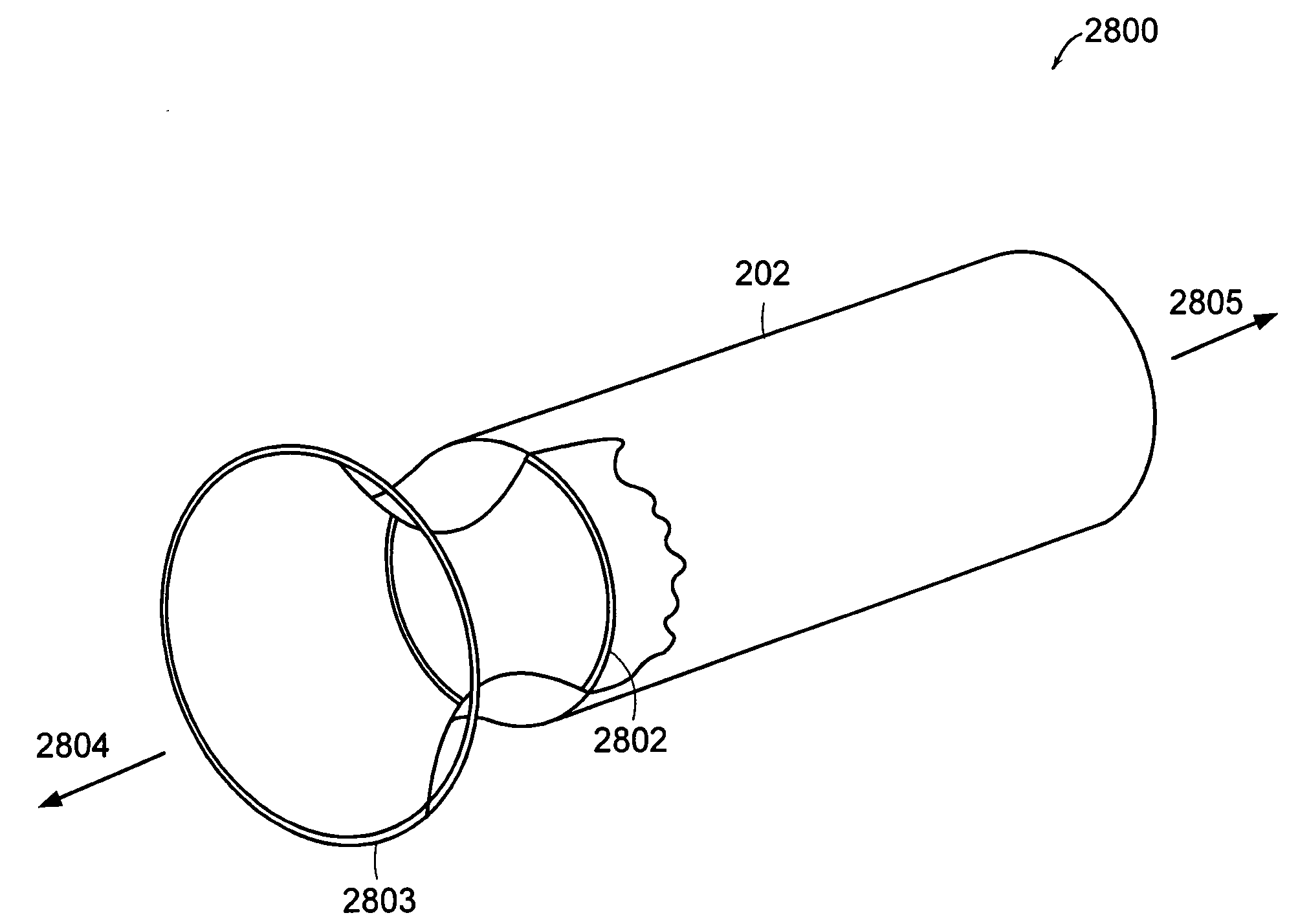
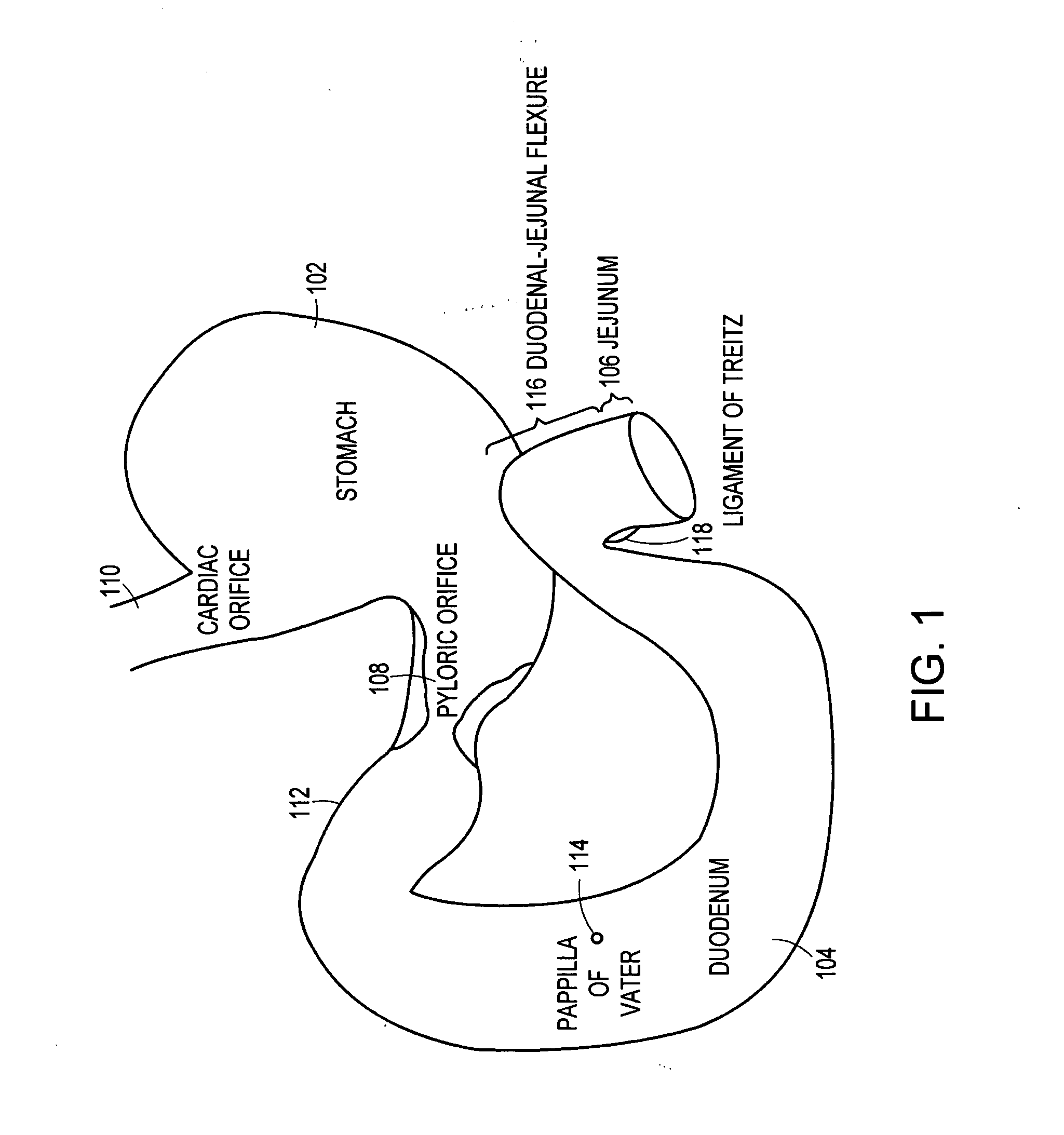
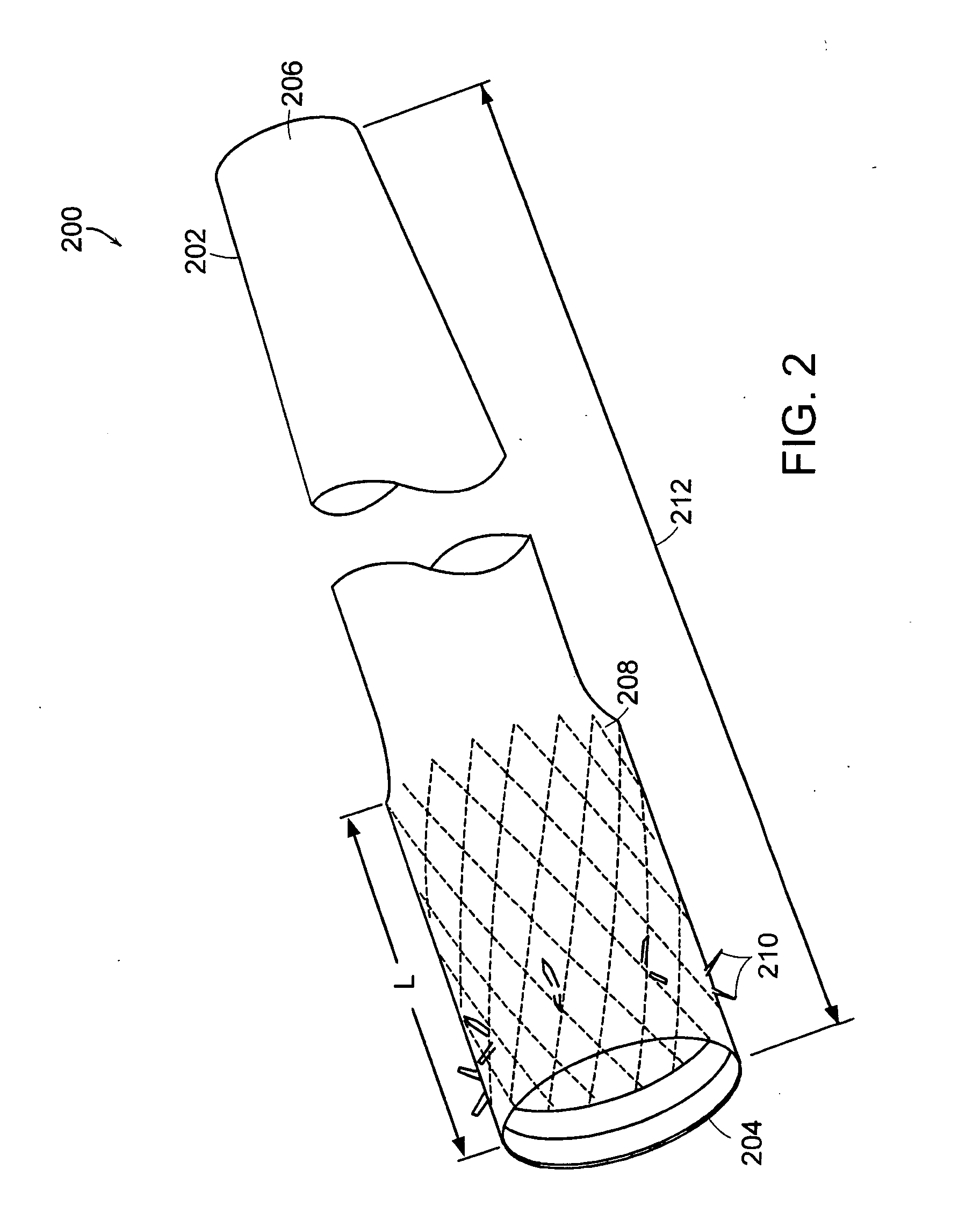
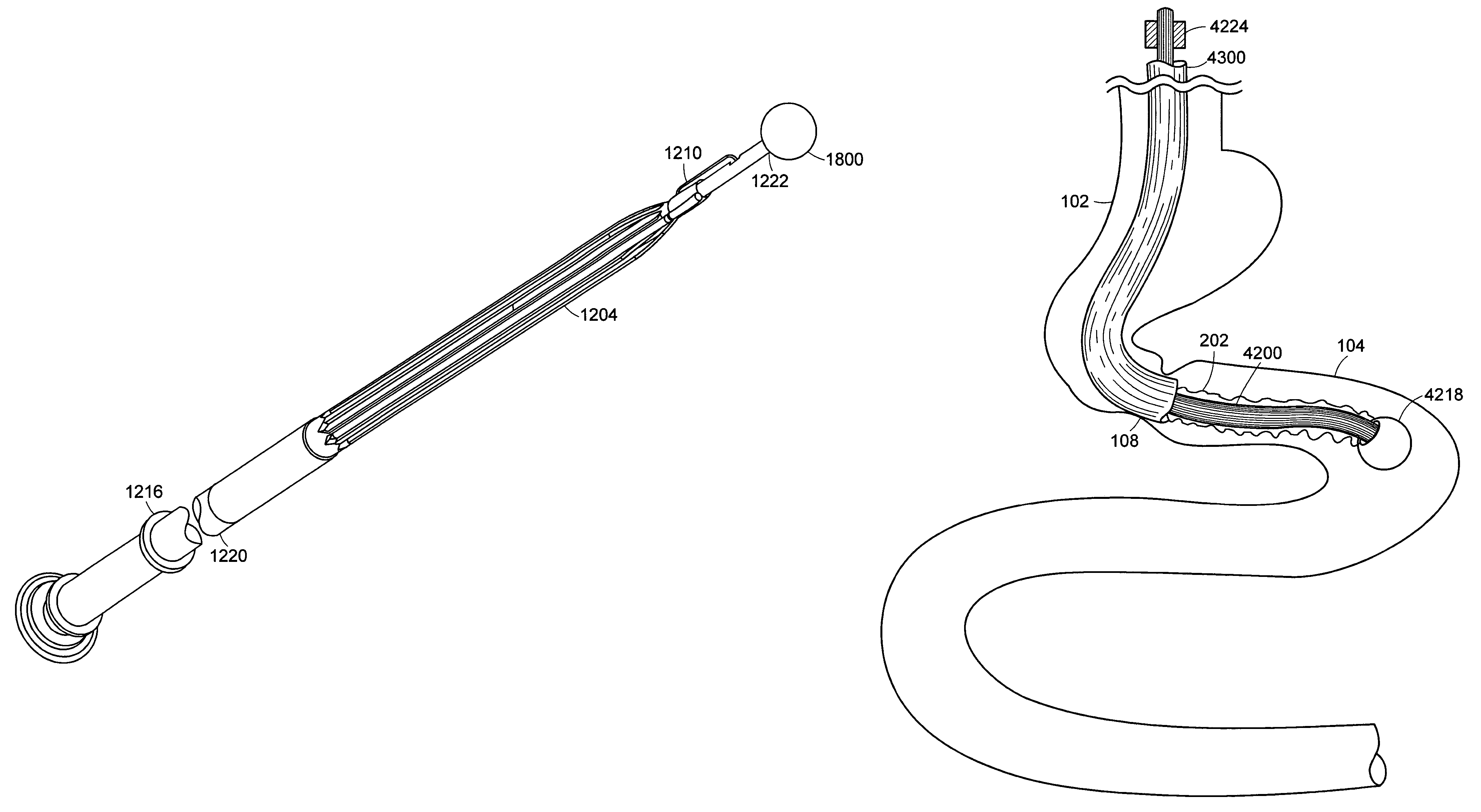
Patents
Literature
395 results about "Duodenum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
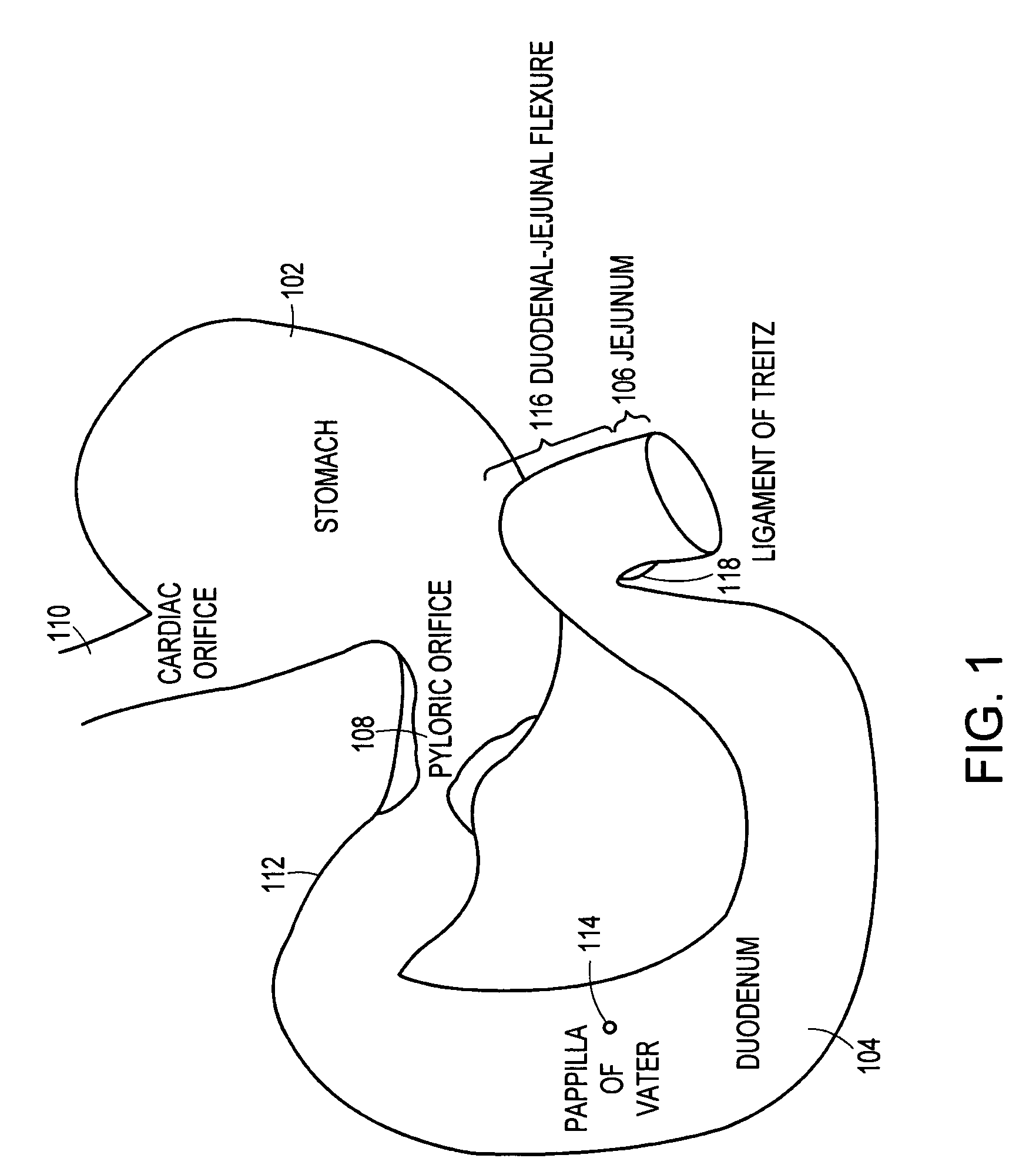
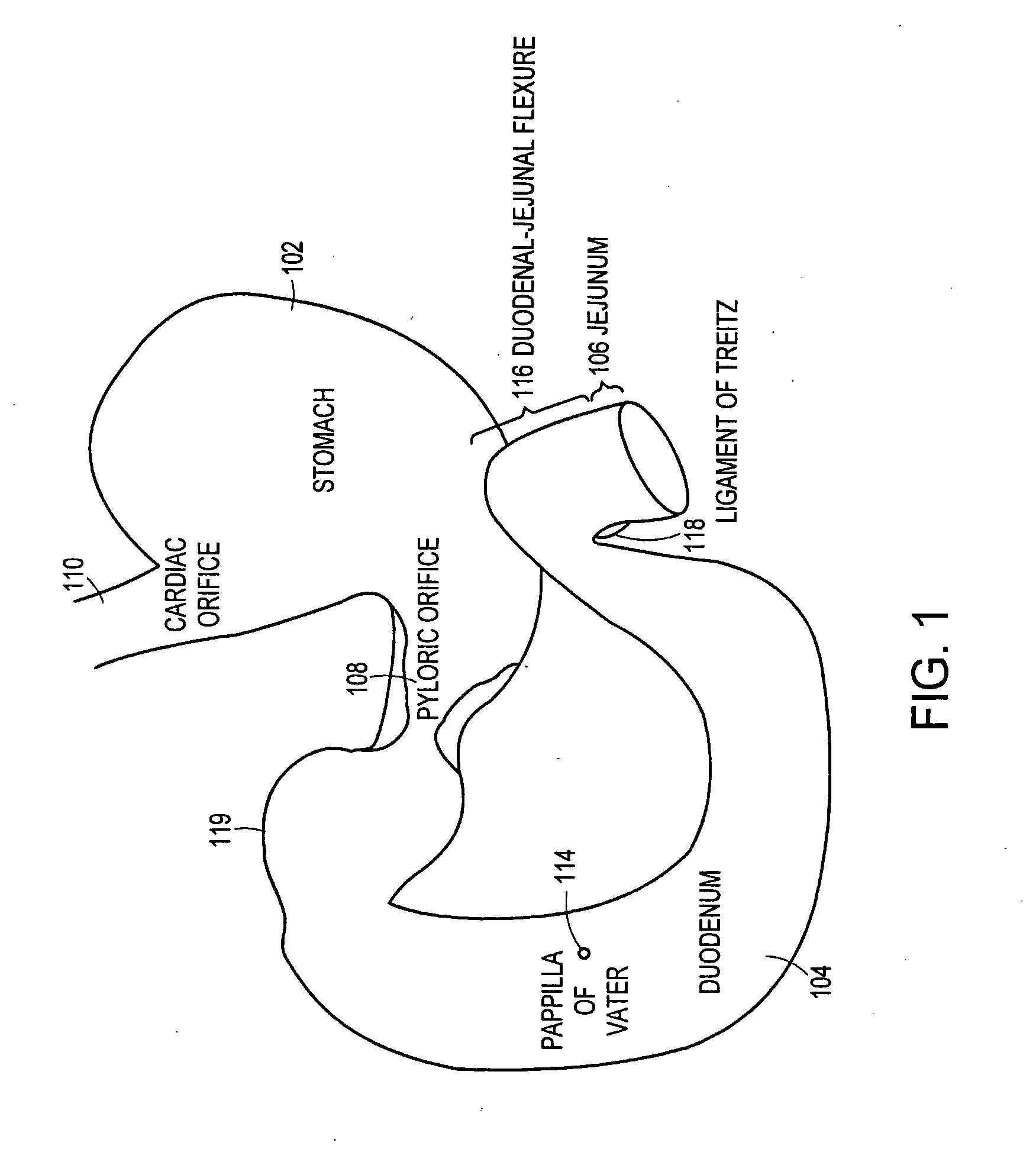
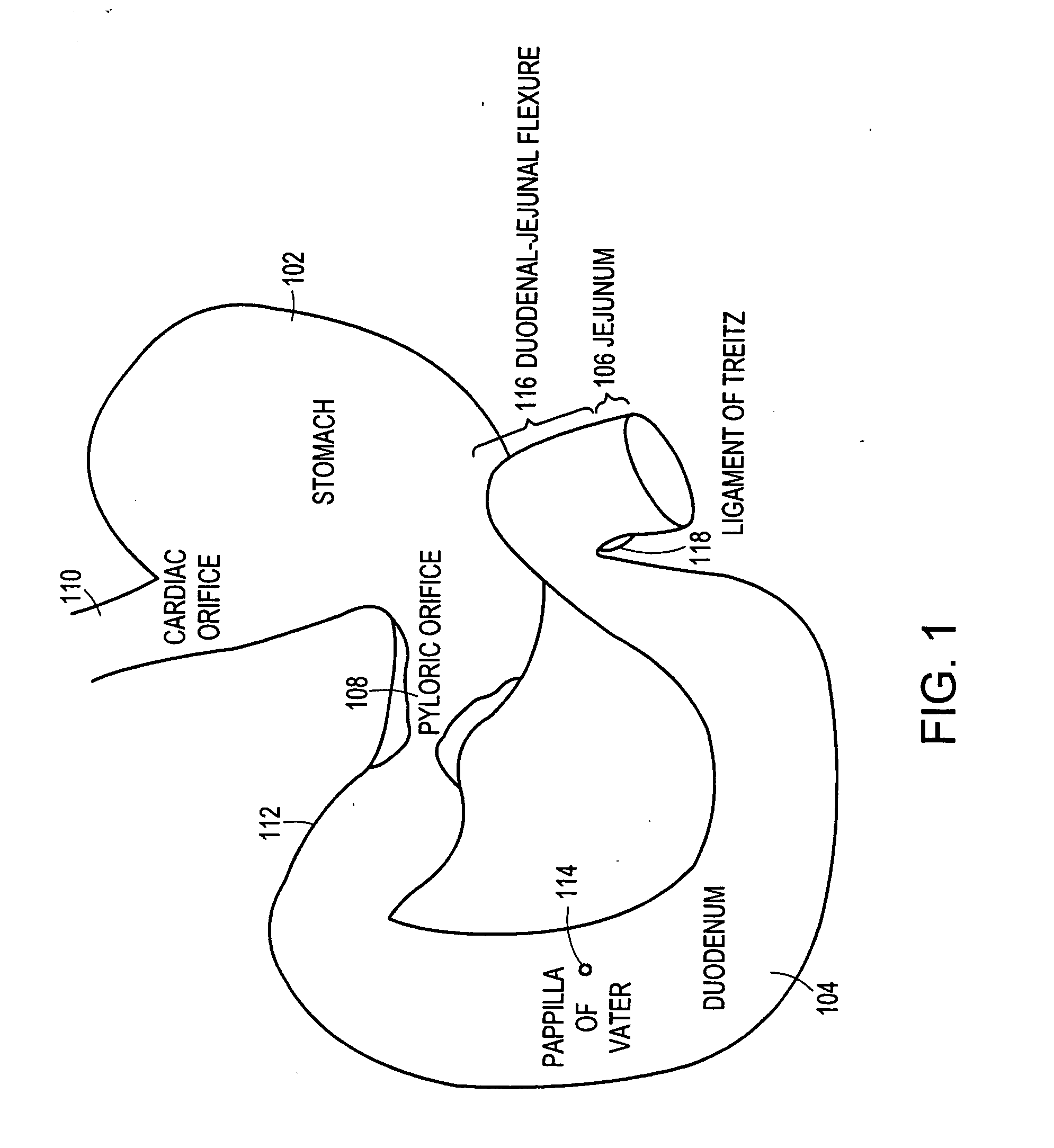
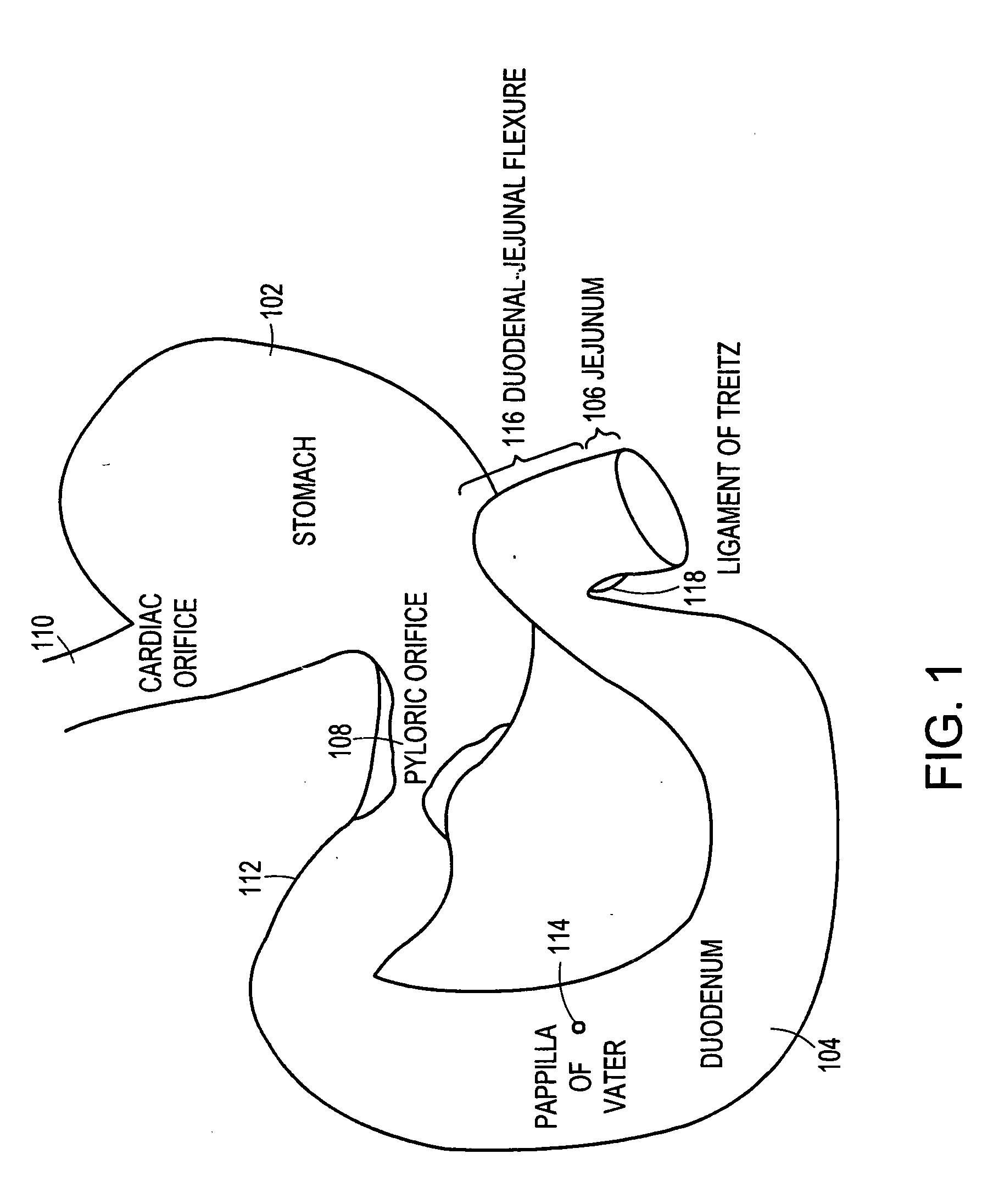
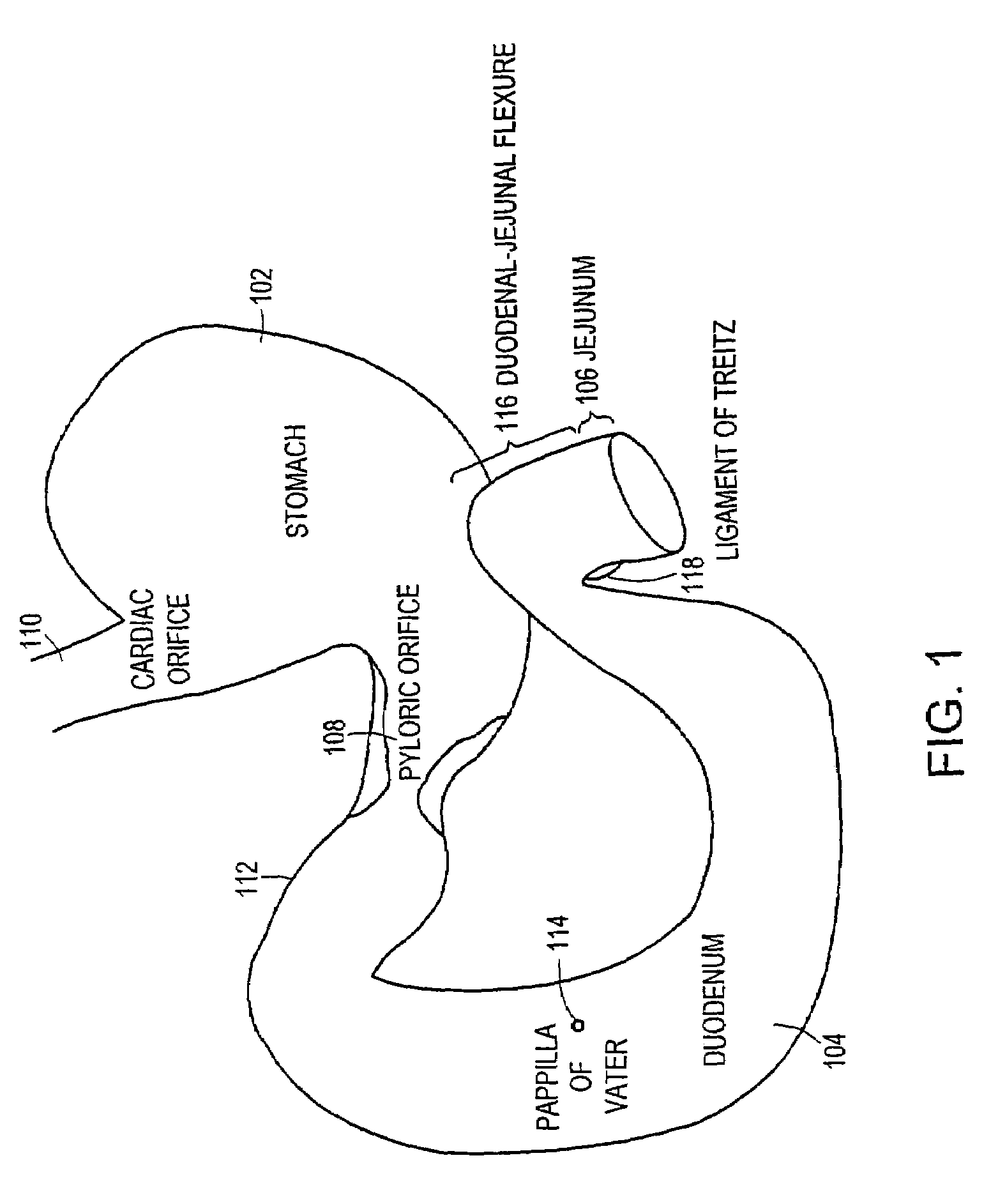
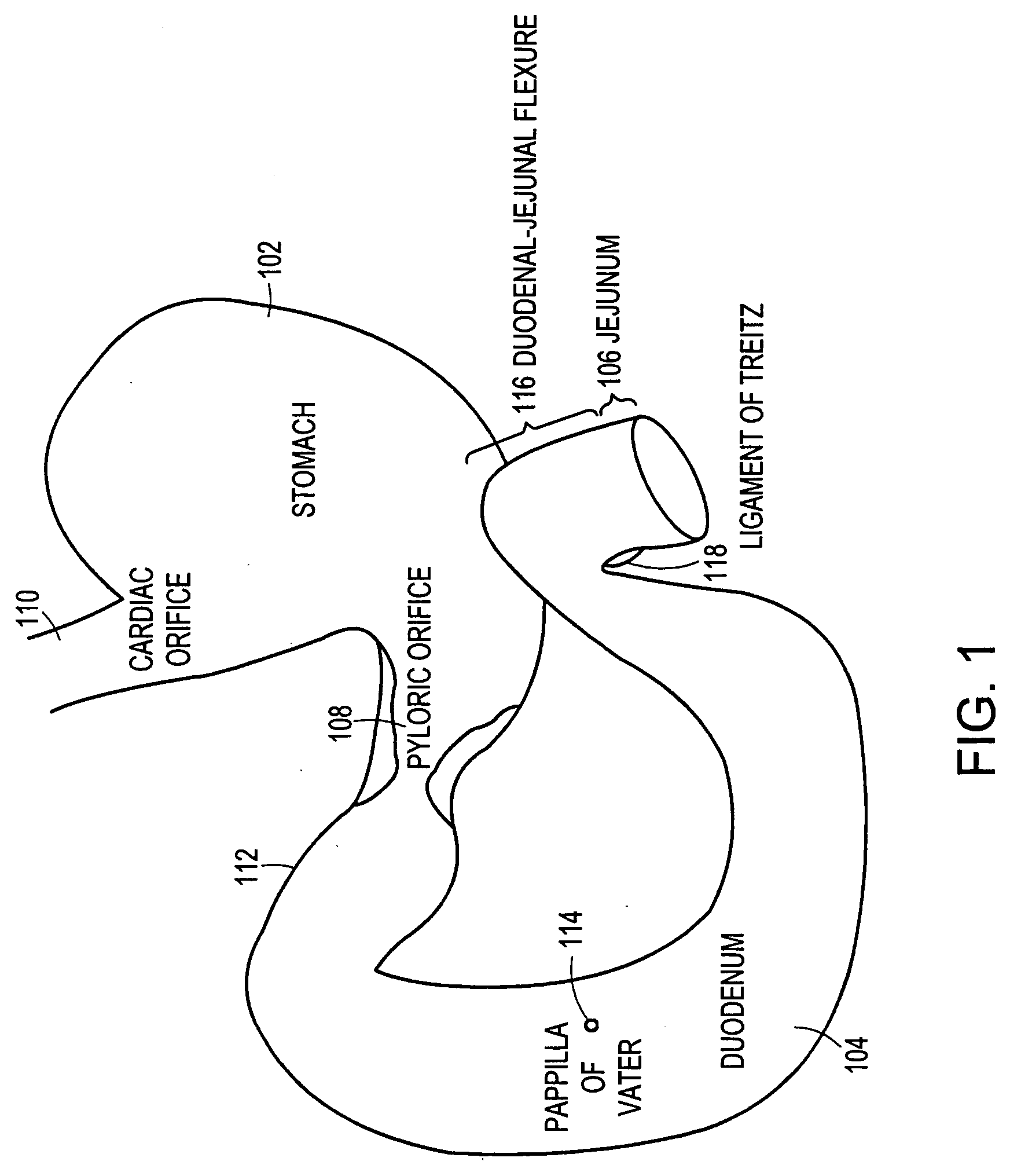
