Patents
Literature
3258 results about "Electrode array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
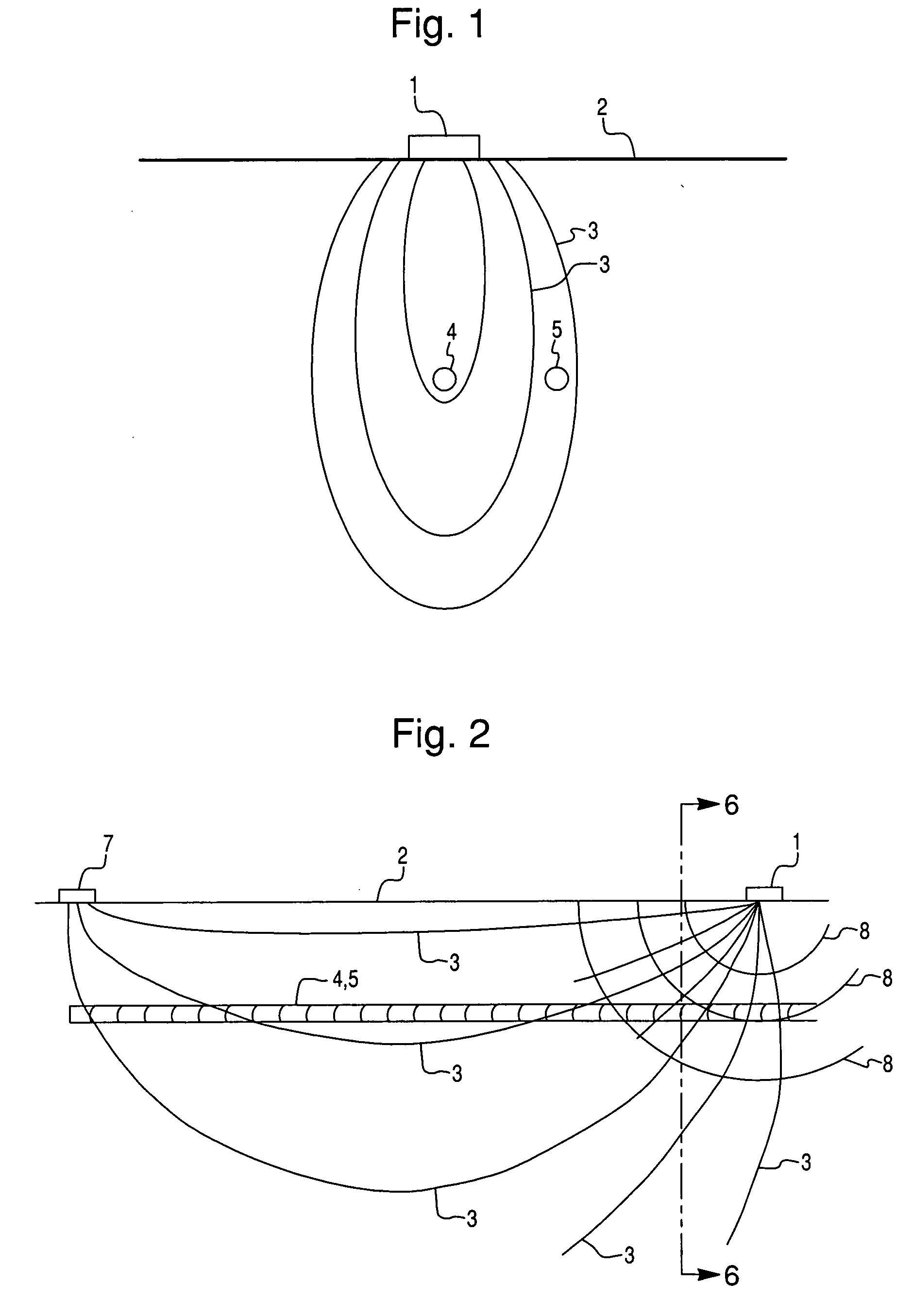
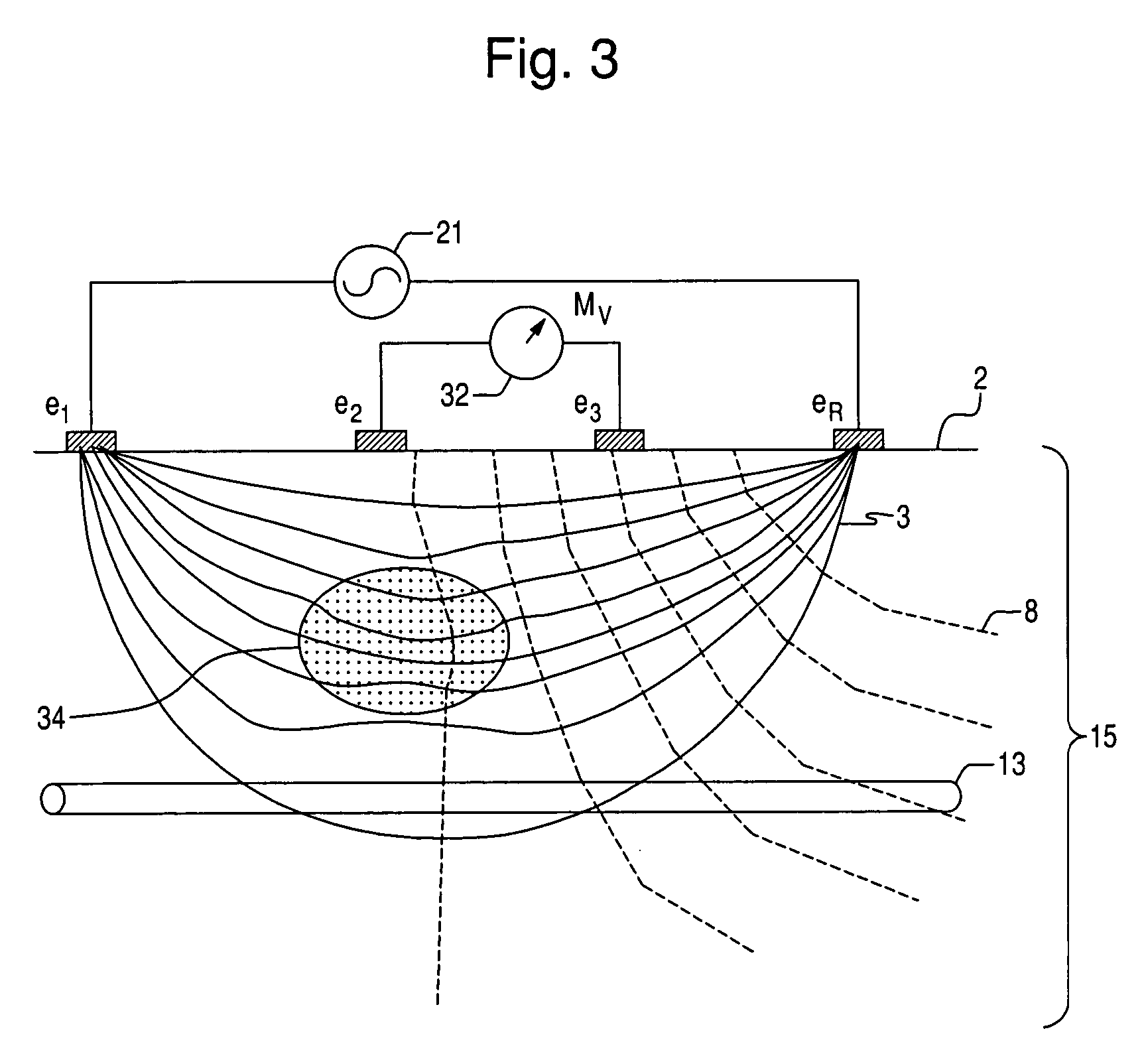
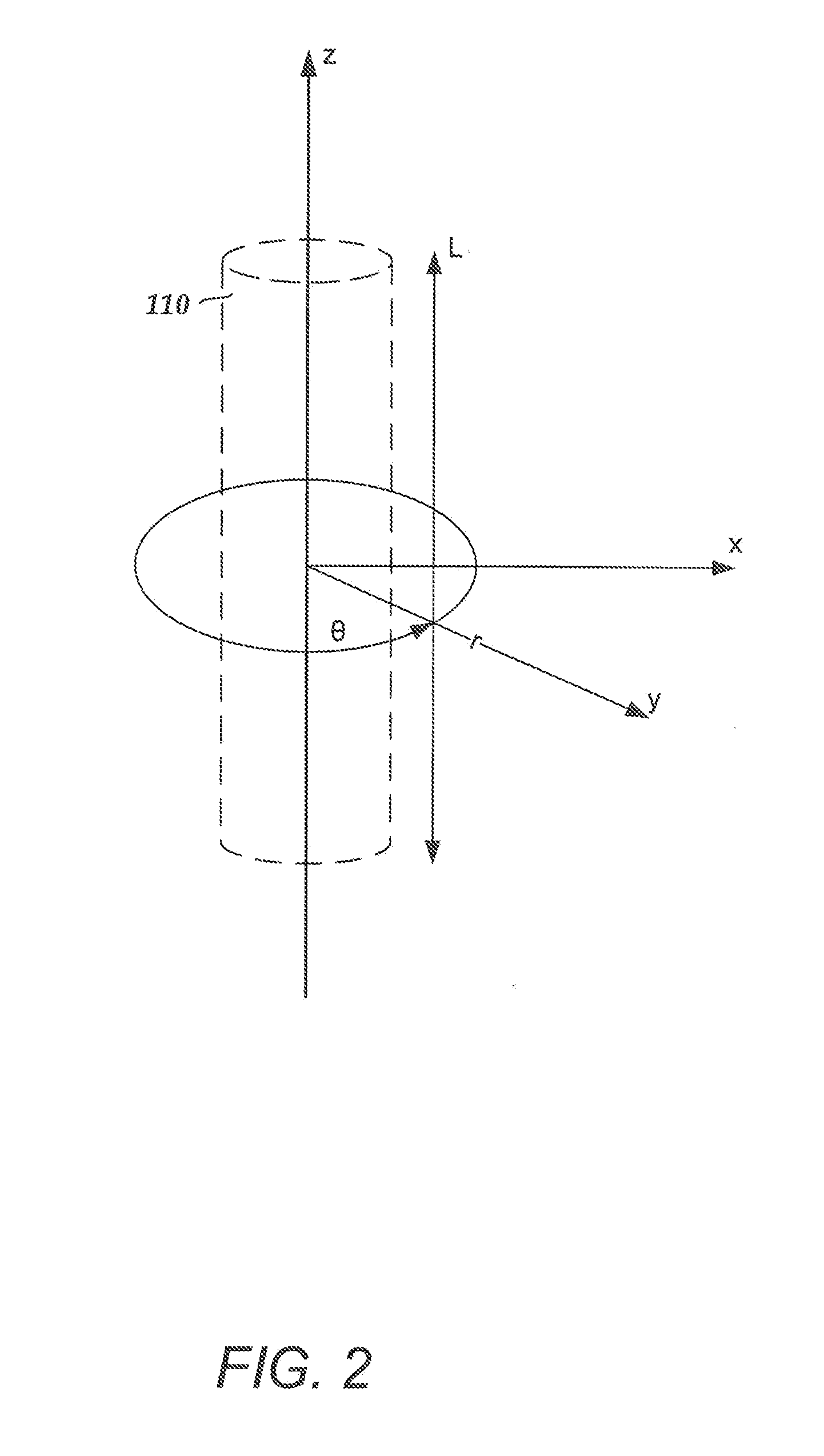
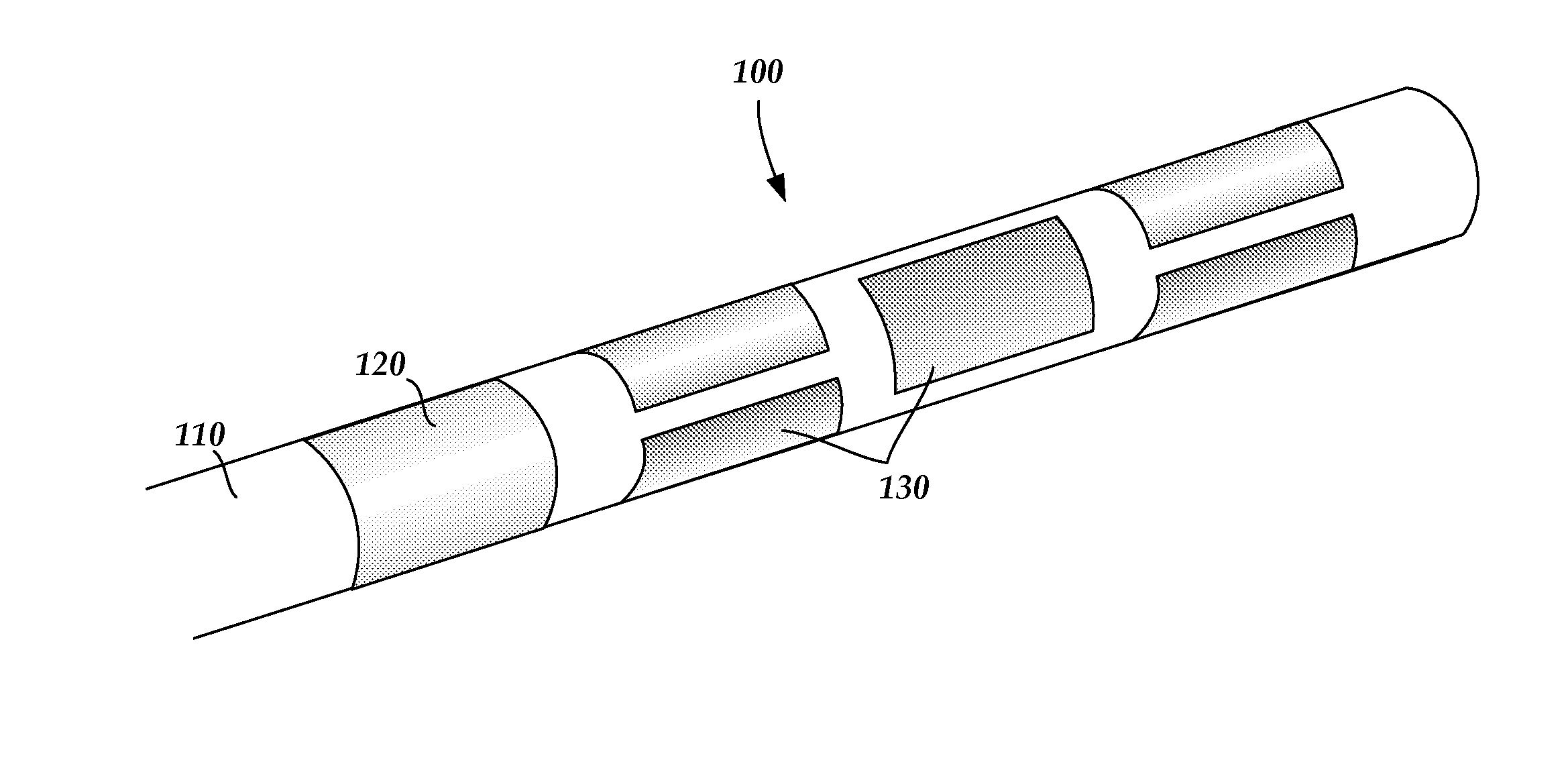
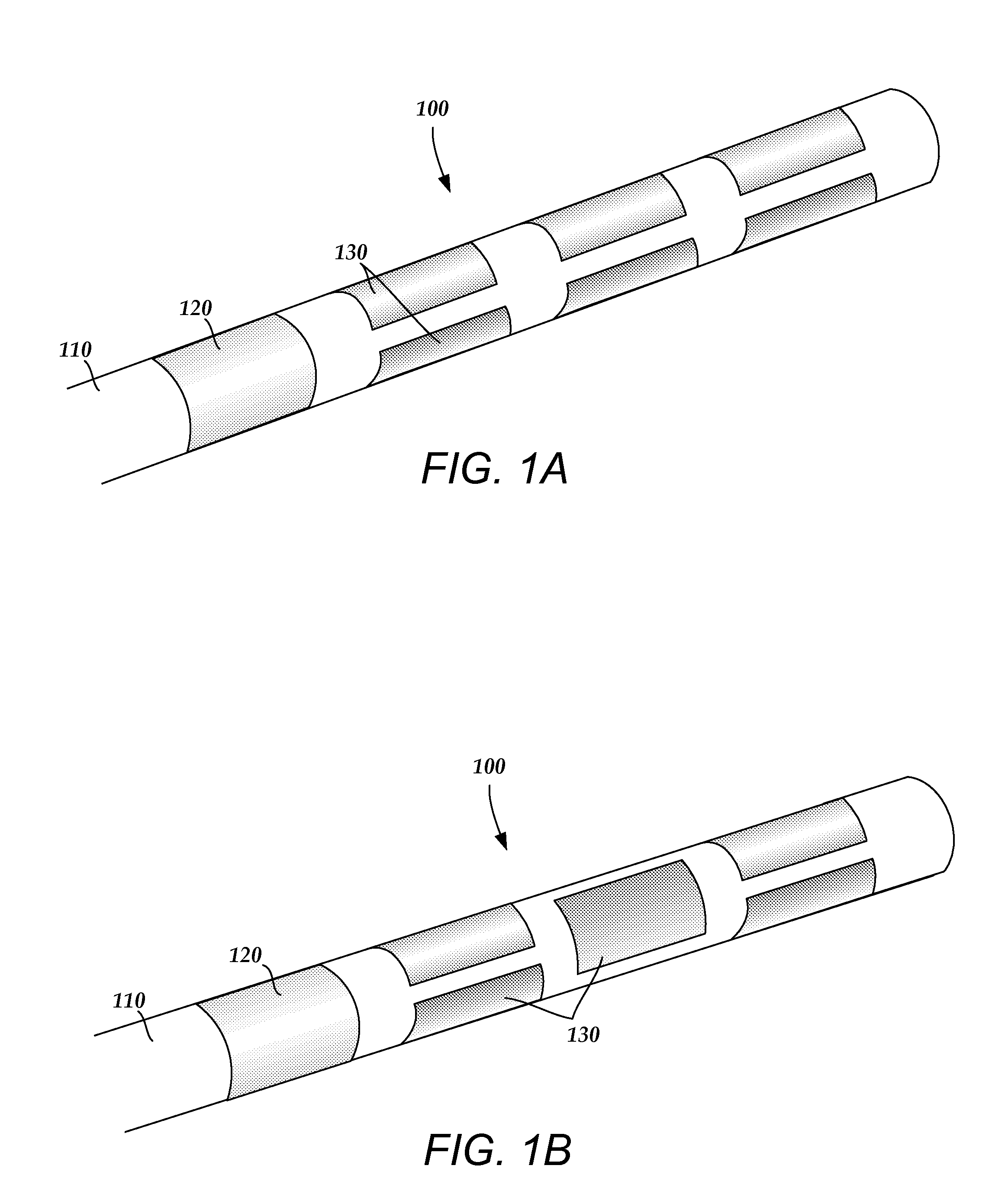
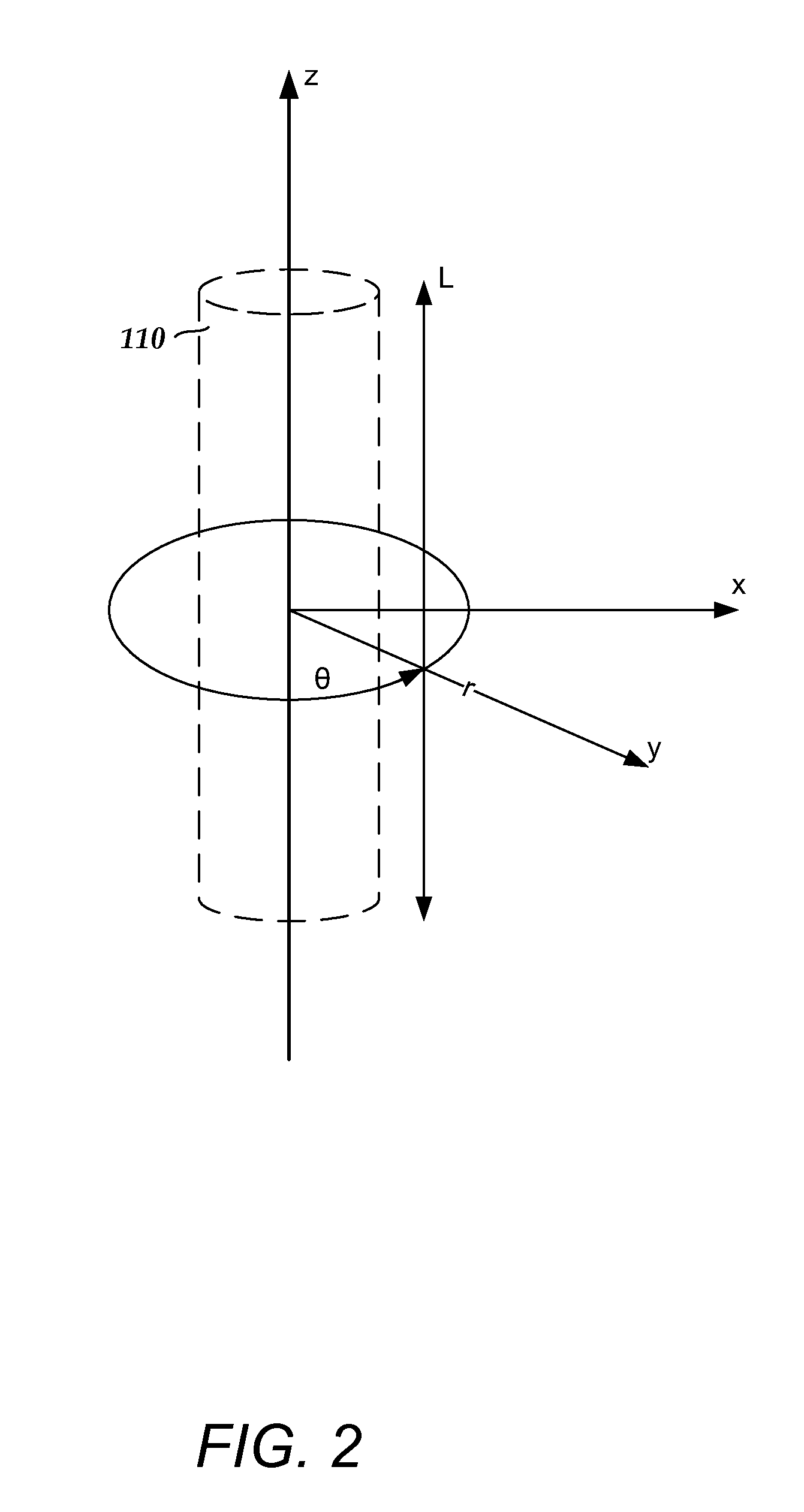
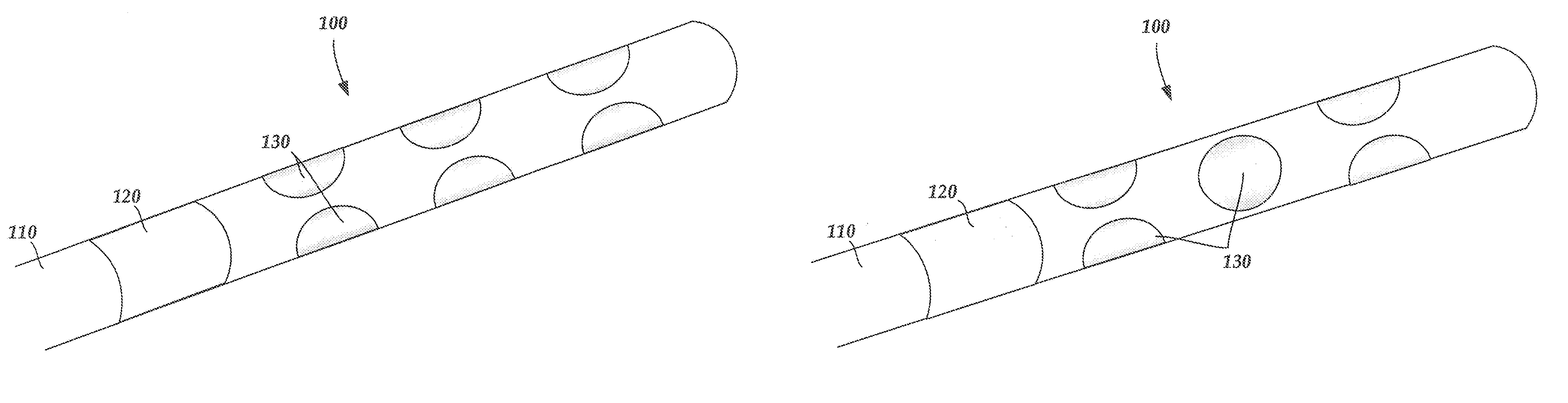
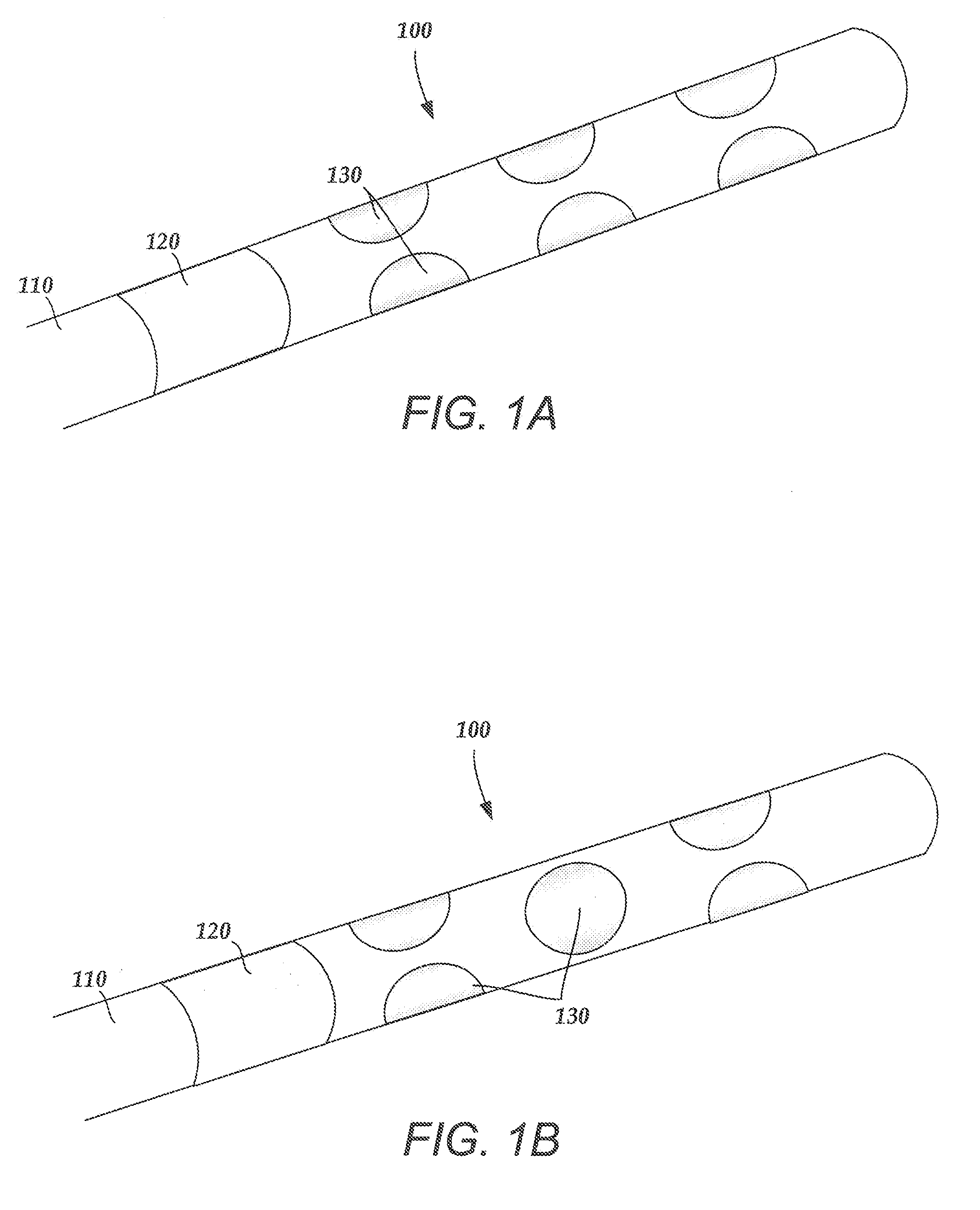
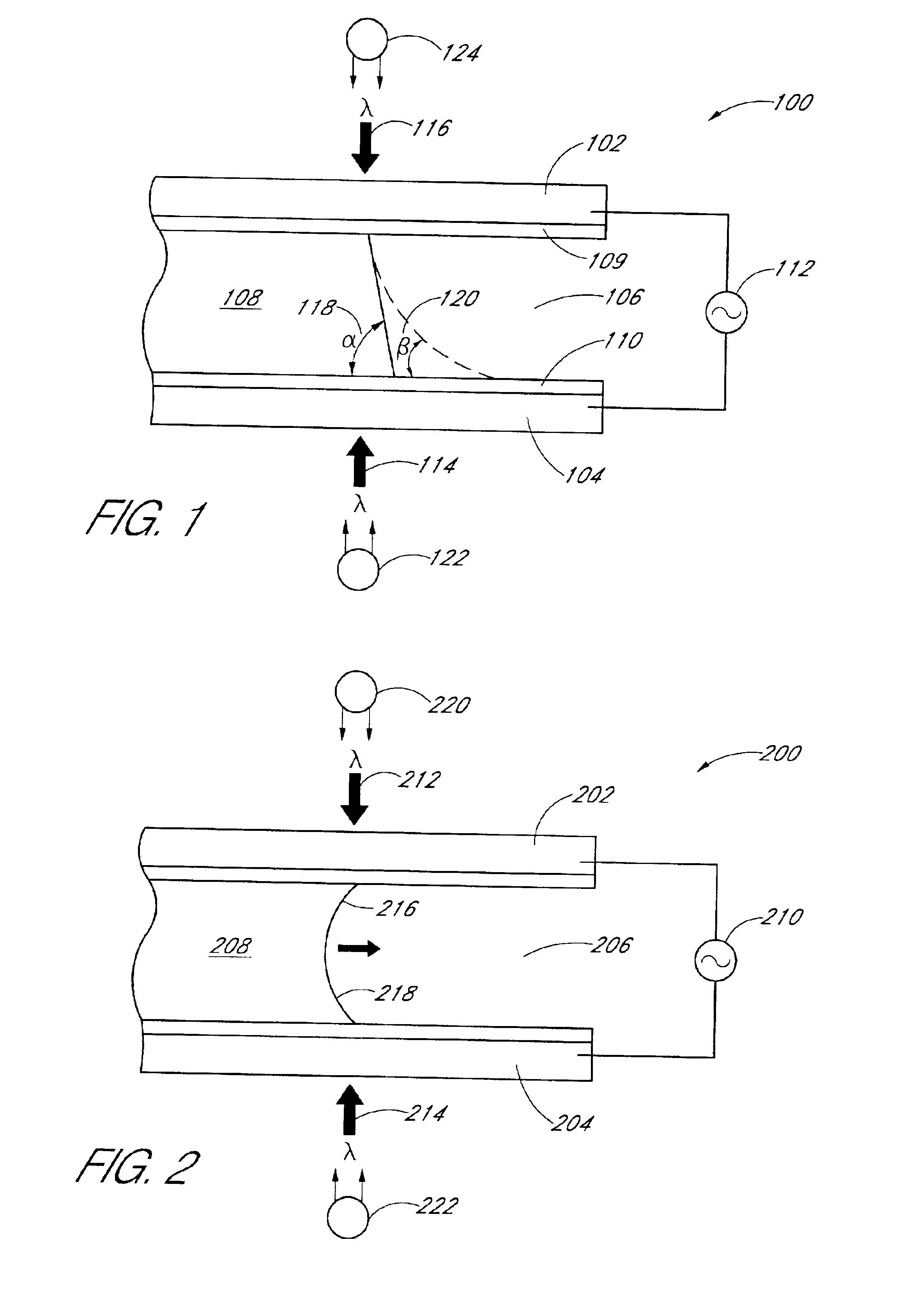
