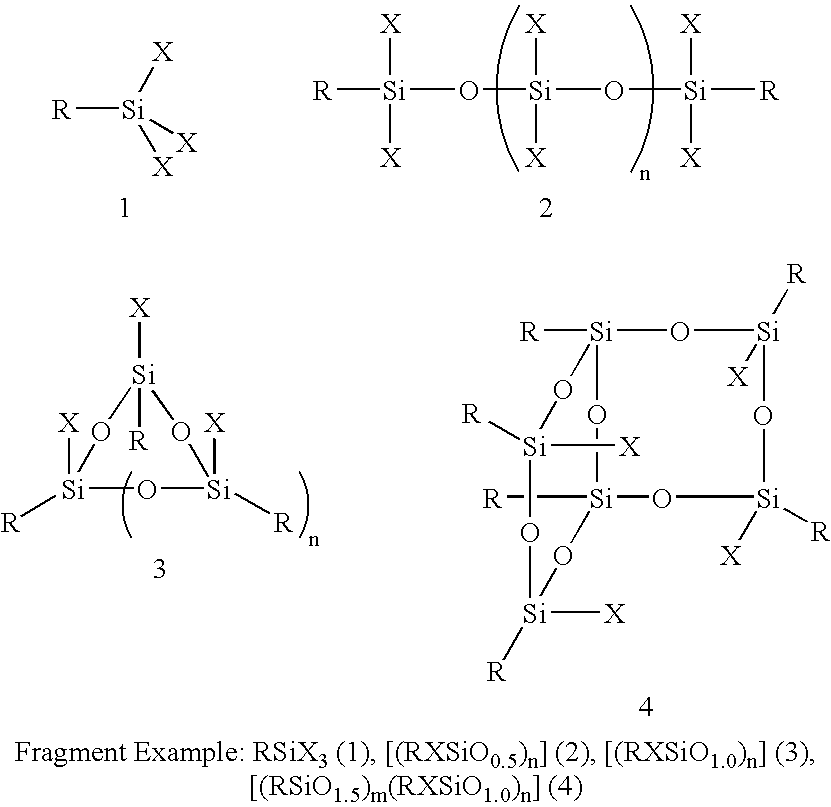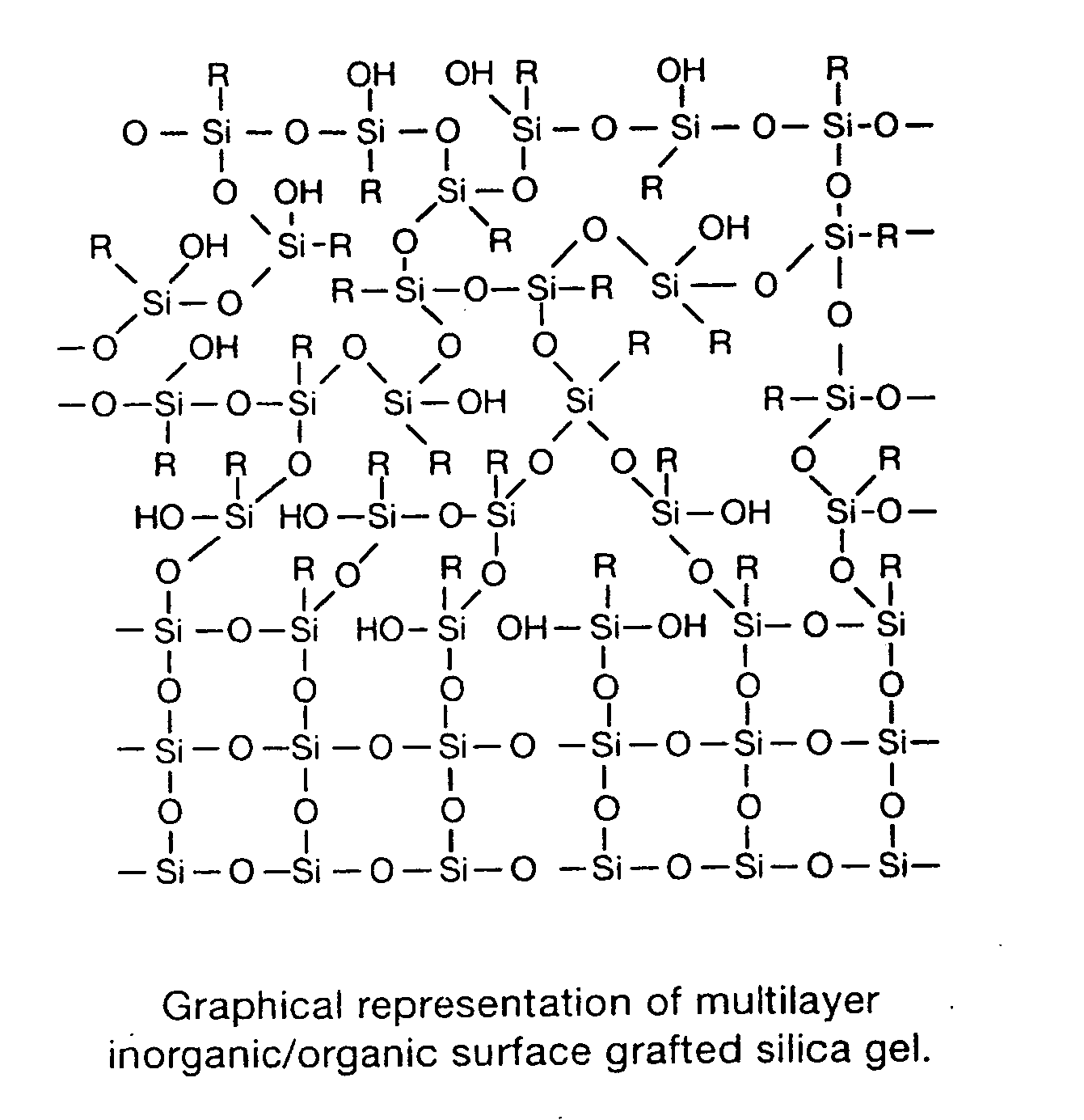Patents
Literature
3504 results about "Grafting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Grafting or graftage is a horticultural technique whereby tissues of plants are joined so as to continue their growth together. The upper part of the combined plant is called the scion (/ˈsaɪən/) while the lower part is called the rootstock. The success of this joining requires that the vascular tissues grow together and such joining is called inosculation. The technique is most commonly used in asexual propagation of commercially grown plants for the horticultural and agricultural trades.
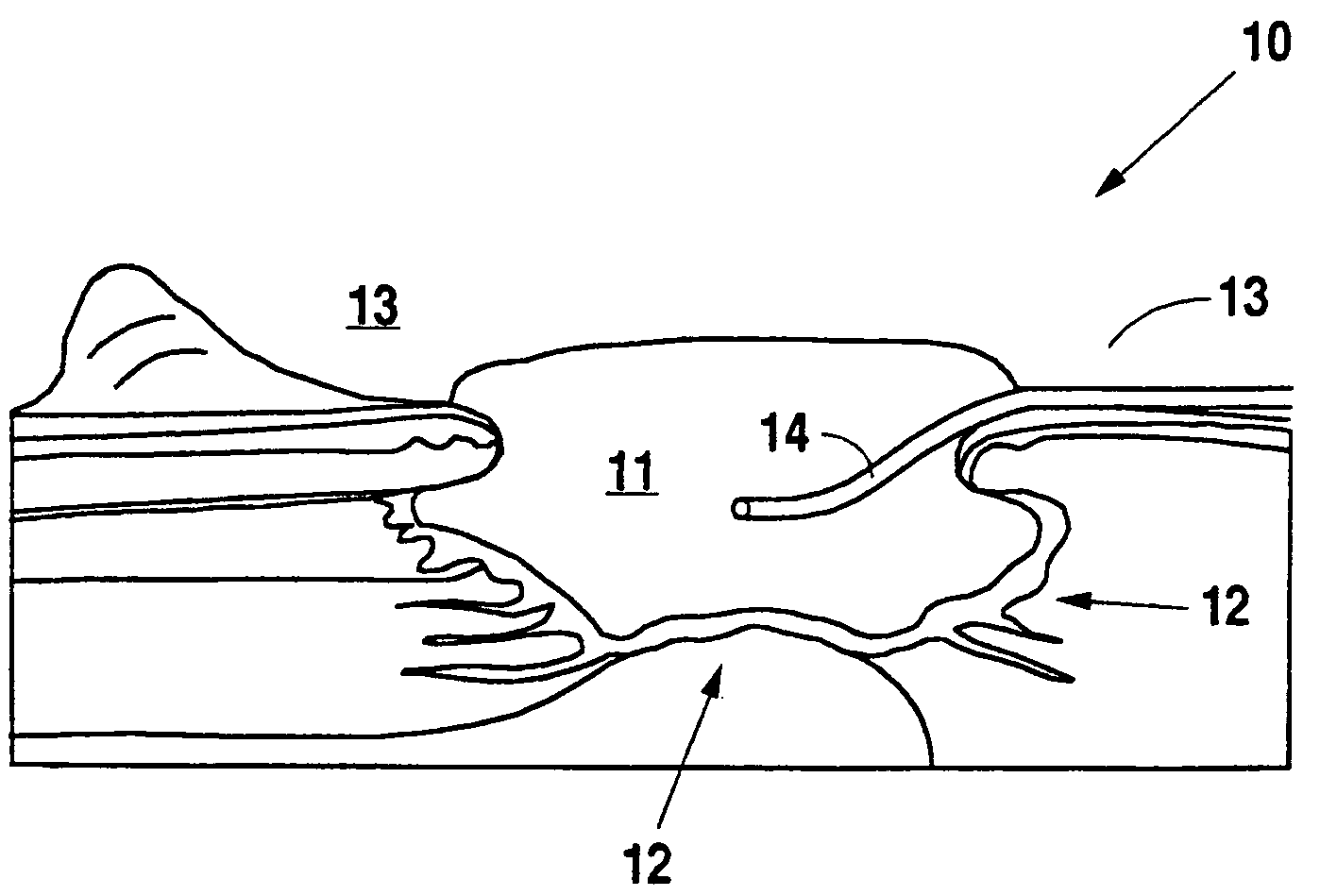
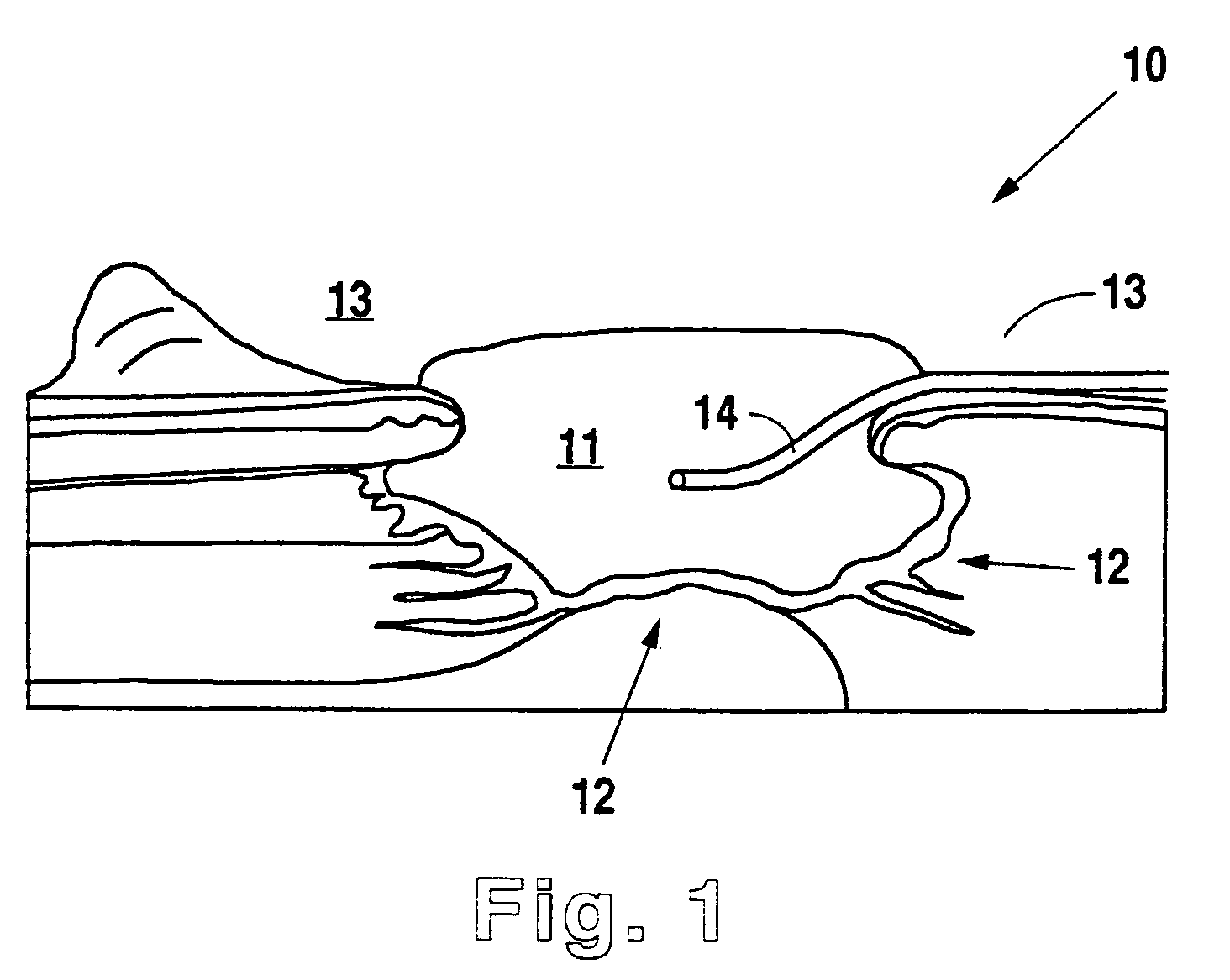
Negative pressure wound therapy system with provision for introduction of an agent
InactiveUS7534240B1Promote wound healingRapid reepithelializationPeptide/protein ingredientsSurgical needlesWound siteGrafting
A method and apparatus for the introduction to a wound under negative pressure therapy of a wound healing agent, generally comprises a foam pad (11) for insertion substantially into a wound site (12), and a wound drape (13) for sealing enclosure of the foam pad at the wound site. The foam pad is placed in fluid communication with a vacuum source for promotion of fluid drainage. Additionally, the foam pad is predisposed, through grafting or other techniques known to those of ordinary skill in the art, with basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), anti-microbial or other factors, also known to those of ordinary skill in the art, for the promotion of increased wound healing.
