Patents
Literature
2303 results about "Surface wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
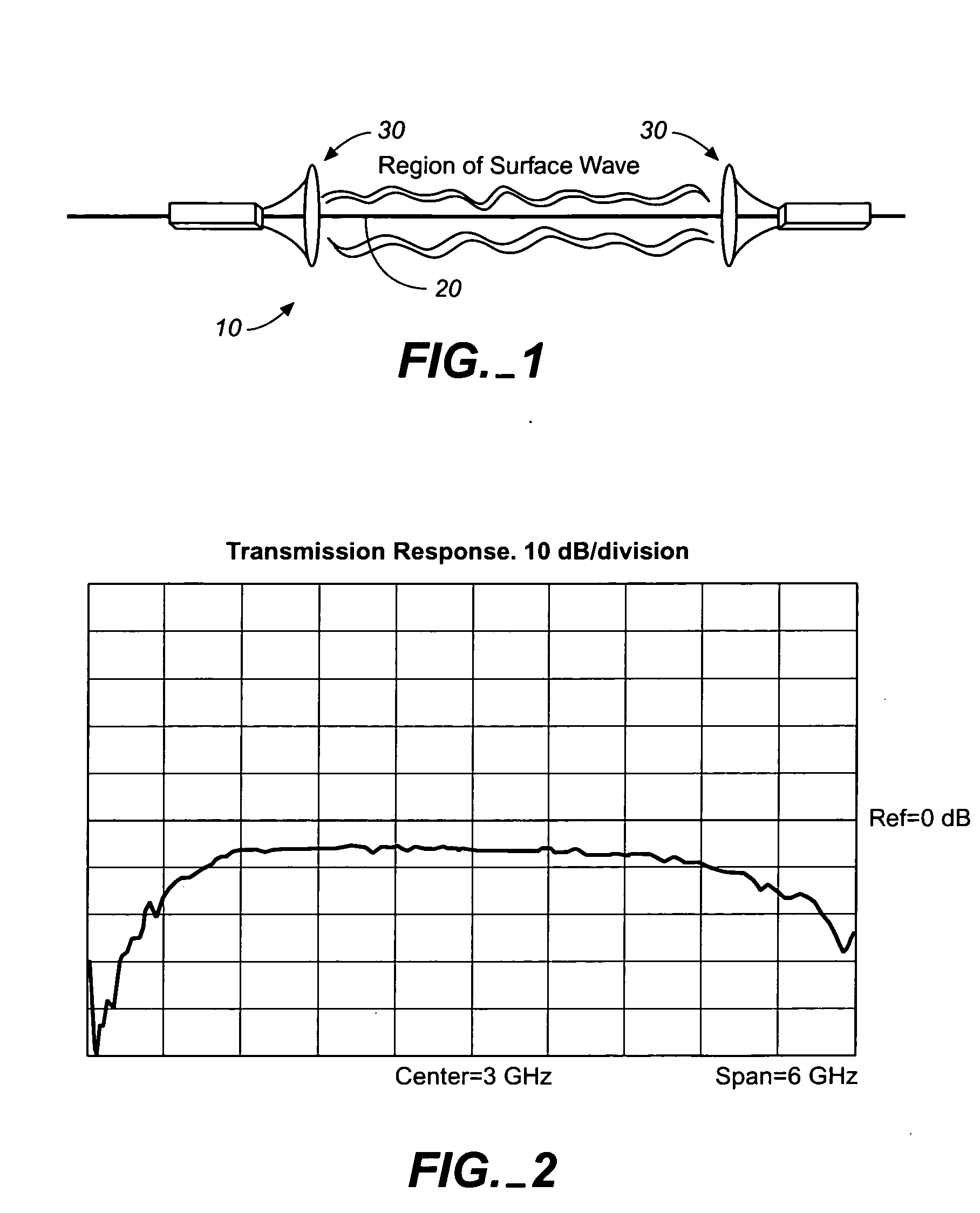
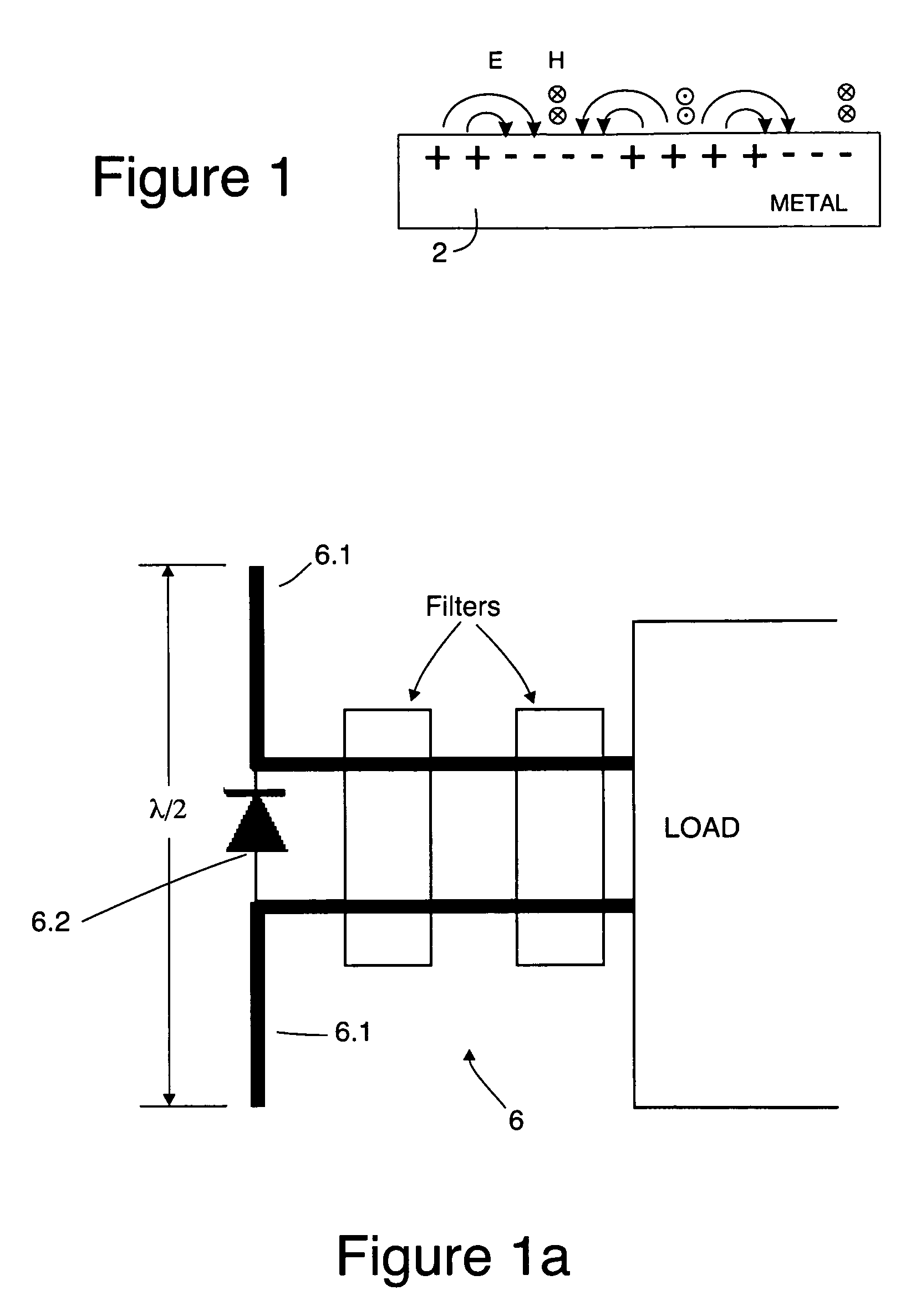
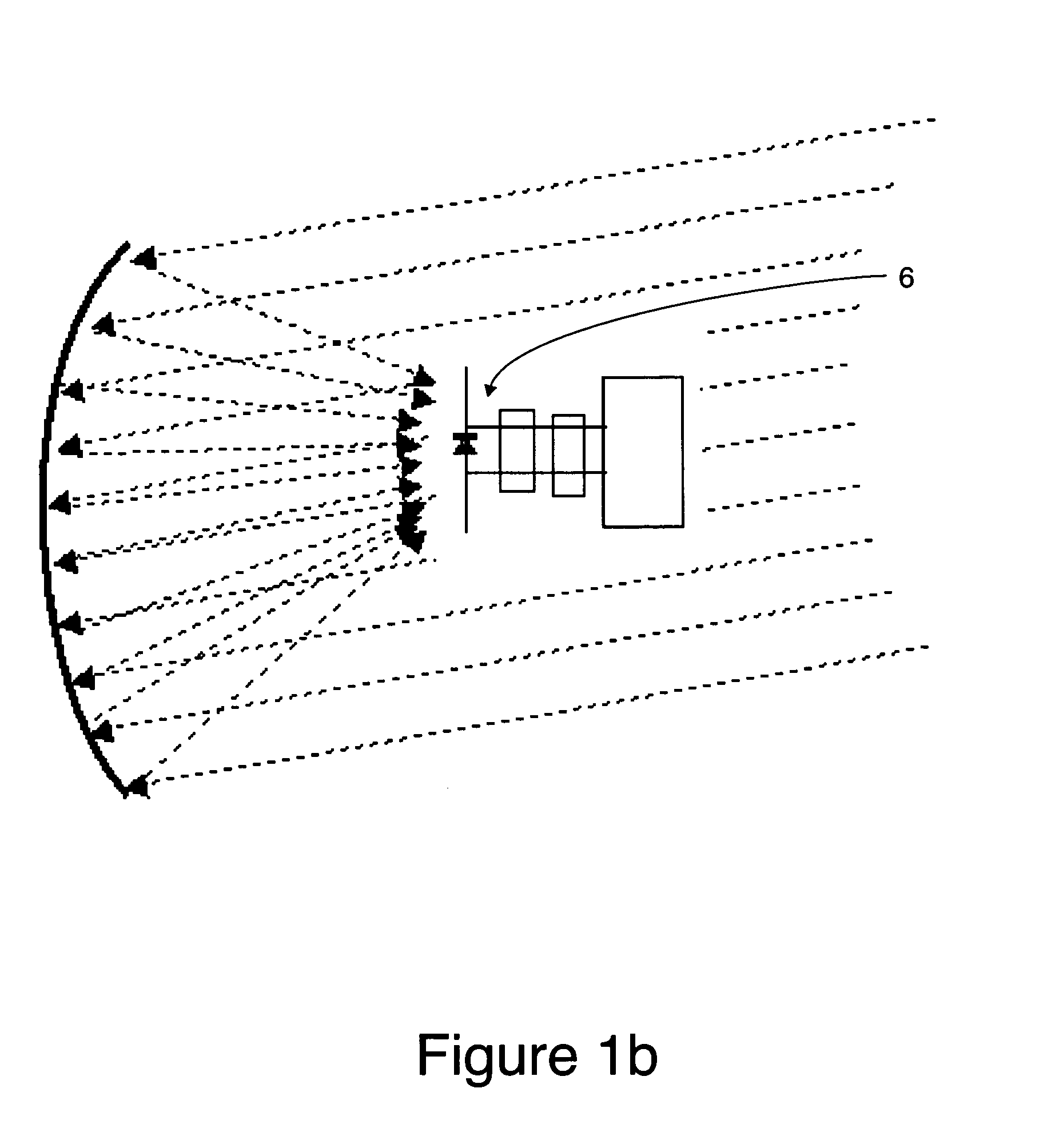
In physics, a surface wave is a 90 degree wave that propagates along the interface between differing media. A common example is gravity waves along the surface of liquids, such as ocean waves. Gravity waves can also occur within liquids, at the interface between two fluids with different densities. Elastic surface waves can travel along the surface of solids, such as Rayleigh or Love waves. Electromagnetic waves can also propagate as "surface waves" in that they can be guided along a refractive index gradient or along an interface between two media having different dielectric constants. In radio transmission, a ground wave is a guided wave that propagates close to the surface of the Earth.
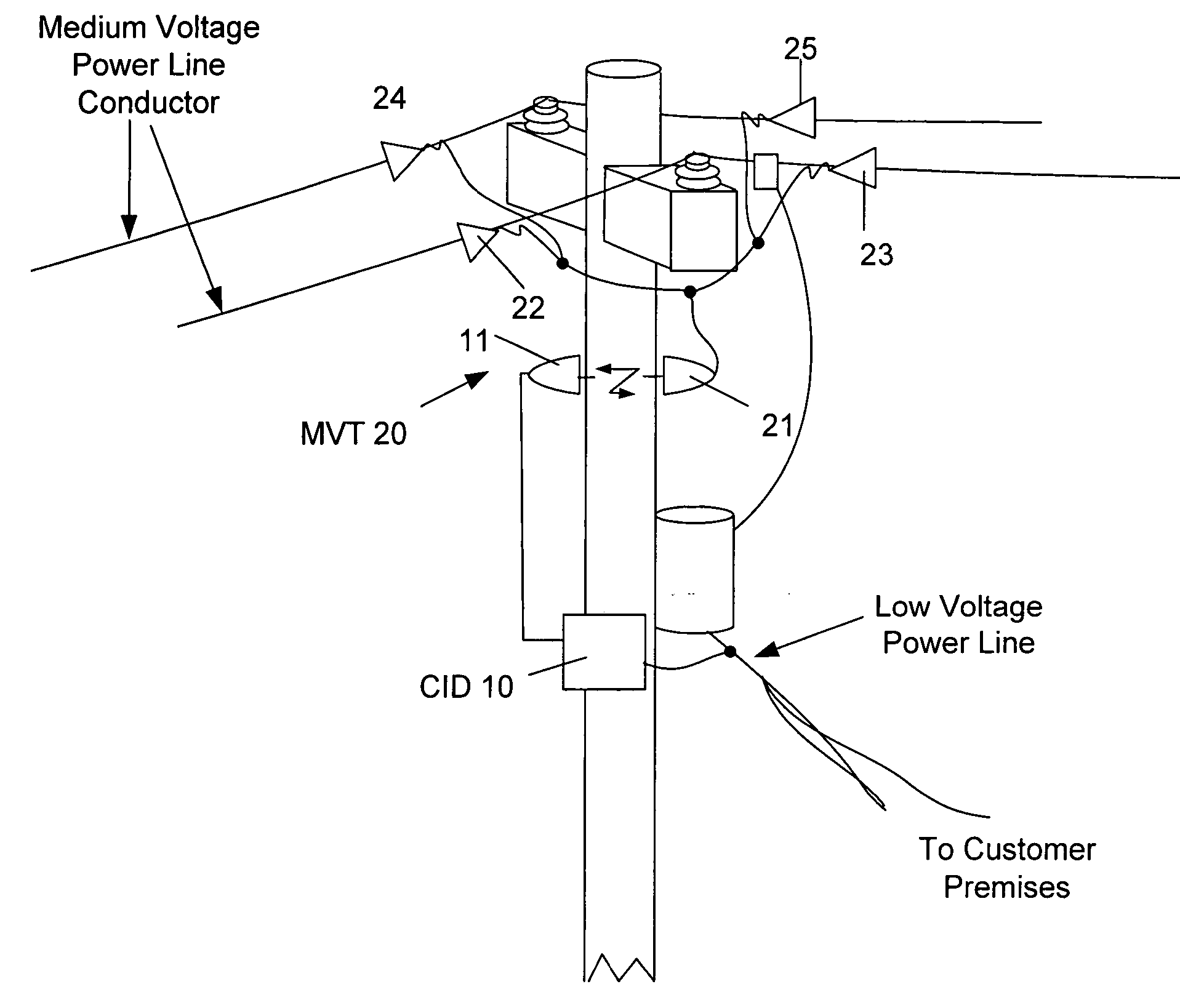
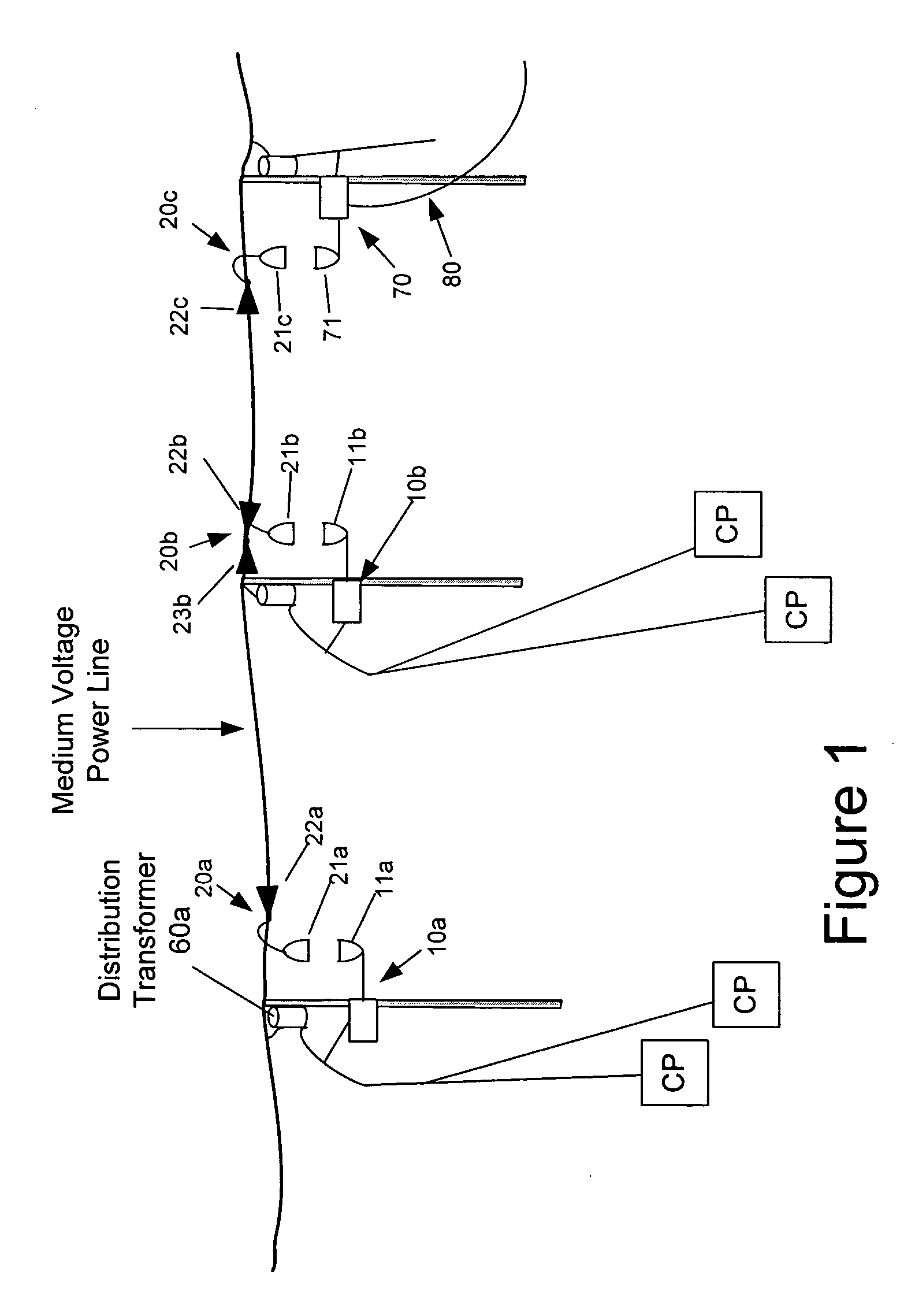
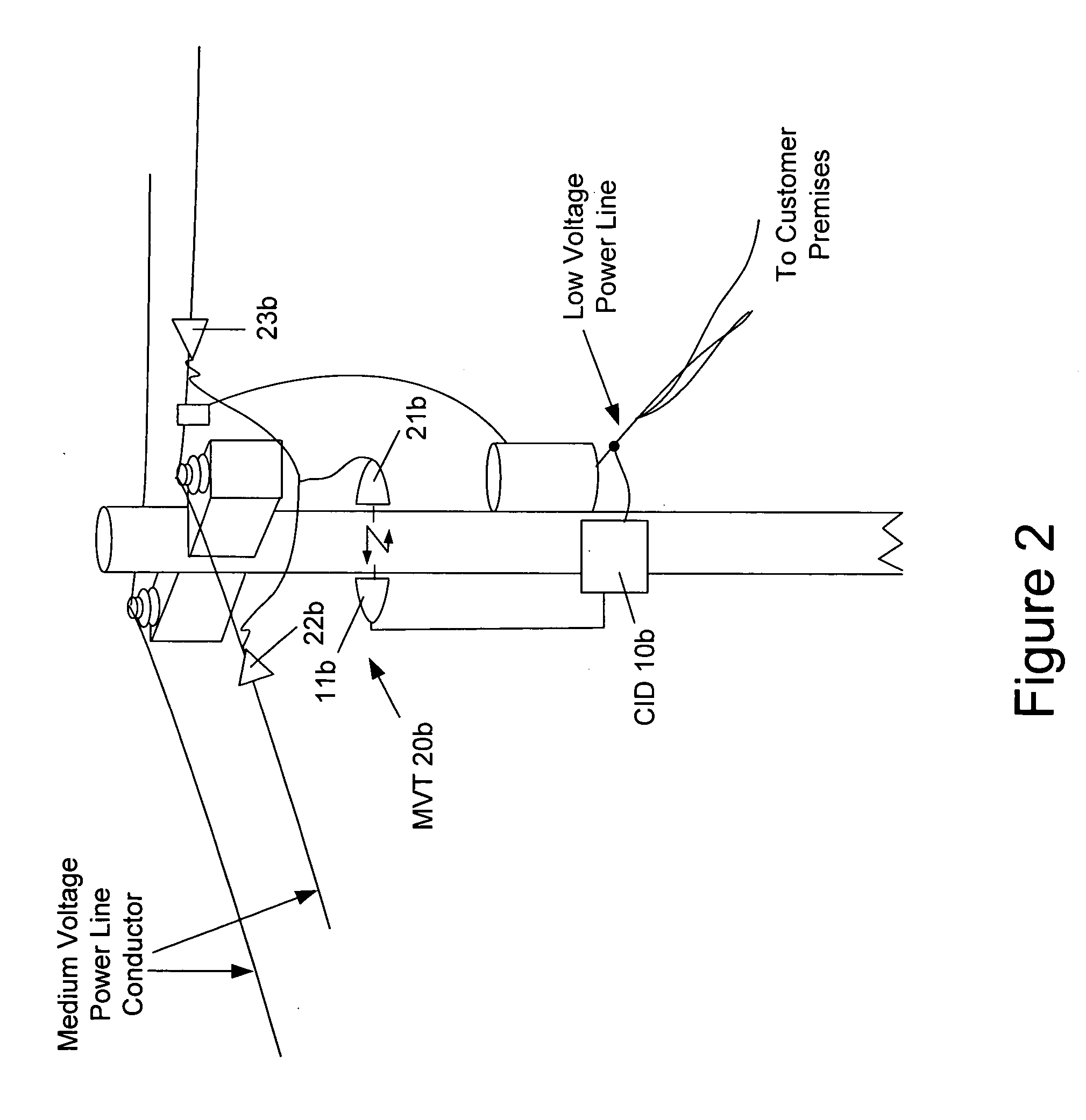
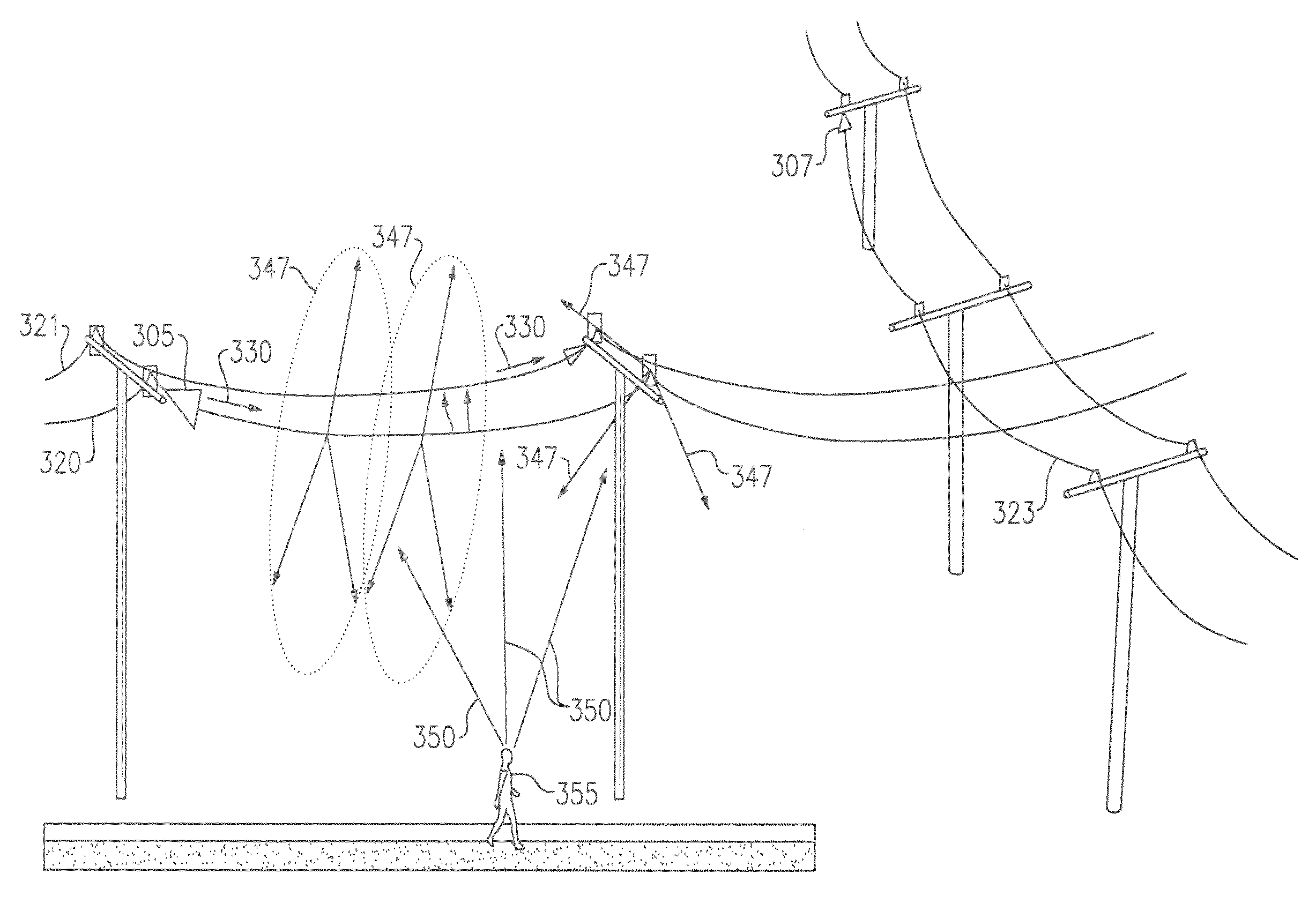
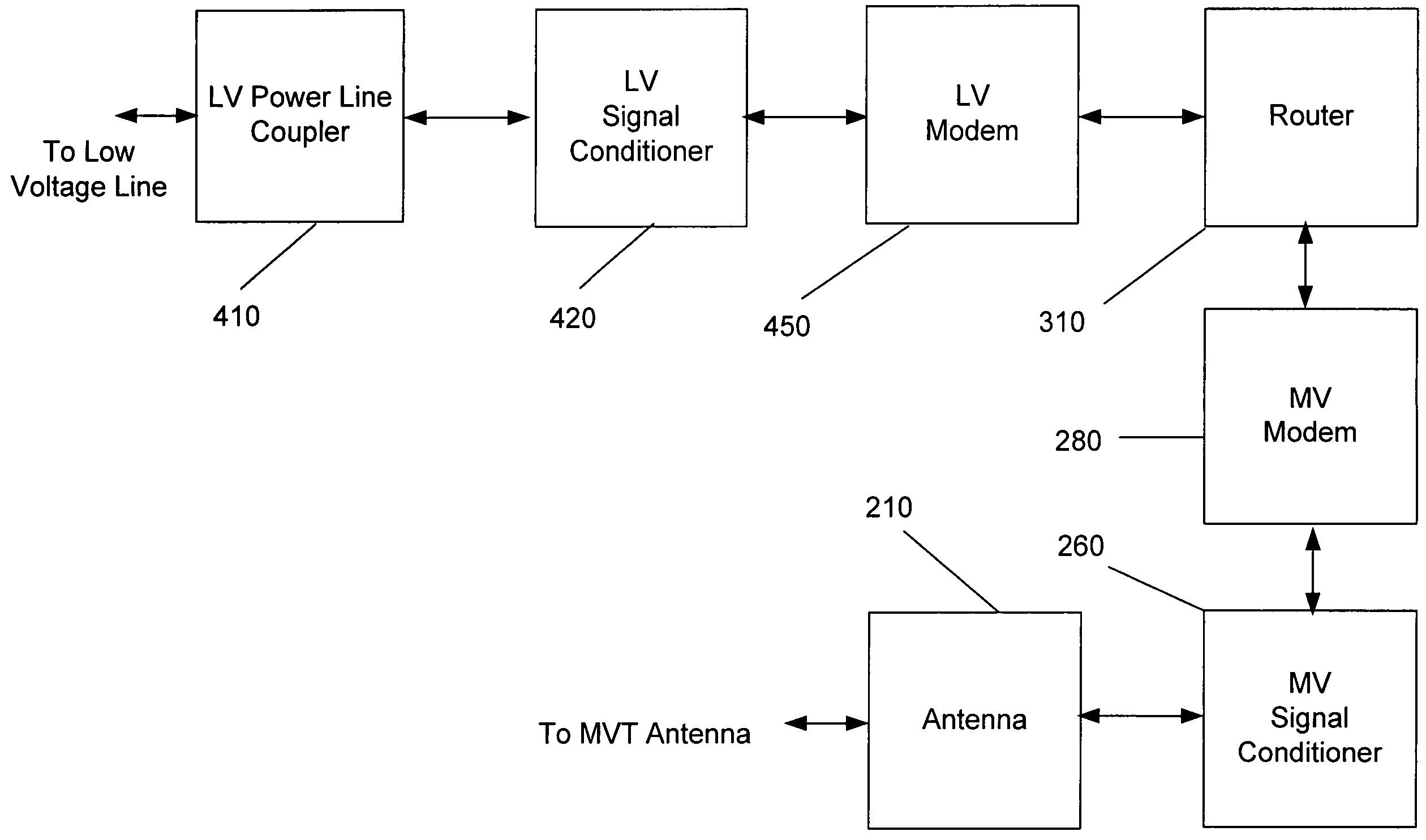
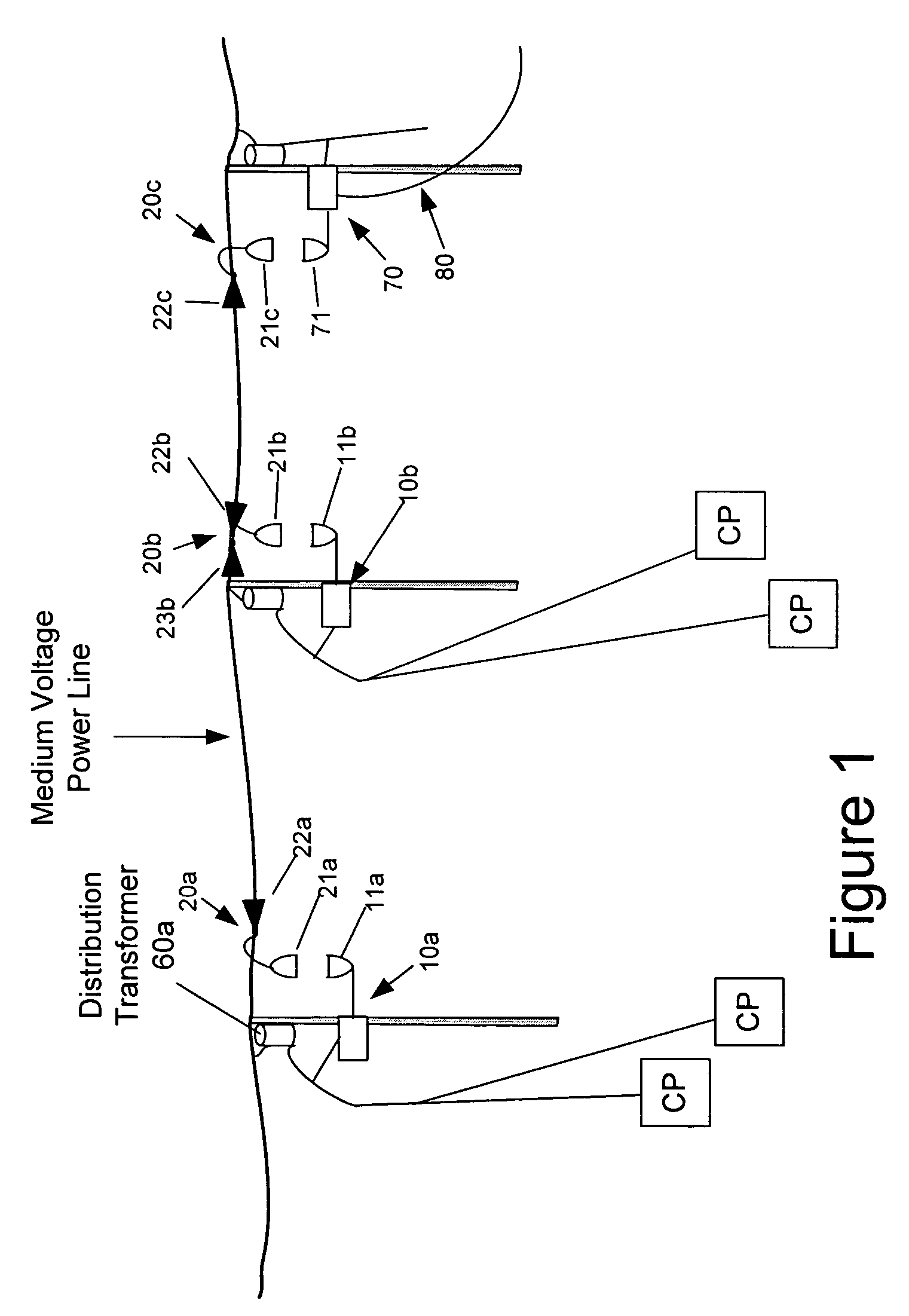
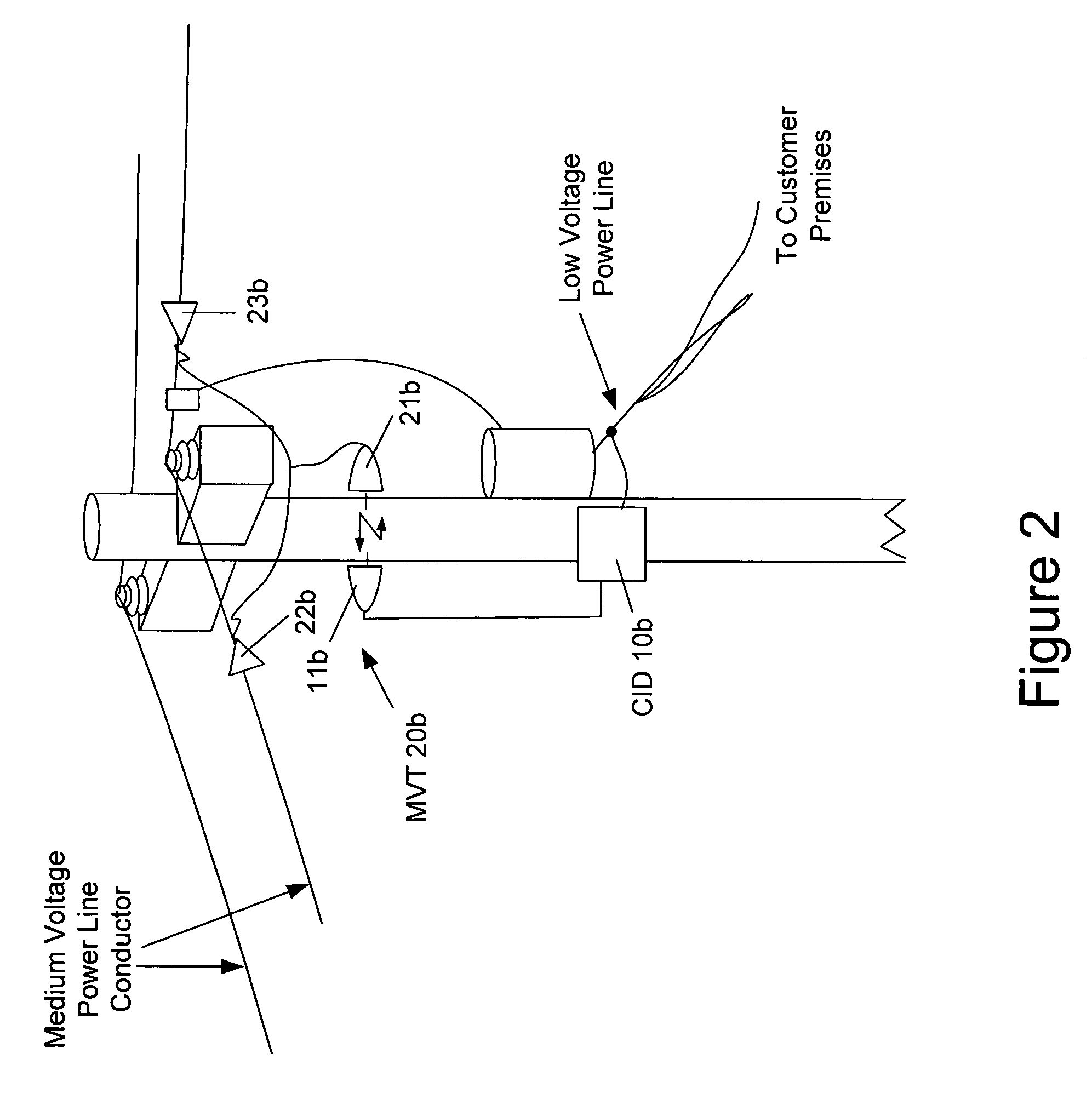
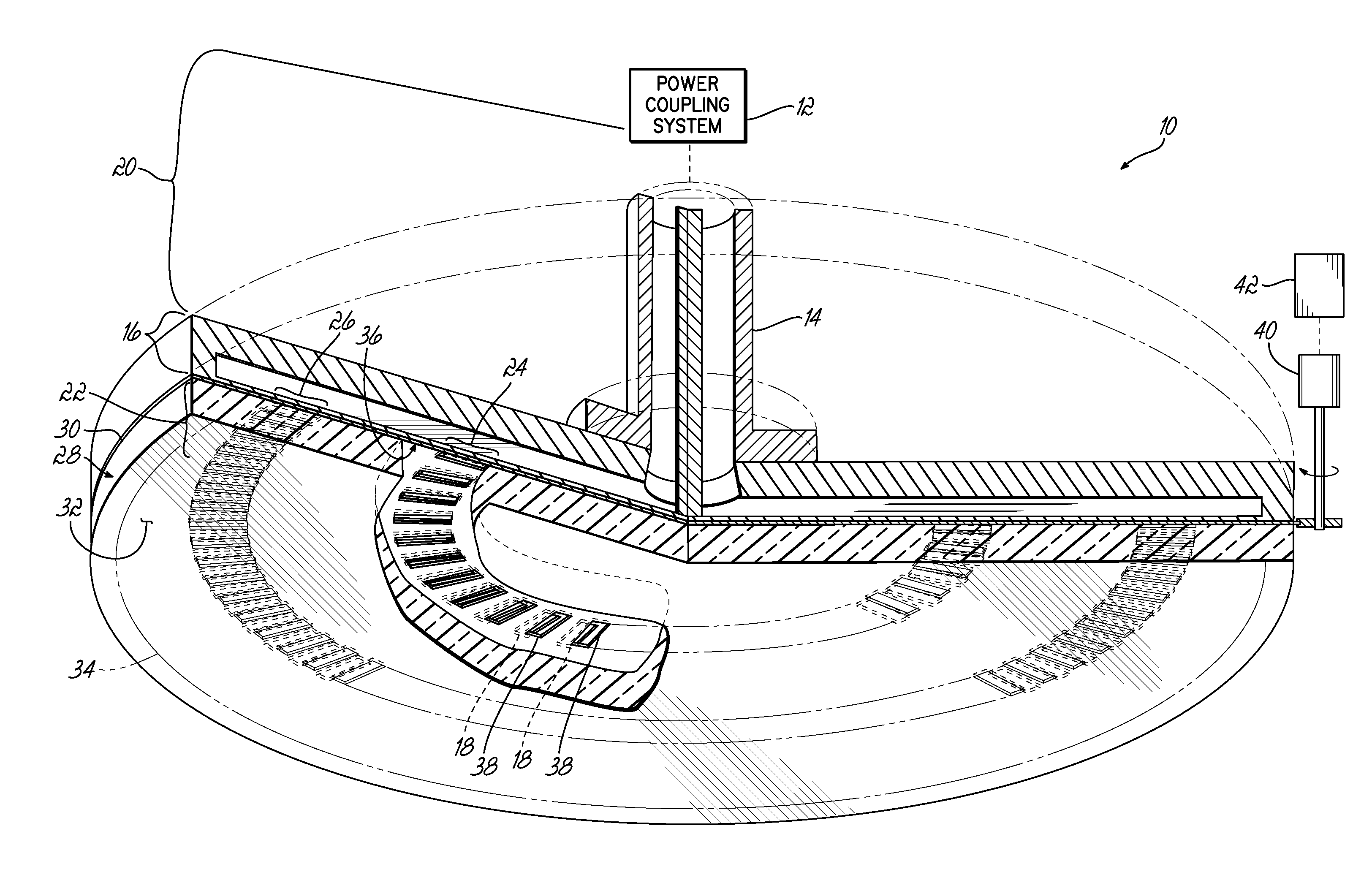
Surface wave power line communications system and method
InactiveUS20050111533A1Electric signal transmission systemsInterconnection arrangementsCommunication interfaceCommunications system
The present invention provides a system for operating a power line communications system that employs surface wave communications and conducted communications. The system is comprised of a plurality of network elements, which may take the form of repeaters, communication interface devices, backhaul devices, medium voltage transducers, distribution points, aggregation points, and others. In one embodiment, surface waves are communicated over the medium voltage power lines and the conducted communications are communicated via the low voltage power lines to and from customer premises.