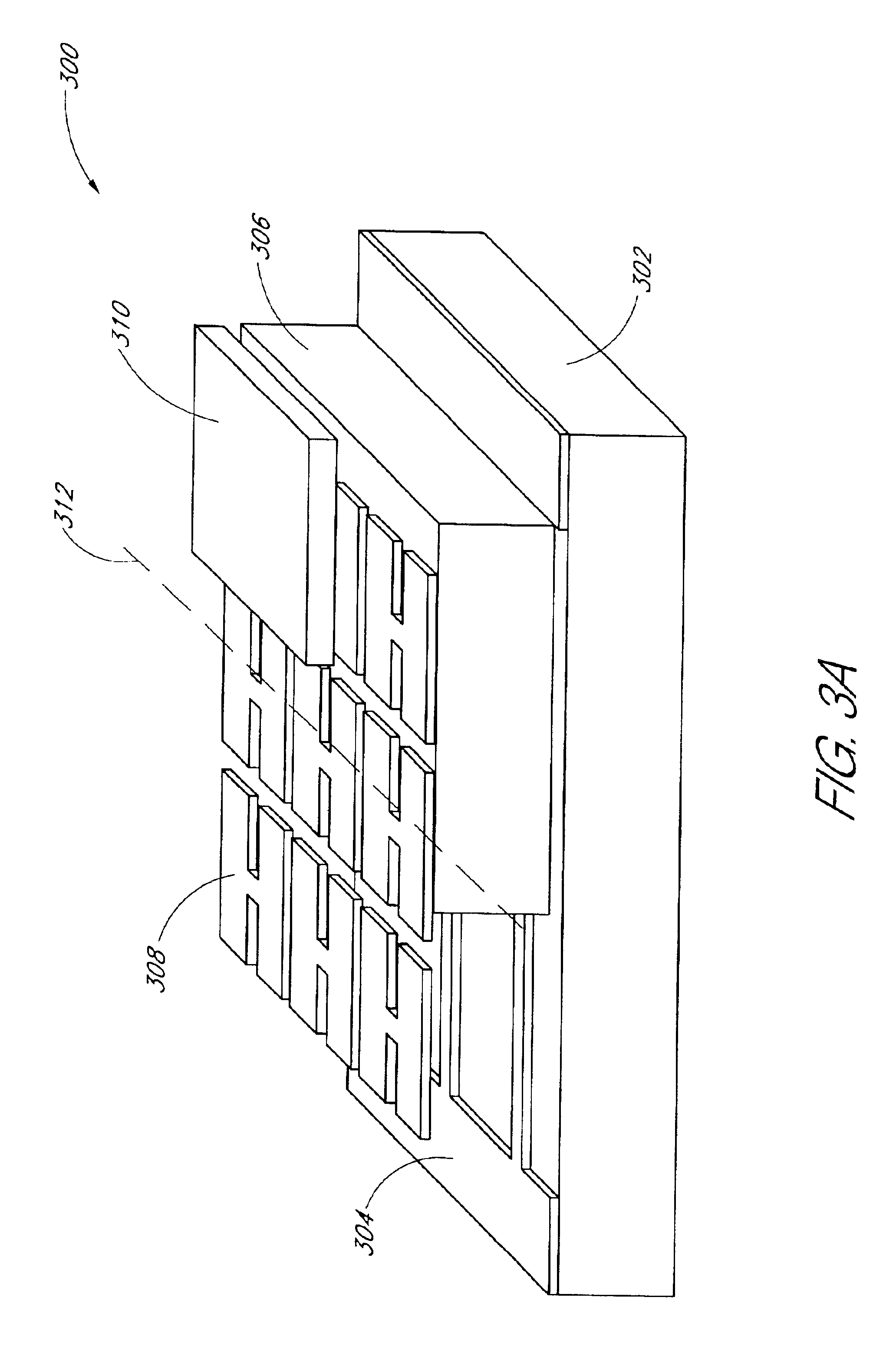
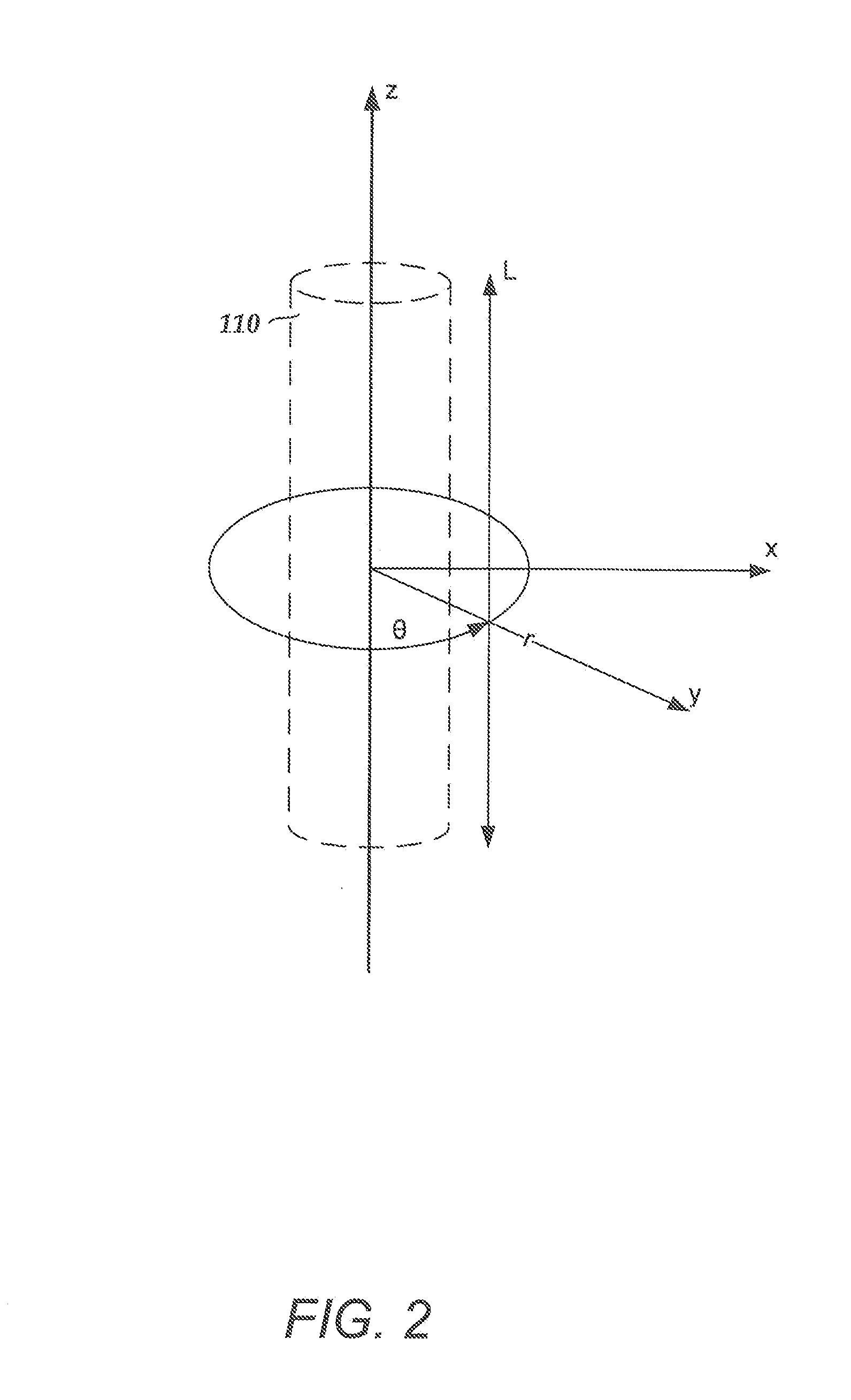
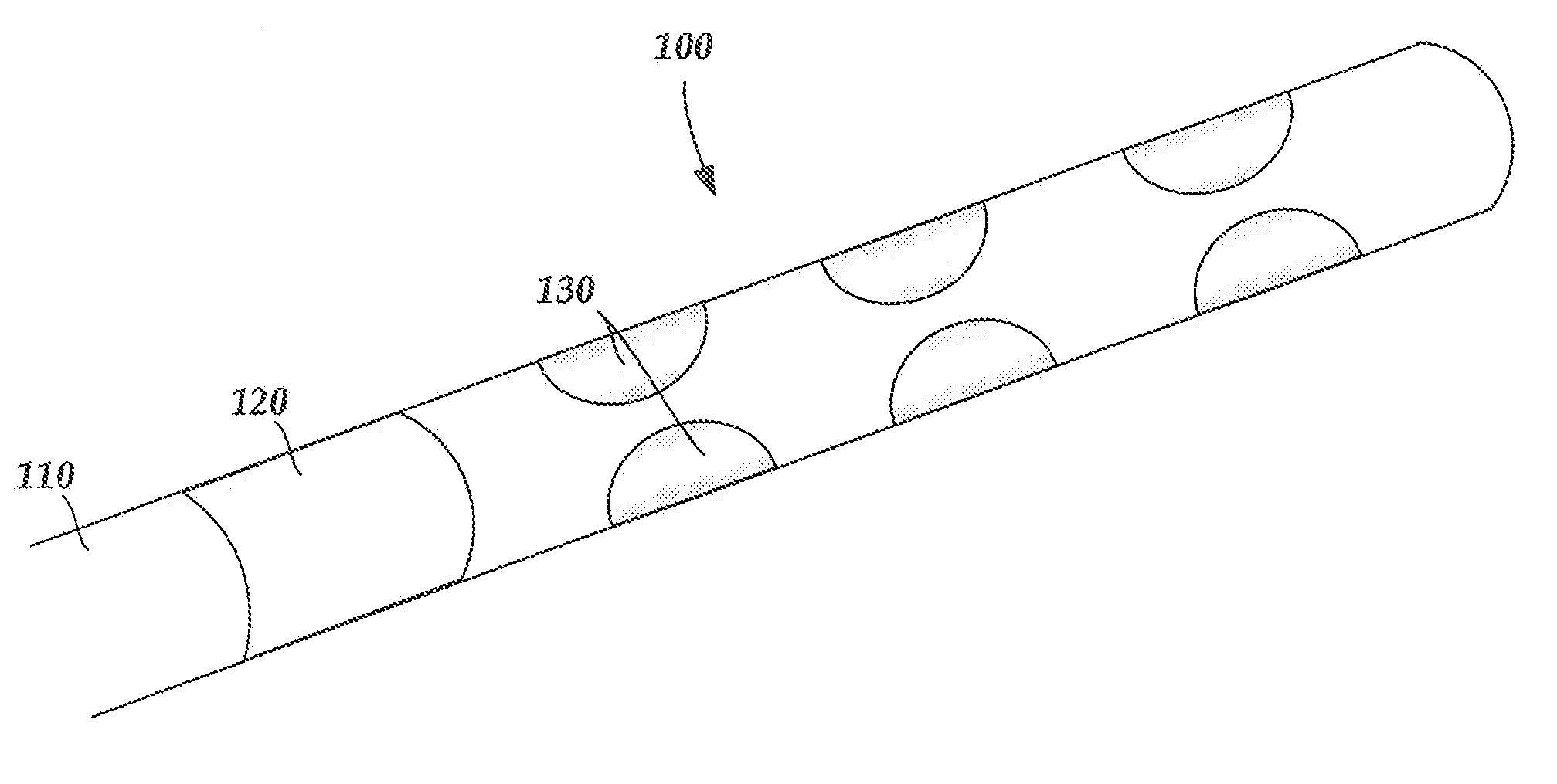
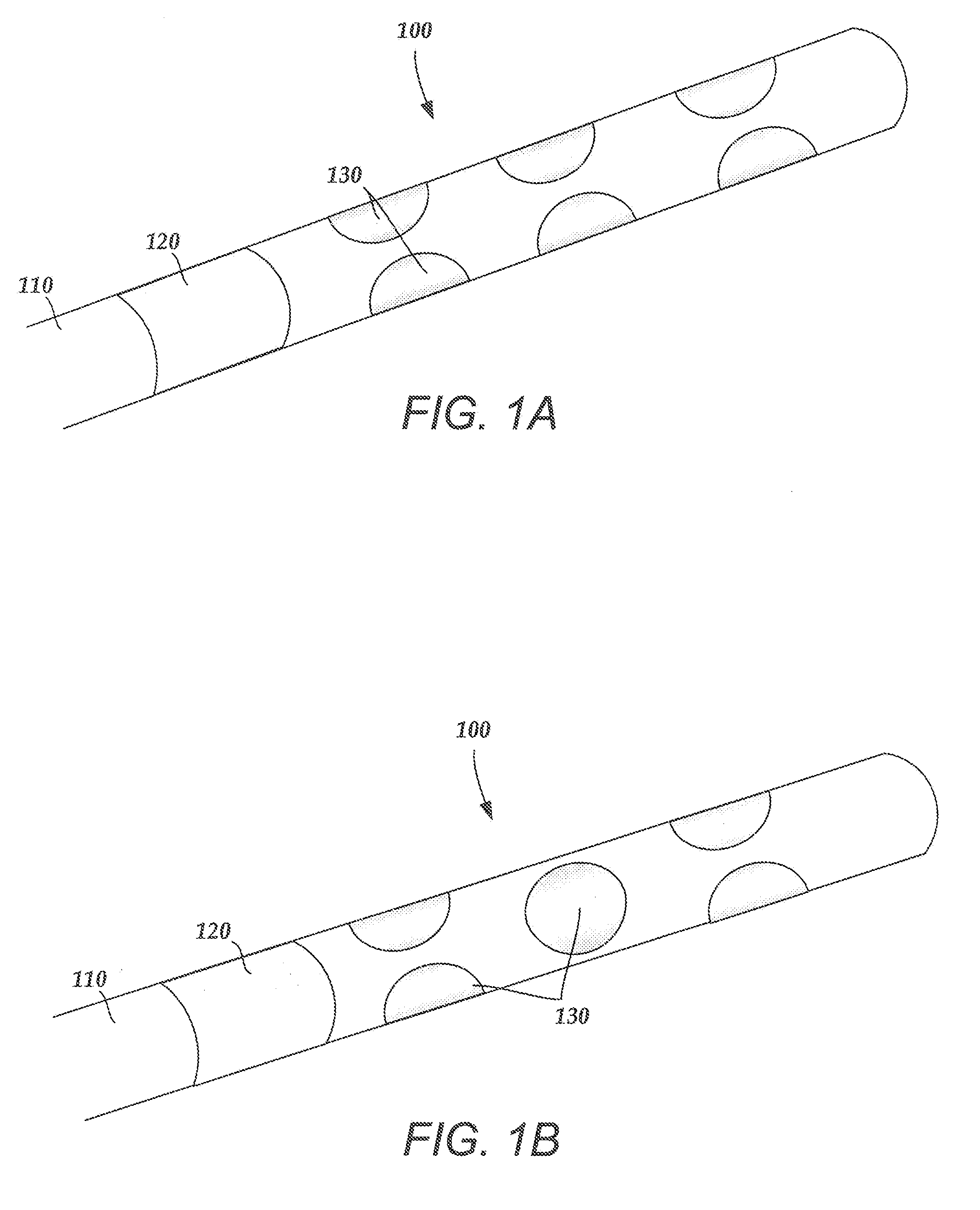
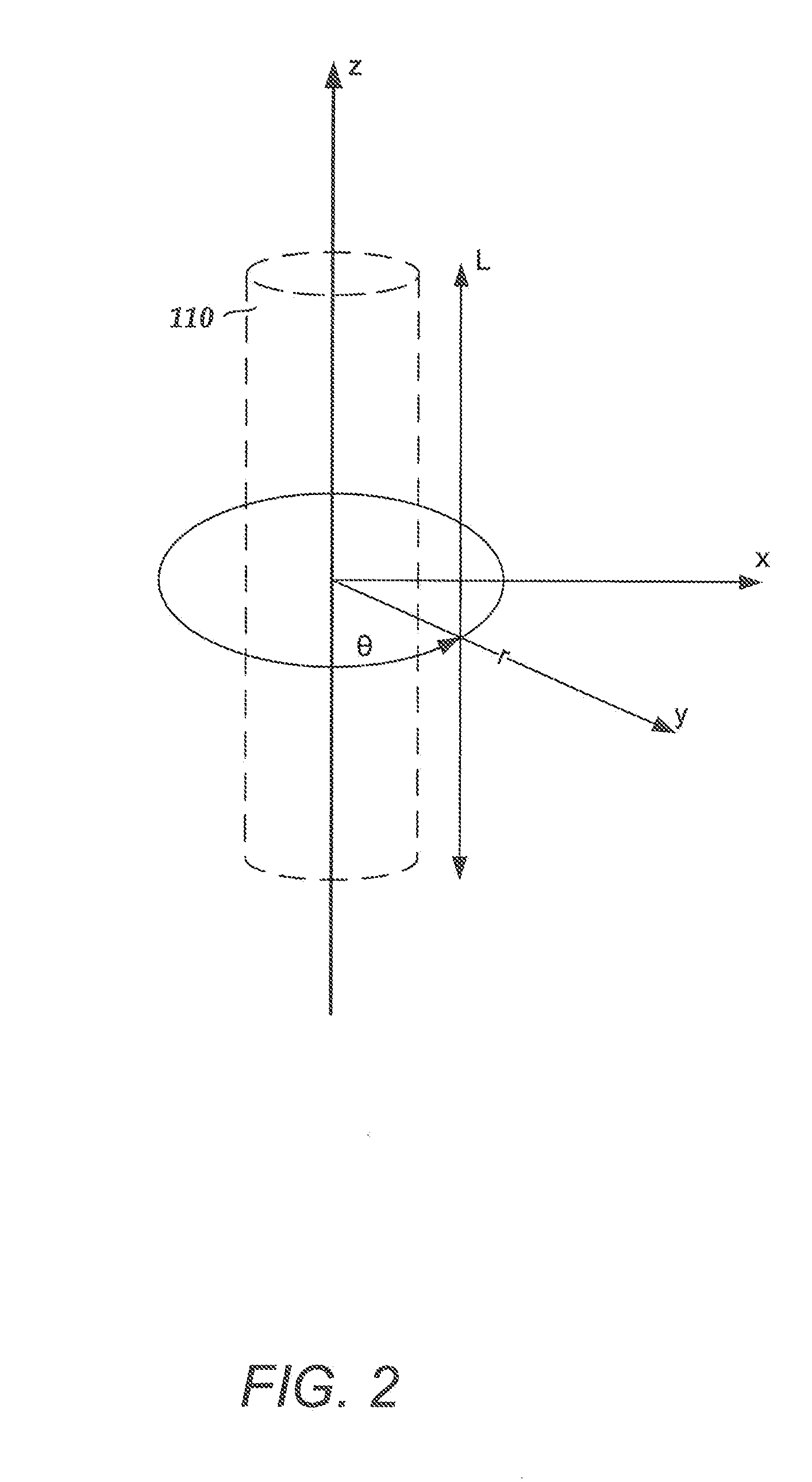
An electrode array is a configuration of electrodes used for measuring either an electric current or voltage. Some electrode arrays can operate in a bidirectional fashion, in that they can also be used to provide a stimulating pattern of electric current or voltage.
