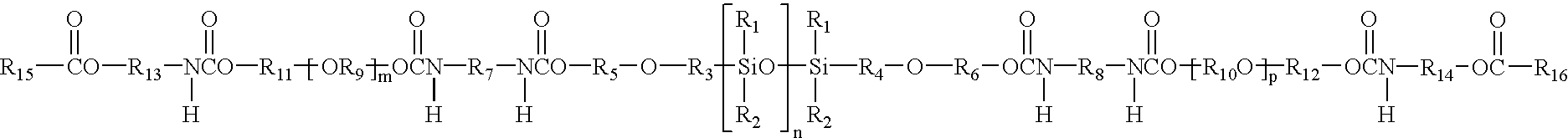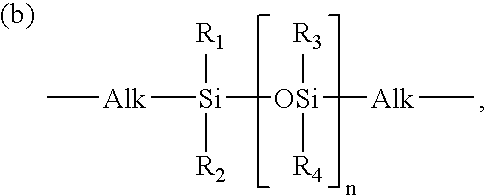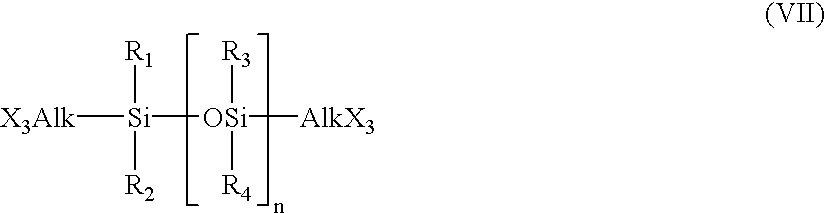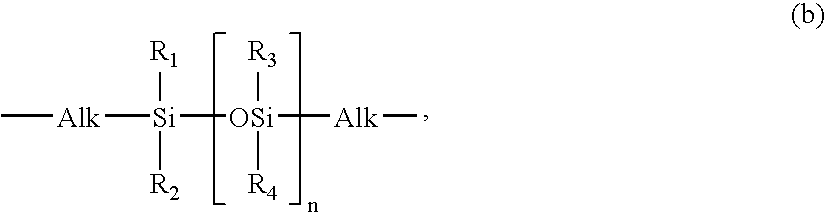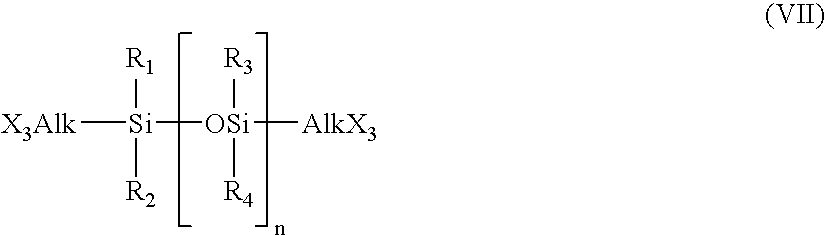Patents
Literature
998results about How to "Extended maintenance period" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
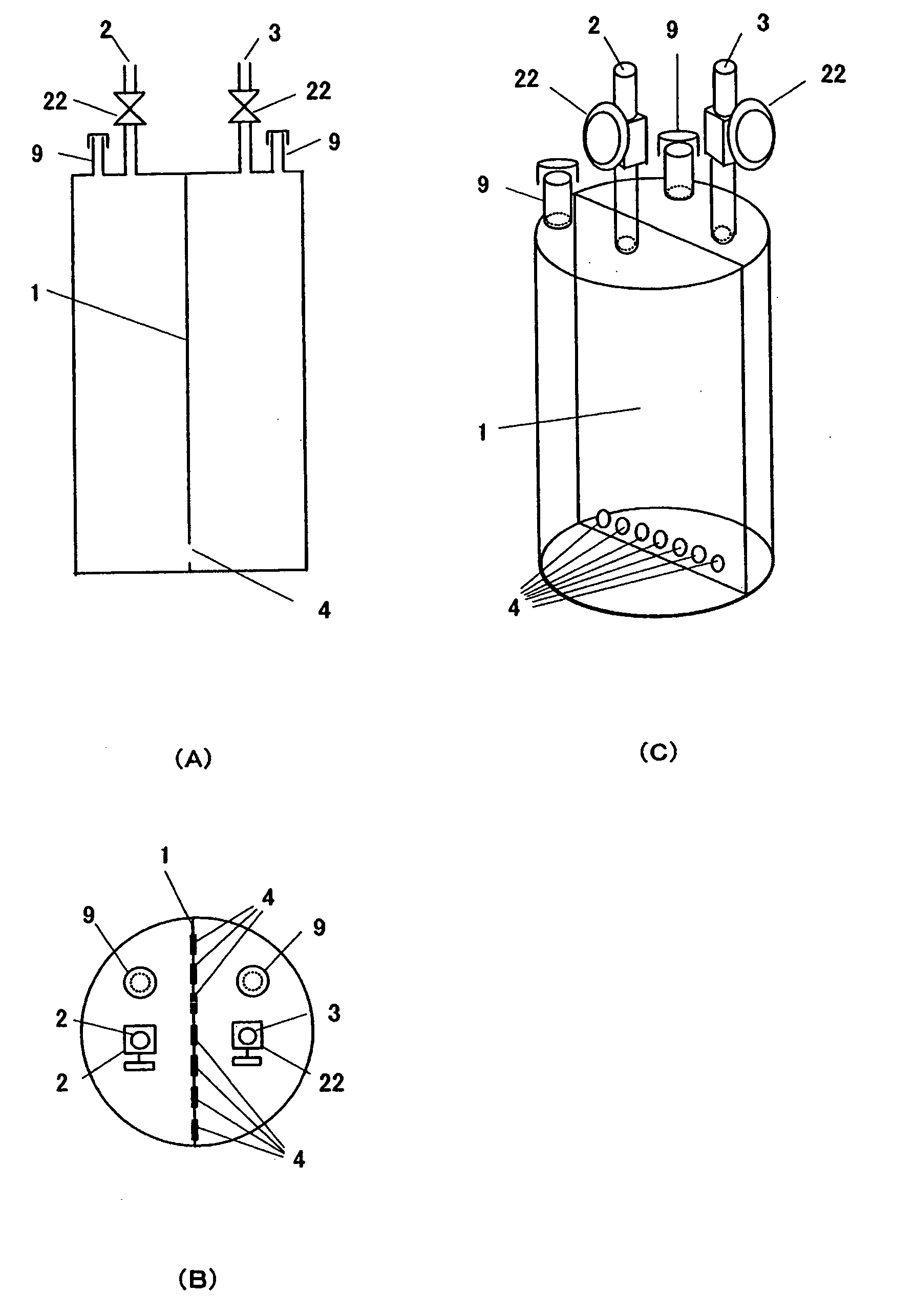
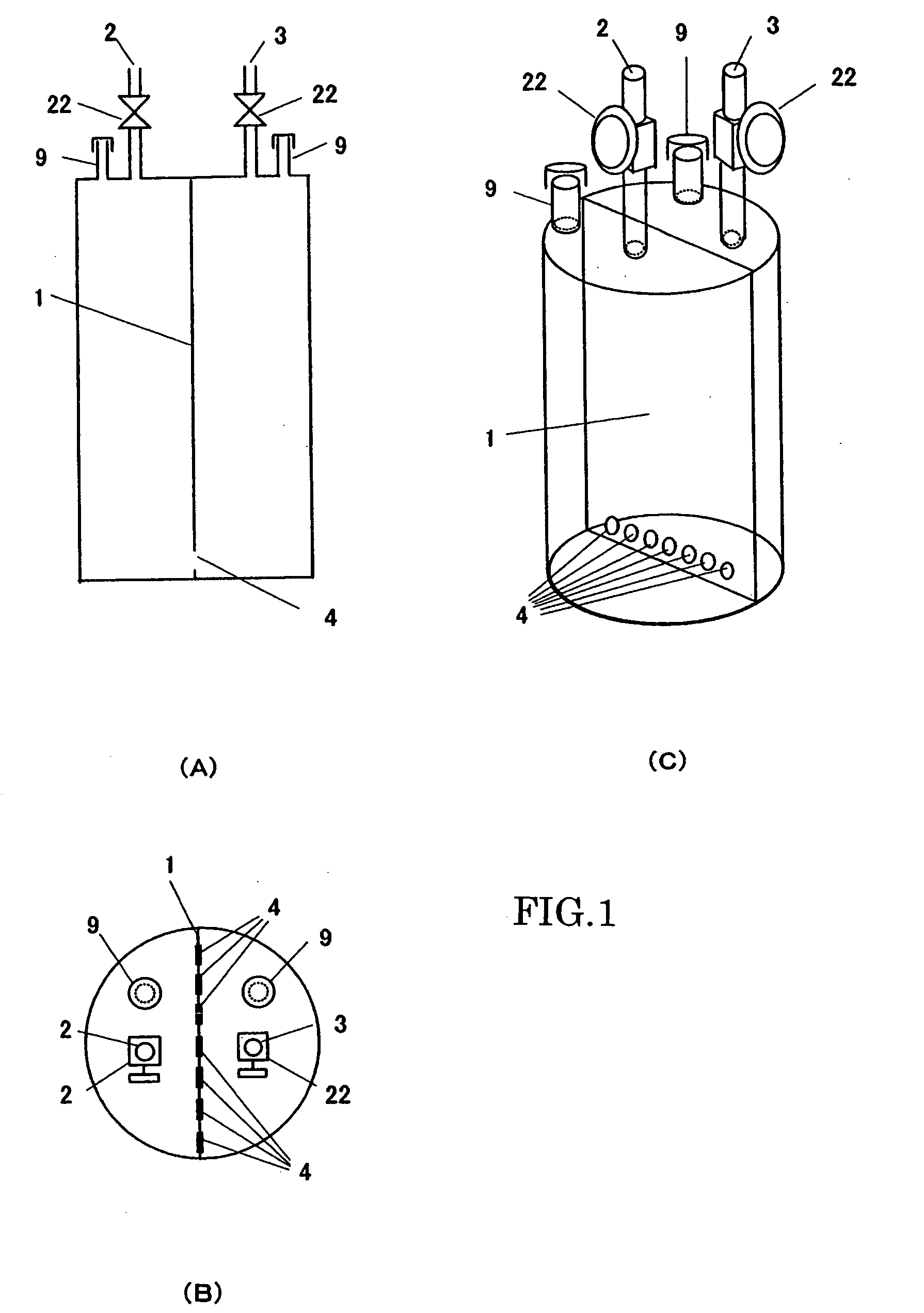
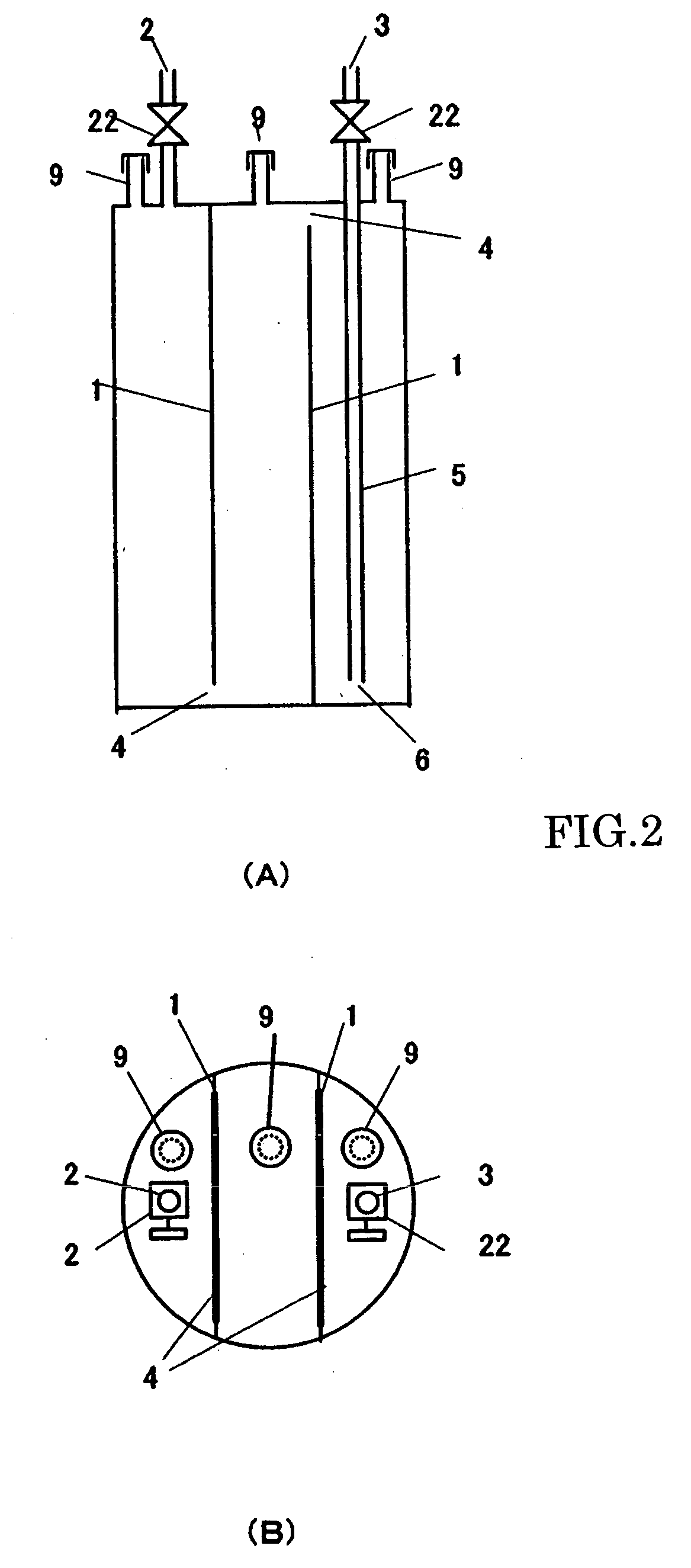
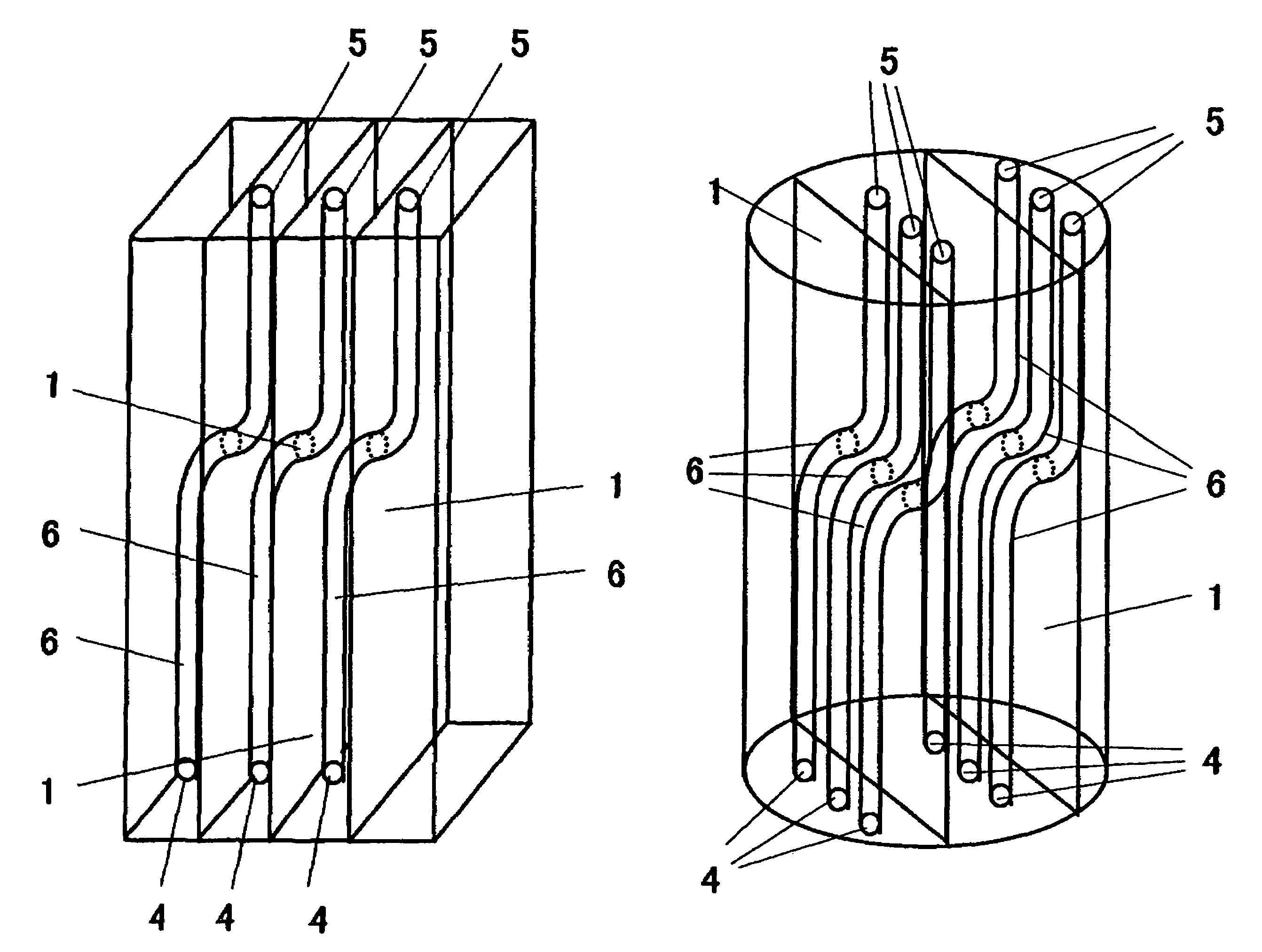
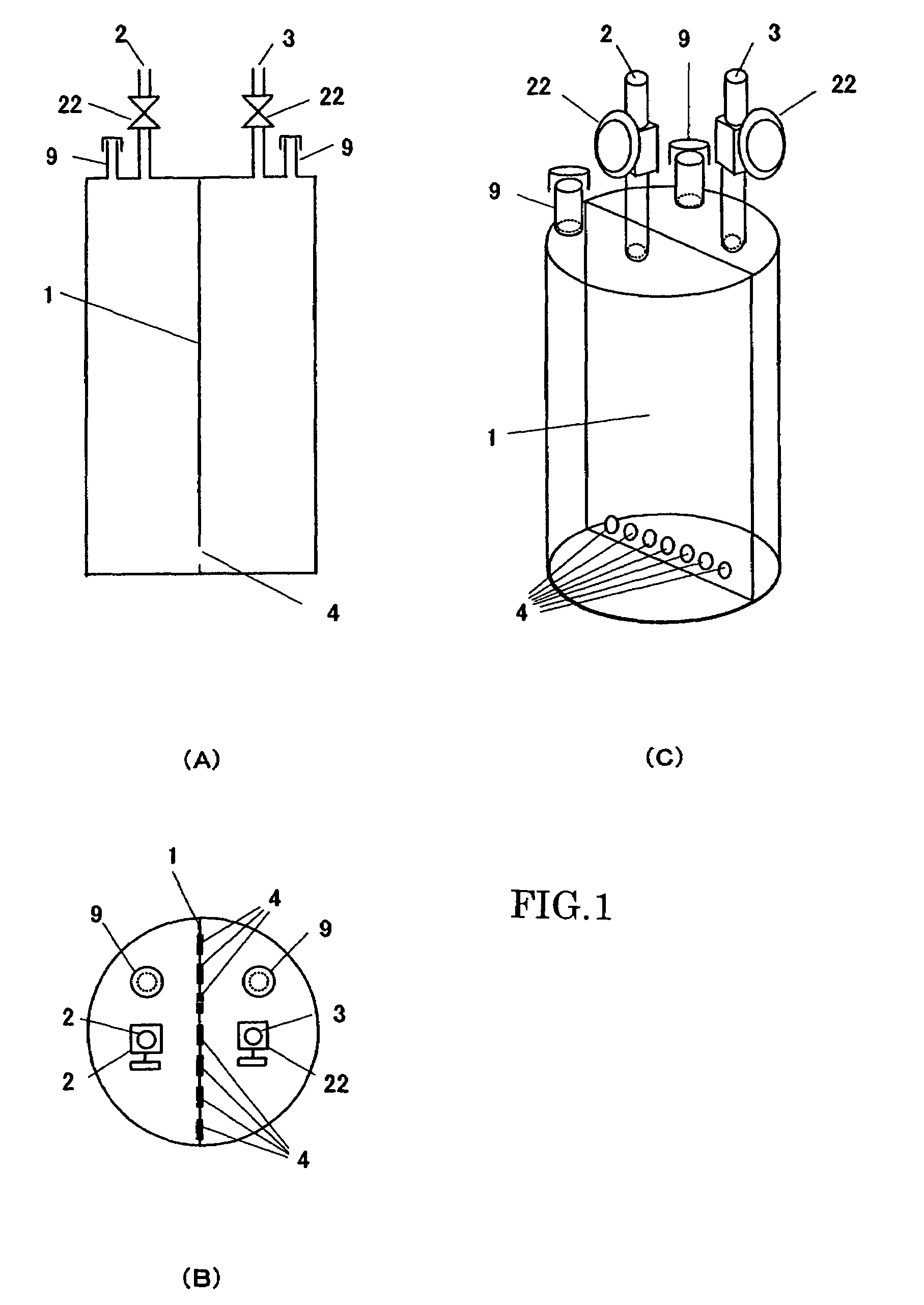
Solid organometallic compound-filled container and filling method thereof
InactiveUS20050008799A1Increasing outer sizeStable supplyEnvelopes/bags making machineryPipe laying and repairEngineeringVapor phase
A novel filled container is provided, which can stably supply an apparatus for vapor phase epitaxial growth such as an MOCVD apparatus with a solid organometallic compound over a long term. The solid organometallic compound-filled container has a carrier gas inlet and a carrier gas outlet. The interior of the filled container is separated into a plurality of vertical compartments. A carrier gas introduced via the carrier gas inlet flows through each of the vertical compartments and is then discharged via the carrier gas outlet.
Owner:TOSOH FINECHEM CORP
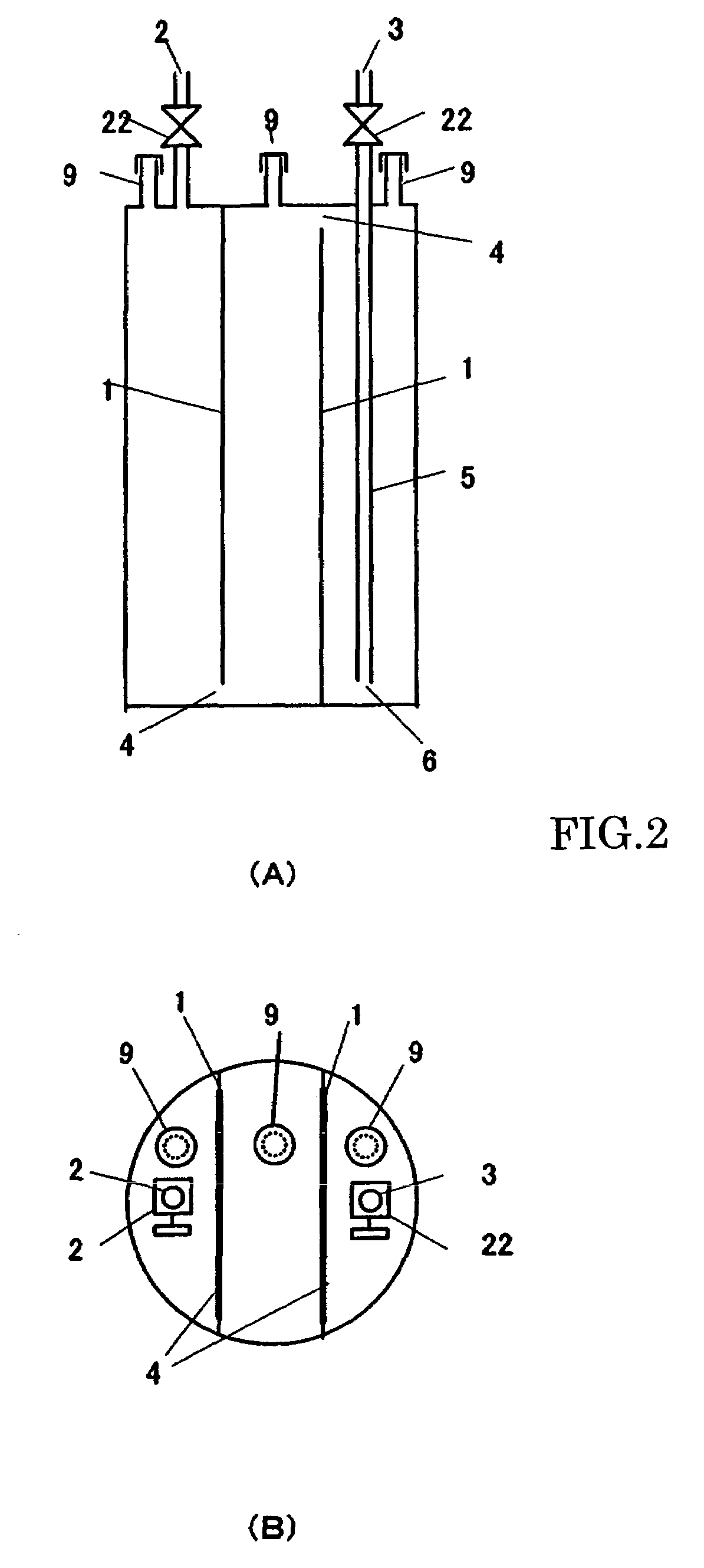
Solid organometallic compound-filled container and filling method thereof
InactiveUS7547363B2Increasing outer sizeExtended maintenance periodEnvelopes/bags making machineryLayered productsGas phaseEngineering
A solid organometallic compound novel filled container stably supplies an apparatus for vapor phase epitaxial growth such as an MOCVD apparatus with a solid organometallic compound over a long term. The solid organometallic compound-filled container has a carrier gas inlet and a carrier gas outlet. The interior of the filled container is separated into a plurality of vertical compartments. A carrier gas introduced via the carrier gas inlet flows through each of the vertical compartments and is then discharged via the carrier gas outlet.
