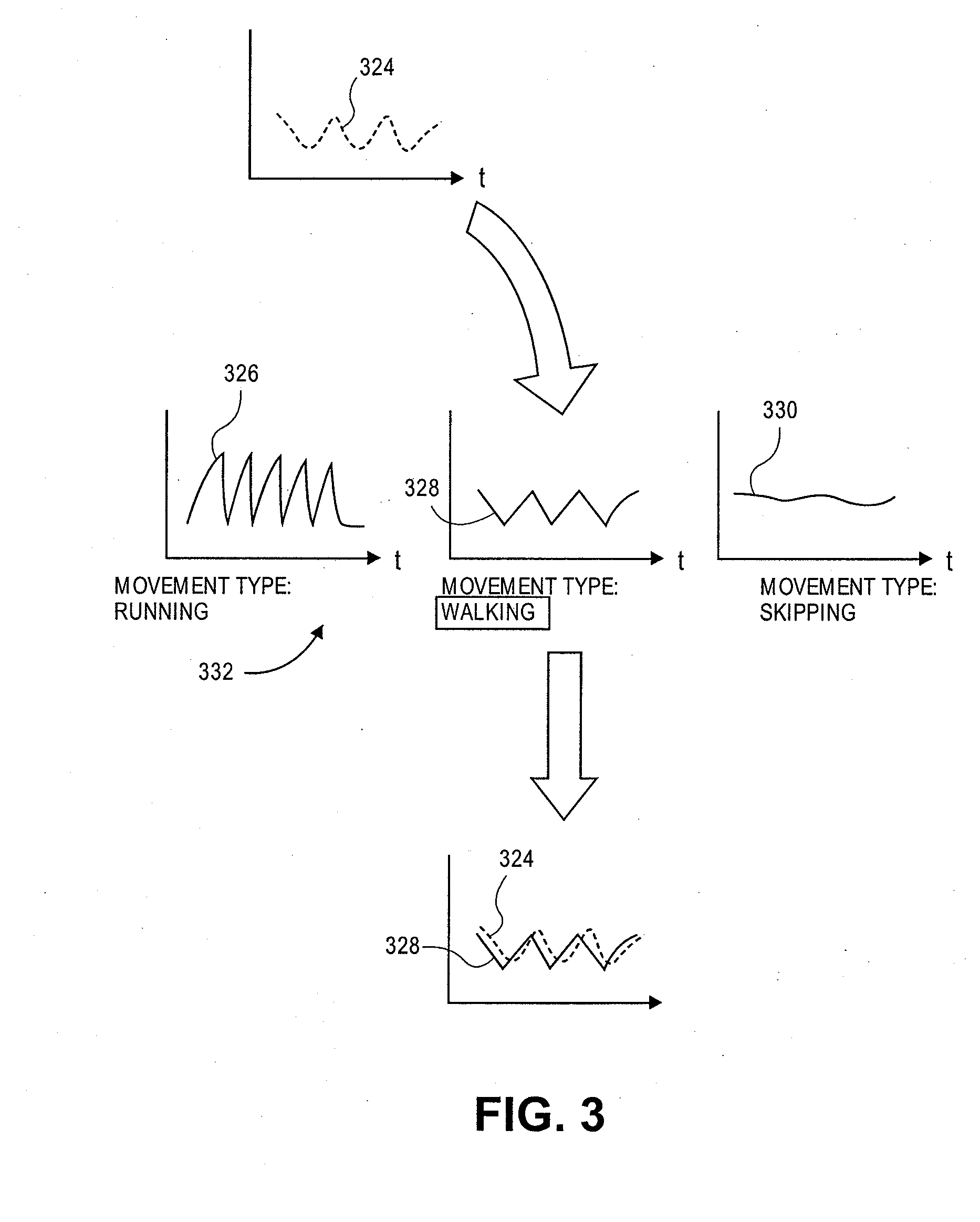
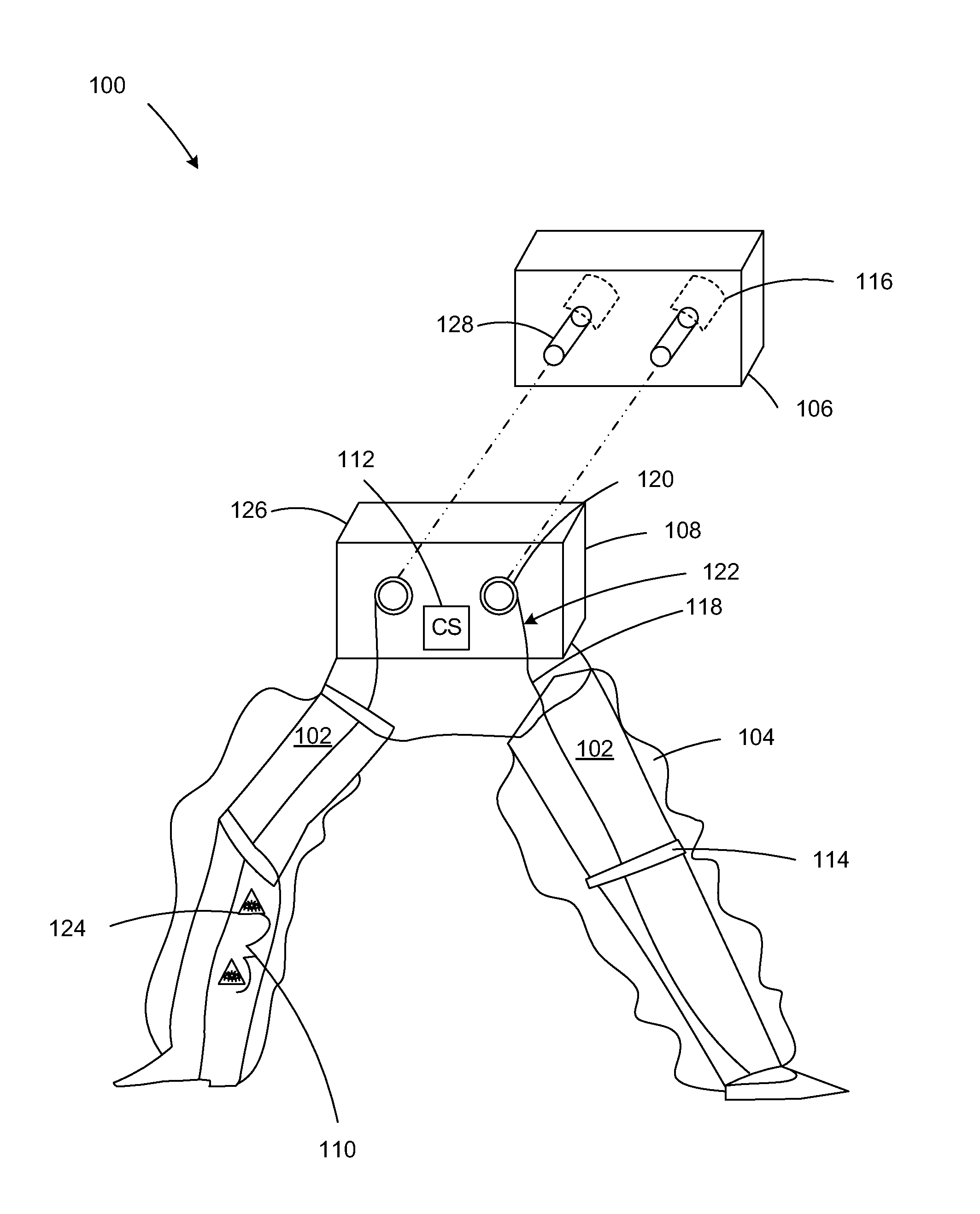
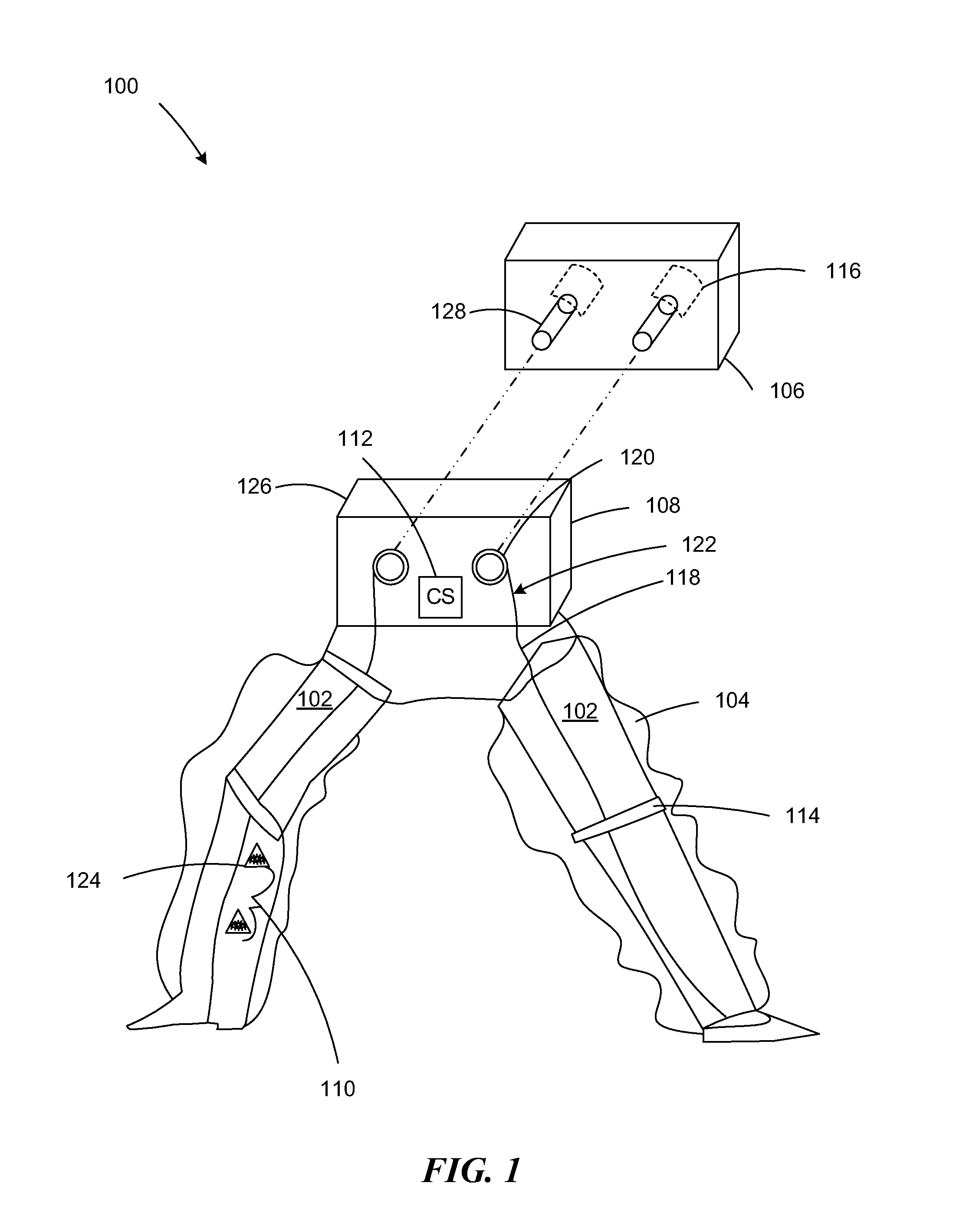
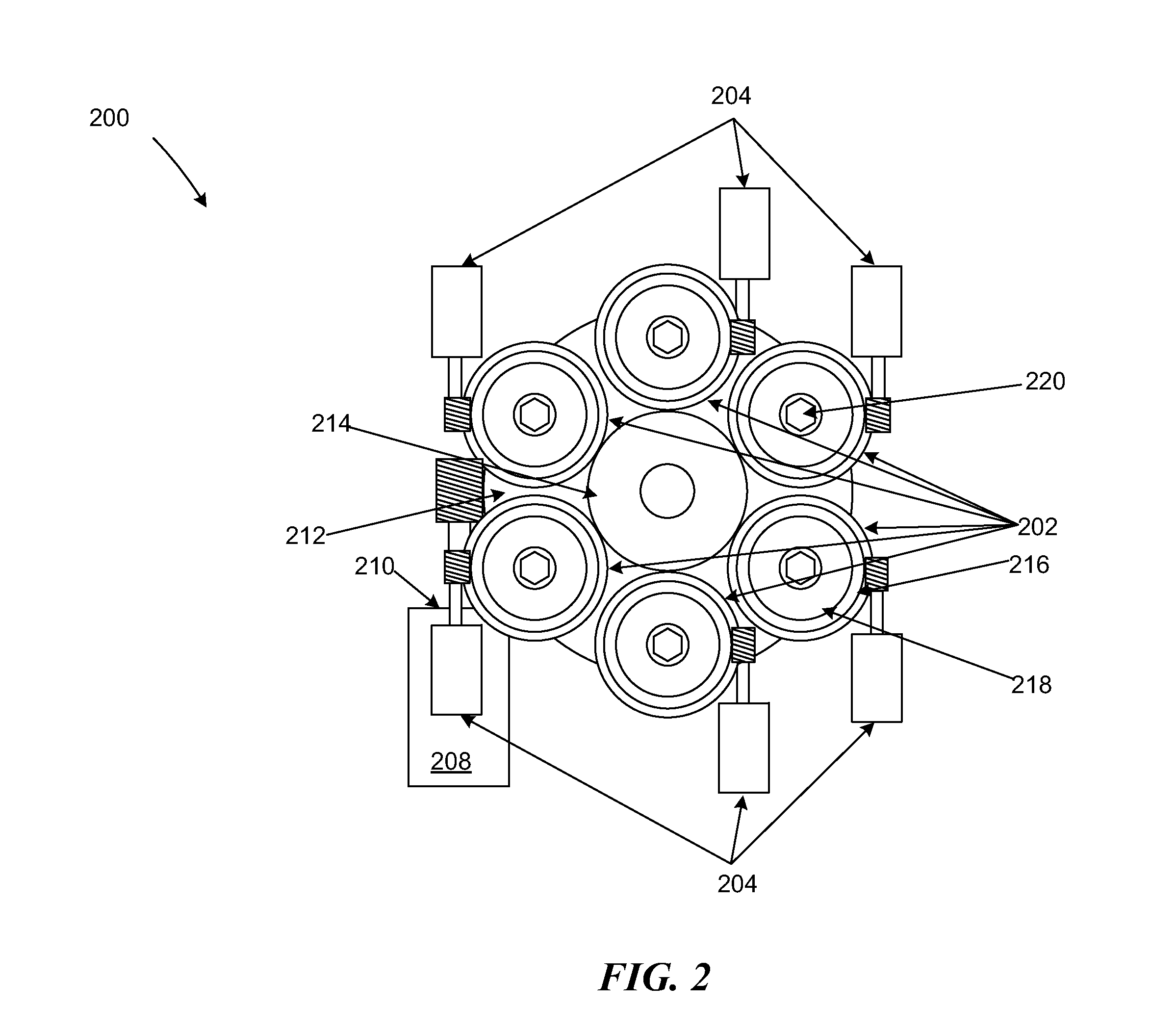
Patents
Literature
1461 results about "Gait" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
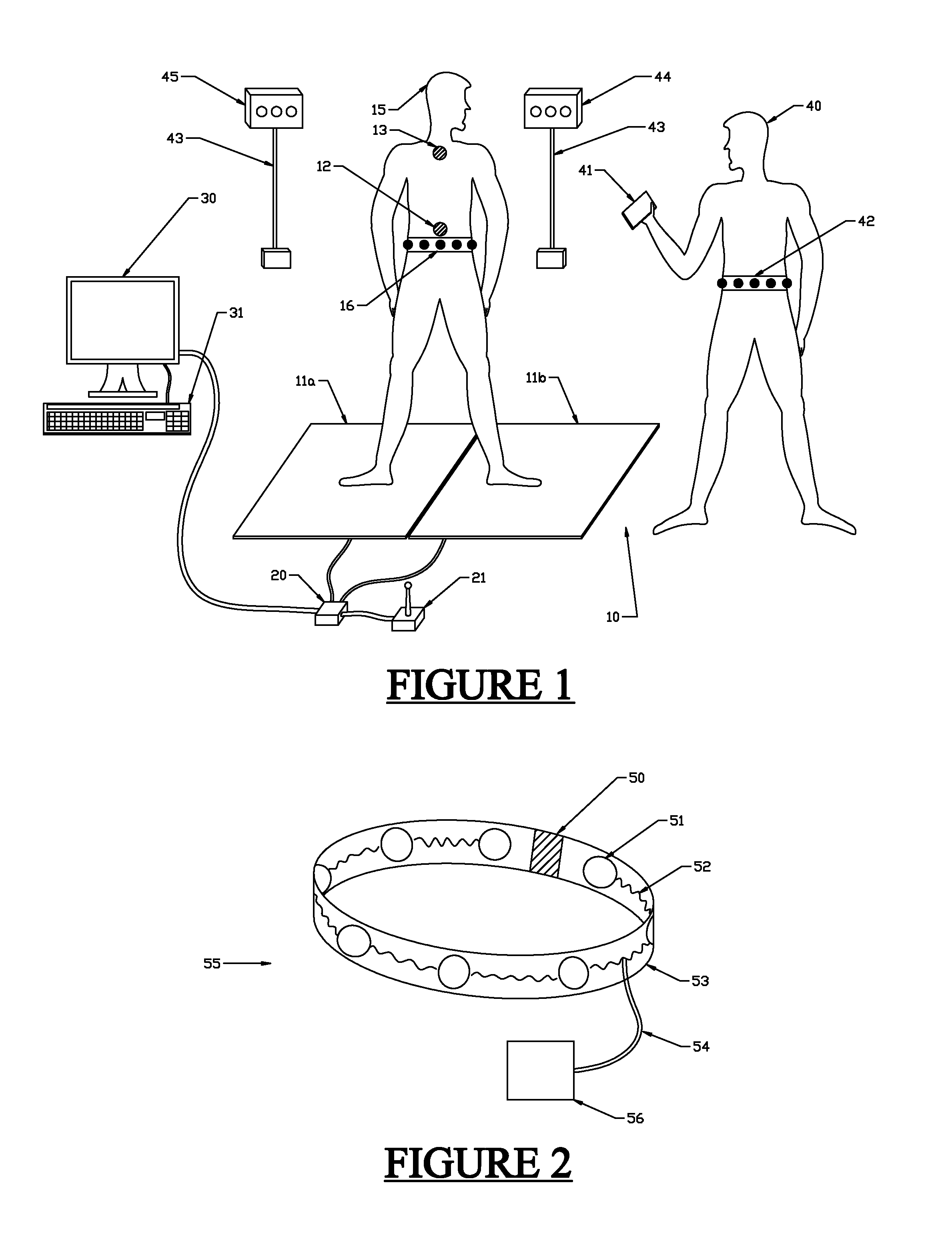
Gait is the pattern of movement of the limbs of animals, including humans, during locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to maneuver, and energetic efficiency. Different animal species may use different gaits due to differences in anatomy that prevent use of certain gaits, or simply due to evolved innate preferences as a result of habitat differences. While various gaits are given specific names, the complexity of biological systems and interacting with the environment make these distinctions 'fuzzy' at best. Gaits are typically classified according to footfall patterns, but recent studies often prefer definitions based on mechanics. The term typically does not refer to limb-based propulsion through fluid mediums such as water or air, but rather to propulsion across a solid substrate by generating reactive forces against it (which can apply to walking while underwater as well as on land).
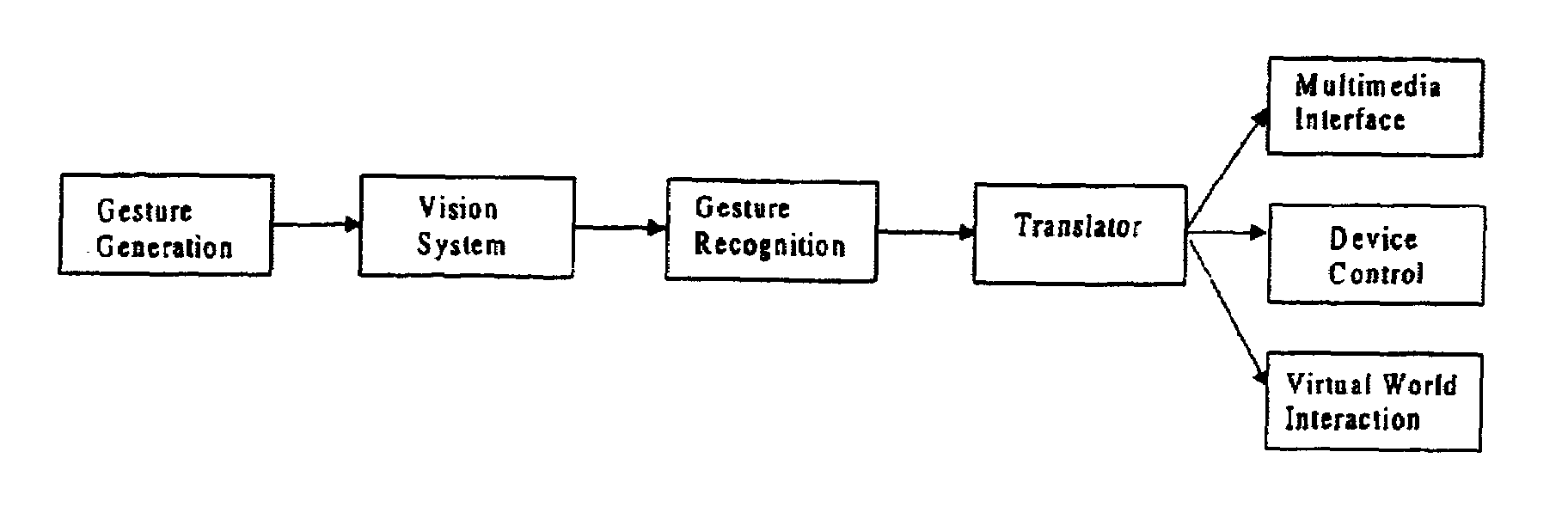
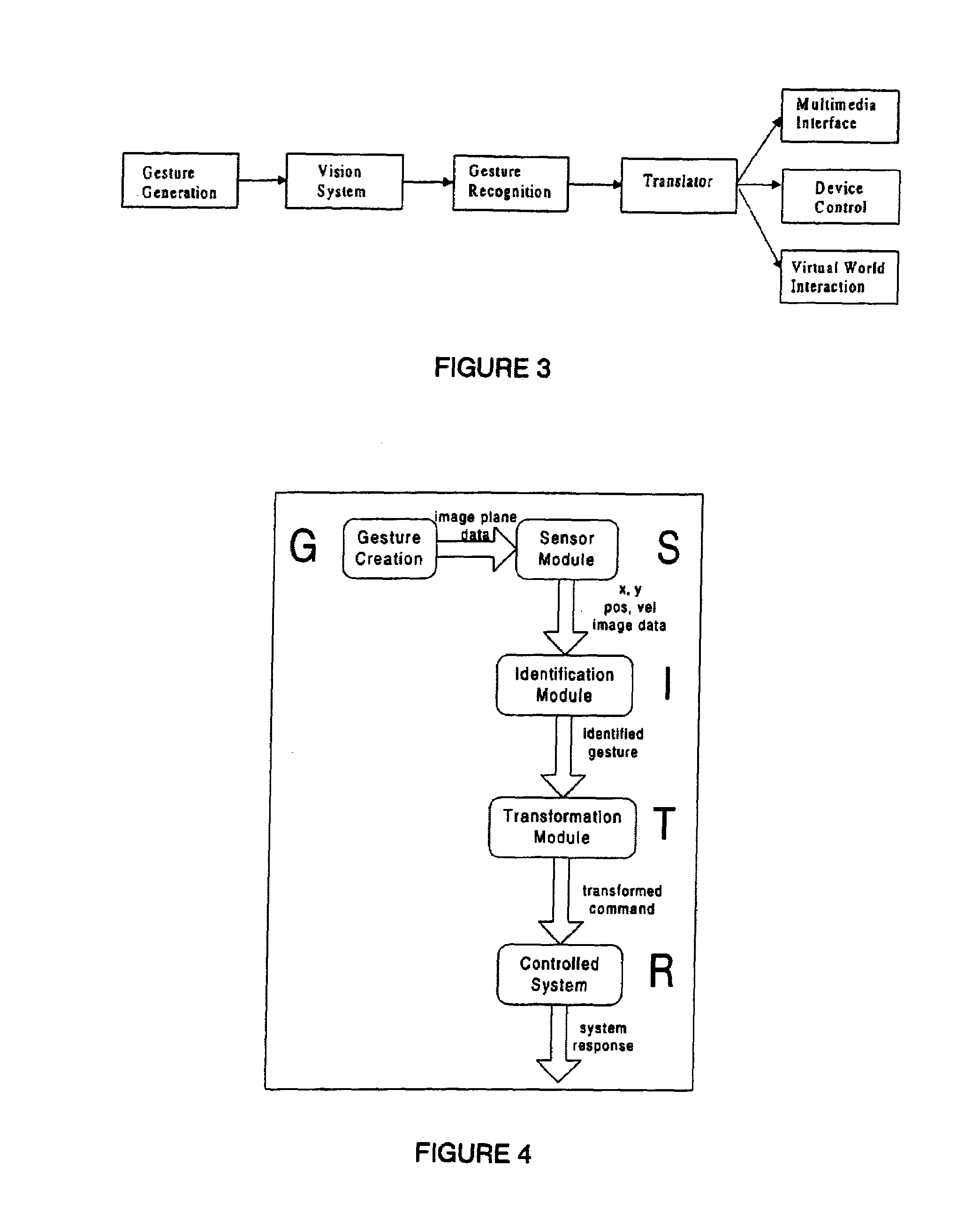
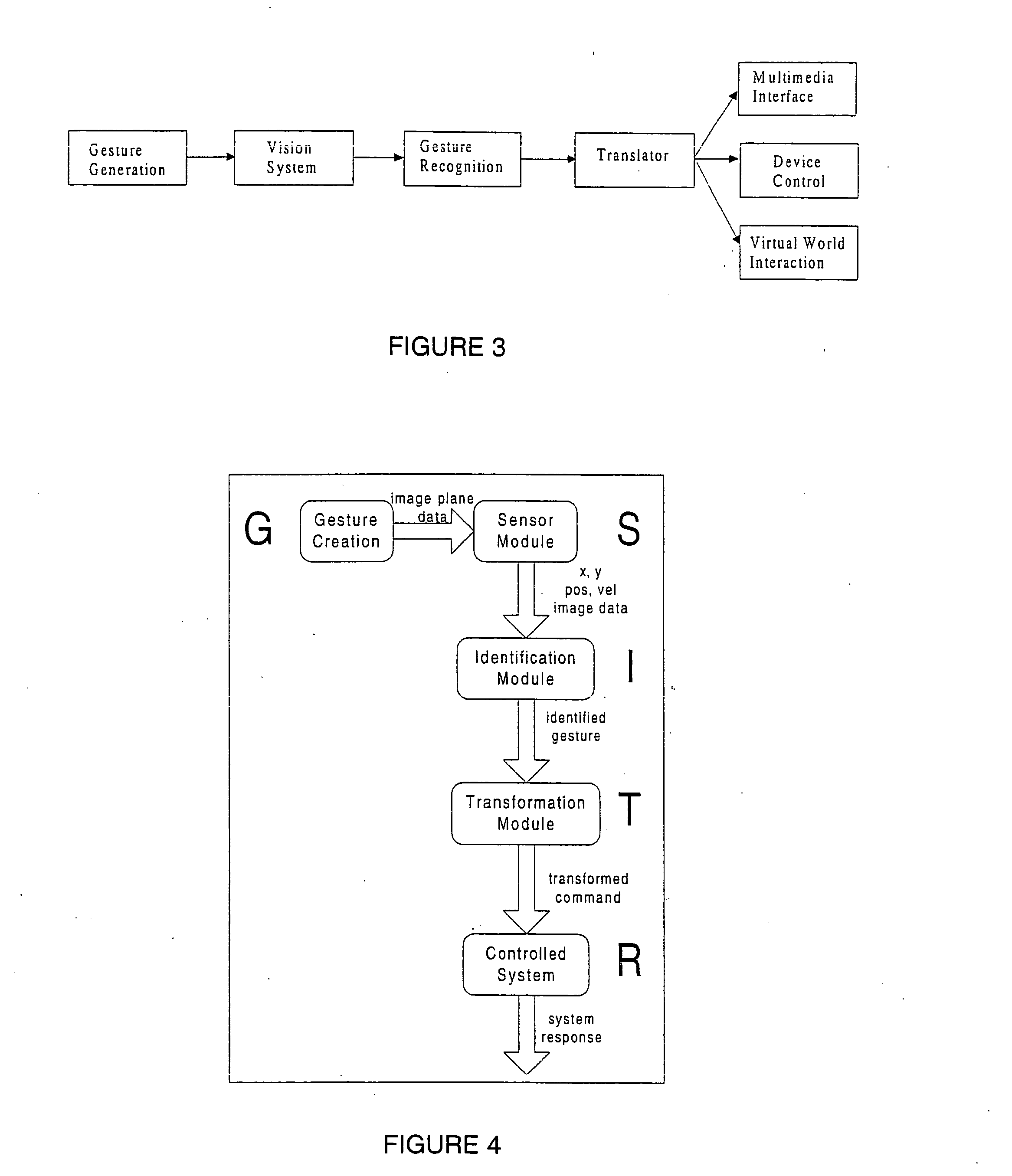
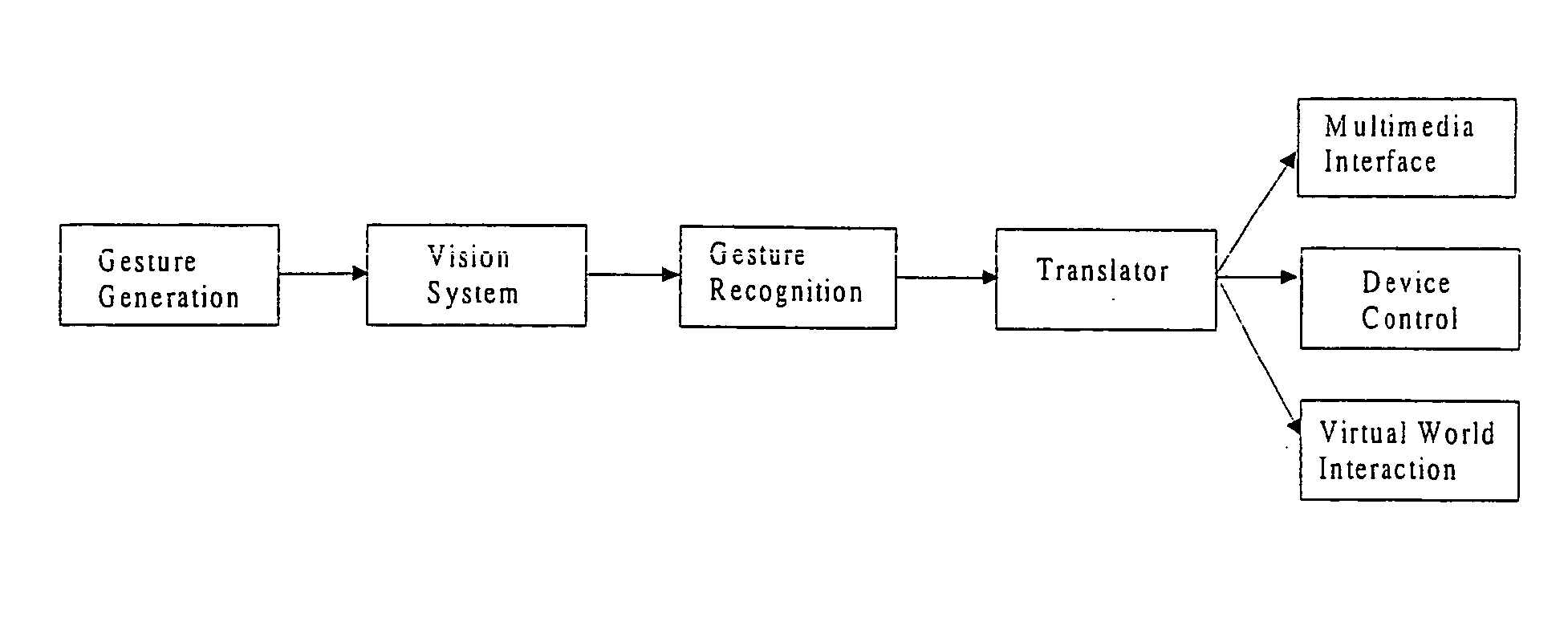
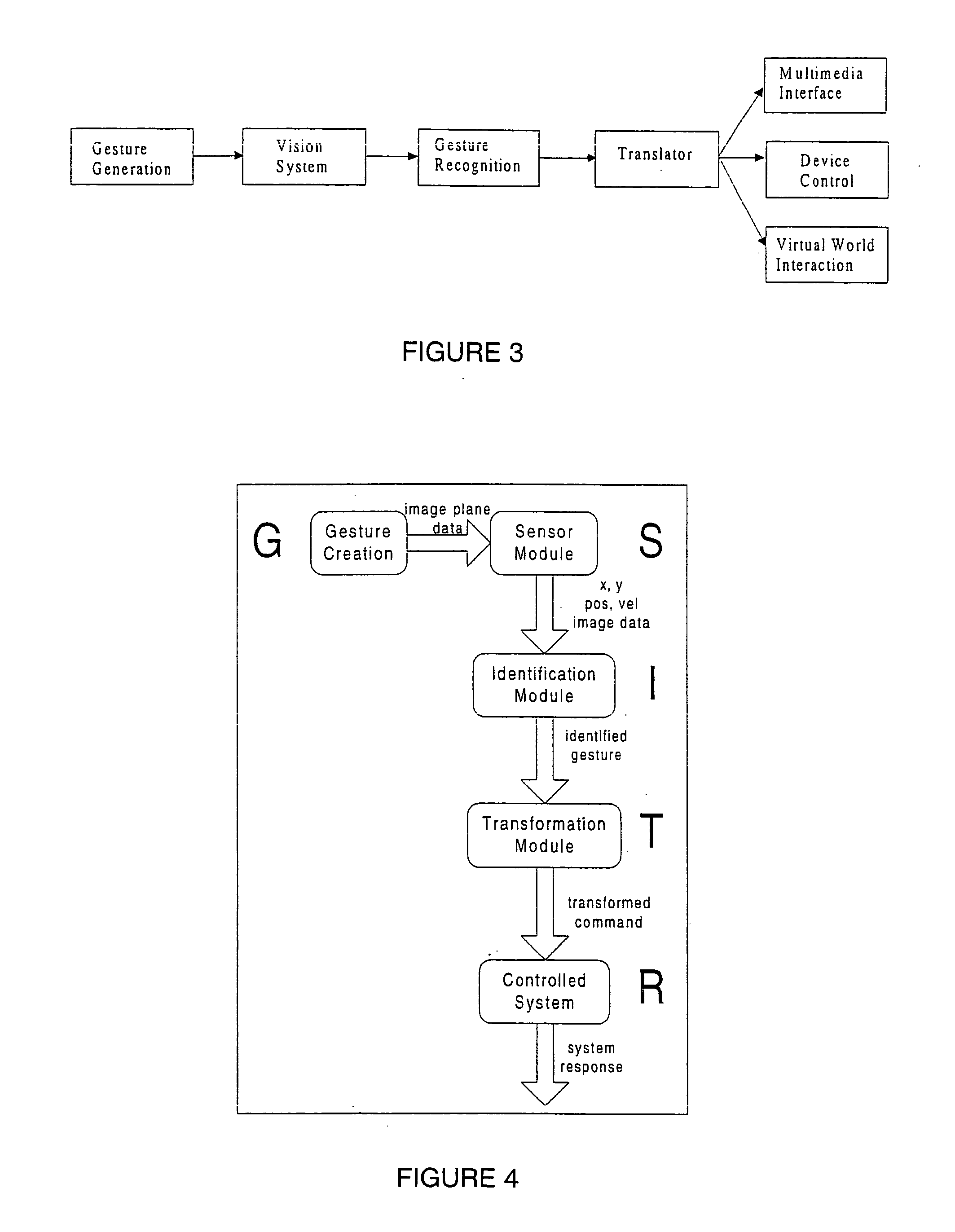
Behavior recognition system
InactiveUS7036094B1Easy to identifyCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGaitBehavior recognition
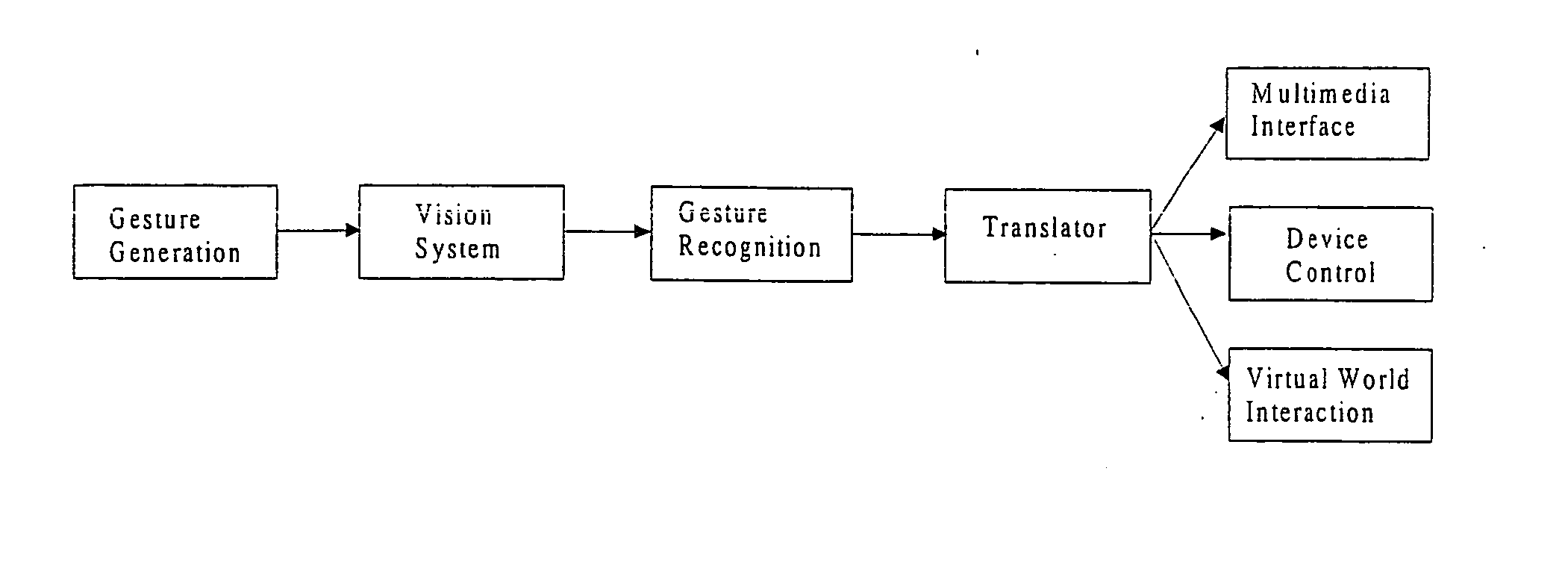
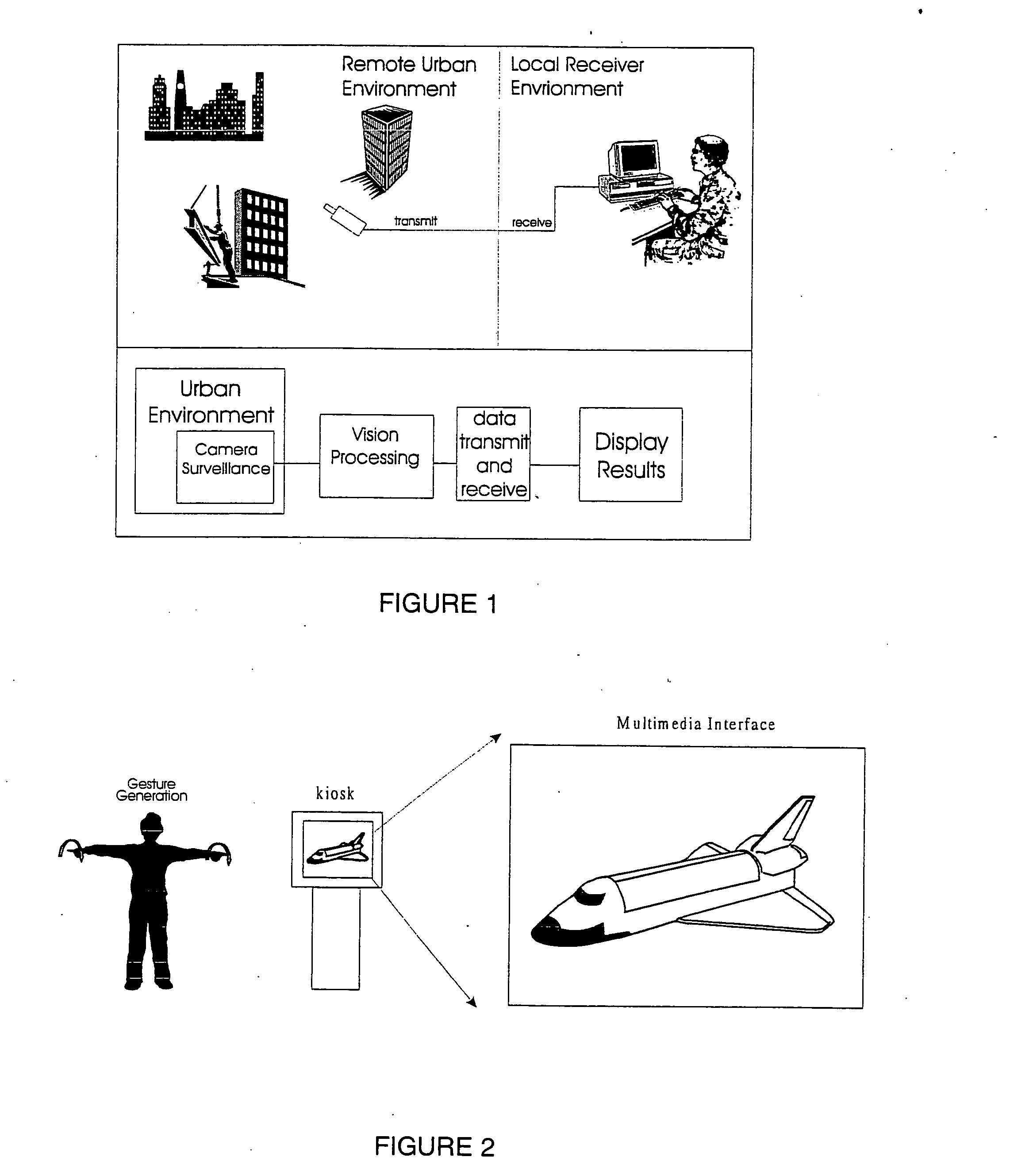
A system for recognizing various human and creature motion gaits and behaviors is presented. These behaviors are defined as combinations of “gestures” identified on various parts of a body in motion. For example, the leg gestures generated when a person runs are different than when a person walks. The system described here can identify such differences and categorize these behaviors. Gestures, as previously