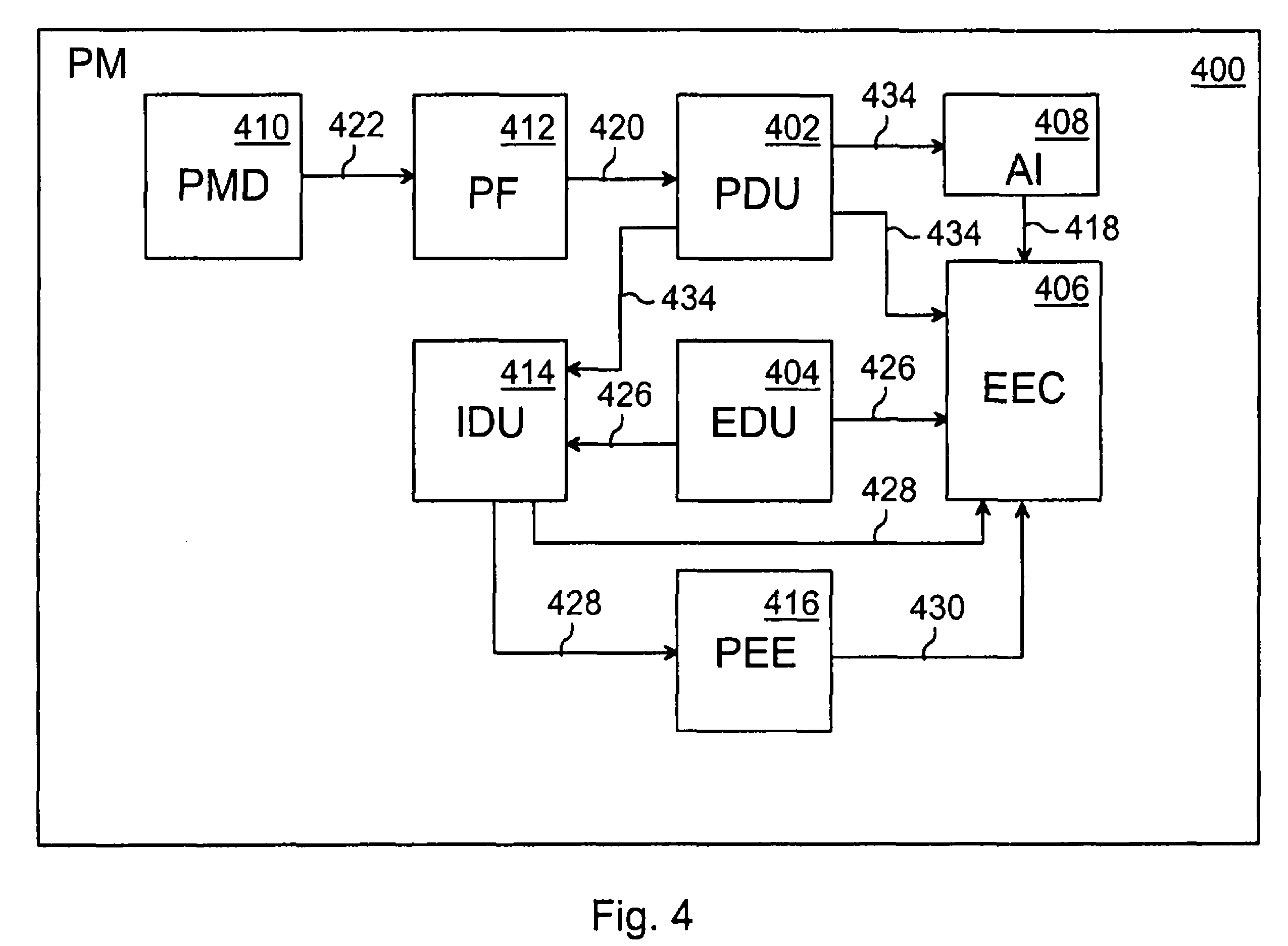
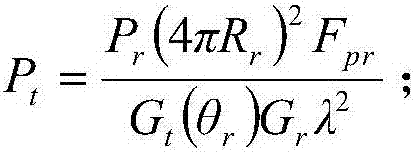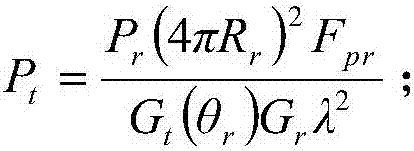Patents
Literature
58 results about "Propagation factor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and apparatus for cancellation of unwanted signals in MWD acoustic tools
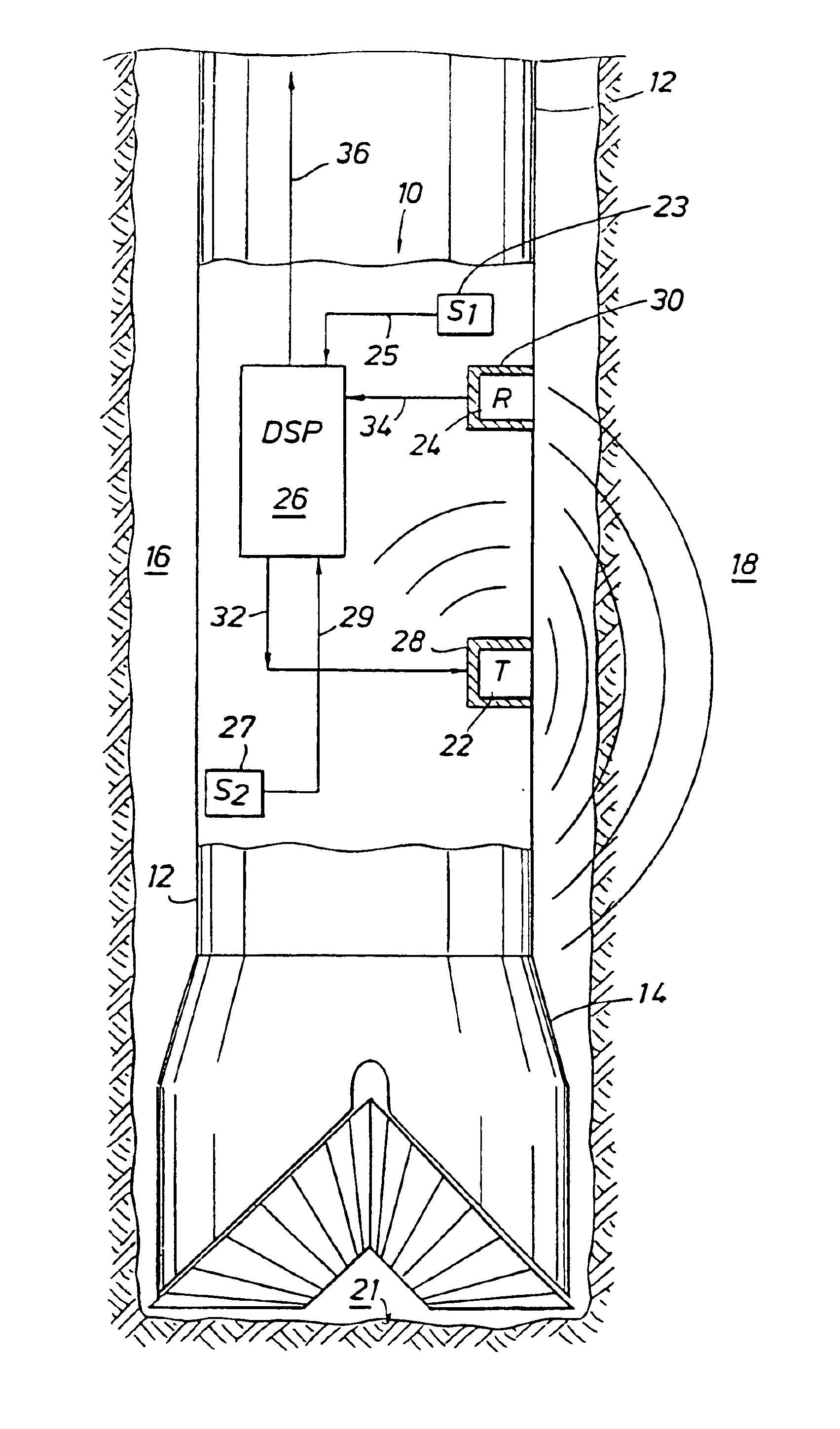
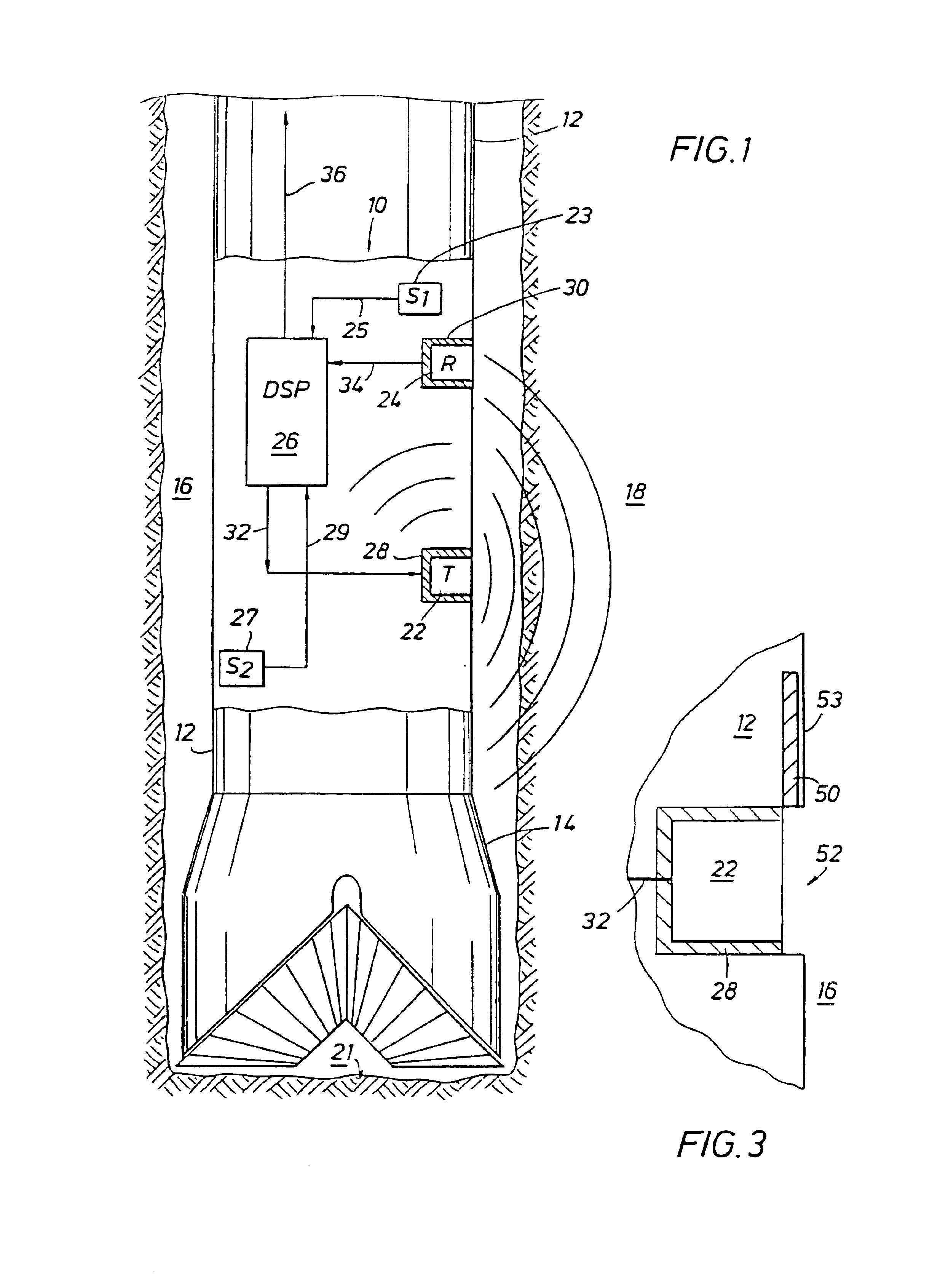
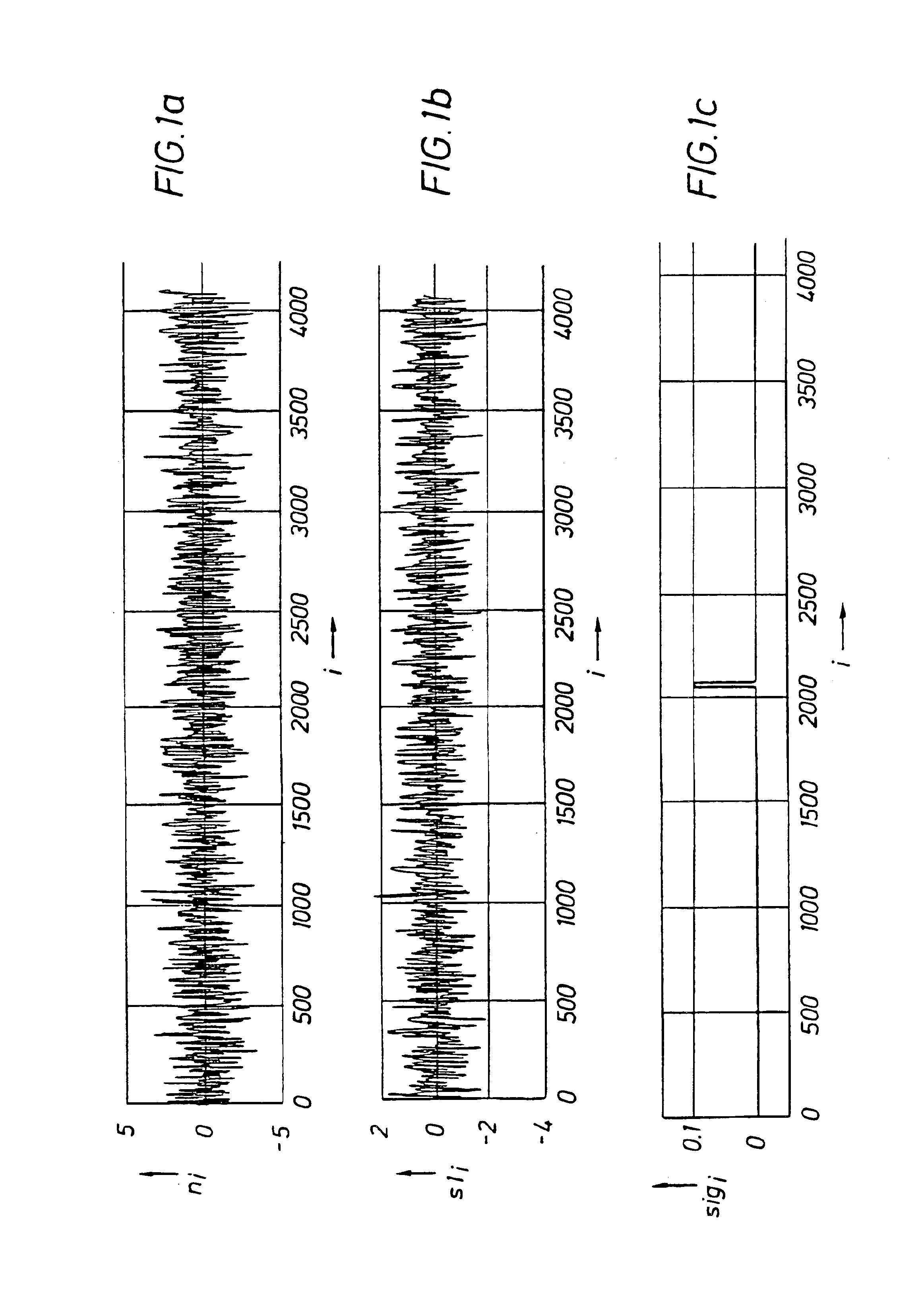
An apparatus (10) and method are disclosed for eliminating a noise signal from at least one source during an acoustic measurement of a subsurface geological formation or borehole. The apparatus (10) includes a longitudinal body for positioning in the borehole and a transmitter (22) supported by the body for transmitting acoustic signals into the formation and borehole. A sensor (23), substantially isolated within the body, is used to detect one or more noise signals and a receiver (24) is carried by the body for receiving acoustic signals traversing the formation and borehole, and for receiving one or more noise signals. A processor (26) is connected to the sensor (23) and receiver (24) for processing the acoustic signals and noise signals coupled from the receiver (24) and the noise signal coupled from the sensor (23) into a preferred formation or borehole signal by determining the noise signal received at the receiver (24) using the noise signal received in the sensor (23) and a propagation factor for the noise signal between the sensor (23) and receiver (24). The determined noise signal is used to identify and eliminate the noise signals from the acoustic signals traversing the formation and borehole.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Academic influence cooperative sequencing method of nodes in scientific and technical literature heterogeneous network
InactiveCN104133843AAvoid Node InfluenceAvoid the phenomenon of positive in-degree correlationWeb data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsNODALTechnical literature
The invention discloses an academic influence cooperative sequencing method of nodes (papers, authors and periodicals / conference) in a scientific and technical literature heterogeneous network. By aiming at the heterogeneity of the scientific and technical literature network, according to the method provided by the invention, two stages of random walk are adopted for calculating and sequencing the academic influence of the nodes in the scientific and technical literature, wherein the two stages of the random walk are respectively the random walk driven by the node network topology on the scientific and technical literature heterogeneous network and the random walk driven by the academic type in a minimum network mode of the scientific and technical literature network; the weight of each edge is calculated in the scientific and technical literature heterogeneous network for configuring the random walk driven by the node network topology; and according to the minimum network mode of the scientific and technical literature heterogeneous network, an average edge betweenness of various relation edges in different fields is counted, a propagation factor is calculated, and the rand walk driven by the node academic type is configured. The method provided by the invention solves the problems caused by the heterogeneity of the heterogeneous network and avoids phenomena of node influence and in-degree positive correlation, so that the sequencing result is relatively accurate.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
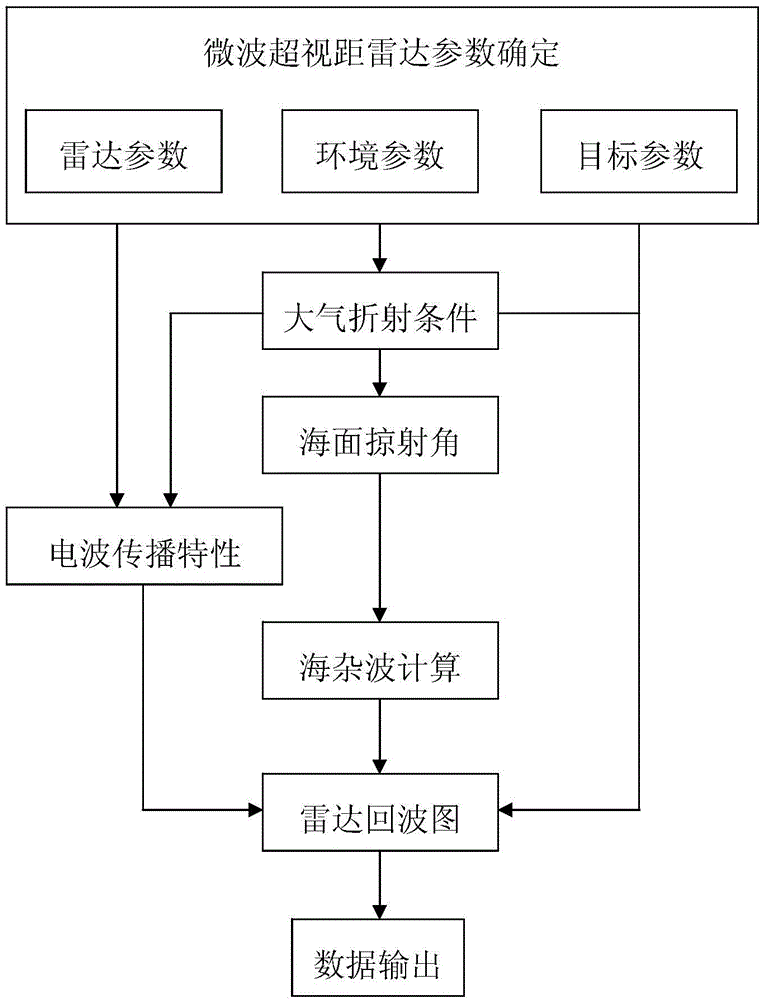
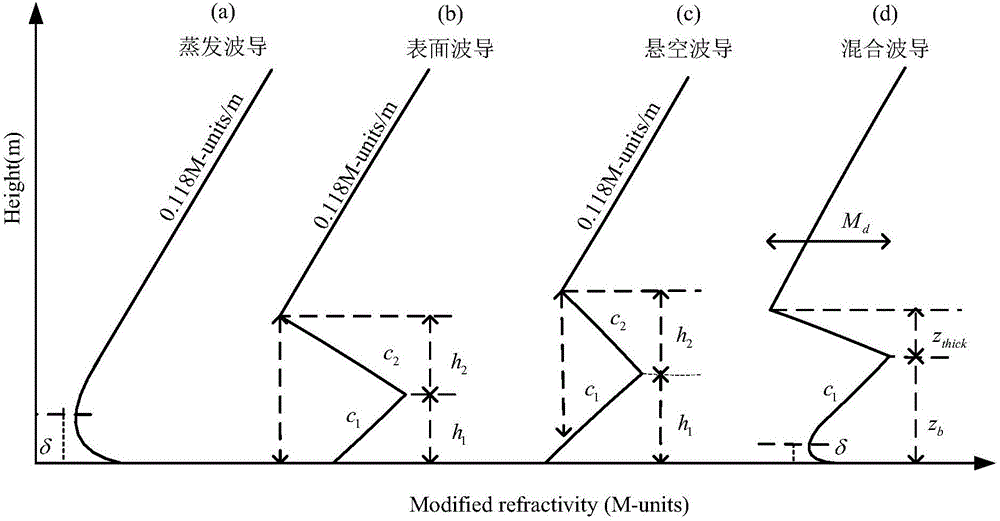
Microwave over-the-horizon radar echo chart calculating method
ActiveCN106772300AFully consider the echoFully consider the impact of the target echoWave based measurement systemsRadar systemsEvaporation
