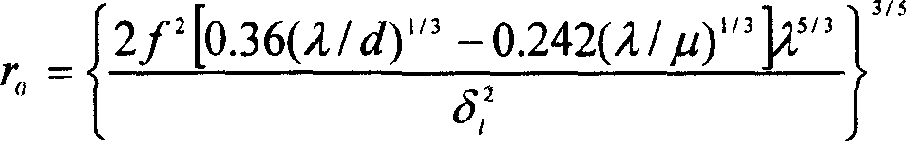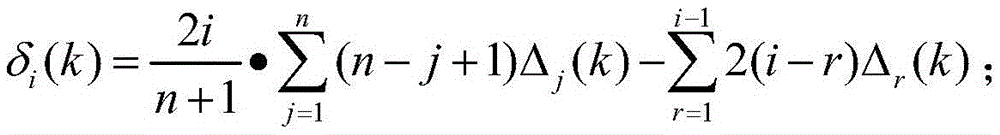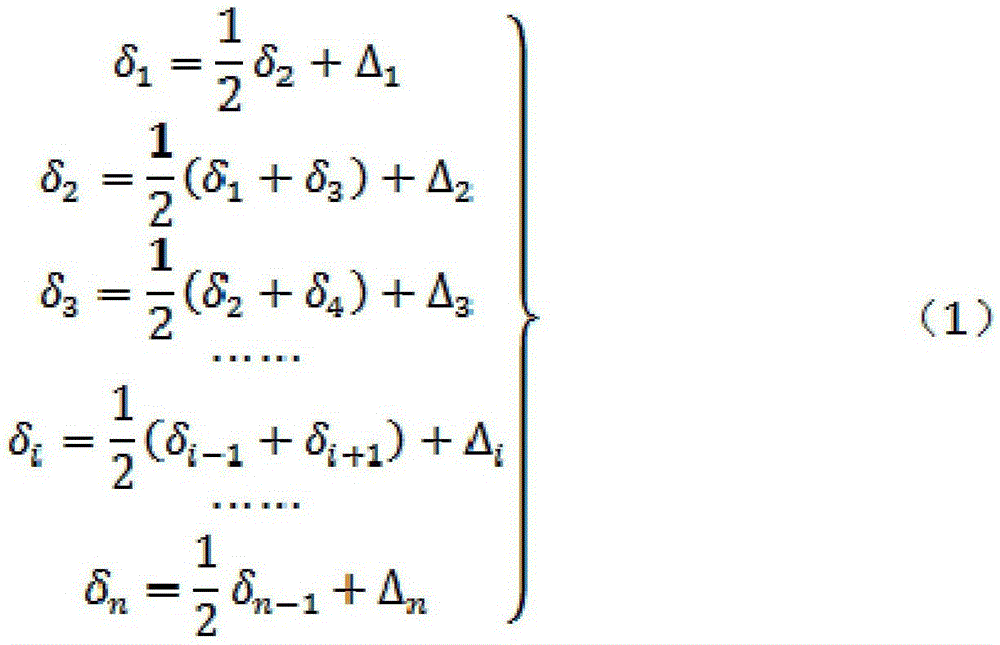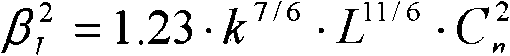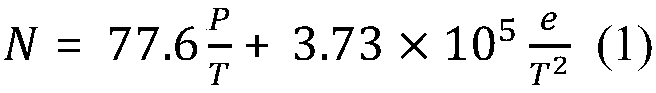Patents
Literature
166 results about "Atmospheric refraction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
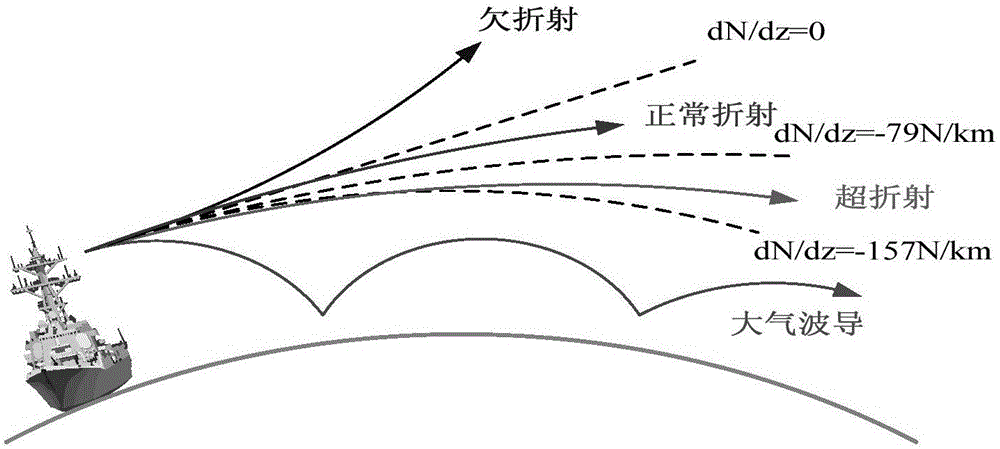
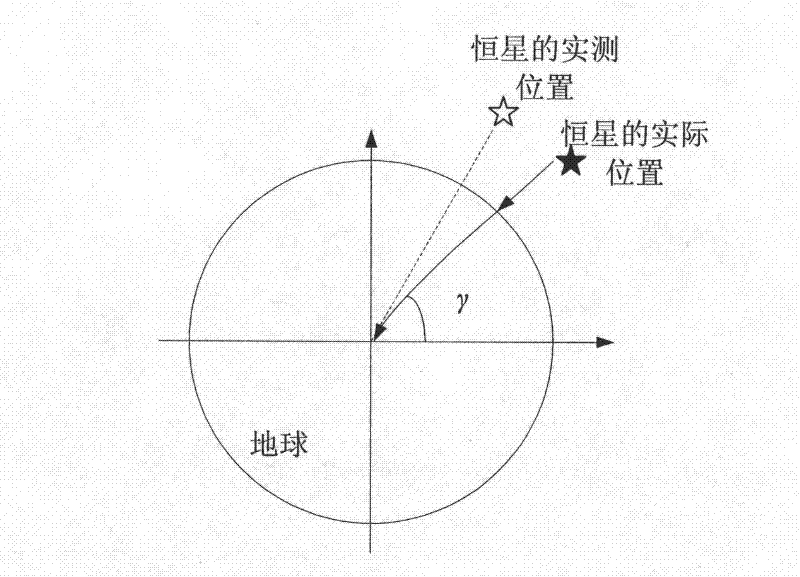
Atmospheric refraction is the deviation of light or other electromagnetic wave from a straight line as it passes through the atmosphere due to the variation in air density as a function of height. This refraction is due to the velocity of light through air, decreasing (the refractive index increases) with increased density. Atmospheric refraction near the ground produces mirages. Such refraction can also raise or lower, or stretch or shorten, the images of distant objects without involving mirages. Turbulent air can make distant objects appear to twinkle or shimmer. The term also applies to the refraction of sound. Atmospheric refraction is considered in measuring the position of both celestial and terrestrial objects.
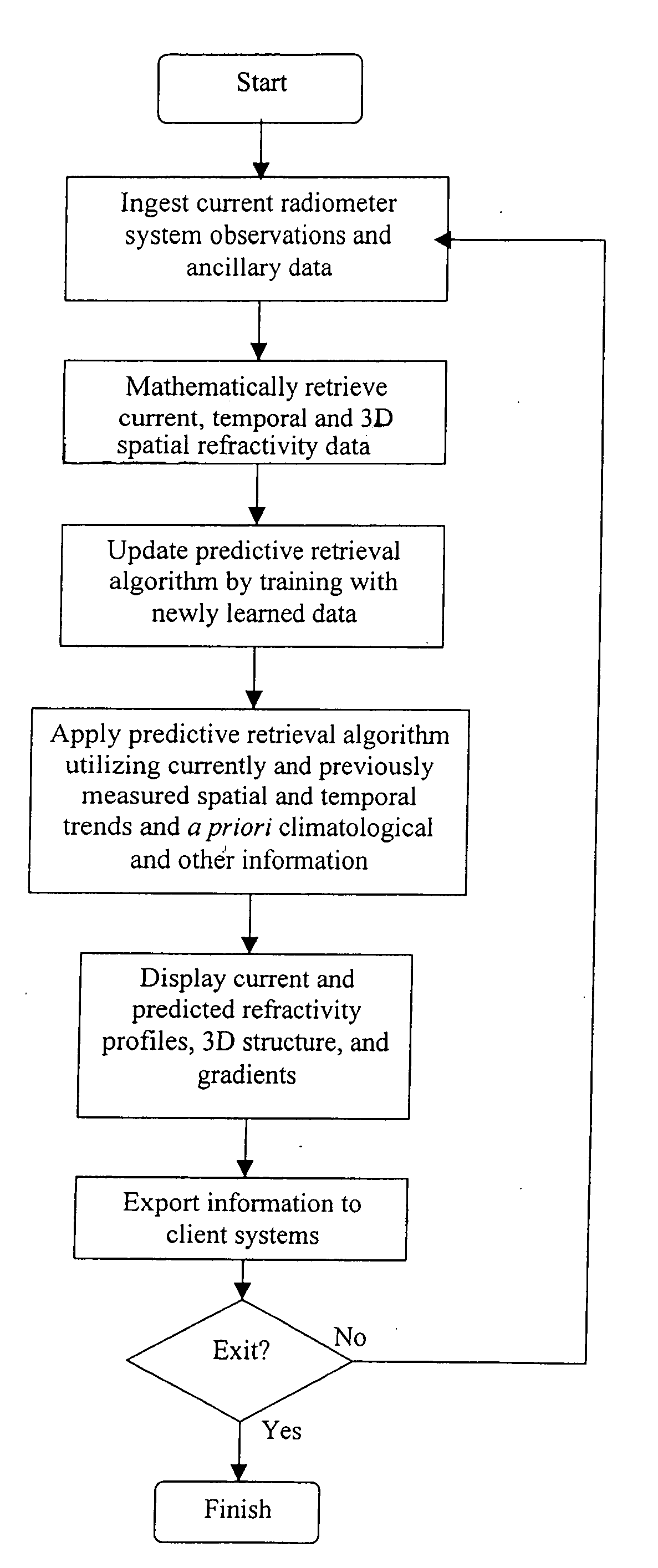
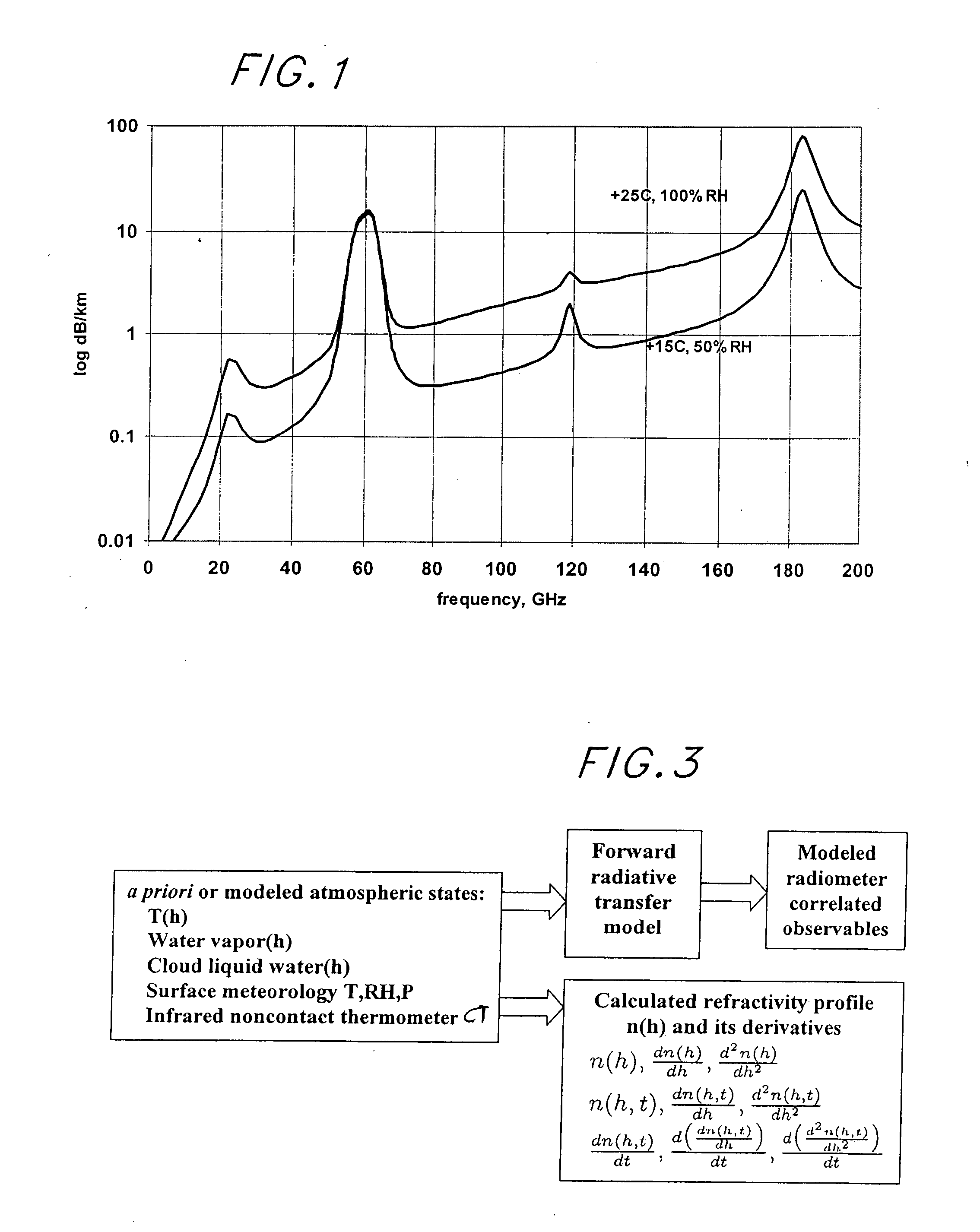
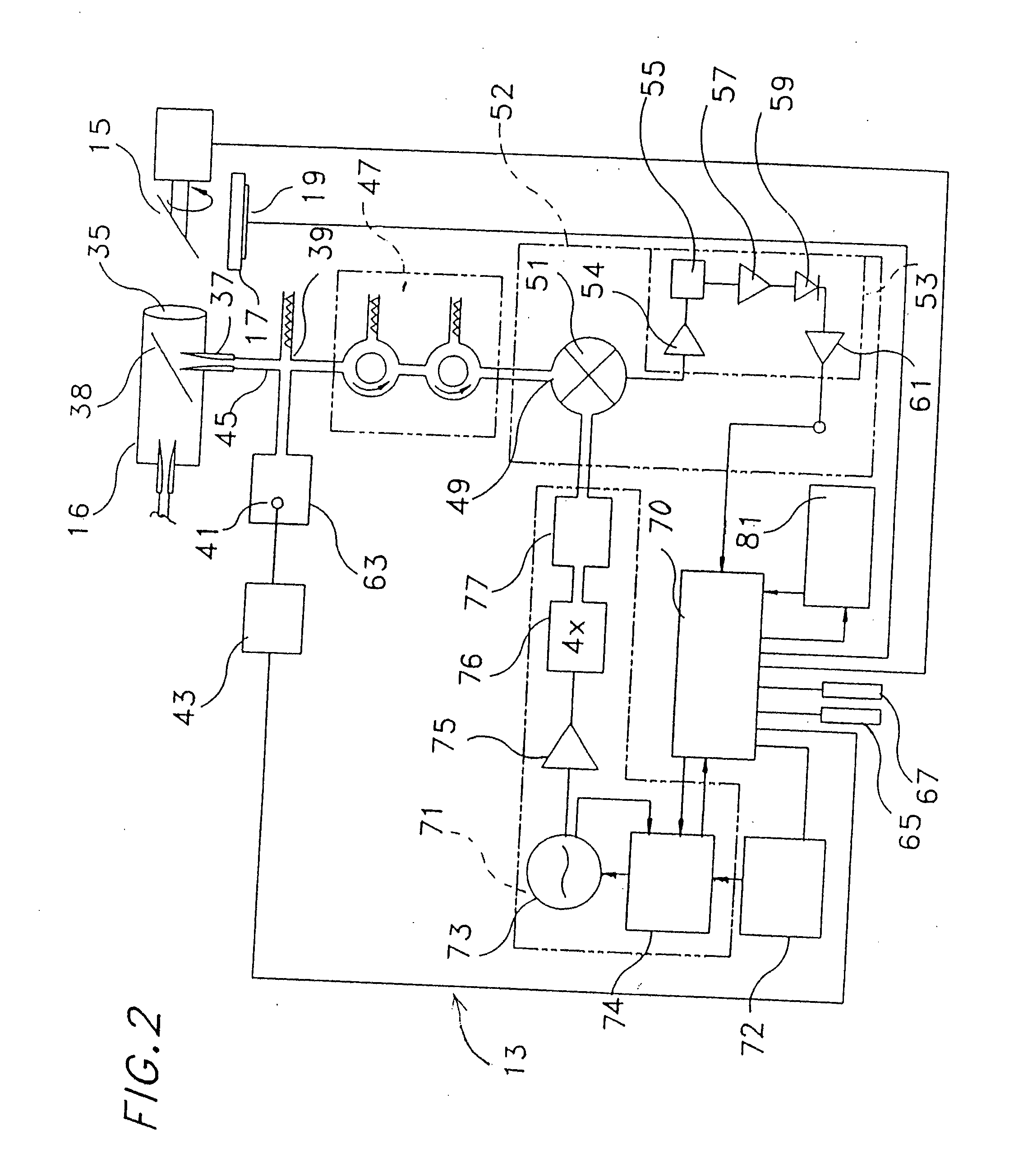
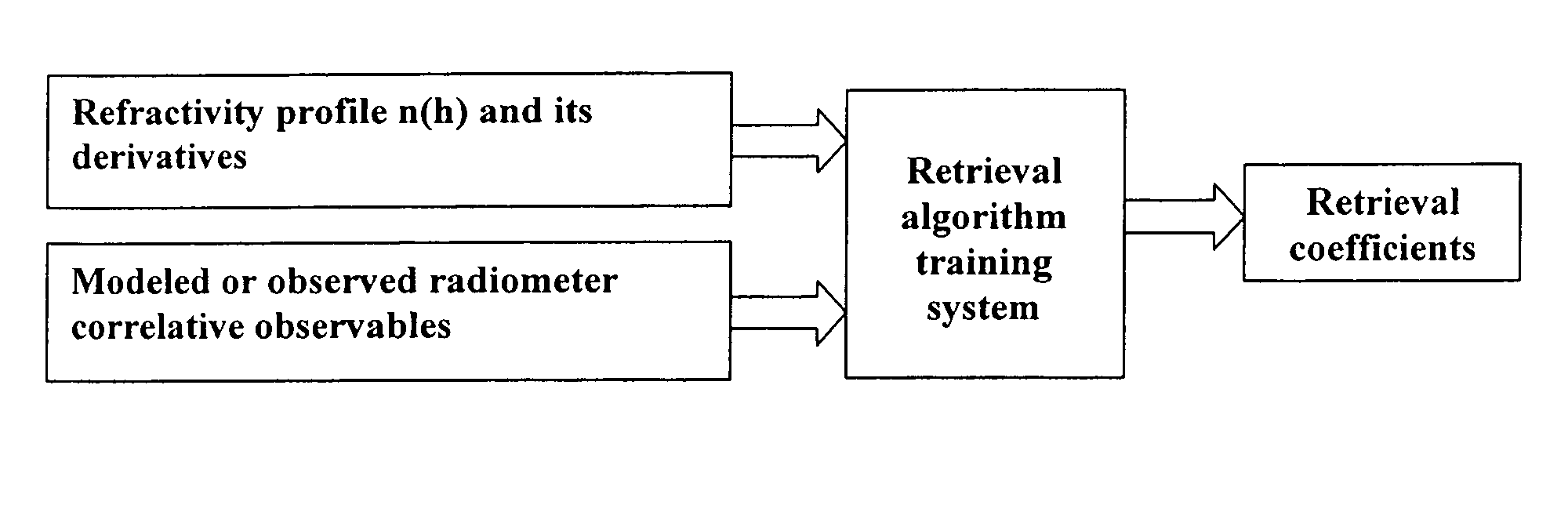
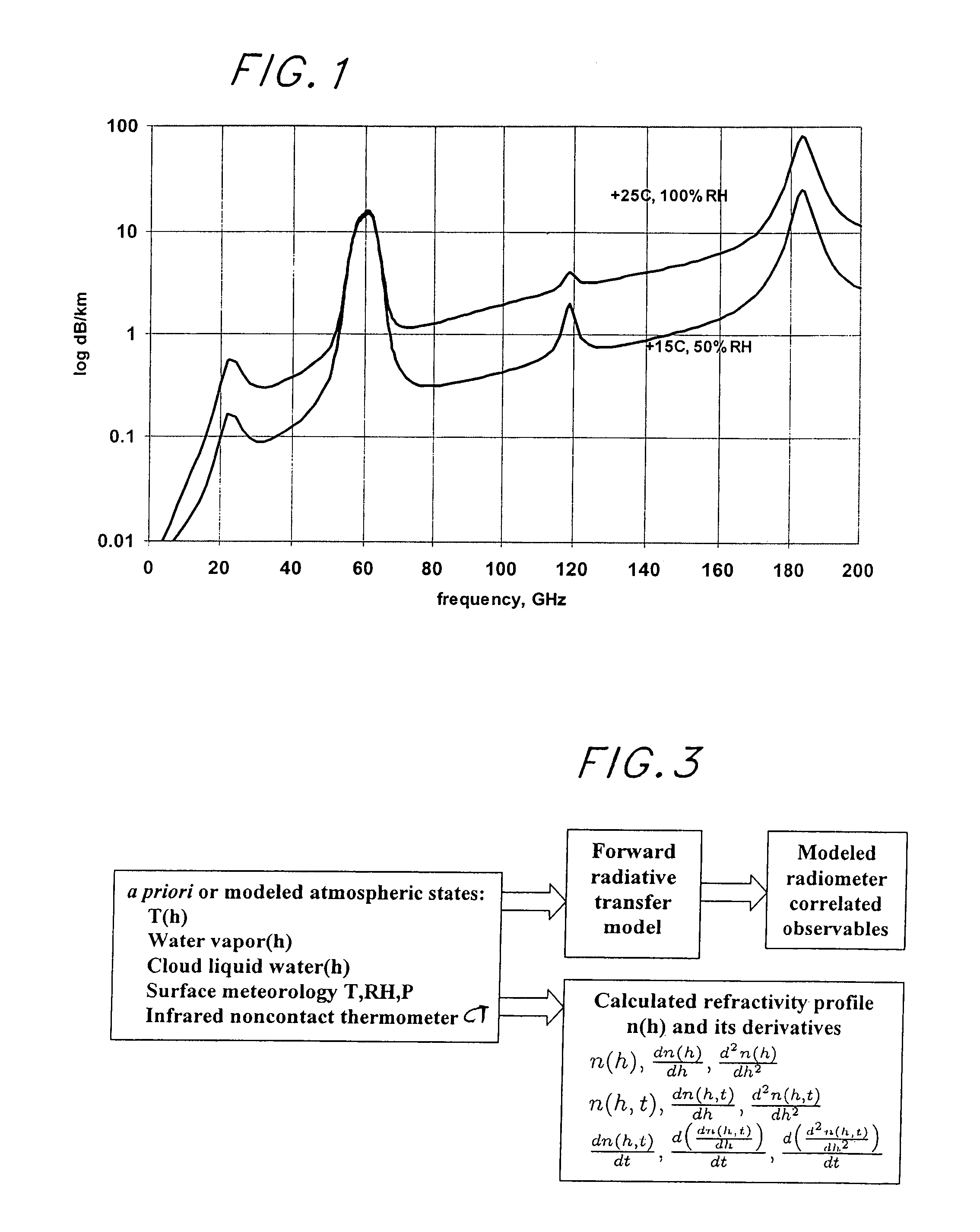
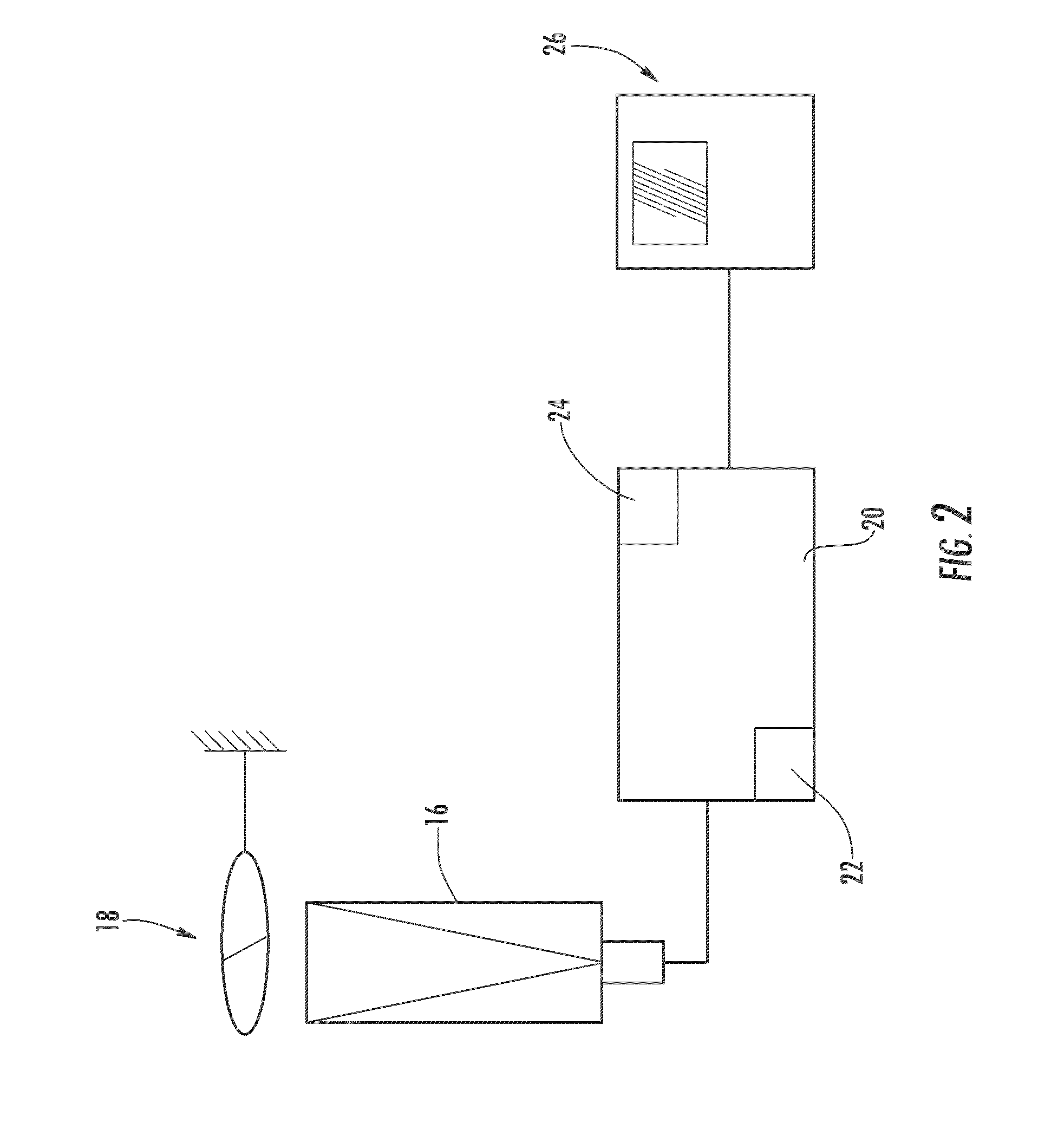
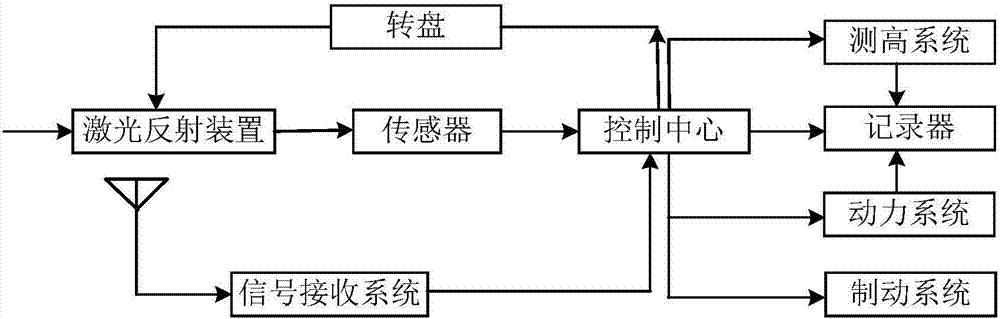
Atmospheric refractivity profiling apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20060164063A1Direction finders using radio wavesThermometers using physical/chemical changesMeasurement deviceSky
Apparatus and methods for characterizing atmospheric refractivity and its evolution in time and space utilizing passive radiation emission measurement devices are disclosed. Based on an instrument such as a passive microwave radiometer, ancillary meteorological measurements and other information and observations, the apparatus and methods provide useful signatures for characterizing atmospheric refractivity. The system can observe to any vector in the sky, giving directional as well as zenithal measurements of the refractivity profile, its spatial and temporal gradients, and the spatial and temporal trending of the profile and its gradients.
Owner:RADIOMETRICS CORP
Atmospheric turbulance detection laser rader using position-sensitive detector
InactiveCN1945355ALow priceHigh sensitivityElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationRayleigh scatteringRefractive index
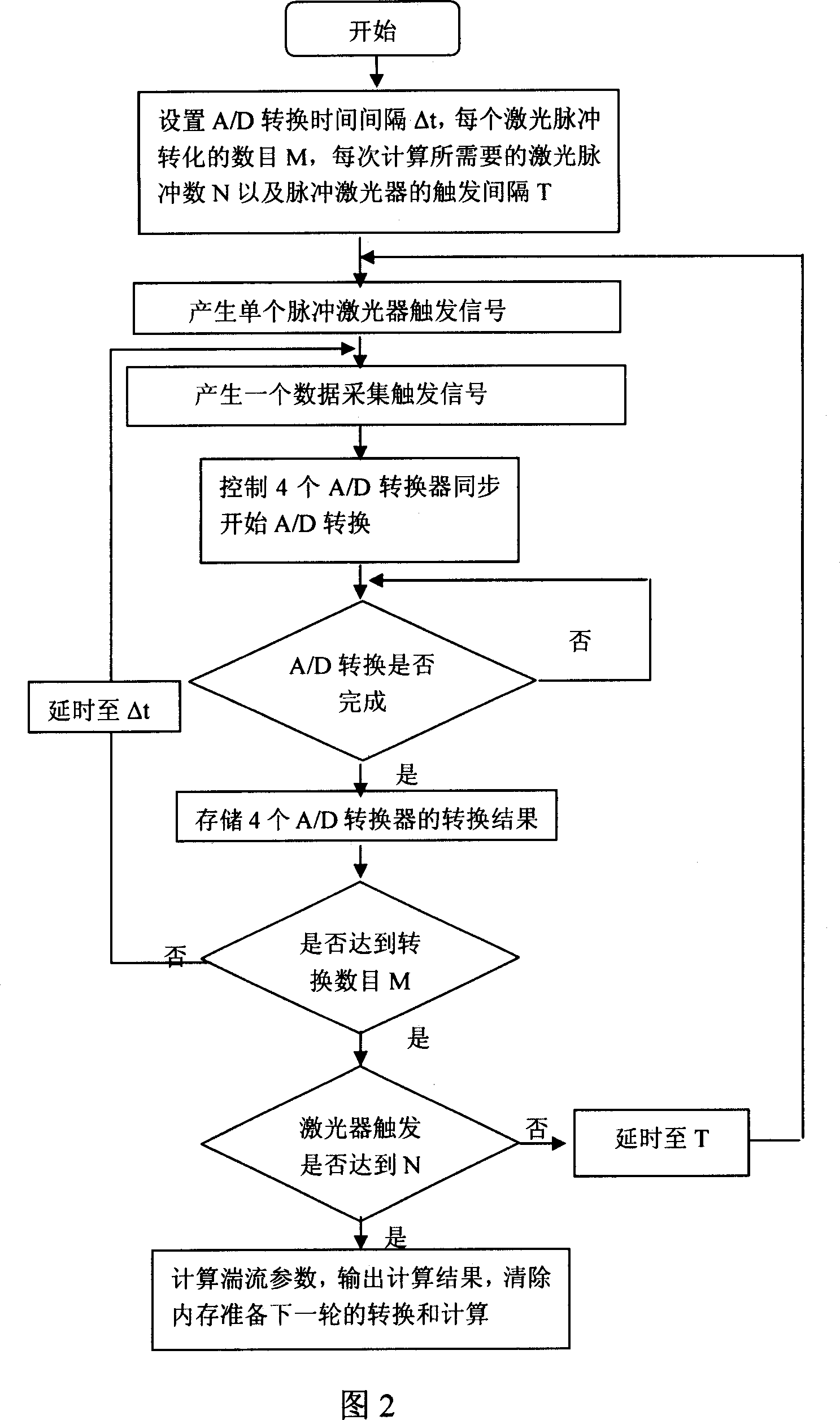