defined, are motions generated by humans, animals, or machines. Where in the previous patent only one gesture was recognized at a time, in this system, multiple gestures on a body (or bodies) are recognized simultaneously and used in determining behaviors. If multiple bodies are tracked by the system, then overall formations and behaviors (such as military goals) can be determined.
Owner:JOLLY SEVEN SERIES 70 OF ALLIED SECURITY TRUST I
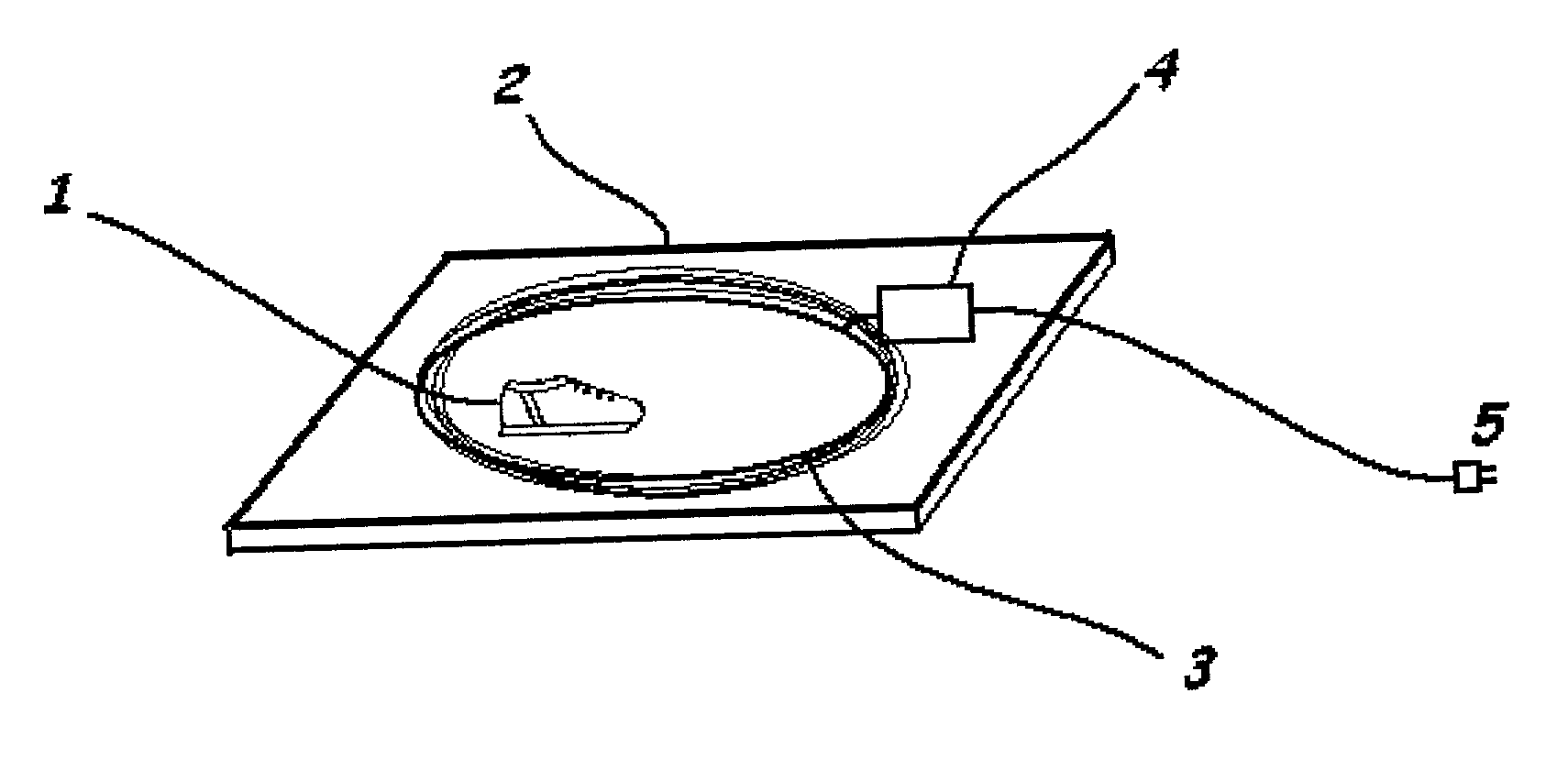
Instrumented insole
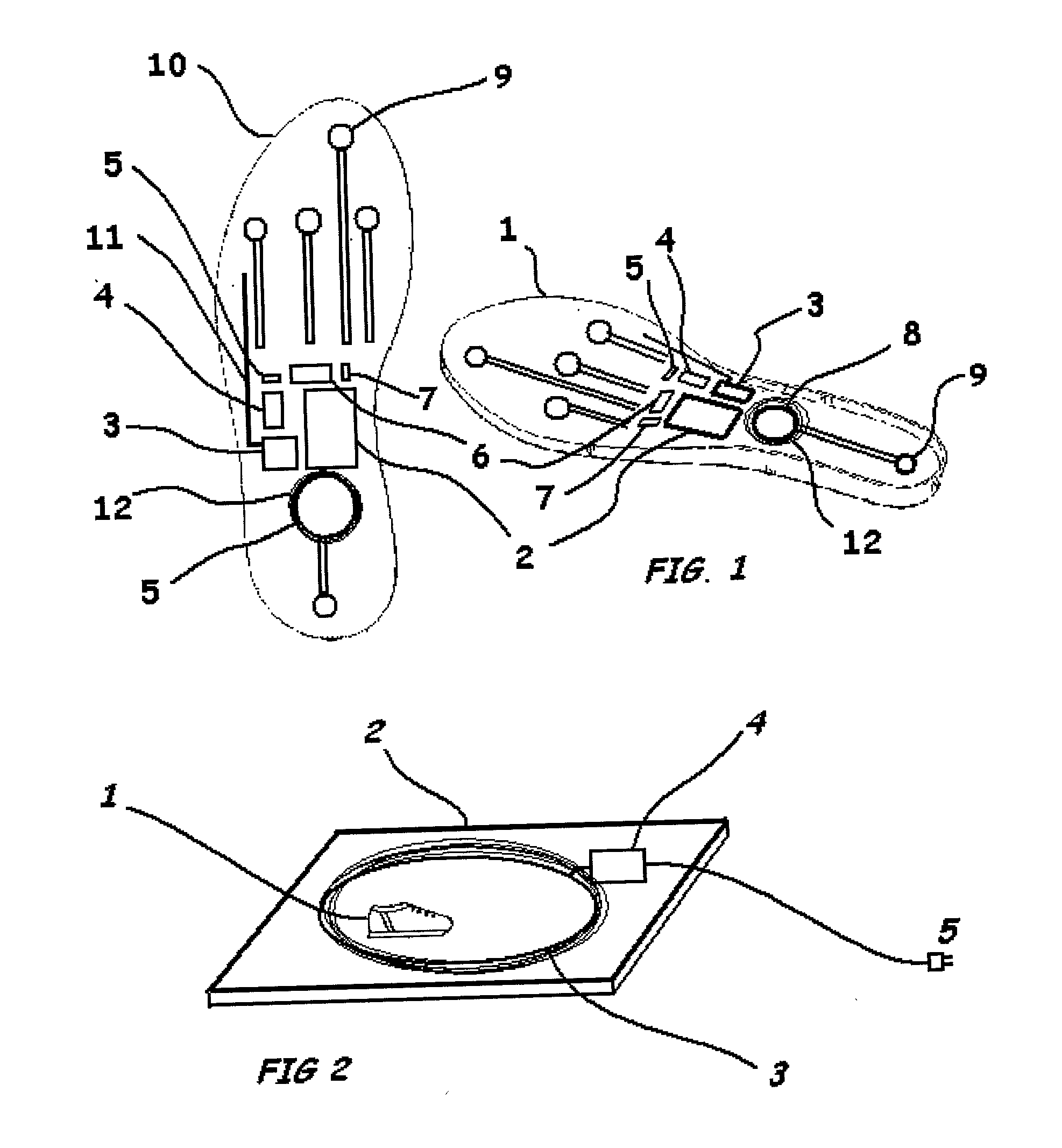
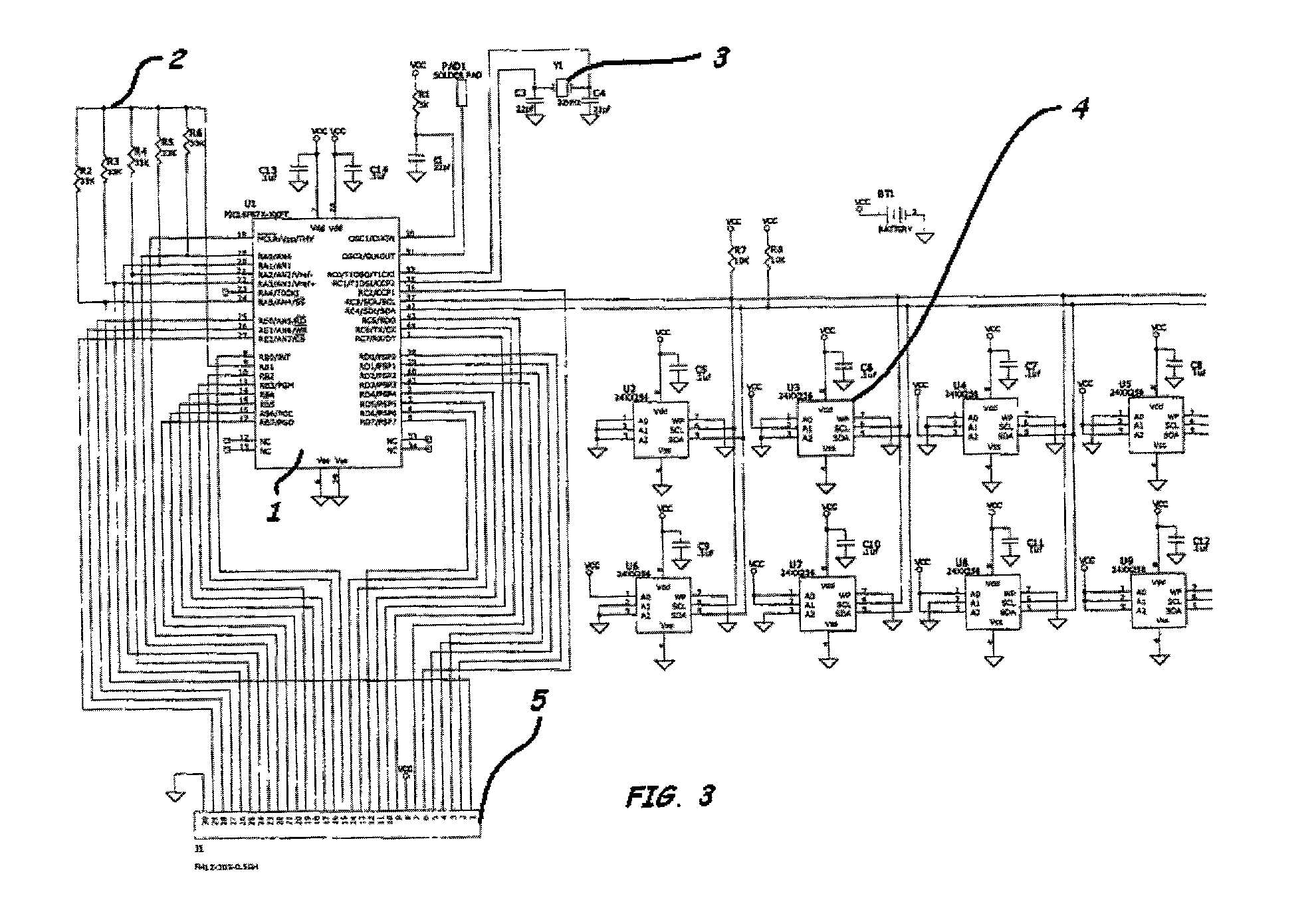
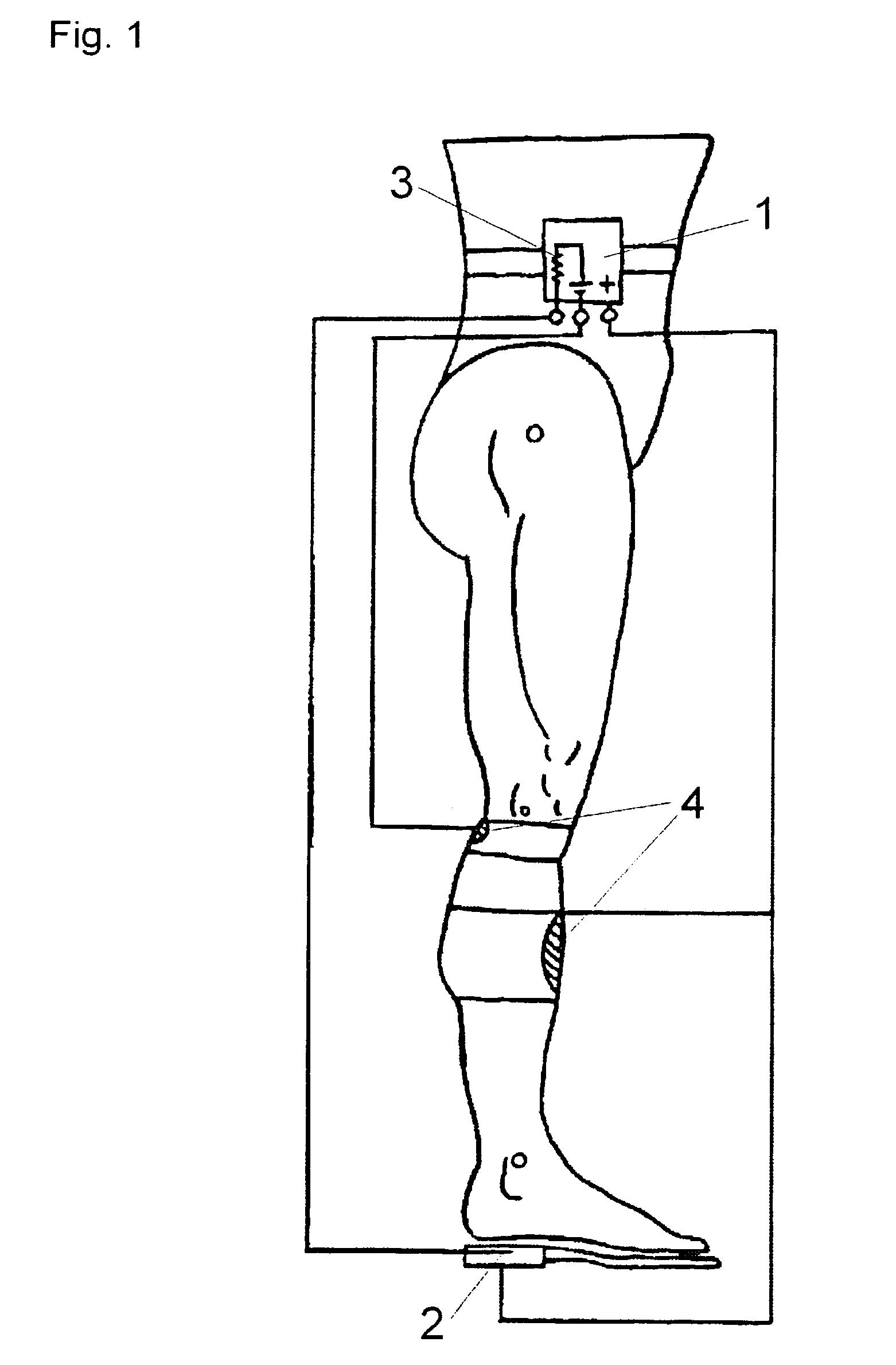
A combination of sensors, including solid-state gyros and force-sensitive resistors, are mounted in an insole suitable for insertion into a shoe. Data from the sensors is recorded by an in situ Programmable Interface Controller (PIC), logged into on-board EEPROM / Flash memory and relayed to a base station computer via a miniature telemetry transmitter triggered by RFID tagging. Software then uses this data to compute the cadence and ankle power of the subject, as well as other parameters, in order to analyze and assess the gait and activity of the subject.
Owner:CATHOLIC UNIV OF AMERICA
Behavior recognition system
InactiveUS20090274339A9Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionBiological motionGait
A system for recognizing various human and creature motion gaits and behaviors is presented. These behaviors are defined as combinations of “gestures” identified on various parts of a body in motion. For example, the leg gestures generated when a person runs are different than when a person walks. The system described here can identify such differences and categorize these behaviors. Gestures, as previously defined, are motions generated by humans, animals, or machines. Multiple gestures on a body (or bodies) are recognized simultaneously and used in determining behaviors. If multiple bodies are tracked by the system, then overall formations and behaviors (such as military goals) can be determined.
