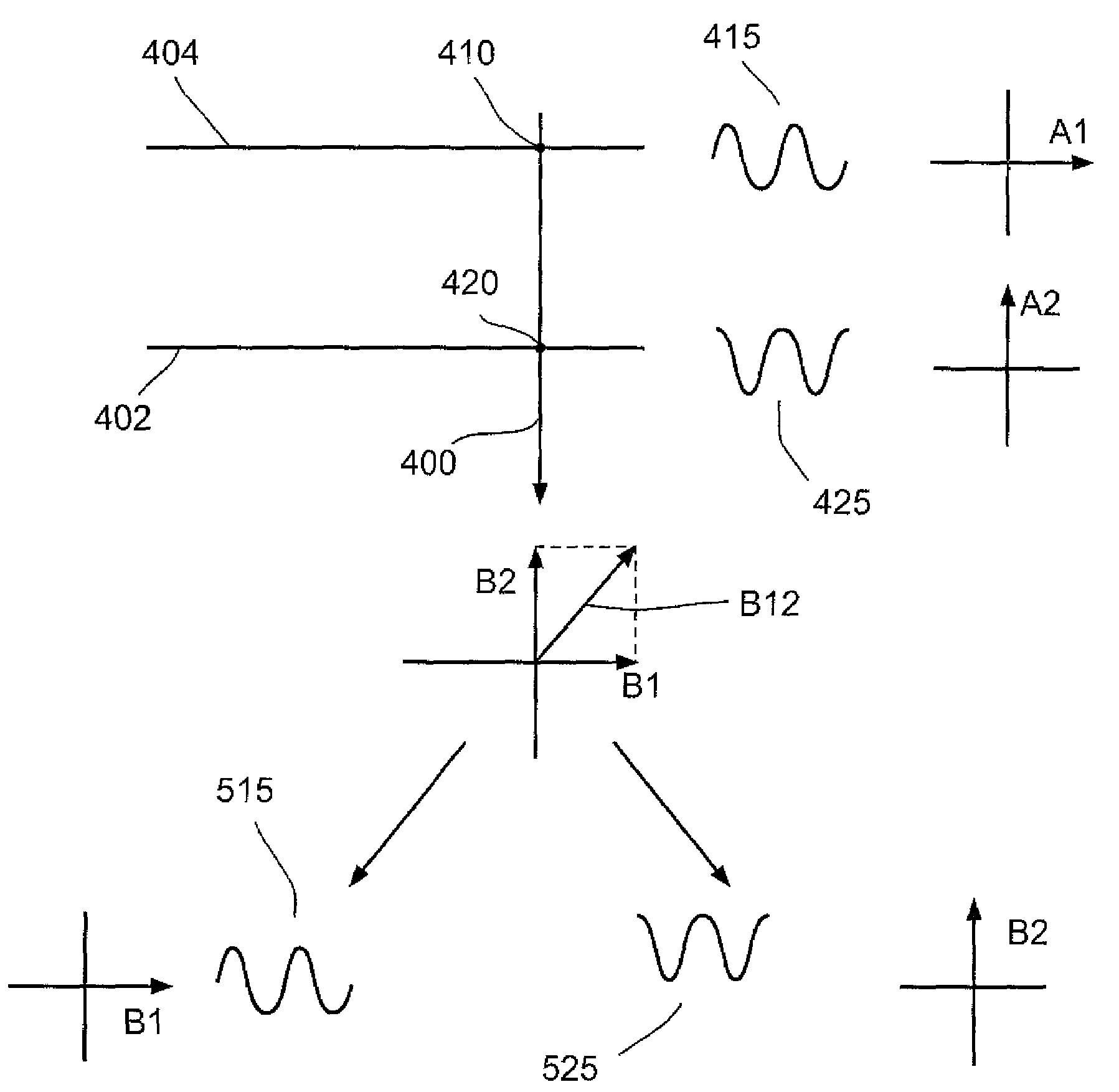Patents
Literature
16199 results about "Signal on" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
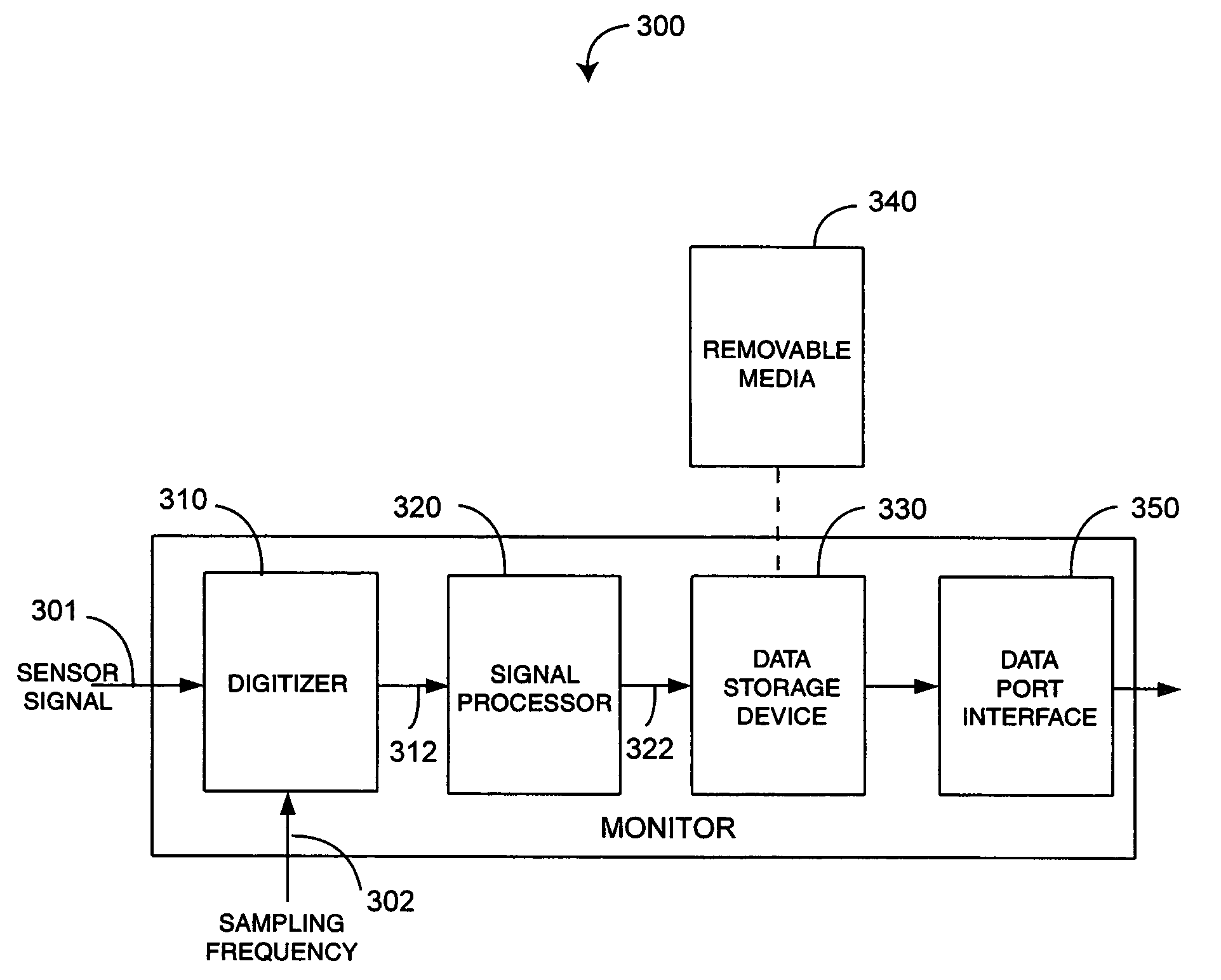
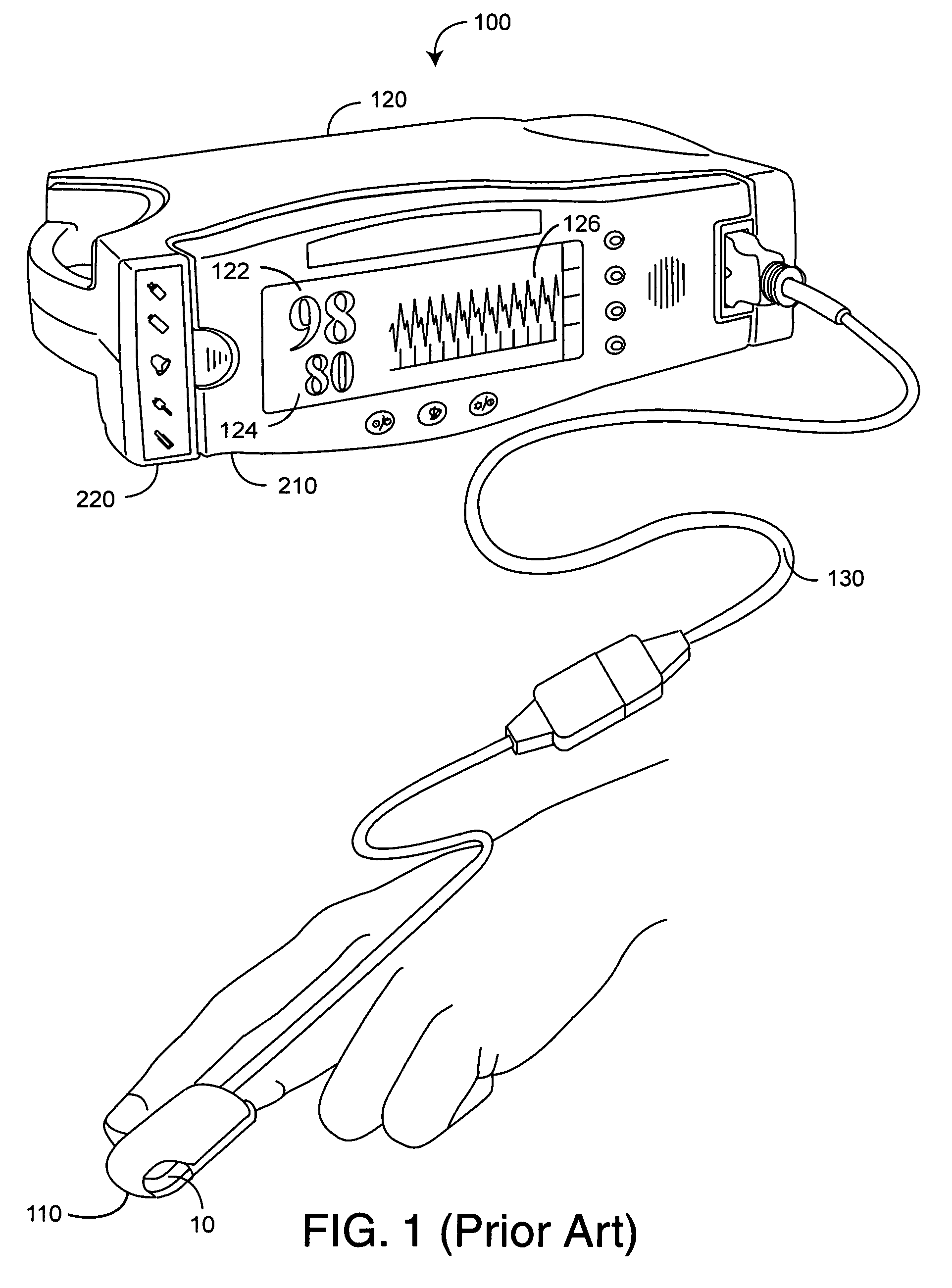
Pulse oximetry data capture system
A data capture system utilizes a sensor with emitters adapted to transmit light into a fleshy medium and a detector adapted to generate intensity signals in response to receiving light after absorption by the fleshy medium. A monitor is configured to input the intensity signals, generate digitized signals from the intensity signals at a sampling rate and compute at least one physiological parameter responsive to magnitudes of the digitized signals. A data storage device is integrated with the monitor and is adapted to record data derived from the digitized signals on a removable storage media at the sampling rate.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
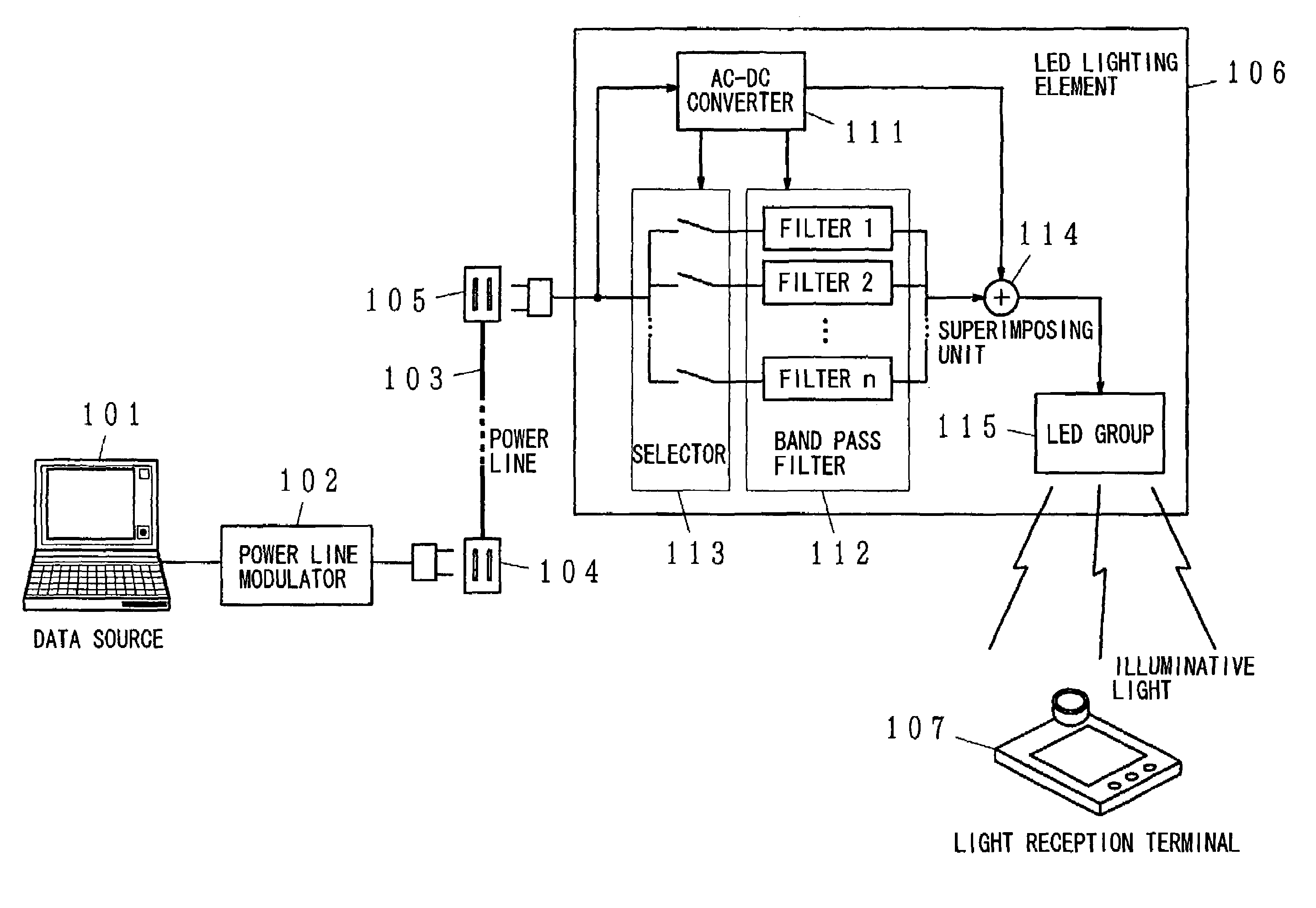
Illuminative light communication device
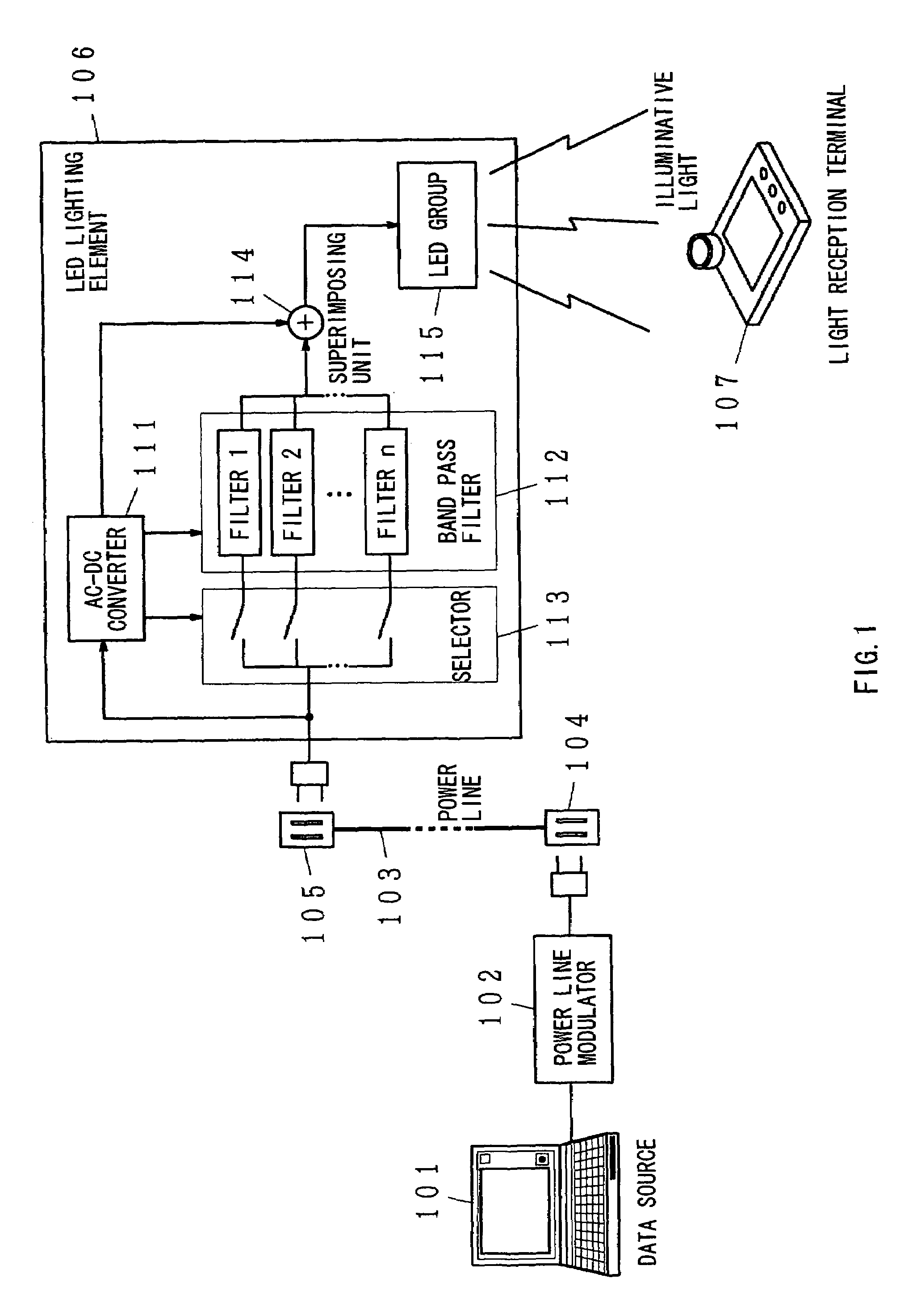
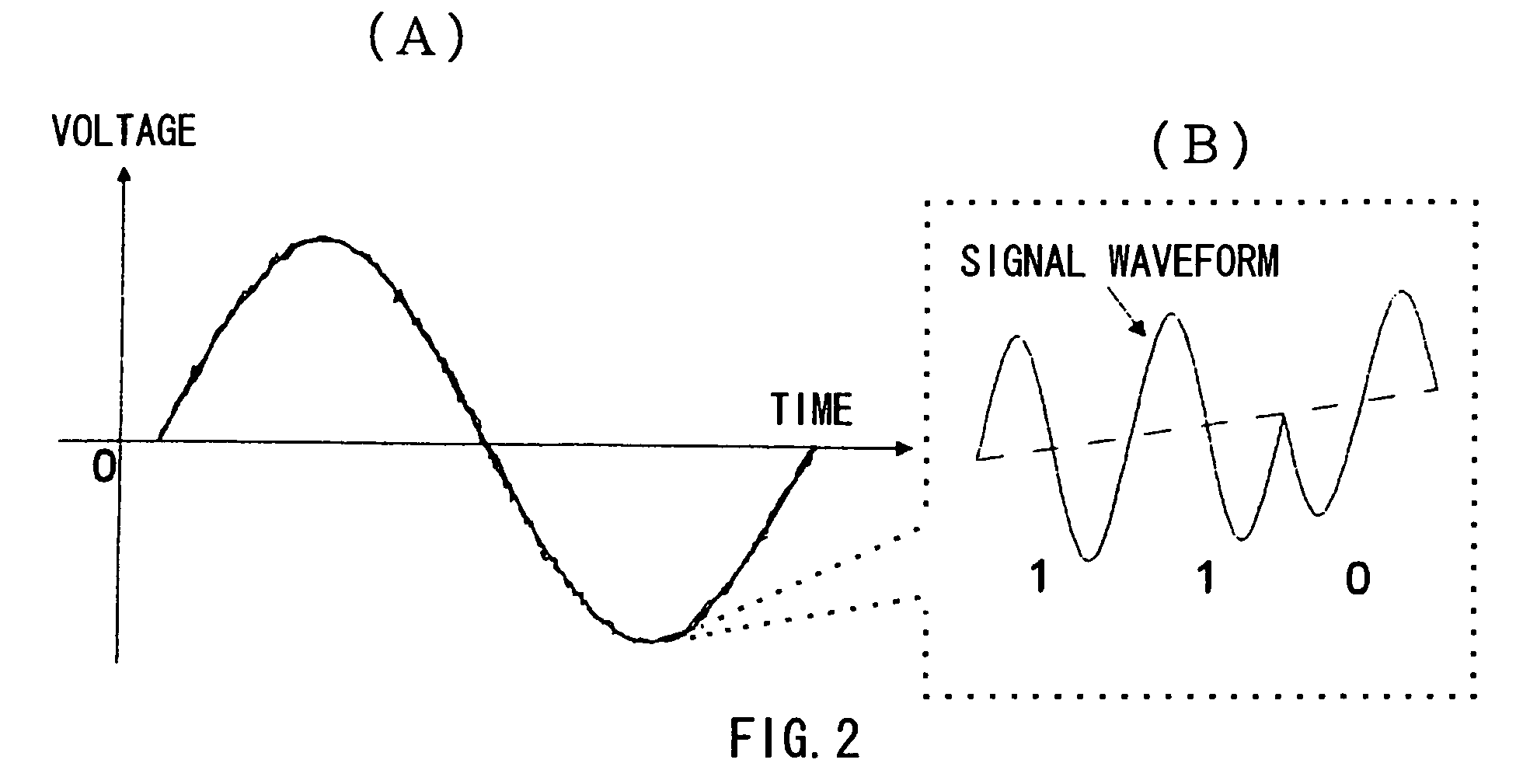
InactiveUS7583901B2Possible to separateWeaken influenceTransmission/receiving by modifying power source wavePoint-like light sourceMultiplexingSignal on
The present invention has been developed considering the above-described problems and aims to provide various structures and applications for illuminative light communication. According to the first aspect of the prevent invention, a broadcast system includes an LED light source 115 for lighting, a power line 103 that supplies electric power to the LED light source 115, a data modulator 102 that modulates and multiplexes a plurality of pieces of data, superimposes the resulting signal on an electric power waveform, and then transmits the resulting superimposed signal waveform to the power line 103, and a filter 112 that selectively separates one or more of a plurality of pieces of modulated data on the power line so as to control light intensity or blinking of the LED light source. Data is transmitted through changes in light intensity or blinking of the LED light source.
