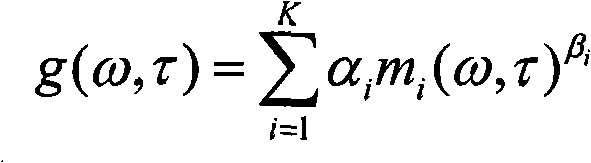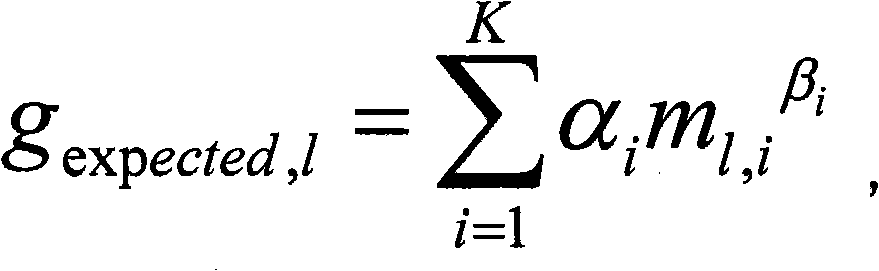Patents
Literature
807 results about "Signal gain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Signal gain is a signal measurement performed at the antenna output. It is usually measured in db or micro volts. The most popular is displayed as dB. This particular measurement has been misused increasingly in the last decade.
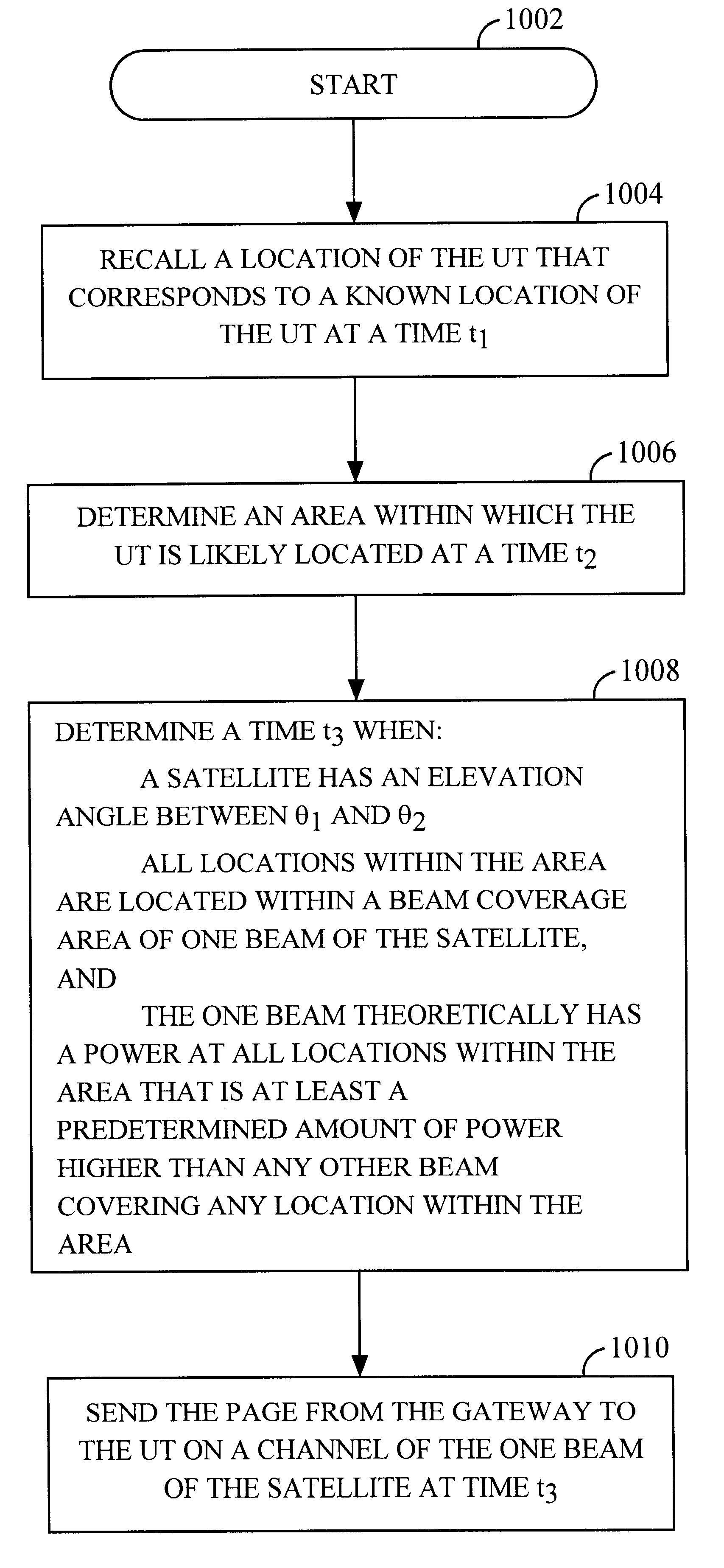
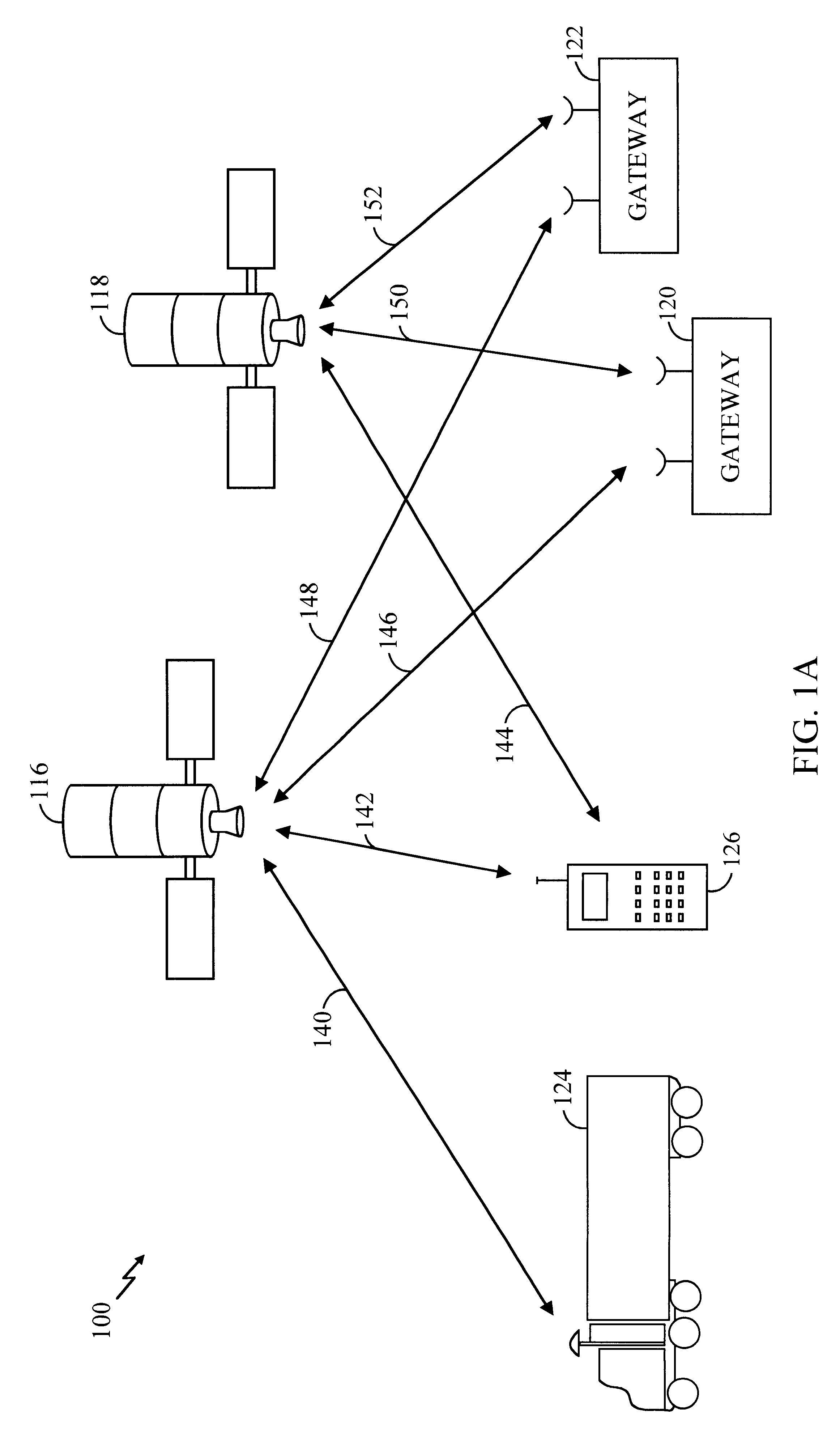
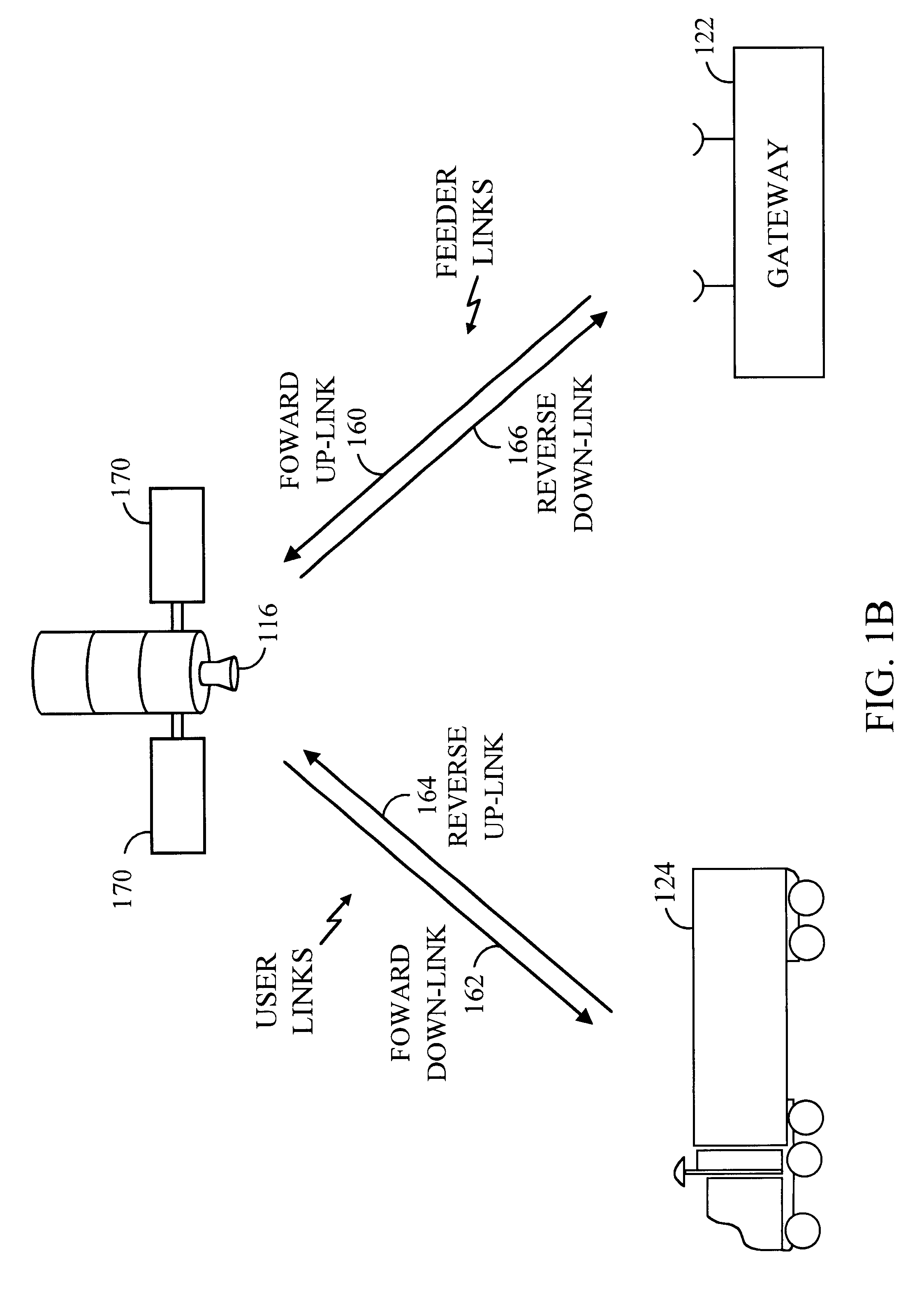
Method and apparatus for paging a user terminal within the "sweet spot" of a satellite
An apparatus and method for paging a user terminal (UT) using a satellite communications system having a gateway and one or more satellites, wherein each satellite produces a plurality of beams and each beam includes a plurality of channels. The method of the present invention includes the step of recalling a location of the UT, wherein the recalled location corresponds to a location of the UT at a time t1. In one embodiment this is accomplished by performing a lookup in a table that includes location information for user terminals at different points in time. The method also includes the step of determining an area, based on the recalled location, within which the UT is assumed to be located at a time t2, where time t2 is later in time than time t1. The next step is to determine a time t3, where t3 is equal to or later in time than time t2, when the following two criteria are satisfied. First a satellite of the one or more satellites has an elevation angle between theta1 and theta2. Second, all locations within the area are located within a footprint of the satellite (that has an elevation angle between theta1 and theta2). The elevation angles theta1 and theta2 can be determined from the perspective of the recalled location. Alternatively, the elevation angle can be determined from the perspective of all locations within the area. This ensures that the UT is in the "sweet spot" of the satellite (where the gain of signals sent from the satellite are highest) when the UT is paged. A page is then sent from the gateway to the UT on a channel of a beam of the satellite at time t3. The page can be sent on a channel of every beam of a plurality of beams that make up the footprint of the satellite at time t3. Alternatively, the page can be sent on a channel of selected beams of the footprint. By waiting until the UT is within the "sweet spot" to page the UT, less power can be used by the satellite. In addition, this type of operation allows the UT to use an antenna that has a substantial gain only when the UT is within the "sweet spot". This allows the use of satellite power to be reduced further.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
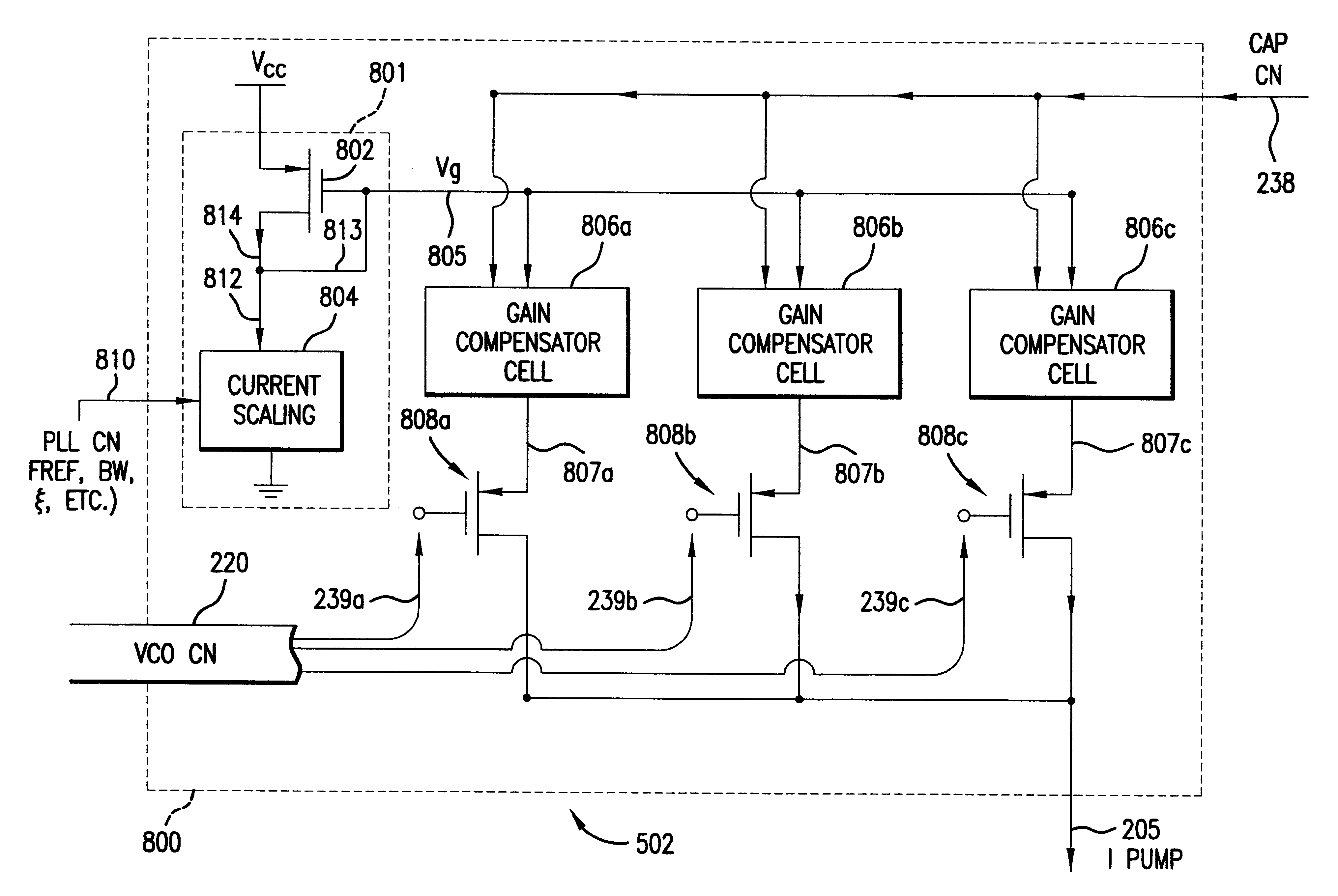
Apparatus and method for phase lock loop gain control using unit current sources
InactiveUS6583675B2Pulse automatic controlDiscontinuous tuning for band selectionFixed capacitorReference current
A gain compensator compensates for the gain variation of a varactor-tuned voltage tuned oscillator (VCO) in a phase lock loop (PLL). The VCO includes a parallel LC circuit having multiple fixed capacitors that can be switched-in or switched-out of the LC circuit according to a capacitor control signal to perform band-select tuning of the VCO. The gain compensator compensates for the variable VCO gain by generating a charge pump reference current that is based on the same capacitor control signal that controls the fixed capacitors in the LC circuit. The gain compensator generates the charge pump reference current by replicating a reference scale current using unit current sources. The number of times the reference scale current is replicated is based on the fixed capacitance that is switched-in to the LC circuit and therefore the frequency band of the PLL. The reference scale current is generated based on a PLL control that specifics certain PLL characteristics such as reference frequency, loop bandwidth, and loop damping. Therefore, the reference pump current can be efficiently optimized for changing PLL operating conditions, in addition to compensating for variable VCO gain.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
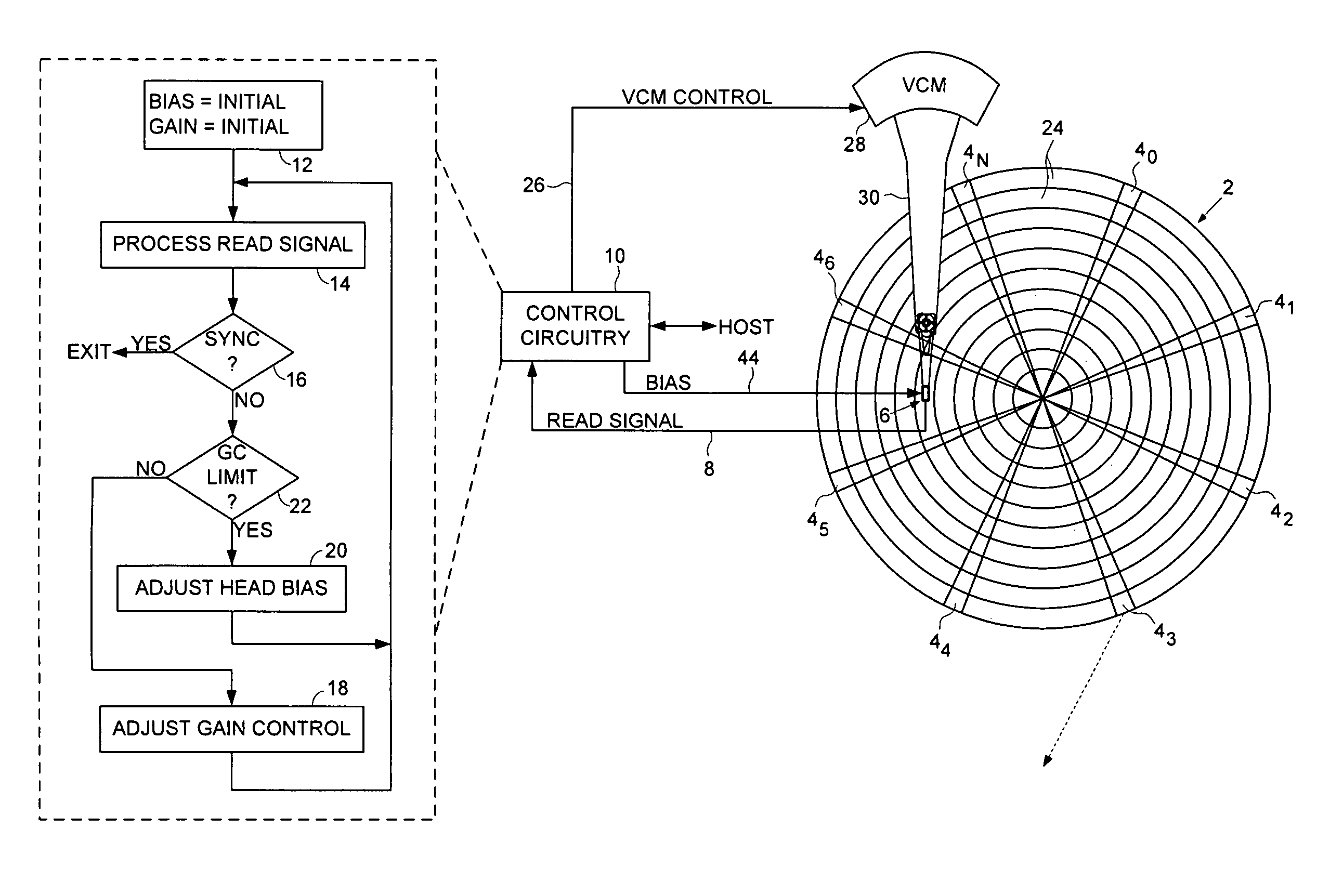
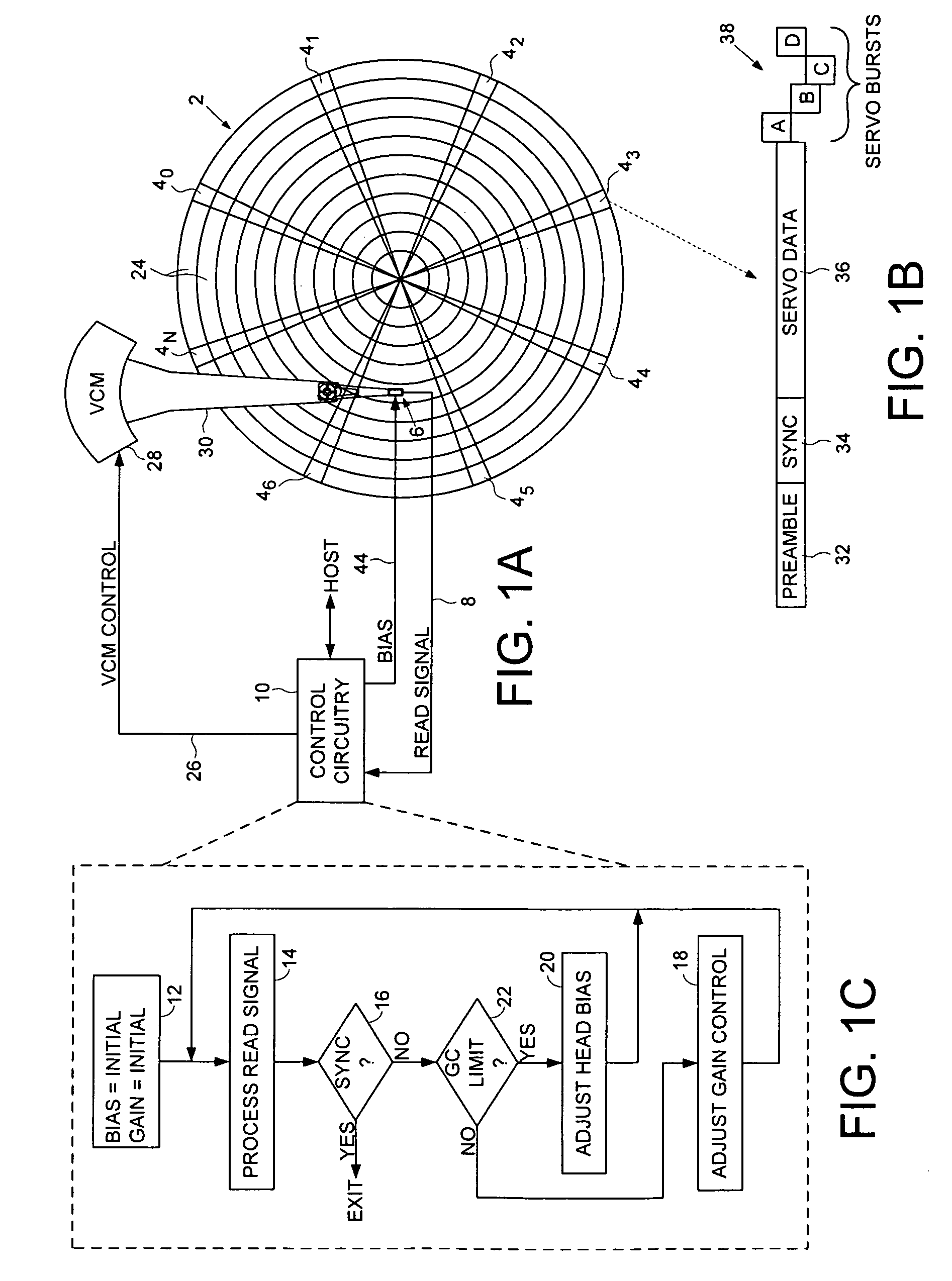
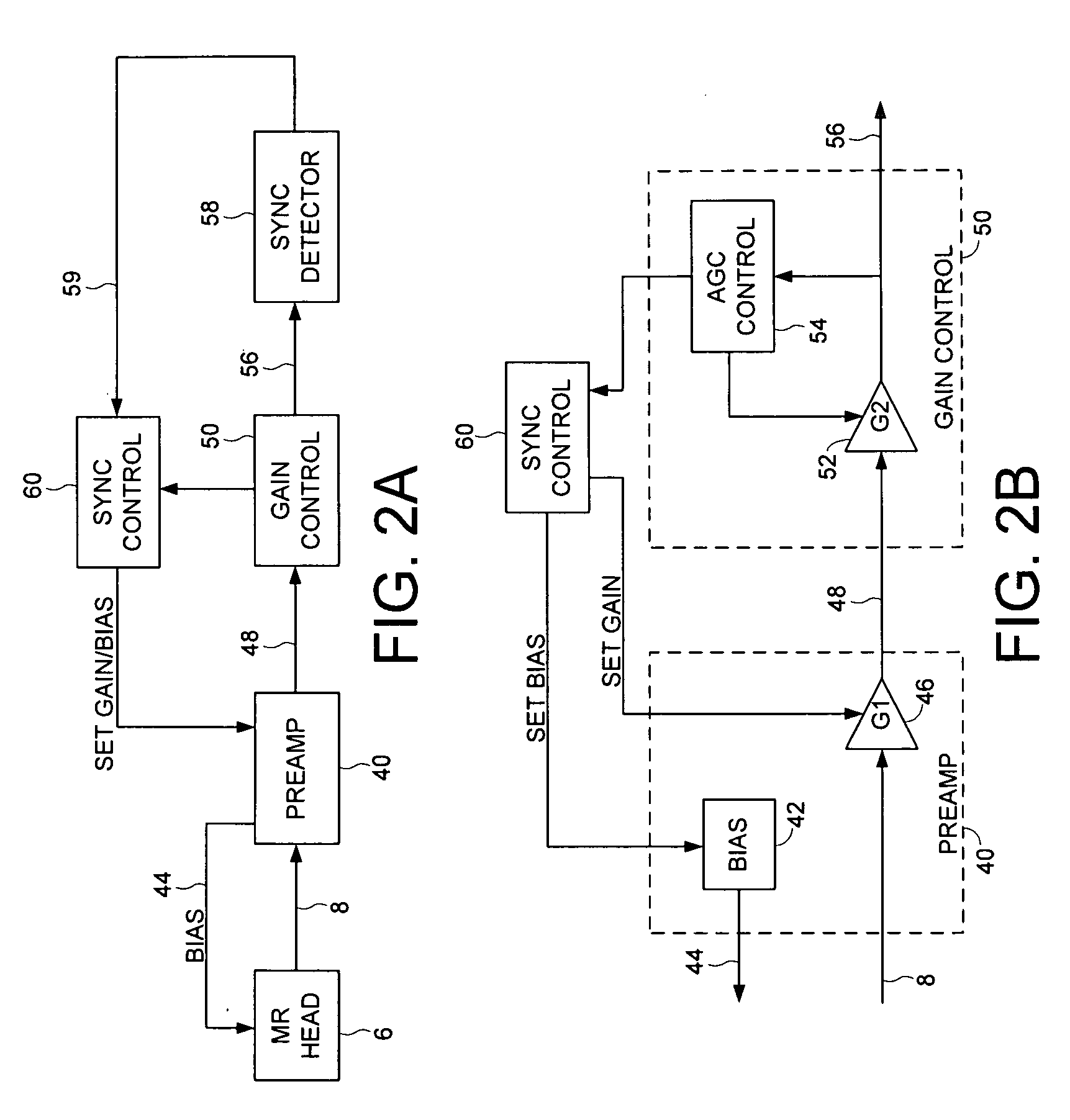
Disk drive adjusting head bias during servo synchronization to compensate for over/under sensitivity
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk including a plurality of servo sectors, a head actuated over the disk, the head for generating a read signal, and a gain control circuit for adjusting a gain of the read signal in response to a gain setting. A bias setting is initialized for the head, and the gain setting for the read signal is initialized. The read signal is processed to detect at least one of the servo sectors, and when at least one of the servo sectors is not detected, the gain setting is adjusted. The read signal is processed with the adjusted gain setting to detect at least one of the servo sectors, and when at least one of the servo sectors is not detected with the adjusted gain setting, the bias setting is adjusted in response to the adjusted gain setting.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
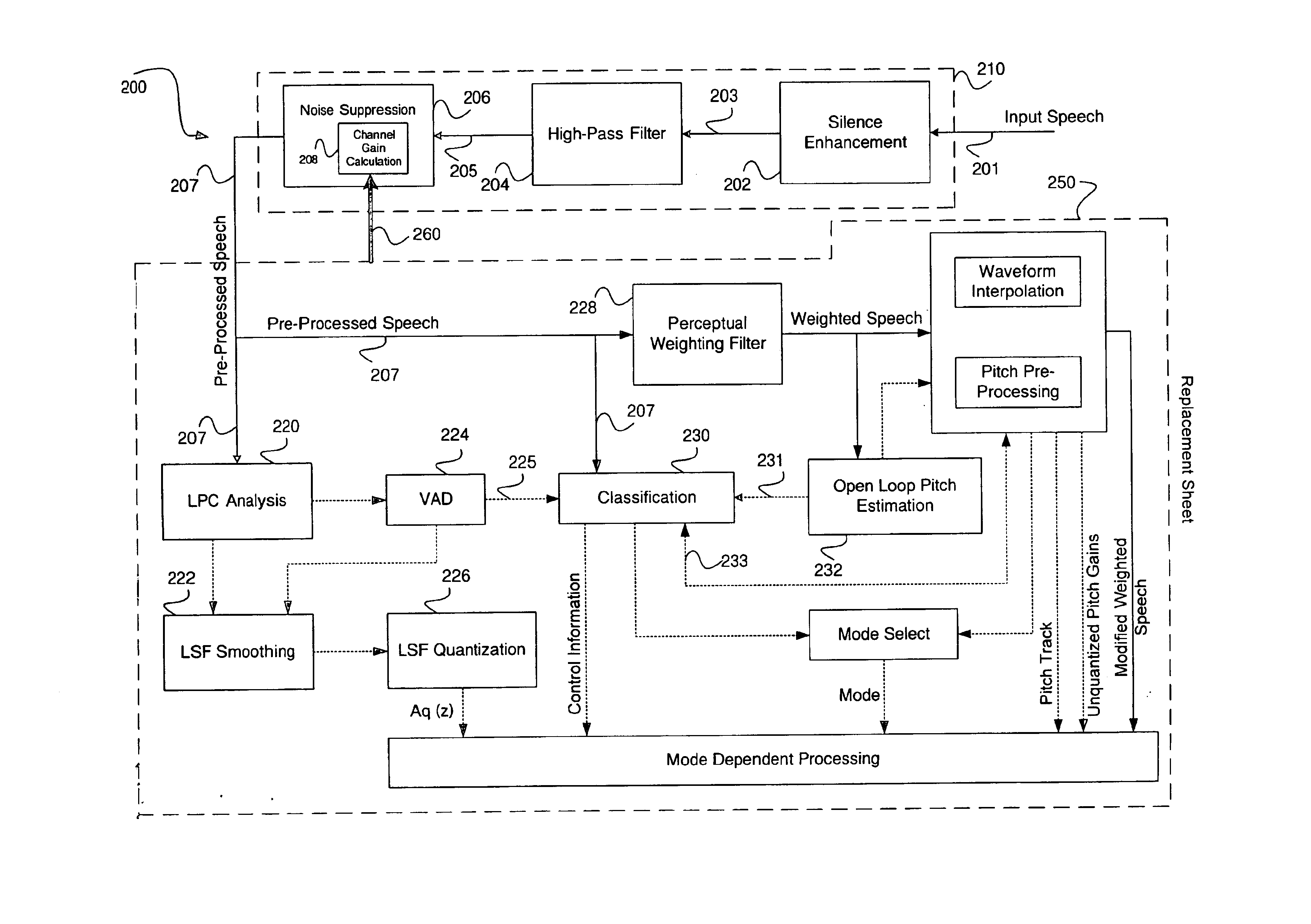
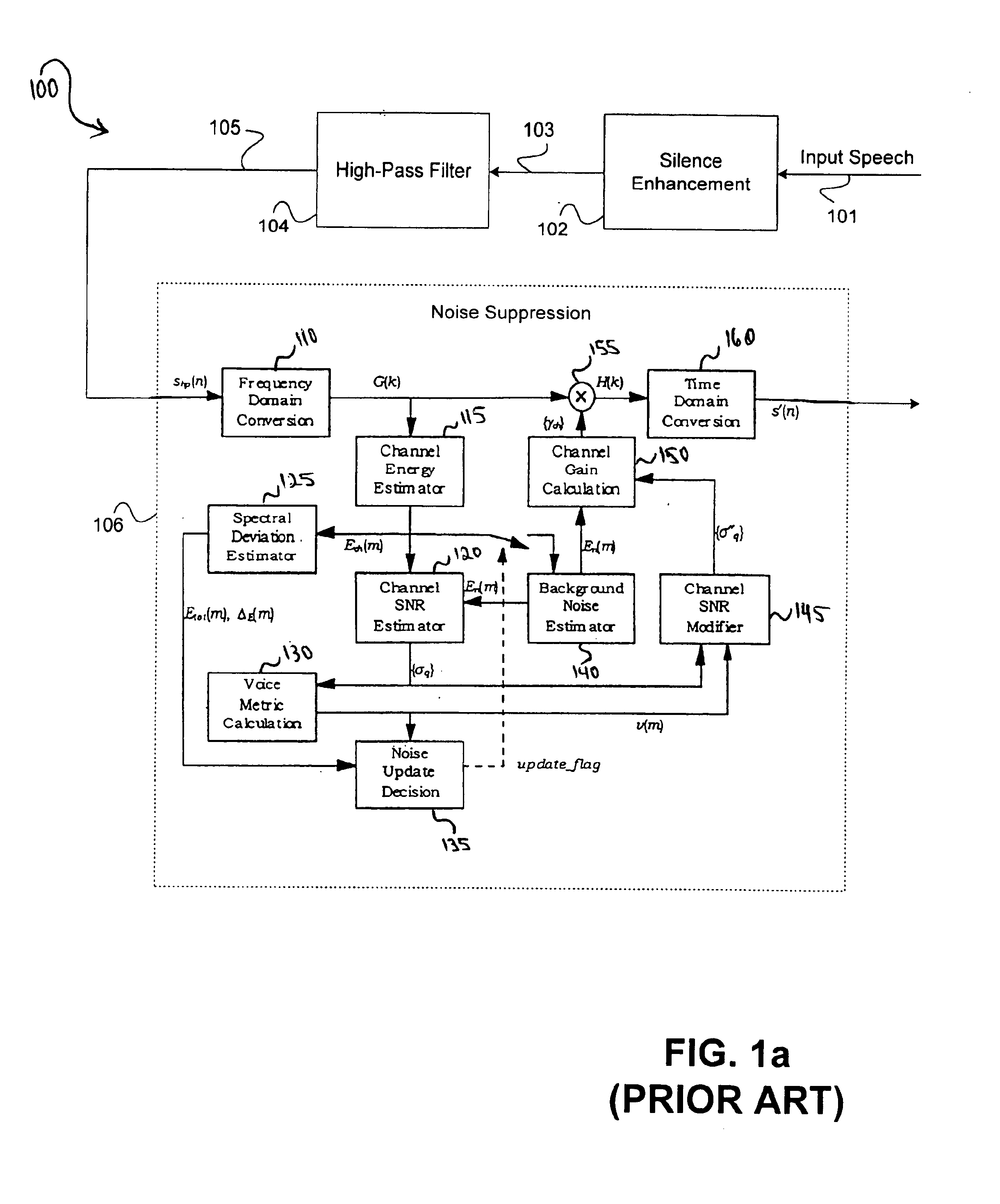
Noise suppression in the frequency domain by adjusting gain according to voicing parameters
