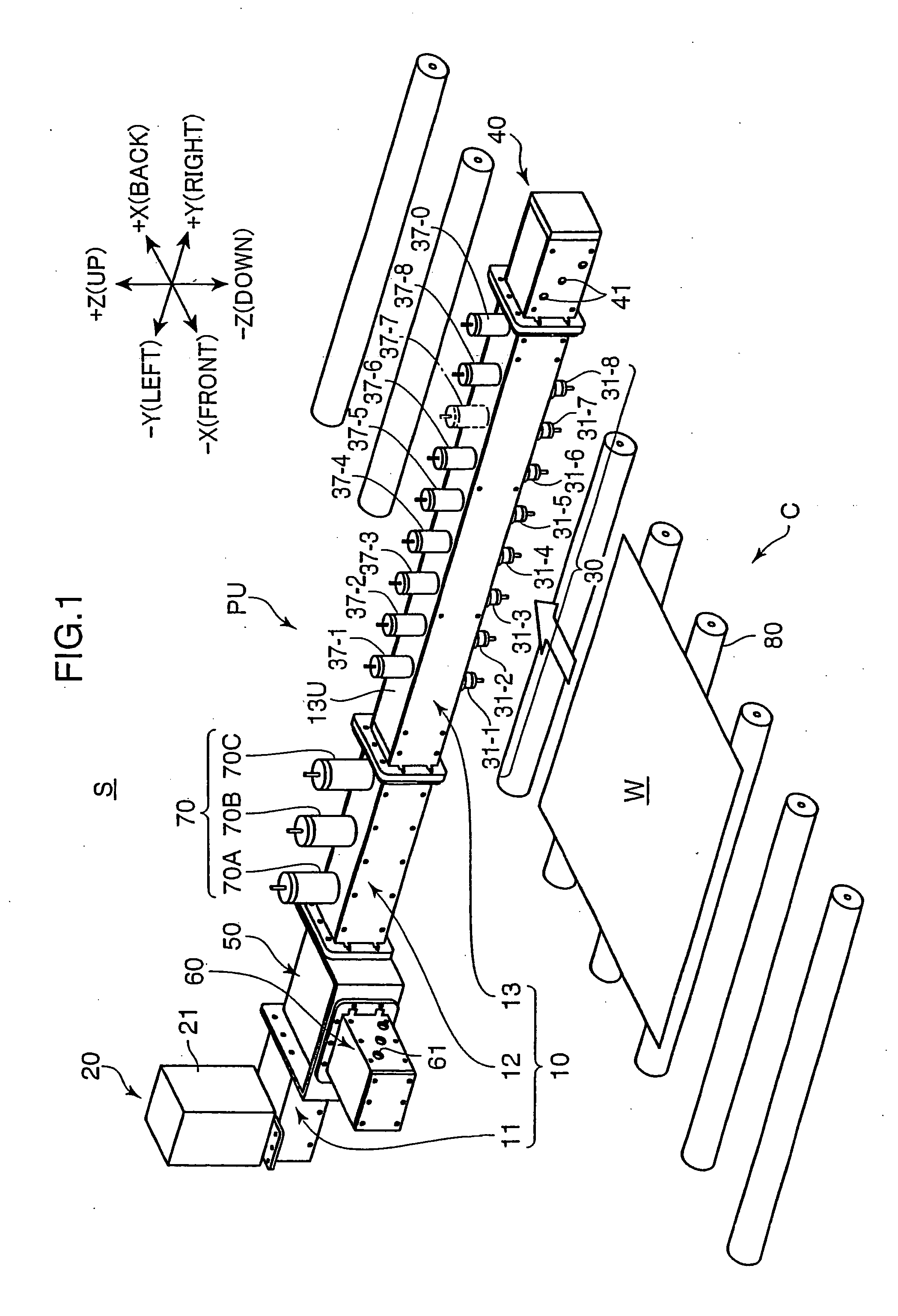
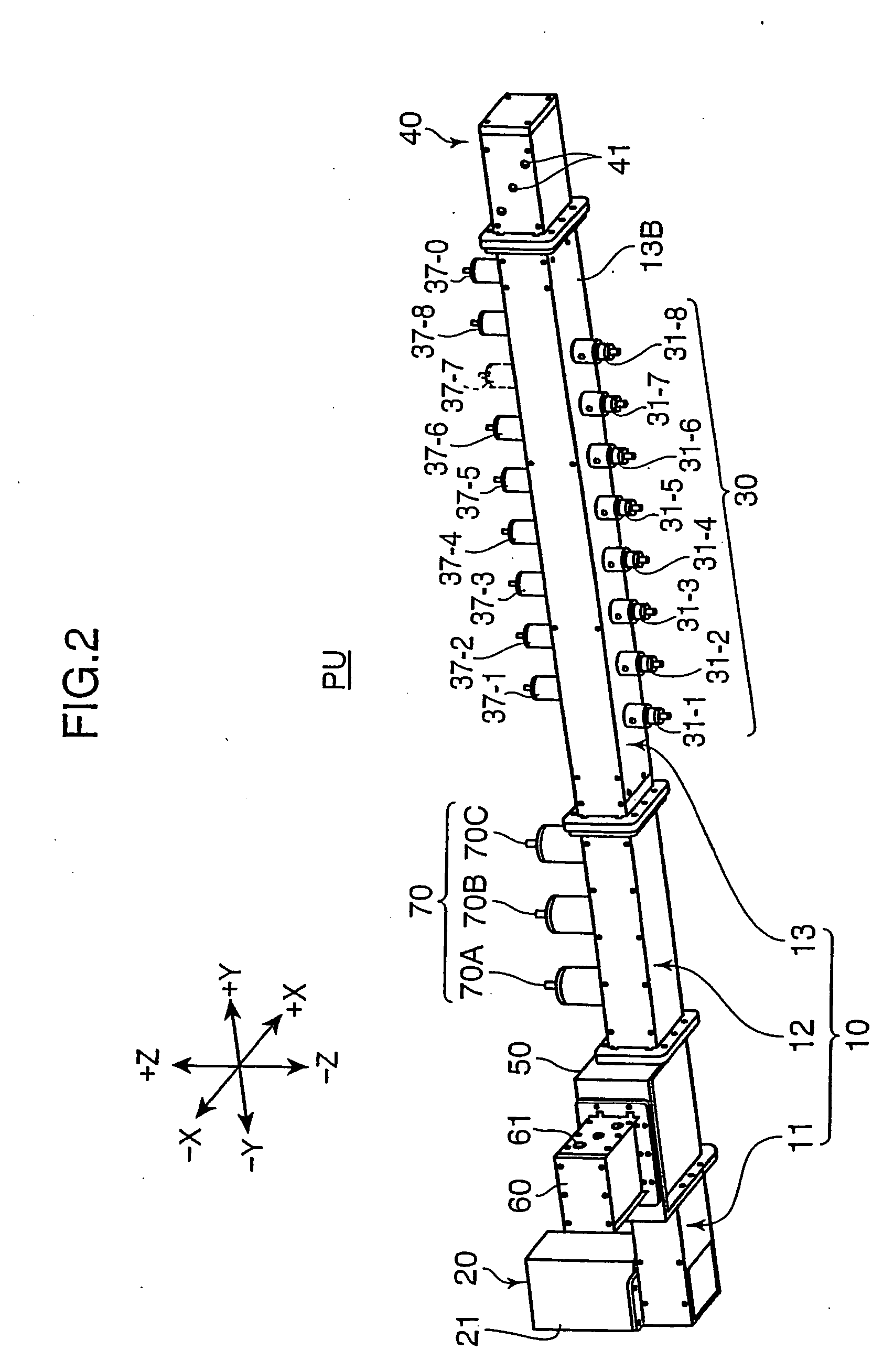
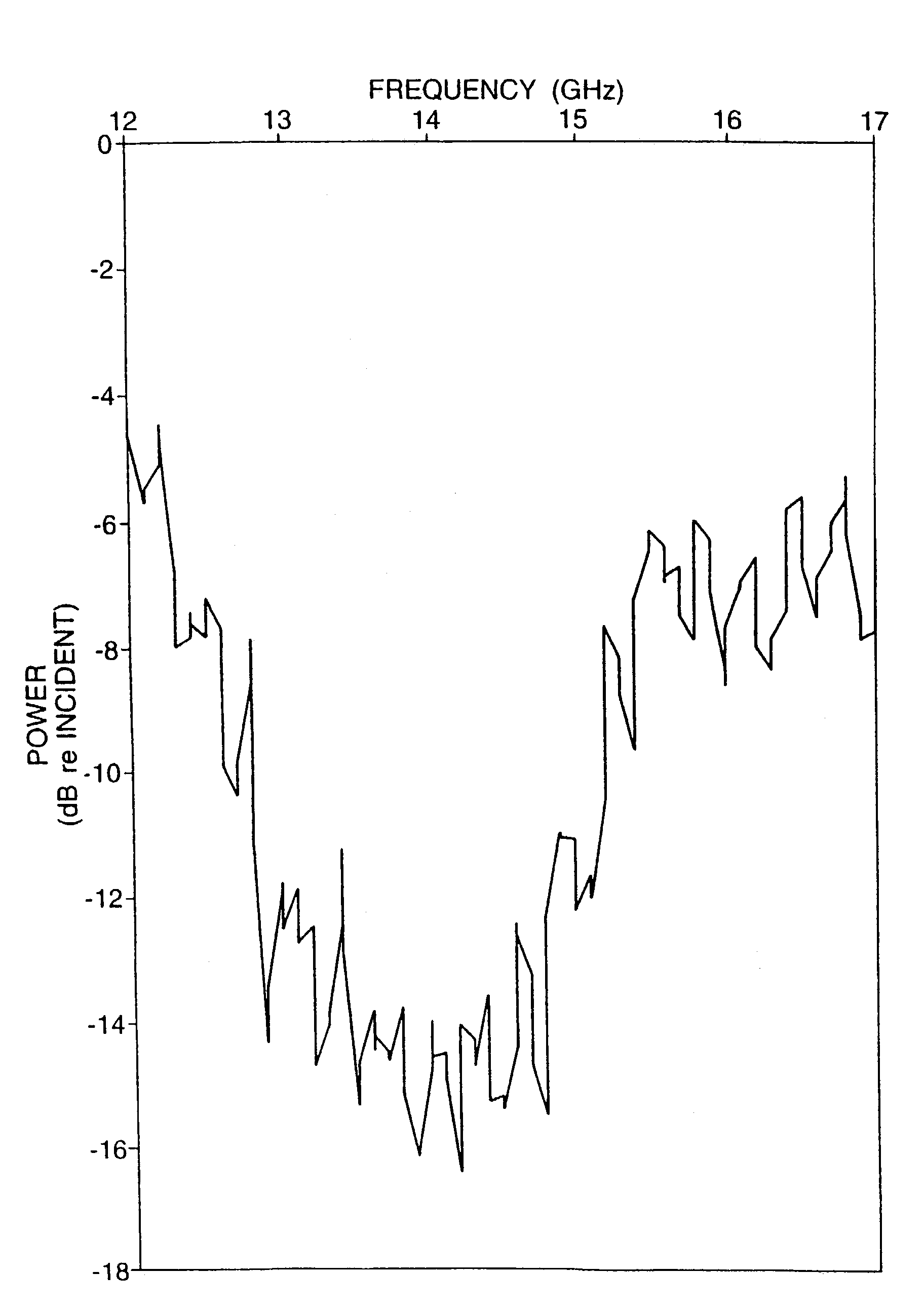
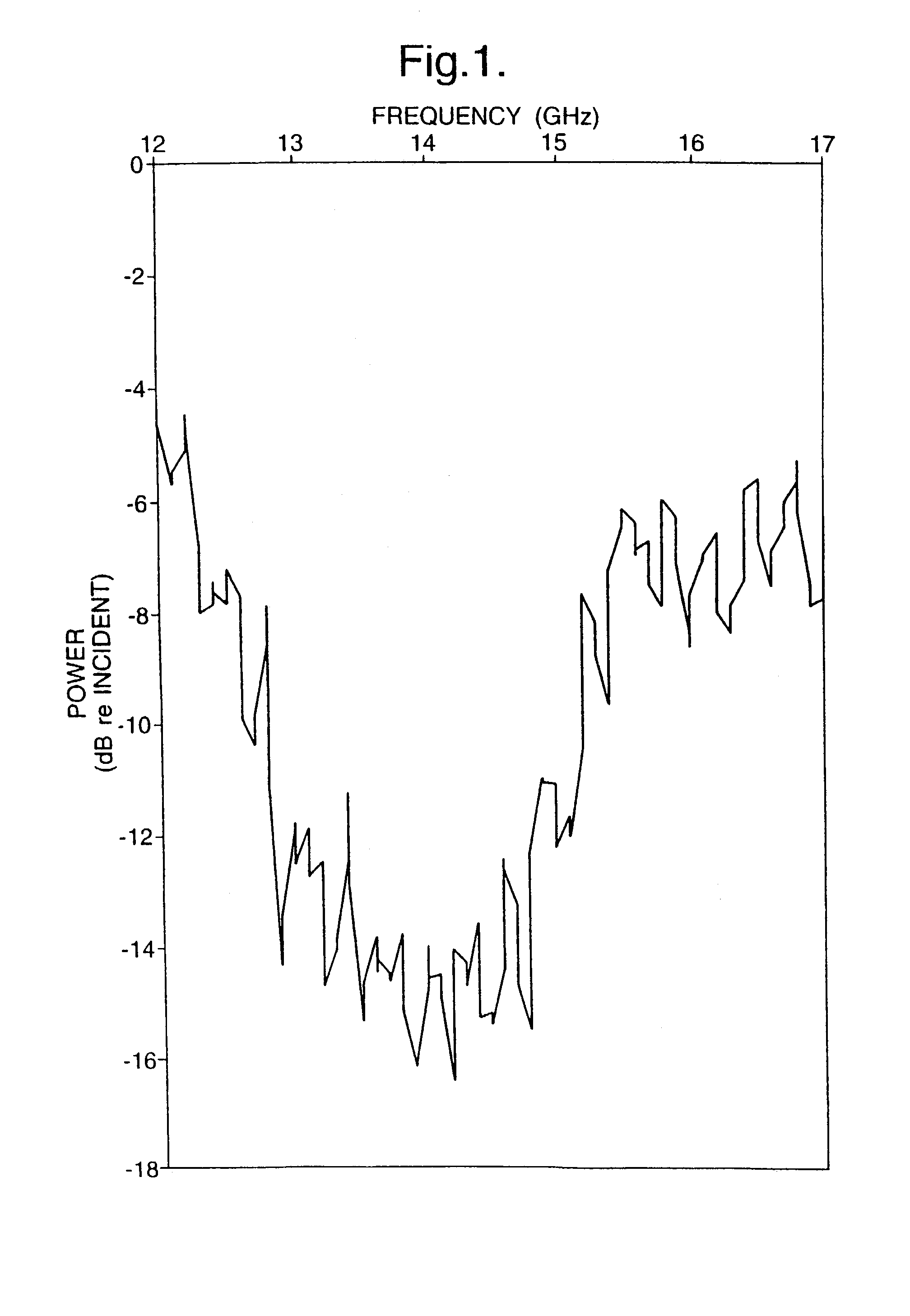
Patents
Literature
40 results about "Microwave propagation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microwave Propagation. Microwave signals usually travel from transmitter to receiver along nearly straight-line paths. There are occasional exceptions. The same atmospheric conditions that cause optical mirages can cause microwavefading problems. Microwave signals bend slightly when passing obliquely through layers of different air density.
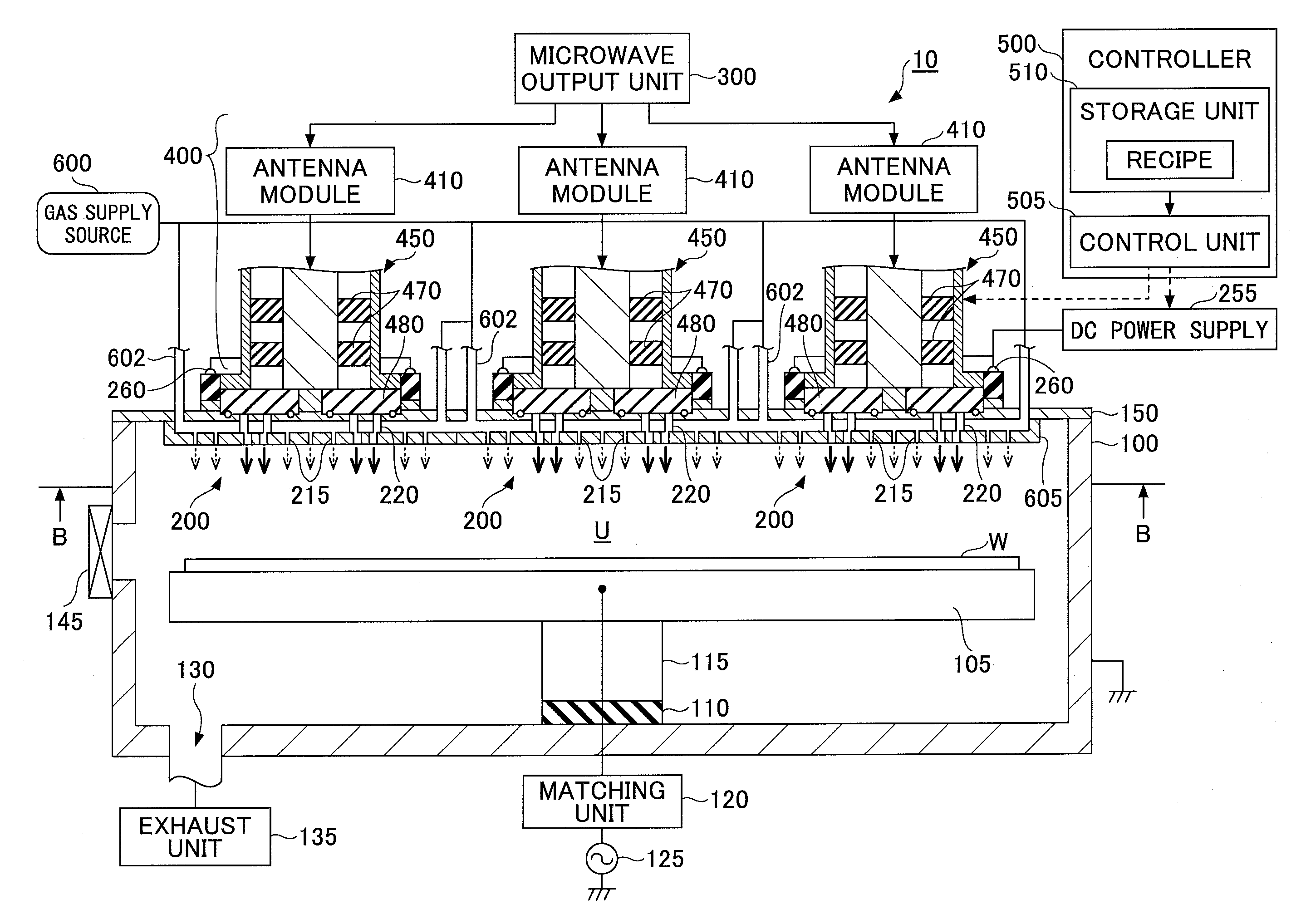
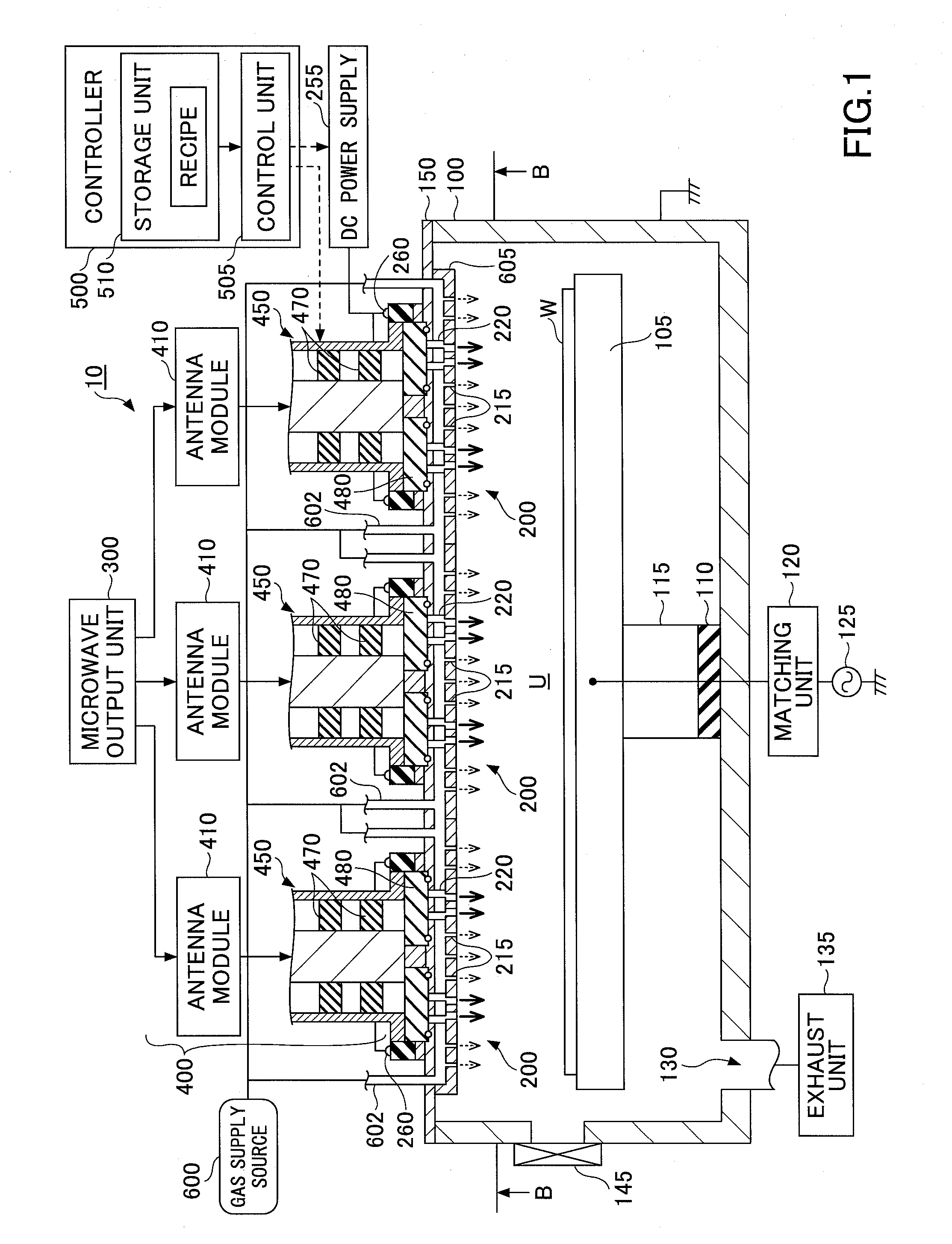
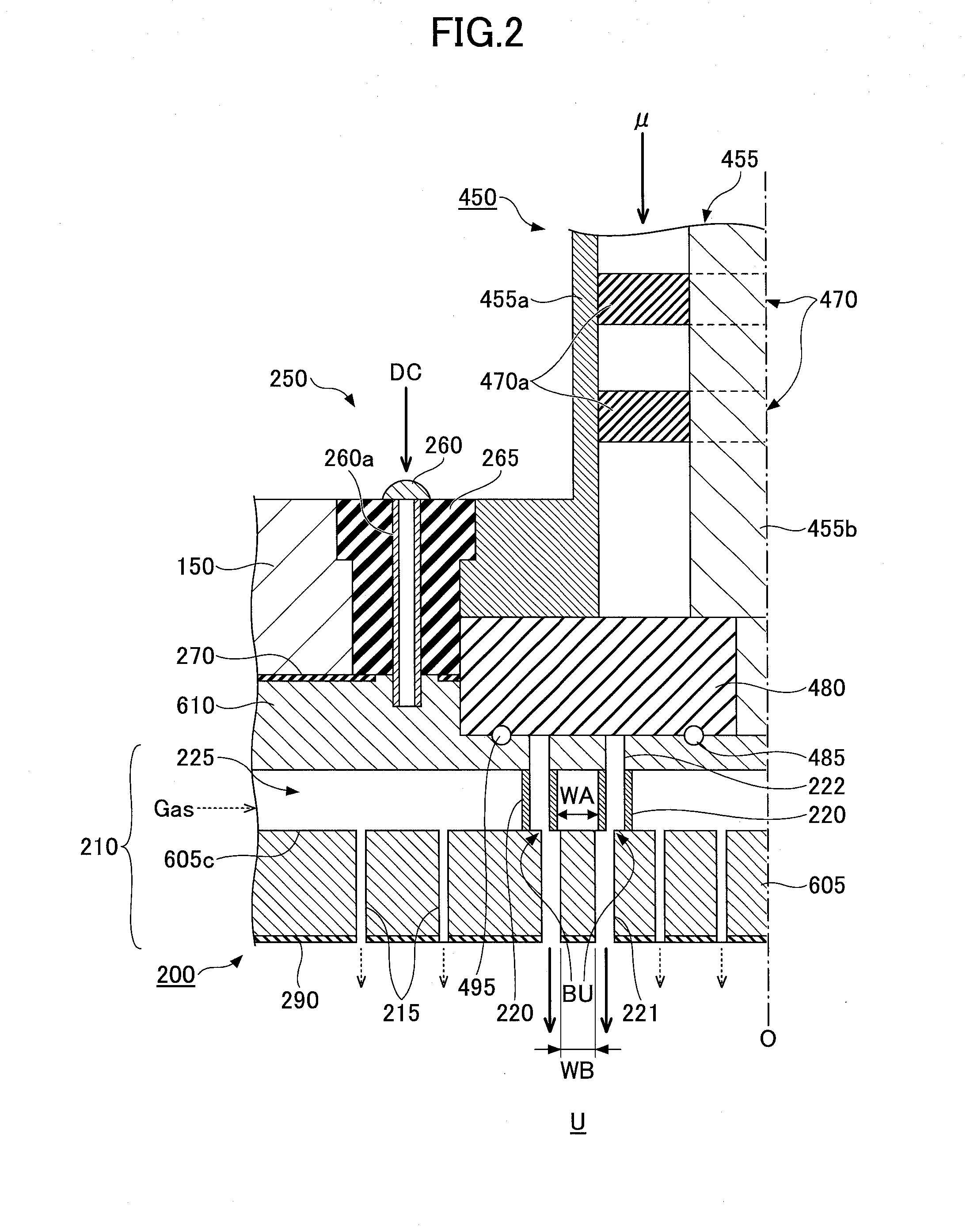
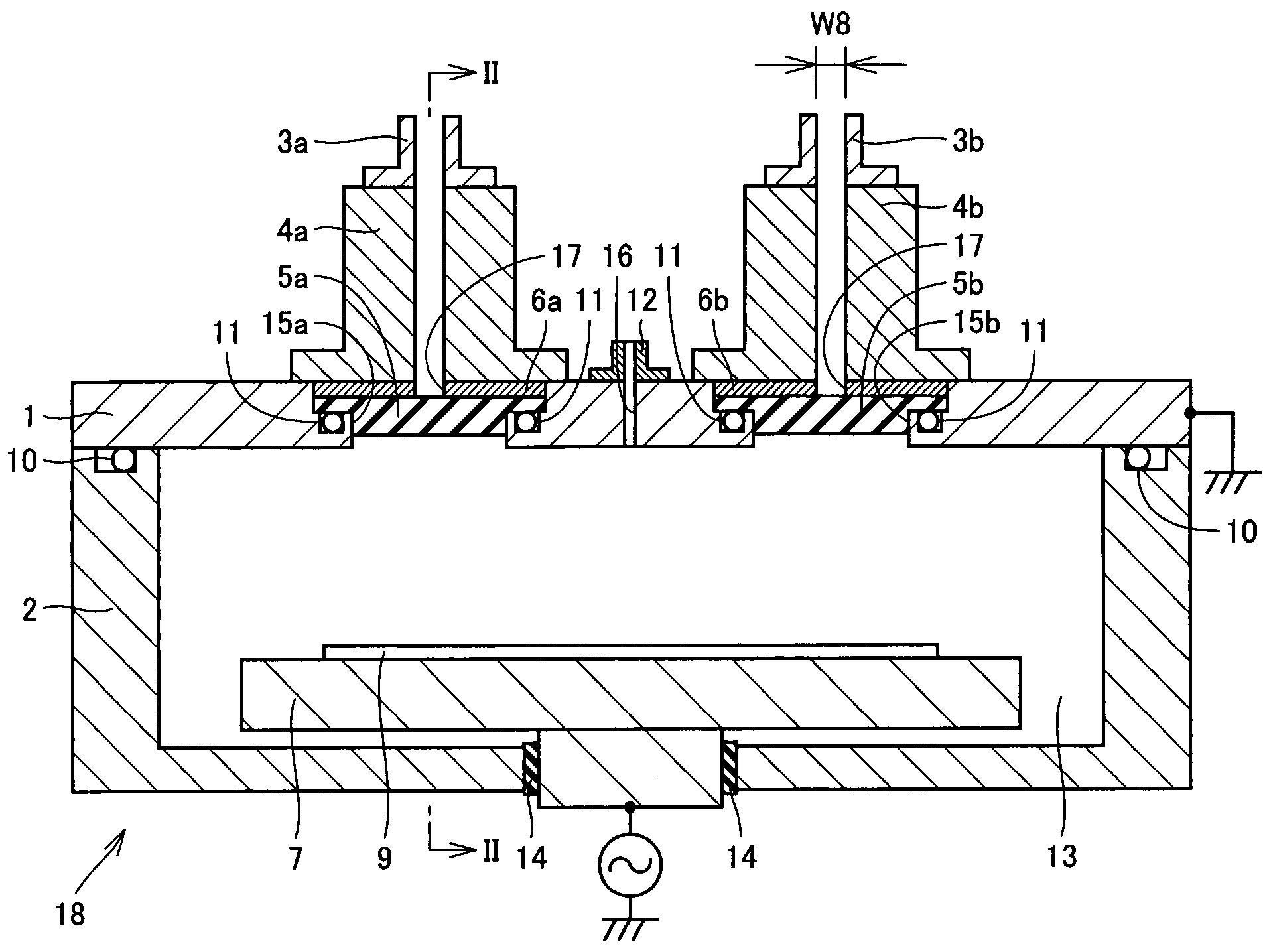
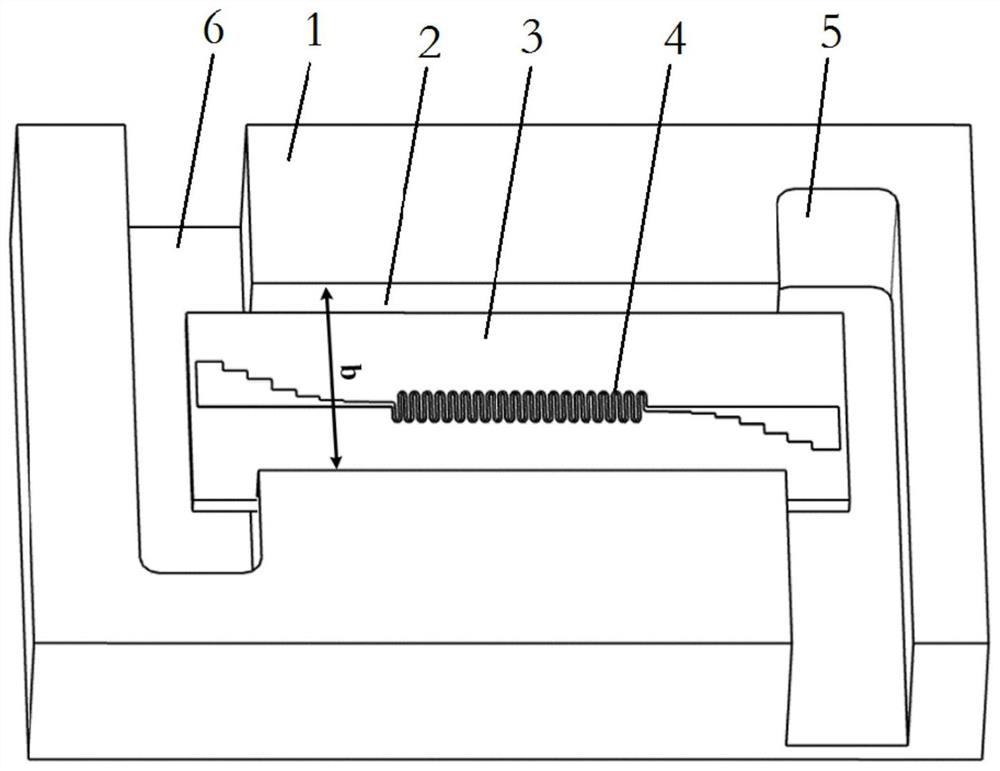
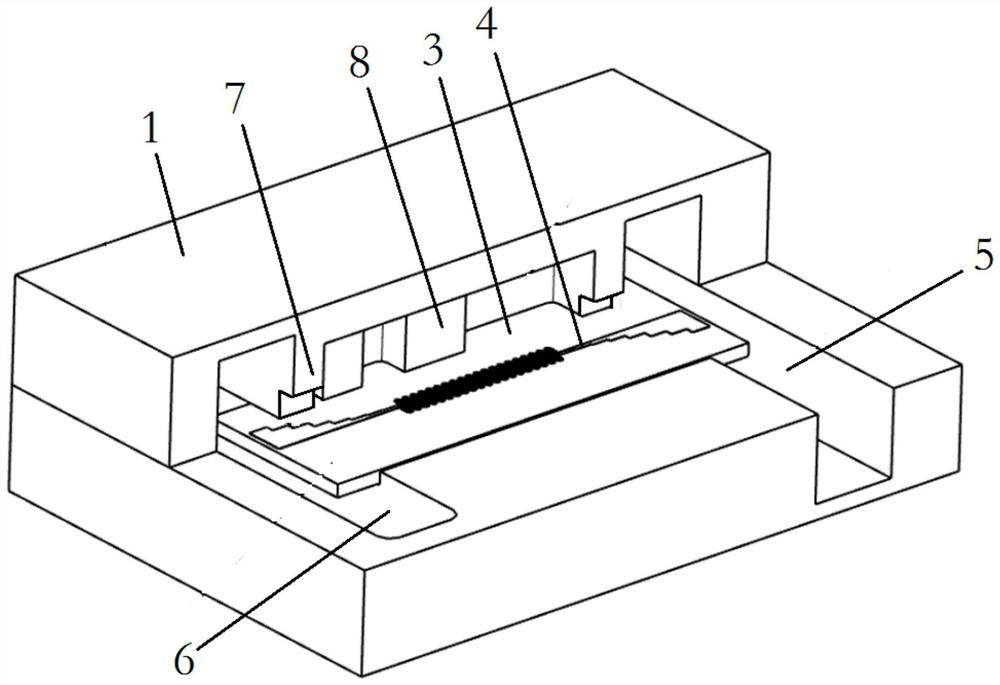
Antenna for plasma generation, plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method
ActiveUS20140339981A1Electric discharge tubesAntenna supports/mountingsMicrowave propagationCoaxial waveguides
An antenna for plasma generation radiates a microwave transmitted through a coaxial waveguide into a processing chamber and propagates the microwave on a metal surface of the processing chamber to convert gas into surface wave plasma. The antenna includes a gas flow path for passing the gas through the antenna, a plurality of gas holes that communicate with the gas flow path and introduce the gas into the processing chamber, and a plurality of slots that are separated from the gas flow path and penetrate through the gas flow path. The slots pass the microwave transmitted through the coaxial waveguide and a slow-wave plate to the processing chamber. A first space between portions of adjacent slots penetrating through the gas flow path is arranged to be wider than a second space between portions of the adjacent slots opening out to a plasma generation space of the processing chamber.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
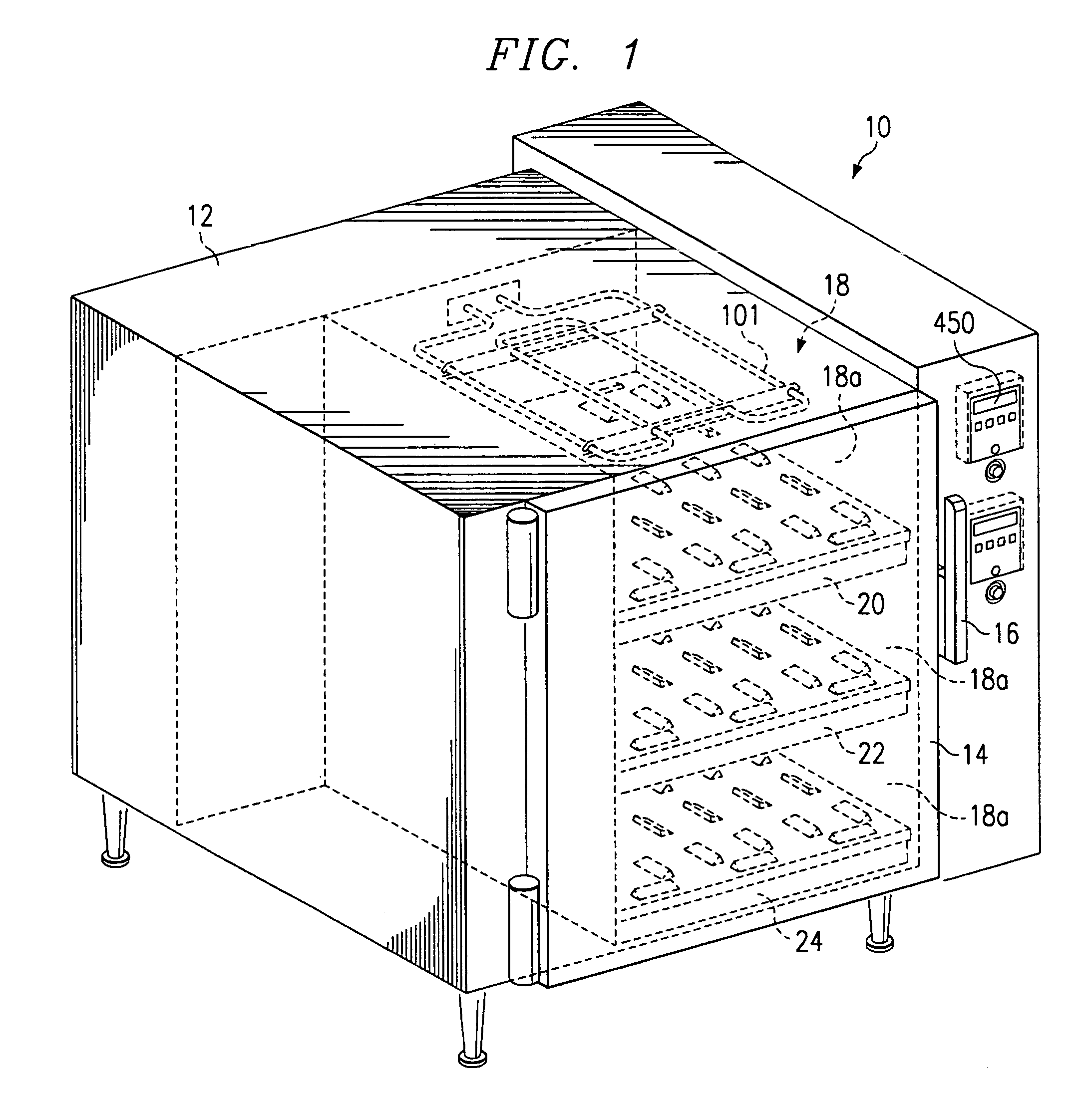
Multi-shelved convection microwave oven
An oven, is provided that includes multiple heat transfer means, including convection and microwave heat transfer means. The oven includes a cooking chamber, a blower and at least a shelf disposed within the cooking chamber. The shelf is designed to act as a food support as well as a conduit through which heated air passes into the cooking chamber. The microwave heating means comprises a microwave source and wave guide through