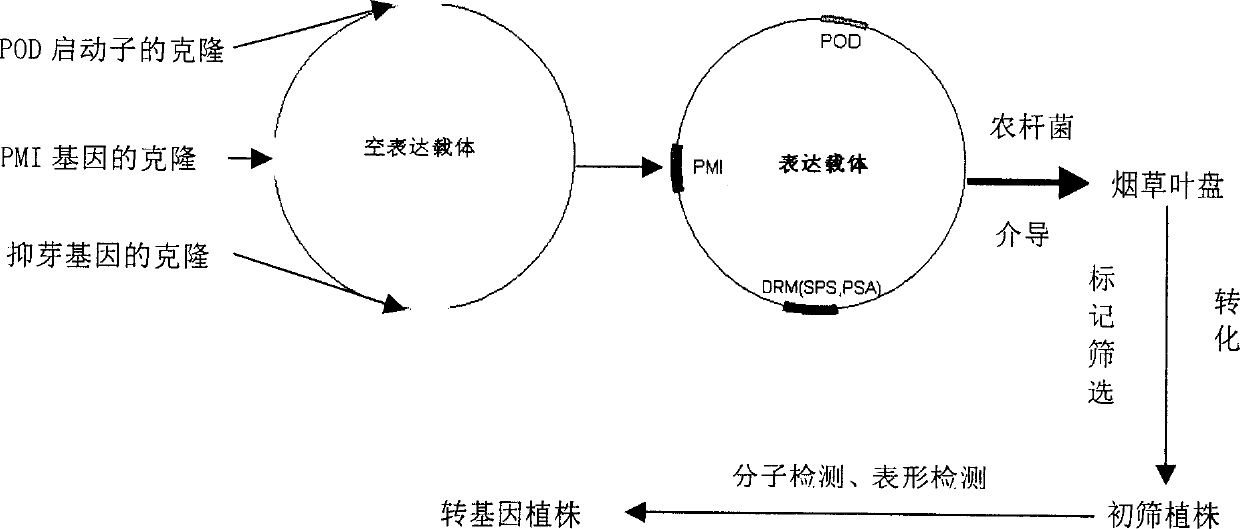
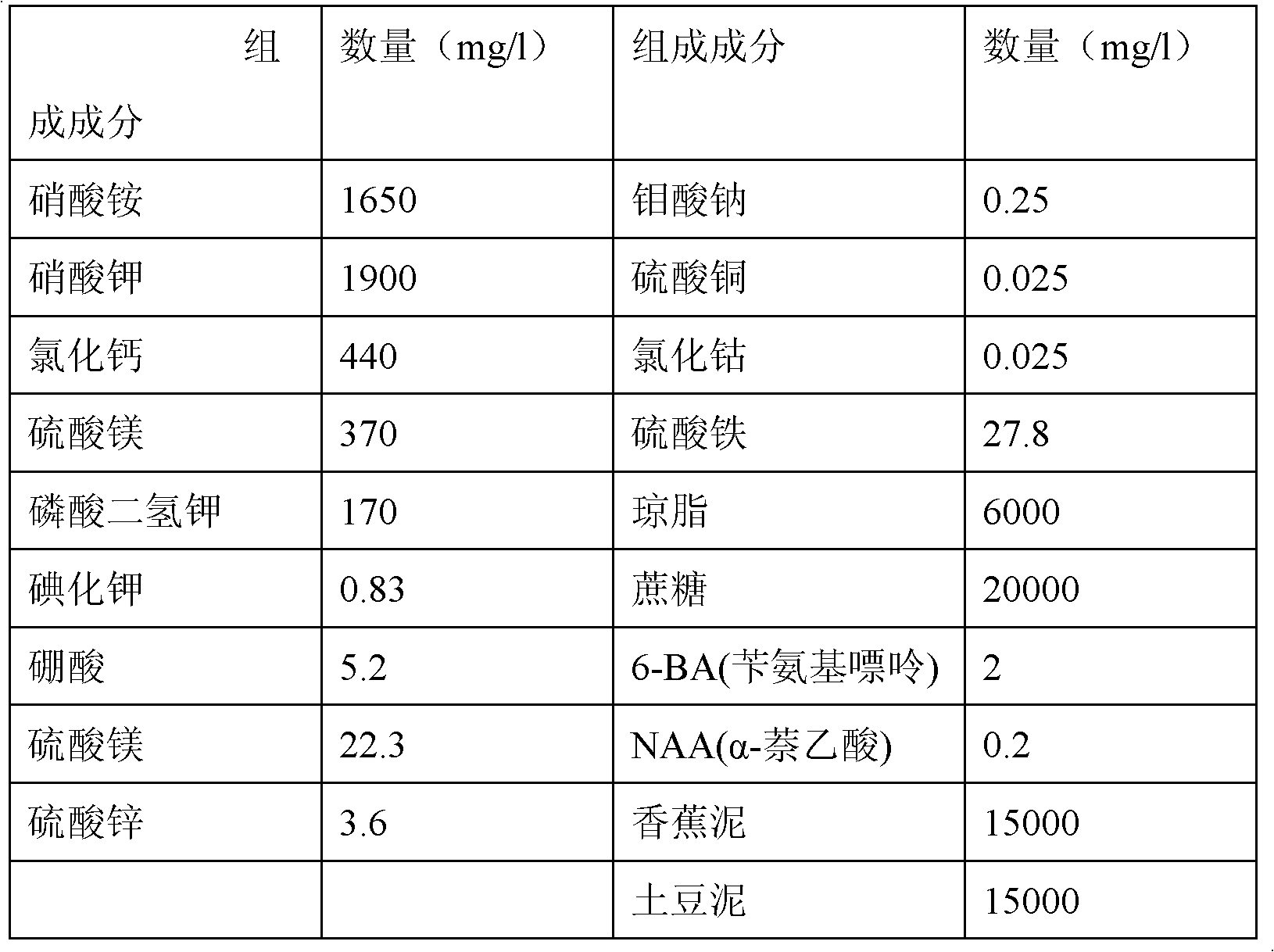
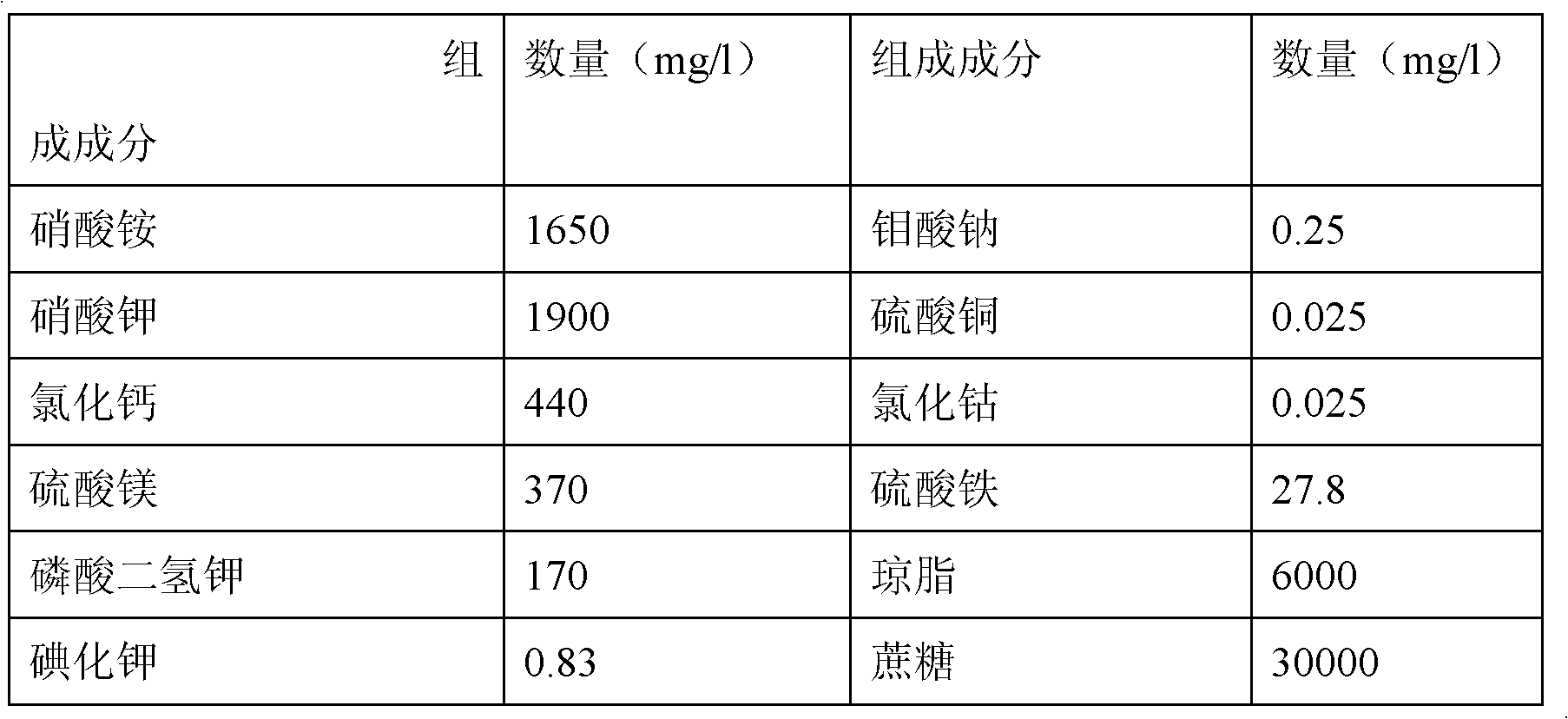
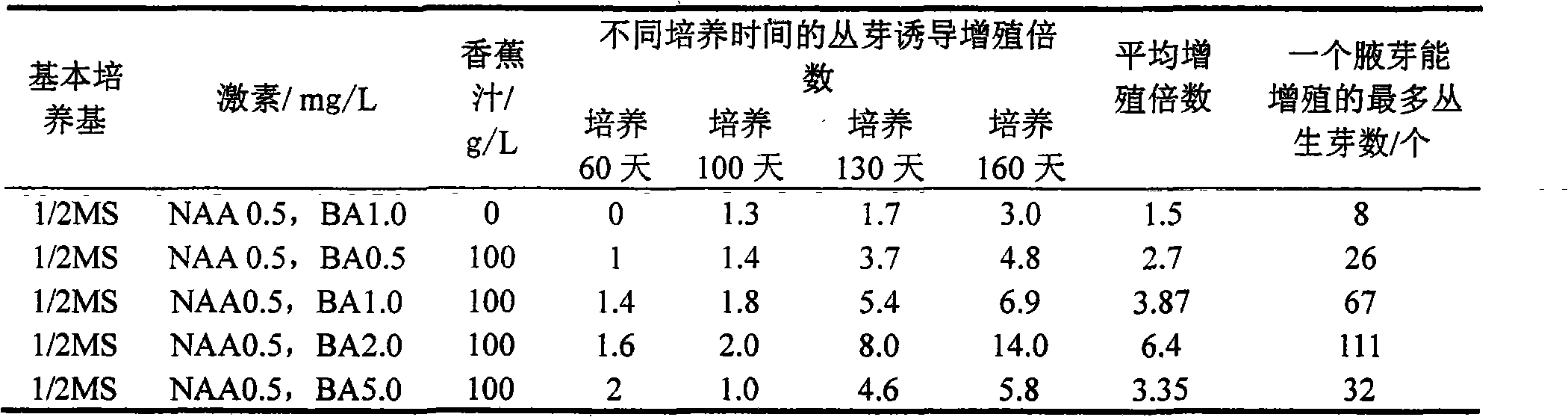
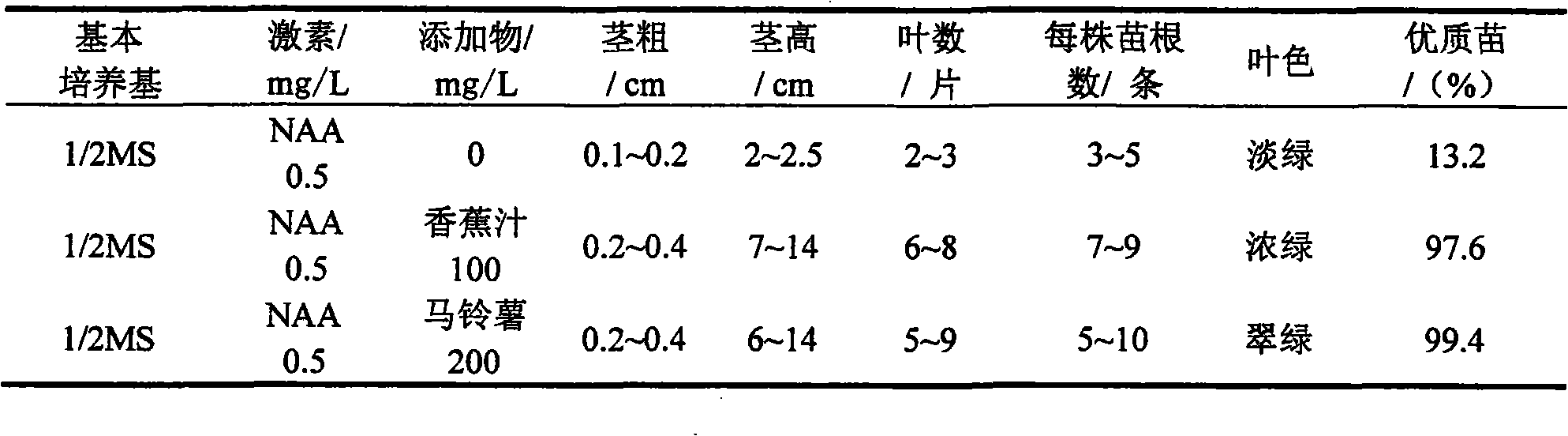
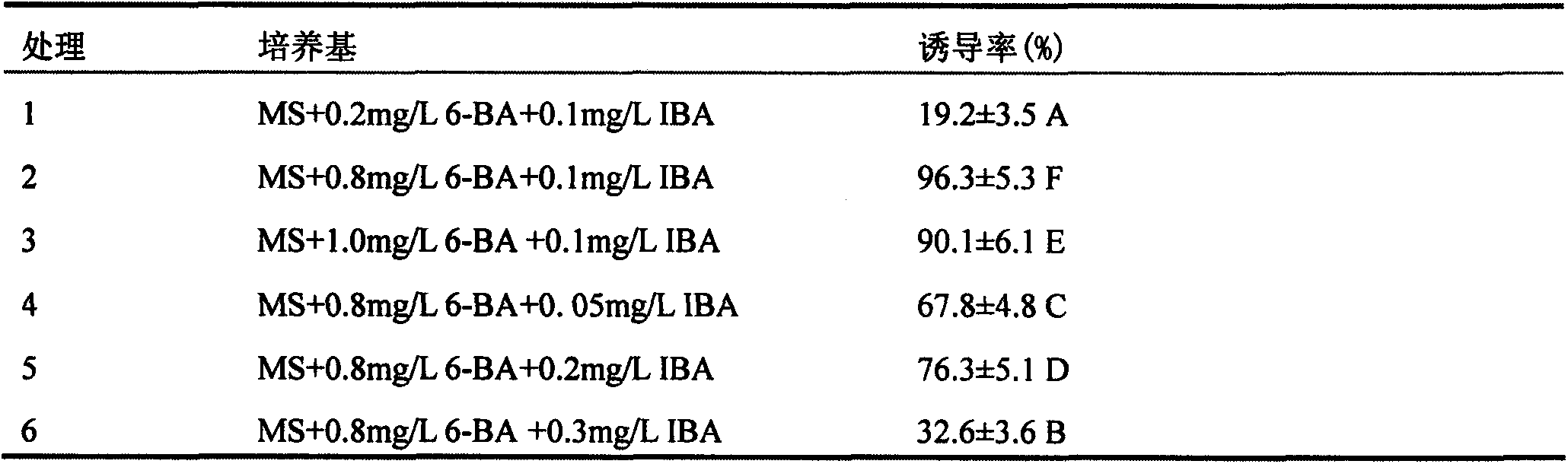
Patents
Literature
1288 results about "Axillary bud" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The axillary bud (or lateral bud) is an embryonic or organogenic shoot located in the axil of a leaf. Each bud has the potential to form shoots, and may be specialized in producing either vegetative shoots (stems and branches) or reproductive shoots (flowers). Once formed, a bud may remain dormant for some time, or it may form a shoot immediately.
Methods for stable transformation of plants
InactiveUS6858777B2Improve conversion efficiencyImprove transformation efficiencyOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationAxillary budNicotiana tabacum
Multiple shoot structures are induced from plant tissues (e.g., shoot apices or axillary buds on an artificial medium) to produce multiple shoot cultures. These multi-shoot cultures are then transformed by known transformation methods. Plants are subsequently regenerated from the transformed cells. Crops that may be efficiently transformed by this method include plants normally recalcitrant to transformation such as sugar beet, sunflower, soybean, cotton, tobacco, tomato, peanuts, melons, watermelon, squash, Brassica, and pepper.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Culturing method of auxilliary bud less tobacco after topping