Owner:JOLLY SEVEN SERIES 70 OF ALLIED SECURITY TRUST I
Behavior recognition system
InactiveUS20060210112A1Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionBiological motionGait
Owner:JOLLY SEVEN SERIES 70 OF ALLIED SECURITY TRUST I
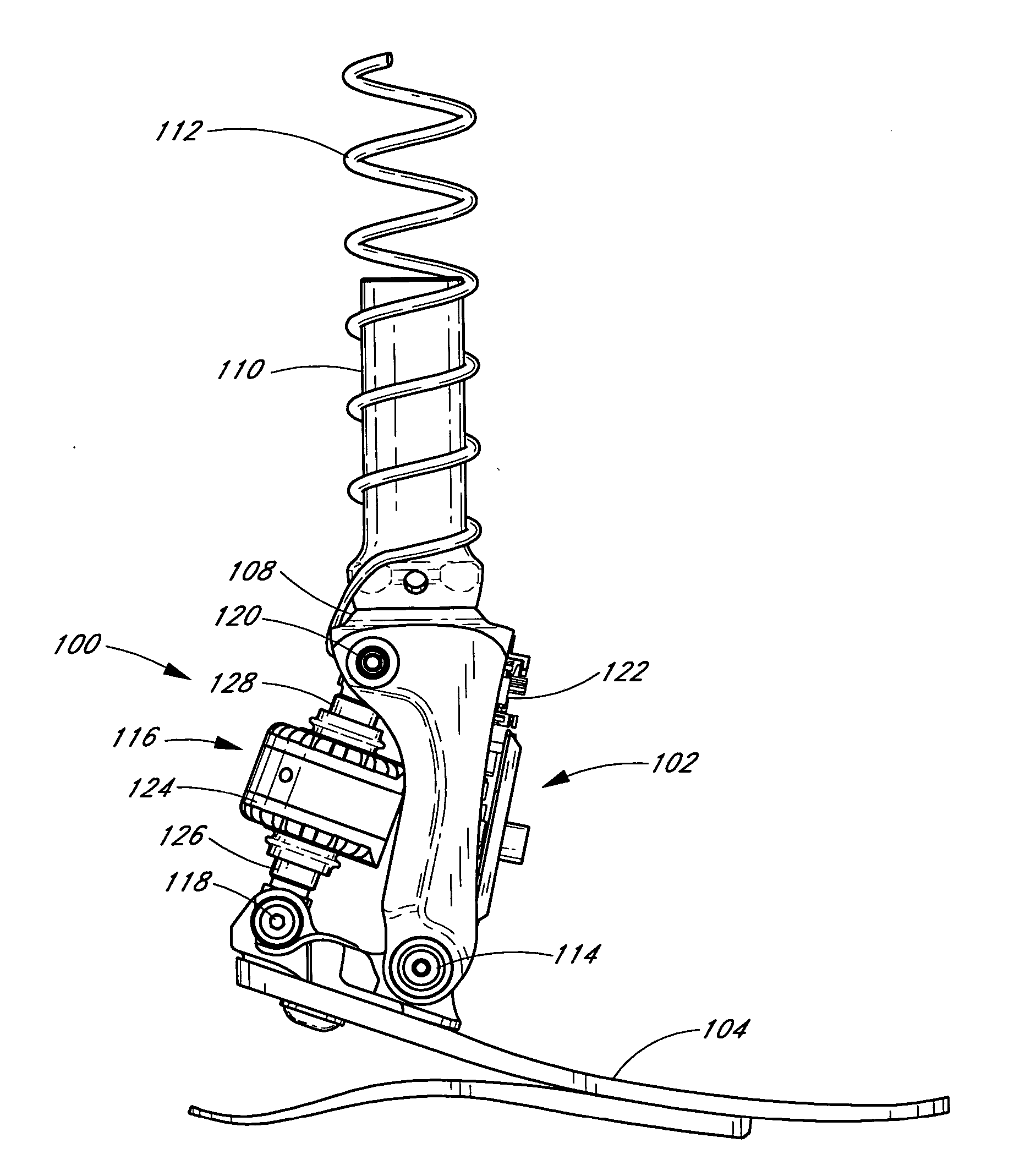
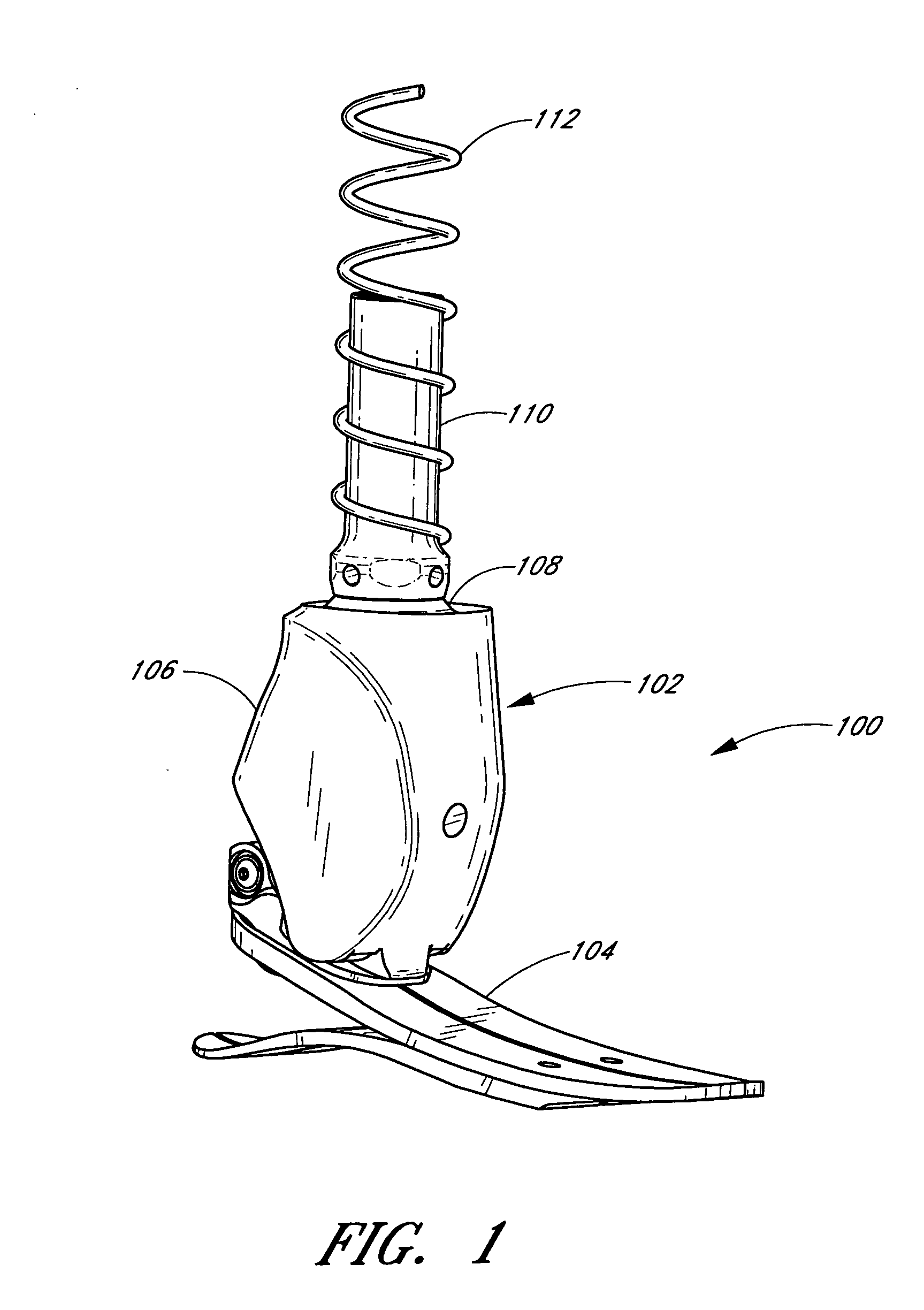
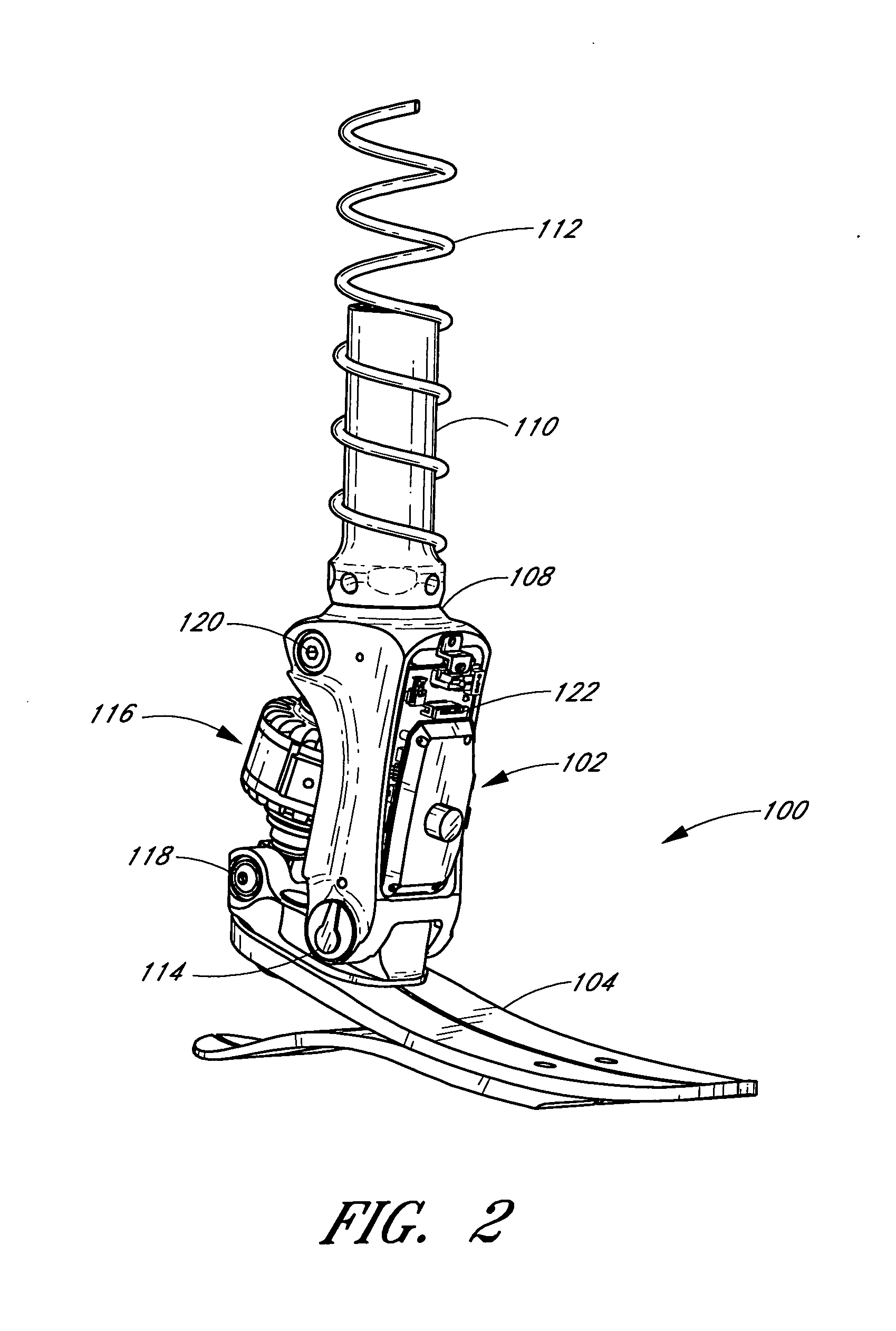
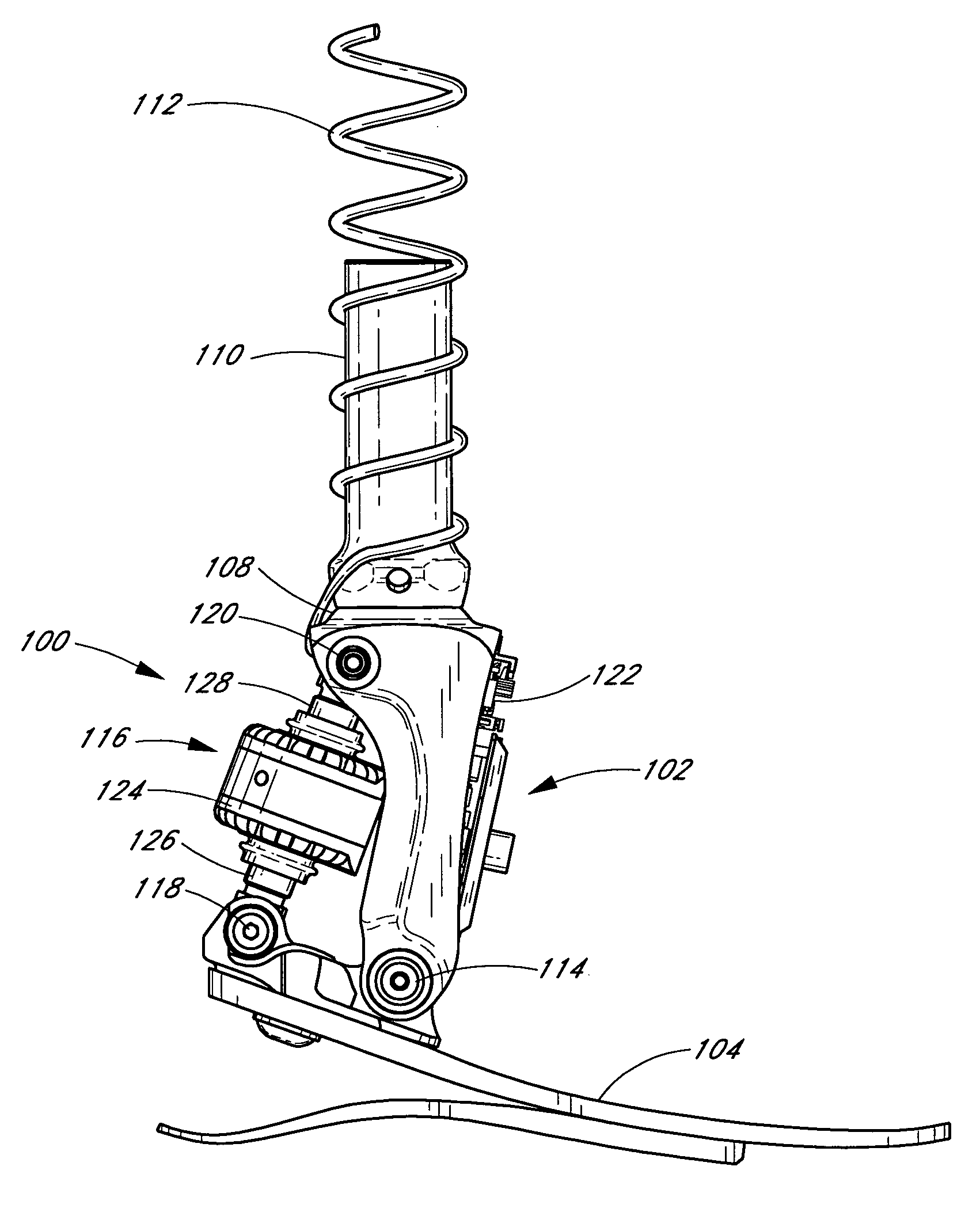
System and method for motion-controlled foot unit
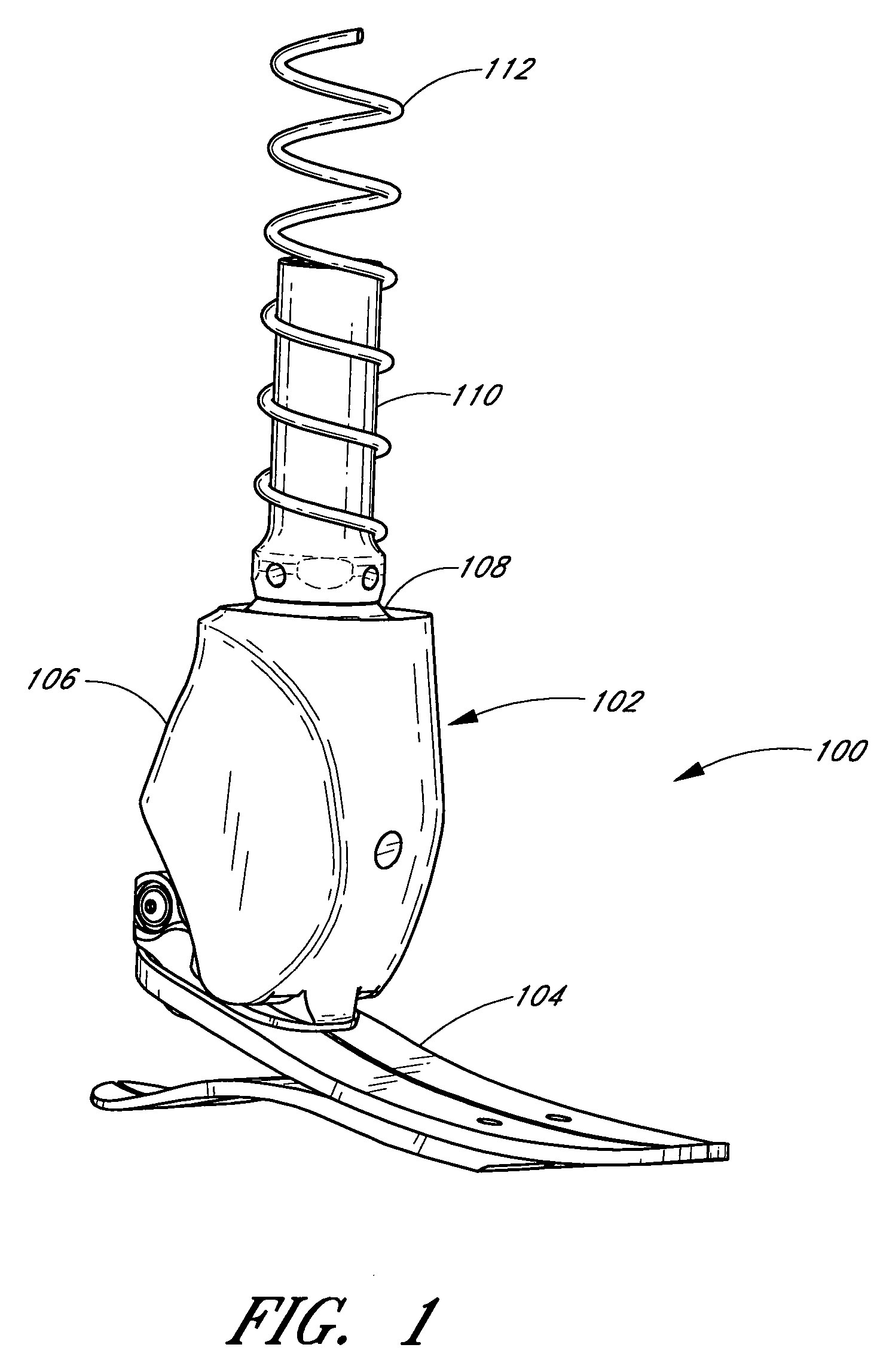
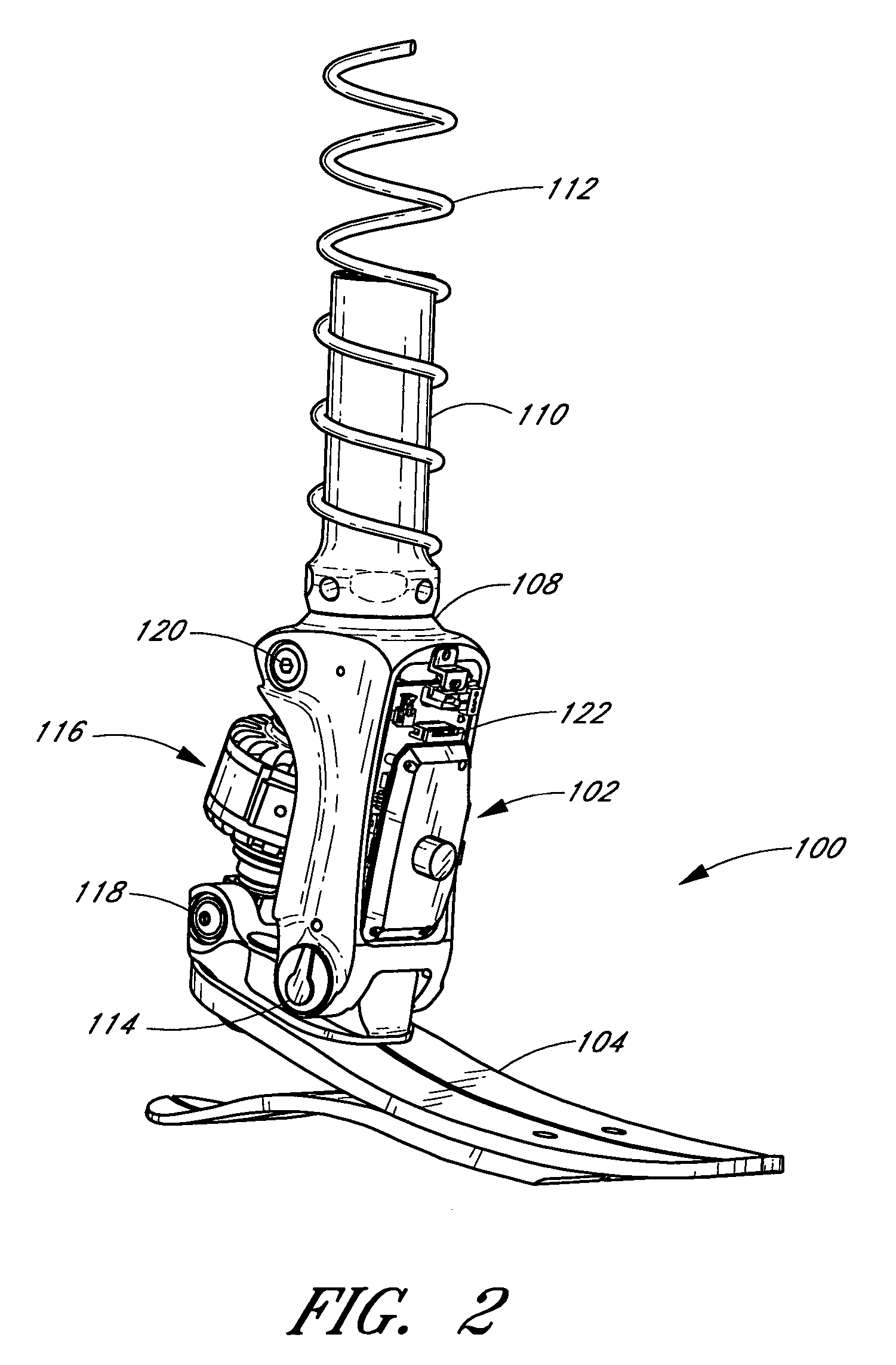
A system and method associated with the movement of a limb. In one example, the system, such as a prosthetic or orthotic system, includes an actuator that actively controls, or adjusts, the angle between a foot unit and a lower limb member. A processing module may control movement of the actuator based on data obtained from a sensor module. For instance, sensing module data may include information relating to the gait of a user and may be used to adjust the foot unit to substantially mimic the movement of a natural, healthy ankle. The system may further accommodate, for example, level ground walking, traveling up / down stairs, traveling up / down sloped surfaces, and various other user movements. In addition, the processing module may receive user input or display output signals through an external interface. For example, the processing module may receive a heel height input from the user.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Prosthetic leg having electronically controlled prosthetic knee with regenerative braking feature
InactiveUS20070050044A1Absorb energyAugment other portionArtificial legsRegenerative brakeElectronic control system
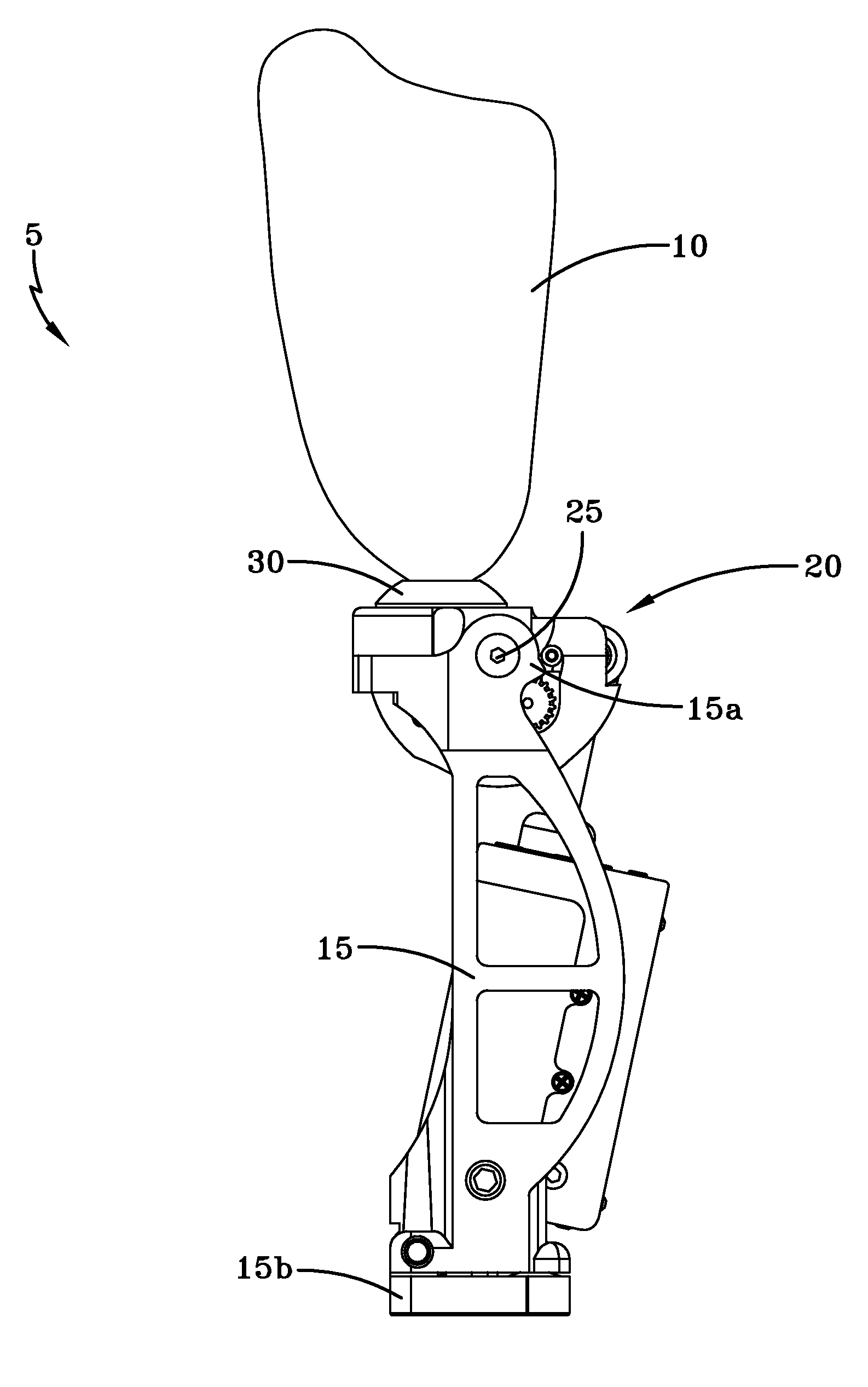
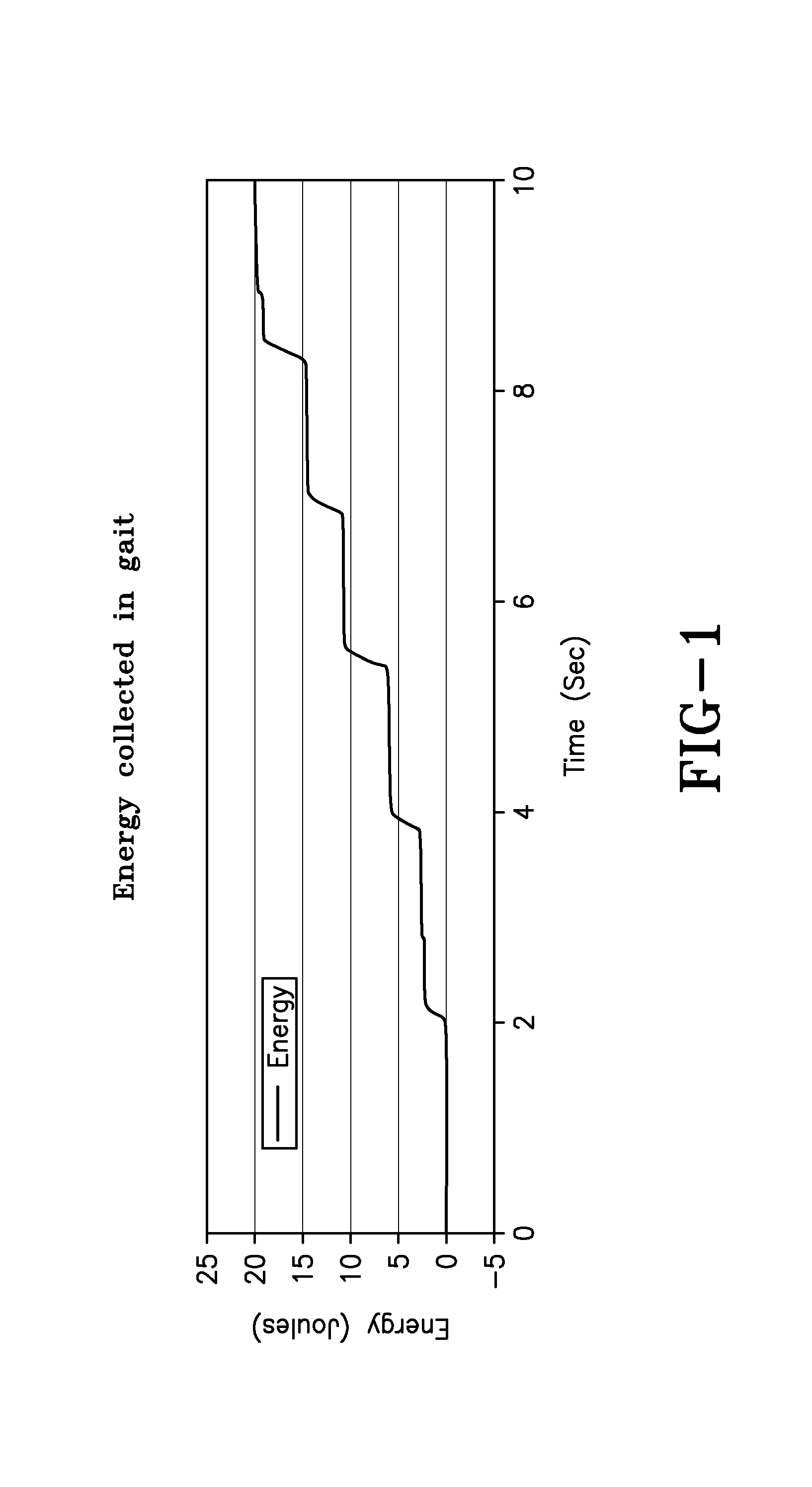
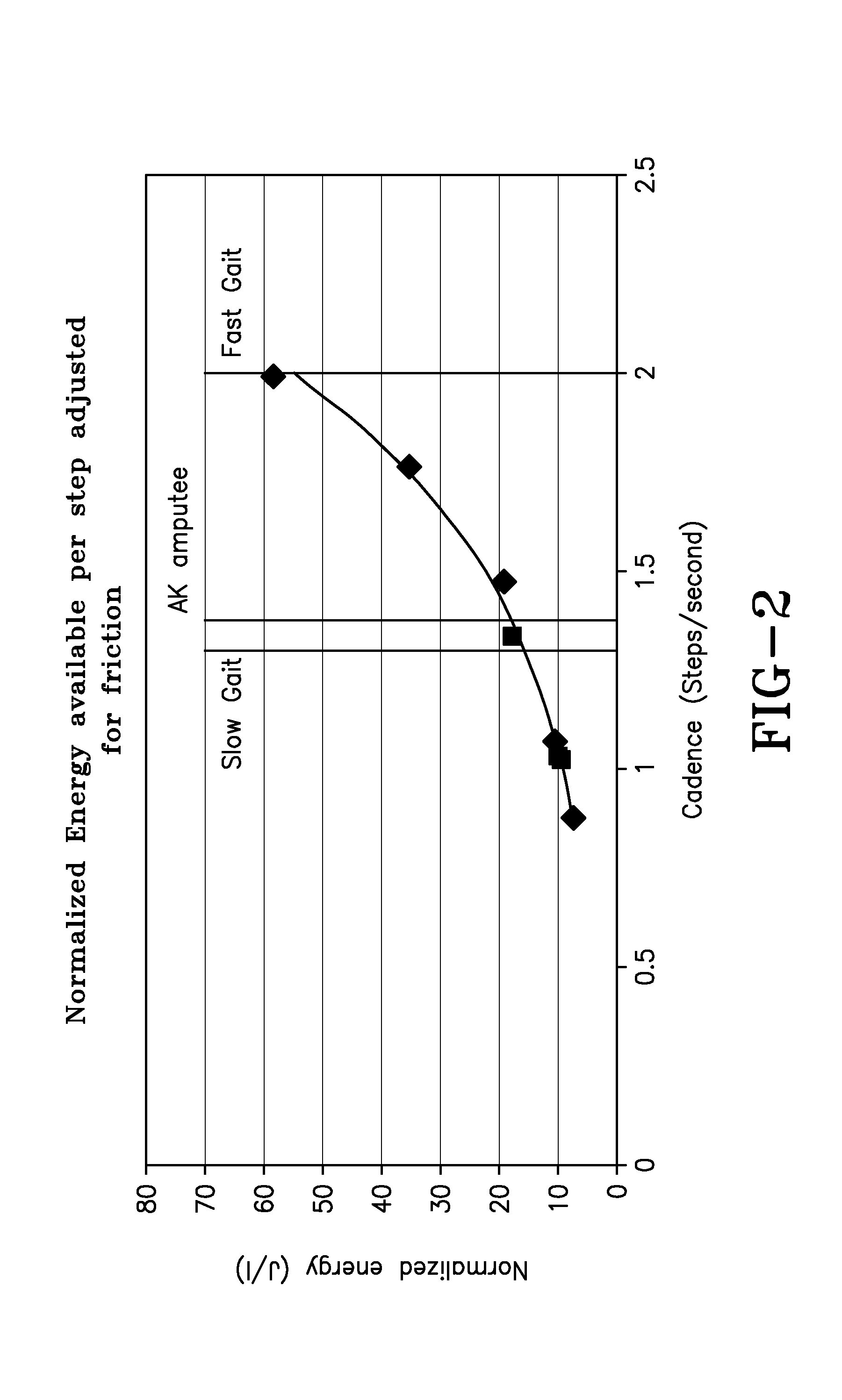
A prosthetic leg having an electronically controlled regenerative prosthetic knee. In certain embodiments of the present invention the knee may be passive, whereby it is used only to generate electrical energy. In other embodiments, the knee may be active, whereby it can be used to assist with or completely control gait, as well as to generate electrical energy. The knee makes use of an actuator motor / generator to control gait and / or to generate electrical energy. An electronic control system is provided to control overall operation of the prosthetic leg, to distribute generated electrical energy, and to transfer excess electrical energy to one or more storage devices for later use. A prosthetic leg of the present invention having an active prosthetic knee may be especially helpful in assisting an amputee with activities that impart a high torque load to the knee joint.
