Patents
Literature
479 results about "Local anesthesia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Local anesthesia is any technique to induce the absence of sensation in a specific part of the body, generally for the aim of inducing local analgesia, that is, local insensitivity to pain, although other local senses may be affected as well. It allows patients to undergo surgical and dental procedures with reduced pain and distress. In many situations, such as cesarean section, it is safer and therefore superior to general anesthesia. It is also used for relief of non-surgical pain and to enable diagnosis of the cause of some chronic pain conditions. Anesthetists sometimes combine both general and local anesthesia techniques.
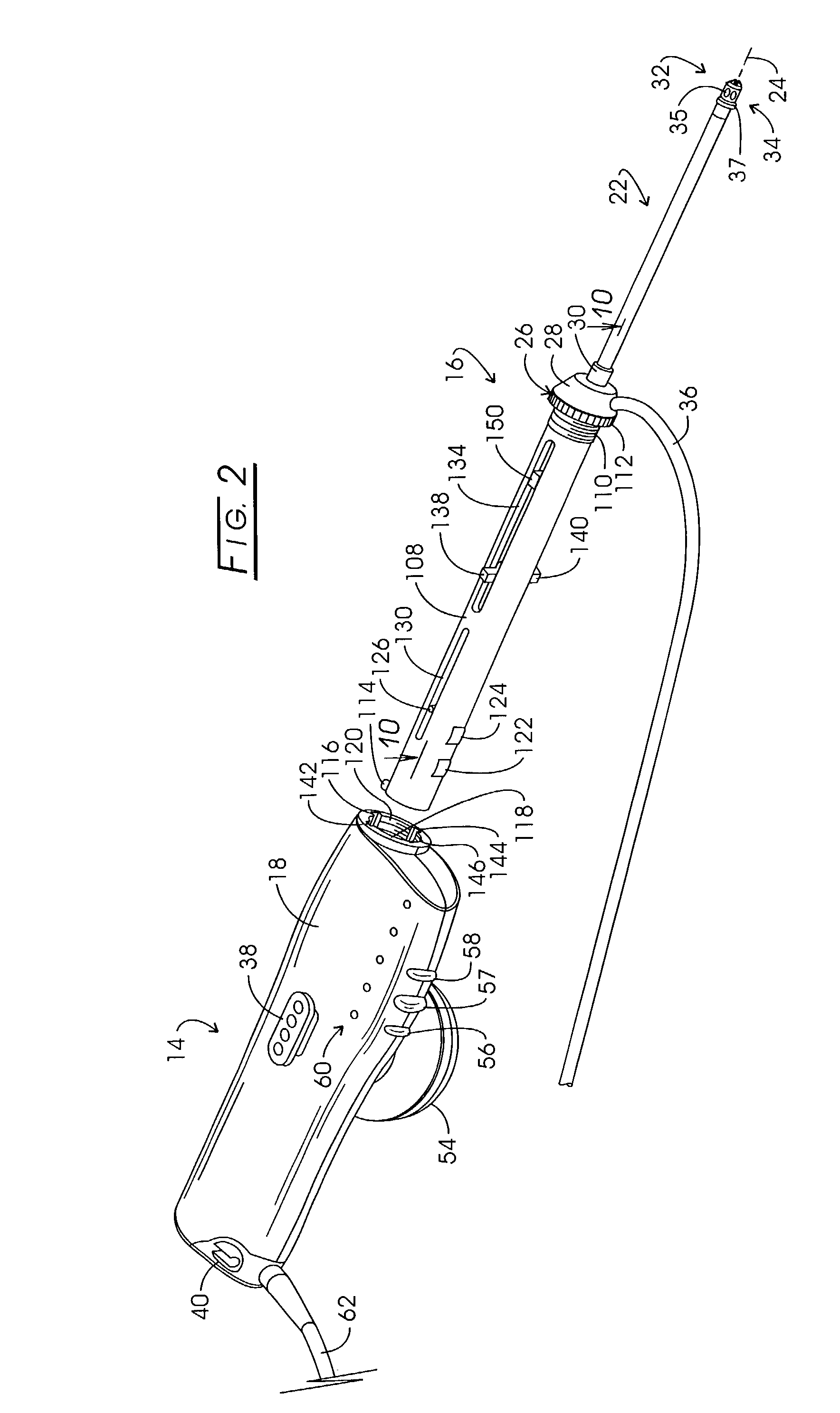
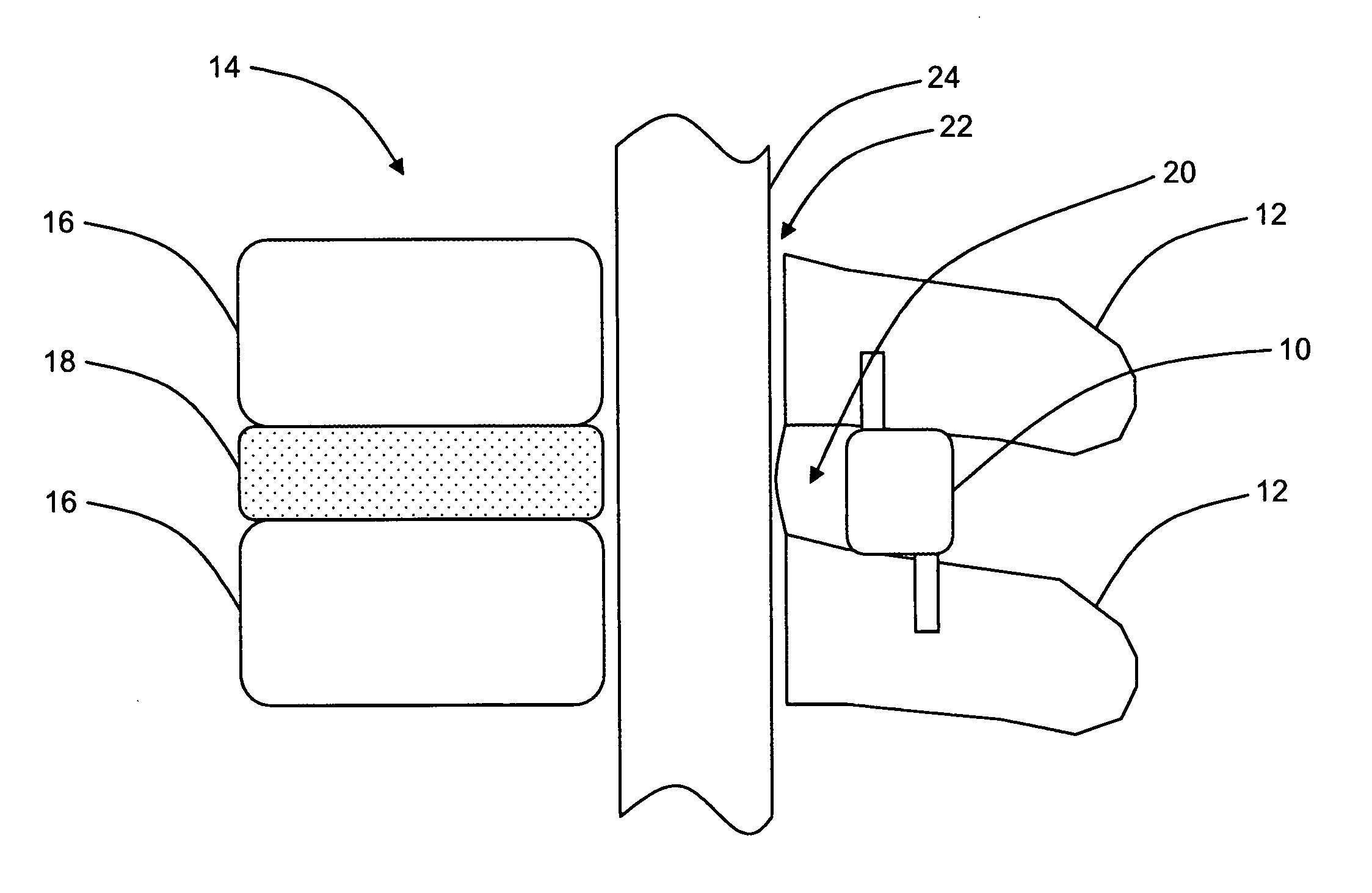
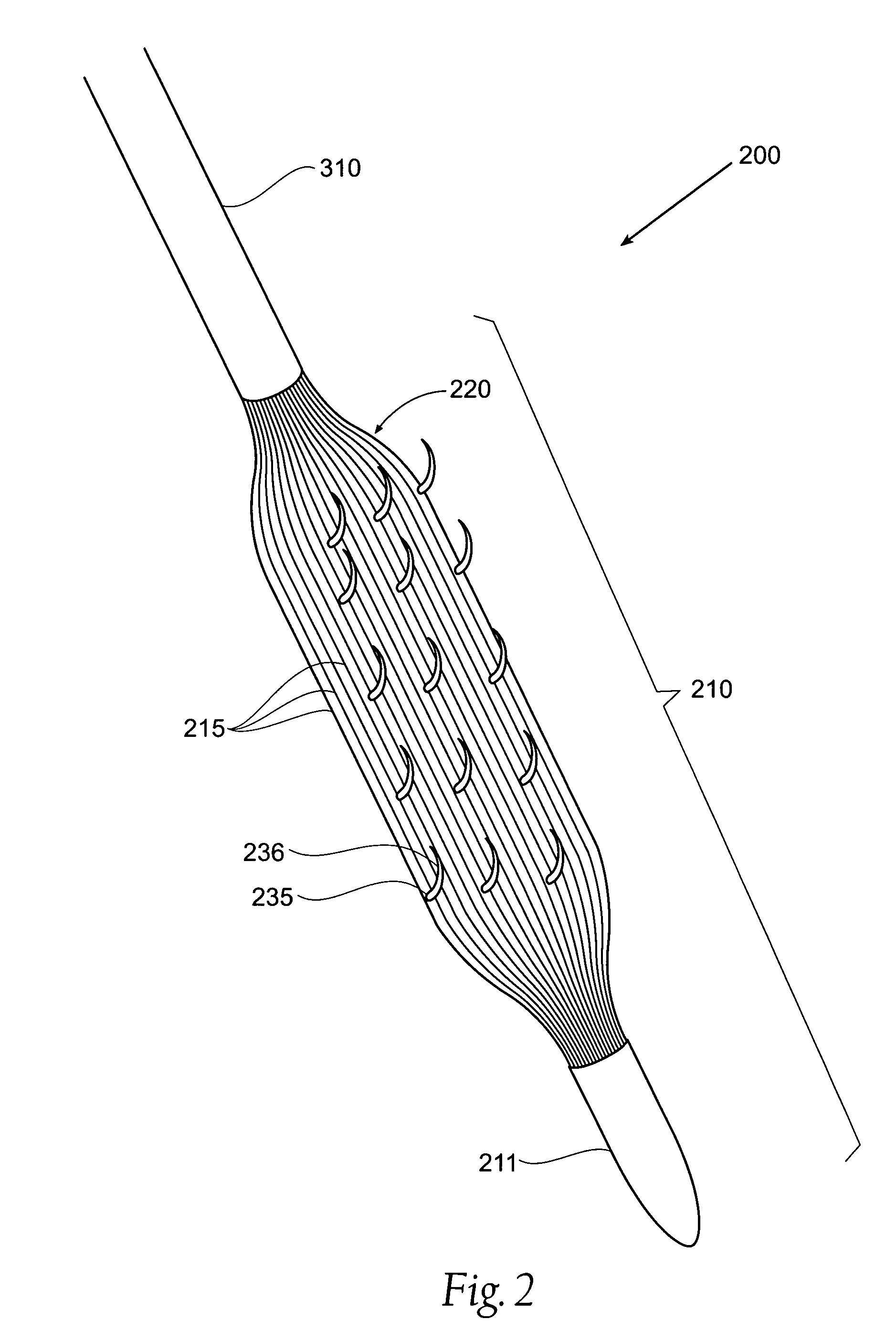
Electrosurgery with infiltration anesthesia
InactiveUS7004174B2AnaesthesiaVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrosurgery
Method for carrying out the recovery of an intact volume of tissue wherein a delivery cannula tip is positioned in confronting adjacency with the volume of tissue to be recovered. The electrosurgical generator employed to form an arc at a capture component extending from the tip is configured having a resistance-power profile which permits recovery of the specimen without excessive thermal artifact while providing sufficient power to sustain a cutting arc. For the recovery procedure, a local anesthetic employing a diluent which exhibits a higher resistivity is utilized and the method for deploying the capture component involves an intermittent formation of a cutting arc with capture component actuation interspersed with pauses of duration effective to evacuate any accumulation or pockets of local anesthetic solution encountered by the cutting electrodes.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Interspinous distraction devices and associated methods of insertion
In various exemplary embodiments, the present invention provides a plurality of novel interspinous distraction devices and associated methods of insertion. The interspinous distraction devices of the present invention are designed and configured to effectively treat such conditions as lumbar spinal stenosis and degenerative disc disease. Advantageously, the interspinous distraction devices of the present invention may be inserted through conventional open procedures, typically requiring a relatively large incision and a general anesthetic, or through novel minimally-invasive procedures, typically requiring only a local anesthetic. These novel minimally-invasive procedures and related enabling devices are also disclosed and described herein.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