Method and apparatus for integrating manual input
InactiveUS6888536B2Simple methodEasy to learnInput/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisLow noiseBiomechanics
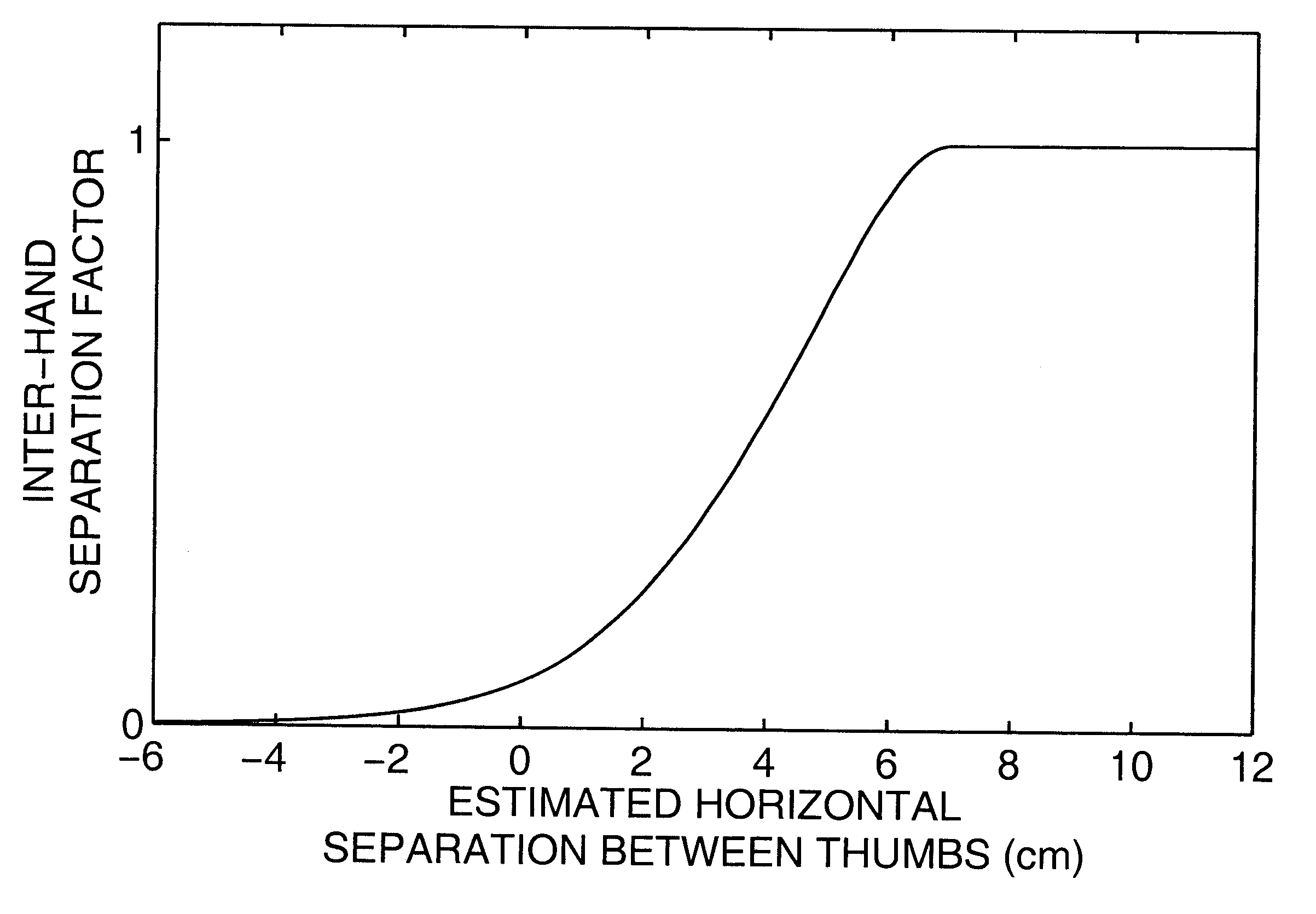
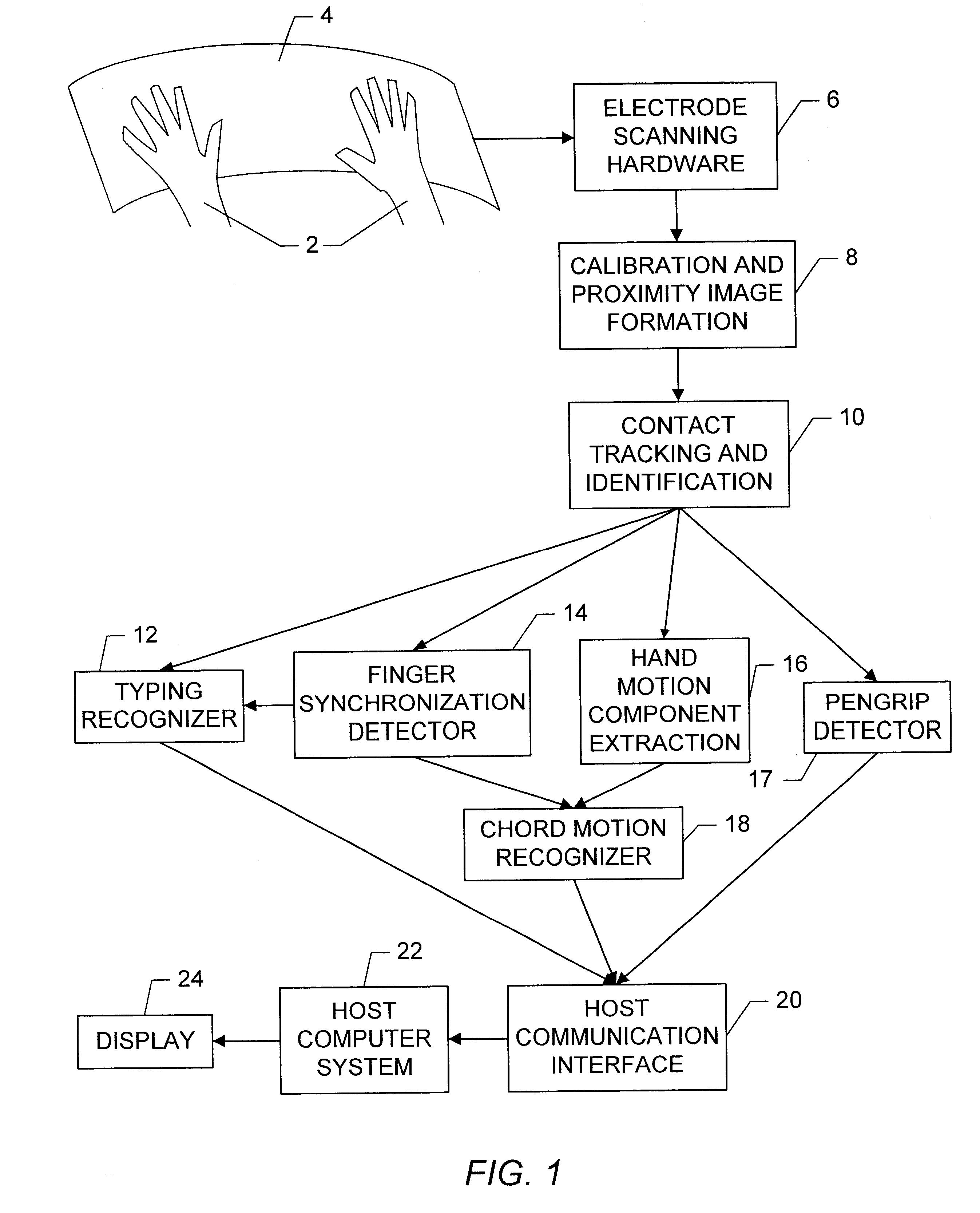
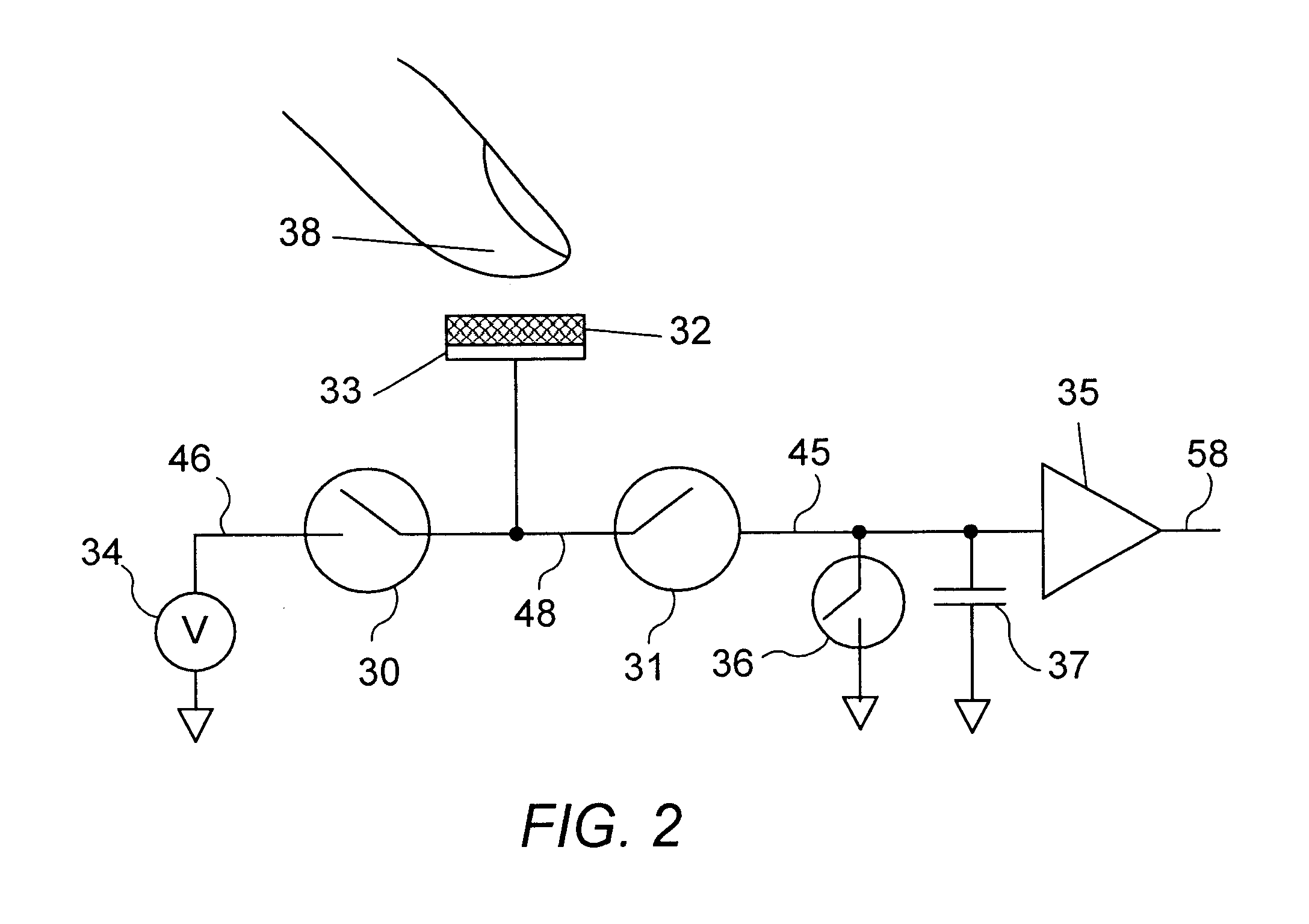
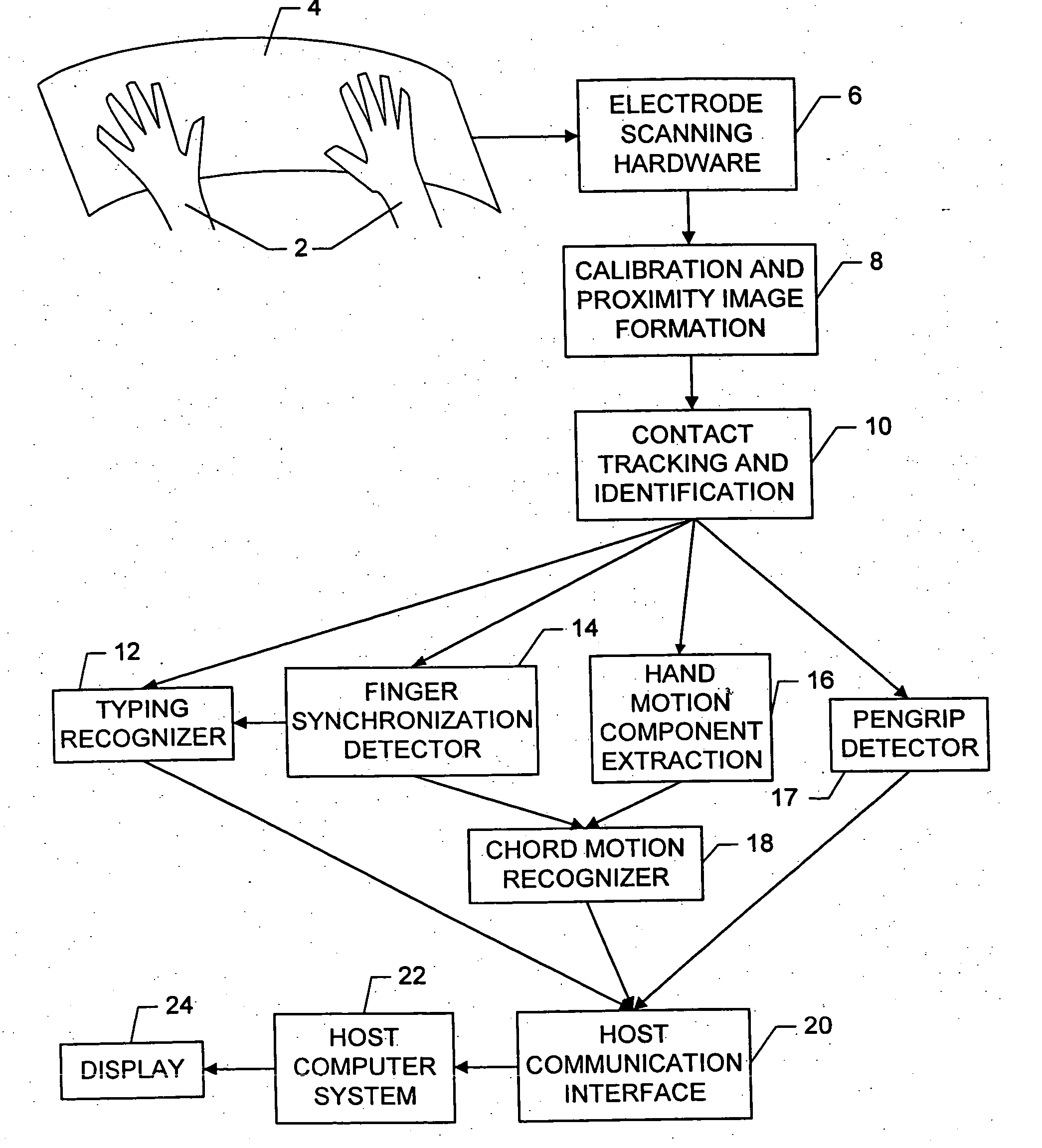
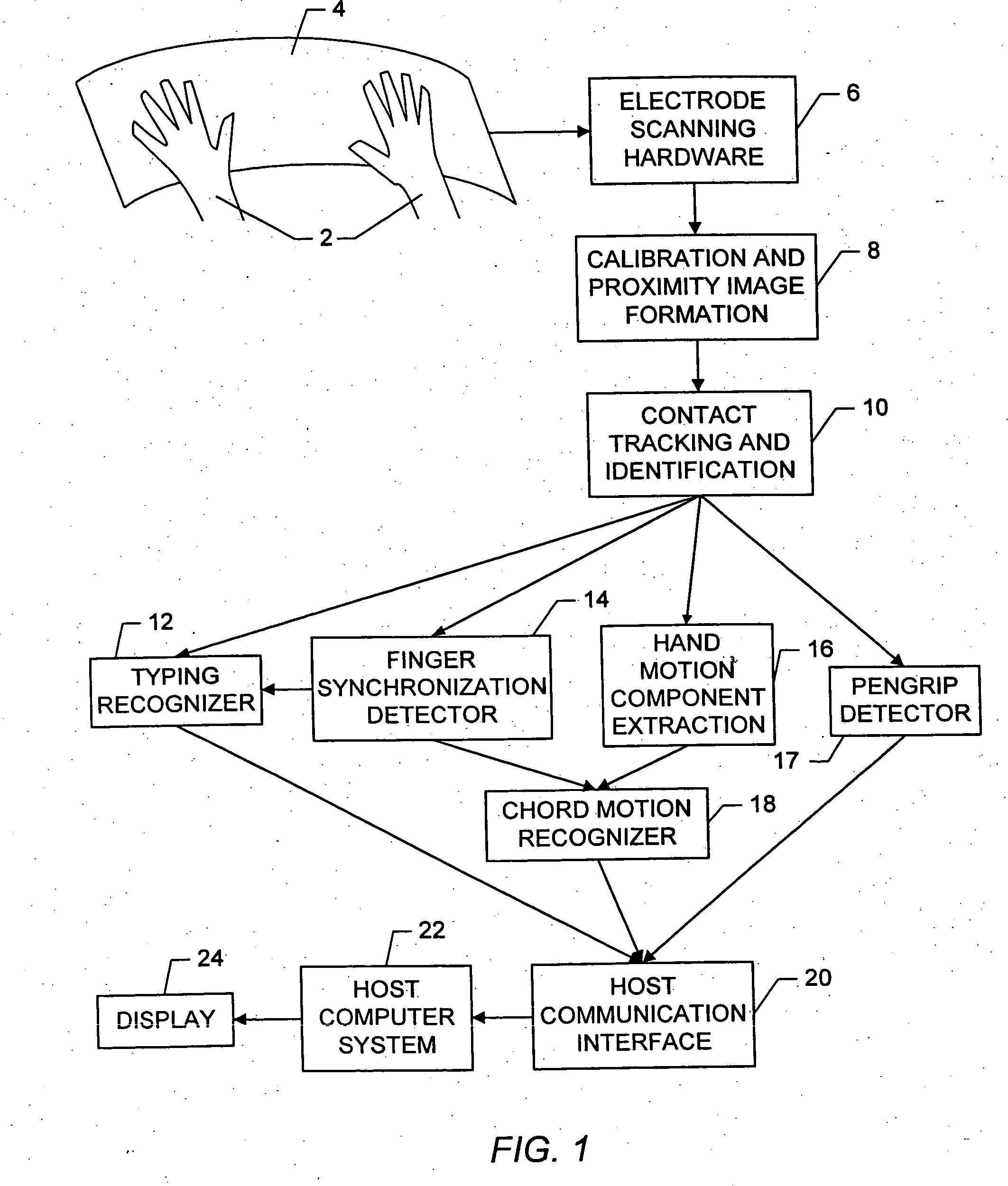
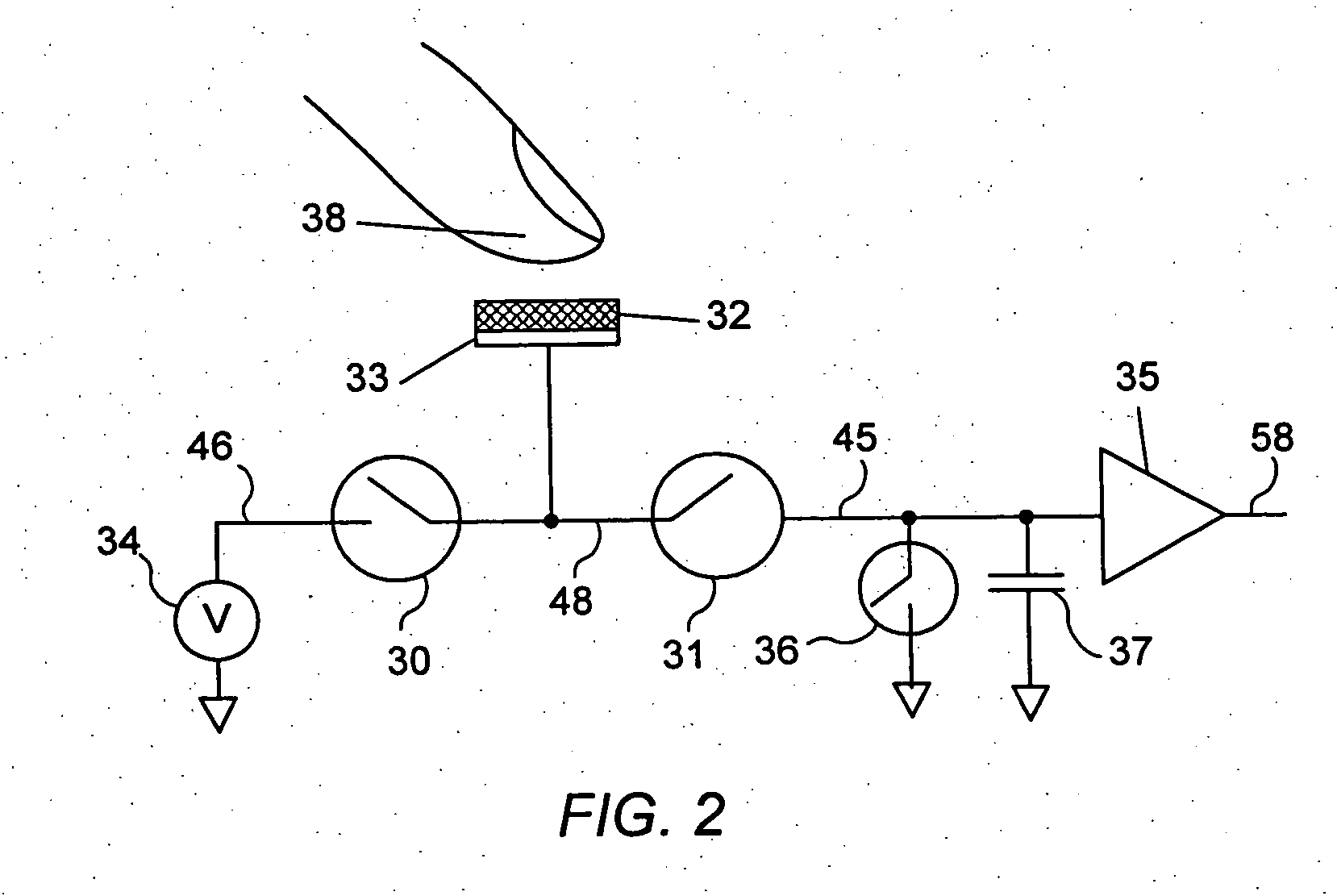
Apparatus and methods are disclosed for simultaneously tracking multiple finger and palm contacts as hands approach, touch, and slide across a proximity-sensing. compliant, and flexible multi-touch surface. The surface consists of compressible cushion, dielectric, electrode, and circuitry layers. A simple proximity transduction circuit is placed under each electrode to maximize signal-to-noise ratio and to reduce wiring complexity. Such distributed transduction circuitry is economical for large surfaces when implemented with thin-film transistor techniques. Scanning and signal offset removal on an electrode array produces low-noise proximity images. Segmentation processing of each proximity image constructs a group of electrodes corresponding to each distinguishable contact and extracts shape, position and surface proximity features for each group. Groups in successive images which correspond to the same hand contact are linked by a persistent path tracker which also detects individual contact touchdown and liftoff. Combinatorial optimization modules associate each contact's path with a particular fingertip, thumb, or palm of either hand on the basis of biomechanical constraints and contact features. Classification of intuitive hand configurations and motions enables unprecedented integration of typing, resting, pointing, scrolling, 3D manipulation, and handwriting into a versatile, ergonomic computer input device.
Owner:APPLE INC
Active electrode, bio-impedance based, tissue discrimination system and methods of use
InactiveUS20060085049A1Accurate identificationAvoid problemsElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityTissues types
Systems and methods for discriminating and locating tissues within a body involve applying a waveform signal to tissue between two electrodes and measuring the electrical characteristics of the signal transmitted through the tissue. At least one of the electrodes is constrained in area so that localized electrical characteristics of the tissue are measured. Such localized electrical characteristics are determined over a portion of a body of the subject by using an array of electrodes or electrodes that can be moved over the body. A controller may implement the process and perform calculations on the measured data to identify tissue types and locations within the measured area, and to present results in graphical form. Results may be combined with other tissue imaging technologies and with image-guided systems.
Owner:NERVONIX INC
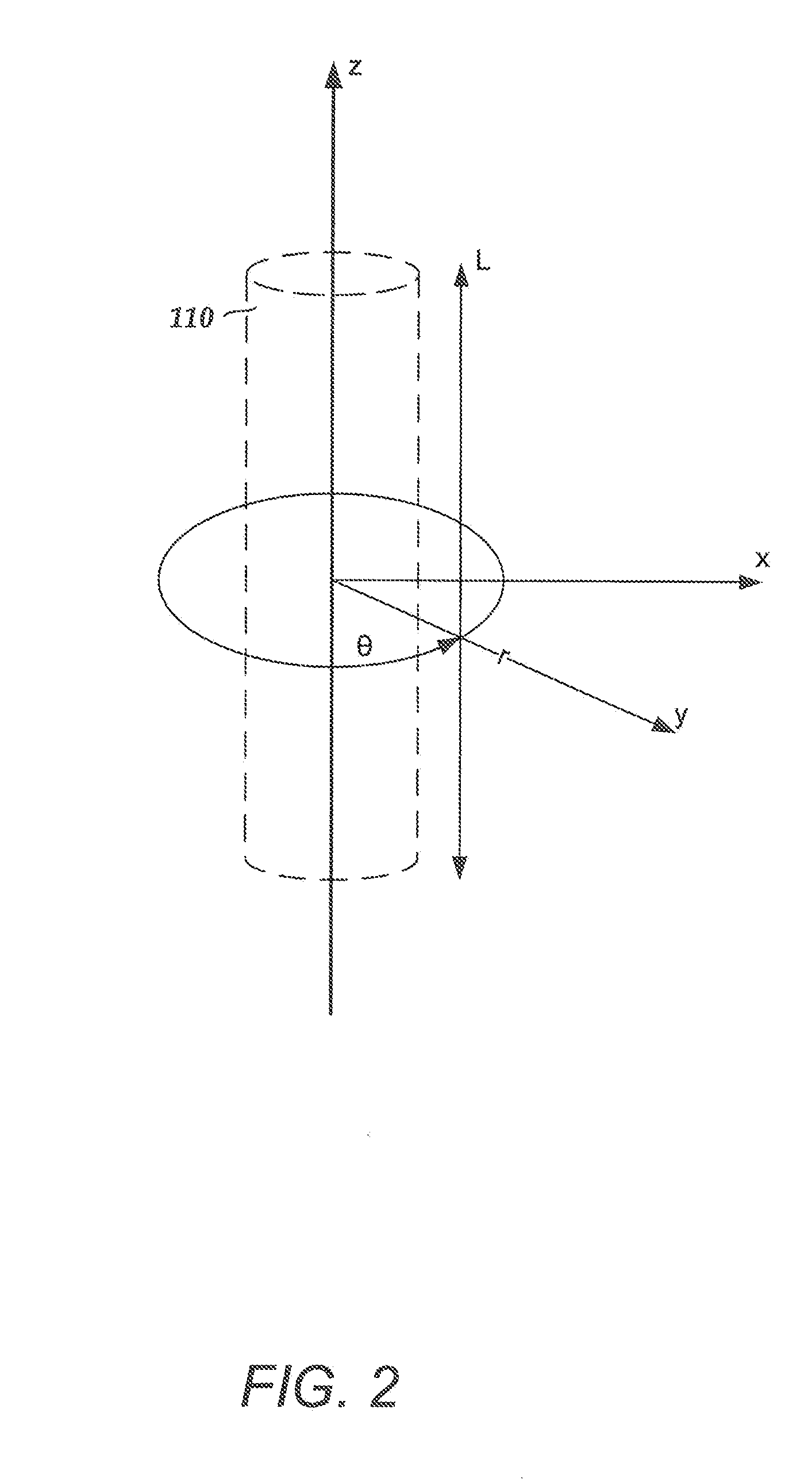
Rolled electrode array and its method for manufacture
InactiveUS20050051427A1Long-term robustnessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEndoradiosondesOptoelectronicsElectrode array
An electrode array for use in an electrochemical device is provided. The electrode array includes at least one electrode material and at least one insulating material arranged in a spiral configuration. The electrode array is manufactured by forming a composite stack of the at least one electrode material and the at least one insulating material, such that the insulating material(s) surrounds the electrode material(s) after which the stack is rolled into a spiral roll. The spiral roll can be cut, sliced, and / or dissected in numerous ways to form the electrode array of the preferred embodiments. Optionally, the sections can be further processed by machining, polishing, etching, or the like, to produce a curvature or stepped configuration.
Owner:DEXCOM
Dynamic heating method and radio frequency thermal treatment
A method and system for the delivery of radiofrequency energy to the tissue, particularly, the prostate, to alleviate the symptoms of BPH is disclosed. The system incorporates a bipolar or multipolar electrode array to create an electric field where the heat created is confined solely to a specific volume of the prostate gland and therefore the heated tissue is defined only by the electrode geometry. The bipolar electrode array provides a variety of three dimensional, symmetric heating patterns within the prostatic tissue depending on the relative electrode lengths and angular separation. The system provides precision tissue temperature and impedance measurements thereby enabling the surgeon to accurately predict heating pattern performance and tissue response to RF heating.