Owner:CURRENT TECH
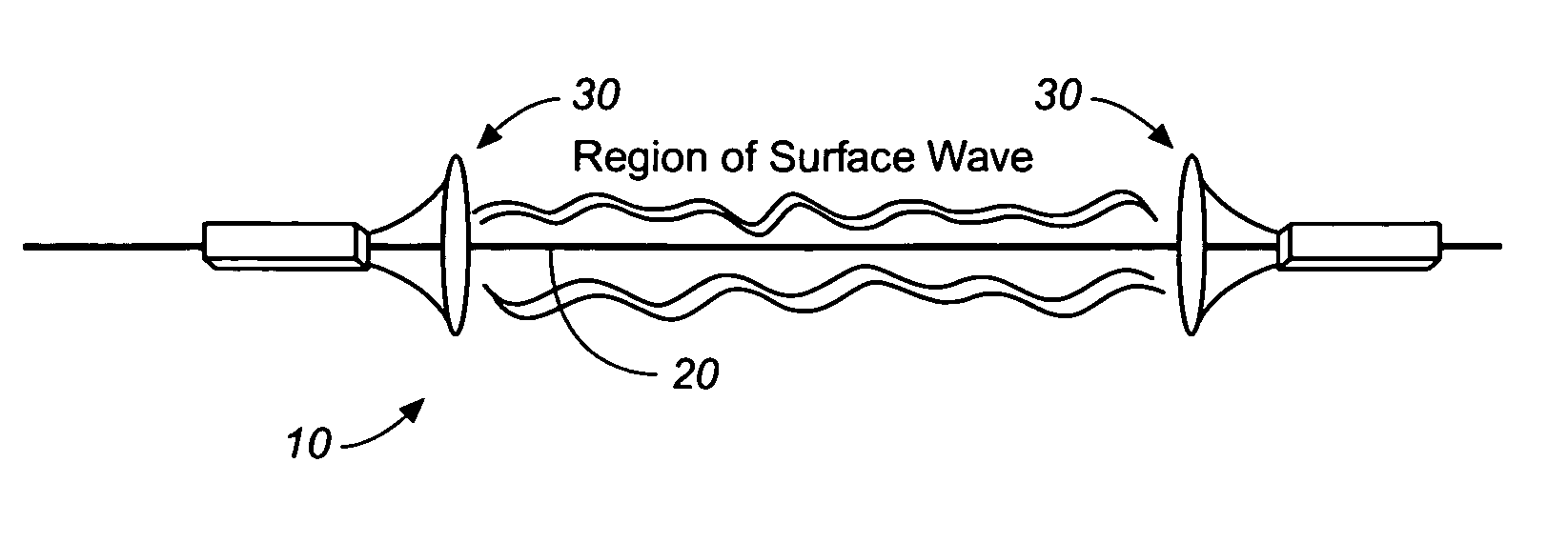
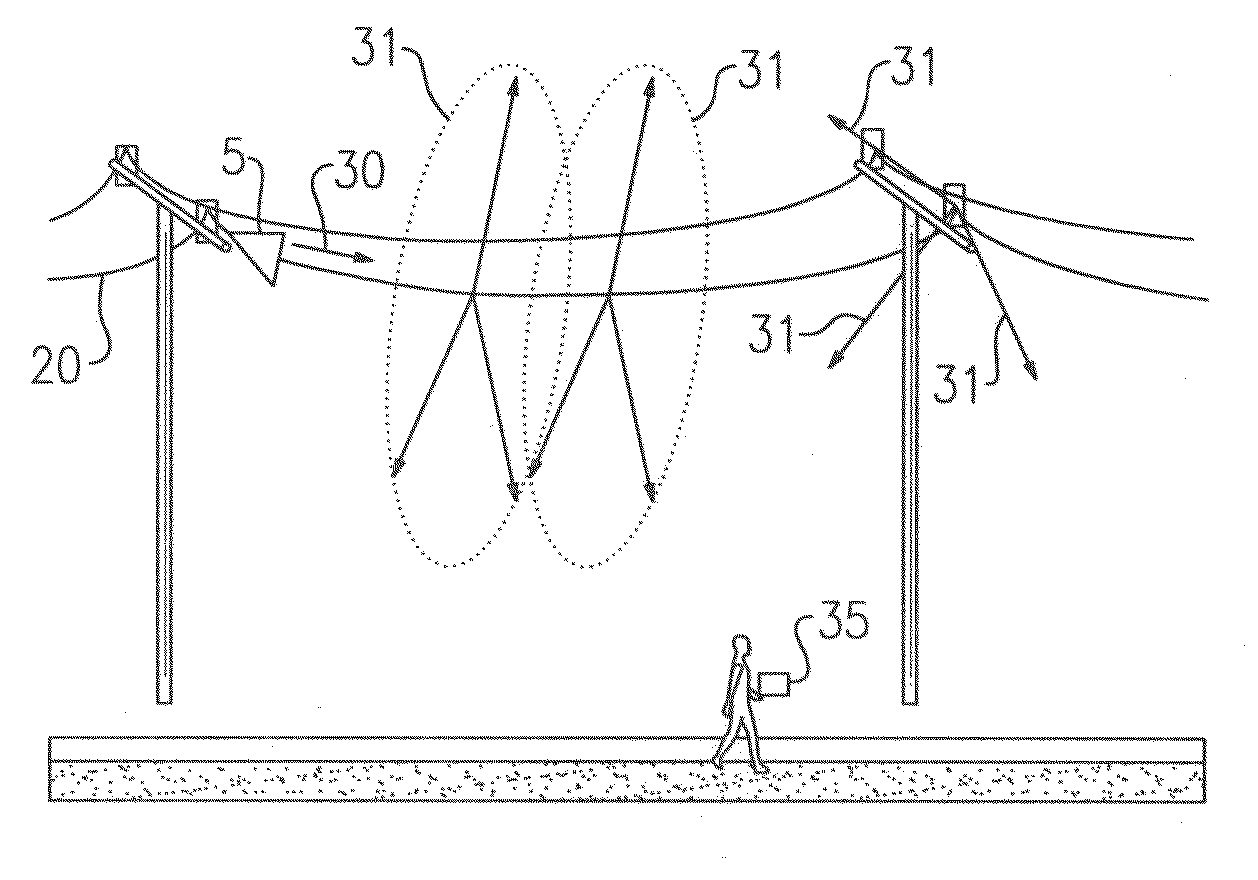
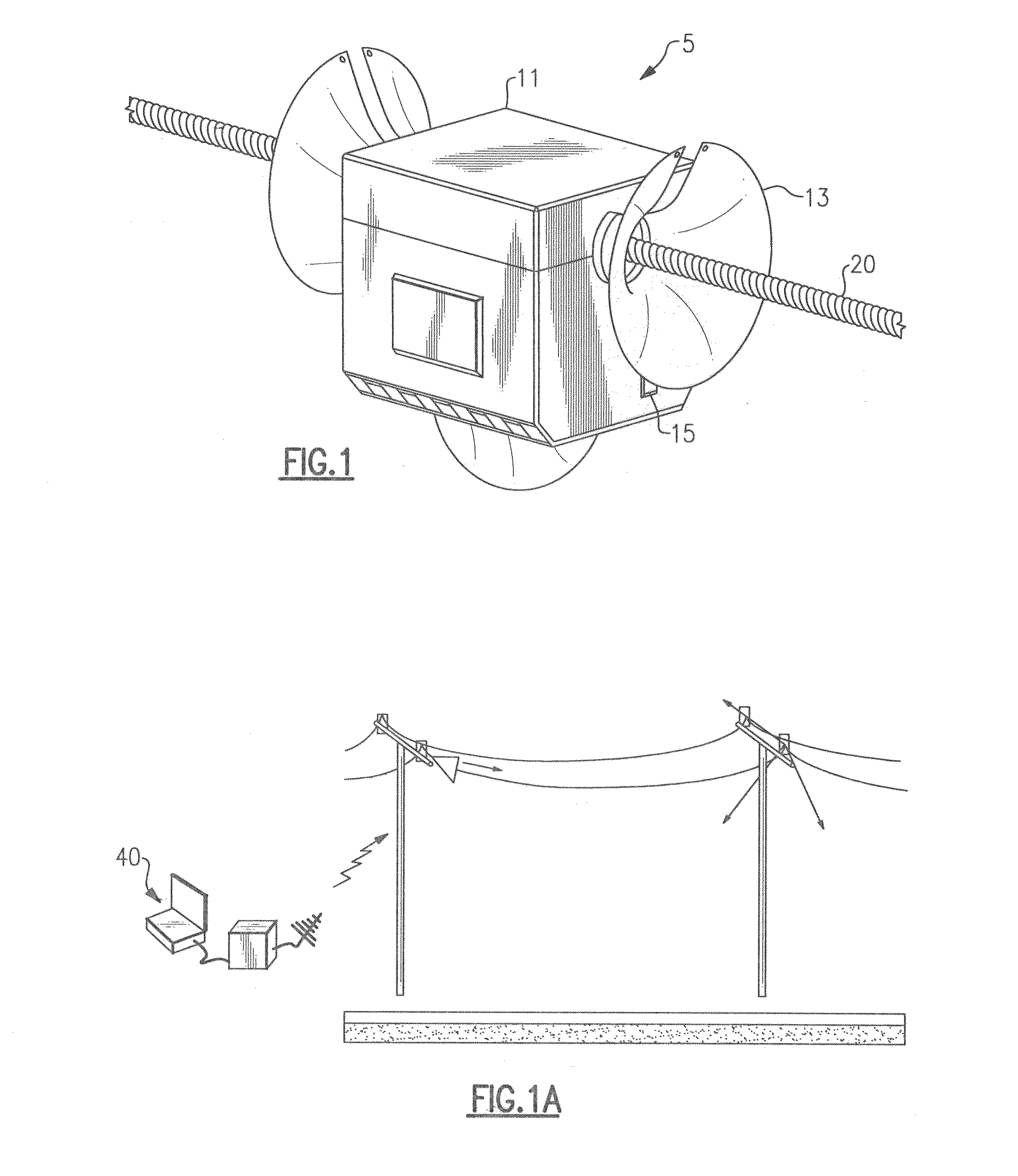
System and method for launching surface waves over unconditioned lines
A low loss transmission system which utilizes a single uninsulated central conducting line segment without any special surface treatment or special enclosing dielectric and having launch devices mounted at each end. The invention provides the use of conductors with circumference approaching and exceeding one wavelength at the propagating frequency. In combination, this invention enables the use of unconditioned and uninsulated conductors and in particular, existing overhead electric power lines which are available worldwide, for the economic and efficient transport of information.
Owner:CORRIDOR SYST INC
Conductive line communication apparatus and conductive line radar system and method
InactiveUS20110187578A1Increase heightAvoid interferenceDuplex signal operationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsTransceiver
A conductive line radar comprising at least one signal surface wave launcher, which comprises a signal surface wave transceiver, which is physically attached to a power line. The signal surface wave transceiver transmits a wave signal along the power line with another signal radiating from the wave signal in a plurality of directions along the power line. The at least one signal surface wave transceiver receives reflected signals from a target within a distance of the power line. The at least one signal surface wave launcher includes at least one RF communications transceiver and can be inductively powered from the power line.
Owner:SENSIS CORPORATION
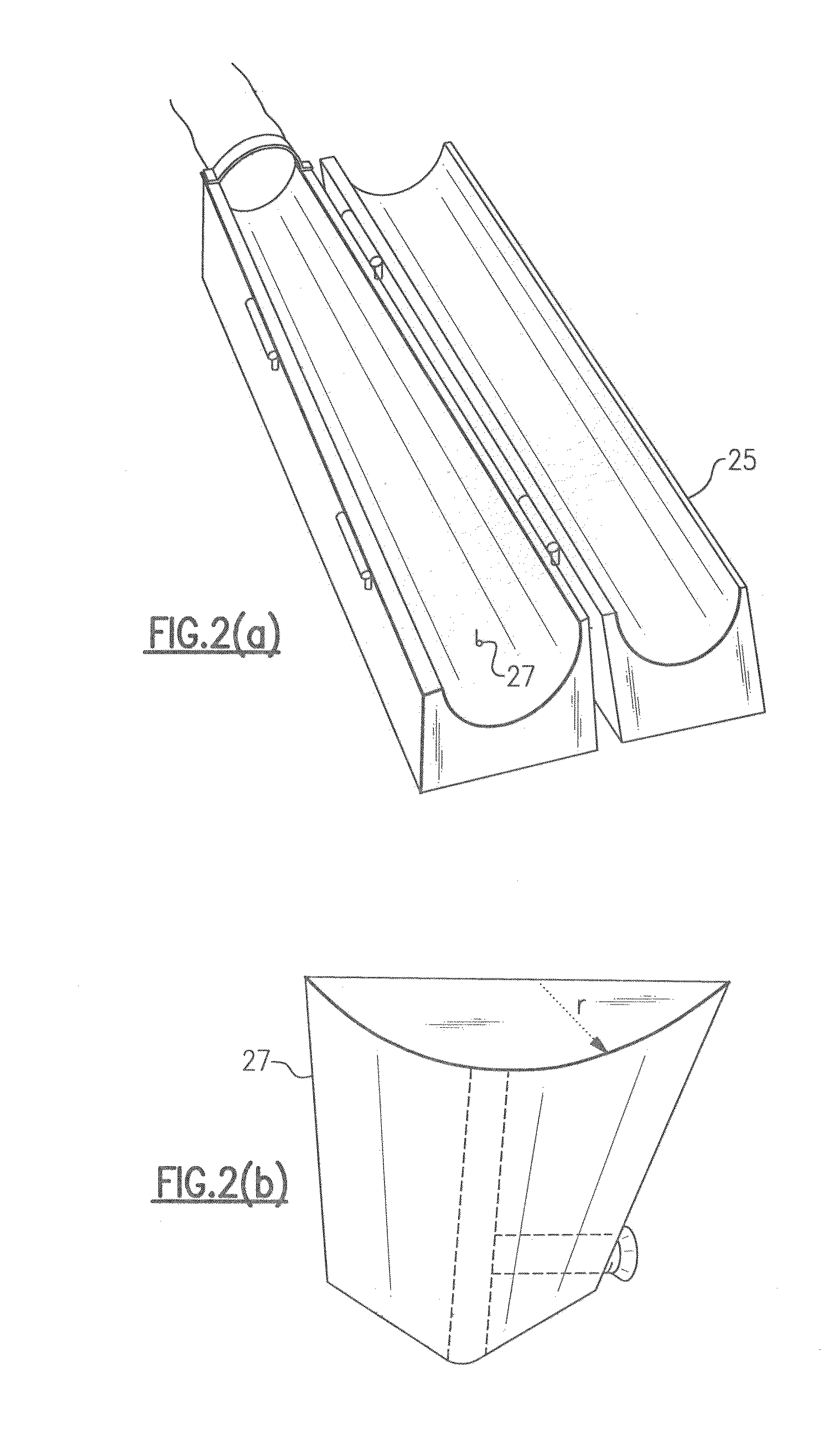
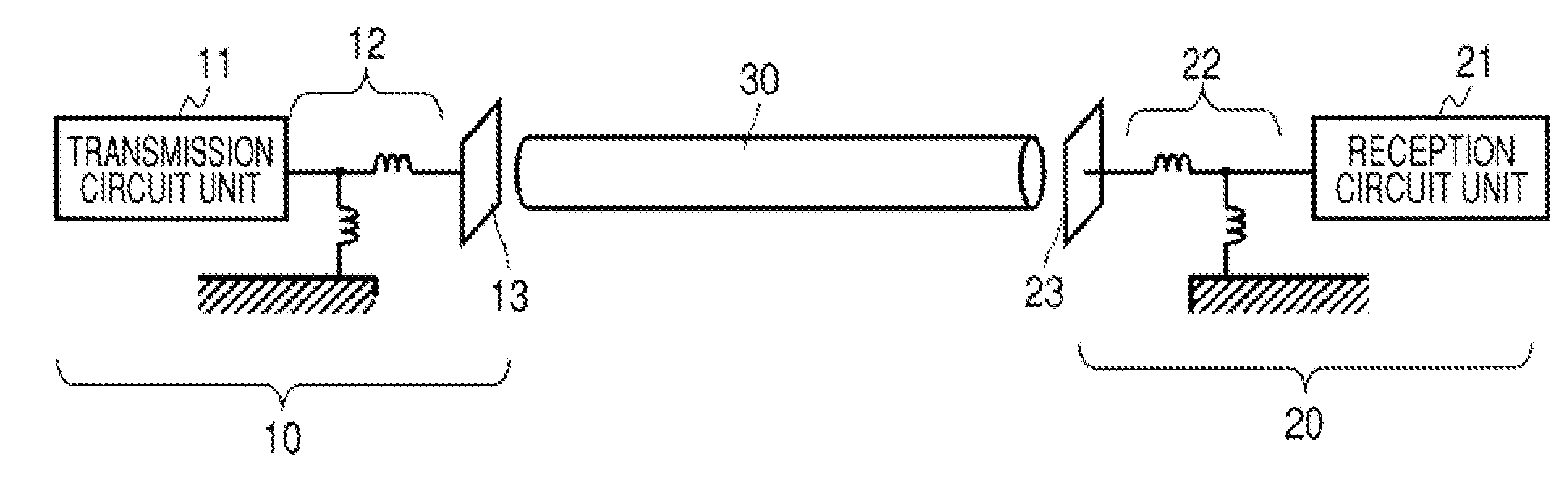
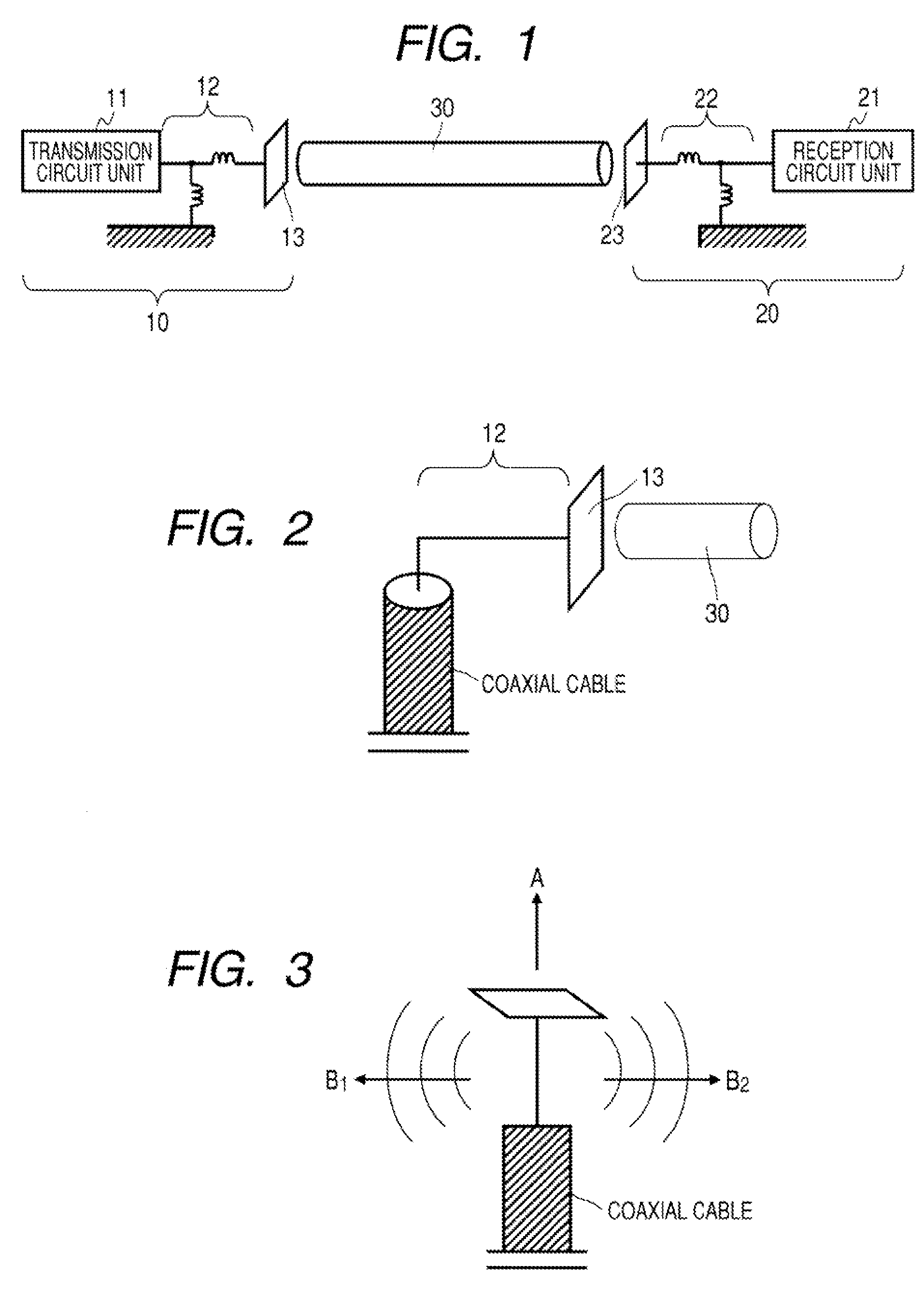
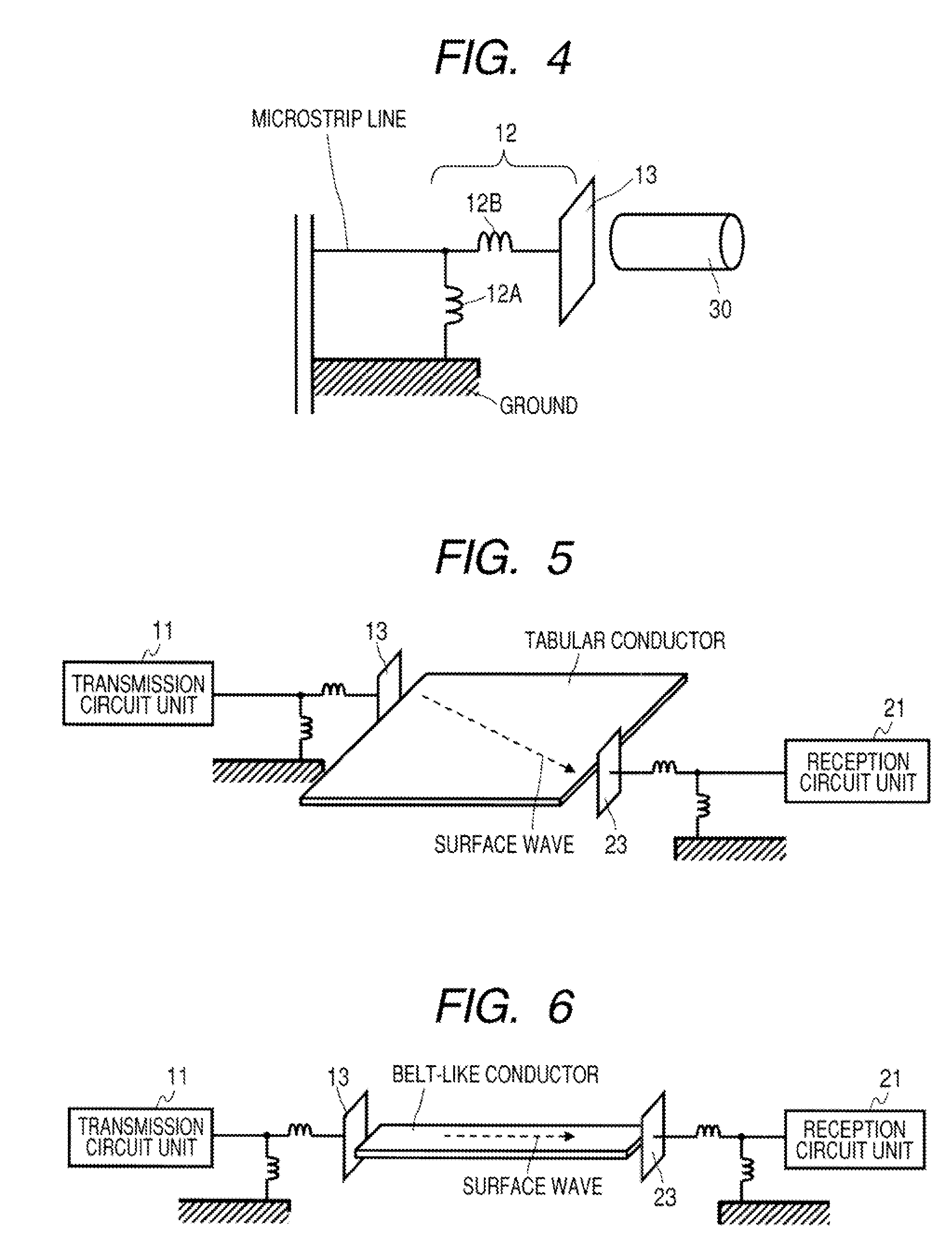
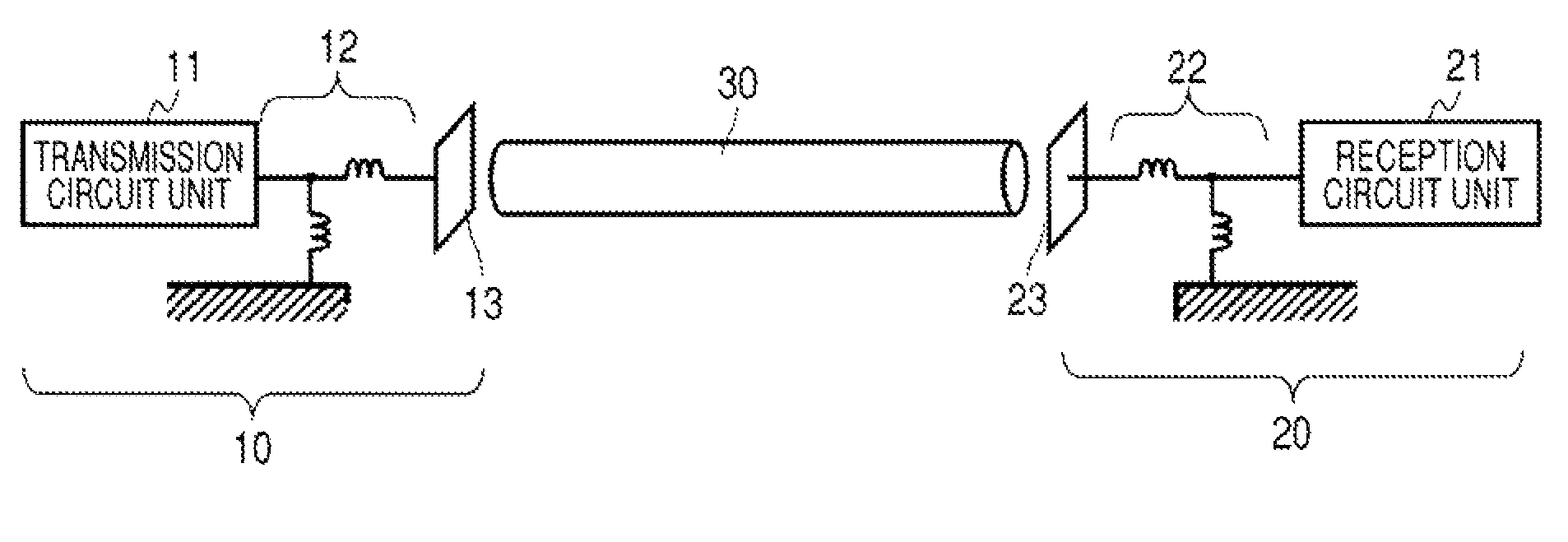
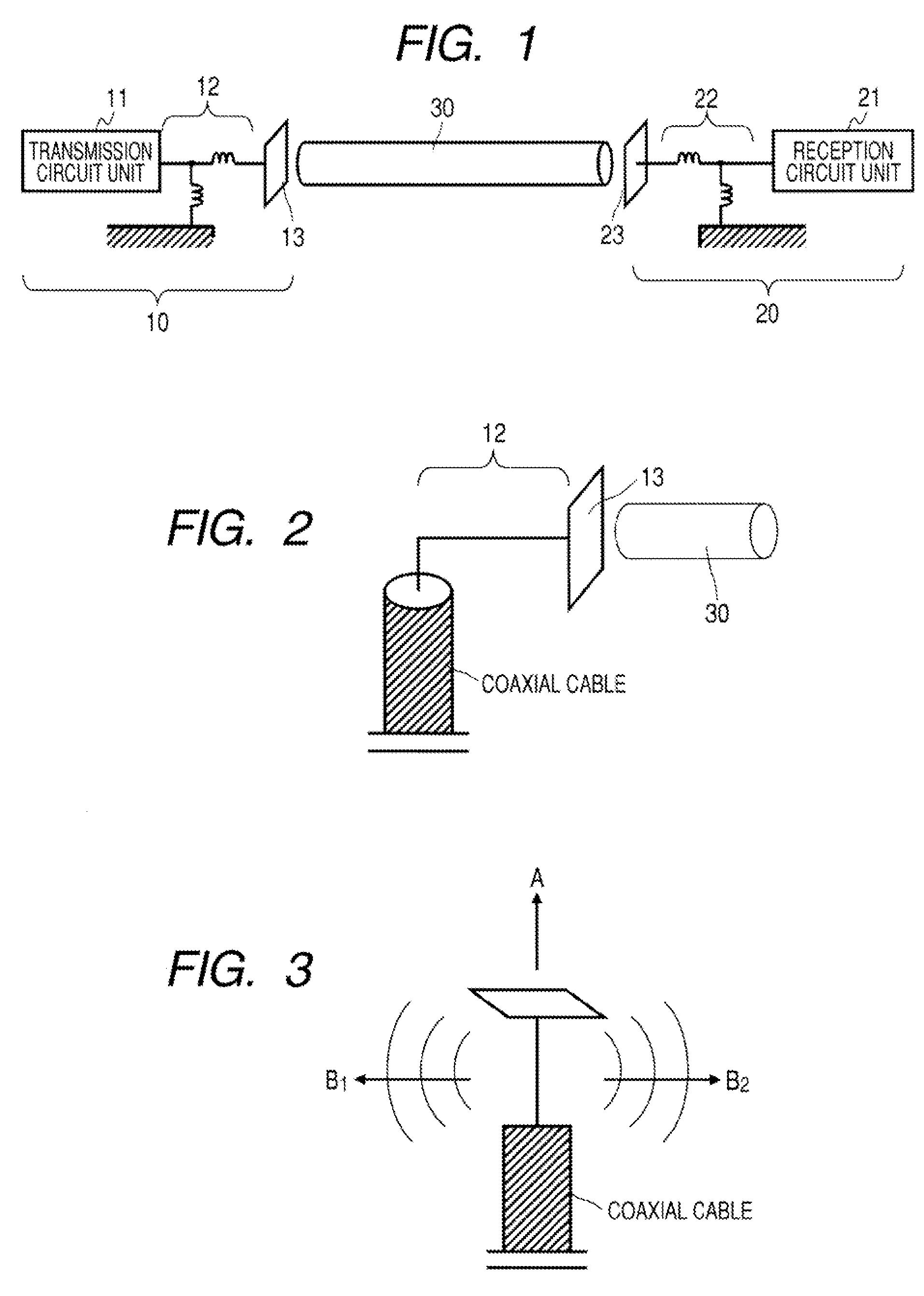
Communication System
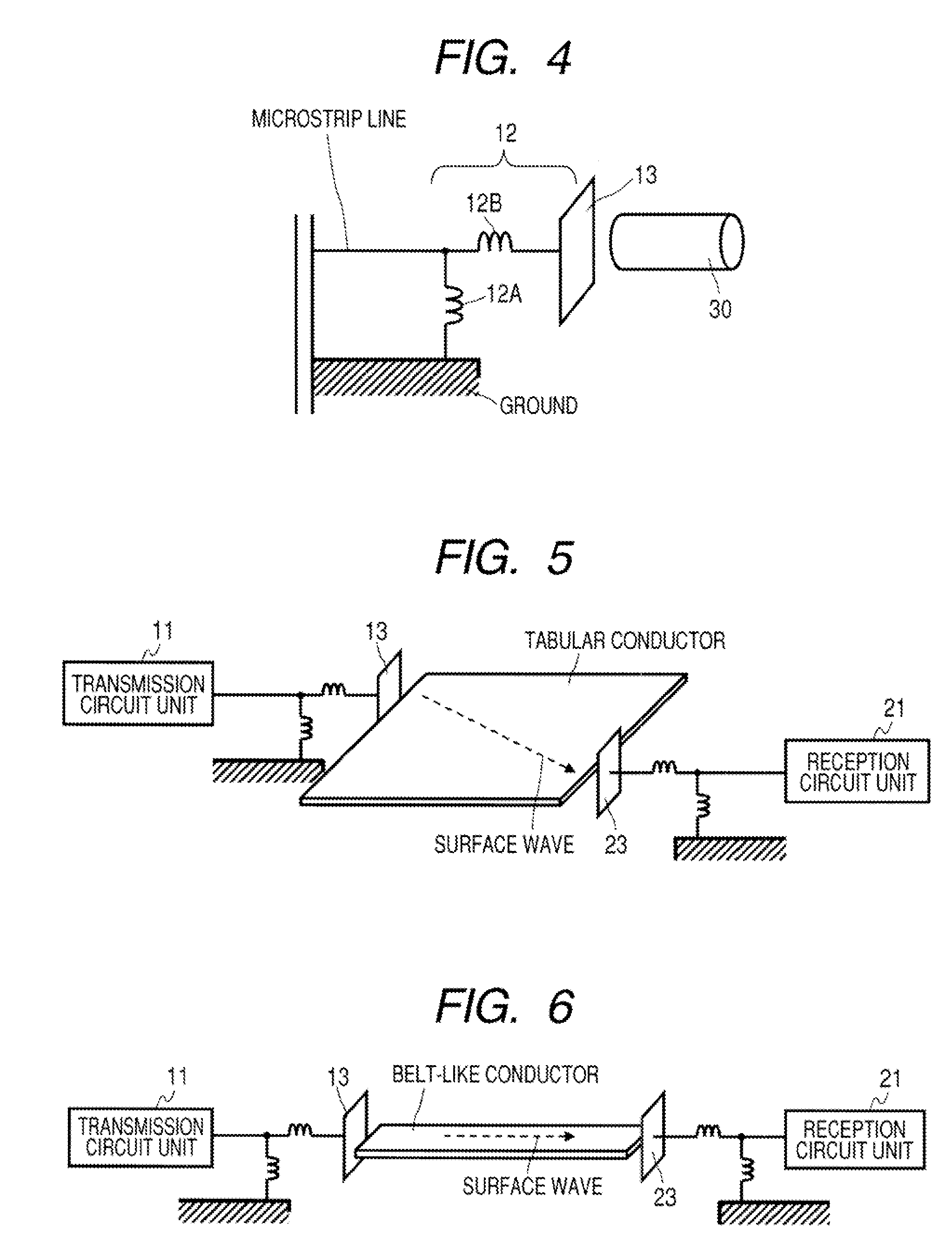
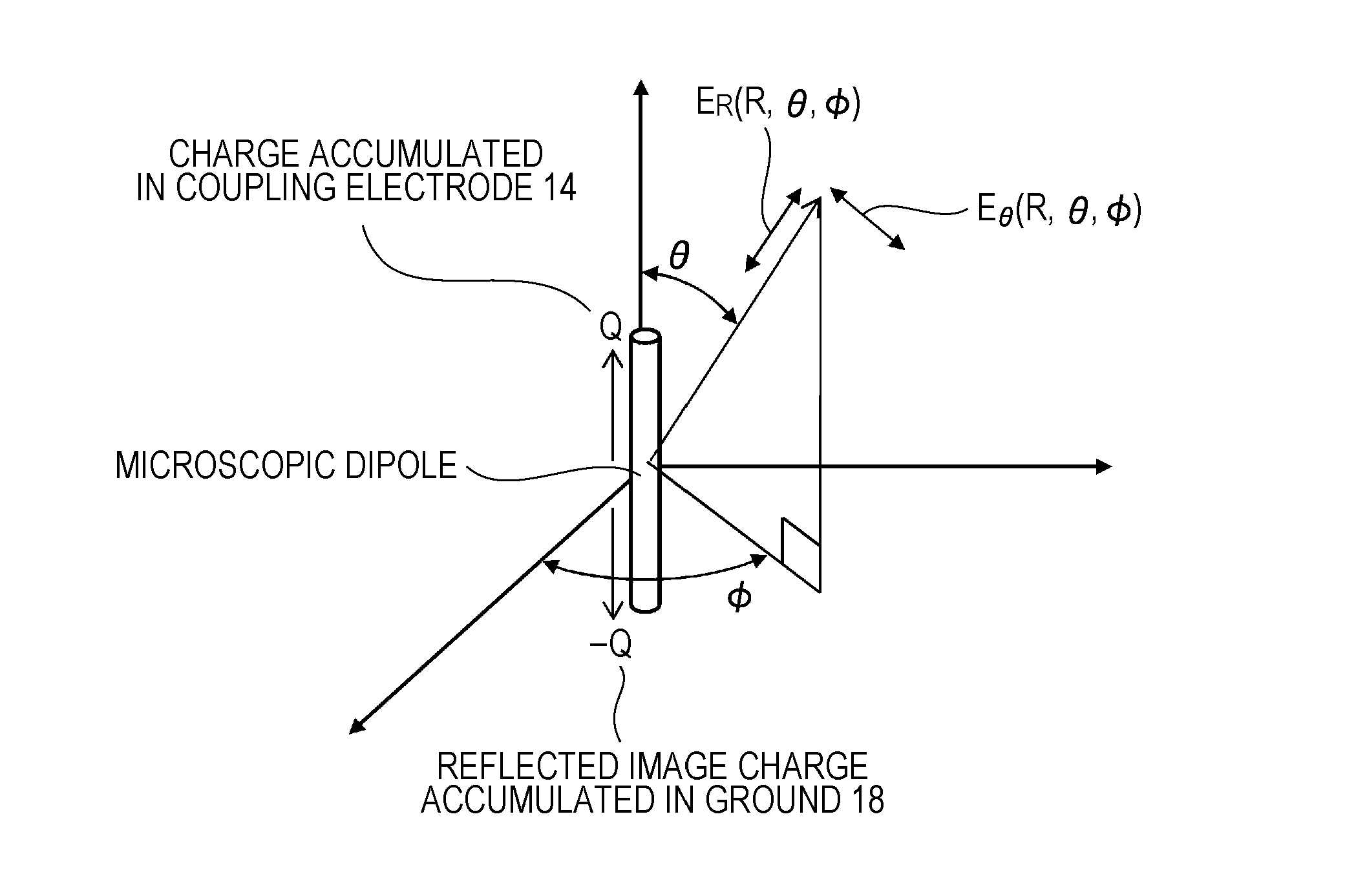
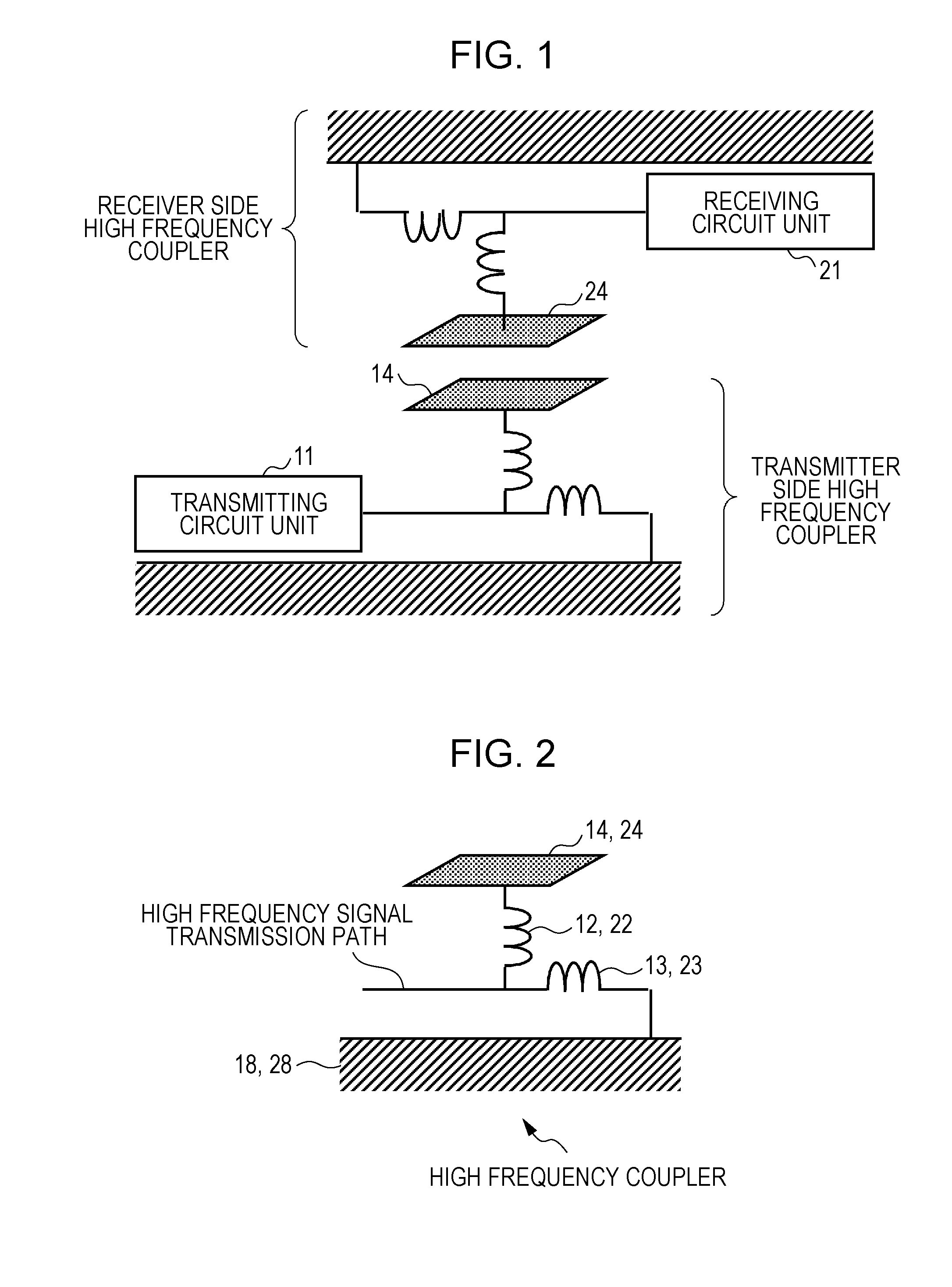
A communication system includes a transmitter including a transmission circuit unit that generates an RF signal for transmitting data and an electric-field-coupling antenna that transmits the RF signal as an electrostatic field, a receiver including an electric-field-coupling antenna and a reception circuit unit that subjects an RF signal received by the electric-field-coupling antenna to reception processing, and a surface-wave propagating means for providing a surface wave transmission line made of a conductor that propagates a surface wave radiated from the electric-field-coupling antenna of the transmitter along a surface of the surface wave transmission line.