Owner:WILLOWWOOD GLOBAL LLC
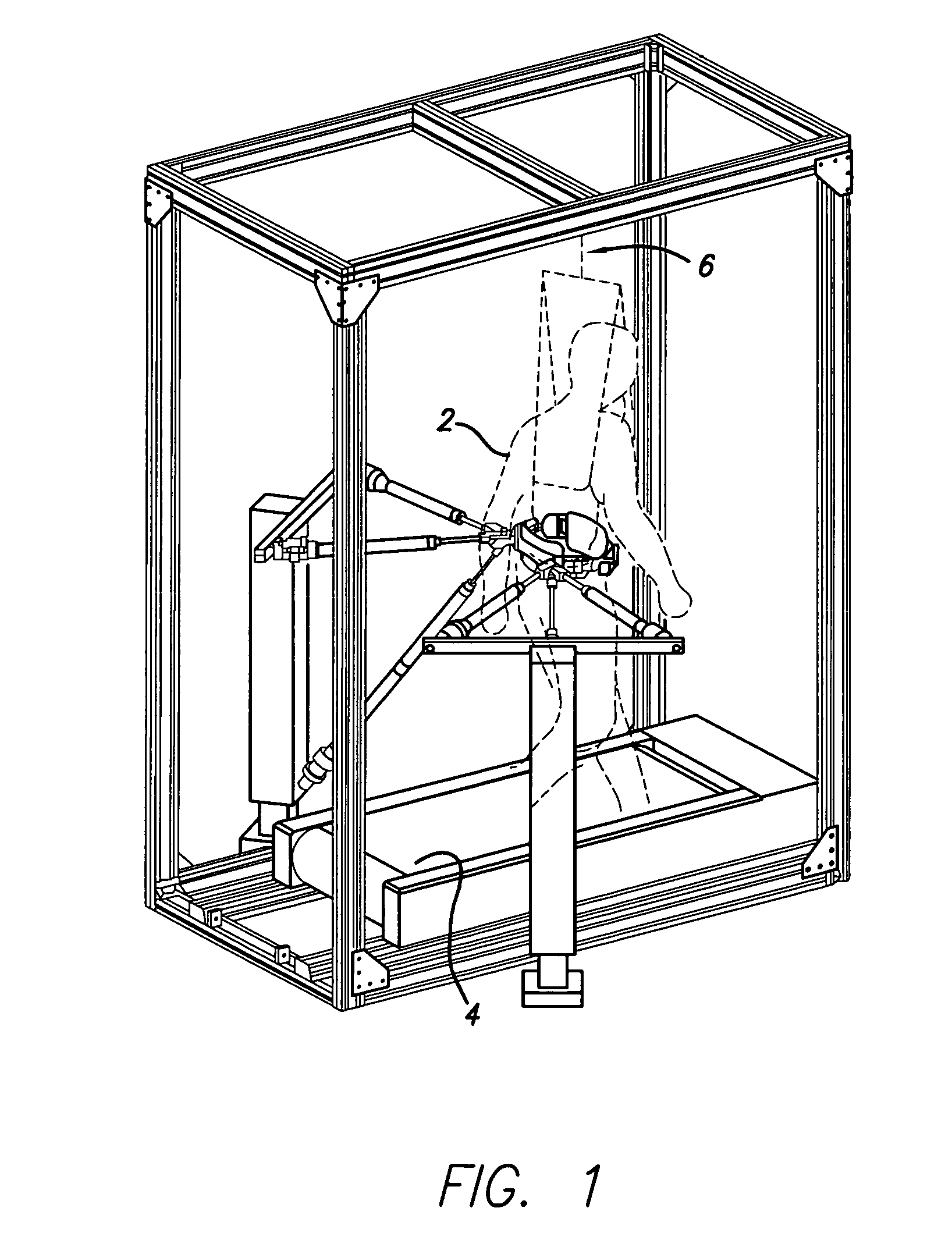
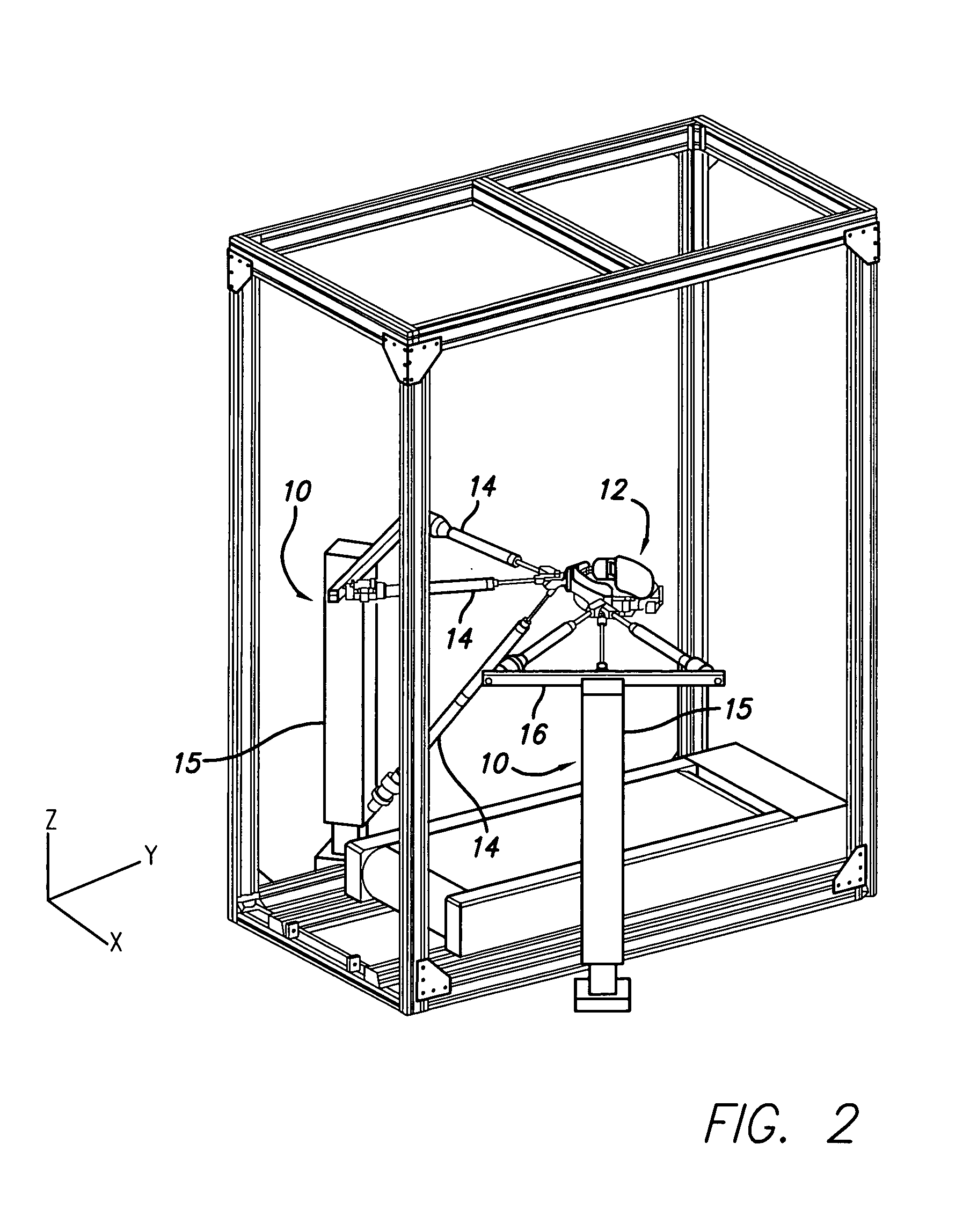
Ambulatory suspension and rehabilitation apparatus
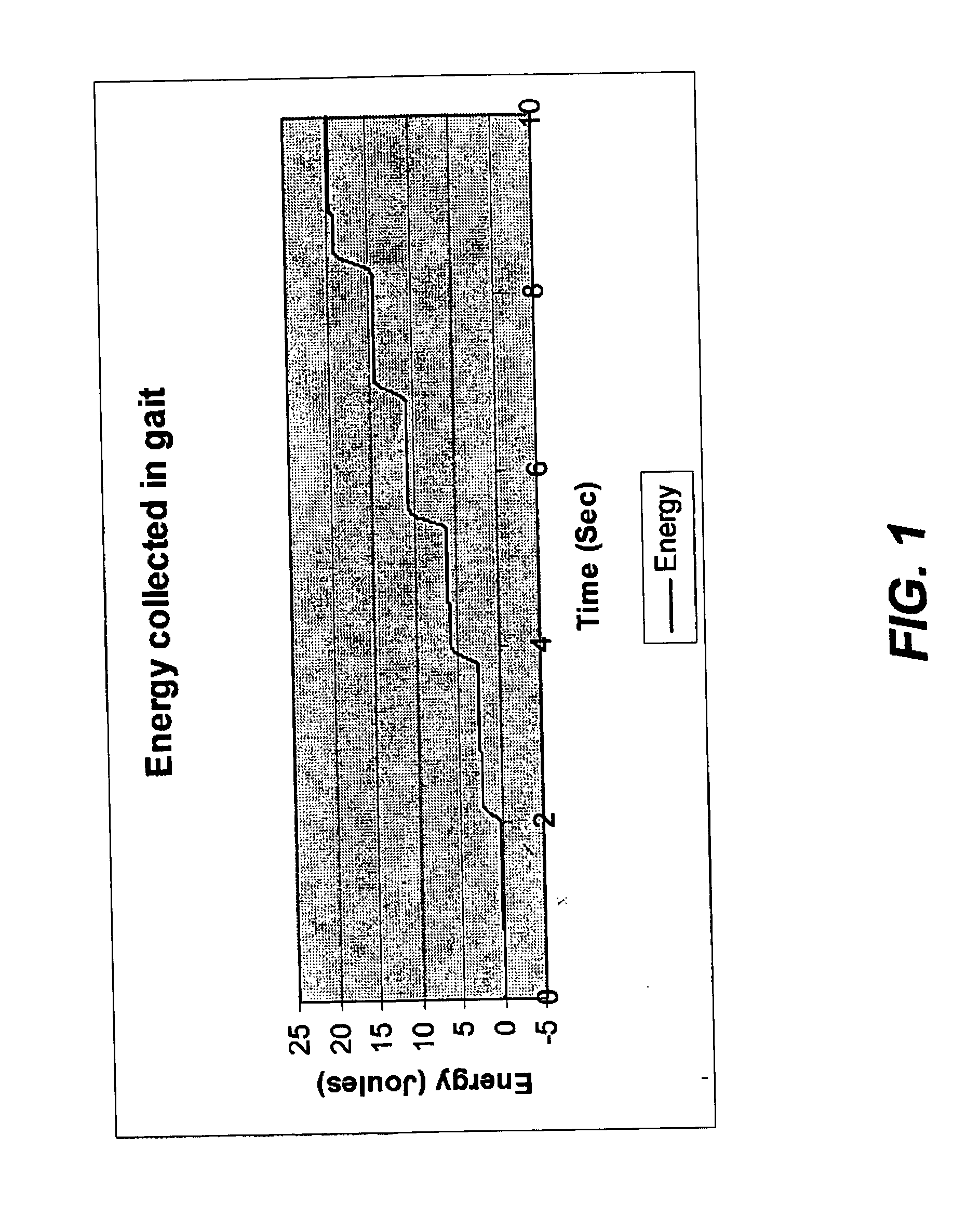
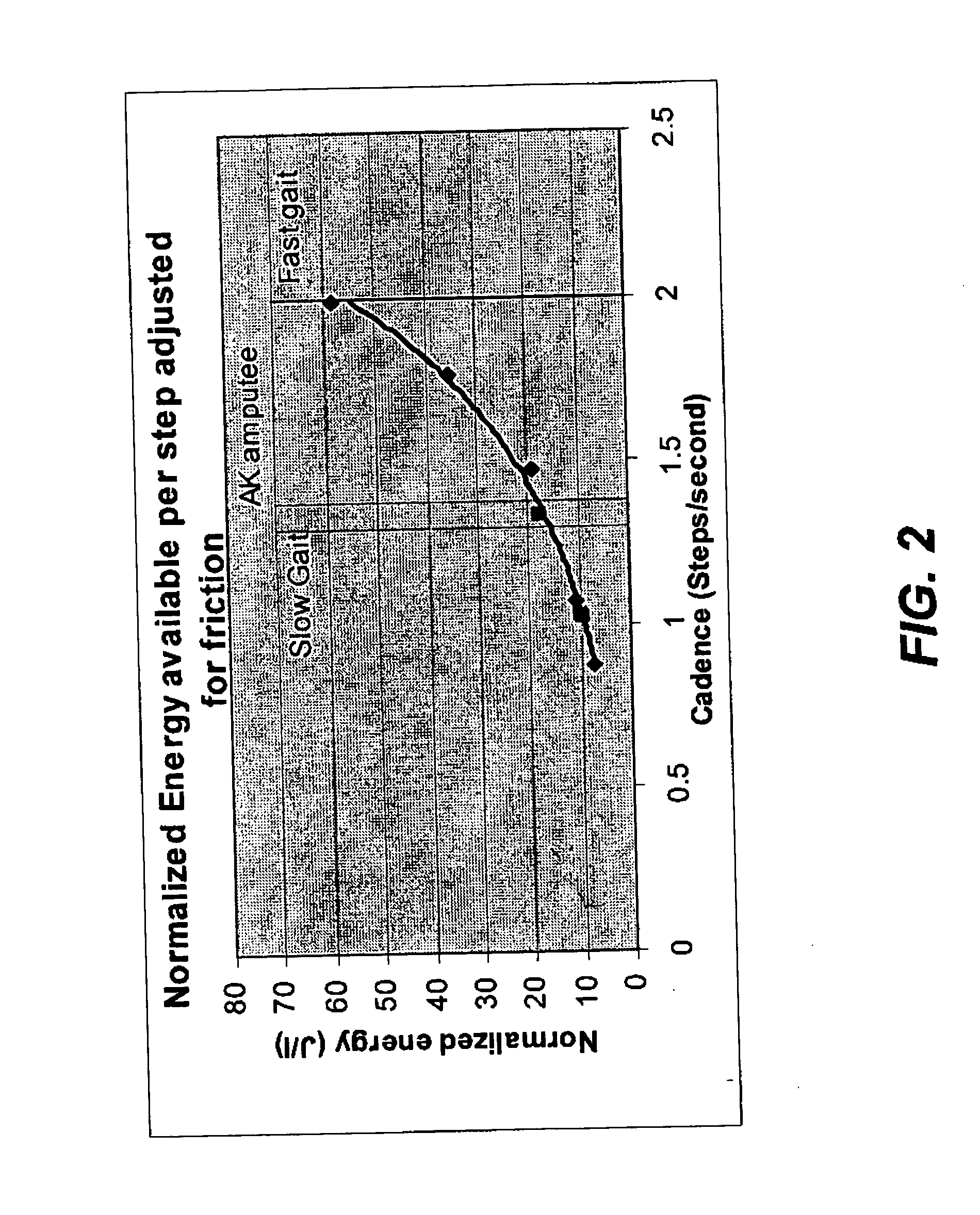
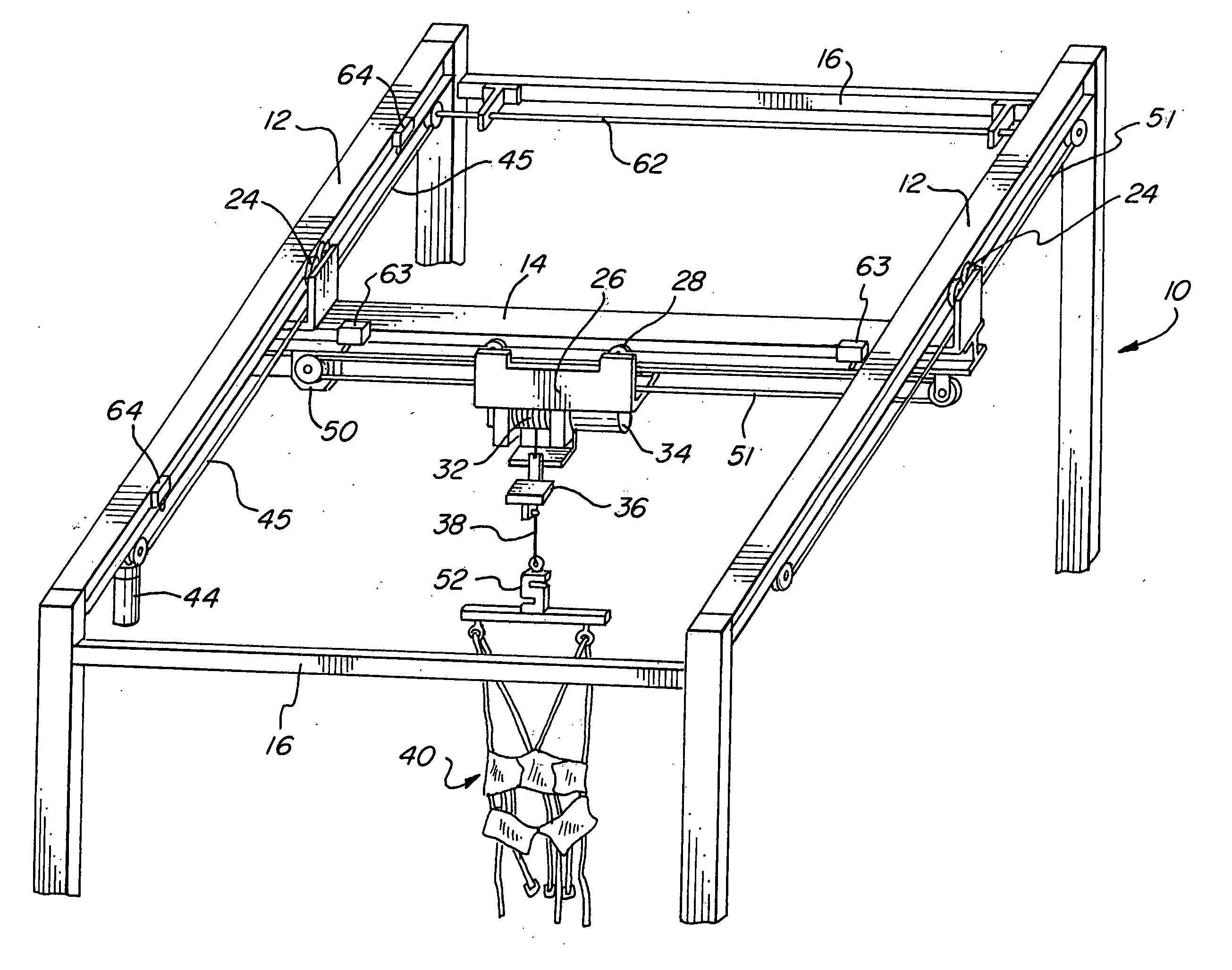
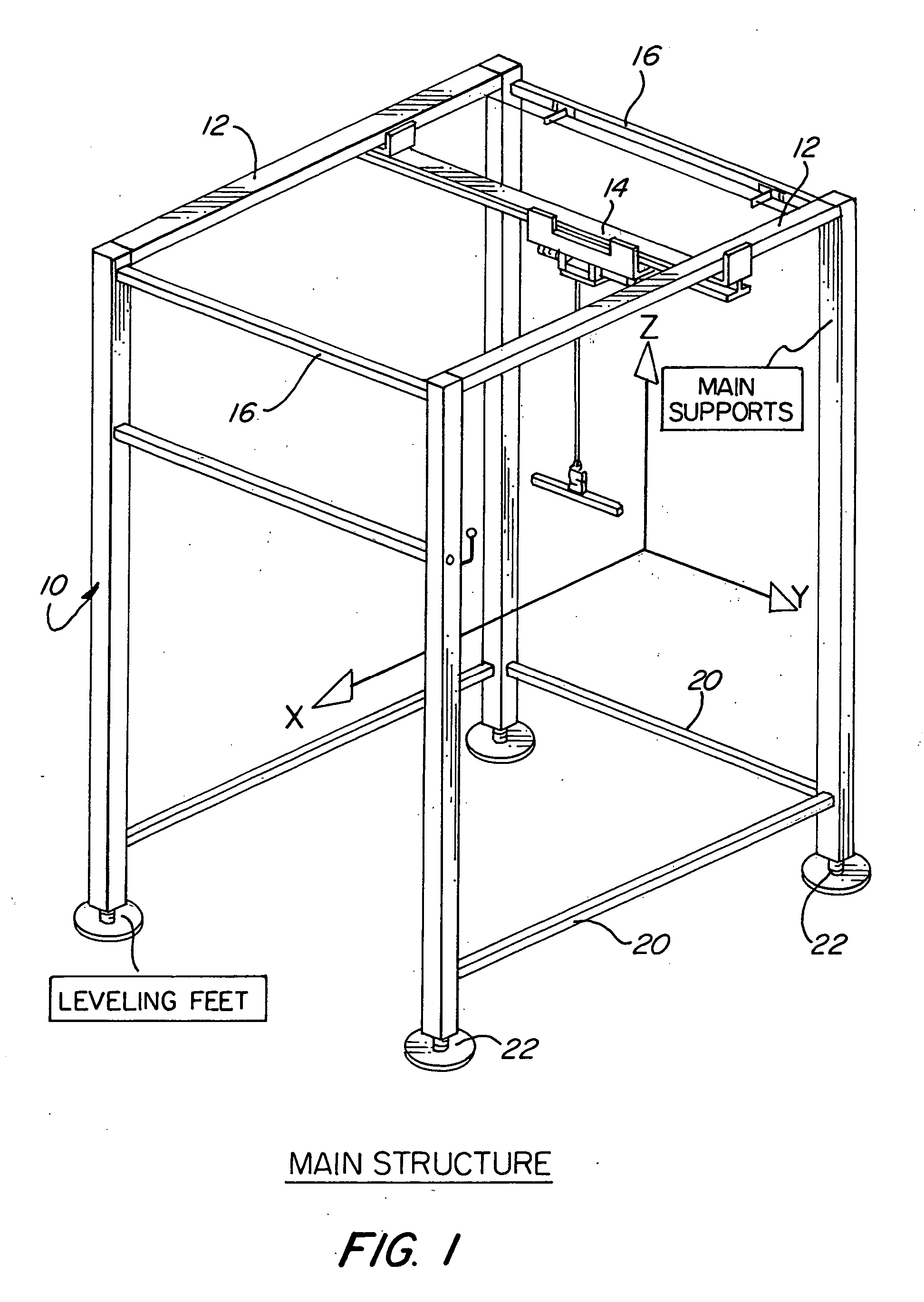
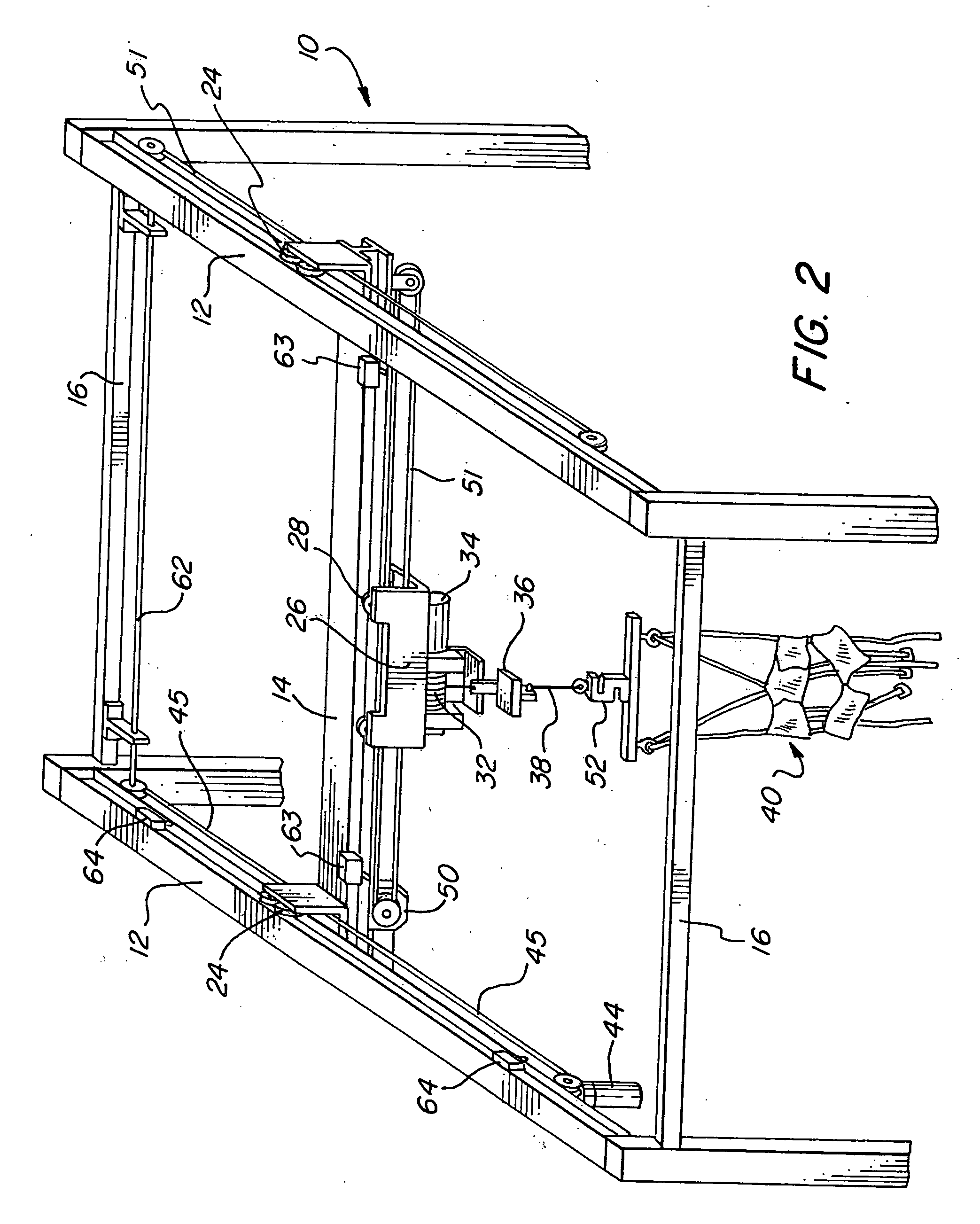
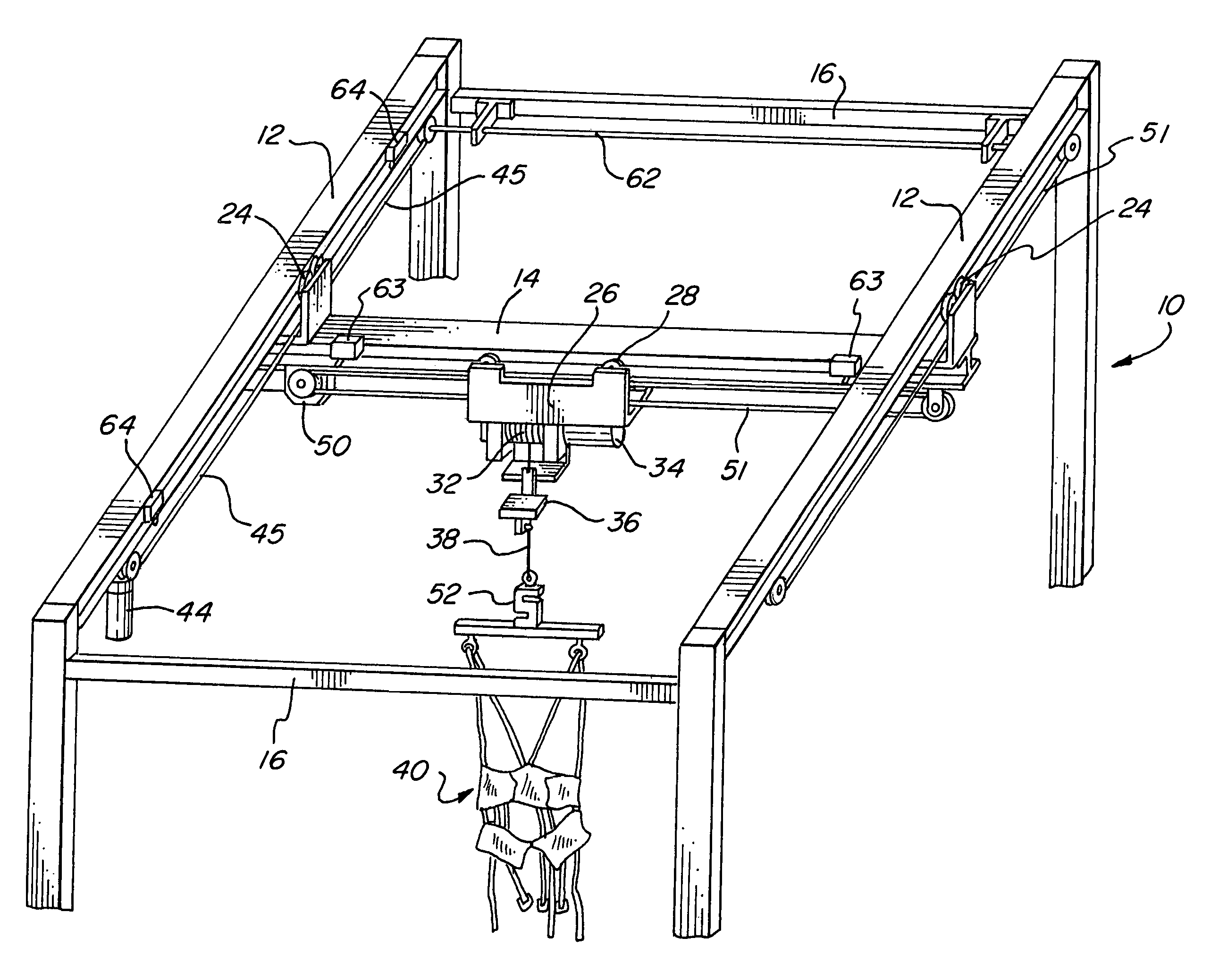
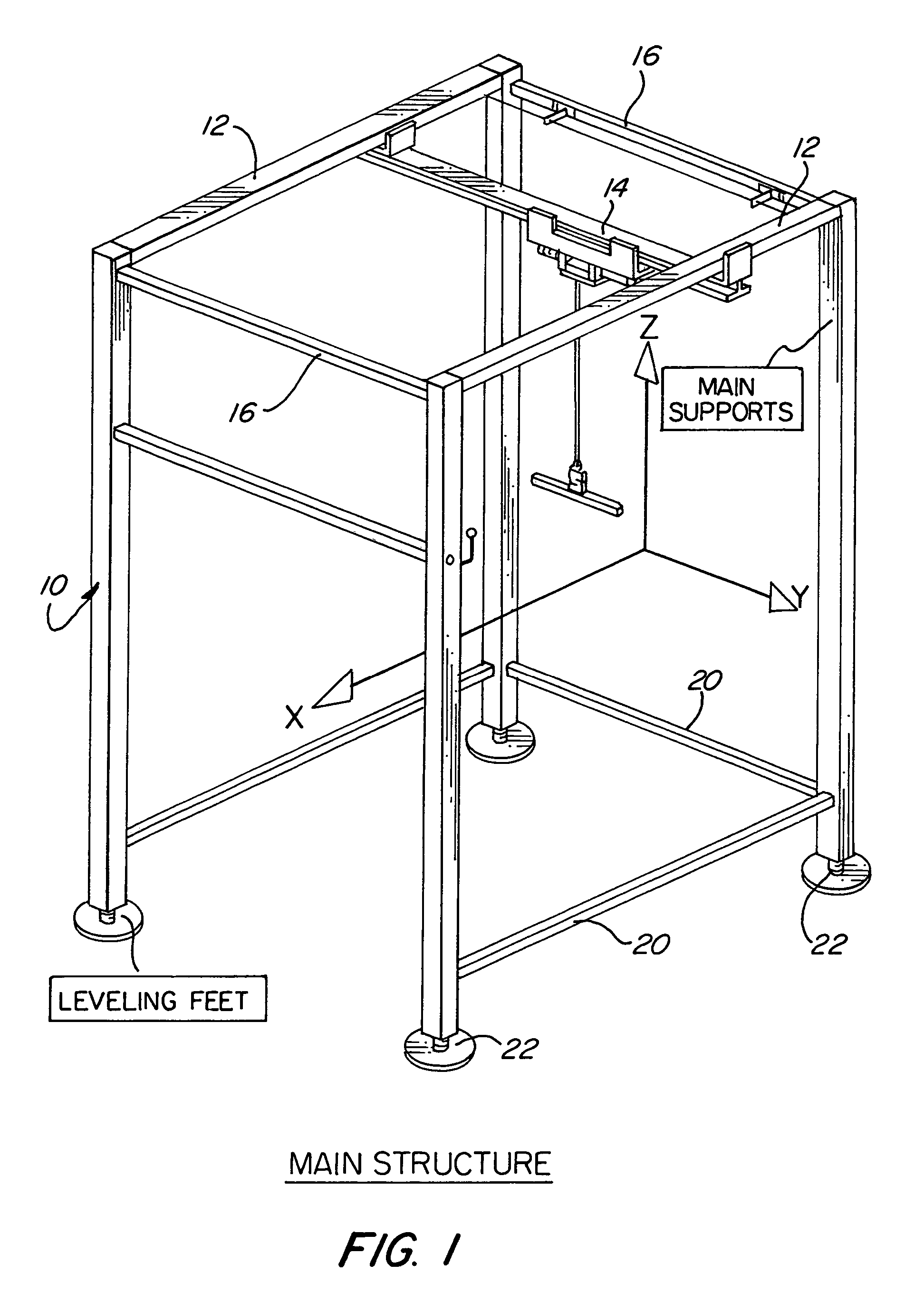
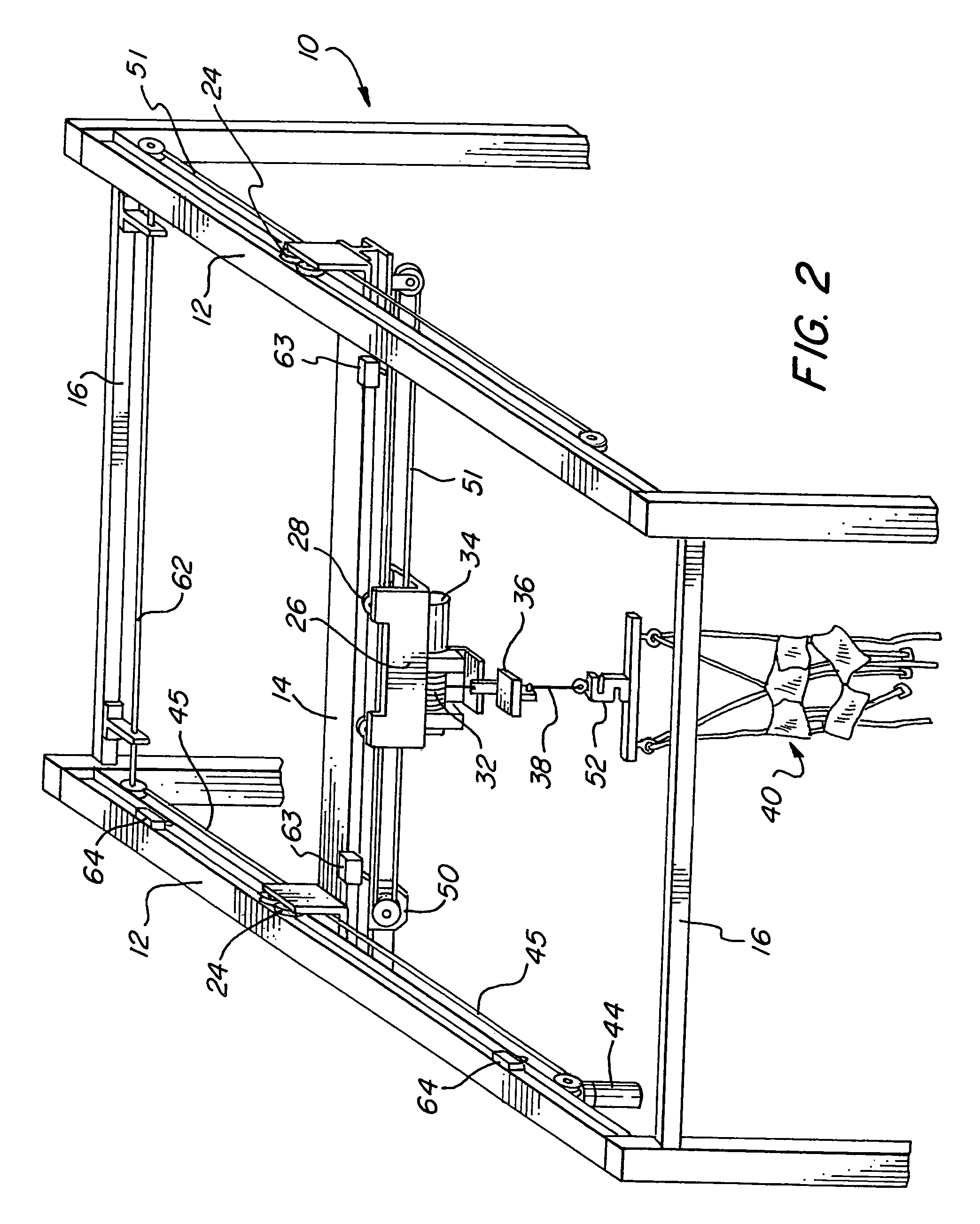
An ambulatory suspension system for gait rehabilitation has a parallel pair of rails bordering the sides of a training area and a bridge extending between and movable along the rails. A trolley is movable along the bridge and includes a motor driven hoist with a cable extending thereabout and depending from the trolley. The hoist is operable to vary the length of the cable depending from the trolley, and a harness is suspended by the cable. Motors move the bridge along the rails and the trolley along the bridge as the sensors sense the direction of movement of the patient in X and Y directions. The falling motion of a patient supported in the harness is sensed and will immediately disable the system. A computer control receives signals from the sensors and operates the motors so that the patient is held in an upright position.