which microwaves travel. The wave guide includes a plurality of openings through which microwaves can pass into said cooking chamber. In the preferred embodiment, the openings in the wave guide are positioned to correspond with the predetermined minima or maxima for the microwave wavelength propagating within the wave guide. An electric heating element may also be disposed within the cooking chamber to provide an alternative heating source.
Owner:ENERSYST DEV CENT
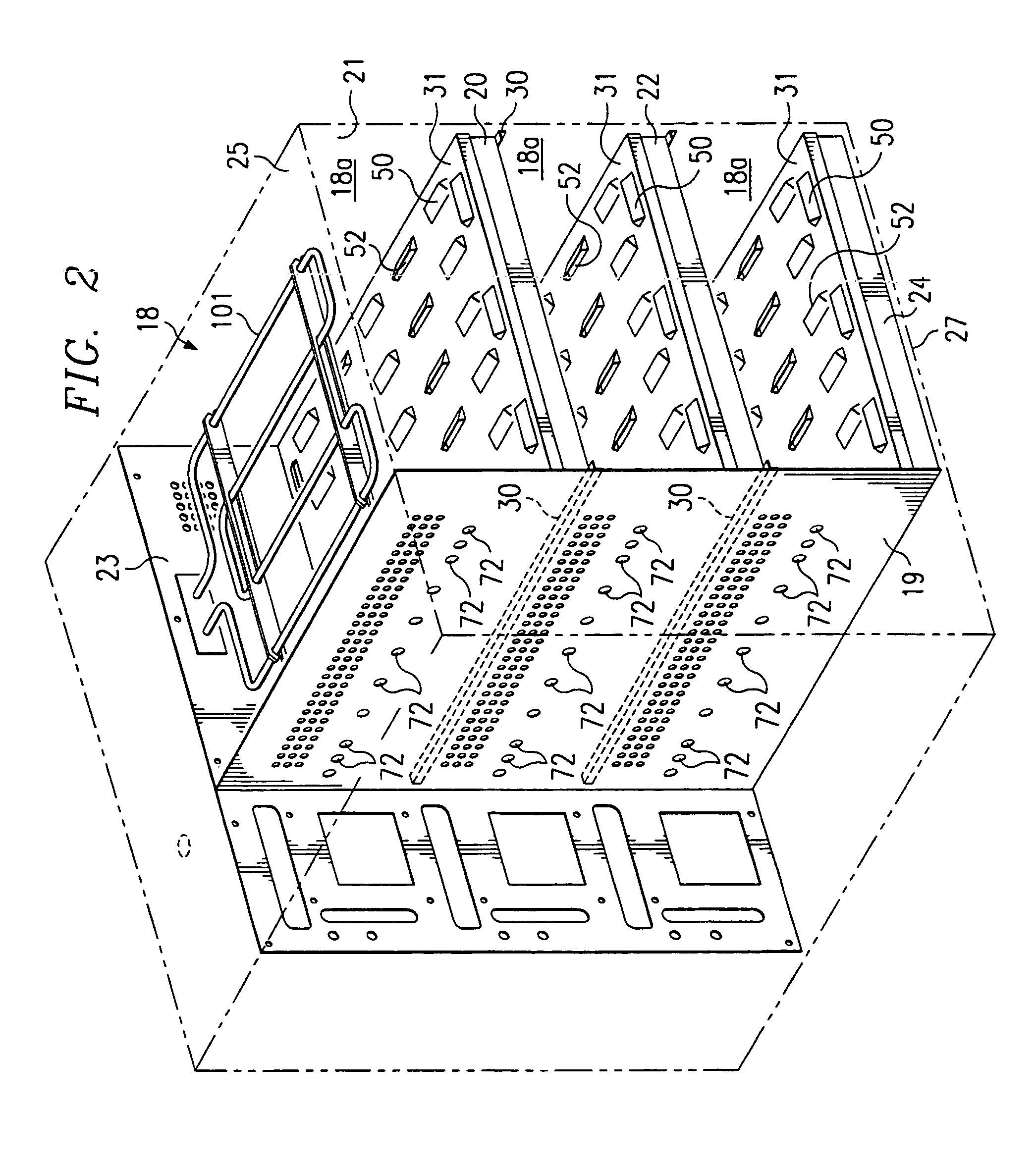
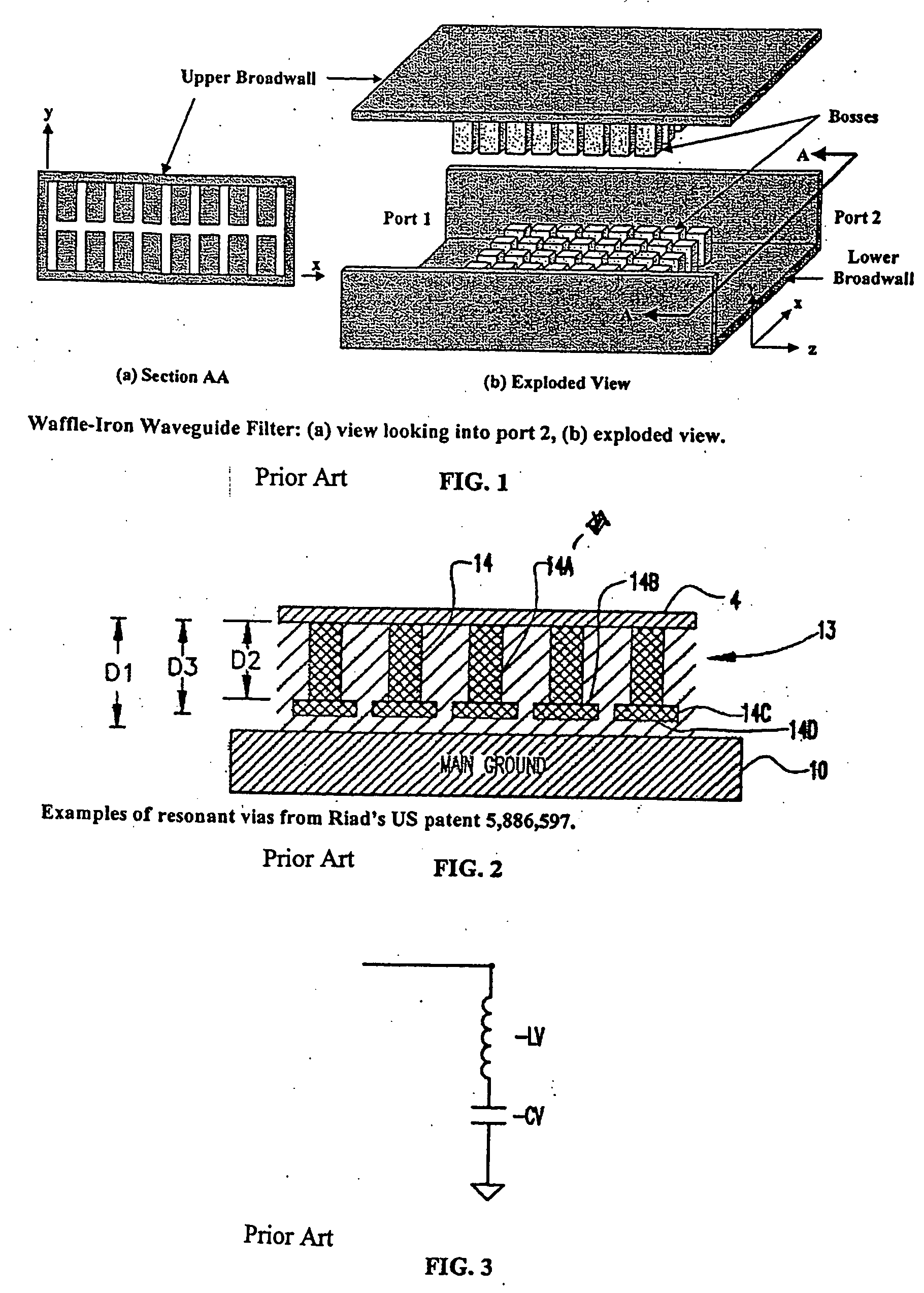
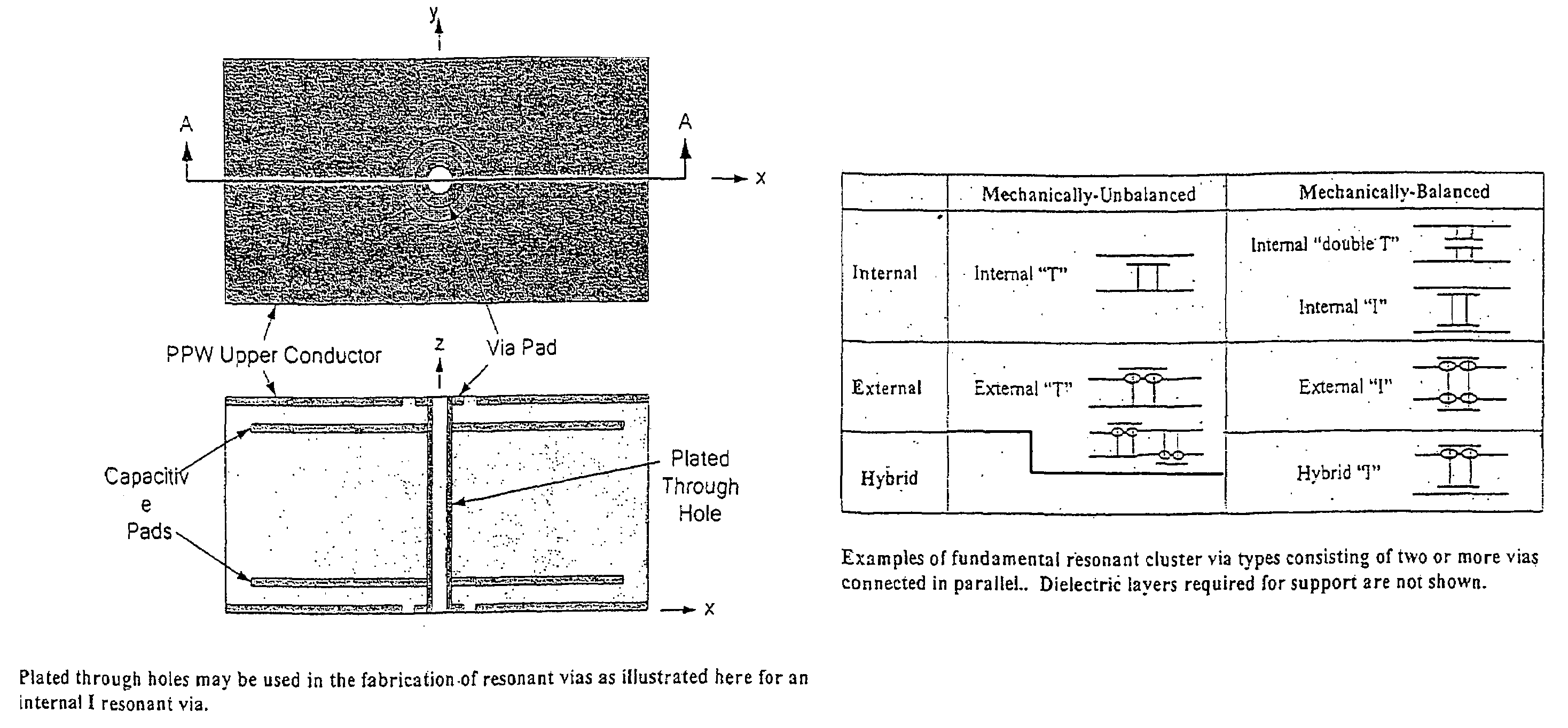
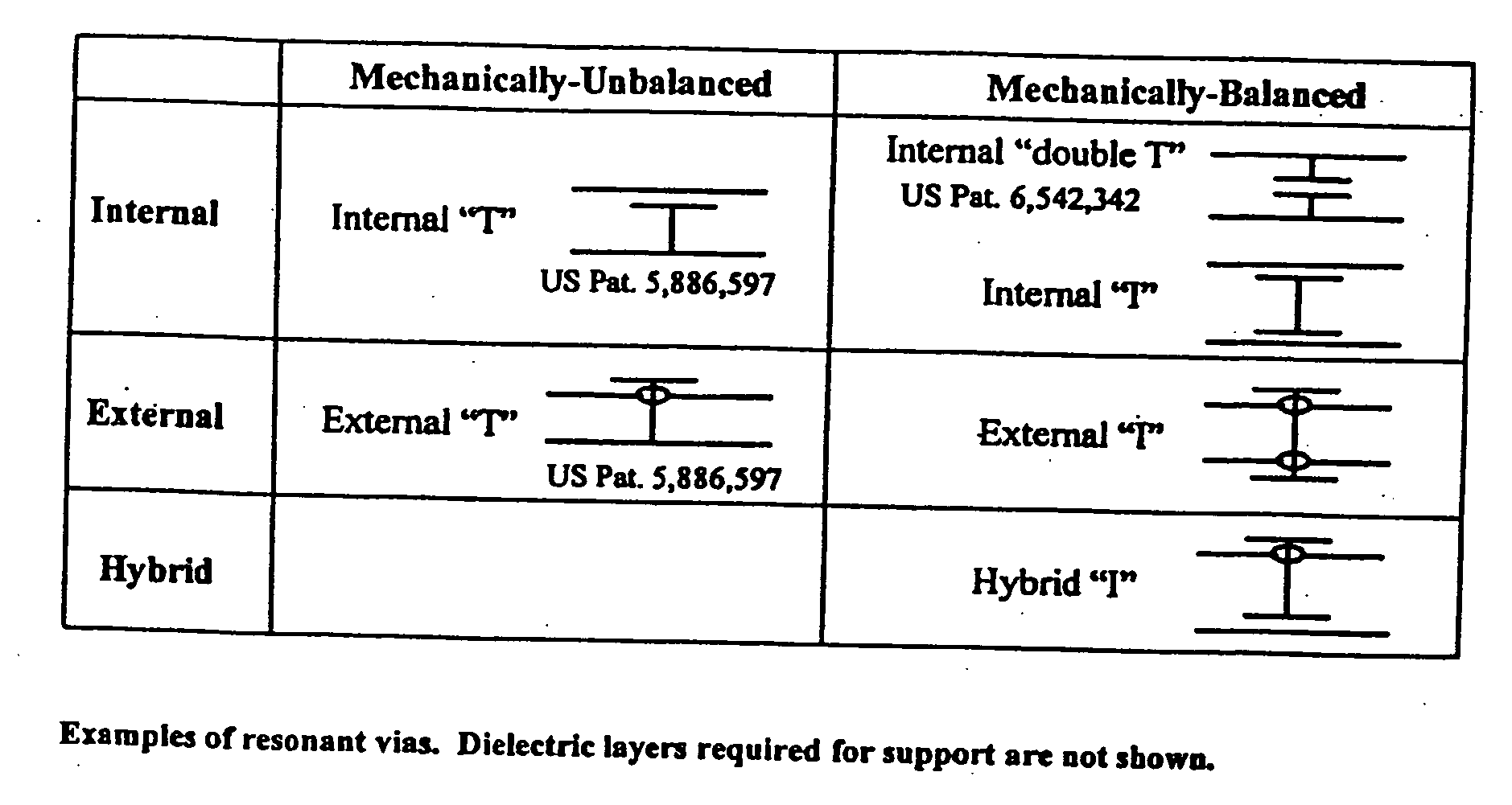
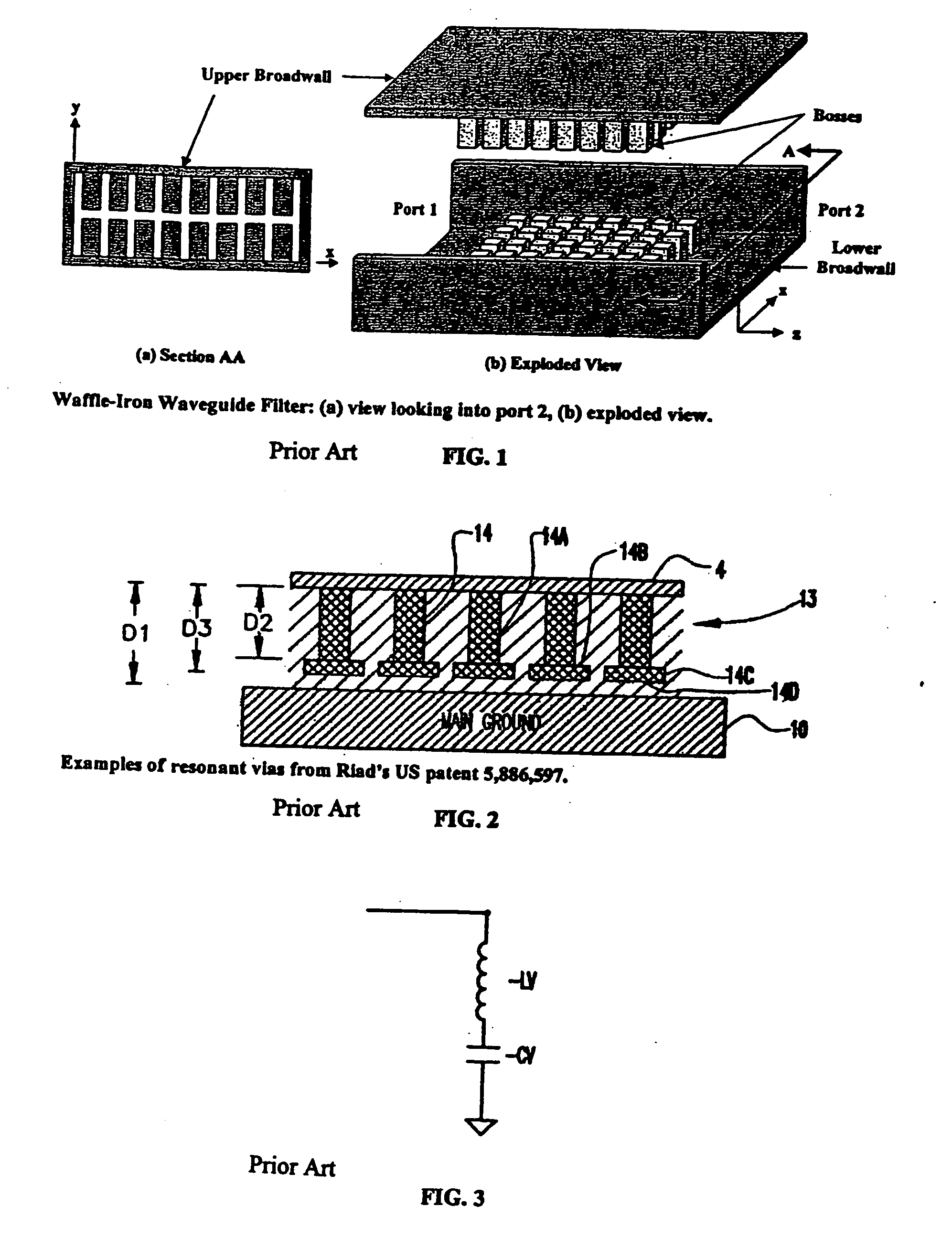
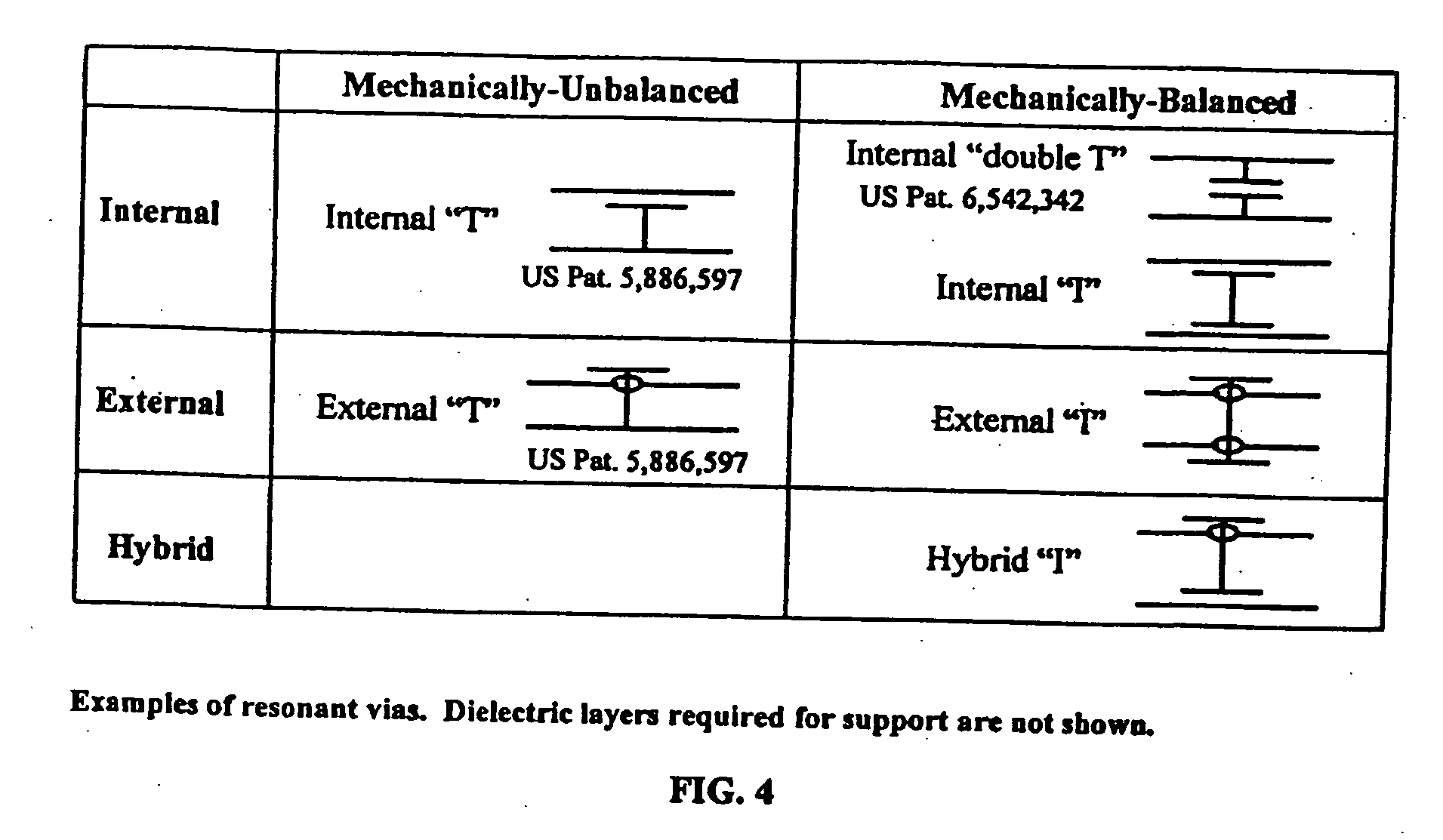
Systems and methods for blocking microwave propagation in parallel plate structures utilizing cluster vias
InactiveUS20060038639A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceIn plane
Systems and methods are taught for blocking the propagation of electromagnetic waves in parallel-plate waveguide (PPW) structures. Periodic arrays of resonant vias are used to create broadband high frequency stop bands in the PPW, while permitting DC and low frequency waves to propagate. Particular embodiments include clusters of small vias that effectively function as one large via, thereby increasing stop band bandwidth and maximizing parallel plate capacitance. Cluster vias can be configured to additionally provide a shielded and impedance matched route within the interior area of the cluster through which signal vias can connect transmission lines disposed in planes lying above and below the PPW. Important applications include electromagnetic noise reduction in layered electronic devices such as circuit boards, ceramic modules, and semiconductor chips.
Owner:WEMTEC
Systems and methods for blocking microwave propagation in parallel plate structures utilizing cluster vias
Systems and methods are taught for blocking the propagation of electromagnetic waves in parallel-plate waveguide (PPW) structures. Periodic arrays of resonant vias are used to create broadband high frequency stop bands in the PPW, while permitting DC and low frequency waves to propagate. Particular embodiments include clusters of small vias that effectively function as one large via, thereby increasing stop band bandwidth and maximizing parallel plate capacitance. Cluster vias can be configured to additionally provide a shielded and impedance matched route within the interior area of the cluster through which signal vias can connect transmission lines disposed in planes lying above and below the PPW. Important applications include electromagnetic noise reduction in layered electronic devices such as circuit boards, ceramic modules, and semiconductor chips.
