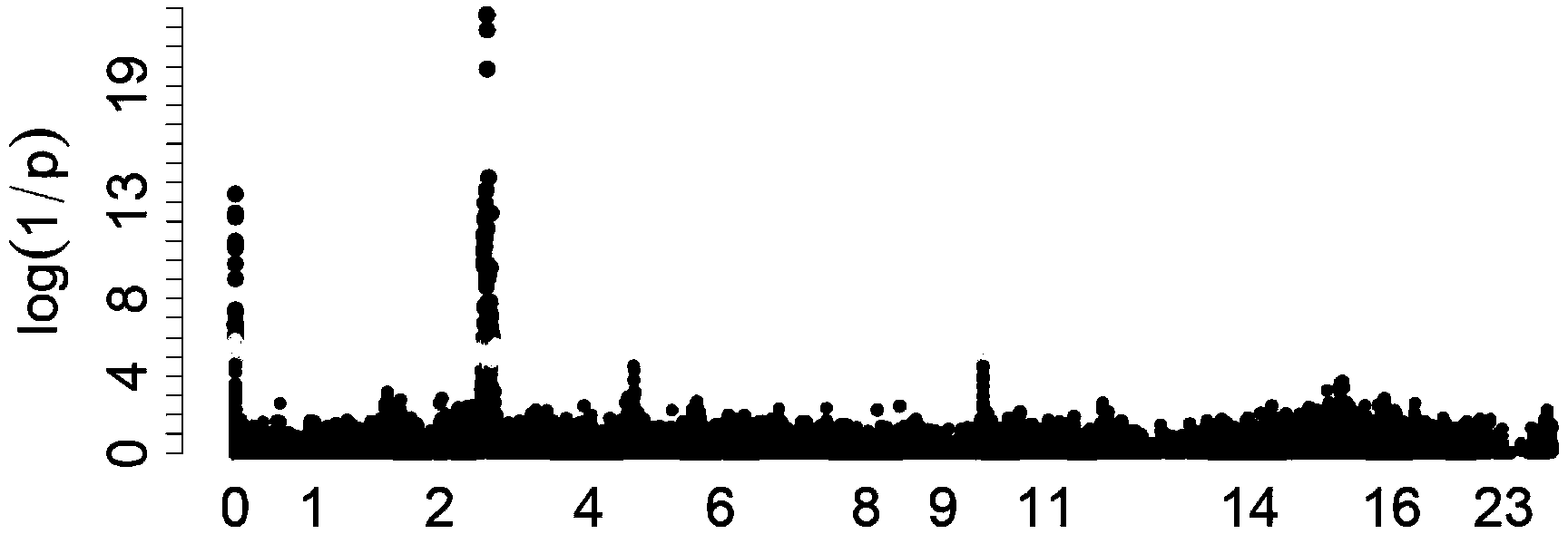
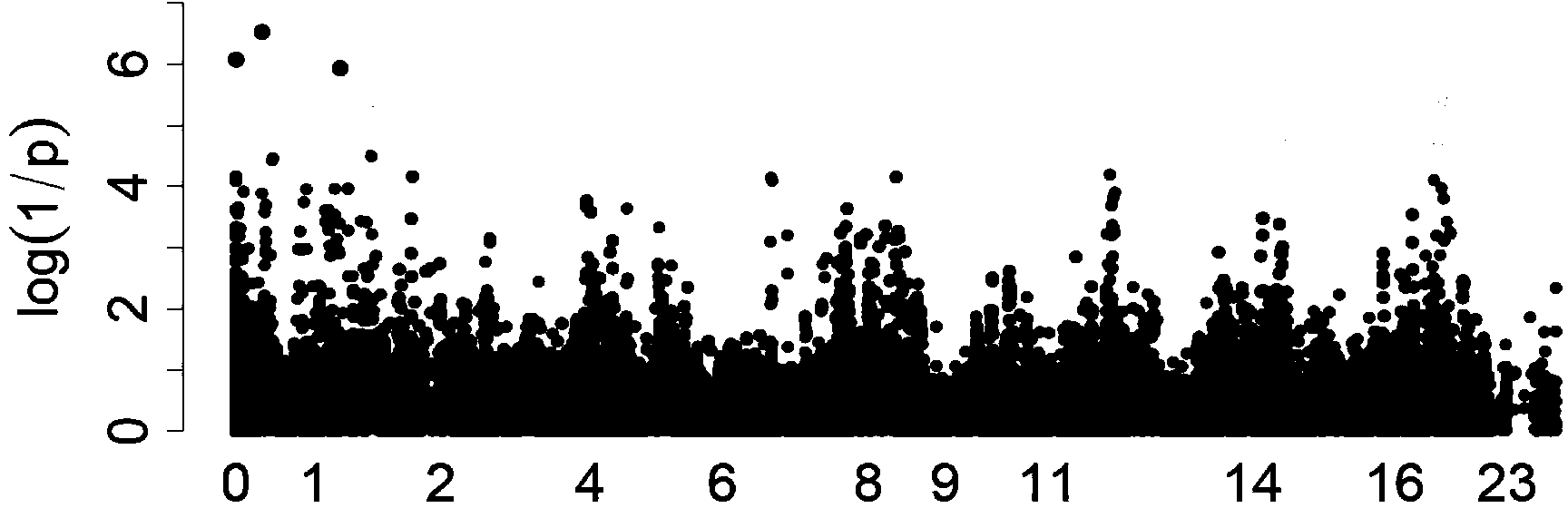
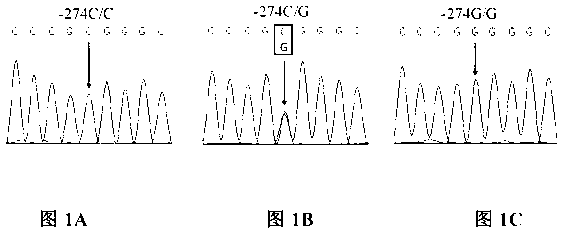
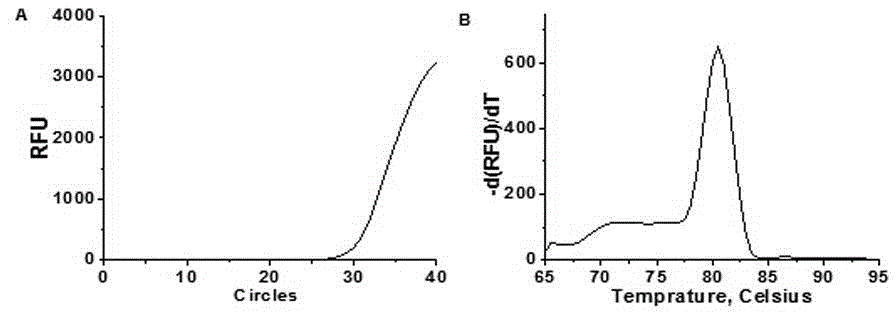
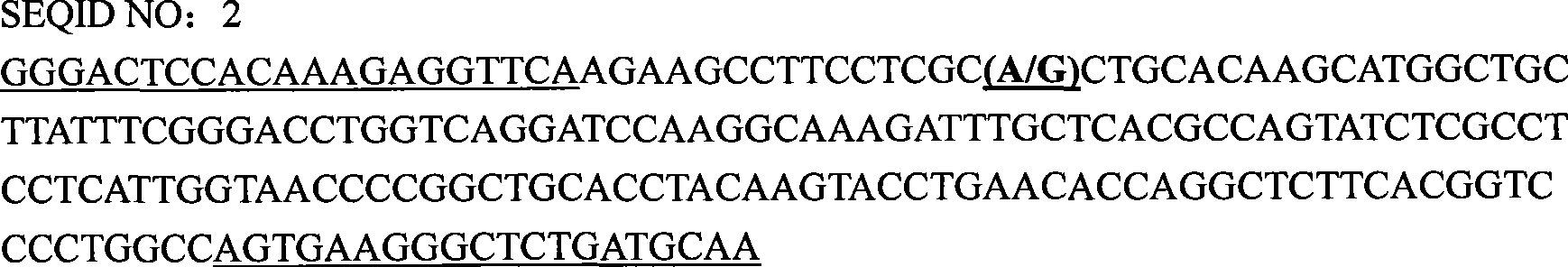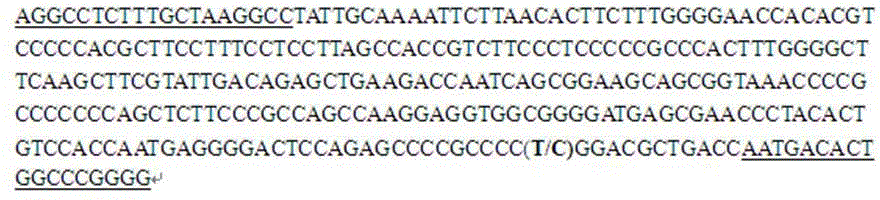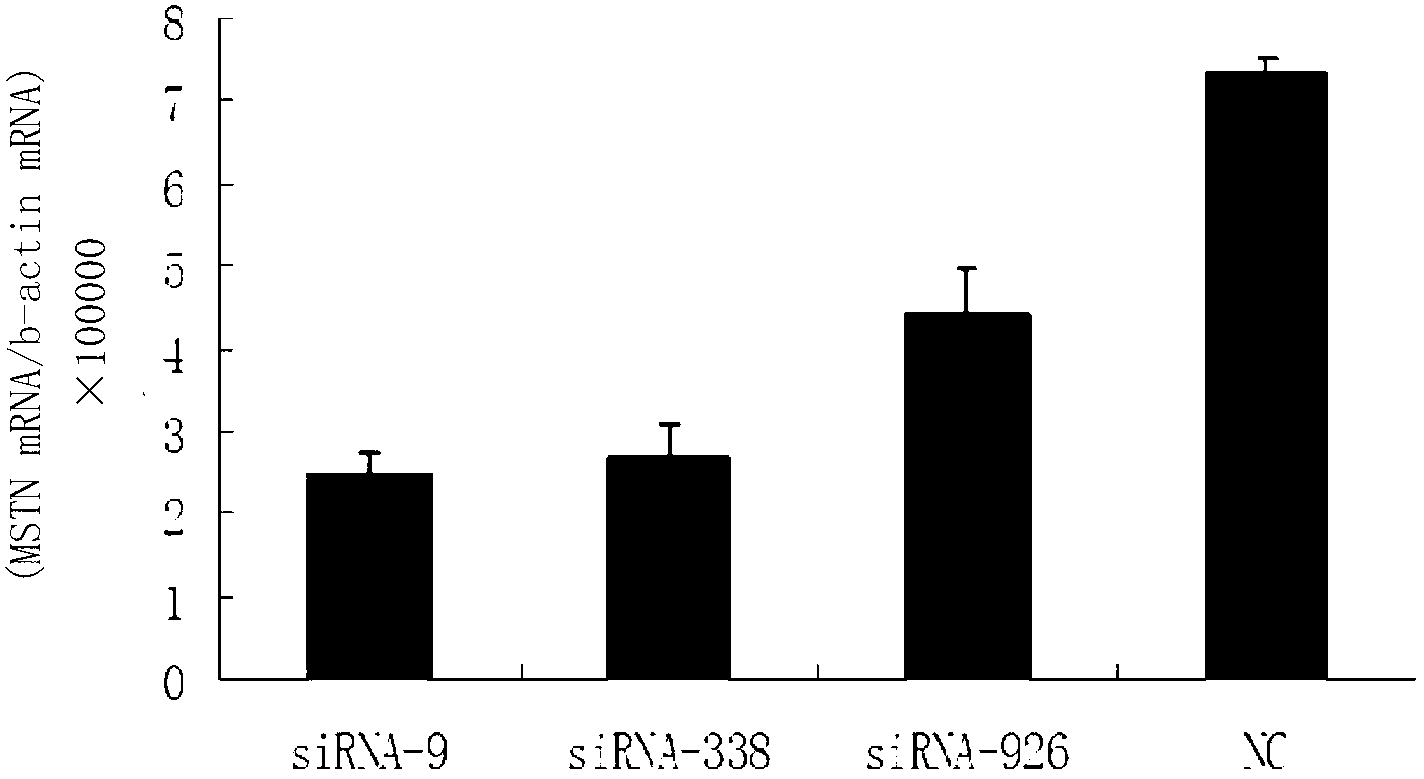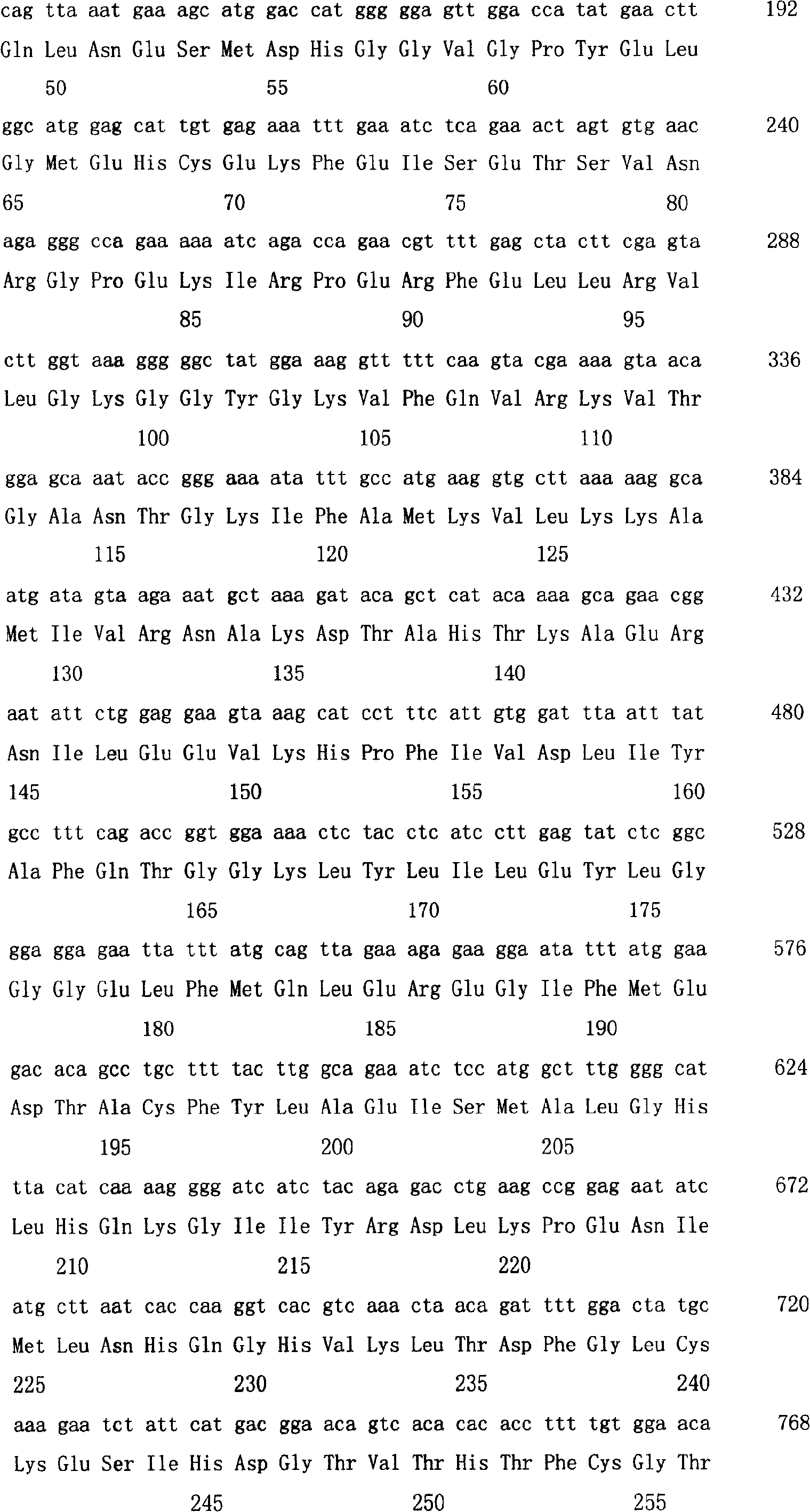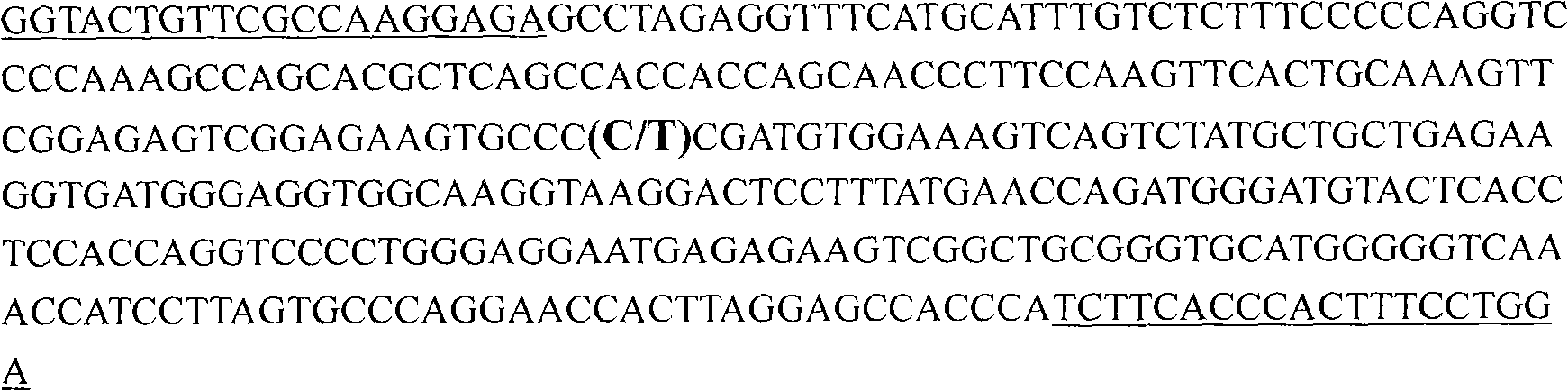Patents
Literature
93 results about "MUSCLE" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
MUltiple Sequence Comparison by Log-Expectation (MUSCLE) is computer software for multiple sequence alignment of protein and nucleotide sequences. It is licensed as public domain. The method was published by Robert C. Edgar in two papers in 2004. The first paper, published in Nucleic Acids Research, introduced the sequence alignment algorithm. The second paper, published in BMC Bioinformatics, presented more technical details.
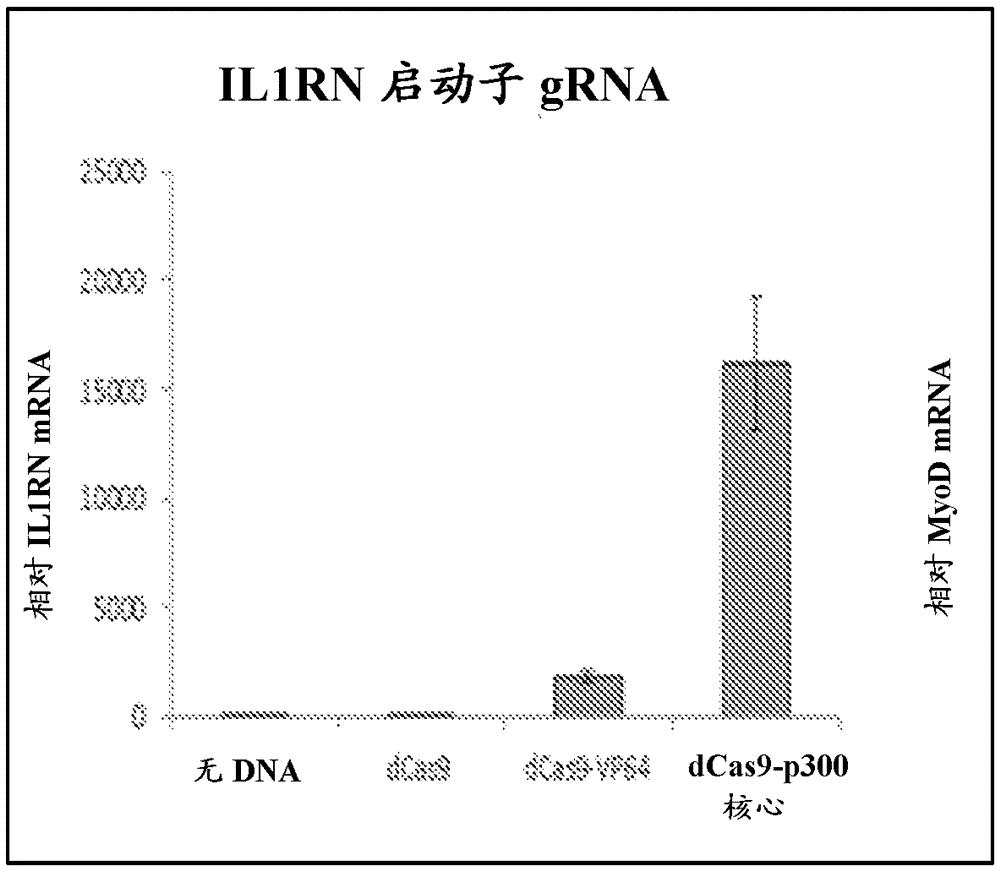
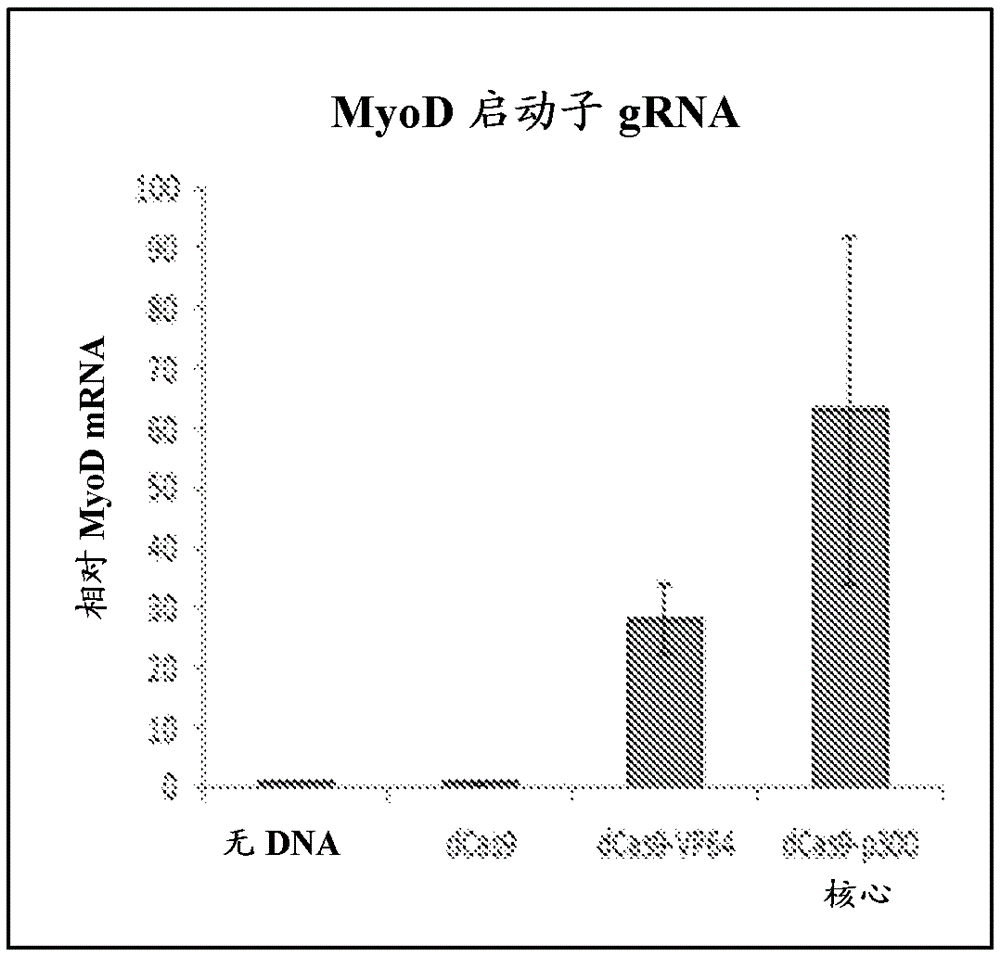
Rna-guided gene editing and gene regulation
Disclosed herein are Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) / CRISPR-associated (Cas) 9-based system related compositions and methods of using said CRISPR / Cas9-based system related compositions for altering gene expression and genome engineering. Also disclosed herein are compositions and methods of using said compositions for altering gene expression and genome engineering in muscle, such as skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
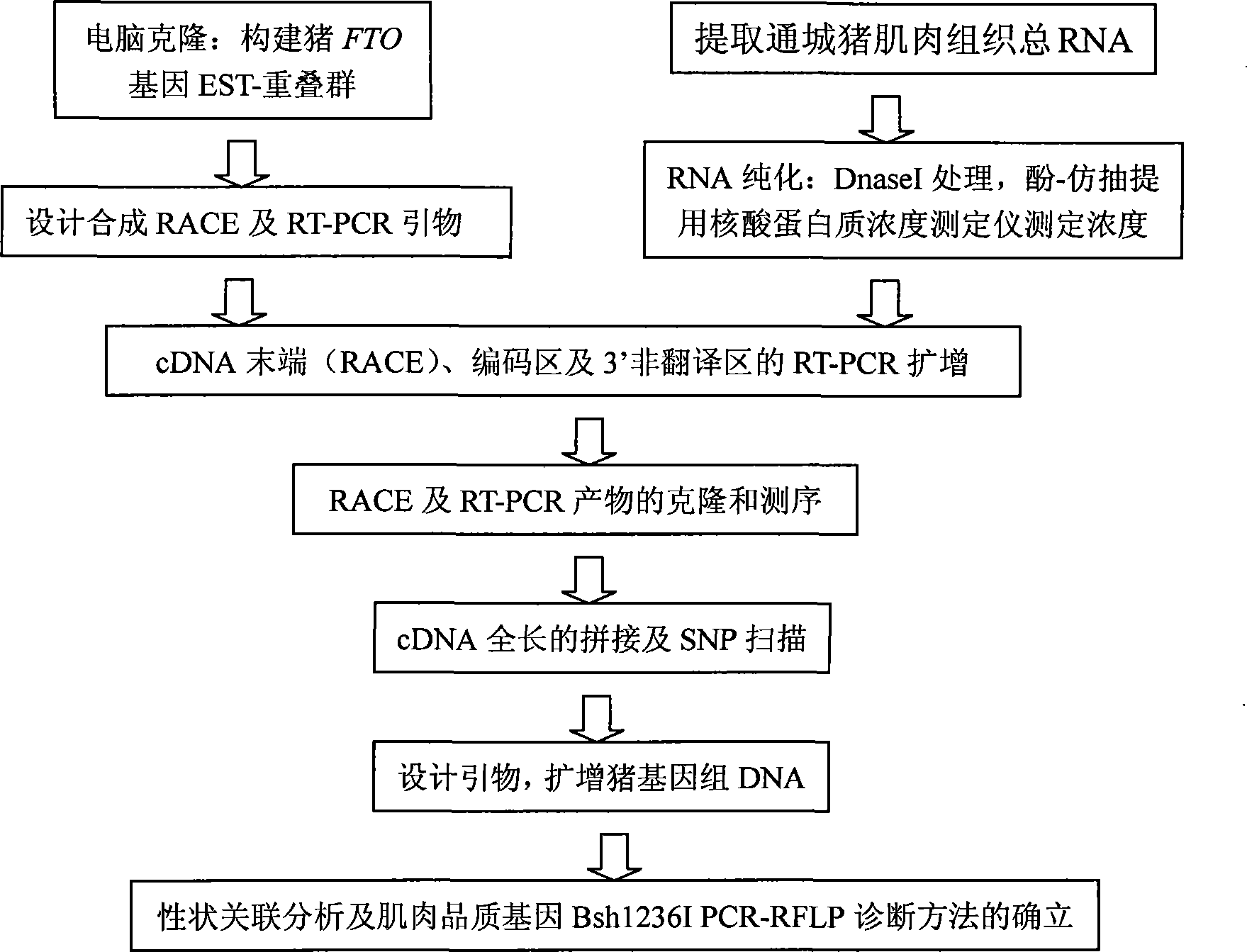
FTO gene clone relating to pig meat quality trait and application of the same as molecular marker
InactiveCN101392255AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationEnzyme digestionAgricultural science
The invention pertains to the technical field of livestock genetic engineering and particularly relates to a molecular marker which is applied to the marker auxiliary select and application of pigs and related to the characteristics of the muscle quality of the pigs, and an application thereof. The molecular marker is cloned by an FTO gene and the cDNA sequence of the molecular marker is shown in a sequence table SEQ ID NO: 1. The substitution of a basic group A37-G37 occurs at the 37th bp of the sequence table SEQ ID NO: 2, which causes the enzyme digestion polymorphism of Bsh1236I PCR-RFLP. The invention also discloses a complete cDNA sequence for amplifying the FTO gene, a primer used by a part of the DNA sequence and a method for testing the polymorphism, thereby providing a new molecular marker for the marker auxiliary select of the pigs.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Detection primer marked by SNP and associated with pinctada martensi adductor muscle weight and application of detection primer
ActiveCN104099415AAmplified SNP lociMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationElectrophoresisBiology
The invention discloses a detection primer marked by SNP and associated with pinctada martensi adductor muscle weight and application of the detection primer. The detection primer comprises the following substances:ASSN815FI: TCCATCGTGGACAAACGTGTAA; ASSN815RI: GTGTCAAAGTAAACTGTATCTCGTGCC; ASSN815FO: TAGAATTGGCAAAGGAACAAGCAT; ASSN815RO: AATAATTCCTAACAGGTGCCCGTC. Through the adoption of the detection primer marked by SNP and associated with pinctada martensi adductor muscle weight, SNP sites of the myostatin genes can be amplified, and the SNP sites are associated with the muscle weight obviously; according to the PCR amplification electrophotogram, the size of the adductor muscle weight between individuals can be compared visually, so that the detection primer can be directly used for follow-up molecular marker assistant breeding, for example, the detection primer can be used for selecting target characters in early growth stage, and then the specific individual is selected for variety breed.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Devices comprising muscle thin films and uses thereof in high throughput assays for determining contractile function
The present invention provides high throughput assays for identifying compounds that modulate a contractile function, as well as devices suitable for use in these assays.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
PHKG1 (phosphorylase kinase, gamma 1) gene and application thereof in genetic improvement for breeding pig meat quality traits
ActiveCN103409440AReduced glycolytic potentialReduce lossesMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesBase JNucleotide
The invention discloses a nucleotide sequence or an amino acid sequence of a PHKG1 (phosphorylase kinase, gamma 1) gene located on pig chromosome 3, wherein a mutation site of the PHKG1 gene is the C-A mutual mutation of a mononucleotide at the 8118th site of a sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; when C is mutated to A, a normal transcript generated by the PHKG1 gene in a transcription process deletes abnormal transcripts of 32 bp fragments, and the deleted 32 bp fragments are located at the 8123rd-8154th base of 5' end of the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; on the basis, disadvantageous genotype individuals are eliminated by selecting advantageous genotype individual reserve breeding pigs, so that population meat quality traits can be remarkably improved, especially, muscle glycogen content can be reduced, drip loss and processing loss can be reduced, and pH value and intramuscular fat content can be increased, thus the pig meat quality is improved.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
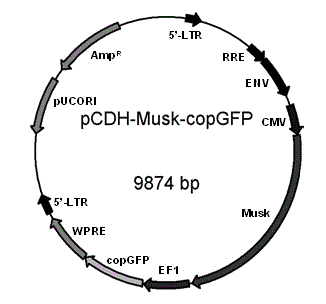
Lentiviral plasmid expression vector as well as construction method and application of lentiviral plasmid expression vector
InactiveCN104017827AImprove the level of clinical diagnosis and treatmentImprove the level of diagnosis and treatmentBiological testingFermentationMuscle specific receptor tyrosine kinase AntibodyStaining
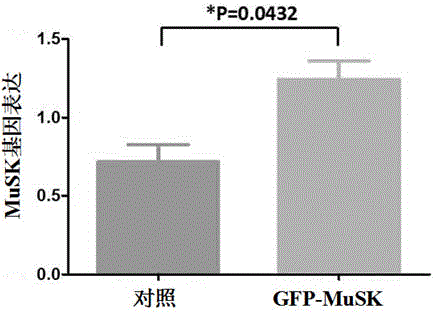
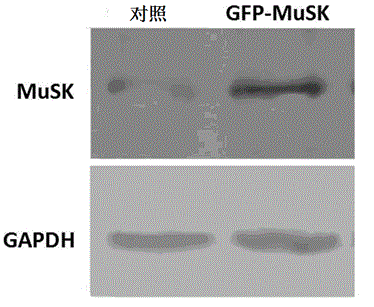
The invention discloses a lentiviral plasmid expression vector as well as a construction method and an application of the lentiviral plasmid expression vector. The lentiviral plasmid expression vector is pCDH-MCS-MuSK-GFP and the nucleotide sequence of the lentiviral plasmid expression vector is shown in SEQ ID NO. 2 in a sequence table. The invention further discloses an application of the lentiviral plasmid expression vector in construction of an anti-muscle-specific receptor tyrosine kinase antibody detection. According to the invention, a stable