An input signal enters a noise suppression system in a time domain and is converted to a frequency domain. The noise suppression system then estimates a signal to noise ratio of the frequency domain signal. Next, a signal gain is calculated based on the estimated signal to noise ratio and a voicing parameter. The voicing parameter may be determined based on the frequency domain signal or may be determined based on a signal ahead of the frequency domain signal with respect to time. In that event, the voicing parameter is fed back to the noise suppression system, for example, by a speech coder, to calculate the signal gain. After calculating the gain, the noise suppression system modifies the signal using the calculated gain to enhance the signal quality. The modified signal may further be converted from the frequency domain back to the time domain for speech coding.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC +1
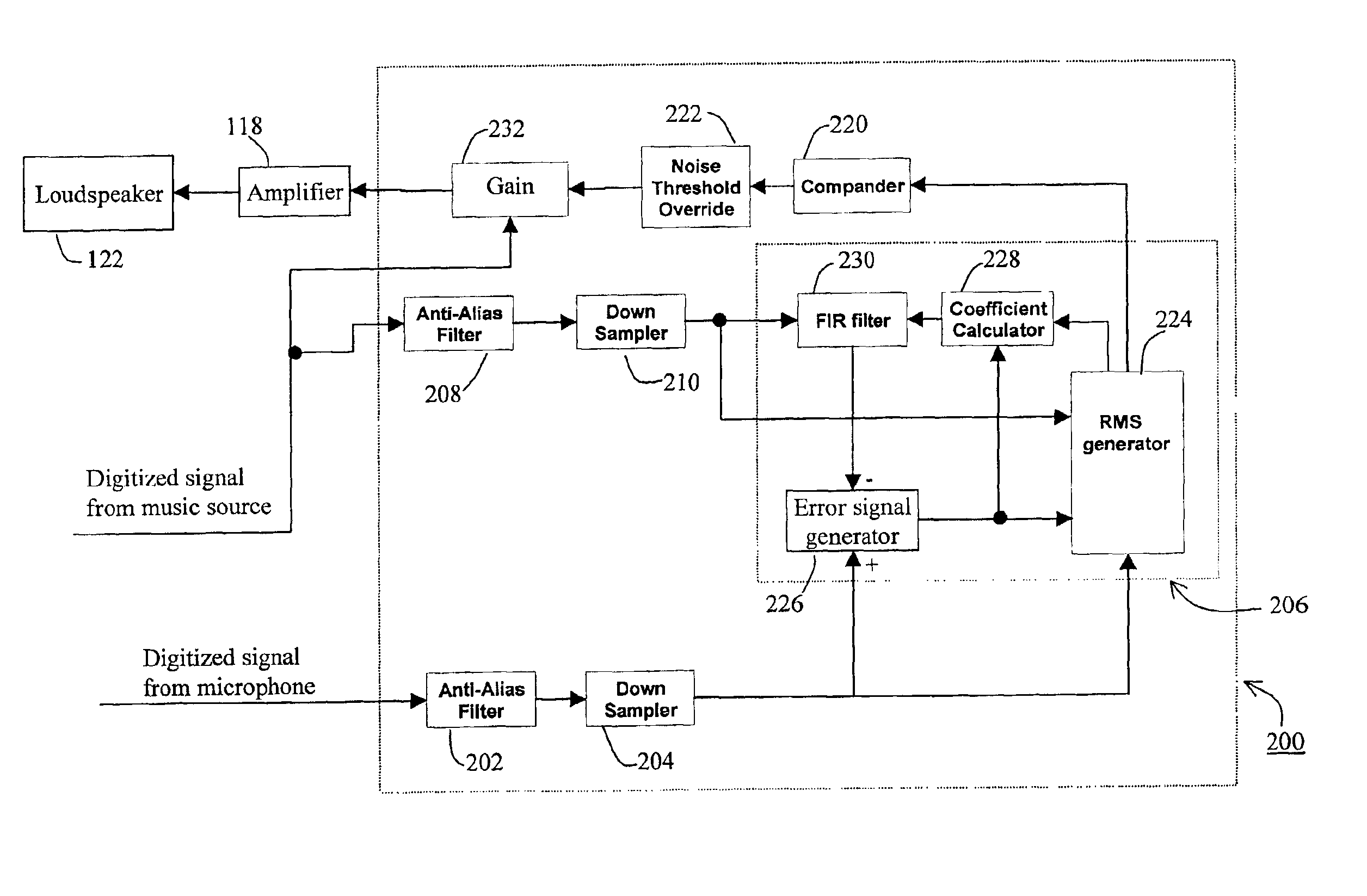
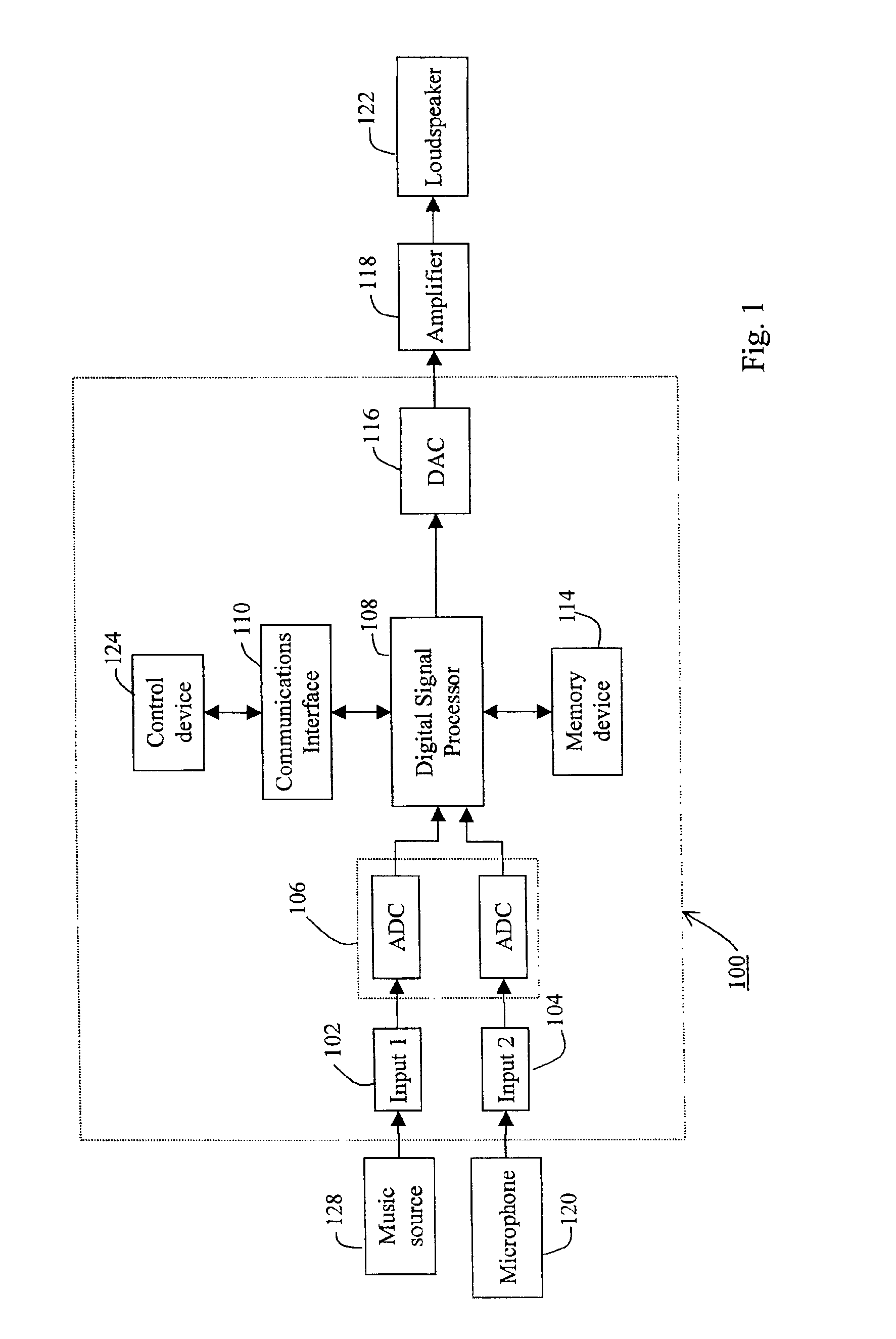
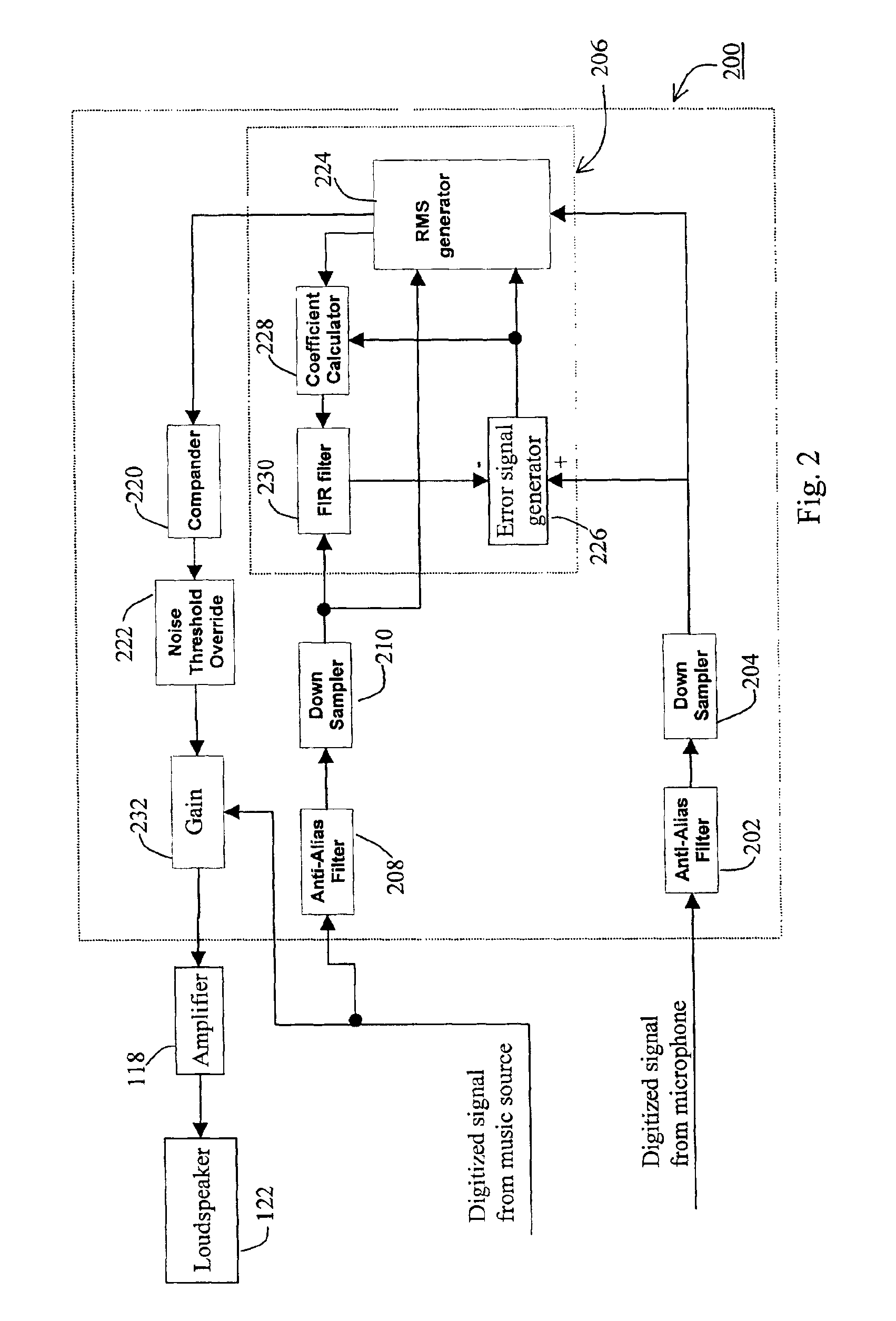
Method and apparatus for automatic volume control in an audio system
InactiveUS6868162B1Quick calibrationSet become largeGain controlAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlAdaptive filterAutomatic control
An audio system (100) is provided with improved adaptive filter (206) to automatically adjust signal gain depending on the ambient noise level. The original music signal passes through a normalized adaptive filter (206), and is subtracted from the ambient room signal detected by a microphone (120), resulting in an error signal that is an estimate of the ambient noise. The error signal is used to update a set of adaptation coefficients so that the normalized adaptive filter more accurately simulates the room transfer function, resulting in an better estimate of the ambient noise. The audio system (100) is calibrated automatically upon initial use to determine adaptation coefficients and noise threshold level to prevent runaway gain. System parameters are adjusted using a controller (124) with a user-friendly interface (400).
Owner:MACKIE DESIGNS
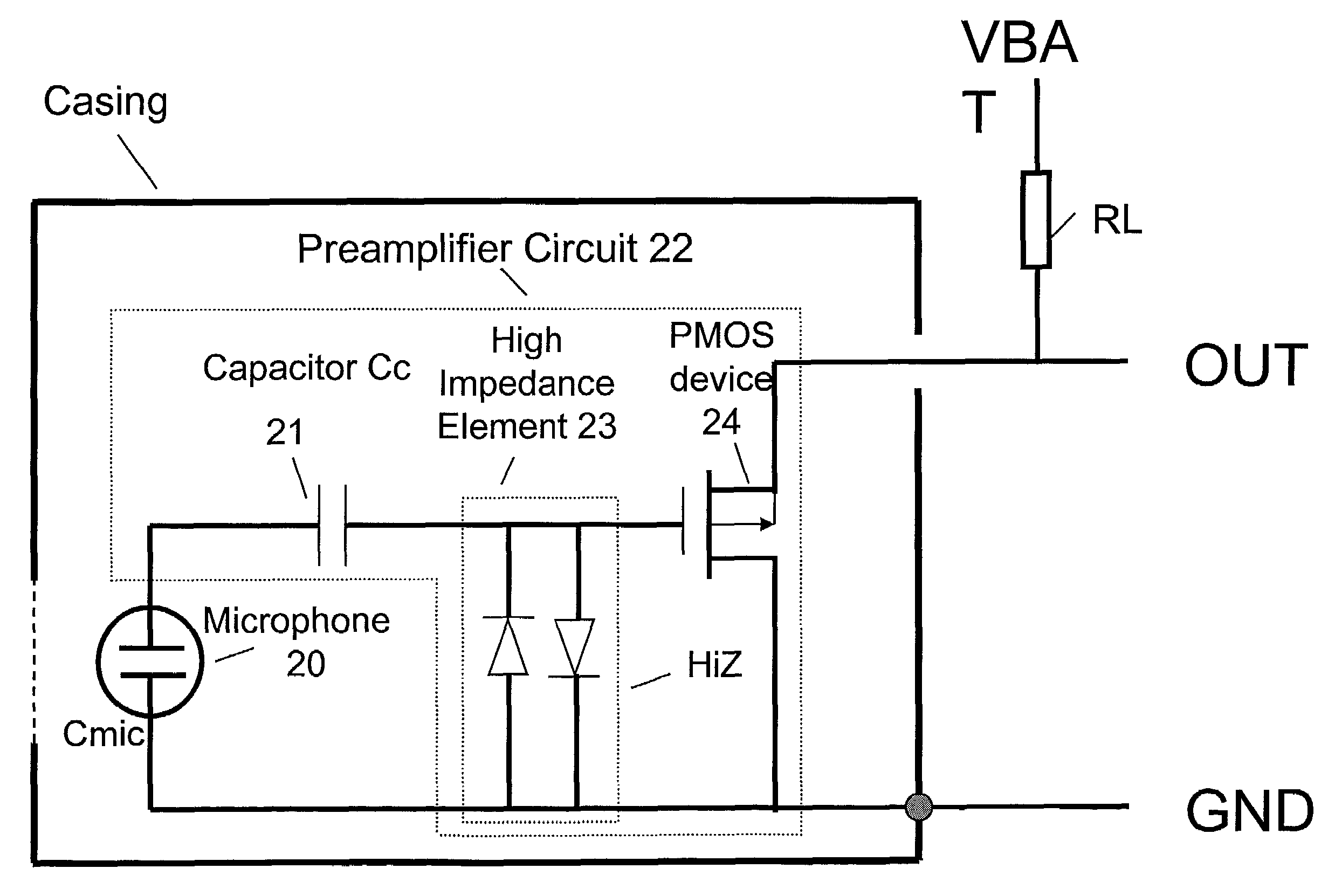
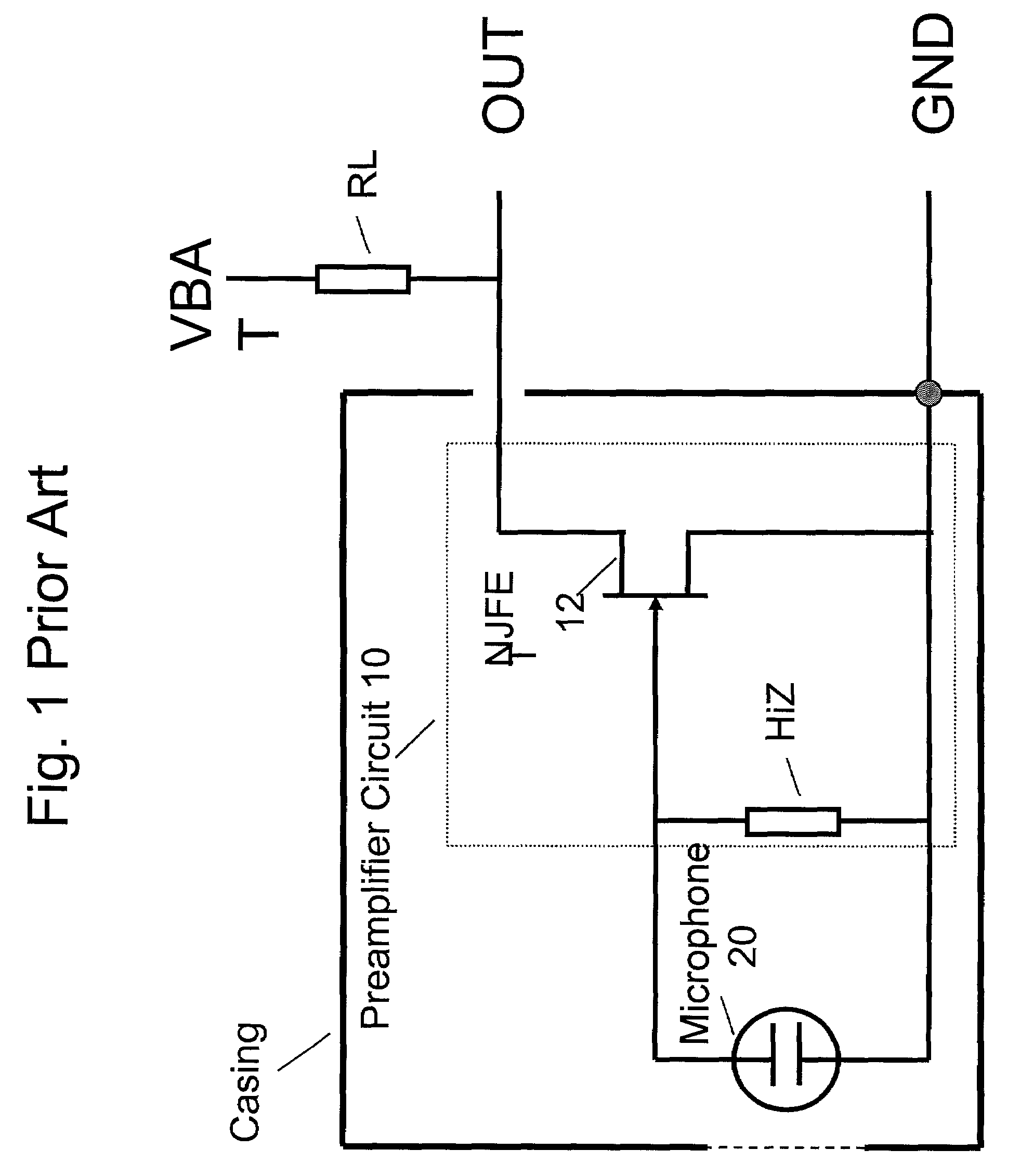
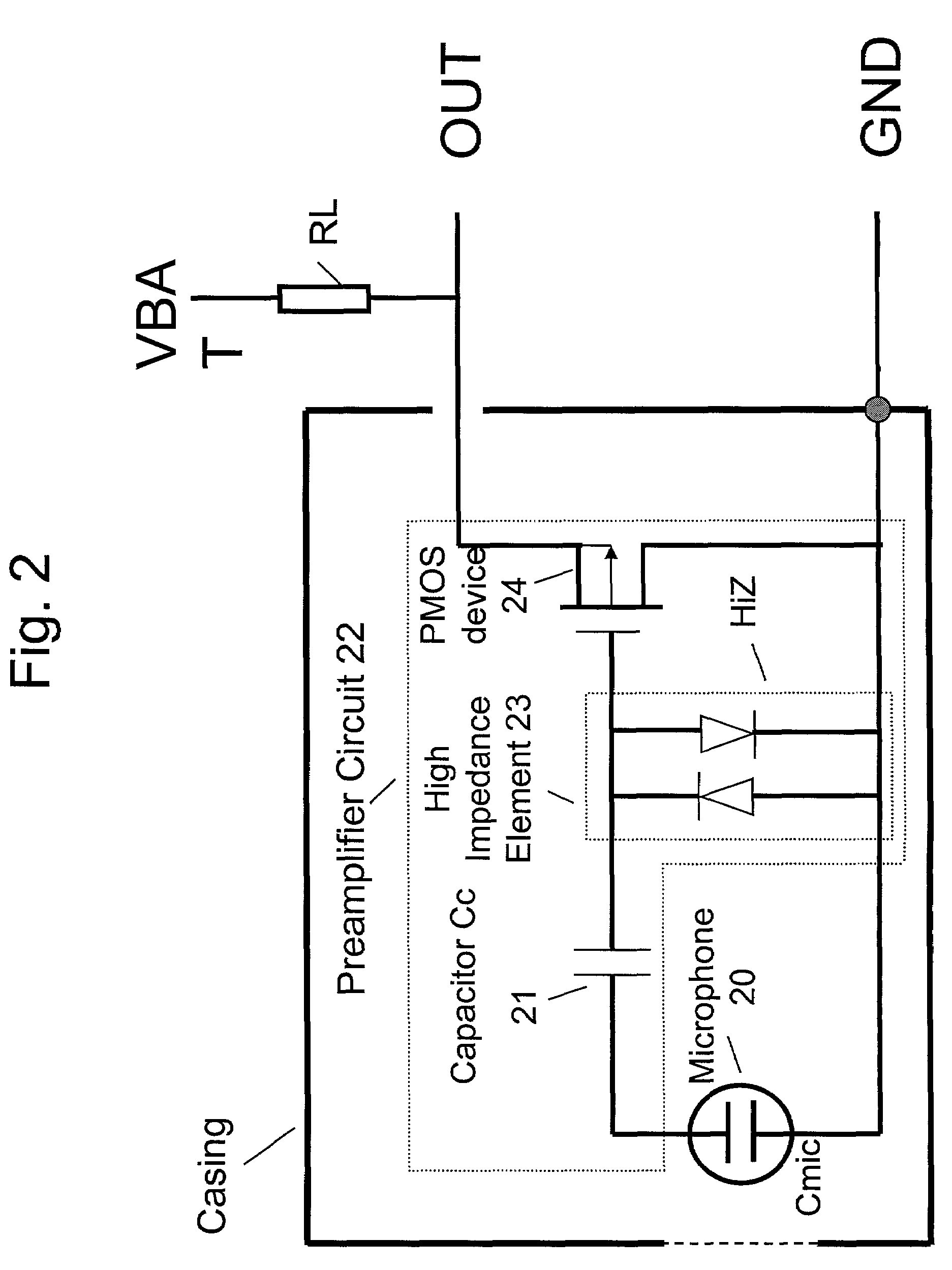
Electret condensor microphone preamplifier that is insensitive to leakage currents at the input
InactiveUS7110560B2Reduce input leakage currentAvoid leakage currentLow frequency amplifiersTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsCapacitanceOperating point
A preamplifier having extremely high input impedance amplifies the electrical signal output from an electret condenser microphone (ECM) without suffering from the effects of a DC leakage current at the input. The preamplifier circuit includes a pair of cross-coupled PN junction diodes setting the input impedance, a PMOS device, and a load resistor configured similarly to a conventional preamplifier. A capacitor is placed between the input and the cross-coupled diodes such that a DC path no longer exists to bias the cross-coupled diodes. Therefore, leakage currents are prevented from upsetting the DC operating point of the preamplifier and biasing the cross-coupled diodes. Consequently, small signal gain distortion, excessive demodulation products and increased noise can be avoided.
Owner:SONION
Passive repeater for wireless communications
InactiveUS20110063181A1Increased RF signal strengthHigh strengthAntenna arraysPassive radio relay systemsSignal gainRadio frequency
Some embodiments provide a relatively small antenna apparatus that acts as a passive repeater. The antenna apparatus can be designed to facilitate radio frequency (RF) signal gain for a collection or range of frequencies. In some embodiments, the antenna apparatus is placed near a device with a wireless receiver and / or transmitter, where the antenna apparatus causes increased RF signal intensity at the device by coupling RF signals from a proximate area of higher RF signal intensity into the area around the device. Accordingly, in some instances, an embodiment of the antenna apparatus can be used to increase the RF signal intensity in a null spot or dead spot by coupling RF signal energy from an area proximate to the null spot that has higher RF signal intensity.
Owner:WALKER MICHAEL CLYDE
Method and apparatus for reducing noise in speech and audio signals
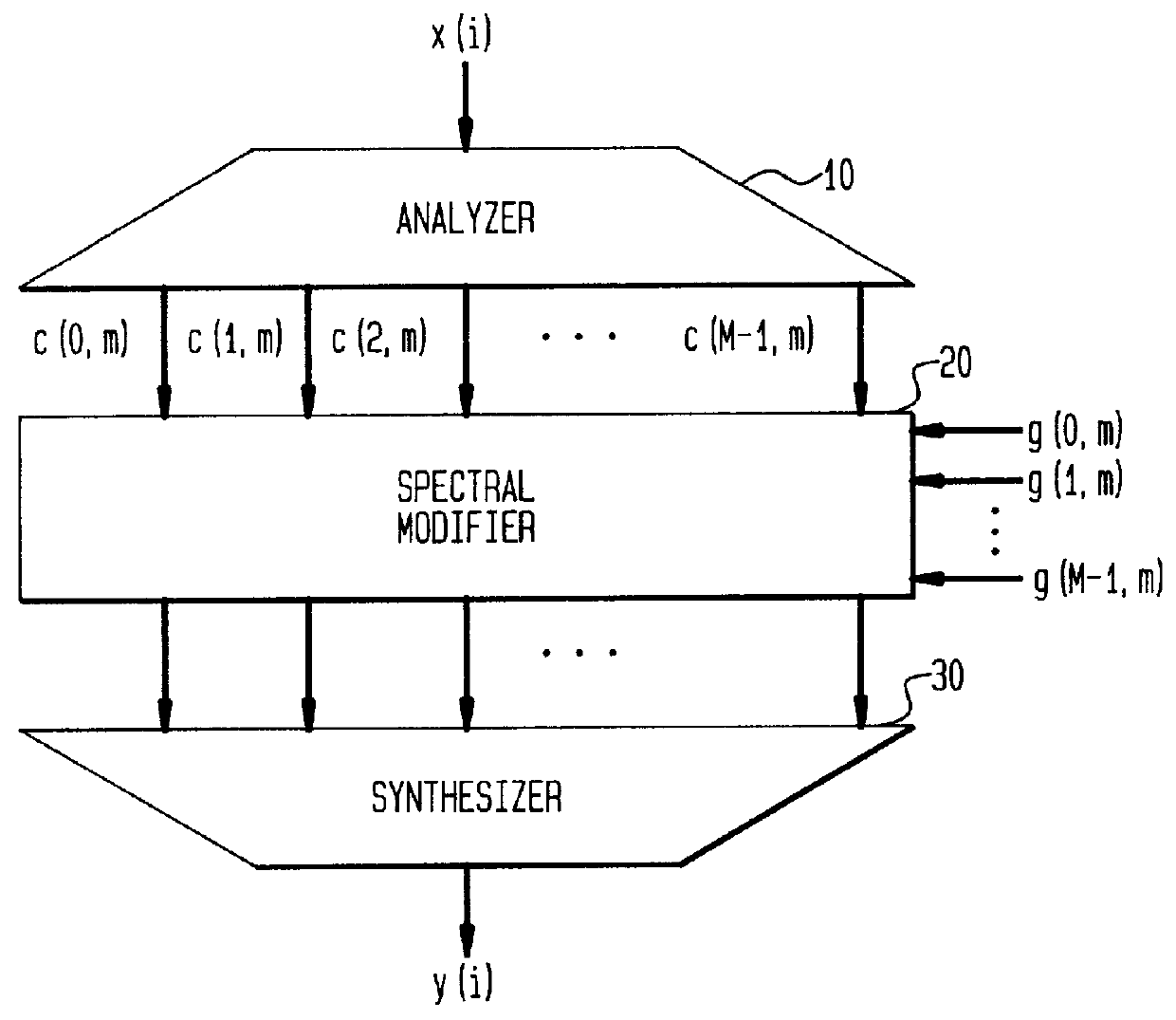
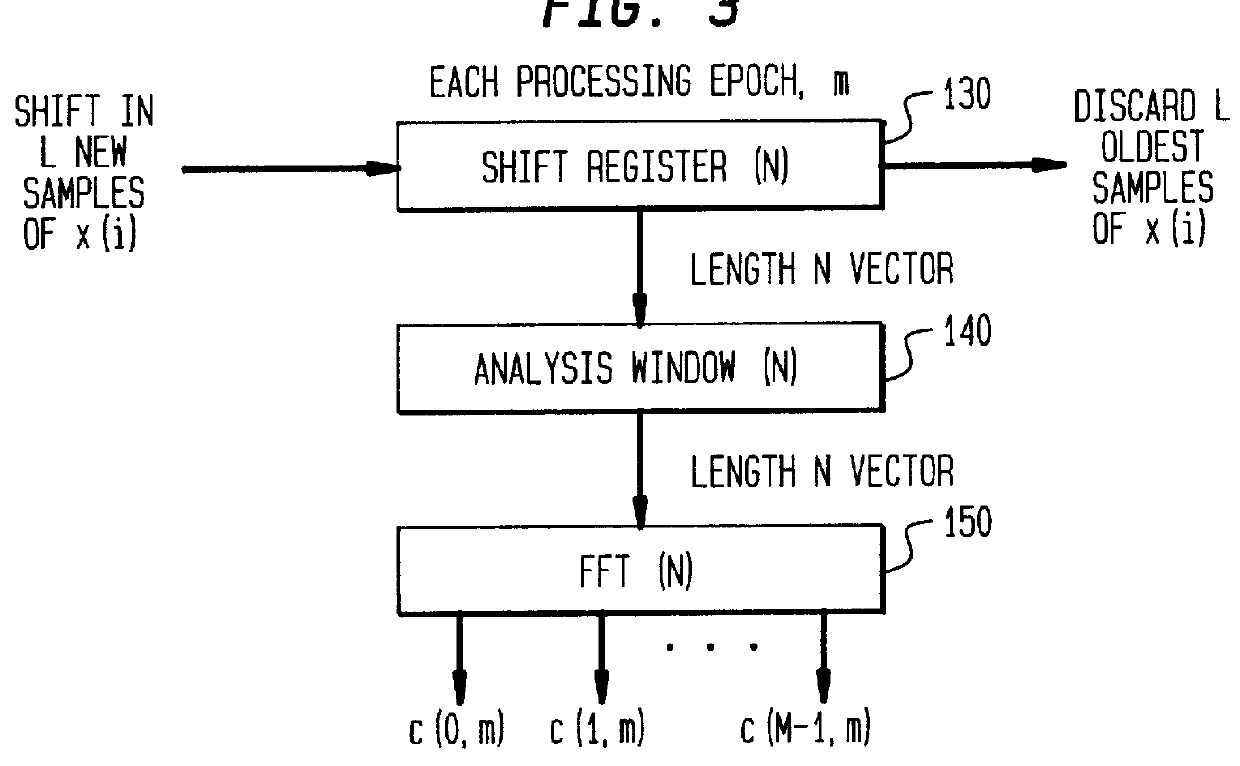
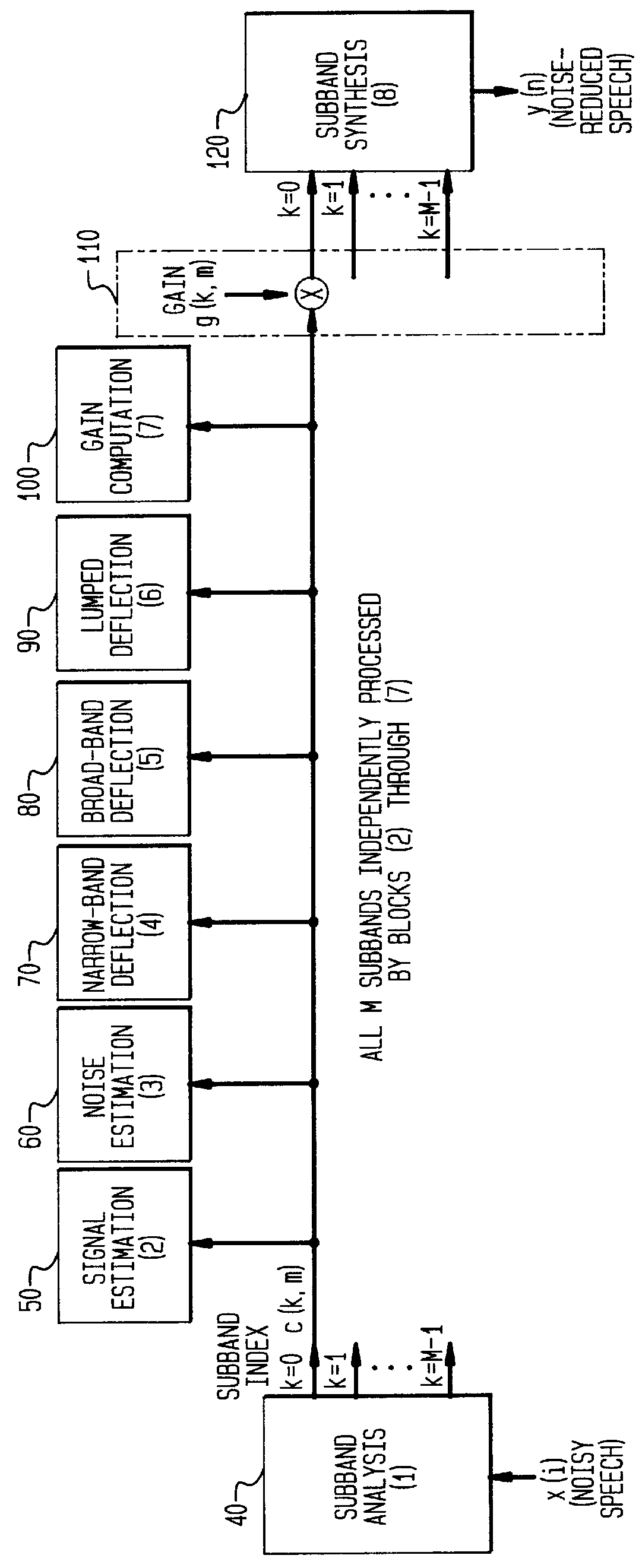
A method and apparatus are disclosed for enhancing, within a signal bandwidth, a corrupted audio-frequency signal. The signal which is to be enhanced is analyzed into plural sub-band signals, each occupying a frequency sub-band smaller than the signal bandwidth. A respective signal gain function is applied to each sub-band signal, and the respective sub-band signals are then synthesized into an enhanced signal of the signal bandwidth. The signal gain function is derived, in part, by measuring speech energy and noise energy, and from these determining a relative amount of speech energy, within the corresponding sub-band. In certain embodiments of the invention, the signal gain function is also derived, in part, by determining a relative amount of speech energy within a frequency range greater than, but centered on, the corresponding sub-band. In other embodiments of the invention, the sub-band noise energy is determined from a noise estimate that is updated at periodic intervals, but is not updated if the newest sample of the signal to be enhanced exceeds the current noise estimate by a multiplicative threshold (i.e., a threshold expressible in decibels). In still other embodiments of the invention, the value of the noise estimate is limited by an upper bound that is matched to the dynamic range of the signal to be enhanced.