Owner:WEMTEC
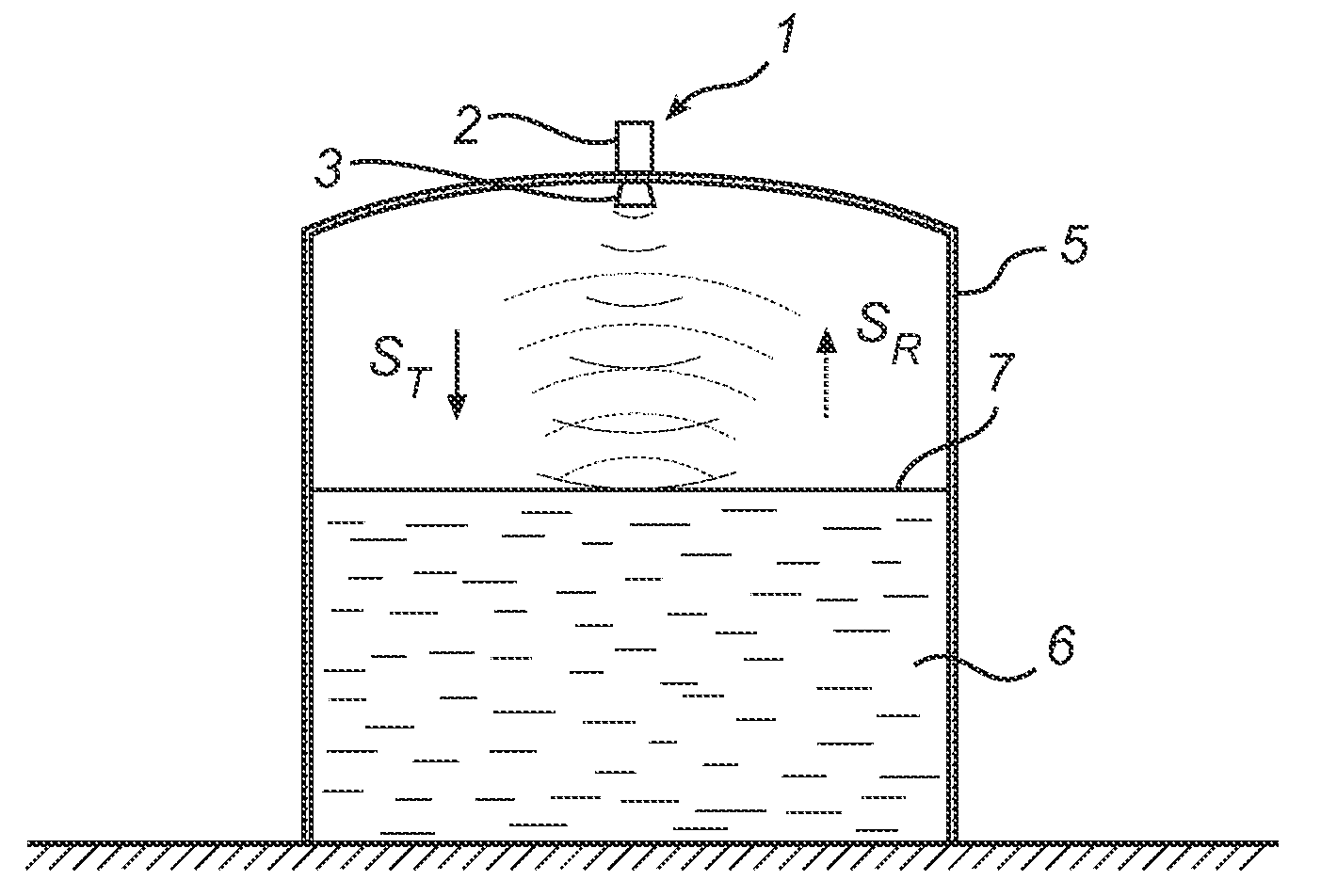
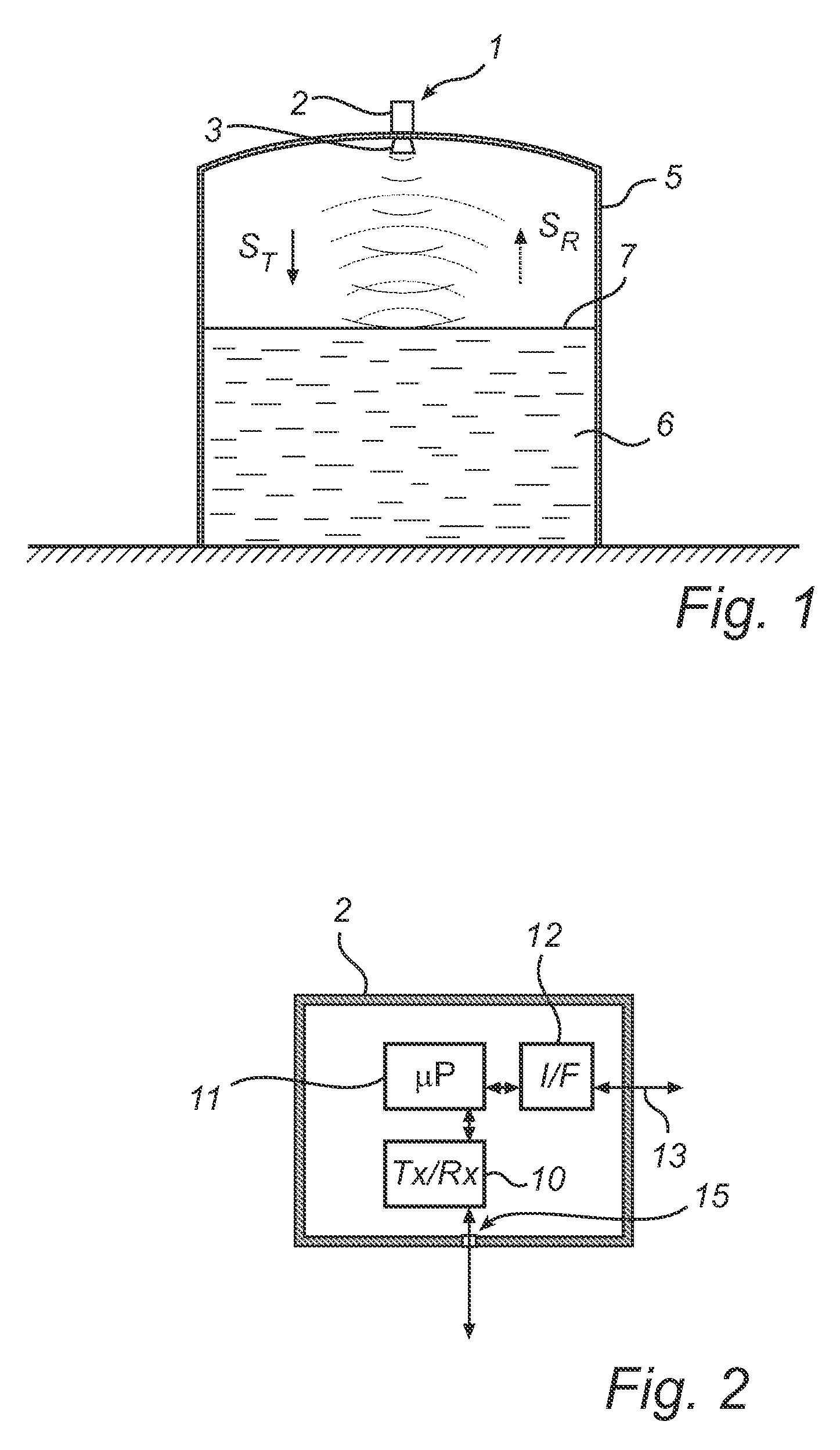
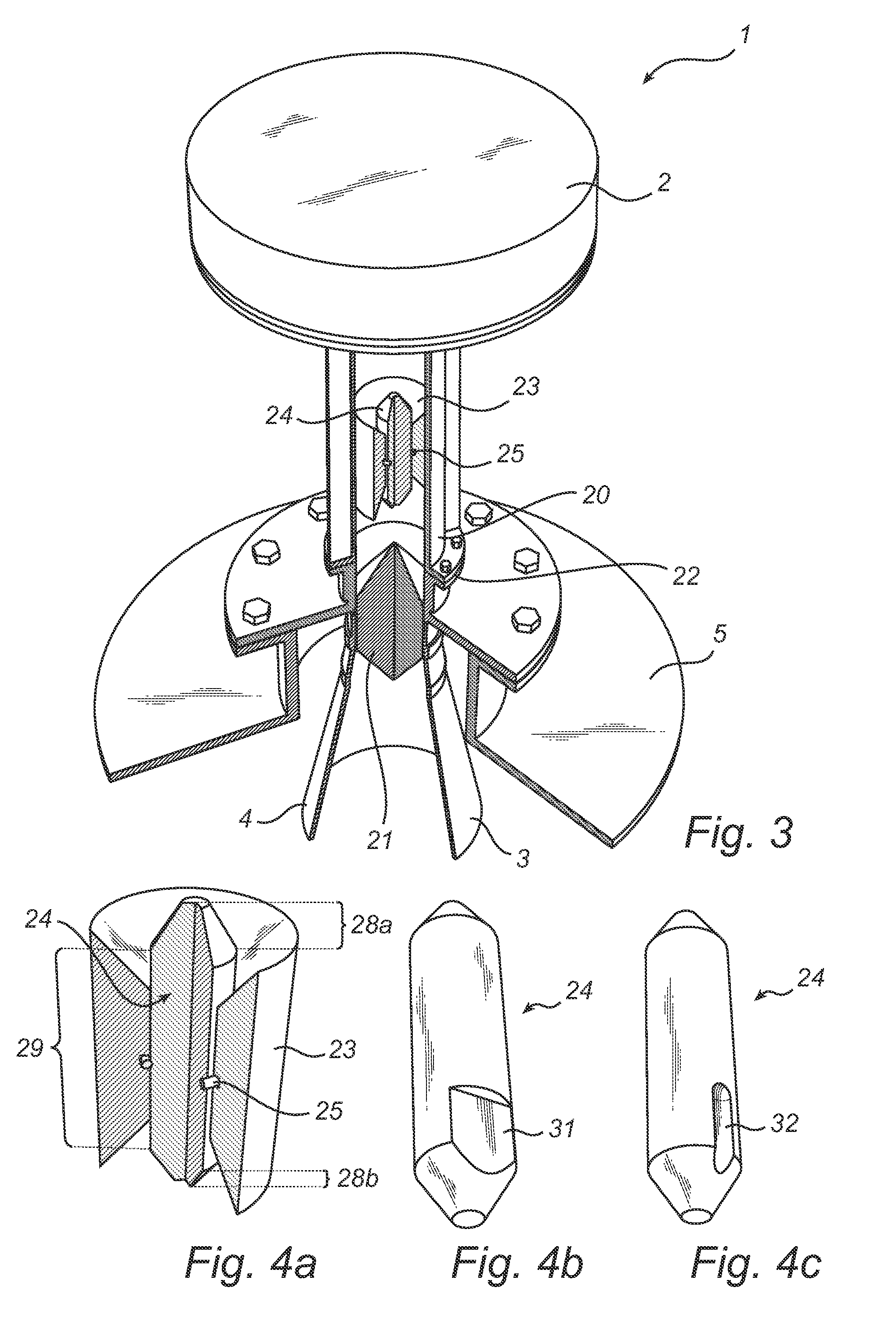
Radar level gauge system with leakage detection
InactiveUS20100231438A1Easily and conveniently changedImprove transmittanceDetection of fluid at leakage pointTesting/calibration apparatusMicrowave propagationTransceiver
A radar level gauge system, for determining a filling level of a product contained in a tank, comprising a transceiver for generating, transmitting and receiving electromagnetic signals; an antenna arranged to direct transmitted electromagnetic signals towards a surface of the product contained in the tank, and to return reflected electromagnetic signals resulting from reflections at impedance transitions encountered by the transmitted electromagnetic signals back to the transceiver; and a hollow waveguide connecting the transceiver and the antenna for guiding the electromagnetic signals therebetween. A sealing member is arranged to seal the waveguide to prevent fluid from passing into the waveguide from an interior of the tank; and the radar level gauge system further comprises processing circuitry connected to the transceiver and configured to determine the filling level based on the reflected electromagnetic signals. The radar level gauge system further comprises a leak indication member being movably arranged inside the hollow waveguide in such a way that a force resulting from leakage of the fluid at the sealing member causes a movement of the leak indication member when acting thereon; and the hollow waveguide is configured in such a way that the movement of the leak indication member causes a change in at least one microwave propagation characteristic of the hollow waveguide.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
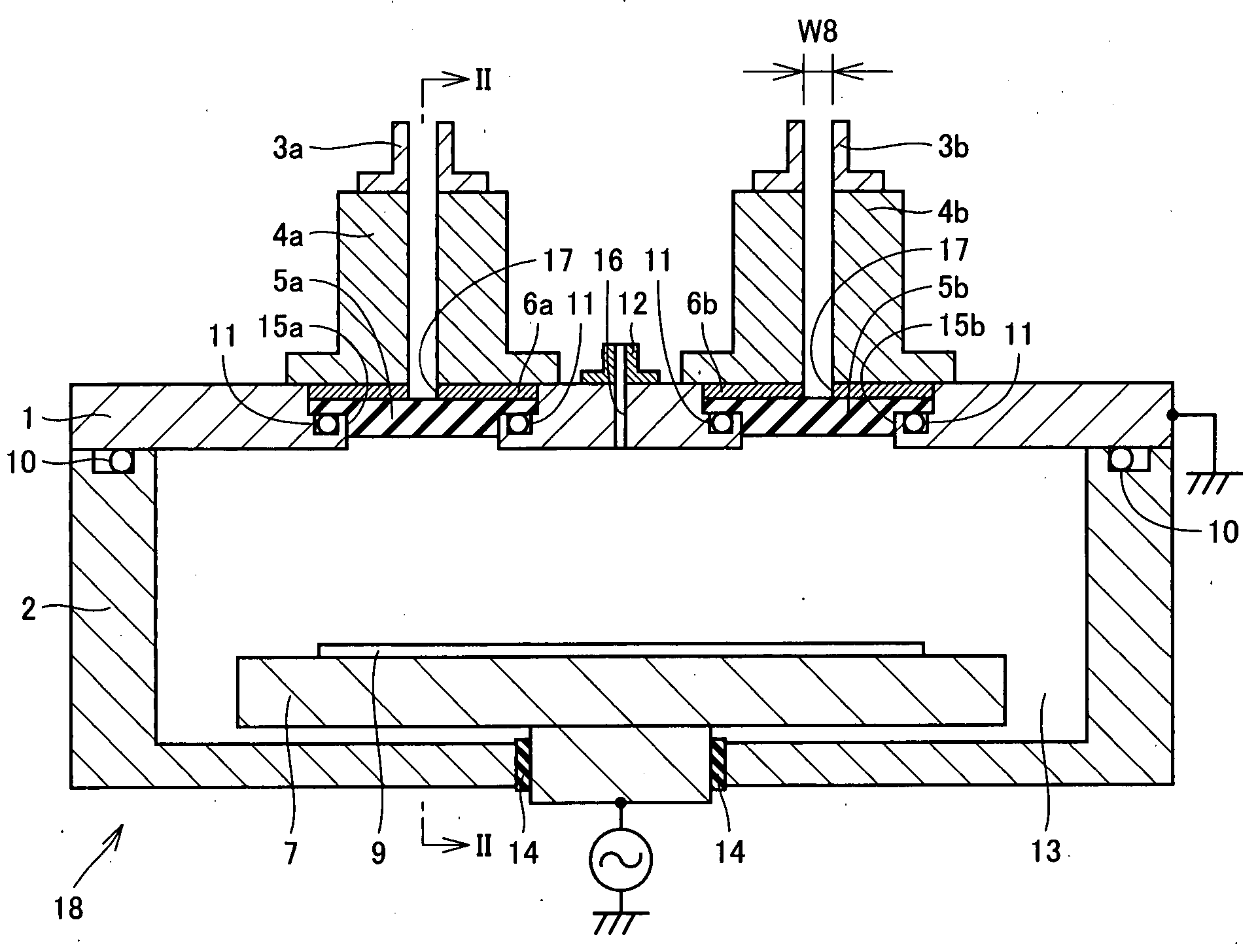
Plasma process apparatus and its processor
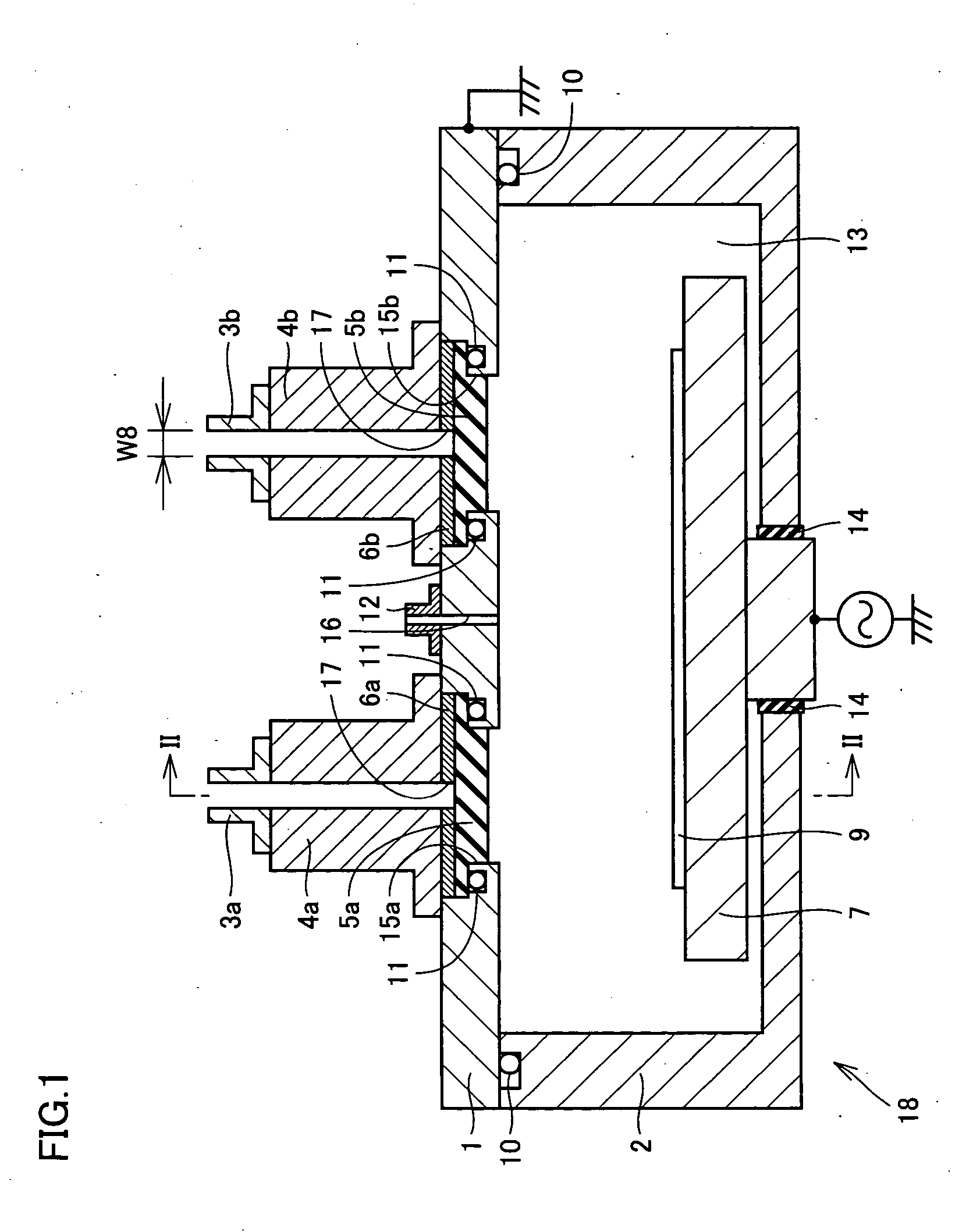
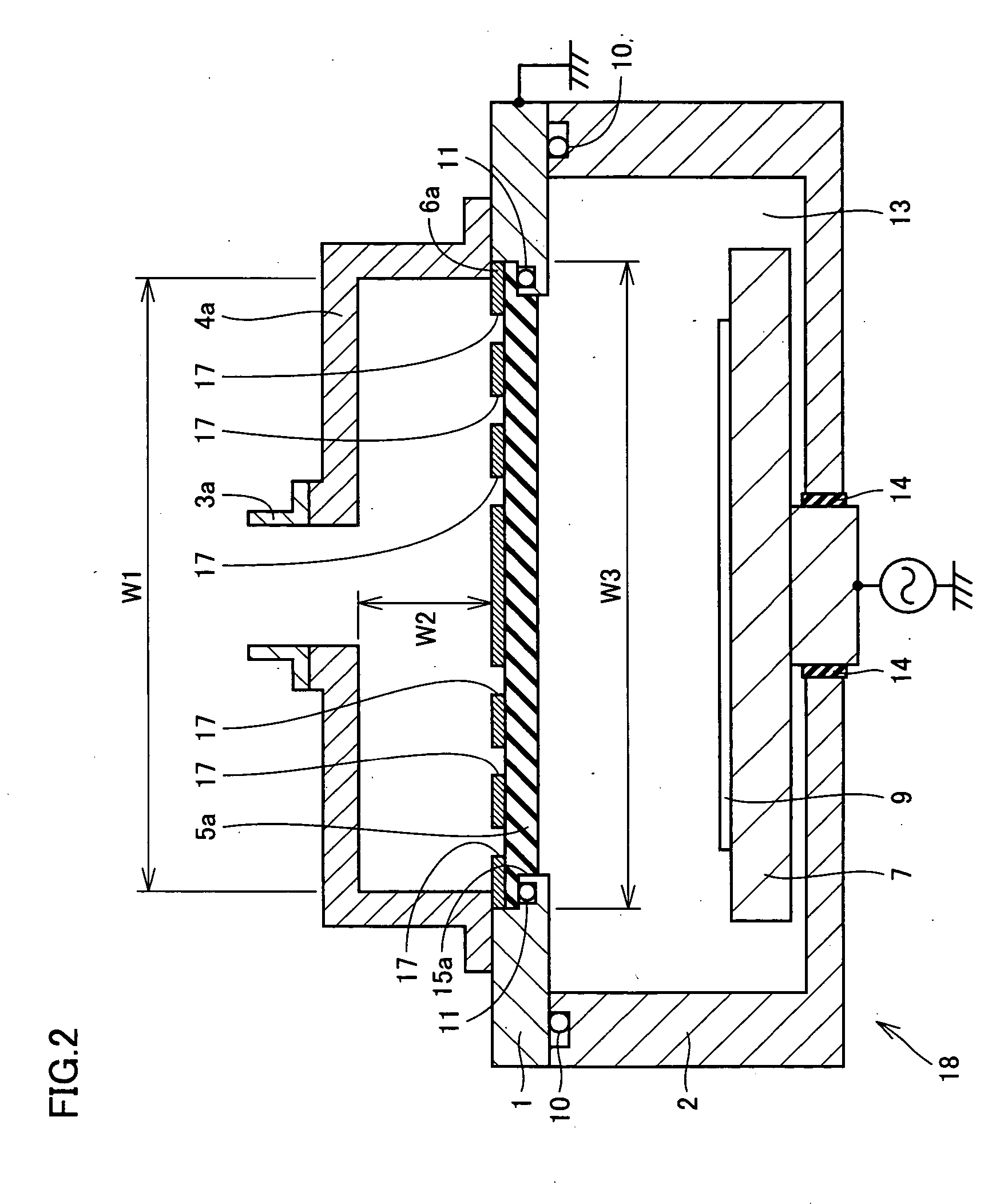
InactiveUS20050011455A1Increase rangeGuaranteed normal transmissionElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricMicrowave propagation
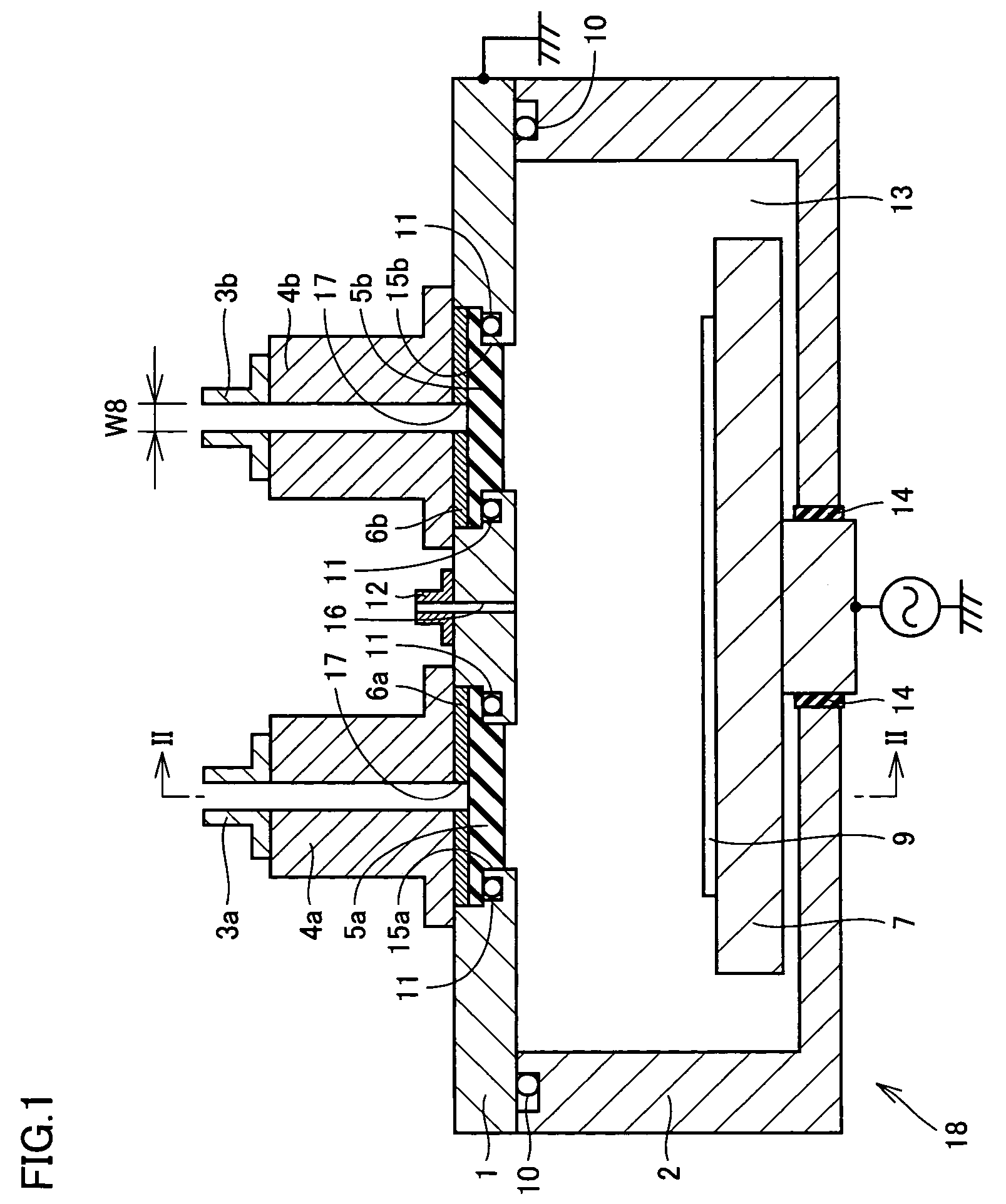
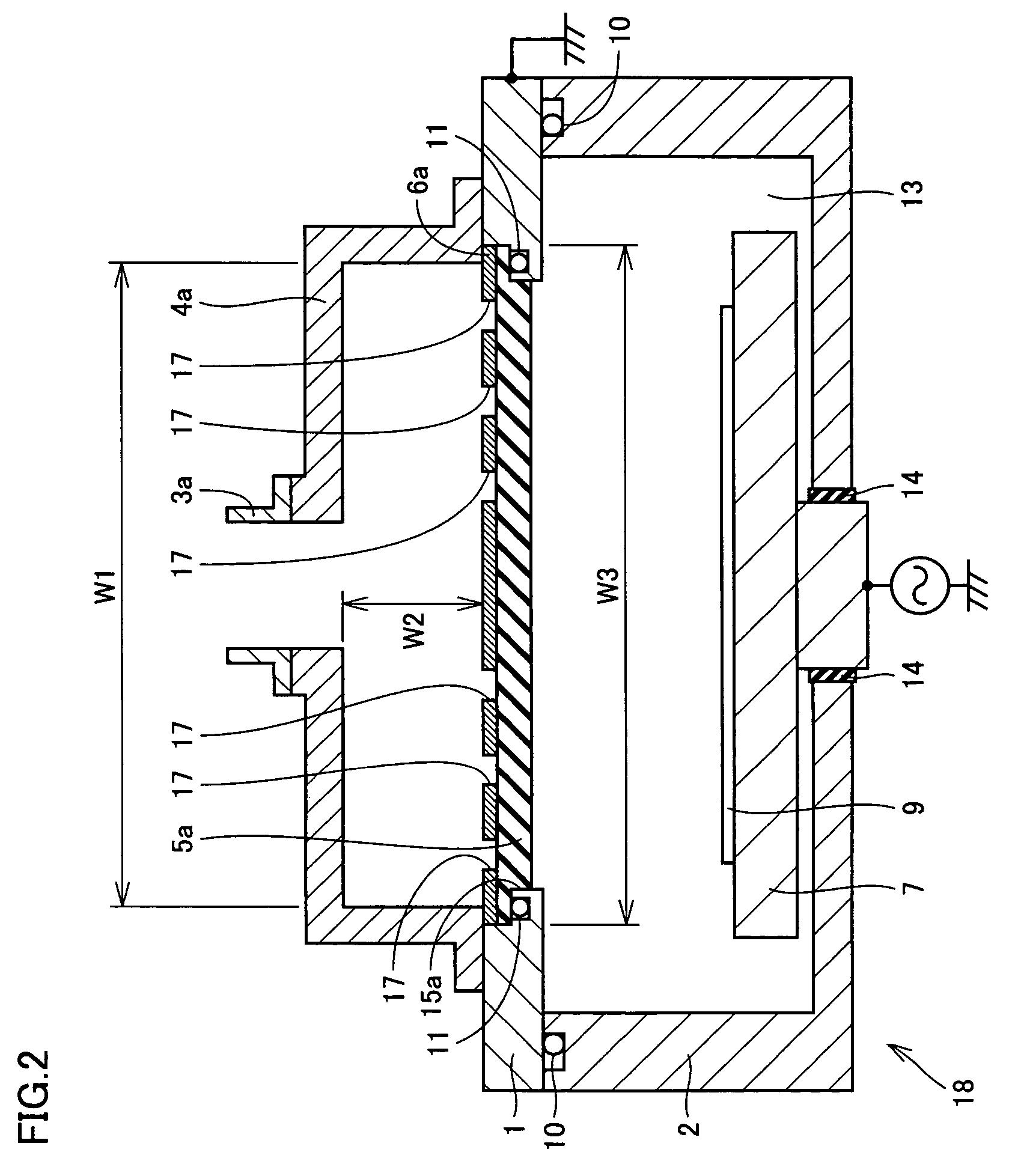
