Patents
Literature
2160results about "Endoradiosondes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
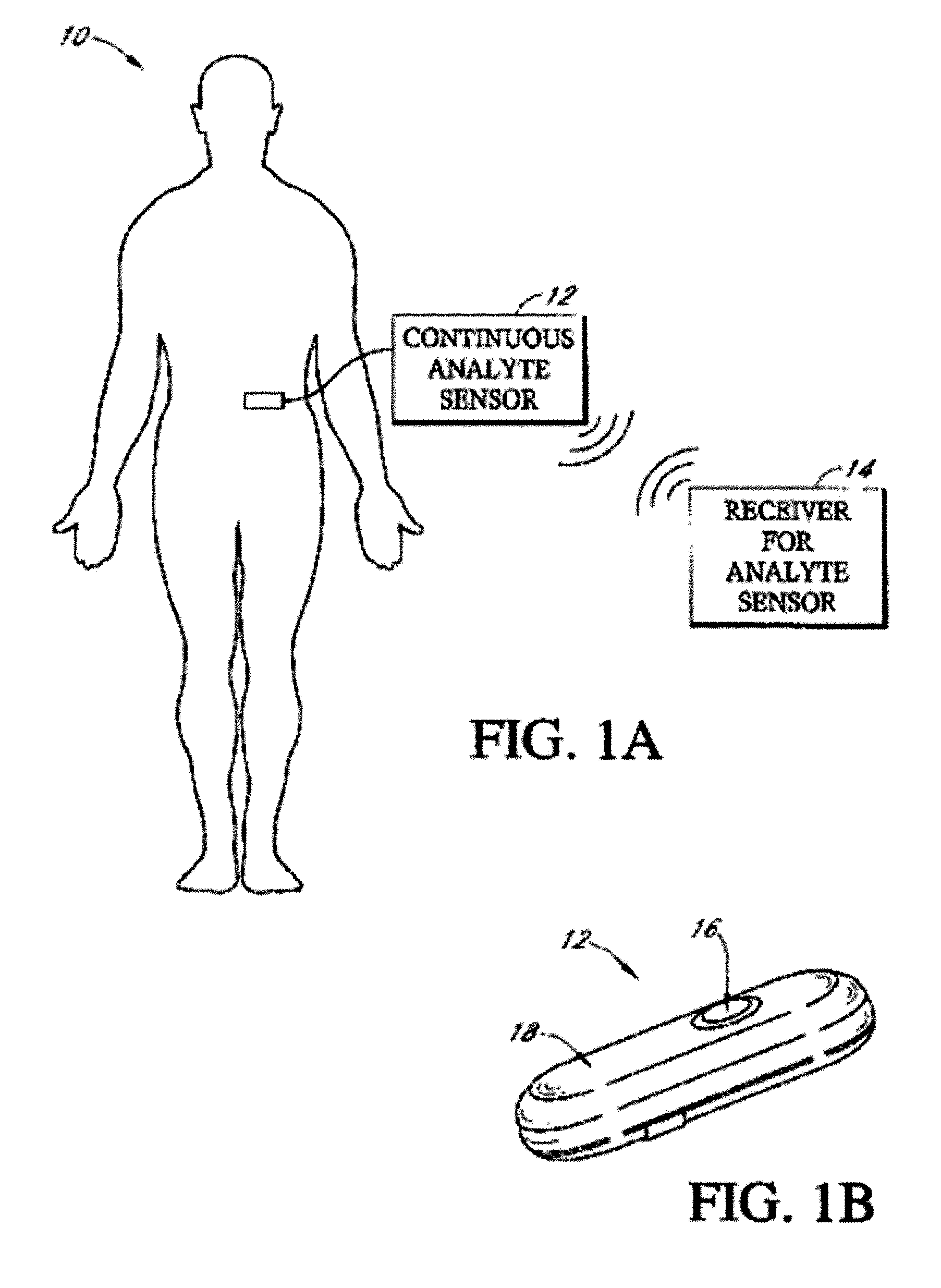
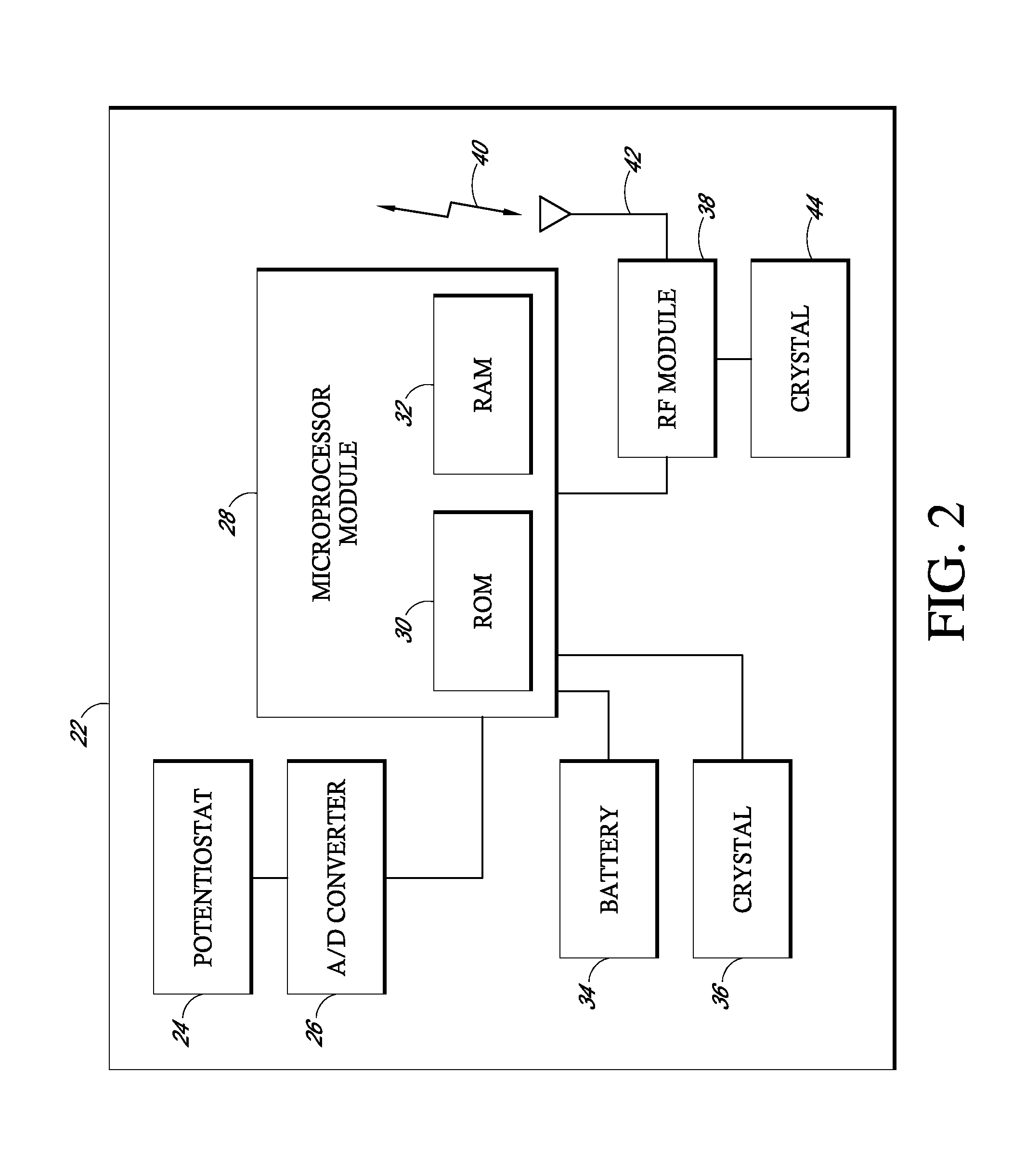
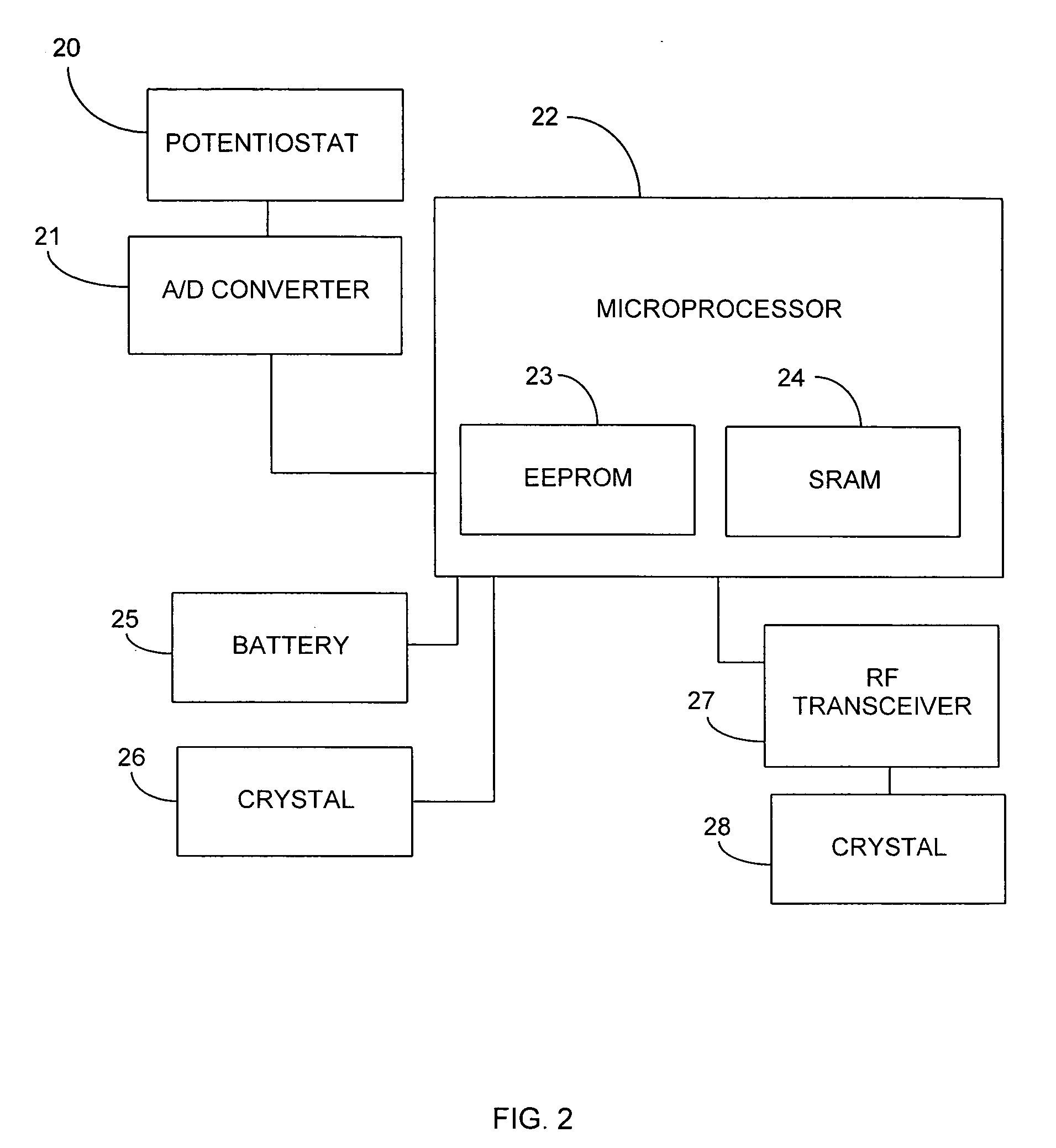
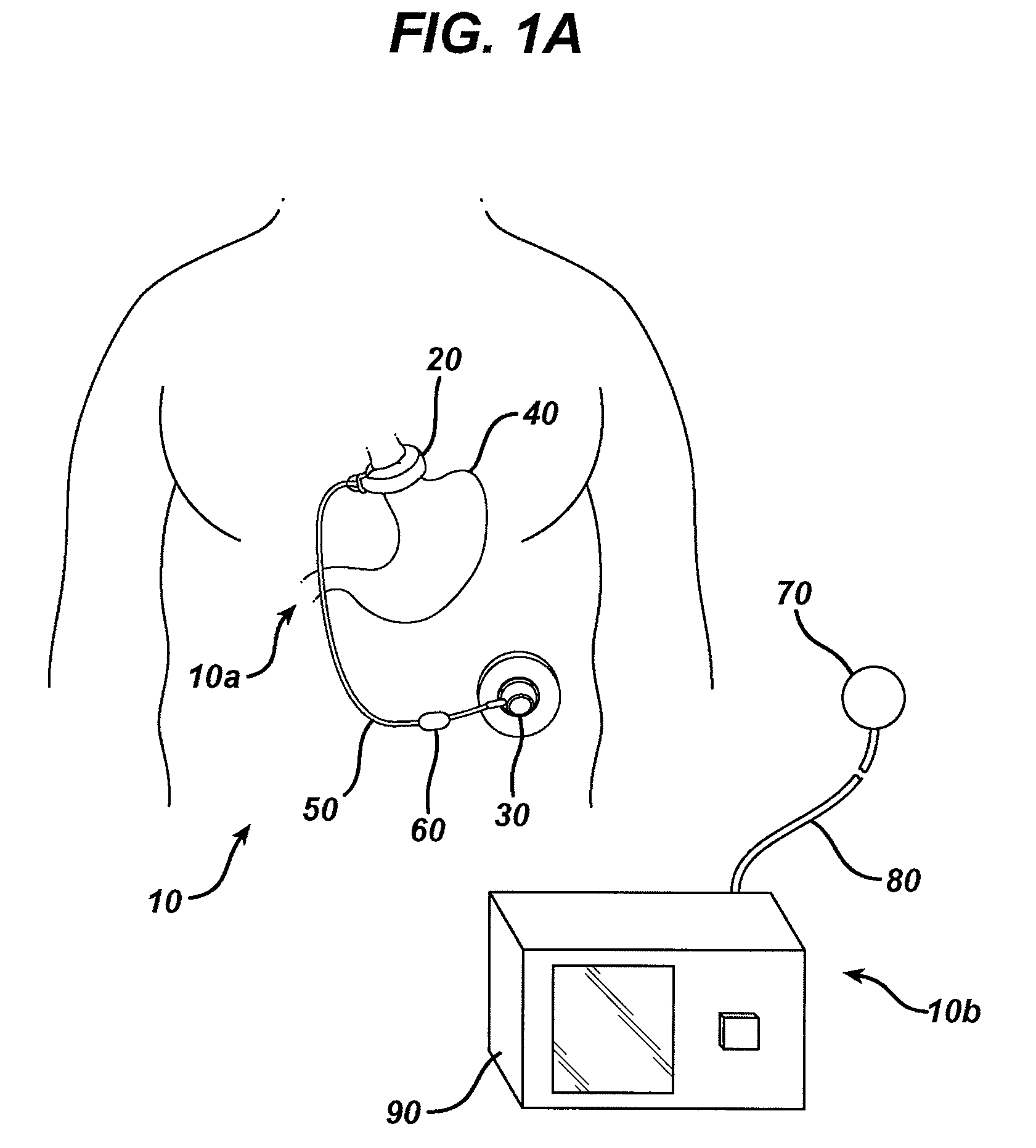
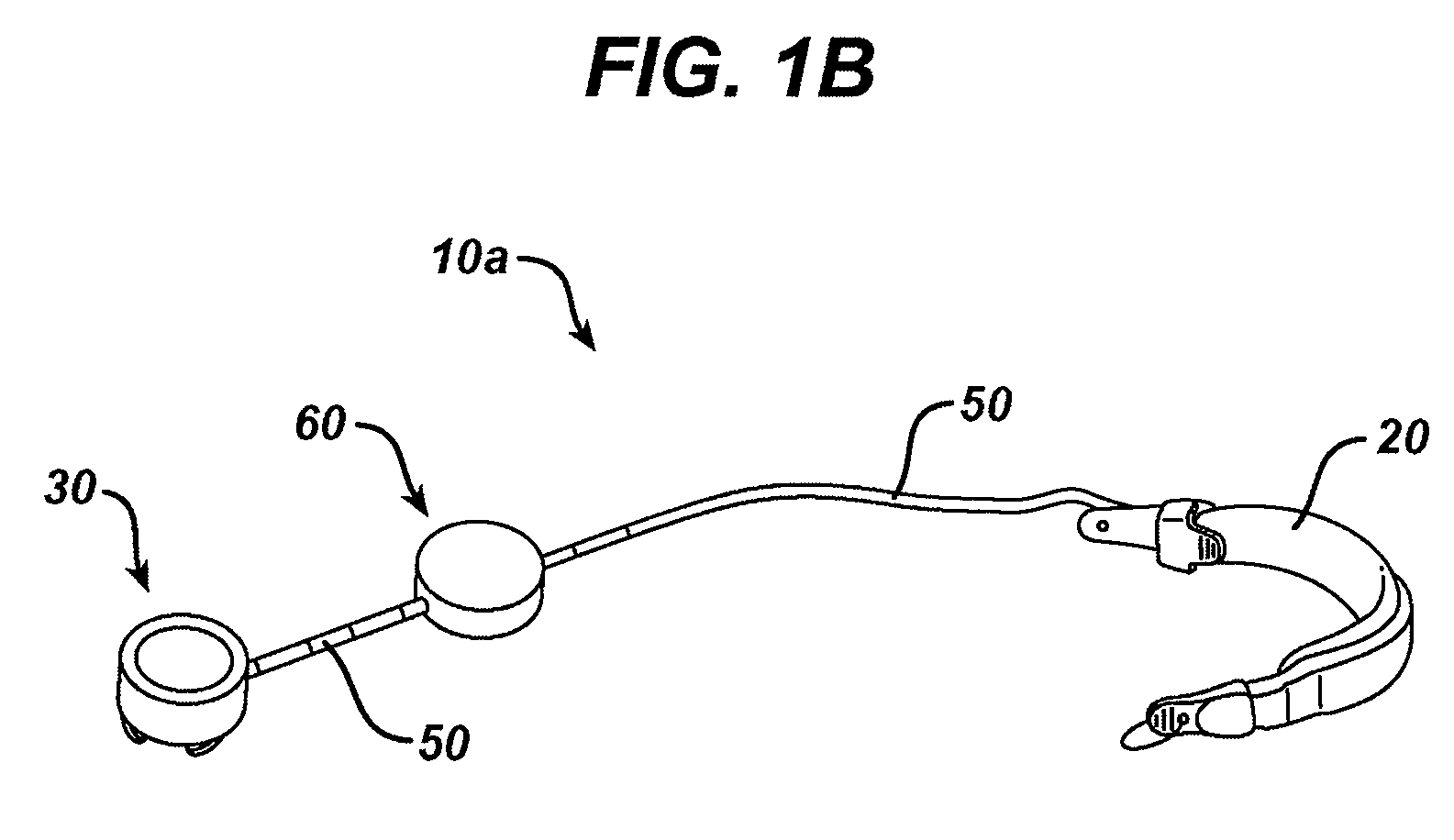
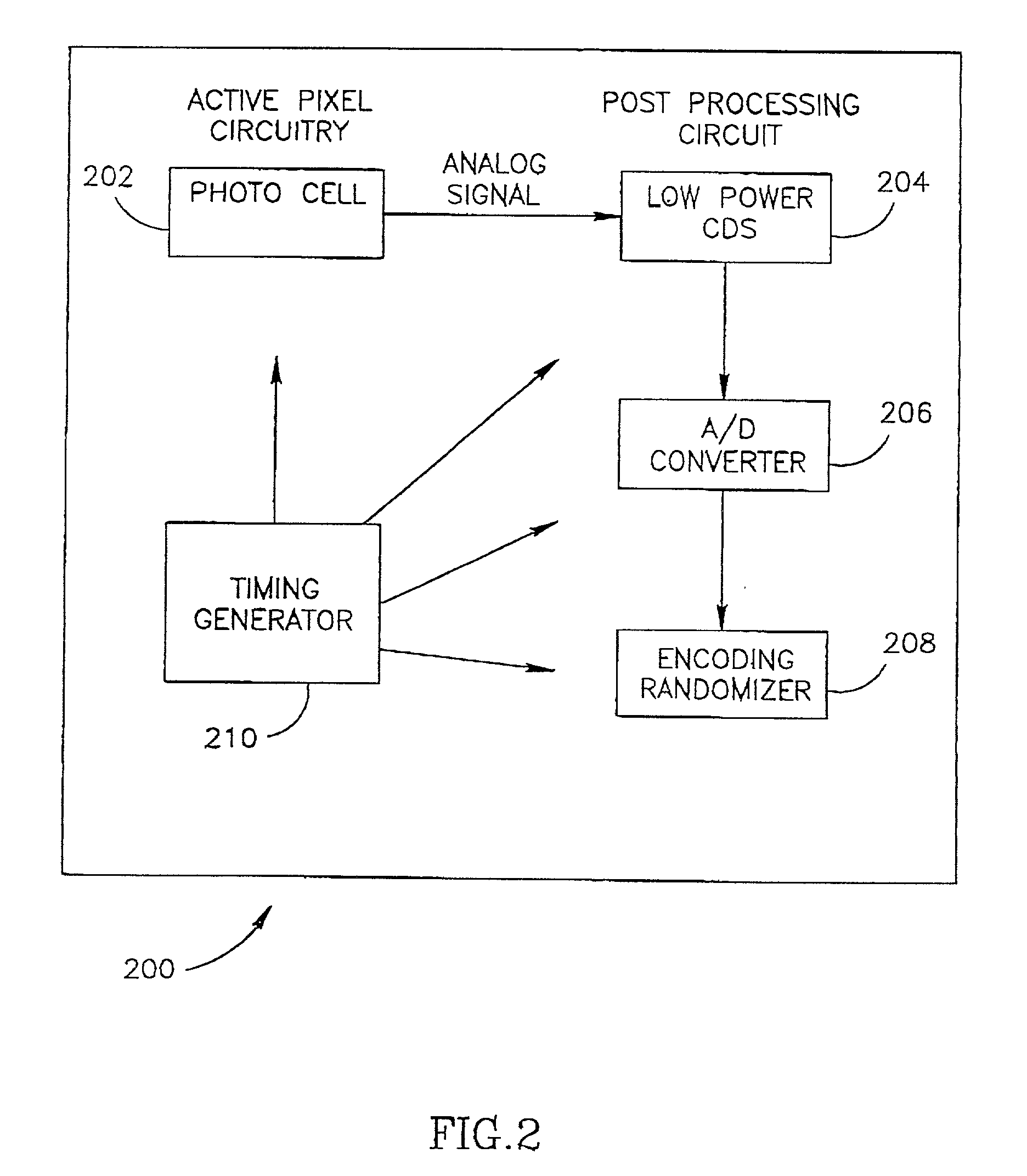
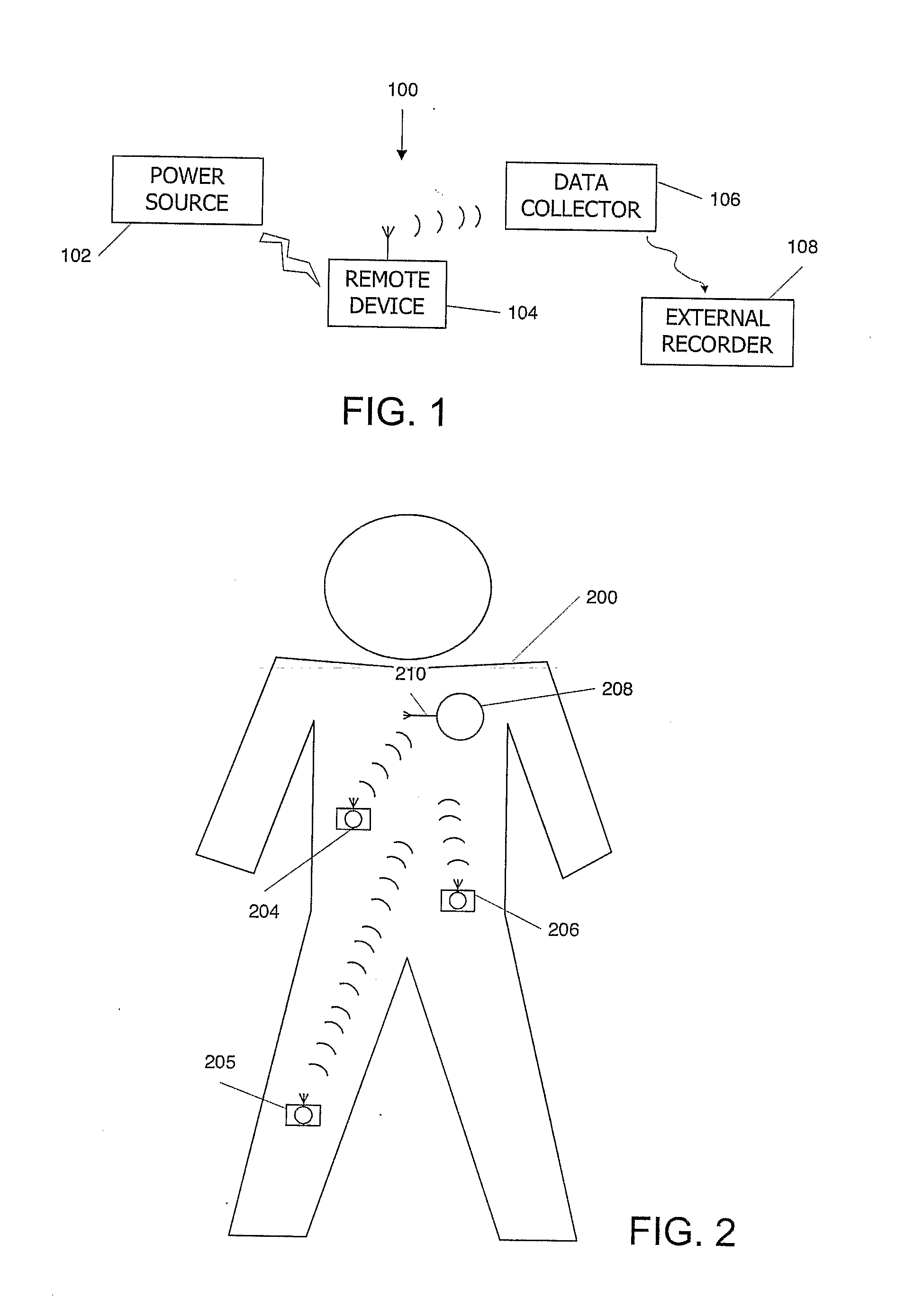
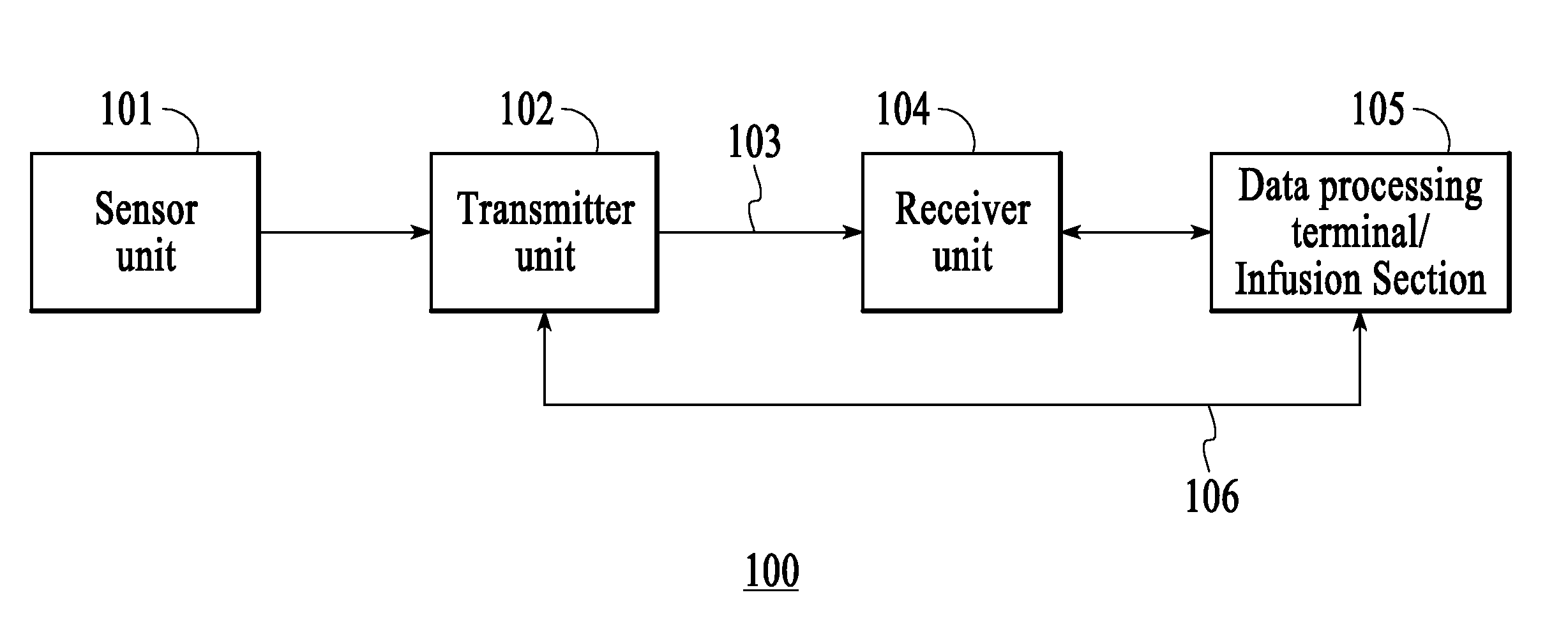
Digital wireless position sensor
ActiveUS7397364B2Fast chargingImprove signal-to-noise ratioElectric signal transmission systemsMagnetic measurementsVoltage dropEngineering
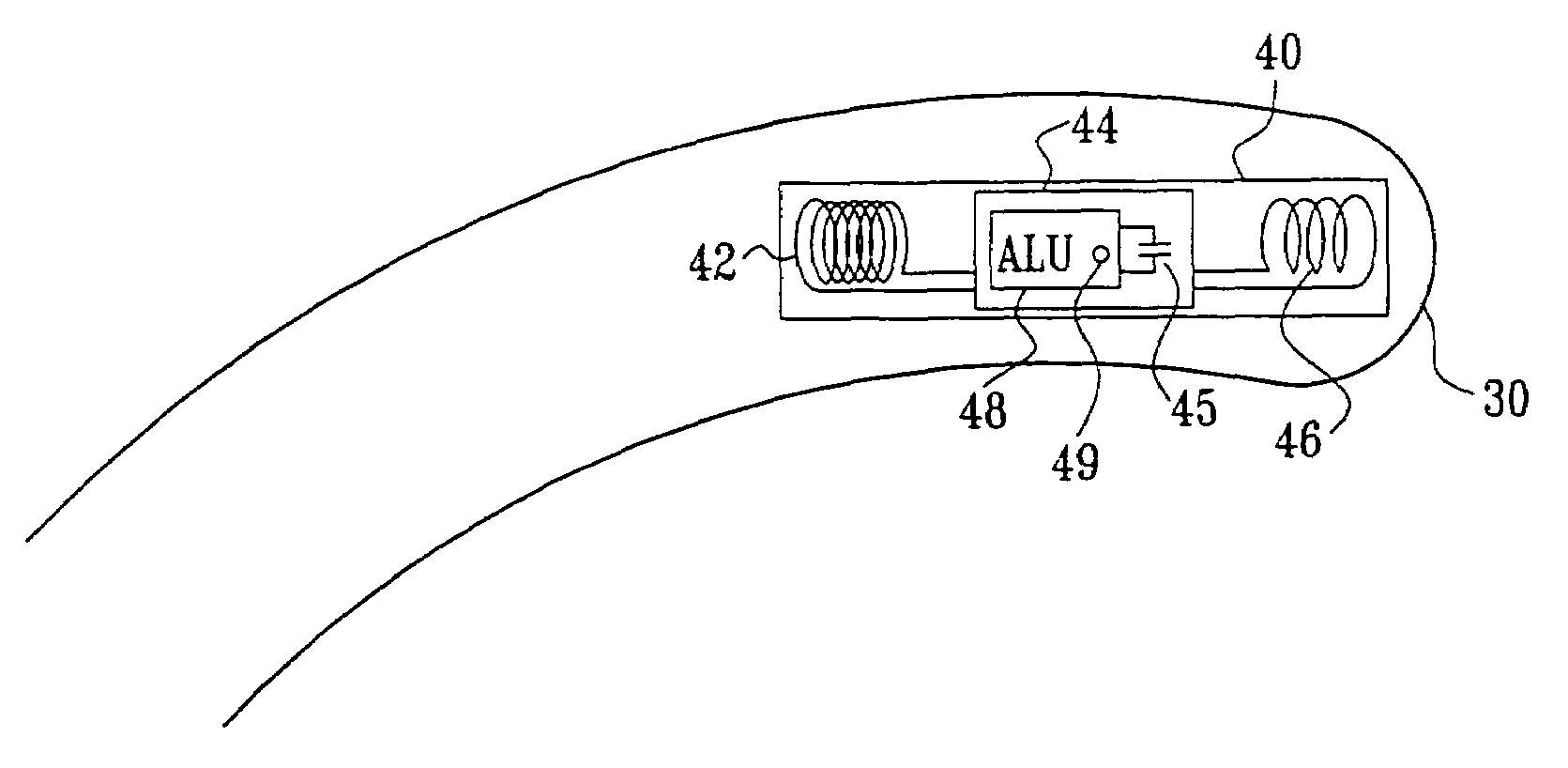
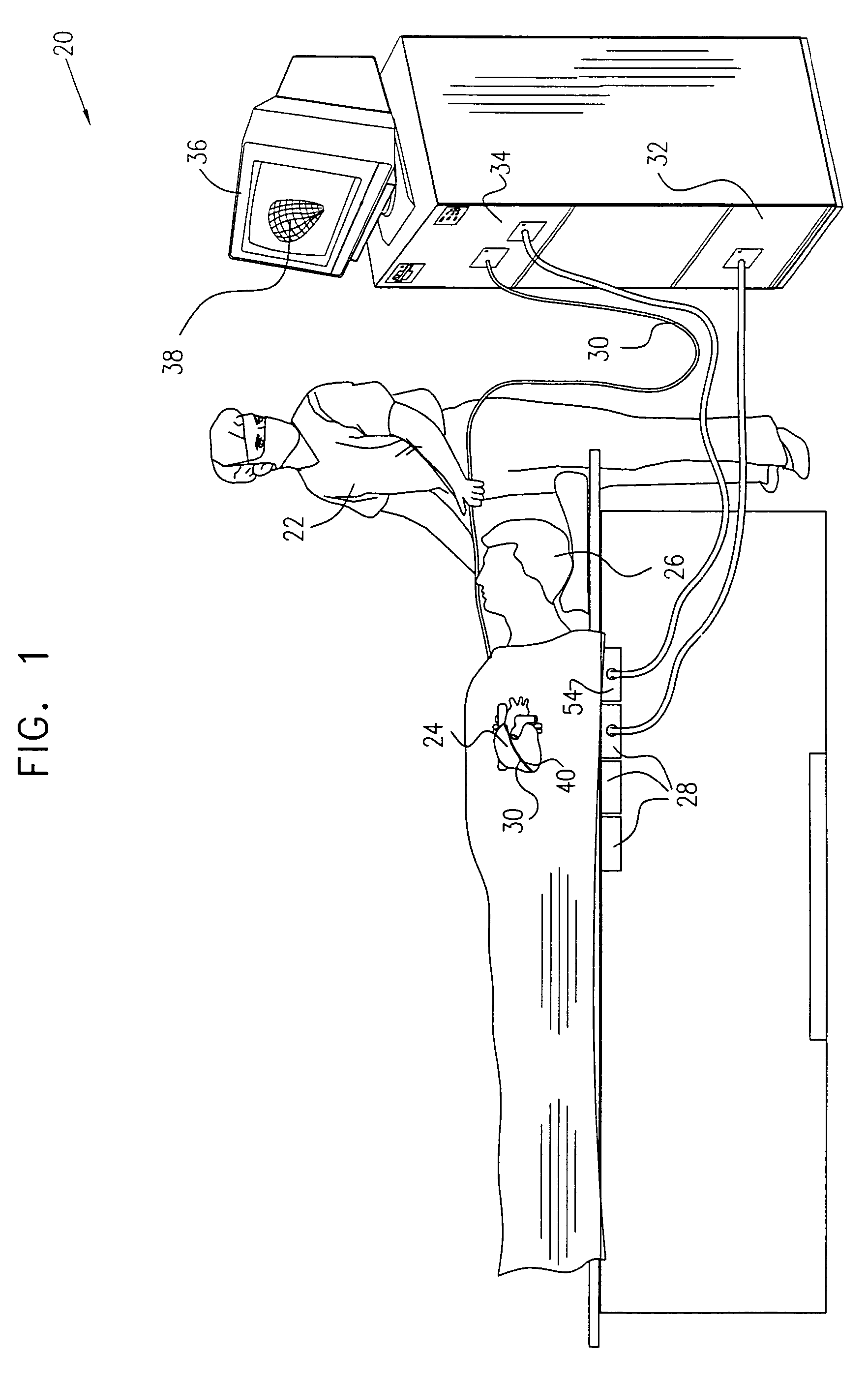
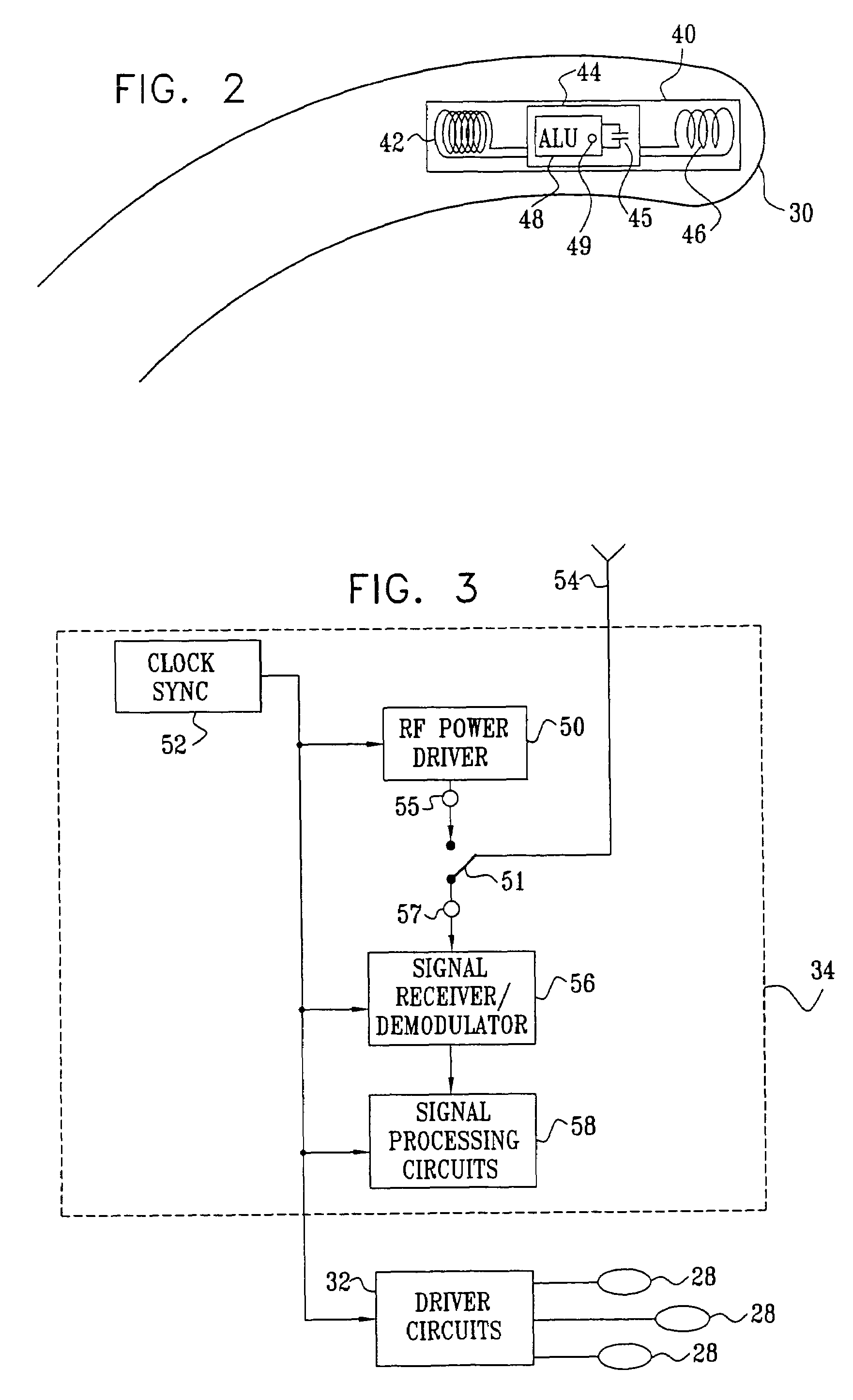
A method is provided for tracking an object, including positioning a radio frequency (RF) driver to radiate an RF driving field toward the object, and fixing to the object a wireless transponder that includes a power coil and at least one sensor coil. The method also includes receiving the RF driving field using the power coil and storing electrical energy derived therefrom. A plurality of field generators are driven to generate electromagnetic fields at respective frequencies in a vicinity of the object that induce a voltage drop across the at least one sensor coil. A digital output signal is generated at the wireless transponder indicative of the voltage drop across the sensor coil, and the generation of the digital output signal is powered using the stored electrical energy. The digital output signal is transmitted from the wireless transponder using the power coil, and the transmission of the digital output signal is powered using the stored electrical energy. The digital output signal is received and processed to determine coordinates of the object.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
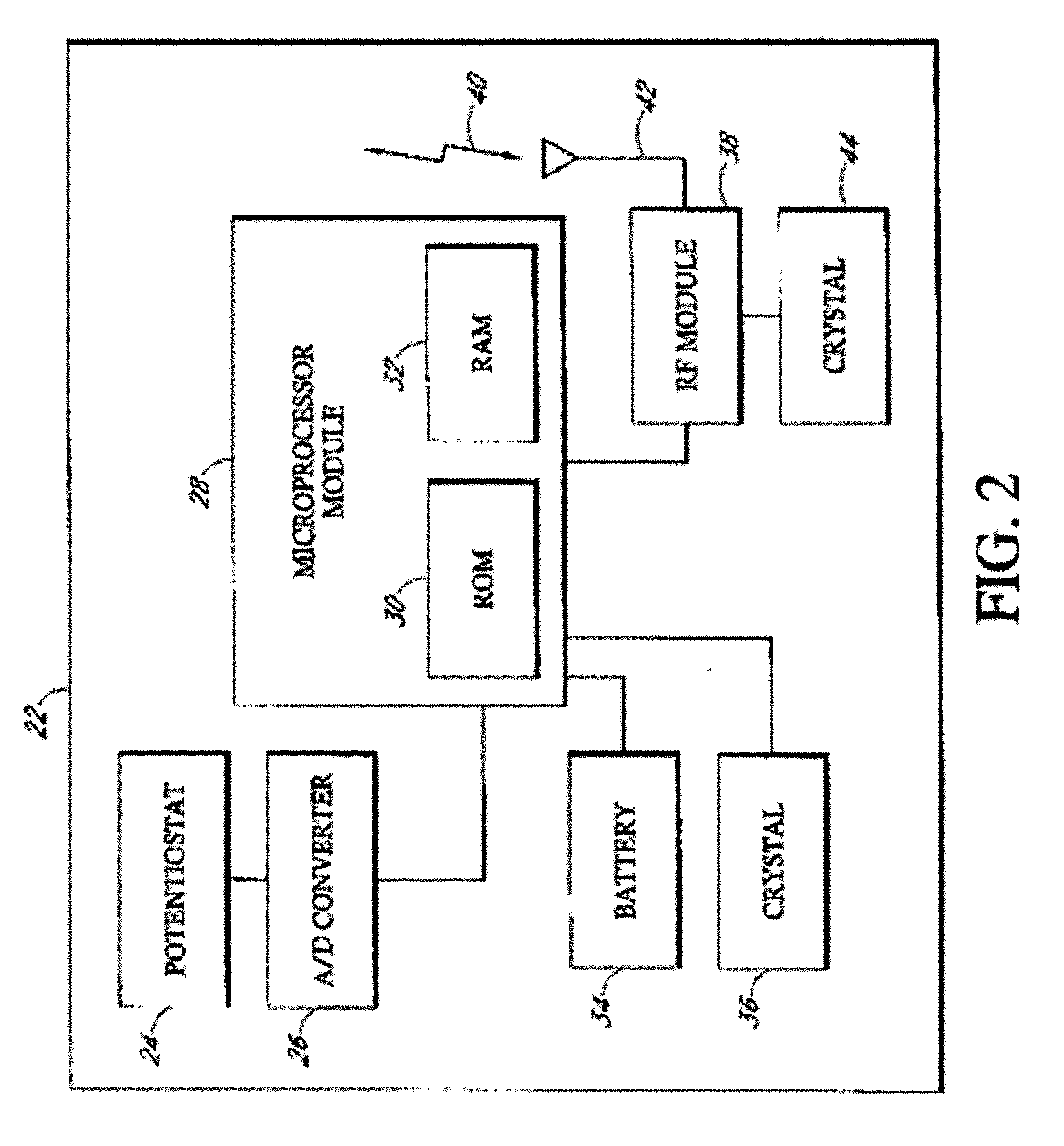
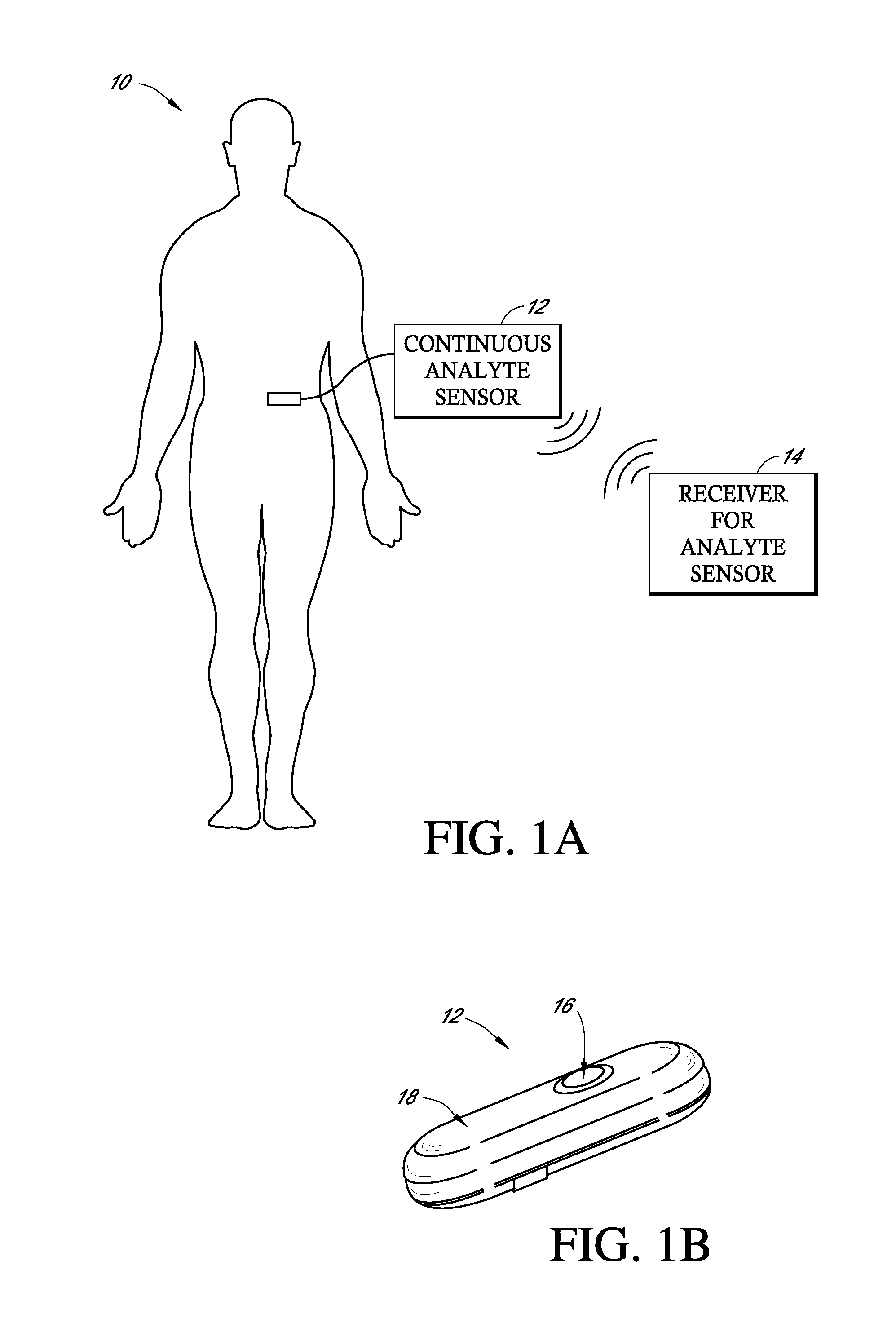
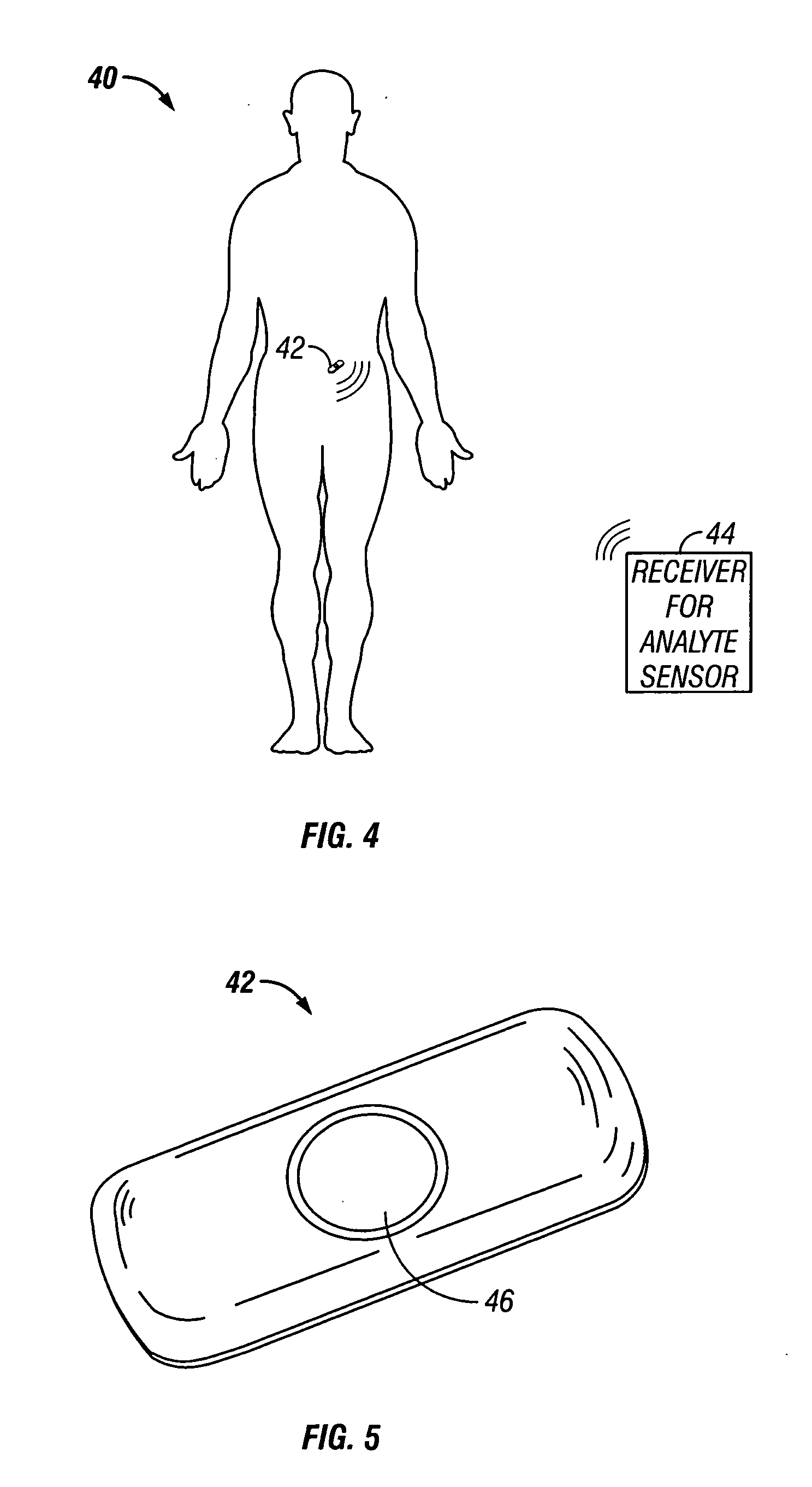
Implantable analyte sensor
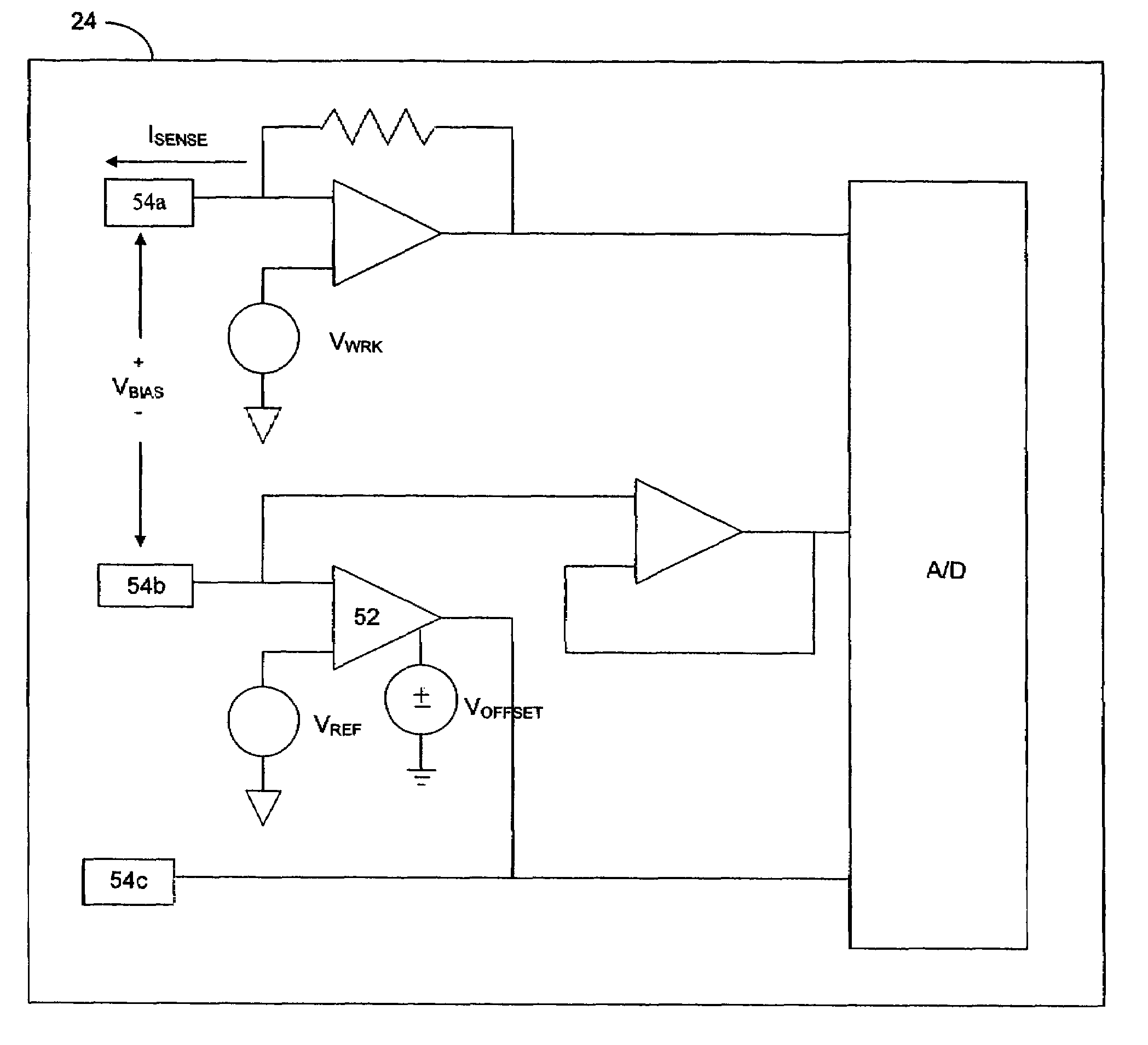
ActiveUS20050245795A1Improved patient convenienceConvenient careImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteEngineering
Abstract of the DisclosureAn implantable analyte sensor including a sensing region for measuring the analyte and a non-sensing region for immobilizing the sensor body in the host. The sensor is implanted in a precisely dimensioned pocket to stabilize the analyte sensor in vivo and enable measurement of the concentration of the analyte in the host before and after formation of a foreign body capsule around the sensor. The sensor further provides a transmitter for RF transmission through the sensor body, electronic circuitry, and a power source optimized for long-term use in the miniaturized sensor body.
Owner:DEXCOM
Implantable analyte sensor
InactiveUS20090030294A1Improve convenienceMinimize movementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteMiniaturization
An implantable analyte sensor including a sensing region for measuring the analyte and a non-sensing region for immobilizing the sensor body in the host. The sensor is implanted in a precisely dimensioned pocket to stabilize the analyte sensor in vivo and enable measurement of the concentration of the analyte in the host before and after formation of a foreign body capsule around the sensor. The sensor further provides a transmitter for RF transmission through the sensor body, electronic circuitry, and a power source optimized for long-term use in the miniaturized sensor body.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
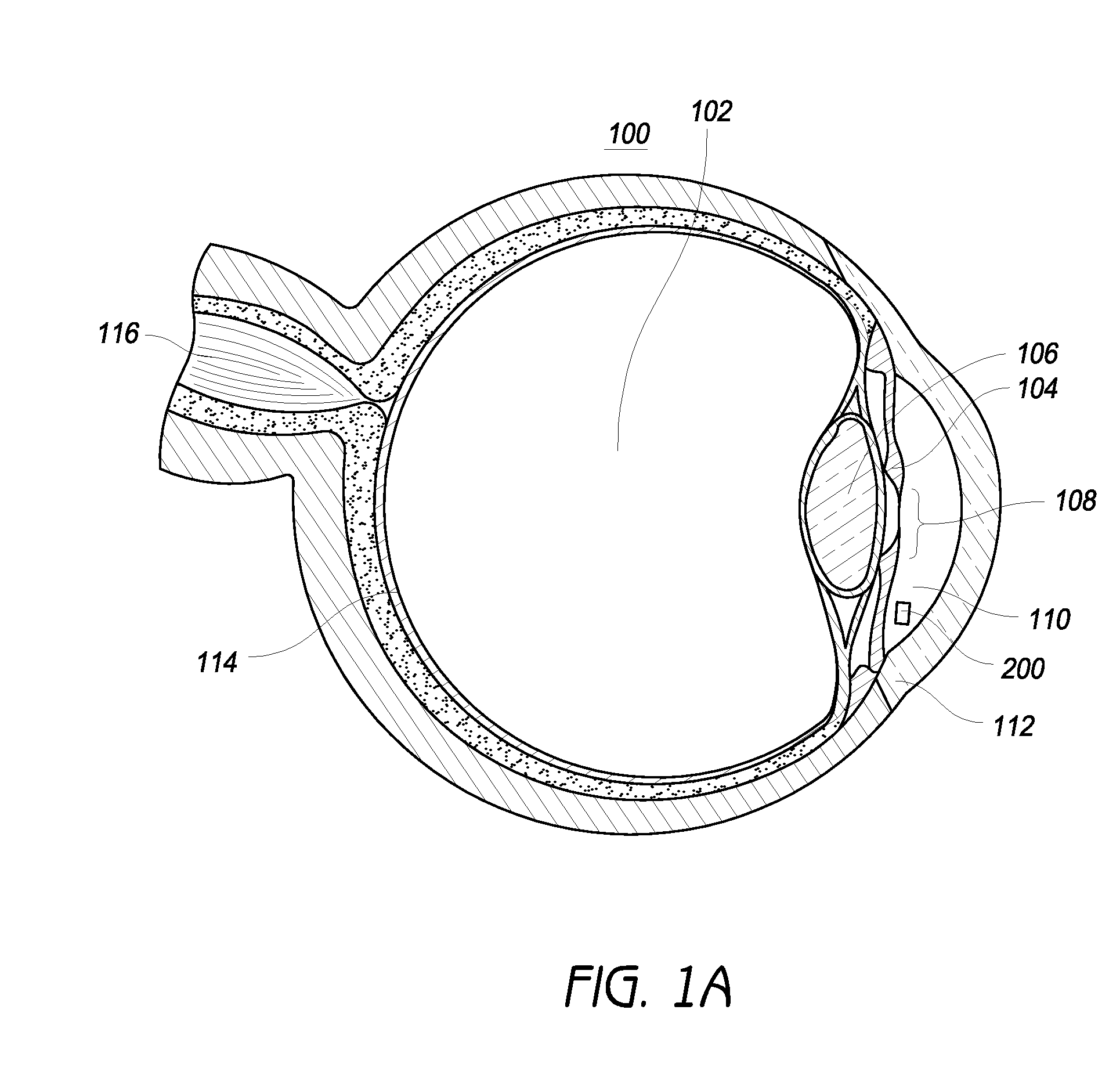
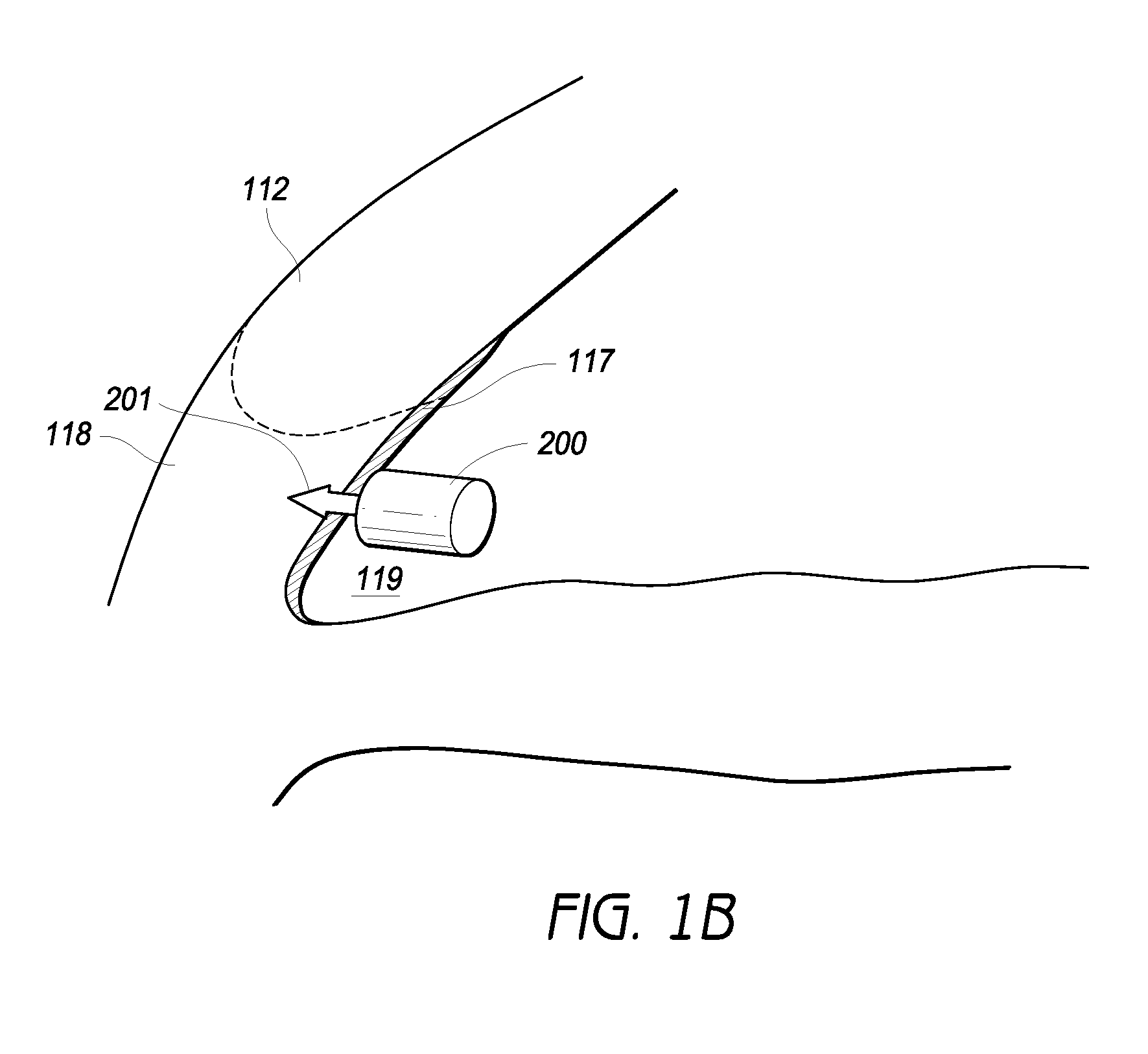
Intraocular physiological sensor
An implantable intraocular physiological sensor for measuring intraocular pressure, glucose concentration in the aqueous humor, and other physiological characteristics. The implantable intraocular physiological sensor may be at least partially powered by a fuel cell, such as an electrochemical glucose fuel cell. The implantable intraocular physiological sensor may wirelessly transmit measurements to an external device. In addition, the implantable intraocular physiological sensor may incorporate aqueous drainage and / or drug delivery features.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
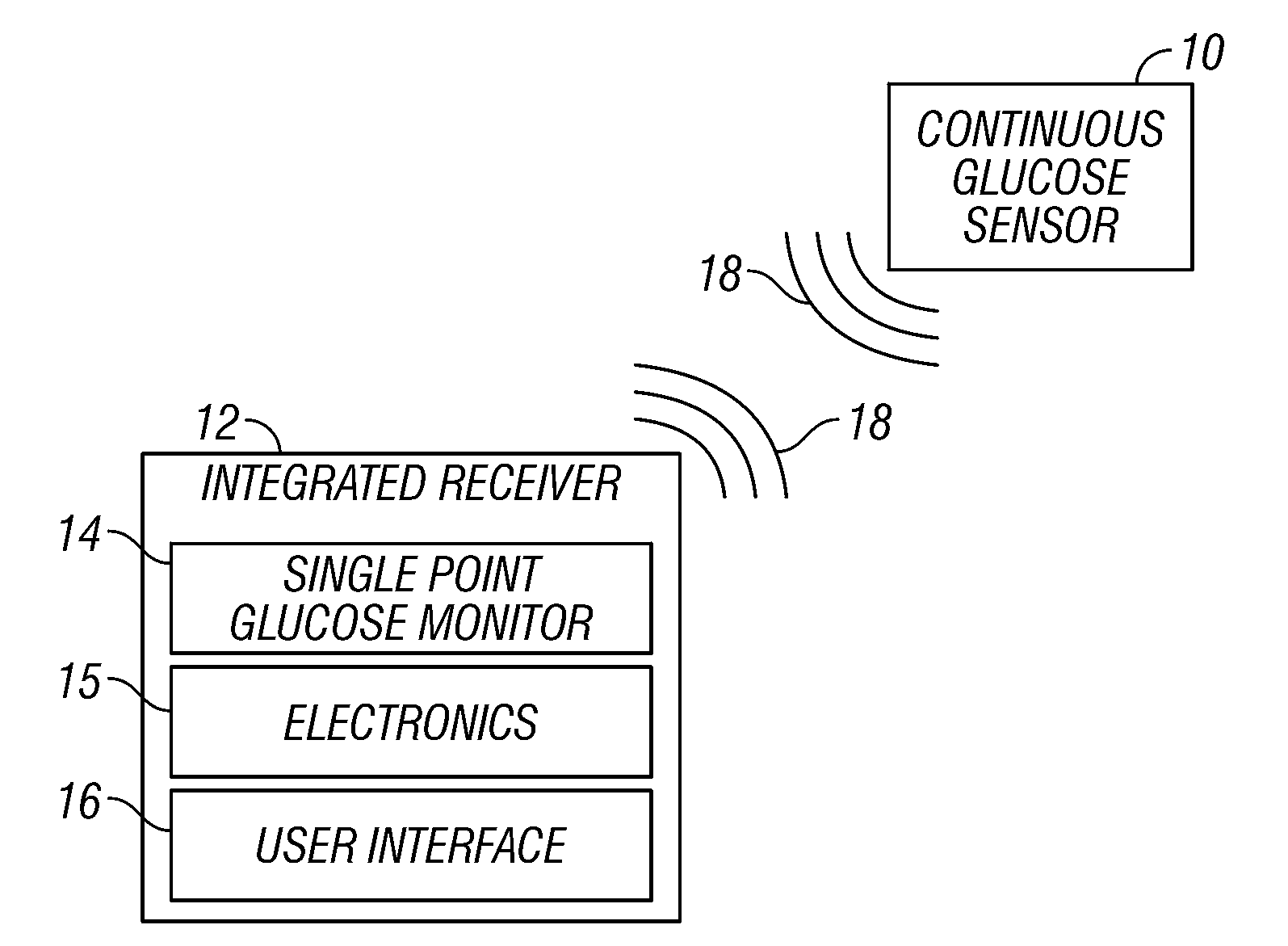
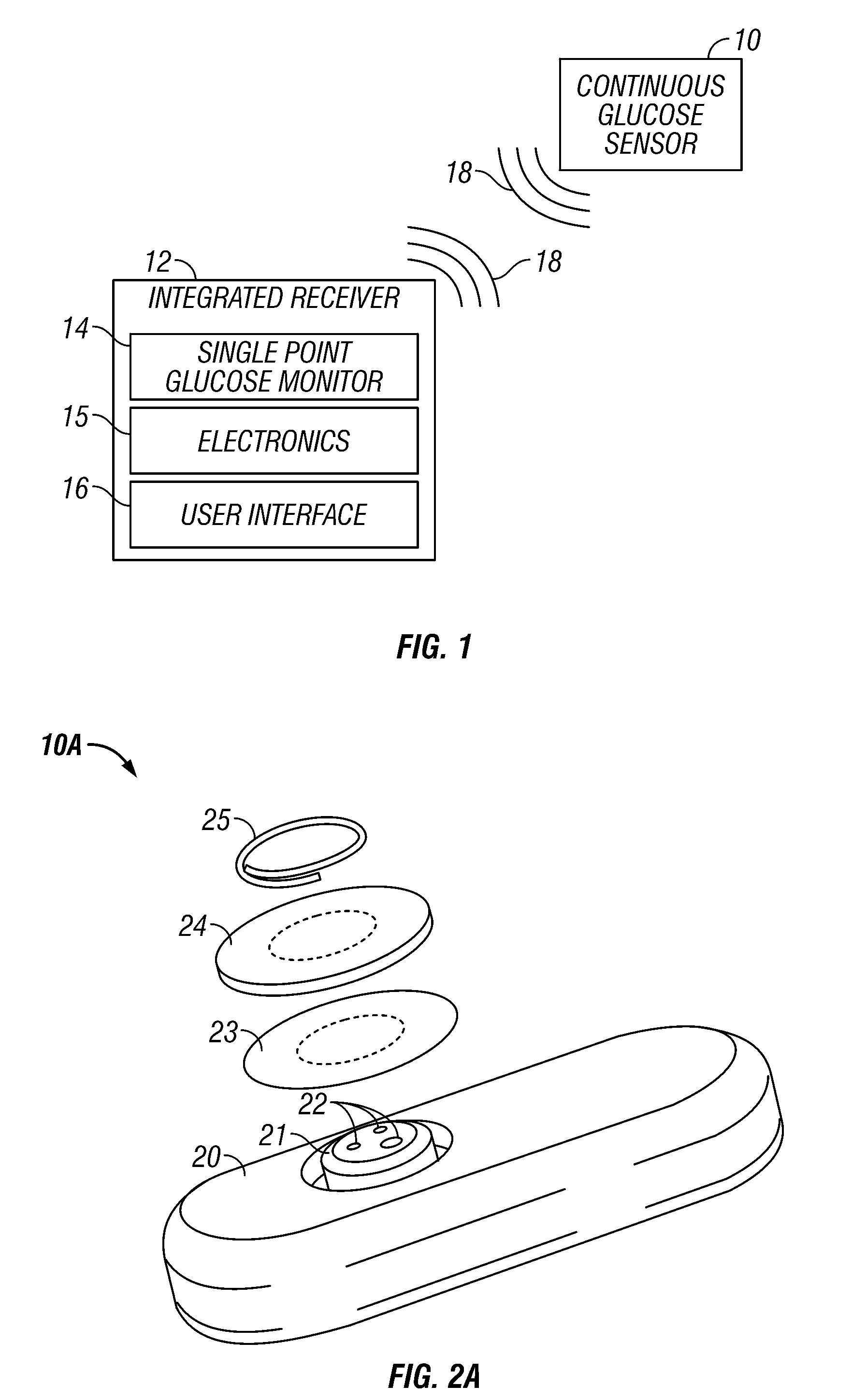
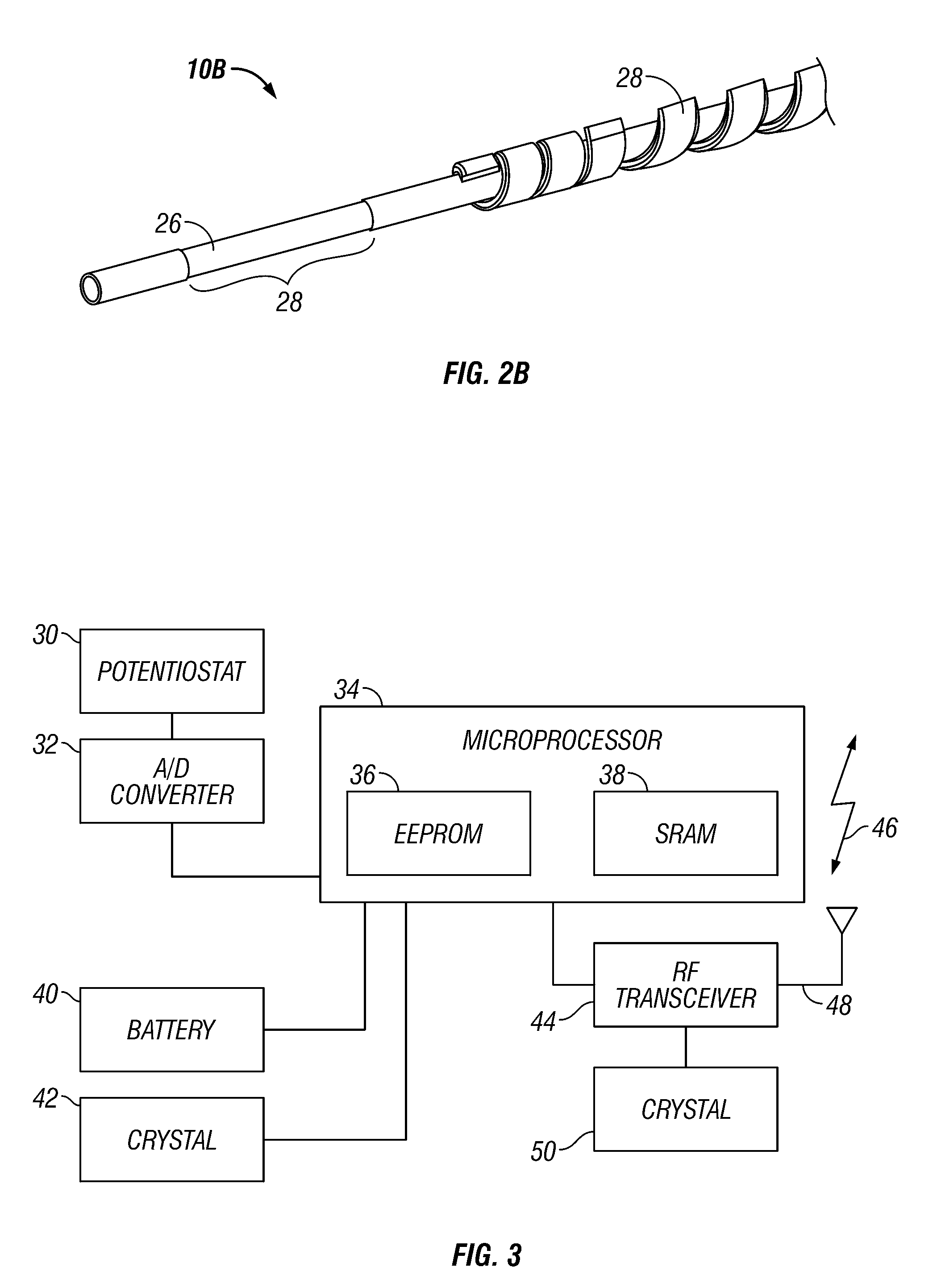
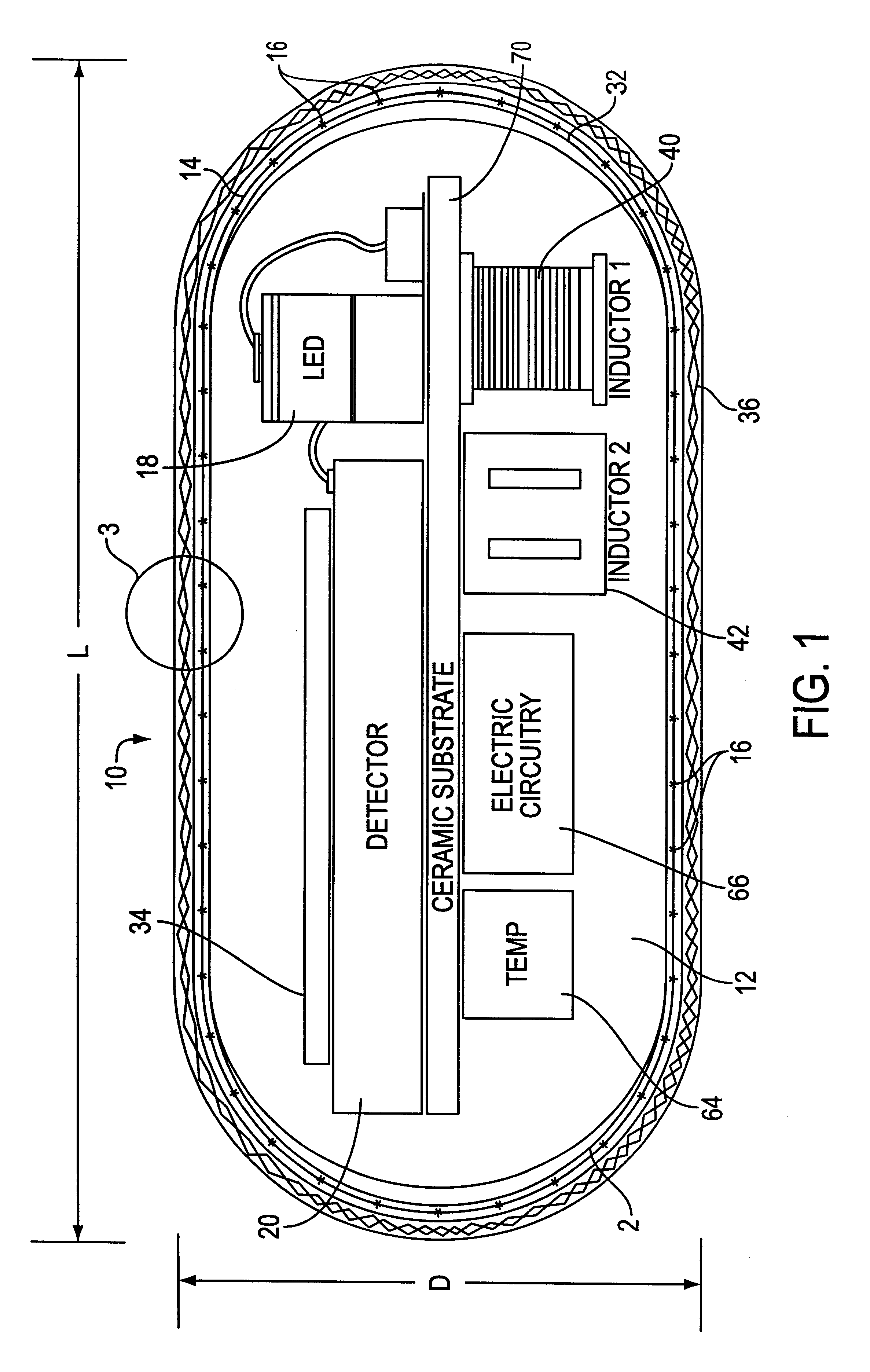
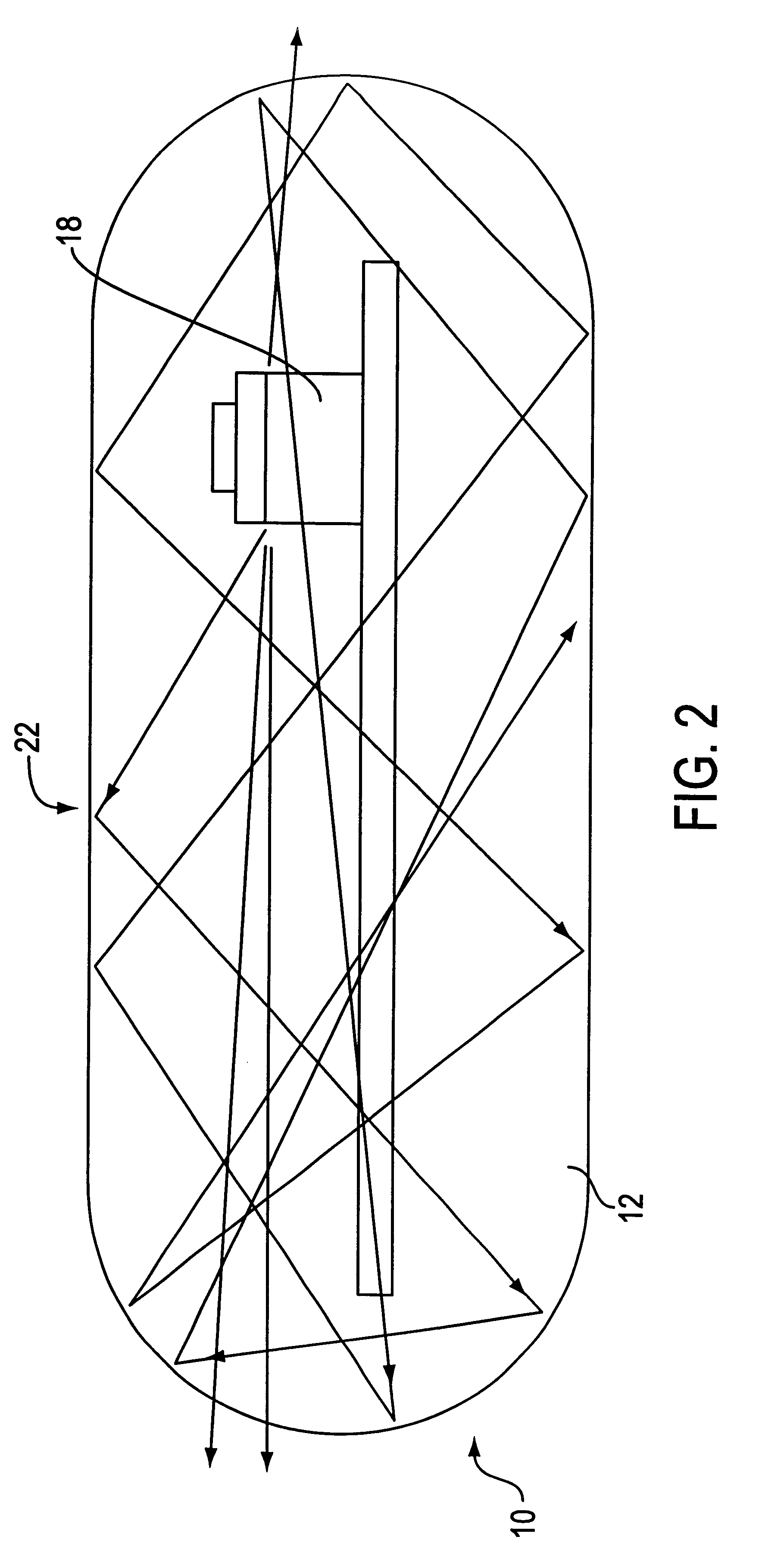
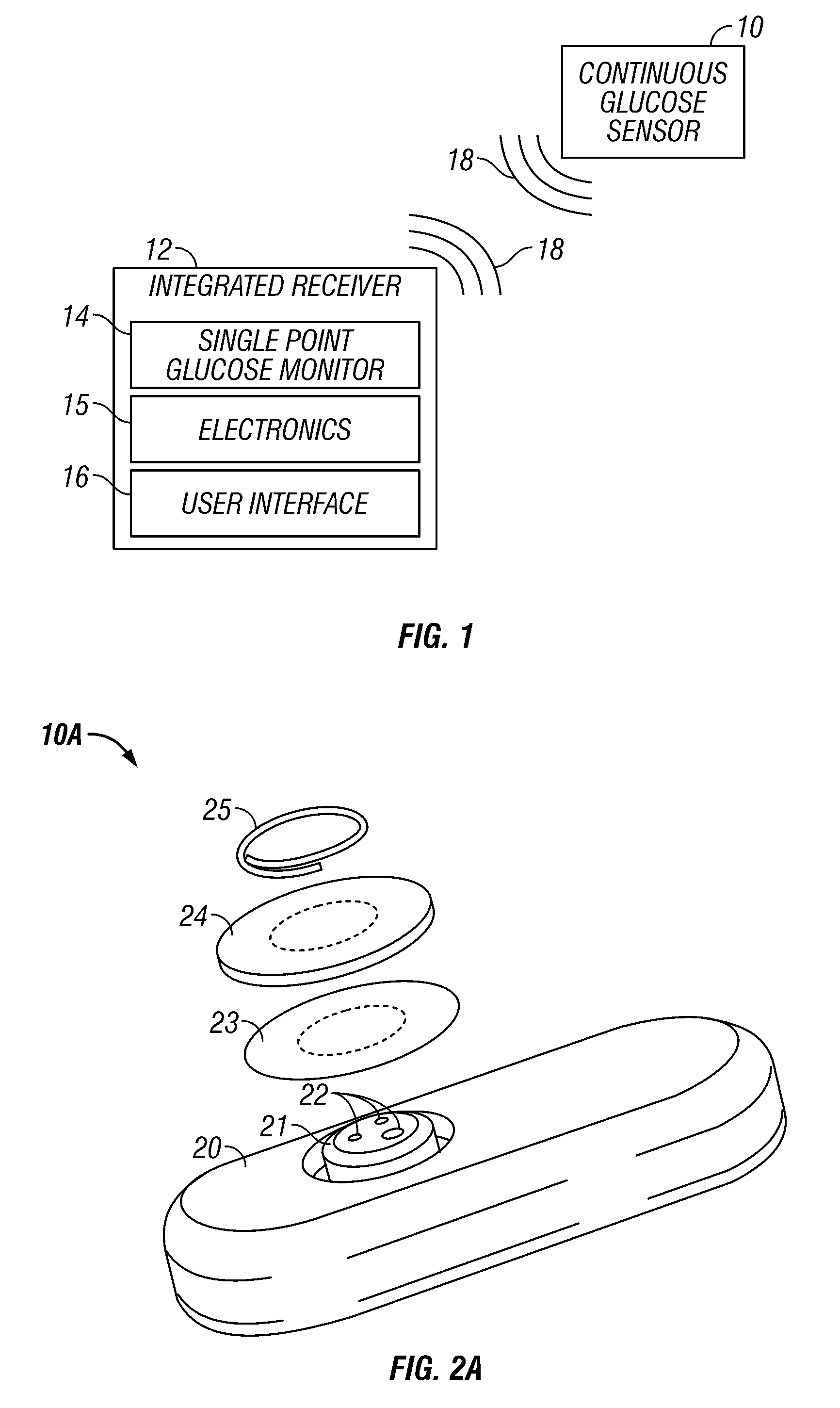
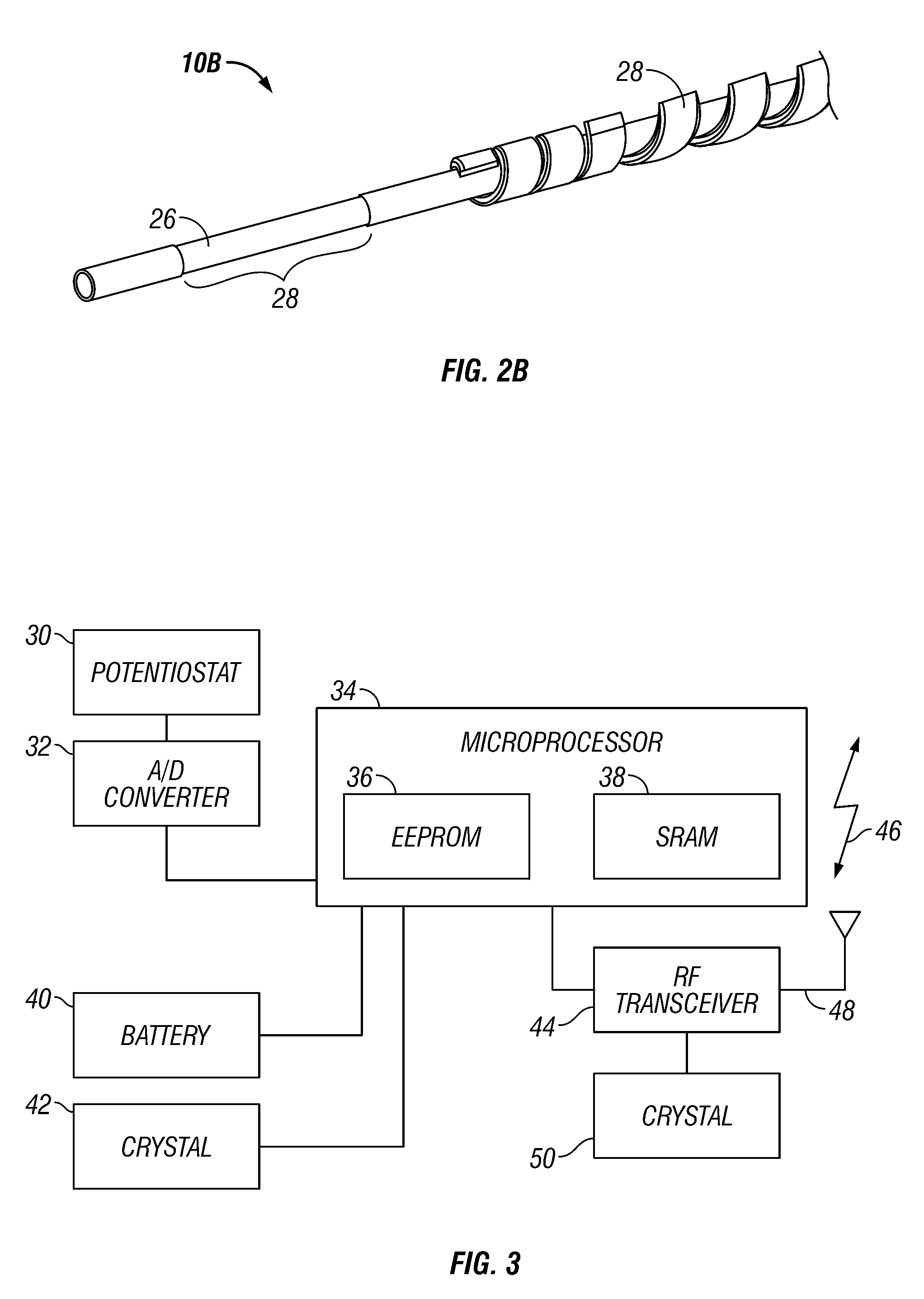
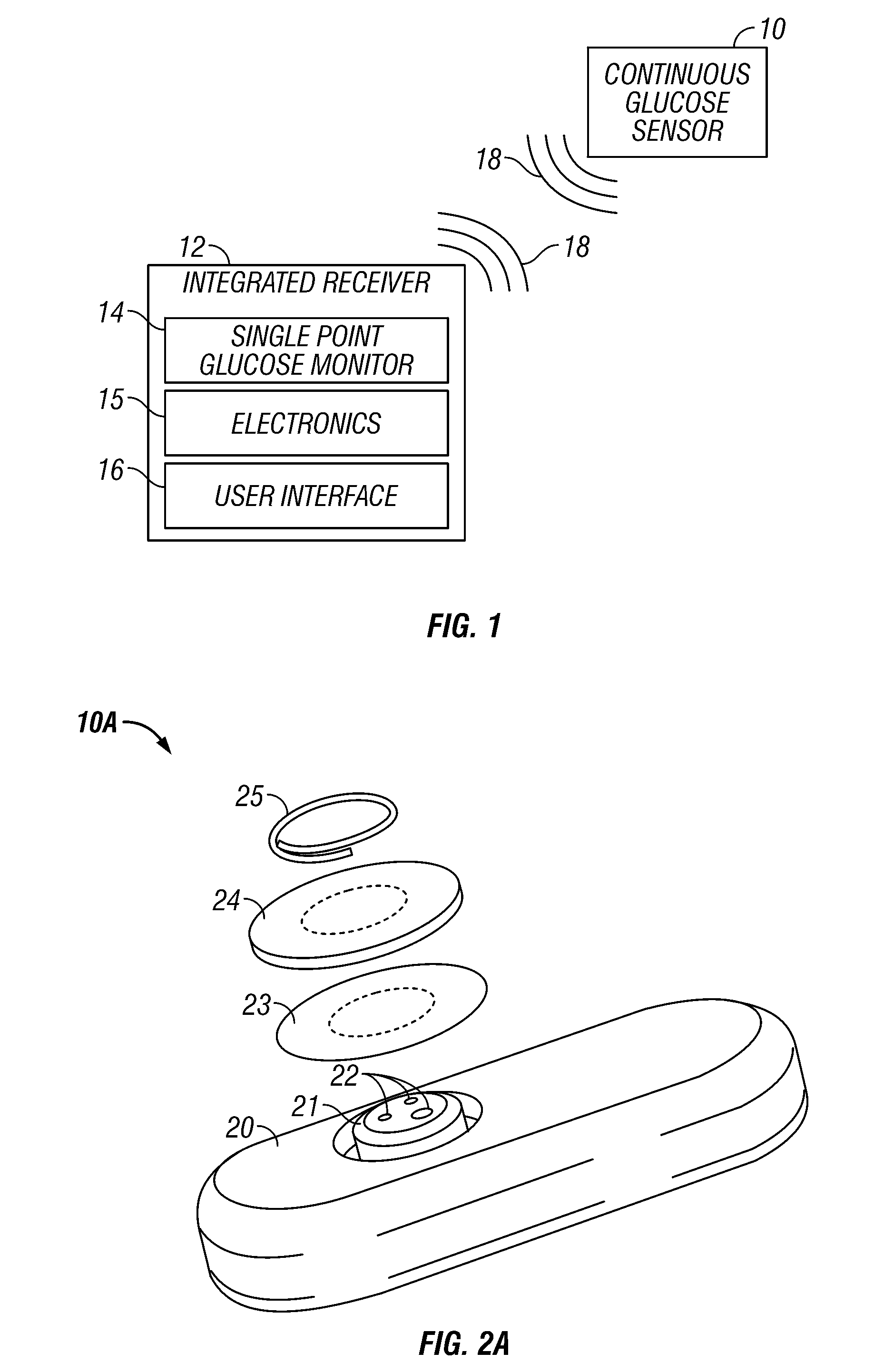
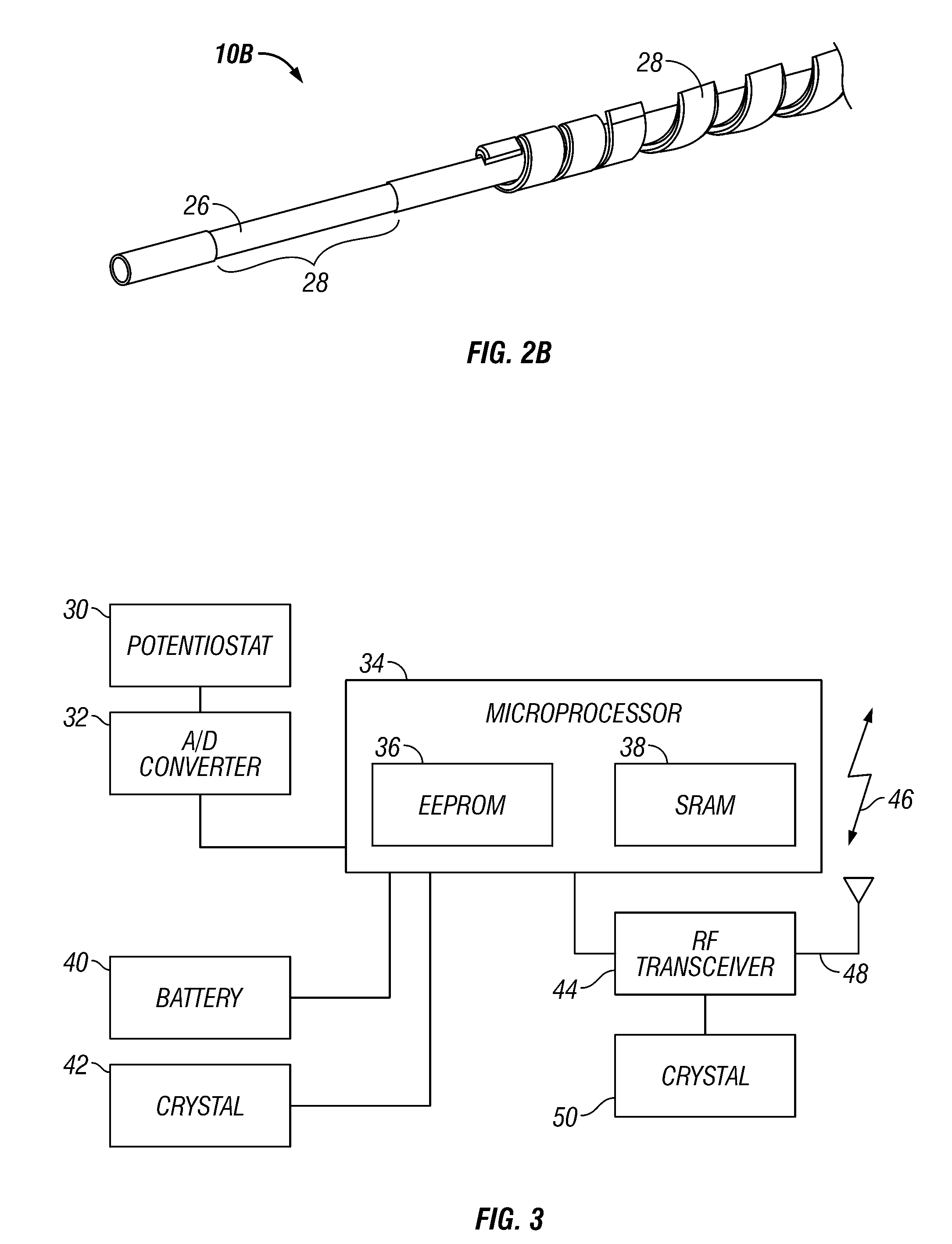
Integrated receiver for continuous analyte sensor
InactiveUS20080287765A1Simpler and few componentReduce errorsEndoradiosondesCatheterGlucose sensorsData stream