Owner:TOSOH FINECHEM CORP
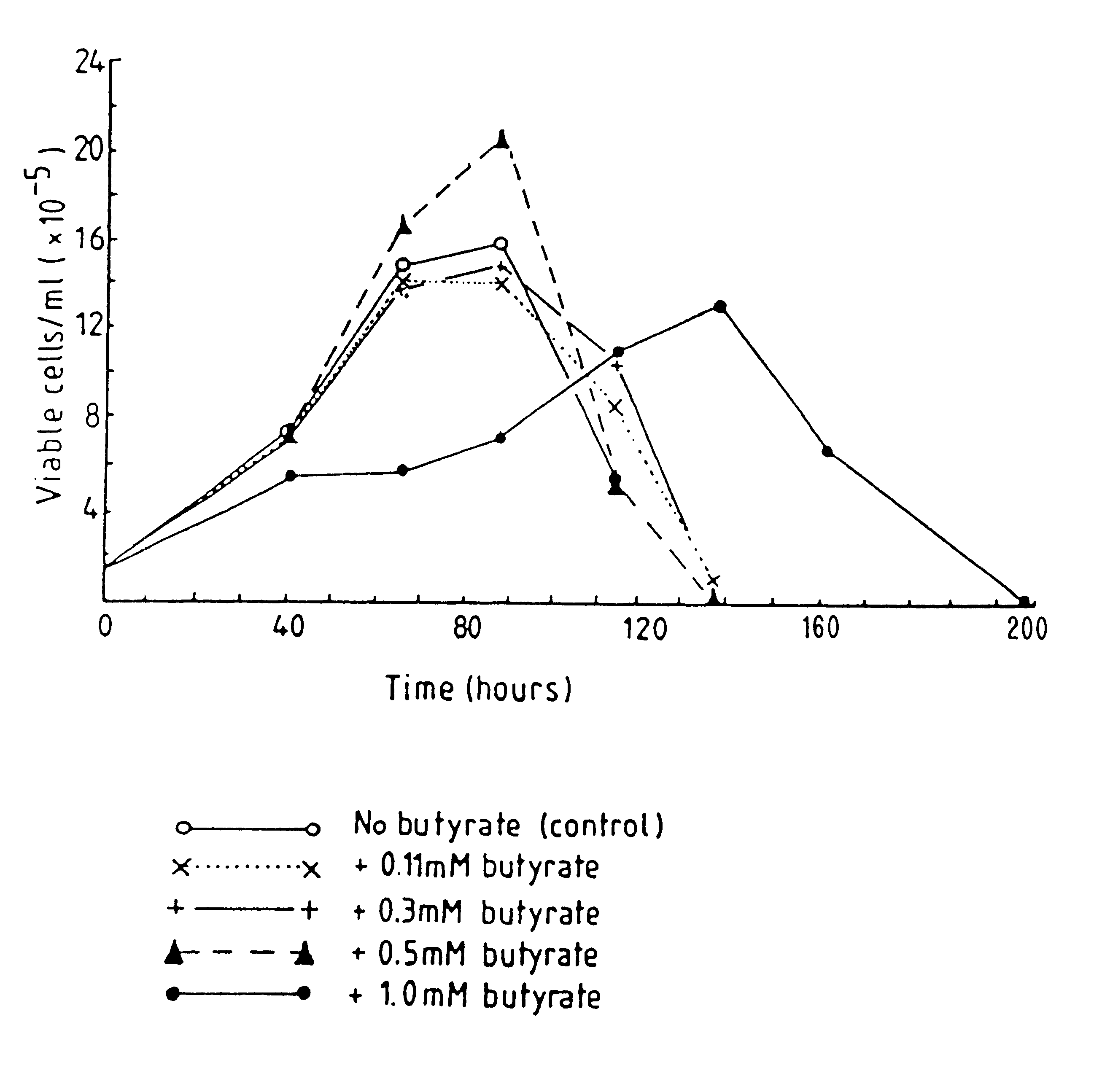
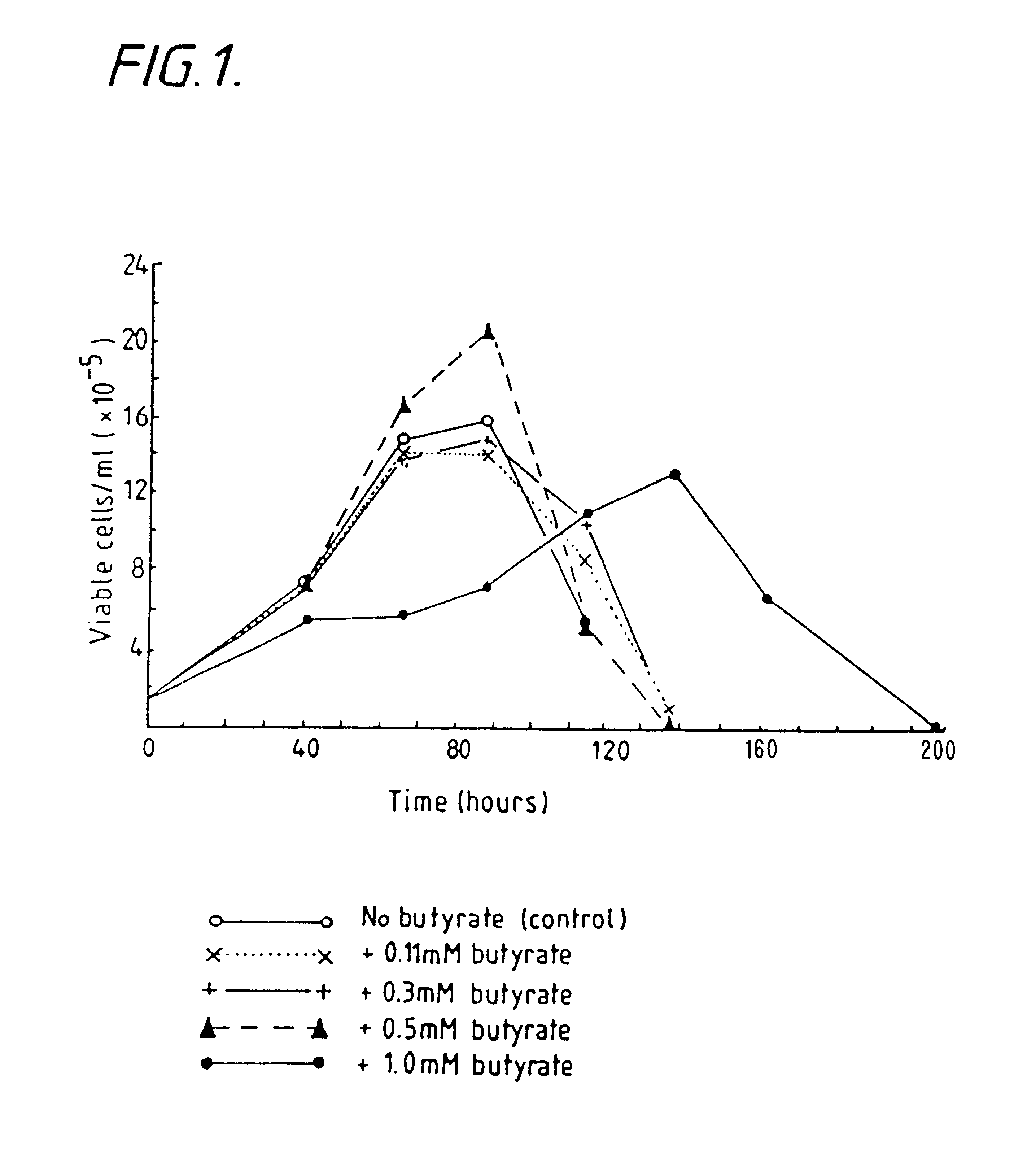
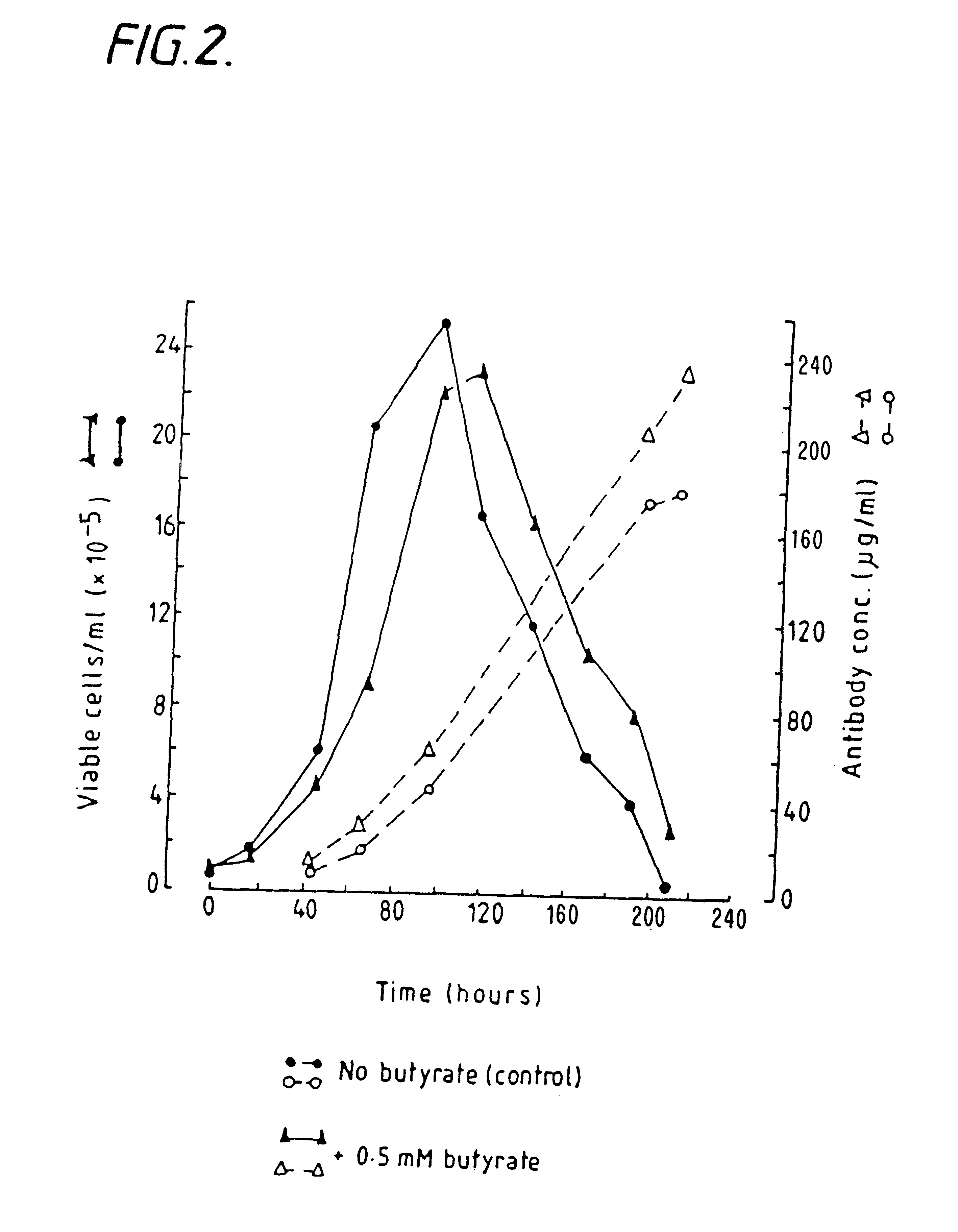
Production of proteins by cell culture
InactiveUS6413746B1High protein yieldReduce cell viabilityImmunoglobulins against blood group antigensPeptide/protein ingredients3D cell cultureBiochemistry
Methods for obtaining a protein by culture of hybridoma cells, wherein said protein is an immunoglobulin, are disclosed. The methods involve culturing animal hybridoma cells in continuous presence of an alkanoic acid or salt thereof, which enhances protein production, wherein said alkanoic acid or salt thereof is present at 2 concentration range of 0.1 mM to 200 mM.
Owner:LONZA LTD
Methods, products, systems, and devices for processing reusable information
InactiveUS20080010365A1Increase subscription periodMinimize useData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsClient-sideTelecommunications link
In a communication network having at least one communication link connecting at least one provider and a client, where the at least one provider is in communication with at least one database storing at least one identifier having variable ownership status, a method includes establishing that at least one identifier of significance to the client is unavailable for ownership by the client, communicating to the at least one provider at least one desired action the at least one provider is to take on behalf of the client to obtain an ownership interest in the at least one identifier of significance to the client, where the at least one identifier of significance to the client is unavailable for ownership by the client at the time of the communication, and determining whether to perform the at least one desired action without monitoring the ownership status of the at least one identifier of significance to the client.
Owner:MEC MANAGEMENT LLC +1
Digital camera using multiple image sensors to provide improved temporal sampling
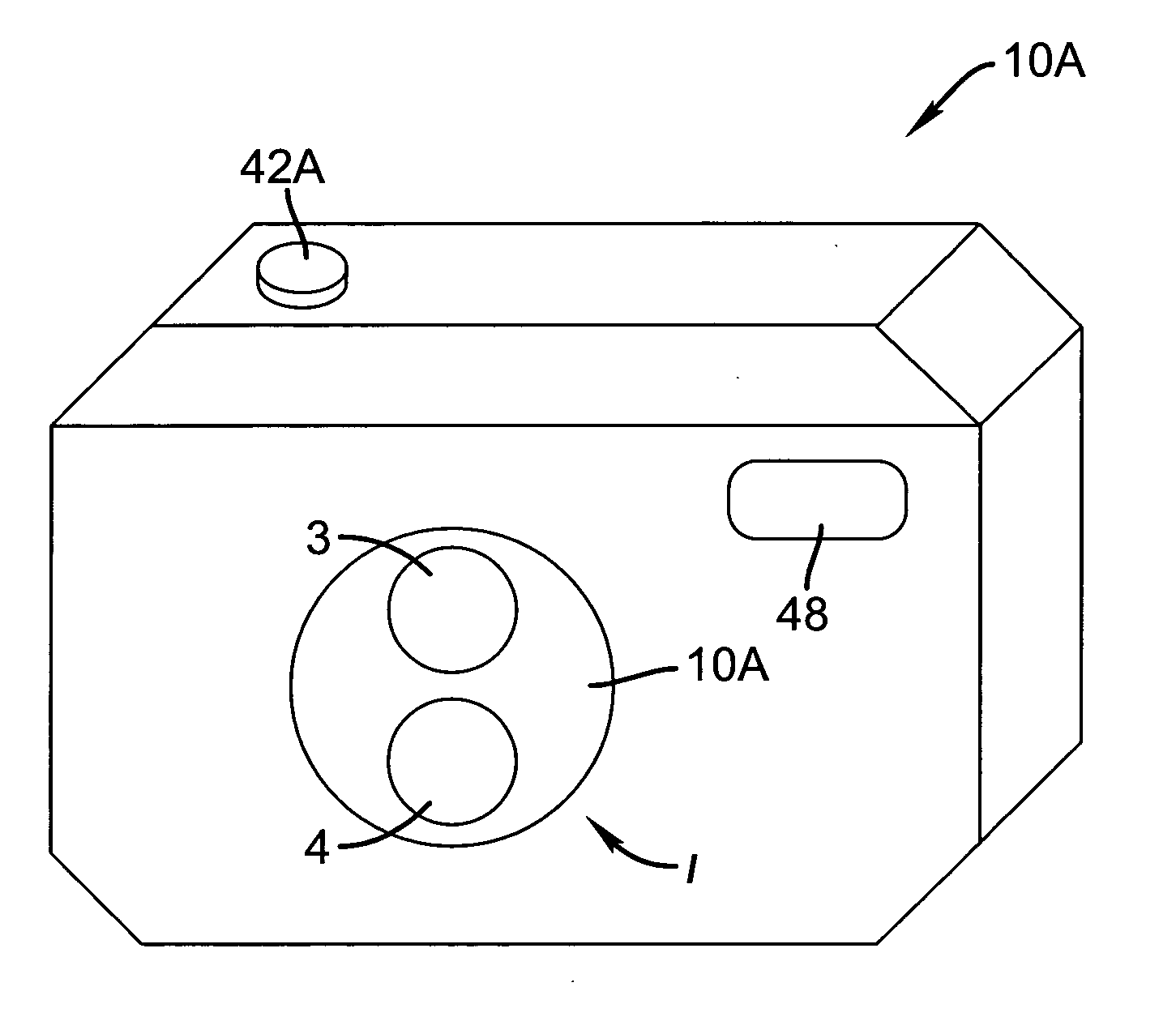
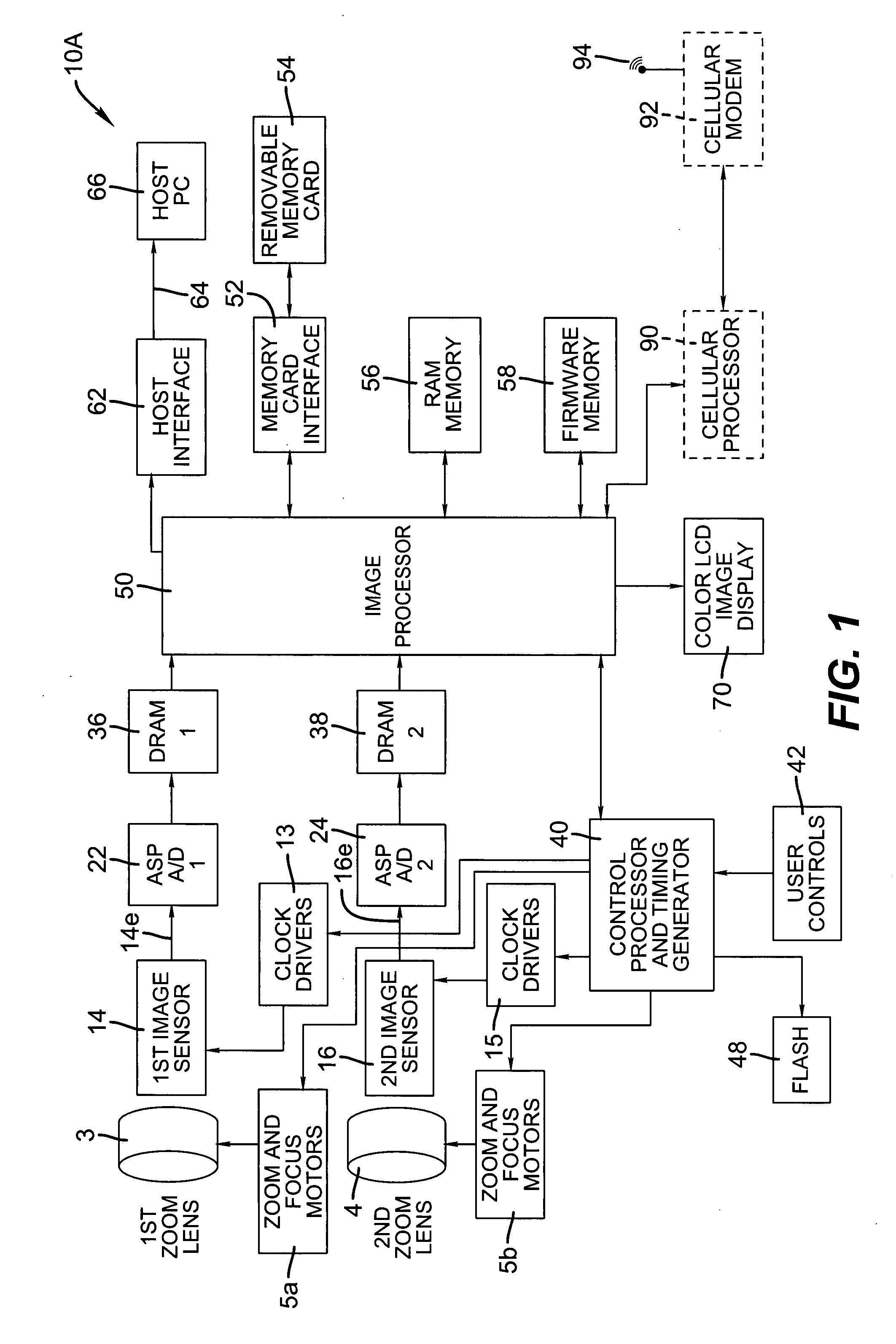
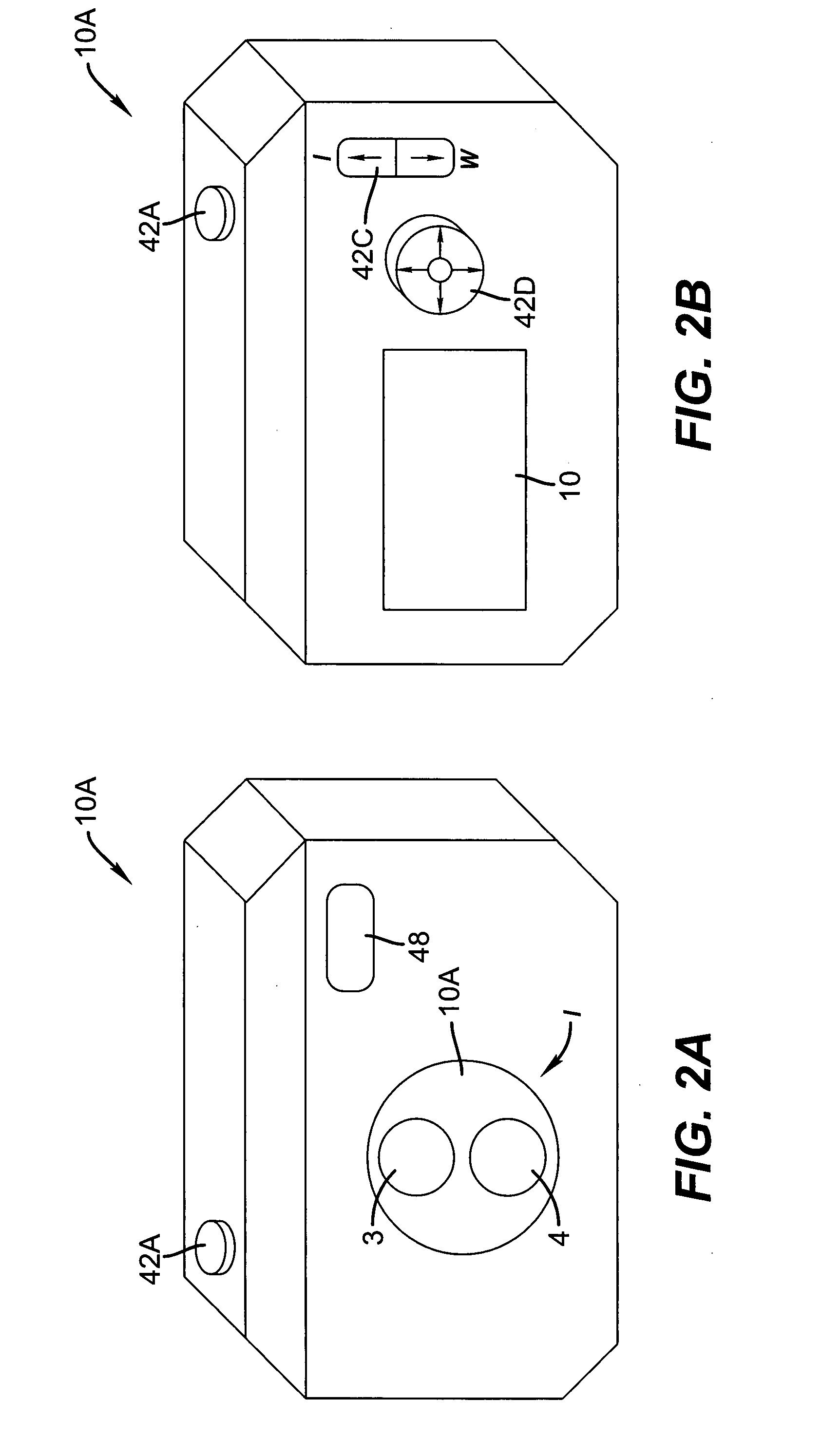
InactiveUS20080211941A1Keep for a long timeImprove spatial resolutionTelevision system detailsSignal generator with multiple pick-up deviceImage resolutionExposure period
A method and apparatus for capturing image data from multiple image sensors and generating an output image sequence are disclosed. The multiple image sensors capture data with one or more different characteristics, such as: staggered exposure periods, different length exposure periods, different frame rates, different spatial resolution, different lens systems, and different focal lengths. The data from multiple image sensors is processed and interleaved to generate an improved output motion sequence relative to an output motion sequence generated from an a single equivalent image sensor.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
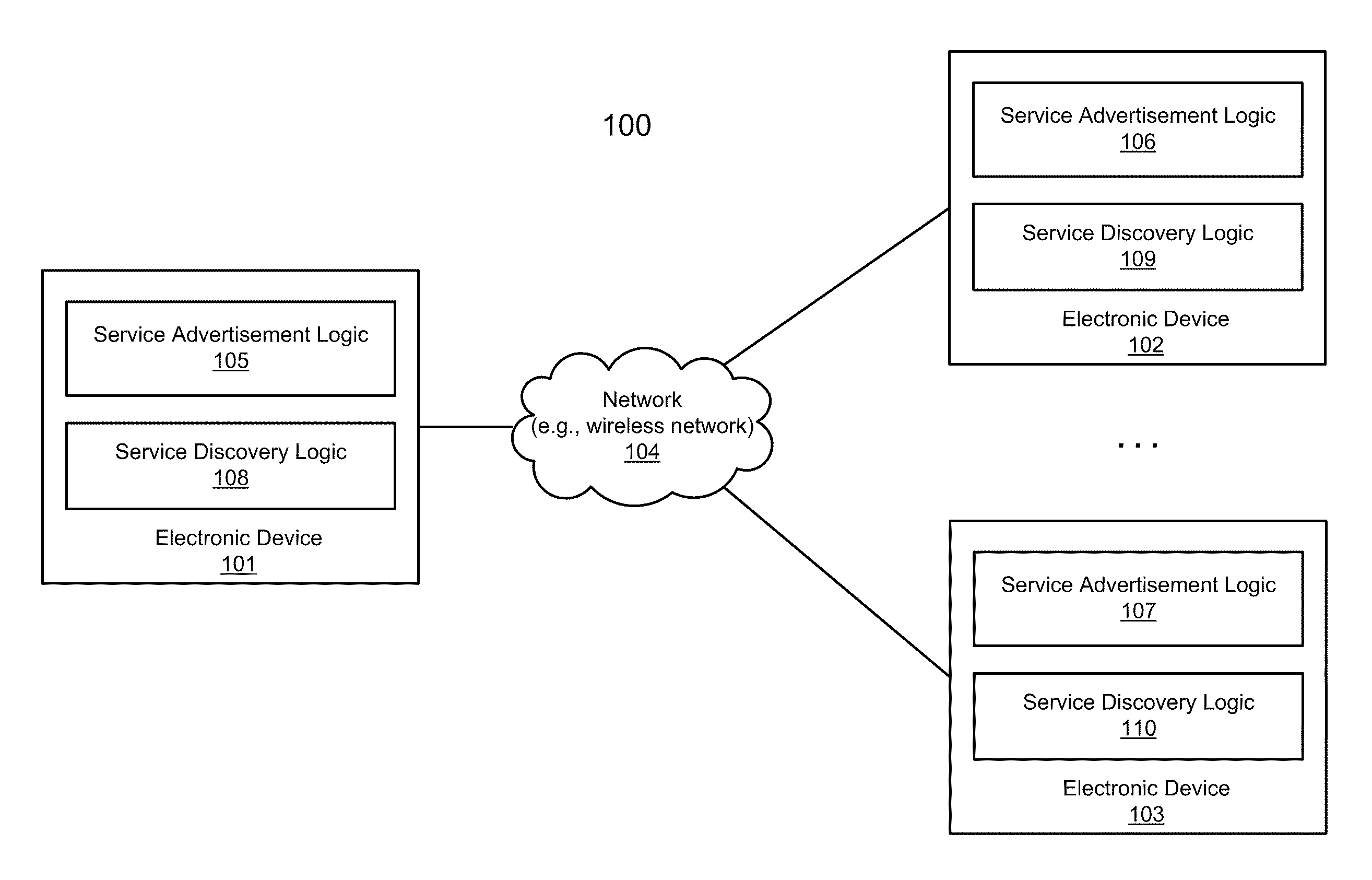
Efficient service advertisement and discovery in a peer-to-peer networking environment with cooperative advertisement
ActiveUS20110153773A1Efficiently discover and advertiseReduce frequencyPower managementEnergy efficient ICTCooperative advertisingPeer-to-peer
Operating conditions of a remote device and operating conditions of a local device are compared, where the local device and the remote device are located within a predetermined proximity of a wireless network. An advertisement request is transmitted from the local device to the remote device based on the comparison of the operating conditions of the local device and the remote device. The advertisement request includes information identifying one or more services advertised by the local device, whereby the remote device is configured to advertise the one or more services on behalf of the local device in the wireless network.