The invention discloses a laser radar for detecting the atmosphere turbulence via a positioning sensitive detector, which relates to the refractive index structure constant profile Cn2 and atmospheric coherence length r0 of the atmosphere turbulence. In the invention, the laser radar takes a pulsed laser as the emission source, and the dual-aperture Rayleigh scattering echo received by the telescopes is focused on the positioning sensitive detector through the reflection prism, and the profile Cn2 and atmospheric coherence length r0 are obtained by micro-processing after the positioning signals are transferred to the digital signals via A / D processor.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
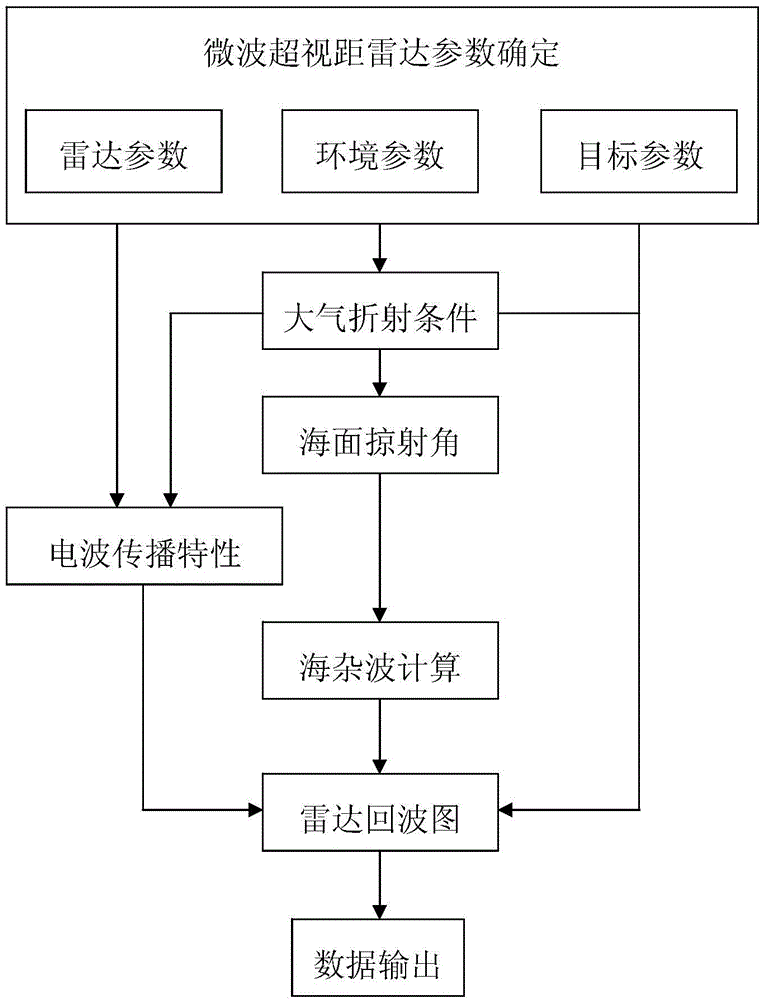
Microwave over-the-horizon radar echo chart calculating method
ActiveCN106772300AFully consider the echoFully consider the impact of the target echoWave based measurement systemsRadar systemsEvaporation
The invention discloses a microwave over-the-horizon radar echo chart calculating method, which comprises the following steps: 1) determination of relevant parameters, target parameters and environment parameters of a microwave over-the-horizon radar; 2) prediction of characteristic parameters of an evaporation waveguide and measurement of characteristic parameters of a surface waveguide; 3) calculation of an atmosphere waveguide or atmosphere refraction propagation sea surface glancing angle; 4) calculation of an atmosphere waveguide or atmosphere refraction propagation factor; 5) calculation of a sea clutter and target echo power diagram; and 6) simulation of a dynamic radar echo chart. The disclosed microwave over-the-horizon radar echo chart calculating method takes influence, formed under ocean hydrological conditions, of atmospheric duct propagation on sea surface echoes and target echoes into full consideration under the actual microwave over-the-horizon radar working environment, provides an actual radar beam sea surface grazing angle calculating method under the atmospheric refraction or atmospheric duct condition on the basis of radar system parameters and marine hydrometeorological parameters, and with relevant sea clutter models being combined, can effectively predicate and estimate the sea surface echo power.
Owner:中国电波传播研究所 +1
Atmospheric refractivity profiling apparatus and methods
InactiveUS7353690B2Direction finders using radio wavesThermometers using physical/chemical changesMeasurement deviceSky
Apparatus and methods for characterizing atmospheric refractivity and its evolution in time and space utilizing passive radiation emission measurement devices are disclosed. Based on an instrument such as a passive microwave radiometer, ancillary meteorological measurements and other information and observations, the apparatus and methods provide useful signatures for characterizing atmospheric refractivity. The system can observe to any vector in the sky, giving directional as well as zenithal measurements of the refractivity profile, its spatial and temporal gradients, and the spatial and temporal trending of the profile and its gradients.
