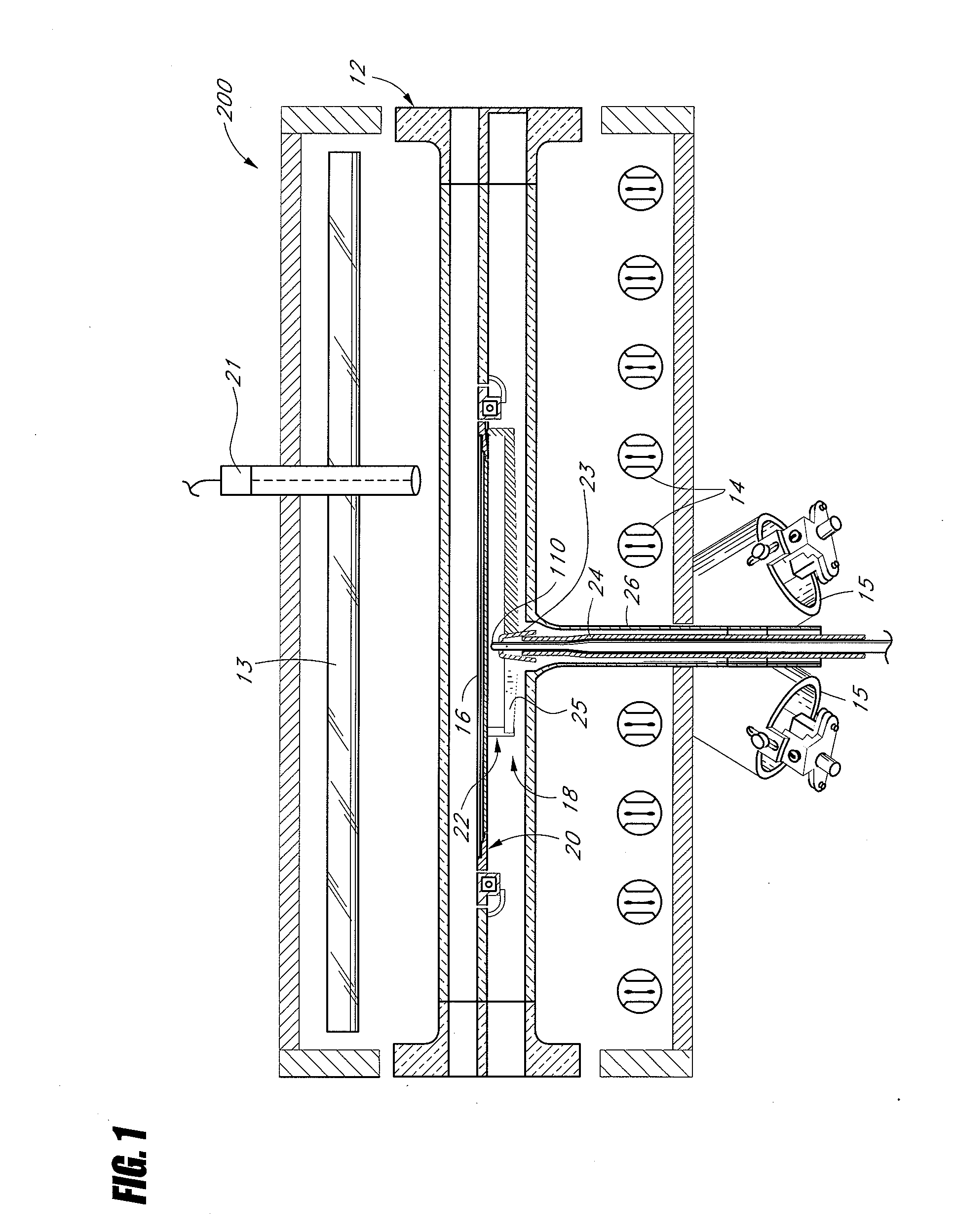
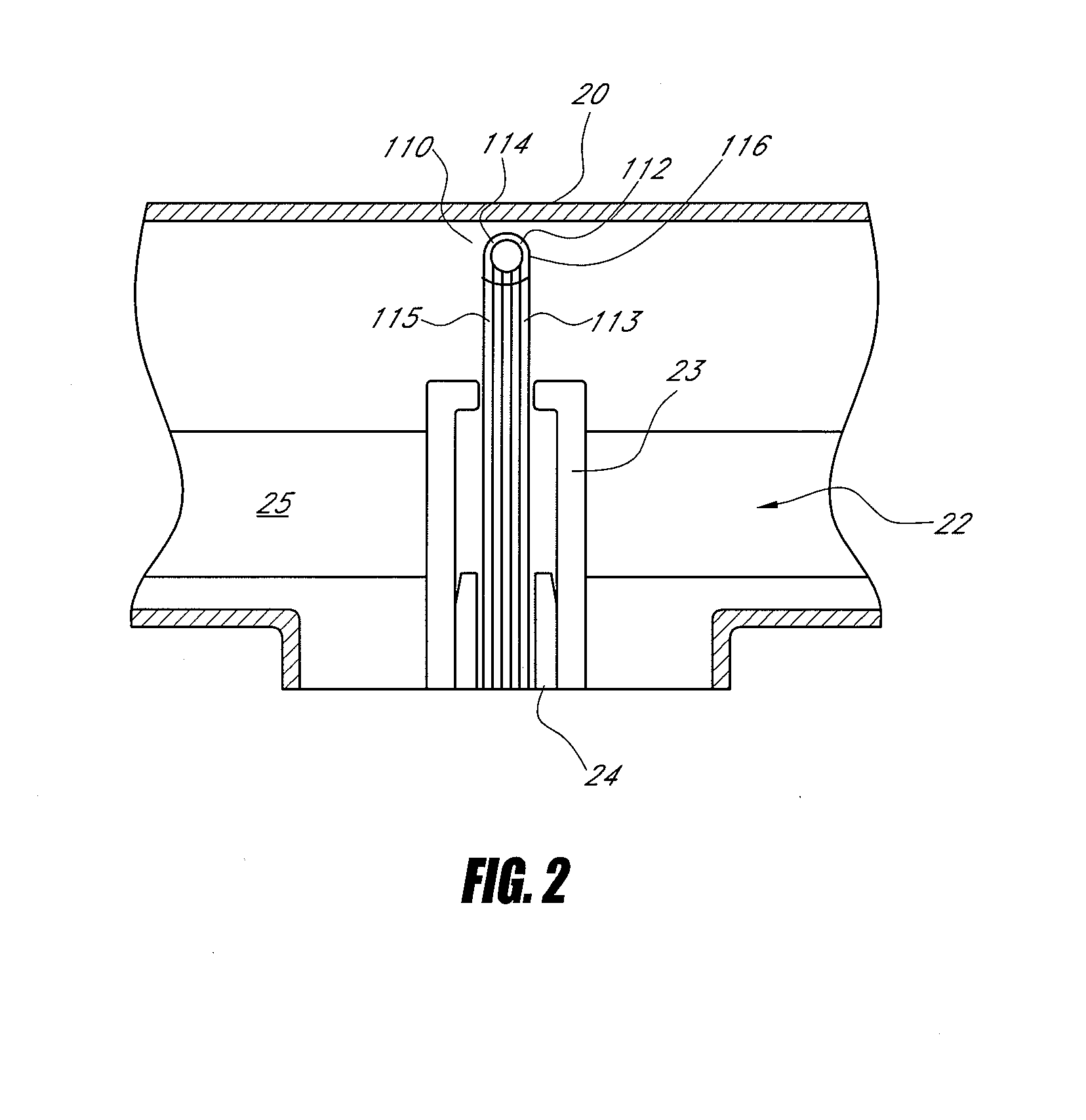
Patents
Literature
38542results about "Using electrical means" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
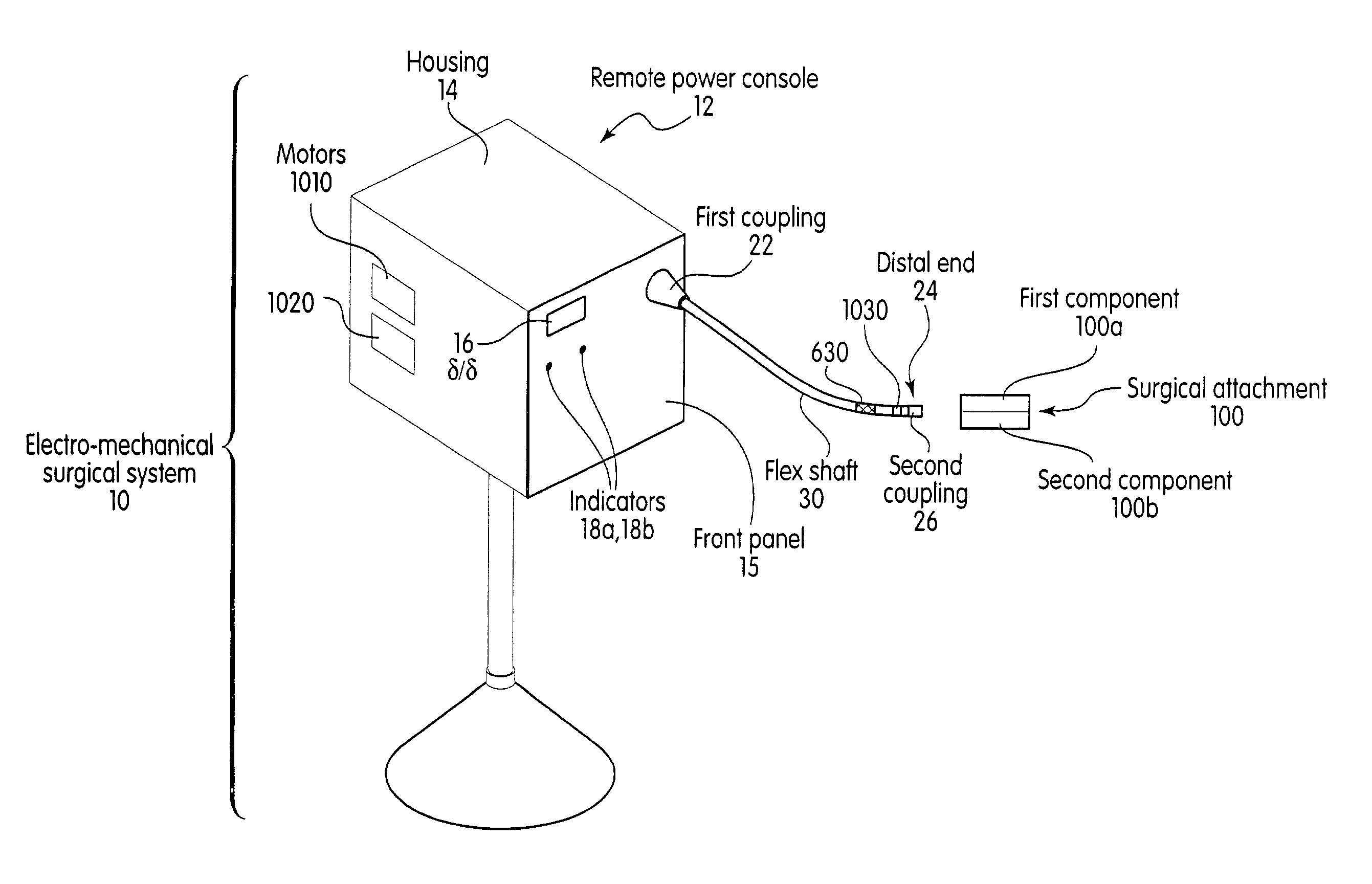
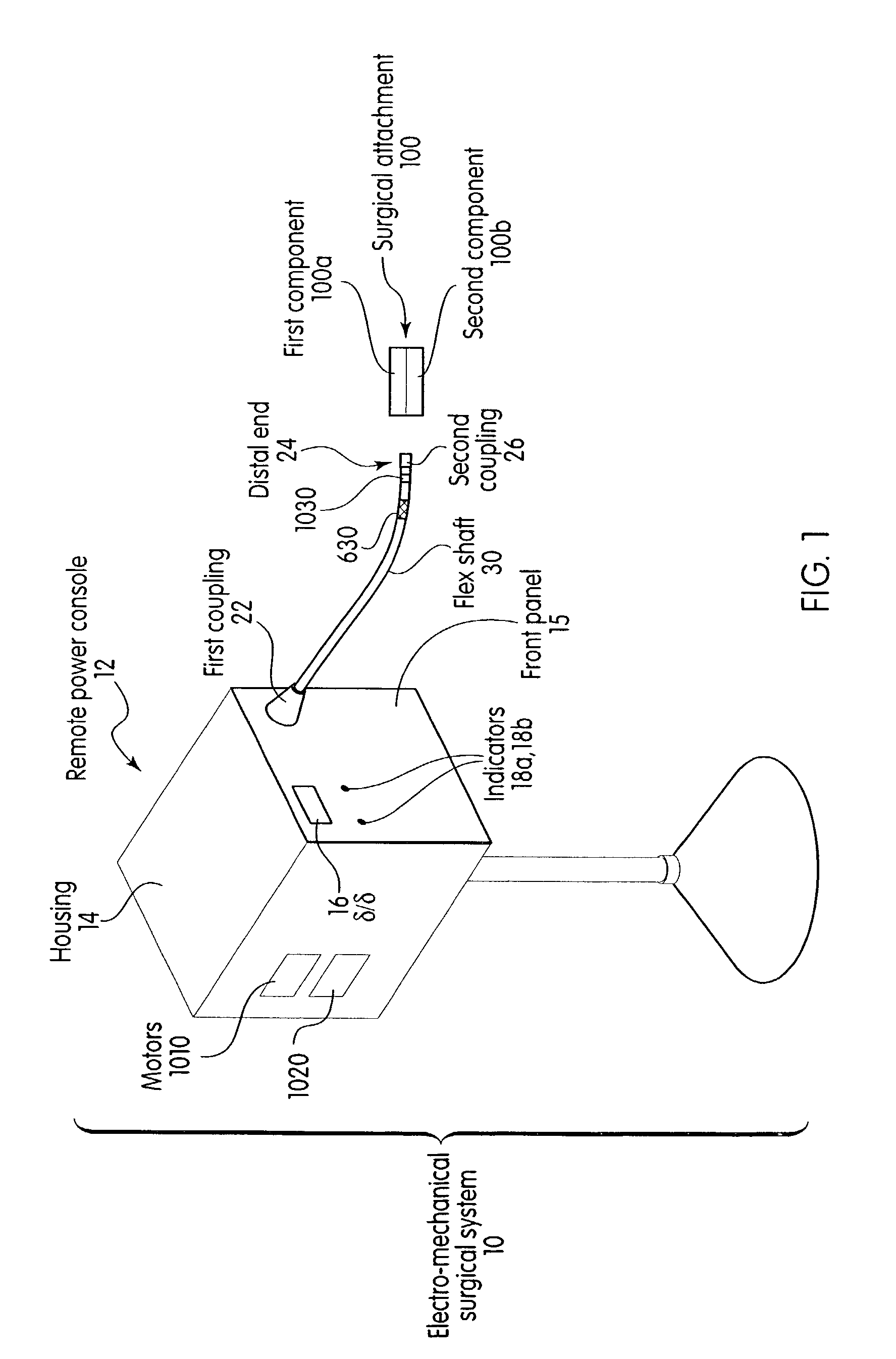
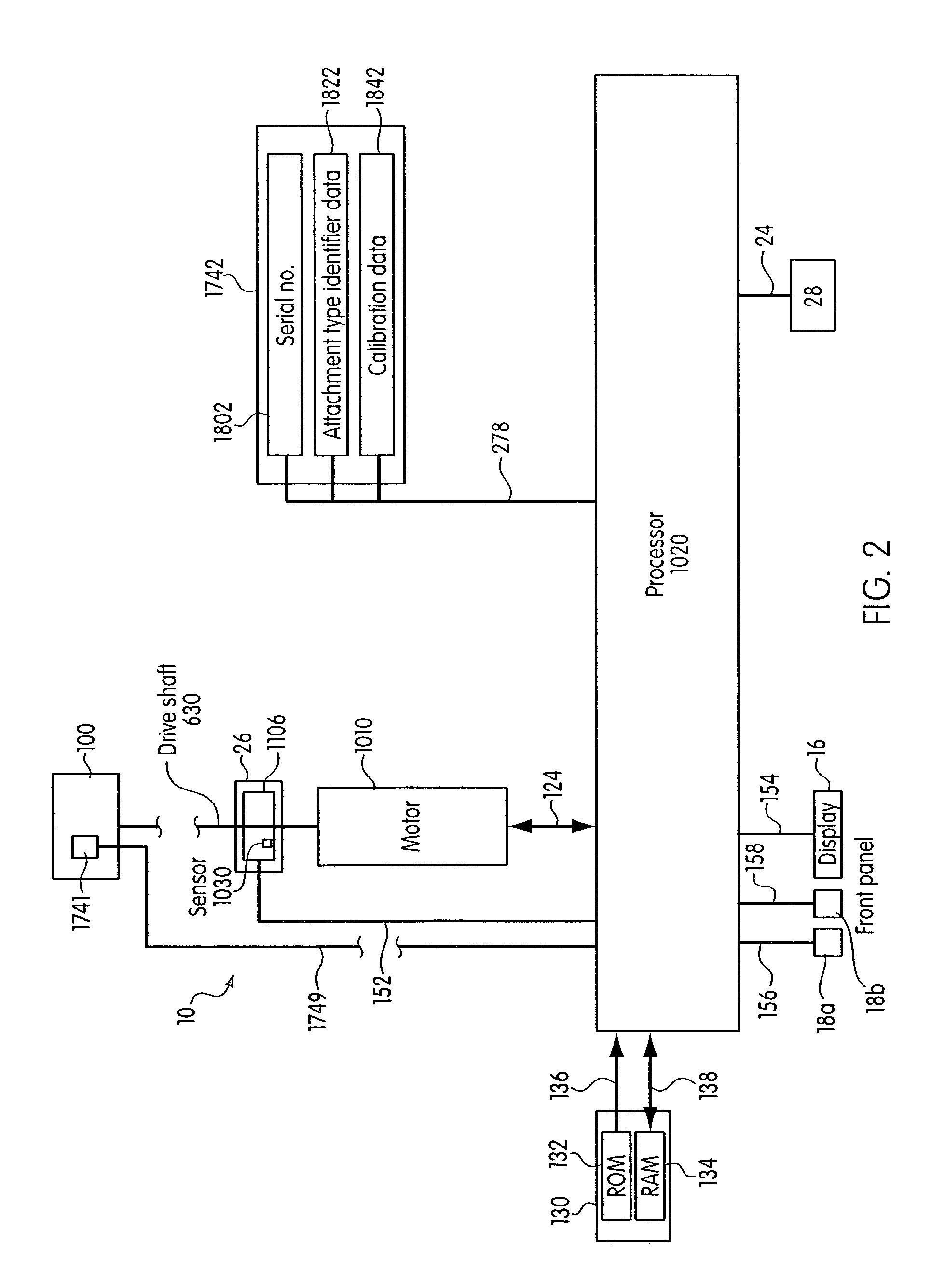
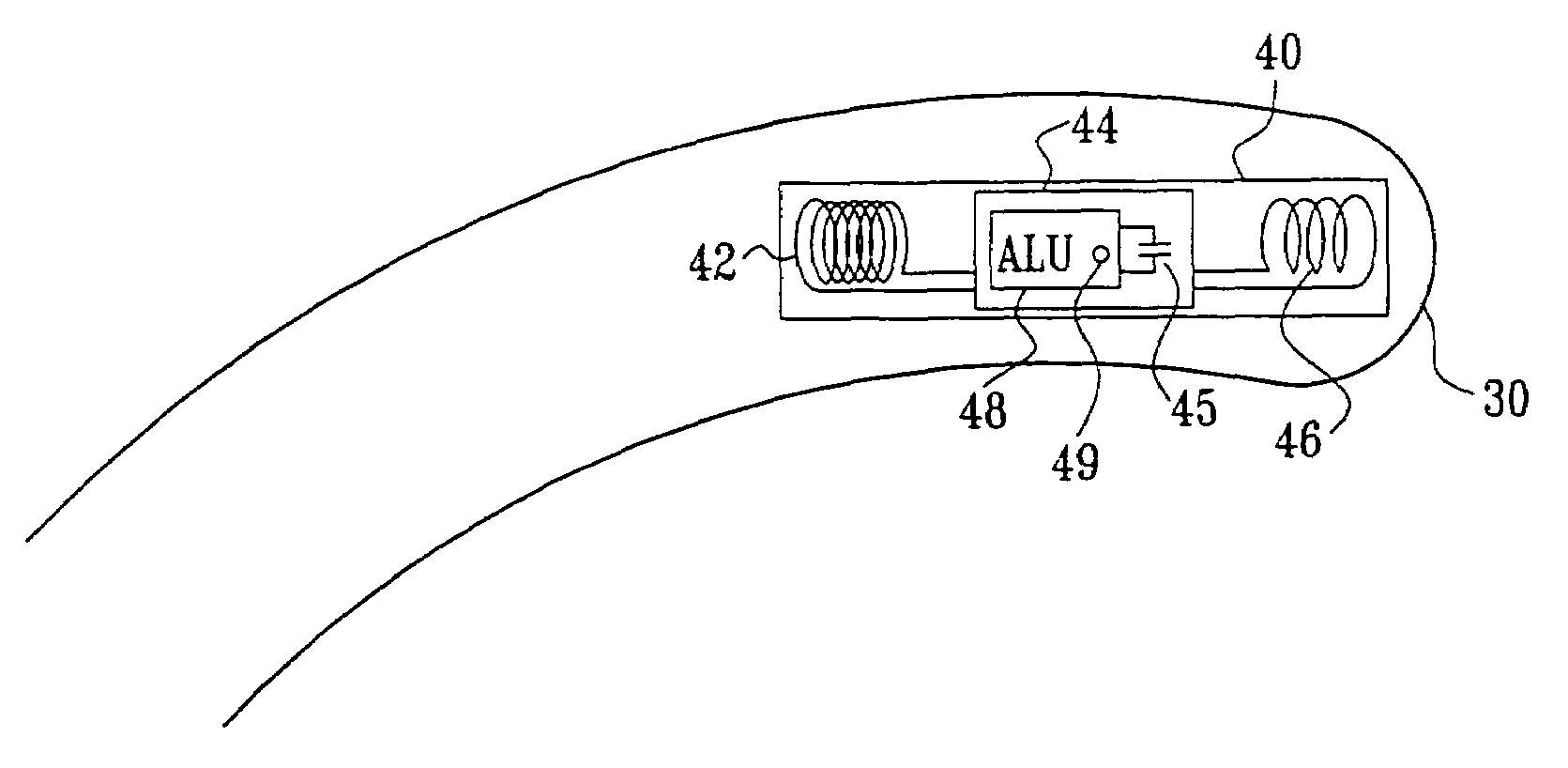
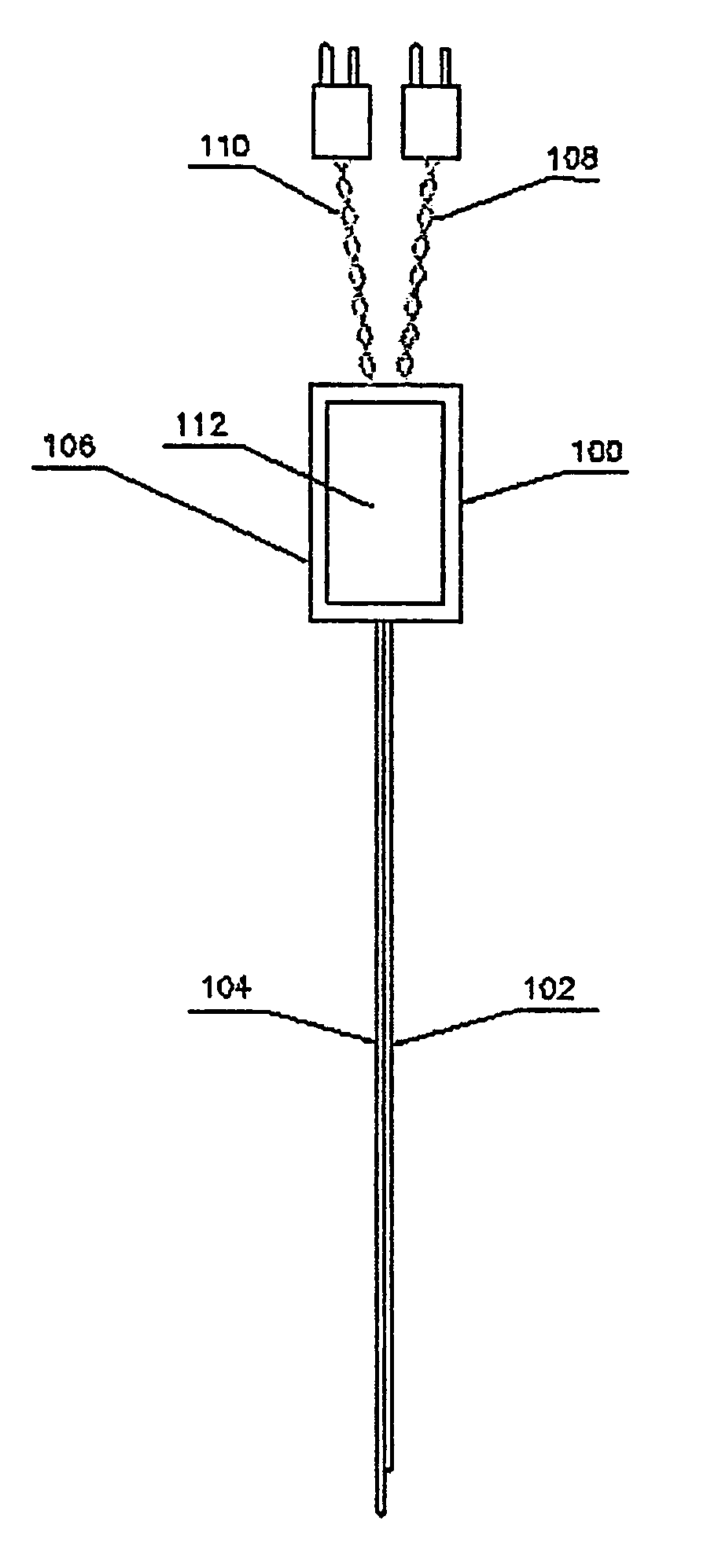
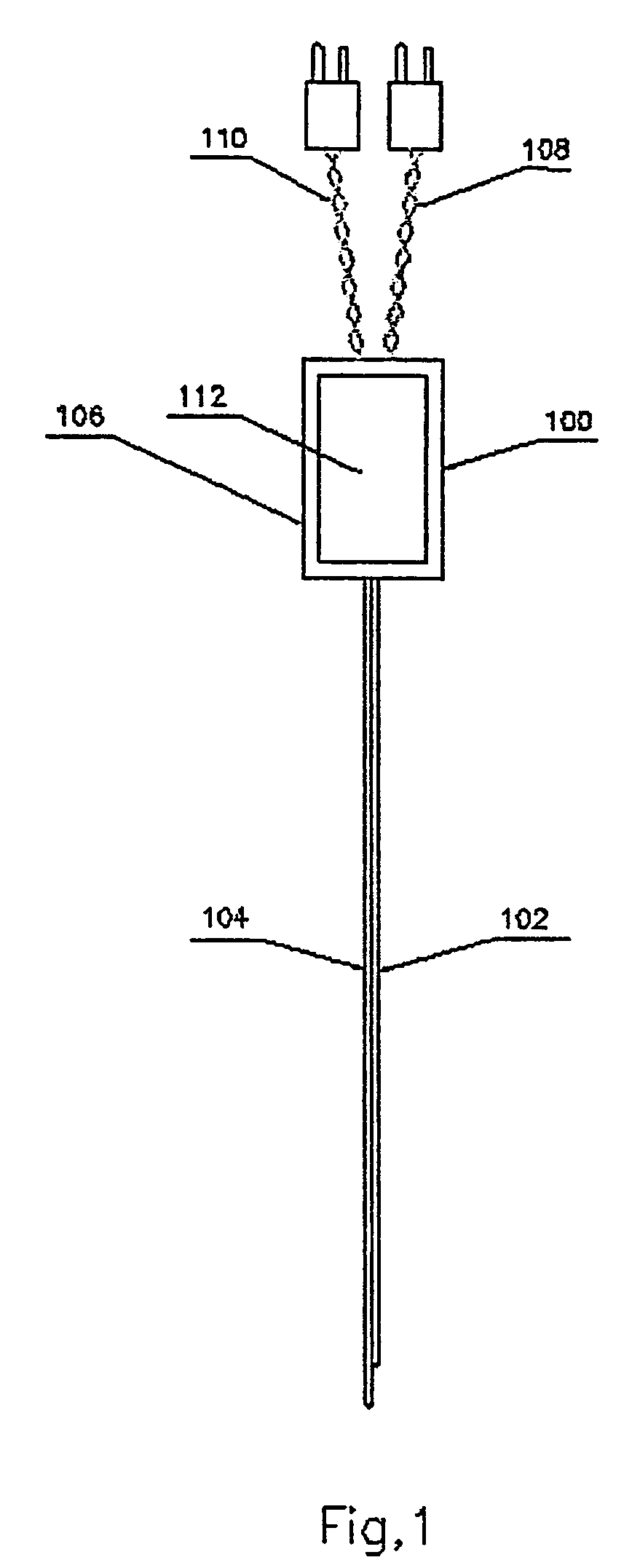
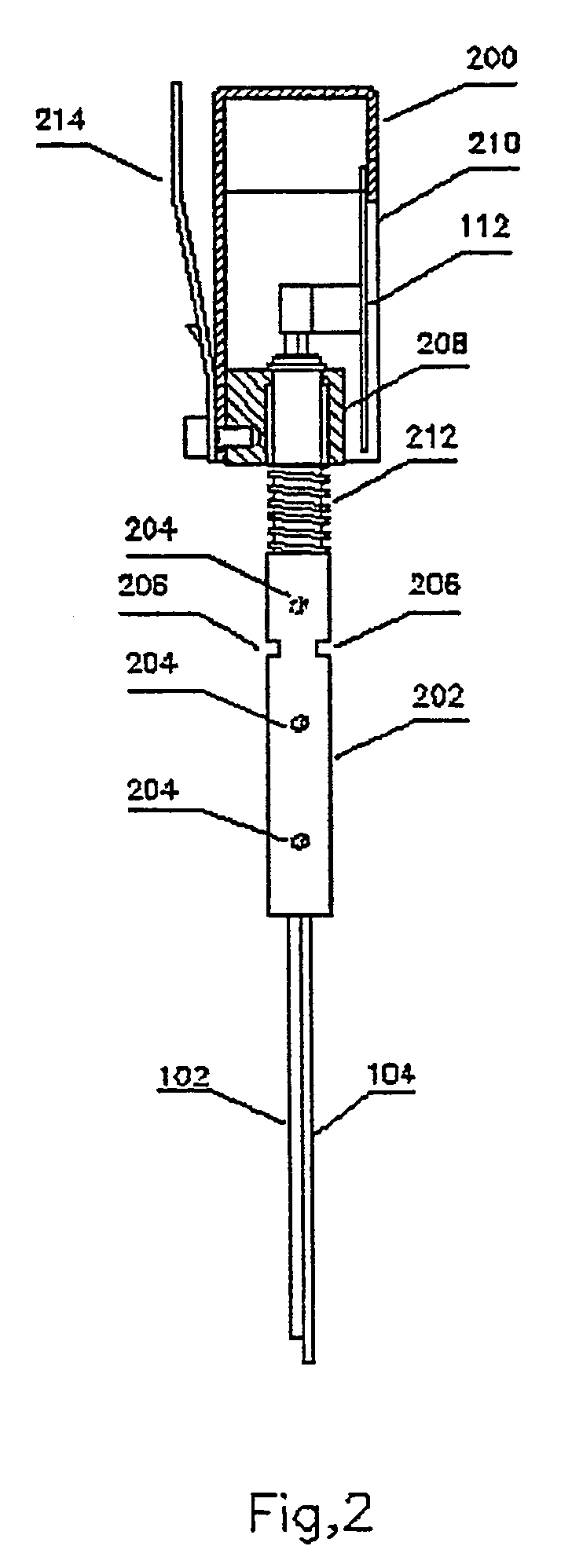
System and method for calibrating a surgical instrument
A calibration system for a surgical instrument. The calibration system includes an actuator, such as a motor system and a flexible shaft. The calibration system also includes a surgical instrument actuatable by the actuator. The calibration system also include calibration data corresponding to the surgical instrument. A processor is configured to process the calibration data for determining a position of the surgical instrument. The calibration system may include a sensor configured to provide a signal corresponding to a movement of the actuator, the processor being further configured to process the signal for determining a position of the surgical instrument.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
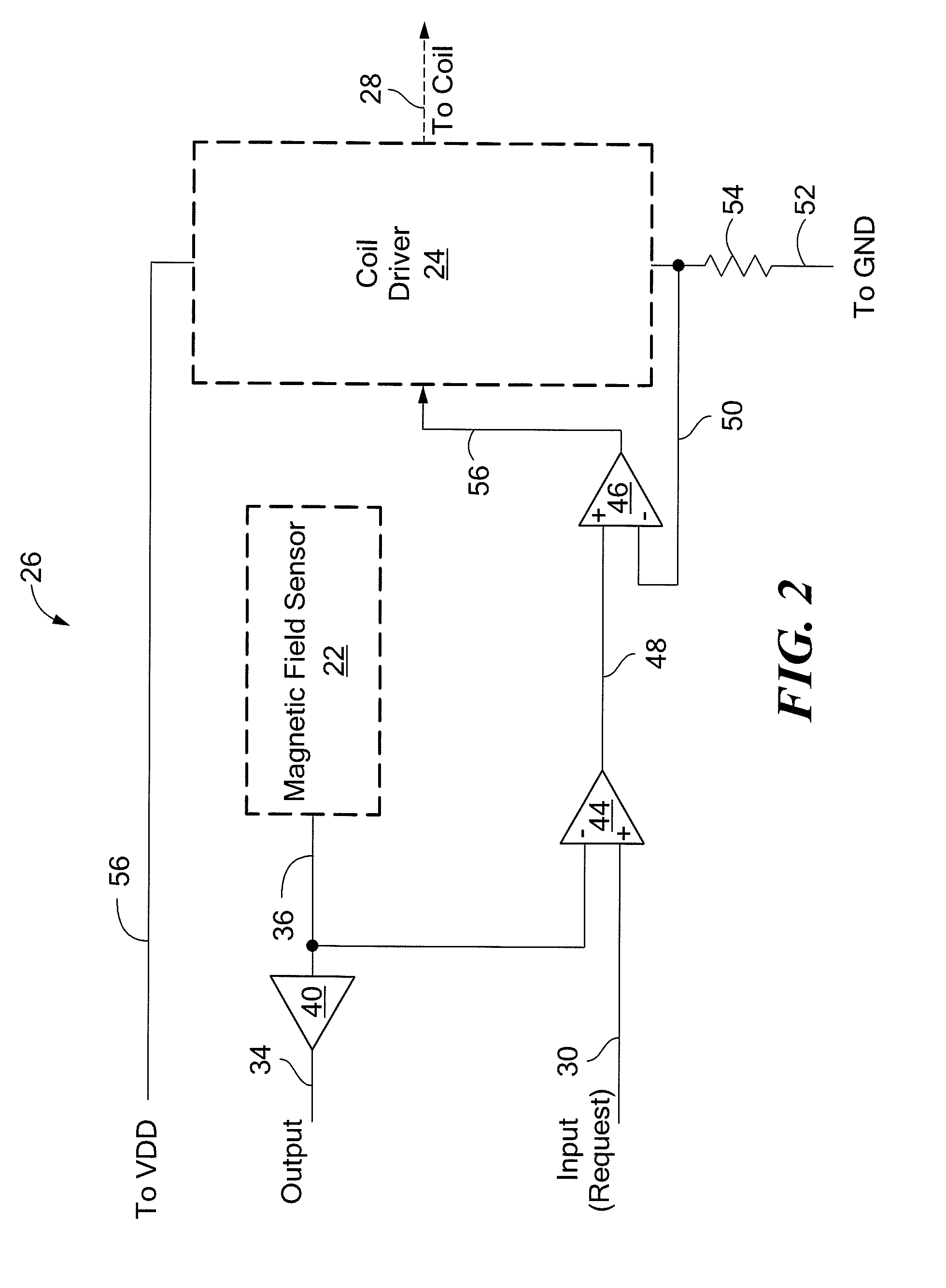
Digital wireless position sensor
ActiveUS7397364B2Fast chargingImprove signal-to-noise ratioElectric signal transmission systemsMagnetic measurementsVoltage dropEngineering
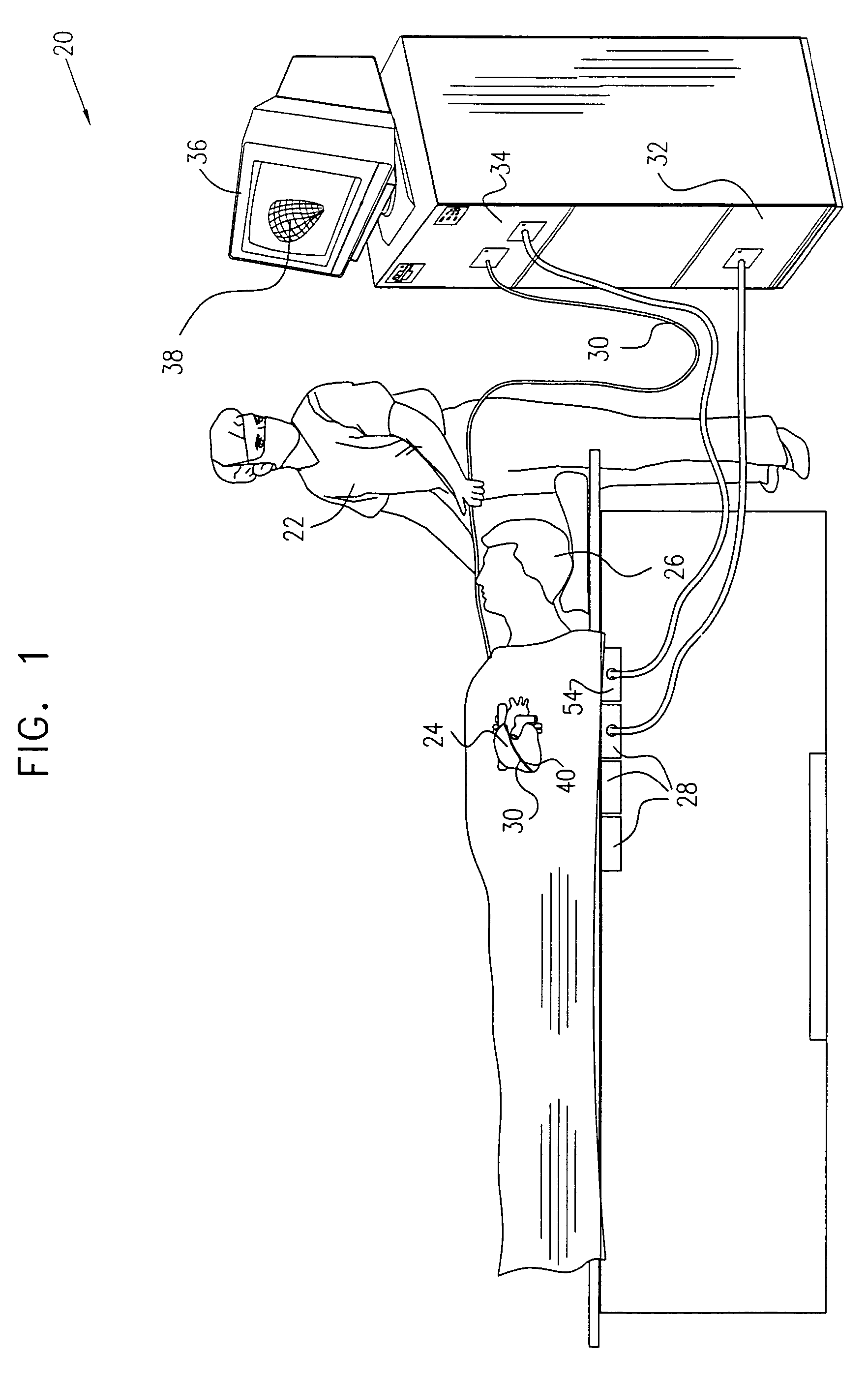
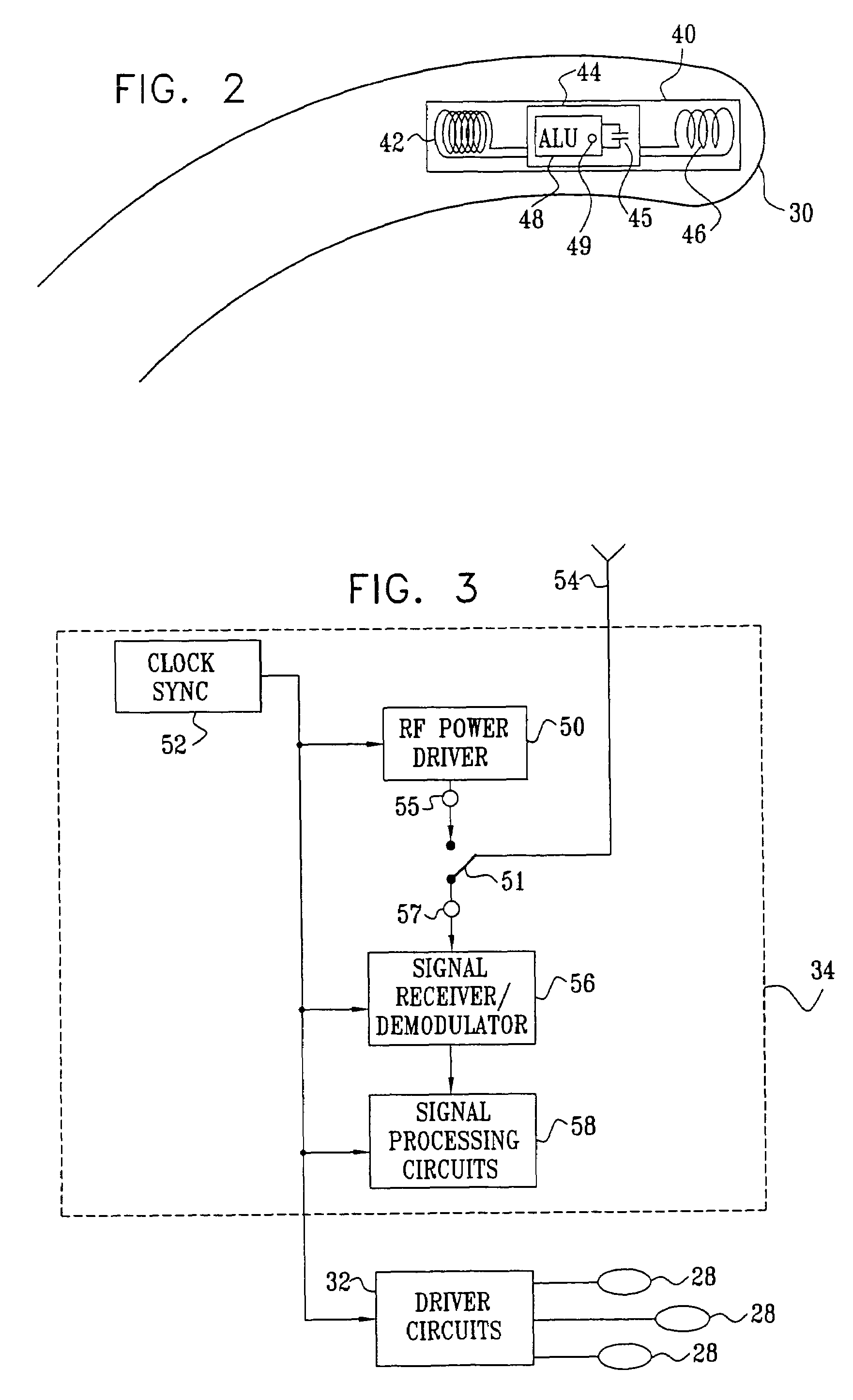
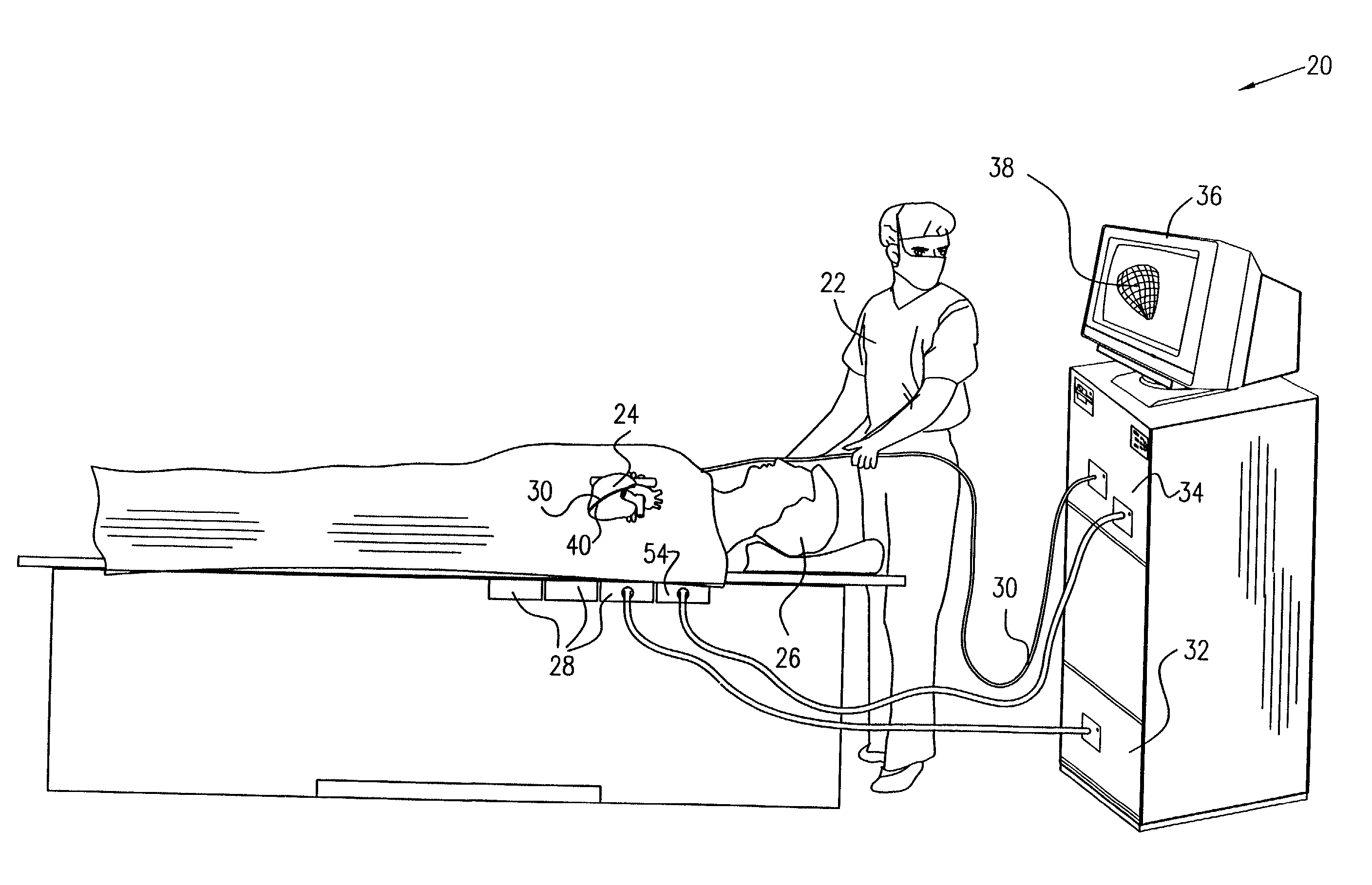
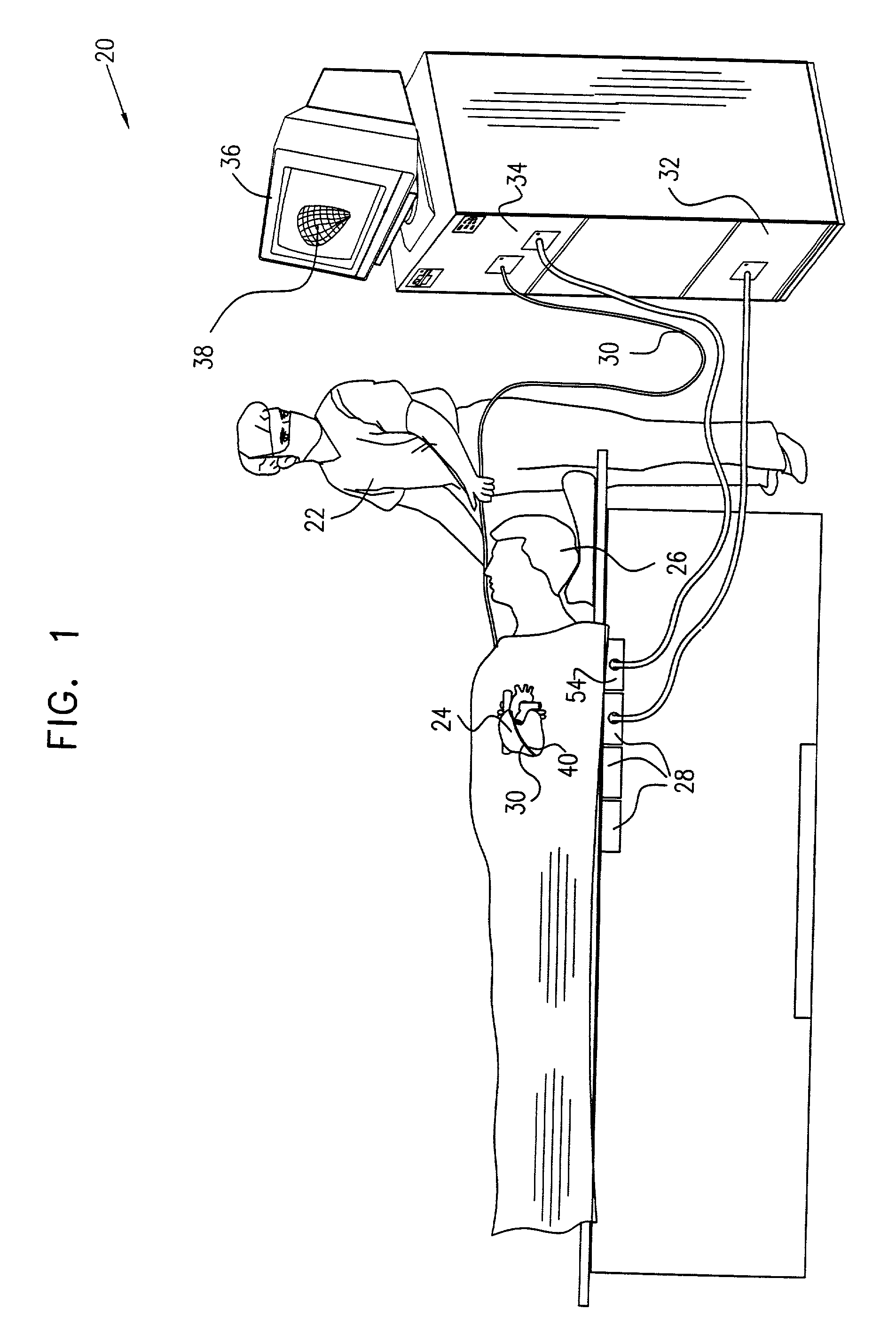
A method is provided for tracking an object, including positioning a radio frequency (RF) driver to radiate an RF driving field toward the object, and fixing to the object a wireless transponder that includes a power coil and at least one sensor coil. The method also includes receiving the RF driving field using the power coil and storing electrical energy derived therefrom. A plurality of field generators are driven to generate electromagnetic fields at respective frequencies in a vicinity of the object that induce a voltage drop across the at least one sensor coil. A digital output signal is generated at the wireless transponder indicative of the voltage drop across the sensor coil, and the generation of the digital output signal is powered using the stored electrical energy. The digital output signal is transmitted from the wireless transponder using the power coil, and the transmission of the digital output signal is powered using the stored electrical energy. The digital output signal is received and processed to determine coordinates of the object.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Wireless position sensor
Apparatus for tracking an object includes a plurality of field generators, which generate electromagnetic fields at different, respective frequencies in a vicinity of the object, and a radio frequency (RF) driver, which radiates a RF driving field toward the object. A wireless transponder is fixed to the object. The transponder includes at least one sensor coil, in which a signal current flows responsive to the electromagnetic fields, and a power coil, which receives the RF driving field and conveys electrical energy from the driving field to power the transponder. The power coil also transmits an output signal responsive to the signal current to a signal receiver, which processes the signal to determine coordinates of the object.