Owner:SONY CORP
Surface wave transmission system over a single conductor having E-fields terminating along the conductor
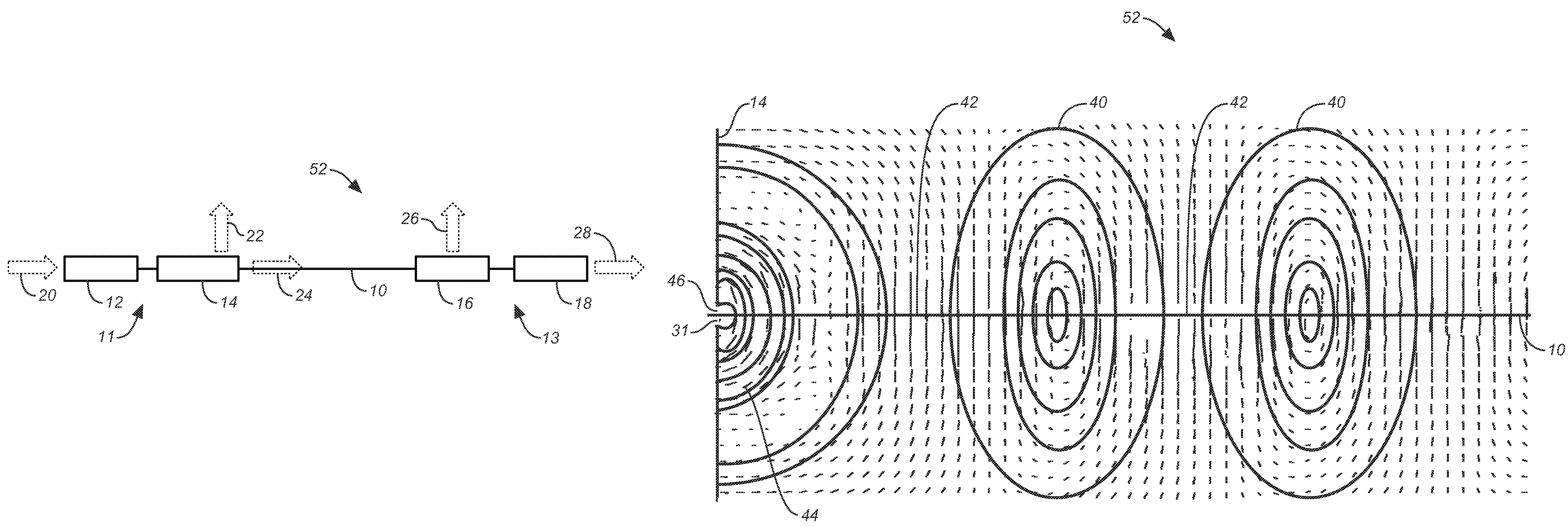
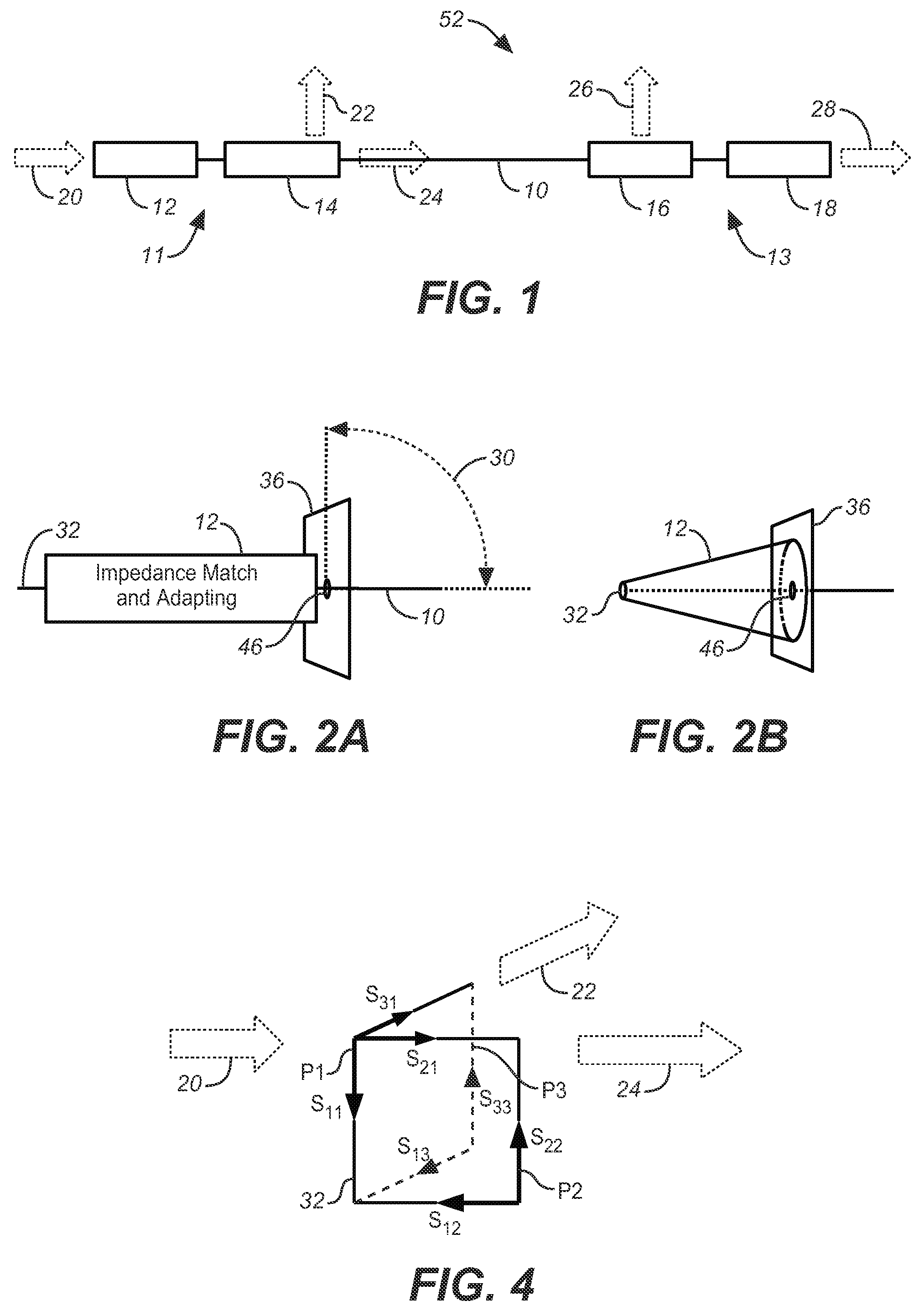
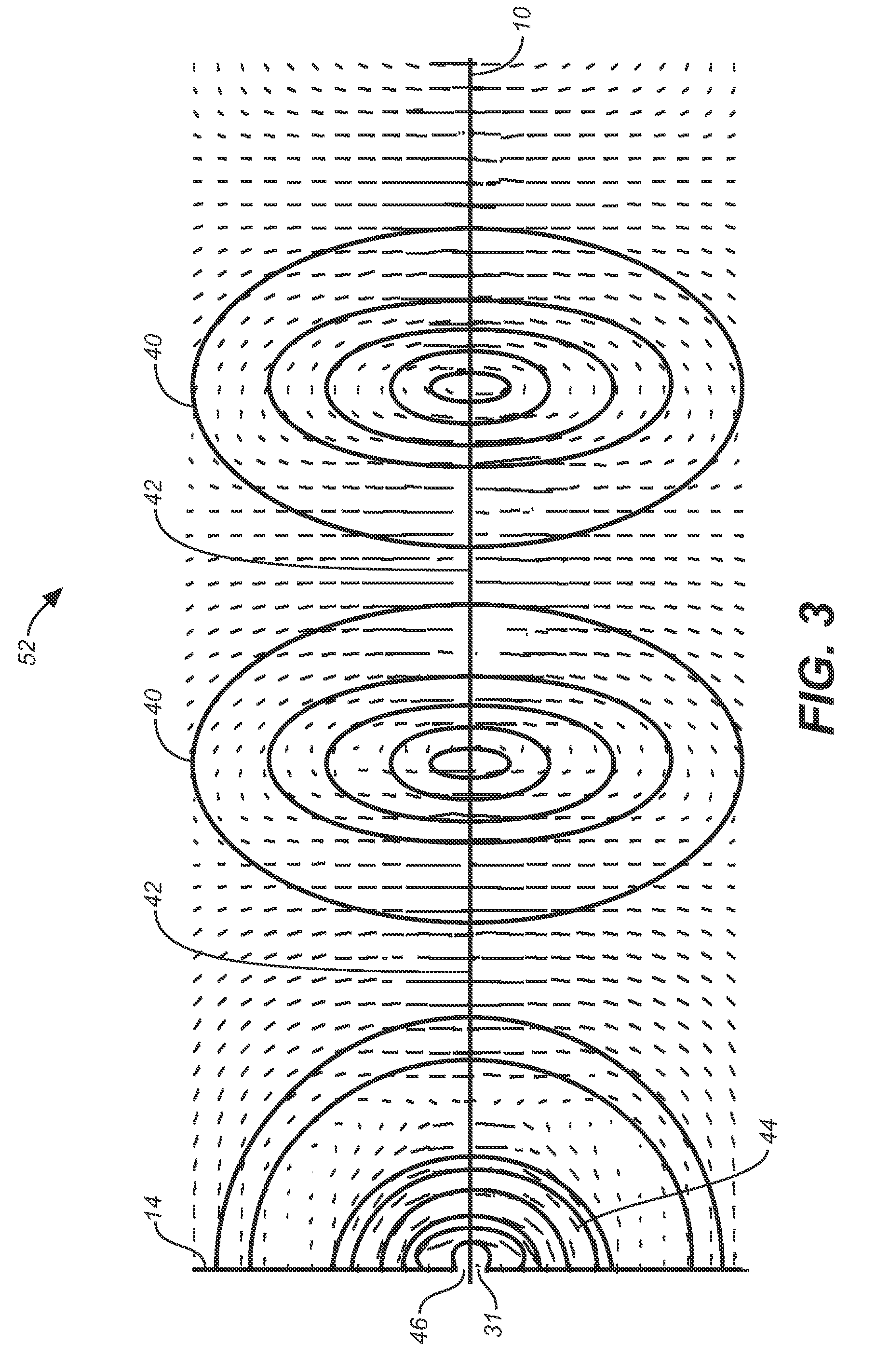
ActiveUS7567154B2Reduce energy costsEnable economicMultiple-port networksWaveguidesElectric power transmissionElectrical conductor
A low attenuation surface wave transmission line system for launching surface waves on a bare and unconditioned conductor, such as are found in abundance in the power transmission lines of the existing power grids. The conductors within the power grid typically lack dielectric and special conditioning. Accordingly, the present invention includes a first launcher, preferably including a mode converter and an adapter, for receiving an incident wave of electromagnetic energy and propagating a surface wave longitudinally on the power lines. The system includes at least one other launcher, and more likely a number of other launchers, spaced apart from one another along the constellation of transmission lines. The system and associated electric fields along any given conductor are radially and longitudinally symmetrical.
Owner:CORRIDOR SYST INC
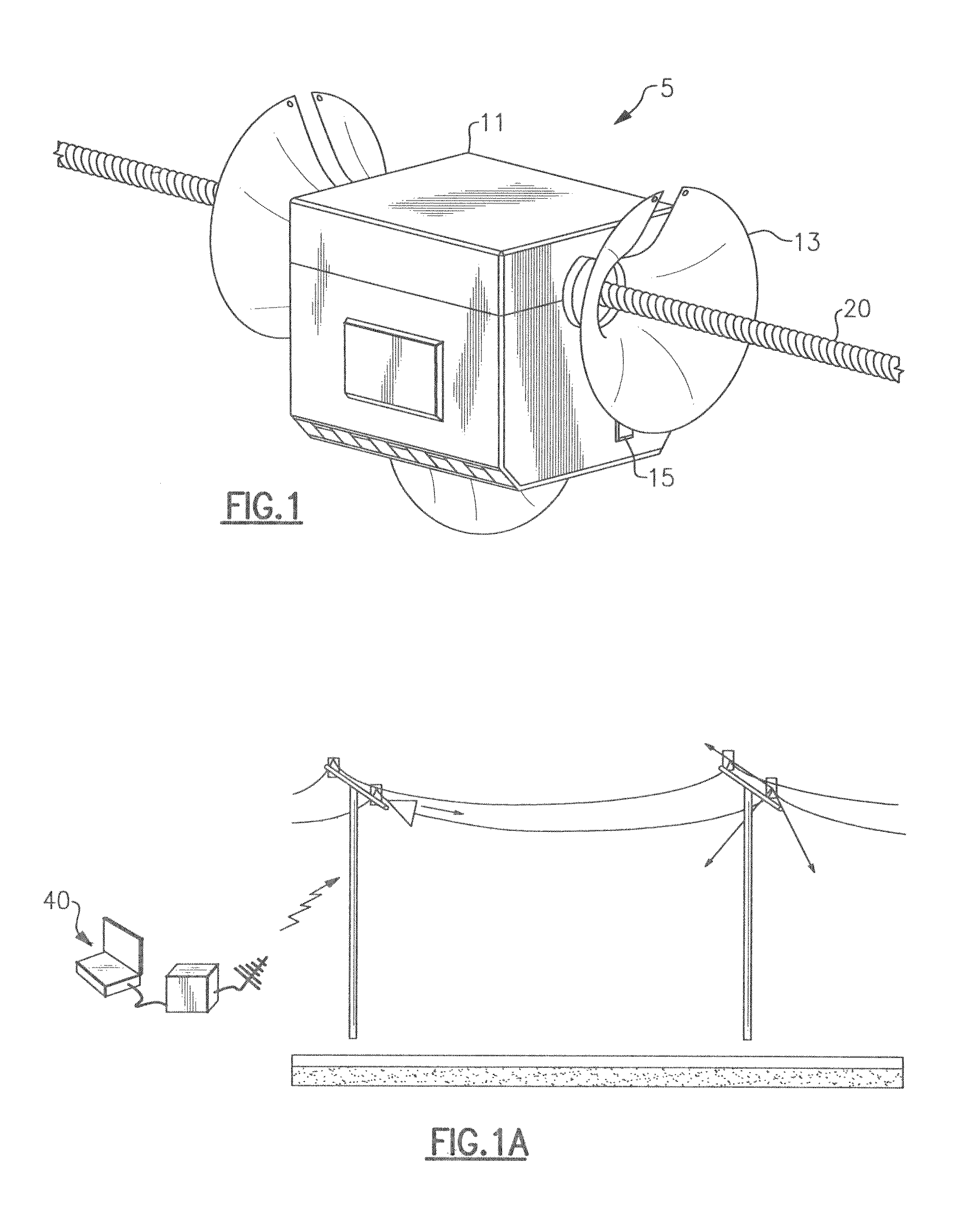
System and apparatus for transmitting a surface wave over a single conductor
ActiveUS20080211727A1Reduce radiationSmall sizeWaveguide hornsMultiple-port networksElectric power transmissionElectrical conductor
A low attenuation surface wave transmission line system for launching surface waves on a bare and unconditioned conductor, such as are found in abundance in the power transmission lines of the existing power grids. The conductors within the power grid typically lack dielectric and special conditioning. Accordingly, the present invention includes a first launcher, preferably including a mode converter and an adapter, for receiving an incident wave of electromagnetic energy and propagating a surface wave longitudinally on the power lines. The system includes at least one other launcher, and more likely a number of other launchers, spaced apart from one another along the constellation of transmission lines. The system and associated electric fields along any given conductor are radially and longitudinally symmetrical.
Owner:CORRIDOR SYST INC
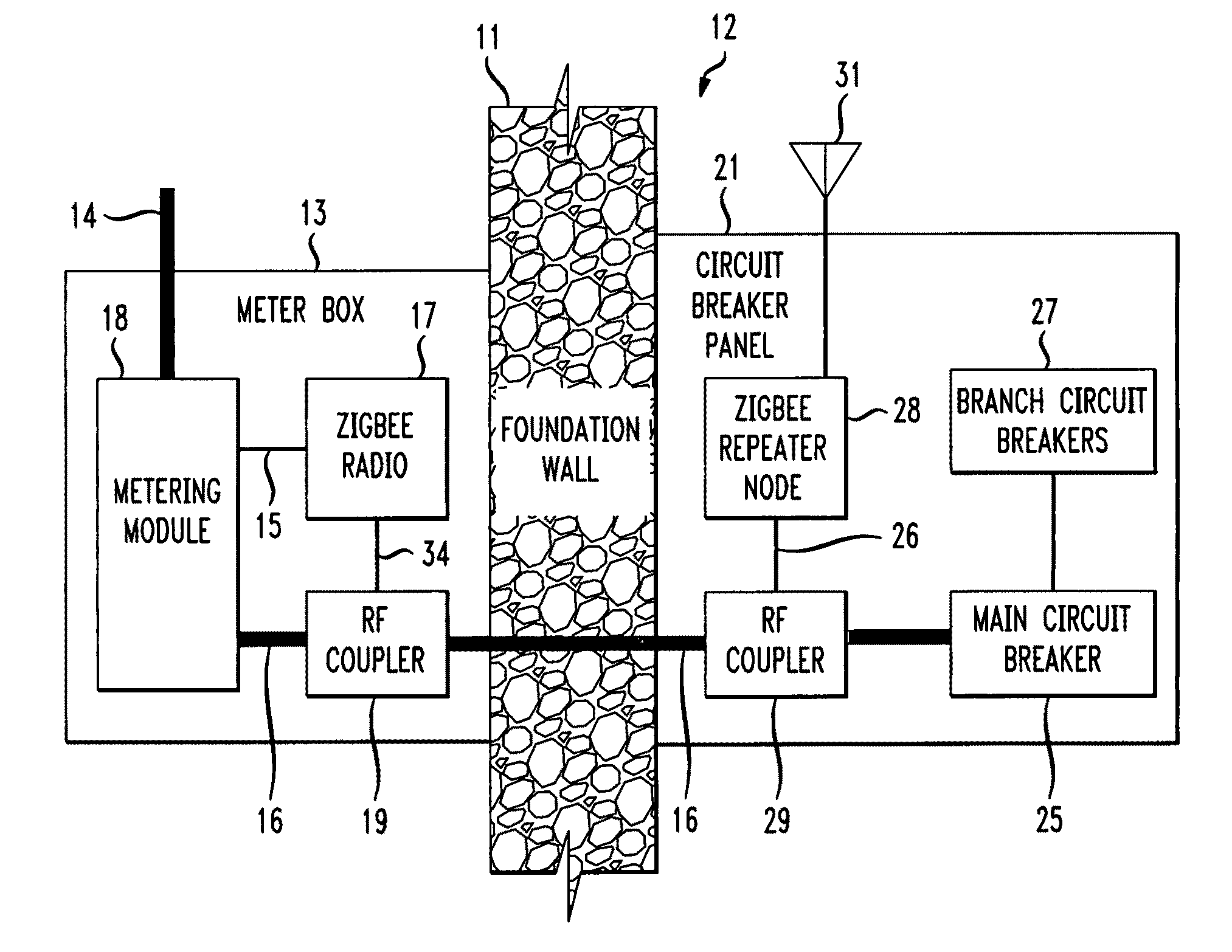
Surface wave coupler
ActiveUS8212635B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsPower distribution line transmissionElectrical conductorEngineering
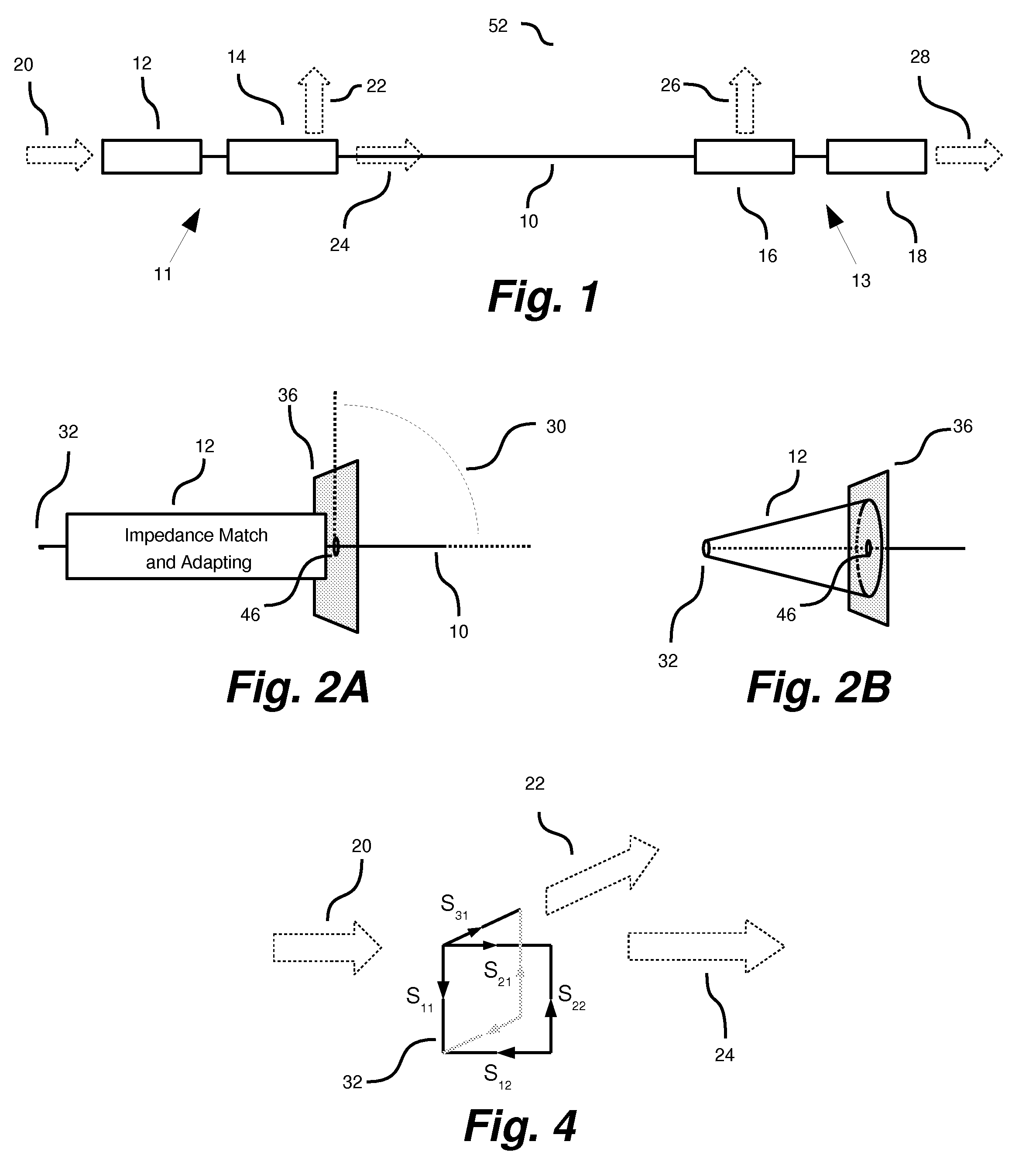
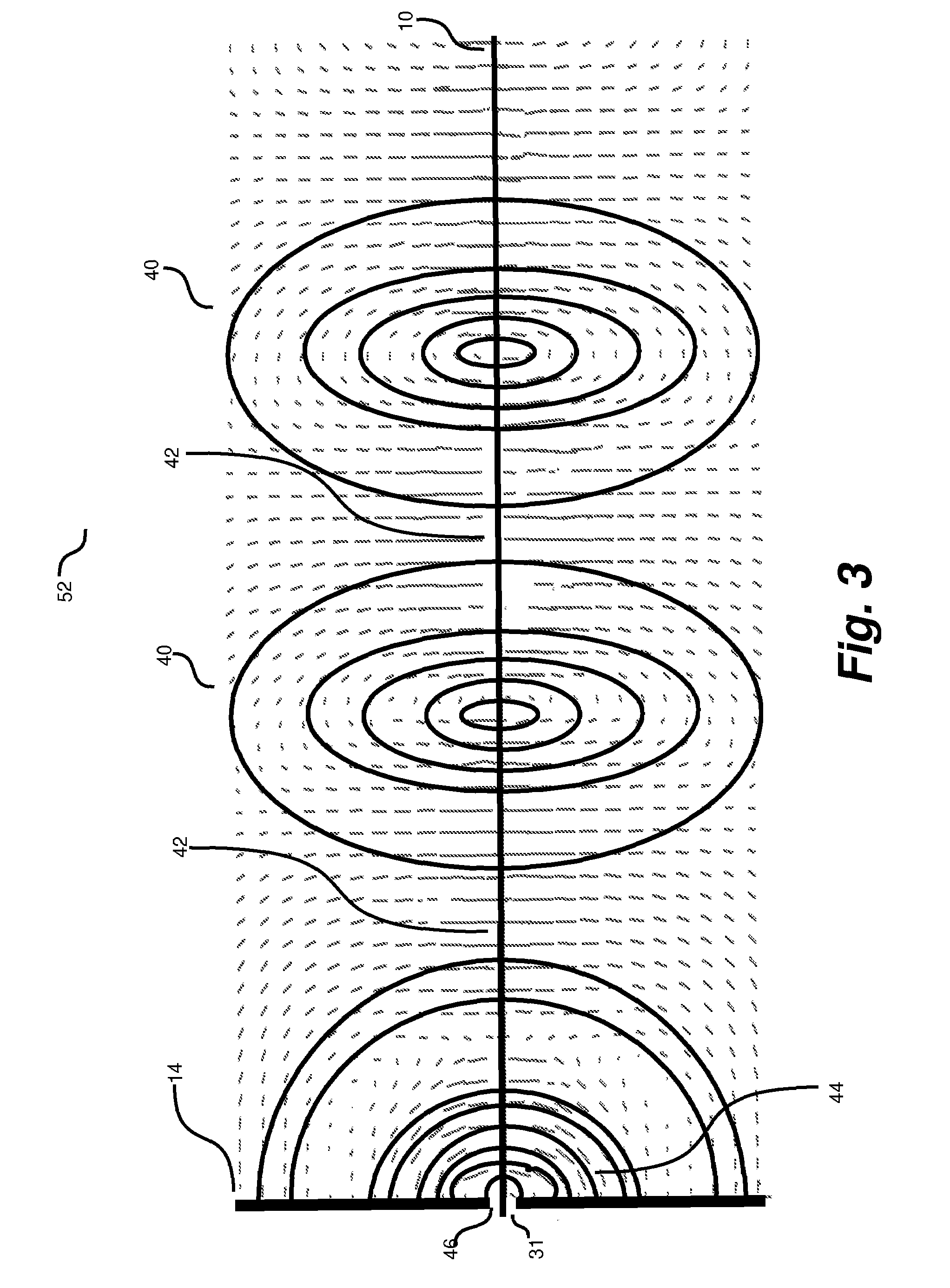
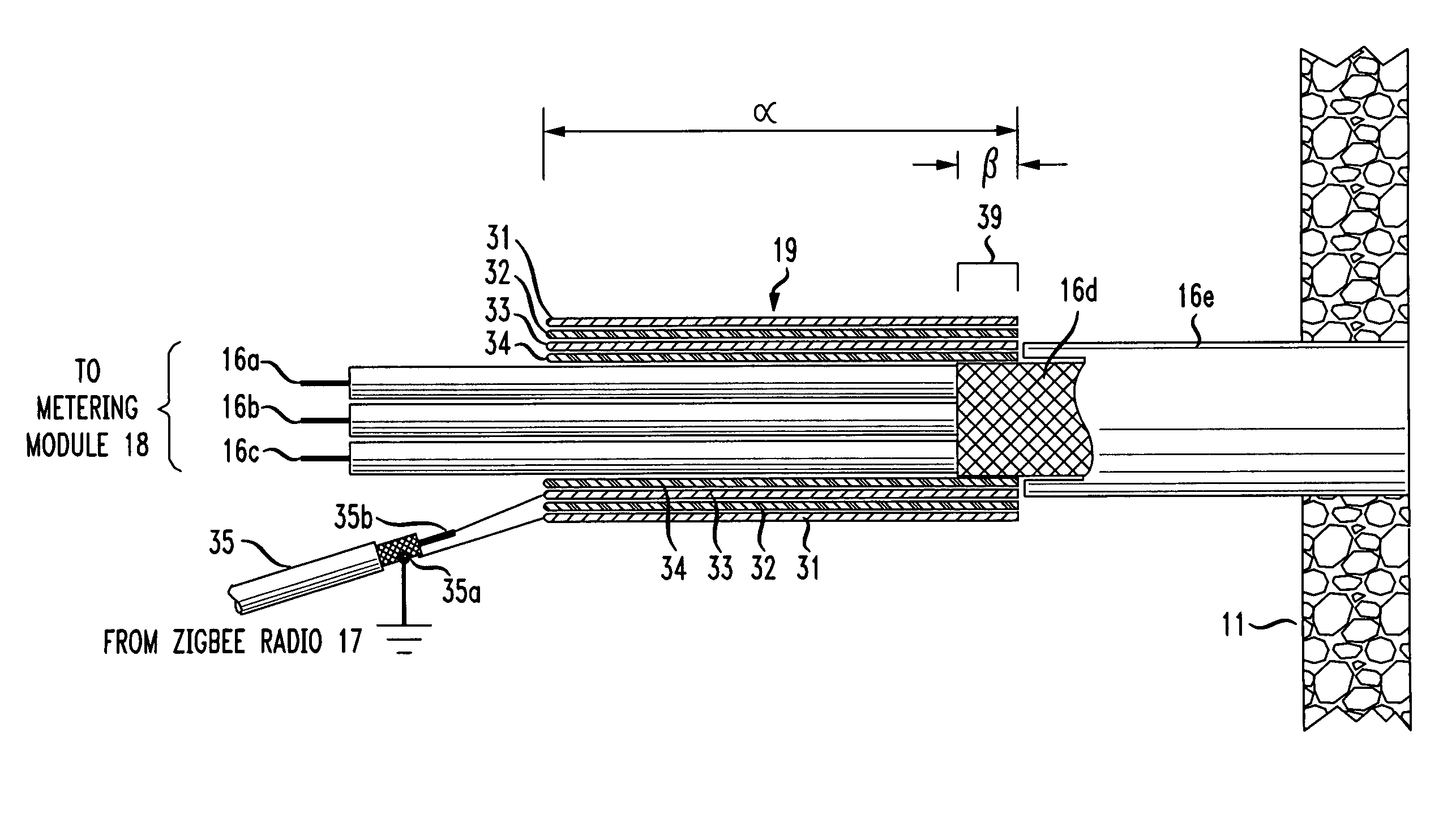
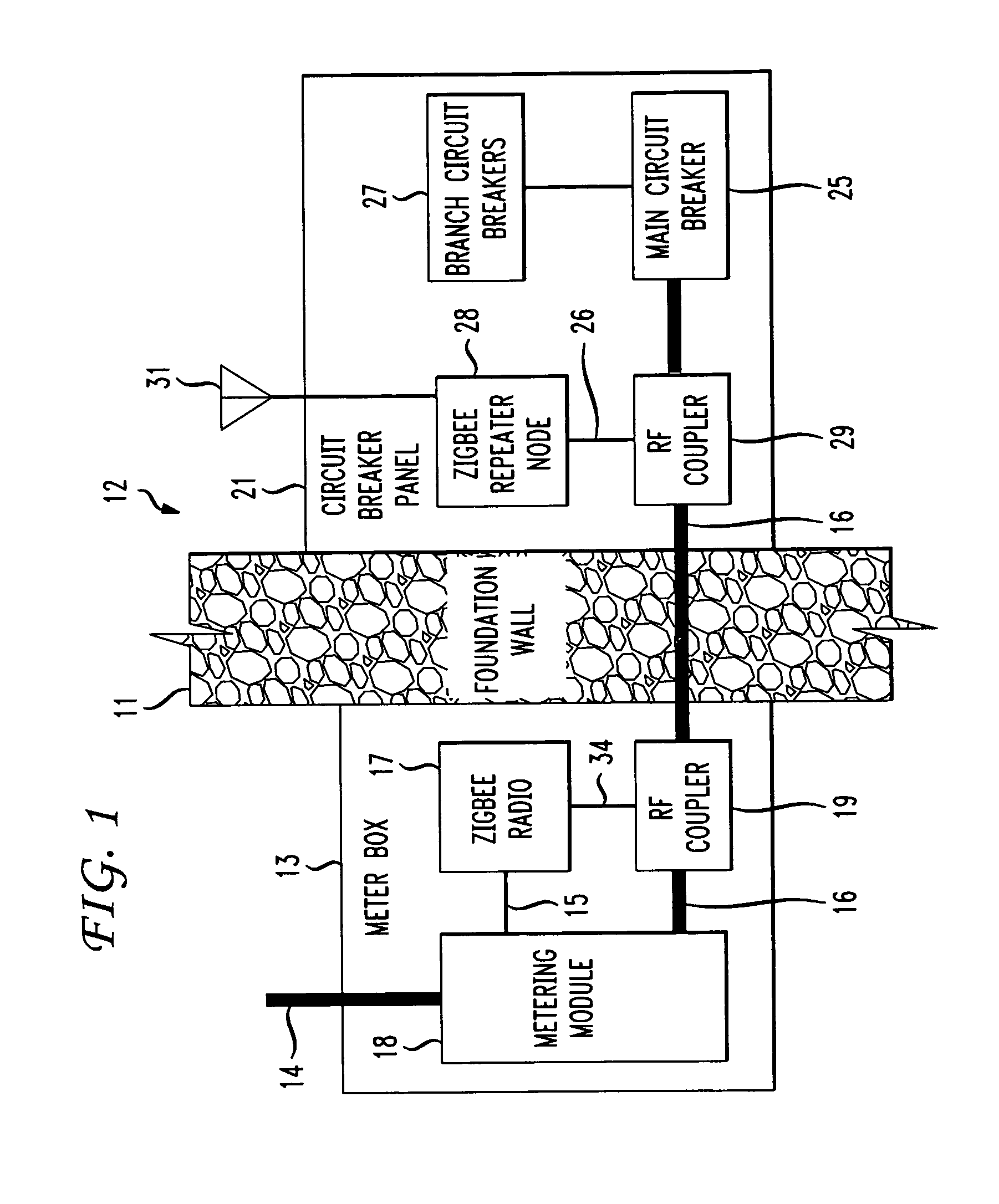
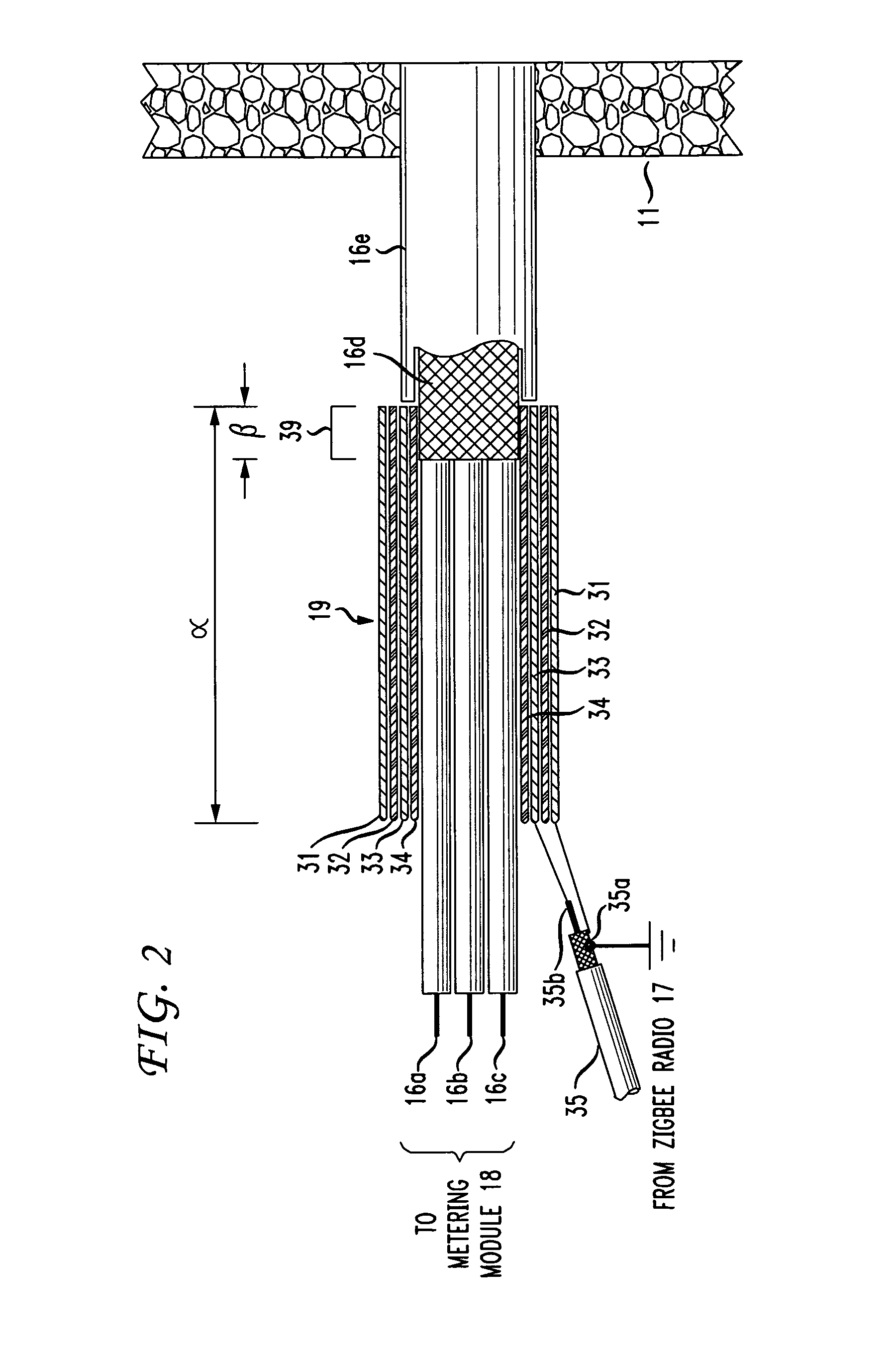
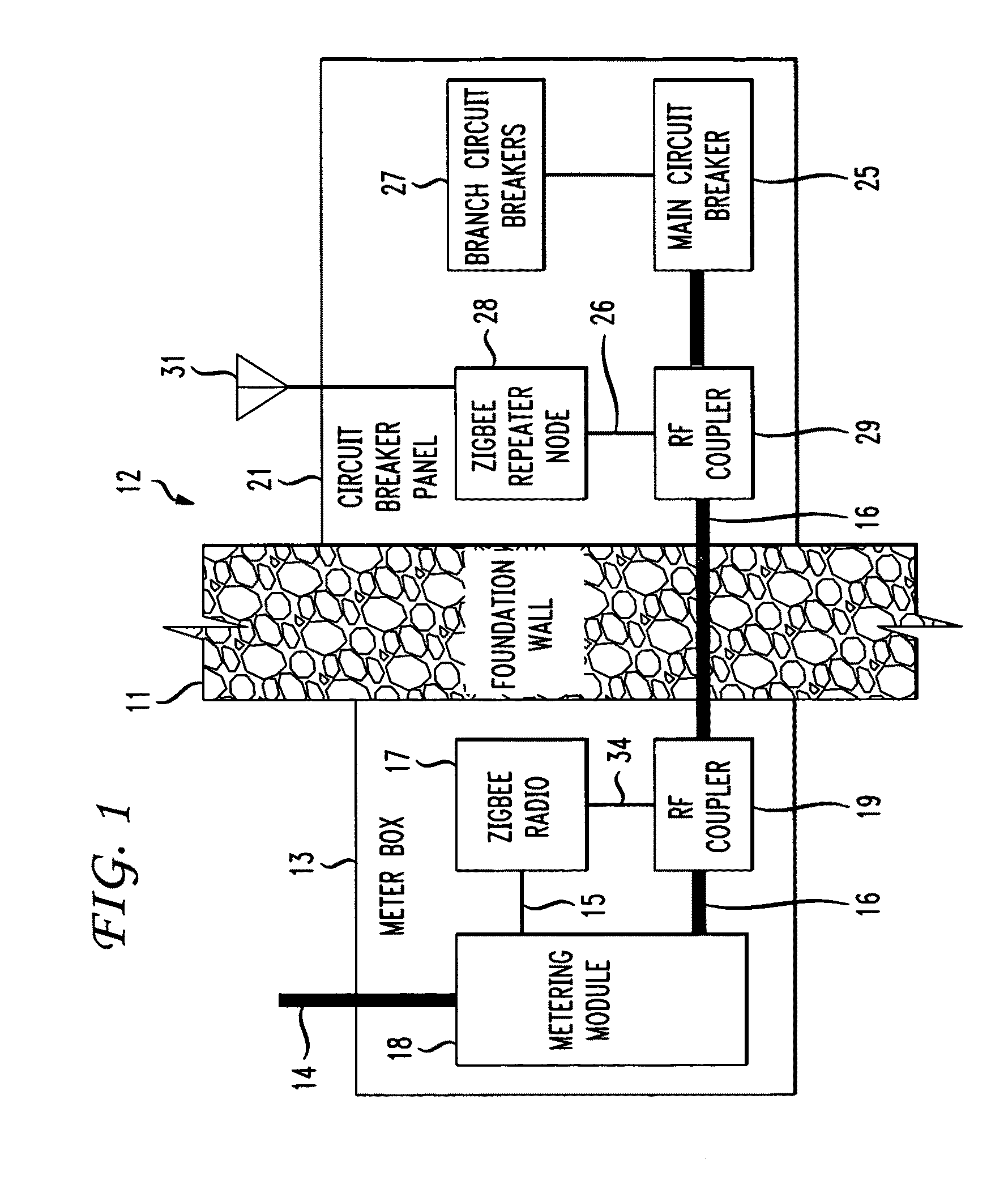
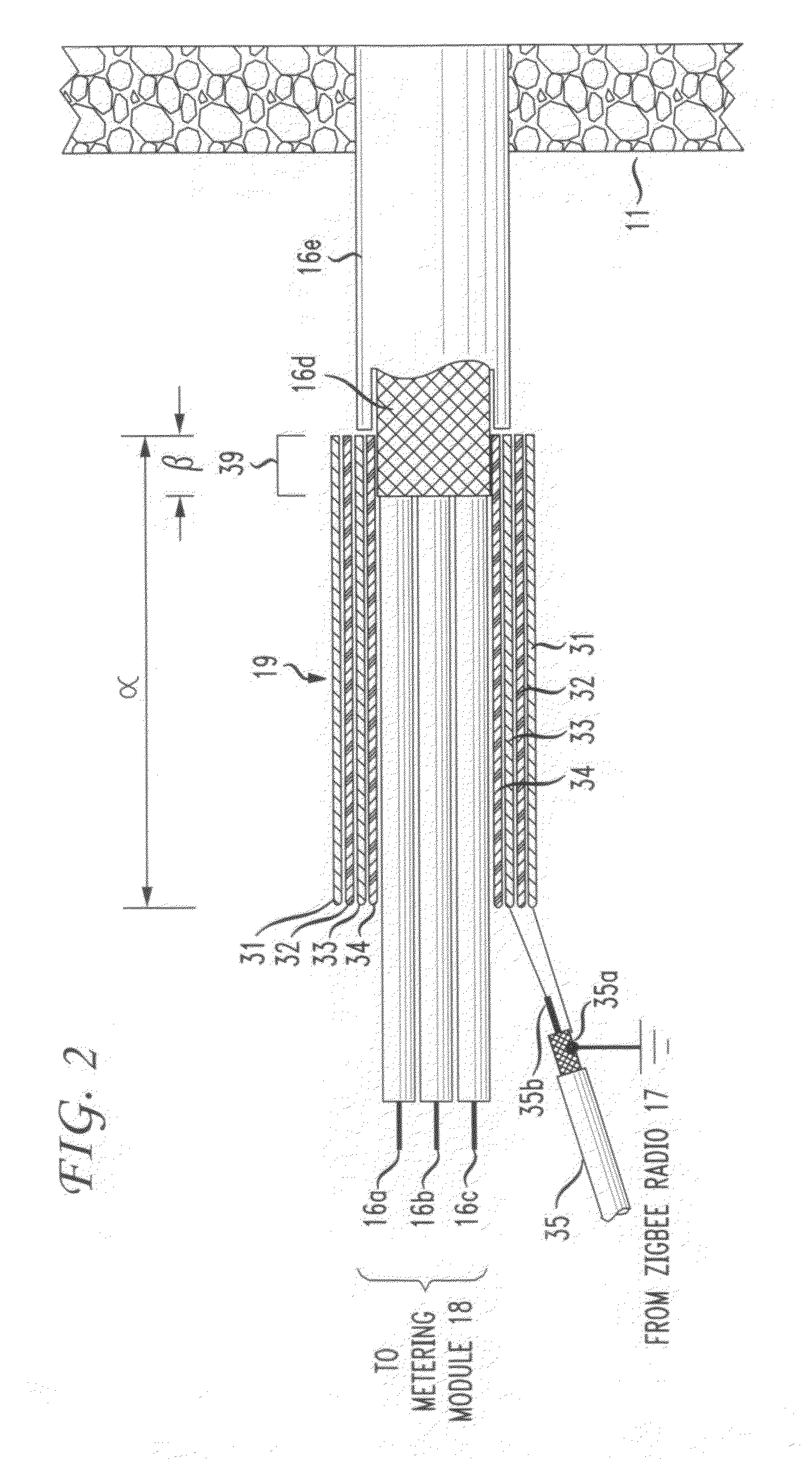
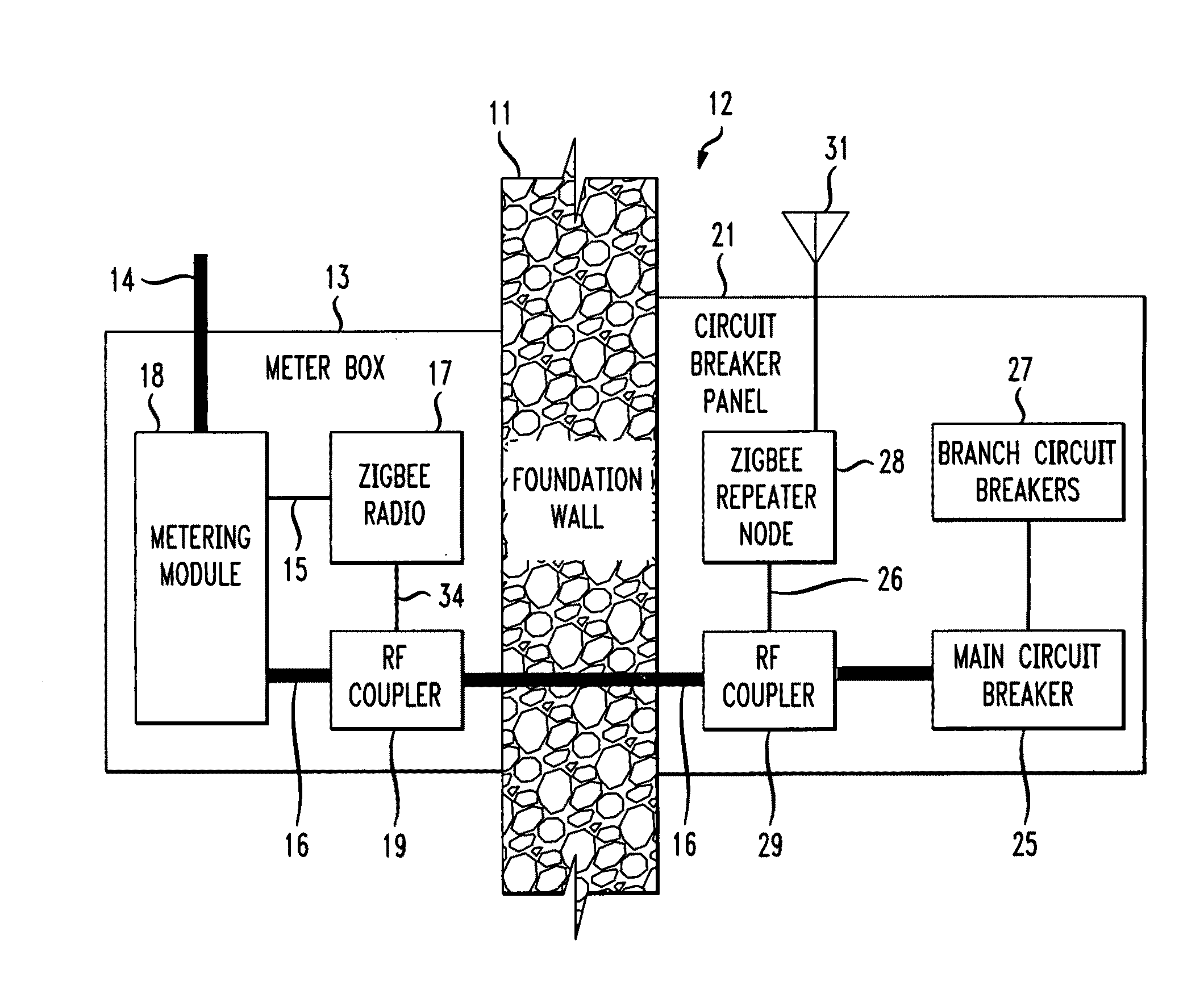
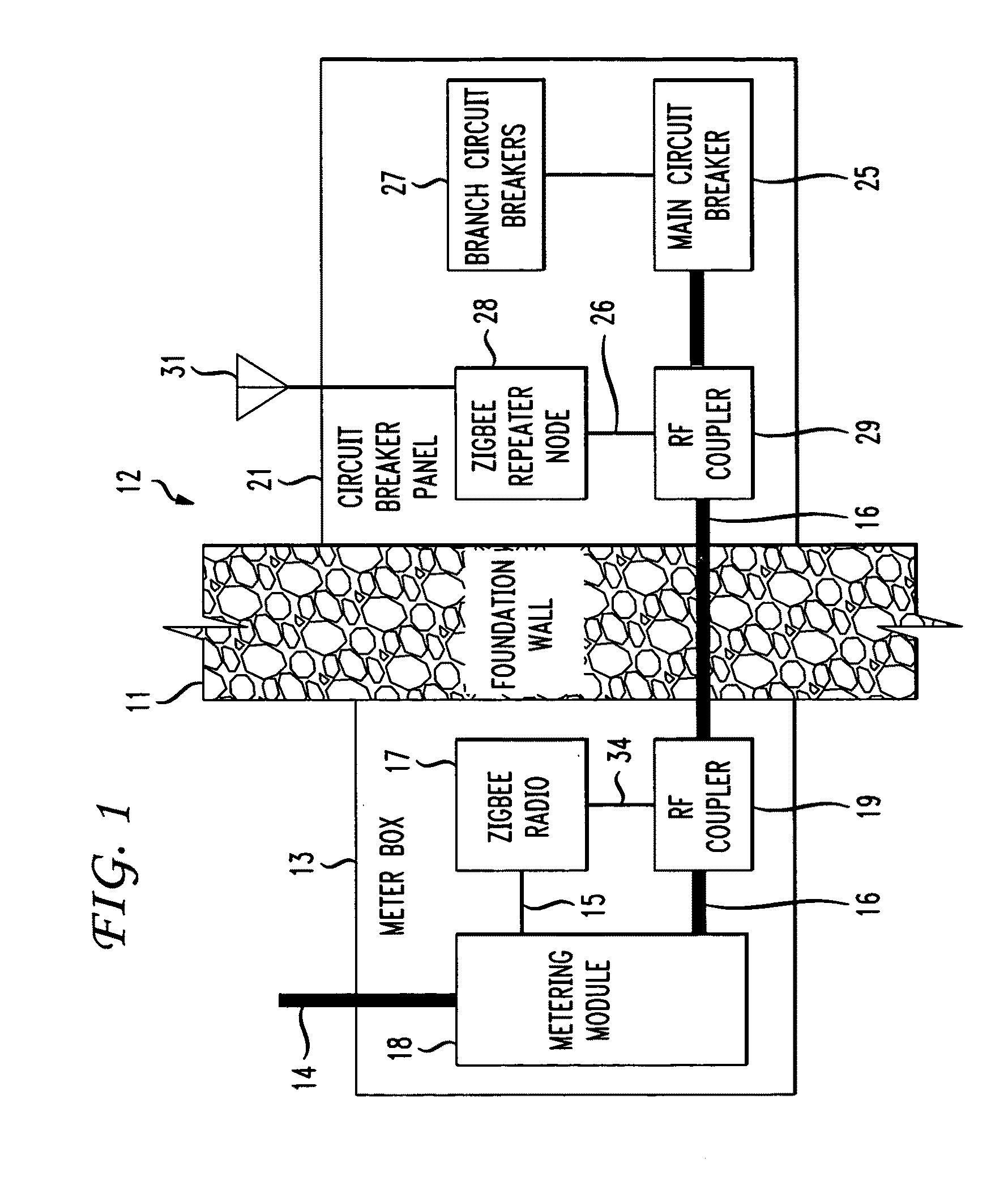
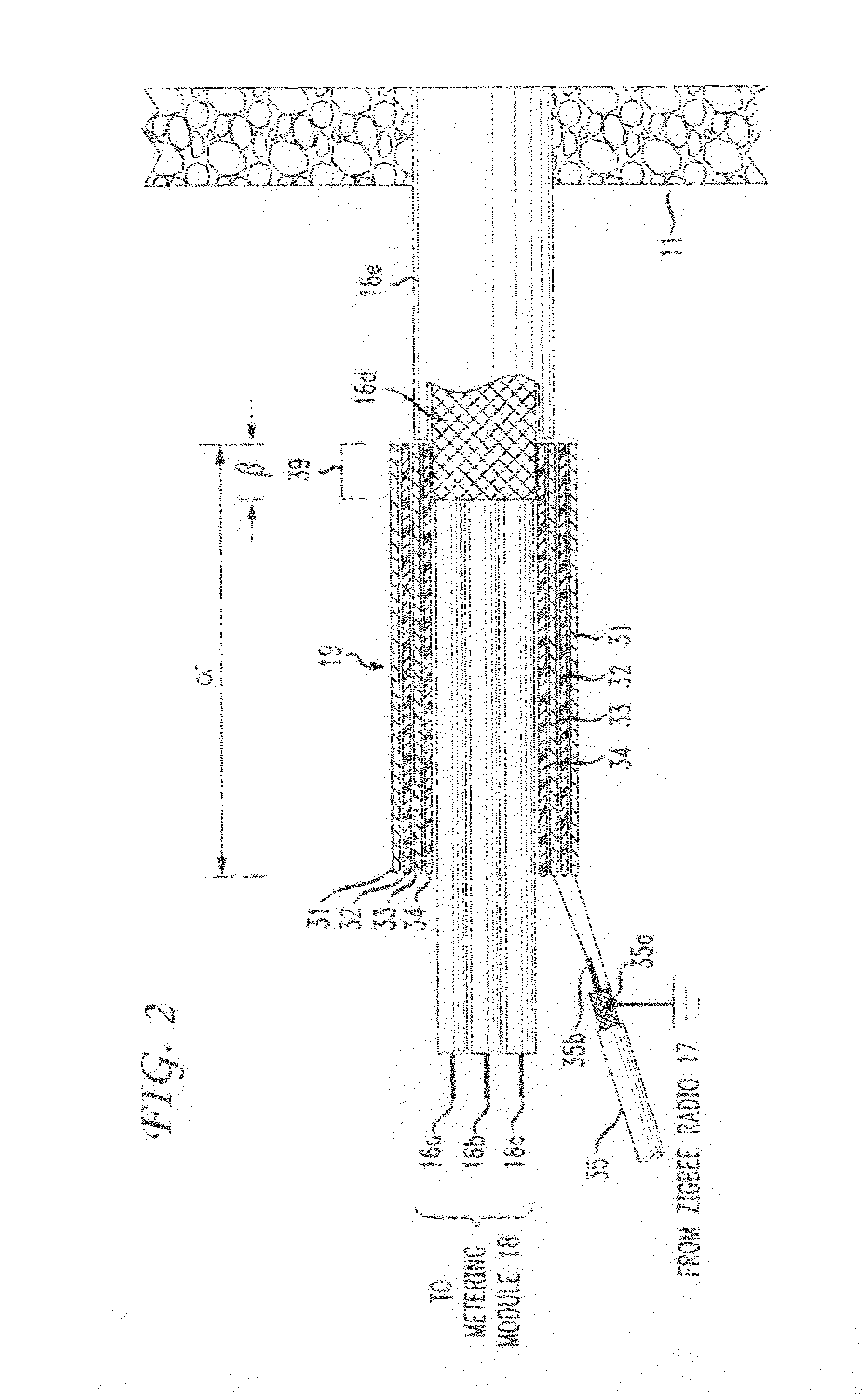
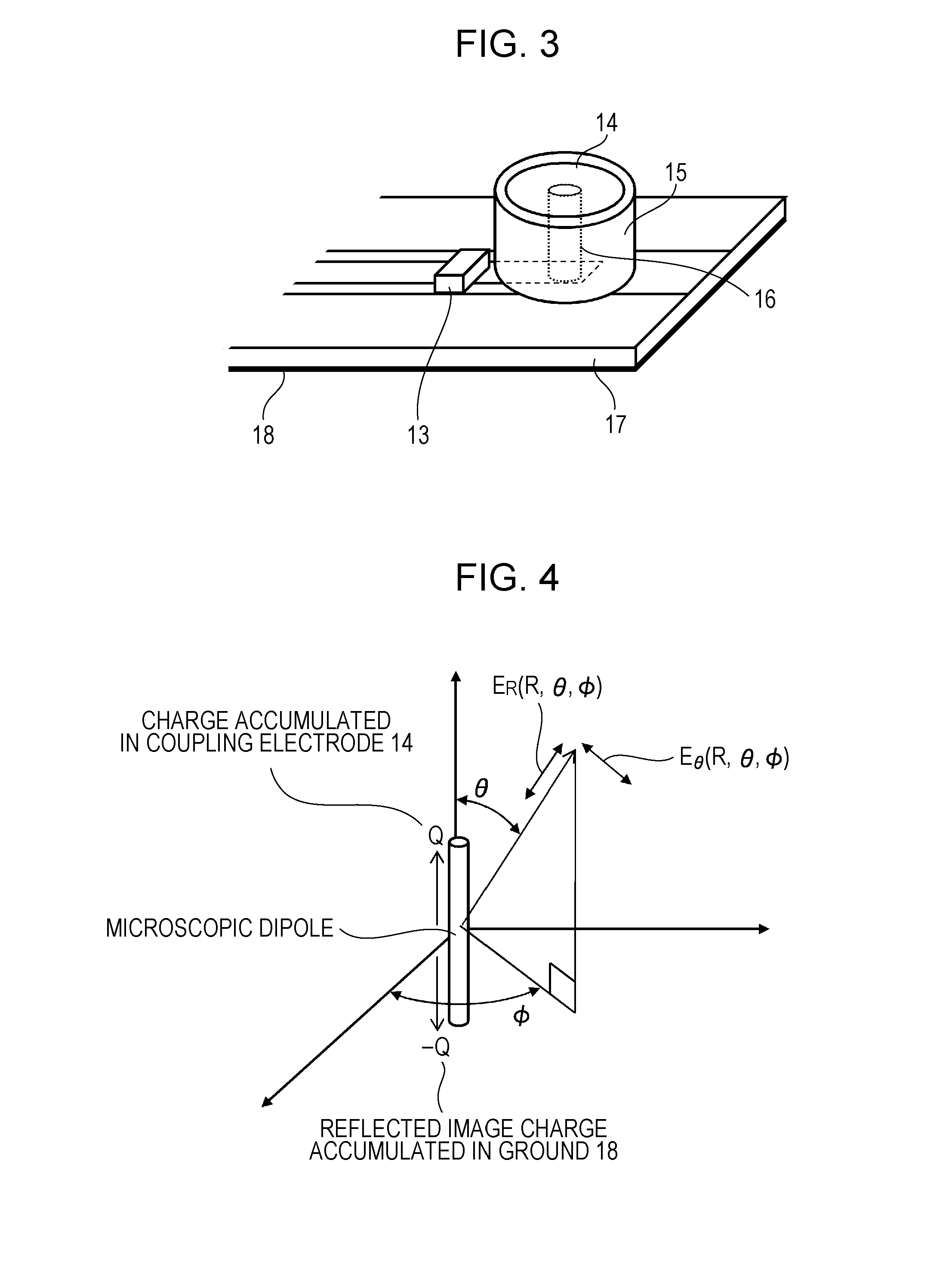
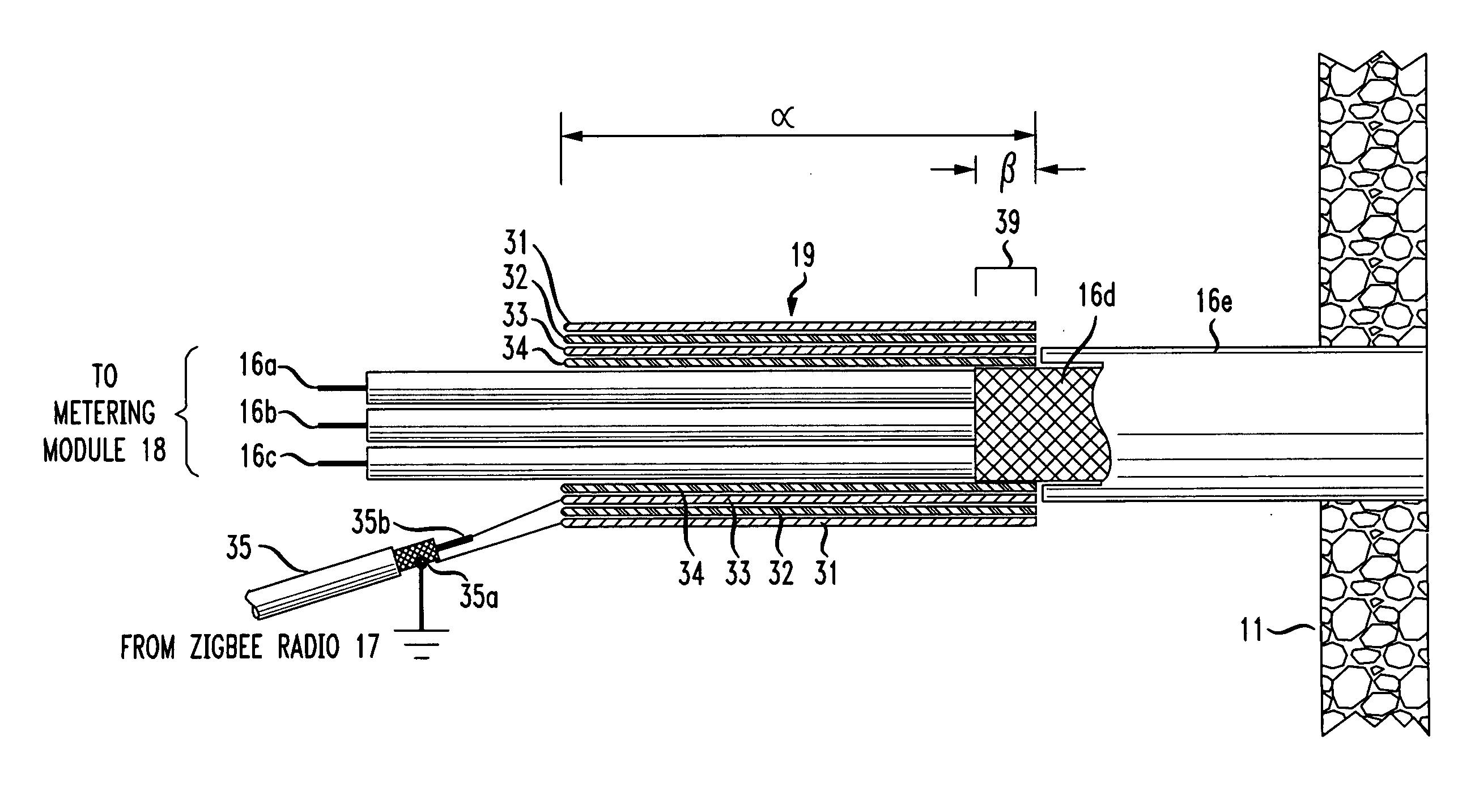
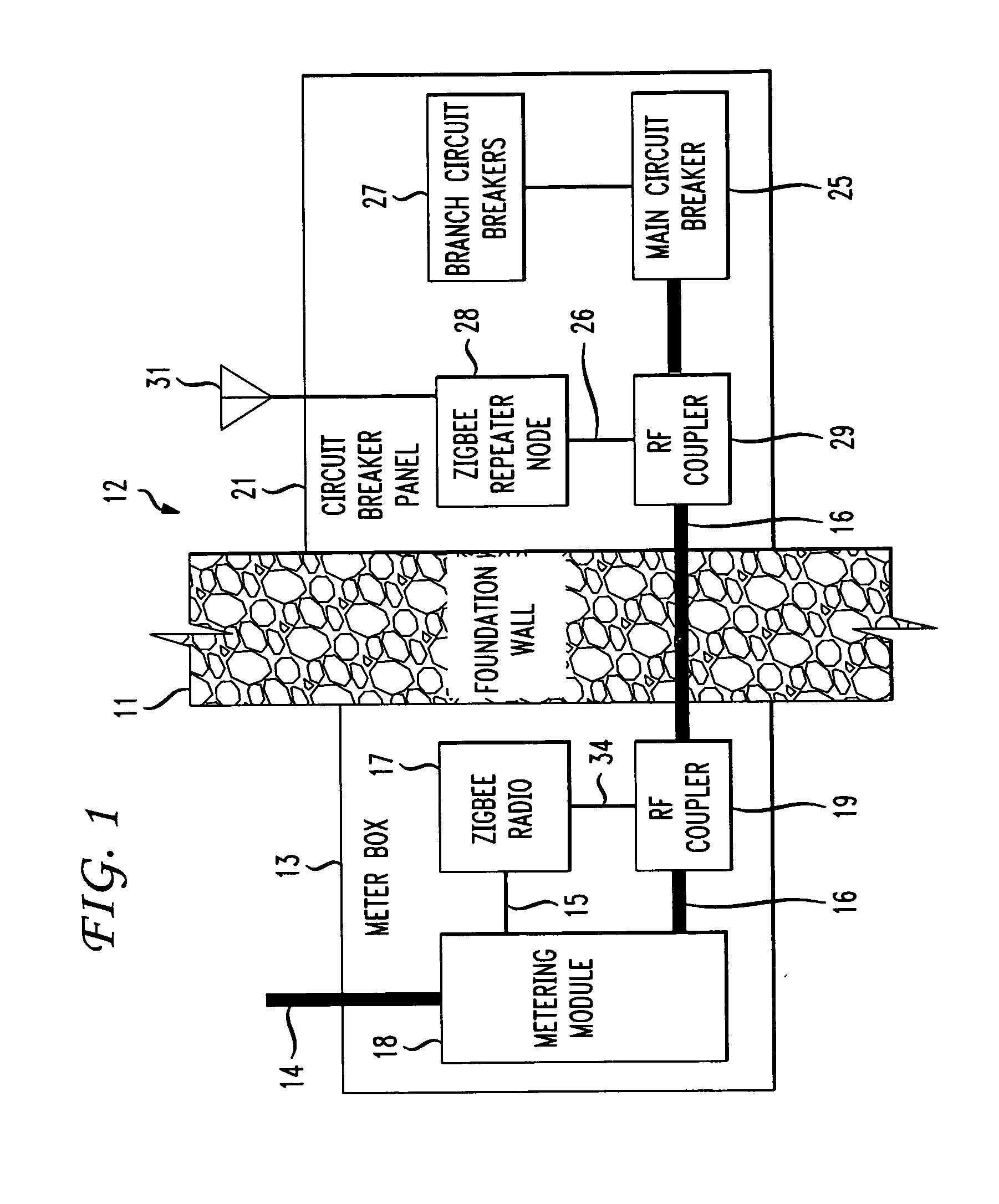
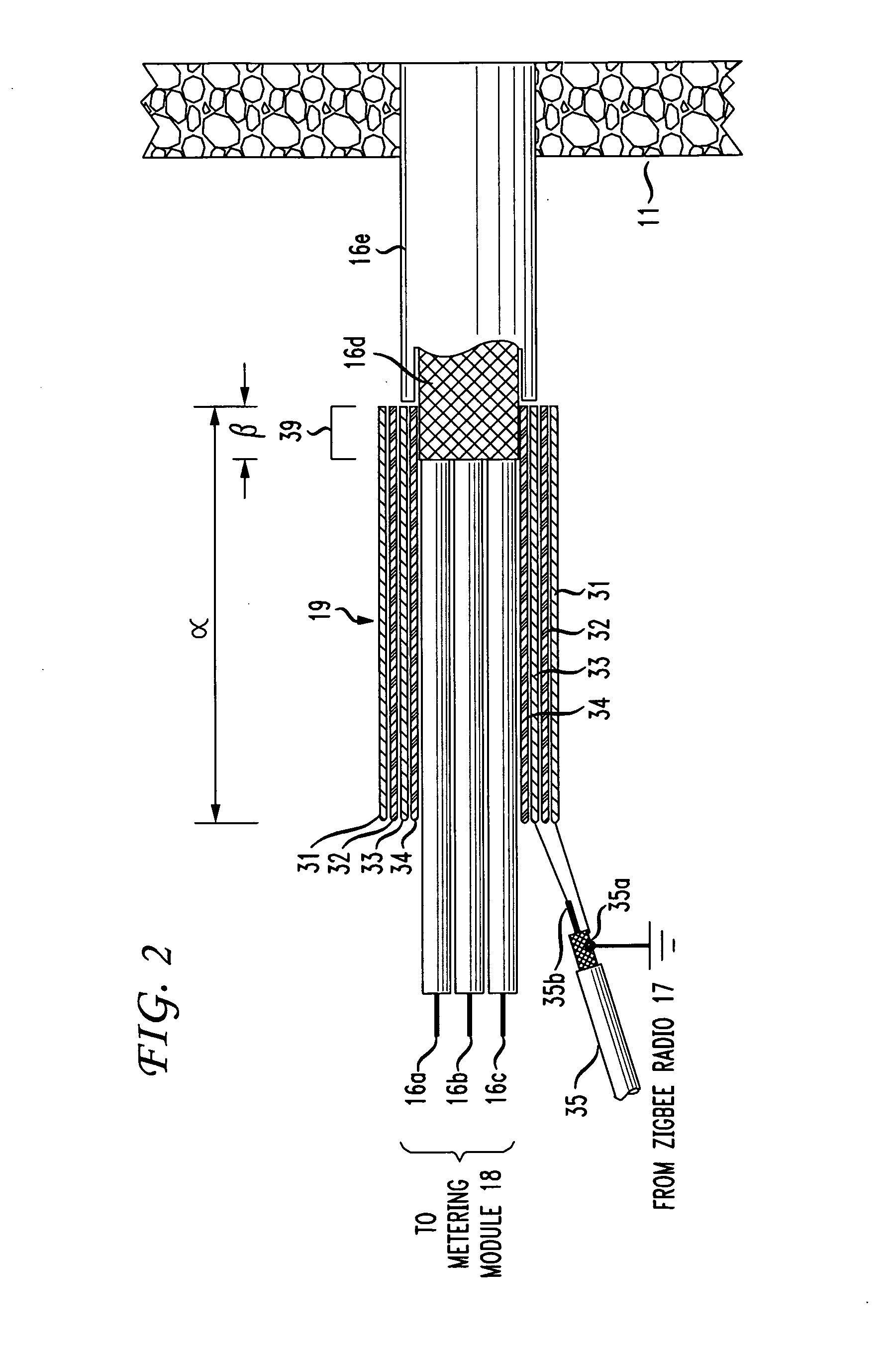
The RF signal generated by a ZigBee radio on the outside of a building structure is conveyed to the interior of the building by guiding it along an electric cable bundle that passes through the building's wall to supply domestic electric power to the interior of the structure. The RF signal is launched by a unique coupler comprising a pair of insulated foil conductors.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I LP