A plasma processing apparatus and a processing apparatus having a widened process condition range allowing plasma generation are obtained by increasing microwave propagation efficiency. The plasma processing apparatus includes a processing chamber (1, 2) where plasma processing is performed, and microwave introduction means (3a-6a, 3b-6b, 19a, 19b) for introducing microwaves into the processing chamber. The microwave introduction means (3a-6a, 3b-6b, 19a, 19b) includes a dielectric member (5a, 5b, 19a, 19b) transmitting the microwaves. The dielectric member has a shape in cross section in a direction approximately perpendicular to a transmitting direction of the microwaves through the dielectric member that allows transmission of the microwaves of substantially a single mode. The dielectric member has a thickness T in the transmitting direction that satisfies a condition of (λ×(2m+0.7) / 4)≦T≦(λ×(2m+1.3) / 4), where λ is a wavelength of the microwaves of the single mode transmitted through the dielectric member and m is an arbitrary integer.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
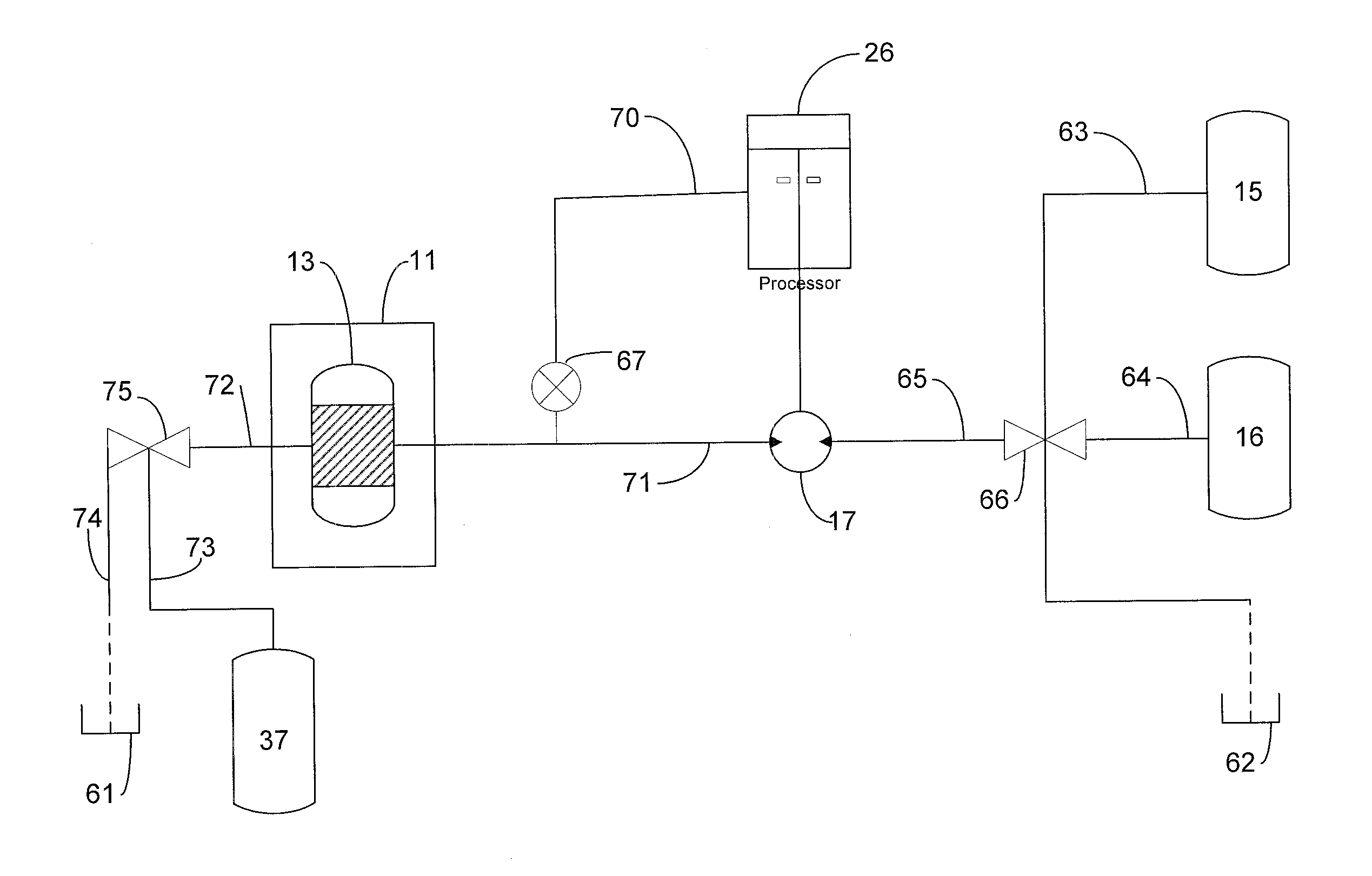
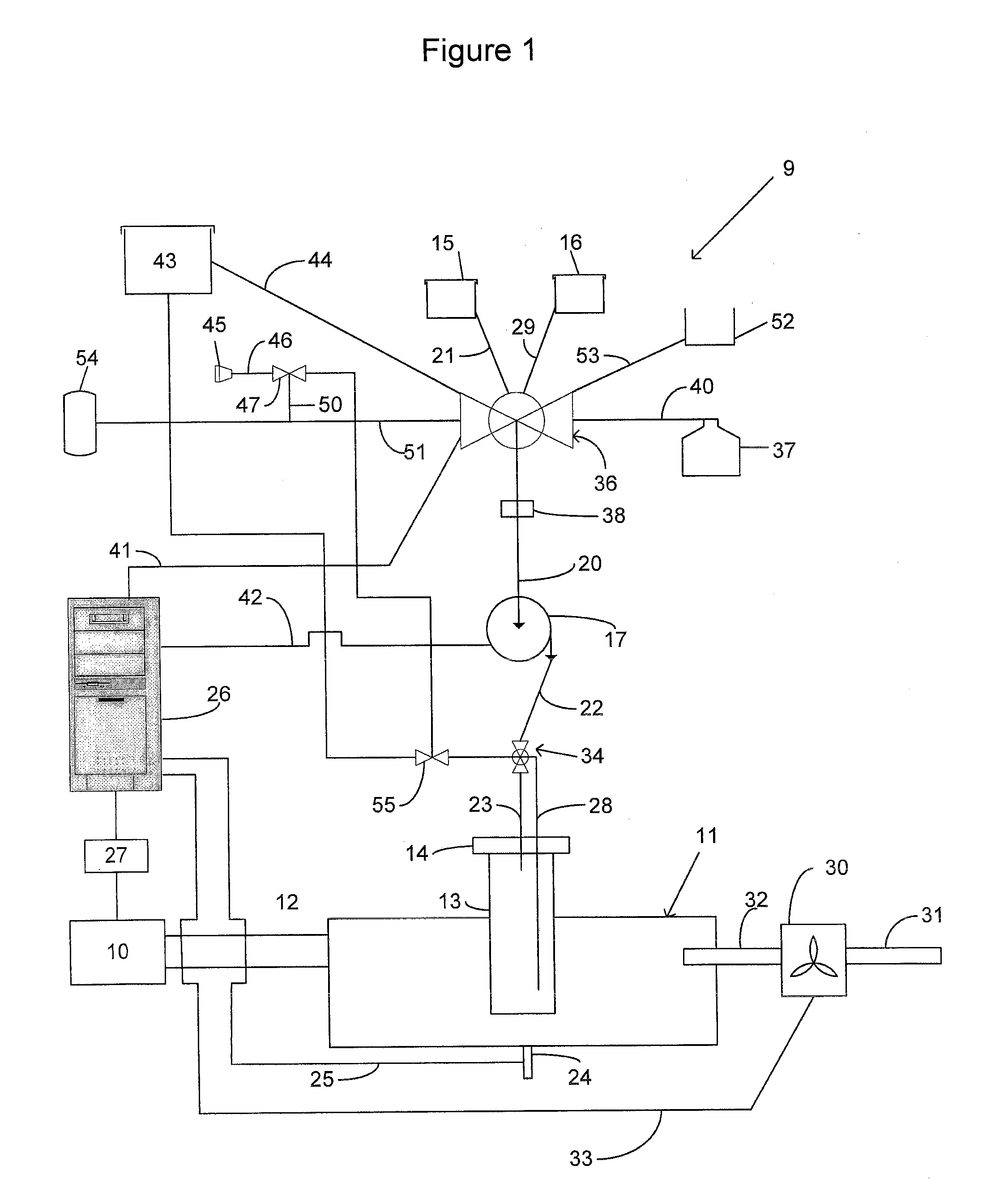
Controlled Flow Instrument For Microwave Assisted Chemistry With High Viscosity Liquids And Heterogeneous Mixtures
A controlled-flow microwave instrument is disclosed for chemical synthesis that includes heterogeneous or highly viscous materials. The instrument includes a fluid reservoir for supplying or receiving fluids, a fluid pump in fluid communication with the reservoir for pumping fluids to or from the reservoir, a microwave transparent reaction vessel in fluid communication with the pump for supplying or receiving fluids to or from the pump and the reservoir, a pressure sensor in fluid communication with the reservoir and the vessel for measuring the pressure of fluids in the instrument at the sensor, and a processor in signal communication with the pressure sensor and the pump for controlling the pump and the flow of fluids in the instrument based at least in part on the pressure measured at the sensor. The instrument also includes a magnetic stirrer bar inside the vessel for agitating reactants in the vessel during exposure to microwave radiation, a first rotating magnet positioned external to and adjacent the cavity to minimize any interaction between the magnetic field of the magnet and microwave propagation in the cavity, and a second rotating magnet inside the cavity for being driven by the first rotating magnet and for driving the rotation of the stirrer bar in the reaction vessel.