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
Surface-functionalized mesoporous carbon materials
ActiveUS9249241B2Effectively and efficiently functionalizedPractical and cost-effective for large scale productionProcess efficiency improvementPolyvinyl polymerSolvent
A functionalized mesoporous carbon composition comprising a mesoporous carbon scaffold having mesopores in which polyvinyl polymer grafts are covalently attached, wherein said mesopores have a size of at least 2 nm and up to 50 nm. Also described is a method for producing the functionalized mesoporous composition, wherein a reaction medium comprising a precursor mesoporous carbon, vinyl monomer, initiator, and solvent is subjected to sonication of sufficient power to result in grafting and polymerization of the vinyl monomer into mesopores of the precursor mesoporous carbon. Also described are methods for using the functionalized mesoporous carbon, particularly in extracting metal ions from metal-containing solutions.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
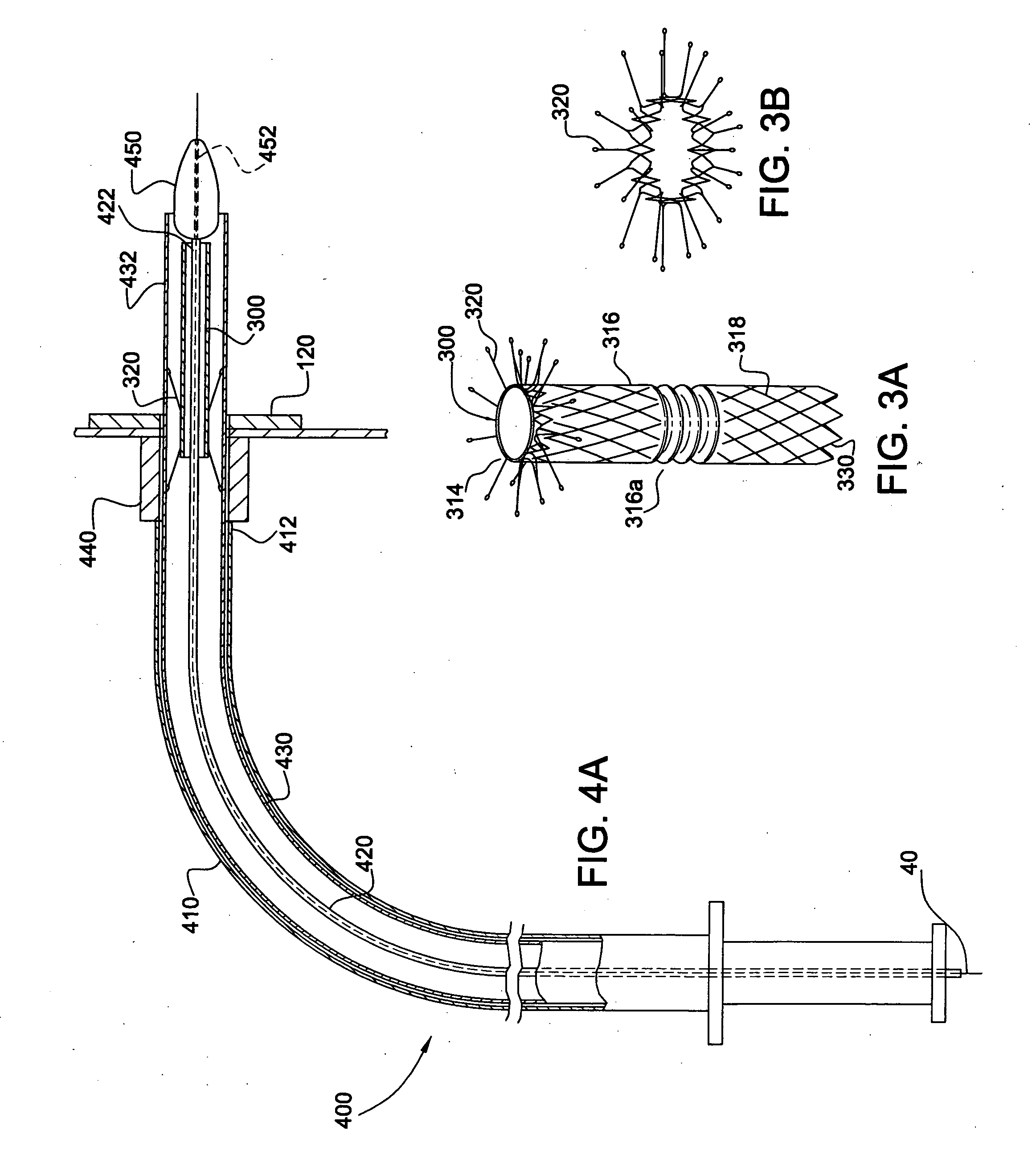
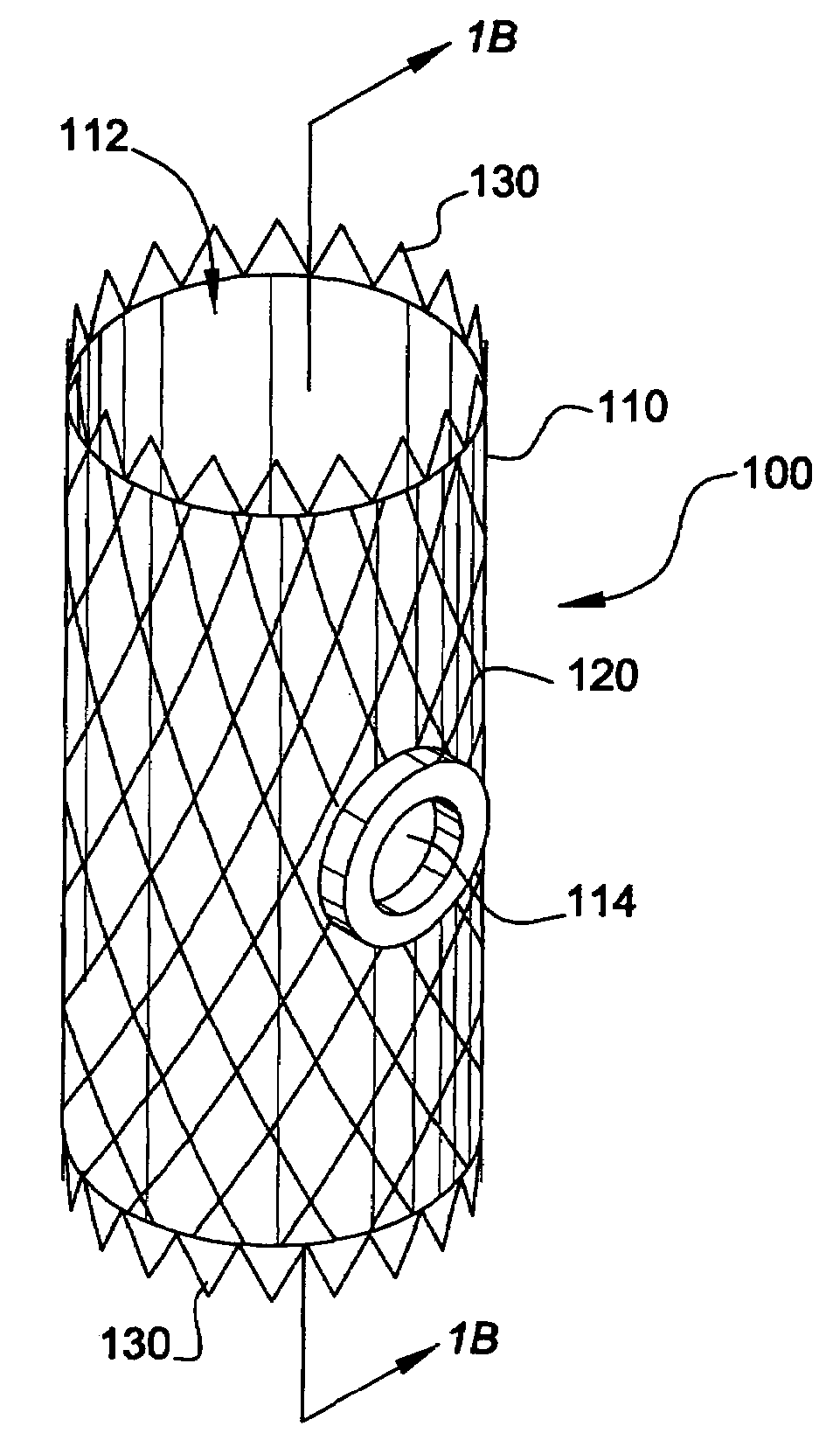
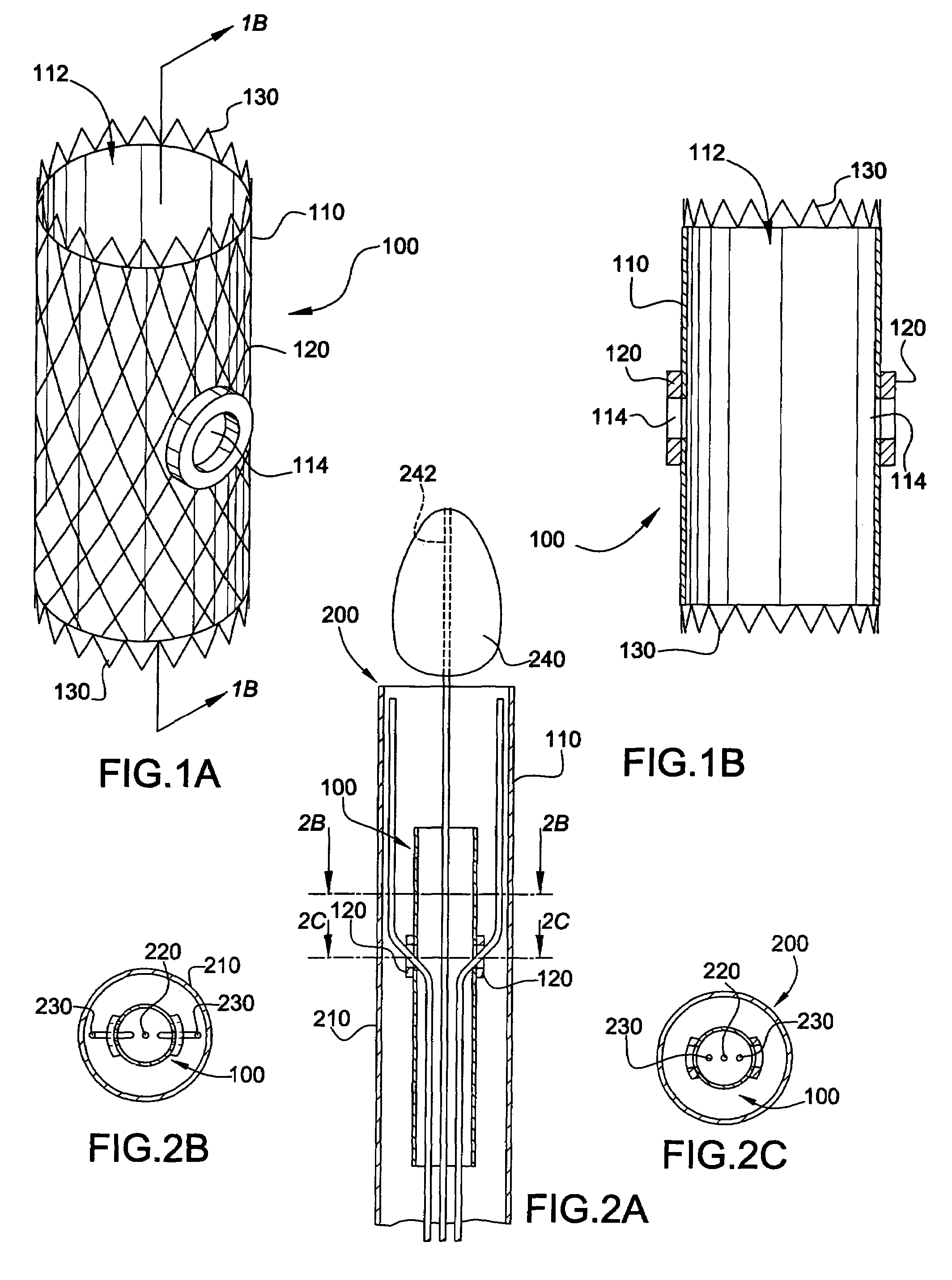
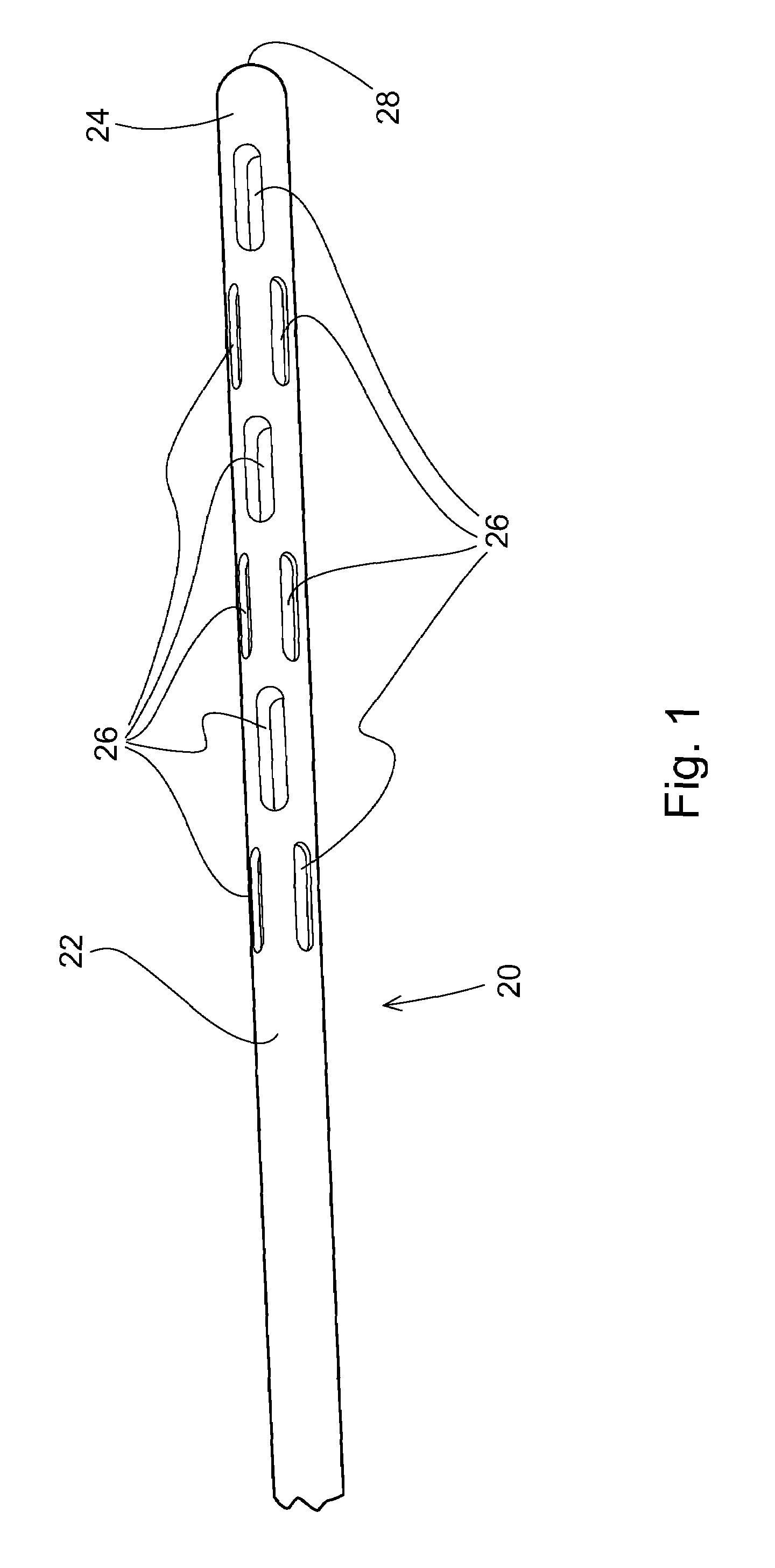
System and method for endoluminal grafting of bifurcated and branched vessels
InactiveUS20050154444A1Improve efficiencyMore aortic aneurysmsStentsBlood vesselsCouplingMetal alloy
A system and method for endoluminal grafting of a main anatomic conduit in its diseased state in which it dilates to pose a life threatening condition and its various conduits that emanate from the main anatomic conduit. The grafting system comprises an endoaortic graft having at least one opening therein and at least one branch graft that is passable through the opening of the endoaortic graft into the branch anatomic conduit(s) such that the junction between the branch graft and the endoaortic graft is substantially fluid tight. A system and method for delivery of the endoaortic graft and also a system and method for efficient alignment and deployment of the branch (e.g., side branch) graft such that the coupling of the branch graft with the endoaortic graft is efficient and exact and fluid-tight; and a system and method for coupling the branch to the endoaortic graft via a coupling mechanism employing a memory metal alloy; a system and method for the proper and exact alignment of the endoaortic graft and the branch using magnetic force of a suitable nature, and which does not use the magnetic force as the coupling mechanism.
Owner:CARDIAQ VALVE TECH
Hydrophilic polymer treatment of an activated polymeric material and use thereof
InactiveUS6830782B2Simple materialImprove nucleationRadiation applicationsFibre typesFiberMicroorganism
A method of modifying a polymeric material which comprises the steps of activation-treatment and a hydrophilic polymer-treatment, or comprises the steps of activation-treatment, a hydrophilic polymer-treatment, and monomer grafting in this order, or comprises the step of a solvent-treatment followed by these steps. Thus, the polymeric material, e.g., polyolefin, is improved in hydrophilicity, adhesion, etc. without lowering the practical strength thereof. The polymeric material thus improved in adhesion and other properties can be used in many applications where water absorption and adhesion are required, such as an absorption material, e.g., a wiping / cleansing material, a water retention material, a material for microorganism culture media, a separator for batteries (or cells), a synthetic paper, a filter medium, a textile product for clothing, a medical / sanitary / cosmetic supply, and reinforcing fibers for composite materials.