Owner:INTEL CORP
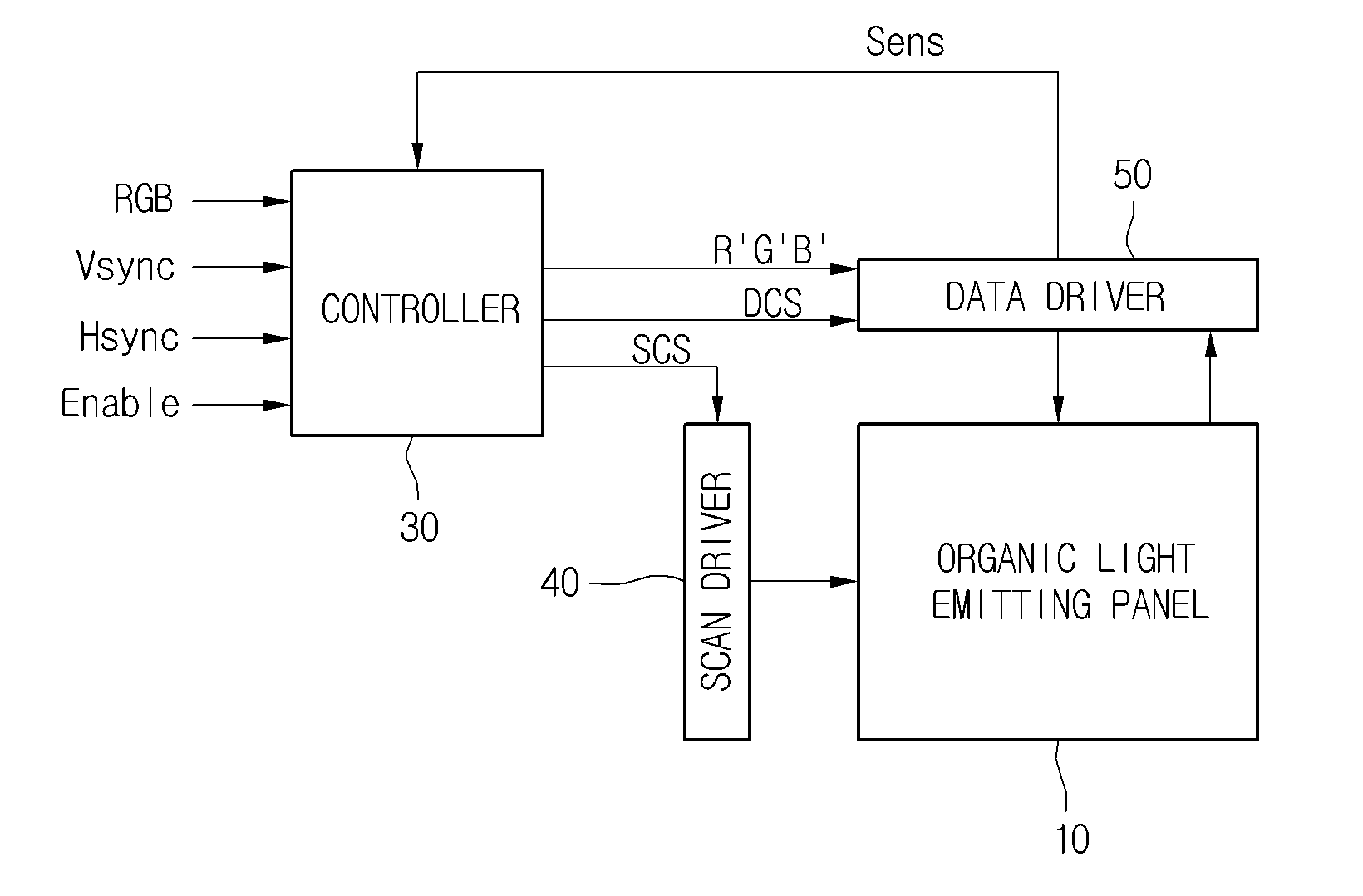
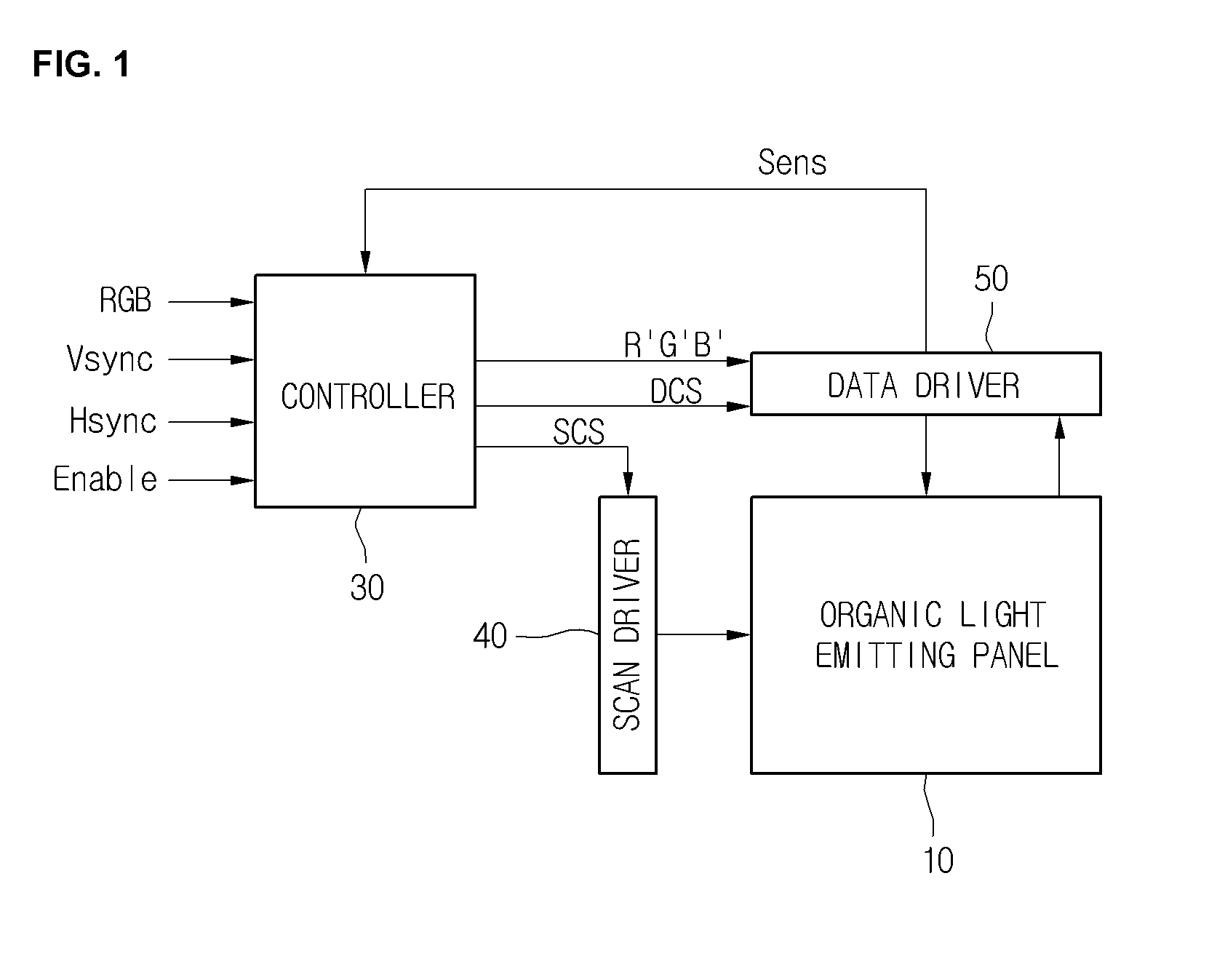
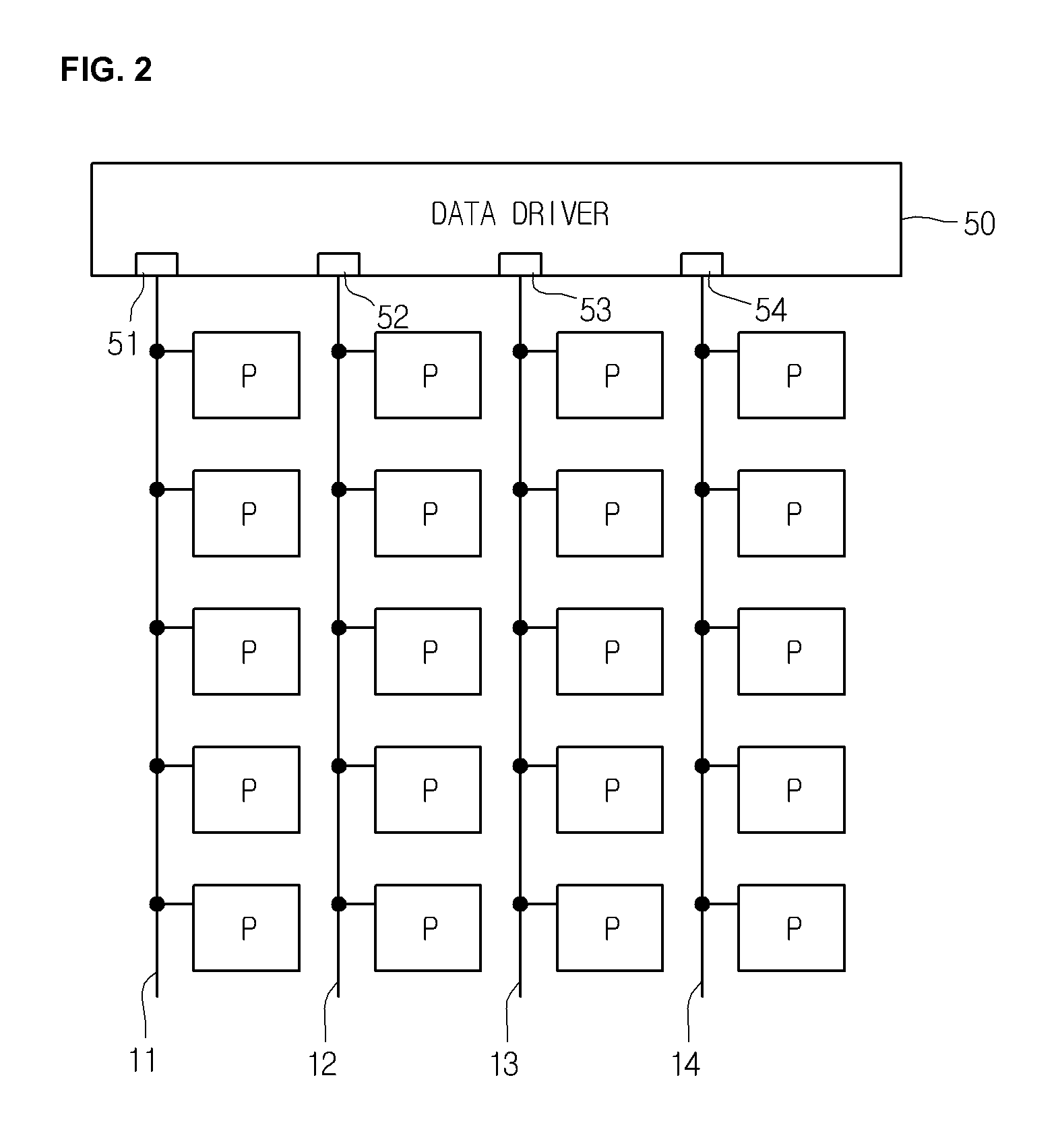
Organic light-emitting display device with data driver operable with signal line carrying both data signal and sensing signal
An organic light emitting display device having a data line that is used for sending data voltage signals to pixels from a data driver as well as send sensor signals for detecting threshold voltage levels of driving transistors in the pixels at different times. By using the same data line to transmit the data voltage signals and the sensor signals, the number of signal lines in the organic light emitting display can be reduced. The data driver also includes switches for selectively coupling the data line to a driver unit or an analog to digital converter (ADC) unit.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
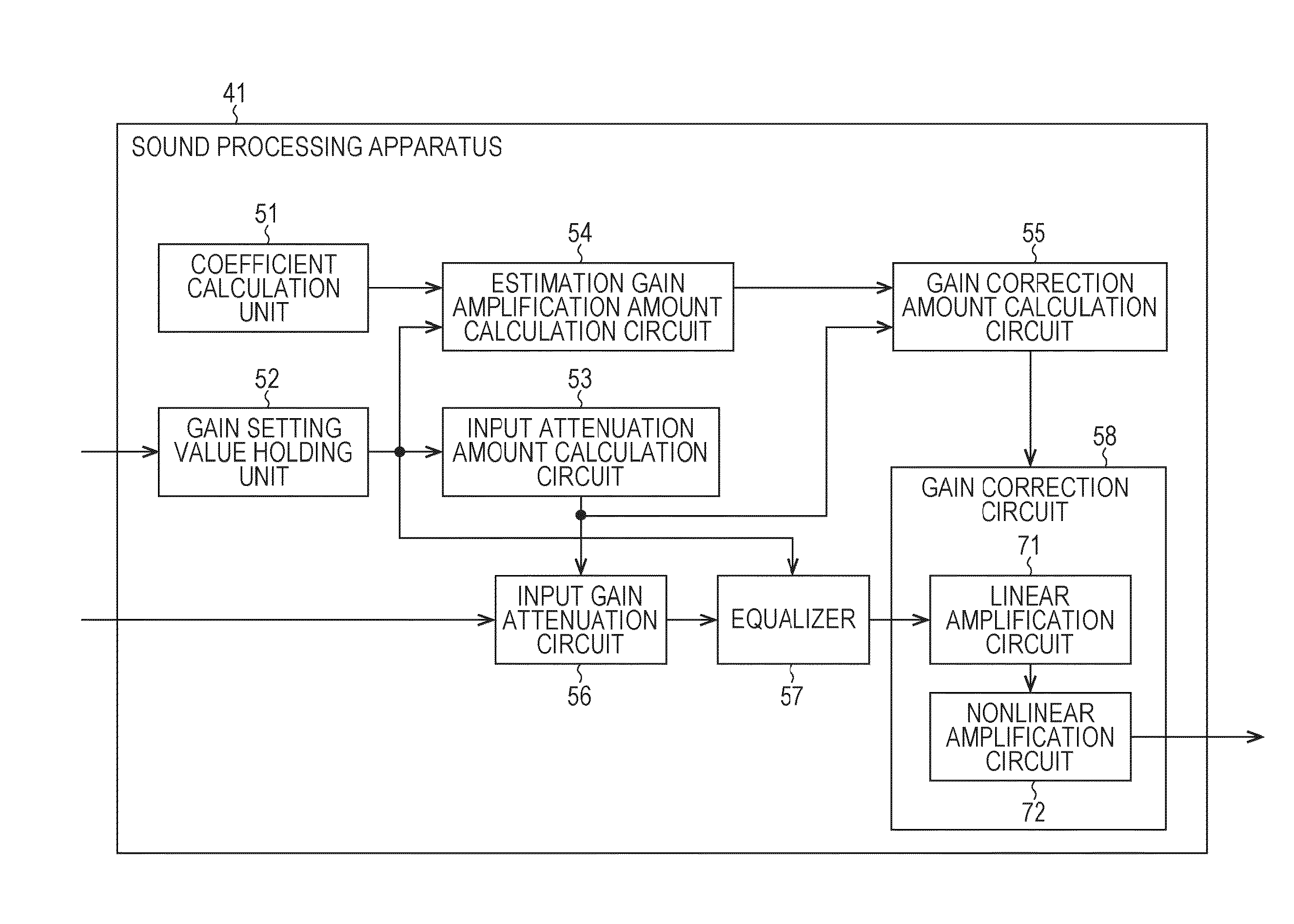
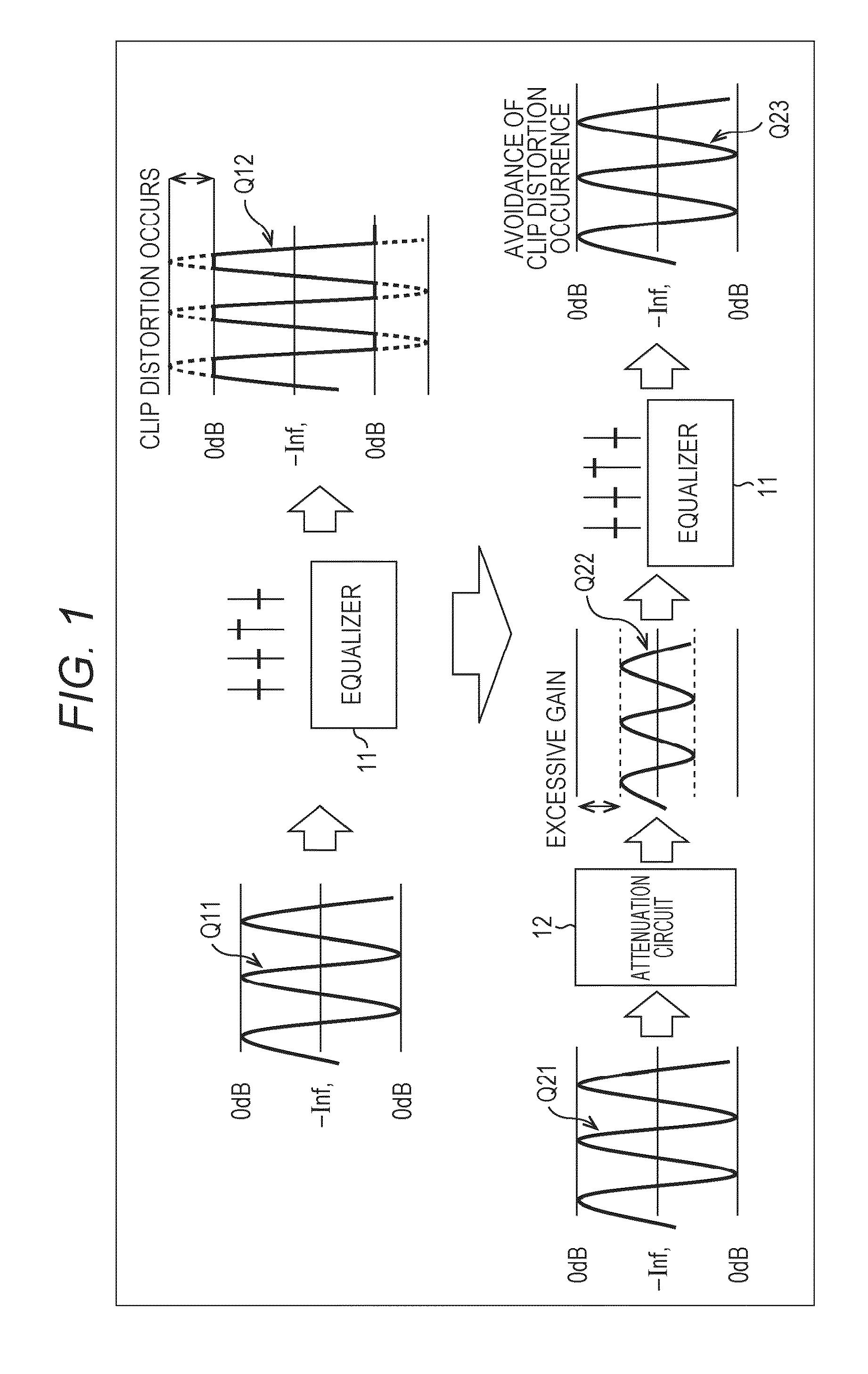
Sound processing apparatus, method, and program
ActiveUS9294062B2Reduce quality degradationQuality improvementAnalog signal digital controlAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlUltrasound attenuationWeight coefficient
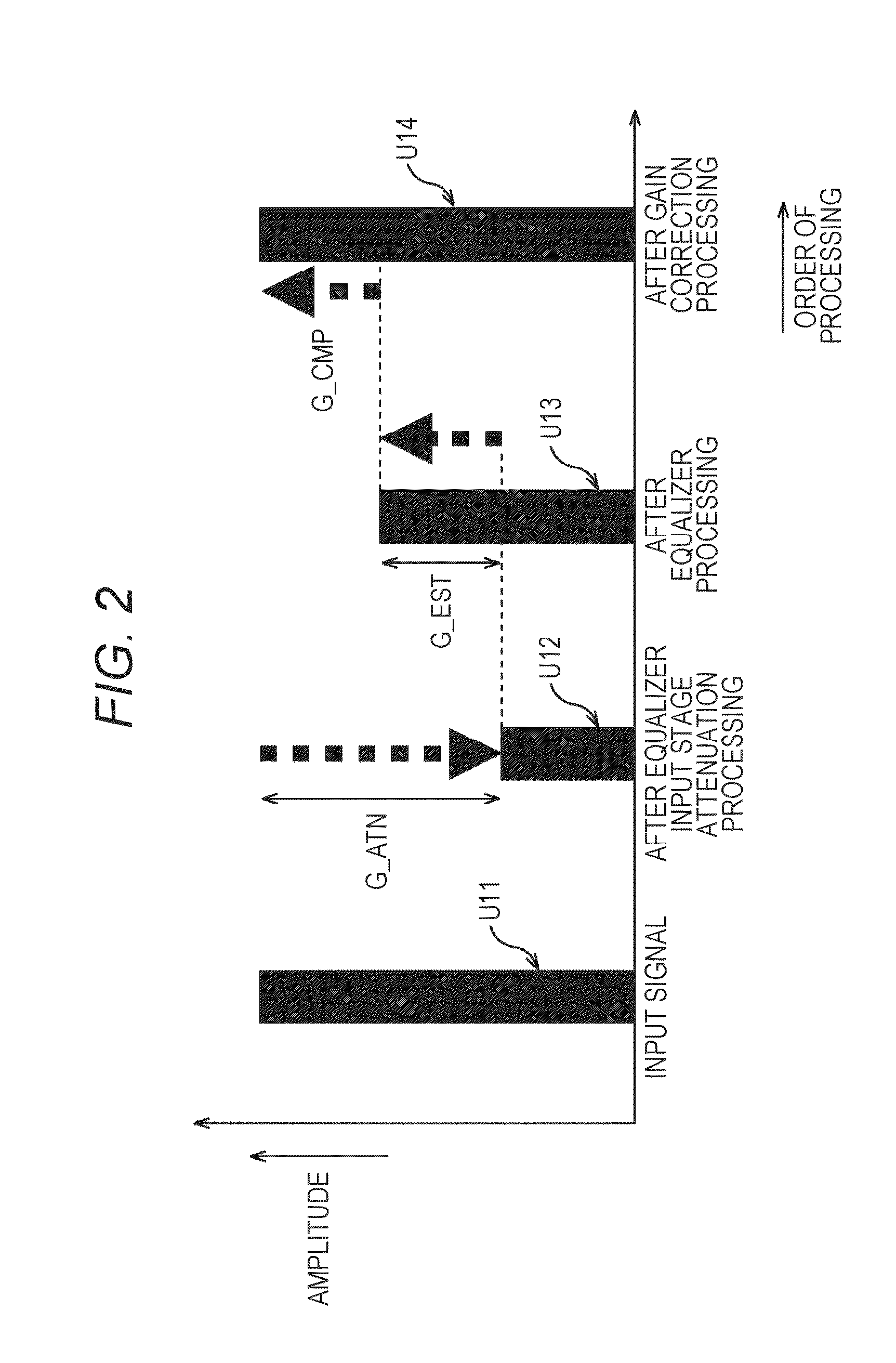
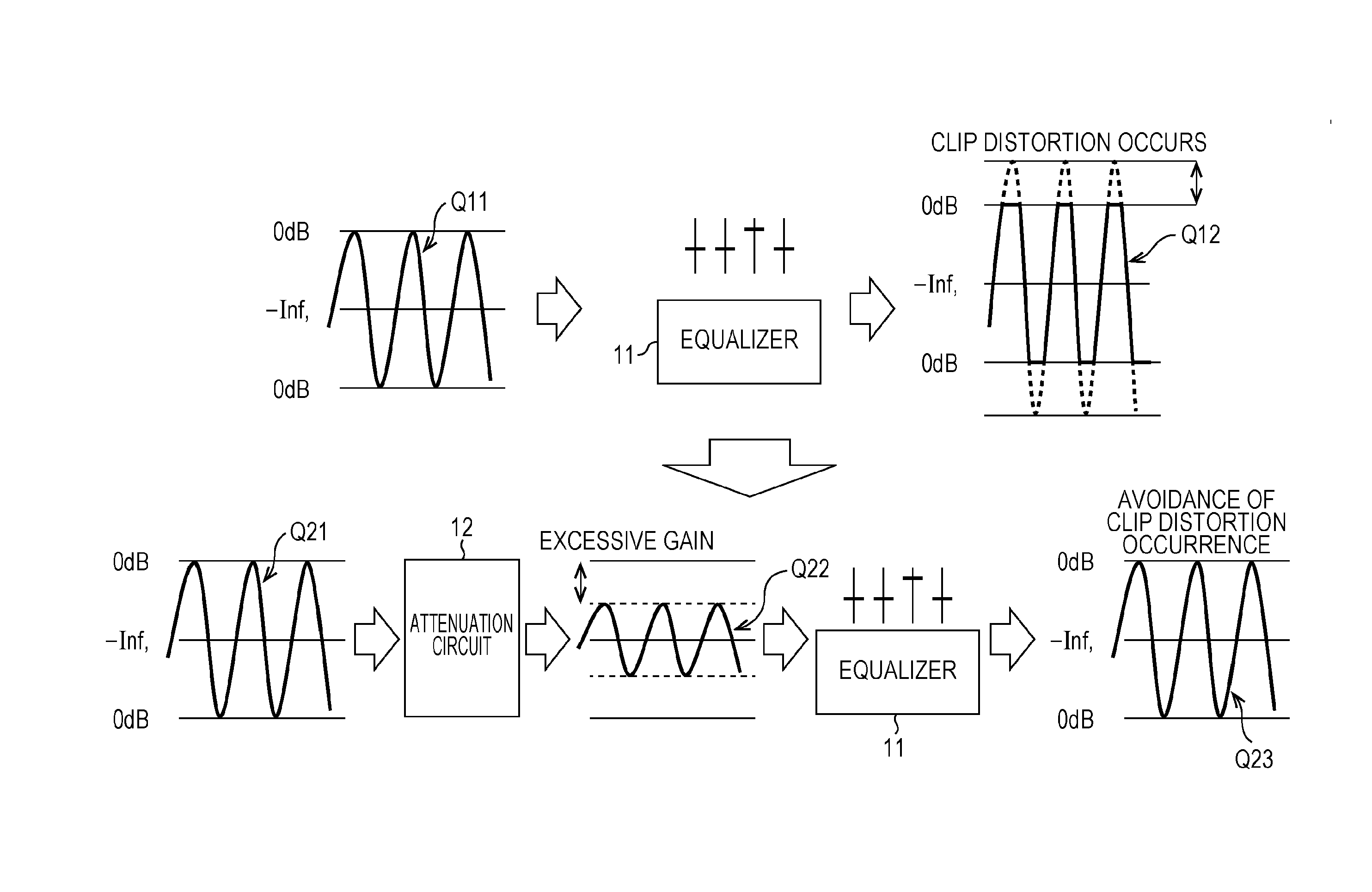
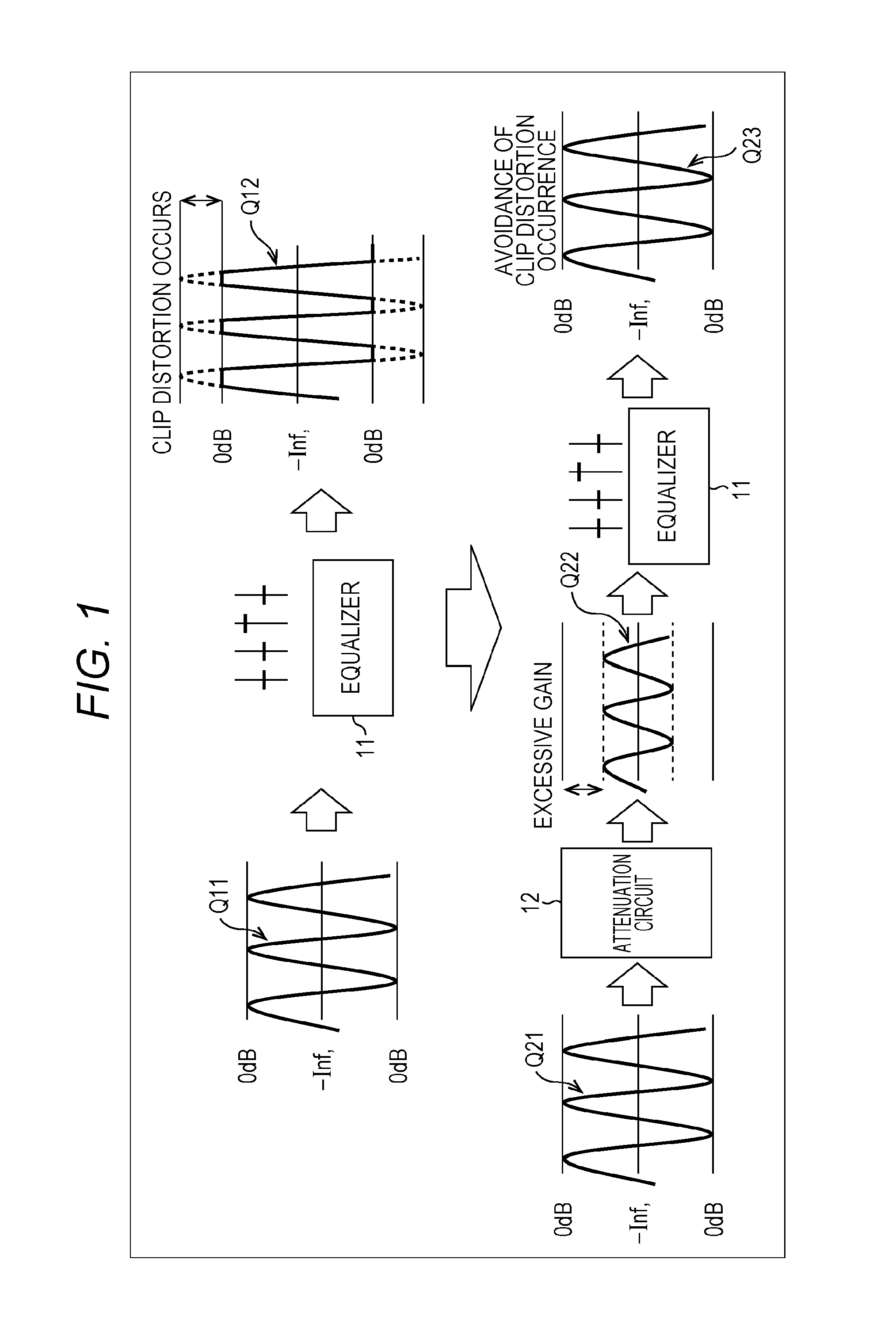
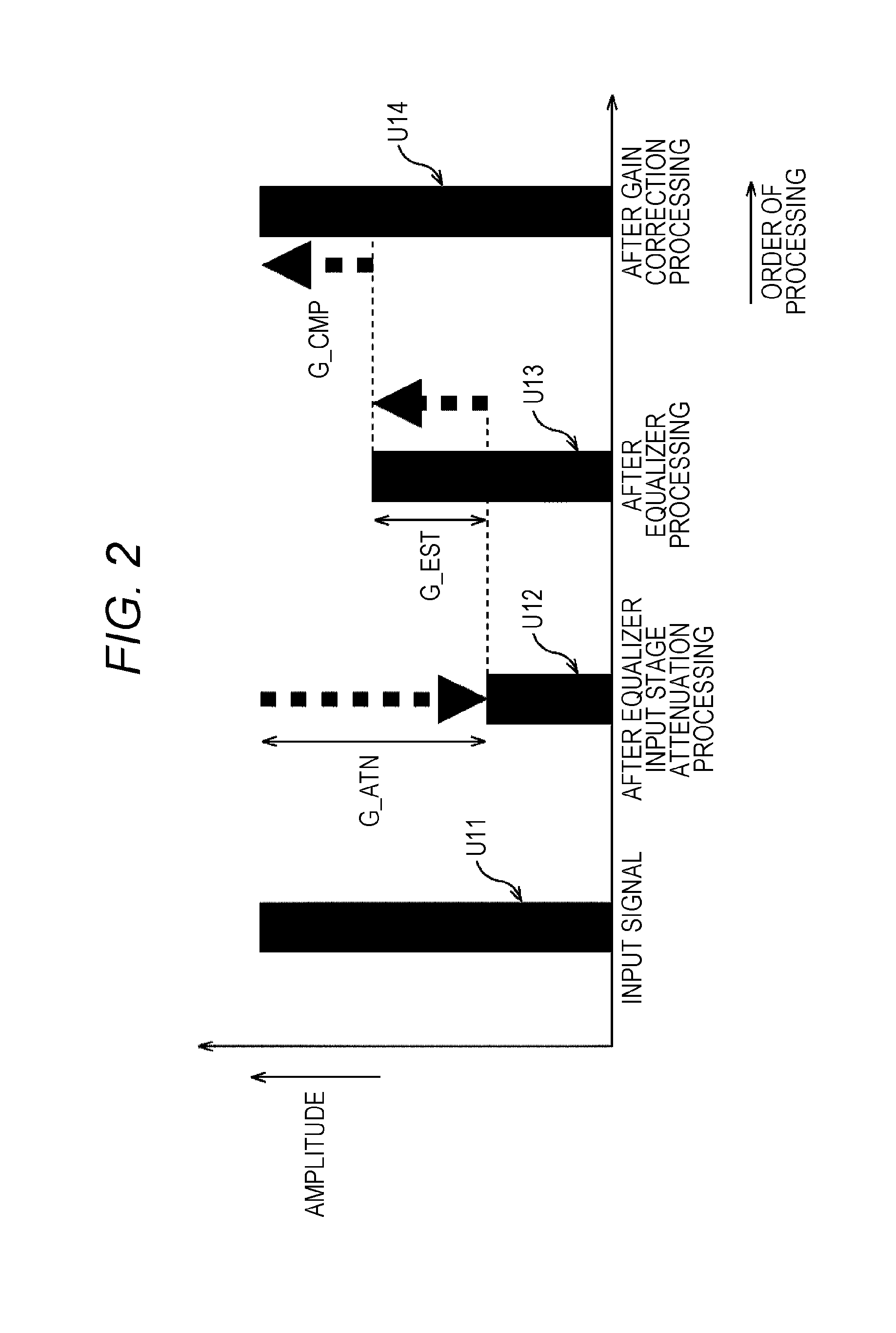
The present technique relates to a sound processing apparatus, a method, and a program capable of alleviating degradation of the quality of sound in a case where the gain of a sound signal is amplified.When equalizer processing for adjusting the gain of each frequency band of an input signal on the basis of a gain setting value is performed, an input signal is attenuated by an input attenuation amount derived from the gain setting value, and the equalizer processing is performed on the input signal attenuated. The amount of amplification of the gain of the input signal in the equalizer processing is estimated on the basis of the gain setting value and a weight coefficient of each frequency band derived from a generally-available music signal prepared in advance, and a difference of the estimation value and the input attenuation amount is calculated as a gain correction amount. Further, nonlinear amplification processing is performed on the input signal so as to actually amplify the input signal, which has been subjected to the equalizer processing, by a gain correction amount, and an output signal is obtained. The present technique can be applied to a sound processing apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
Closed loop power control with high dynamic range
ActiveUS20060170499A1Gain controlAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesTransmitted powerClosed loop
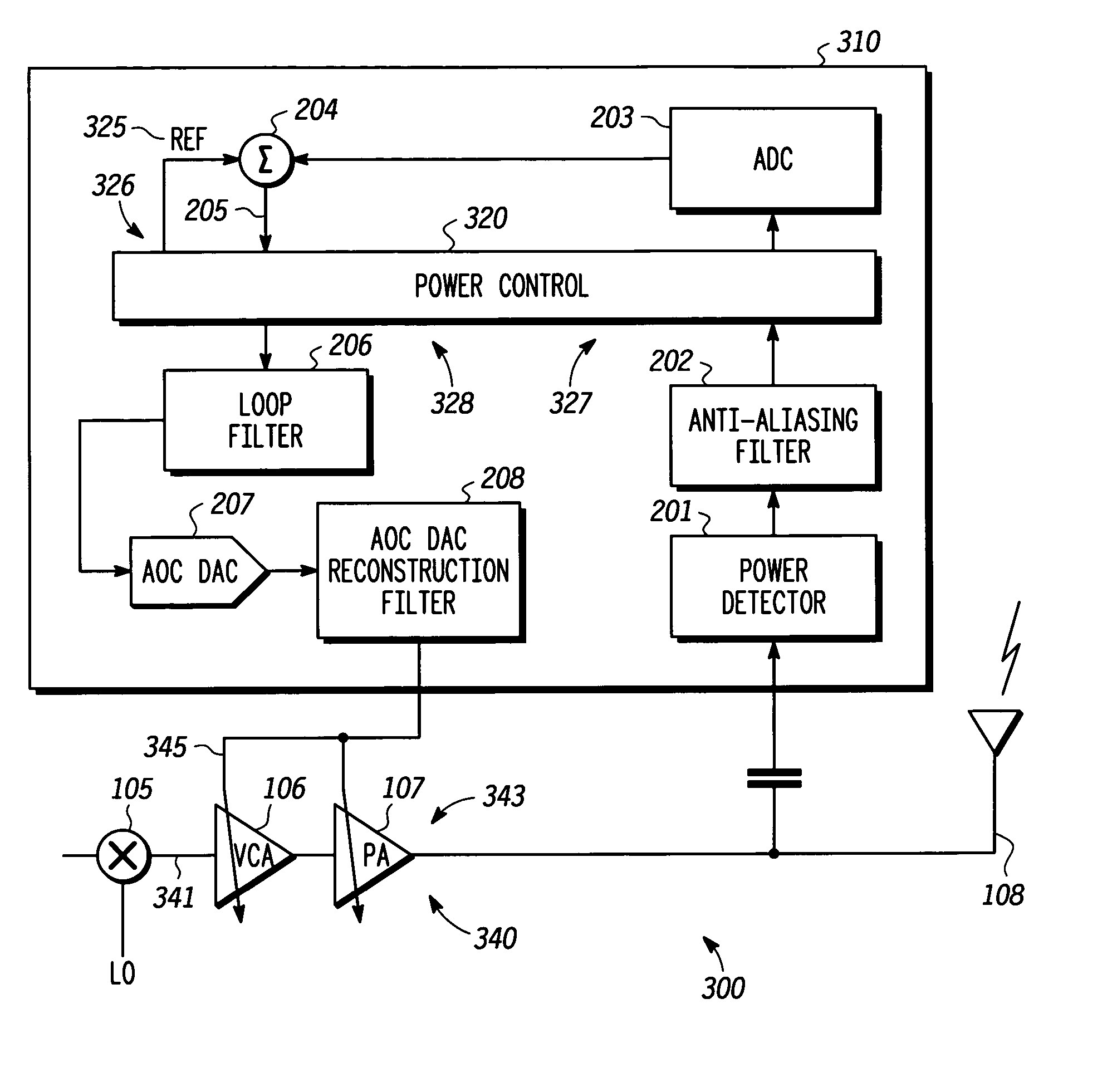
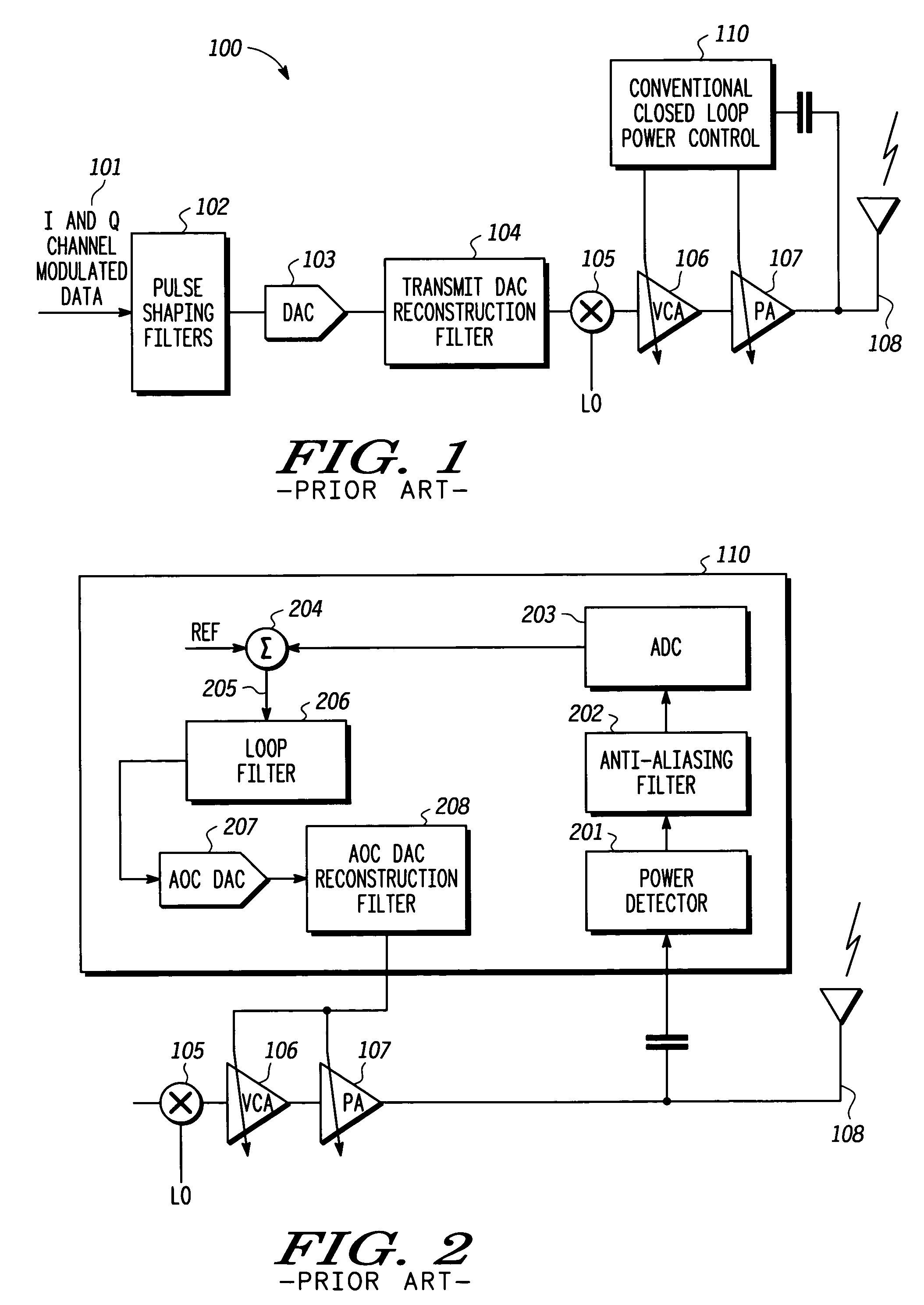
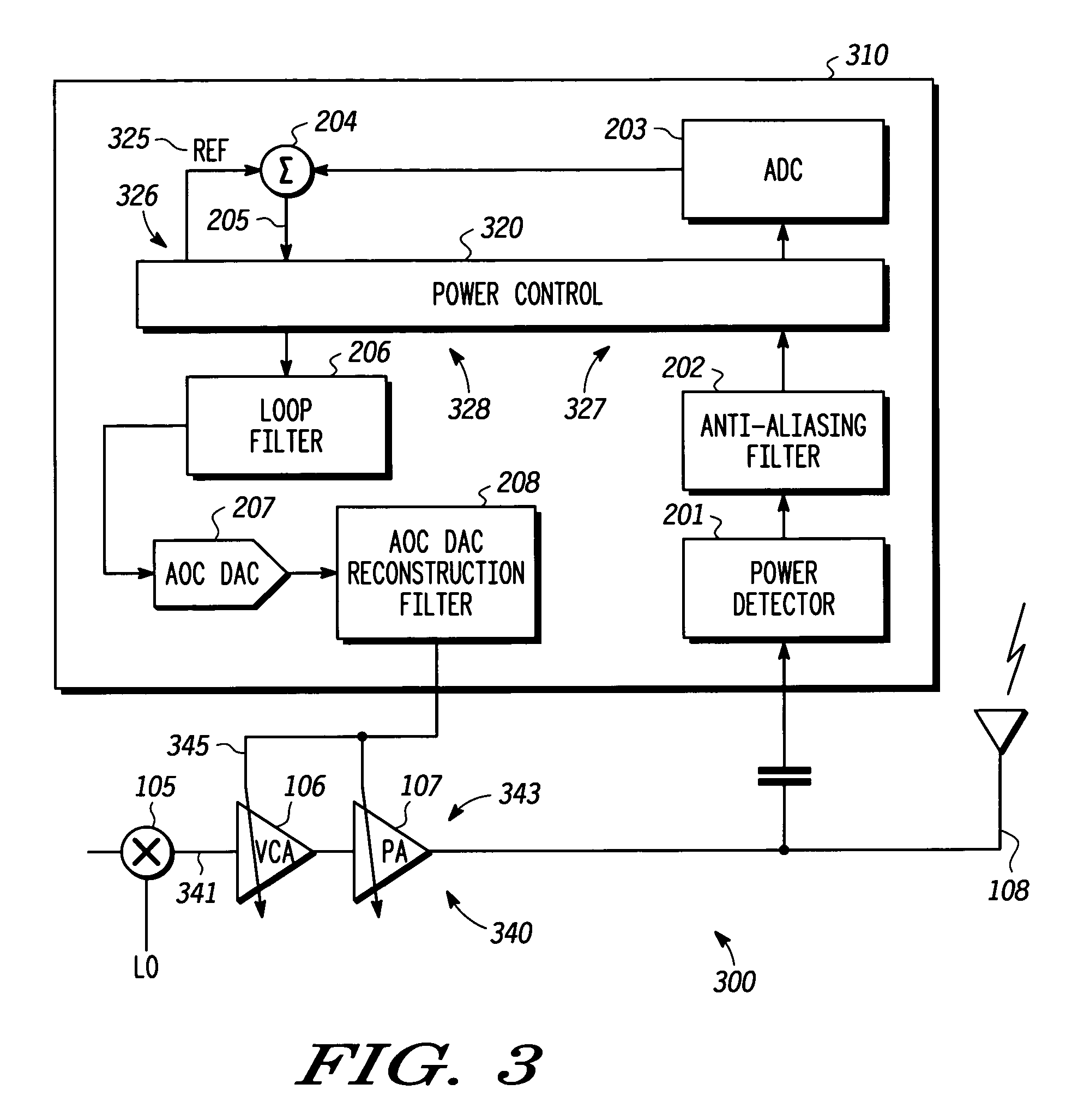
A method (500) and apparatus (300, 400, 601) facilitate closed loop transmit power control in a power control loop at and during a transition from one transmit power level to another transmit power level in a transmitter. The apparatus includes a reference path (326) configured to provide a reference signal (325) and a gain compensation signal (417), a detect path (327) configured to process, in accordance with the gain compensation signal, a detected signal corresponding to a power level to provide a gain compensated detected signal; and a power control path (328) configured to generate a power control value in accordance with the reference signal, the gain compensated detected signal, and a loop compensation factor associated with the gain compensation signal where the power control value is suitable for setting the power level for the transmission.