transfected cell line of MuSK is established by constructing a viral vector, a MuSK antibody is qualitatively and quantitatively detected clinically by an immunofluorescence staining method with relatively high sensitivity and specificity in combination with a flow cytometry, the detection results are more stable and manpower and time costs are greatly saved. The diagnosis and treatment levels of myasthenia gravis are greatly improved by the establishment of the project, the labor capacity and life quality of patients are improved and the lentiviral plasmid expression vector has significant social and economic benefits.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Utilization of nucleotide probes for the measurement of specific mRNA for the molecular diagnosis of autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy
InactiveUS20030049627A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismNucleotide
The present invention concerns the development of a quantitative method for the molecular diagnosis of autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) by measuring the amount of cytosolic mRNA from human muscle cells. Both the procedure using radioactive material and the Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) nonradioactive method were developed using 32P-dCTP labeled and biotinylated nucleotide probes. The results obtained demonstrate that the measurement of mRNA could be used as a quantitative method for the molecular diagnosis of SMA. There was a perfect concordance of the results obtained between the procedure using radioactive material, the ELISA method and the single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis regarding the negative and positive SMA samples. The methods developed in this study may be applicable to the diagnosis (detection of homozygous and heterozygous deletions in exons 7 and 8 of the SMN gene) and the control of mRNA concentrations in the future gene therapy of patients with SMA.
Owner:NGUYEN HUYNH MAI THI
Preparation method for procambarus clarkia simple sequence repeats (SSR) primer
ActiveCN104726554AEasy to filterQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationProcambarusMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a preparation method for a procambarus clarkia simple sequence repeats (SSR) primer. The preparation method comprises the steps: (1), extracting procambarus clarkia genome DNAs: extracting the genome DNAs from procambarus clarkia abdominal muscles; (2), hybridizing a probe and a target segment: hybridizing the biotin labeled probe and the target segment to obtain a hybridization product; (3), enriching magnetic beads: enriching the hybridization product by a magnetic bead enrichment method to obtain an enrichment product; (4), performing positive clone sequencing, and designing a primer amplification gene DNA according to a microsatellite flanking sequence; (5), performing SSR primer detection. The preparation method for the procambarus clarkia SSR primer has the advantages that a microsatellite sequence of the procambarus clarkia whole genome can be simply and quickly screened; a large number of SSR primers can be developed at a short time; technical measures are provided for germ plasma conservation and genetic improvement of the procambarus clarkia.