Owner:HARTFORD THE UNIV OF +1
Wearable device having feedback characteristics
InactiveUS8025632B2Avoid injuryImprove rigidityElectrotherapyStrain gaugeEngineeringSacroiliac joint
Owner:OSSUR HF
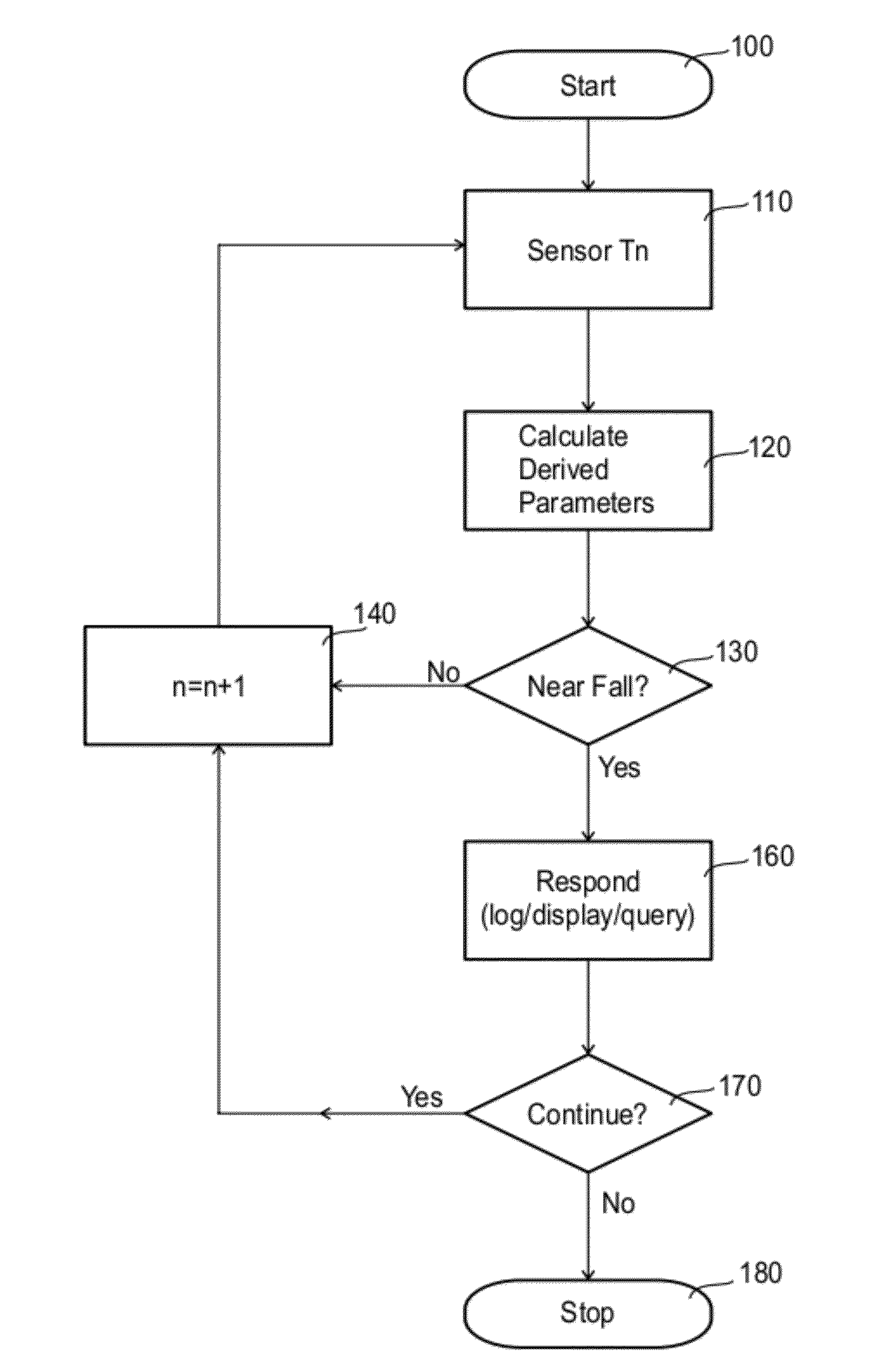
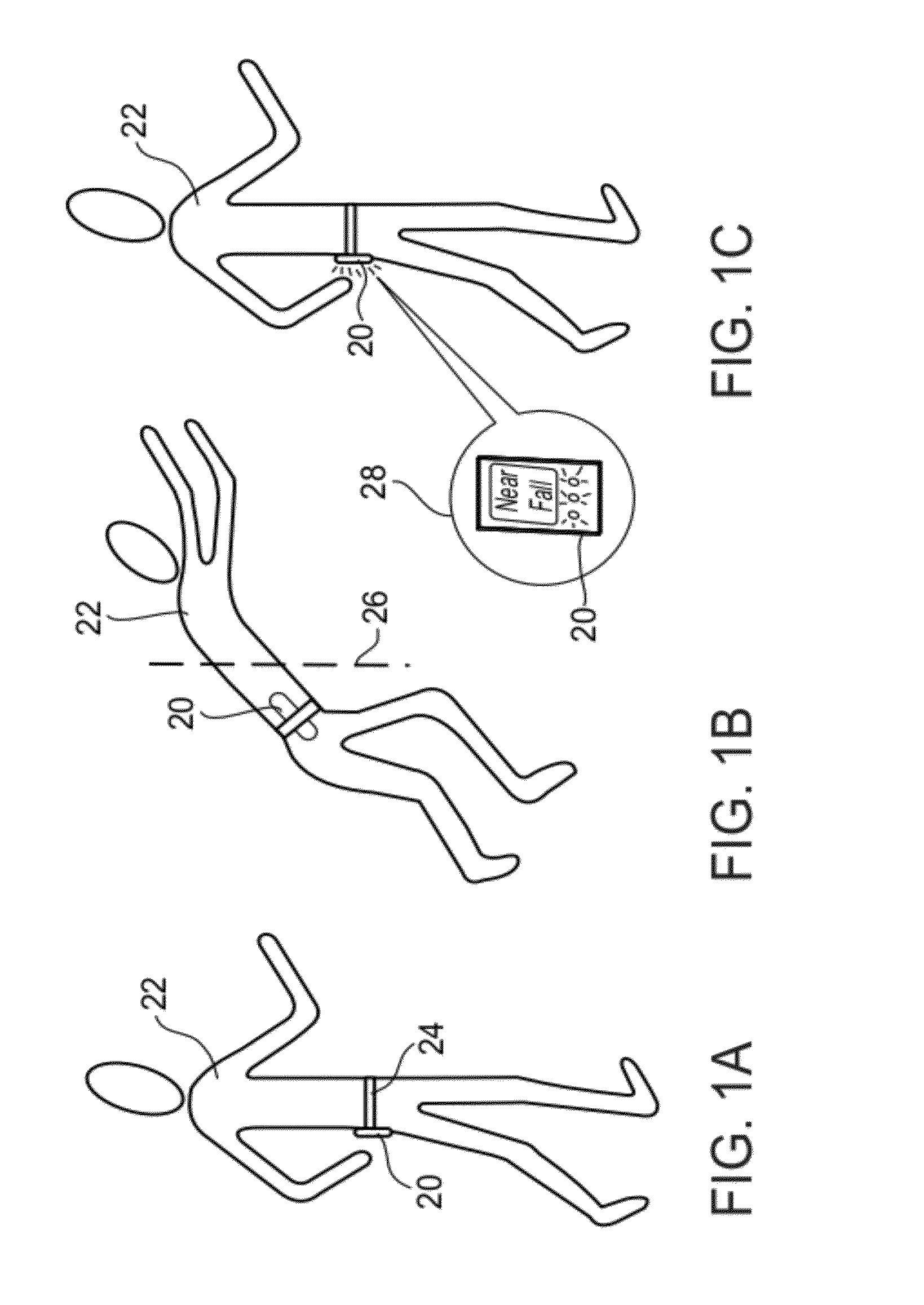
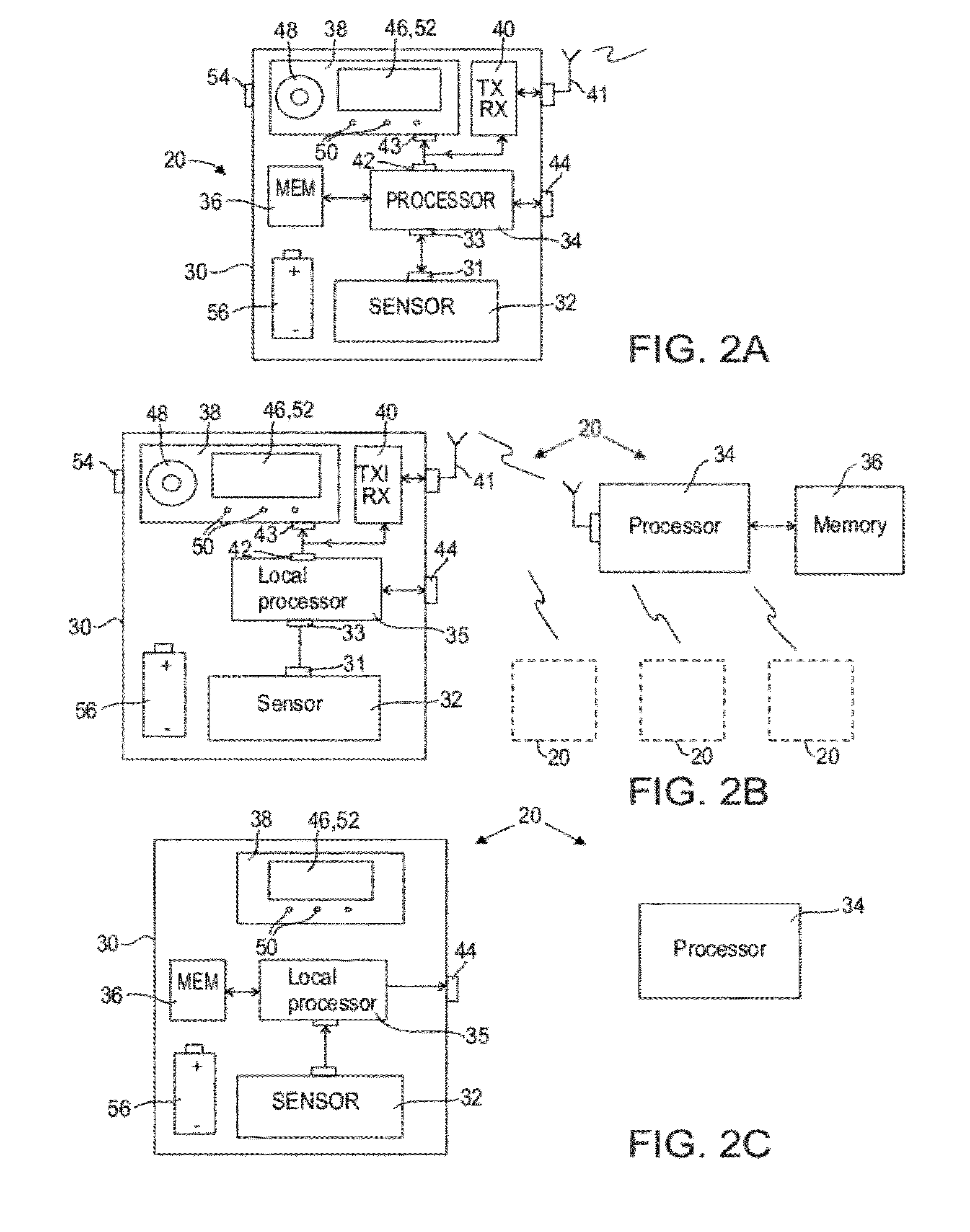
Automated near-fall detector
A method of gait data collection, the method comprising collecting movement data, determining from the data a movement parameter that includes a third order derivative of position, comparing the movement parameter with a threshold value, and counting at least a near fall if the movement parameter exceeds the threshold value.
Owner:THE MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & HEALTH SERVICES FUND OF THE TEL AVIV MEDICAL CENT
System and method for motion-controlled foot unit
A system and method associated with the movement of a limb. In one example, the system, such as a prosthetic or orthotic system, includes an actuator that actively controls, or adjusts, the angle between a foot unit and a lower limb member. A processing module may control movement of the actuator based on data obtained from a sensor module. For instance, sensing module data may include information relating to the gait of a user and may be used to adjust the foot unit to substantially mimic the movement of a natural, healthy ankle. The system may further accommodate, for example, level ground walking, traveling up / down stairs, traveling up / down sloped surfaces, and various other user movements. In addition, the processing module may receive user input or display output signals through an external interface. For example, the processing module may receive a heel height input from the user.
Owner:OSSUR HF
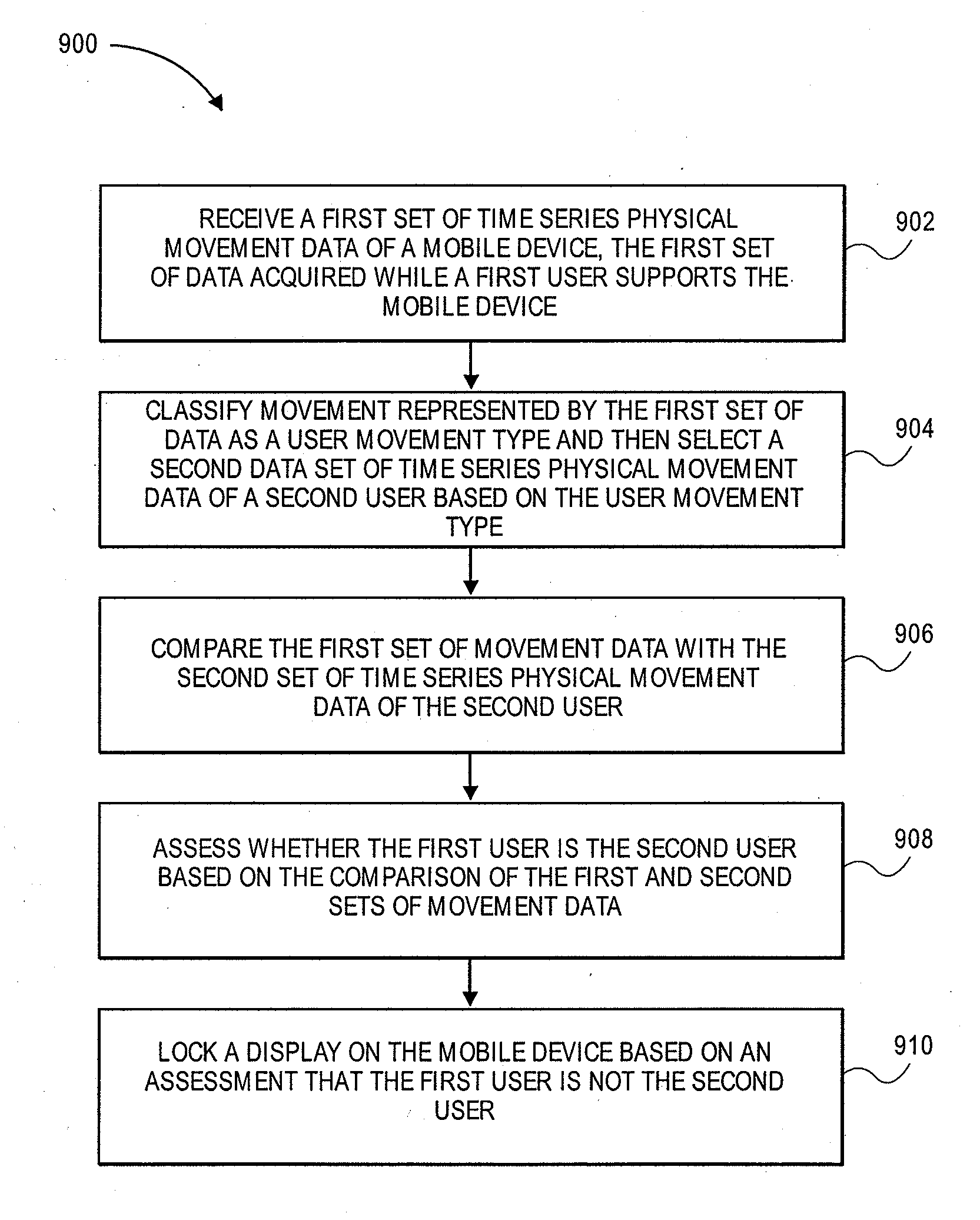
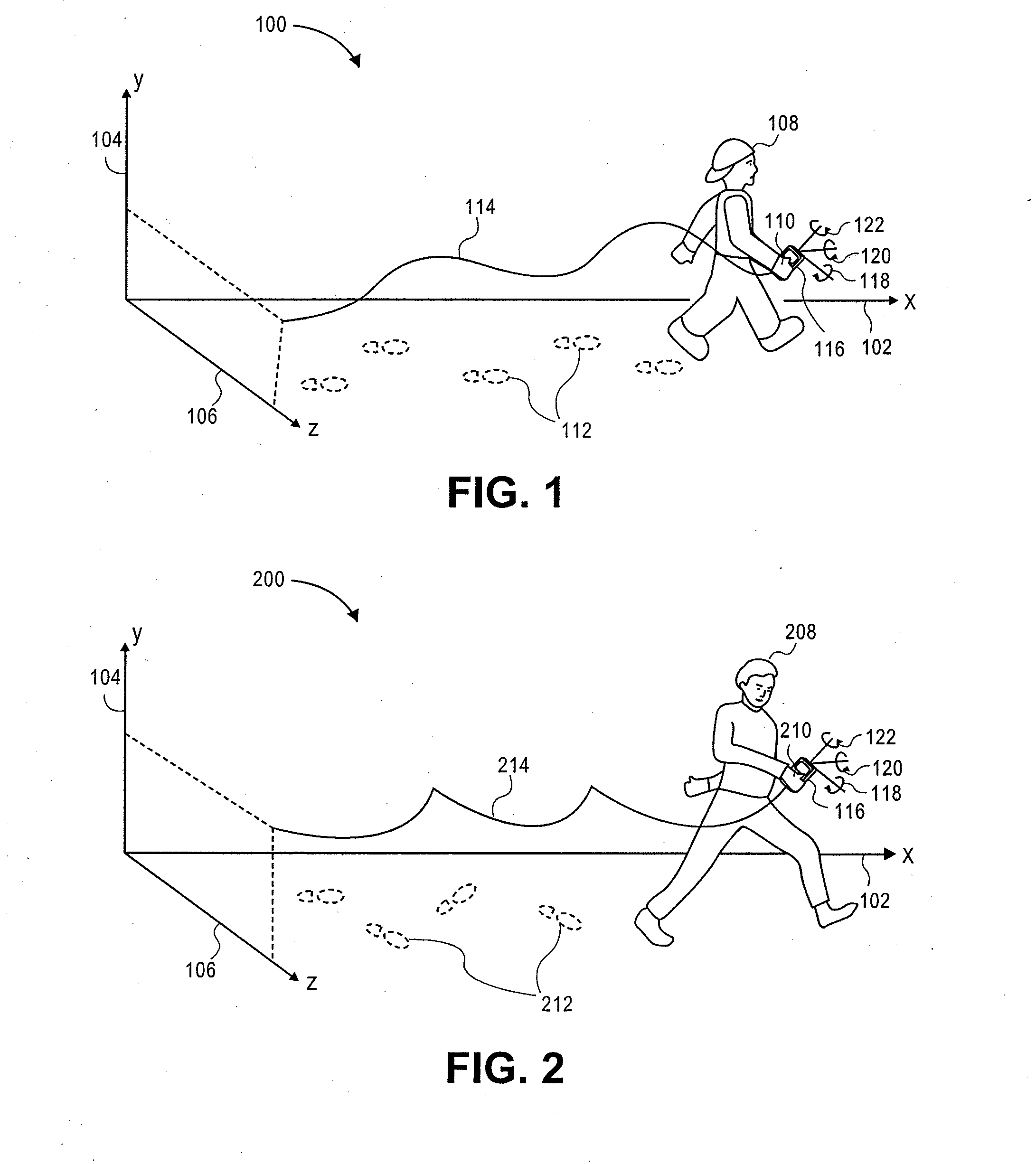
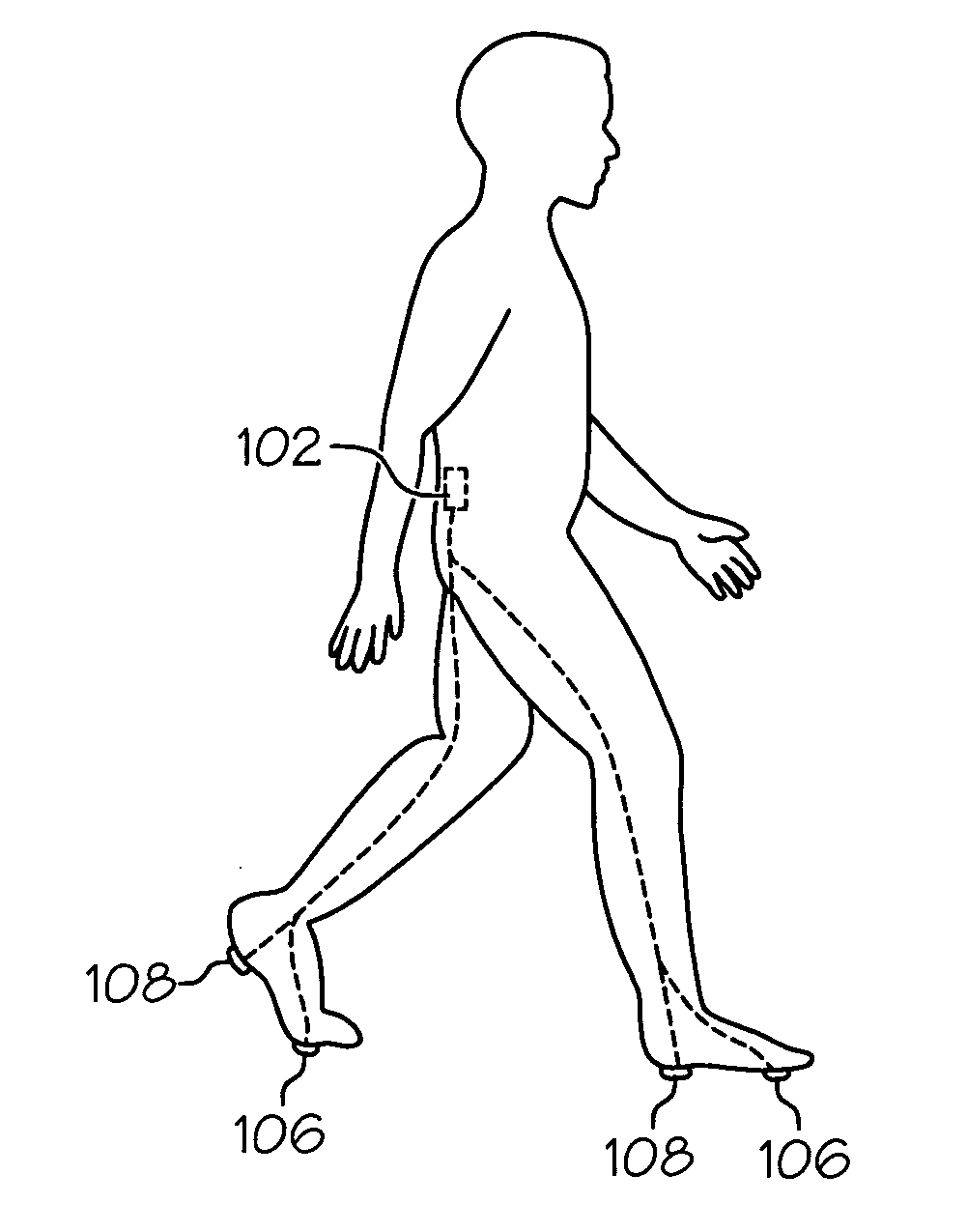
Authentication and human recognition transaction using a mobile device with an accelerometer
ActiveUS20110159850A1Discounts/incentivesUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionAccelerometerMobile device
Methods, devices, and systems are presented for screen locking or delaying the screen locking of mobile devices, such as smart phones, based on whether the gait of the current user match that of its true, authorized owner. A user's gait can be measured using accelerometers embedded in the device. Other movements, such as where a user normally goes to work, can be measured using GPS or other positional location data and used to lock or delay locking of the screen.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
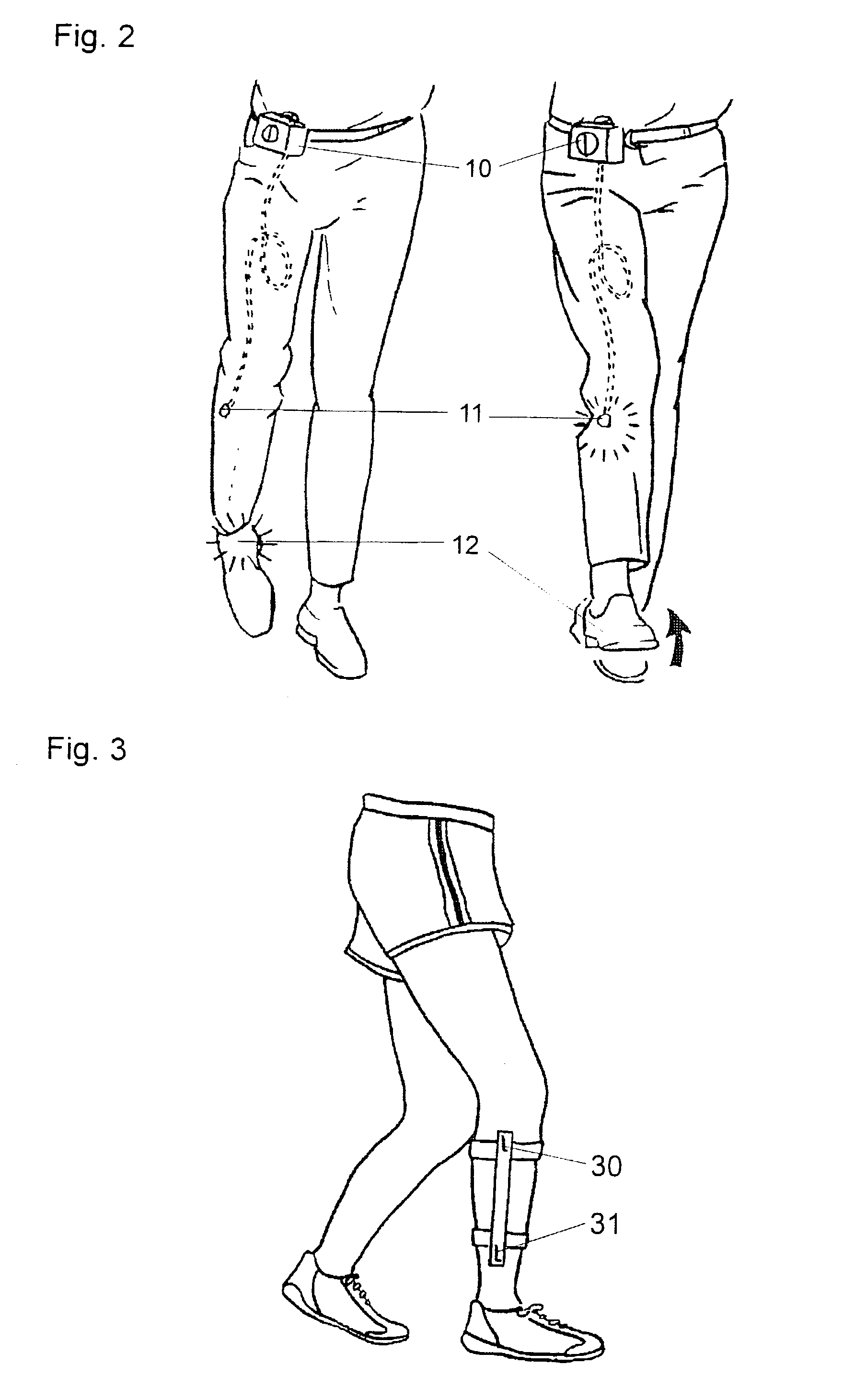
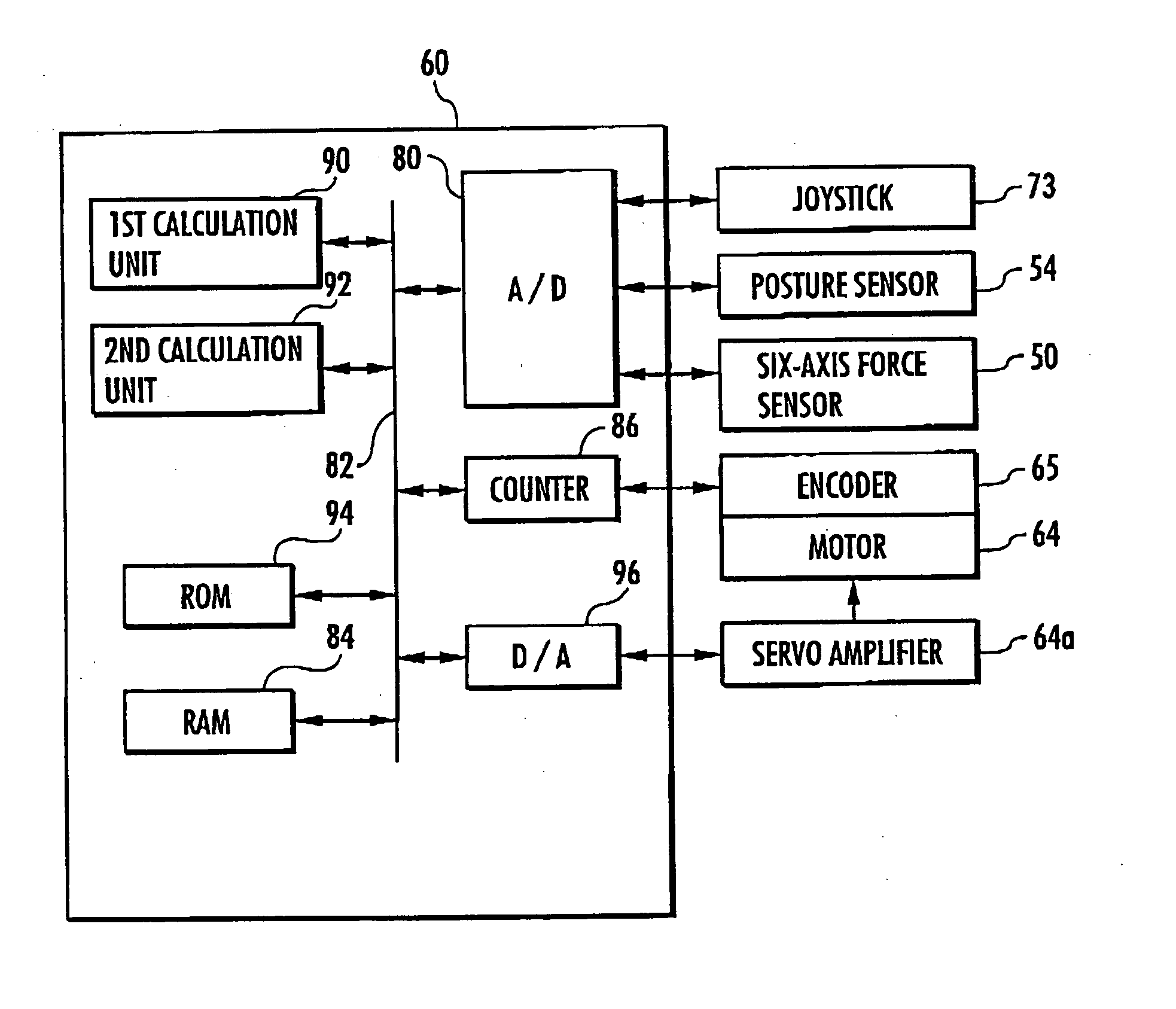
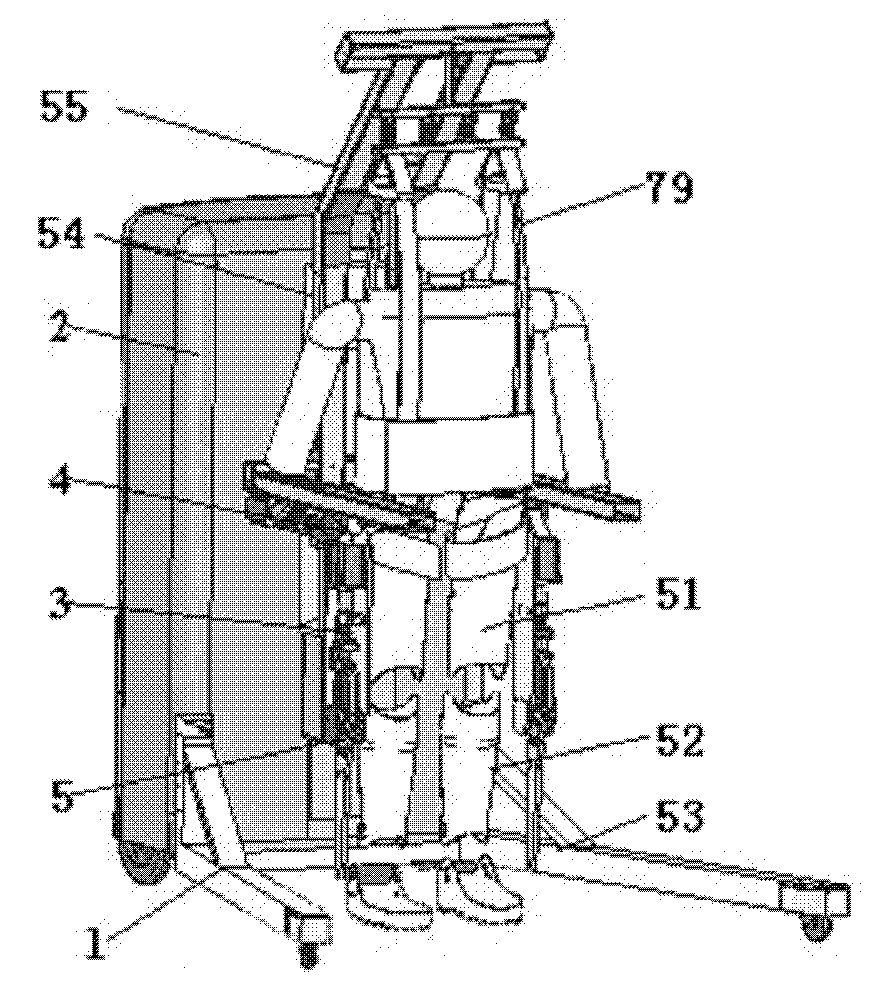
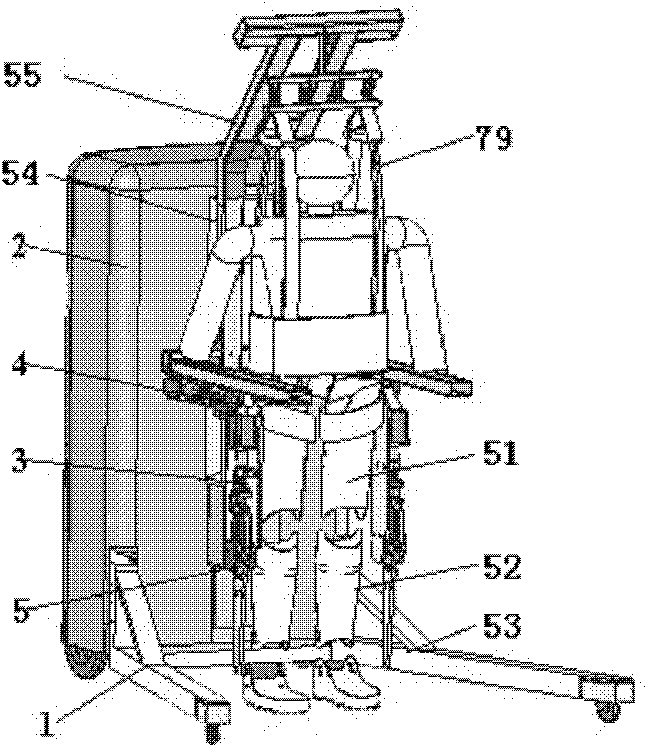
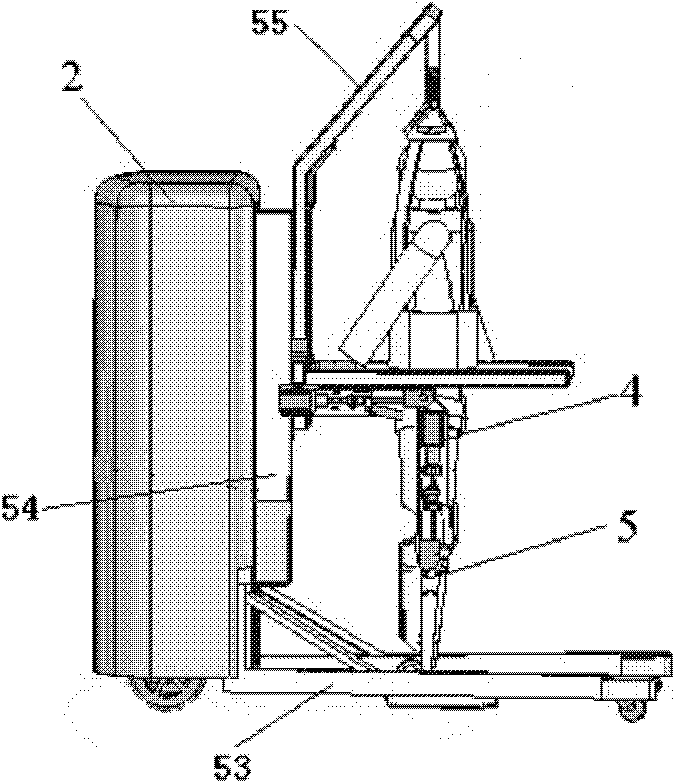
Exoskeleton for gait assistance and rehabilitation
A method of operating an exoskeleton device includes: receiving sensor information; connecting a clutch system to a pulley system in; determining whether to engage a drive train gear to the clutch system based on the sensor information; engaging the drive train gear through the clutch system when determined to engage the drive train gear; and powering a first motor to drive the drive train gear for controlling a joint or segment of exoskeleton device.
Owner:LEONIS MEDICAL CORP
Wearable device having feedback characteristics
ActiveUS20090024062A1Avoid injuryImprove rigidityElectrotherapyStrain gaugeEngineeringSacroiliac joint