Owner:APPLE INC
Liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20050122441A1Reduce angle dependenceImprove display qualityCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsCapacitanceLiquid-crystal display
A liquid crystal display of the invention includes a plurality of pixels each of which has a liquid crystal layer and a plurality of electrodes for applying a voltage to the liquid crystal layer and which are arranged in a matrix of rows and columns, wherein: each of the plurality of pixels has a first sub-pixel and a second sub-pixel which can apply mutually different voltages to the liquid crystal layer, where the first sub-pixel has a higher brightness than the second sub-pixel in certain gradations; the first sub-pixel and the second sub-pixel each has: a liquid crystal capacitor formed by a counter electrode and a sub-pixel electrode opposing the counter electrode via the liquid crystal layer, and a storage capacitor formed by a storage capacitor electrode connected electrically to the sub-pixel electrode, an insulating layer, and a storage capacitor counter electrode opposing the storage capacitor electrode via the insulating layer; the counter electrode is a single electrode shared by the first sub-pixel and the second sub-pixel, and the storage capacitor counter electrodes of the first sub-pixel and the second sub-pixel are electrically independent of each other; and the storage capacitor counter electrode of the first sub-pixel in any of the plurality of pixels and the storage capacitor counter electrode of the second sub-pixel of a pixel adjacent to any of the pixels in the column direction are electrically independent of each other.
Owner:SHARP KK
Self contained ambulatory blood pressure cincture
InactiveUS6251080B1Extended maintenance periodReduce power consumptionEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterAmbulatory blood pressureWrist
A long term ambulatory blood pressure monitor is disclosed in which all elements of the monitor are compactly and inconspicuously contained in / on a cincture housing mounted on an inflatable arm band fixedly and comfortably positioned on the patient arm. System control and display modules are efficiently placed in a flip top mode on the cincture housing itself and alternatively in a wrist watch mode on the patient wrist. Non volatile EEPROM blood pressure data memory is disposed adjacent EPROM system memory and microprocessor controller circuitry on a compact PCB within the cincture housing along with pneumatic motor / pump and solenoid for inflation / deflation of the arm band to obtain systolic / diastolic blood pressure readings via the oscillatory detection method.
Owner:SPACELABS HEALTHCARE LLC
Method and apparatus for controlling power drawn from an energy converter
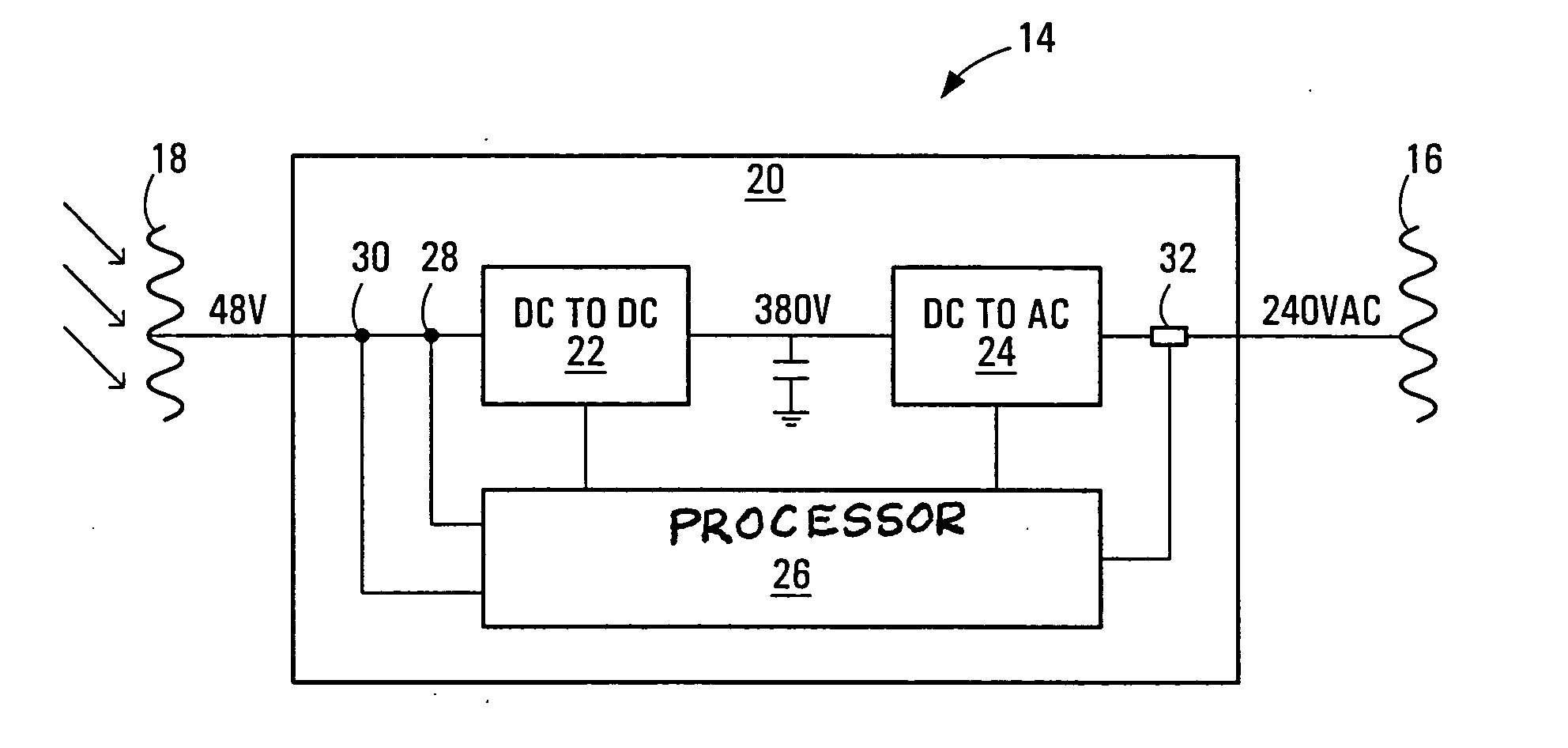
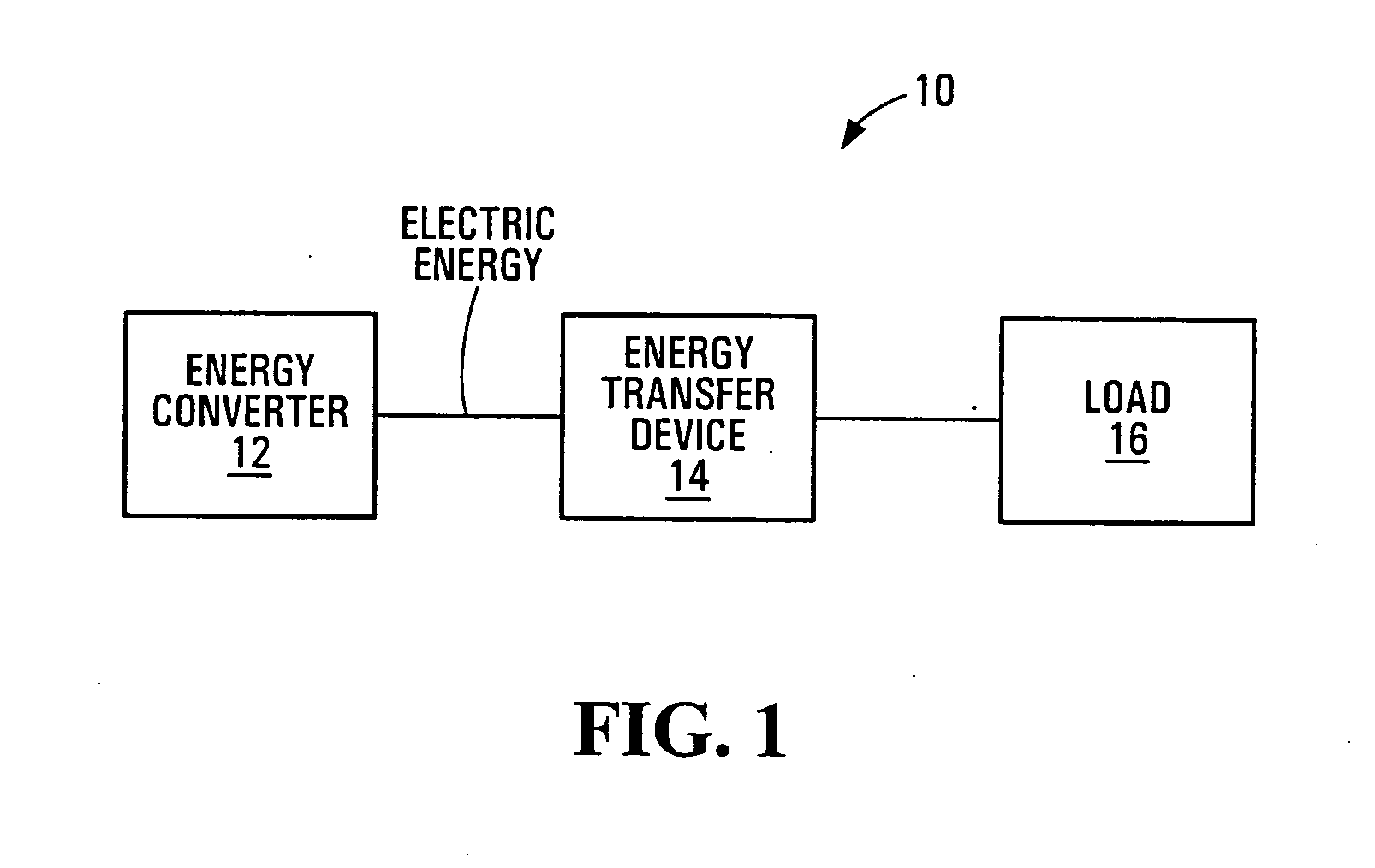
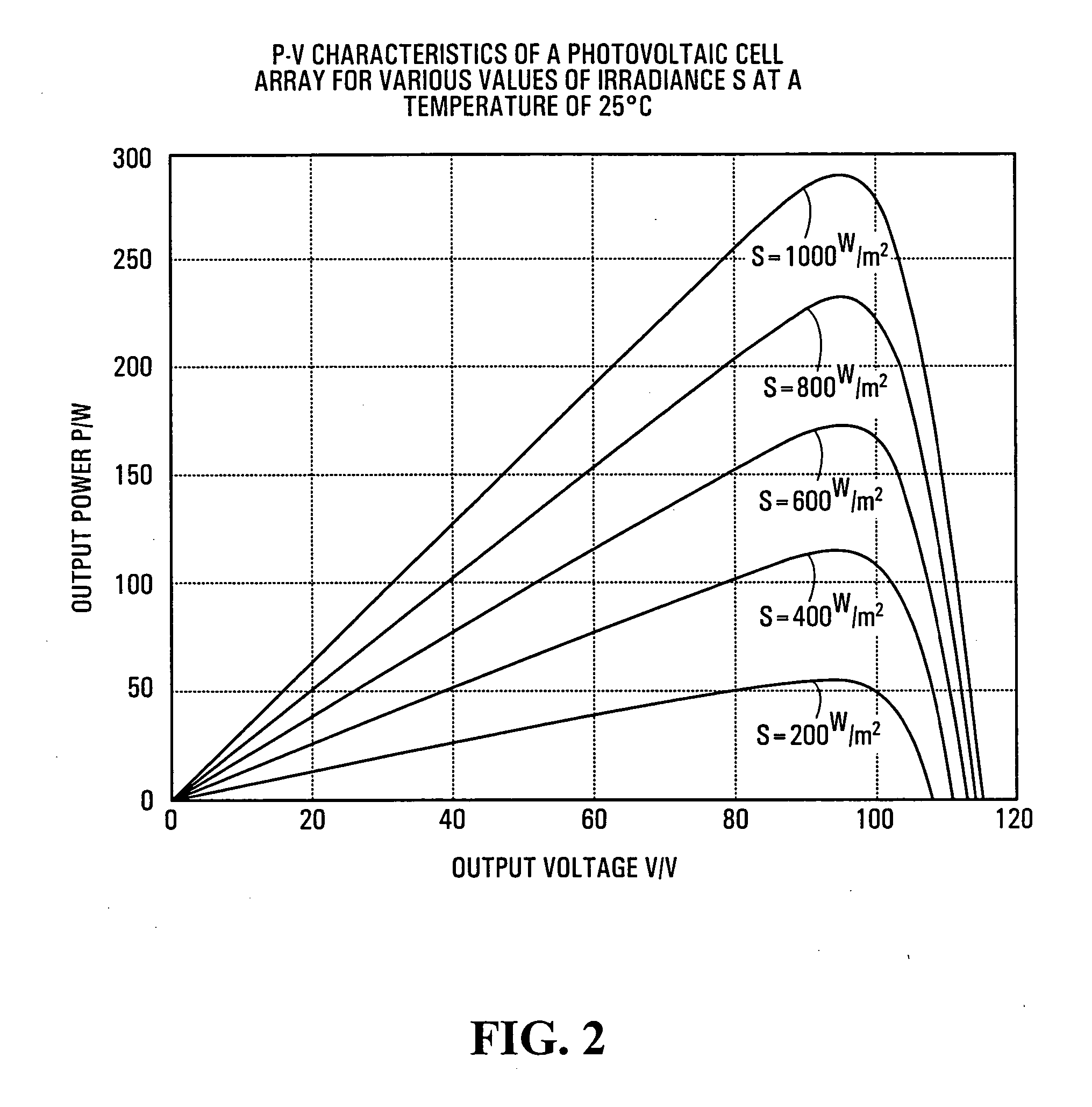
ActiveUS20050068012A1Extended maintenance periodShorten the overall cycleSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAc network voltage adjustmentEngineeringEnergy converter
Methods, apparatus, media and signals for controlling power drawn from an energy converter to supply a load, where the energy converter is operable to convert energy from a physical source into electrical energy. Power drawn from the energy converter is changed when a supply voltage of the energy converter meets a criterion. The criterion and the change in the amount of power drawn from the energy converter are dependent upon a present amount of power supplied to the load. The methods, apparatus, media and signals described herein may provide improvements to DC to AC maximum power point tracking in an energy conversion system such as a photovoltaic power generation system.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SOLAR INVERTERS USA
Extended wear ophthalmic lens
InactiveUS6951894B1Sufficient for corneal healthSubstantial adverse impact on ocular health or consumerLiquid surface applicatorsEye implantsExtended wear contact lensesEye movement
An ophthalmic lens suited for extended-wear periods of at least one day on the eye without a clinically significant amount of corneal swelling and without substantial wearer discomfort. The lens has a balance of oxygen permeability and ion or water permeability, with the ion or water permeability being sufficient to provide good on-eye movement, such that a good tear exchange occurs between the lens and the eye. A preferred lens is a copolymerization product of a oxyperm macromer and an ionoperm monomer. The invention encompasses extended wear contact lenses, which include a core having oxygen transmission and ion transmission pathways extending from the inner surface to the outer surface.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
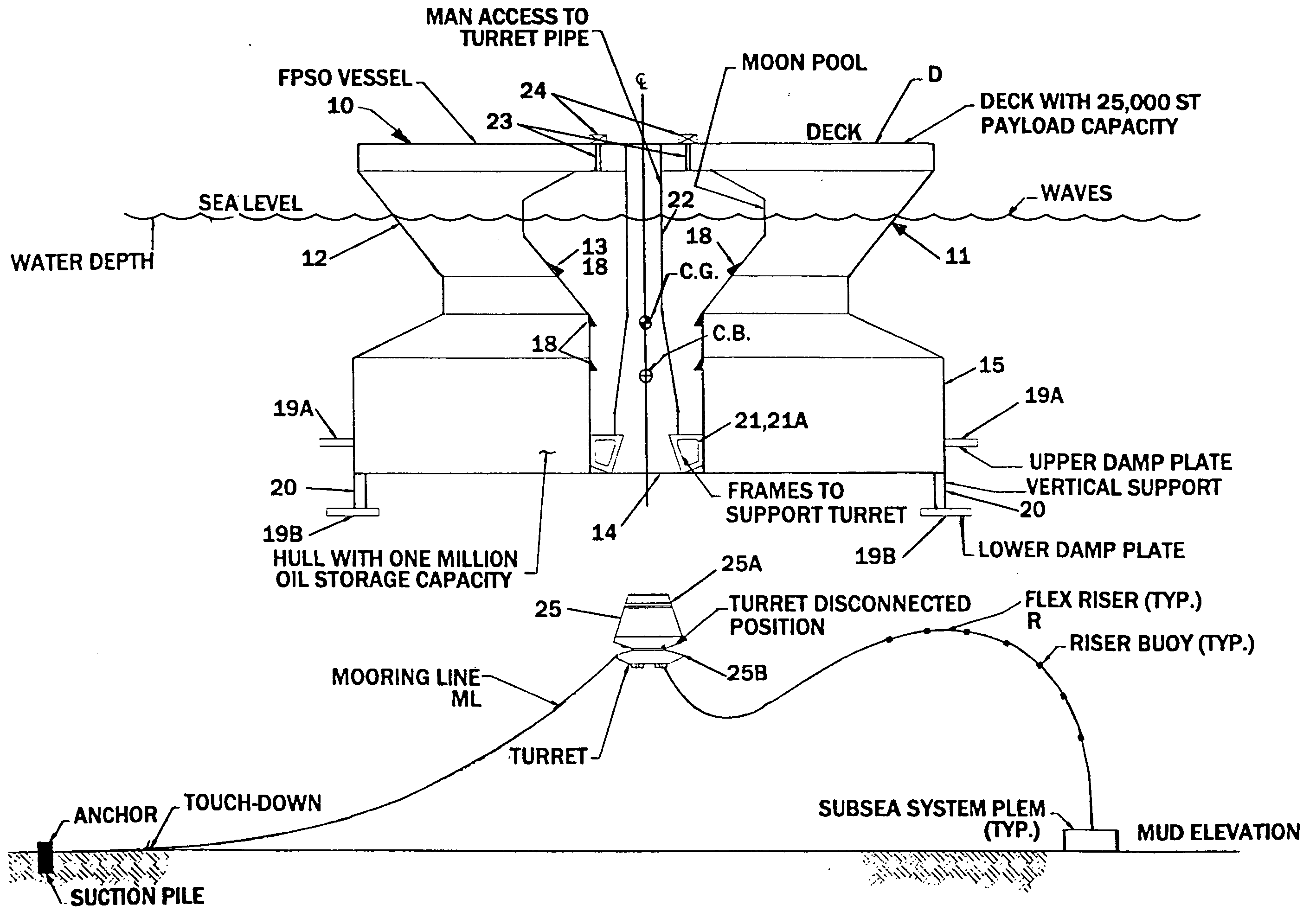
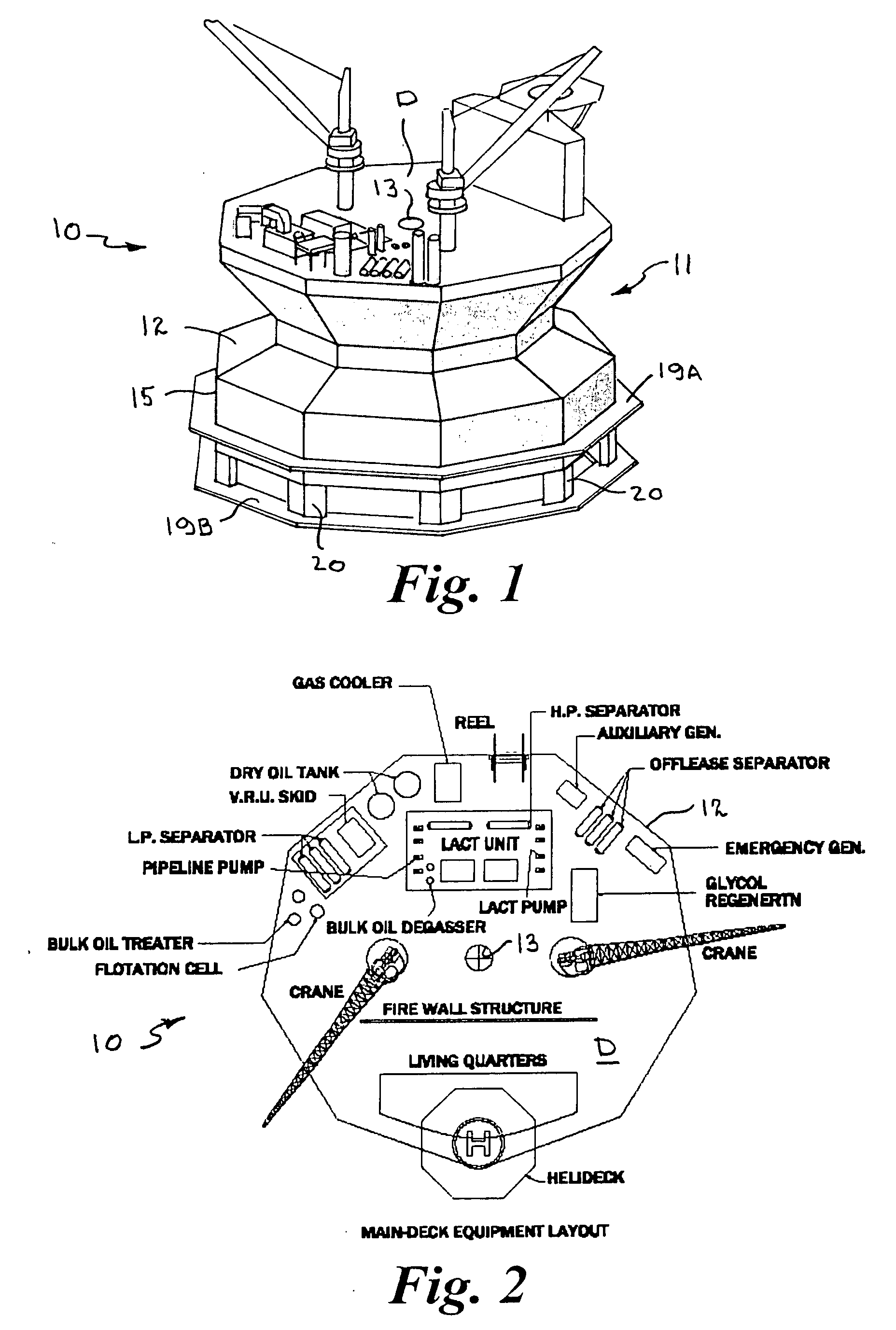
Offshore floating production, storage, and off-loading vessel for use in ice-covered and clear water applications
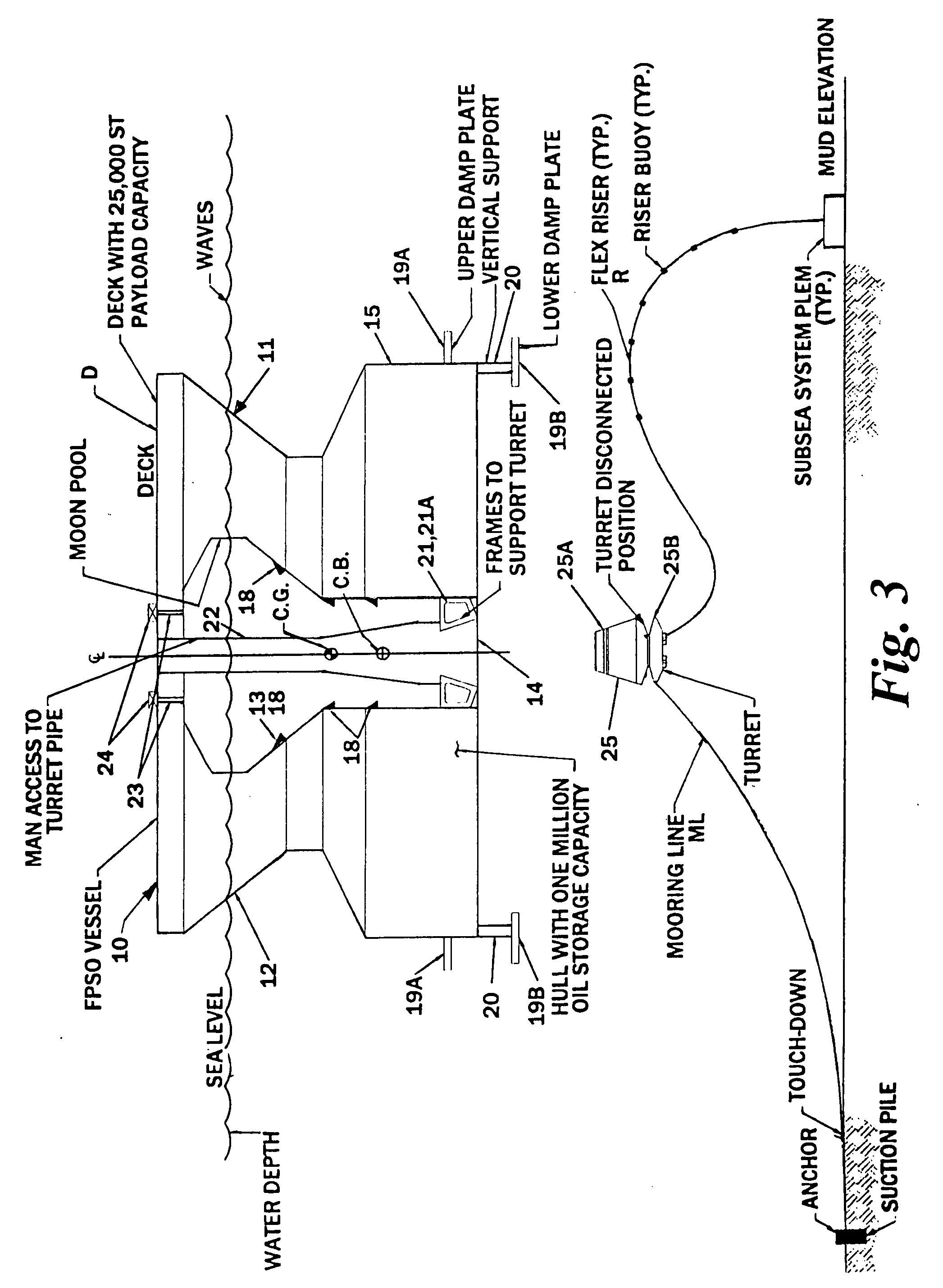
InactiveUS20090126616A1Reduces dynamic amplificationReduce resonanceProtective foundationMovement controllersResonanceBuoy
An offshore floating production, storage, and off-loading vessel has a monolithic non ship-shaped hull of polygonal configuration surrounding a central double tapered conical moon pool and contains water ballast and oil storage compartments. The exterior side walls of the hull have flat surfaces and sharp corners to cut ice sheets, resist and break ice, and move ice pressure ridges away from the structure. An adjustable water ballast system induces heave, roll, pitch and surge motions of the vessel to dynamically position and maneuver the vessel to accomplish ice cutting, breaking and moving operations. The moon pool shape and other devices on the vessel provide added virtual mass capable of increasing the natural period of the roll and heave modes, reducing dynamic amplification and resonance due to waves and vessel motion, and facilitate maneuvering the vessel. The vessel may be moored by a disconnectable turret buoy received in a support frame at the bottom of the moon pool and to which flexible well risers and mooring lines are connected.