The present invention discloses a tobacco cultivation method. Said method is characterized by that it adopts a molecular biological technique to identify key gene capable of promoting axillary bud germination and growth after the tip is pruned, then uses nocuity inducible promoter to drive antisense RNA and make it promptly express after the tip is pruned so as to inhibit the expression of said key gene capable of promoting axillary bud germination and growth and make the axillary bud can not be germinated or grown.
Owner:贾朝钧
Plant regeneration method for butterfly orchid
InactiveCN103004603AReduce manufacturing costReproduce fastPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAxillary budAnthesis
The invention discloses a plant regeneration method for butterfly orchid, belonging to the field of butterfly orchid planting. The plant regeneration method comprises the following steps of: selecting pedicel axillary bud stems with length of 2-5 centimeters on butterfly orchid plants; carrying out induction culture on stem apexes for 2-3 weeks for gradually forming protocorms after 25-30 days; continuously splitting the protocorms to implement subculture acceleration reproduction; moving seedlings with height of one centimeter to a strong seedling culture medium to be cultured for 3-6 months; and inducing the seedlings to root for 20-25 days, and transplanting the strong seedlings with height of 8-10 centimeters, wherein the survive rate of the seedlings is higher than 95%, nursery-grown plants grow well after surviving. The plant regeneration method enables the excellent butterfly orchids to form sterile strains within a short time for implementing large-scale industrial production, can be produced yearly, has a high reproduction speed, and provides novel, fresh, fragrant and colorful flowers with various colors and consistent model. Moreover, a production technology with high technical content is provided to enterprises, so that the plants are consistent in size for facilitating control on flowering phases and uniform management of industrialization, the production costs of the enterprises are reduced, and giant economical benefits are created.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Rapid propagation method for tissue cultivation of dendrobium candidum stem
InactiveCN103053425AAddressing Inadequate SterilizationHigh pollution rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAxillary budSocial benefits
The invention relates to a rapid propagation method for tissue cultivation of a dendrobium candidum stem, belonging to the technical field of artificial cultivation of dendrobe. The method comprises the following steps of preparing an explant, inducing axillary bud and protocorm, conducting propagation cultivation, and rooting and seeding cultivation. The rapid propagation method has the beneficial effects that the technical problems of insufficient explant sterilization, high pollution rate, incapability of conducting axenic cultivation, slow protocorm differentiation, less differentiation, long propagation period, high production cost and the like can be well solved. Compared with the prior art, the rapid propagation method has the advantages that rapid propagation can be achieved; and the propagation period can be reduced by over 60 days. In addition, according to the rapid propagation method, seeding genetic traits are stable, the variation is small, the variety is pure, and the parent characteristics and features can be well kept. Thus, excellent seeding guarantee is provided for development of plant industry of dendrobium candidum, and the rapid propagation method has good economic benefit and social benefit.
