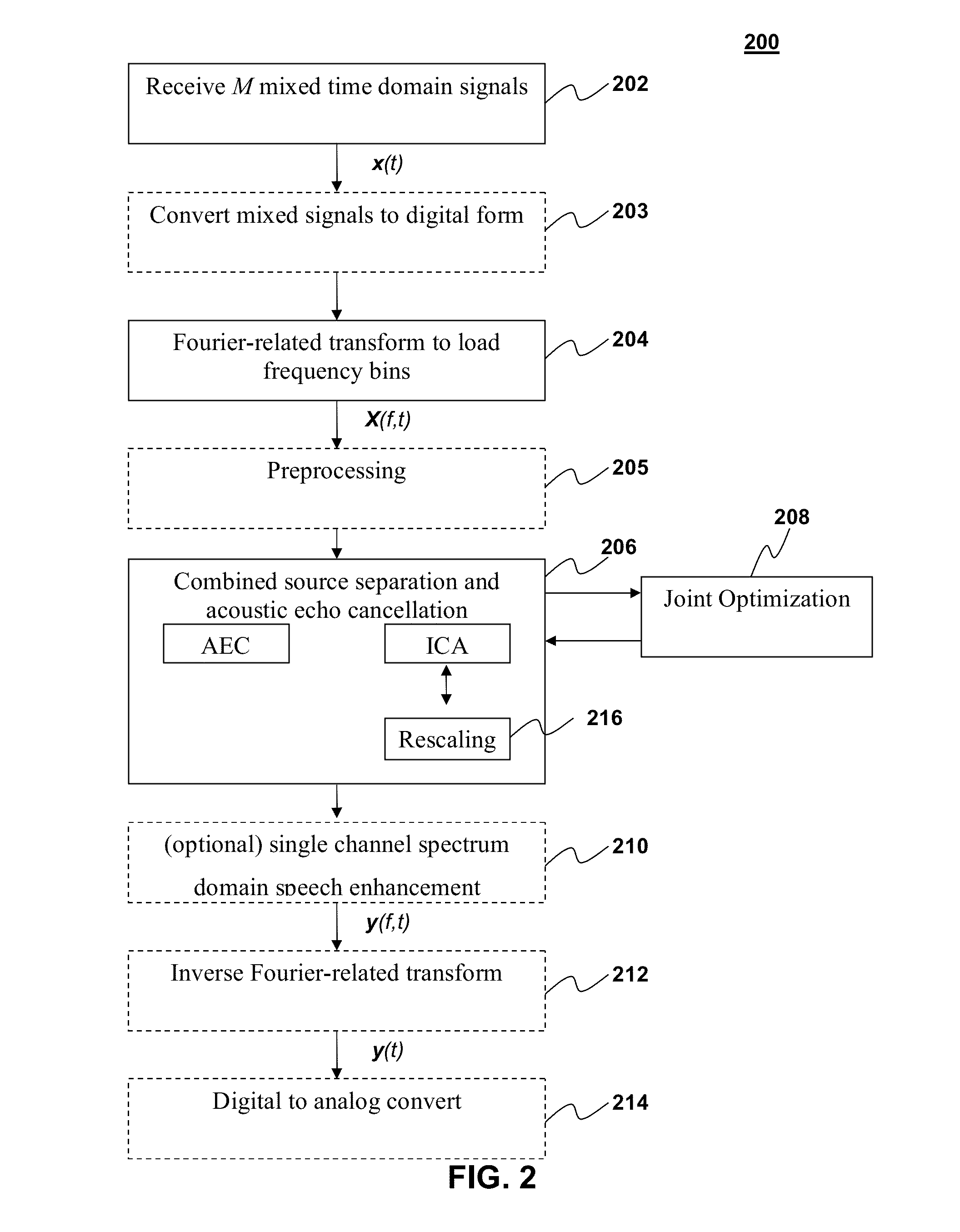
Source separation by independent component analysis in conjuction with optimization of acoustic echo cancellation
Methods and apparatus for signal processing are disclosed. Source separation can be performed to extract source signals from mixtures of source signals and perform acoustic echo cancellation. Independent component analysis may be used to perform the source separation in conjunction with acoustic echo cancellation on the time-frequency domain mixed signals to generate at least one estimated source signal corresponding to at least one of the original source signals. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
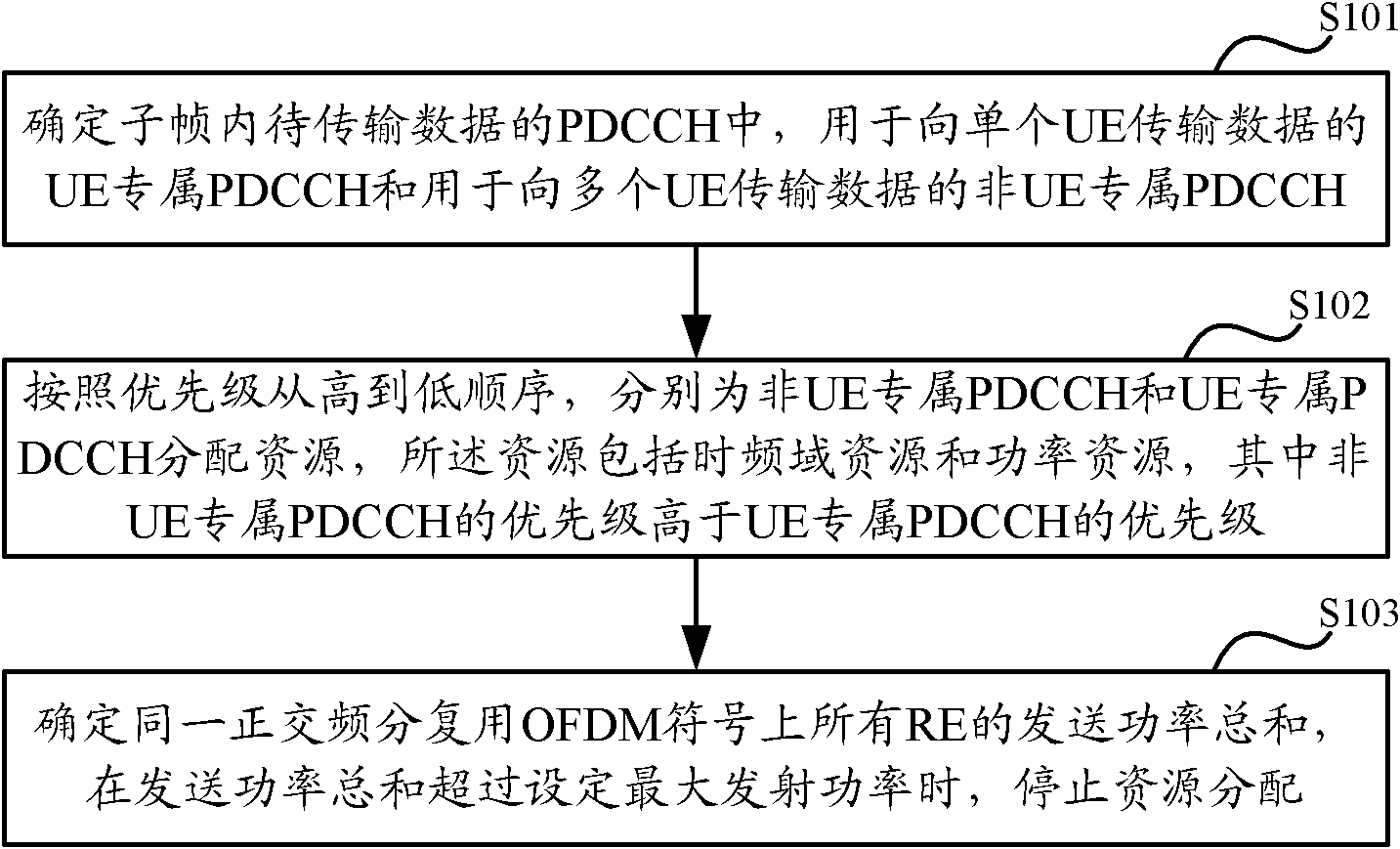
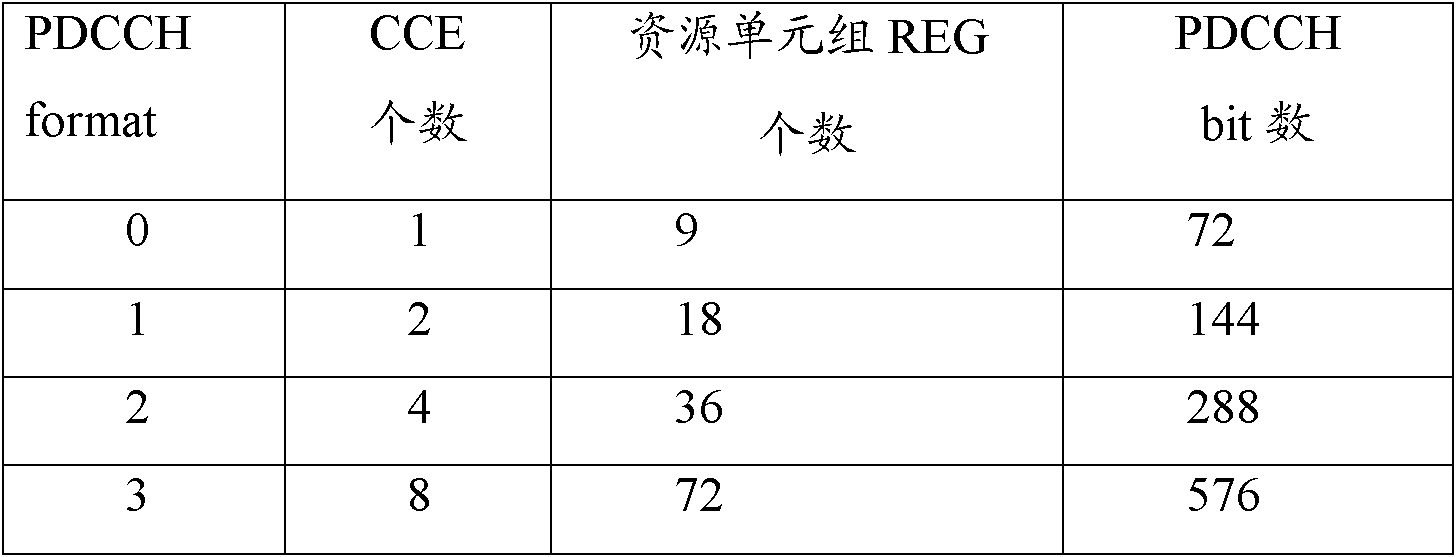
Combined adaptive resource allocation method and device for PDCCH (Physical Downlink Control Channel)
ActiveCN102143593AAddress detection performanceWireless communicationTelecommunicationsControl channel
The invention discloses a combined adaptive resource allocation method and device for a PDCCH (Physical Downlink Control Channel). The method comprises the following steps of: determining a UE (User Equipment) dedicated PDCCH for transmitting data to single UE and a non-UE dedicated PDCCH for transmitting data to a plurality of UE in the PDCCH to be used for transmitting data in a subframe; and allocating resources to the non-UE dedicated PDCCH and the UE dedicated PDCCH from high to low according to priority respectively, wherein the resources comprise a time