Regional anesthetic
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
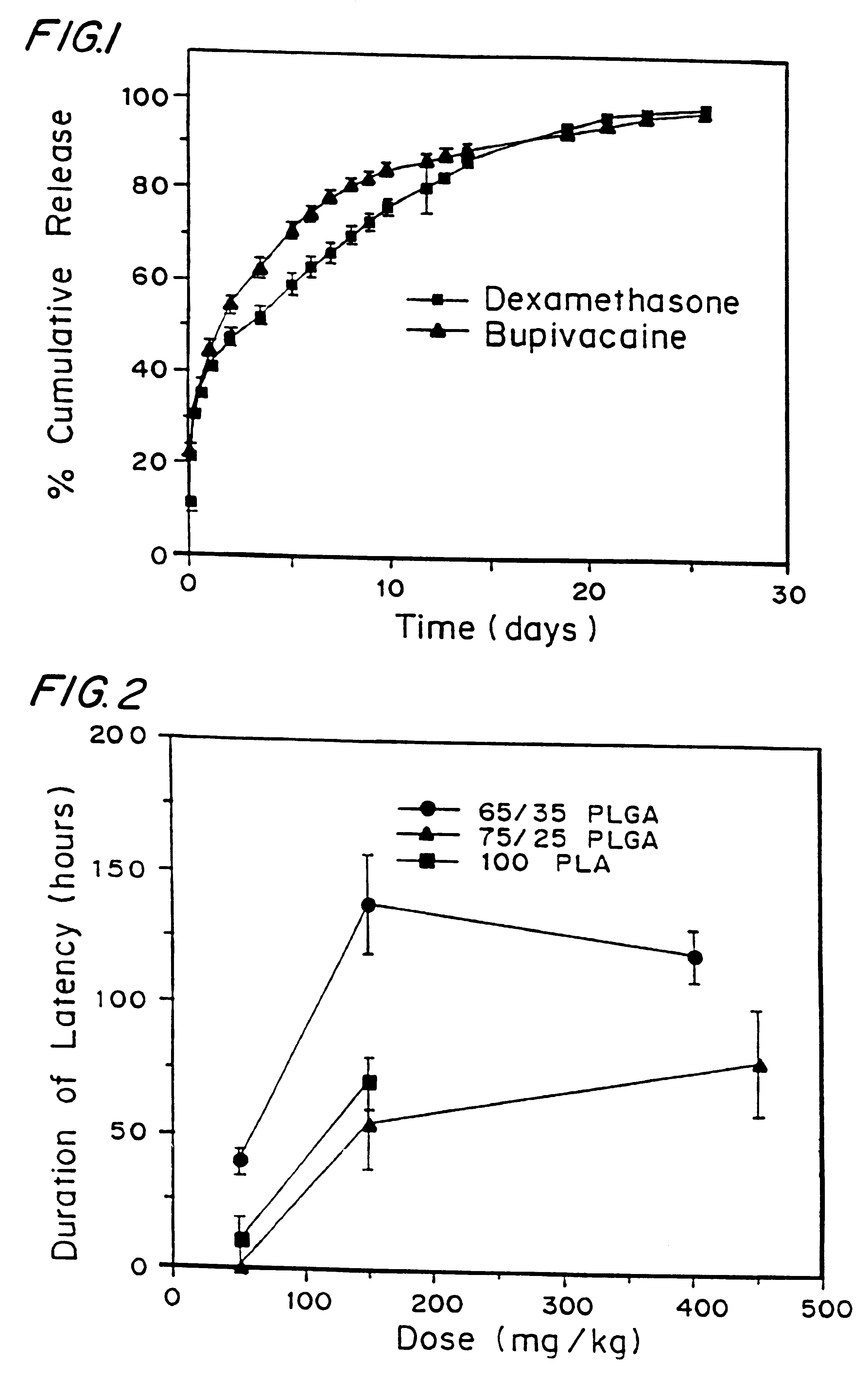
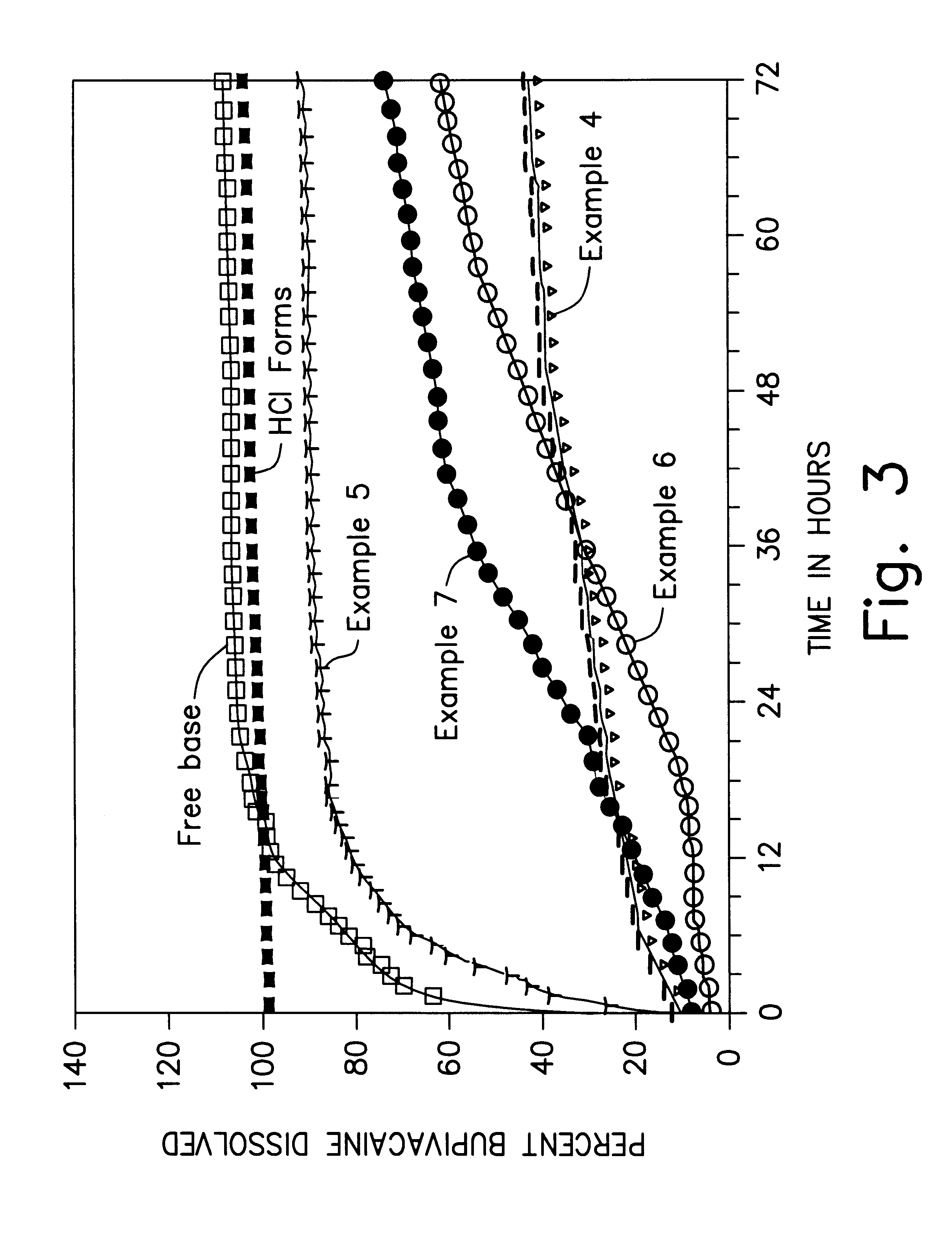
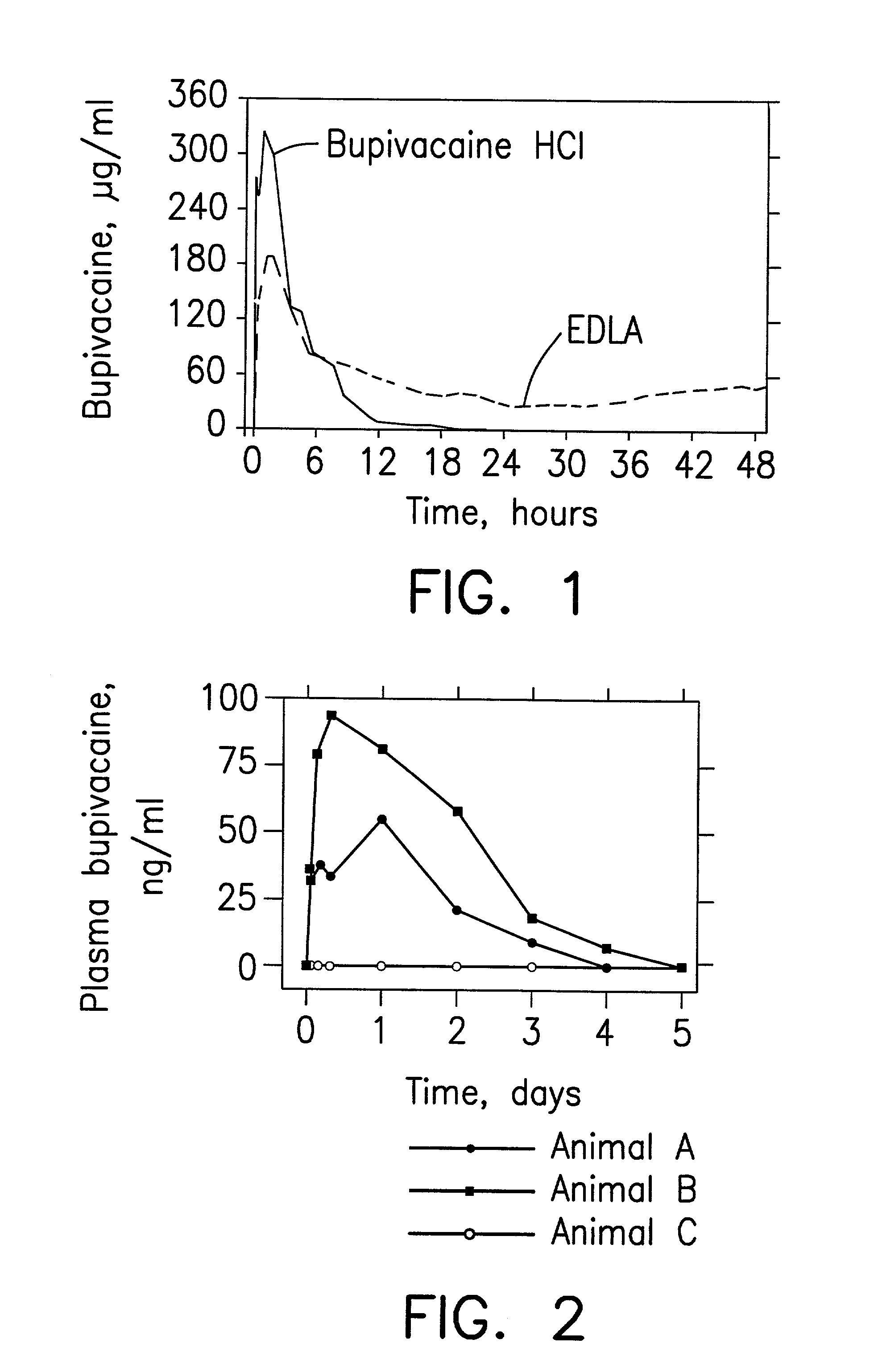
High load formulations and methods for providing prolonged local anesthesia
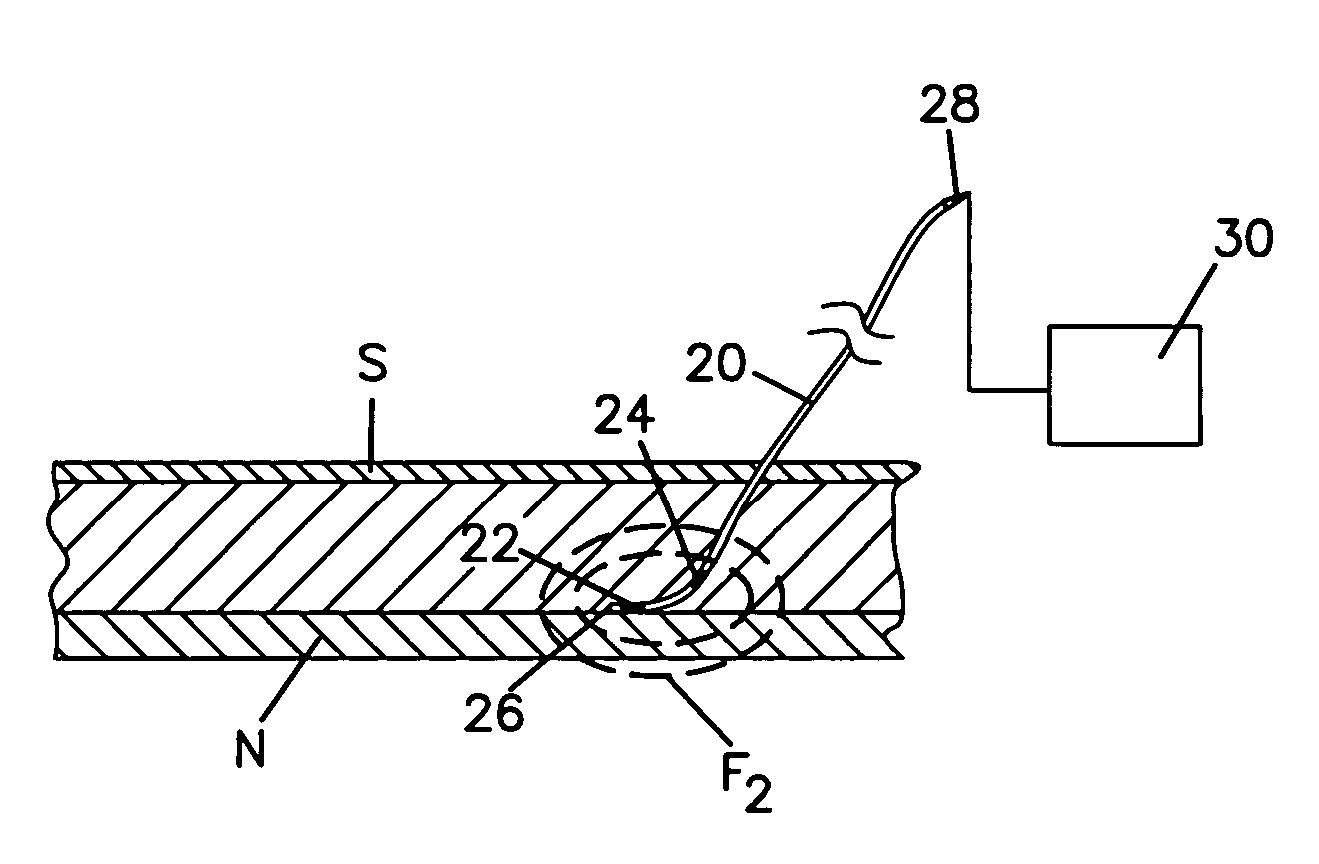
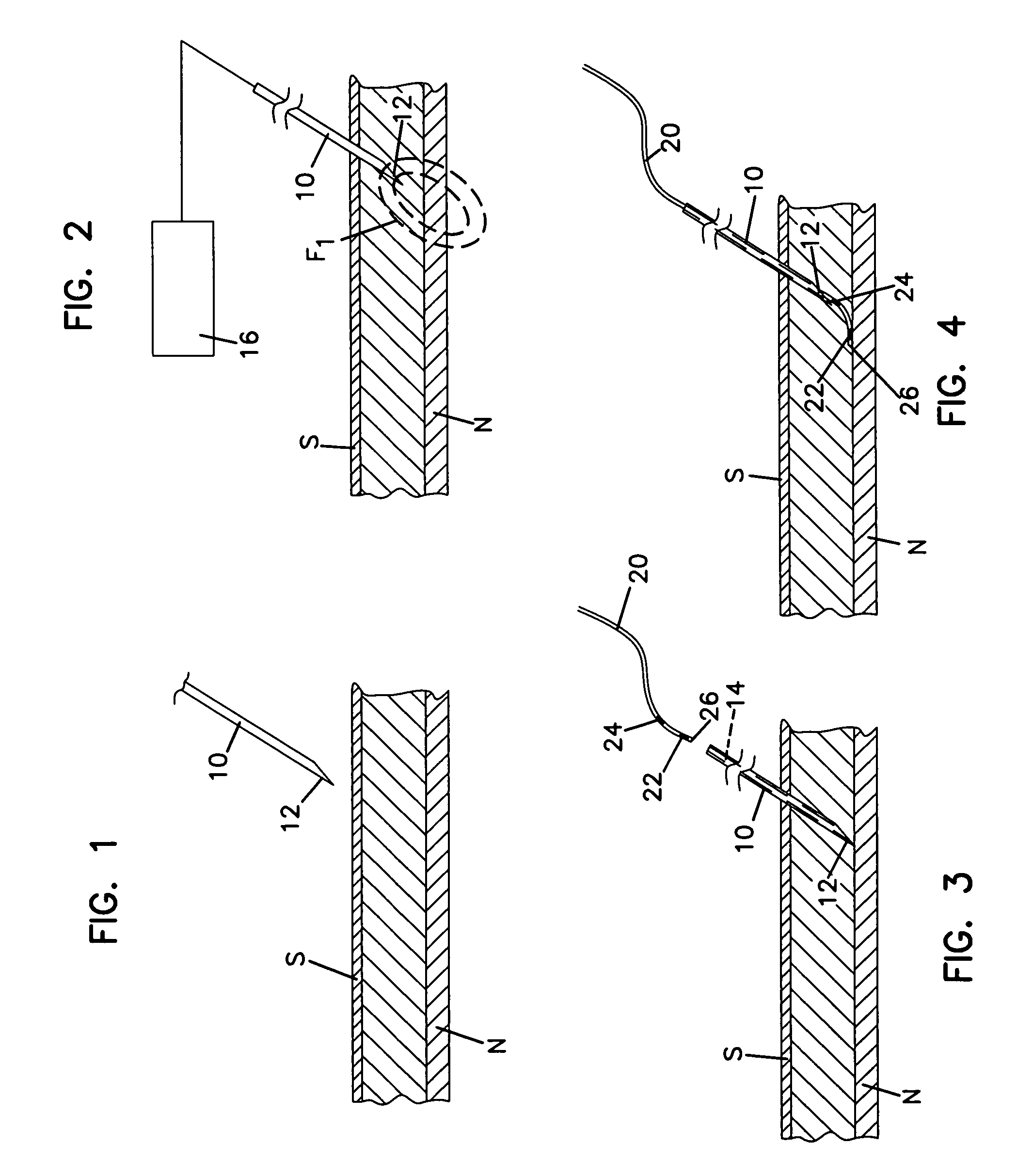
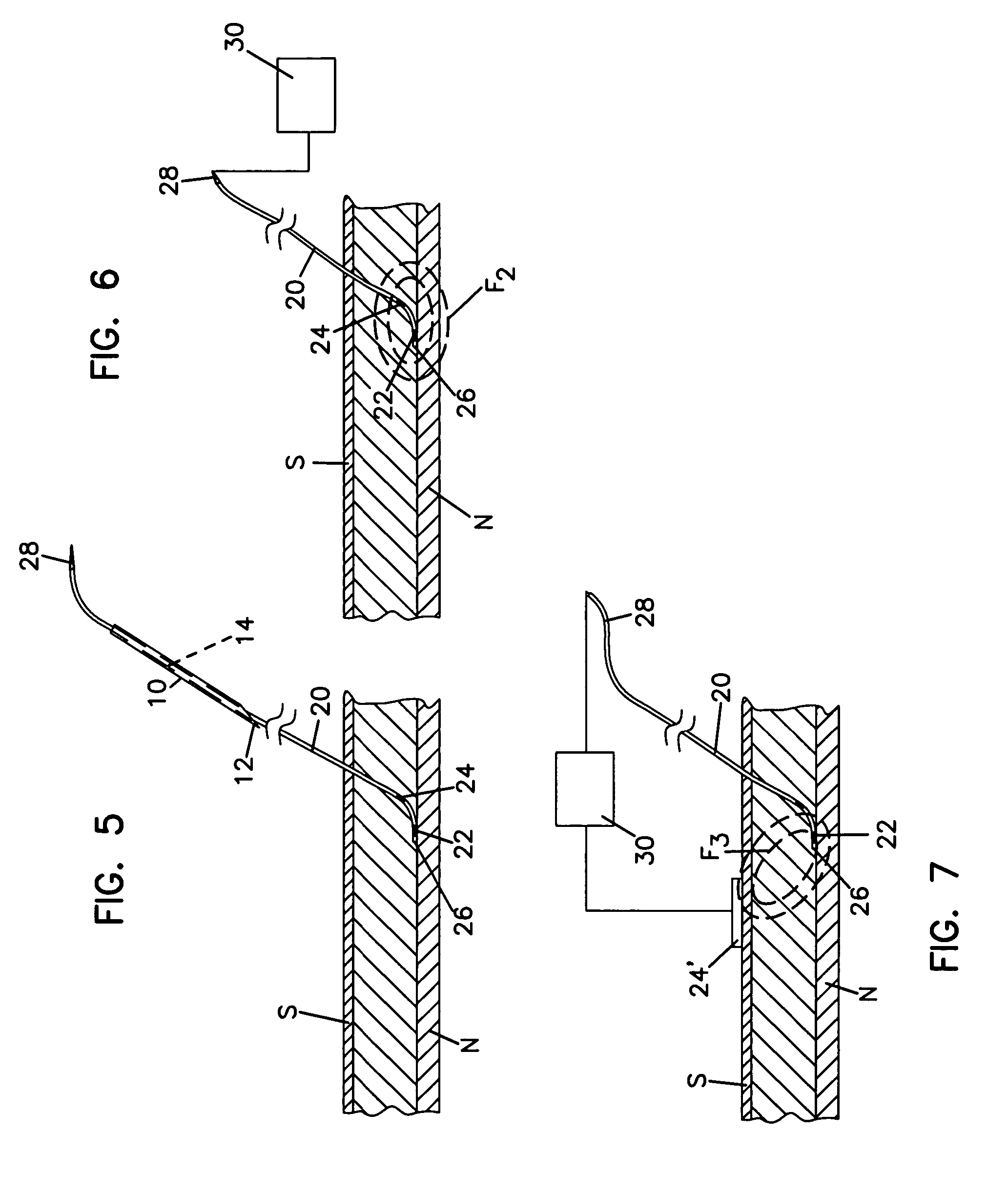
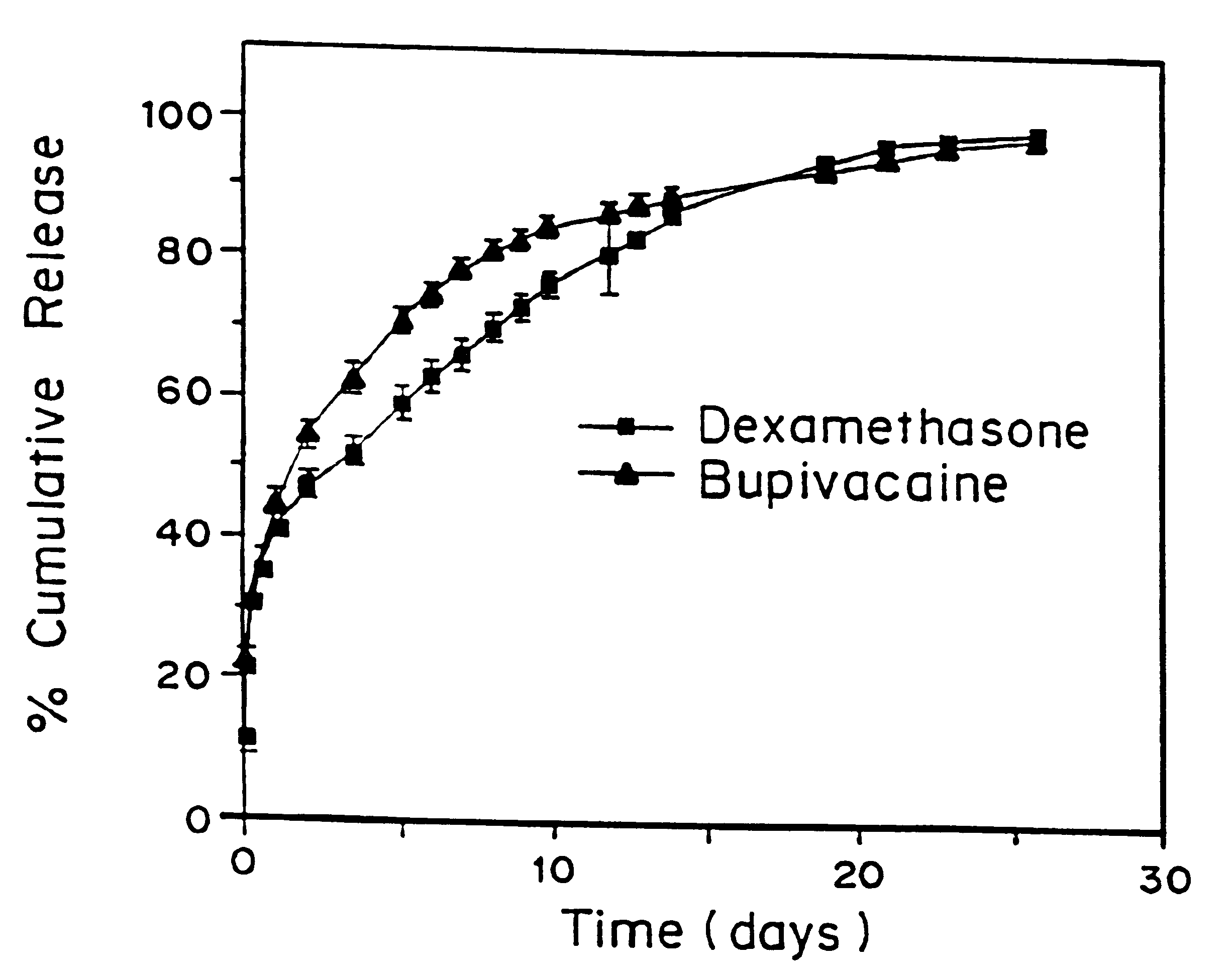
A formulation for inducing sustained local anesthesia in a patient comprising a substrate comprising a high load of local anesthetic by weight and an effective amount of a biocompatible, controlled release material to obtain a. reversible nerve blockade or anesthesia effect when implanted or injected in a patient, and a non-toxic glucocorticosteroid agent effective to prolong the duration of the local anesthesia for a time period longer than that obtainable from the substrate without the glucocorticosteroid agent.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Surgical weight control device
InactiveUS7326207B2Optimize quantityEasy to eatStentsBalloon catheterCurative treatmentPhysical therapy
This invention provides a method and system for the curative treatment of obesity. A first aspect of this invention is that it enables identification of the nerves responsible for the relaxation of the stomach muscles that occurs prior to and during eating. A second aspect of the invention is that it allows the physician to identify focal nerve sites in the stomach and upper duodenum that are associated with producing sensations of hunger and satiety. Nervous transmission from these sites can be modulated or blocked all together so as to minimize the sensation of hunger. A third aspect of this invention is that allows a physician to shrink selected portions of the innermost oblique muscle and middle circular muscle layers of the stomach. This can be performed in a physician's office using local anesthesia. Shrinkage of these muscles produces a feeling of satiety that enhances the patient's efforts to restrict his caloric intake.
Owner:MEDERI RF LLC
Topical compositions and methods for treating pain
InactiveUS6638981B2Avoid painComposition is stableBiocideNervous disorderNR1 NMDA receptorPreventing pain
Topical compositions and methods for treating pain. The invention provides oil-in-water emulsions comprising an antidepressant; an NMDA-receptor antagonists; a lipophilic component; water; and a surfactant. The compositions induce a local-anesthetic effect when topically administered to intact skin thereby treating or preventing pain, for example, neuropathic pain.