Owner:BIOSENSE
Magnetic rotary system for input devices
InactiveUS20110025311A1Easy to manufactureMagnetization is simpleDigital data processing detailsUsing electrical meansMagnetizationEngineering
Embodiments of the present invention include a roller for an input device, where the roller's absolute angular position is measured by a magnetic encoder. A magnet is attached to the roller, possibly inside the roller so as to make the embodiment more compact. In one embodiment, the magnetization is simple and low cost. Further, tight tolerances are not required, and such a system is easy to manufacture. In one embodiment, the sensor is covered by any non-ferromagnetic material, to protect it from foreign particles, and to reduce ESD. In one embodiment, the wheel consumes much less power than conventional wheels in input devices. In one embodiment, the tilting of the wheel is measured using the same sensor that is used for measuring the rotation of the wheel. In one embodiment, a ratcheting feel provided to the user when rotating the wheel is synchronized with the rotation signal.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
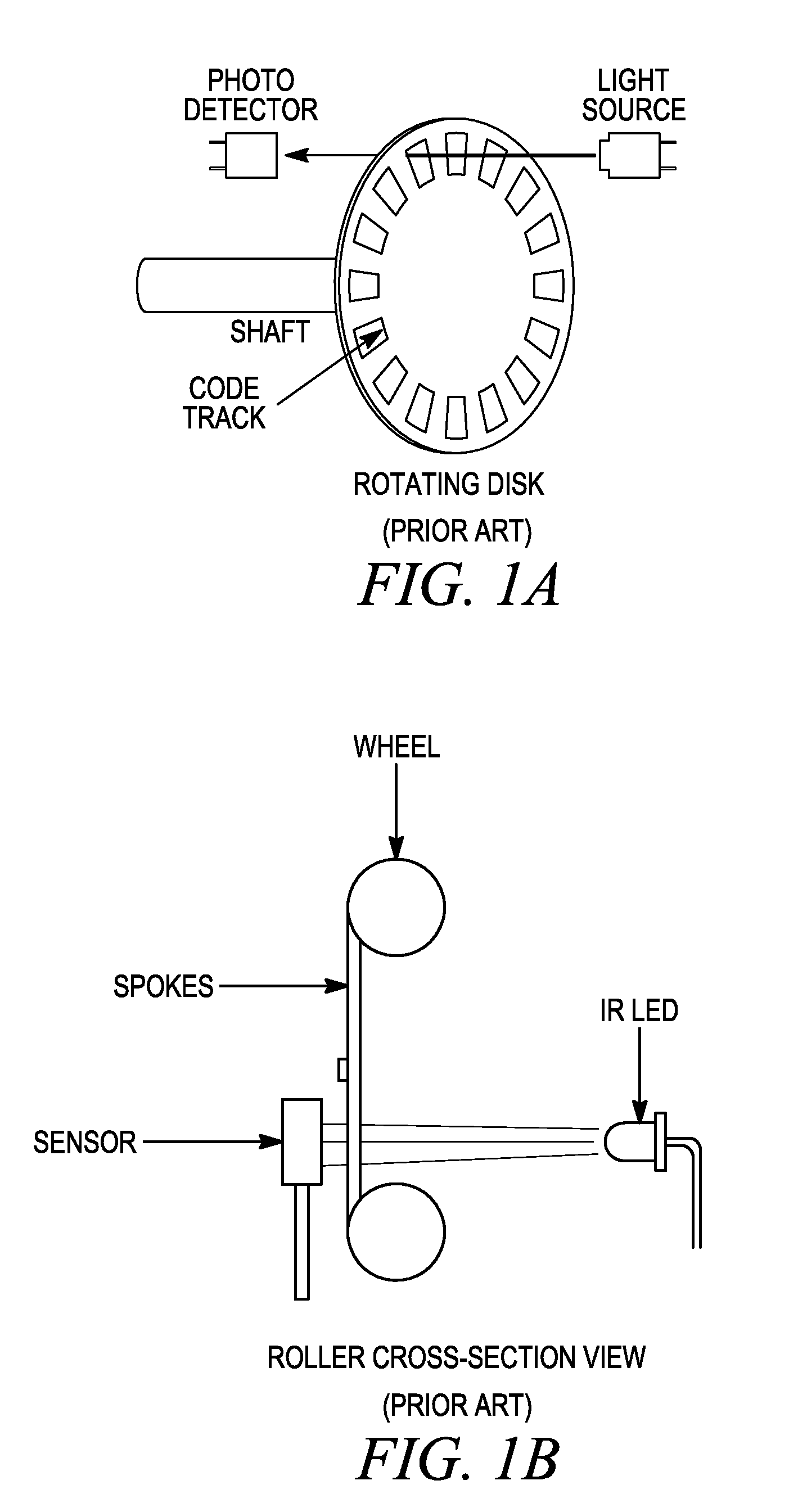
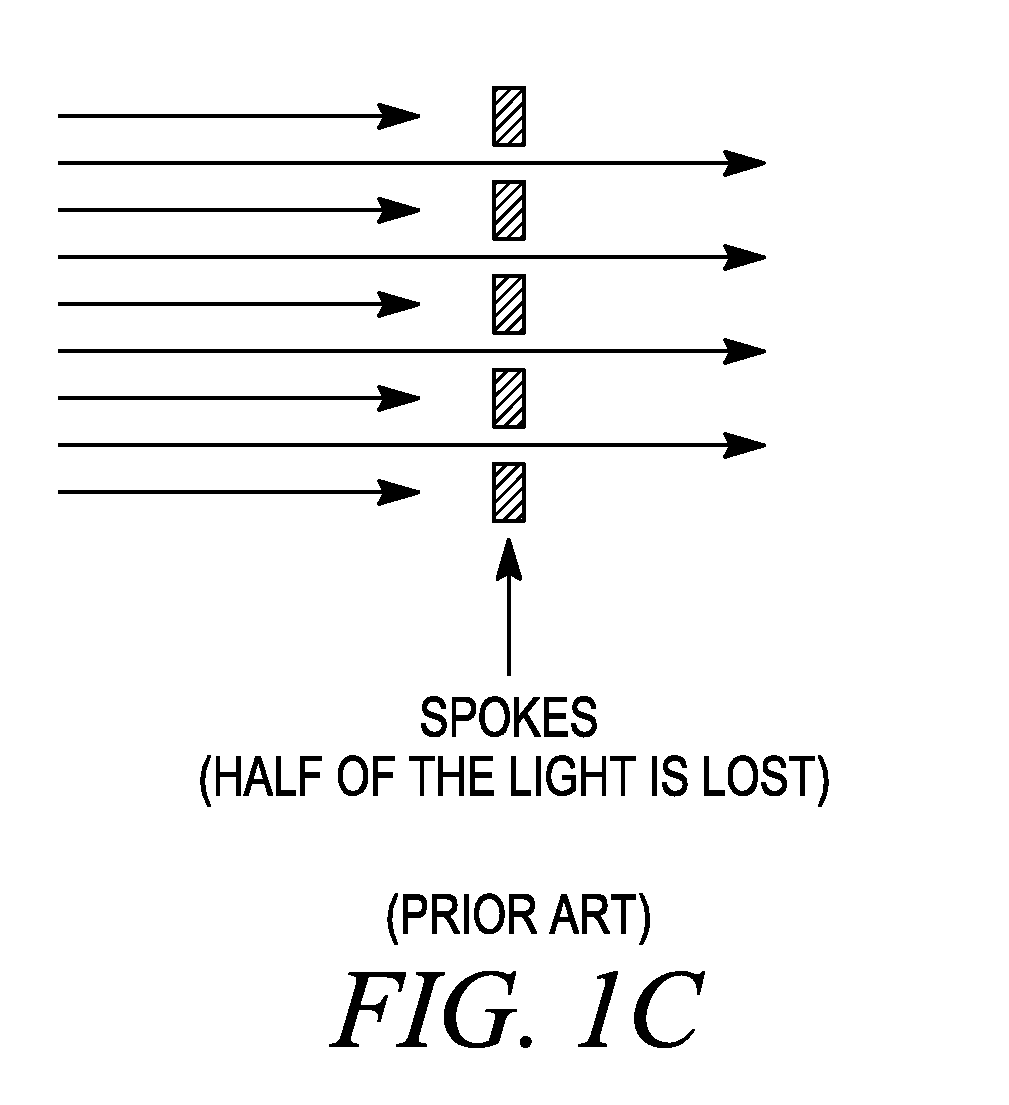
Method for detecting transverse mode vibrations in an ultrasonic hand piece/blade
InactiveUS6588277B2Low costRecuperation increasedVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResonanceEngineering
A method for detecting transverse mode vibrations in an ultrasonic hand piece / blade for determining the existence of unwanted vibration in the hand piece / blade. A tracking filter centered at the drive frequency of the generator, is used to monitor the drive frequency of the ultrasonic generator and attenuate the drive signal when it exceeds a predetermined level. The tracking filter has a wide pass band. Alternatively, a tracking filter having a pass band which is divided into several regions is used to avoid other longitudinal resonances, such as a resonance at a second harmonic, or other spectral features that would otherwise detract from the tracking accuracy of the filter.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
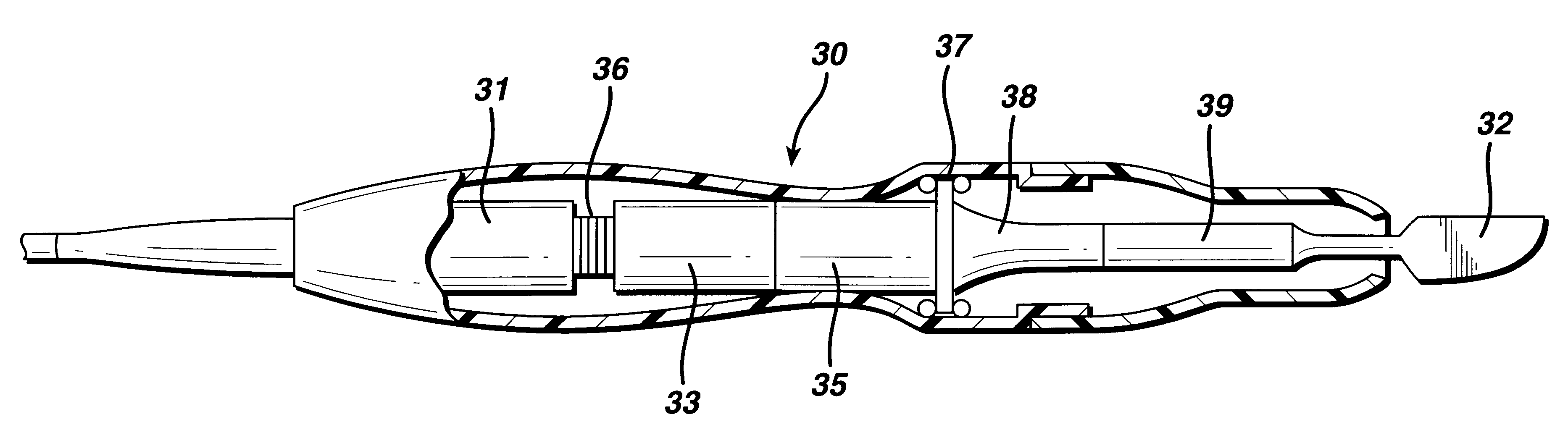
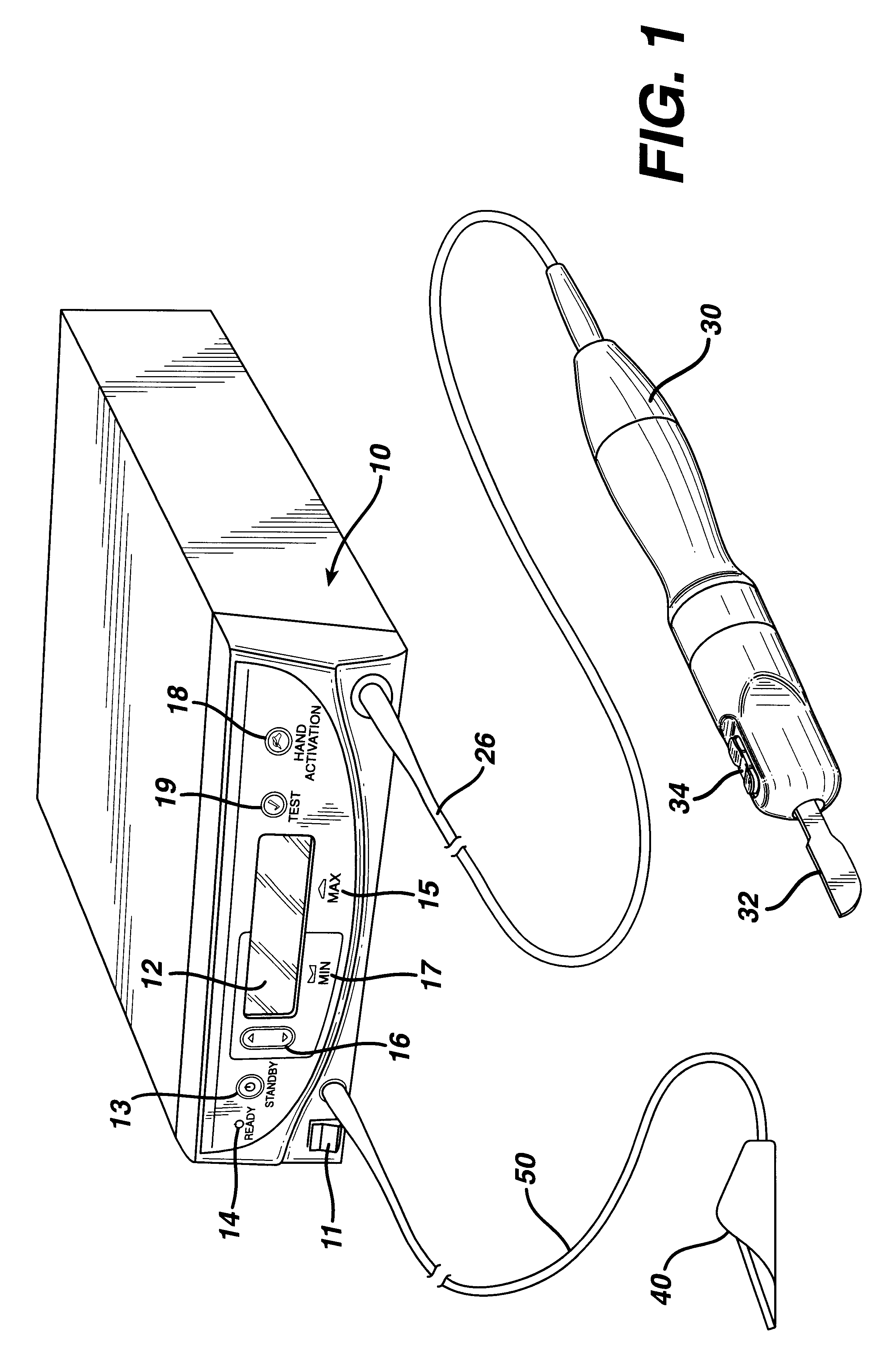
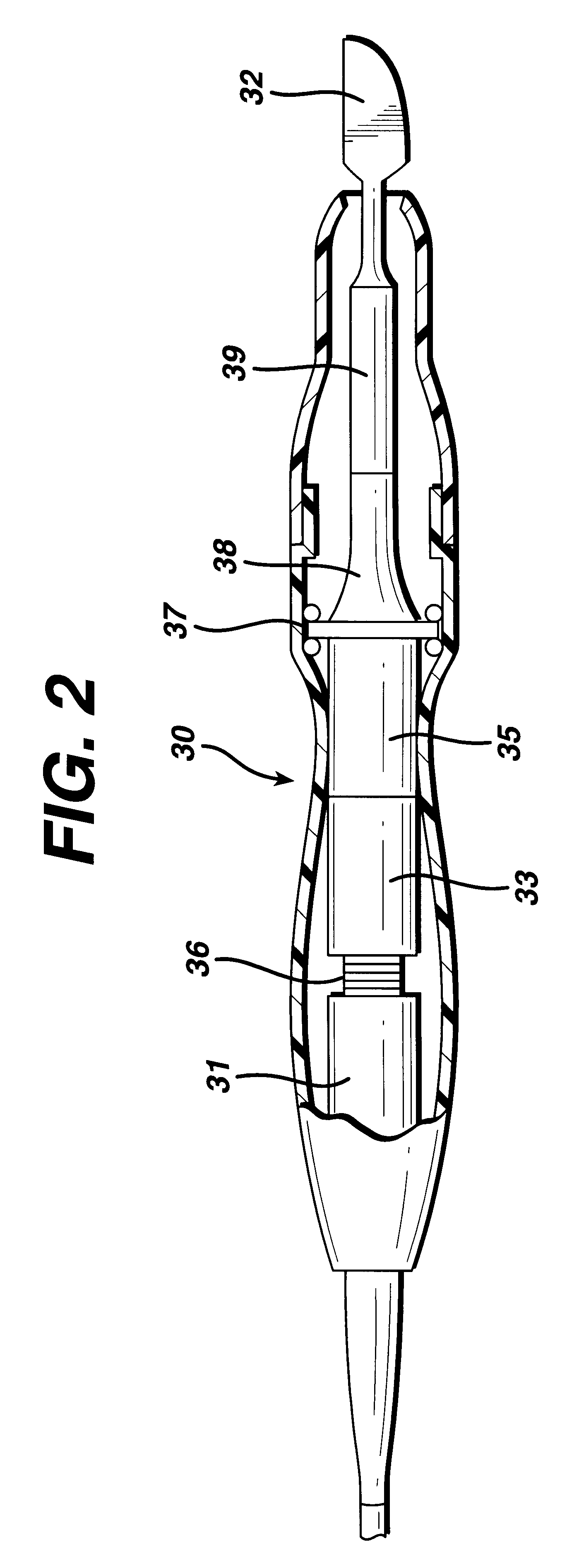
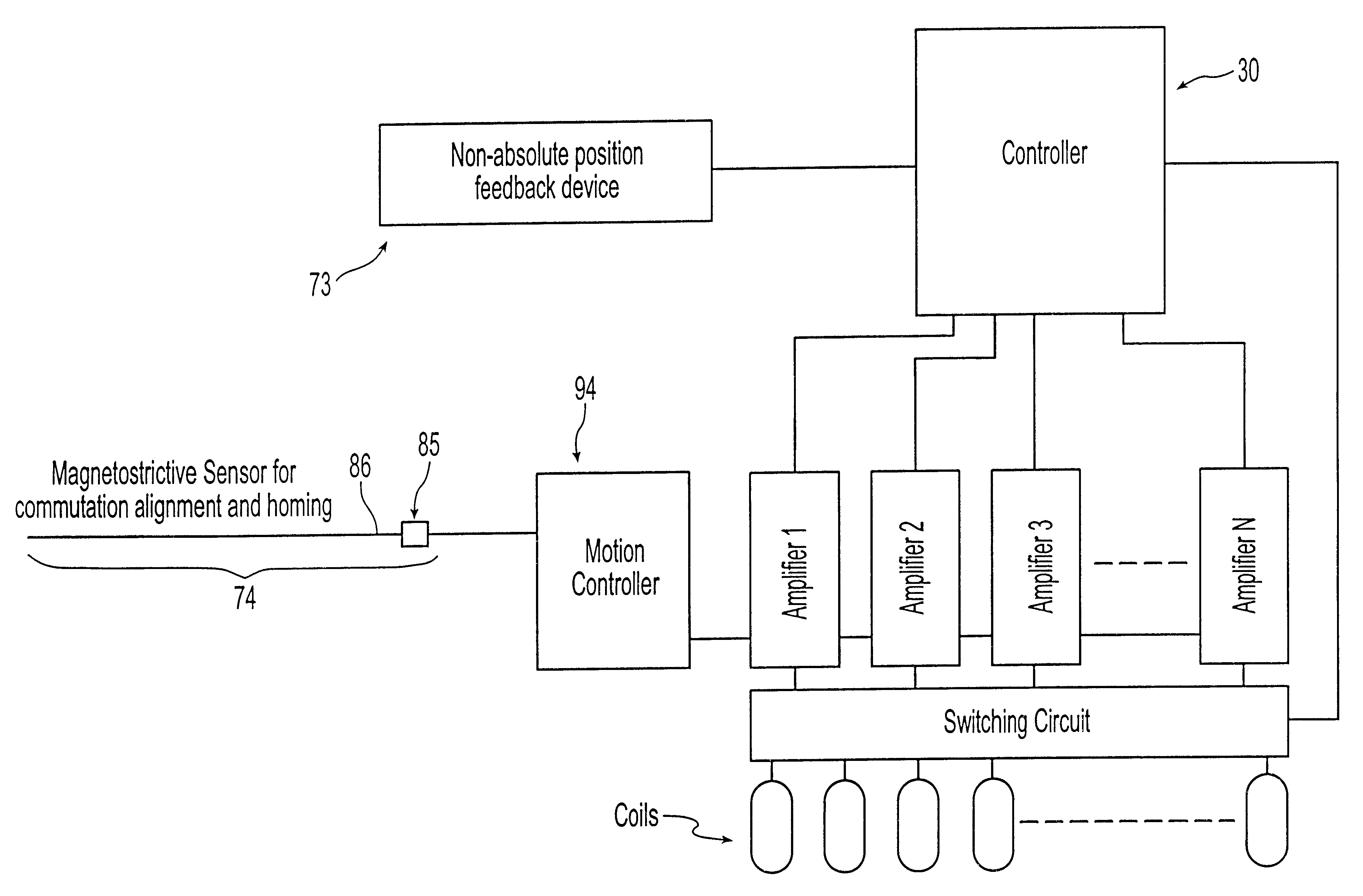
Position feedback system and method for use thereof
InactiveUS6625517B1Solid-state devicesSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringVirtual sensors
The present invention is directed to a machine with a position feedback system and a method for use thereof. The machine includes at least one movable element mounted for movement on a path and at least one programmable controller. The machine further includes at least two absolute or magnetostrictive sensors or the machine includes an absolute sensor and a non-absolute sensor. The programmable controller uses positional information from the sensors to determine the position of the movable elements on the path and control the movable elements. The method includes determining a known position for the movable elements, linking at least two magnetostrictive sensors into one virtual sensor, and / or performing commutation alignment for the movable elements. Determining the position and commutation alignment can occur when the movable elements are stationary or moving.