Surface wave communications between a remote antenna and a base station that is co-located with another base station
ActiveUS7590404B1Interconnection arrangementsNetwork traffic/resource managementSurface waveBase station
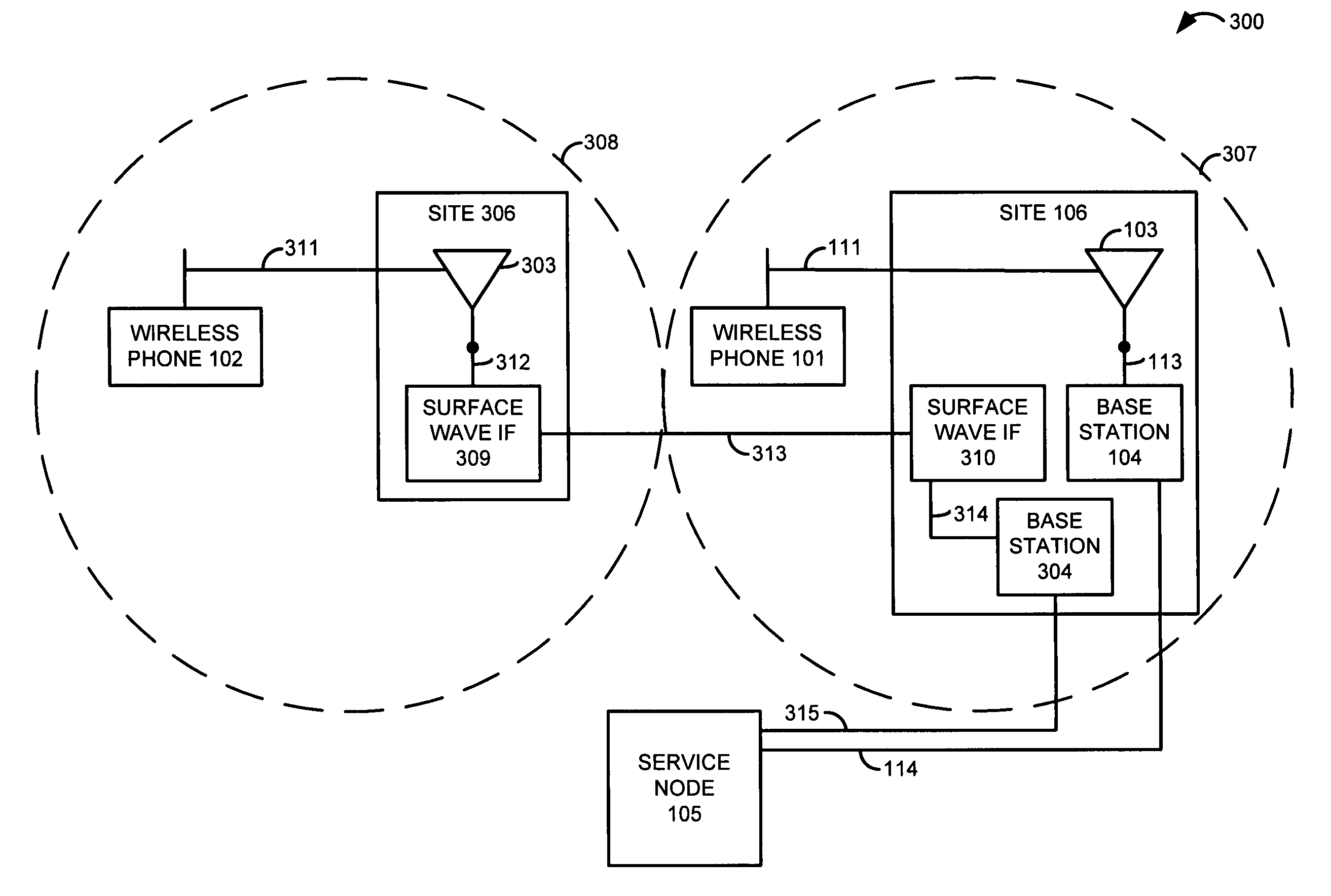
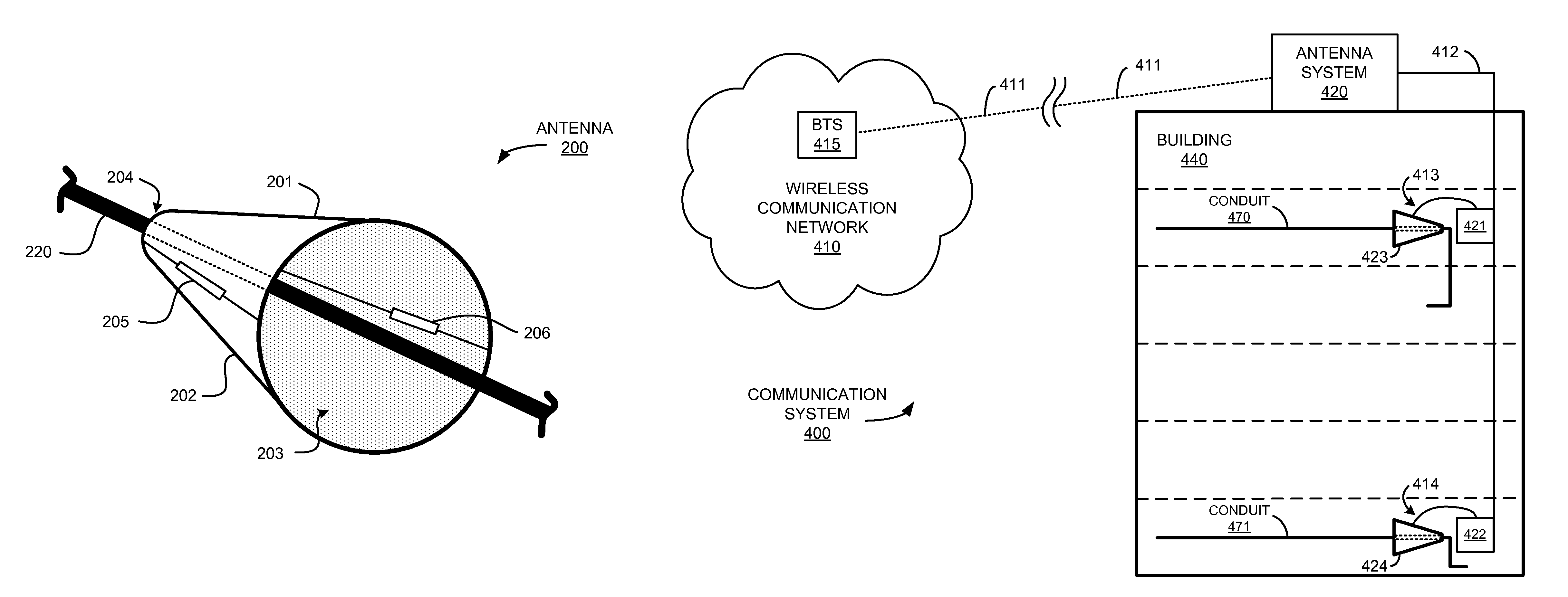
At a first site, a first antenna exchanges first communications with wireless devices, and exchanges the first communications with a first base station. The first base station exchanges the first communications with a service node. At a second site, a second antenna exchanges second communications with other wireless devices, and exchanges the second communications with a first surface wave interface. The first surface wave interface exchanges the second communications with a second surface wave interface at the first site. The second surface wave interface exchanges the second communications with a second base station at the first site. The second base station exchanges the second communications with the service node. The service node processes the first and second communications to provide a communication service to the wireless devices.
Owner:T MOBILE INNOVATIONS LLC
Conductive line communication apparatus and conductive line radar system and method
InactiveUS8159385B2Eliminate the effects ofIncrease the areaDuplex signal operationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTransceiverRadar systems
A conductive line radar comprising at least one signal surface wave launcher, which comprises a signal surface wave transceiver, which is physically attached to a power line. The signal surface wave transceiver transmits a wave signal along the power line with another signal radiating from the wave signal in a plurality of directions along the power line. The at least one signal surface wave transceiver receives reflected signals from a target within a distance of the power line. The at least one signal surface wave launcher includes at least one RF communications transceiver and can be inductively powered from the power line.
Owner:SENSIS CORPORATION
Using an electric power cable as the vehicle for communicating an information-bearing signal through a barrier
ActiveUS8253516B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsOne-port networksPower cableElectrical conductor
The RF signal generated by a ZigBee radio on the outside of a building structure is conveyed to the interior of the building by guiding it as a surface wave along an electric cable bundle that passes through the building's wall to supply domestic electric power to the interior of the structure. The RF signal is launched by a unique coupler comprising a pair of insulated foil conductors.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
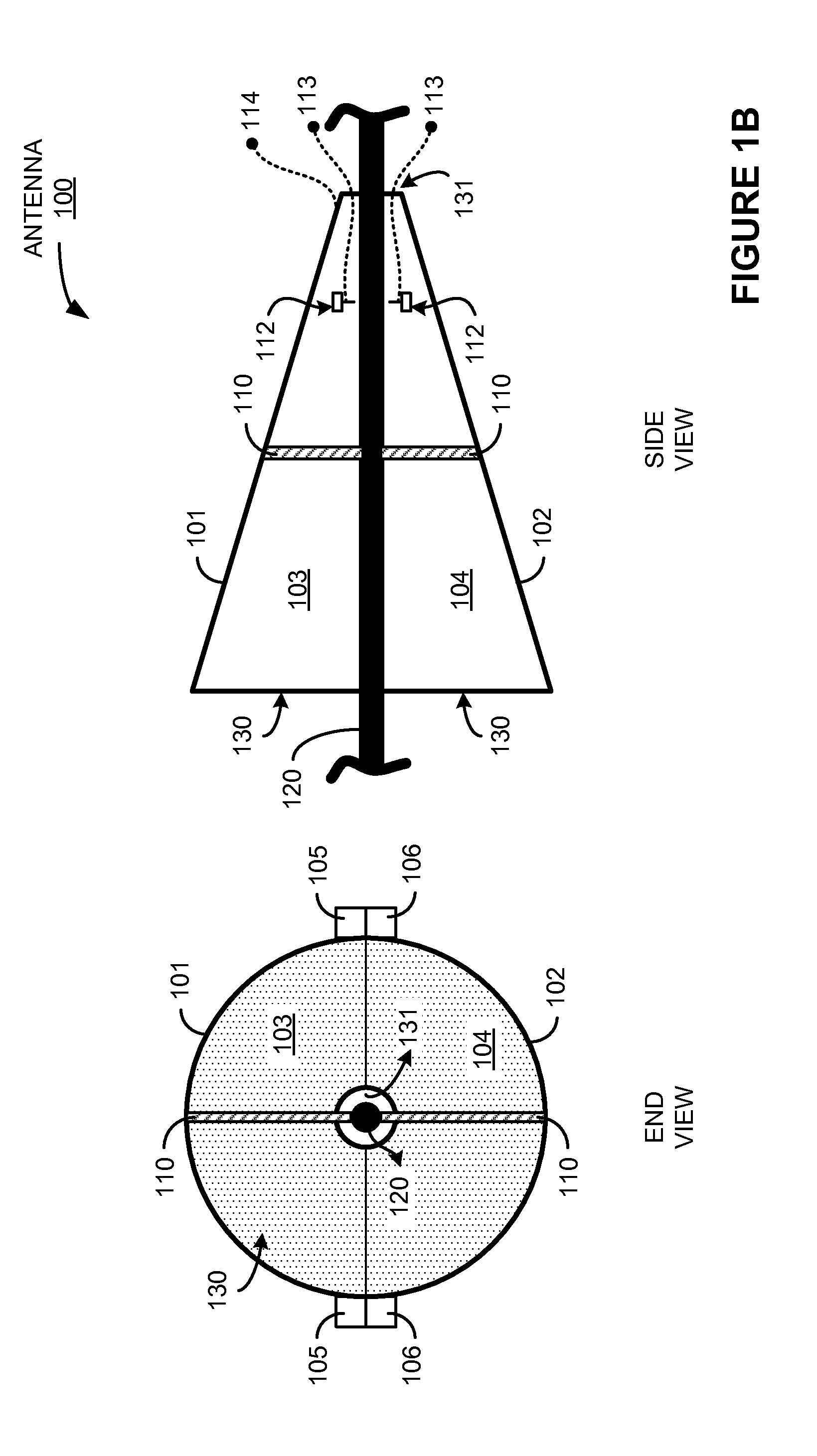
Surface wave antenna mountable on existing conductive structures
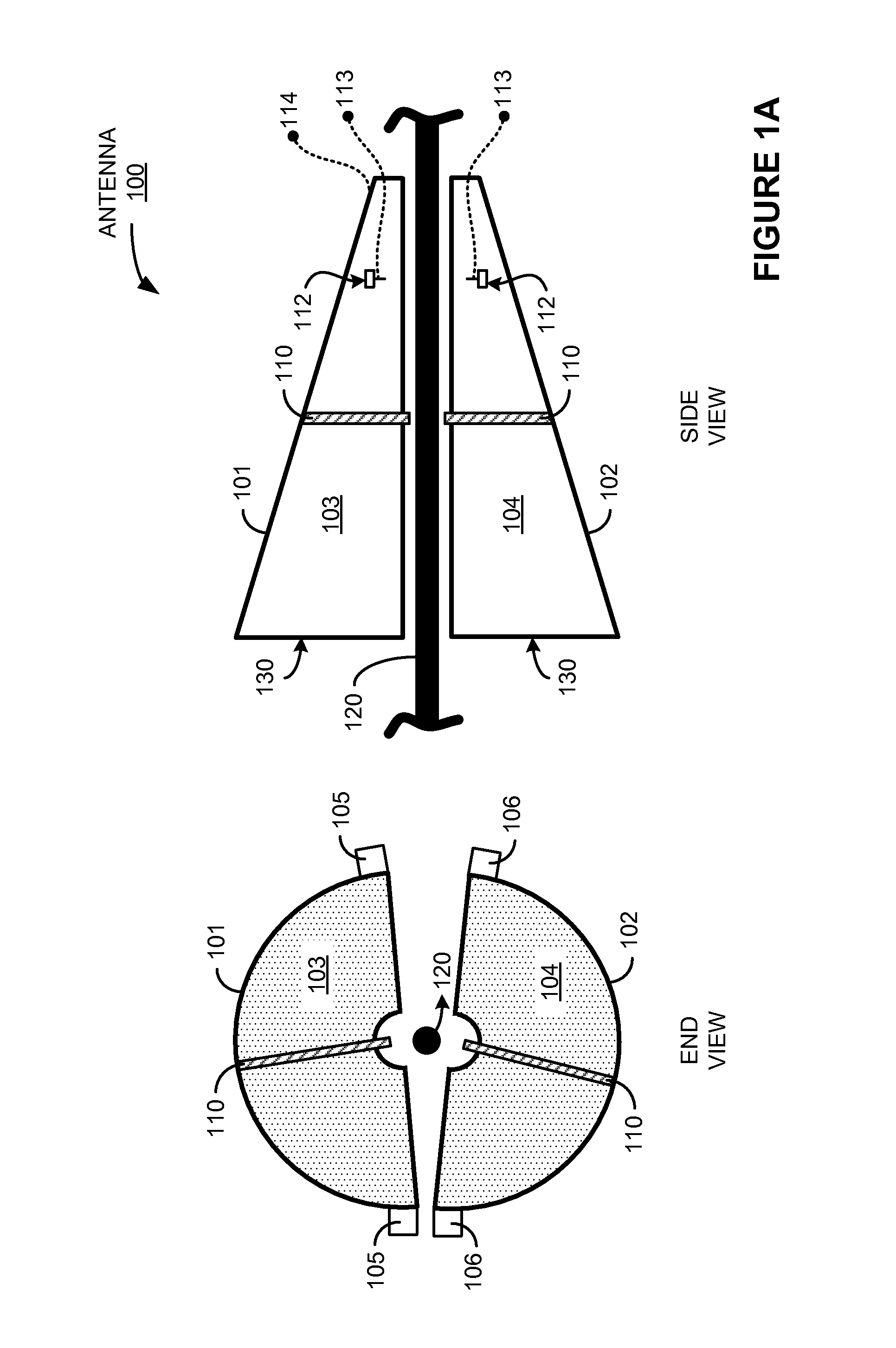