Owner:RADIOMETRICS CORP
Collimation line deformation measurement method
InactiveCN105571559AReduce the impactSimple methodMeasurement devicesMeasurement pointReference line
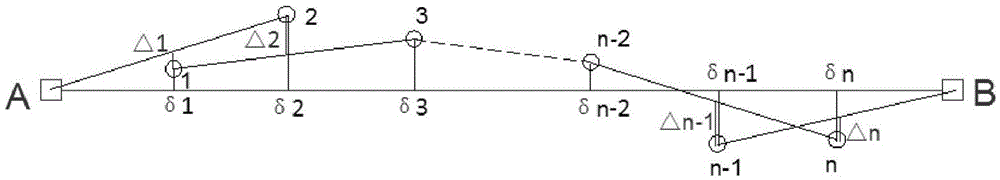
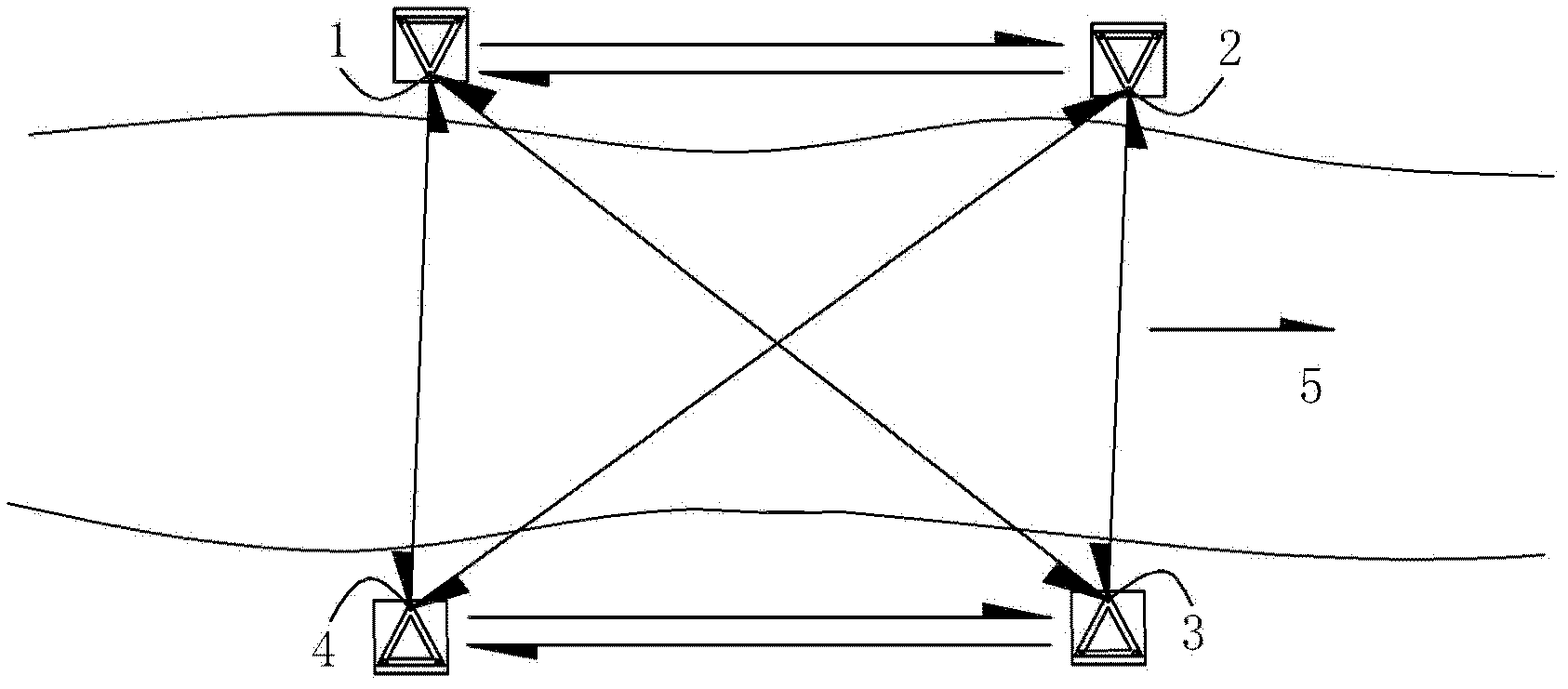
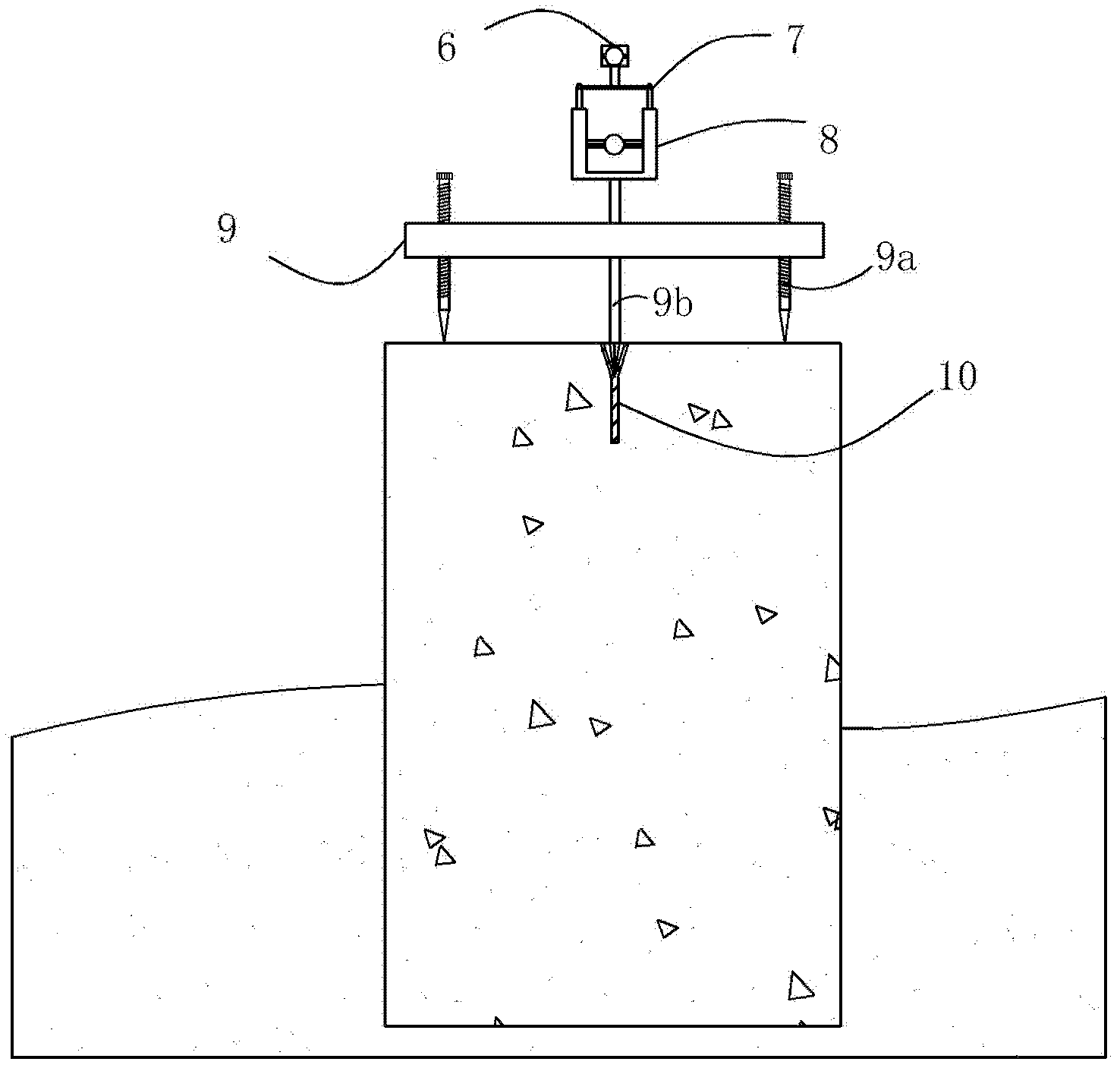
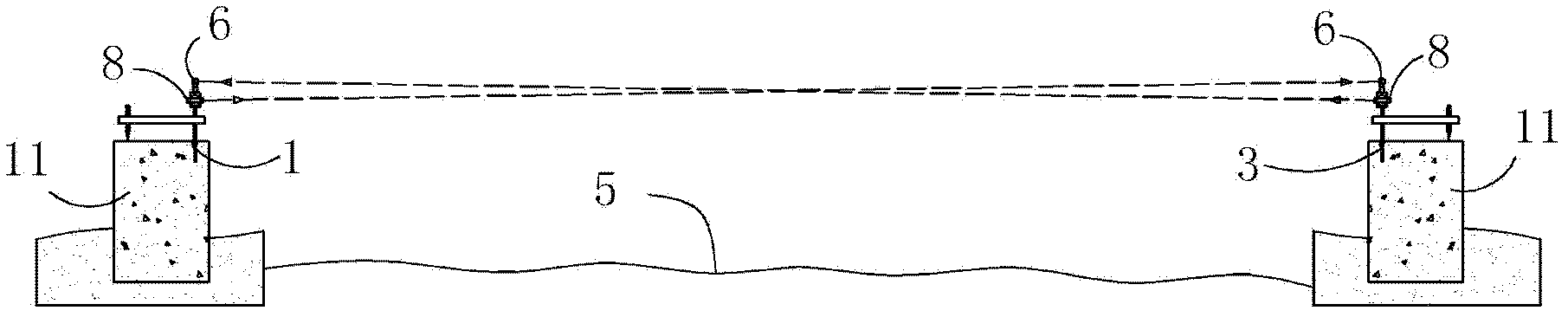
The invention discloses a collimation line deformation measurement method. A kth period observation deviation value delta(k) of the ith measurement point of a long distance collimation line relative to a reference line is calculated by utilizing the following formula (the formula is expressed in the specification), wherein n is the number of the measurement points of the long distance collimation line, delta<j>(k) is a kth period observation local deviation value of the jth measurement point relative to the reference line formed by the connecting line of the (j-1)th measurement point and the (j+1) measurement point, and r=2,3,..., n+1; and the deformation value of the ith measurement point is difference of the kth period observation deviation value of the ith measurement point and the first period observation deviation value of the ith measurement point. The problems that the reference line of total length acts as a collimating reference, and the target is vague, collimating accuracy is poor, a backsight point and the measurement point are far apart from each other and influence of focusing error of a telescope is high when the reference line is long can be effectively solved so that influence of atmospheric refraction on the observation result can be effectively reduced. The method is simple, high in measurement accuracy and convenient in application in actual work.
Owner:POWERCHINA ZHONGNAN ENG
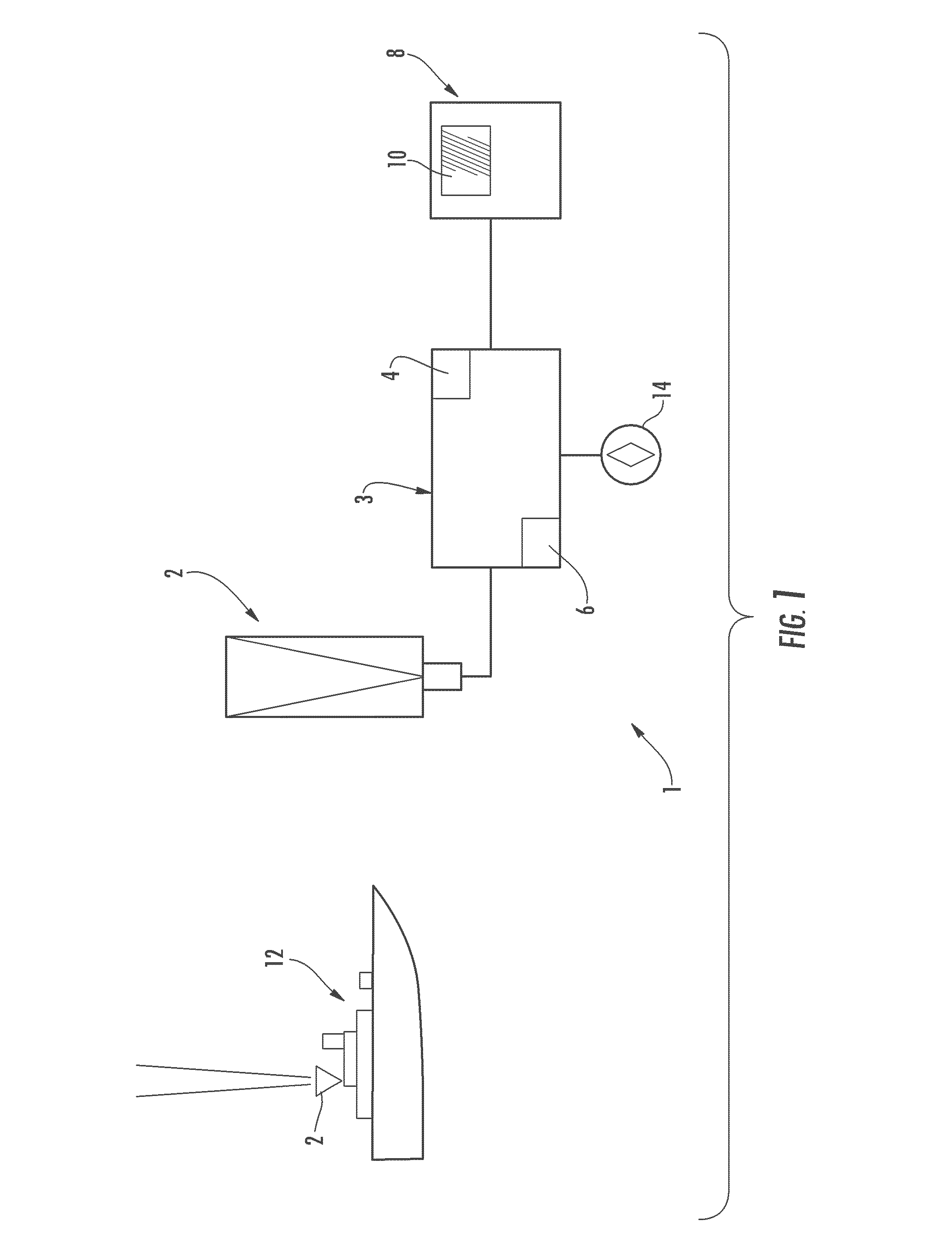
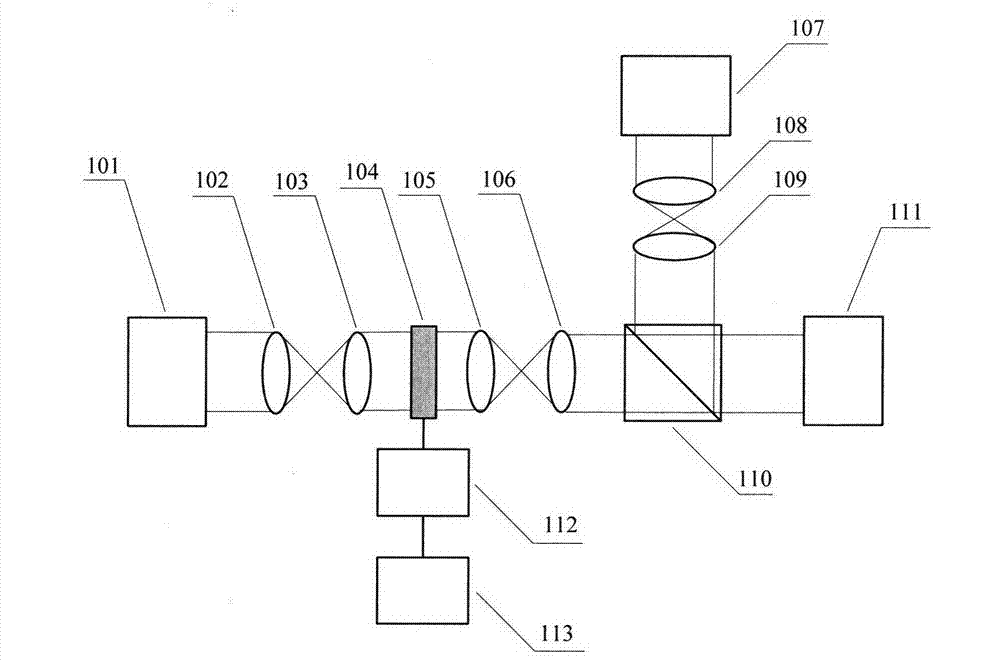
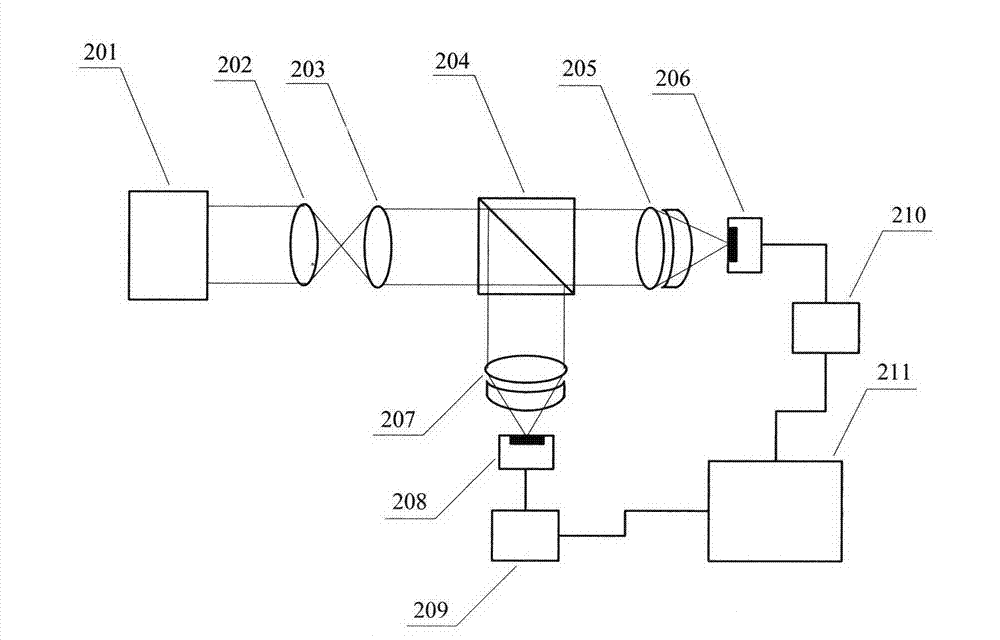
Testing device for influence of atmospheric turbulence to spacing laser communication
InactiveCN101272183AImprove measurement accuracyTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsTime domainPhotovoltaic detectors
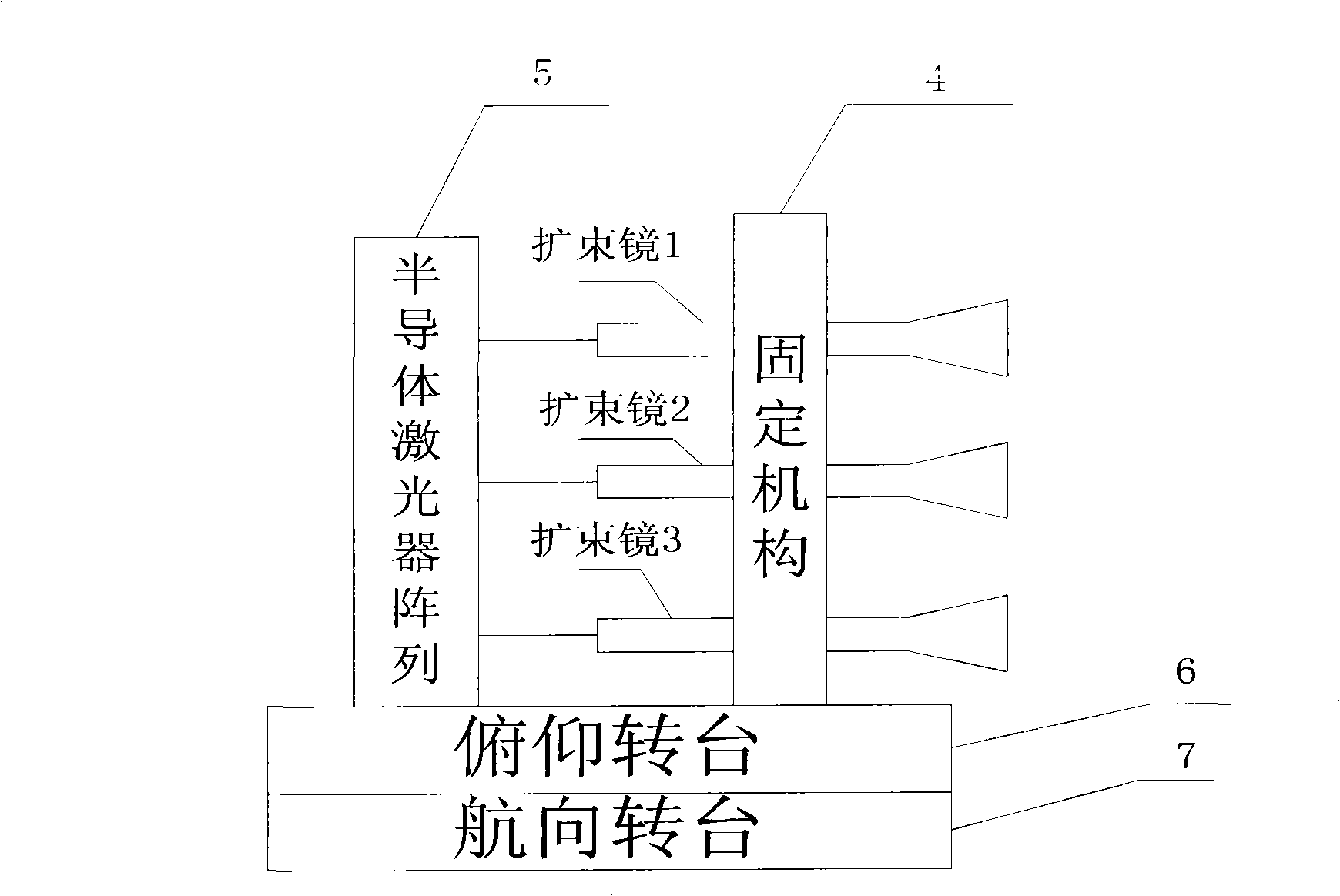
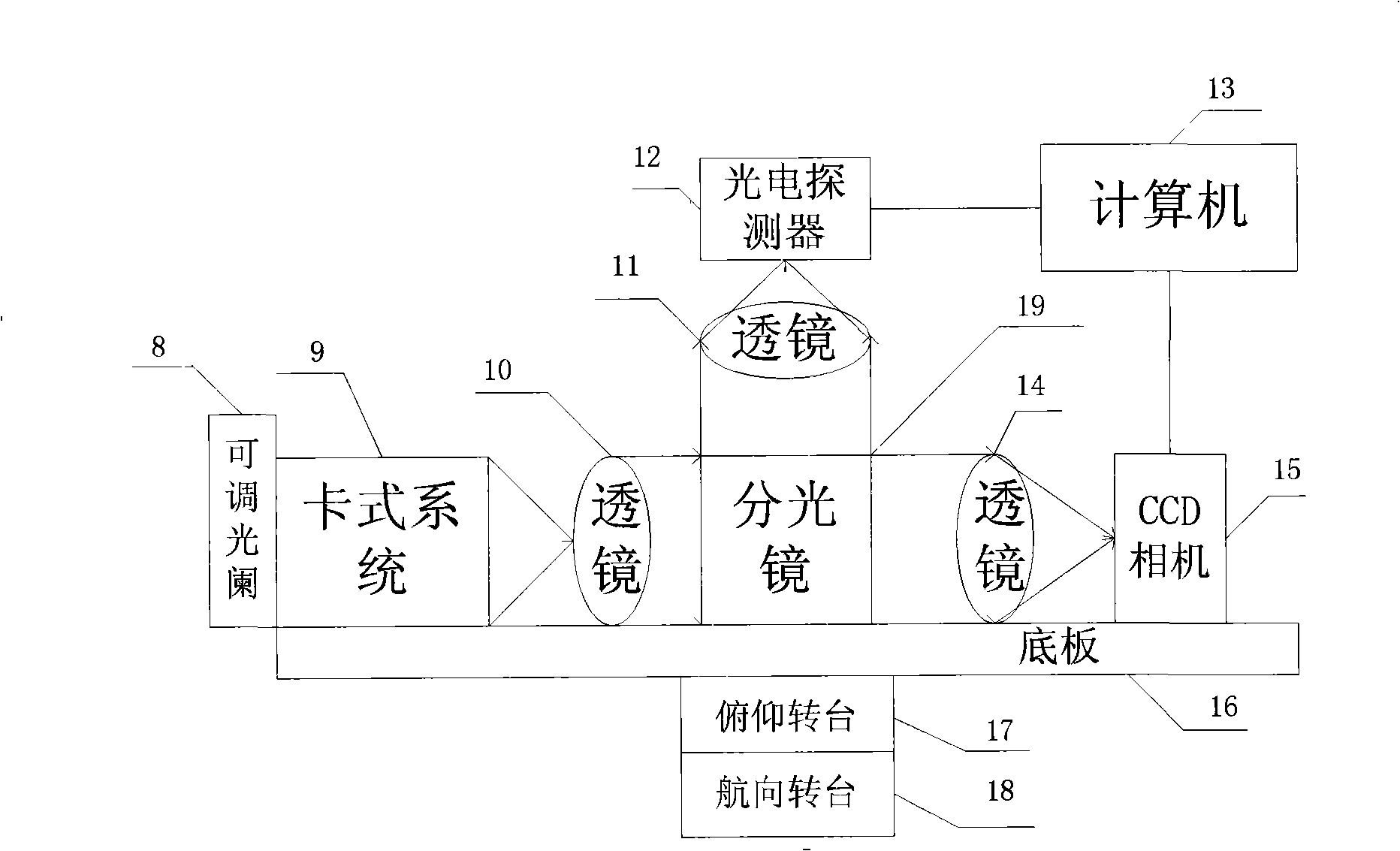
A device for detecting the effects of an atmospheric turbulence to space laser communication provided by the invention consists of an emitting terminal and a receiving terminal; the emitting terminal consists of a laser expanding lens (1), a laser expanding lens (2), a laser expanding lens (3), a fixing mechanism (4), a semiconductor laser array (5), a pitch rotating floor (6) and a course rotating floor (7); the receiving terminal consists of an adjustable diaphragm (8), a card type system (9), a lens (10), a lens (11), a photodetector (12), a computer (13), a lens (14), a CCD camera (16), a pitch rotating floor (17), a course rotating floor (18) and a dispersion prism(19). The detecting device can realize the detecting of the effects of the atmospheric turbulence to space laser communication, can measure an atmospheric refraction index constant, can validate different receiving calibers and different CCD integral times as well as an atmospheric twinkling variance during multi-caliber emitting and can give the time domain and space domain distribution situations of light intensity.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ship-borne high-precision star sensor setting angle calibrating method
InactiveCN105387874AHigh measurement accuracyAutomate calculationMeasurement devicesFixed starsReference vector
The invention discloses a ship-borne high-precision star sensor setting angle calibrating method, and relates to the field of spacecraft attitude control ground application to solve the problem of unable reaction of accurate calibration of the setting angle of a ship-borne star sensor in the prior art. A ship-borne radar equipment pedestal is provided with a star sensor; when a ship docks, a ship-borne alignment calibration theodolite determines the course angle of a measurement ship through a star measurement or azimuth vane tracking technology, and the horizontal reference pitching angle and rolling angle of a whole ship are calibrated to obtain an inertial navigation horizontal system to deck coordinate system transformation matrix; and the star sensor shoots a star atlas, the observation vectors and the reference vectors of i fixed stars are obtained, the azimuths and the pitching angles of the i fixed stars in a view field are calculated, the pitching angles undergo atmospheric refraction correction one by one, the inertial navigation horizontal system reference vectors of the i fixed stars are reconstructed, and star sensor attitude matrix and the ship-borne star sensor setting matrix under the inertial navigation horizontal system are calculated to resolve the setting angle. The method improves the measurement precision of the attitude of the body of a spaceflight measurement ship.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for measuring second-grade river-crossing leveling height difference by using intelligent total station
InactiveCN102322851ASave manpower and material resourcesImprove work efficiencyOpen water surveyHeight/levelling measurementHeight differenceTotal station
The present invention discloses a method for measuring second-grade river-crossing leveling height difference by using an intelligent total station. The method is characterized in that, various river-crossing leveling points are firstly arranged; the height difference among the river-crossing leveling points is measured; an intelligent total station and a reflecting prism are adopted among the river-crossing leveling points positioned on different banks during the measurement process to carry out the synchronous and opposite observation of both banks of the river. According to the present invention, the equipment height is fixed, the alignment is forced to be performed, the intelligent total station and the reflecting prism are arranged integratedly; because the optical alignment and the measurement of the equipment height are not required, the error of the optical alignment and the error of the measurement of the equipment height are avoided; the synchronously-performed river-crossing leveling height measurement counteracts the atmospheric refraction error so as to substantially improve work efficiency and measurement accuracy.