Owner:SRINIVASAN NAGAN
Barriers for polymer-coated implantable medical devices and methods for making the same
InactiveUS6953560B1Reduce and prevent and inflammationReduce and prevent proliferationStentsSurgeryHafniumPt element
An implantable medical device and methods for making the implantable medical device are disclosed. The implantable medical device includes a substrate. At least a portion of the substrate is coated with a first layer including a polymer containing a drug. A barrier overlies the first layer. The barrier significantly reduces the rate of release of the drug from the polymer, thereby sustaining release of the drug from the medical device for a longer time.The barrier may be a homogeneous layer overlying the first layer, or a number of discrete deposits over the first layer. Alternatively, the barrier may be intermixed with an outer portion of the first layer. The barrier material is biocompatible, and typically has a thickness ranging from about 50 angstroms to about 20,000 microns. Suitable materials for the barrier include, but are not limited to, inorganic compounds, such as inorganic silicides, oxides, nitrides, carbides, as well as pure metals such as aluminum, chromium, gold, hafnium, iridium, niobium, palladium, platinum, tantalum, titanium, tungsten, zirconium, and alloys of these metals. The barriers disclosed may be applied to the first layer by several techniques, depending on the material being applied. Exemplary deposition techniques include physical vapor deposition, alkoxide hydrolysis, and electroless plating.The implantable device may be a stent or a graft, among other possibilities.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Dosage form containing a morphine derivative and another drug
InactiveUS20050232987A1Extended maintenance periodBiocidePill deliveryPharmaceutical drugBlood plasma
A pharmaceutical dosage form which comprises a first drug which comprises at least one morphine derivative with antitussive activity and at least one second drug. The dosage form provides a plasma concentration within the therapeutic range of the at least one second drug over a period which is coextensive with at least about 70% of the period over which the dosage form provides a plasma concentration within the therapeutic range of the first drug. This abstract is neither intended to define the invention disclosed in this specification nor intended to limit the scope of the invention in any way.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PHARMA
Extended wear ophthalmic lens
InactiveUS7468398B2Sufficient for corneal healthSubstantial adverse impact on ocular health or consumerOptical articlesProsthesisExtended wear contact lensesEye movement
An ophthalmic lens suited for extended-wear periods of at least one day on the eye without a clinically significant amount of corneal swelling and without substantial wearer discomfort. The lens has a balance of oxygen permeability and ion or water permeability, with the ion or water permeability being sufficient to provide good on-eye movement, such that a good tear exchange occurs between the lens and the eye. A preferred lens is a copolymerization product of a oxyperm macromer and an ionoperm monomer. The invention encompasses extended wear contact lenses, which include a core having oxygen transmission and ion transmission pathways extending from the inner surface to the outer surface.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Method and system for providing a virtual presentation including a virtual companion and virtual photography
ActiveUS20110086702A1Easy to attachRaise the possibilityVideo gamesSpecial data processing applicationsComputerized systemDisplay device
A method and computer system for providing a virtual presentation is provided. A plurality of different groups of virtual objects within a virtual world on a display device, wherein at least one of the different groups is selectable by a user. The desired group of virtual objects are to be displayed within a virtual optical viewfinder. A selection tool is provided within the virtual optical viewfinder and is controllable by the user to select a target virtual object from the desired group of virtual objects displayed within the virtual optical viewfinder. The user is presented with a magnified image of the target virtual object and revealing an identity of the target virtual object that has been selected in response to selection of the target virtual object by the user.
Owner:GANZ
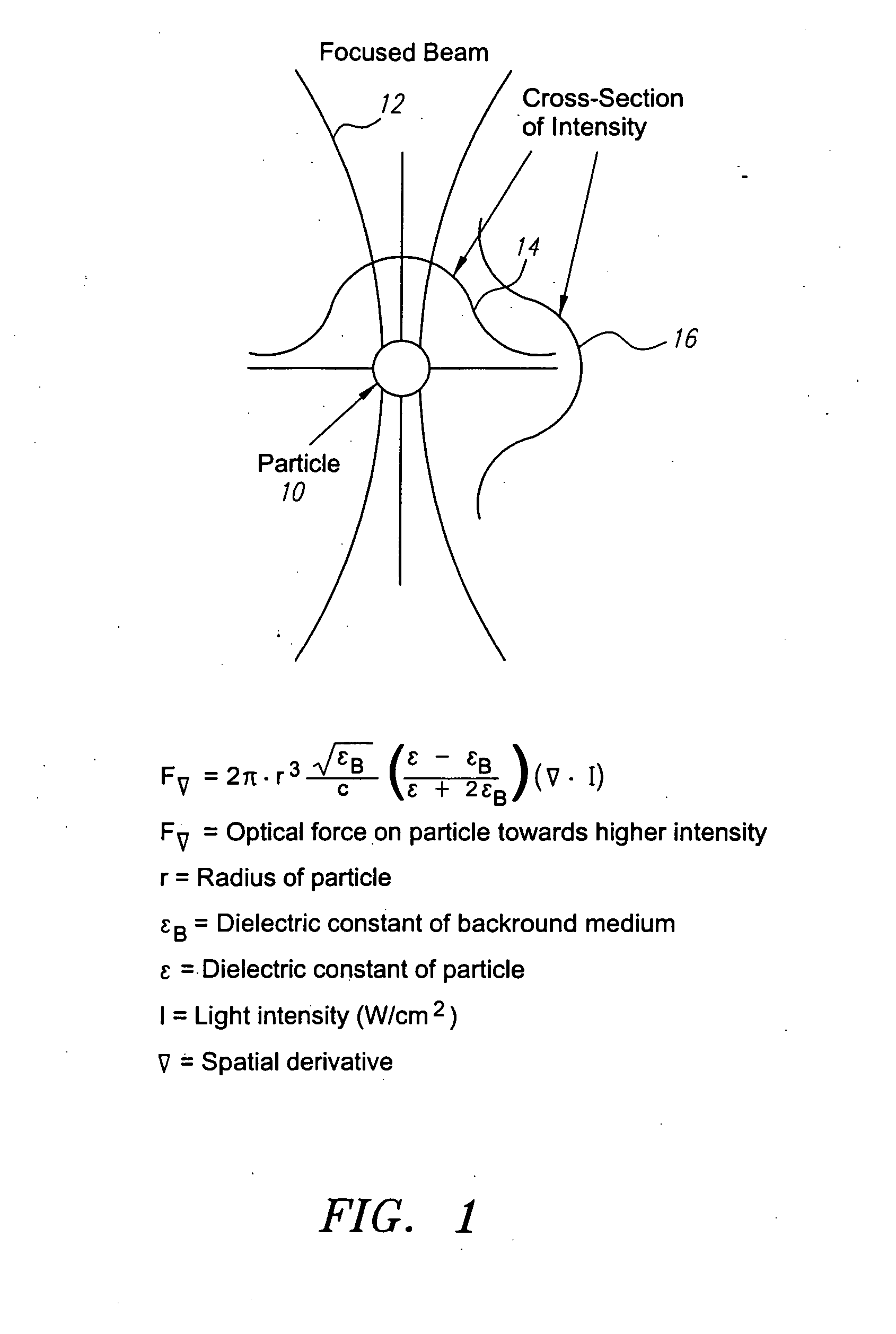
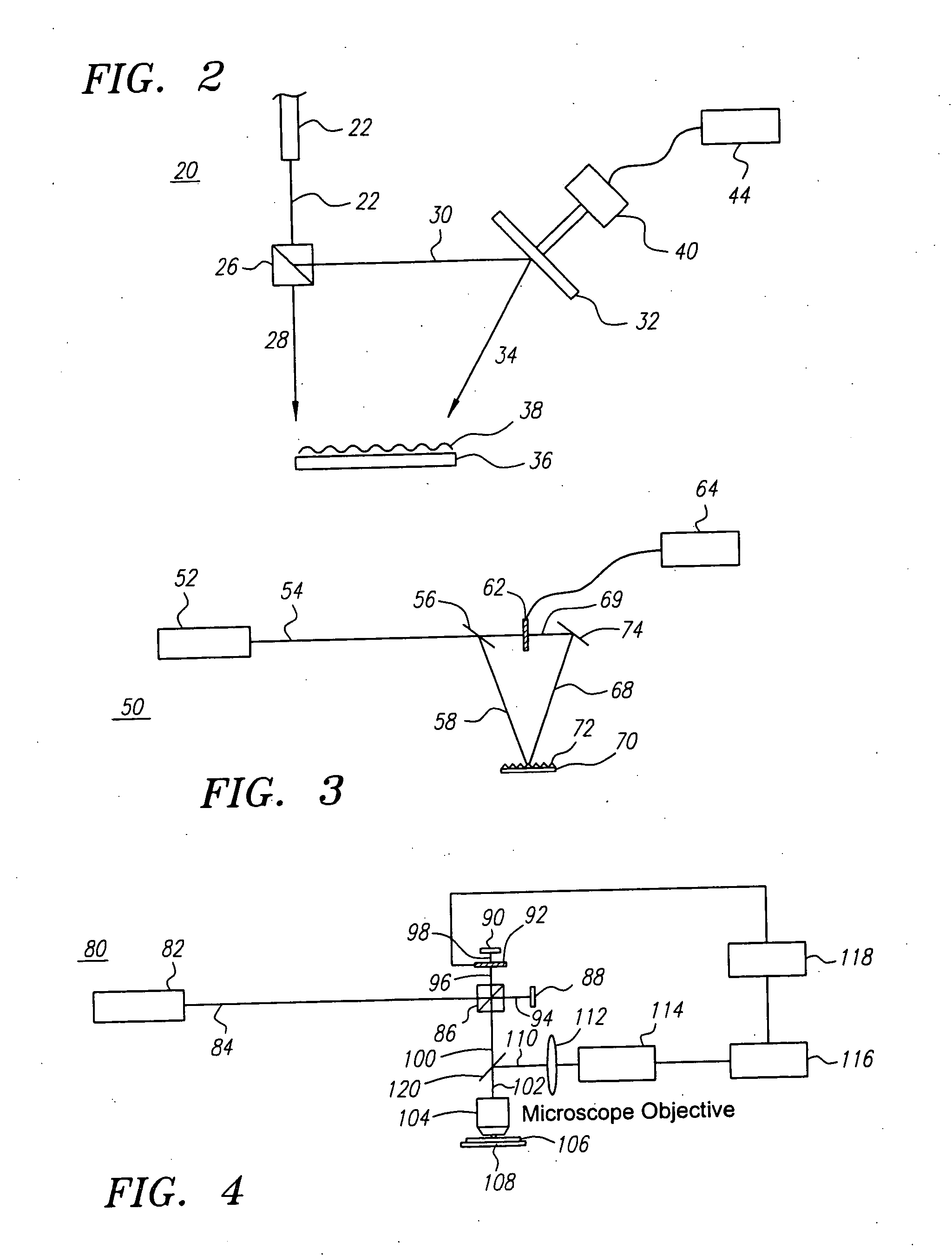
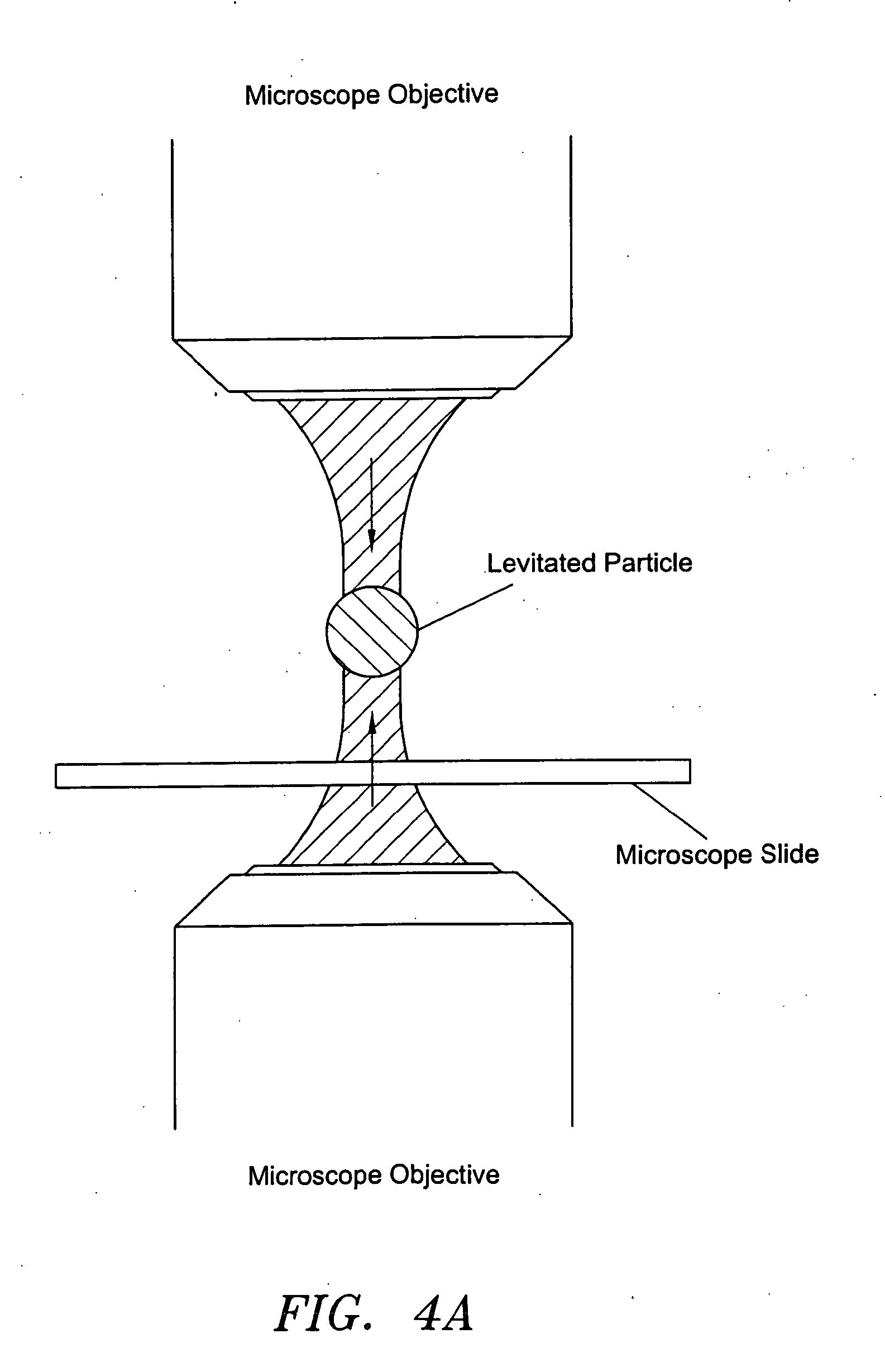
Methods and apparatus for use of optical forces for identification, characterization and/or sorting of particles
InactiveUS20060060767A1Reduce pollutionSimple and efficientLaser detailsComponent separationPhysicsMechanical force
Apparatus and methods are provided for interacting light with particles, including but not limited to biological matter such as cells, in unique and highly useful ways. Optophoresis consists of subjecting particles to various optical forces, especially optical gradient forces, and more particularly moving optical gradient forces, so as to obtain useful results. In biology, this technology represents a practical approach to probing the inner workings of a living cell, preferably without any dyes, labels or other markers. In one aspect, a particle may be characterized by determining its optophoretic constant or signature. For example, a diseased cell has a different optophoretic constant from a healthy cell, thereby providing information, or the basis for sorting. In the event of physical sorting, various forces may be used for separation, including fluidic forces, such as through the use of laminar flow, or optical forces, or mechanical forces, such as through adhesion. Various techniques for measuring the dielectric constant of particles are provided.