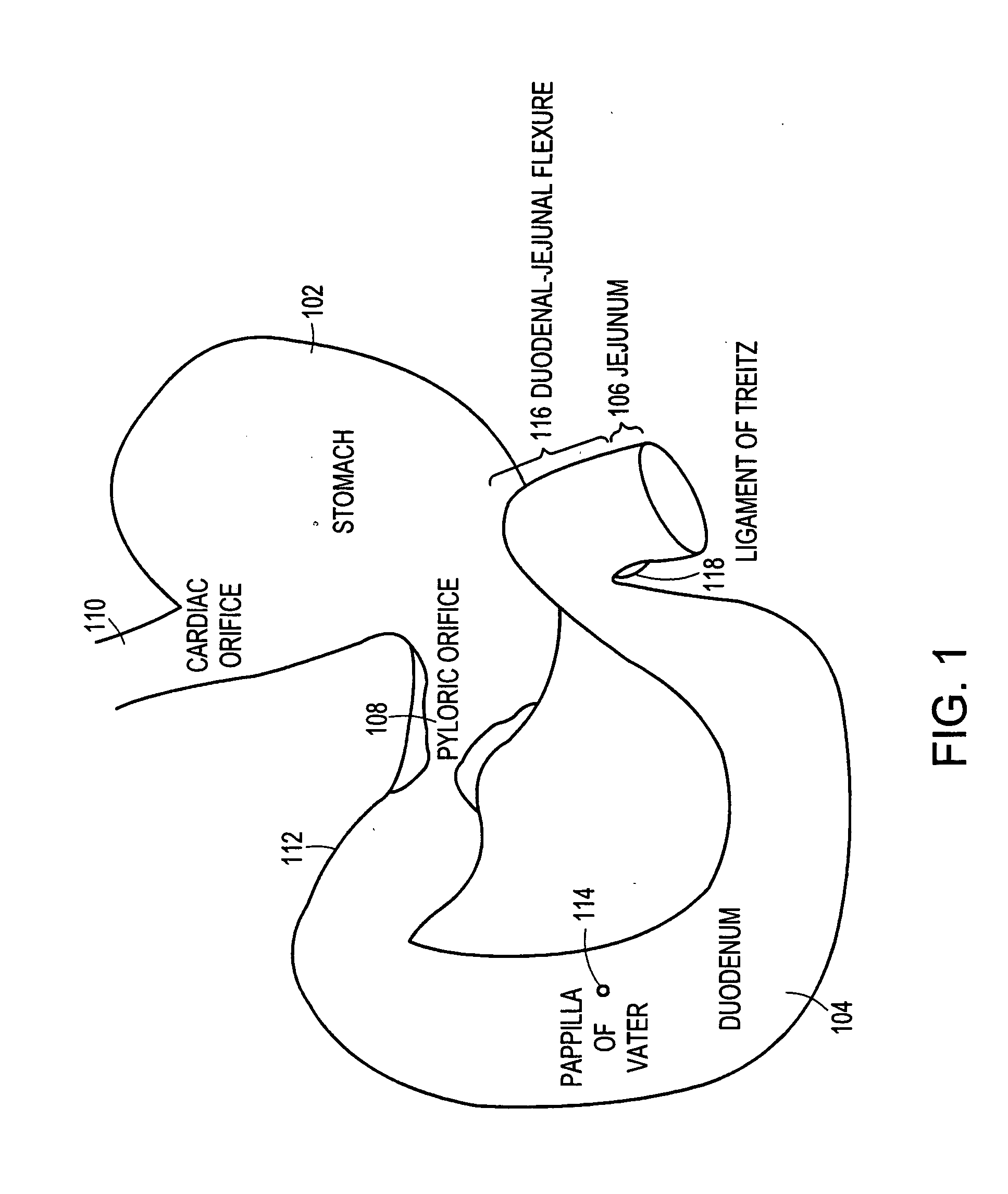
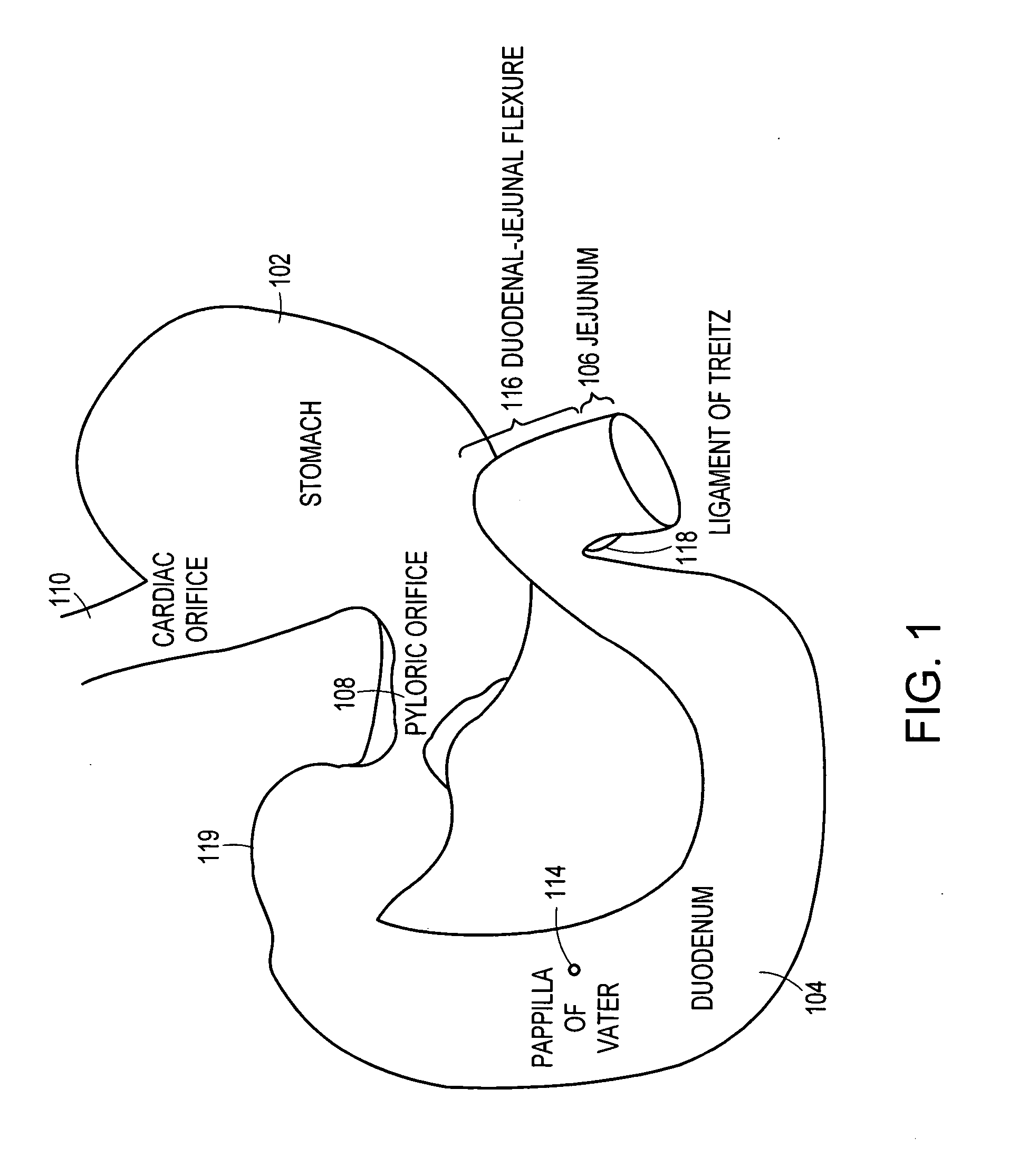
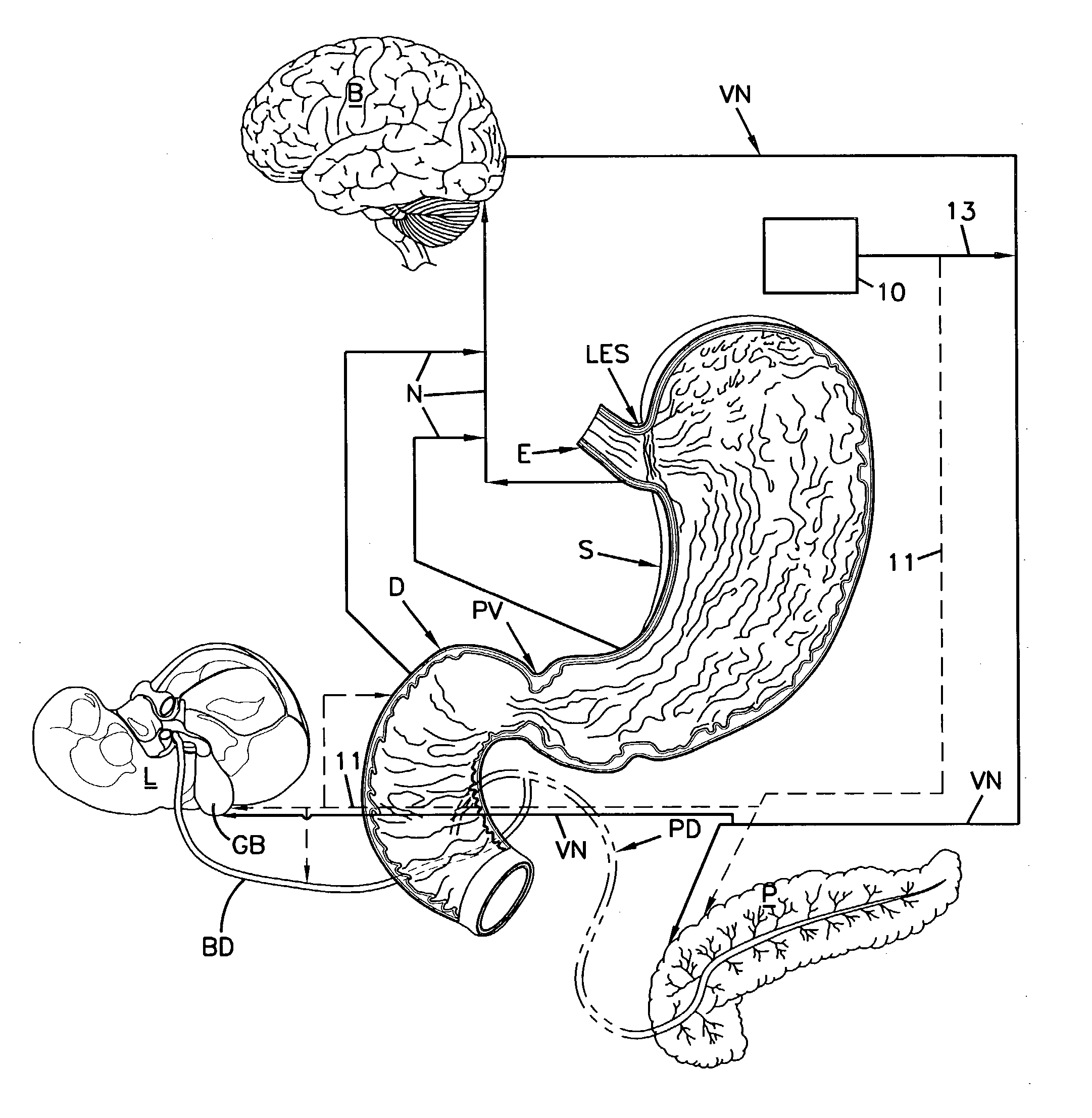
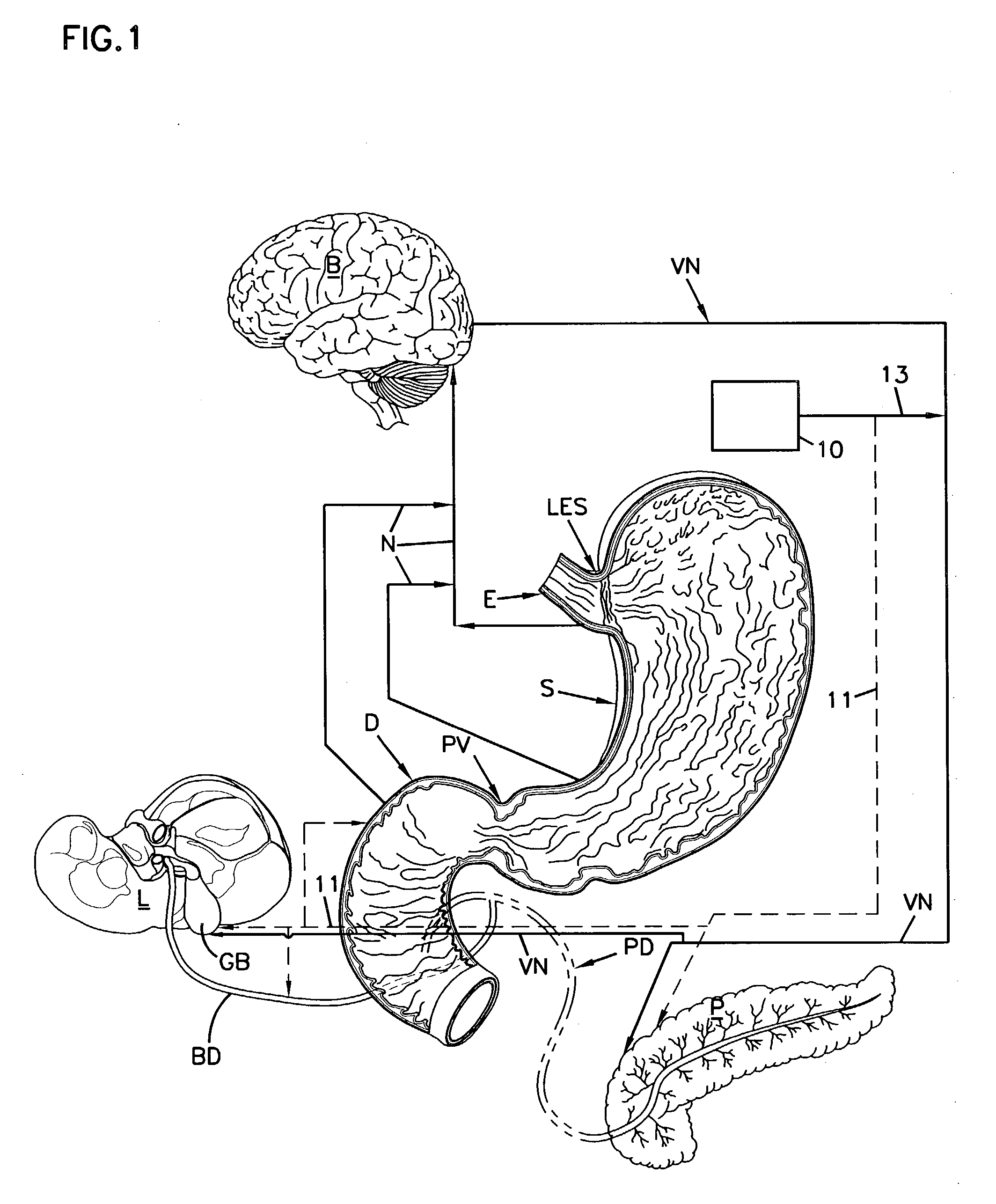
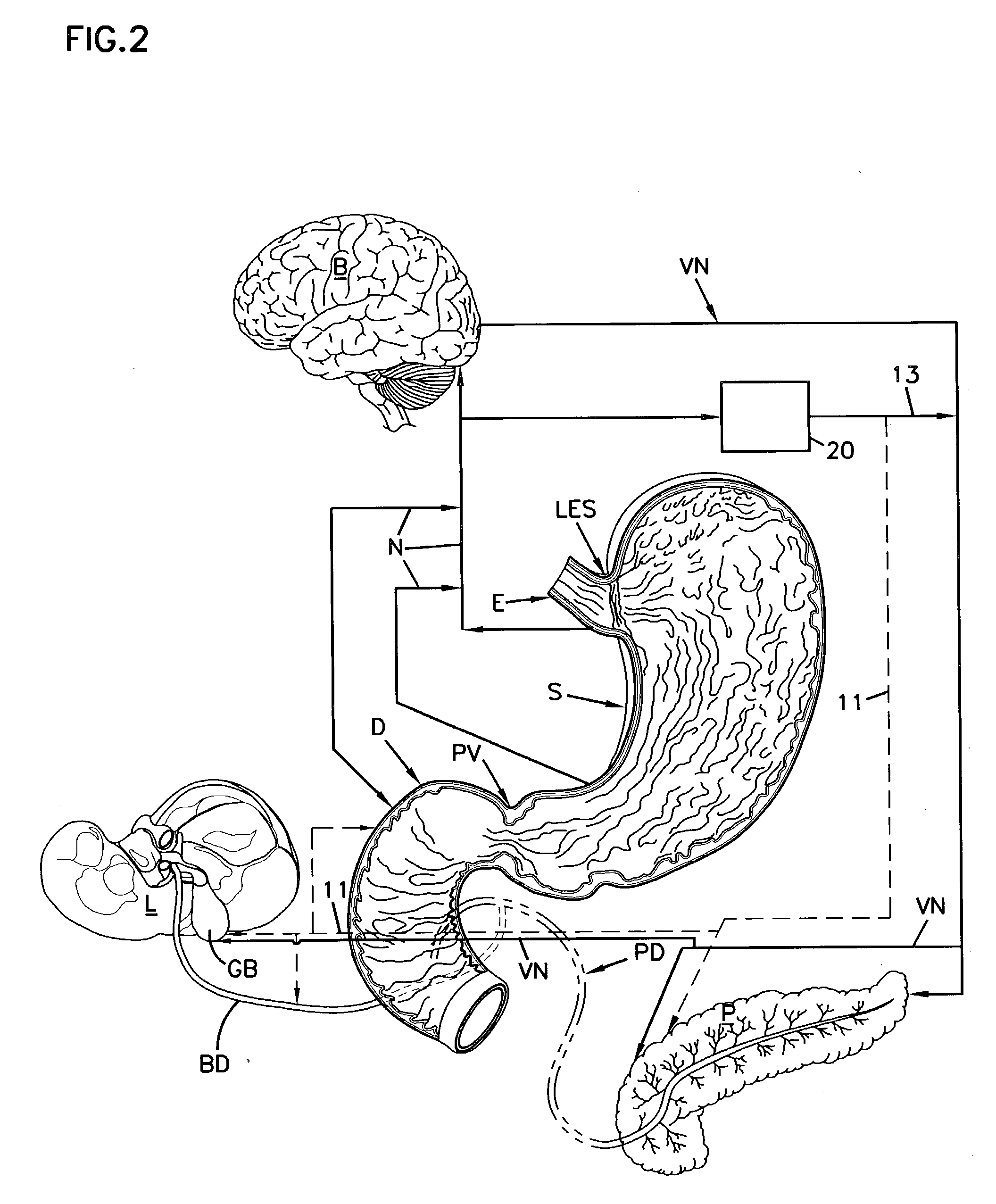
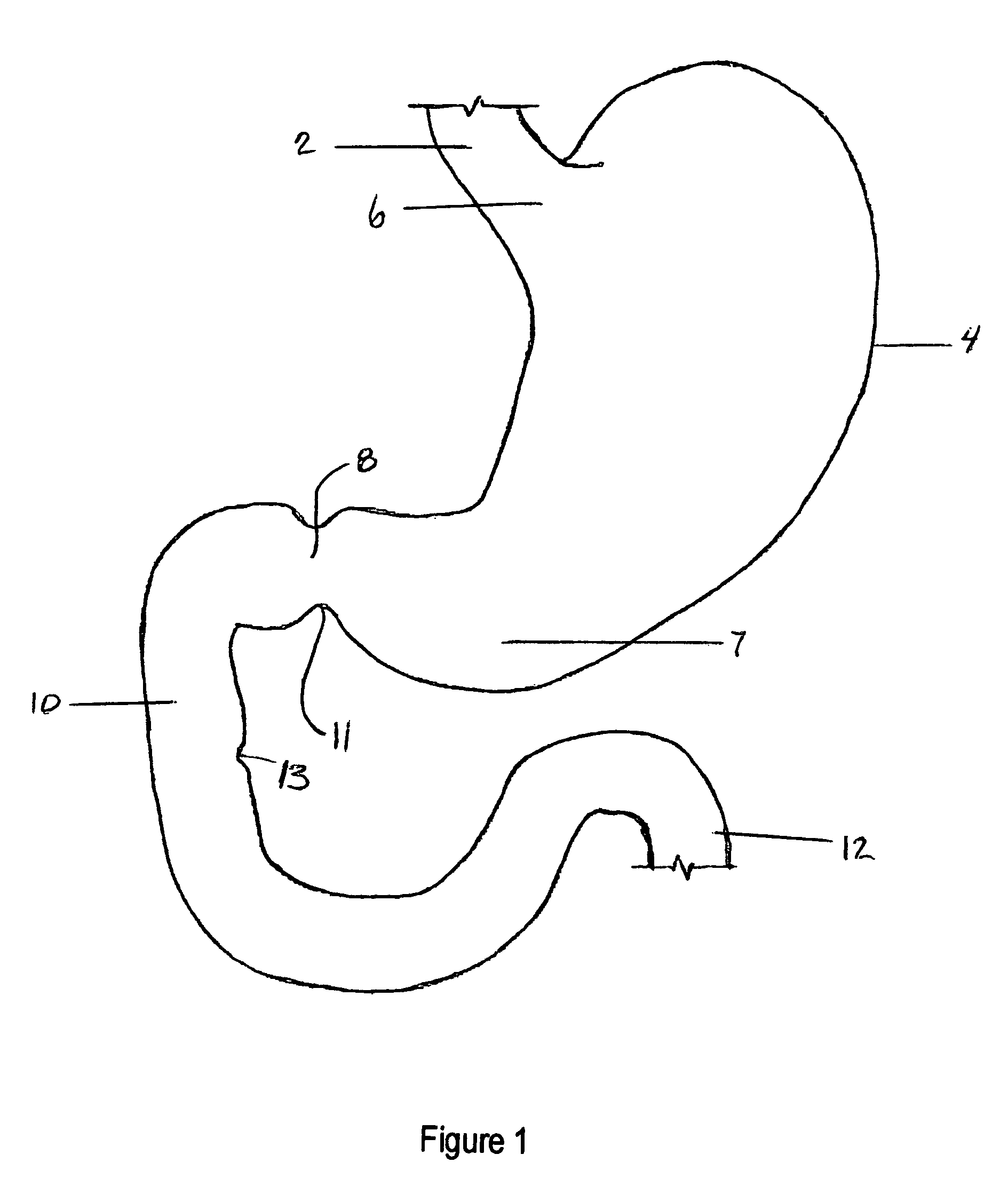
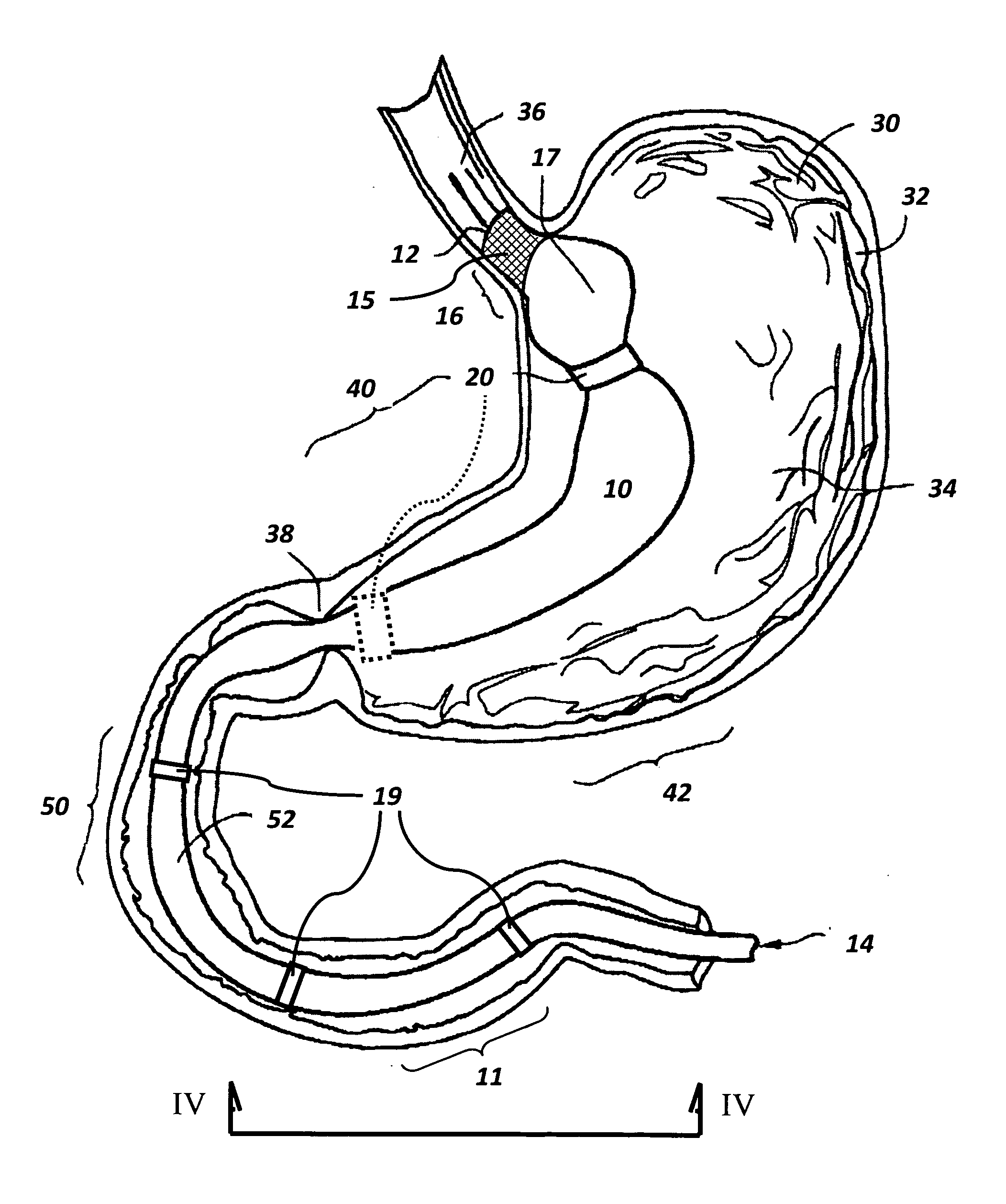
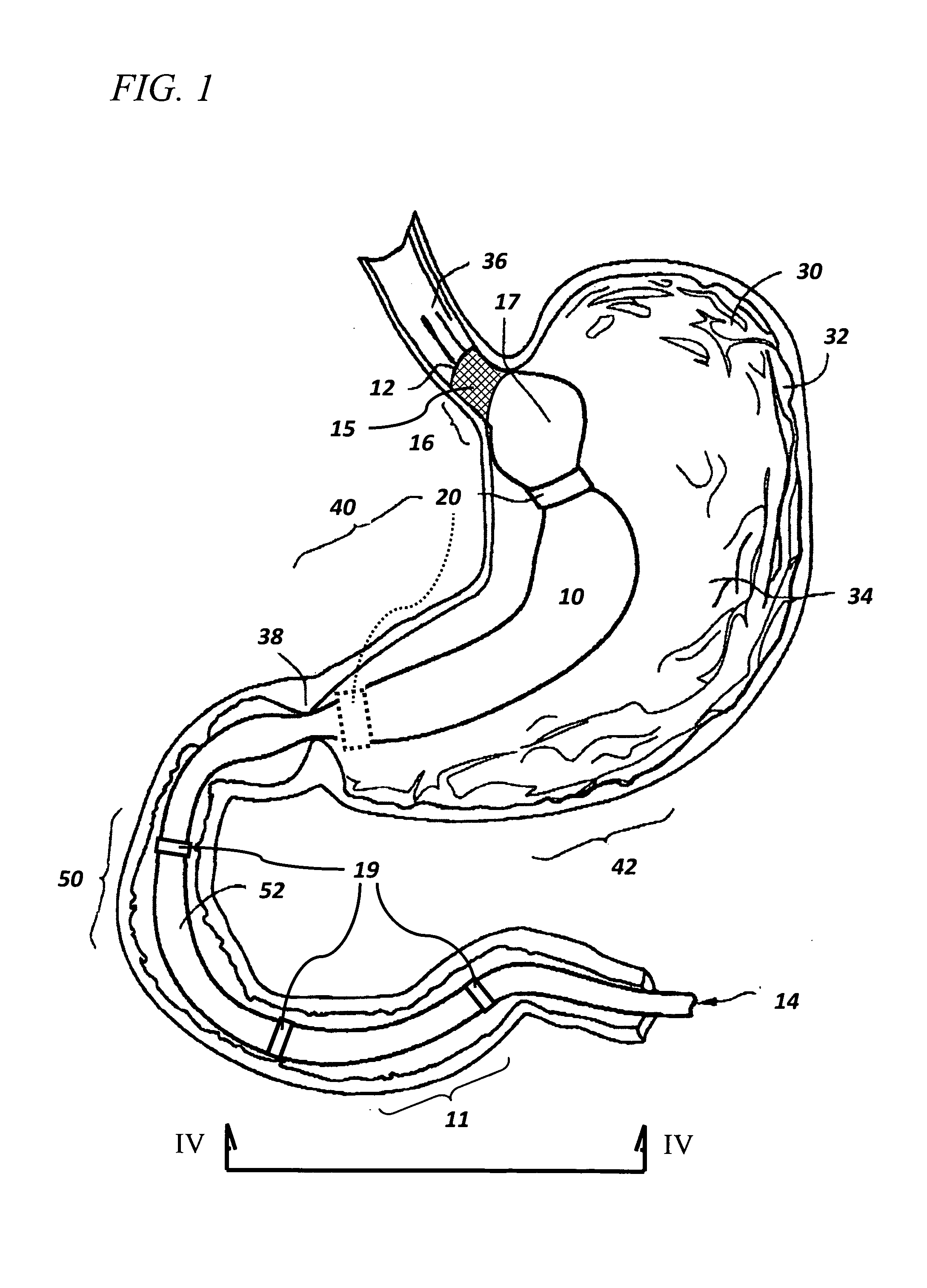
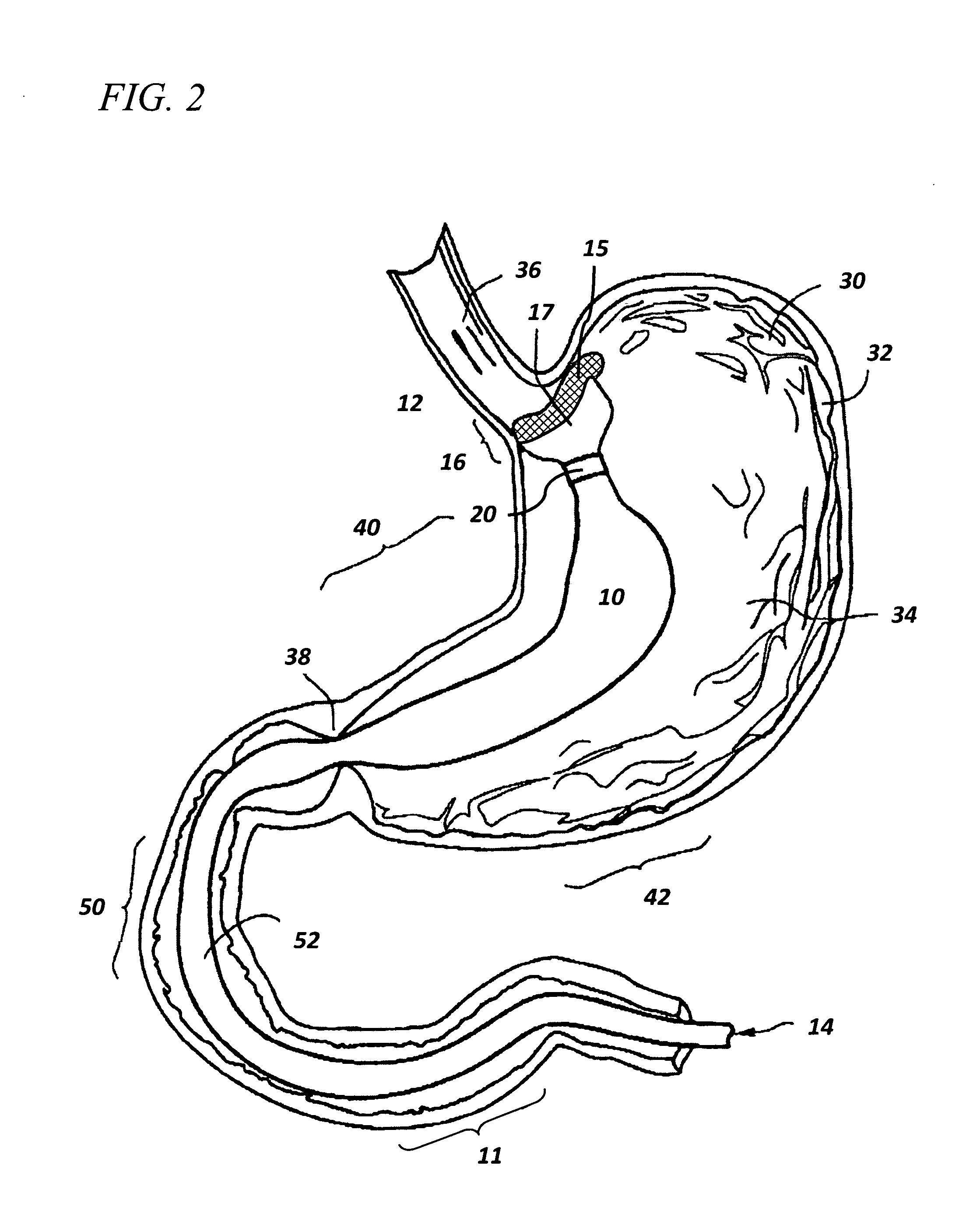
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine may be used instead of duodenum. In mammals the duodenum may be the principal site for iron absorption.