Owner:THE FIRST ENG CO LTD OF CTCE GRP
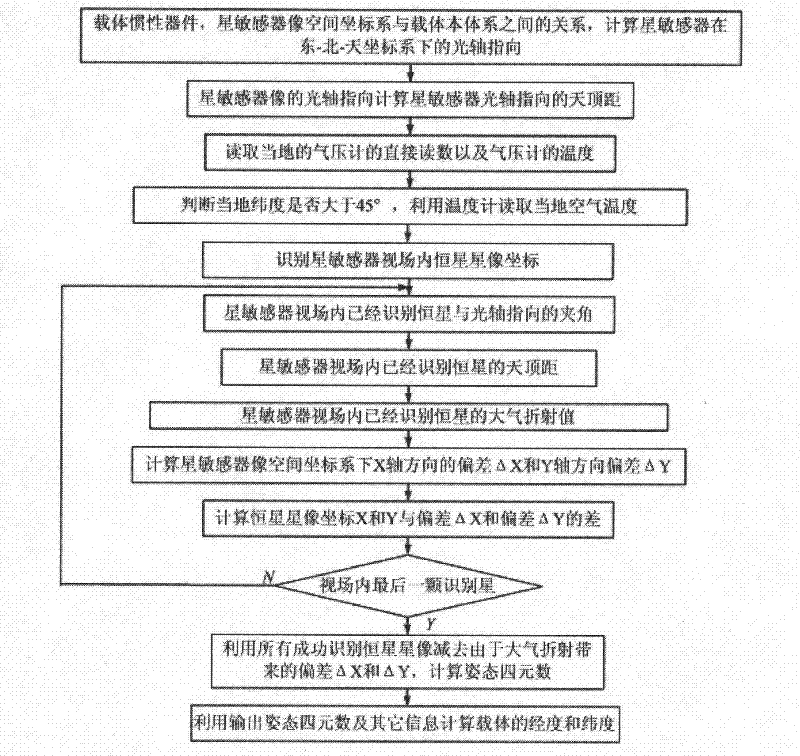
A Method of Correcting the Influence of Atmospheric Refraction on the Accuracy of Star Sensor
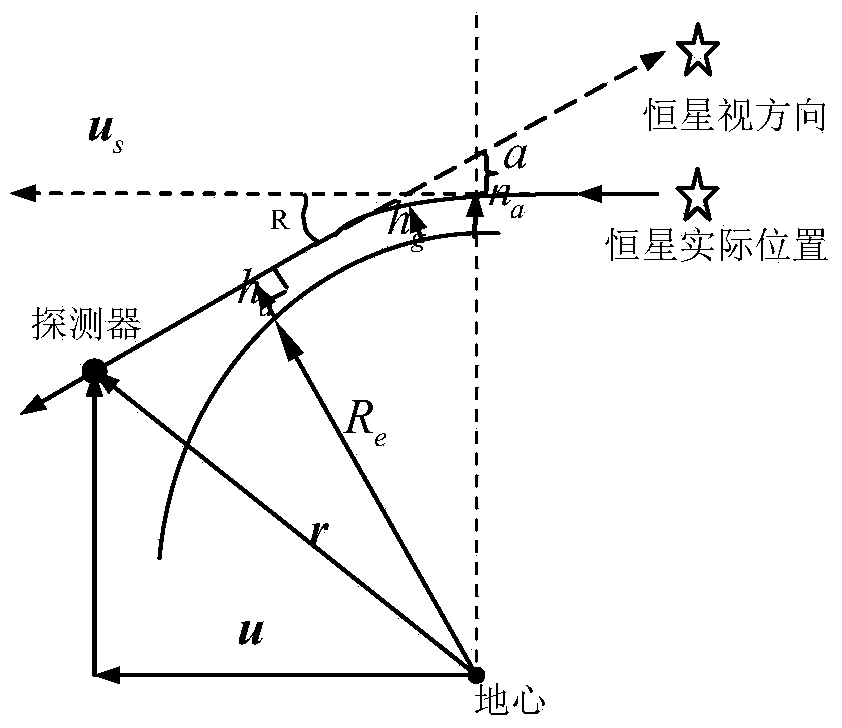
The invention provides a method for correcting the influence of atmospheric refraction on the precision of a star sensor, which comprises the following steps: according to the optic axis orientation of an image of the star sensor, calculating the zenith distance of the optic axis orientation of the star sensor; recognizing the star image coordinates of fixed stars in the viewing field of the starsensor by using a star map recognition algorithm; calculating the zenith distances of the recognized fixed stars in the viewing field of the star sensor; decomposing an atmospheric refraction value into an X-axis direction component and a Y-axis direction component under an image space coordinate system of the star sensor; and subtracting the deviation delta X and delta Y (arising from the atmospheric refraction value) from all successfully-recognized star images of the fixed stars, thus calculating attitude quaternions. When the influence of atmospheric refraction is eliminated, the star sensor can provide high-precision navigation information for shipborne, missile-mounted and airborne aircraft and other aircraft which carry out low-altitude flying; and after carriers adopt atmospheric-refraction-corrected high-precision navigation information, a basis is provided for planning a better navigation path for the carriers, thereby further reducing the fuel consumption of the carriers and improving the efficiency.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
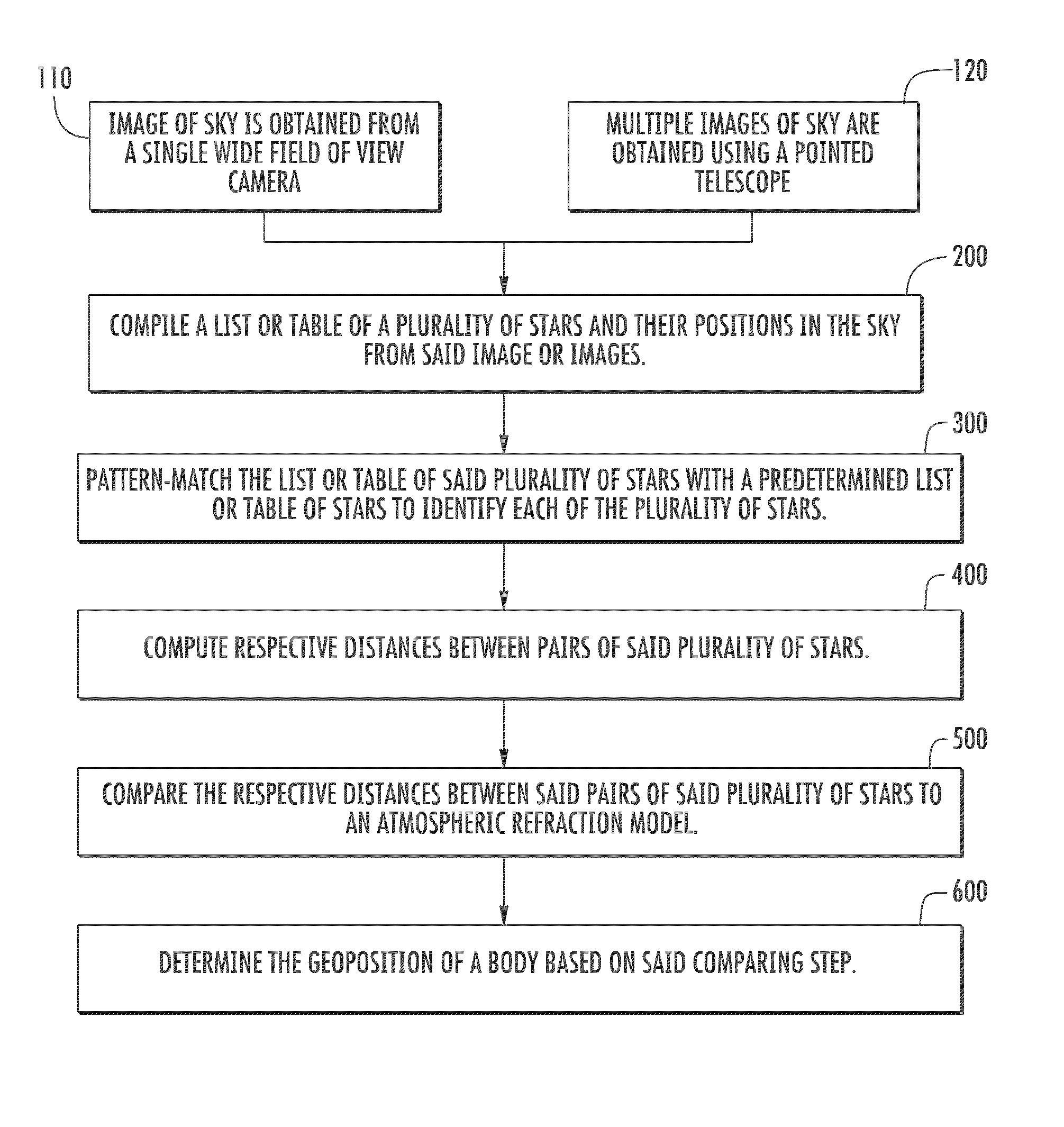
Geoposition determination by starlight refraction measurement
A system and method are disclosed for determining geoposition of an observer. The system includes a sensor such as a wide field of view camera or telescope that can capture an image of the sky. The image of the sky is used to compile a table or list of the stars in the sky along with their positions. This table or list is pattern-matched with a predetermined list or table of stars to identify each star. In one embodiment, the distances between all stars in the image are computed and compared to star images from an atmospheric refraction model. A comparison of the measured table or list and the refraction model, using an optimization algorithm, is performed to determine the geoposition of the observer. In an alternative embodiment, a sensor capable of measuring two different frequency bands obtains two images of each star in the sky simultaneously. A difference in displacement is determined between the two frequencies for each imaged star; and a magnitude and direction of the difference in displacement is used to determine the geoposition of a body.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
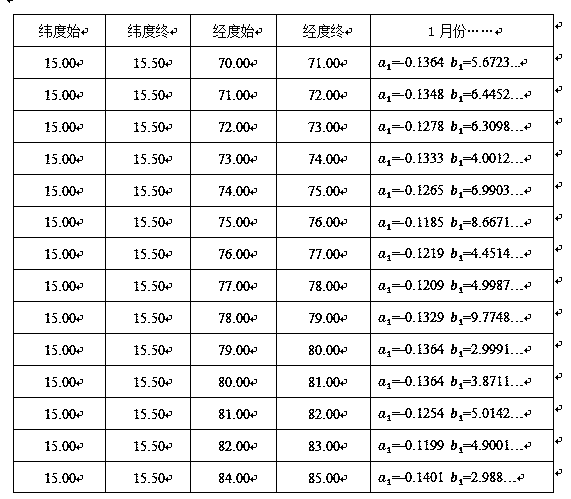
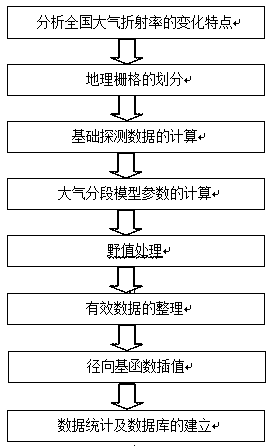
Prediction method for national tropospheric refractive index profile
InactiveCN108898252AImproved refraction error correction accuracyForecastingPredictive methodsLongitude
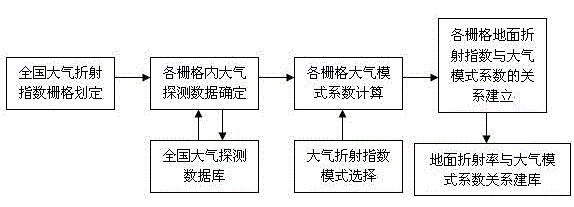
The invention relates to a prediction method for the national tropospheric refractive index profile. The established national tropospheric refractive index profile prediction database includes the following two aspects: first, the longitude and latitude information of each grid after the national atmospheric environment is gridded according to certain longitude and latitude intervals; the other isthe relationship coefficient between the atmospheric section profile model coefficients G, C1 and the surface refractive index N0 of each month in each grid. The main steps of establishing the national tropospheric refractive index profile prediction database are listed as follows: analyzing the characteristics of the national atmospheric refractive index variation, dividing the geographic grid,processing the basic sounding data, calculating the atmospheric section model parameters, processing the outliers, sorting out the valid data, interpolating the radial basis function, data statisticsand establishing the database. The refraction error correction precision can be improved from the source, and the real-time variation of the refractive index in different regions of the country can beobtained conveniently and quickly.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
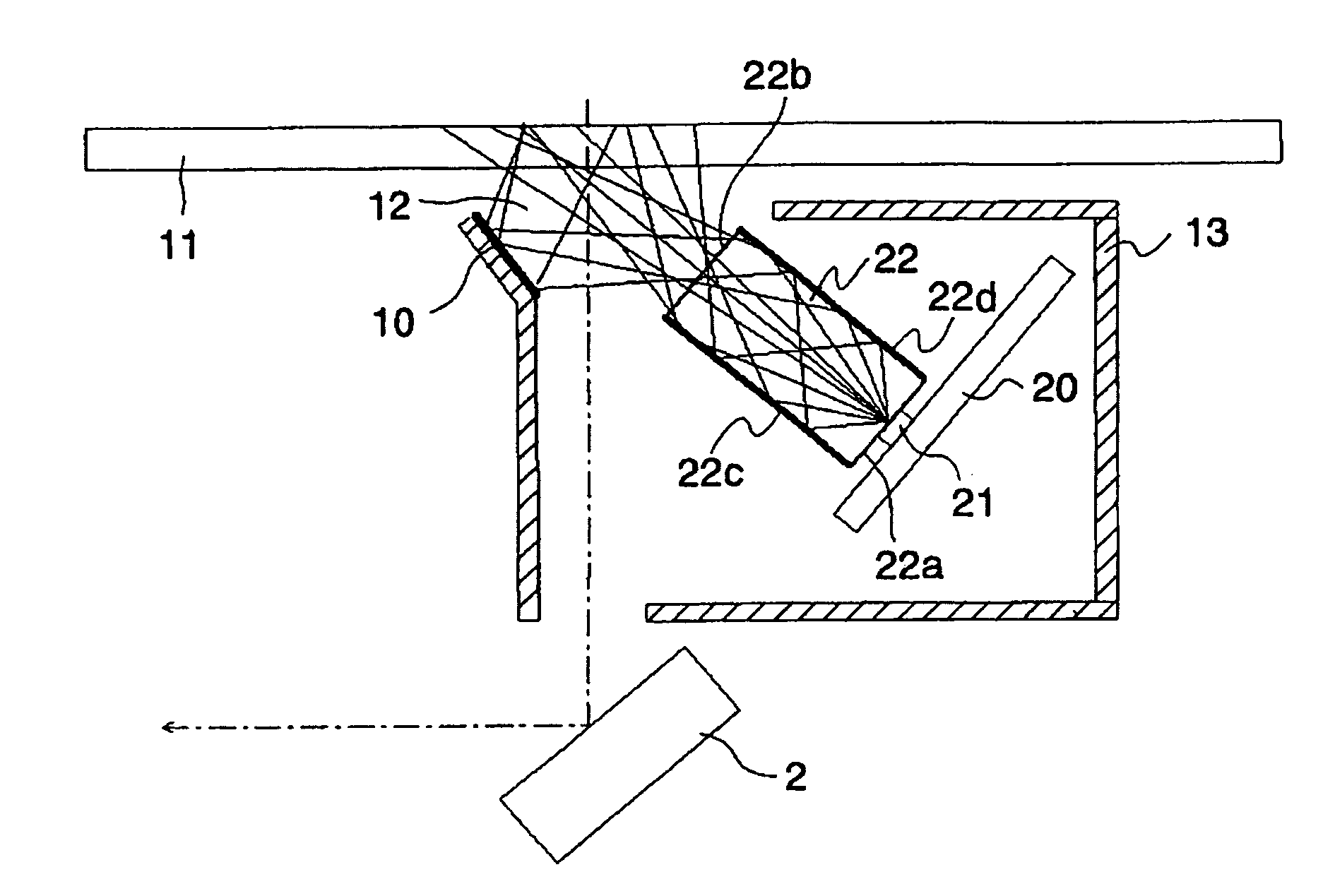
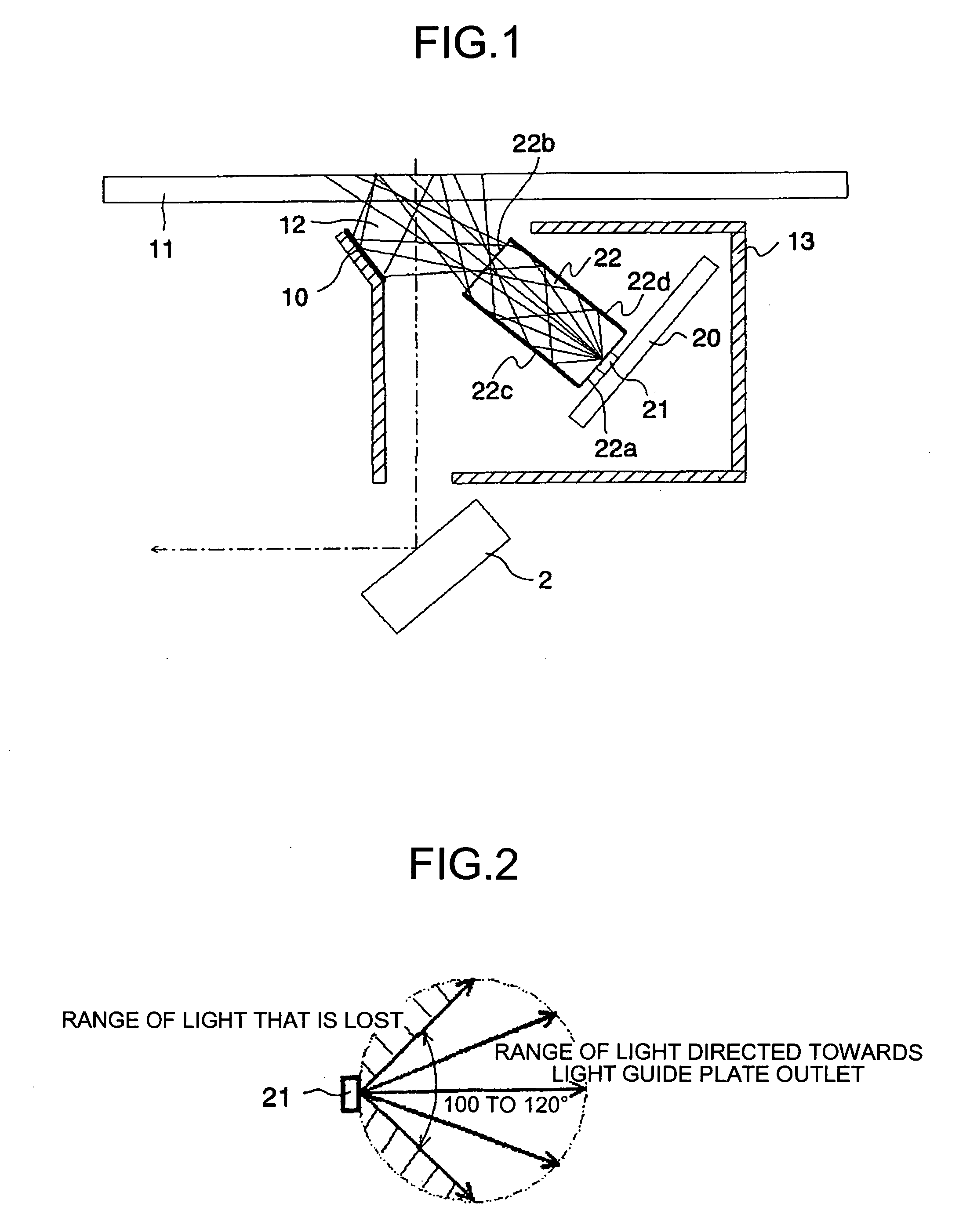
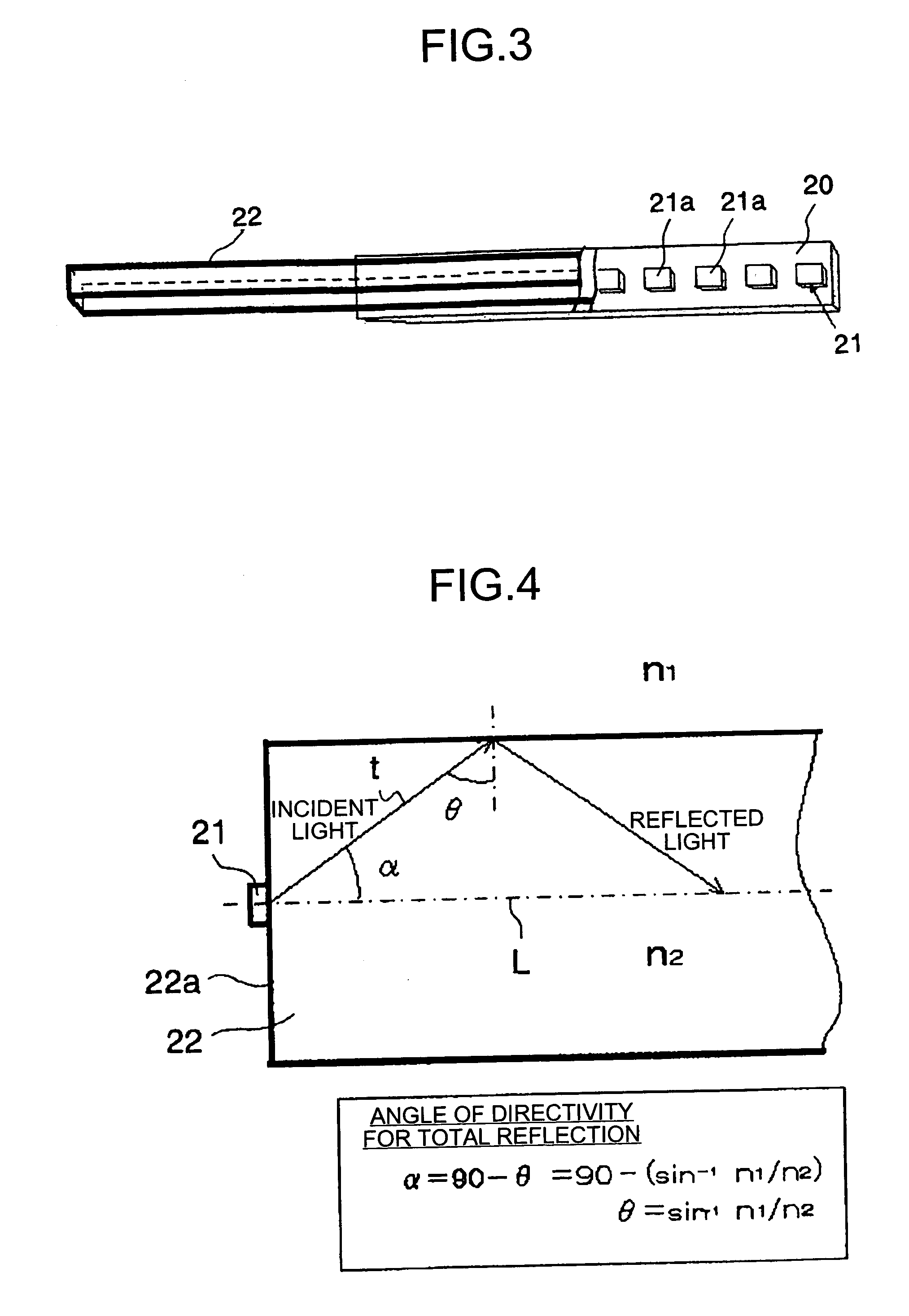
Illumination device, image reading device, and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20060197822A1Solve problemsMaterial analysis by optical meansFibre light guidesLight guideRefractive index