A system is provided for monitoring glucose in a host, including a continuous glucose sensor that produces a data stream indicative of a host's glucose concentration and an integrated receiver that receives the data stream from the continuous glucose sensor and calibrates the data stream using a single point glucose monitor that is integral with the integrated receiver. The integrated receiver obtains a glucose value from the single point glucose monitor, calibrates the sensor data stream received from the continuous glucose sensor, and displays one or both of the single point glucose measurement values and the calibrated continuous glucose sensor values on the user interface.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Optical-based sensing devices
InactiveUS6330464B1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSurgeryAnalyteFluorescence
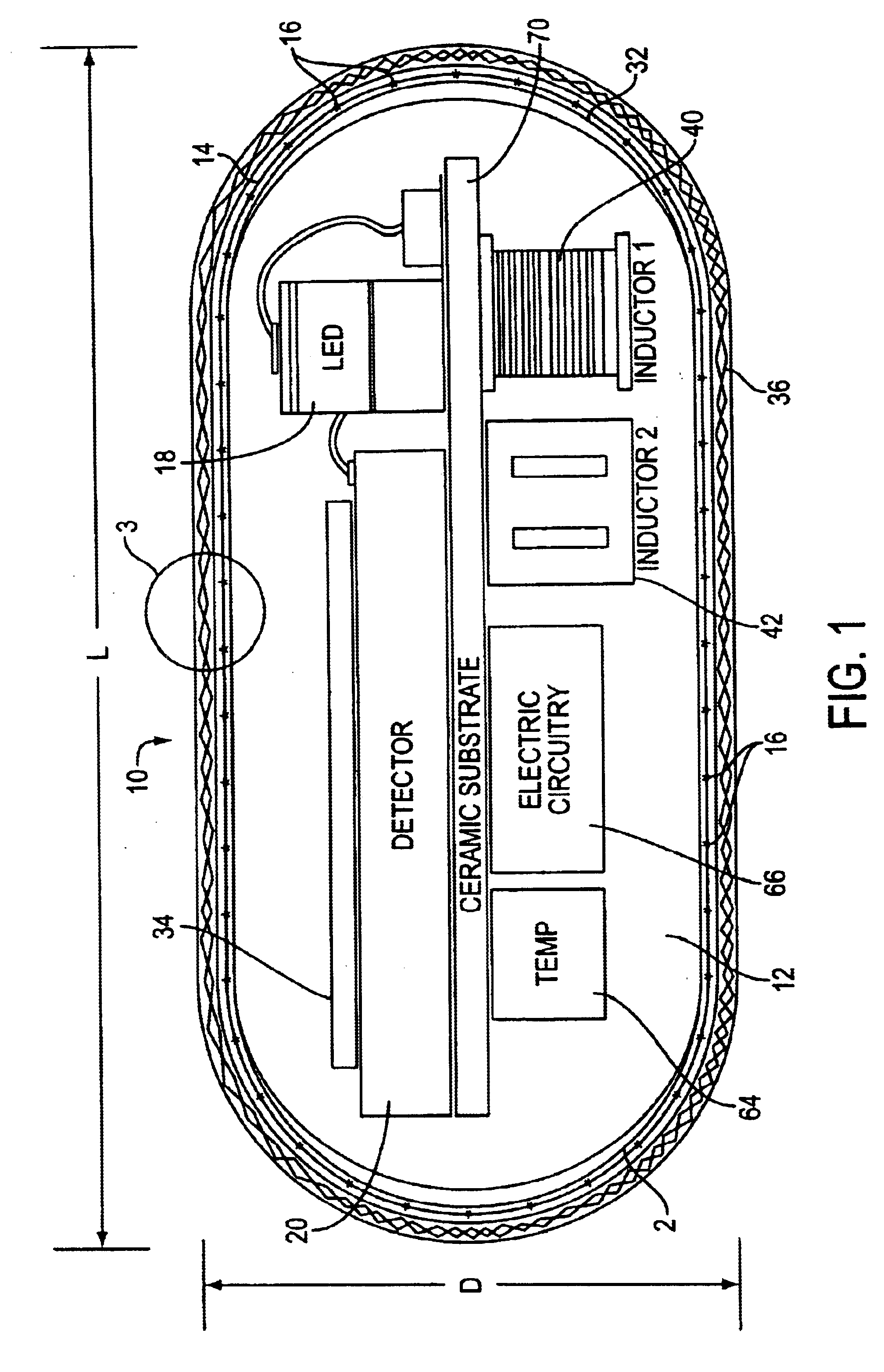
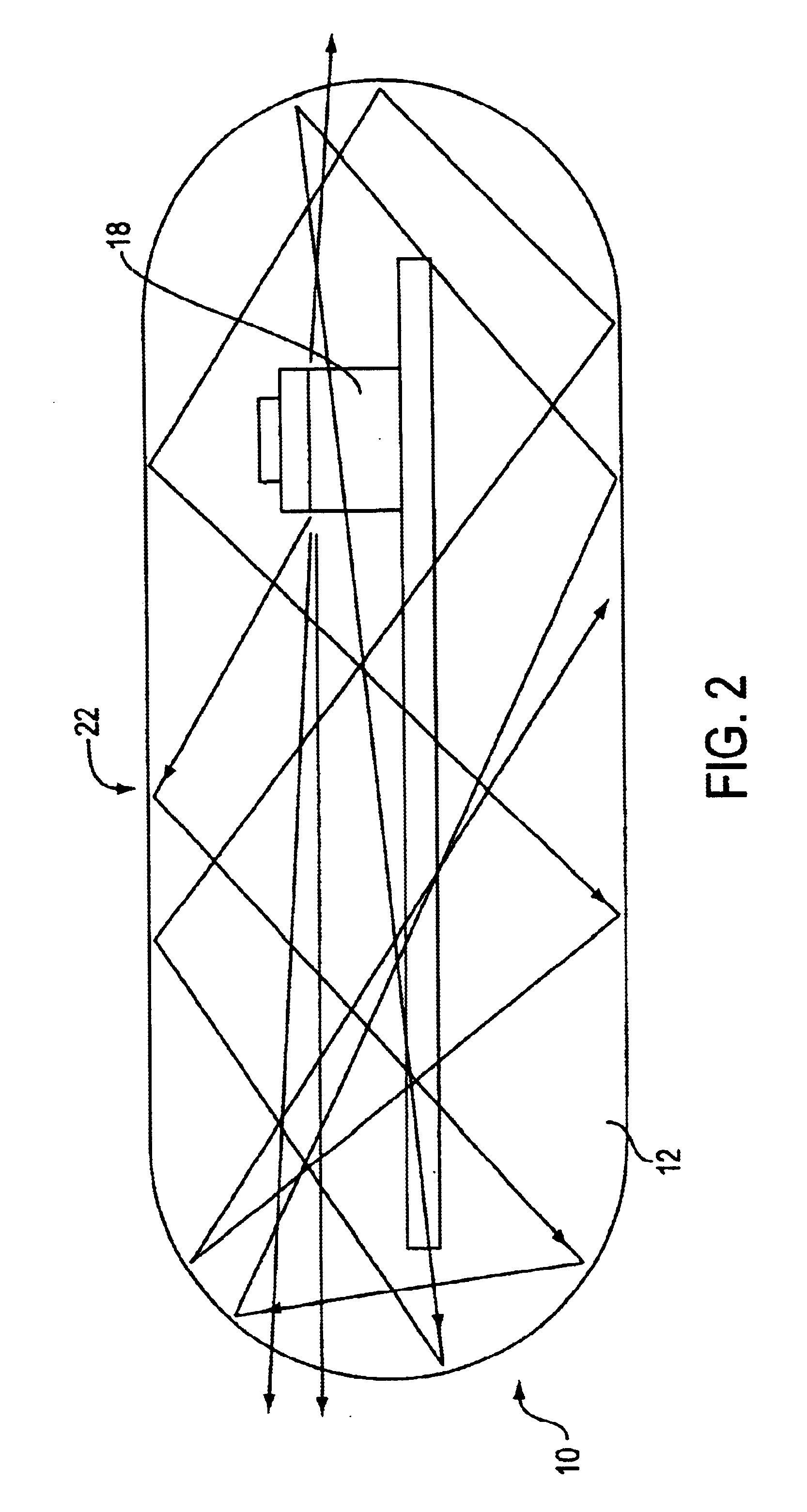
An optical-based sensor for detecting the presence or amount of an analyte using both indicator and reference channels. The sensor has a sensor body with a source of radiation embedded therein. Radiation emitted by the source interacts with indicator membrane indicator molecules proximate the surface of the body. At least one optical characteristic of these indicator molecules varies with analyte concentration. For example, the level of fluorescence of fluorescent indicator molecules or the amount of light absorbed by light-absorbing indicator molecules can vary as a function of analyte concentration. In addition, radiation emitted by the source also interacts with reference membrane indicator molecules proximate the surface of the body. Radiation (e.g., light) emitted or reflected by these indicator molecules enters and is internally reflected in the sensor body. Photosensitive elements within the sensor body generate both indicator channel and reference channel signals to provide an accurate indication of the concentration of the analyte. Preferred embodiments are totally self-contained and are sized and shaped for use in vivo in a human being. Such embodiments preferably include a power source, e.g. an inductor, which powers the source of radiation using external means, as well as a transmitter, e.g. an inductor, to transmit to external pickup means the signal representing the level of analyte.