Owner:TETRA LAVAL HLDG & FINANCE SA
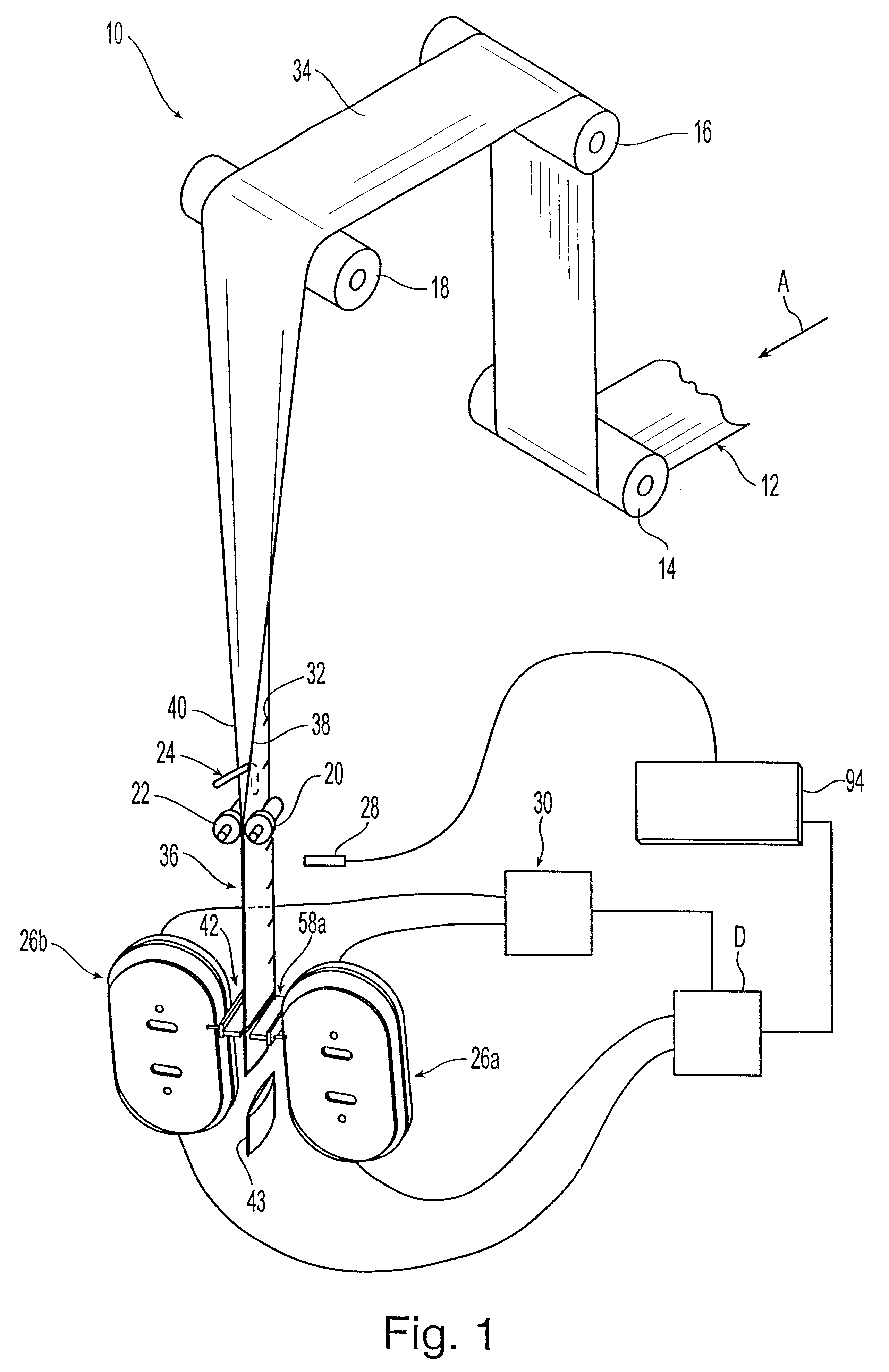
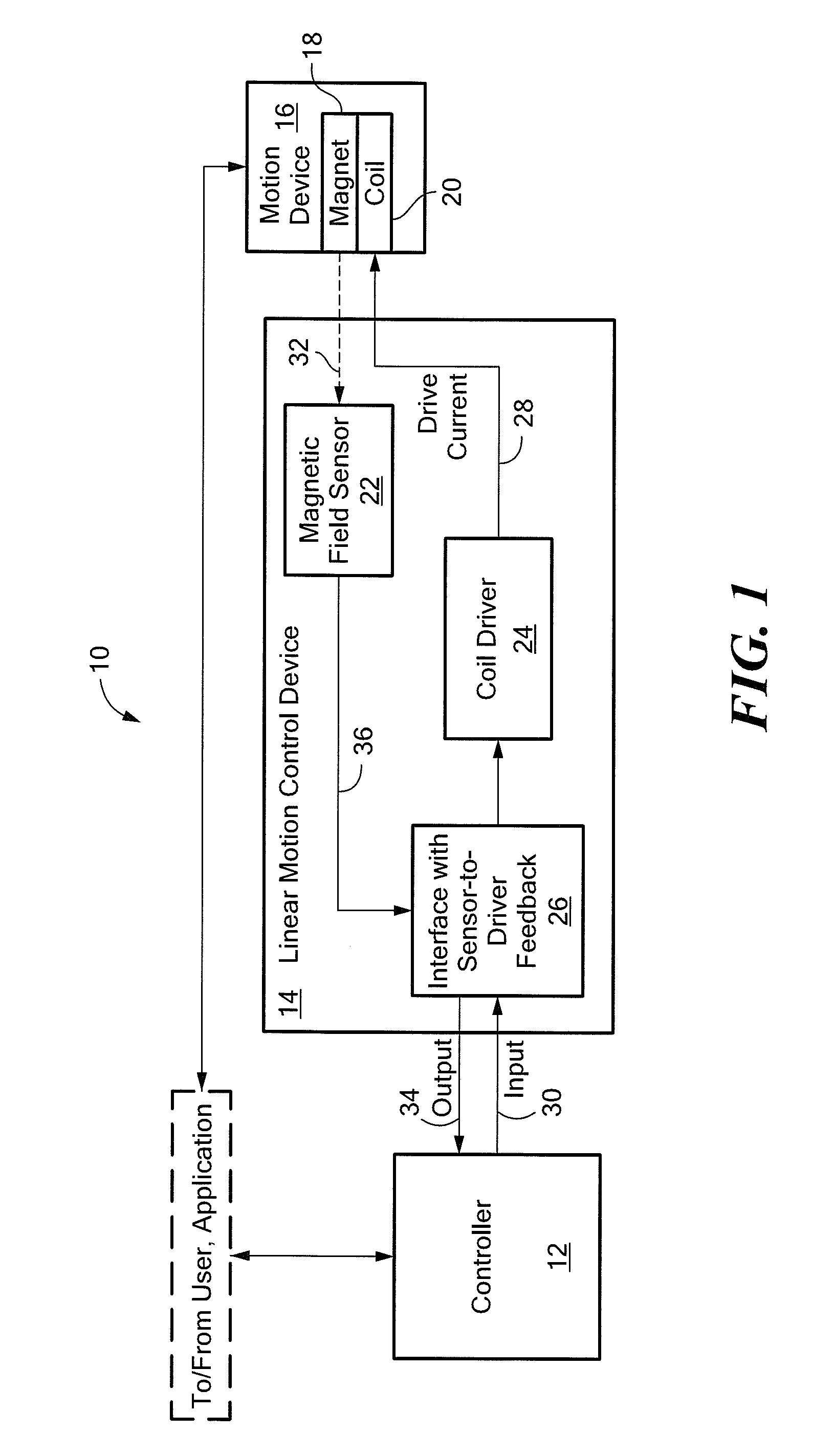
Hall-effect based linear motor controller
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
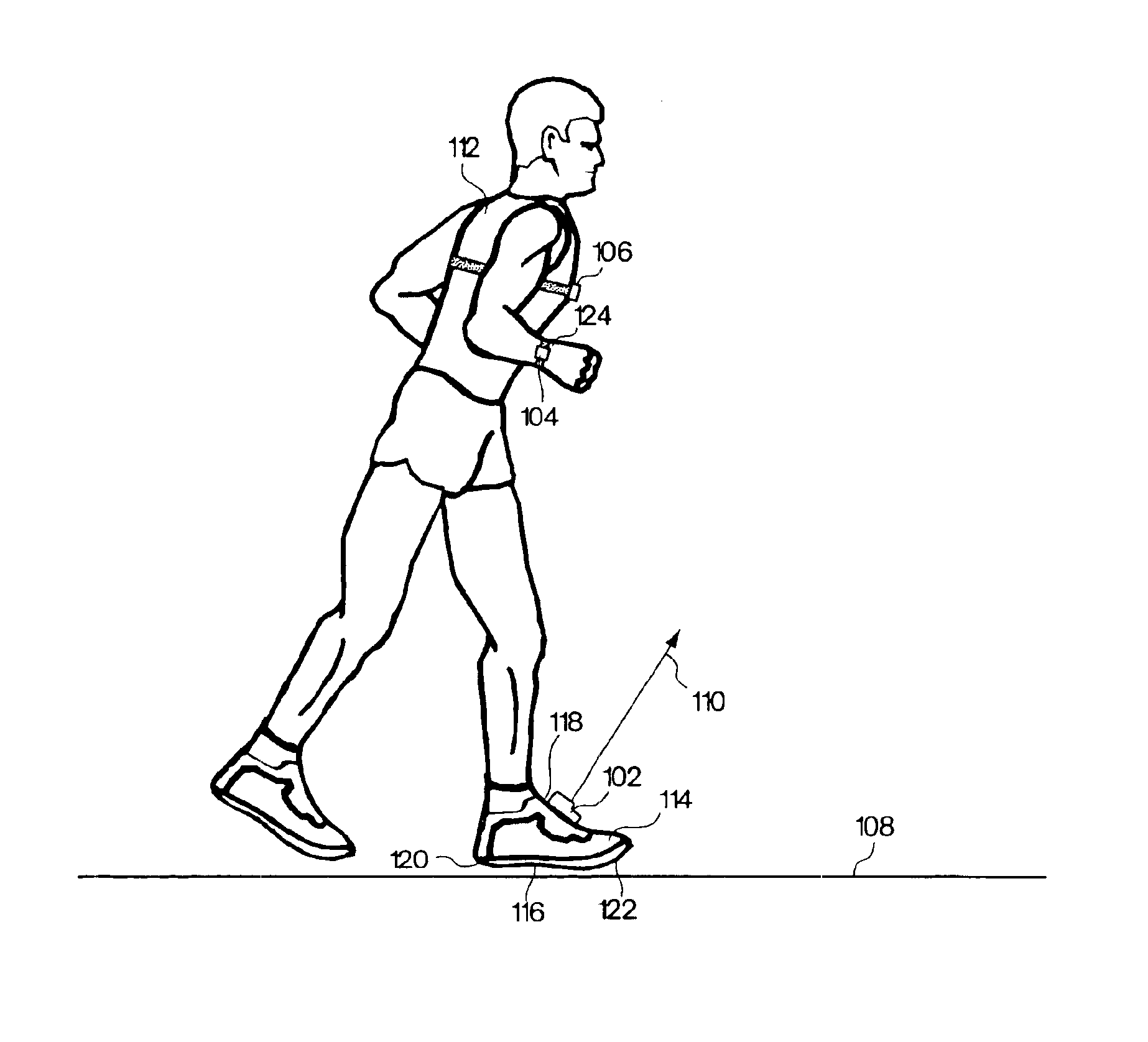
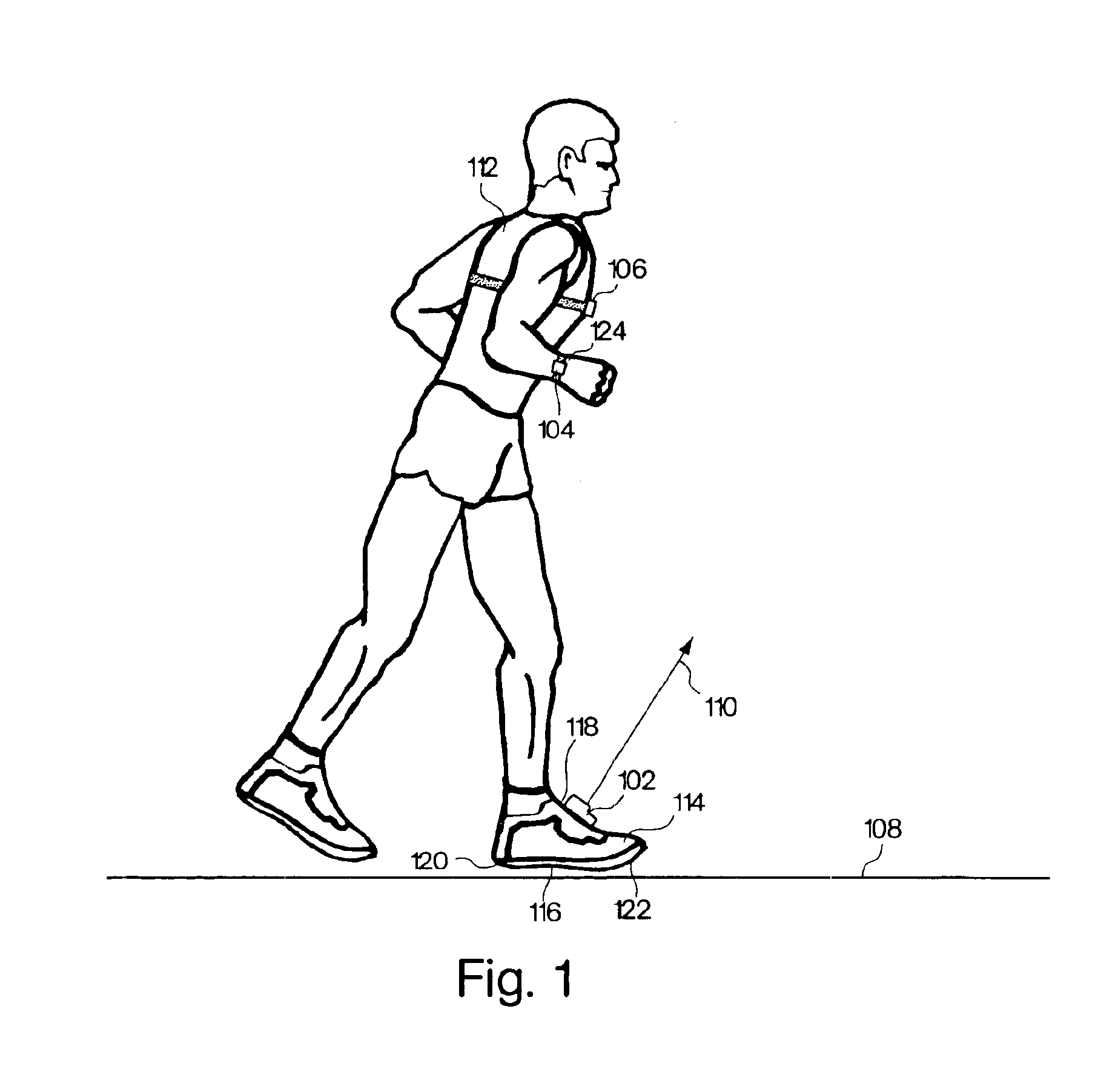
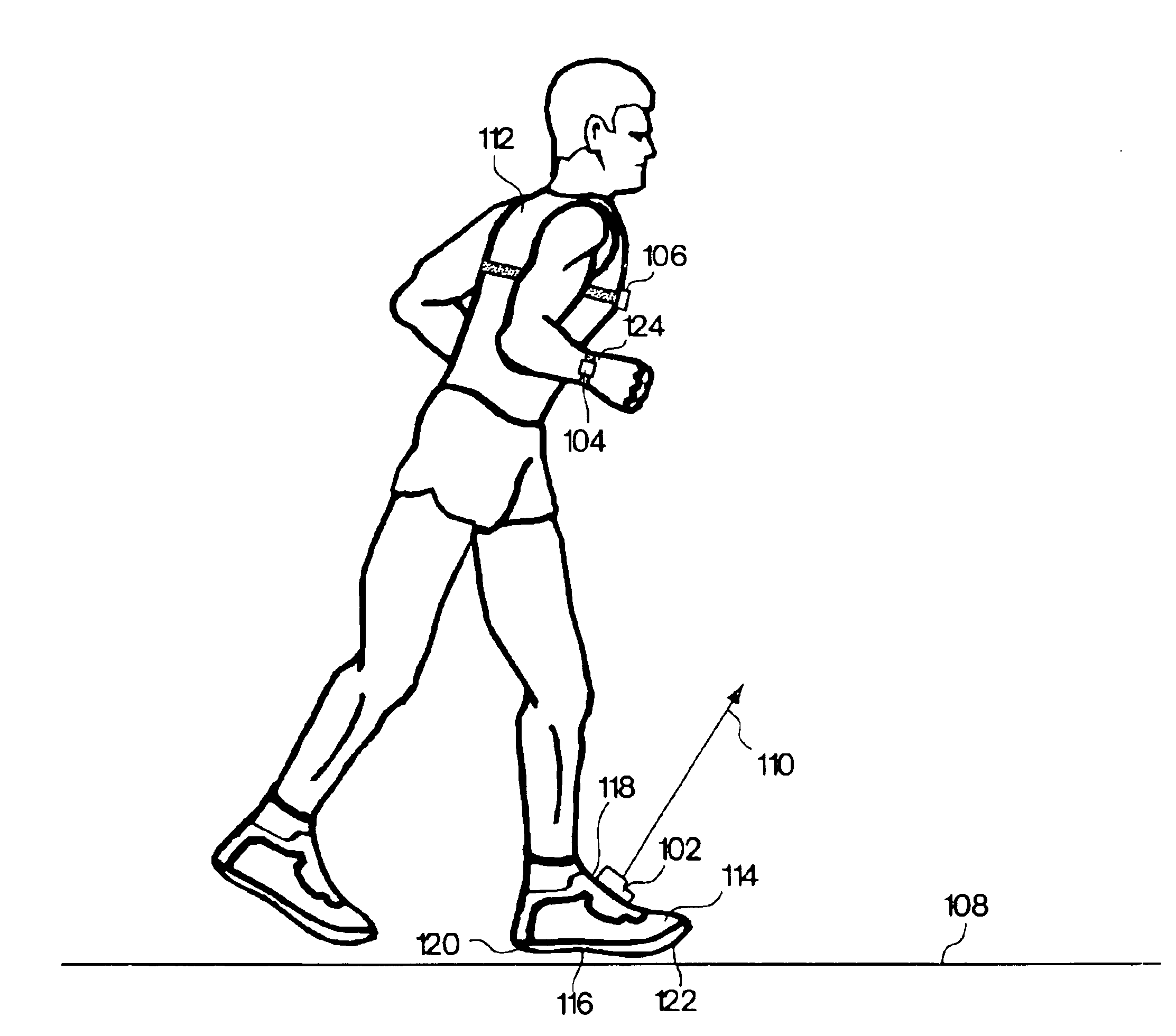
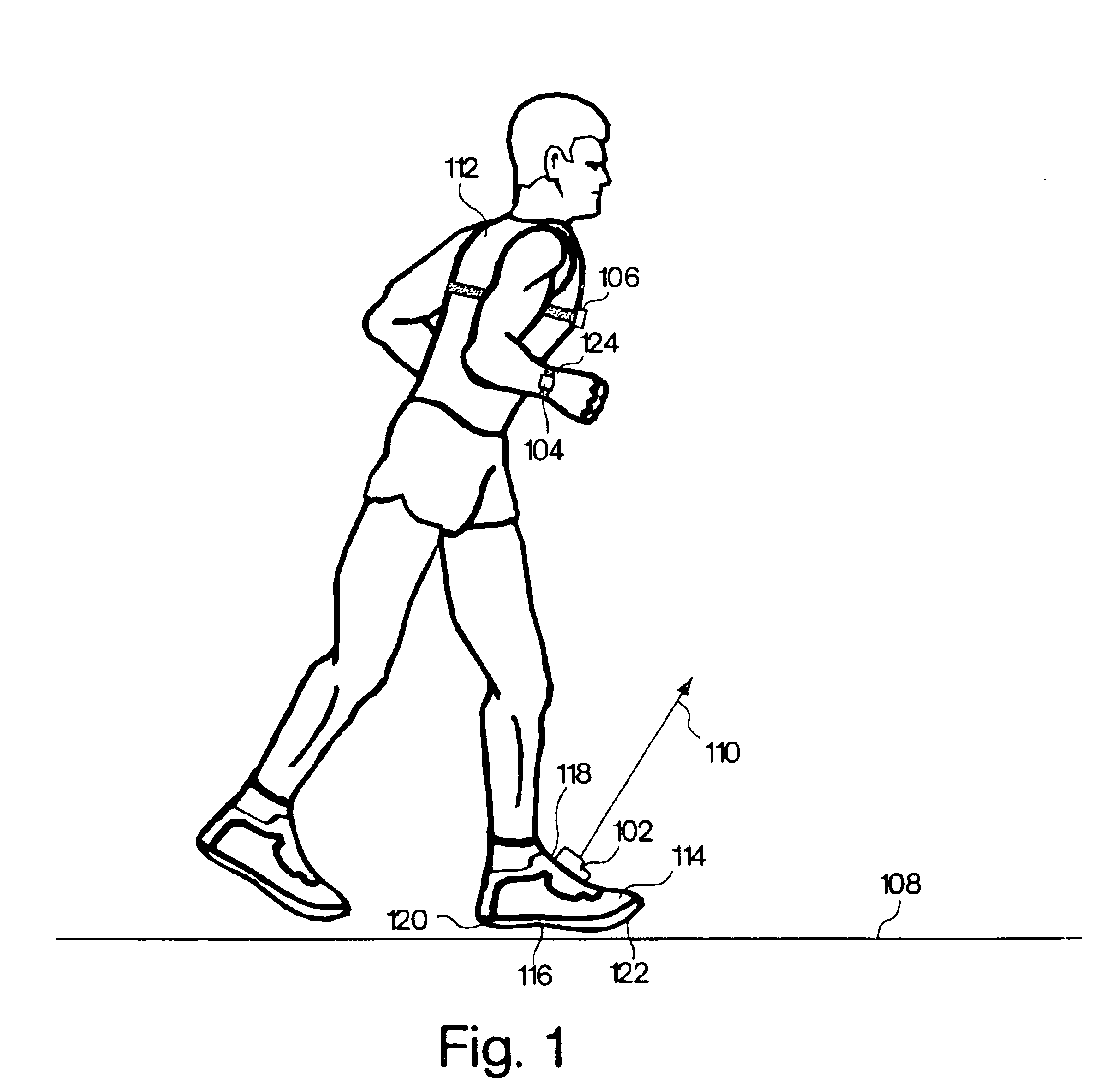
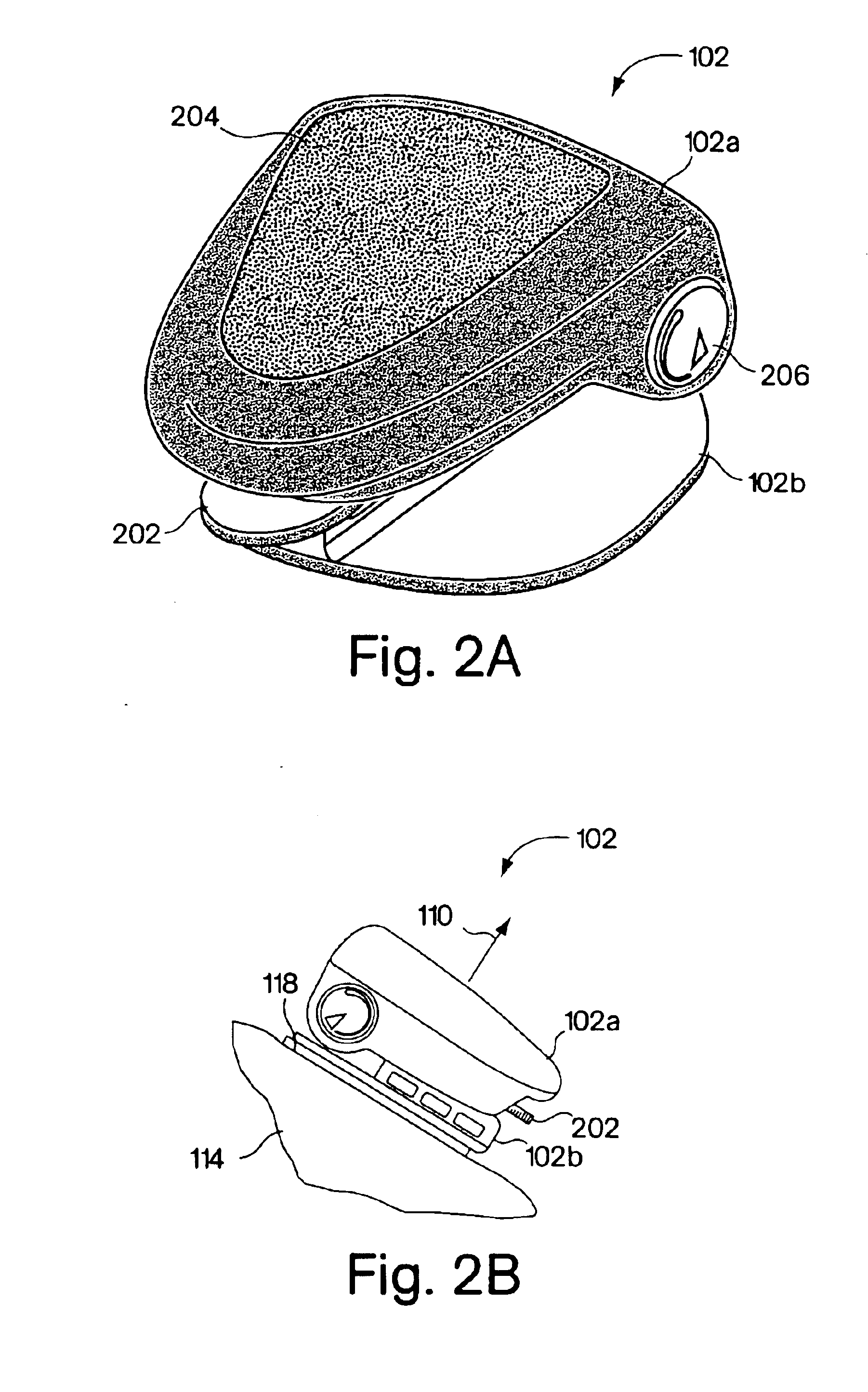
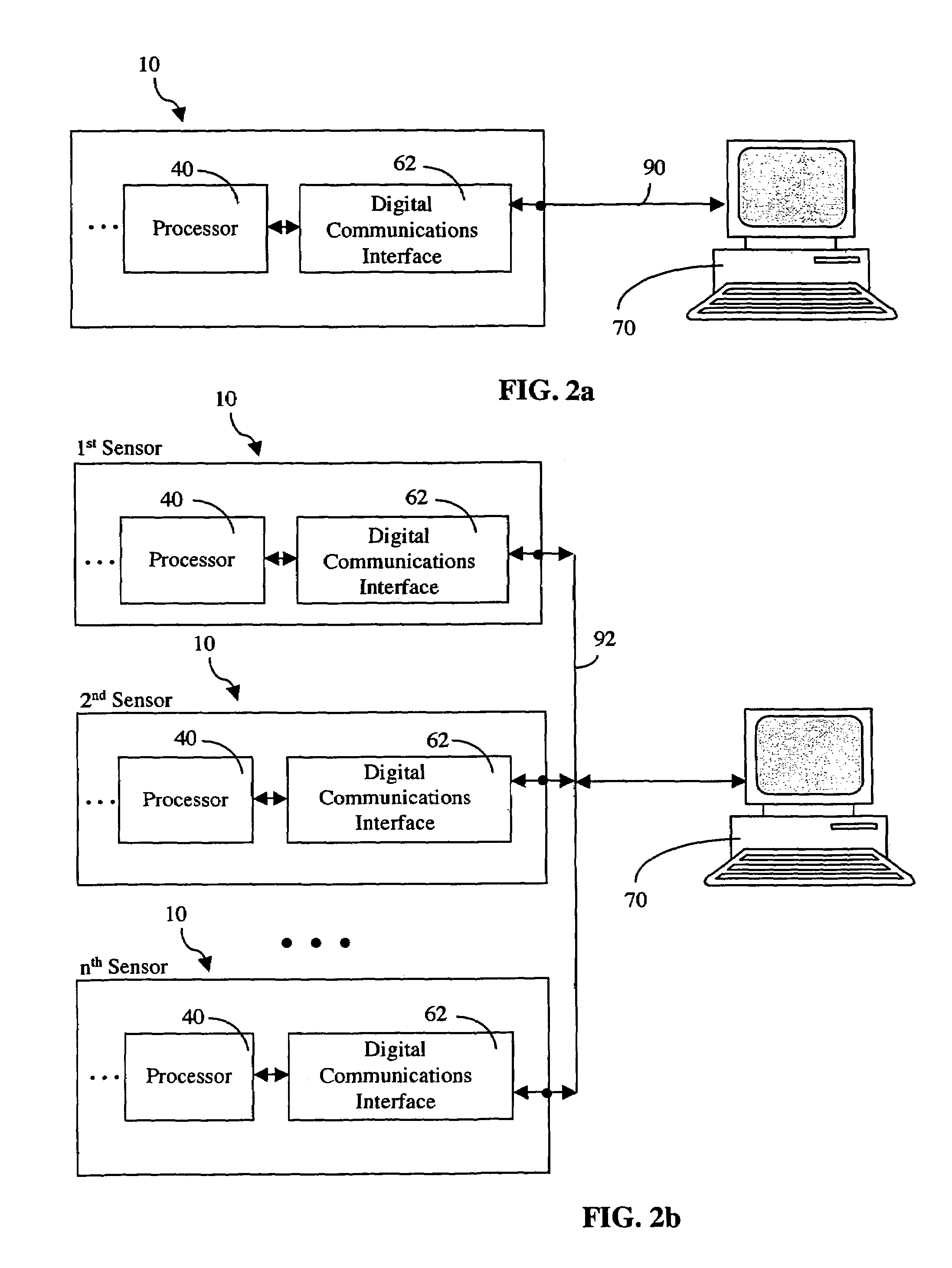
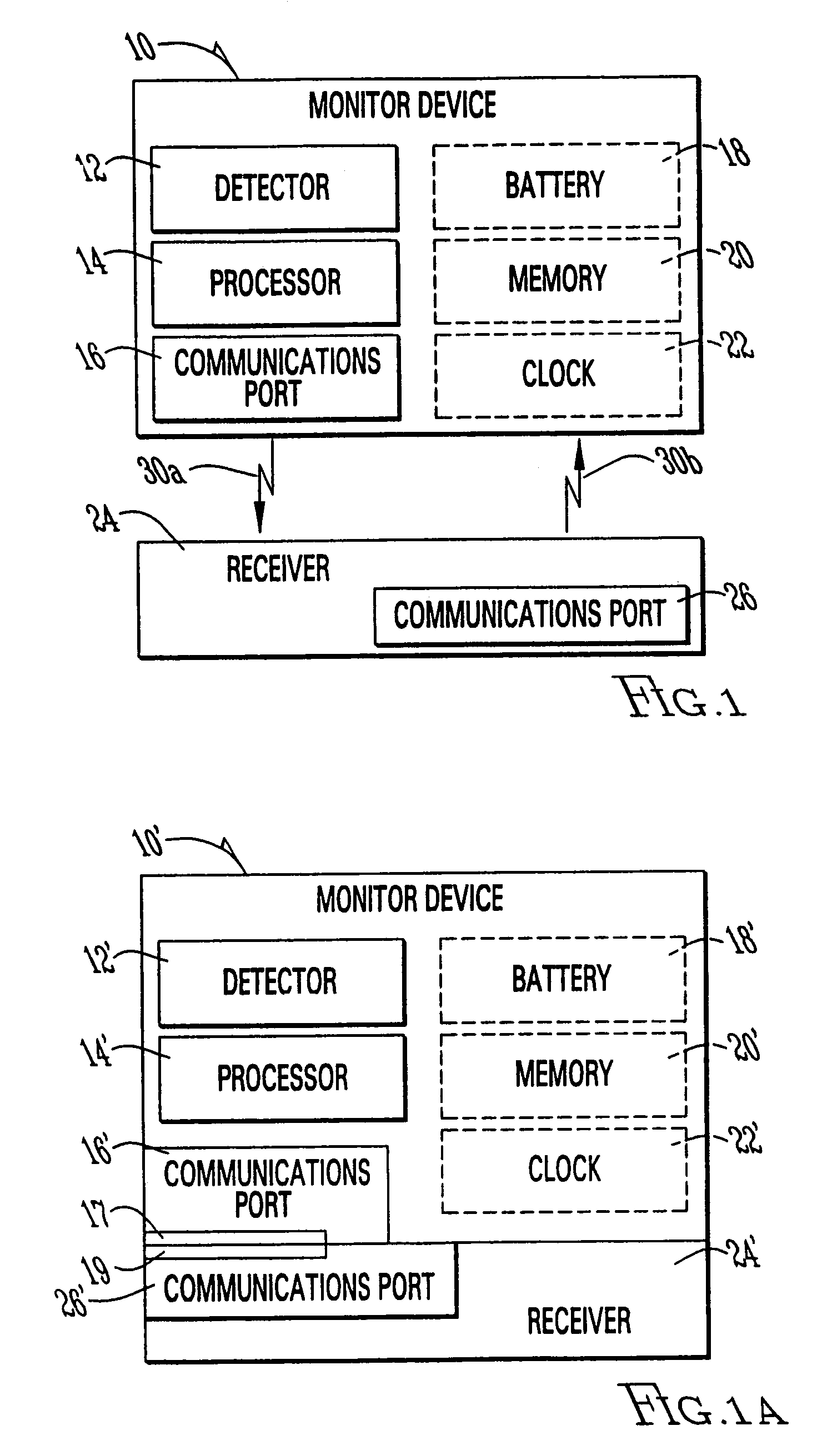
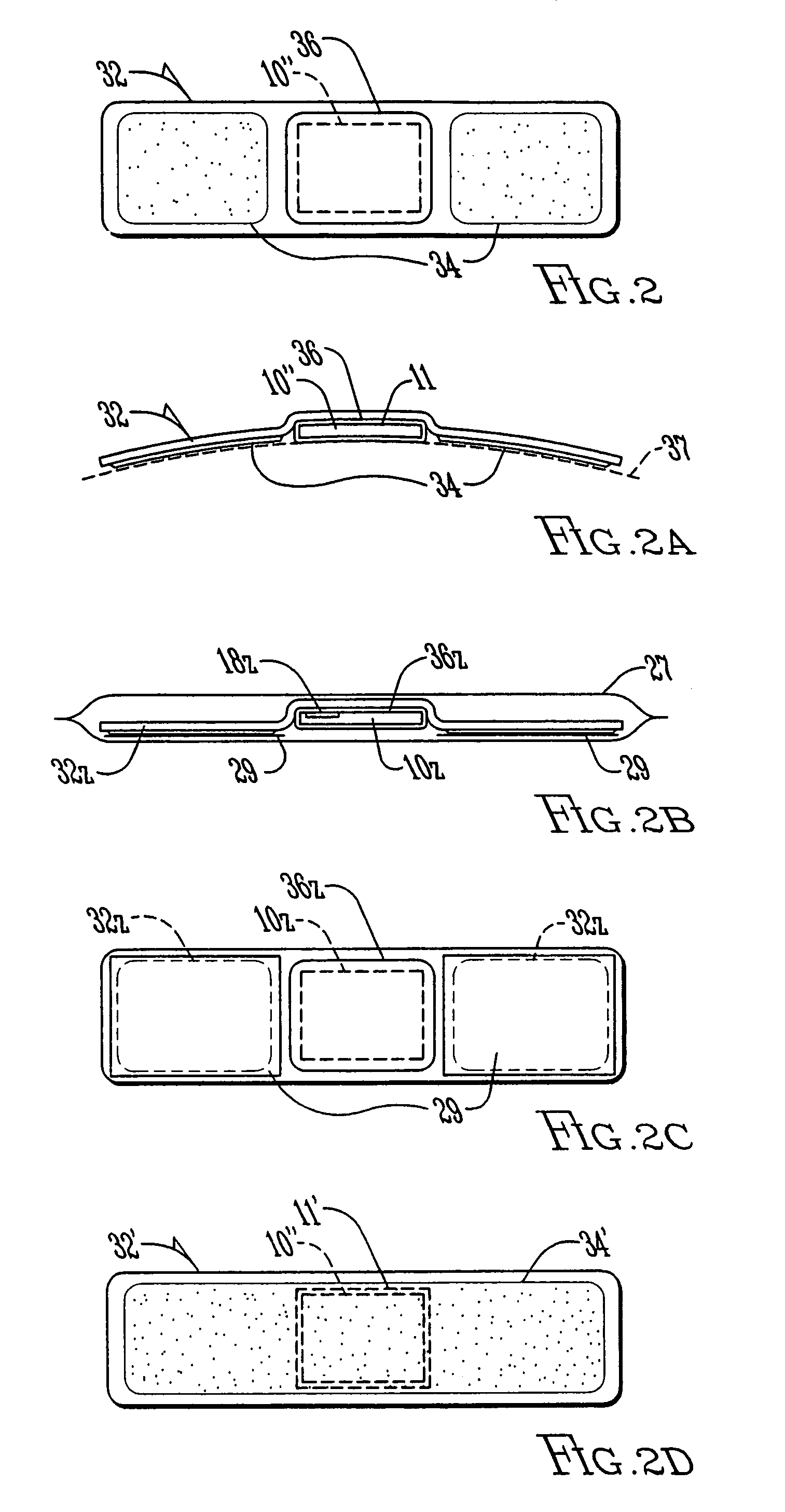
Monitoring activity of a user in locomotion on foot
InactiveUS6882955B1Time indicationSynchronous motors for clocksHuman–computer interactionVisual perception
In one embodiment, a display unit to be mounted on a wrist of a user includes a display screen, a base, and at least one strap. The display unit is configured such that, when it is worn by the user, the display screen is oriented at an angle with respect to a surface of the user's wrist. In another embodiment, visually-perceptible information indicative of determined values of the instantaneous pace of a user and the average pace of the user are displayed, simultaneously. In another embodiment, visually-perceptible information indicative of the determined values of the at least one variable physiological parameter of the user and the at least one performance parameter of the user are displayed, simultaneously.