Owner:KB INT
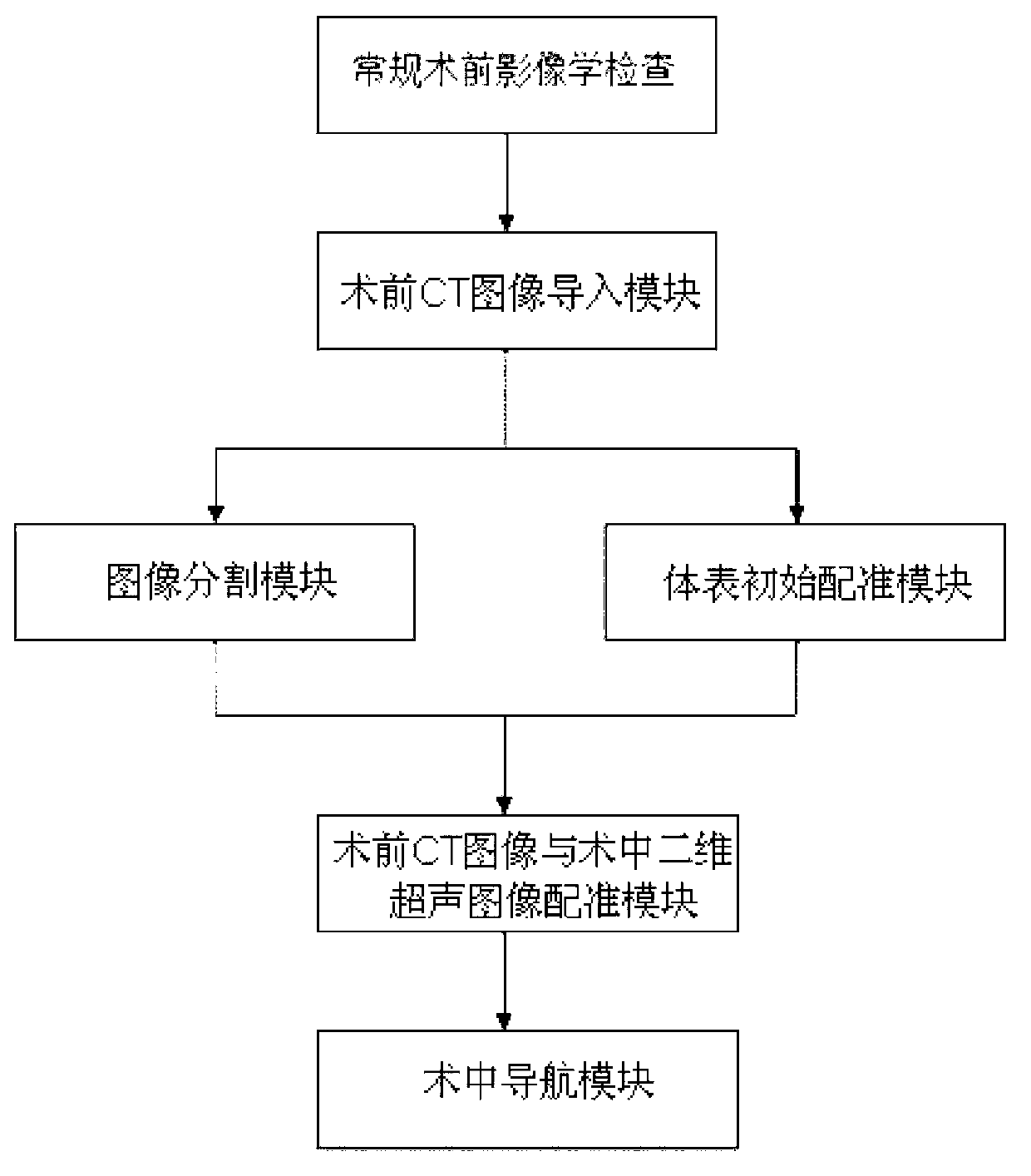
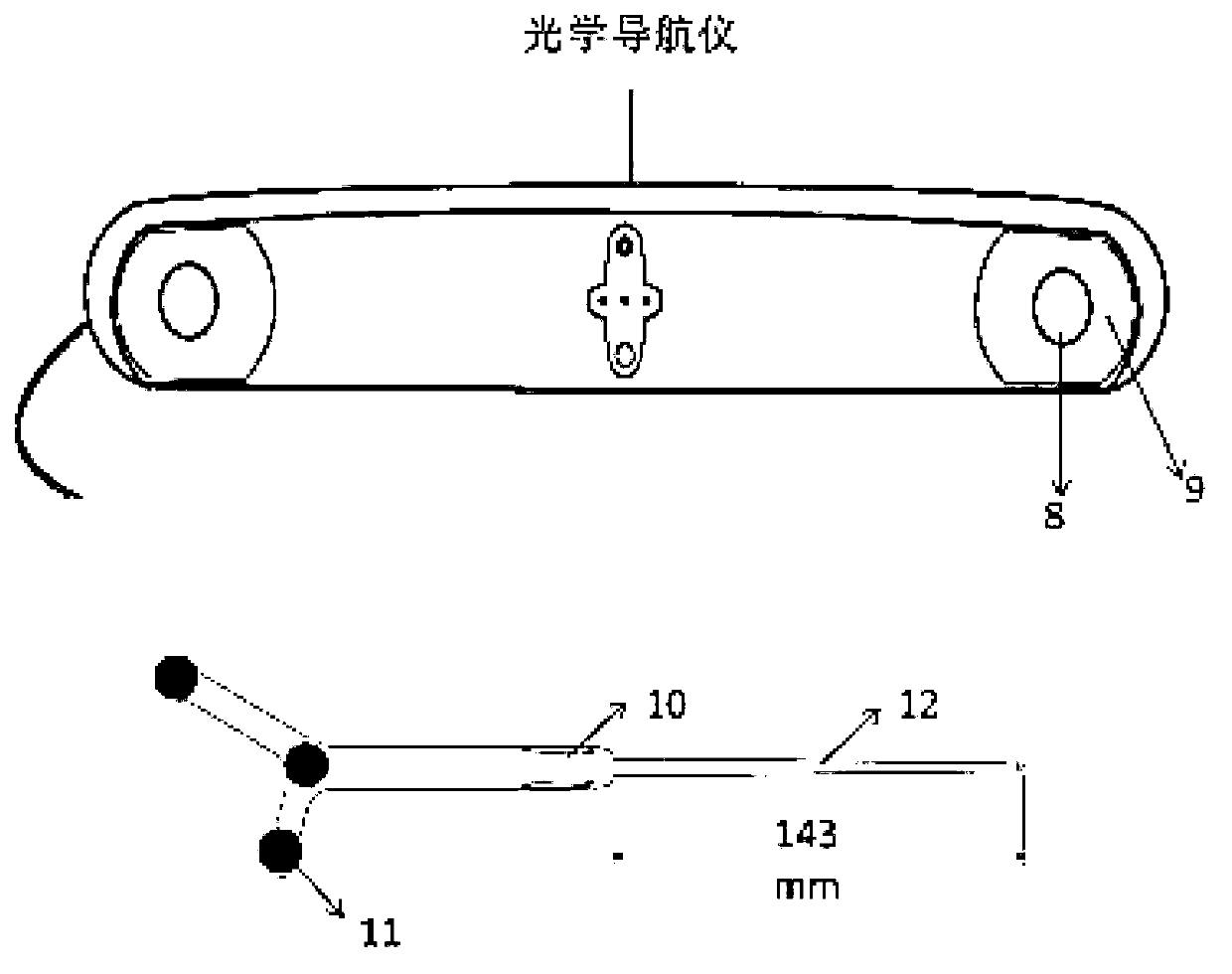
Optical navigation positioning system based on CT (computed tomography) registration results and navigation method thereby
ActiveCN102999902AResolve uncertaintyImage analysisDiagnosticsImage segmentationIntraoperative ultrasound
Disclosed are an optical navigation positioning system based on CT (computed tomography) registration results and a navigation method thereby. The system comprises a preoperative CT image guide input module, an image segmentation module, a body surface initial-registration module, a preoperative CT image and intraoperative two-dimensional ultrasound image module and an intraoperative navigation module. By combining virtual reality and intraoperative ultrasound, intraoperative positioning errors caused by factors such as breathing are compensated, and accordingly a target point for coronary artery bypass grafting is accurately positioned and navigated. Cardiac and coronary vessel tree in preoperative cardiac CT image data is manually segmented and reconstructed, an augmented virtual reality environment integrating endoscope and virtual endoscope is built by the aid of optical navigation apparatus and CT-ultrasound-based intraoperative registration error correction, and accordingly the target point of coronary artery bypass grafting is accurately positioned and navigated.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
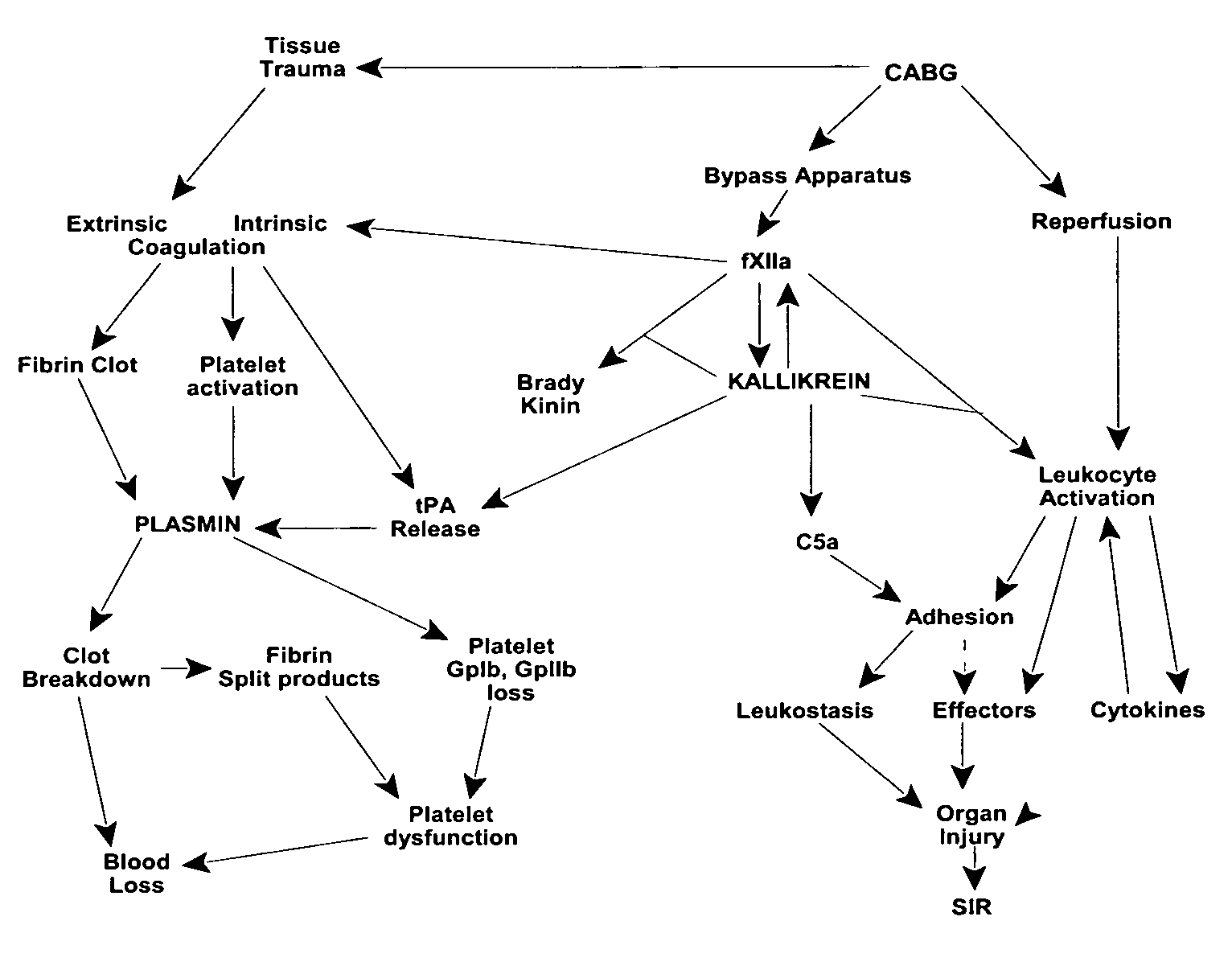
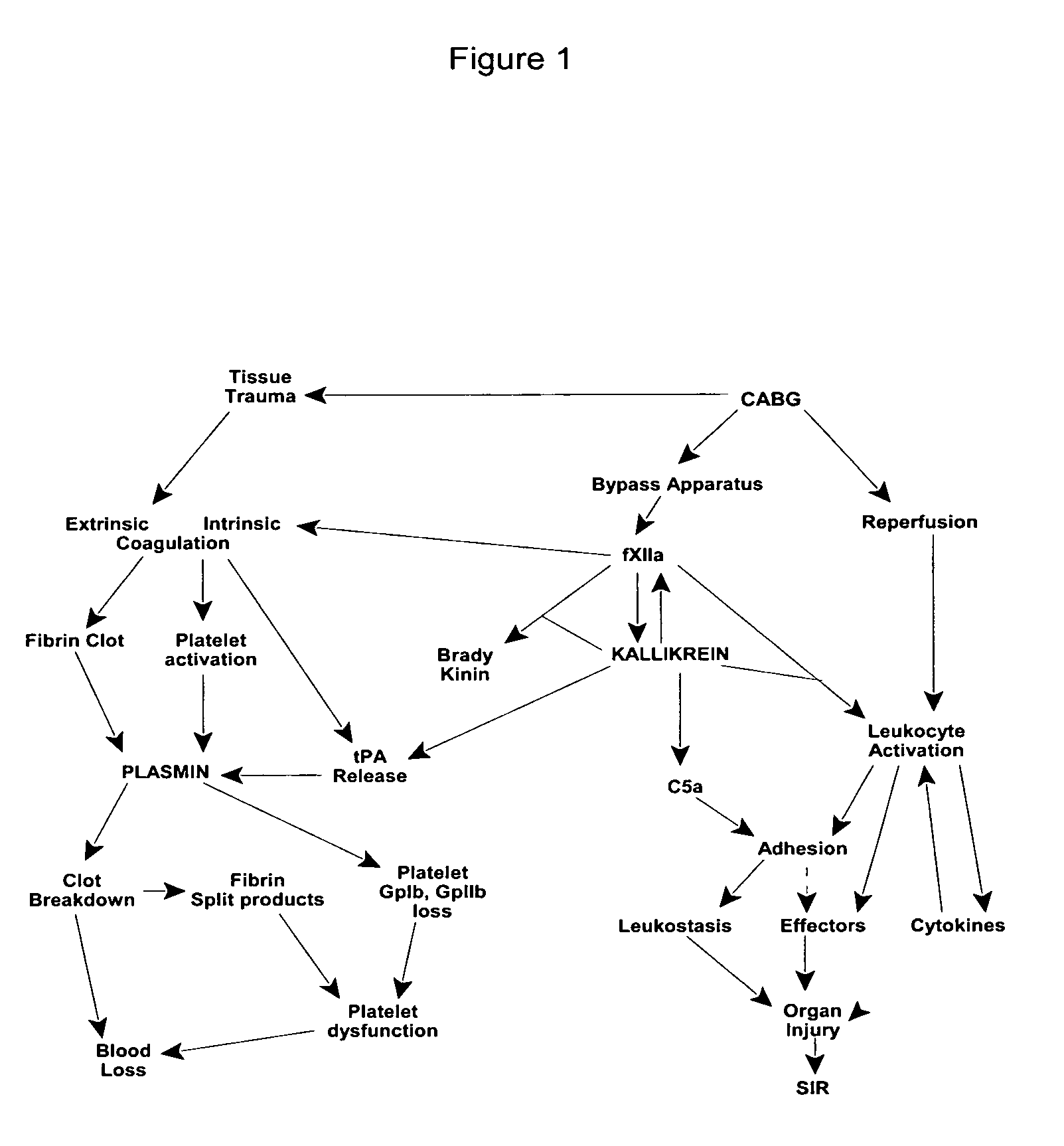
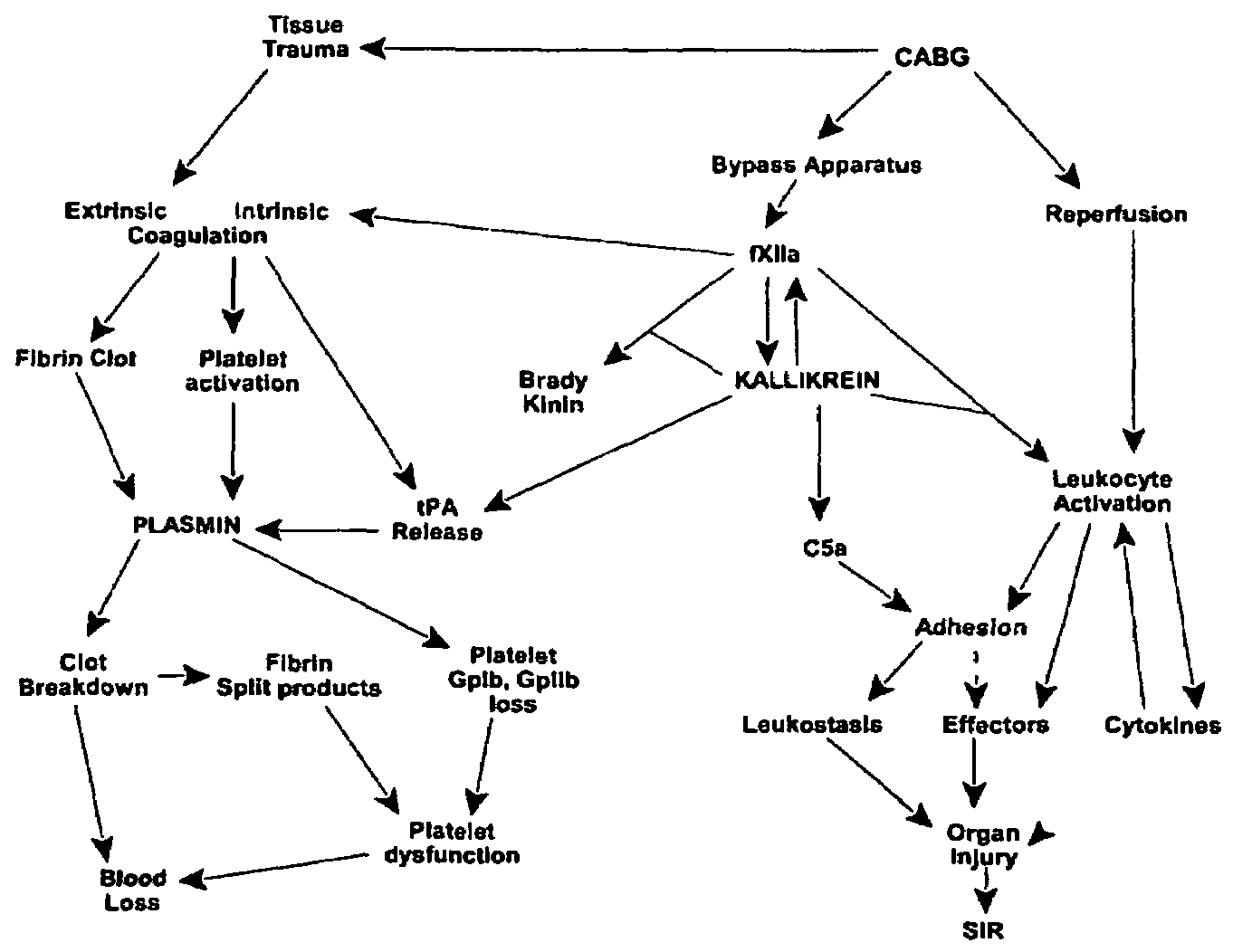
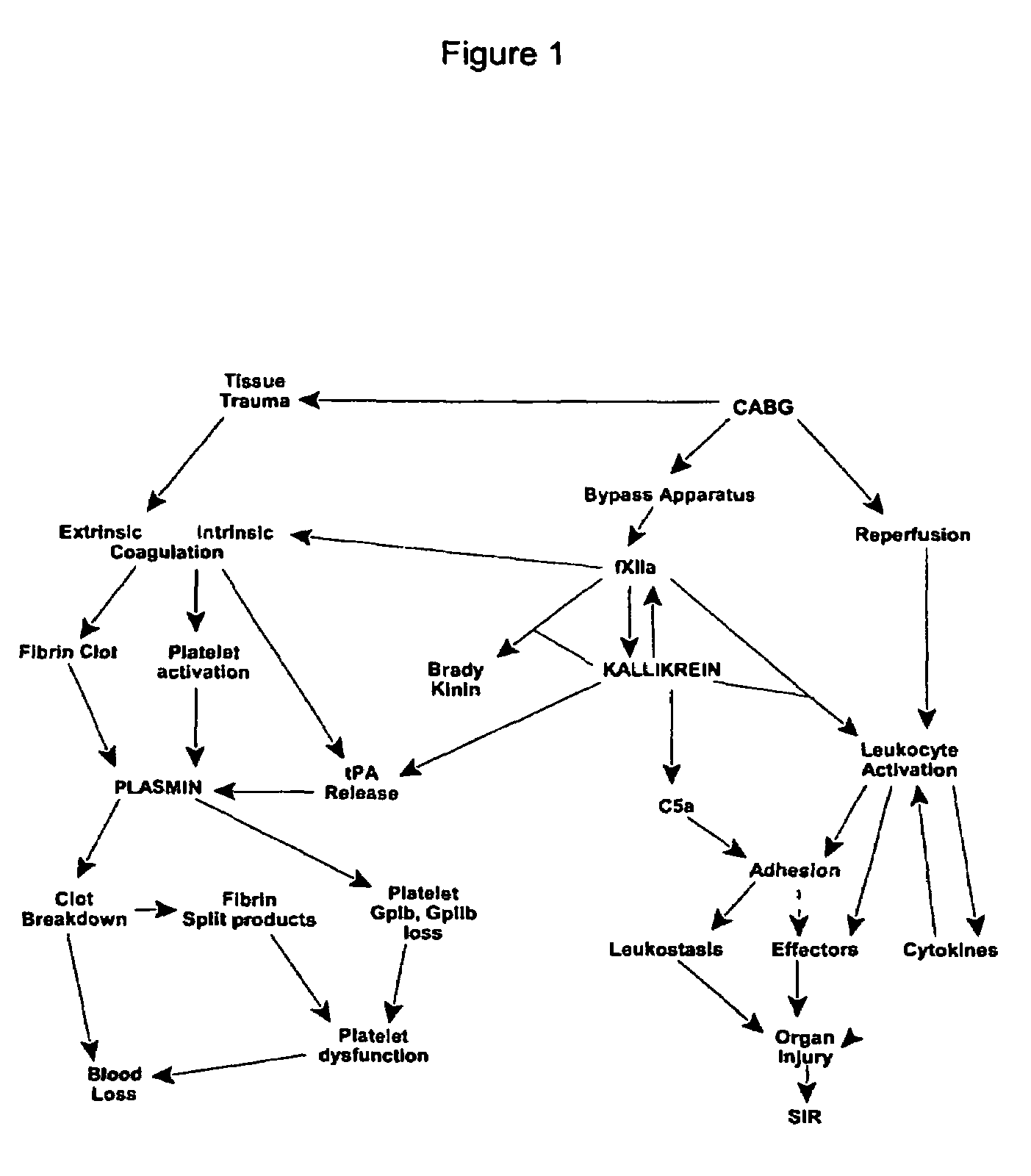
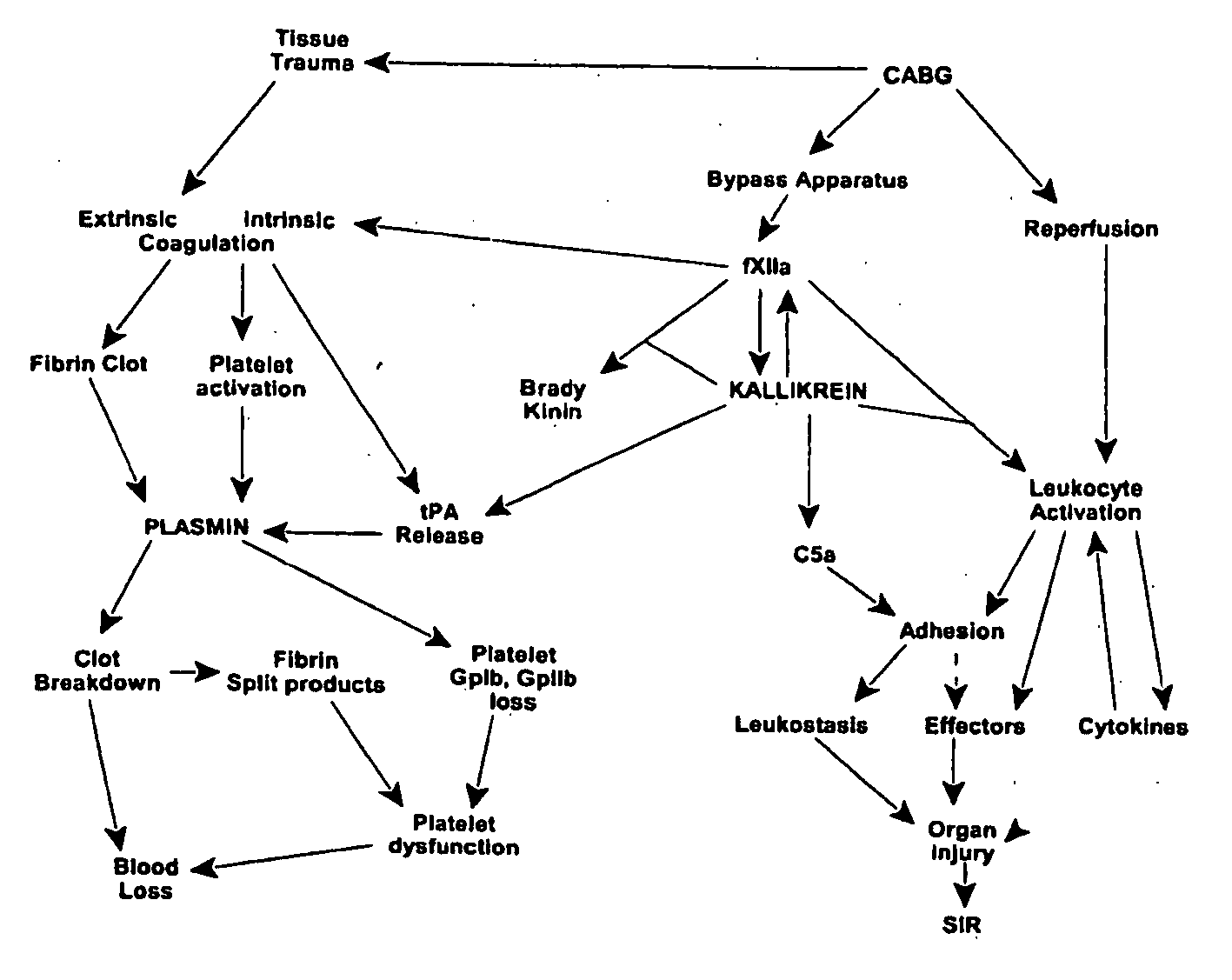
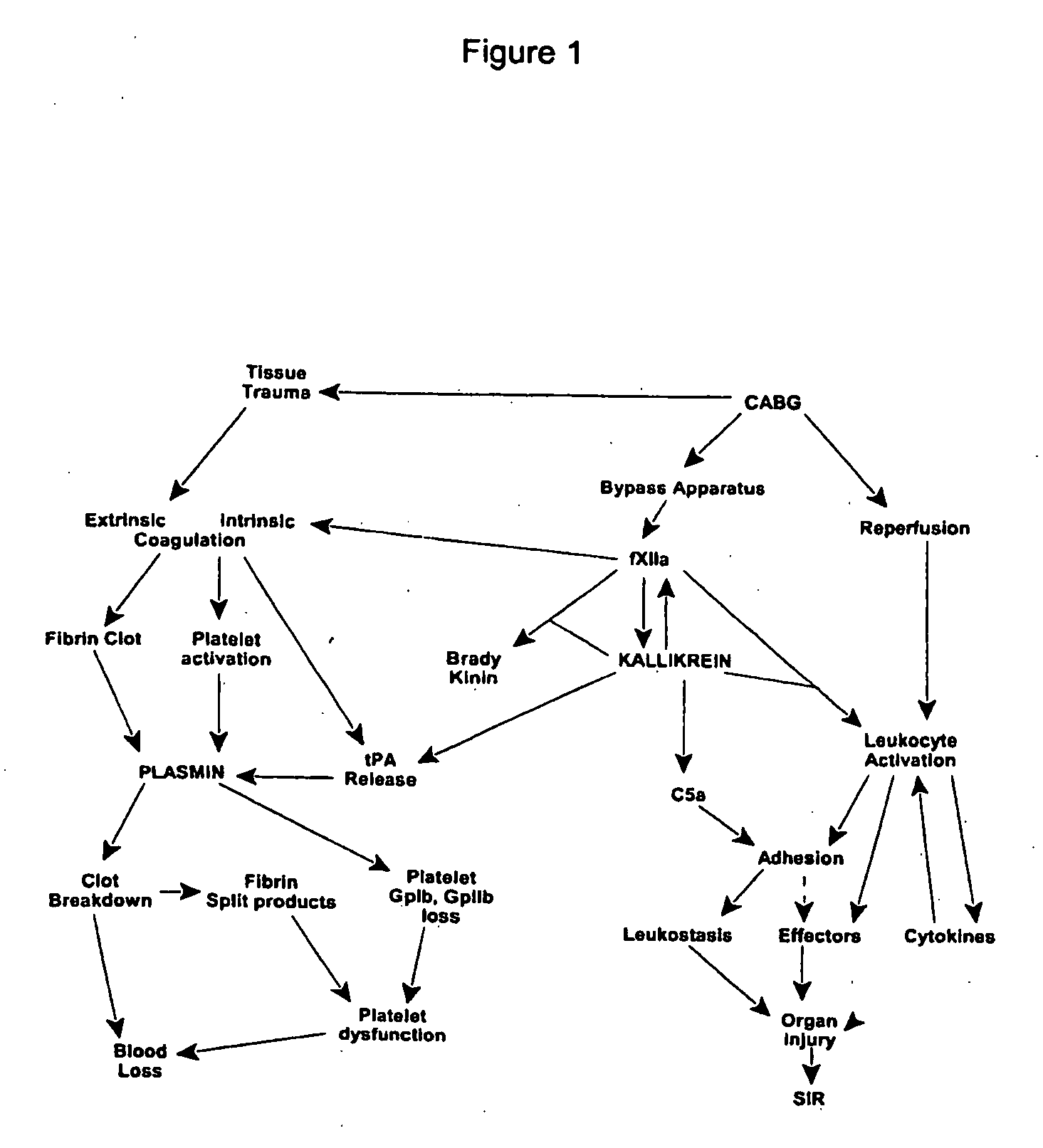
Prevention and reduction of blood loss
InactiveUS7064107B2Preventing and reducing onsetReduce and preventNervous disorderHydrolasesWhole bodySurgical department
Methods are described for preventing or reducing ischemia and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient such as perioperative blood loss and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient subjected to cardiothoracic surgery, e.g., coronary artery bypass grafting and other surgical procedures, especially when such procedures involve extra-corporeal circulation, such as cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Prevention and reduction of blood loss
Methods are described for preventing or reducing ischemia and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient such as perioperative blood loss and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient subjected to cardiothoracic surgery, e.g. coronary artery bypass grafting and other surgical procedures, especially when such procedures involve extra-corporeal circulation, such as cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