Owner:EPICEPT CORP
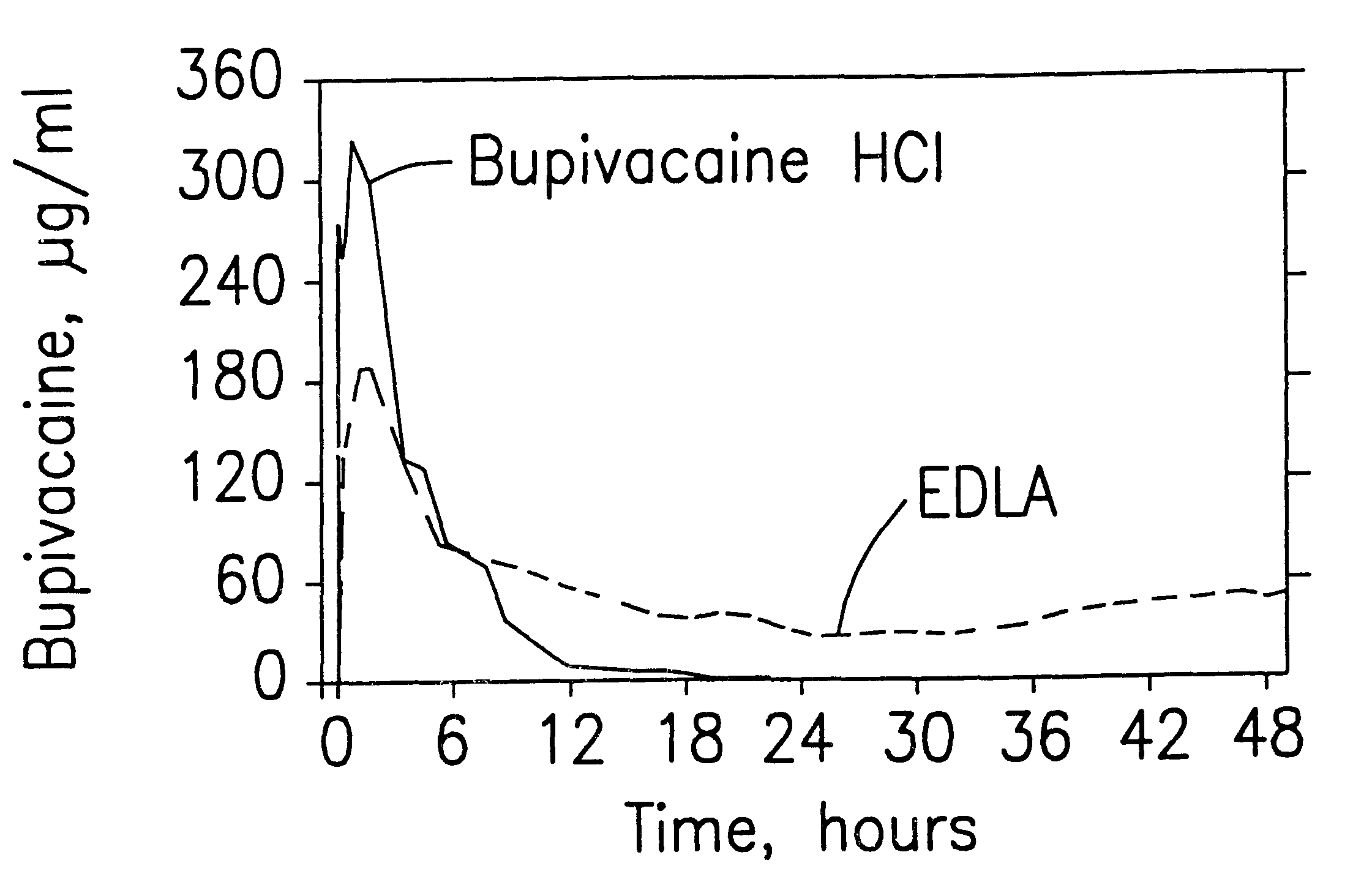
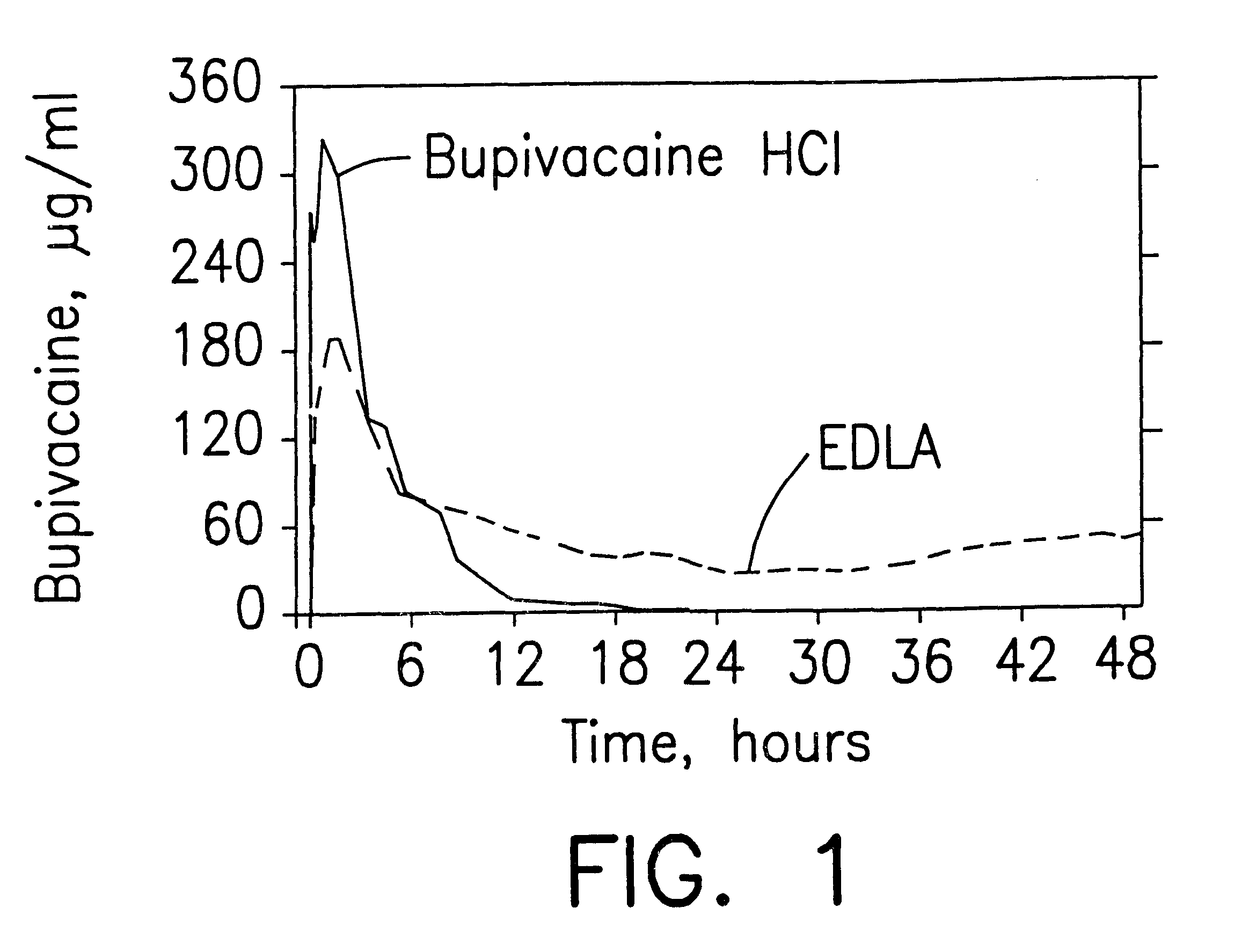
Formulations and methods for providing prolonged local anesthesia
InactiveUS6451335B1Slow in-vitro releaseRelease the local anestheticAnaesthesiaGranular deliveryControlled releaseAnesthetic Agent
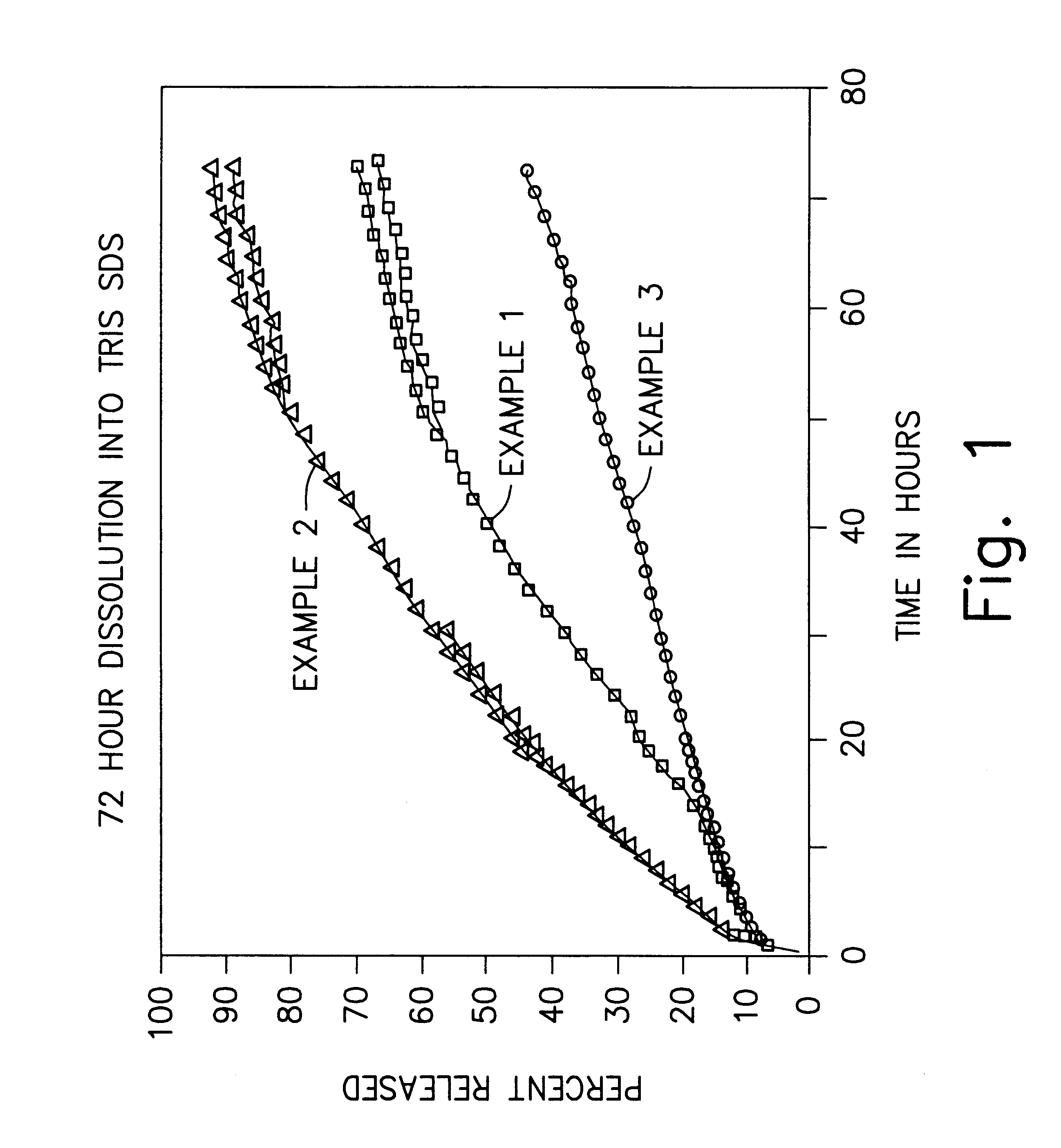
A formulation for inducing sustained regional local anesthesia in a patient comprising a substrate comprising a local anesthetic and an effective amount of a biocompatible, biodegradable, controlled release material prolonging the release of the local anesthetic from the substrate to obtain a reversible local anesthesia when implanted or injected in a patient, and a non-toxic augmenting agent effective to prolong the duration of the local anesthesia for a time period longer than that obtainable from the substrate without the augmenting agent. In preferred embodiments, the controlled release material is a low molecular weight, acid-terminated polymer. A further aspect of the invention is directed to such formulations which release the local anesthetic in two phases, the first a rapid "bolus" to initiate anesthesia and a second, slower release to maintain anesthesia.
Owner:EURO-CELTIQUE SA
Brachytherapy apparatus for asymmetrical body cavities
InactiveUS20070270627A1Reduce in quantityOptimize treatment planX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPartial Breast IrradiationAbdominal trocar
The present disclosure provides a brachytherapy apparatus, system and method that delivers partial breast irradiation treatment for post-lumpectomy patients via introduction of a catheter-like device through a trocar. The apparatus may be introduced post-surgically with local anesthesia under image guidance into the previous excision site and into a cavity by a surgeon. The brachytherapy apparatus includes one or more thin-walled tubes, each of said thin-walled tubes being configured to contain one or more radioactive sources, at least one radiation source configured to deliver a prescribed dose of radiation, a whisk adjuster configured to permit adjustment of each of the one or more thin-walled tubes so that the tubes substantially conform to a size of the body cavity; and an expansion element configured to expand outwardly said one or more thin-walled tubes within the cavity so that the thin-walled tubes substantially conform to a shape and / or size of the body cavity.
Owner:PORTOLA MEDICAL
Mechanically registered videoscopic myringotomy/tympanostomy tube placement system
InactiveUS20060155304A1Facilitate performing treatment procedureSmooth rotationEar treatmentDiagnosticsMedicineLight beam
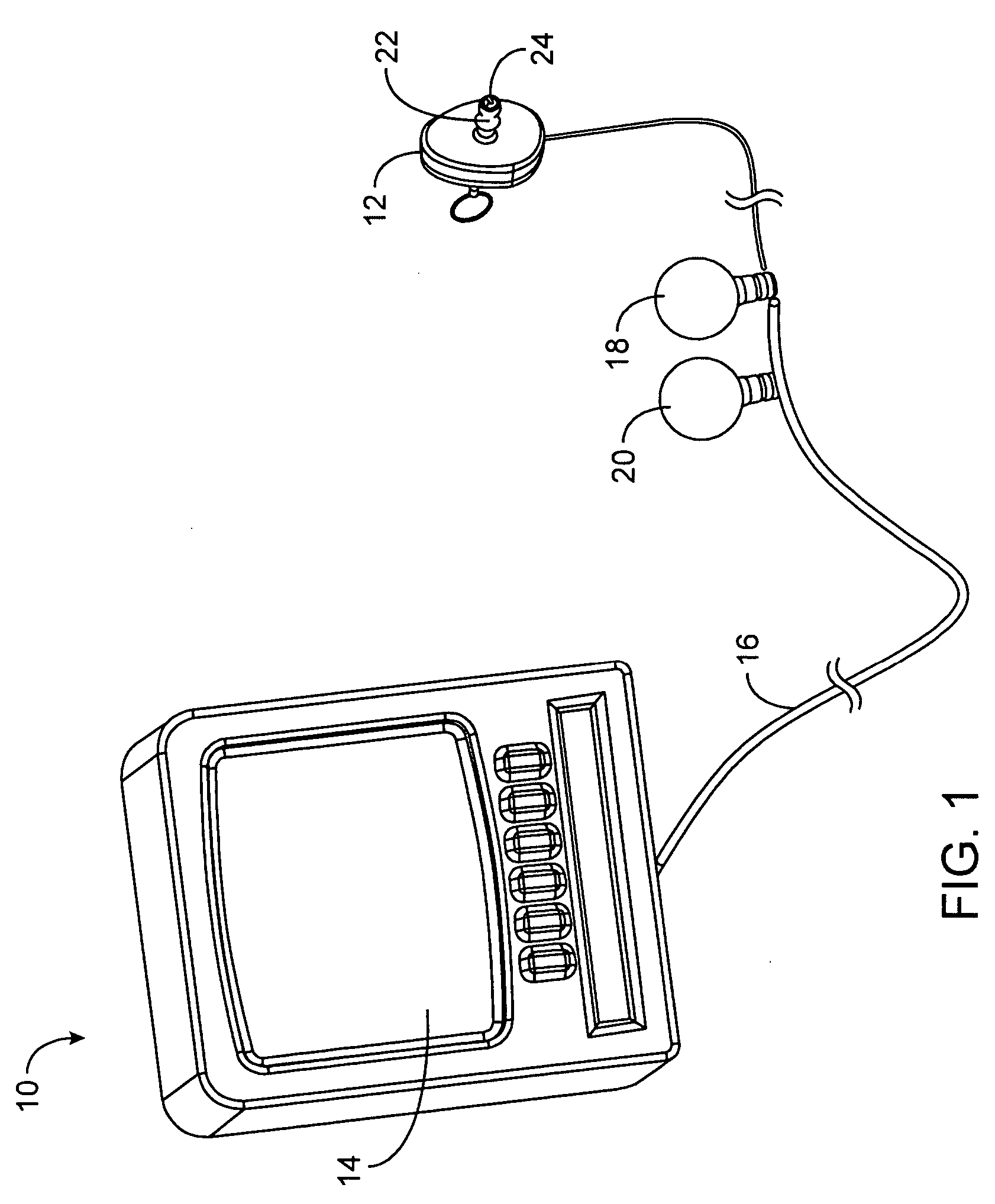
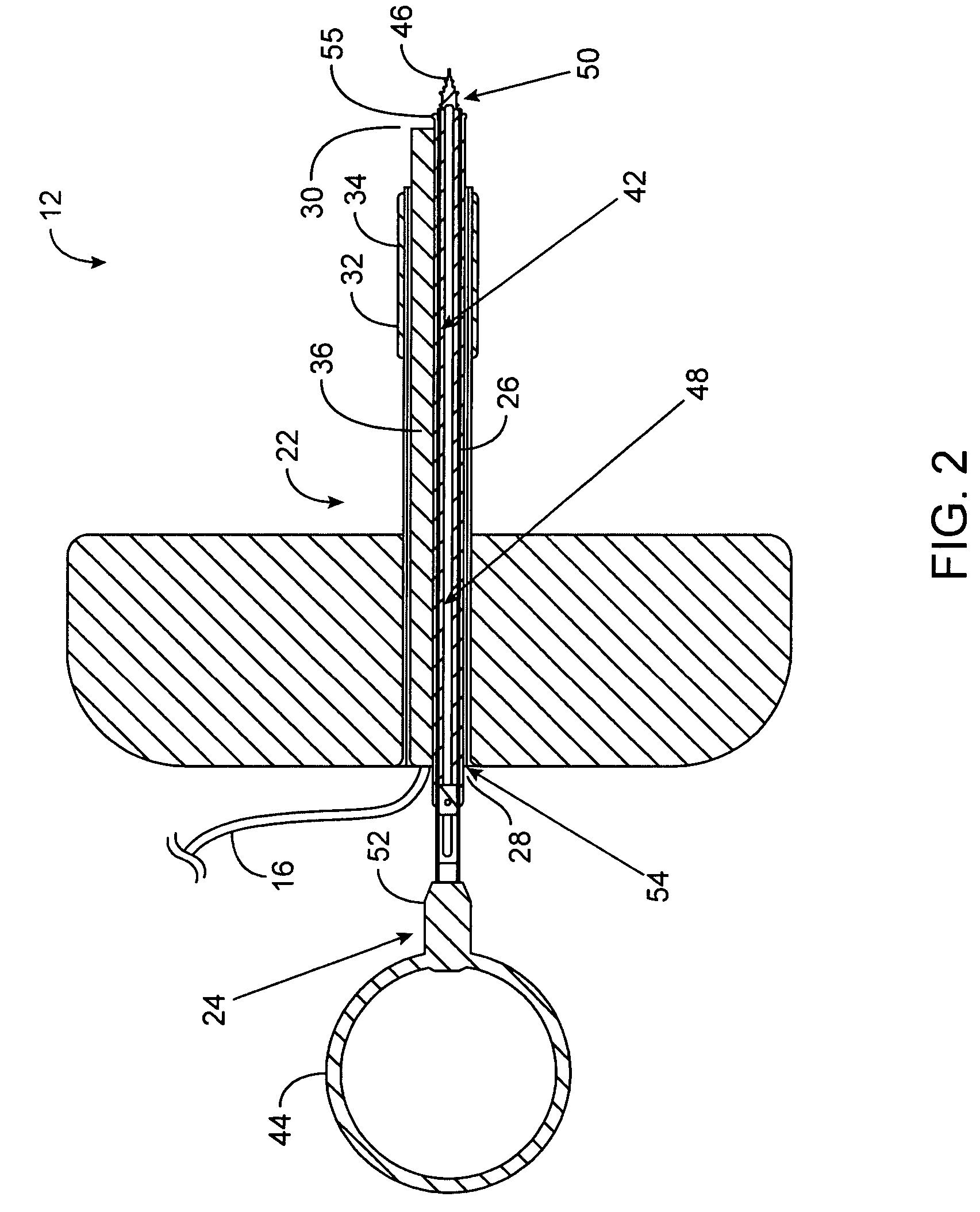
Devices, systems, methods, and kits for treating the tissue structures of the ear make use of a guide structure that can mechanically register a treatment probe with a target region of a target tissue, the guide structure being fittingly received in an auditory canal and often comprising a conformable body such as a compressible foam, or the like. The guide structure may include an articulating mechanism for selectively orienting the treatment probe toward the target region of, for example, a tympanic membrane. The guide structure may also support a videoscopic image capture device, illumination transmitting optical fibers, an aiming beam transmitter, and the like. Such structures facilitate myringotomy, tympanostomy tube placement, and the like, under local anesthesia in a doctor's office.
Owner:TUSKER MEDICAL
Methods for providing safe local anesthesia
InactiveUS6699908B2Reduce riskImproved therapeutic indexBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAnesthetic AgentControlled release
Methods and formulations for inducing substantially safer local anesthesia in a patient are provided. The methods comprise administering, to a patient in need thereof, a substrate containing a local anesthetic and an effective amount of a biocompatible, biodegradable, controlled release material to safely obtain a reversible nerve blockade when implanted or injected in a patient.
Owner:PURDUE PHARMA LP
Topical compositions and methods for treating pain
InactiveUS20030082214A1Treating and preventing painAvoid painBiocideNervous disorderPreventing painNR1 NMDA receptor
Topical compositions and methods for treating pain. The invention provides oil-in-water emulsions comprising an antidepressant; an NMDA-receptor antagonists; a lipophilic component; water; and a surfactant. The compositions induce a local-anesthetic effect when topically administered to intact skin thereby treating or preventing pain, for example, neuropathic pain.
Owner:EPICEPT CORP
Mechanically registered videoscopic myringotomy/tympanostomy tube placement system
InactiveUS7704259B2Facilitate performing treatment procedureSmooth rotationEar treatmentDiagnosticsMedicineLight beam
Owner:TUSKER MEDICAL
Organ arrest, protection, preservation and recovery
InactiveUS20050202394A1Reduced uptakeBiocideOrganic active ingredientsPotassium channel openerPotassium
The present invention relates to a composition for controlling viability of a tissue including a potassium channel opener or adenosine receptor agonist, a compound for inducing local anaesthesia and a compound for reducing the uptake of water by a cell in the tissue. The present invention also realtes to the use of the composition accordng to the invention for controlling viability of a tissue.
Owner:HIBERNATION THERAPEUTICS A KF
Treatment of retinal detachment
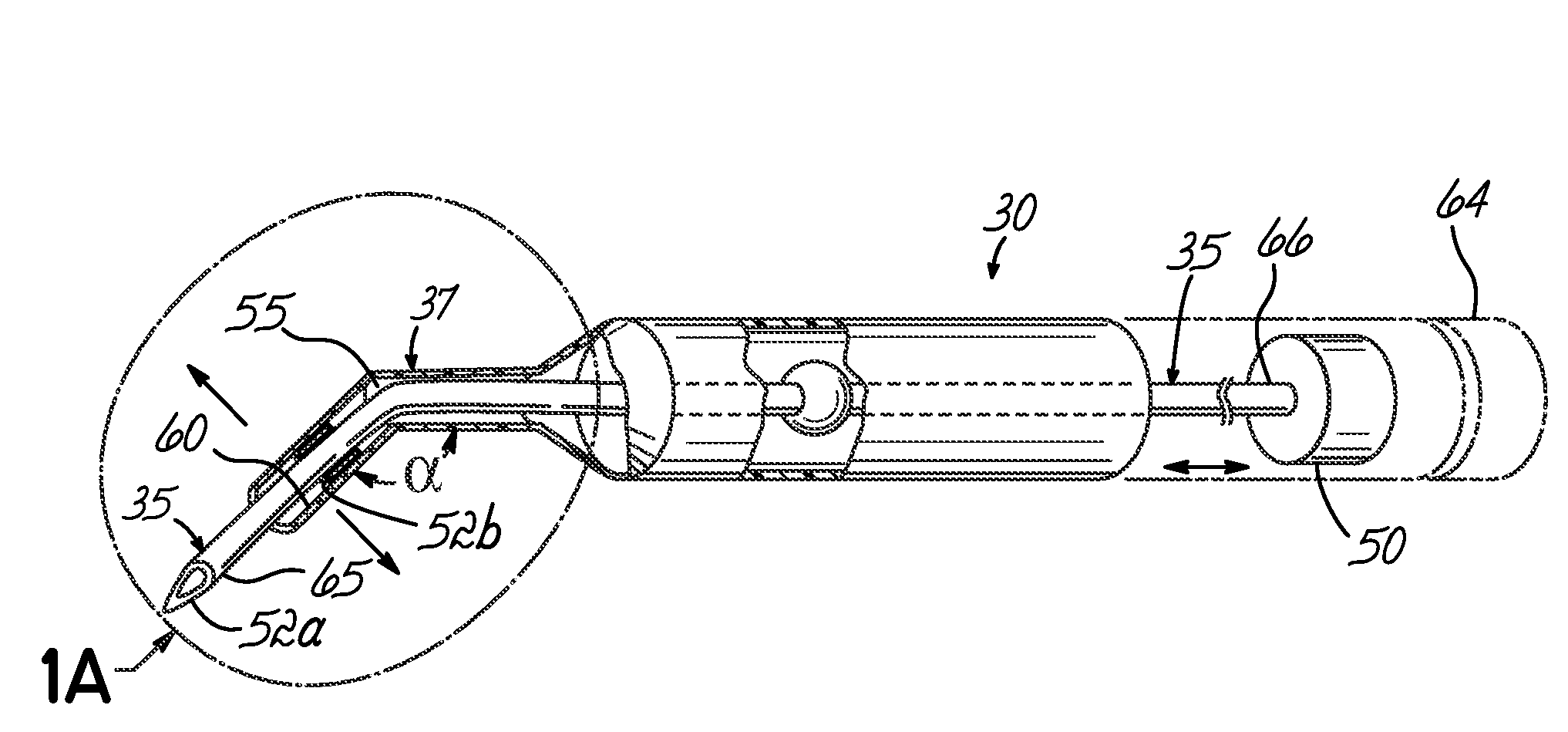
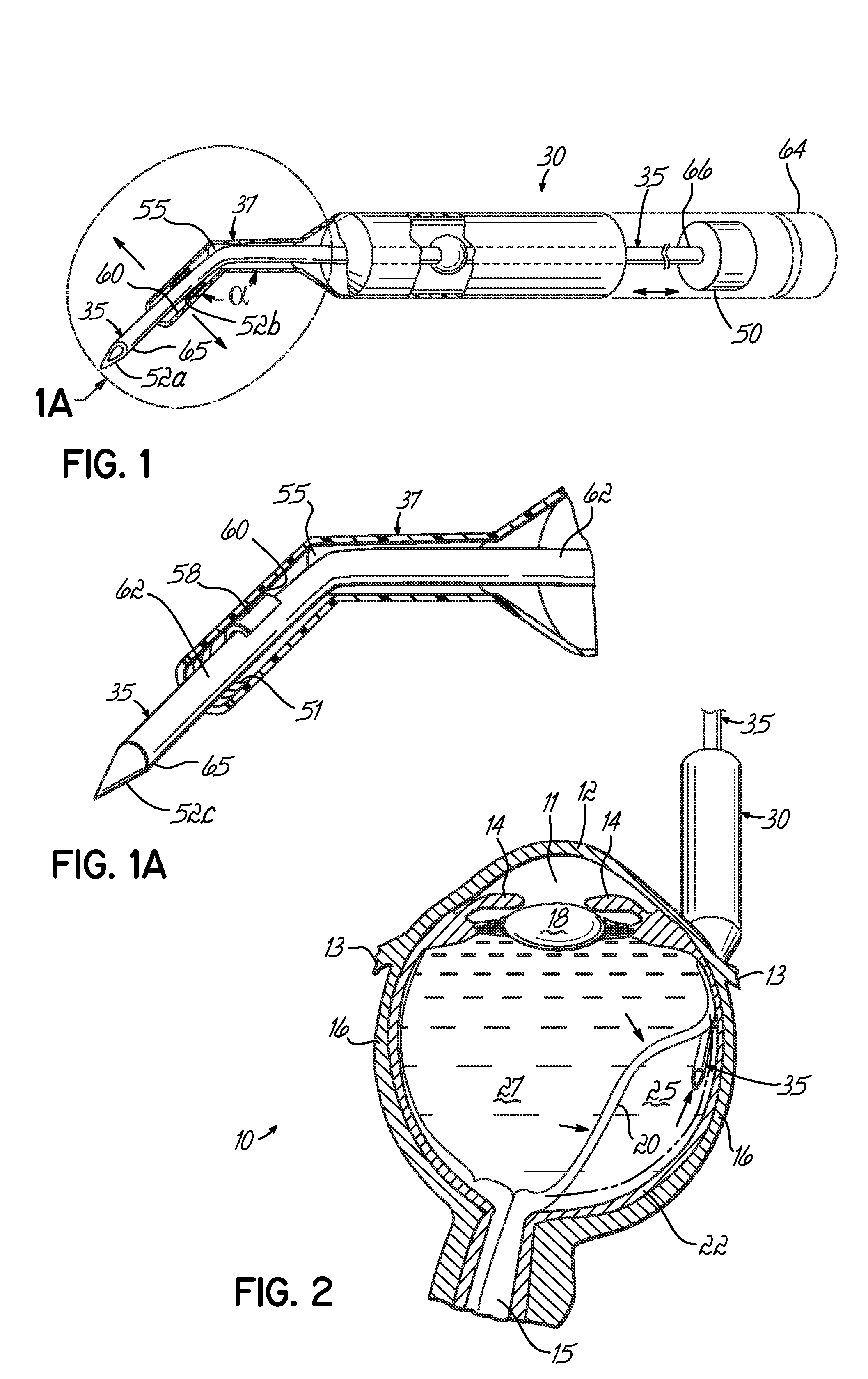
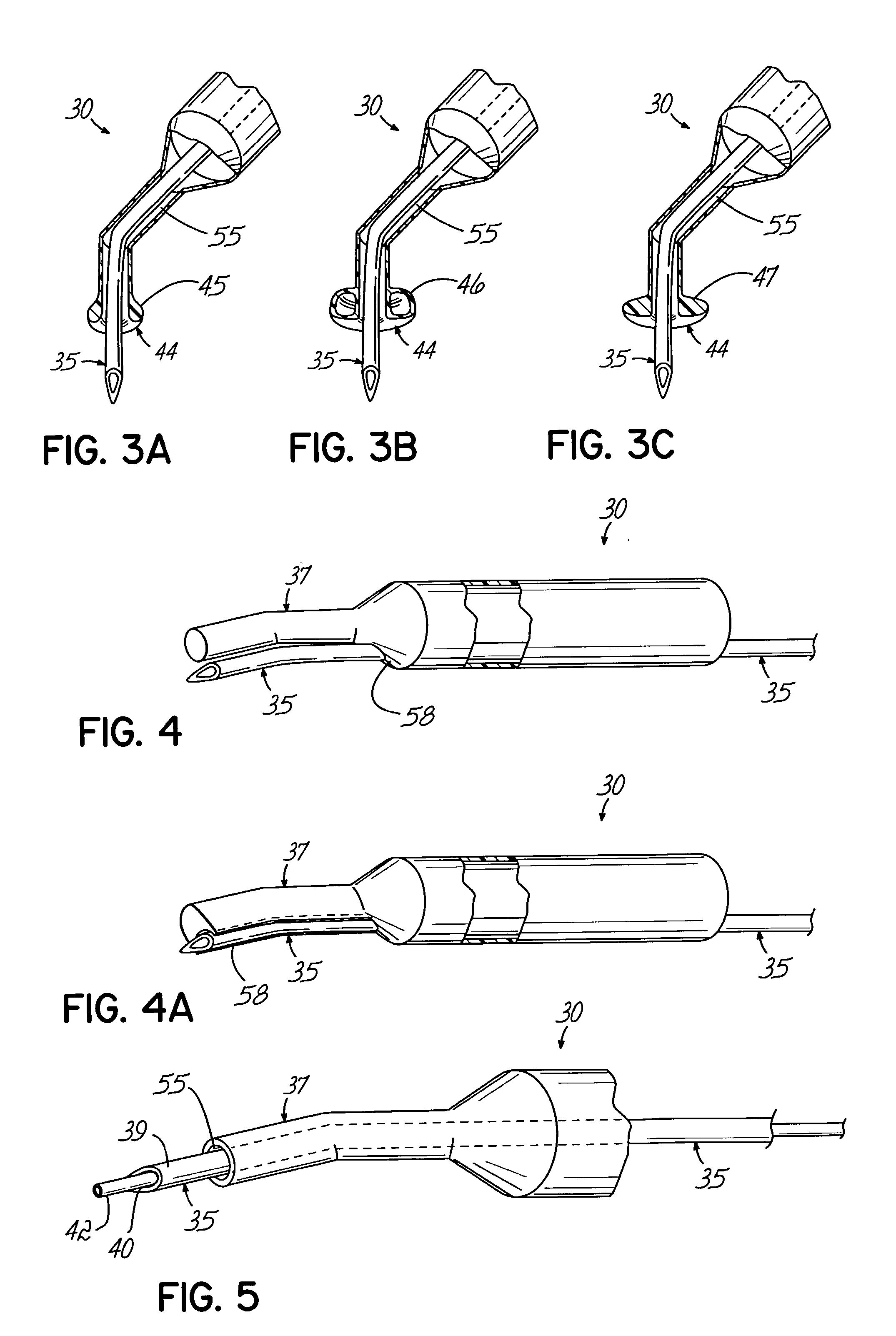
An apparatus and minimally invasive method for removing fluid from a subretinal space to allow a detached retina to flatten. An apparatus, comprising a fluid withdrawal device and a guide for advancing and placing the device, is positioned on the exterior eye surface at the detachment site. Various embodiments of the apparatus are disclosed. Using the guide, the surgeon advances the device into the fluid-filled space and drains fluid, allowing the retina to flatten. Additional injection of saline or gas into the vitreous cavity normalizes intraocular pressure, and the patient is ambulatory immediately afterward. Unlike other retinal attachment techniques, in the inventive procedure the patient receives only a local anesthetic, and has no restraint on head movement.