Owner:APPLE INC
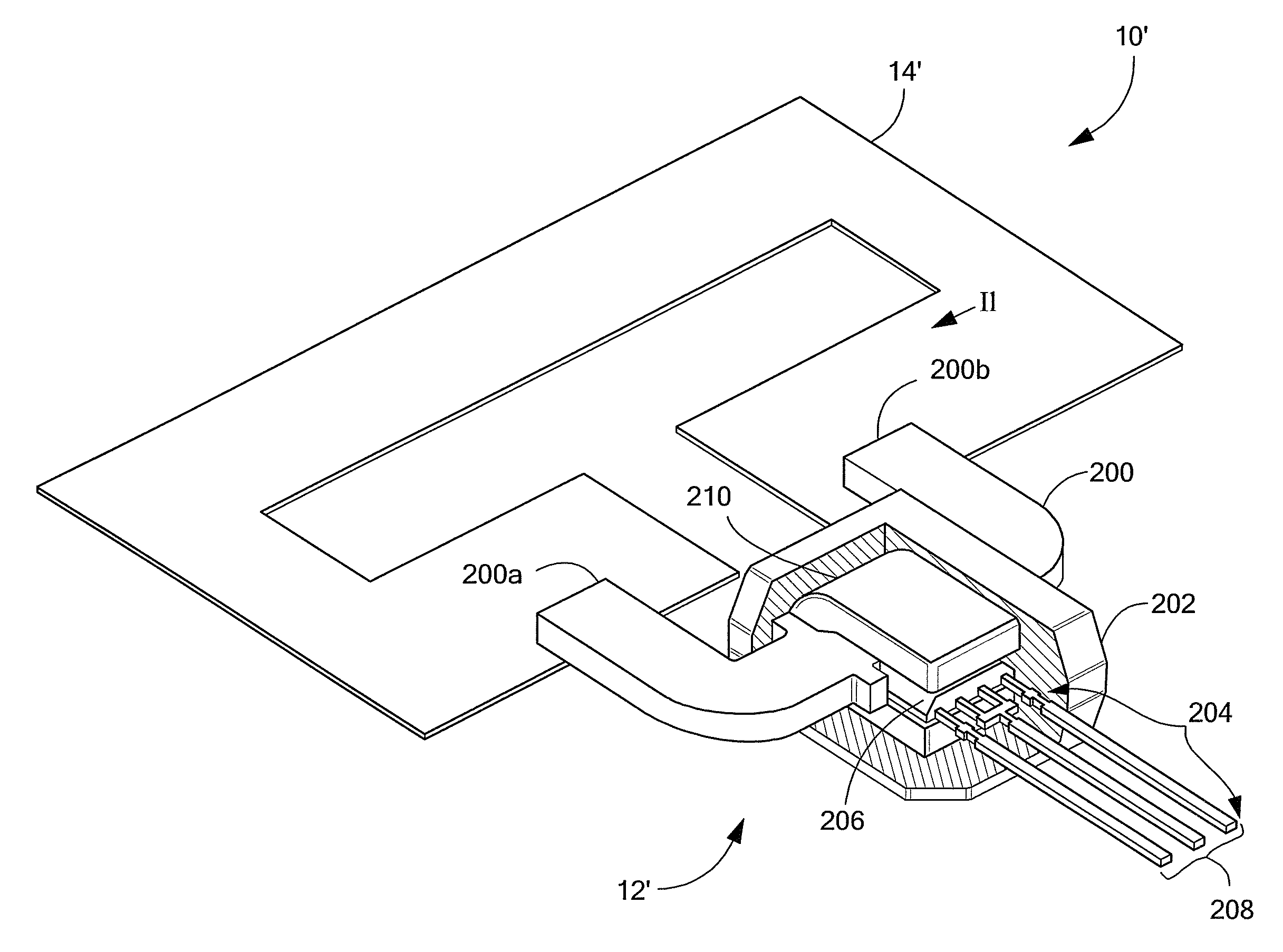
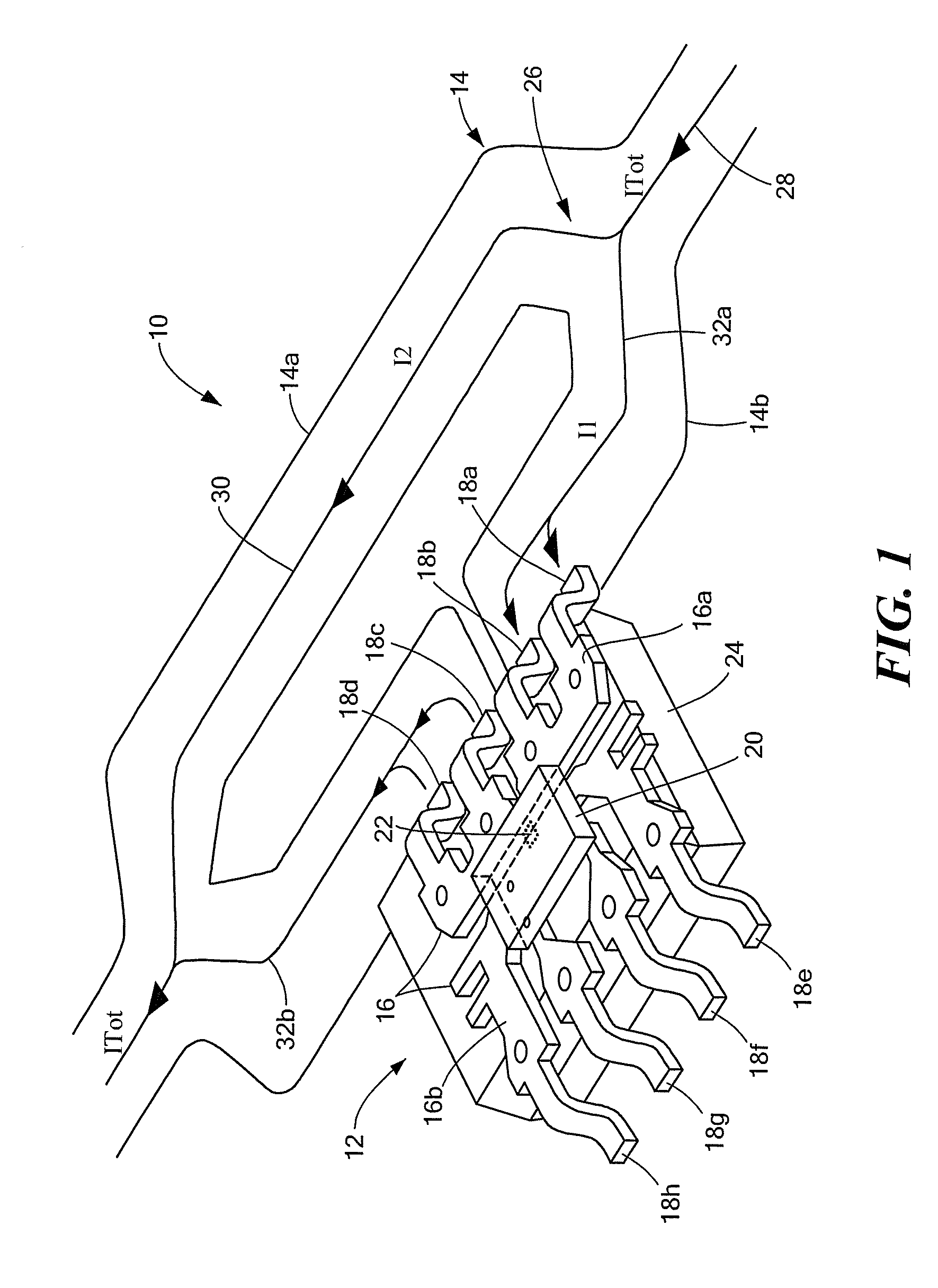
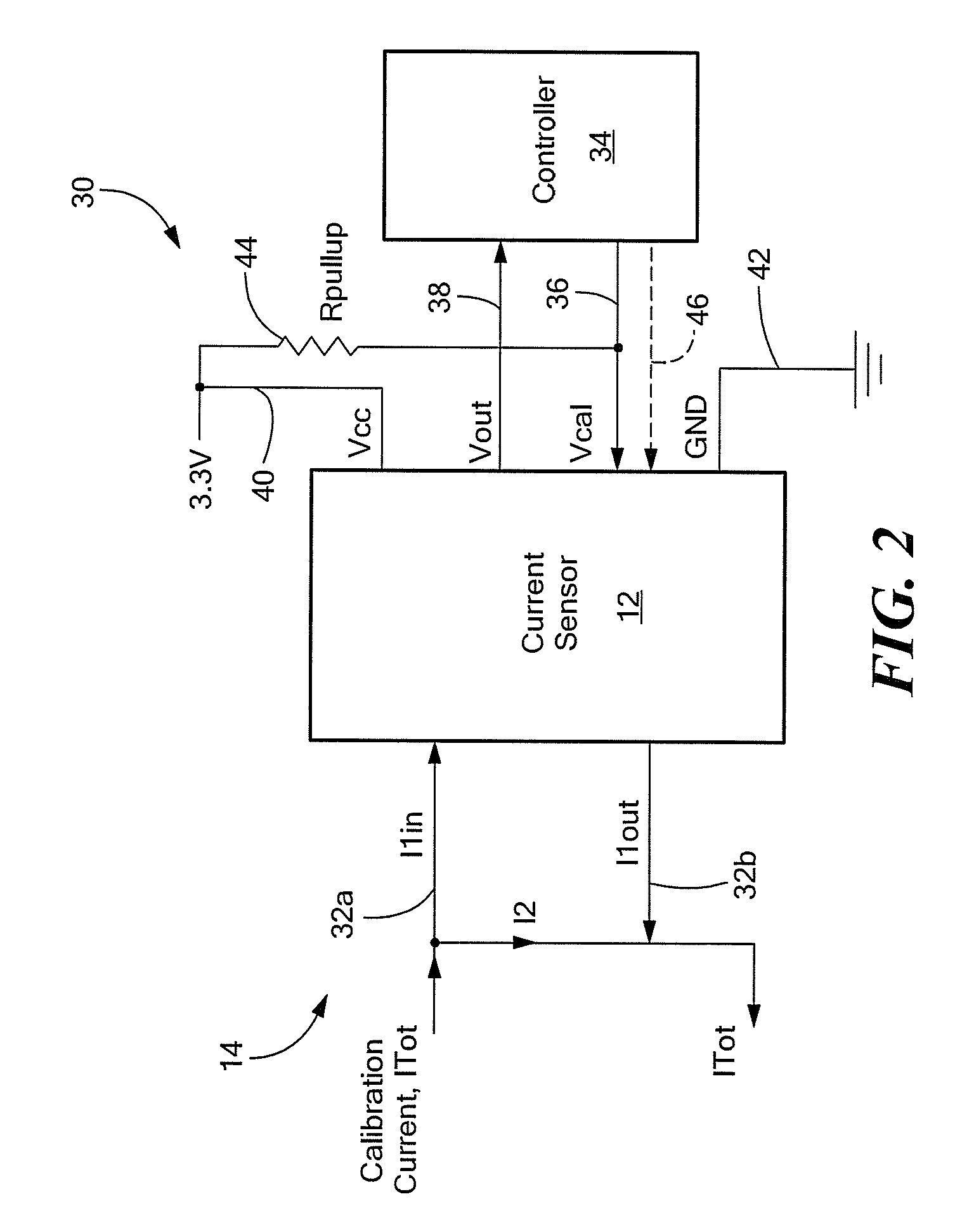
Current sensor with calibration for a current divider configuration
ActiveUS20130015843A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesBase element modificationsShunt DeviceElectrical conductor
An integrated circuit (IC) current sensor that self-calibrates to adjust its signal gain when employed in a current divider configuration is presented. The current sensor includes an integrated current conductor, a magnetic field transducer, a controllable gain stage and a calibration controller. The integrated current conductor is adapted to receive a portion of a calibration current. The calibration current corresponds to a full scale current. The magnetic field transducer, responsive to the calibration current portion, provides a magnetic field signal having a magnitude proportional to a magnetic field generated by the calibration current portion. The controllable gain stage is configured to amplify the magnetic field signal with an adjustable gain to provide an amplified magnetic field signal. The calibration controller is responsive to a calibration command signal to adjust the adjustable gain of the controllable gain stage to a calibrated gain in order to provide the amplified magnetic field signal at a predetermined voltage level that corresponds to a desired current sensor output signal voltage level if the full scale current were received by the integrated current conductor.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
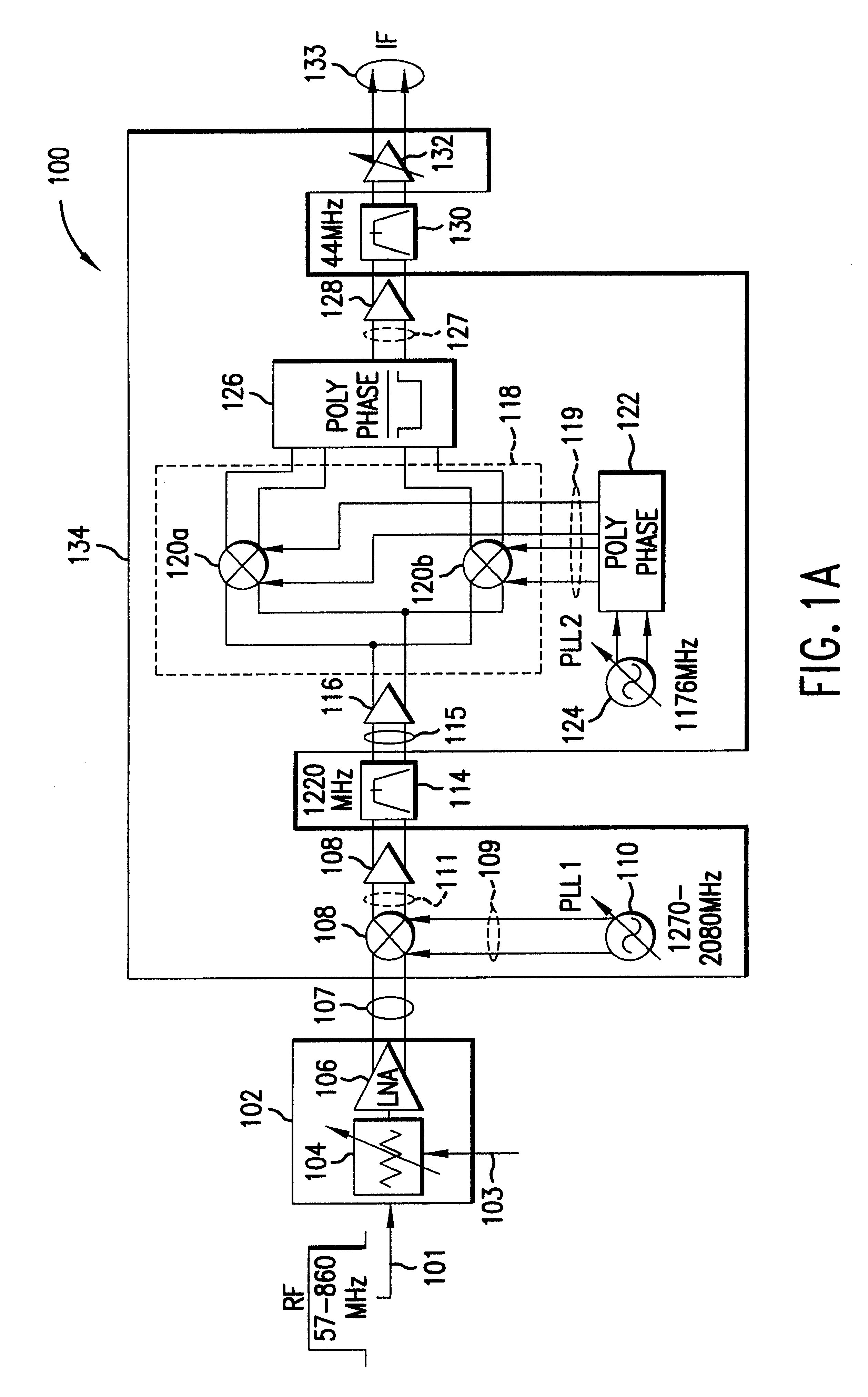
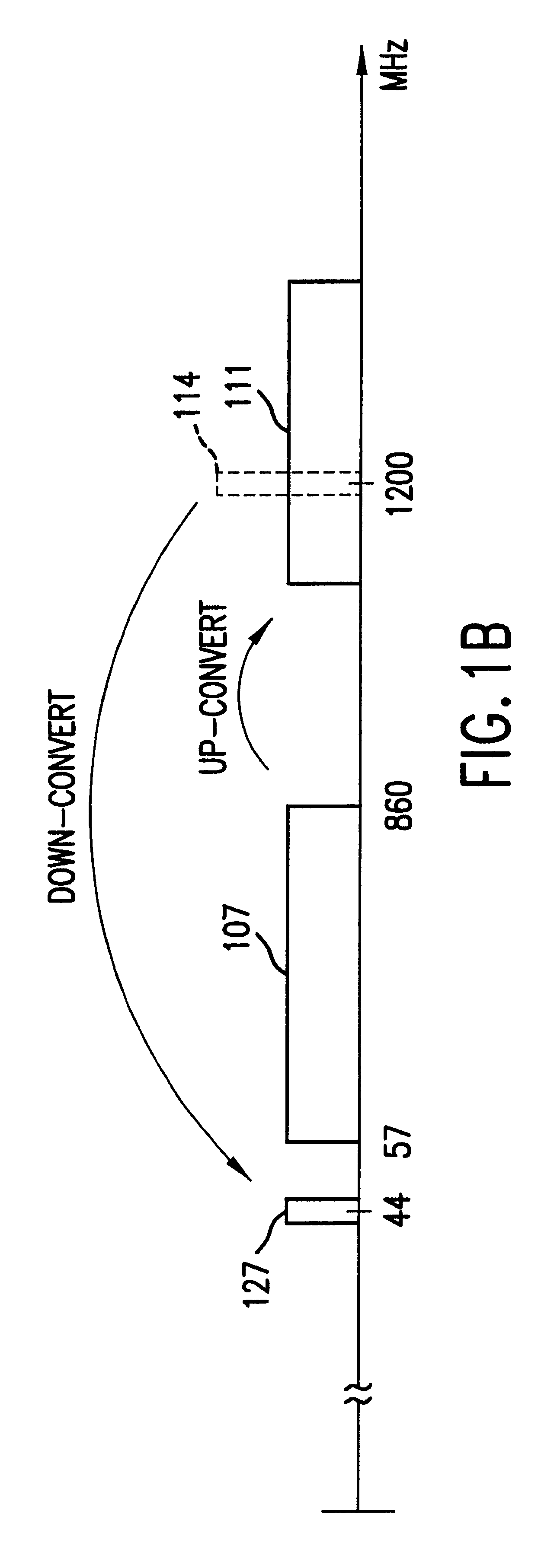
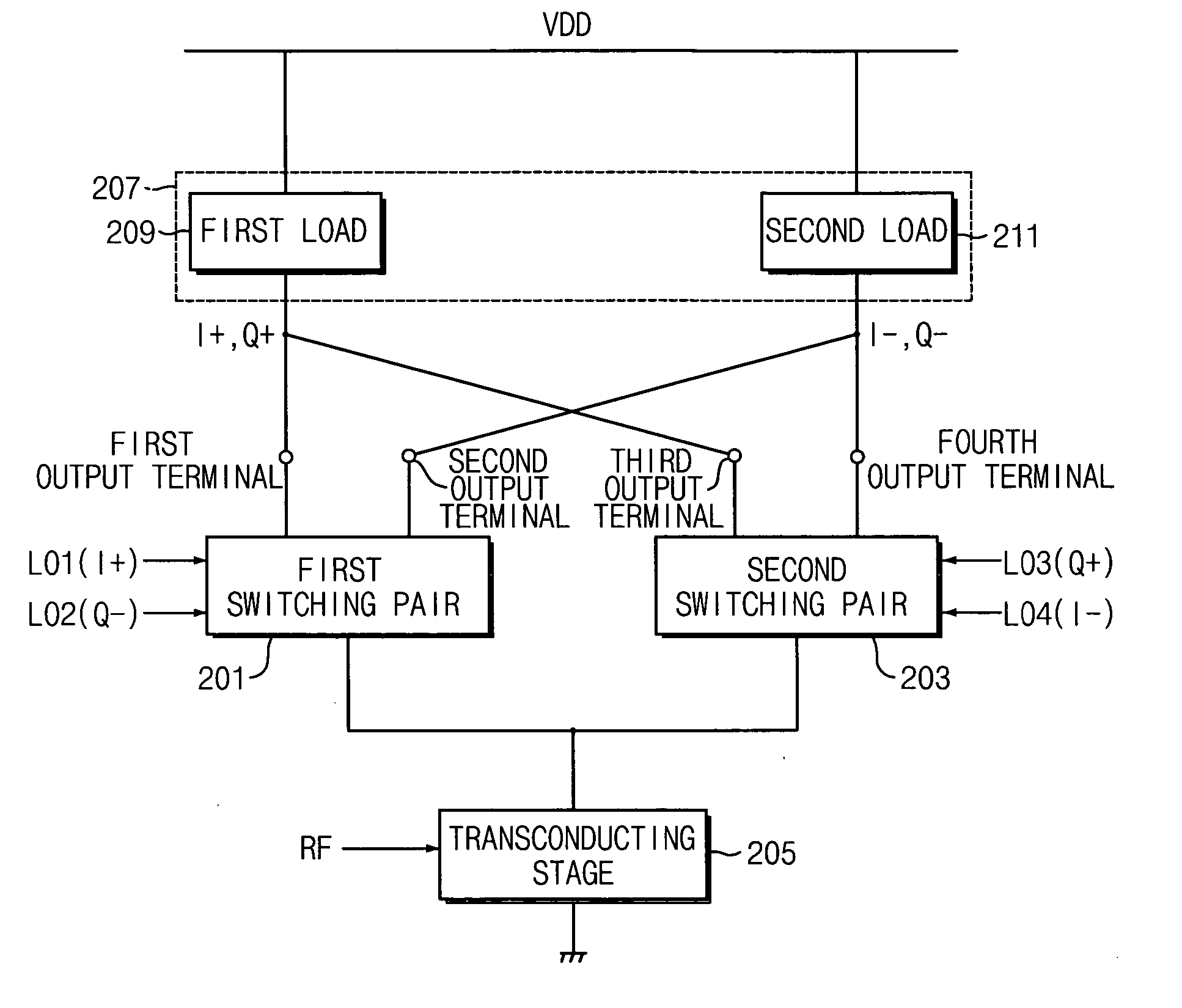
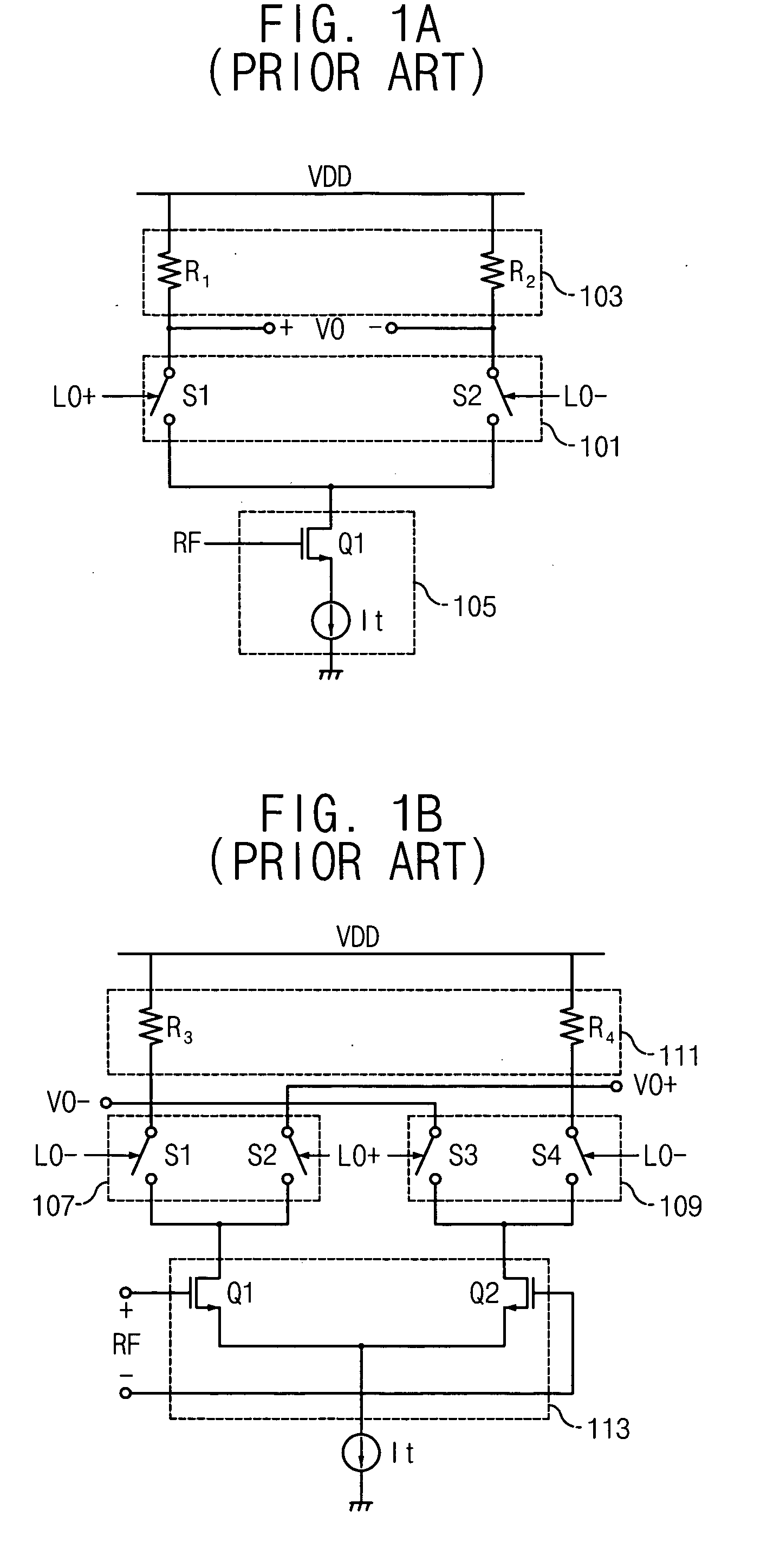
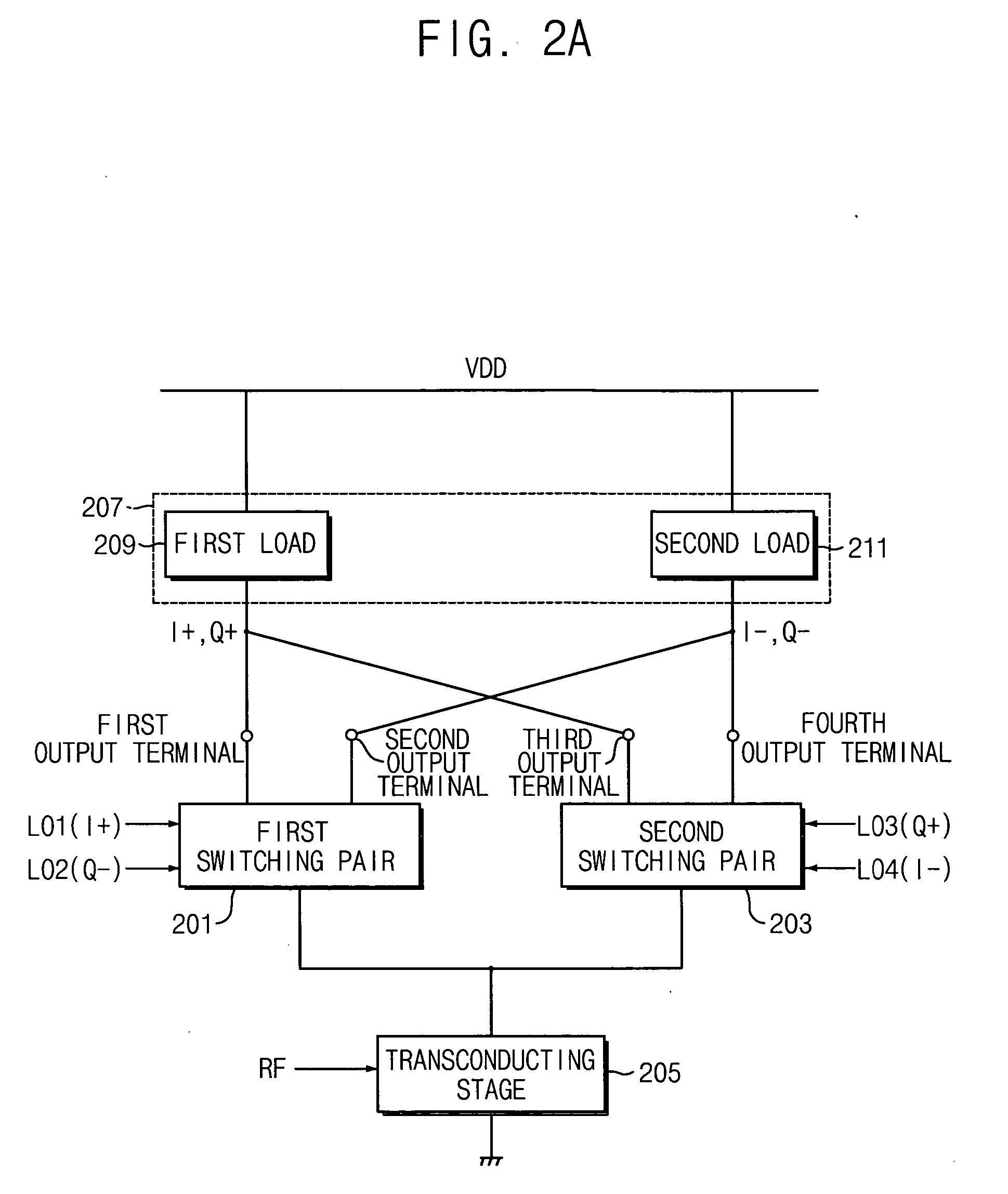
Mixer circuit for direct conversion transceiver with improved IP2
InactiveUS20050170806A1Improved IP characteristicImprove featuresModulation transference balanced arrangementsVibration massagePhase shiftedFrequency mixer
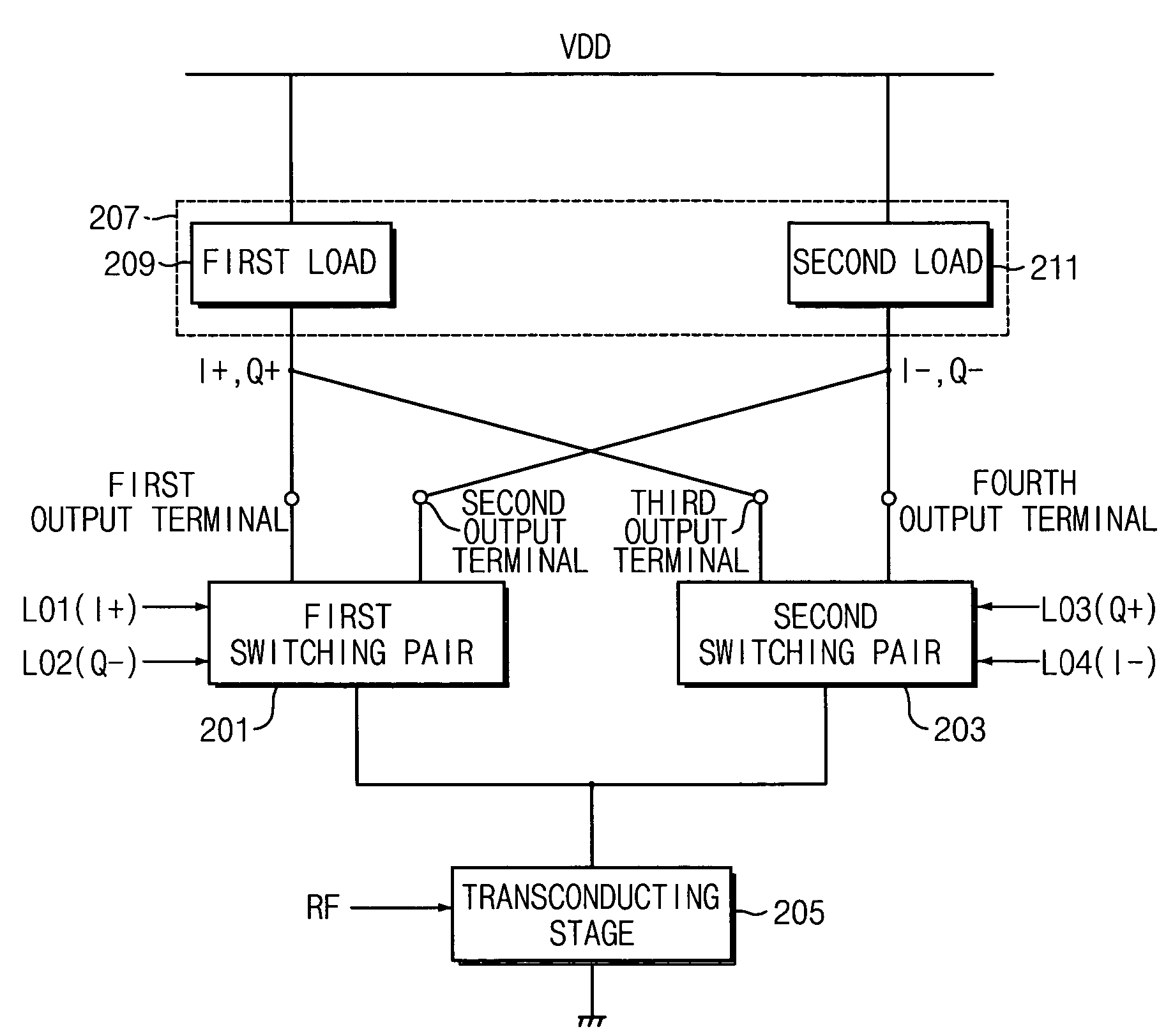
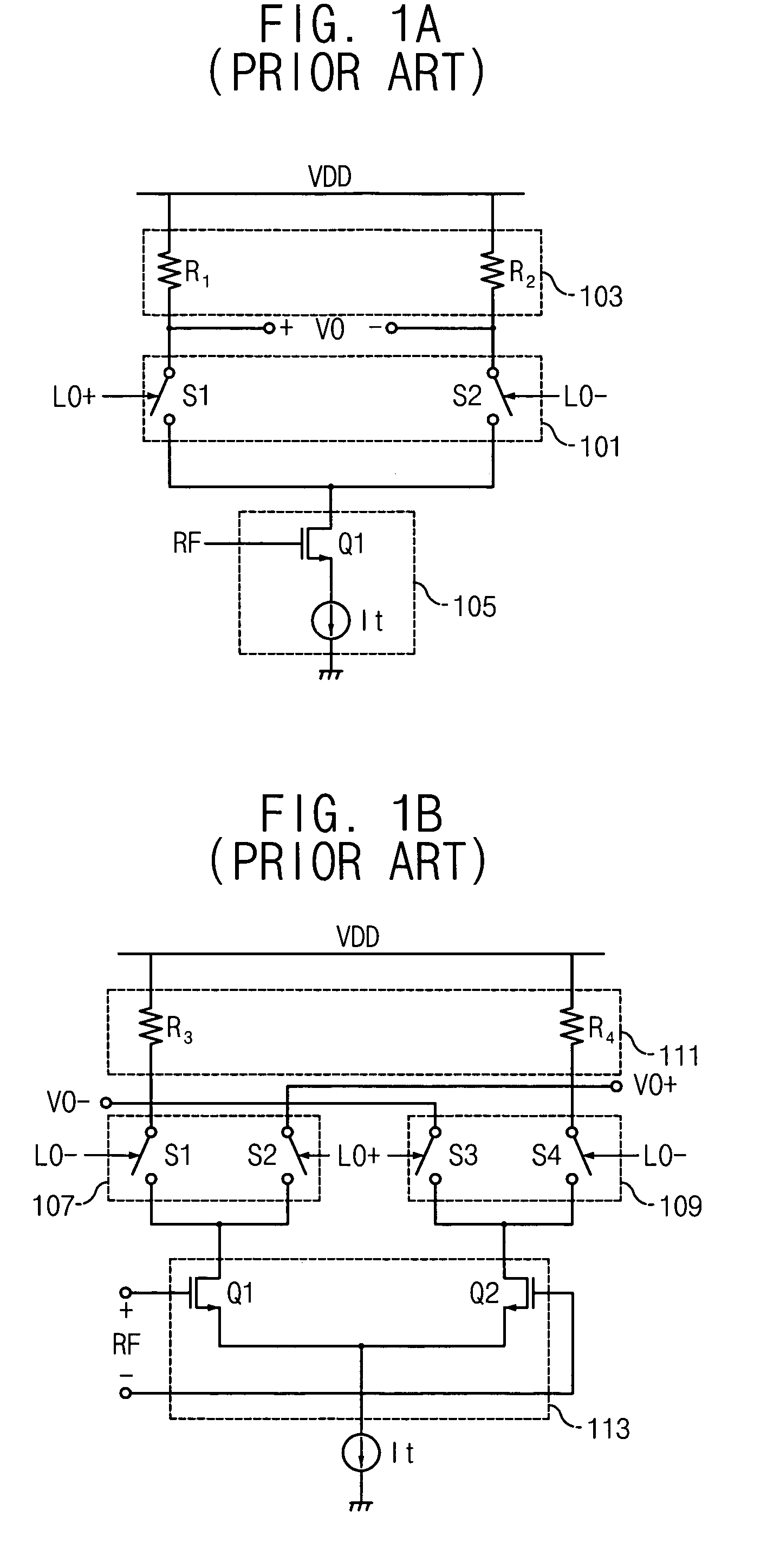
A mixer for direct conversion transmitters and receivers using four phase-shifted local oscillation signals that are orthogonal each other to control a plurality of switches for outputting signals that are orthogonal each other. Two output signals that are orthogonal to each other do not mutually interfere and have a predetermined small signal gain. Further, a mixer may include four or eight switches controlled by four phase-shifted local oscillation signals that are orthogonal each other for outputting signals that are orthogonal to each other on an I-Q plot. The signals outputted from the switches controlled by four phase-shifted local oscillation signals remove I-Q mismatch and a DC component, and improve IP2 characteristics.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
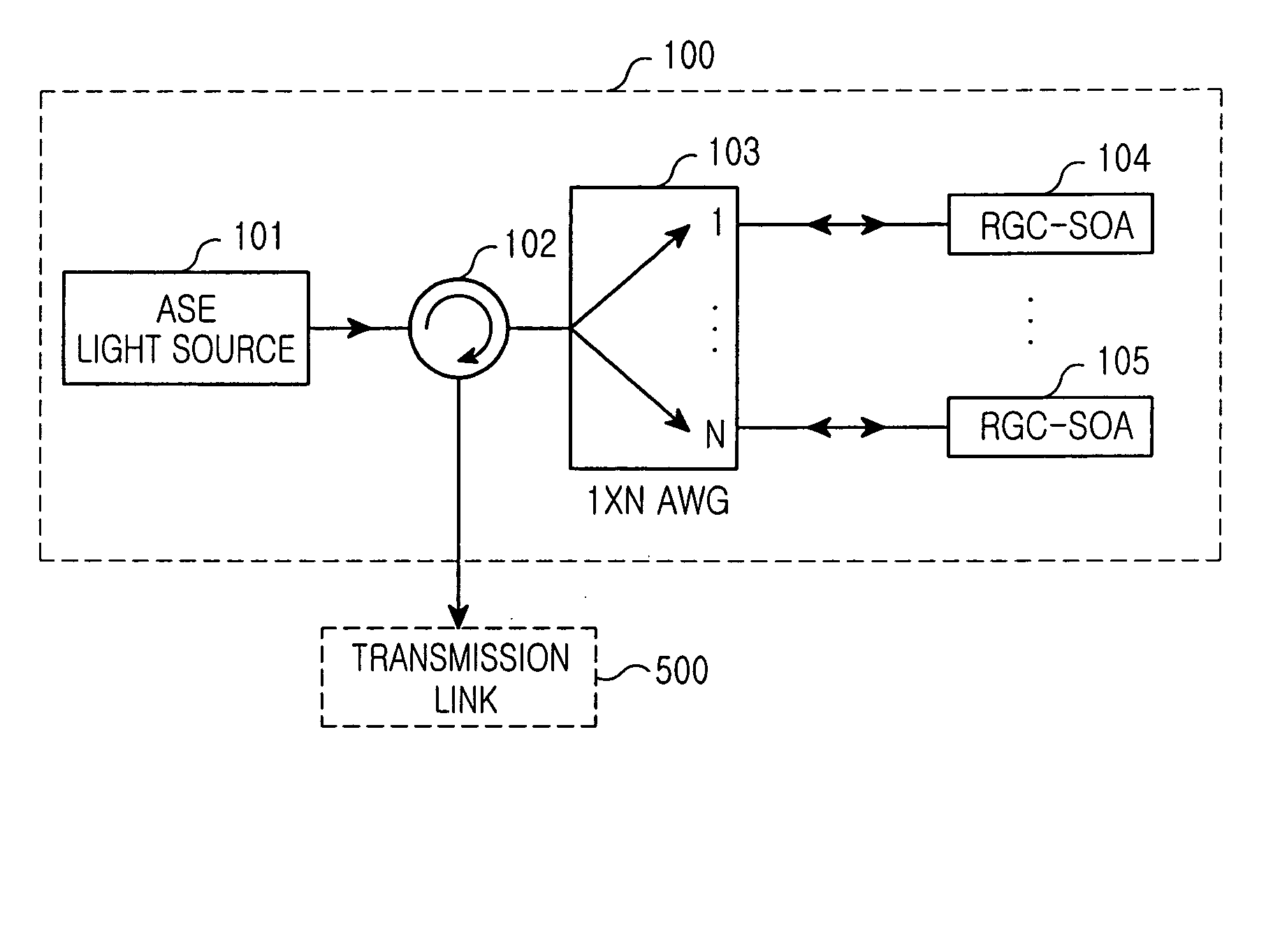
Optical signal transmission apparatus including reflective gain-clamped semiconductor optical amplifier
InactiveUS20050088724A1Improve modulation speedIncrease optical powerWavelength-division multiplex systemsSemiconductor laser optical deviceAudio power amplifierOptical power
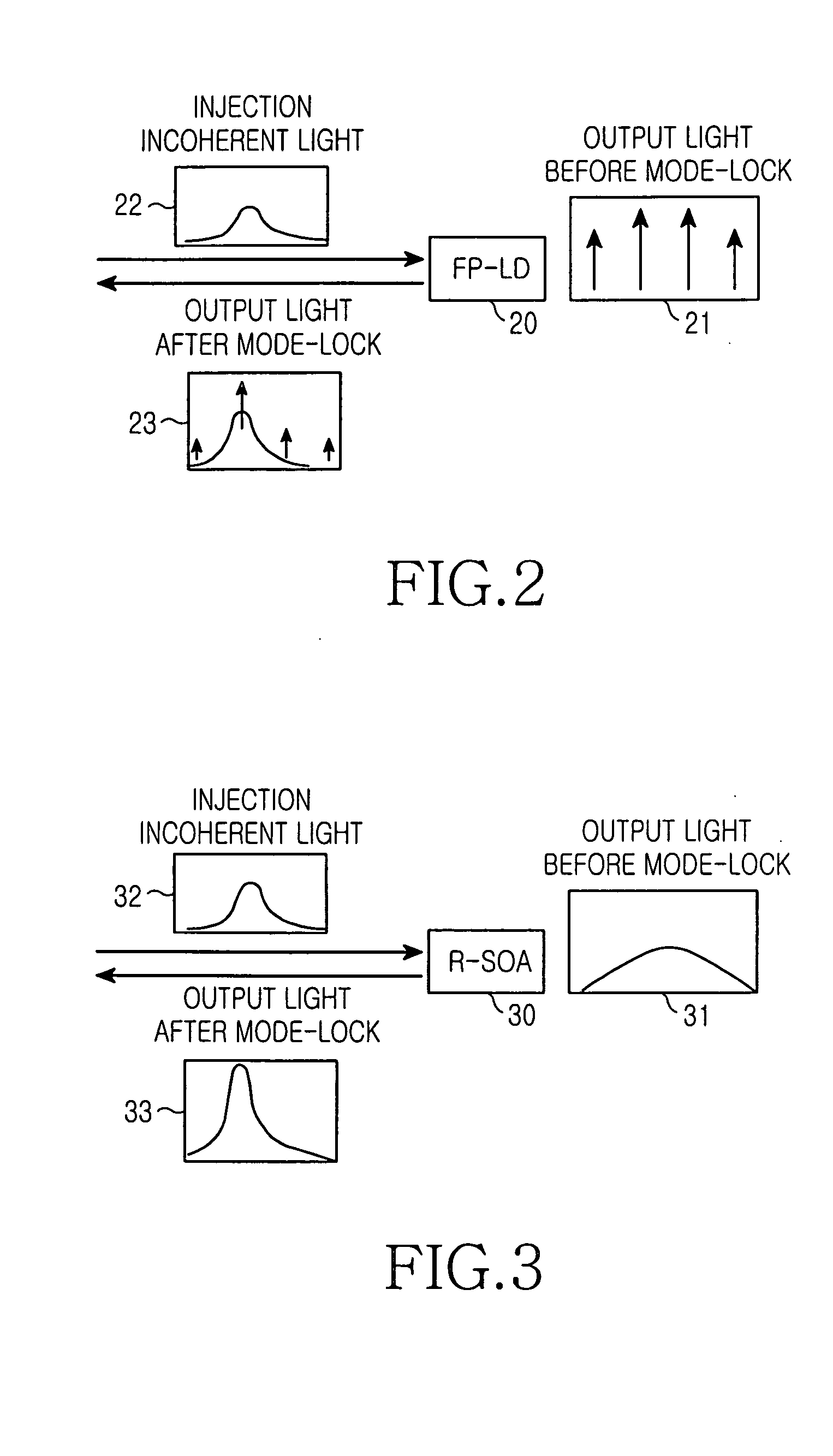
Disclosed are optical signal transmission apparatus including a reflective gain-clamped semiconductor optical amplifier and optical communication system using the optical signal transmission apparatus, which can improve modulation speed and optical power by effectively suppressing intensity noise of an incoherent light source. The optical signal transmission apparatus comprises a light source; a reflective gain-clamped semiconductor optical amplifier to generate gain-clamped optical signals having a substantially constant output intensity in a gain saturation region; a wavelength division multiplexing apparatus configured to spectrum-slice light from the light source, provide the spectrum-sliced light to the reflective gain-clamped semiconductor optical amplifier, and multiplex optical signals gain-clamped by the reflective gain-clamped optical amplifier. and a circulator for inputting the light generated by the light source to the wavelength division multiplexing apparatus, and outputting the optical signal multiplexed by the wavelength division multiplexing apparatus to a transmission link.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods, systems and apparatus for steering wheel vibration reduction in electric power steering systems
ActiveUS20120061169A1Short response timeEasy to implementElectrical steeringElectric power steeringElectric power system