frequency domain resource and a power resource, and the priority of the non-UE dedicated PDCCH is higher than that of the UE dedicated PDCCH. By adopting the method and the device, the resource is preferably allocated to the non-UE dedicated PDCCH compared with the UE dedicated PDCCH, so that the non-UE dedicated PDCCH is not limited to the PDCCH allocation, and the problem of conflict between PDCCH detection performance and increase in number of supportable scheduled users is solved.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Method of separating sound signal
InactiveUS20110058685A1Easy to getMinimizing smoothnessSpeech analysisTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsFrequency spectrumAudio frequency
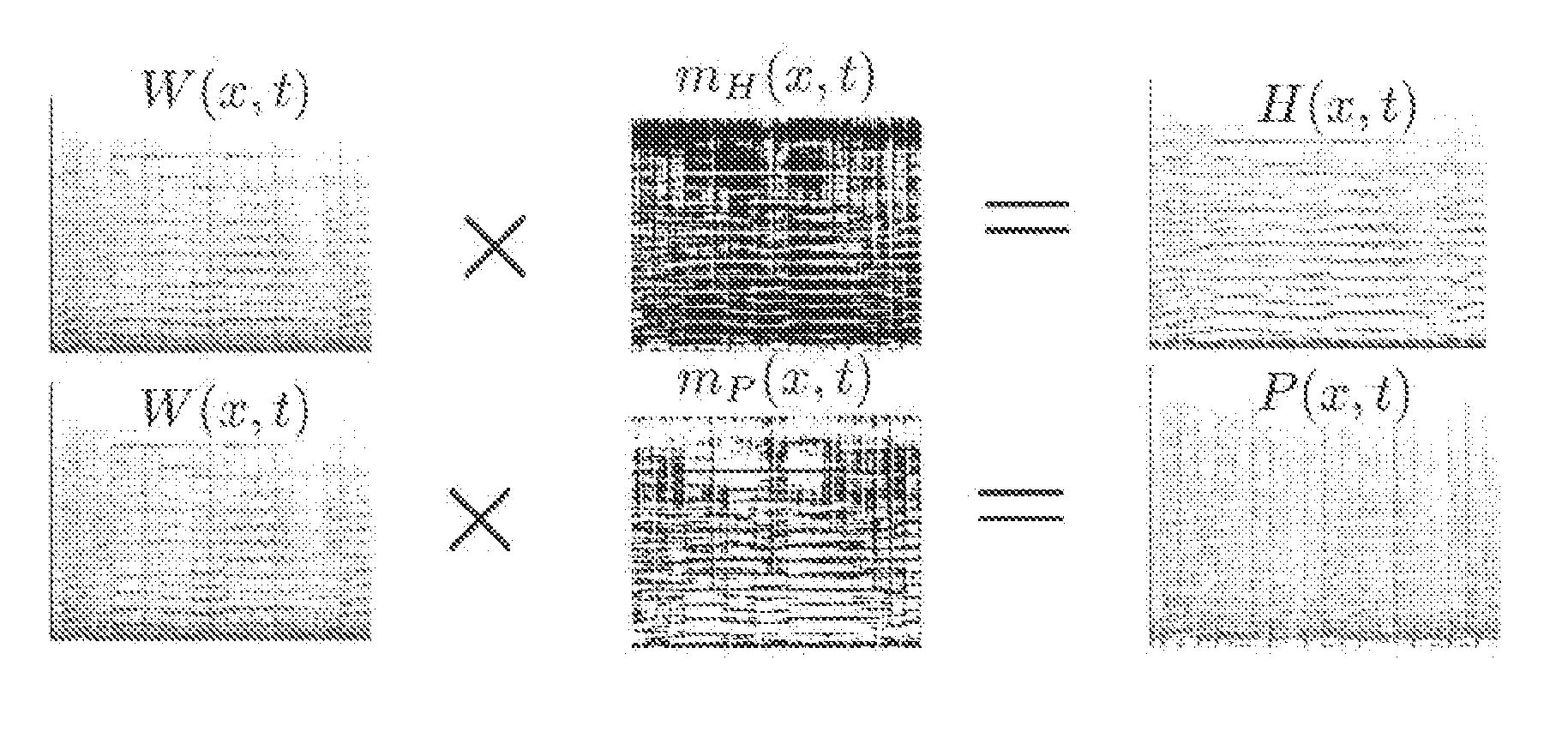
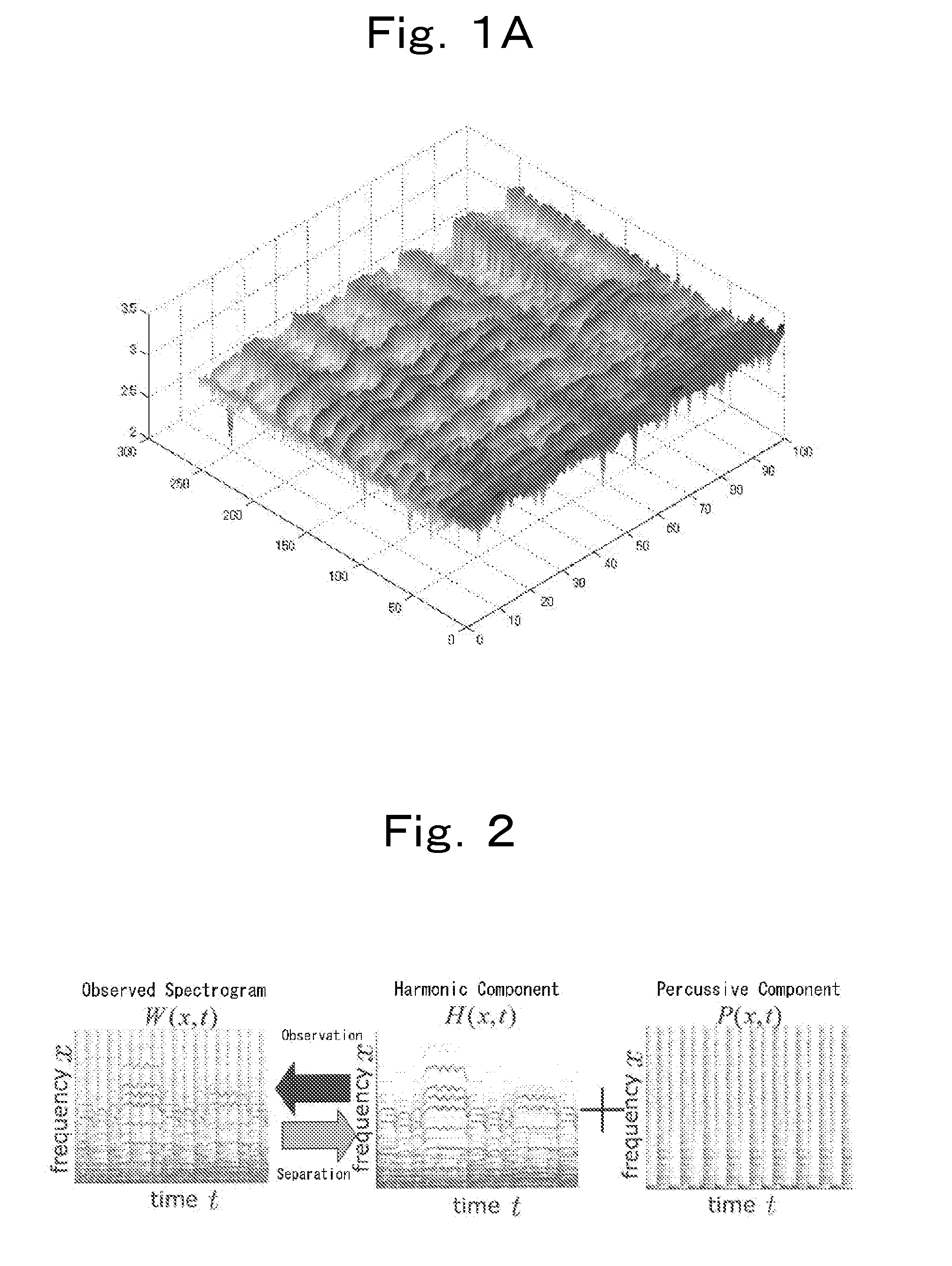
The present invention obtains a separated signal from an audio signal based on the anisotropy of smoothness of spectral elements in the time-frequency domain. A spectrogram of the audio signal is assumed to be a sum of a plurality of sub-spectrograms, and smoothness of spectral elements of each sub-spectrogram in the time-frequency domain has directionality on the time-frequency plane. The method comprises obtaining a distribution coefficient for distributing spectral elements of said audio signal in the time-frequency domain to at least one sub-spectrogram based on the directionality of the smoothness of each sub-spectrogram on the time-frequency plane, and separating at least one sub-spectrogram from said spectral elements of said audio signal using said distribution coefficient.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Wind turbine generator gear case fault diagnosis method based on VMD and FA_PNN