Owner:ZHEJIANG INST OF FRESH WATER FISHERIES
Fluorescence quantitative PCR detection primer and method for type and composition of yak muscle fibers
ActiveCN105039515AChemical assessment is accurateAccurate quantitative determinationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyReference genes
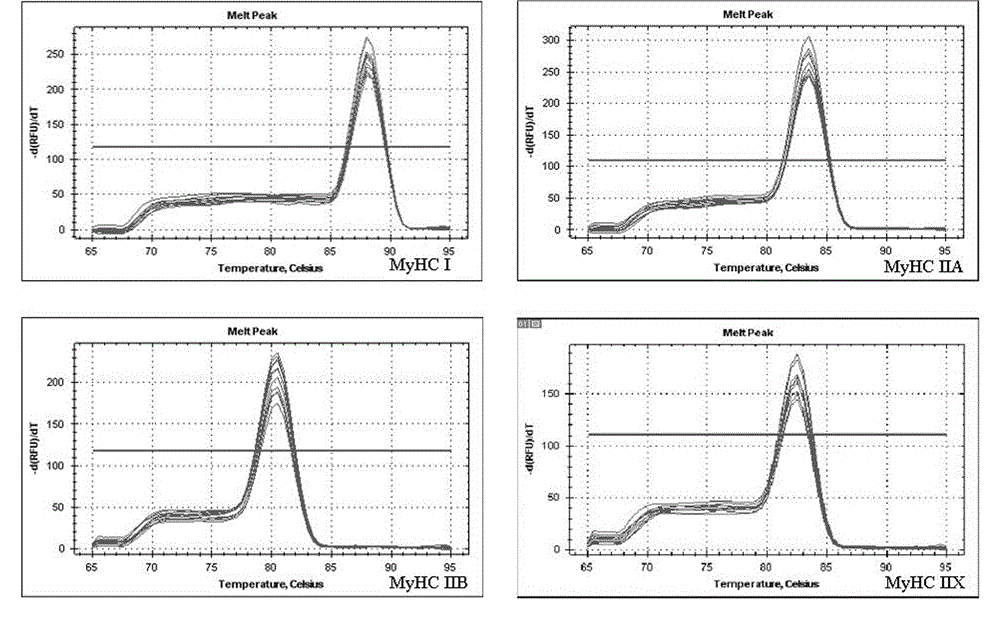
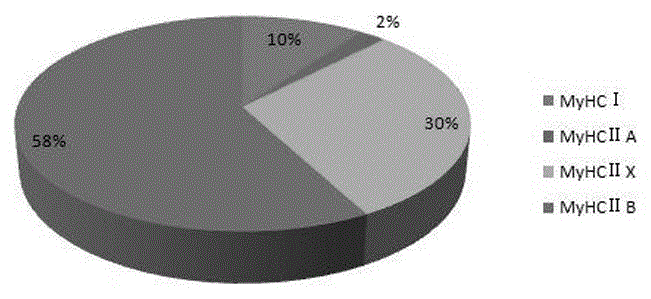
The invention discloses a fluorescence quantitative PCR detection method for type and composition of yak muscle fibers. According to the fluorescence quantitative PCR detection method, yak muscle tissues are taken for total RNA extraction, the RNA purity and concentration are detected, the total RNA is subjected to inverse transcription to generate cDNA, then quality detection is carried out by taking GAPDH genes of yak as internal genes, and then a special detection primer is adopted for carrying out fluorescence quantitative PCR reaction, meanwhile, the GAPDH genes of yak are taken as reference genes for statistic analysis. The detection method and the detection primer provided by the invention are more accurate and more reliable than histochemistry evaluation; with the molecule quantitative classification method, accurate quantitative and analysis can be carried out on the type composition of the various muscle fibers in muscles at different parts of the yak, so that a technological base is laid for further study on the relevance between the muscle fibers and the meat quality trait of the yak, and meanwhile, compared with other methods, the fluorescence quantitative PCR detection method has the advantages of low workload and low cost, and high efficiency.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
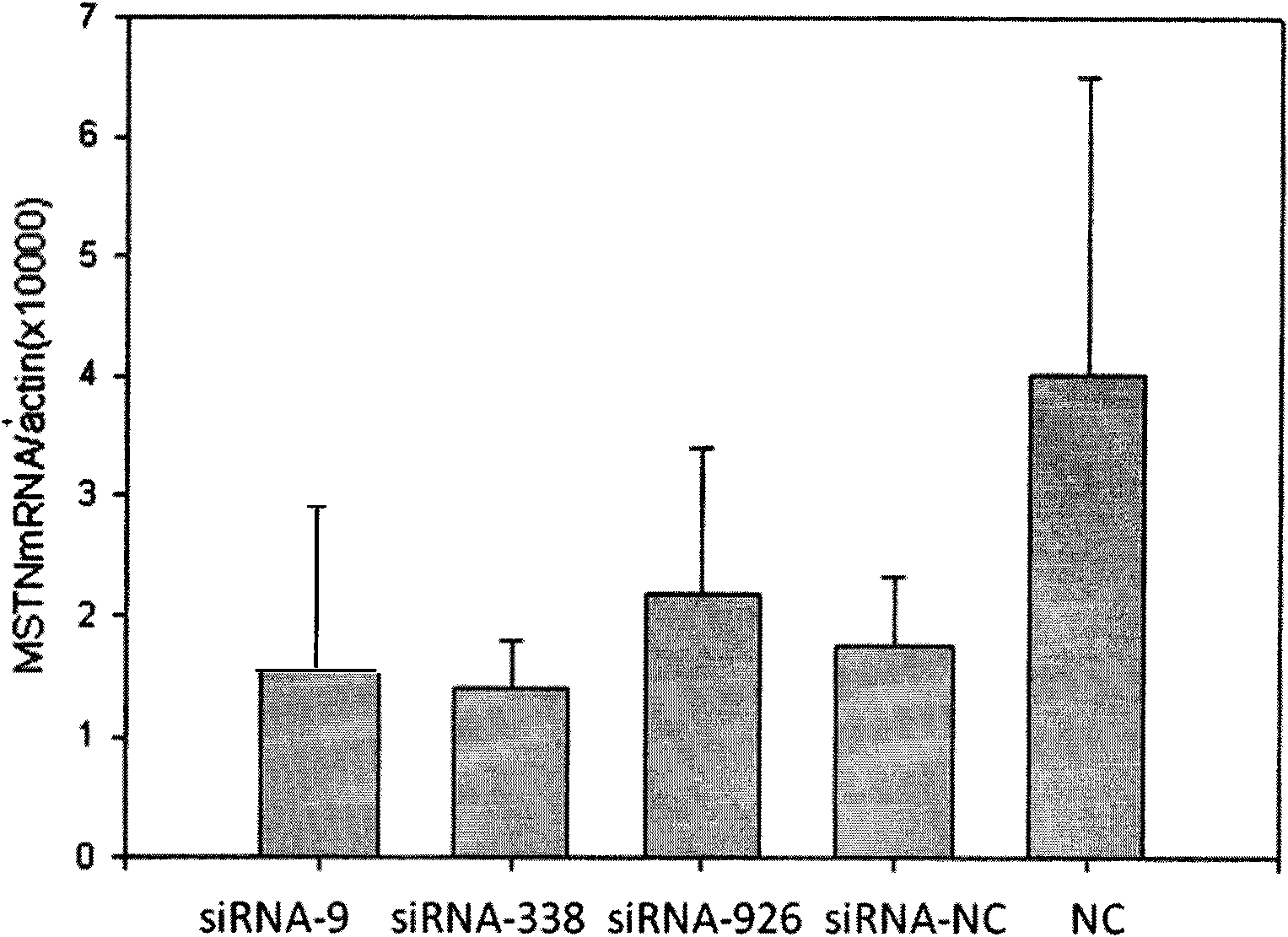
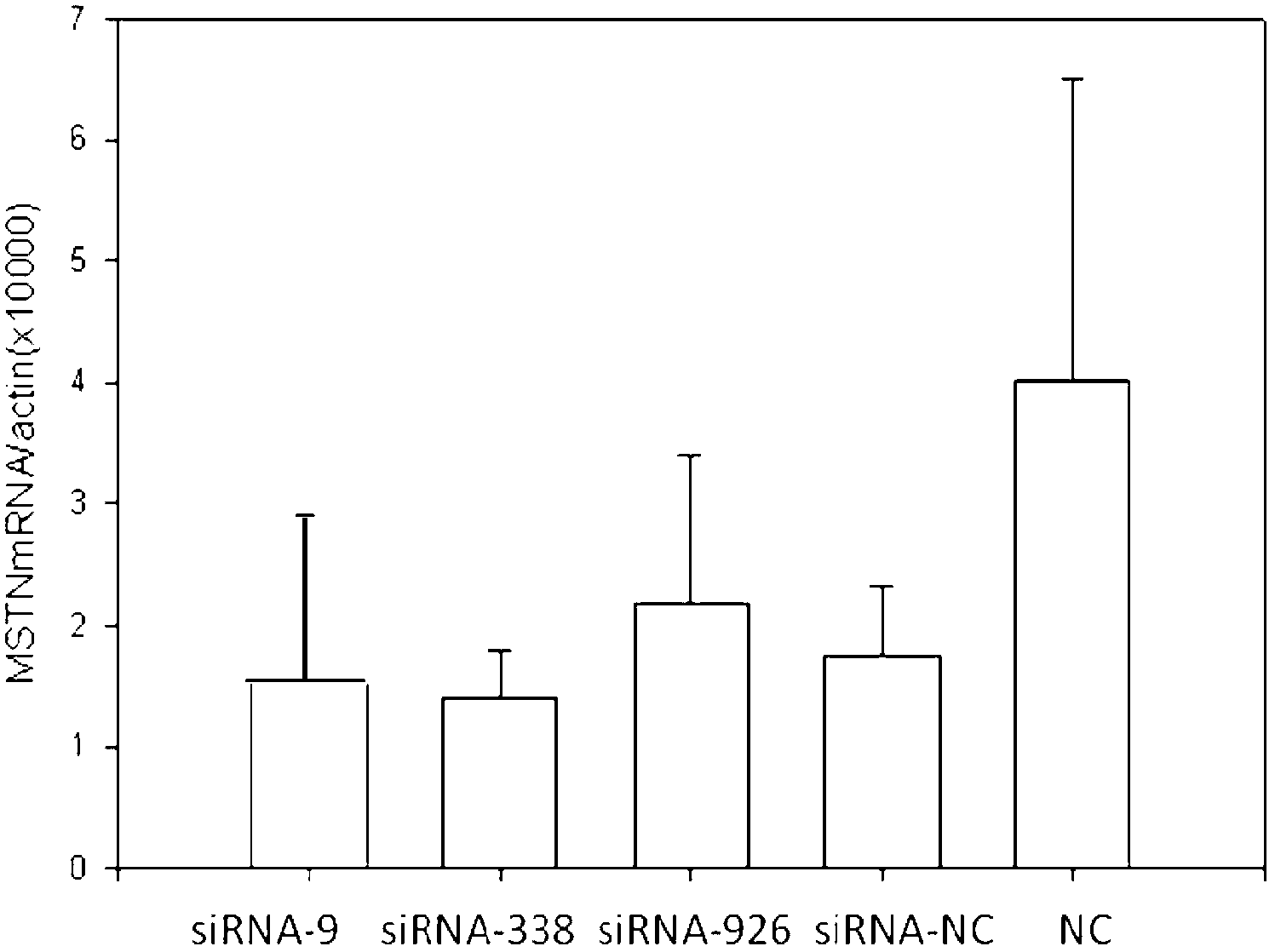
Small interfering RNA (siRNA) inhibiting expression of myostatin (MSTN) gene in chicken and application thereof
InactiveCN102041257ASkeletal muscle enlargementIncrease meat productionMicroencapsulation basedDNA/RNA fragmentationMyostatinBreeding chicken
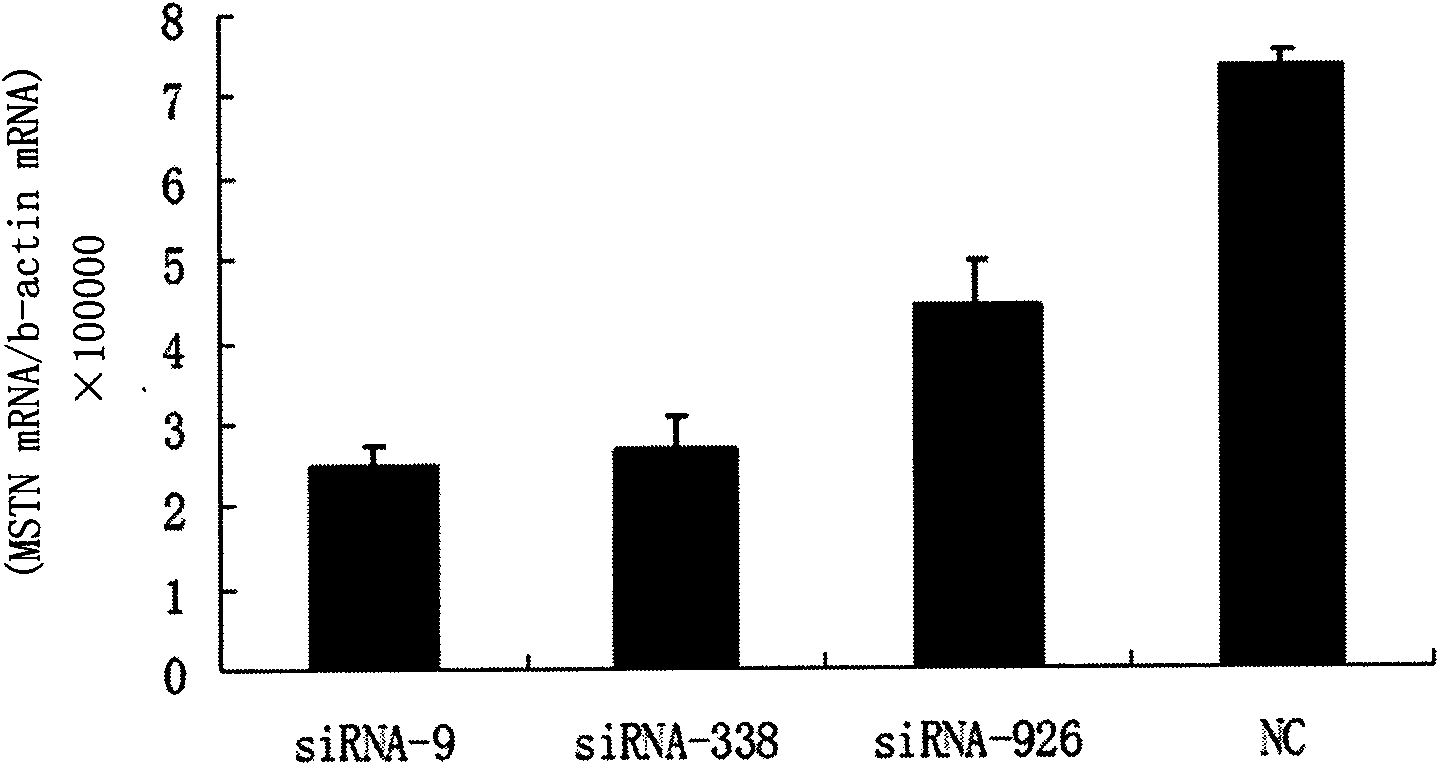
The invention discloses a small interfering RNA (siRNA) inhibiting expression of a myostatin (MSTN) gene in chicken and application thereof. The invention provides an siRNA which acts on the MSTN gene, wherein the siRNA is a) a double-stranded RNA composed of the sequence 1 and the sequence 2 in a sequence table, b) a double-stranded RNA composed of the sequence 3 and the sequence 4 in the sequence table or c) a double-stranded RNA composed of the sequence 5 and the sequence 6 in the sequence table. The invention obtains the siRNA effectively inhibiting expression of the MSTN gene in chicken,real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) verifies that the siRNA effectively reduces expression of MSTN in molecular biology, and chicken with skeletal muscles obviously increased are successively obtained through microinjection test in embryology. The above results show that the siRNA provided by the invention can be used for breeding chicken, thus improving the meat yields of broilers, especially high quality chicken.