Owner:WANG MARK M +8
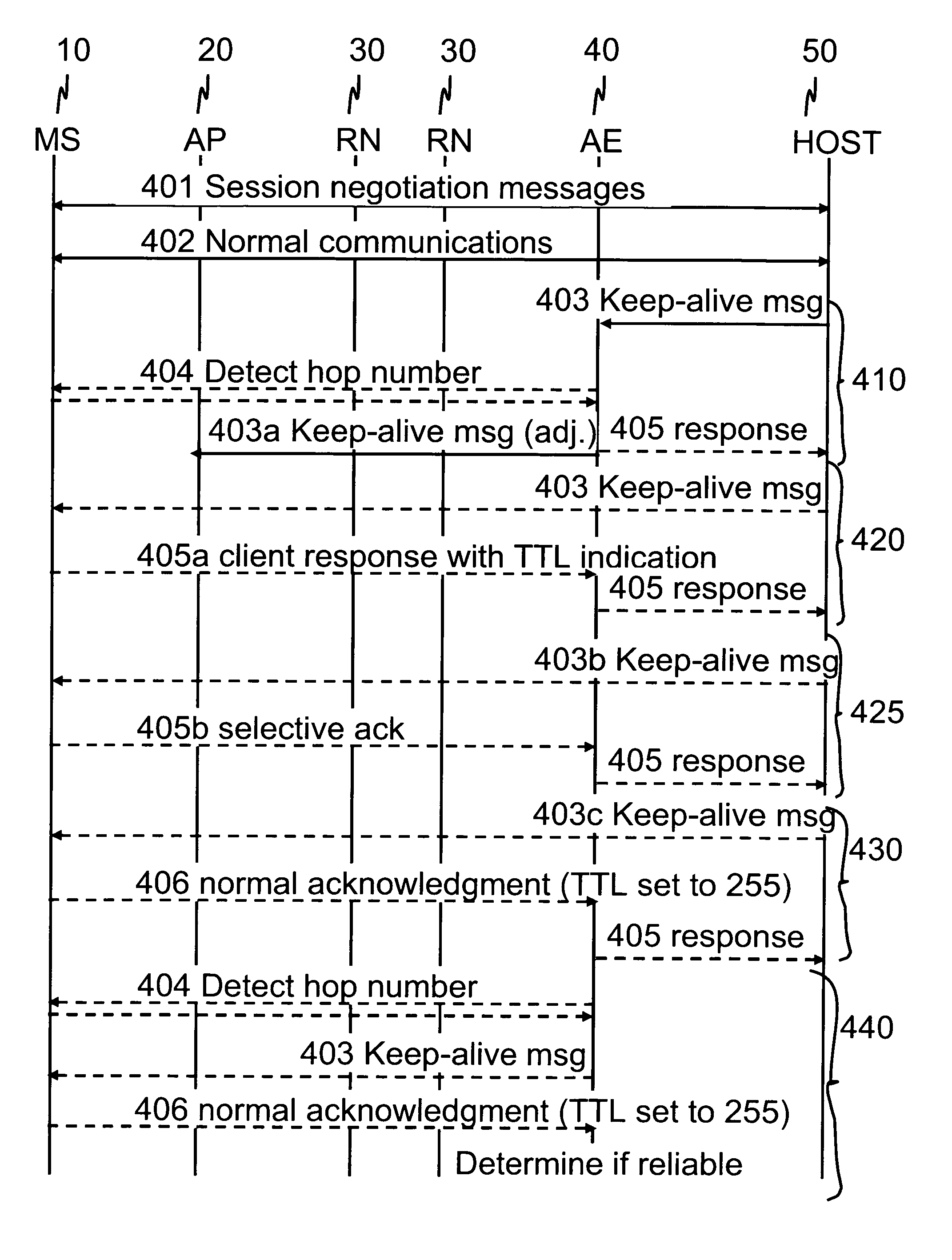
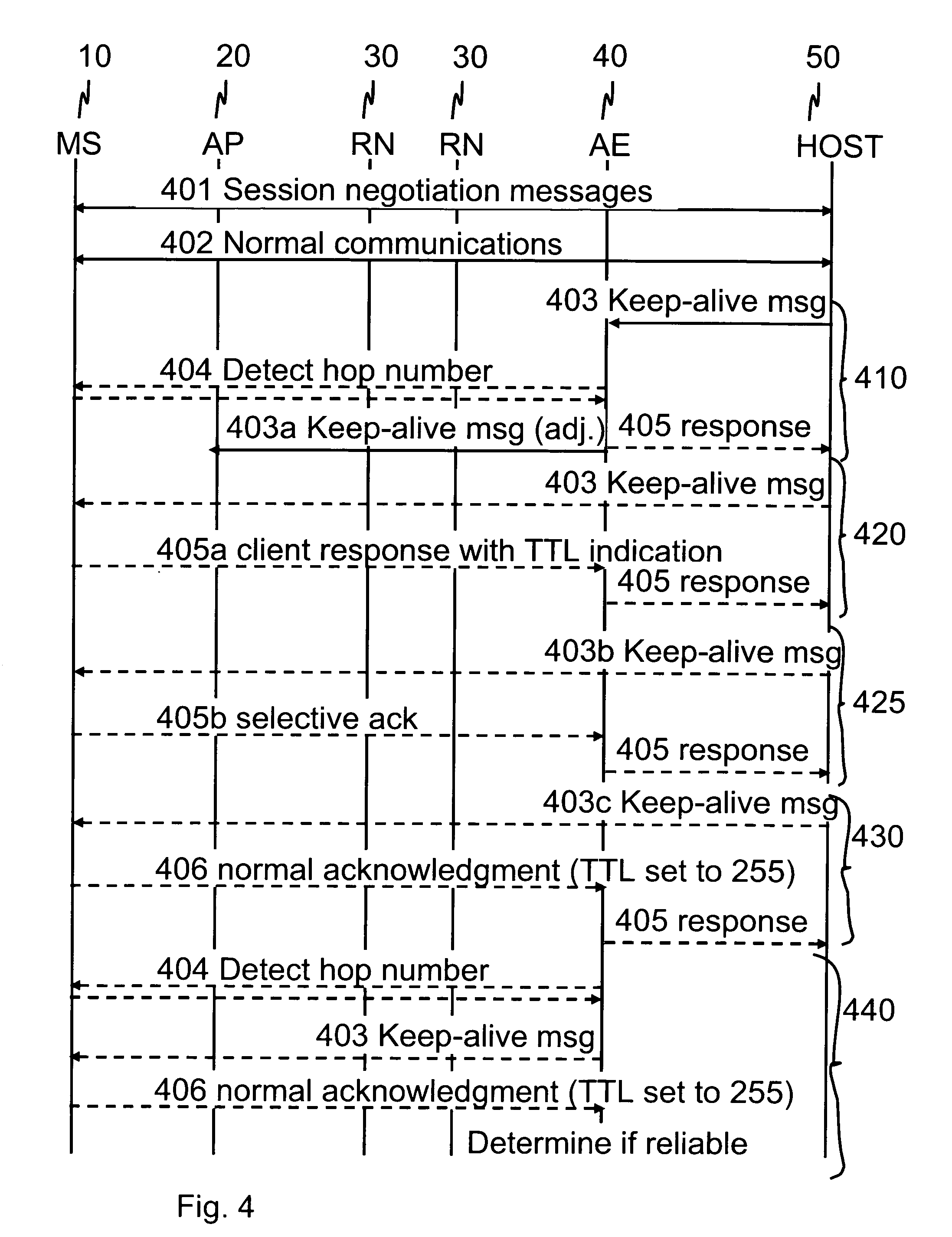
Communications control for extending the period over which a terminal is able to have an open connection with a host accessible via a packet data network
ActiveUS7684346B2Reduce power consumptionExtended maintenance periodError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityThe Internet
A client and a host communicate in a packet data network including a plurality of routing nodes such as routers and firewalls. The host is configured to provide the client with a session and to detect the accessibility of the client by repeatedly sending keep-alive messages to the client. In order to reduce the traffic actually arriving at the client, at least some of the keep-alive message are adjusted such that their routing towards the client will be stopped before the client by storing in a Time-To-Live field specified in the Internet Protocol a value of maximum routing hops defined to correspond with the last routing node before the client on a route from the host to the client. The adaptation of the keep-alive message can also be configured to allow some keep-alive message to reach the client to occasionally test the communication path between the client and server.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Implantable RF telemetry devices with power saving mode
ActiveUS20060229053A1Low power consumptionProlonging sniff periodElectrotherapySubstation equipmentPower savingRadio receiver
An electronic implantable device with a power saving circuit incorporates a radio frequency receiver with low power consumption. A high power radio receiver is normally turned off during a period of inactivity. When an analyzer detects a predetermined identification code in a received radio frequency signal, it outputs a signal to turn on the high power receiver.
Owner:MICROSEMI SEMICON
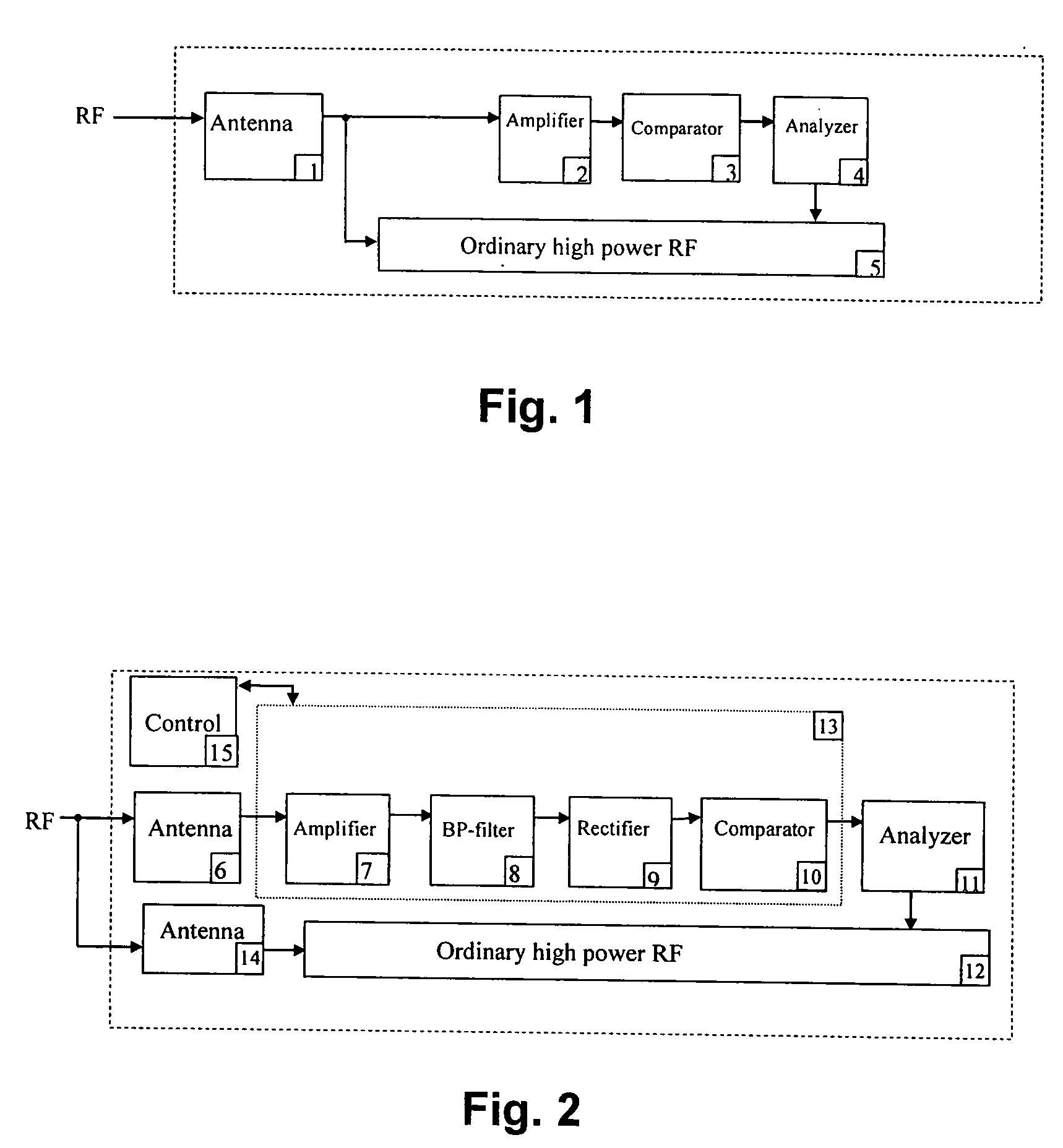
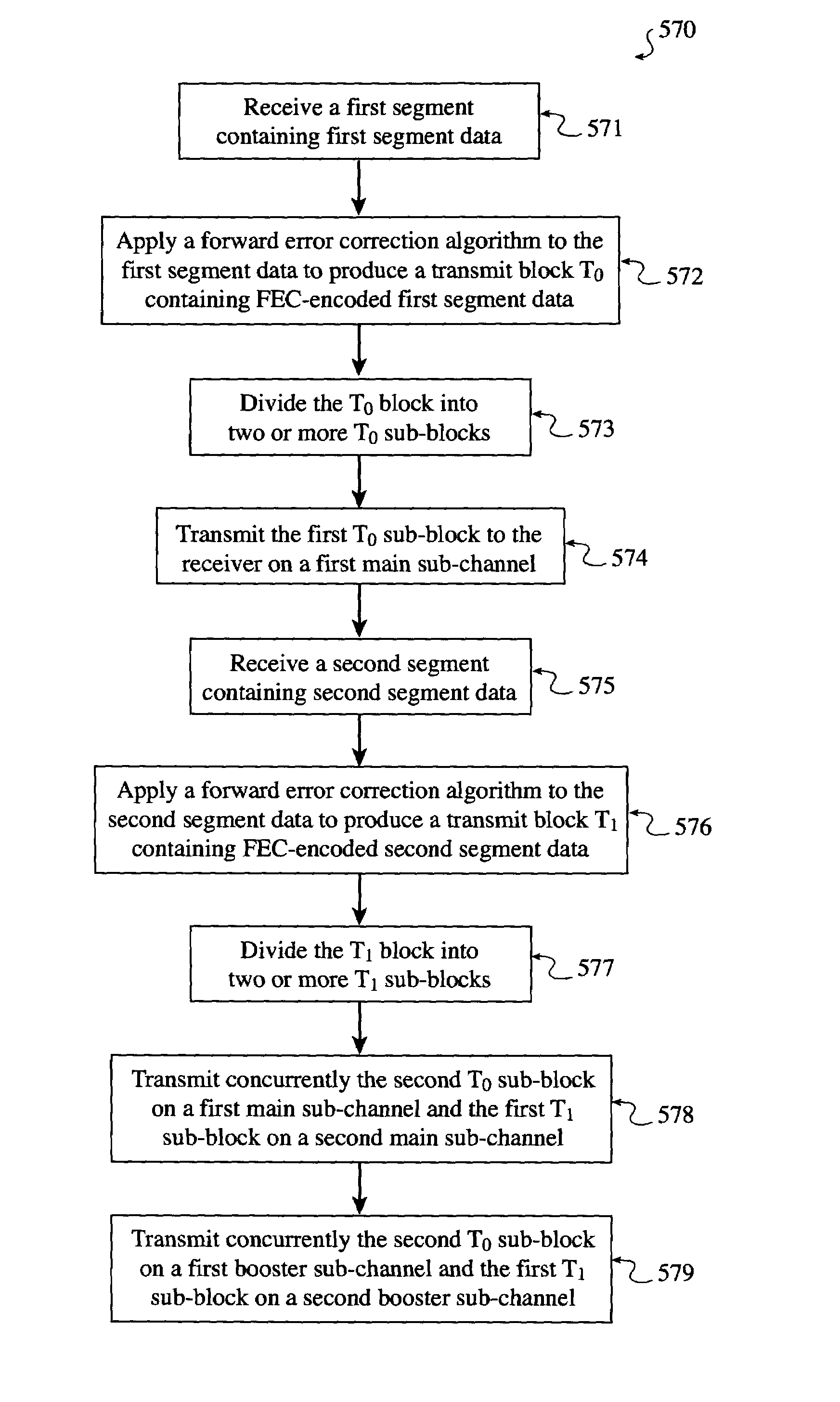
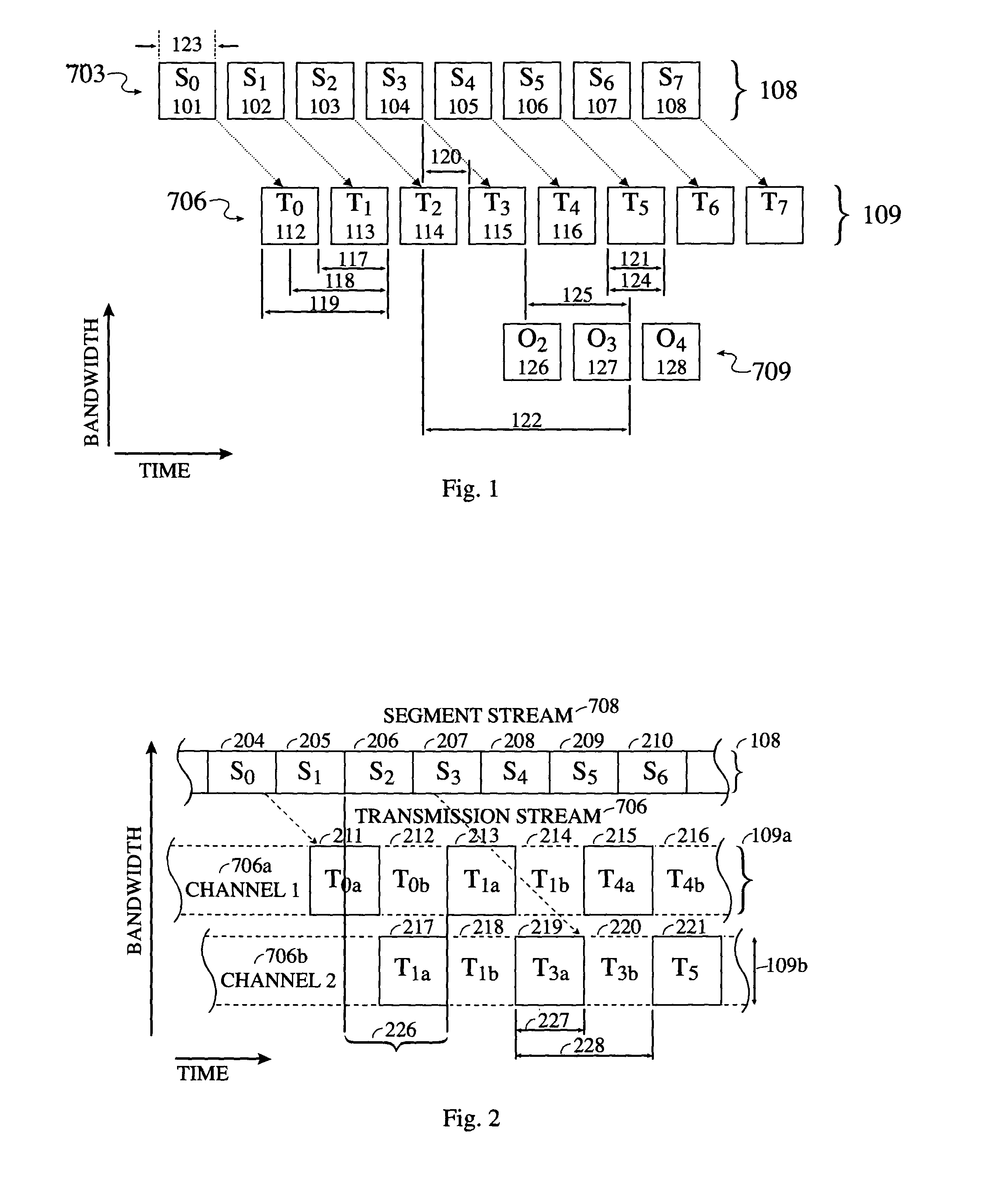
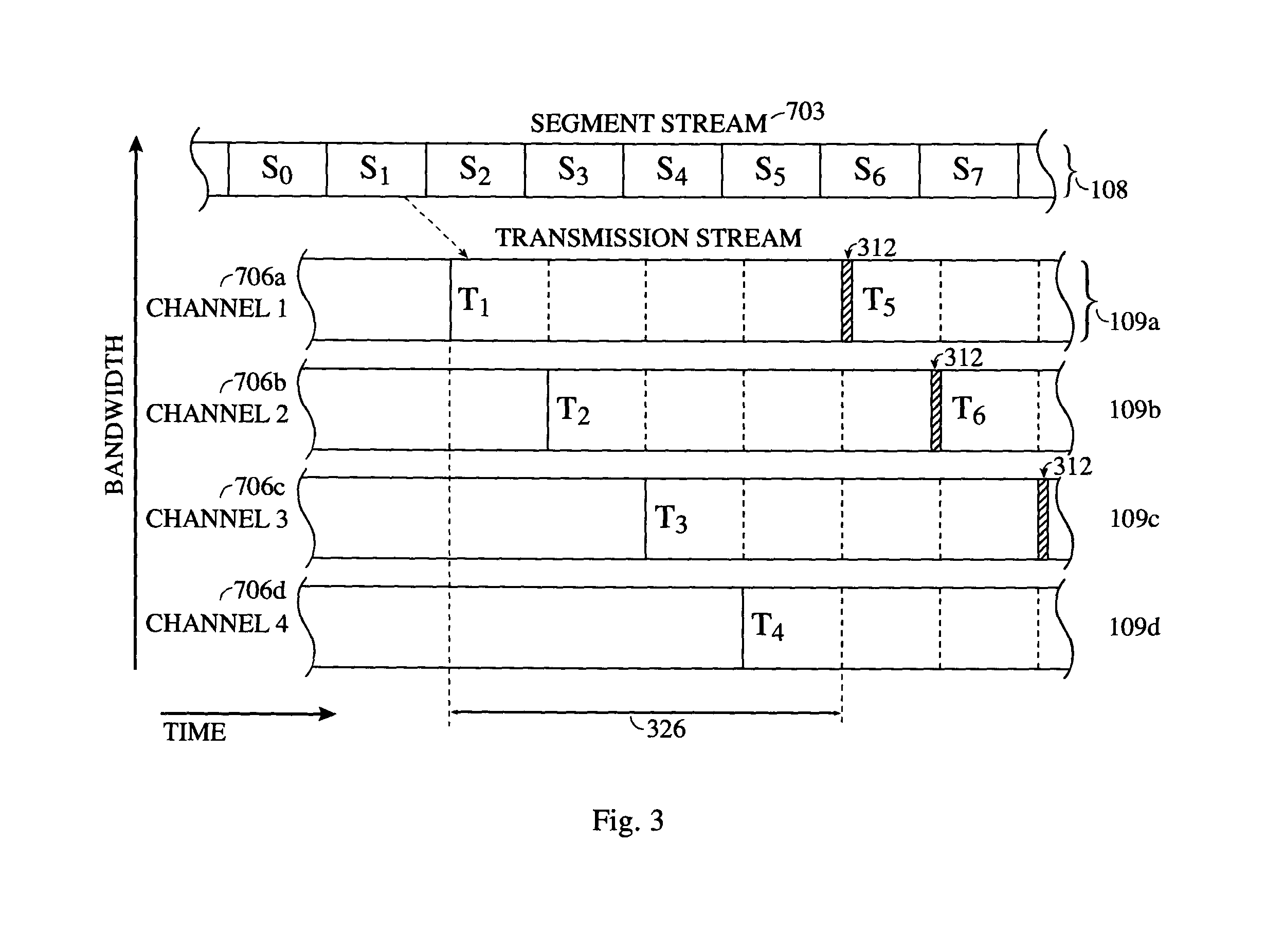
System and method for reliably communicating the content of a live data stream
InactiveUS7249291B2Reliable communicationIncreased start-up timePulse modulation television signal transmissionError detection/correctionComputer hardwareData stream
A method for communicating the content of a live data stream to a receiver using a plurality of channels comprising two encoder channels used to encode the live data content prior to transmission. Initially a plurality of segments of a live data stream are received, wherein each segment contains segment data. A forward error correction algorithm is applied to each segment's data, thereby producing FEC-encoded segment data. The FEC-encoded segment data is contained within an FEC-encoded block, resulting in a corresponding plurality of FEC-encoded blocks