Owner:PEYMAN GHOLAM A
Topical anesthetic for rapid local anesthesia and method of applying a topical anesthetic
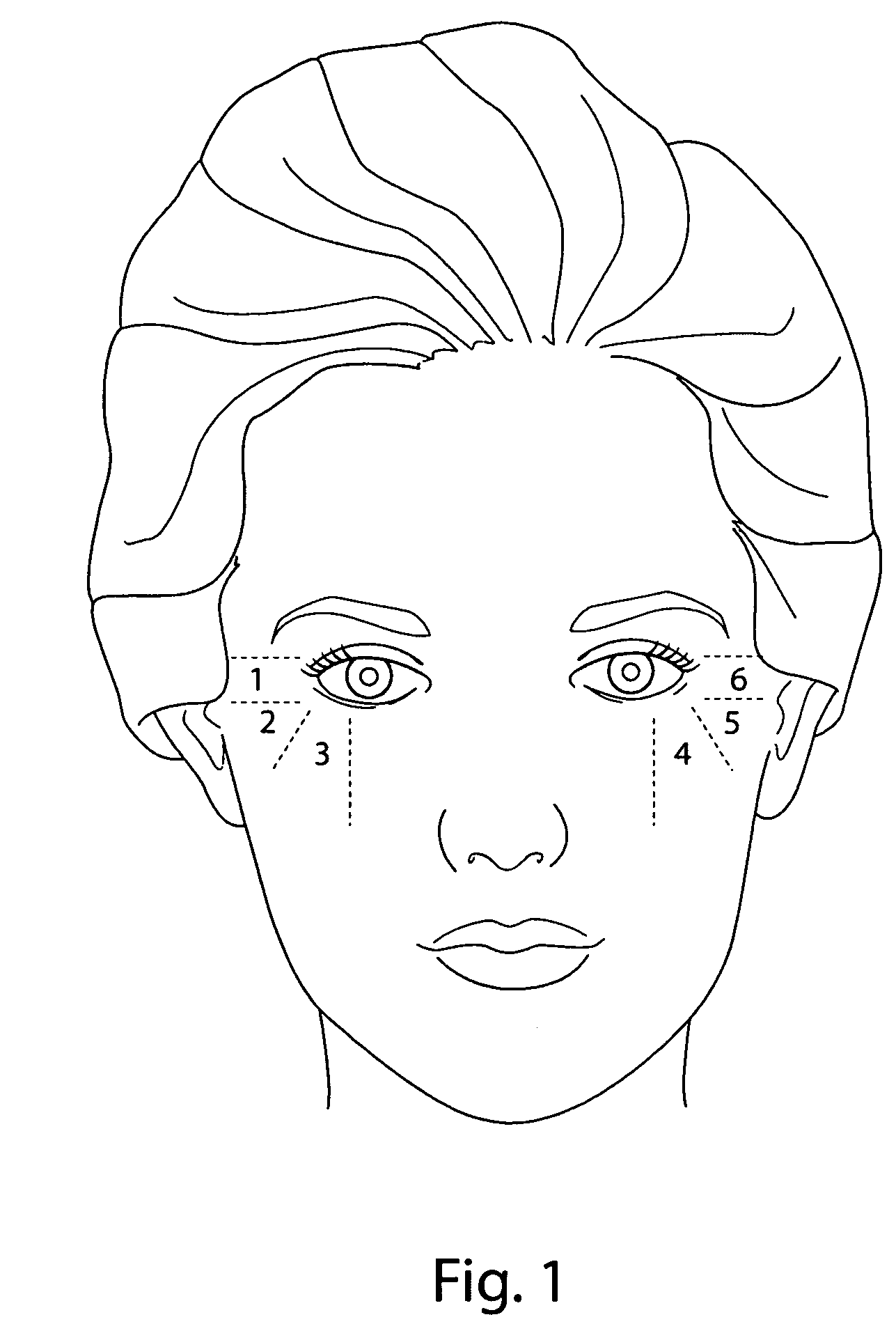
The invention relates to a drug delivery system for the topical administration of anesthetic agents. For example, a topical anesthetic for rapid local anesthesia is provided. The topical anesthetic includes an anesthetic, volatile and non-volatile solvents, and an optional thickener. In addition, a method is taught for applying the topical anesthetic to the face of a patient without occlusion. The anesthetic is applied topically to an area for injection such that the dermatological procedure (cosmetic injections) can be performed in fifteen minutes.
Owner:JUVENTIO
Ion channel modulating compounds and uses thereof
Ion channel modulating compounds are disclosed. The compounds of the present invention may be incorporated in compositions and kits. The present invention also discloses a variety of in vitro and in vivo uses for the compounds and compositions, including the treatment of arrhythmia and the production of analgesia and local anesthesia.
Owner:CORREVIO INT SARL
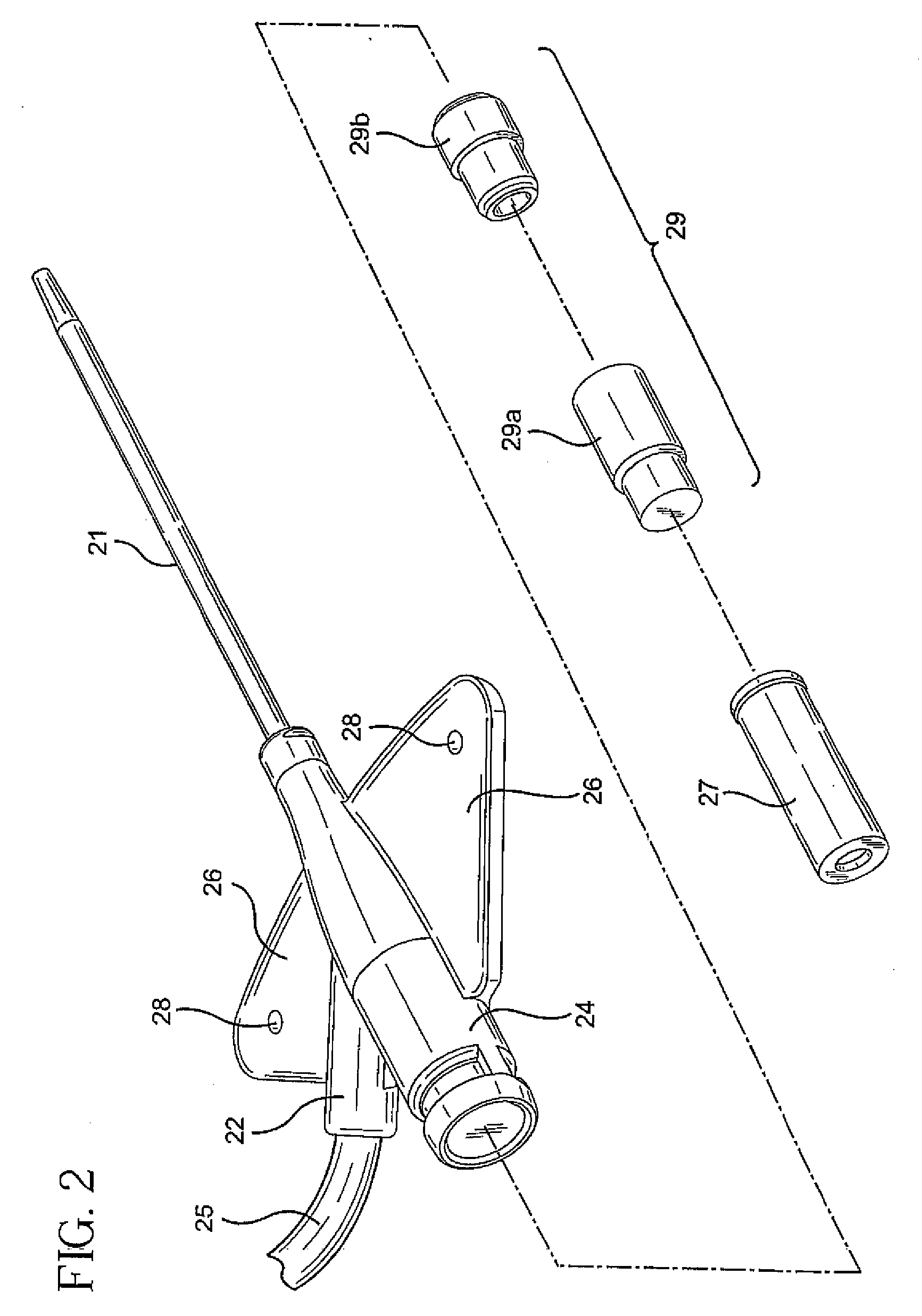
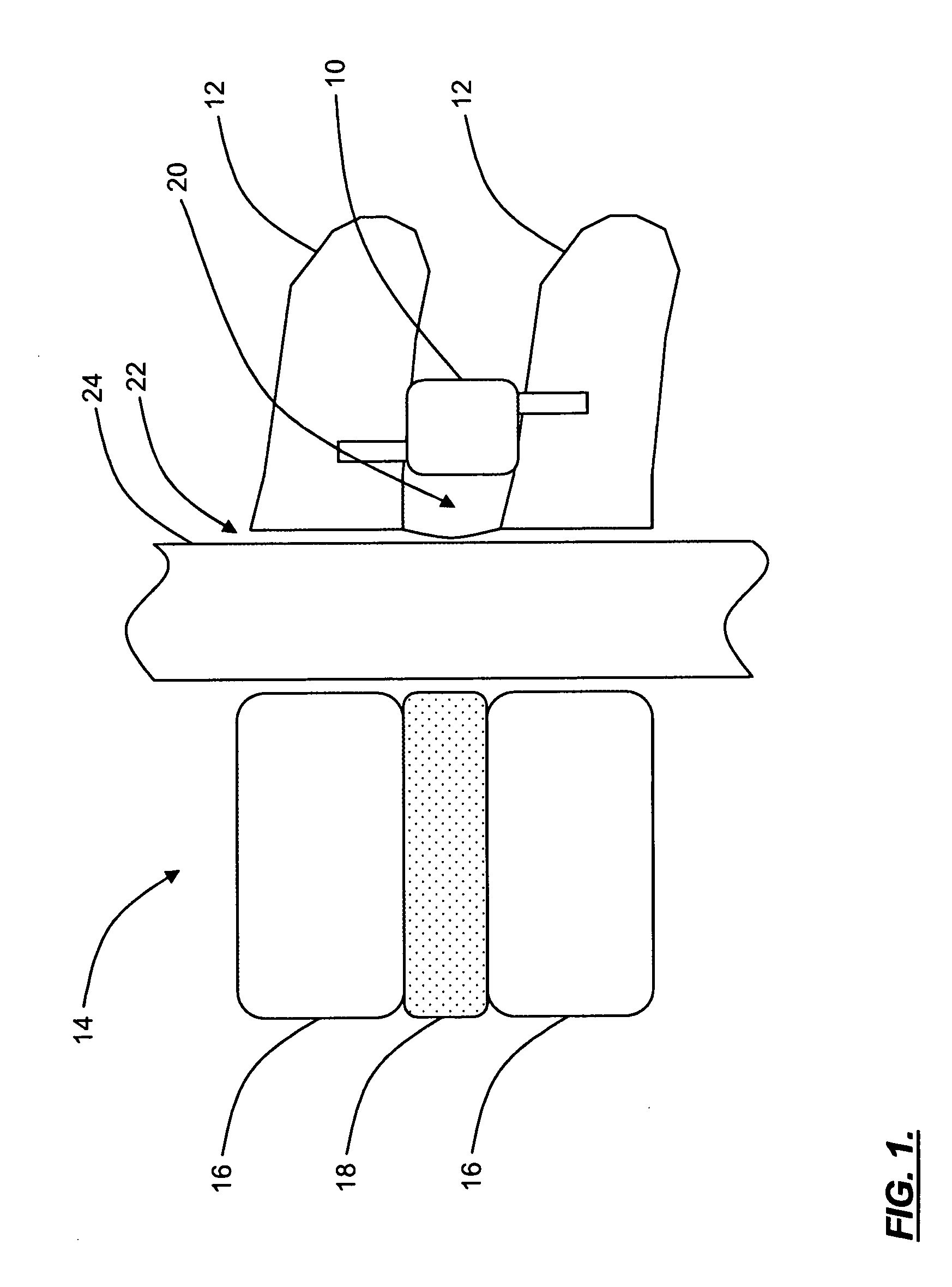
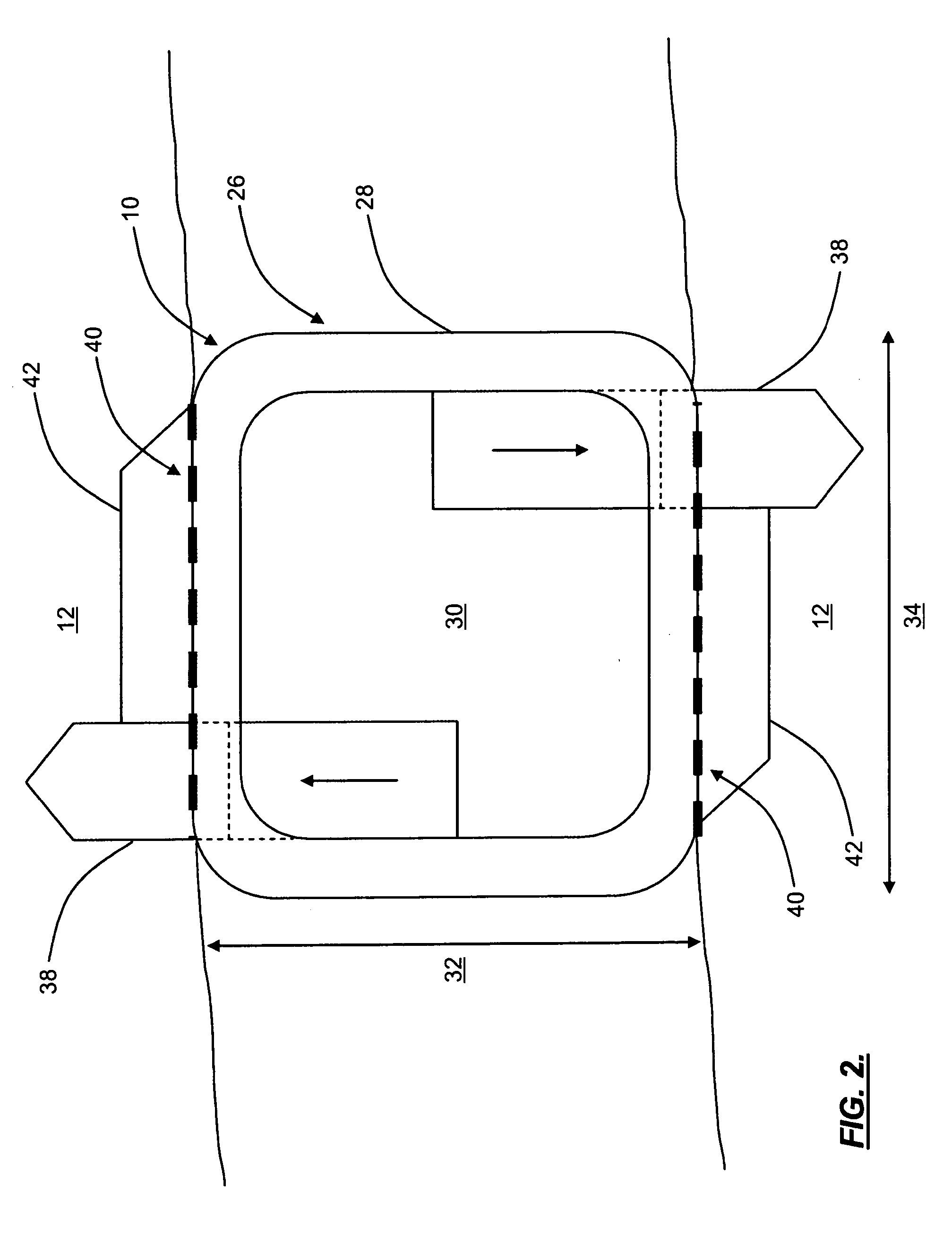
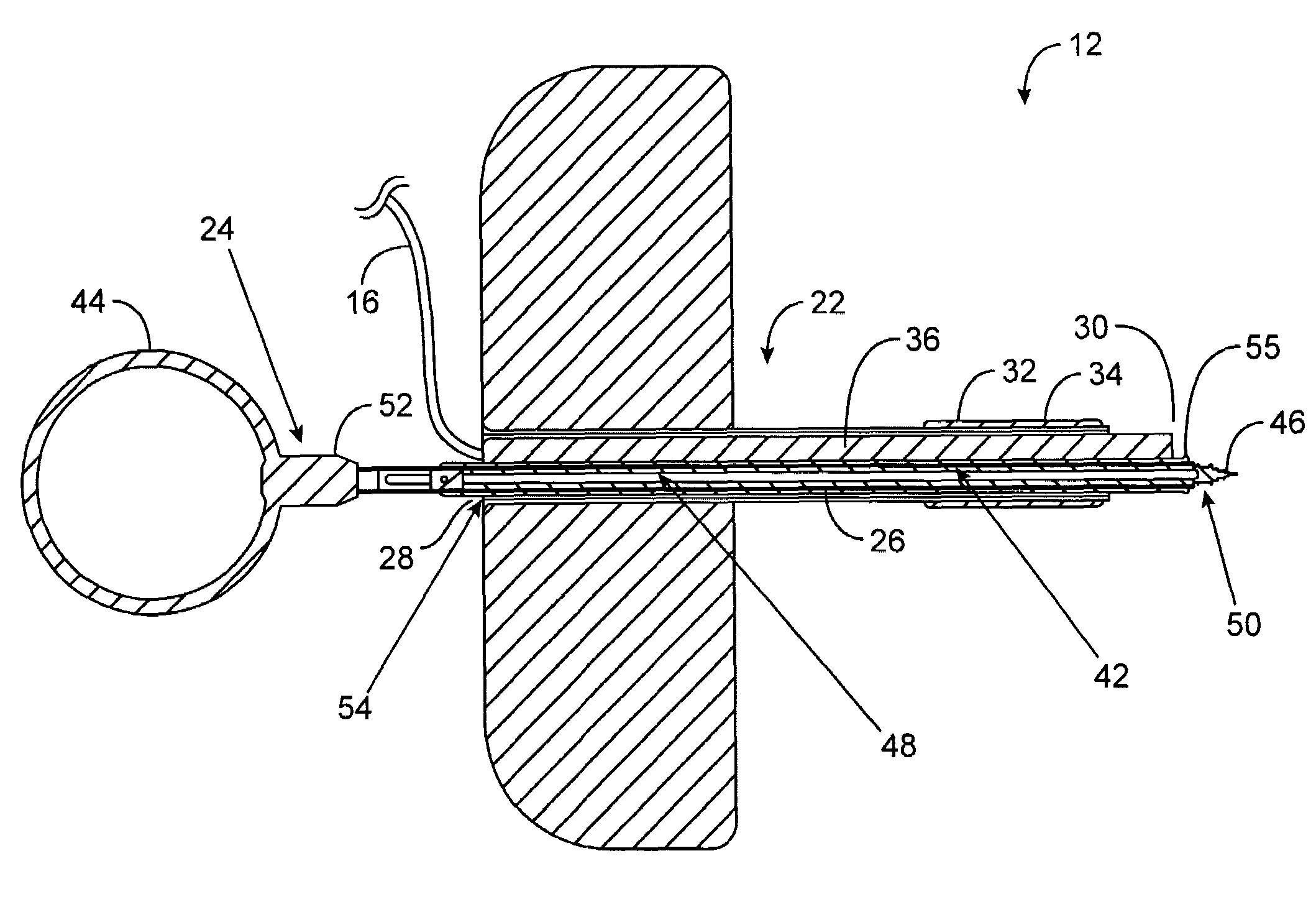