The invention discloses a microwave over-the-horizon radar echo chart calculating method, which comprises the following steps: 1) determination of relevant parameters, target parameters and environment parameters of a microwave over-the-horizon radar; 2) prediction of characteristic parameters of an evaporation waveguide and measurement of characteristic parameters of a surface waveguide; 3) calculation of an atmosphere waveguide or atmosphere refraction propagation sea surface glancing angle; 4) calculation of an atmosphere waveguide or atmosphere refraction propagation factor; 5) calculation of a sea clutter and target echo power diagram; and 6) simulation of a dynamic radar echo chart. The disclosed microwave over-the-horizon radar echo chart calculating method takes influence, formed under ocean hydrological conditions, of atmospheric duct propagation on sea surface echoes and target echoes into full consideration under the actual microwave over-the-horizon radar working environment, provides an actual radar beam sea surface grazing angle calculating method under the atmospheric refraction or atmospheric duct condition on the basis of radar system parameters and marine hydrometeorological parameters, and with relevant sea clutter models being combined, can effectively predicate and estimate the sea surface echo power.
Owner:中国电波传播研究所 +1
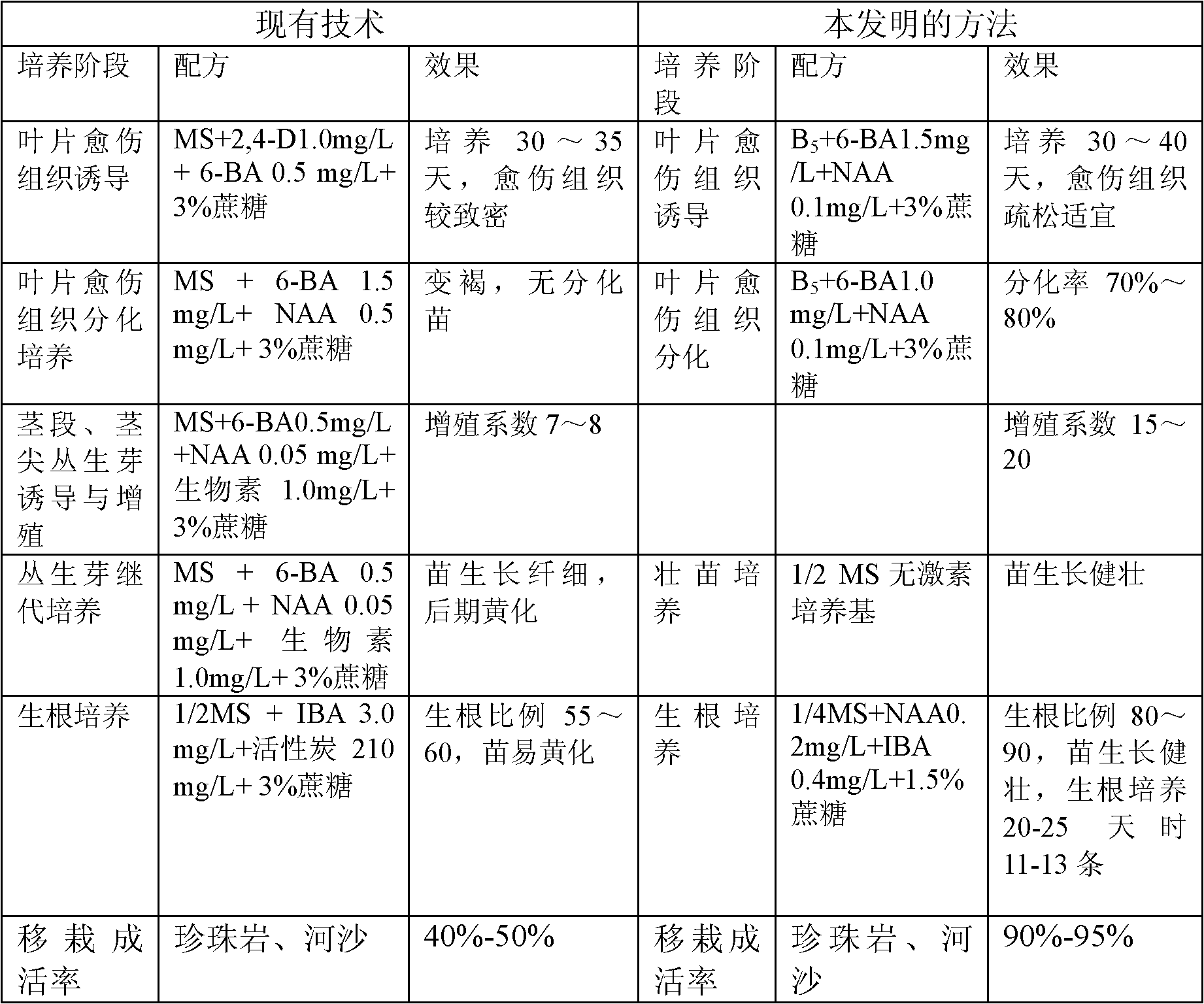
Rapid propagation technique of Dendrobium candidum axillary buds
ActiveCN102369881AIncrease the number ofPromote recoveryPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAxillary budBud
The invention discloses a rapid propagation technique of Dendrobium candidum axillary buds. According to the technique, Dendrobium candidum axillary buds are used as explants directly to induce fasciculated buds; influences of combinations of different types of hormones with different concentration and different natural extracts on survival and growth of axillary buds, induction and multiplication of fasciculated buds and seedlings are compared, the quantity and quality of seedlings growing from fasciculated buds are researched and explored, the optimal culture medium formula in each stage is screened, and therefore, a fasciculated-bud-way high-efficiency rapid propagation system is established, so that plants obtained through rapid propagation are consistent with parent plants genetically so as to provide basis for restoration of wild population of Dendrobium candidum, and furthermore, wild resources are protected. Compared with vegetative propagation, the rapid propagation technique provided by the invention greatly improves propagation factor. A high-efficiency rapid propagation system of Dendrobium candidum which is an endangered plant provides a technical probability for the large-scale production and is beneficial to the restoration of wild population.
Owner:SHANGHAI XCT HEALTH FOOD
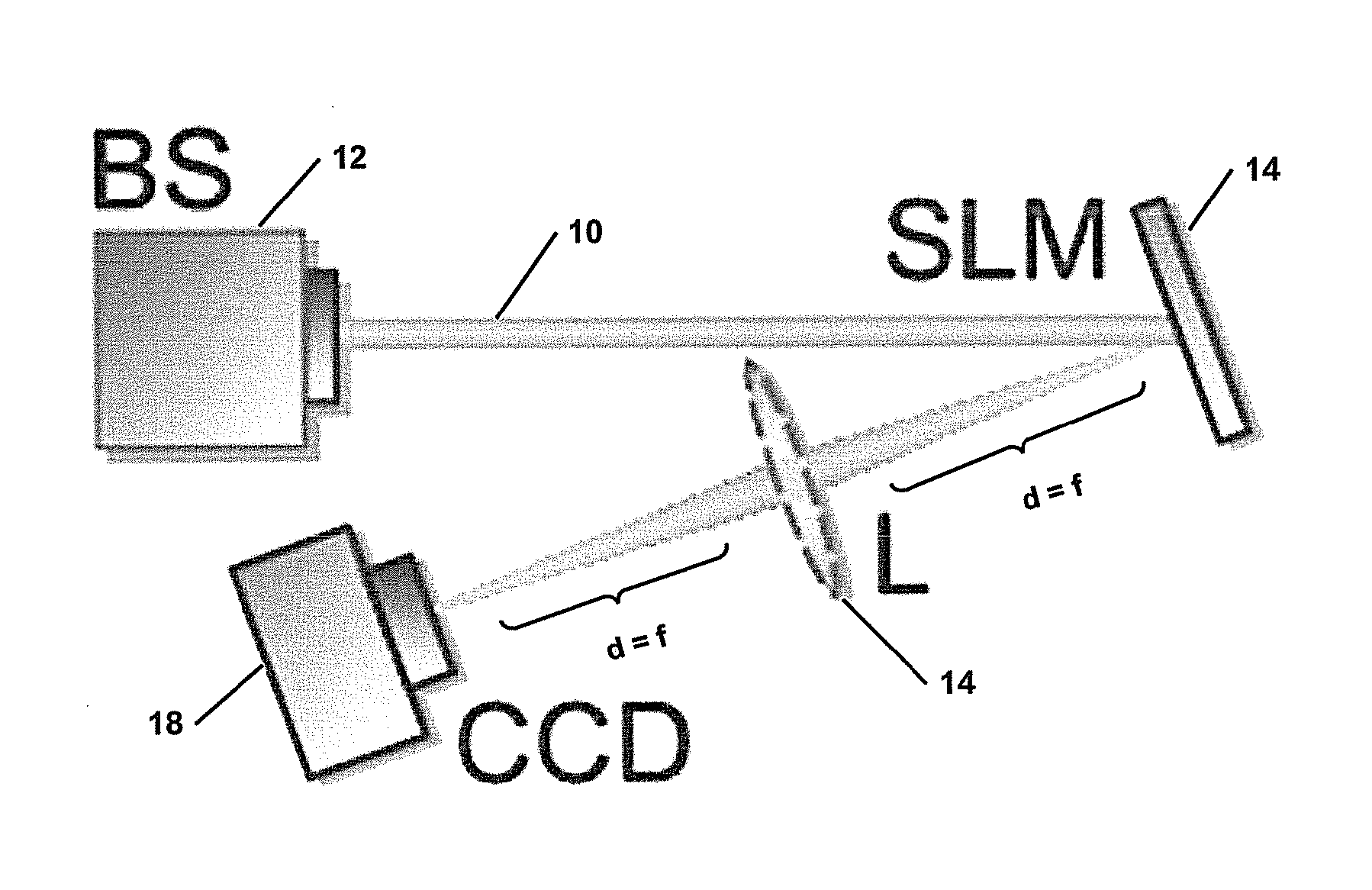
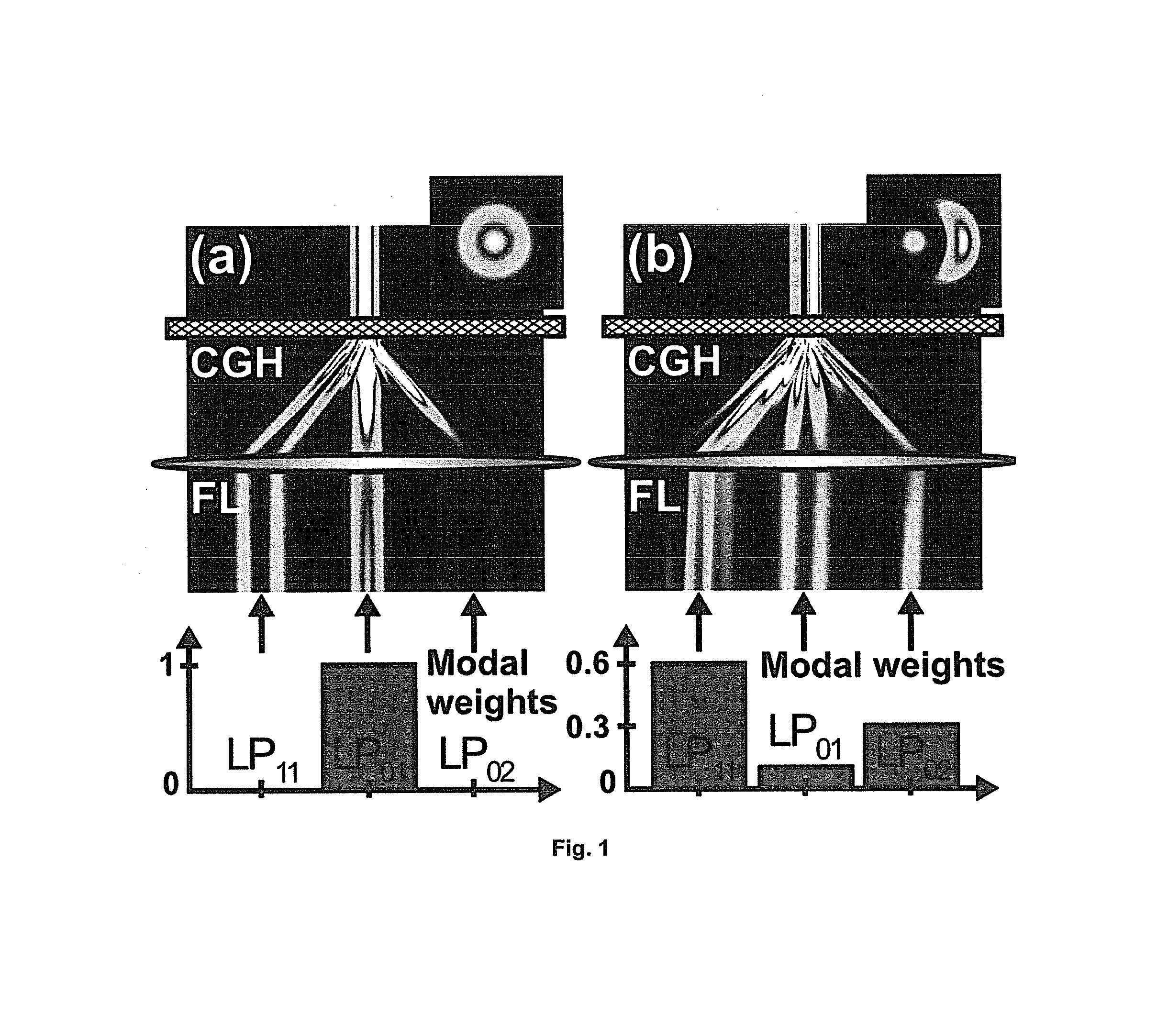
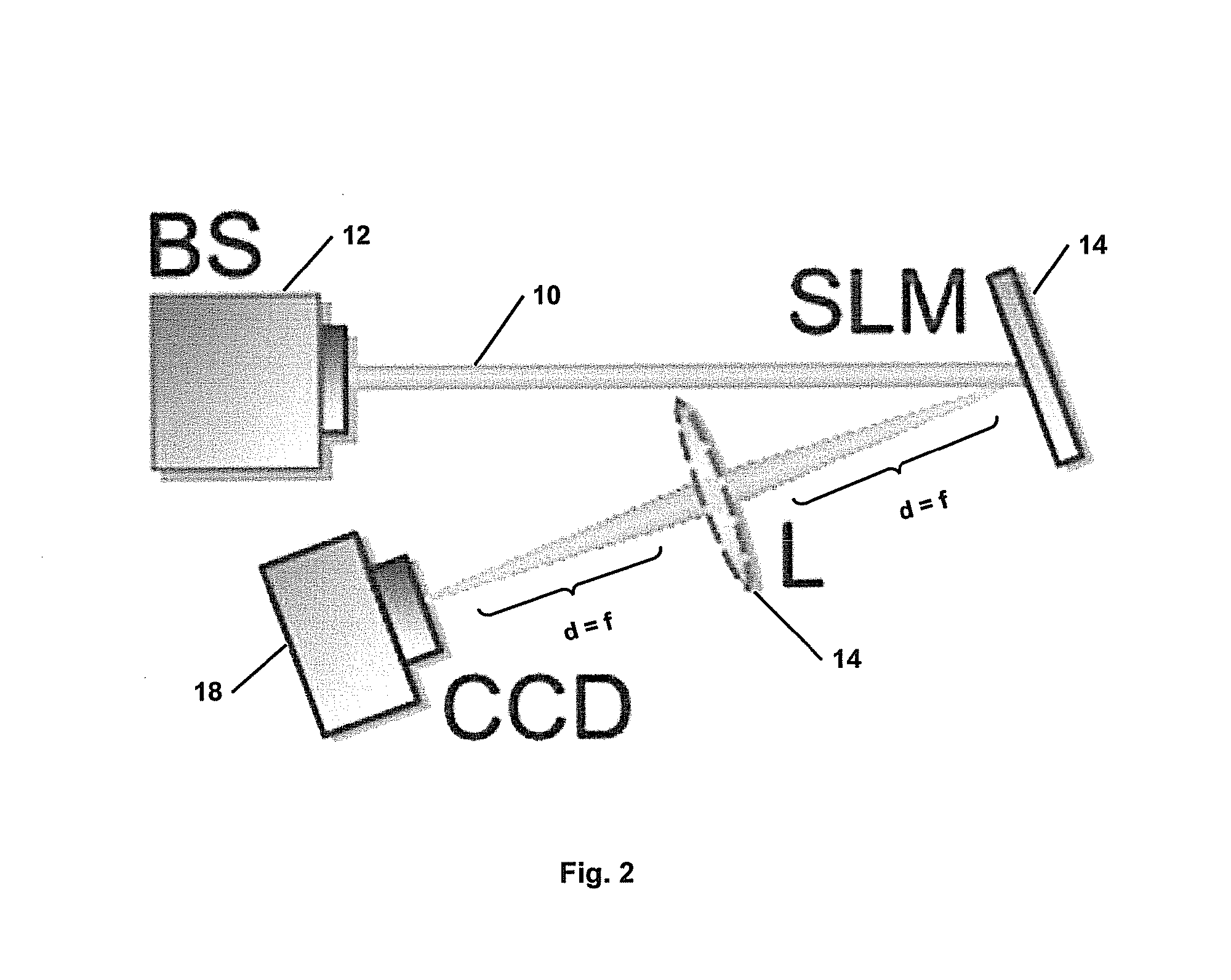
Modal decomposition of a laser beam
InactiveUS20150292941A1Measurement fast and flexibleEasy to createOptical measurementsOptical devices for laserSpatial light modulatorDecomposition
A method and apparatus for performing a modal decomposition of a laser beam are disclosed. The method includes the steps of performing a measurement to determine the second moment beam size (w) and beam propagation factor (M2) of the laser beam, and inferring the scale factor (wO) of the optimal basis set of the laser beam from the second moment beam size and the beam propagation factor, from the relationship: wO=w / M2. An optimal decomposition is performing using the scale factor wO to obtain an optimal mode set of adapted size. The apparatus includes a spatial light modulator arranged for complex amplitude modulation of an incident laser beam, and imaging means arranged to direct the incident laser beam onto the spatial light modulator. Fourier transforming lens is arranged to receive a laser beam reflected from the spatial light modulator. A detector is placed a distance of one focal length away from the Fourier transforming lens for monitoring a diffraction pattern of the laser beam reflected from the spatial light modulator and passing through the Fourier transforming lens. The apparatus performs an optical Fourier transform on the laser beam reflected from the spatial light modulator and determines the phases of unknown modes of the laser beam, to perform a modal decomposition of the laser beam.
Owner:CSIR
Intestinal health food and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102379392AGood for healthIncrease the number ofFood preparationBifidobacteriumIsomaltooligosaccharide
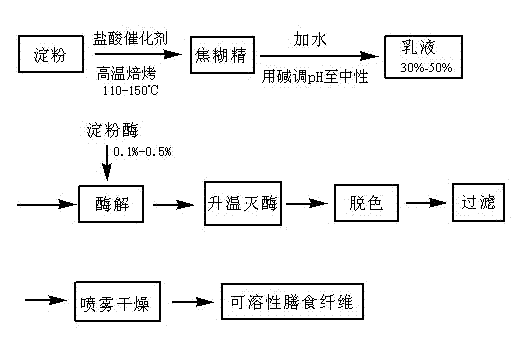
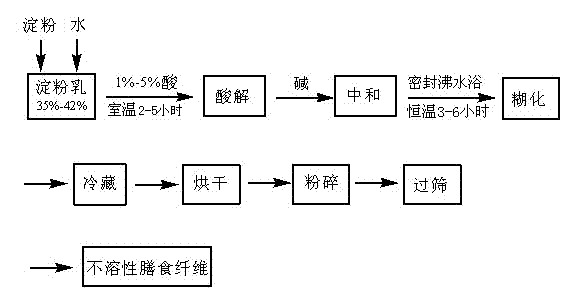
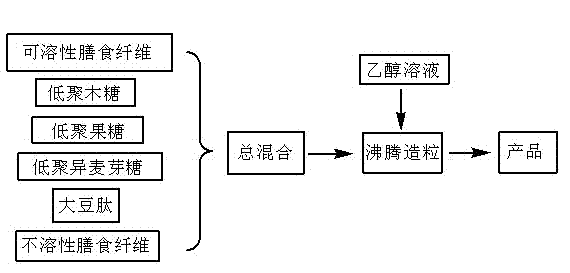