Owner:ICHIMARU
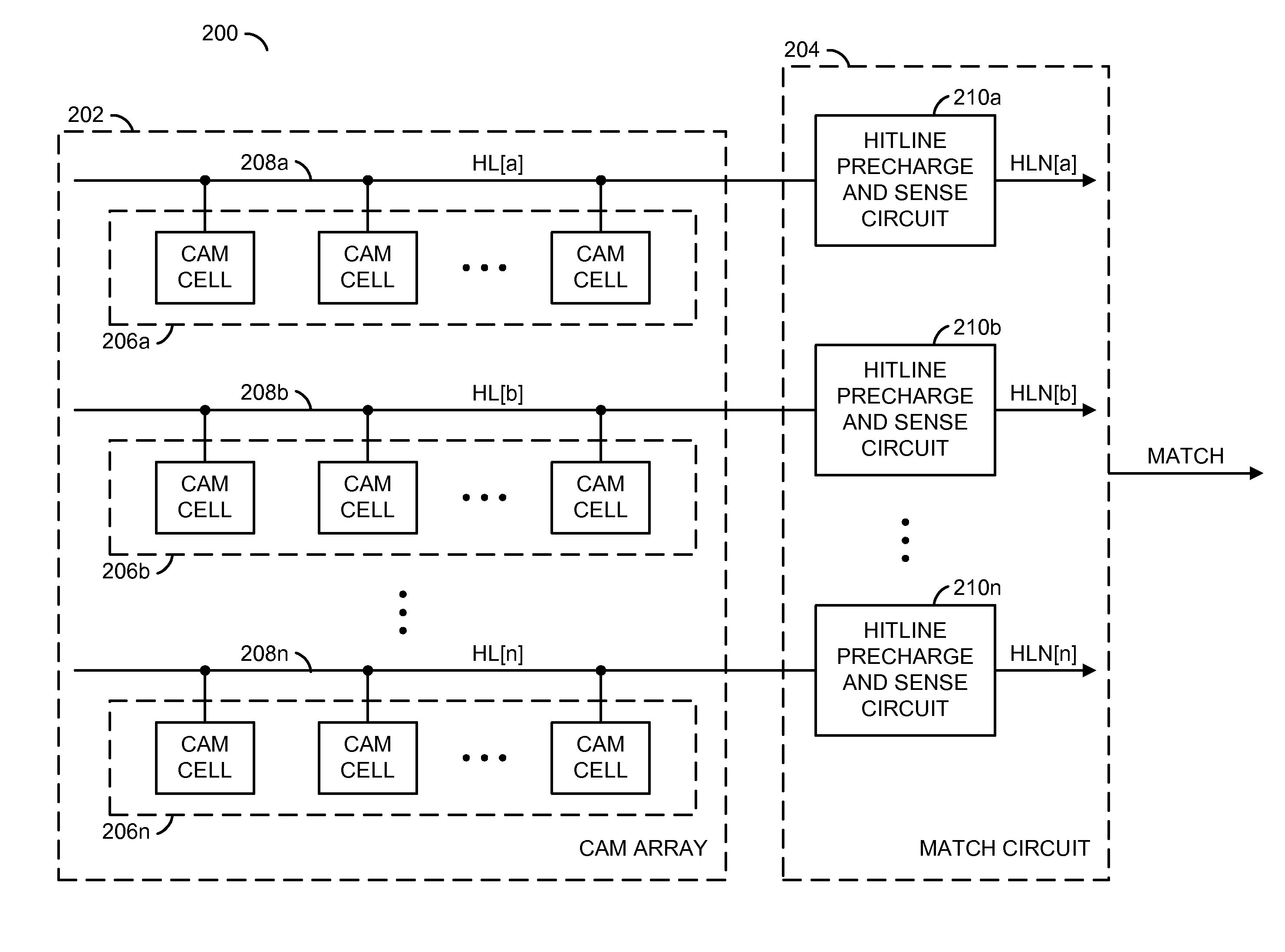
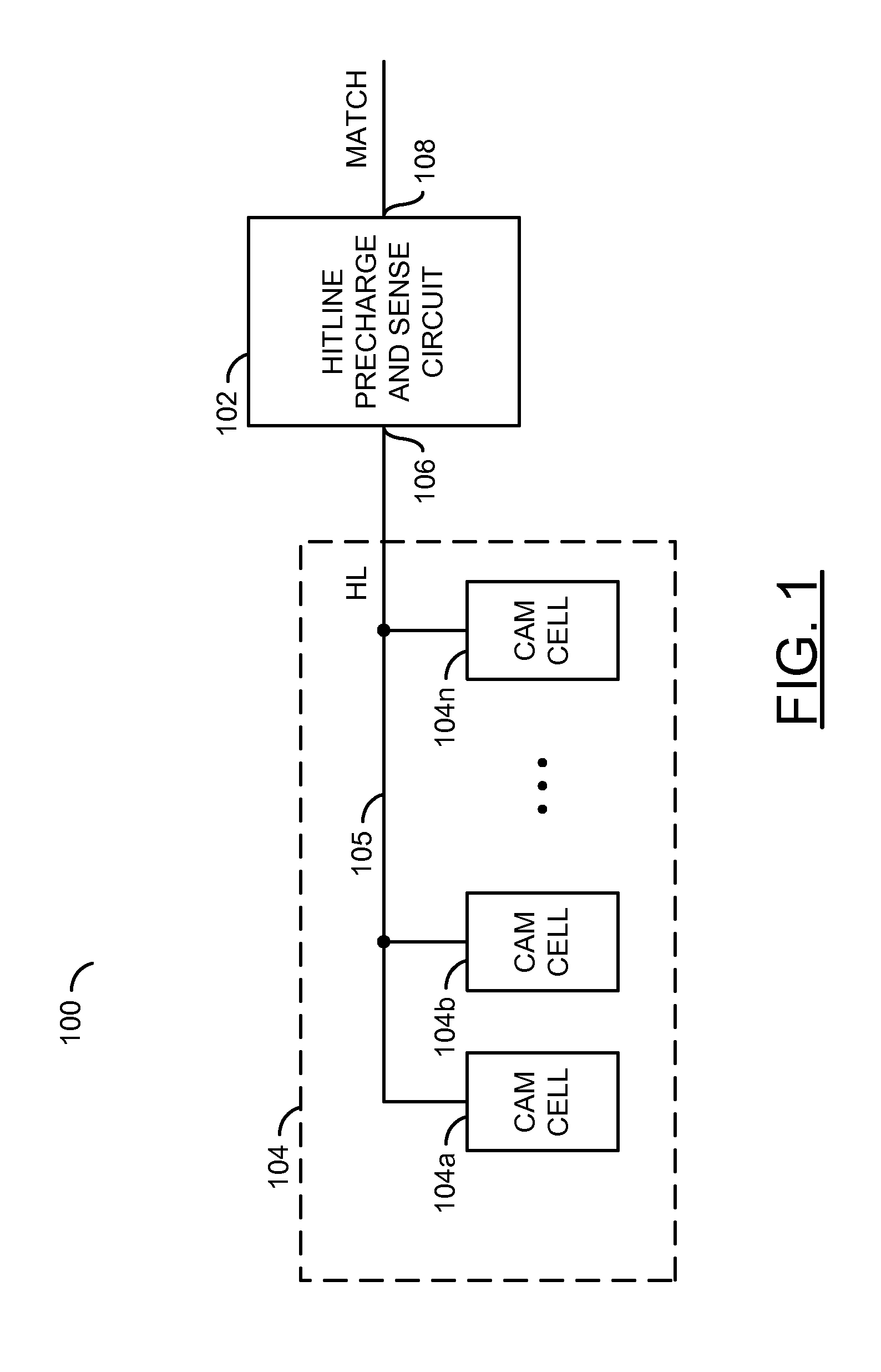
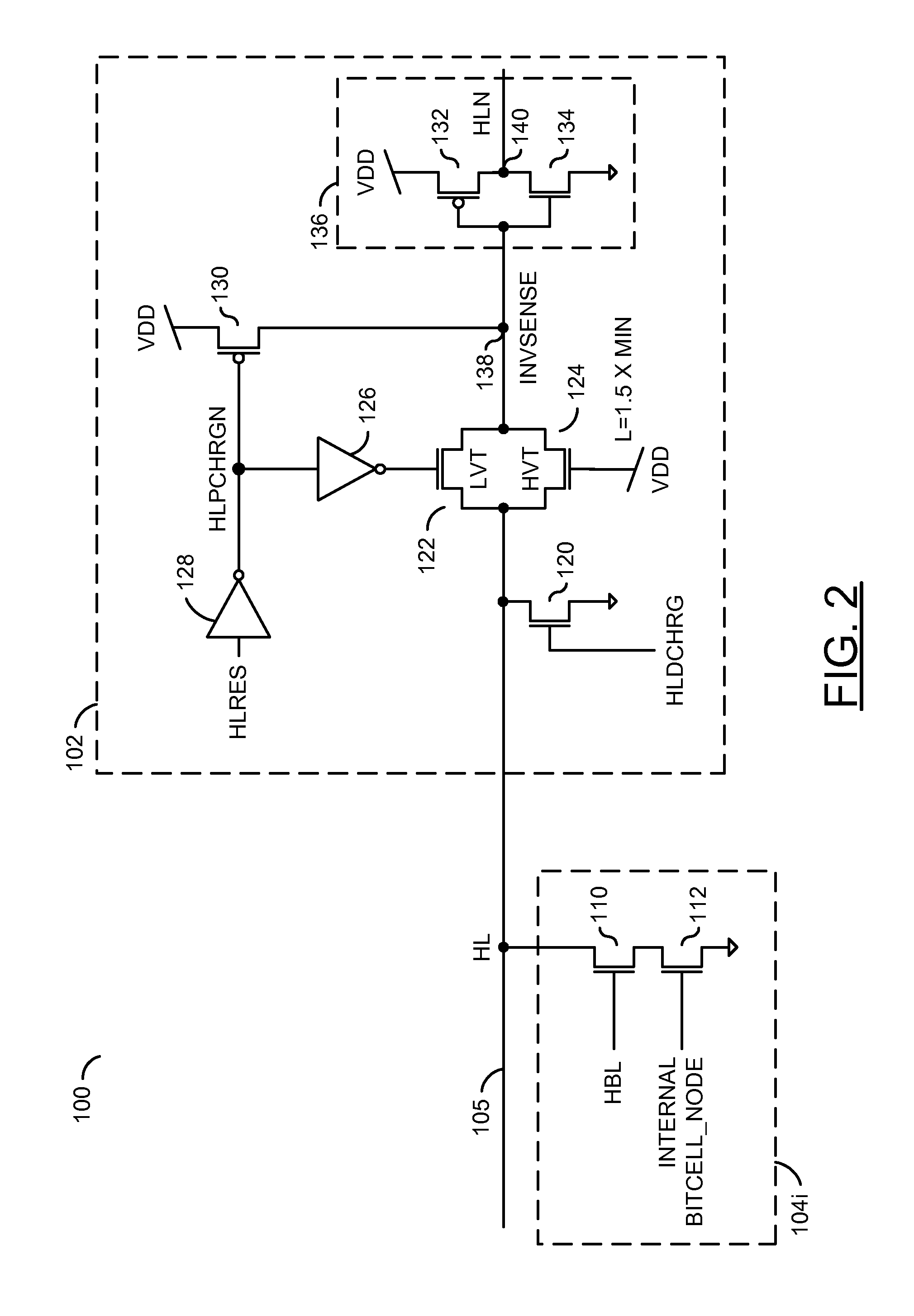
Low power content addressable memory hitline precharge and sensing circuit
An apparatus and a method of operating the apparatus. The apparatus includes a driver circuit and a memory circuit. The driver circuit may be configured to precharge a hitline in response to a predetermined voltage level and a control signal and sense a result of a compare operation based upon a hitline signal on the hitline. The driver circuit generally precharges the hitline to a voltage level lower than the predetermined voltage level and senses the result of the compare operation using the full predetermined voltage level. The memory circuit may be configured to perform the compare operation using the hitline.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
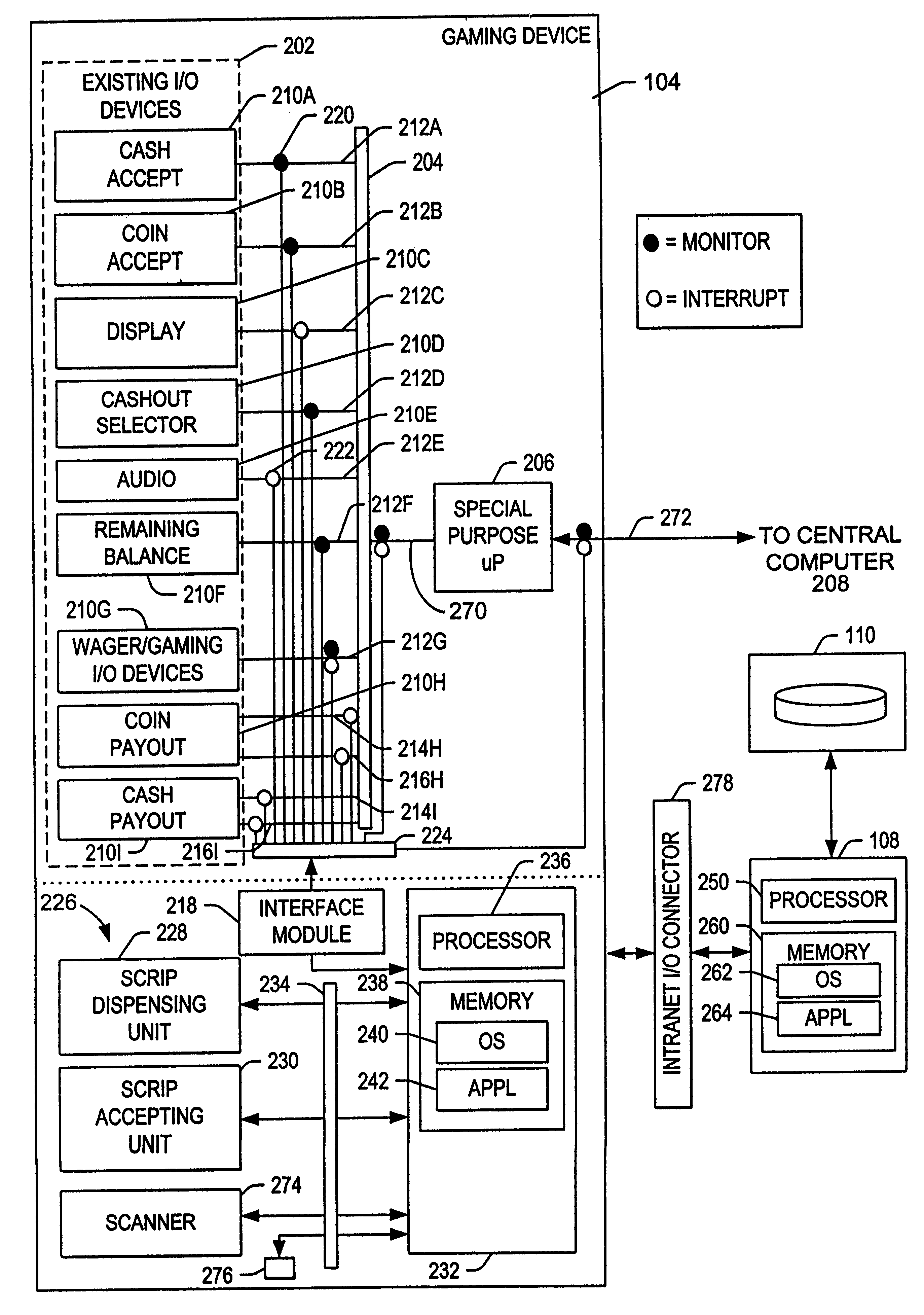
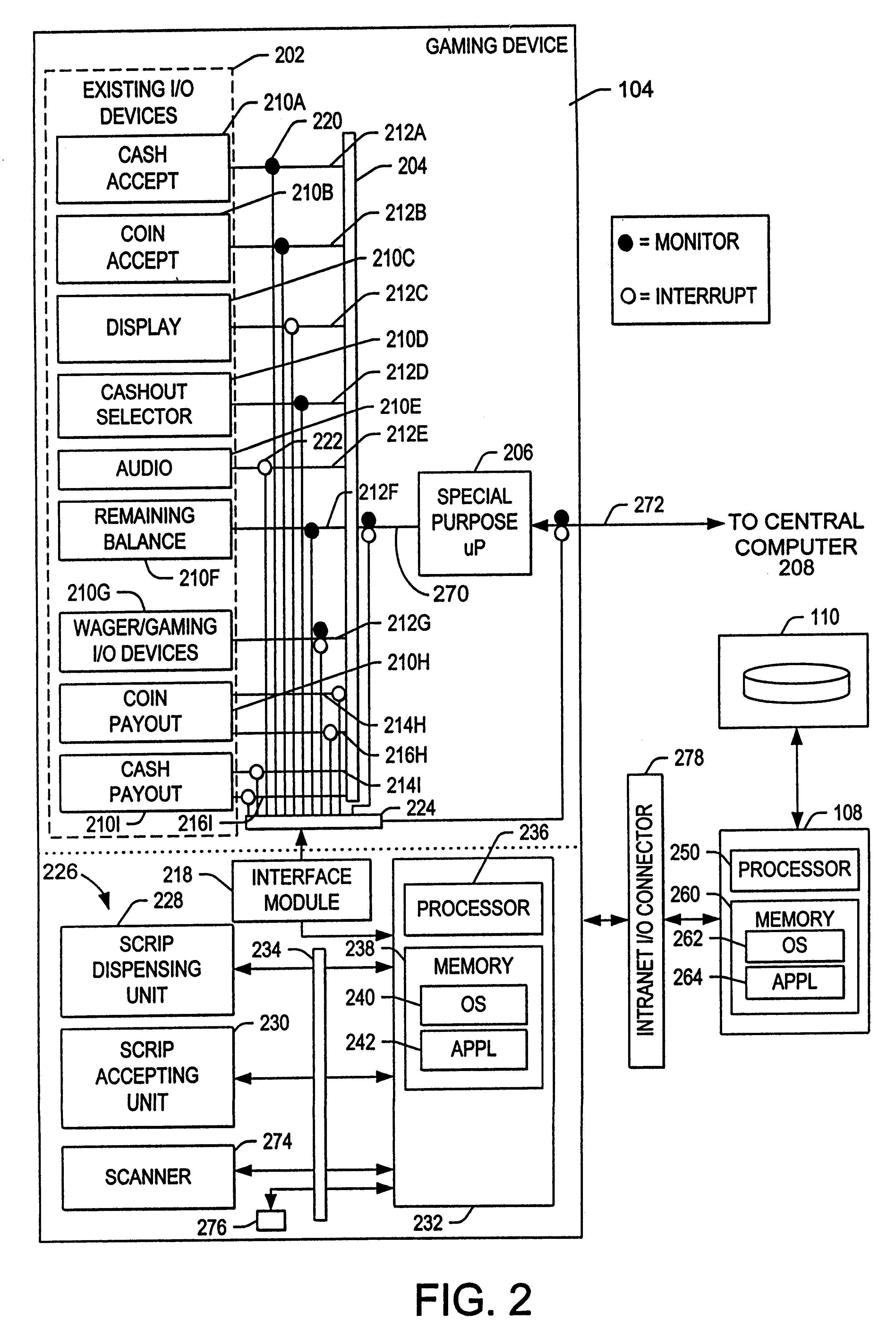
Method and apparatus for modifying gaming machines to provide supplemental or modified functionality
A method, apparatus, and article of manufacture for enhancing a gaming device is disclosed. The gaming device has a plurality of legacy I / O devices for communicating I / O device signals to a legacy gaming device processor via a plurality of legacy communication paths. The apparatus comprises an interface module, communicatively coupled to at least one of the legacy I / O communication paths between the legacy I / O device and the legacy gaming device processor to monitor the I / O device signal; and a local processor, communicatively coupled to the interface module and to a remote processor, the local processor performing instructions comprising instructions for controlling the interface module, for receiving the monitored I / O signals, and for transmitting the monitored signal to the remote processor. The method comprises the steps of modifying at least one of the legacy communication paths to monitor at least one of the I / O device signals; and providing the I / O device signal on the monitored I / O device signals to a remote processor external to the gaming device. In one embodiment, the method further comprises the steps of interrupting at least one of the I / O device signals communicated on a legacy communication path; generating a substitute I / O device signal; and providing the substitute I / O device signal on the legacy communication path.
Owner:WESTERN GAMING PROPERTIES
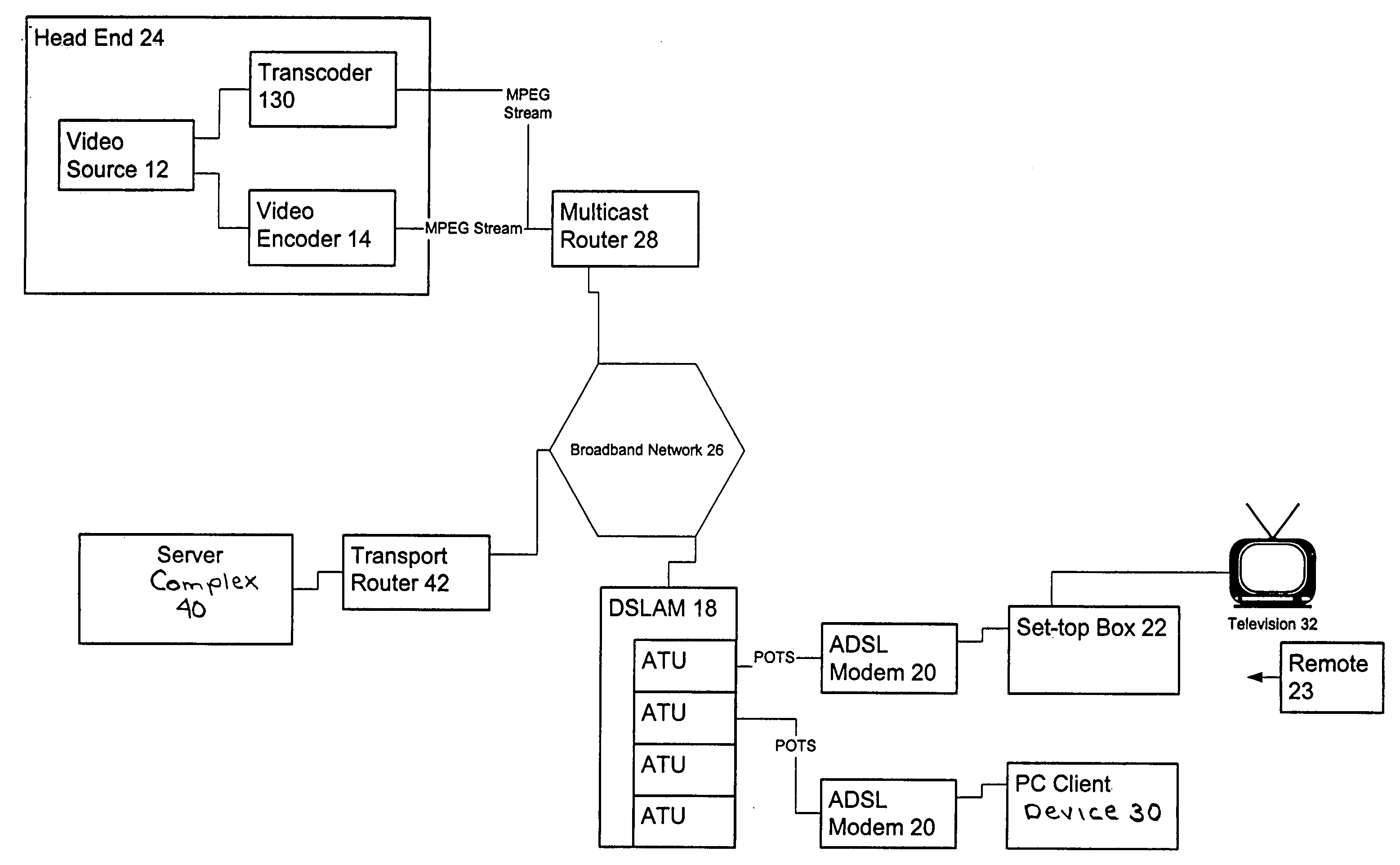
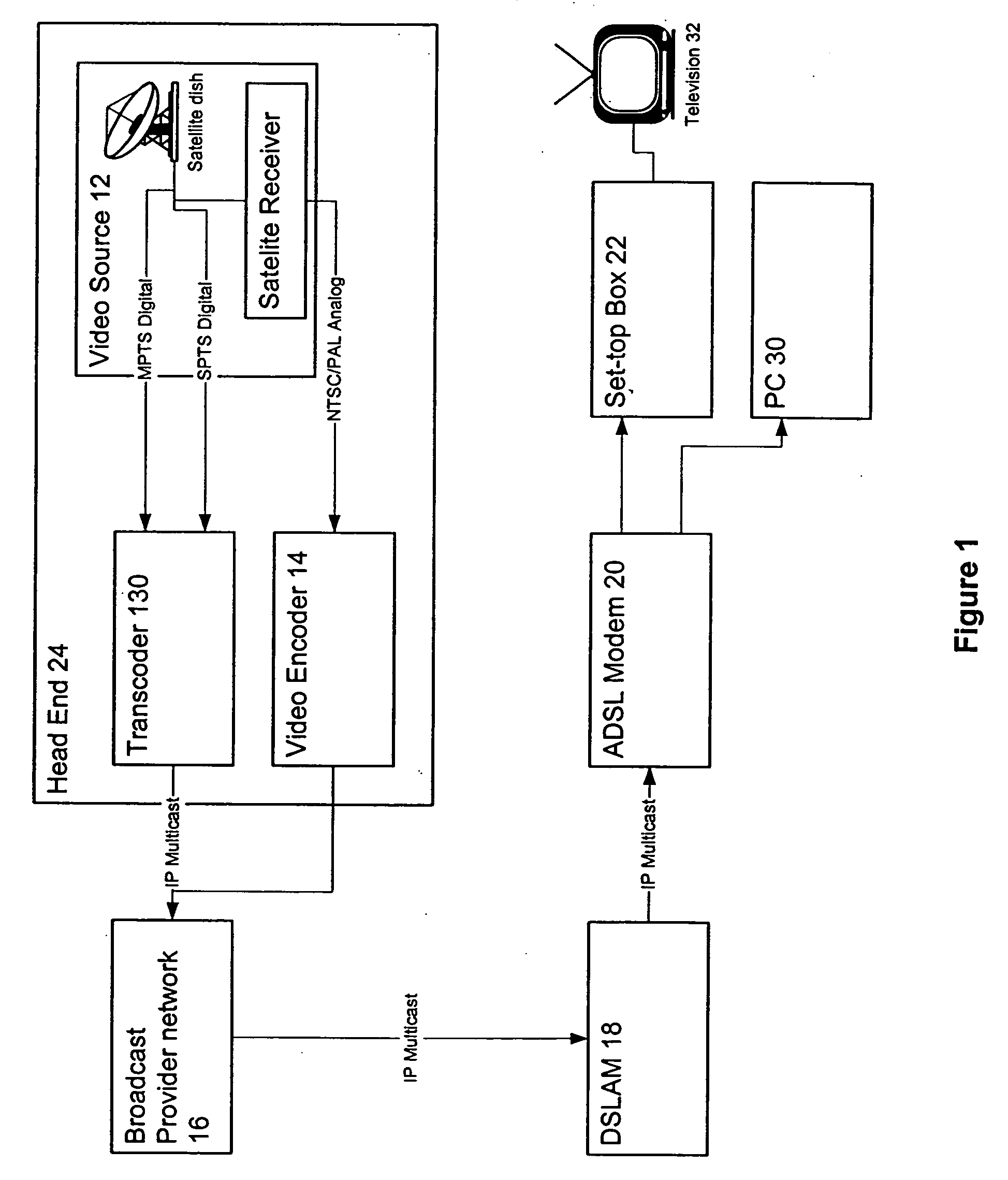
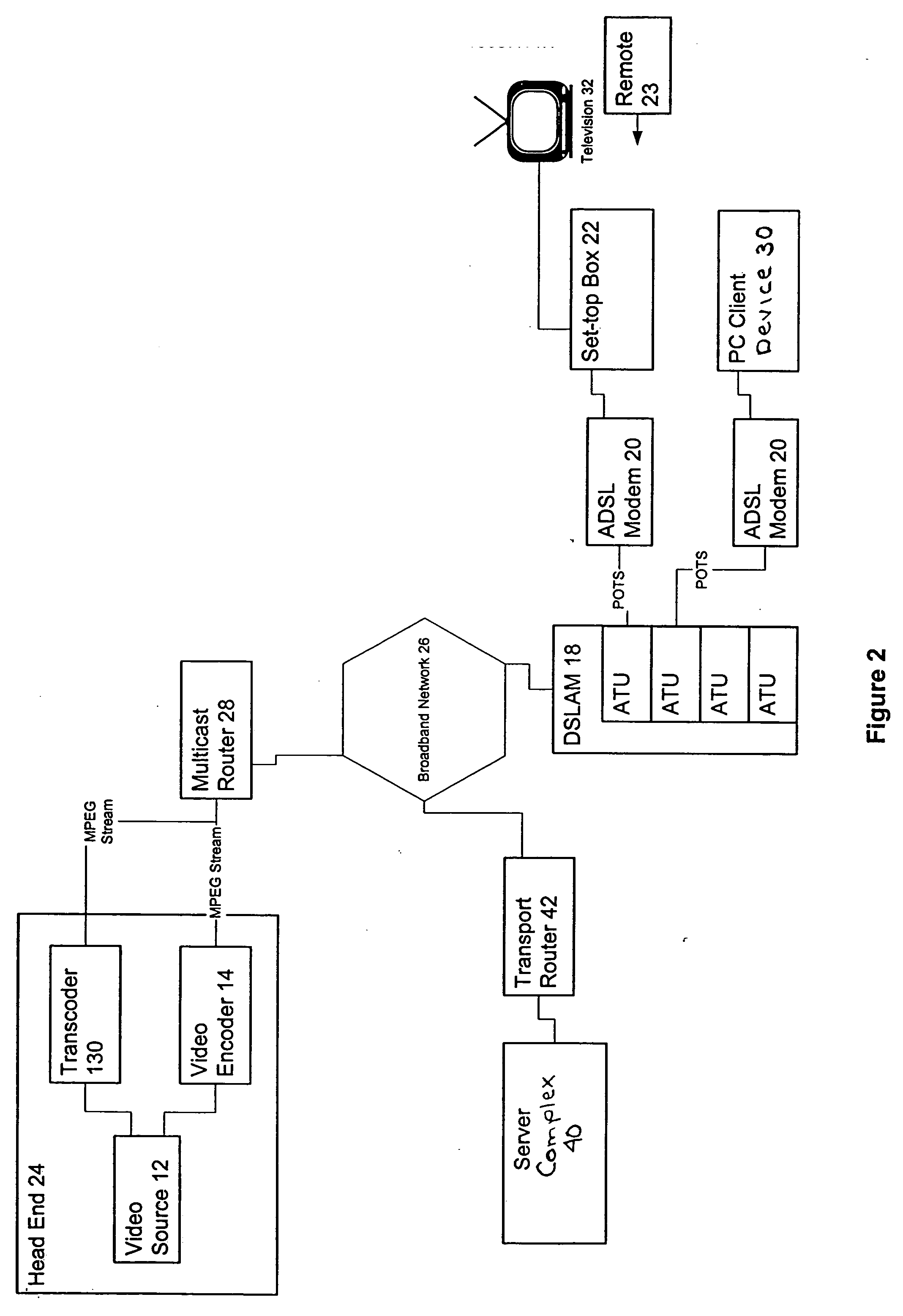
Digital interactive delivery system for TV/multimedia/internet
InactiveUS20050028206A1Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsSignal onIP multicast
Owner:IMAGICTV
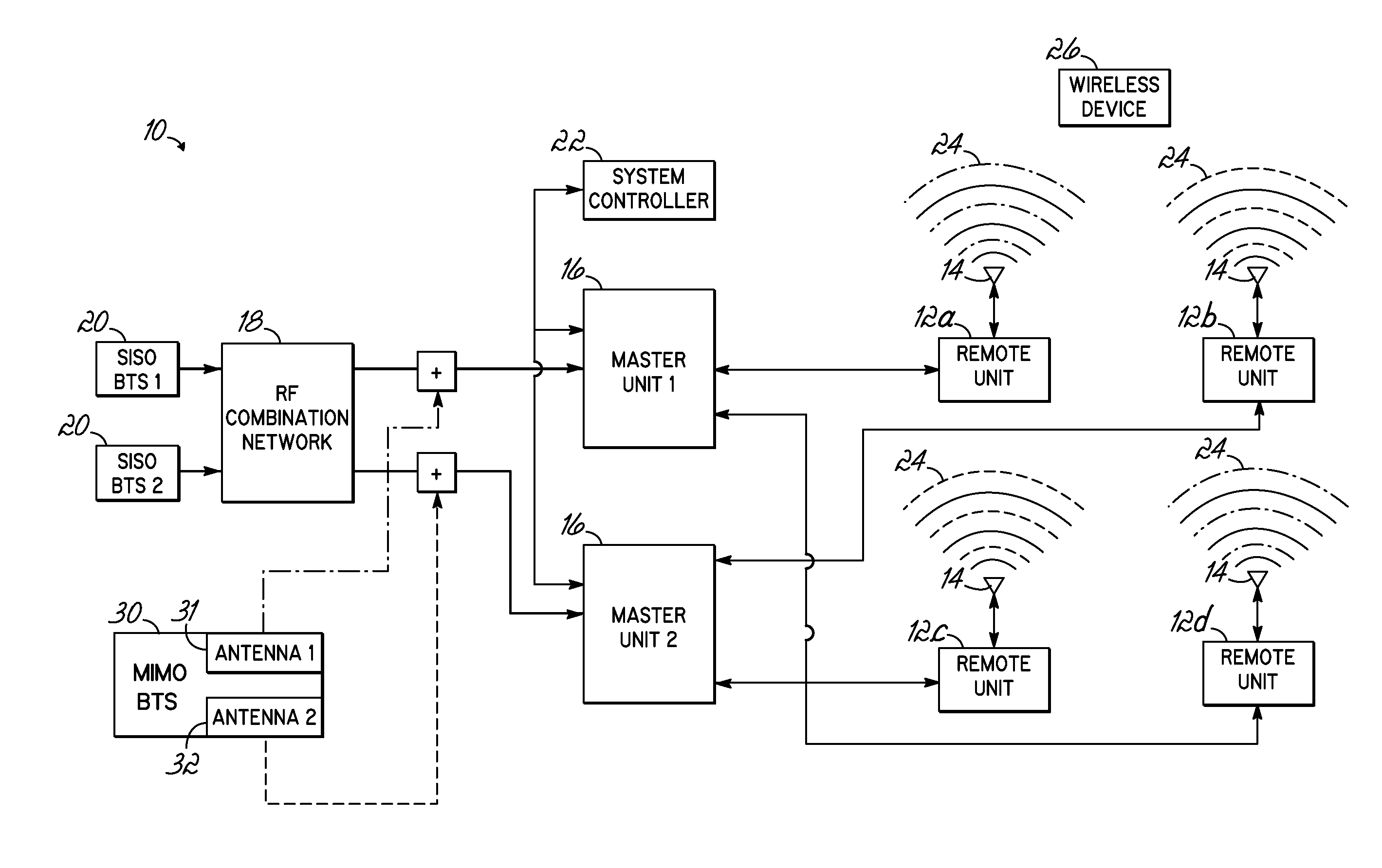
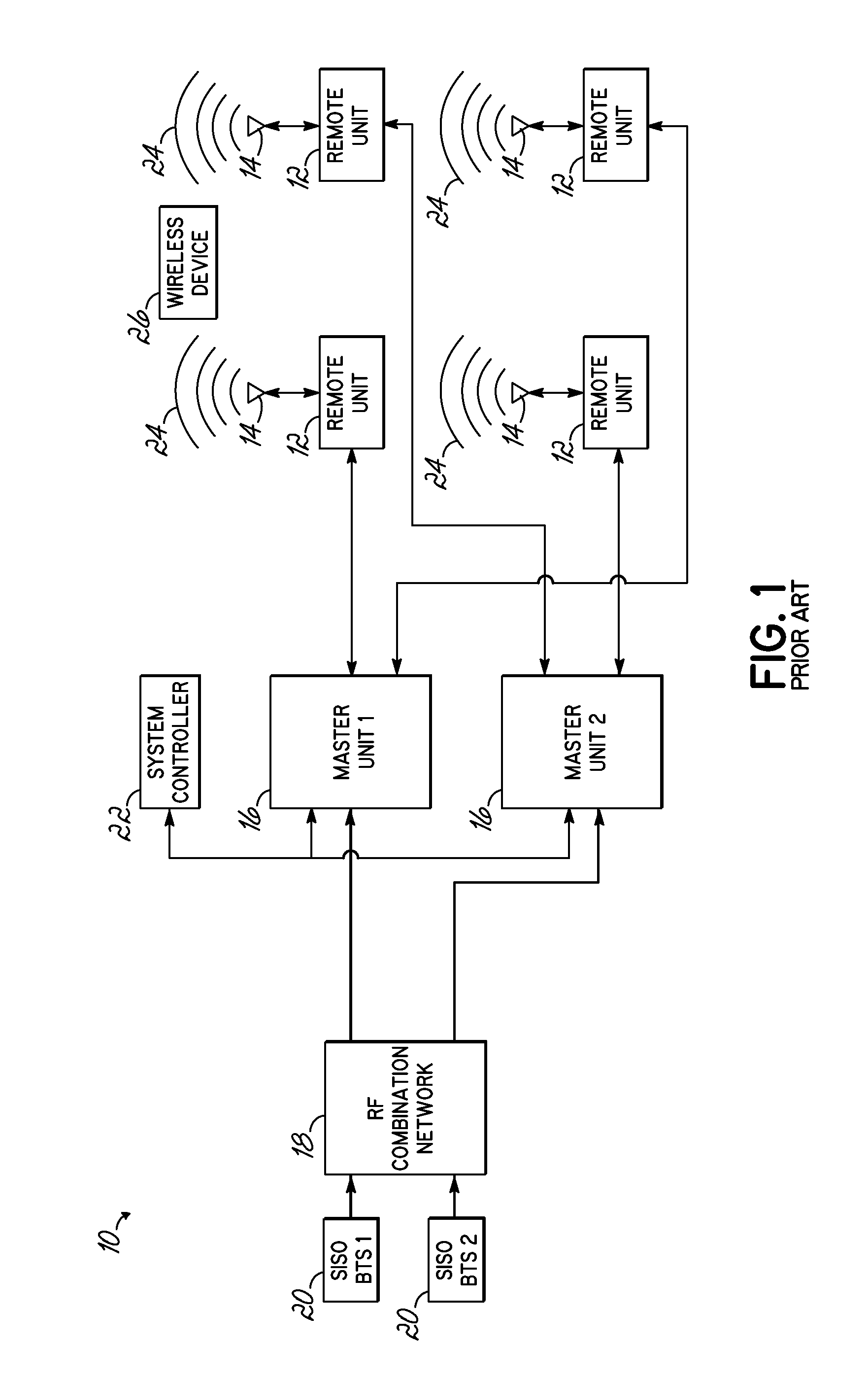
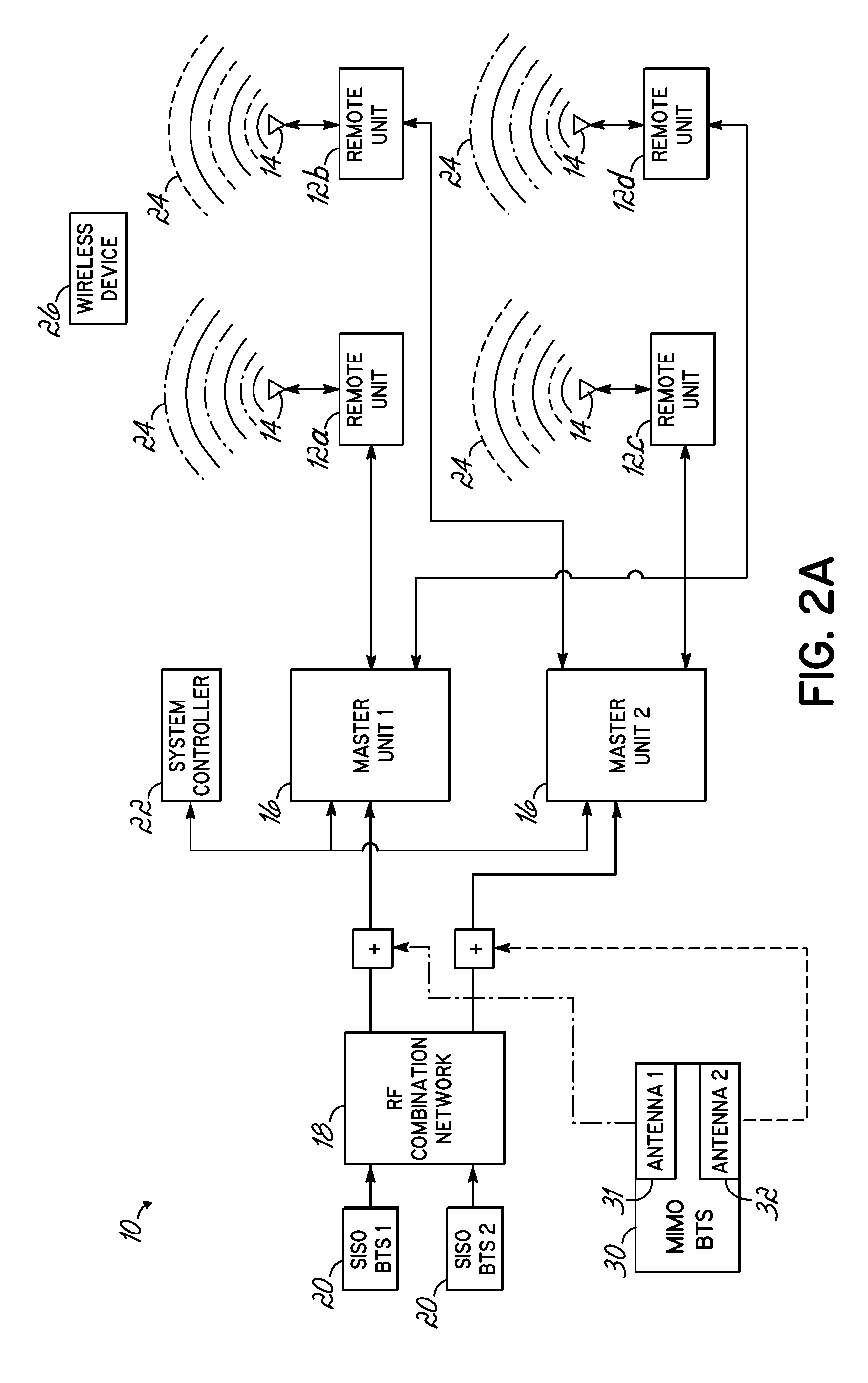
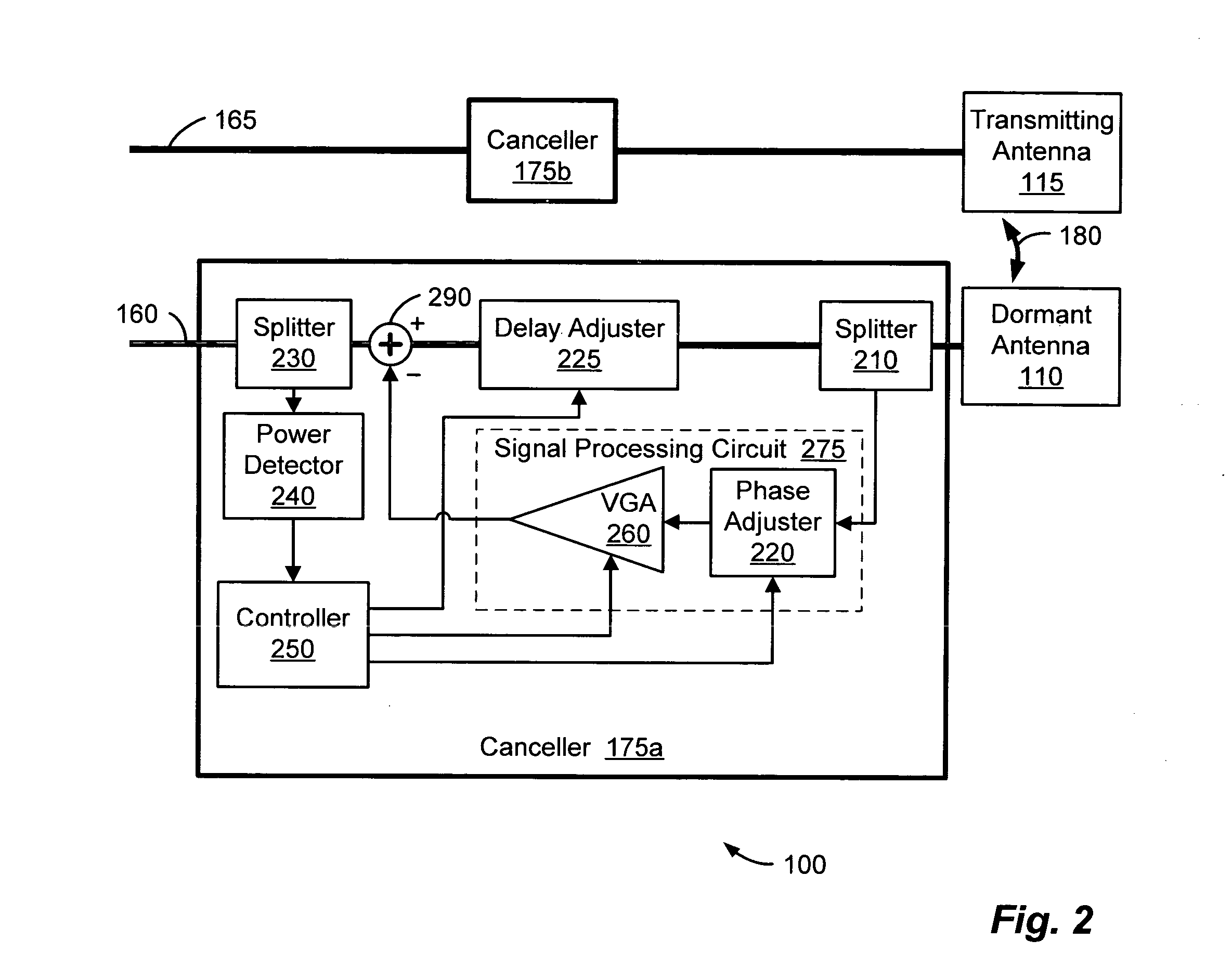
Distributed antenna system for MIMO signals
ActiveUS20110135308A1Site diversityWavelength-division multiplex systemsHybrid couplerDistributed antenna system
A distributed antenna system (DAS) includes a multiple-input and multiple-output (“MIMO”) base station configured to output at least a first and second signal, and a hybrid coupler coupled thereto, the coupler configured to receive the first and second signal from the MIMO base station on respective first and second ports and provide an output signal on at least one output port, the output signal including at least a portion of the first signal and at least a portion of the second signal. The DAS further includes a master unit communicating with the coupler and configured to receive at least the output signal, and at least one remote unit communicating with the master unit and configured to communicate the output signal to a device.