An illumination device that illuminates an original document by propagating an illuminating light beam output from each of a plurality of light emitting diodes from a first end surface of a light guide to a second end surface of the light guide. Assuming that A is a dimension from the first end surface of the light guide to the second end surface of the light guide, B is an interval between adjoining light emitting diodes, the light emitting diodes being arranged in an array format in a main scanning direction, n1 is a refractive index of atmosphere outside of the light guide, and n2 is a refractive index of the light guide, a condition of tan−1(B / 2A)≦β≦π / 2−{sin−1(n1 / n2)} is satisfied.
Owner:RICOH KK
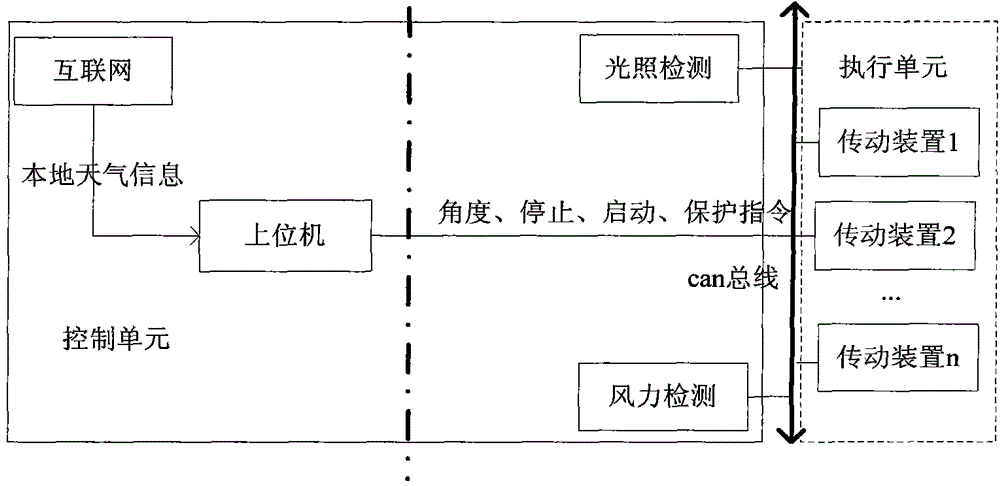
Solar energy sun chasing and state monitoring system and method thereof
InactiveCN103605378AImprove power generation efficiencyLow costControl using feedbackSkyMonitoring system
The invention discloses a solar energy sun chasing and state monitoring system and a method thereof. According to the system, an upper computer is used as a control center; an astronomical calendar theory expansion formula is used to calculate an azimuth angle and a height angle of the sun. Then, an error caused by atmospheric refraction and an altitude is corrected, a horizontal angle and a pitch angle of a power generation plate are calculated and are transmitted to each tracking transmission mechanism so that sun chasing motion is executed. Simultaneously, software acquires local weather phenomena through a network, such as a cloudy sky, rain, snow, wind and other information, complements on-site illumination and a wind power detection result, and sends instructions of protection, stopping, starting, tracking and the like to a sun chasing control device. The system has the advantages that concentration control is used; cost is low; an anti-interference performance is strong and a tracking error is small.
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
Systems and methods for improved atmospheric monitoring and GPS positioning utilizing GNSS tomographic refractivity
The disclosed technology relates to systems and methods for determining three-dimensional atmospheric and ionospheric density using refraction of electromagnetic waves. A method is provided for receiving, at a processing system, and from a plurality of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) stations, navigation data corresponding to computed positions of the plurality of GNSS stations. The method can further include determining, based at least in part on received navigation data and received GNSS transmitter information, ionosphere and atmosphere refractivity corresponding to intersections of two or more GNSS signals. The method can include calculating, based on the determined 3D density states, data fields of a model representing the three-3D density states. The method can include transmitting position adjustment data to calibrate a navigation position of at least one of the plurality of the GNSS stations based at least in part on the calculated data fields of the model.
Owner:SPIRE GLOBAL
Autonomous celestial navigation method for deep space probe on near-earth parking orbit
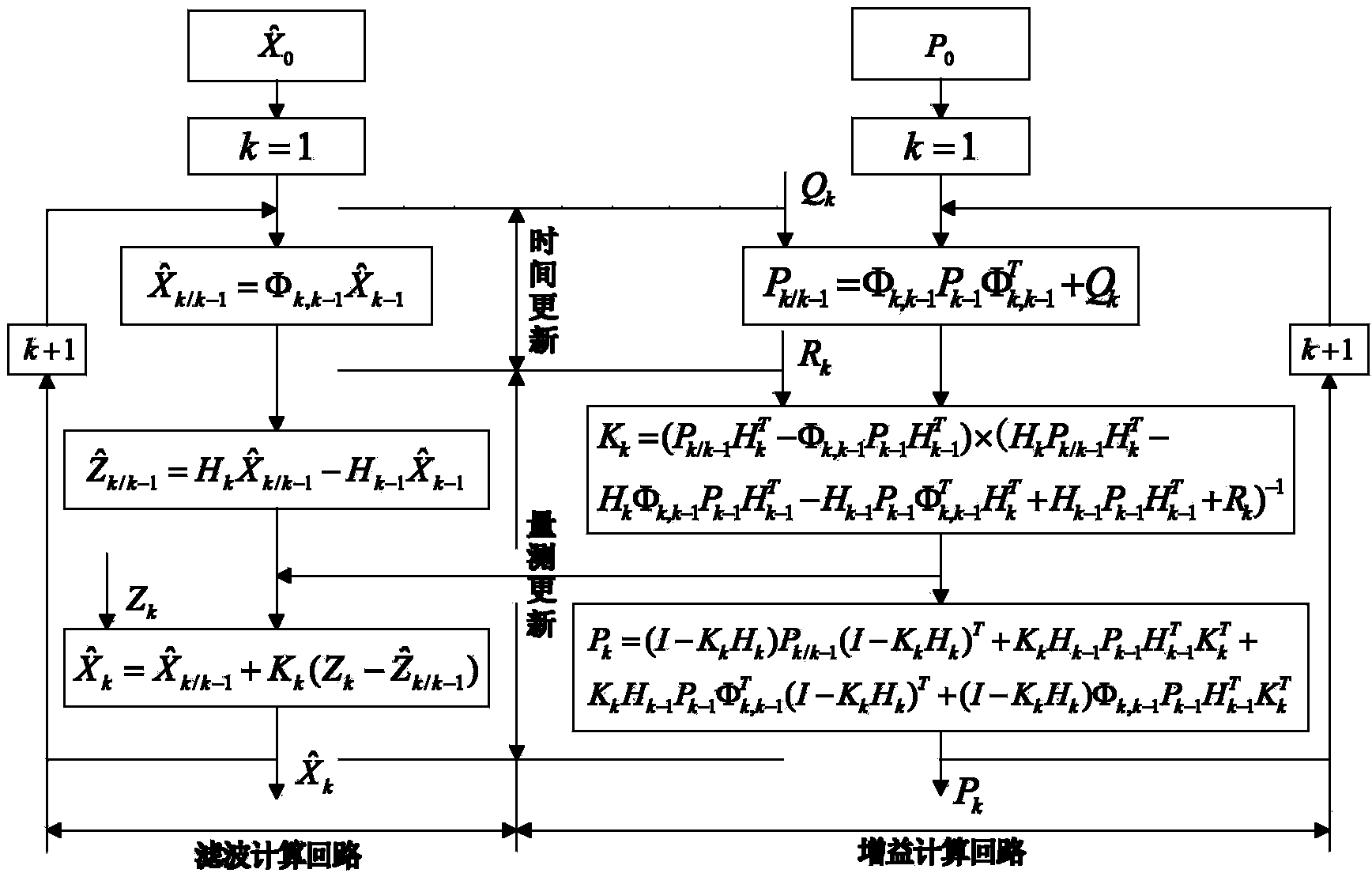
ActiveCN103968834AHigh precisionEliminate the effects ofNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by astronomical meansSpace probeStratosphere
The invention relates to an autonomous celestial navigation method for a deep space probe on a near-earth parking orbit. The method comprises the following steps: performing continuous height (20-50km) modeling and fitting in the stratosphere on density scale height H according to data given by United States atmosphere standard in 1976, establishing a stellar atmospheric refraction model, establishing a novel measurement model by taking height difference at adjacent moments as observed quantity, and estimating the navigation parameters by adopting a method for correspondingly improving extended Kalman filter parameters. The autonomous celestial navigation method is applied to navigational positioning of the deep space probe on the near-earth parking orbit, errors caused by the environment can be eliminated on the basis that extra observed quantity is not increased, and the navigation accuracy is guaranteed.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High orbit area array optical satellite in orbit geometry calibration method considering atmospheric refraction rectification
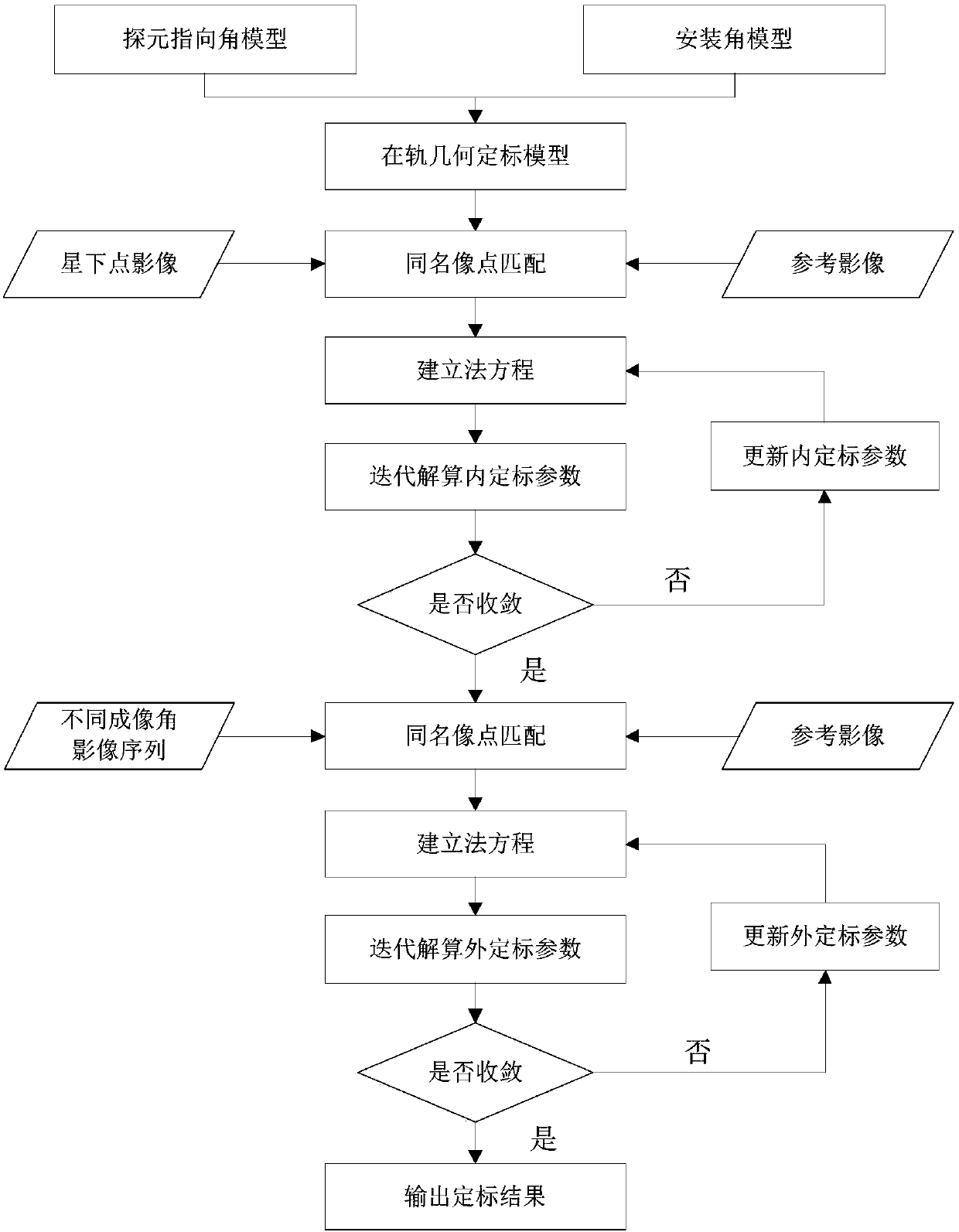
InactiveCN107564057AImproving Direct Geometry Positioning AccuracyImage analysisAtmospheric refractionSatellite imagery