Methods, system and apparatus are provided for suppression of steering wheel vibrations generated by an electric power steering system of a vehicle. A feedback controller is provided that extracts information from ABS pulse trains communicated over the vehicle's LAN to generate estimates of instantaneous tire position and angular velocity. The estimated tire position is used to generate carrier signals. The carrier signals are then processed with a measured dynamic disturbance signal to extract periodic content of the torque sensor. The estimated tire frequency is applied to a stored inverse motor drive-to-sensor torque transfer function to generate gain and phase adjustments that, along with the extracted periodic content of the torque sensor, can be applied to carrier signals to generate a gain-and-phase-compensated motor drive signal. The gain-and-phase-compensated motor drive signal is fedback to the electric motor to suppress the periodic content in the output signal of the torque sensor to suppress vibrations at the vehicle's steering wheel.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Predictive and adaptive weather radar detection system and method
ActiveUS7808422B1Tune performancePosition fixationNavigation instrumentsWeather radarPosition dependent
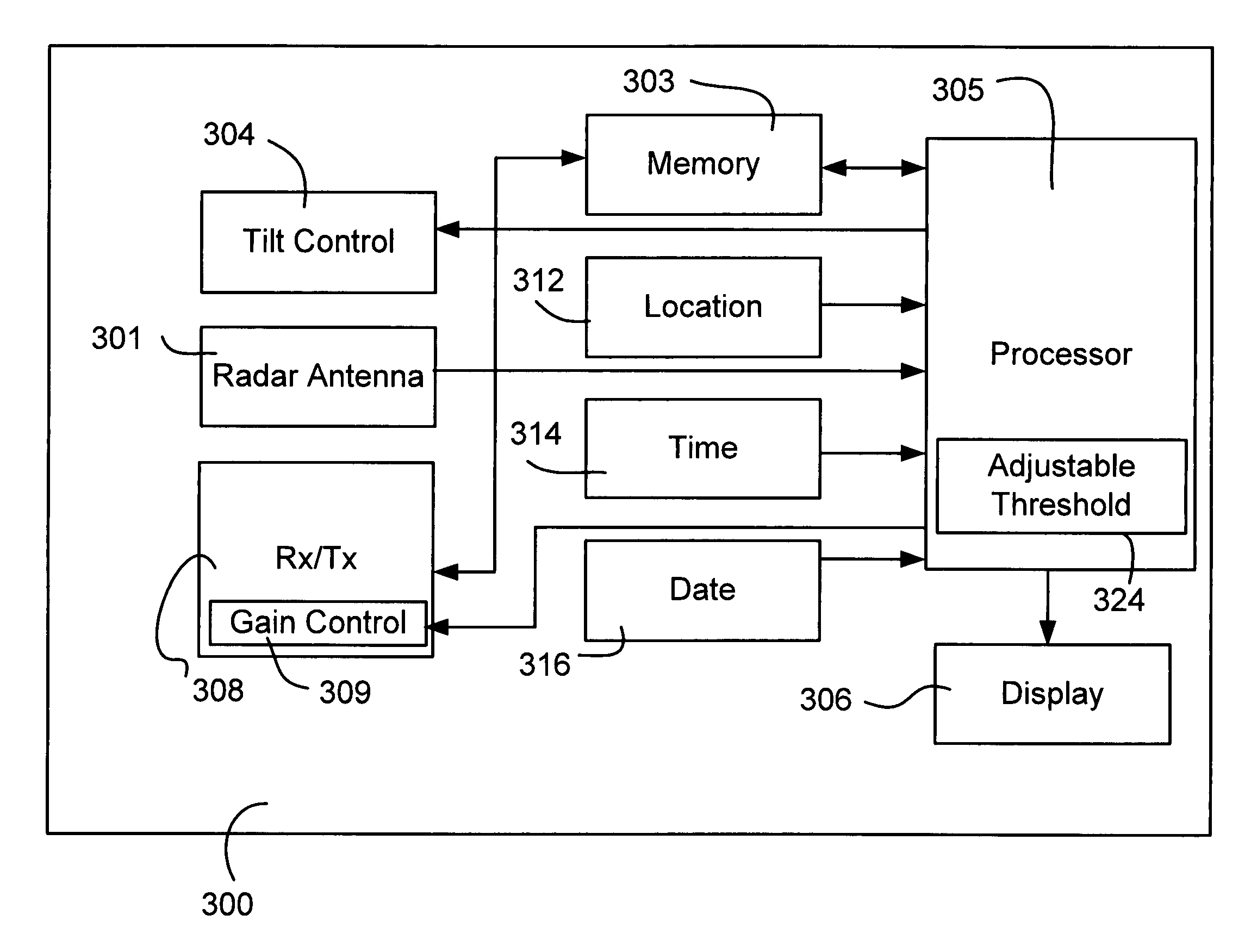
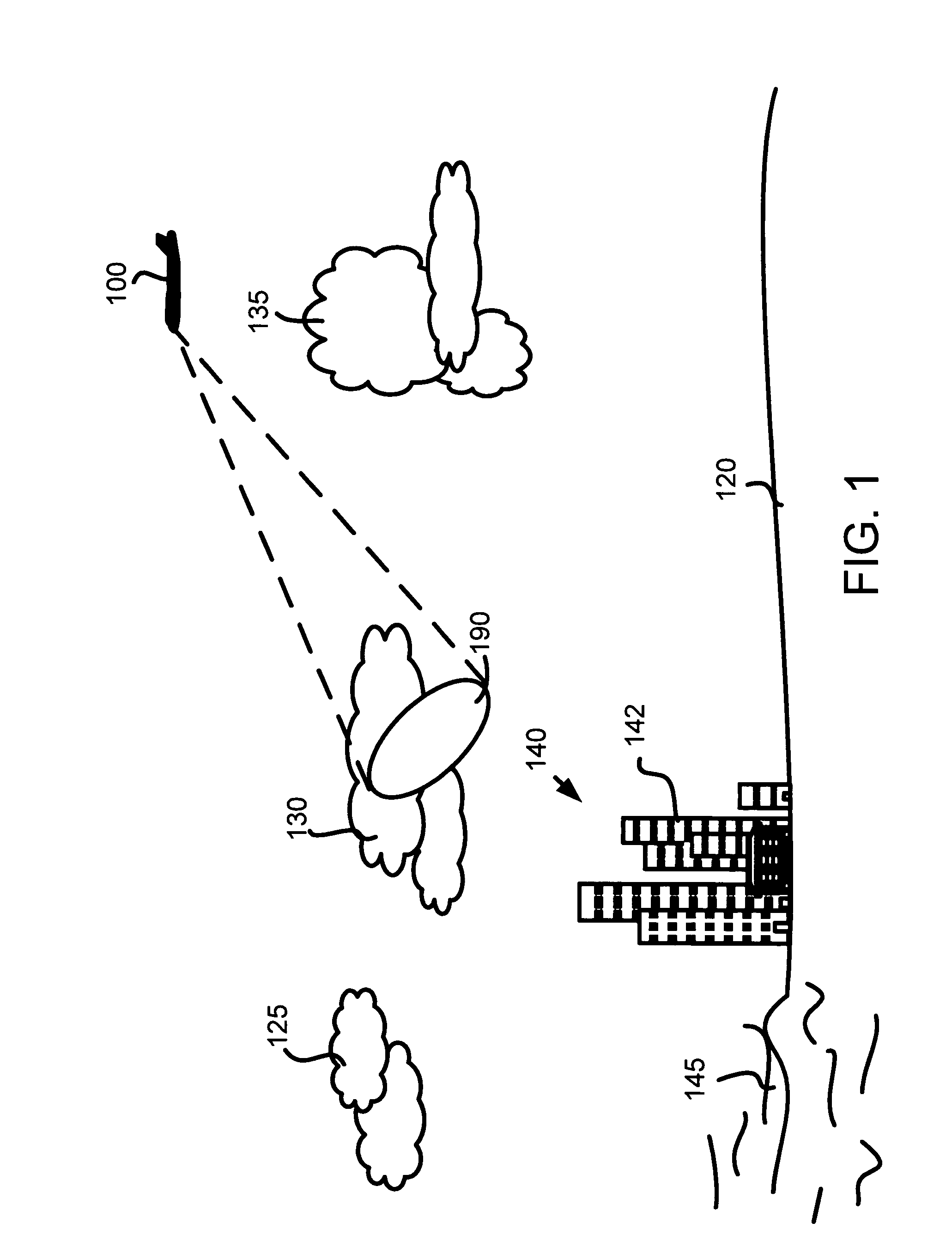
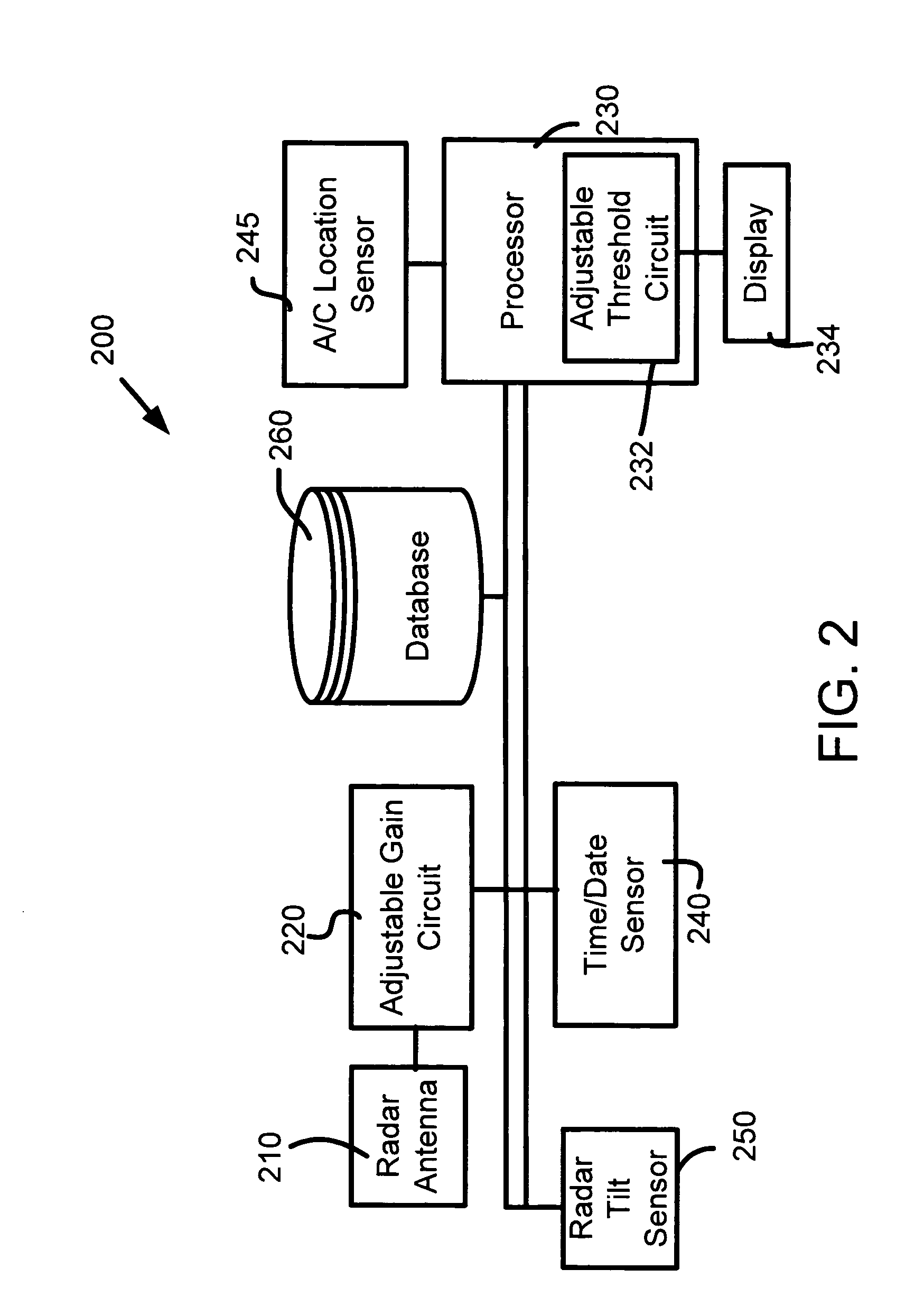
A method of detecting weather on an aircraft uses a weather radar system. The method includes determining a location of a reflective radar target, accessing a database having stored information relating to ground clutter of a reflective radar target, retrieving weather radar information associated with the location, and automatically adjusting the weather radar return threshold in response to the information. The method can adjust a threshold for a weather radar display, adjust a weather radar signal gain, adjust a tilt angle of the weather radar, or adjust a ground clutter suppression threshold. The method can be implemented by hardware and / or software.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Decoupling sampling clock and error clock in a data eye
ActiveUS20120170621A1Well formedMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsPhase correctionTransceiver
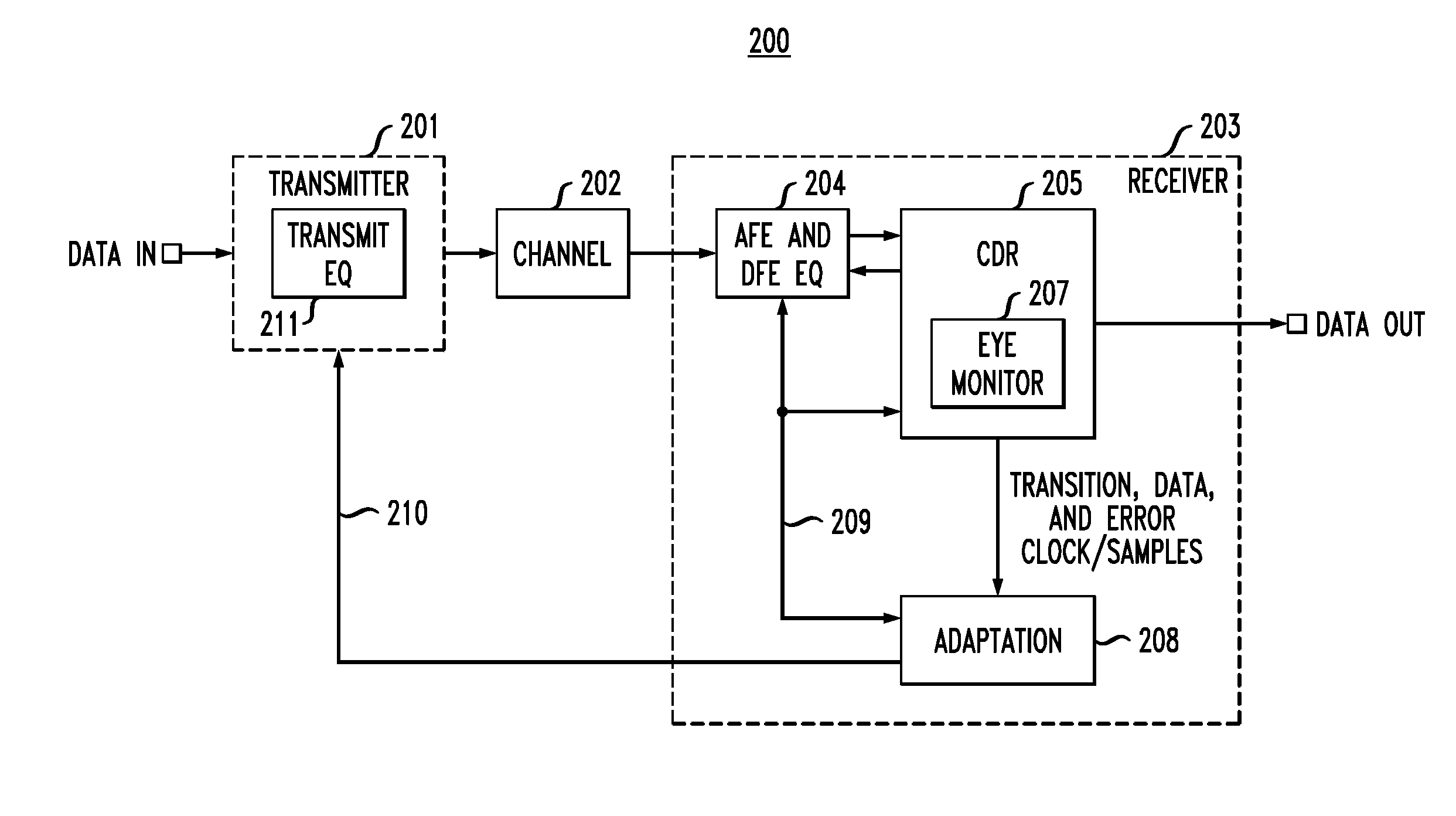
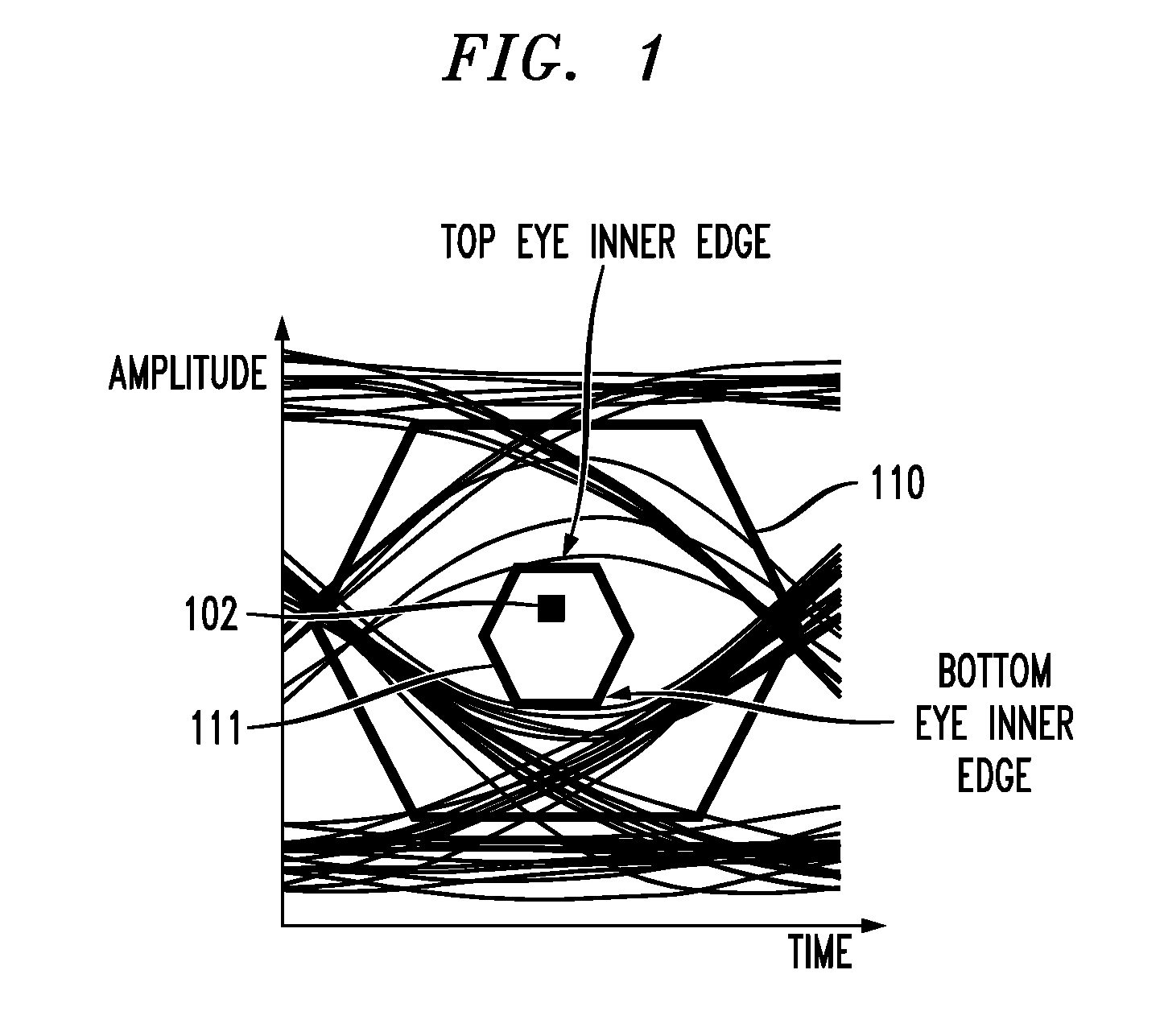
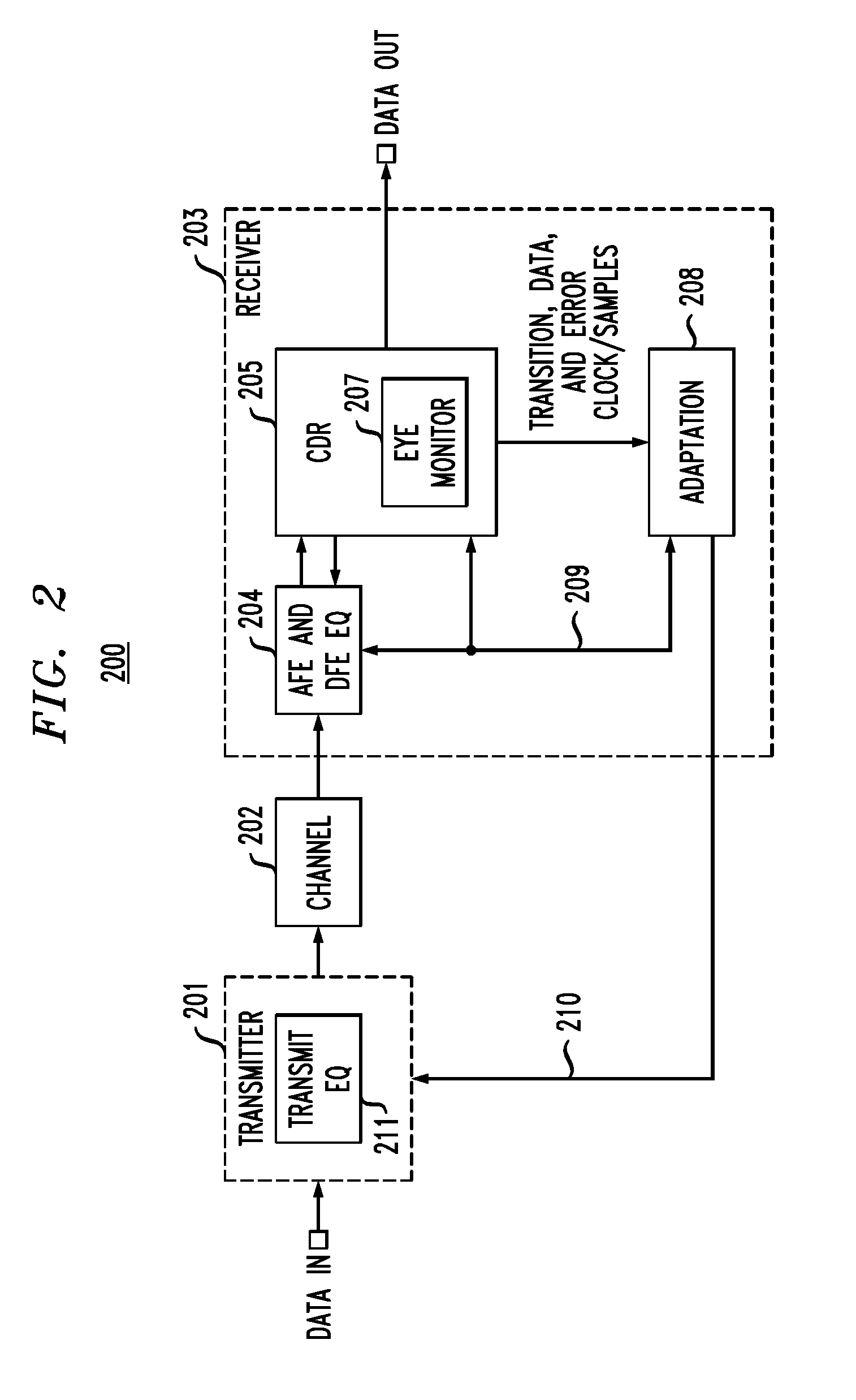
In described embodiments, a transceiver includes an eye monitor, clock and data recovery, and adaptation modules. Data sampling clock phase and error clock phase determined from a data eye are decoupled in the transceiver during a sampling phase correction process. Decoupling these clock phases during the sampling phase correction process allows relative optimization of system equalization parameters without degradation of various adaptation algorithms. Such adaptation algorithms might be employed for received signal gain and equalization such as, for example, Decision Feedback Equalizer (DFE) adaptation. Deriving the data sampling clock and error clock phases from the same clock generation source and with independent clock control enables an iterative sampling phase correction process that allows for accelerated clock and data recovery (CDR) without disturbing the data eye shape.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Mixer circuit for direct conversion transceiver with improved IP2
InactiveUS7457606B2Enhanced IPImprove featuresModulation transference balanced arrangementsVibration massageTransceiverPhase shifted
A mixer for direct conversion transmitters and receivers using four phase-shifted local oscillation signals that are orthogonal each other to control a plurality of switches for outputting signals that are orthogonal each other. Two output signals that are orthogonal to each other do not mutually interfere and have a predetermined small signal gain. Further, a mixer may include four or eight switches controlled by four phase-shifted local oscillation signals that are orthogonal each other for outputting signals that are orthogonal to each other on an I-Q plot. The signals outputted from the switches controlled by four phase-shifted local oscillation signals remove I-Q mismatch and a DC component, and improve IP2 characteristics.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and device for correcting in-vivo sensor drift
ActiveUS7025718B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsEngineeringIn vivo
A method and device for reducing signal drift on a balloon catheter mounted pressure sensor by adjusting for signal gain and / or zero offset, and by separately calibrating the constant signal component and the time-varying signal component of an uncalibrated source signal to produce a calibrated source signal.