Owner:ANDREW WIRELSS SYST
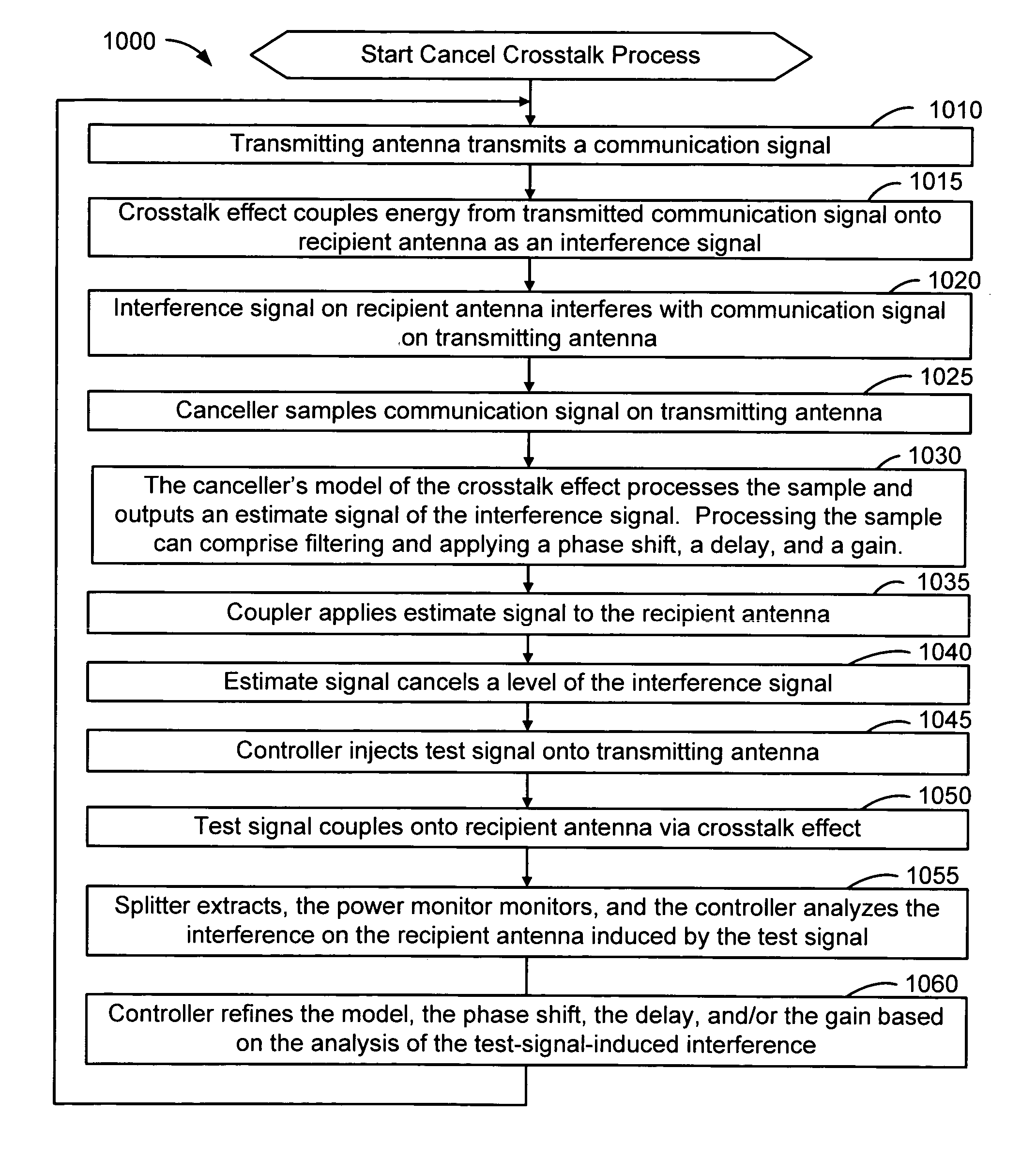
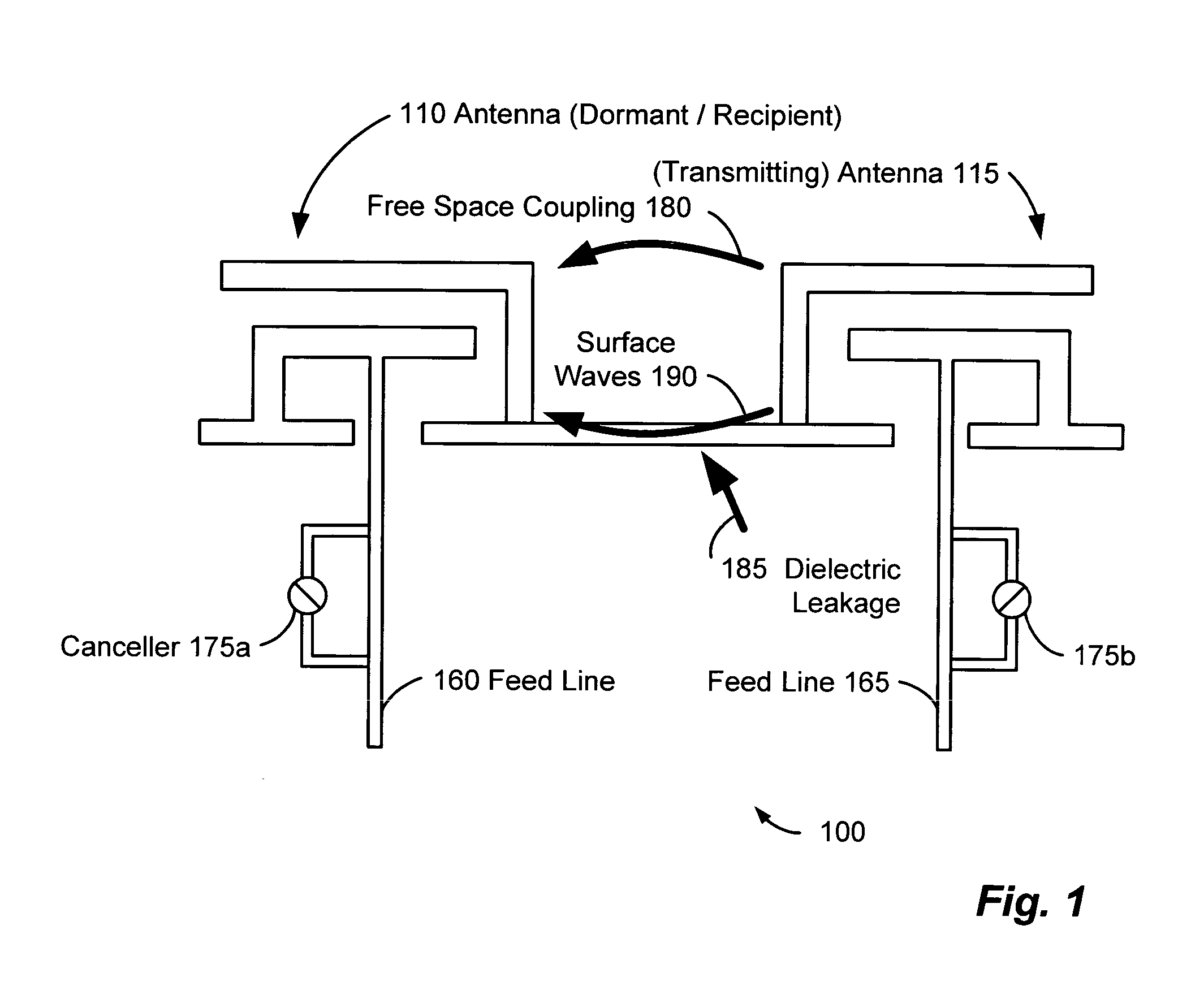
Method and system for antenna interference cancellation
InactiveUS20050226353A1Improve signal qualityHigh bandwidthCorrect operation testingLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemSignal on
A wireless communication system can comprise two or more antennas that interfere with one another via free space coupling, surface wave crosstalk, dielectric leakage, or other interference effect. The interference effect can produce an interference signal on one of the antennas. A cancellation device can suppress antenna interference by generating an estimate of the interference signal and subtracting the estimate from the interference signal. The cancellation device can generate the estimate based on sampling signals on an antenna that generates the interference or on an antenna that receives the interference. The cancellation device can comprise a model of the crosstalk effect. Transmitting test signals on the communication system can define or refine the model.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Systems and methods for communicating video data between a mobile imaging system and a fixed monitor system
A system for communicating video data is described. The system includes a mobile imaging system, at least one monitor fixed to a room in a medical facility, and a video transmitter assembly coupled to the mobile imaging system to transmit a video signal. The system for communicating video data also includes a video receiver assembly coupled to the at least one monitor to receive the video signal and display the video signal on the at least one monitor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Transmission with collision detection and mitigation for wireless communication
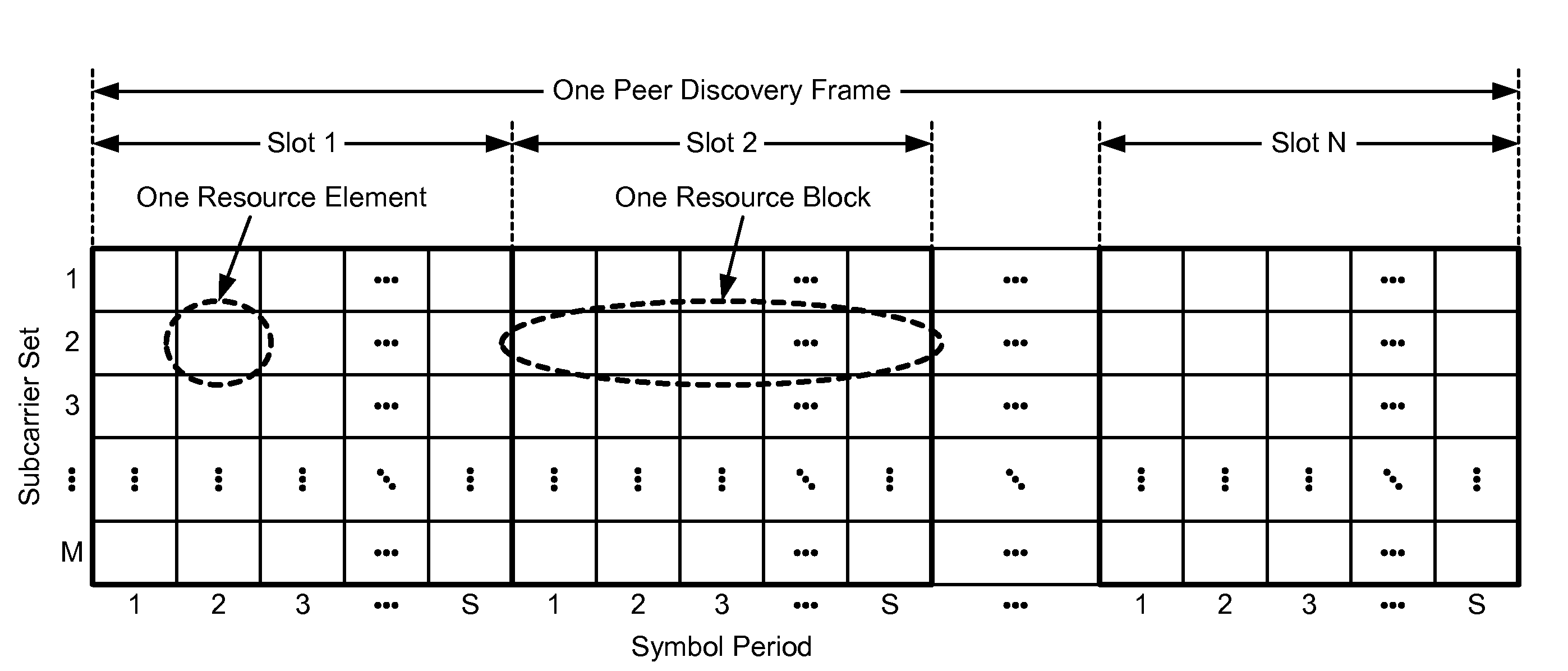
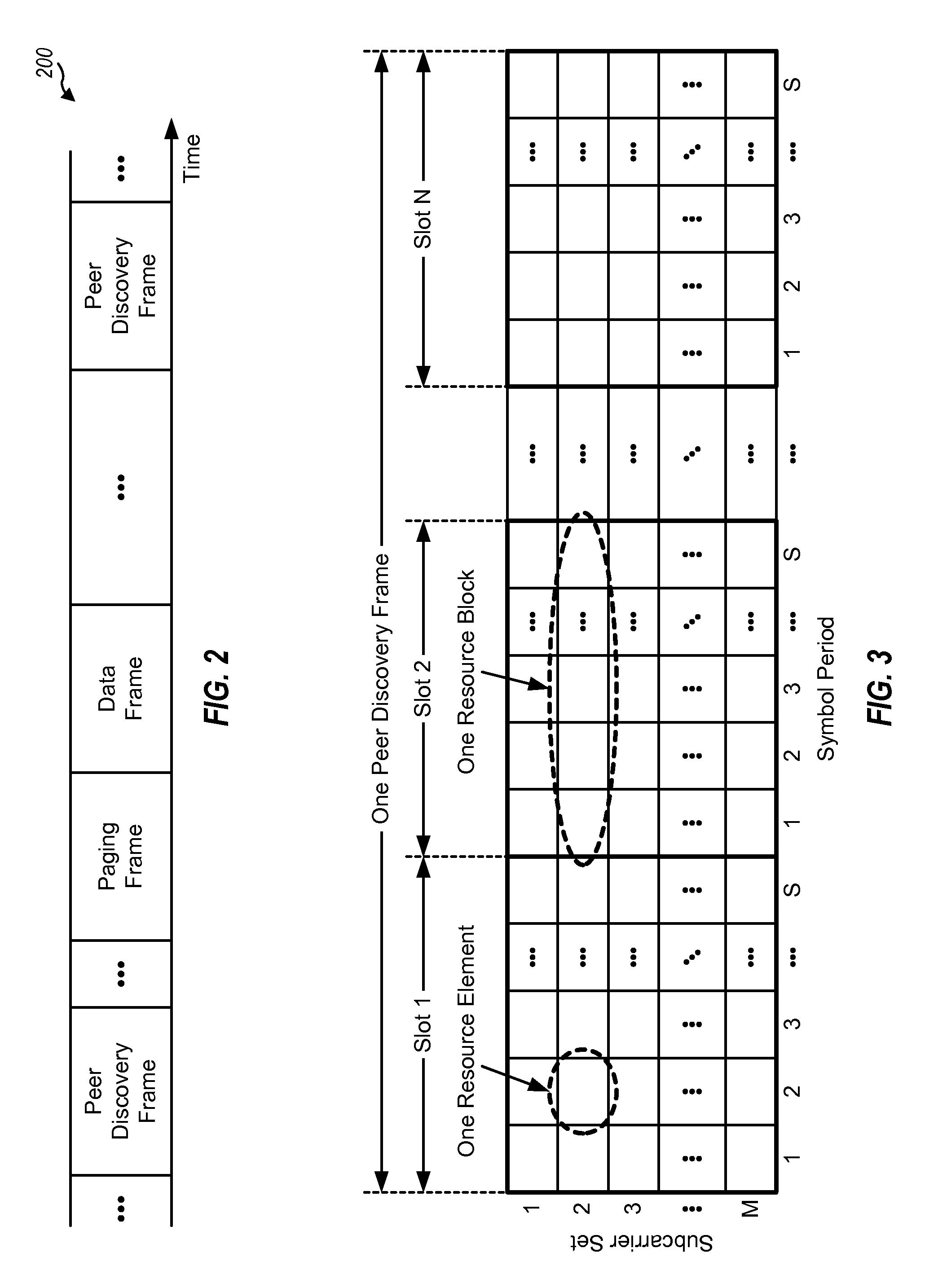
ActiveUS20100202400A1Improve interferenceWireless commuication servicesNetwork data managementTelecommunicationsResource element
Techniques for transmitting signals on shared resources in a manner to detect and / or combat collision are described. In an aspect, a terminal may transmit a signal on a subset of resource elements in a resource block, and at least one null resource element with no signal may be used to detect for collision of the signal. In another aspect, different terminals may simultaneously transmit their signals on different subsets of resource elements in a resource block. These different subsets of resource elements may be pseudo-randomly selected to randomize interference. In one design, a terminal may determine a resource block to use for transmission of a signal, select a subset of the resource elements in the resource block, and transmit the signal on the selected resource elements, e.g., to at least one other terminal for peer-to-peer communication. The signal may be a peer discovery signal, a paging signal, etc.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
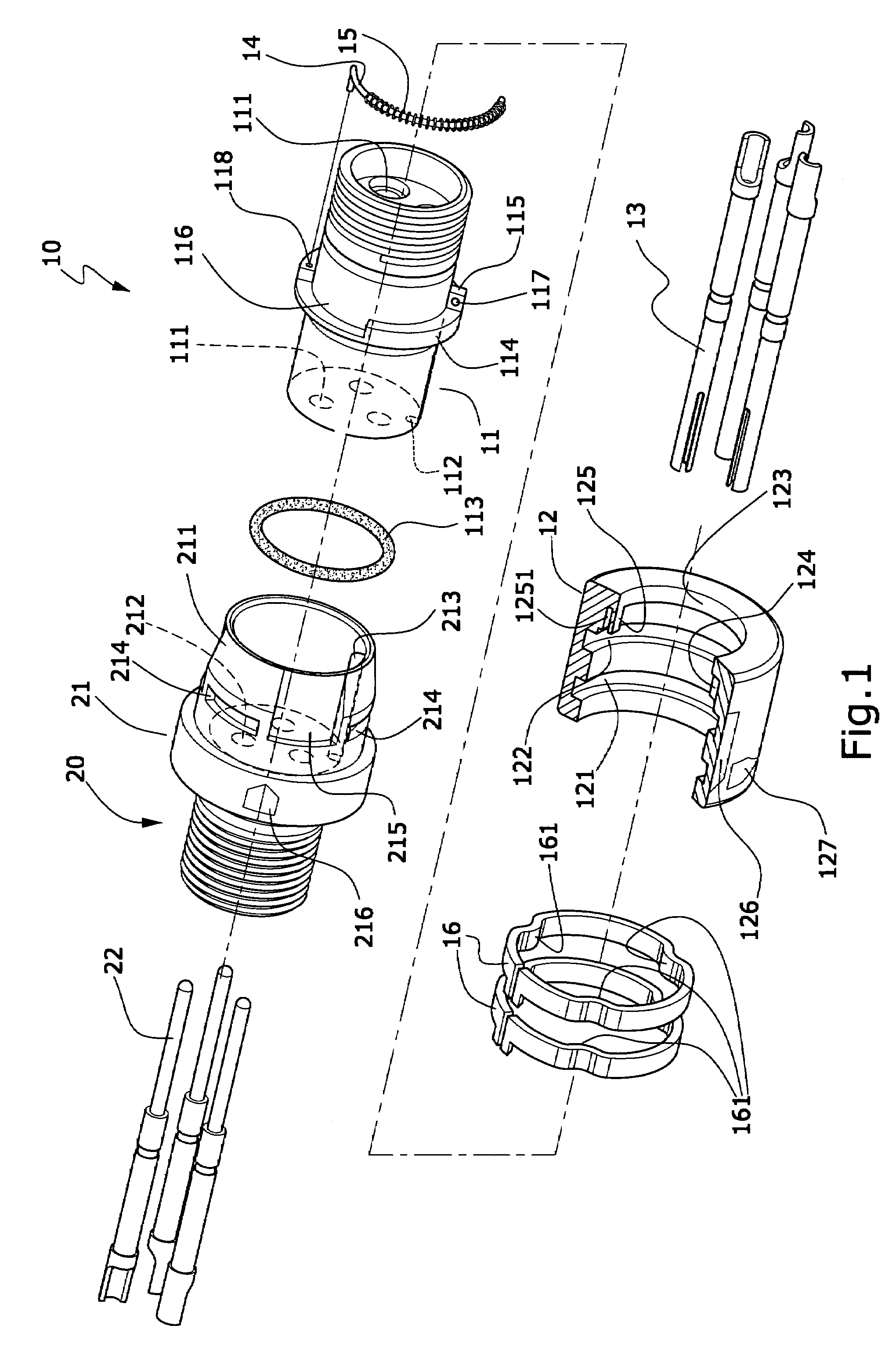
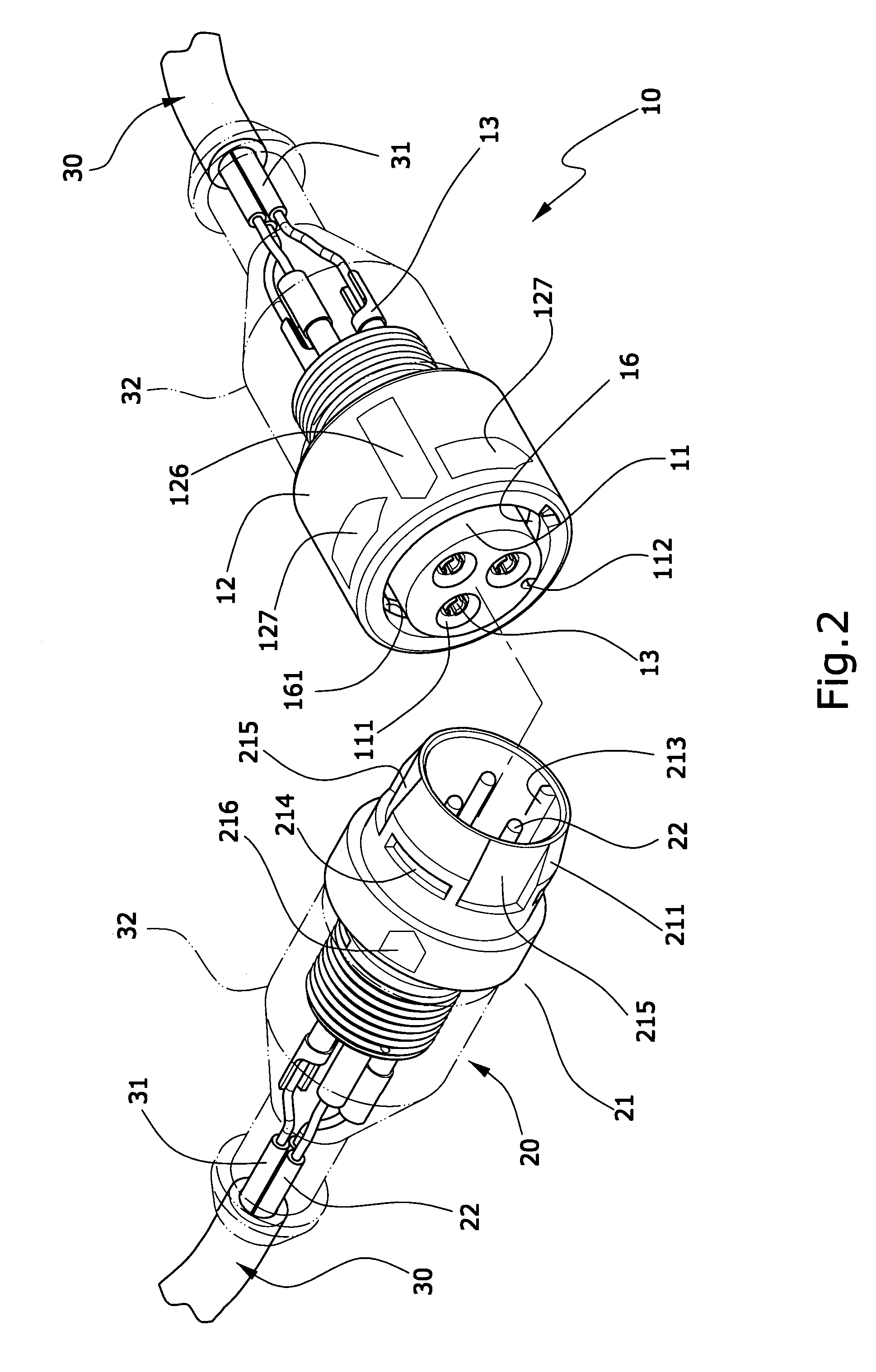
Fast coupling structure of waterproof cable connector
InactiveUS7422463B2Firmly connectedEasy to disassembleElectrically conductive connectionsSecuring/insulating coupling contact membersCouplingElectric power system
The invention relates to a fast coupling structure of waterproof cable connector, mainly comprising a male connecting joint and a female connecting joint, both are positioned on the cable end for connection of electric power source or signals on an electric apparatus; the invention enables both of the male and the female connecting joints to have the fast coupling function and the waterproof effects; therefore, a user is able to easily and quickly connect or disassemble the coupling structure.
Owner:KUO KO AN
Mobile devices and methods employing haptics
ActiveUS20120028577A1Precise positioningDisplayed-facilitating its purchaseNear-field transmissionRepeater circuitsTablet computerTouch Perception
A variety of haptic improvements useful in mobile devices are detailed. In one, a smartphone captures image data from a physical object, and discerns an object identifier from the imagery (e.g., using watermark, barcode, or fingerprint techniques). This identifier is sent to a remote data structure, which returns data defining a distinct haptic signature associated with that object. This smartphone then renders this haptic signal to the user. (Related embodiments identify the object using other means, such as location, or NFC chip.) In another arrangement, haptic feedback signals social network information about a product or place (e.g., the user's social network friends “Like” a particular brand of beverage). In yet another arrangement, the experience of watching a movie on a television screen is augmented by tactile effects issued by a tablet computer on the viewer's lap. In still another arrangement, commercial vendors bid for rights to employ different ones of a library of haptic signals on one or more users' smartphones, e.g., to alert such user(s) to their products / services. A great variety of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Method and a device for maintaining the performance quality of a code-division multiple access system in the presence of narrow band interference
InactiveUS6807405B1Reduce adverse effectsReducing and eliminating disruptionPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementContinuous scanningTime division multiple access
A method and device which dynamically detects, tracks and filters interfering signals with sufficient speed (i.e. within one IS-95 CDMA data frame period, or 20ms and fidelity to eliminate or greatly reduce the deleterious effects of narrow band interferor signals on a CDMA link. When inserted in an RF signal path an Adaptive Notch Filter (ANF) detects narrow band interferors above a threshold level within the CDMA signal. Detection is accomplished by continuous scanning of a preset excision band, e.g. a specified narrow band associated with an AMPS system. Detected interferors are then automatically acquired and suppressed. This is achieved by electronically placing a rejection notch at the frequency of the interferors. Multiple notch filters may be used to simultaneously suppress multiple interferors. In the absence of interferors a bypass mode is selected allowing the RF signal to bypass the notch. Upon detection of an interferor, a switch is made to a suppression mode where the interferor is steered through a first notch section and suppressed. Alternatively, an external control line may be used to select the bypass mode so that the signal is allowed to pass the notch section, regardless of interferer content.