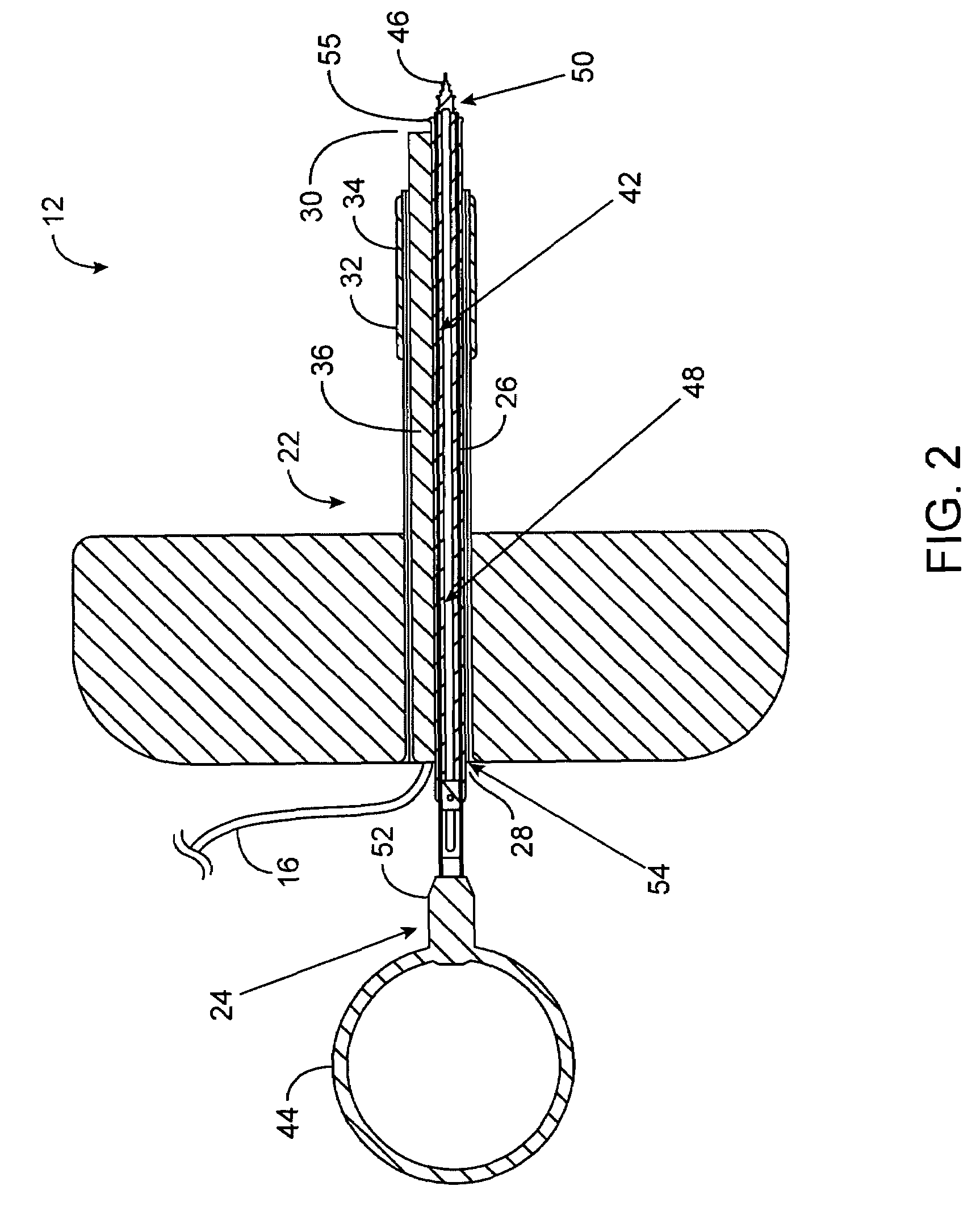
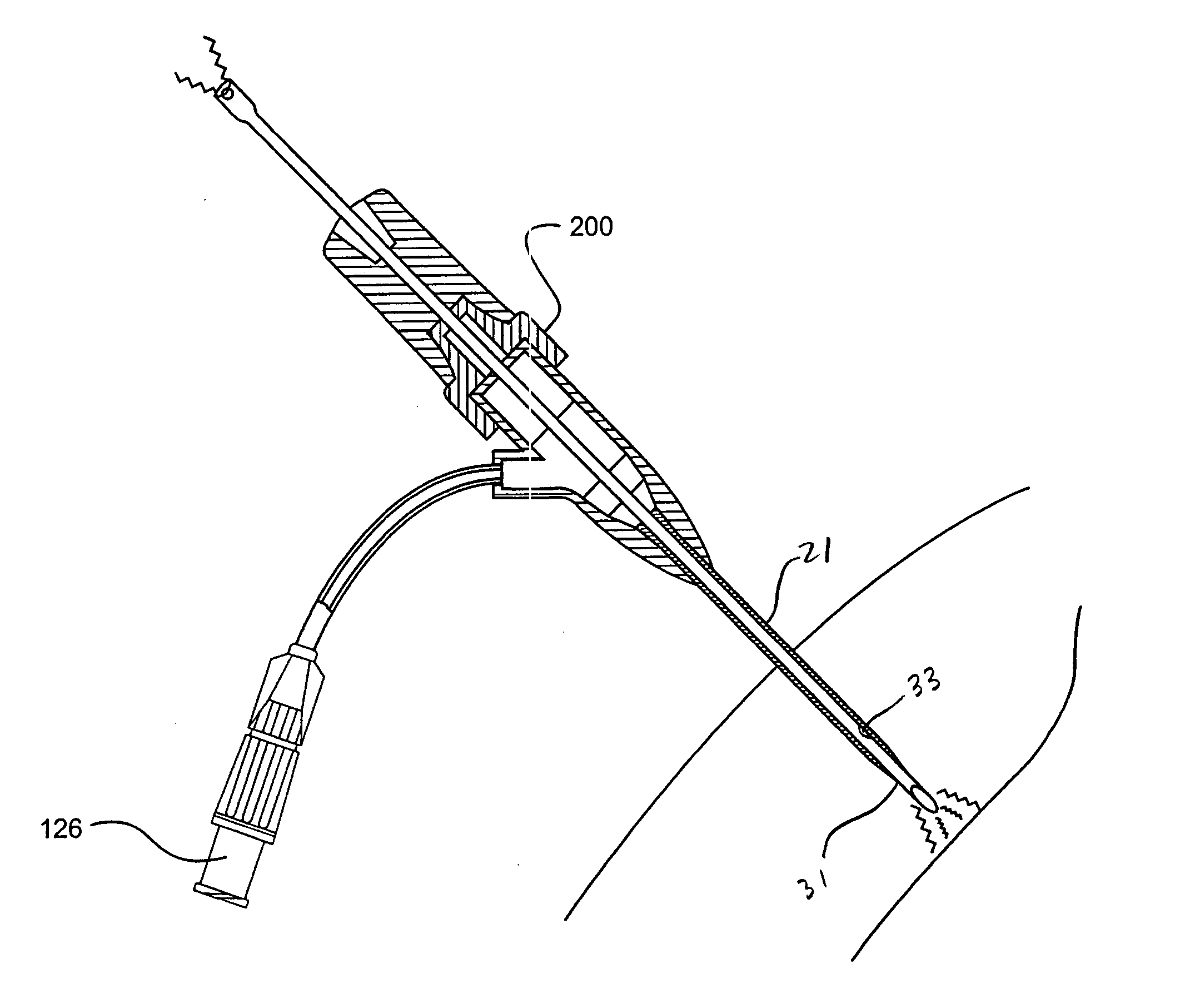
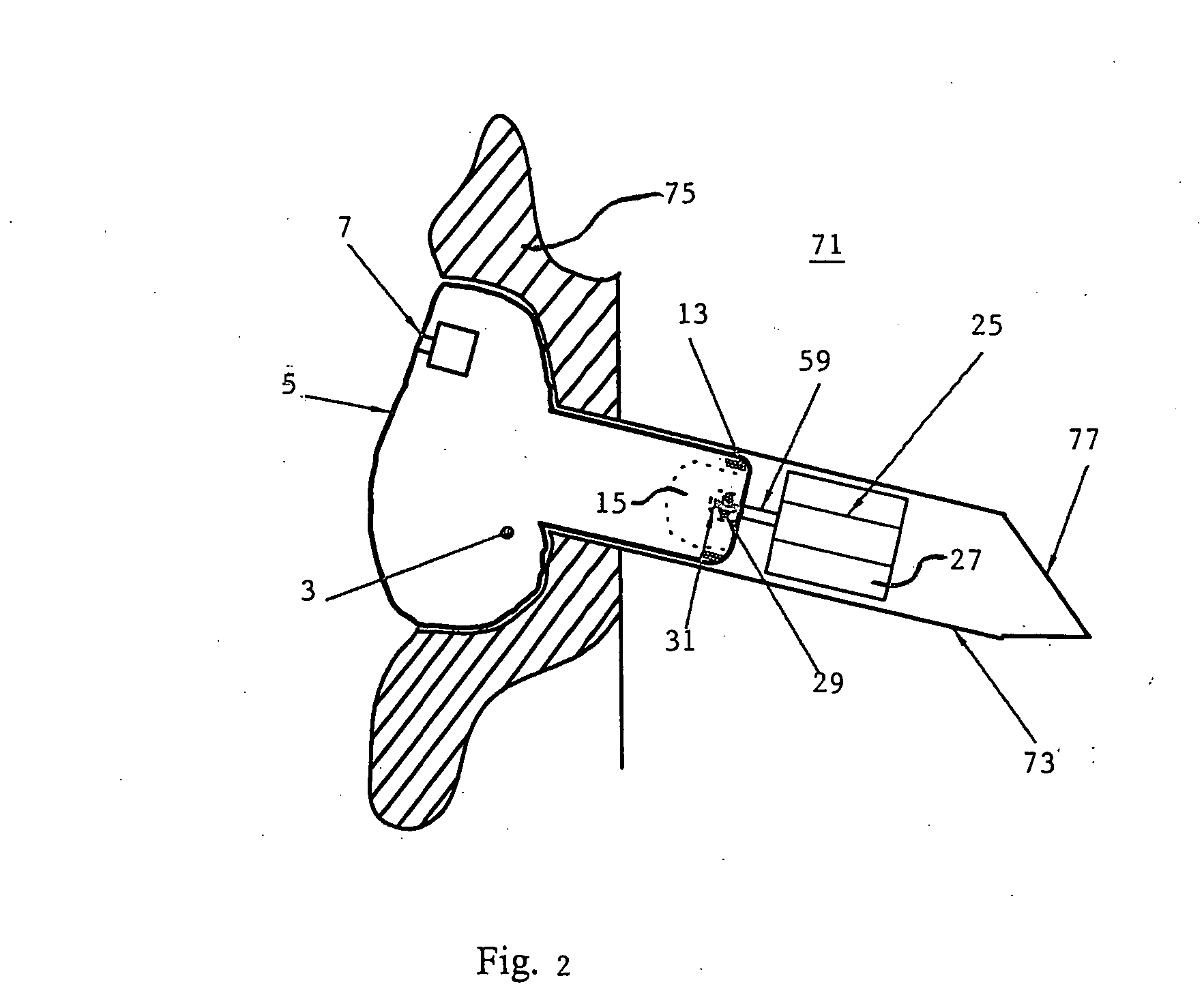
System and method of delivering local anesthesia
A catheter and introducer needle assembly is provided including a catheter adapter at its proximal end. The catheter adapter includes a side port in fluid communication with the catheter. A septum is located in the proximal end of the catheter adapter proximal of the side port. The introducer needle is connected at its proximal end to a needle hub and includes at least one notch formed therein in communication with the introducer needle lumen. The notch is formed in the needle such that blood can flow into the open distal end of the needle, through the lumen in the needle and through the notch into the catheter lumen (specifically, the annular space between the outside of the introducer needle and the inside of the catheter and catheter adapter). Thereafter, the blood can flow through the annular space and then through the side port and extension tube that extends from the catheter adapter. Similarly, liquids delivered to the side port flow to the annular space between the needle and the catheter, through the notch into the lumen within the needle, and out of the tip of the needle. Liquid anesthesia thus