Owner:DATASCOPE
Adaptive quantizer, adaptive quantization method and adaptive quantization program
InactiveUS20070201553A1Small step sizeSuppress noiseColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionErrors and residualsSignal gain
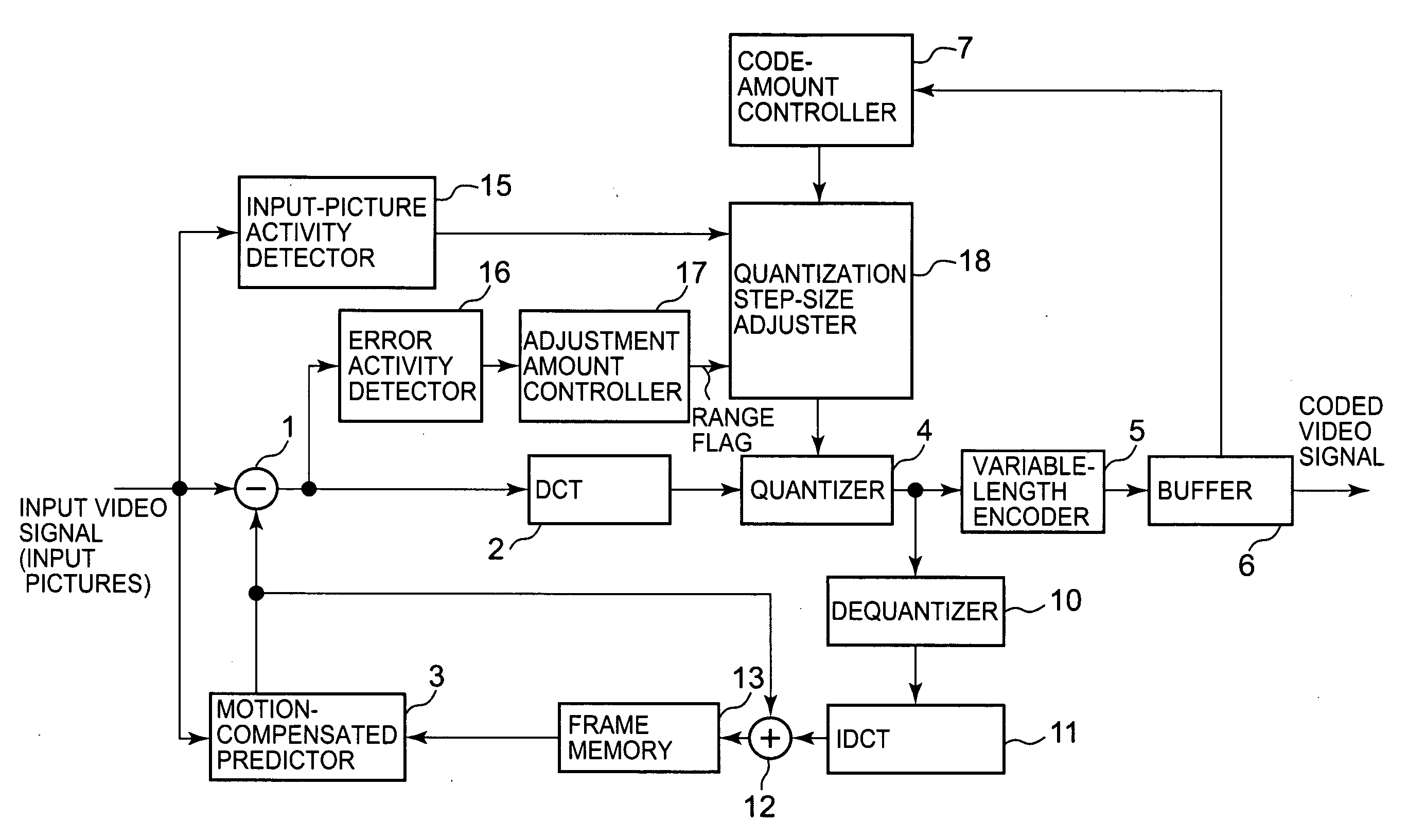
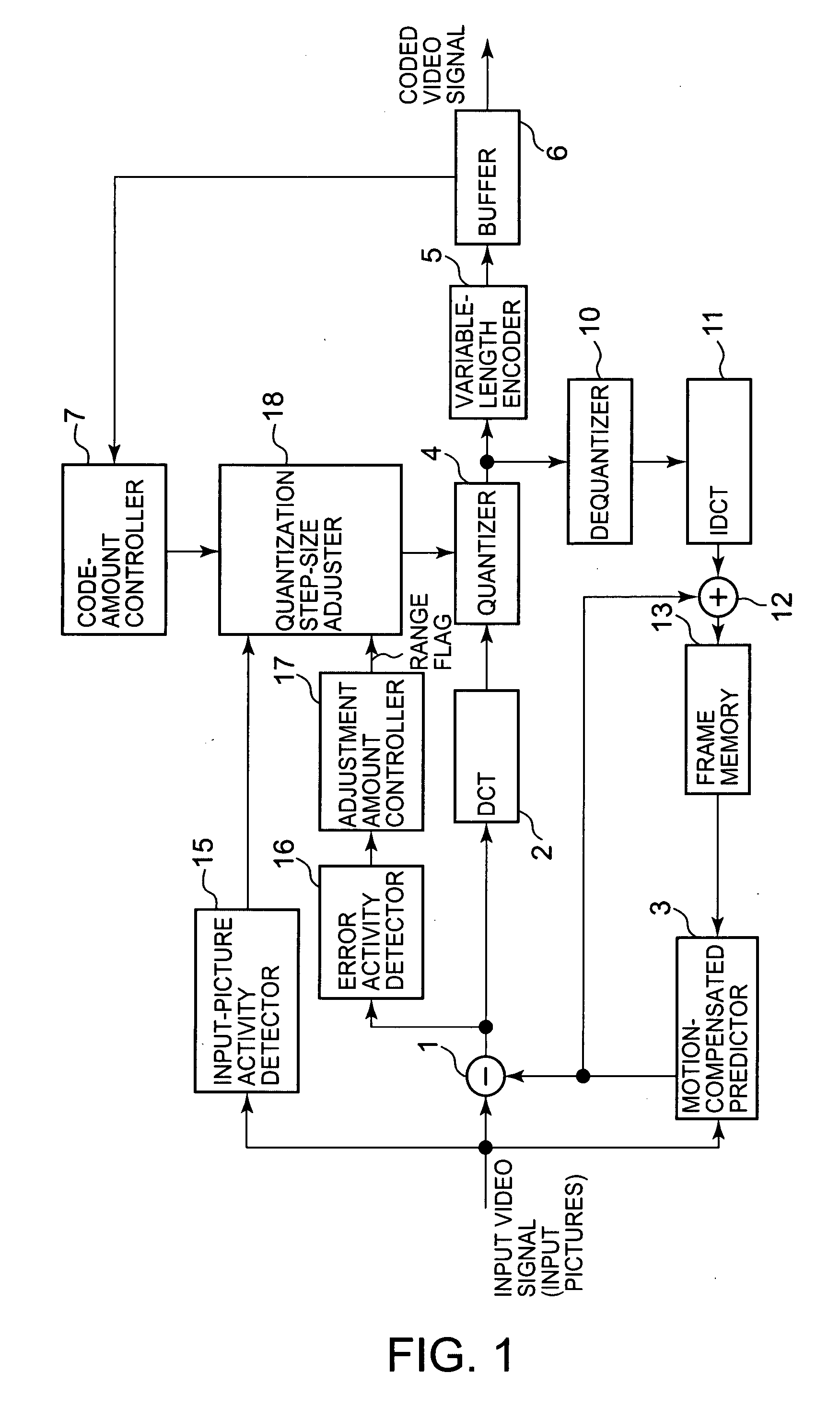
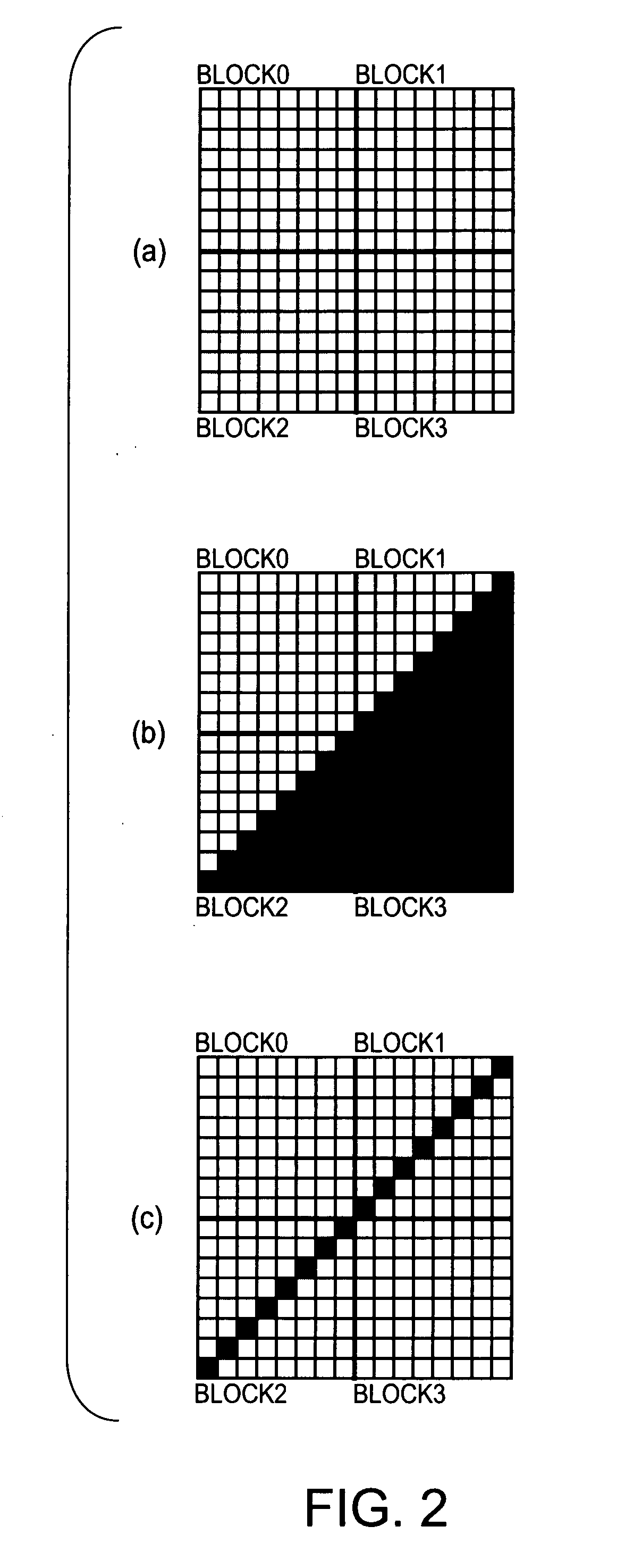
Adaptive quantization in coding pictures carried by an input video signal. The pictures include first pictures to be coded with motion-compensated prediction and second pictures to be coded with no motion-compensated prediction. Activities of the input video signal are obtained for a plurality of subblocks that compose each of a plurality of macroblocks that compose each picture of the input video signal. The smallest activity is detected among the activities as an input-picture activity per macroblock. Obtained next are activities of a motion-compensated predictive signal gained in motion-compensated prediction per first picture and activities of the input video signal per second picture, for the subblocks of each macroblock. A mean value of the obtained activities is obtained per macroblock for each of the first and second pictures, as an error activity per macroblock. Obtained further is a mean error activity of error activities in each picture. The error activity per macroblock is compared with the mean error activity in each picture. A quantization step size to be used in quantization of the video signal is adjusted per macroblock, according to the input-picture activity, so that the quantization step size becomes smaller when the error activity is equal to or larger than the mean error activity than when the error activity is smaller than the mean error activity.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Optical receiver with monolithically integrated photodetector
InactiveUS20120141122A1High bandwidthTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsCMOSPhotovoltaic detectors
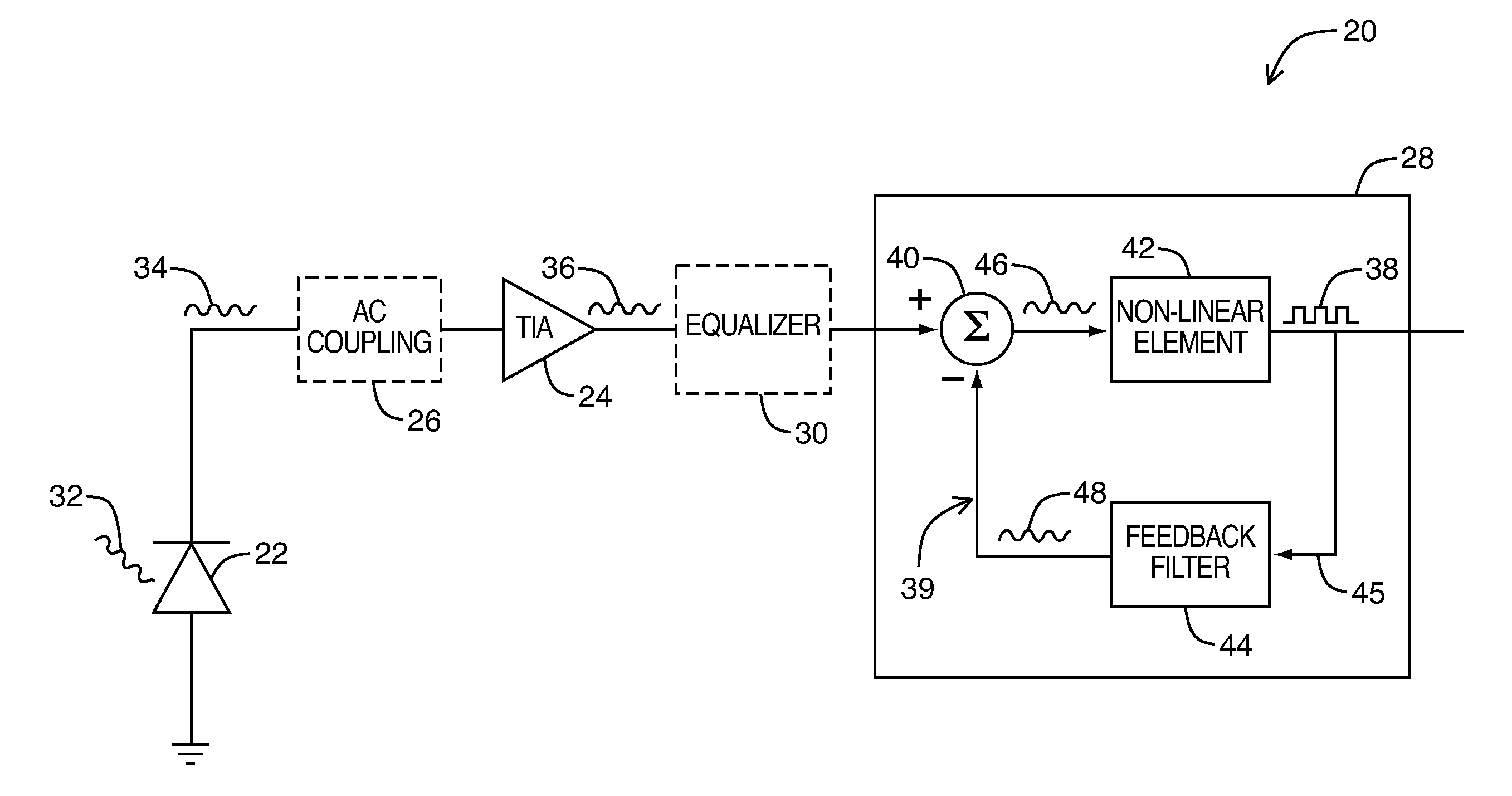
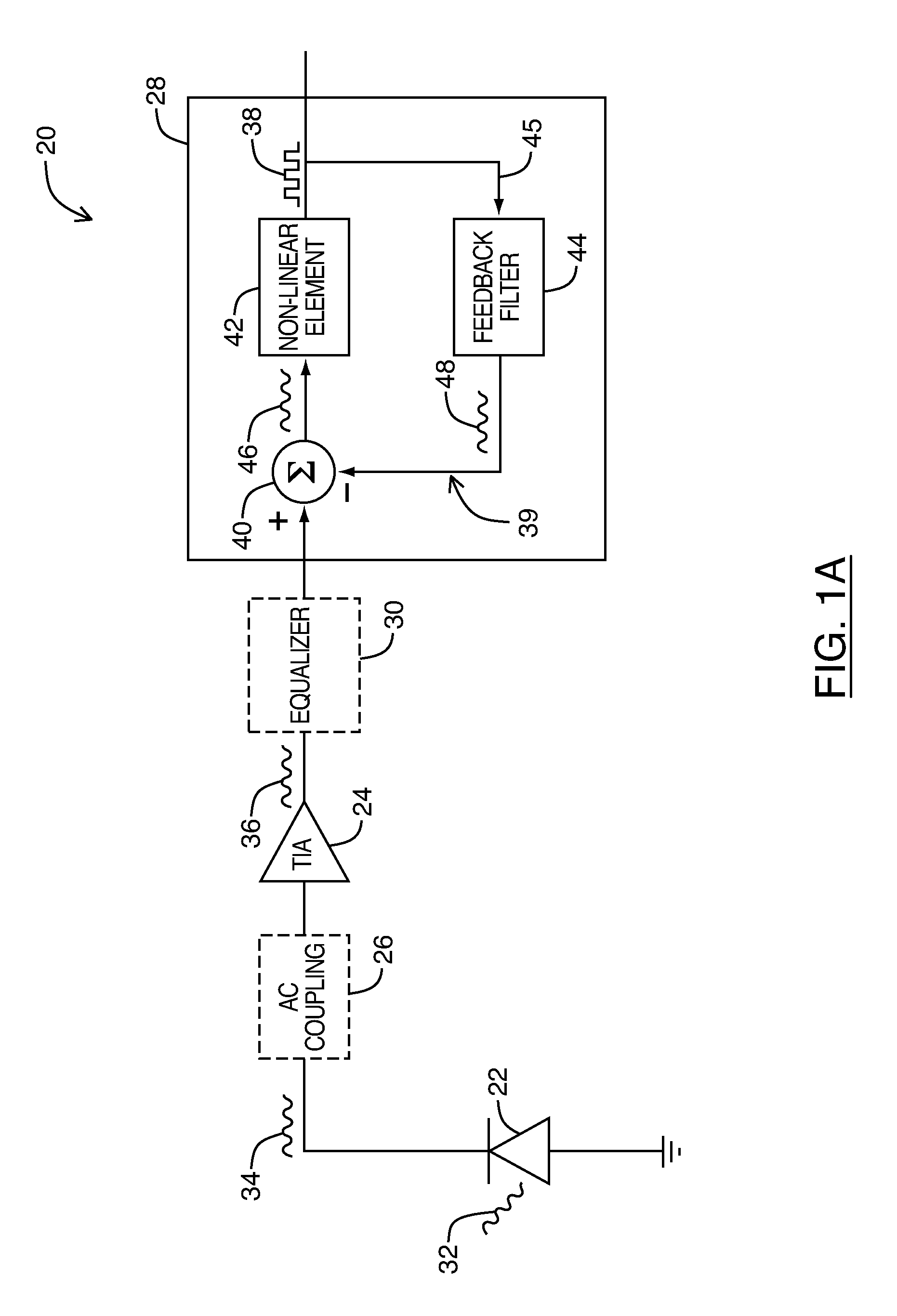
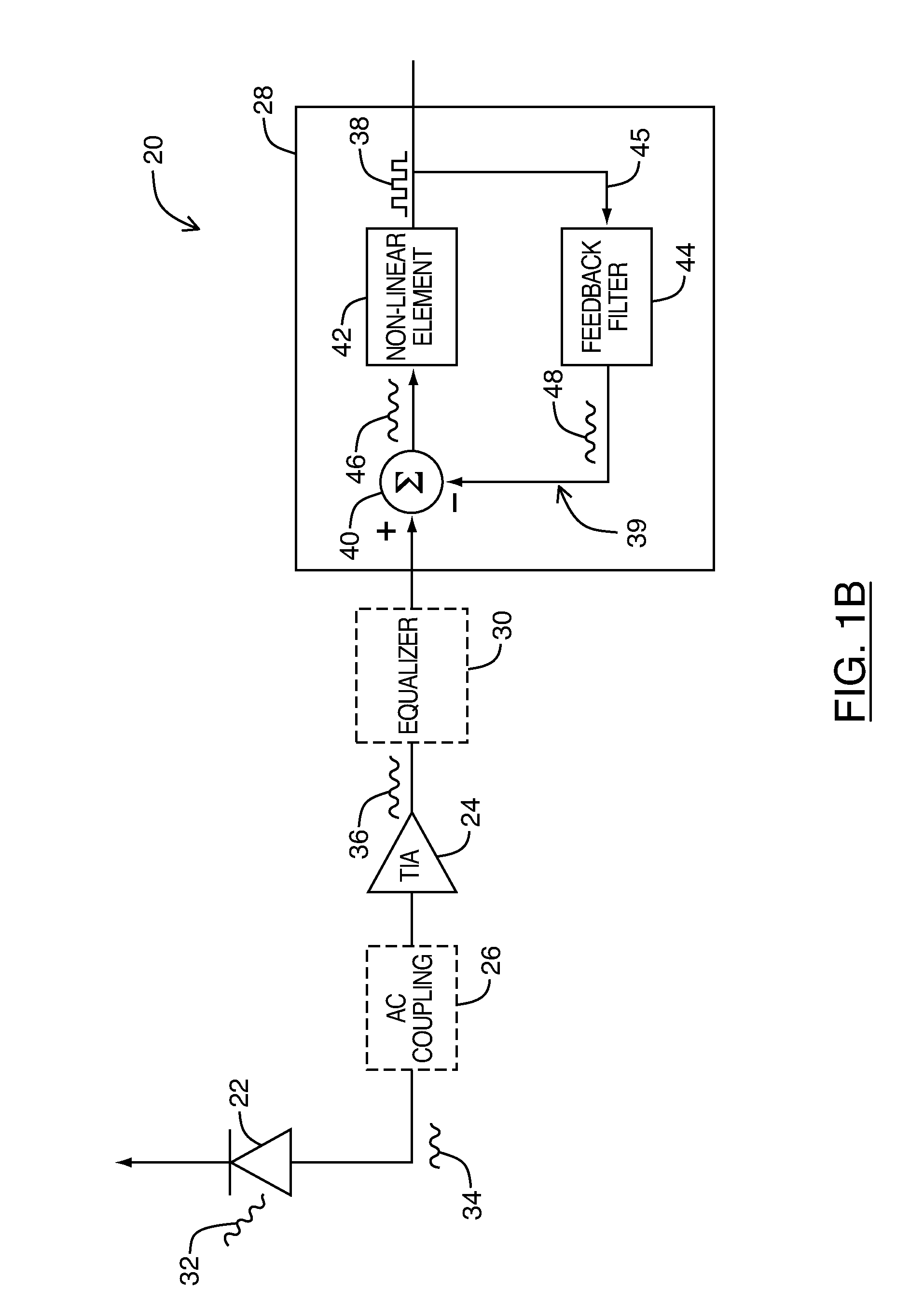
An optical receiver includes a photodetector for detecting incoming optical data signals and an amplifier for providing signal gain and current to voltage conversion. The detection signal generated by the photodetector may include a distortion component caused by an operating characteristic of the photodetector. A signal compensating circuit may reconstruct the received optical data signal by effectively canceling the distortion component. For this purpose, the signal compensating circuit may include a decision feedback equalizer implemented using at least one feedback filter matched to the operating characteristic of the photodetector causing the signal distortion so as to reproduce the distortion component for cancellation. Use of a control module may also configure the optical receiver in real time to account for other operating and environmental conditions of the optical receiver. Data rates in excess of 5 Gbps may be realized in monolithic CMOS photodetectors when the signal compensating circuit is properly matched.