Owner:SENSEONICS INC
Integrated receiver for continuous analyte sensor
InactiveUS20080287764A1Simpler and few componentReduce errorsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismEndoradiosondesGlucose sensorsData stream
A system is provided for monitoring glucose in a host, including a continuous glucose sensor that produces a data stream indicative of a host's glucose concentration and an integrated receiver that receives the data stream from the continuous glucose sensor and calibrates the data stream using a single point glucose monitor that is integral with the integrated receiver. The integrated receiver obtains a glucose value from the single point glucose monitor, calibrates the sensor data stream received from the continuous glucose sensor, and displays one or both of the single point glucose measurement values and the calibrated continuous glucose sensor values on the user interface.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Integrated receiver for continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS20080287766A1Simpler and few componentReduce errorsEndoradiosondesCatheterGlucose sensorsData stream
A system is provided for monitoring glucose in a host, including a continuous glucose sensor that produces a data stream indicative of a host's glucose concentration and an integrated receiver that receives the data stream from the continuous glucose sensor and calibrates the data stream using a single point glucose monitor that is integral with the integrated receiver. The integrated receiver obtains a glucose value from the single point glucose monitor, calibrates the sensor data stream received from the continuous glucose sensor, and displays one or both of the single point glucose measurement values and the calibrated continuous glucose sensor values on the user interface.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Implantable analyte sensor
ActiveUS7657297B2Improve convenienceMinimize movementImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteMiniaturization
An implantable analyte sensor including a sensing region for measuring the analyte and a non-sensing region for immobilizing the sensor body in the host. The sensor is implanted in a precisely dimensioned pocket to stabilize the analyte sensor in vivo and enable measurement of the concentration of the analyte in the host before and after formation of a foreign body capsule around the sensor. The sensor further provides a transmitter for RF transmission through the sensor body, electronic circuitry, and a power source optimized for long-term use in the miniaturized sensor body.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
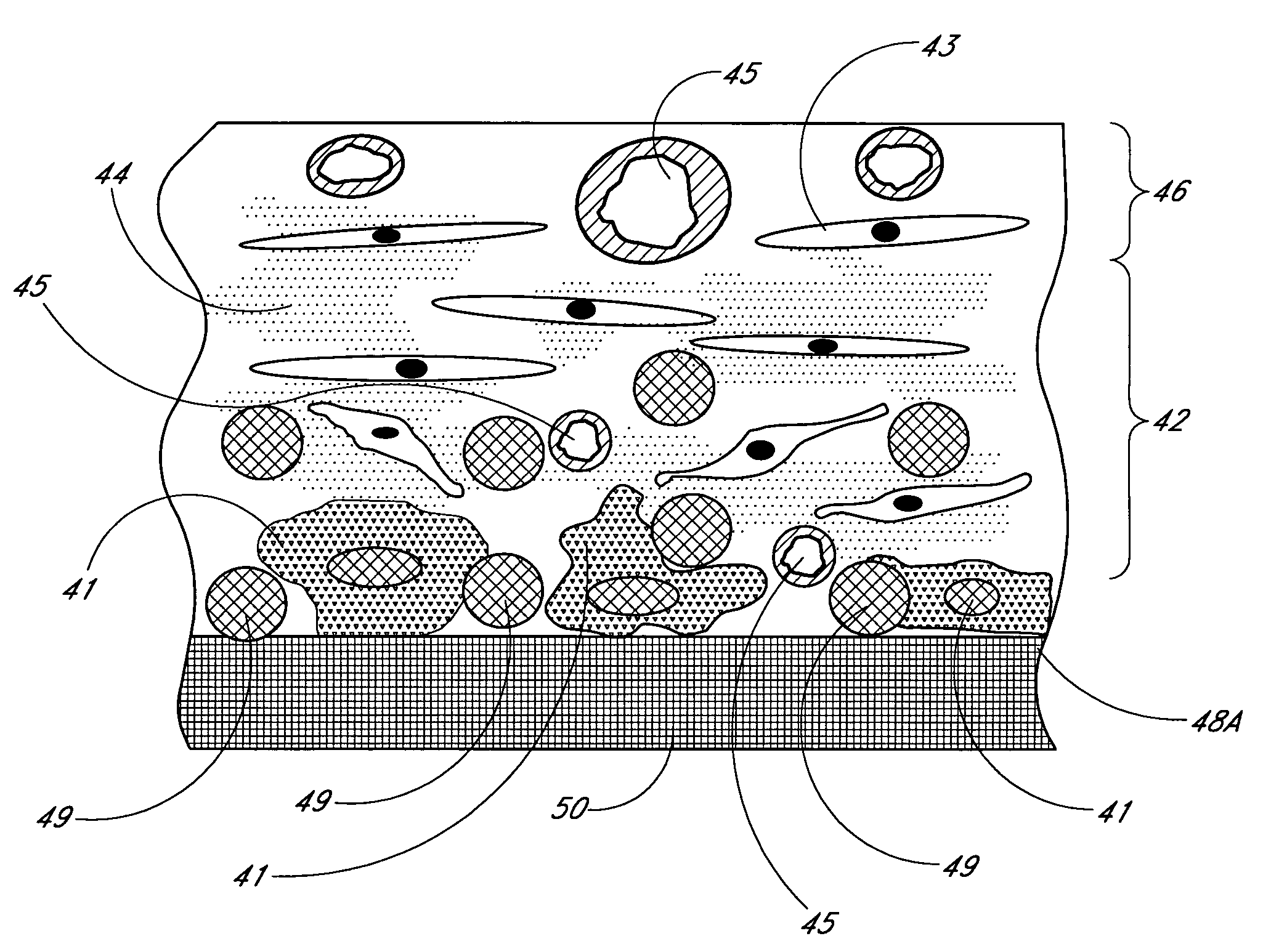
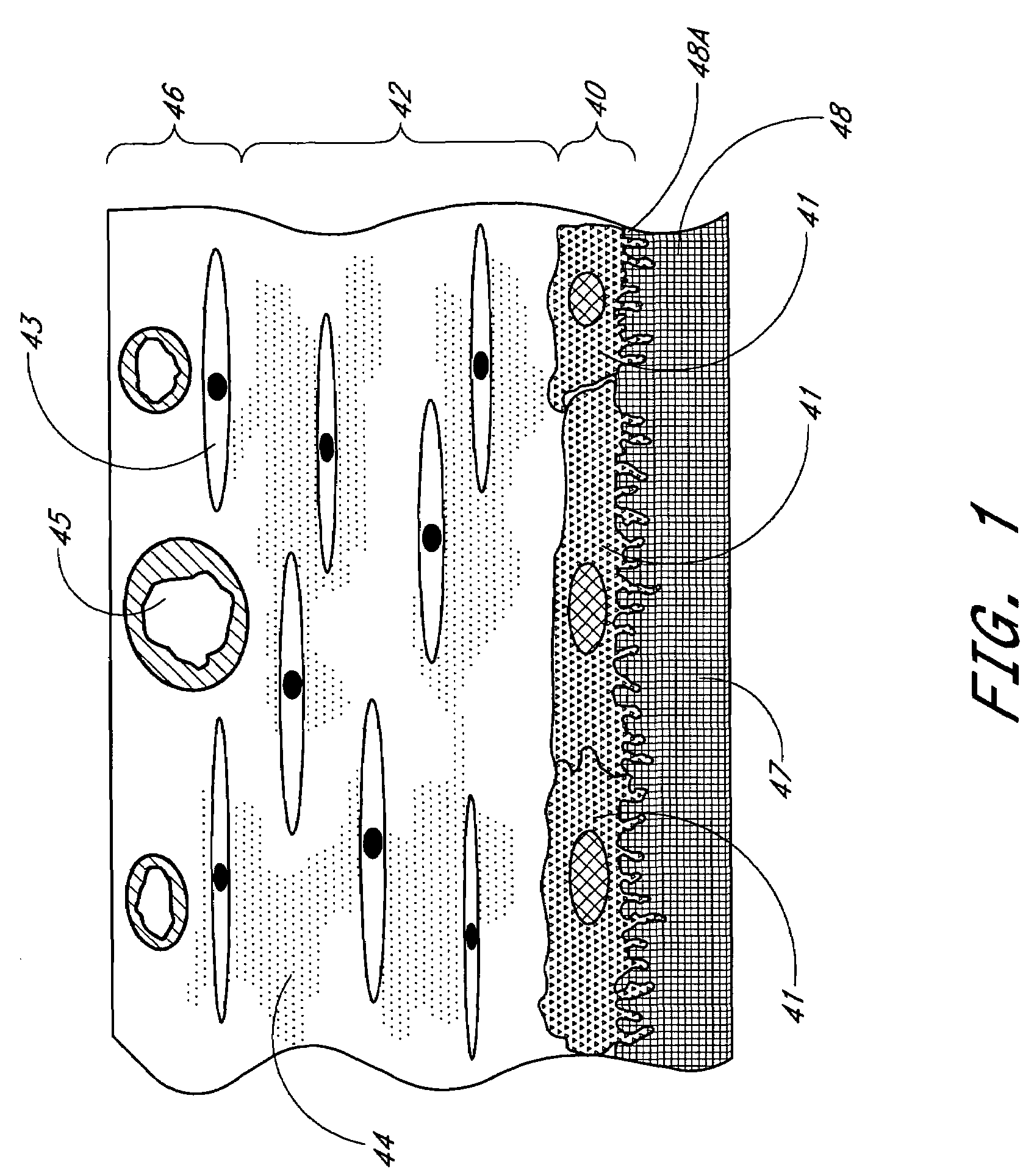
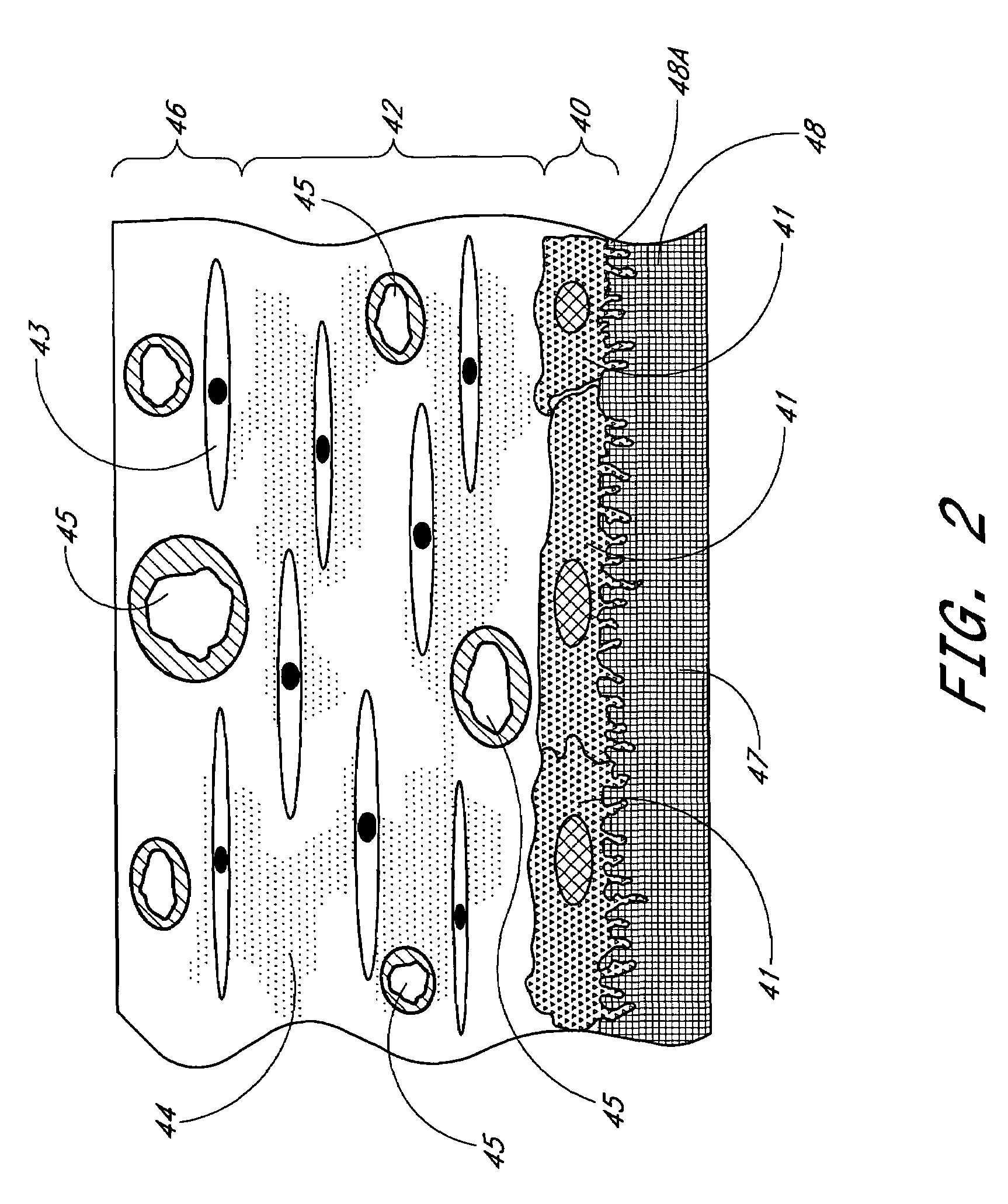
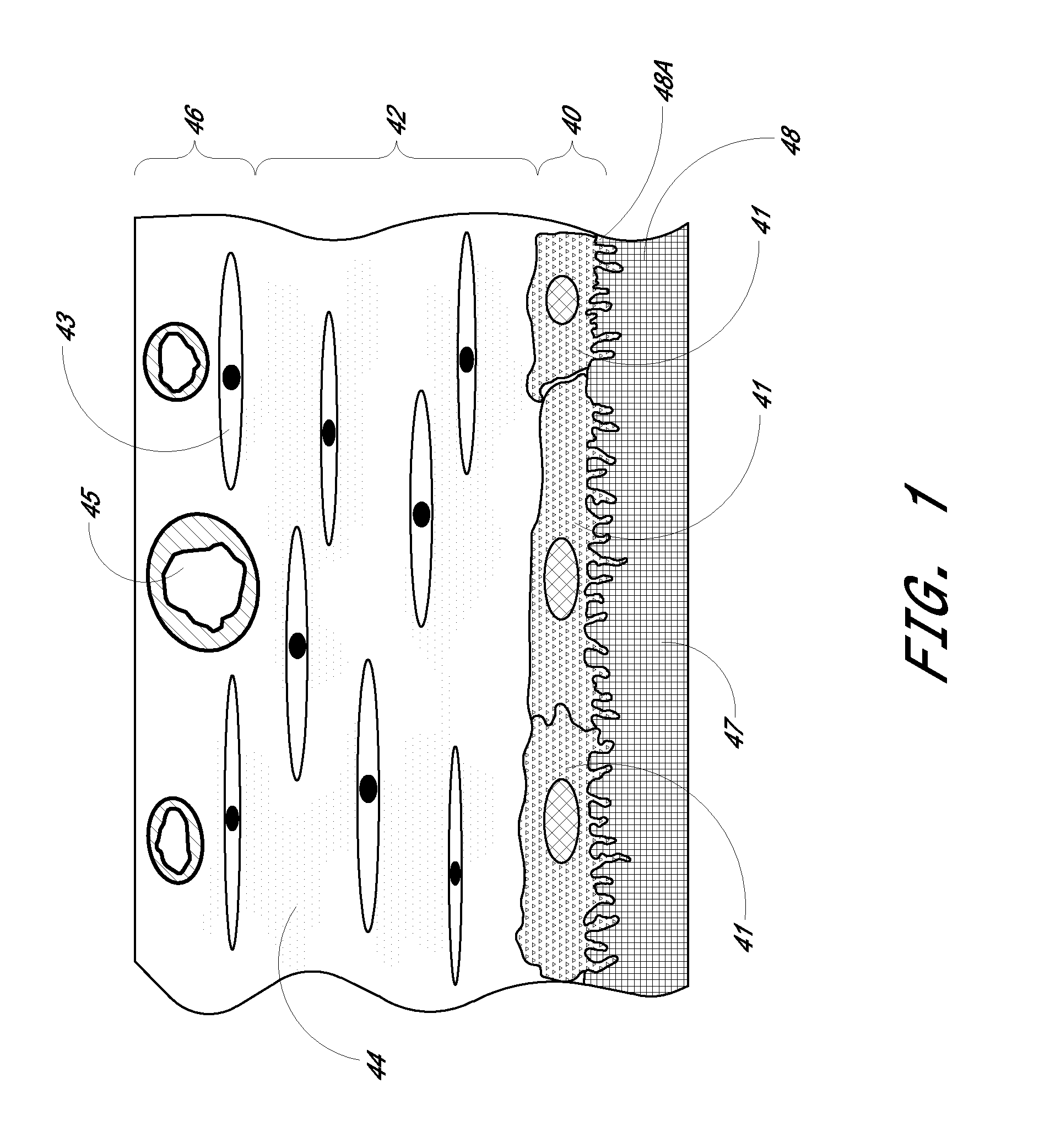
Membrane for use with implantable devices
The present invention provides a biointerface membrane for use with an implantable device that interferes with the formation of a barrier cell layer including; a first domain distal to the implantable device wherein the first domain supports tissue attachment and interferes with barrier cell layer formation and a second domain proximal to the implantable device wherein the second domain is resistant to cellular attachment and is impermeable to cells. In addition, the present invention provides sensors including the biointerface membrane, implantable devices including these sensors or biointerface membranes, and methods of monitoring glucose levels in a host utilizing the analyte detection implantable device of the invention. Other implantable devices which include the biointerface membrane of the present invention, such as devices for cell transplantation, drug delivery devices, and electrical signal delivery or measuring devices are also provided.
Owner:DEXCOM
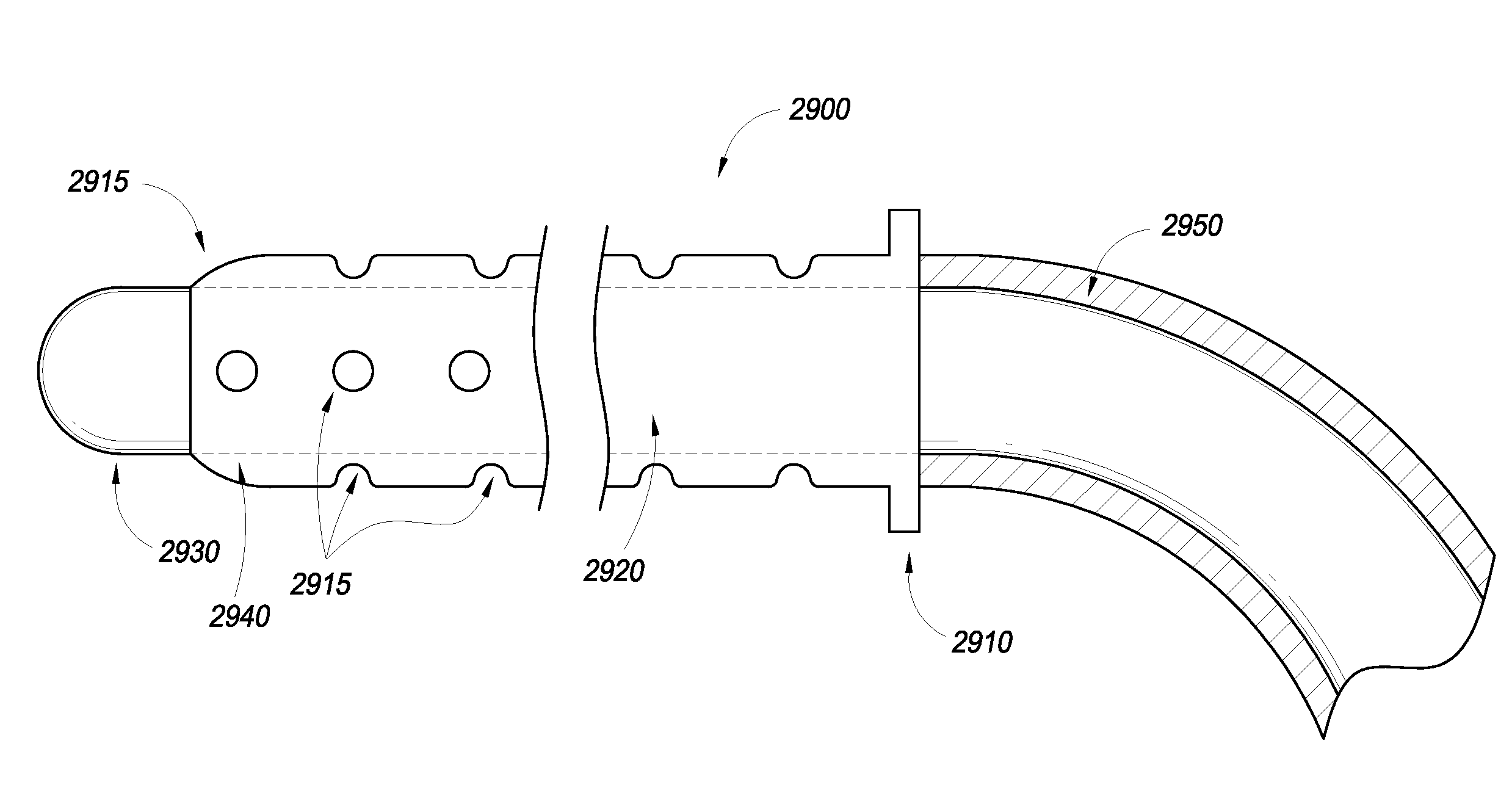
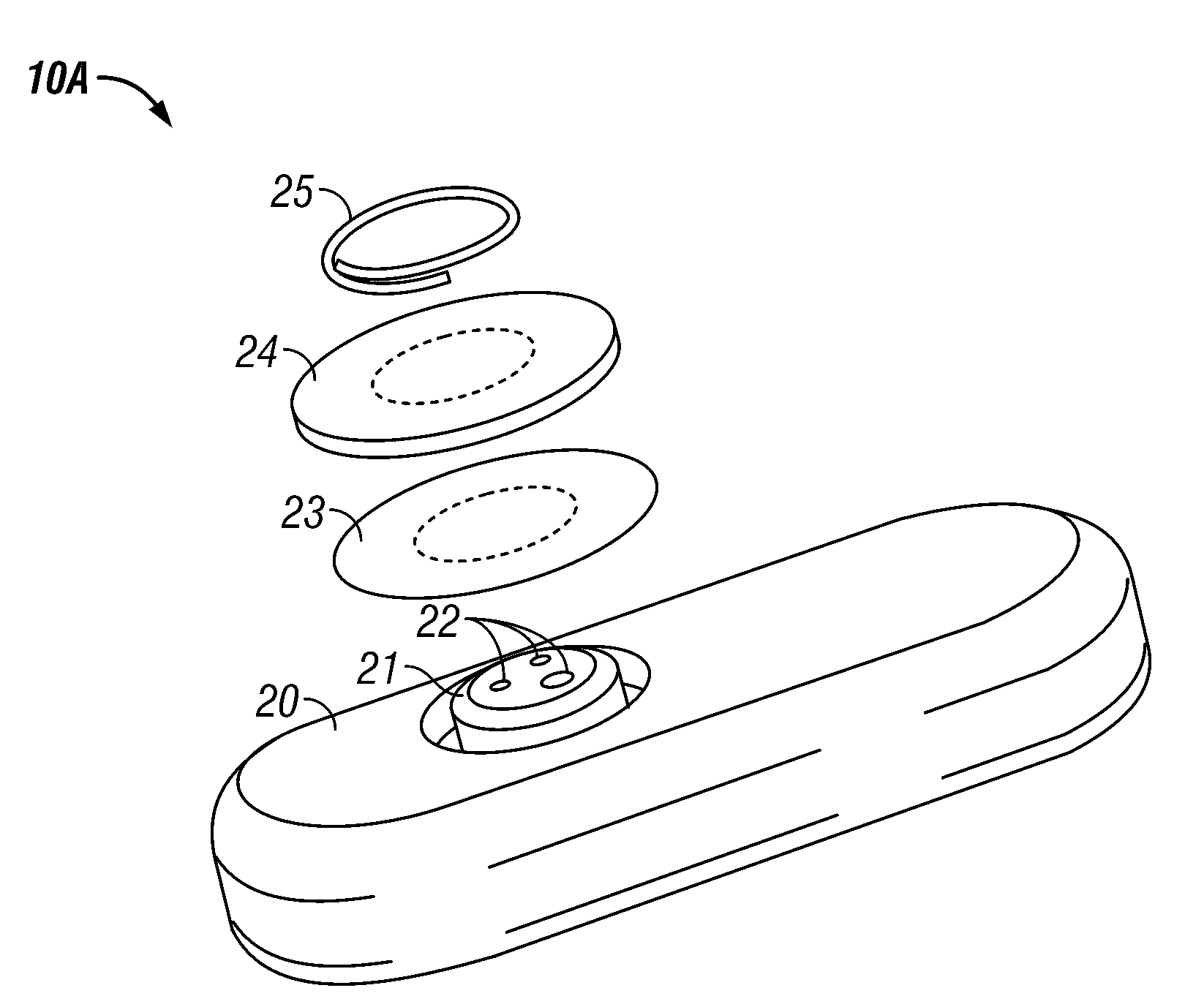
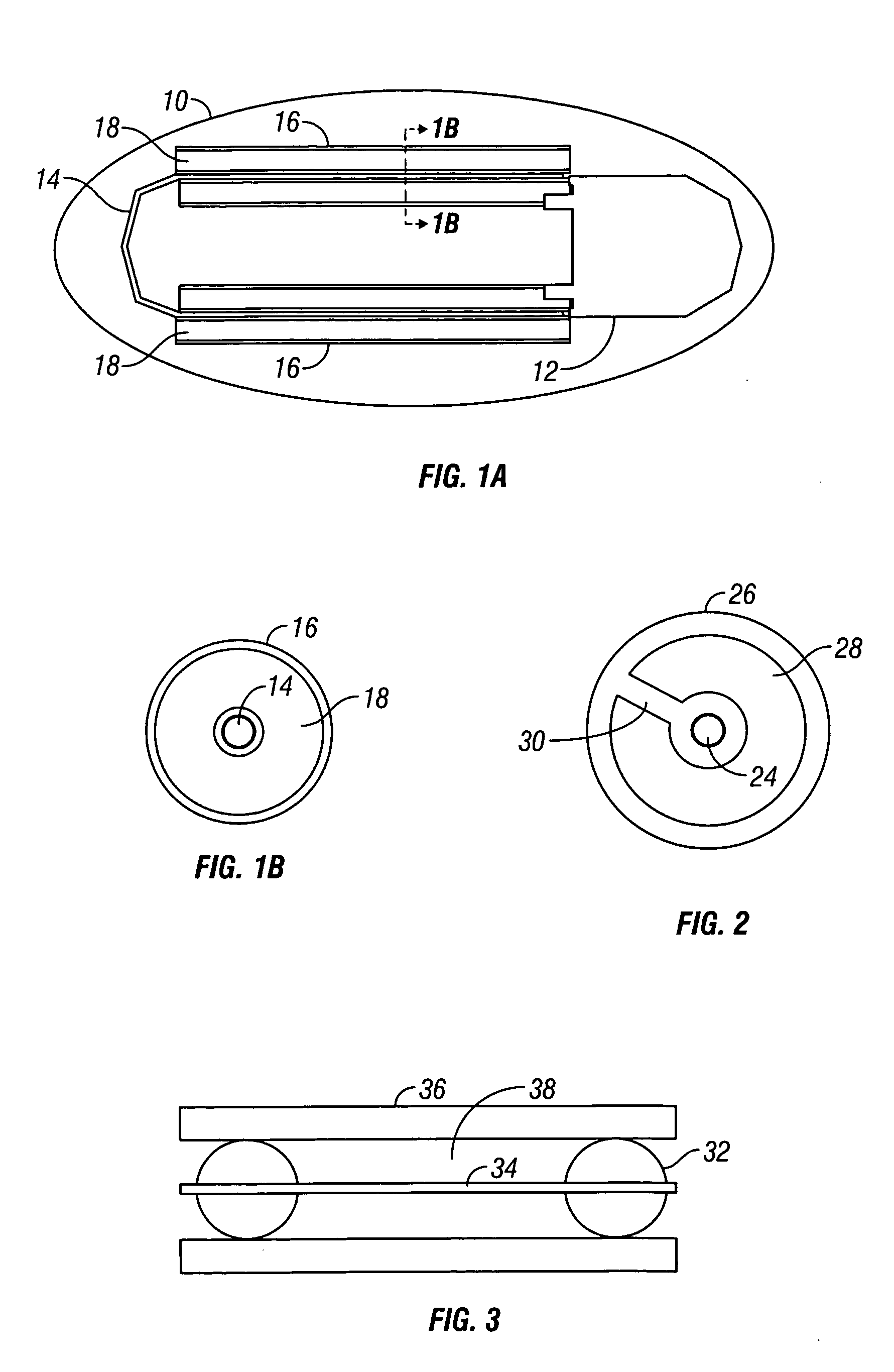
Rolled electrode array and its method for manufacture
InactiveUS20050051427A1Long-term robustnessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEndoradiosondesOptoelectronicsElectrode array
An electrode array for use in an electrochemical device is provided. The electrode array includes at least one electrode material and at least one insulating material arranged in a spiral configuration. The electrode array is manufactured by forming a composite stack of the at least one electrode material and the at least one insulating material, such that the insulating material(s) surrounds the electrode material(s) after which the stack is rolled into a spiral roll. The spiral roll can be cut, sliced, and / or dissected in numerous ways to form the electrode array of the preferred embodiments. Optionally, the sections can be further processed by machining, polishing, etching, or the like, to produce a curvature or stepped configuration.