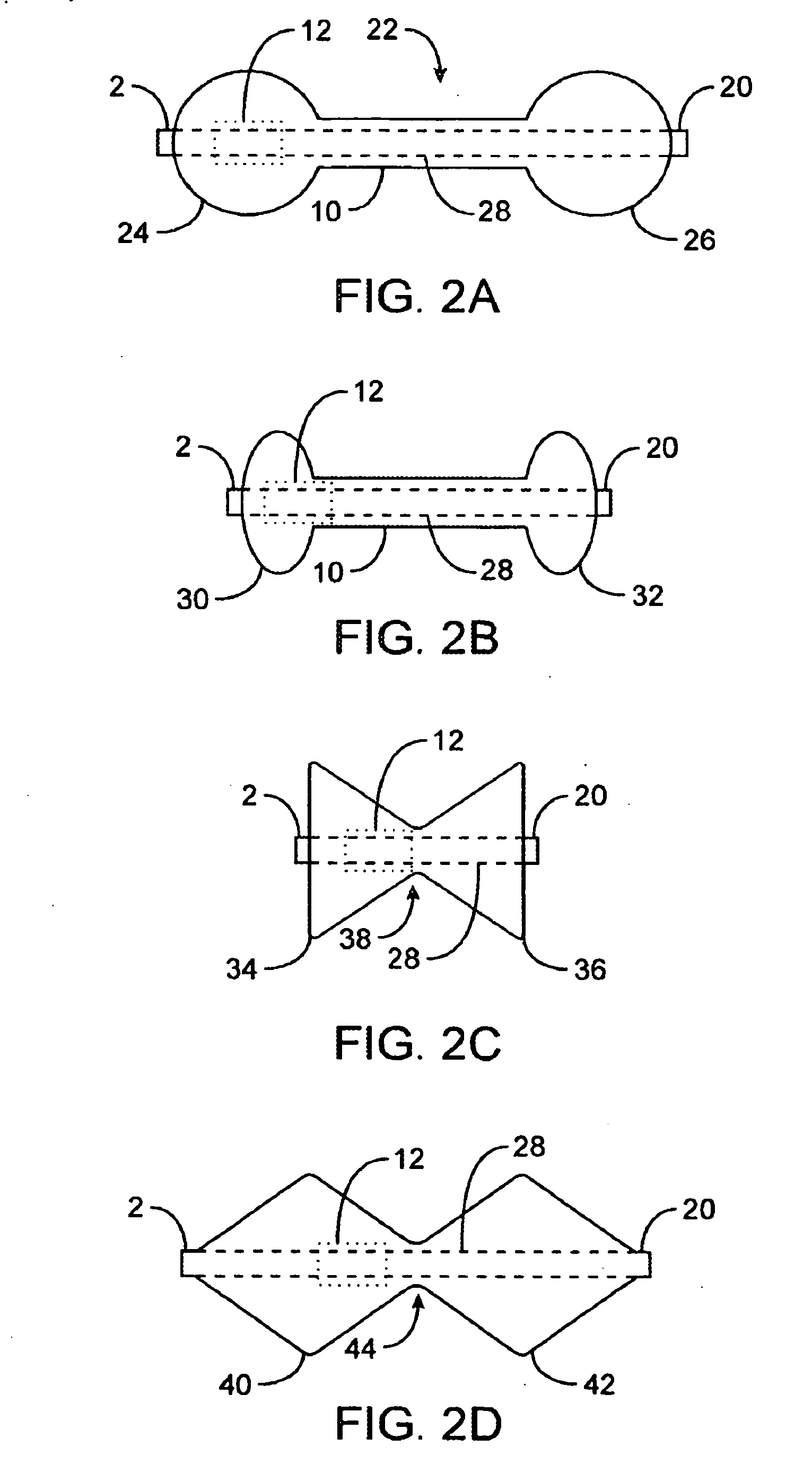
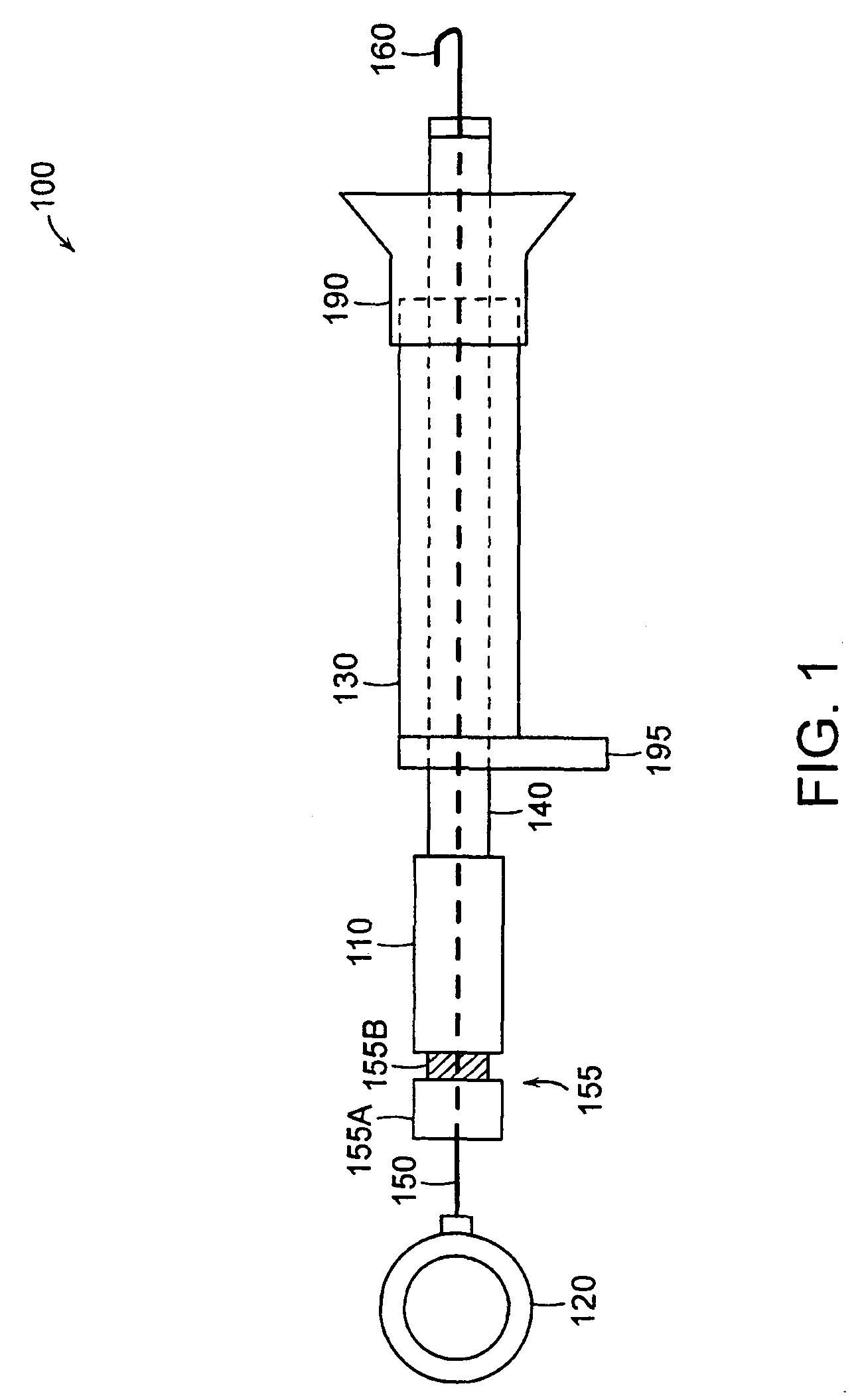
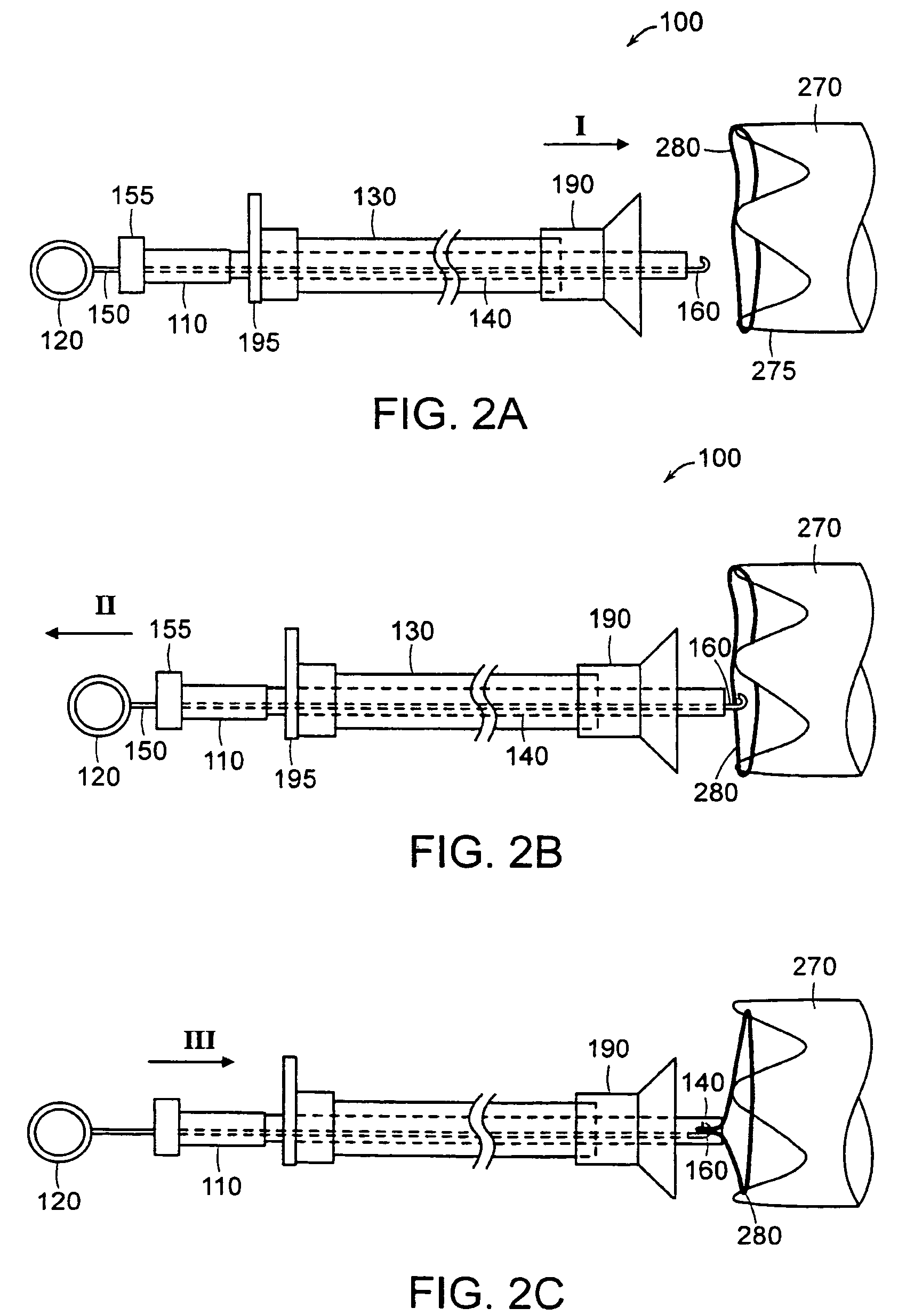
Anti-obesity devices
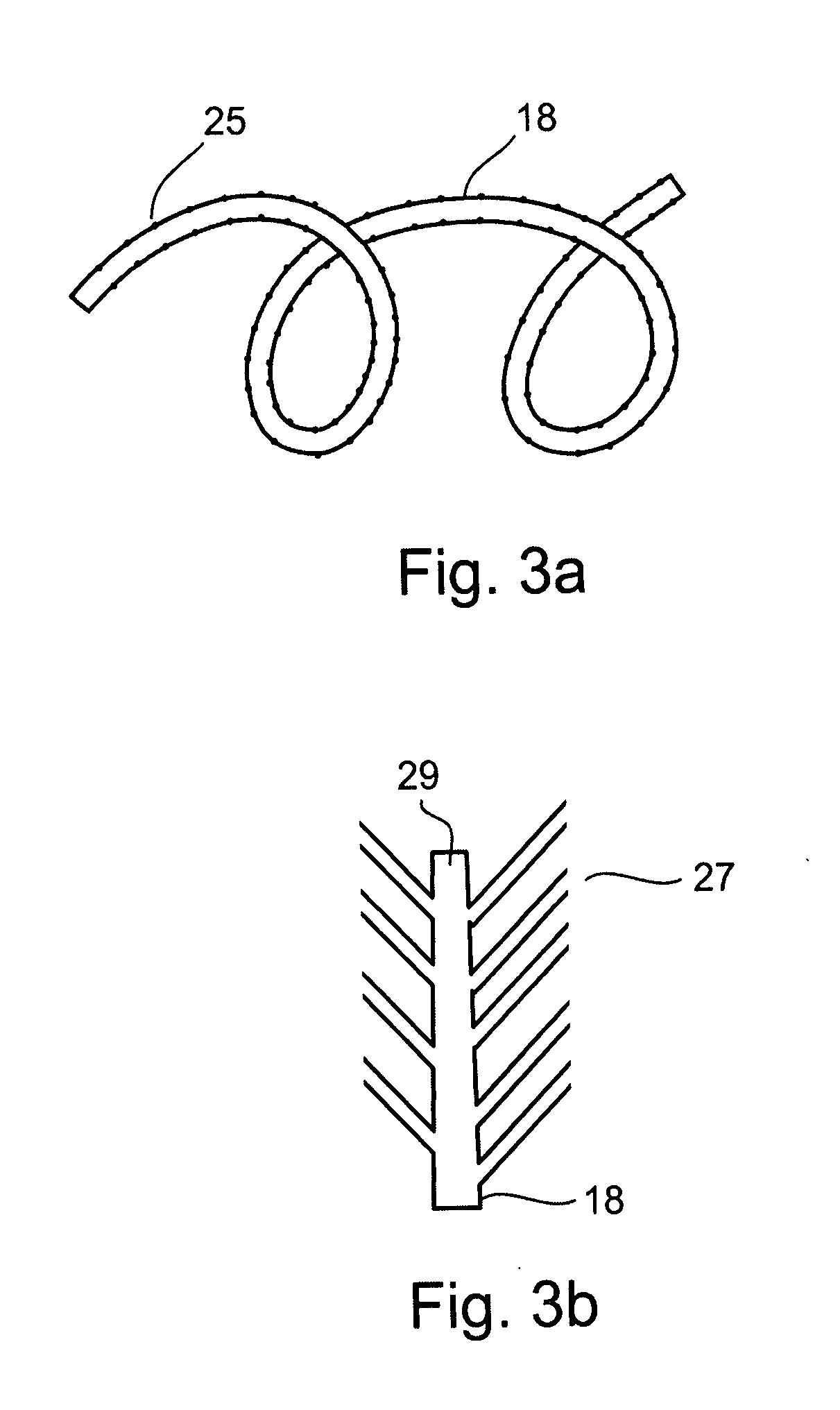
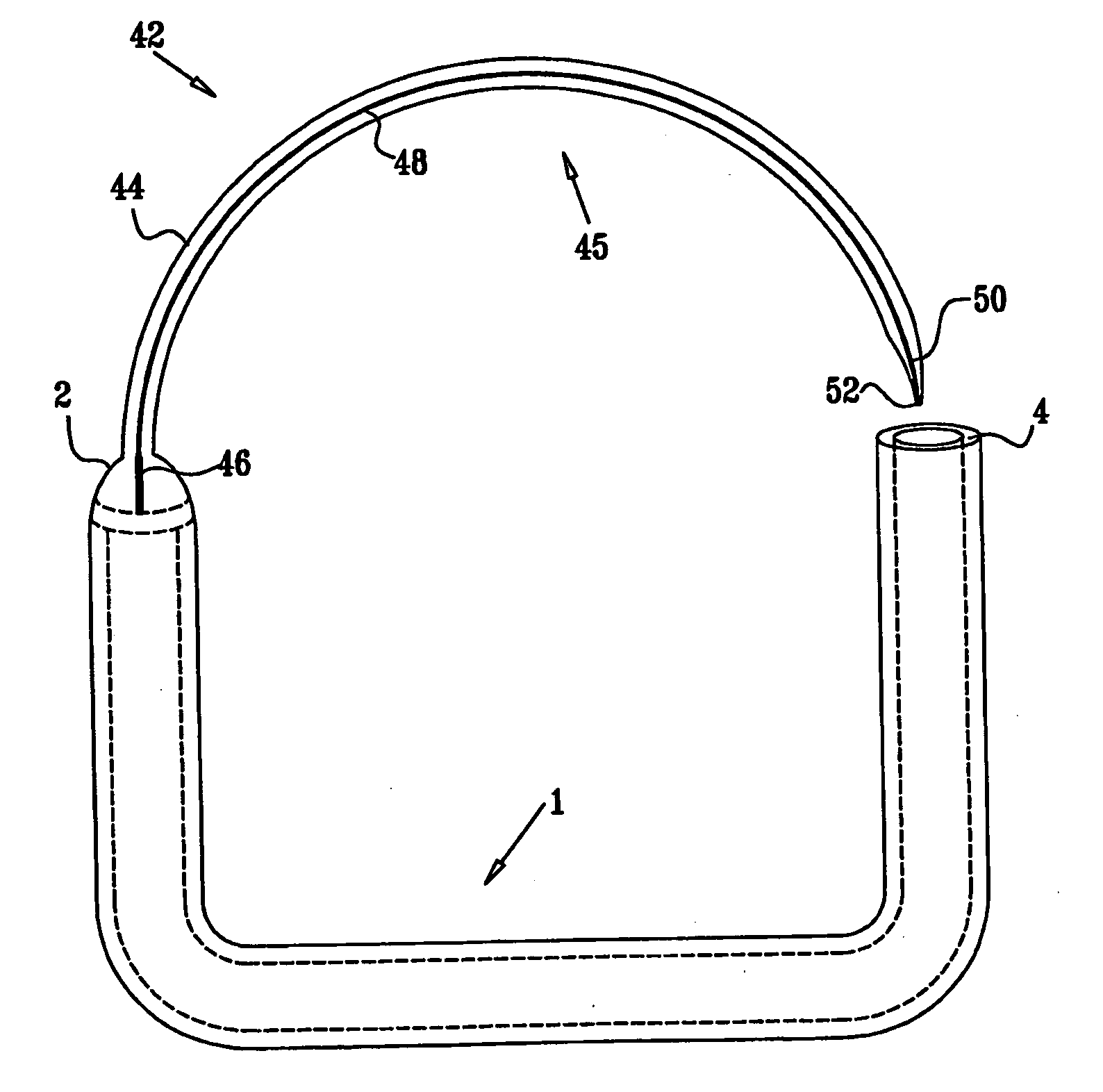
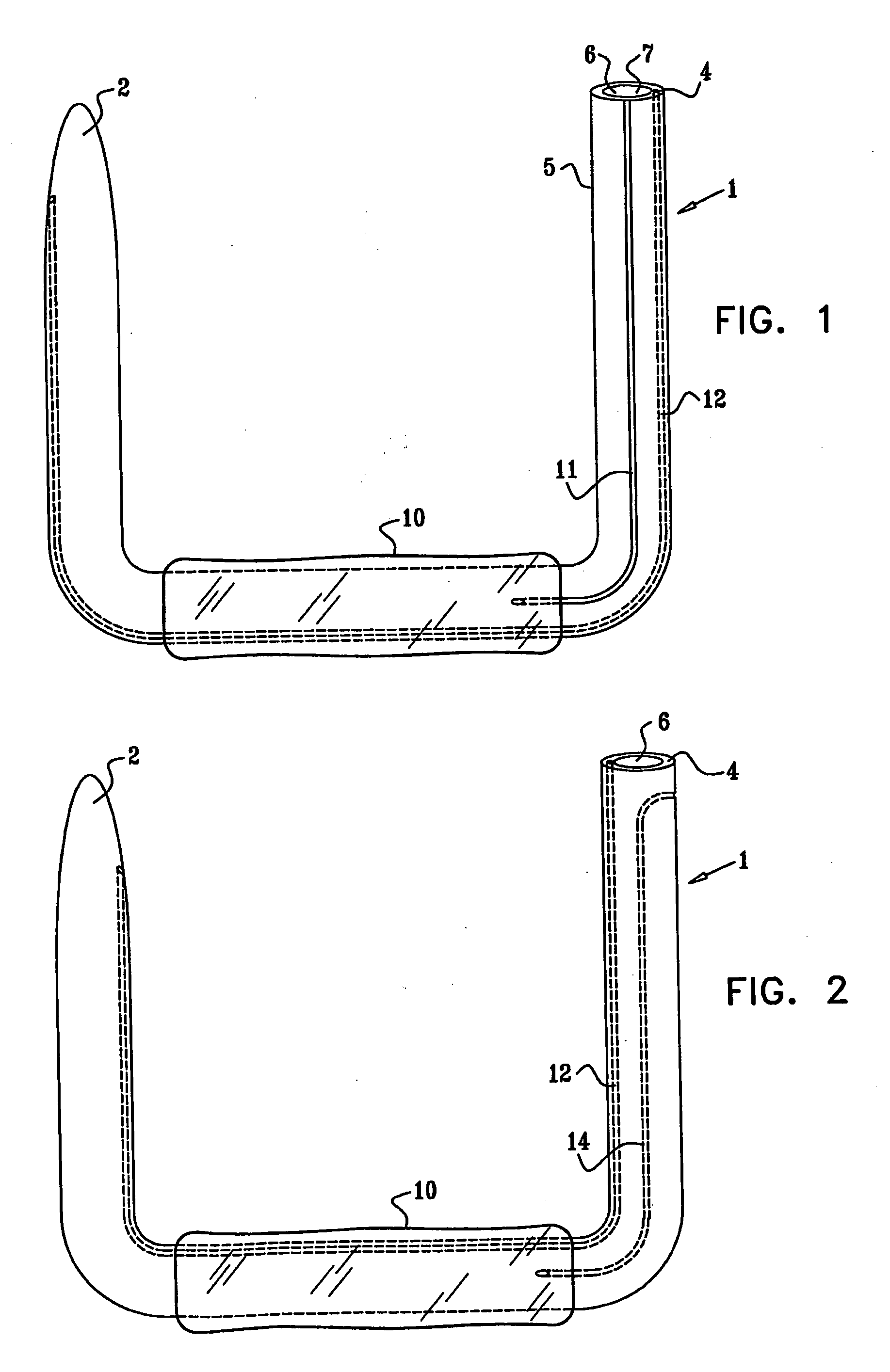
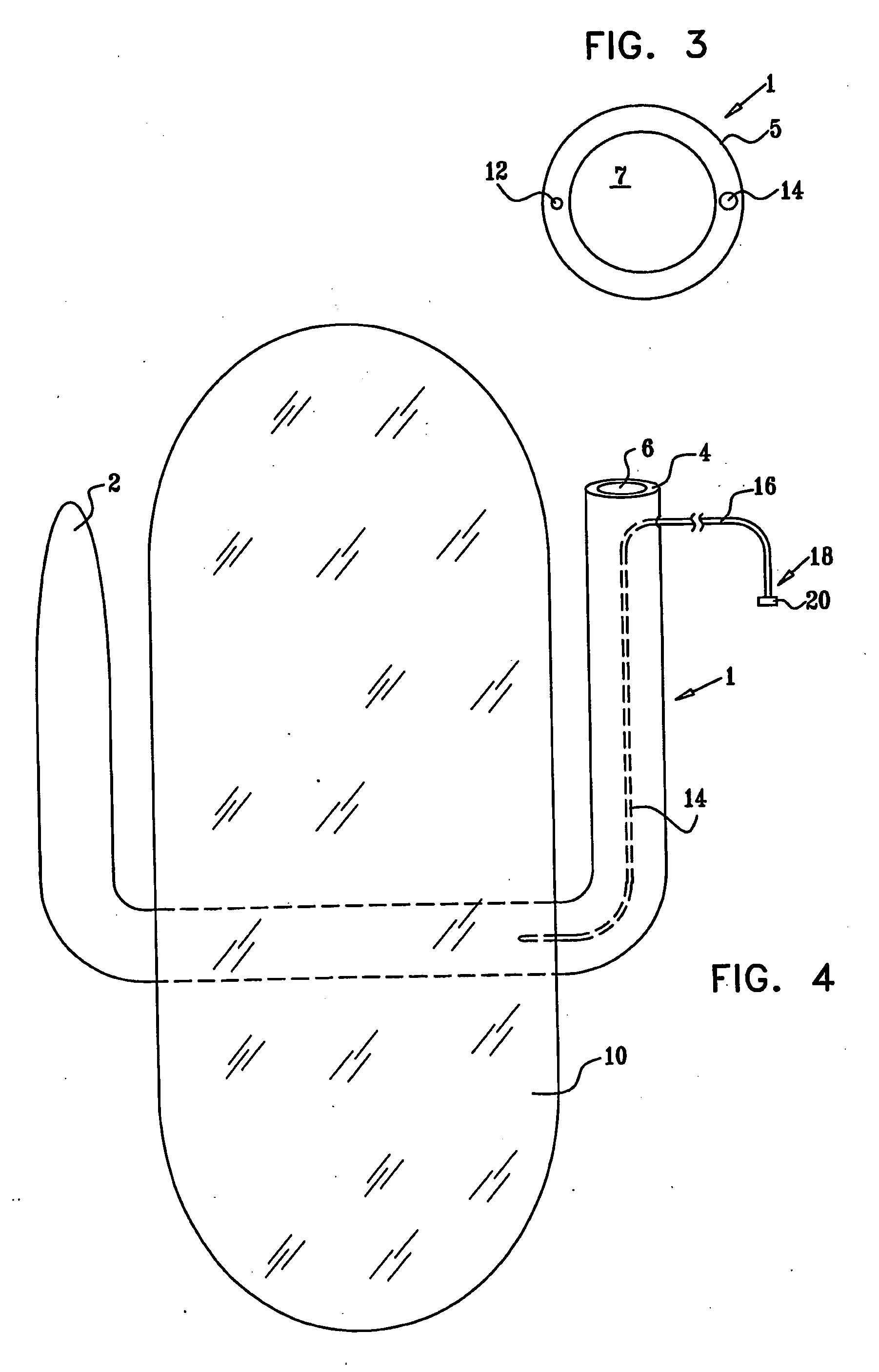
InactiveUS20050085923A1Controlled absorptionChange habitsSuture equipmentsStentsGastrointestinal deviceLigament structure
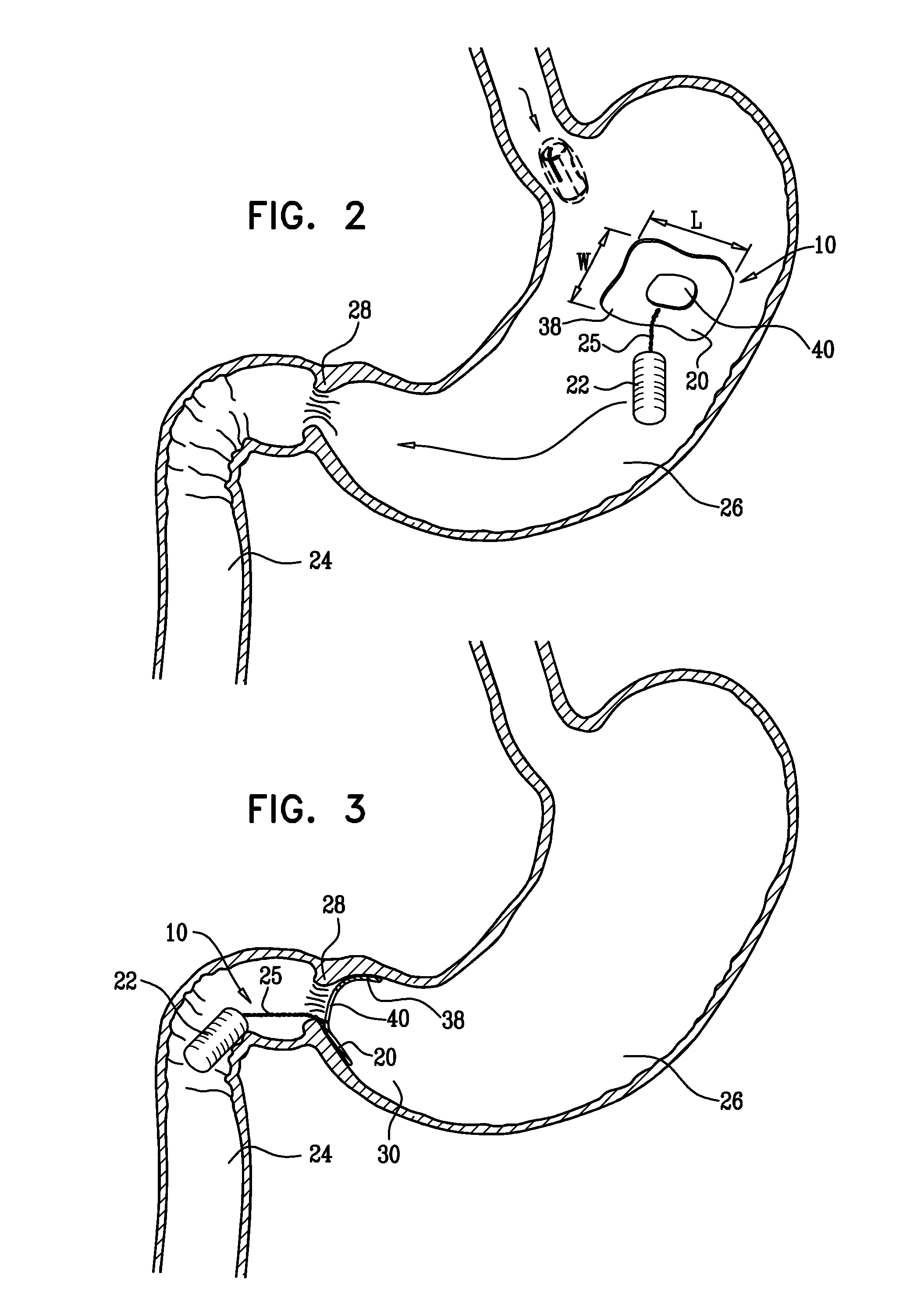
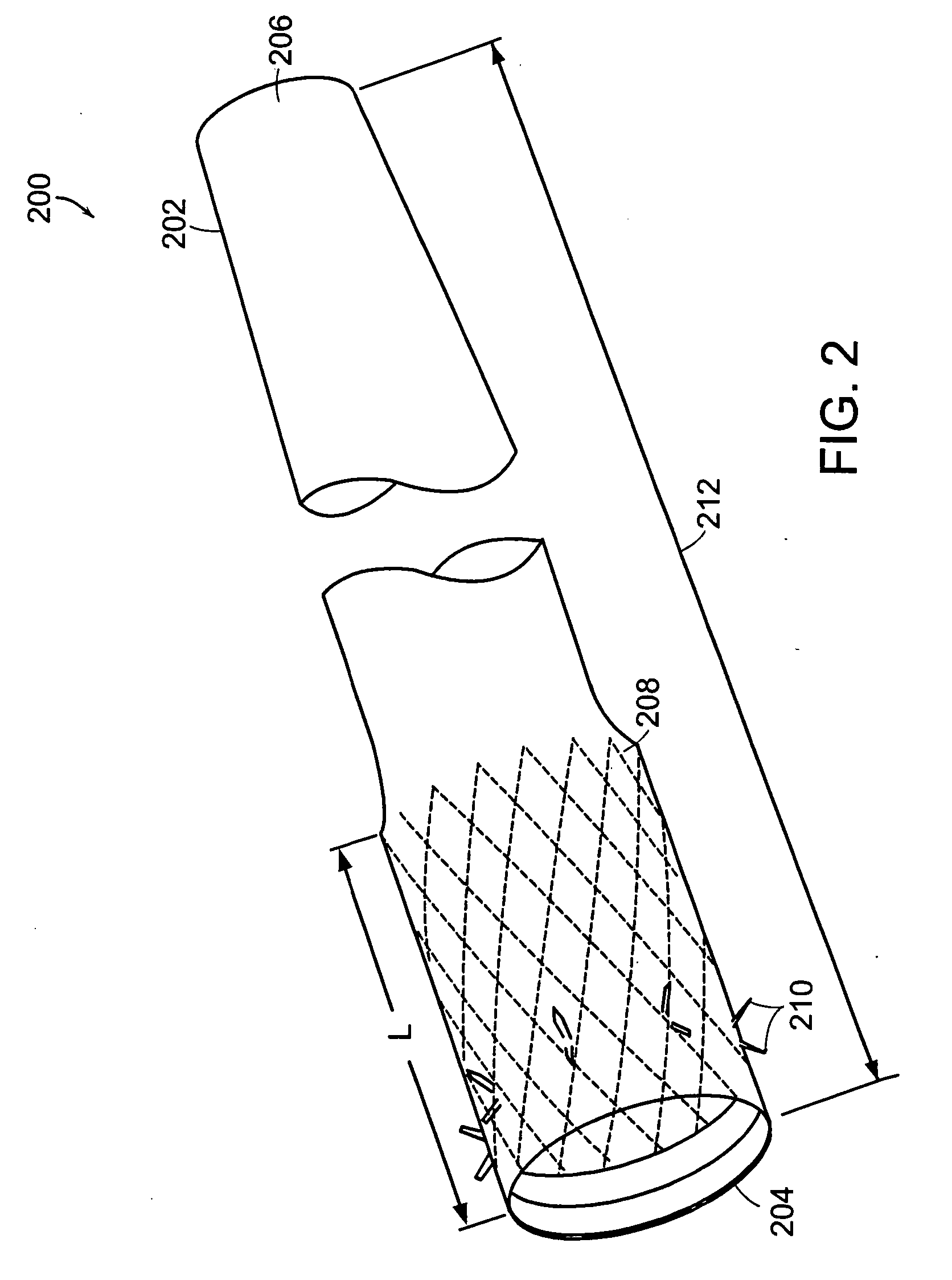
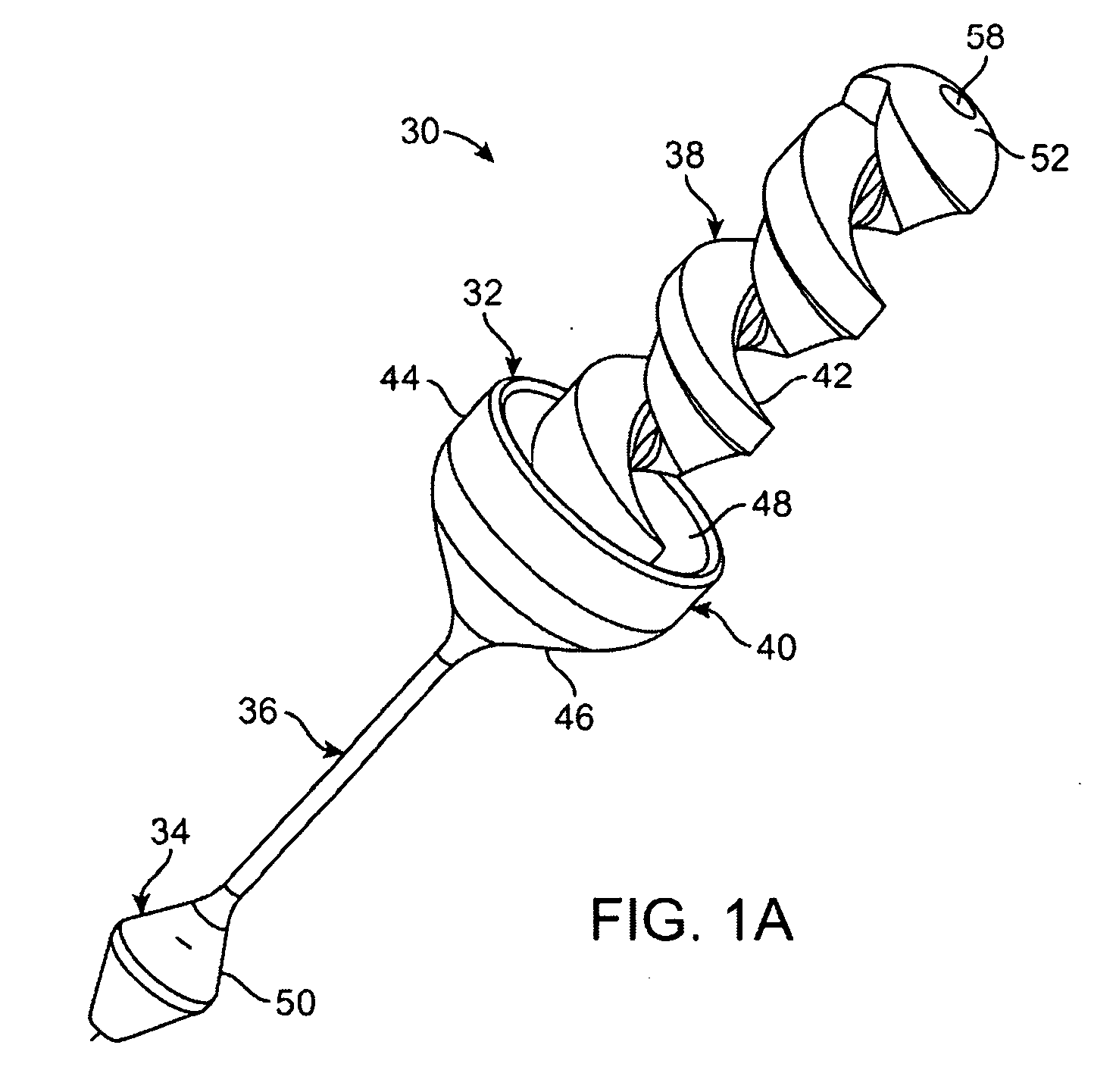
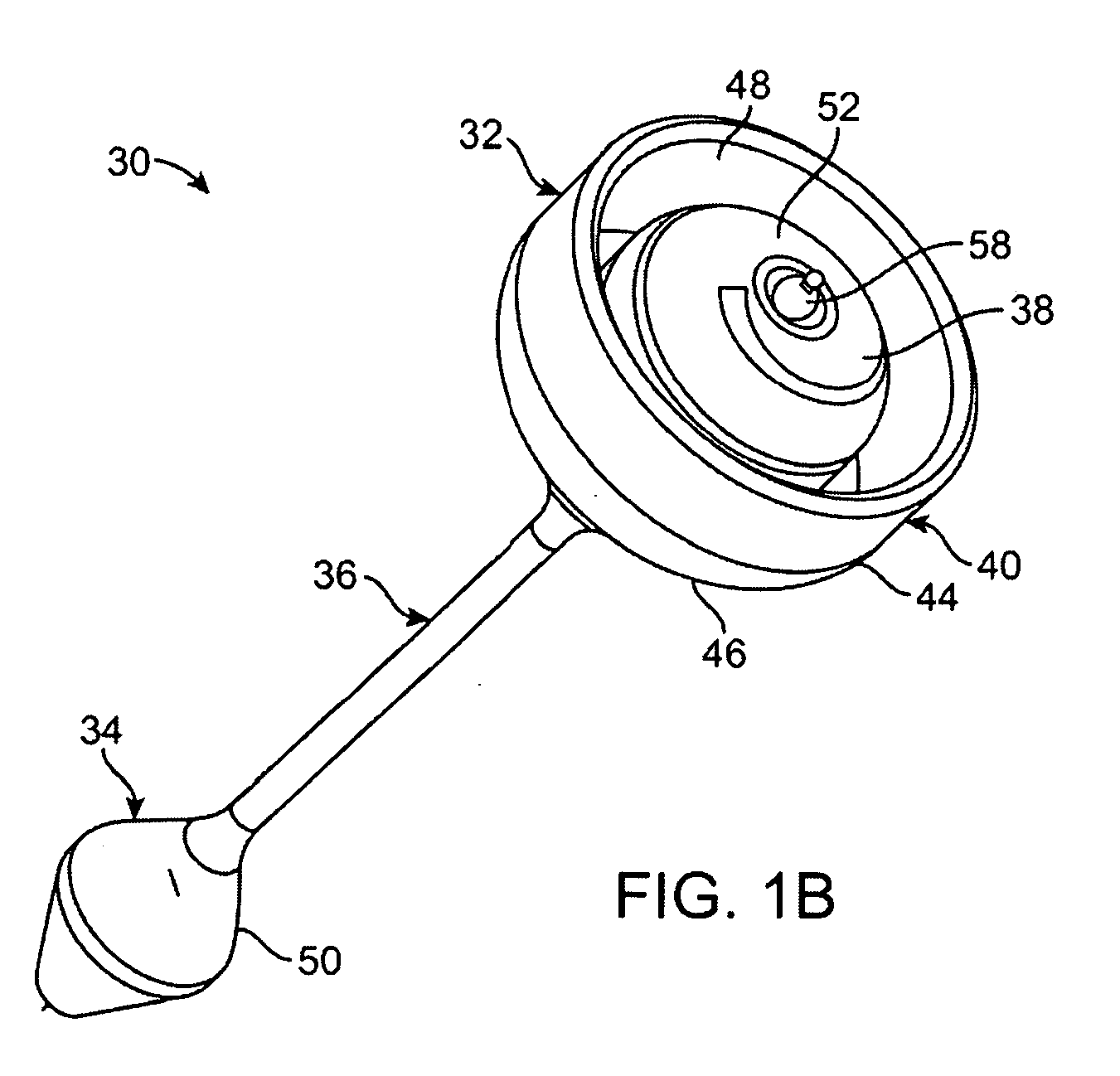
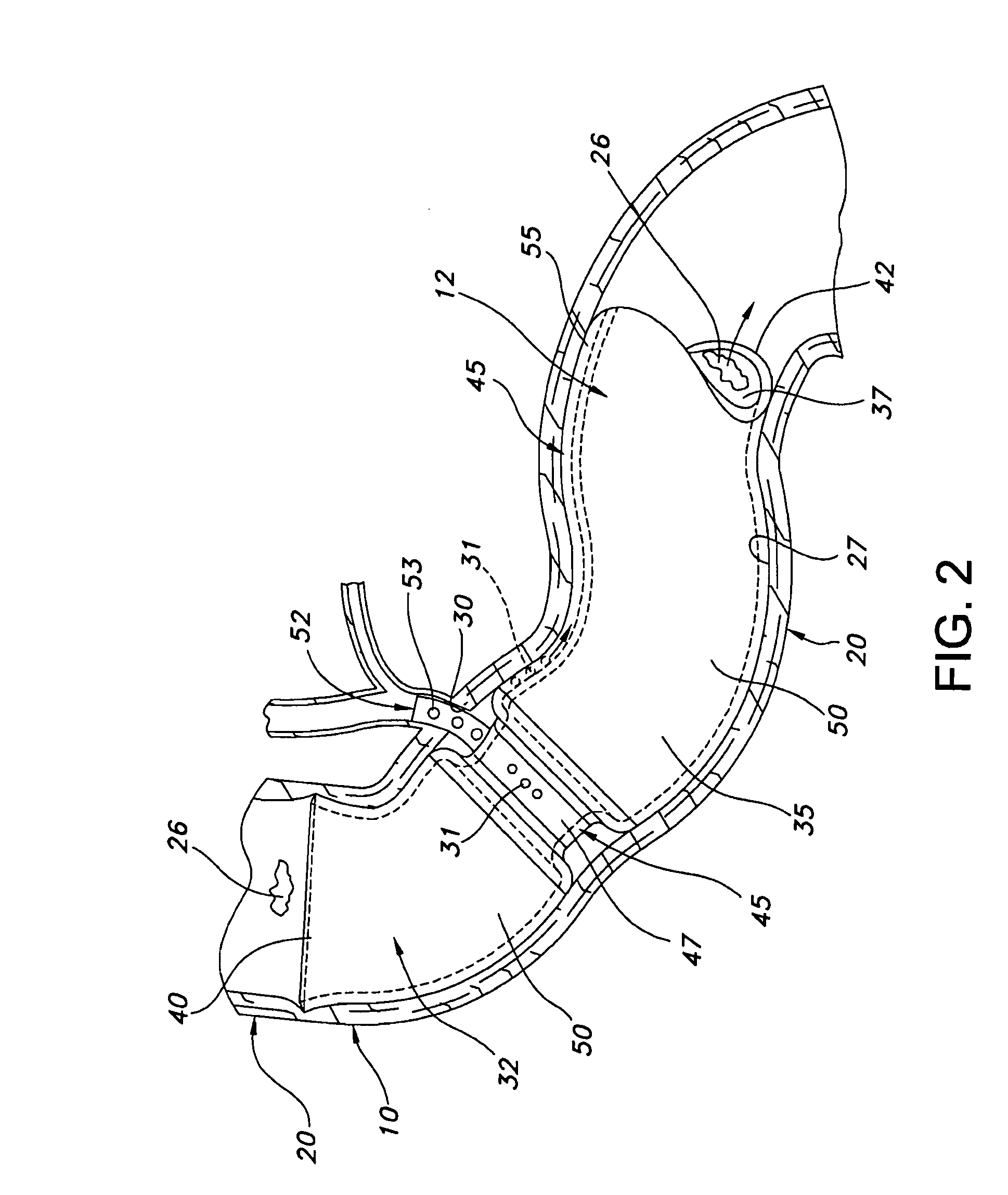
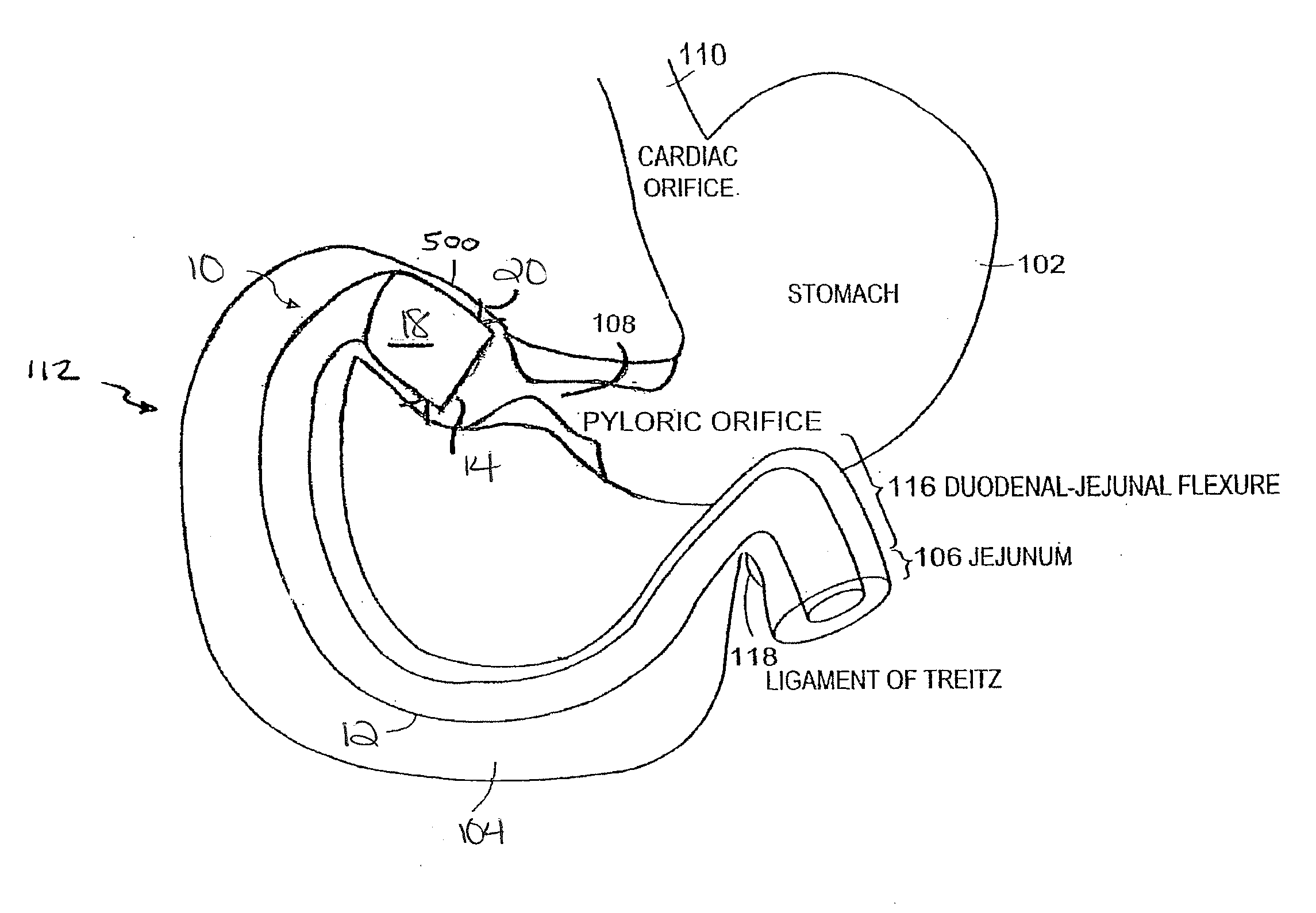
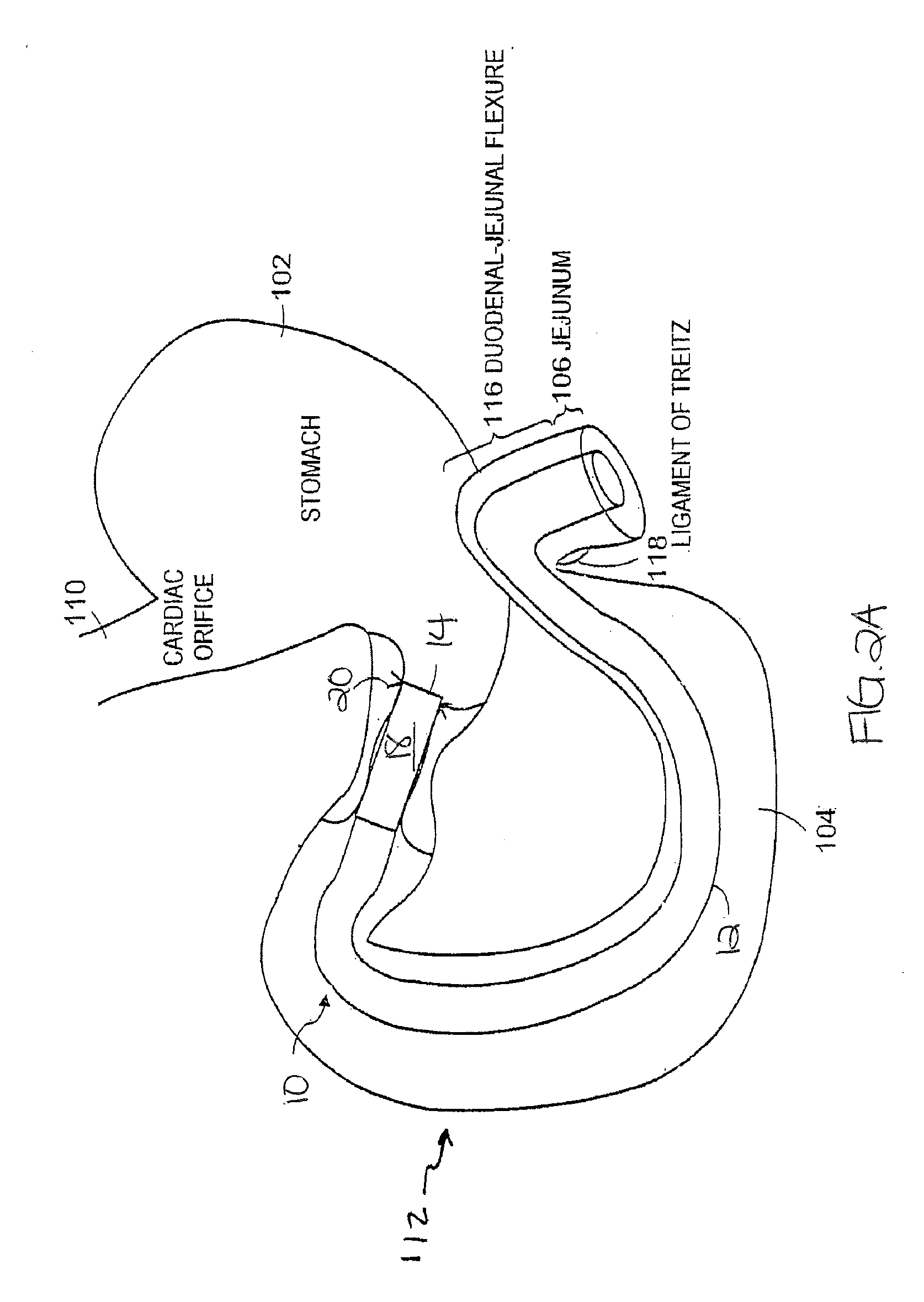
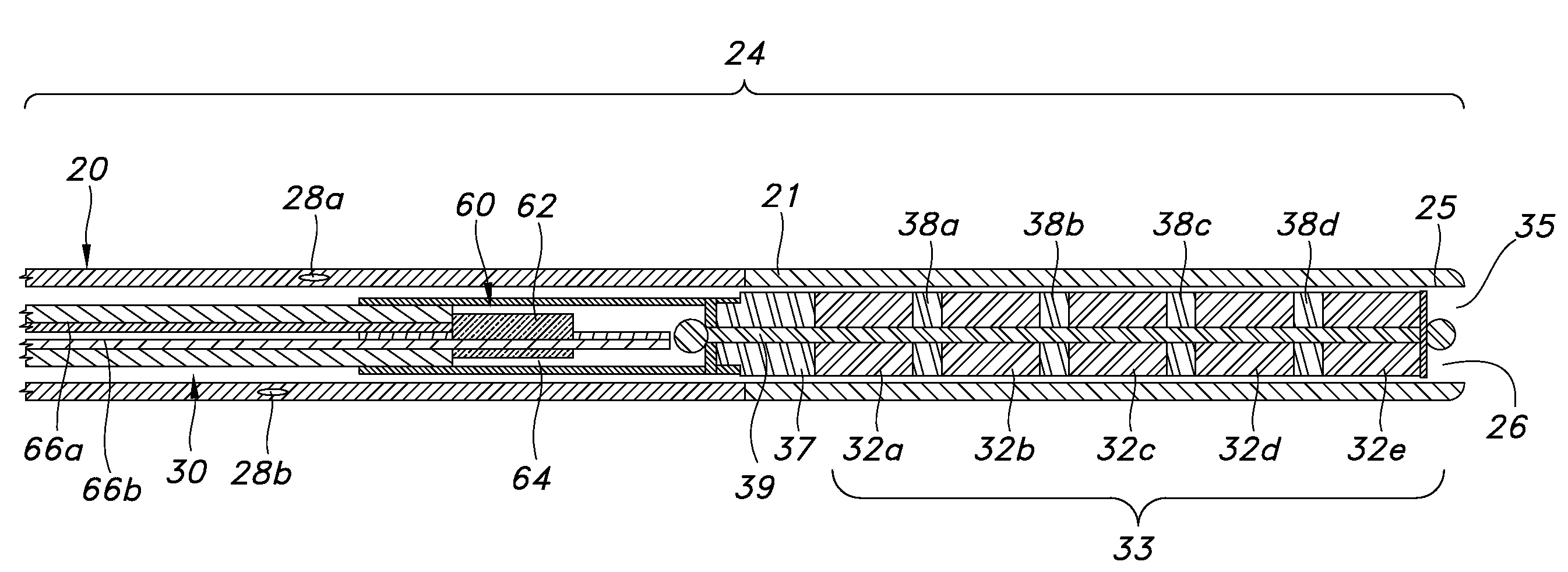
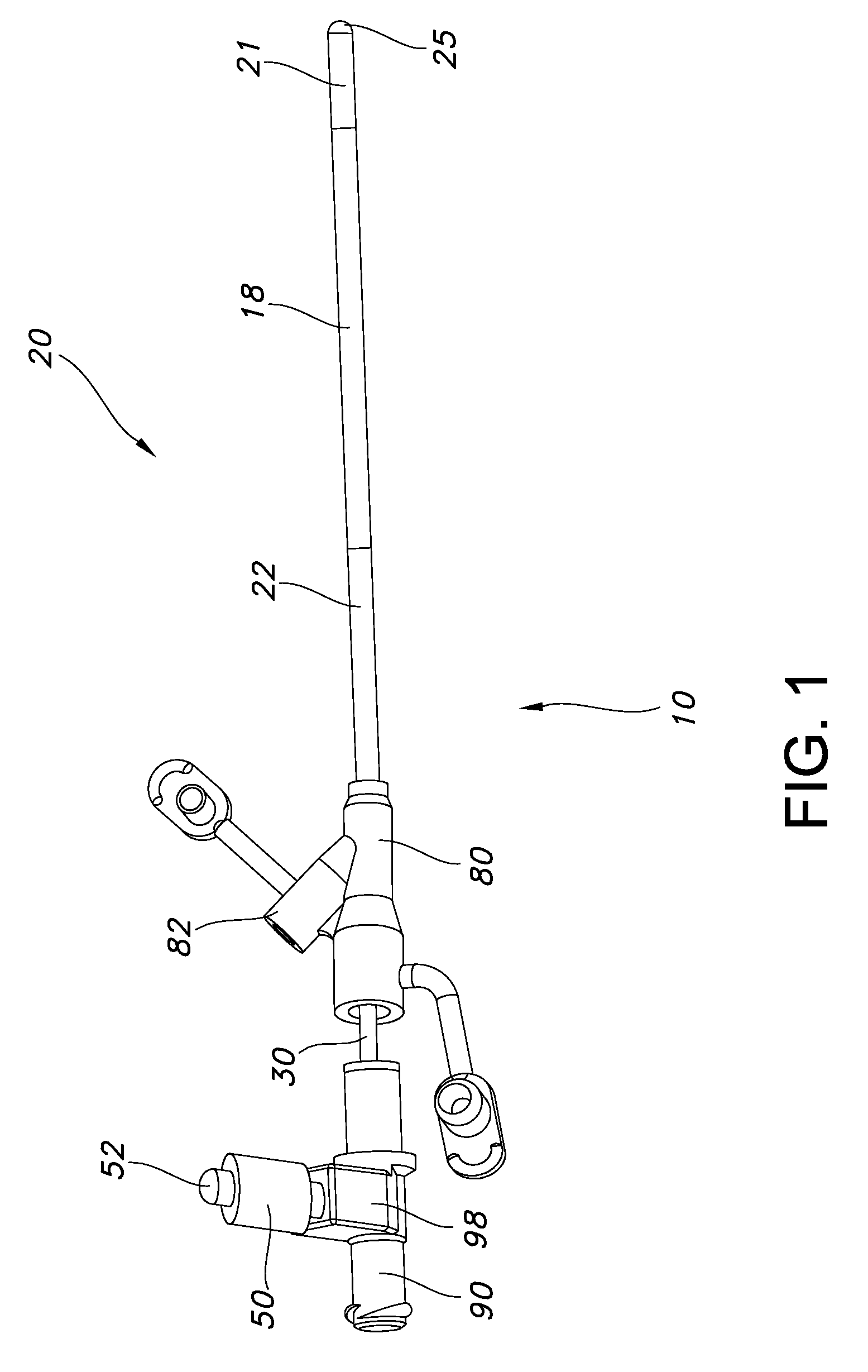
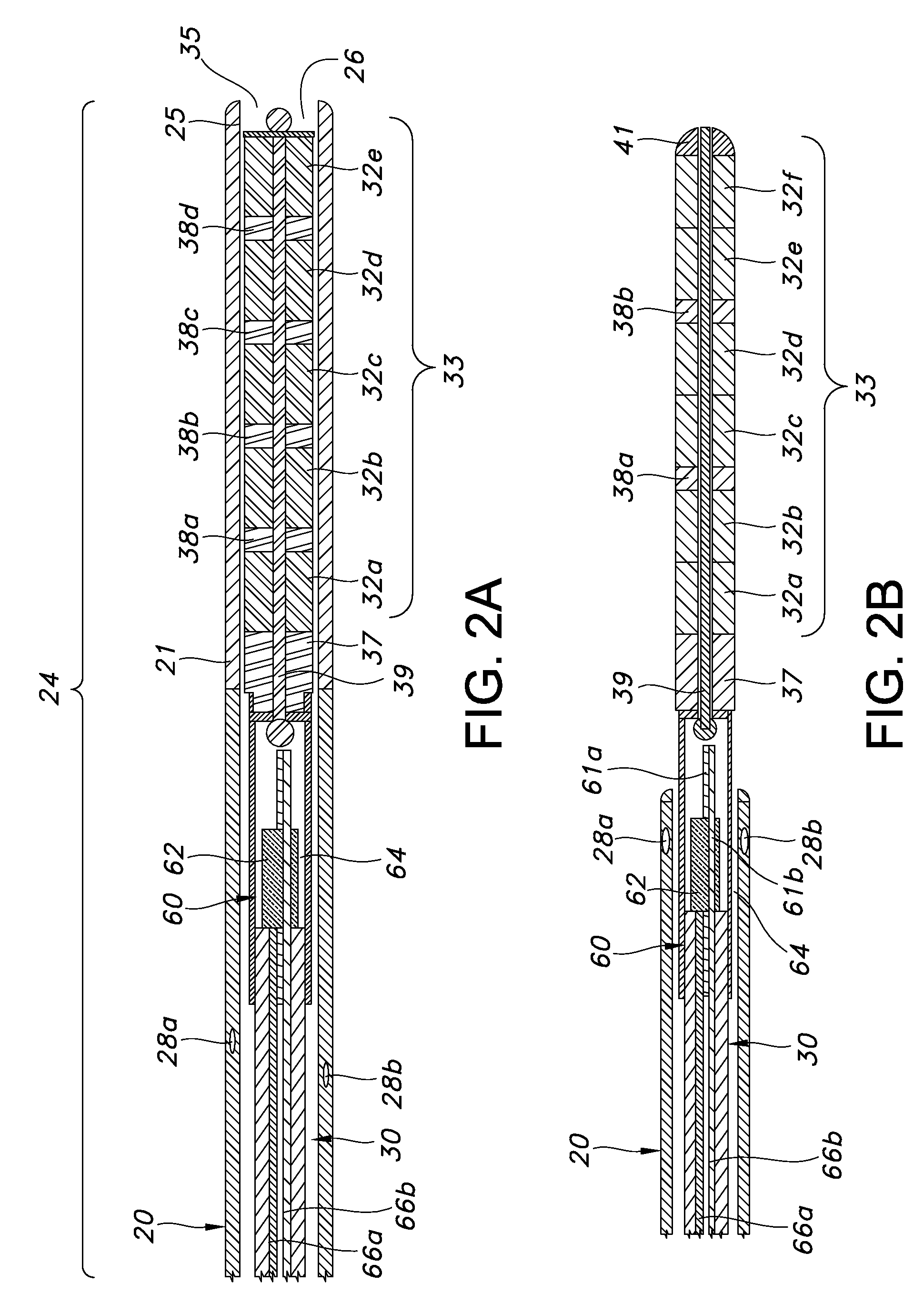
Method and apparatus for limiting absorption of food products in specific parts of the digestive system is presented. A gastrointestinal implant device is anchored in the stomach and extends beyond the ligament of Treitz. All food exiting the stomach is funneled through the device. The gastrointestinal device includes an anchor for anchoring the device to the stomach and a flexible sleeve to limit absorption of nutrients in the duodenum. The anchor is collapsible for endoscopic delivery and removal.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
Anti-obesity devices
InactiveUS7122058B2Limit absorptionModify their heating habitsSuture equipmentsStentsGastrointestinal deviceImplanted device
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
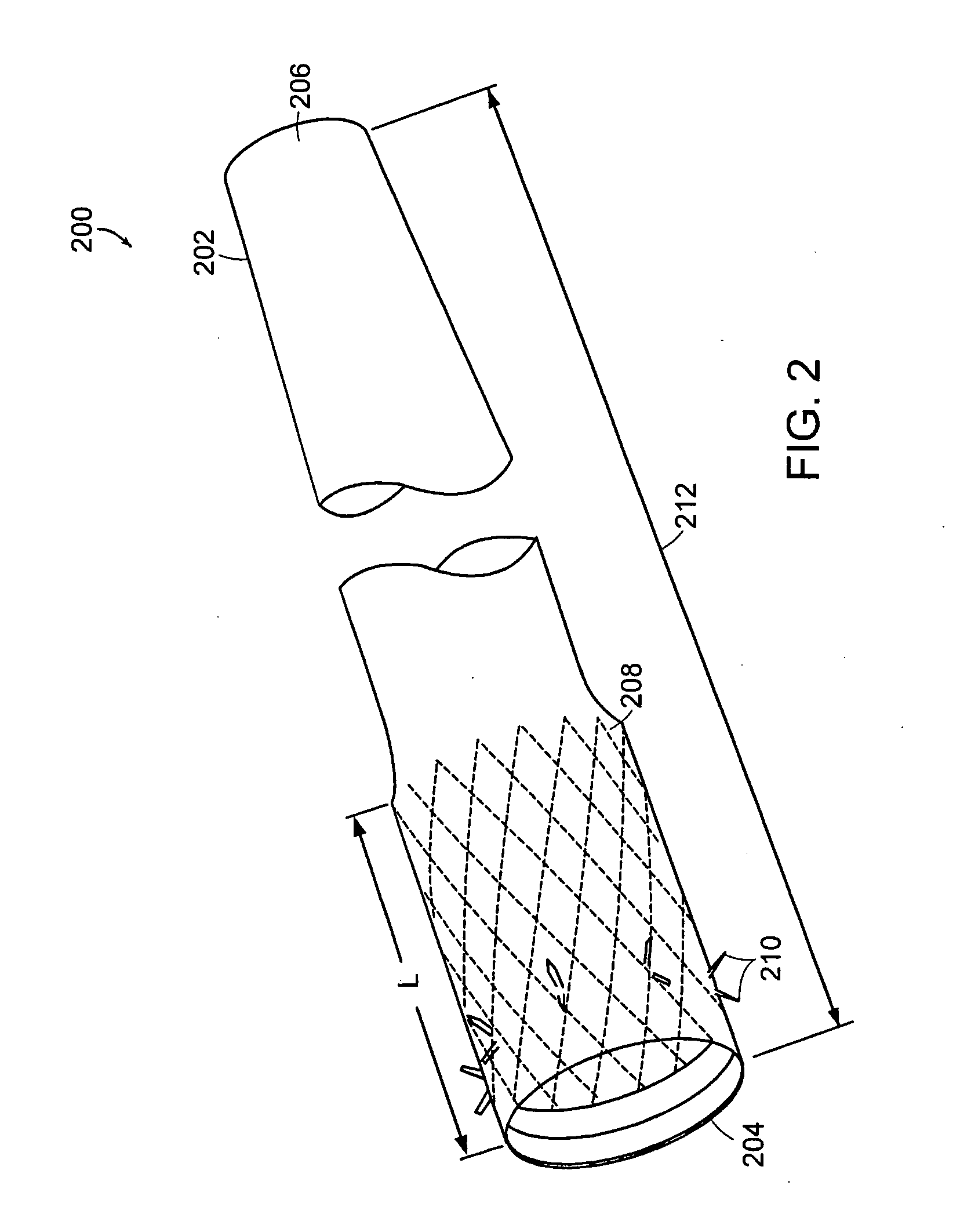
Intestinal sleeve
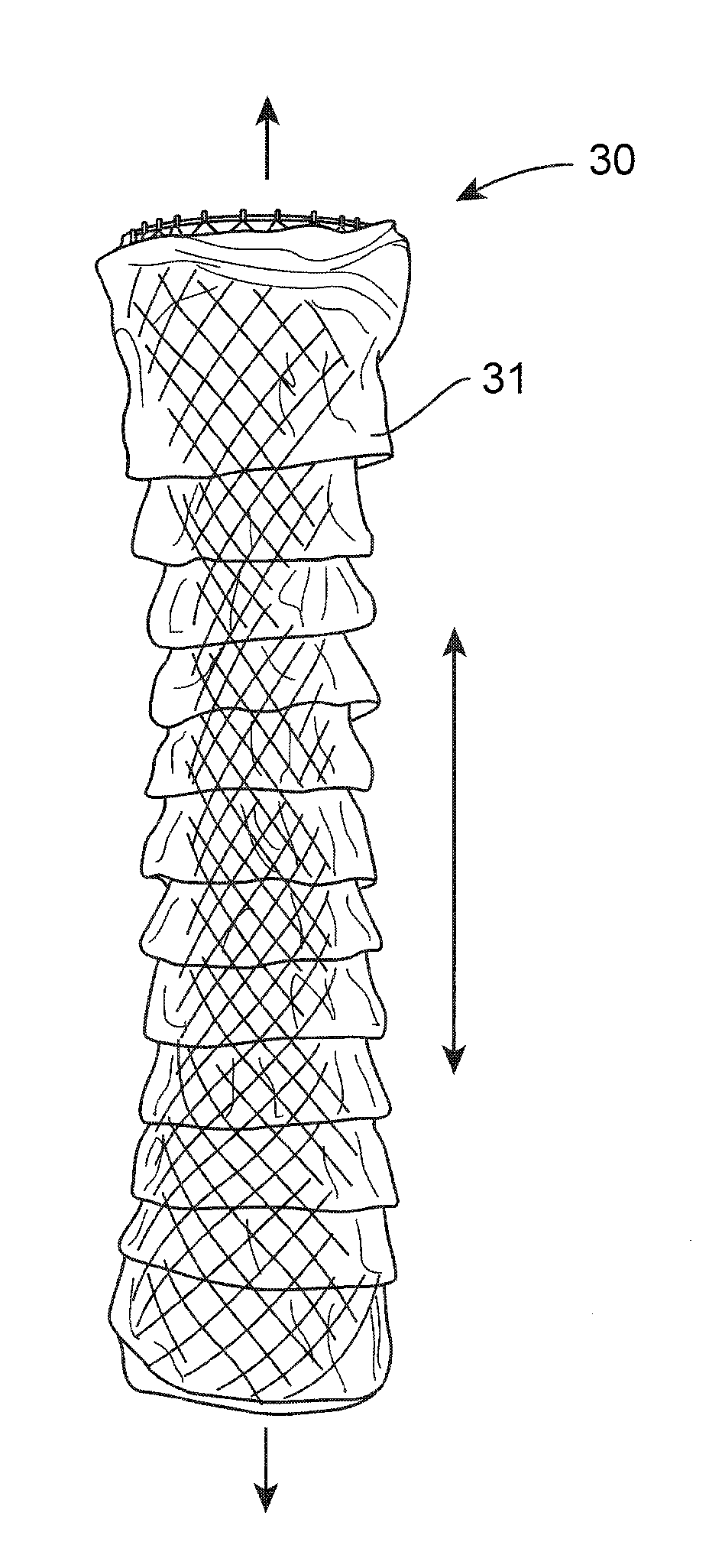
ActiveUS20050125075A1Controlled absorptionChange habitsSuture equipmentsStentsGastrointestinal deviceInsertion stent
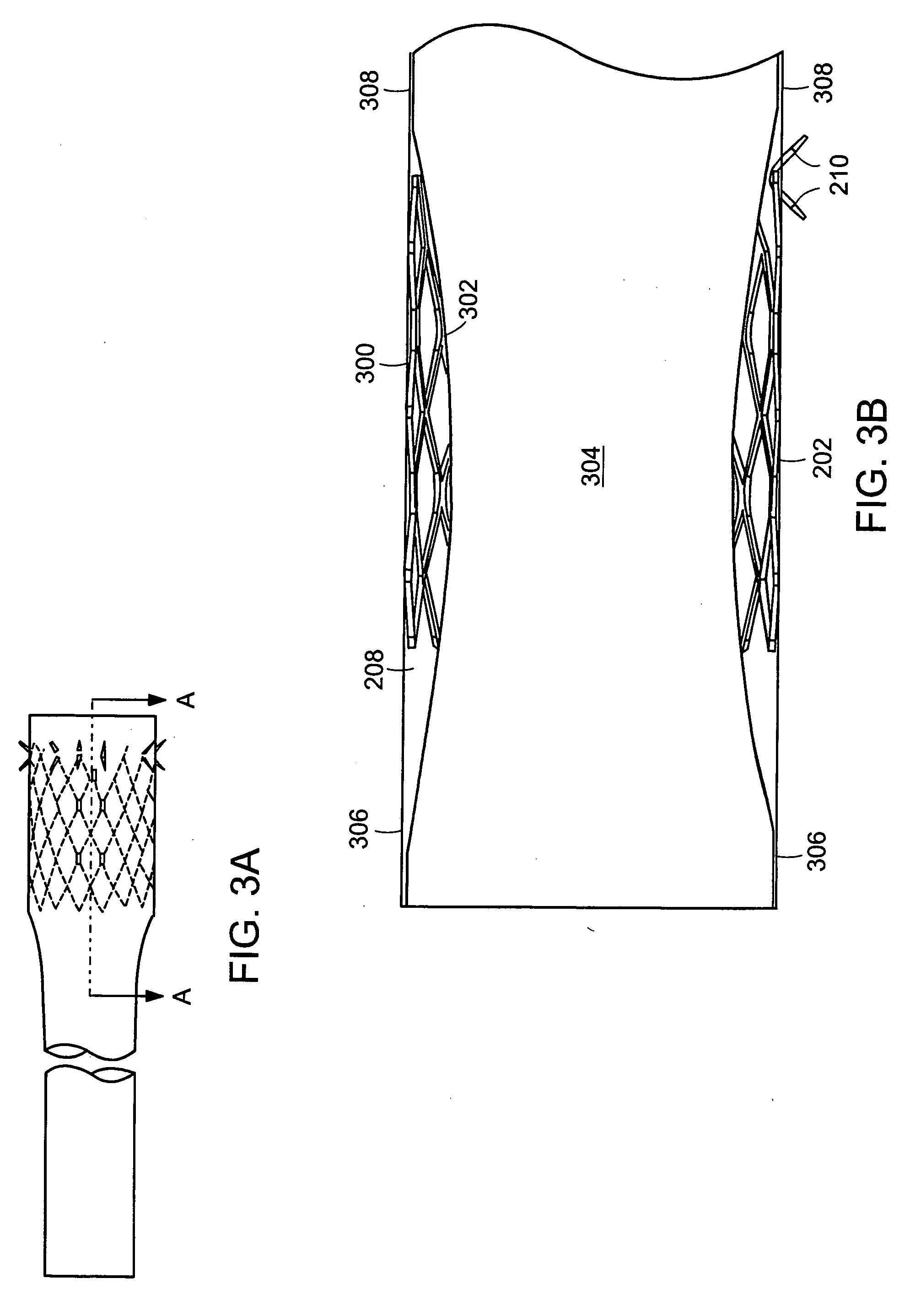
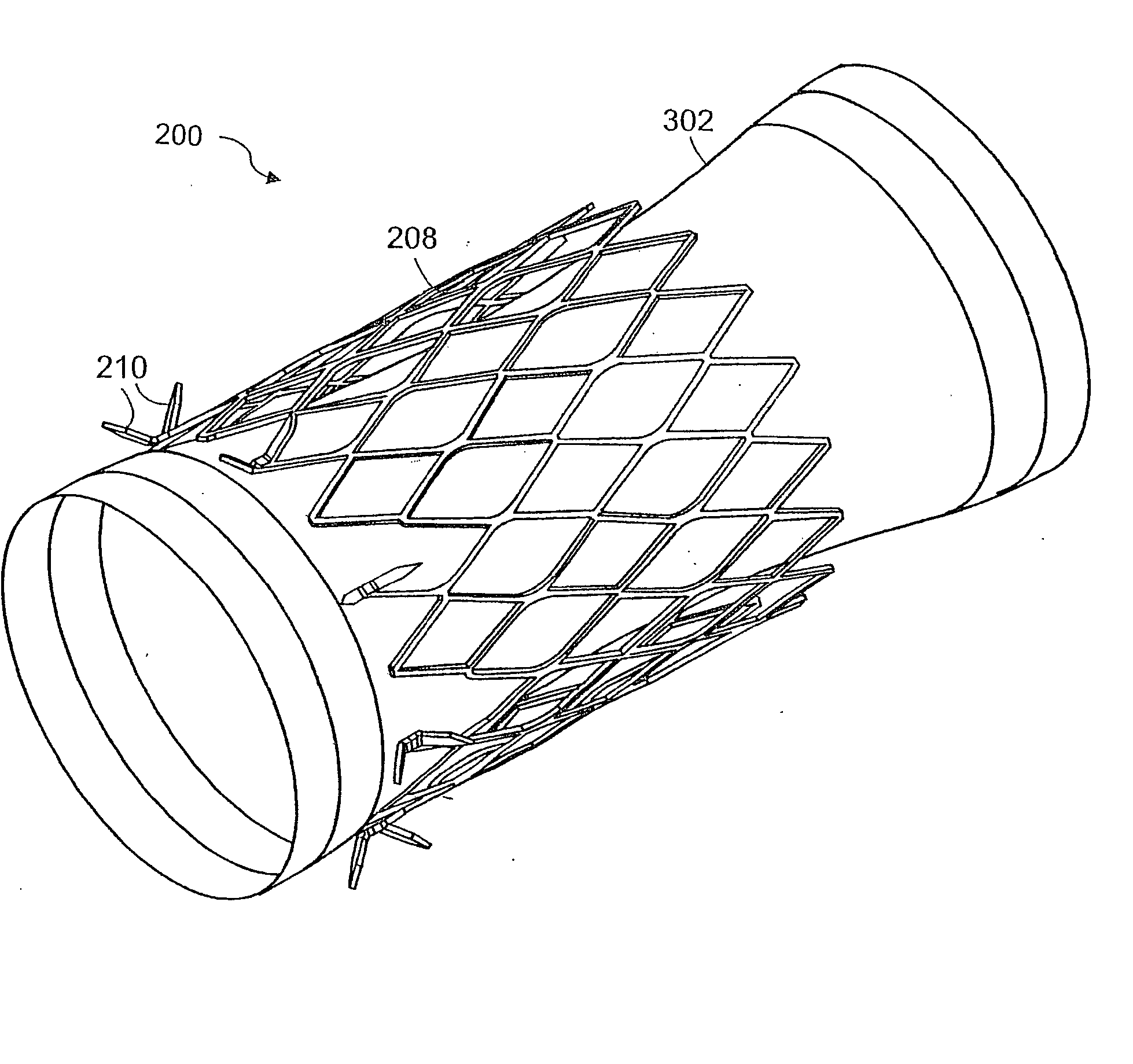