Owner:ILLINOIS SUPER CONDUCTOR CANADA CORP A CO INC UNDER THE LAWS OF CANADA +1
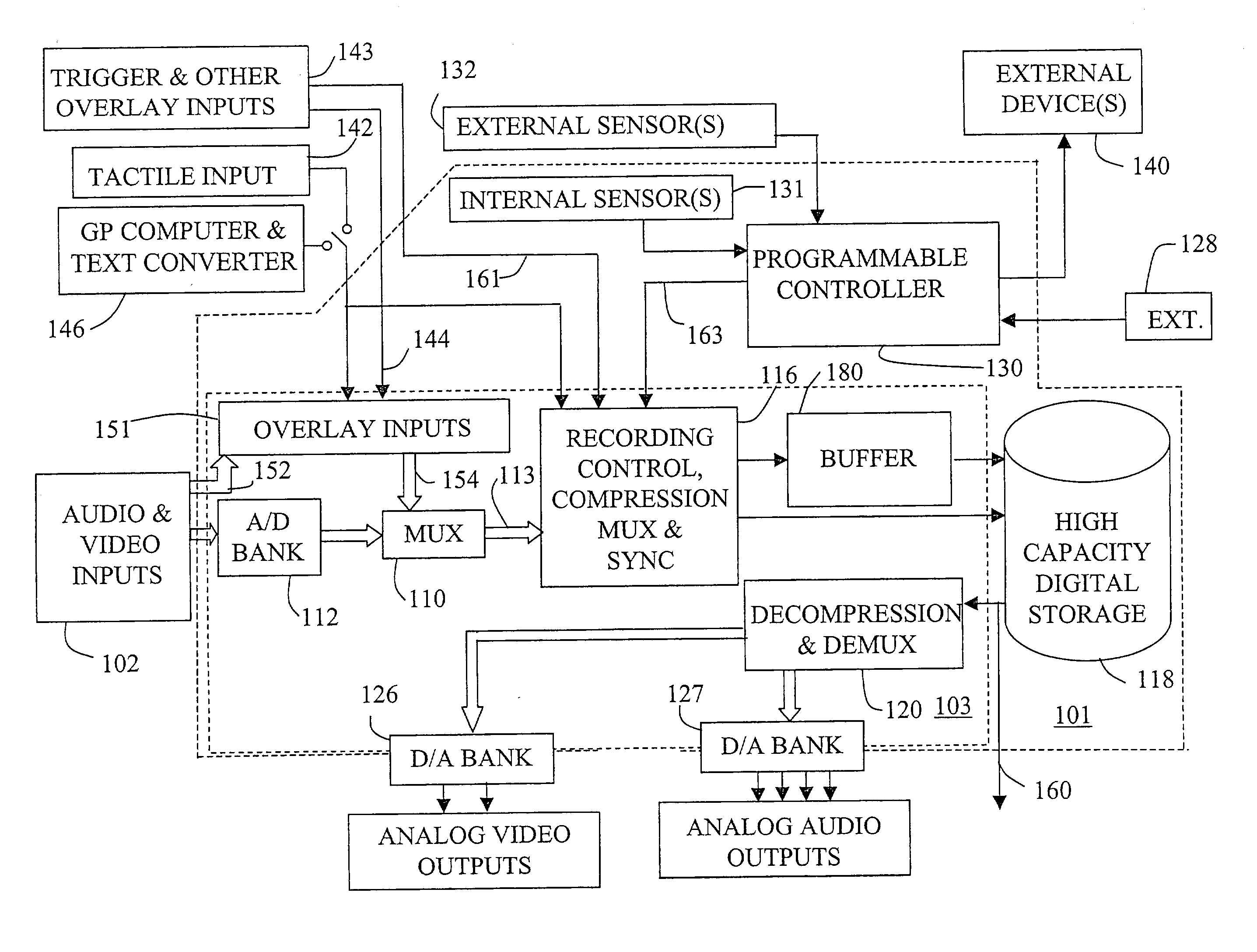
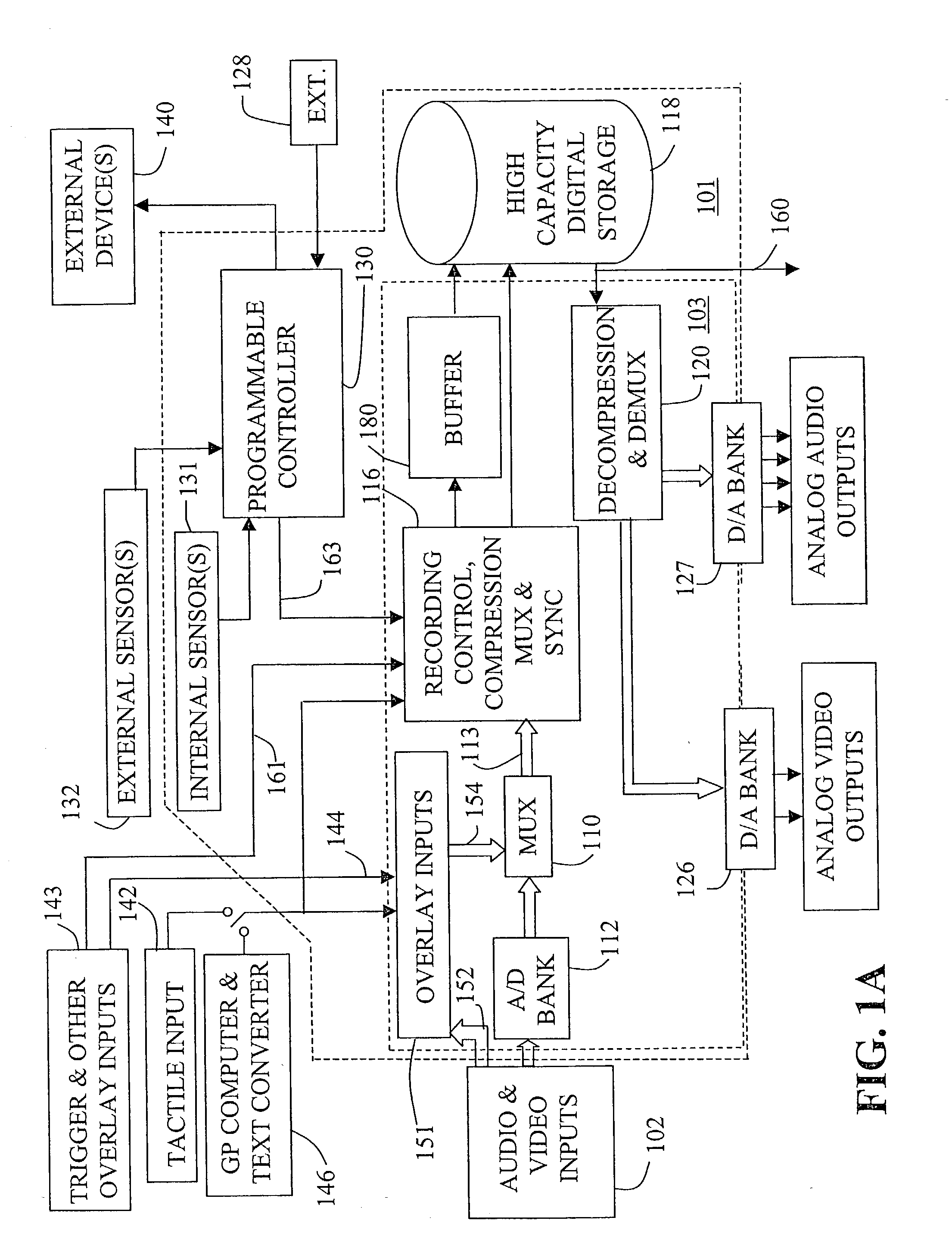
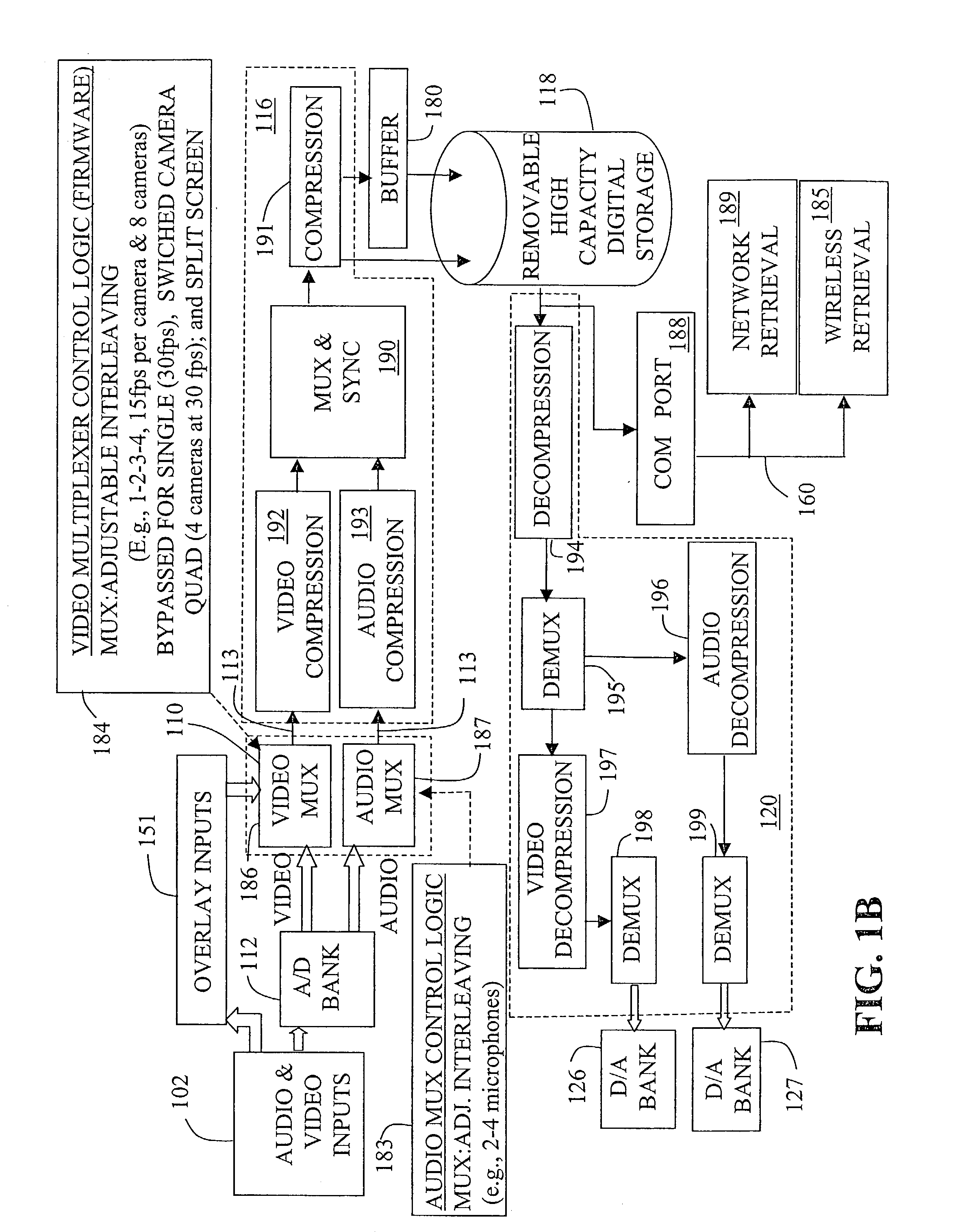
Mobile video recorder control and interface
InactiveUS20030081934A1Quick analysisSimple processTelevision system detailsDisc-shaped record carriersVideocassette recorderComputer graphics (images)
Provided are systems and techniques for recording video in a mobile environment, in which camera means mounted at a first location in a vehicle generates a video signal based upon an observed scene. Video recording means mounted at a second location in the vehicle inputs and records the video signal on a tangible medium. General-purpose computing means, mounted at a third location in the vehicle and running a general operating system and user-installed application programs, communicates with the video recording means, is loaded with software to provide a user interface to control recording and playback by the video recording means, and includes means for wireless communication with a central base station.
Owner:HUBB SYST
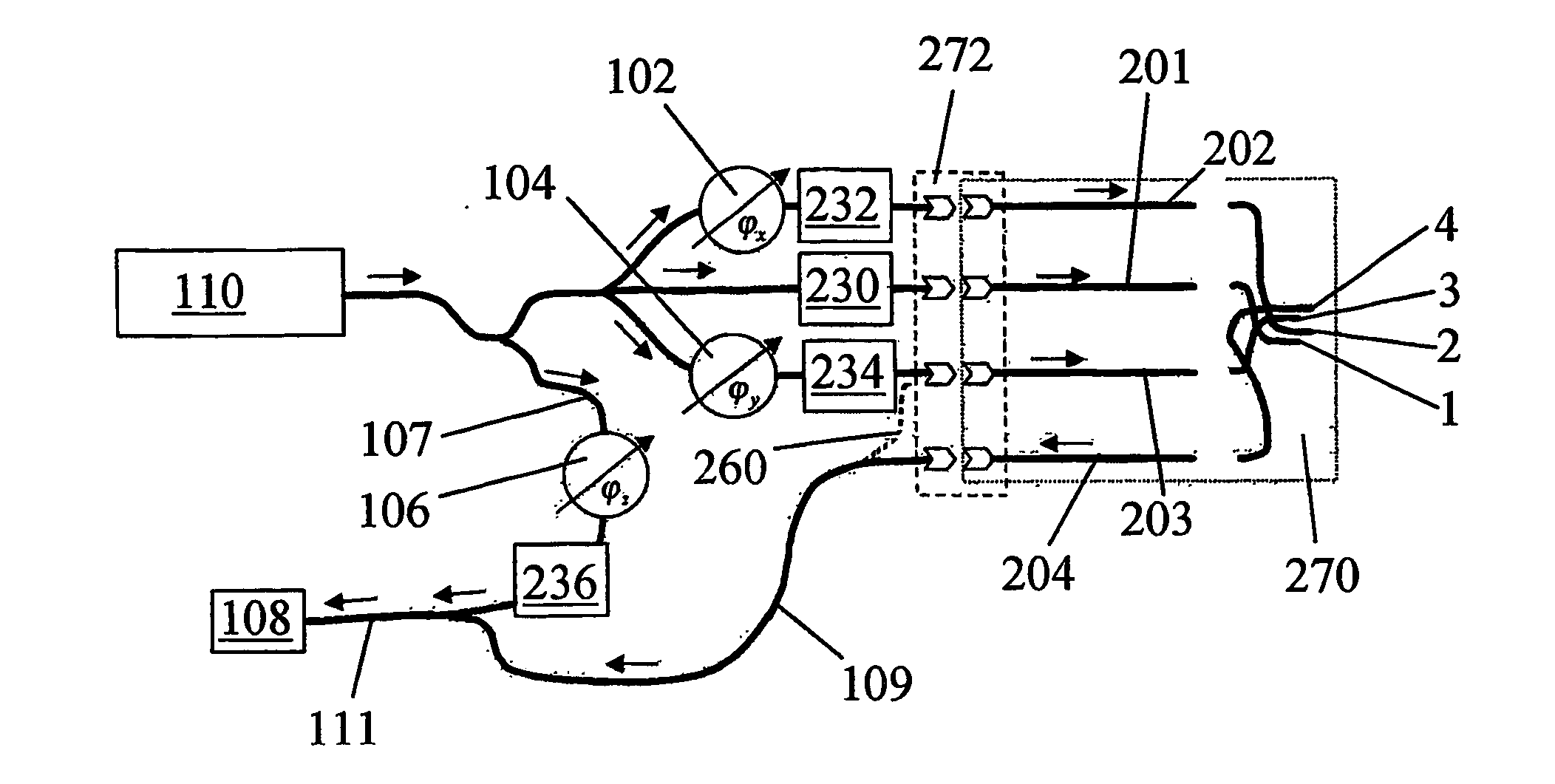
Optical coherence tomography with 3d coherence scanning
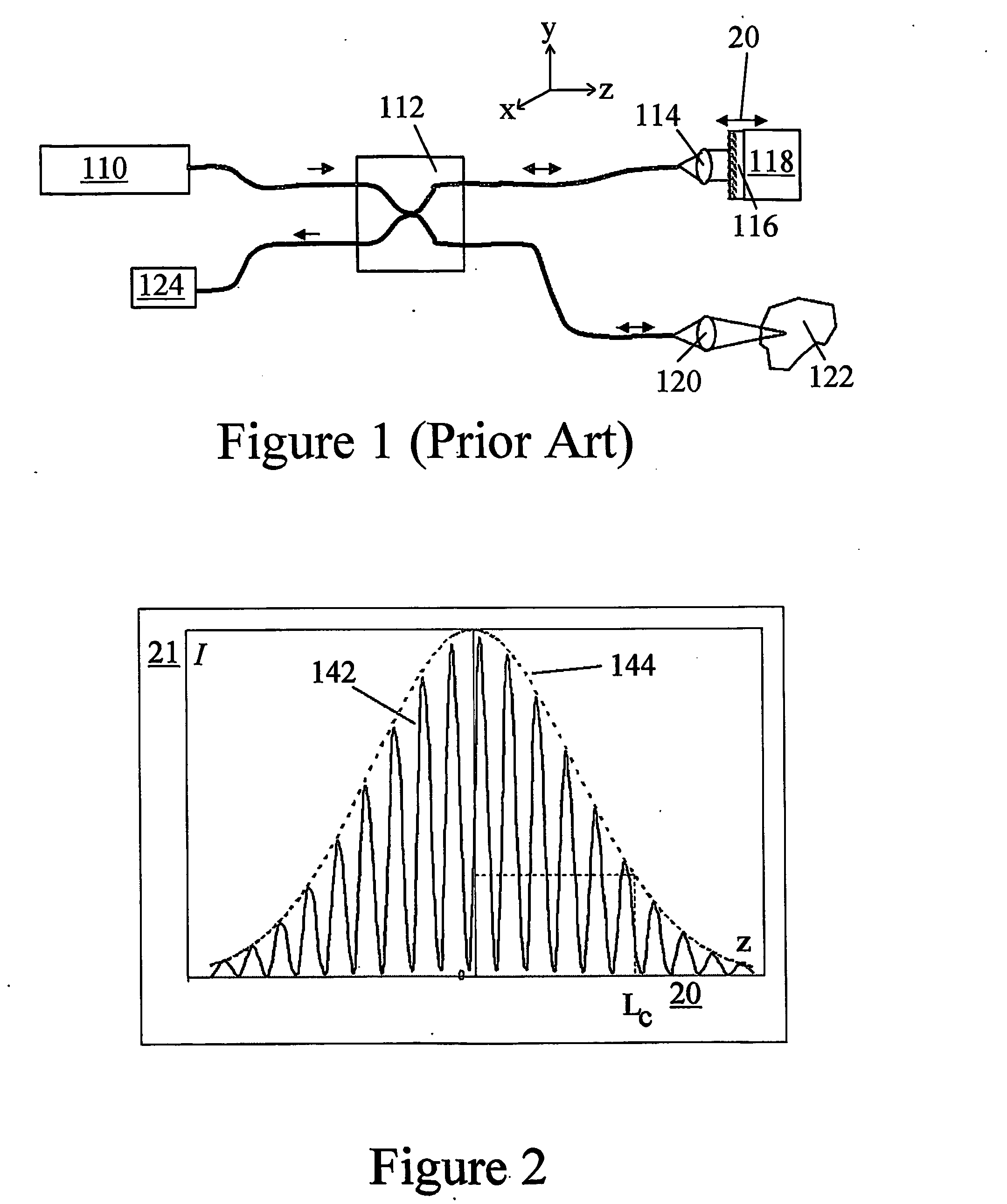
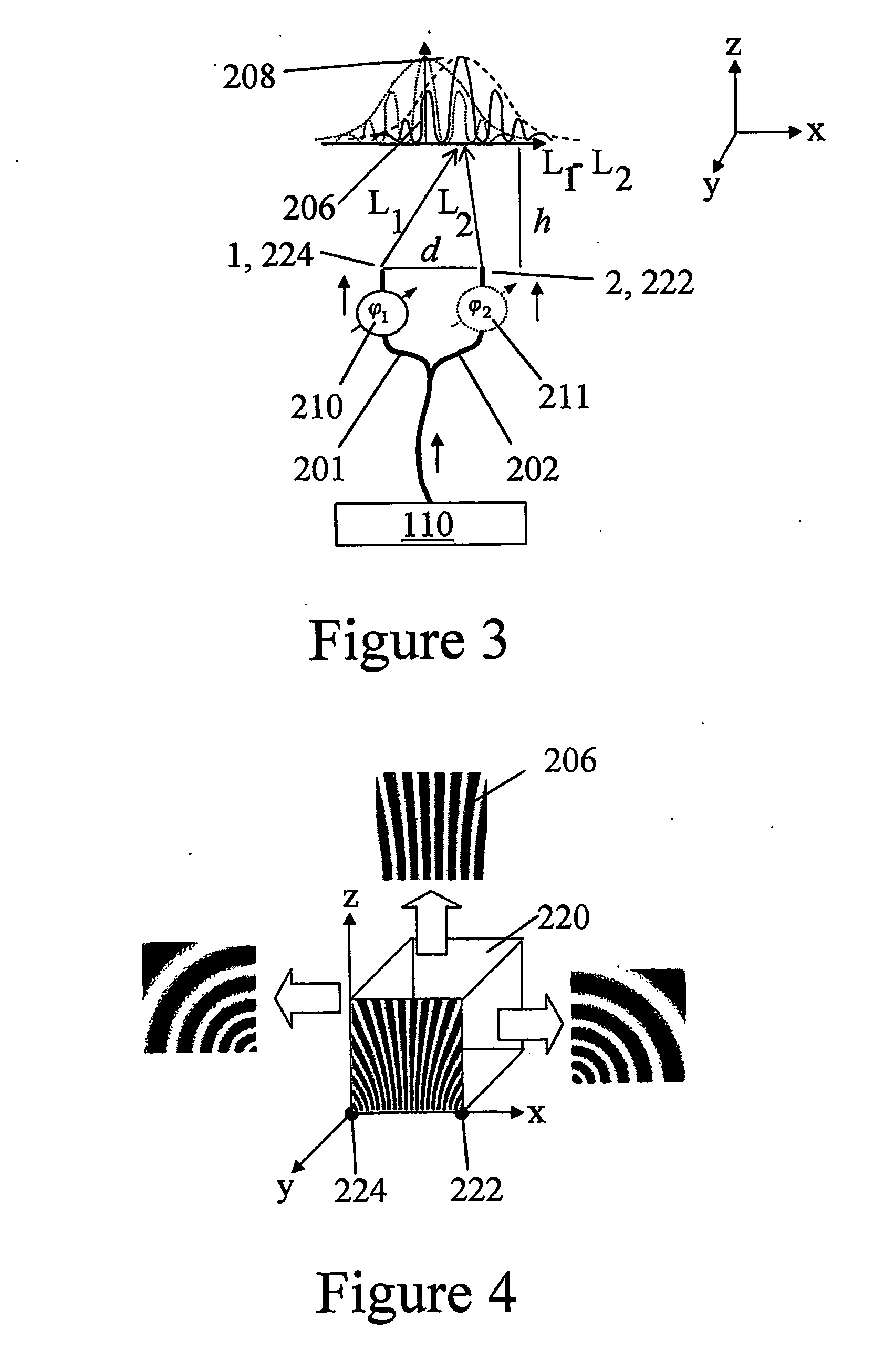
Optical coherence tomography with 3D coherence scanning is disclosed, using at least three fibers (201, 202, 203) for object illumination and collection of backscattered light. Fiber tips (1, 2, 3) are located in a fiber tip plane (71) normal to the optical axis (72). Light beams emerging from the fibers overlap at an object (122) plane, a subset of intersections of the beams with the plane defining field of view (266) of the optical coherence tomography apparatus. Interference of light emitted and collected by the fibers creates a 3D fringe pattern. The 3D fringe pattern is scanned dynamically over the object by phase shift delays (102, 104) controlled remotely, near ends of the fibers opposite the tips of the fibers, and combined with light modulation. The dynamic fringe pattern is backscattered by the object, transmitted to a light processing system (108) such as a photo detector, and produces an AC signal on the output of the light processing system (108). Phase demodulation of the AC signal at selected frequencies and signal processing produce a measurement of a 3D profile of the object.
Owner:APPLIED SCI INNOVATIONS +1
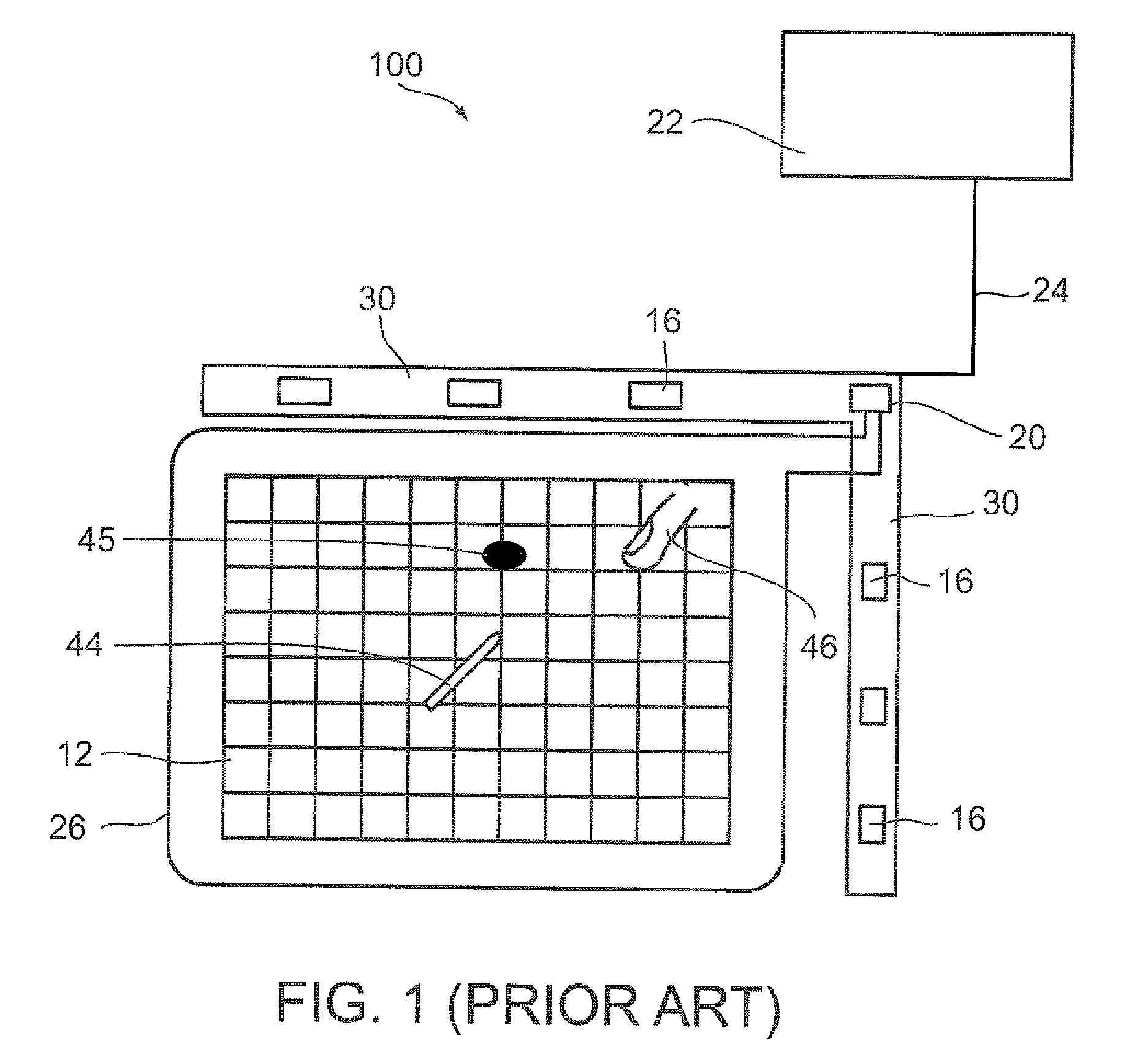
System and method for detection with a digitizer sensor
A method for detection on a digitizer sensor, the method comprises simultaneously transmitting orthogonal signals having the same frequency on at least two conductors of a digitizer sensor; sampling a signal on at least one other conductor crossing the at least two conductors, wherein the signal is responsive to capacitive coupling at cross-junctions formed between the at least two conductors and at least one other conductor; decomposing the sampled signal into orthogonal components; and analyzing the orthogonal components to detect user interaction at each cross junction.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
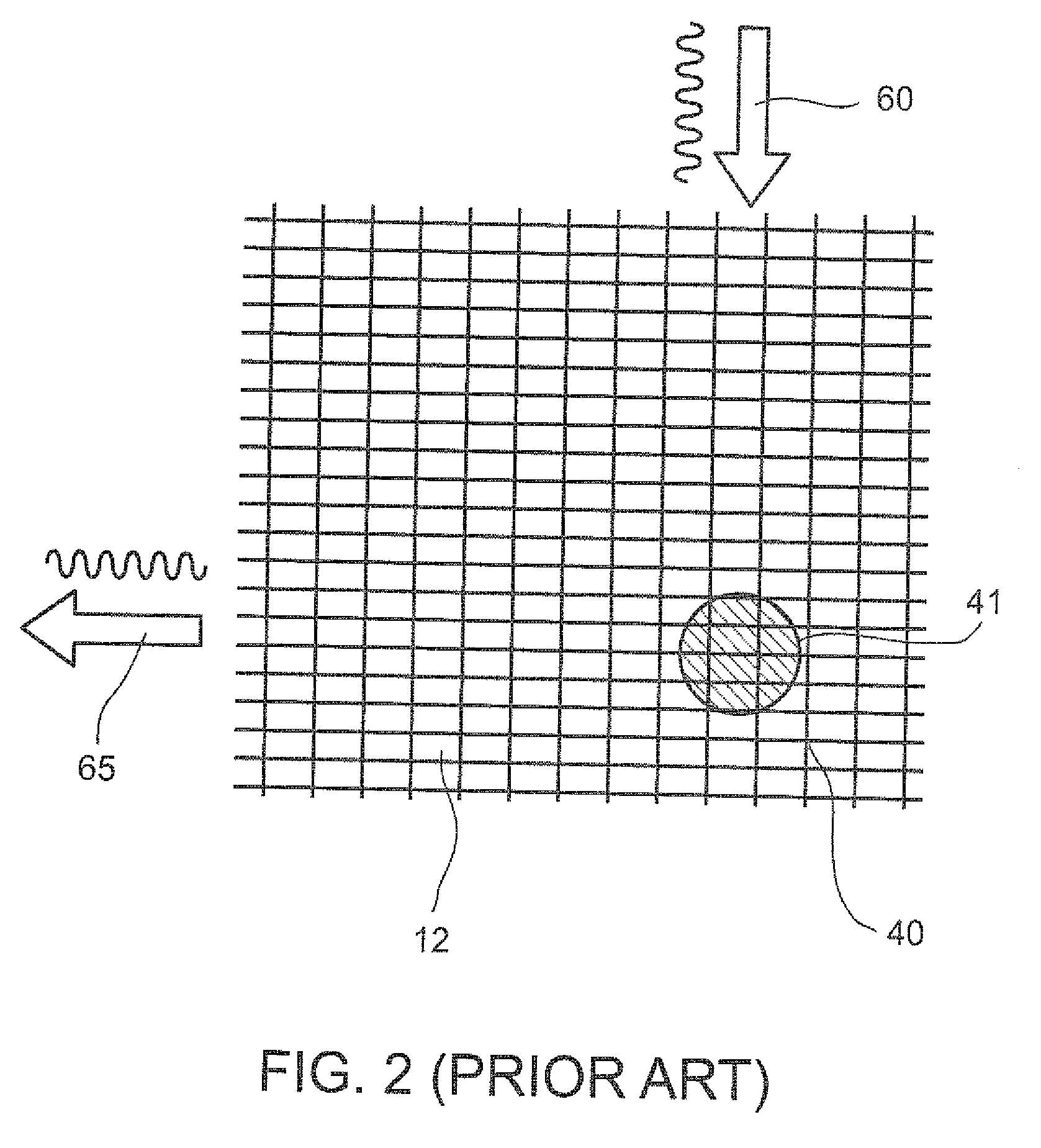
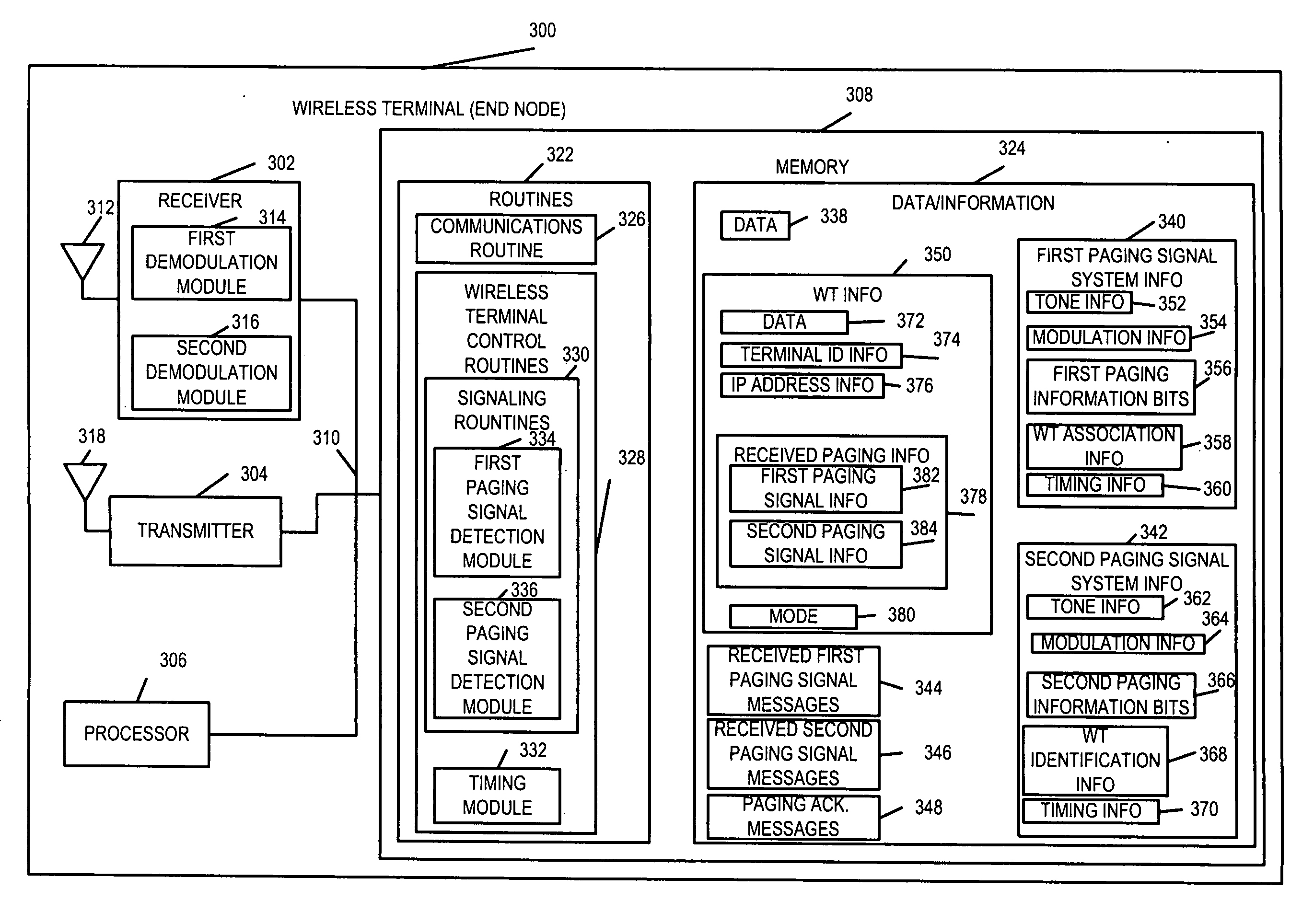
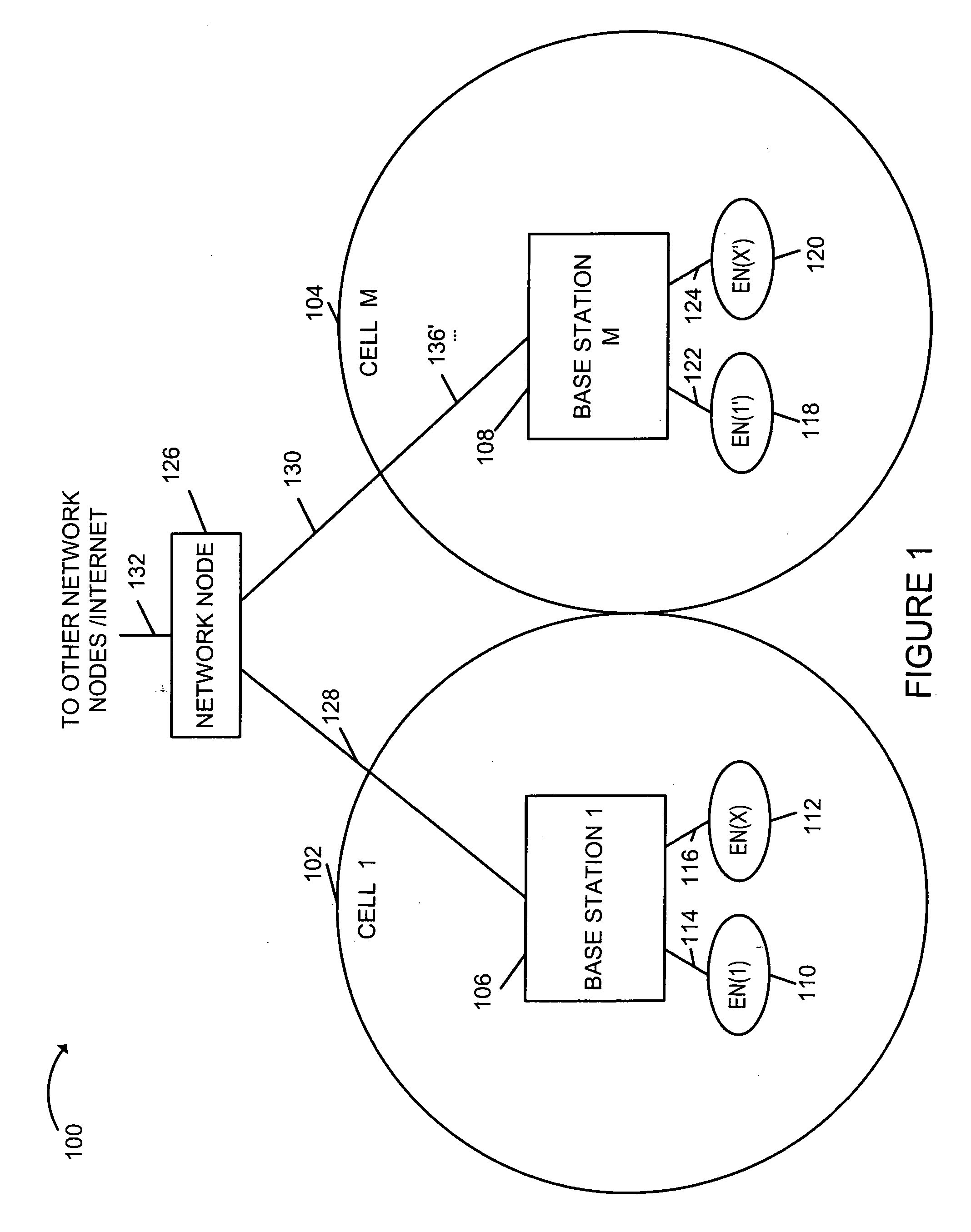
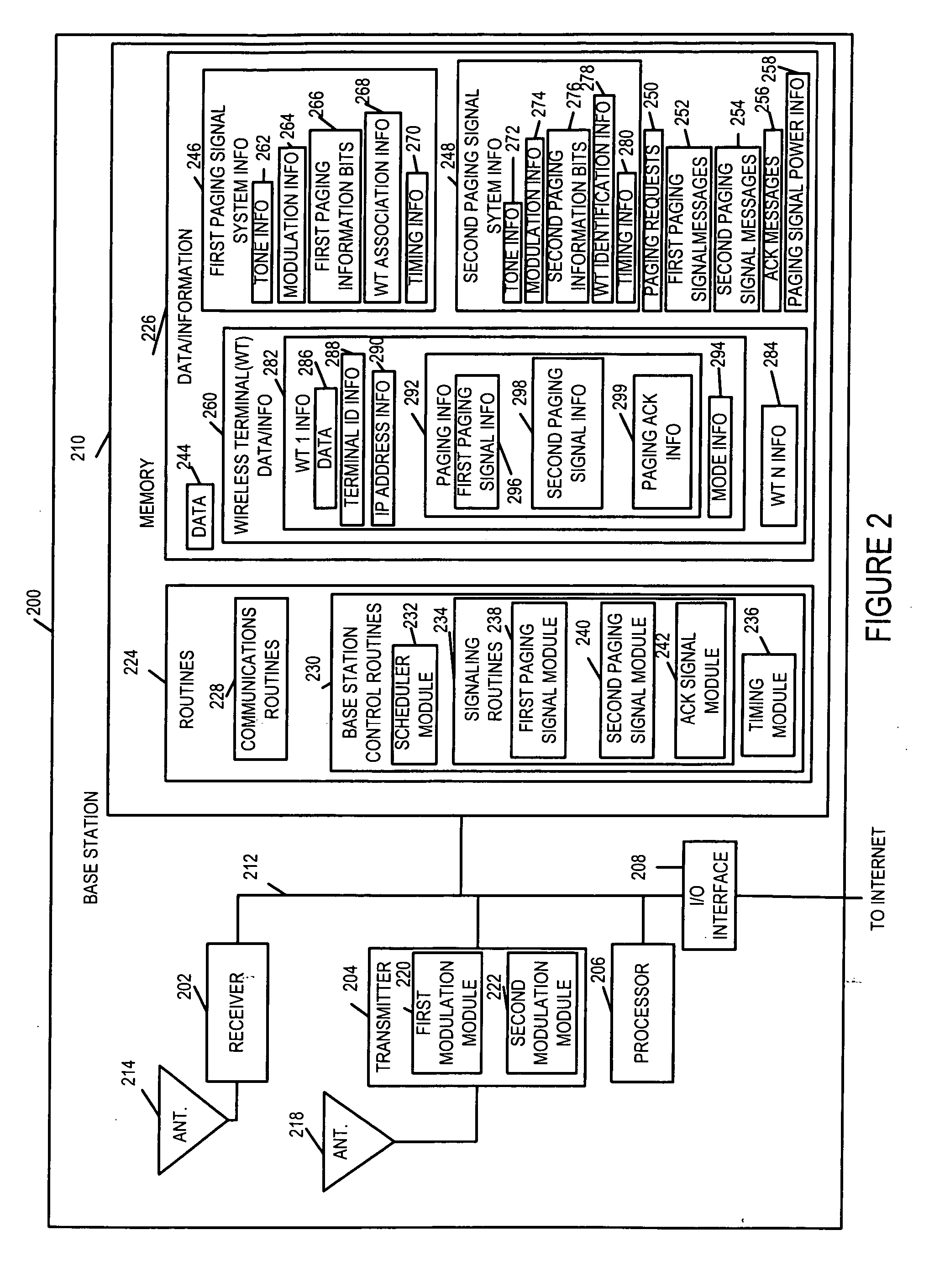
Efficient paging in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20050277429A1High bit rateFast decodingEnergy efficient ICTRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemSignal on
Methods and apparatus for efficient two-stage paging wireless communications systems are described. Wireless terminals are assigned to paging groups. A few first paging message information bits are modulated (using non-coherent modulation) into a first paging signal and communicated from a base station to wireless terminals. WTs wake-up, receive the first paging signal and quickly ascertain whether its paging group should expect a second paging signal, if so, the WT is operated to receive the second paging signal; otherwise, the WT goes back to sleep conserving power. The base station modulates (using coherent modulation) a number of second message information bits into a second paging signal and transmits the signal to WTs. From the information in first and second paging signals, a WT can determine that it is the paged WT and process the paging instructions. The intended paged WT can transmit an acknowledgement signal on a dedicated uplink resource.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
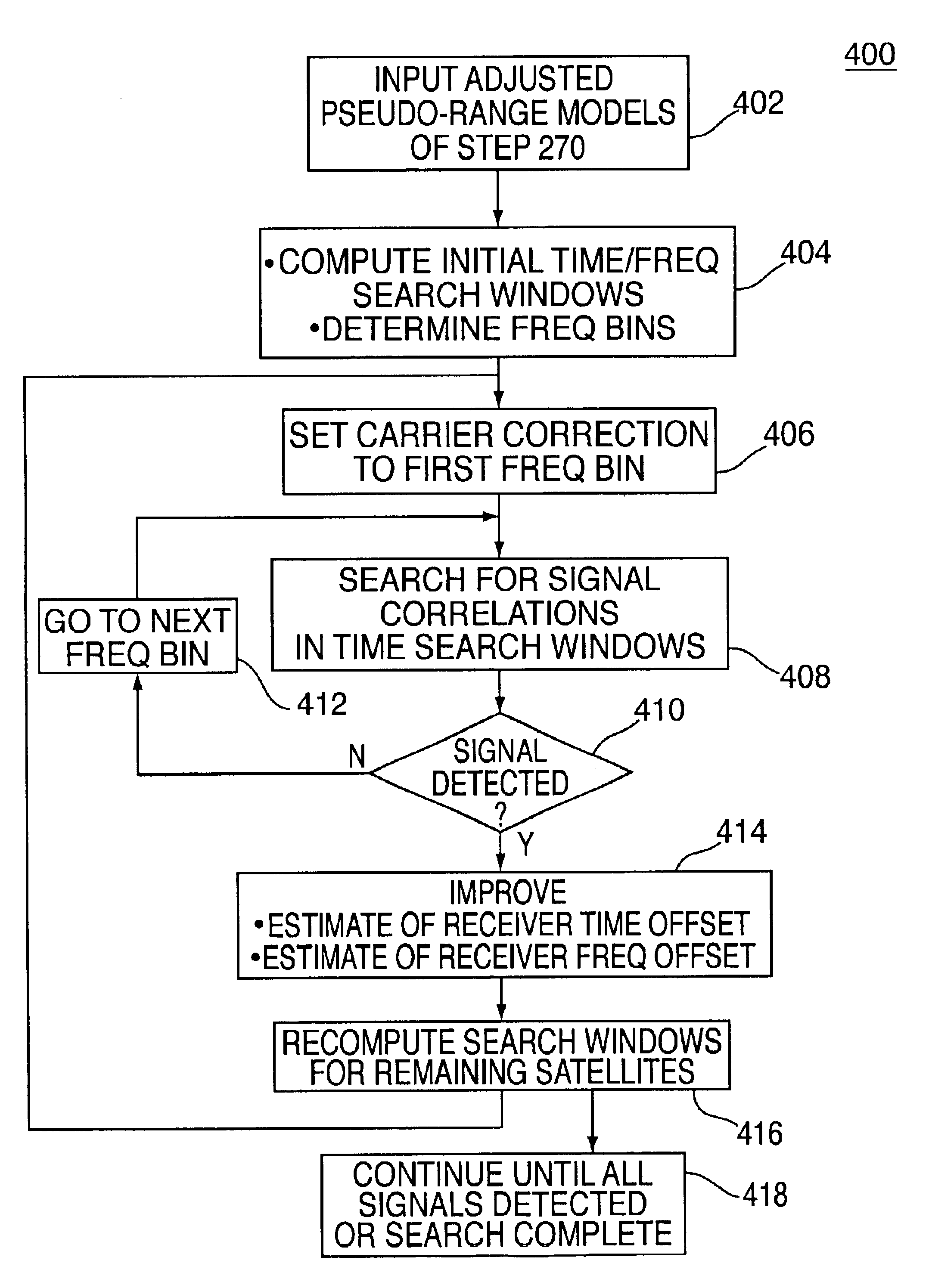
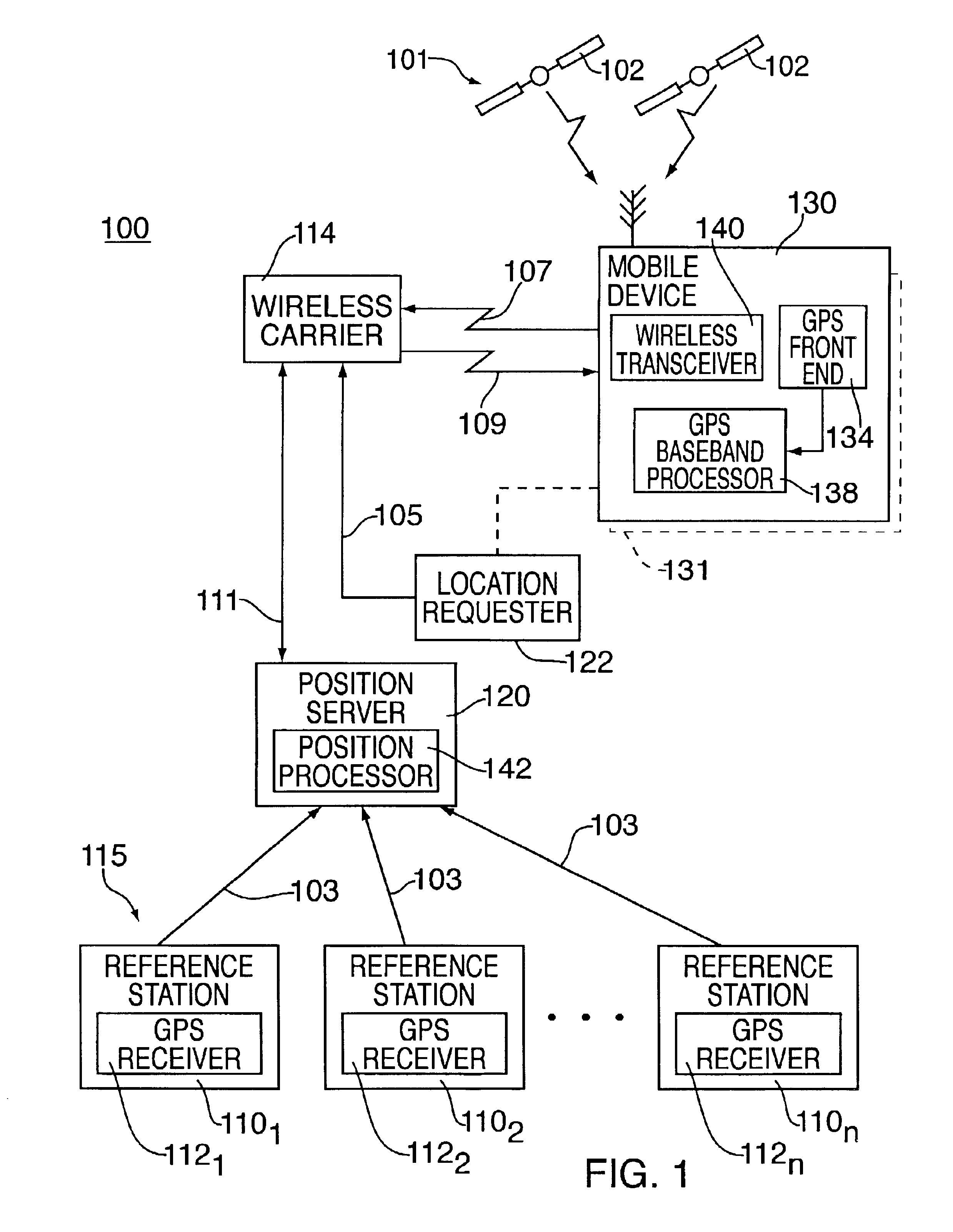
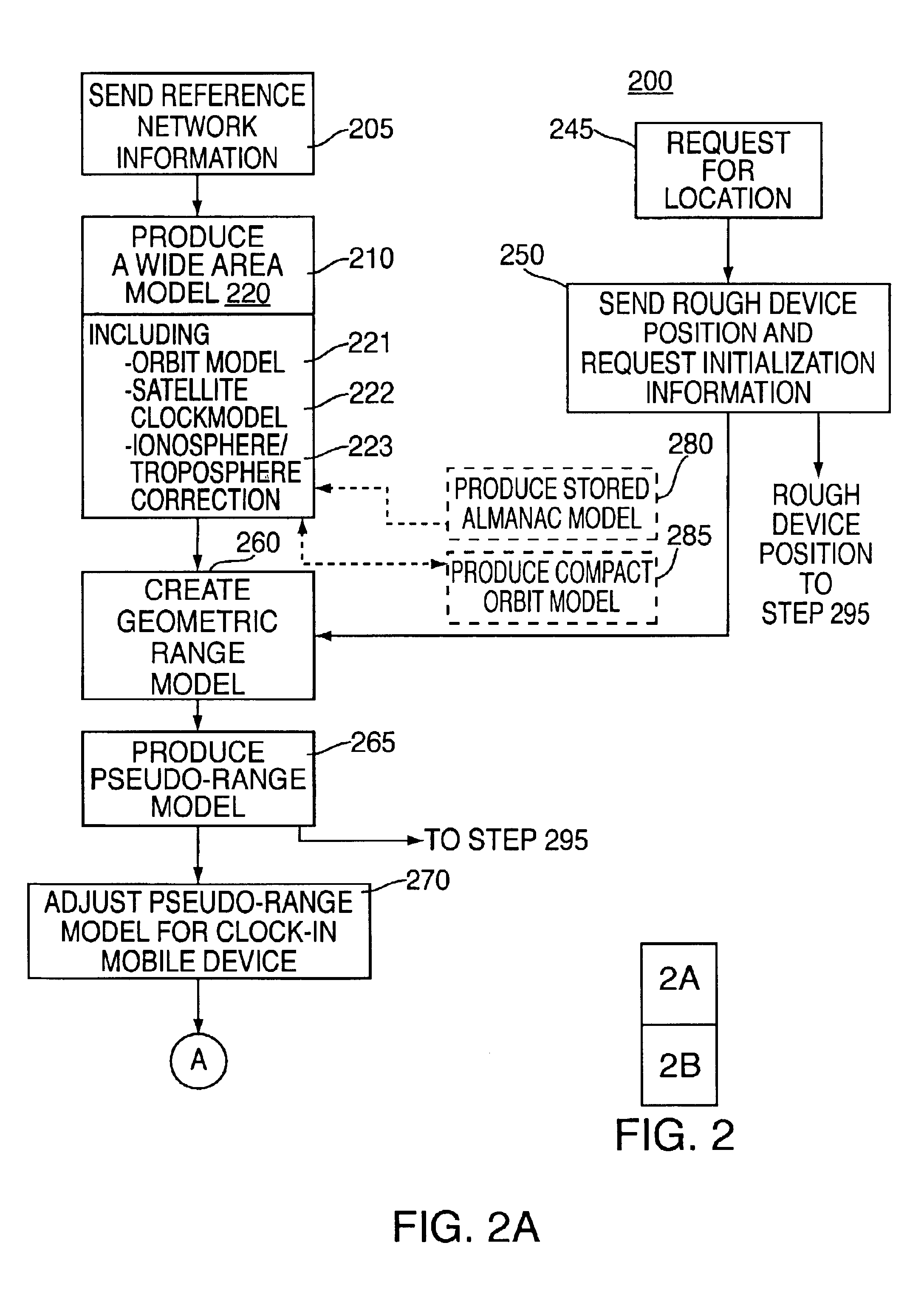
Method and apparatus for forming a pseudo-range model
InactiveUS6853916B2Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTelecommunications linkSignal on