can be delivered to the patient's tissue surrounding the needle tip be delivering the liquid through the side port. An electrical connection may be provided to the needle via the needle hub to. carry an electrical charge to the patient's tissue. After withdrawing the needle from the catheter, the catheter remains in place, with the tip of the catheter disposed in the tissue being anesthetized. The clinician may provide additional anesthesia via the catheter through the extension tube set.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
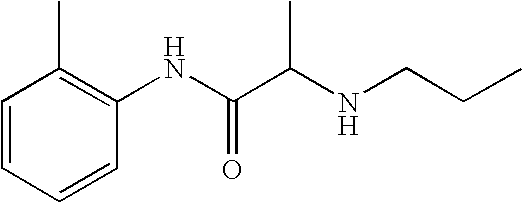
R-isomer of 2-{2[N-(2-indanyl)-N-phenylamino]ethyl}piperidine and other dermal anesthetics
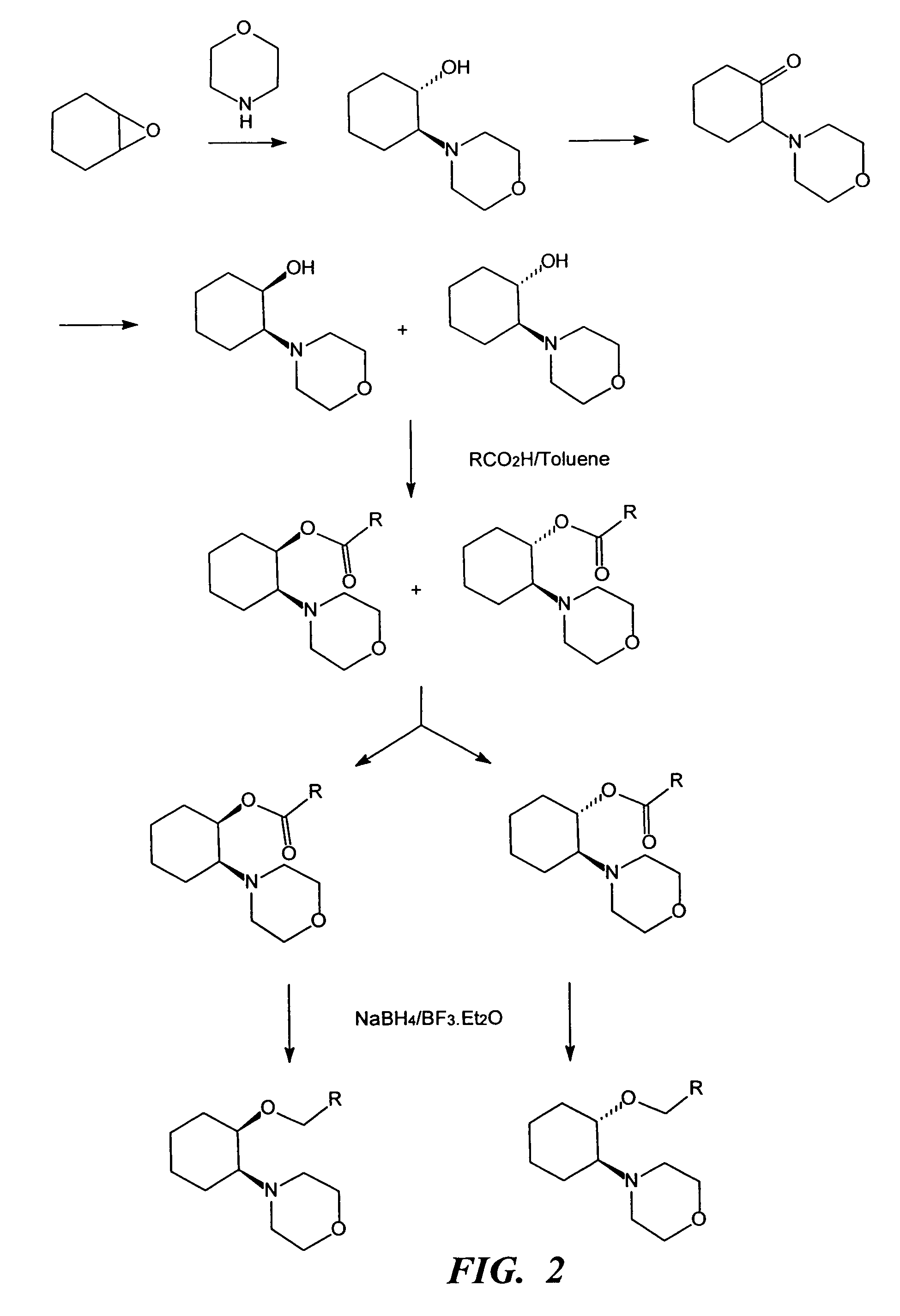
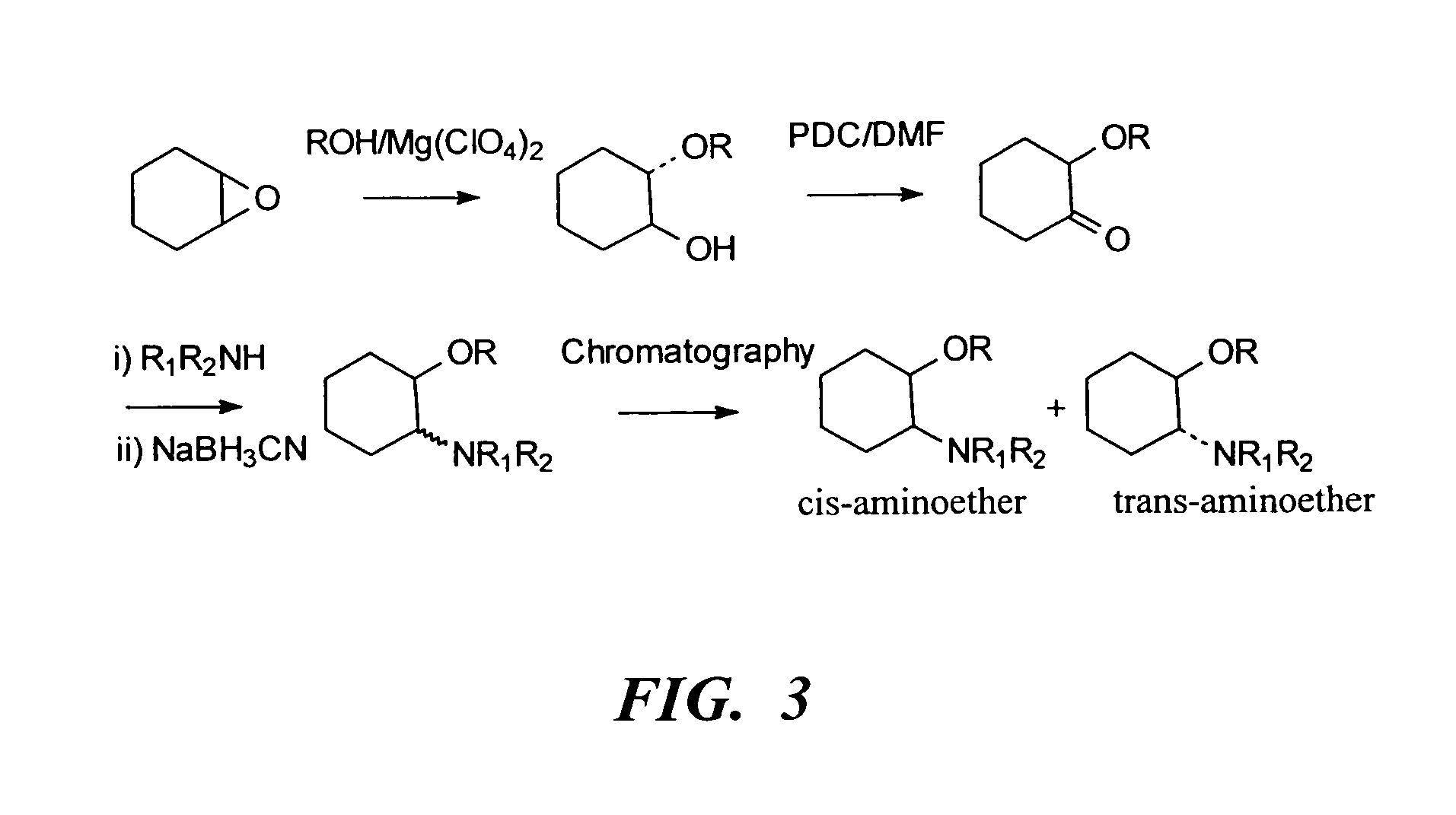
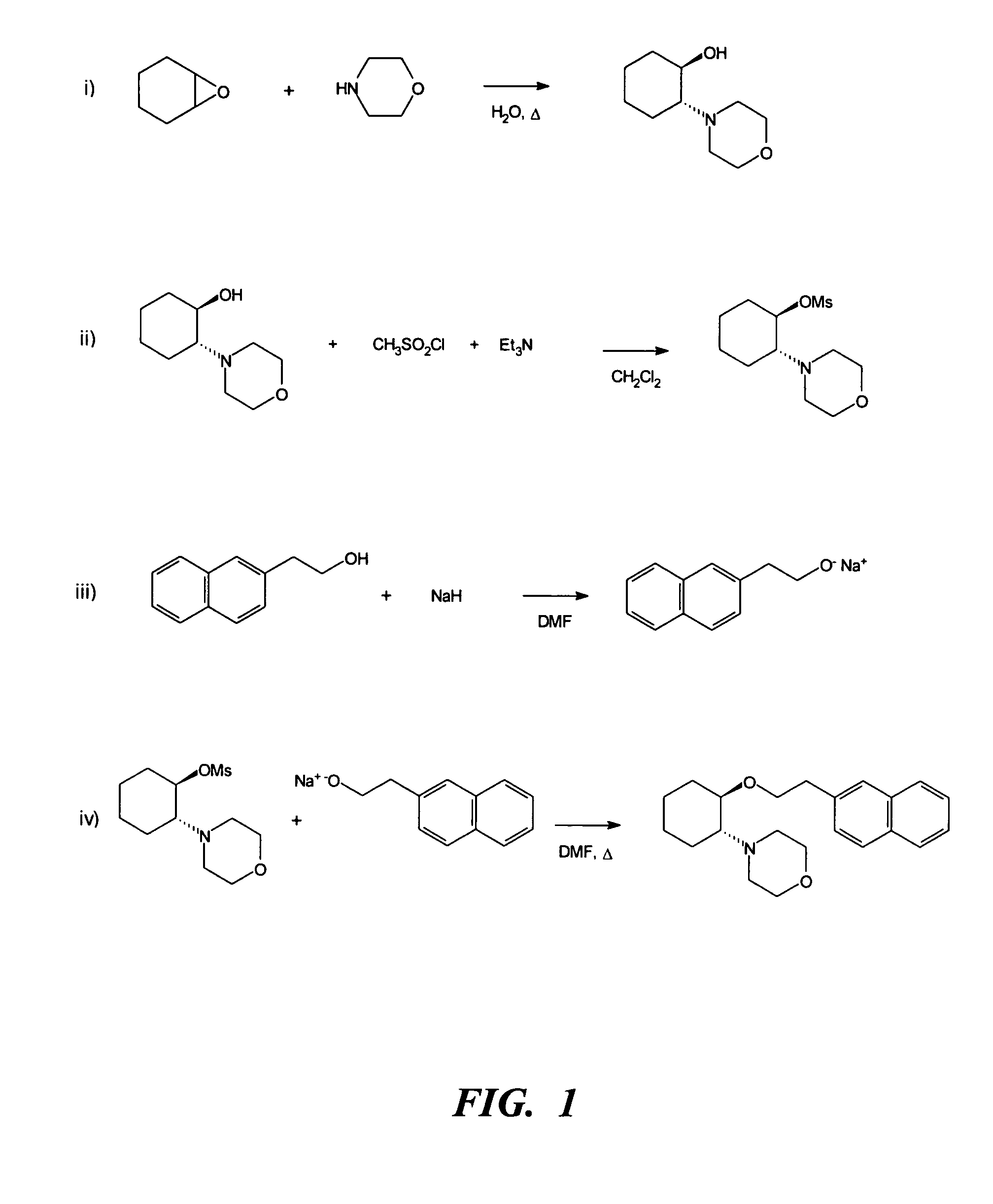
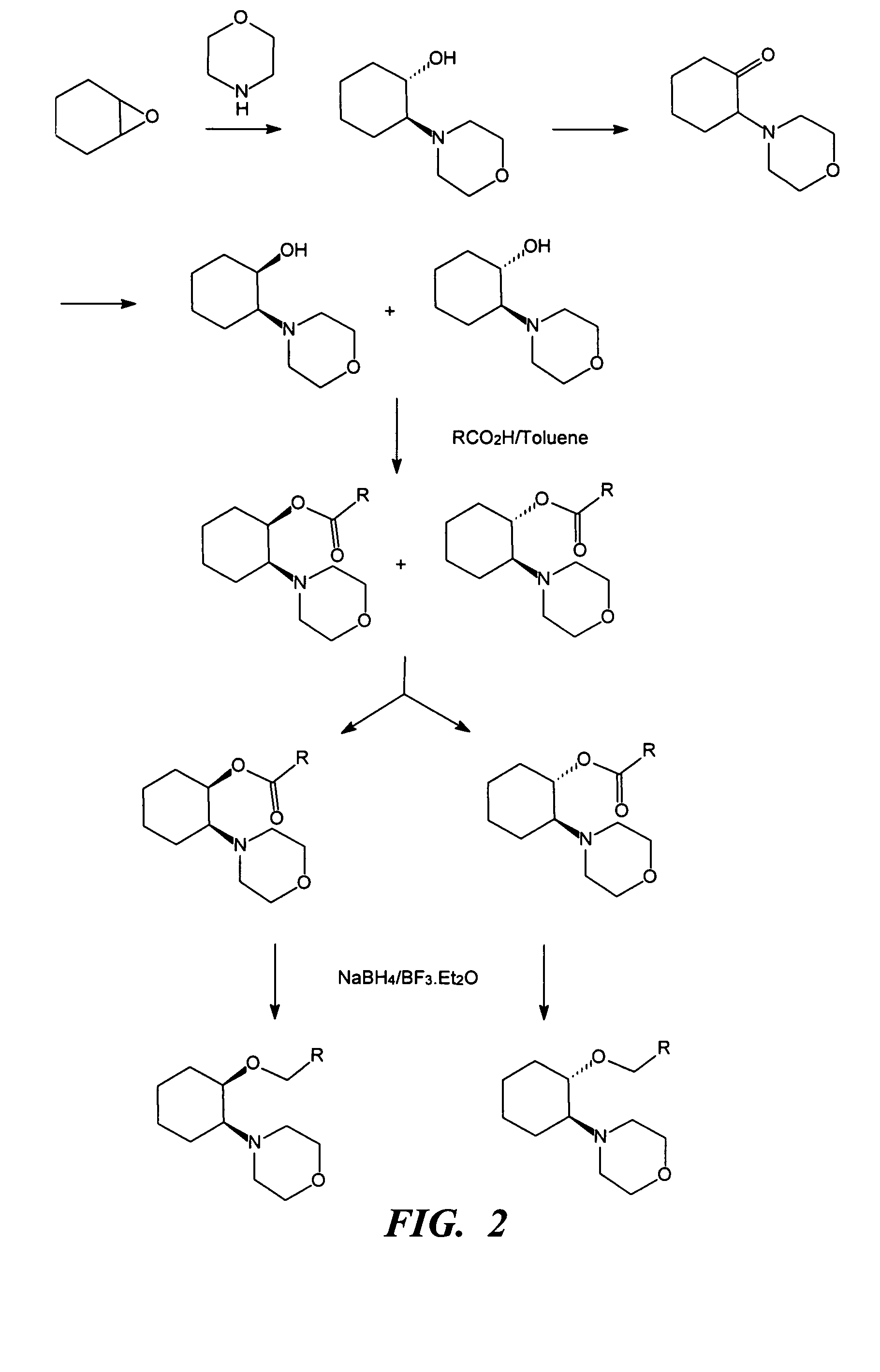
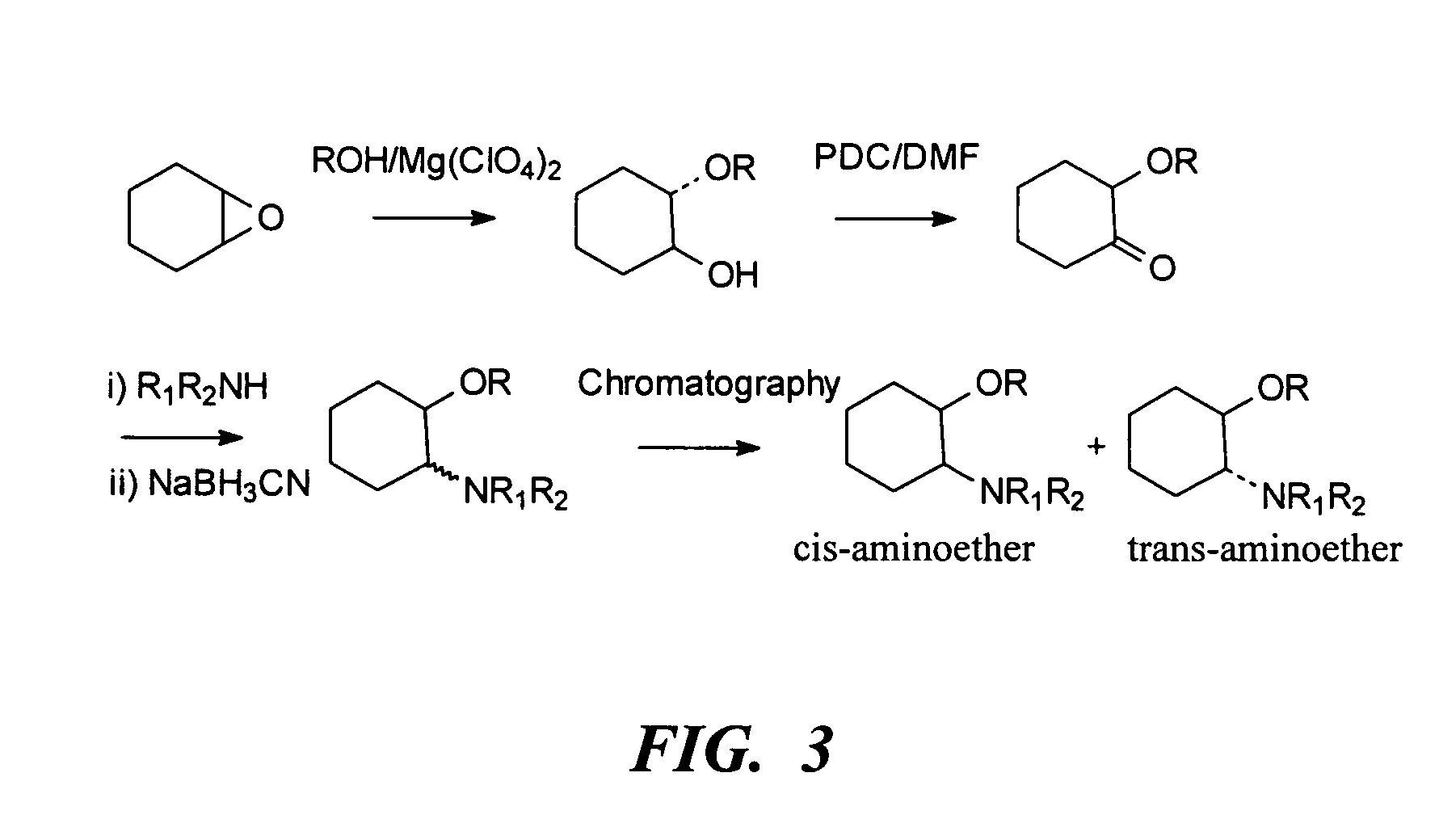
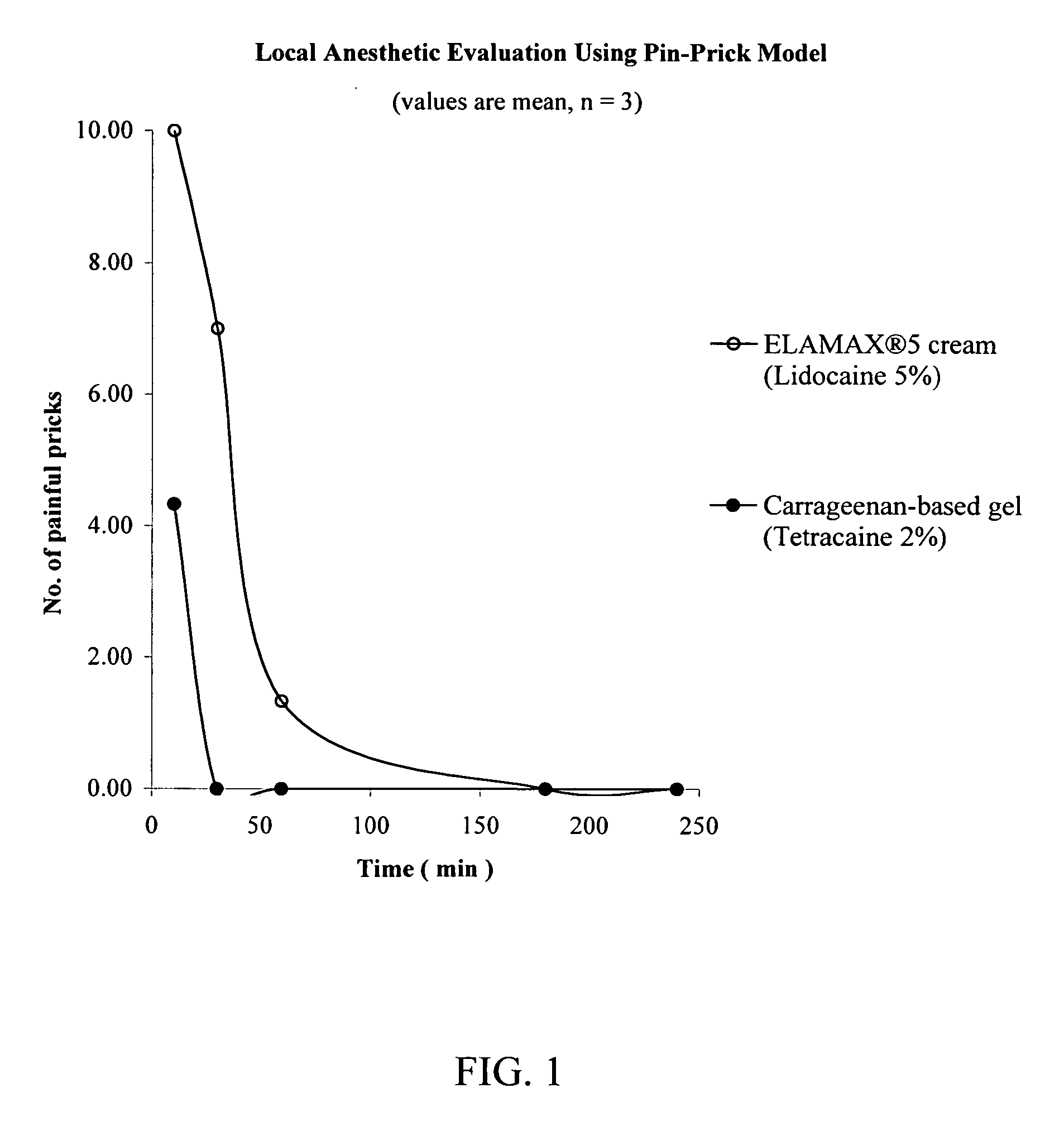
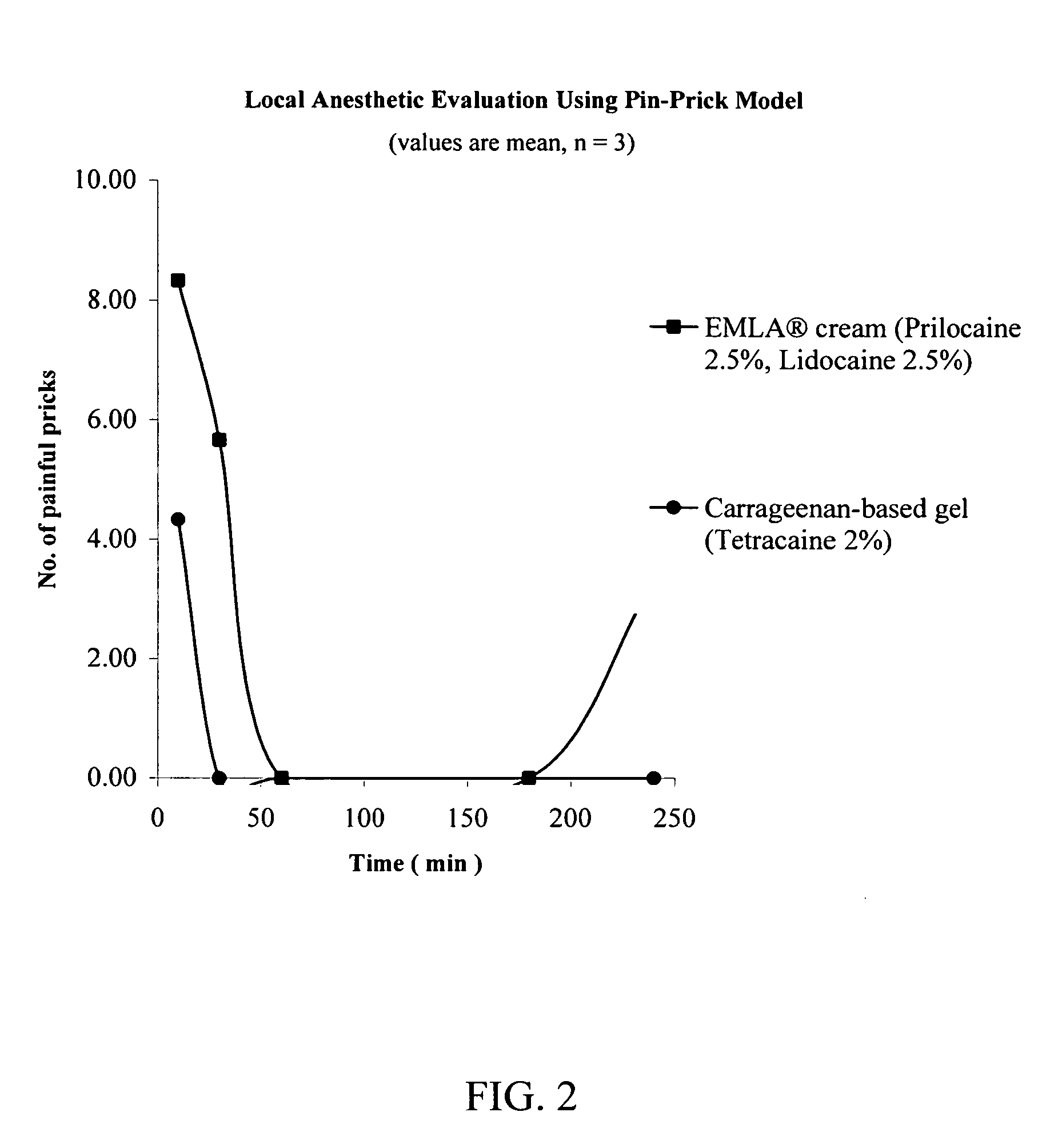
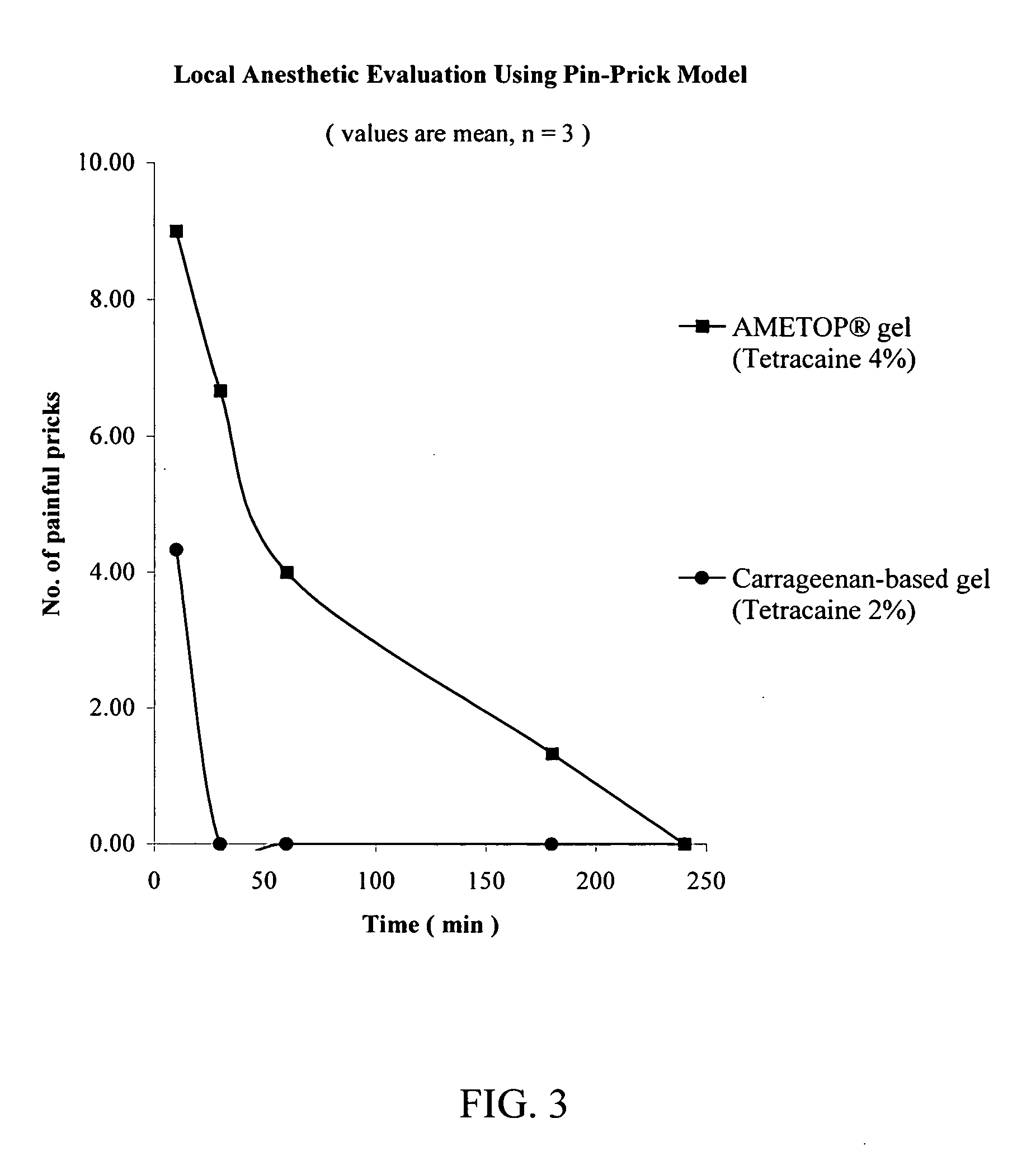
InactiveUS20060079558A1Desired effectImprove sleepingBiocideOrganic chemistryLocal anesthesiaAnesthetic
The present invention relates to the R-isomers of anesthetic compounds, the methods of treatment therewith, the compounds being useful for inducing local anesthesia, analgesia and sleep.