Method and apparatus for limiting absorption of food products in specific parts of the digestive system is presented. A gastrointestinal implant device is anchored in the duodenum and extends beyond the ligament of Treitz. All food exiting the stomach is funneled through the device. The gastrointestinal device includes an anchor for attaching the device to the duodenum and an unsupported flexible sleeve to limit absorption of nutrients in the duodenum. The anchor can include a stent and / or a wave anchor and is collapsible for catheter-based delivery and removal.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
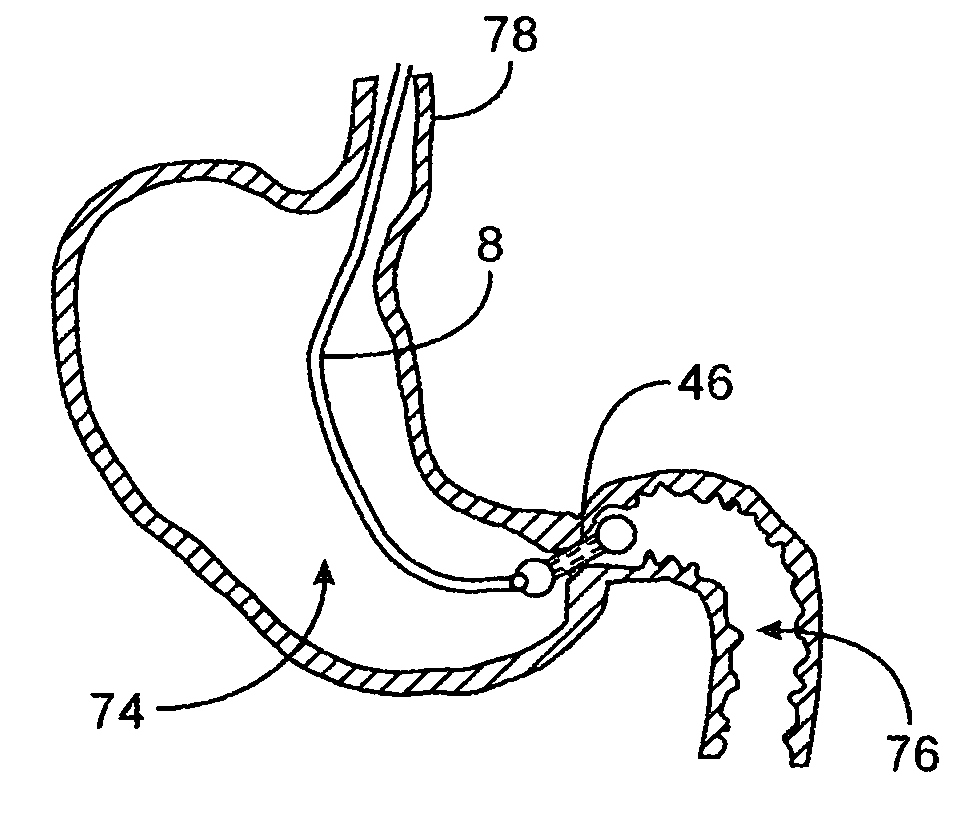
Gastrointestinal stimulation device
A fixation device for holding stimulating electrodes in electrical contact with the wall of a portion of the gastrointestinal tract is provided. In one embodiment, the fixation device includes an expandable member that fixes the electrodes in electrical contact with the gastrointestinal tract wall. Also provided is an implantable device and method for controlling the opening and / or closing of the pylorus. In particular a device and method is provided for stimulating the duodenum to control the closing / and or opening of the pylorus. Finally, a method is provided for treating obesity by controlling the pylorus to retain food in the stomach for a desired period of time, among other things to provide a feeling of satiety and / or to reduce hunger. One aspect includes controlling the pylorus's contraction by electrical stimulation of the duodenum.
Owner:INTRAPACE
Pyloric valve corking device and method
InactiveUS6994095B2Reduce trafficEasy to placeDiagnosticsDilatorsGastric ContentBiomedical engineering
Pyloric valve corking devices and methods are described herein. The devices generally include an occluding member which expands from a first configuration to a larger second configuration and a bridging member extending from the occluding member. The bridging member has a length which passes at least partially through the gastric opening such that the occluding member obstructs the gastric opening, and wherein the length permits the occluding member to intermittently move relative to the gastric opening. A second occluding member may be attached to the distal end of the bridging member. The reduction in flow of gastric contents into the duodenum can be tightly regulated using a pump or valve. Otherwise, the flow can be passively regulated with the occluding device.