Owner:CEM CORP
Radar level gauge system with leakage detection
InactiveUS7855676B2Rapid and remote detectionMinimize damageDetection of fluid at leakage pointTesting/calibration apparatusMicrowave propagationTransceiver
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
Transmission line microwave apparatus including at least one non-reciprocal transmission line part between two parts
ActiveUS8294538B2Small sizeGood effectRadiating elements structural formsWaveguidesCapacitanceMicrowave propagation
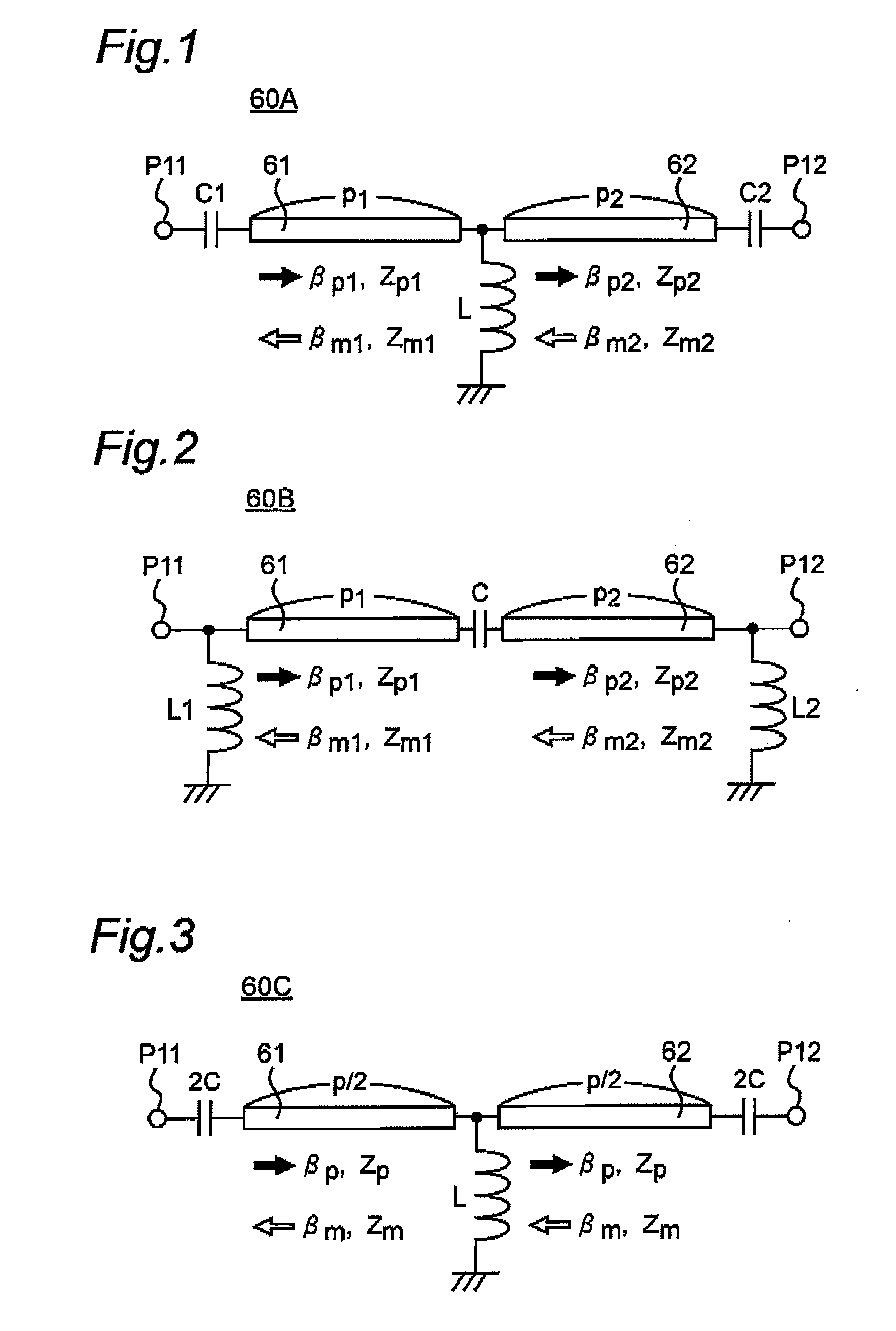
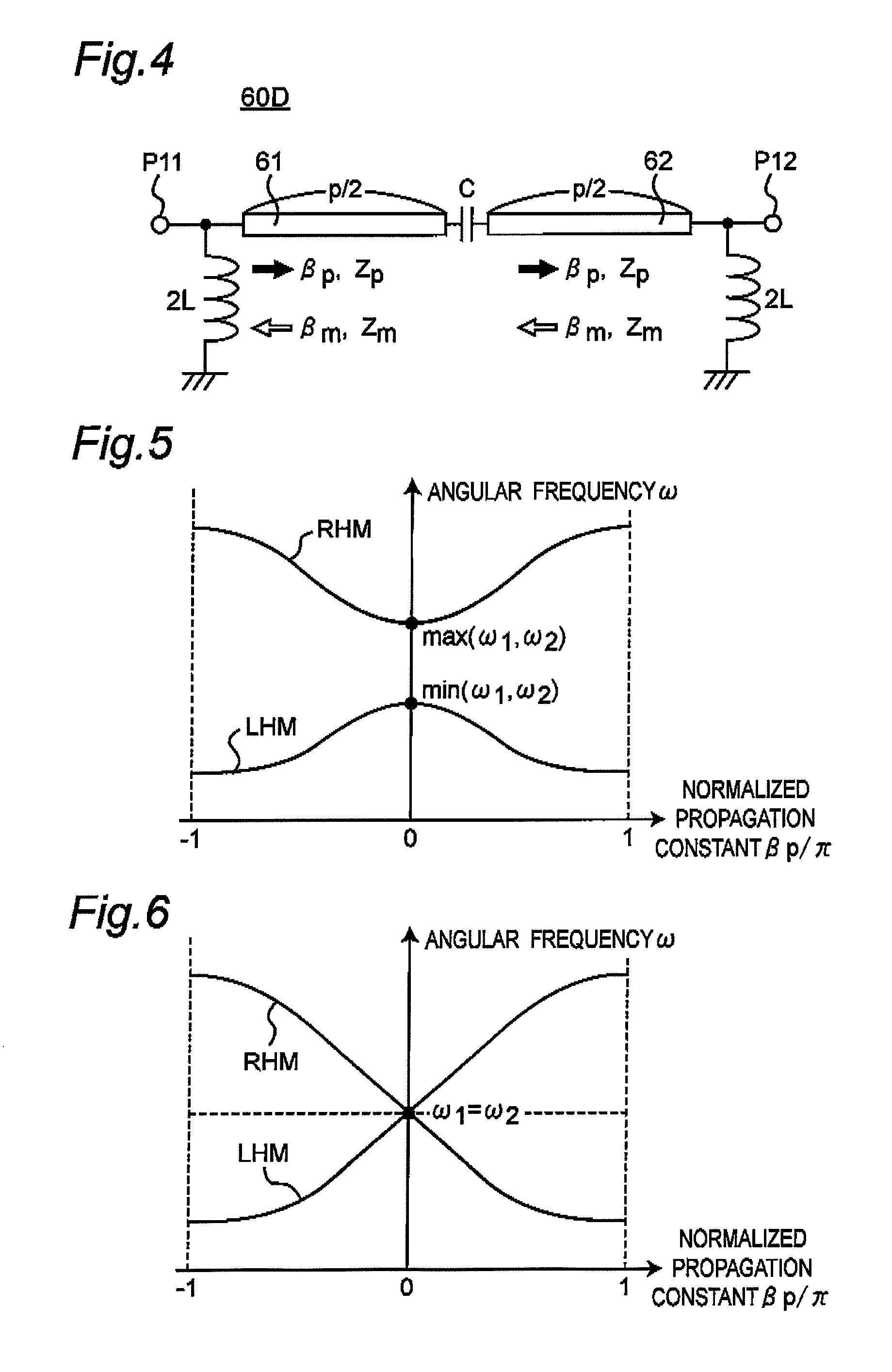
A transmission line microwave apparatus includes at least one nonreciprocal transmission line part, which includes a series branch circuit equivalently including a capacitive element and a shunt branch circuit equivalently including an inductive element. The nonreciprocal transmission line part has gyrotropic characteristic by being magnetized in a magnetization direction different from the propagation direction of a microwave, and has an asymmetric structure to a plane formed by the propagation direction and the magnetization direction. The nonreciprocal transmission line part has a propagation constant and an operating frequency set in a dispersion curve that represents a relation between the propagation constant and the operating frequency so that the propagation constant in the forward direction and the propagation constant in the backward direction have nonreciprocal phase characteristics different from each other. A microwave transmission line is constituted by cascade-connecting at least one non-reciprocal transmission line part between first and second ports.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Plasma generator and work processing apparatus provided with the same
ActiveUS20090200910A1Amount be controlSolid cathode detailsGas discharge lamp detailsMicrowave propagationPlasma generator
A plasma generator is provided which includes: a microwave generation portion which generates a microwave; a wave guide for propagating the microwave; a plurality of plasma generation nozzles which are attached to the wave guide so as to be apart from each other in the direction where the microwave is propagated, receive the microwave, and generate and emit a plasmatic gas based on the energy of this microwave; and a plurality of stabs which correspond to a part or the whole part of the plasma generation nozzles and are each disposed in the wave guide so as to lie in a rear position a predetermined distance apart from each other in the direction where the microwave is propagated.
Owner:RECARBON INC
Dielectric media
InactiveUS7338615B2Additive manufacturing apparatusLiquid organic insulatorsDesign phaseComputer design
A novel method of fabrication of periodic dielectric composites involving a flexible computer design stage, rapid growth of a second dielectric component. Laser stereolithography is used to form the polymer material layer by layer by photopolymerisation of a liquid. Certain materials constructed in this fashion exhibit a complete loss-free barrier to microwave propagation through the material for a desired band of frequencies and are commonly known as photonic band gap crystals. Such materials could provide a novel medium for all-angle wide- and narrow-band blocking filters, narrow-band transmission filters, reflective and loss-free substrates for planar antennas, and novel loss-free media for oscillator cavities and waveguides. In addition a novel crystal structure, particularly suited to the fabrication method mentioned above and consisting of concatenated polyhedrons, is revealed.
Owner:X POINT SOLUTIONS L L C
Coupled-waveguide microwave applicator for uniform processing
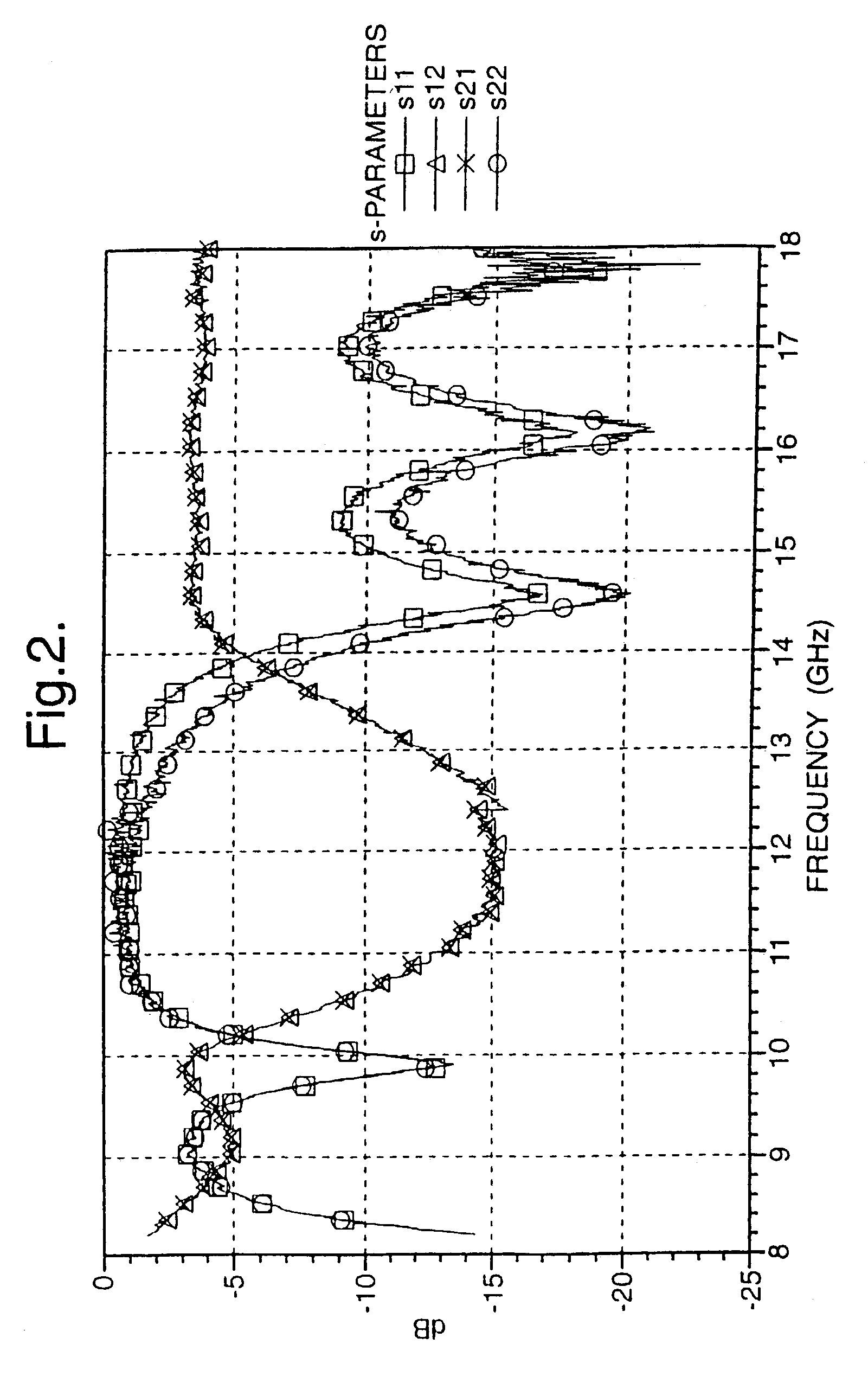
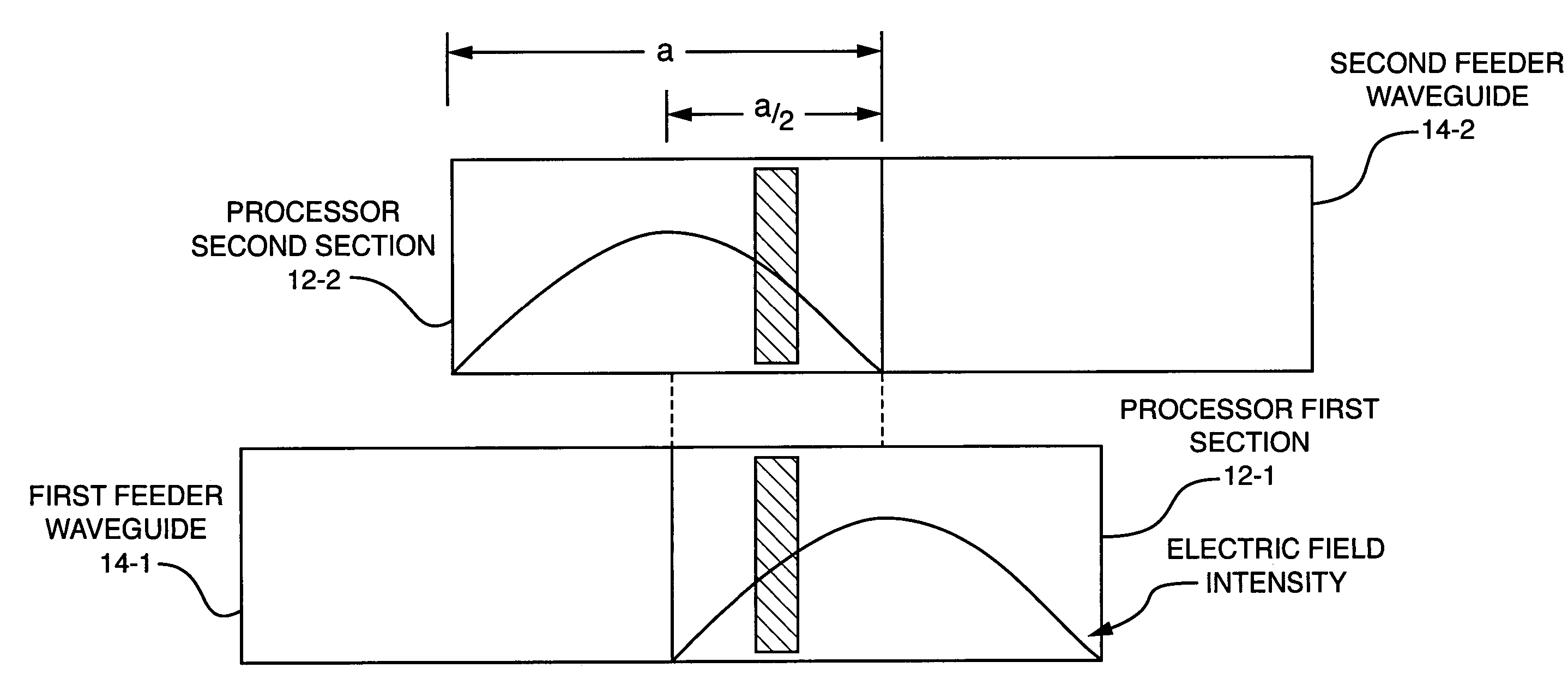
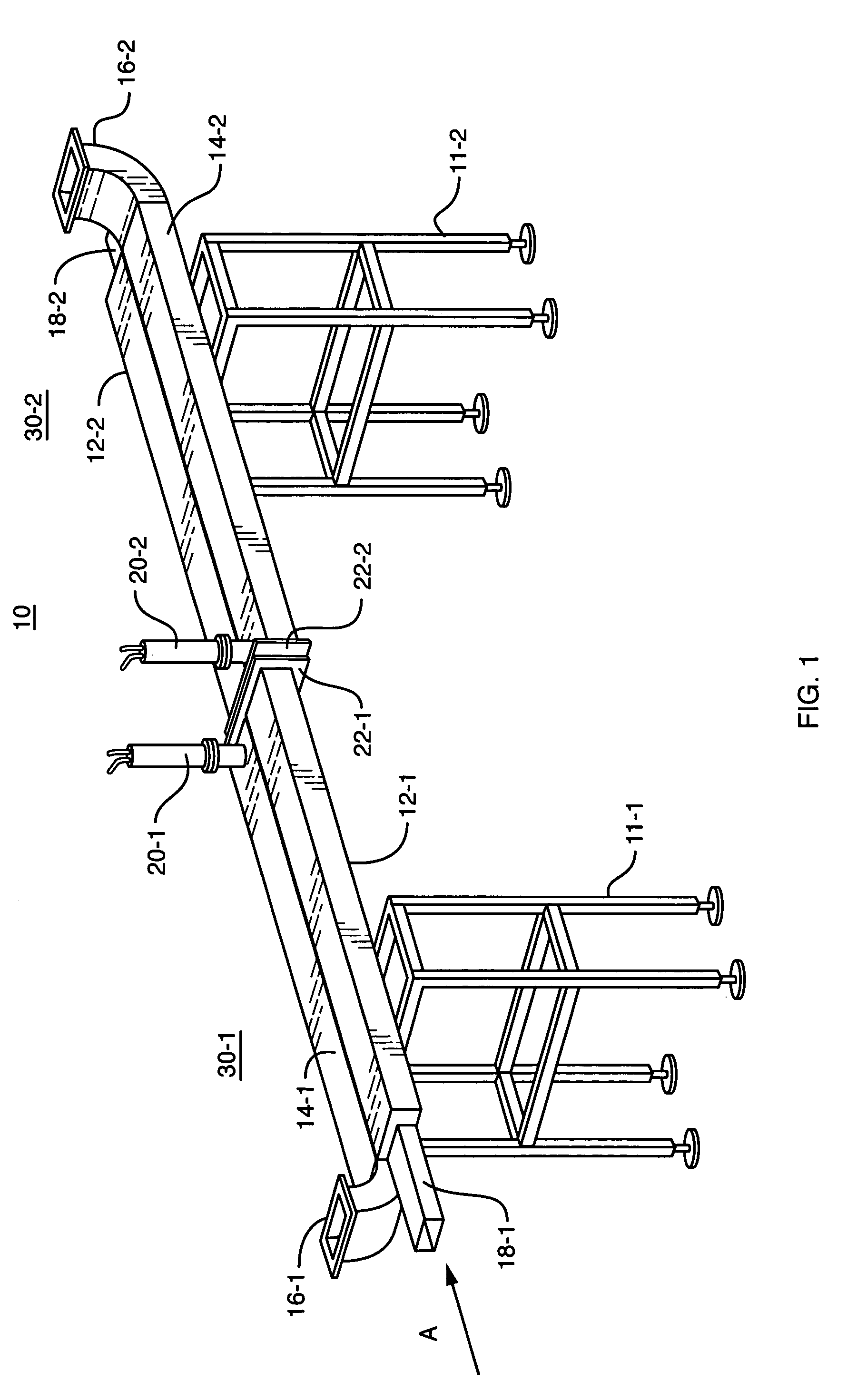
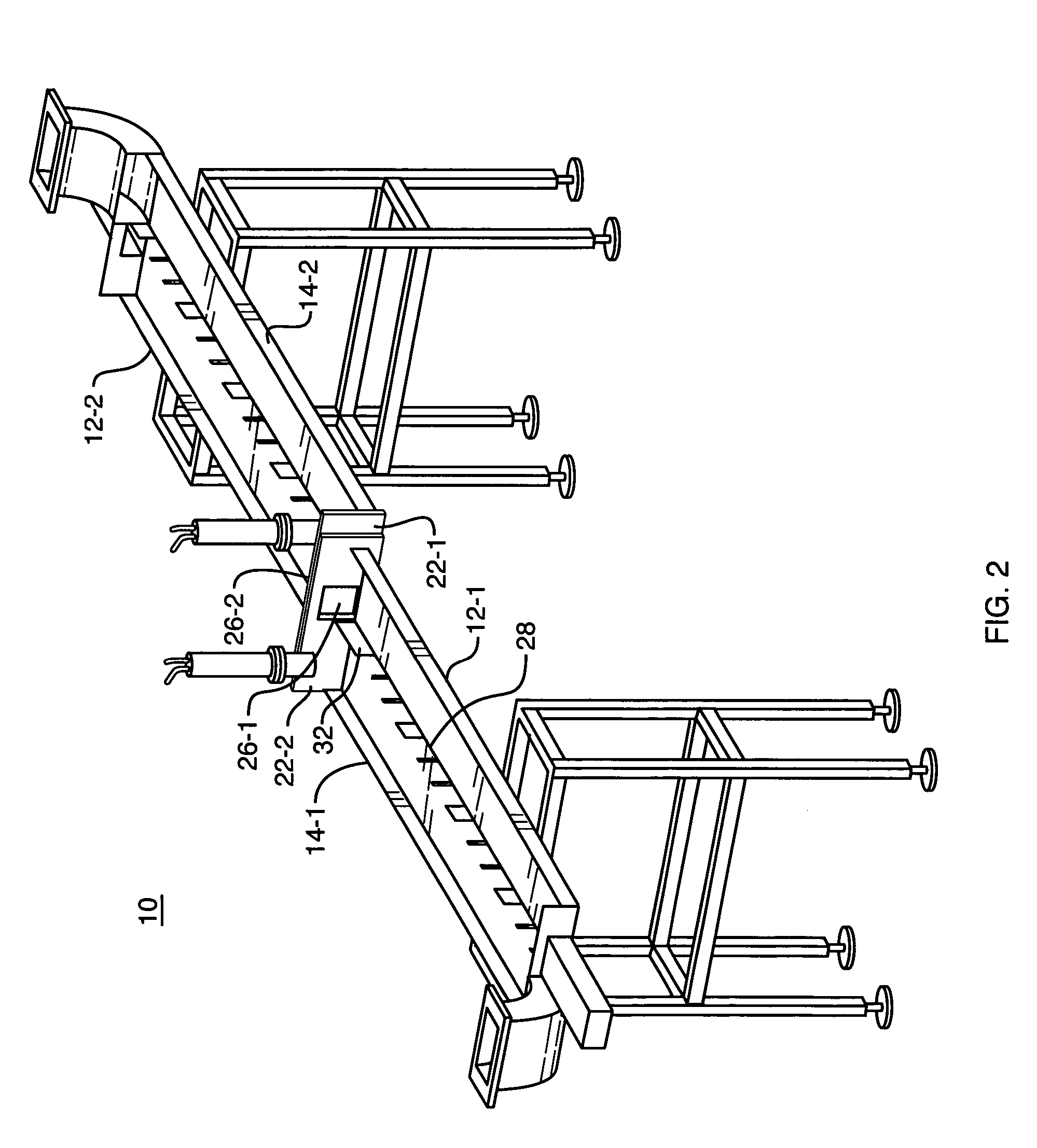
An apparatus providing uniform microwave processing of products especially those that are likely to absorb microwave energy such as meat and the like. The apparatus uses at least a pair of complimentary processing waveguides. The waveguides are offset along at least one axis thereof so that the energy coupled to the product when traveling through a first waveguide section is presented with a complimentary or mirror image of the field variation applied to the product when traveling in the second waveguide. Energy may be fed to the elongated waveguides through a broad open wall or a wall having narrow openings. Coupling values can therefore be adjusted to transfer a higher percentage of energy in the feeder waveguide as microwaves propagate but then are diminished by a previous coupling section.