Owner:杨宝明
Tissue culture rapid propagation method of liquorice
InactiveCN104686345ASolve large-scale productionPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAxillary budShoot
The invention discloses a tissue culture rapid propagation method of liquorice. The axillary bud stems of the liquorice are taken as the explants to establish a liquorice in-vitro rapid propagation system, and a foundation is laid for the large-scale production of the liquorice. The stem with the axillary buds is taken as the explant, and the tissue culture rapid propagation of the liquorice is realized by use of the processes of multiple shoot induction, multiplication culture, root and shoot induction, test-tube plantlet acclimatization and transplant and the like; the technical support is provided for the industrialization development of the liquorice.
Owner:陈桂容
Tissue culture and tachytelic propagating method for alpine rhododendron
InactiveCN1568670ANot affected by seasonGrow fastHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAxillary budLactalbumin hydrolysate
The invention relates to alpine rhododendron tissue culture quick-propagation method. All the medium is prepared according to following material: medium for inducing explant: 1 / 4MS, MS ferric salt, VitB50.2mg, lactalbumin hydrolysate 300mg, sucrose 30g+Kt1.0mg / L; medium for propagating cluster sprout: 1 / 2MS, Kt0.5mg / L; medium for rooting: 1 / 2MS, NAA5mg / L, active carbon 0.5%. The method of alpine rhododendron tissue culture quick-propagation is characterized as test tube sprout provisional planting method adopting tender stem segment axillary bud culture method and 'two-step' method. The advantages of the invention lie in: the growth is not influenced by season, plant has strong resistance to stress, and the plant has big colorful flowers.
Owner:上海市闵行区农业科学研究所
Rapid propagation technique of Dendrobium candidum axillary buds
ActiveCN102369881AIncrease the number ofPromote recoveryPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAxillary budBud
The invention discloses a rapid propagation technique of Dendrobium candidum axillary buds. According to the technique, Dendrobium candidum axillary buds are used as explants directly to induce fasciculated buds; influences of combinations of different types of hormones with different concentration and different natural extracts on survival and growth of axillary buds, induction and multiplication of fasciculated buds and seedlings are compared, the quantity and quality of seedlings growing from fasciculated buds are researched and explored, the optimal culture medium formula in each stage is screened, and therefore, a fasciculated-bud-way high-efficiency rapid propagation system is established, so that plants obtained through rapid propagation are consistent with parent plants genetically so as to provide basis for restoration of wild population of Dendrobium candidum, and furthermore, wild resources are protected. Compared with vegetative propagation, the rapid propagation technique provided by the invention greatly improves propagation factor. A high-efficiency rapid propagation system of Dendrobium candidum which is an endangered plant provides a technical probability for the large-scale production and is beneficial to the restoration of wild population.
Owner:SHANGHAI XCT HEALTH FOOD
Tender stem callus plant regeneration induction culture medium for lonicera caerulea
InactiveCN102119657APromote healthy growthPromote productionPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAxillary budCalla
The invention relates to a tender stem callus plant regeneration induction culture medium for lonicera caerulea and solves the problems of low plant differentiation rate and high culture medium cost problem of the auxiliary bud or stem tip culture, which is the main tissue culture of lonicera caerulea. The culture medium consists of a large amount of macroelements, microelements and hormone, wherein the hormone consists of 6-benzyl aminopurine at a concentration of 1.0 to 2.0mg / L and indolebutyric acid or naphthylacetic acid at a concentration of 0.05 to 0.2mg. When the LD1 culture medium of the invention is used, the tender stems of lonicera caerulea can be easily induced to form calla, and the induction rates of the calla are all over 90 percent; and the probability of the induction of the calla into plants is high, the plant differentiation rate is up to 50 to 82 percent which is 66.6 to 173.3 percent higher than that of the conventional Murashige-Skoog (MS) culture medium, and the cost is saved by 45.1 percent compared with the reference MS culture medium.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Tissue-culturing rapid propagation method of Actinidia macrosperma
InactiveCN1826878AImprove qualityConservation of Germplasm ResourcesCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue cultureAxillary budRoot growth
The invention provides a method of rapid breeding of kiwi fruit with large seed by tissue culture. The invention comprises steps of selecting and treating explant, inducing culture medium, root culturing and replanting, etc. The invention takes MS culture medium as basis and adds BA, NAA, GA, ZT and other external plant growth regulator to induce the growth of axillary bud of the said kiwi fruit and strengthen sprout and root. The root growth rate is as high as 100%, the average bud height is 6.28 cm and the average replanting survival rate is 91% after 35 days culture. The invention solves the technique problem of rapid breeding of said kiwi fruit and provides a method of short period, high breeding rate and low cost for the industrial production of kiwi fruit with large seed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for rapid propagation and timely flowering of China rose
The invention relates to a method for rapid propagation and timely flowering of China rose, and relates to the technical field of flower planting. The method comprises the following steps: in January and February, scissoring annual stingless wild rose branches, and reserving one or two bud points to be taken as stocks for grafting; selecting annual China rose branches as scions, reserving one or two bud joints, cutting the upper ends of the scions to be flat, cutting the lower ends of the scions to be inclined planes with the angles of 30-45 degrees, wherein the distances between pruning wounds and axillary buds are 1 cm; putting the cut stocks and scions in nutrient solution and soaking for 10-20 minutes, then grafting the soaked stocks with the scions together, tightening grafting ports with plastic films, and then daubing rooting powder on the roots of the stocks and inserting the roots of the stocks in soil; beginning to transplant two months later after the stocks are alive through cottage, irrigating and fertilizing according to a conventional management method 15-20 days later, wherein the China rose can be flowered in May. The method is simple and feasible; compared with a traditional grafting method, the survival rate can reach more than 90%, nursery stocks grow strongly, the China rose can be flowered timely, the planting cost is reduced, and the economic benefit is improved.