Owner:BARONOVA
System and Method for Treating Nausea and Vomiting by Vagus Nerve Stimulation
ActiveUS20080208266A1Relieve nauseaReduce vomitingInternal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsIntestinal structureAbdomen
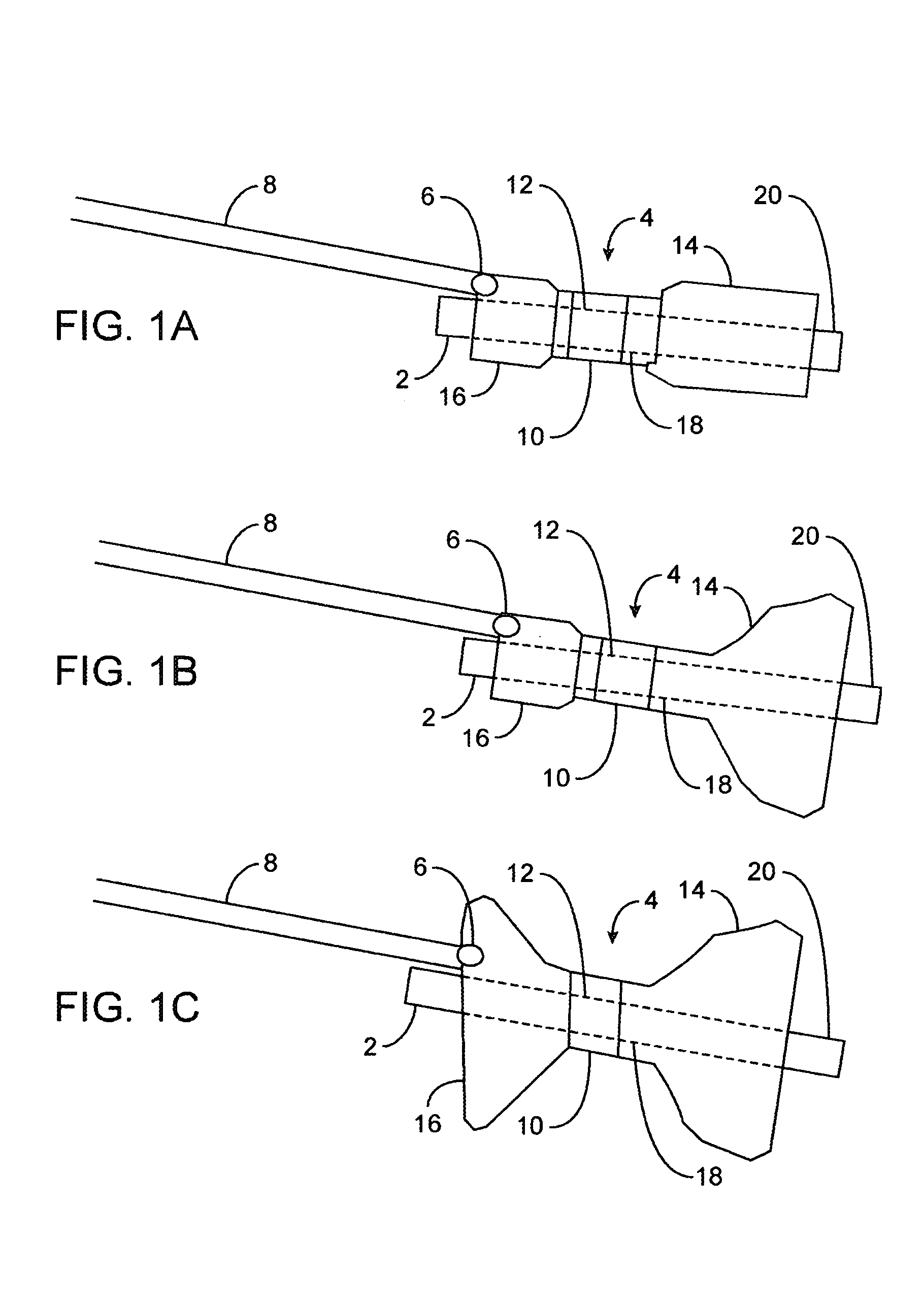
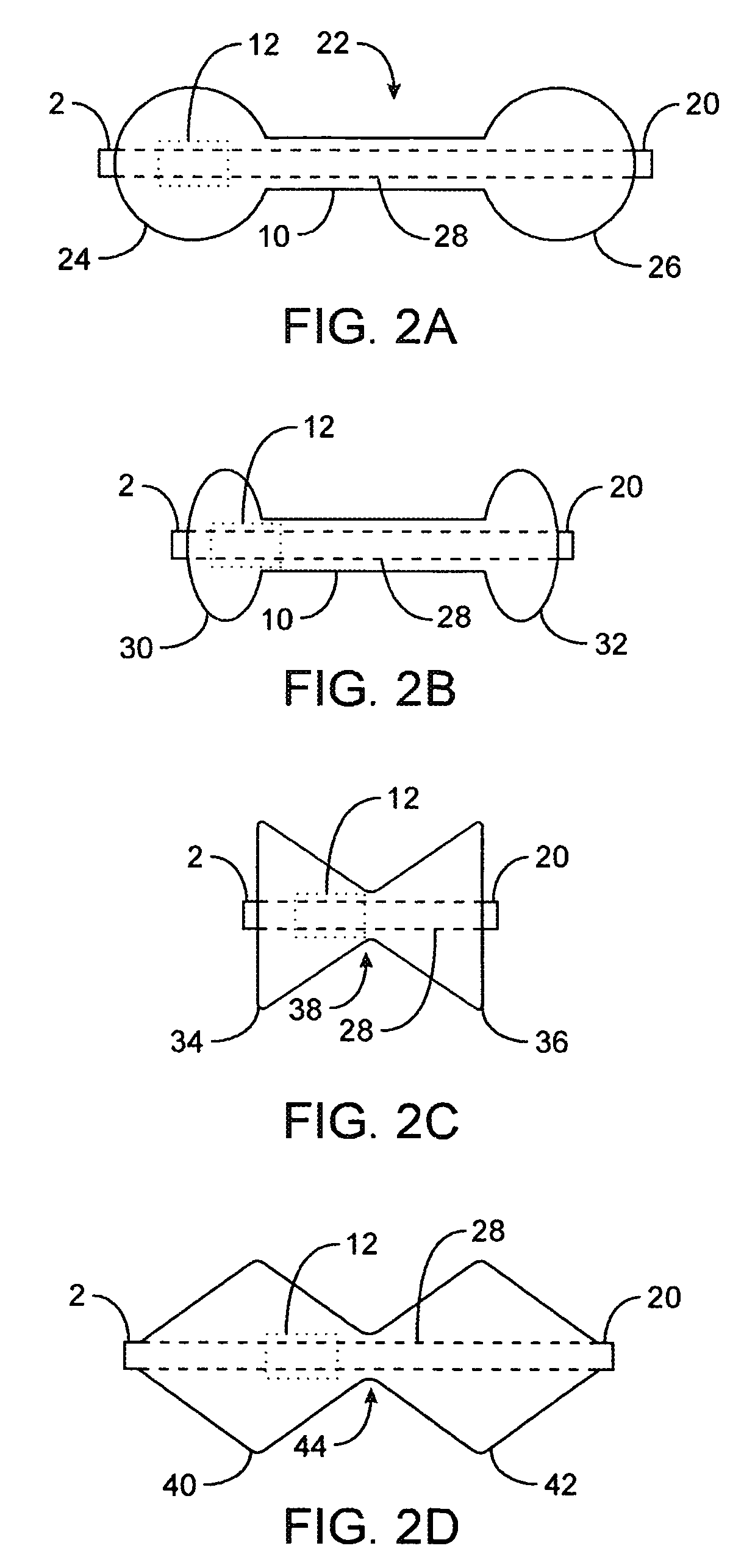
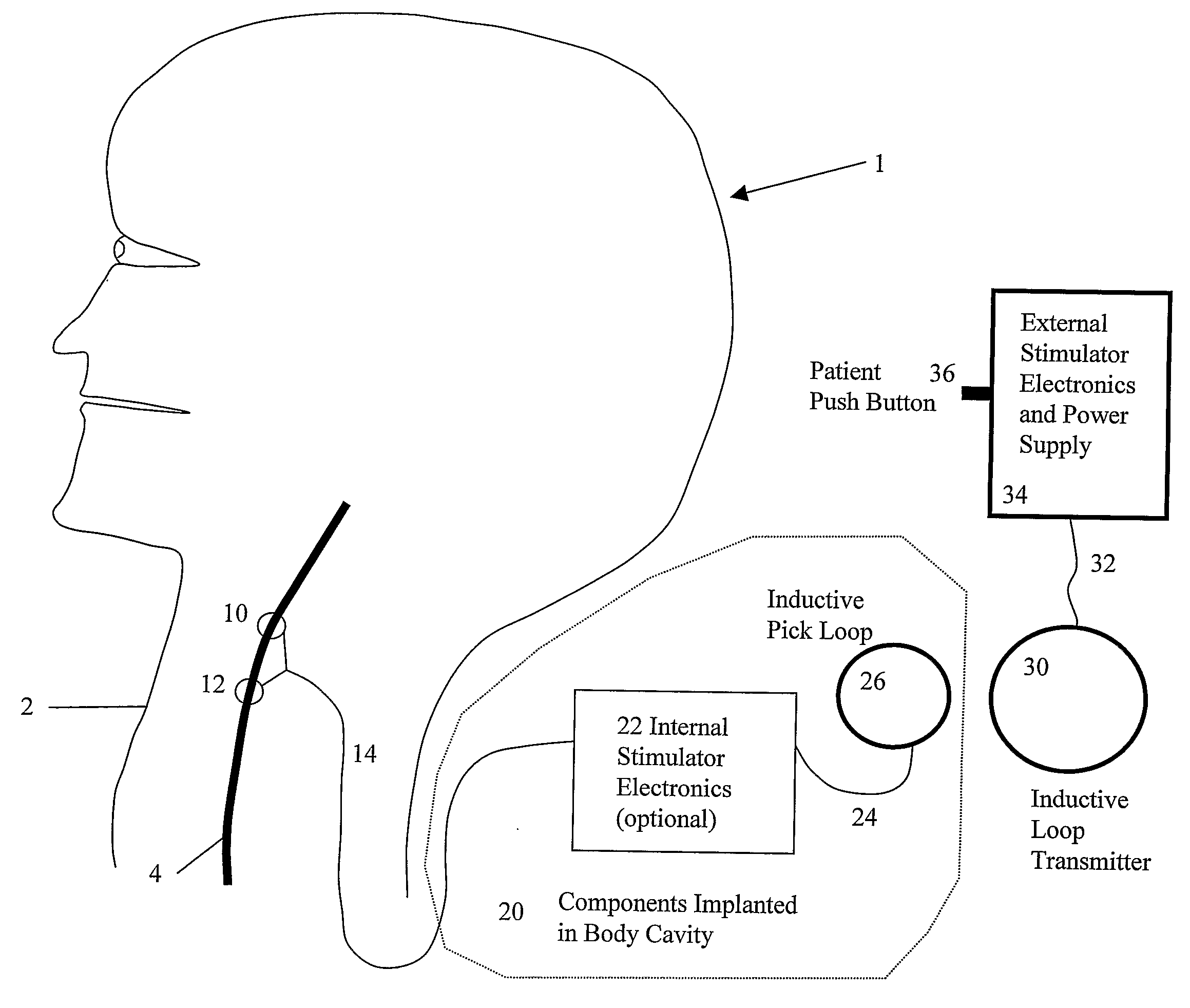
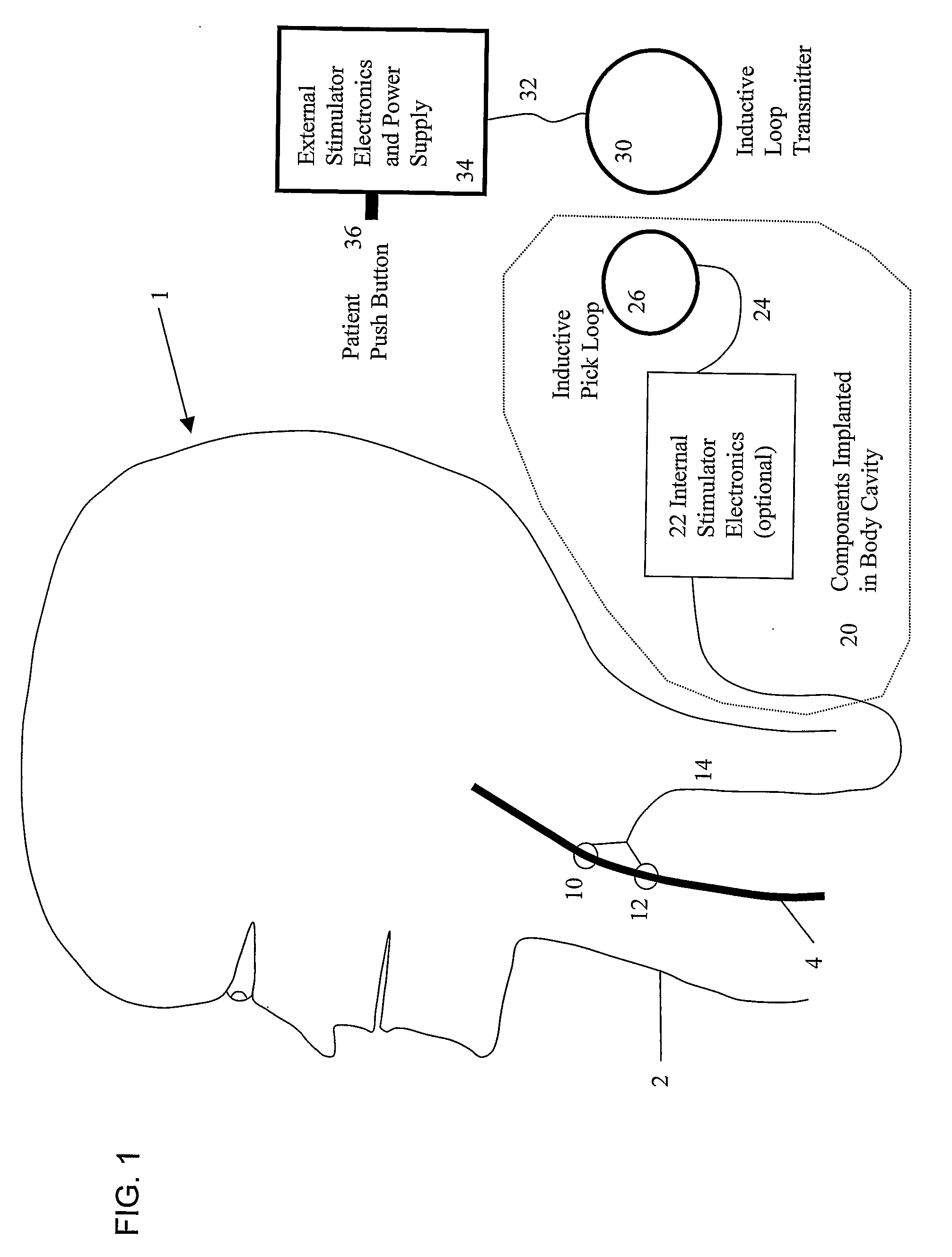
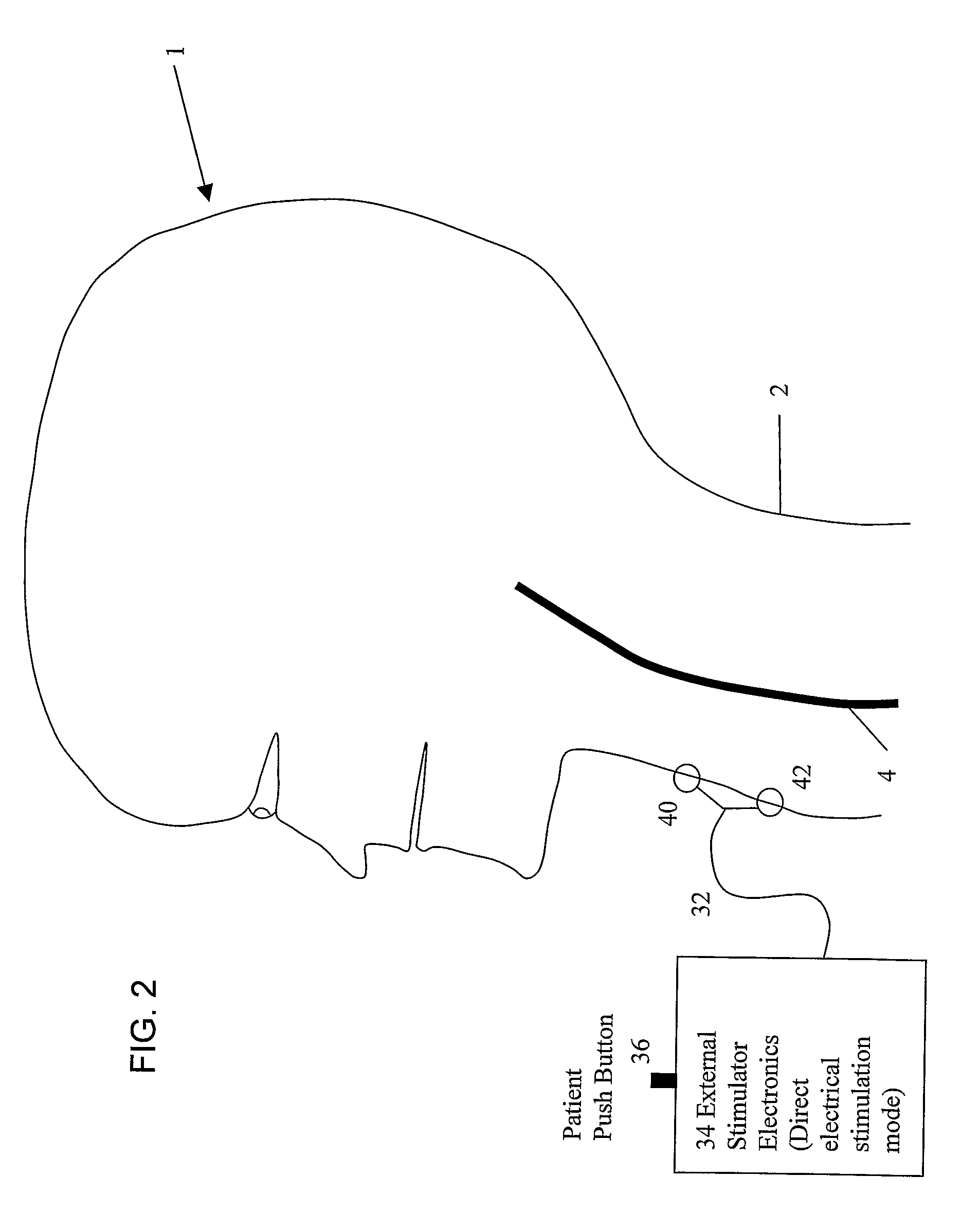
A system and method for treating nausea and vomiting are provided, including one or more electrodes (10, 12) applied on or under the skin, the electrodes being connected to an external current source (34). The electrodes can be implanted under the skin and connect to internal stimulator electronics (22), which can form a magnetic inductive link to the external current source (34). Alternatively, the electrodes can be placed on the skin and directly linked by wires to the external current source. As a further alternative, the vagus nerve can be directly stimulated in the neck, or the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, or intestines can be directly stimulated by magnetic stimulation. The electrodes can stimulate the vagus nerve in the neck to reduce nausea and vomiting, or can be arranged near the chest or abdomen, so as to stimulate the esophagus, stomach, duodenum or intestines. Because the current source is provided outside the body, it is not necessary to implant batteries or another power supply in the body.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Device and Method for Treating Weight Disorders
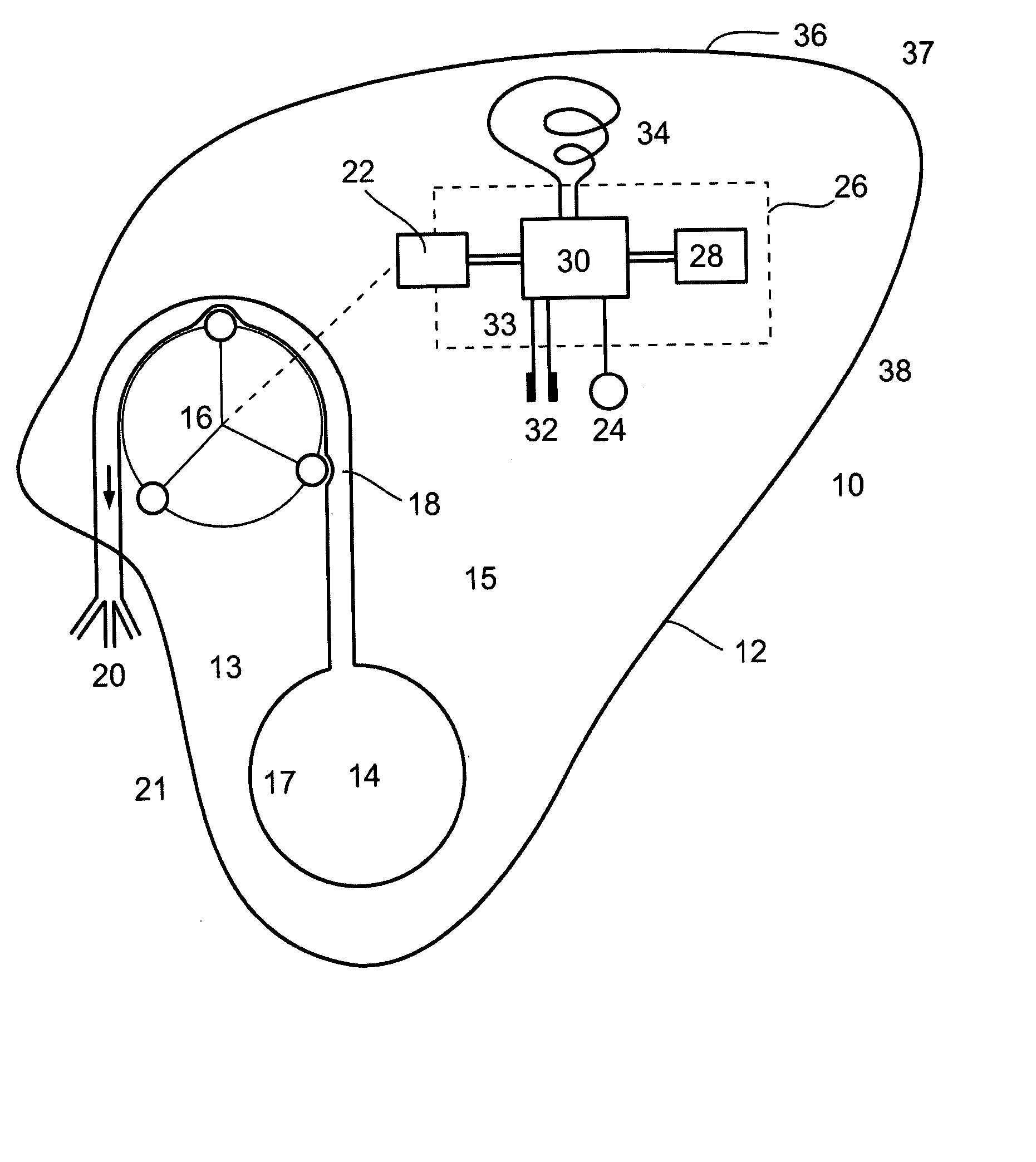
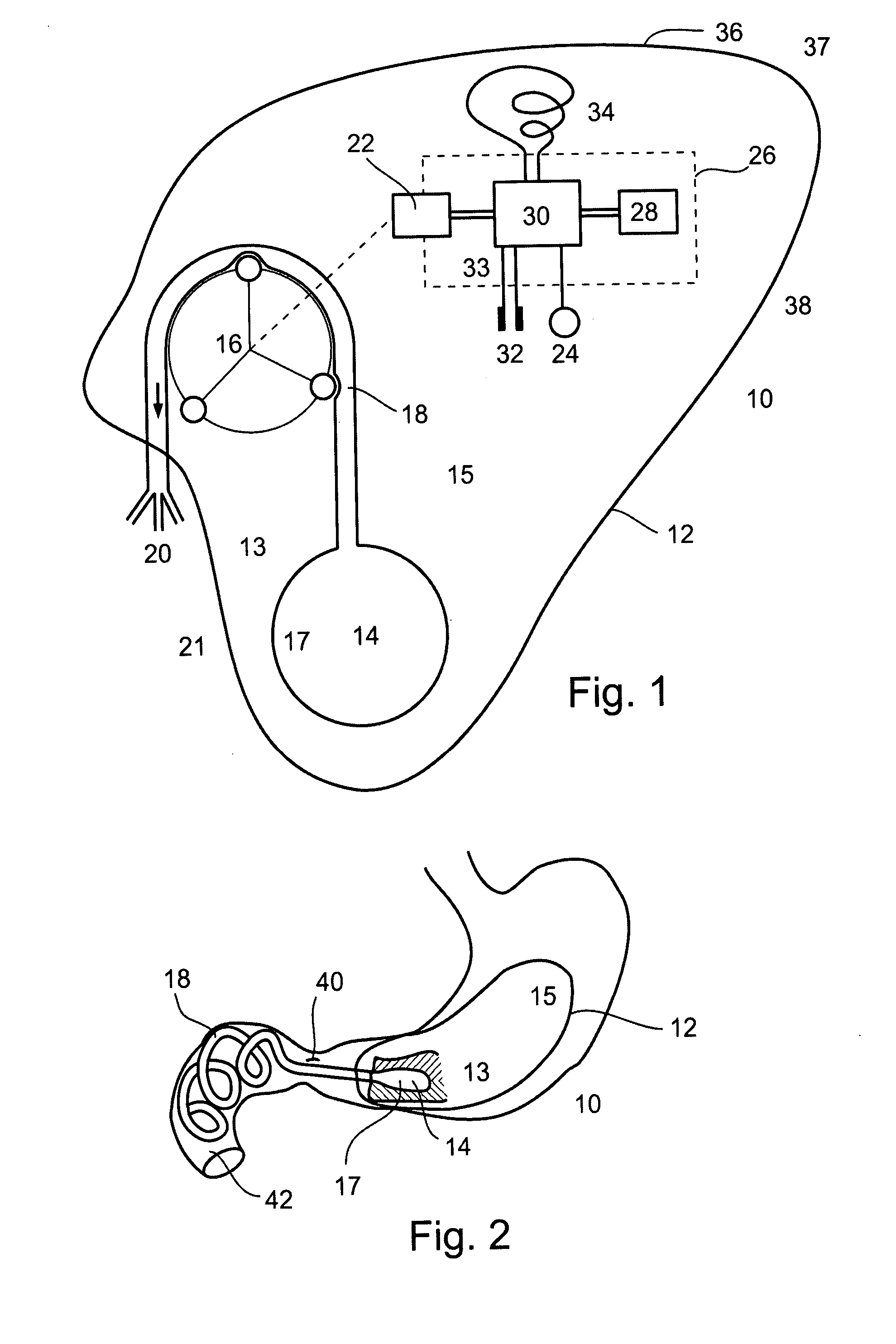
An apparatus and a method for treating a weight disorder in a subject are provided. The apparatus comprising an implantable device such as an inflatable balloon and electrodes capable of sensing a physiological change associated with food ingestion or hunger and a mechanism adapted for directly stimulating a region such as the duodenum which is responsive to a gastrointestinal satiety agent, such a mechanism can be a drug reservoir containing a drug such as CCK or analogs thereof which is contained within an inflatable balloon being implantable in a stomach of the subject. The apparatus and method provided here combine synergistic approaches to limiting meal size, i.e., chemo and mechano receptor activation of vagal satiety stimuli, electric stimulation of specific vagal pathways and limitations of gastric space.
Owner:DUOCURE
Bariatric sleeve
InactiveUS20050075622A1Reduce twistDelayed bucklingSuture equipmentsStentsGastrointestinal deviceLigament structure
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
Bariatric sleeve removal devices
Method and apparatus for limiting absorption of food products in specific parts of the digestive system is presented. A gastrointestinal implant device is anchored in the stomach and extends beyond the ligament of Treitz. All food exiting the stomach is funneled through the device. The gastrointestinal device includes an anchor for anchoring the device to the stomach and a flexible sleeve to limit absorption of nutrients in the duodenum. The anchor is collapsible for endoscopic delivery and removal.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
Surgical weight control device
InactiveUS7326207B2Optimize quantityEasy to eatStentsBalloon catheterCurative treatmentPhysical therapy
This invention provides a method and system for the curative treatment of obesity. A first aspect of this invention is that it enables identification of the nerves responsible for the relaxation of the stomach muscles that occurs prior to and during eating. A second aspect of the invention is that it allows the physician to identify focal nerve sites in the stomach and upper duodenum that are associated with producing sensations of hunger and satiety. Nervous transmission from these sites can be modulated or blocked all together so as to minimize the sensation of hunger. A third aspect of this invention is that allows a physician to shrink selected portions of the innermost oblique muscle and middle circular muscle layers of the stomach. This can be performed in a physician's office using local anesthesia. Shrinkage of these muscles produces a feeling of satiety that enhances the patient's efforts to restrict his caloric intake.
Owner:MEDERI RF LLC
Gastric anchor
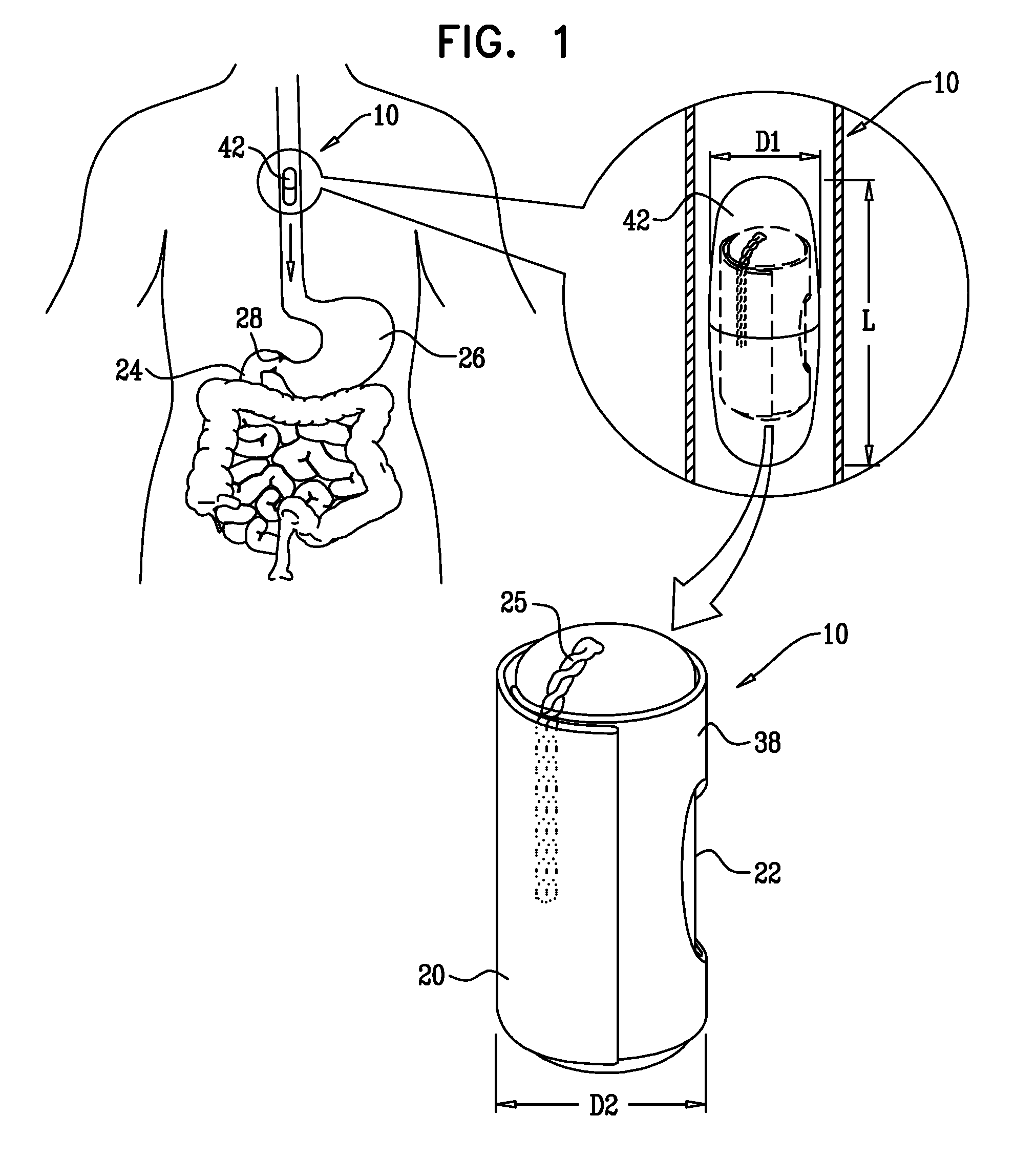
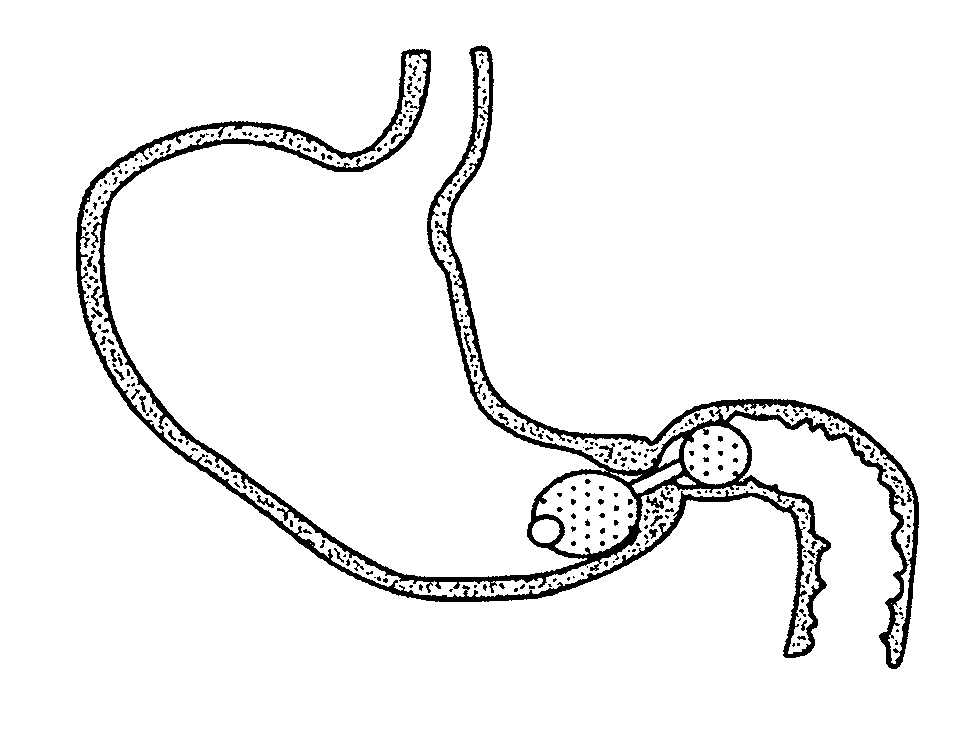
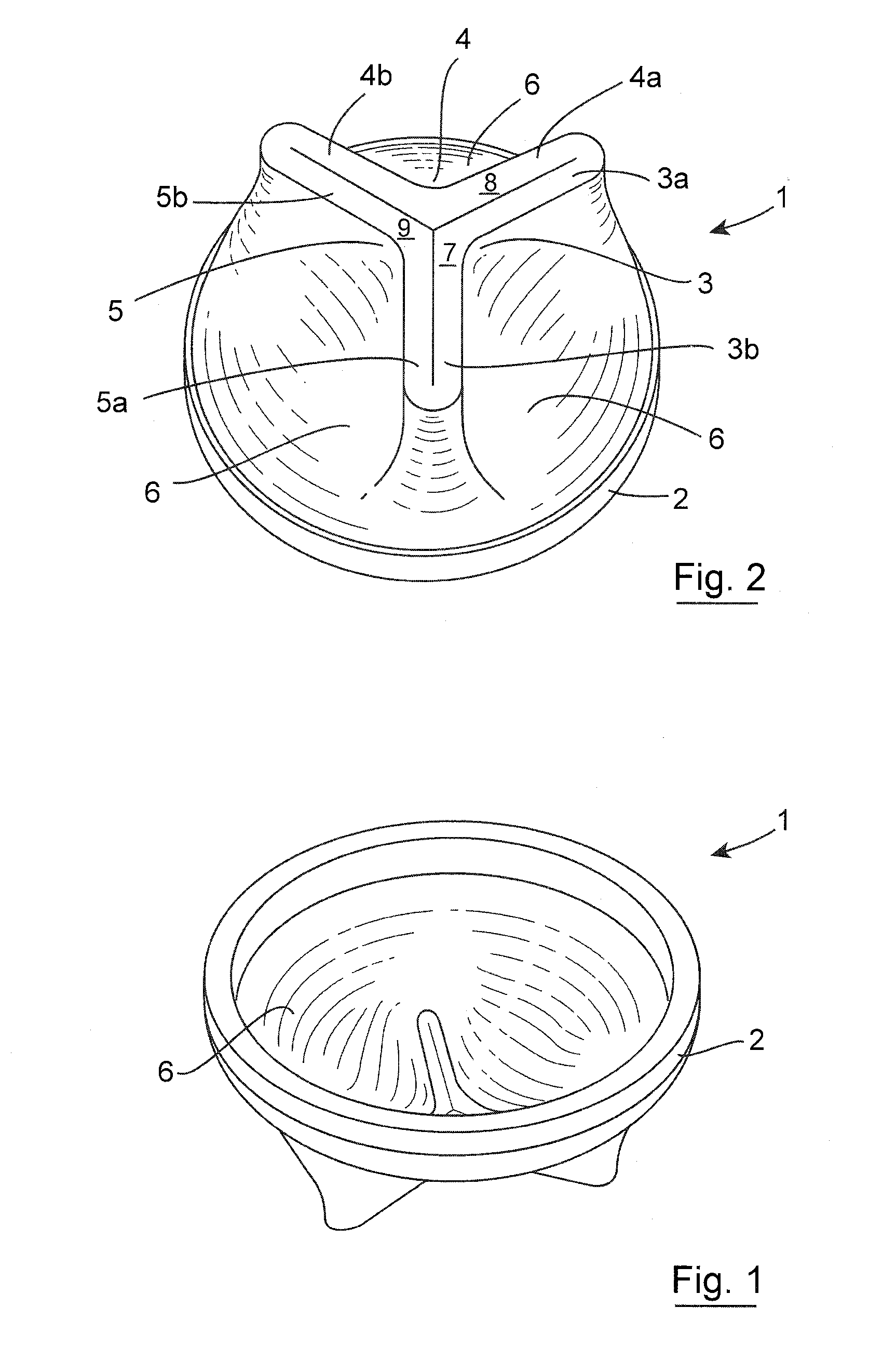
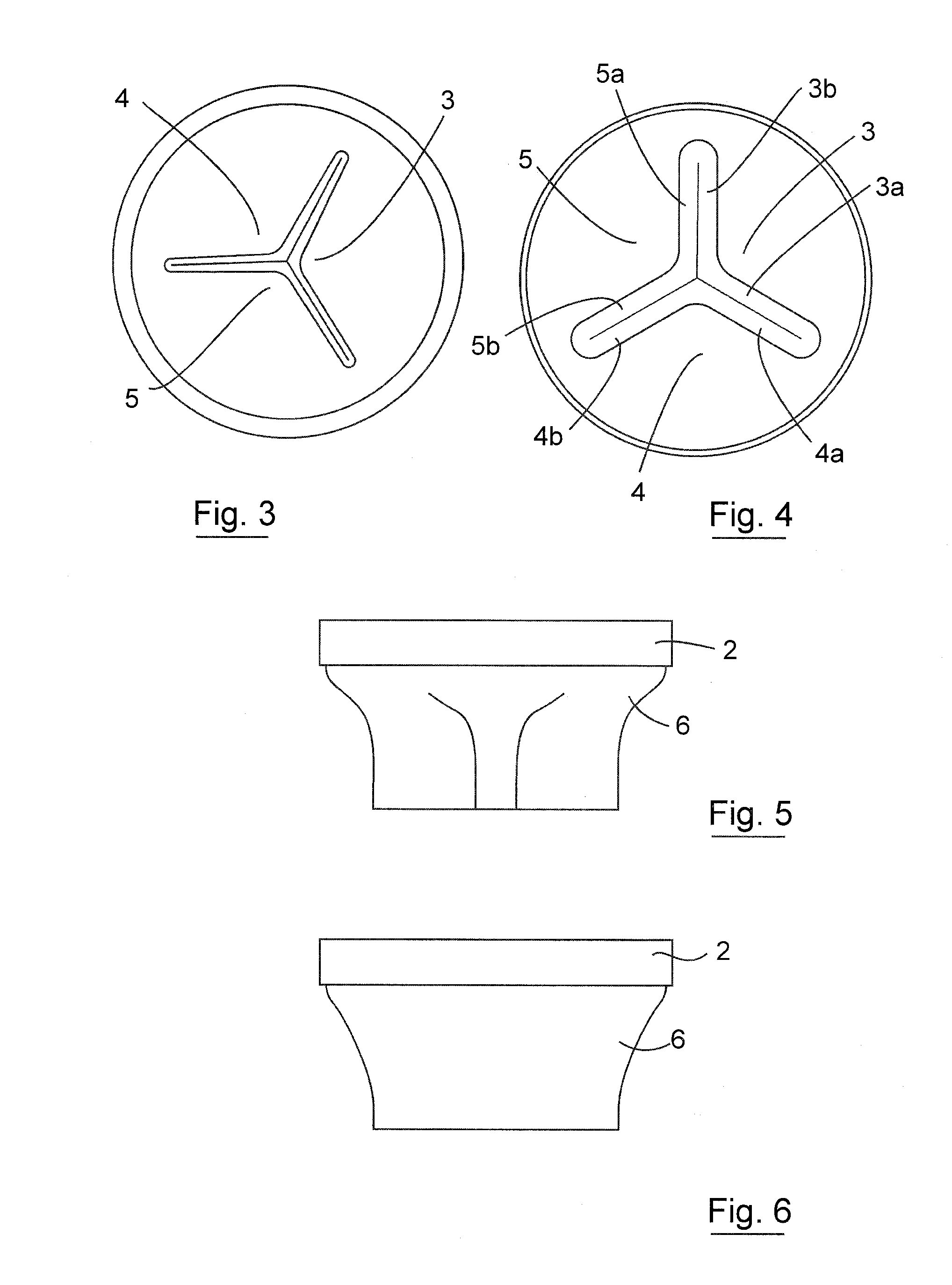
A swallowable medical treatment device is configured to initially assume a contracted state having a volume of less than 4 cm3. The device includes a gastric anchor, which initially assumes a contracted size, and which is configured to, upon coming in contact with a liquid, expand sufficiently to prevent passage of the gastric anchor through a round opening having a diameter of between 1 cm and 3 cm. The device also includes a duodenal unit, which is configured to pass through the opening, and which is coupled to the gastric anchor such that the duodenal unit is held between 1 cm and 20 cm from the gastric anchor. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:RAINBOW MEDICAL LTD
Methods of treatment using a bariatric sleeve