Owner:DEXCOM
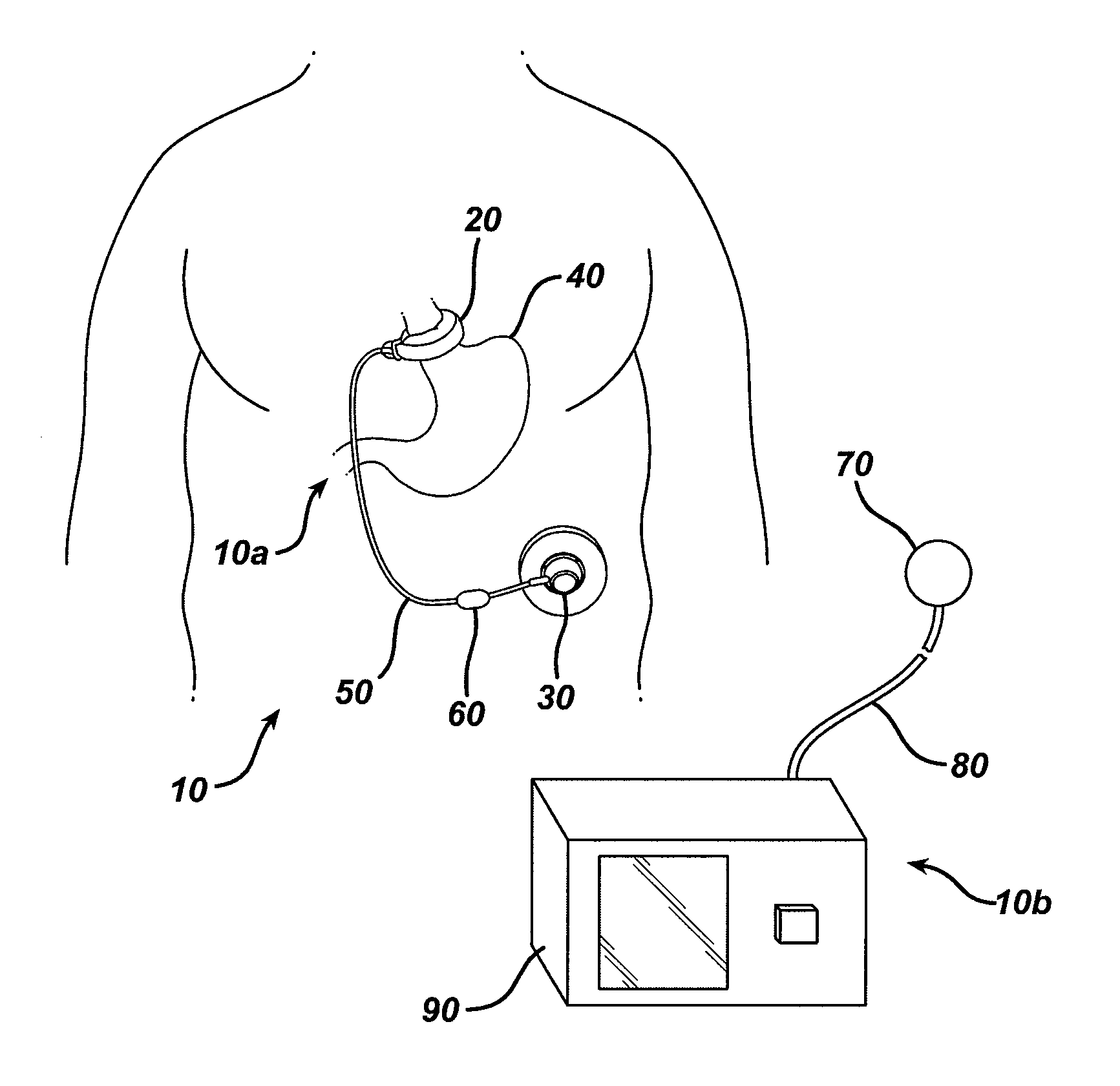
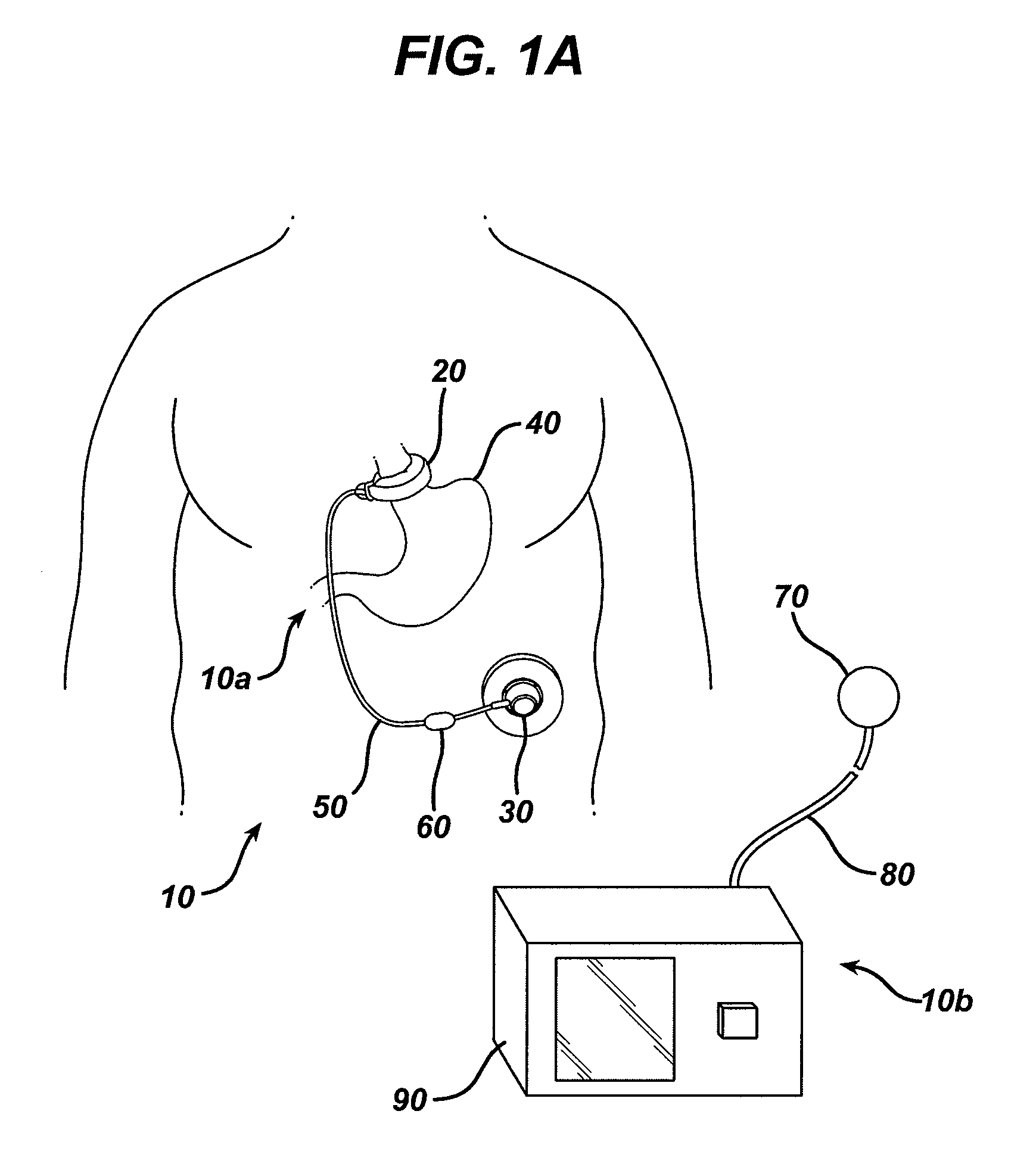
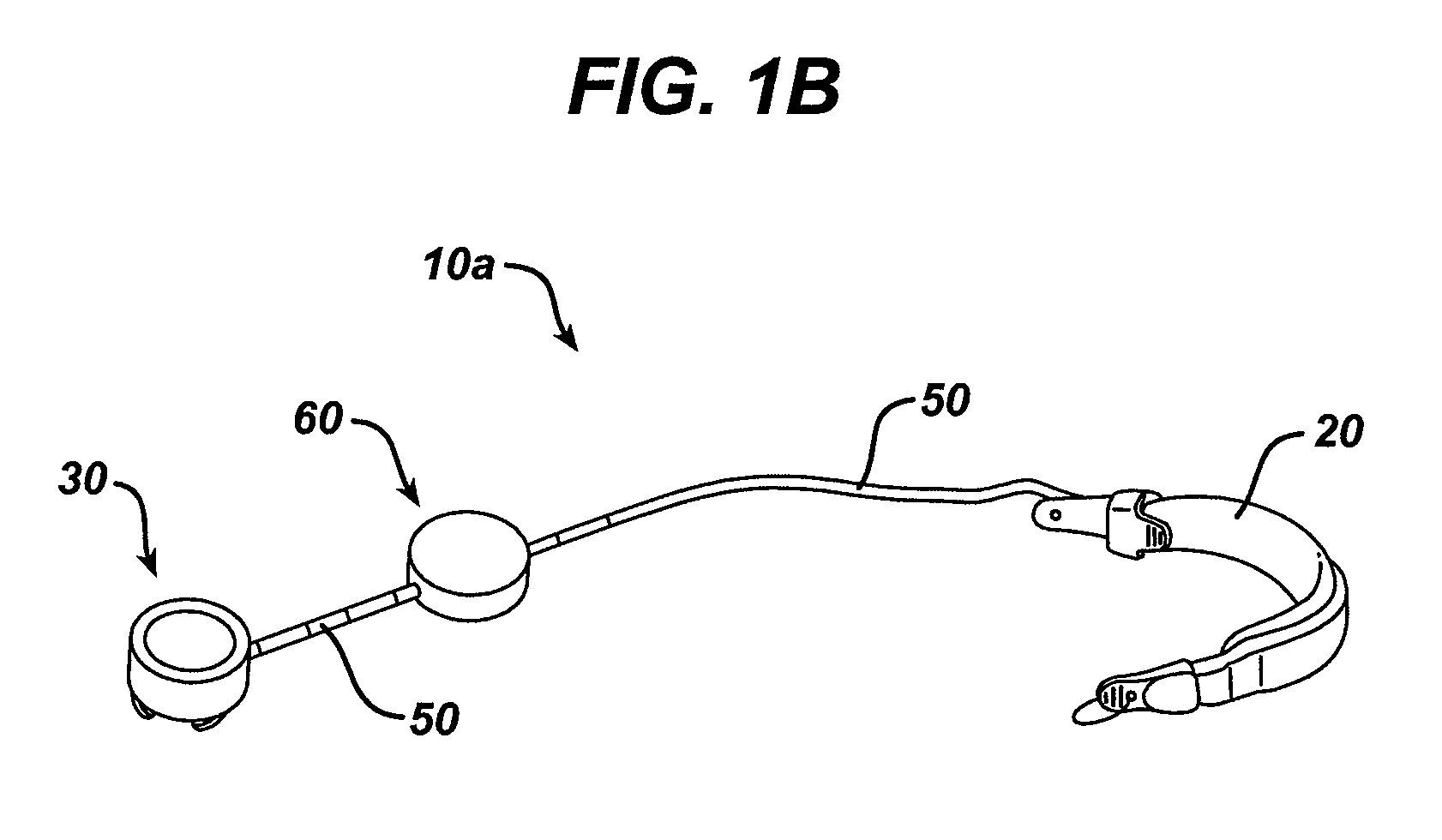
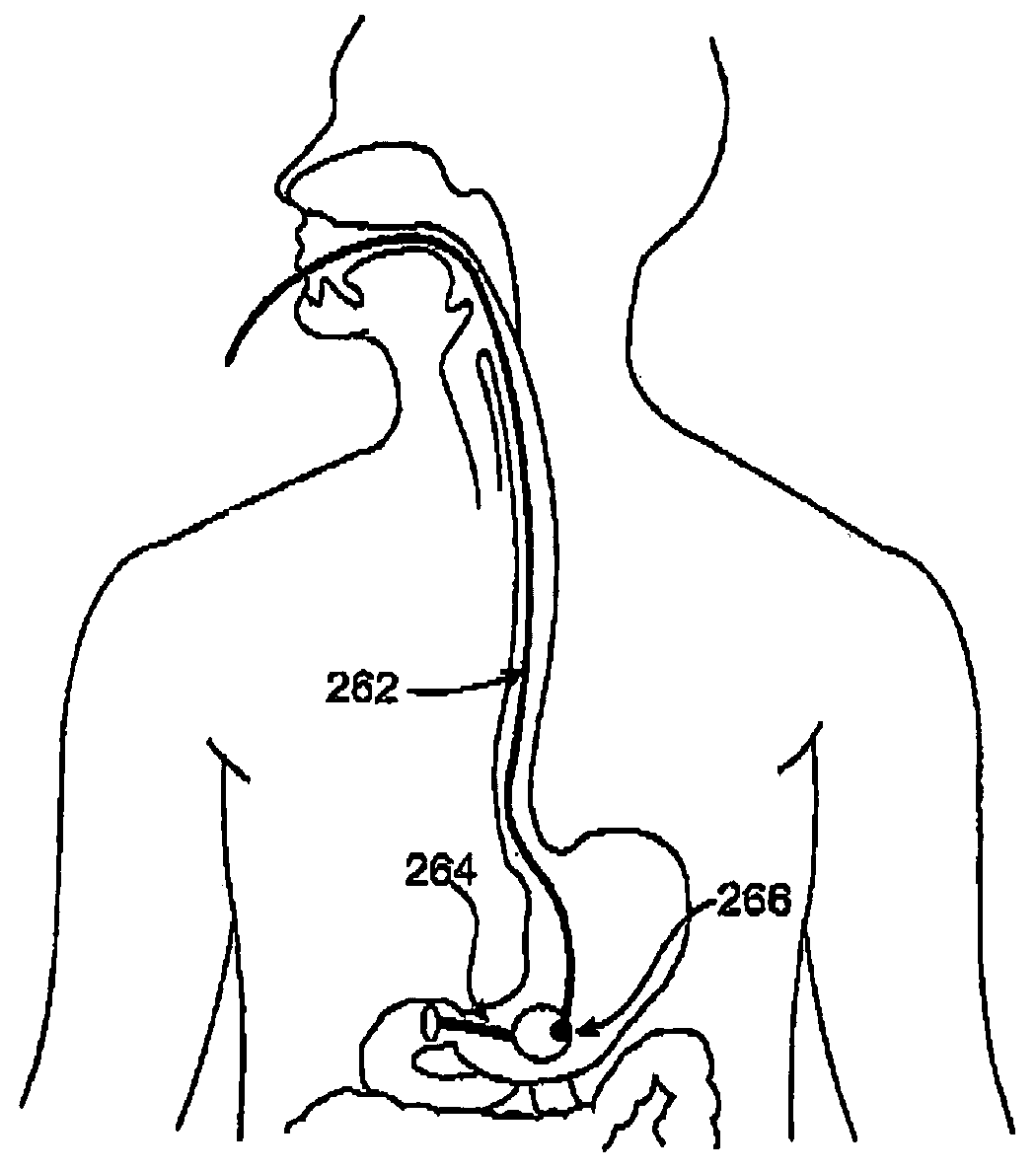
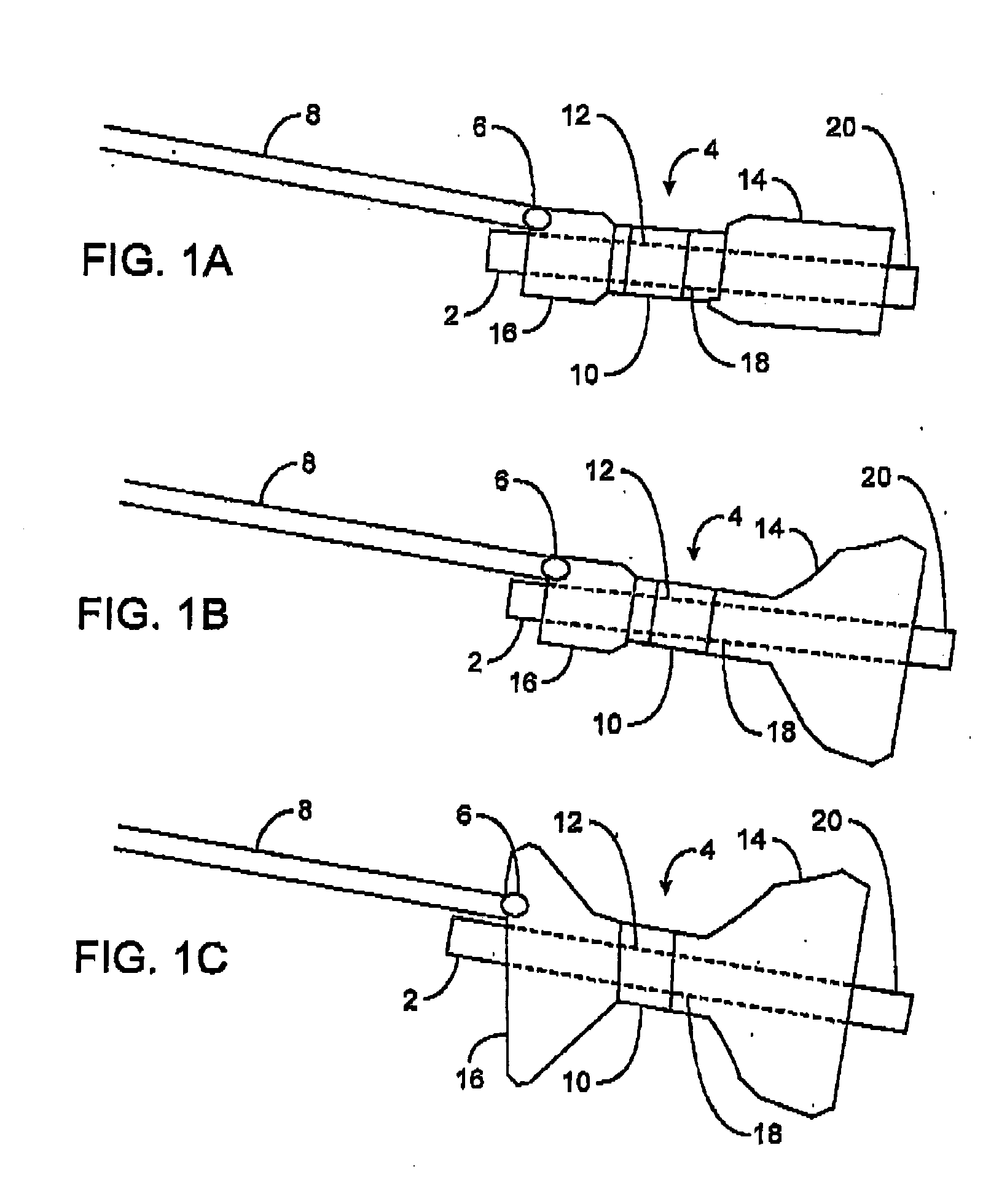
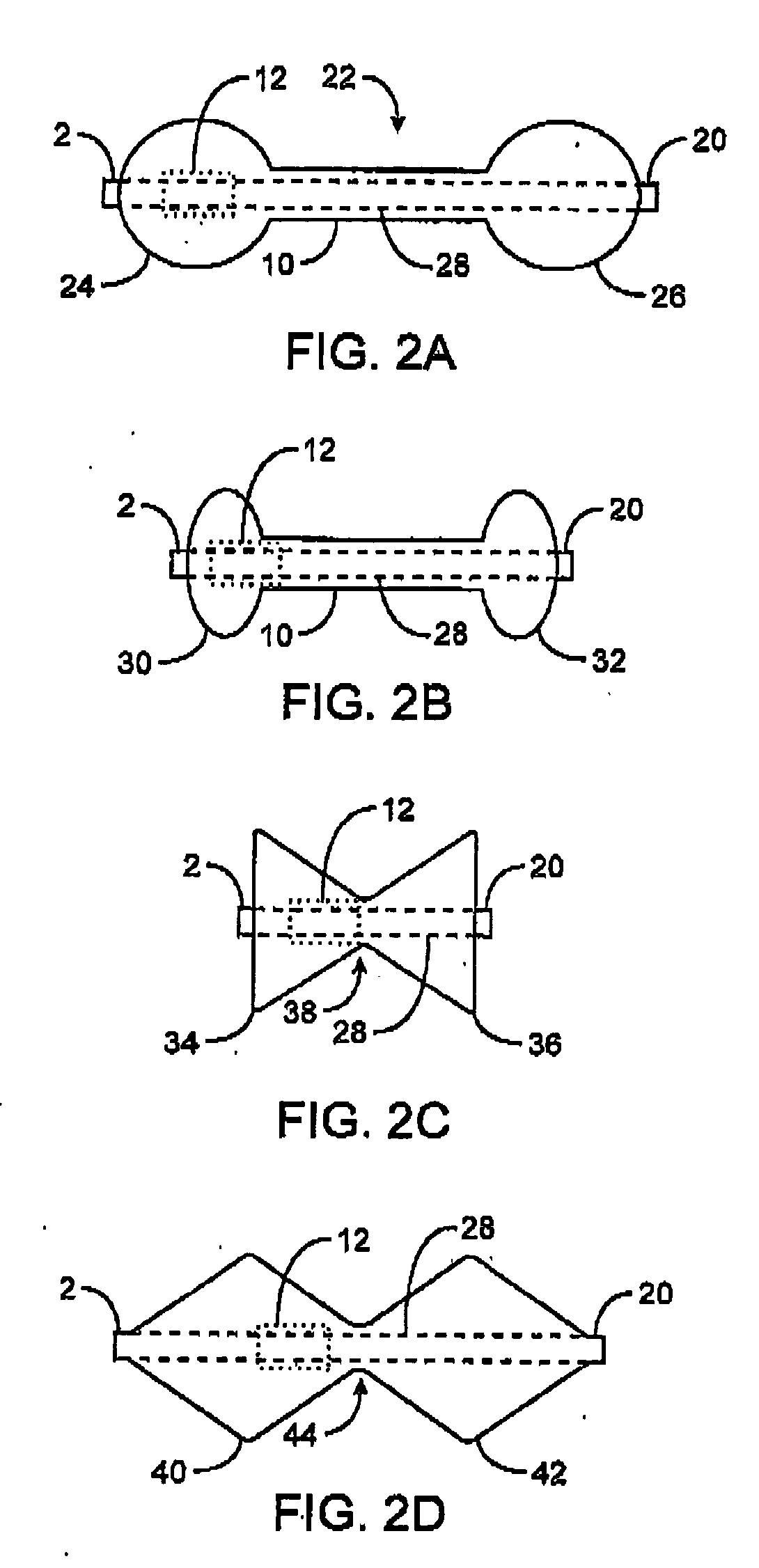
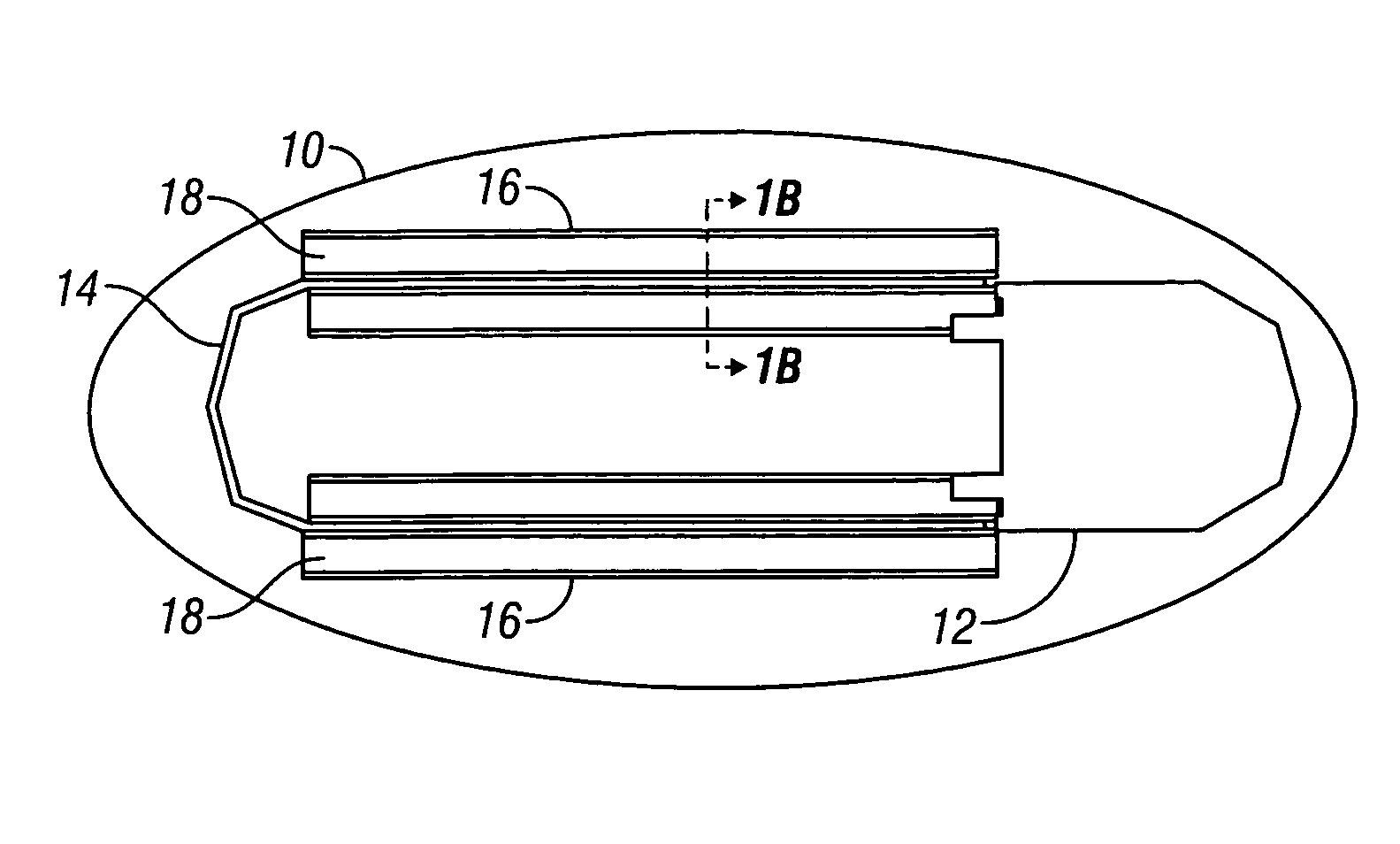
Sensor trigger
Methods and devices for effecting a gastric restriction system are disclosed. In one exemplary embodiment, a restriction system for forming a restriction in a patient is provided and can include an implantable restriction device and at least one implantable sensor that is in communication with the restriction device. In general, the implantable restriction device can be adjustable and can be configured to form a restriction in a patient. The implantable sensor(s) can be defaulted to a dormant power usage mode and can have a triggering mechanism that is configured to place the sensor(s) in a use configuration upon the occurrence of a triggering event.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
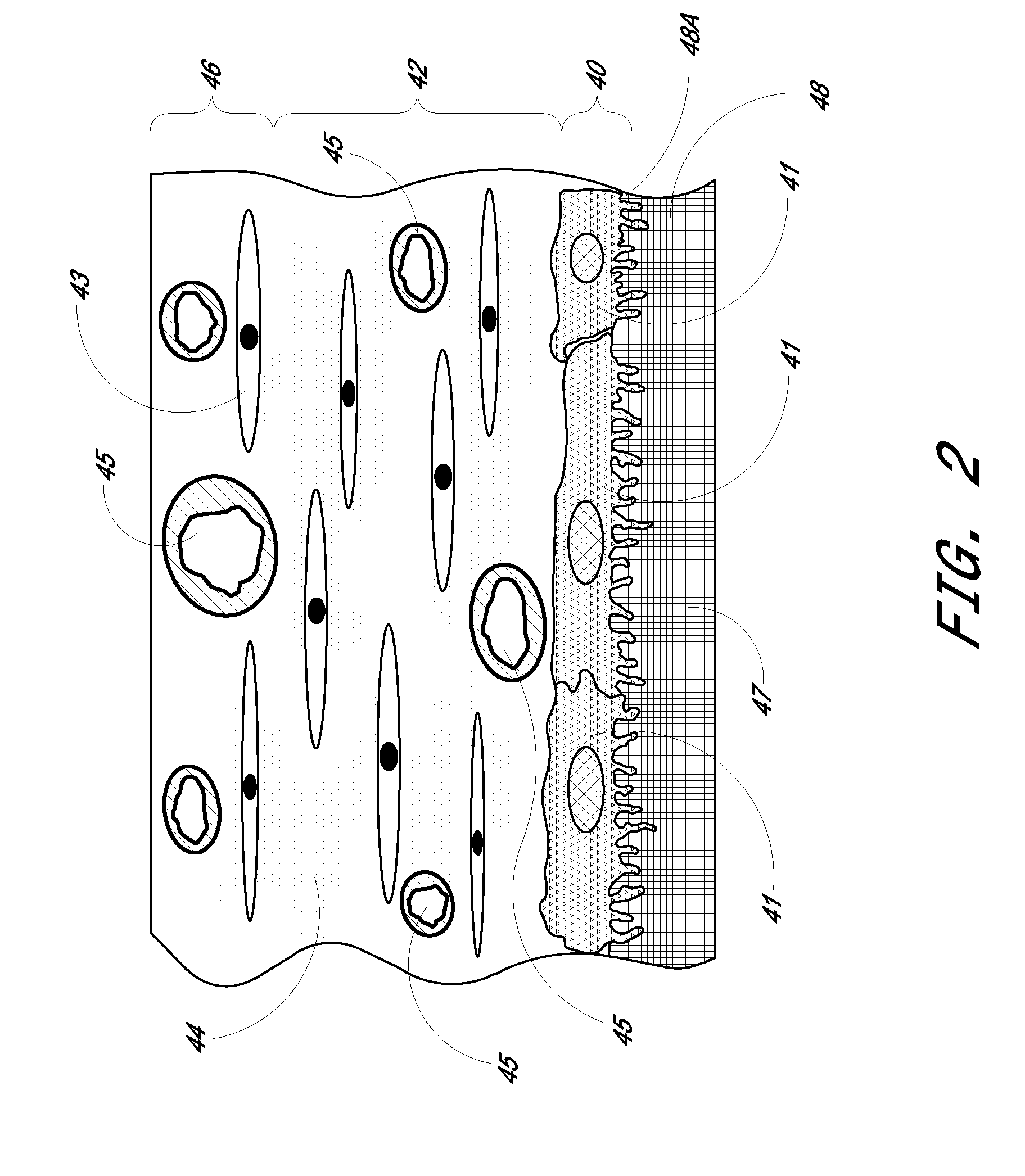
Membrane for use with implantable devices
ActiveUS20100087724A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteBiointerface
The present invention provides a biointerface membrane for use with an implantable device that interferes with the formation of a barrier cell layer including; a first domain distal to the implantable device wherein the first domain supports tissue attachment and interferes with barrier cell layer formation and a second domain proximal to the implantable device wherein the second domain is resistant to cellular attachment and is impermeable to cells. In addition, the present invention provides sensors including the biointerface membrane, implantable devices including these sensors or biointerface membranes, and methods of monitoring glucose levels in a host utilizing the analyte detection implantable device of the invention. Other implantable devices which include the biointerface membrane of the present invention, such as devices for cell transplantation, drug delivery devices, and electrical signal delivery or measuring devices are also provided.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Methods and devices for measuring impedance in a gastric restriction system
Methods and devices are provided for gathering impedance data related to implantable restriction devices. In general, the methods and devices can enable patients, health care providers, and others to use gathered data as a feedback mechanism to non-invasively monitor efficacy of an implantable restriction device in a patient and to identify, modify, and / or prescribe a treatment plan for the patient considering the gathered data. Impedance data can be gathered and analyzed for tissue proximate to the restriction device, e.g., a fat pad between a gastric band and the patient's stomach. Electrodes in contact with the tissue can measure an impedance of the tissue, with the impedance between the electrodes changing as the tissue reduces in size (e.g., as fat cells shrink) and / or changes configuration.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
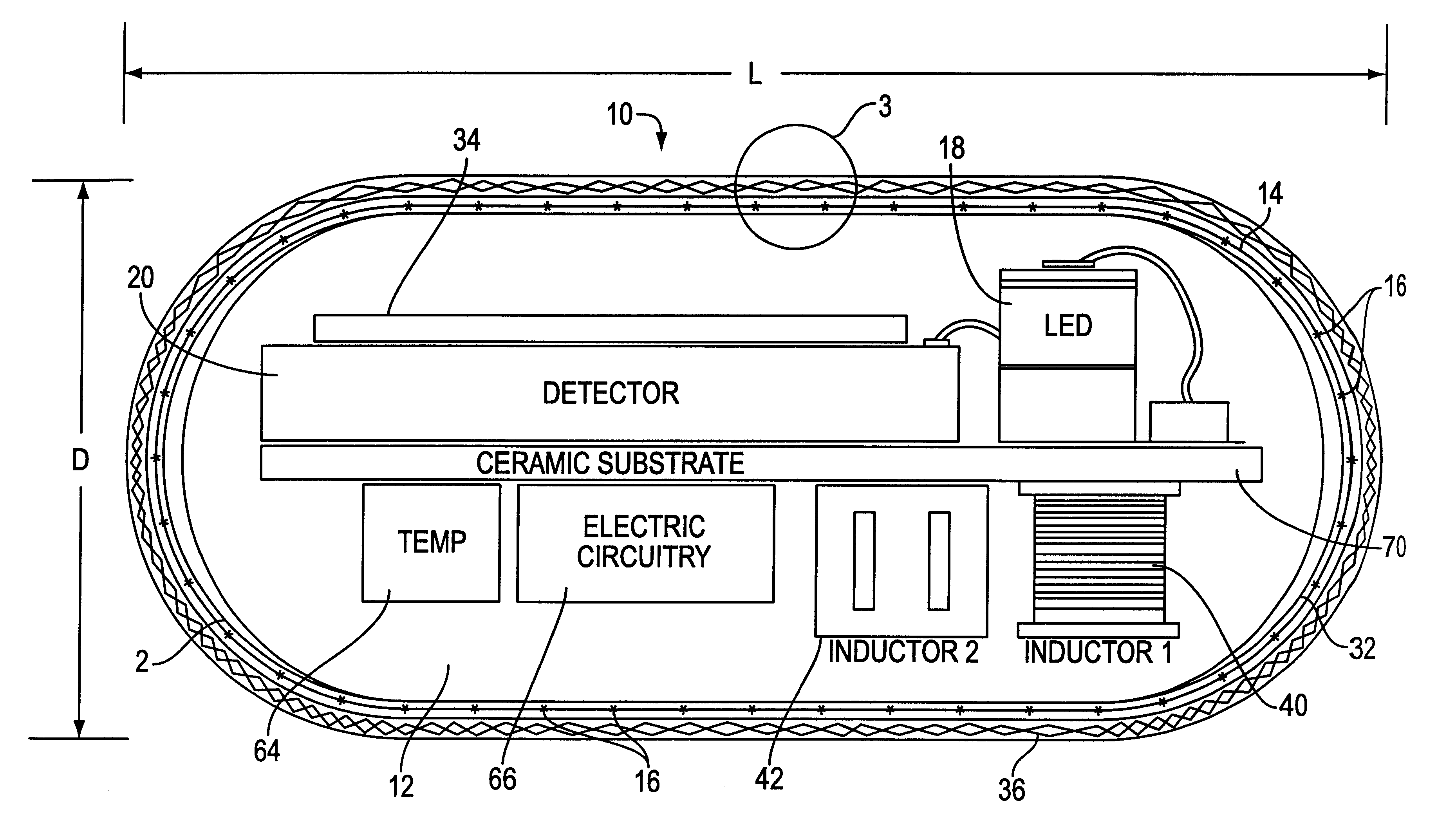
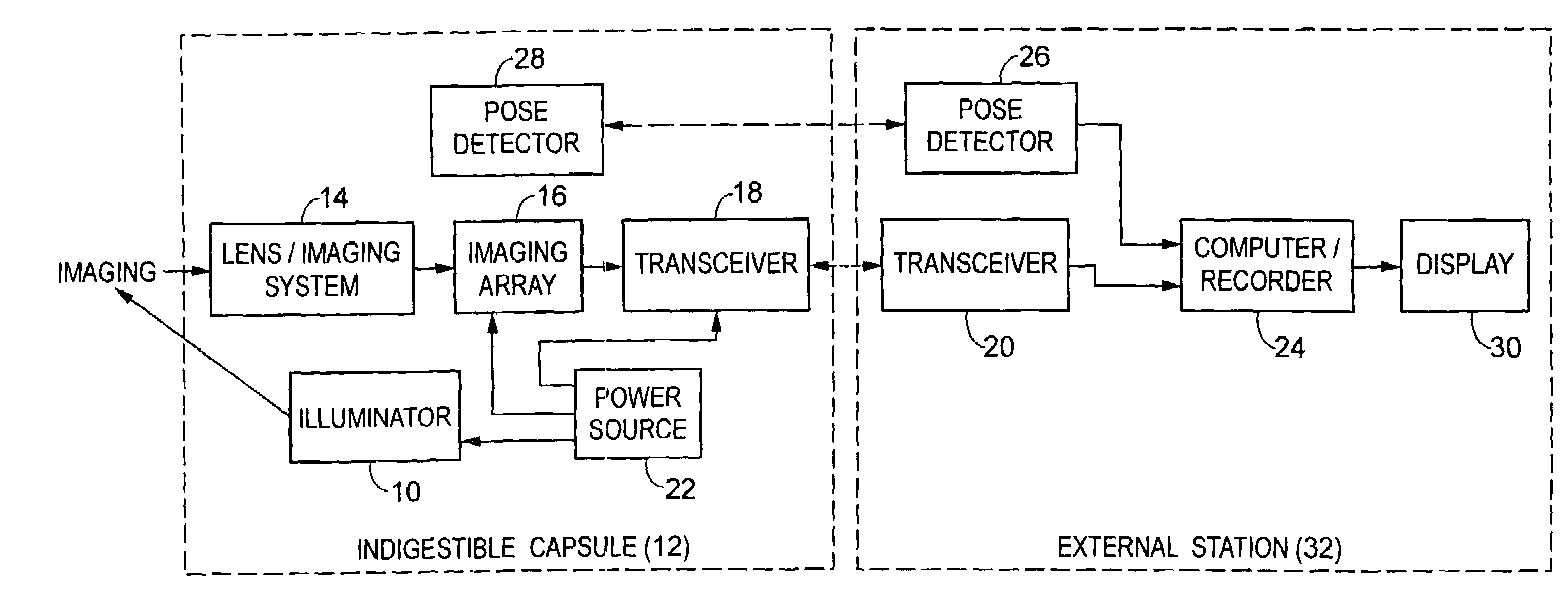
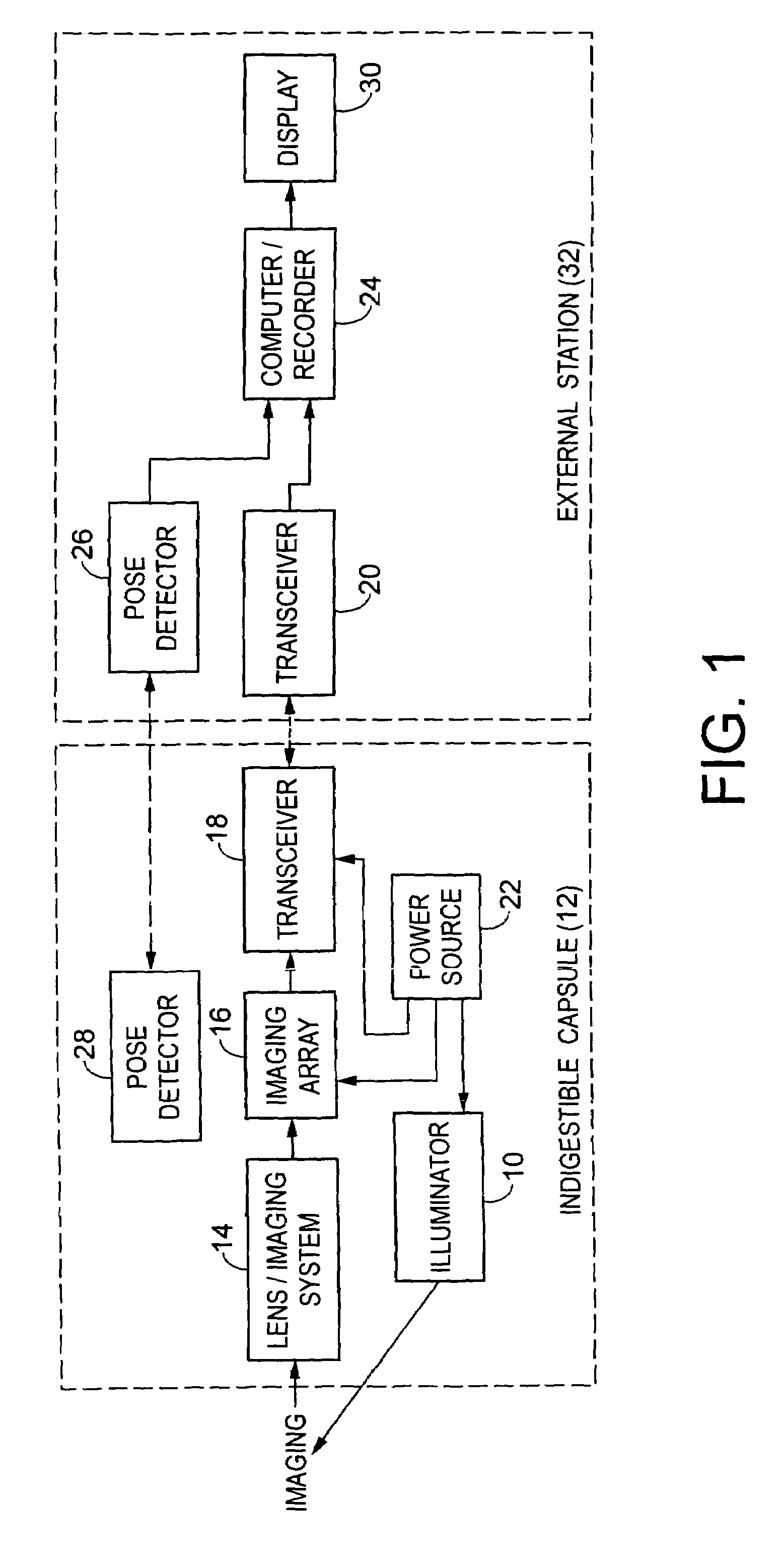
Device for in-vivo imaging
ActiveUS7009634B2Quality improvementTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringIn vivo
The present invention provides a system and method for obtaining in vivo images. The system contains an imaging system and an ultra low power radio frequency transmitter for transmitting signals from the CMOS imaging camera to a receiving system located outside a patient. The imaging system includes at least one CMOS imaging camera, at least one illumination source for illuminating an in vivo site and an optical system for imaging the in vivo site onto the CMOS imaging camera.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
Devices and methods for pyloric anchoring
ActiveUS20050055039A1Avoiding erosion and ulcerationSuture equipmentsElectrotherapyPylorusPatient characteristics
A device for performing one or more functions in a gastrointestinal tract of a patient includes an anchoring member and at least one actuator, sensor, or combination of both coupled with the anchoring device. The anchoring device is adapted to maintain at least part of the device within a pyloric portion of the patient's stomach and to intermittently engage, without directly attaching to, stomach tissue. Actuators perform any suitable function, such as transmitting energy to tissue, acting as a sleeve to reduce nutrient absorption, occupying space in the stomach, eluting a drug and / or the like. Sensors may be adapted to sense any suitable patient characteristic within the patient's gastrointestinal tract, such as pH, temperature, bile content, nutrient content, fats, sugars, alcohol, opiates, drugs, analytes, electrolytes and / or hemoglobin.