A wearable device having feedback characteristics including a compliant article that is arranged to extend over an anatomical portion of a wearer. Sensors provided with the wearable device detect the orientation of a joint and send signals to a processor for analysis. When the processor determines that the joint is in an unsafe or potentially injurious configuration, a feedback or response mechanism is activated to alert the user to such a condition and / or to provide substantially rigid structural support to the joint. The device may also be used to condition users to maintain the joint in proper orientations to avoid injuries, or to condition an amputee to use more effective motions to achieve a more natural gait.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Method and implantable systems for neural sensing and nerve stimulation
InactiveUS7403821B2Easy to controlIncrease stimulationSpinal electrodesEndoradiosondesControl signalSacral nerve stimulation
The present invention relates to methods and apparatuses for the detection of neural or muscular activity, analysis of the signals and the subsequent stimulating of neural or muscular tissue based thereon. According to a first aspect of the invention an apparatus for producing a muscular action is provided, comprising a combined sensing and stimulation electrode device comprising at least one neurosense electrode means capable of sensing a nerve signal from a peripheral nerve and at least one stimulation electrode means capable of stimulating a peripheral motor nerve fiber, means for receiving and processing the sensed neurosignals to identify a signal indicative of a specific action, especially a component of the gait performed by the patient and for producing a control signal in response thereto, and means for operating the at least one stimulation electrode means in response to the control signal to produce a stimulation of a peripheral motor nerve fiber.
Owner:NEURODAN A S
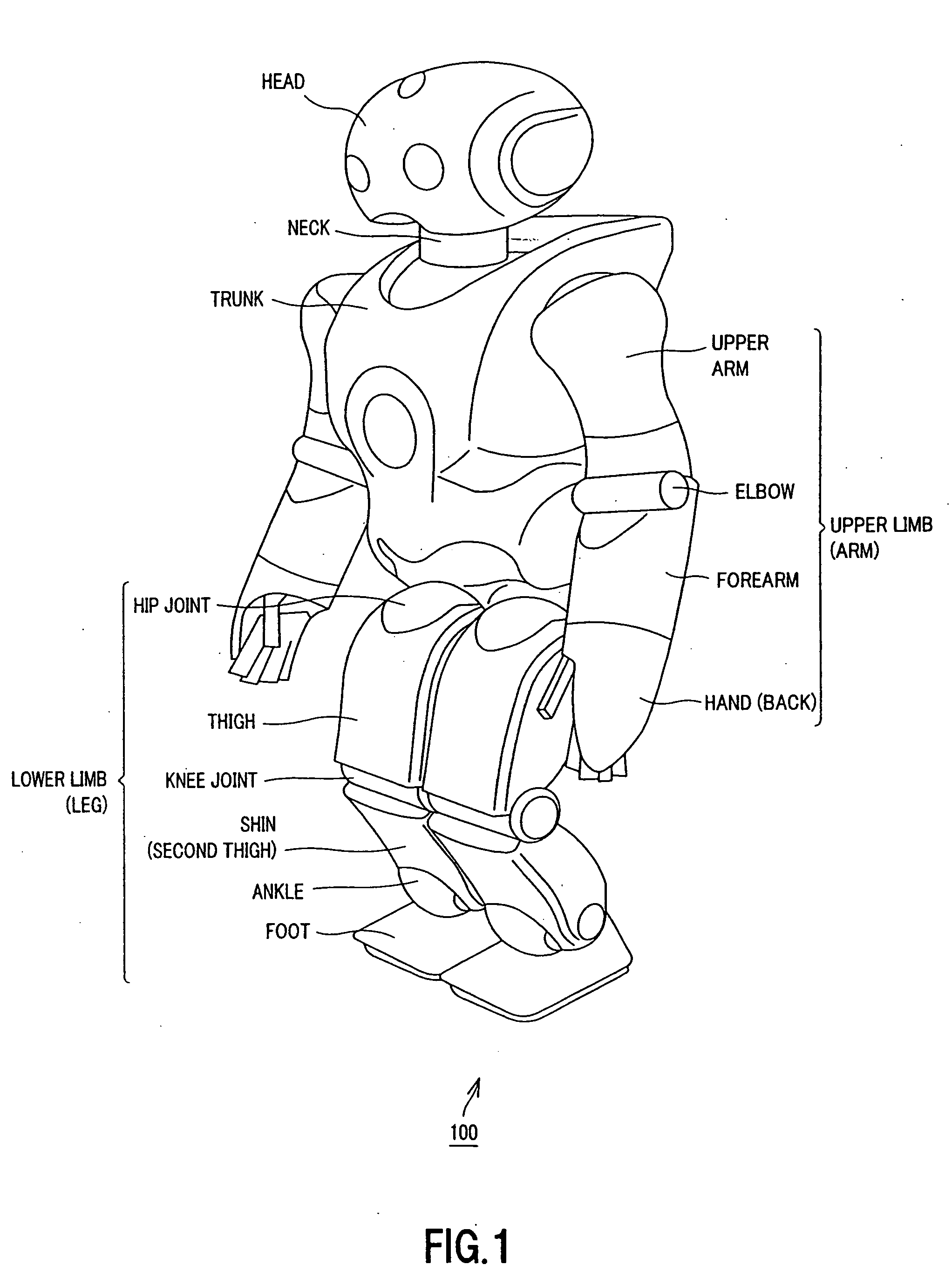
Motion editing apparatus and method for robot device, and computer program
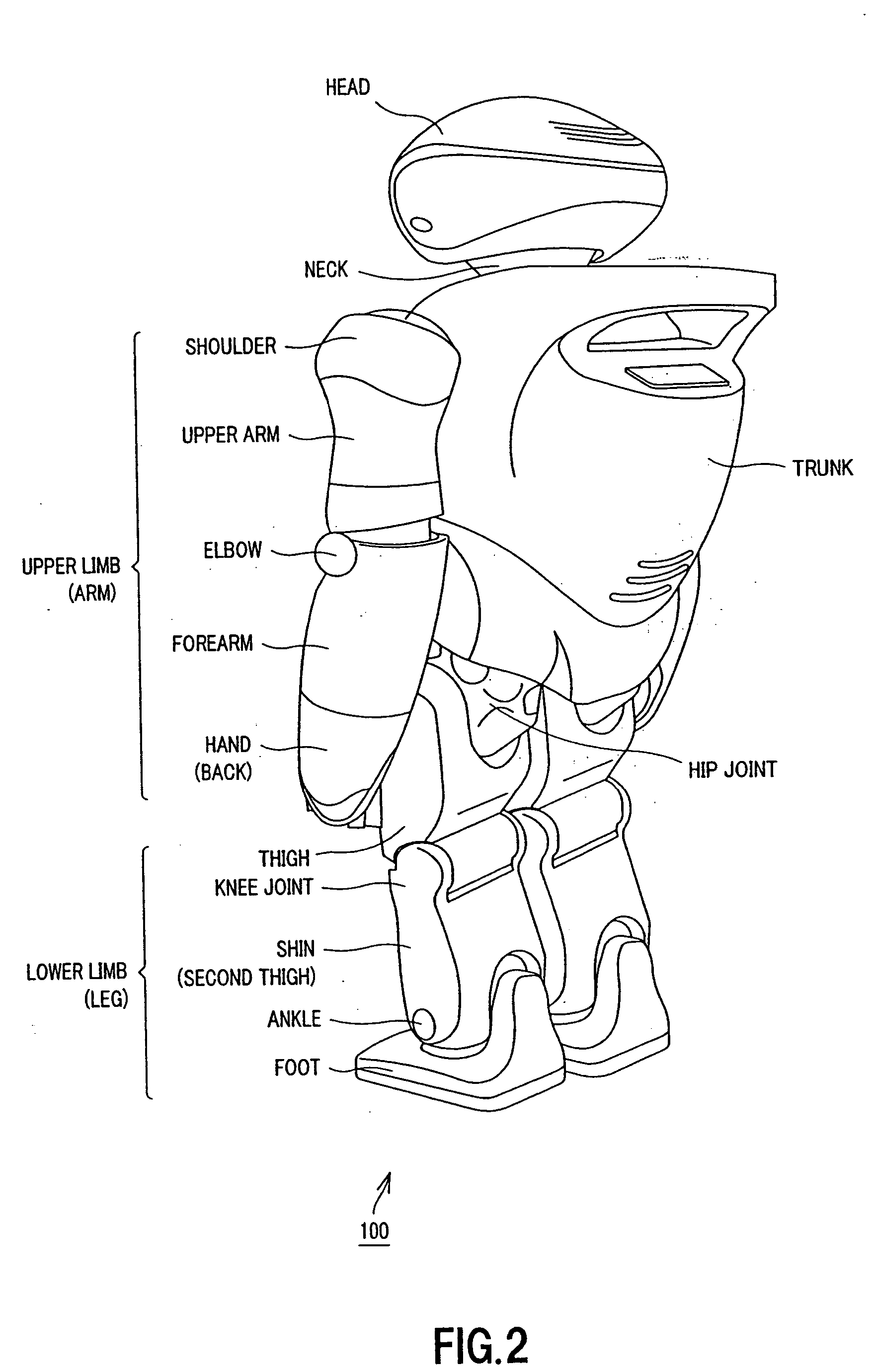
ActiveUS20050125099A1Motion is lowEasy to editProgramme-controlled manipulatorArtificial lifeWhole bodySimulation
To implement a dynamic, elegant motion performance of an actual robot, a motion editing system is provided which includes a motion editor to edit motions of an upper body and whole body of the robot and a foot trajectory editor to create a gait pattern and lower-body motion to stabilize the entire robot. The foot trajectory editor includes the same gait pattern generator and motion stabilized as those installed in the actual robot. Before performing the edited motions on the actual robot, the motions are created, corrected and stabilized on a 3D viewer.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Gait Rehabilitation Methods and Apparatuses
InactiveUS20080234113A1Assist with balance trainingEntry and exit can be easedElectromyographyChiropractic devicesGait
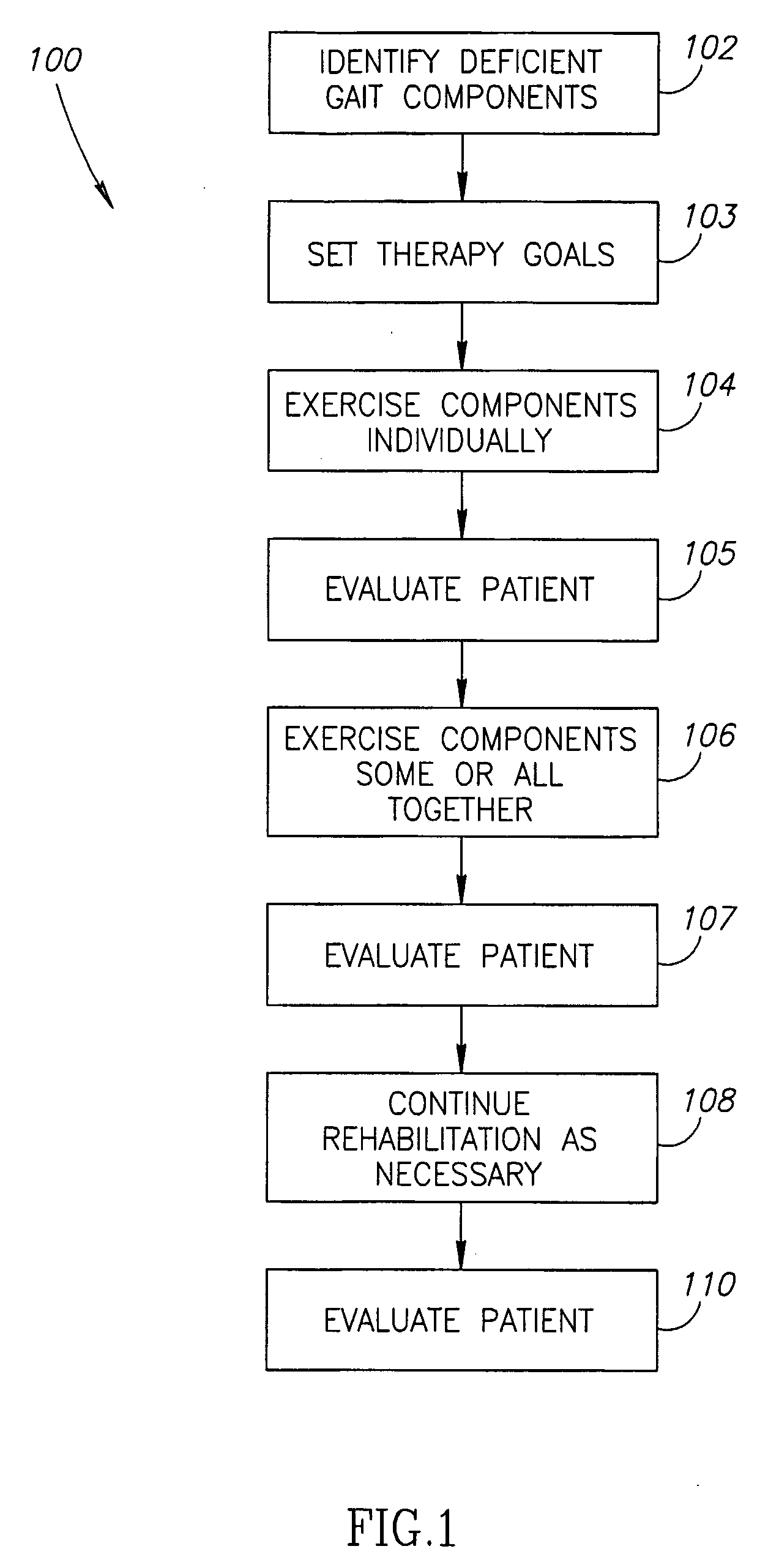
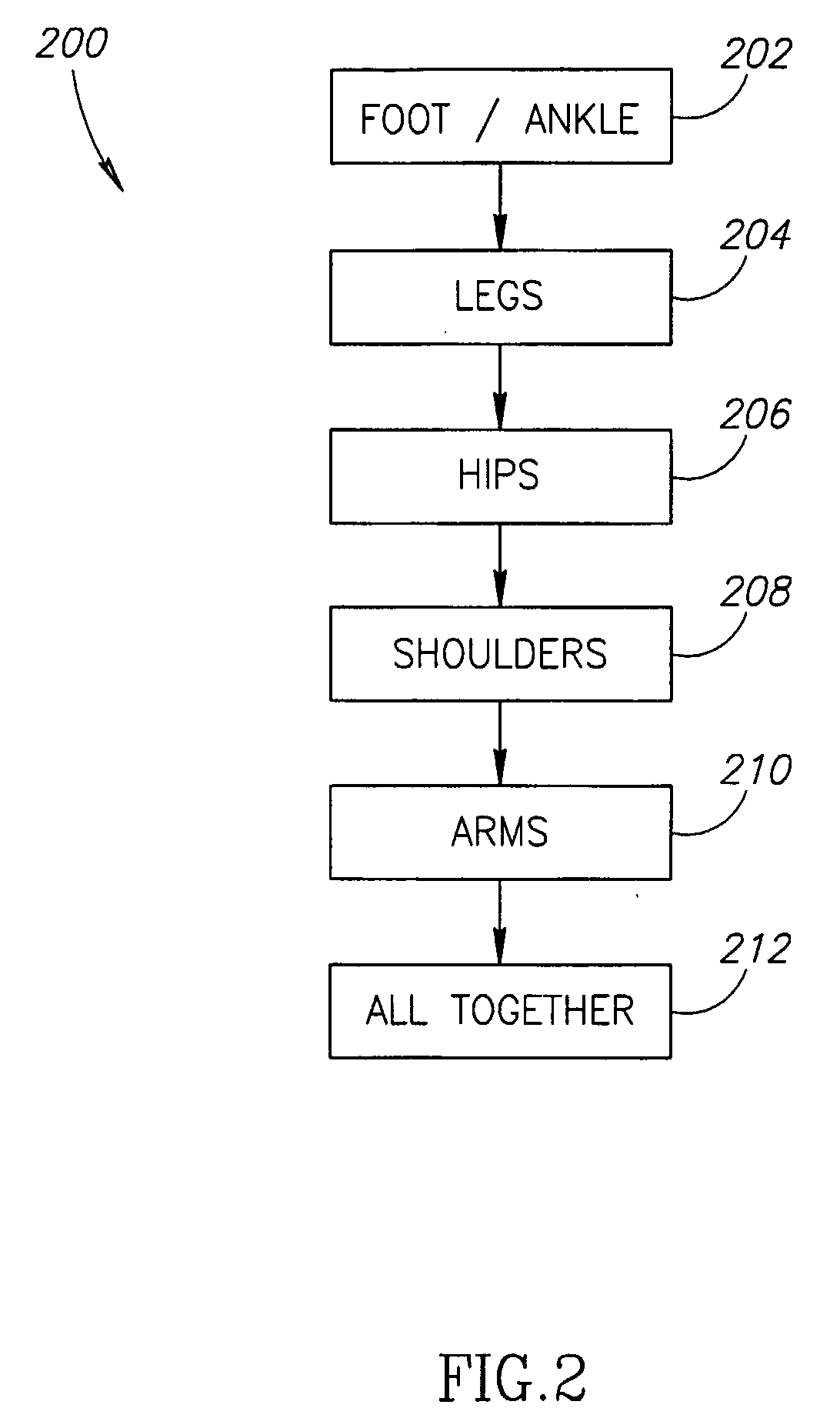
A method for gait rehabilitation, comprising, identifying at least one deficient gait element; exercising said deficient gait element individually using a rehabilitation apparatus; and exercising said deficient gait element in concert with at least one other gait element using said rehabilitation apparatus.
Owner:MOTORIKA
Ambulatory suspension and rehabilitation apparatus
An ambulatory suspension system for gait rehabilitation has a parallel pair of rails bordering the sides of a training area and a bridge extending between and movable along the rails. A trolley is movable along the bridge and includes a motor driven hoist with a cable extending thereabout and depending from the trolley. The hoist is operable to vary the length of the cable depending from the trolley, and a harness is suspended by the cable. Motors move the bridge along the rails and the trolley along the bridge as the sensors sense the direction of movement of the patient in X and Y directions. The falling motion of a patient supported in the harness is sensed and will immediately disable the system. A computer control receives signals from the sensors and operates the motors so that the patient is held in an upright position.