InactiveCN110595765AVerify validityVerify feasibilityMachine part testingEngineeringFirefly optimization
The invention discloses a wind turbine generator gear case fault diagnosis method based on VMD and FA_PNN. Firstly, gear case vibration signals acquired by a sensor are subjected to de-trending processing, then, the processed gear case vibration signals are subjected to VMD variation modal decomposition under the condition of different decomposition numbers and penalty factors, k modal componentsare obtained with a Pearson's correlation coefficient method, singular value entropy, power spectral entropy, marginal spectral entropy and instantaneous energy spectral entropy of the k modal components are extracted from three angles of time domain, frequency domain and time-frequency domain, a feature vector matrix capable of describing operating states of a wind turbine generator gear case ina quantization manner is formed, and finally, test sample data are tested with well-trained firefly optimized probabilistic neural network FA_PNN, so that fault diagnosis of the wind turbine generatorgear case is completed. Classified recognition of faults of the wind turbine generator gear case is realized.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
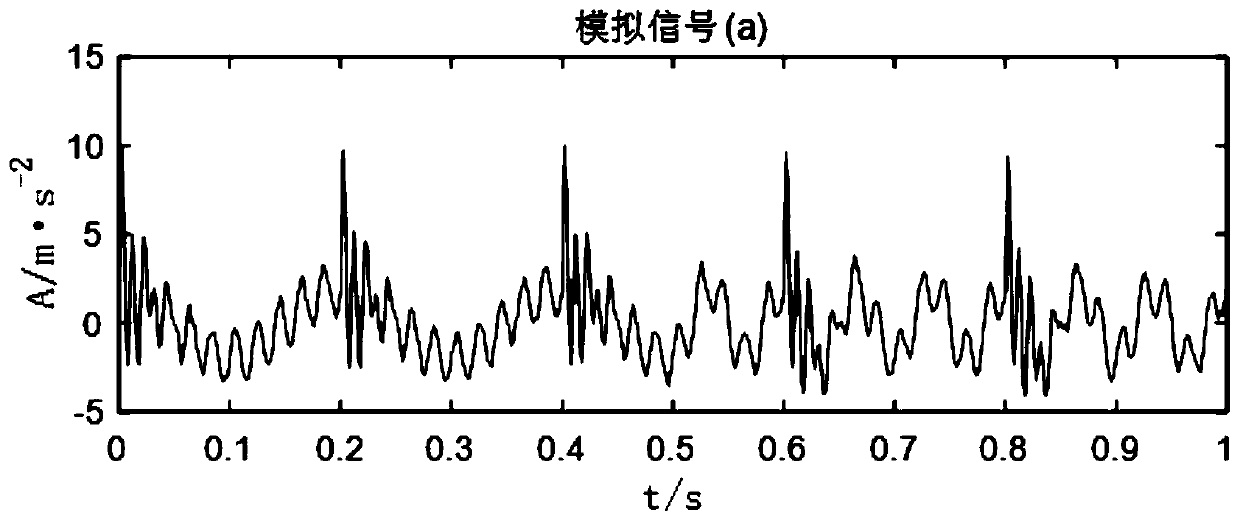