What is disclosed is a surface wave antenna configured to install on an electrically conductive structure. The surface wave antenna includes a first portion comprising a conductive element and an attachment element, and a second portion comprising a conductive element and an attachment element. The conductive element of the first portion and the conductive element of the second portion are configured to each form a conductive longitudinal portion of a horn receive element, and the attachment elements are configured to conductively couple the conductive elements together to form the horn receive element. The surface wave antenna also includes a dipole element comprising a first transmit element and a second transmit element. The surface wave antenna also includes a mounting element comprising a first dielectric mount and a second dielectric mount.
Owner:T MOBILE INNOVATIONS LLC
Surface wave power line communications system and method
InactiveUS7280033B2Electric signal transmission systemsInterconnection arrangementsCommunication interfaceCommunications system
The present invention provides a system for operating a power line communications system that employs surface wave communications and conducted communications. The system is comprised of a plurality of network elements, which may take the form of repeaters, communication interface devices, backhaul devices, medium voltage transducers, distribution points, aggregation points, and others. In one embodiment, surface waves are communicated over the medium voltage power lines and the conducted communications are communicated via the low voltage power lines to and from customer premises.
Owner:CURRENT TECH
Using an electric power cable as the vehicle for communicating an information-bearing signal through a barrier
ActiveUS20110136432A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsPower distribution line transmissionElectrical conductorPower cable
The RF signal generated by a ZigBee radio on the outside of a building structure is conveyed to the interior of the building by guiding it as a surface wave along an electric cable bundle that passes through the building's wall to supply domestic electric power to the interior of the structure. The RF signal is launched by a unique coupler comprising a pair of insulated foil conductors.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
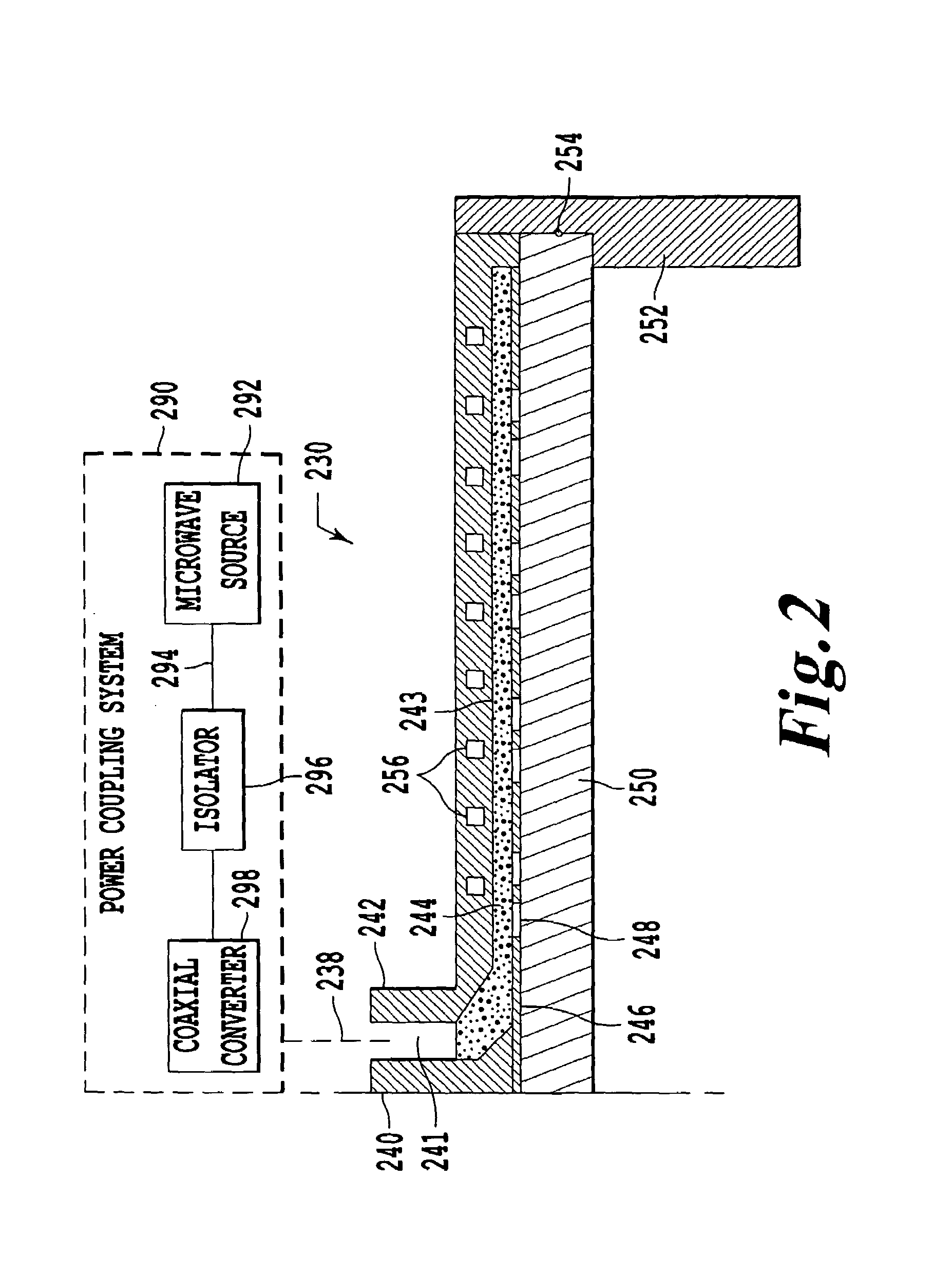
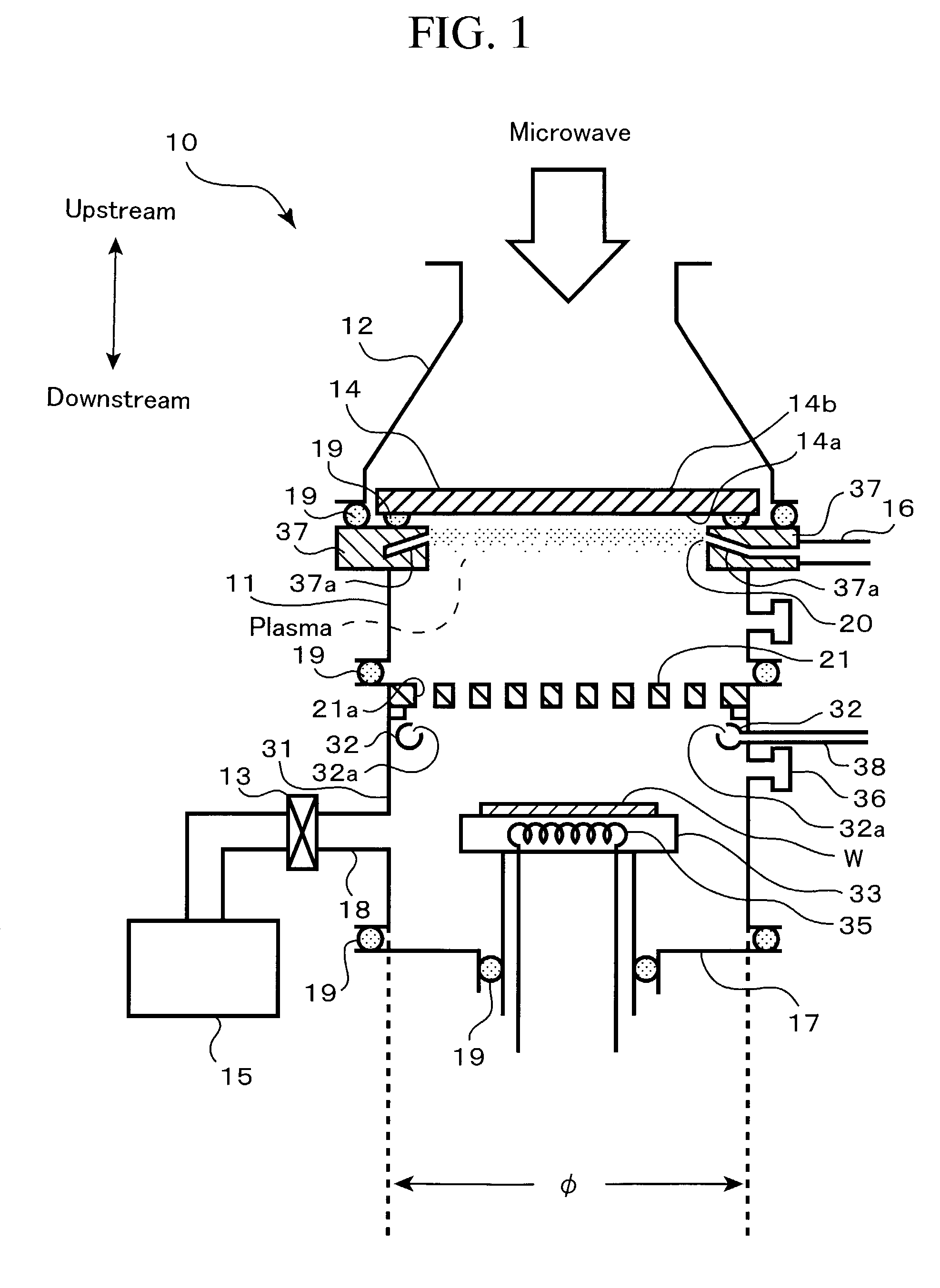
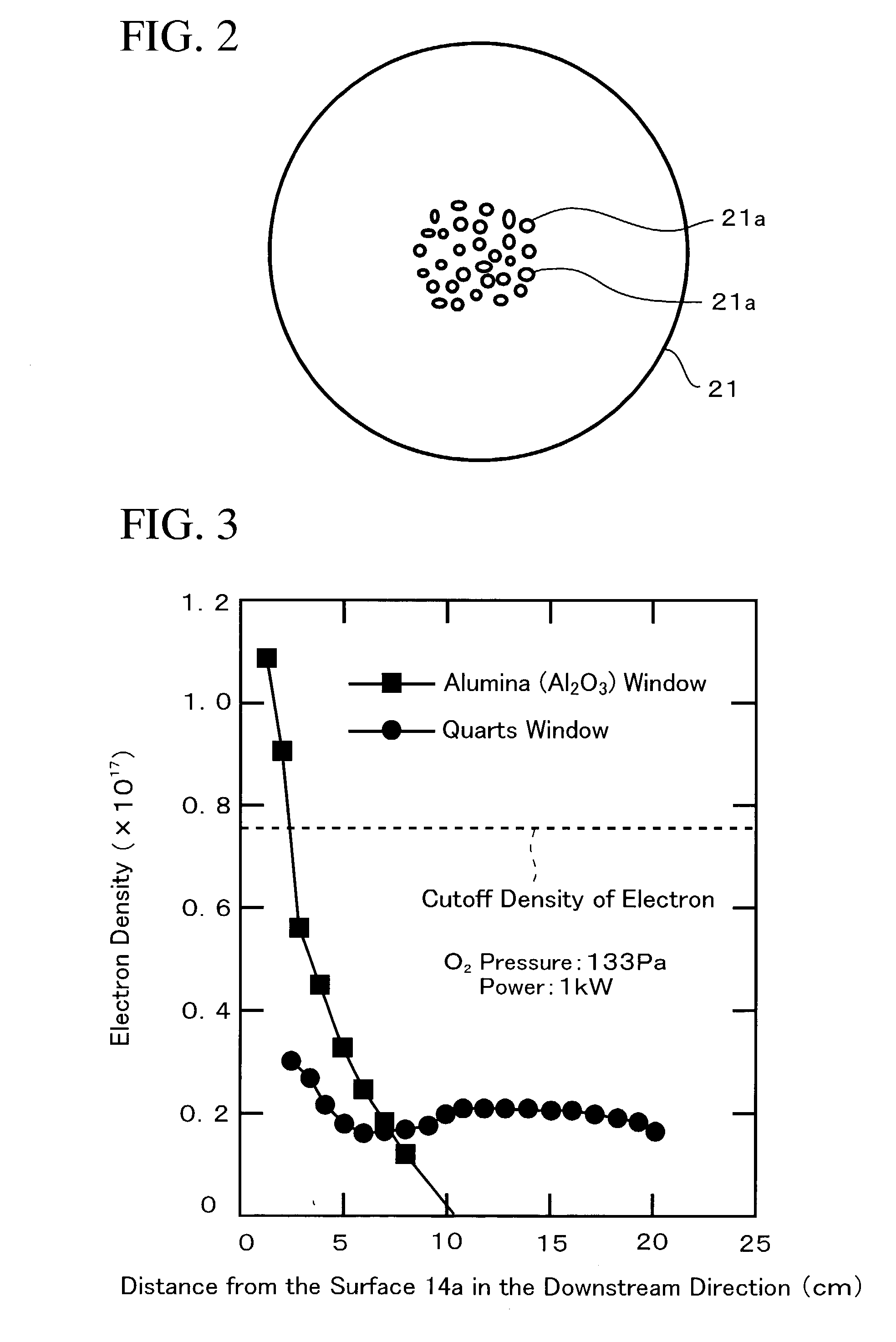
Surface wave plasma processing system and method of using
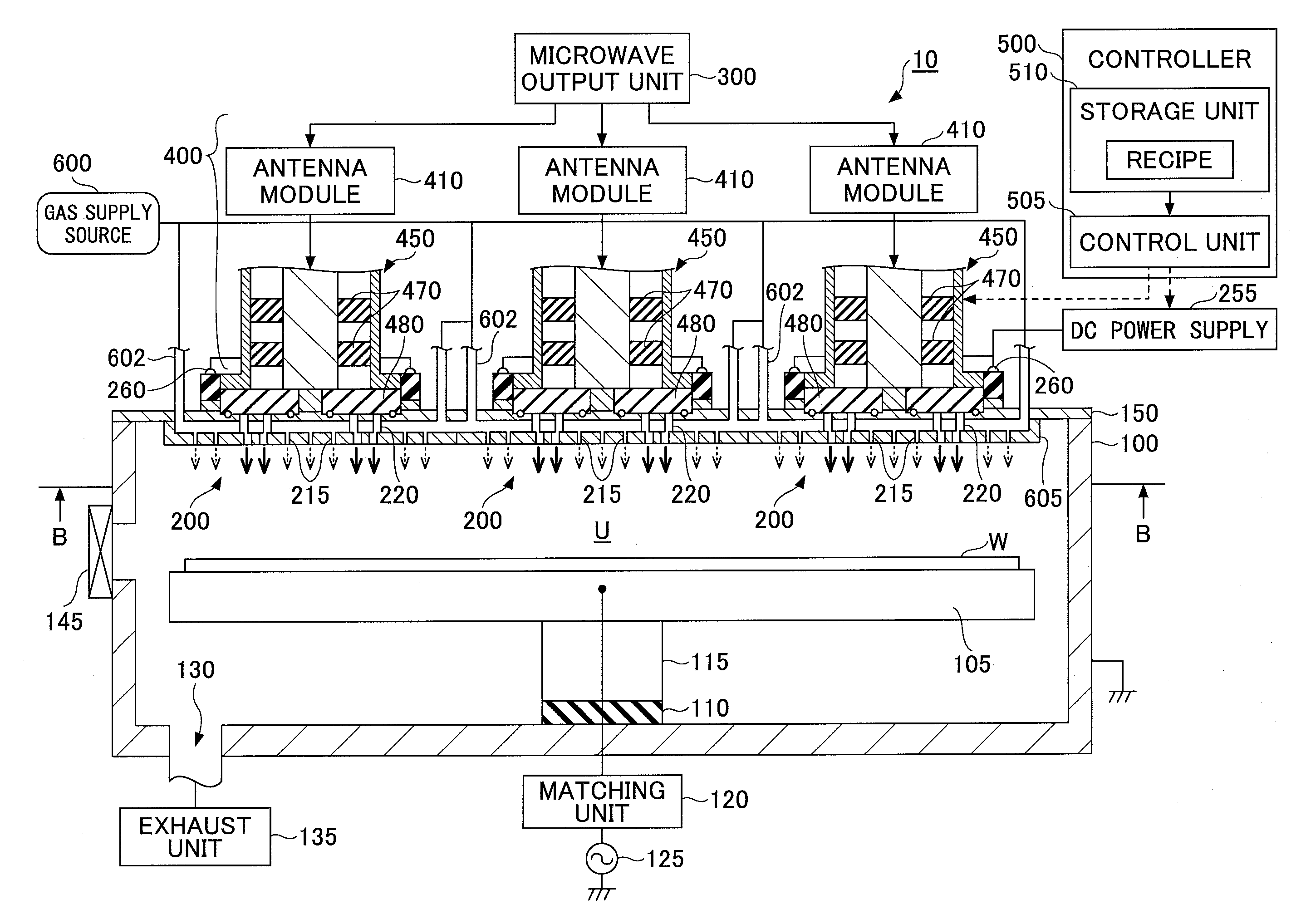
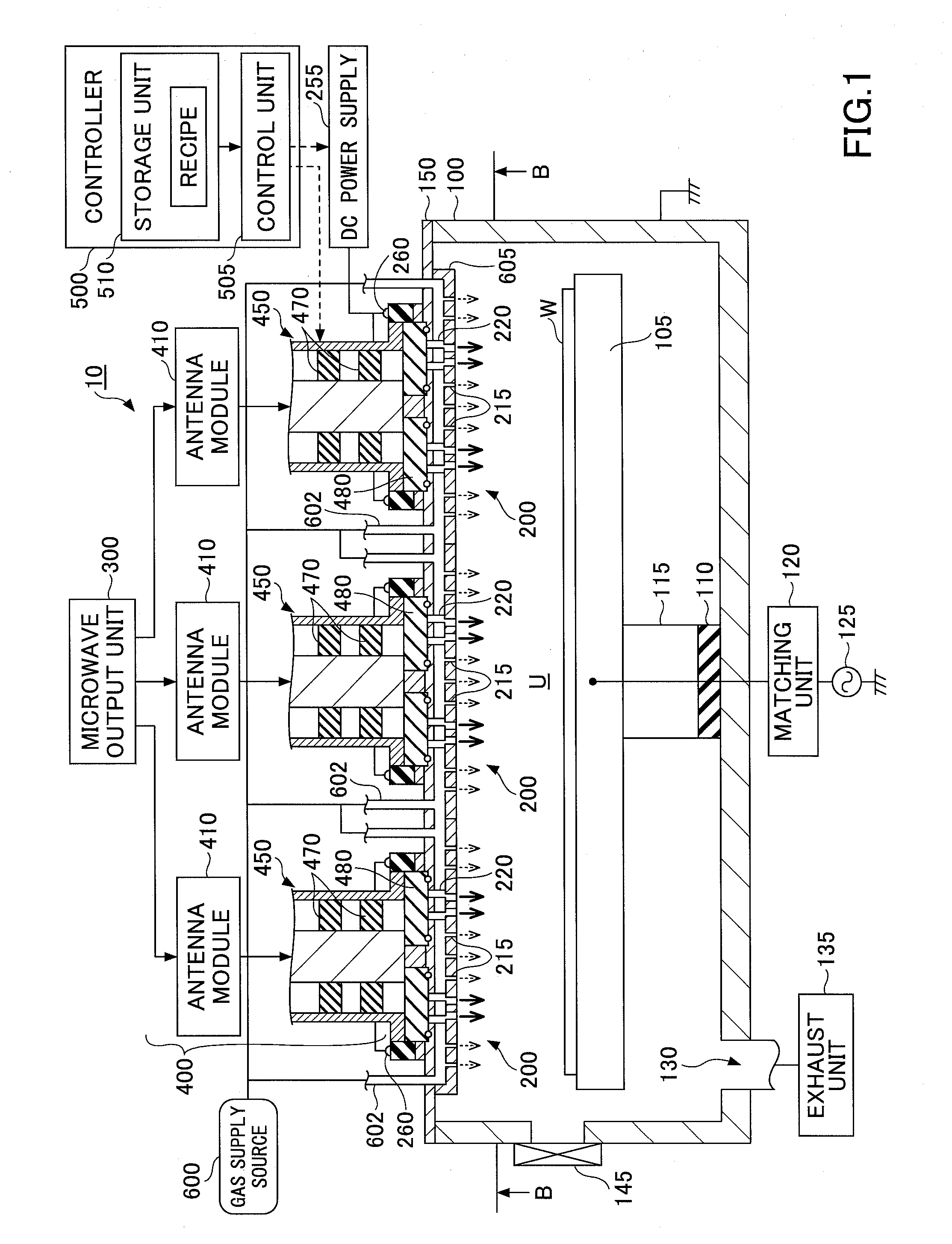
InactiveUS7138767B2Reduce harmReduce the possibility of damageElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsPower couplingPlasma processing
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Communication system
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and apparatus for information conveyance and distribution
InactiveUS20040054425A1Sufficient signal to noise ratioReduce distortion problemsComputer controlElectromagnetic transmissionLow distortionSpread spectrum
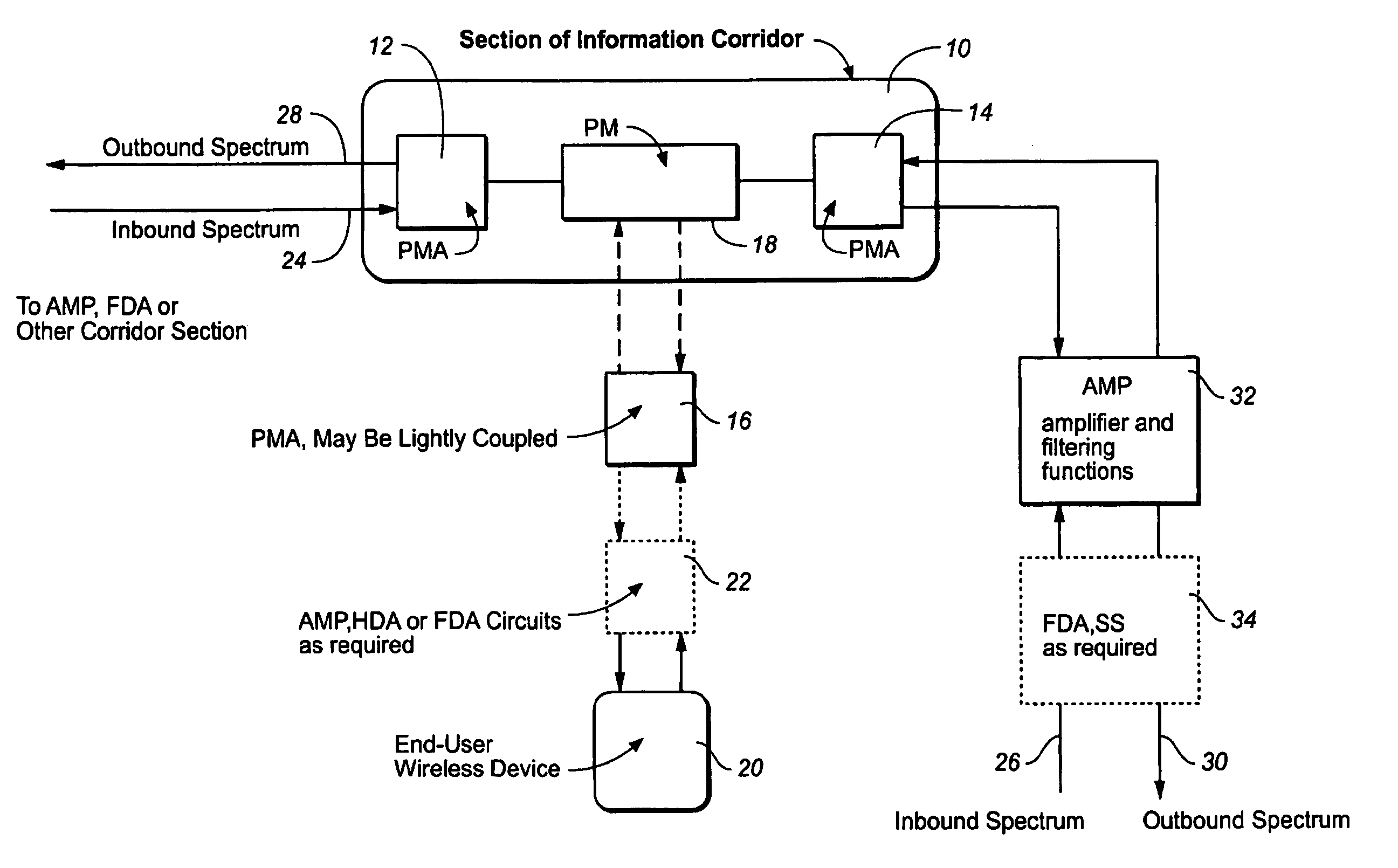
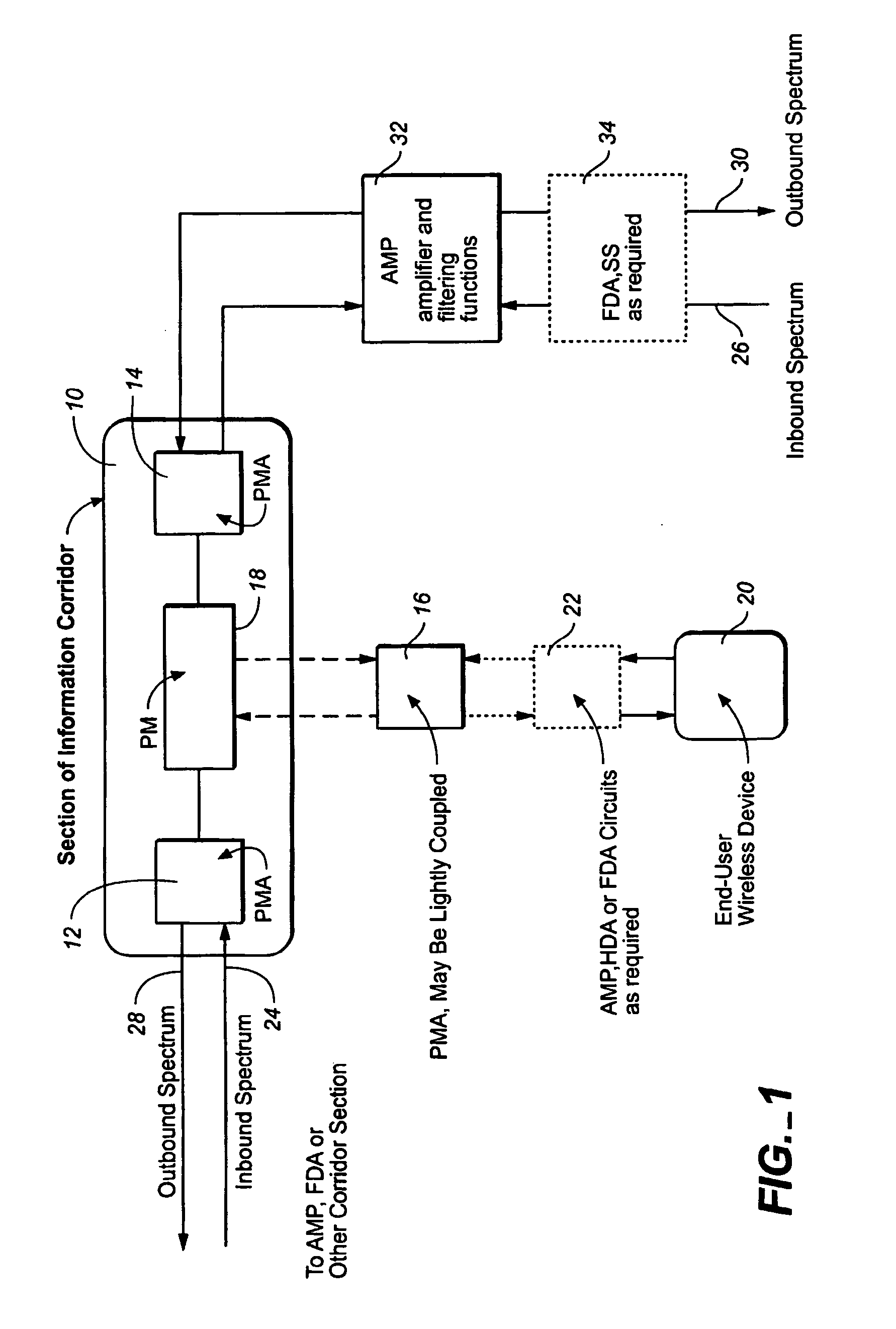
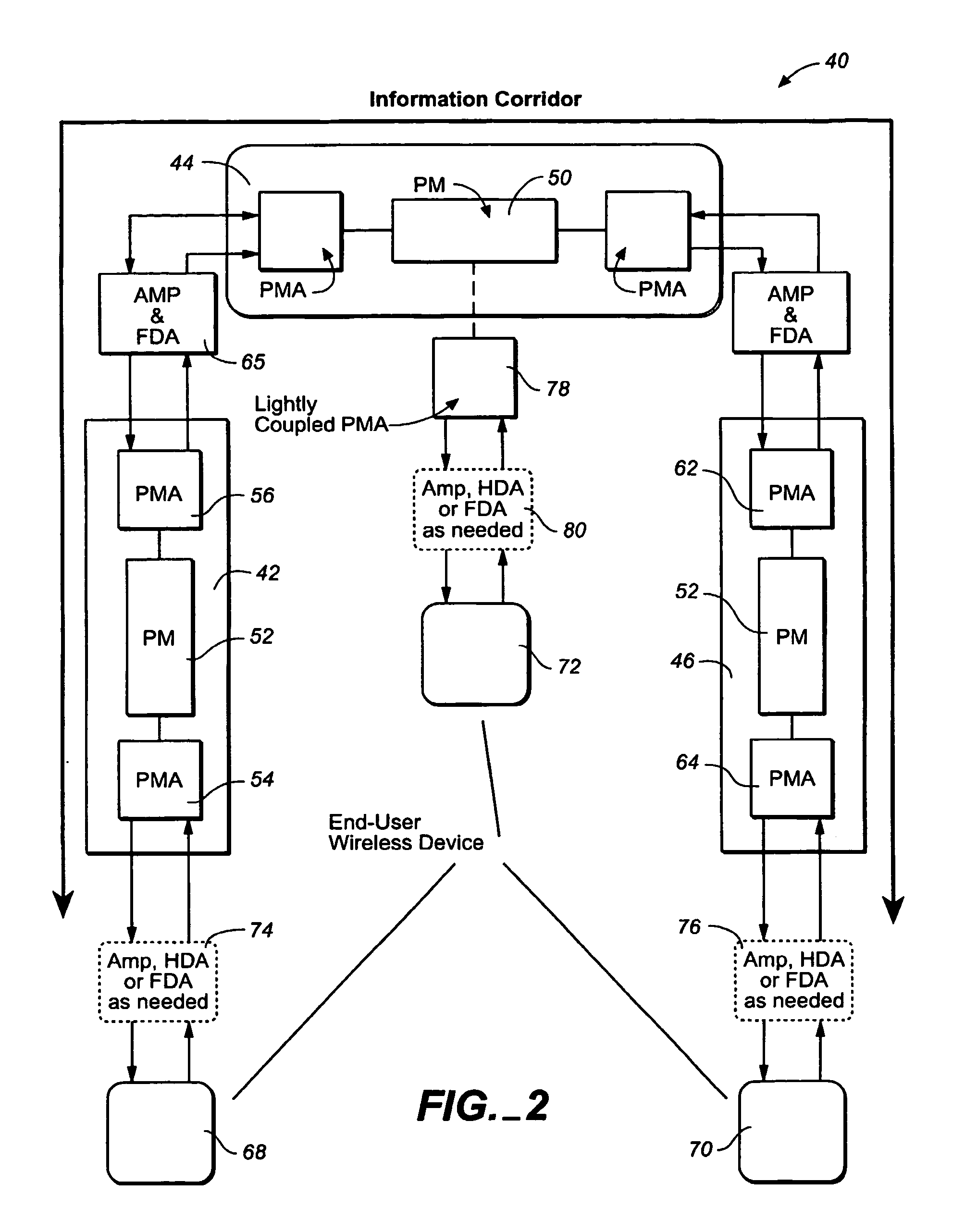