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Molecular marker related to pig muscle pH value character and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of a pig genetic marker, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a pig muscle pH value related molecular marker and application of the pig muscle pH value related molecular marker on auxiliary marker selection. The molecular marker is obtained by cloning a GYS1 gene promoter sequence, and the nucleotide sequence of the molecular marker is as shown in the sequence table SEQ ID NO: 1; and a C267-T267 basic group on the 267th basic group of a sequence as shown in the sequence table SEQ ID NO: 2 is mutated to cause MvaIPCR-RFLP polymorphism. The invention also discloses application of the preparation method for obtaining the molecular marker and a polymorphism detection method. The preparation method disclosed by the invention provides a new genetic marker for carrying out the auxiliary marker selection of a high-muscle quality pig.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
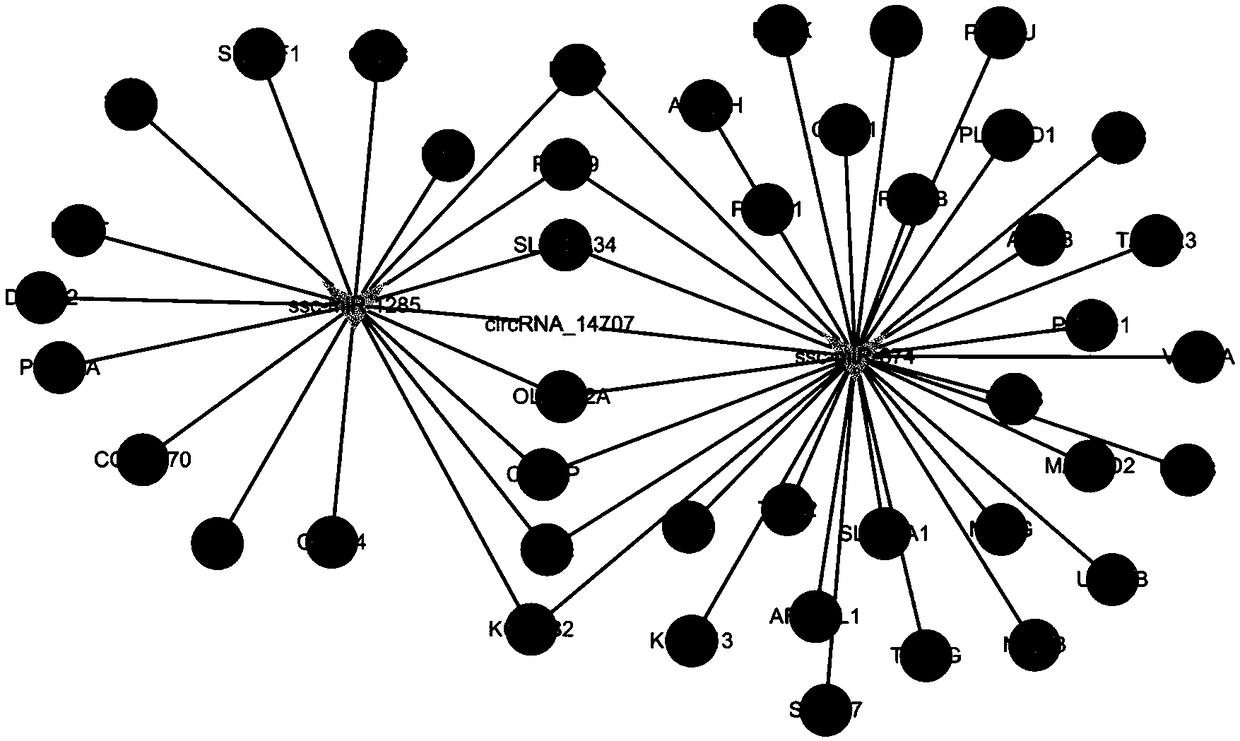
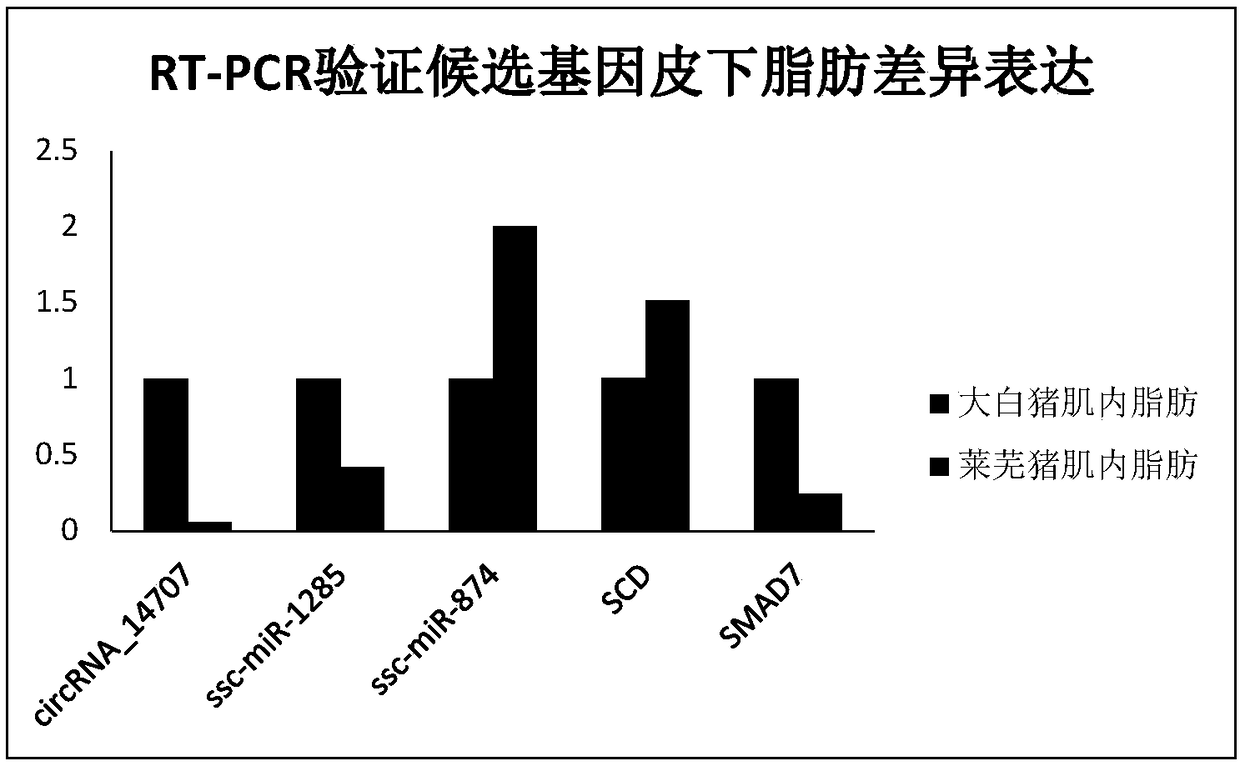
CircRNA_14707 and application thereof in molecular assistant breeding
ActiveCN108893540AImprove sequencing efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBreeding pigBiology
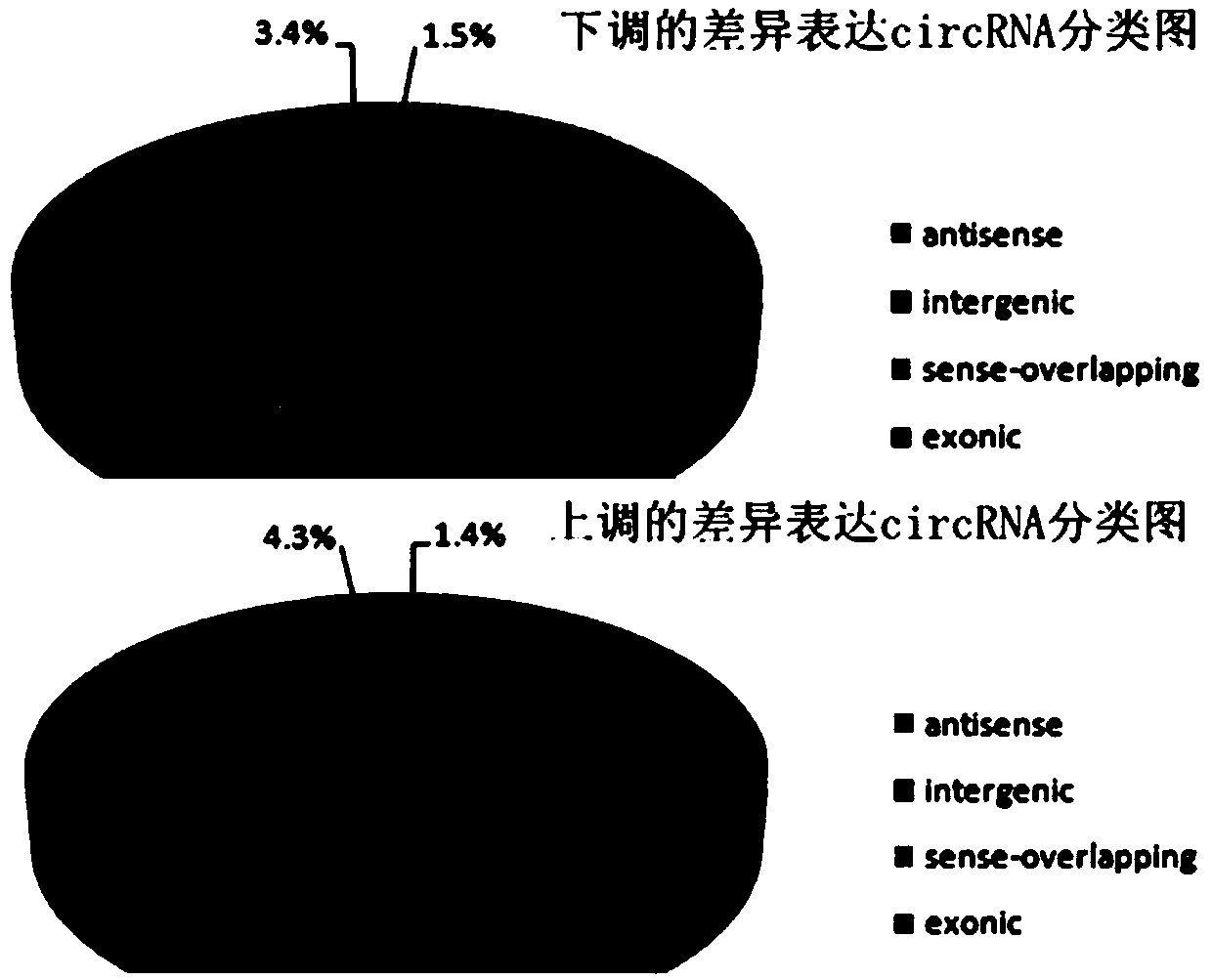
The invention relates to circRNA_14707 and an application thereof in molecular assistant breeding. By means of high-throughput sequencing on expression conditions of circRNA in subcutaneous fat tissues of a big white pig and a Laiwu pig and integrated analysis performed by combining previous miRNA and mRNA of a laboratory, a result shows that differential expressions of the circRNA_14707 and related miRNA are quite obvious and the circRNA_14707 and related miRNA can serve as molecular markers for detecting the subcutaneous fat contents of the pigs. The circRNA_14707 has a very good applicationprospect in the fields of predicating or assisted predicting pork quality and breeding pigs with different muscle qualities and the like.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Application of adiponcetin gene expression level in beef cattle muscle marbling grade identification
InactiveCN102477461AIncreased sensitivityGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMedicineGene expression level
The invention relates to an application of an adiponcetin gene expression level in beef cattle muscle marbling grade identification, which is characterized in that a cloned adiponcetin gene cDNA complete sequence is used to establish a real-time fluorescence quantitative detection method of adiponcetin mRNA; and the application of the adiponcetin gene expression level in beef cattle muscle marbling grade identification is determined. The method which adopts fluorescence quantitative RT-PCT to detect ADPNmRNA has very good sensitivity and repeatability. In the detection results, a copy number is used to express the content of an initial template, which is more accurate and reliable than a comparison value in semi-quantitative RT-PCR; the ADPNmRNA level is negatively correlated with the muscle marbling of fattening cattle (Yanbian cattle r=-0.87; P<0.001, n=9) and (red steppe cattle r=-0.79; P<0.001, n=9). The accuracy rate is up to 95%.