Owner:KASEVICH RAYMOND S
Method and apparatus for integrating manual input
InactiveUS20050104867A1Easy to learnEasy to identifyInput/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisLow noiseDielectric
Owner:APPLE INC
Electrosurgical probe having circular electrode array for ablating joint tissue and systems related thereto
InactiveUS6991631B2Low aspiration rateIncrease inhalation rateSurgical instruments for heatingTherapyMeniscal tissueElectrode array
Electrosurgical methods, systems, and apparatus for the controlled ablation of tissue from a target site, such as a synovial joint, of a patient. An electrosurgical probe of the invention includes a shaft, and a working end having an electrode array comprising an outer circular arrangement of active electrode terminals and an inner circular arrangement of active electrode terminals. The electrode array is adapted for the controlled ablation of hard tissue, such as meniscus tissue. The working end of the probe is curved to facilitate access to both medial meniscus and lateral meniscus from a portal of 1 cm. or less.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
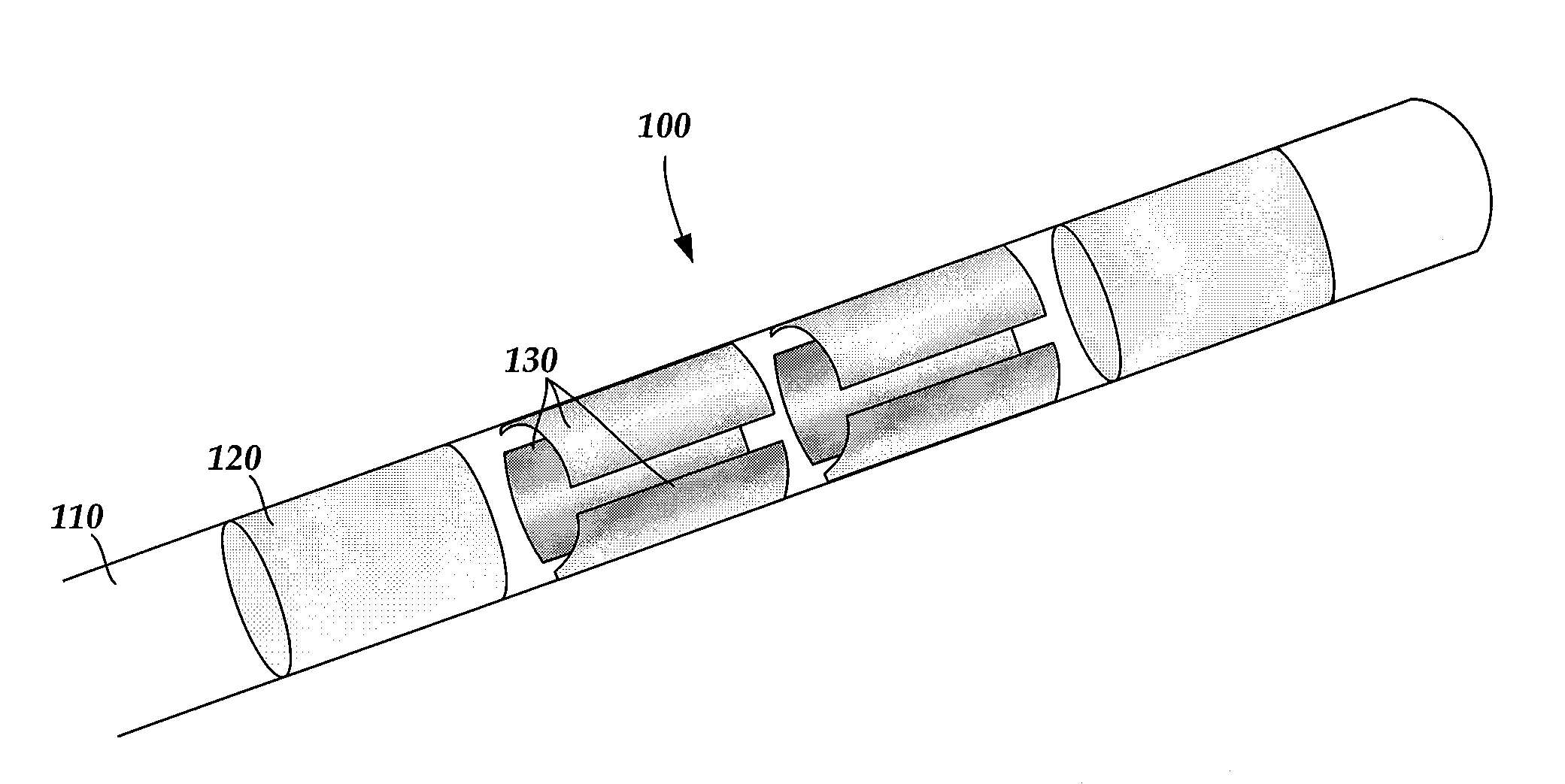
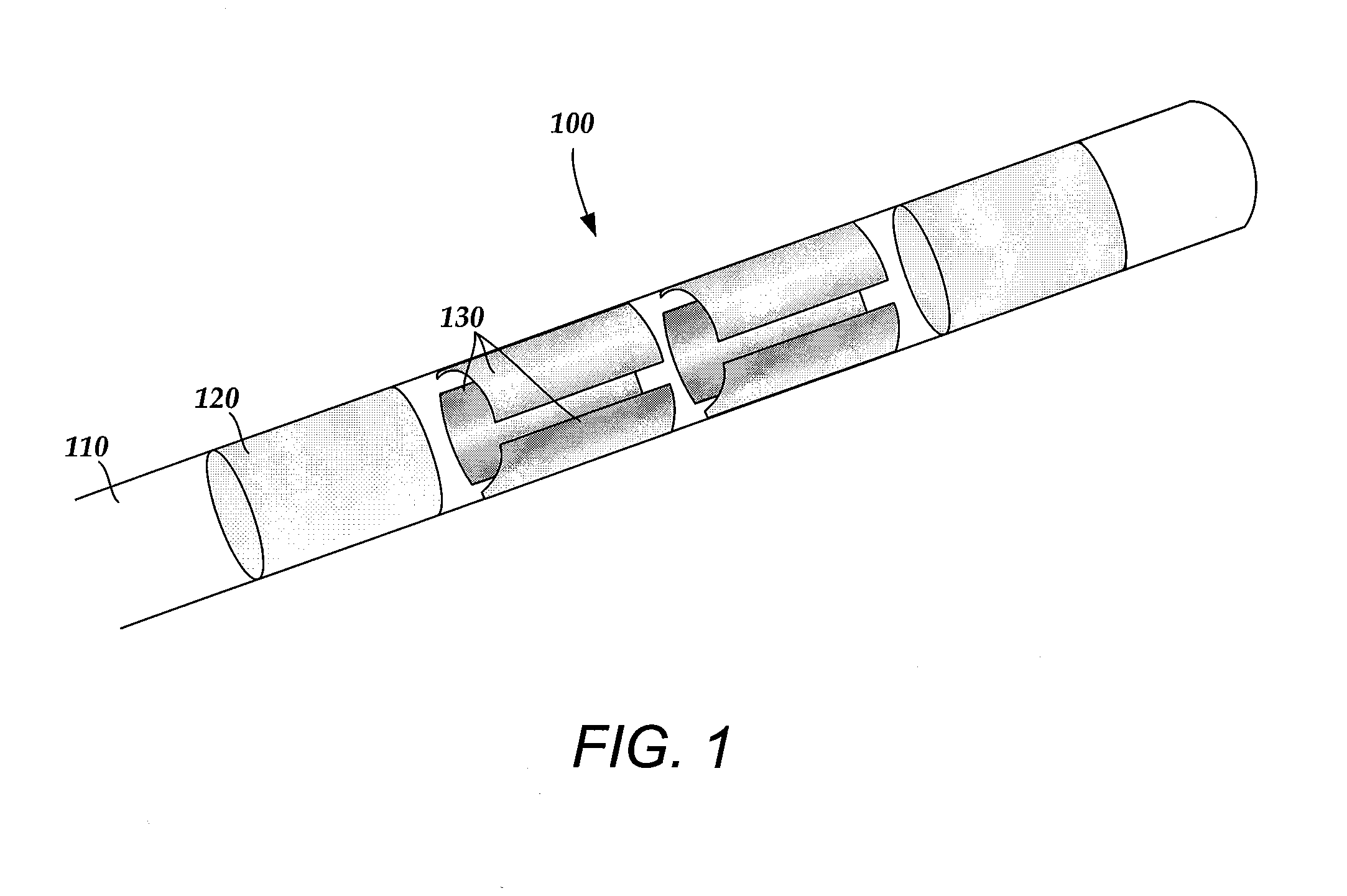
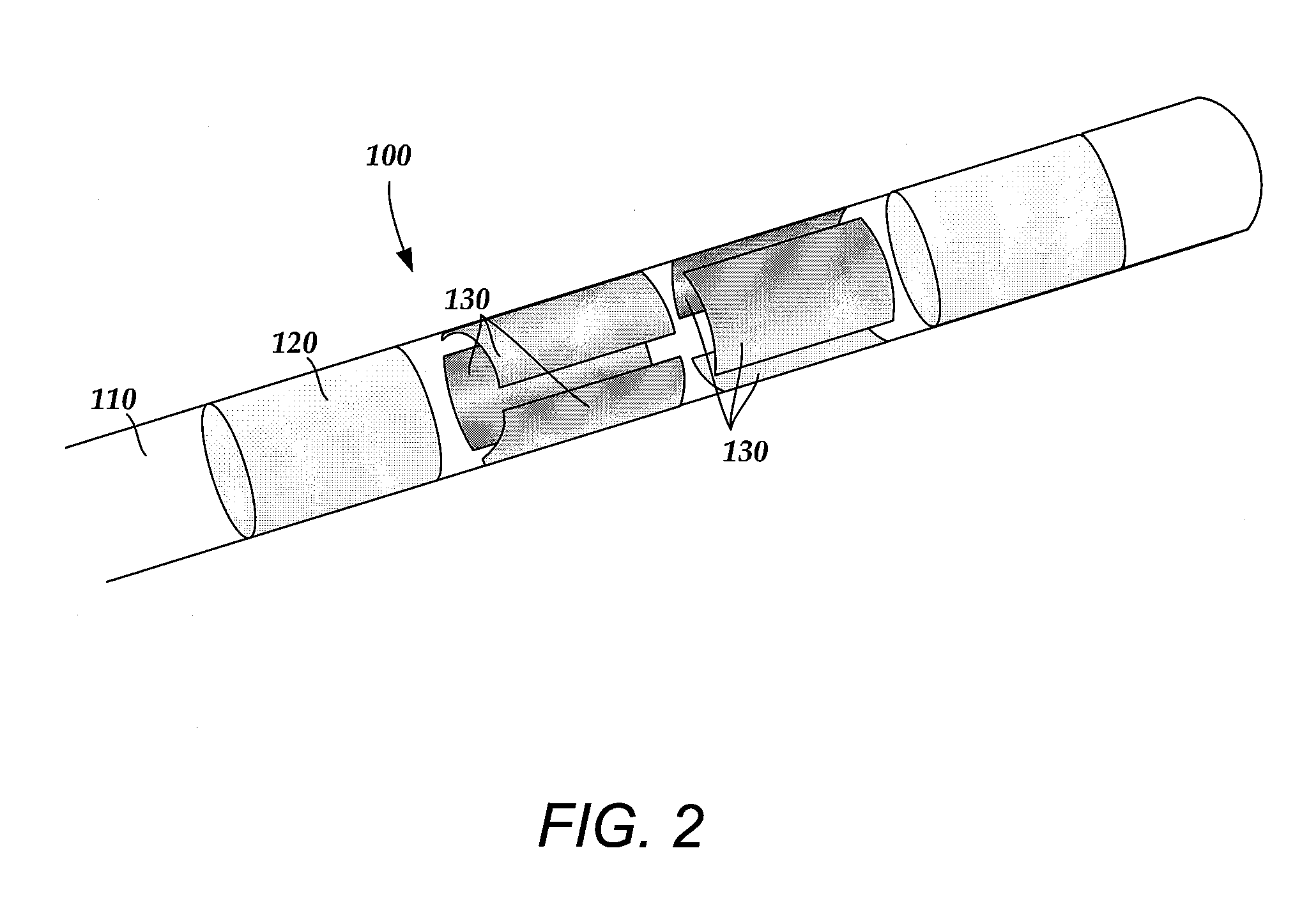
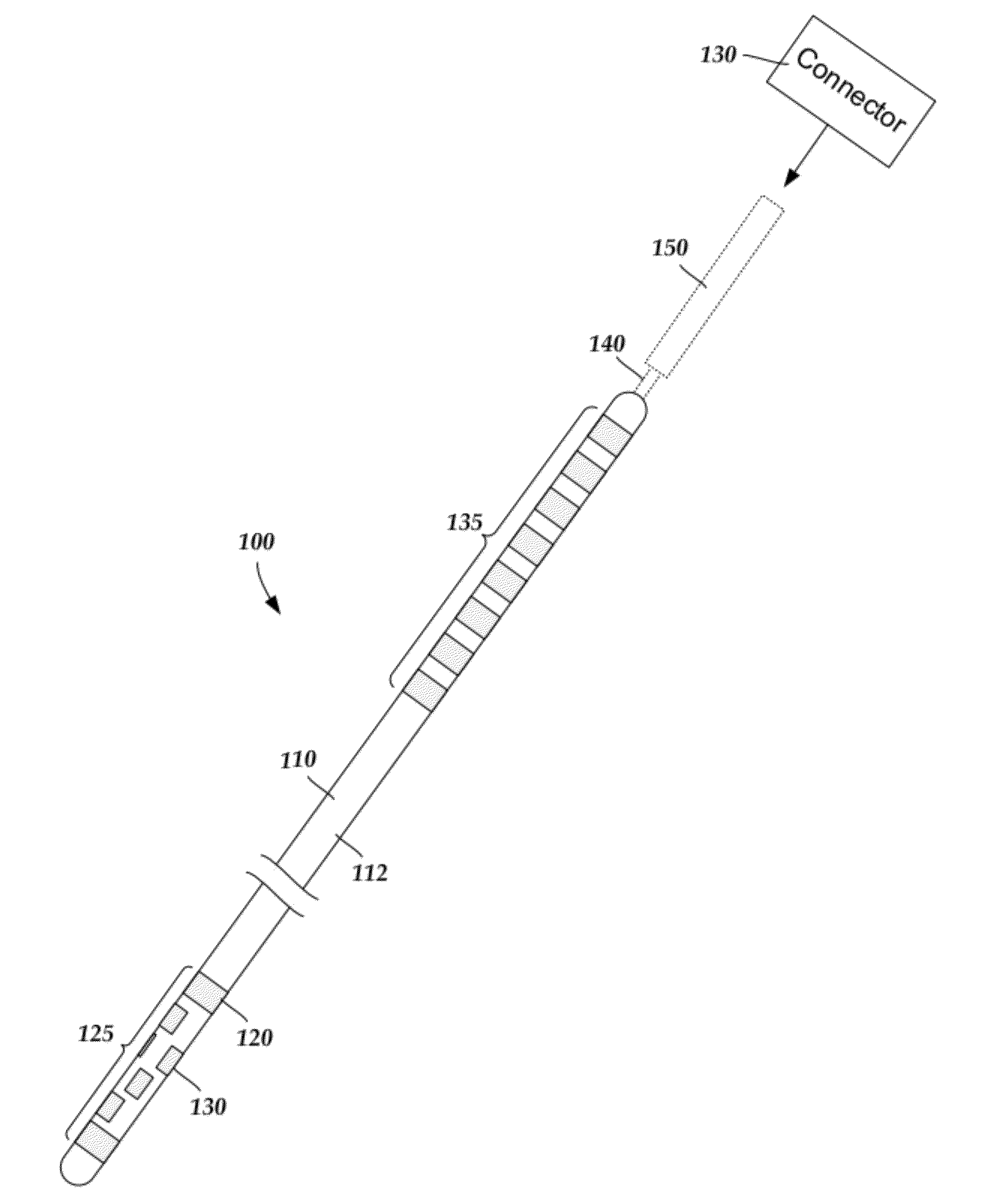
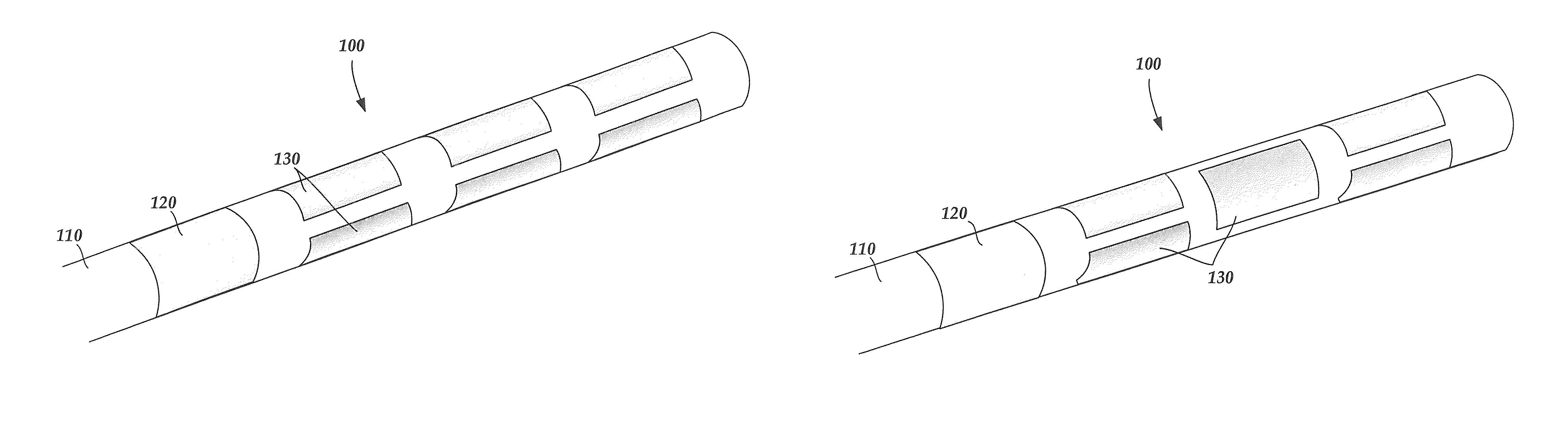
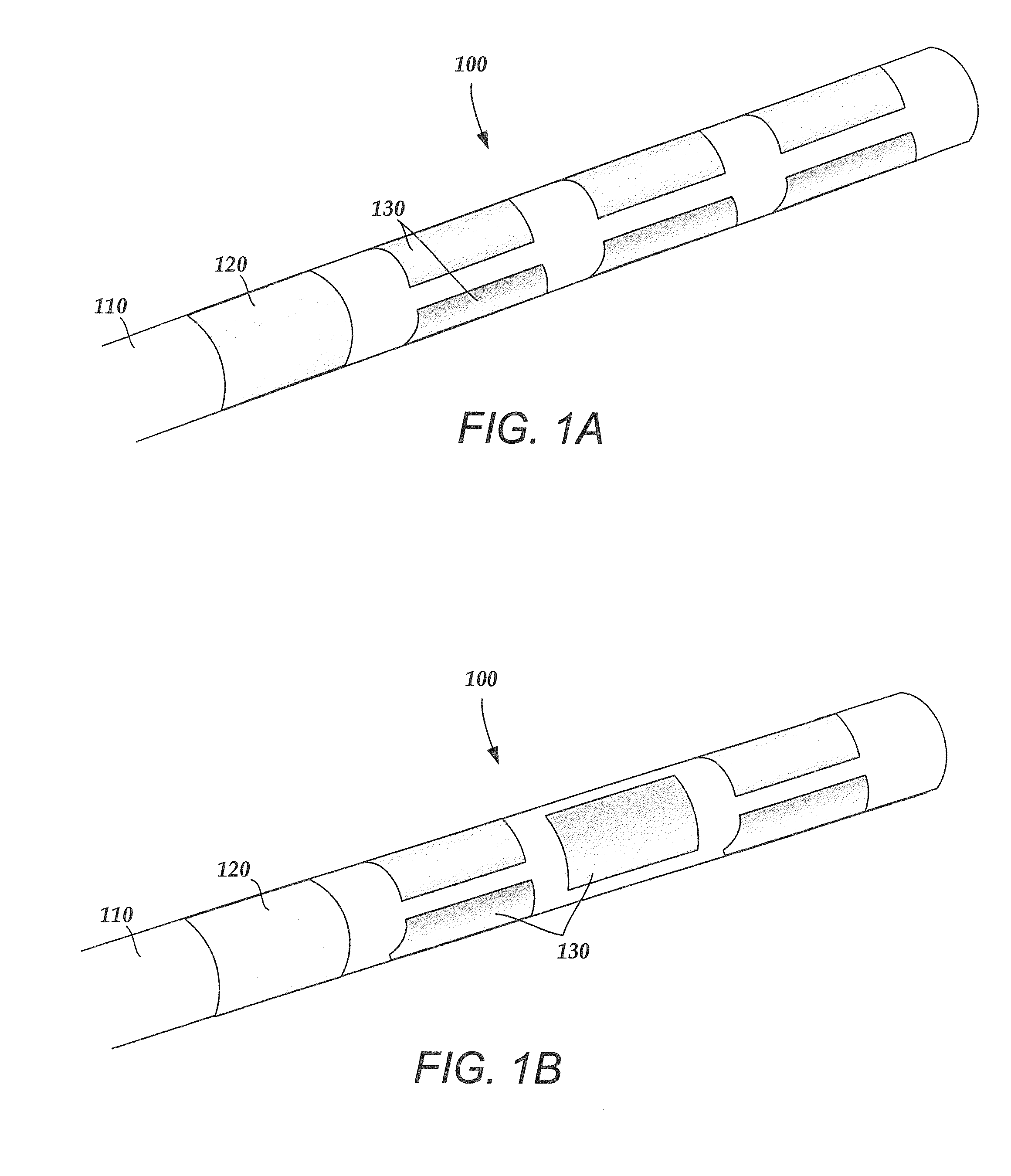
Electrode array having concentric split ring electrodes and methods of making the same
ActiveUS20110130818A1Line/current collector detailsLiquid surface applicatorsSplit ringElectrode array
A device for brain stimulation includes a lead body having a longitudinal surface and a distal end. The device further includes at least one ring array. The at least one ring array includes a plurality of split ring electrodes disposed on the distal end of the lead body. Each of the plurality of split ring electrodes includes a stimulating portion and a base portion coupled to the stimulating portion. The split ring electrodes of the at least one ring array are arranged about the circumference of the lead body. At least a portion of the base portion of at least one of the plurality of split ring electrodes is disposed below, and insulated from, at least a portion of the stimulating portion of another of the plurality of split electrodes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Electrode array having embedded electrodes and methods of making the same
ActiveUS20110313500A1Line/current collector detailsHead electrodesElectrode arrayBiomedical engineering
A method of manufacturing a device for brain stimulation includes forming a lead body having a distal end section and coupling at least one pre-electrode to the distal end section of the lead body. The pre-electrode defines a divider with a plurality of partitioning arms, and has a plurality of fixing lumens. A portion of the pre-electrode aligned with the portioning arms is removed to divide the pre-electrode into a plurality of segmented electrodes. Each of the plurality of segmented electrodes defines at least one of the plurality of fixing lumens at least partially disposed through the segmented electrode. A material is introduced through the at least one fixing lumen to couple the plurality of segmented electrodes to the lead body.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Systems and leads with a radially segmented electrode array and methods of manufacture
A method of making a lead for a stimulation device includes forming at least one pre-electrode in the shape of a ring, the at least one pre-electrode comprises at least two thin-walled portions separated by at least two thick-walled portions; disposing the at least one pre-electrode near a distal end of a lead body; joining at least one conductor to each thick-walled portion of the at least one pre-electrode; and grinding the lead body and the at least one pre-electrode to remove the thin-walled portions of the at least one pre-electrode to form segmented electrodes from the thick-walled portions of the at least one pre-electrode.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Leads with spiral of helical segmented electrode arrays and methods of making and using the leads
ActiveUS20120197375A1Line/current collector detailsHead electrodesElectrode arrayBiomedical engineering