Owner:NIKE INC +1
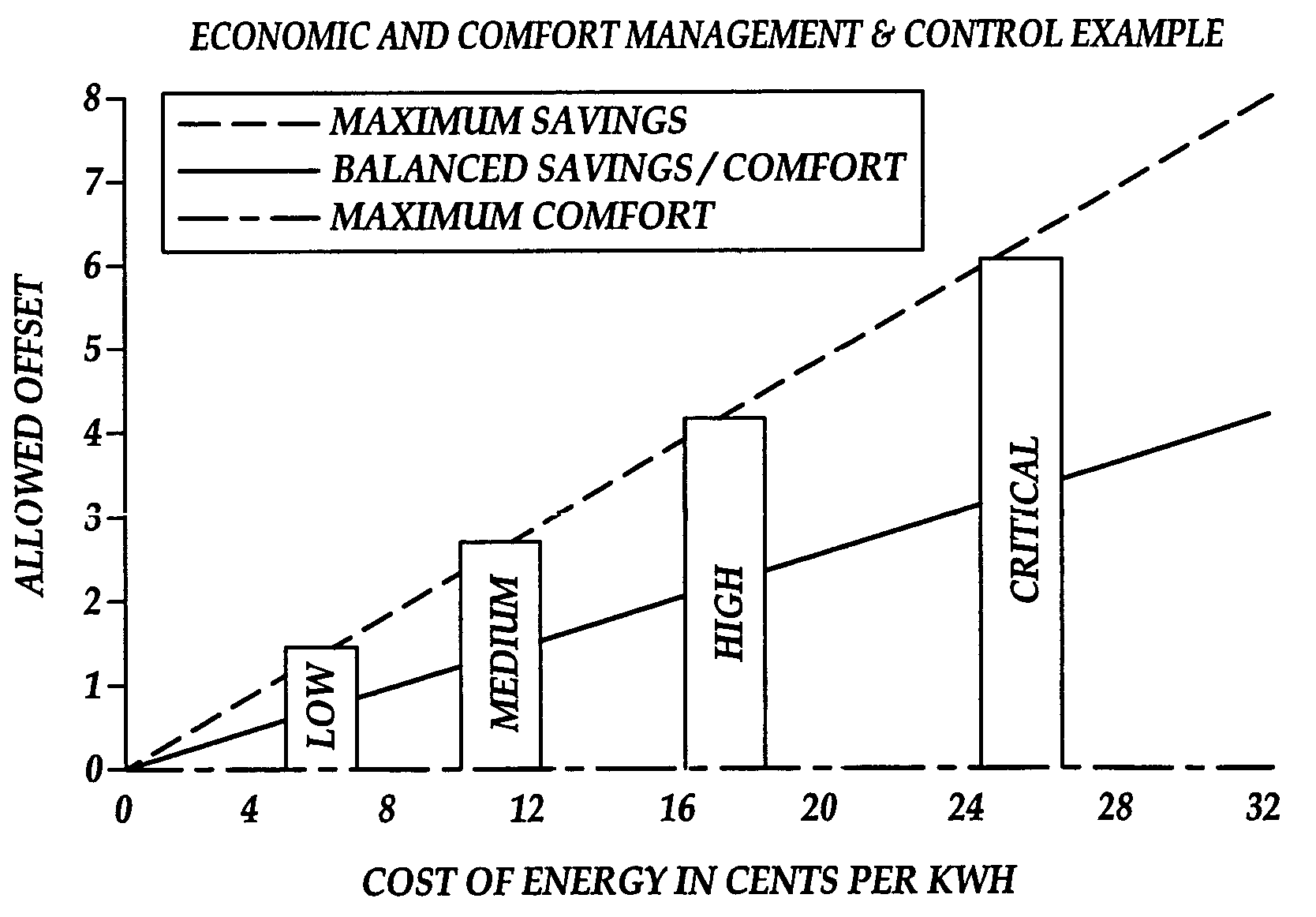
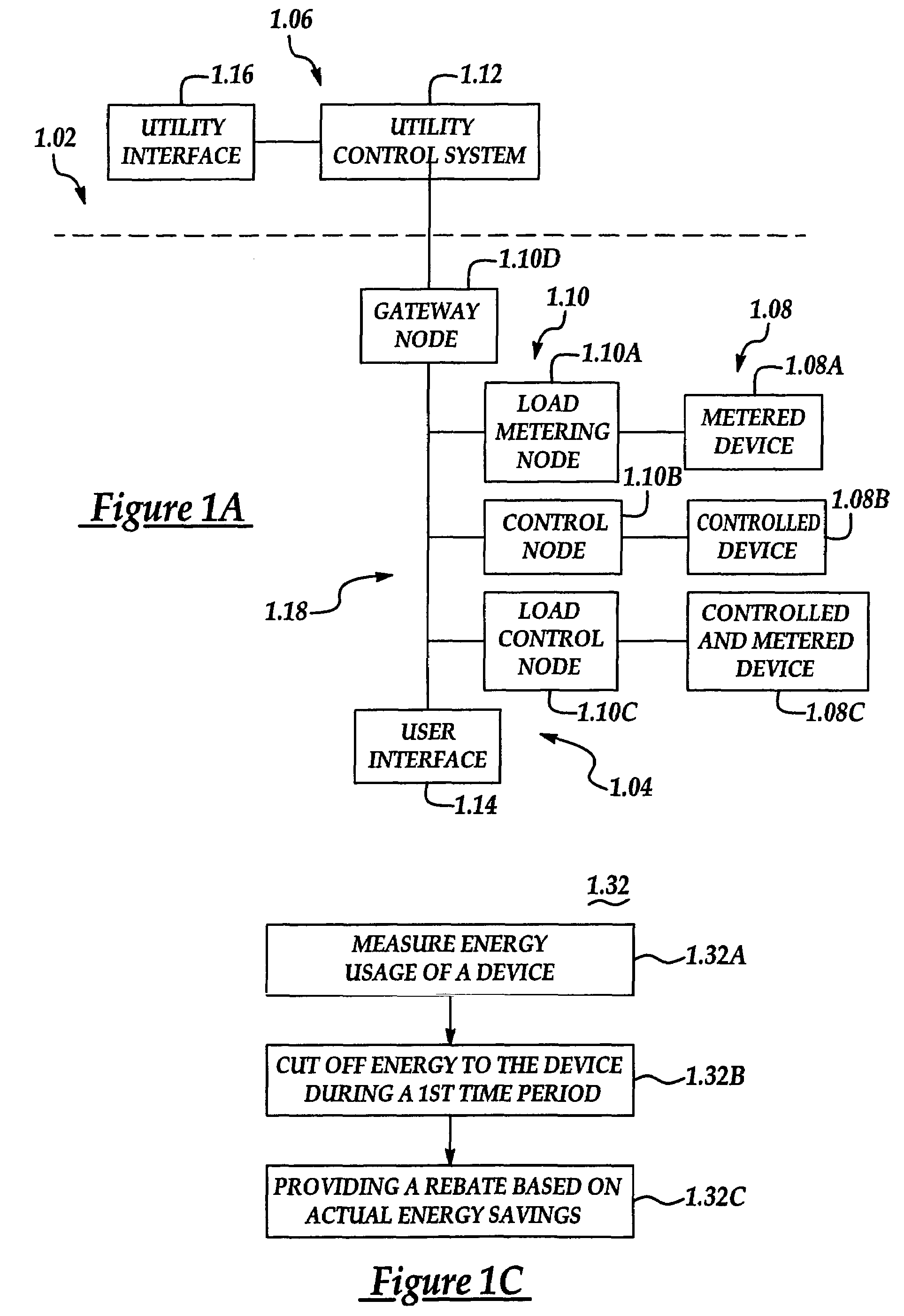
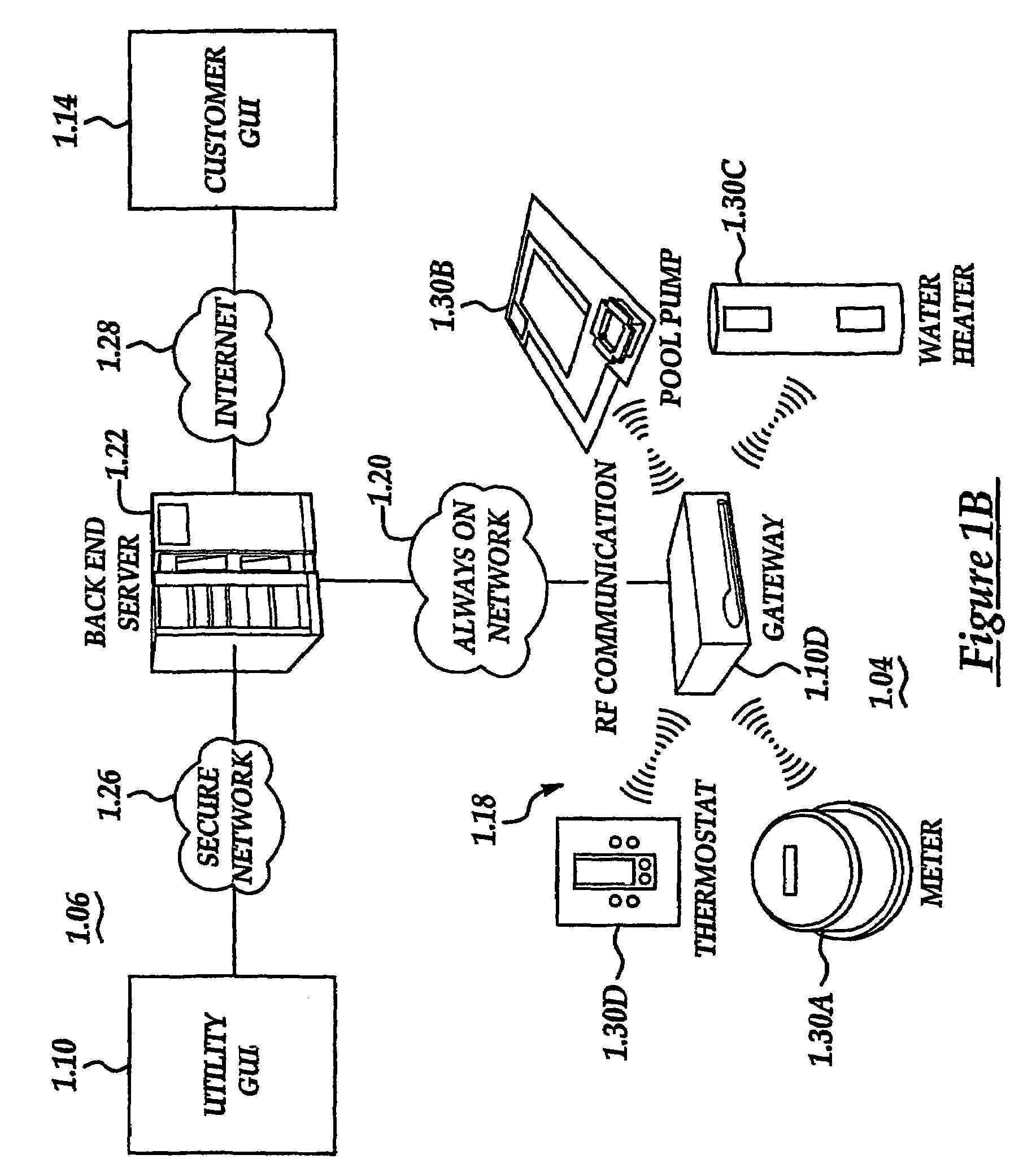
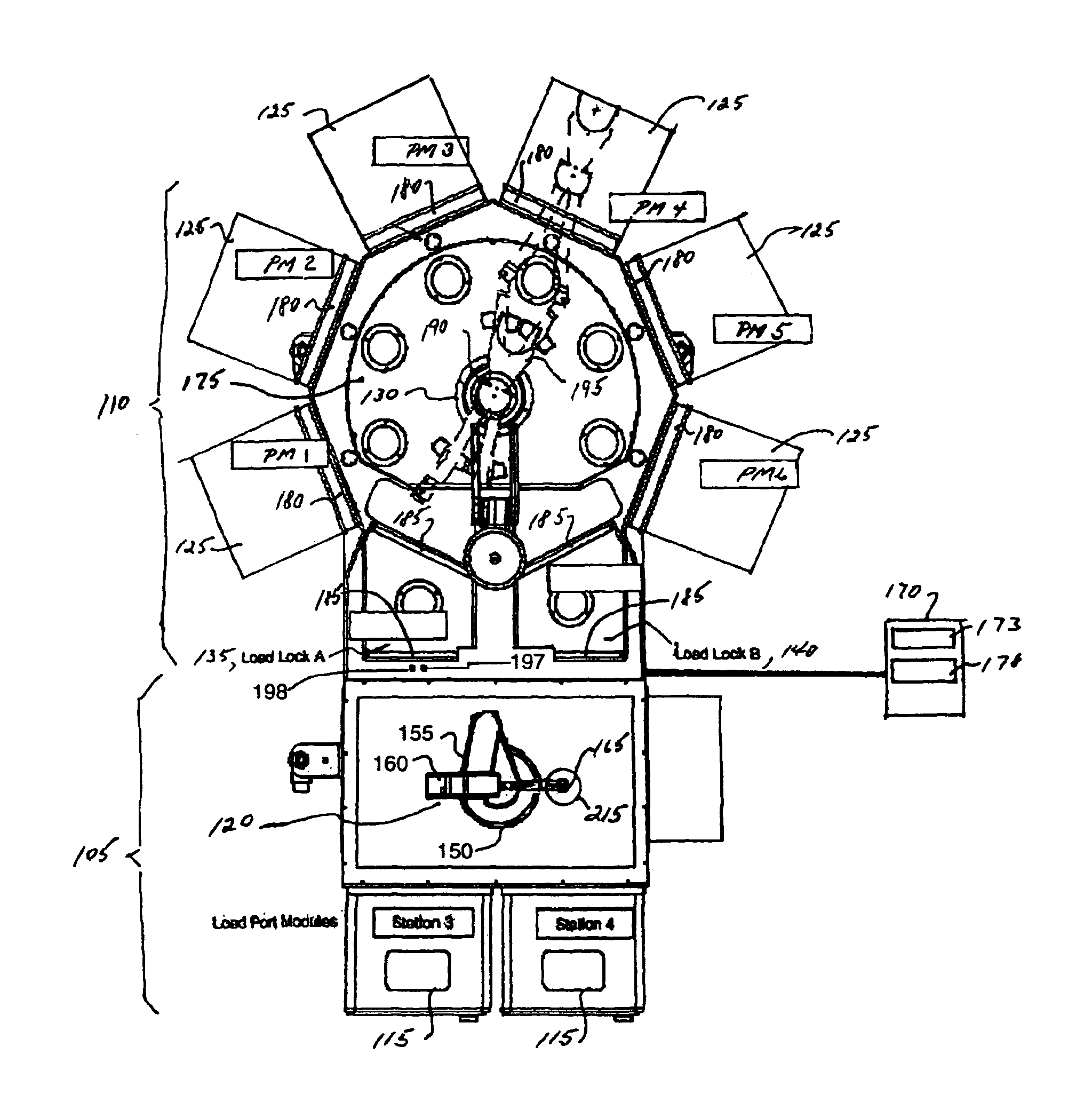
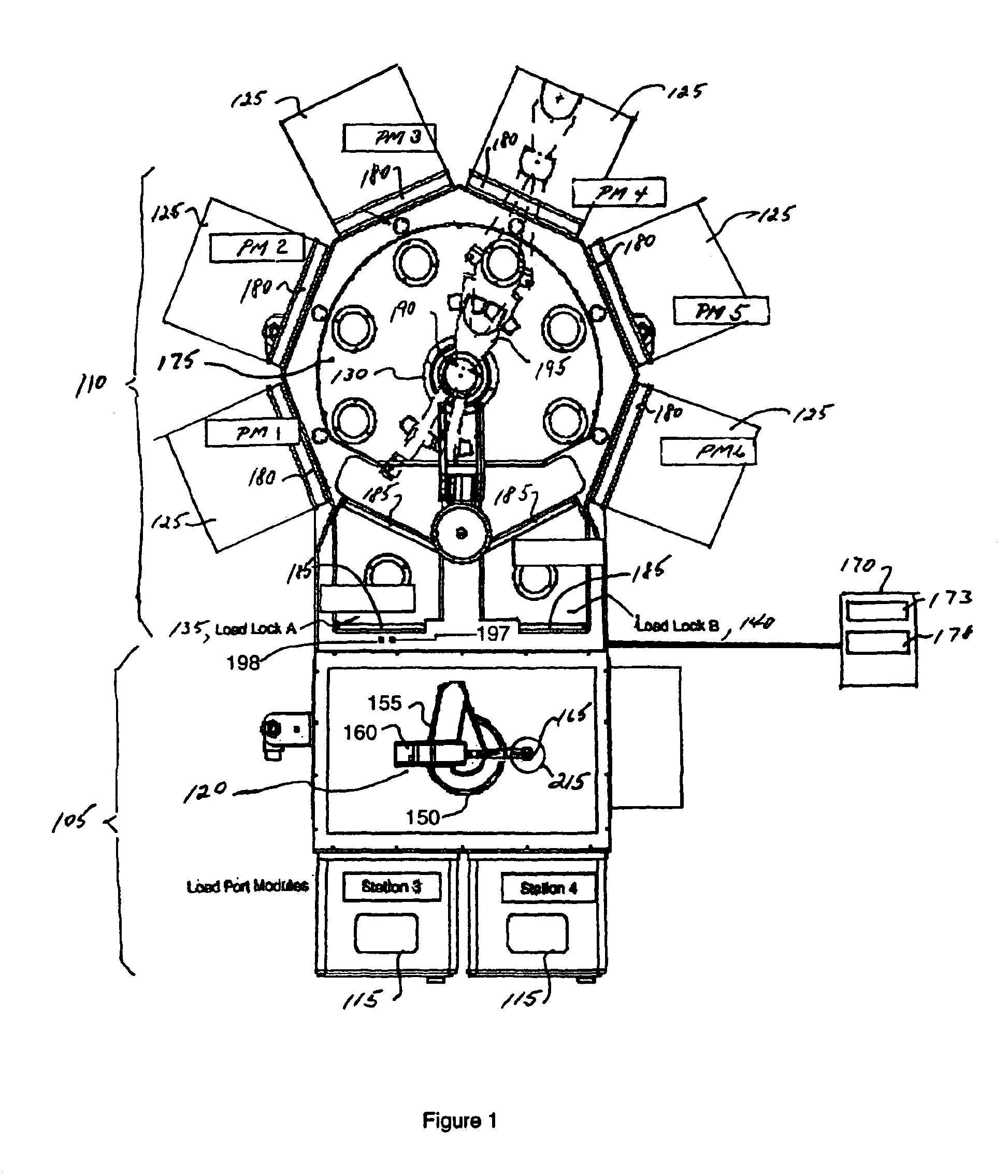
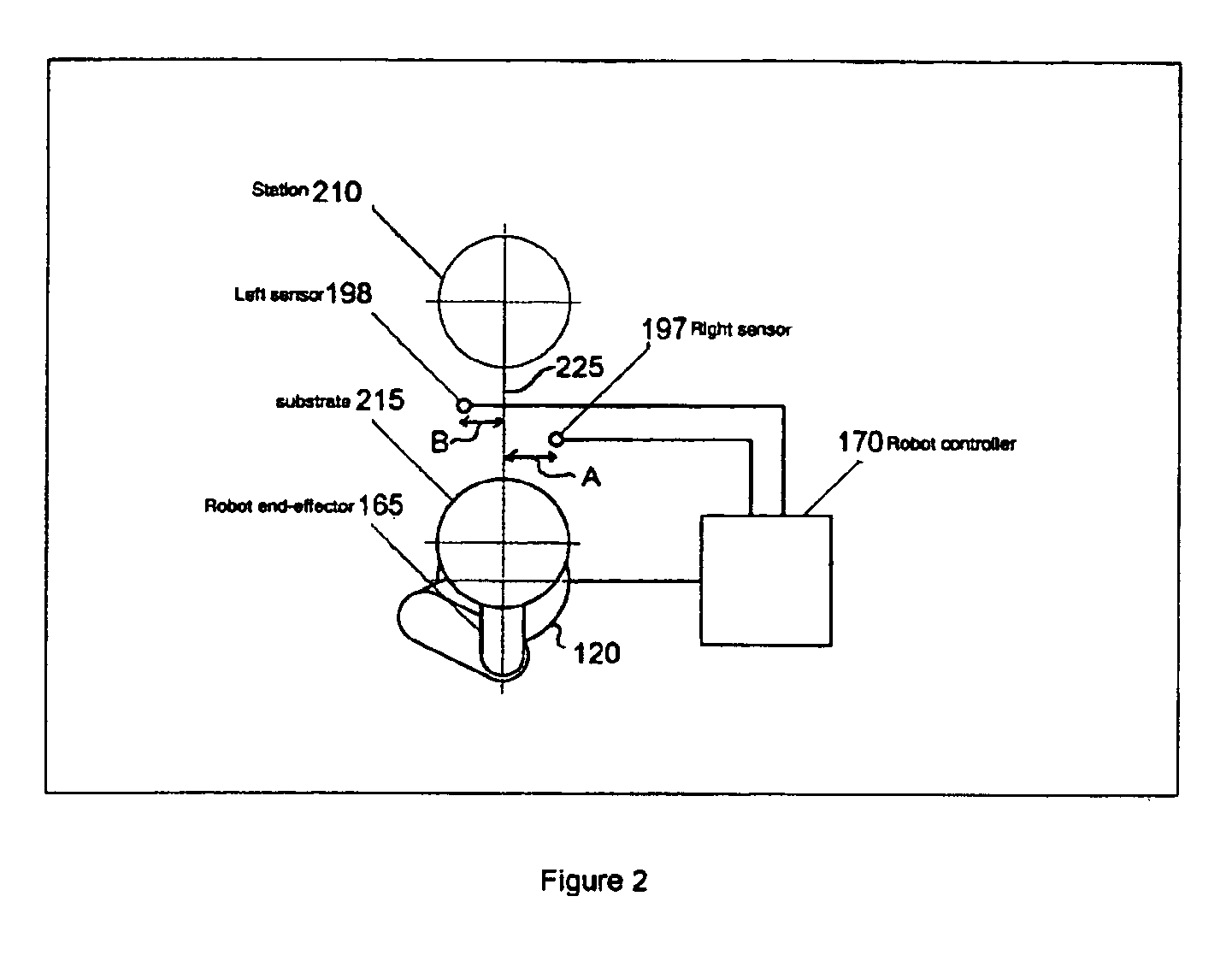
System and method of controlling an HVAC system
A system and method manage delivery of energy from a distribution network to one or more sites. Each site has at least one device coupled to the distribution network. The at least one device controllably consumes energy. The system includes a node and a control system. The node is coupled to the at least one device for sensing and controlling energy delivered to the device. A control system is coupled to the node and distribution network for delivery to the node at least one characteristic of the distribution network. The node controls the supply of energy to the device as a function of the at least one characteristic.
Owner:INVENSYS SYST INC
Monitoring activity of a user in locomotion on foot
InactiveUS6898550B1Physical therapies and activitiesTime indicationPhysical medicine and rehabilitationSimulation
Owner:NIKE INC +1
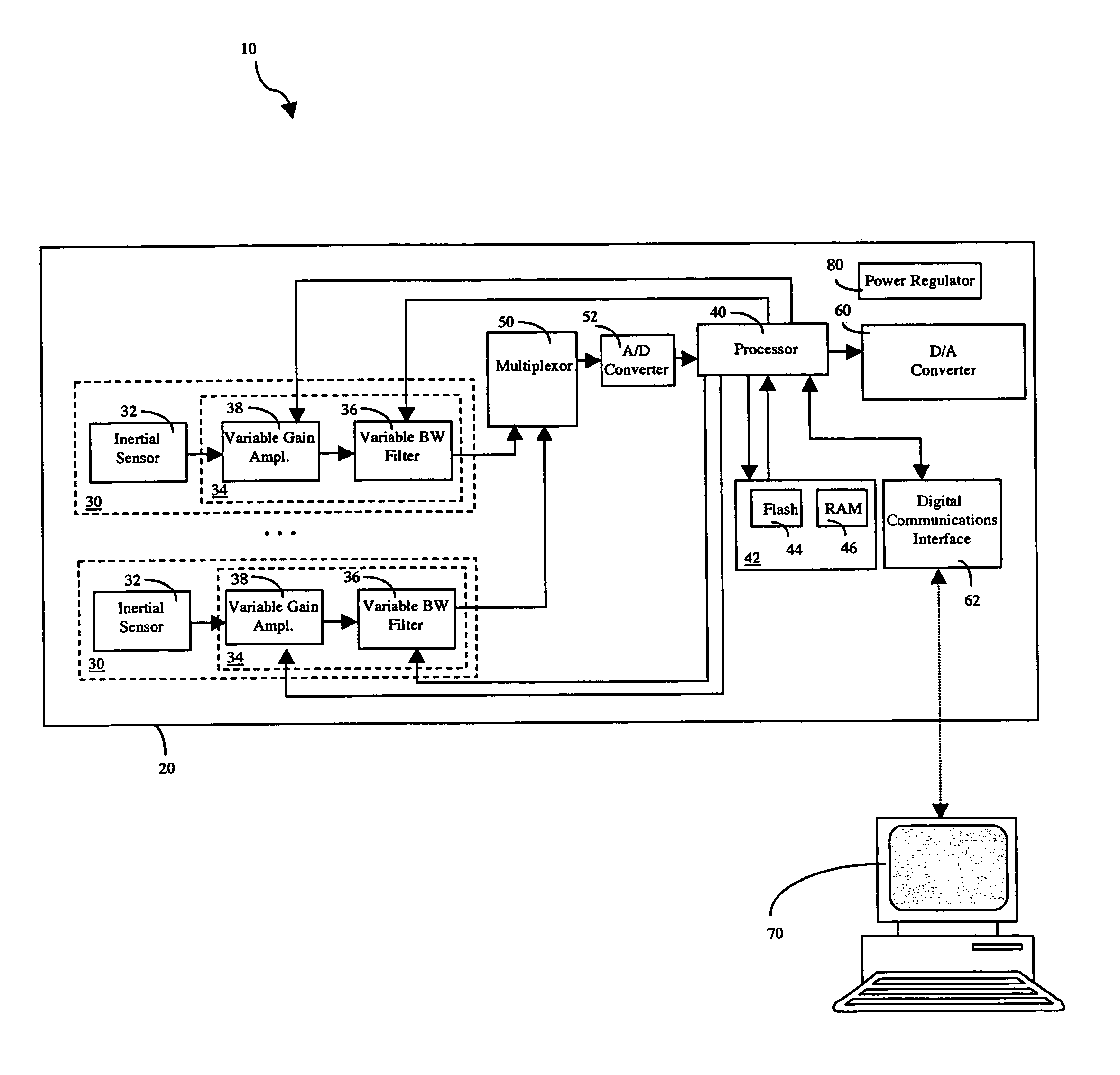
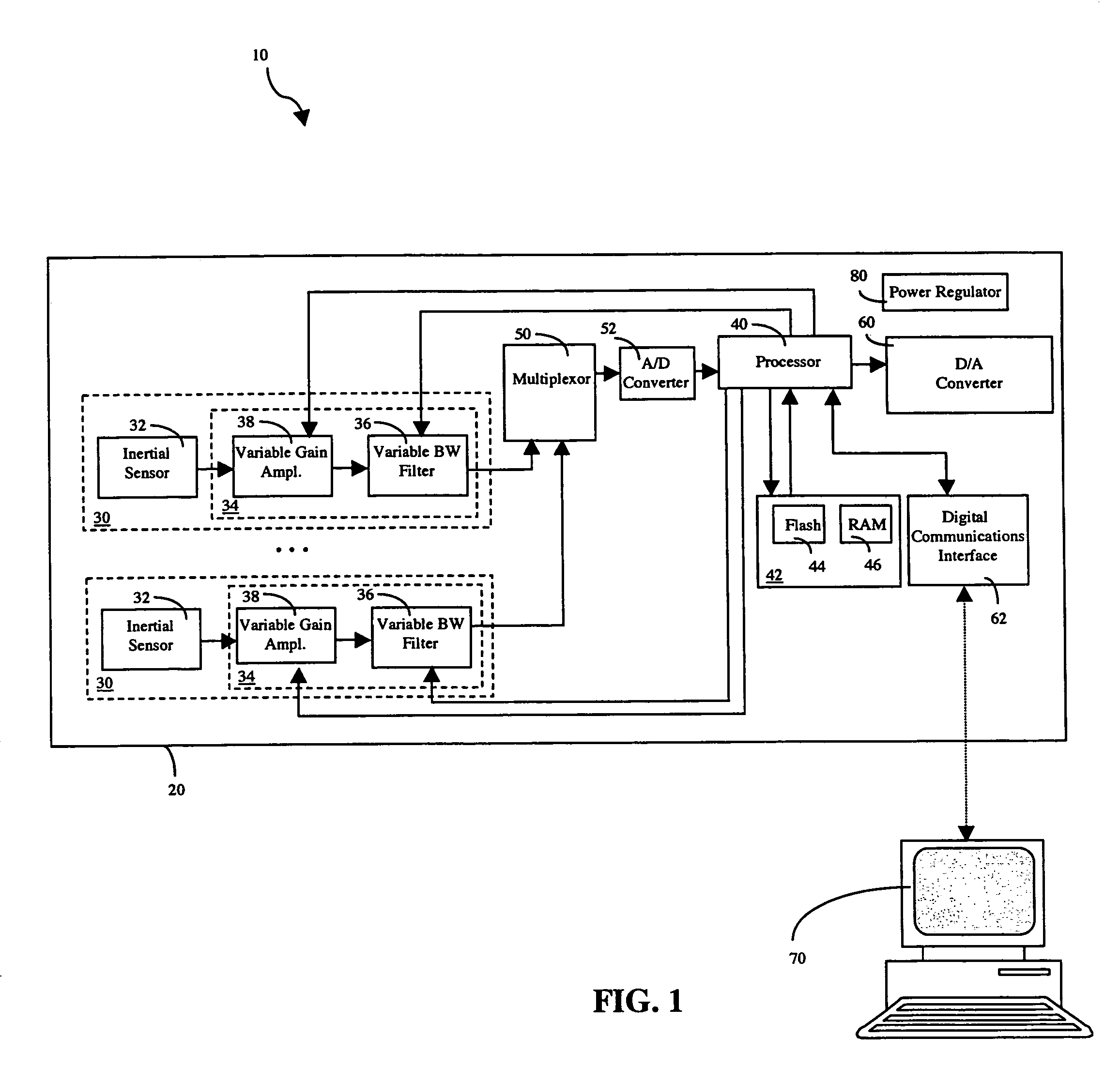
Configurable vibration sensor
InactiveUS7093492B2Vibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingVibration measurementVariable-gain amplifier
A configurable vibration sensor having a sensor circuit, an analog-to-digital converter and a processor is provided. The sensor circuit employs a vibration sensing element and a variable bandwidth filter controllable by the processor. In addition to the variable bandwidth filter, other configurable elements may also be employed in the sensor circuit, including a variable gain amplifier. These configurable elements allow the configurable vibration sensor to be configured for different vibration measurement applications when measuring vibrations from vibrating structures such as machinery and the like.