Owner:JILIN AGRI SCI & TECH COLLEGE
siRNA capable of restraining chicken myostatin gene expression and application thereof
ActiveCN102703449ASkeletal muscle enlargementIncrease meat productionMicroencapsulation basedAnimal husbandrySmall interfering RNABroiler
The invention discloses a siRNA capable of restraining chicken myostatin (MSTN) gene expression and application of the siRNA; small interfering RNA (ribonucleic acid) acted on myostatin gene is provided by the invention and is a) or b) or c) as follows: a) double-stranded RNA composed of a sequence 1 of a sequence table and a sequence 2 of the sequence table; b) double-stranded RNA composed of a sequence 3 and a sequence 4 of the sequence table; and c) double-stranded RNA composed of a sequence 5 and a sequence 6 of the sequence table; according to the invention, the small interfering RNA effectively capable of restraining chicken MSTN gene expression is obtained and is proved to effectively reduce expression of MSTN through real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) on molecular biology; chicks with obviously enlarged skeletal muscle is successfully acquired through a micro-injection test on embryology; above-mentioned results show that the small interfering RNA provided by the invention can be used for breeding the chicks, so that chicken yield of the chicks specifically high-quality chicks is increased.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
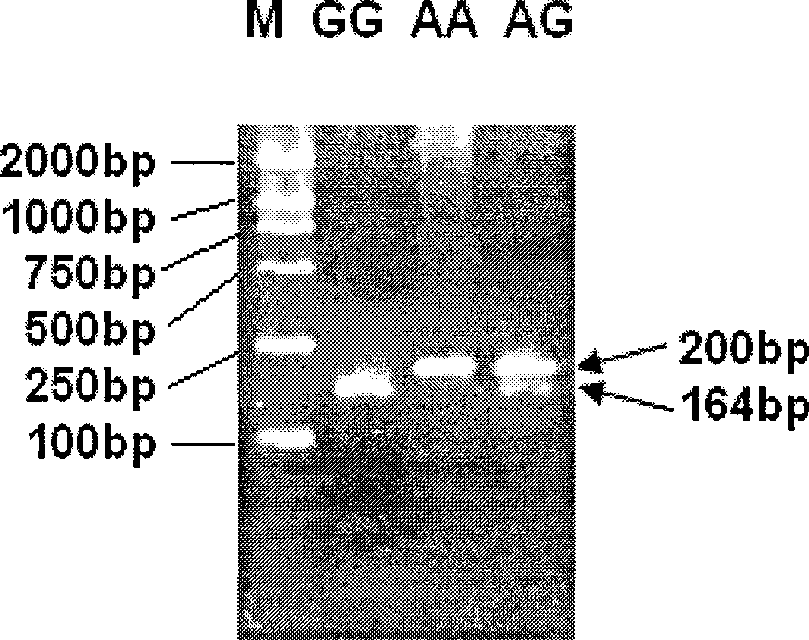
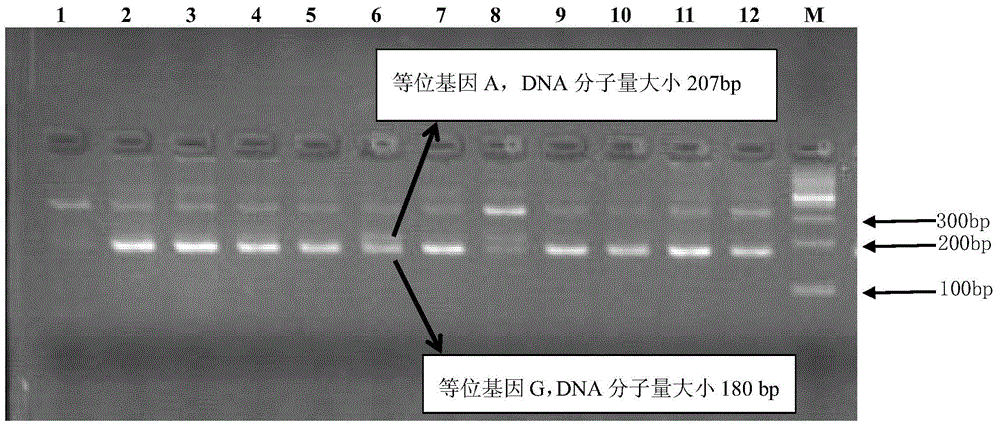
Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) molecular marker associated with pH and dropping loss character of pig muscles and application of SNP molecular marker
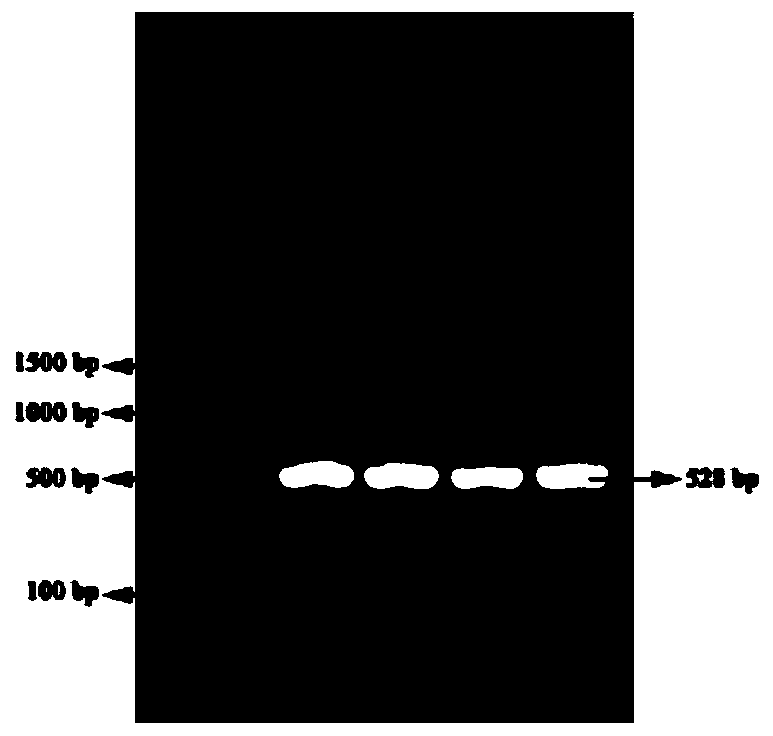
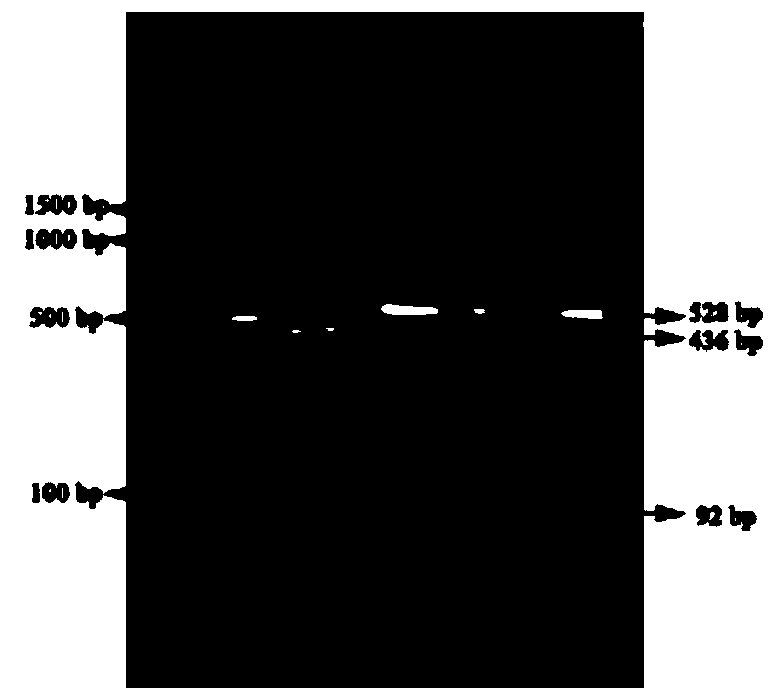
The invention belongs to the technical field of pig molecular marker preparation, and relates to a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) molecular marker associated with the pH and a dropping loss character of pig muscles and application of the SNP molecular marker. The SNP molecular marker nucleotide sequence is an obtained specific DNA fragment obtained by cloning from a second exon area of a pigKLF5 gene, and the DNA fragment has 528 bp, wherein A / G mutations are found at the 160 bp and the 436 bp in the sequence correspondingly. According to the SNP molecular marker associated with the pHand the dropping loss character of the pig muscles and application of the SNP molecular marker, the specific DNA fragment is obtained by cloning from the exon area of the pig KLF5 gene, SNP sites arelooked for, a corresponding detection method is established, and the new molecular marker is provided for selection and breeding of pork quality traits of pigs.