Owner:HARTFORD THE UNIV OF +1
Robotic gait rehabilitation by optimal motion of the hip
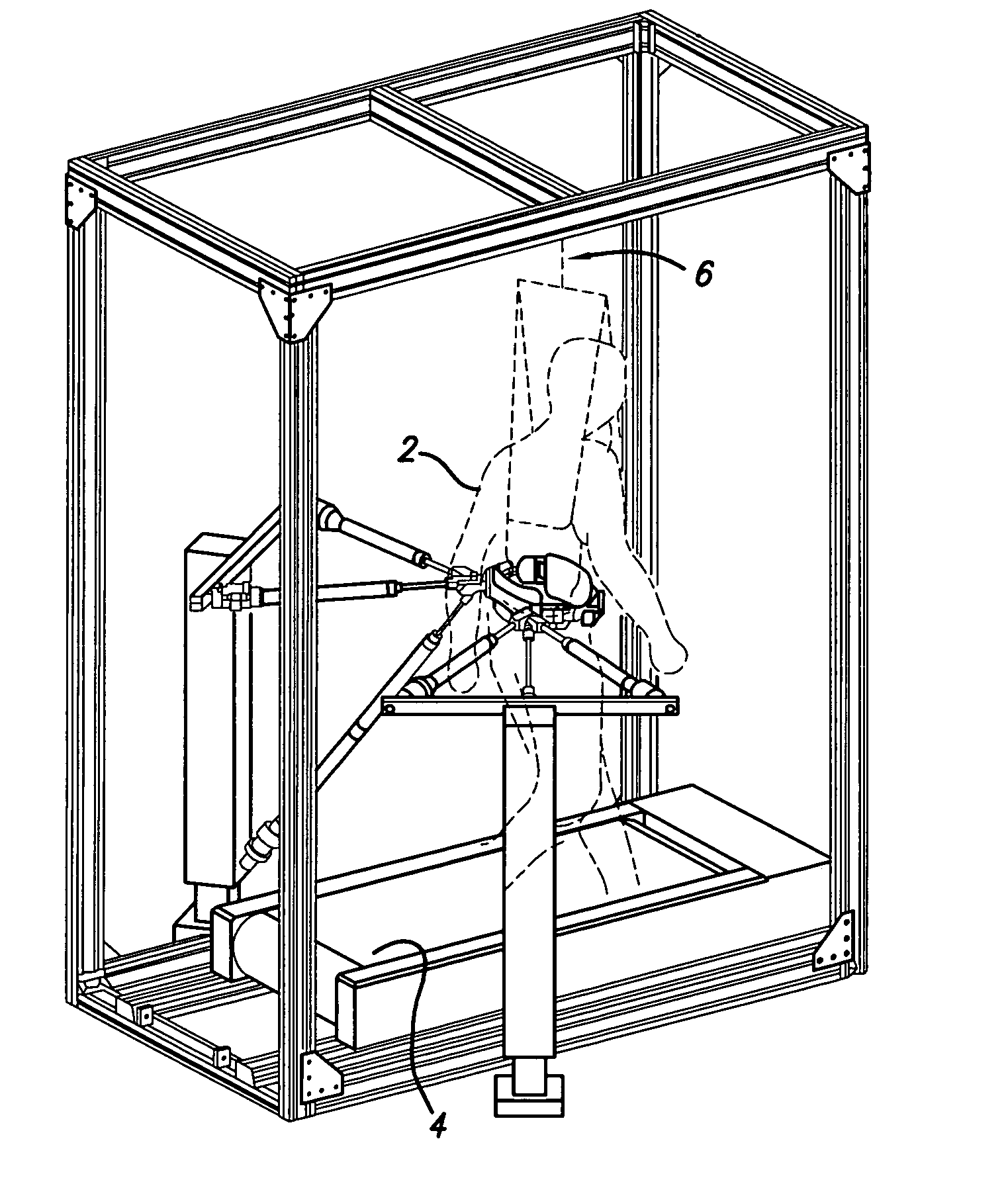
A method and a robotic device for locomotion training. The method involves shifting a subject's pelvis without directly contacting the subject's leg, thereby causing the subject's legs to move along a moveable surface. The device comprises two backdriveable robots, each having three pneumatic cylinders that connect to each other at their rod ends for attachment to the subject's torso. Also provided is a method of determining a locomotion training strategy for a pelvic-shifting robot by incorporating dynamic motion optimization.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
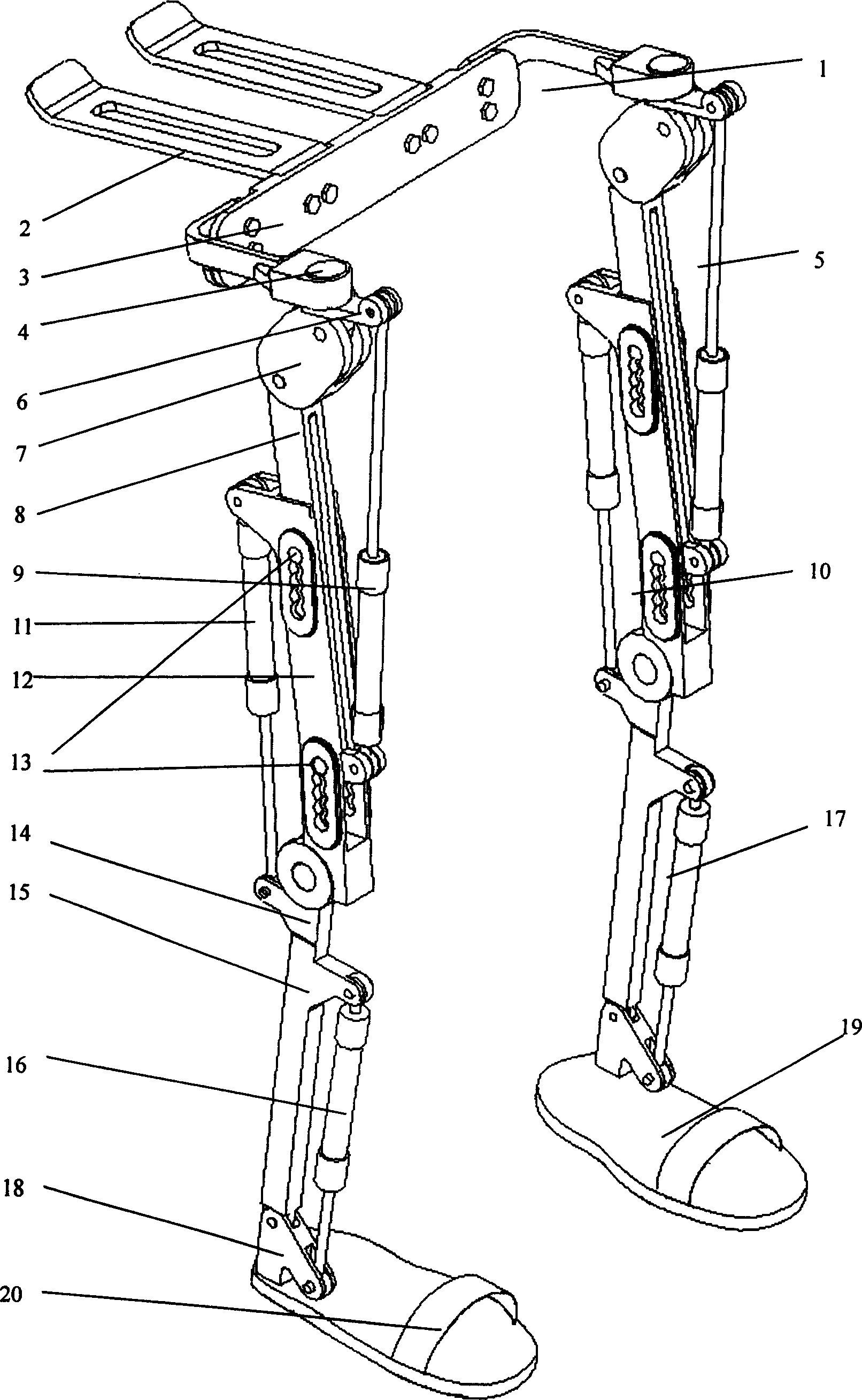
Lower limb walking external skeleton capable of being worn
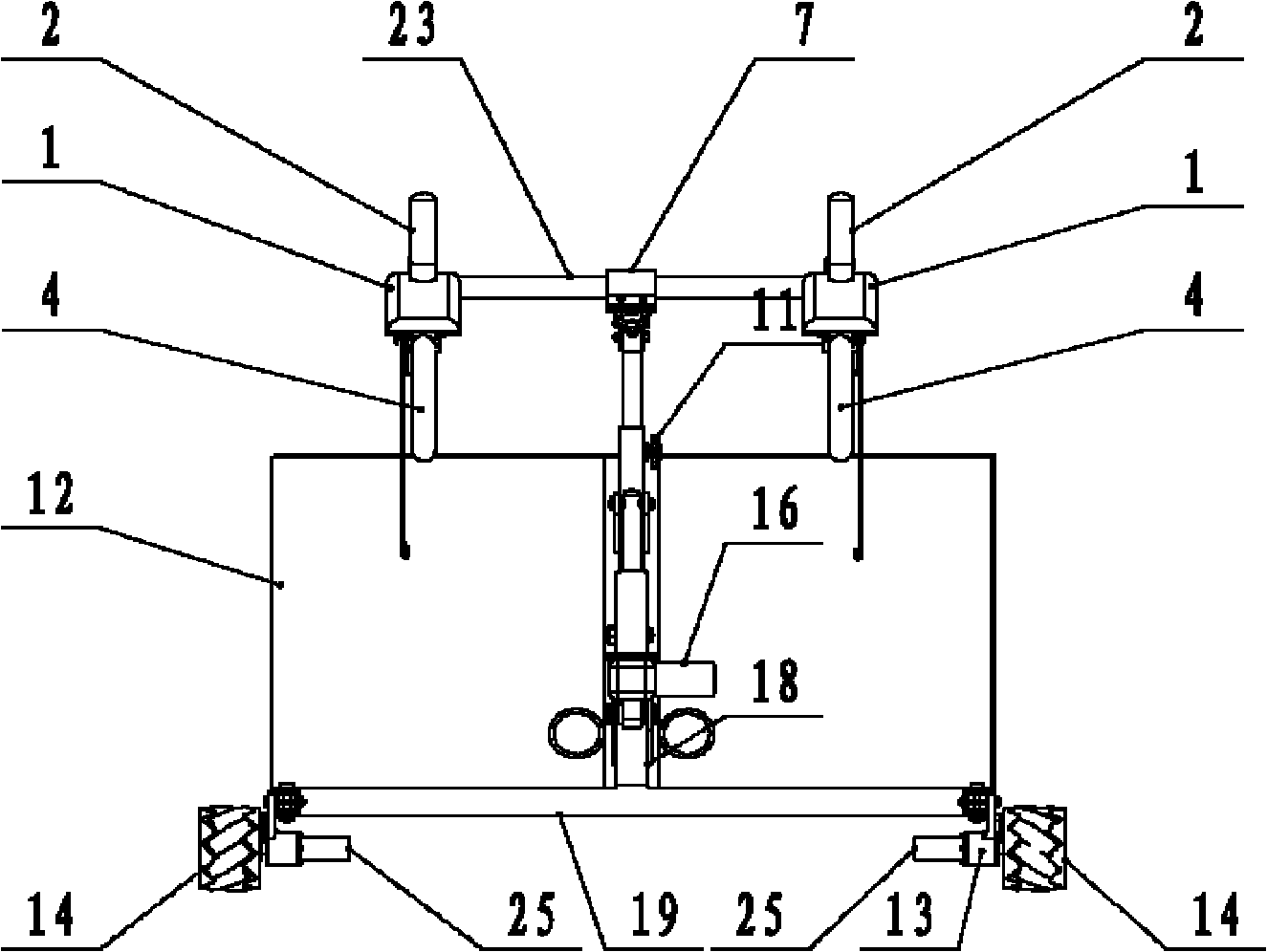
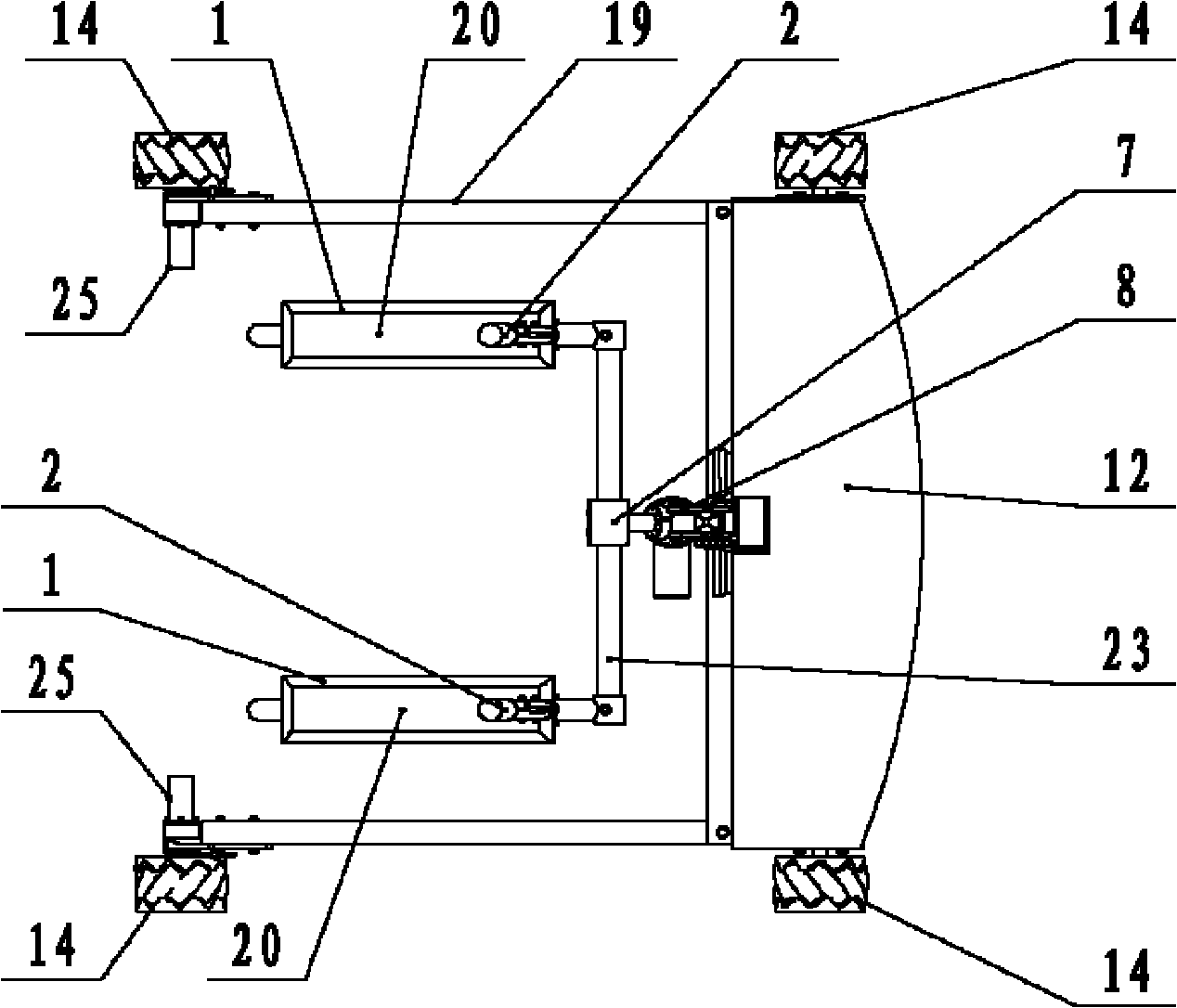
InactiveCN1586434AEnhance walking abilityReduce fatigueArtificial legsMuscular dystrophyHuman motion
The wearable lower limb walking external skeleton consists of waist support, four-rod hip mechanism, four-rod knee mechanism, four-rod heel knee mechanism and planta support connected successively. For amputated patient or muscular dystrophy patient, the present invention has auxiliary program written in advance for assisting walking. For tourist and the weak, the present invention is worn and the wearer walks, so that the displacement sensors acquires the motion gesture signals of the wearer, and the gait is recorded in the computer and copied to strengthen the walking ability of the wearer. The present invention is used as the walking aid for the patients and the equipment for walking tourist.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Enhanced system and method for assessment of disequilibrium, balance and motion disorders
A system and method for providing therapy and assessment utilizing vibrotactile feedback is disclosed. Such treatment is useful for the assessment and treatment of disequilibrium, movement and balance disorders. The system and method measures a subject's performance of predetermined tasks with respect to expected parameters using sensors such as force plates, inertial sensors, and three dimensional cameras. Predetermined motions are motions such as stand, sit-to-stand, reach, bend, functional gait, functional gait plus headshake, and other functional tasks. Vibrotactile stimulation may be applied during the subject's performance as disruptive input. Variance and rate of change of variance between measured and expected parameters is used as a tool for assessment of said subject, and is also used for providing real-time vibrotactile training to said subject. The invention is useful in the treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI), neurologic disorders causing disequilibrium and balance disorders, and the like.
Owner:ENG ACOUSTICS
Retail store motion sensor systems and methods
ActiveUS20160180440A1Physical therapies and activitiesDiagnostic recording/measuringMovement activityComputer module
A method for providing a recommendation to an individual about an article of footwear includes receiving data about the individual from a sensor module associated with the individual during a first athletic activity engaged in by the individual, determining a first characteristic about the individual's gait based on the data related to the first athletic activity, providing a recommendation about a first article of footwear to the individual based on the first characteristic, receiving data about the individual from the sensor module associated with the individual during a second athletic activity engaged in by the individual, determining a second characteristic about the individual's gait based on the data related to the second athletic activity, comparing the first characteristic with the second characteristic, and providing a recommendation about a second article of footwear to the individual based on the comparison.
Owner:ADIDAS
Force sensor system for use in monitoring weight bearing
InactiveUS20060282017A1Quality improvementNormalize gait patternElectrotherapySolesEngineeringBiological activation
A force sensor system for use in monitoring weight bearing on a location. The force sensor system comprises at least one a foot force sensor, a palm force sensor, and a knee force sensor. The foot force sensor comprises a flexible insole containing a plurality of inflatable pockets that are inflated with air or liquid. The palm force sensor and knee force sensor each comprise a wrap to be worn around the palm and knee, respectively. Each wrap comprises a pocket. Each pocket is connected to a tube that, in turn, connects with a pressure sensor and a connector coupling that is remote from the pocket. Each coupling contains a valve. The valve opens to allow inflation and deflation of each inflatable pocket. The pressure sensors measure the air or liquid pressure within each of the inflatable pockets, and convert the corresponding pressure signal into a suitable output signal medium, usually electrical signals. The output signal from the sensors provides accurate real time input data to a weight bearing biofeedback system or to control a stimulator for activation of an electronic orthosis to normalize dynamic gait patterns.
Owner:ANDANTE MEDICAL DEVICES
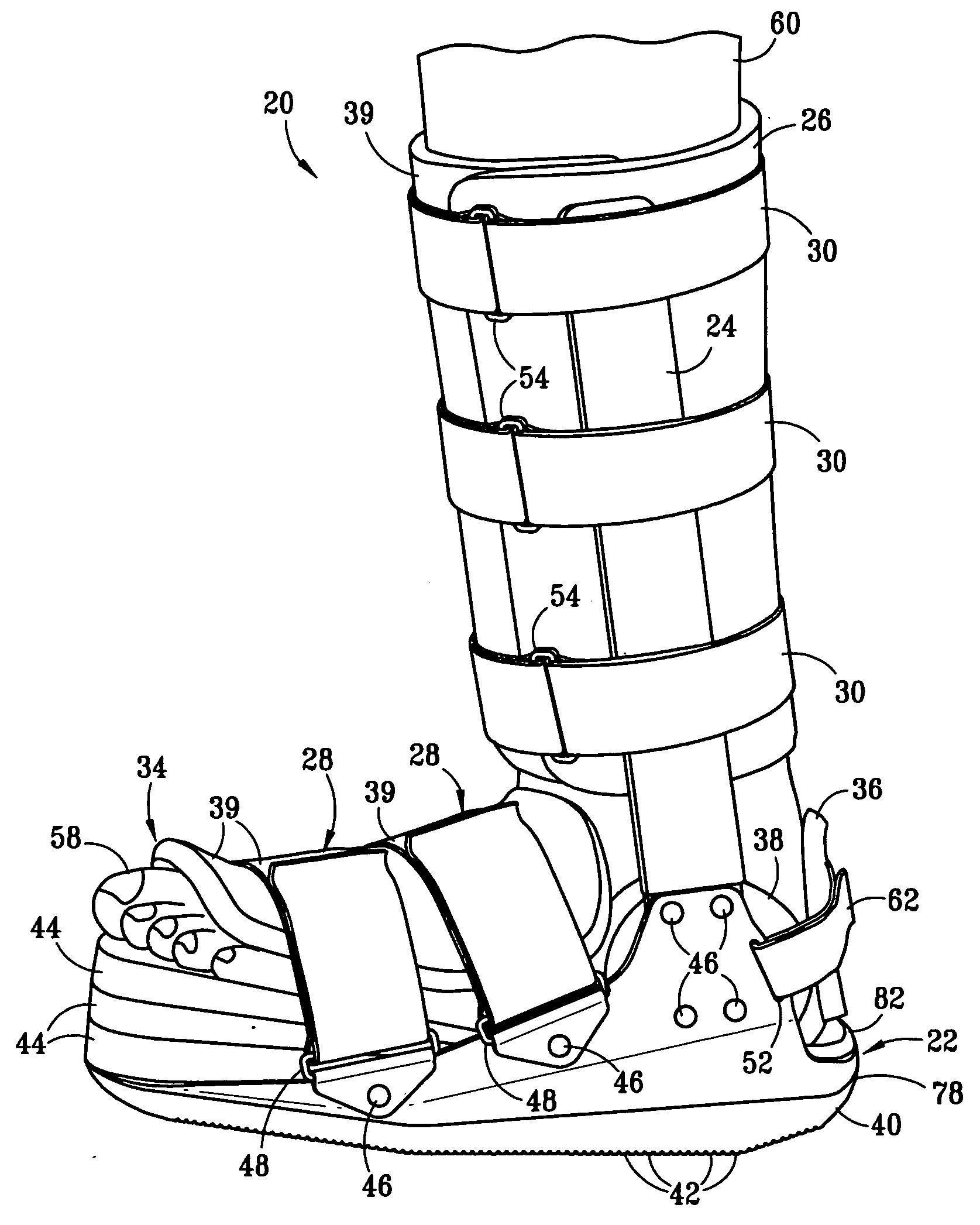
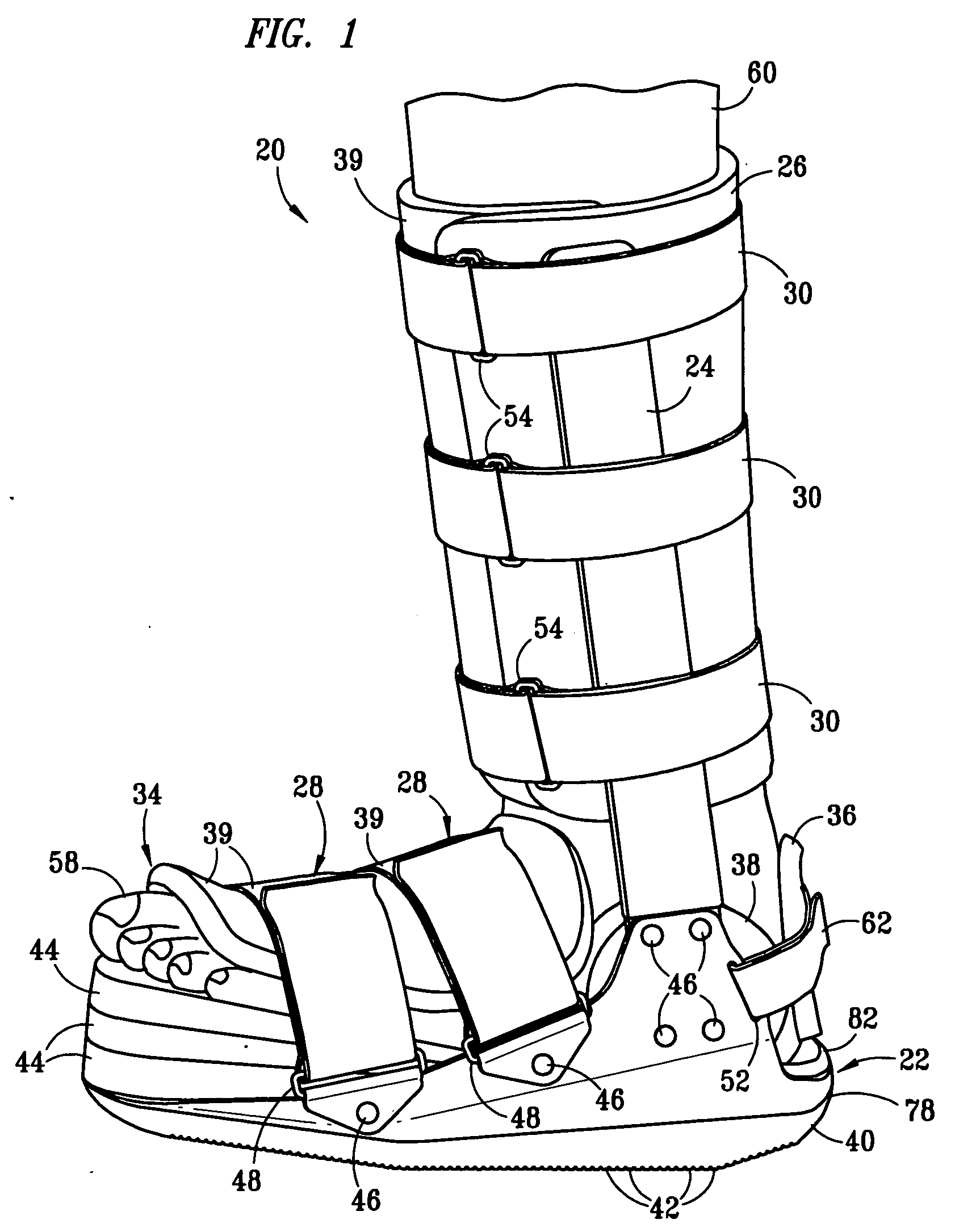
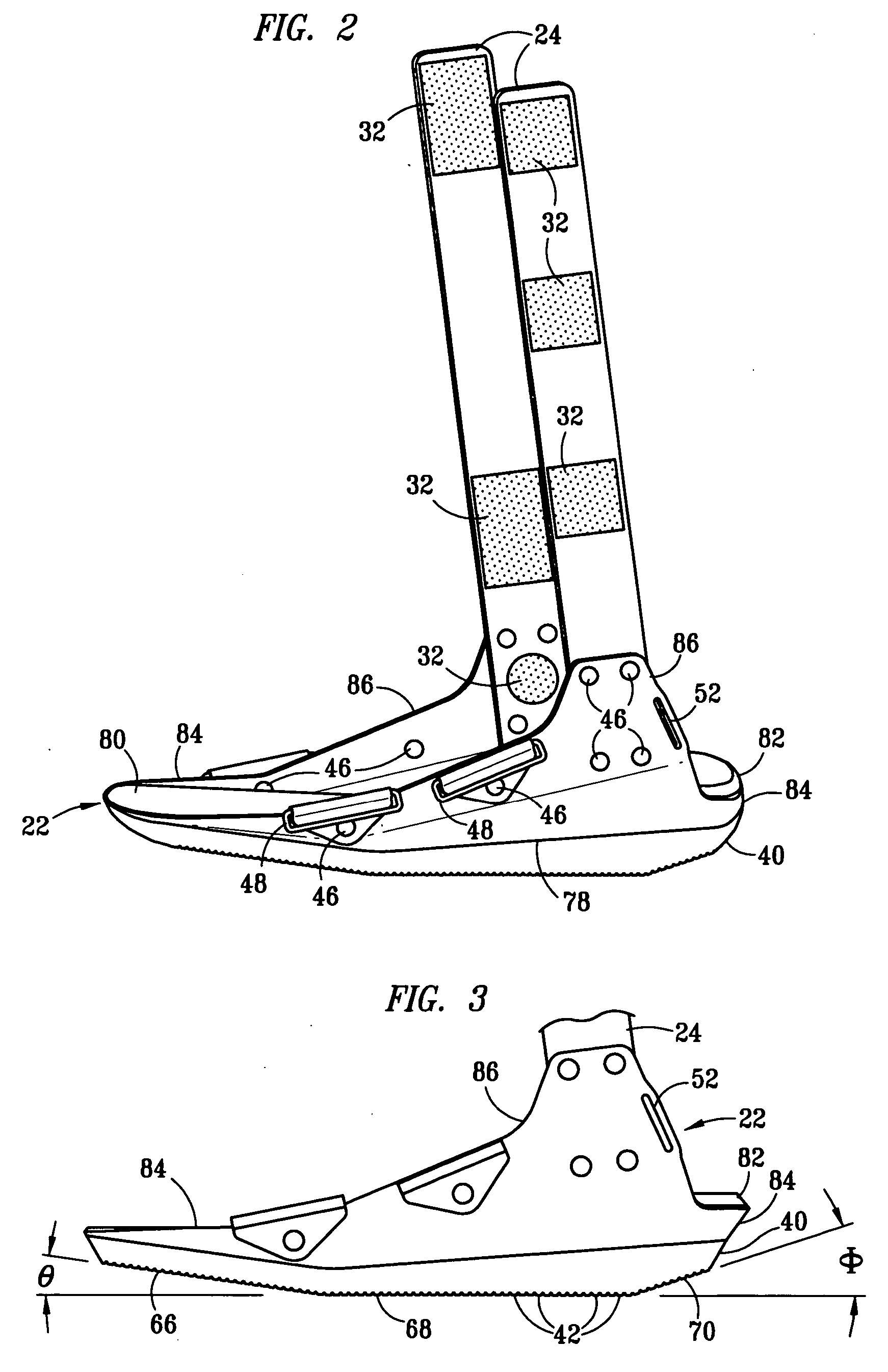
Boot for treatment of plantar fasciitis
InactiveUS20050131324A1Avoid attenuationMinimize further damageNon-surgical orthopedic devicesGaitFoot dorsiflexion
A boot for use in the treatment of plantar fasciitis. The boot places the foot in the desired amount of dorsiflexion, preferably from 5° to 20°, which stretches the Achilles tendon and is believed to prevent the shortening of the plantar fascia. The boot also provides protection for the foot while walking or engaging in other load bearing activities, to minimize further damage to and / or inflammation of the plantar fascia. The boot has a sole that is shaped to allow as close to a natural walking gait as possible while maintaining the foot in the desired degree of dorsiflexion. Preferably, the amount of dorsiflexion of the foot is controlled through the addition wedges on the base of the boot.