Owner:BRIDGE PHARMA INC
Cochlear ear implant
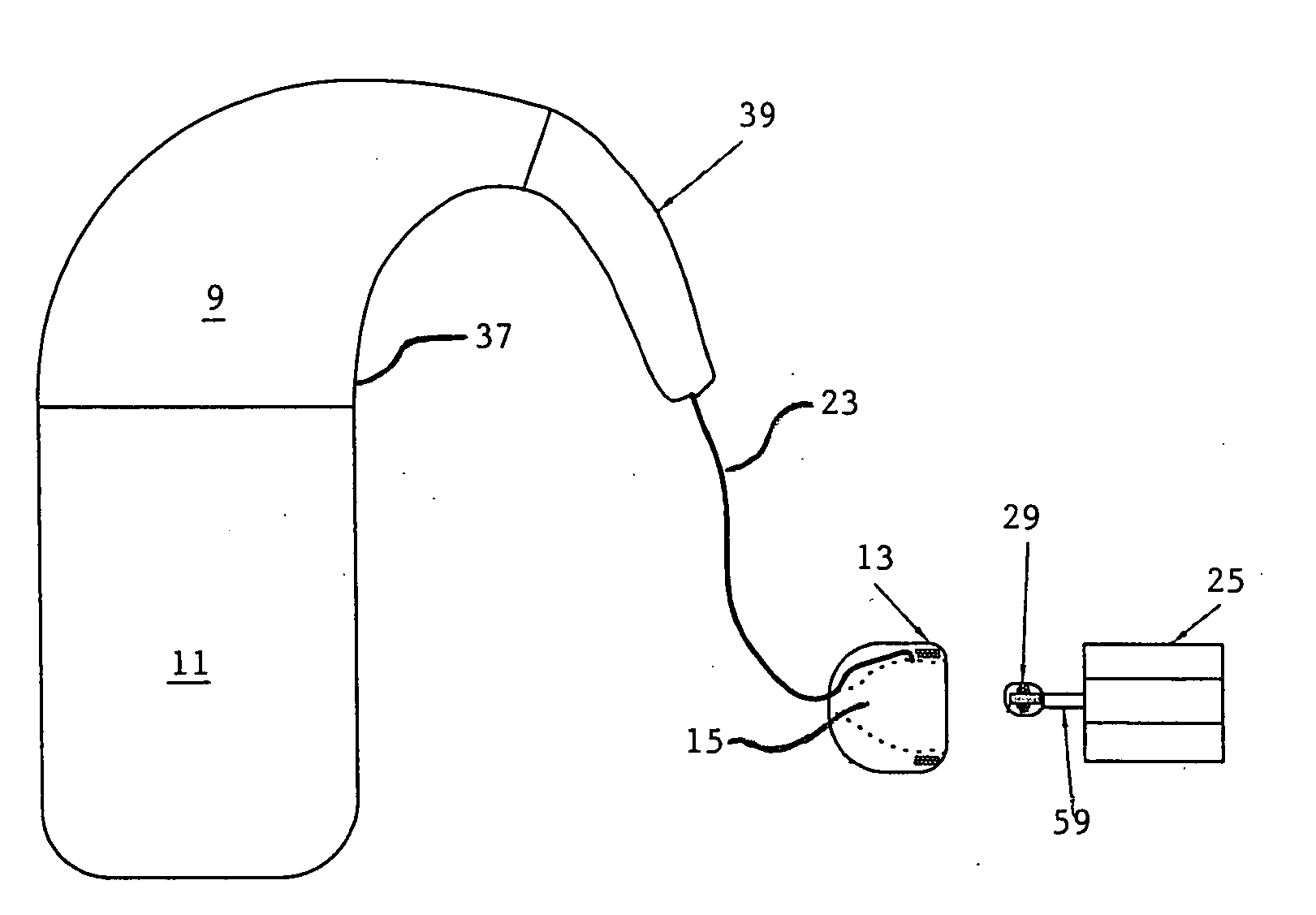
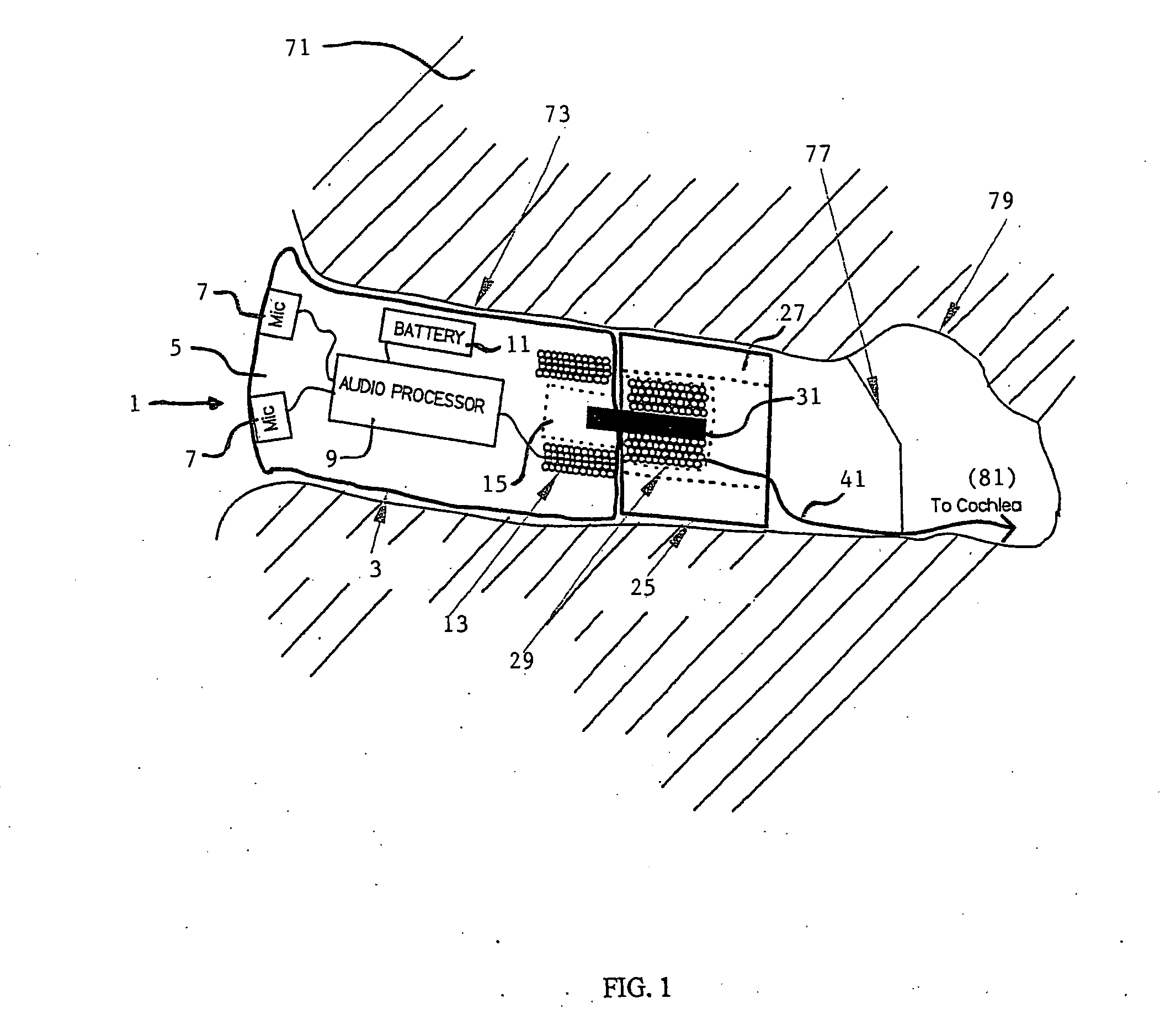
InactiveUS20050033384A1Not destroy residual hearingHead electrodesExternal electrodesHearing perceptionElectrode array
A simple cochlear implant is provided that can be implanted in a doctor's office under local anesthesia, which does not destroy residual hearing, and in a preferred embodiment, which is small enough to fit within a person's ear canal. The cochlear ear implant includes an exterior ear module, an interior ear module, and a cochlear electrode array. The exterior ear module includes a hollow housing within which are located the active electrical components including a microphone, power supply, and processor. The exterior ear module is easily removable from the body without surgery and is positioned in the auditory canal, the concha bowl or behind the pinna. The interior ear module is a semi-permanent assembly located immediately exterior to the tympanic membrane. It is a simple passive module for relaying signals to the electrode array. The communication of auditory signals from the exterior ear module to the interior ear module may be achieved by various techniques including by direct electrical transmission. However, the communication between the exterior and interior ear modules is preferably accomplished using a transcanal induction link. The electrode array extends from the interior ear module through the tympanic membrane to engage the cochlea. The electrode array includes an implanted active electrode, a return electrode, and a biocompatible miniature connector for connecting to the interior ear module.
Owner:SACHA MIKE K
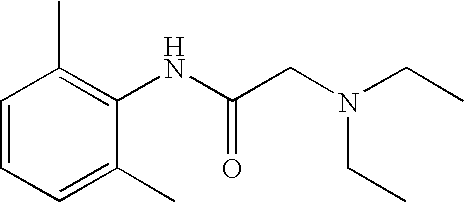
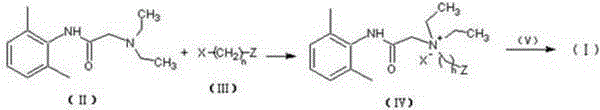
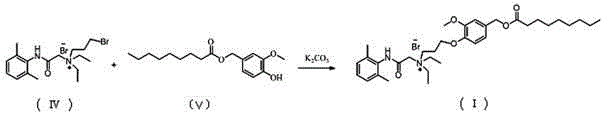
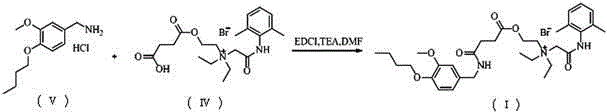
N-diethylaminoacetyl-2,6-dimethylaniline derivatives, preparation method and applications thereof
The invention provides N-diethylaminoacetyl-2,6-dimethylaniline derivatives, a preparation method and applications thereof. The structure of the derivatives is represented by the formula (I). The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out reactions between N-diethylaminoacetyl-2,6-dimethylaniline and halogenated compounds to obtain a corresponding quaternary ammonium salt intermediate, and then subjecting the quaternary ammonium salt intermediate to react with corresponding 2-methoxyl-4-subsituted phenol derivative raw material so as to obtain the N-diethylaminoacetyl-2,6-dimethylaniline derivatives. The derivatives can be used as a long-acting local anesthetic drug or a pain relieving drug capable of separating the motion and the feeling, can exert a reversible and lasting local anesthetic effect in organism bodies, do not affect motor function in a certain dosage range, and have an ideal retardant effect on separation of motion and feeling.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
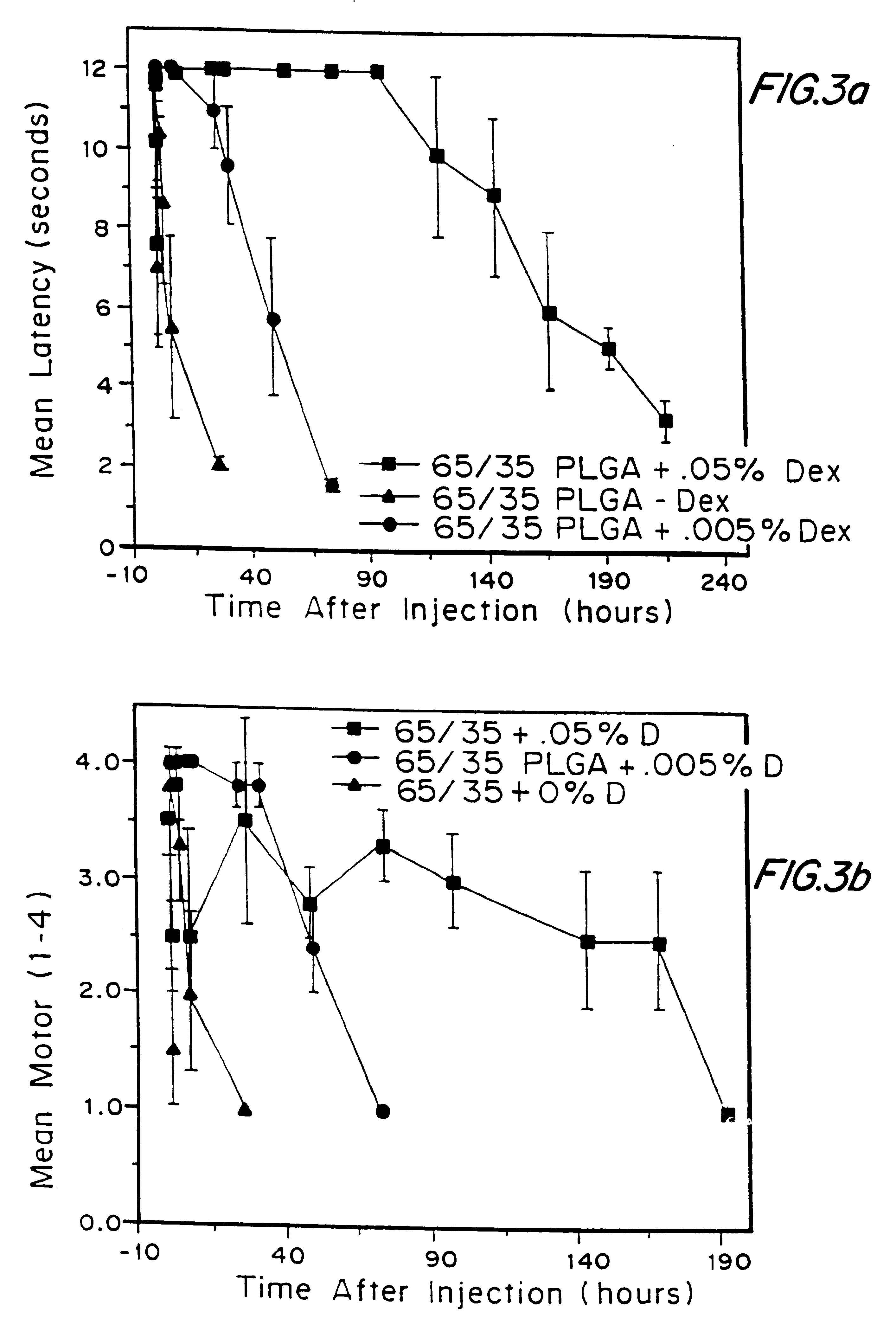
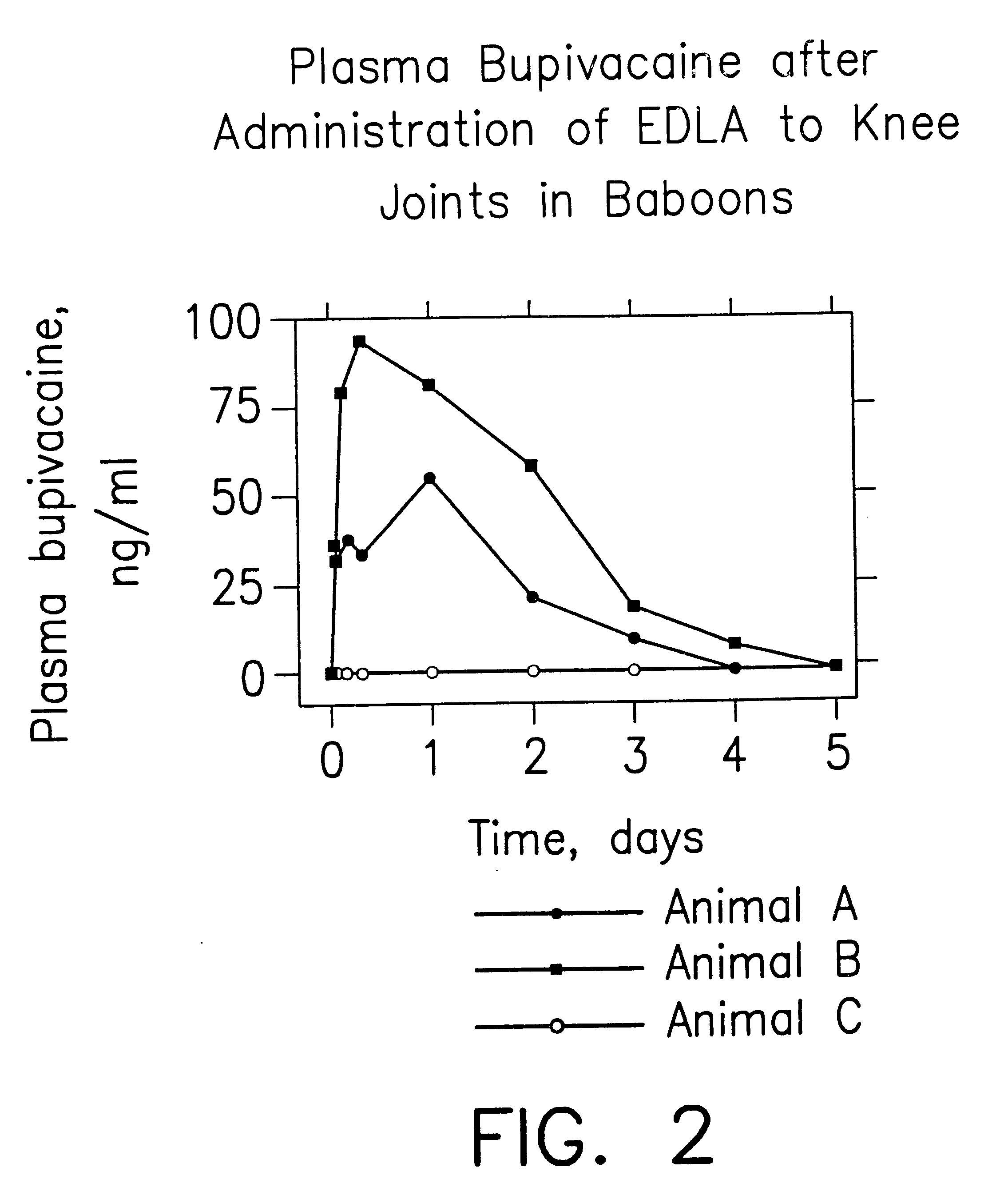
Prolonged anesthesia in joints and body spaces
InactiveUS20020054915A1Enhance and prolong local anesthesiaGood effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAnaestheticsAnesthetic AgentMicroparticle
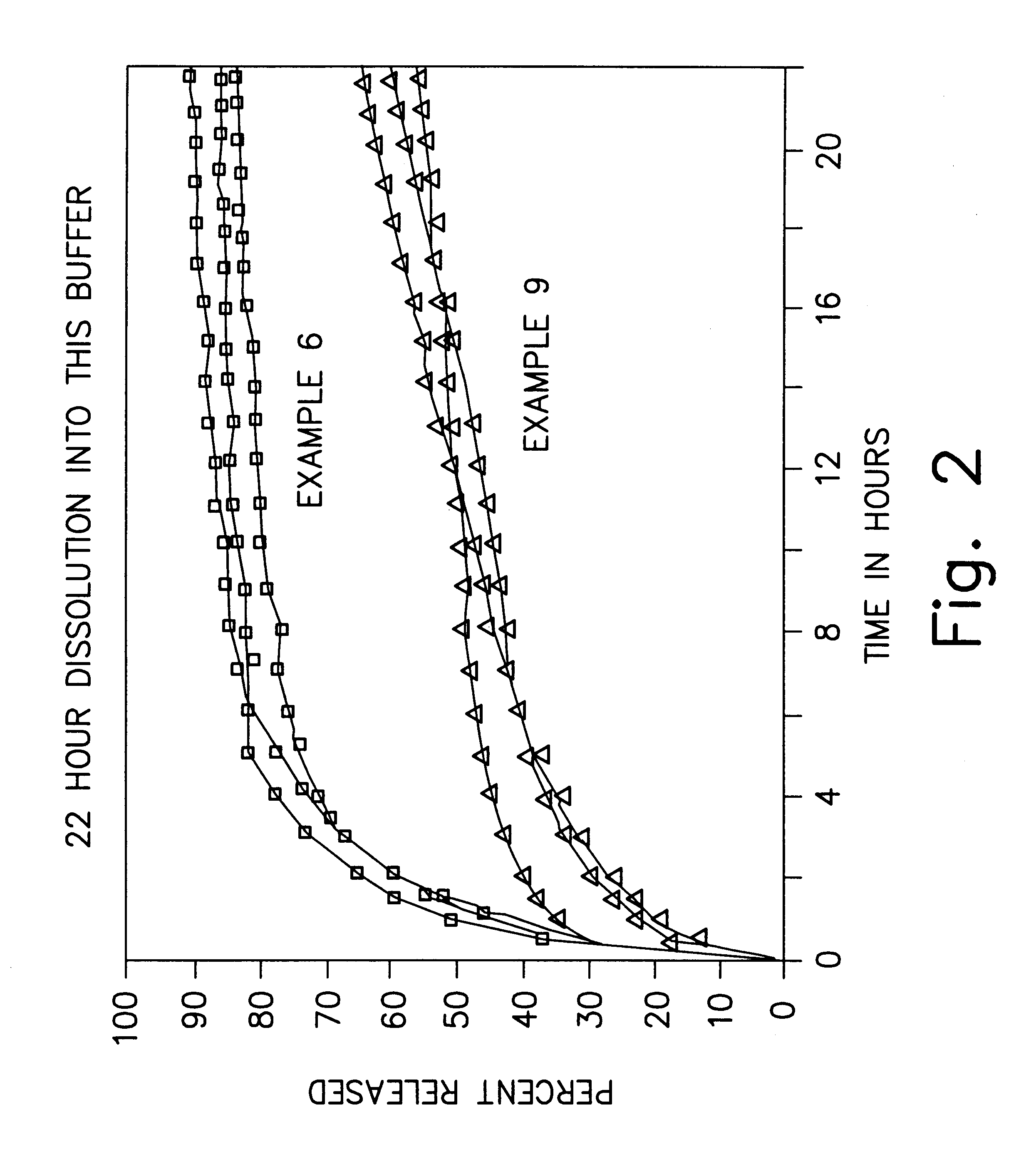
Sustained release local anesthetic formulations are administered intra articularly and / or into body spaces / cavities. The formulation is preferably a plurality of injectable microparticles including a local anesthetic and an effective amount of a biocompatible, biodegradable, sustained release material prolonging the release of the local anesthetic and optionally and a pharmaceutically acceptable, i.e., non-toxic, augmenting agent effective to prolong the duration of the local anesthesia for a time period longer than that obtainable without the augmenting agent.