Owner:MECHWORKS SYST
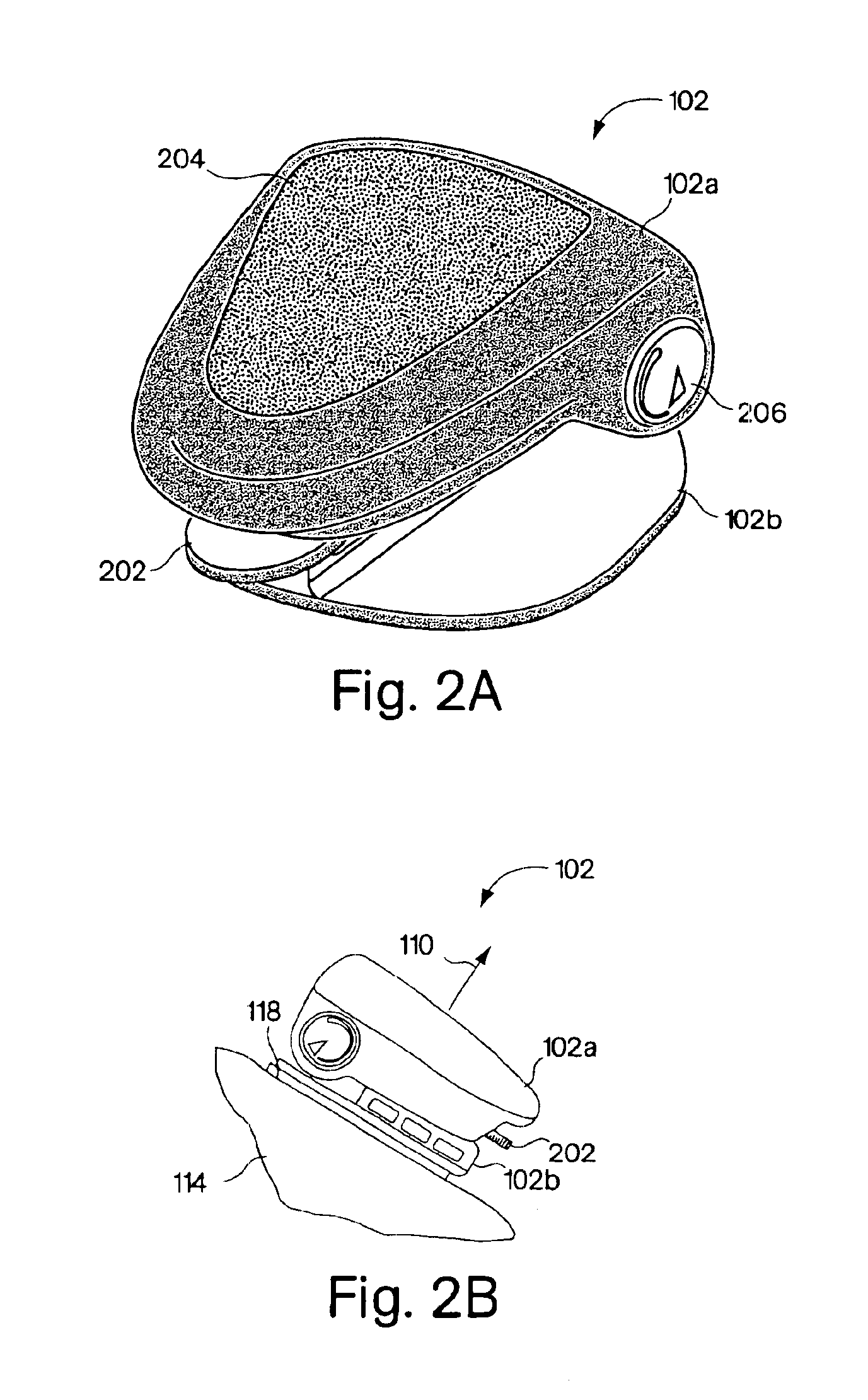
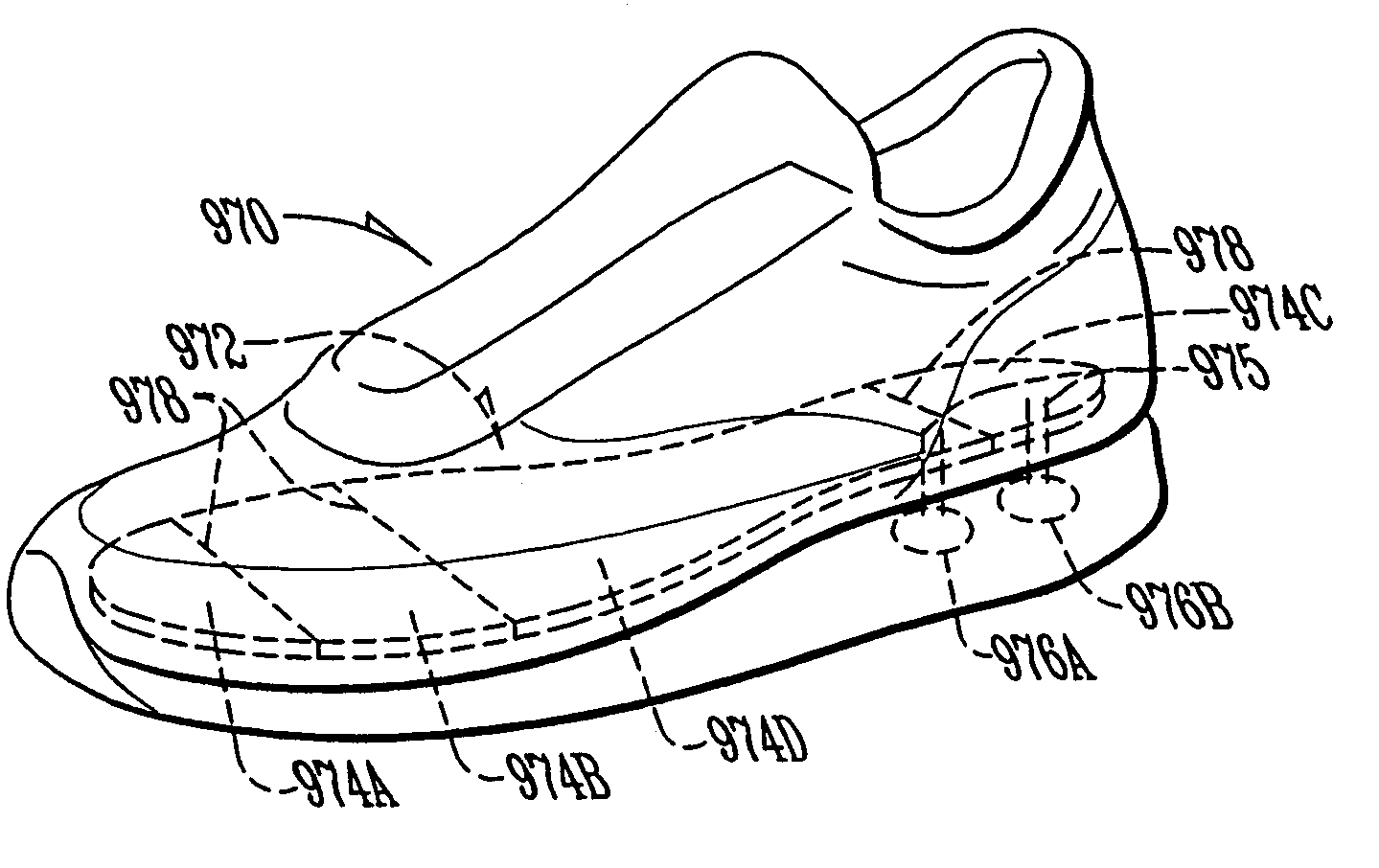
Shoes employing monitoring devices, and associated methods
InactiveUS7171331B2Soften contactAvoid breakingBroadcast transmission systemsLinear/angular speed measurementAccelerometerEngineering
Owner:APPLE INC
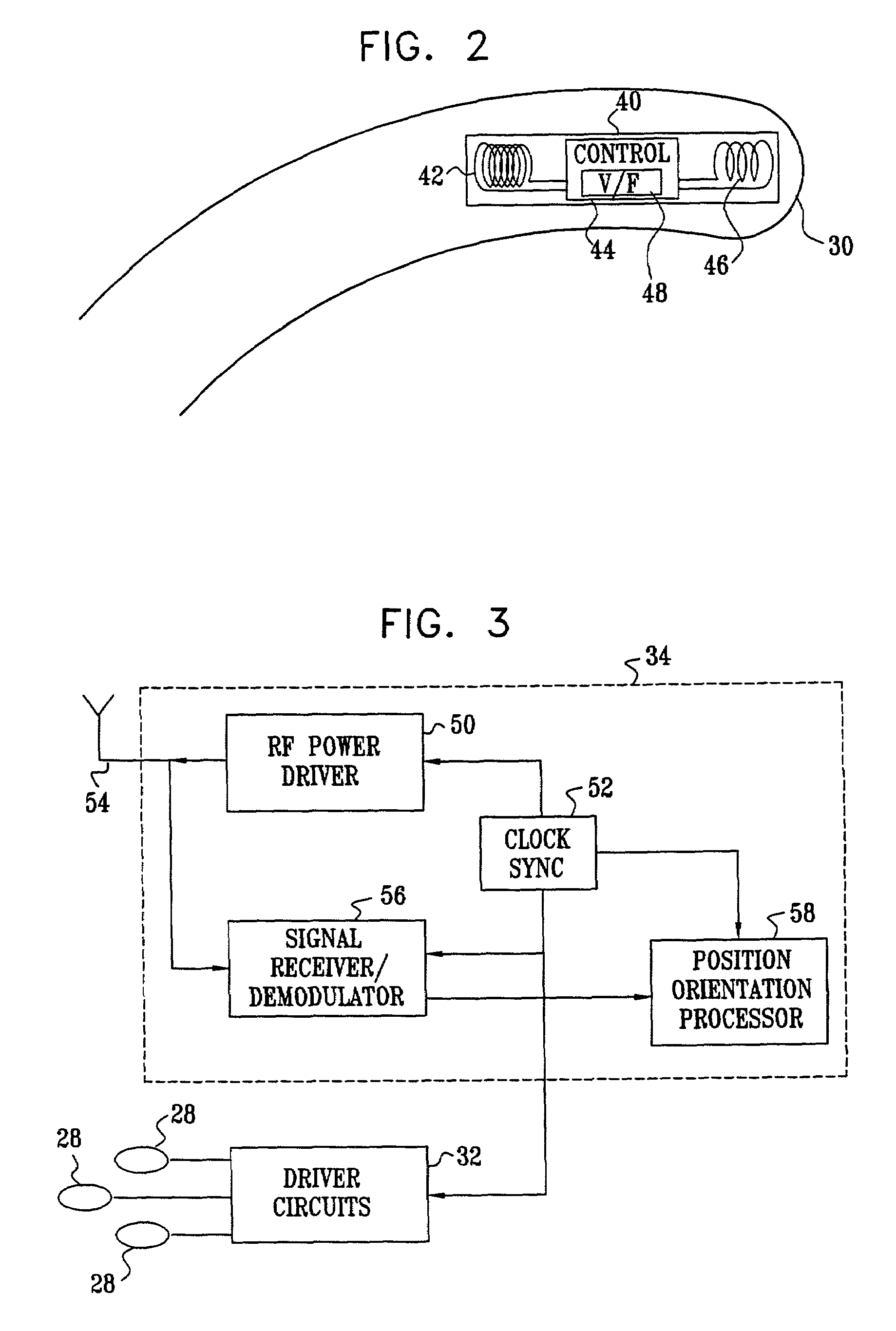
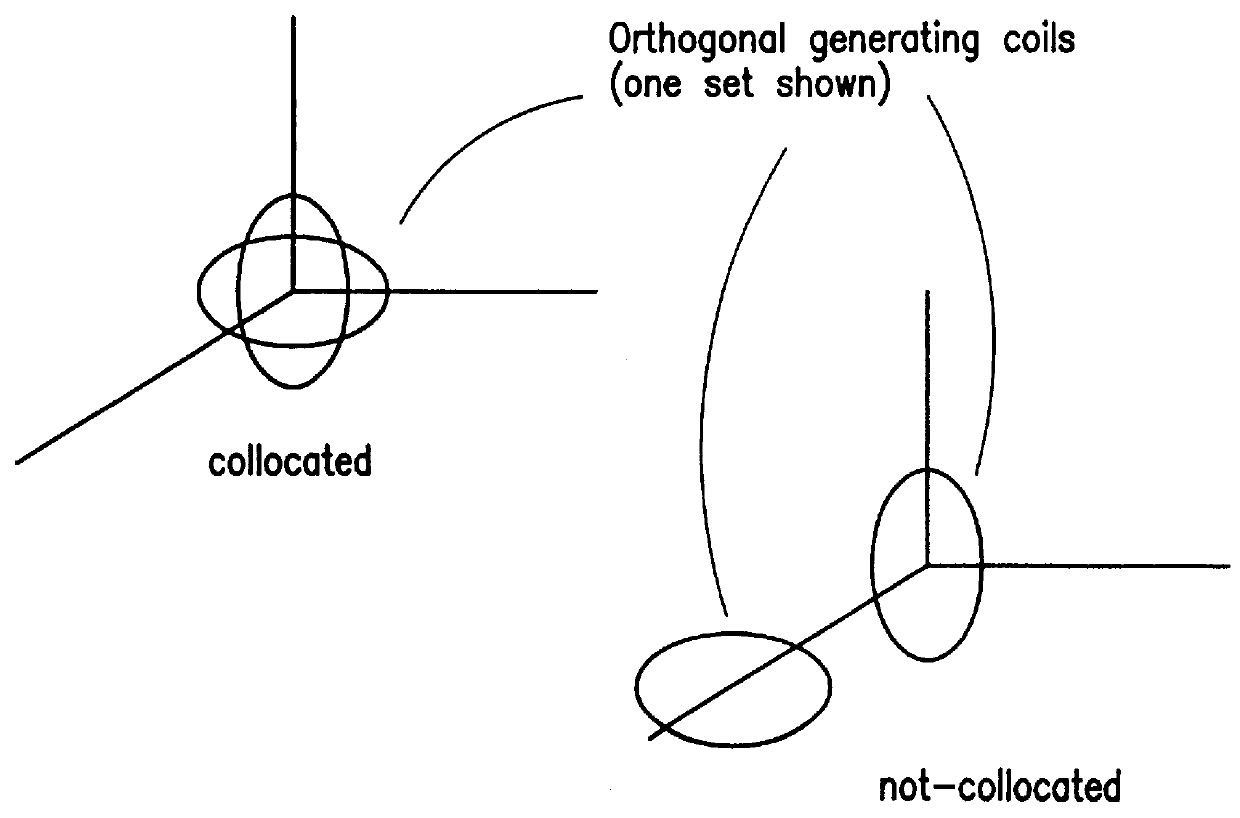
Measuring position and orientation using magnetic fields
InactiveUS6073043APrecise positioningMinimize timeMagnetic measurementsSurgeryMagnetic trackingMagnetic field coupling
A method and apparatus for determining the position and orientation of a remote object relative to a reference coordinate frame includes a plurality of field-generating elements for generating electromagnetic fields, a drive for applying, to the generating elements, signals that generate a plurality of electromagnetic fields that are distinguishable from one another, a remote sensor having one or more field-sensing elements for sensing the fields generated and a processor for processing the outputs of the sensing element(s) into remote object position and orientation relative to the generating element reference coordinate frame. The position and orientation solution is based on the exact formulation of the magnetic field coupling as opposed to approximations used elsewhere. The system can be used for locating the end of a catheter or endoscope, digitizing objects for computer databases, virtual reality and motion tracking. The methods presented here can also be applied to other magnetic tracking technologies as a final "polishing" stage to improve the accuracy of their P&O solution.
Owner:CORMEDICA
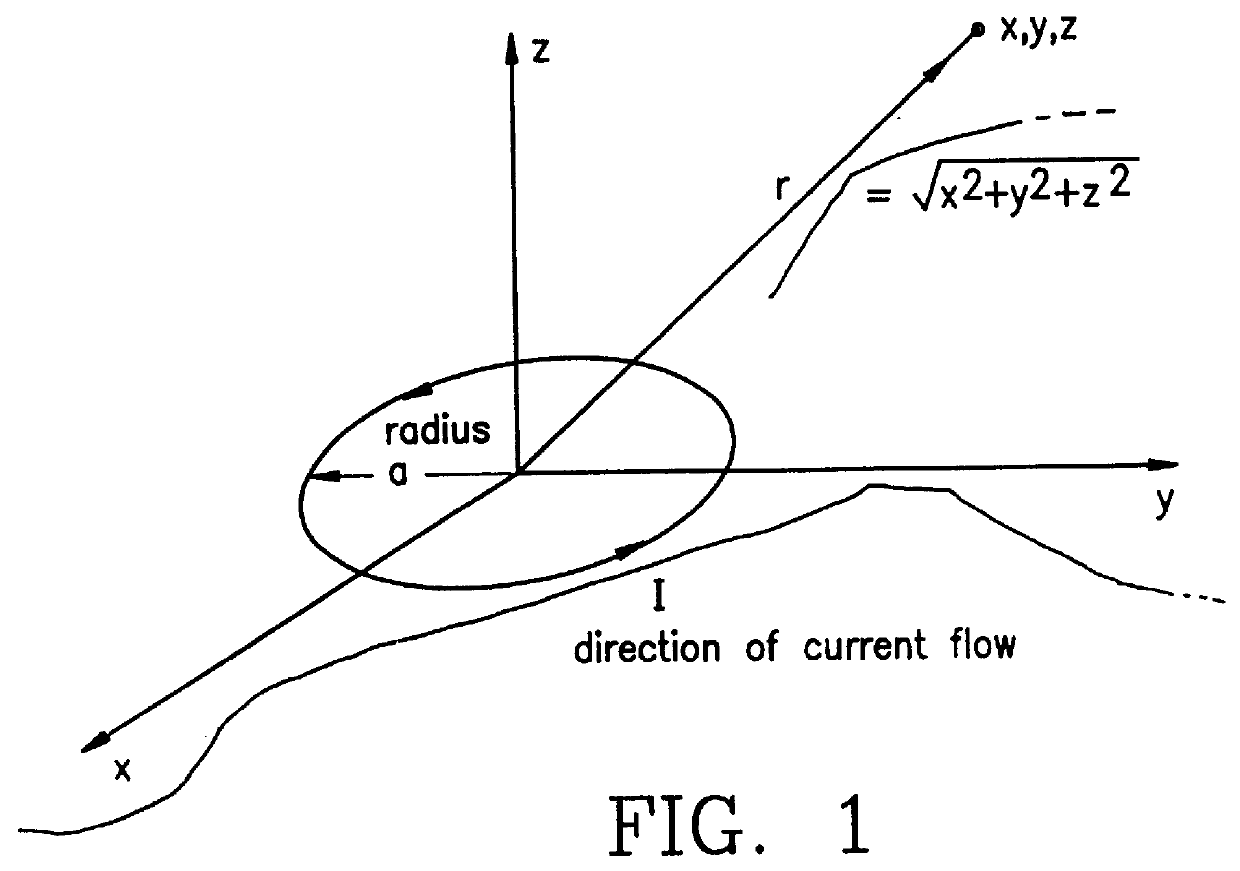
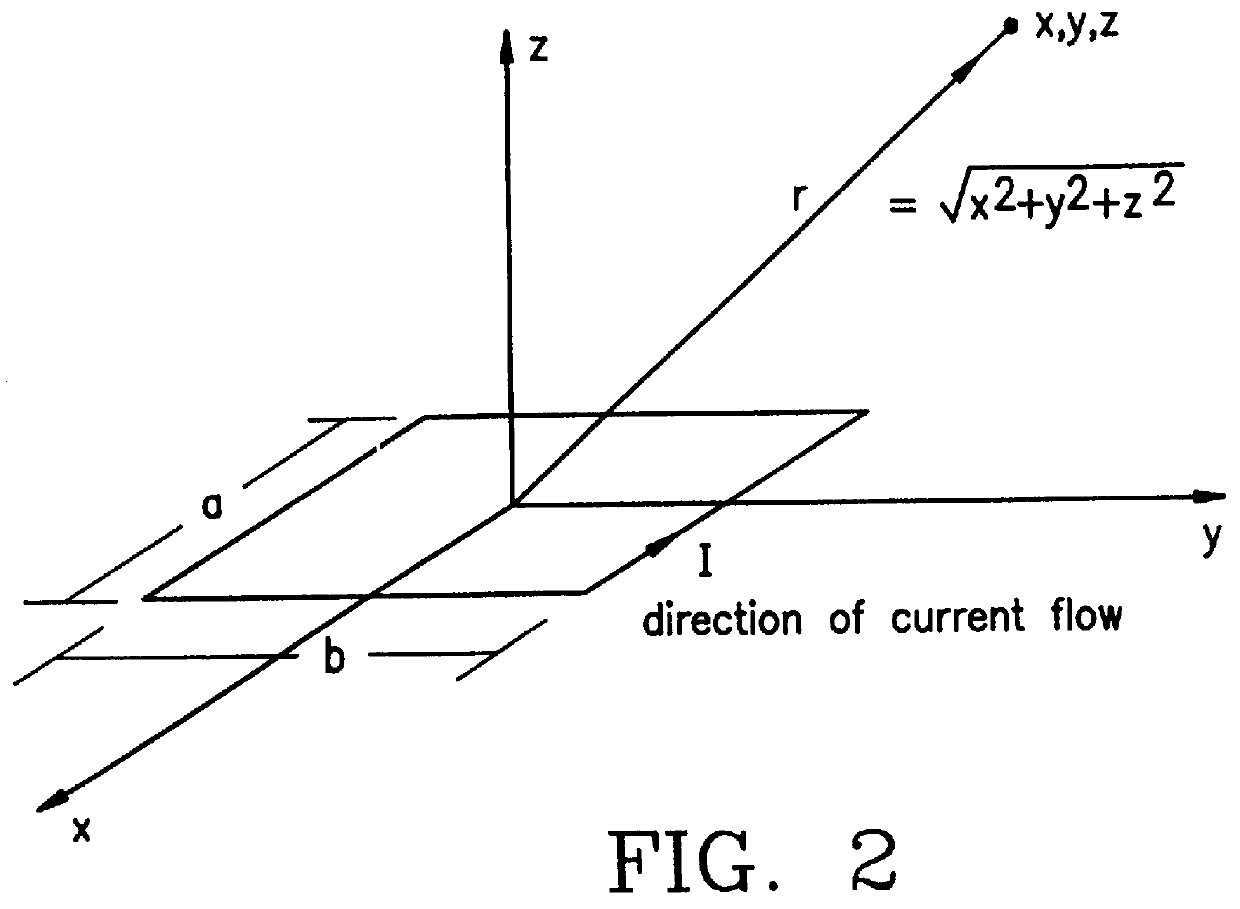
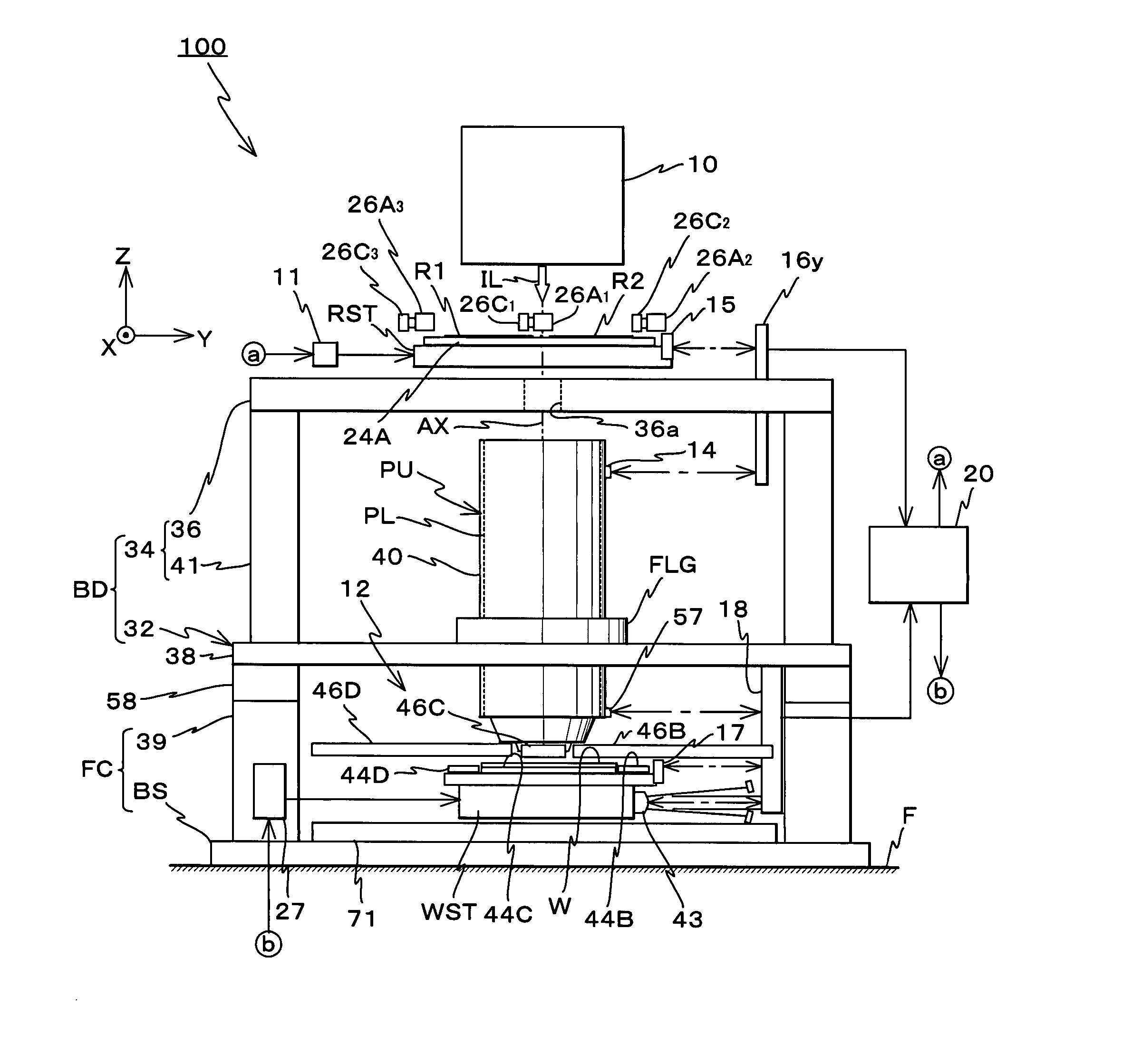
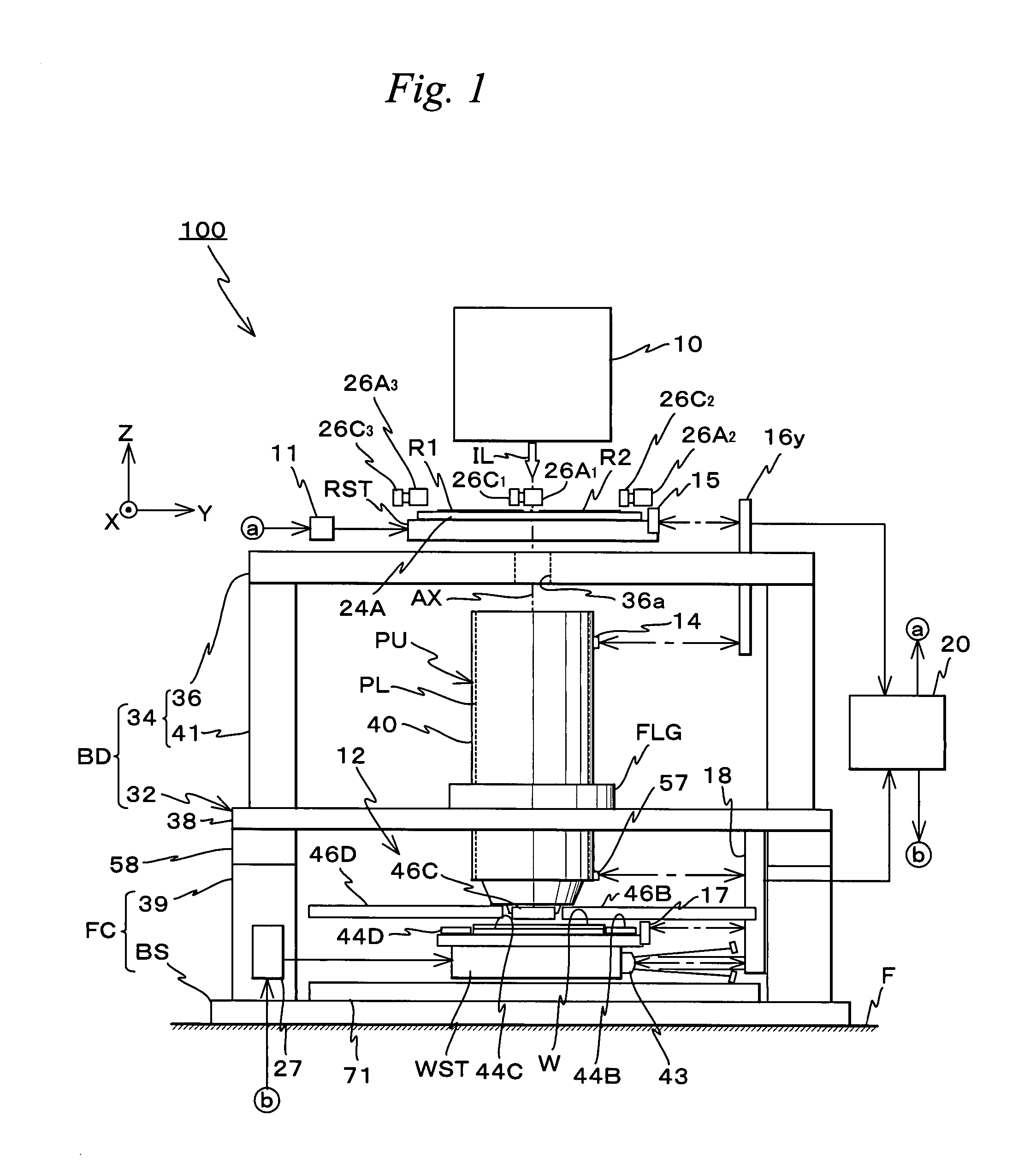
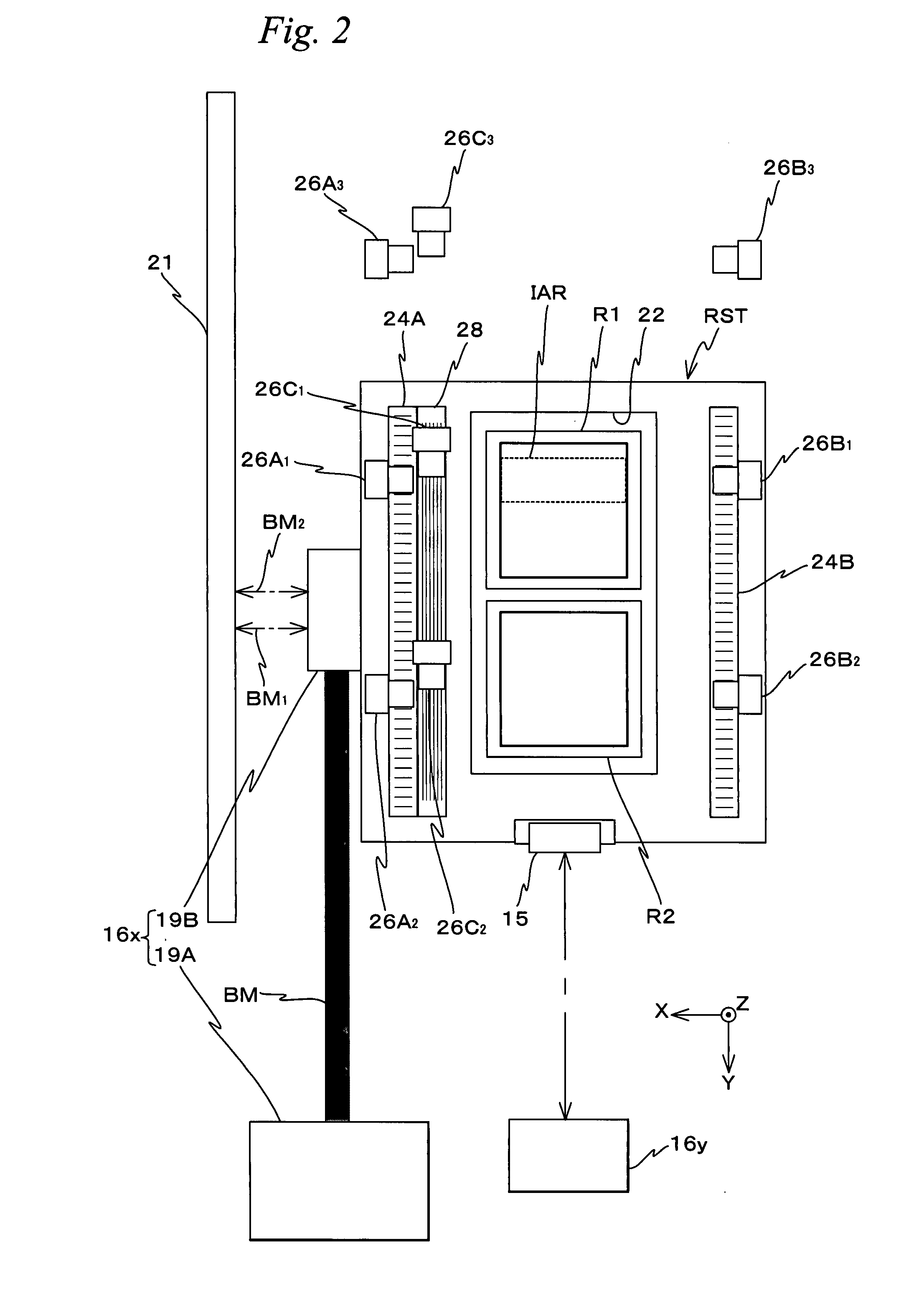
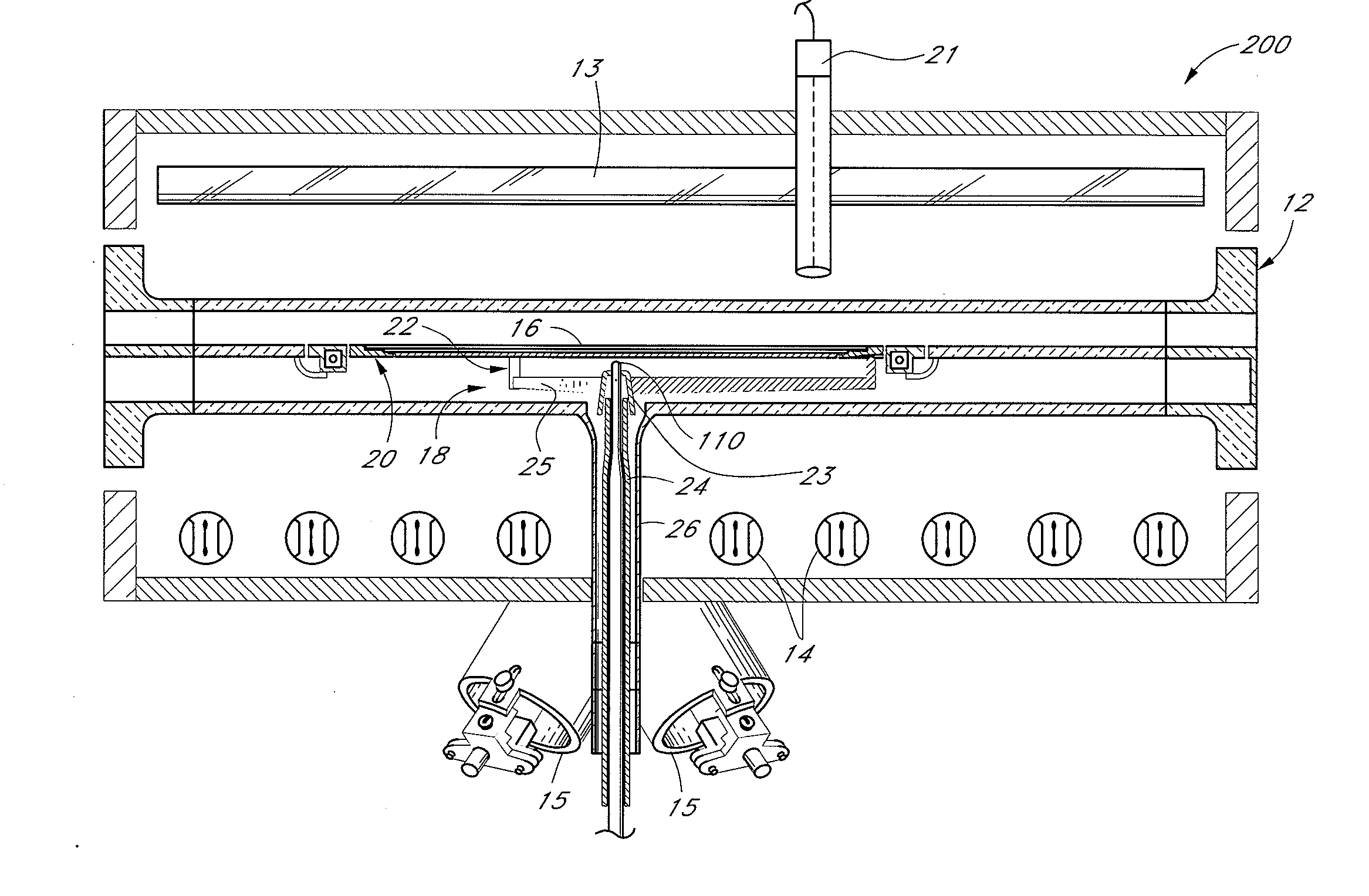
Movable body drive method, movable body drive system, pattern formation method, pattern forming apparatus, exposure method, exposure apparatus, and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20070288121A1Improve accuracyScaling errorDigital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputational physicsShort term stability
Positional information of a movable body in a Y-axis direction is measured using an interferometer and an encoder whose short-term stability of measurement values excels when compared with the interferometer, and based on the measurement results, a predetermined calibration operation for obtaining correction information for correcting measurement values of the encoder is performed. Accordingly, by using measurement values of the interferometer, correction information for correcting the measurement values of the encoder whose short-term stability of the measurement values excels the interferometer is obtained. Then, based on the measurement values of the encoder and the correction information, the movable body is driven in the Y-axis direction with good precision.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Transducer and transducer module
InactiveUS20130069483A1Enhanced Haptic FeedbackEnhance propagationMagnetic circuit rotating partsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerAcoustic propagation
Transducers and transducer modules having the transducers are disclosed. An embodiment discloses a transducer that includes a conductive layer having a U-shaped slit toward its swing end. The slit is configured to enhance a haptic feedback or an acoustic propagation, or adjust a resonant mode.