A stimulation lead includes a lead body having a longitudinal surface, a distal end, a proximal end, and a shaft extending along at least a portion of the distal end of the lead body. The stimulation lead also includes multiple segmented electrode members disposed on the shaft along the longitudinal surface of the lead body near the distal end of the lead body. Each segmented electrode member includes a ring structure which forms at least a partial ring and is disposed on the shaft, and a segmented electrode coupled to the ring and having an exposed surface configured and arranged for stimulating tissue when the stimulation lead is implanted.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Implantable medical electrical stimulation lead fixation method and apparatus
InactiveUS6999819B2Optimize locationQuick placementSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesMuscle tissueMedicine
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC +1
Implantable generator having current steering means
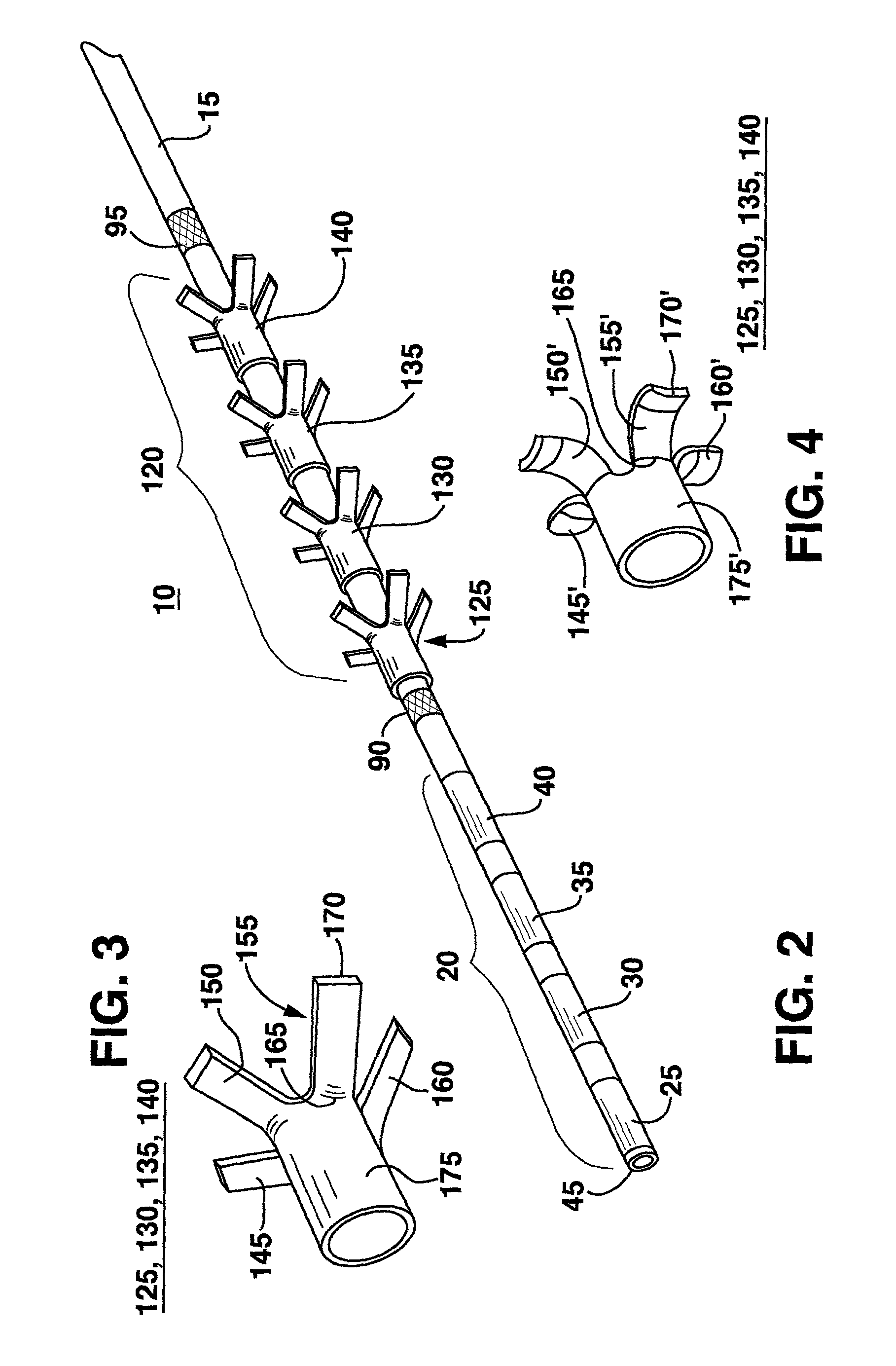
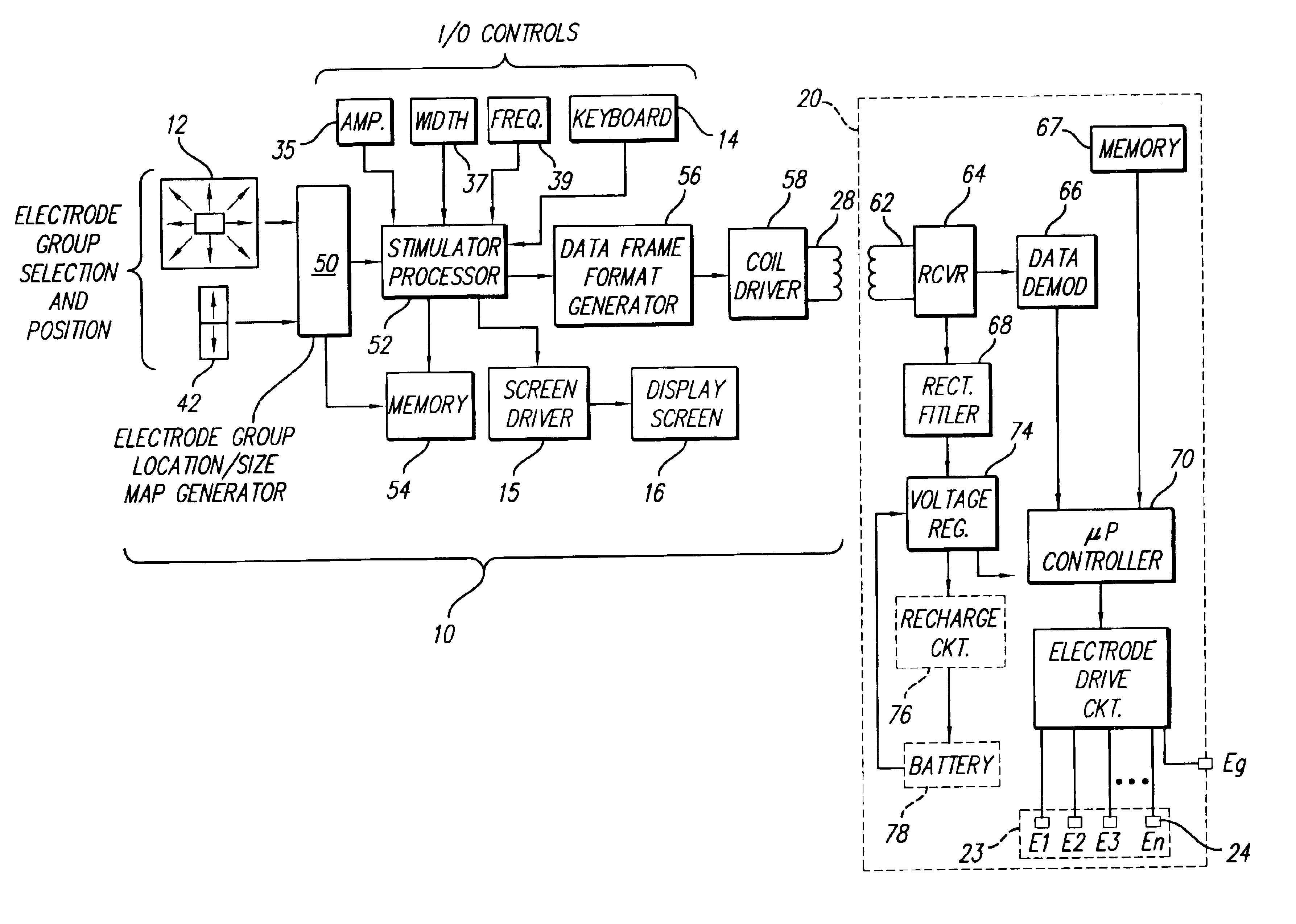
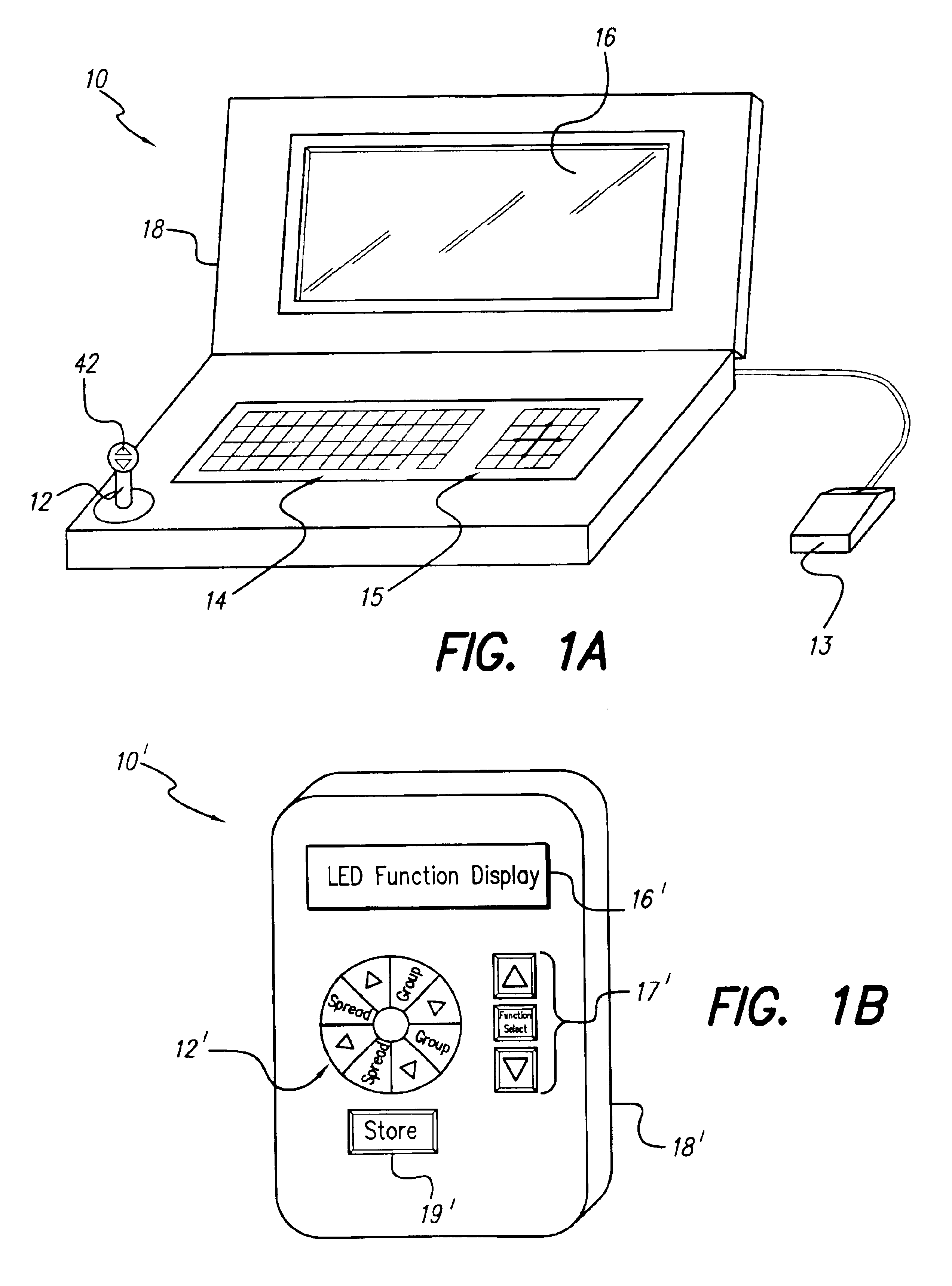
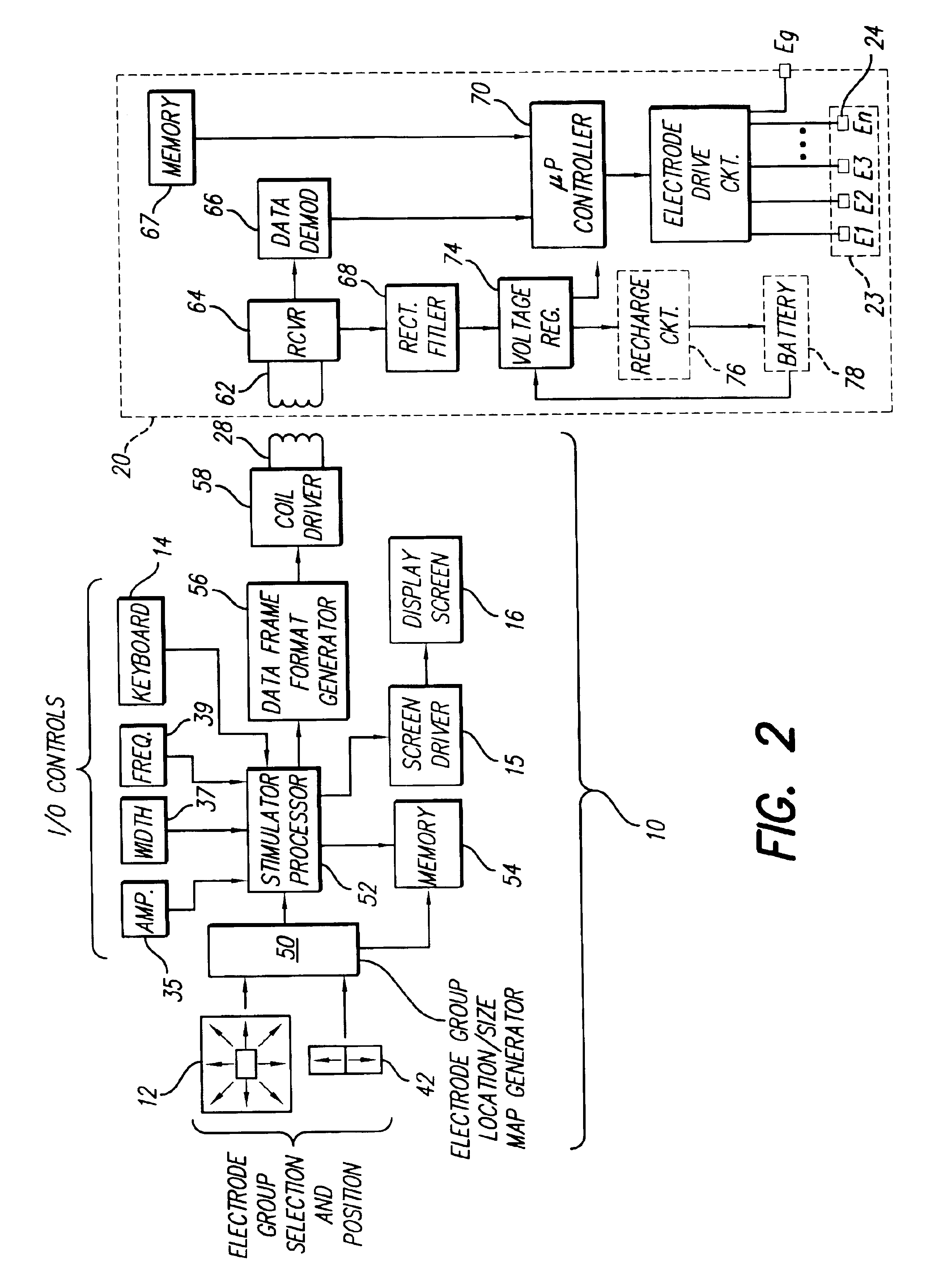
An implantable pulse generator includes a current steering capability that allows a clinician or patient to quickly determine a desired electrode stimulation pattern, including which electrodes of a group of electrodes within an electrode array should receive a stimulation current, including the amplitude, width and pulse repetition rate of such current. Movement of the selected group of electrodes is facilitated through the use of remotely generated directional signals, generated by a pointing device, such as a joystick. As movement of the selected group of electrodes occurs, current redistribution amongst the various electrode contacts takes place. The redistribution of stimulus amplitudes utilizes re-normalization of amplitudes so that the perceptual level remains fairly constant. This prevents the resulting paresthesia from falling below the perceptual threshold or above the comfort threshold.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Electrode array with electrodes having cutout portions and methods of making the same
A lead for brain stimulation includes a lead body having a distal end. At least one cable extends within the lead body, each cable comprising at least one conductor. The lead further includes a plurality of electrodes coupled to the at least one cable. Each of the plurality of electrodes defines a cutout portion that receives and attaches to a one of the at least one cable.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Systems and methods for optical actuation of microfluidics based on opto-electrowetting
InactiveUS6958132B2Improve performanceSludge treatmentMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectricityMicrofluidics
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of fabricating a light emitting diode display with integrated defect detection test
ActiveUS20140267683A1Reduce probabilityImage analysisStatic indicating devicesLED displayDisplay device
A display panel and method of manufacture are described. In an embodiment, a display substrate includes a pixel area and a non-pixel area. An array of subpixels and corresponding array of bottom electrodes are in the pixel area. An array of micro LED devices are bonded to the array of bottom electrodes. One or more top electrode layers are formed in electrical contact with the array of micro LED devices. In one embodiment a redundant pair of micro LED devices are bonded to the array of bottom electrodes. In one embodiment, the array of micro LED devices are imaged to detect irregularities.
Owner:APPLE INC
System and method for performing ablation and other medical procedures using an electrode array with flex circuit
InactiveUS20060100618A1Easy to makeSmall sizeSurgical instruments for heatingFlexible circuitsElectrode array
An ablation catheter having distal and proximal ends for performing ablation on a human tissue region comprises at least one electrode. These elements are formed on a conductive sheet situated at the distal end of the catheter. A flex circuit assembly couples the at least one electrode to a measurement and power circuit attached to the proximal end of the catheter. The measurement and power circuit supplies power to the at least one electrode via the flex circuit.
Owner:RUI XING
Electrode array having concentric windowed cylinder electrodes and methods of making the same