The invention provides a high orbit area array optical satellite in orbit geometry calibration method considering atmospheric refraction rectifications; the method comprises the following steps: usingpolynomial fitting probe directional angles to build an internal calibration model, parsing influence rules on the image geometry precision by the atmospheric refraction, building an external calibration model considering the atmospheric refraction rectification, and introducing the internal and external calibration models into a strict geometry imaging model so as to build a high orbit optical satellite in orbit geometry calibration model; parsing internal and external calibration parameter initial values according to sub-satellite point images; using the parsed internal calibration parameter as the true-value, using images obtained by different sequence imaging angles, and parsing the external calibration parameter according to the external calibration parameter initial value. In the high orbit optical satellite in orbit geometry calibration process, the method can fully consider the influences on the imaging geometry precision by the atmospheric refraction, thus building the more strict in orbit geometry calibration model, and obviously improving the high orbit optical satellite image direct geometry positioning precision.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for forward simulation of occultation
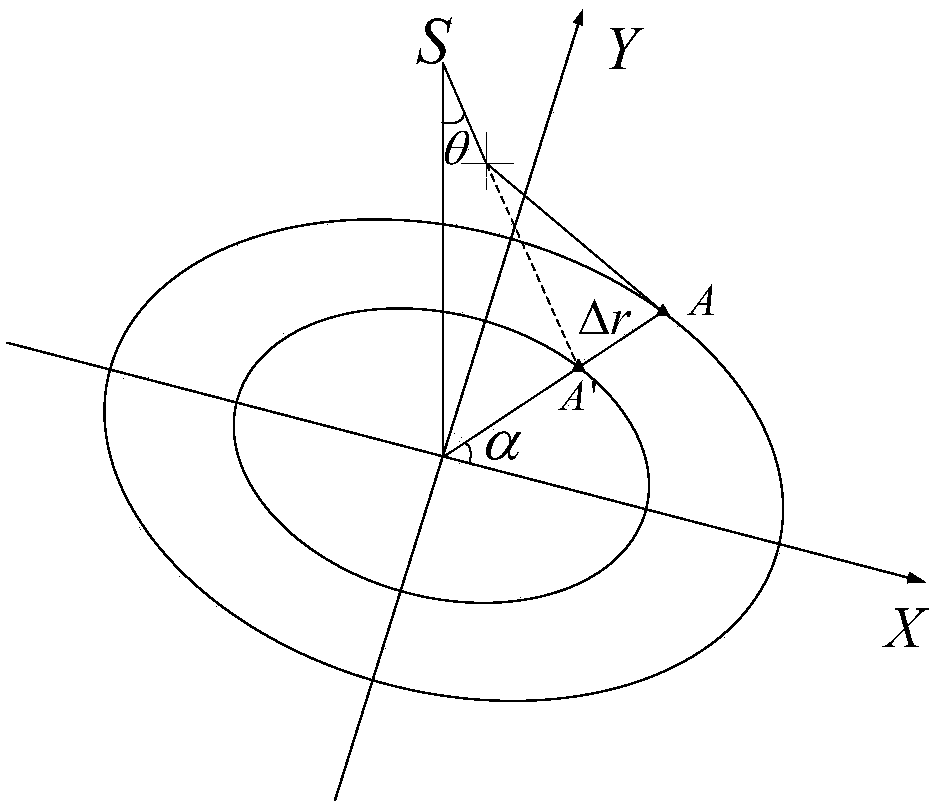
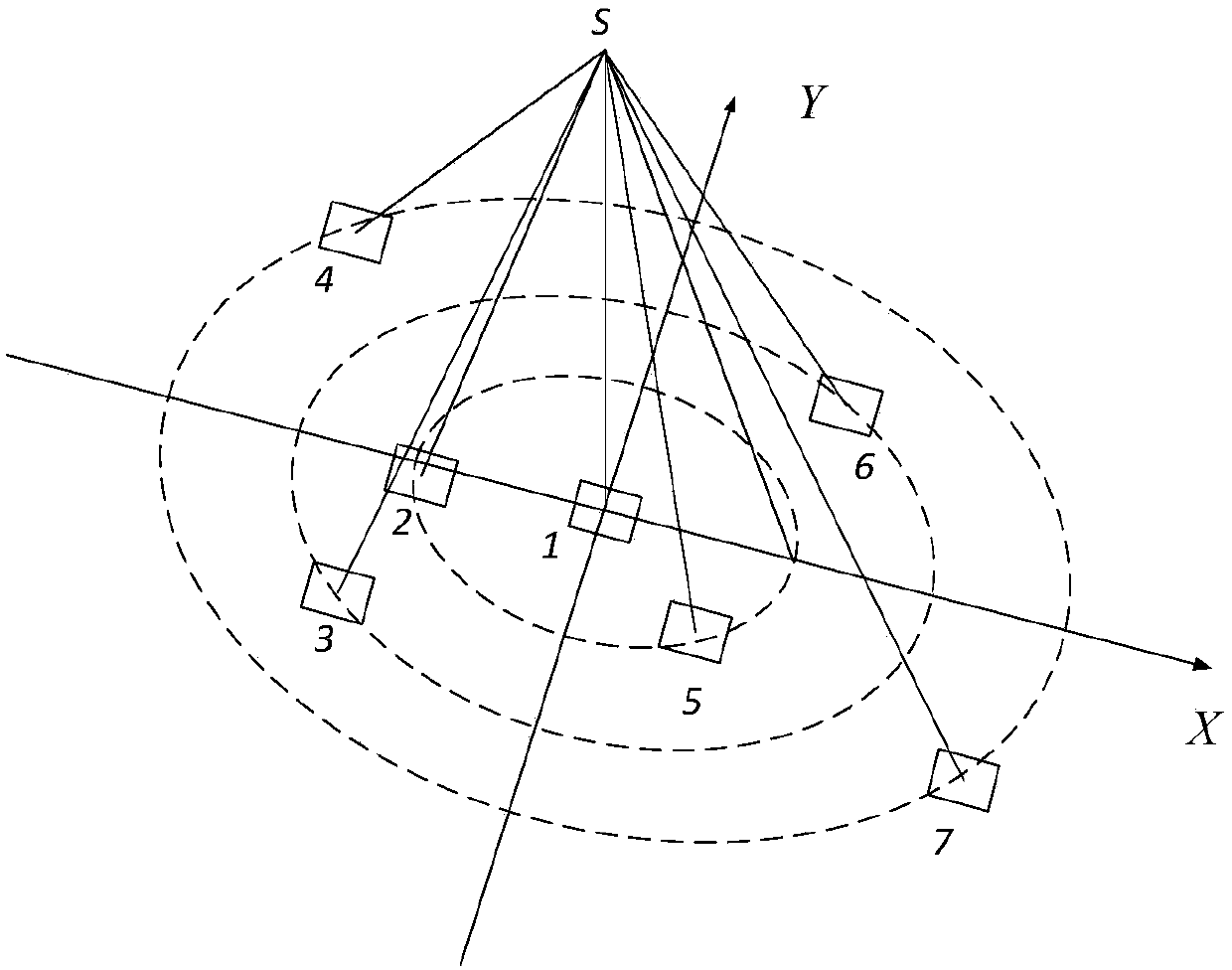
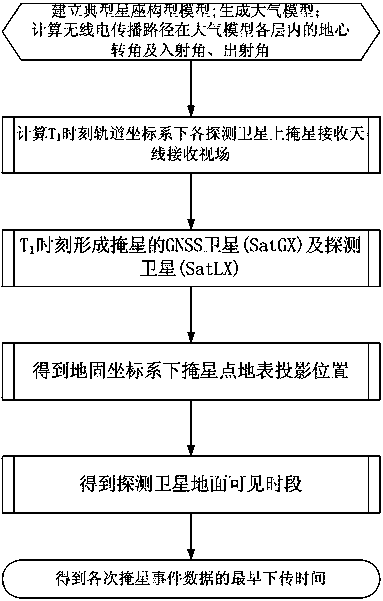
The invention provides a method for forward simulation of occultation. The method is applicable to the GNSS earth atmosphere occultation exploration constellation design and analysis application. According to the method, satellite orbit parameters serve as design input, constellation construction parameters are supplemented to serve as design input, and constellation design and analysis application are facilitated; influence of atmospheric refraction is taken into comprehensive consideration in the process of occultation event judgment and positioning, and occultation measuring point positioning accuracy is improved; ground data transmission station modeling is added, and downloading timeliness of occultation exploration data can be supplemented and analyzed.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG DEV LTD
Method for on-line correcting low-angle radar electric wave refraction error
InactiveCN105093195ARealize the online correction function of radio wave refraction errorHigh positioning accuracyWave based measurement systemsMeasuring instrumentDevice form
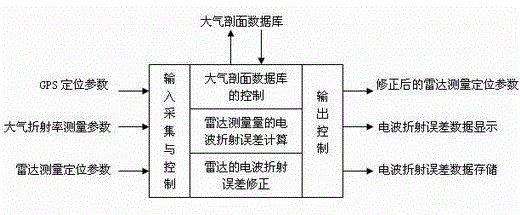
The invention discloses a method for on-line correcting low-angle radar electric wave refraction error. When a radar measures a target, radar measured parameter distance and angle are used to obtain radar positioning parameters with atmosphere refraction errors eliminated through a device formed by a GPS receiver, a ground atmospheric refractivity measuring instrument, an atmosphere profile database, a control and data processor and related interface circuits. The parameters are used for positioning a target, and the radar positioning precision is improved. The refraction error correction method is simple, and low in computation burden, short in time, high in precision, high in automation level and easy for realization. The method realizes on-line correcting radar electric wave refraction error in a high-precision way.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Technique for Telescope Polar Alignment
A polar scope for a telescope mount includes a reticle having a pattern with multiple markings that allows users to accurately position pole stars for precise polar alignment. A system and mount may be provided including a polar scope of this kind. The polar scope may be provided with a controller that calculates the apparent position of a pole star, while accounting for errors, such as proper motion, precession of the earth's axis, and / or atmospheric refraction.
Owner:XU NING +1
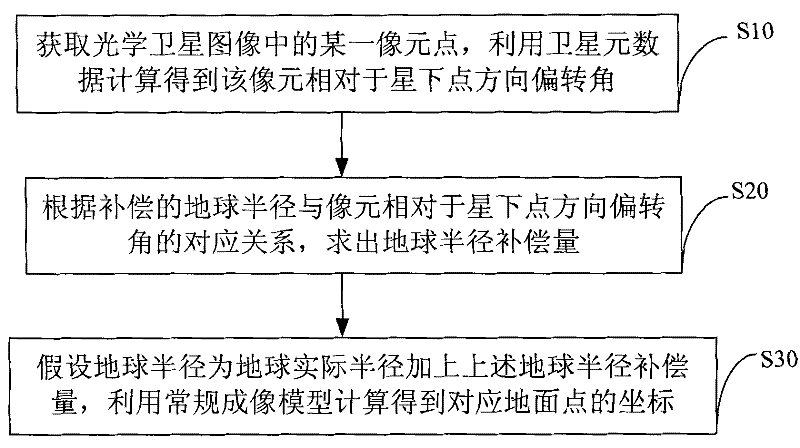
Method and system for compensating atmospheric refraction in optical satellite remote sensing data geographic positioning
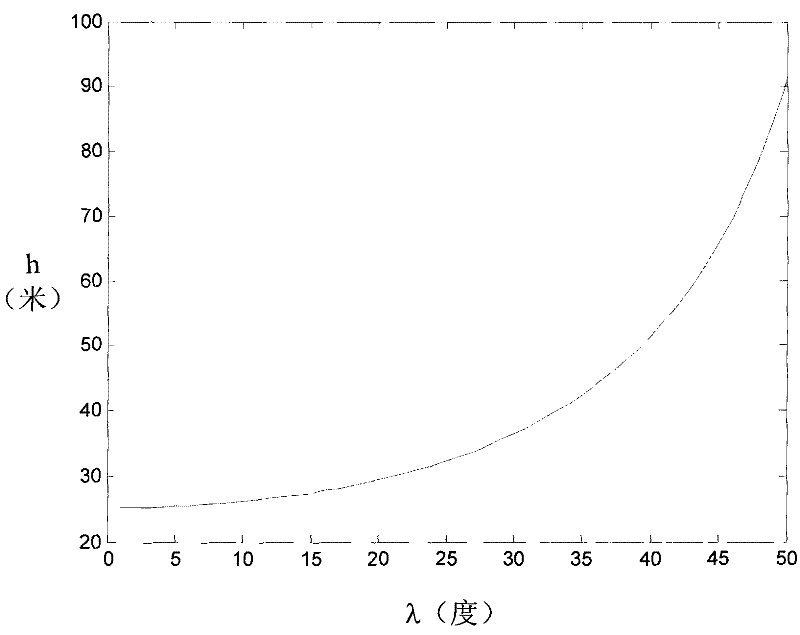
The invention discloses a method and a system for compensating atmospheric refraction in optical satellite remote sensing data geographic positioning. The method for compensating the atmospheric refraction in the optical satellite remote sensing data geographic positioning comprises an earth radius compensating step, and is used for calculating the coordinate of a ground point corresponding to a certain pixel point in a satellite image by supposing that the earth radius is equal to the summation of the actual earth radius and the compensation amount of the earth radius. The method not only can be used for performing correction on the remote sensing data of SPOT-5, but also can be used for performing correction on other satellite remote sensing data; and due to the adoption of the method, the positioning accuracy after the compensation of the atmospheric refraction is obviously improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Star sensor calibrating method based on detection data of high-precision telescope
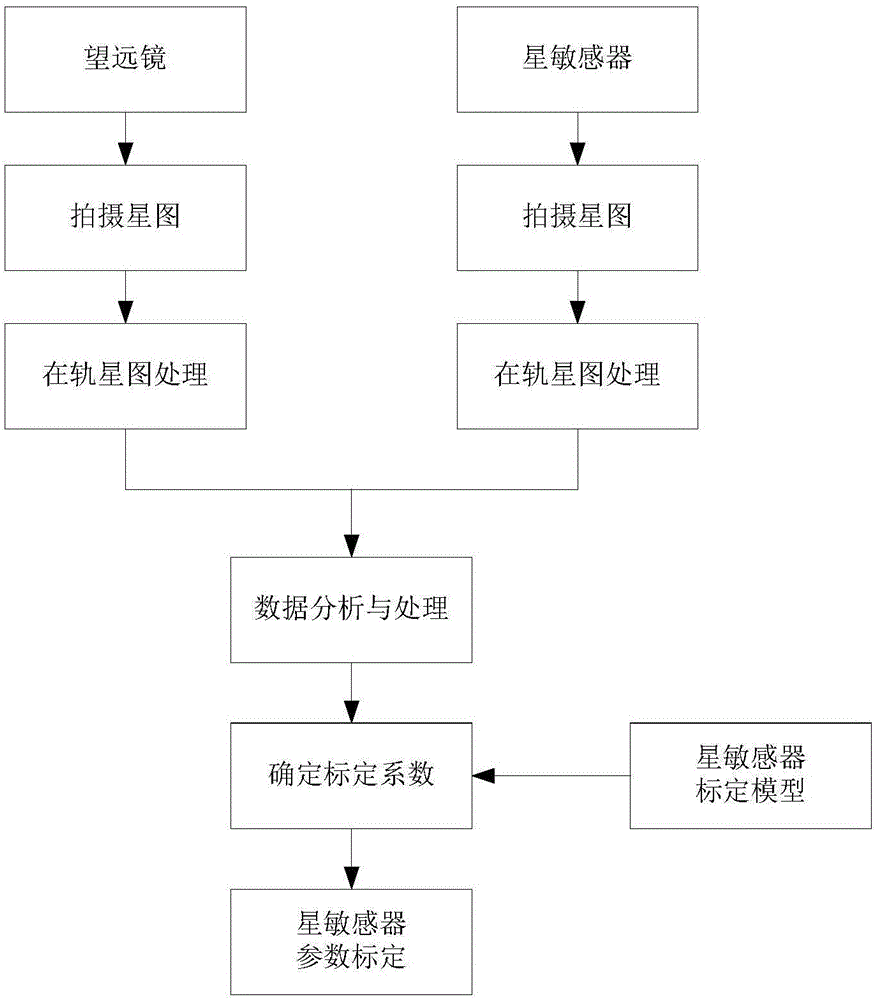
InactiveCN106441373AAchieve high-precision attitude measurementImprove attitude measurement accuracyMeasurement devicesObservation dataMultiple frame