Owner:湖南省畜牧兽医研究所
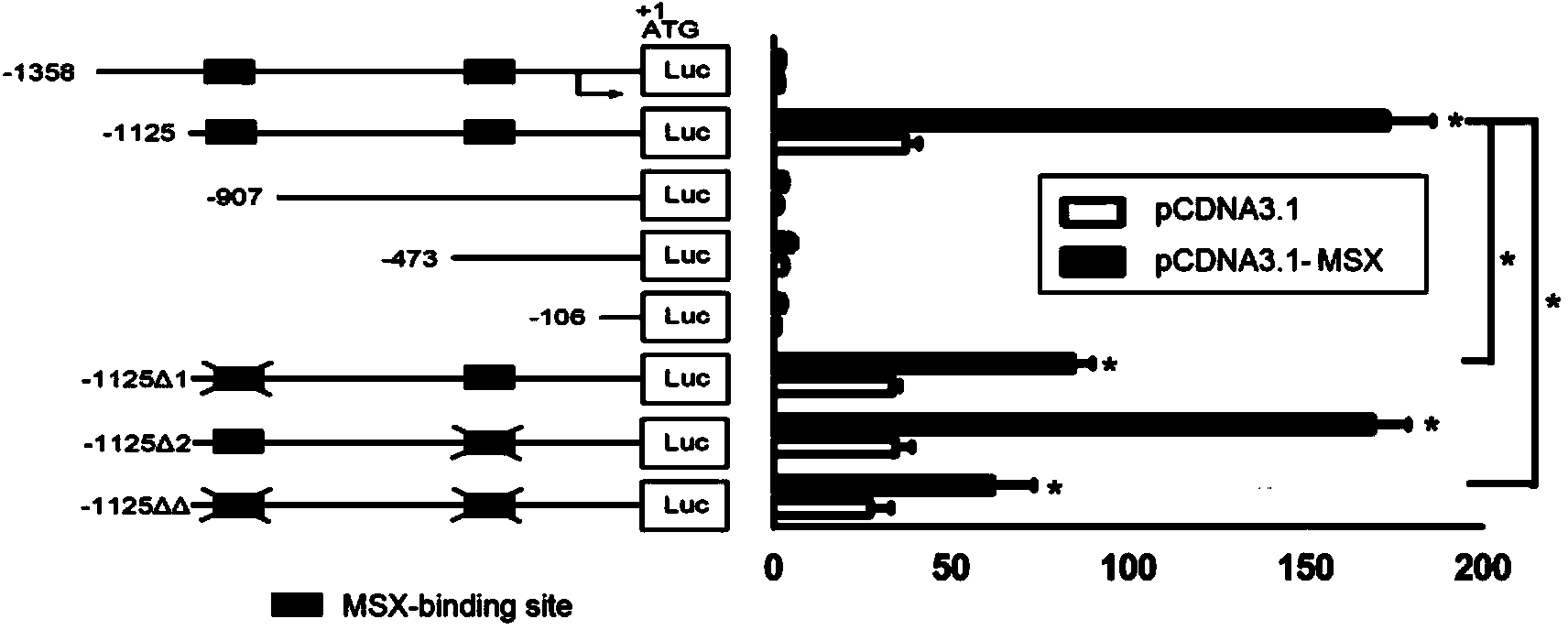
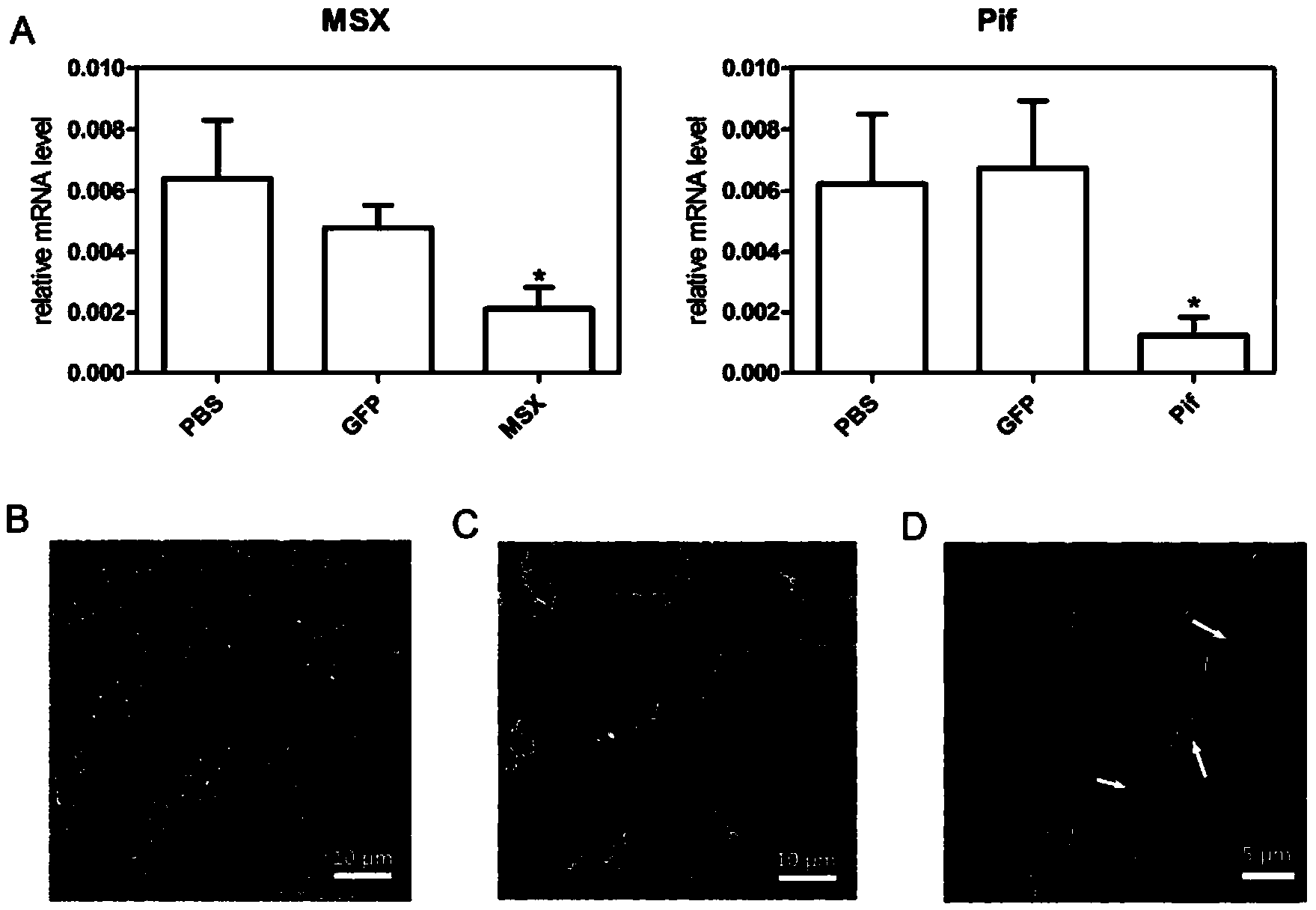
Pif promoter capable of being activated by pinctada martensii MSX (muscle segment homeobox) gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103820453AVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideBinding site
The invention discloses a Pif promoter capable of being activated by pinctada martensii MSX (muscle segment homeobox) genes and application of the Pif promoter. The nucleotide sequence of the Pif promoter is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. A Pif promoter sequence is obtained through amplification by a genome walking method. The Pif promoter has a binding site 1 and a binding site 2, which can be bound to the MSX genes. Through the establishment of wild type carriers and mutant type carriers of Pif promoters of different fragment lengths, a dual-luciferase reporter gene system is applied to identify the fact that the MSX genes act on the Pif promoter through the binding site 1. The Pif promoter can start the downstream target gene expression, thereby promoting the growth of pearls or pearl oysters.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
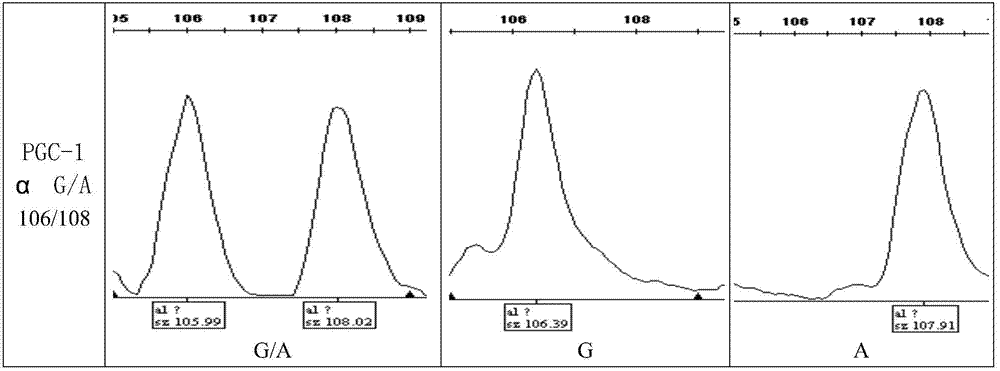
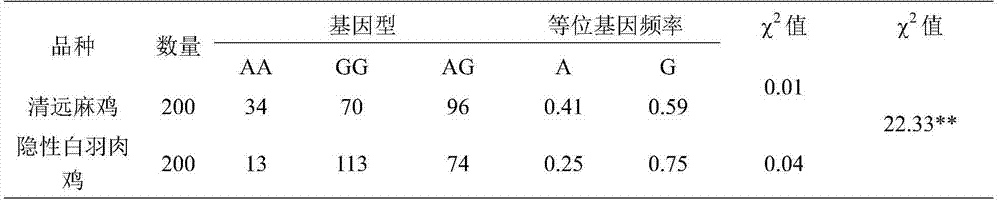
Chicken muscle fiber-type property-related gene molecule marker and use thereof
InactiveCN104762373AEasy to filterSlow-twitch fibersMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideExon
The invention discloses a chicken muscle fiber-type property-related gene molecule marker and a use thereof. A 646th nucleotide G-to-A mutational site of a PGC-1 alpha gene exon is used as a molecule marker, the molecule marker has a nucleotide sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO. 1, and at 97th bp of the nucleotide sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO. 1, G97-A97 base mutation is produced. The molecule marker provides a fast, simple and low cost gene analysis method for breeding of chicken with chicken muscle fiber-type properties, is conducive to screening of chicken with high slow muscle fiber content and good meat quality and can guide molecule marker-assistant breeding of chicken with chicken muscle fiber-type properties.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF POULTRY SCI
Polypeptide in small molecule of endothelium inhibin, nucleotide sequence for encoding the polypeptide and complementary strand
ActiveCN1916023ASmall molecular weightPromote absorptionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic engineeringNucleotideGenetic engineering
This invention relates to endostatin small molecular polypeptide, its coding nucleotide sequence and complementary strand. The endostatin small molecular polypeptide has 30 amino acid residues corresponding to a nucleotide sequence with a full length of 90 bp and a complementary strand with a length of 88 bp. The endostatin small molecular polypeptide avoids the defects of the current endostatin such as high molecular weight, limit to subcutaneous injection and intramuscular injection, large dosage and unsafety in intravenous injection. The endostatin small molecular polypeptide has such advantages as low molecular weight and no medicine accumulation, and is suitable for intravenous, intramuscular and subcutaneous injection. The coding nucleotide sequence and complementary strand can be synthesized by an automatic synthesizer, and used to manufacture endistatin in large scale by genetic engineering after recombination and transformation.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for rapidly detecting third exon single base mutation of myostatin gene
InactiveCN101724700AGood polymorphismPolymorphic shortcutMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMarker-assisted selection
The invention provides a method for rapidly detecting the third exon single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of a beef myostatin gene. In the method, aiming at the G-to-A mutation of a third exon of the myostatin gene, two groups of PCR primer pairs for respectively amplifying an upstream sequence and a downstream sequence of a G938A single base polymorphism site are designed, wherein the primer pairs are respectively provided with a mismatched primer for mutation site, and the 3' tail end of the primer is positioned on the mutation site. By utilizing the primers, different beef DNA samples can obtain different amplification results, thereby judging the polymorphism of the third exon of the myostatin gene. The method has low cost, and simple, rapid and accurate operation, is suitable for popularization and application, and is important to rapidly and accurately carry out marker-assisted selection of beef, accelerate the beef selecting and breeding process and research a rapid PCR detecting method of the field of molecular biology.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Goat S6K1 gene cDNA encoding zone nucleotide sequence