A device for brain stimulation includes a lead body having a distal end section and at least one inner conductive cylinder with at least one inner window cut out from the inner cylinder. The inner cylinder is disposed at the distal end section of the lead body. The device also includes an outer conductive cylinder with at least one outer window cut out from the outer cylinder. The outer cylinder is secured to and disposed concentric to the inner cylinder with a portion of each of the at least one inner cylinder aligned with the at least one outer window of the outer cylinder. The device further includes an insulator configured and arranged to electrically insulate each of the at least one inner cylinder and the outer cylinder.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Apparatus and method for treating tumors near the surface of an organ
InactiveUS6337998B1Avoid flowPrevent heat lossElectrotherapySurgical needlesAbnormal tissue growthTherapeutic Area
A system for treating a target region in tissue beneath a tissue surface comprises a probe for deploying an electrode array within the tissue and a surface electrode for engaging the tissue surface above the treatment site. Preferably, surface electrode includes a plurality of tissue-penetrating elements which advance into the tissue, and the surface electrode is removably attachable to the probe. The tissue may be treated in a monopolar fashion where the electrode array and surface electrode are attached to a common pole on an electrode surgical power supply and powered simultaneously or successively, or in a bipolar fashion where the electrode array and surface electrode are attached to opposite poles of the power supply. The systems are particularly useful for treating tumors and other tissue treatment regions which lie near the surface.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Electrode array having concentric windowed cylinder electrodes and methods of making the same
A device for brain stimulation includes a lead body having a distal end section and at least one inner conductive cylinder with at least one inner window cut out from the inner cylinder. The inner cylinder is disposed at the distal end section of the lead body. The device also includes an outer conductive cylinder with at least one outer window cut out from the outer cylinder. The outer cylinder is secured to and disposed concentric to the inner cylinder with a portion of each of the at least one inner cylinder aligned with the at least one outer window of the outer cylinder. The device further includes an insulator configured and arranged to electrically insulate each of the at least one inner cylinder and the outer cylinder.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Electrode array with electrodes having cutout portions and methods of making the same
ActiveUS20110130816A1Line/current collector detailsHead electrodesElectrical conductorElectrode array
A lead for brain stimulation includes a lead body having a distal end. At least one cable extends within the lead body, each cable comprising at least one conductor. The lead further includes a plurality of electrodes coupled to the at least one cable. Each of the plurality of electrodes defines a cutout portion that receives and attaches to a one of the at least one cable.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Electrode addressing method
InactiveUS20090192044A1Reduce in quantitySimplify line selection meanElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentElectrode arrayEngineering
A device for addressing an electrode array of 2n lines of an electro-fluidic device, each line having N electrodes (n≦N). The device includes, on each line, n selection electrodes, all of the line selection electrodes being connected to 2n line selection conductors, 2n−1 line selection electrodes of 2n−1 lines being connected to each line selection conductor, and selection devices for selecting one or more line selection conductors.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
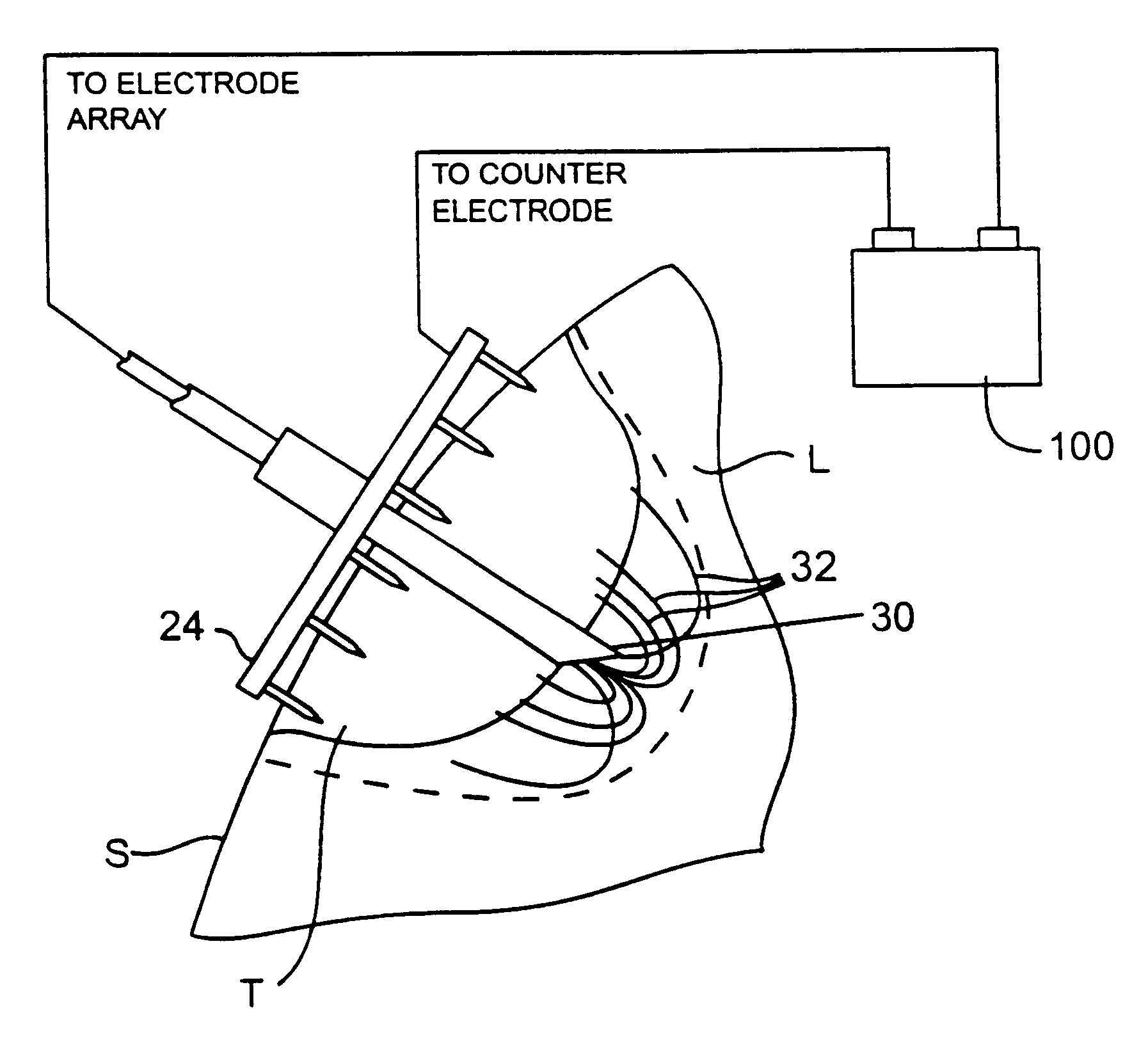
Method for electrosurgical tissue treatment near a patient's heart
InactiveUS7217268B2Control depthControl damageEnemata/irrigatorsHeart valvesElectricityHigh frequency power
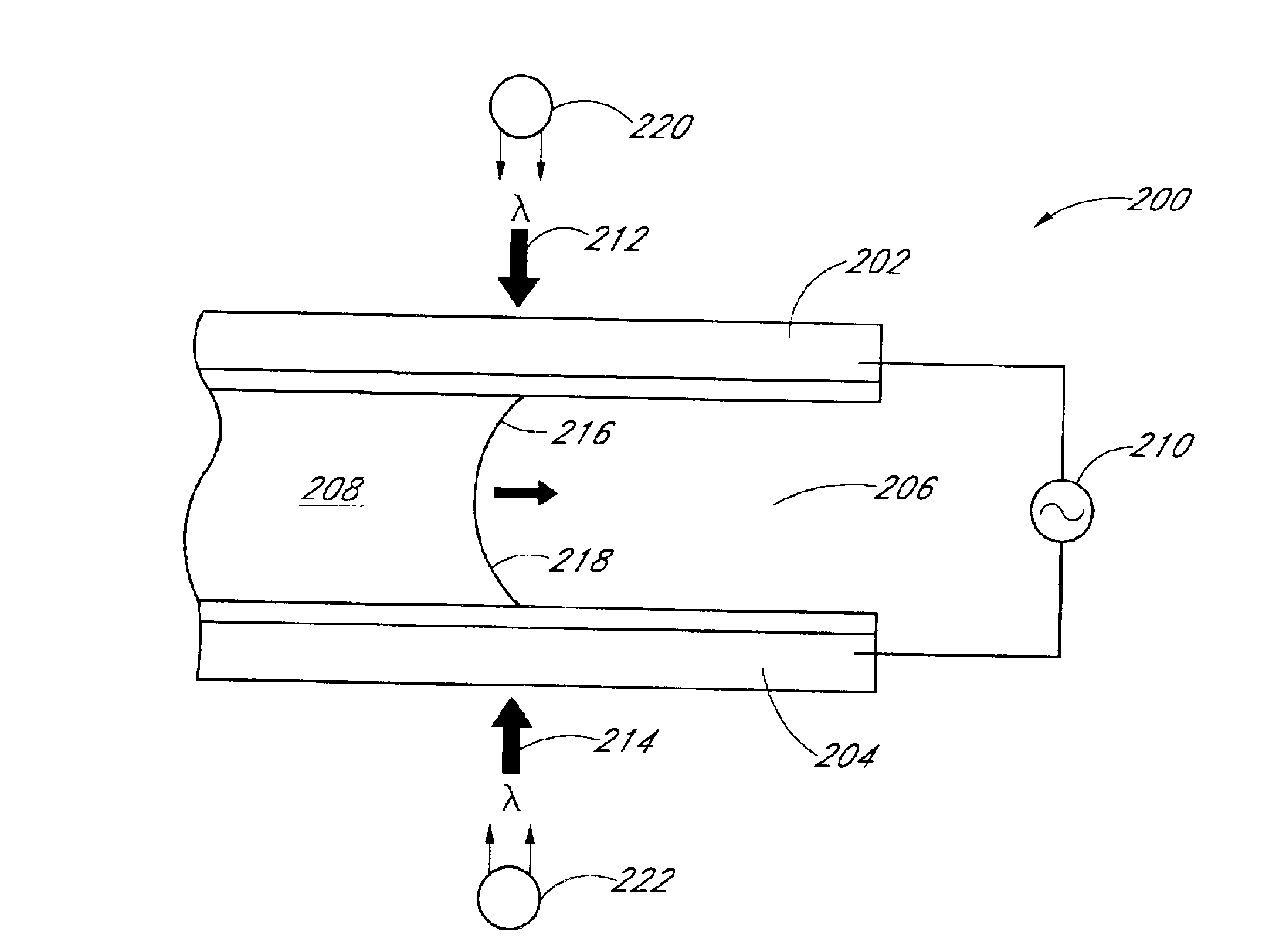
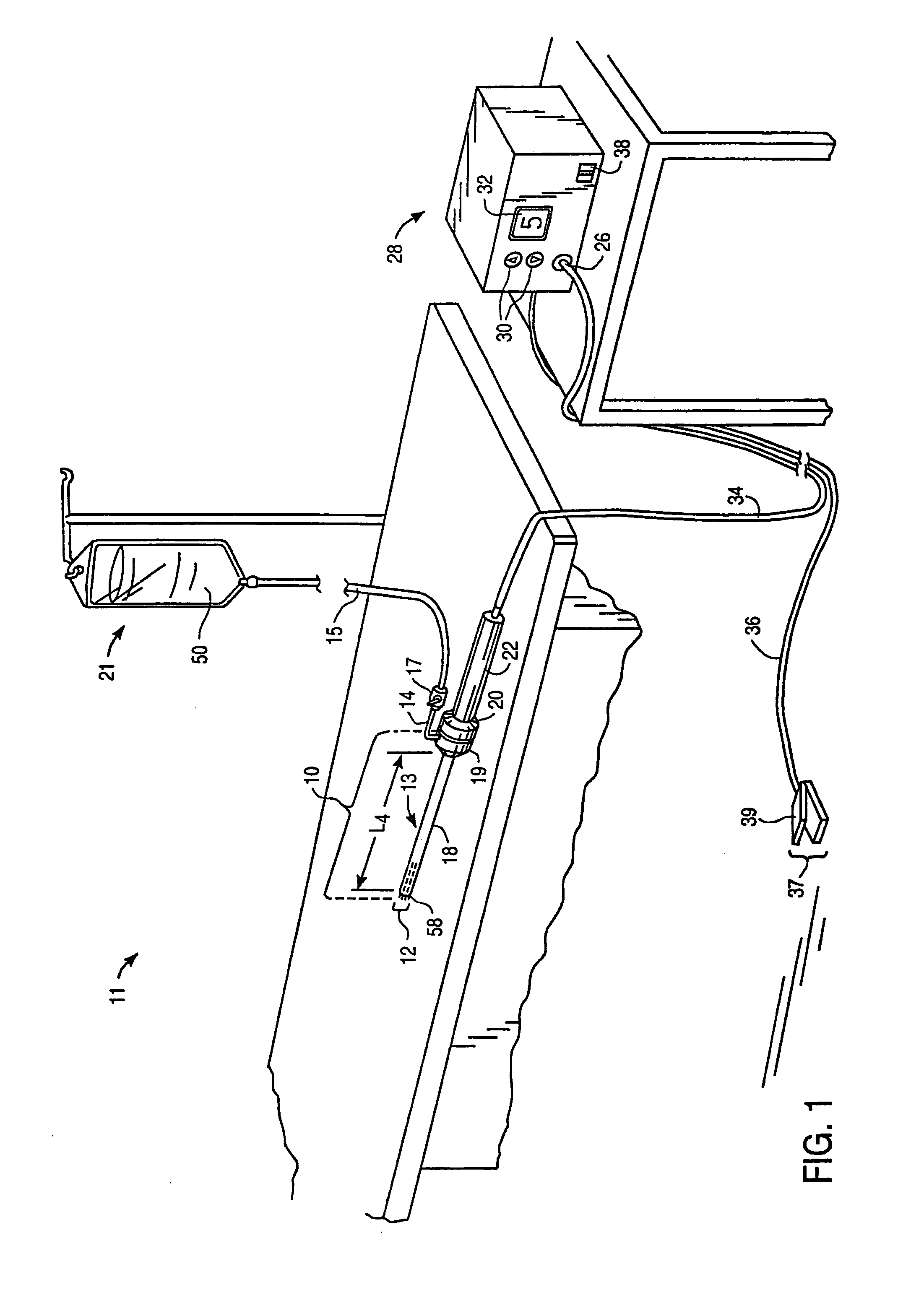
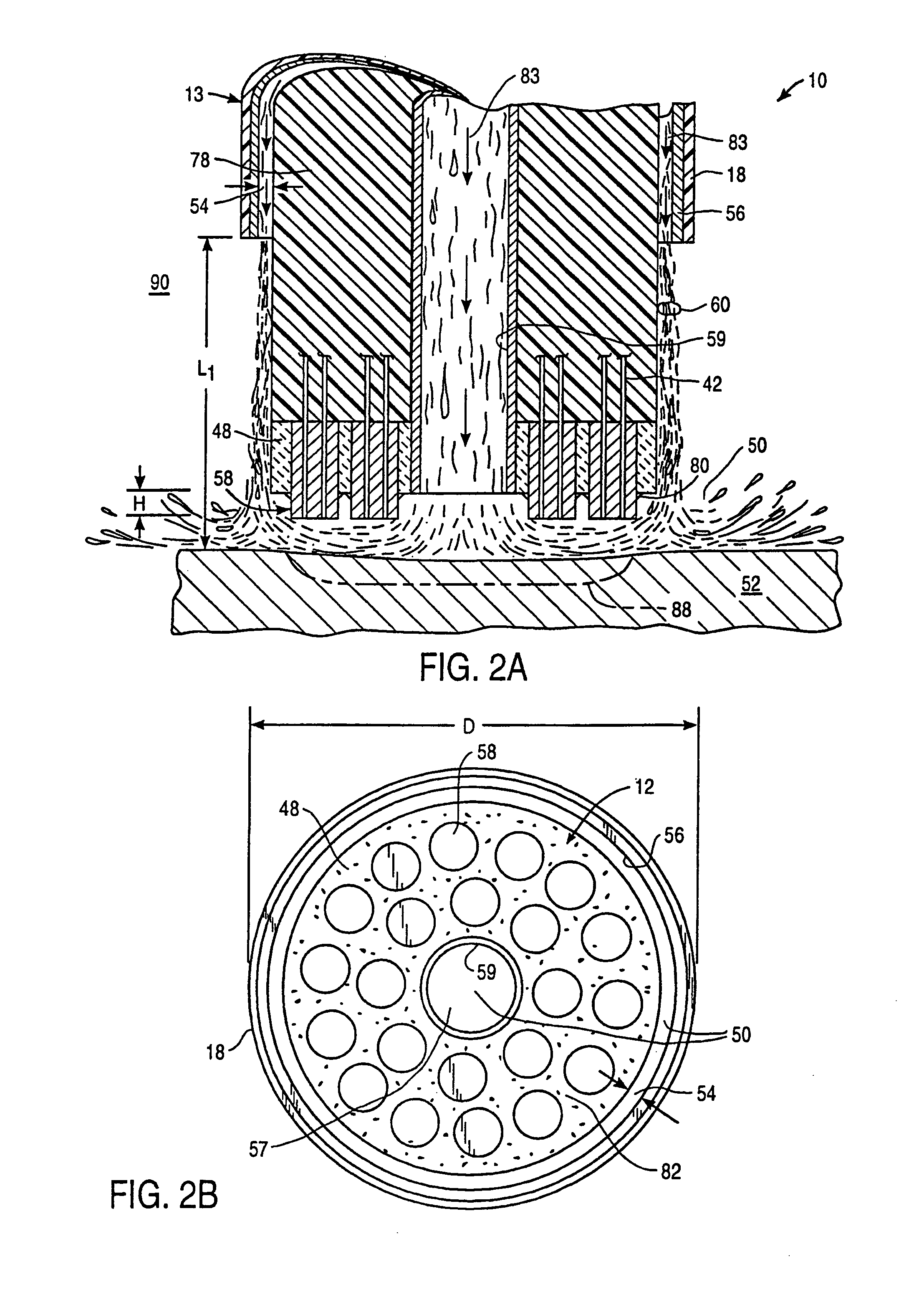
An electrosurgical probe (10) comprises a shaft (13) having an electrode array (58) at its distal end and a connector (19) at its proximal end for coupling the electrode array to a high frequency power supply (28). The shaft includes a return electrode (56) recessed from its distal end and enclosed within an insulating jacket (18). The return electrode defines an inner passage (83) electrically connected to both the return electrode and the electrode array for passage of an electrically conducting liquid (50). By applying high frequency voltage to the electrode array and the return electrode, the electrically conducting liquid generates a current flow path between the return electrode and the electrode array so that target tissue may be cut or ablated. The probe is particularly useful in dry environments, such as the mouth or abdominal cavity, because the electrically conducting liquid provides the necessary return current path between the active and return electrodes.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Apparatus and method for treating tumors near the surface of an organ