Owner:THE FERRITE
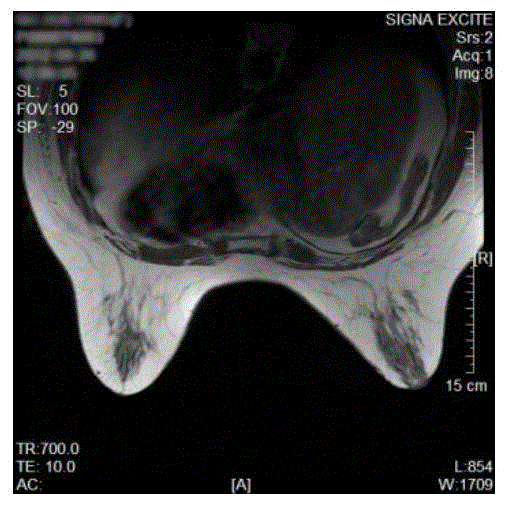
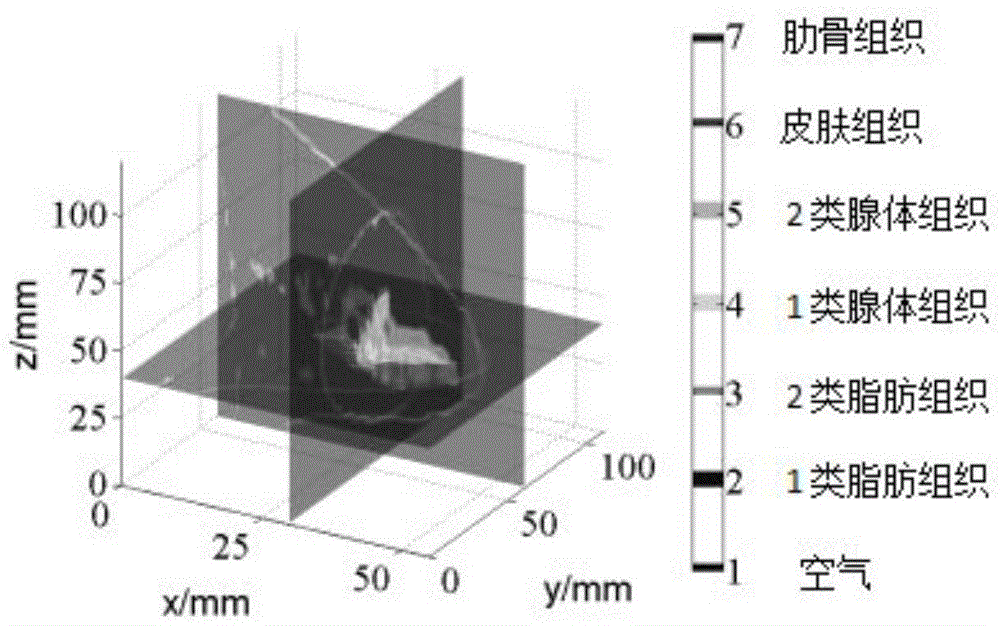
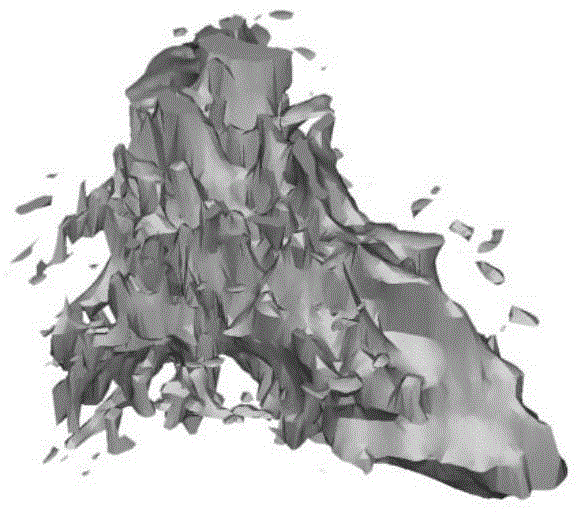
Ultra-wideband breast tumor imaging method based on magnetic resonance image compensation
InactiveCN105701814AEmbody practicalityReduce imaging position deviationImage enhancementImage analysisTime errorUltra-wideband
The invention relates to an ultra-wideband breast tumor imaging method based on magnetic resonance image compensation. The method comprises the following steps of based on a MRI slice atlas based on breasts, constructing a three-dimensional discrete breast model of a gland; modeling a gland structure and approximating structures of gland tissues in the breasts into an elliptic cone shape; using spatial coordinate transformation and ''righting'' an elliptic cone to an auxiliary coordinate system; creating an isosceles triangle area in a plane projection area of the elliptic cone, carrying out a finite element on the area and determining an elliptic cone surface capable of best describing a change trend of a rough gland surface; and carrying out microwave propagation time error estimation and accurate imaging. In the invention, ultra-wideband breast tumor imaging can be accurately performed.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
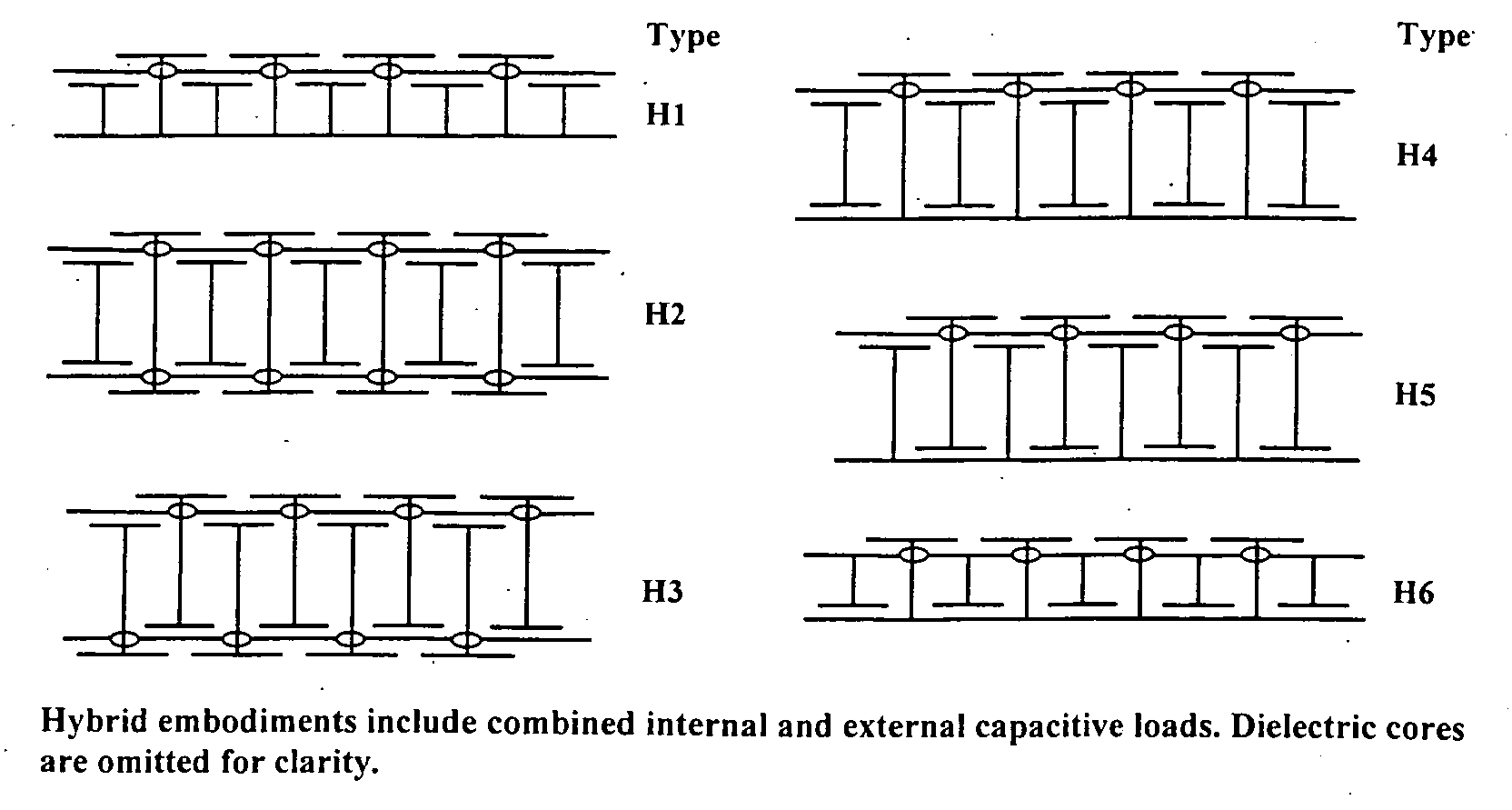
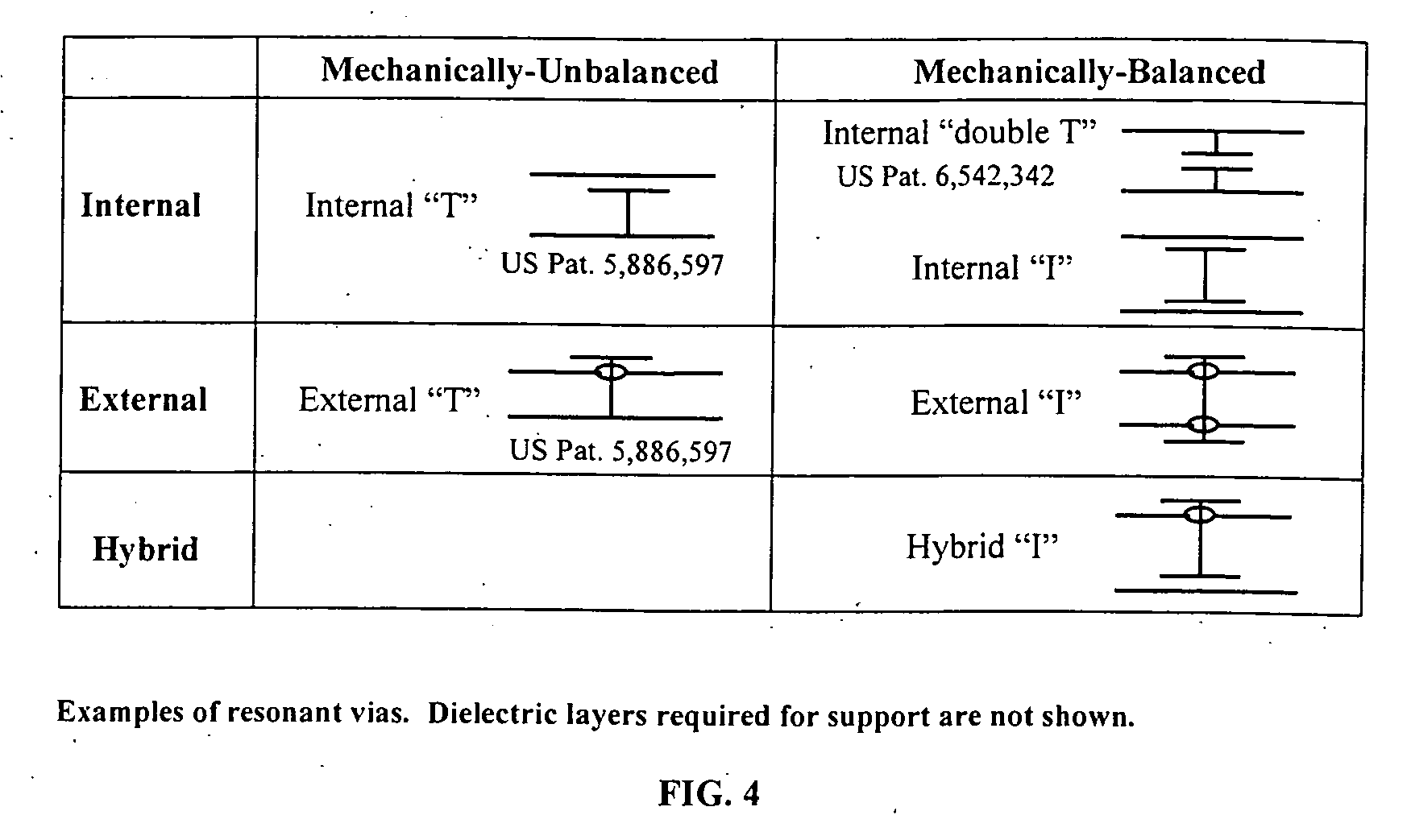
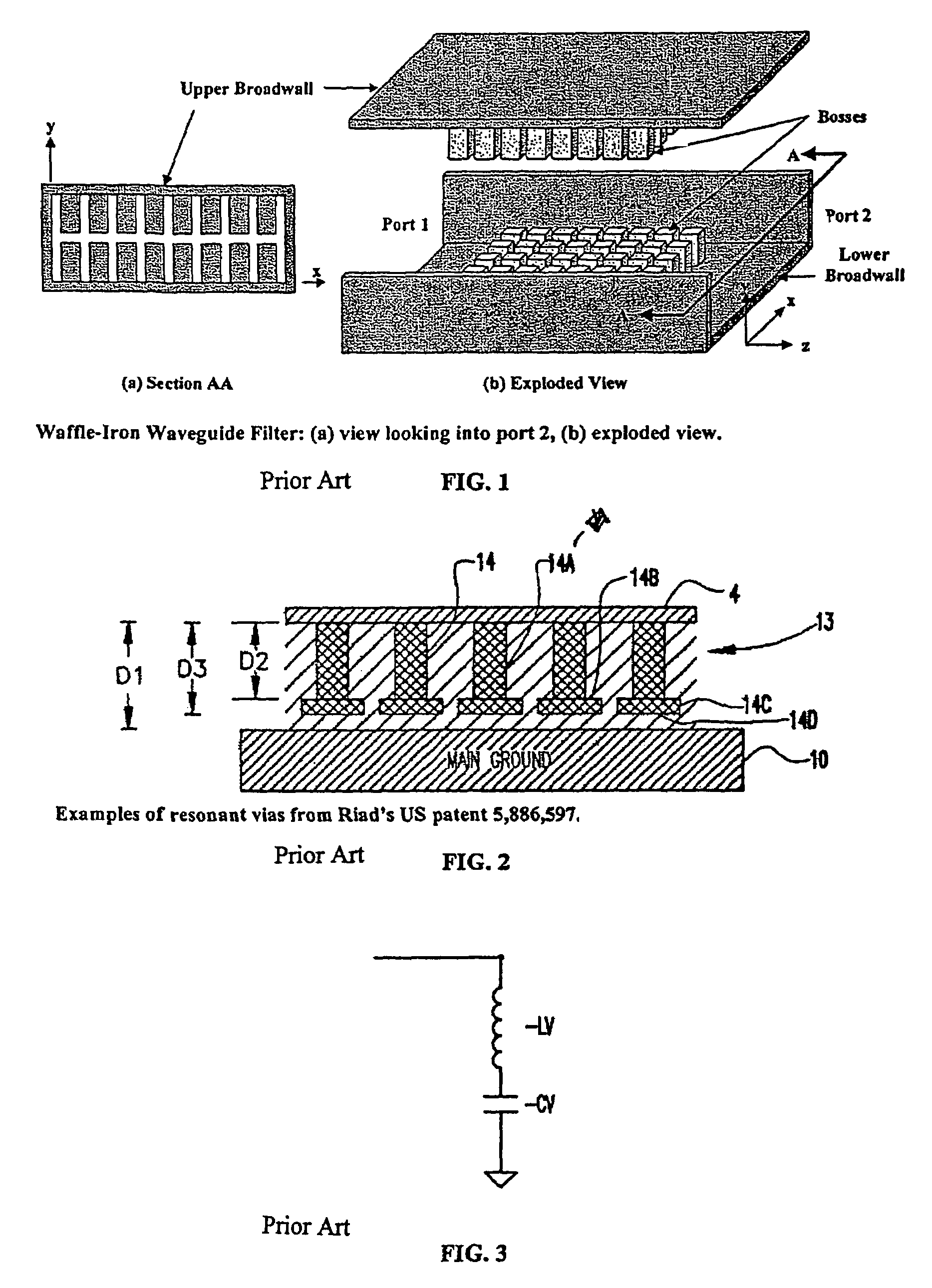
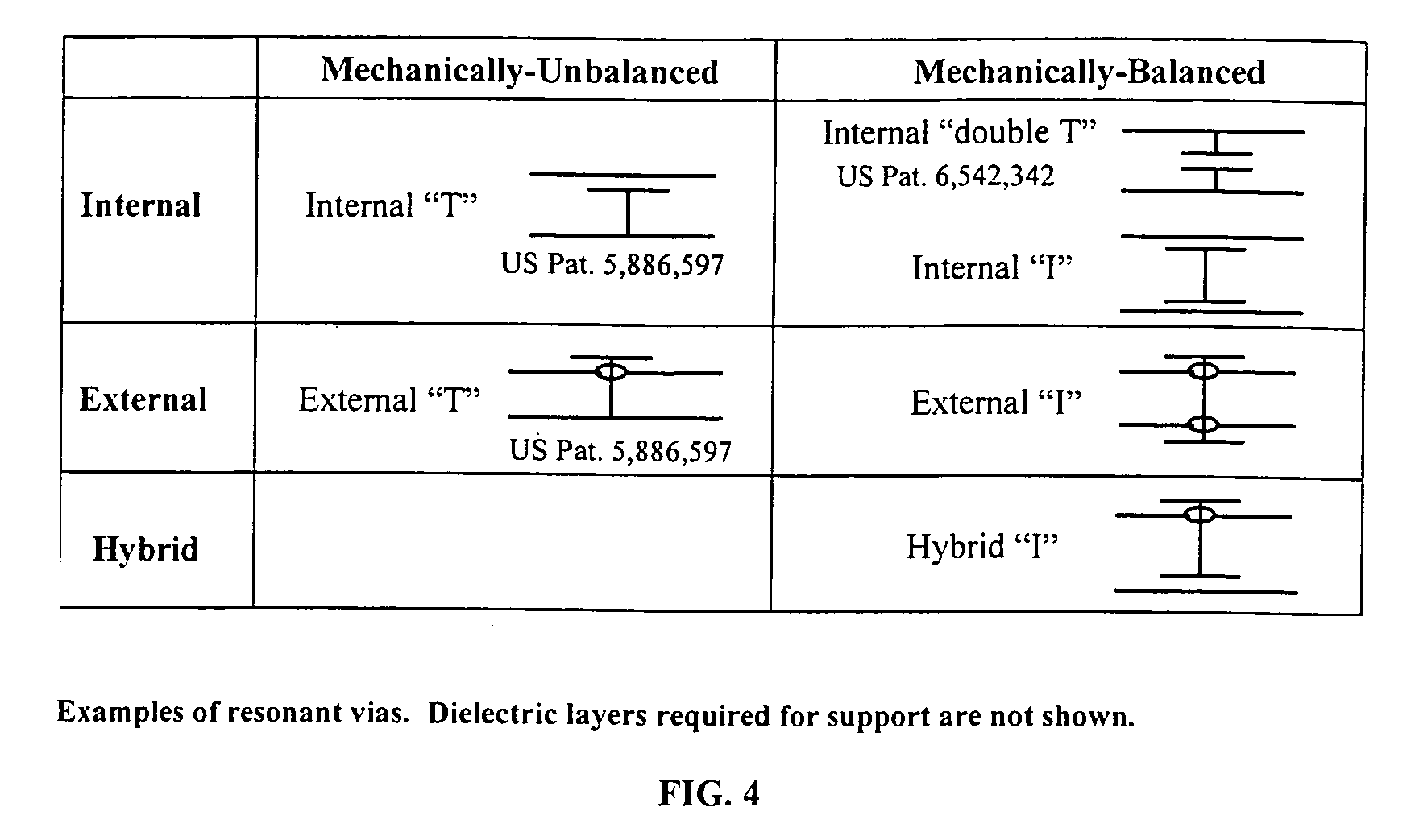
Systems and methods for blocking microwave propagation in parallel plate structures
InactiveUS20060202784A1Cross-talk/noise/interference reductionHigh frequency circuit adaptationsMicrowave propagationParallel plate
Systems and methods are taught for blocking the propagation of electromagnetic waves in parallel-plate waveguide (PPW) structures. Periodic arrays of resonant vias are used to create broadband high frequency stop bands in the PPW, while permitting DC and low frequency waves to propagate. Some embodiments of resonant via arrays are mechanically balanced, which promotes improved manufacturability. Important applications include electromagnetic noise reduction in layered electronic devices such as circuit boards, ceramic modules, and semiconductor chips.
Owner:WEMTEC
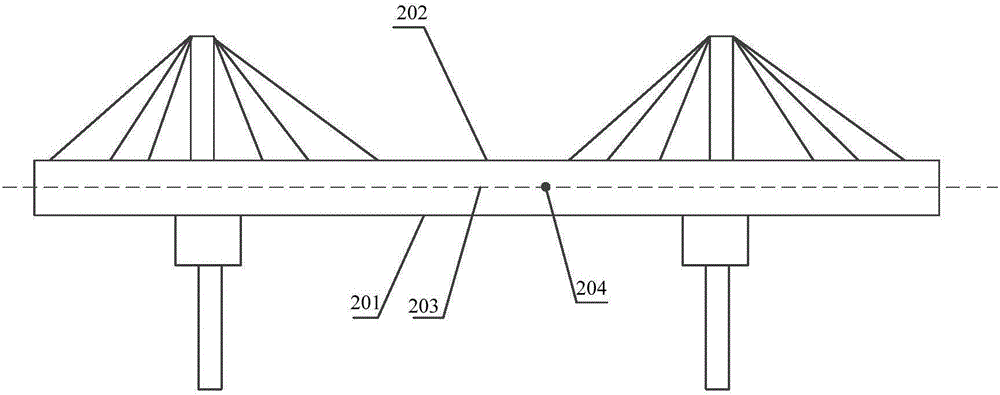
Bridge dynamic deflection detection method and device based on microwave interference
InactiveCN106441749AImprove detection accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionElasticity measurementMicrowave propagationAtmospheric air
The invention discloses a bridge dynamic deflection detection method and device based on microwave interference. The method includes the steps: S1 acquiring geometrical characteristic parameters of a microwave interference detection system for a bridge to be detected in the detection process, and acquiring atmospheric dry temperature, atmospheric steam partial pressure and atmospheric dry air partial pressure in detection; S2 calculating an atmospheric refraction index in detection according to the atmospheric dry temperature, the atmospheric steam partial pressure and the atmospheric dry air partial pressure; S3 calculating dynamic deflection of the bridge in detection by a bridge dynamic deflection correction model according to the atmospheric refraction index and the geometrical characteristic parameters. According to the method, the influence of the atmospheric dry temperature, the atmospheric steam partial pressure and the atmospheric dry air partial pressure on the microwave propagation process is taken into consideration, the influence of environmental factors such as temperature, humidity and atmospheric pressure on ground microwave interference detection precision due to season and time difference is avoided, and dynamic deflection detection precision of the bridge is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CIVIL ENG & ARCHITECTURE
Microwave short circuit ring
ActiveCN102632572AEasy to get close toEliminate potential safety hazardsMicrowave propagationLength wave
The invention discloses a microwave short circuit ring comprising a hollow chamber, wherein N grooves are formed on the inner wall of the chamber; N is an integer greater than or equal to 1; when N is greater than or equal to 2, the distance between two adjacent grooves is greater than one half of a microwave wavelength and less than the wavelength of two microwaves; the width of the groove in the microwave propagation direction is one quarter of the microwave wavelength and the tolerance of the width is + / -1 mm; and the depth of the groove is a multiple of one quarter of the microwave wavelength and the tolerance of the depth is + / -2 mm. The microwave short circuit ring has the following beneficial effects that the dose of microwave leakage at the inlet and outlet of a rubber vulcanizing apparatus can be quickly attenuated to be below 30 mu W / cm so that operating personnel can conveniently and freely work by approaching the rubber vulcanizing apparatus; the potential safety hazard is eliminated and the labor productivity is improved; the length of the short circuit ring is one third of the length of the previous short circuit ring; and the equipment manufacture and use costs are reduced.
Owner:浙江百纳橡塑设备有限公司
Plasma process apparatus and its processor
InactiveUS7478609B2Increase rangeGuaranteed normal transmissionElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrowave propagationElectricity
A plasma processing apparatus and a processing apparatus having a widened process condition range allowing plasma generation are obtained by increasing microwave propagation efficiency. The plasma processing apparatus includes a processing chamber where plasma processing is performed, and microwave introducer for introducing microwaves into the processing chamber. The microwave introducer includes a dielectric member transmitting the microwaves. The dielectric member has a shape in cross section in a direction approximately perpendicular to a transmitting direction of the microwaves through the dielectric member that allows transmission of the microwaves of substantially a single mode. The dielectric member has a thickness T in the transmitting direction that satisfies a condition of (λ×(2m+0.7) / 4)≦T≦(λ×(2m+1.3) / 4), where λ is a wavelength of the microwaves of the single mode transmitted through the dielectric member and m is an arbitrary integer.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
Lithium niobate electrooptical modulator
The invention relates to a lithium niobate electrooptical modulator, in particular to a low half-wave voltage lithium niobate electrooptical modulator, and belongs to the technical field of lithium niobate electrooptical modulators. According to the lithium niobate electrooptical modulator, a travelling wave electrode and a direct current bias electrode are combined into one, it is achieved that only direct current voltage is loaded on a central electrode of the travelling wave electrode through a capacitor of a match circuit, and carrying out direct current modulation is ensured. In addition,an access high frequency property of the capacitor is utilized, microwave propagation is not influenced, and high speed modulation of the modulator is ensured. The device integration is improved, andunder the circumstances of not changing length of a chip and whole size of the modulator, the electrode length of the chip is greatly increased, therefore direct current half-wave voltage and microwave half-wave voltage of the modulator are greatly reduced.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE TIMES OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH
A method for improving the quiet zone performance of a microwave anechoic chamber and a modular dielectric barrier
InactiveCN104005483BSmall sizeReduce construction costsBuilding constructionsMicrowave propagationVertical plane
The present invention relates to the field of propagation technology for microwave anechoic chamber isolation from the external environment, and in particular to a method for improving the performance of the quiet zone of the microwave anechoic chamber and a modular dielectric barrier. It is connected with a rectangular base, the acute angle of the right-angled triangle is 20-30°, the right-angled surface of the modular dielectric fence faces the electromagnetic radiation source, and the slope of the modular dielectric fence faces the center of the quiet zone; and the slope of the right-angled triangle is set There is a wave-absorbing material layer, and the wave-absorbing material layer is respectively arranged on the right-angled surface of the vertical surface of the right-angled triangle and the shielding body of the ground plane of the microwave anechoic chamber; the modularized dielectric barrier is fixed or movable. The invention uses multiple dielectric barriers to suppress ground reflection or wall reflection of the microwave anechoic chamber, which can reduce the size of the microwave anechoic chamber, directly reduce the construction cost of the microwave anechoic chamber, and further improve the quiet zone performance of the microwave anechoic chamber.