The method and apparatus for information conveyance and distribution to bidirectionally focus or guide a wide spectrum of electromagnetic waves propagated over a possible variety of propagation media, including free space or wireless, surface wave, and cable or wired transmission lines. The apparatus communicates with information devices immediately adjacent to these media wherein the devices, which are not themselves part of the apparatus, may have electromagnetic access to one another. The apparatus maintains adequate signal to noise ratio and low distortion for a possible variety of different signal modulation and encoding types which it can support while permitting transparent, simultaneous communications among a variety of devices. Spread spectrum techniques may be used within the apparatus to mitigate propagation medium distortions and impairments as well as to control access and provide a means for securing information within the corridor and for obtaining revenue. Adapters may be employed to provide either full or half duplex access to the information devices which utilize it.
Owner:CORRIDOR SYST INC
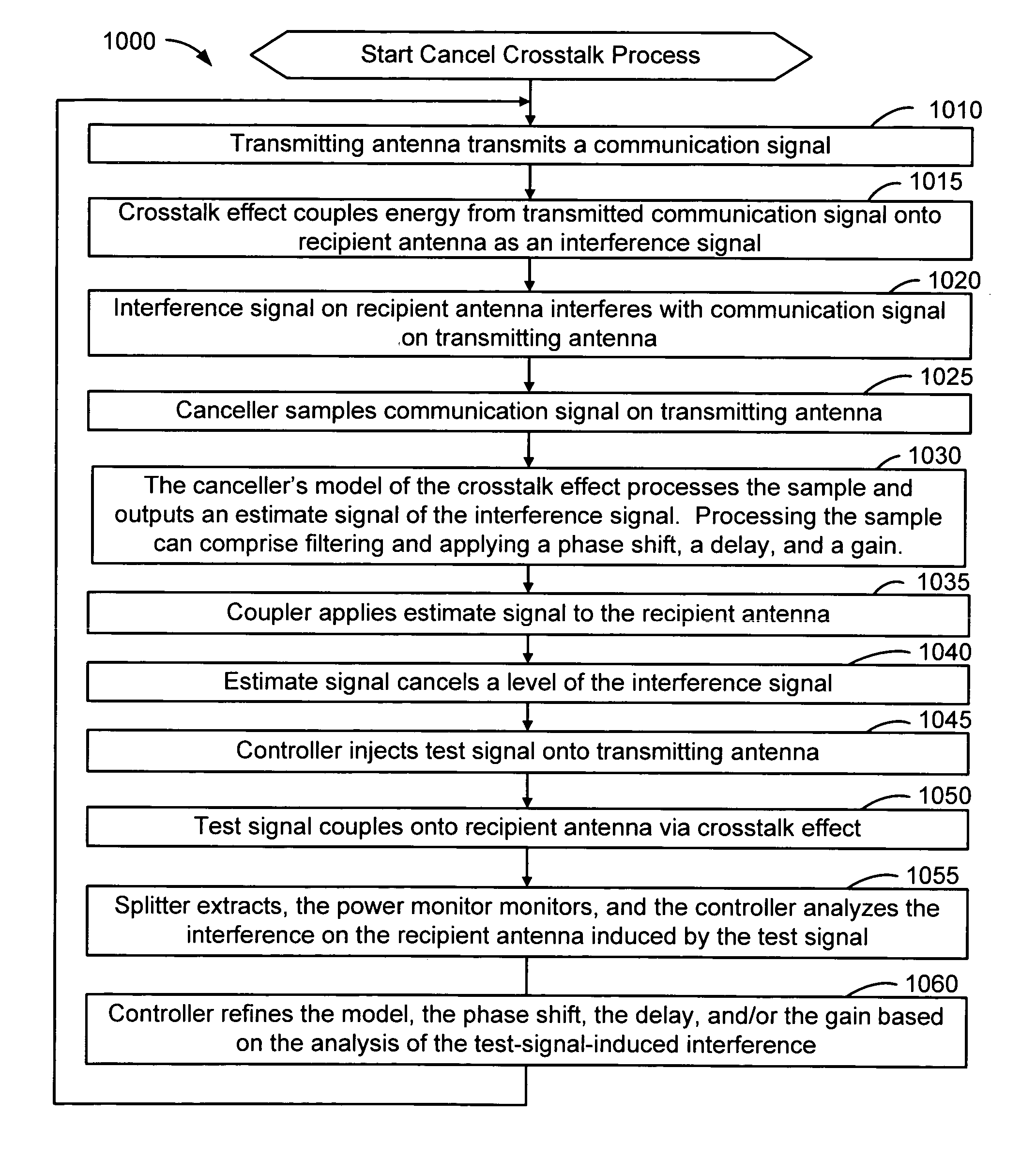
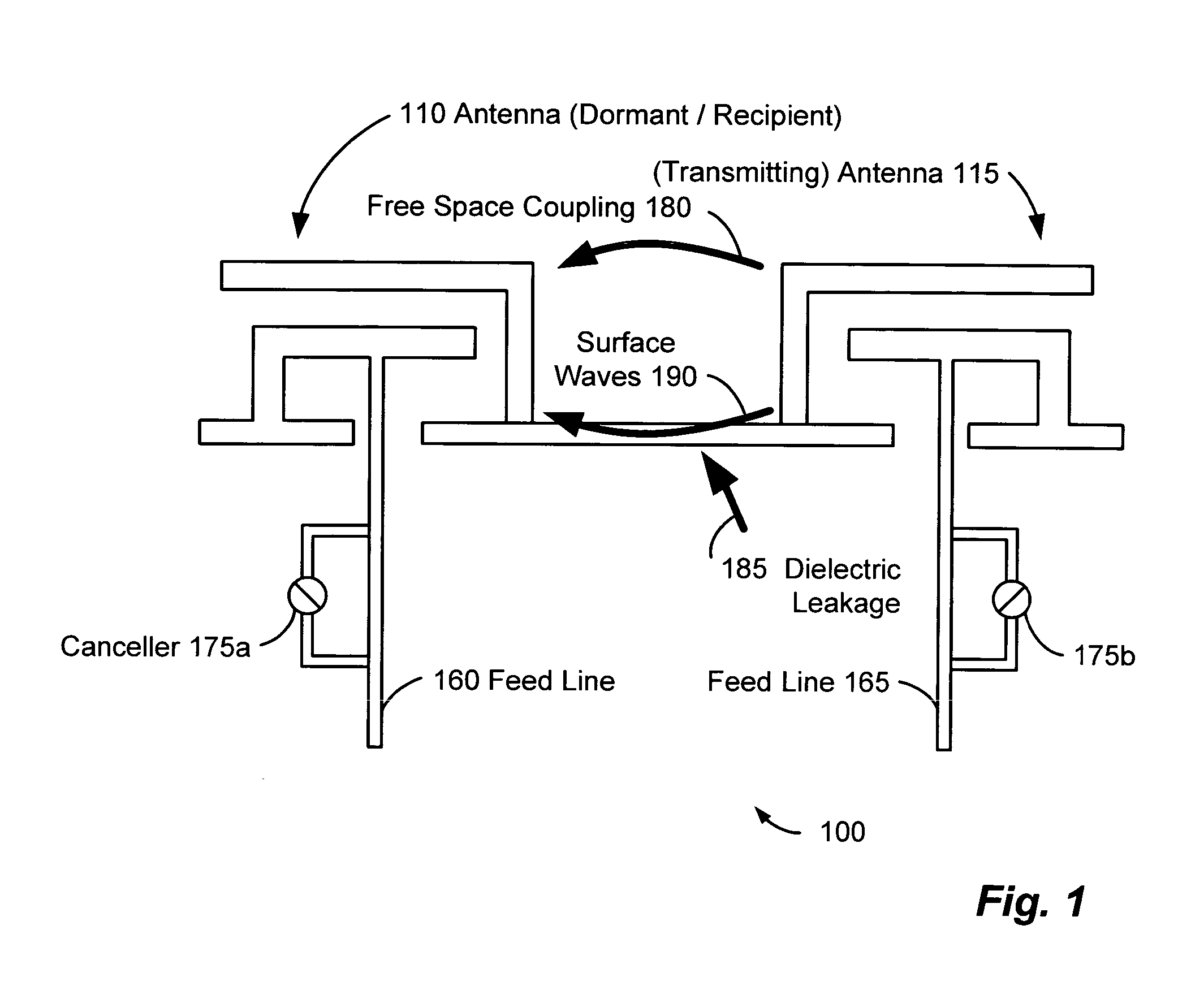
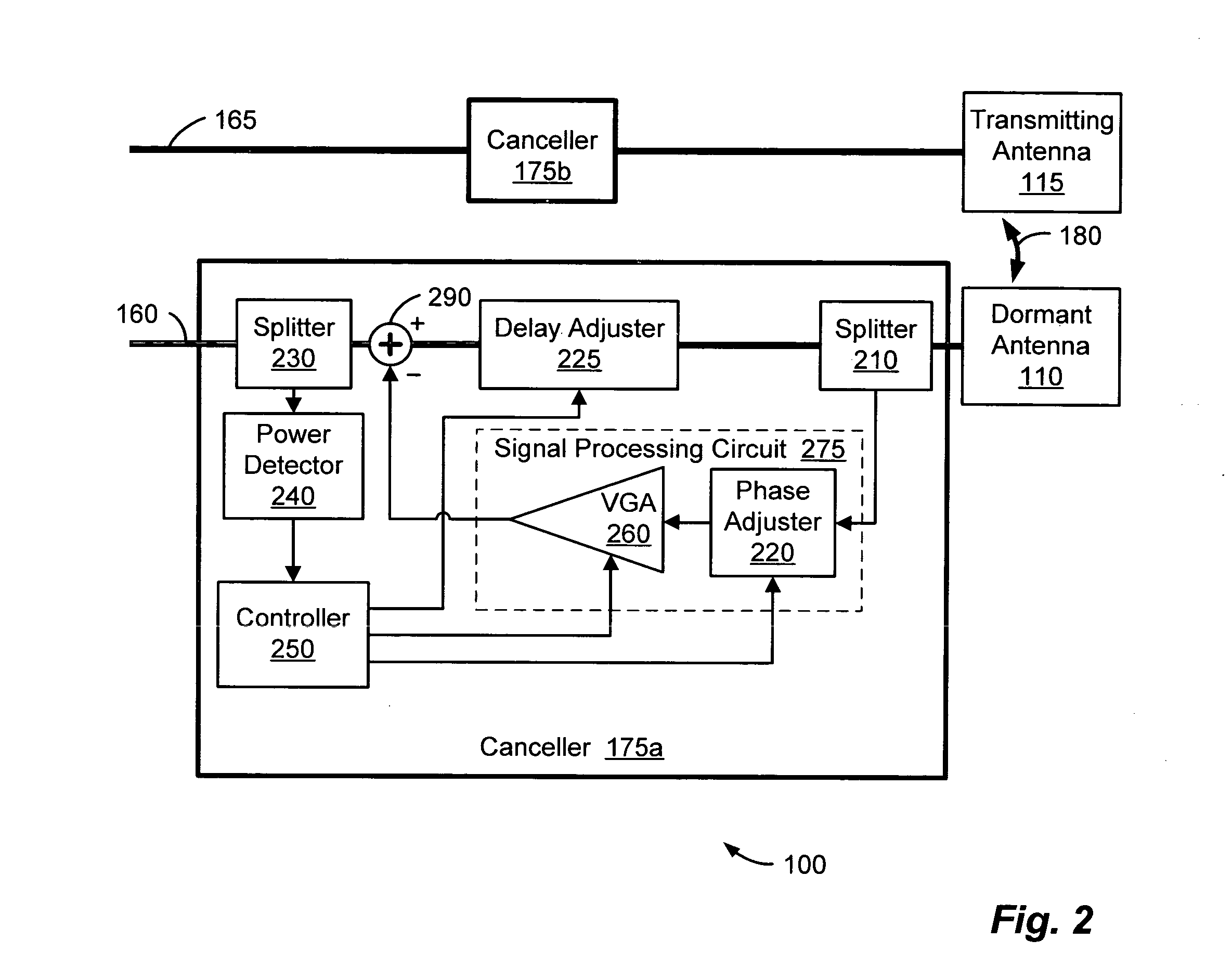
Method and system for antenna interference cancellation
InactiveUS20050226353A1Improve signal qualityHigh bandwidthCorrect operation testingLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemSignal on
A wireless communication system can comprise two or more antennas that interfere with one another via free space coupling, surface wave crosstalk, dielectric leakage, or other interference effect. The interference effect can produce an interference signal on one of the antennas. A cancellation device can suppress antenna interference by generating an estimate of the interference signal and subtracting the estimate from the interference signal. The cancellation device can generate the estimate based on sampling signals on an antenna that generates the interference or on an antenna that receives the interference. The cancellation device can comprise a model of the crosstalk effect. Transmitting test signals on the communication system can define or refine the model.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Deposition method, deposition apparatus, and semiconductor device
InactiveUS20030077883A1Avoid it happening againAvoid breakingFrom solid stateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMicrowaveReactive gas
To provide a deposition method and a deposition apparatus, in which deposition can be performed under a low temperature and a substrate does not suffer from charge-up damage, and a semiconductor device produced thereby. The deposition method is that reactive gas is made to pass through communication holes and guided toward downstream of the communication holes after the gas is exposed to surface wave of microwave, and it is reacted with silicon compound gas to deposit a silicon-containing film on a substrate arranged in the downstream.
Owner:ARIES RES
Communication device
InactiveUS20110228814A1Suppress mutationHigh dielectric constantHigh level techniquesNear-field systems with capacitive couplingCommunication deviceTelecommunications equipment
A communication device includes a case, a high frequency coupler that is disposed inwards from the surface of the case so as to be spaced apart from the surface and transmits and receives a signal of an induction electric field, and a surface wave transmission path that is disposed between the radiation surface of the induction electric field of the high frequency coupler and the surface of the case.