System and method for endoluminal grafting of bifurcated and branched vessels
A system and method for endoluminal grafting of a main anatomic conduit in its diseased state in which it dilates to pose a life threatening condition and its various conduits that emanate from the main anatomic conduit. The grafting system comprises an endoaortic graft having at least one opening therein and at least one branch graft that is passable through the opening of the endoaortic graft into the branch anatomic conduit(s) such that the junction between the branch graft and the endoaortic graft is substantially fluid tight. A system and method for delivery of the endoaortic graft and also a system and method for efficient alignment and deployment of the branch (e.g., side branch) graft such that the coupling of the branch graft with the endoaortic graft is efficient and exact and fluid-tight; and a system and method for coupling the branch to the endoaortic graft via a coupling mechanism employing a memory metal alloy; a system and method for the proper and exact alignment of the endoaortic graft and the branch using magnetic force of a suitable nature, and which does not use the magnetic force as the coupling mechanism.
Owner:CARDIAQ VALVE TECH
Closed System and Method for Atraumatic, Low Pressure, Continuous Harvesting, Processing, and Grafting of Lipoaspirate
ActiveUS20080167613A1Reduce excessFat graft survivalMelt-holding vesselsMedical devicesFat graftingEngineering
A closed system for harvesting fat through liposuction, concentrating the aspirate so obtained, and then re-injecting the concentrated fat into a patient comprises as its main components a low pressure cannula having between about 7 to 12 side holes of about 1-2 mm by 2.0 to 4.0 mm, a spring loaded syringe holder with a helicoidal spring to apply a substantially constant pressure over the full excursion of the plunger, and a preferably flexible collection bag which is also preferably graduated, cylindrical over most of its body and funnel shaped at its bottom, all of which are connected through flexible tubings to a multi-port valve. The multi-port valve has two flutter / duck bill valves which restrict the fluid flow to a one way direction which effectively allows the syringe to be used to pump fat out of a patient and into a collection bag in a continuous manner. After the bags are centrifuged to concentrate the fat, the excess fluids are separated and the valve is re-connected to permit the syringe pump to reverse fluid flow to graft the concentrated fat back into the patient.