ActiveUS7695446B2Promote healingControlled absorptionSuture equipmentsStentsDiseaseIntestinal structure
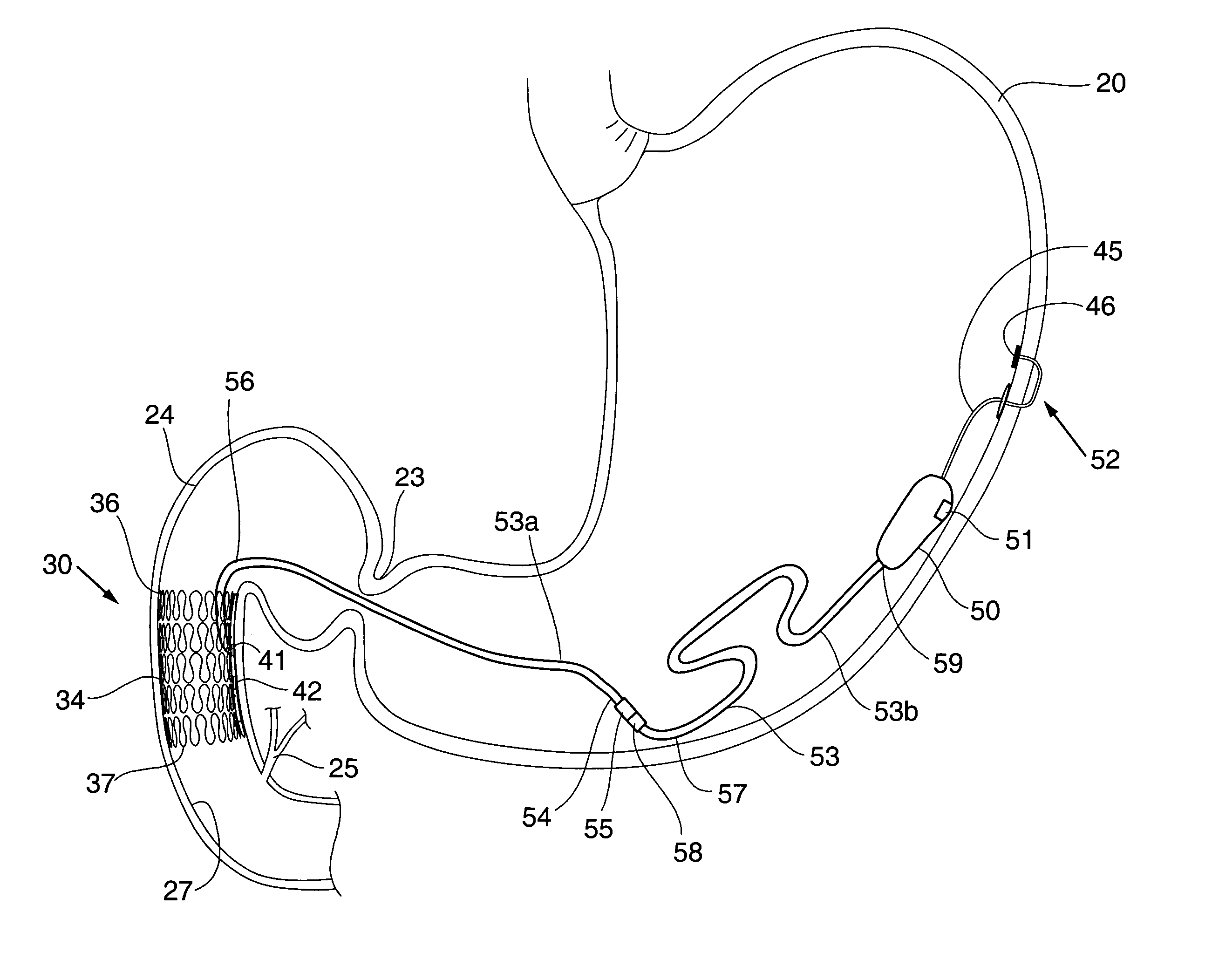
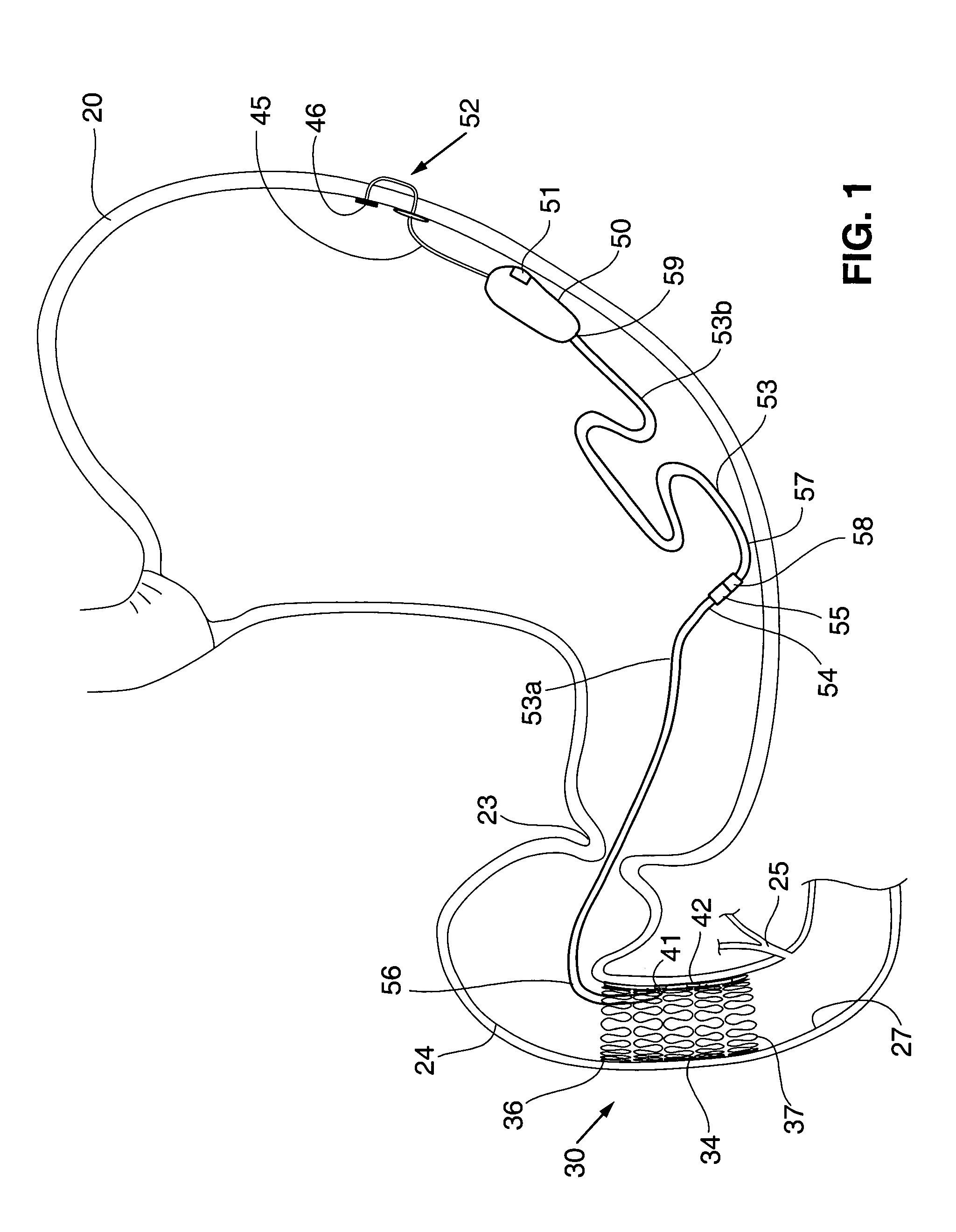
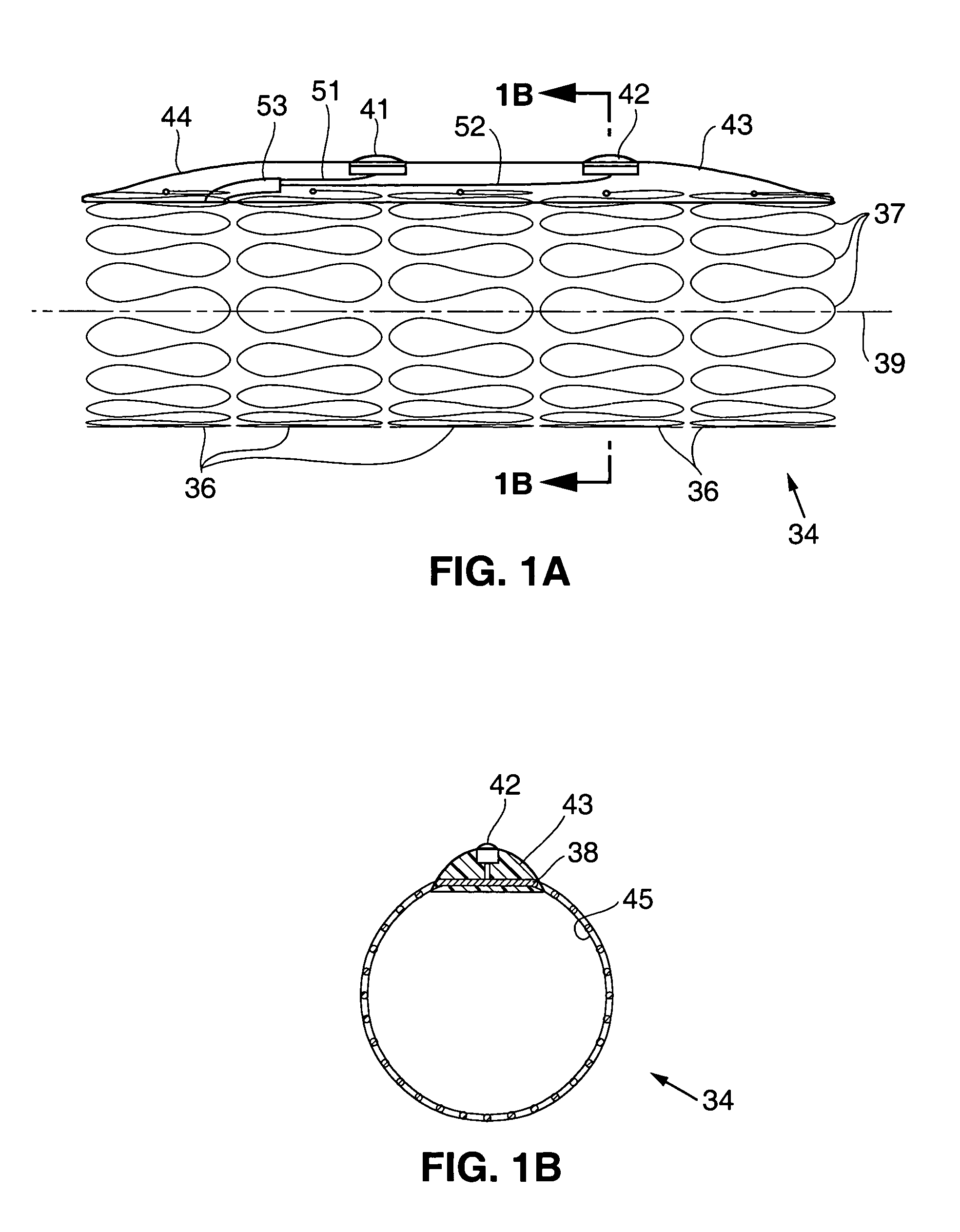
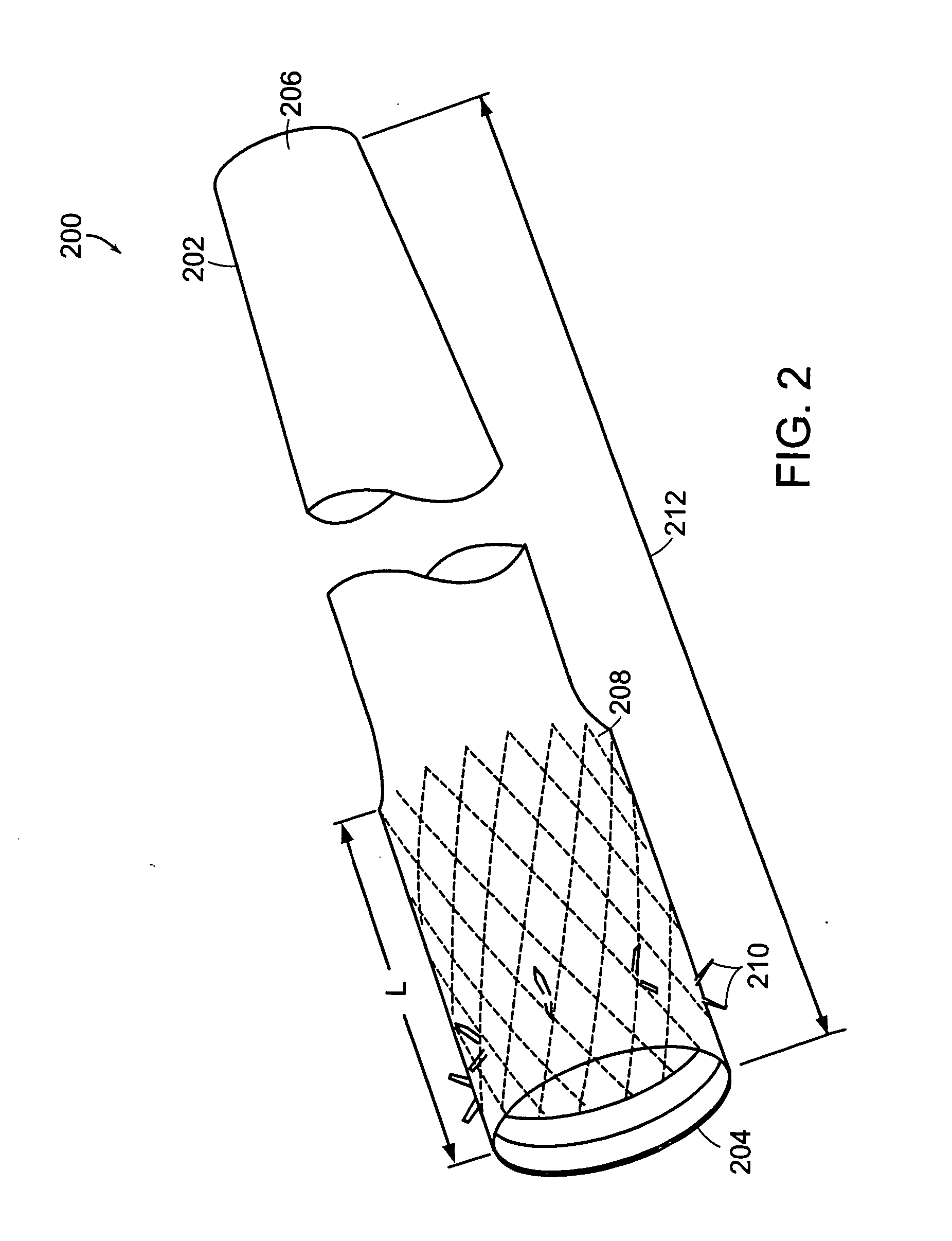
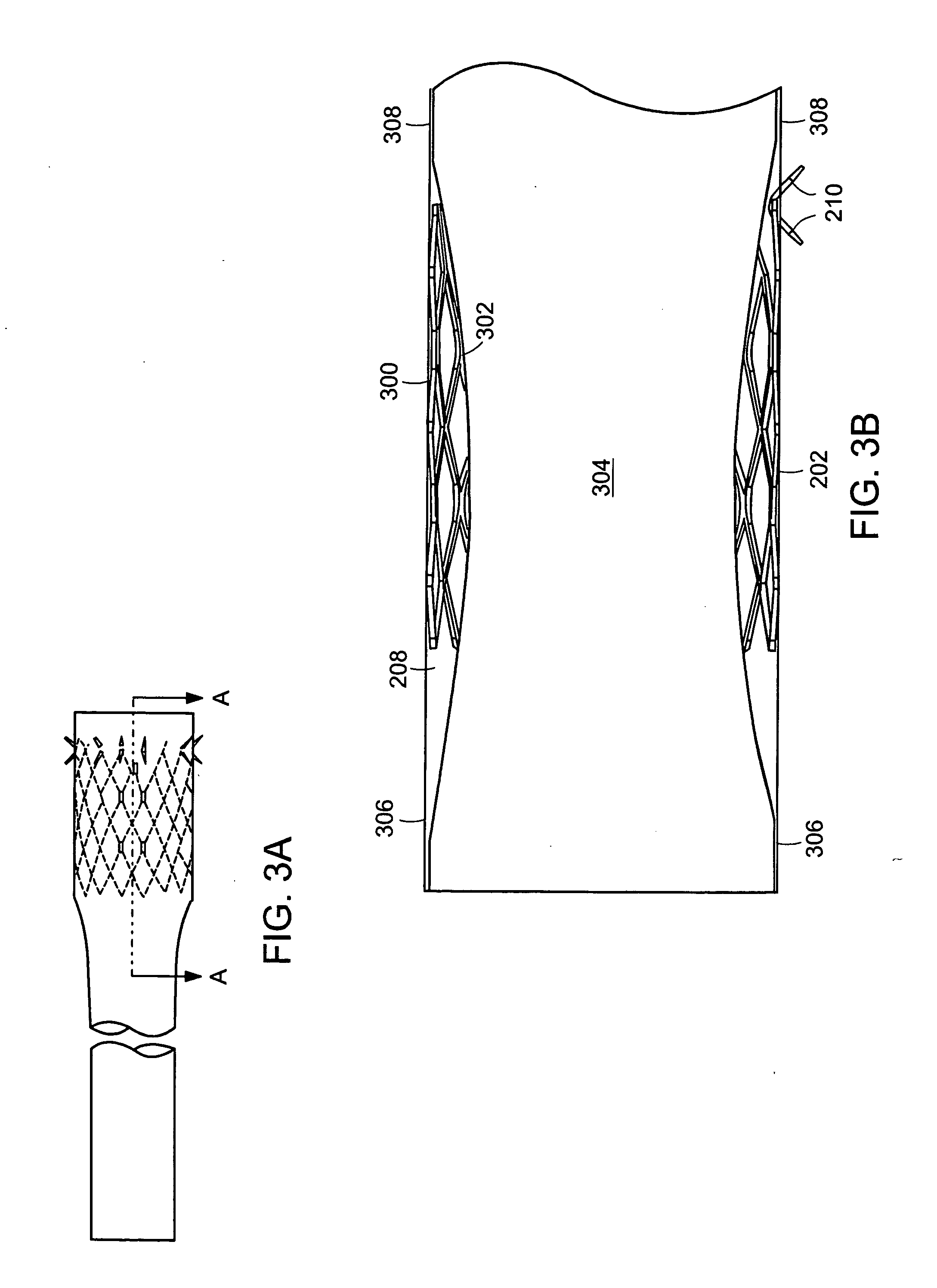
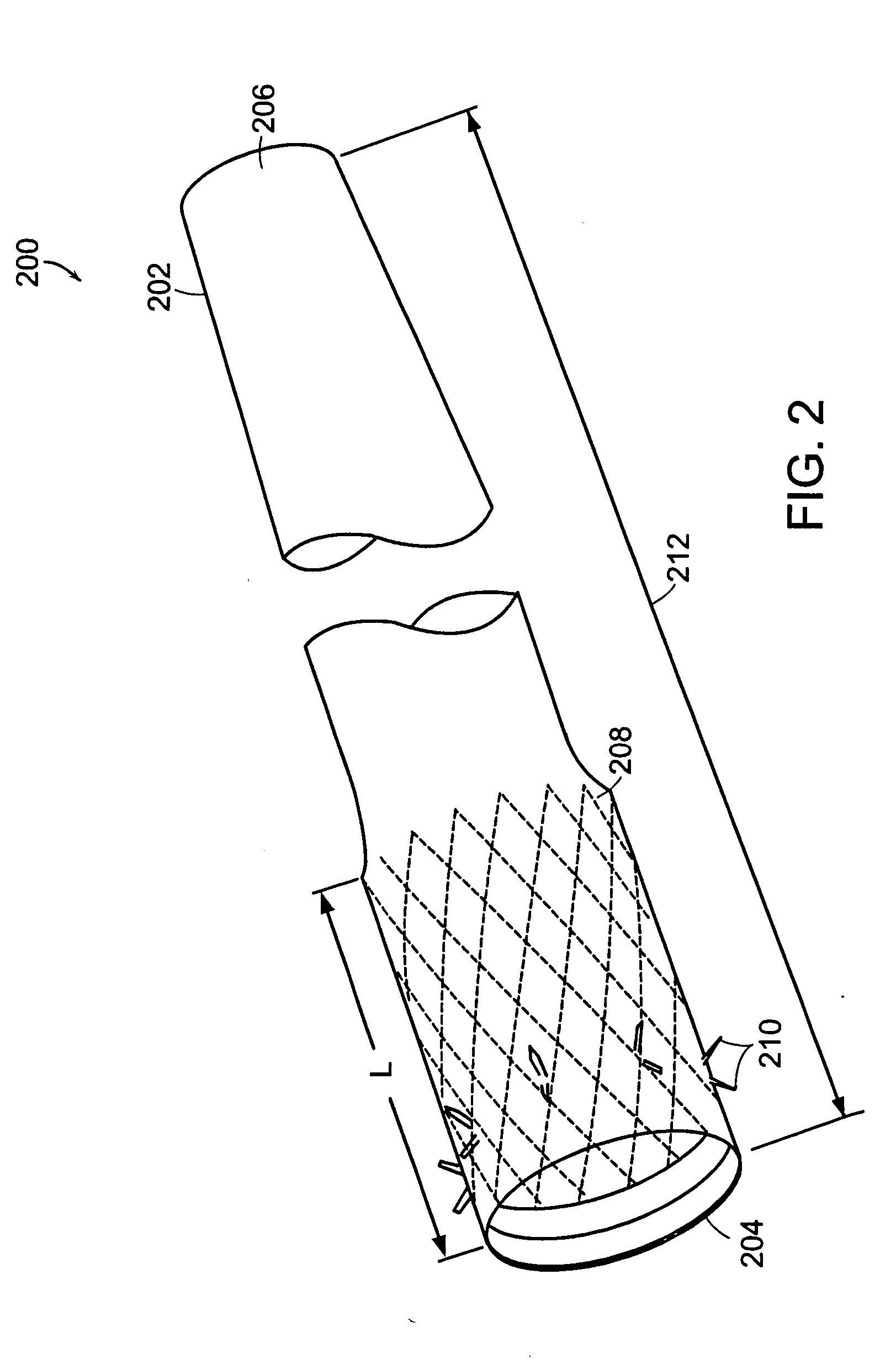
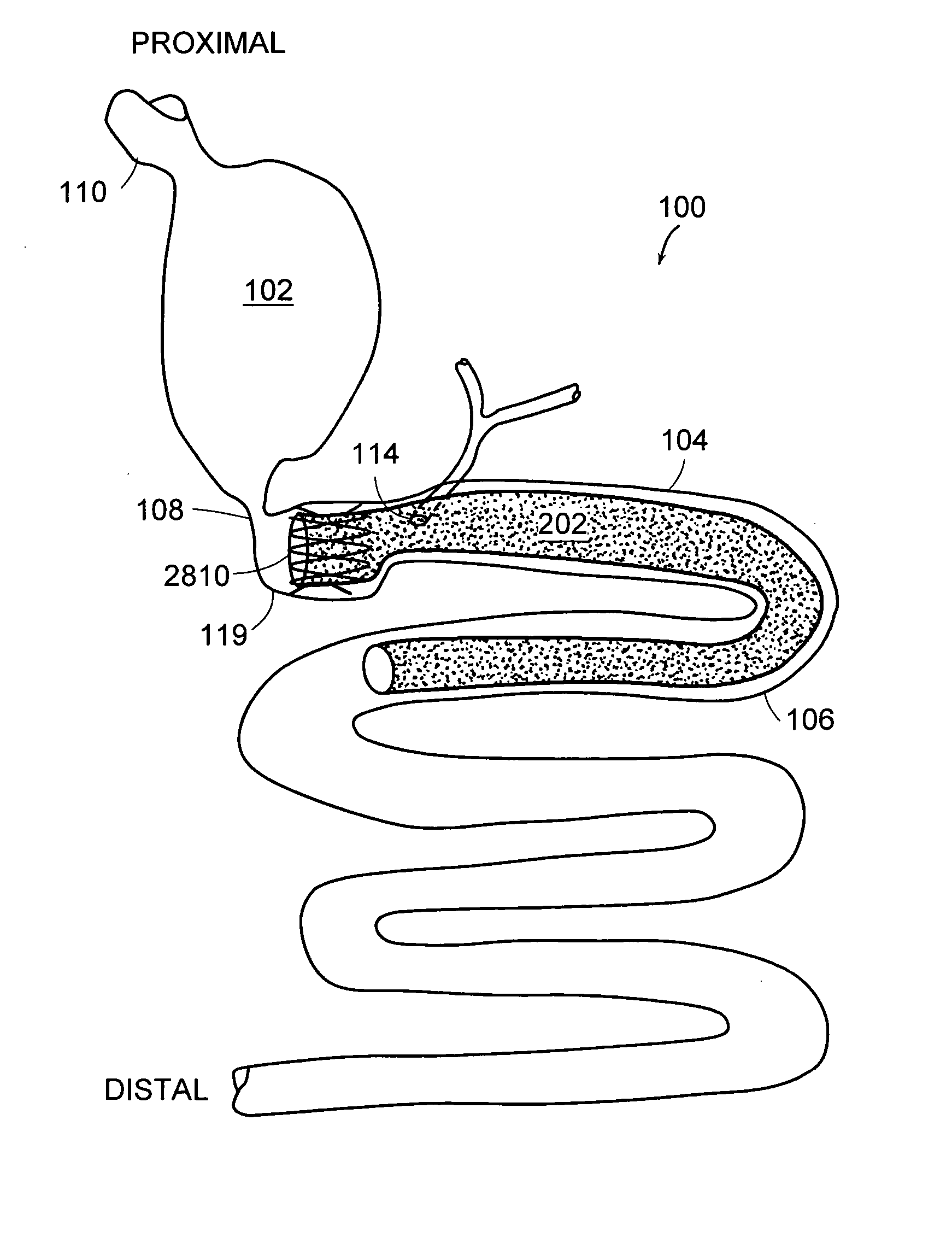
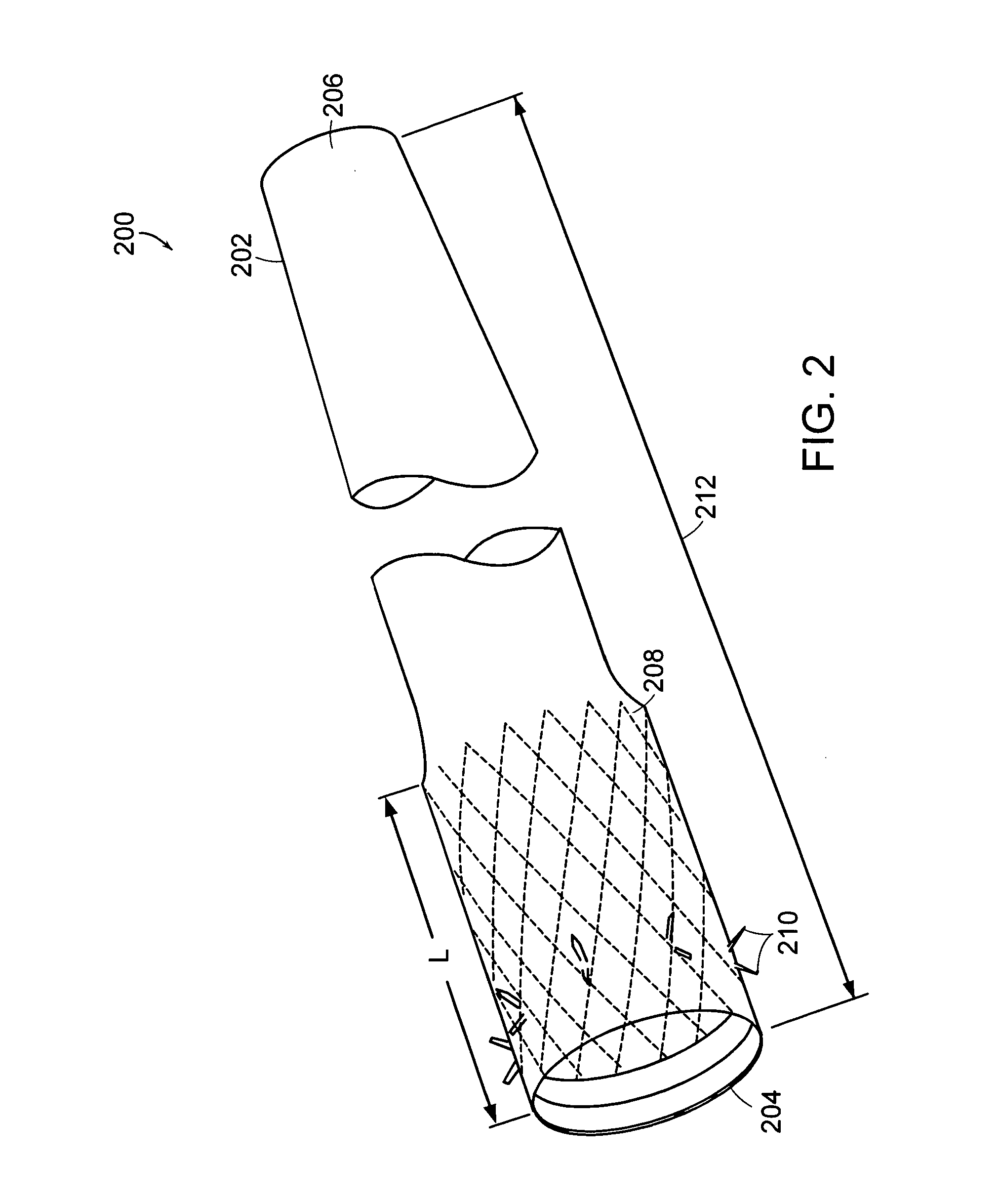
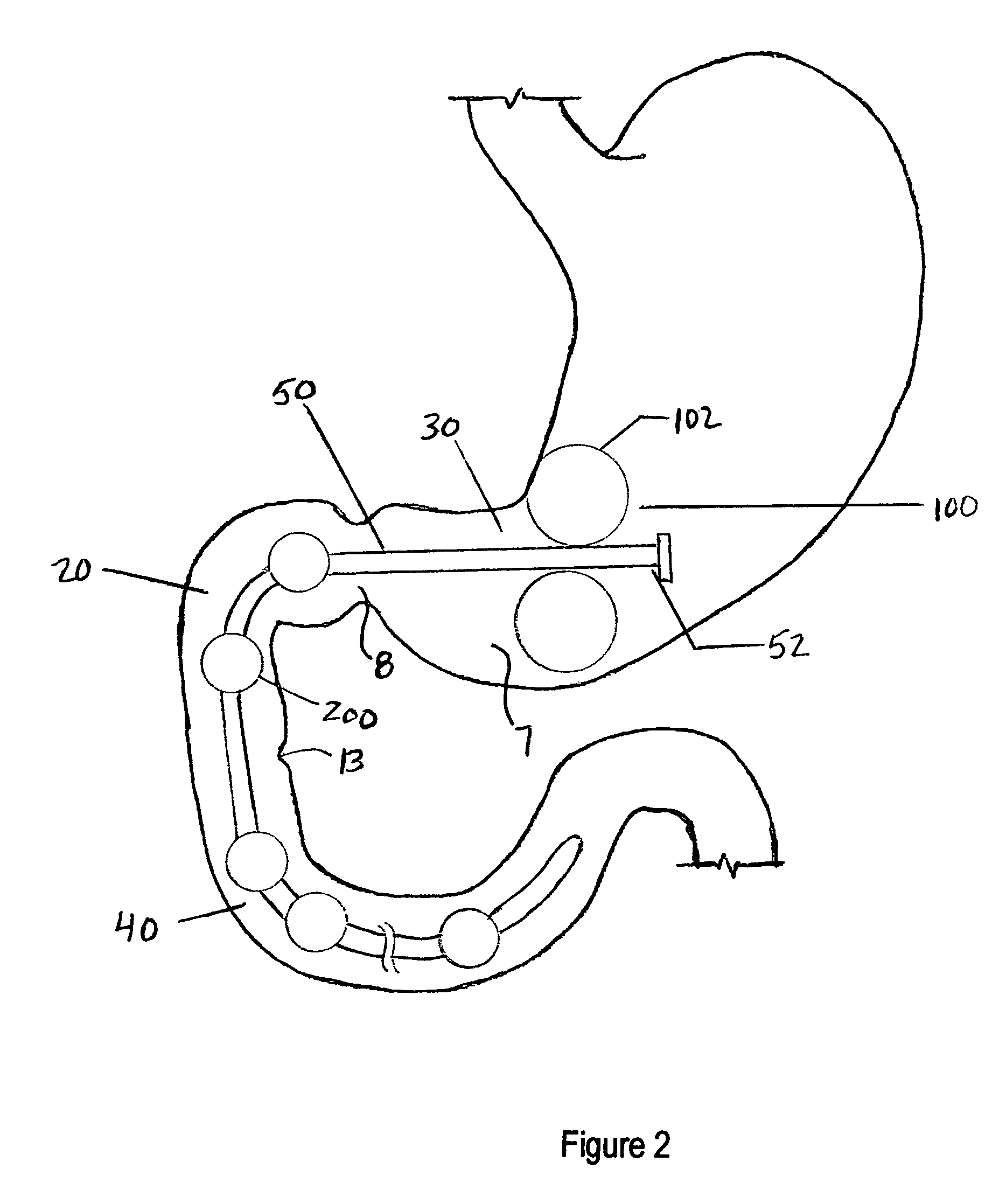
Methods of treatment using a gastrointestinal implant device removably anchored within an animal's gastrointestinal tract. For example, the implant device includes a collapsible anchor for anchoring the device coupled to a proximal end of a flexible sleeve. The implant device can be anchored within the stomach, within the pyloric orifice, and / or distal to the pylorus and extended into the duodenum. All partially-digested food, or chyme, exiting the stomach is funneled through the device. Methods of treatment include treating obesity by one or more of: limiting the absorption of nutrients within the duodenum; delaying the mixing of chyme with digestive enzymes; alter hormonal triggers; and providing negative feedback. Alternatively or in addition, the desired result includes treating a diseases, such as diabetes, or temporarily shielding a portion of the intestine to promote healing within the intestine.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS INC
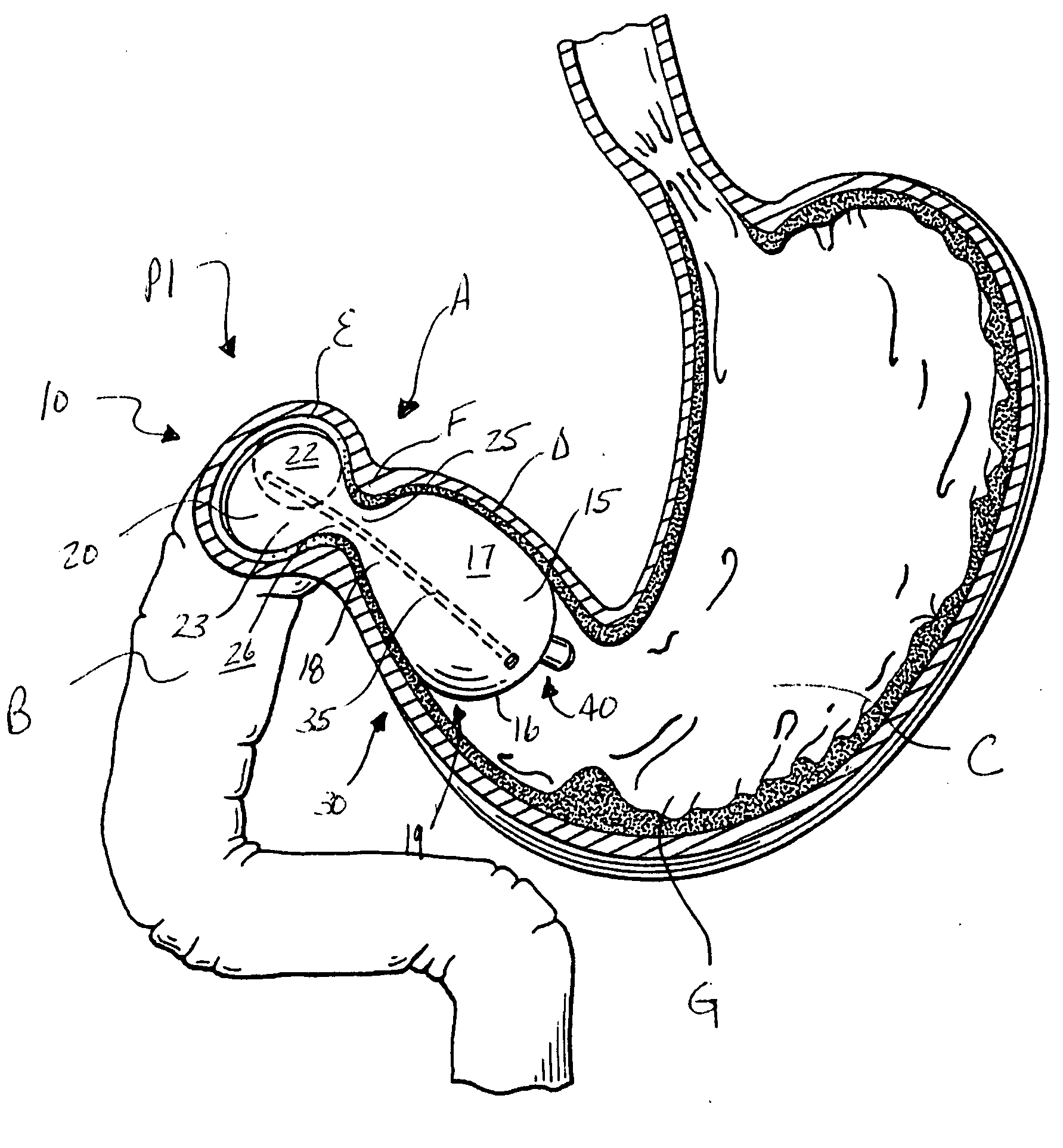
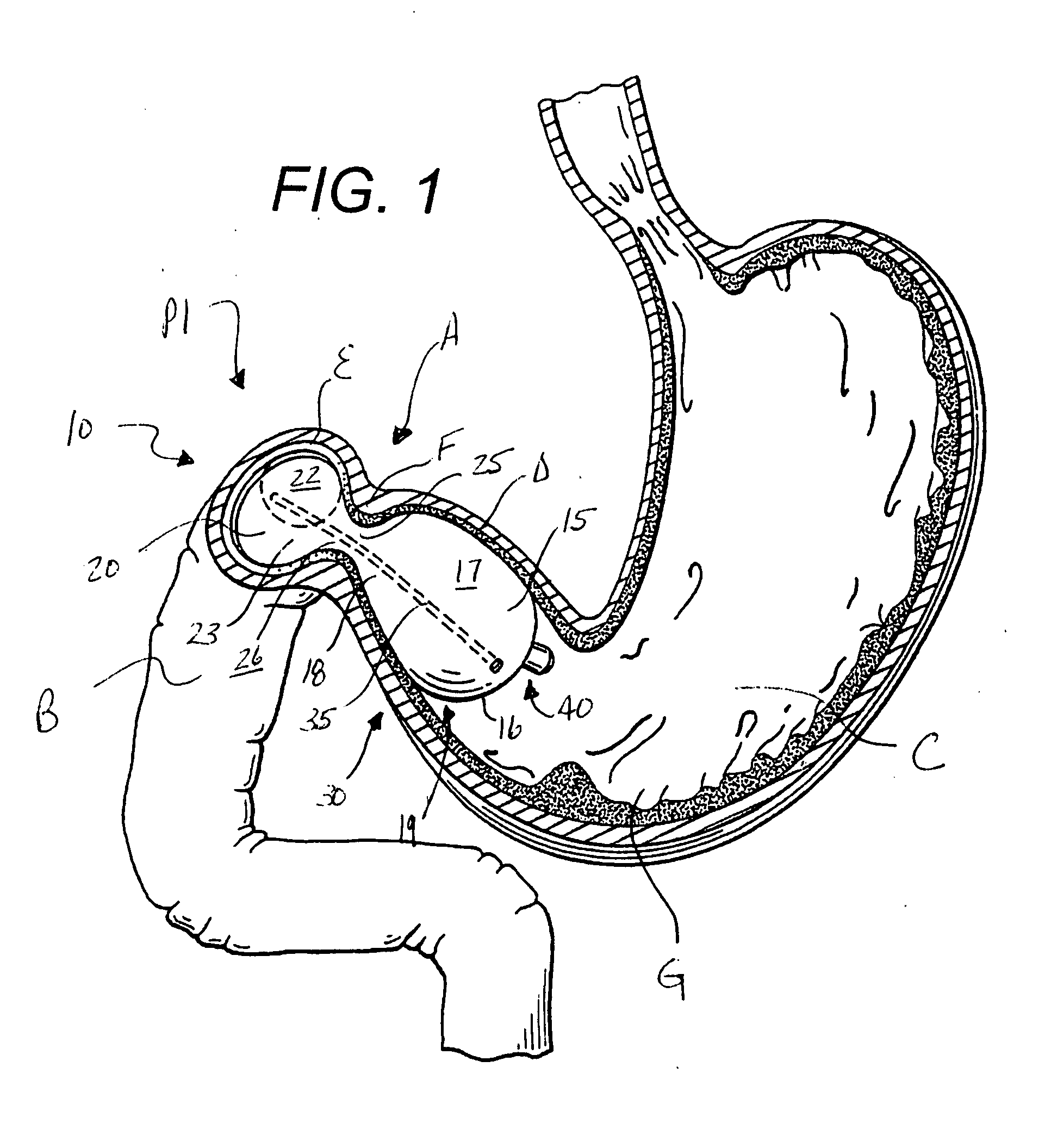
Floating gastrointestinal anchor
ActiveUS20090287231A1Improve overall senseSlowing gastric emptyingDilatorsObesity treatmentGas-filled tubeGastrointestinal tract
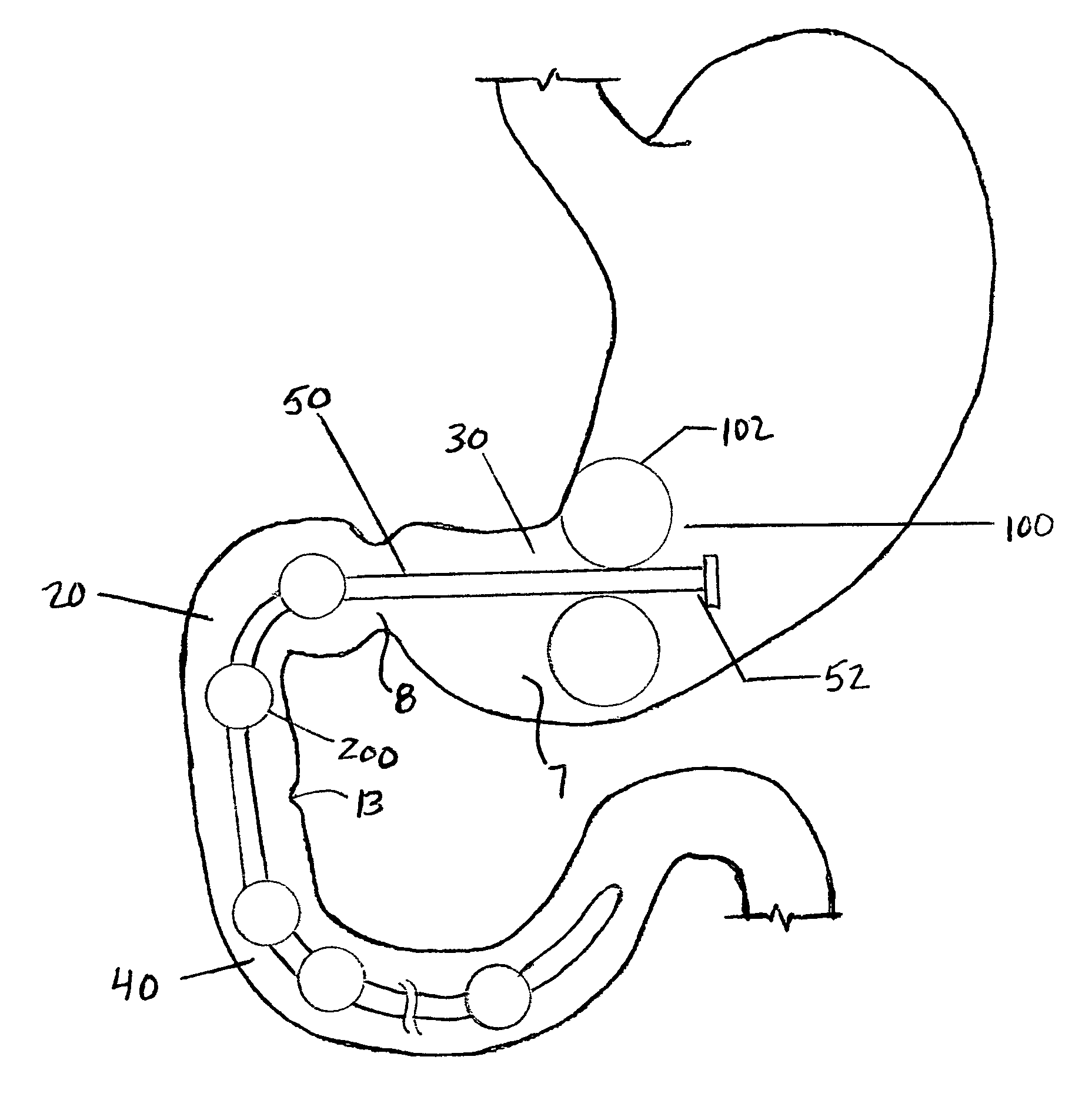
Apparatus (90) is provided for use in a stomach of a subject. The apparatus includes a balloon (92), adapted for placement in the stomach, and all anchor (102), coupled to the balloon. The anchor is adapted to prevent the balloon from passing into a duodenum of the subject. The apparatus further includes an inflation tube (96), coupled to the balloon to permit inflation of the balloon, and is adapted to stretch from the stomach to a mouth of the subject to facilitate inflation of the balloon. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:SPATZ FGLA INC (US)
Methods of treatment using a bariatric sleeve
InactiveUS20050080395A1Reduce twisting and bucklingReduce penetrationSuture equipmentsStentsGastrointestinal deviceLigament structure
Method and apparatus for limiting absorption of food products in specific parts of the digestive system is presented. A gastrointestinal implant device is anchored in the stomach and extends beyond the ligament of Treitz. All food exiting the stomach is funneled through the device. The gastrointestinal device includes an anchor for anchoring the device to the stomach and a flexible sleeve to limit absorption of nutrients in the duodenum. The anchor is collapsible for endoscopic delivery and removal.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
Bariatric sleeve delivery devices
Method and apparatus for limiting absorption of food products in specific parts of the digestive system is presented. A gastrointestinal implant device is anchored in the stomach and extends beyond the ligament of Treitz. All food exiting the stomach is funneled through the device. The gastrointestinal device includes an anchor for anchoring the device to the stomach and a flexible sleeve to limit absorption of nutrients in the duodenum. The anchor is collapsible for endoscopic delivery and removal.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
Intestinal sleeve
InactiveUS20060265082A1Reduce twisting and bucklingMinimize traumaSuture equipmentsStentsGastrointestinal deviceInsertion stent
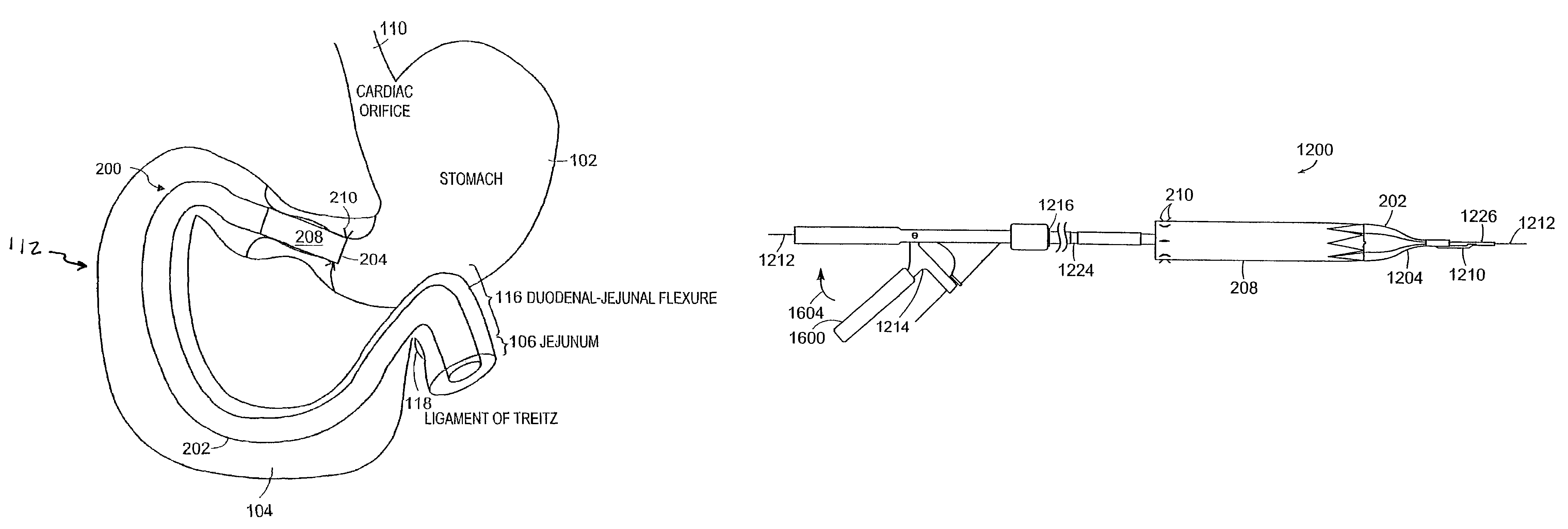
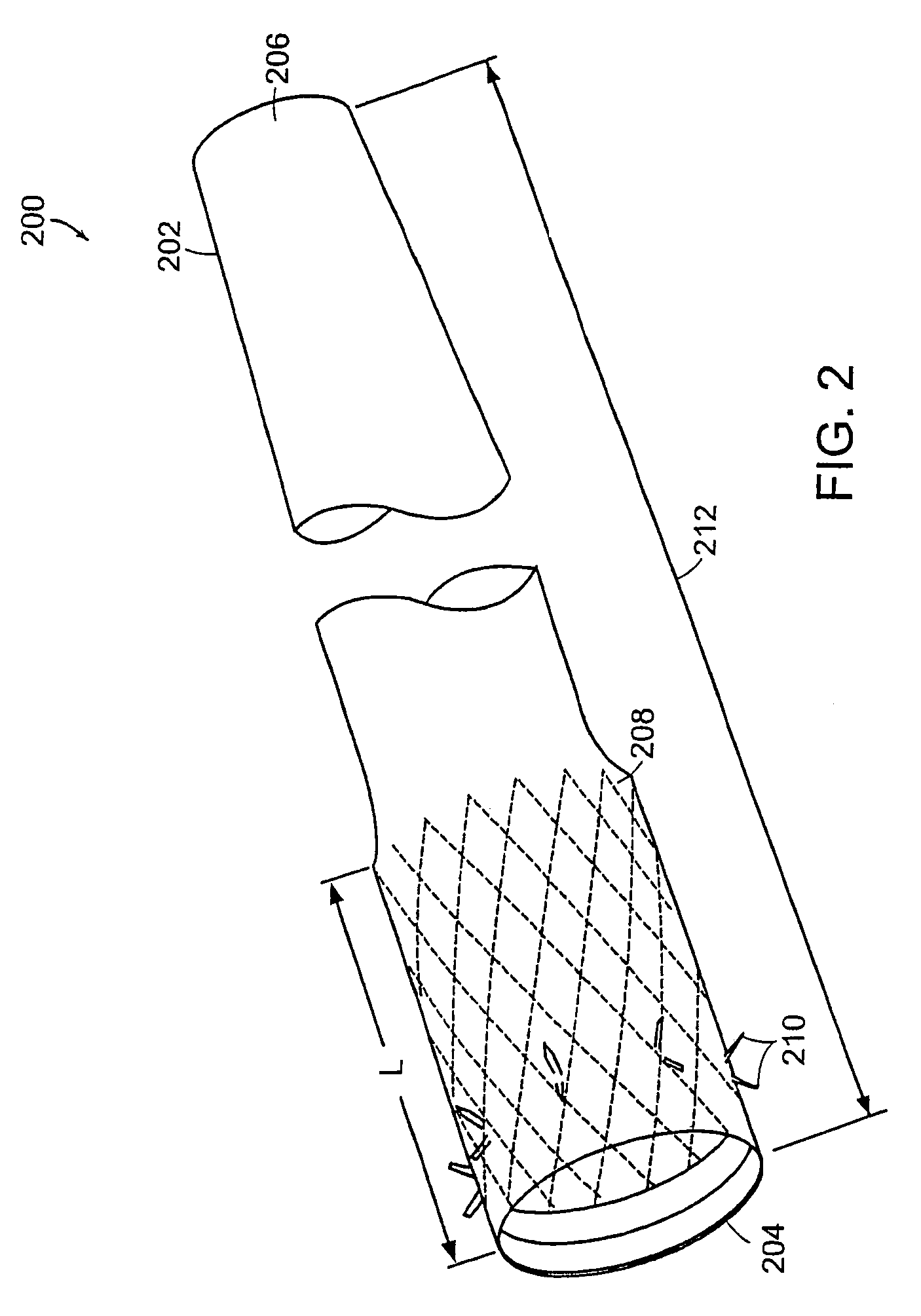
A gastrointestinal implant device is anchored in the duodenum and extends beyond the ligament of Treitz. All food exiting the stomach is funneled through the device. The gastrointestinal device includes an anchor for attaching the device to the duodenum and an unsupported flexible sleeve. The anchor can include a stent and / or a wave anchor and is collapsible for catheter-based delivery and removal.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
Pyloric valve corking device and method
ActiveUS20050033332A1Prevent premature passageMaintain sensationDiagnosticsDilatorsGastric ContentBiomedical engineering
Pyloric valve corking devices and methods are described herein. The devices generally include an occluding member which expands from a first configuration to a larger second configuration and a bridging member extending from the occluding member. The bridging member has a length which passes at least partially through the gastric opening such that the occluding member obstructs the gastric opening, and wherein the length permits the occluding member to intermittently move relative to the gastric opening. A second occluding member may be attached to the distal end of the bridging member. The reduction in flow of gastric contents into the duodenum can be tightly regulated using a pump or valve. Otherwise, the flow can be passively regulated with the occluding device.