Owner:SONY CORP
Surface wave coupler
ActiveUS20110133867A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTelephonic communicationElectrical conductorElectric cables
The RF signal generated by a ZigBee radio on the outside of a building structure is conveyed to the interior of the building by guiding it along an electric cable bundle that passes through the building's wall to supply domestic electric power to the interior of the structure. The RF signal is launched by a unique coupler comprising a pair of insulated foil conductors.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
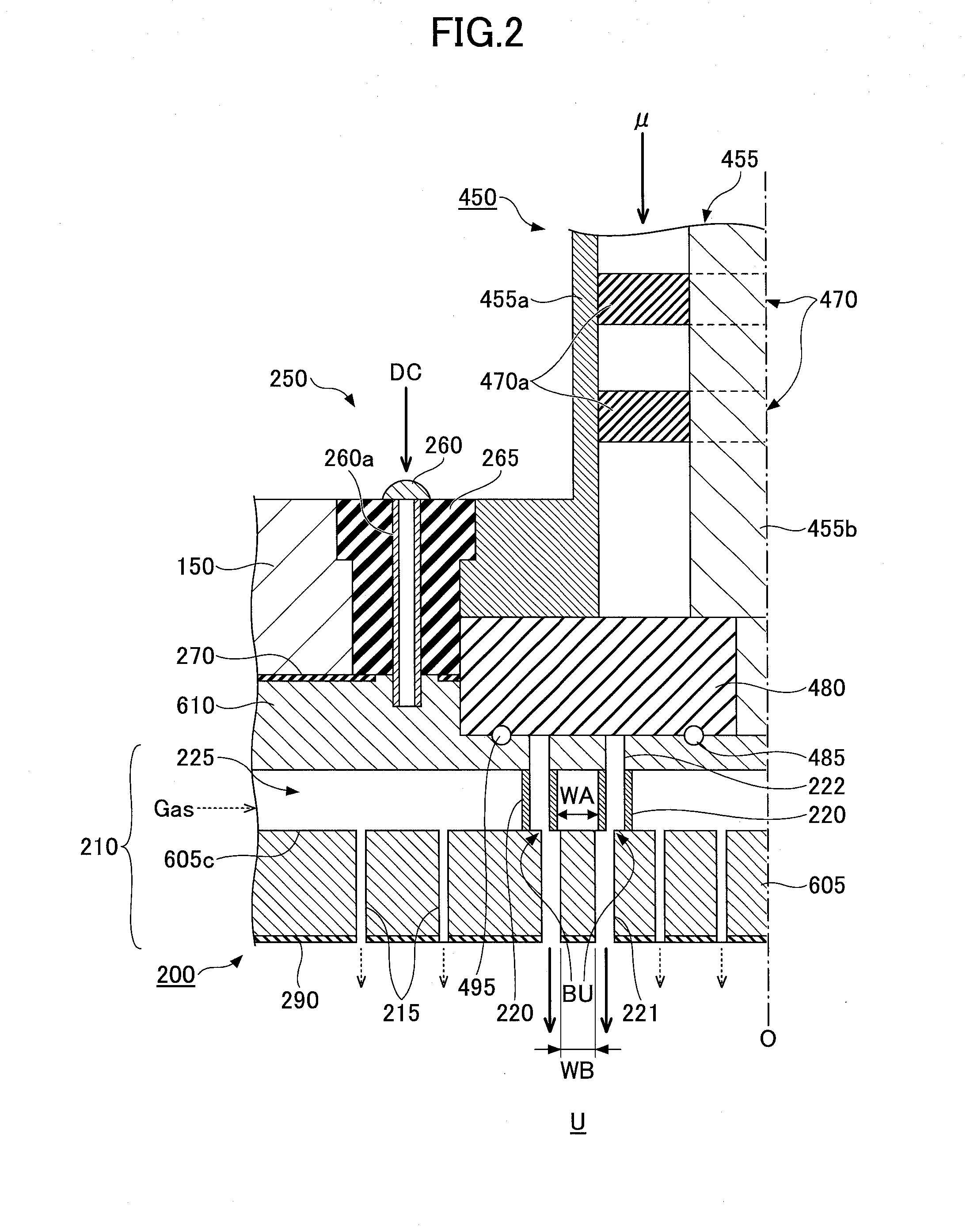
Antenna for plasma generation, plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method
ActiveUS20140339981A1Electric discharge tubesAntenna supports/mountingsMicrowave propagationCoaxial waveguides
An antenna for plasma generation radiates a microwave transmitted through a coaxial waveguide into a processing chamber and propagates the microwave on a metal surface of the processing chamber to convert gas into surface wave plasma. The antenna includes a gas flow path for passing the gas through the antenna, a plurality of gas holes that communicate with the gas flow path and introduce the gas into the processing chamber, and a plurality of slots that are separated from the gas flow path and penetrate through the gas flow path. The slots pass the microwave transmitted through the coaxial waveguide and a slow-wave plate to the processing chamber. A first space between portions of adjacent slots penetrating through the gas flow path is arranged to be wider than a second space between portions of the adjacent slots opening out to a plasma generation space of the processing chamber.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Adjustable slot antenna for control of uniformity in a surface wave plasma source
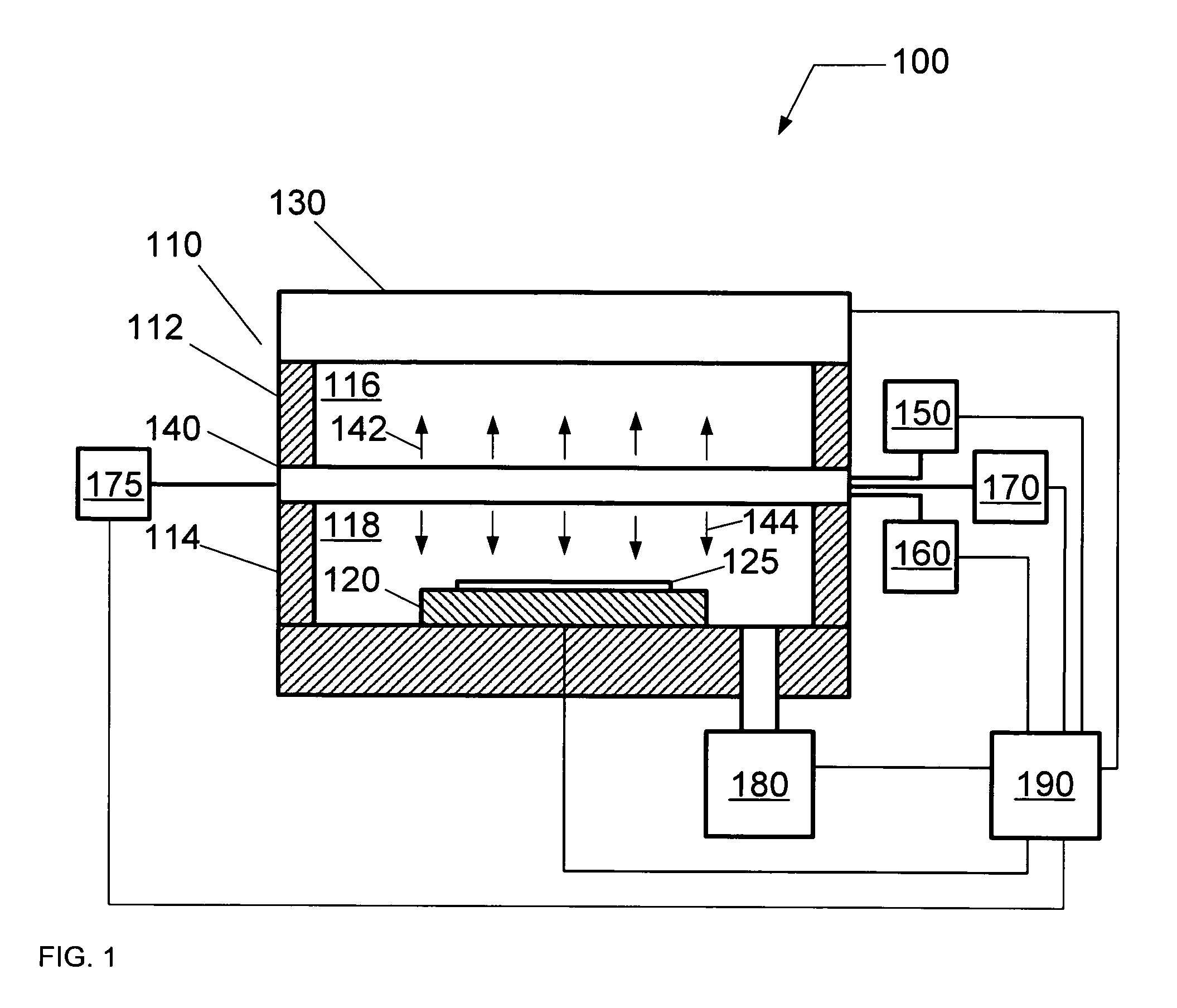
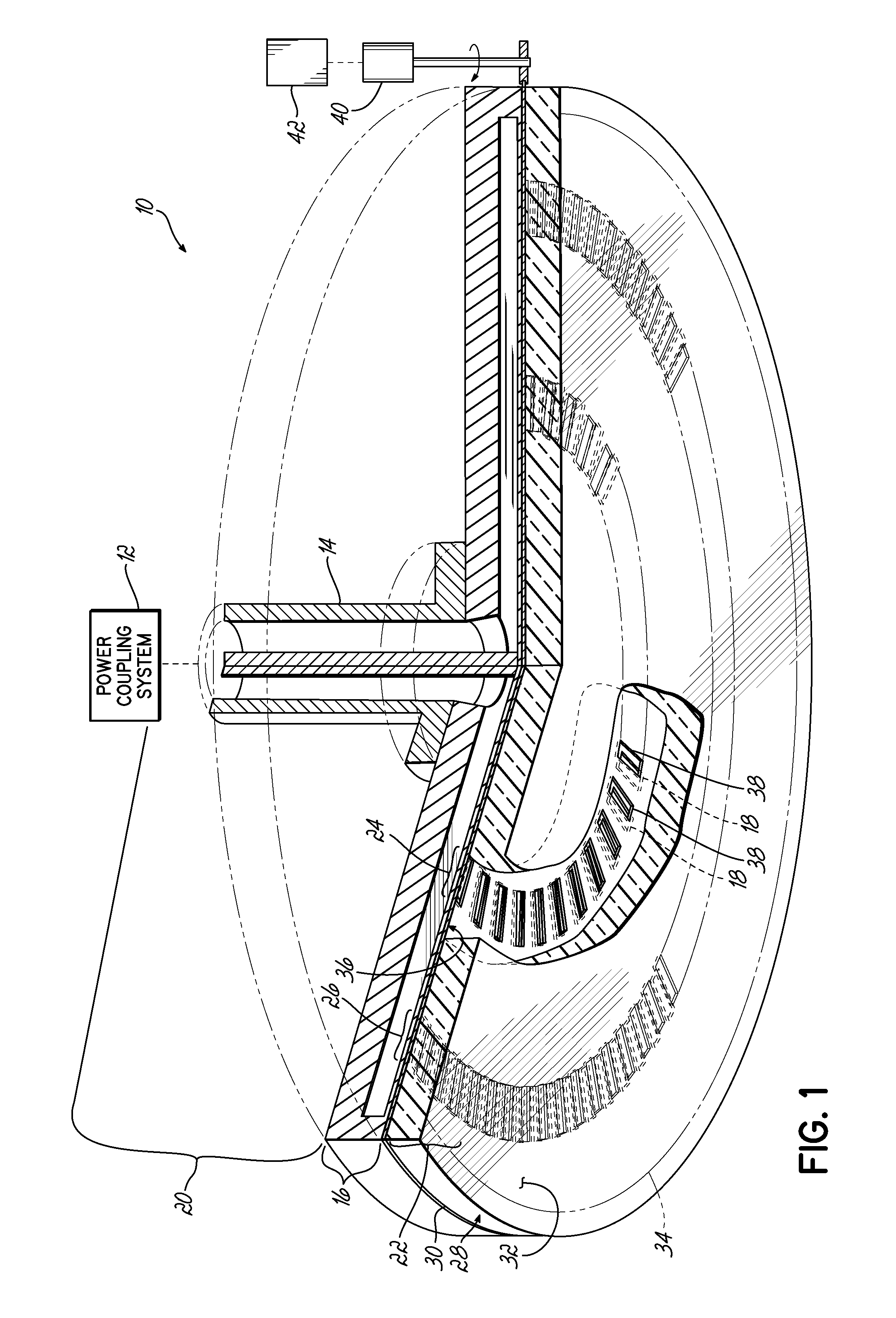
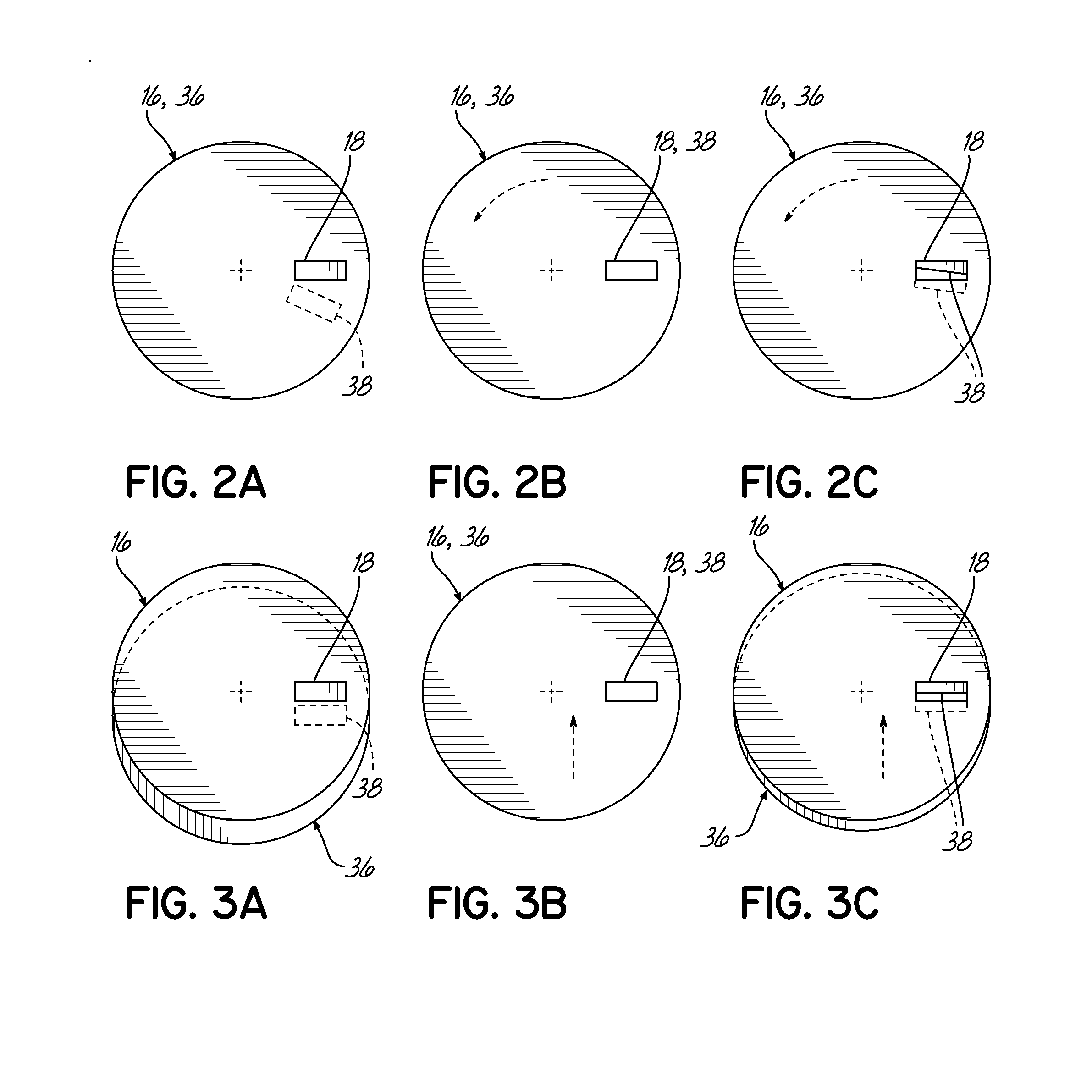
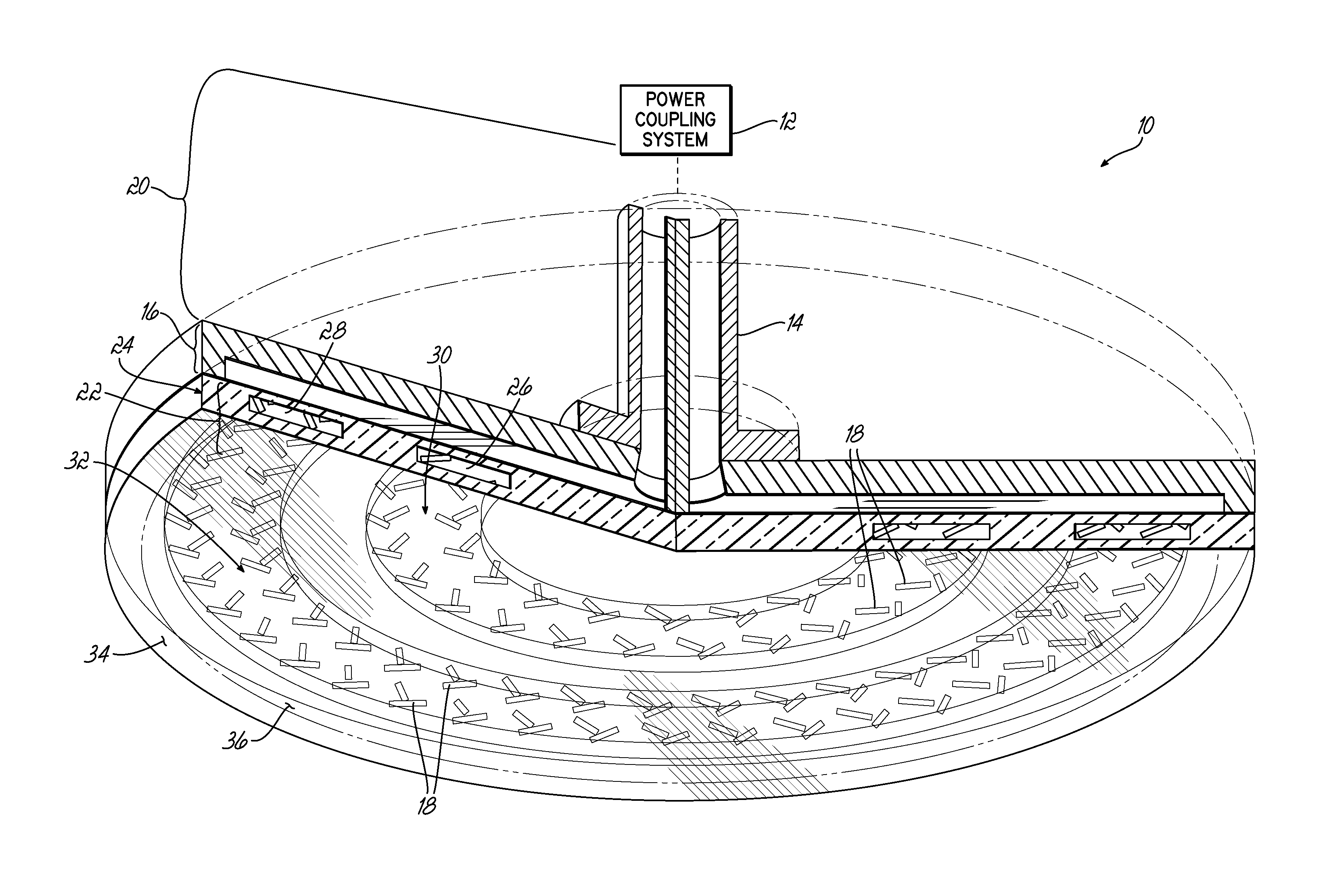
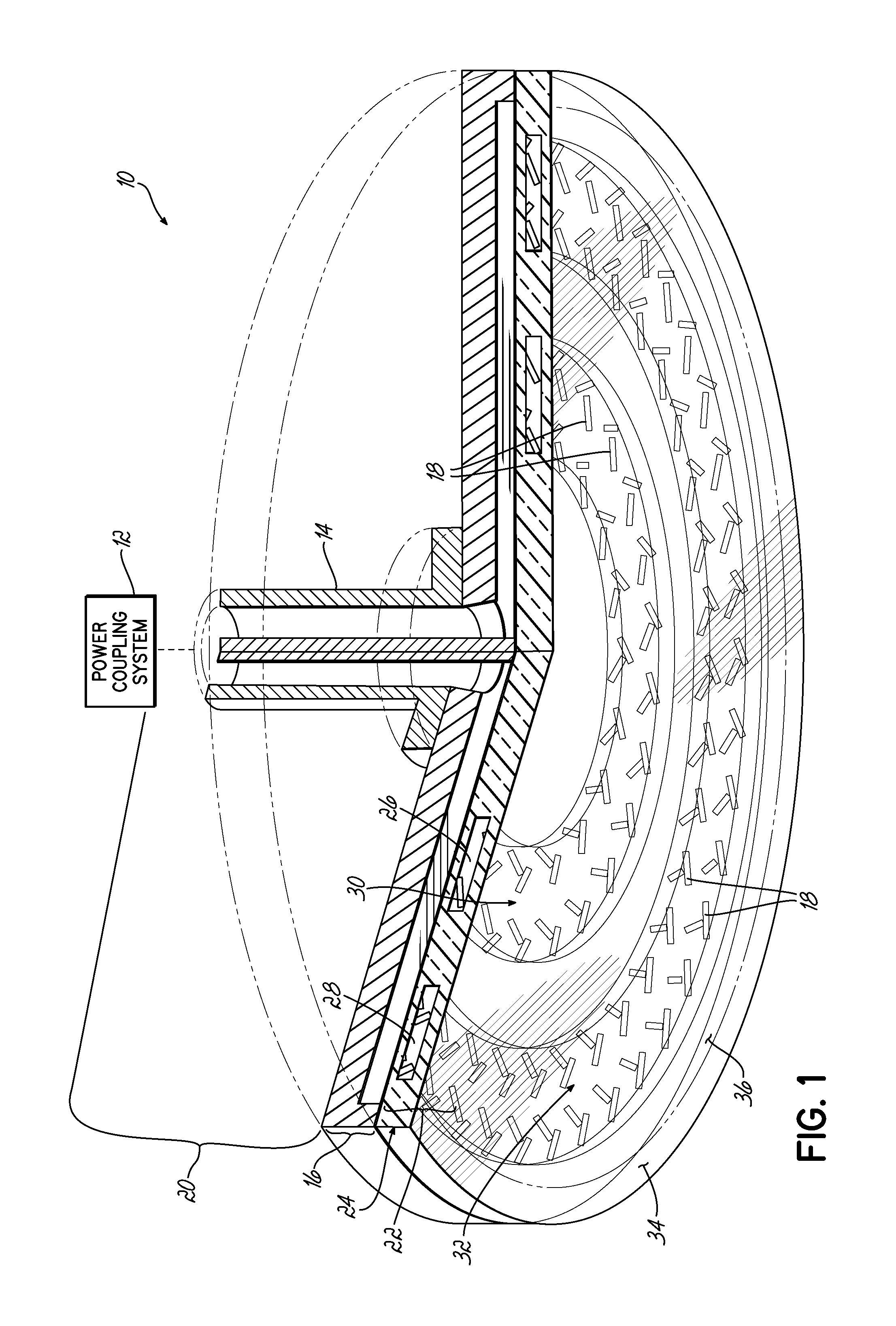
ActiveUS20140028190A1Avoid passingElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsPower couplingSurface wave
The present invention provides a surface wave plasma source including an electromagnetic (EM) wave launcher comprising a slot antenna having a plurality of antenna slots configured to couple the EM energy from a first region above the slot antenna to a second region below the slot antenna, and a power coupling system is coupled to the EM wave launcher. A dielectric window is positioned in the second region and has a lower surface including the plasma surface. A slotted gate plate is arranged parallel with the slot antenna and is configured to be movable relative to the slot antenna between variable opacity positions including a first opaque position to prevent the EM energy from passing through the first arrangements of antenna slots, and a first transparent position to allow a full intensity of the EM energy to pass through the first arrangement of antenna slots.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Control of uniformity in a surface wave plasma source
A surface wave plasma source (SWPS) is disclosed, having an electromagnetic (EM) wave launcher including a slot antenna configured to couple EM energy in a desired EM wave mode to a plasma by generating a surface wave on a plasma surface of the SWPS adjacent the plasma. The SWPS also includes a dielectric window positioned below the slot antenna, having a lower surface and the plasma surface. The SWPS further includes an attenuation assembly disposed between the slot antenna and the plasma surface. The attenuation assembly includes a first fluid channel substantially aligned with a first arrangement of slots in the slot antenna, and is configured to receive a first flow of a first fluid at a first fluid temperature. The SWPS finally includes a power coupling system coupled to the EM wave launcher and configured to provide EM energy to the EM wave launcher for forming the plasma.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Plasma processing apparatus
In a plasma processing apparatus, microwaves being transmitted in a waveguide pass through a microwave transmitted window via first and second slot antennas provided in a magnetic field side, so as to form surface waves. Process gas in a chamber is excited by the surface waves so as to generate surface wave plasma. A substrate is processed by the plasma. Each first slot antenna is provided with an aperture, which has a curved or bent shape and whose longitudinal direction extends substantially to follow the lines of magnetic force of the microwaves. Each second slot antenna is provided with an aperture which has a rectangular shape.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Method for the packaging of electronic components
InactiveUS6492194B1Improve seal qualityEfficient electromagnetic shieldingImpedence networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHermetic sealElectronic component
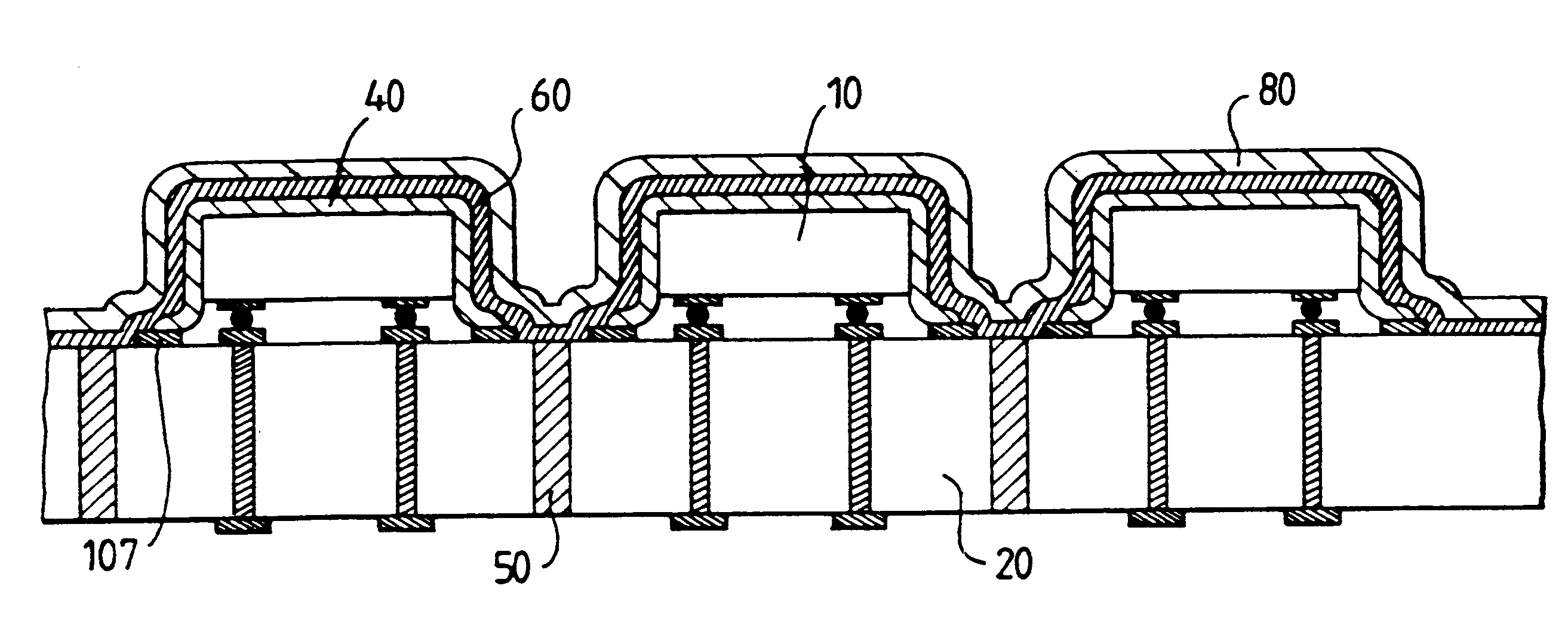
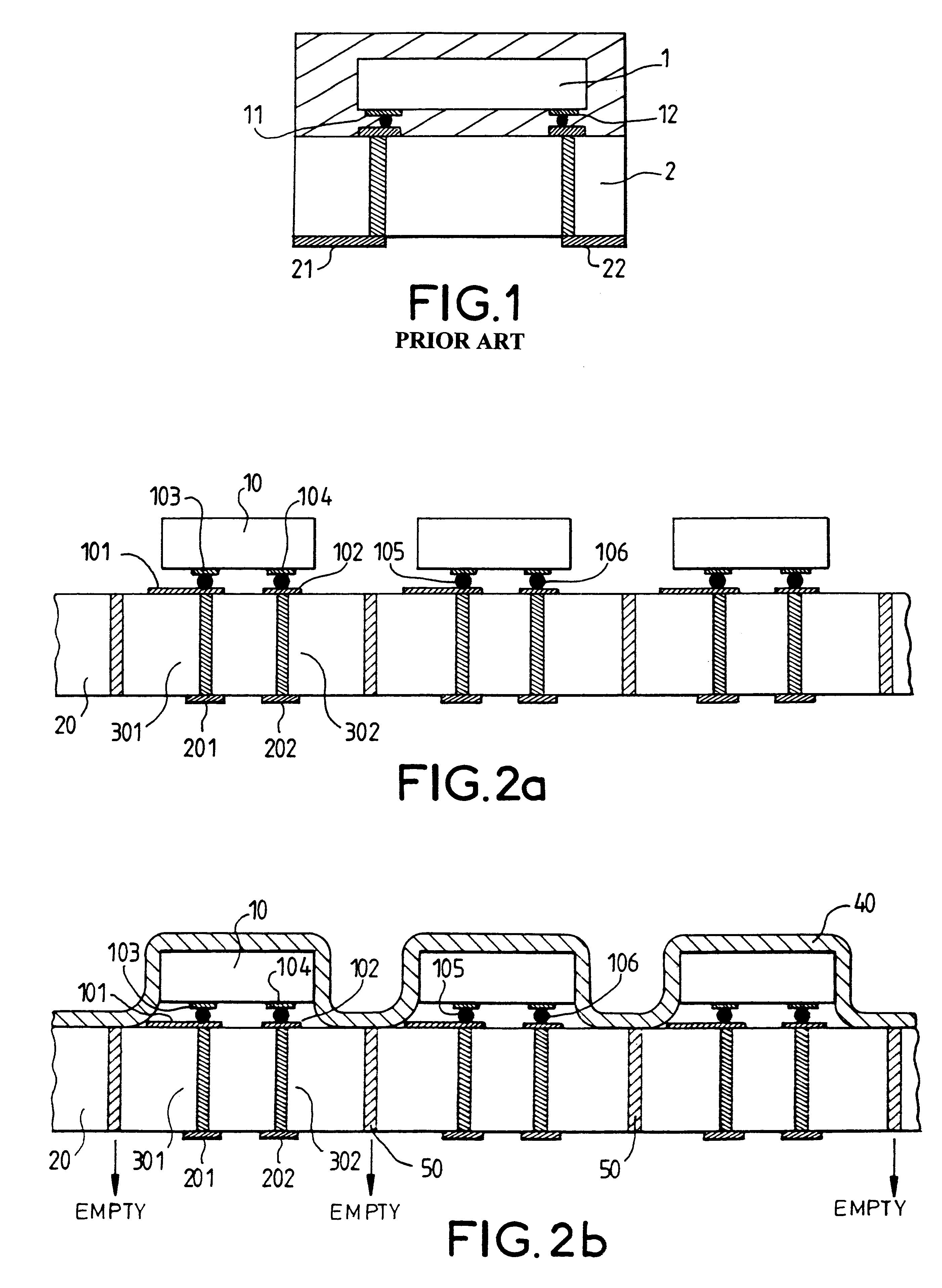
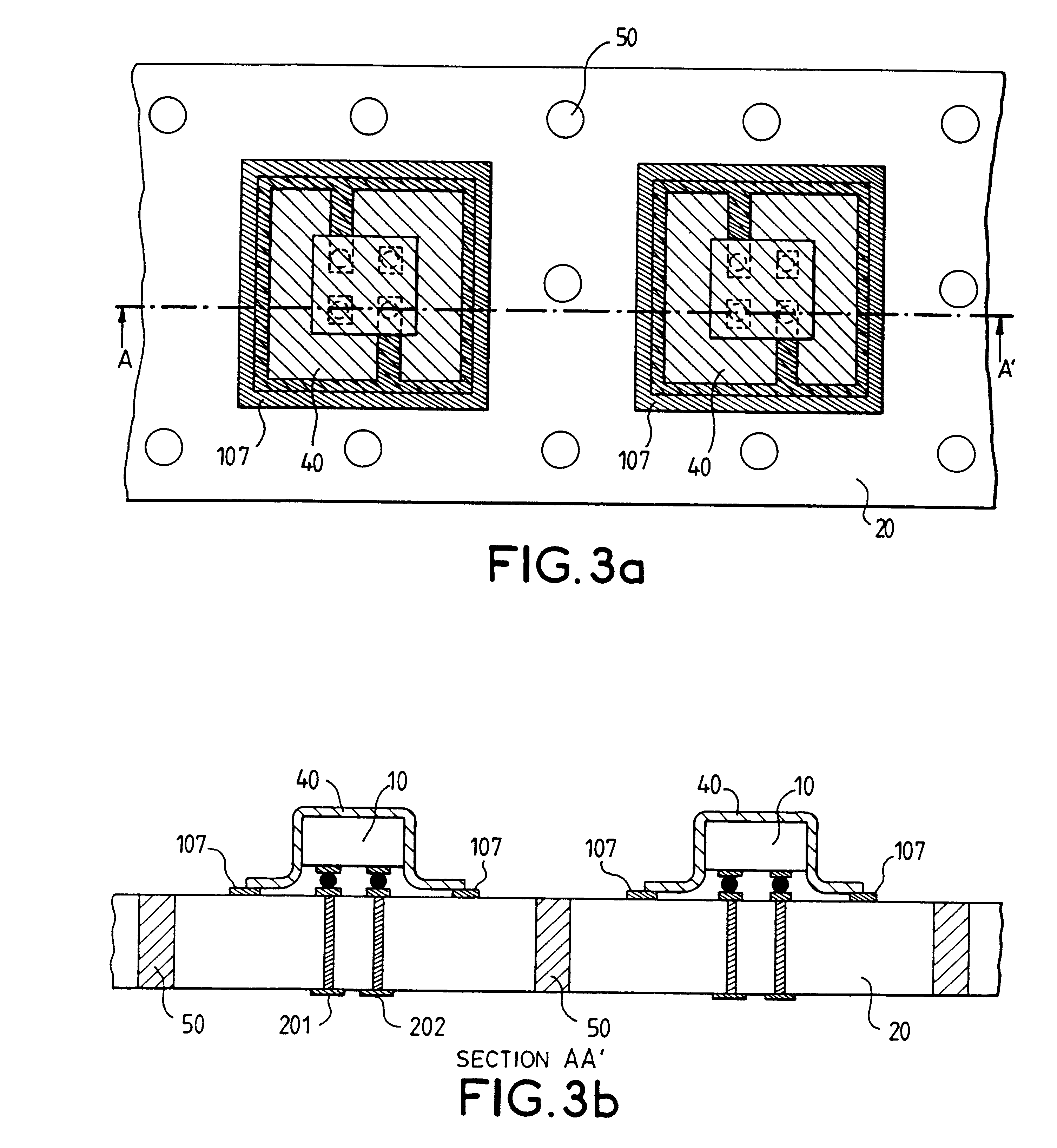
A method for the packaging of electronic components, including the mounting of at least one electronic component on its active face side to a base, the base including electrical contacts on an external face and connection pads on a face opposite the external face, and including a first series of via holes connecting the electrical contacts and the connection pads and a second series of holes for use in aspiration. A deformable film is deposited on the face opposite to the active face of the electronic component or components. The deformable film is aspirated through the second series of holes from the face opposite the external face of the base, so as to sheath the electronic component or components. The method may furthermore include, on top of the deformable film, a mineral deposition to provide for the hermetic sealing of the components and a conductive deposition to provide for the shielding. Such an application may find particular application to surface wave filters.
Owner:THOMSON CSF SA
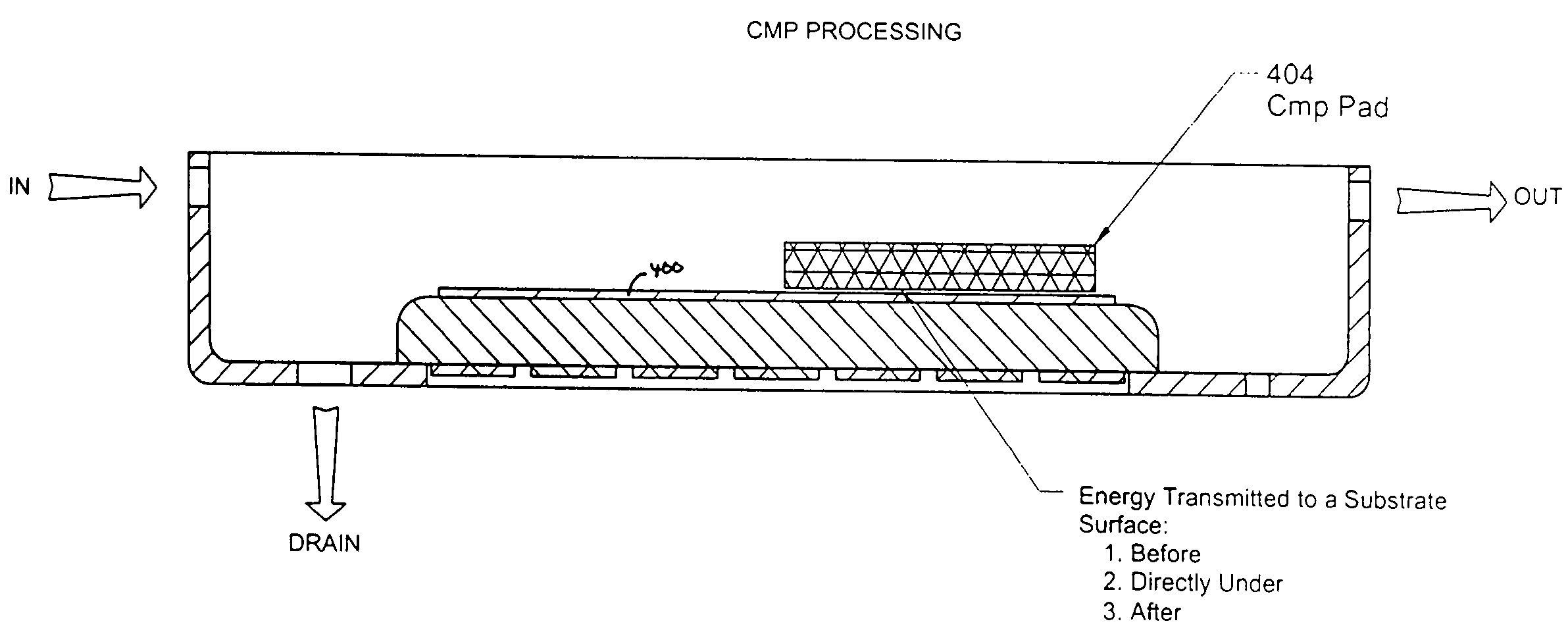
Method and apparatus to process substrates with megasonic energy
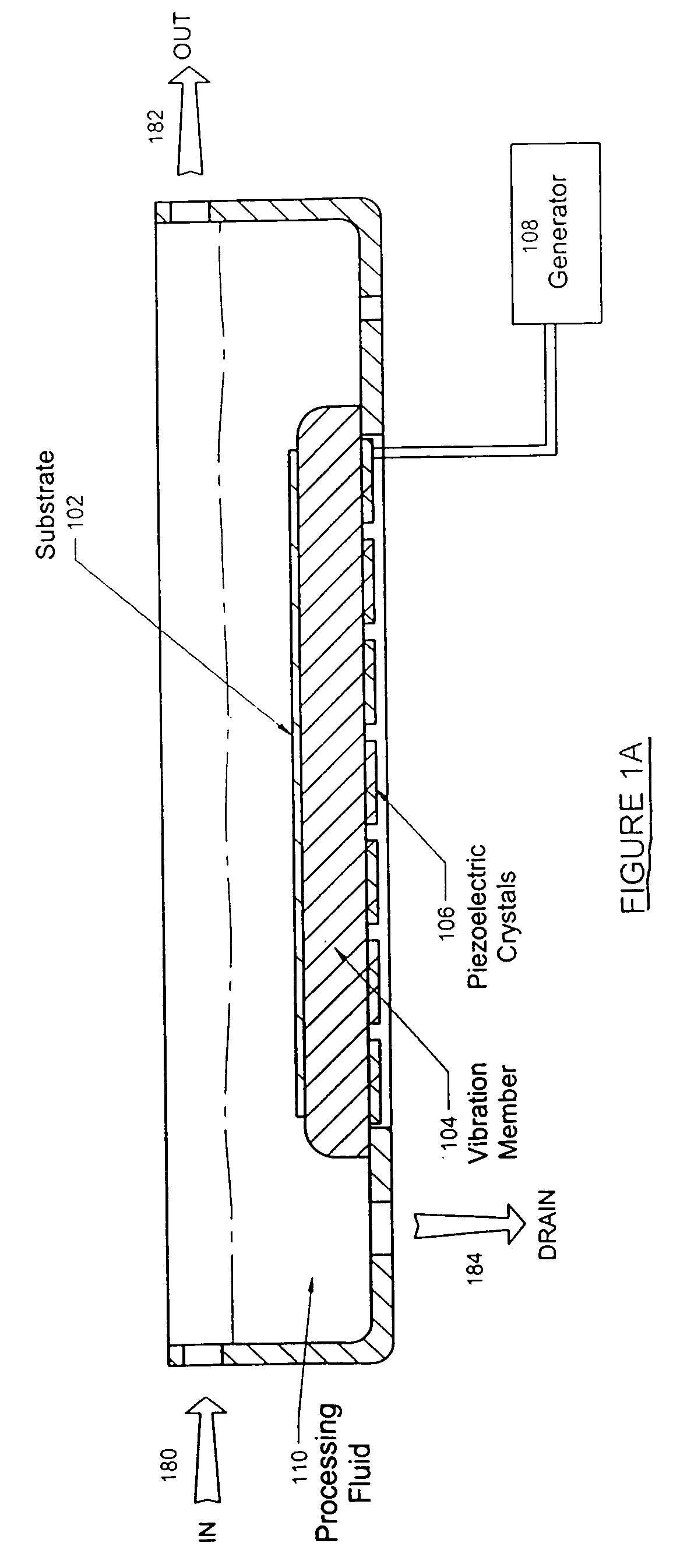
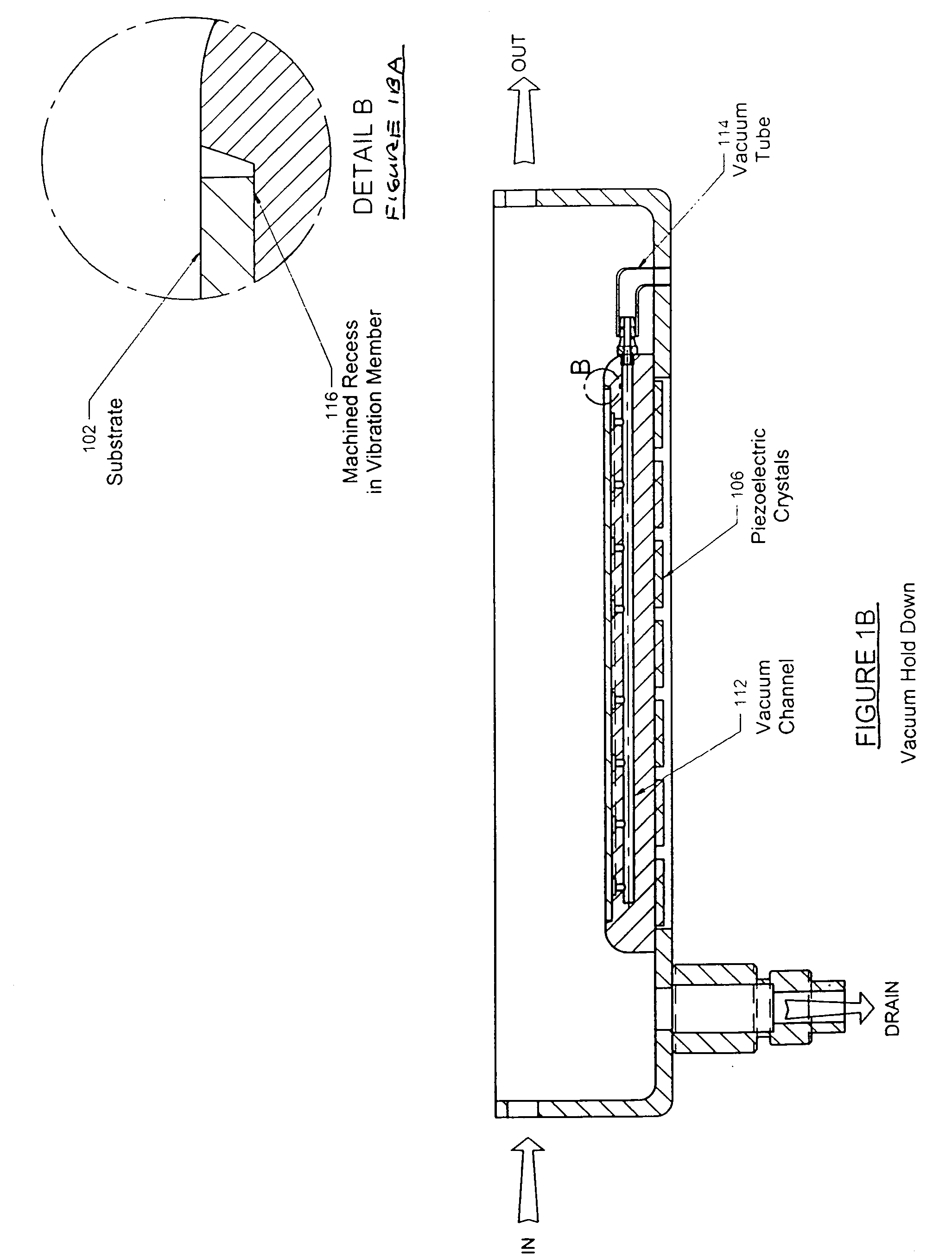
ActiveUS20050003737A1Uniform energyImprove uniformityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsLiquid surface applicatorsEngineeringSubstrate surface
A variety of techniques may be employed, alone or in combination, to enhance contact between a processed substrate and applied megasonic energy. In accordance with one embodiment of the new invention, the vibration plate is brought into intimate contact with one surface of the substrate, while cleaning or processing fluid contacts the other. In accordance with an alternative embodiment of the present invention, a reflecting surface may be provided to cause emanated energy to be reflected back into the near field and make it more uniform. In accordance with another alternative embodiment of the present invention, energy may be transferred across a substrate bounded on both sides by liquid with incidence of megasonic energy that is either normal to the substrate surface or within a critical range of incident angles. In yet another embodiment, generated dilatational waves may be converted to surface waves prior to contacting the substrate.