being generated. Each FEC-encoded block is copied to a sub-channel on both a first encoder channel and a second encoder channel, resulting in a plurality of FEC-encoder blocks residing on the first and second encoder channels. The first and second encoder channels differ in the number of sub-channels they contain (interleaving depth), and accordingly the arrangement of the FEC-encoded blocks in the first and second encoder channels are different. A first cross-section of the FEC-encoded segment data contained within the FEC-encoded blocks resident in the first encoder channel is added to a first transmit block T0. Similarly, A first cross-section of the FEC-encoded segment data contained within the FEC-encoded blocks resident in the second encoder channel is added to a second transmit block T1. The first and second transmit blocks are then communicated to the receiver.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
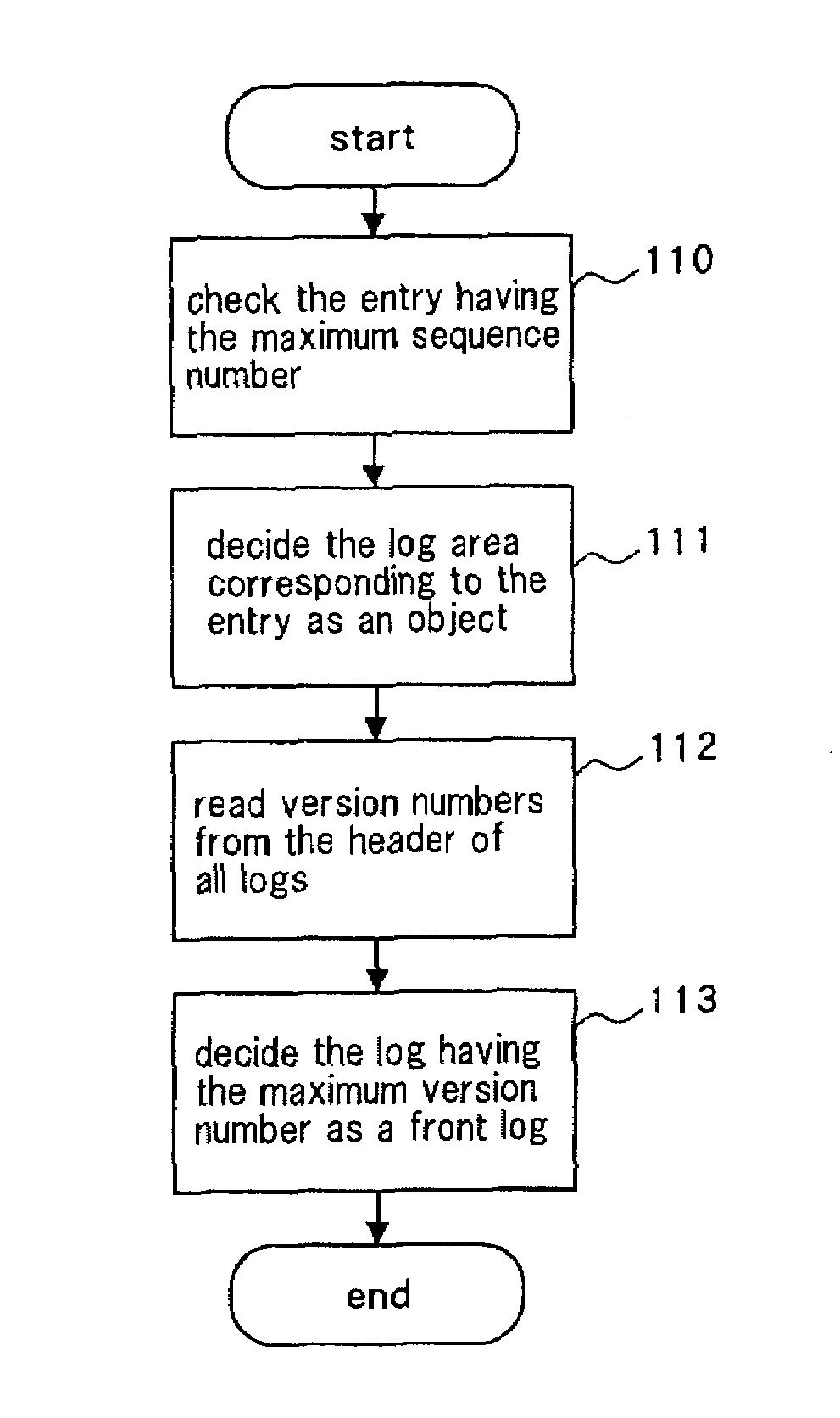
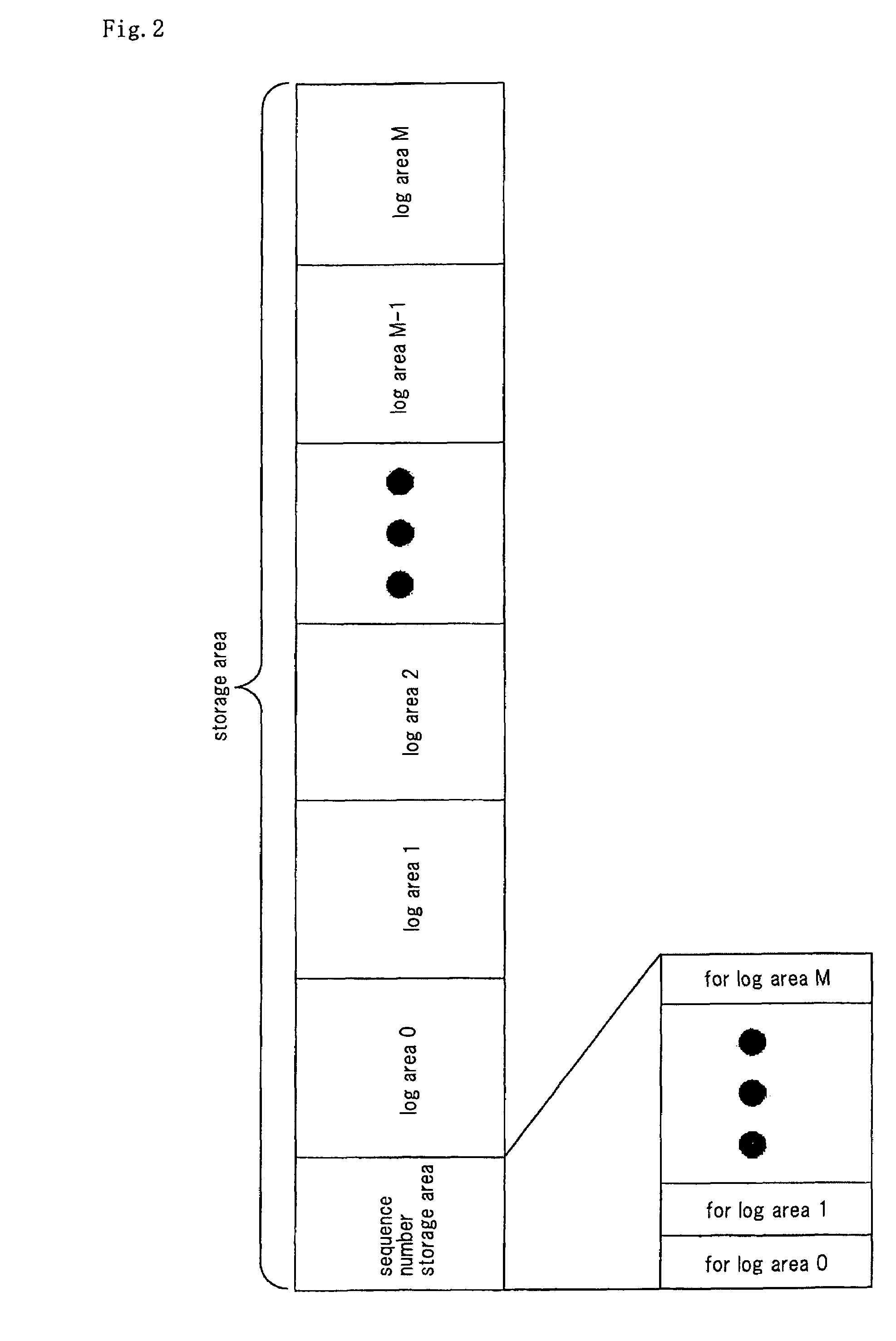
File management method for log-structured file system for sequentially adding and storing log of file access
ActiveUS7680837B2Extended maintenance periodReduce usage timeMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data information retrievalFile systemManagement area
There is disclosed a file management method in a log-structured file system for storing accesses to files that are sequentially performed by sequentially adding logs. A storage area of a storage medium is previously divided into a data area for storing a log including data of the file and a management area that can store management information related to the log stored in said data area for a plurality of entries. Then, the management information including a first number indicating the order of writing the entry is added and stored in the management area as a new entry.
Owner:ZOOM VIDEO COMM INC
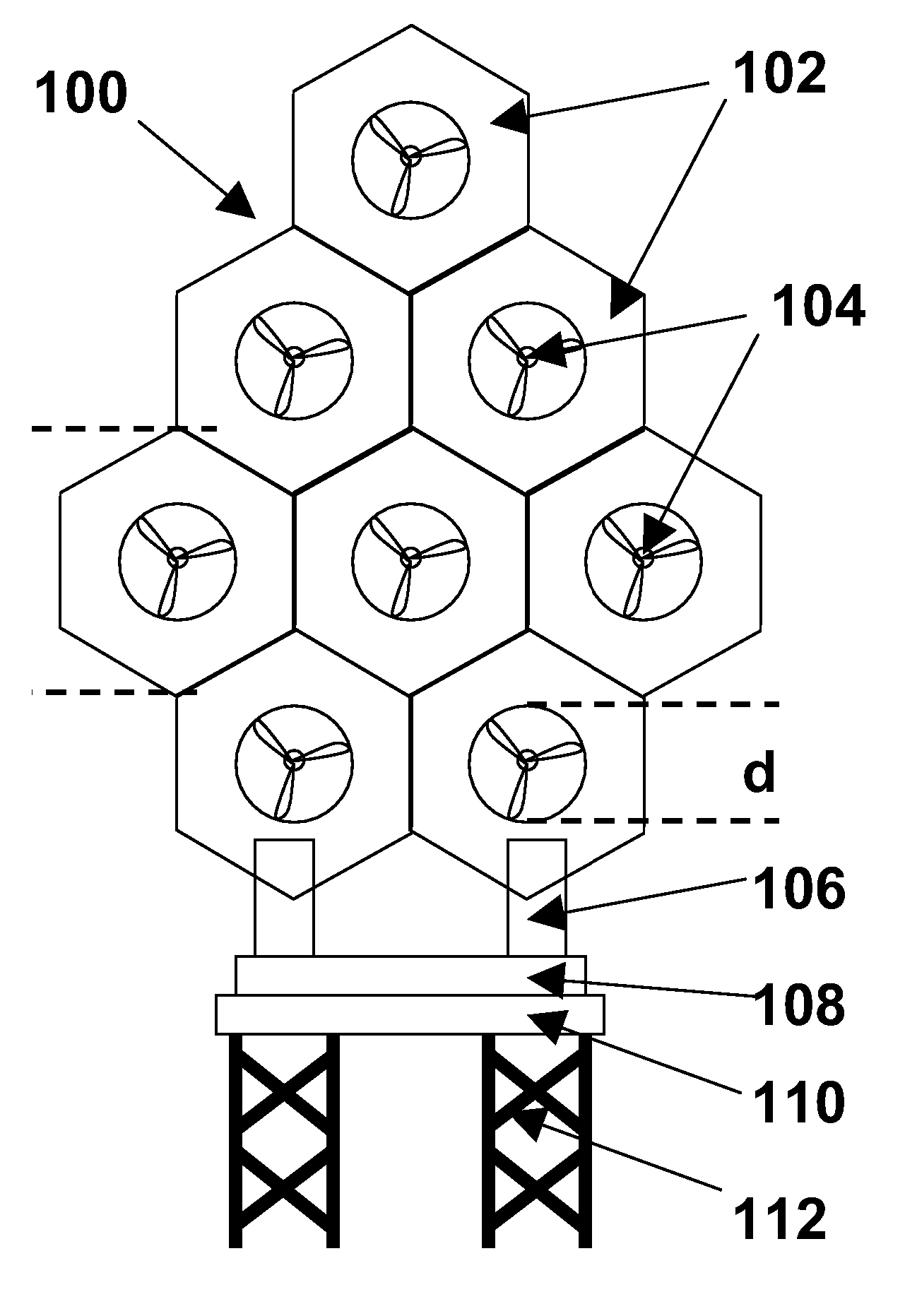
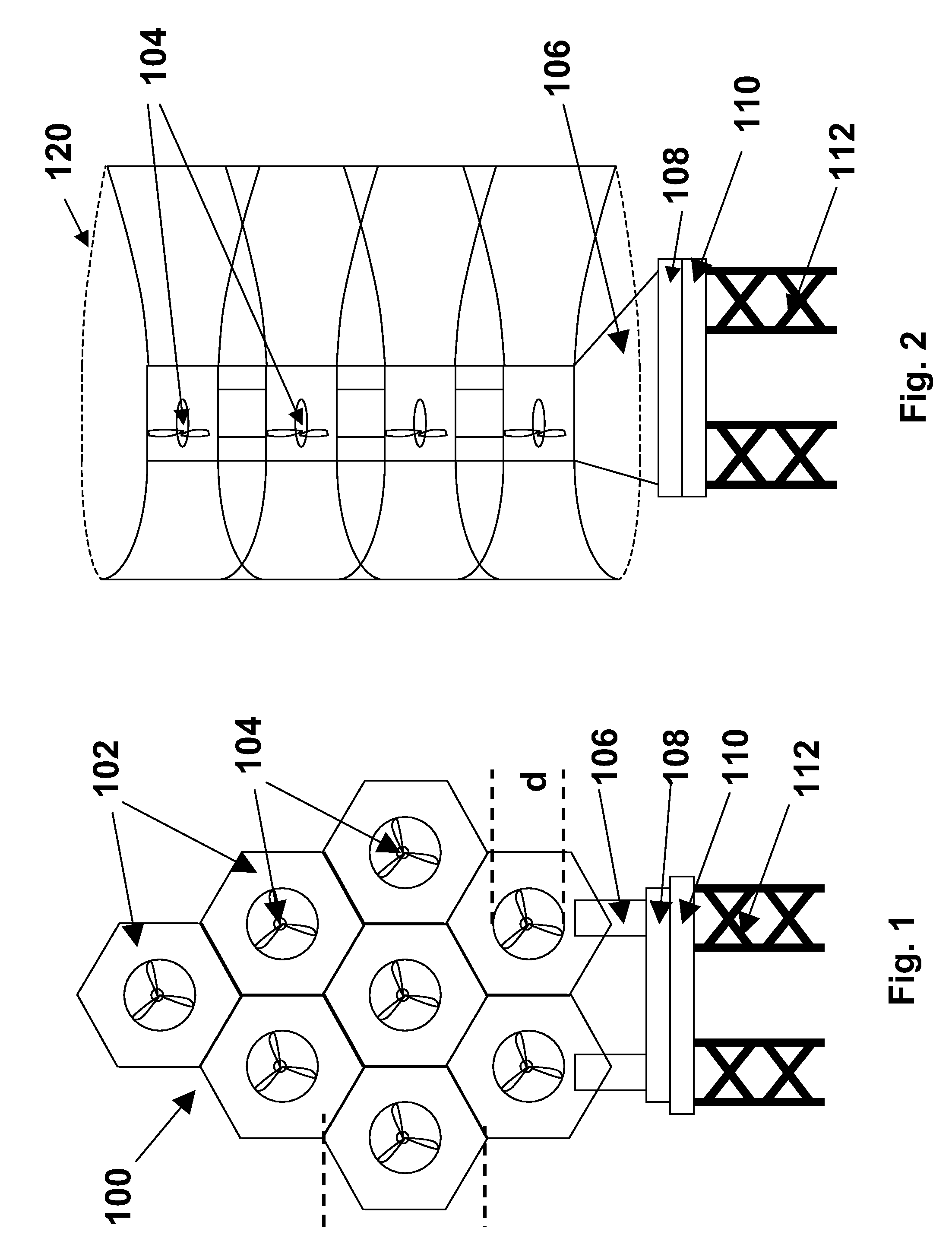
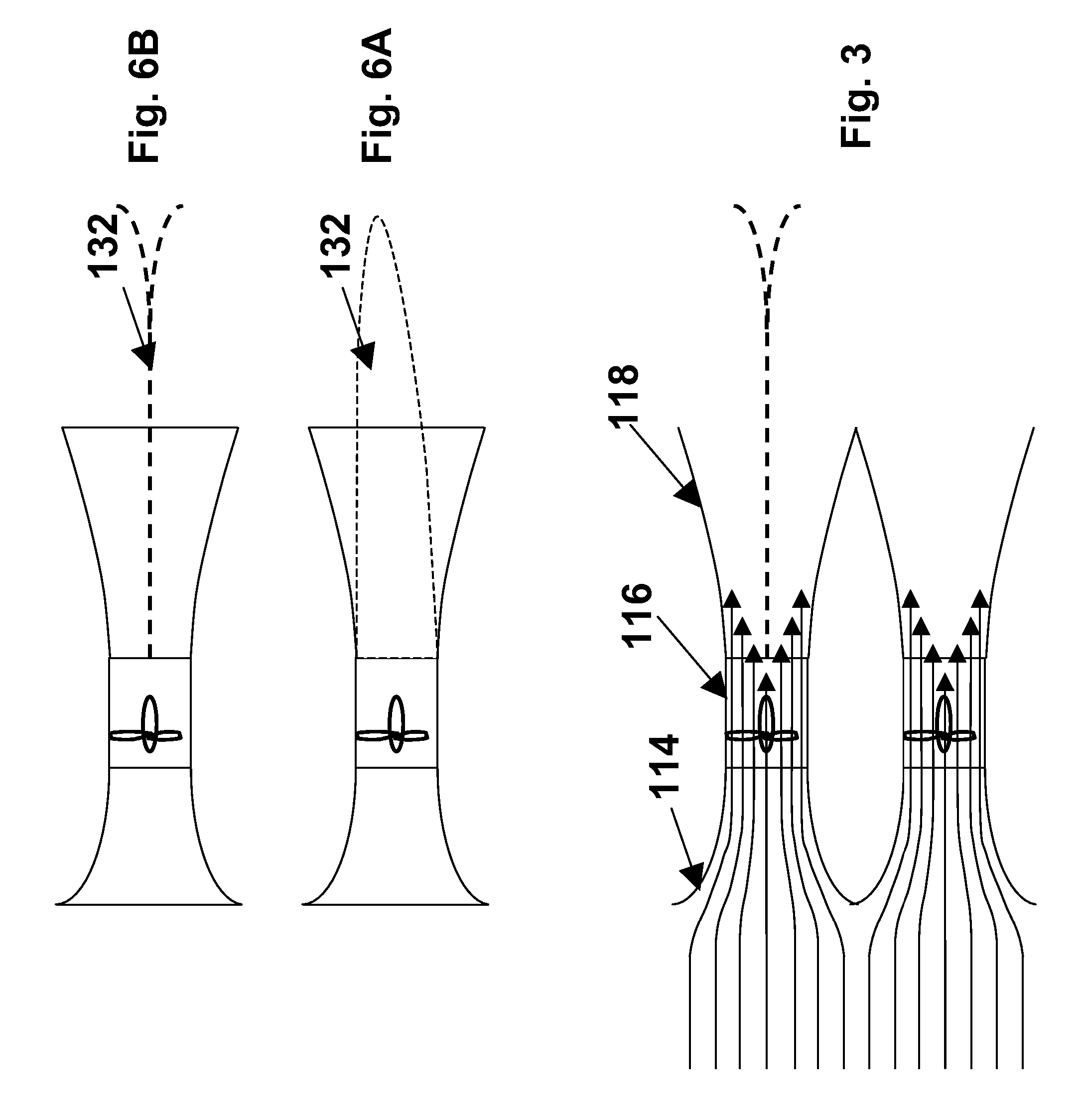
Power generation assemblies, and apparatus for use therewith
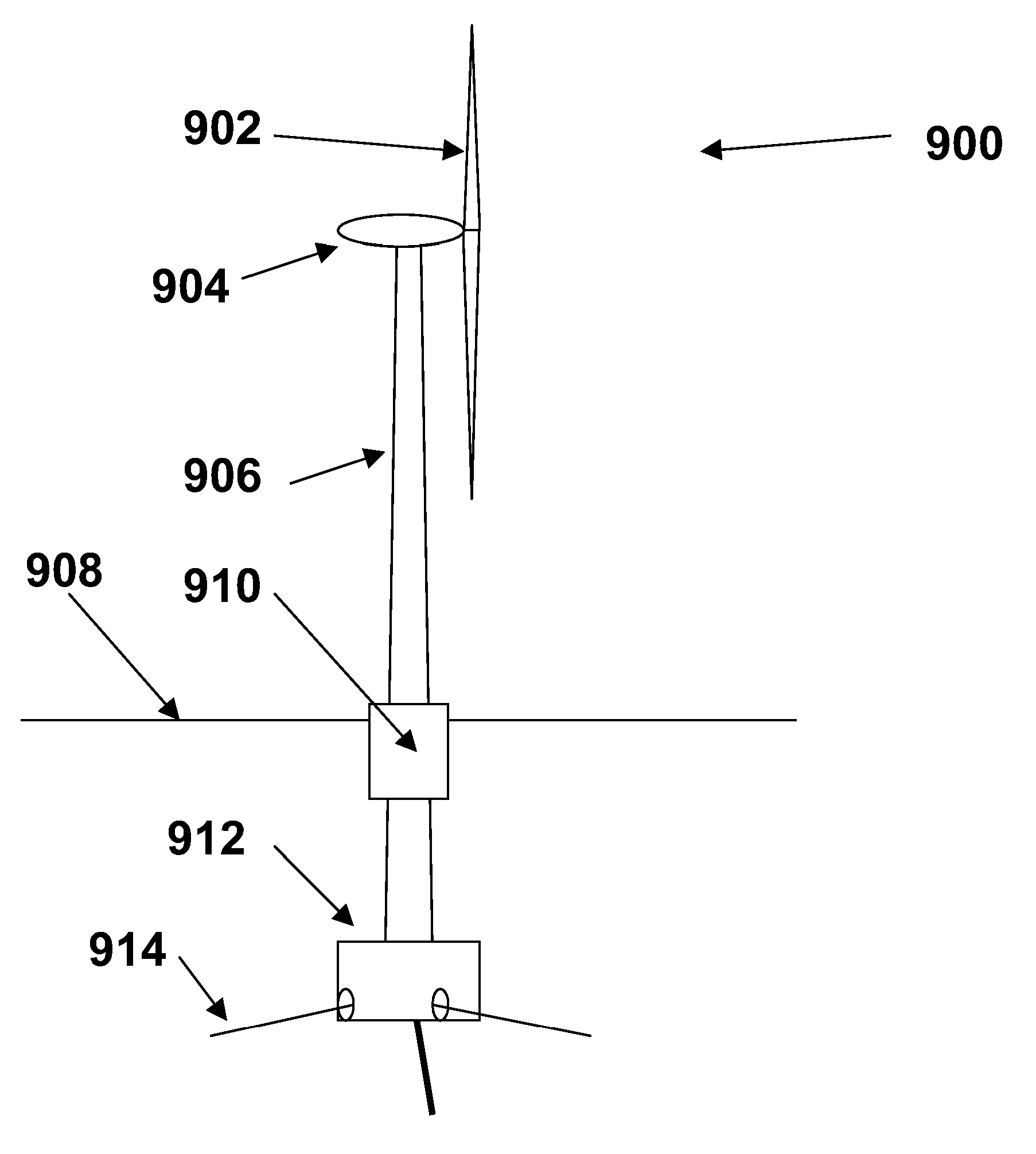
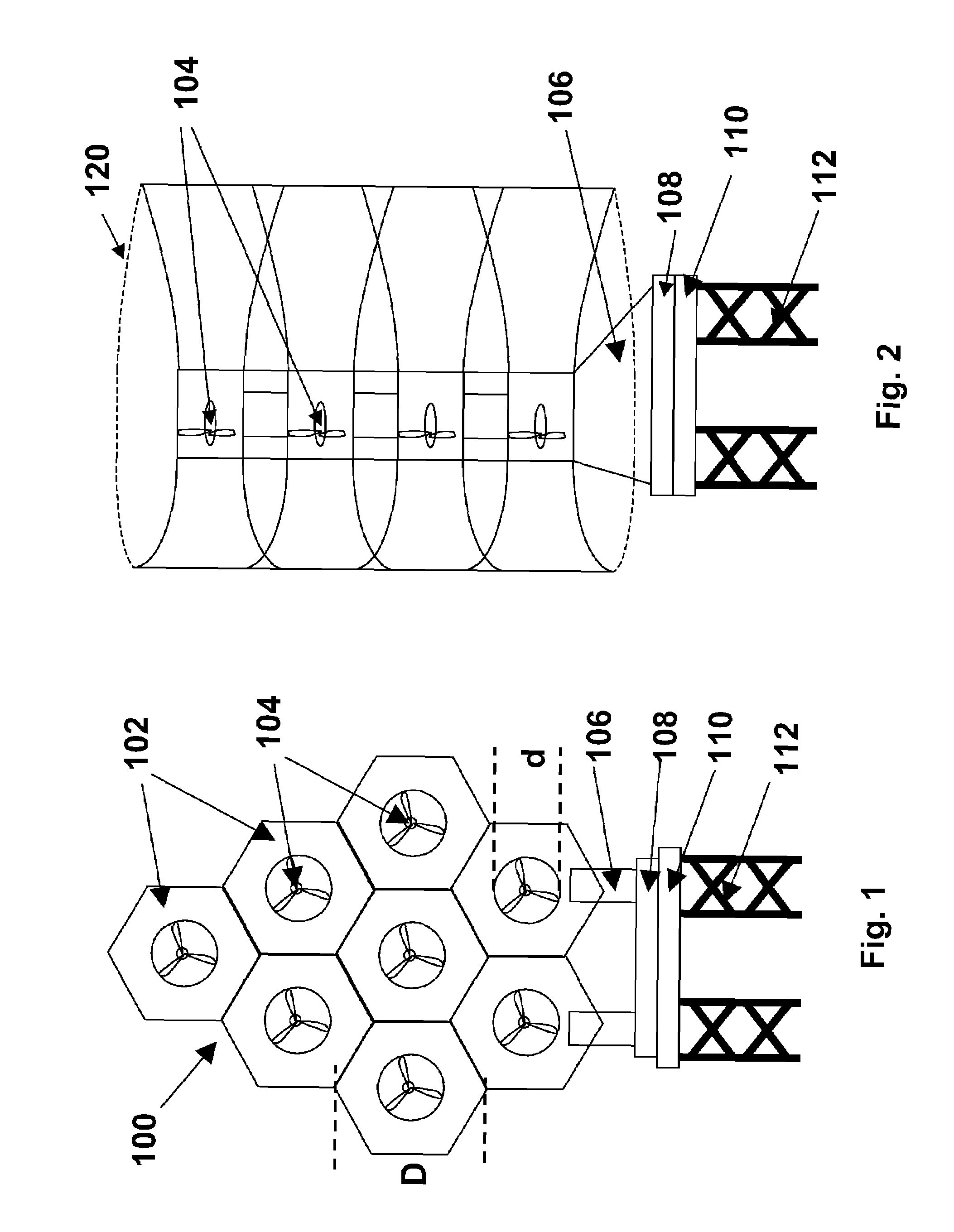
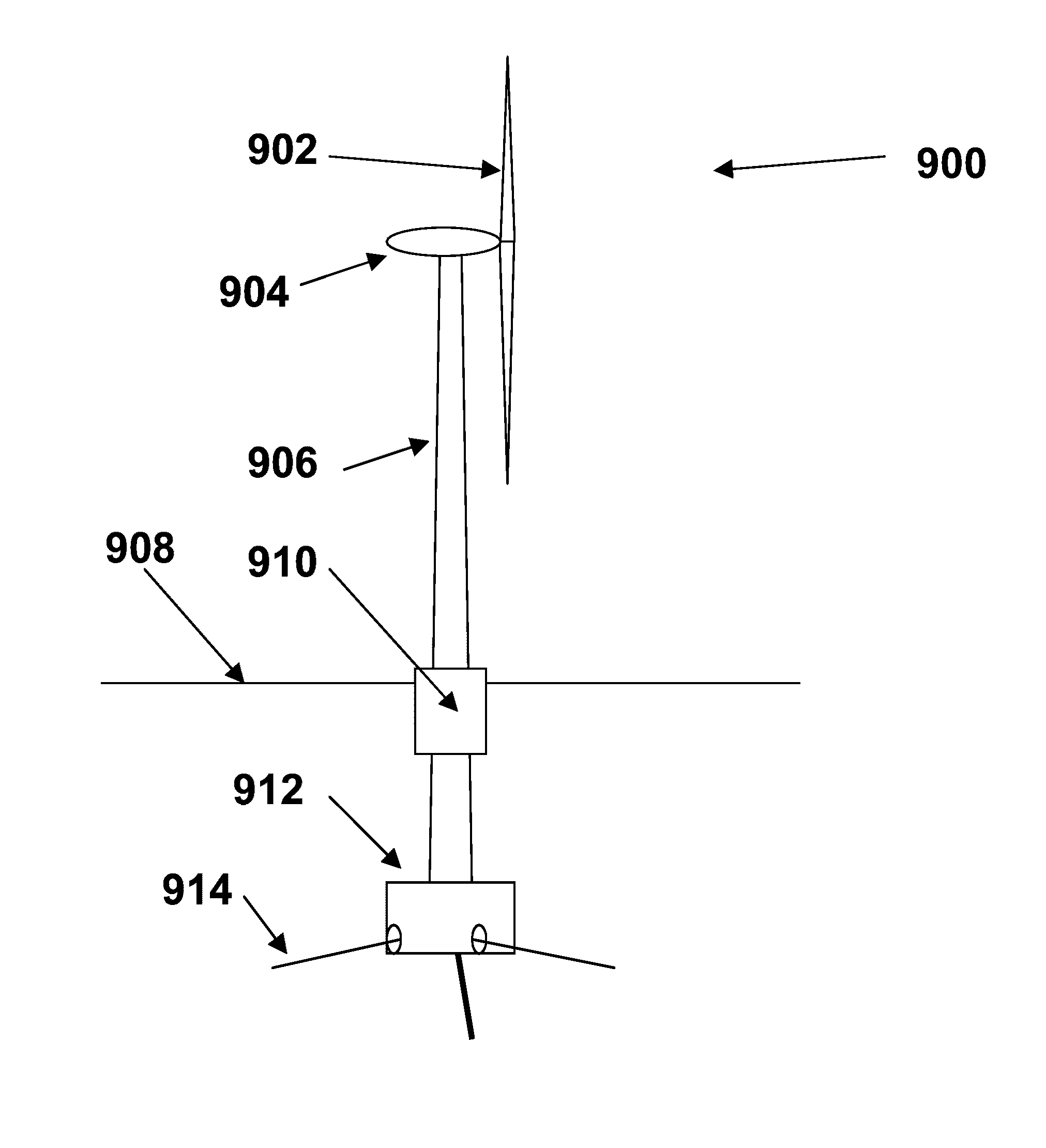
ActiveUS7293960B2Increase hydrodynamic massExtended maintenance periodPropellersWind motor controlIsoetes triquetraMarine engineering
A floating power generation assembly comprises at least three floating units (900) floating on a body of water, and at least three anchors (916) secured to a solid surface beneath the body of water, each of the floating units (900) being provided with a power generator, the floating units (900) being arranged substantially at the vertices of at least one equilateral triangle. Ship borne apparatus for deploying the floating units of such a power generation assembly and a novel multiple wind turbine assembly are also described.