Owner:THE GOVERNING COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORONTO
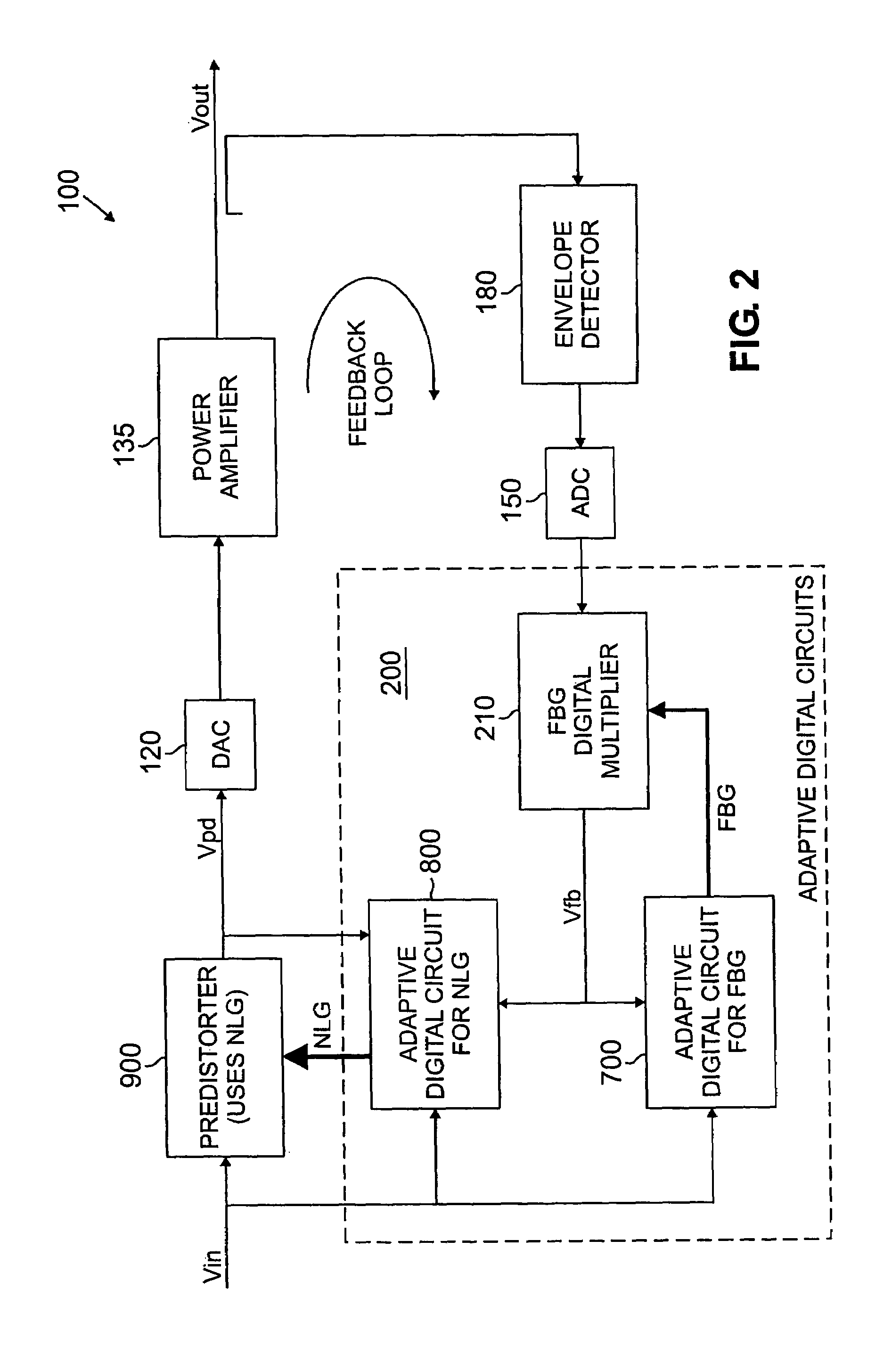
Method and apparatus for adaptive digital predistortion using nonlinear and feedback gain parameters
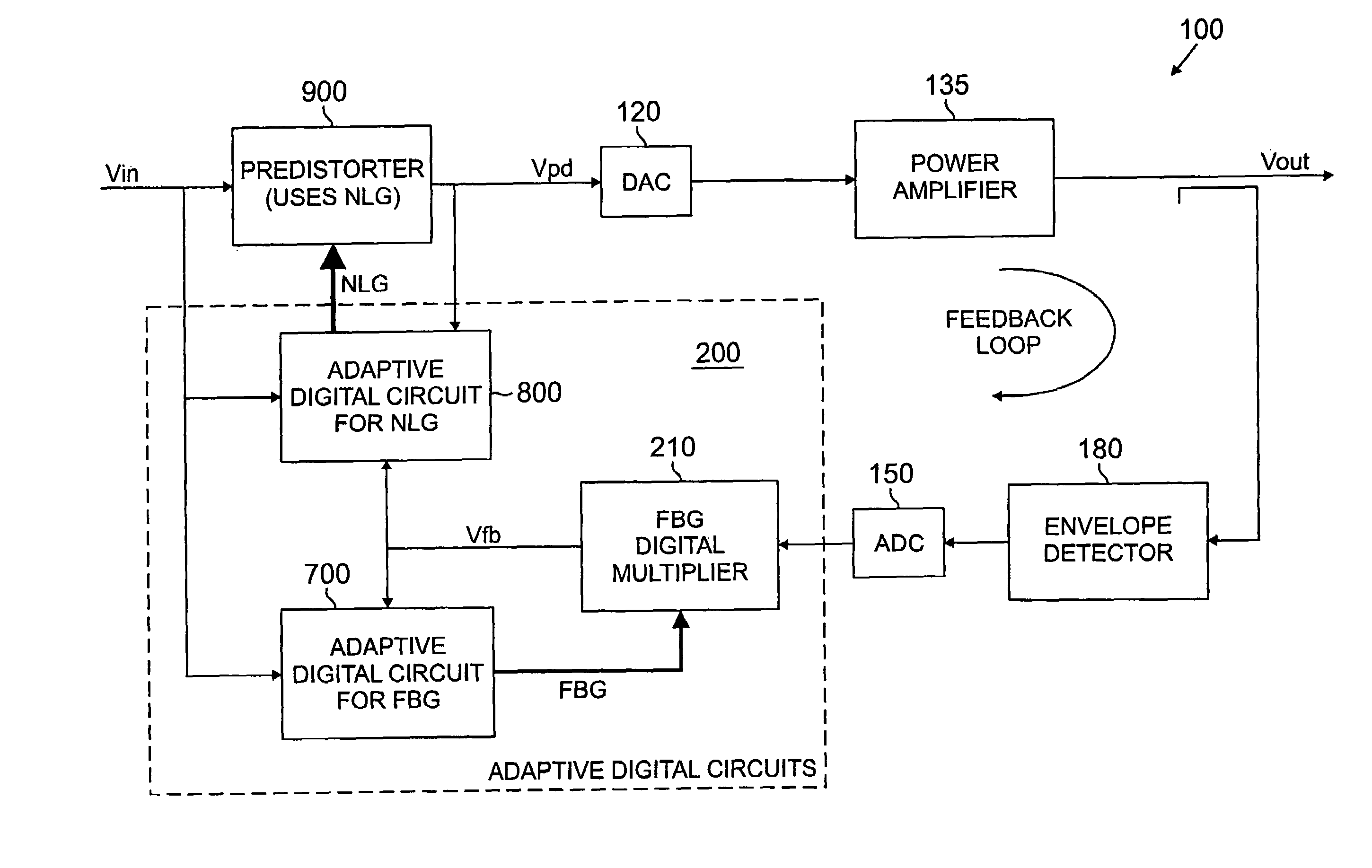
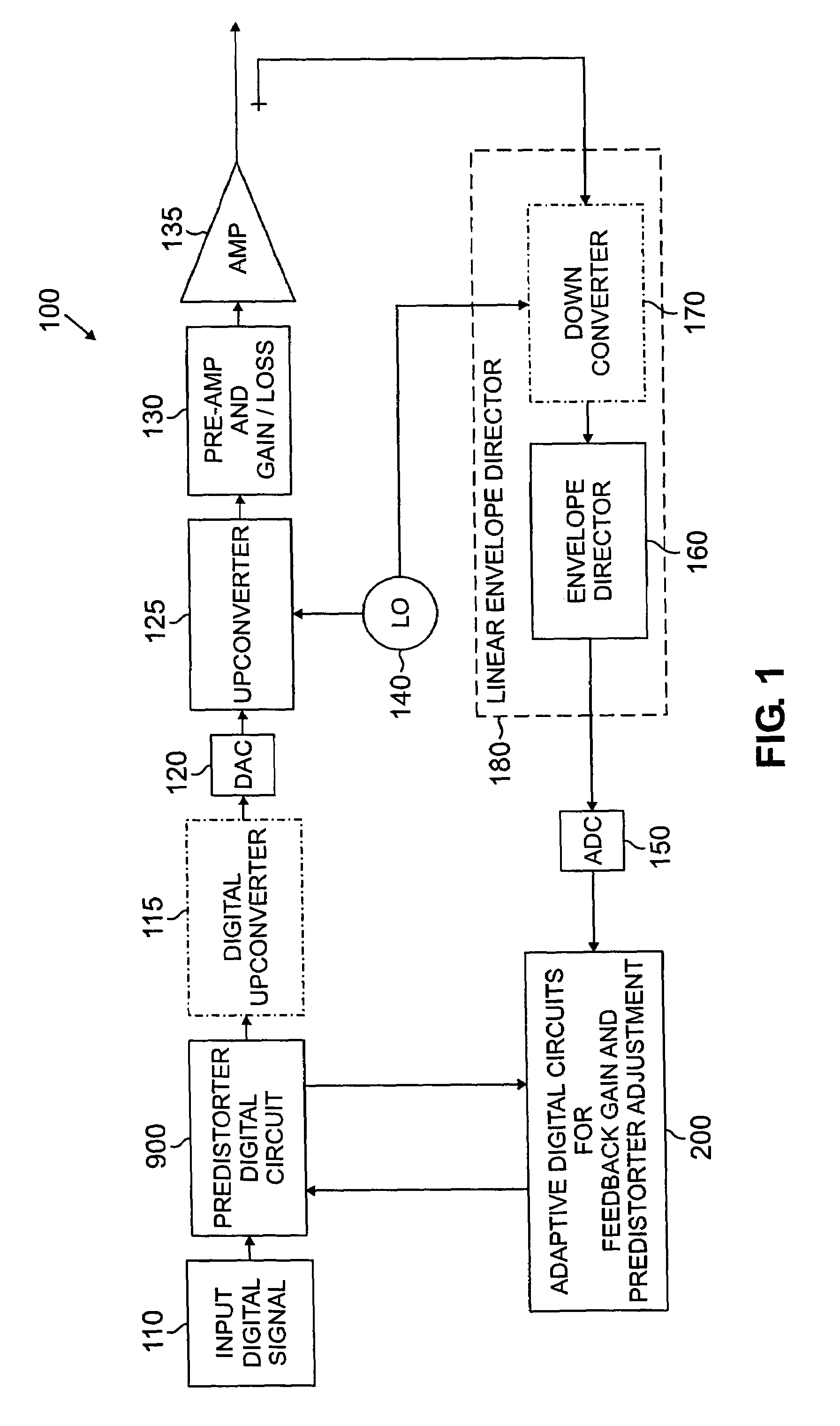
ActiveUS7113036B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
A predistorter is disclosed that predistorts an input signal based on one or more static coefficients that are representative of a non-linear distortion characteristic of an amplifier. The input signal is also processed based on a non-linear gain parameter that reduces an error metric between the input signal and a feedback signal. The nonlinear gain parameter adapts an amount of nonlinearity introduced by the predistorter. The non-linear gain adaptation is performed, for example, when the input voltage is above a threshold input voltage. The input signal can be processed by multiplying the input signal by the non-linear gain parameter followed by table-coefficient processing, or by both multiplying the input by the non-linear gain parameter followed by dividing the table-coefficient processed output signal by the same non-linear gain parameter. The input signal can also be processed based on a feedback gain parameter that compensates for a small-signal gain of the feedback loop. The feedback gain parameter attempts to maintain a small-signal gain of approximately unity.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
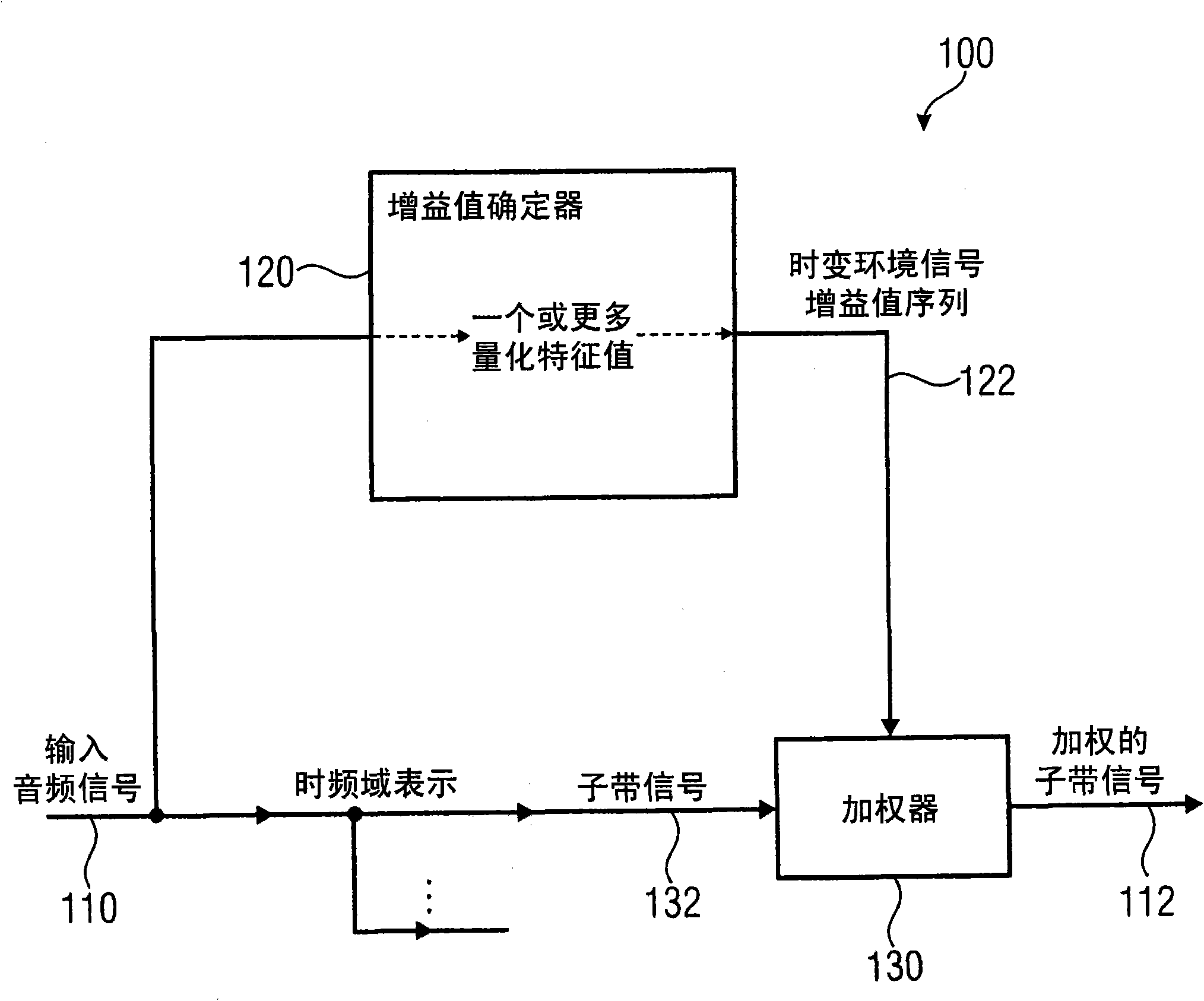
Apparatus and method for extracting an ambient signal in an apparatus and method for obtaining weighting coefficients for extracting an ambient signal and computer program
An apparatus for extracting an ambient signal from an input audio signal comprises a gain-value determinator configured to determine a sequence of time-varying ambient signal gain values for a given frequency band of the time-frequency distribution of the input audio signal in dependence on the input audio signal. The apparatus comprises a weighter configured to weight one of the sub-band signals representing the given frequency band of the time-frequency-domain representation with the time-varying gain values, to obtain a weighted sub-band signal. The gain-value determinator is configured to obtain one or more quantitative feature-values describing one or more features of the input audio signal and to provide the gain-value as a function of the one or more quantitative feature values such that the gain values are quantitatively dependent on the quantitative values. The gain value determinator is configured to determine the gain values such that ambience components are emphasized over non-ambience components in the weighted sub-band signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Signal-on architecture for electronic, oligonucleotide-based detectors
ActiveUS20070154909A1Enhanced detection signalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSignal onOxidation-Reduction Agent
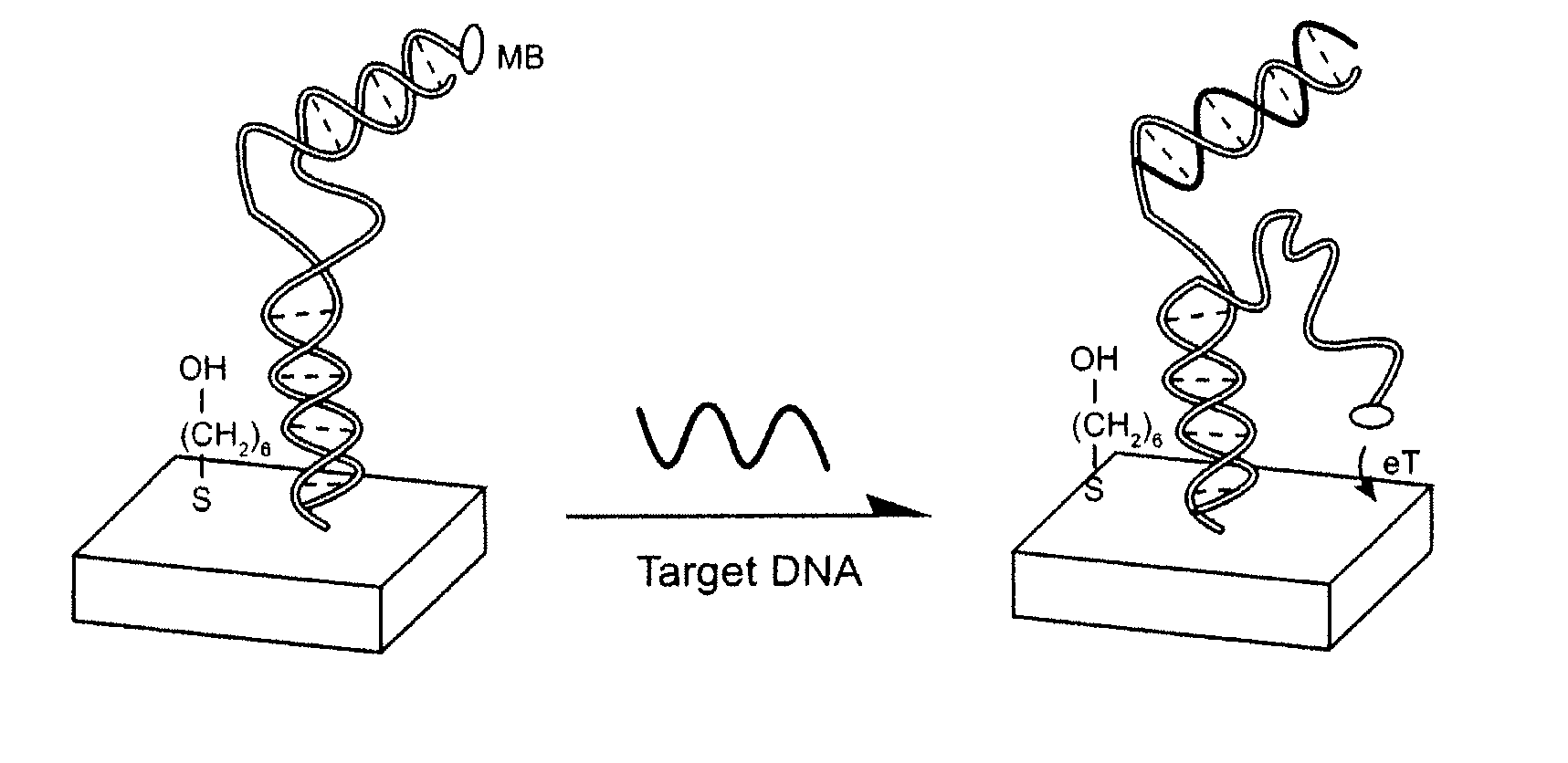
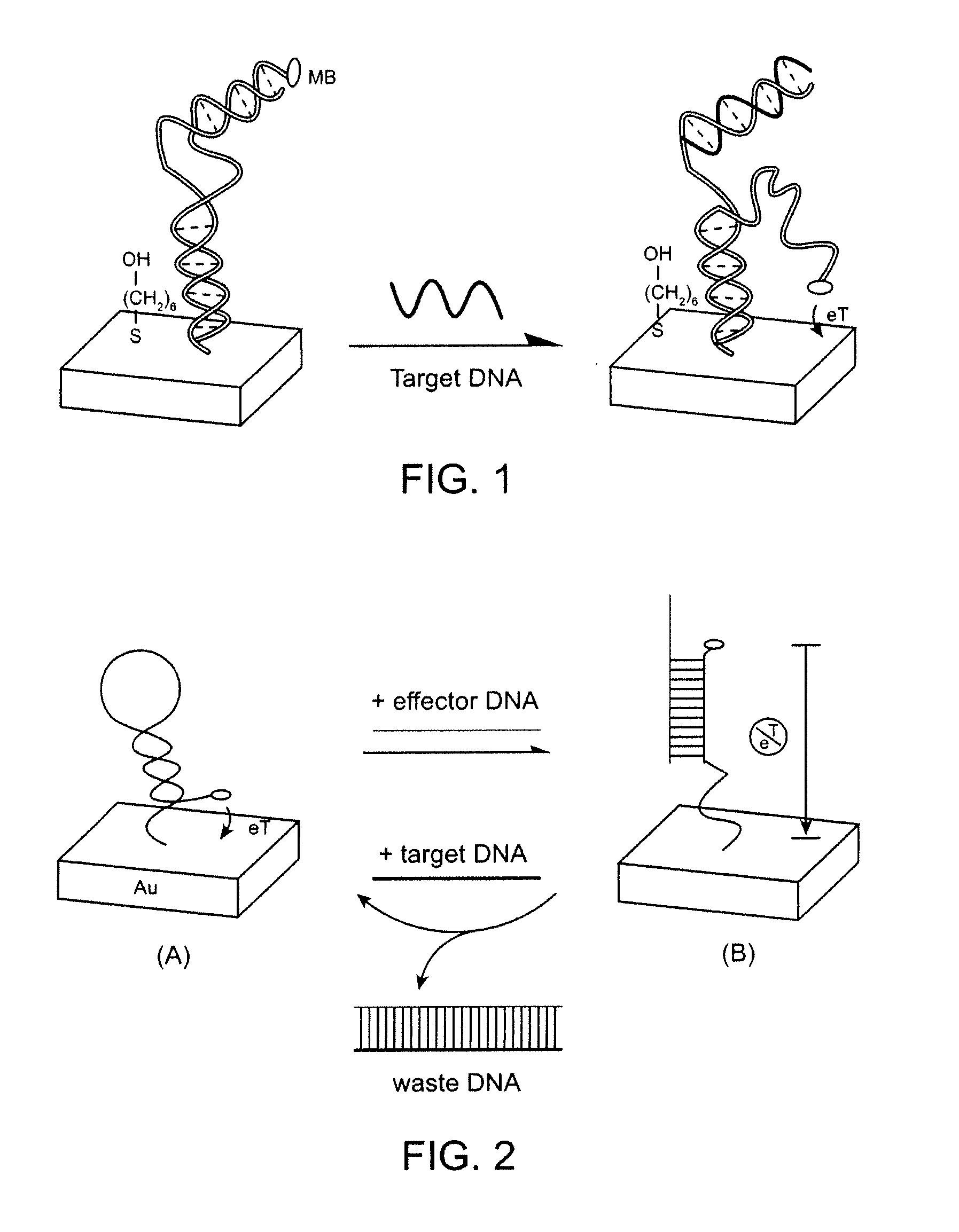
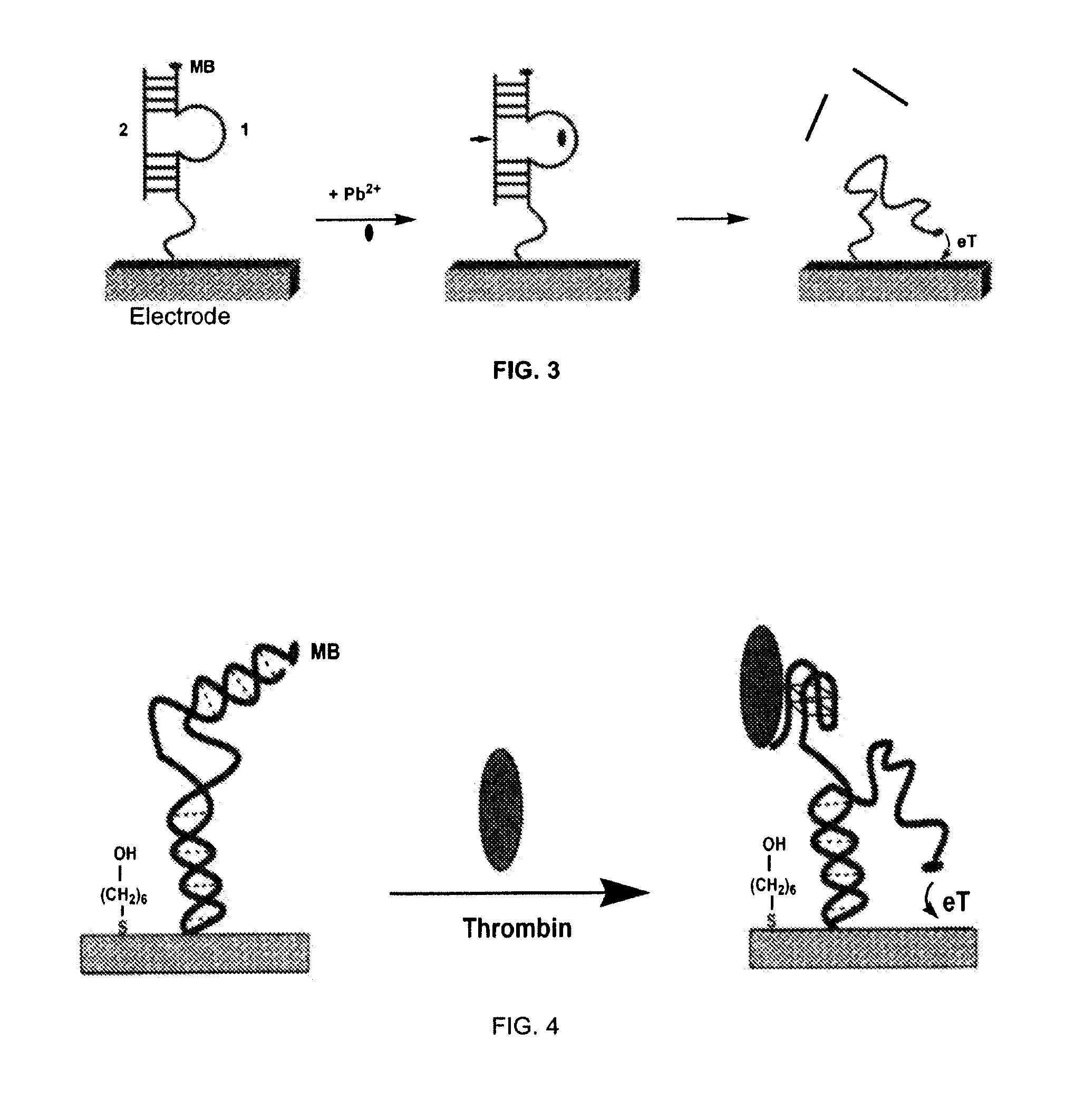
The invention provides a general “signal-on” architecture for oligonucleotide-based detectors that leads to order of magnitude increases in signal gain and sensitivity as compared to prior art detectors. The detectors of the invention rely on base pairing between two oligonucleotide strands, the sensor strand and the blocker strand. In the ‘off’ position of the detector, i.e., in the absence of target, the blocker strand and sensor strand are base-paired. As shown in FIG. 1, the formation of comparatively rigid, duplex DNA prevents the redox moiety from approaching the electrode surface, thereby suppressing Faradaic currents. When target is added to the system, the target displaces the blocker strand, binds to the sensor strand, liberating the end of the redox-labeled oligonucleotide to produce a flexible element. This, in turn, allows the redox moiety to collide with the electrode surface, producing a readily detectable Faradaic current.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
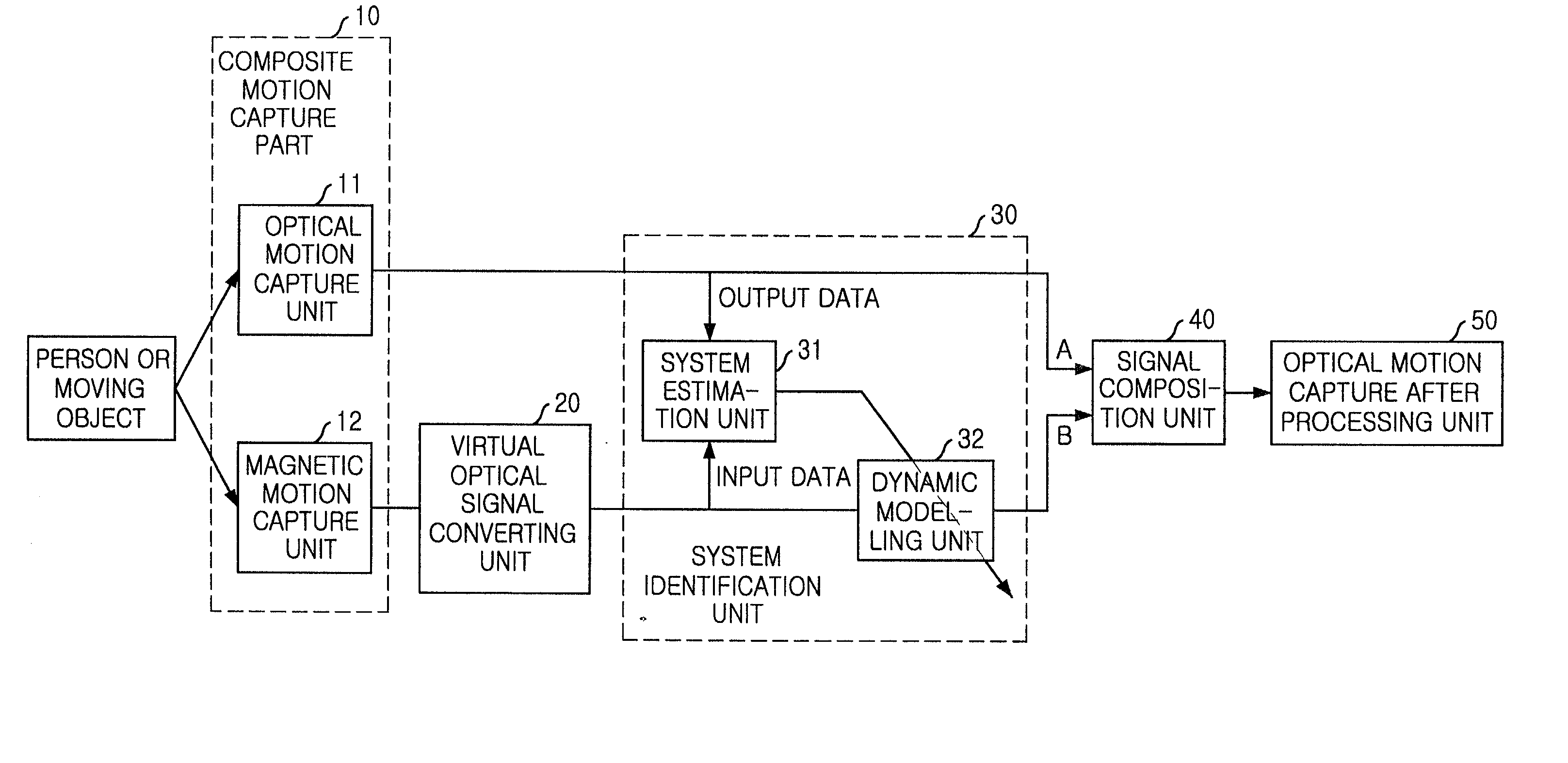
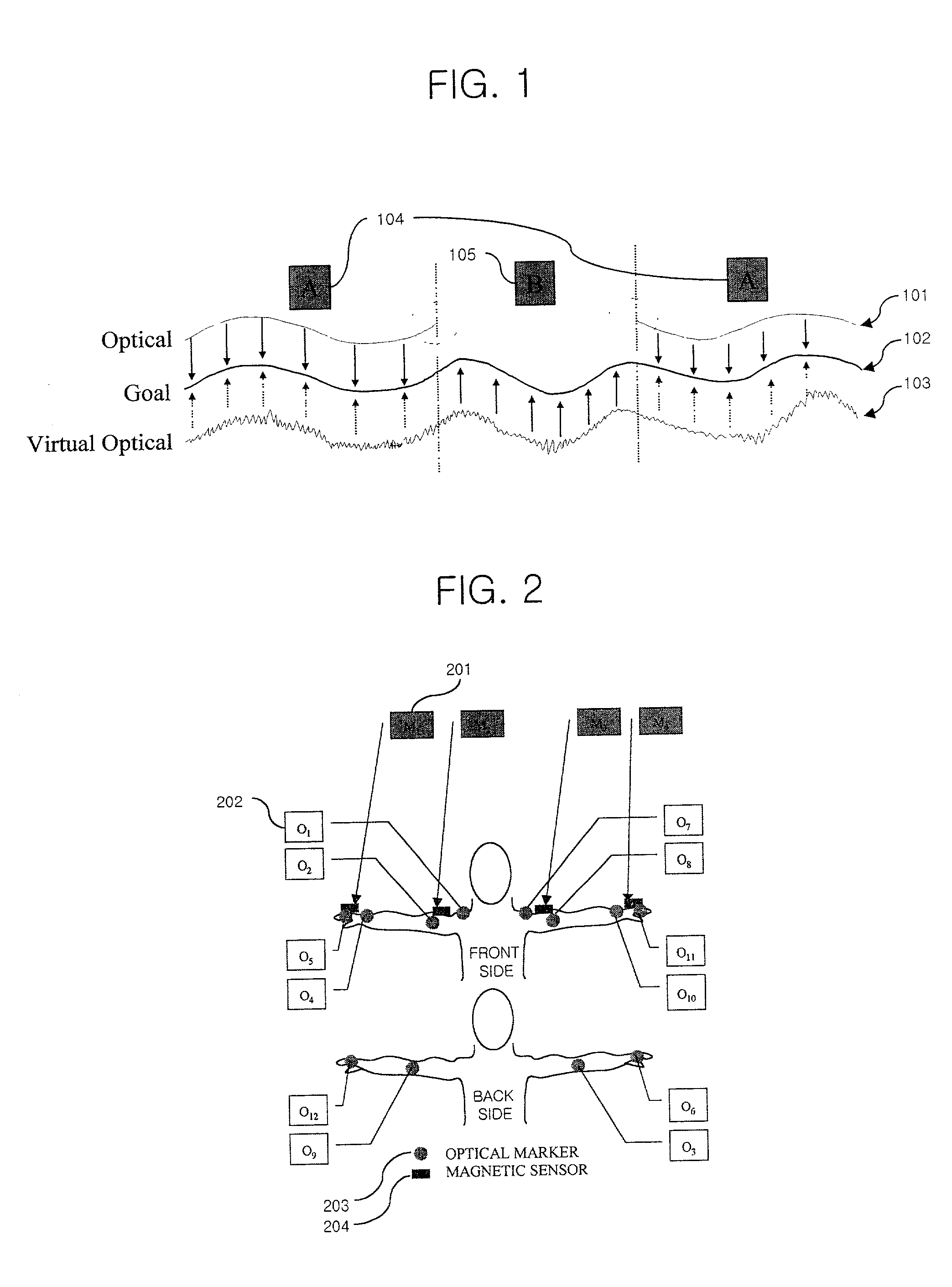
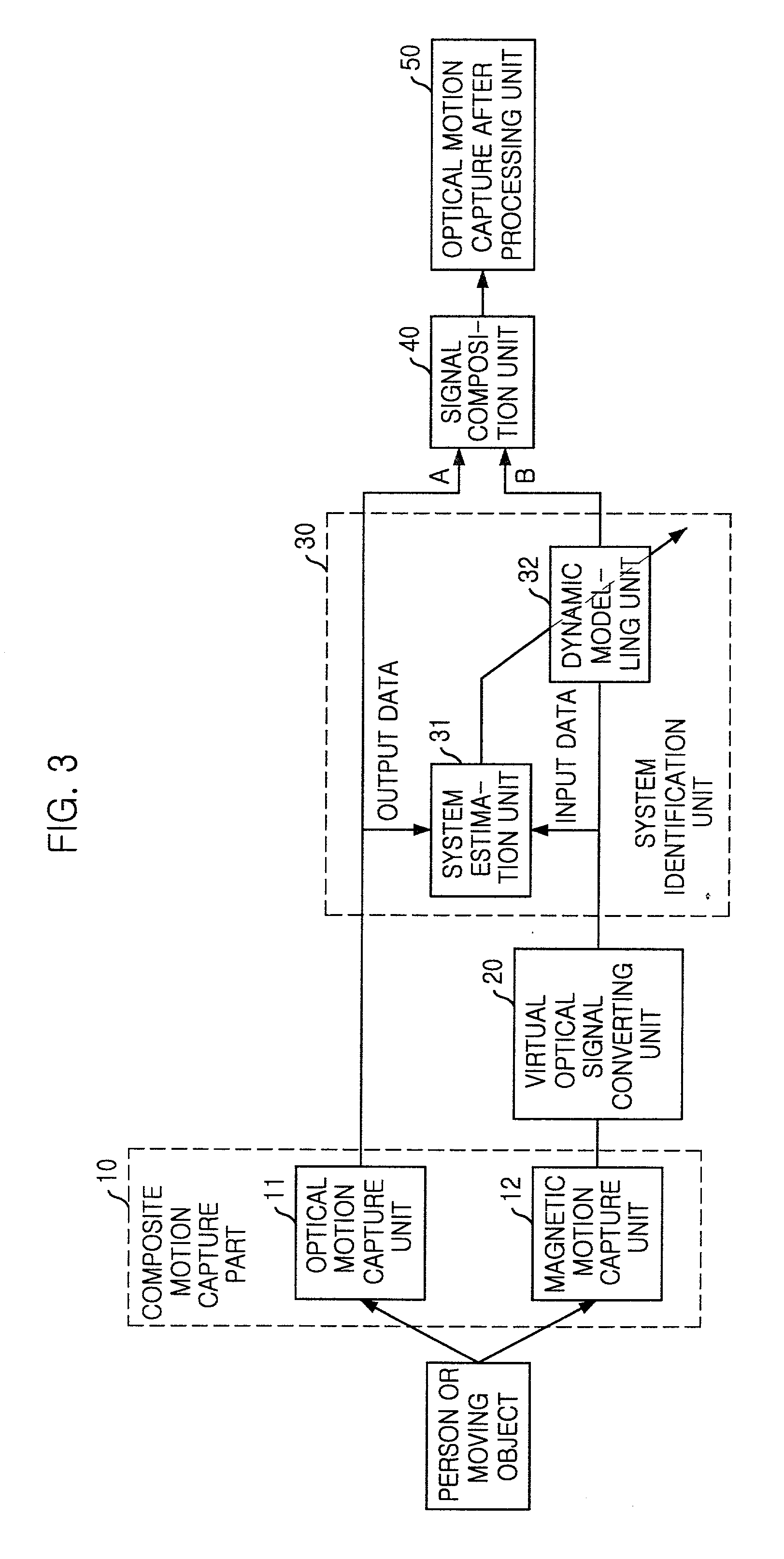
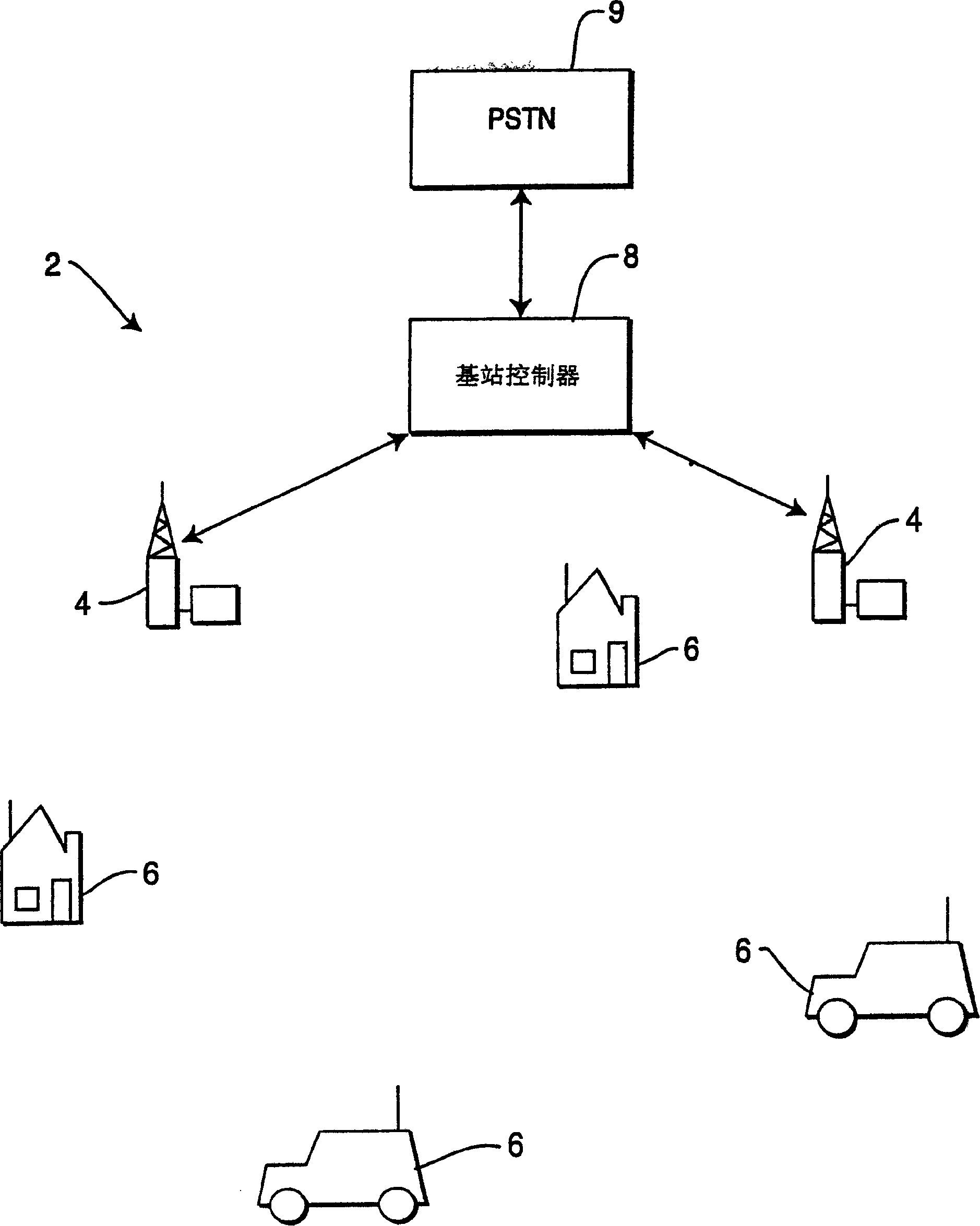
Sensor fusion apparatus and method for optical and magnetic motion capture systems
InactiveUS20020097245A1Reduce the burden onAccurate gainImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionDynamic modelsRead through
In a sensor fusion apparatus and method for optical and magnetic motion capture systems and a record medium capable of being read through a computer having a writing of a program to realize the inventive method, in which a shortcoming of respective systems can be overcome and merits can be led by simultaneously using the optical motion capture system (OMCS) and the magnetic motion capture system (MMCS) to obtain motion capture data more precisely, the method includes a first step of obtaining an optical marker signal and a magnetic sensor signal for the motion capture object; a second step of converting the magnetic sensor signal into a corresponding optical marker signal, and acquiring a virtual optical marker signal; a third step of modeling a relation between the virtual optical marker signal and the optical marker signal to a dynamic model through a system identification; and a fourth step of using the optical marker signal as it is, when the optical marker signal is normal, and using a signal gained by inputting the virtual optical signal into the dynamic model, as a usage for a correction of the optical marker signal, by using the dynamic model when the optical marker signals are discontinuous, according to a normal or abnormal state of the optical marker signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Communication station with multiple antennas