Owner:P C T SYST
Electro-optical device and electronic equipment having touch panel with resin having particular elastic modulus
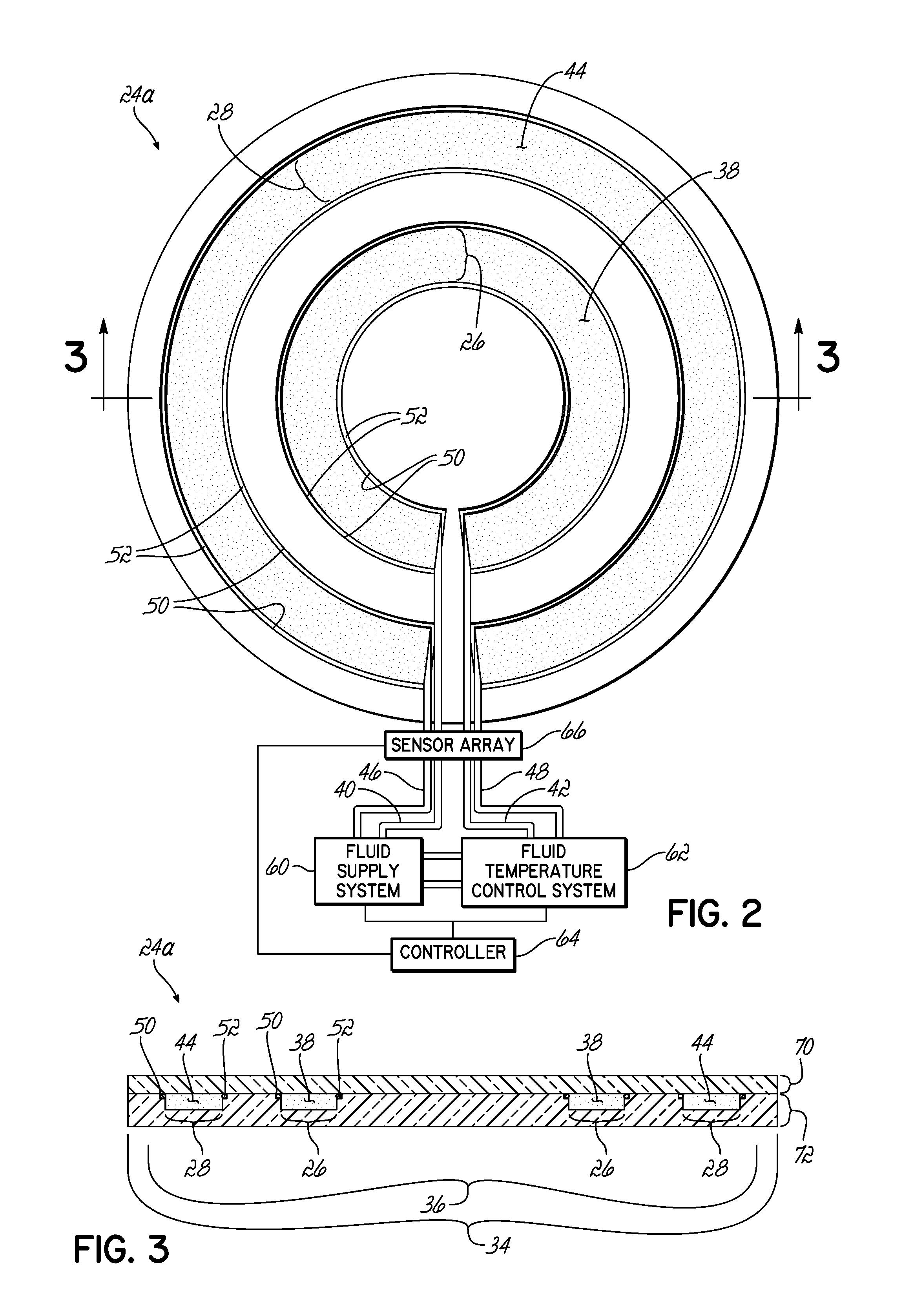
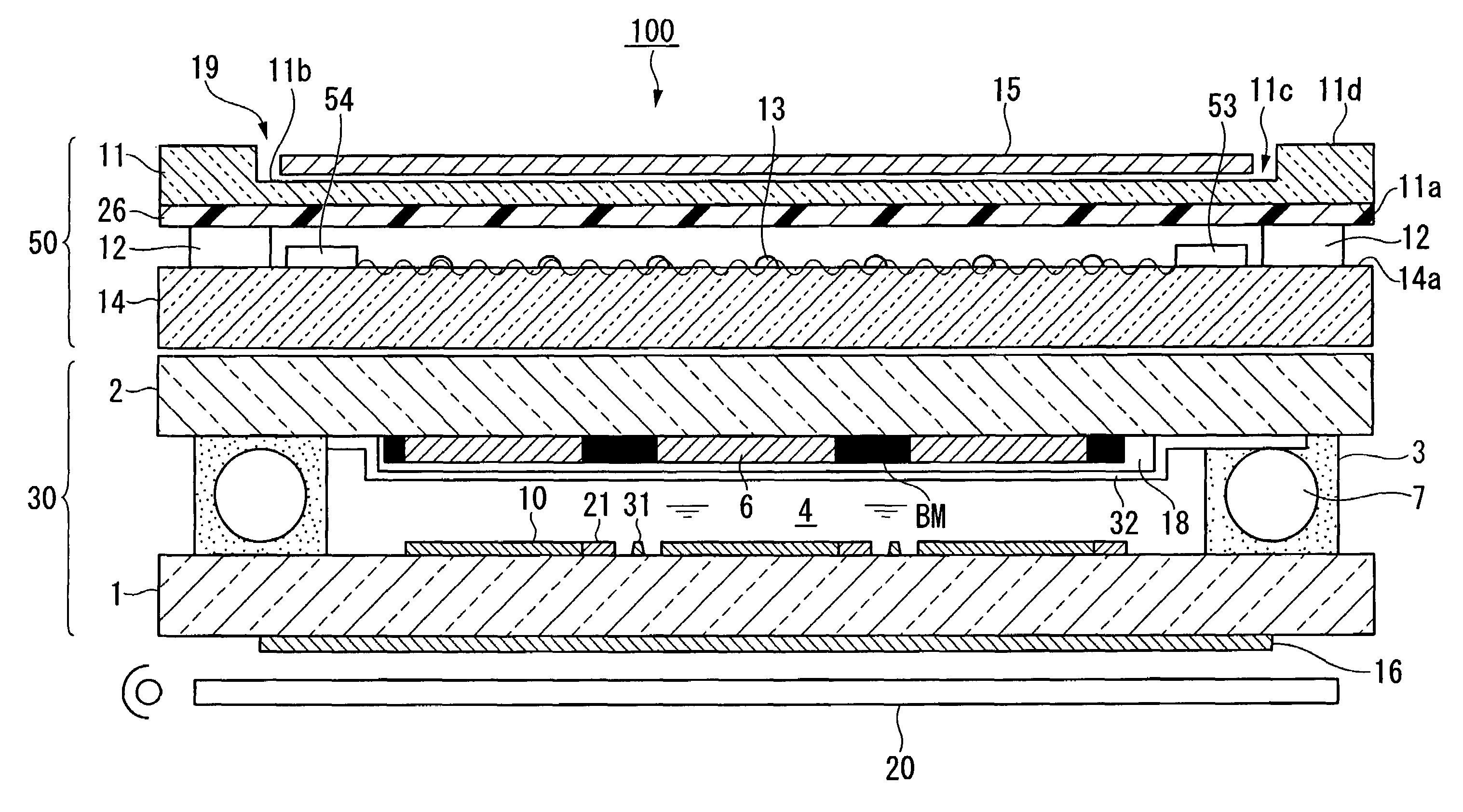
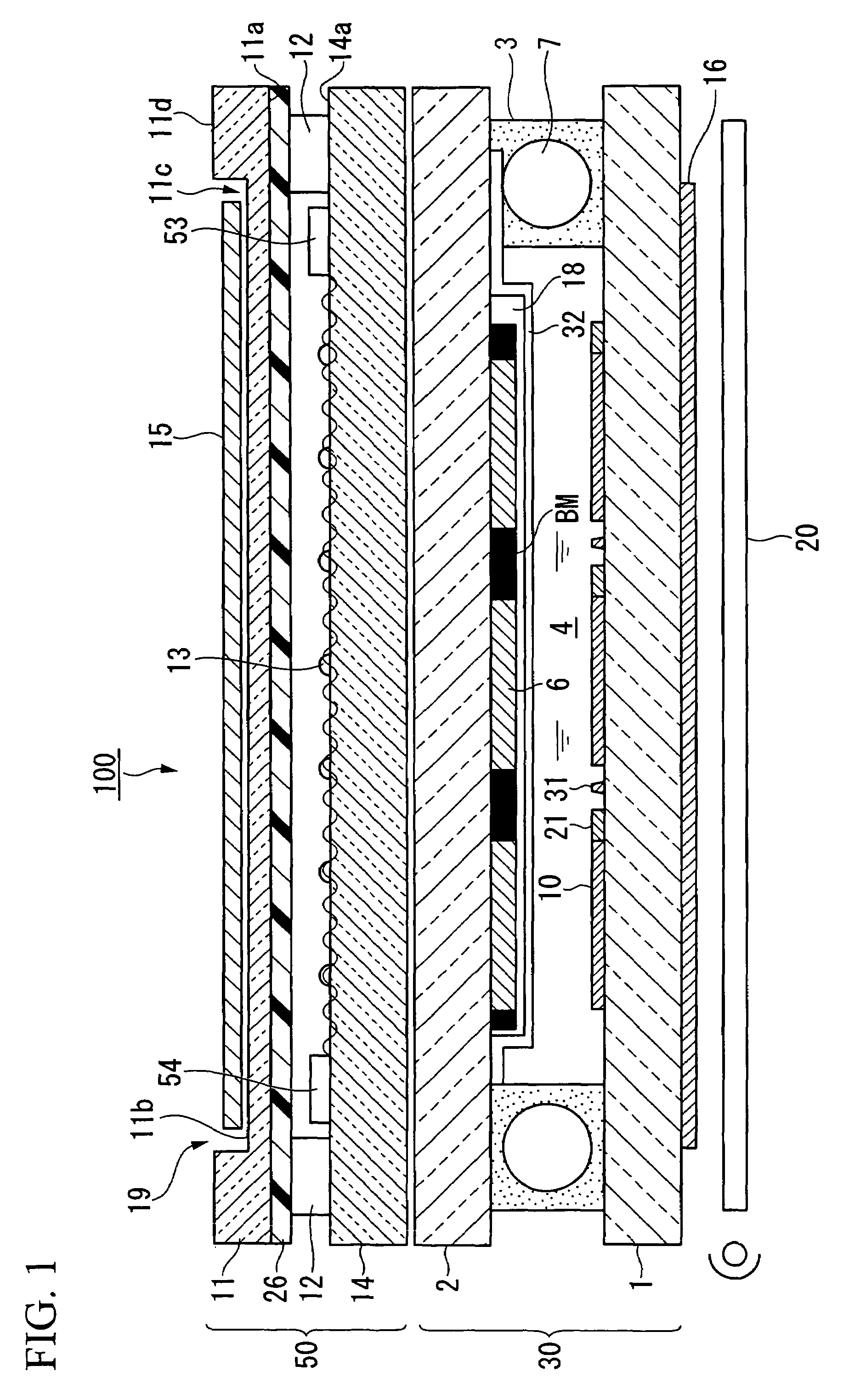
ActiveUS7593067B2The detection position is accurateAvoid failureNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringTouch panel
An electro-optical device includes: an electro-optical panel having a first substrate, a second substrate, and an electro-optical substance interposed between the first and the second substrates; a third substrate arranged on the second substrate; a fourth substrate having a flexibility and arranged on the third substrate via a spacer; a position detector provided on the third substrate and detecting a pressed position on the fourth substrate based on changes in surface waves generated on the third substrate; and a resin film provided on the fourth substrate and opposed to the third substrate.
Owner:138 EAST LCD ADVANCEMENTS LTD
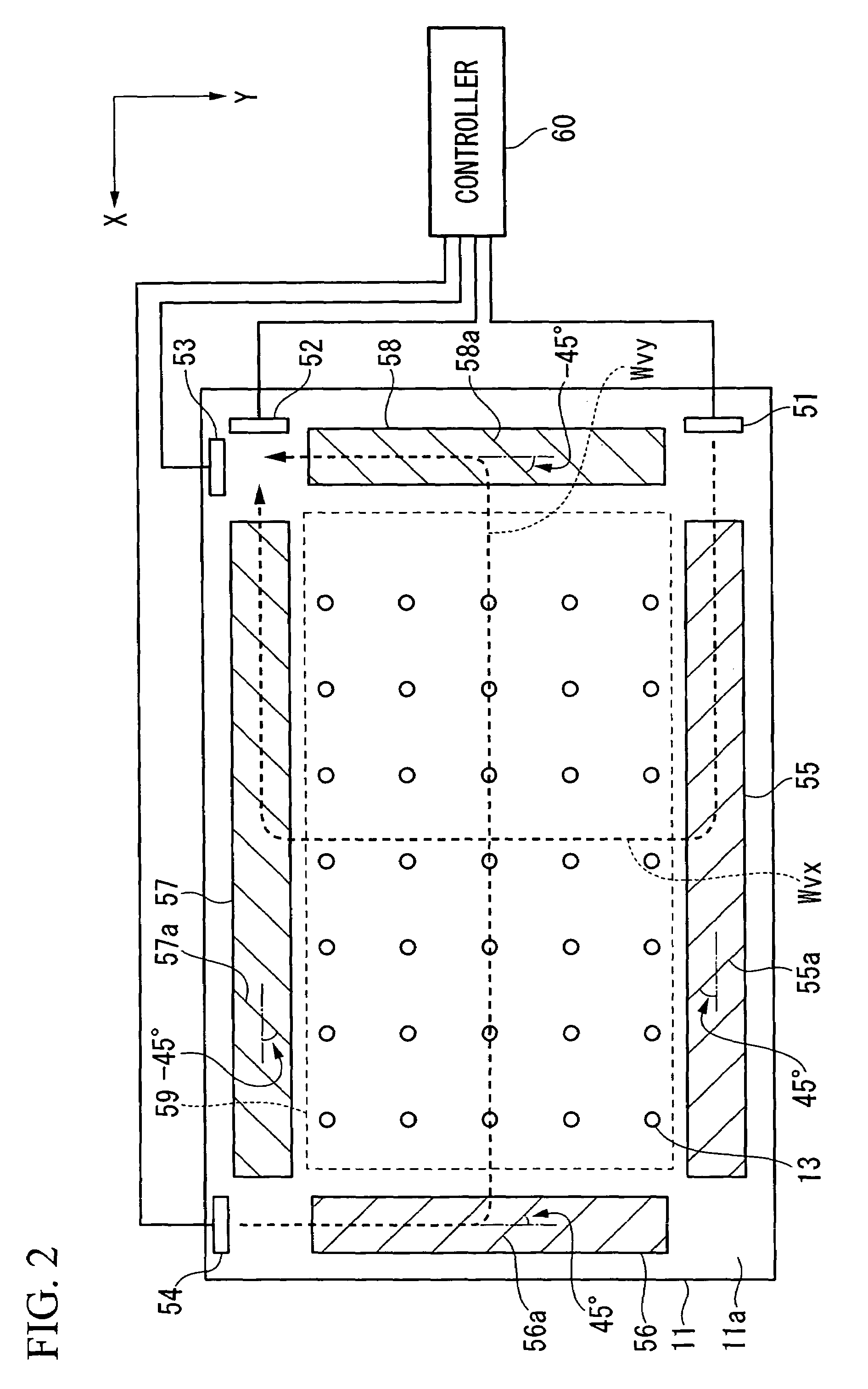
Large-scale adaptive surface sensor arrays
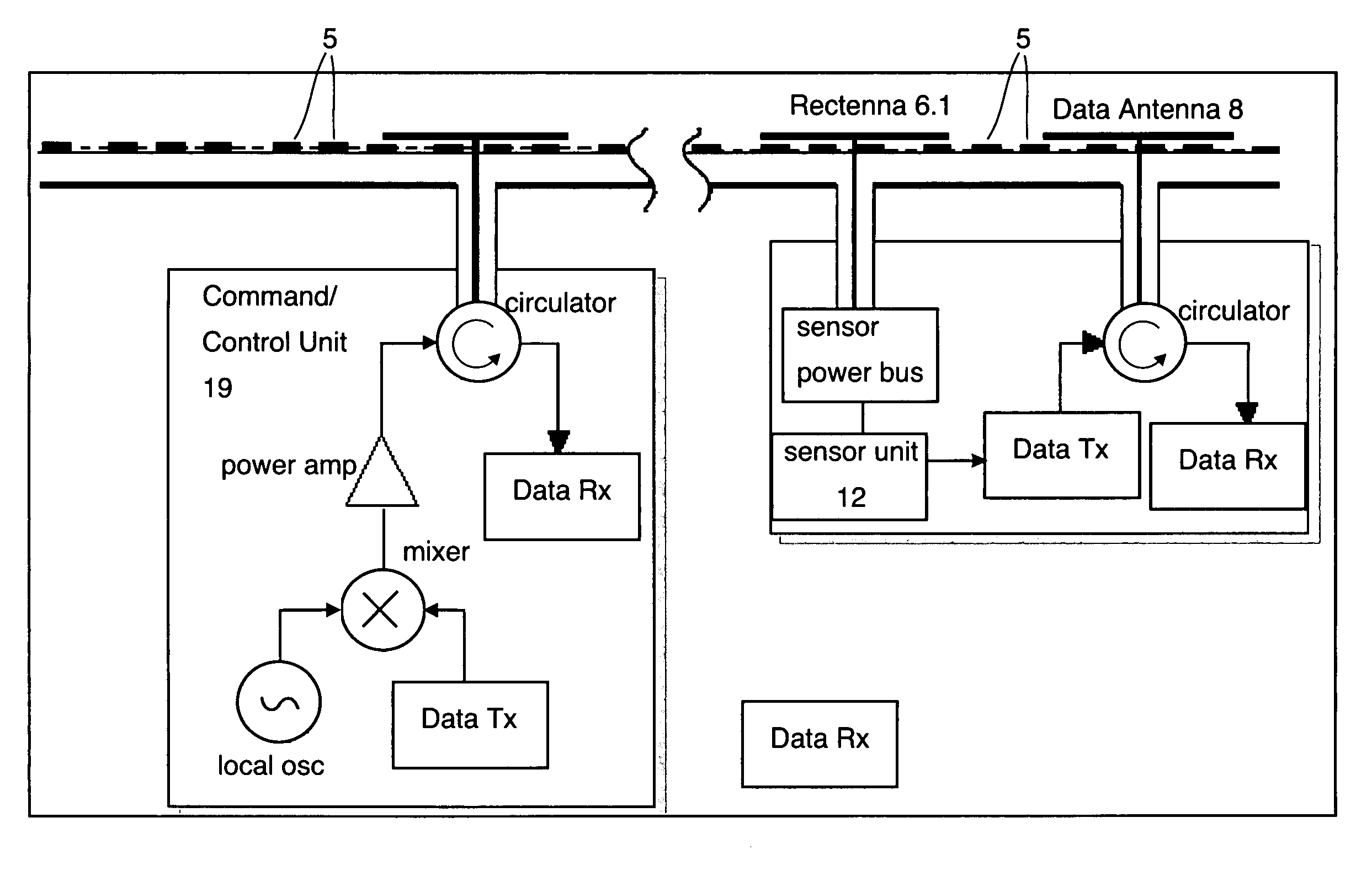
An adaptive surface has a dielectric surface with a repeating pattern of electrically conductive structures disposed thereon or therein, the dielectric surface in combination with repeating pattern of electrically conductive structures forming a metasurface for binding surface waves thereto. A plurality of actuators on the dielectric surface alter the shape of the metasurface in response to control signals. A plurality of sensors on the dielectric surface for measuring a desired parameter and converting it to data. A plurality of rectennae disposed on the dielectric surface for providing electrical power to said actuators and to said sensors. A plurality of data antennas are disposed on or in the dielectric surface, the data antennas being coupled with data receivers and data transmitters for receiving data from an external source for controlling the actuators and for transmitting data from said sensors to an external receiver.
Owner:HRL LAB
Substrate transport device and substrate processing apparatus
ActiveUS20170178939A1Prevent movementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConveyor partsEngineeringSurface wave
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
In vivo simulator for microwave treatment
InactiveUS6175768B1Reduce the possibilityWide bandwidthElectrotherapyLavatory sanitoryPeristaltic pumpVentricular tachycardia
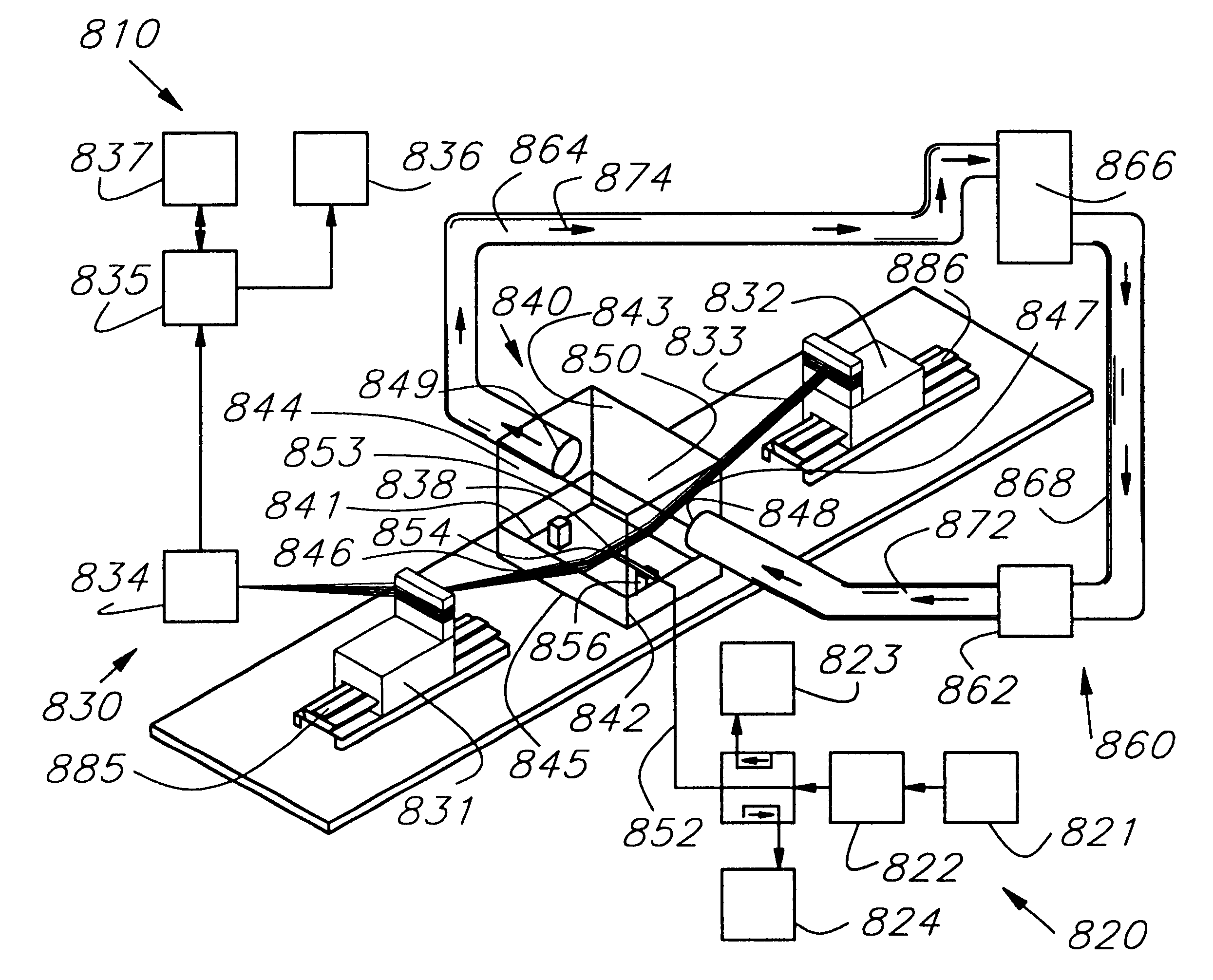
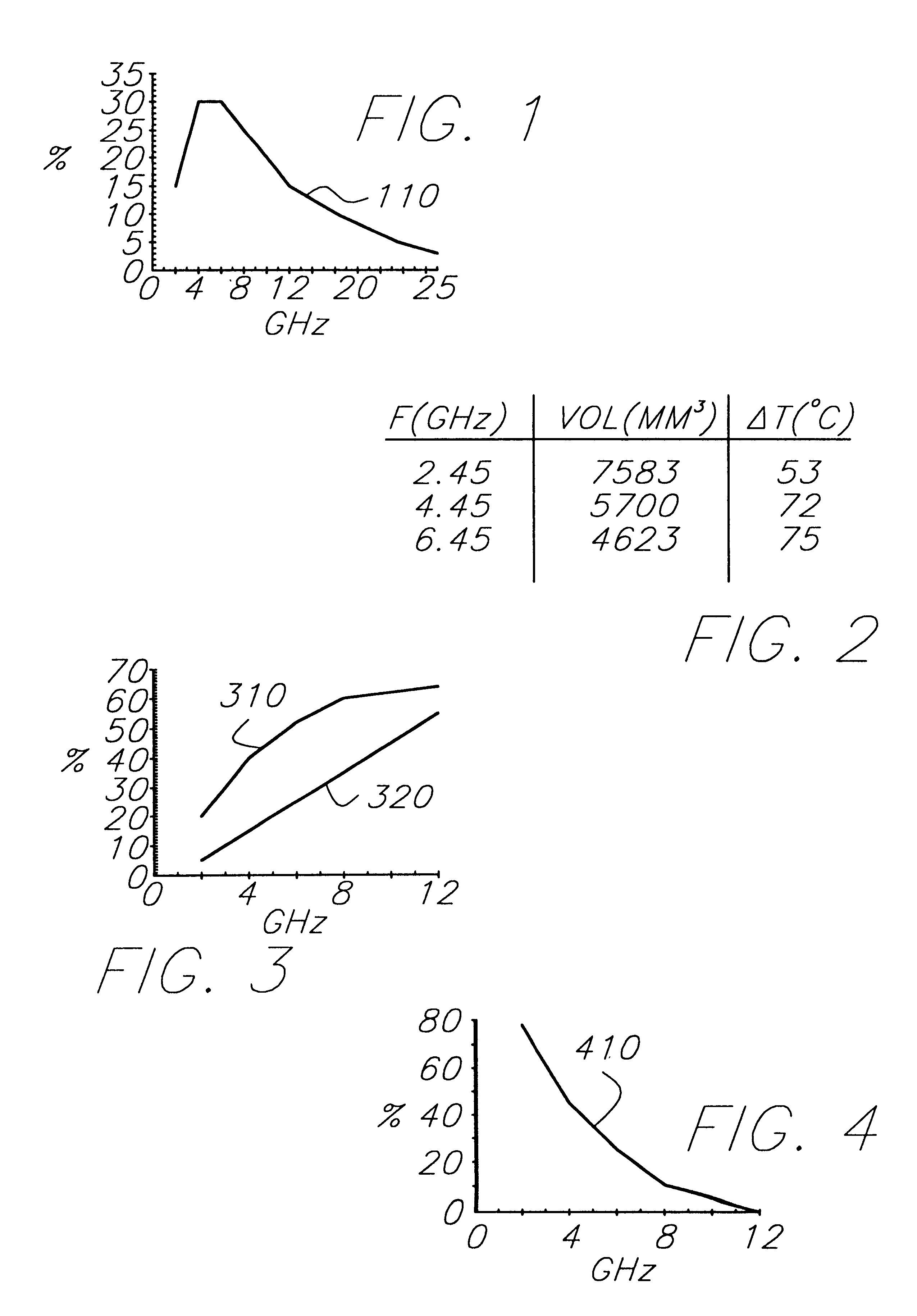
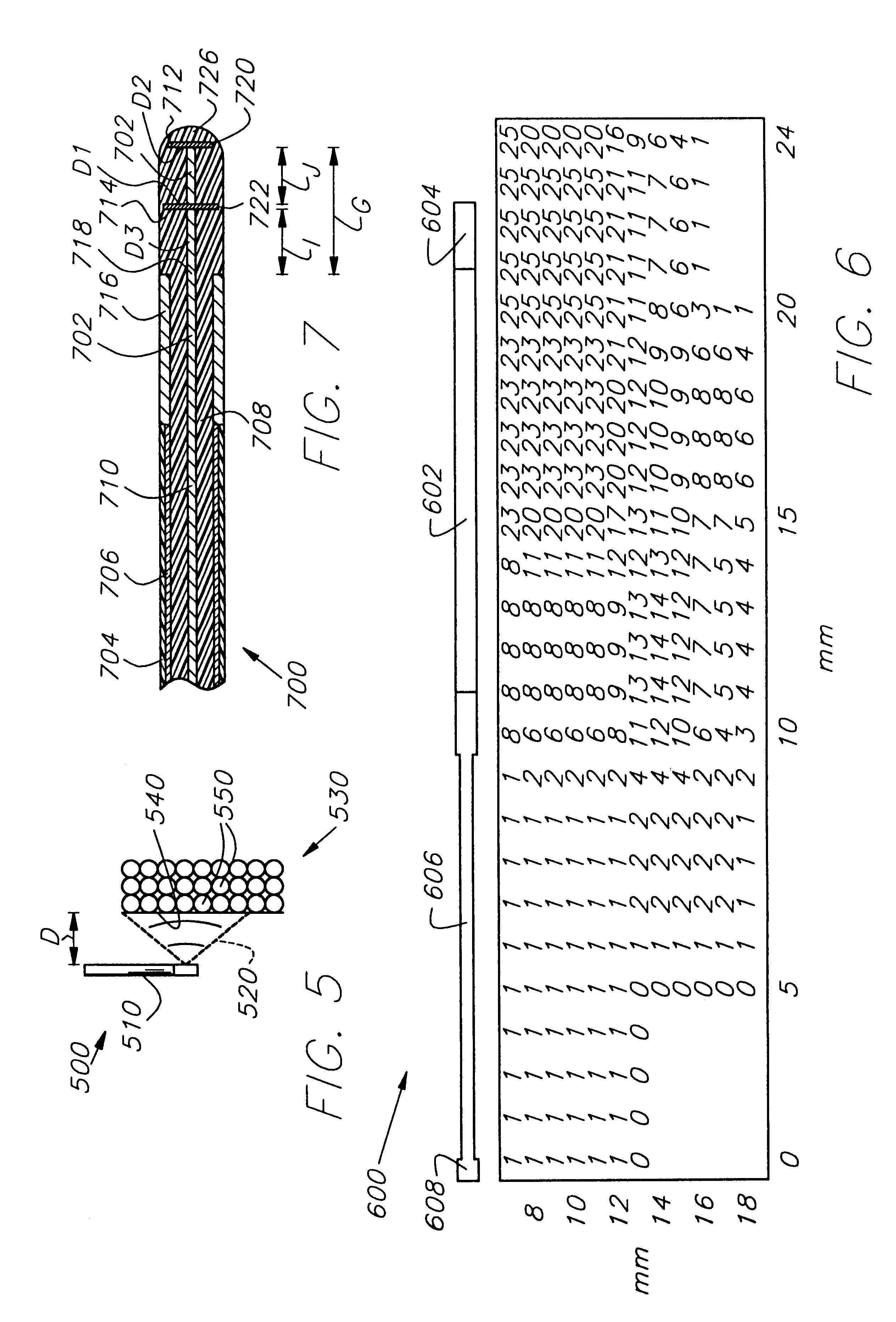
Method and apparatus are provided for propagating microwave energy into heart tissues to produce a desired temperature profile therein at tissue depths sufficient for thermally ablating arrhythmogenic cardiac tissue to treat ventricular tachycardia and other arrhythmias while preventing excessive heating of surrounding tissues, organs, and blood. A wide bandwidth double-disk antenna (700) is effective for this purpose over a bandwidth of about six gigahertz. A computer simulation provides initial screening capabilities for an antenna such as antenna, frequency, power level, and power application duration. The simulation also allows optimization of techniques for specific patients or conditions. In operation, microwave energy between about 1 Gigahertz and 12 Gigahertz is applied to monopole microwave radiator (600) having a surface wave limiter (606). A test setup provides physical testing of microwave radiators (854) to determine the temperature profile created in actual heart tissue or ersatz heart tissue (841). Saline solution (872) pumped over the heart tissue (841) with a peristaltic pump (862) simulates blood flow. Optical temperature sensors (838) disposed at various tissue depths within the heart tissue (841) detect the temperature profile without creating any electromagnetic interference. The method may be used to produce a desired temperature profile in other body tissues reachable by catheter (510) such as tumors and the like.
Owner:NASA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com