A method and apparatus for locating mobile device over a broad coverage area using a wireless communications link that may have large and unknown latency. The apparatus comprises at least one mobile device, a reference network, a position server, a wireless carrier, and a location requester. The mobile device is in communication with the wireless carrier and receives global positioning system (GPS) signals from a plurality of satellites in the GPS satellite constellation. The reference network is coupled to the position server and provides GPS data. The mobile receiver receives GPS signals, performs rudimentary signal processing and transmits the processed signals to the wireless carrier. The wireless carrier passes the signals on to the position server. The position server processes the mobile receiver's GPS data and the reference network ephemeris data to identify the location of the mobile receiver. The location is sent to the location requester.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
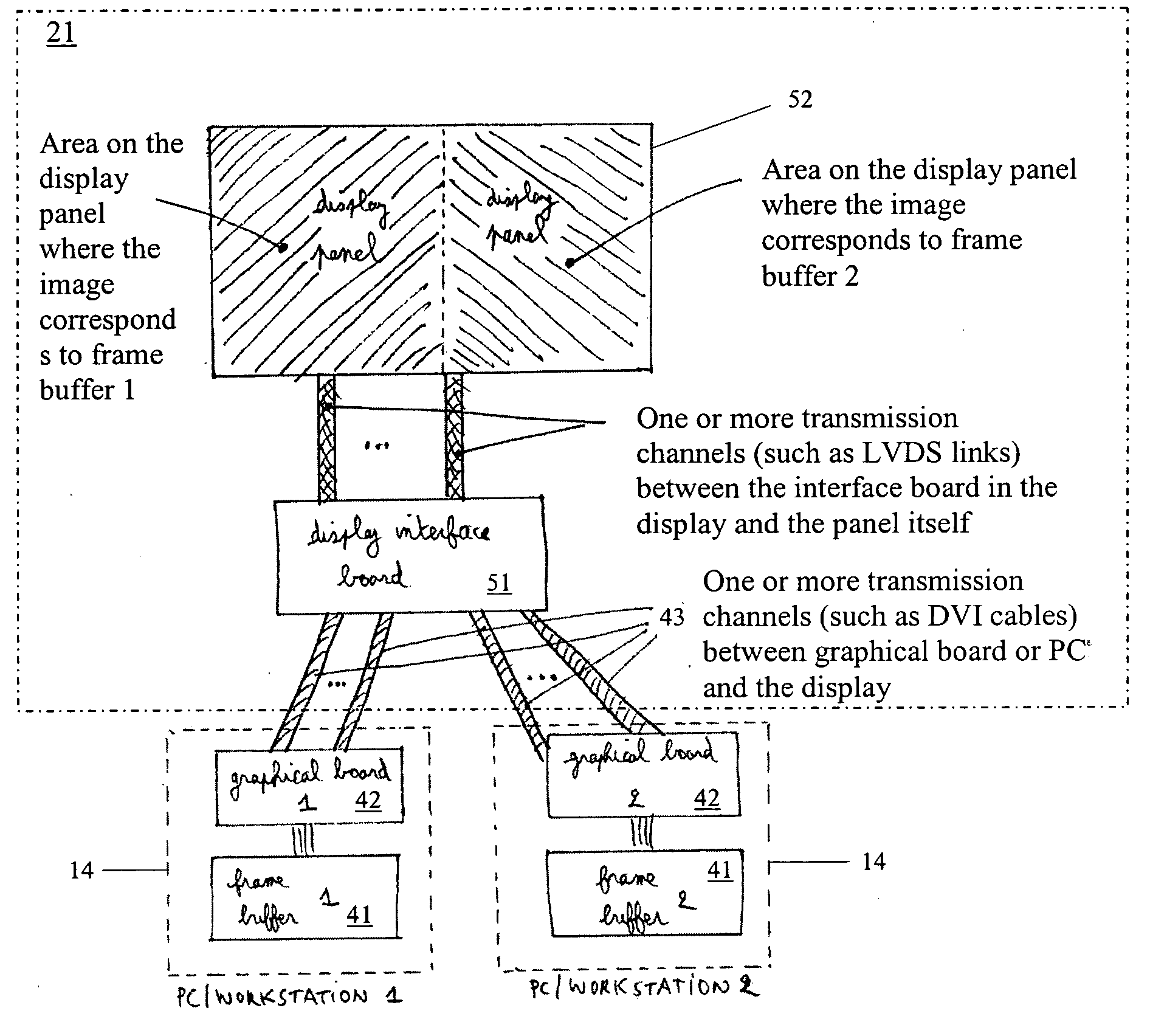
Display system for viewing multiple video signals
InactiveUS20070120763A1Improve the quality of workImprove efficiencyCathode-ray tube indicatorsMedical imagesSignal onComputer graphics (images)
The present invention provides a method and device for displaying a plurality of video signals on one single display. According to embodiments of the present invention a plurality of display systems can be replaced by one display system being fully backwards compatible without the need to change any software or hardware components such as application software, graphical boards, . . . The present invention can also guarantee that even though a plurality of displays are being replaced by one single display still individual characteristics of those plurality of displays are being retained by the new display.
Owner:BARCO NV
Method for selecting an operating mode for a frame-based communications network
ActiveUS6888844B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelEnergy efficient ICTFrame basedSignal on
A method for selecting an operating mode for a frame-based communications network consisting of a plurality of stations attached to a transmission medium. The plurality of stations include both a first type station and a second type station. The first type station is capable of transmitting and receiving first protocol frames in accordance with a first protocol. The second type station is capable of transmitting and receiving both first protocol frames and second protocol frames in accordance with a second protocol. The first protocol and the second protocol each use different signals on the transmission medium. The first type station is not capable of reliably detecting second protocol frames. The first protocol has a first protocol frame format containing at least two reserved bits in a first protocol frame header which are ignored in received frames by first type stations and always sent with a same fixed value by first type stations. The first protocol frame format is redefined to provide an updated first protocol frame header wherein two reserved bits in the first protocol frame header are allocated as a mode selection indicator field in the updated first protocol frame header. The mode selection indicator field has meaning for second type stations.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Automatic charging apparatus of autonomous mobile robot and automatic charging method using the same
InactiveUS20080174268A1Improve convenienceBatteries circuit arrangementsSuction cleanersMicrocomputerElectricity
Disclosed are an automatic charging apparatus of an autonomous mobile robot and an automatic charging method using the same in that a moving robot can automatically detect infrared signals emitted from a charging station and can automatically induce charging station so as to automatically charge a battery of the robot, whereby improving convenience thereof. The automatic charging apparatus of the autonomous mobile robot, comprises a charging station having connecting terminals for charging the battery and an infrared signal generator for emitting infrared signals on a position information thereof; and a moving robot having an infrared receiving apparatus for receiving the infrared signals from the infrared signal generator in a cast that a remnant capacity of the battery is insufficient or a charging order is inputted, a microcomputer for controlling a traveling of the moving robot by using a detected position information of the charging station through the infrared signals received from the infrared receiving apparatus, and charging terminals for charging the battery with electricity through the contact with the connecting terminal.