InactiveUS6889089B2Enhances uniform electrosurgical treatment of tissueEliminate needSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingAbnormal tissue growthElectrode array
A system for treating a target region in tissue beneath a tissue surface comprises a probe for deploying an electrode array within the tissue and a surface electrode for engaging the tissue surface above the treatment site. Preferably, surface electrode includes a plurality of tissue-penetrating elements which advance into the tissue, and the surface electrode is removably attachable to the probe. The tissue may be treated in a monopolar fashion where the electrode array and surface electrode are attached to a common pole on an electrode surgical power supply and powered simultaneously or successively, or in a bipolar fashion where the electrode array and surface electrode are attached to opposite poles of the power supply. The systems are particularly useful for treating tumors and other tissue treatment regions which lie near the surface.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
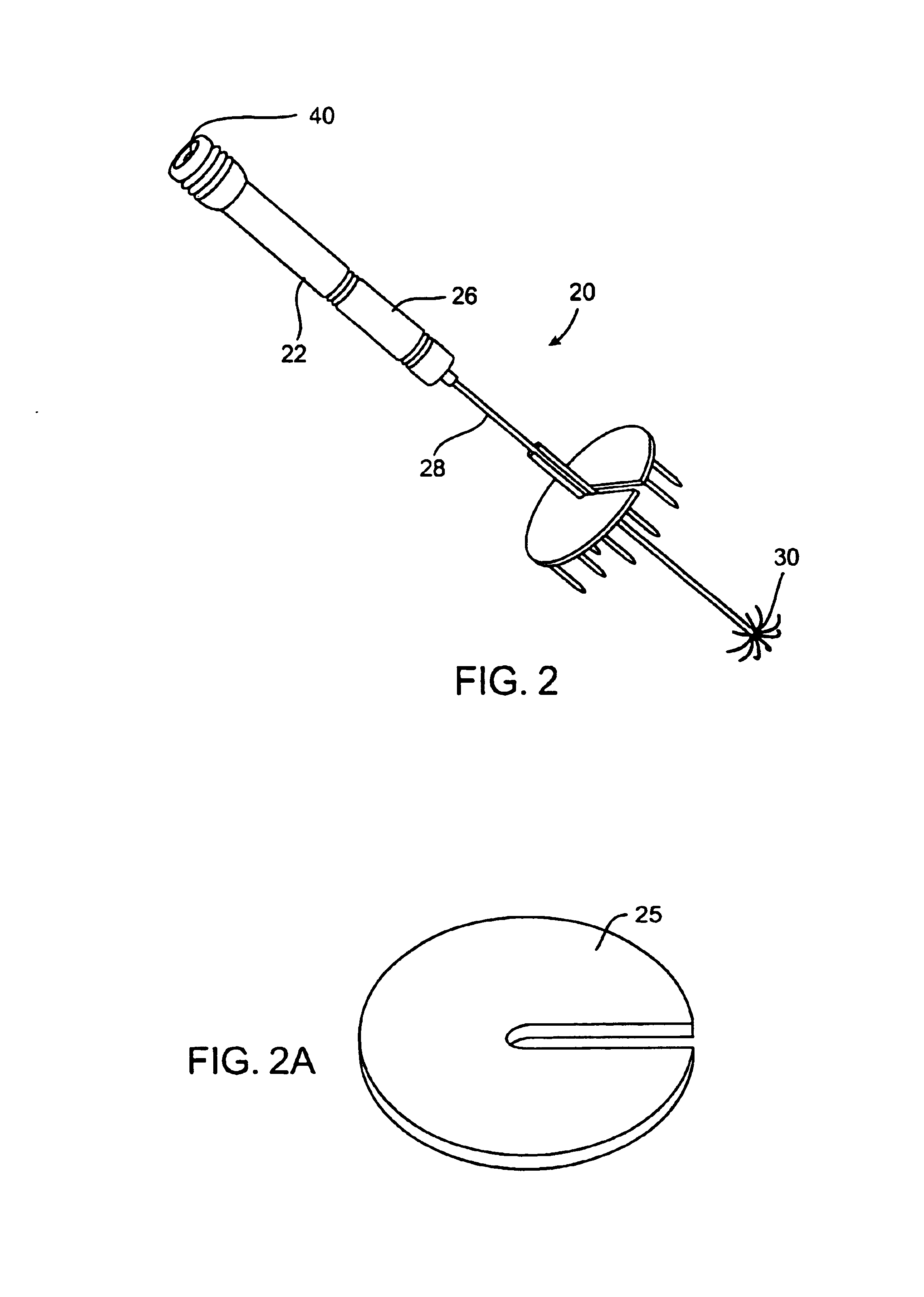
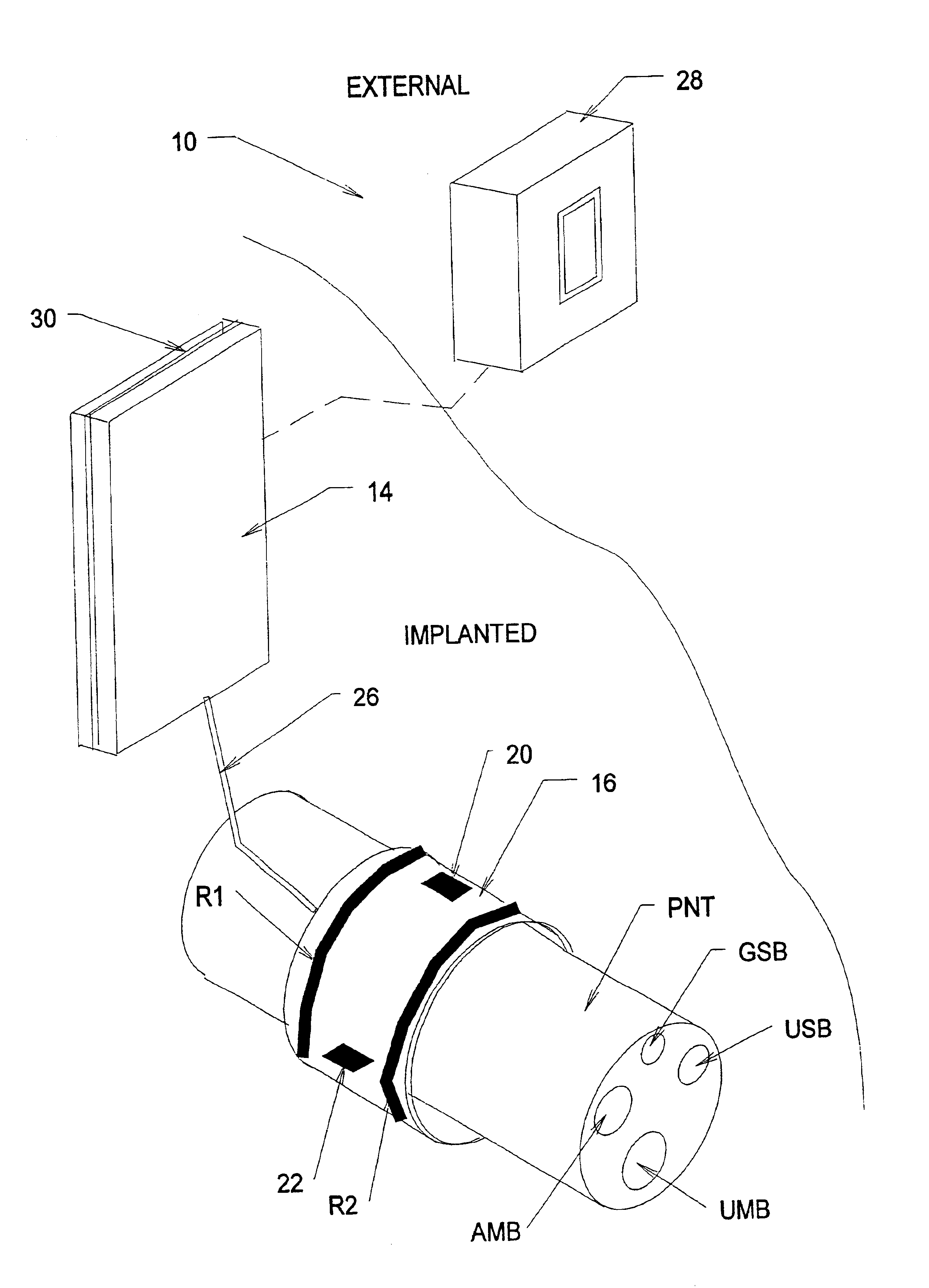
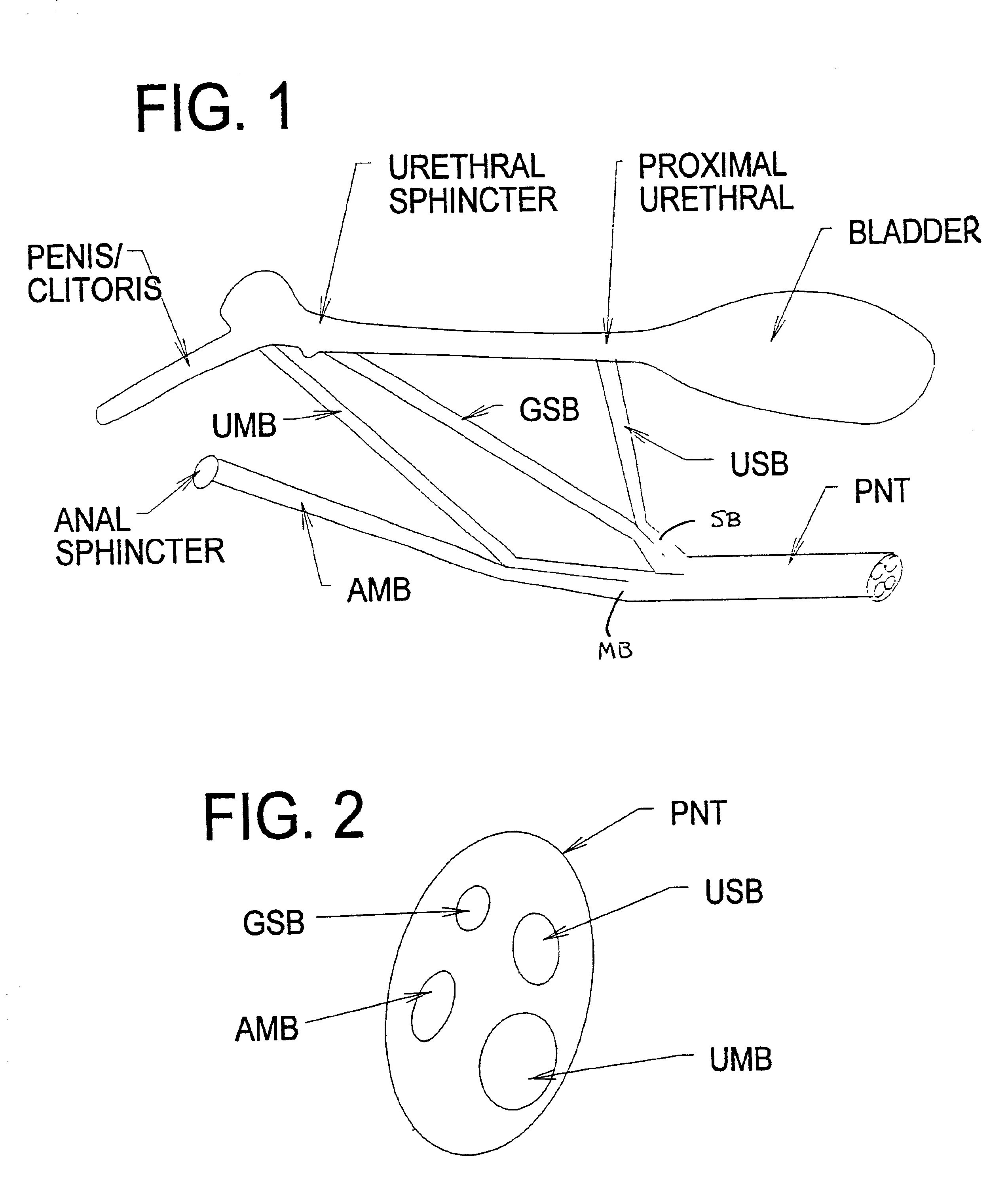
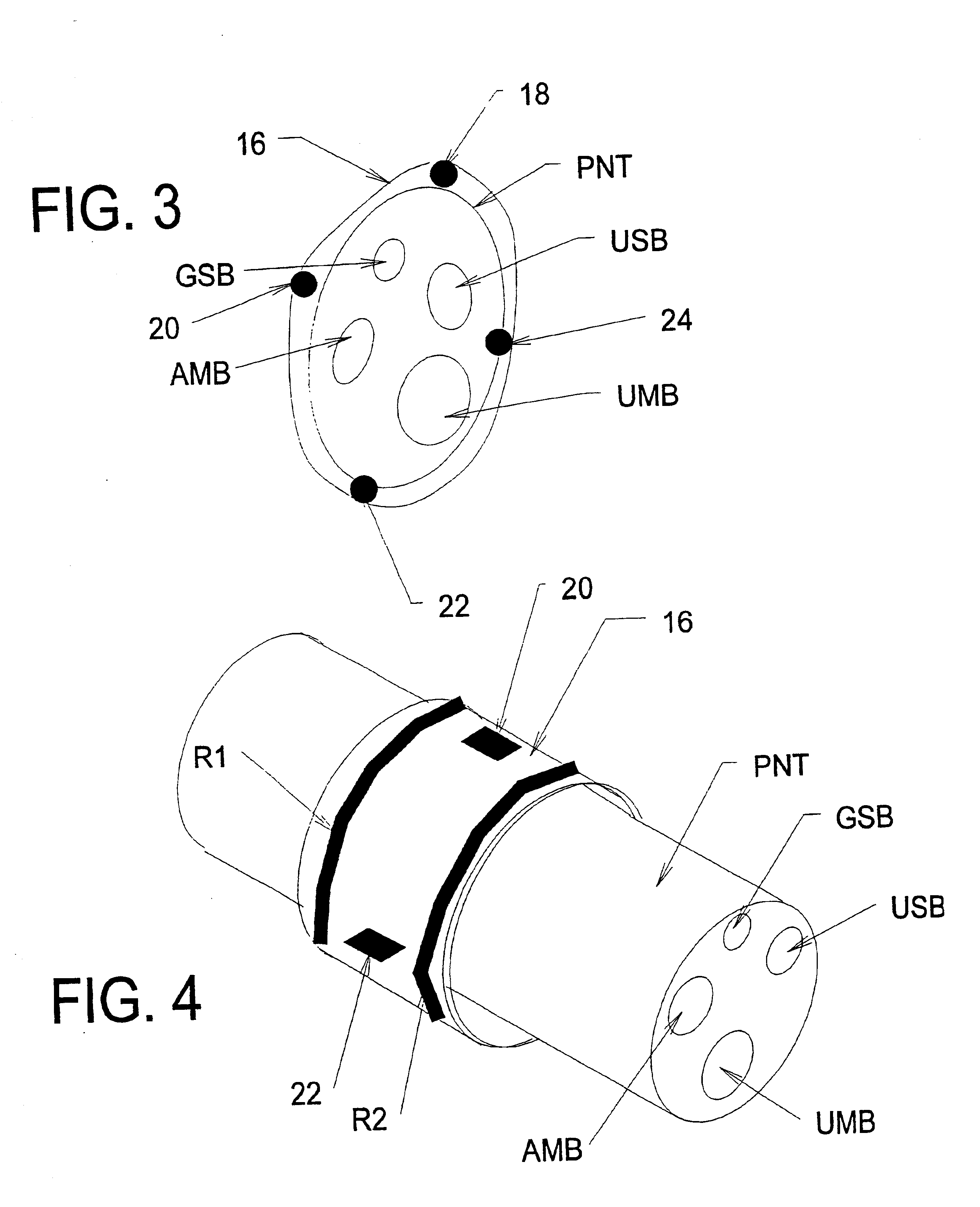
Systems and methods for selectively stimulating components in, on, or near the pudendal nerve or its branches to achieve selective physiologic responses
ActiveUS6907293B2Easy to defecatePromote contractionSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesMedicineMultielectrode array
Systems and methods selectively stimulate components of the pudendal nerve away from the sacral root to evoke desired physiologic responses in persons who lack the ability to otherwise produce these responses—e.g., maintain continence and / or produce micturition, and / or provide male / female sexuality responses, and / or provide bowel responses. The systems and methods use a multiple electrode array, or individual electrodes, placed on, in, or near the pudendal nerve. The electrode array, or individual electrodes, in association with a pulse generator, provide selective stimulation of individual fascicles within the pudendal nerve, to achieve different physiologic responses.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Sensor systems having multiple probes and electrode arrays
ActiveUS20110319734A1Improve reliabilityImprove sensor accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSensor arrayDiabetes mellitus
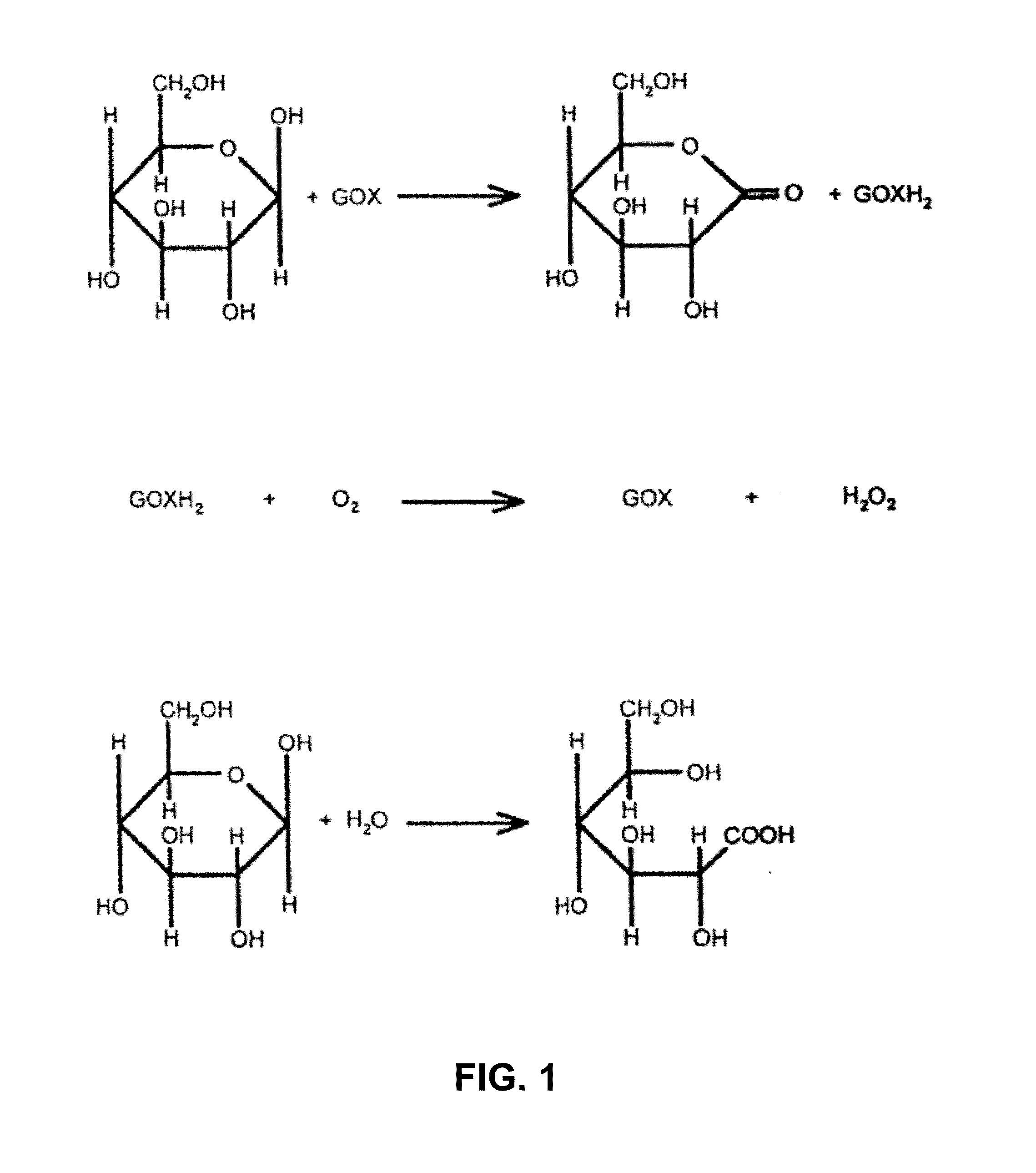
Embodiments of the invention provide amperometric analyte sensors having multiple related structural elements (e.g. sensor arrays comprising a working, counter and reference electrode) and algorithms designed for use with such sensors. While embodiments of the innovation can be used in a variety of contexts, typical embodiments of the invention include glucose sensors used in the management of diabetes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
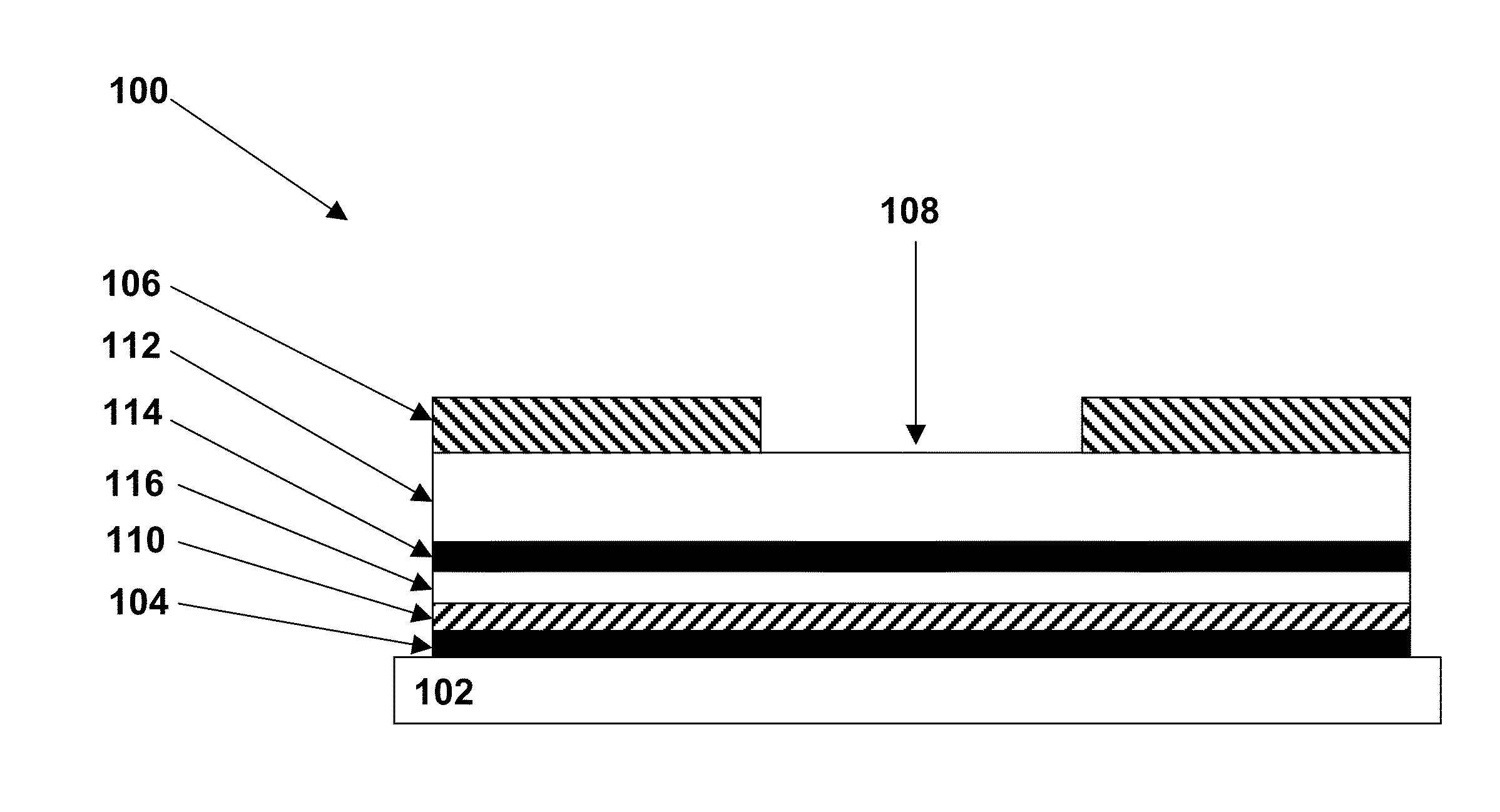
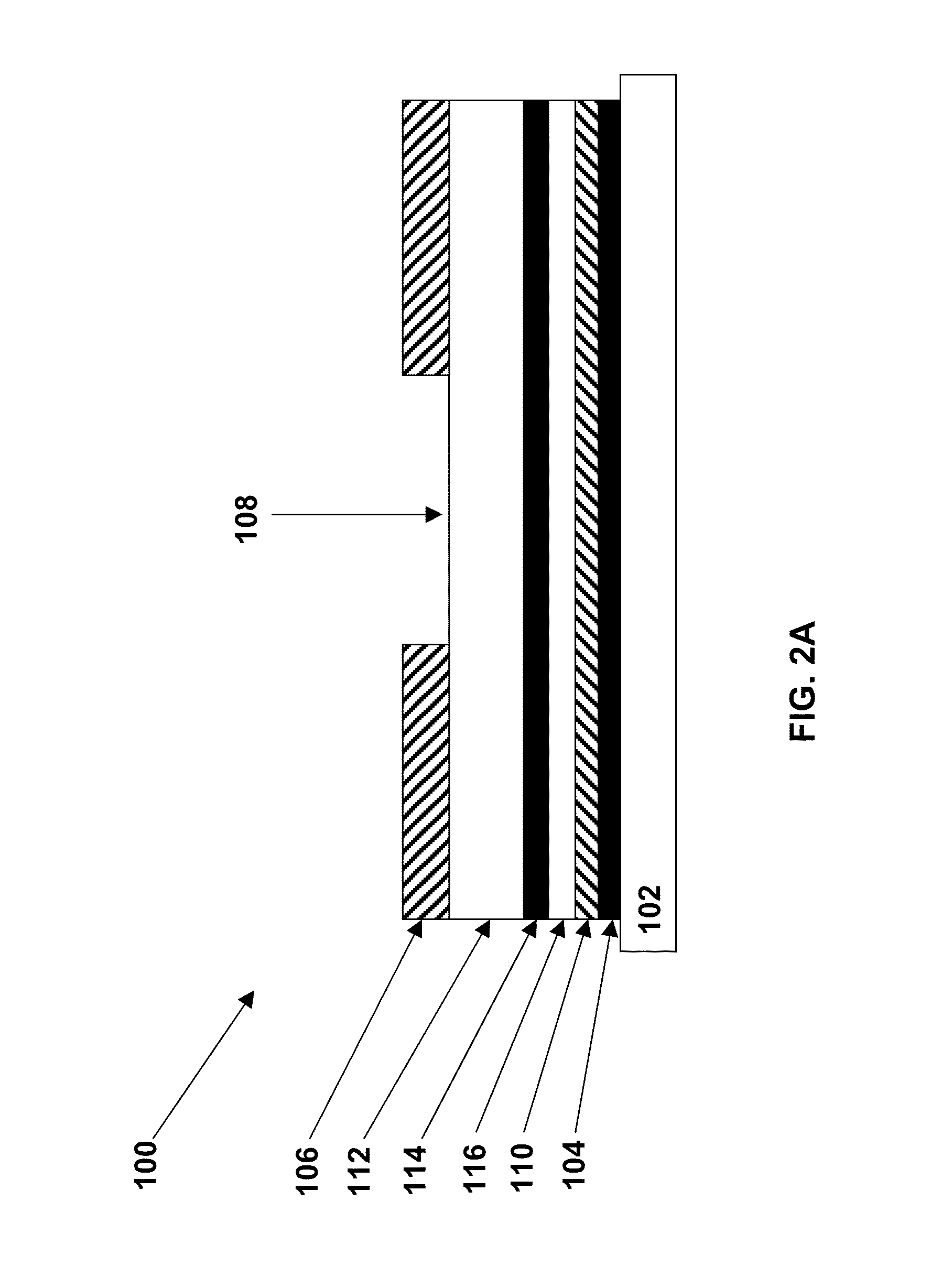
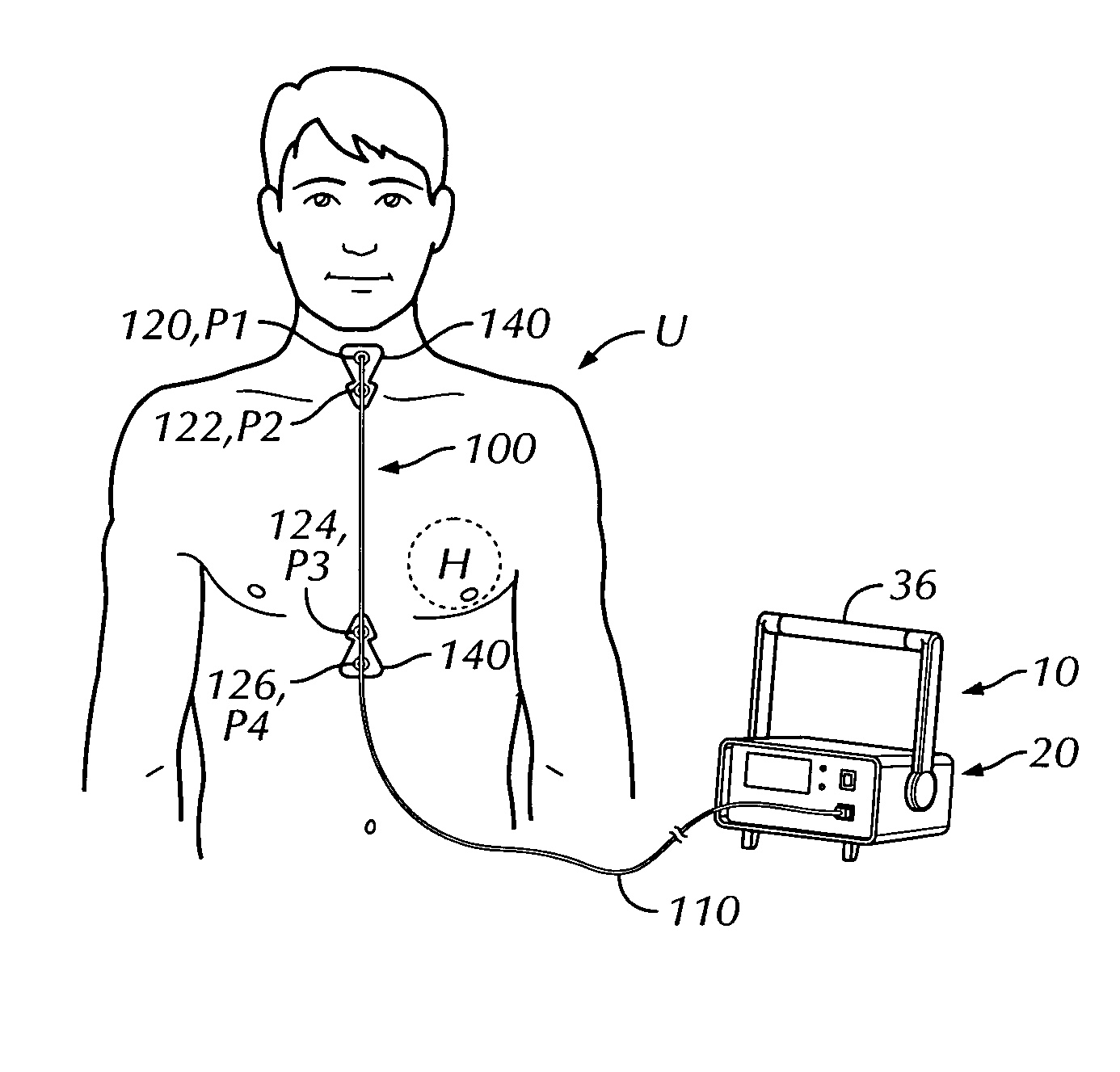
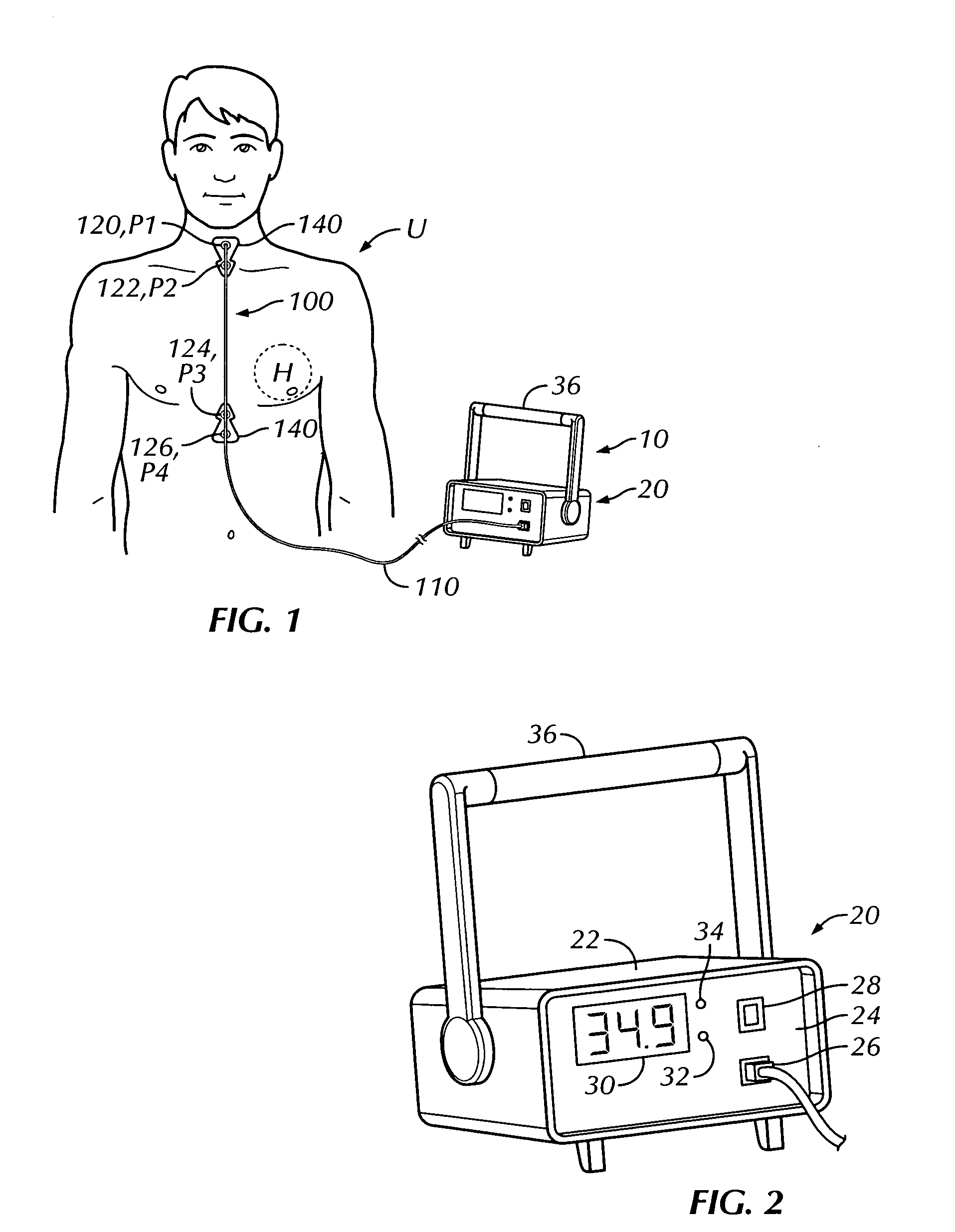
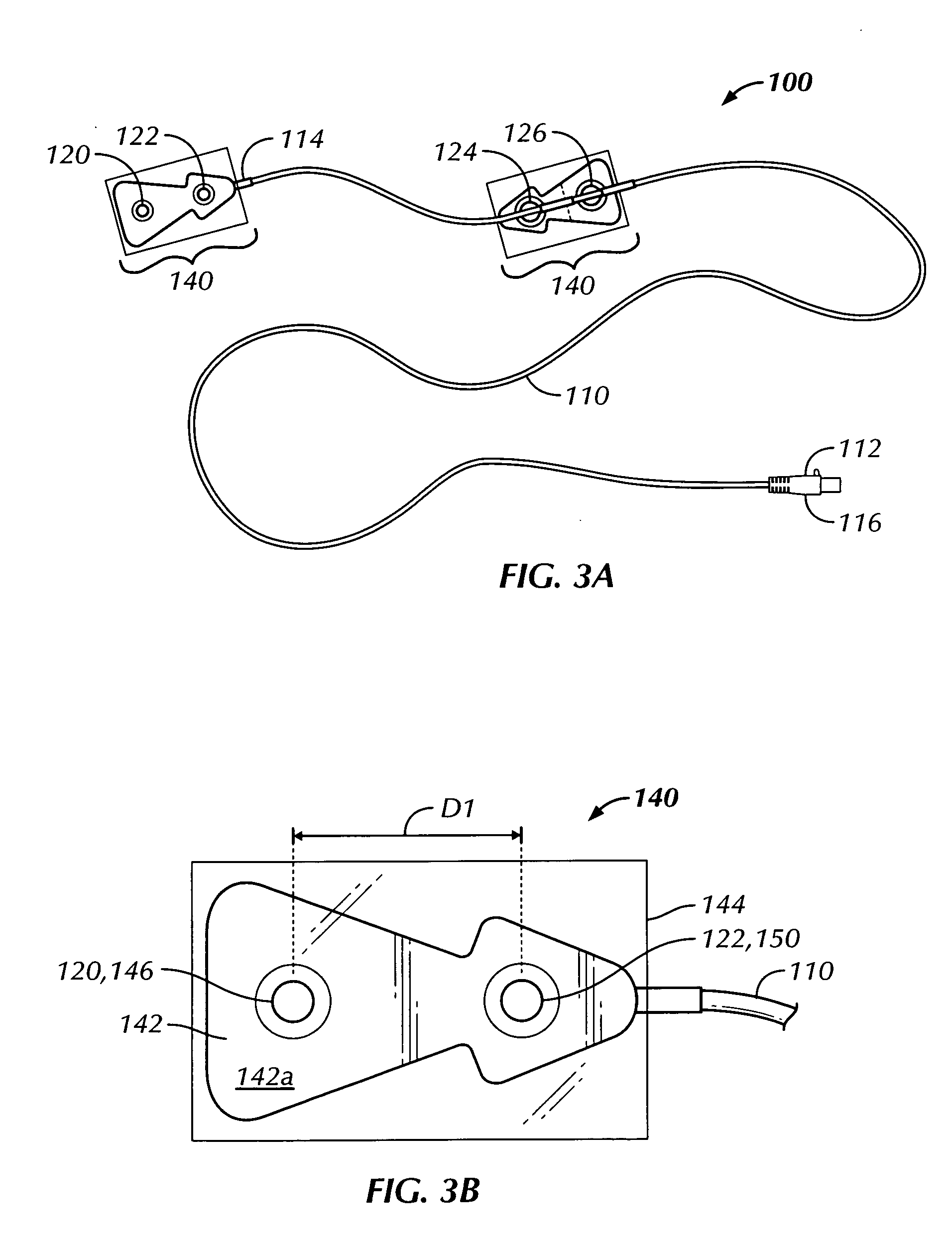
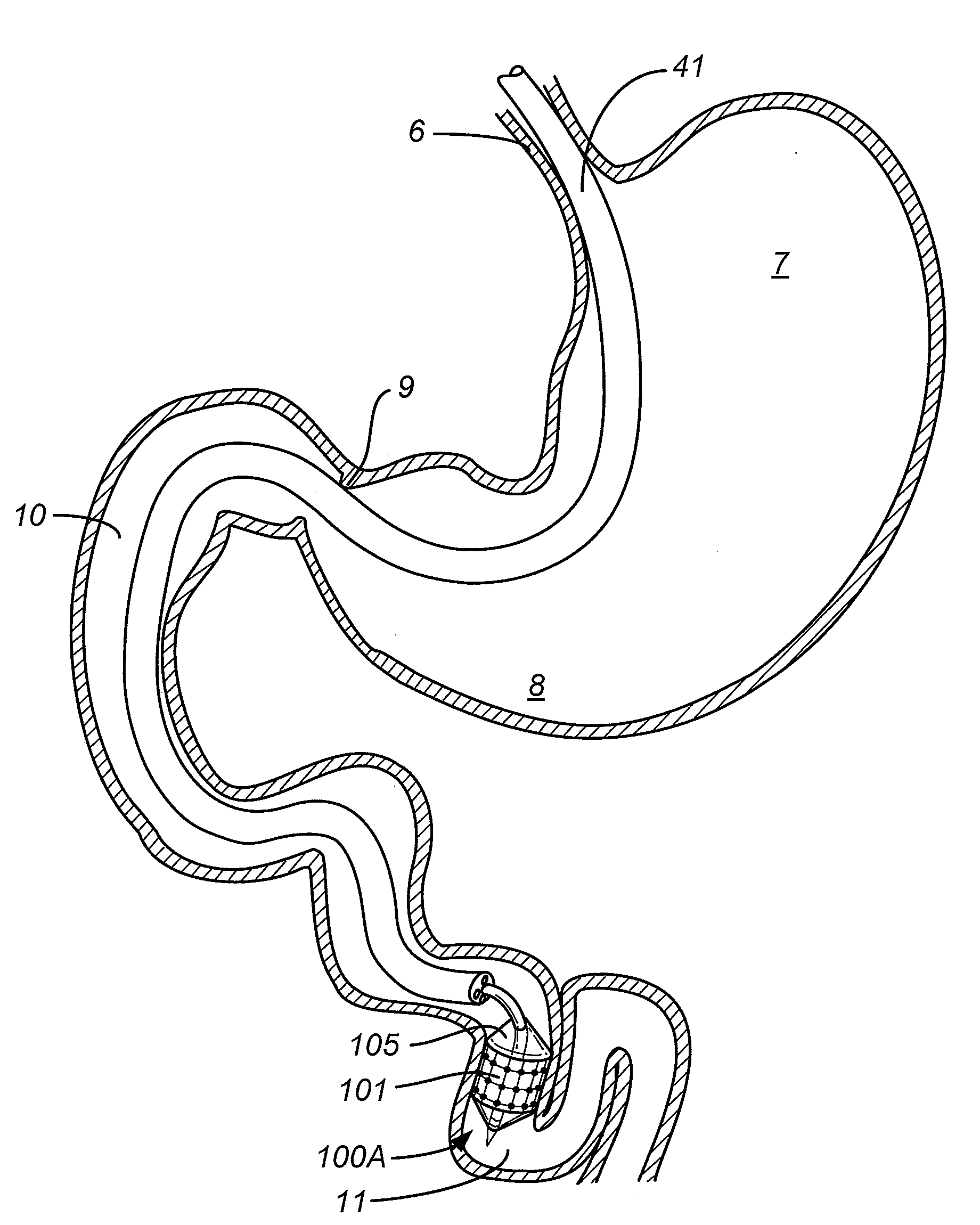
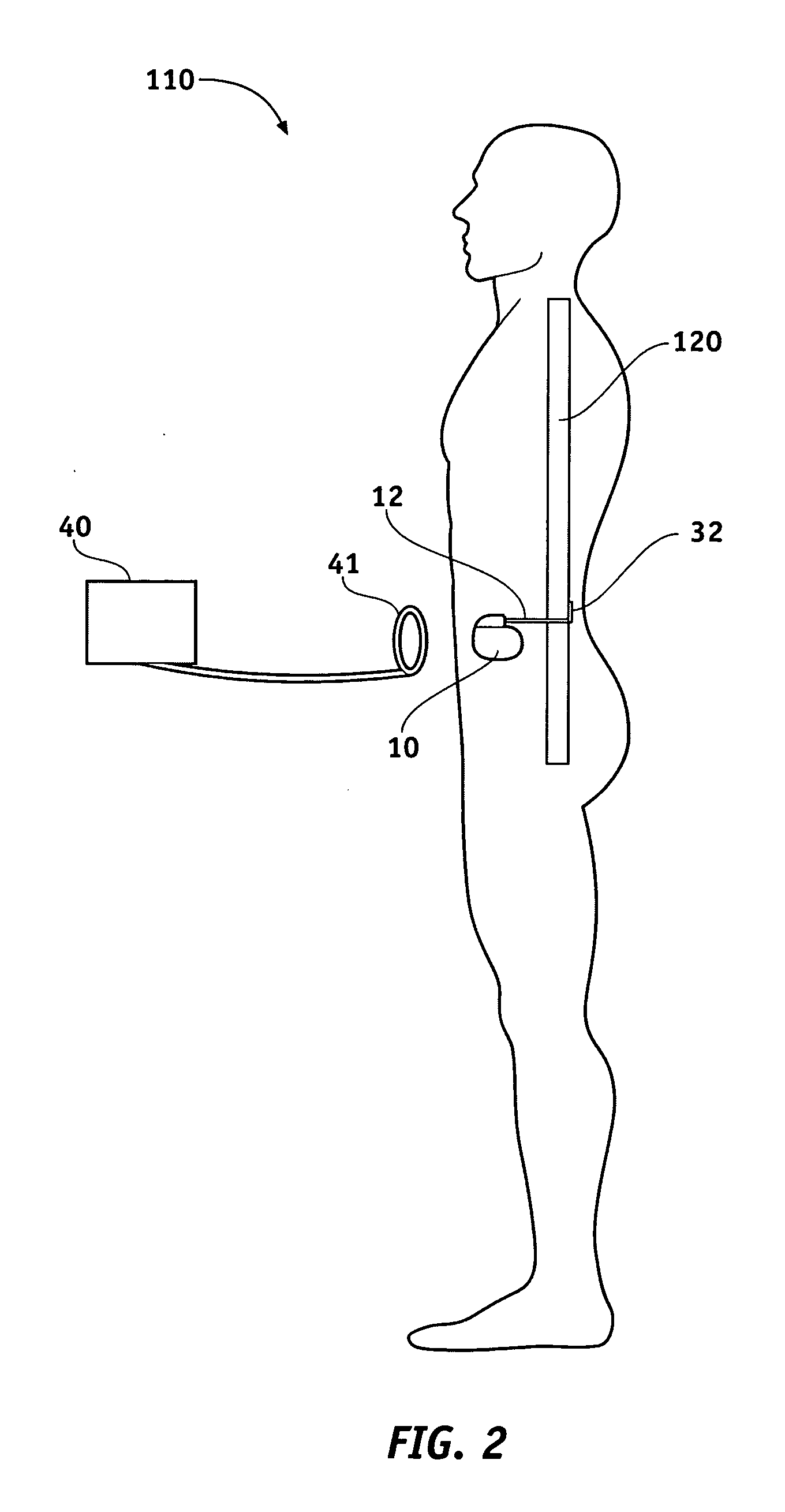
Thoracic impedance monitor and electrode array and method of use
A portable thoracic impedance monitor for monitoring thoracic fluid levels, an electrode array assembly having a single linear electrode array lead with first, second, third, and fourth electrodes arranged sequentially and axially along the linear electrode array lead, and a method of use of the thoracic impedance monitor. A measurement of the user's thoracic impedance is obtained by connecting the second electrode to the user's body at the junction of the clavicles, superior to the sternum, the third electrode to the user's body at the xyphiod-sternal junction, and the first and fourth electrodes to the user's body substantially along a centerline of the user's sternum respectively at a first pre-determined distance above the second electrode and a second predetermined distance below the third electrode, followed by initiating operation of the monitor.