The invention relates to a star sensor calibrating method based on detection data of a high-precision telescope. The star sensor calibrating method comprises the following steps: shooting on a number of star maps in the current view field on an orbit by using the telescope and a star sensor respectively, and in order to reduce influence of a random error, performing multi-frame averaging on star coordinates of the star maps and performing other on-orbit processing; performing comparative analysis on observation data of the high-precision telescope and star map data of the star sensor; according to a star sensor calibrating model, determining a star sensor calibrating coefficient so as to achieve high-precision calibration of the star sensor. By the star sensor calibrating method based on the detection data of the high-precision telescope, provided by the invention, influence of atmospheric refraction and other factors on ground calibration can be eliminated, calibration parameter changes caused by temperature, vibration and other reasons can be compensated, high-precision on-orbit calibration of the star sensor can be achieved, and the accuracy of star sensor measurement is further improved; therefore, the star sensor calibrating method has an engineering application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
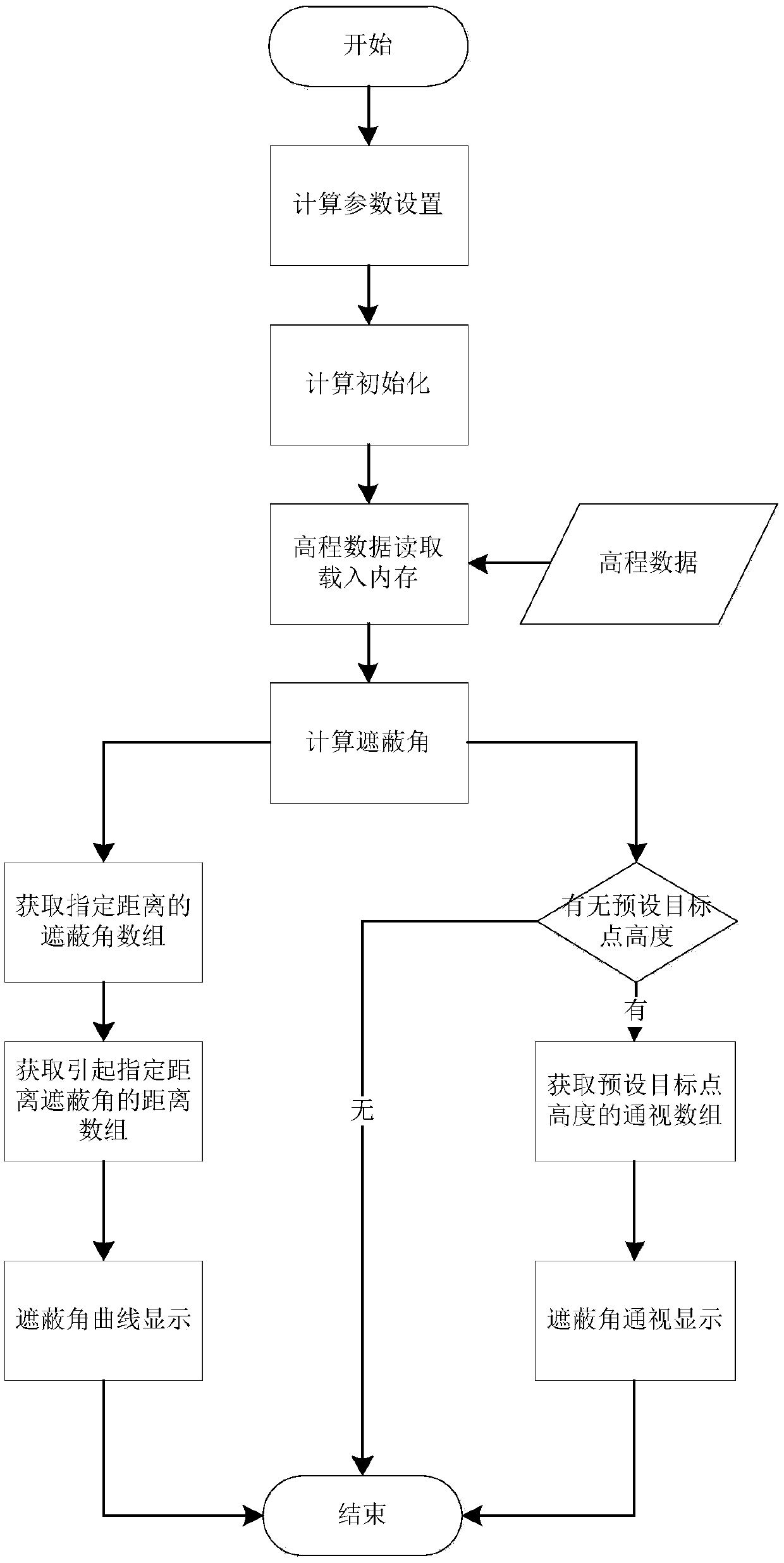
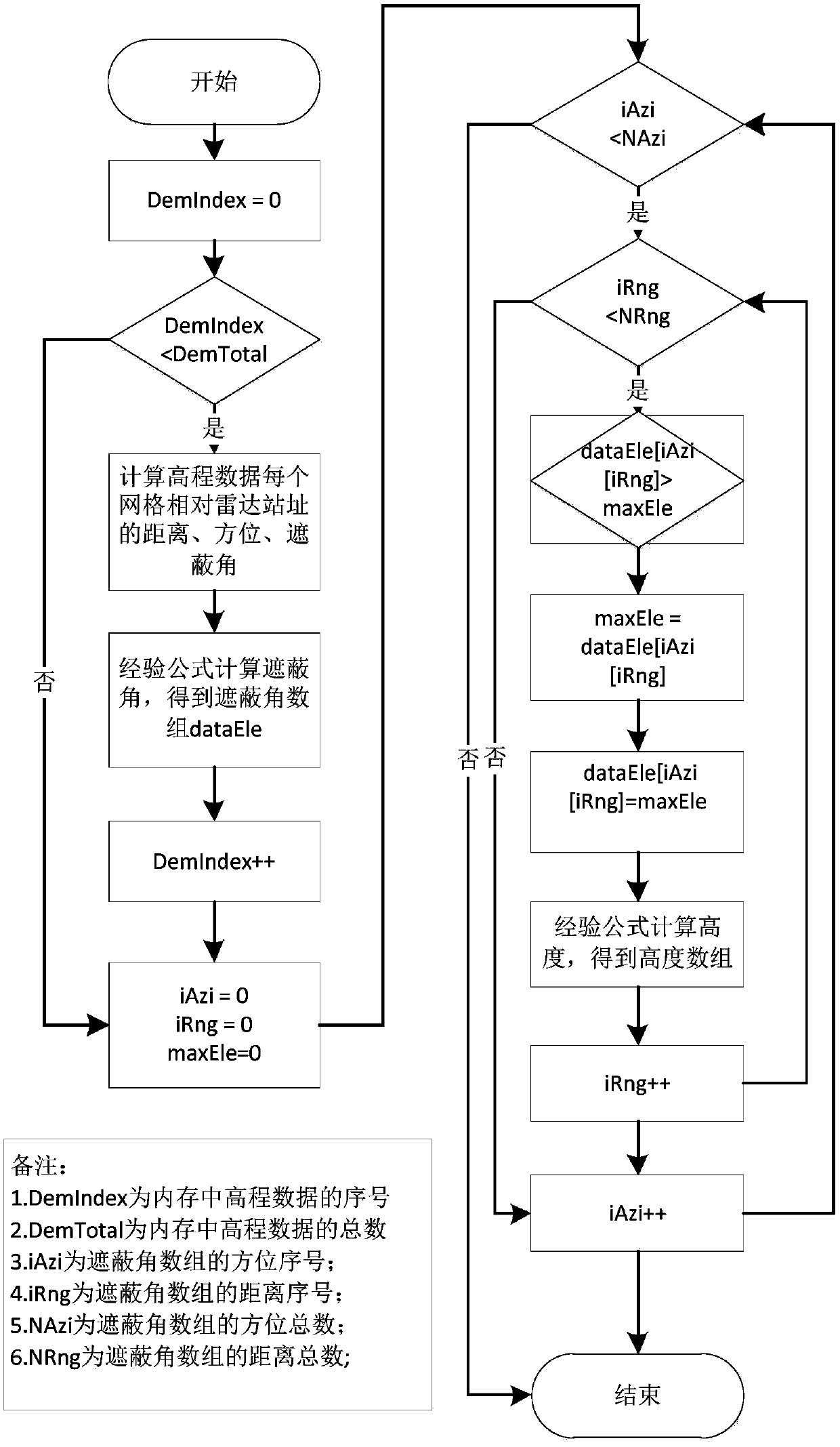
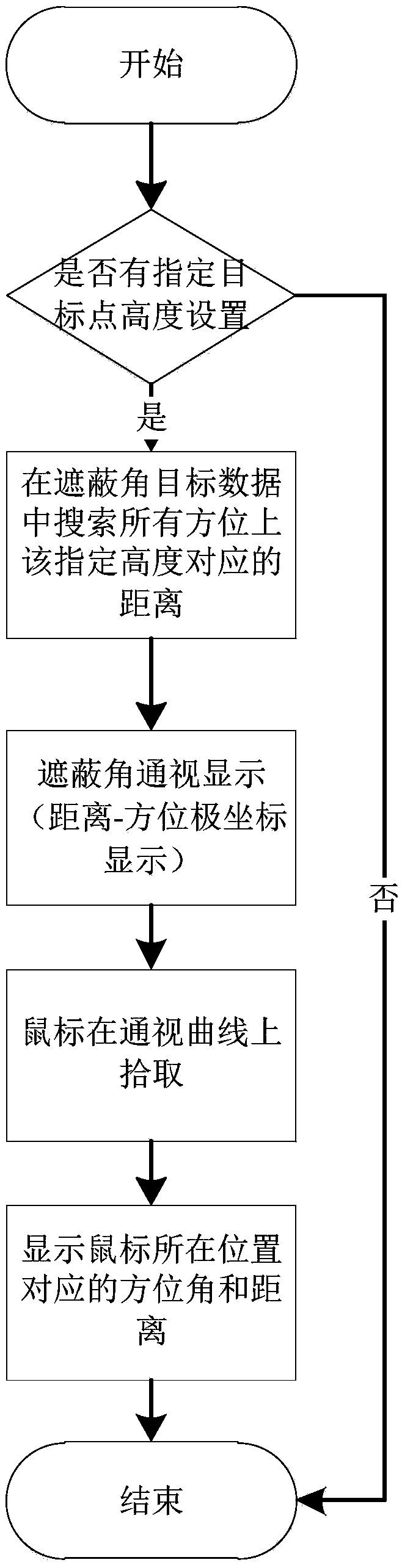
Radar terrain masking analysis and display method
The invention discloses a radar terrain masking analysis and display method which comprises the steps of: according to a longitude, a latitude and a height of a radar site, which are set by a user, and a longitude and latitude range which needs to be calculated, carrying out loading on elevation data by taking the radar site as the center and taking the longitude and latitude range as a radius; according to a radar detection minimum elevation angle, a maximum detection distance, azimuth accuracy and distance accuracy which are set by the user, initializing radar masking data; according to theloaded elevation data, analyzing a radar terrain masking condition; and constructing a multi-dimension display mode by using the calculated radar terrain masking data. A space is partitioned in two dimensions of a distance and an azimuth, and terrain masking information of each unit is respectively analyzed; a calculation method of a masking angle adopts an empirical formula considering various factors such as atmospheric refraction and the like; on the basis of calculating the masking angle, a visibility range of a radar for a fixed height target is calculated; display of the visibility rangeand display of a masking angle curve provide an approach for multi-azimuth multi-angle observation and analysis of the radar terrain masking condition.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
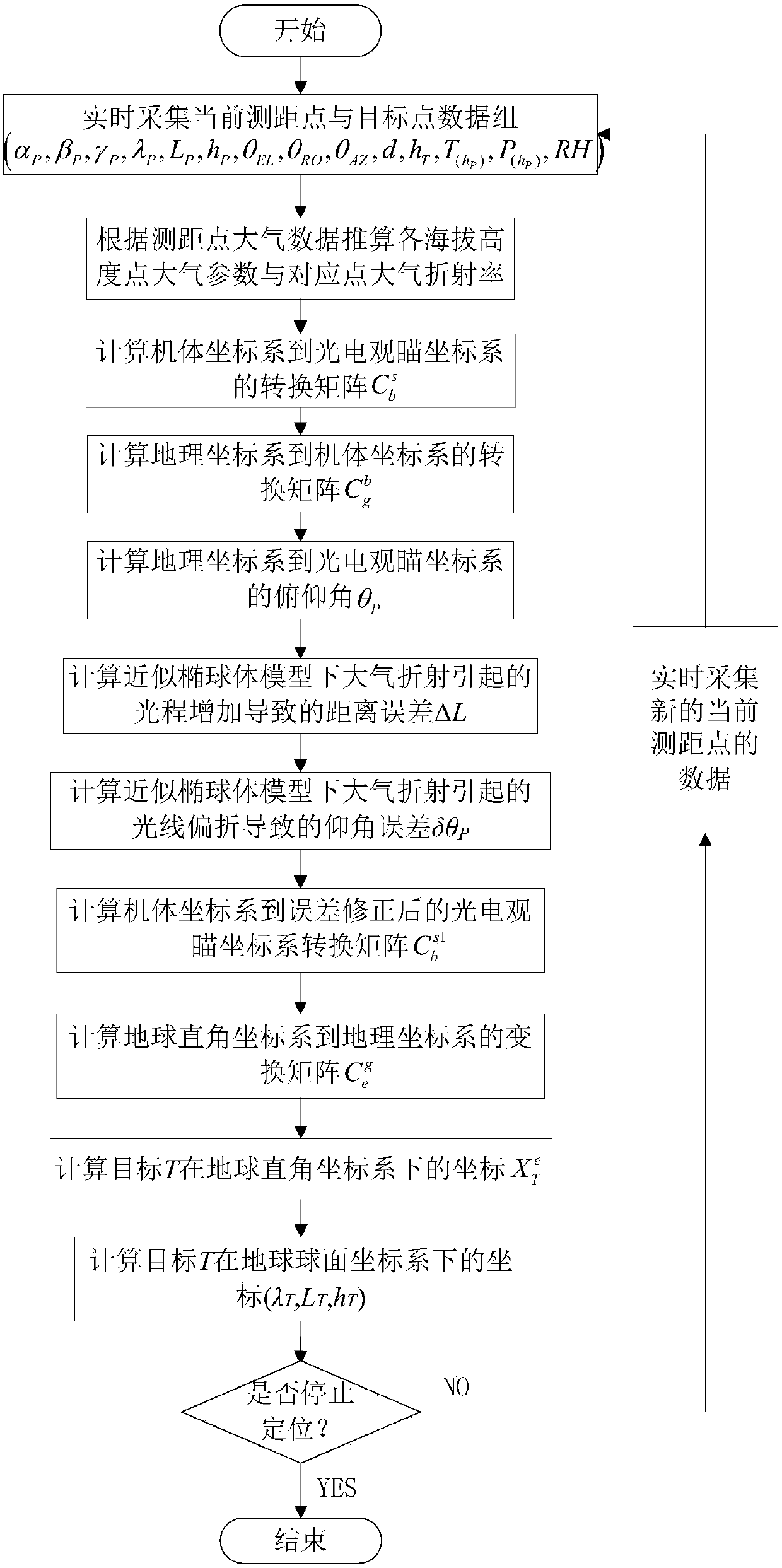
Target positioning method applicable to vehicle-mounted photoelectric watching-aiming system with atmospheric refraction
InactiveCN108535715AImprove description accuracyHigh solution accuracyWave based measurement systemsNavigational calculation instrumentsLaser rangingAtmospheric sciences
The invention discloses a target positioning method applicable to a vehicle-mounted photoelectric watching-aiming system with atmospheric refraction and belongs to the technical field of vehicle-mounted photoelectric observation. By adopting the target positioning method, geographical location information of a target can be solved in real time by modifying light deflection with atmospheric refraction and implementing coordinate conversion calculation of different coordinate systems according to geographical location information of a carrying vehicle, posture angles of the carrying vehicle, angles of a photoelectric turret, laser ranging values, the altitude of a target point and atmospheric parameters of a carrying vehicle point. By adopting the target positioning method, target positioning errors caused by atmospheric refraction can be modified on the basis of a conventional vehicle-mounted target positioning way, that is, vehicle-mounted target positioning precision is improved through innovation of techniques, and the method has the characteristics of being high in calculation precision, simple to operate, and the like.
Owner:西安应用光学研究所
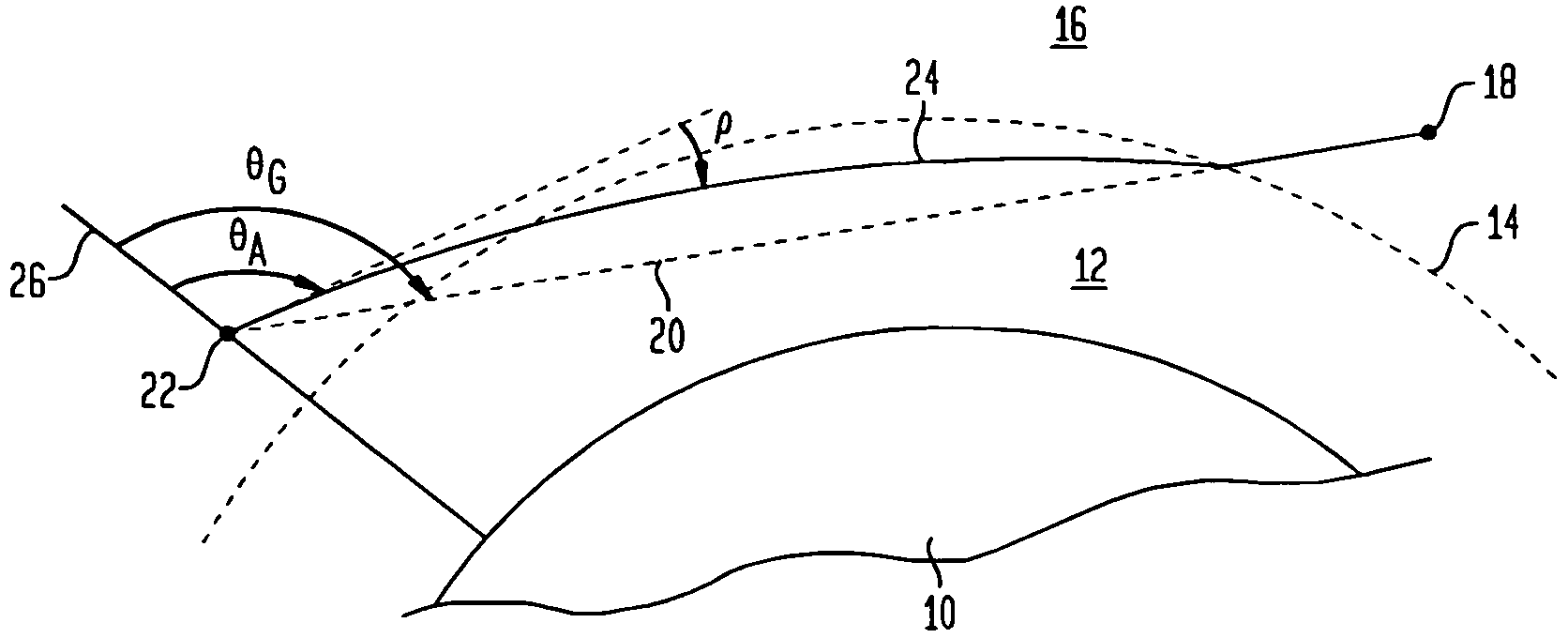
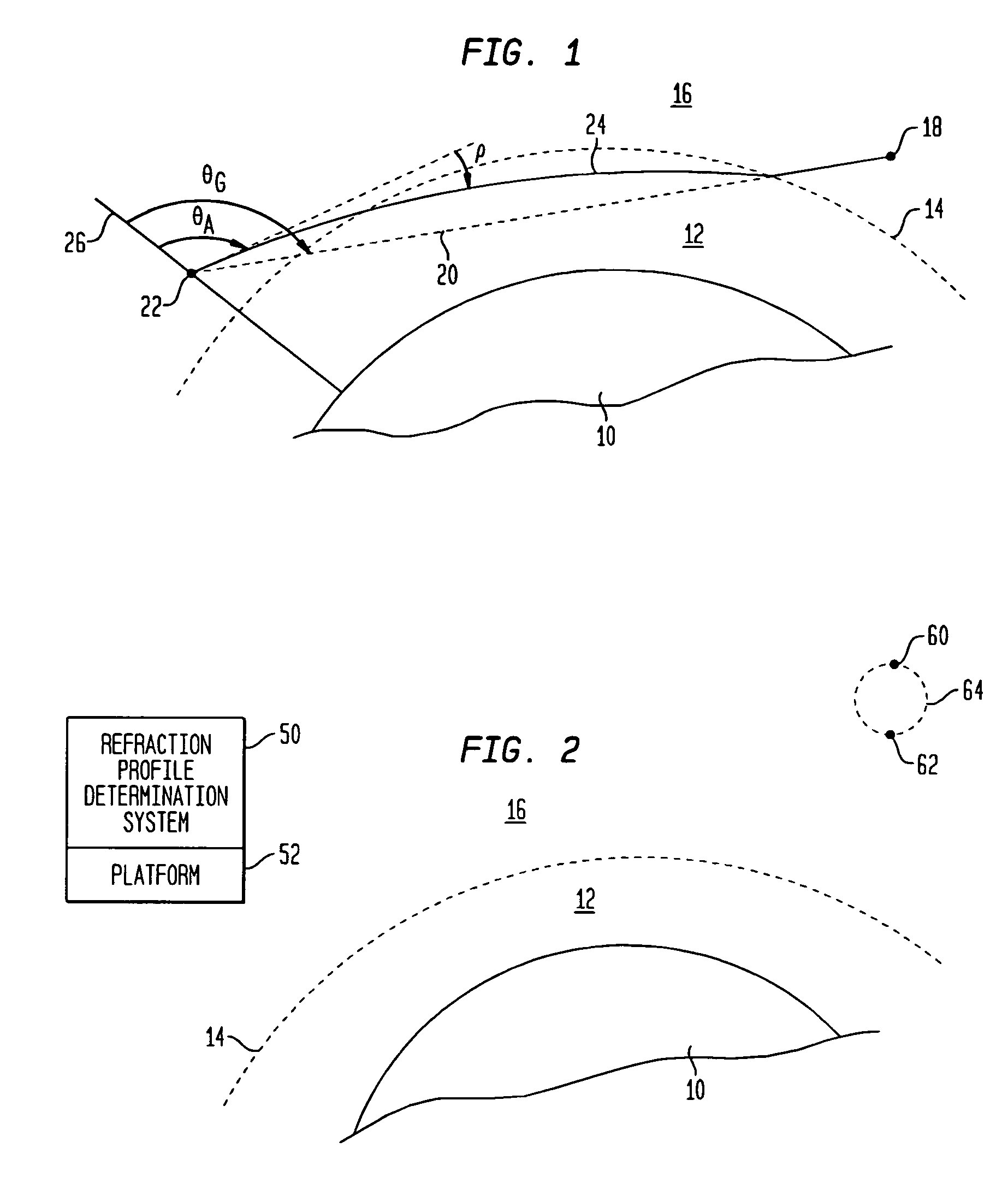
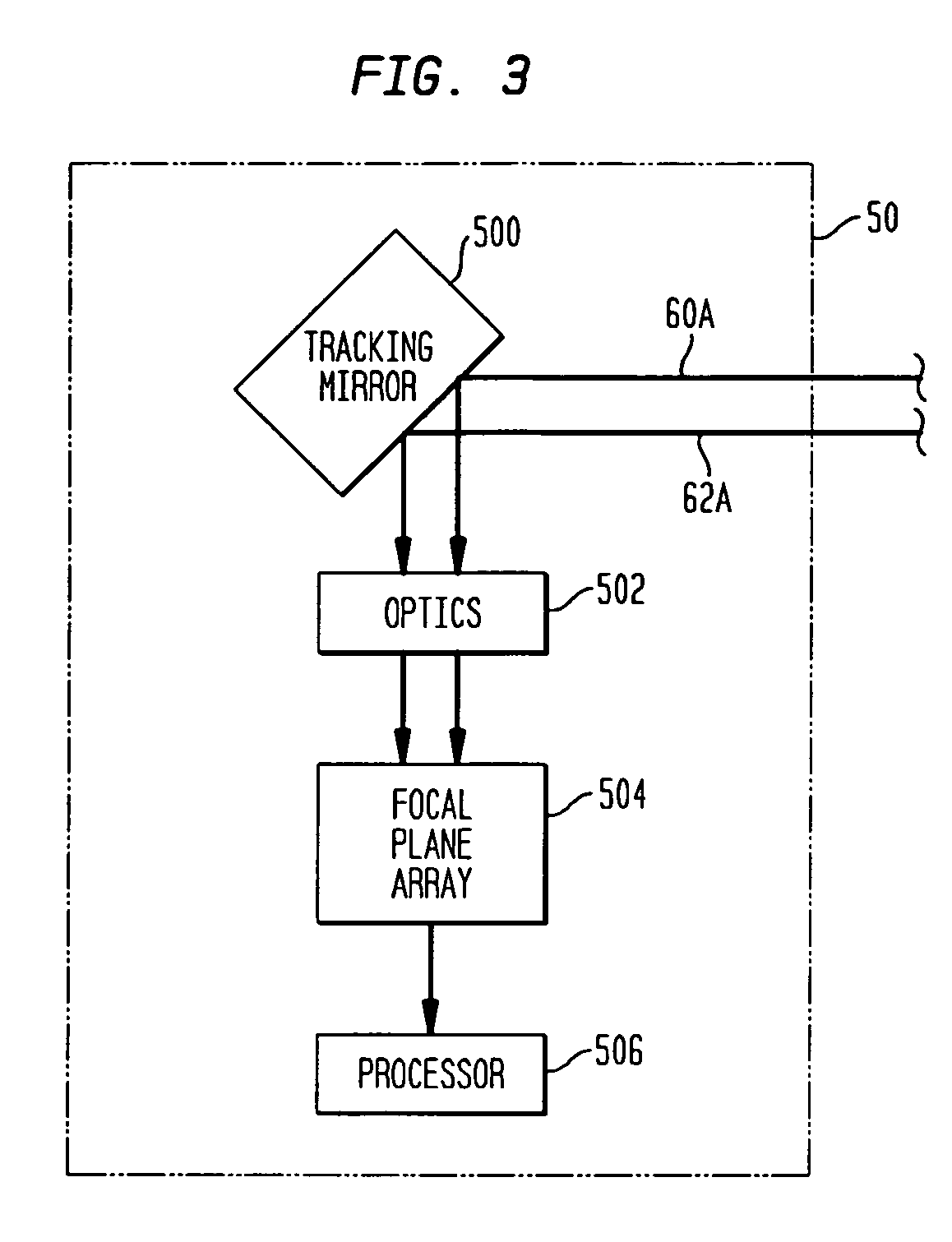
Method of determining atmospheric refraction profile using two spatially separated light sources
An atmospheric refraction profile is determined using an imaging system positioned at a location that is simultaneously within line-of-sight of two celestial light sources. A variety of active or passive methods can be employed to cause the line-of-sight to vertically traverse through a refractive portion of an atmosphere. Images of the two celestial light sources are captured as the line-of-sight vertically traverses through the refractive portion of the atmosphere. Each such image indicates an apparent distance between the two celestial light sources. The apparent distances are used to determine refraction angles.