The invention relates to an intestinal health food and a preparation method thereof. A technical problem to be solved is to provide a food for promoting the propagation factor of an intestinal bifidobacterium to increase the number of the intestinal bifidobacterium and promote the intestinal health and a preparation method thereof. The intestinal health food of the invention is prepared from the following raw materials, by weight, 15-35 parts of a soluble dietary fiber, 15-35 parts of an insoluble dietary fiber, 2-6 parts of a xylooligosaccharide, 6-16 parts of a fructooligosaccharide, 10-25 parts of an isomaltooligosaccharide and 3-10 parts of a soy peptide (preferably defatted milk powder and sucralose). The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing the soluble dietary fiber; 2, preparing the insoluble dietary fiber; 3, mixing; and 4, granulating.
Owner:山东众友生物科技有限公司
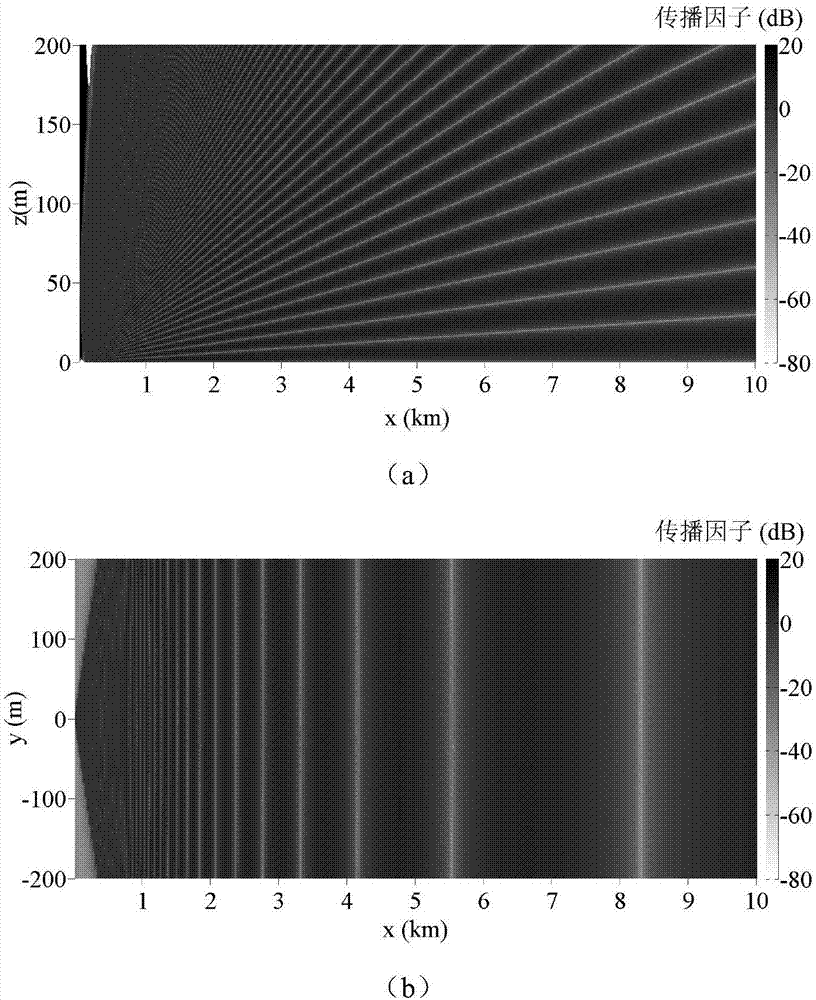
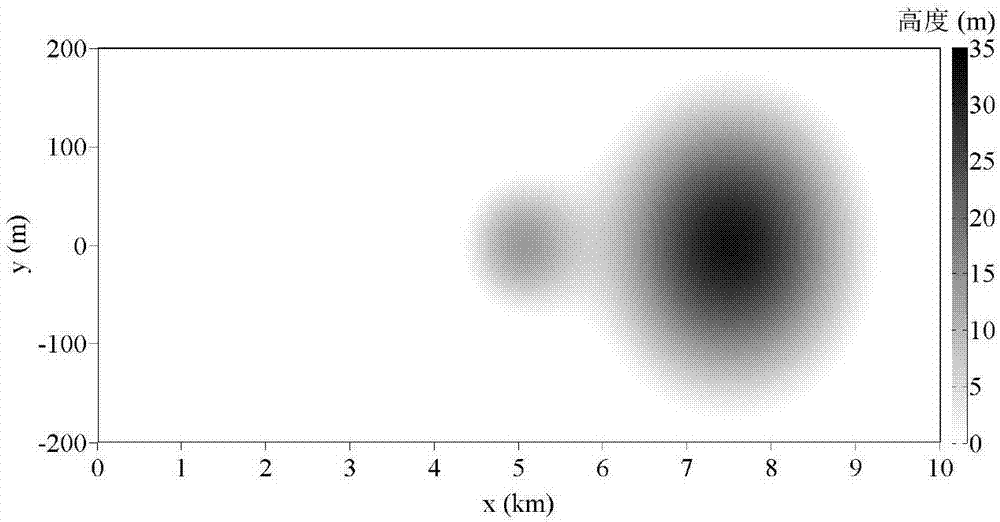
Irregular terrain radio wave propagation factor prediction method based on three-dimensional parabolic equation
InactiveCN107545104AImprove forecast accuracyAvoid the influence of radio wave propagationSpecial data processing applications3D modellingLandformGps positioning
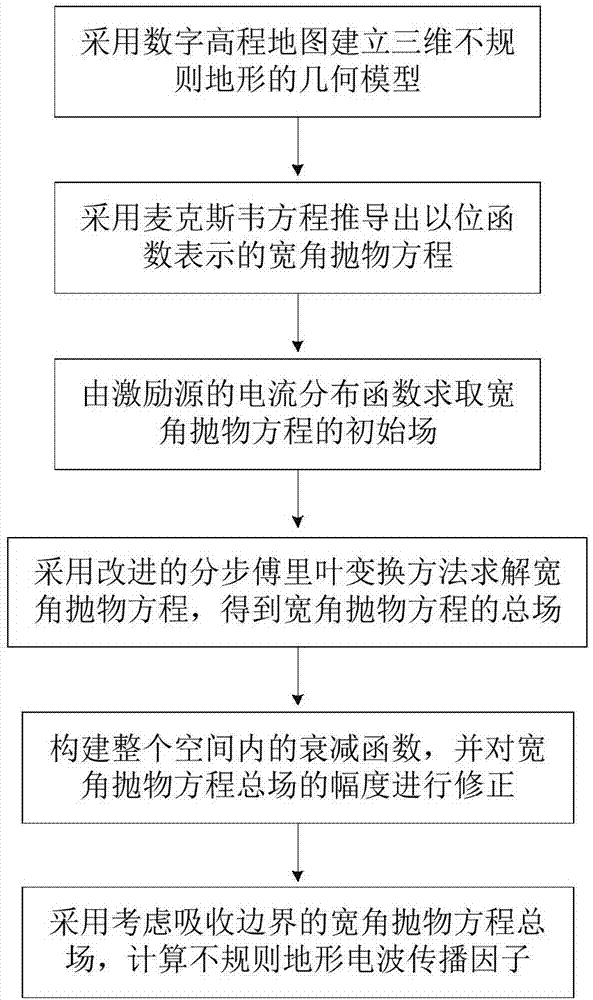
The invention provides an irregular terrain radio wave propagation factor prediction method based on a three-dimensional parabolic equation for solving the problem that a two-dimensional parabolic equation cannot consider the influence of transverse terrain to radio wave propagation properties. The irregular terrain radio wave propagation factor prediction method comprises the following steps: establishing a three-dimensional irregular terrain geometric model by using a digital elevation map; deducing a wide angle parabolic equation expressed by a bit function by using a maxwell equation; figuring out an initial field of the wide angle parabolic equation by using a current distribution function of an excitation source; figuring out the wide angle parabolic equation by using an improved step-by-step Fourier transform method to obtain a total field of the wide angle parabolic equation; constructing an attenuation function in a whole space, and correcting the amplitude of the total fieldof the wide angle parabolic equation; and calculating an irregular terrain radio wave propagation factor by using the total field of the wide angle parabolic equation considering the absorption boundary. By adoption of the irregular terrain radio wave propagation factor prediction method, the precision of prediction of the three-dimensional parabolic equation is improved, the application range ofthe digital elevation map is expanded, and the irregular terrain radio wave propagation factor prediction method can be applied to wireless communication and GPS positioning in complex environments.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
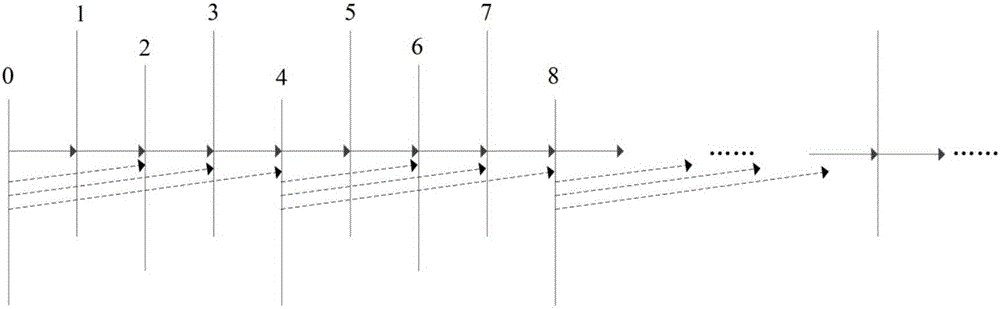
Method for optimizing time domain rate-distortion in low-delay video coding
The invention belongs to the technical field of video coding, and particularly relates to a rate-distortion optimizing method based on time domain dependence in low-delay video coding. A circulating group of picture (GOP) structure is adopted, a GOP is formed by every four frames, the frames in the GOPs are allocated to different layers, and the frames in the same layer follow the similar reference frame and QP allocation rule. The time domain dependence of a hierarchical structure in the low-delay video coding is analyzed, a time domain propagation chain shown in picture 2 is established according to the time domain dependence in the low-delay coding, and then rate-distortion optimal modeling of time domain dependence is carried out. A propagation factor omega a and global lagrangian multiplier lambda g are got. Finally, according to the propagation factor omega a, time domain rate-distortion optimizing is achieved only by adjusting the global lagrangian multiplier lambda g.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Telecommunication customer loss forecasting method based on nervous-netowrk improved algorithm
The method comprises: firstly using BP neural network to build a client running off model; then using the error propagation factor to make normalization process for the data with a normalization formula: x'=0.8(x-xmin / xmax-xmin)+0.1, and wherein, x is an inputted parameter, xmin is a minimum inputted parameter, xmax is a maximum parameter, x is a normalized inputted parameter.