Owner:CHIEF LAND ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Thermal measurments of electronic devices during operation
InactiveUS20050114068A1Thermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionElectricityEngineering
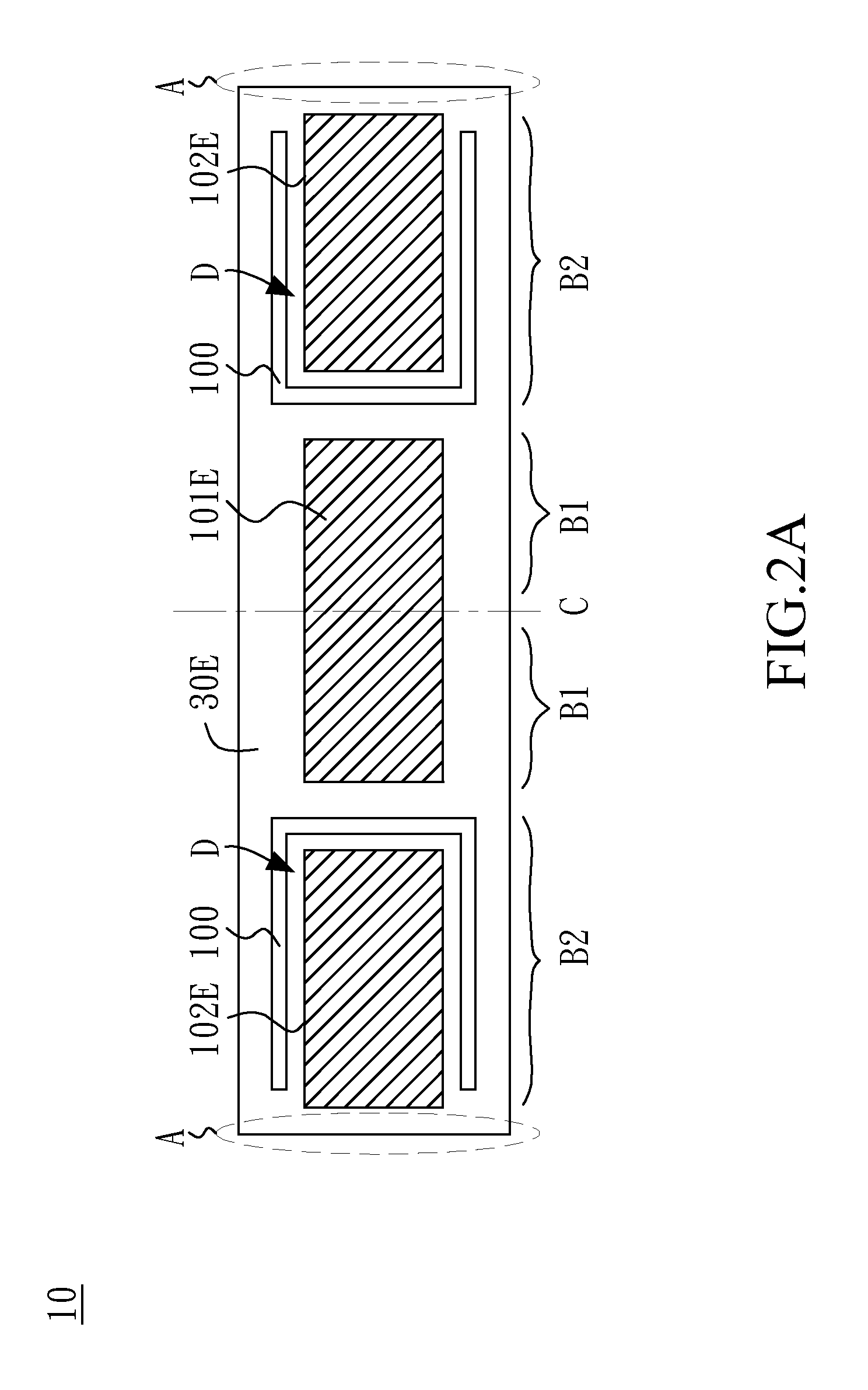
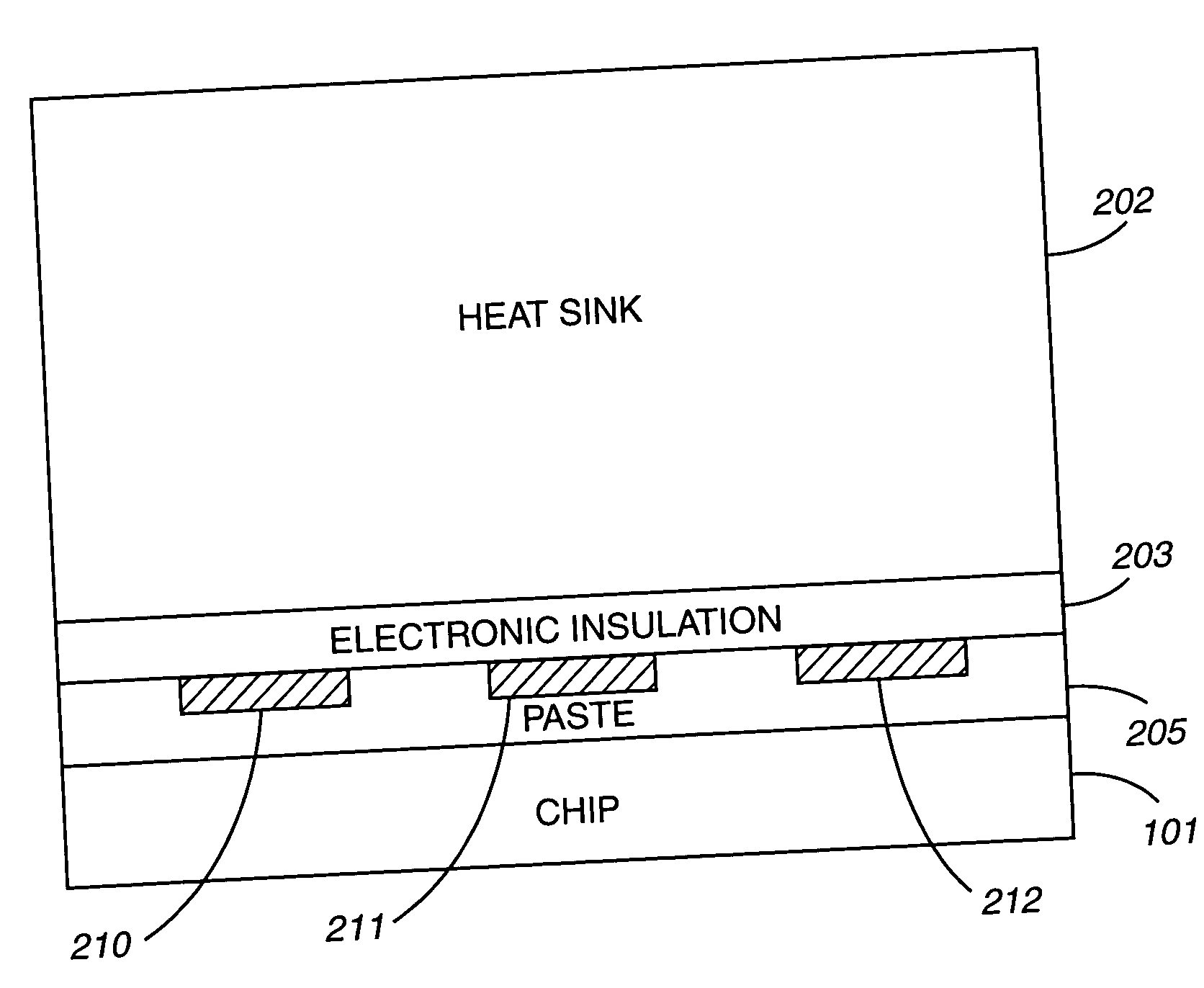
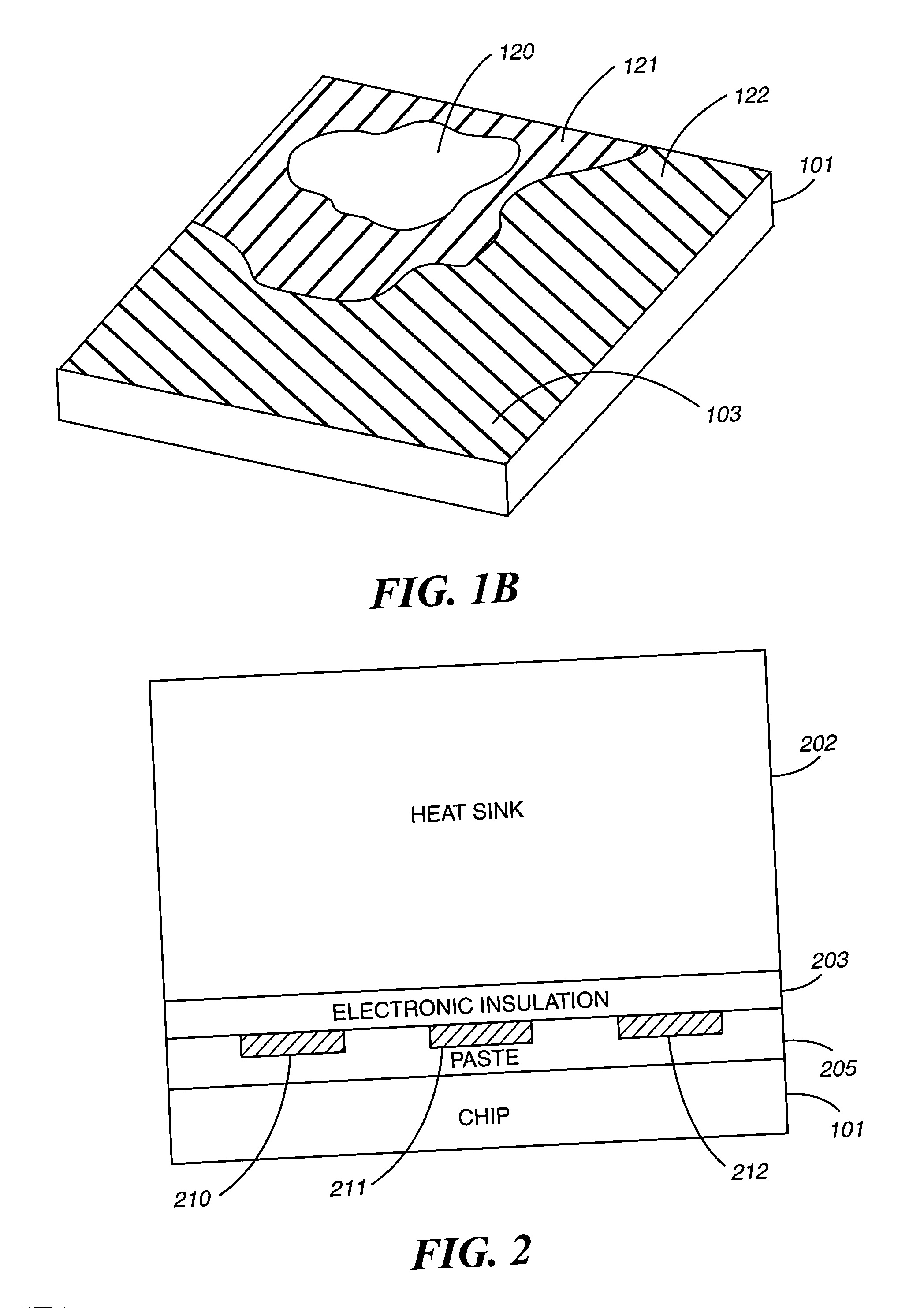
A system and method for measuring thermal distributions of an electronic device during operation is disclosed. The system includes an electronic device, a heat sink adjacent to the electronic device and an electrical-insulating layer disposed on the electronic device so as to separate the electronic device and the heat sink. The system further includes a plurality of thermal sensors located on the electrical-insulating layer, each of the plurality of thermal sensors in a different location. The plurality of thermal sensors is located within one or more thin film circuit layers disposed adjacent to the electrical insulating layer. The system further includes a module for receiving thermal information from the plurality of thermal sensors during operation of the electronic device. The system further includes a processor coupled to the module for generating a thermal distribution of the electronic device based on the thermal information received from the plurality of thermal sensors.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for controlling a temperature-controlled probe
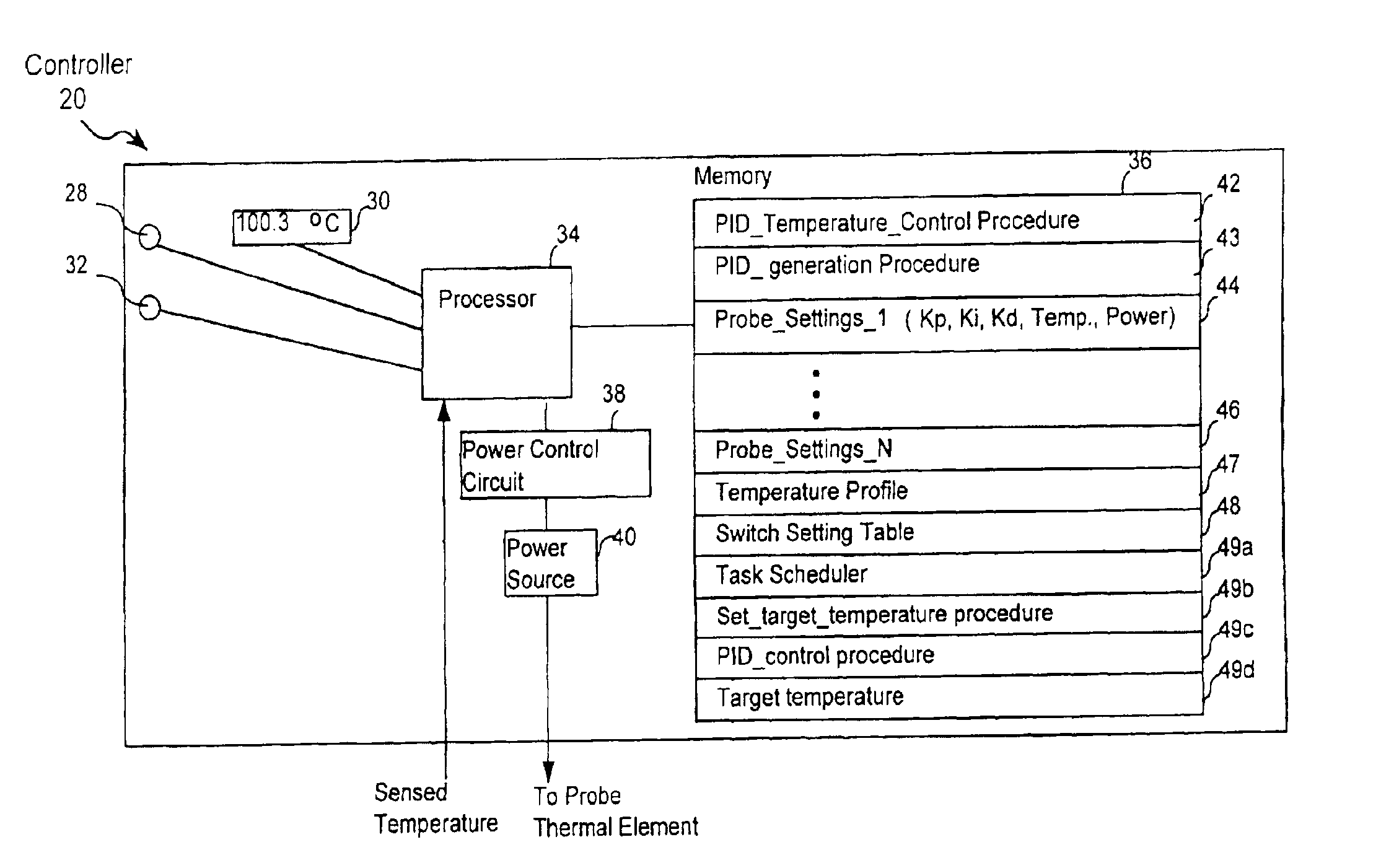
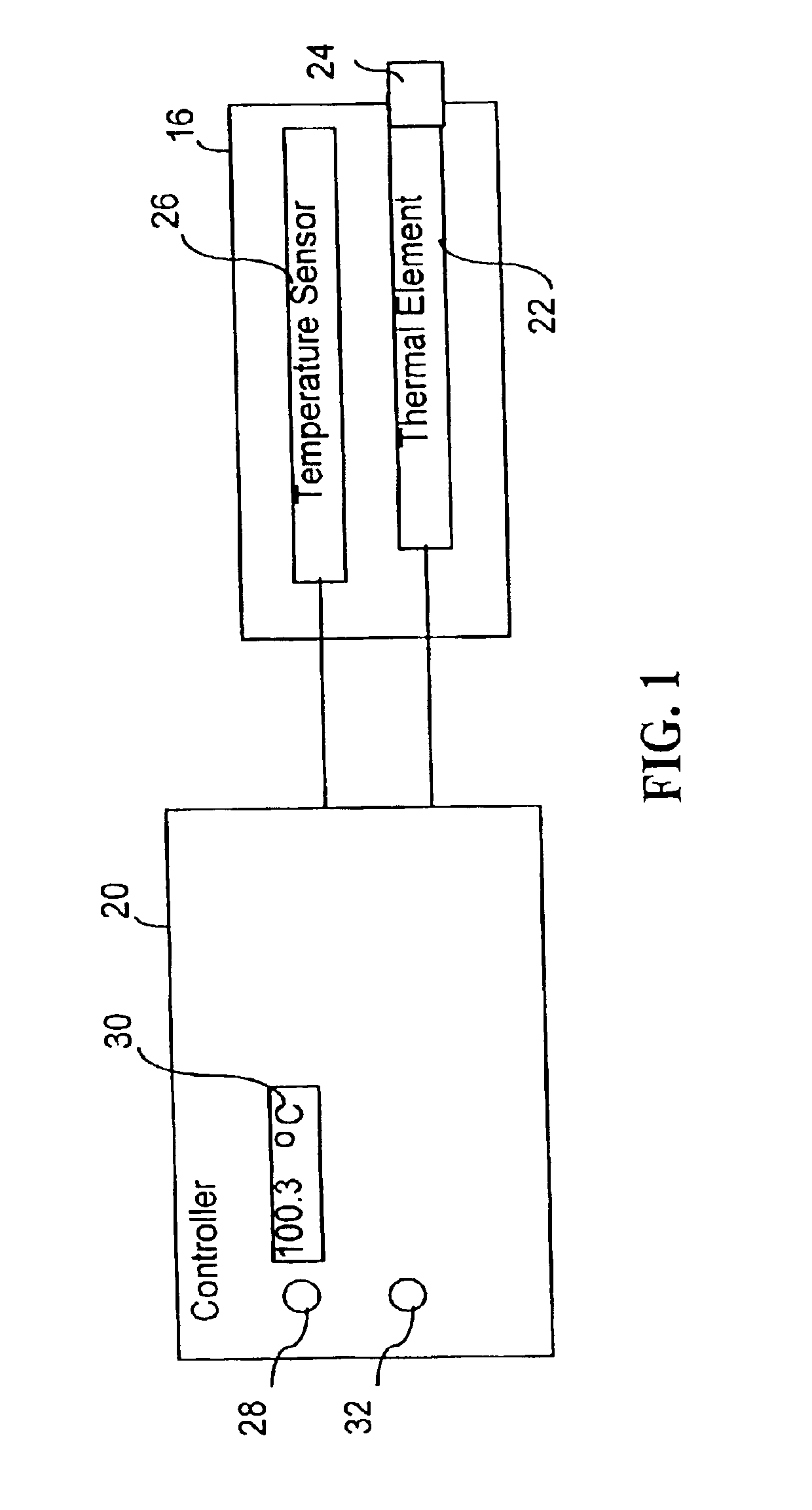
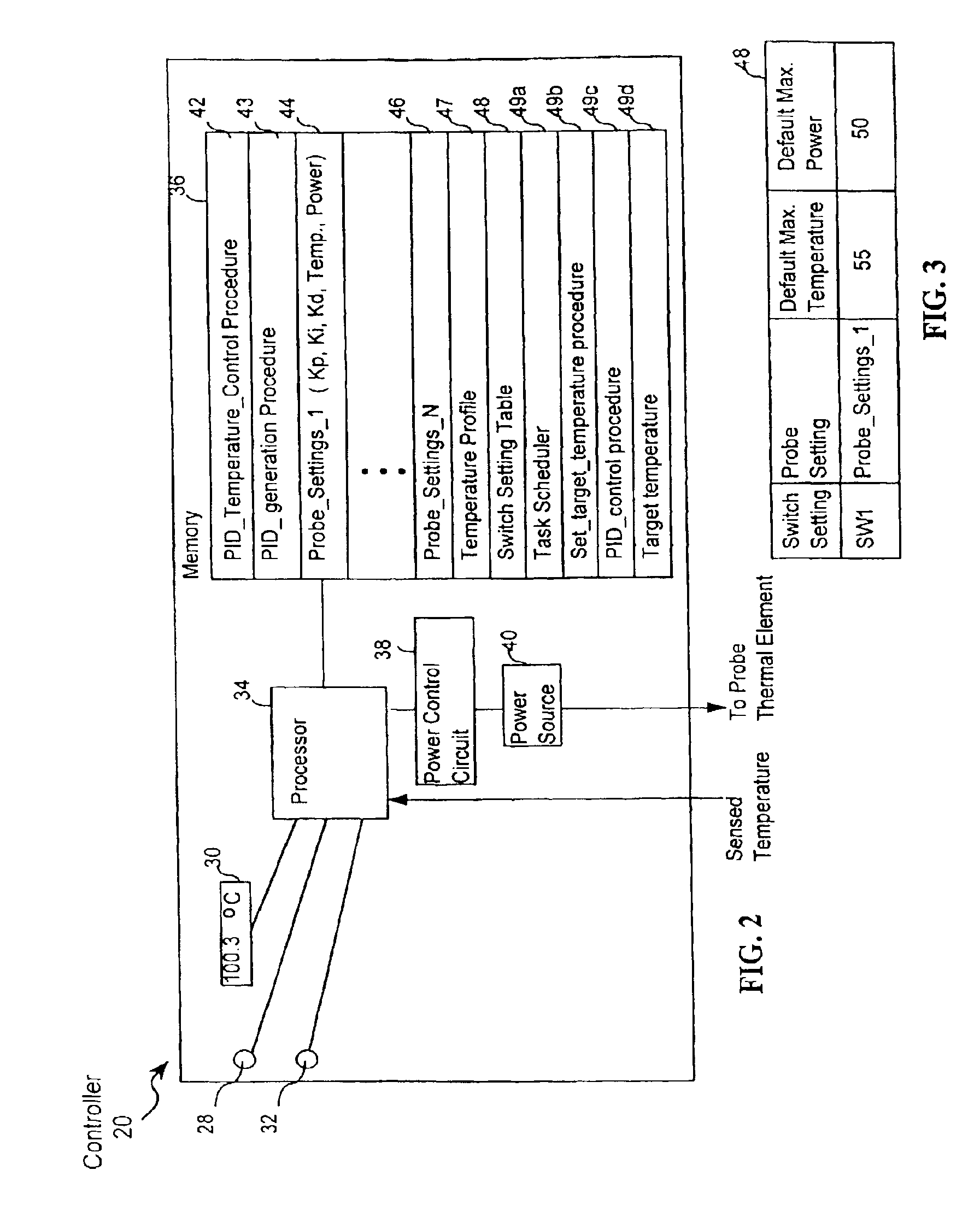
InactiveUS6939346B2Finer granularity of controlMinimize overshootThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansThermal energyMedicine
A thermal energy controller system useful in medical procedures includes a controller coupled to a probe, and a thermal element to vary probe temperature. The controller includes memory storing a non-continuous algorithm that permits user-selectable settings for various probe types such that controller operation is self-modifying in response to the selected probe setting. Probe output power Pout is constant in one mode to rapidly enable probe temperature to come within a threshold of a target temperature. The controller can then vary Pout dynamically using a proportional-integral-derivative (PID) algorithm Pout=Kp·P+Ki·I+Kd·D, where feedback loop coefficients Kp, Ki, Kd can vary dynamically depending upon magnitude of an error function e(t) representing the difference between a user-set desired target temperature and sensed probe temperature. Advantageously, target temperature can be rapidly attained without overshoot, allowing the probe system to be especially effective in arthroscopic tissue treatment.
Owner:ORATEC INTERVENTIONS
Motion analysis system
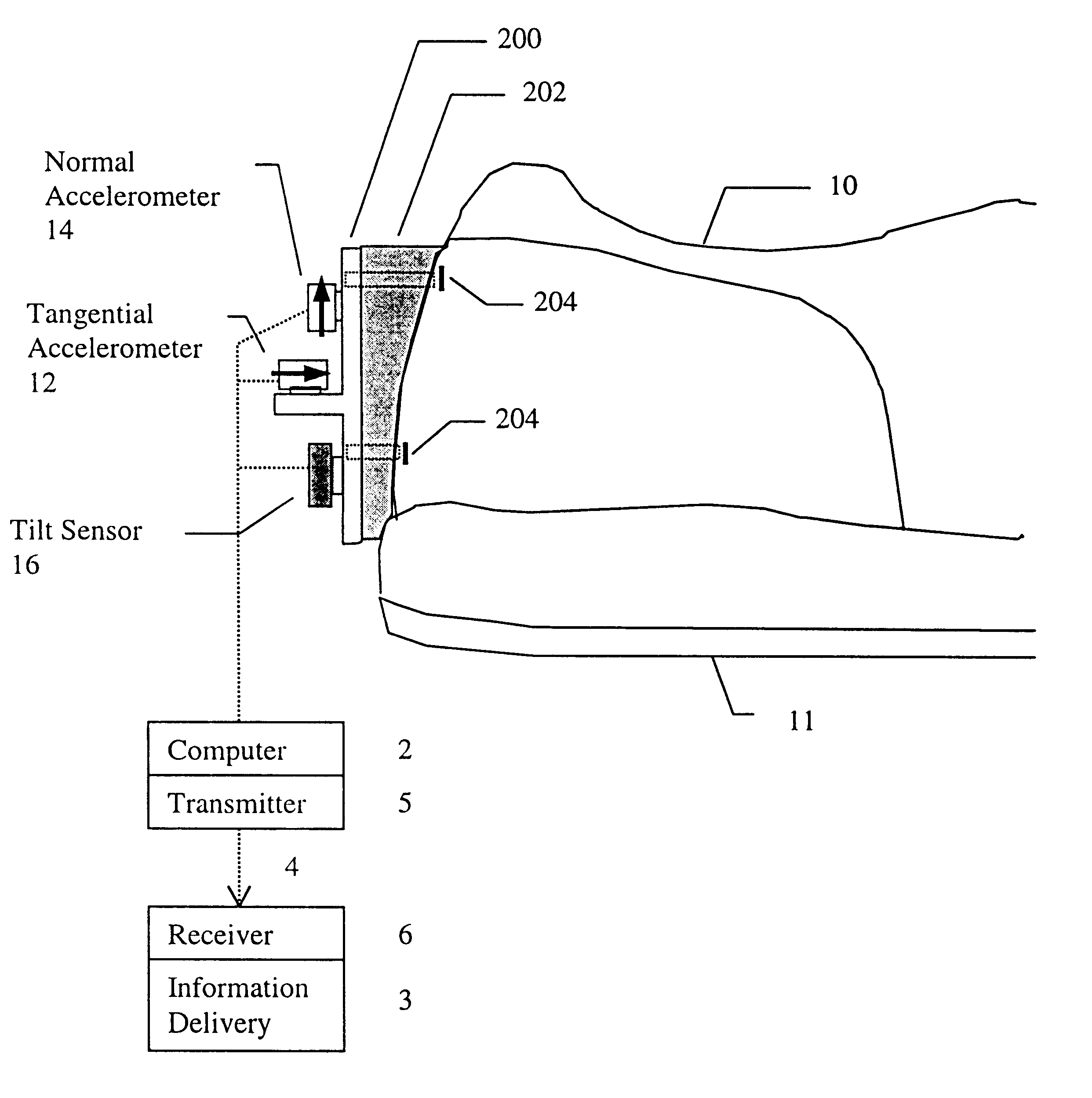
InactiveUS6301964B1Accurately determine velocity and distance traveledAcceleration measurement using interia forcesGymnastic exercisingAccelerometerTarget Motion Analysis
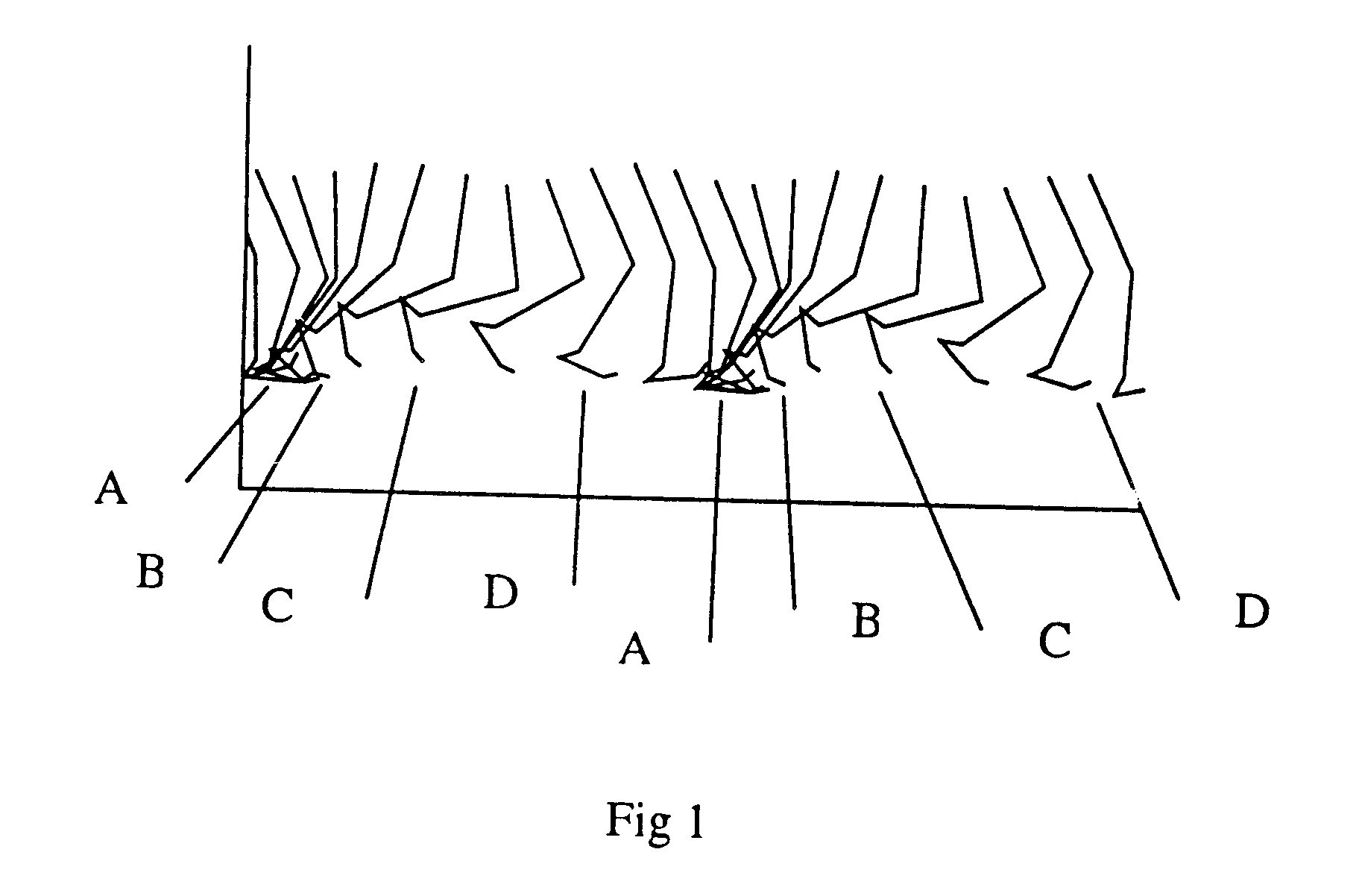
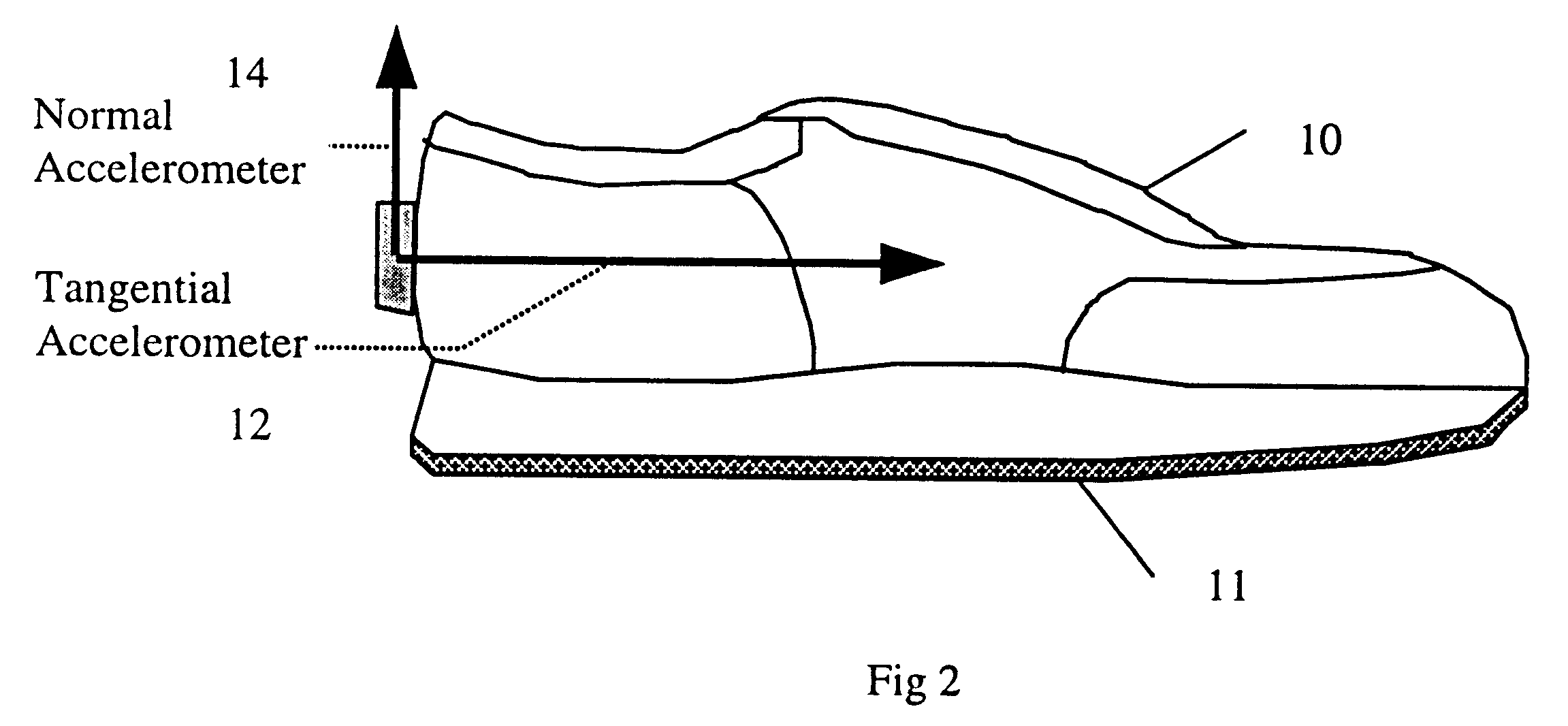
A device comprised of at least a pair of accelerometers and a tilt sensor mounted in fixed relation to a datum plane defining surface (sole of a shoe) may be used for extracting kinematic variables including linear and rotational acceleration, velocity and position. These variables may be resolved into a selected direction thereby permitting both relative and absolute kinematic quantities to be determined. The acceleration is determined using a small cluster of two mutually perpendicular accelerometers mounted on a shoe. Angular orientation of the foot may be determined by double integration of the foot's angular acceleration (which requires a third accelerometer substantially parallel to one of the two orthogonal accelerometers). The two orthogonal accelerations are then resolved into a net horizontal acceleration or other selected direction which may be integrated to find the foot velocity in the selected direction. The average of the foot velocity corresponds to the subject's gait speed.