Owner:UNIT 63892 OF PLA
Coupler for microwave pyrolysis systems
PendingCN113939954AElectrical coke oven heatingPyrolysis reactionsMicrowave propagationMicrowave pyrolysis
There is described a coupler for propagating microwaves into a microwave pyrolysis reactor, the coupler comprising: an elongated hollow body for propagating the microwaves, the elongated hollow body extending between a receiving end for receiving the microwaves and a transmitting end mountable to the microwave pyrolysis reactor for propagating the microwaves therein, the receiving end having a rectangular cross-sectional shape and the transmitting end having a circular cross-sectional shape, a shape of the elongated allow body being designed so as to convert a transverse (TE) mode of propagation for the microwaves at the receiving end thereof into a linearly polarized (LP) mode of propagation for the microwaves at the transmitting end thereof; and a barrier body inserted into the hollow body for isolating the receiving end of the elongated hollow body from the transmitting end thereof.
Owner:파이로웨이브인크
Flat antenna
InactiveCN1130797CAvoid resonanceEasy to assembleIndividually energised antenna arraysResonant antennasMicrowave propagationCoupling
A flat aperture-coupled antenna with a multilayer structure is disclosed. A rear side of the antenna comprises a metal reflector device including a hollow structure (3, 5) with separate box-like compartments, located in registry with radiating patches, corresponding pairs of orthogonal slots and feed elements, whereby microwave propagation within the hollow metal structure is substantially interrupted and any mutual coupling between the orthogonal slots is avoided.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Microwave frequency attenuation and red-shift experimental device and method based on Chen Shouyuan effect
InactiveCN109036035AConvenient researchEducational modelsUltrasound attenuationMicrowave propagation
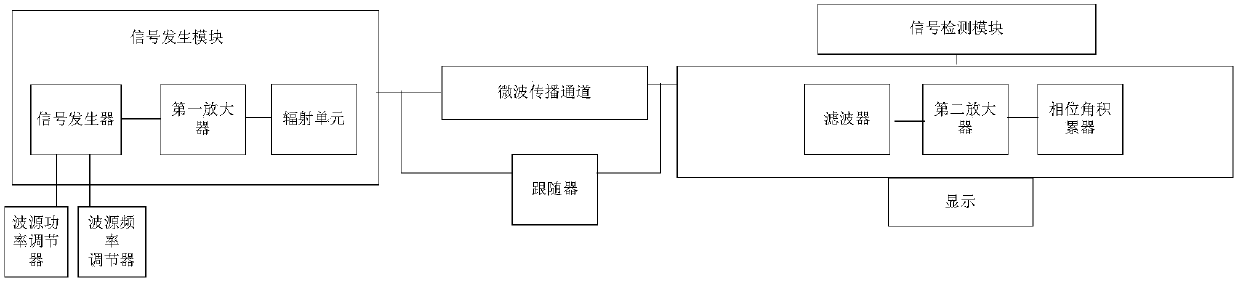
The invention relates to an experimental device and method for microwave frequency attenuation and red-shift with propagation distance based on a Chen Shouyuan effect. The experimental device comprises a signal generating module, a microwave propagation channel and a signal detecting module; wherein the signal generating module is used for generating a microwave with set frequency and amplitude; the microwave reaches the signal detecting module through the microwave propagation channel; the signal detecting module observes the attenuation of the microwave frequency based on the propagation distance by measuring the frequency of the microwave; and the sound source position where the signal generating module generates the microwave, and the measuring point position of the microwave propagation channel and the signal detecting module remain relatively stationary.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
A liquid crystal microwave modulation device and modulation method thereof
ActiveCN106374170BLight in massAvoid deformationWaveguide type devicesDielectricMicrowave propagation
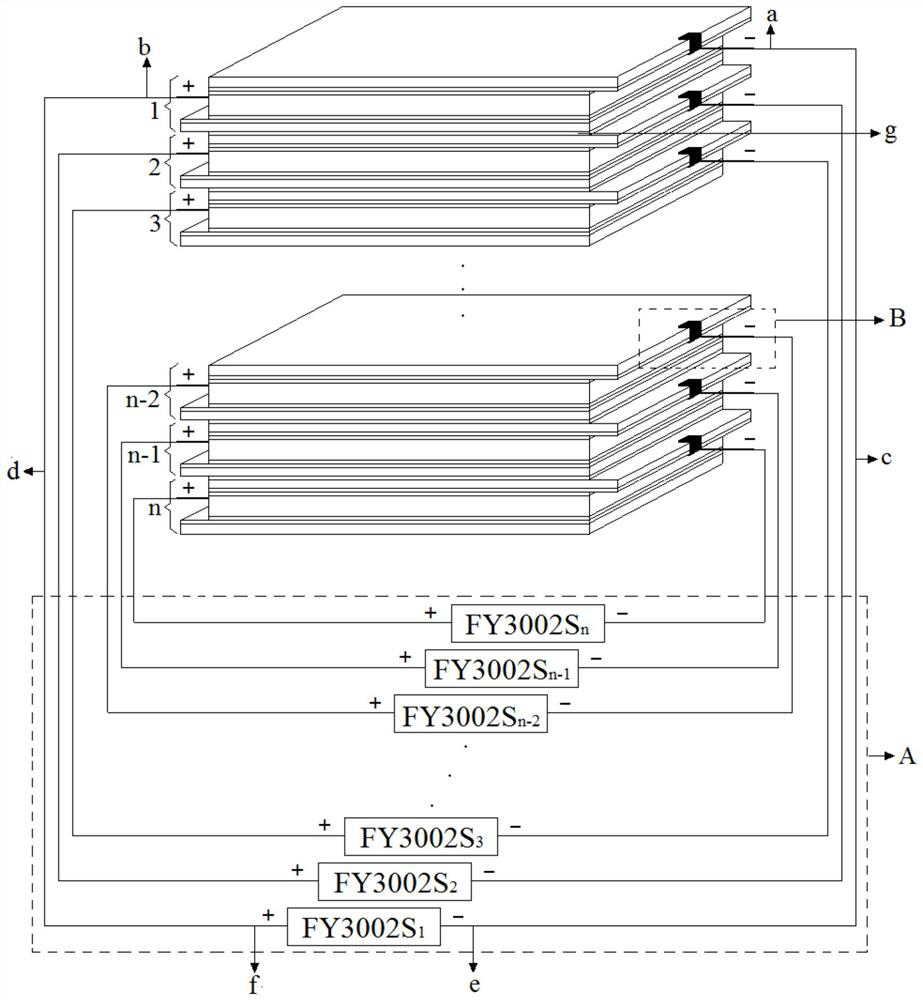
The invention relates to a liquid crystal microwave modulation device and a modulation method thereof. The device consists of n liquid crystal cells with the same structure and n channels of driving voltage signal sources A, n=2~10; the structure of the liquid crystal cell is as follows from top to bottom: the first glass substrate, the first ITO electrode, the first An alignment layer, a liquid crystal layer, a second alignment layer, a second ITO electrode, and a second glass substrate; wherein, spherical resin spacers are placed in the liquid crystal layer, and the n liquid crystal cells with the same structure are stacked sequentially from top to bottom , the n-channel drive voltage signal source A is composed of n mutually independent waveform signal generators, and each waveform signal generator is correspondingly connected to a liquid crystal cell. In the present invention, the dielectric constant of each layer of liquid crystal in the direction of microwave propagation can be changed according to the multi-channel driving voltage signals set by the user, and the results of outgoing microwave interference and diffraction can be adjusted.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
High-power broadside longitudinal slot waveguide slot array
PendingCN113782985ASuppress disturbanceIncreased power capacityIndividually energised antenna arraysAntenna couplingsMicrowave propagationSlot-waveguide
The invention discloses a high-power broadside longitudinal slot waveguide slot array. The array comprises a waveguide and an elliptical slot; the waveguide is a broadside longitudinal-seam rectangular waveguide, and a short-circuit surface is arranged at the tail end of the waveguide in a microwave propagation direction; and the slot is distributed on one side of the waveguide in a staggered mode along the two sides of the center line of the broadside of the waveguide, the long axis of the slot is parallel to the center line of the broadside of the waveguide, and the short axis of the slot is in the direction of the broadside of the waveguide. According to the high-power broadside longitudinal slot waveguide slot array, the slot area of the waveguide slot array is larger, and the high power capacity is achieved.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
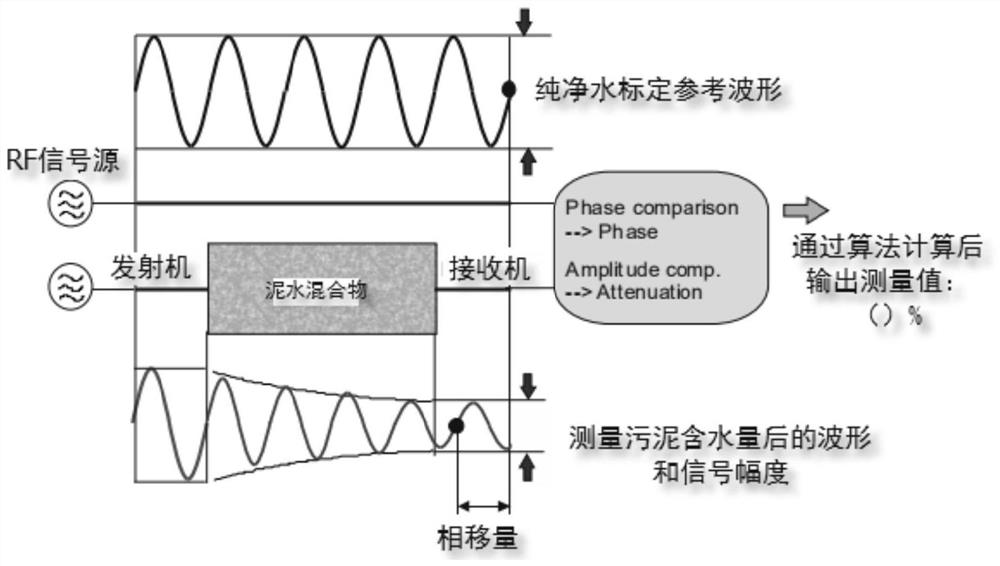
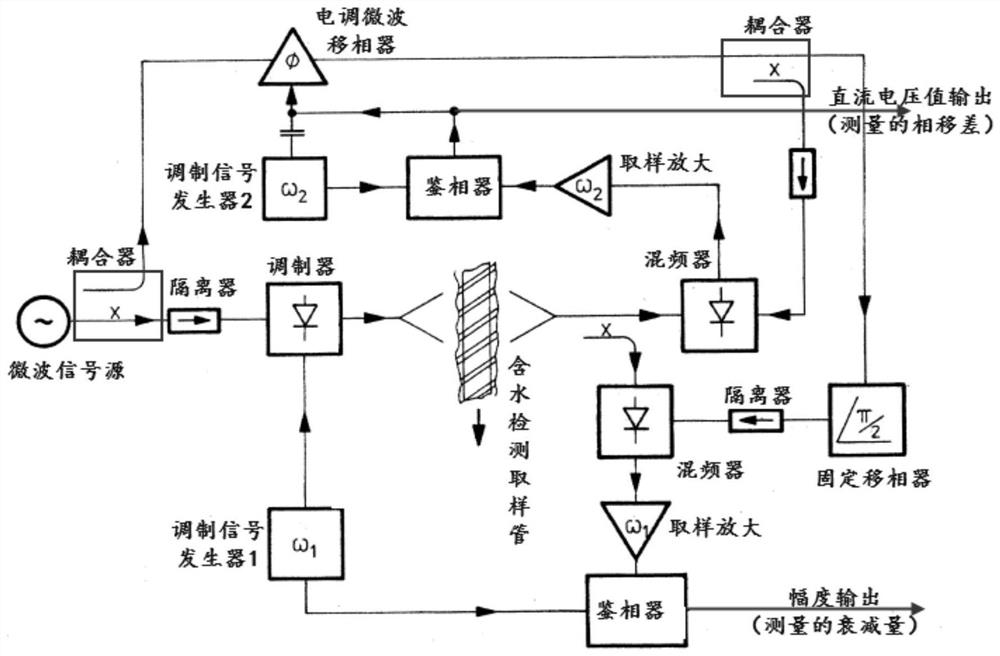
Sludge concentration online measurement method and device, electronic equipment and medium
PendingCN112730464AEasy to installDoes not affect productionMoisture content investigation using microwavesMicrowave propagationSludge
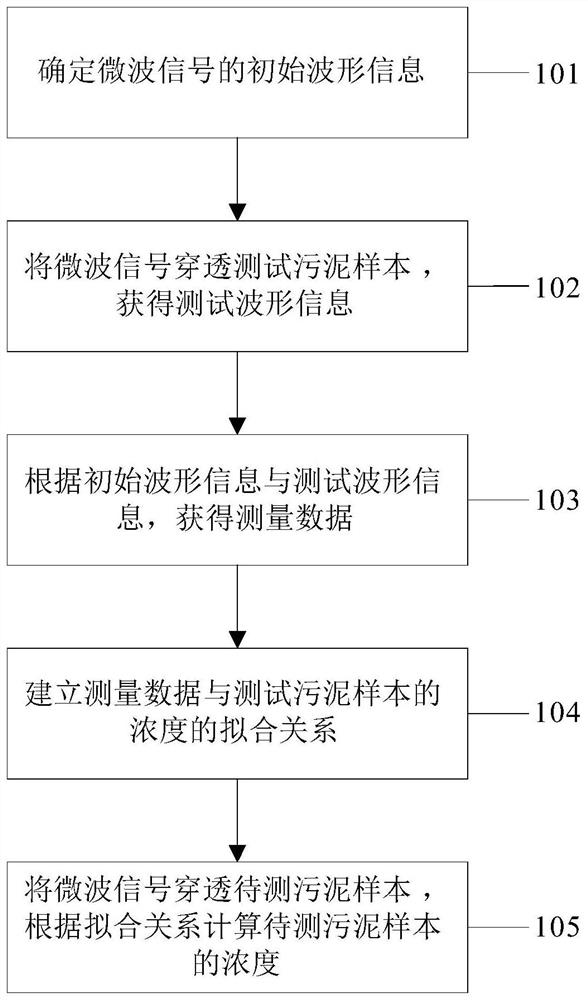
The invention discloses a sludge concentration online measurement method and device, electronic equipment and a medium. The method comprises the following steps: determining initial waveform information of a microwave signal; enabling the microwave signal to penetrate through a test sludge sample to obtain test waveform information; obtaining measurement data according to the initial waveform information and the test waveform information; establishing a fitting relationship between the measurement data and the concentration of the test sludge sample; enabling the microwave signal to penetrate through a to-be-detected sludge sample, and calculating the concentration of the to-be-detected sludge sample according to the fitting relationship. The sludge concentration test is carried out based on the microwave propagation principle, and the test result ensures the test precision.
Owner:BEIJING DRAINAGE GRP CO LTD
Pipeline inner wall detection system and method
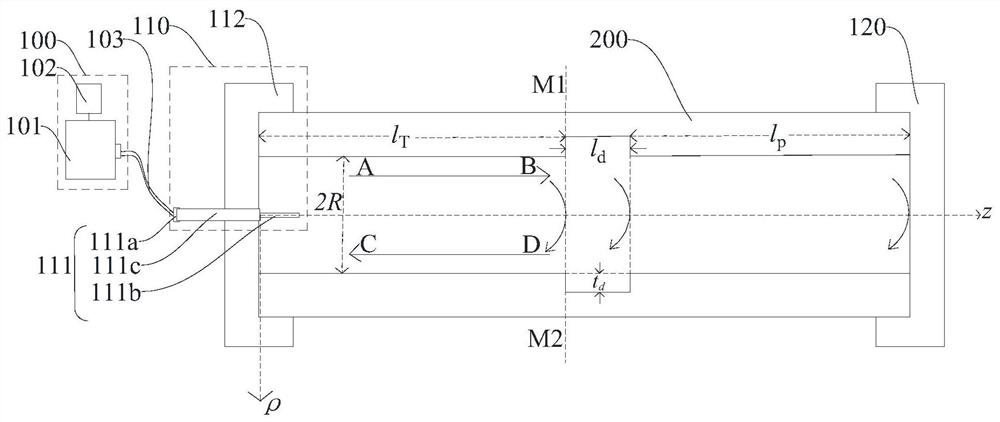
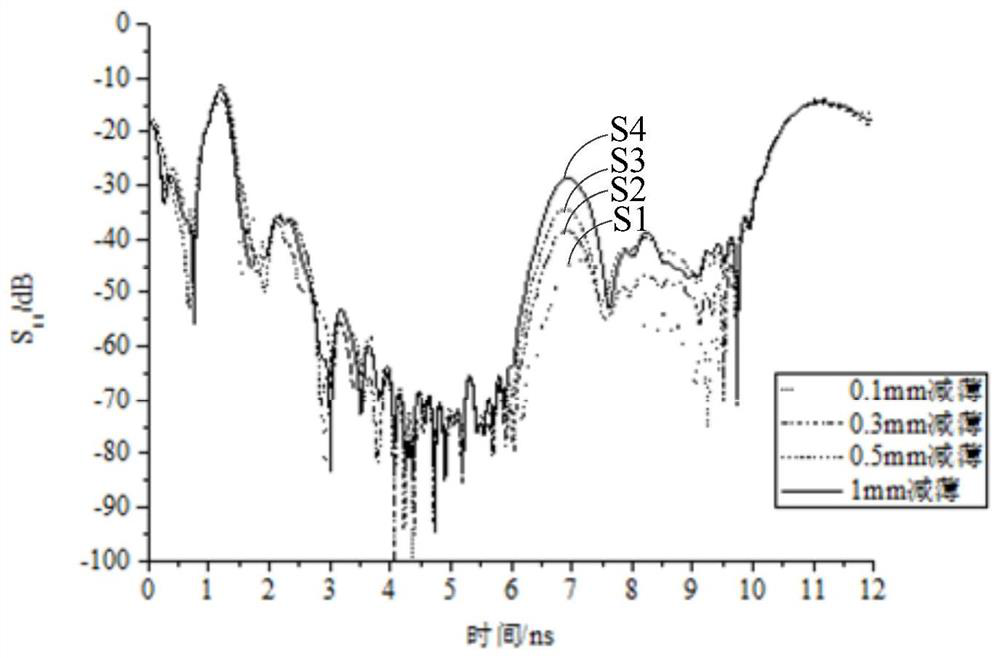
ActiveCN107703159BUsing wave/particle radiation meansFlaw detection using microwavesTime domainMicrowave propagation
A pipeline inner wall detection system and method provided in embodiments of the present invention relate to the technical field of pipeline inner wall detection. The method comprises that the vector network analyzer device outputs microwaves and transmits the microwaves to the coaxial feeding end cover device; the coaxial feeding end cover device transmits the received microwaves into the pipeline to be tested, and when there is a When thinning, receive the echo signal reflected back by the thinning part of the inner wall of the pipe to be tested in the microwave; then the coaxial feeding end cover device will also transmit the received echo signal to the vector network analyzer device; the vector network The analyzer device also processes the echo signals to obtain thinning information at the thinning of the inner wall of the pipe under test. The wave impedance changes at the thinned part of the inner wall of the pipeline to be tested through microwaves, resulting in impedance mismatch, which causes the microwave to reflect at the thinned part in the time domain, and then processes the reflected echo signal to obtain the measured Thinning information at the thinning of the inner wall of the pipe. Improve detection accuracy.
Owner:LASER RES INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
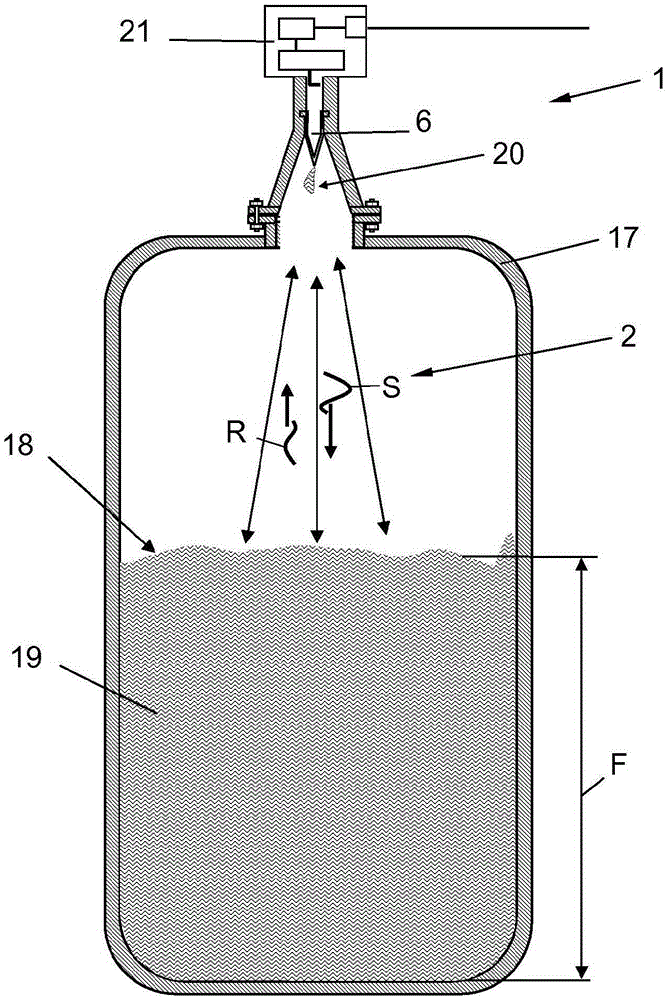
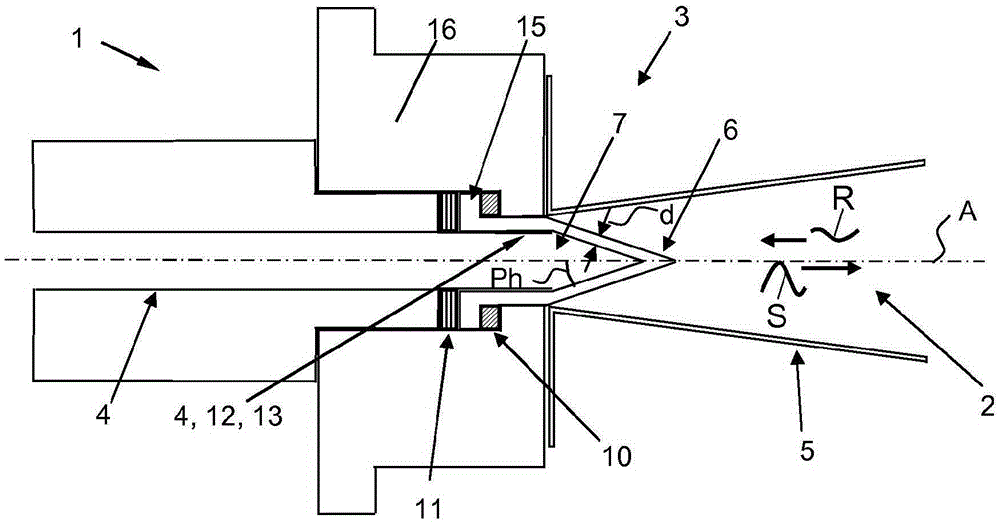
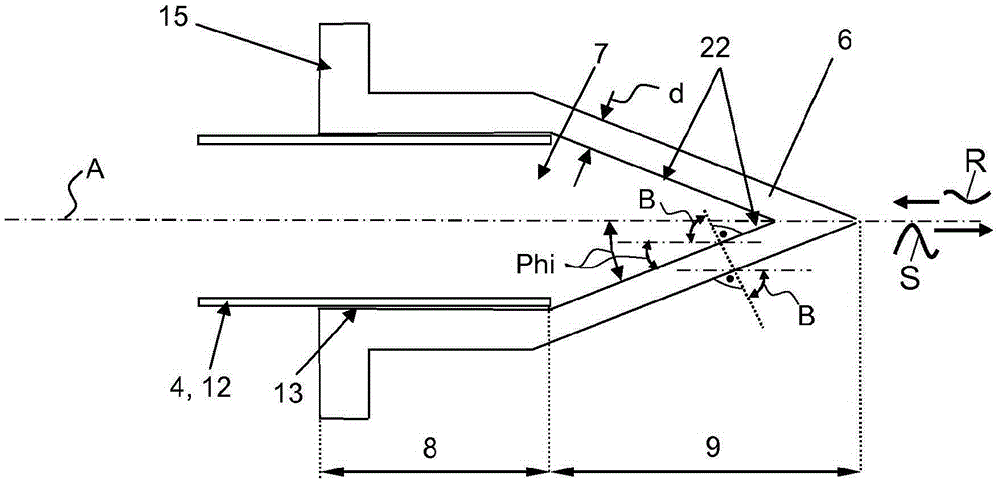
Fill level measuring device for determining and monitoring the fill level of a medium in the process space of a container by microwave transit time measurement
ActiveCN103003677BImprove temperature stabilityGood chemical stabilityWaveguide hornsResistance/reactance/impedenceMicrowave propagationElectrical conductor
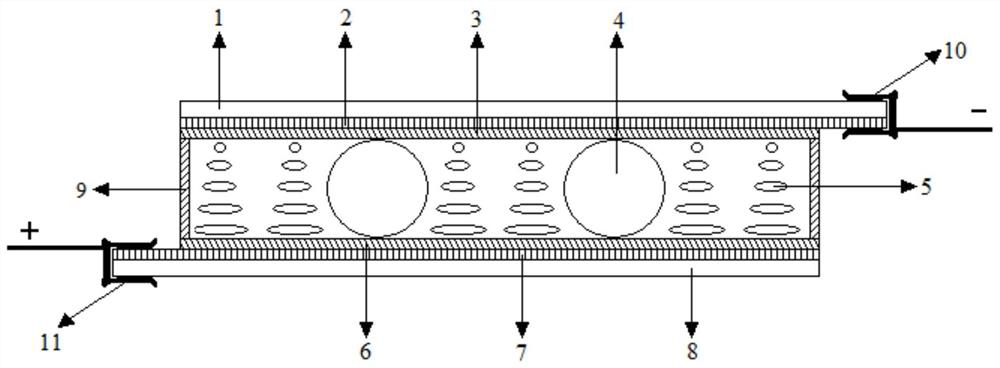
A fill-level measuring device for ascertaining and monitoring fill level of a medium located in the process space of a container by means of a microwave travel time measuring method. The device comprises a measurement transmitter and an antenna unit, which is constructed at least of a hollow conductor and a radiating element A microwave transmissive, process isolating element is inserted for process isolation into the hollow conductor between the measurement transmitter and the horn shaped radiating element contacting the process space. The process isolating element is embodied as a hollow body having at least one tubular hollow body region matched to the shape of the hollow conductor, and a pointed hollow body region neighboring the hollow body region in the direction of the radiating element and having a wall thickness selected based on reflection, or lack thereof, of the microwave signals.