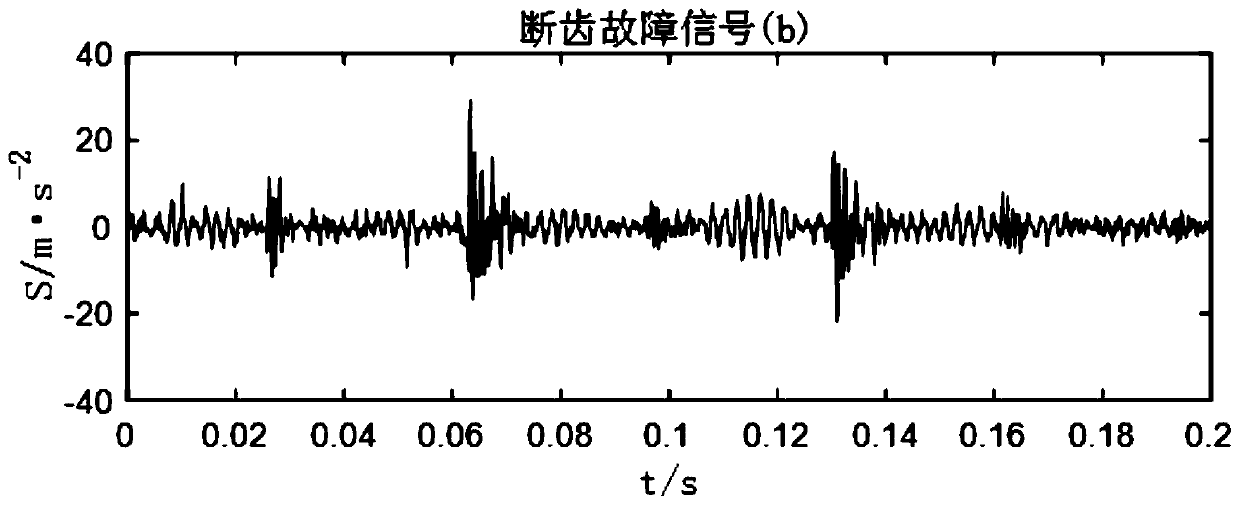
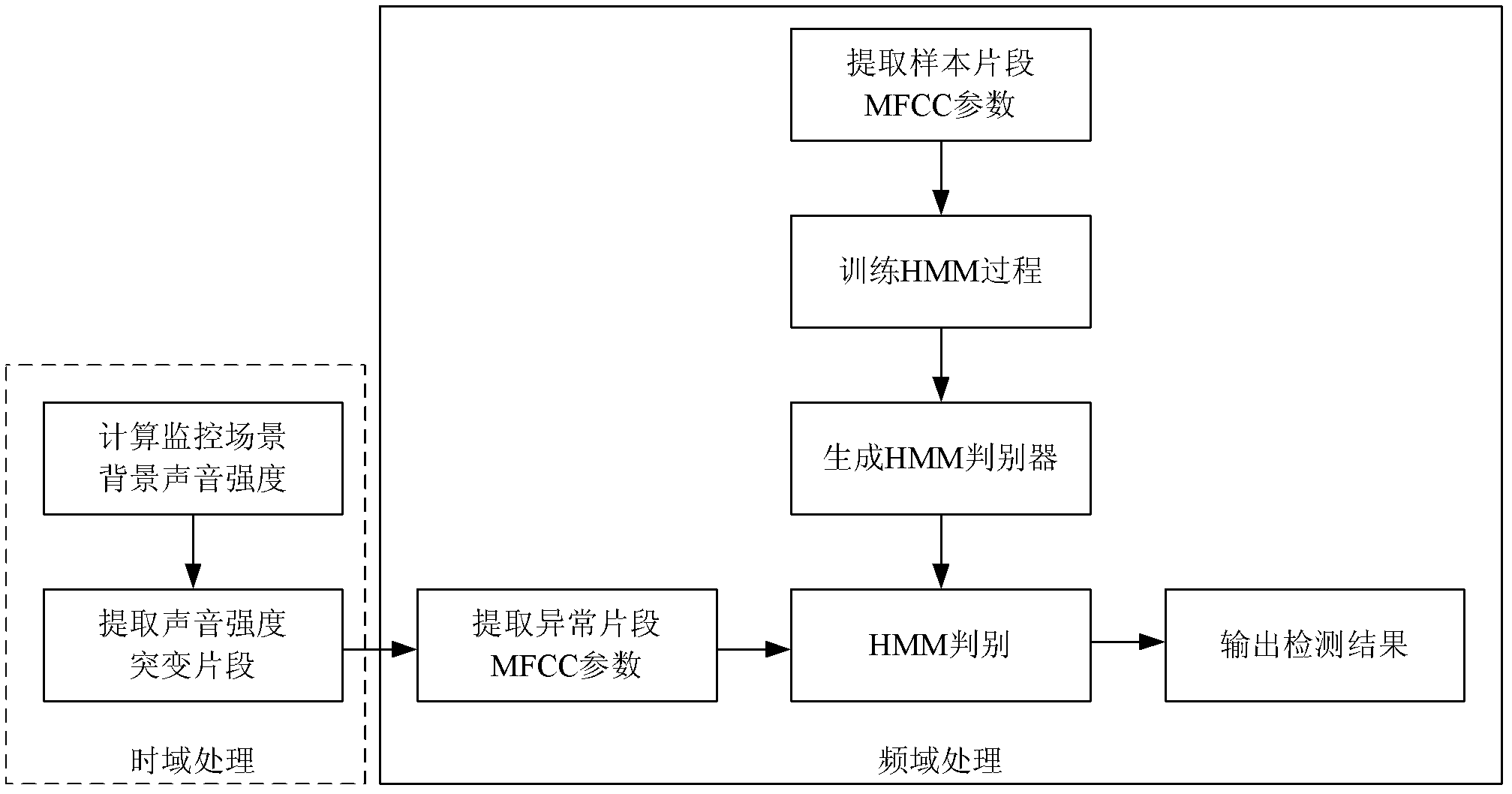
Abnormal voice detecting method based on time-domain and frequency-domain analysis
ActiveCN102664006AIncrease flexibilityImprove noise immunitySpeech recognitionTime domainMel-frequency cepstrum
The invention relates an abnormal voice detecting method based on time-domain and frequency-domain analysis. The method includes computing the background sound intensity of a monitored scene updated in real time at first, and detecting and extracting suddenly changed fragments of the sound intensity; then extracting uniform filter Mel frequency cepstrum coefficients of the suddenly changed fragments; and finally using the extracted Mel frequency cepstrum coefficients of sound of the abnormal fragments as observation sequences, inputting a trained modified hidden Markov process model, and analyzing whether the abnormal fragments are abnormal voice or not according to frequency characteristics of voice. Time sequence correlation is improved when the hidden Markov process model is added. The method is combined with time-domain extraction of suddenly changed energy frames and verification within a frequency-domain range, the abnormal voice can be effectively detected, instantaneity is good, noise resistance is high, and robustness is fine.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
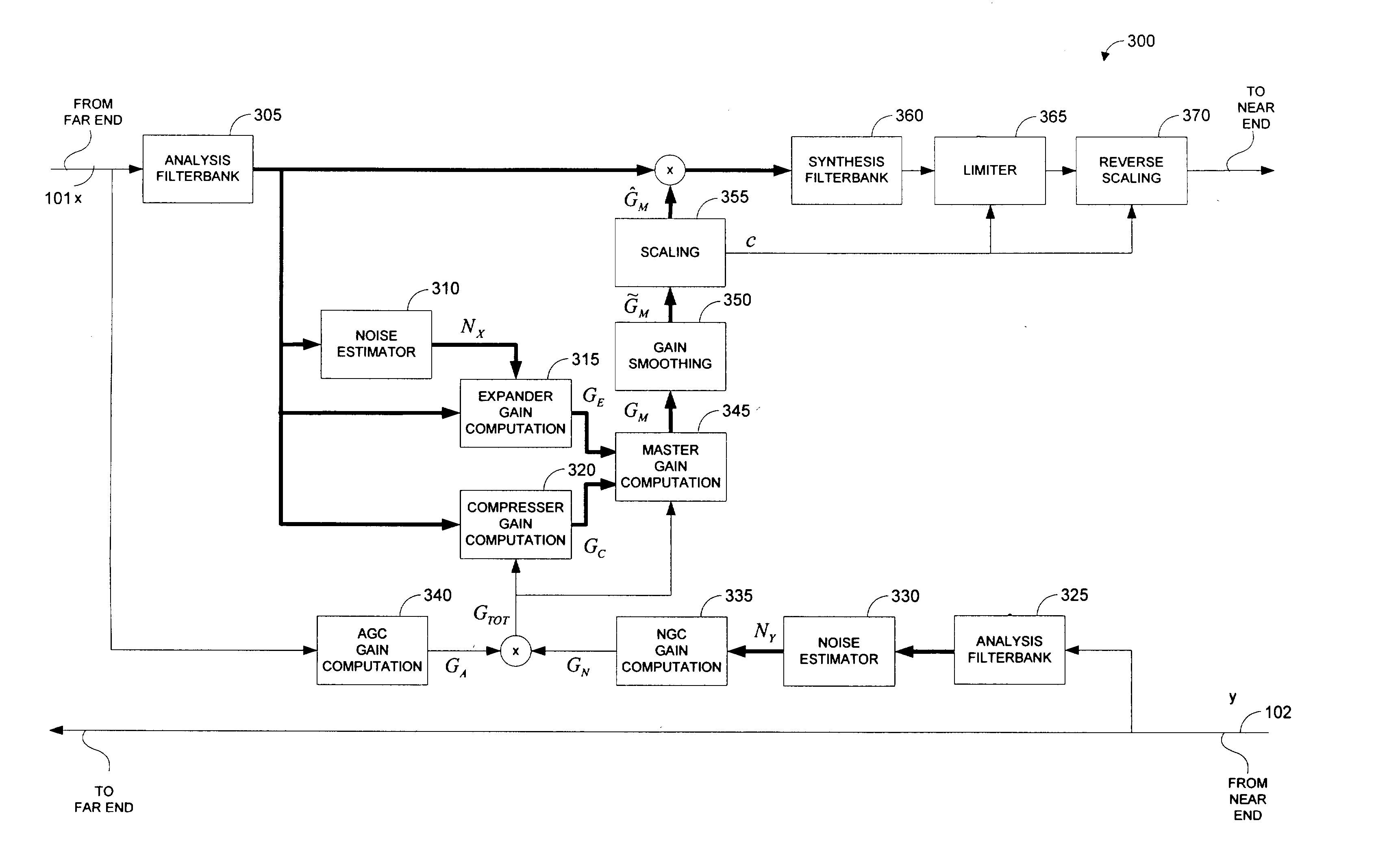
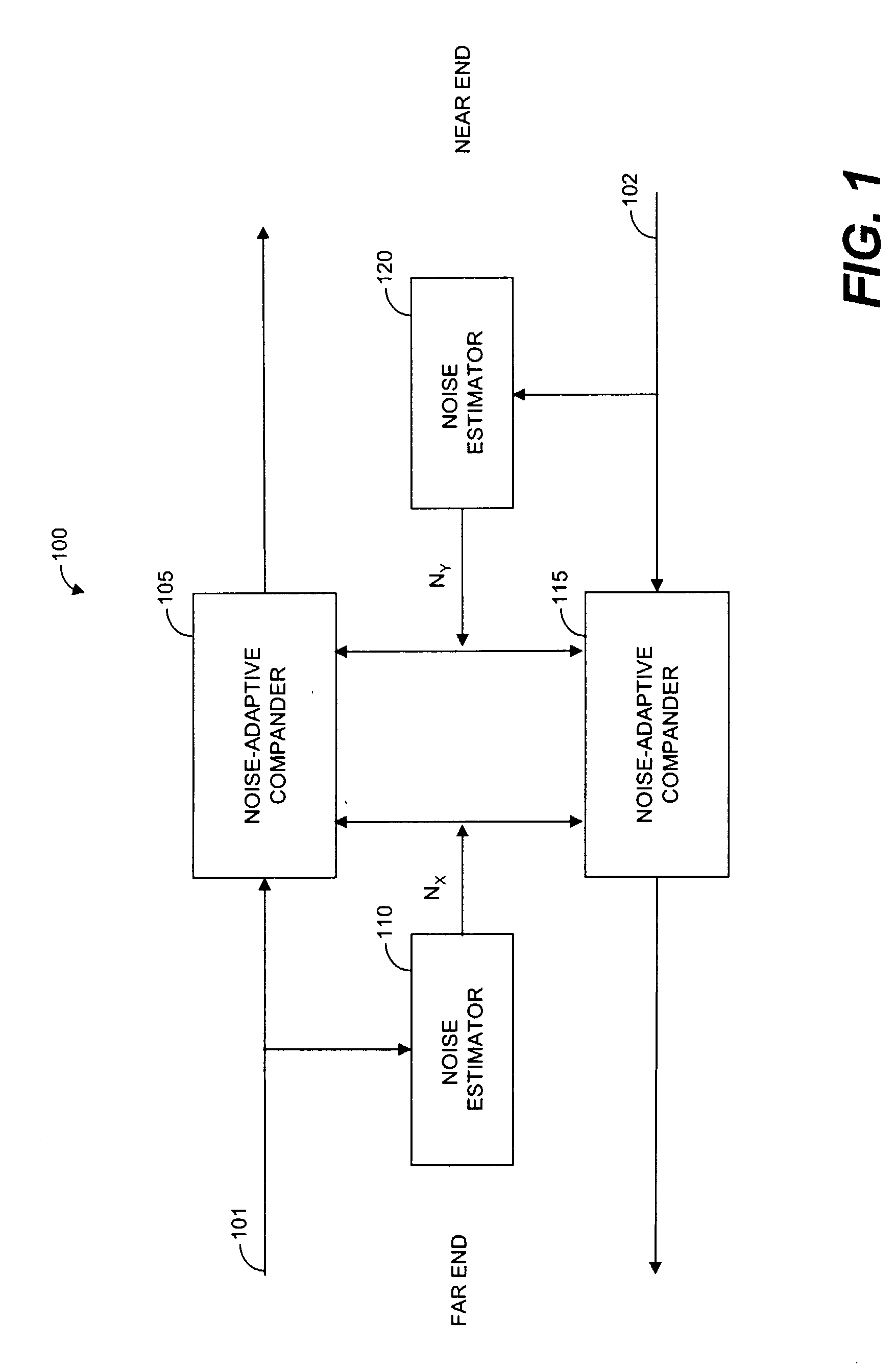
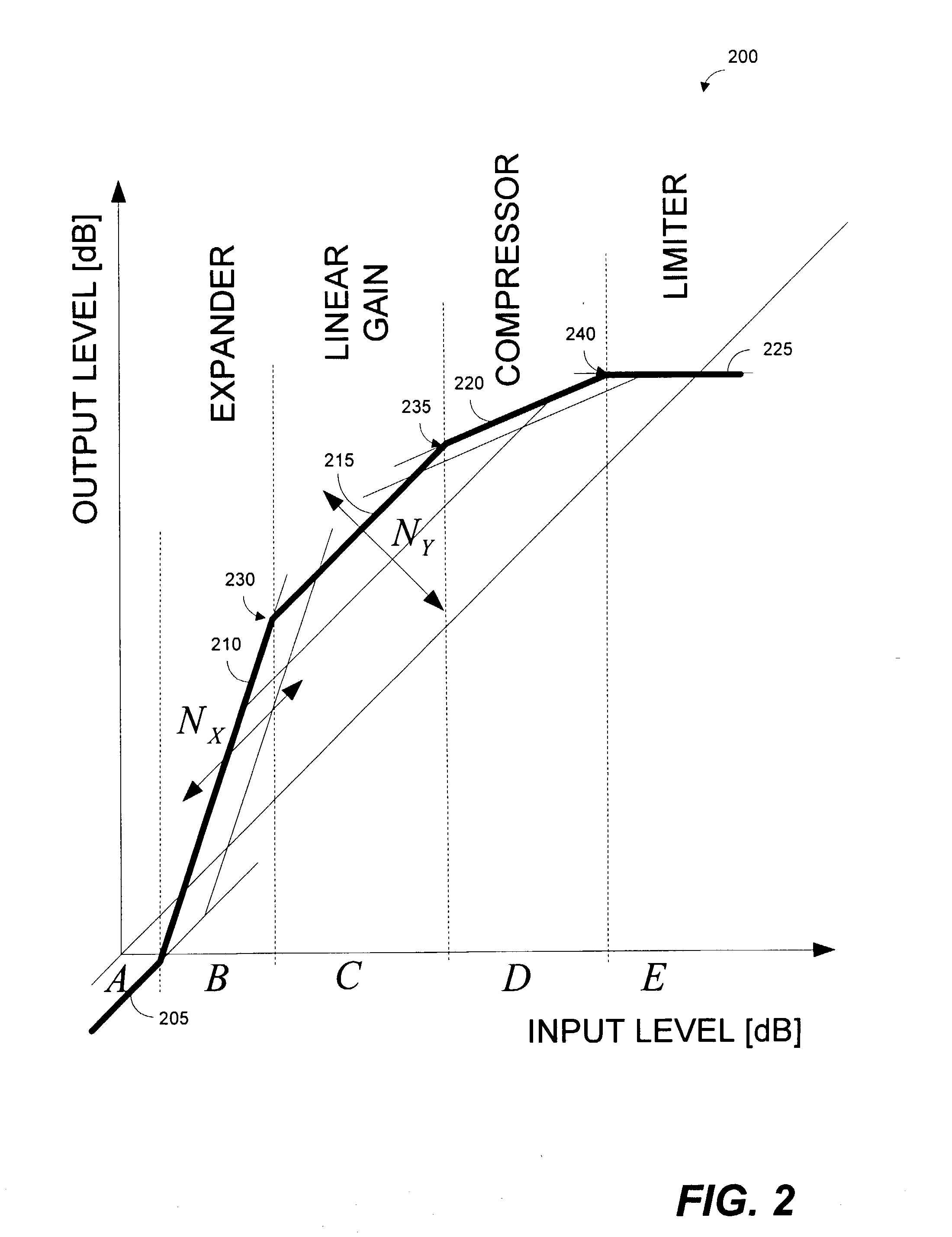