Owner:OCEAN WIND TECH
Power generation assemblies and apparatus
InactiveUS20100219645A1Increase hydrodynamic massExtended maintenance periodWind motor assemblyWind motor supports/mountsQuadrilateralTension-leg platform
A floating power generation assembly has at least three floating units (3400) provided with power generation means (3402, 3404) and floating in a body of water. At least one of the three floating units (3400) is a tension leg platform. The assembly also comprises first anchors secured to a surface beneath the water, and first cables (3414, 3416) connecting the buoyant body (3400) to the first anchors. Second anchors are secured to the underwater surface and connected by second cables (3412) to the floating units (3400). The floating units (3400) are arranged substantially at the vertices of at least one triangle or quadrilateral.
Owner:YAMAMOTO SHIGEYUKI +1
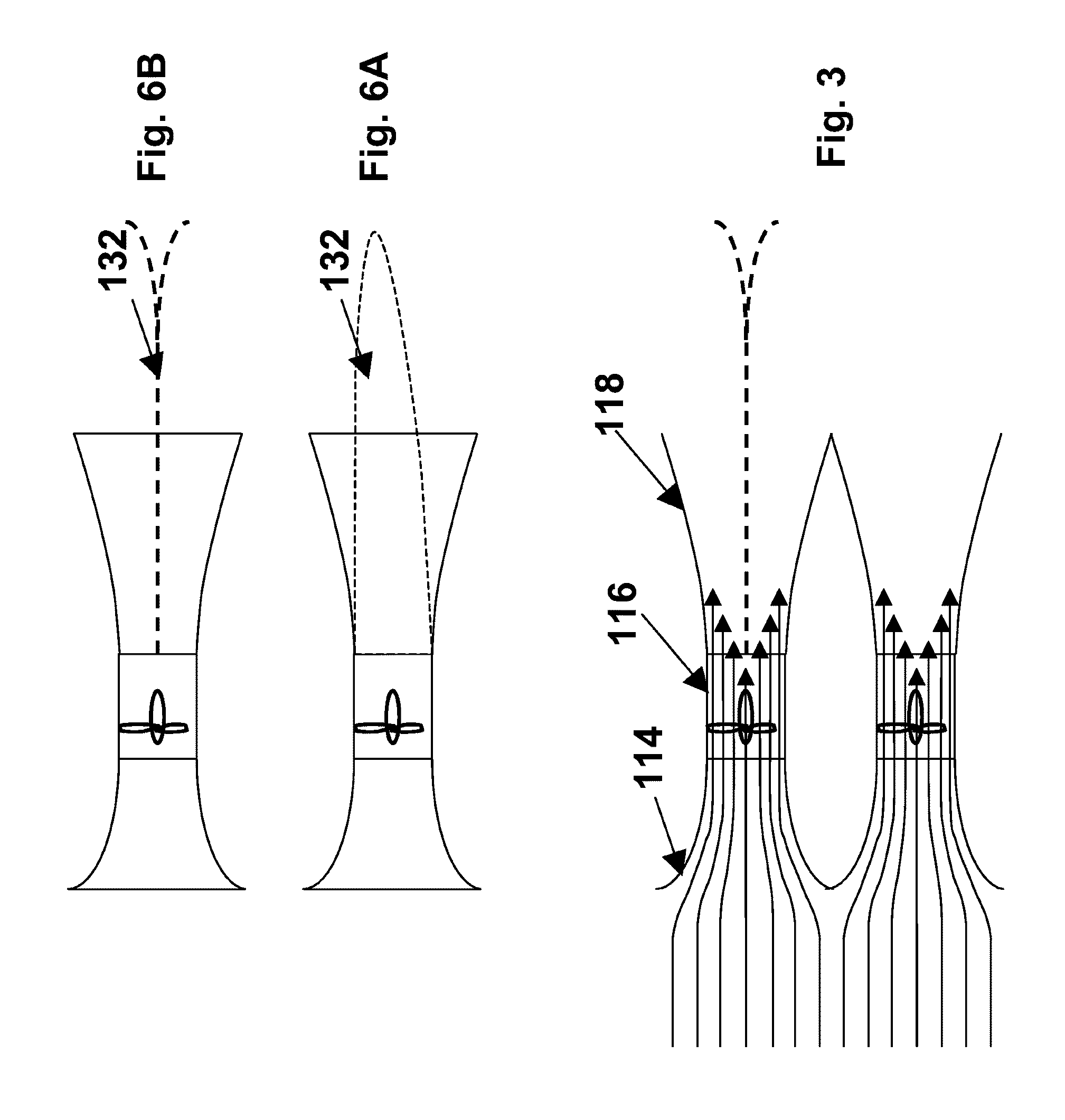
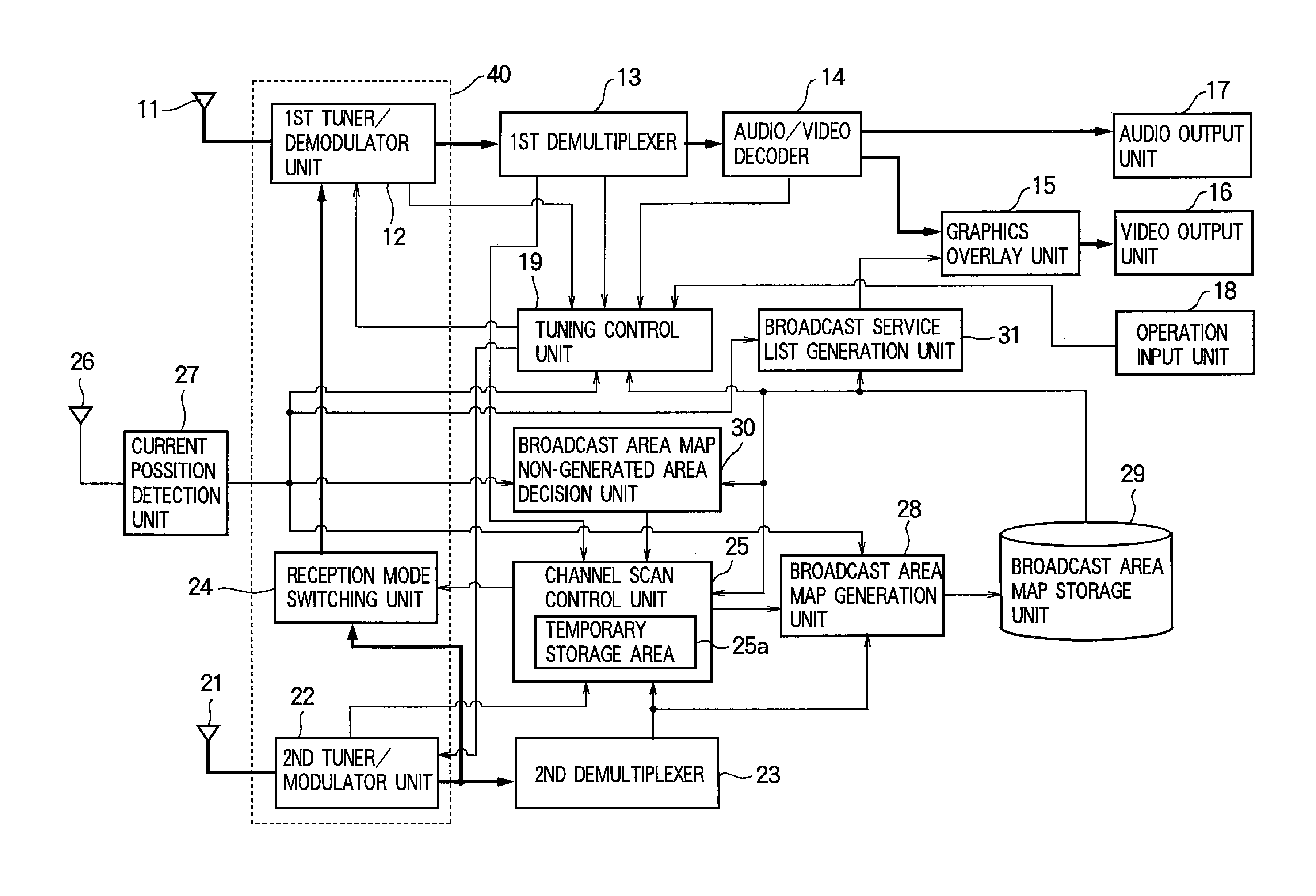
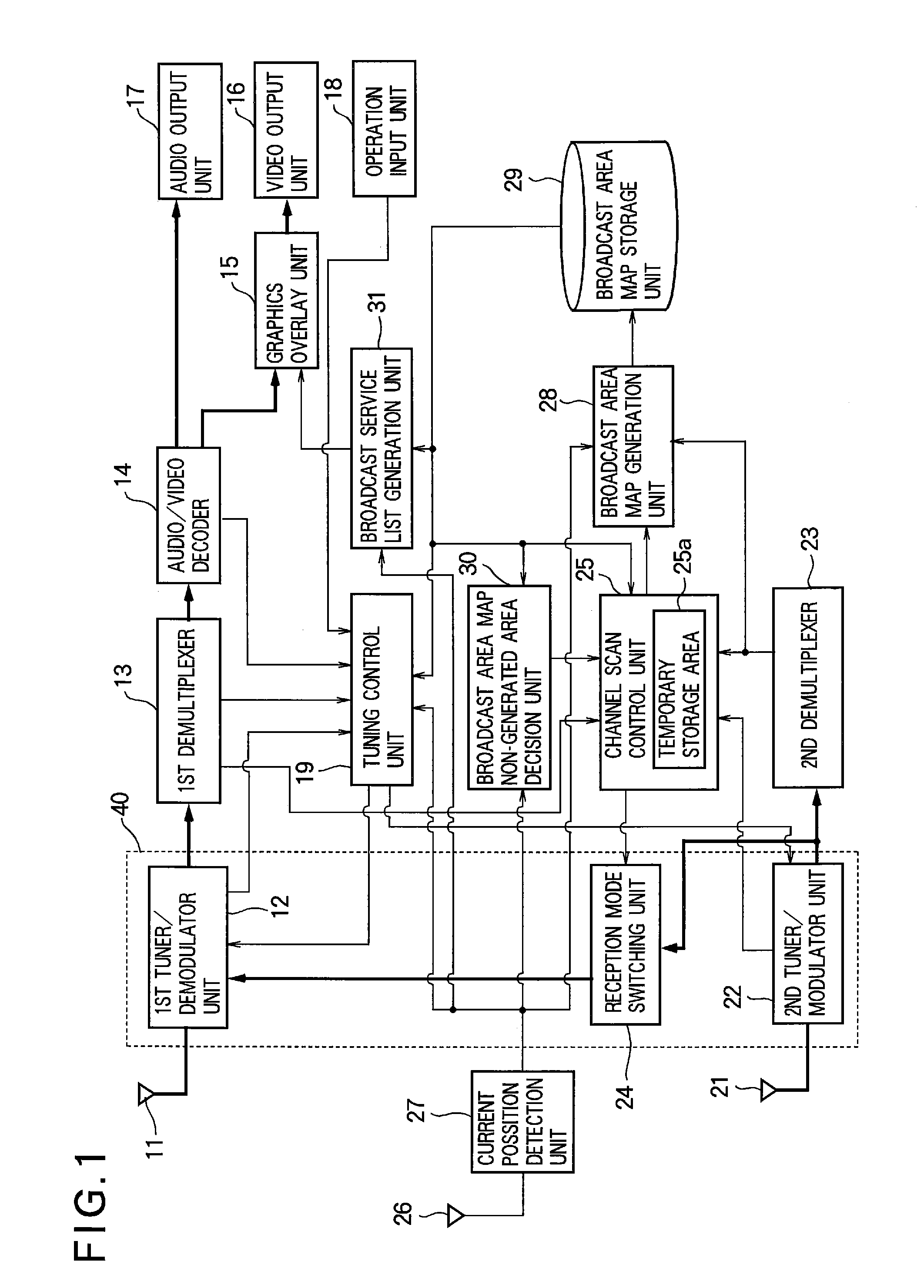
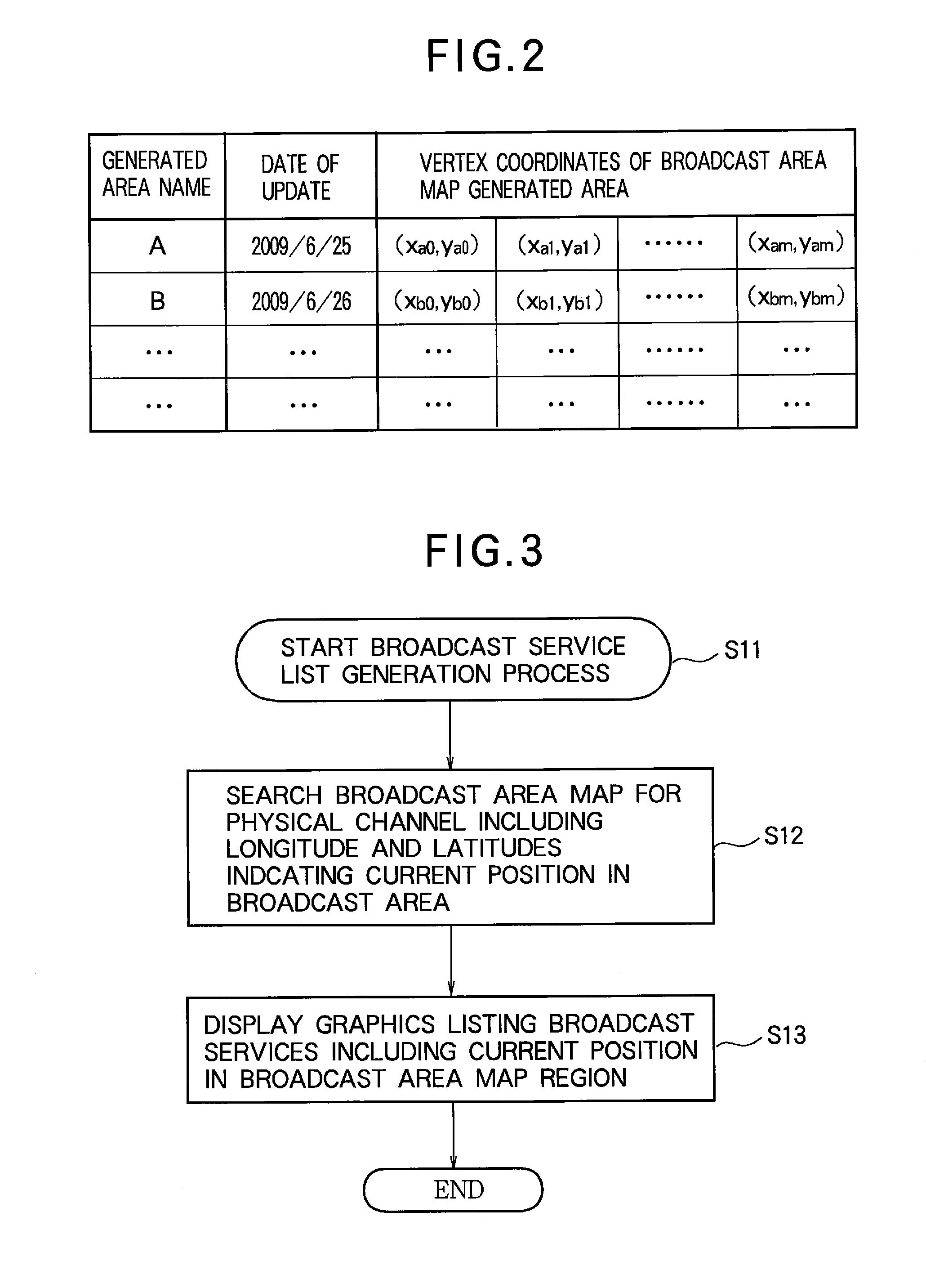
Digital broadcast reception device and digital broadcast reception method
InactiveUS20120133840A1Improve listeningReduce frequencyTelevision system detailsSpatial transmit diversityLocation detectionTelecommunications
Disclosed is a digital broadcast reception device that includes a plurality of tuner / demodulator units; a tuning control unit; a current position detection unit for detecting a current position; a channel scan control unit that has one of the plurality of tuner / demodulator units perform tuning for program viewing or listening, and has another one of the plurality of tuner / demodulator units perform a channel scan by tuning to the physical channels sequentially and detecting receivable physical channels; a broadcast area map generation unit for generating broadcast area maps including the receivable physical channels when the channel scan is executed, broadcast service information regarding broadcast content of the physical channels, and receivable position information; and a broadcast area map storage unit for storing the generated broadcast area maps.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Gastric retentive oral dosage form with restricted drug release in the lower gastrointestinal tract
ActiveUS7976870B2Minimizes variabilityMinimizes deliveryAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryUpper gastrointestinalActive agent
Controlled release oral dosage forms are provided for the continuous, sustained administration of a pharmacologically active agent to the upper gastrointestinal tract of a patient in whom the fed mode as been induced. The majority of the agent is delivered, on an extended release basis, to the stomach, duodenum and upper regions of the small intestine, with drug delivery in the lower gastrointestinal tract and colon substantially restricted. The dosage form comprises a matrix of a biocompatible, hydrophilic, erodible polymer with an active agent incorporated therein, wherein the polymer is one that both swells in the presence of water and gradually erodes over a time period of hours, with swelling and erosion commencing upon contact with gastric fluid, and drug release rate primarily controlled by erosion rate.