Owner:GARMIN
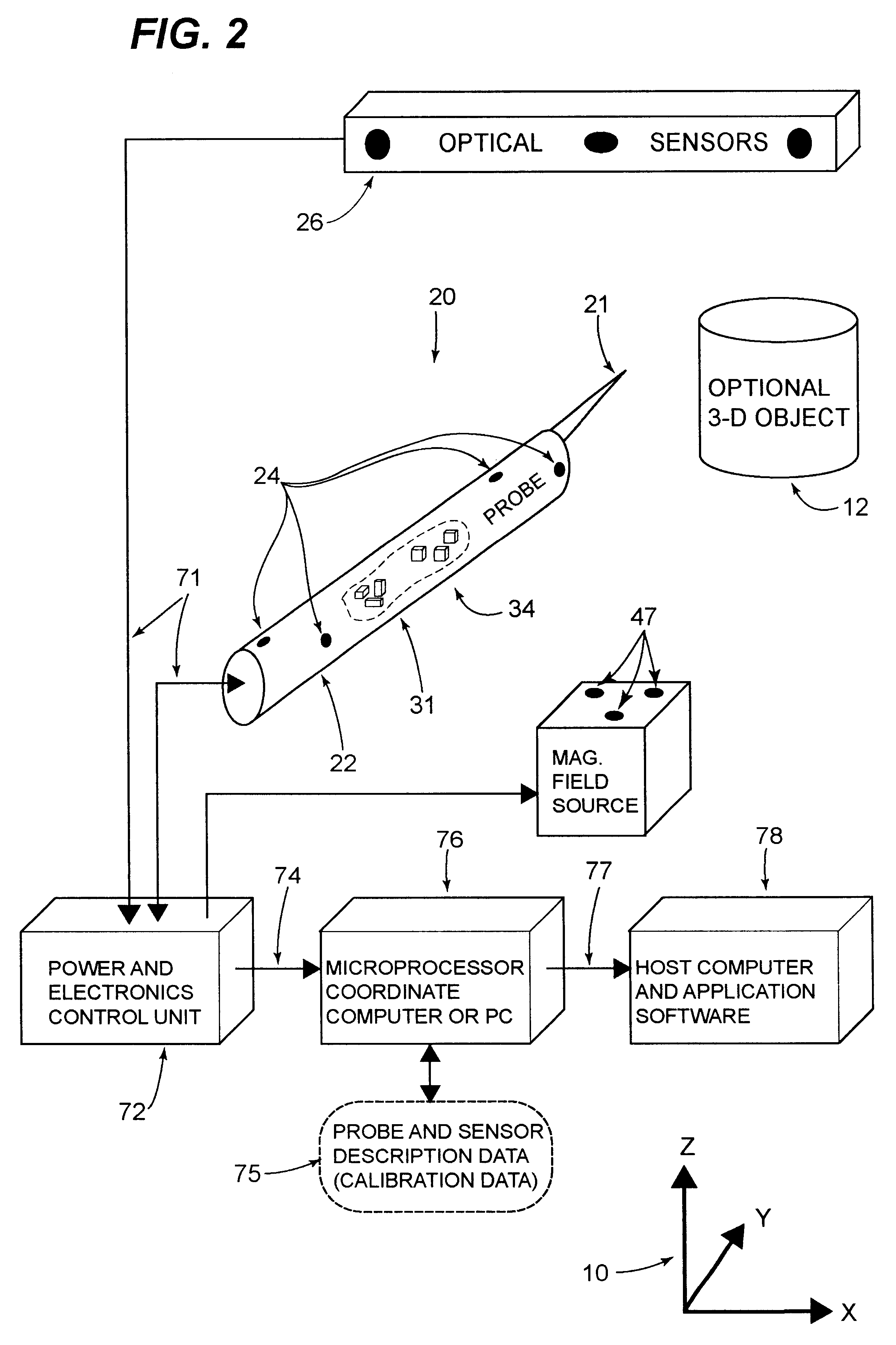
Hybrid 3-D probe tracked by multiple sensors
InactiveUS6611141B1Surgical navigation systemsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsMultiple sensorQuantum system
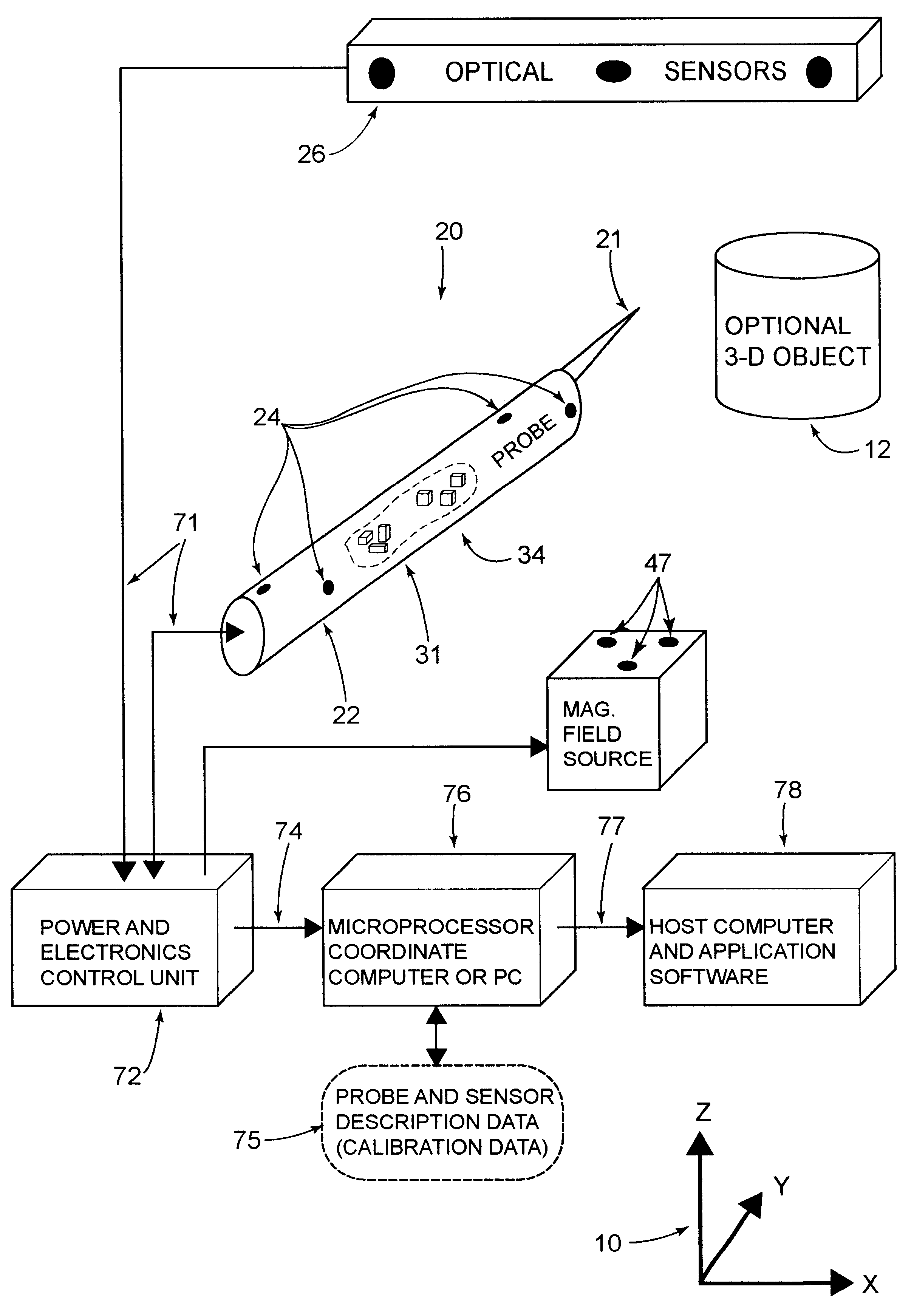
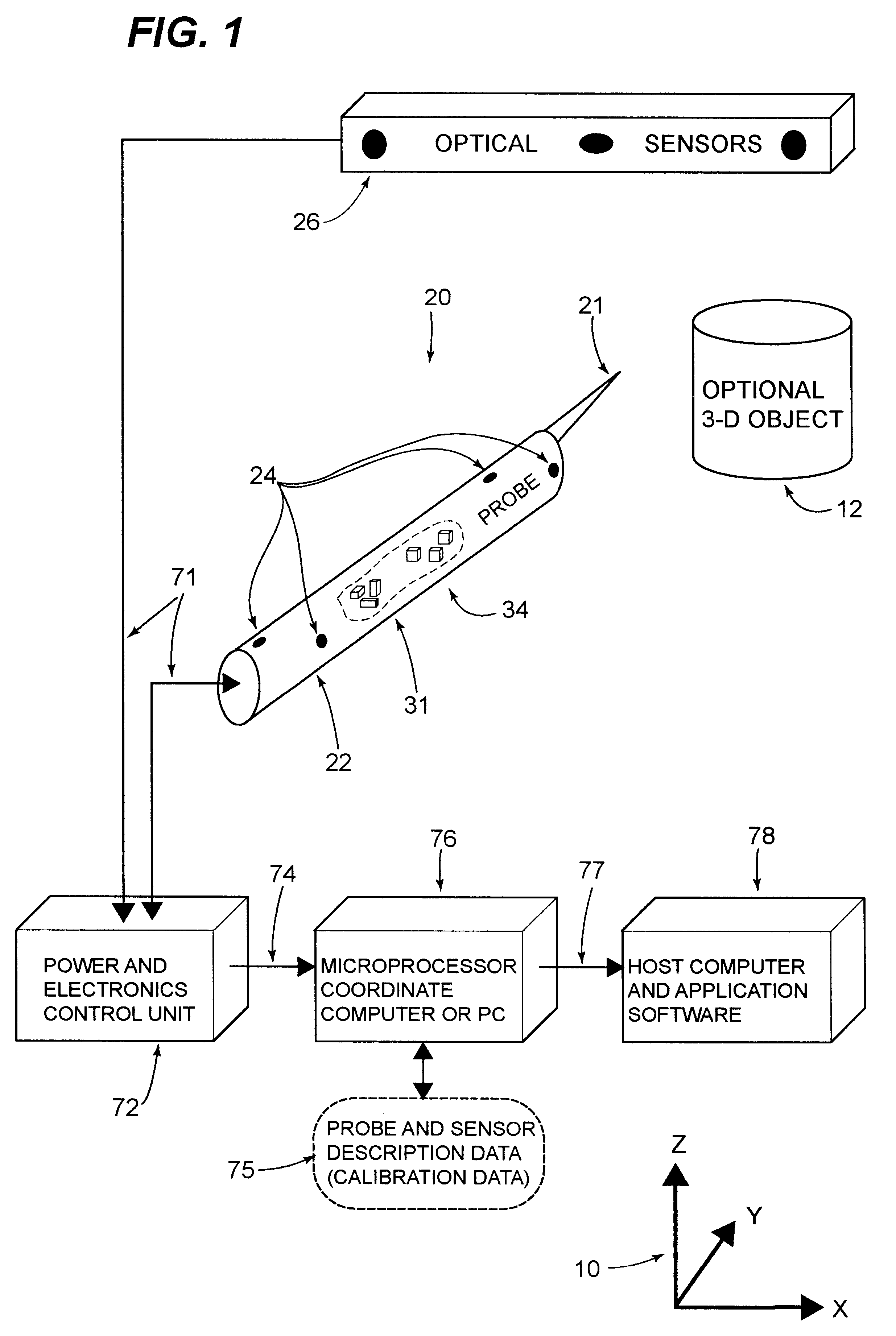
This invention is a system that tracks the 3-dimensional position and orientation of one or more bodies (20) in a volume by a light based as well as at least one non-light based mensuration sub-system. This overcomes the limitation of light based mensuration systems to the necessity of the bodies (20) to be in constant line-of-sight of its light based position sensors (26). The invention possesses most of the accuracy and stability of its light based position measurement sub-system (24, 26, 72), but can also work without direct line of sight either for short periods of time or within certain parts of the volume. It does so by incorporating other sensors (31, 34), such as inertial or magnetic, which are frequently recalibrated against the light based sub-system (24, 26, 72) while the bodies (20) are visible by the light based sub-system (24, 26, 72).
Owner:STRYKER CORP
System and method for on-the-fly eccentricity recognition
Owner:BOOKS AUTOMATION US LLC
Apparatus and method for measuring biologic parameters
ActiveUS20090105605A1Prevent dehydrationAvoid overhydrationThermometer detailsTelevision system detailsInfraredVideo transmission
Support structures for positioning sensors on a physiologic tunnel for measuring physical, chemical and biological parameters of the body and to produce an action according to the measured value of the parameters. The support structure includes a sensor fitted on the support structures using a special geometry for acquiring continuous and undisturbed data on the physiology of the body. Signals are transmitted to a remote station by wireless transmission such as by electromagnetic waves, radio waves, infrared, sound and the like or by being reported locally by audio or visual transmission. The physical and chemical parameters include brain function, metabolic function, hydrodynamic function, hydration status, levels of chemical compounds in the blood, and the like. The support structure includes patches, clips, eyeglasses, head mounted gear and the like, containing passive or active sensors positioned at the end of the tunnel with sensing systems positioned on and accessing a physiologic tunnel.
Owner:BRAIN TUNNELGENIX TECH CORP
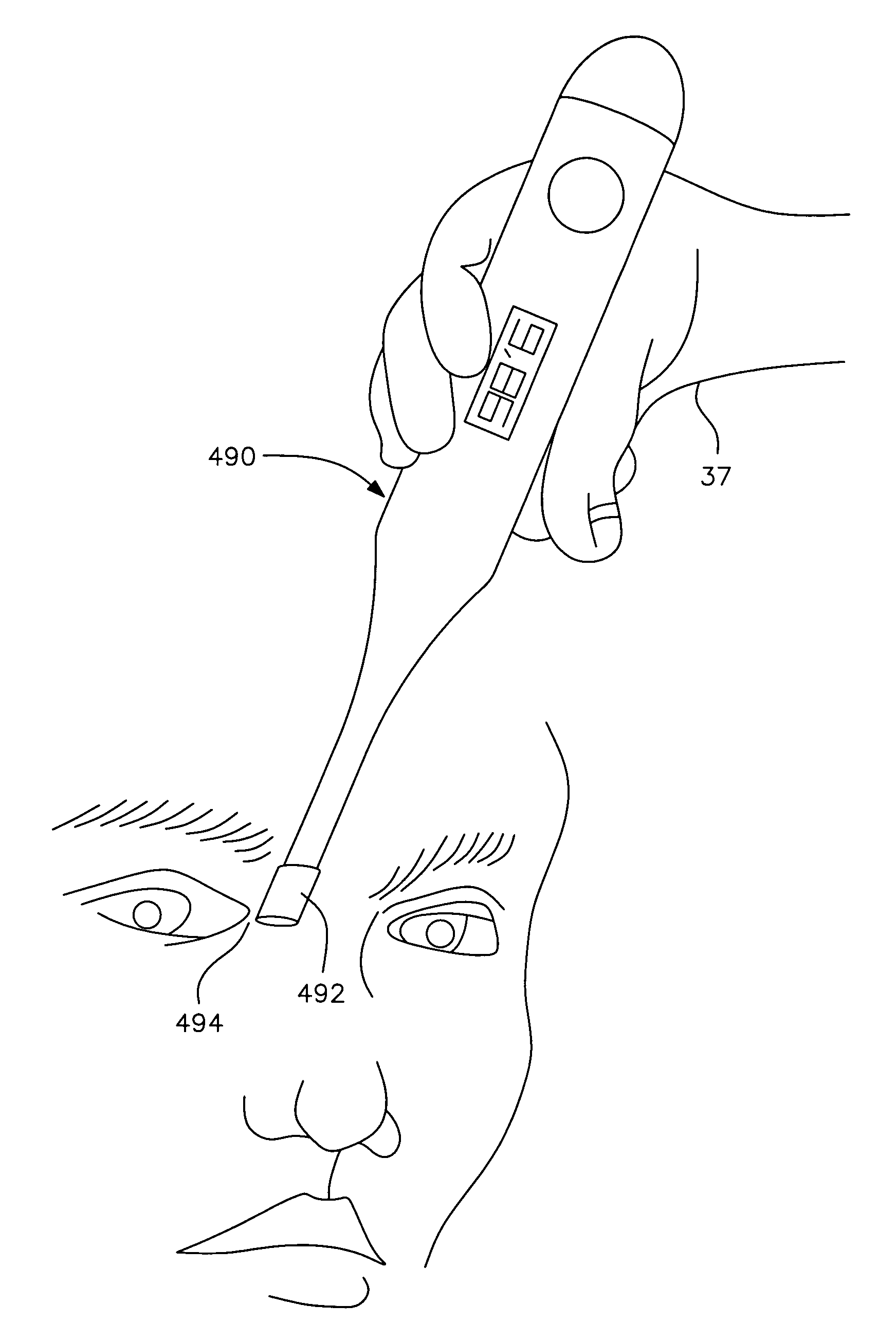
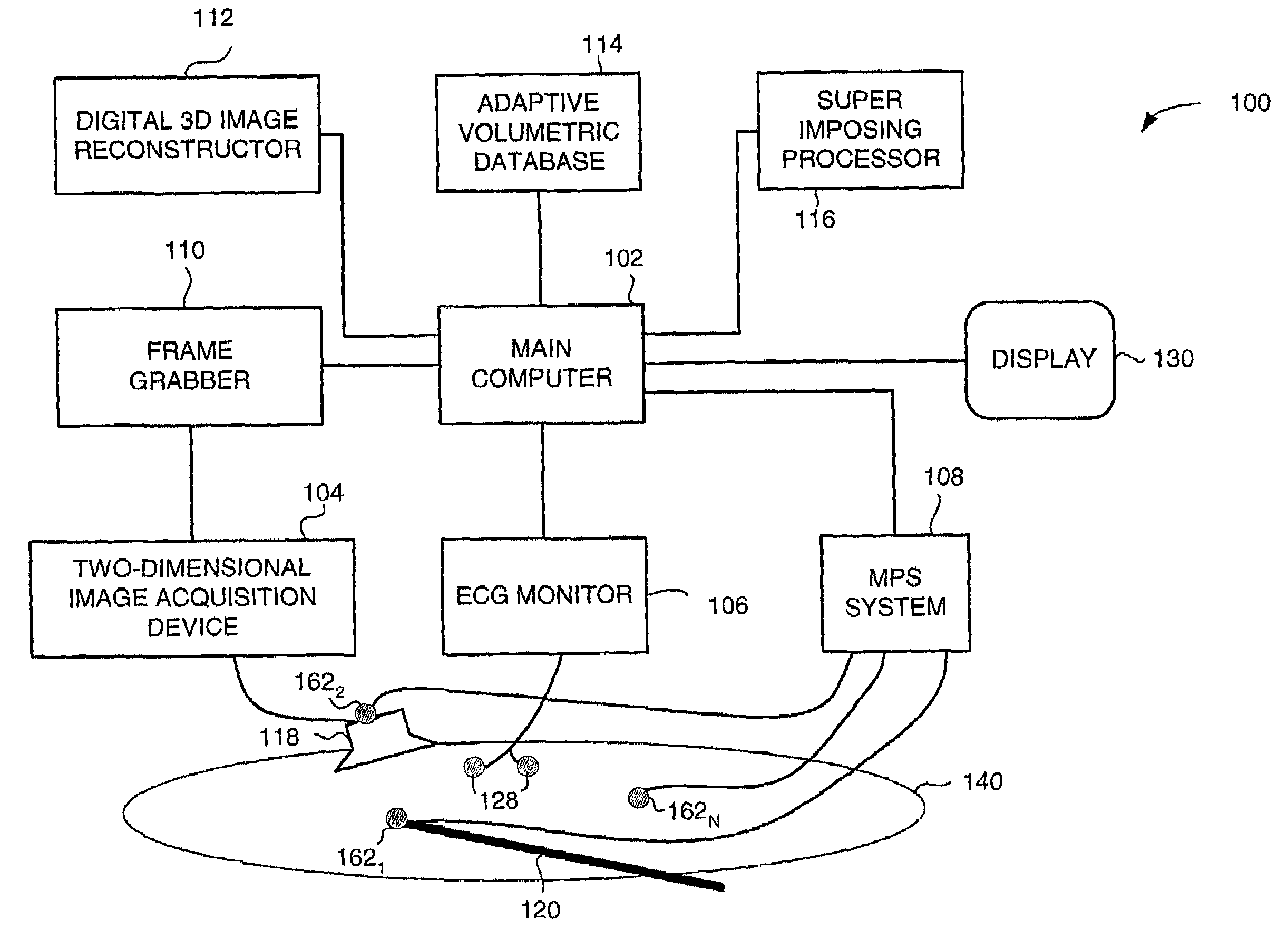
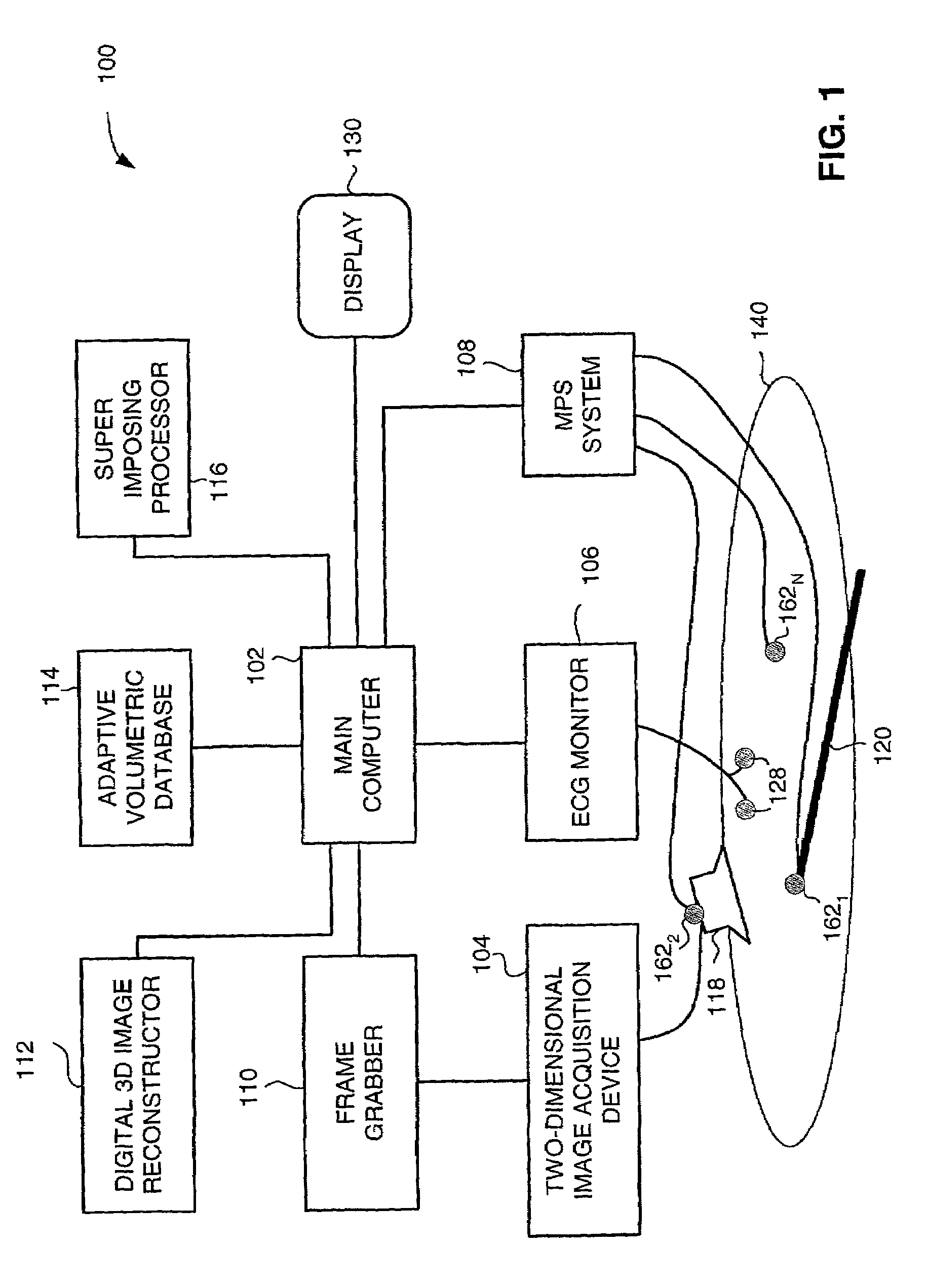
Method and apparatus for real time quantitative three-dimensional image reconstruction of a moving organ and intra-body navigation
InactiveUS7343195B2Operating tablesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansImage detectionMedical imaging
Medical imaging and navigation system including a processor, a medical positioning system (MPS), a two-dimensional imaging system and an inspected organ monitor interface, the MPS including an imaging MPS sensor, the two-dimensional imaging system including an image detector, the processor being coupled to a display unit and to a database, the MPS being coupled to the processor, the imaging MPS sensor being firmly attached to the image detector, the two-dimensional imaging system being coupled to the processor, the image detector being firmly attached to an imaging catheter.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
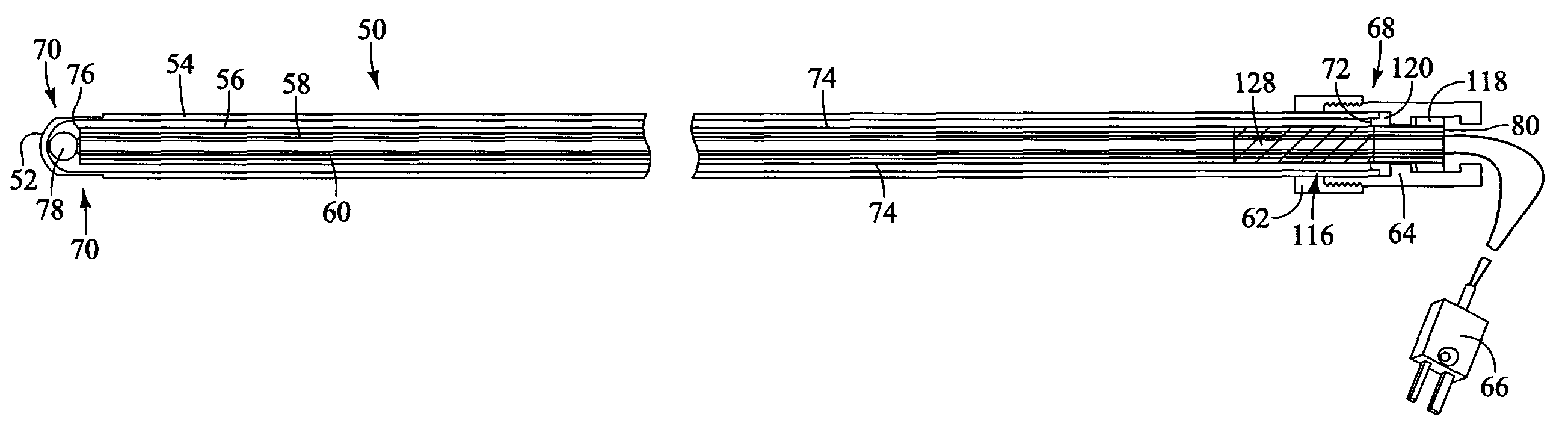
Ceramic sheath type thermocouple
InactiveUS6102565AThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsHeat resistanceWhiskers
This ceramic sheath type thermocouple has a long service life, an improved temperature measuring responsibility and an improved temperature measuring precision, and enables repetitive use. The ceramic sheath type thermocouple has its protective tube 1 formed of a heat resisting ceramics selected from silicon nitride, sialon and silicon carbide. In the protective tube 1 are installed a pair of W-Re wires that are connected to form a joint portion constituting a temperature measuring point 5. A filler made of Si3N4 reaction-sintered ceramics is loaded into the front end portion of the protective tube to enclose the W-Re wires. Another filler made of SiC whisker with a heat conductivity smaller than that of the filler of the front end portion is loaded into the rear portion of the protective tube. An inert gas is sealed in the protective tube. Alternatively, the temperature measuring portion may be formed by exposing from the front end portion of the protective tube the joint portion where the ends of the W-Re wires are connected. The temperature measuring portion is coated with a cover film that is made of silicon carbide, silicon nitride or a composite of these, all having excellent heat resisting and corrosion resisting properties.
Owner:ISUZU MOTORS LTD
Magnetic field permeable barrier for magnetic position measurement system
InactiveUS6246231B1SurgeryElectric/magnetic position measurementsOrientation measurementMetallic Object
A magnetic field position and orientation measurement system contains, confines and re-directs the magnetic field from one or more transmitters such that the fields are attenuated in areas outside of the operating volume in areas where metallic objects are commonly found. A thin barrier made of a highly permeable material such as ferrite or mumetal is placed on top of a conductive plate. The thickness of the permeable layer is from 0.01 inches to 0.25 inches while the conductive plate, preferably made of an aluminum alloy, may preferably be from {fraction (3 / 16)} of an inch to ¼ inch in thickness. On top of the permeable barrier, a rhombic three axis transmitter is placed. In the preferred embodiment, the transmitter consists of a PC board carrying the transmitter. PC boards having thicknesses varying from 0.03125-0.125 inches may be employed. Thus, the entire "stack" including the transmitter, the permeable barrier and the conductive plate may only be from ½ inch to ⅝ of an inch in thickness. The permeable barrier may have a flat, planar configuration. Alternatively, it may be made to resemble, in cross-section, a cake pan having a flat central region with uplifted peripheral edges. Alternatively, the permeable barrier may have a generally flat configuration with peripheral edges that taper outwardly from the top surface thereof to the bottom surface thereof with the taper making an angle with the bottom surface in the range of, preferably, 30° to 85°.