Owner:BARONOVA
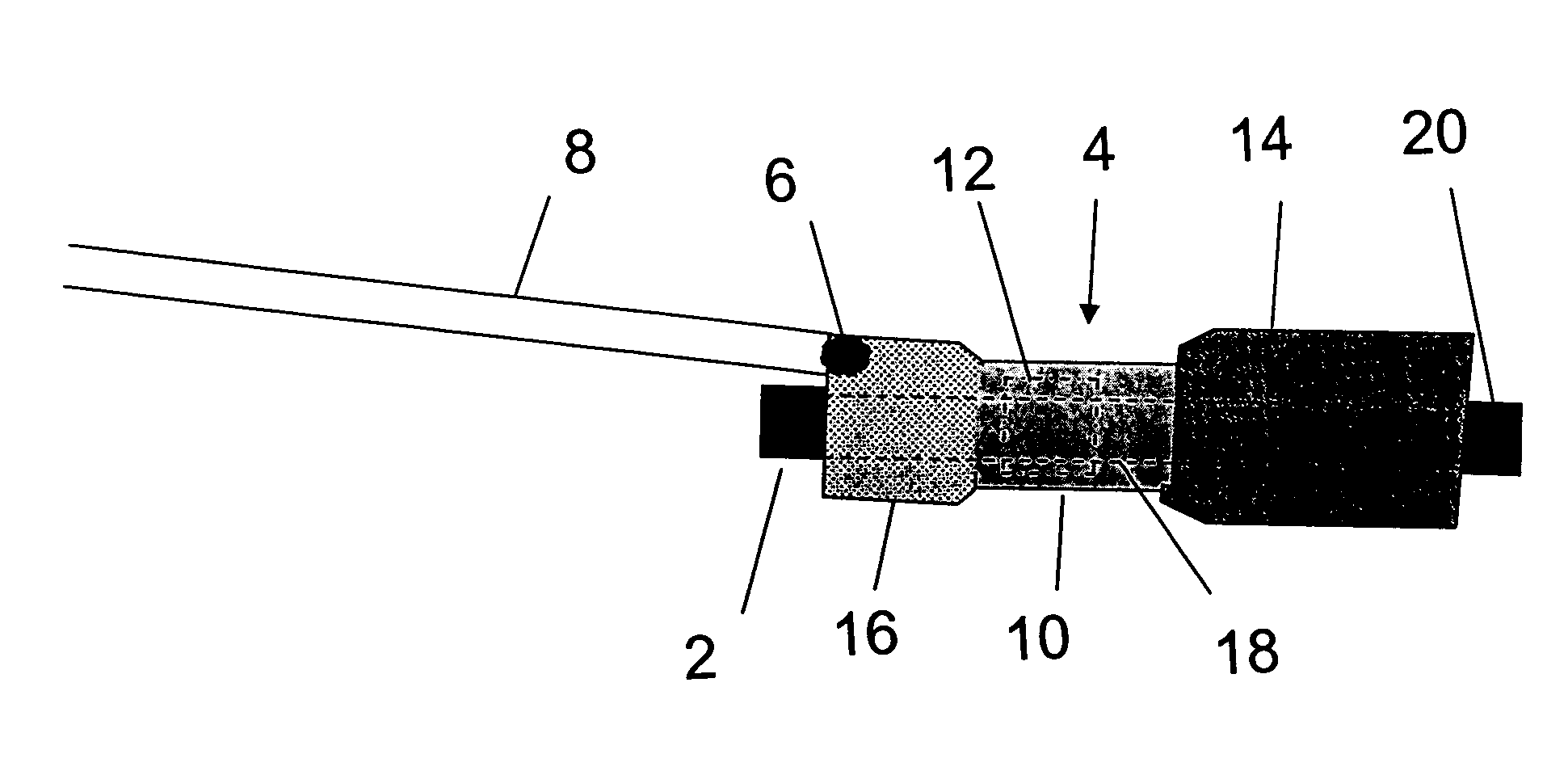
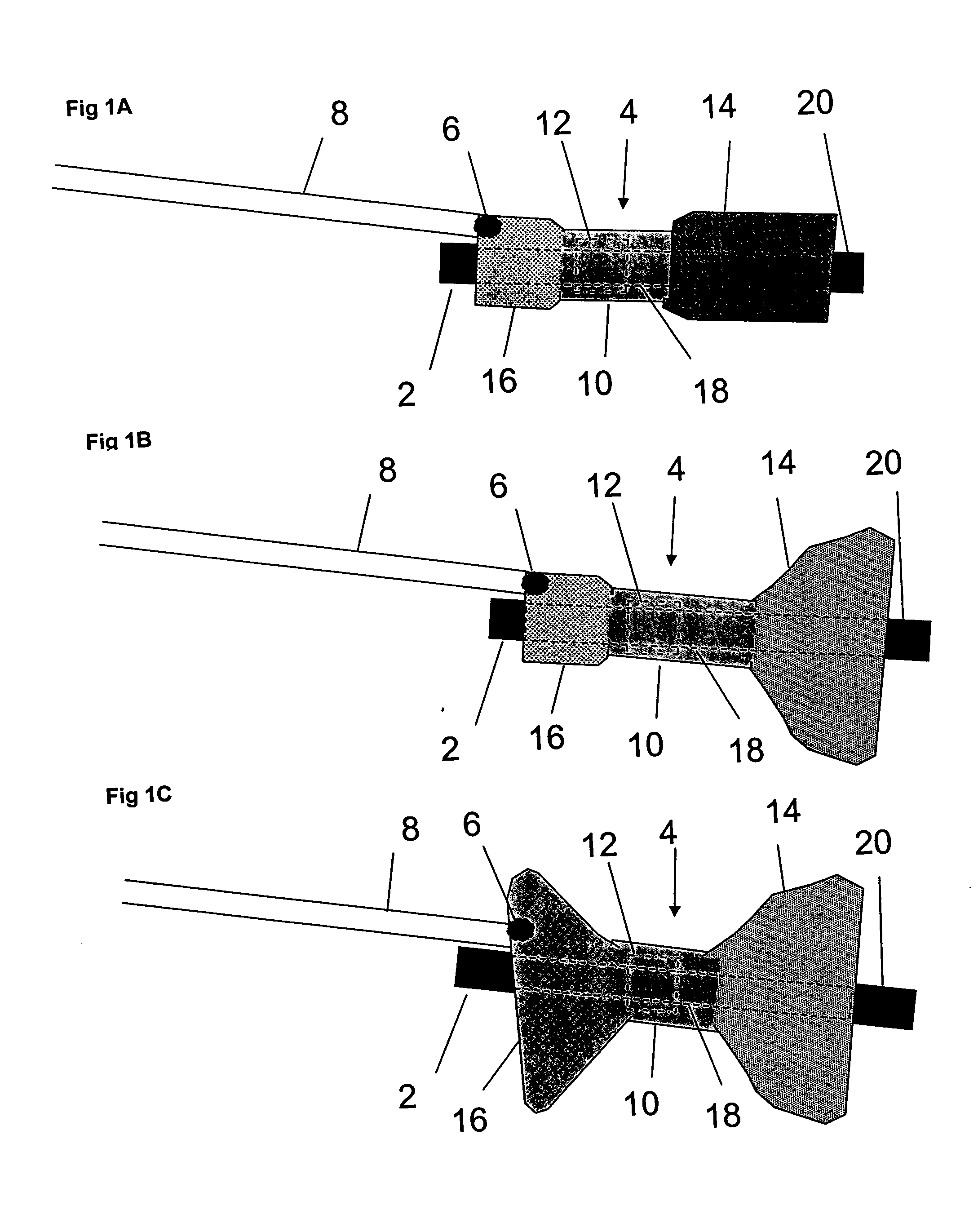
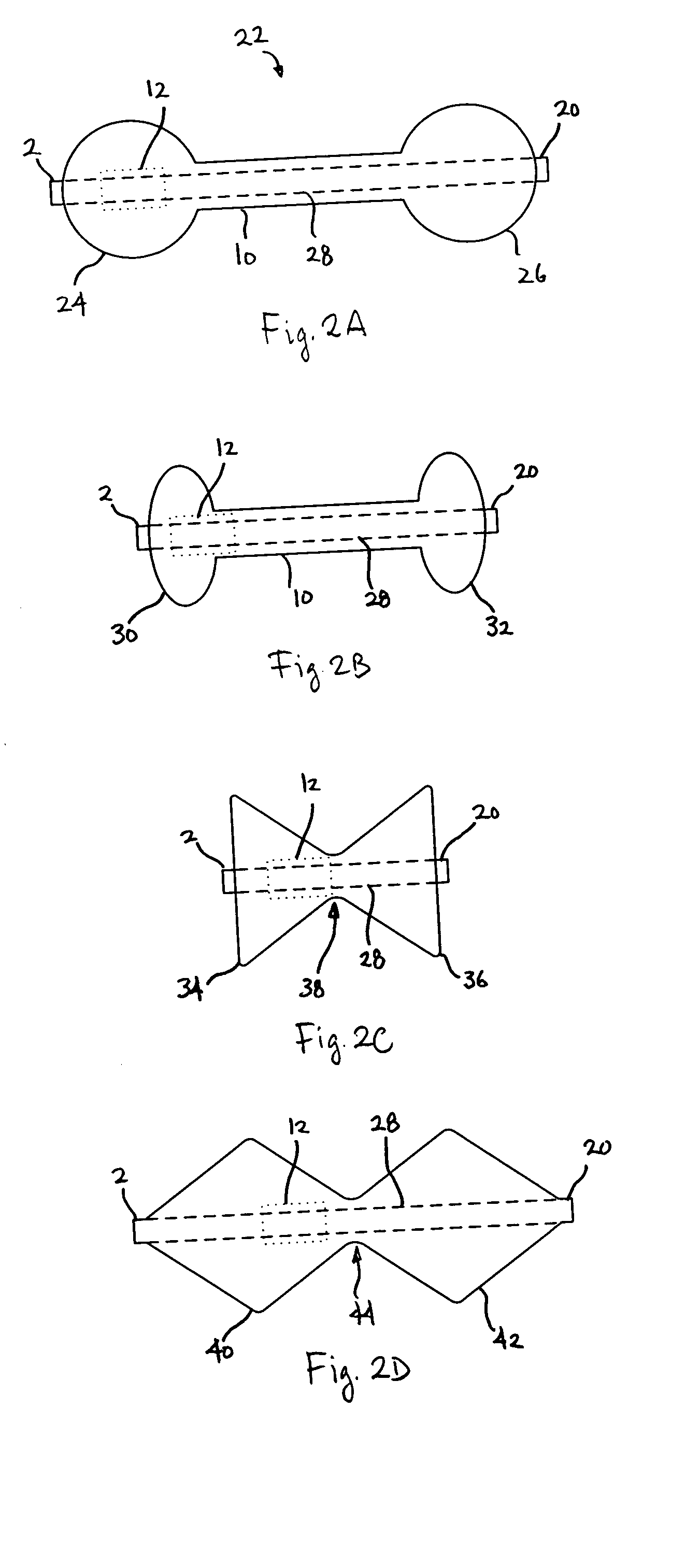
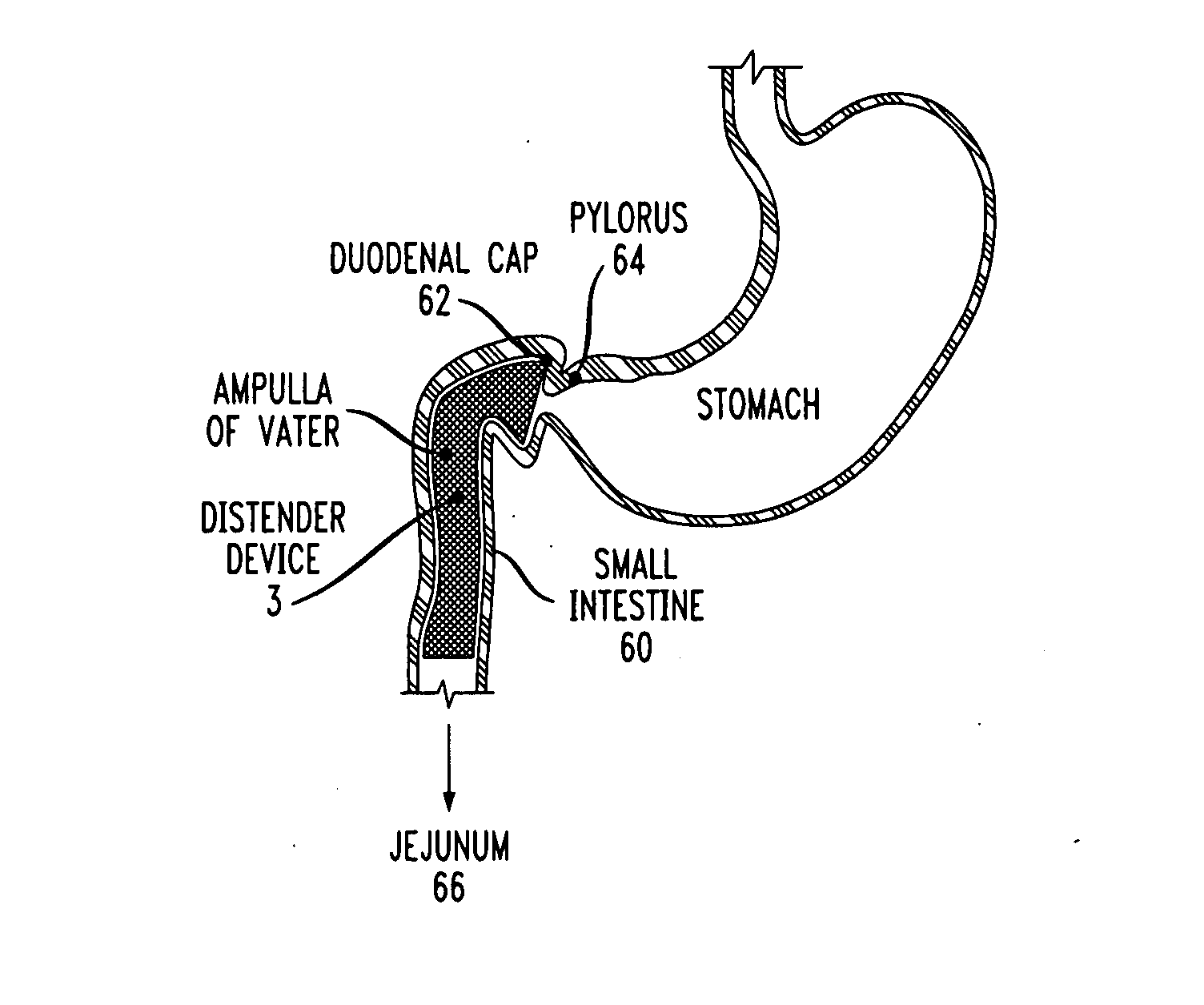
Distender device and method for treatment of obesity and metabolic and other diseases
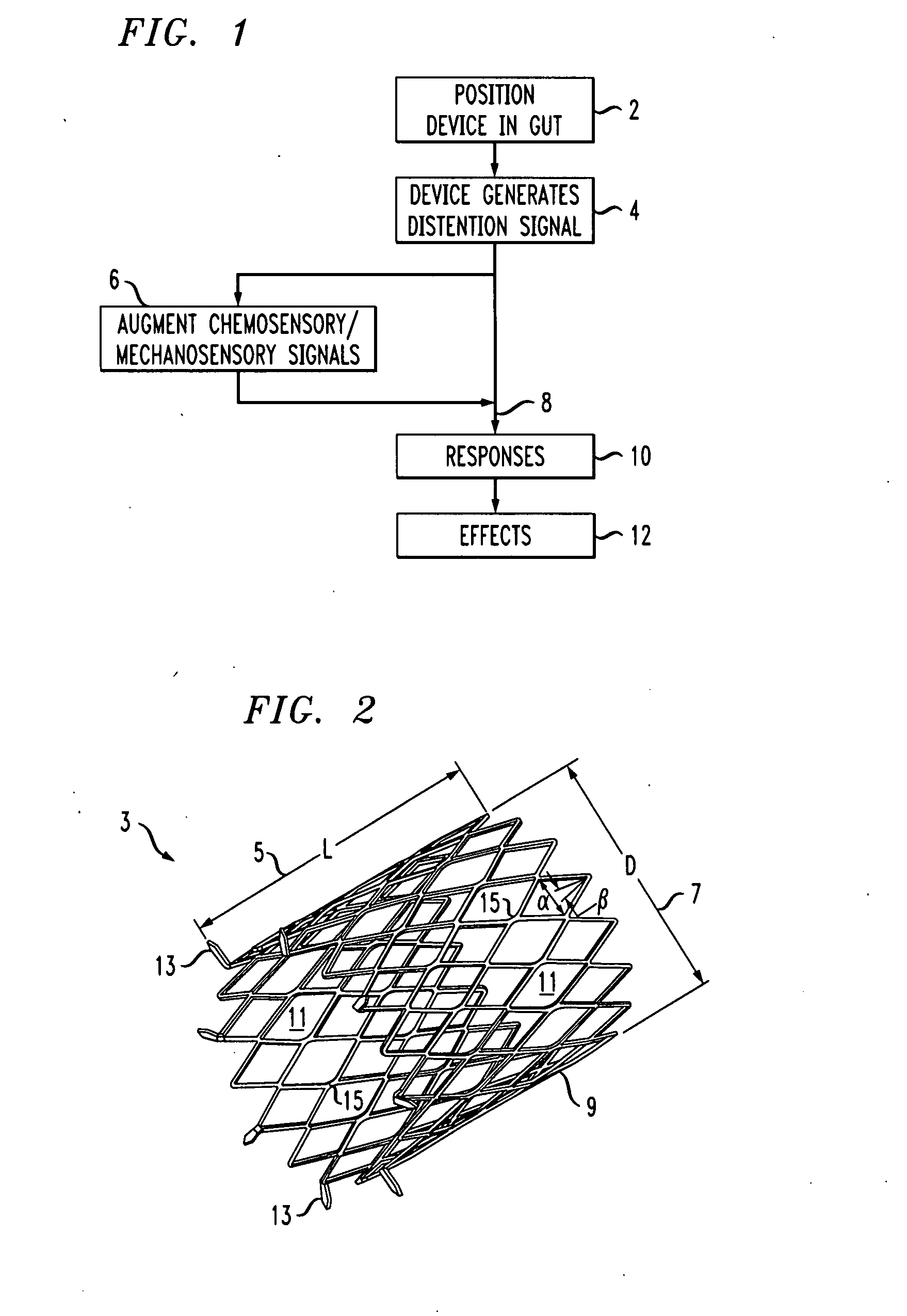
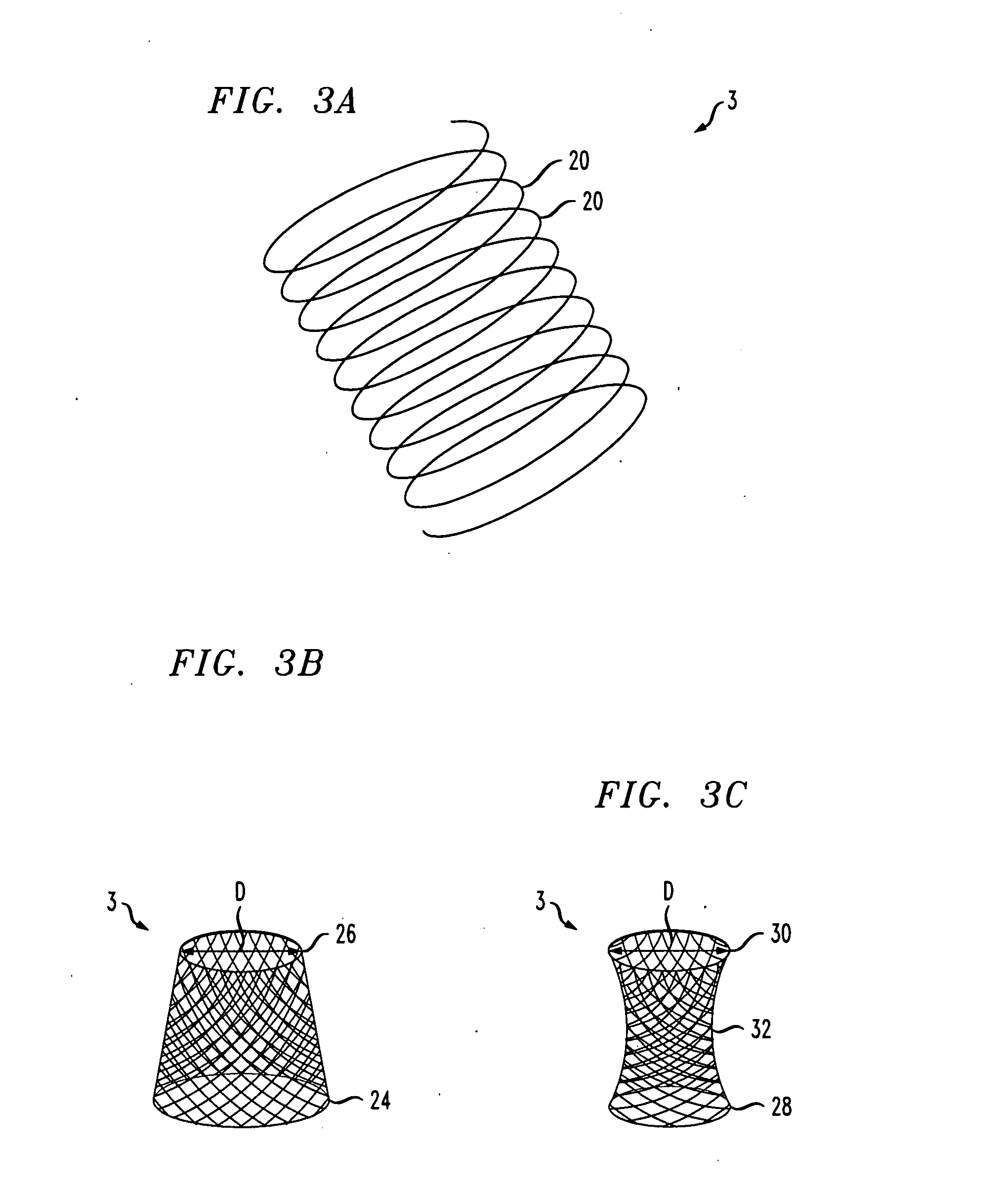
A gastrointestinal implant device is positioned in a patient's small intestine or rectum and produces an outward force that itself produces a distension signal which is a therapeutically useful neural or humoral signal that evokes satiogenic or weight loss effects by itself. The device may advantageously be placed in the duodenum adjacent the pylorus or in the jejunum, ileum or rectum. The distension signals may amplify chemosensory or mechanosensory signals such as enteroendocrine secretions within the patient. The device may be a mesh and include a low material density that allows for unrestricted chyme absorption within the small intestine and unrestricted chyme flow through the gastrointestinal system. A method includes inserting the device into the patient then either retrieving the device after treatment is complete or allowing a device formed of a biodegradable material to degrade in time after treatment is complete.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Semi-stationary balloon in the gastric antrum provided with connecting an anchoring rod for inducing weight reduction in human beings
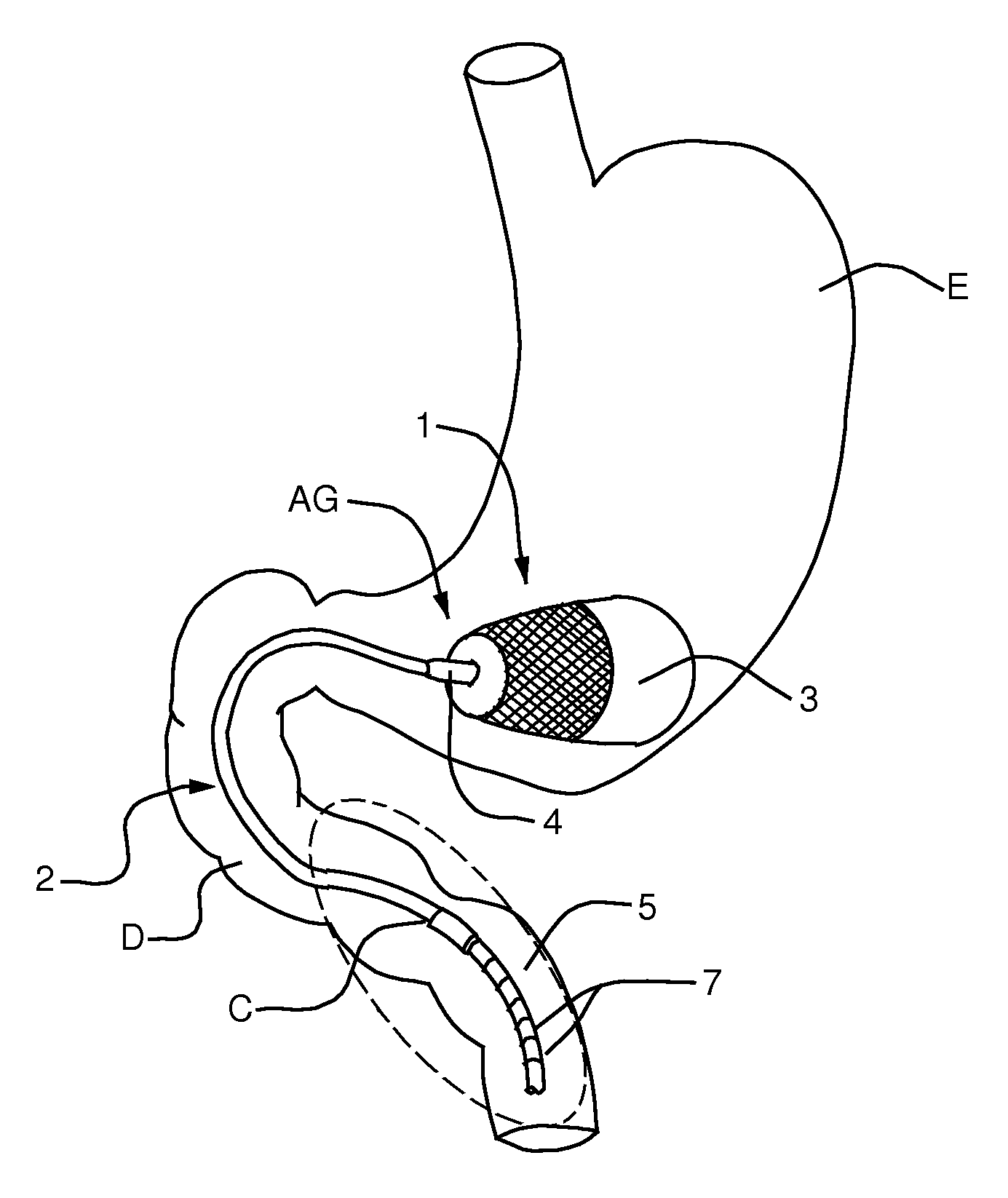
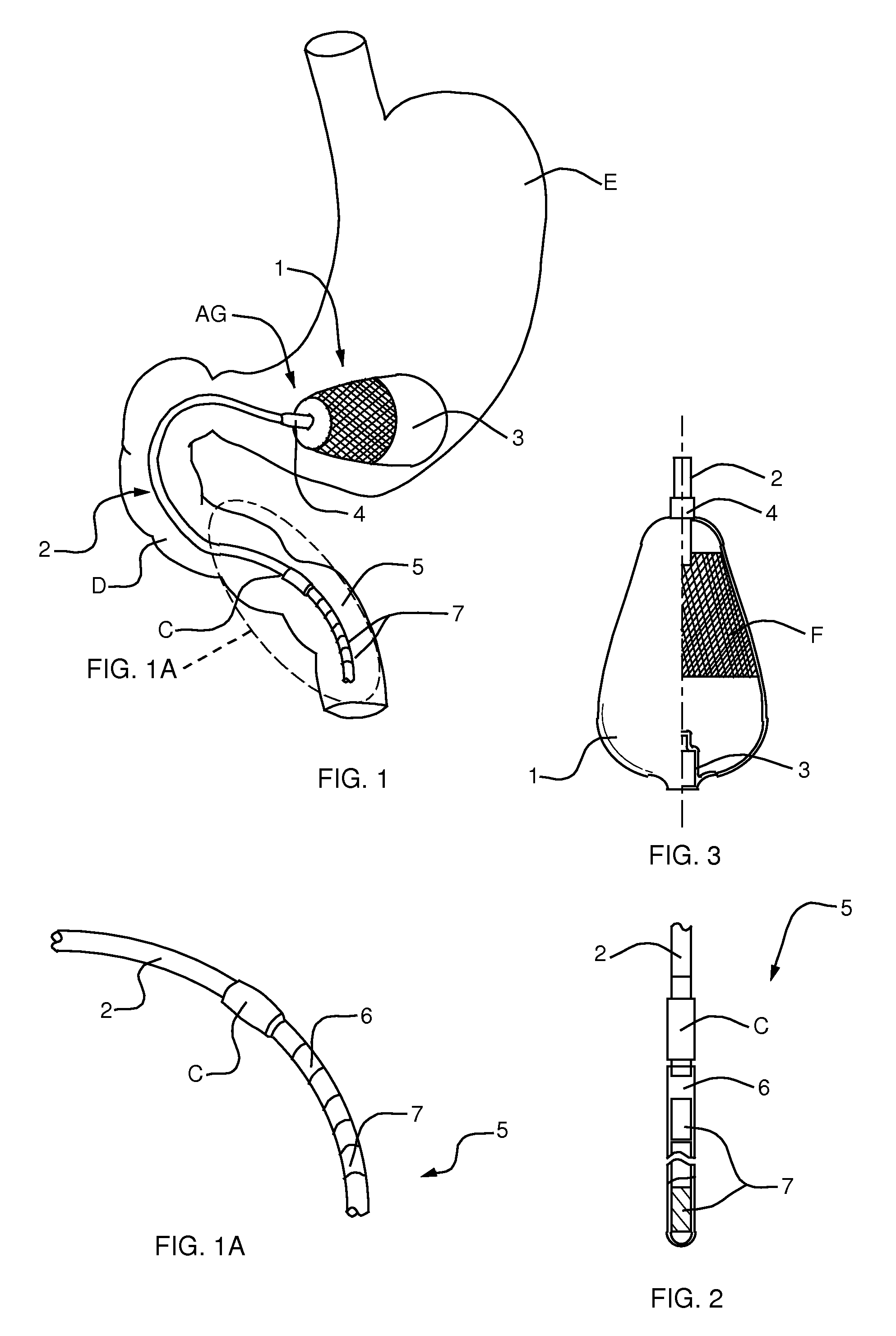
A semi-stationary balloon in the gastric antrum provided with an anchoring rod for inducing weight reduction in human beings is disclosed, a device for inducing a lesser appetite and early prandial satiety, said balloon being made of inflatable per-os medical grade silicone having a volume of up to 240 ml, with an average space of 120 ml to be filled with non-elastic fluid provided with radio-opaque contrast and dye, preferably methylene blue, so that the maximum diameter of 8 cm is reached after it is filled up with a volume of up to 240 ml and the average diameter of 6 cm with a volume of 120 ml, to be endoscopically placed inside the stomach (E); said intra-gastric balloon (1) being positioned in a semi-stationary way in the gastric antrum (GAC) and provided with an anchoring or duodenal rod (2) having a distal counter-weight (5) installed in the duodenum (D); particularly, the inner face of the pear-shaped medium portion of lesser diameter is coated with a malleable ribbon (f) that provides said balloon (1) with resistance and flexibility.
Owner:GAZI BASHIR MUSSA +2
Method and apparatus for treatment of gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD)
InactiveUS20040172084A1Easy dischargeSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsBody organsGastro-esophageal reflux disease
Owner:RESHAPE LIFESCIENCES INC
Device for intermittently obstructing a gastric opening and method of use
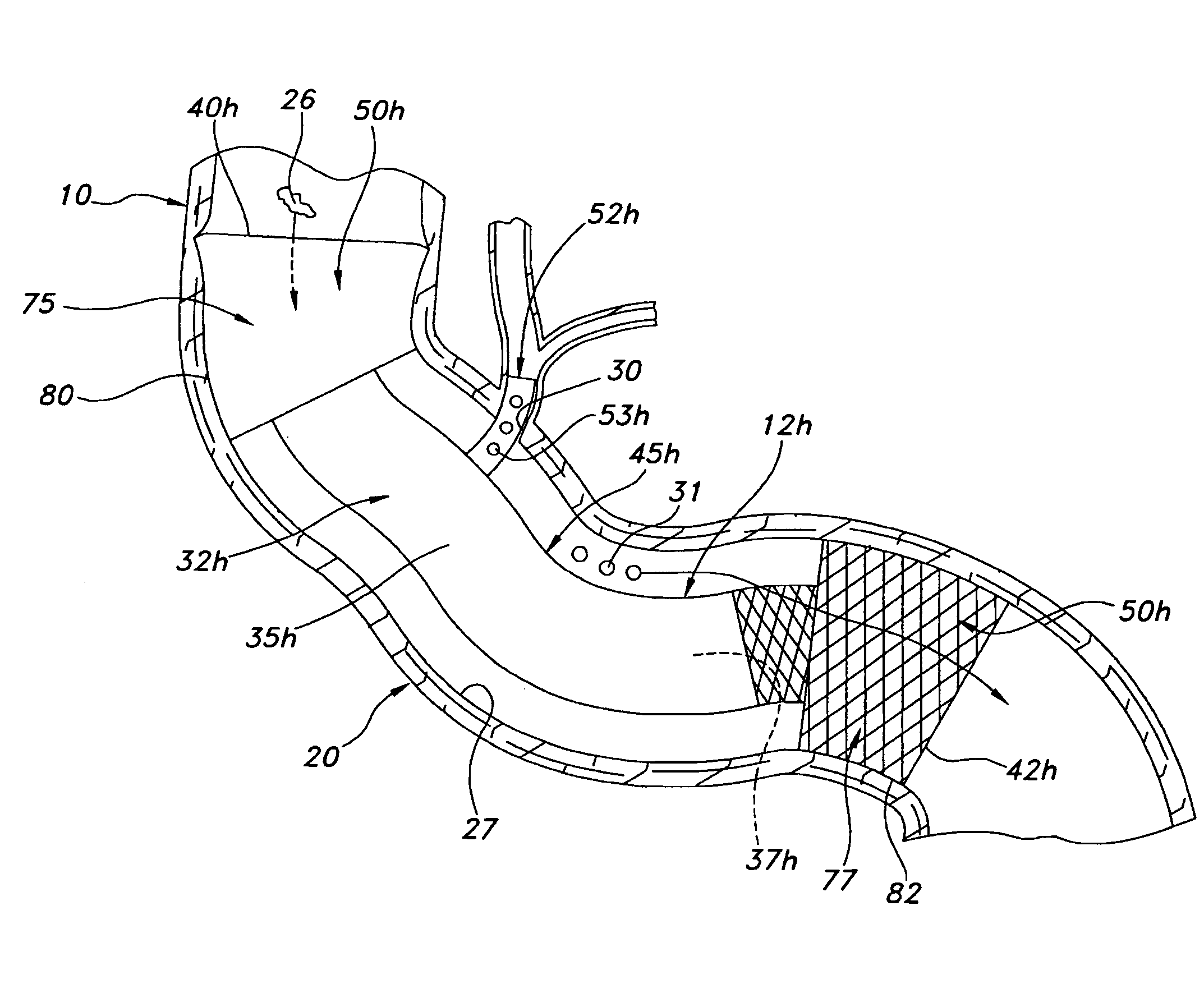
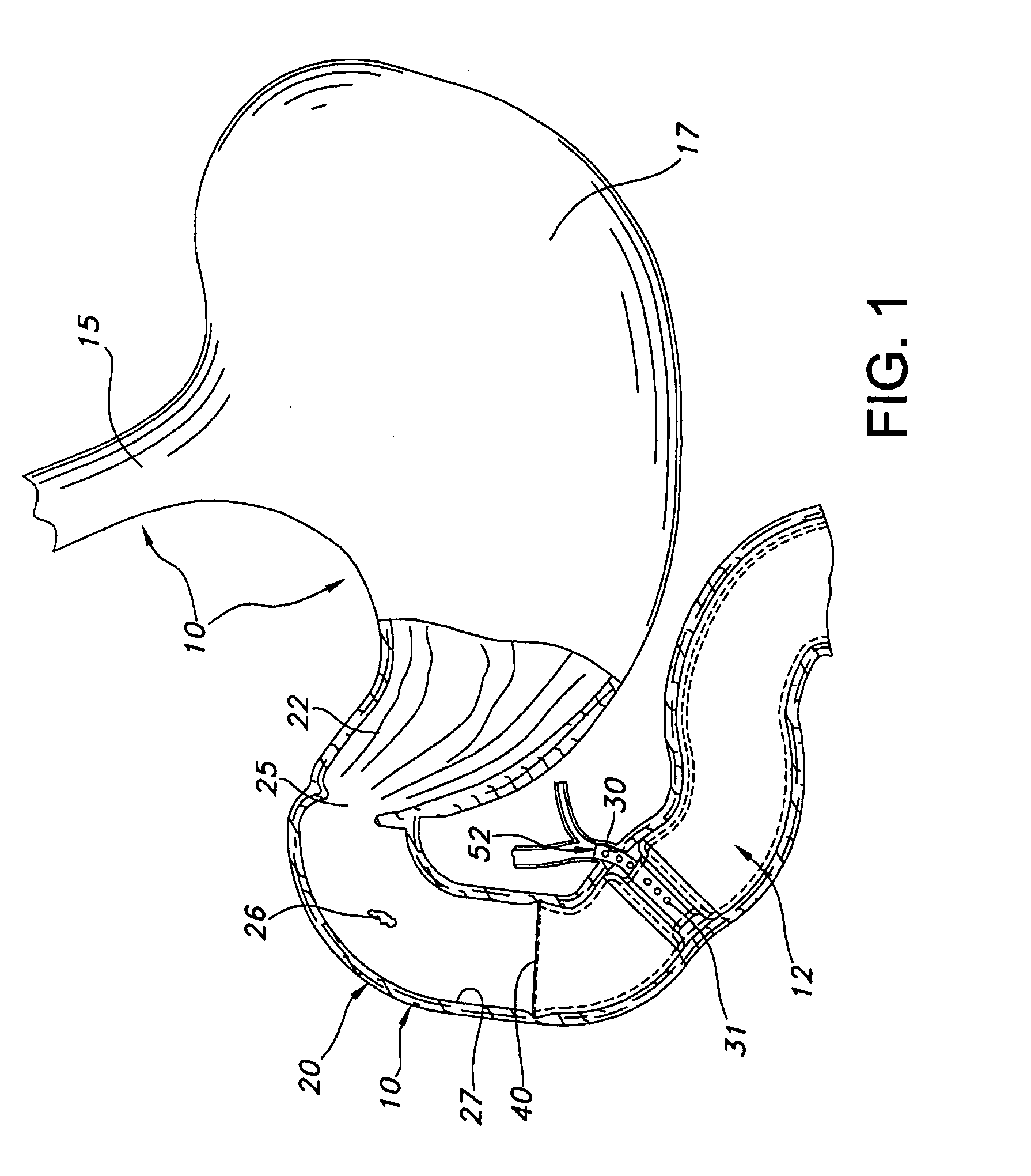
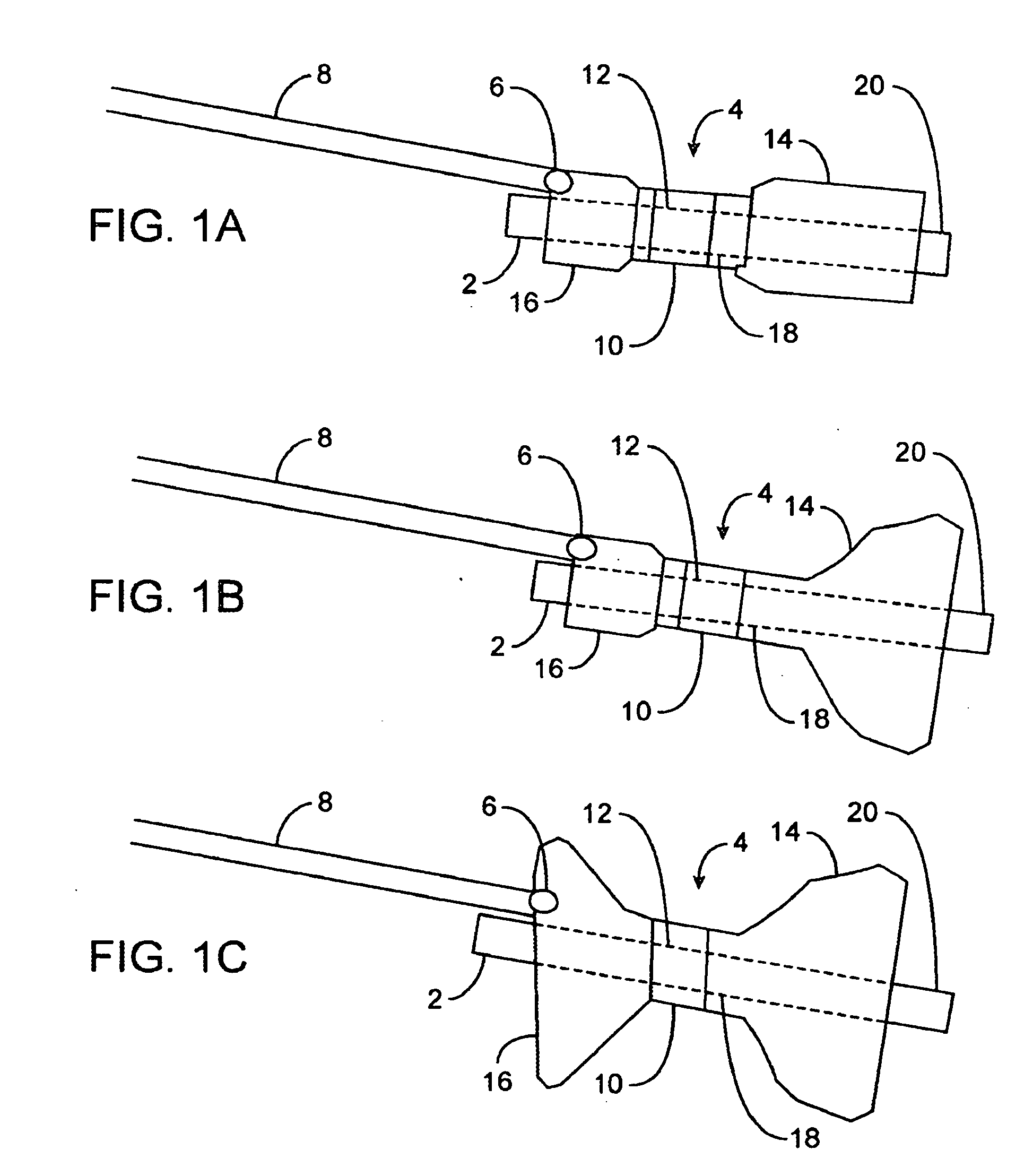
The present invention relates to a device for intermittently obstructing a bodily opening, such as a gastric opening, and includes a proximal member connected to a distal member by a tether. The proximal member includes an apron member surrounding a first occluding member, which is formable from an elongated and narrower configuration to a contracted or expanded but wider configuration. When employed in the stomach, the device of the present invention is arranged transluminally, with the distal member disposed in the duodenum and the proximal member disposed against the pyloric valve, intermittently occluding the pyloric valve and preventing or delaying the flow of gastric contents through the pyloric valve. In certain embodiments, a reservoir may be included for releasing a substance of interest, for example for releasing insulin from a reservoir disposed in the distal member. Sensors, actuators, and data transmission devices may also be included.