Owner:LIPOCOSM LLC
Methods and compositions for altering skin coloration
Novel compositions and methods and pharmaceutical compositions for altering skin coloration. The methods include administering a cytokine to a dermal region desired to be altered. The cytokine is formulated for local administration. The cytokine is preferably administered in conjunction with a therapeutic procedure. The therapeutic procedure is preferably selected from the group consisting of excision, dermabrasion, laser therapy, cryosurgery, grafting, camouflaging, scarification, and salabrasion.
Owner:KYTHERA BIOPHARMLS INC
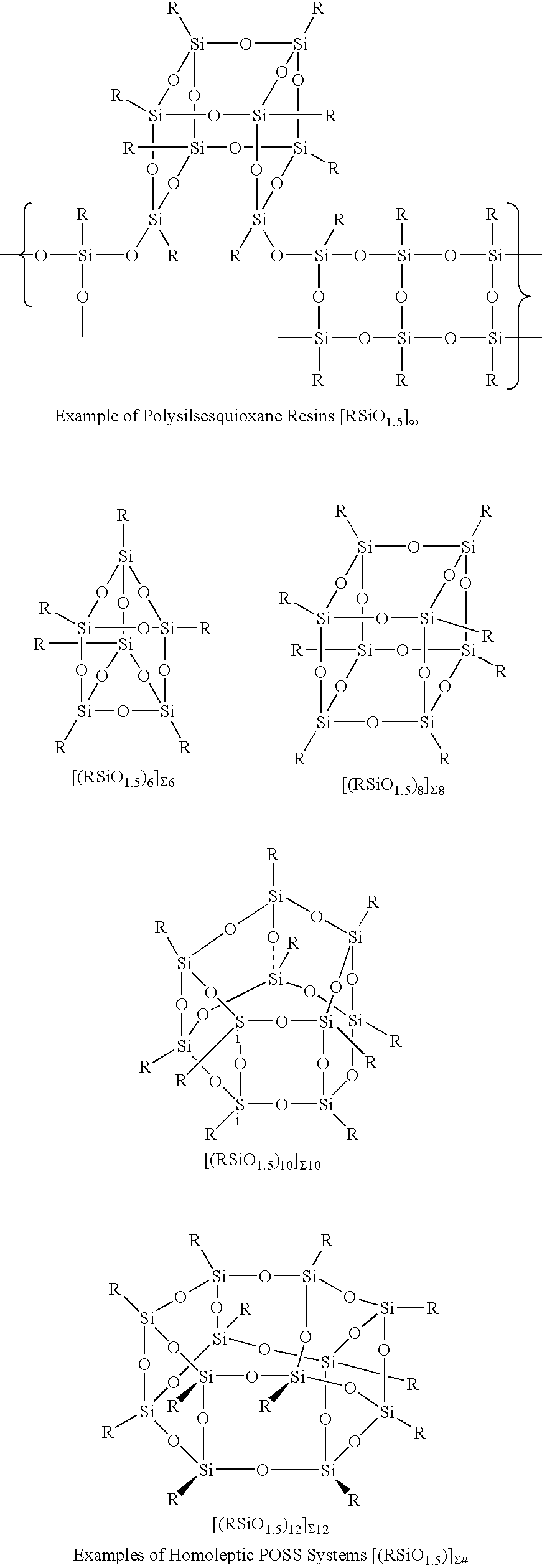
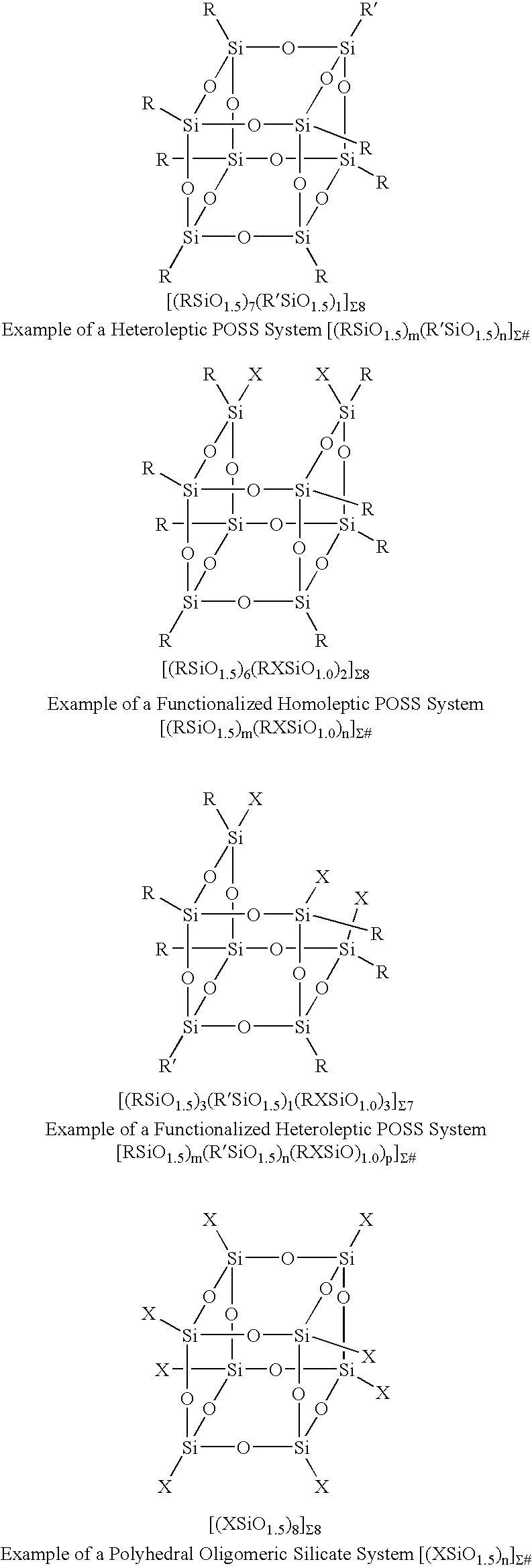
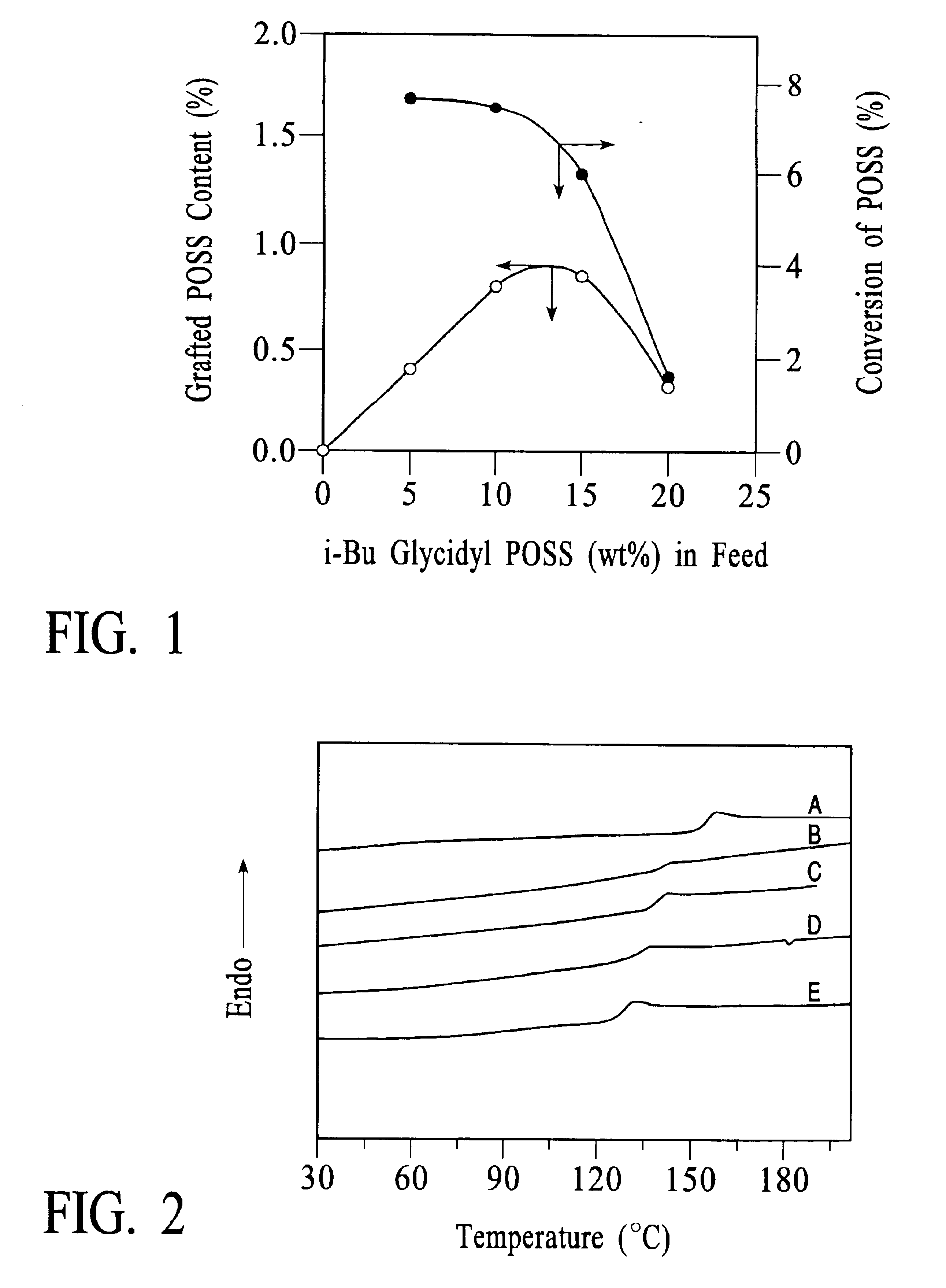
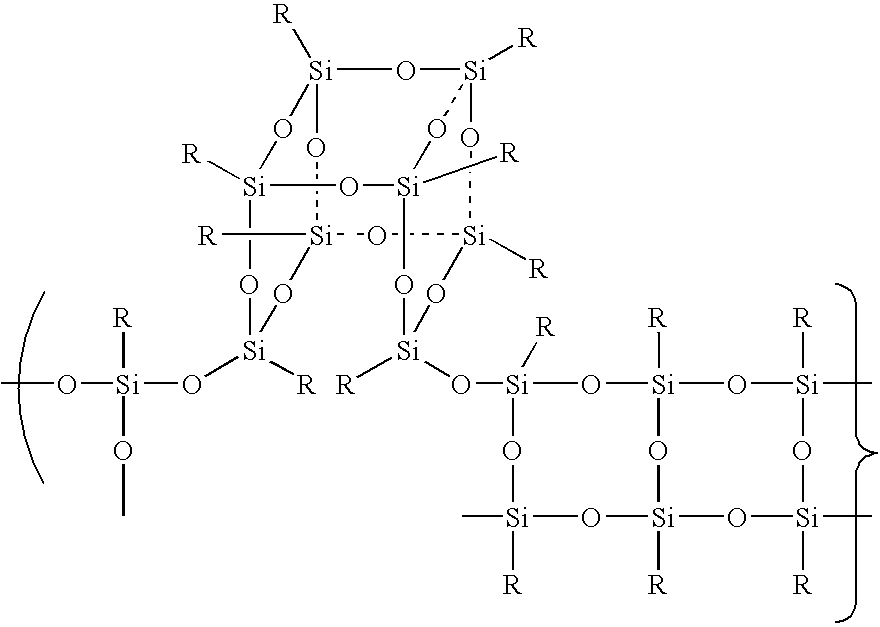
Process for the formation of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes
Three processes for the manufacture of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes (POSS) which utilize the action of bases that are capable of either attacking silicon or any compound that can react with a protic solvent (e.g. ROH, H2O etc.) and generate hydroxide [OH]−, alkoxide [RO]−′, etc. The first process utilizes such bases to effectively redistribute the silicon-oxygen frameworks in polymeric silsesquioxanes [RSiO1.5]28 where ∞=1-1,000,000 or higher into POSS nanostructures of formulas [(RSiO1.5)nΣ#, homoleptic, [(RXSiO1.5)n]Σ#, functionalized homoleptic, [(RSiO1.5)m(R′SiO1.5)n]Σ#, heteroleptic, and {(RSiO1.5)m(RXSiO1.0)n}Σ#, functionalized heteroleptic nanostructures. The second process utilizes base to aid in the formation of POSS nanostructures of formulas [(RSiO1.5)n]Σ# homoleptic and [(RSiO1.5)m(R′SiO1.5)n]Σ# heteroleptic and [(RSiO1.5)m(RXSiO1.0)n]Σ# functionalized heteroleptic nanostructures from silanes RSiX3 and linear or cyclic silsesquioxanes of the formula RX2Si—(OSiRX)m—OSiRX2 where m=0-10, X=OH, Cl, Br, I, alkoxide OR, acetate OOCR, peroxide OOR, amine NR2, isocyanate NCO, and R. The third process utilizes base to selectively ring-open the silicon-oxygen-silicon (Si—O—Si) bonds in POSS structures to form POSS species with incompletely condensed nanostructures. These processes also afford stereochemical control over X. The three processes result in new POSS species that can undergo additional chemical manipulations to ultimately be converted into POSS-species suitable for polymerization, grafting, or other desirable chemical reactions.
Owner:HYBRID PLASTICS INC
Cross-linkable polymers, method for the production thereof, and shaped bodies made of cross-linked polymers
InactiveUS6528585B1Low levelExtended maintenance periodPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsCross-linkPolymer science
The invention relates to a process for preparing crosslinkable polymers containing silane groups having at least one hydrolyzable radical by free-radical-initiated grafting of the base polymers with an olefinically unsaturated silane having at least one hydrolyzable radical, wherein the grafting is carried out in the presence of(a) an alkylsilane of the formula I, whereR1 is a monovalent hydrocarbon radical having from 1 to 33 carbon atoms or a divalent hydrocarbon radical having from 4 to 24 carbon atoms,R2 is a hydrocarbon radical having from 1 to 10 carbon atoms,X are identical or different hydrolyzable radicals,n is 0, 1 or 2 andm is 1 or 2 and / or(b) a fluoroalkylsilane of the formula whereR3 is a fluoroalkyl radical,R4 is an alkyl radical andX is a hydrolyzable radical,x is an integer from 1 to 3,y is 0, 1 or 2 andz is an integer from 1 to 3, with the proviso that the sum x+y+z=4.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Prevention and reduction of blood loss
InactiveUS20080064637A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsWhole bodyCardiopulmonary bypass time
Methods are described for preventing or reducing ischemia and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient such as perioperative blood loss and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient subjected to cardiothoracic surgery, e.g. coronary artery bypass grafting and other surgical procedures, especially when such procedures involve extra-corporeal circulation, such as cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:DYAX CORP
Reactive grafting and compatibilization of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes
InactiveUS6933345B1Rapid low cost modificationEasy to controlMaterial nanotechnologyFiberSilsesquioxane
The nanoscopic dimensions of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes (POSS) and polyhedral oligomeric silicates (POS) materials ranges from 0.7 nm to 5.0 nm and enables the thermomechanical and physical properties of polymeric materials to be improved by providing nanoscopic reinforcement of polymer chains at a length scale that is not possible by physically smaller aromatic chemical systems or larger fillers and fibers. A simple and cost effective method for incorporating POSS / POS nanoreinforcements onto polymers via the reactive grafting of suitably functionalized POSS / POS entities with polymeric systems amenable to such processes is described. The method teaches that the resulting POSS-grafted-polymers are particularly well suited for alloying agents by nongrafted POSS entitles such as molecular silicas. The successful alloying of POSS-polymers is aided because their interfacial tensions are reduced relative to non-POSS containing systems.