Owner:YUJIN ROBOT
Wireless broadcast link to remote receiver
InactiveUS6256303B1Increase rangeImprove noise qualityTelevision system detailsFrequency-division multiplex detailsSignal onCarrier signal
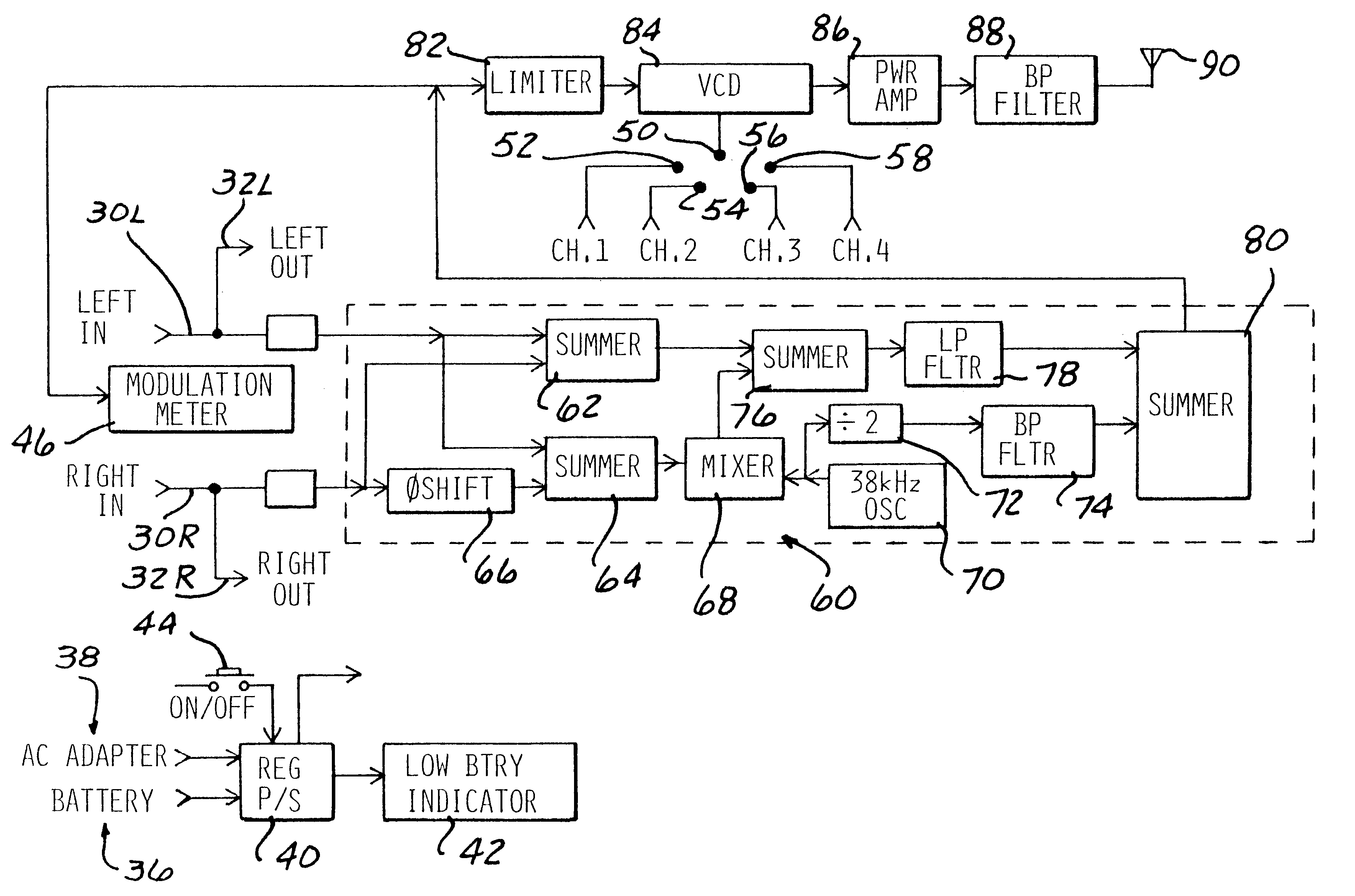
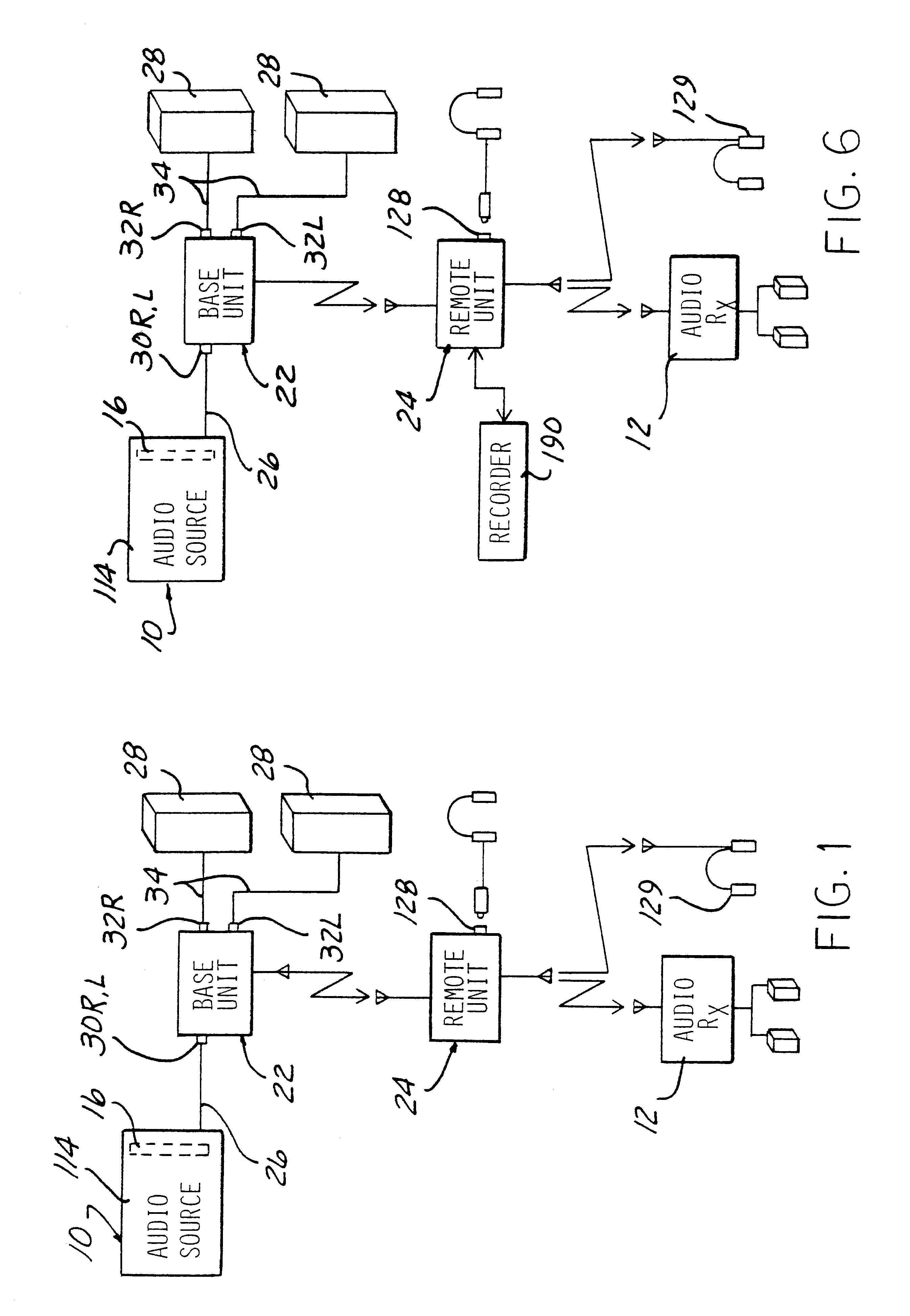
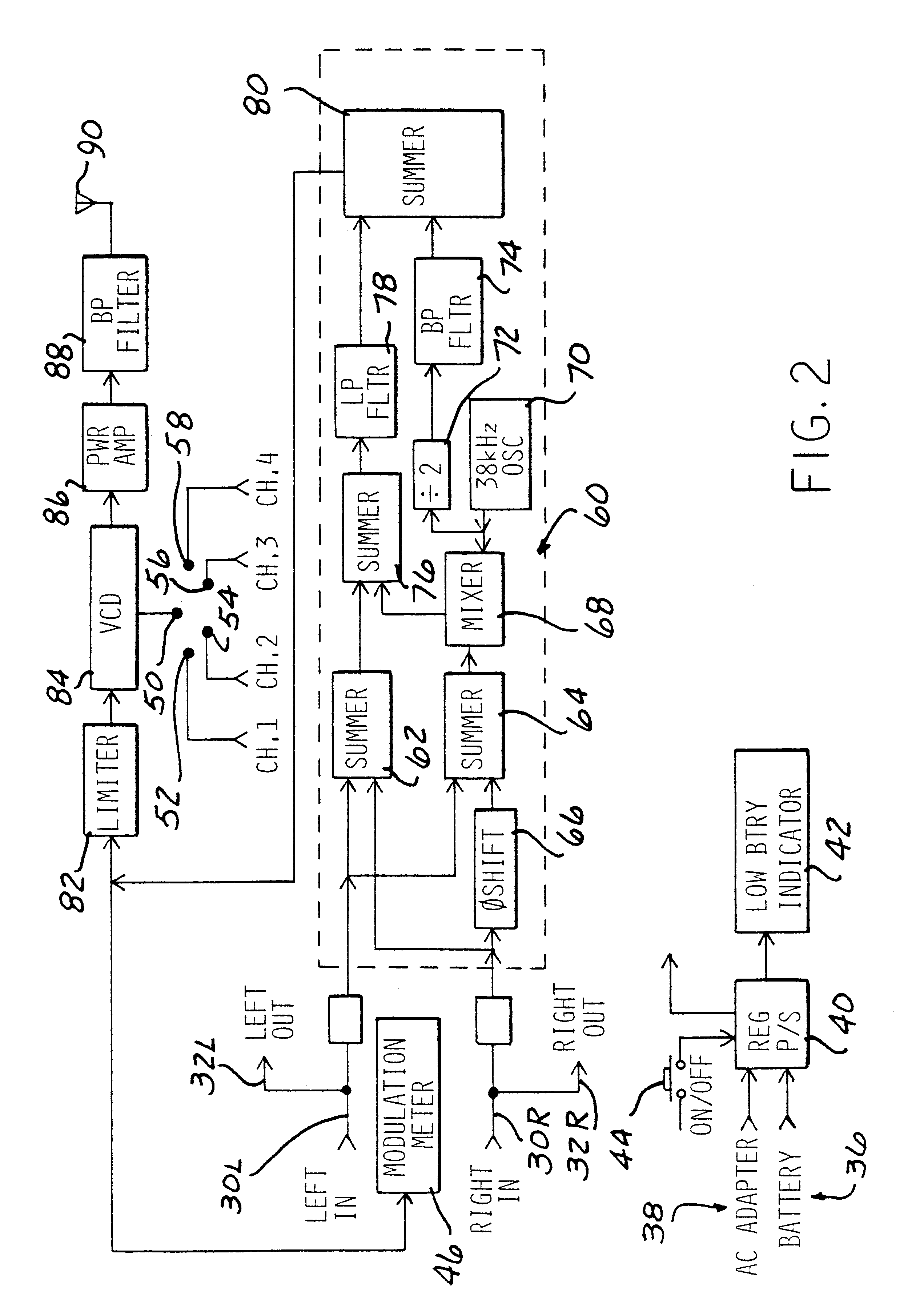
A high frequency signal transmission apparatus includes a transmitter for transmitting received signals from a signal source as a modulated signal on a high frequency 900 MHz carrier to a remote receiver. The remote receiver converts the high frequency carrier in at least one conversion step to a lower frequency carrier signal. The lower frequency carrier signal carrying the modulated signal is then converted to another carrier signal and retransmitted as a modulated second signal to another remote receiver capable of demodulating the signal and broadcasting the audio sounds or video images. The oscillators in the transmitter and receiver are selectable to operate at discrete frequencies. Automatic fine tuning control is provided in the receiver to accommodate drift of the oscillator in the receiver. A recorder is coupled to the receiver for temporarily storing a demodulated first signal from the transmitter and then outputting the stored signals to a second transmitter for retransmission to a remote output device.
Owner:CONCERT TECH
Touch-sensitive interface and method using orthogonal signaling
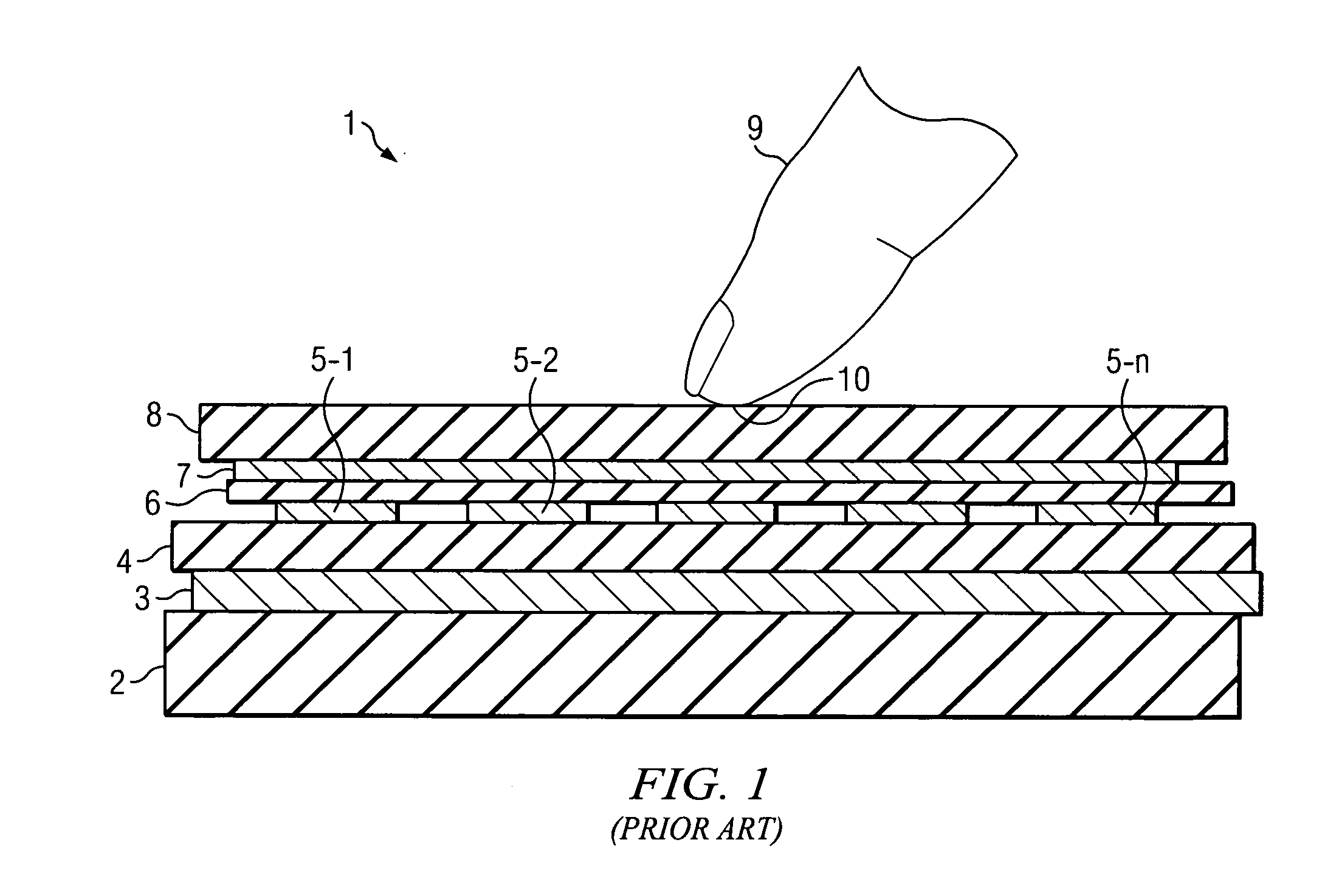
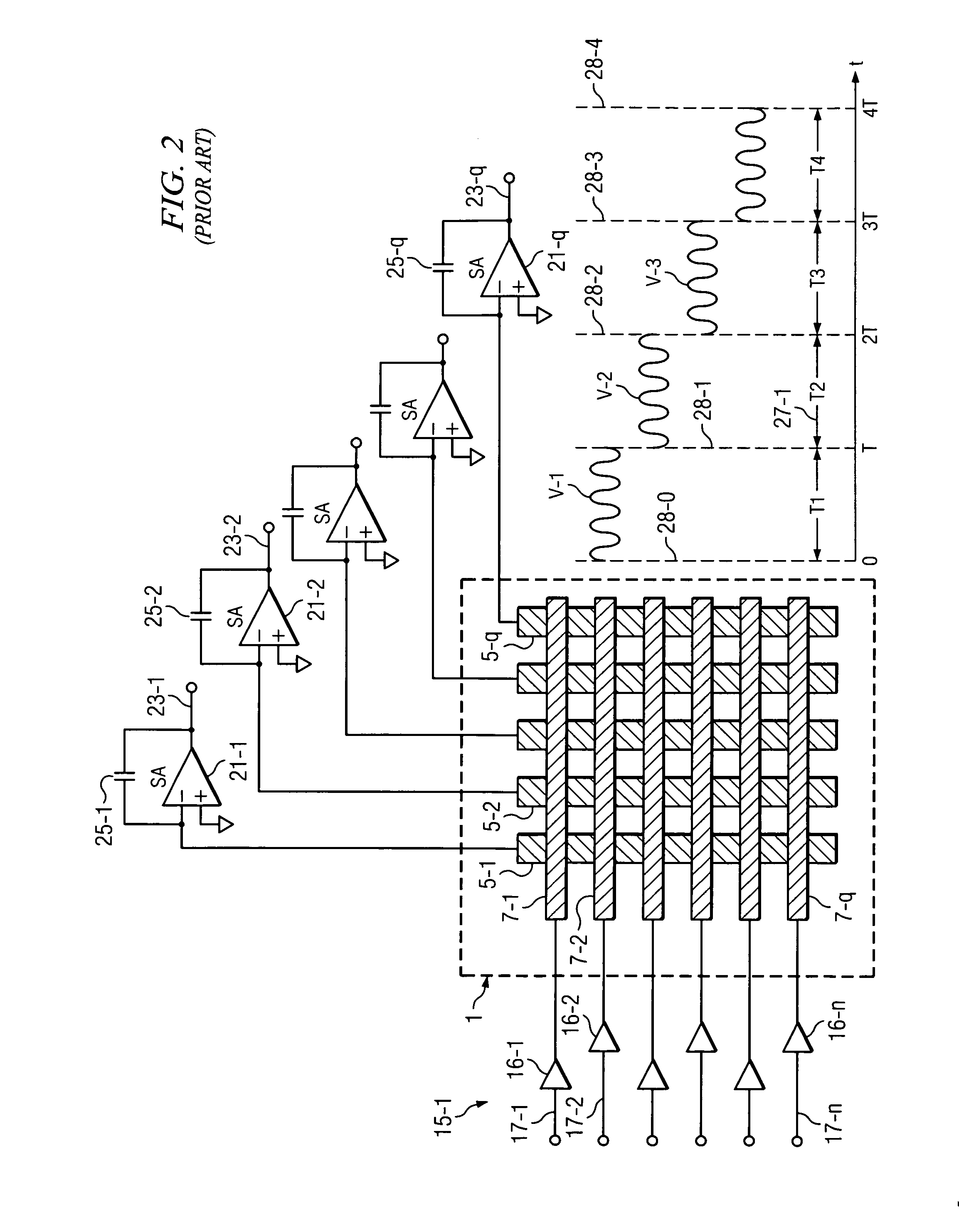
InactiveUS20120056841A1Improve touch sensitivityScan rate can be decreasedCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
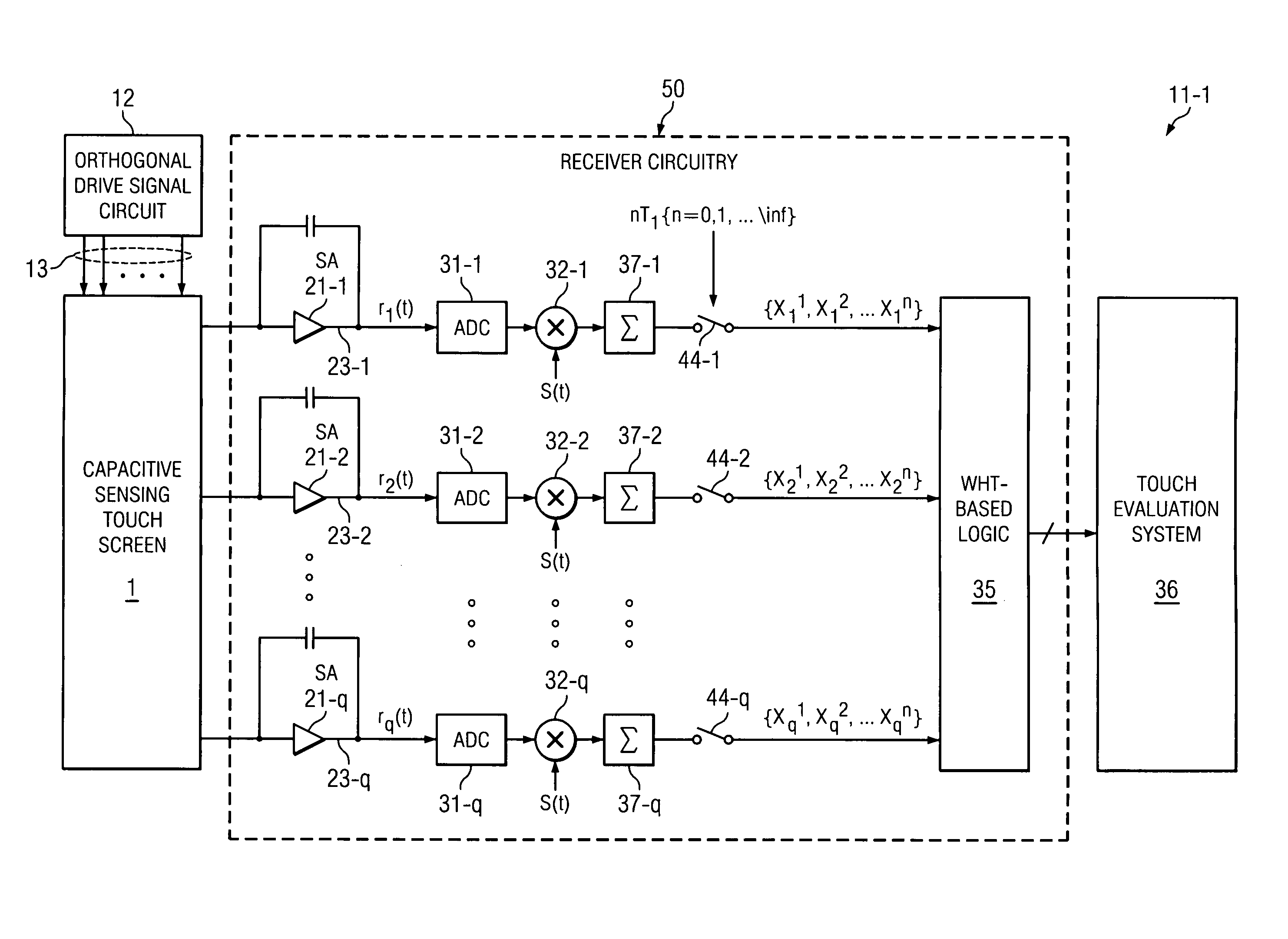
A touch screen system includes a capacitive touch screen (1) including a plurality of row conductors (7-1,2 . . . n) and a column conductor (5-1). A plurality of cotemporaneous orthogonal excitation signals (S1(t), S2(t) . . . Sn(t)) are simultaneously driven onto the row conductors, respectively. The capacitively coupled signals on the column conductor may be influenced by a touch (10) on the capacitive touch screen. Receiver circuitry (50) includes a sense amplifier (21-1) coupled to generate an amplifier output signal (r1(t)) in response to signals capacitively coupled onto the column conductor. WHT-based circuitry (35) determines amounts of signal contribution capacitively coupled by each of the excitation signals, respectively, to the amplifier output signal.
Owner:INTEL CORP
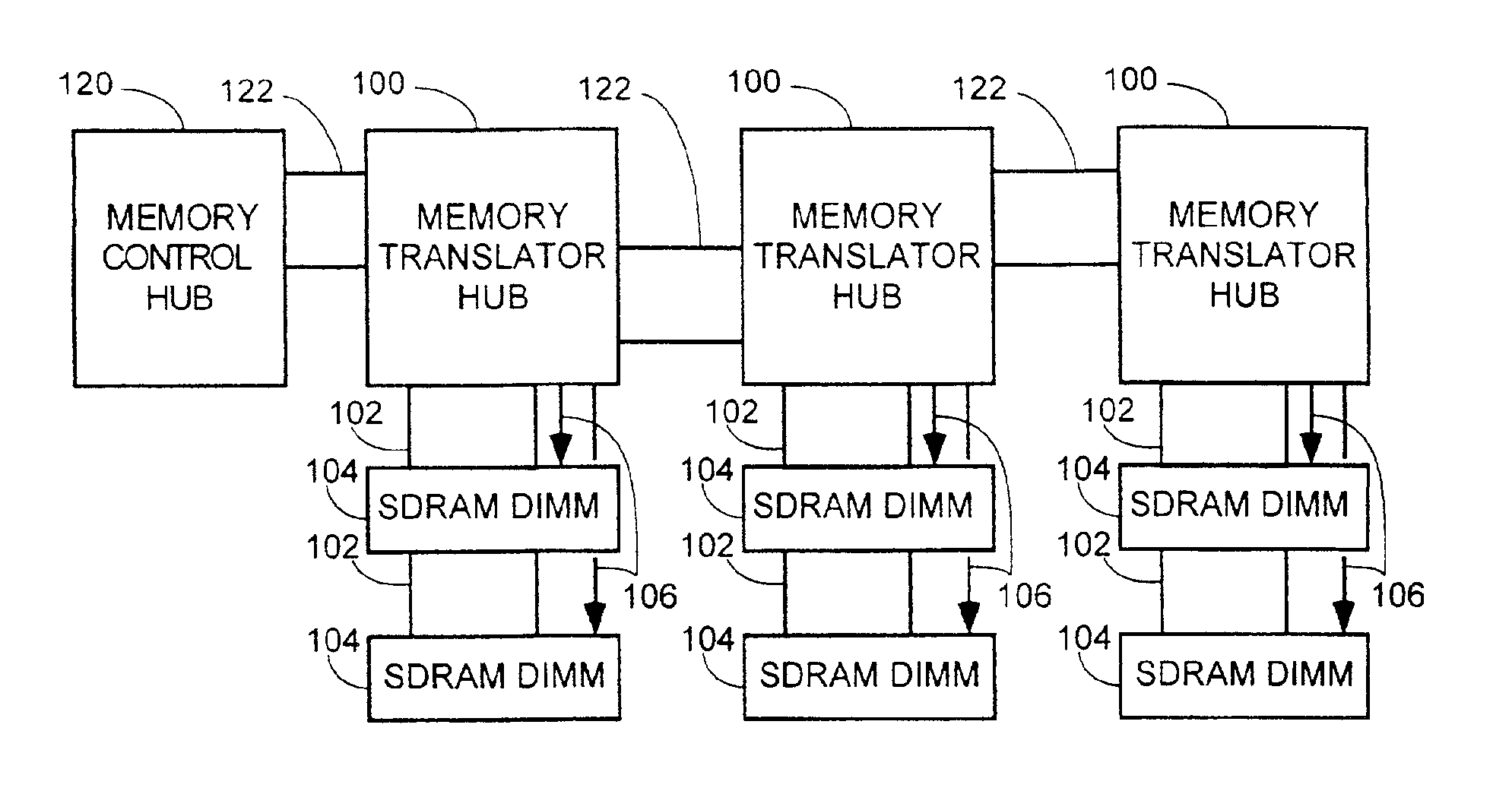
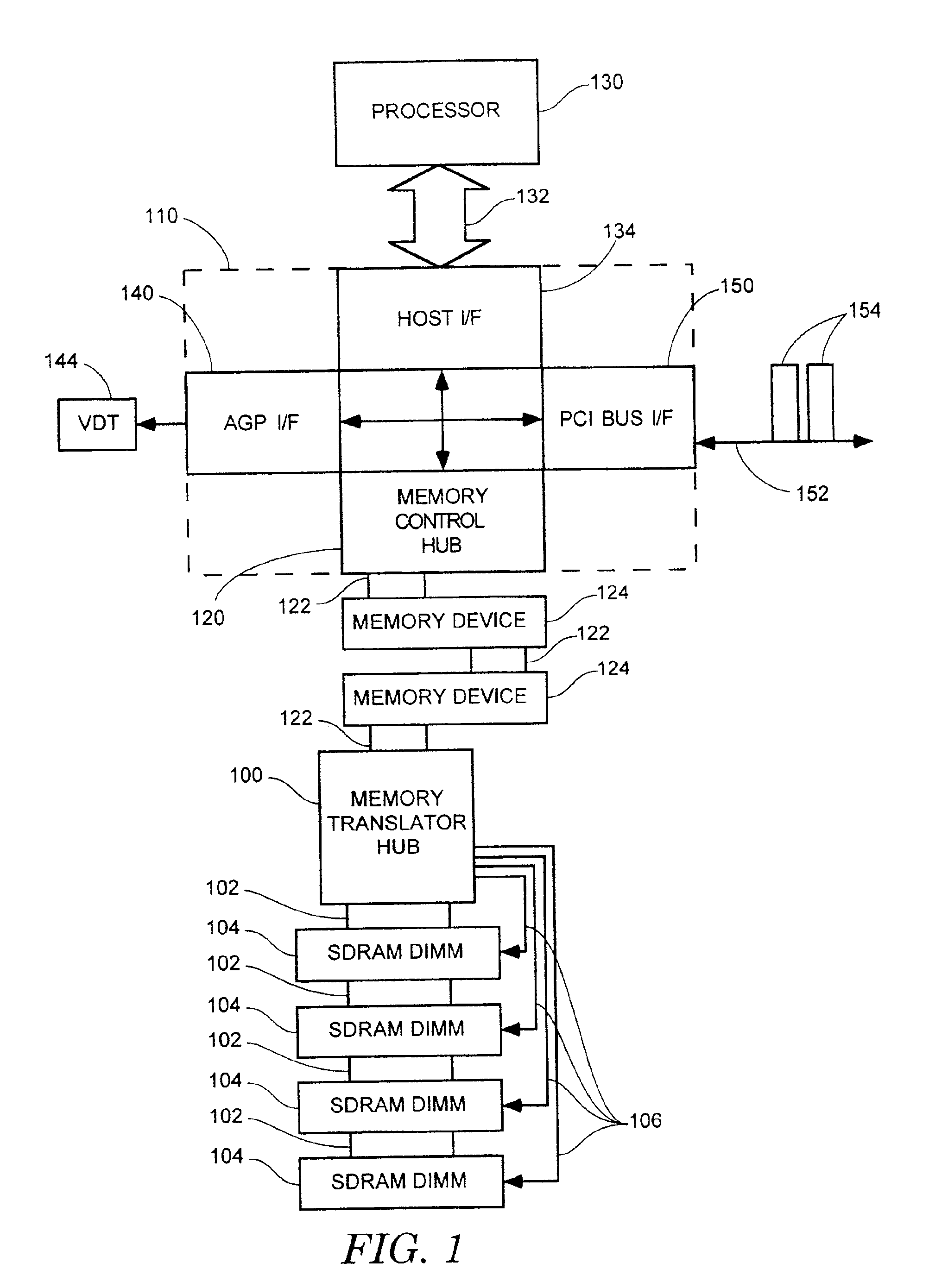
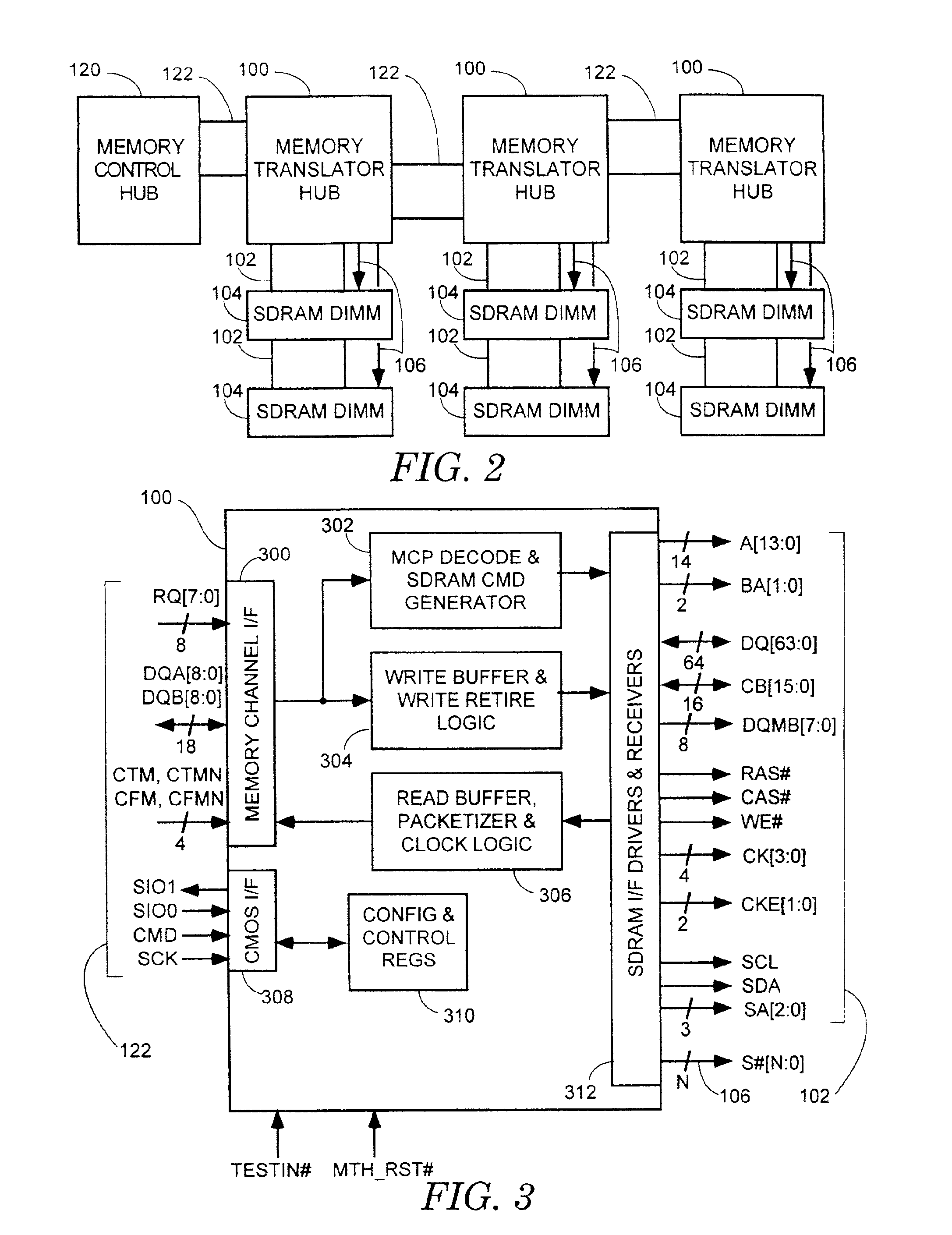
Method and apparatus for supporting SDRAM memory
A memory translation hub comprising a memory channel interface, a memory bus interface, and a command generator coupled to the memory channel interface and to the memory bus interface. The memory channel interface receives a memory control packet from a memory channel. The memory bus interface provides a memory bus. The command generator causes the memory bus interface to provide memory control signals on the memory bus responsive to the memory control packet.