Owner:ANHUI BAIHUI GARDEN
In vitro conservation method of churysanthemum by reducing macroelements in the medium
InactiveCN101006774ANormal growthKeep material stableDead plant preservationHorticulture methodsAxillary budNormal growth
The invention relates to a method for conserving chrysanthemum in vitro through reducing major element in the medium, which is special for the in vitro conservation of the chrysanthemum germplasm resource. The invention comprises the steps of: taking the suckers of the chrysanthemum as the explants, and axillary buds for subculture, and conserving on the 1 / 2MS, 1 / 2MS (1 / 2NH4+) or 1 / 4MS medium containing 6-BA0.3mg / L and NAA0.1mg / L. The survival rate for a 12-month conservation is 100%, 8 months longer than that of conservation on the normal MS medium. After the conservation material recovers to normal growth, the descendant is proved to have no genetic variance through the detection of POD, EST and ISSR. The invention uses the method of conserving chrysanthemum test-tube plantlet through reducing major element in the medium and identifies the genetic stability of the descendant, which proves that the plants grow normally after one-year conservation and the descendant has no genetic variation.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Modified medium for improving propagation of stems of Dendrobium officinale and propagation method
InactiveCN102613082AAchieve high efficiencyAchieve securityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAxillary budSucrose
The invention discloses a modified medium for improving propagation of stems of Dendrobium officinale and a propagation method. The medium comprises MS (Murashige and Skoog) basal medium, cane sugar 20g / l, agar 6g / L, 6-BA (benayl aminopurine) 2mg / l, NAA (alpha-naphthaleneacetic acid) 0.2-0.5mg / l, banana mash 15-20g / l, potato mash 15-20g / l, and common tap water replacing distilled water. The modified MS medium is used to propagate the stems with axillary buds of Dendrobium officinale, alkaloid and polysaccharide content of Dendrobium officinale is evidently increased, and Dendrobium officinale grow normally. By the method, consumption of cane sugar is reduced, the tap water is used to replace the distilled water, and accordingly tissue culture technology for Dendrobium officinale is more convenient, more efficient and resource-saving.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for propagating dendrobium candidum test-tube plantlets
ActiveCN101810140AIncrease profitGrow neatlyMicrobiological testing/measurementHorticulture methodsAxillary budShoot
The invention provides a mthod for propagating dendrobium candidum test-tube plantlets, which comprises the following steps: a. adopting dendrobium candidum stem sections or stem section axillary buds as explants, wherein chloroplasts of the stem sections or the stem section axillary buds have gene sequences with the GenBank login number of FJ530946; and b. carrying out the processes of axillary bud survival and growth, cespitose shoot inducement and multiplication, and plantlet formation, wherein the culture conditions include the culture room temperature of 26+ / -2 DEG C, the illumination intensity of 20001x, the pH value between 5.8 and 6.0, the light source of a fluorescent lamp or an LED light source, and the illumination time of 12 h per day. The method of the invention aims at the defects of the existing dendrobe tissue culture method, improves the existing dendrobe tissue culture method, and provides a fast propagation method of the dendrobium candidum germchits. The method can meet the requirements of germchits required by large-scale production in a short time, and has the characteristics of low cost, regular germchit growth, simplicity and easy implementation of a domestication method, good inheritance stability and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN WANAN DENDROBIUM IND DEV
Method of somatic embryogenesis of cassava and rapid propagation of regenerated plant
The invention relates to a tissue culture propagating method of Manihot esculenta Crantz. As one of the global three-top tuber crops and the number one alimentarn crop in Africa, the Manihot esculenta Crantz is currently ranked as a vital biological energy crop in our country. Stem section vegetative cottage is commonly adopted for propagation, and the low propagation rate thereof is a restrictive factor for popularizing the new variety and shortening the breeding period. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: the Manihot esculenta Crantz stem section with stem apexes or lateral buds is taken as an explant, and the Manihot esculenta Crantz tissue culture plantlets are quickly obtained in virtue of the micro-propagation method; young leaves, stem apexes and axillary buds of the sterile plantlets obtained from micro-propagation are taken as explants, somatic embryo generation and plant regeneration are induced, thus the Manihot esculenta Crantz somatic cell regeneration system is established. By adopting the method, the Manihot esculenta Crantz has the advantages of high propagation rate, no genotype dependence, and the like; the method has high value on the quick propagation and large-scale production of the Manihot esculenta Crantz improved variety in a short term, and establishes a technical basis for the Manihot esculenta Crantz transgene and other breeding.
Owner:朱文丽 +4
Vegetative propagation method for butterfly orchid
InactiveCN102613076AReproductive features that break monostem sexResolve source issuesHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAxillary budSocial benefits
The invention relates to a vegetative propagation method for cattleya, in particular to a vegetative propagation method for butterfly orchid. The vegetative propagation method for butterfly orchid, provided by the invention, comprises the following steps of: by taking pedicel and axillary bud of butterfly orchid as explant, inoculating the explant into a culture medium for culturing; and performing subculture, rooting culture and transplanting culture on the induced new buds in turn. According to the method provided by the invention, the tillering of the butterfly orchid is realized in an artificially prepared culture medium; the single-stalk reproduction feature of the butterfly orchid is broken through; an induced pedicel seedling can be obtained without hurting a butterfly orchid stock plant according to the method; and the pedicel of the same stock plant can be repeatedly used. The seedlings produced according to the method are robust, trim and consistent; the source problem of excellent butterfly orchid seedlings during production is solved; and more economic and social benefits can be created.
Owner:吴海红
Method for quickly planting cynodon dactylon on ecological concrete slope
ActiveCN104969749AStrong resilienceStem segment grows wellHops/wine cultivationTurf growingAxillary budEcological environment
The invention provides a method for quickly planting cynodon dactylon on an ecological concrete slope. The method comprises the following steps of 1 slope surface preparing; 2 lattice frame constructing, wherein multiple lattice frames adjacent to one another are poured and are all backfilled with planting matrixes, the planting matrixes are leveled, tamped and covered with first non-woven fabric; 3 ecological concrete pouring; 4 cynodon dactylon planting, wherein the stolons of cynodon dactylon are sheared into cynodon dactylon stems; 5 curing. According to the method, the cynodon dactylon which is good in stress resistance, resistant to trampling and poor soil and high in recovery capacity is adopted to serve as the planting species, the survival rate is high, and the selected cynodon dactylon is at least two years old; after twenty days, the coverage rate of the cynodon dactylon can reach 80 percent, the cynodon dactylon stems grow well, adventitious roots are grown, axillary buds on the stems begin to grow into branches on the ground, and new stolons begin to tiller; after thirty days, the vegetation coverage rate is more than 95 percent. By adopting the method, vegetation landscapes can be quickly formed, the slope ecology environment can be improved, and slope ecology protection can be achieved.