Systems and methods for far-end noise reduction and near-end noise compensation in a mixed time-frequency domain compander to improve signal quality in communications systems
InactiveUS20040101038A1Improve clarityReduce inconvenienceTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsFrequency-modulated carrier systemsTime domainCommunications system
Methods and systems for a mixed time-frequency domain compander, where the expander and compressor are applied in the frequency domain (subbands), while the limiter and the linear gain are applied in the time-domain (full band). Far-end noise reduction is achieved by adapting the expander gain to the far-end noise, near-end noise compensation is achieved by adapting the linear gain and the compressor gain to the near-end noise. The range of the linear gain section is set individually for each subband, but the linear gain is essentially applied to the full band signal via a scaling procedure. The scaling procedure first reduces the compander gain in the frequency domain by a scaling factor and then performs the reciprocal reverse scaling in the time domain. Far-end noise reduction is coupled to near-end noise compensation in order to avoid cross-modulation of the far-end noise by the near-end noise.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
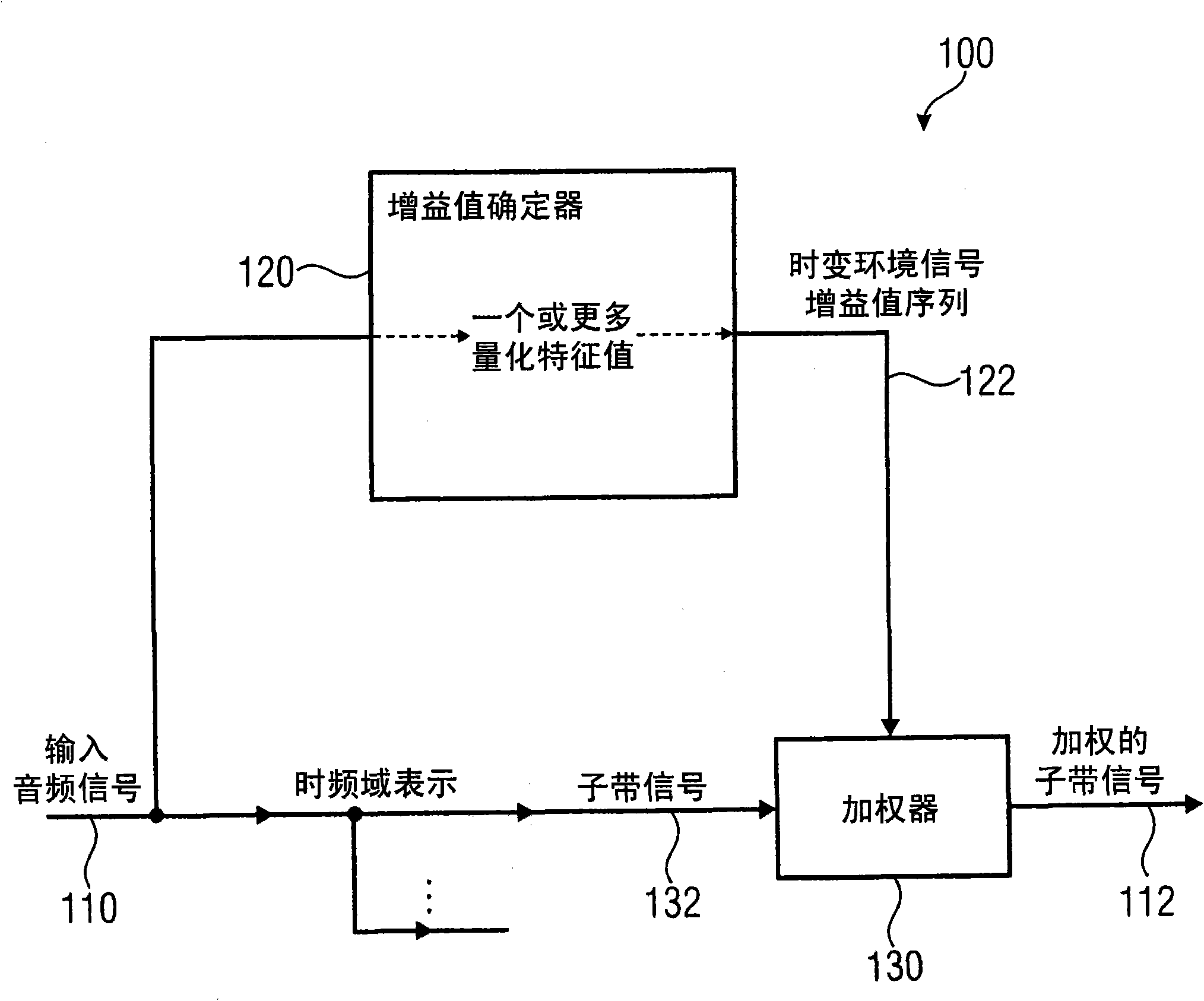
Apparatus and method for extracting an ambient signal in an apparatus and method for obtaining weighting coefficients for extracting an ambient signal and computer program