Owner:ASCENSION TECH
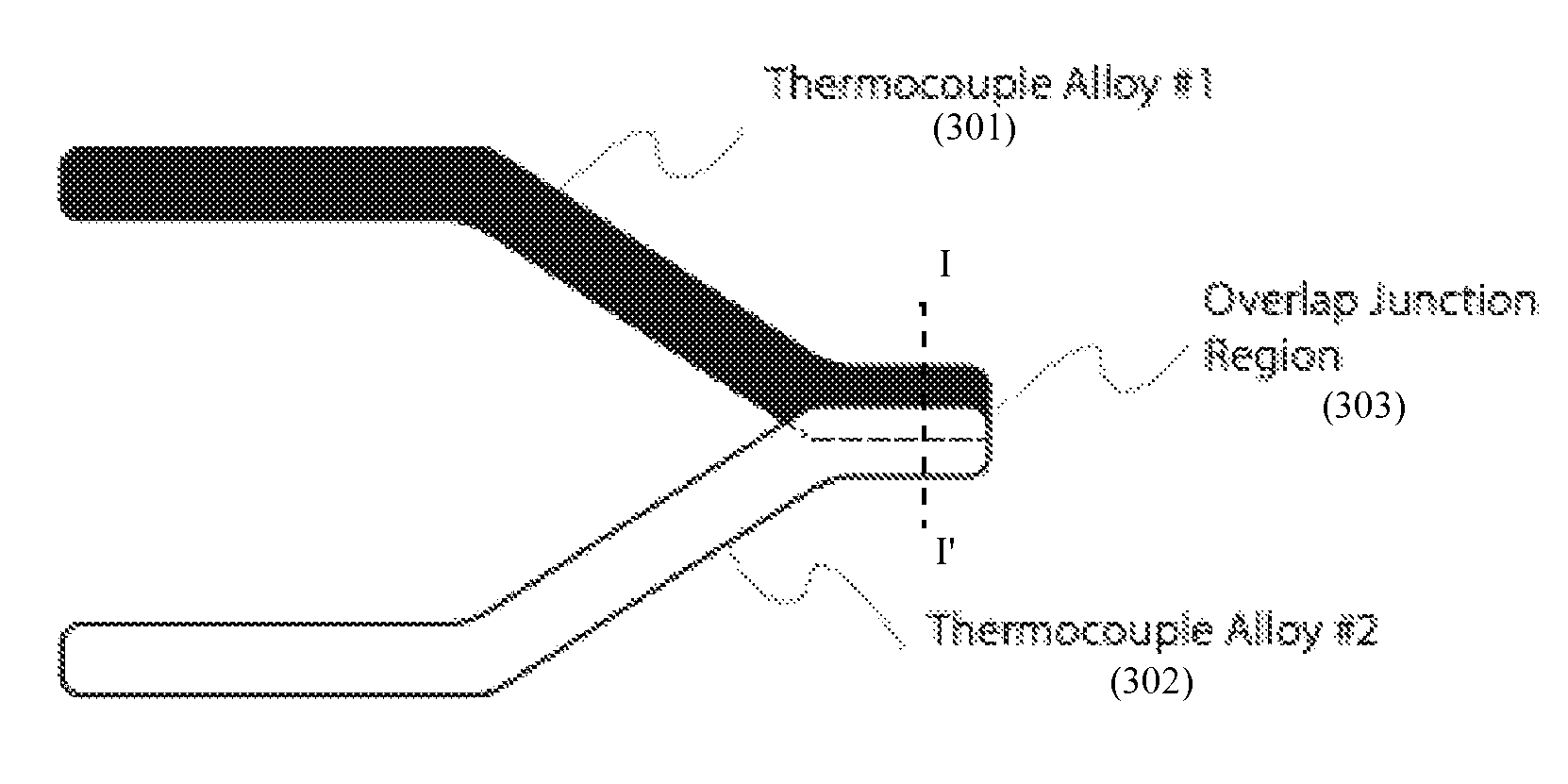
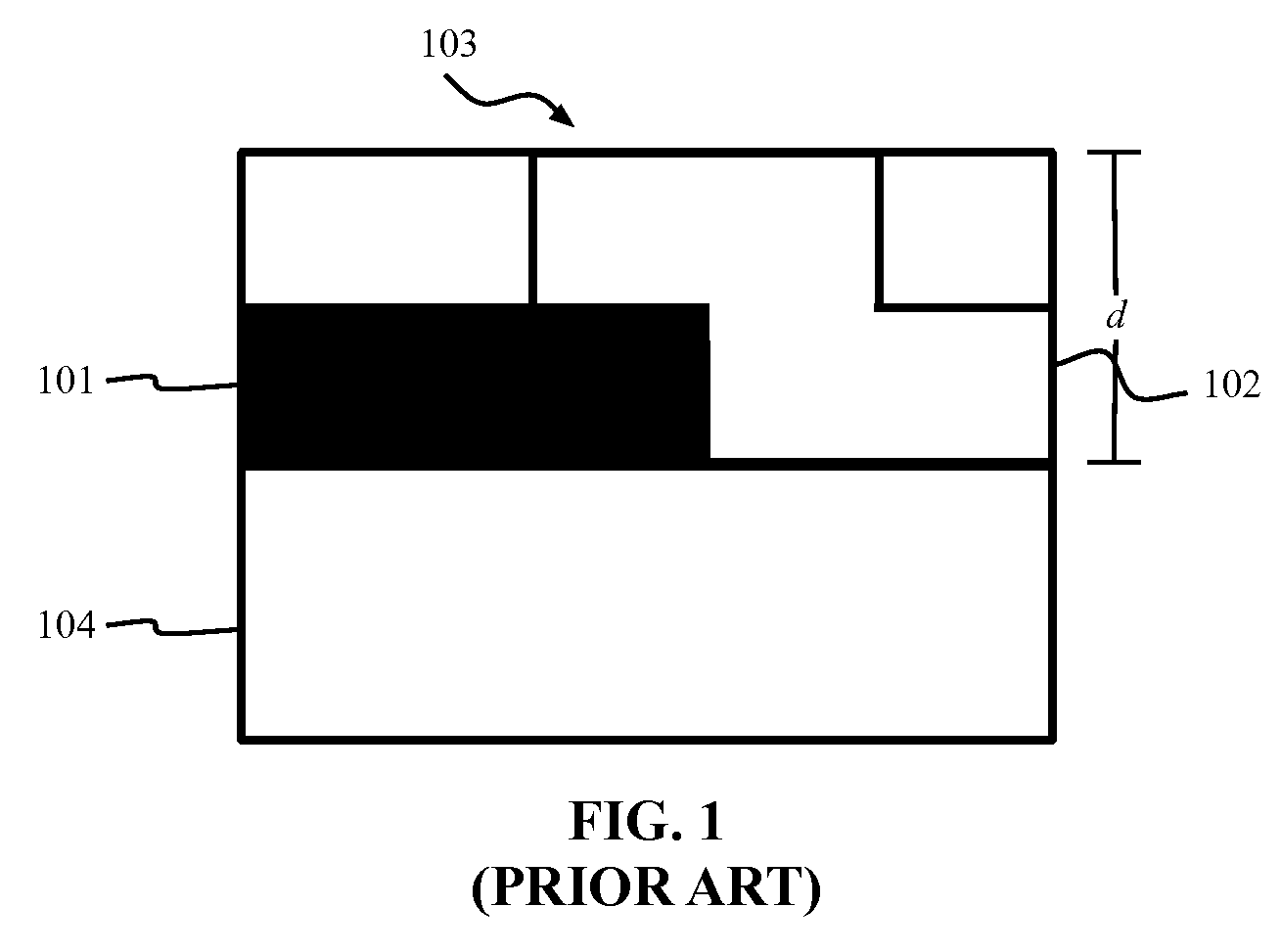
Thermocouple
ActiveUS8100583B2Thermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsEngineeringThermocouple device
A thermocouple having at least one inner alignment feature or at least one outer alignment feature, or a combination thereof for positively positioning and aligning at least one thermocouple junction within a bore formed in a susceptor ring of a semiconductor substrate processing reactor. The outer alignment feature is configured to positively align the junction(s) longitudinally within the bore. The inner alignment feature configured to positively position the junction(s) rotationally within the sheath of the thermocouple relative to the bore.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
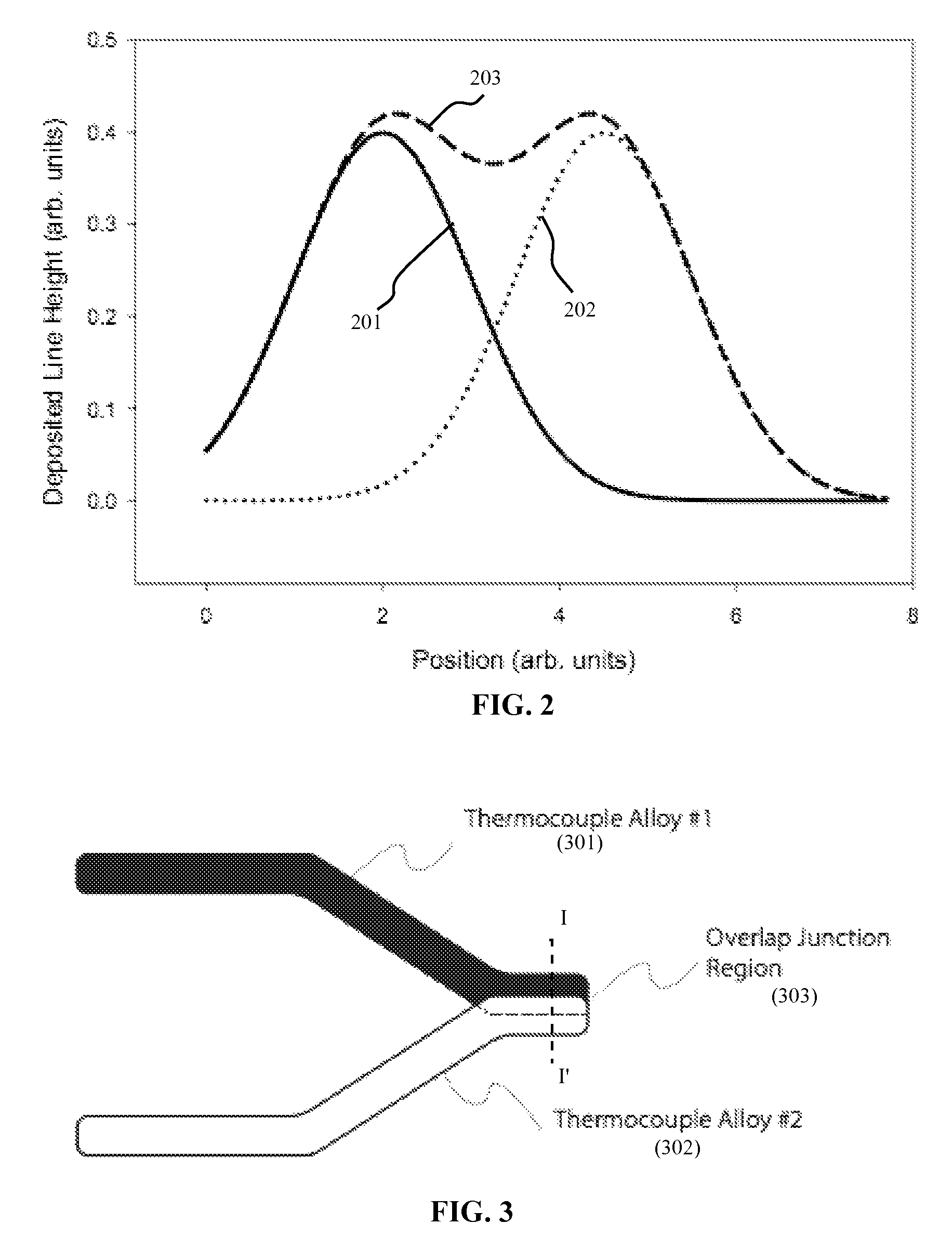
Thermocouples
ActiveUS7753584B2Thermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsThermoelectric materialsEngineering
A thermocouple disposed on a substrate comprises a first leg of thermoelectric material, a second leg of thermoelectric material, and a thermocouple junction electrically connecting the first leg and the second leg, wherein a height of the thermocouple junction is substantially a height of the first or second legs.
Owner:CVD MESOSCRIBE TECH CORP
Temperature gauge and ceramic susceptor in which it is utilized
InactiveUS7090394B2Shorten the timeEasy to replaceThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsSusceptorMetallurgy
Temperature gauge, and ceramic susceptors and semiconductor manufacturing equipment utilizing the temperature gauge, in which the thermocouple may be easily replaced even if damaged, and in which heat from the temperature-gauging site is readily transmitted to the temperature-gauging contact, shortening time until the measurement temperature stabilizes. A temperature-gauging contact (12) in the tip of the thermocouple contacts, in an exposed-as-it-is state, a temperature-gauging site on a ceramic susceptor (1), and by means of a circular cylindrical-shaped retaining member (11) screwed into female threads in the ceramic susceptor (1) is detachably pressed upon and retained against the ceramic susceptor. Thermocouple lead lines (13), passing through a through-hole (14) in the retaining member (11), stretch from one end face to the other end face thereof. The retaining member may be provided with a flange having threaded holes and screwlocked into female screws in the ceramic susceptor.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Temperature measuring device and temperature measuring method
InactiveUS20050141591A1Low production costFree replacementThermometer detailsElectric signal transmission systemsSingle-Use DeviceMeasurement device
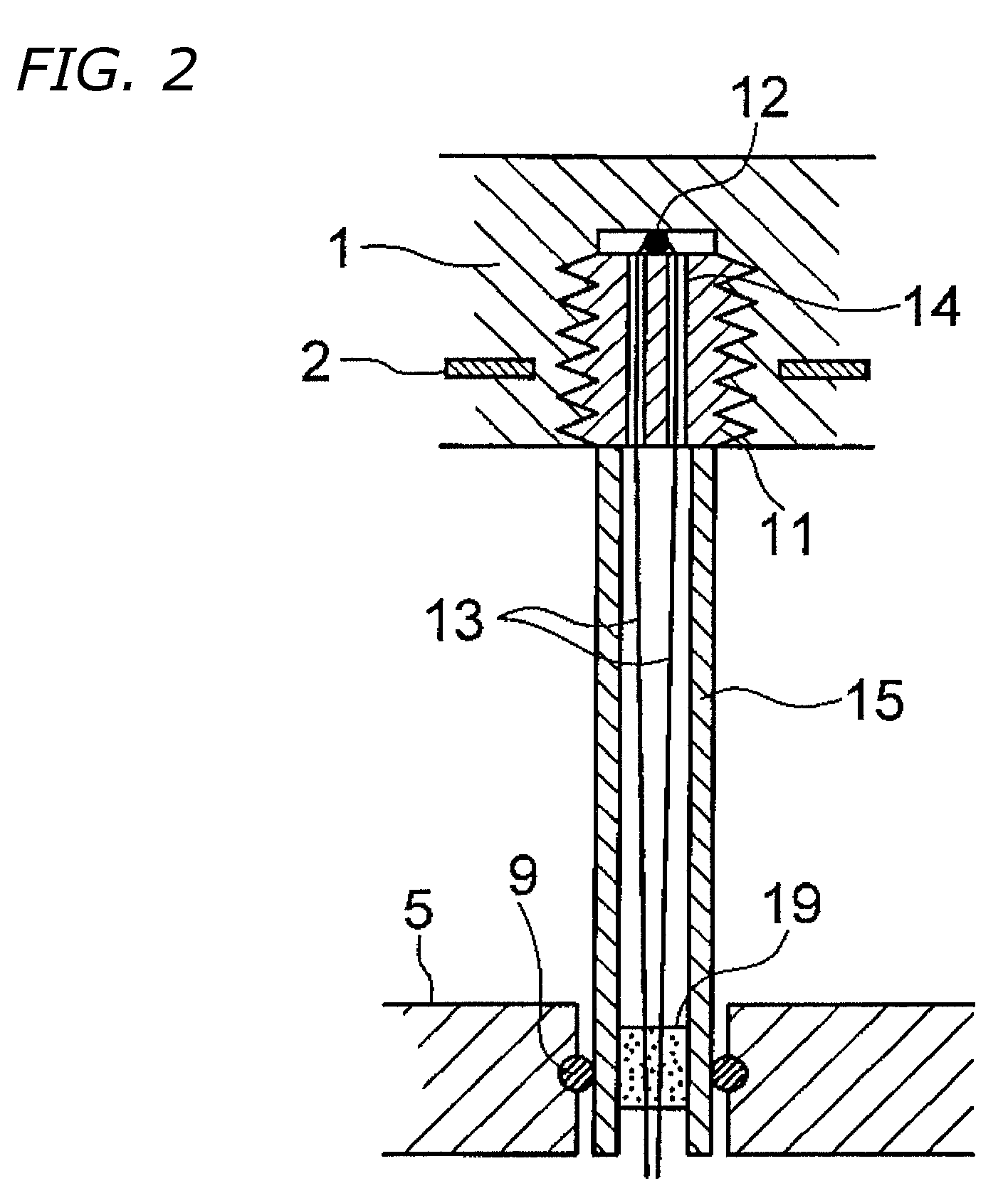
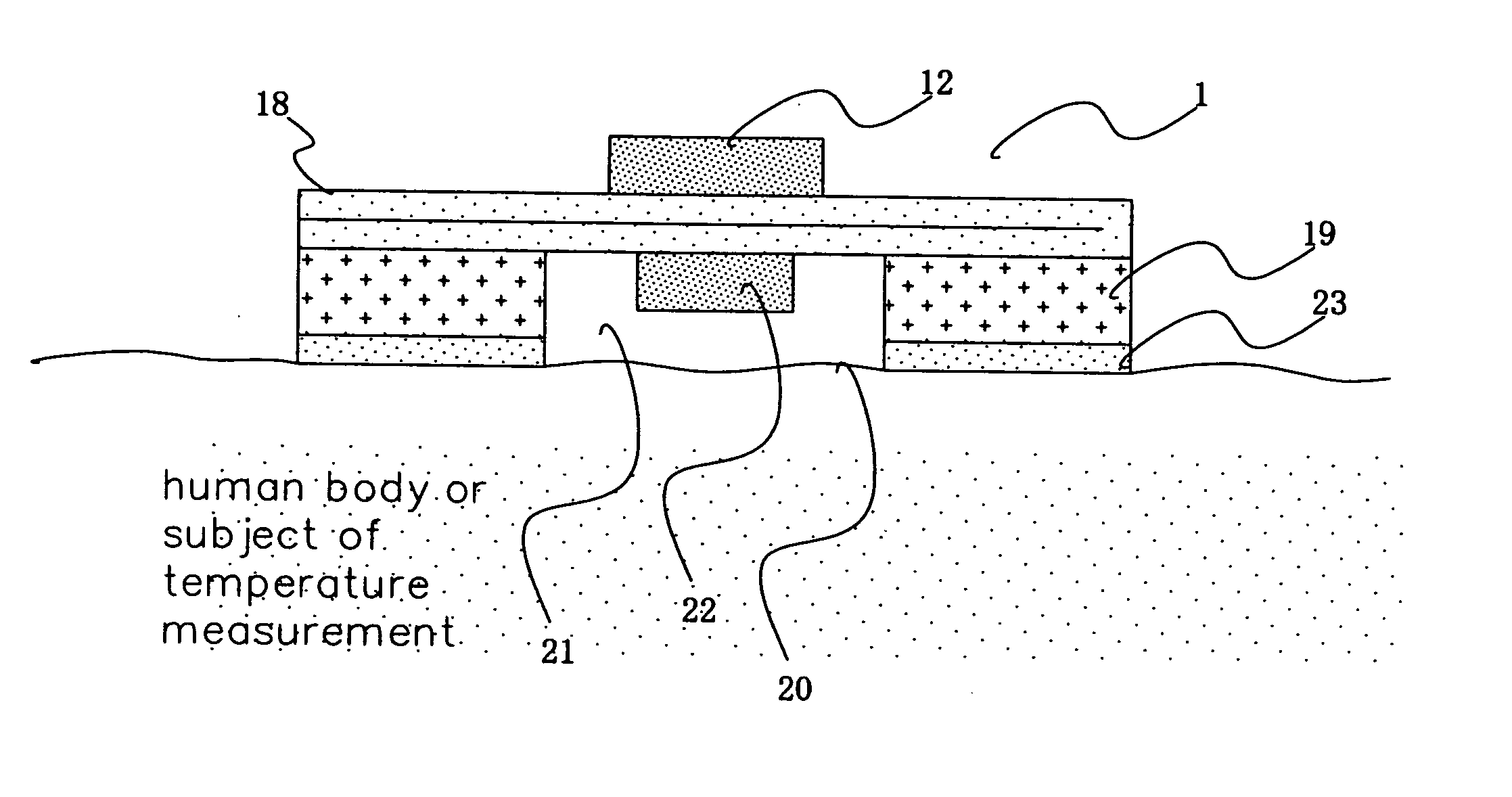
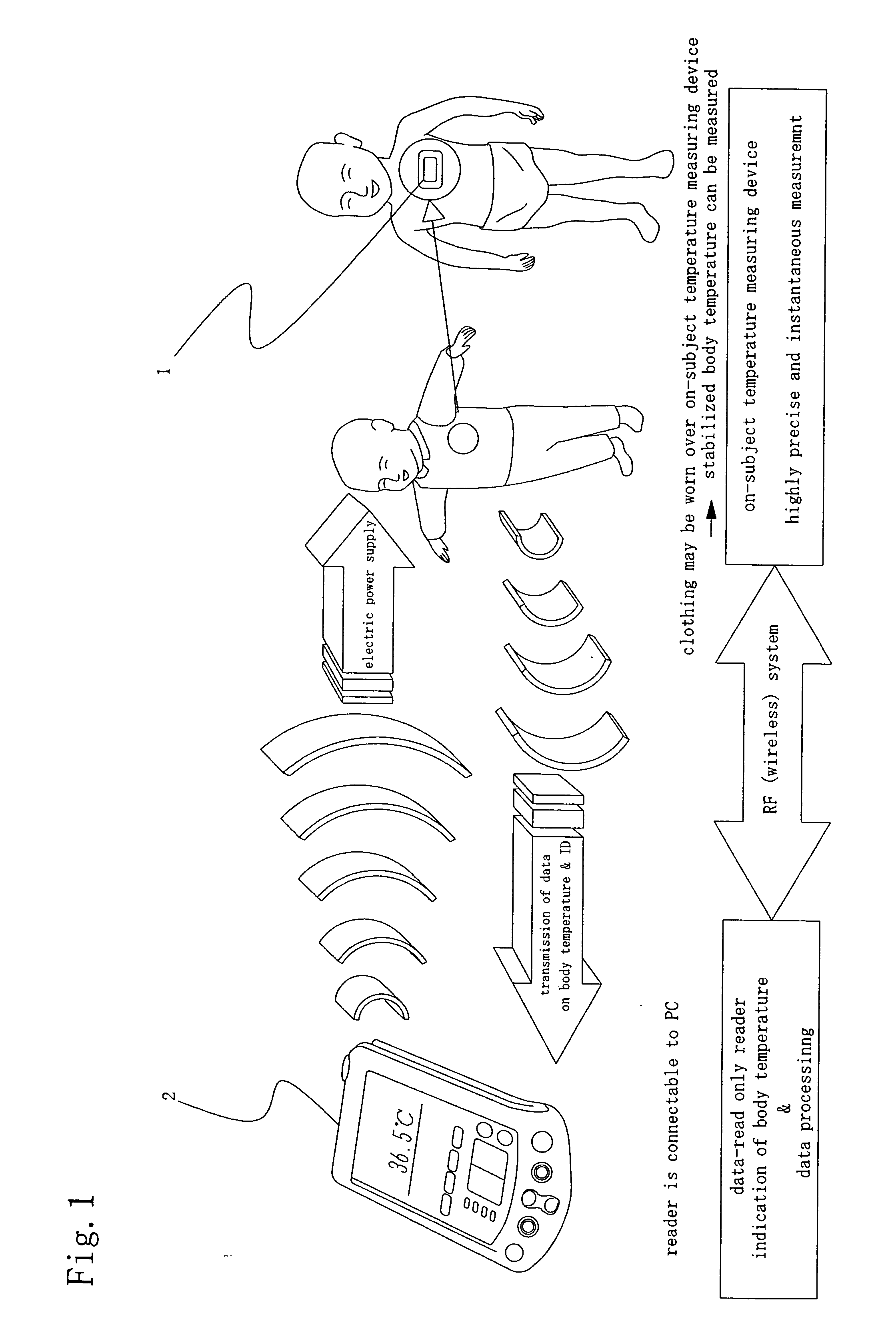
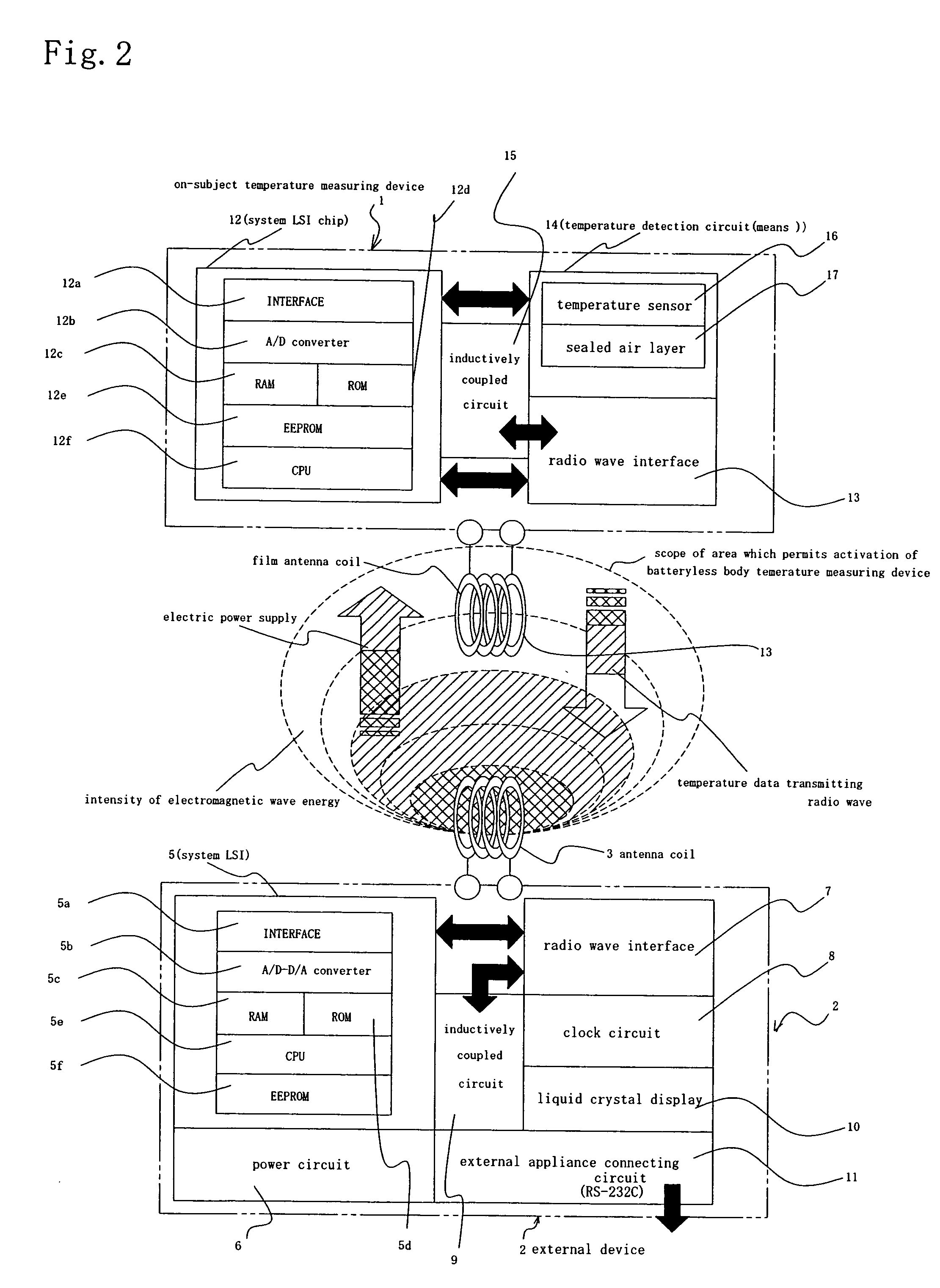
A temperature measuring device and a temperature measuring method are provided which are capable of obtaining precise measured temperature values with respect even to old persons, sucklings or infants, which device may be formed into a disposable type according to need, which method may be carried out using such a disposable type device according to need, and which enable precise temperature measurement in real time. An on-subject temperature measuring device 1, which is attached to a subject when a temperature of the subject is measured, receives a radio wave from a reader 2 as an external device and is thereby electrically powered. Using the electric power, temperature measurement is performed in the on-subject temperature measuring device 1. The results of the measurement are transmitted through radio waves to the reader 2 in the form of a temperature of the subject and ID data. The reader 2 is so constructed as to be connectable to a personal computer (not shown), and data processing by the personal computer is performed according to need.
Owner:SAKANO KAZUHITO +2
Method and a device for thermal analysis of cast iron
InactiveUS7168852B2Improve accuracyEliminate sourceThermometer detailsWithdrawing sample devicesCooling curveComputer module
Owner:SINTERCAST
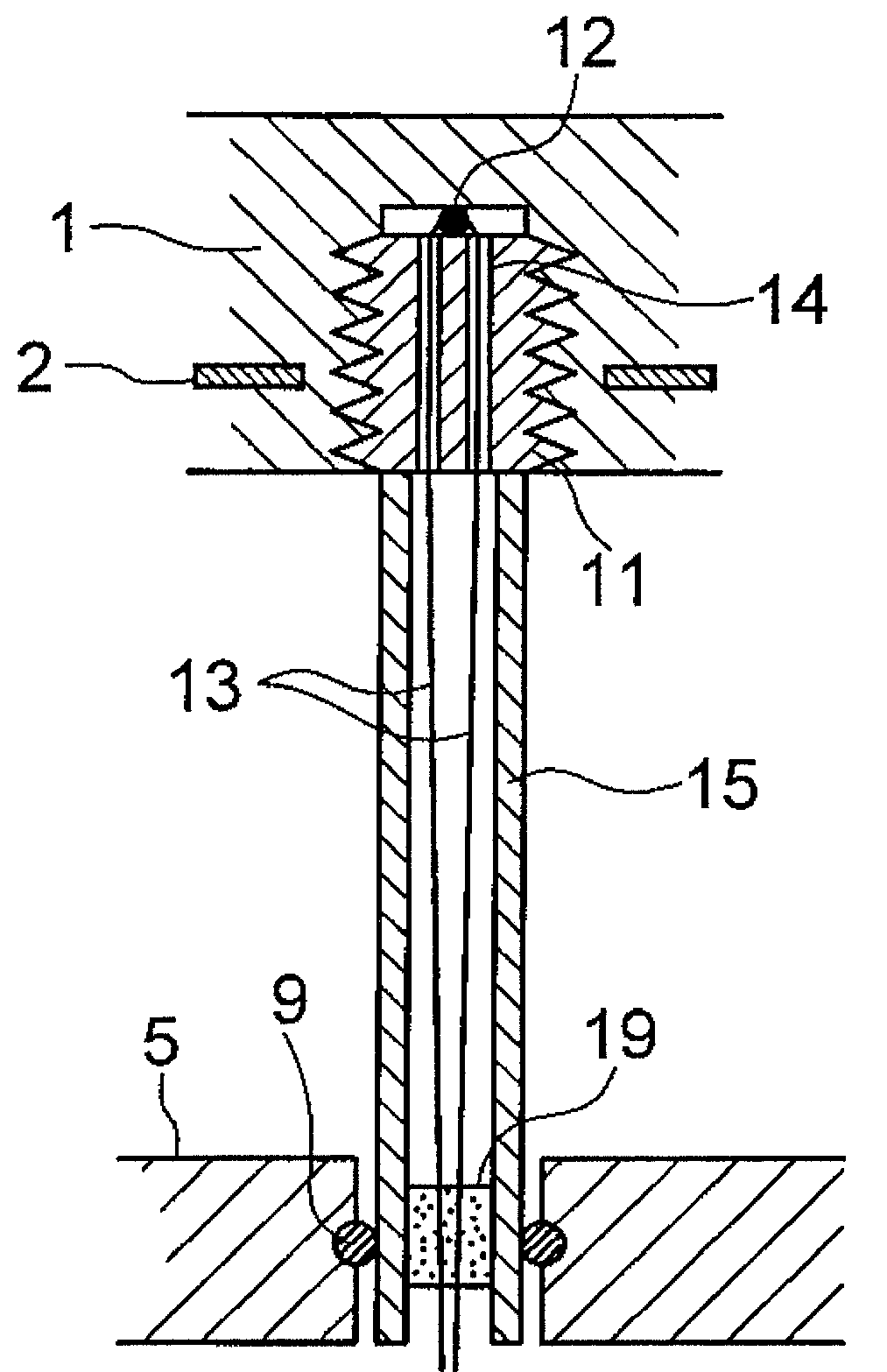
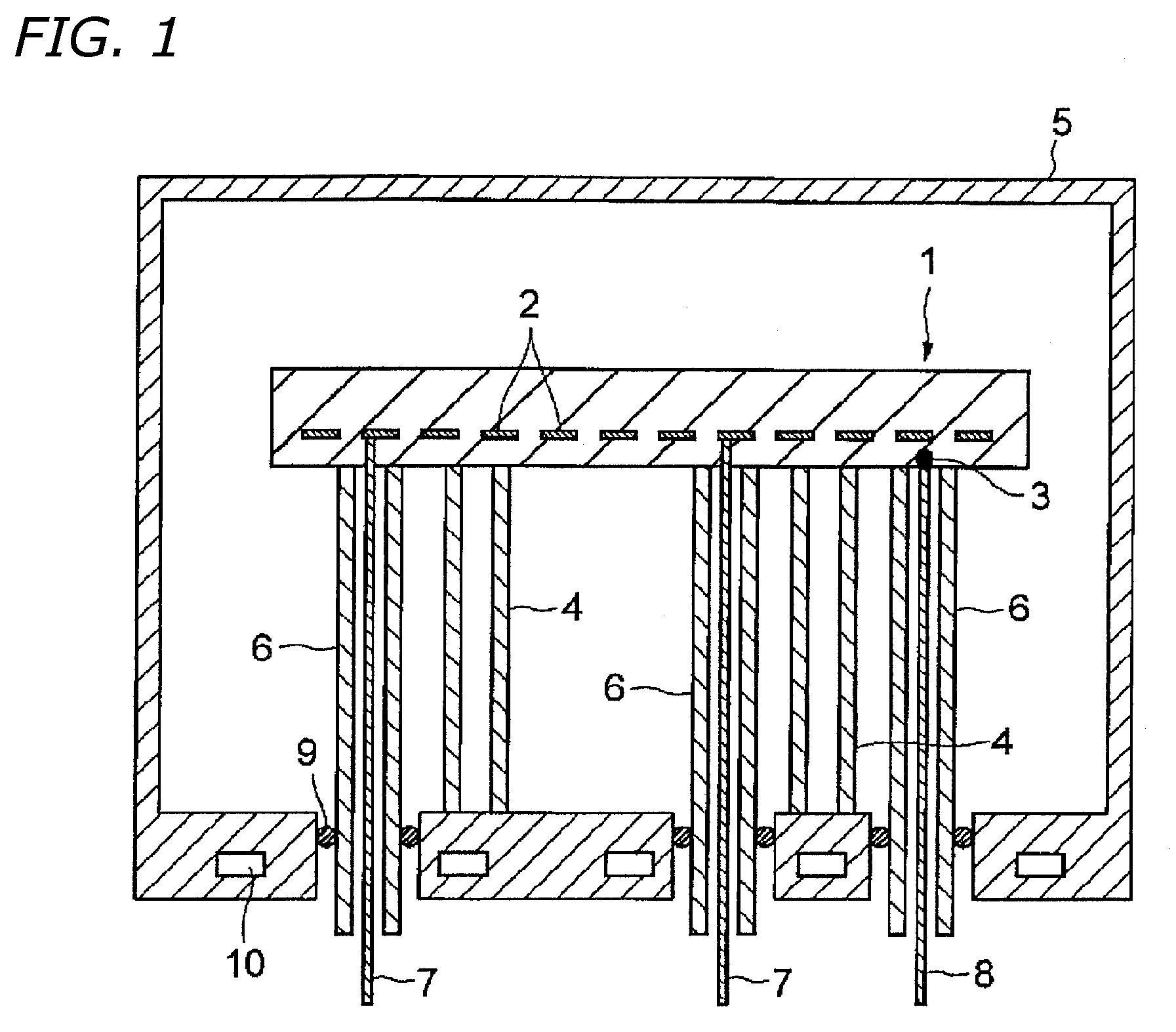
Redundant temperature sensor for semiconductor processing chambers
Systems are provided for measuring temperature in a semiconductor processing chamber. Embodiments provide a multi-junction thermocouple comprising a first junction and a second junction positioned to measure temperature at substantially the same portion of a substrate. A controller may detect failures in the first junction, the second junction, a first wire pair extending from the first junction, or a second wire pair extending from the second junction. The controller desirably responds to a detected failure of the first junction or first wire pair by selecting the second junction and second wire pair. Conversely, the controller desirably responds to a detected failure of the second junction or second wire pair by selecting the first junction and first wire pair. Systems taught herein may permit accurate and substantially uninterrupted temperature measurement despite failure of a junction or wire pair in a thermocouple.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com