Owner:INTEL CORP
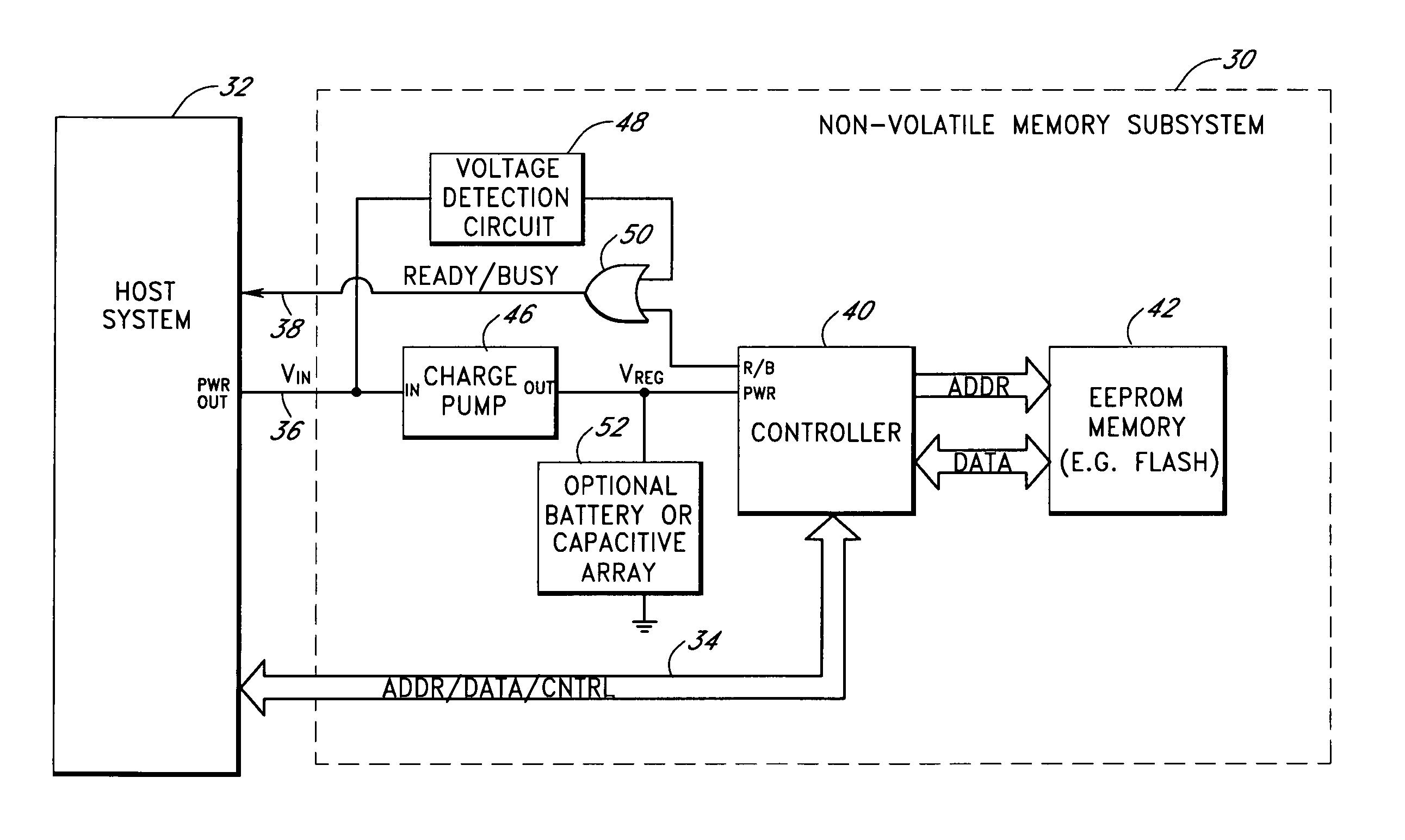
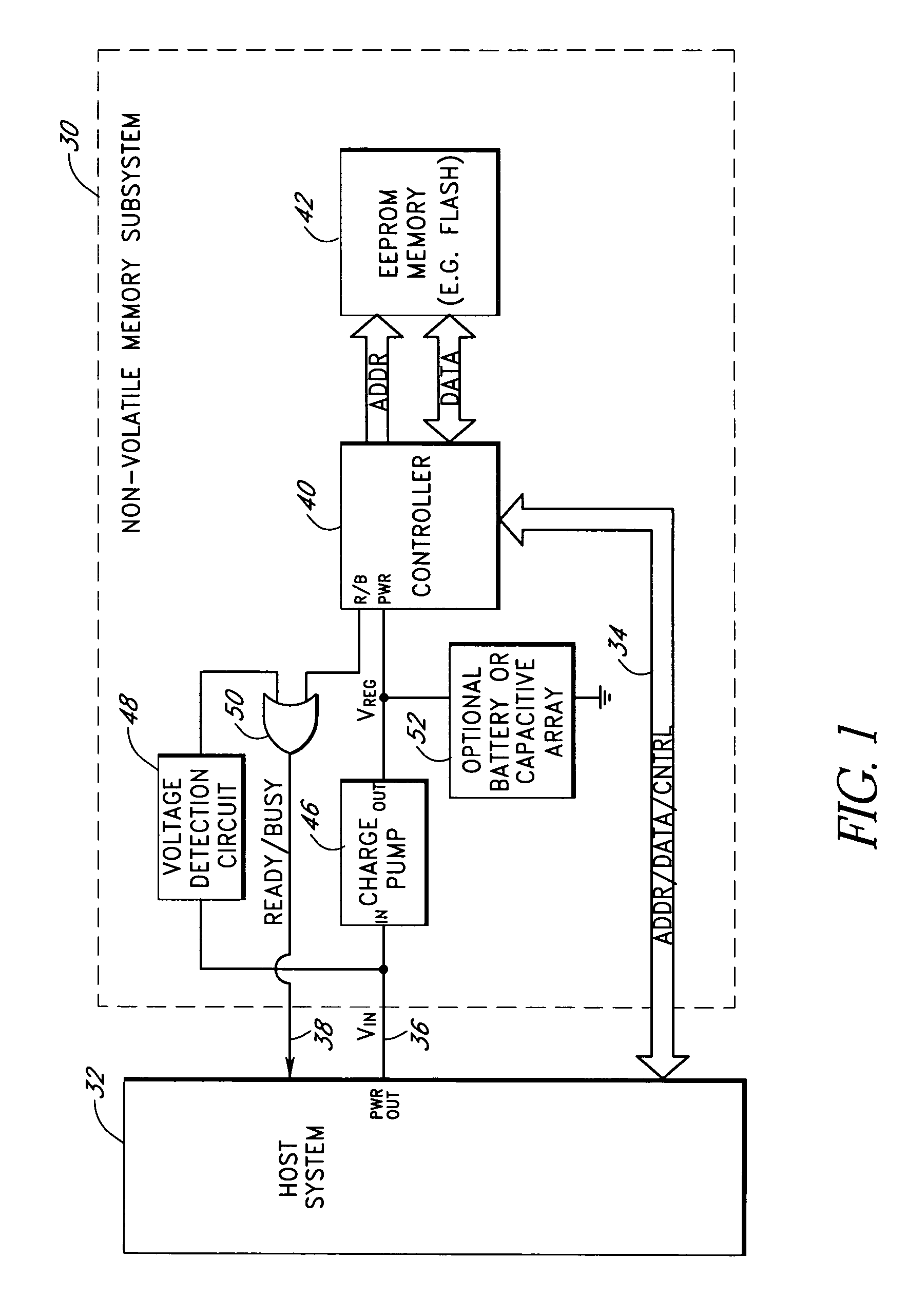
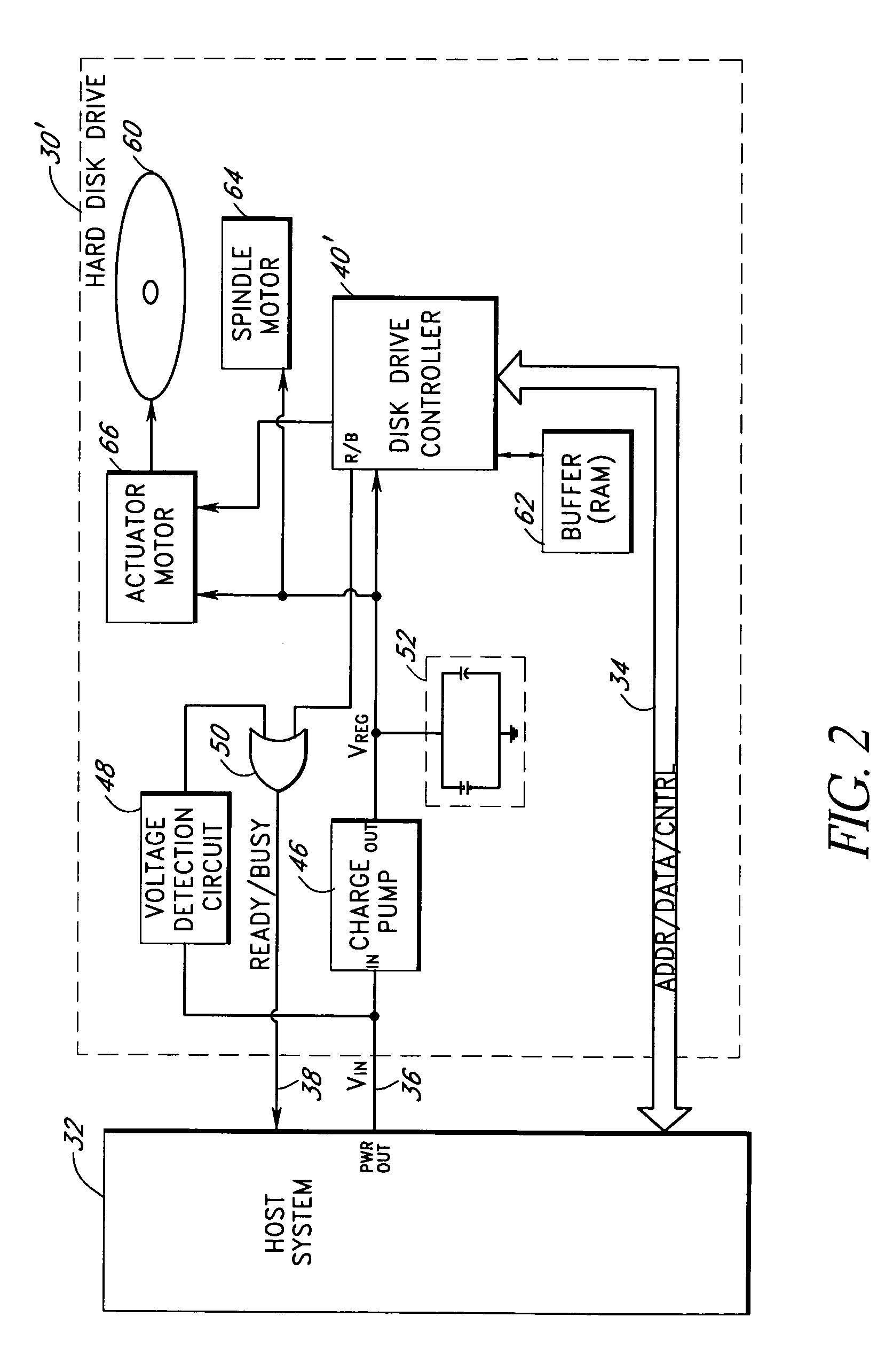
Storage subsystem with embedded circuit for protecting against anomalies in power signal from host
A storage subsystem, such as a flash memory card, includes a voltage detection circuit that monitors the power signal from a host system to detect anomalies. The voltage detection circuit responds to a power signal anomaly by asserting a signal, such as a busy signal on a standard ready / busy signal line, to block the host system from performing write operations to the storage subsystem during presence of the anomaly. The storage system may also include a backup power source, such as a charge pump circuit, a capacitive array, and / or a rechargeable battery, that provides power to a controller of the storage subsystem during the presence of the anomaly, such that the storage system can complete outstanding operations.
Owner:INNOVATIVE MEMORY SYST INC
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20060051122A1Improve detection accuracyDc-dc conversionElectric light circuit arrangementTemperature controlElectricity
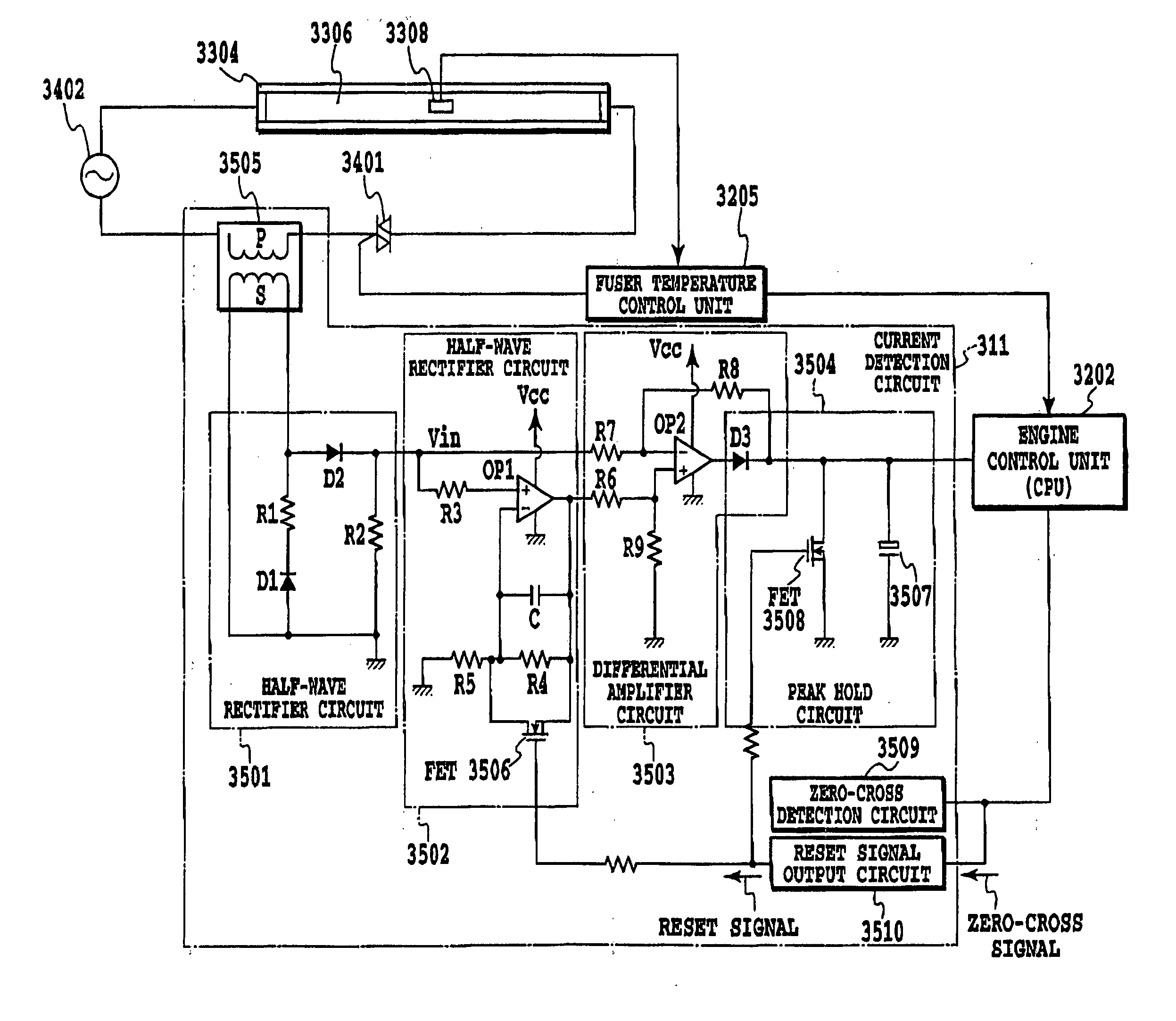
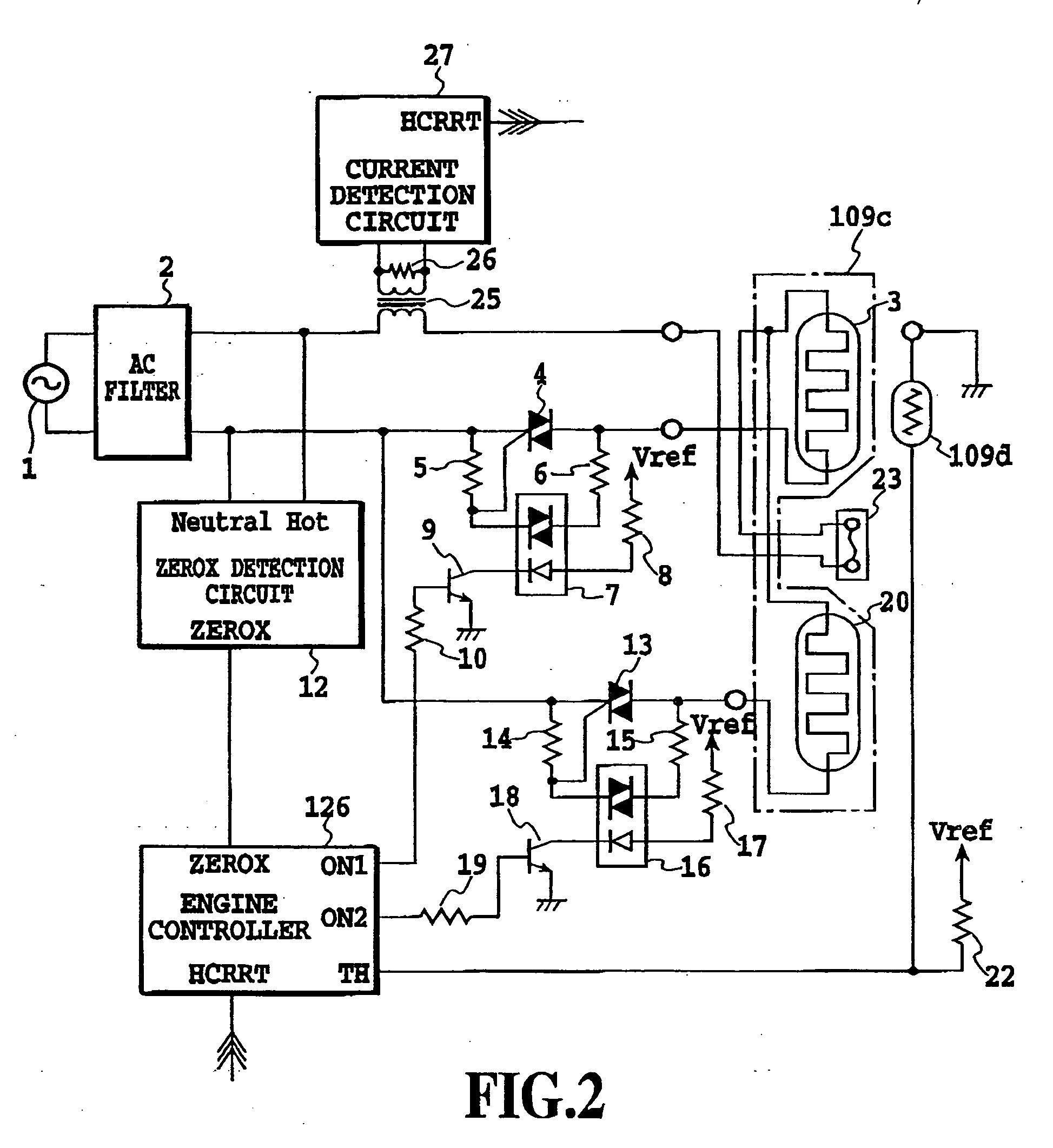
This invention is intended to control the amount of power to be supplied to a fusing heater below a maximum applicable current value. The engine controller supplies electricity to both of two heating bodies at the same fixed duty D1. At a phase angle α1 corresponding to the fixed duty D1, pulse signals ON1 and ON2 are issued in response to a ZEROX signal as a trigger. A current value I1 is detected based on a HCRRT signal from the current detection circuit. The engine controller calculates an upper limit of applicable power duty Dlimit based on the detected current value I1, the fixed duty D1 and the preset applicable current value Ilimit. Then, a PI temperature control is performed at a duty below the upper limit duty Dlimit.
Owner:CANON KK
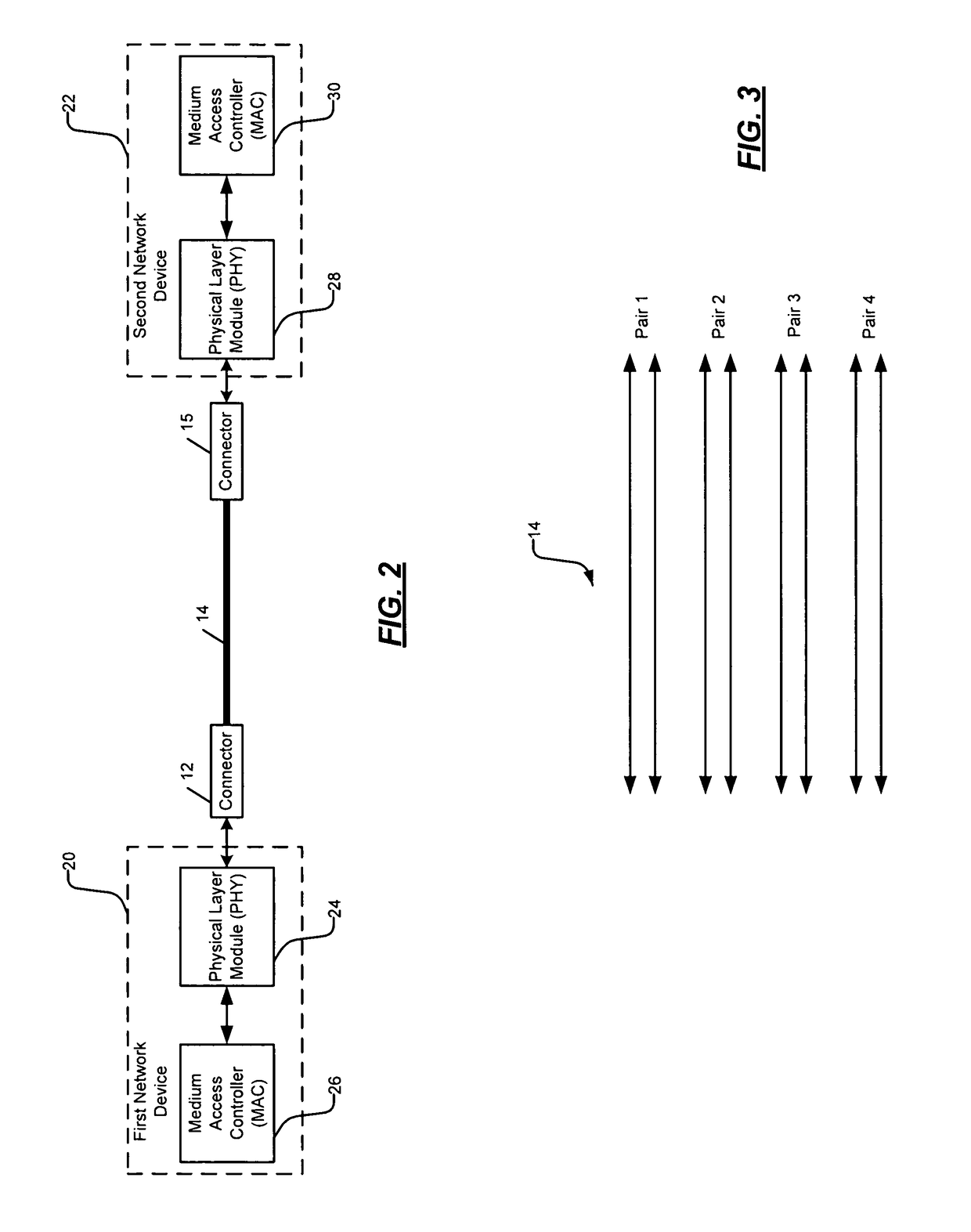
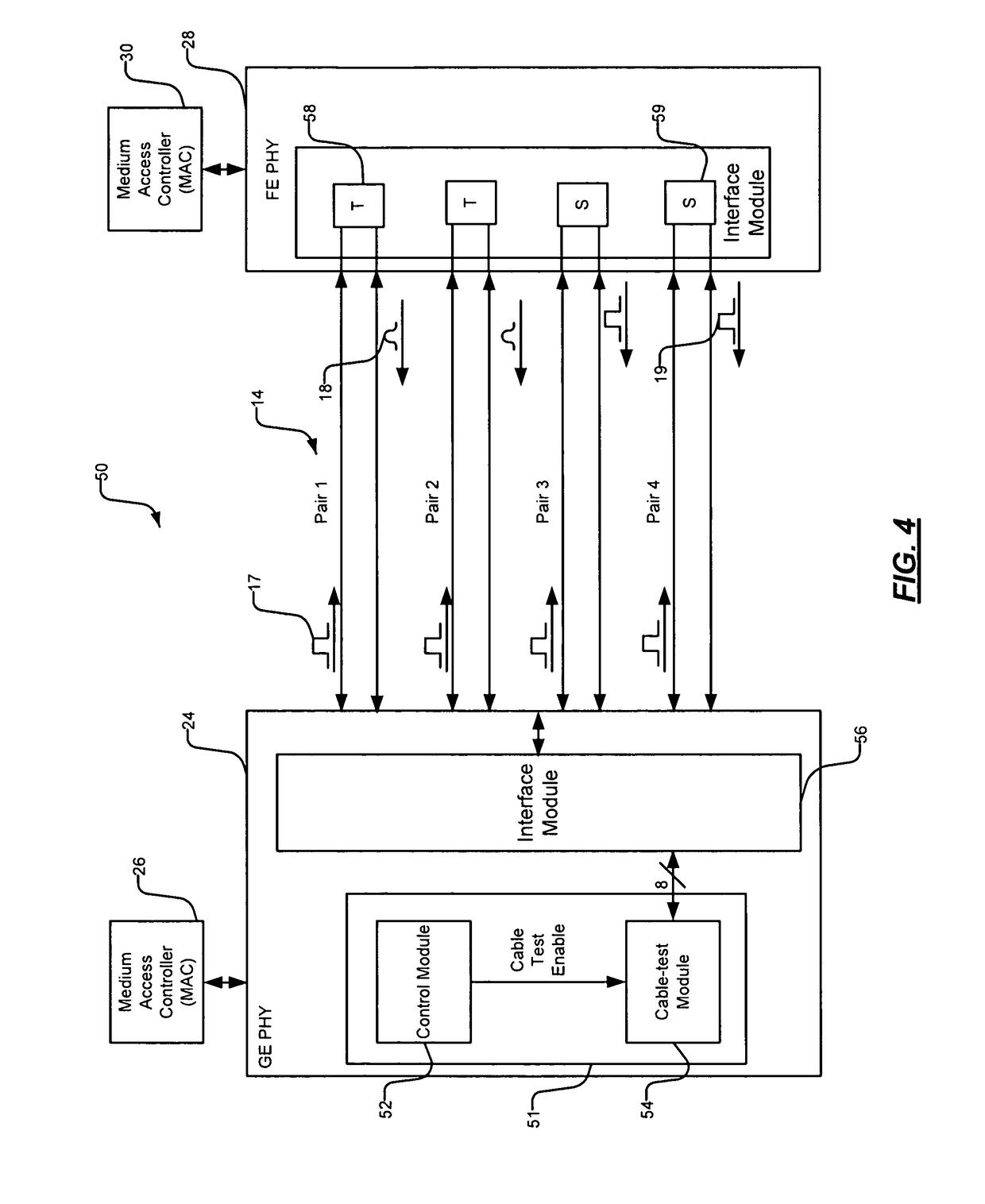
Cable tester
ActiveUS7906973B1Fault location by pulse reflection methodsLine-transmission monitoring/testingSignal onPhysical layer
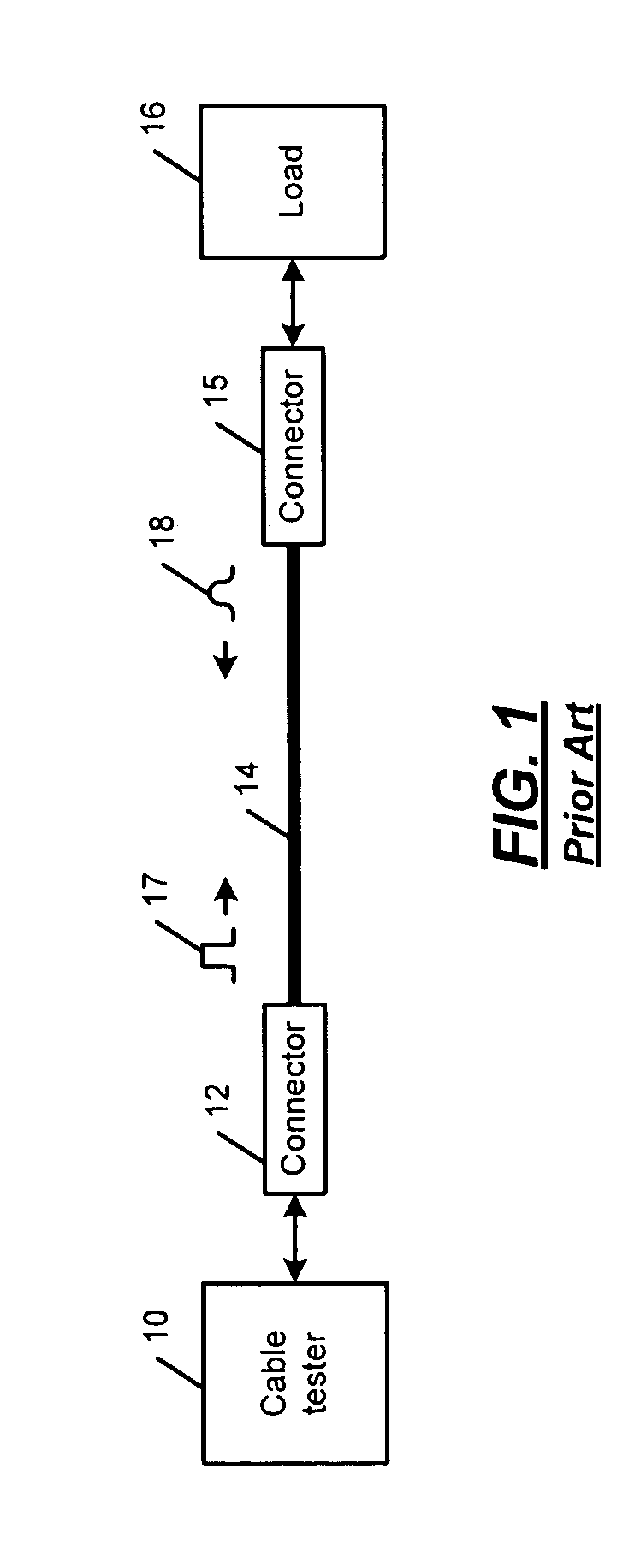
A physical layer module (PHY) of a network device includes a control module and a cable-test module. The control module selectively generates a cable-test enable signal to test a cable including four pairs of twisted wire. The cable-test module tests the cable based on the cable-test enable signal. The cable-test module transmits test signals on the four pairs at a first time and receives return signals. The cable-test module determines that the cable is not faulty when the return signals received on first and second pairs of the four pairs have an amplitude less than a first predetermined amplitude, and when the return signals received on third and fourth pairs of the four pairs have an amplitude greater than a second predetermined amplitude and are received substantially contemporaneously.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Movement disorder stimulation with neural block
InactiveUS20050070970A1Ameliorate disorderReduce adverse effectsInternal electrodesExternal electrodesBlocking nerveSignal on
A method and apparatus for treating patients suffering from involuntary movement disorders (including epilepsy) by stimulating a selected cranial nerve of the patient with an electrical signal applied to induce a signal at brain by applying an electrical signal at the nerve to ameliorate the disorder and by applying a neural conduction block at the nerve selected to at least partially block nerve impulses on said nerve at a blocking site and reduce adverse effects of said signal on an organ.