Owner:LINKAGE SYST INTEGRATION
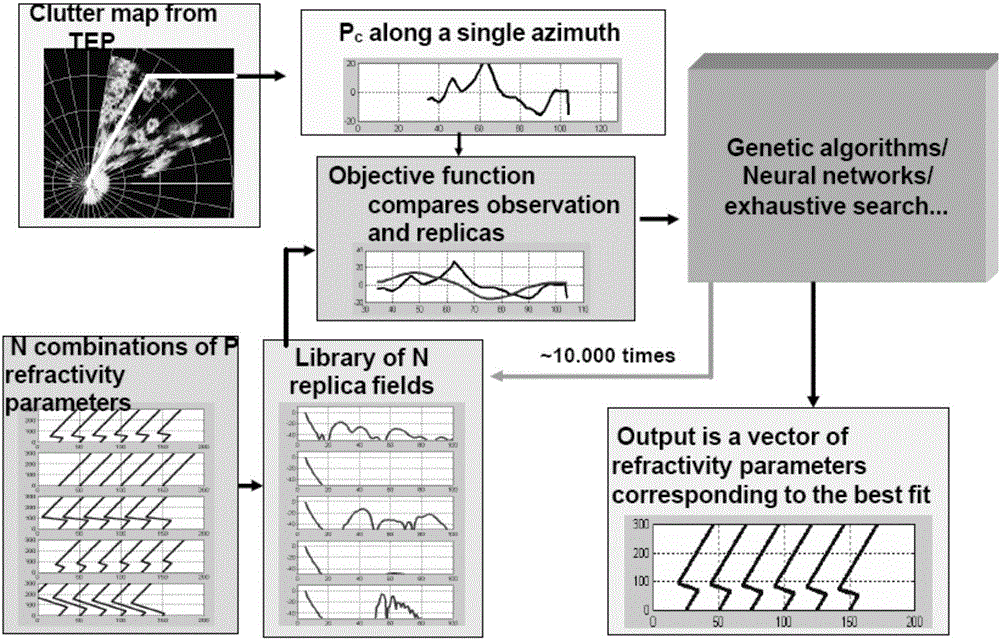
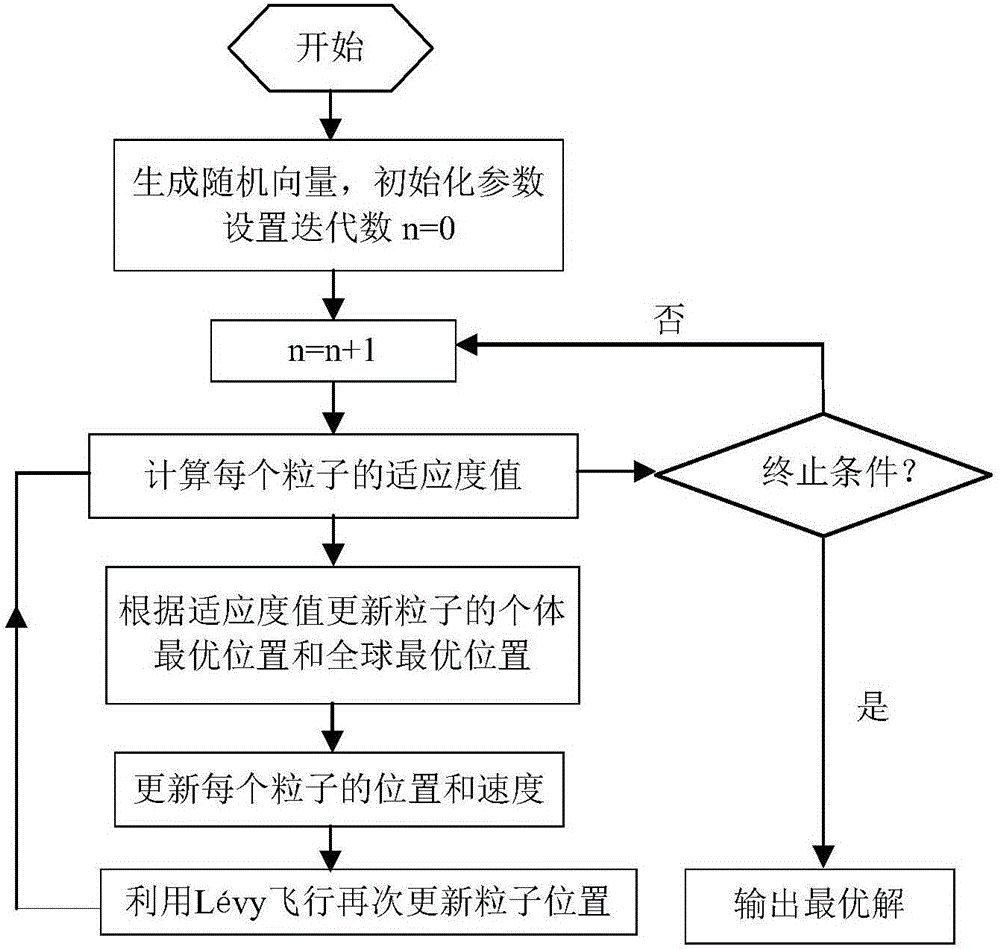
Method of inversing atmospheric duct by radar echo through LPSO algorithm
InactiveCN106772386AReal-time atmospheric ductEfficient Atmospheric WaveguideDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsRadar systemsBoundary value problem
The invention discloses a method of inversing atmospheric duct by radar echo through an LPSO algorithm; the method includes steps of 1), building up air refractive index outline parameterization by using a five-parameter experience model mentioned by Gerstoft or offshore air environment; 2), calculating the radar echo power Pc; according to low incidence angle of the radar, forming a linear function relationship with the propagation distance of a radar electromagnetic wave; 4) based on a propagation model of a parabolic equation (PE), writing the radar electromagnetic wave propagation as an initial side value problem; 5), making 'Fourier conversion' and ' Fourier inverse transformation' of above formula, and acquiring the solution; 6) defining the ratio of the actual field intensity at one point of the space and by using the directional diagram propagation factor F and the field intensity of the same one emitting antenna at the same distance point in the free space along the maximum emitting direction of the antenna; 7), at last, calculating the single-way propagation loss value L at the propagation path (x, z) by the formula below; combining with the real air refractive index outline and the radar system parameter, and calculating the radar echo power by a forward modeling model; 8) establishing a target function by using the actual measured radar echo power and the simulated radar echo power; using the established target function, and inversing the atmospheric duct parameter by LPSO algorithm.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
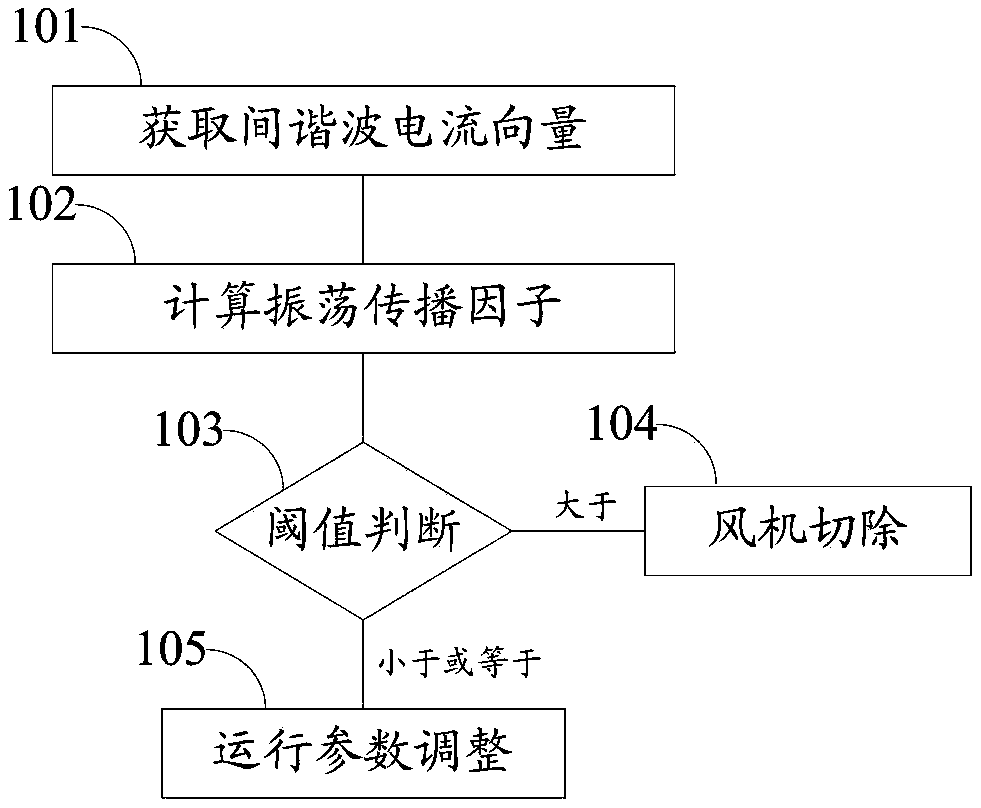
Safe operation method and system for subsynchronous oscillation wind power grid-connected system
ActiveCN109617121AGuaranteed safe operationReduce operating control costsGenerator control circuitsFlicker reduction in ac networkElectricityHarmonic
The invention discloses a safe operation method and system for a subsynchronous oscillation wind power grid-connected system. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining inter-harmonic currentobtained by carrying out real-time monitoring on inter-harmonics in the wind power grid-connected system so as to obtain an inter-harmonic current vector; inputting the inter-harmonic current vectorto calculate an oscillation propagation factor; judging whether the oscillation propagation factor is greater than a preset threshold value so as to obtain a judging result, when the judging result indicates that the oscillation propagation factor is greater than the preset threshold value, determining that subsynchronous oscillation is propagated to an electric generator to be measured, and cutting off draught fans causing subsynchronous oscillation from the wind power grid-connected system, and when the judging result indicates that the oscillation propagation factor is smaller than or equalto the preset threshold value, determining that subsynchronous oscillation is propagated in the range of a draught fan group only, and adjusting the operating parameter suppression inter-harmonics ofthe draught fan group. According to the safe operation method and system for the subsynchronous oscillation wind power grid-connected system disclosed by the invention, subsynchronous oscillation canbe monitored, and safe operation of the wind power grid-connected system is guaranteed when subsynchronous oscillation occurs.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
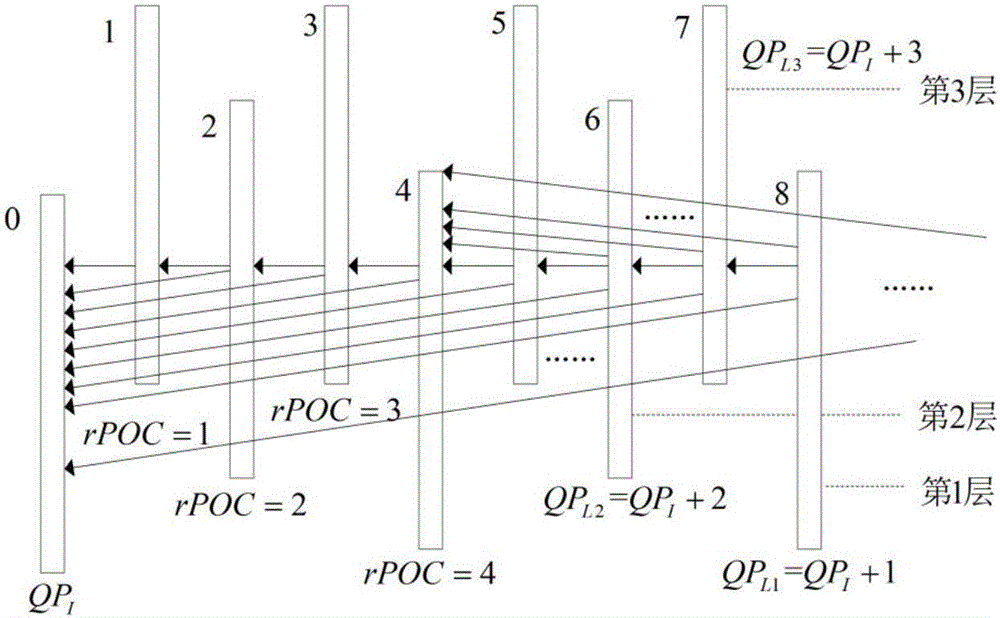
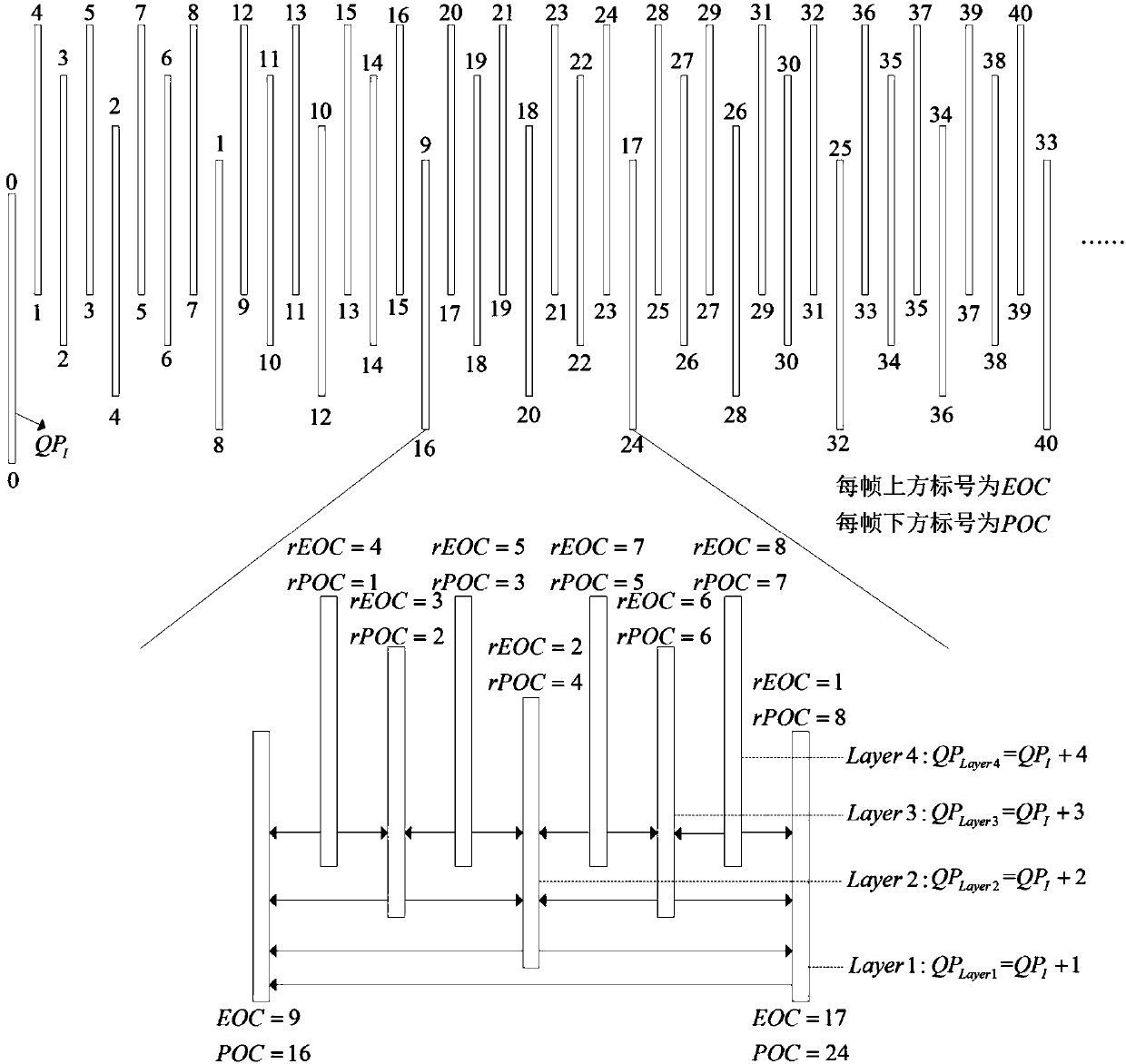