Owner:CALDWELL SIMPSON LLC
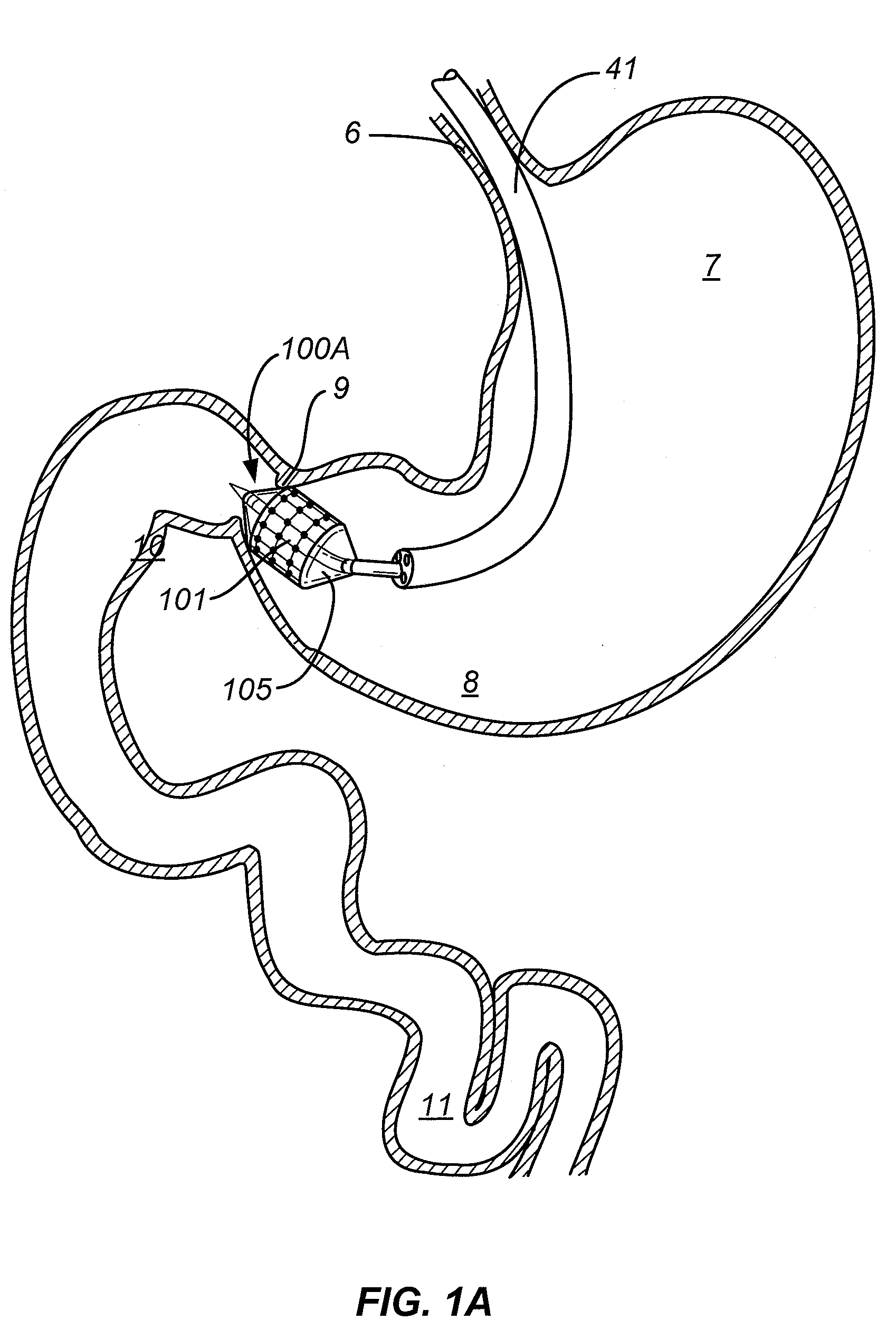
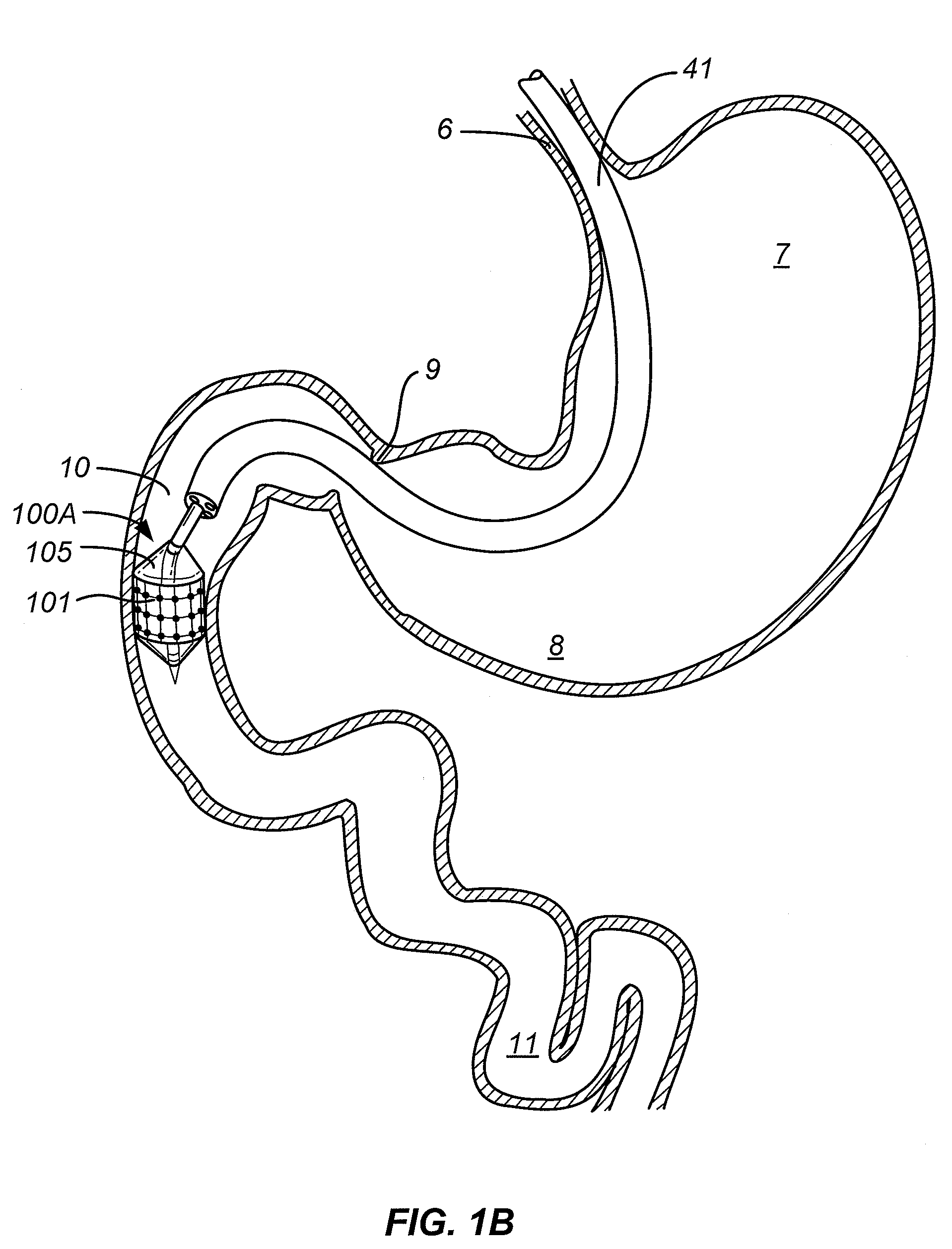
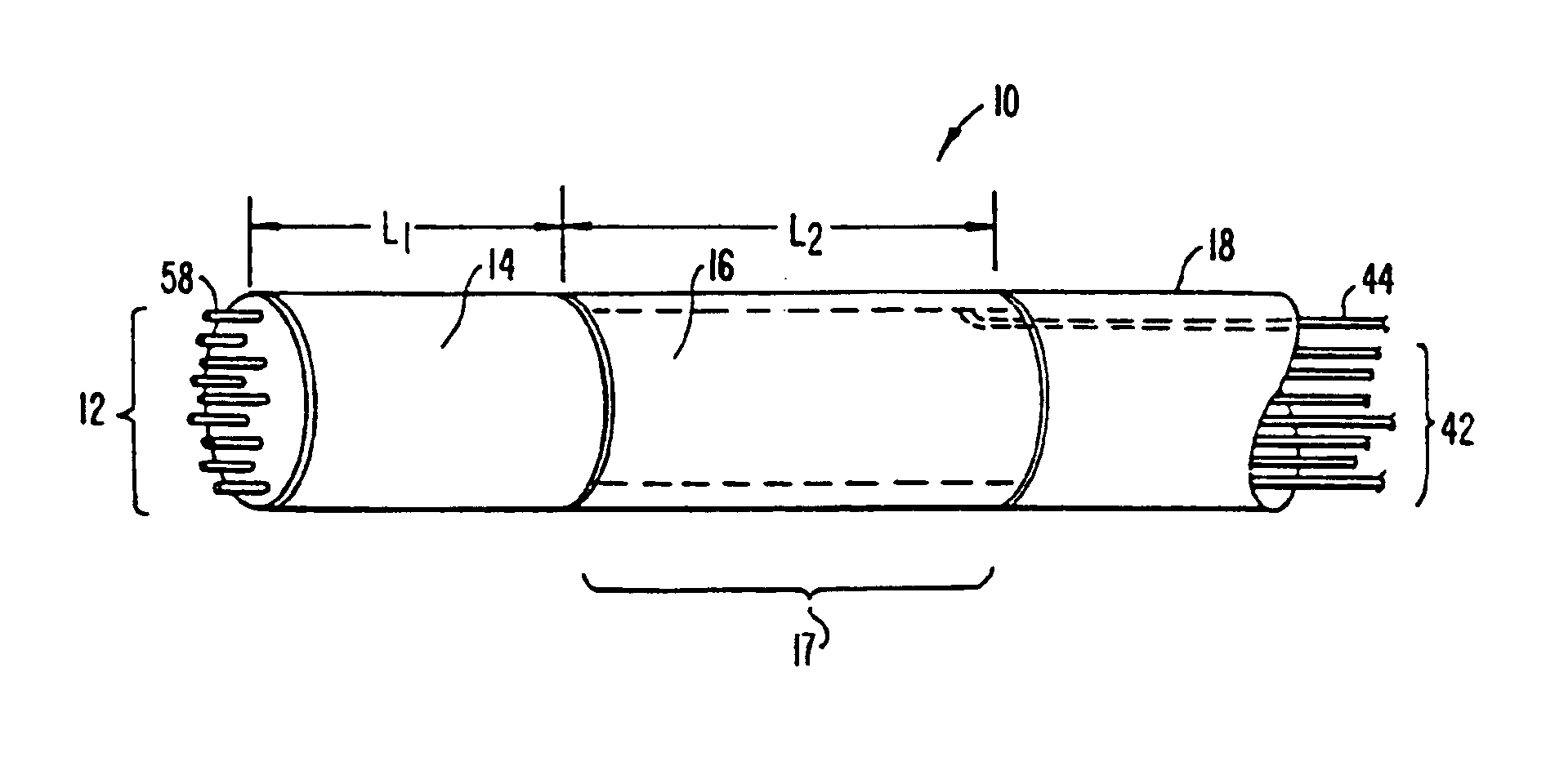
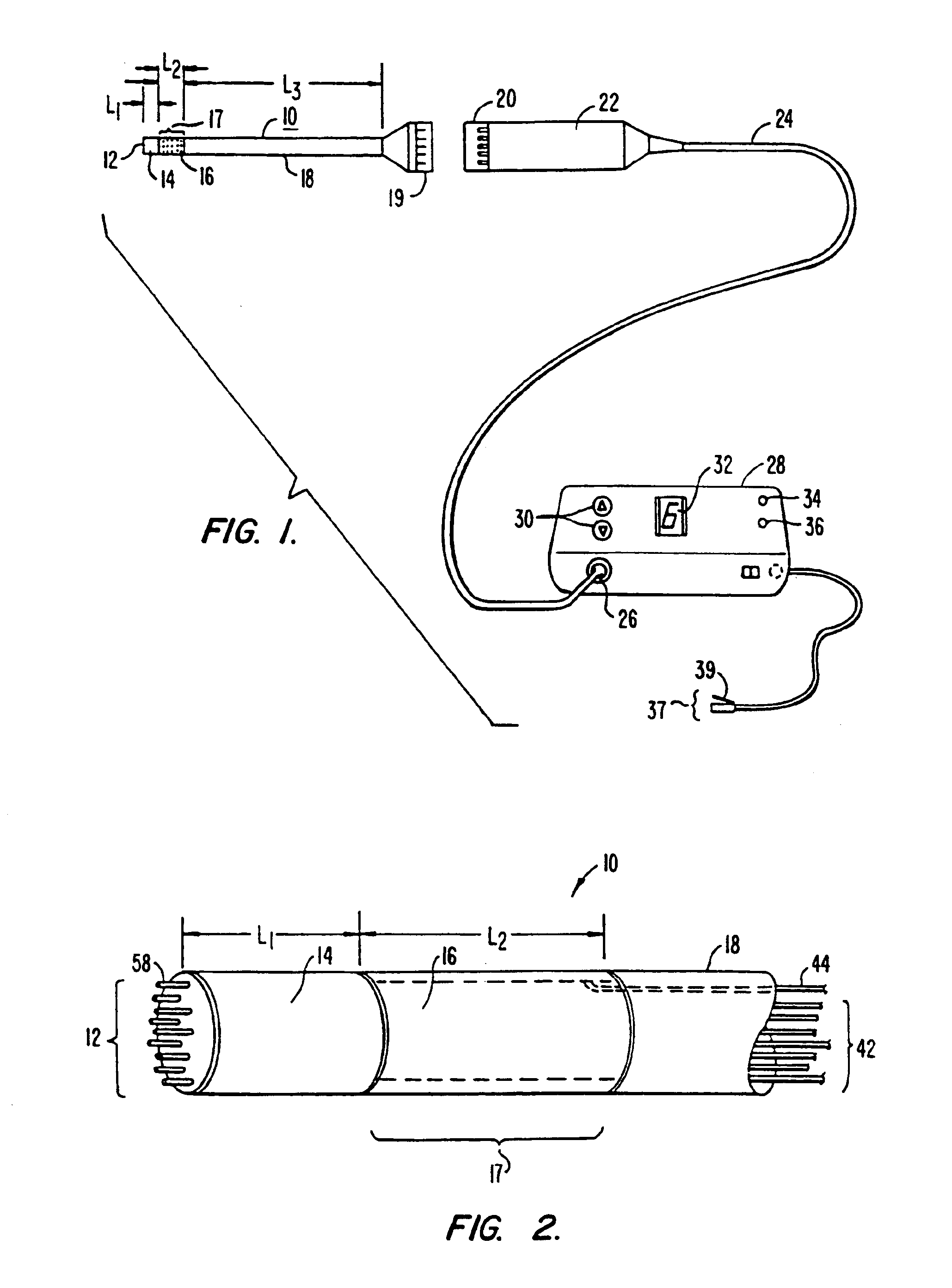
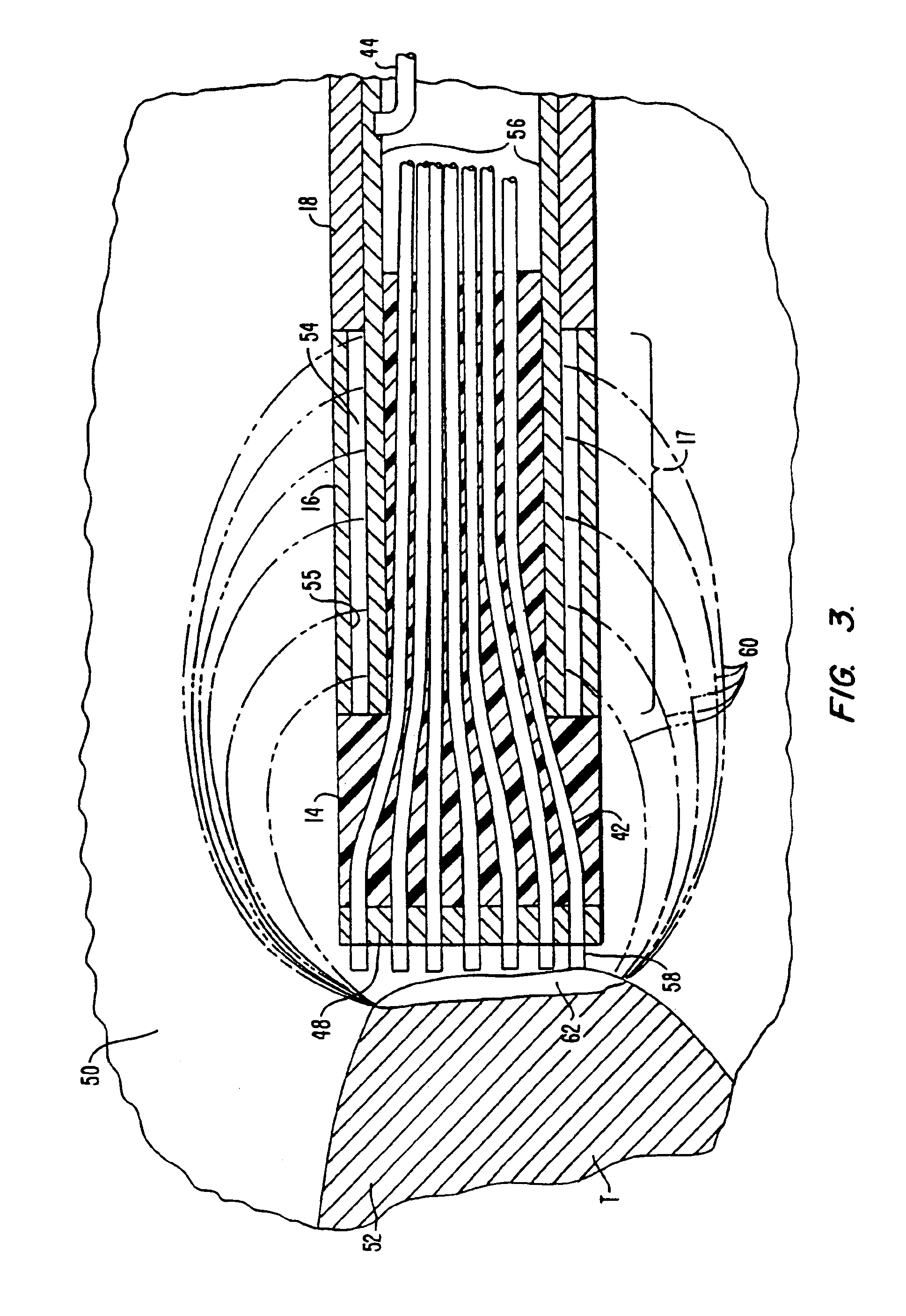
Method and apparatus for gastrointestinal tract ablation for treatment of obesity
ActiveUS20080275445A1Reduce rateSlowing of gastric emptyingCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingBiological activationElectrode array
Devices and methods for ablating tissue in the wall of various organs of the gastrointestinal tract of a patient in order to cure or ameliorate metabolic pathophysiological conditions such as obesity, insulin resistance, or type 2 diabetes mellitus are provided. Ablational treatment of target areas may be fractional or partial, rendering a post-treatment portion of target tissue ablated and another portion that is substantially intact. Fractional ablation is achieved by controlling the delivery of ablational energy across the surface area being treated, and controlling the depth of energy penetration into tissue. Surface area control of energy delivery may controlled by the spatial pattern of distributed ablation elements or by the selective activation of a subset of a dense pattern of ablation elements. Embodiments of the device include an ablational electrode array that spans 360 degrees and an array that spans an arc of less than 360 degrees.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Electrosurgical method using laterally arranged active electrode
InactiveUS6960204B2Control depthReducing power deliveryHeart valvesDiagnosticsActive electrodeElectrode array
An electrosurgical probe comprises a shaft having an electrode array (12) at its distal end and a connector at its proximal end. The array (12) includes a plurality of isolated electrode terminals, and an electrosurgical power supply (28) is provided with a multiplicity of independently limited or controlled current sources and a connector. The electrosurgical probe and the power supply may be connected through their respective connectors so that the independent current sources are connected to individual electric terminals. By applying very high frequency electrical energy to the electrode array, target tissue may be cut or ablated while heat dissipation through low impedance paths, such as blood and normal saline, will be minimized.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
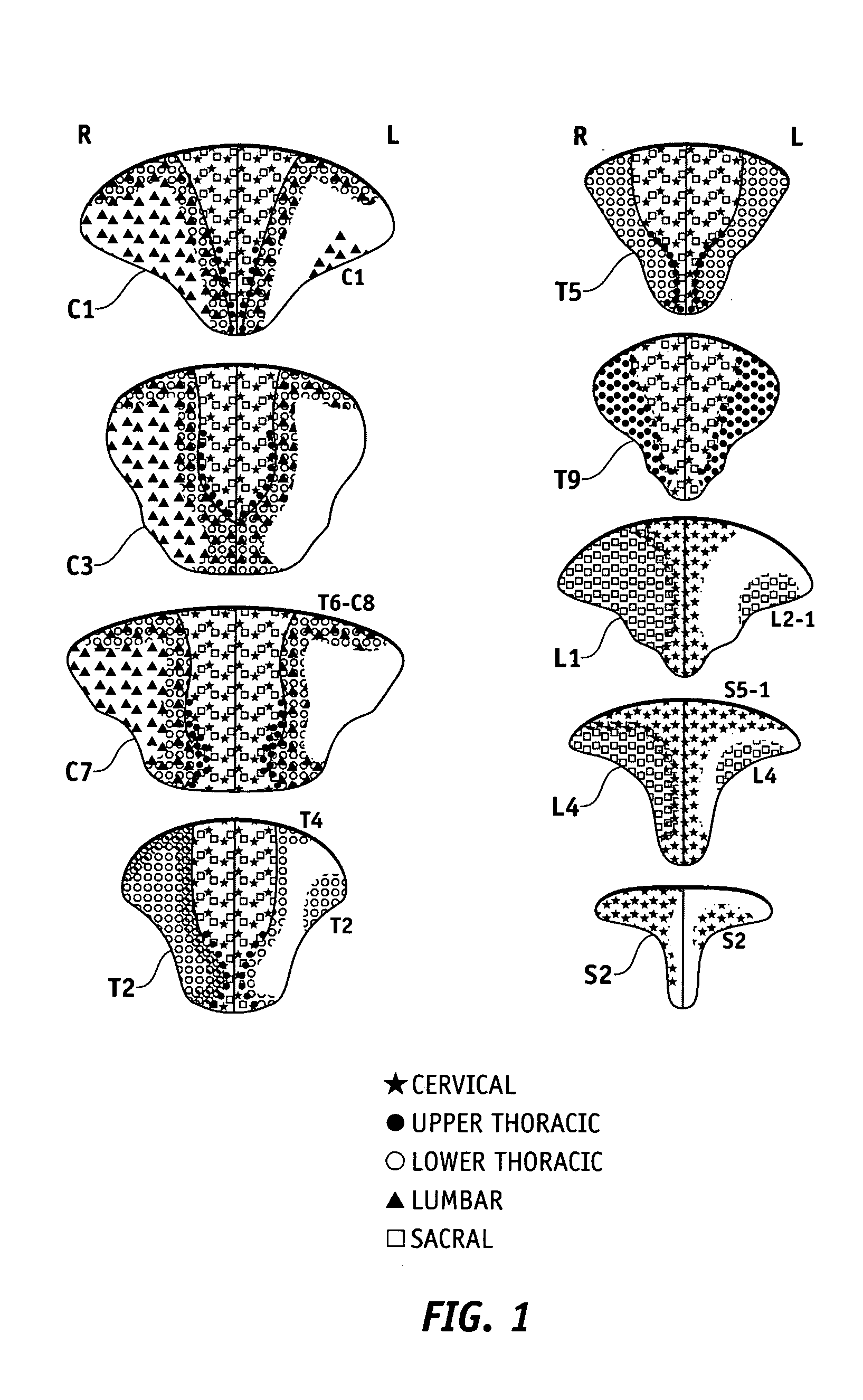
Sensor assembly for monitoring an infant brain
InactiveUS20040030258A1Risk minimizationGood flexibilityElectroencephalographyDiagnostics using lightNeuronal swellingTreatment effect
A flexible, conformable, sensor assembly is provided, including an electrode array especially adapted for stable, long-term recording of EEG signals from a pre-term or neonatal infant in intensive care. A kit or sterile pack includes guidance for placement of the electrodes over a designated area of the infant's brain, an area likely to be injured. The sensor assembly includes a left-side and a right-side flexible strip bearing at least electrodes and optional temperature, motion, and optical sensors provide for the monitoring of an extended range of parameters including aspects of cerebral perfusion and metabolism. Optional impedance measurements provide an indication of neuronal swelling. Stable performance over from three days to about a week is intended so that progress, effects of treatment, and outcome can be considered.
Owner:TRU TEST
Field steerable electrical stimulation paddle, lead system, and medical device incorporating the same
An implantable electrode paddle is adapted to receive an electrical signal from a medical device and generate an electrical field to stimulate selected body tissue. The paddle includes a housing including walls that define an interior space and a plurality of windows formed through at least a first one of the walls for transmitting the electrical field to the body tissue, an electrode array including a plurality of electrode groups, each electrode group including at least two electrodes individually secured in a respective window and spaced between about 0.1 mm and about 10 mm apart, and a plurality of wires, each of the wires being coupled to a respective electrode and routed within the interior space to receive the electrical signal. A lead assembly and an implantable medical device can include the paddle.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com