Owner:RESHAPE LIFESCIENCES INC
Lighting control system and method
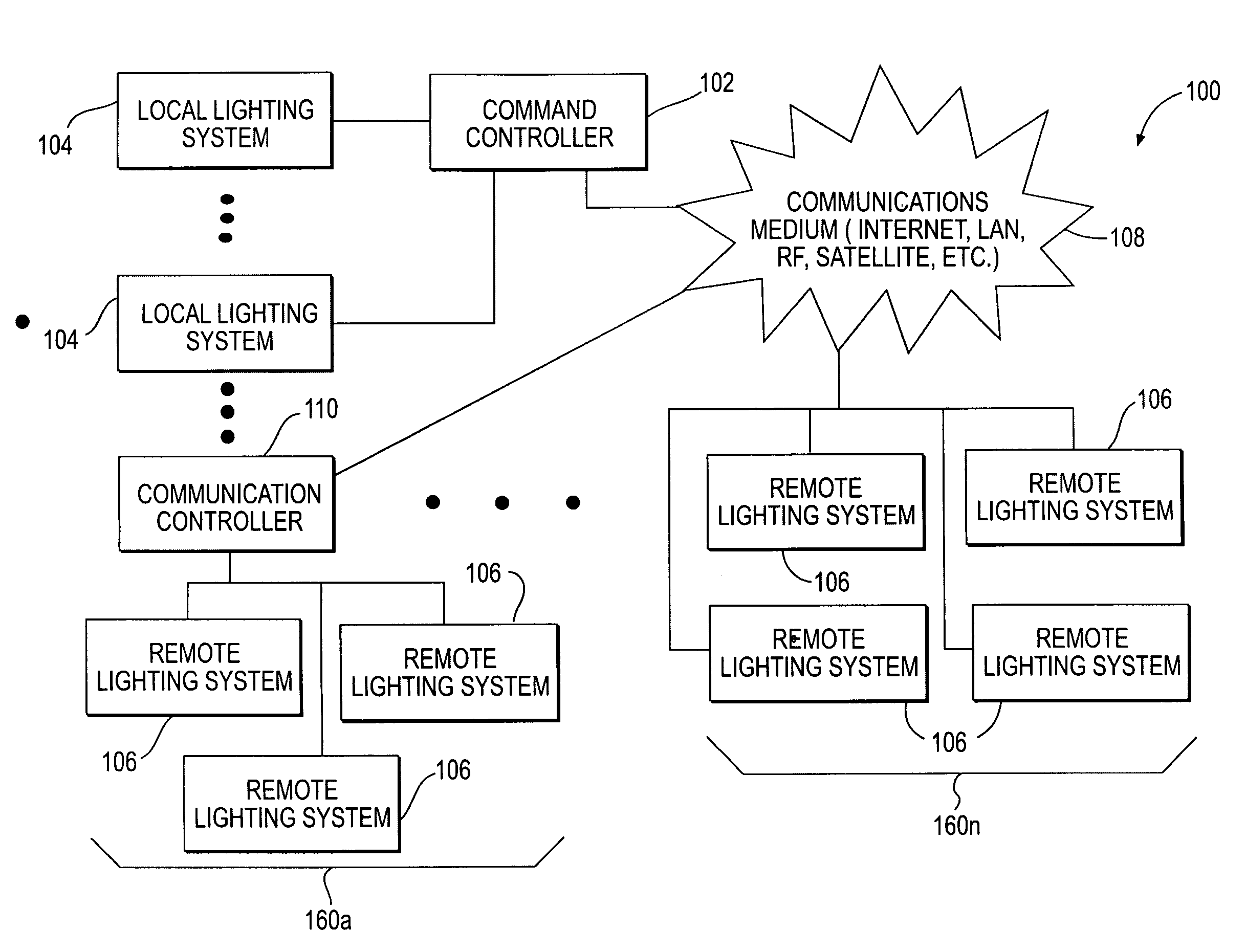
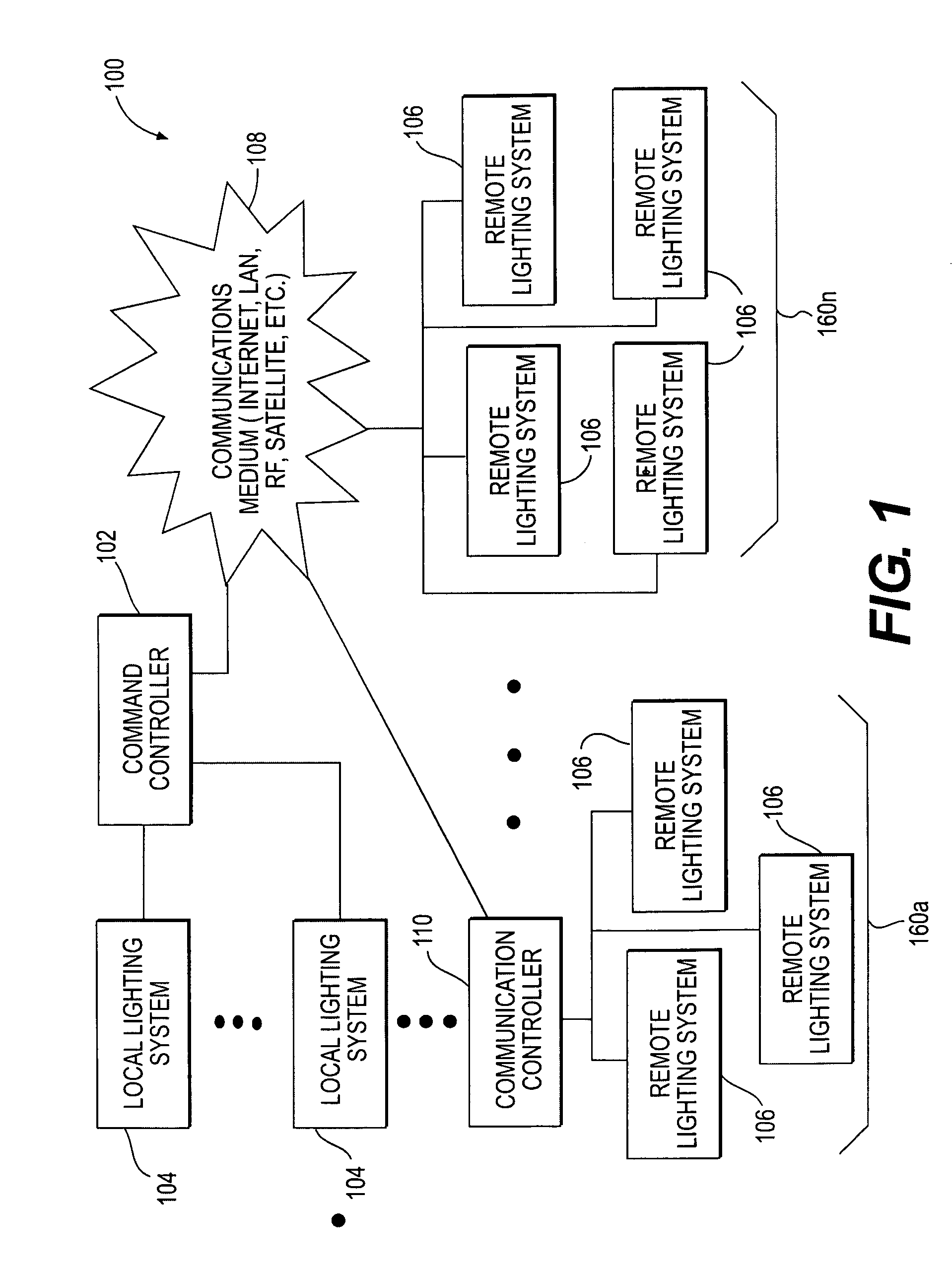
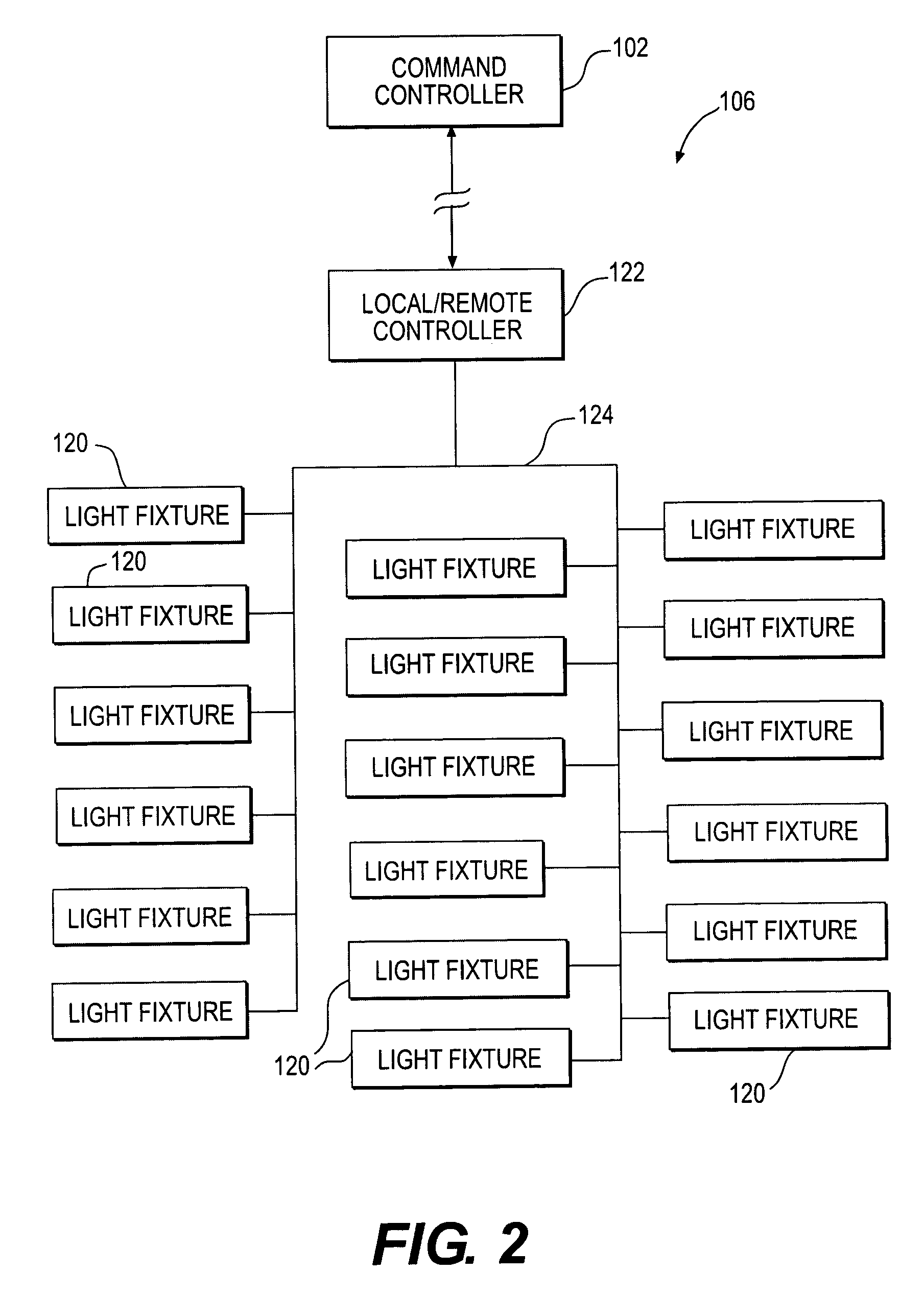
A control system for allowing remote control of a load. The control system includes a command controller for running a control program that provides a command signal. The command controller has a first wireless interface for transmitting the command signal on a first wireless network. A remote controller has a second wireless interface for receiving the command signals from the command controller via the first wireless network. The remote controller includes a controller for adapting the received command signals for communication on a second wireless network. The remote controller has a third wireless interface for transmitting the adapted command signals via a second wireless network to the load.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE LIGHTING LP
System and method for determining reentrant ventricular tachycardia isthmus location and shape for catheter ablation
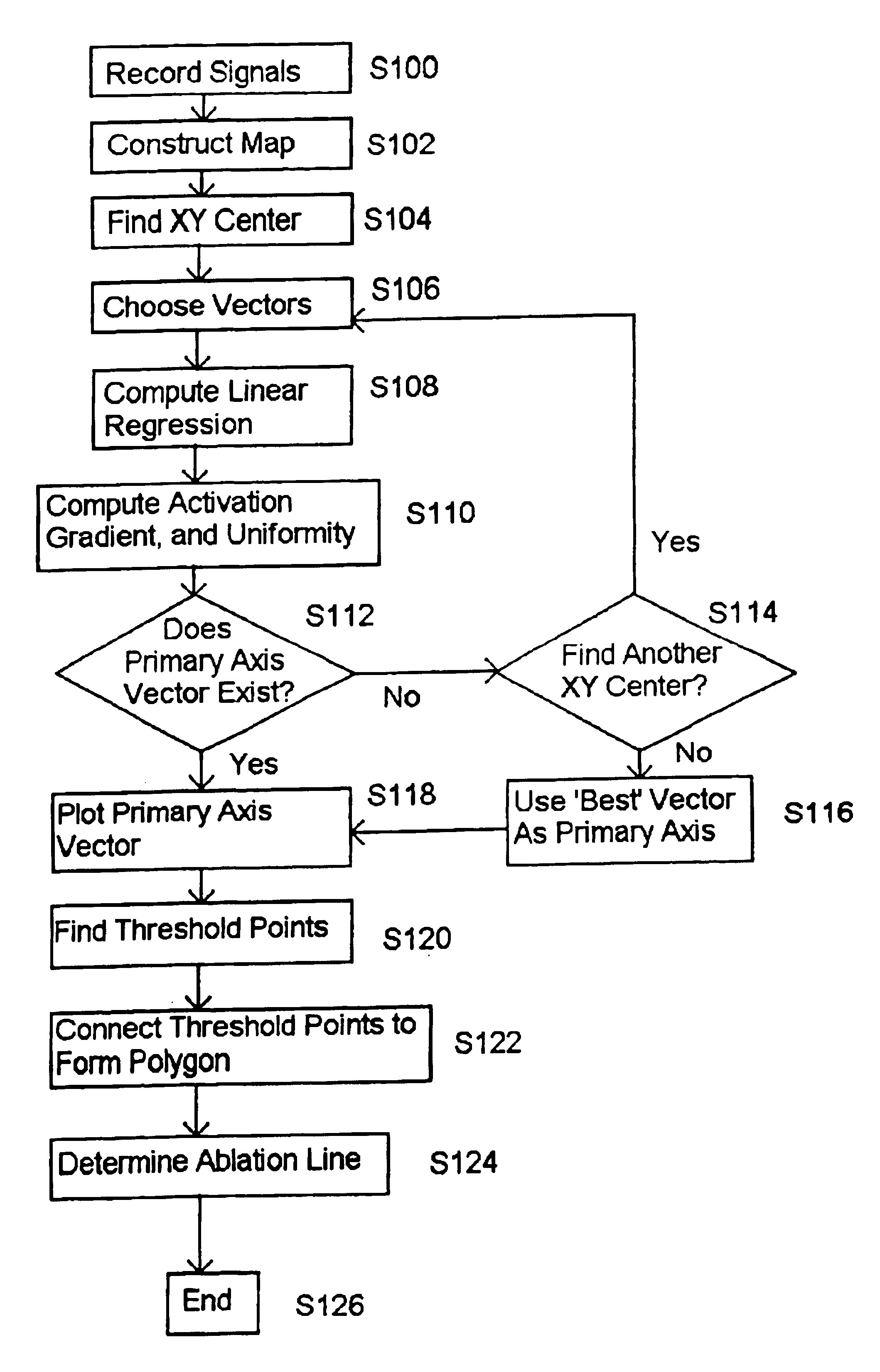
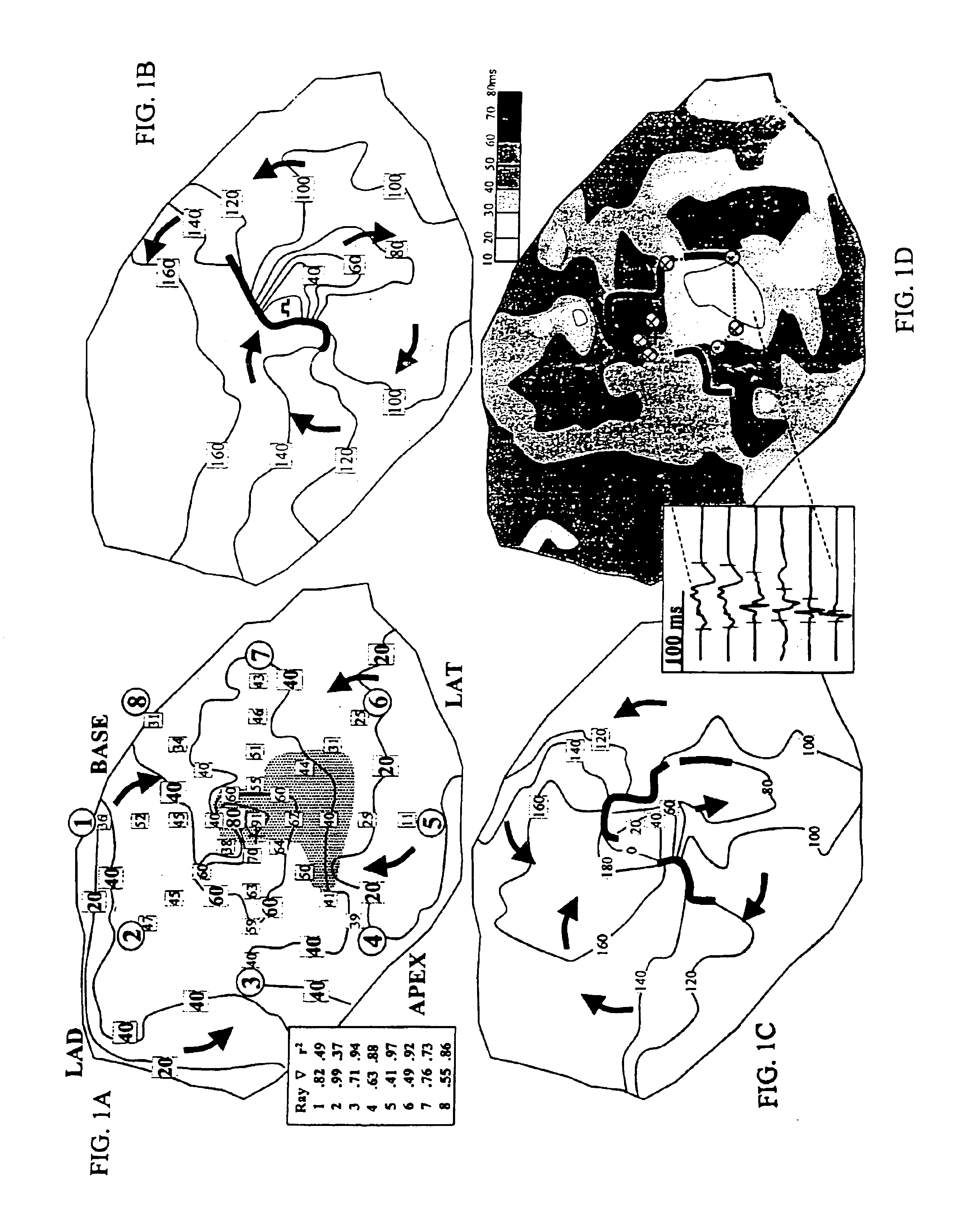
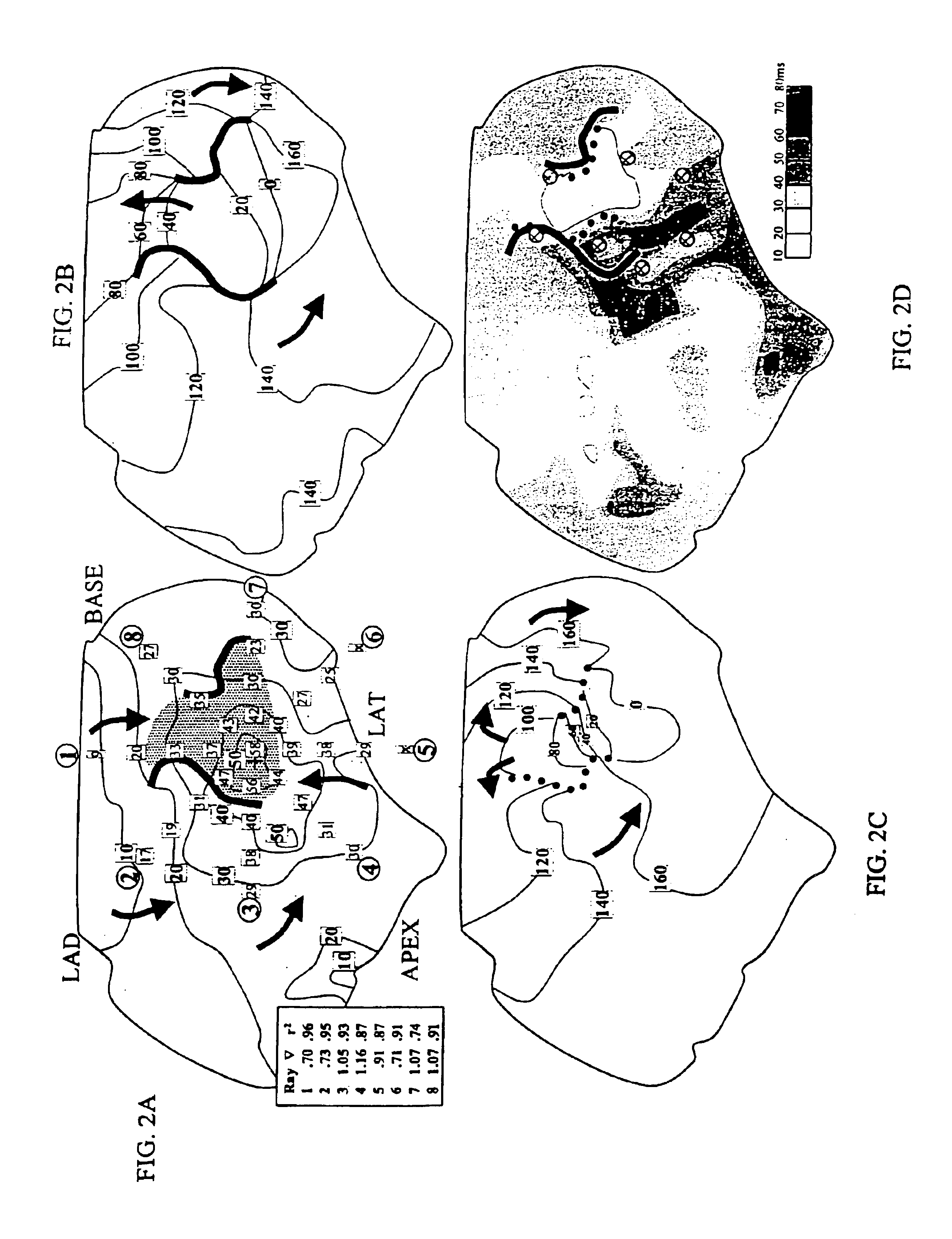
A method for identifying and localizing a reentrant circuit isthmus in a heart of a subject during sinus rhythm, including: a) receiving electrogram signals from the heart during sinus rhythm via electrodes; b) storing the electrogram signals; c) creating a map based on the electrogram signals; d) finding a center reference activation location on the map; e) defining measurement vectors originating from the center reference activation location; f) selecting from the measurement vectors a primary axis vector indicating a location of the reentrant circuit isthmus in the heart; g) finding threshold points of electrogram signals on the map; h) connecting the threshold points to form a polygon indicating a shape of the reentrant circuit isthmus in the heart.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
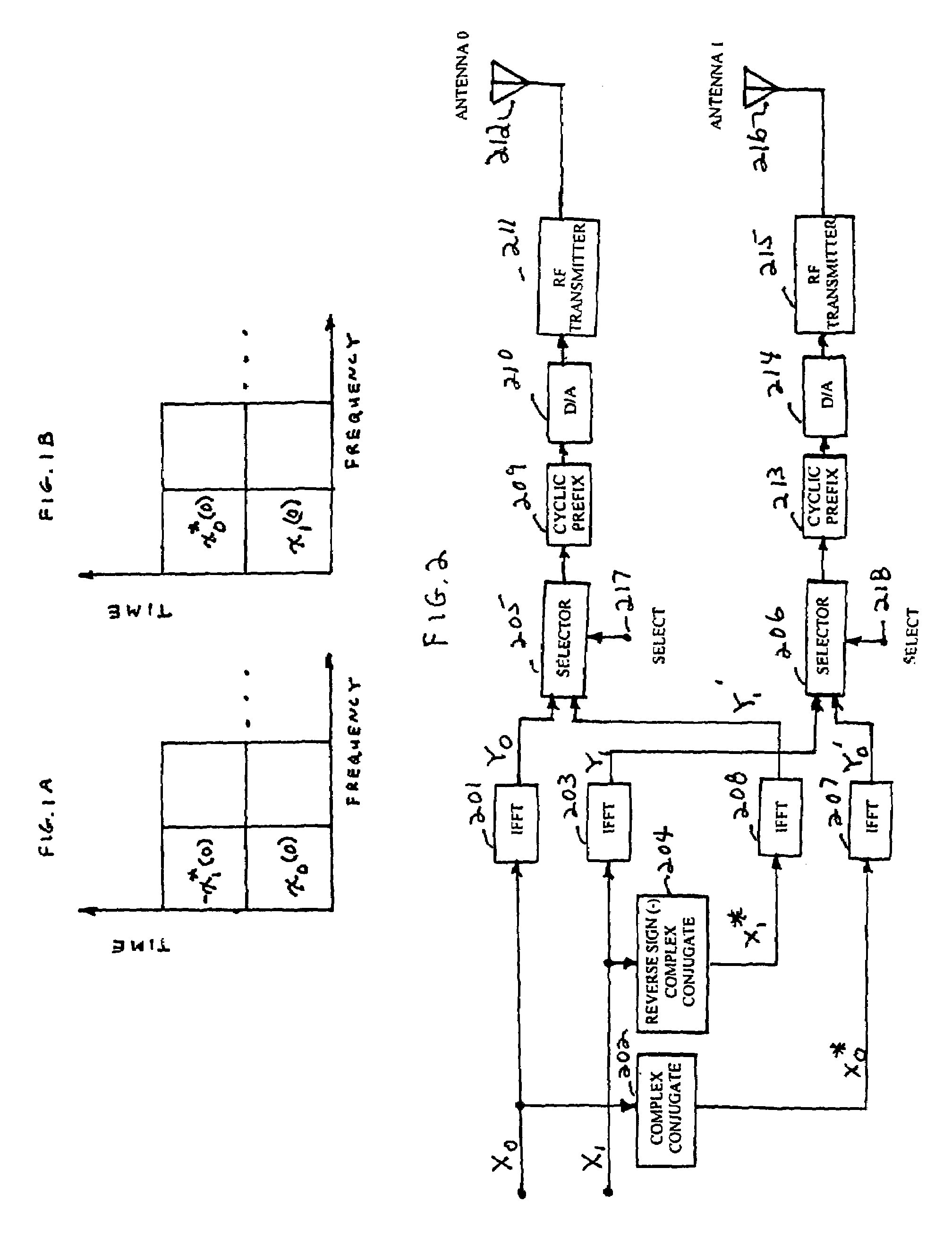
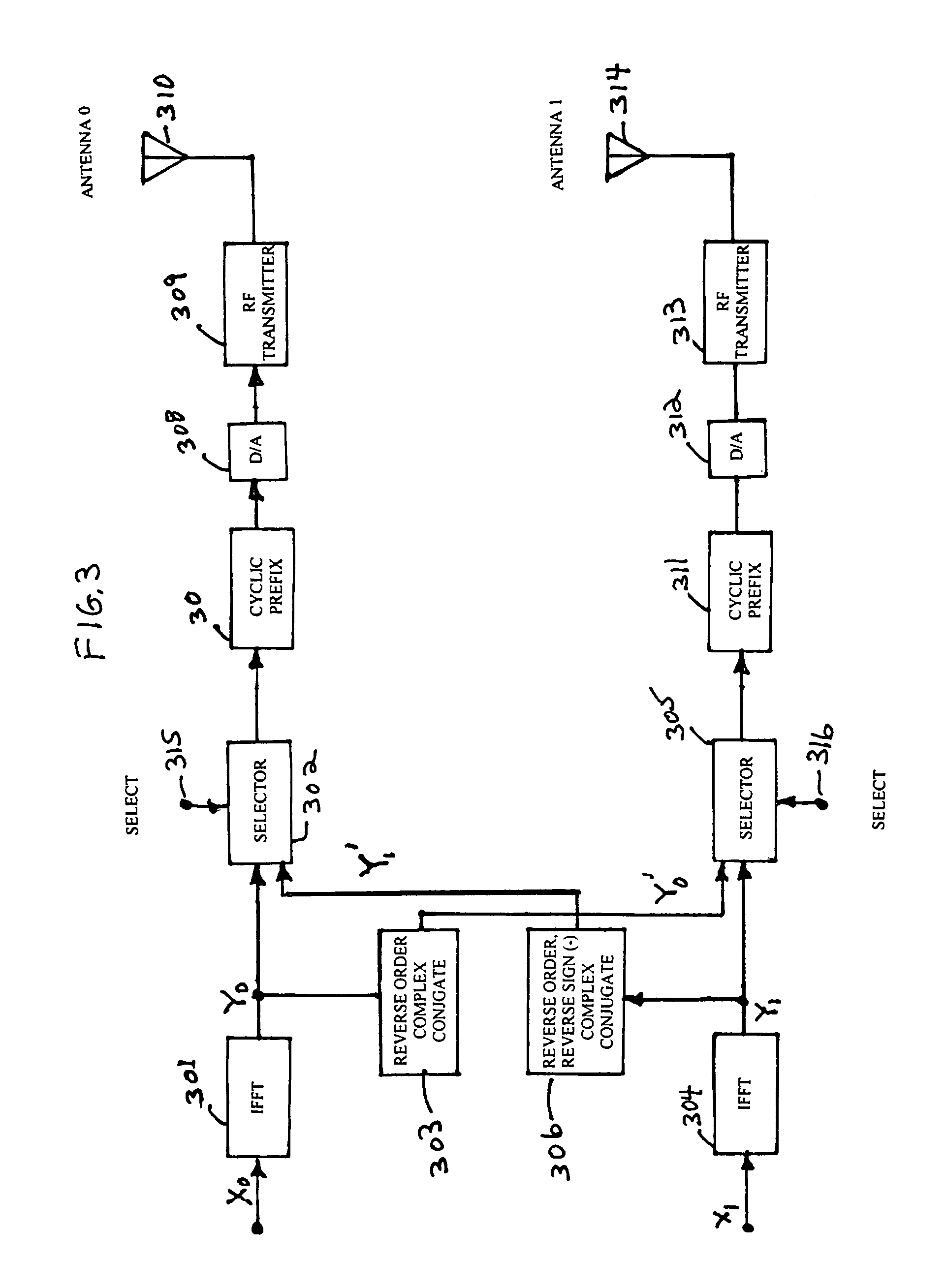
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing transmit diversity system for frequency-selective fading channels
InactiveUS7020072B1Reduce complexityIncrease transmission diversitySpatial transmit diversityFrequency-division multiplexReverse orderSignal on
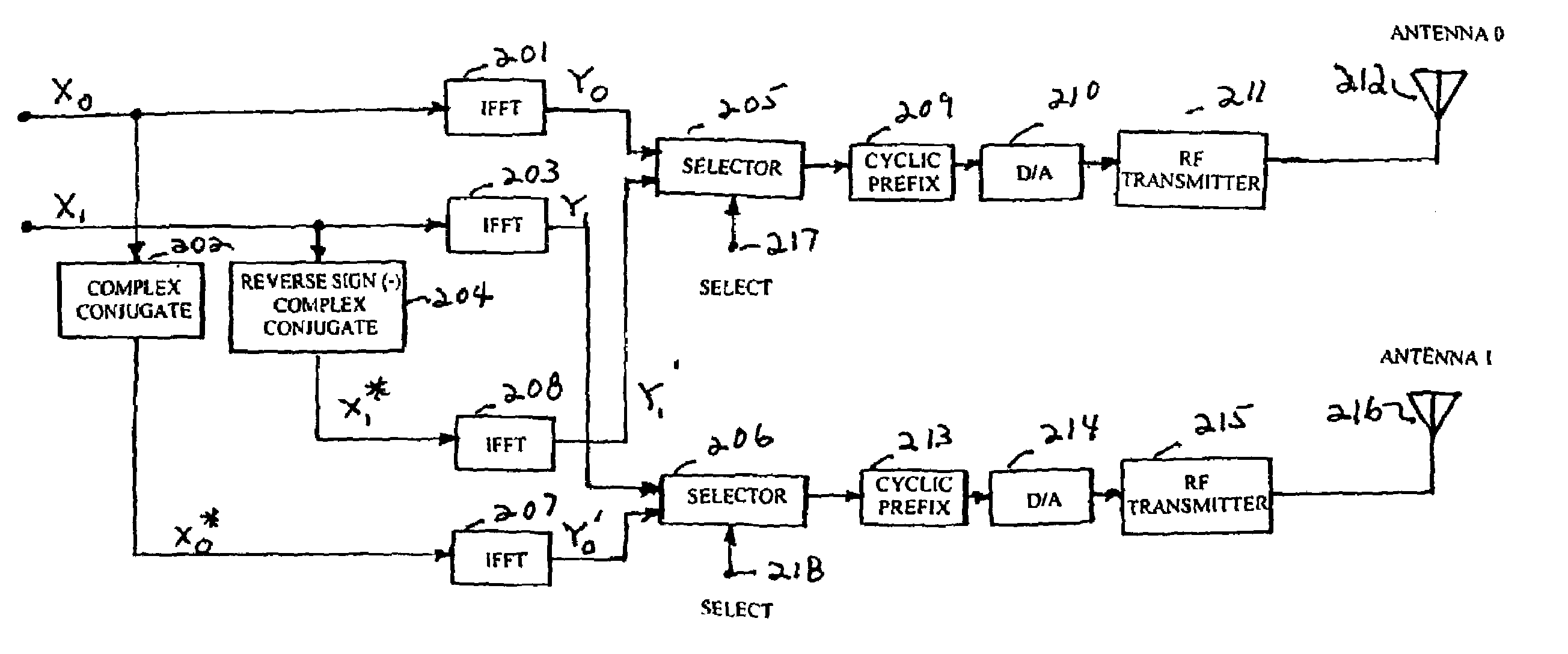
Wireless communications for frequency-selective fading channels is realized by employing a system including orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) in combination with an at least two antenna transmit diversity arrangement. Specifically, OFDM converts a multipath channel into a plurality of narrowband subchannels each having flat fading. Then, the signals on the same frequency subchannels of the at least two antennas are grouped together. Considering a first frequency subchannel, during a first OFDM time interval, a first signal and a second signal are transmitted on the first frequency subchannel from a first antenna (0) and from a second antenna (1), respectively. During a second OFDM time interval, a reverse sign (−) complex conjugate of the second signal and a complex conjugate of the first signal are transmitted from the first antenna and the second antenna, respectively. In a specific embodiment of the invention, reduced complexity in the implementation is realized by a reverse order complex conjugate and a reverse order, reverse sign (−) complex conjugate and judicious selection of the processed data signals in order to transmit the appropriate ones of the signals during the first and second OFDM intervals. Again, if the channel remains constant over the two OFDM intervals, diversity combination is realized for each frequency subchannel. In another embodiment of the invention, antenna-group hopping is employed in conjunction with pairing in time of the OFDM frequency subchannel signals to realize increased transmit diversity without rate loss.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com