Method for layering time domain rate-distortion optimization in random access video coding
The invention belongs to the technical field of video coding, and particularly relates to a method for layering time domain rate-distortion optimization in random access video coding. A cyclic group of picture (GOP) structure is adopted, every eight frames form one GOP and are distributed to different layers, frames on the same layer abide by similar reference frame and QP distribution rules, as shown in figure 1, the coding sequence of frames is represented by EOC, and the playing sequence / time sequence of frames is represented by POC. Time domain dependency on the same layer and different layers among coding units in random access coding is analyzed, nested layering time domain propagation chains are established according to time domain dependency in random access coding, as shown in figure 3, and then layering time domain dependency rate-distortion optimal modeling is conducted and propagation factor kv and global lagrangian multiplier lambda g are obtained. Finally, according to the propagation factor kv, time domain rate-distortion optimization is achieved by adjusting the global lagrangian multiplier lambda g.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
In-vitro culture and planting regeneration and propagation method of Xianglei honeysuckle leaves and culture medium
InactiveCN102657082AReduce concentrationIncrease the multiplication factorHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureObserved SurvivalSeedling
The invention discloses an in-vitro culture and planting regeneration and propagation method of Xianglei honeysuckle leaves and a culture medium. When being used for culturing Xianglei honeysuckle, the method and the culture medium provided by the invention can effectively solve the problems that in the existing in-vitro culture and propagation technology of the Xianglei honeysuckle, the propagation factor is low, the rooting of the obtained strains is little, the required time is long, the cost is high, the quality is low, the transplanting survival rate is low, and the market requirement onhigh-quality seedlings is difficult to meet.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
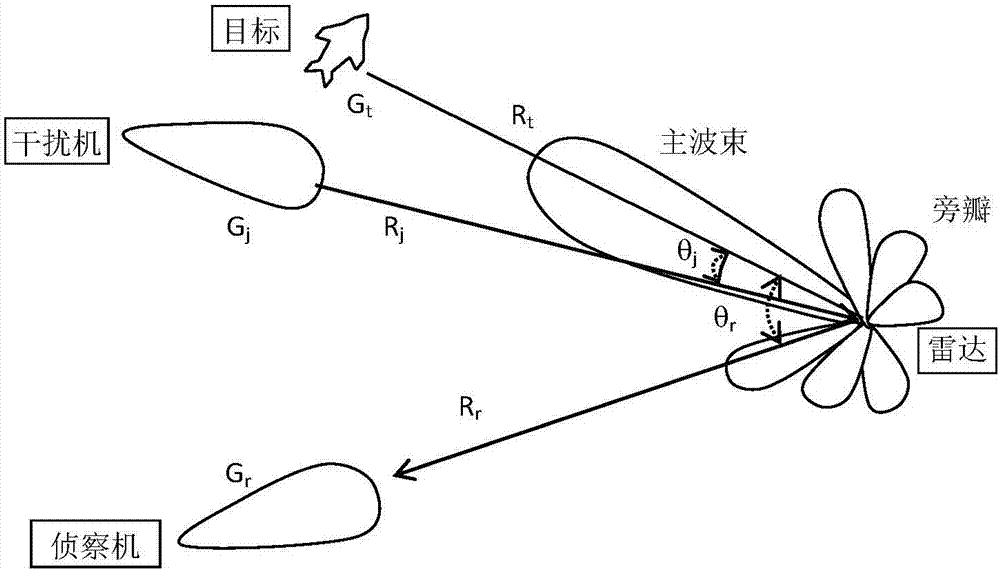
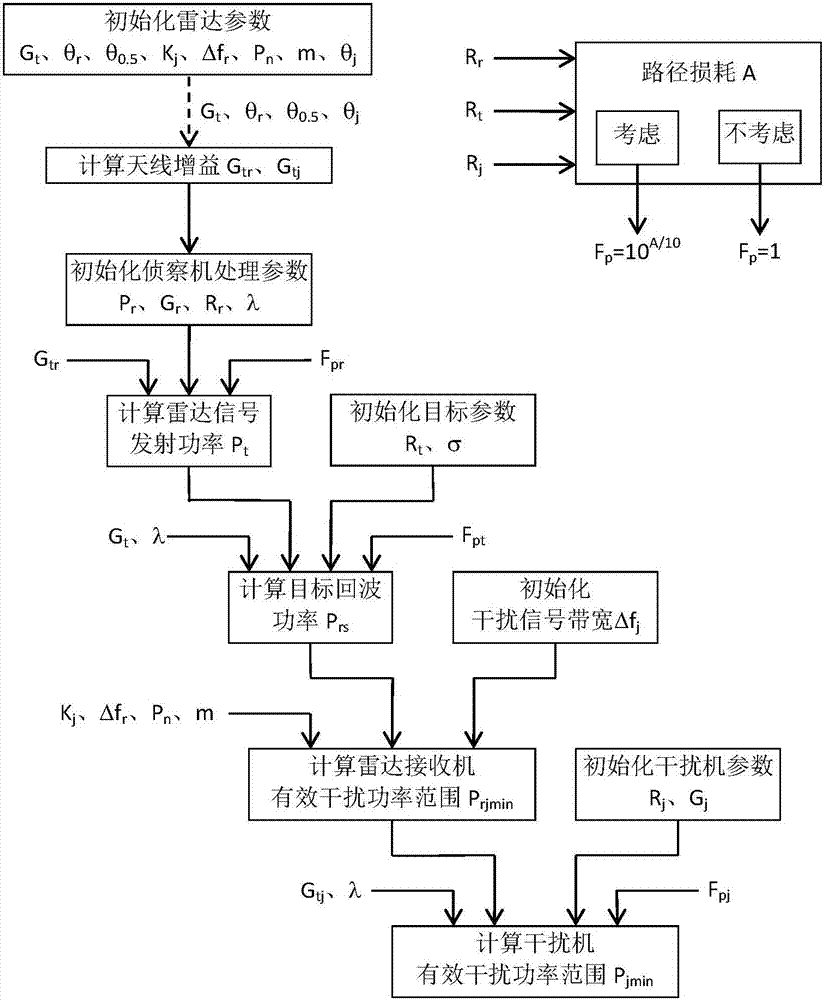
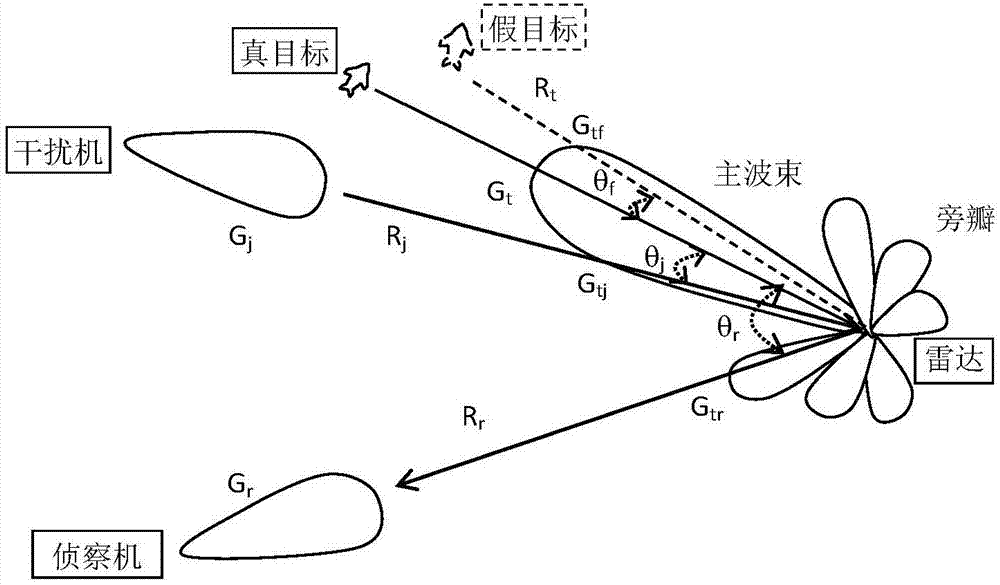
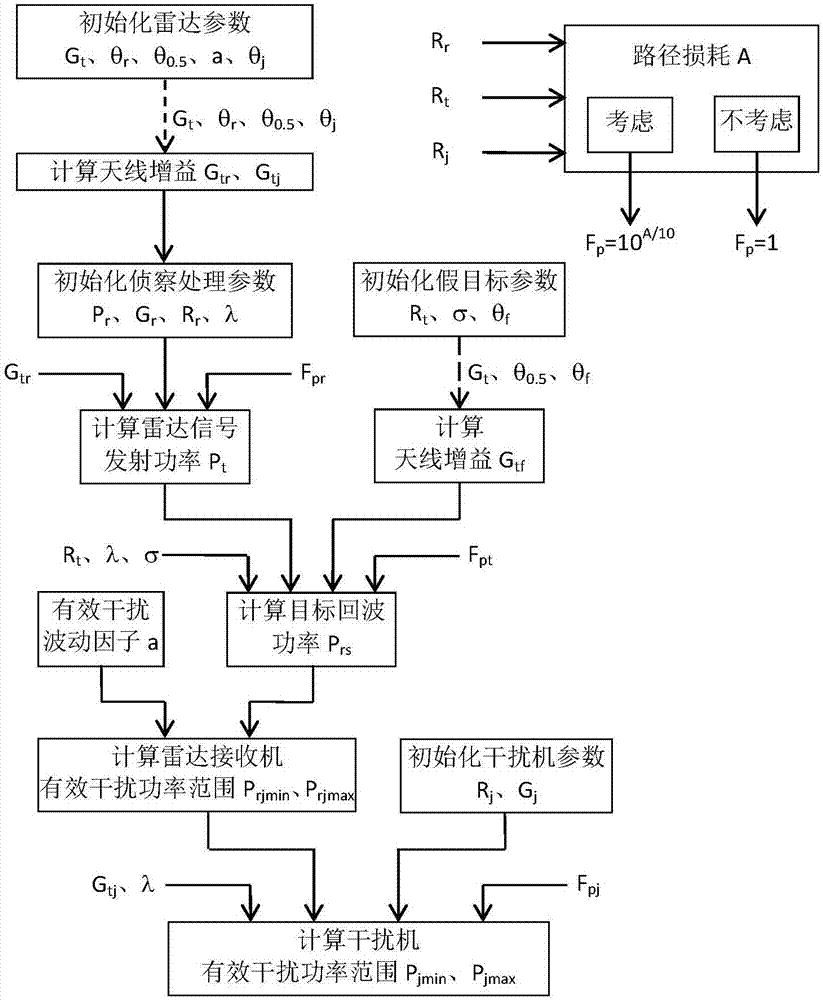
Blanketing jamming signal transmission power estimation method
ActiveCN107390186AEstimated transmit powerAccurately estimate target echo powerWave based measurement systemsUltrasound attenuationEstimation methods
The invention relates to a blanketing jamming signal transmission power estimation method. The method comprises the following steps that: a radar beam points to a target, a radar transmitter transmits radar signals, a reconnaissance plane intercepts the radar signals and estimates the transmitting power of the radar signals; a radar receiver receives target echoes and estimates the power of the target echoes; the power of interference signals received by the radar receiver under a condition that desired interference is generated is estimated; and the transmission power of interference signals transmitted by a jammer is estimated according to the power of the interference signals received by the radar receiver. According to the blanketing jamming signal transmission power estimation method of the invention, the attenuation of signal space propagation caused by environmental factors are considered; the attenuation is embodied on a propagation factor in the estimation process of the transmission power of the signals; and therefore, the signal transmission power of the jammer for blanketing jamming under an effective interference condition can be obtained more accurately.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
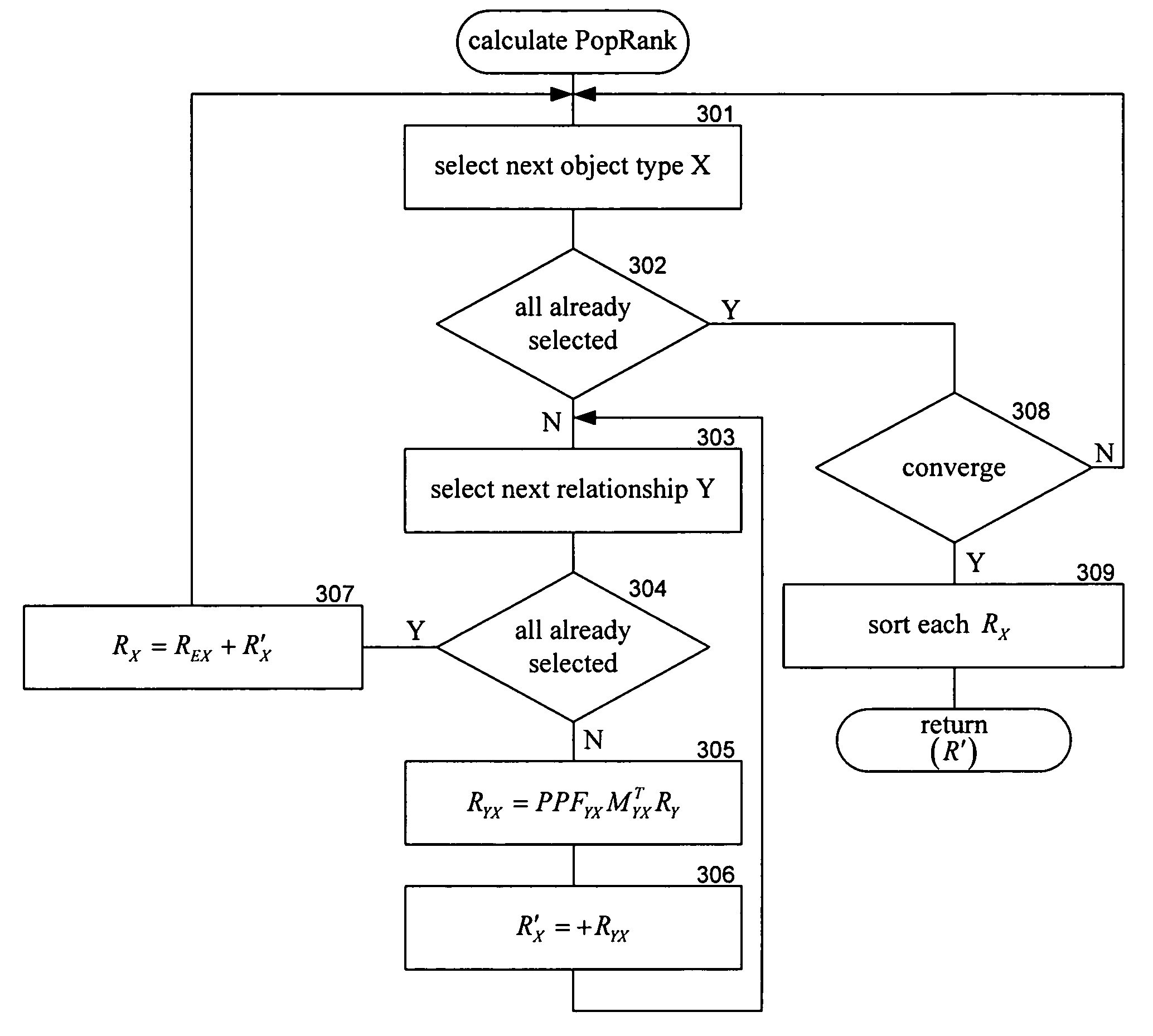