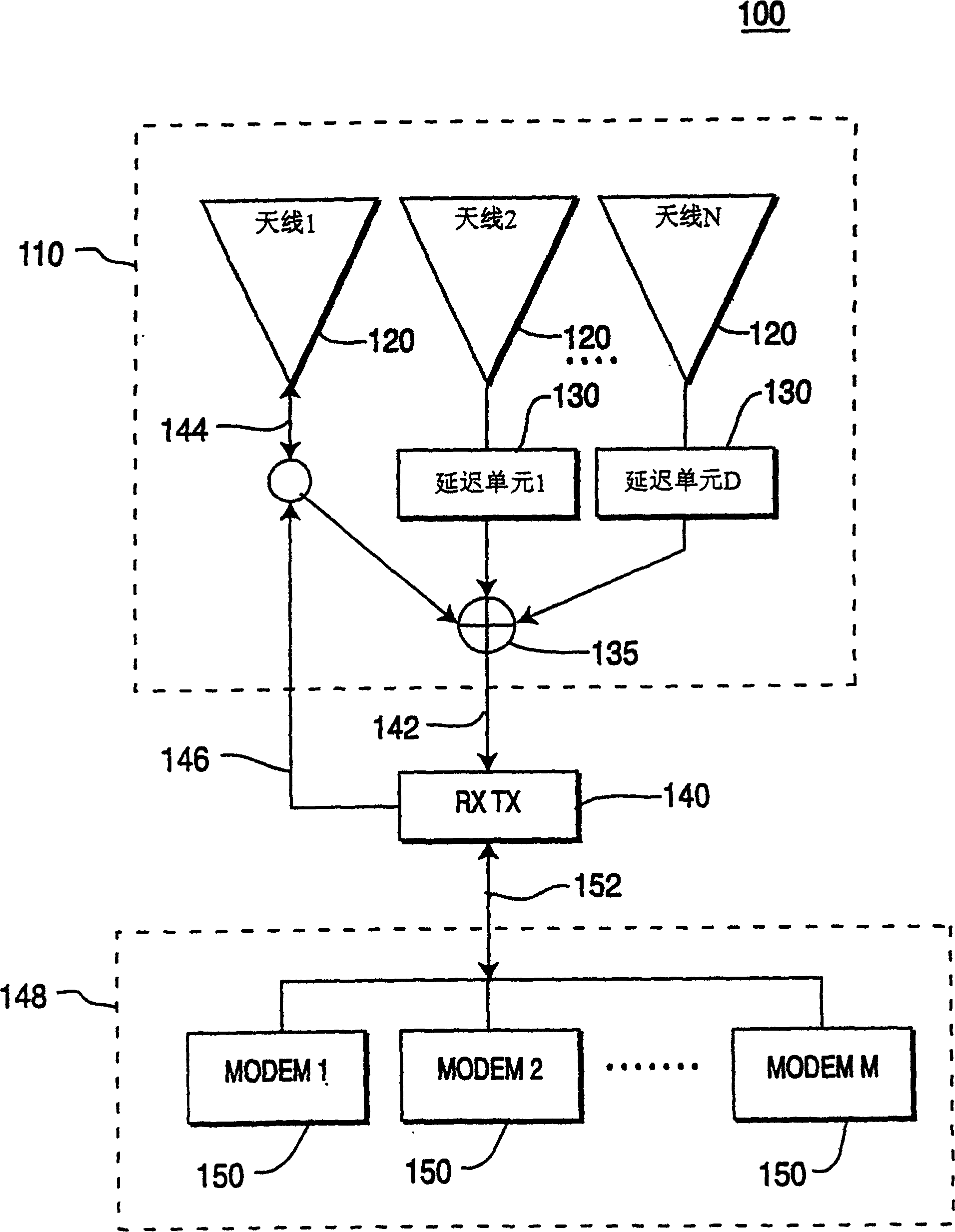
InactiveCN1538636AIncrease signal strengthPower managementSpatial transmit diversityModem deviceTransmitted power
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
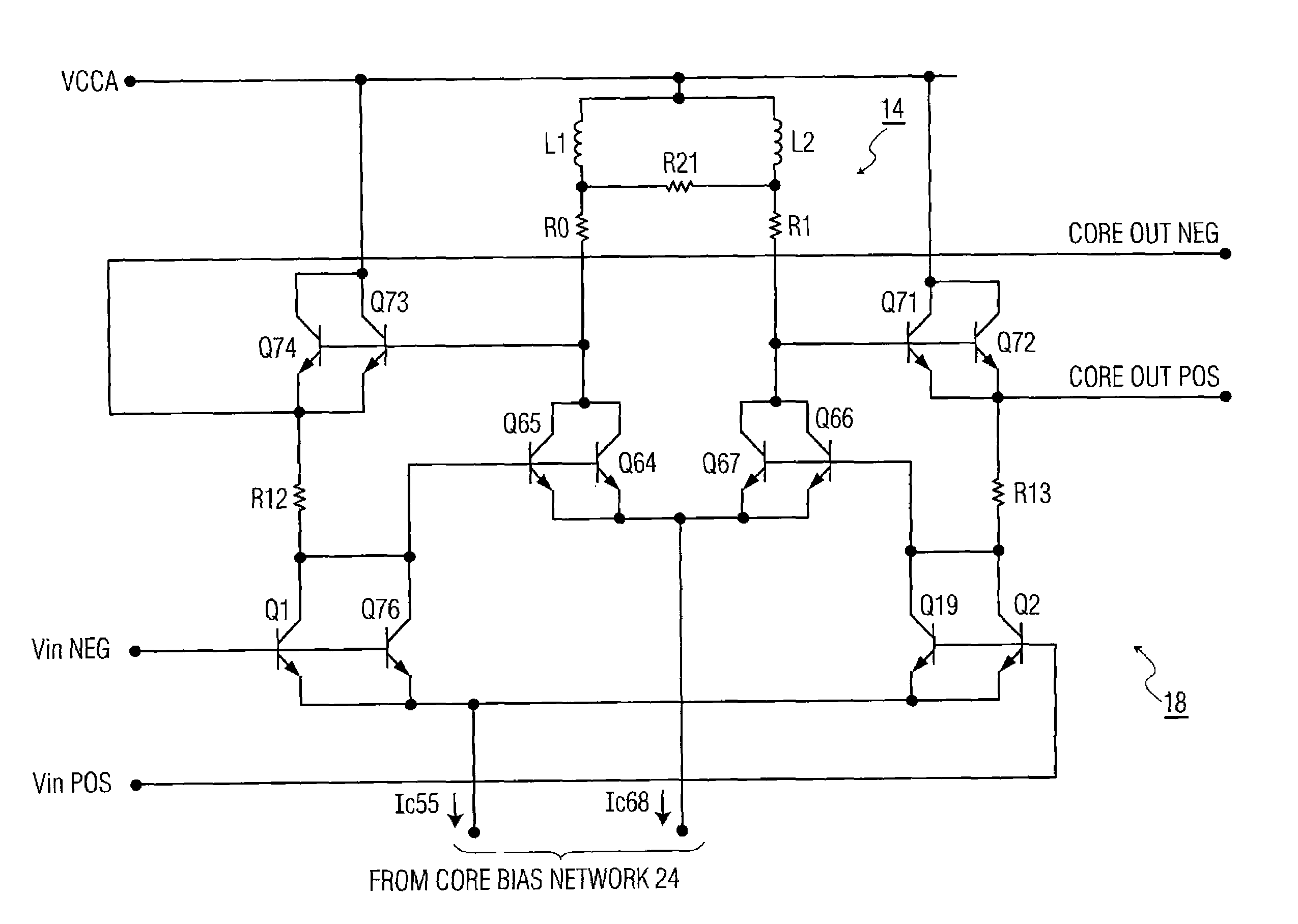
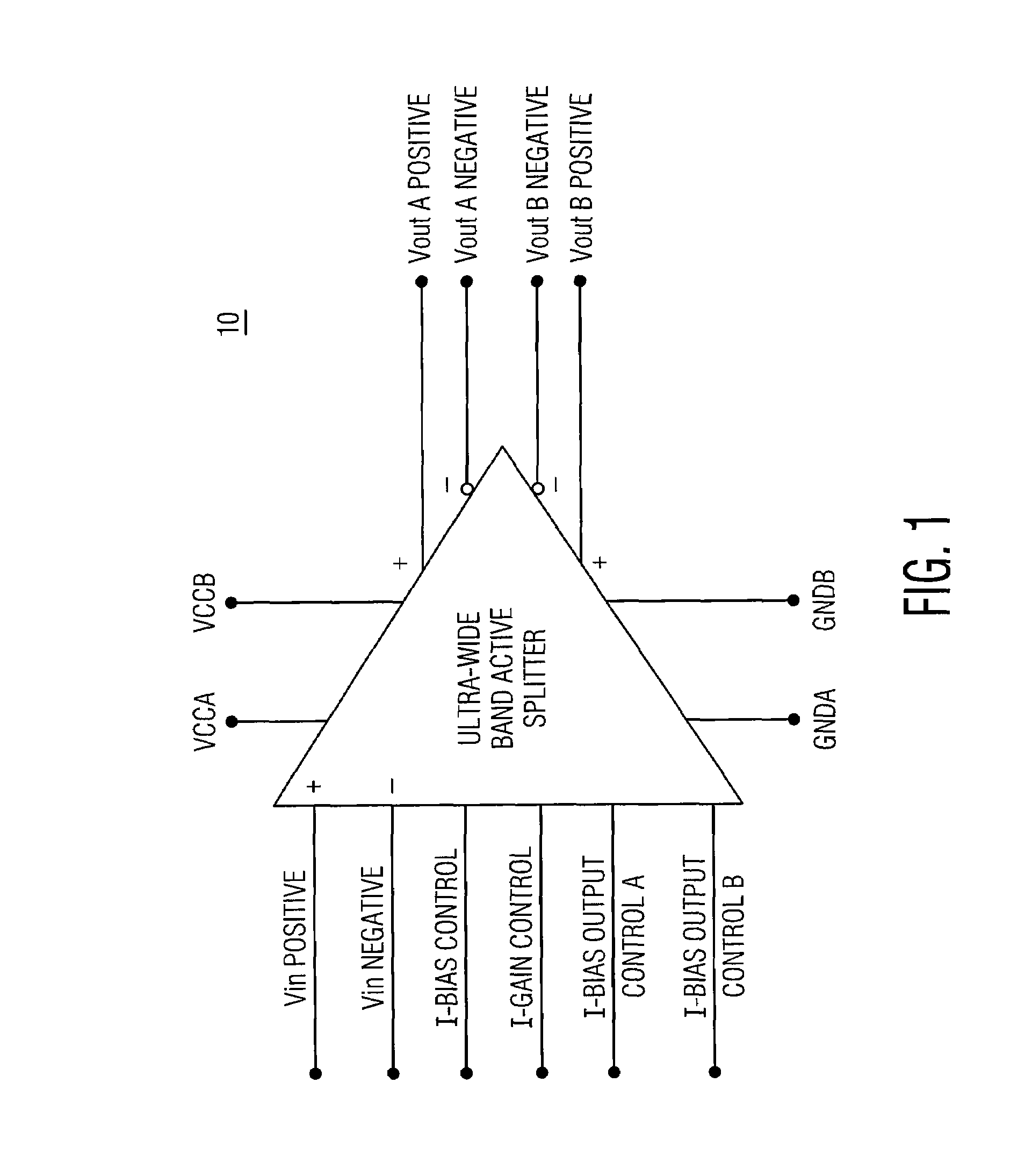
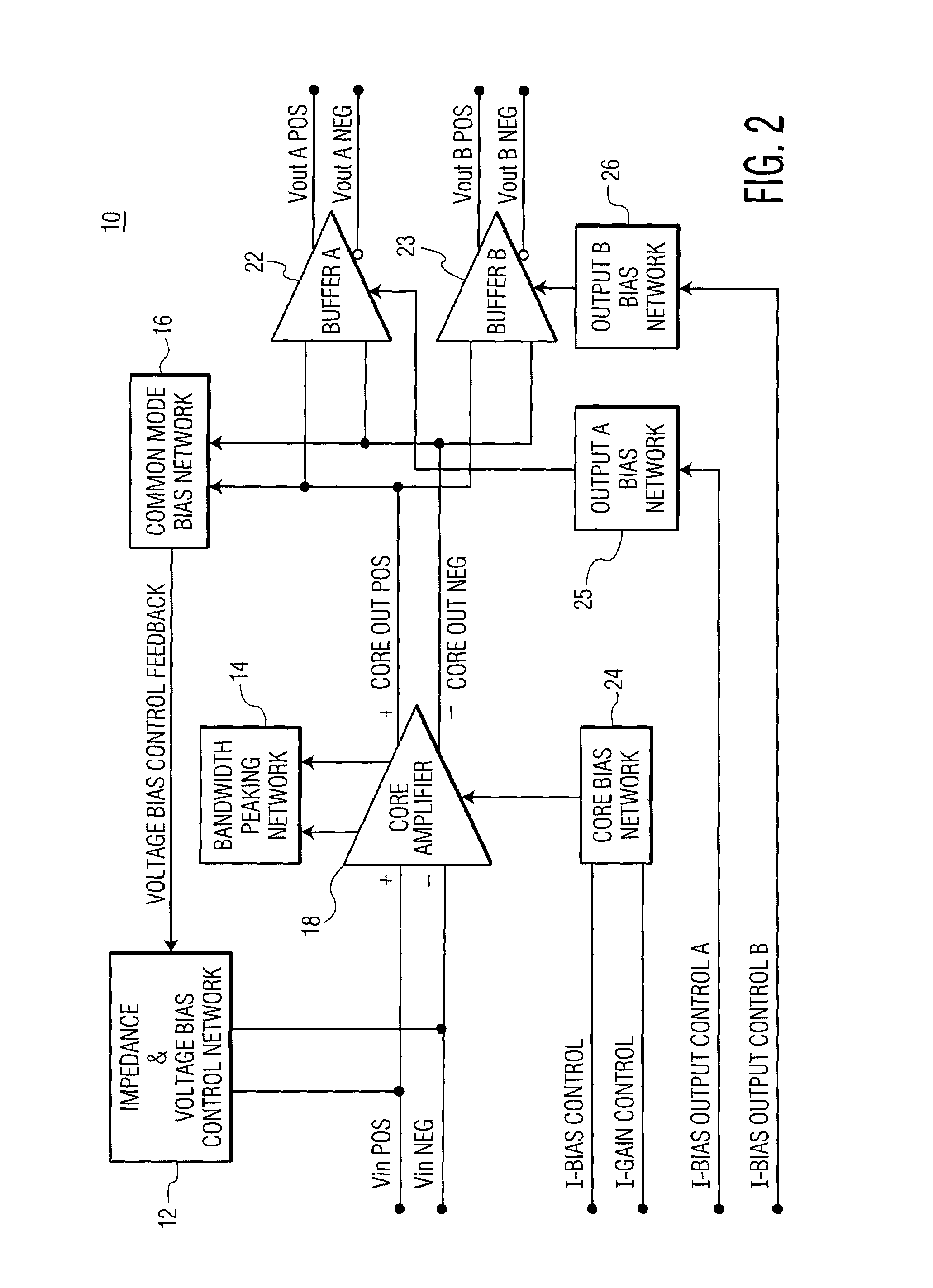
Ultra wide band, differential input/output, high frequency active splitter in an integrated circuit
ActiveUS7400193B2Increase frequency bandwidthAmplifier combinationsDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
A wideband splitter includes a core amplifier for receiving a single pair of differential input signals and providing first and second pairs of differential output signals. The first pair of differential output signals and the second pair of differential outputs have substantially identical characteristics. A signal gain is implemented between the received single pair of differential input signals and the first and second pair of differential output signals. The signal gain is substantially constant across the frequency bandwidth of the core amplifier. A bandwidth peaking network is coupled to the core amplifier and includes (a) a first coil and a first resistor connected in series and (b) a second coil and a second resistor connected in series. The bandwidth peaking network is configured to increase the frequency bandwidth of the core amplifier.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
DC offset cancellation in a direct-conversion receiver
InactiveUS20050110550A1Reduce silicon areaSave powerPulse automatic controlDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceIntegrator
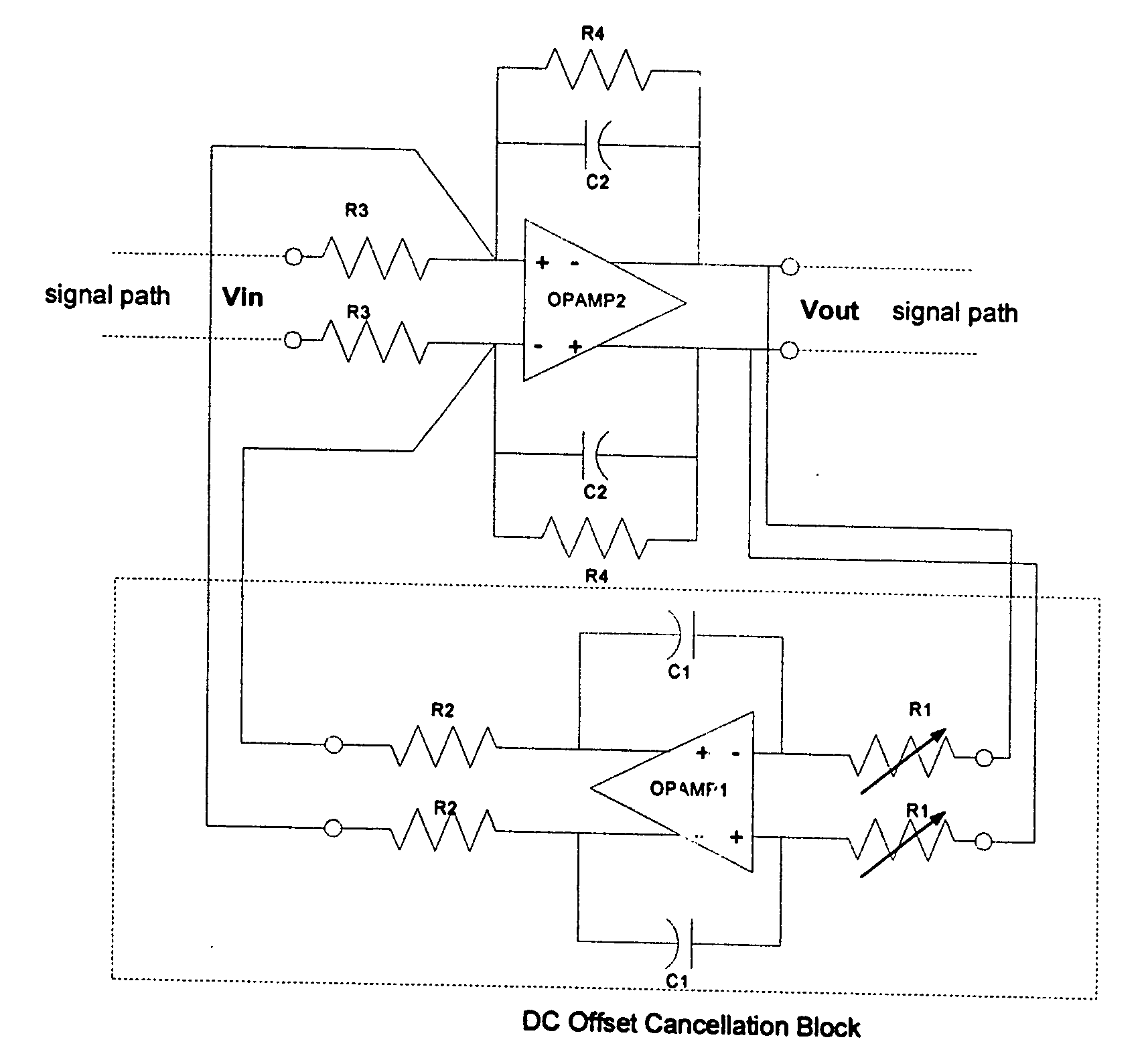
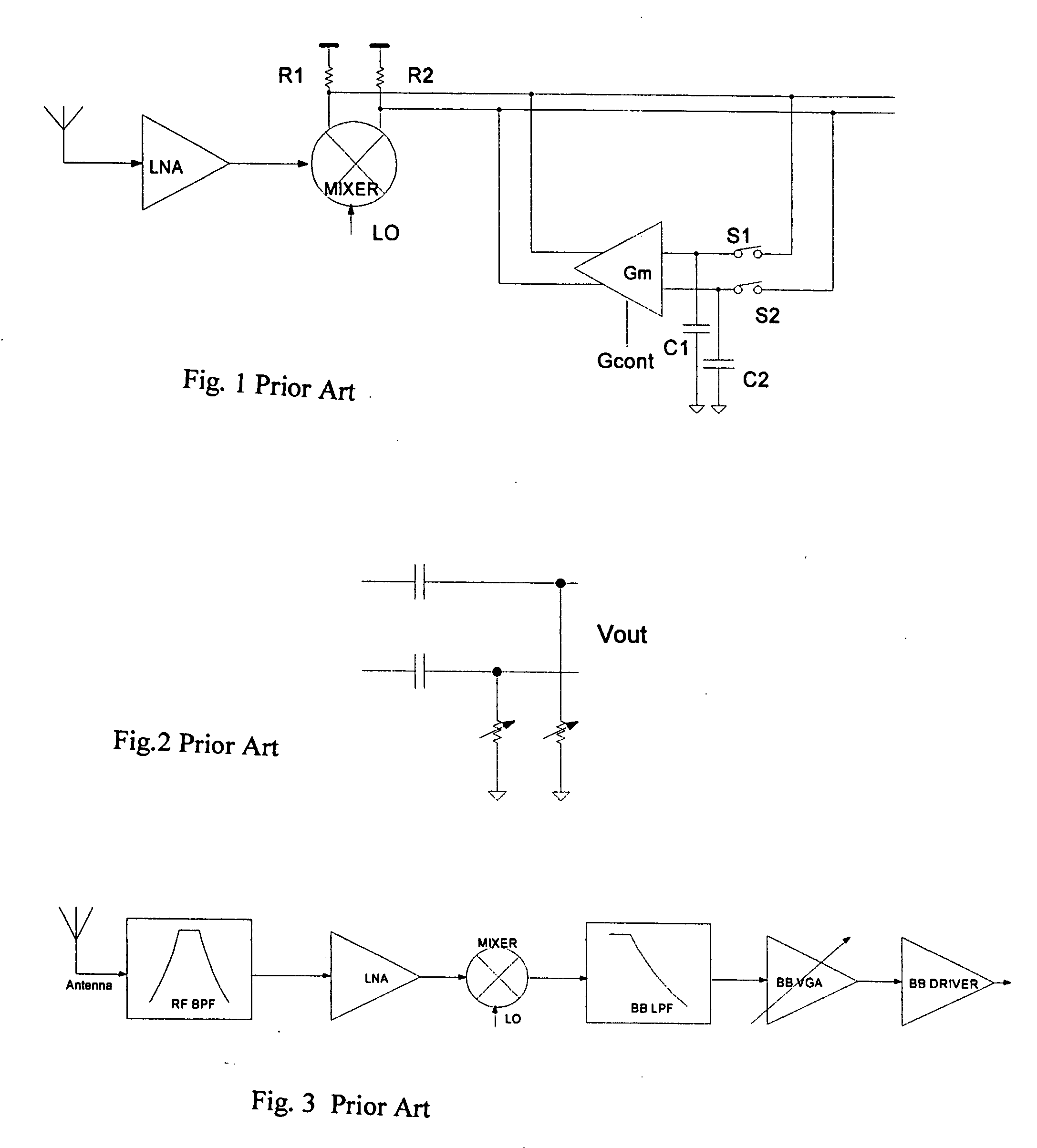
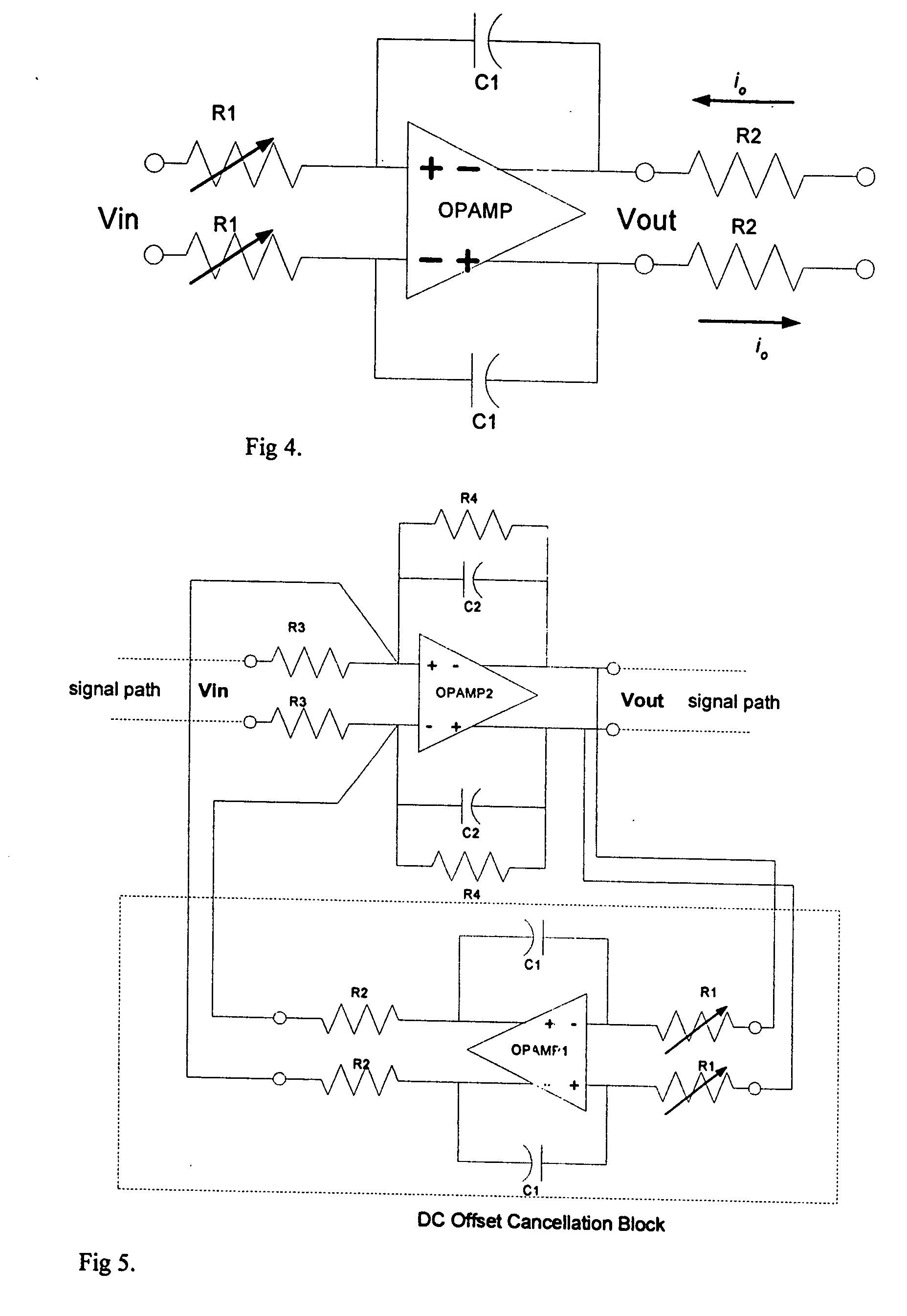
The DCOC block is used in ZIF BB to form HPF function to cancel dc offset with a penalty of small silicon area and low power consumption. It is a LPF plus a voltage to current conversion (VIC) resistor, and can hook up with any BB opamp used in signal path, to form a feedback loop, with or without signal gain stages in the loop. The BB opamp is used as a summing point. The summing method is input current summing. The cutoff frequency of the HPF function is thus defined by the integrator, the VIC resistor, and the feedback resistor in the summing opamp. The presence of the VIC resistor can drastically reduce the integrator capacitor and resistor values and thus save silicon area or improve receiver performance.
Owner:PROMINENT COMM
Sound processing apparatus, method, and program
ActiveUS20140205111A1Reduce quality degradationQuality improvementAnalog signal digital controlAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlUltrasound attenuationSignal on
The present technique relates to a sound processing apparatus, a method, and a program capable of alleviating degradation of the quality of sound in a case where the gain of a sound signal is amplified.When equalizer processing for adjusting the gain of each frequency band of an input signal on the basis of a gain setting value is performed, an input signal is attenuated by an input attenuation amount derived from the gain setting value, and the equalizer processing is performed on the input signal attenuated. The amount of amplification of the gain of the input signal in the equalizer processing is estimated on the basis of the gain setting value and a weight coefficient of each frequency band derived from a generally-available music signal prepared in advance, and a difference of the estimation value and the input attenuation amount is calculated as a gain correction amount. Further, nonlinear amplification processing is performed on the input signal so as to actually amplify the input signal, which has been subjected to the equalizer processing, by a gain correction amount, and an output signal is obtained. The present technique can be applied to a sound processing apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
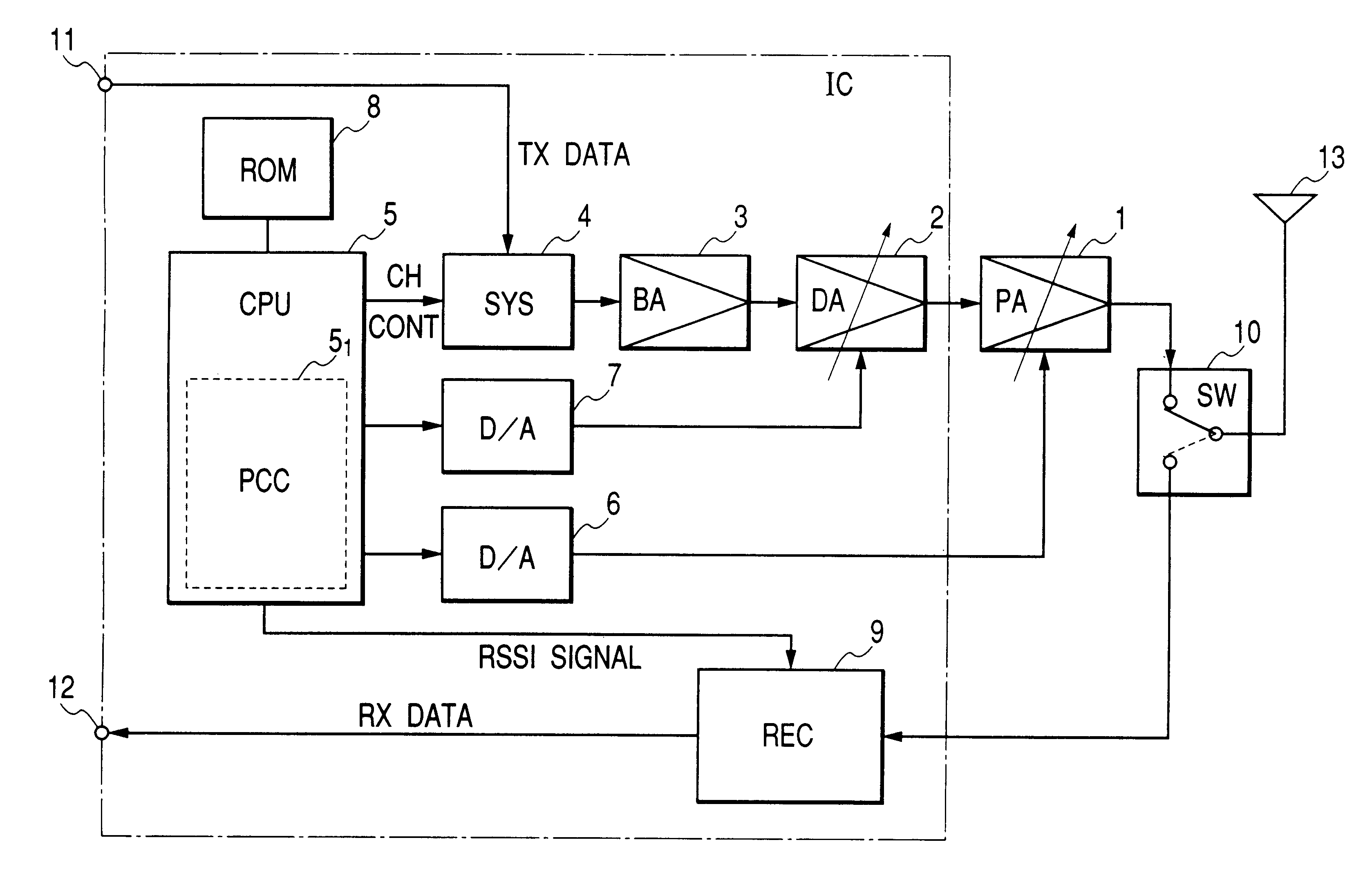
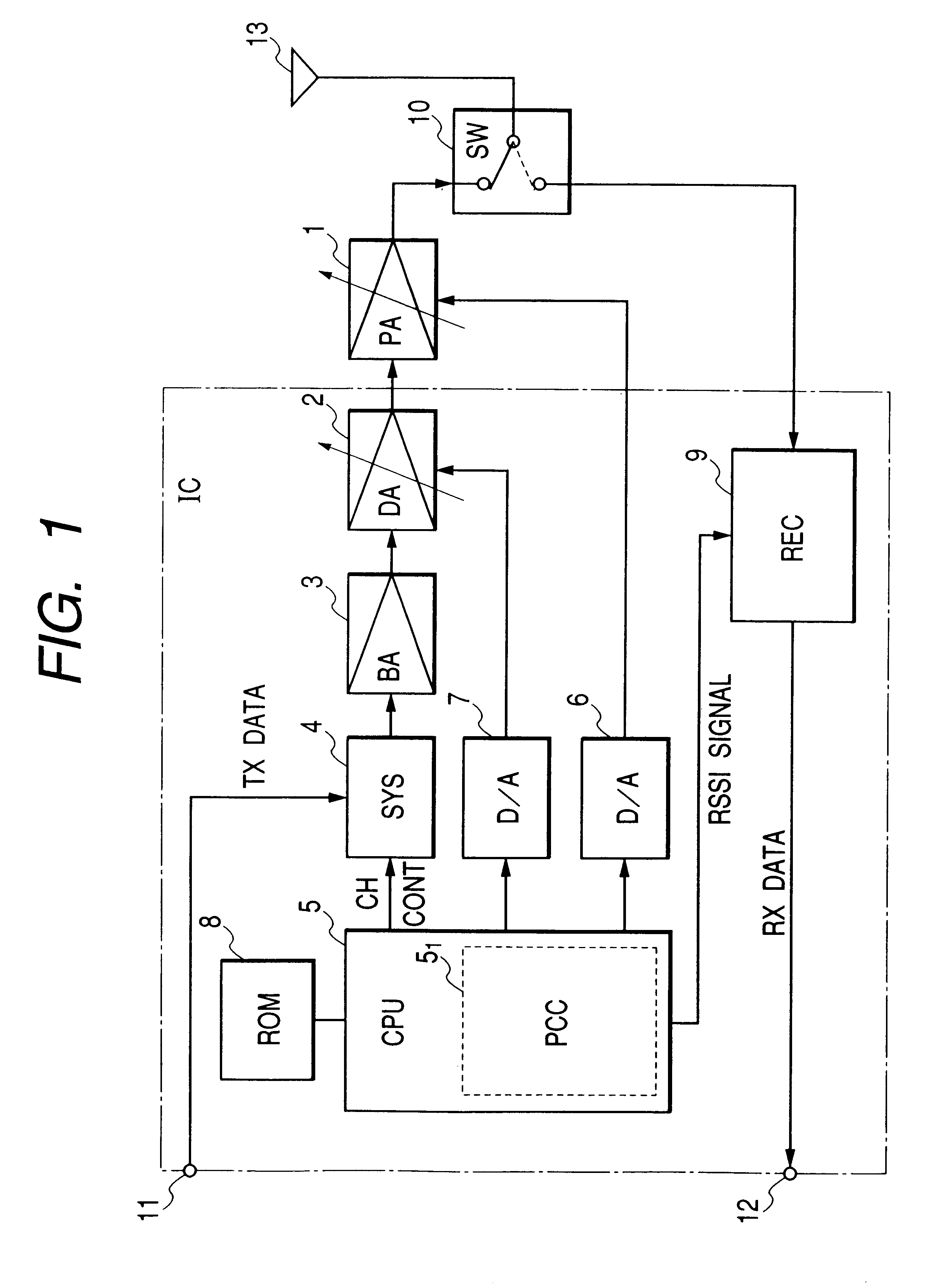
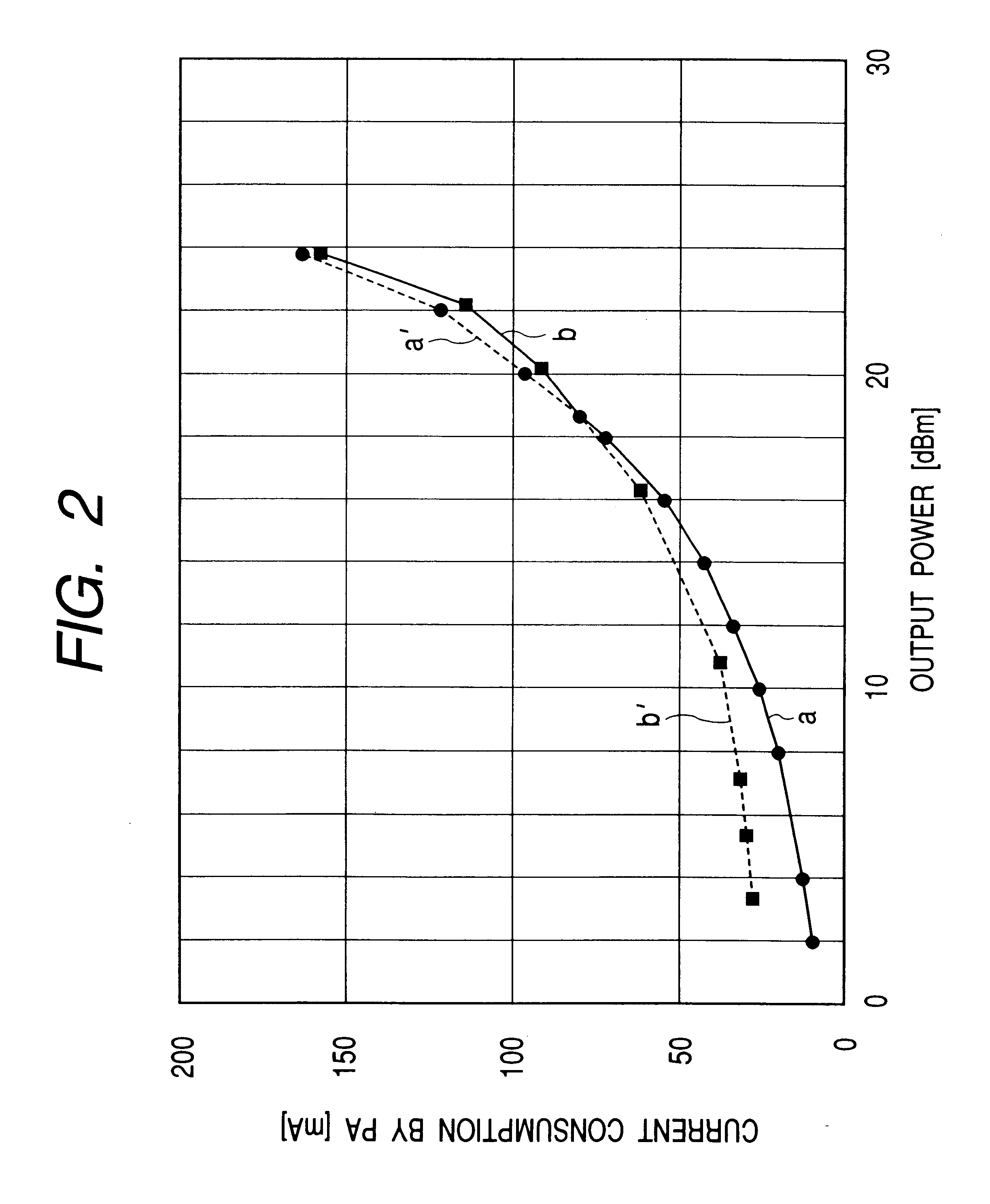
Transmitter adjusting output power
The transmitter adjusting output power is provided with a signal generator for generating a transmit signal, a variable-gain drive amplifying stage, a variable-gain power amplifying stage for amplifying in power the amplified transmit signal, and a control voltage generator for generating a first gain control voltage for adjusting the signal gain of the variable-gain drive amplifying stage and a second gain control voltage for adjusting the signal gain of the variable-gain power amplifying stage, wherein the control voltage generator generates the second gain control voltage to adjust the signal gain of the variable-gain power amplifying stage when the required signal level is not higher than a certain fixed level and generates a first gain control voltage to adjust the signal gain of the variable-gain drive amplifying stage when the required signal level is not lower than a certain fixed level.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com