Owner:HYBRID PLASTICS INC
Method for grafting polymer on inorganic material surface
The present invention discloses a method of grafting a polymer on the surface of the inorganic materials. The polyethylene oxide or polyethylene glycol which contains amino or hydroxyl at the chain-end by a covalent bond or an ionic bond, or a compound containing glucose units is firstly fixed at the surface of the inorganic materials, so as to have a reductive organic chemical group on the surface; then a high cerium salt and a polymerizable monomer are added, the present invention makes use of the high cerium salt and the reductive organic group on the surface of the inorganic materials to constitute an oxidation-reduction initiation system, so as to initiate the monomer polymerization under the acidic condition, further to graft the polymer on the surface of the inorganic materials. The method of the present invention can graft the polymer on the surface of the inorganic materials easily, which has the advantages of simple reaction process, mild reaction condition and high grafting rate, so the present invention is particularly applicable for the grafting of a water-soluble polymer or a polymer hydrogel thin layer on the surface of the inorganic materials.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Prevention and reduction of blood loss
InactiveUS20070249807A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass time
Methods are described for preventing or reducing ischemia and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient such as perioperative blood loss and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient subjected to cardiothoracic surgery, e.g. coronary artery bypass grafting and other surgical procedures, especially when such procedures involve extra-corporeal circulation, such as cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
PH stable chromatographic media using templated multilayer organic/inorganic grafting
ActiveUS20060070937A1Ion-exchange process apparatusPhysical/chemical process catalystsChromatographic separationSorbent
An advanced silica gel sorbent for use in chromatographic separations that has been chemically modified by surface polycondensation of a trifunctional and / or difunctional organosilane. The chromatographic media exhibits a wider pH range and improved pH stability as compared to other silica gel based sorbents, while retaining all other positive aspects attributed to silica gel based sorbents. A method of forming the advanced silica gel sorbent by Templated Multilayer Inorganic / Organic Grafting.
Owner:PHENOMENEX INC
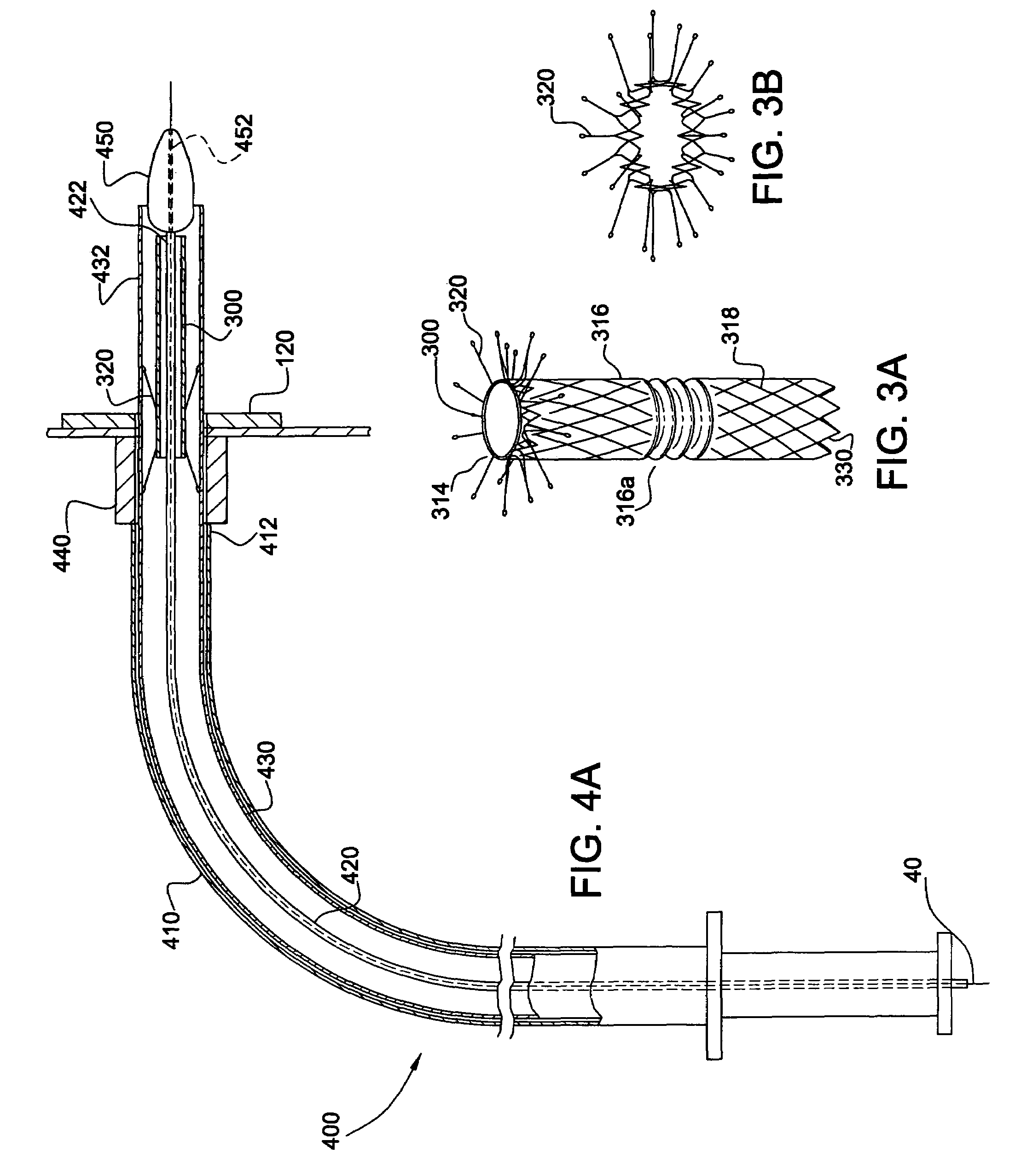
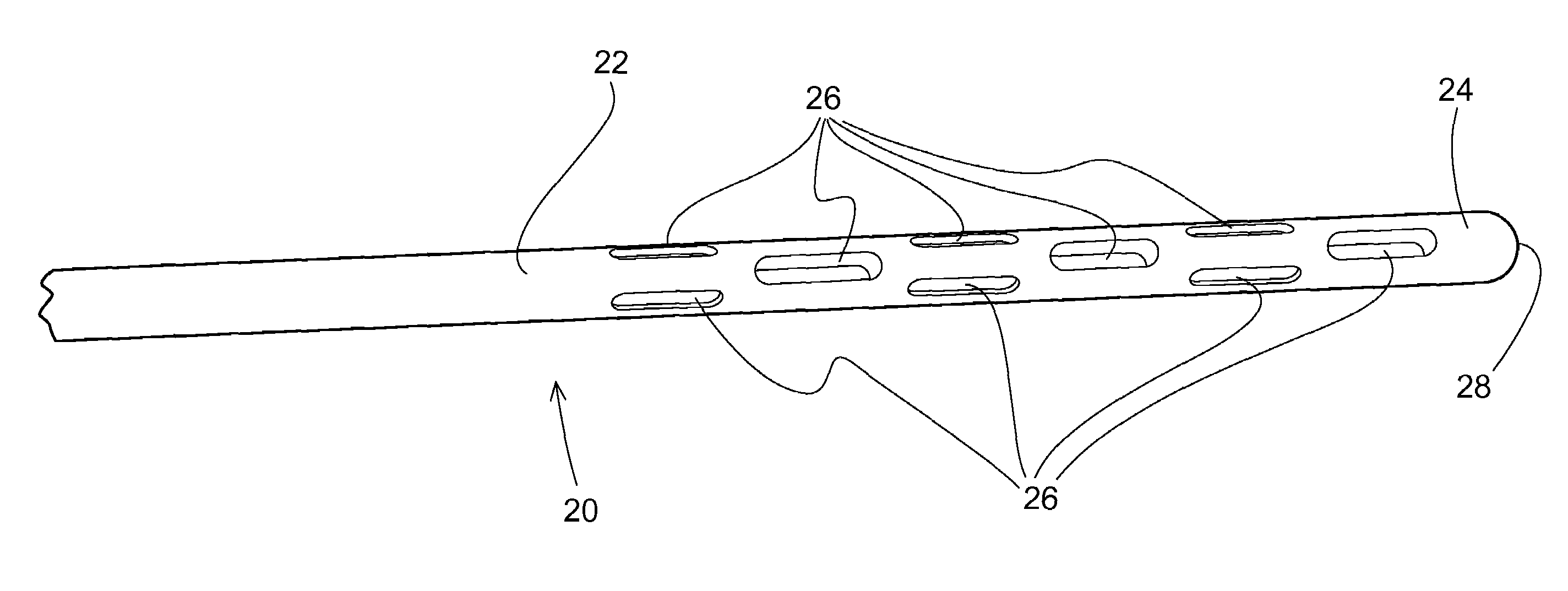
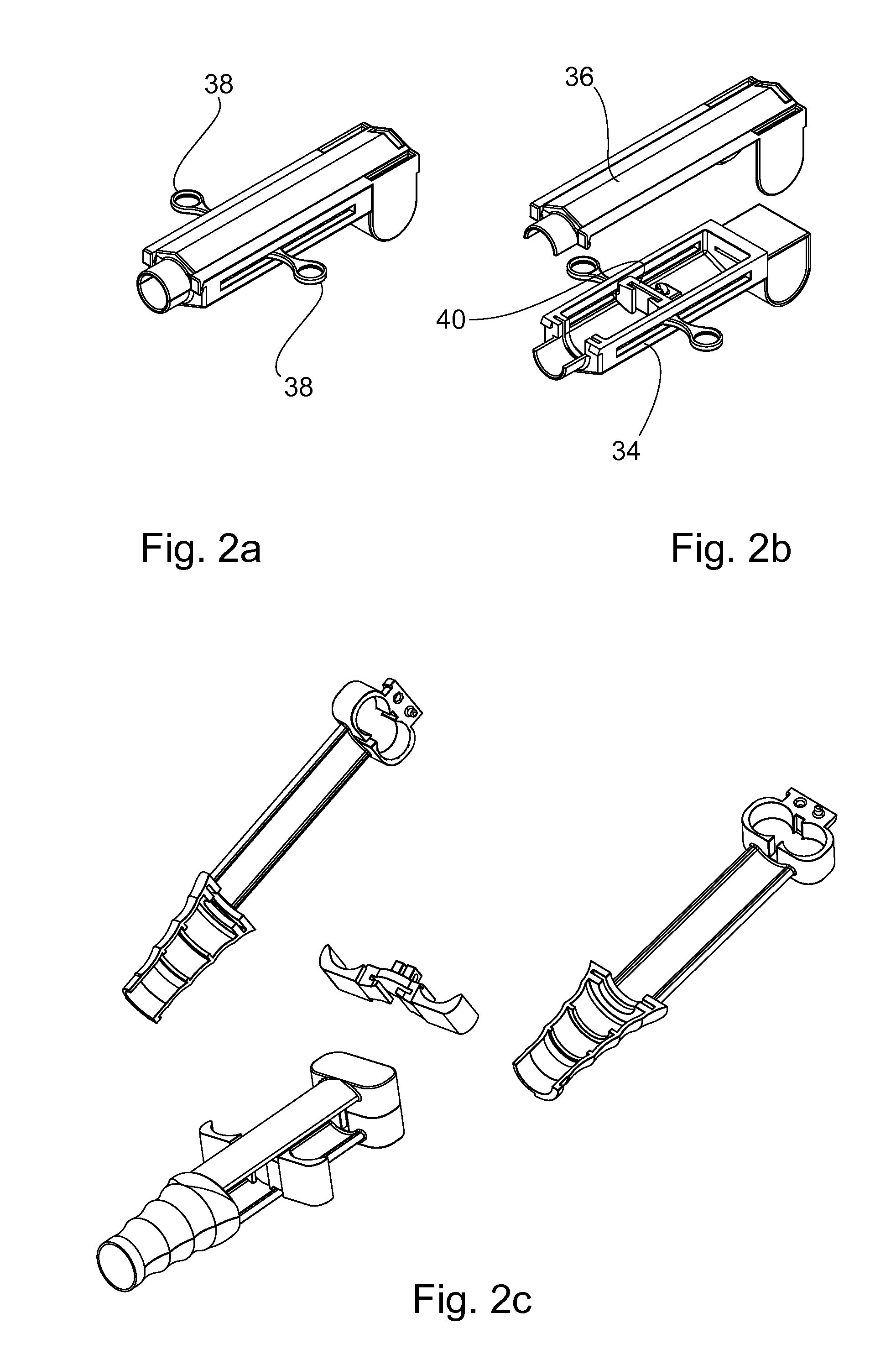
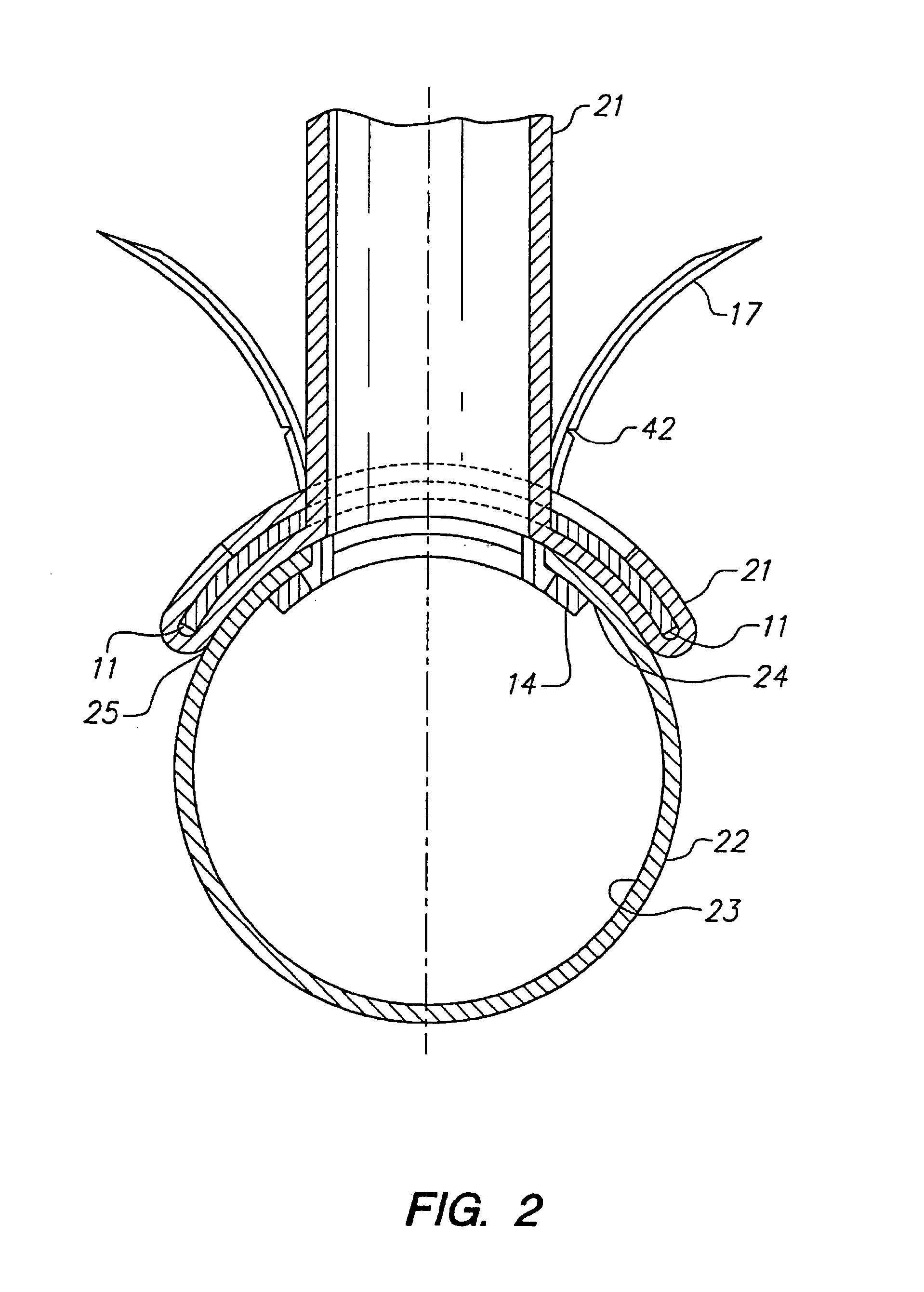
Method and system for attaching a graft to a blood vessel
InactiveUS7018388B2Minimizing restenosisMinimizing thrombosisDiagnosticsStaplesCoronary arteriesInsertion stent