Owner:DEPOMED SYST INC
Method of controlling engine system and engine system
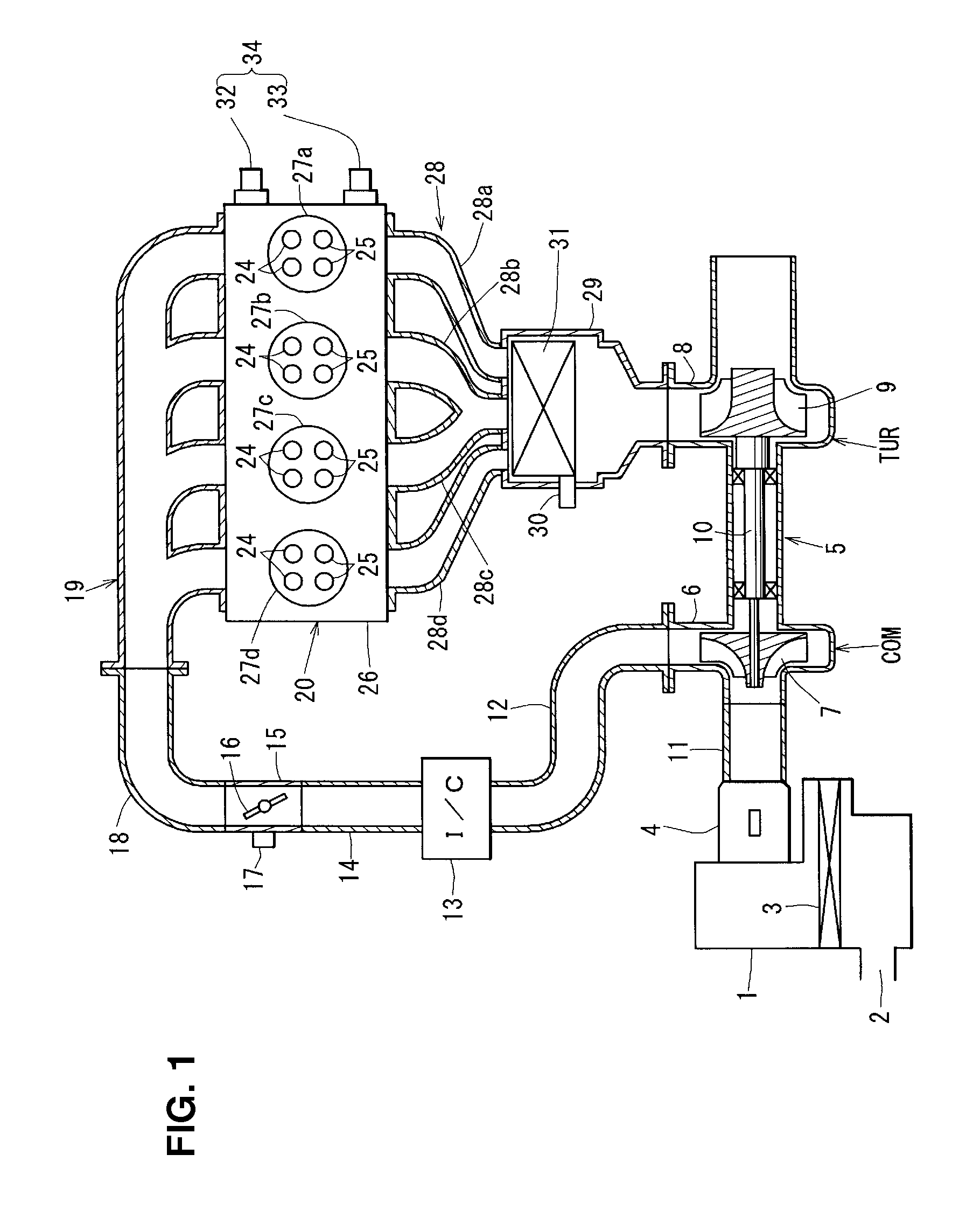
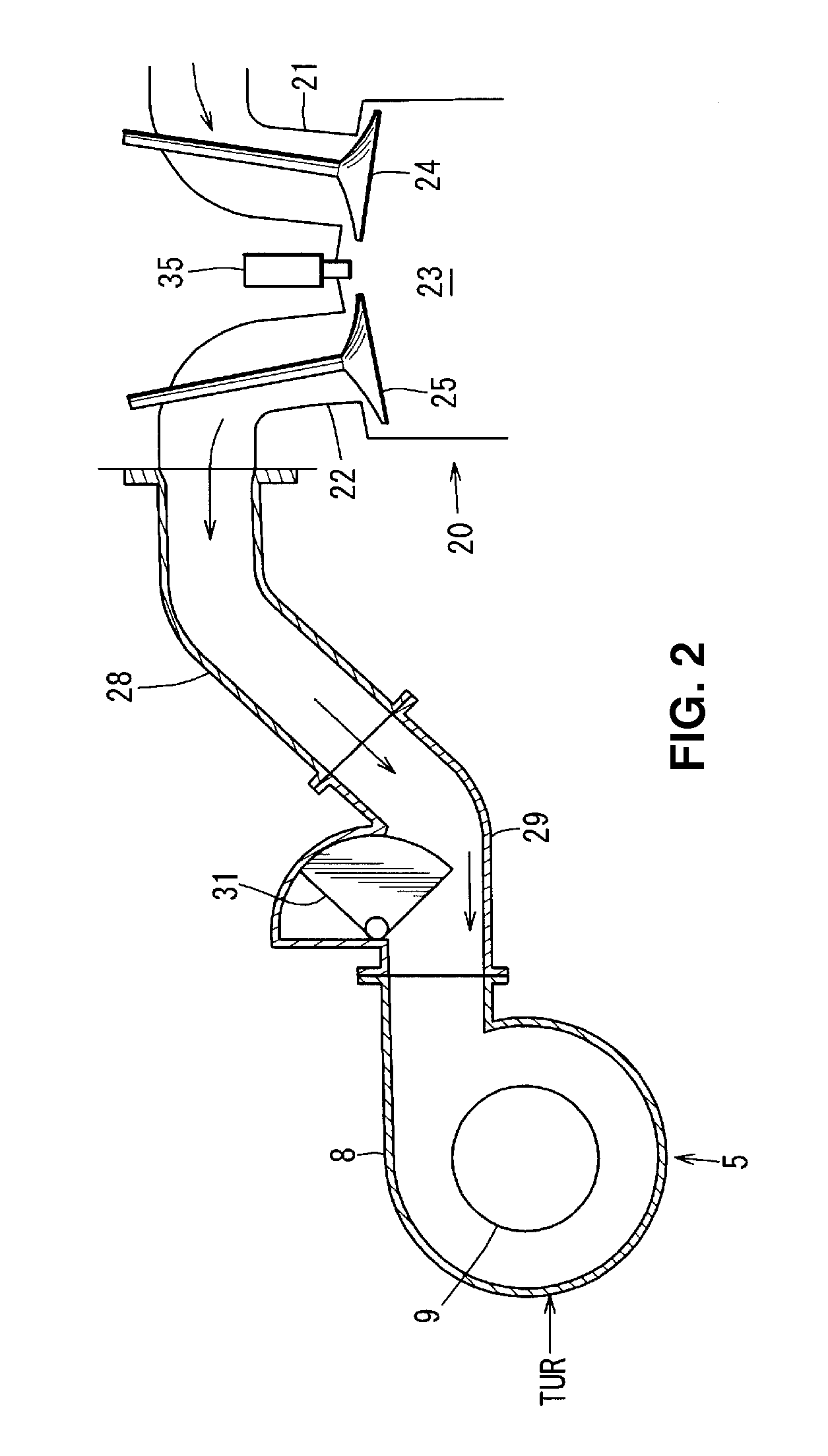
InactiveUS20100217504A1Improve drivabilitySmooth torque curveAnalogue computers for vehiclesValve arrangementsExhaust valveInlet valve
A valve overlap period is increased as a desired torque of an engine increases by advancing an opening timing of an intake valve at a rate greater than that of retarding a closing timing of an exhaust valve in a low engine-torque area in which the desired torque of the internal combustion engine is relatively low (step S16). The valve overlap period is increased as the desired torque of the engine increases by retarding the closing timing of the exhaust valve at a rate greater than that of advancing the opening timing of the intake valve in a high engine-torque area in which the desired torque of the internal combustion engine is relatively high (step S17). Accordingly, the drivability can be improved by obtaining the proper torque and the smooth torque curve in the wide driving area.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
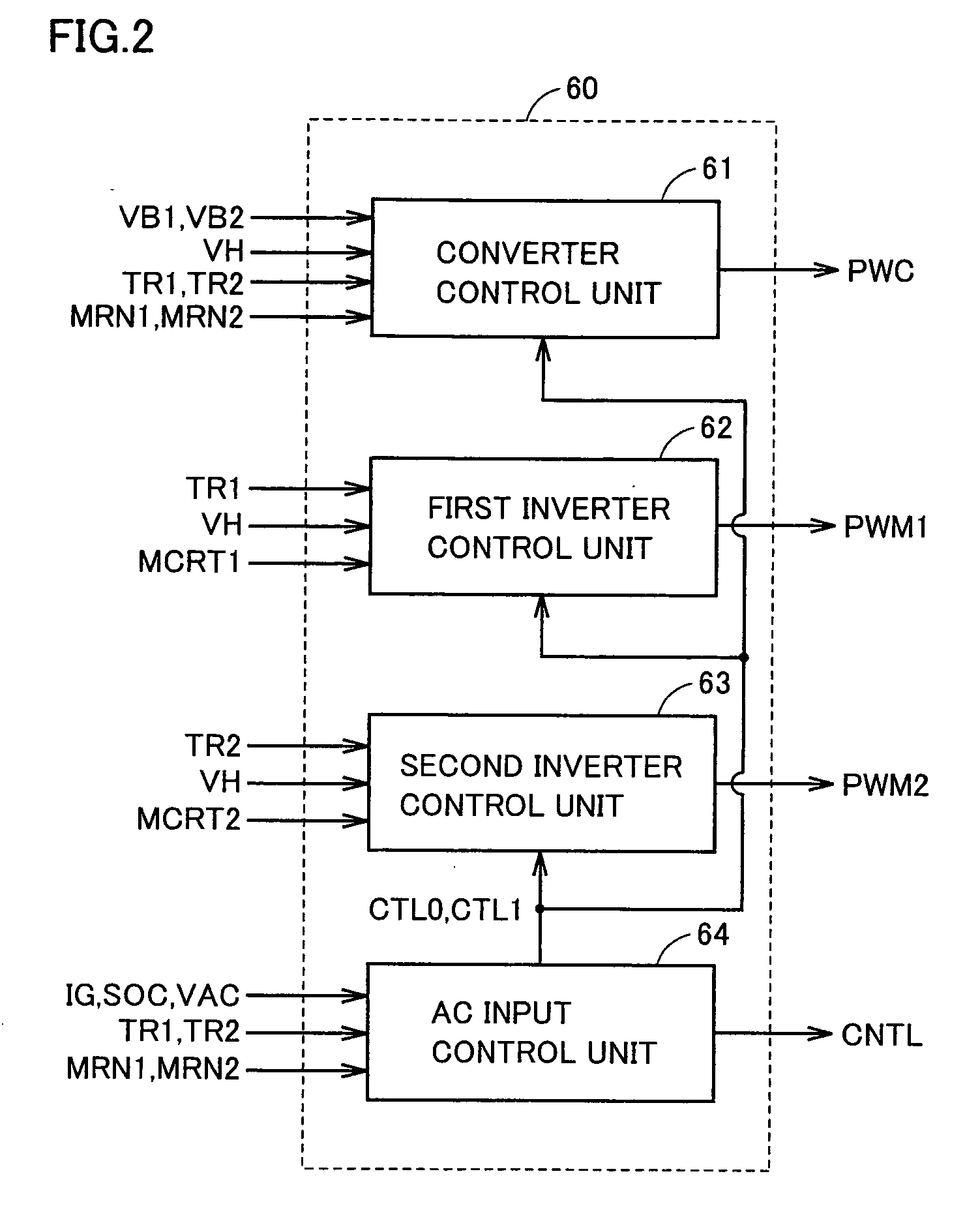
Power supply device for vehicle and method of controlling the same
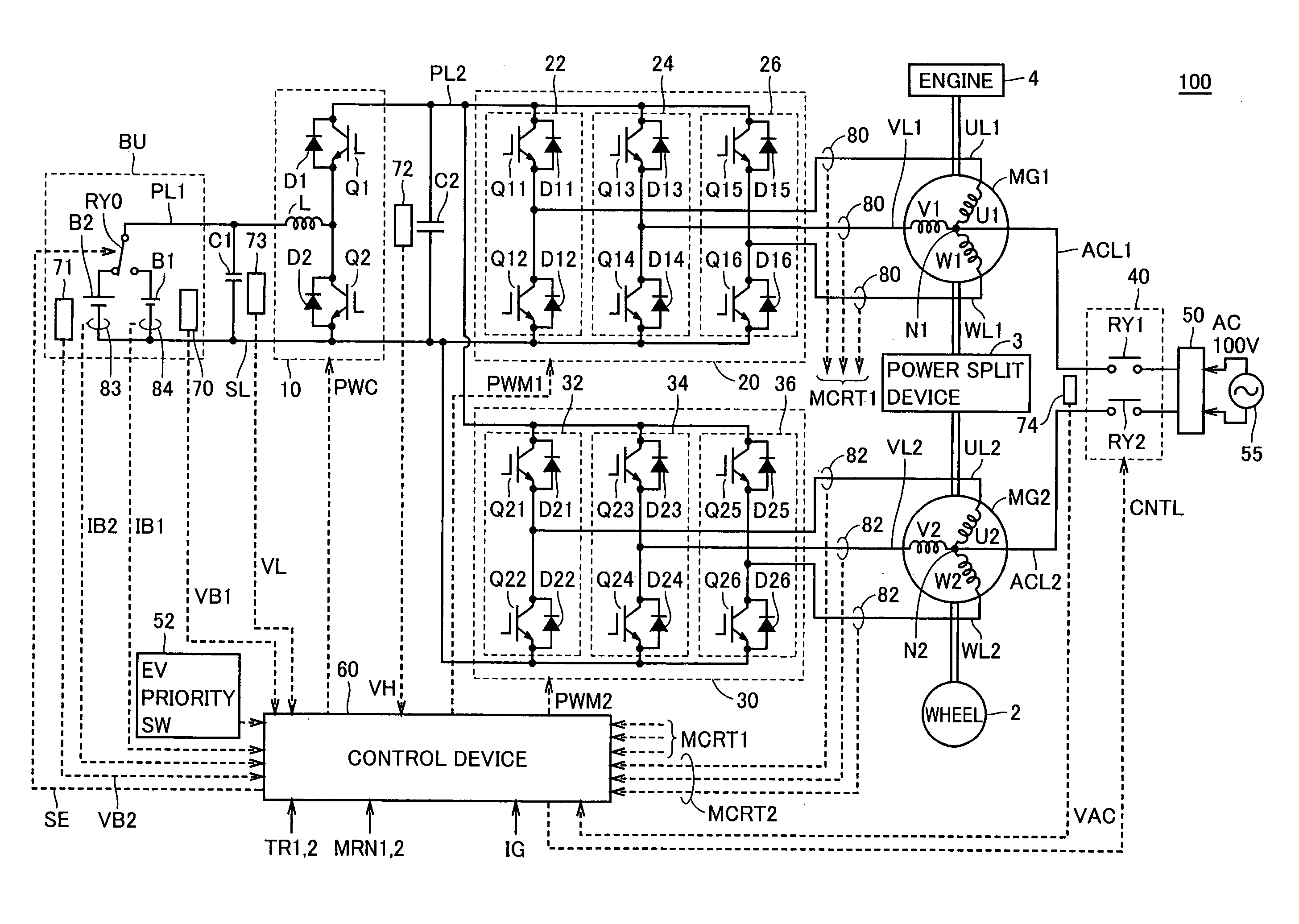
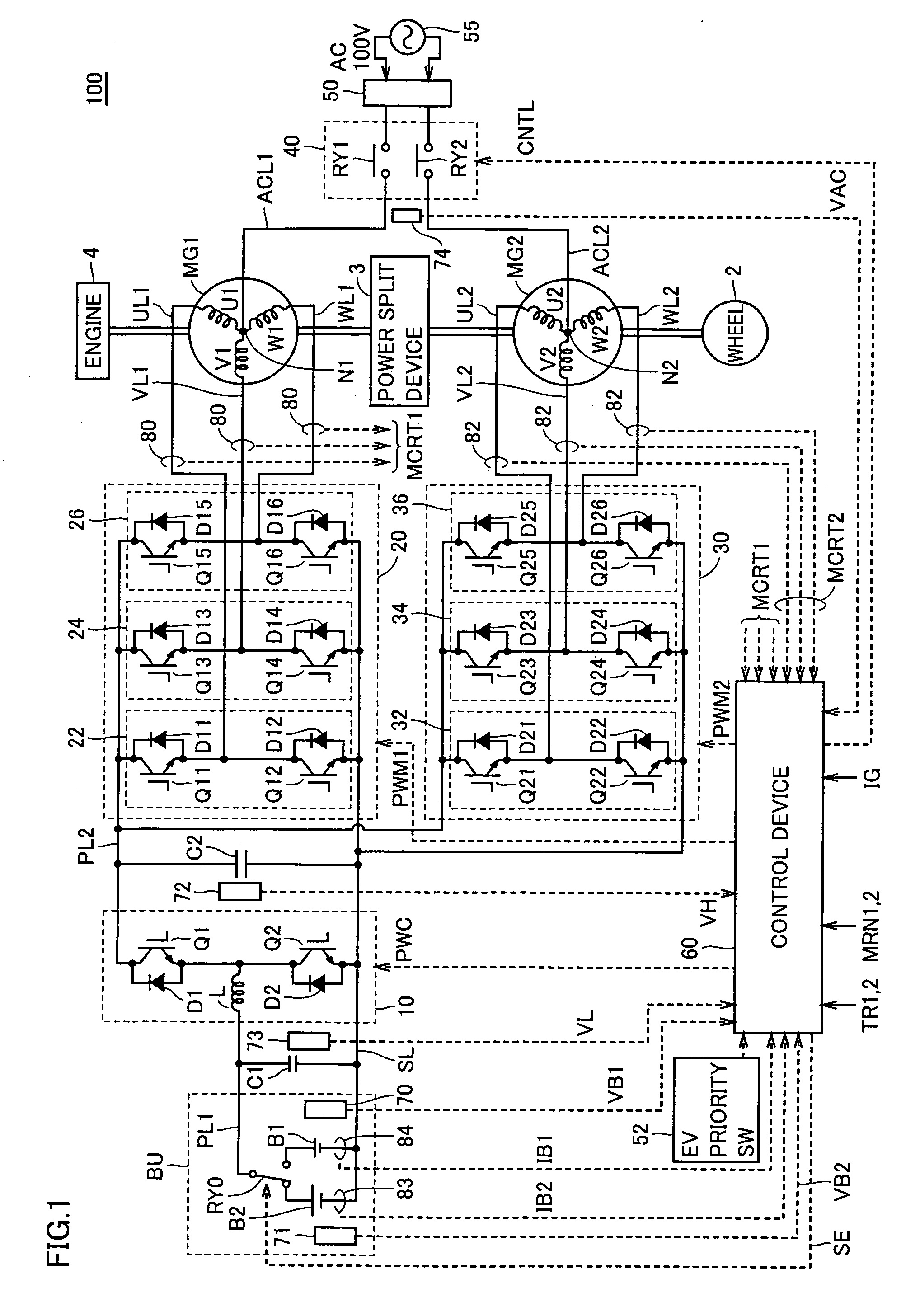
InactiveUS20070029986A1Improve energy efficiencyLong-time drivingMultiple ac dynamo-electric motors controlPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingElectricityElectrical battery
A power supply device for a vehicle includes a battery serving as a first electric storage device, a battery serving as a second electric storage device, a motor generator driving a wheel, a selection switch selecting one of the first and second electric storage devices and connecting the selected electric storage device to the motor generator, and a control device controlling switching of the selection switch in accordance with a state of charge of each of the first and second electric storage devices. In the case where the selection switch selects the first electric storage device, when charging is performed and the state of charge of the first electric storage device becomes higher than a first prescribed level, the control device instructs the selection switch to select the second electric storage device.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Power generation assemblies, and apparatus for use therewith
ActiveUS20060171798A1Increase hydrodynamic massExtended maintenance periodPropellersWind motor controlIsoetes triquetraEngineering
A floating power generation assembly comprises at least three floating units (900) floating on a body of water, and at least three anchors (916) secured to a solid surface beneath the body of water, each of the floating units (900) being provided with power generation means, the floating units (900) being arranged substantially at the vertices of at least one equilateral triangle. The invention also provides ship-borne apparatus for deploying the floating units of such a power generation assembly and a novel multiple wind turbine assembly.
Owner:OCEAN WIND TECH
Cross-linkable polymers, method for the production thereof, and shaped bodies made of cross-linked polymers
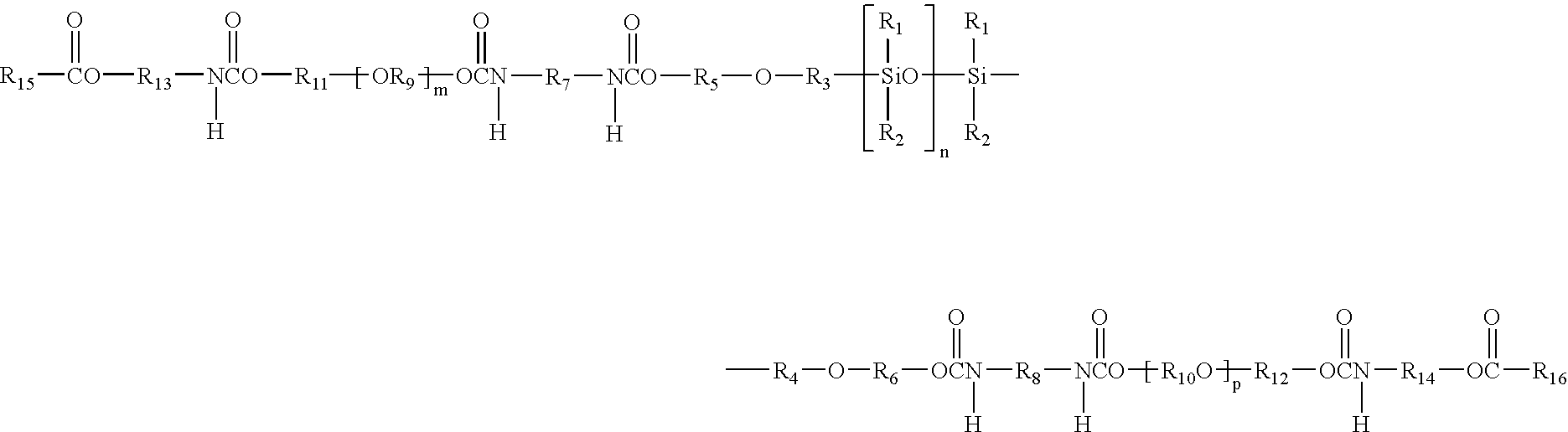
InactiveUS6528585B1Low levelExtended maintenance periodPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsCross-linkPolymer science
The invention relates to a process for preparing crosslinkable polymers containing silane groups having at least one hydrolyzable radical by free-radical-initiated grafting of the base polymers with an olefinically unsaturated silane having at least one hydrolyzable radical, wherein the grafting is carried out in the presence of(a) an alkylsilane of the formula I, whereR1 is a monovalent hydrocarbon radical having from 1 to 33 carbon atoms or a divalent hydrocarbon radical having from 4 to 24 carbon atoms,R2 is a hydrocarbon radical having from 1 to 10 carbon atoms,X are identical or different hydrolyzable radicals,n is 0, 1 or 2 andm is 1 or 2 and / or(b) a fluoroalkylsilane of the formula whereR3 is a fluoroalkyl radical,R4 is an alkyl radical andX is a hydrolyzable radical,x is an integer from 1 to 3,y is 0, 1 or 2 andz is an integer from 1 to 3, with the proviso that the sum x+y+z=4.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Barriers for polymer-coated implantable medical devices and methods for making the same
InactiveUS20050208098A1Reduce and prevent and inflammationReduce and prevent proliferationStentsSurgeryBiomedical engineeringMedical treatment
A drug eluting medical device is disclosed. The device includes a barrier layer for reducing the rate of release of a drug.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Adipocytic differentiated adipose derived adult stem cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20040092011A1Less lipidGreat propensityArtificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixStromal cell
The present invention is differentiated adipose tissue-derived stromal cells that exhibit the improved properties of increased extracellular matrix proteins and / or a lower amount of lipid than a mature isolated adipocyte. Methods for the expansion and differentiation of these cells are also provided. The cells of the invention are used for the treatment, repair, correction and / or regeneration of soft tissue cosmetic defects.
Owner:WILKISON WILLIAM O +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com