Owner:MEDICAL TECH
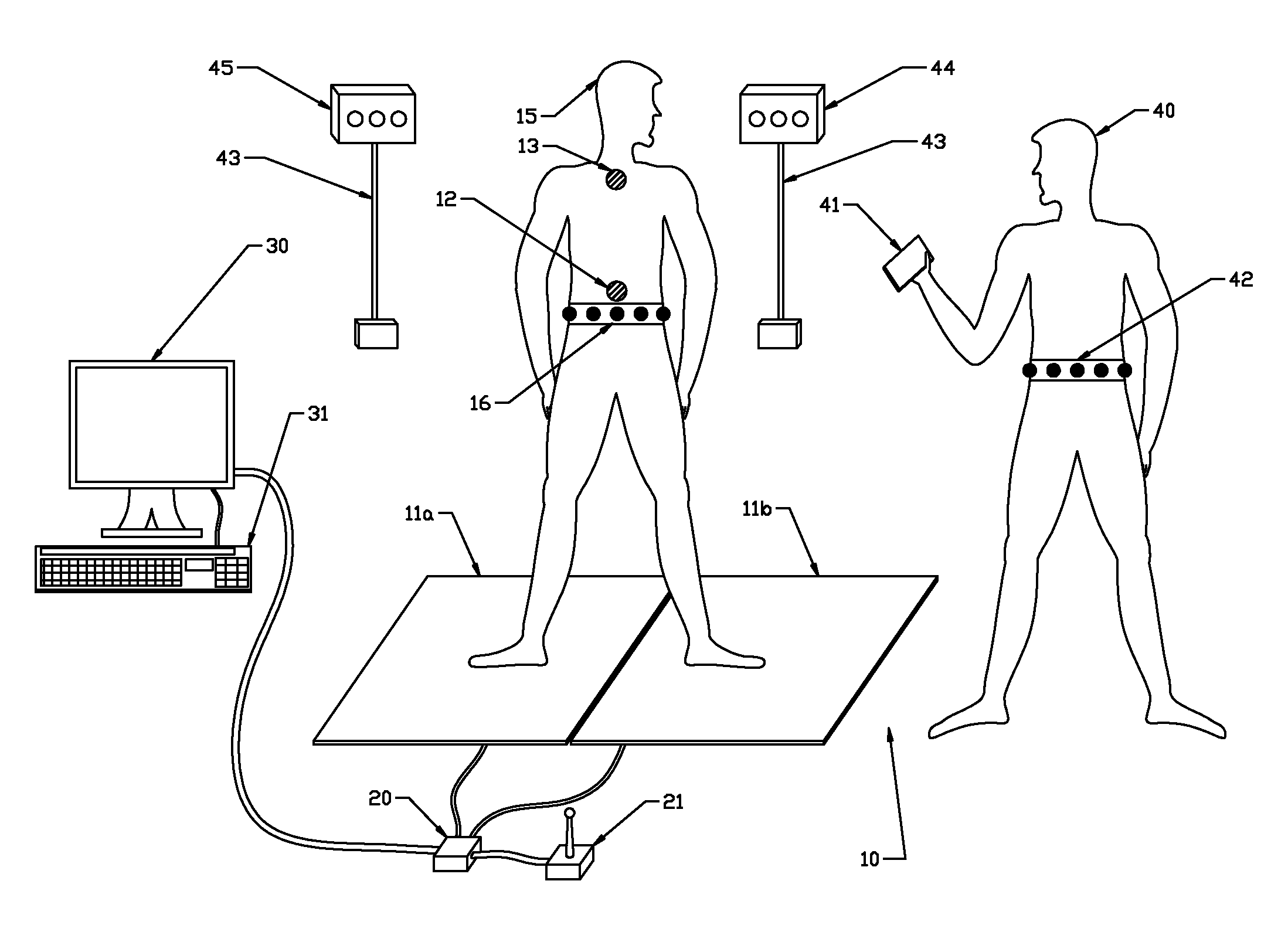
Method and system for assessing locomotive bio-rhythms
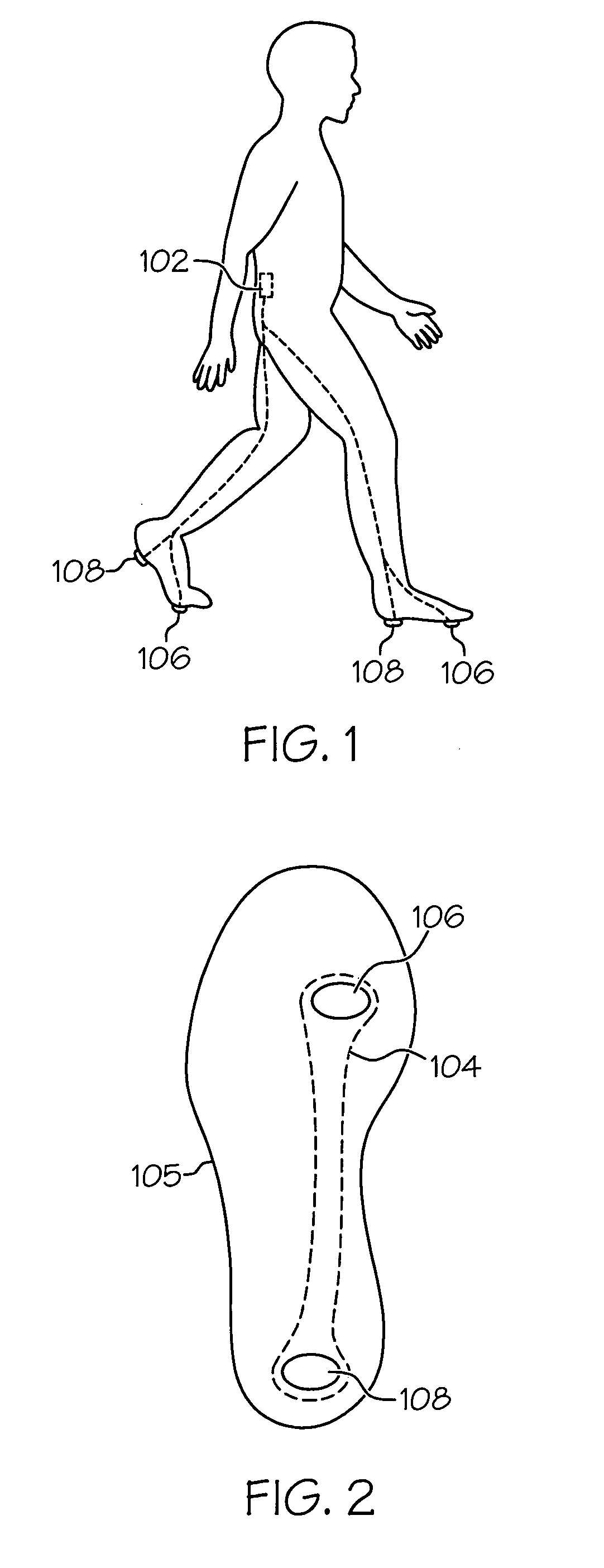
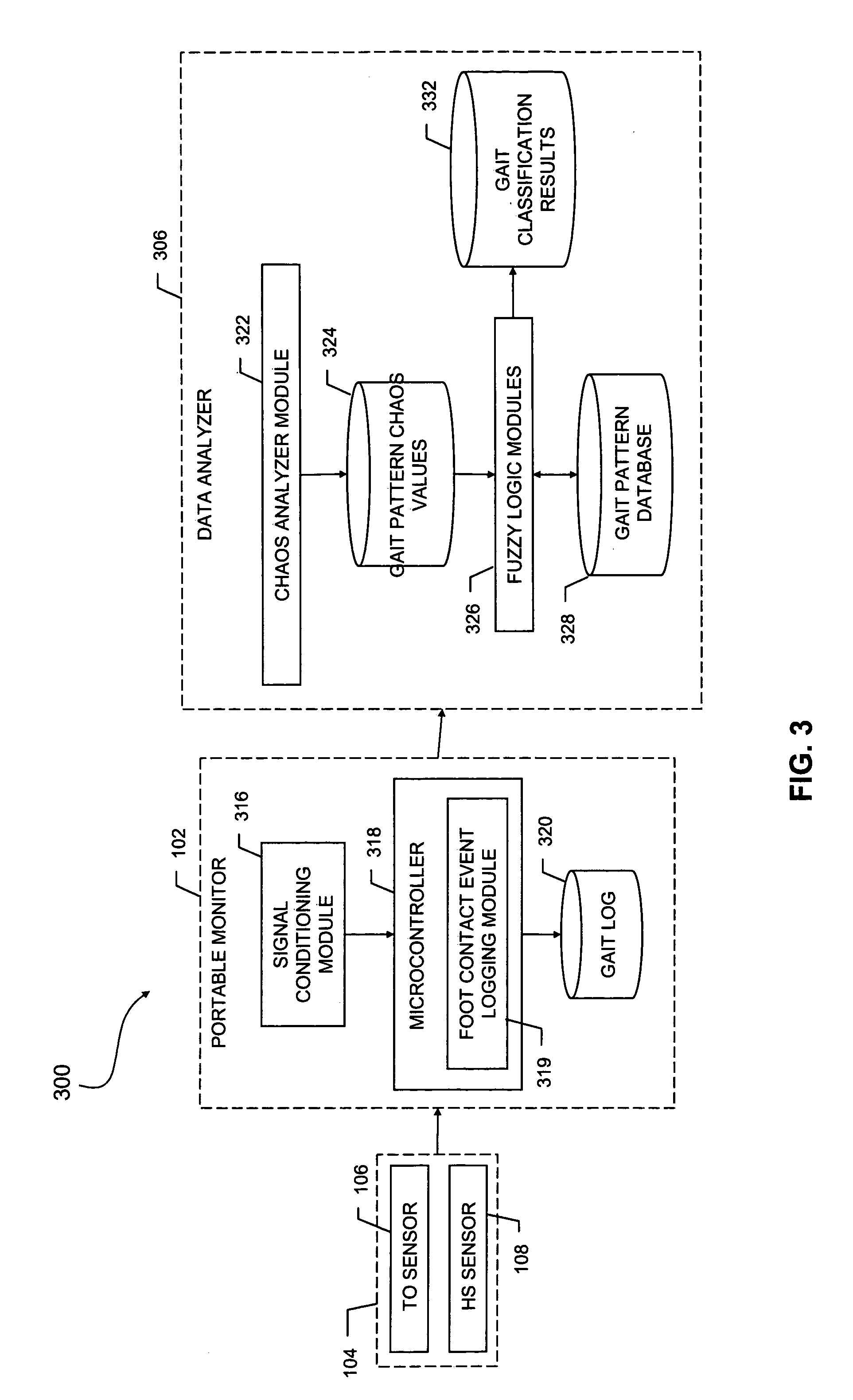
A method, system, and article of manufacture for detecting, recording, quantifying, and classifying gait data. In one embodiment, the method of the invention includes a step of detecting foot contact events using a portable sensor device. Stride data is collected by processing the detected foot contact events to obtain and record gait pattern data. At least one gait stability value is determined from the gait pattern data using a specified gait stability metric. The gait stability value is preferably a mathematical chaos value which is processed utilizing clustering correlation to classify the gait pattern data in association with a neuromuscular status. In a preferred embodiment, fuzzy logic is utilized to correlate the determined gait stability value with a plurality of gait stability values each associated with a distinct neuromuscular status.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Variable-impedance lower limb rehabilitation robot control method based on brain muscle information
ActiveCN105213153AHigh precisionReal-time recovery assessmentGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesFeature vectorMan machine
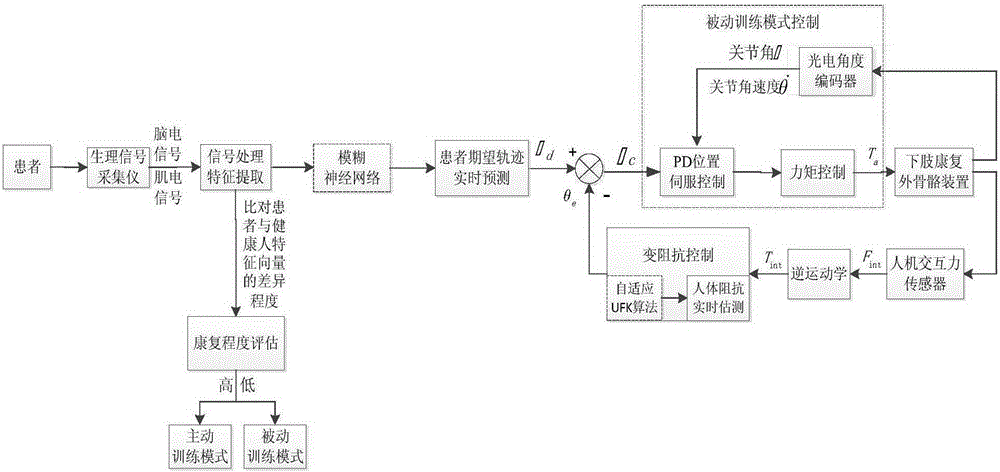
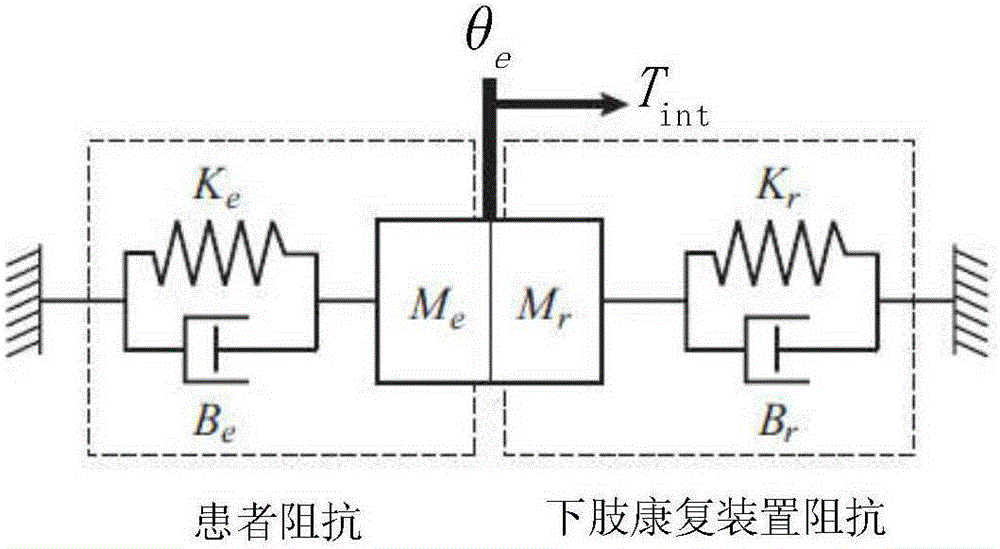
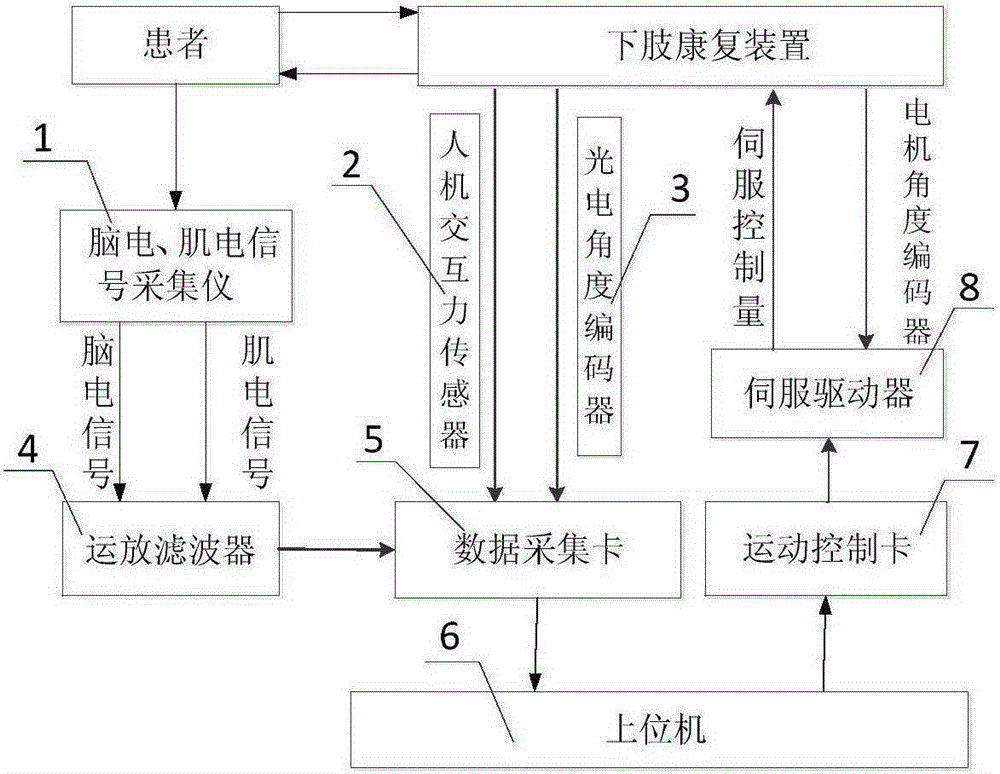
The invention discloses a variable-impedance lower limb rehabilitation robot control method based on brain muscle information. The method includes: collecting electroencephalogram and surface electromyogram signals of a patient in real time through an electroencephalogram and surface electromyogram signal collector, and monitoring and evaluating rehabilitation degree of the patient; adopting different rehabilitation training strategies; when the rehabilitation degree is low, implementing passive training control, adopting a PD position servo control method, and controlling a lower limb rehabilitation device to enable the patient to move with a correct physiological gait track; when the rehabilitation degree is high, adopting an active control mode, and predicting a movement intention of the patient by extracting feature vectors of electroencephalogram signals and surface electromyogram signals of the patient in real time; using a fuzzy neutral network algorithm to integrate the electroencephalogram signals and the surface electromyogram signals to generate a movement gait track curve expected by the patient in real time; utilizing a variable-impedance control method to realize active, realtime and synergistic control of a lower limb rehabilitation robot man-machine system.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Wearing type dynamic real-time fall detection method and device
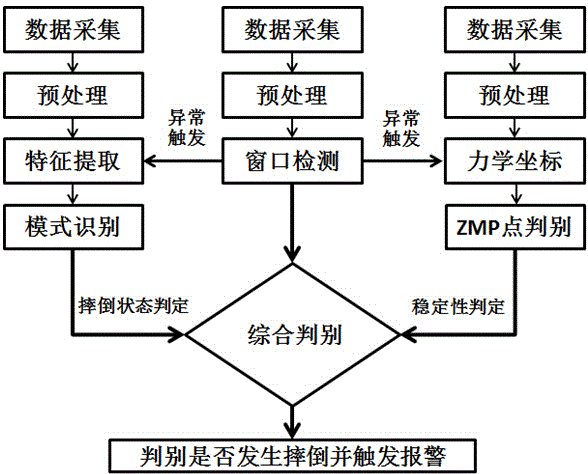
ActiveCN103976739AAchieve protectionHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman bodyHardware structure
The invention discloses a wearing type dynamic real-time fall detection method and device. The wearing type detection device comprises a specific hardware structure consisting of a foot part, a waist part, a wrist part and a back part. According to the dynamic real-time fall detection method, real-time judgment of the fall of human body in any state can be finished. The core algorithm of the detection device comprises a threshold opening logic structure caused by sudden change of gait acceleration, a human body posture dynamic stability judgment algorithm based on zero moment point (ZMP), and a fall mode identification algorithm based on a human body motion database. A complete dynamic real-time detection system is constructed, and the aims of wide application field, low dependence on the application environment and real-time detection are fulfilled. Moreover, the detection method and the detection device are high in accuracy, and have the advantages of low system cost, small system size and good convenience in wearing.
Owner:BEWIS TECH
Prosthetic leg having electronically controlled prosthetic knee with regenerative braking feature
InactiveUS7485152B2Augment other portionReducing necessary energy expenditureArtificial legsRegenerative brakeElectronic control system
A prosthetic leg having an electronically controlled regenerative prosthetic knee. In certain embodiments of the present invention the knee may be passive, whereby it is used only to generate electrical energy. In other embodiments, the knee may be active, whereby it can be used to assist with or completely control gait, as well as to generate electrical energy. The knee makes use of an actuator motor / generator to control gait and / or to generate electrical energy. An electronic control system is provided to control overall operation of the prosthetic leg, to distribute generated electrical energy, and to transfer excess electrical energy to one or more storage devices for later use. A prosthetic leg of the present invention having an active prosthetic knee may be especially helpful in assisting an amputee with activities that impart a high torque load to the knee joint.
Owner:WILLOWWOOD GLOBAL LLC
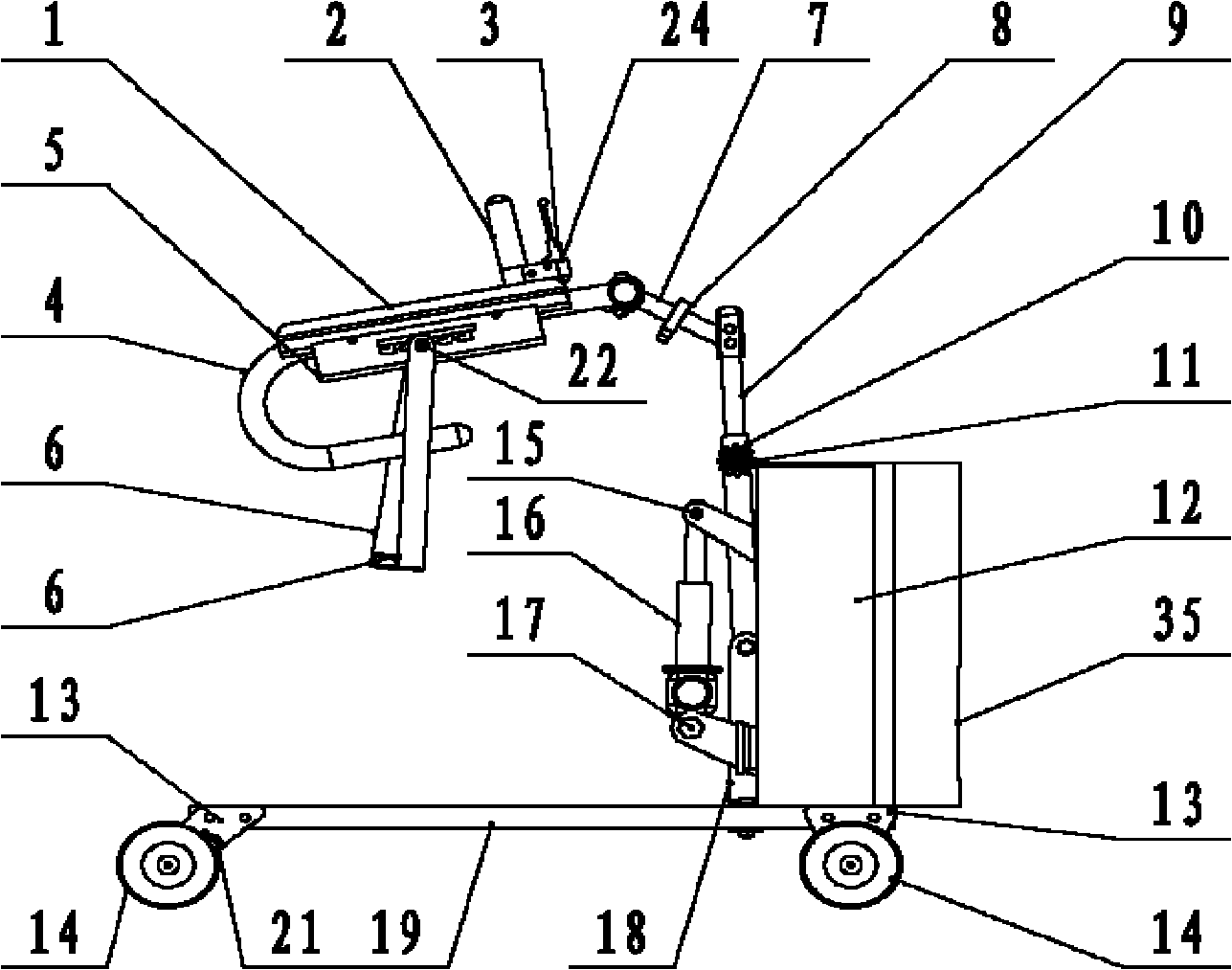
Multifunctional intelligent rehabilitation robot for assisting stand and walk
The invention discloses a multifunctional intelligent rehabilitation robot for assisting stand and walk. The whole robot comprises three parts basically: a mechanical stand assisting device, a chassis moving device and a monitoring control device, wherein the mechanical stand assisting device comprises a support base, a swing arm, an electric push rod and a handrail device; the chassis moving device comprises a base, a motor fixing frame, four Mecanum wheels, a braking ratchet wheel, a braking sheet, and the like; the monitoring control device comprises a force sensor array, a vision sensor, a distance-measuring sensor, and the like; and in addition, the robot also comprises a power source storage battery, and the like. The robot can realize the auxiliary stand and walk assistance to a user, can lift the user up safely and comfortably under the condition of sitting posture, judge the motion intention of the user in the walking process and carry out all-sided collaborative motion; meanwhile, the robot can also detect the moving tread of the user so as to judge the stability of the user and do corresponding assistance to the user at the real time; and the robot can safely and effectively assist patients with lower limbs being injured to carry out rehabilitation training and assist the daily activities of weak old people.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Controller of legged mobile robot
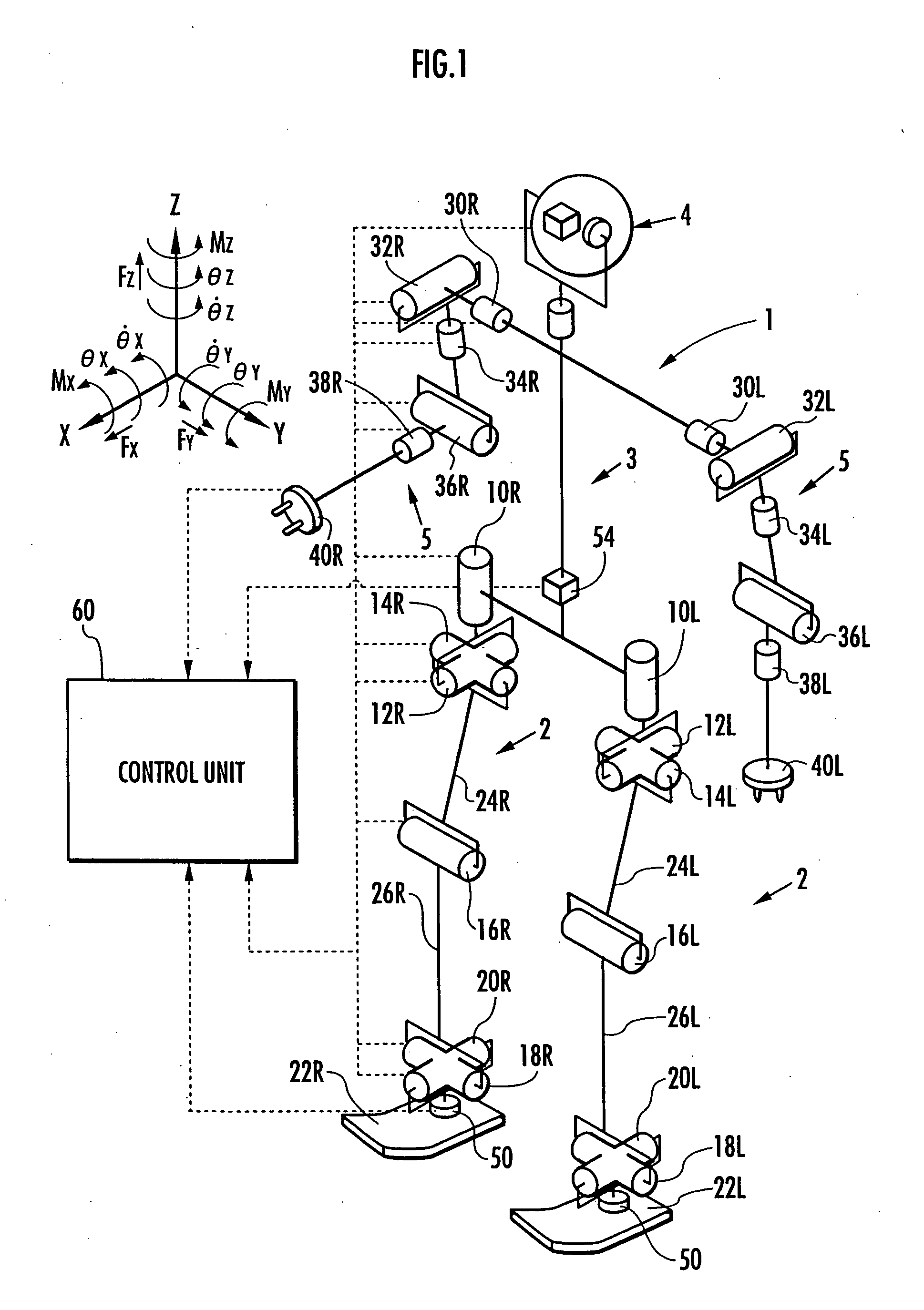
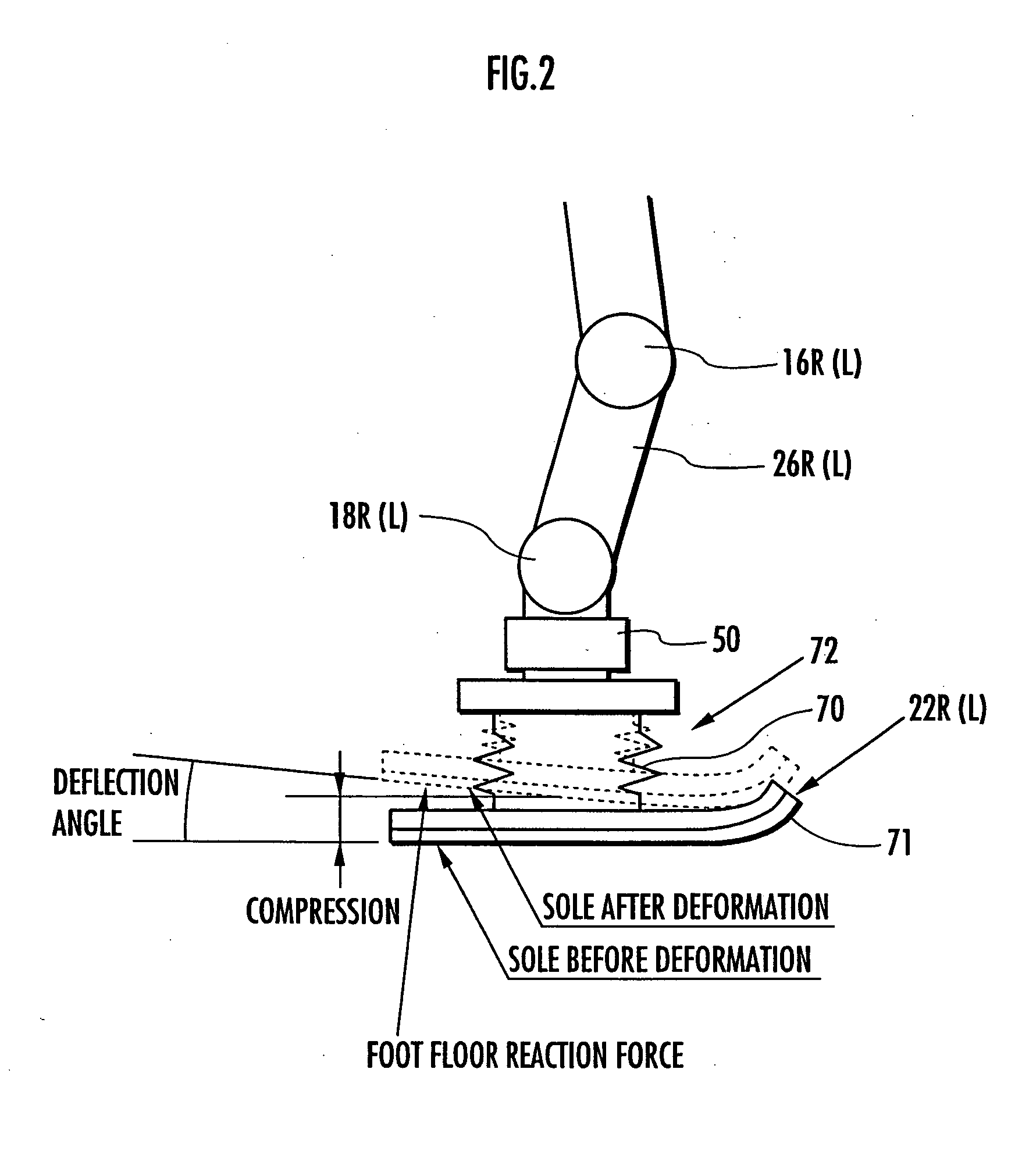
InactiveUS20060173578A1Inhibition is effectiveQuick fixProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlMobile robot controlMomentum
The occurrence of a slippage of a robot in operation, following a desired gait, is determined, and the permissible range of a restriction object amount, such as a floor reaction force horizontal component or a floor reaction force moment vertical component to be applied to the robot, is variably set according to a slippage determination result. A provisional motion of a desired gait is determined using a dynamic model, and if the restriction object amount defined by the provisional motion deviates from the permissible range, then the motion of a desired gait is determined by correcting the provisional motion by changing the changing rate of the angular momentum of the robot from the provisional motion so as to limit the restriction object amount to the permissible range, while satisfying a dynamic balance condition.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Walking aid exoskeleton rehabilitation robot
InactiveCN101810533ACompact designLarge range of joint rotationChiropractic devicesWalking aidsHuman bodyRehabilitation engineering
The invention discloses a walking aid exoskeleton rehabilitation robot in the technical field of rehabilitation engineering, which comprises a mobile auxiliary mechanism, a control mechanism and an exoskeleton prosthesis mechanism, wherein the mobile auxiliary mechanism is connected with the exoskeleton prosthesis mechanism, and the control mechanism is connected with the mobile auxiliary mechanism and the exoskeleton prosthesis mechanism respectively. The exoskeleton prosthesis mechanism has compact design structure and large rotation range of each joint, and can meet the requirement on actual motion of a human body. By adopting a servo motor to drive, the control precision is high, and the output torque is large; and the mobile auxiliary mechanism rotates under the driving of the servo motor, can freely move, and has higher climbing capacity and movement speed. The height of the mobile auxiliary mechanism is adjusted to be applied to people with different heights. When the patient undergoes gait rehabilitation training, the human gravity center is actively adjusted to accord with the characteristics that the human body is fluctuated along with alternative gait. The mobile auxiliary mechanism also can support the human body, prevent people from tumbling in walking, and guarantee the whole stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com