Owner:BARONOVA
Anti-obesity stent
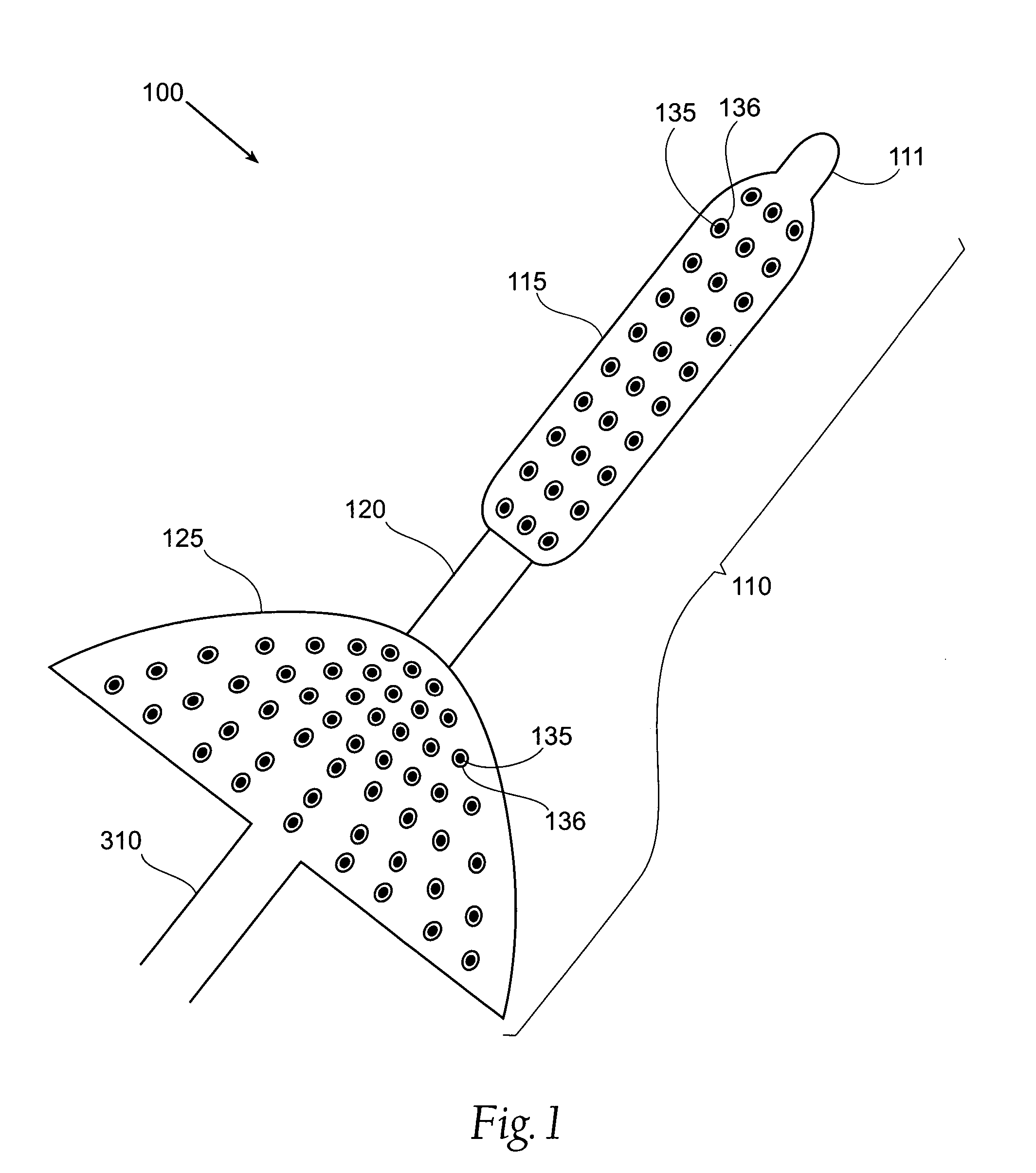
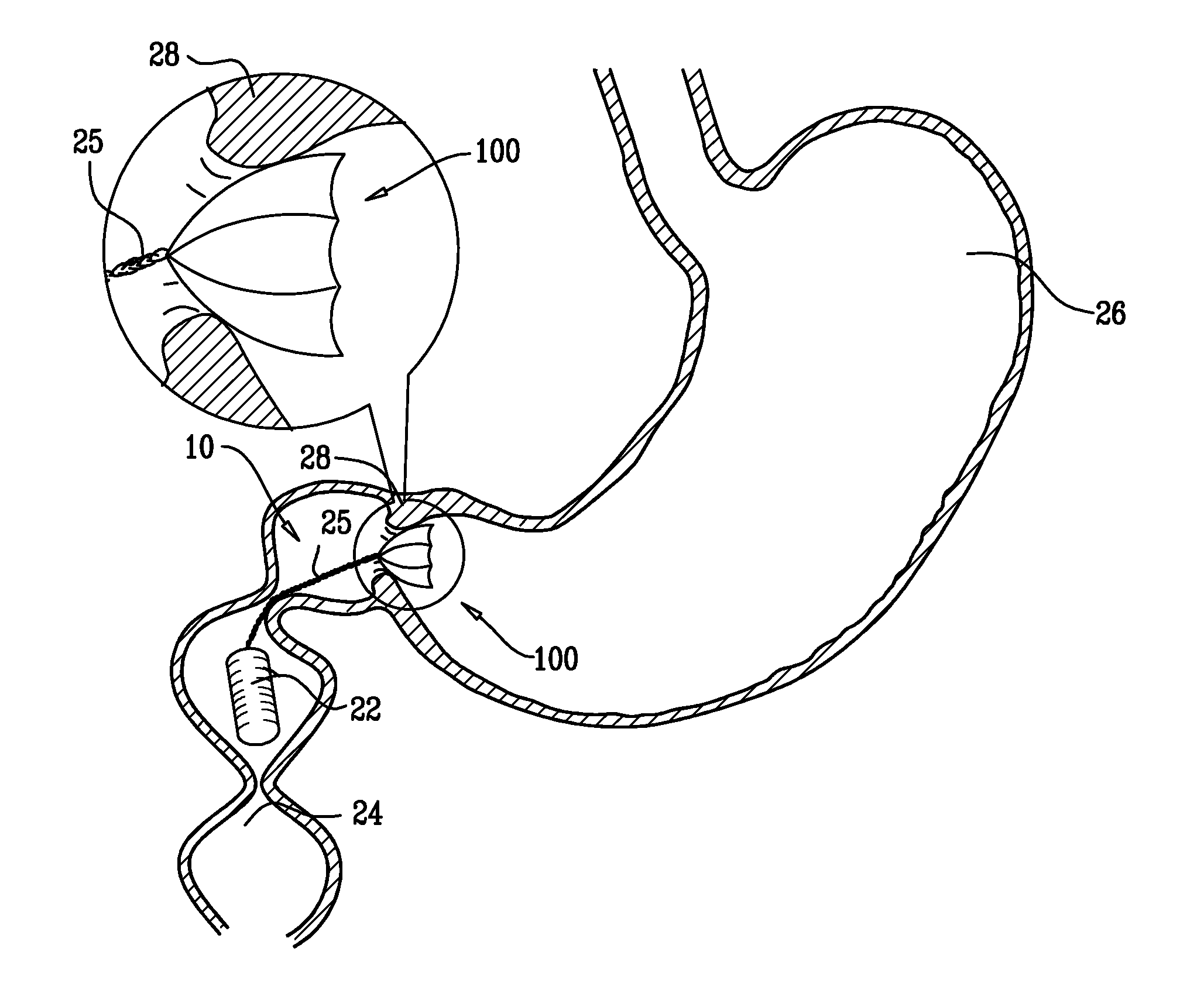
The anti-obesity stent includes a tubular structure having outer and inner surfaces and proximal and distal ends. The tubular structure is sized to fit within a duodenum in substantially coaxial relation therewith. The tubular structure is impervious or semi-permeable to digestive substances and chyme within the duodenum. The anti-obesity stent includes a transport structure at least a part of which is coincident with or connected to the outer surface. The transport structure extends to the distal end of the tubular structure. At least one retainer structure is connected to the tubular structure. The retainer structure secures the tubular structure within the duodenum such that the transport structure is positioned to receive digestive fluids from a papilla of Vater on an inner surface of the duodenum. The transport structure provides a conduit for the digestive fluids therein to flow to the distal end.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method for gastric volume reduction surgery
ActiveUS20090276055A1Avoid interactionSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesAbdominal cavityGastric Content
A method for treating a patient includes creating at least one incision to gain access to an petitoneal cavity, performing a gastric volume reduction procedure and introducing a device to prevent gastric contents from interacting with at least a portion of the duodenum.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Guided catheter with removable magnetic guide
A feeding tube apparatus, a kit containing the feed tube apparatus and method for intubating a patient to deliver the feeding tube apparatus to the desired location for delivering nutrients and / or medication are described herein. The feeding tube apparatus (10) contains at least a catheter (20) and a removable stylet (30), where the removable stylet contains one or more magnetic materials (32a-j). In one embodiment, the stylet contains more than one magnetic material in the form of a magnet stack (33). The feeding tube apparatus is used in combination with a suitable external magnet (40) which a medical practitioner can use to guide the feeding tube apparatus (10) through the intestinal tract. Optionally, the feeding tube apparatus contains additional components, such as a spring wire guide. The feeding tube apparatus is inserted into the patient's body and the external magnet (40) is applied to the patient's body within the minimum distance required to create a magnetic field between the external magnet (40) and the magnetic material(s) (32) located at the distal end (34) of the stylet (30) that is sufficiently strong to allow the external magnet to guide the catheter and stylet through the intestinal tract, and into the distal duodenum (470) of the small intestine. Once the catheter is placed in the desired location, the stylet is removed, thereby removing the magnetic material(s) from the feeding tube apparatus. This allows for the catheter to remain in place while the patient undergoes diagnostic testing, such as magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:SYNCRO MEDICAL INNOVATIONS
Method and apparatus for reducing obesity
Method and apparatus for treatment of morbid obesity by placement of a series of flow reduction elements in the small intestine to induce satiety are disclosed. The flow reduction elements restrict the movement of partially digested food and reduce the flow rate through the small intestine which causes the emptying of the stomach and the duodenum to occur slower. The flow reduction elements are attached to an elongated tube and are constructed from various shapes and configurations. The flow reduction elements may be inflated with fluid or may be constructed from self-expandable materials. The device is anchored in the antrum of the stomach with an anchoring member. The transoral gastric device can be inserted with a delivery catheter through the working lumen of an endoscope or alongside an endoscope and may be removed with the aid of an endoscope if desired.
Owner:ENDOSPHERE
Pyloric valve corking device
ActiveUS20070135831A1Reduce trafficEasy to placeSuture equipmentsElectrotherapyGastric ContentBiomedical engineering
Pyloric valve corking devices are disclosed herein that generally include an occluding member, expanding from a first configuration to a larger second configuration, and a bridging member extending from the occluding member. The bridging member has a length that is adapted to pass at least partially through the gastric opening, so to enable the occluding member to obstruct the gastric opening, and that is also adapted to permit the occluding member to intermittently move relative to the gastric opening. A second occluding member may be attached to the distal end of the bridging member. The reduction in flow of gastric contents into the duodenum can be actively regulated using a pump or valve, or can be passively regulated with movements of the occluding device.
Owner:BARONOVA
Devices and methods for endolumenal therapy
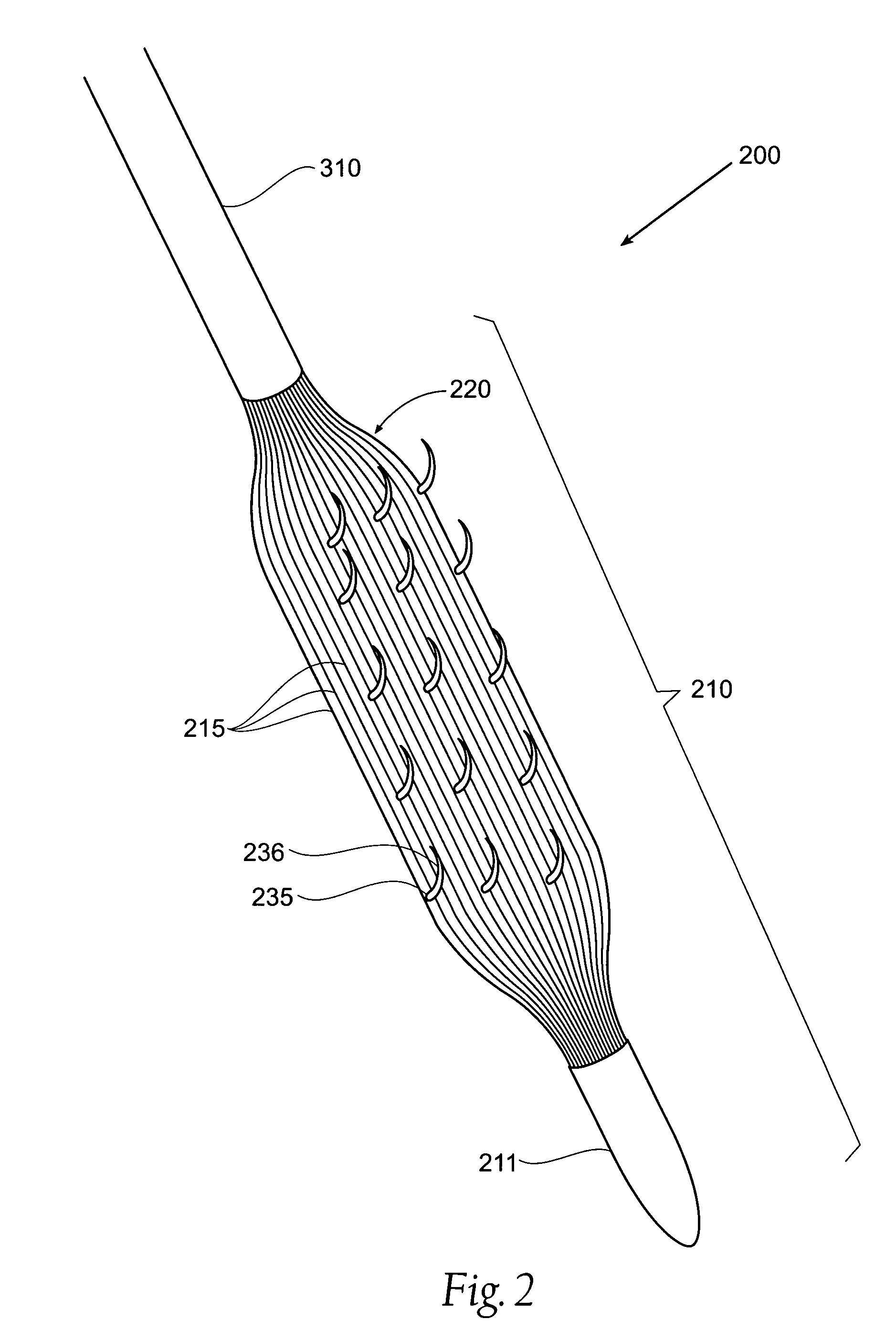
InactiveUS20090093767A1Promoting tissue in-growthAltering abilityDiagnosticsSurgeryGastrointestinal deviceLower esophagus
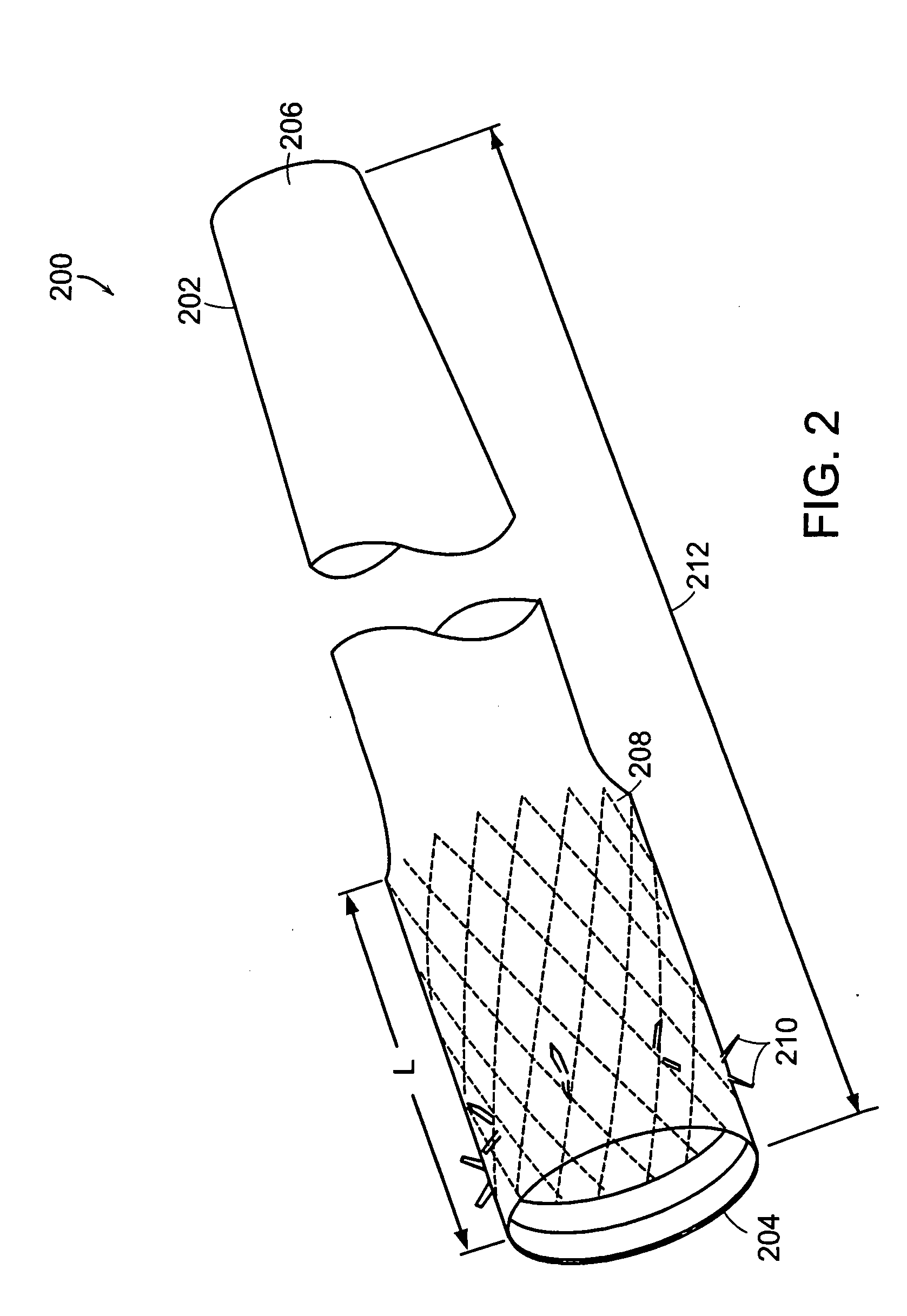
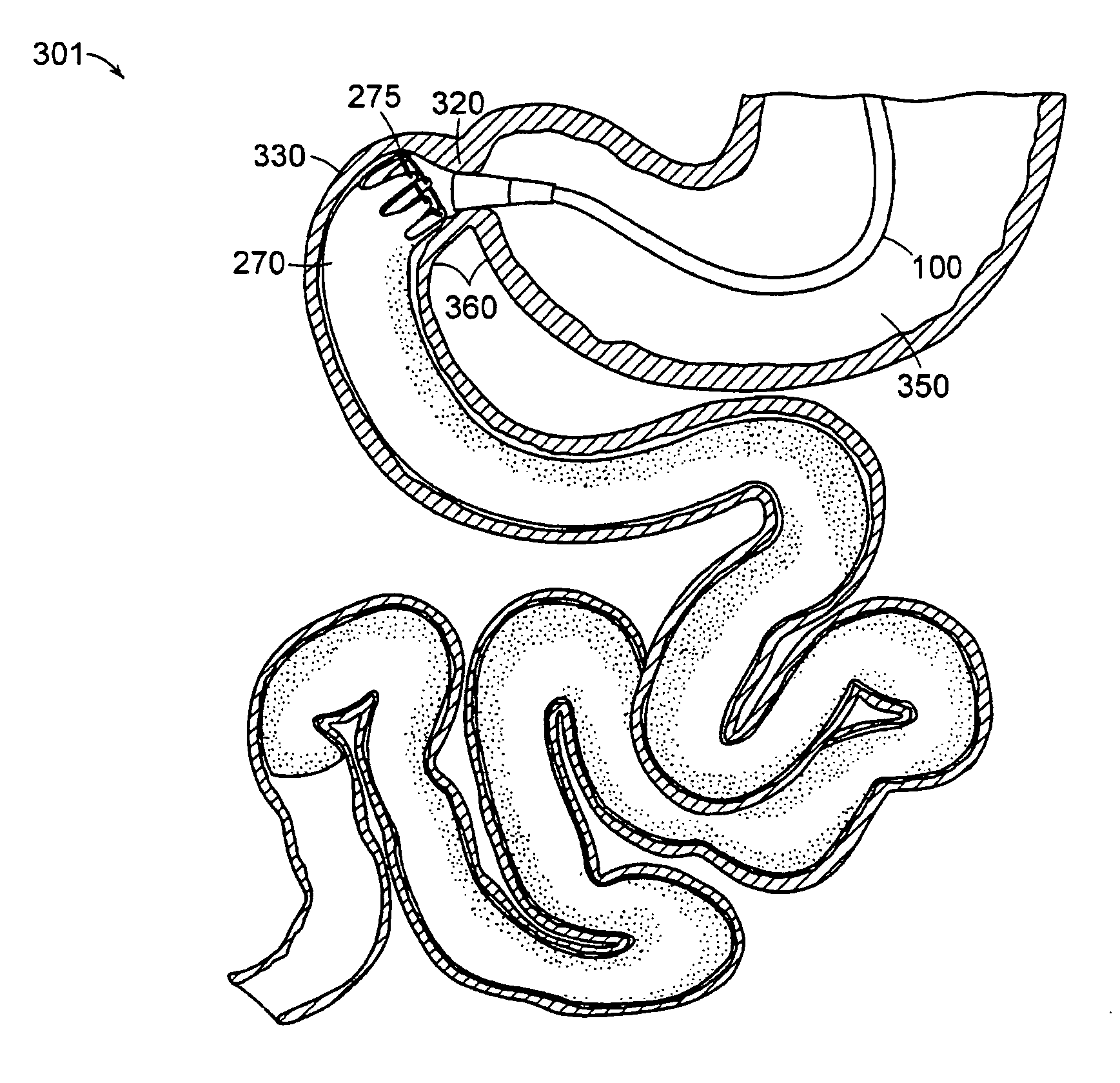
The present invention is directed generically to a means for altering the ability of the mammalian body to absorb nutritive content from ingested foodstuffs, and more specifically to an apparatus and method of use for an endolumenal sleeve (referred to also as an “intragastrointestinal device” or “gastrointestinal device”) positioned in the mammalian gastrointestinal (GI) tract. A suitable endolumenal sleeve is comprised of an anchor element and an opening at a proximal end, an elongate lumen or hollow open-ended tube having a transverse dimension, and a distal orifice. Optionally, an exterior aspect of the elongate lumen may include additional modes of attachment to the tissues walls of the GI tract through the use of one or more means for promoting tissue in-growth. The endolumenal sleeve is retained in the GI tract such that a substantial fraction of the food and liquids passing through the GI tract is channeled into the proximal opening and through an interlumenal space defined within the interior space of the endolumenal sleeve. Within the endolumenal sleeve there may be one or more restrictive means to constrain, impede or otherwise control the operative flow of material through the device. An individual restrictive means can either be of a fixed geometry or such means may include one or more elements which are adjustable in nature or function. The elongate lumen of the endolumenal sleeve is formed of a polymer composition suitable for controlled ingress of biological secretions, egress of certain selected nutritional elements, and may comprise either a single tubular structure or a multi-section (i.e. articulated and / or multiple lumen) assembly. When the endolumenal sleeve is in situ within the mammalian gastro-intestinal system, ingested foodstuffs are conveyed from the proximal end to said distal orifice. In typical applications, the proximal end of the endolumenal sleeve is positioned within the physiological region extending from the lower esophagus to the duodenum and the distal orifice is positioned within the physiological region extending from the upper duodenum to the lower jejunum, though further extension into the lower intestine is possible. Through proper selection of position for the endolumenal sleeve proximal and distal ends, combined by selection of the composition used in the fabrication of the elongate lumen, it is possible to finitely control the degree of nutritive absorption performed by the gastrointestinal tract.
Owner:KELLEHER BRIAN
Gastrointestinal implant
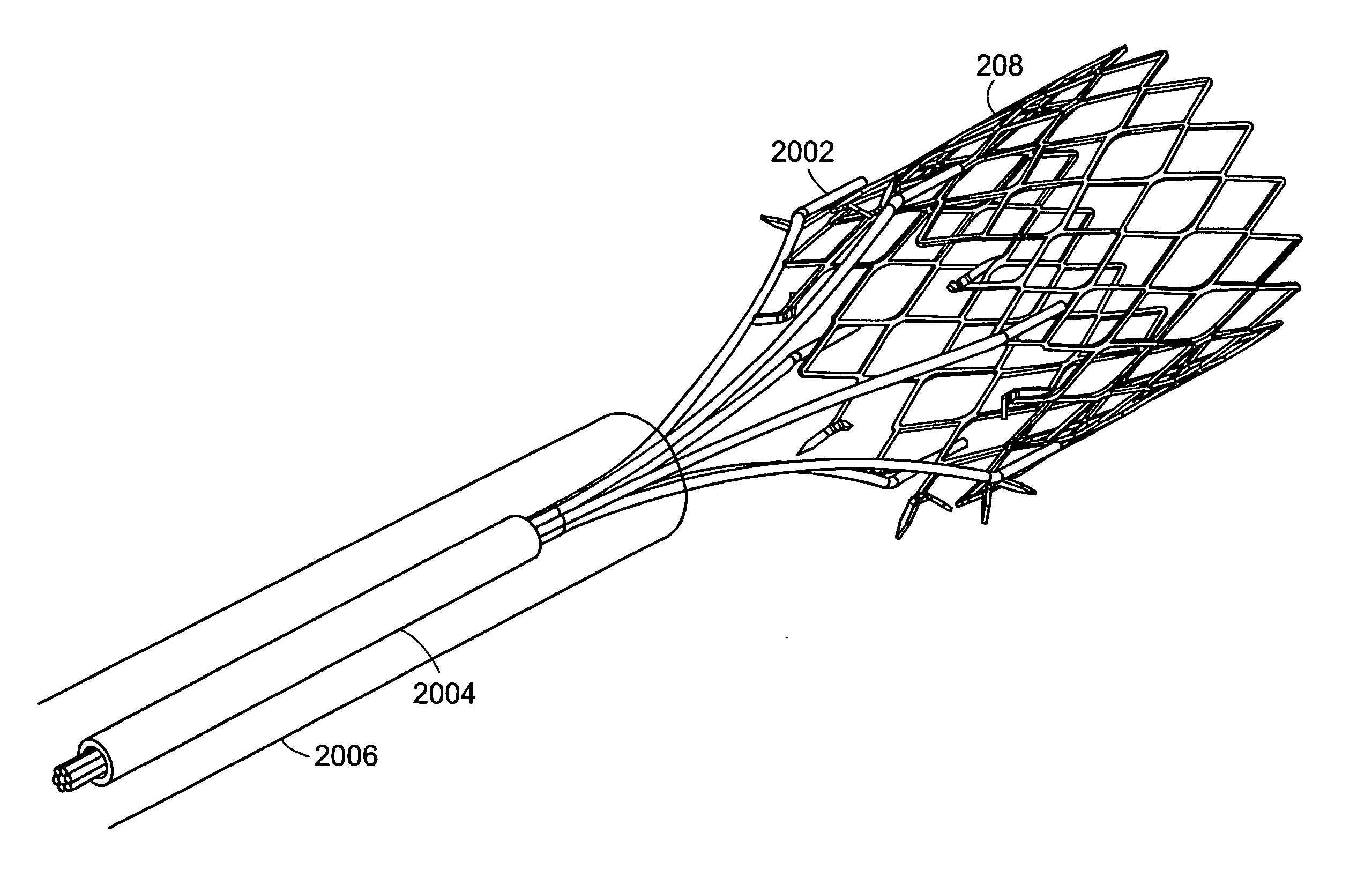
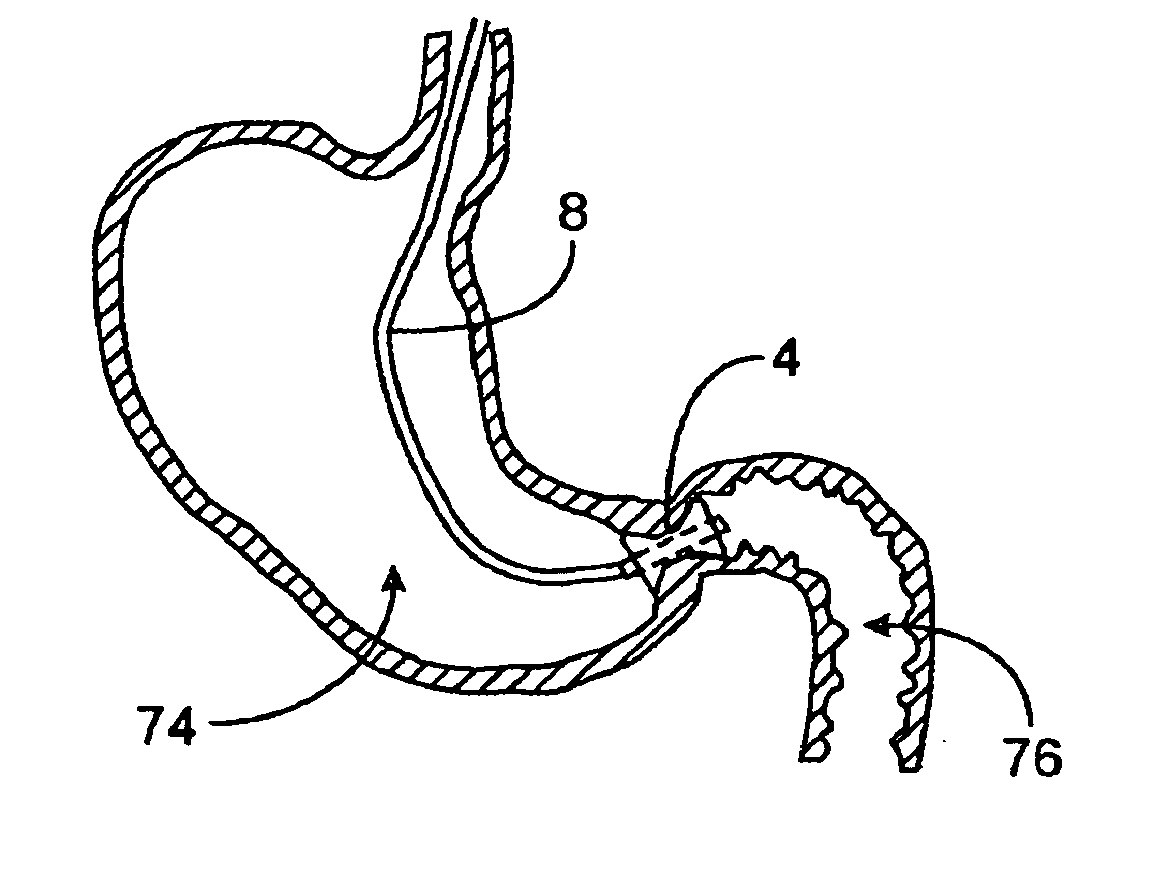
A gastrointestinal implant device comprises a sleeve for extending into the duodenum and an artificial valve for placement at the pylorus to control flow from the stomach into the duodenal sleeve. The implant device also comprises a support structure for the valve.
Owner:VYSERA BIOMEDICAL
Gastrointestinal implant with drawstring
A gastrointestinal implant device includes a flexible, floppy sleeve, open at both ends, that extends into the duodenum. The device further includes a collapsible anchor coupled to the proximal portion of the sleeve. The device further includes a drawstring that is threaded through a proximal end of the anchor, and barbs that extend from the exterior surface of the anchor. The collapsible anchor can be a wave anchor. The drawstring can be used to collapse at least a proximal portion of the implant device. This is useful in removing or repositioning the implant device.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
Method for treating obesity using an implantable weight loss device
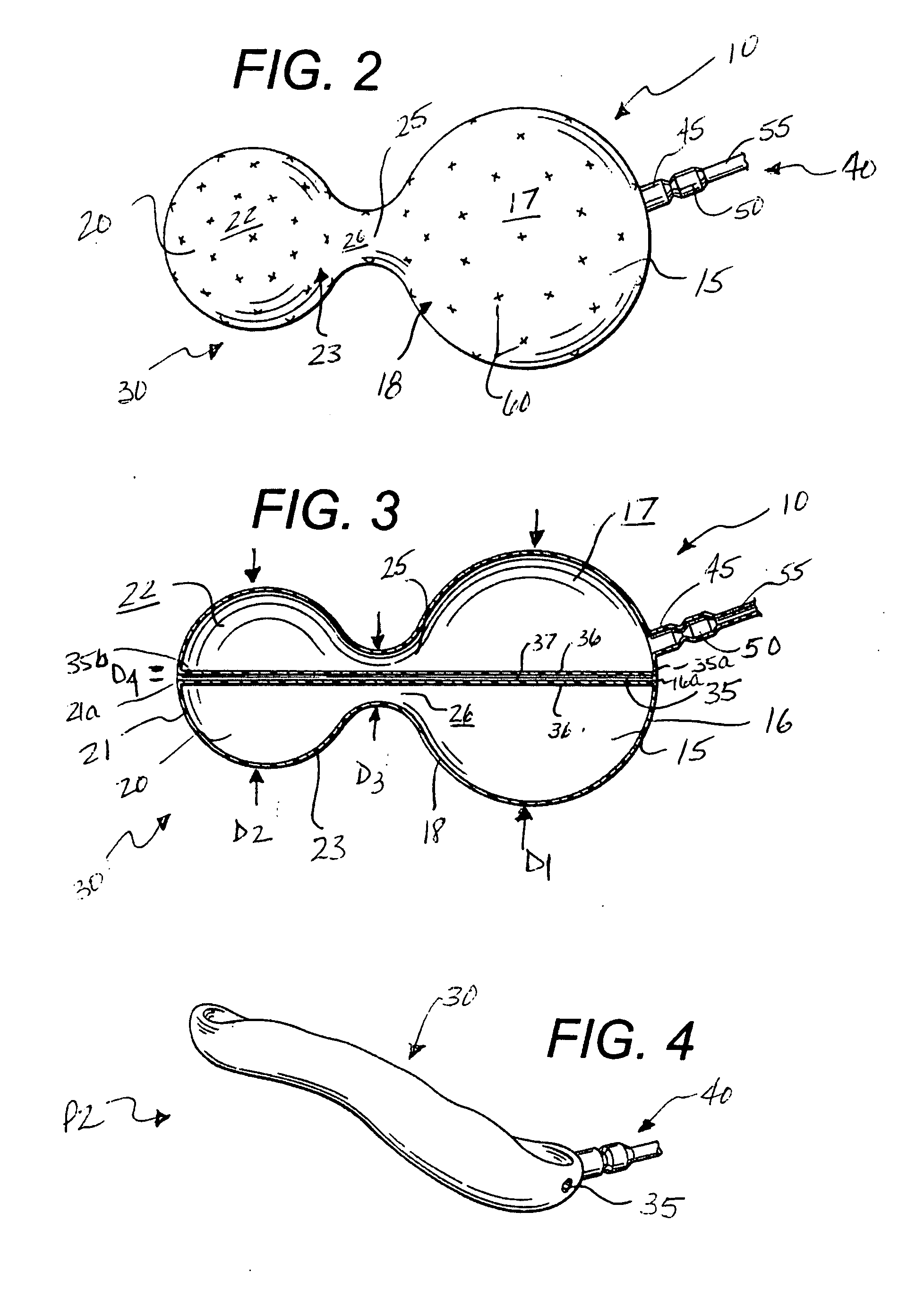
InactiveUS20080208239A1Reduce the overall diameterAccelerate the accumulation processSurgeryDilatorsPylorusProximate
The present invention provides methods of treating overweight or obese patients with an inflatable weight control device that is implanted in the patient's digestive tract. A first method comprises the steps of providing the weight control device which includes an inflatable body having a first bulb, a second bulb, an intermediate portion, and an internal passageway extending from the first bulb through the intermediate portion and to the second bulb. The inflatable body includes a valve assembly that is grasped by the endoscope during insertion of the weight control device in the patient's pylorus. Next, the endoscope is used to position the weight control device within the pylorus such that the intermediate portion resides within the pyloric valve and the first bulb resides within the pyloric antrum. The weight control device is then inflated with the endoscope such that the first bulb engages an inner surface of the pyloric antrum to form an outlet obstruction within the pyloric antrum. This obstruction causes chyme to accumulate proximate the first bulb prior to entering the internal passageway where it is then transported through the body and discharged from the second bulb into the patient's duodenum. The accumulation of chyme in pyloric antrum and the stomach causes the patient to feel full and stop eating. Thus, the treatment method provides a gastric outlet obstruction that slows the passage of chyme into the duodenum and as a result, the patient feels full and stops eating after consuming relatively small portions.
Owner:AGT INC (US)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com