Owner:BARONOVA
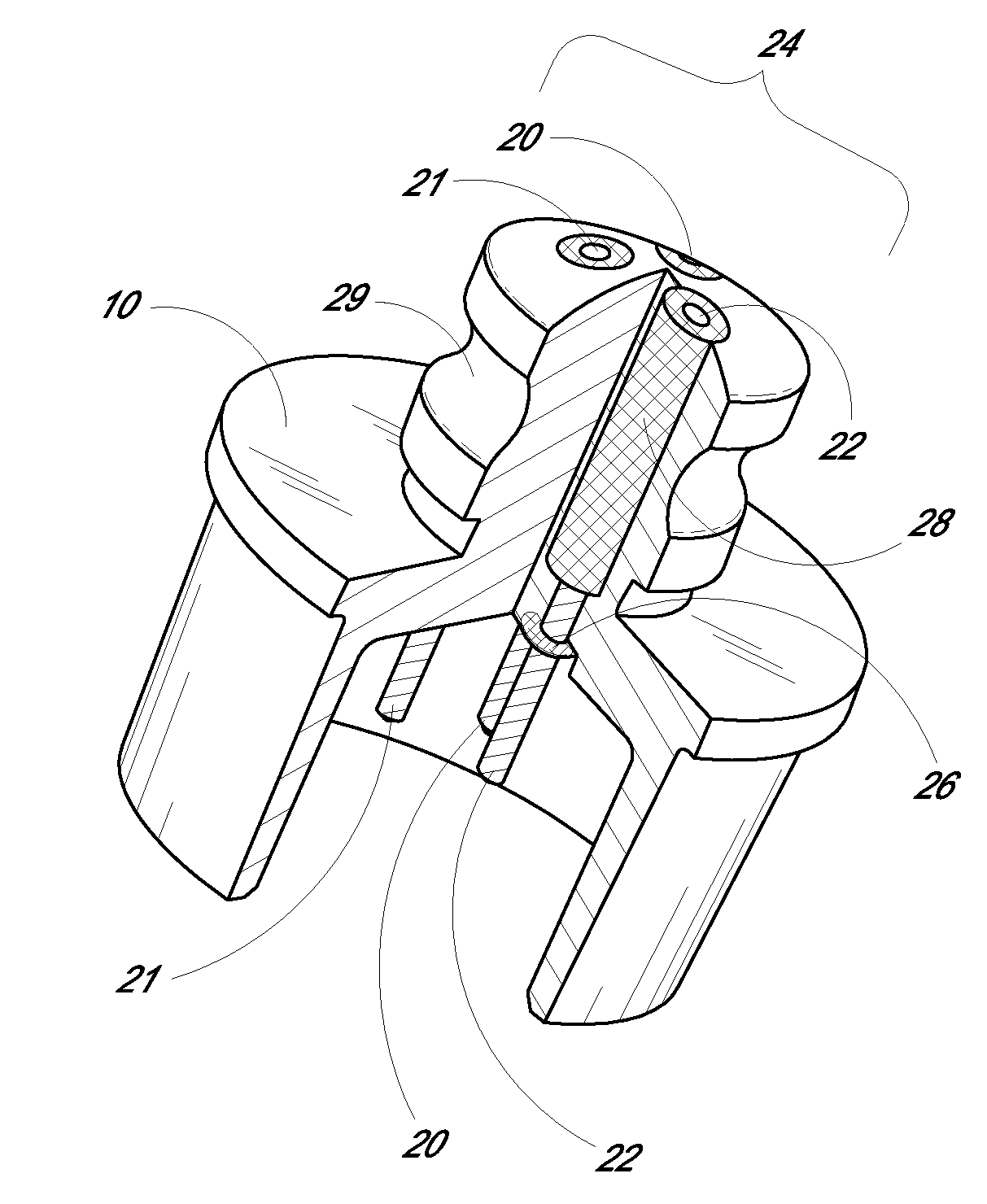
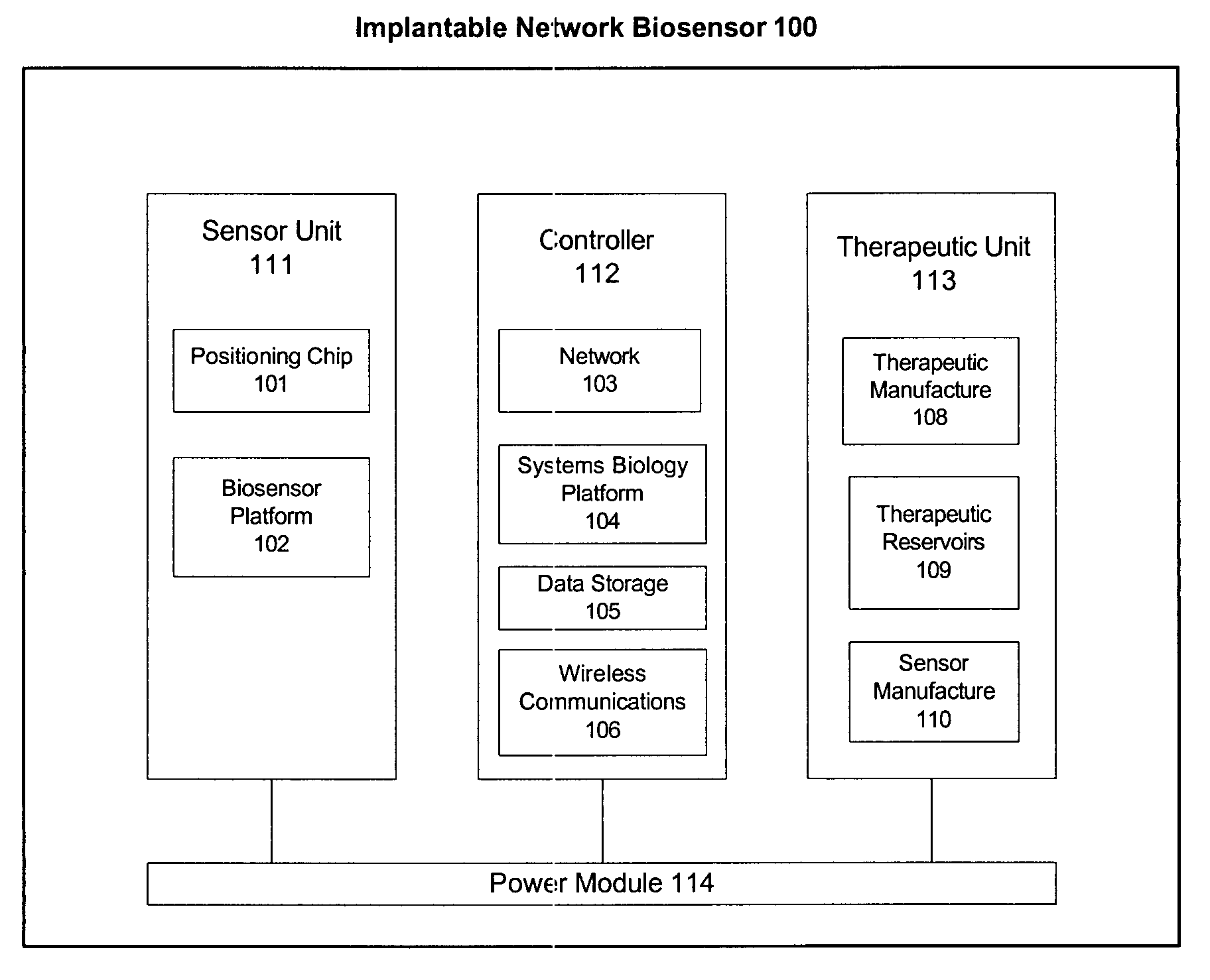
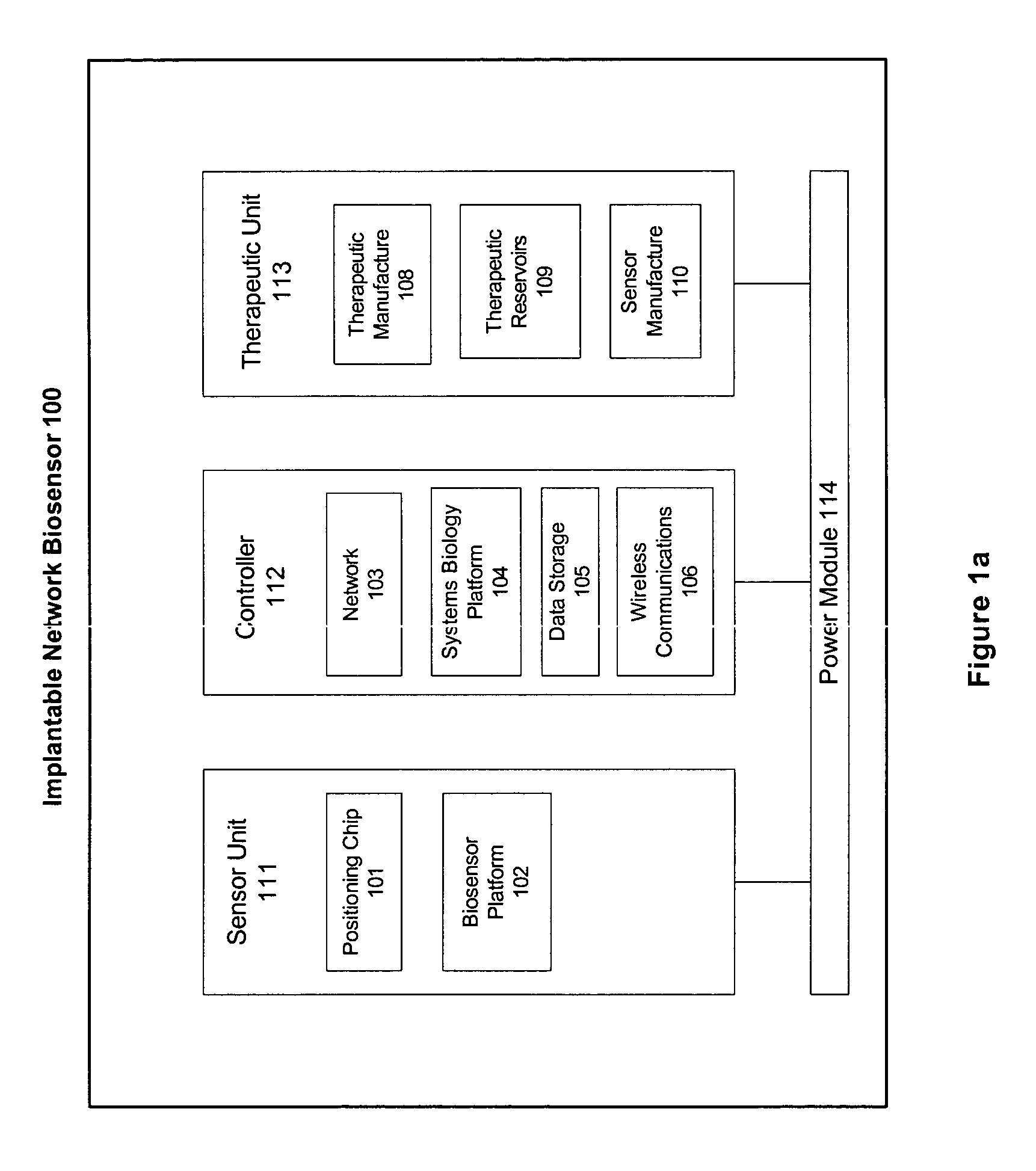
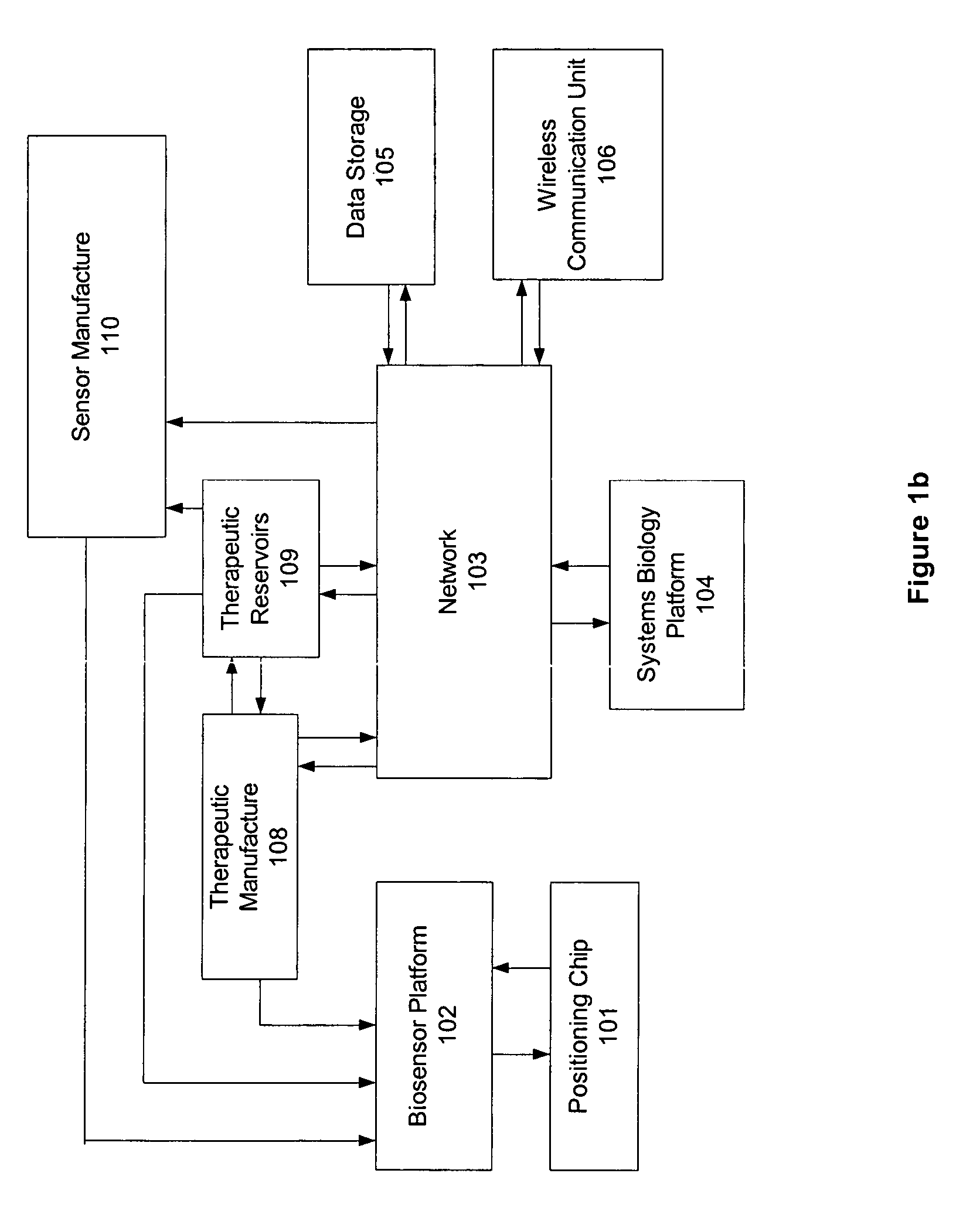
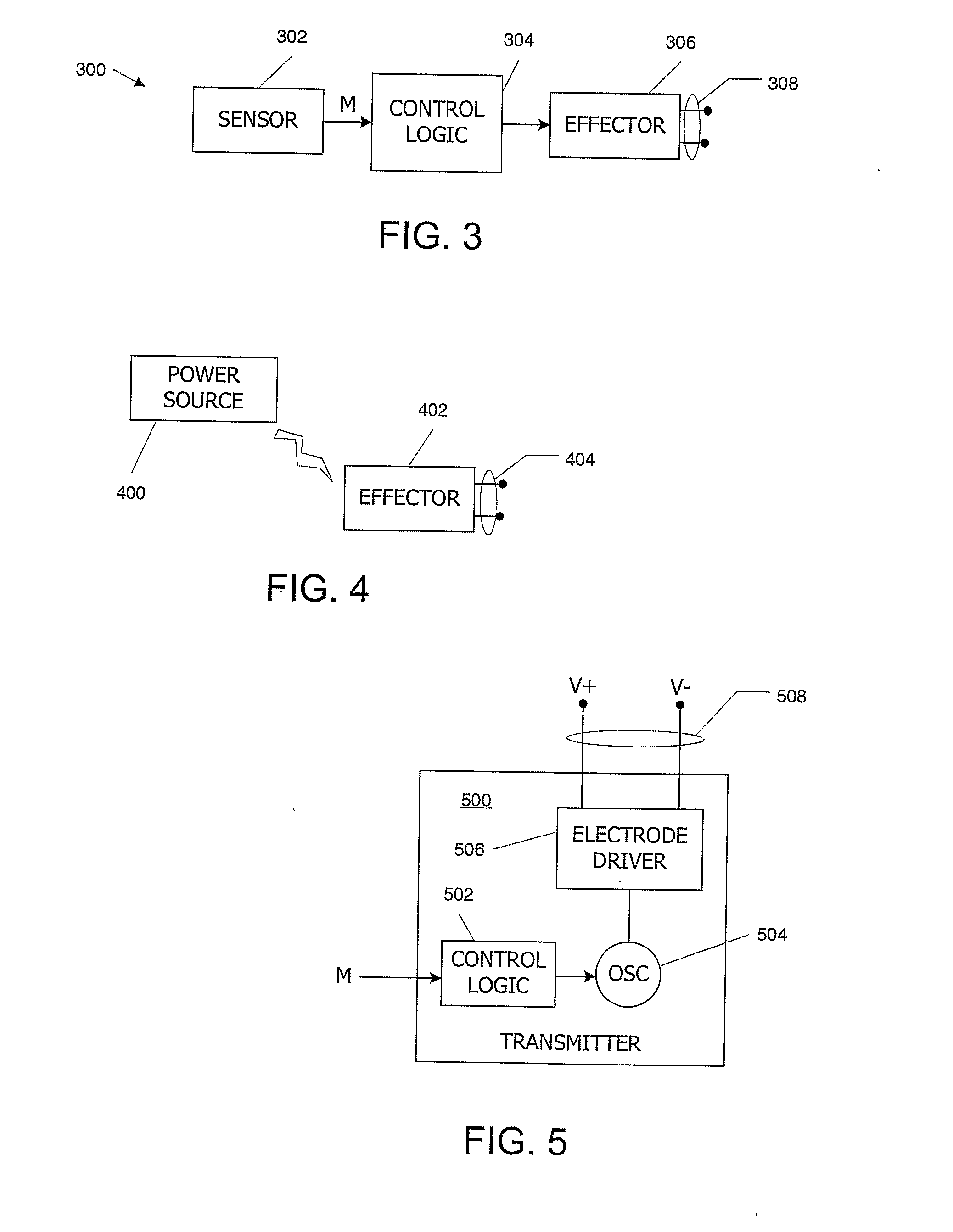
Implantable device with improved radio frequency capabilities
Owner:GRIFFIN ADAM +2
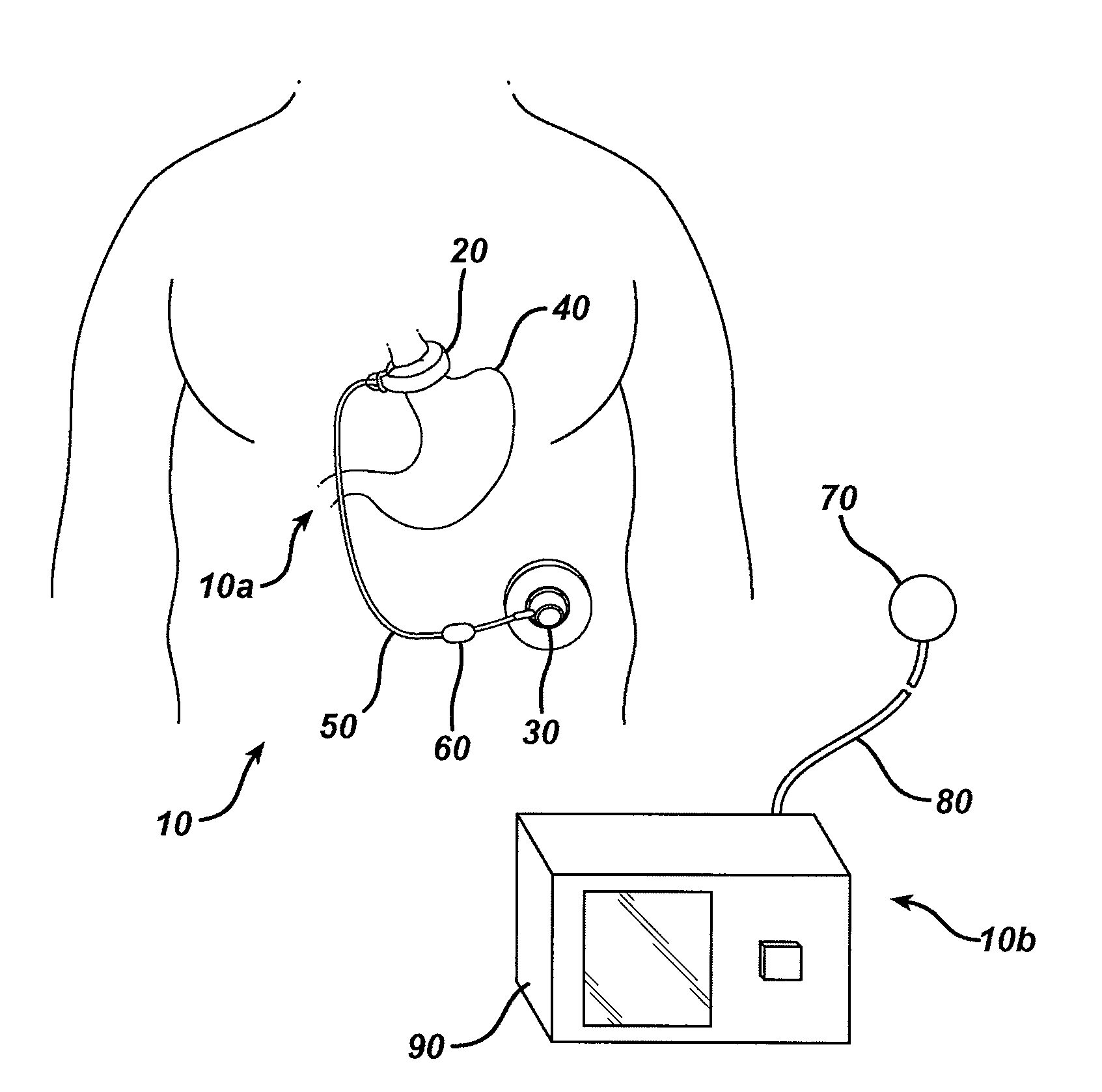
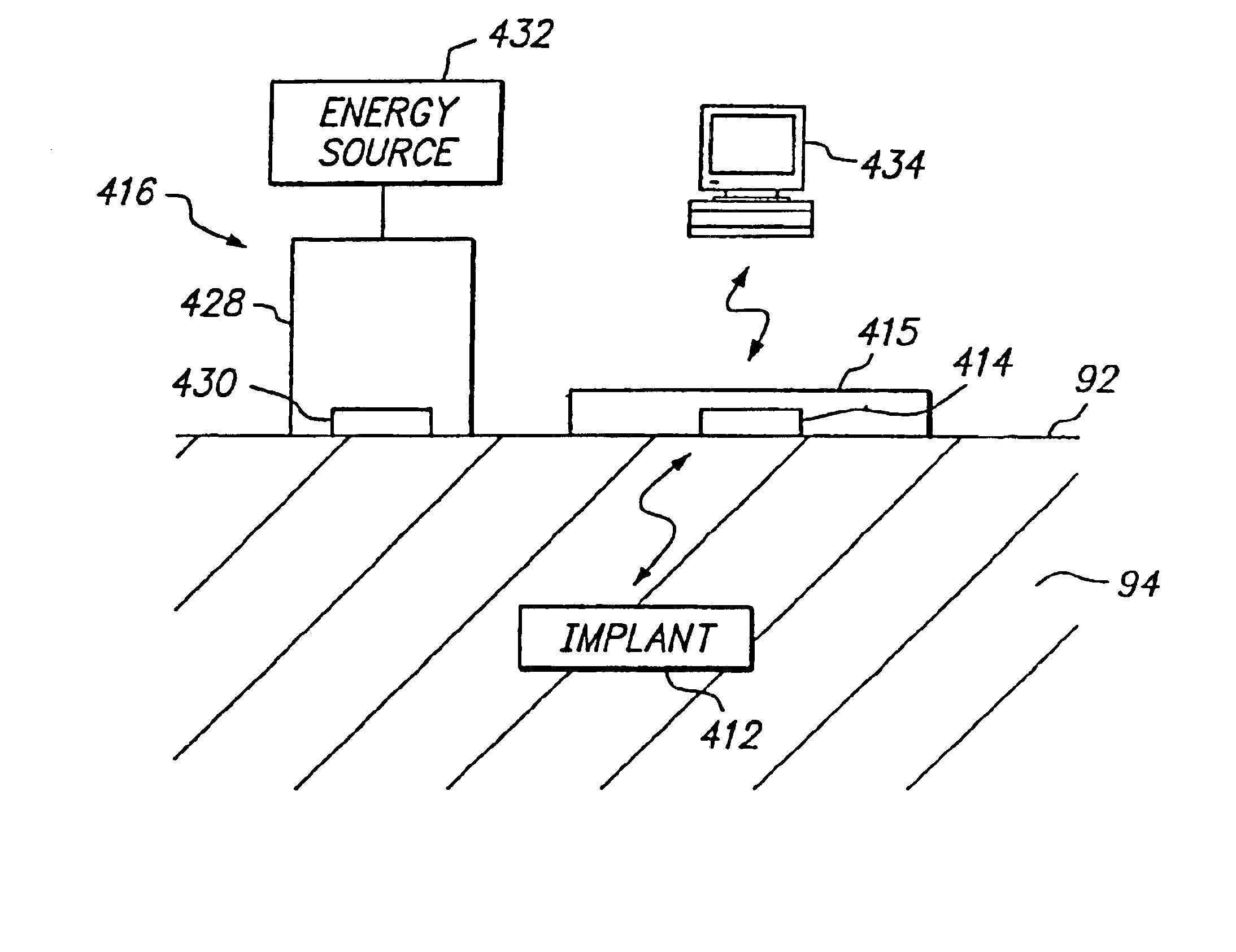
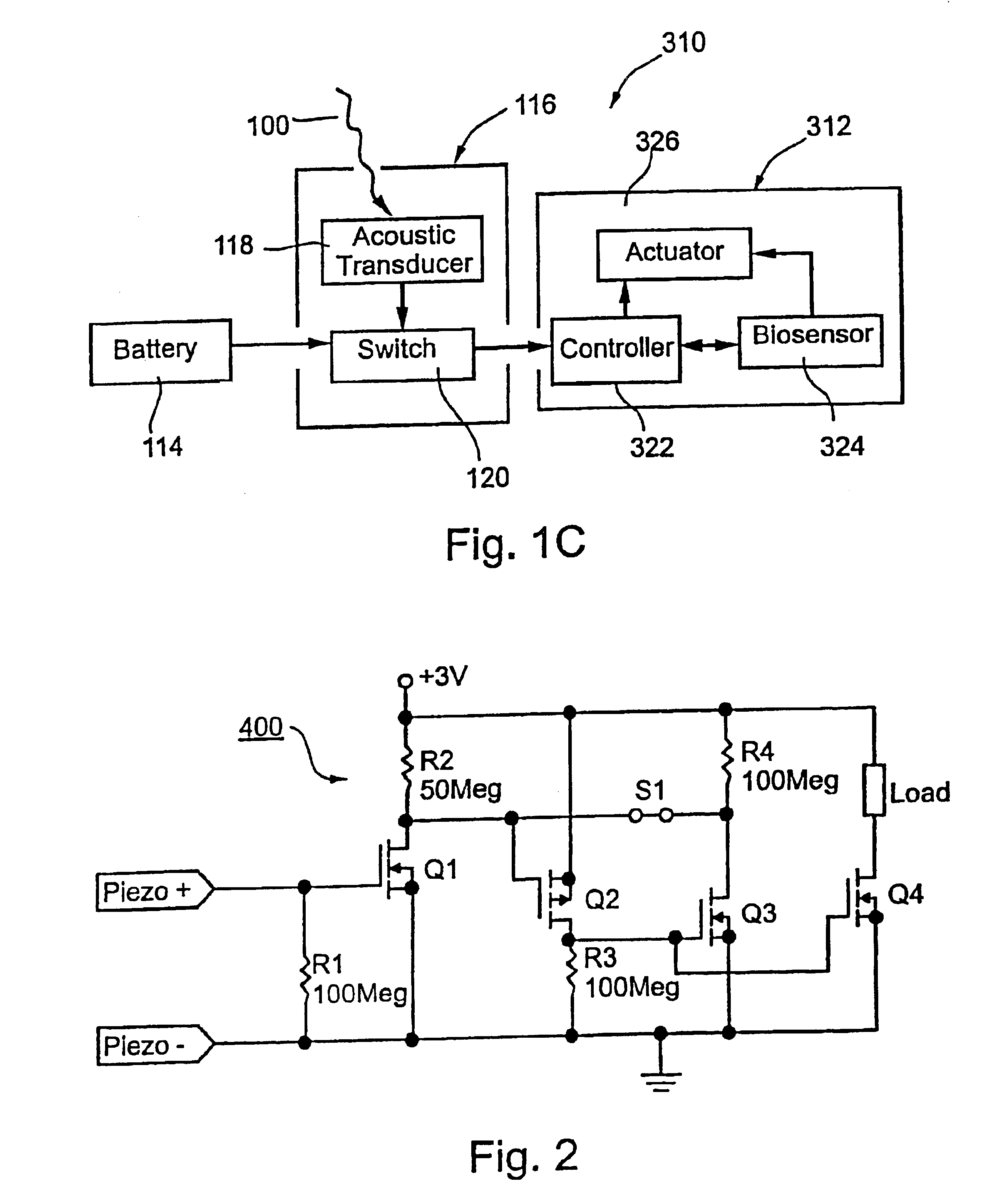
Systems and methods for communicating with implantable devices
Systems and methods for communicating with an implant within a patient's body using acoustic telemetry includes an external communications device attachable to the patient's skin. The device includes an acoustic transducer for transmitting acoustic signals into the patient's body and / or for receiving acoustic signals from the implant. The device includes a battery for providing electrical energy to operate the device, a processor for extracting data from acoustic signals received from the implant, and memory for storing the data. The device may include an interface for communicating with a recorder or computer, e.g., to transfer data from the implant and / or to receive instructions for controlling the implant. The device is secured to the patient's skin for controlling, monitoring, or otherwise communicating with the implant, while allowing the patient to remain mobile.