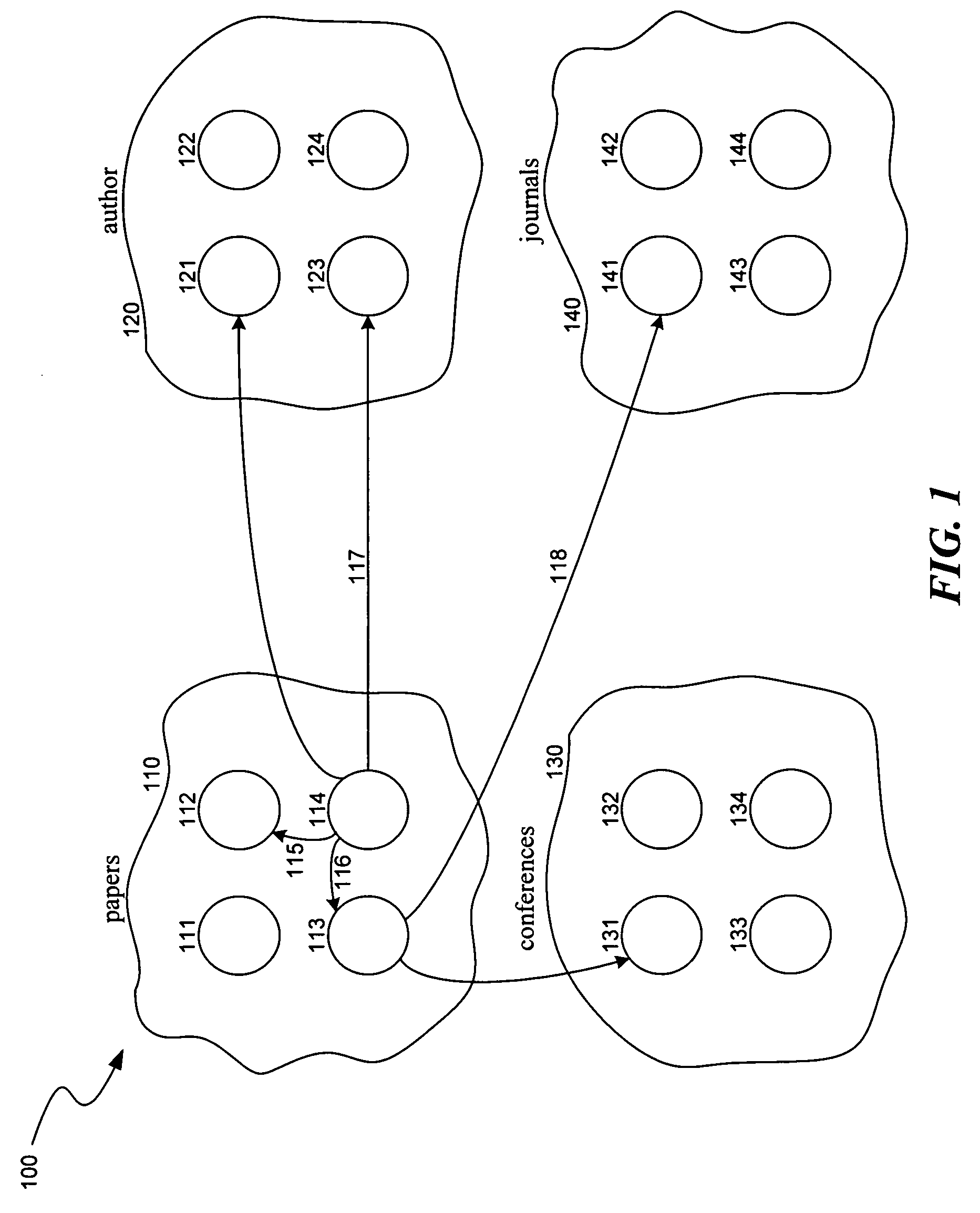
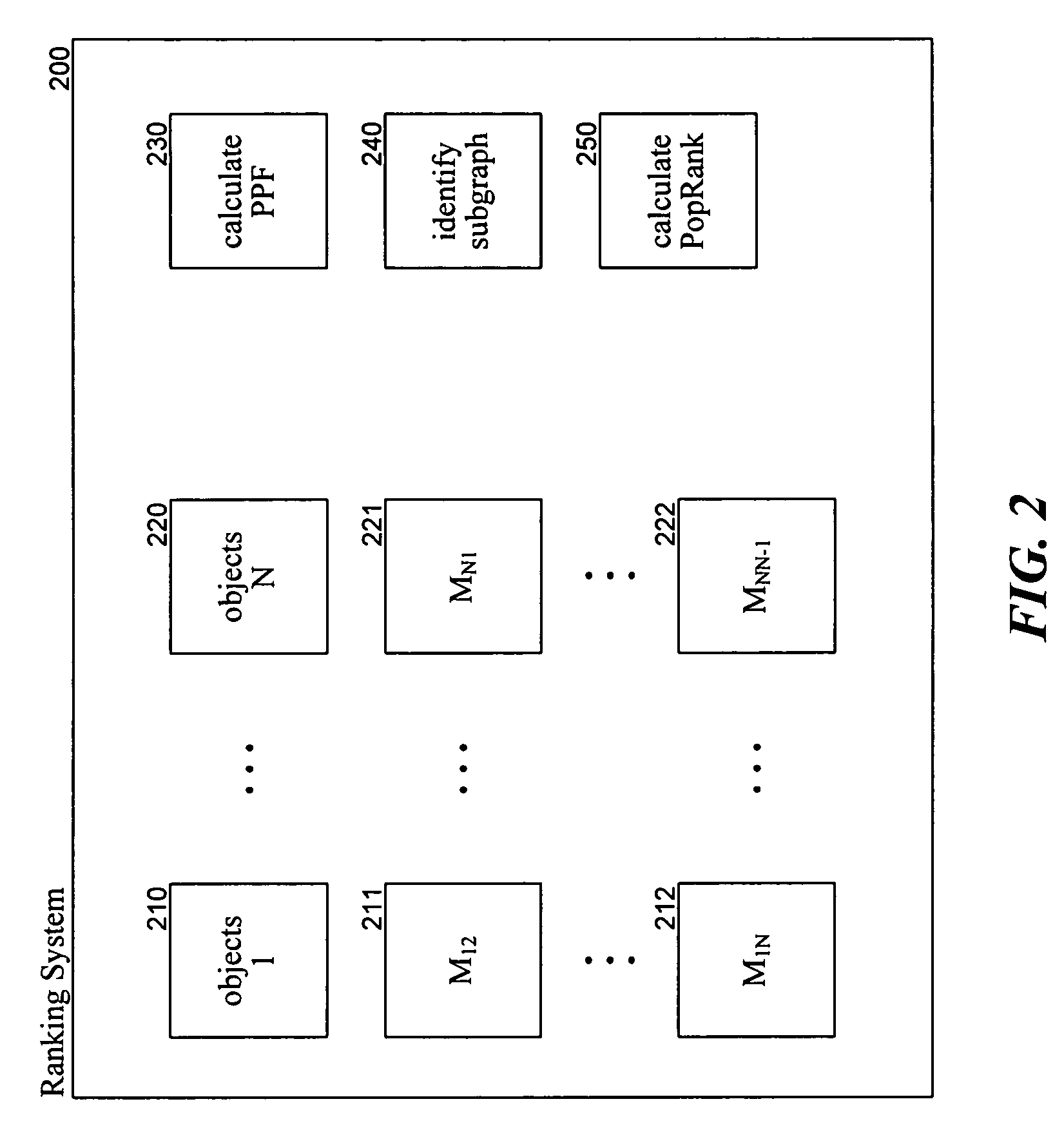
Method and system for ranking objects of different object types
A method and system for ranking objects of different object types based on their popularity is provided. A ranking system calculates the popularity of objects based on relationships between the objects. A relationship indicates how one object is related to another object. Thus, objects of one object type may have one or more relationships with objects of another object type. One goal of the ranking system is to rank the objects of the different object types based on their popularity. The objects and their relationships can be represented using a graph with nodes representing objects and links representing relationships between objects. The ranking system assigns a popularity propagation factor to each relationship to represent its contribution to the popularity of objects of that type.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for analyzing song popularity under influence of social relationship in music information network
InactiveCN105956040AReasonable analysisAnalysis method is reasonableSpecial data processing applicationsNODALInformation networks
The invention relates to a method for analyzing song popularity under the influence of a social relationship in a music information network. The method comprises the steps of firstly obtaining an information sub-network and a network mode of the information sub-network from the music information network, and obtaining the social relationship related to the information sub-network; secondly calculating mean edge betweenness of different types of relational edges in the information sub-network; thirdly making a calculation according to the mean edge betweenness to obtain propagation factors of the different types of relational edges; fourthly designing edge weights in the information sub-network according to the social relationship and selecting nodes from nodes of the same type according to the edge weights to perform random walk; and finally performing random walk in the information sub-network in combination with the propagation factors and the edge weights to obtain a node influence ranking in the network so as to obtain the song popularity. According to the method proposed by the invention, the influence of a user group on songs is considered, so that the final popularity analysis is more reasonable.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
User-specific performance monitor, method, and computer software product
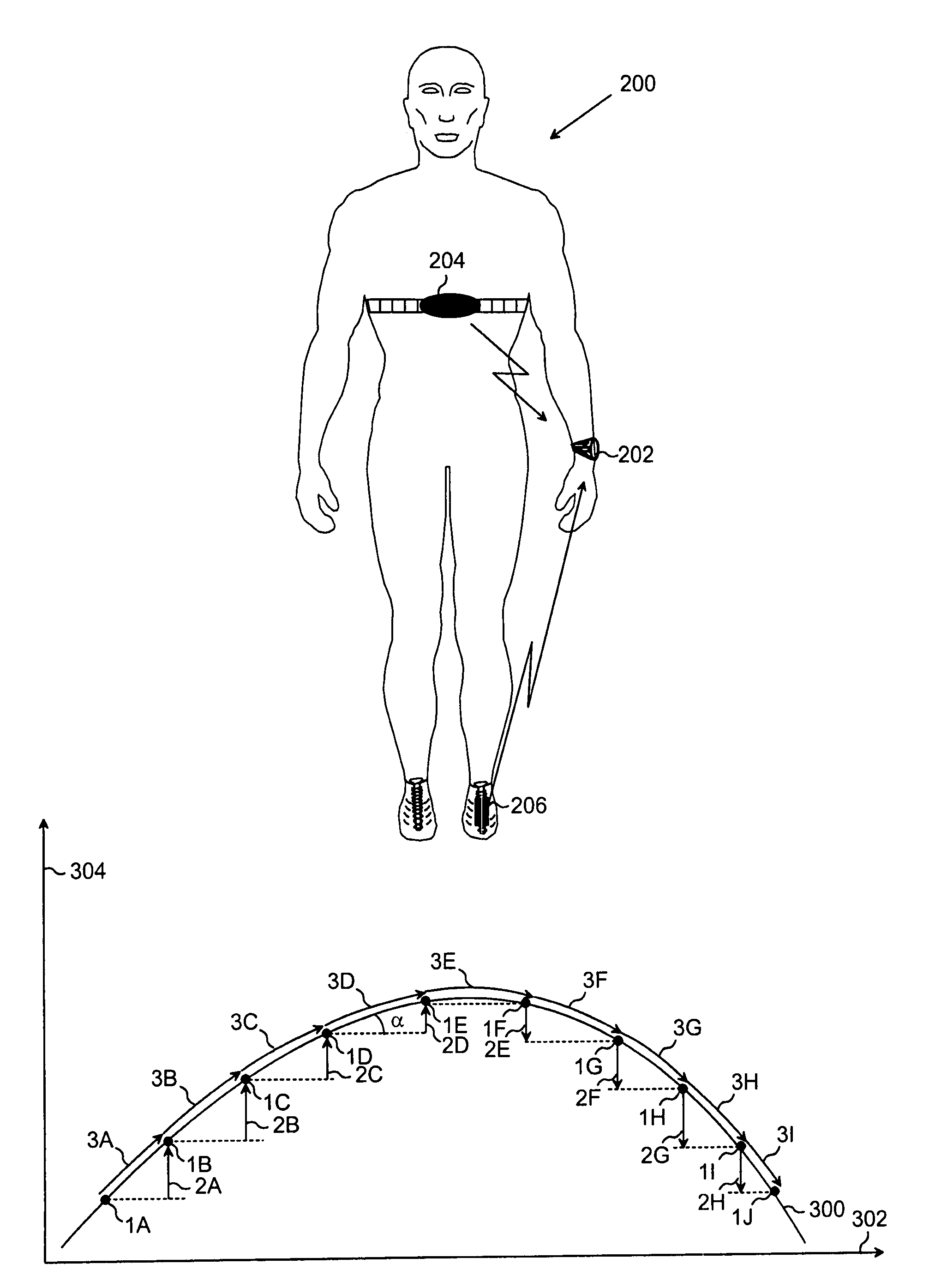
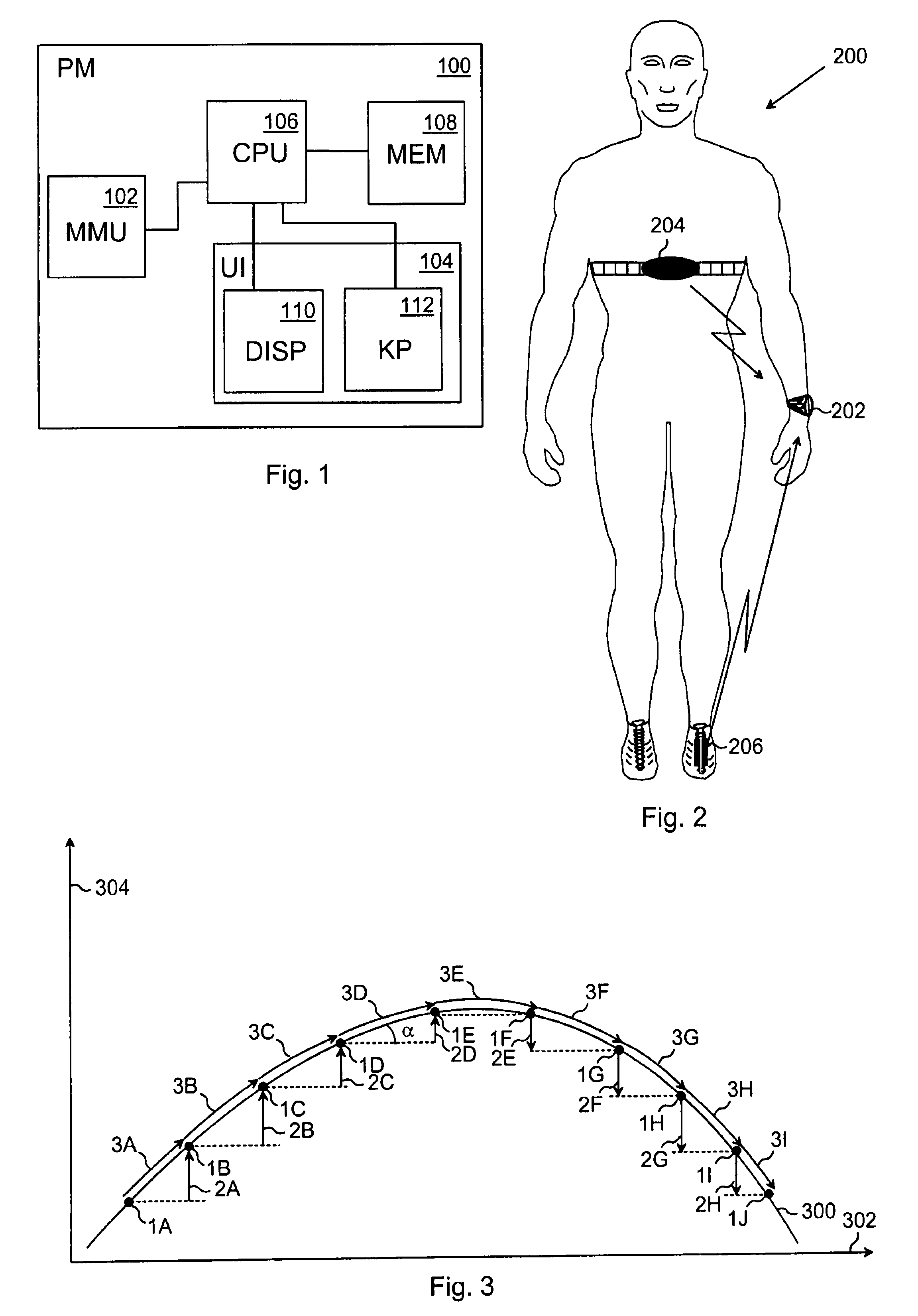
ActiveUS7901326B2Reliable estimateCosmonautic condition simulationsGymnastic exercisingExertionEngineering
A method for determining an exertion parameter during physical exercise, user-specific performance monitor implementing the method, and computer software product. The method includes determining a propagation variable characterizing the user's propagation; determining a gravitational motion variable characterizing the user's motion in the direction of the gravitational field; calculating an inclination factor proportional to the inclination of a propagation base in accordance with the propagation variable and the gravitational motion variable; calculating a propagation factor proportional to propagation efficiency characterizing the user's ability to move with respect to the inclination of the propagation base, the propagation factor having a different calculated value based on whether the inclination factor is positive or negative for the same base value of the inclination factor; and calculating an exertion parameter that characterizes the user's energy consumption along the propagation route in accordance with the propagation variable, the gravitational motion variable, and the propagation factor.