Anastomotic stents for connecting a graft vessel to a target vessel, and methods of use thereof. The anastomotic stents of the invention are suitable for use in a variety of anastomosis procedures, including coronary artery bypass grafting. One embodiment of the invention comprises a large vessel anastomotic stent for use with large diameter target vessels such as the aorta or its major side branches. Another embodiment of the invention comprises a small vessel anastomotic stent for use on a target vessel which has a small diameter such as a coronary artery. Another aspect of the invention involves applicators for use with the stents of the invention.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
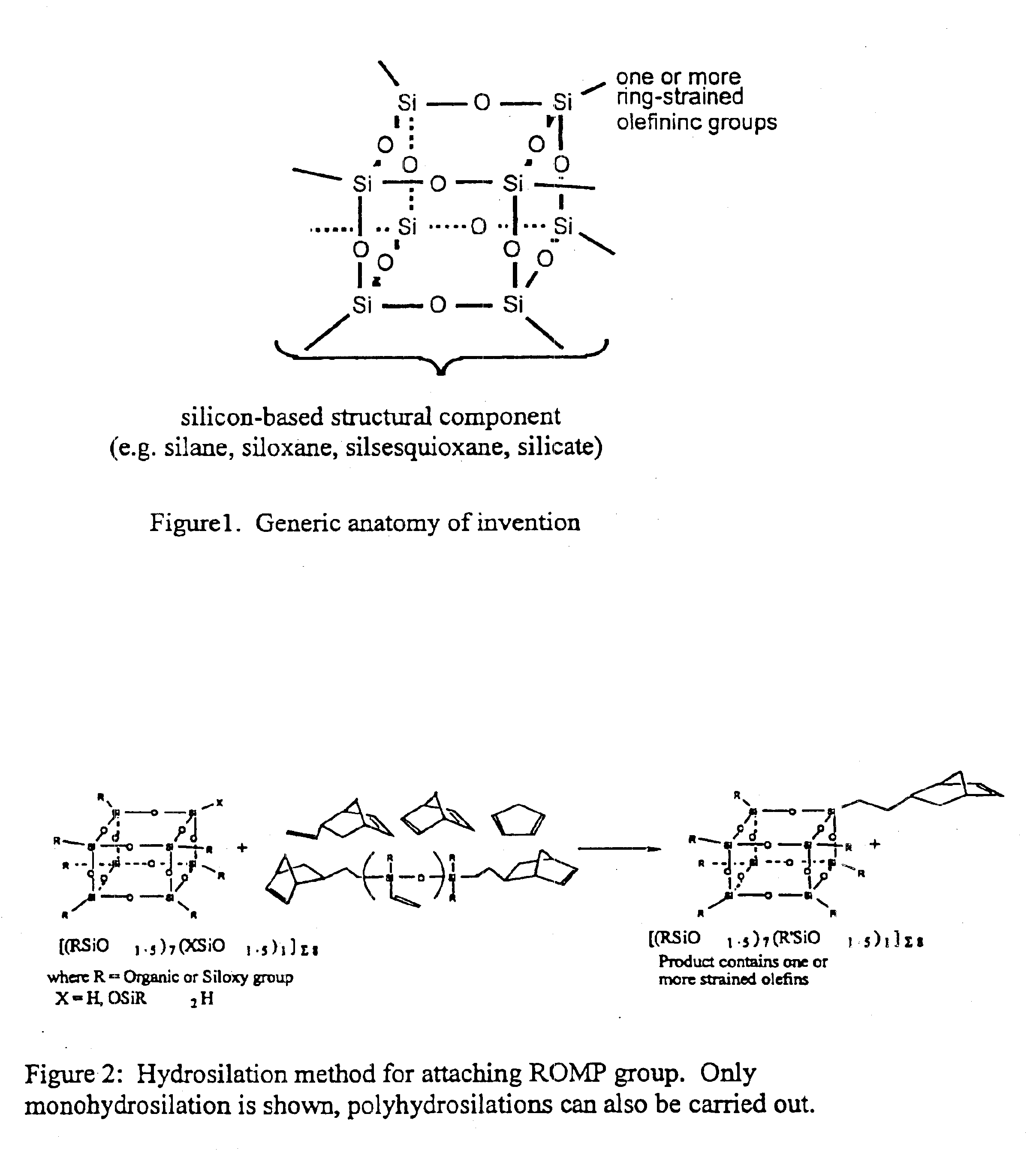
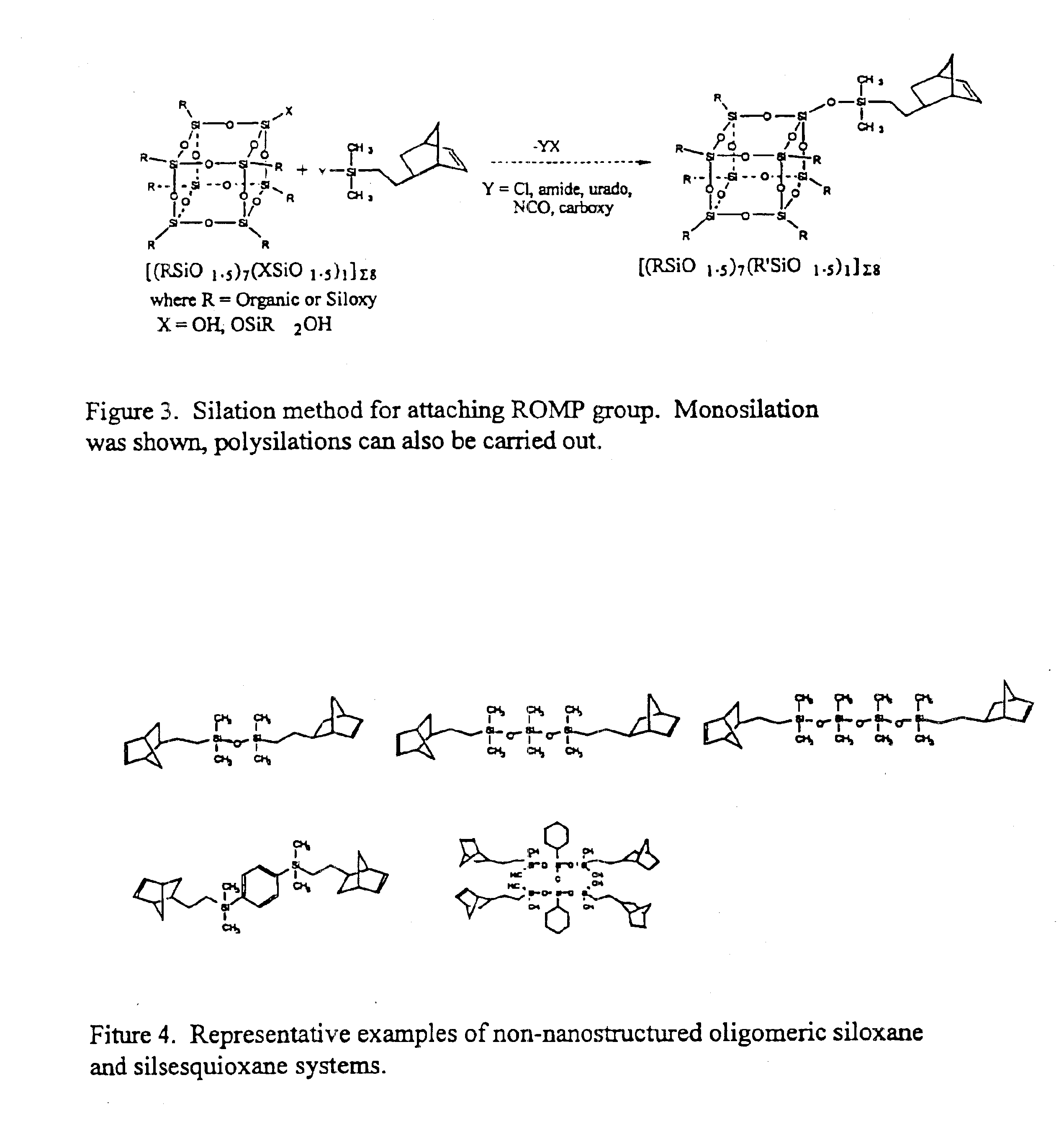
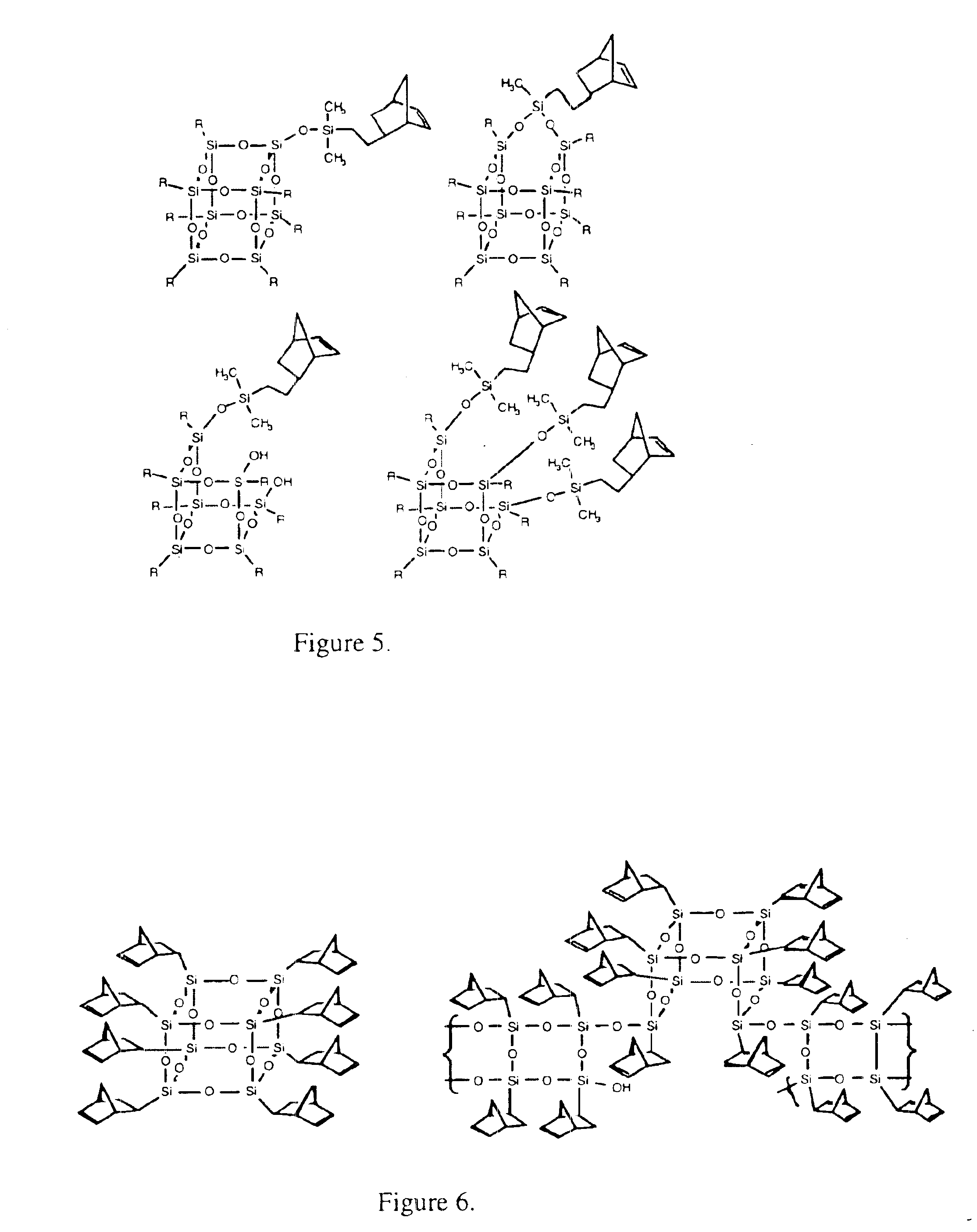
Polyhedral oligomeric -silsesquioxanes, -silicates and -siloxanes bearing ring-strained olefinic functionalities
InactiveUS6911518B2Improving biocompatabilityImprove fire resistanceSilicon organic compoundsGroup 6/16 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesAlkaline earth metalChemical reaction
Processes have been developed for the manufacture of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes (POSS), polysilsesquioxanes, polyhedral oligomeric silicates (POS), and siloxane molecules bearing reactive ring-strained cyclic olefins (e.g. norbornenyl, cyclopentenyl, etc. functionalities). The preferred manufacturing processes employ the silation of siloxides (Si—OA, where A=H, alkaline or alkaline earth metals) with silane reagents that contain at least one reactive ring-strained cyclic olefin functionality [e.g., X3-ySi(CH3)y(CH2)2 where y=1-2 and X=OH, Cl, Br, I, alkoxide OR, acetate OOCR, peroxide OOR, amine NR2, isocyanate NCO, and R]. Alternatively, similar products can be prepared through hydrosilation reactions between silanes containing at least one silicon-hydrogen bond (Si—H) with ring-strained cyclic olefin reagents [e.g., 5-vinyl, 2 norbornene CH2═CH, cyclopentadiene]. The two processes can be effectively practiced using polymeric silsesquioxanes [RSiO1.5]∞ where ∞=1-1,000,000 or higher and which contain unreacted silanol or silane groups at chain terminus or branch points, on POSS nanostructures of formulas [(RSiO1.5)n]Σ#, homoleptic, [(RSiO1.5)m(R′SiO1.5)n]Σ#, heteroleptic, and {(RSiO1.5)m(RXSiO1.0)n}Σ#, functionalized heteroleptic nanostructures, on silanes RSiX3, linear, cyclic, oligomeric and polymeric siloxanes (polymeric formula RX2Si—(OSiRX)m—OSiRX2 where m=0-1000, X=OH, Cl, Br, I, alkoxide OR, acetate OOCR, peroxide OOR, amine NR2, isocyanate NCO, and R). Each of the processes result in new chemical species bearing one or more ring strained olefins that can undergo polymerization, grafting, or other desirable chemical reactions to form polymeric products. These polymeric systems are most desirably utilized in polymerizations for the modification of properties of thermoplastic or thermoset resin systems or for the preparation of polymers with utility in electronics, medical devices, sporting goods, and aerospace as coatings and structural components.