Owner:武汉植物园园艺中心有限公司
Method of cutting propagation of peony immature stem
ActiveCN103493677AEasy to synthesizeAccelerates and induces divisionCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsAxillary budGrowth retardant
The invention belongs to the field of plant tissue cultivation, and particularly relates to a method of cutting propagation of a peony immature stem. The method includes the steps of material selection, cutting cultivation, indoor management, oversummer maintenance, overwinter management and strong seedling cultivation. By using low-frequency ultrasonic waves to conduct processing, rooting can be promoted, plant cell division can be remarkably accelerated and induced, the cell growth is stimulated, protein synthesis of protoplast can be accelerated, and the adventitious bud reproducibility can be improved. Due to the fact that intermittent irradiation is adopted, no drastic cavitation effect can be produced, and partial damage to cells caused by the ultrasonic waves can be avoided. Due to the fact that cultivation and rooting are conducted in the dark cultivation process, growth inhibitor is greatly reduced, and rooting is facilitated. The complete and specific method including the steps of oversummer maintenance, auxiliary bud inducing, overwinter management and strong seedling cultication is provided, and therefore application of the peony rapid cutting propagation technology in actual production is promoted, and the method has significance in large-scale production of peony seedlings.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for suppressing browning of carya cathayensis sarg explant
InactiveCN103004602AGuaranteed induction rateEffect of inhibiting browningHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureCarya cathayensisAxillary bud
The invention relates to a forest tree seedling breeding technology and in particular relates to a method for suppressing browning of a carya cathayensis sarg explant. The method is characterized by selecting a carya cathayensis sarg stem with axillary buds as an explant in spring, disinfecting the explant, then inoculating the explant into a culture medium to which catechins and anti-browning agents are added, and firstly culturing a tissue culture vessel in the low temperature dark environment and then transferring the tissue culture vessel to the routine culture environment at the initial stage of inoculation. The method can conduce to obvious reduction of the browning rate of the carya cathayensis sarg explant and improvement of inductivity of the carya cathayensis sarg explant, is simple and convenient to operate, has a better browning suppression effect, and provides a technical support for tissue culture and asexual reproduction of carya cathayensis sarg.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +2
Method for building bamboo reed tissue culture system
InactiveCN102919127AEasy to sterilizeGrow fastCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue cultureAxillary budCulture mediums
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant tissue culture and particularly relates to a method for building a bamboo reed tissue culture system. The method comprises the steps of (1) explant disinfection, wherein axillary buds of bamboo reeds are fully soaked in 75% of ethanol for 10 seconds and then moved into 0.2% of mercury bichloride solution for 10 minutes; (2) primary culture, wherein a culture medium is formed by adding cane sugar 30g / L and agar 8g / L in MS, then adding 6-BA 5mg / L and IBA 0.5mg / L and finally adjusting potential of hydrogen (pH) to 5.8; (3) secondary culture, wherein a culture medium and culture conditions of the secondary culture are the same as the culture medium and culture conditions for the primary culture; (4) strong bud and root culture, wherein the buds are cultured in the secondary culture medium for one month to finish strong bud culture and then planted in a rooting culture medium, and the rooting culture medium is formed by adding IBA 0.5 mg / L into the MS; and (5) domestication and transplantation, wherein the domestication is performed by using a floating bed domestication system for one week and then transplantation is performed. By means of the method, the efficient breeding of the bamboo reeds can be achieved.
Owner:HUZHOU TEACHERS COLLEGE
Method for grafting of cucumber on black-seed pumpkin in Yunnan
The invention discloses a method for grafting of a cucumber on a black-seed pumpkin in Yunnan, belonging to the field of crop breeding. According to the method, the black-seed pumpkin in Yunnan is used as a stock, a growing point and axillary buds on two sides of the stock are removed by a blade, a special bamboo stick of 0.5cm is vertically inserted into the center of the growing point and is maintained in a stem, a cucumber seedling is taken, the under-cotyledon part is removed by obliquely cutting at 0.4-0.6cm under the cotyledon of the cucumber seedling for an angle of 25-30 degrees, the bamboo stick is taken out, the cucumber seedling is inserted into a grafting hole, and the cotyledon of the cucumber and the cotyledon of the stock are arranged in a cross-shaped vertical shape; and after grafting is performed, moisture is kept for 3-5 days in an enclosed environment in a greenhouse, the temperature is maintained at 25-30 DEG C at daytime and 18-20 DEG C at night for seedling hardening, then ventilation is performed gradually, and complete ventilation is performed on the ninth or tenth day. The black-seed pumpkin in Yunnan is used as the stock in the method, diseases which can easily occur to certain cucumber seedlings can be eliminated completely, and the stress tolerance and disease resistance can be better improved. Since direct insertion is adopted for grafting, the rate of incidence of adventive roots is very low, and the survival rate of grafted seedlings can be guaranteed to be up to 98 percent.
Owner:句容市旺华大棚蔬菜专业合作社
Pruning, reshaping and yield-increasing method of kiwi fruit in mountain land
The invention provides a pruning, reshaping and yield-increasing method of kiwi fruit in a mountain land. The method comprises the following steps: shearing the tip of the main stem of the kiwi fruit so that two buds at the upper end are cultured to form main branches and tendrils which respectively grow along the two sides of a shed frame; shearing and removing unnecessary main branches and tendrils and binding the branches and tendrils in parallel at the end of the year; in the second year, leaving axillary buds at the even number positions of the main branches and tendrils to be used as fruiting mother branches in the same year, and eliminating the axillary buds at the odd number positions of the main branches and tendrils to be used as the fruiting mother branches in the next year; and after fruiting on the fruiting mother branches and harvesting, pruning the fruiting mother branches in the end of the same year so that new buds can grow in the next year and become growing branches, in such a way, alternatively culturing and pruning the axillary buds at the even and odd number positions and the fruiting mother branches, and culturing and pruning repeatedly and circularly annually. The method provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that unnecessary branches are sheared and removed annually and abstemiously according to different positions and a planned way, the unnecessary axillary buds are eliminated, fruiting branches after harvesting are sheared and removed, the fruiting mother branches and the growing branches alternatively develop and mature annually, and nutrition substances in soil are concentrated to mainly be supplied to fruits, so that the yield per mu is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING HONGYI AGRI
Tissue cultivating method of spiceberry melaleuca alternifolia
InactiveCN101032223AResolution cycleSolve the survival ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAxillary budMelaleuca alternifolia
The present invention discloses tissue culture process of alternate leaf cajeputtree as one kind of perfume plant. The tissue culture process includes the following steps: cutting axillary bud as the explant from the mother body, washing and sterilizing; the subsequent inducing culturing in inducing culture medium comprising 7 / 10MS-MS, 6-BA 0.1-0.3 mg / L and NAA 0.1-0.3 mg / L; secondary culturing in secondary culture medium comprising 7 / 10 MS-MS, 6-BA 0.4-0.6 mg / L and NAA 0.05-0.15 mg / L; and final rooting culturing in rooting culture medium comprising 2 / 5MS -3 / 5MS, and IBA 0.5-0.7 mg / L. The tissue culture process has the culturing conditions including illumination intensity of 2500-3000Lux, and temperature of 26+ / -1 deg.c. The tissue culture process is suitable for fast propagation in industrial scale.