Owner:POLAR ELECTRO
Method for estimating transmission power of deception jamming signal
ActiveCN107422312AAccurate estimateImprove interferenceWave based measurement systemsUltrasound attenuationRadar beam
The invention provides a method for estimating the transmission power of a deception jamming signal. The method comprises the steps that: a radar beam points at a real target, a radar transmitter transmits a radar signal, a reconnaissance plane intercepts the radar signal, and the transmission power of transmitting the radar signal by the radar transmitter is estimated; a false target for realizing a deception jamming effect is realized, and the echo power of a real target at the position of the false target received by a radar receiver is estimated; the jamming signal power received by the radar receiver when effective jamming is generated is estimated; and according to the power range of the jamming signal received by the radar receiver, the transmission power of the jamming signal is estimated. According to the method, through considering the attenuation of signal space propagation by environmental factors and reflecting the attenuation to a propagation factor in the estimation process of the signal transmission power, the jammer transmission signal power for deception jamming under an effective jamming condition can be more accurately obtained.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for embryo culture in vitro and plant regeneration of euscaphis konishii hayata
InactiveCN101595845AGrow vigorouslyPromote growthCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsEmbryoPlantlet
The invention provides a method for embryo culture in vitro and plant regeneration of euscaphis konishii hayata, and belongs to the technique of culturing euscaphis konishii hayata embryo. The method solves the problems existing in the prior art that the seed germination rate of the euscaphis konishii hayata embryo is low, and well purified tissue culture seedlings cannot be provided in large amount. In the method, the full seeds in the same year are selected as materials, and the embryo undergoes induced culture for 15 to 20 days to grow strong seedlings; after proliferation for 20 to 30 days and induced rooting for 20 to 25 days, the seedlings are grown and transplanted, and the survival rate is as high as more than 95 percent; and the propagation factor is higher, and the survived seedlings are tall and strong, and well grown.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method for culturing cephalotaxus excised embryos and regenerating plants
InactiveCN101611698AGrow vigorouslyPromote growthPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsEmbryoPlantlet
The invention provides a method for culturing cephalotaxus excised embryos and regenerating plants, which belongs to the cephalotaxus culture technology. The method aims to solve the problem that the prior art is difficult to get ideal germination rate and more robust seedlings because of the long dormancy period of cephalotaxus seeds, long emergence time and low emergence rate. The method is characterized in that fresh plump seeds are selected as materials and subjected to induction culture; robust sprouts can be germinated from embryos after 15 to 20 days; seedlings can be formed and transplanted after 20 to 25 days of proliferation and 25 to 30 days of root induction; and the survival rate is as high as above 90 percent. The method has the advantage of high propagation factor, and surviving seedlings are good in growth, robust and upright.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
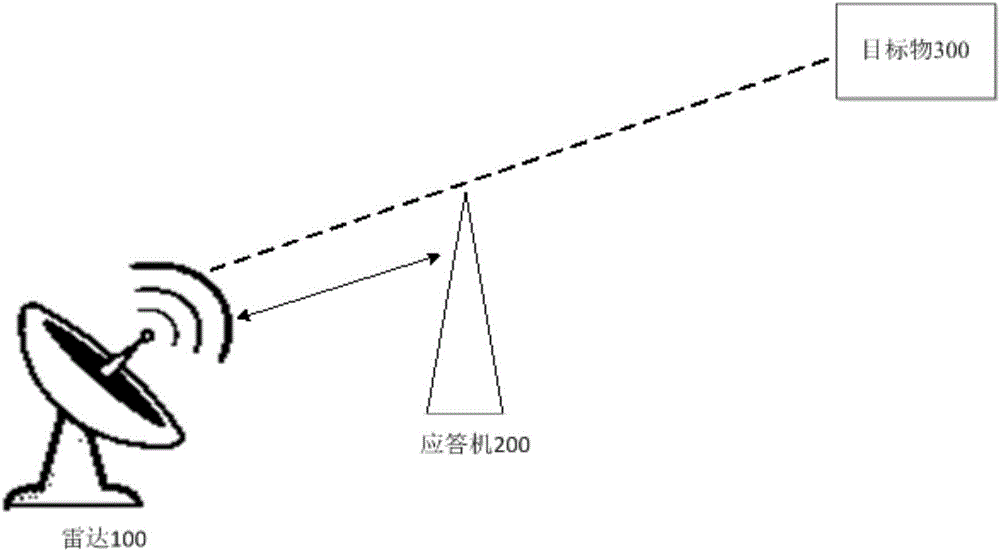
Responder power calibration method and device
The invention discloses a responder power calibration method and device. The method comprises the steps that multiple echo signals returned by multiple calibration targets which are mutually different in distance to radar in the same scope of the beams of the radar are received; a directional diagram propagation factor calibration value is acquired according to the received multiple echo signals; and the power control factor of a responder of the preset position is acquired according to the directional diagram propagation factor calibration value so as to calibrate the output power of the responder of the preset position. The following beneficial effects can be obtained by applying the scheme: the directional diagram propagation factor calibration value is acquired according to the echo signals of at least two calibration targets so as to acquire the power control factor of the responder to calibrate the output power of the responder. Therefore, the calibrated responder is enabled to accurately simulate the echo characteristics of the target objects so as to perform more accurate detection and assessment on the detection performance index of the radar.
Owner:INST OF RADAR & ELECTRONICS CONFRONTATION ARMY AIR FORCE EQUIP RES INST OF PLA
Method for establishing high-frequency regeneration system of euscaphis konishii hayata leaves and quickly reproducing euscaphis konishii hayata leaves
InactiveCN101595846AGrow vigorouslyPromote growthCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue cultureCataphyllEmbryo
The invention provides a method for establishing a high-frequency regeneration system of euscaphis konishii hayata leaves and quickly reproducing euscaphis konishii hayata leaves, and belongs to the technique of culturing euscaphis konishii hayata embryo. The method solves the problems existing in the prior art that the seed germination rate of the euscaphis konishii hayata embryo is low, and well purified tissue culture seedlings cannot be provided in large amount. In the method, partial tender leaves removed during the sub-transplanting in the stem reproduction or seed reproduction are selected as materials, and the tender leaves undergo induced culture for 15 to 20 days to grow strong seedlings; after proliferation culture for 20 to 30 days and induced rooting for 20 to 25 days, the seedlings are grown and transplanted, and the survival rate is as high as more than 95 percent; and the propagation factor is higher, and the survived seedlings are tall and strong, and well grown.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Volume fracture dynamic flow-back simulation device and method
The invention discloses a volume fracture dynamic flow-back simulation device and method. The simulation device comprises an airtight cavity defined by an airtight shell, an upper steel plate and a lower steel plate. The airtight cavity is divided by a movable sealing plate into a high-temperature and high-pressure work cavity and a dynamic control cavity. The movable sealing plate can move between the high-temperature and high-pressure work cavity and the dynamic control cavity. A three-dimensional rock core model is arranged in the high-temperature and high-pressure work cavity, and a sand carrying liquid injection pipe is arranged in the three-dimensional rock core model. A liquid injection pipe is arranged on an upper steel plate of the dynamic control cavity. By means of the volume fracture dynamic flow-back simulation device and method, the fracture simulation three-dimensional rock core model is adopted, design for dynamically controlling pressure control of the cavity is adopted, the formation mechanism of joint nets such as a coal bed gas reservoir and a shale gas reservoir can be studied, and the micro-crack propagation factor can be studied. By means of the volume fracture dynamic flow-back simulation device and method, due to the fact that the volume fracture dynamic flow-back system matched with field fracture construction is designed, the physical effect rule of fracture liquid retention on three-dimensional core models of coal petrography, shale and the like can be studied.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
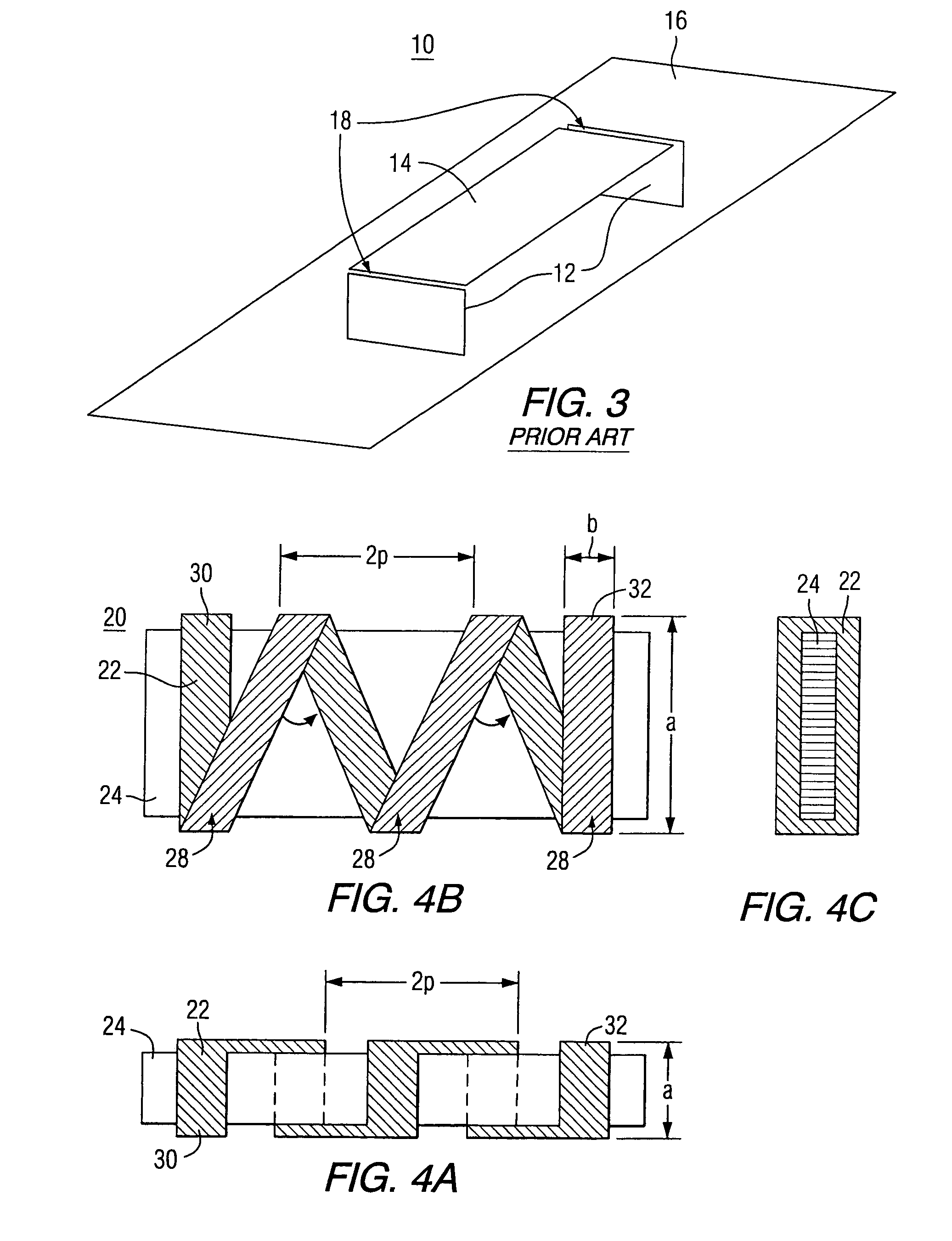
Broadband antenna structures
InactiveUS6965348B2Comparable and enhanced performanceImproved broadband operationResonant long antennasRadiating elements structural formsWave structureElectrical conductor
There is disclosed an antenna exhibiting resonance over a broad frequency band or over a plurality of closely-spaced frequency bands, comprising a ground plane, a non-driven element affixed substantially perpendicular to the ground plane, a driven element affixed substantially perpendicular to the ground plane and a horizontal conductor electrically connected between the driven and the non-driven elements and disposed substantially parallel to the ground plane. The non-driven and the driven elements further comprise periodic slow wave structures. The periodic slow wave structures are configured to provide a substantially constant propagation factor with respect to the applied signal frequency, such that the antenna exhibits broad resonance characteristics.