Owner:REMON MEDICAL TECH
Medical Diagnostic and Treatment Platform Using Near-Field Wireless Communication of Information Within a Patient's Body
ActiveUS20080306359A1Efficient communicationSmall sizeElectric signal transmission systemsCircuit arrangementsMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
The present invention provides implantable systems that communicate wirelessly with each other using a unique format that enables devices configurations and applications heretofore not possible. Embodiments of the present invention provide communication apparatuses and methods for exchanging information with implantable medical devices. In some embodiments, two implantable devices communicate with each other using quasi-electrostatic signal transmission in a long wavelength / low frequency electromagnetic band, with the patient's body acting as a conductive medium.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
Capsule and method for treating or diagnosing the intestinal tract
ActiveUS7160258B2Comprehensive knowledgeElectrotherapyPerson identificationMedicineElectrical stimulations
A device and method for mapping, diagnosing and treating the intestinal tract is provided using a capsule passing through the intestinal tract. Further, a capsule tracking system is provided for tracking a capsule's location along the length of an intestinal tract as various treatment and / or sensing modalities are employed. In one variation, an acoustic signal is used to determine the location of the capsule. A map of sensed information may be derived from the pass of a capsule. Capsules may be subsequently passed through to treat the intestinal tract at a determined location along its length. One variation uses an electrical stimulation capsule to treat and / or diagnose a condition in the intestinal tract.
Owner:ENTRACK INC
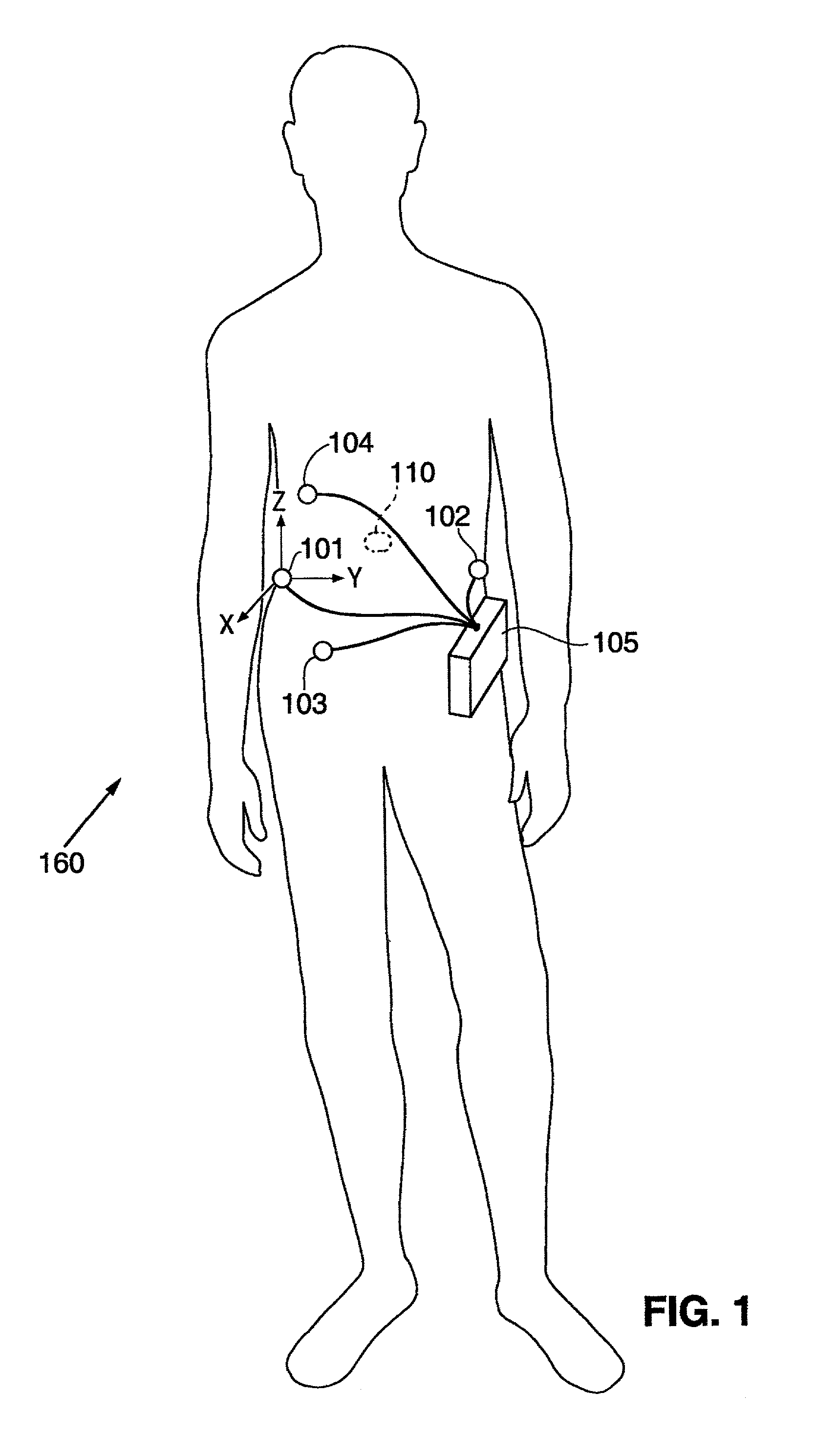
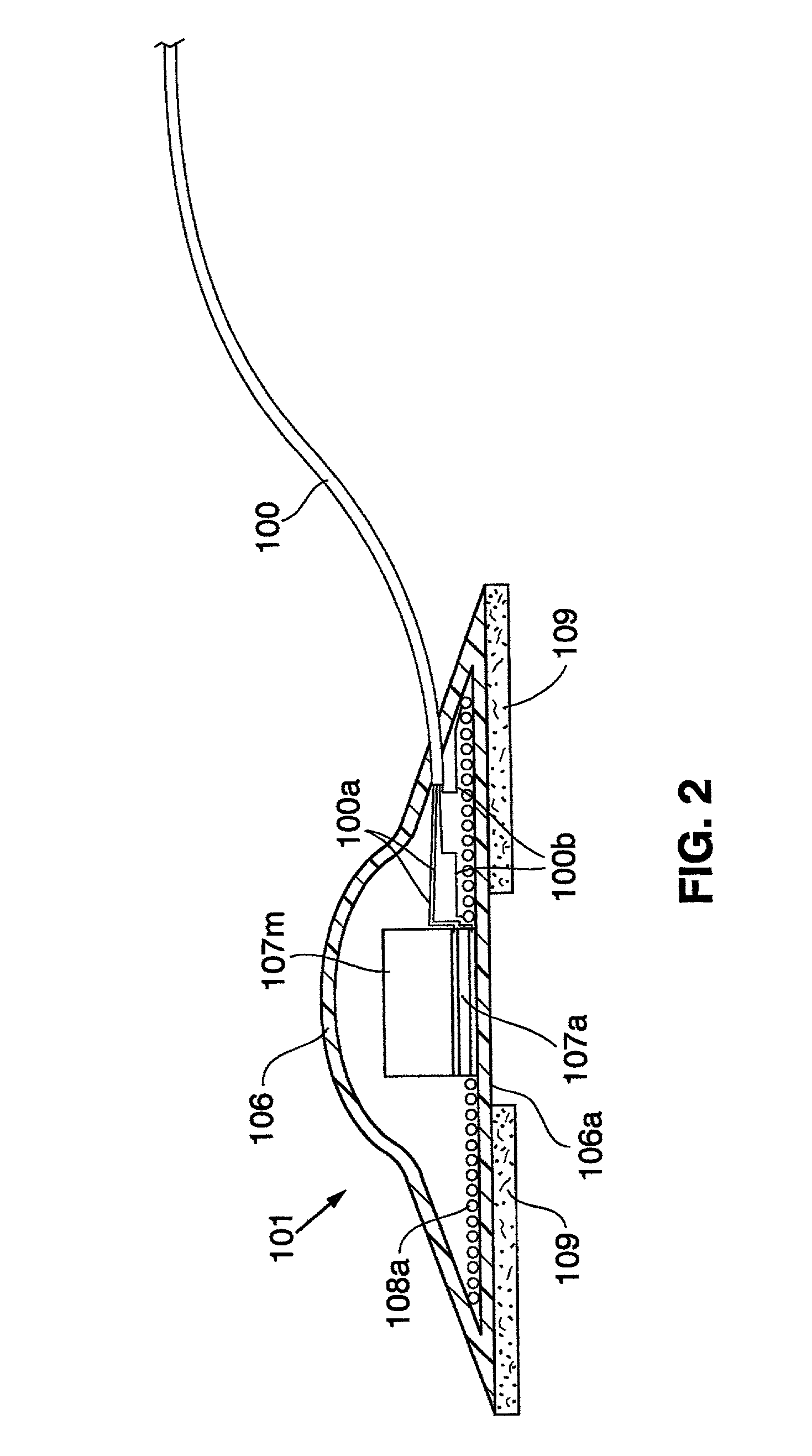
Miniature ingestible capsule
A miniature ingestible imaging capsule having a membrane defining an internal cavity and being provided with a window is provided. A lens is disposed in relation to said window and a light source disposed in relation to the lens for providing illumination to outside of the membrane through the window. An imaging array is disposed in relation to the lens, wherein images from the lens impinge on the imaging array. A transmitter is disposed in relation to the imaging array for transmitting a signal from the imaging array to an associated transmitter outside of the membrane. The lens, light source imaging array, and transmitter are enclosed within the internal cavity of the capsule.
Owner:NAIR PADMANABHAN P +1
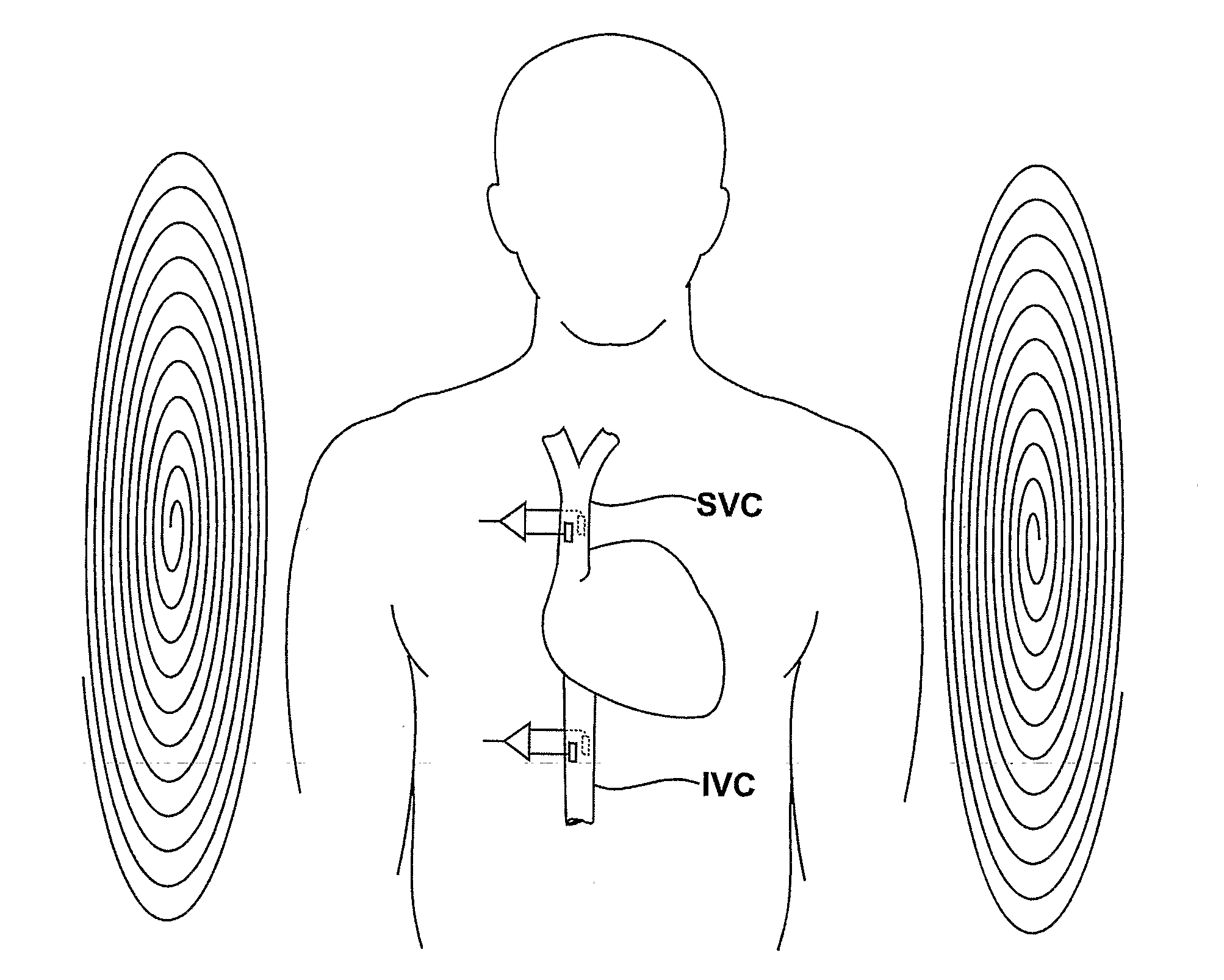
Guided Radiation Therapy System
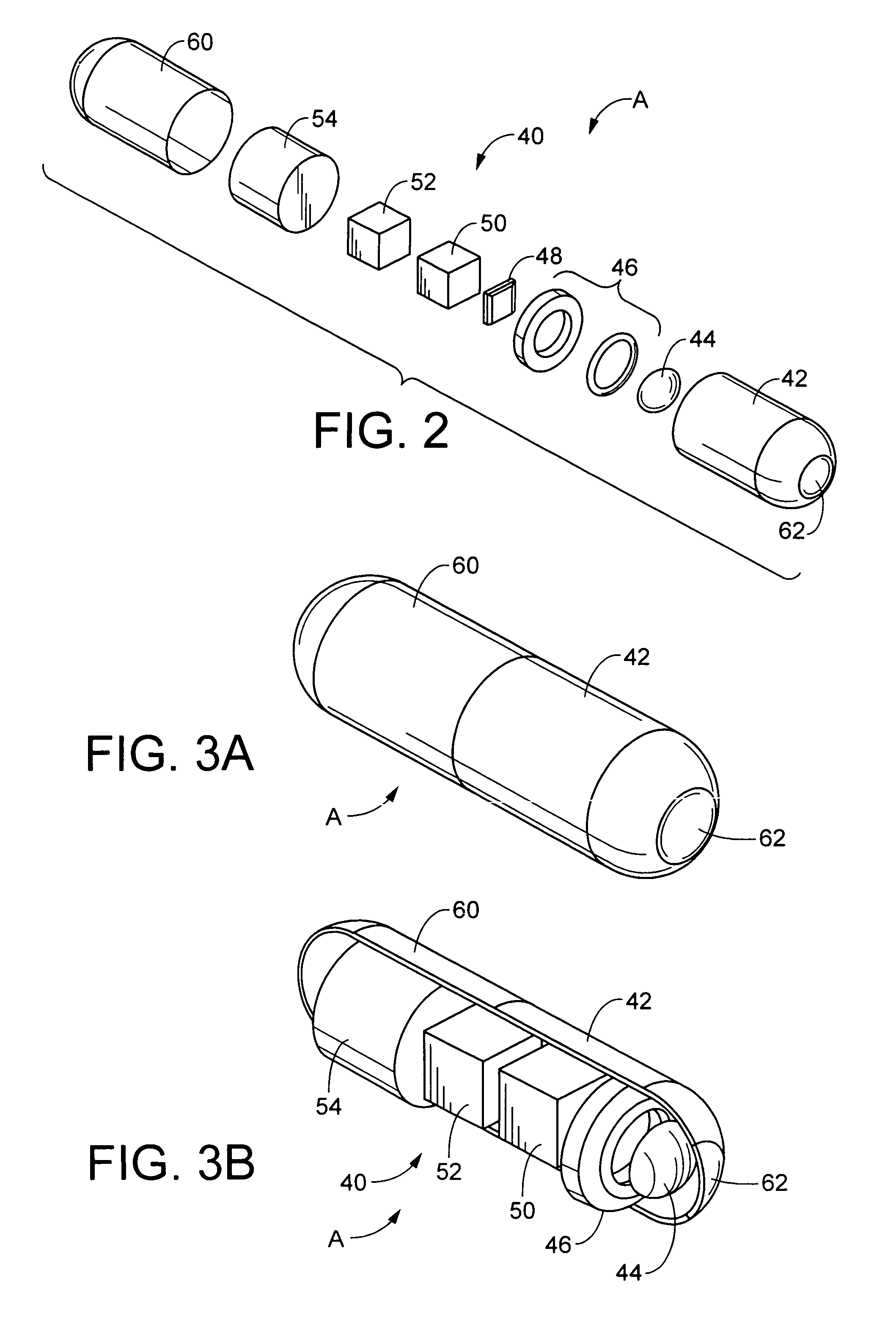
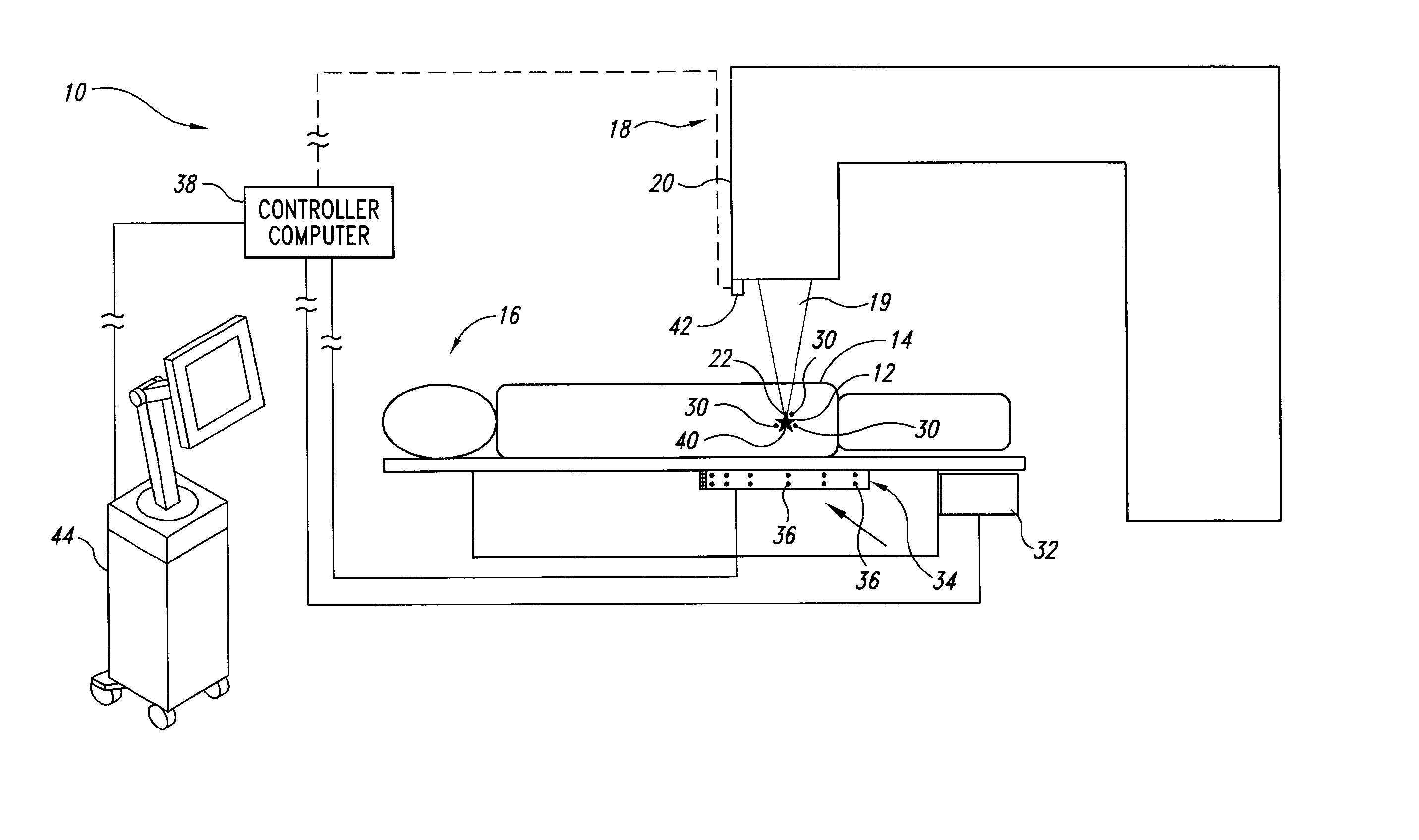
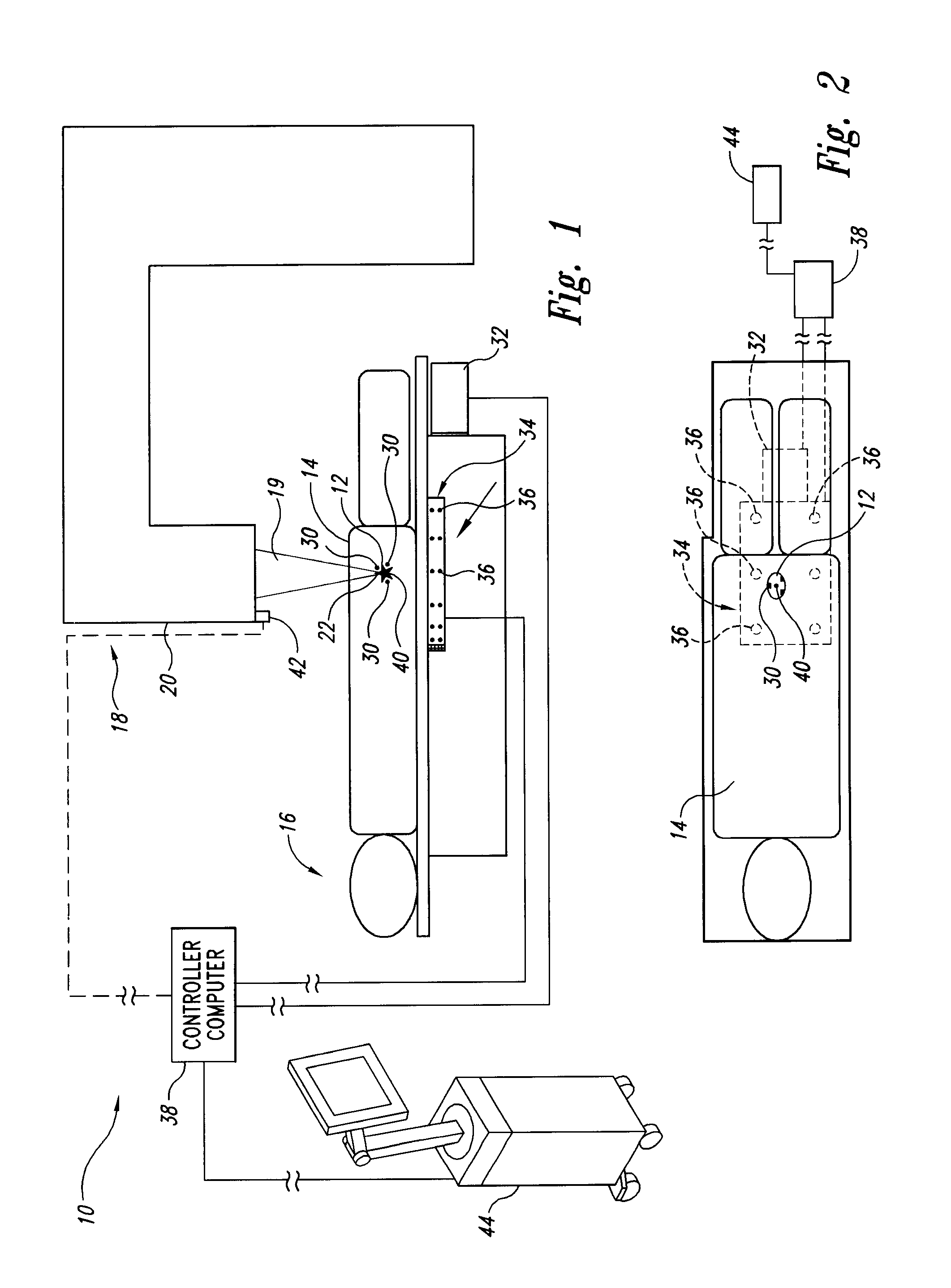
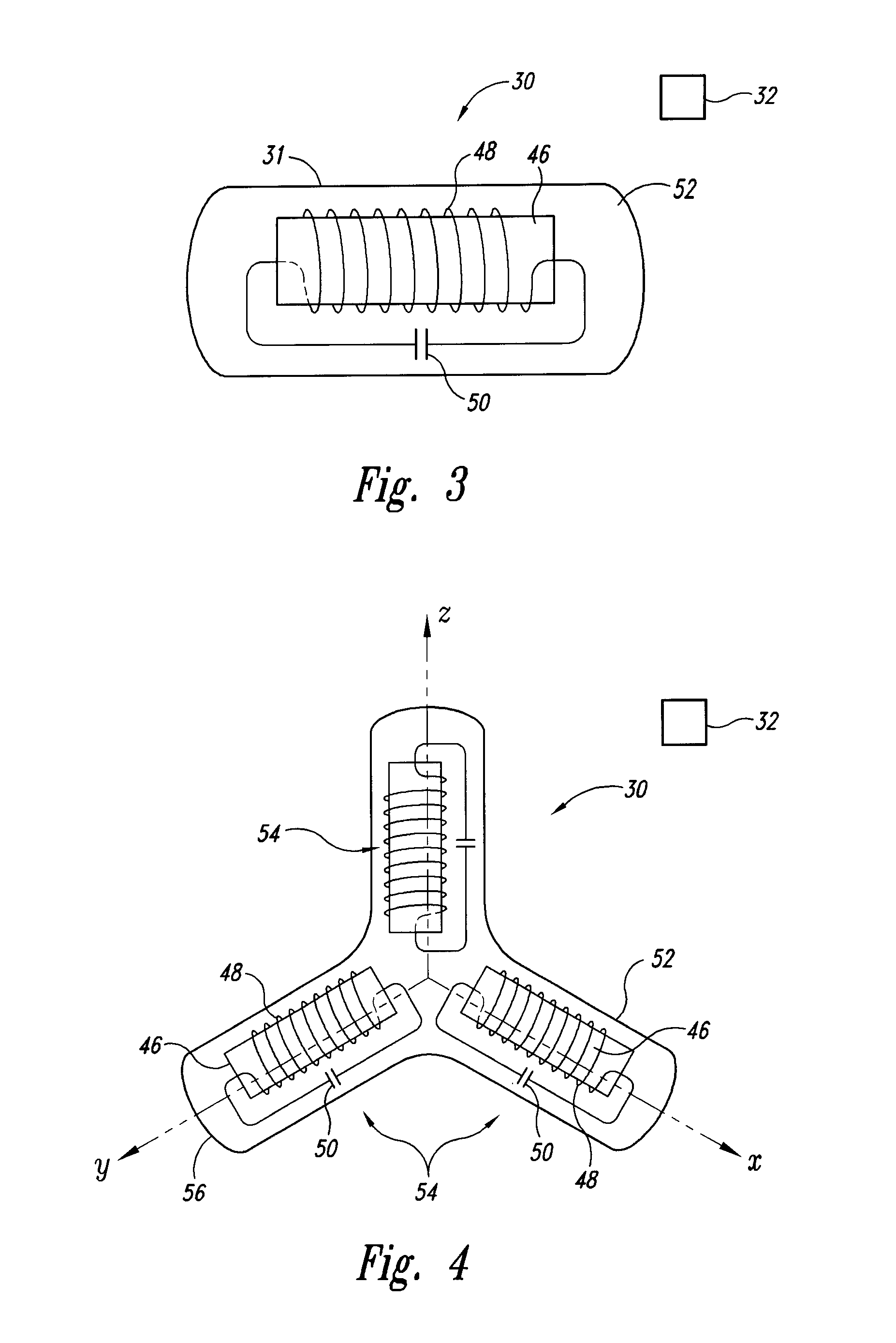
InactiveUS20020193685A1Accurate locationAccurate trackingSurgical navigation systemsPosition fixationMonitoring systemIsocenter
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> A system and method for accurately locating and tracking the position of a target, such as a tumor or the like, within a body. In one embodiment, the system is a target locating and monitoring system usable with a radiation delivery source that delivers selected doses of radiation to a target in a body. The system includes one or more excitable markers positionable in or near the target, an external excitation source that remotely excites the markers to produce an identifiable signal, and a plurality of sensors spaced apart in a known geometry relative to each other. A computer is coupled to the sensors and configured to use the marker measurements to identify a target isocenter within the target. The computer compares the position of the target isocenter with the location of the machine isocenter. The computer also controls movement of the patient and a patient support device so the target isocenter is co-incident with the machine isocenter before and during radiation therapy.