Owner:厦门涌泉科技有限公司
Asexual rapid propagation method for radix glycyrrhizae
ActiveCN105340747AConducive to survivalBreed fastPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAxillary budSocial benefits
The invention discloses an asexual rapid propagation method for radix glycyrrhizae. The asexual rapid propagation method comprises the following steps: inoculating an explant of a radix glycyrrhizae stem section into a culture medium for cultivation to obtain an aseptic seedling; then cutting the aseptic seedling into a terminal bud explant, a stem section explant with one axillary bud and an explant with one axillary bud and a root, inoculating the explants into the same culture medium for cultivation to obtain a subculture-multiplicative aseptic seedling; and transplanting the subculture-multiplicative aseptic seedling into the culture medium to realize asexual rapid propagation for the radix glycyrrhizae. The formula of the used culture medium is that IBA with the concentration of 0.1mg / L is added to the MS culture medium, and the using amounts of KNO3 and NH4NO3 in the MS culture medium are halved respectively, and the pH value of the MS culture medium is 5.8. According to the asexual rapid propagation method, the root-inducing rate of the aseptic seedling is 100%, so that seedling emergence can be realized after 40 days, the seedling can be transplanted into a large field after 50 days, and the survival rate in the large field is higher than 80%. The asexual rapid propagation method can be suitable for rapid propagation of a plurality of excellent strain systems of a plurality of radix glycyrrhizae varieties, and has remarkable ecological, economic and social benefits in sustainable development of the radix glycyrrhizae.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for propagating tissue cultured millettia specisoa champ seedling
InactiveCN101124891AReal resourceHigh quality resourcesPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAxillary budGreenhouse
The invention provides a method for tissue culturing and reproducing the millettia speciosa champ germchit. By using the tissue culture method and taking the fresh apical bud and the axillary bud of the wild millettia speciosa champ as the explant, the explant is disinfected and sterilized by the 75 percent alcohol and 0.1 percent mercuric chloride solution; after that, according to different periods, different culture medium formulas are adopted respectively for the bud induction culture, bud subculture proliferation and the rooting culture to obtain the container seedling of the millettia speciosa champ, wherein, the bud induction culture medium has a formula of MS+6-BA0.4mg.L-1+IBA0.2mg.L-1+3 percent white granulated sugar+0.35 percent agar, the formula of the bud subculture proliferation culture medium is MS+6-BA0.6mg.L-1+NAA0.5mg.L-1+3 percent white granulated sugar+0.35 percent agar, and the formula of the rooting culture medium is 1 / 2MS+ABT10.8mg.L-1+IBA0.4mg.L-1+3 percent white granulated sugar+0.35 percent agar; moreover, when the height of the container seedling is grown about 2 cm, the container seedling is again transplanted to a seedbed of a greenhouse for culturing; after reaching over 20cm, the container seedling is the grown seedling of the millettia speciosa champ germchit.
Owner:钦州市中医药研究所
Sugarcane detoxication tissue culturing and fast propagating method
InactiveCN101138321AIncrease in sizeEasy to inoculateCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsAxillary budBud
The present invention relates to a method for virus-free tissue culture and rapid propagation of sugarcane belonging to the technical field of plant propagation. The method comprises the following steps that the terminal buds or auxiliary buds of the sugar cane is taken as the explants and the virus-free tissue culture seedlings are propagated in mass after the callus tissue inducement and culture, plant differentiation culture, proliferation culture, radication culture and virus test. The present invention is characterized in that the explants adopted are large and the operation is easy; the inoculation survival rate is high; the detoxification is simple, convenient, fast and thorough; the propagation coefficient per month is 5 to 10 times and the speed is fast which is fit for breeding in factory and commercial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
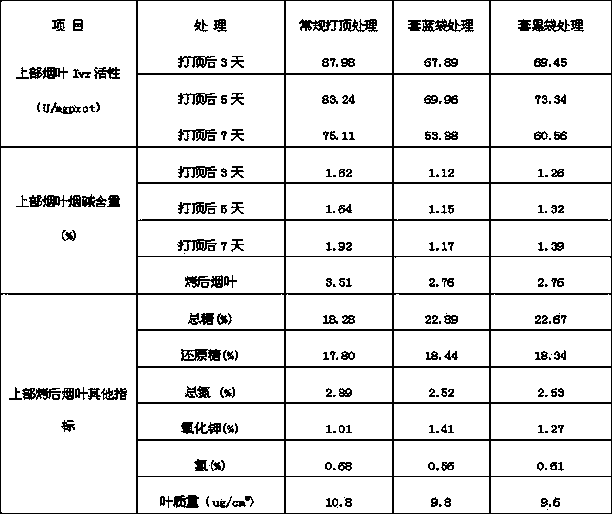
Tobacco field management method for improving quality of upper tobacco leaves
The invention relates to a tobacco field management method for improving quality of upper tobacco leaves. By the adoption of a cultivation method that the tops of tobacco are sleeved with plastic bags instead of topping, from the first blooming stage to the full blooming stage of the tobacco, all inflorescences together with three to five small tobacco leaves at the topmost portion are sleeved with shading materials instead of traditional manual topping, and therefore flowers and the leaves at the tops of the tobacco gradually die under the high-temperature, high-humidity and dark environment in the bags. Compared with the prior art, the tobacco field management method has the advantages that the apical dominance of the tobacco fades away, nutrients of the tobacco and coordination of chemical components of the tobacco leaves are guaranteed, and the effect of improving the quality of the upper tobacco leaves is obvious; the apical dominance of tobacco plants fades away, growth and development of axillary buds are restrained, the use quantity of suckercides is reduced, and quality safety of the tobacco leaves is improved; if bud picking is carried out manually, the frequency of bud picking is reduced, and labor is relieved; the bags are made of blue or black plastic materials convenient to obtain, cost is low, the bags are cleared away together with tobacco stems later, and no environment pollution is caused.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO SCI RES INST