Owner:SKYCROSS CO LTD
Time domain rate distortion optimization method based on distortion type propagation analysis
ActiveCN111314703ASolving the problem of rate-distortion optimization in the time domainExcellent global rate-distortion performanceDigital video signal modificationAlgorithmPropagation factor
The invention belongs to the technical field of video encoding and decoding, and particularly relates to a time domain rate distortion optimization method based on distortion type propagation analysis. The method comprises the following steps of: analyzing according to a time domain dependency relationship under an LD structure and distortion propagation under a skip mode and an inter mode; the dependence rate distortion optimization problem based on time domain distortion propagation is reconcluded; a time propagation chain is constructed; estimating aggregation distortion of the current coding unit and the affected future coding unit; and calculating a propagation factor of a coding unit in the time domain distortion propagation model, further adjusting a Lagrange multiplier through themore accurate propagation factor to realize time domain dependence rate distortion optimization, and meanwhile, realizing time domain dependence rate distortion optimization of the I frame by using asecondary coding technology for the I frame.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
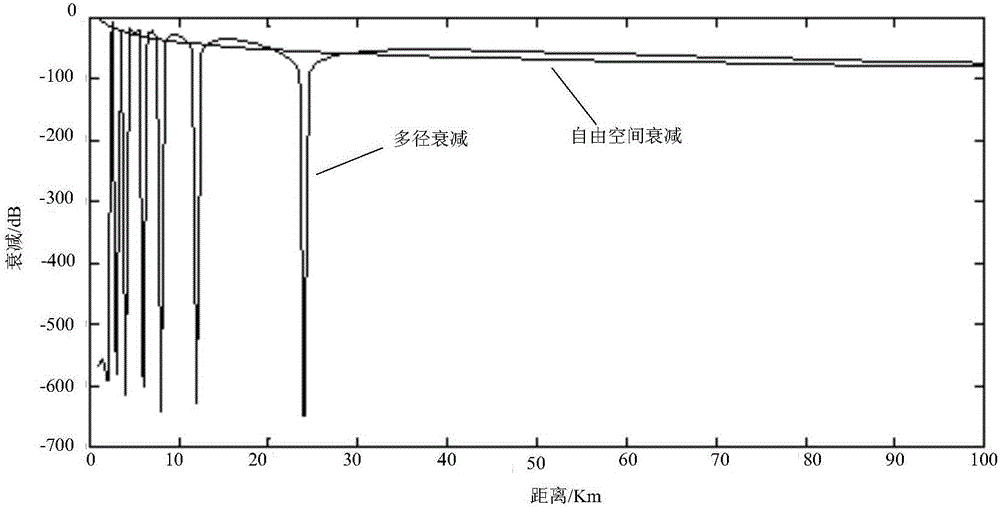
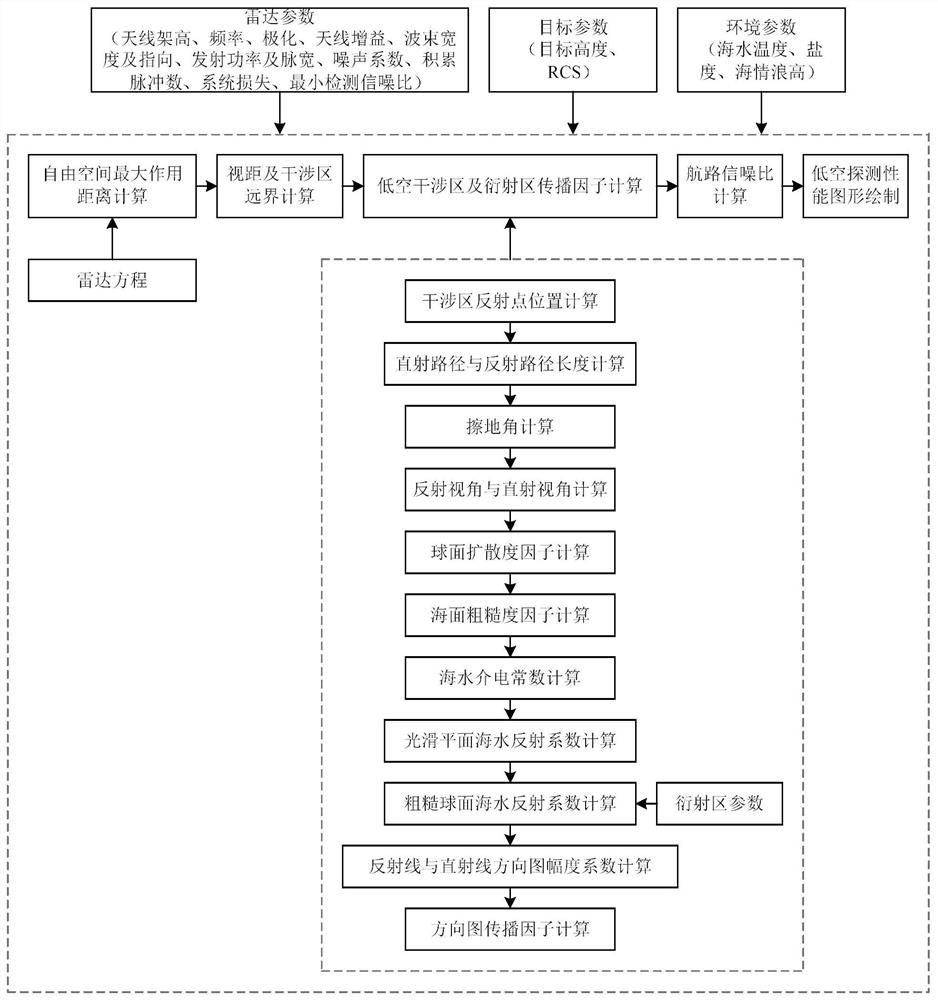
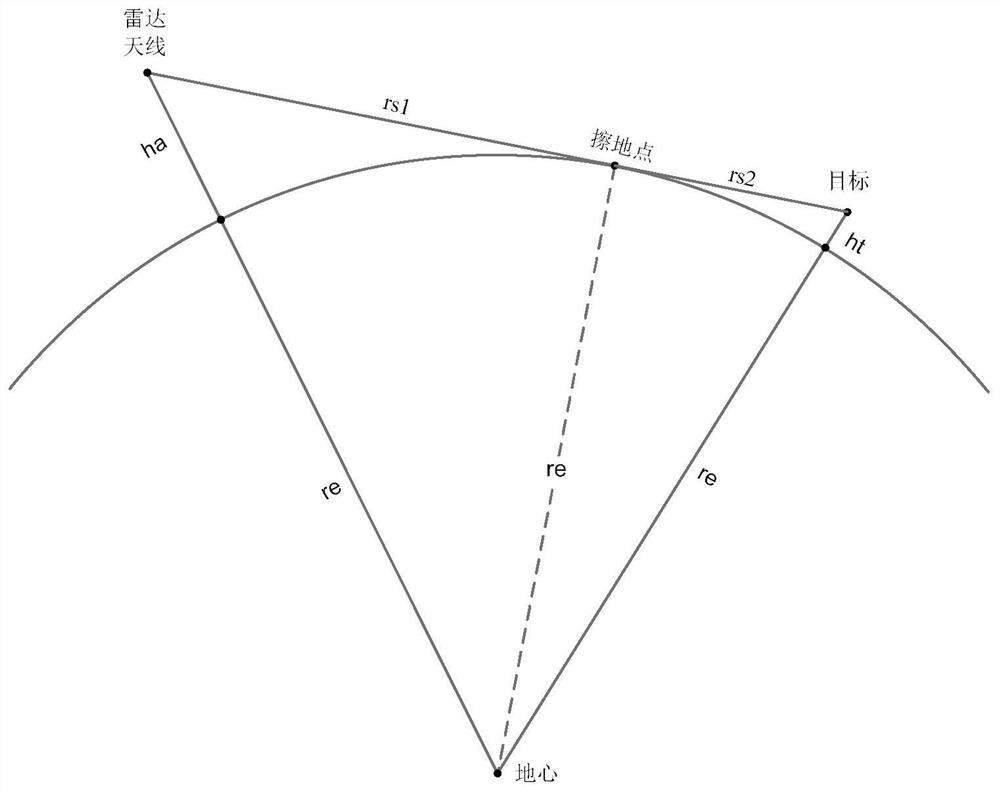
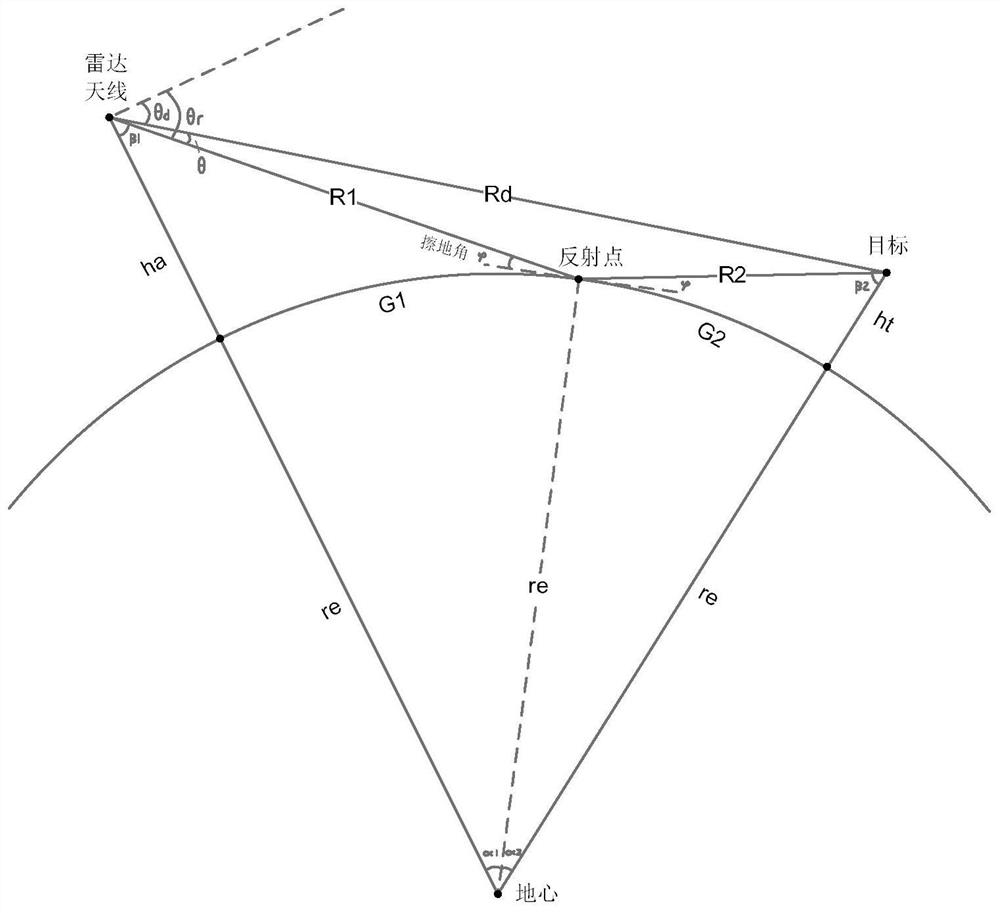
Radar sea surface low-altitude detection performance simulation method and simulation model
PendingCN111896924ASimulation results are real and accurateStrong adaptability to application scenariosWave based measurement systemsAirwayEngineering
The invention discloses a radar sea surface low-altitude detection performance simulation method and simulation model. The model comprises a free space maximum action distance calculation module whichis used for calculating the free space maximum action distance of a radar for target detection through a radar equation, a sight distance and interference area far-field calculation module which is used for solving the interference area far-field distance, an interference region and diffraction region propagation factor calculation module which is used for calculating an interference region propagation factor and a diffraction region propagation factor, an airway signal-to-noise ratio calculation module which is used for calculating an echo signal signal-to-noise ratio and a free space signal-to-noise ratio of each point of the sea surface low-altitude target airway in an interference region and a diffraction region, and a low-altitude detection performance graph drawing module which is used for drawing a low-altitude detection performance curve graph according to the echo signal signal-to-noise ratio and the free space signal-to-noise ratio of each point position of the target airway. Compared with other conventional models, the established simulation model provided by the invention has more real and accurate simulation result and higher application scene adaptability.
Owner:扬州船用电子仪器研究所
Method for batch production of mat grass through one-step culture
InactiveCN106613969AImprove good featuresImprove consistencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsPaddy fieldPlantlet
The invention discloses a method for batch production of mat grass through one-step culture. The method comprises the following steps of (1) acquiring basic seedlings: selecting tillering nodes of find mat grass plants as explants, sterilizing the explants, culturing the sterilized explants on 1 / 2MS+6-BA 1.2 to 4.5 mg / L of solid agar culture, and inducing the tillering nodes; (2) carrying out batch production: inoculating the tillering nodes acquired through the step (1) onto a solid agar culture with 1 / 2MS+6-BA 1.2 to 4.5 mg / L + NAA 0.02 to 1.0 mg / L + IAA 0.02 to 1.0mg / L + paclobutrazol 0.5 to 5.0mg / L for propagating and rooting; (3) carrying out field production: before taking seedlings out of a test-tube for transplanting, opening a test-tube cap for hardening the seedlings, taking out for cleaning the culture medium on the root part, and then directly transplanting the seedlings into a paddy field. The method is excellent in culture effect, high in propagation factor, good in stability and low in production cost, and is a fast propagation method for acquiring a large number of test-tube plantlets within the shortest time.
Owner:INST OF SUBTROPICAL AGRI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Radar detection capability simulation method and device
ActiveCN114781190AIncrease authenticityWave based measurement systemsDesign optimisation/simulationRadar antennasMultipath effect
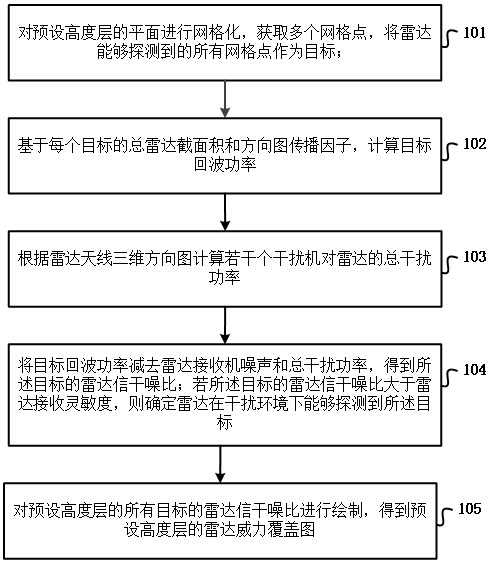
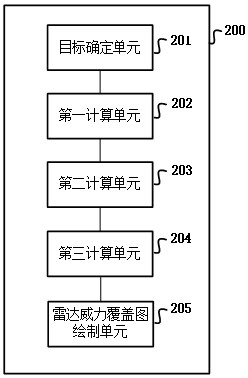
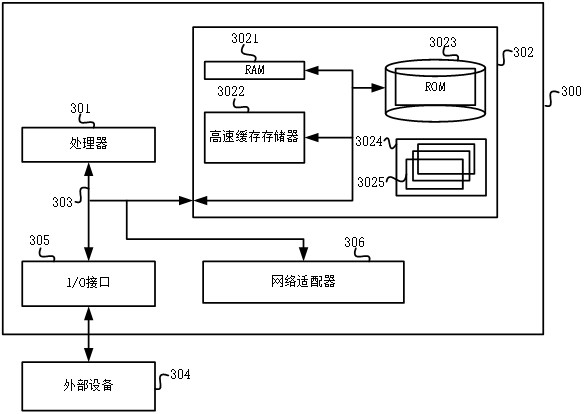
The invention provides a radar detection capability simulation method and device, and relates to the technical field of radar detection, and the method specifically comprises the steps: carrying out the meshing of a plane of a preset height layer, and obtaining a plurality of grid points; taking all grid points which can be detected by the radar as targets; target echo power is calculated based on the total radar sectional area and the directional diagram propagation factor of each target; calculating the total interference power of the plurality of jammers to the radar according to the three-dimensional directional diagram of the radar antenna; subtracting the radar receiver noise and the total interference power from the target echo power to obtain the radar signal to interference plus noise ratio of the target; if the radar signal to interference plus noise ratio of the target is greater than the radar receiving sensitivity, determining that the radar can detect the target in an interference environment; and drawing the radar signal to interference plus noise ratios of all targets of the preset height layer to obtain a radar power coverage map of the preset height layer. According to the method, the target total radar sectional area and multipath effect calculation are added in radar detection, so that the authenticity of simulation is improved.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE HONGTU INFORMATION TECH
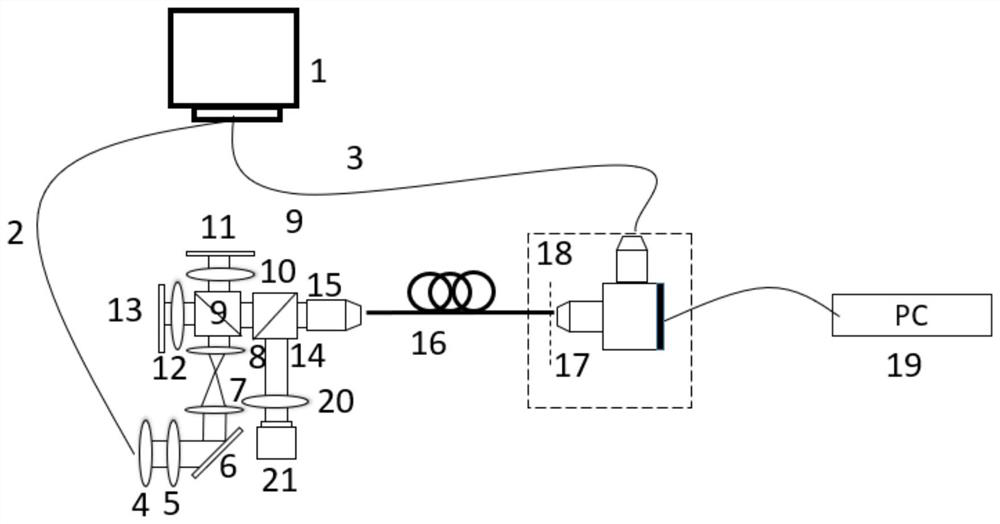
Full-vector modulation single-fiber high-signal-to-noise-ratio three-dimensional imaging method and device
The invention discloses a full-vector modulation single-fiber high-signal-to-noise-ratio three-dimensional imaging method and device. The device comprises a laser, a spatial light modulator, a polarization modulation module, an orthogonal polarization microscopic module and the like. Exciting light generated by the laser device passes through the spatial light modulator and the polarization modulation module to form a light field with any controllable phase, polarization and amplitude. And after the light enters the optical fiber, a full-vector transmission matrix is reconstructed through the cross-polarization microscopic module. And mode coupling, mode loss and polarization dispersion in the long-distance large-curvature multimode optical fiber are compensated through numerical processing of the transmission matrix. And axial scanning with a high signal-to-noise ratio is obtained by adding a propagation factor in a virtual frequency domain of an optical fiber emergent end, and high-signal-to-noise-ratio, high-resolution and large-depth imaging is realized, so that the method can be widely applied to the aspect of biomedicine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB
Method for quickly propagating breeding peanut seeds
InactiveCN102246696AHigh reproductive coefficientPreserve ancestral characteristicsPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBudCell budding
The invention discloses a method for quickly propagating breeding peanut seeds, which comprises: performing tissue culture of the peanut seeds; slicing young leaves of obtained peanut plants; subjecting the slices to tissue culture in a bud induction culture medium, an elongation culture medium and a rooting medium; and planting the tissue culture seedlings. When the method is used, the propagation factor of a breeding seed is improved by over 6,000 times, the propagation factor of the peanut breeding seeds is improved greatly, the hereditary characteristics of the peanut breeding seeds are retained, and the promotion of high-quality peanut breeding seeds is accelerated.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com