Owner:EHNDRESS KHAUZER GMBKH KO KG
A Microstrip Slow-wave Structure Transmission System Suitable for Wide Dielectric Substrate
ActiveCN113345779BImprove transmission performanceTo filter waveguide modesWaveguidesTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureMicrowave propagation
The invention discloses a microstrip slow-wave structure transmission system suitable for wide dielectric substrates, and relates to the field of microwave electric vacuum technology. Protrusions, two groups of first protrusions and two groups of second protrusions are located on the side of the microstrip slow wave line in the dielectric substrate; two groups of first protrusions and two groups of second protrusions are located along the microstrip slow wave line The microwave propagating direction of the line is arranged at intervals, and two groups of second protrusions are located between two groups of first protrusions; the lateral width of the first protrusions is greater than that of the second protrusions. The present invention changes the shape of the inner wall of the metal shell innovatively, so that the cut-off frequency of microwave propagation in multiple places changes suddenly, that is, a new capacitive reactance and inductive reactance are introduced into the slow wave structure, so as to filter out the waveguide mode and improve the efficiency of the slow wave structure. The role of transmission performance effectively overcomes the problem of large reflection and transmission loss when the wide dielectric substrate microstrip slow-wave structure transmits microwave signals.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
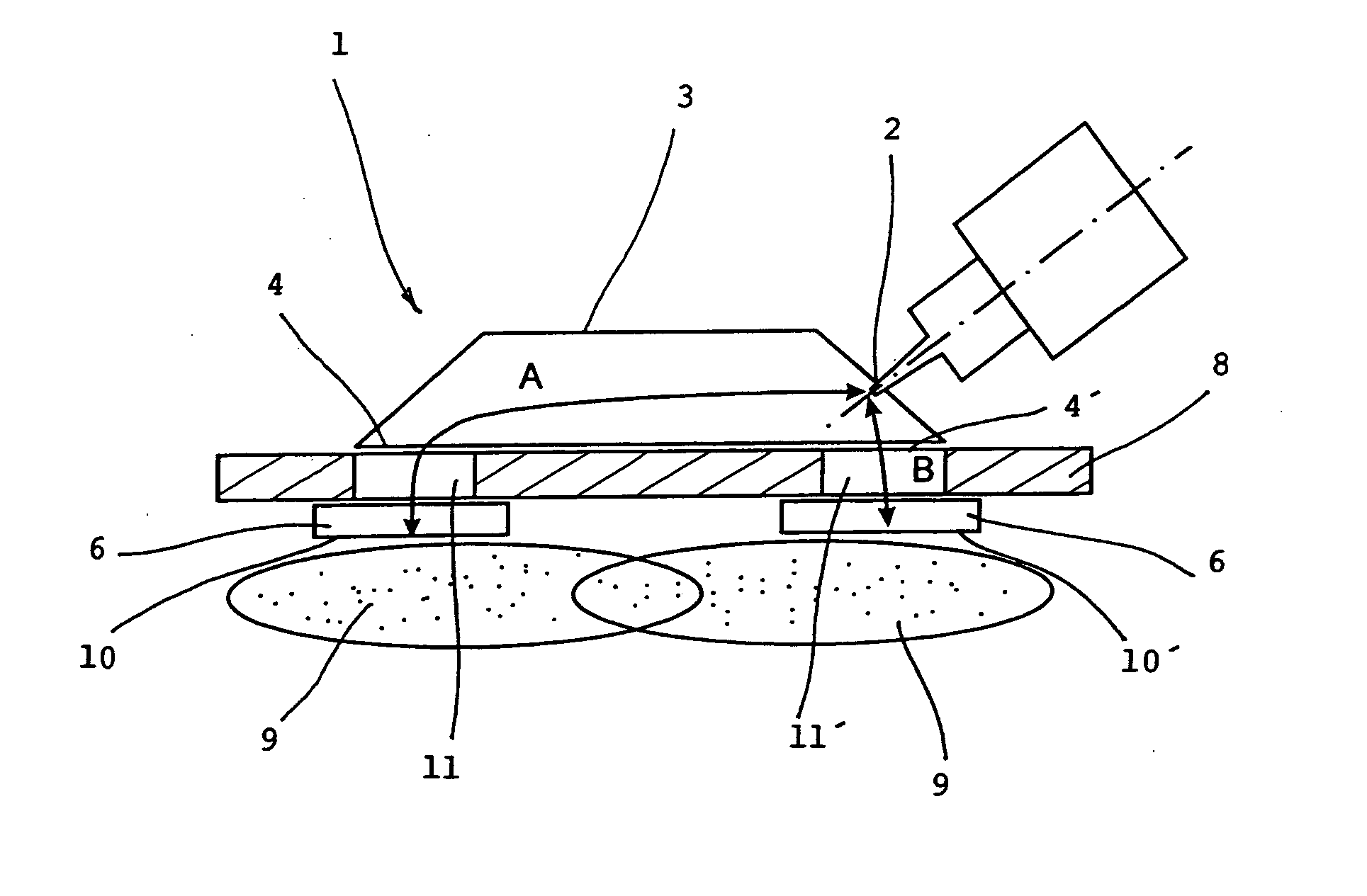
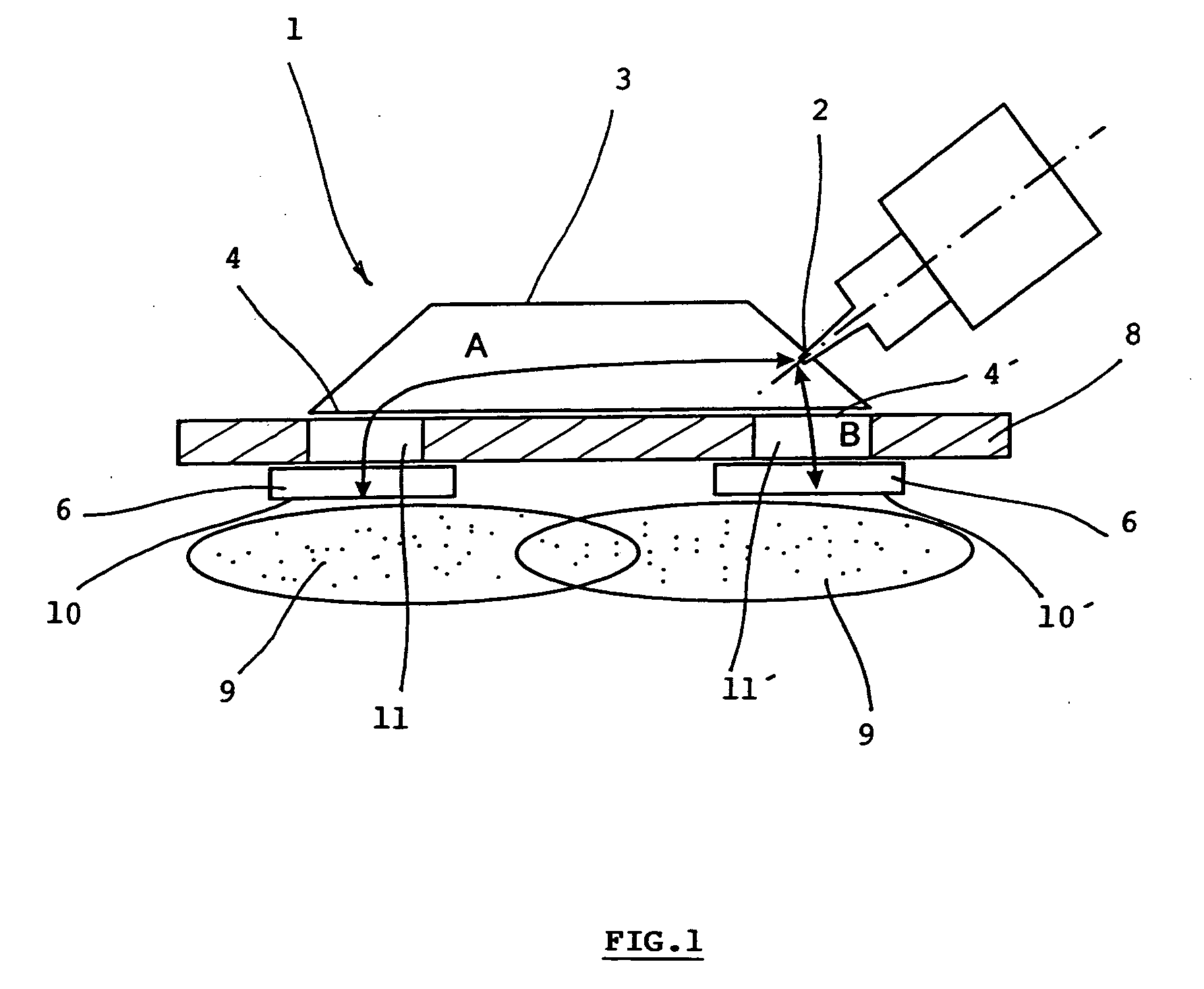
Applicator of microwave plasma generator and microwave plasma generator including this applicator
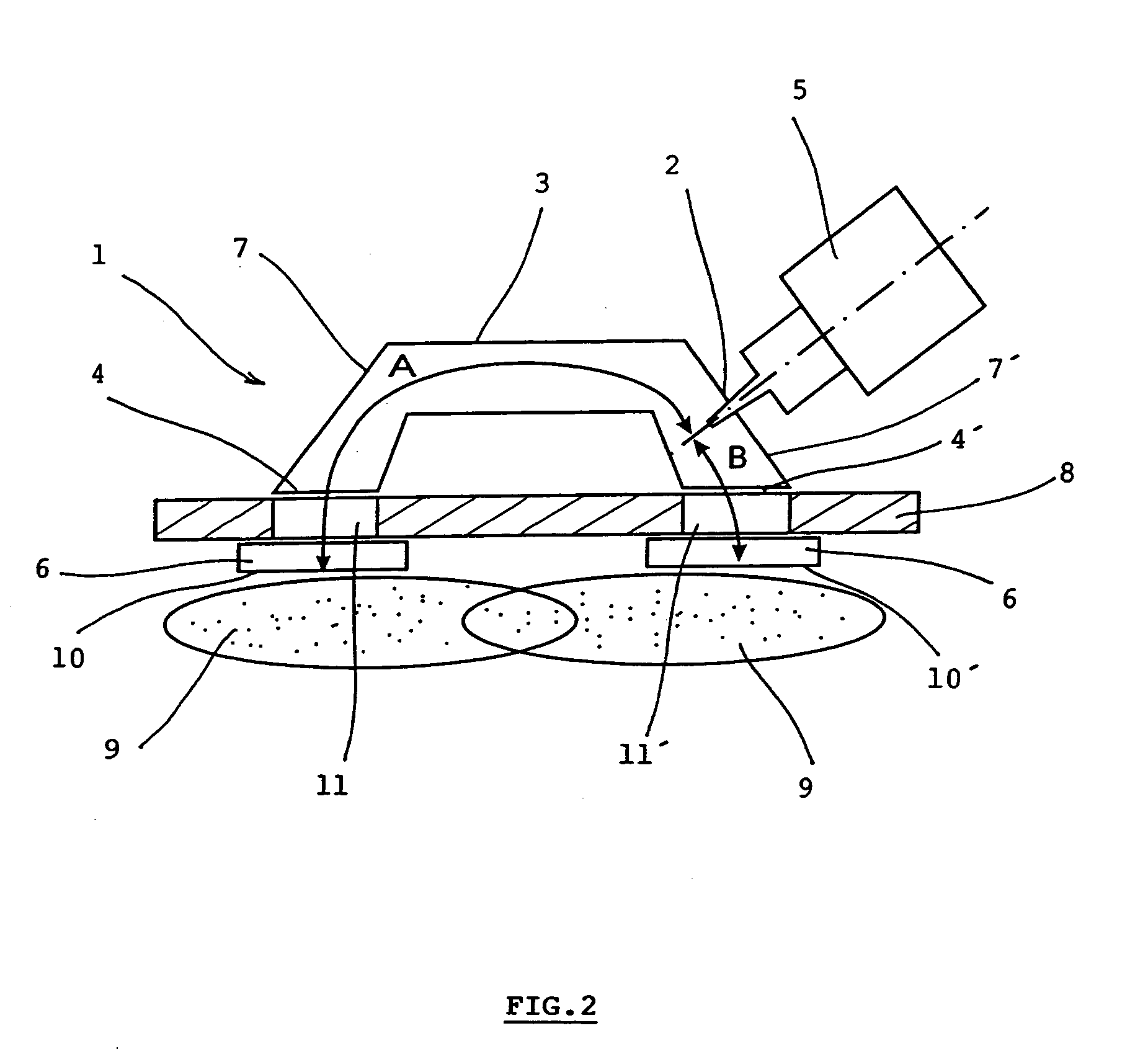
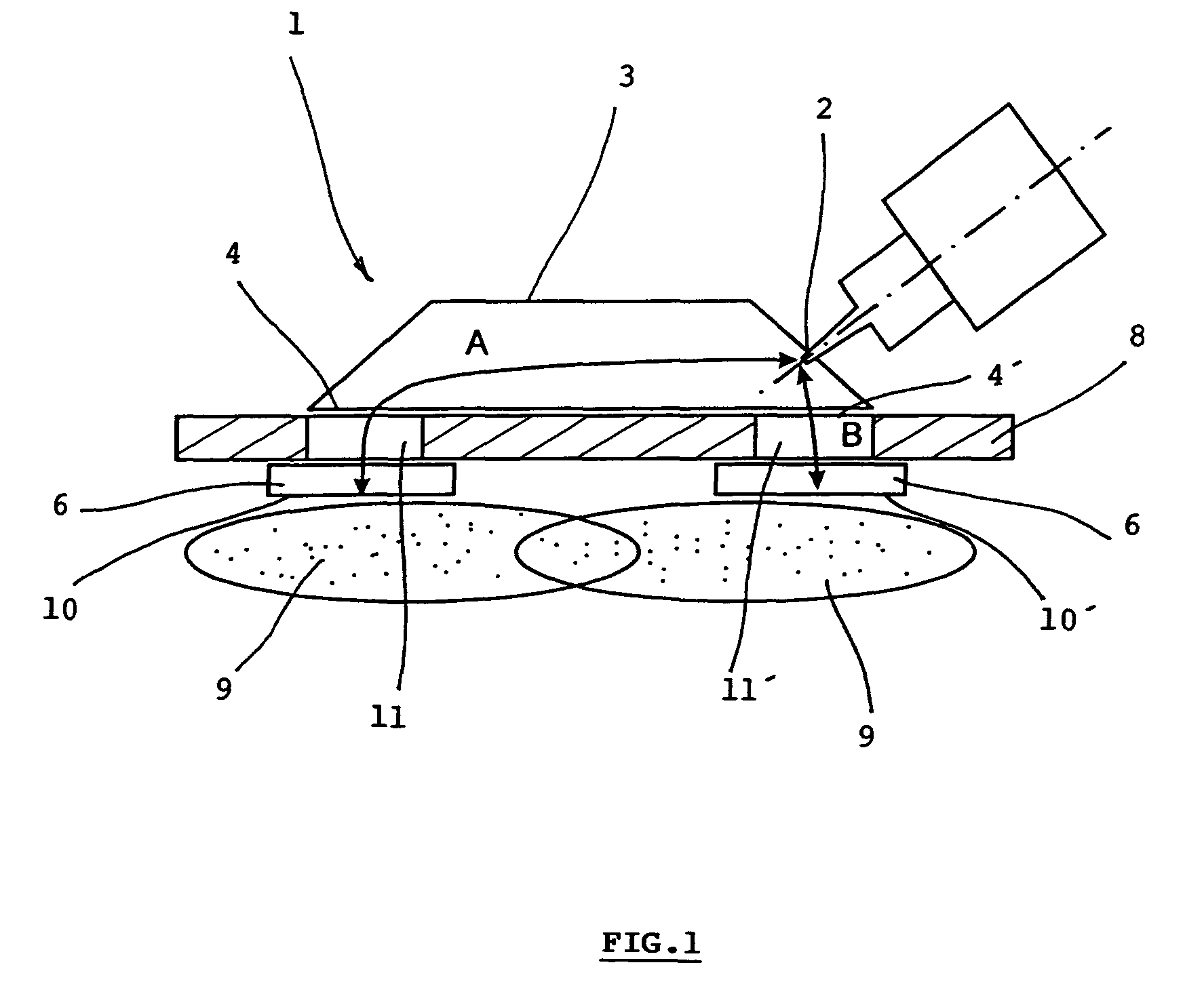
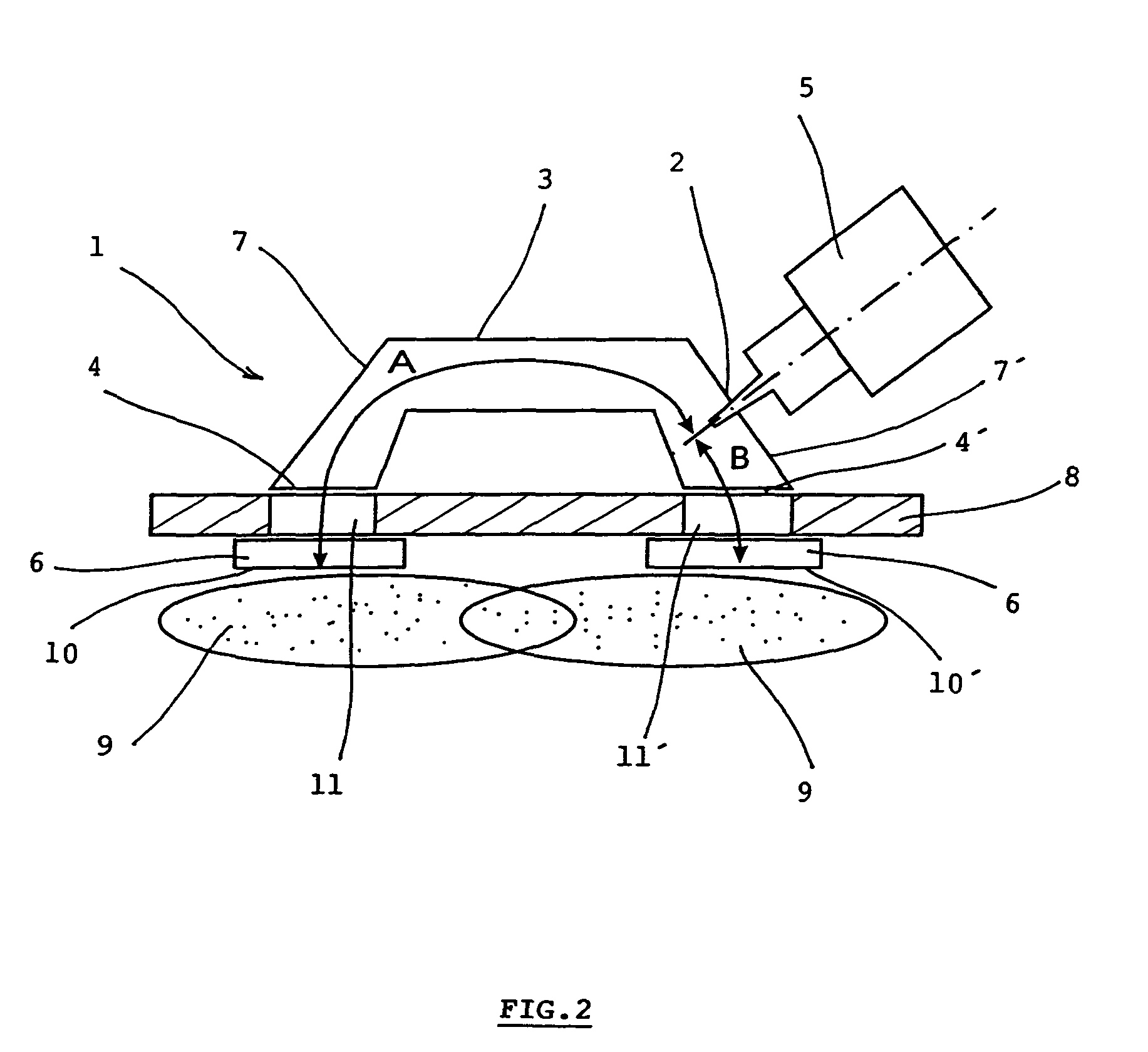
InactiveUS20100301753A1Simple and compactEasy to transportElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsMicrowave propagationPlasma generator
The microwave plasma generator is applied to transmission of electromagnetic field into plasma. The invention consists of the fact that the guiding part (3) has two outputs (4, 4′) between which an input (2) of microwave is placed generated from the microwave power source (5). The input (2) is in the distance (A) from the separation (10) of the first output (4) and in the distance (B) from the separation (10′) of the second output (4′) while the absolute value of the difference of the distances A-B or B-A equals λ / 2 where λ is the wave length of the microwave and distances A and B correspond to the trajectory of microwave propagation. A microwave plasma generator including microwave power source (magnetron) (5) is connected to the input (2) of the guiding part (3) of the applicator (1)
Owner:SPATENKA PETR
Applicator of microwave plasma generator and microwave plasma generator including this applicator
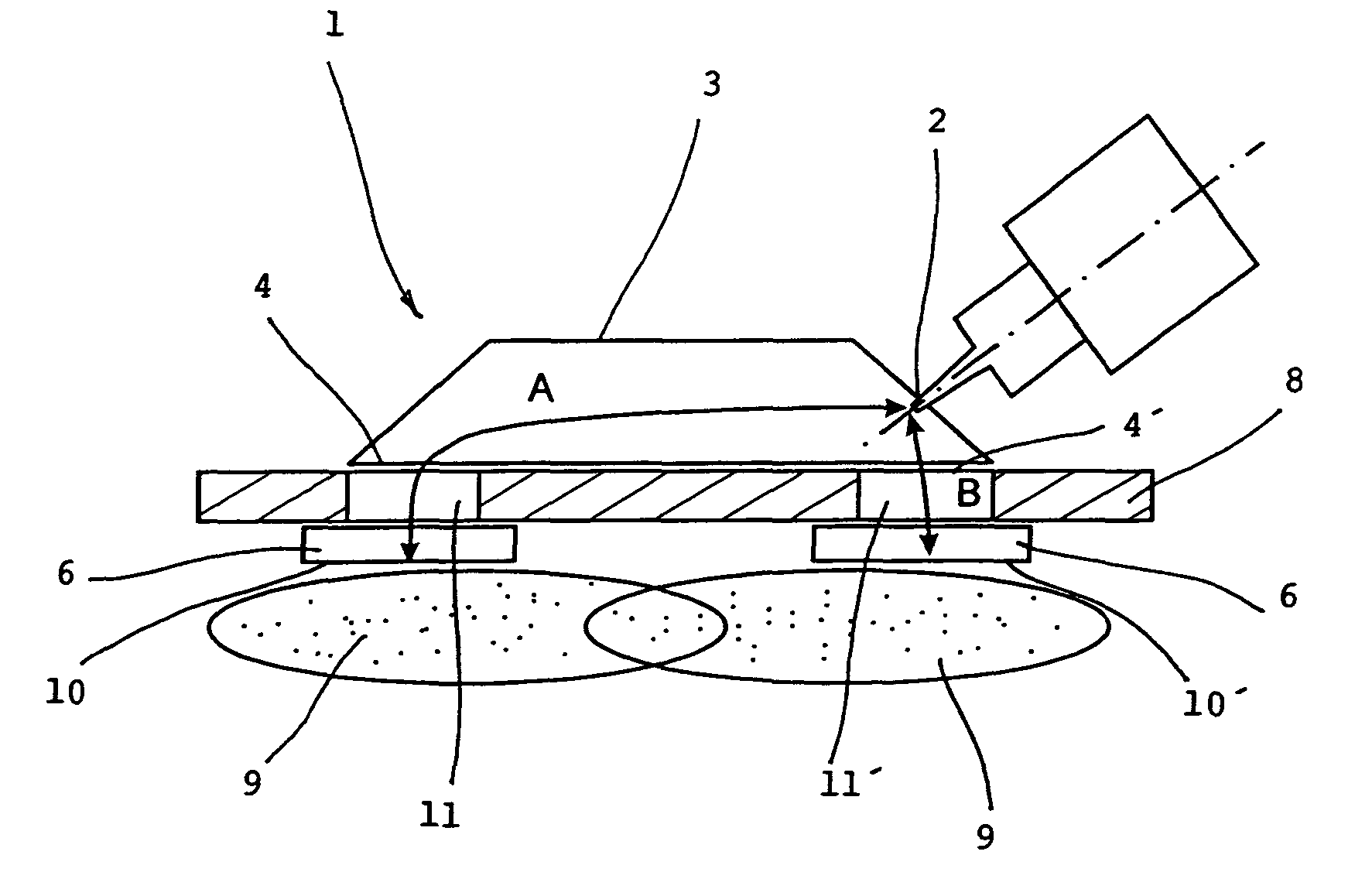
InactiveUS8299714B2Elimination of partGood body shapeElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsMicrowave propagationPlasma generator
The microwave plasma generator is applied to transmission of electromagnetic field into plasma. The invention consists of the fact that the guiding part (3) has two outputs (4, 4′) between which an input (2) of microwave is placed generated from the microwave power source (5). The input (2) is in the distance (A) from the separation (10) of the first output (4) and in the distance (B) from the separation (10′) of the second output (4′) while the absolute value of the difference of the distances A-B or B-A equals λ / 2 where λ is the wave length of the microwave and distances A and B correspond to the trajectory of microwave propagation. A microwave plasma generator including microwave power source (magnetron) (5) is connected to the input (2) of the guiding part (3) of the applicator (1).
Owner:SPATENKA PETR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com