Owner:PURDUE PHARMA LP
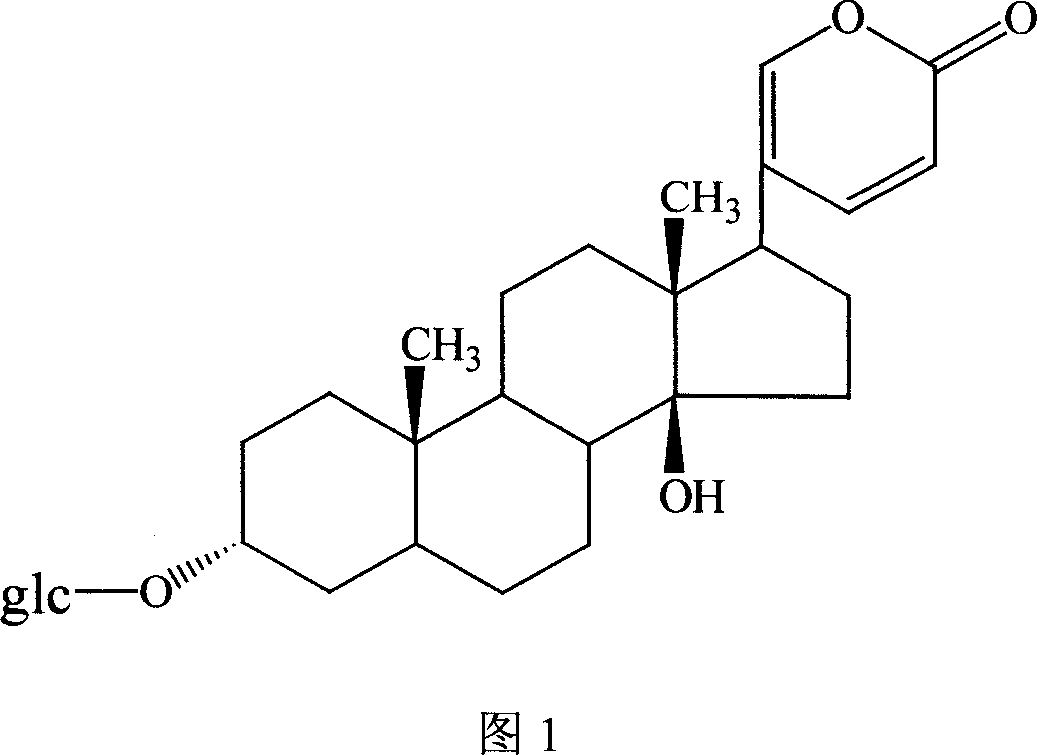
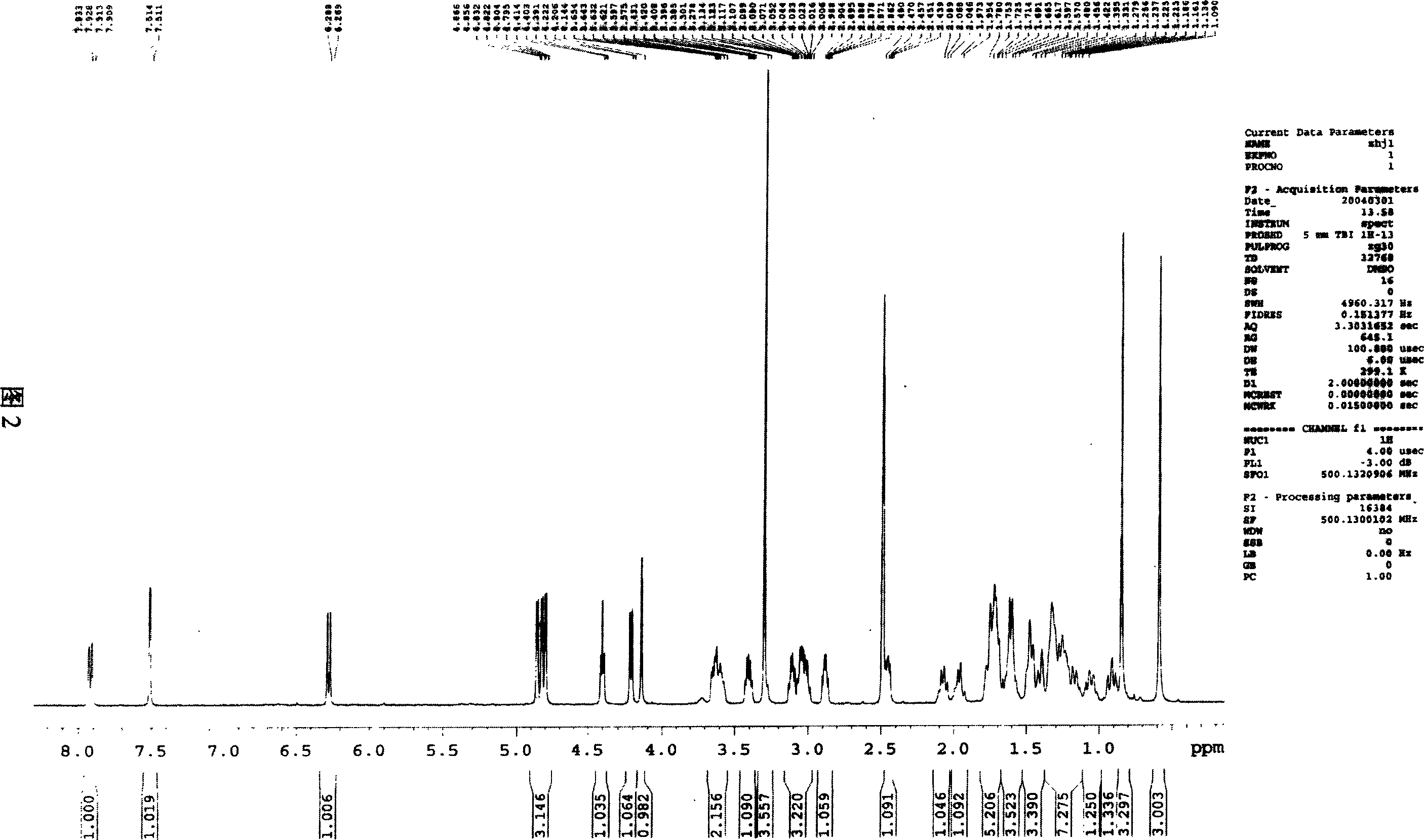
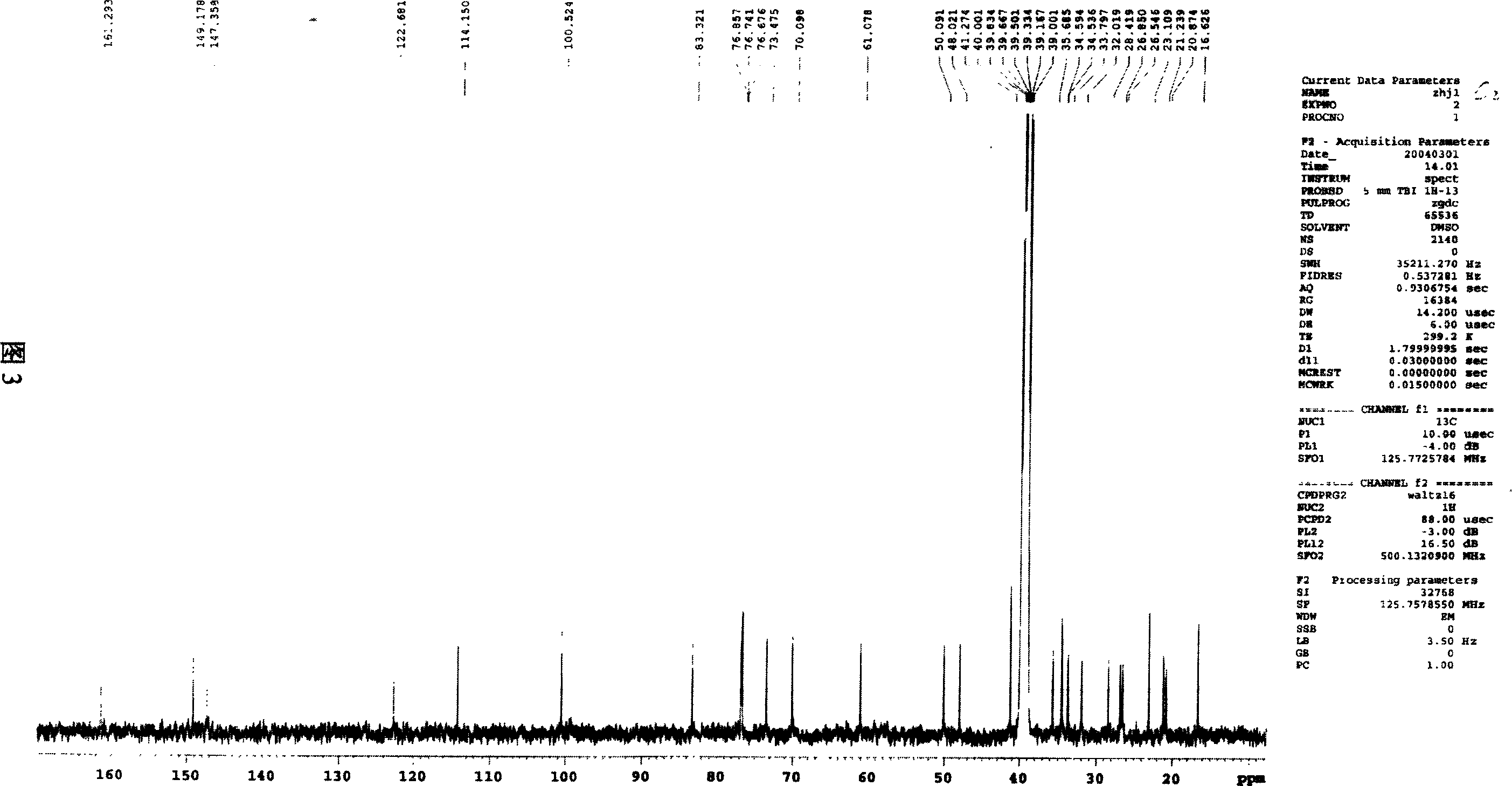
Toad sterene compounds and application thereof in pharmaceutical preparation
ActiveCN101016326AInhibitory activityGood water solubilityAntiviralsPill deliveryCancer cellMedicine
Owner:ANHUI CHINA RESOURCES JINCHAN PHARMA CO LTD
Compositions and delivery systems for administration of a local anesthetic agent
InactiveUS20050152957A1Good effectLocal effectBiocideAdhesive dressingsActive agentHydrophobic polymer
A pharmaceutical composition is provided for topical administration of a local anesthetic agent. The composition comprises (a) a therapeutically effective amount of a local anesthetic agent and (b) a pharmaceutically acceptable, nonliposomal carrier comprised of a monohydric alcohol, a penetration enhancer, and polymer, which may be a hydrophilic polymer, a hydrophobic polymer or a combination thereof. The composition can be in the form of a gel, or it may form a film following application to a patient's body surface and evaporation of the monohydric alcohol. The composition provides rapid onset of local anesthesia as well as penetration of the active agent into the skin. Methods and drug delivery systems for administration of local anesthetic agents are also provided.
Owner:CORIUM INT
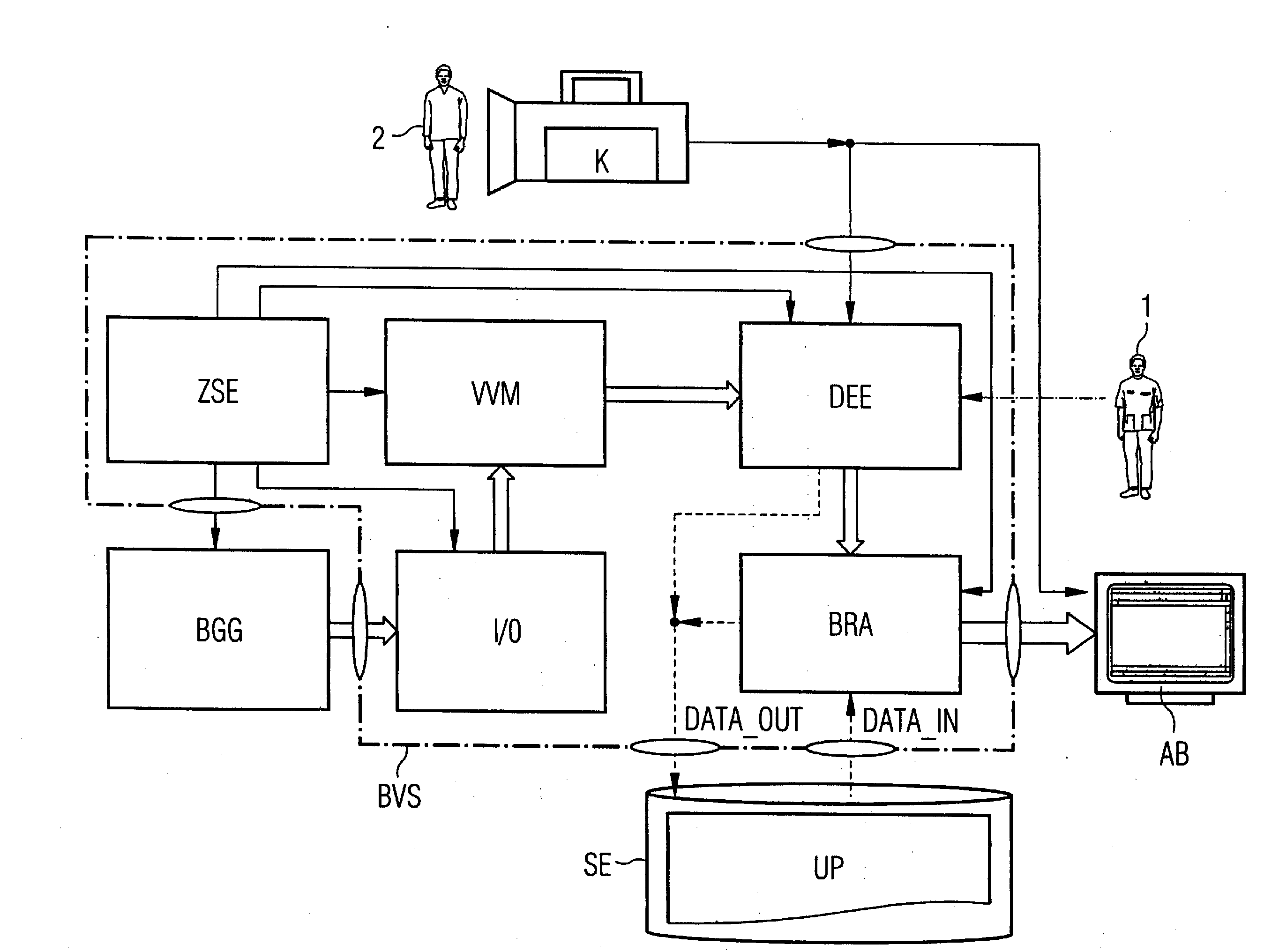
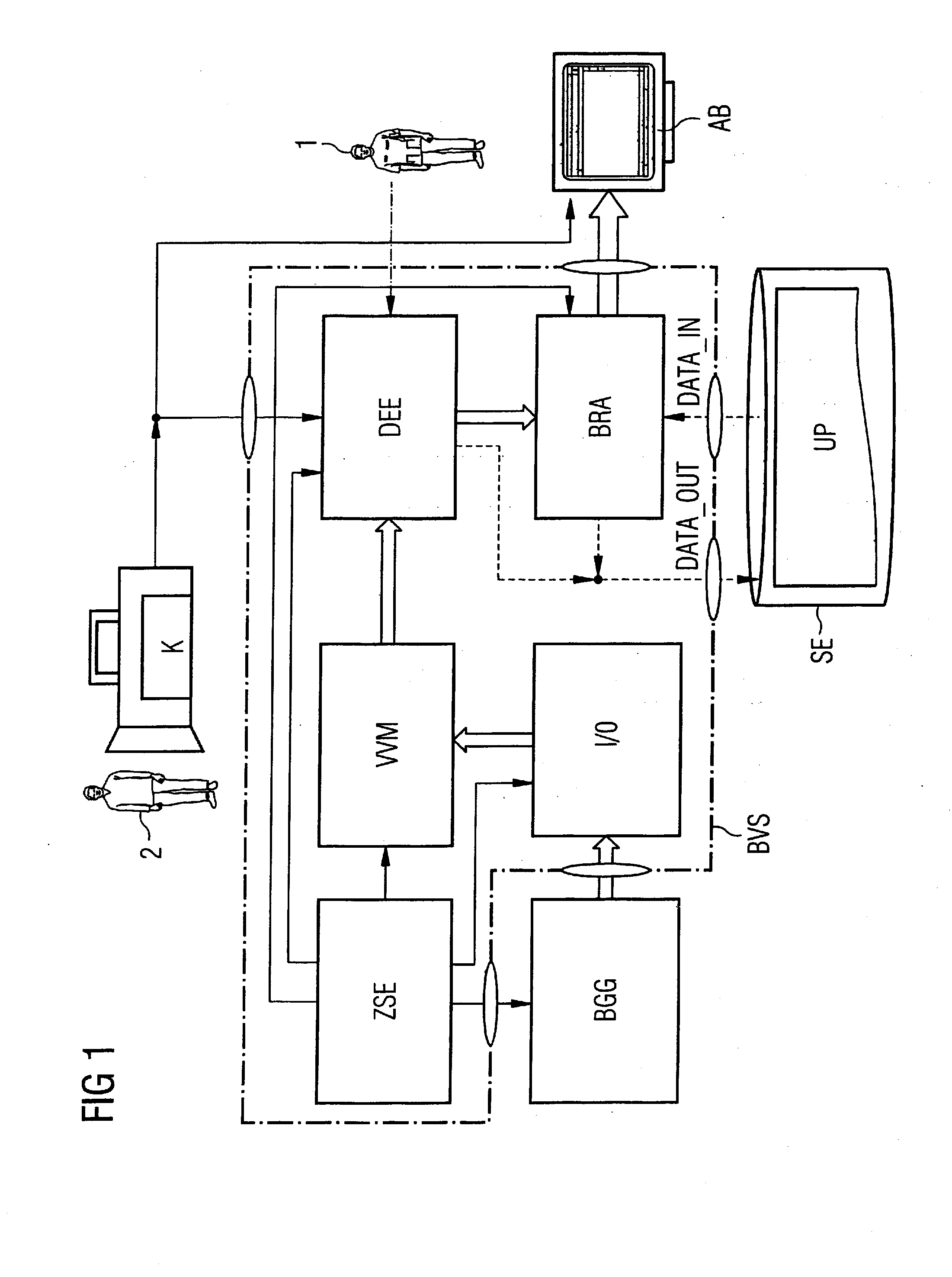
Image acquisition, archiving and rendering system and method for reproducing imaging modality examination parameters used in an initial examination for use in subsequent radiological imaging
InactiveUS20080310698A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingDiagnostic Radiology ModalityTumor Examination
A CT- or MRT-assisted image acquisition, image archiving and image rendering system allows generation, storage, post-processing, retrieval and graphical visualization of computed or magnetic resonance tomography image data that, for example, can be used in the clinical field in the framework of radiological slice image diagnostics as well as in the framework of interventional radiology. Moreover, a method implemented by this system allows reproduction of patient-specific examination parameters of an initial examination implemented by means of computed or magnetic resonance tomography imaging in the framework of CT or MRT follow-up examinations (“follow-ups”), for example in a post-operative tumor examination implemented under slice image monitoring in connection with a histological tissue sample extraction (biopsy) implemented under local anesthesia or a minimally-invasive intervention implemented for tumor treatment. Acquisition, measurement, 2D and / or 3D reconstruction parameters from a radiological initial examination of the patient conducted by means of CT, PET-CT or MRT as well as position data to establish the position adopted by this patient on the examination table of a computed tomography or magnetic resonance tomography apparatus are electronically documented, retrievably and persistently stored, and are automatically reused given subsequent CT-, PET-CT- or MRT-based monitoring examinations, or CT-controlled or MRT-controlled interventional or operative procedures.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
S-isomer of 2-{2[N-(2-indanyl)-N-phenylamino]ethyl}piperidine and other dermal anesthetics
InactiveUS20060079559A1Prolong the action timeDesired effectBiocideNervous disorderLocal anesthesiaAnesthetic
The present invention relates to the S-isomers of anesthetic compounds, the methods of treatment therewith, the compounds being useful for inducing local anesthesia, analgesia and sleep.
Owner:BRIDGE PHARMA INC
Brachytherapy apparatus
InactiveUS20070142694A1Reduce in quantityOptimize treatment planX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyAdemetionineRadioactive seed
The present disclosure provides a brachytherapy apparatus that delivers a low dose, partial breast irradiation treatment for post-lumpectomy patients via introduction of a catheter-like device through a cannula. The apparatus may be introduced post-surgically with local anesthesia under image guidance into the previous excision site and into a cavity by a surgeon. The brachytherapy apparatus includes a seed containment device configured to contain a plurality of low-dose radioactive seeds therein. The seed containment device may be one or more thin-walled tubes. The apparatus is further configured to expand so that at least a portion of the seed containment device is positioned against the remaining tissue and the plurality of radioactive seeds are disposed at the perimeter of the seed containment device. Also described are various clamps for the apparatus, and sleeves for adjusting the size of the device to fit a cavity when the apparatus is in use.
Owner:PORTOLA MEDICAL
System and method of delivering local anesthesia
A catheter and introducer needle assembly is provided including a catheter adapter at its proximal end. The catheter adapter includes a side port in fluid communication with the catheter and a septum located in the proximal end of the catheter adapter proximal of the side port. The introducer needle is connected at its proximal end to a needle hub and includes at least one notch in communication with the introducer needle lumen. The notch allows blood to flow into the open distal end of the needle and through the notch into the catheter lumen (specifically, the annular space between the outside of the introducer needle and the inside of the catheter and catheter adapter). Thereafter, the blood can flow through the annular space and then through the side port and extension tube that extends from the catheter adapter.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Compositions and Methods for Treating Premature Ejaculation
Compositions and methods for the treatment of premature ejaculation have been developed. It has been discovered that premature ejaculation can be treated by administering a local anesthetic to the glans penis. The local anesthetic may be formulated as an emulsion, lotion, paste, gel, cream, ointment, shea butter, suspension, solution, balm, salve, foam, or in the form of a pump spray to achieve local anesthesia of the dorsal neurons of the penis.
Owner:SHIONOGI PHARMA
Local anesthetic methods and kits
Methods of reversing local anesthesia are disclosed. The methods comprise administering a local anesthetic and alpha adrenergic receptor agonist to induce local anesthesia followed by reversing anesthesia with a low dose of an alpha adrenergic receptor antagonist. Also disclosed are kits comprising a local anesthetic, an alpha adrenergic receptor agonist and a low dose of an alpha adrenergic receptor antagonist.
Owner:SEPTODONT HLDG
Ion channel modulating compounds and uses thereof
InactiveUS7101877B2Reduce actionIncrease heart rateSenses disorderNervous disorderIn vivoLocal anesthesia
Ion channel modulating compounds are disclosed. The compounds of the present invention may be incorporated in compositions and kits. The present invention also discloses a variety of in vitro and in vivo uses for the compounds and compositions, including the treatment of arrhythmia and the production of analgesia and local anesthesia.
Owner:CORREVIO INT SARL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![R-isomer of 2-{2[N-(2-indanyl)-N-phenylamino]ethyl}piperidine and other dermal anesthetics R-isomer of 2-{2[N-(2-indanyl)-N-phenylamino]ethyl}piperidine and other dermal anesthetics](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/75863e11-eb15-4fac-b728-e31a43c24920/US20060079558A1-20060413-D00001.png)
![R-isomer of 2-{2[N-(2-indanyl)-N-phenylamino]ethyl}piperidine and other dermal anesthetics R-isomer of 2-{2[N-(2-indanyl)-N-phenylamino]ethyl}piperidine and other dermal anesthetics](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/75863e11-eb15-4fac-b728-e31a43c24920/US20060079558A1-20060413-C00001.png)
![R-isomer of 2-{2[N-(2-indanyl)-N-phenylamino]ethyl}piperidine and other dermal anesthetics R-isomer of 2-{2[N-(2-indanyl)-N-phenylamino]ethyl}piperidine and other dermal anesthetics](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/75863e11-eb15-4fac-b728-e31a43c24920/US20060079558A1-20060413-C00002.png)
![S-isomer of 2-{2[N-(2-indanyl)-N-phenylamino]ethyl}piperidine and other dermal anesthetics S-isomer of 2-{2[N-(2-indanyl)-N-phenylamino]ethyl}piperidine and other dermal anesthetics](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/3fa5434c-3354-478a-ac7e-e46f8387547c/US20060079559A1-20060413-D00001.png)
![S-isomer of 2-{2[N-(2-indanyl)-N-phenylamino]ethyl}piperidine and other dermal anesthetics S-isomer of 2-{2[N-(2-indanyl)-N-phenylamino]ethyl}piperidine and other dermal anesthetics](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/3fa5434c-3354-478a-ac7e-e46f8387547c/US20060079559A1-20060413-C00001.png)
![S-isomer of 2-{2[N-(2-indanyl)-N-phenylamino]ethyl}piperidine and other dermal anesthetics S-isomer of 2-{2[N-(2-indanyl)-N-phenylamino]ethyl}piperidine and other dermal anesthetics](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/3fa5434c-3354-478a-ac7e-e46f8387547c/US20060079559A1-20060413-C00002.png)