Owner:GLOBAL ATMOSPHERIC TECH & SCI INC
Method for observing deformation of blast furnace
ActiveCN103114164ALess investmentReliable deformation dataBlast furnace detailsChecking devicesTotal stationOptimal design
The invention belongs to the field of deformation measurement of buildings and structures, and in particular relates to a method for observing the deformation of a blast furnace. The method for observing the deformation of the blast furnace is characterized in that deformation observing points are respectively set on a brace and a crane beam representing the basic deformation of the blast furnace for using as deformation observing objects for reflecting the incline degree of the furnace body, with the aid of a laser total station and a leveling instrument, the measurement is respectively performed by the planar method and the elevation method, and then the arithmetic mean value of the two measurement results are used as the deformation of the blast furnace. Compared with the prior art, the method for observing the deformation of the blast furnace has the beneficial effects that (1) the cost is saved, the investment is reduced, and important actual guiding significance is provided; (2) reference is provided for the optimal design of the blast furnace; (3) influence of environment, pressure, temperature and atmospheric refraction on the measurement is reduced; and (4) the evaluation of the blast furnace is much closer to the real situation.
Owner:鞍钢集团工程技术有限公司
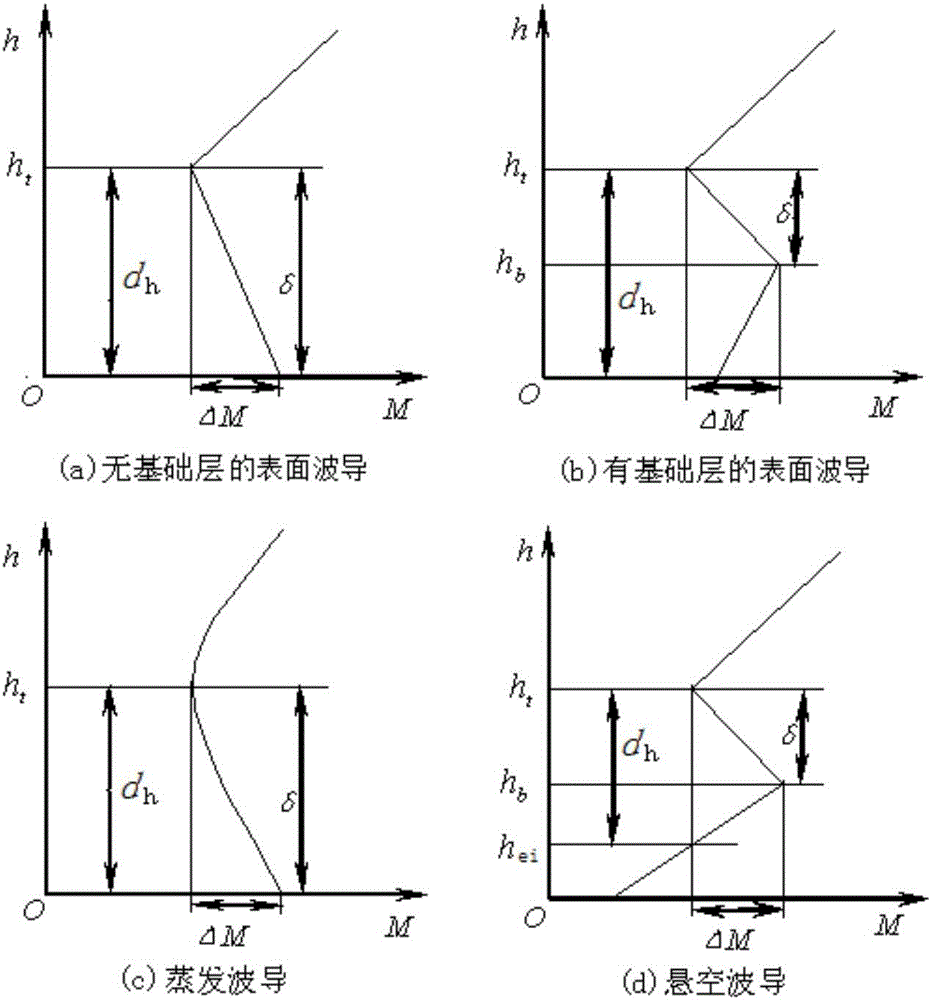
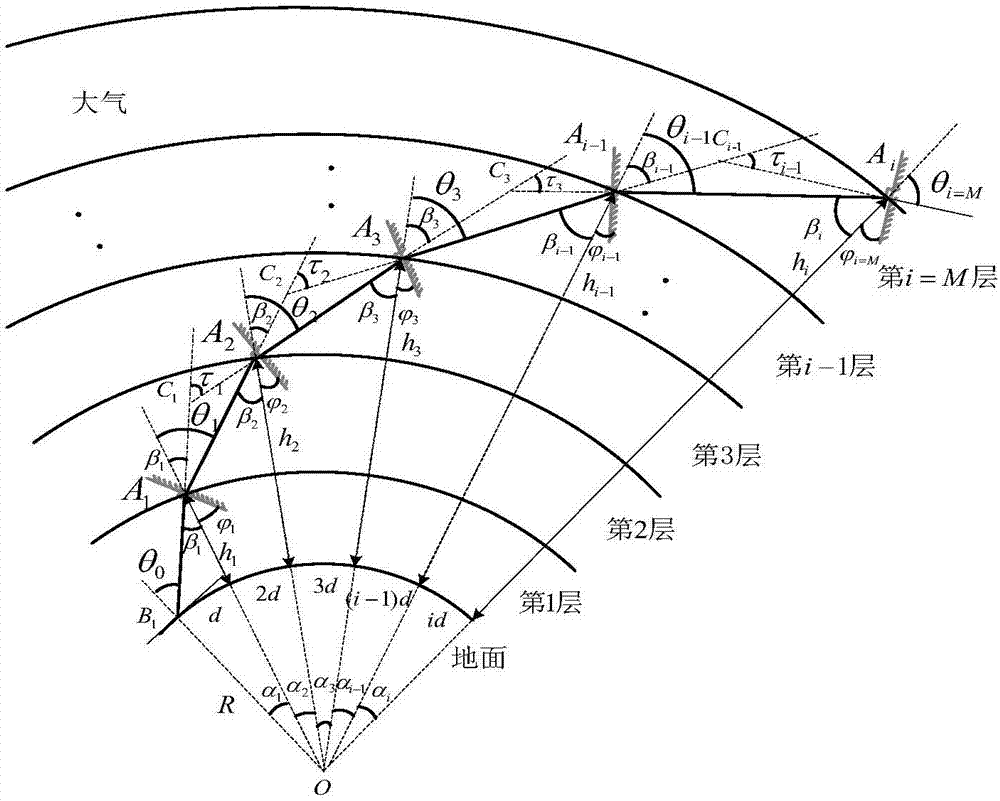
Inversion method of atmospheric refractivity profile
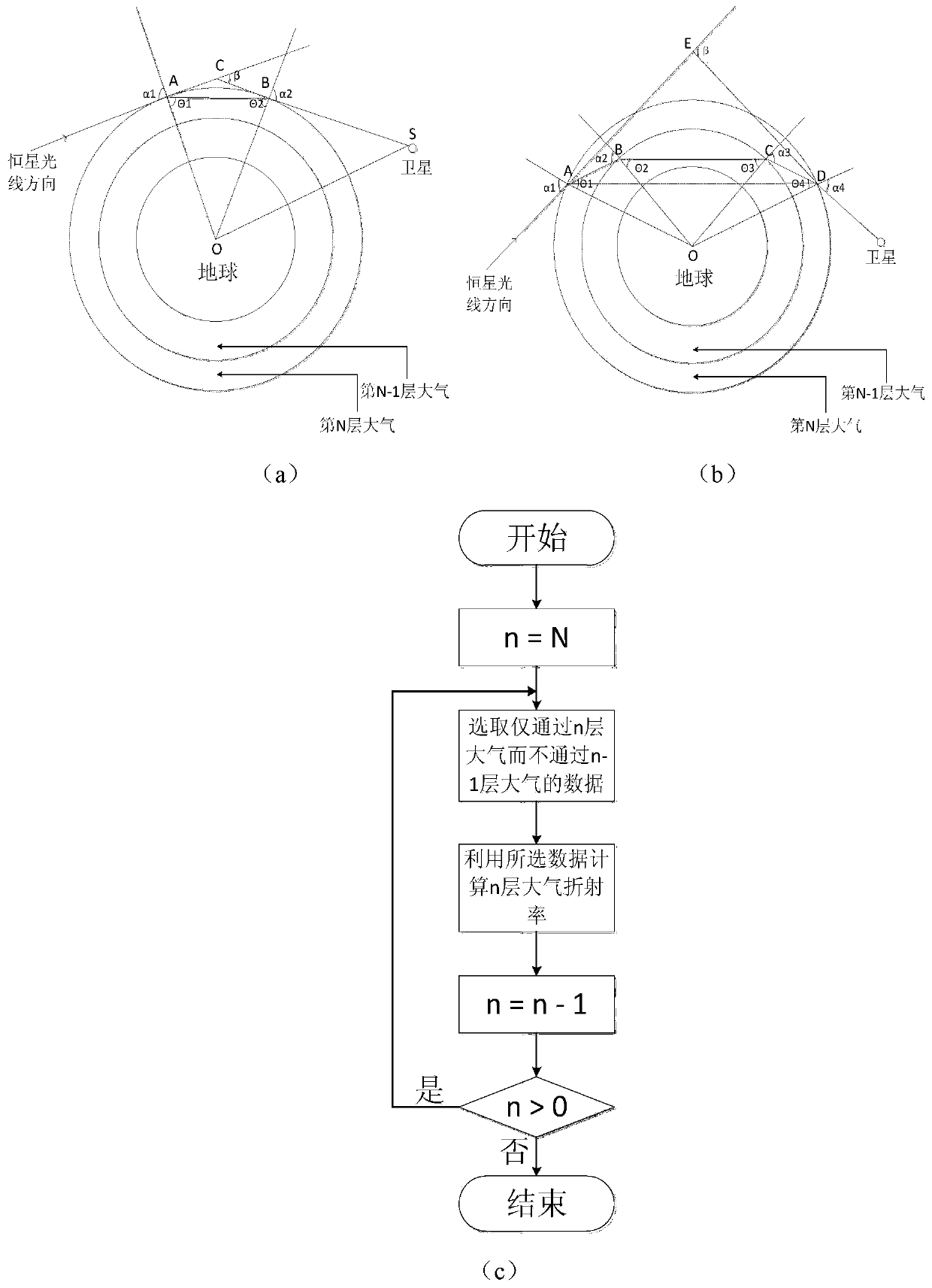
ActiveCN107219193ASolve engineering problemsPhase-affecting property measurementsRefractive indexAtmospheric sciences
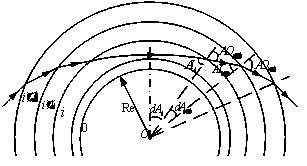
The invention relates to an inversion method of the atmospheric refractivity profile. The method comprises the steps that an atmospheric layer is layered; beacon laser is emitted; air sounding equipment vertically ascends to the sounding height of each atmospheric sub layer; the deflection angle of a reflector when the reflector in the air sounding equipment intercepts and captures the beacon laser and returns the beacon laser to a laser receiver, and the received light intensity is maximum is measured; the geocentric angle of the reflector in each atmospheric sub layer and the incidence angle of the beacon laser in each atmospheric sub layer are calculated; the total refraction angle of each atmospheric sub layer and the gradient of the atmospheric refractivity along with the height change are calculated; a drawing is made by using the height as the X axis, the atmospheric refractivity as the Y axis, the atmospheric refractivity of each atmospheric sub layer as a starting point and the gradient of the atmospheric refractivity along with the height change as the slope at each section; the atmospheric refractivity profile is obtained. The inversion method disclosed by the method has the advantages that the atmospheric refractivity profile can be reversed in real time on the spot; technical support and theoretical support are provided for laser application to various engineering fields of satellite high-precision orbit determination, space high-precision measurement and the like which use precise phase information as a basis.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Test system and method for scintillation characteristic of fake partially coherent light transmitted in atmosphere turbulence
InactiveCN102739314ASimple designIncrease flexibilityElectromagnetic transmissionTime conditionRefractive index
The invention discloses a test system and method for scintillation characteristic of fake partially coherent light transmitted in atmosphere turbulence, and belongs to the technical field of laser signal transmission and detection in an atmospheric channel. The test system comprises a light beam emission sub system and a light beam receiving and detecting sub system, wherein different variances are used to count and calculate parameters, so that a scintillation variance of the fake partially coherent light transmitted in the atmosphere turbulence under different detector integral time conditions is calculated. The system and the method provided by the invention can synchronously measure the scintillation variance of coherent lasers transmitted in the atmosphere turbulence, and a correspondence between the measured scintillation variance and an actual structural constant value of atmospheric. The result tested by the system and the method disclosed by the invention is helpful for optimizing the design of the application system using the fake partially coherent light to restrain the scintillation caused by the atmosphere turbulence.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Infrared multispectral original image processing method
InactiveCN104992411ASave on repurchase costsFix unreadableImage enhancementImage analysisEarth's rotationSpectral response
The invention discloses an infrared multispectral original image processing method comprising image restoration, radiation correction, and geometric correction. Image restoration includes missing element filling, forward and reverse scanning mismatch correction, forward and reverse scanning consistency correction, spectral response consistency correction, B7 spectrum interference removing, B7 spectrum missing row filling, B9 band interpolation, B9 band pinstripe removing, and B9 band stripe tail removing. Geometric correction includes correction of deformation caused by imaging and projecting modes, image distortion caused by earth curvature change, influence of atmospheric refraction and influence of earth rotation. Compared with the prior art, the image processing level is improved obviously, and the project image quality is obviously improved than ever before by adopting the method of the invention.
Owner:SHAANXI GEOLOGICAL & MINERAL SURVEY & DEV CORP
Method for correcting atmospheric refraction of optical imaging satellite through utilizing fixed star observation data
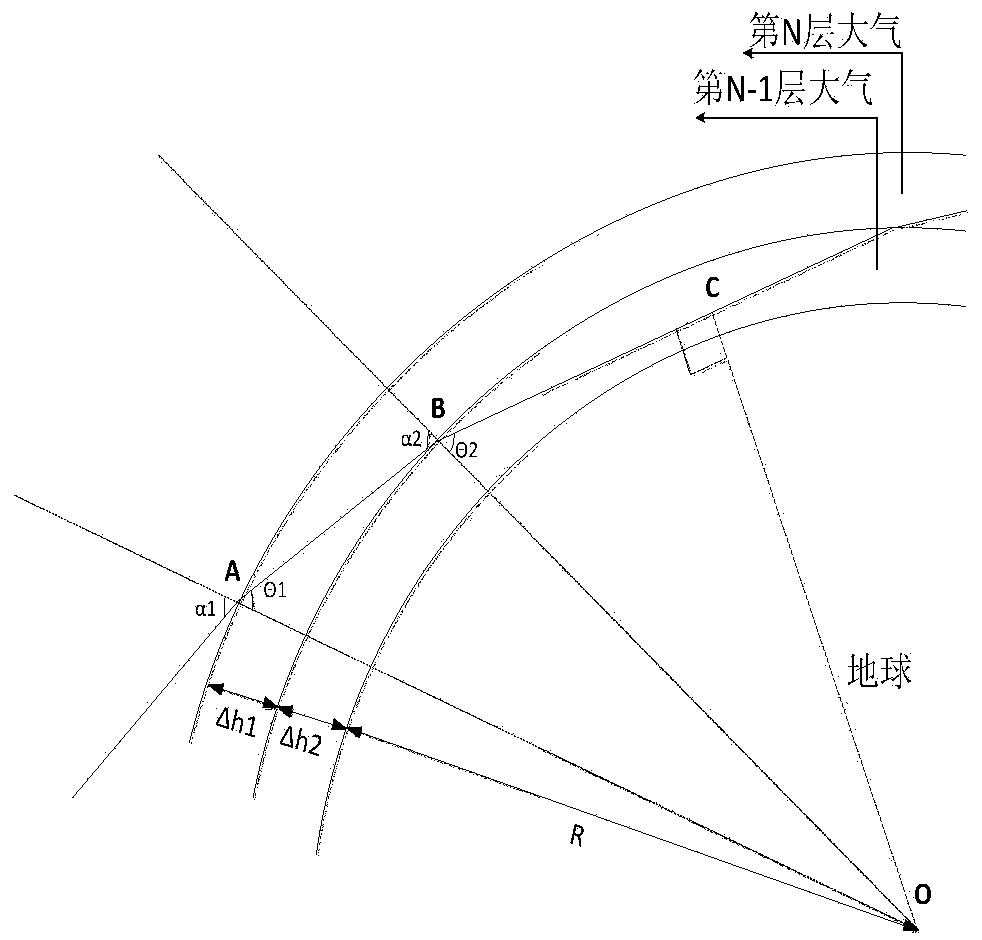
ActiveCN109900658AReflect volatilityPhase-affecting property measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsFixed starsNatural satellite
The invention relates to a method for correcting atmospheric refraction of an optical imaging satellite through utilizing fixed star observation data and belongs to the technical field of remote sensing image processing. The method comprises steps that S1, an atmospheric layering model is established according to a light wave band of an observed satellite image; S2, a fixed star light refraction model is established, and the atmospheric refractive index is calculated through utilizing the observed fixed star deflection phenomenon and the layer-by-layer forward iterative algorithm; S3, the deflected fixed start light is corrected through the fixed star light refraction model and the atmospheric refractive index, and the atmospheric refractive index is updated through the correction result;and S4, the fixed star light refraction phenomenon is predicted through the fixed star light refraction model, the coplanar nature of a satellite and the updated atmospheric refractive index. The method is advantaged in that the atmospheric refractive index is estimated based on the observed fixed star deflection phenomenon, volatility characteristics of the atmospheric refractive index can be better reflected, and the method can further be used in the case where a satellite observation space target is refracted twice by the atmosphere.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method for correcting influences of atmosphere inclination on ground star observation values
ActiveCN102879013AHigh measurement accuracyImprove observation accuracyMeasurement devicesSpecial data processing applicationsMeasuring instrumentLongitude
The invention belongs to the technical field of astrometry and relates to a method for correcting influences of atmosphere inclination on ground star observation values. The method is used for correcting influences of the atmosphere inclination on astronomical longitude and latitude measured values obtained during ground star observation and solves the problem of inaccuracy of existing atmospheric refraction error correction. The method includes the steps: firstly, selecting a plurality of stars as sample stars, establishing a regression model among the observation values of the sample stars, and resolving influence quantity of atmosphere isodensity layer inclination caused by factors such as climate change in observation of each star group; and secondly, correcting the observation values of the stars according to the resolved quantity of the atmosphere isodensity layer inclination. By the method, an apparent zenith distance measured value of each star obtained by observation and star passing record moments can be accurately corrected for atmosphere isodensity layer inclination, and measurement accuracy of astrometric and geodetic instruments is improved.
Owner:YUNNAN ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com