Owner:CALYPSO MEDICAL +1
Chronically-implanted device for sensing and therapy
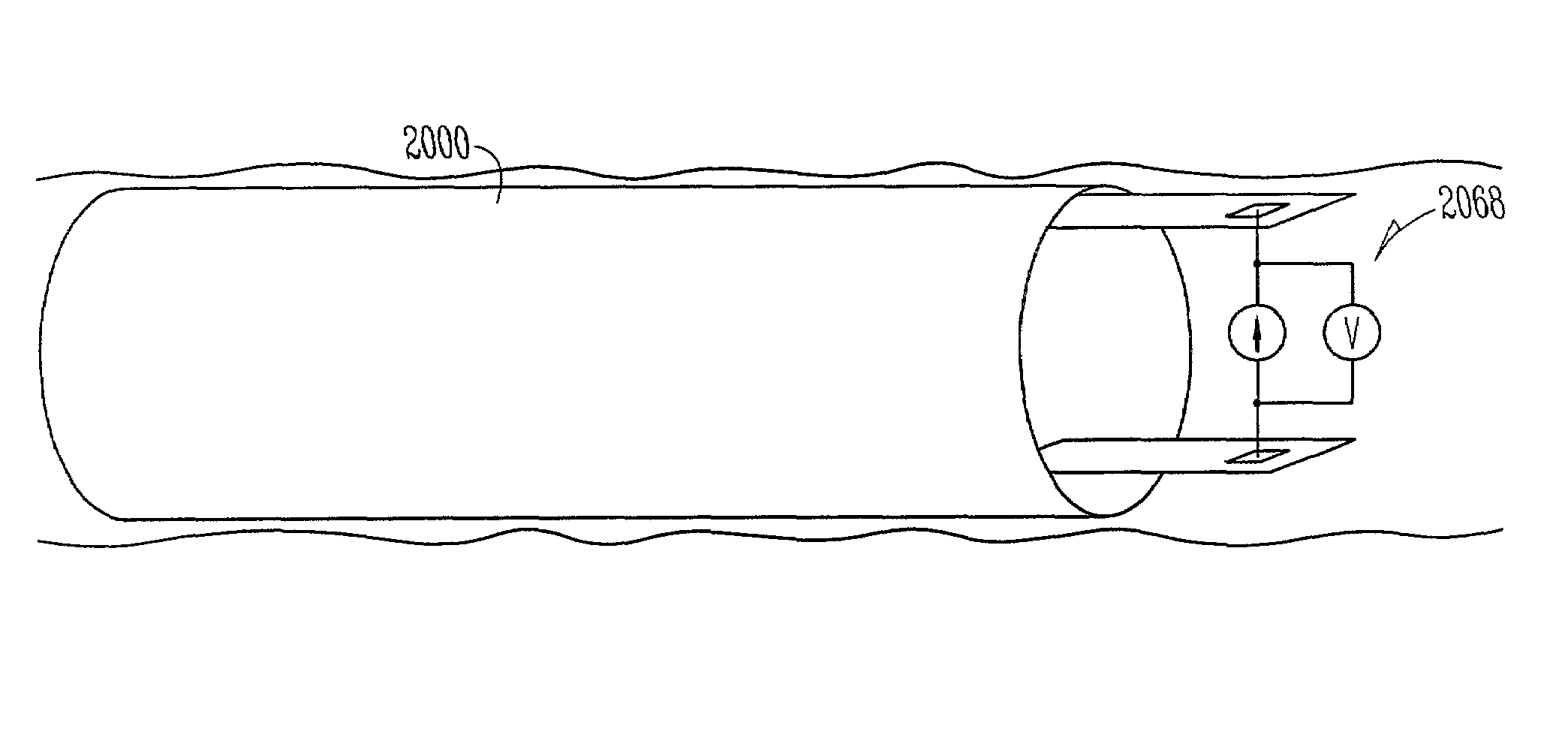
InactiveUS7236821B2Easy to solvePrevent restenosisStentsEndoradiosondesElectricityTherapeutic Devices
Systems, devices and methods are provided for providing sensing and therapy functions using a chronically-implanted device. According to one embodiment, the device includes a structure adapted to be chronically placed within a biosystem, and further includes sensing circuitry and therapy-providing circuitry attached to the structure. The sensing circuitry is adapted to sense mechanical parameters in the biosystem. The therapy-providing circuitry is adapted to provide therapy to the biosystem. According to various embodiments of the device, the sensing circuitry is further adapted to sense electrical and / or chemical parameters in the biosystem, and / or is adapted to provide electrical therapy and / or to provide drug-eluting therapy. One embodiment of the device includes a stent-like structure adapted to be chronically placed intravascularly in the biosystem.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
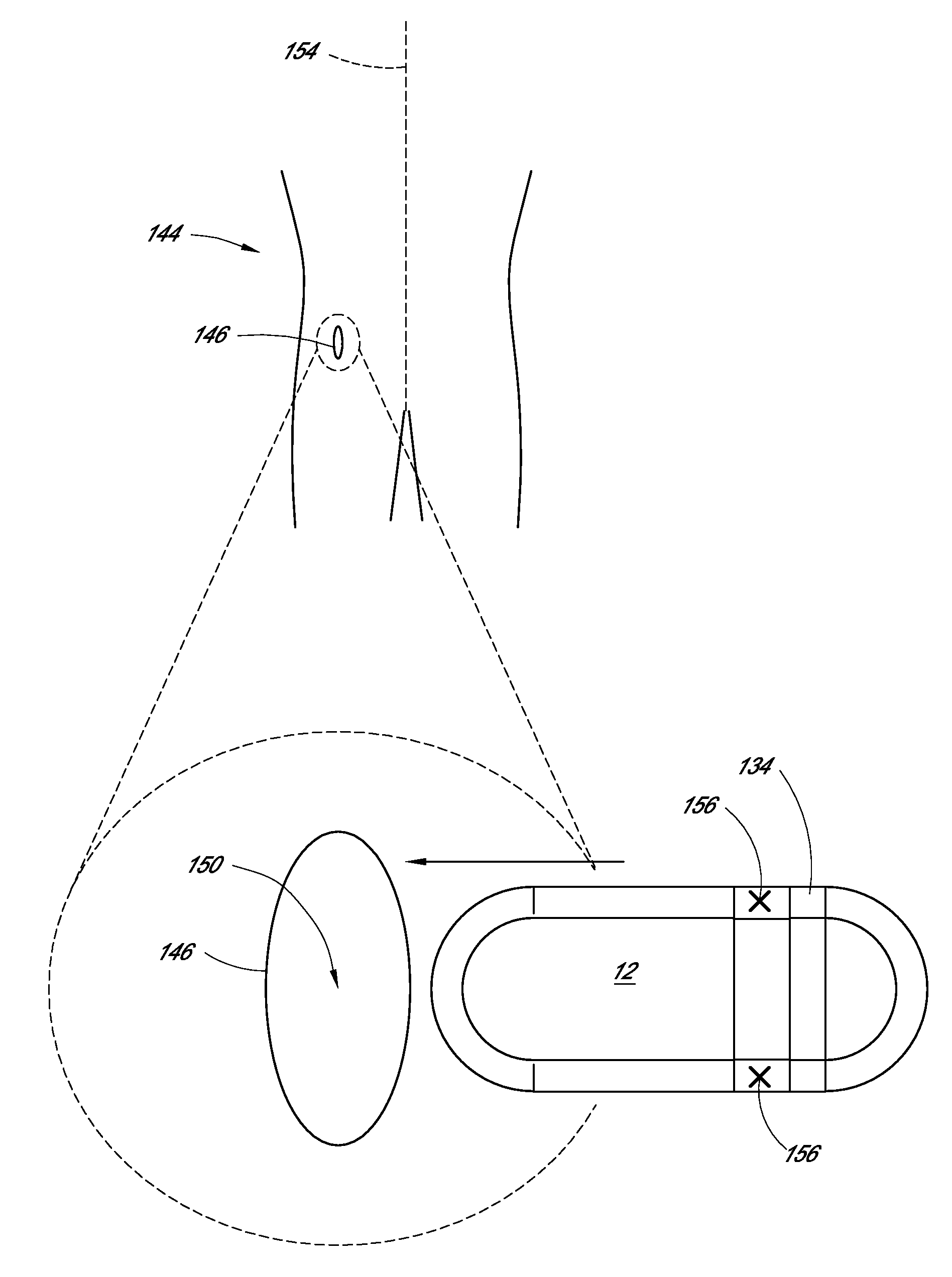
Reusable analyte sensor site and method of using the same
A reusable analyte sensor site for use with a replaceable analyte sensor for determining a level of an analyte includes a site housing and a resealable insertion site coupled to one end of the site housing. Preferably, the site housing is formed to have an interior cavity, and includes an outer membrane made of a material selected to promote vascularization and having a first pore size, and an inner membrane made of a material selected to be free of tissue ingress. Also, the site housing permits the analyte to pass through the site housing to the interior cavity to permit measurement by the replaceable analyte sensor. The resealable insertion site is provided for inserting the replaceable analyte sensor into the interior cavity of the site housing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
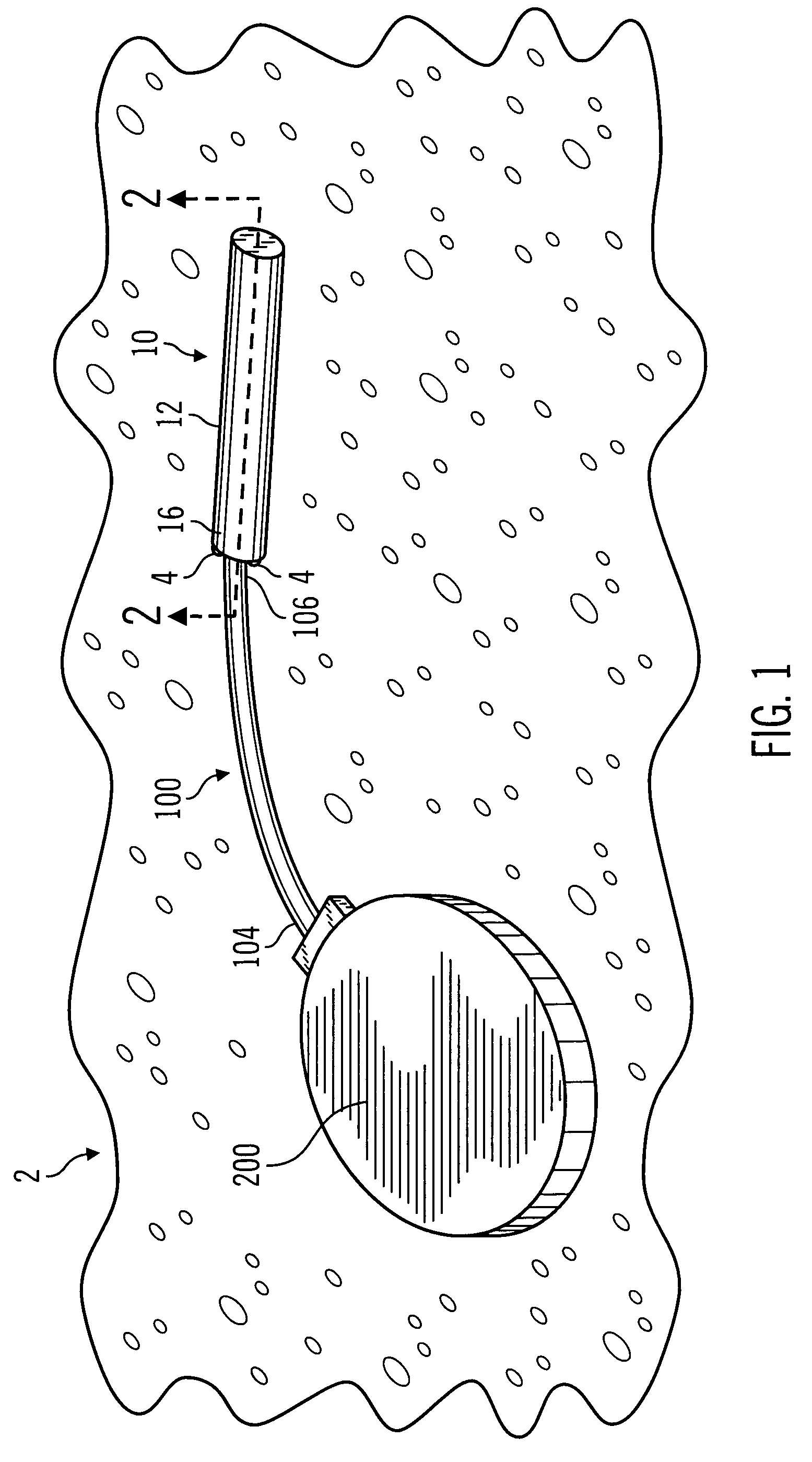
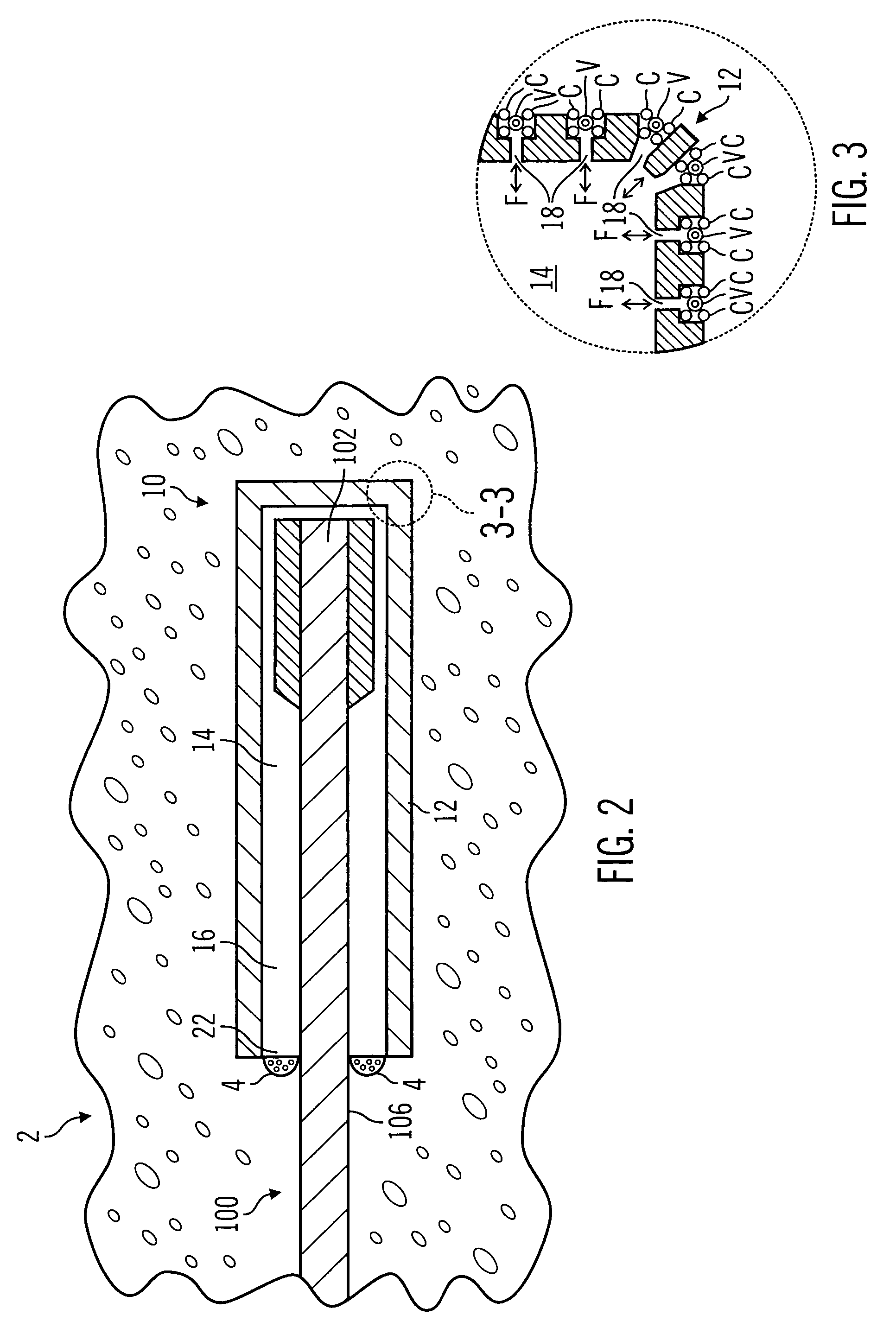
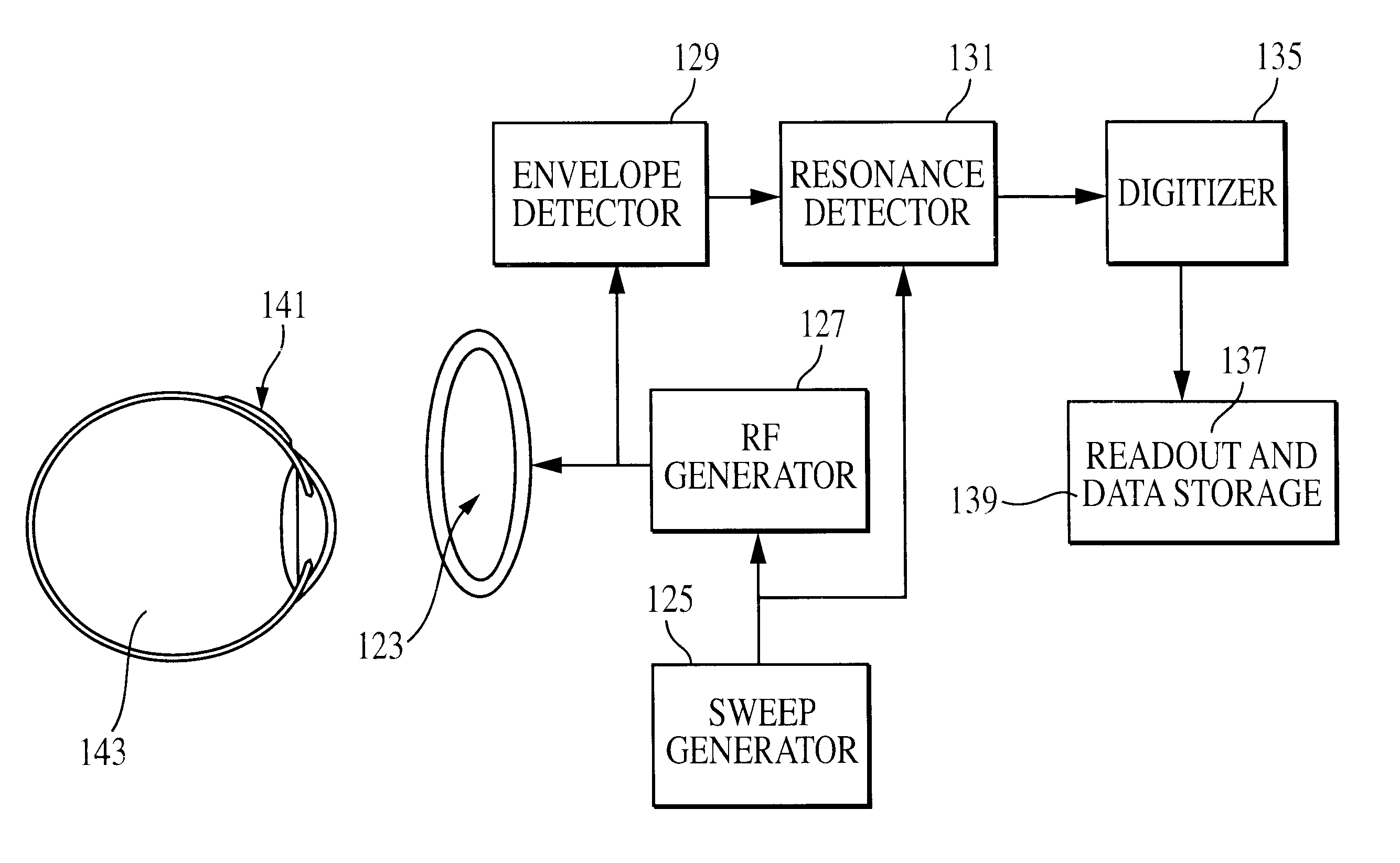
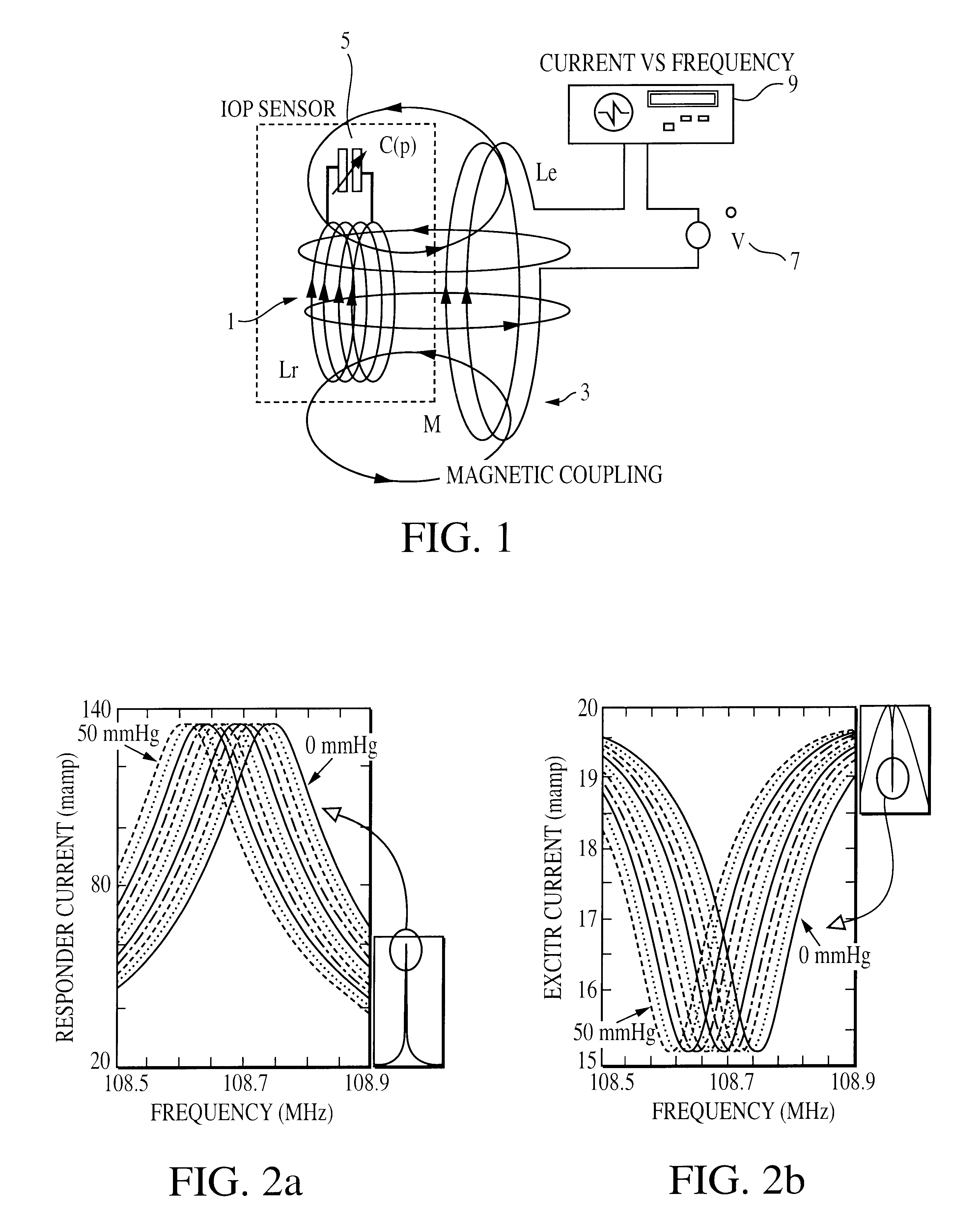
Method for monitoring intraocular pressure using a passive intraocular pressure sensor and patient worn monitoring recorder
A device for passively measuring intraocular pressure of a patient including an in vivo sensor and an instrument external to the patient for remotely energizing the sensor, thereby permitting the instrument to determine the intraocular pressure. The device directly and continuously measures the intraocular pressure of a patient. The in vivo sensor in the intraocular pressure monitor includes a capacitive pressure sensor and an inductive component. An instrument, external to the patient, measures the pressure, provides readout of the pressure values and determines the intraocular pressure.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Internal drug dispenser capsule medical device
The present invention provides a swallowable internal drug medical device. The device includes a swallowable capsule. A sensing module is disposed in the capsule. A bioactive substance dispenser is disposed in the capsule. A memory and logic component is disposed in the capsule and in communication with the sensing module and the dispenser.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
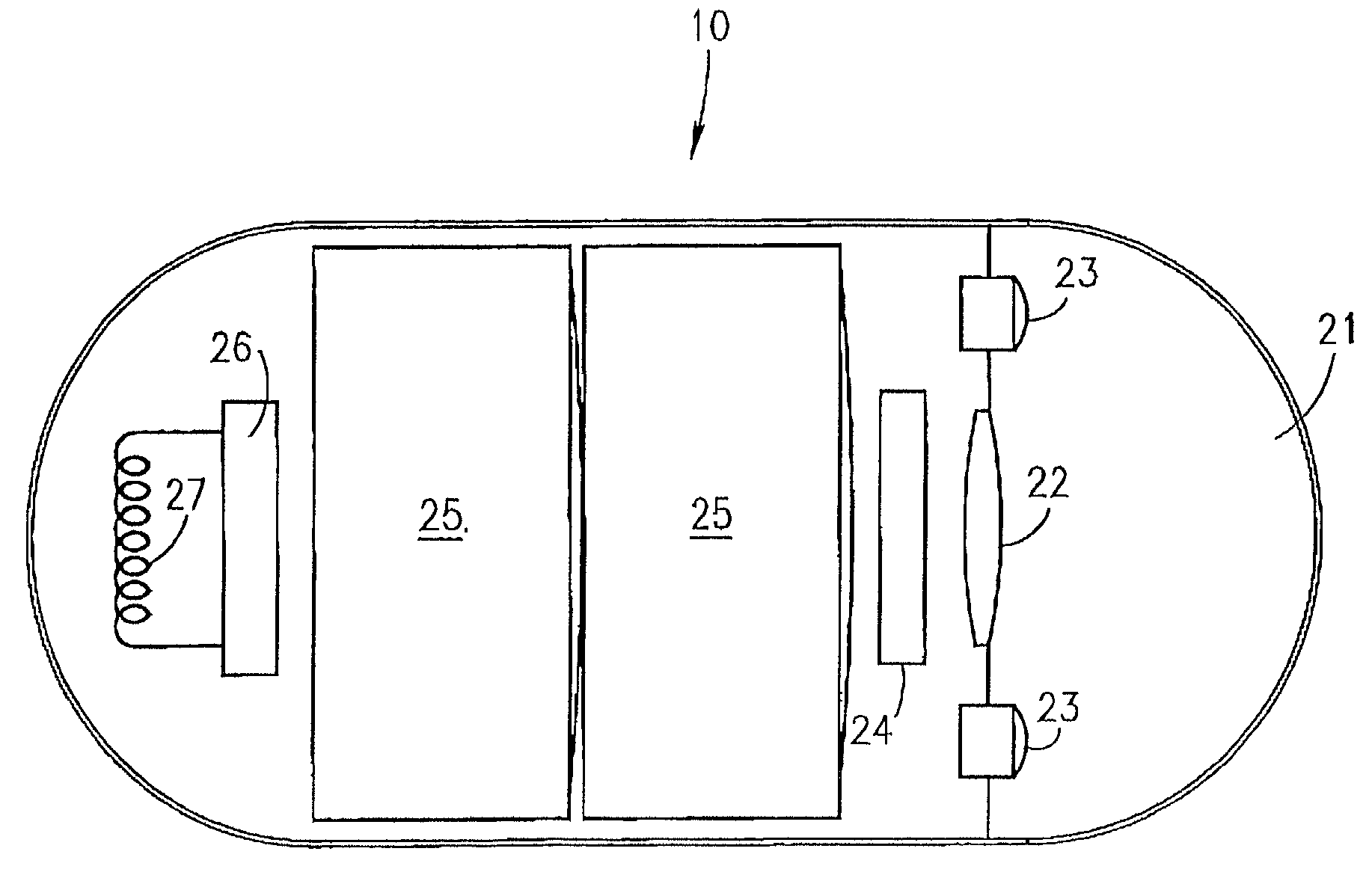
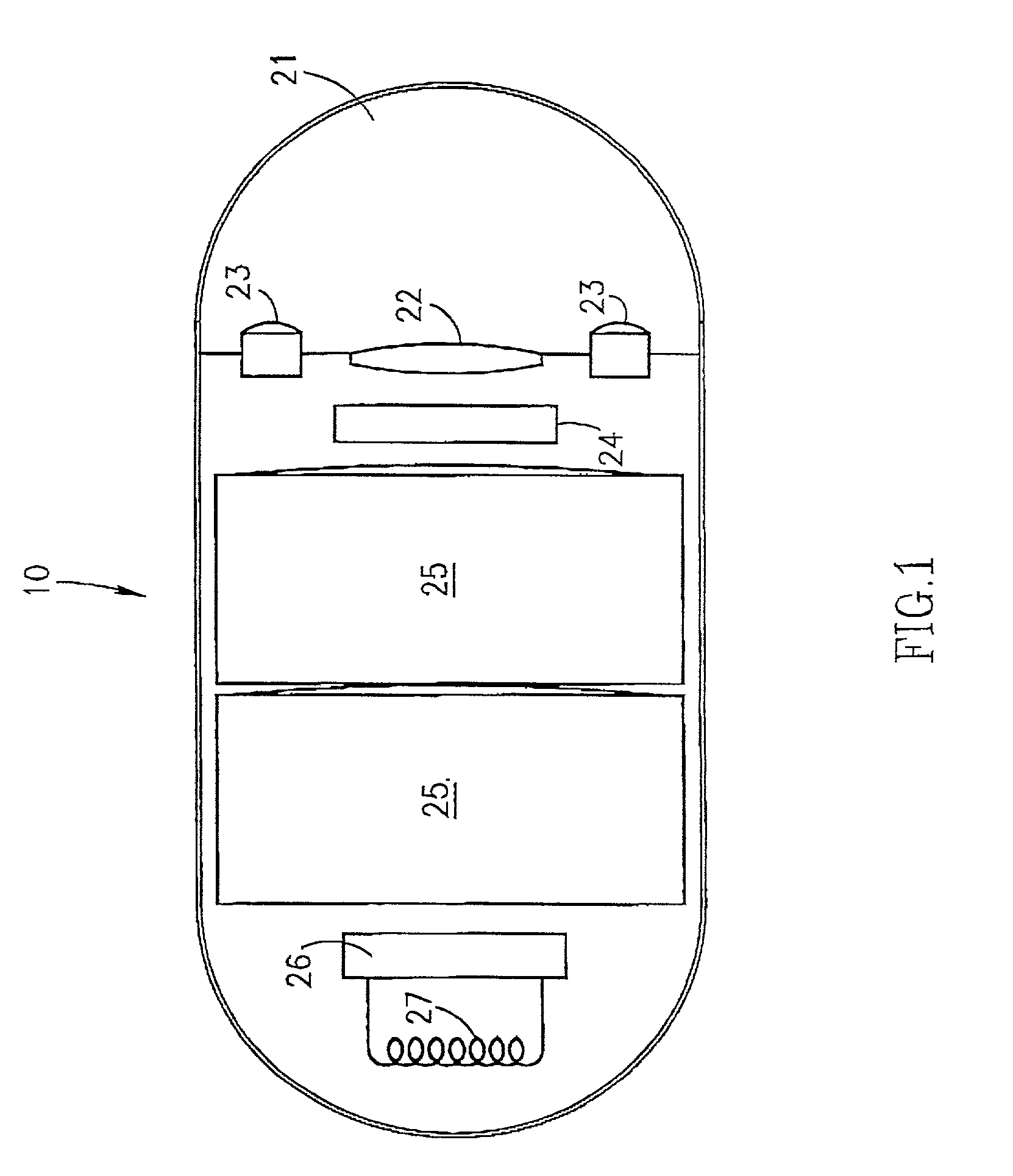
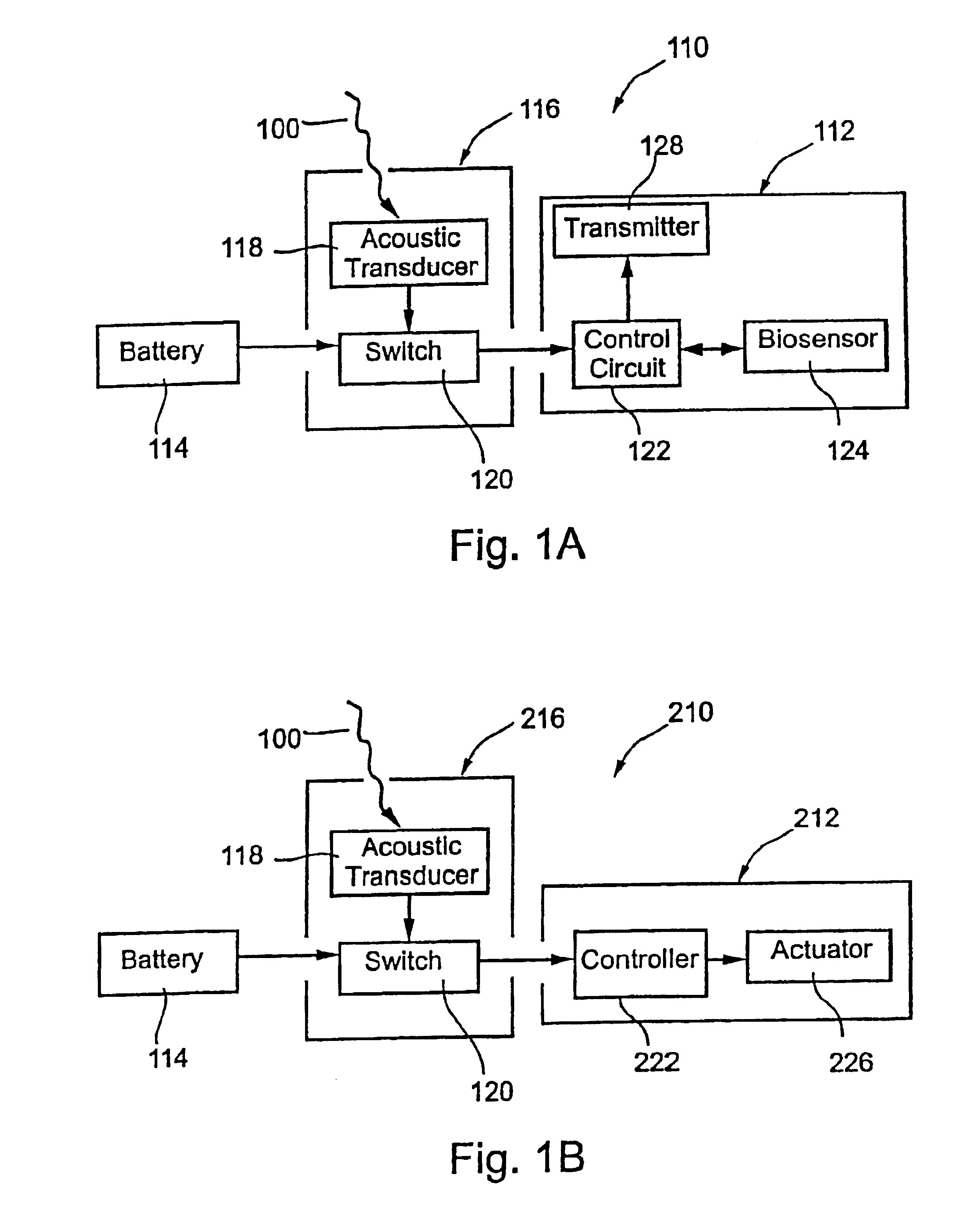
Embedded bio-sensor system
InactiveUS7125382B2Improve accuracyAccurate measurementTelemedicineEndoradiosondesGlucose sensorsConcentrations glucose
Provided is a bio-sensor system which utilizes radio frequency identification technology and which includes a remote transponder in wireless communication with an implantable passively-powered on-chip transponder. The bio-sensor system is specifically adapted to provide a substantially stable and precise sensor reference voltage to a sensor assembly that is included with the on-chip transponder. The remote transponder is also configured to remotely receive data representative of a physiological parameter of the patient as well as identification data and may enable readout of one or more of the physiological parameters that are measured, processed and transmitted by the on-chip transponder upon request by the remote transponder. The precision and stability of the sensor reference voltage is enhanced by the specific circuit architecture of the glucose sensor to allow for relatively accurate measurement of the physiological parameter such as measurement of glucose concentration by a glucose sensor without the use of a microprocessor.
Owner:JAMM TECH INC
Optical-based sensing devices
InactiveUS6711423B2Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSurgeryAnalyteFluorescence
An optical-based sensor for detecting the presence or amount of an analyte using both indicator and reference channels. The sensor has a sensor body with a source of radiation embedded therein. Radiation emitted by the source interacts with indicator membrane indicator molecules proximate the surface of the body. At least one optical characteristic of these indicator molecules varies with analyte concentration. For example, the level of fluorescence of fluorescent indicator molecules or the amount of light absorbed by light-absorbing indicator molecules can vary as a function of analyte concentration. In addition, radiation emitted by the source also interacts with reference membrane indicator molecules proximate the surface of the body. Radiation (e.g., light) emitted or reflected by these indicator molecules enters and is internally reflected in the sensor body. Photosensitive elements within the sensor body generate both indicator channel and reference channel signals to provide an accurate indication of the concentration of the analyte. Preferred embodiments are totally self-contained and are sized and shaped for use in vivo in a human being. Such embodiments preferably include a power source, e.g. an inductor, which powers the source of radiation using external means, as well as a transmitter, e.g. an inductor, to transmit to external pickup means the signal representing the level of analyte.
Owner:SENSEONICS INC
Popular searches
Electric/electromagnetic visible signalling Using electrical means Radio/inductive link selection arrangements Electric signalling details Burglar alarm by hand-portable articles removal Radiation diagnostics Sampling Biochemistry cleaning apparatus Biomass after-treatment Enzymology/microbiology apparatus
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com