An apparatus for extracting an ambient signal from an input audio signal comprises a gain-value determinator configured to determine a sequence of time-varying ambient signal gain values for a given frequency band of the time-frequency distribution of the input audio signal in dependence on the input audio signal. The apparatus comprises a weighter configured to weight one of the sub-band signals representing the given frequency band of the time-frequency-domain representation with the time-varying gain values, to obtain a weighted sub-band signal. The gain-value determinator is configured to obtain one or more quantitative feature-values describing one or more features of the input audio signal and to provide the gain-value as a function of the one or more quantitative feature values such that the gain values are quantitatively dependent on the quantitative values. The gain value determinator is configured to determine the gain values such that ambience components are emphasized over non-ambience components in the weighted sub-band signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method for predicting service life of screw pair of numerical control machine on basis of performance degradation model
InactiveCN101870075APrecise real-timeAccurate predictionMachine gearing/transmission testingMeasurement/indication equipmentsNumerical controlVibratory signal
The invention provides a method for predicting the service life of a screw pair of a numerical control machine on the basis of a performance degradation model. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring vibration signals, carrying out time-frequency domain analysis, extracting the sensitive characteristic data vectors of the performance degradation of the screw pair, and forming a sensitive characteristic matrix in a time-sequence manner; calculating the load Pi of the screw pair and recording the operating time ti at the same time; calculating the rated life time Lhi, the total time t' that the screw pair has run under the current working condition, and the expected residual life LDi according to Pi, and forming an expected residual life vector T of the expected residual life in a time-sequence manner; and fitting the mapping relation between the inputted sensitive characteristic matrix and the expected residual life vector by using a degradation model formed by a double-layer dynamic fuzzy neural network, and outputting the prediction result of the service life. By taking the impact on the performance degradation of the screw pair caused by the load change thereof under various working conditions of the numerical control machine into consideration, the method of the invention can achieve the prediction of the residual life when the screw pair is used, and ensure the high prediction accuracy and high value in actual application.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Seismic wave absorption and attenuation compensation method
ActiveCN102109612AImprove signal-to-noise ratioHigh resolutionSeismic signal processingFrequency spectrumCurve fitting
The invention relates to a seismic wave absorption and attenuation compensation method, and belongs to the geophysical exploration data processing technology. The method comprises the following steps: selecting one of VSP (vertical seismic profiling) initial data as reference data, carrying out generalized S-transform on the reference data, selecting sampling points as reference points, and recording the time and time-frequency spectrums of the sampling points; carrying out generalized S-transform on data of each sampling point, and dividing the time-frequency spectrum of corresponding frequency in the time-frequency spectrums of the reference points by the time-frequency spectrum of each sampling point so as to obtain an absorption and attenuation curve; determining a natural logarithm to figure out a phase compensation operator according to a formula of frequency difference of absorption and attenuation signals in a time frequency domain; and carrying out absorption and attenuation compensation and phase compensation in the time frequency domain to obtain a fine VSP wave field profile. The method has the advantages that noise can be eliminated during the process of fitting the absorption and attenuation curve; generalized S-inverse transform without energy loss is realized; signal-to-noise ratio and resolution of the data are improved after compensation; log resolution control is realized; the reference points are selected flexibly; and algorithm is simple and efficient.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com