Tissue culture method for increasing multiplication coefficient of catalpa bungei
InactiveCN104054580AReduce ambient humidityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAxillary budObserved Survival
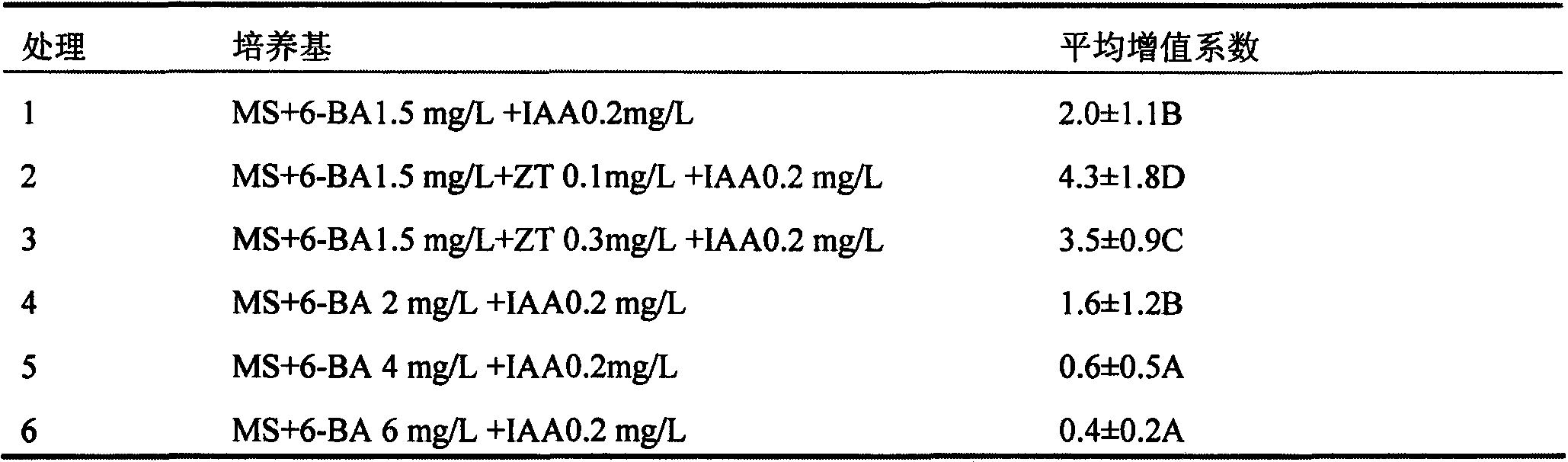
The invention discloses a tissue culture method for increasing the multiplication coefficient of catalpa bungei. The tissue culture method comprises five steps of building sterile culture, inducing axillary bud, performing multiplication of the axillary bud, performing rooting culture of bud seedling and performing tissue culture of seedling. The method is used for culturing tissue and quickly culturing seedling of the catalpa bungei; the method has the advantages of high bud induction rate, large multiplication coefficient, high rooting rate and high transplanting survival rate. By virtue of the method, an optimal culture medium formula of the catalpa bungei is selected and prepared by 1.5mg / L of MS+BA, 0.1mg / L of ZT and 0.2mg / L of IAA, and a subculture method for subculturing stem and root callus during subculturing is also selected; the multiplication coefficient of catalpa bungei is 11.0-23.2, and the average multiplication coefficient is 15.3. By virtue of the method, a seedling culturing method good in multiplication speed, short in production cycle and good in stability is provided for large-scale cultivation of the catalpa bungei in the forestry production.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Non-tube quick reproduction method for seedings of jatropha curcas L.
InactiveCN101057557AReduce in quantitySave germplasm materialHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAxillary budNutrient solution
The invention discloses a non-tube method for fast breeding aleurite seedling, comprising: taking disinfected stem carrying axillary bud of 2-3cm length as explant; enclosing its morphological upper notch, immersing its morphological lower notch in indolebutyric acid solution, cutting it in sand disk, dressing nutritional solution to keep sand disk wet, culturing it for 16. 2-20. 2 days under conditions of 25-28 Deg. C, 70-80% of relative humidity, 2000-3000 lx lighting strength and light period of 12 hour lighting / 12 hour dark, and getting rooting and integral plant. The invention is characterized by fast breeding, free from influence of national factors such as season and region, low variation rate, simple process and low cost.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for cultivating dendrobium fimbriatum
The invention discloses a method for cultivating dendrobium fimbriatum. The method comprises the following steps of: after an axillary bud of a dendrobium fimbriatum pseudobulb grows into a high-bud seedling, cutting the high-bud seedling and transplanting onto a seedling adaptation substrate; and transplanting to the field for cultivating. In the cultivating method, the high-bud seedling grown by the dendrobium fimbriatum pseudobulb on a dendrobium fimbriatum stock plant is cut, so that each high-bud seedling does not damage the stock plant, the accelerated formation of a new high-bud seedling on the stock plant is stimulated, the reproduction speed and efficiency of a dendrobium fimbriatum germchit are increased, the reproduction quantity of the dendrobium fimbriatum germchit is increased, the reproduction period is shortened, and the dendrobium fimbriatum stock plant is brought into full play; moreover, the high-bud seedlings are transplanted to the field after seedling adaptation, so that the survival rate of the seedlings is up to about 98 percent and the germchits are ordered and consistent; and the method has the advantages of low cost, high survival rate and the like, and is suitable for scale culture and cultivation of seedlings.
Owner:安龙县欣蔓生物科技有限责任公司
Method for quickly breeding Akebia trifoliata Koidz fruit seedling in test tube
InactiveCN102090327AImproving Rapid Propagation MethodsPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAxillary budPlant cell
The invention relates to a method for quickly breeding an Akebia trifoliata Koidz fruit seedling in a test tube, comprising the following steps of: inducing Akebia trifoliata Koidz to generate cluster buds, placing the cluster buds into a culture medium for rooting and culturing; then culturing a plant to the height of about 7cm at the temperature of 25 + / - 2 DEG C in an illumination environment; taking out the cluster buds from the culture medium; cutting the seedling in the test tube with a scalpel into stem sections with axillary buds of about 1cm for rooting and culturing; and then illuminating the plant to grow into about 7cm again, i.e. illuminating again and transplanting the plant to a cultivation substrate for growing. By adopting a genetic engineering technology of plant cells, the method can greatly shorten the breeding time, quicken the breeding progress and obtain a new species with more ideal characteristics purposefully.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com