Owner:HYBRID PLASTICS INC
Surface hydrophilic modification method for polytetrafluoroethylene bulked membrane
InactiveCN101890314ASimple processEfficient treatment processSemi-permeable membranesWater layerLow pressure plasma
The invention relates to a surface hydrophilic modification method for a polytetrafluoroethylene bulked membrane, which is characterized by comprising the steps of: pretreating a polytetrafluoroethylene membrane by adopting low-pressure glow discharge plasma to make the surface of the polytetrafluoroethylene membrane generate active groups, and grafting acrylic acid to form a relatively stable hydrophilic layer. The method has the advantages that: the active groups are generated on the surface of the polytetrafluoroethylene membrane by low-pressure plasma treatment, and the relatively stable hydrophilic layer can be formed on the surface of the membrane by acrylic acid grafting treatment, so that the hydrophilicity of the polytetrafluoroethylene membrane is effectively improved, and the effect is lasting; and the polytetrafluoroethylene membrane is treated by the low-pressure plasma induction and acrylic acid grafting, so the treatment method is simple, high-efficiency, water and energy-saving, and suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
ZSM-5 molecular sieve modified catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
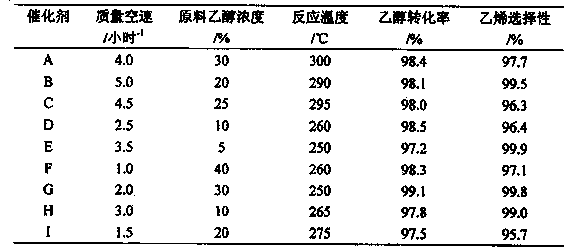
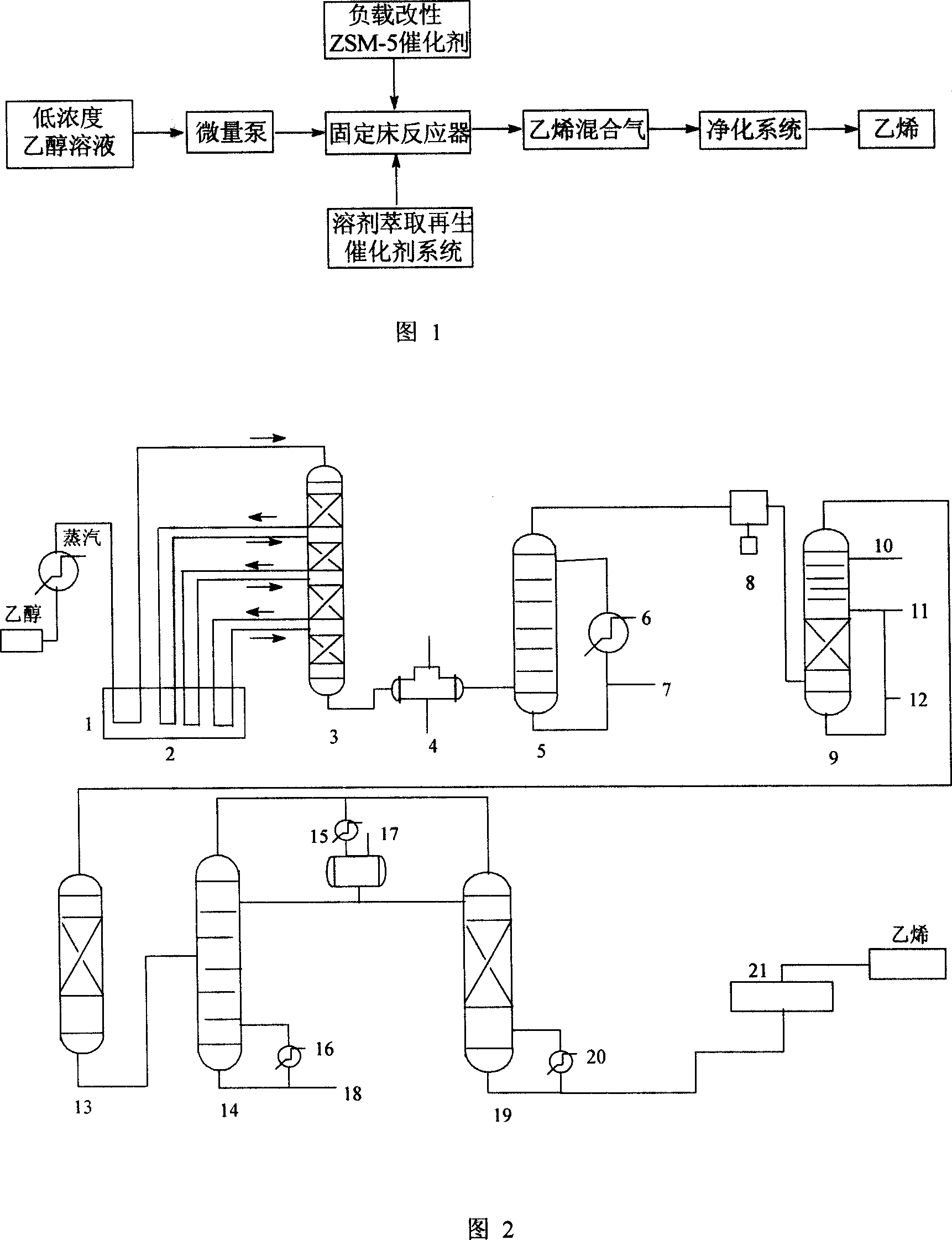
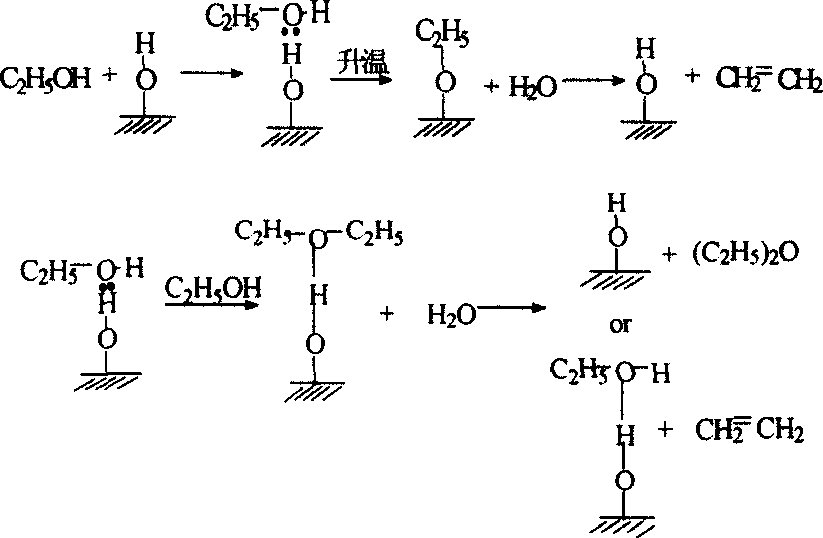
InactiveCN103521257AAchieve growthAchieve transformationMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsReaction temperatureFixed bed
The invention relates to a ZSM-5 molecular sieve modified catalyst. The ZSM-5 molecular sieve modified catalyst comprises the following porous crystal materials in molar ratio: Al2O3 to nSiO2. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the ZSM-5 molecular sieve modified catalyst, a load modified catalyst which is used for low-concentration ethanol dehydration reaction and is specifically prepared performing radical grafting and surface modification by taking a ZSM-5 molecular sieve as a carrier and, and a preparation method for preparing ethylene through dehydration of low-concentration ethanol on a fixed bed reactor. In the preparation method, the low-concentration ethanol dehydration catalyst prepared by loading a modified ZSM-5 molecular sieve has the characteristics of high catalytic activity, high selectivity, easiness in regeneration and the like. Through long-term continuous running on the fixed bed reactor, the ZSM-5 molecular sieve modified catalyst shows the low reaction temperature and low energy consumption performances when used in a low-concentration ethanol dehydration process, the ethanol conversion ratio is high, the ethylene selectivity and yield are high, and the catalyst has the advantages of being stable in activity, convenient to regenerate, stable to operate and the like.
Owner:连云港阳方催化科技有限公司
Seedling growing method of apocarya
ActiveCN103039254ARealize industrializationImprove the survival rate of graftingSeed and root treatmentHorticultureFruit treeRootstock
The invention relates to a seedling growing method of apocarya and belongs to the technical field of fruit trees and forest cultivation. The method includes the steps of sprouting breeding, grafting and post-grafting management. By means of the method, a large amount of scions are obtained each year and are grafted on the stock and the seedling with strong affinity in due time, so that stock grafting survival rate of the apocarya is improved. Grafted seedling preserving rate after large-amount grafting is over 90%. Further, the method achieves tree body stuntedness, shortens the juvenile phase and enables tree bodies to fruit earlier in the fourth year after grafting. The fruiting time is 6-8 years earlier than before. Simultaneously, the method provides a growing method for apocarya stock grafting seedlings and with strong operability for batch and variety seedling growing of the apocarya and greatly increases economical value of the apocarya.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Short-spike and root-grafting rapid propagation method for camellia azalea
ActiveCN102960172AEasy to operateImprove ergonomicsCultivating equipmentsHorticultureStratification (seeds)Camellia oleifera
The invention discloses a short-spike and root-grafting rapid propagation method for camellia azalea. The short-spike and root-grafting rapid propagation method comprises the following steps: selecting general camellia oleifera seeds, sterilizing the general camellia oleifera seeds with potassium permanganate solution and then carrying out stratification, sprouting and anvil culture; after radicles are 3-4 cm in length, grafting the radicles; selecting one-year branches with strongly-grown crown peripheries, full sprout eyes, no pest and disease damage and half lignification to lignification as scions with the length of 2-3 cm; soaking base parts with a plant growth regulator solution; after the scions are grafted, planting the grafted scions in a container bag filled with nutrient-rich substrate on a seed bed in a sunshelter for culturing; and covering, humidifying, shielding and carrying out standard management to form a high-quality grafted container seedling of the camellia azalea. According to the short-spike and root-grafting rapid propagation method, the grafting is realized at the smooth parts of radicles and the root systems of plants are developed, so that the survival rate and the growth amount of nursery stock can be effectively increased and the culture time of the stock is greatly shortened; and the scions are short, and thus the utilization rate and the propagation coefficient of the scions are improved. The short-spike and root-grafting rapid propagation method has the advantages of convenience for operation, high work efficiency and better economic benefit and social benefit; and according to the method, the scale propagation effect of the camellia azalea stock is ensured.
Owner:GUANGXI FORESTRY RES INST
ZSM-5 molecular sieve modified catalyst and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN101007283AImprove conversion rateHigh catalytic activityMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsAlcoholFixed bed
The invention involves preparation of ZSM-5 molecular sieve modified catalysts and the technology of using said catalysts in low concentration ethanol dehydration reaction, specifically a method uses ZSM-5 molecular sieve as carrier and prepares load modified catalysts through group grafting and surface modification, and a preparation method is used for preparing ethane through low concentration alcohol dehydration on fixed bed reactor. The low concentration alcohol dehydration catalyst prepared by load modified ZSM-5 molecular sieve in the invention has characteristics of high catalytic activity, high selectivity and it is easy to regenerate. When it is operated for low concentration alcohol dehydration art through fixed-bed reactor device long time and continuously, it displays advantages of low reaction temperature, low energy consumption, high conversion rate of ethanol, high ethylene selectivity and yield, stable catalyst activity, convenient regeneration and smooth operation.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Polyolefins and method for the production thereof
Process for producing polyolefins, comprising the following steps:a) grafting of acid groups onto polyolefins by means of a graftable monomer bearing at least one functional group chosen from a carbonyl and an acid anhydride, optionally in the presence of another graftable monomer bearing a vinyl unsaturated group and, optionally, one or more aromatic rings;b) purification, consisting in removing at least some of the graftable monomer bearing at least one functional group chosen from a carbonyl and an acid anhydride that has not reacted with the polyolefins;c) neutralization of the acid groups by at least one neutralizing agent.Polyolefin obtained.
Owner:ADDCOMP HOLLAND
Method and system for attaching a graft to a blood vessel
InactiveUS7041110B2Prevent movementMinimizing restenosisStaplesNailsCoronary arteriesInsertion stent
Owner:AESCULAP AG
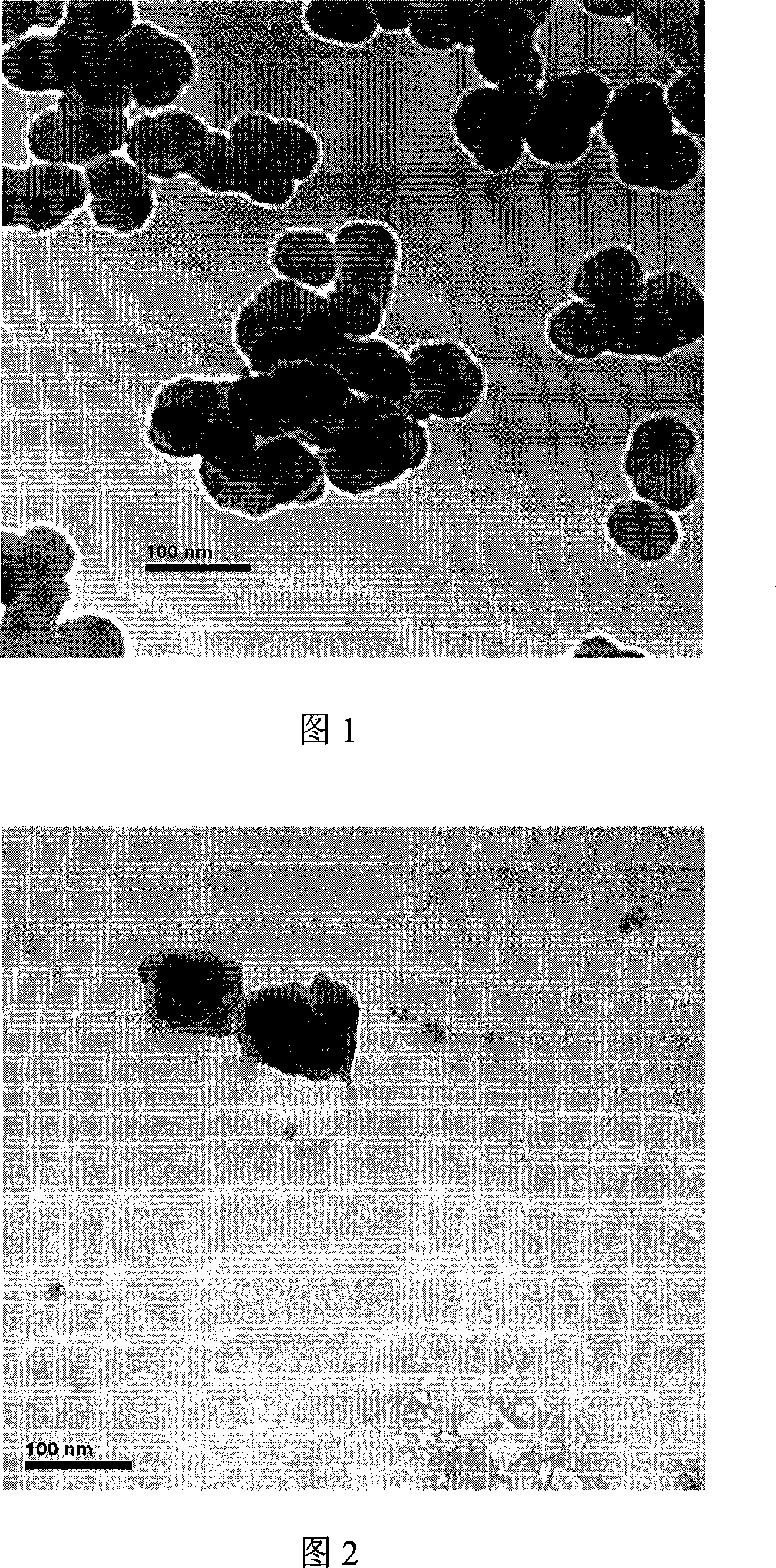
Composite polyolefin/sio2 nano particle and its prepn
The present invention belongs to the field of polymer material technology. Inorganic nano Sio2 partticle, organic olefin monomer and coupler as raw materials are subjected to emulsion polymerization or suspension polymerization in water as medium in the presence of various emulsifiers and initiator, so that the olefine polymer is grafted to the surface of inorganic nano SiO2 particle to form inorganic nano SiO2 particle core-organic olefin polymer shell structure. The composite particle is spherical, has homogeneous particle size smaller than 100 nm, and has high grafting rate and high grafting efficiency. The prepared compoisite olefin polymer / SiO2 particle material has wide application in the development of nano technology.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method of modifying polymeric material and use thereof
InactiveUS20030087982A1Improve hydrophilicityImprove adhesionAlkaline accumulatorsFibre typesFiberPolyolefin
A method of modifying a polymeric material which comprises the steps of activation-treatment and a hydrophilic polymer-treatment, or comprises the steps of activation-treatment, a hydrophilic polymer-treatment, and monomer grafting in this order, or comprises the step of a solvent-treatment followed by these steps. Thus, the polymeric material, e.g., polyolefin, is improved in hydrophilicity, adhesion, etc. without lowering the practical strength thereof The polymeric material thus improved in adhesion and other properties can be used in many applications where water absorption and adhesion are required, such as an absorption material, e.g., a wiping / cleansing material, a water retention material, a material for microorganism culture media, a separator for batteries (or cells), a synthetic paper, a filter medium, a textile product for clothing, a medical / sanitary / cosmetic supply, and reinforcing fibers for composite materials.
Owner:KB INT
Method for grafting branch onto tree
InactiveCN103081732AImprove survival rateGood ornamental valueHorticulture methodsGraftingAgroforestry
The invention discloses a method for grafting a branch onto a tree. According to the method for grafting the branch onto the tree, a scion tree which is in the same type as the tree where the branch is to be grafted is selected; the scion tree is transplanted beside the tree where the branch is to be grafted; the time of grafting is chosen to be in March to May, 60% to 70% of the skin of an inarching portion of the scion tree is stripped to expose the xylem of the scion tree, a groove where the inarching portion of the scion tree can be inserted is formed in an inarching portion of the tree where the branch is to be grafted, the groove is deep enough to reach the xylem of the tree where the branch is to be grafted, and after the inarching portion of the scion tree and the groove are sterilized, the inarching portion of the scion tree and the groove are bonded closely; nails are used for fixing the inarching portion of the scion tree and the groove, and then a grafting film is used for tying up the scion tree and the groove; the grafting film is untied after two to three months; in the inarching growing period, the situation that the scion three is provided with suitable soil, water and fertilizer for facilitating the growth of the scion tree is maintained; and if the scion tree is alive after the grafting, the portion, under the joint portion of the scion tree and the tree, of the scion three is cut and sealed with tree wound sealing glue, wherein the cutting time is chosen to be in October to November and at least one year after the grafting date.
Owner:长沙县奥景花卉苗木专业合作社
Method for fixing functional molecules on biomedical material surface with dopamine serving as bridging
InactiveCN102813963AFunction is not brokenSolve the problem of stabilization of assembled substancesCoatingsProsthesisChemical reactionDopamine
The invention discloses a method for fixing functional molecules on a biomedical material surface with dopamine serving as a bridging. The method uses the dopamine to serve as a bridging medium, firstly uses strong auto polymerization characters of the dopamine under certain pH environment to be assembled on the biomedical material surface to form a poly-dopamine layer, and then a chemical reaction is used for stem grafting of the functional molecules on the poly-dopamine layer to build the biomedical material surface with biological activity. The method does not damage the biological activity of the functional molecules and can change assembling thickness of the poly-dopamine layer by controlling reaction time so as to change grafting percent of the functional molecules on the surface. The method is simple and practical in process, good in repeatability and capable of widely applying to surface functionalization modification of biomedical materials such as intervention materials and tissue engineering materials, and has good clinical application prospects.
Owner:高长有
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com