The invention relates to a cDNA nucleotide sequence which encodes S6K1 protein and is separated from a goat muscle cell and the corresponding amino acid sequence. The invention finds a conservation region by comparing the cDNA nucleotide sequences of the known human, rat, rabbit and cattle S6K1 genes and then designs a pair of primers for a cDNA coding area fragment of an RT-PCR amplified goat S6K1 gene according to the cDNA sequence of a cattle S6K1 gene (GenBank landing number is AY396564), the primers are used for amplifying the specific fragment by the PT-PCR method, the nucleotide sequence of 1563bp of the cDNA coding area of the goat S6K1 gene and the corresponding amino acid sequence are obtained after sequencing. The obtained 1563bp nucleotide sequence can be further used for full-length cDNA cloning of the goat S6K1 gene and detecting the tissue expression specificity of the S6K1 gene by the RT-PCR or the hybridization method, which can also be used for preparing an antibody for detecting the S6K1 after recombinant expression.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
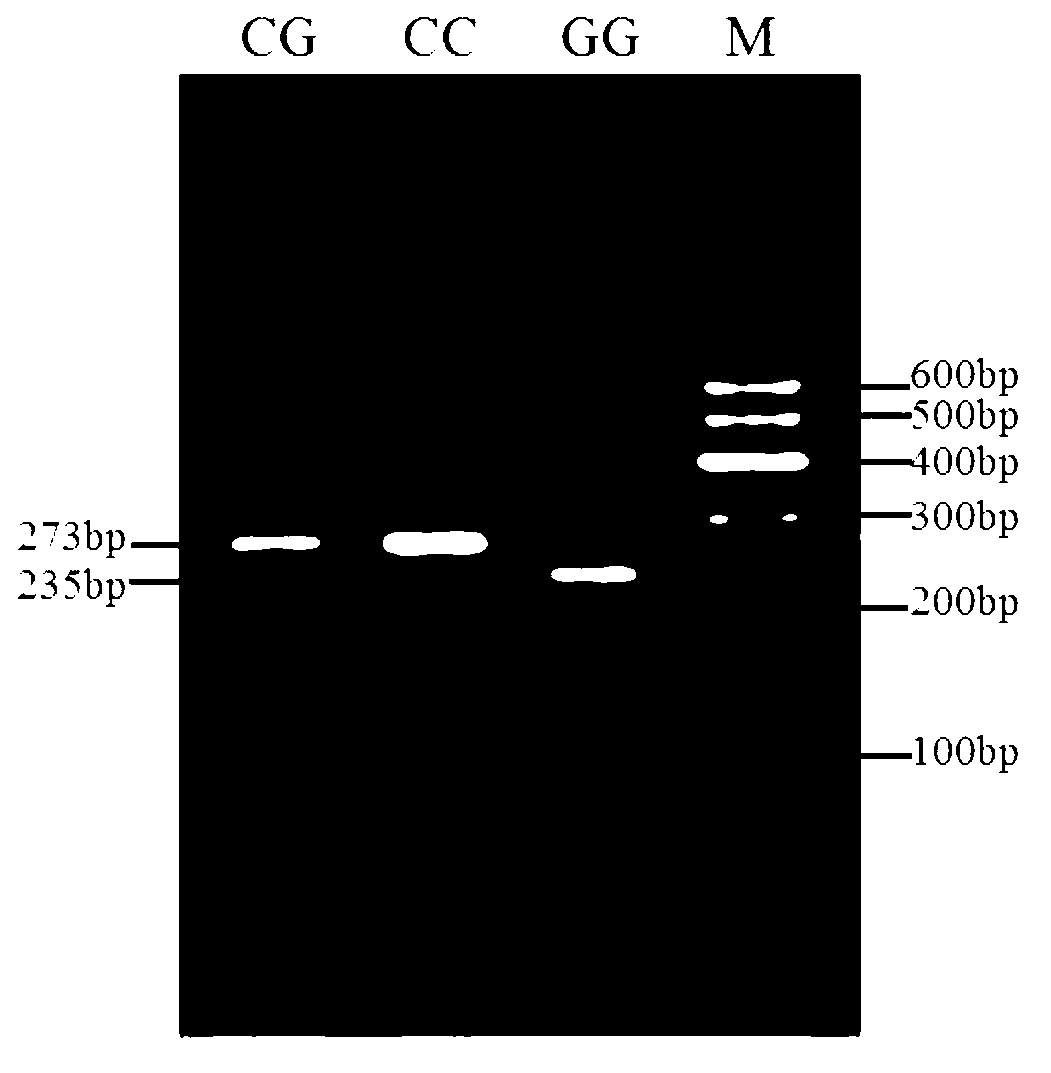
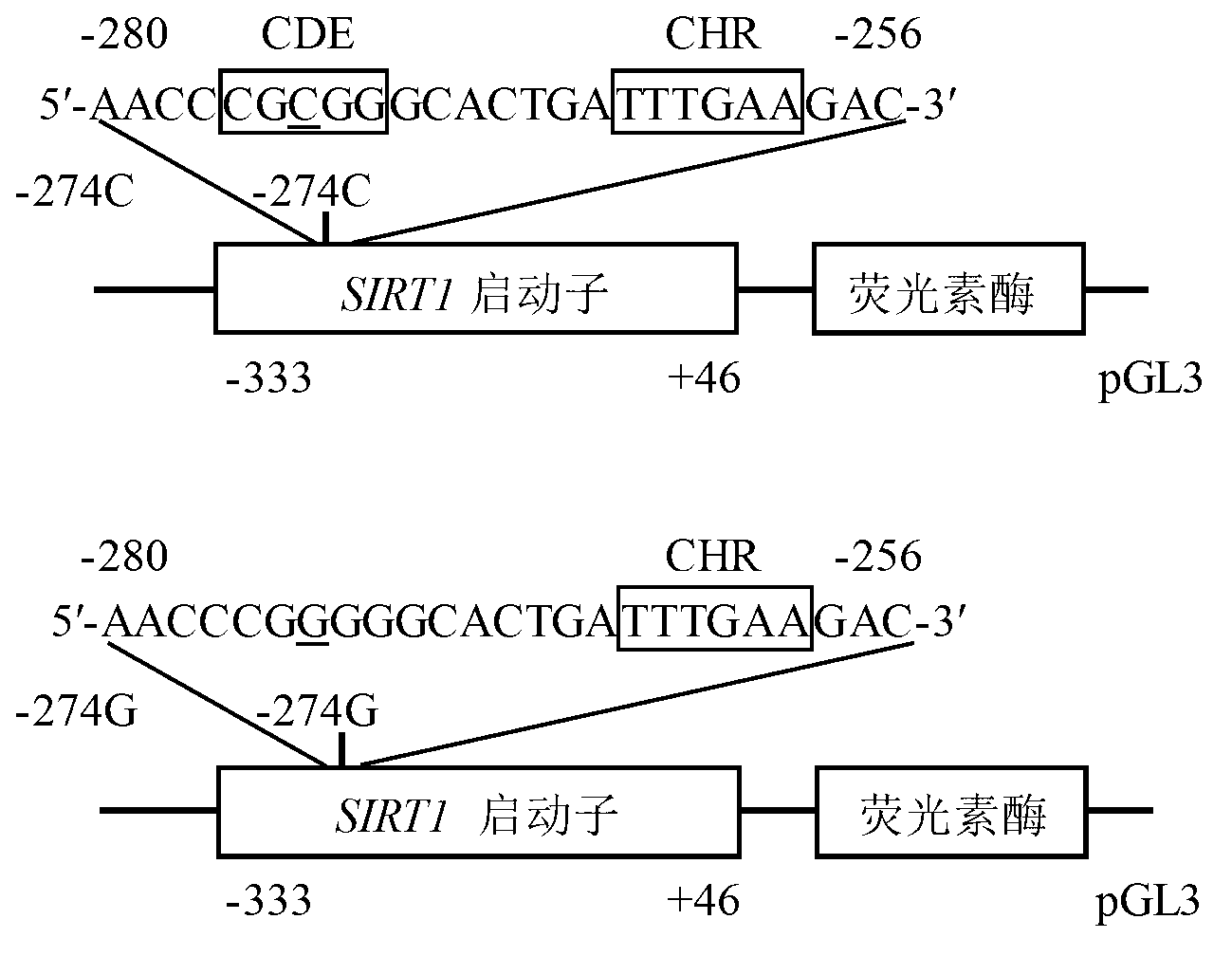
Method for quickly detecting RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism) of SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) of common ox SIRT1 (silent information regulator 1) gene
The invention discloses a method for quickly detecting RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism) of SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) of a common ox SIRT1 (silent information regulator 1) gene promotor region. The method comprises the following steps of: taking whole genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of common ox blood as a template and a primer pair P (F and R) as a primer; performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on the common ox SIRT1 gene promotor region; digesting a PCR amplification product by using restriction endonuclease SmaI; performing agarose gel electrophoresis on segments after enzyme digestion; and identifying the SNP of the common ox SIRT1 promotor region according to a result of the agarose gel electrophoresis. Because important functions including muscle differentiation, lipogenesis and the like related to the SIRT1 are closely related to common ox meat quality characteristics, and the SNP can significantly affect the promotor activity of the SIRT1 gene and is related to various important economic characteristics of the common ox, the detection method provided by the invention lays a foundation for the establishment of the relationship between the SNP and growth characteristics of the SIRT1 gene, and can be used for marker assisted selection of the growth characteristics of the Chinese common ox so as to facilitate rapid establishment of common ox populations with excellent genetic resources.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Sinkiang Alaska grayling heritable variation detection method utilizing microsatellite marker Thymalag
ActiveCN105779614AEasy accessSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic markerSpecific primers
The invention discloses a Sinkiang Alaska grayling heritable variation detection method utilizing a microsatellite marker Thymalag. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a genome DNA in Sinkiang Alaska grayling muscle is extracted and diluted for use; then, a microsatellite core sequence contained in a Sinkiang Alaska grayling DNA sequence is utilized, and specific primers are designed at the two ends of the sequence; then, the primers are used for performing PCR amplification on genome DNA of different geographic stocks or individuals inside Sinkiang Alaska grayling, and a PCR product is detected; strips of the product are analyzed, the gene type of each individual is determined, and a genetic polymorphic map of Sinkiang Alaska grayling is obtained. The method has the advantages that the genetic variation map of the genetic marker Thymalag of Sinkiang Alaska grayling can be obtained rapidly, and the method is simple and convenient to implement.
Owner:广东华轻质量检测服务中心有限公司
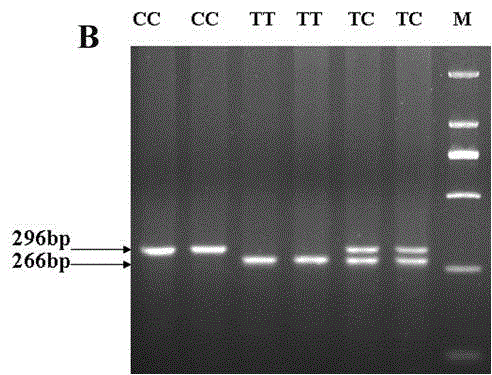
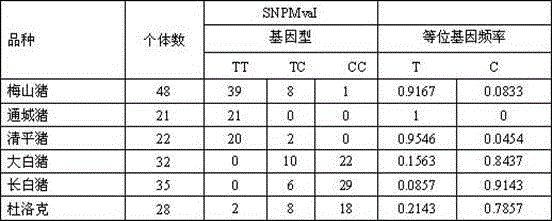
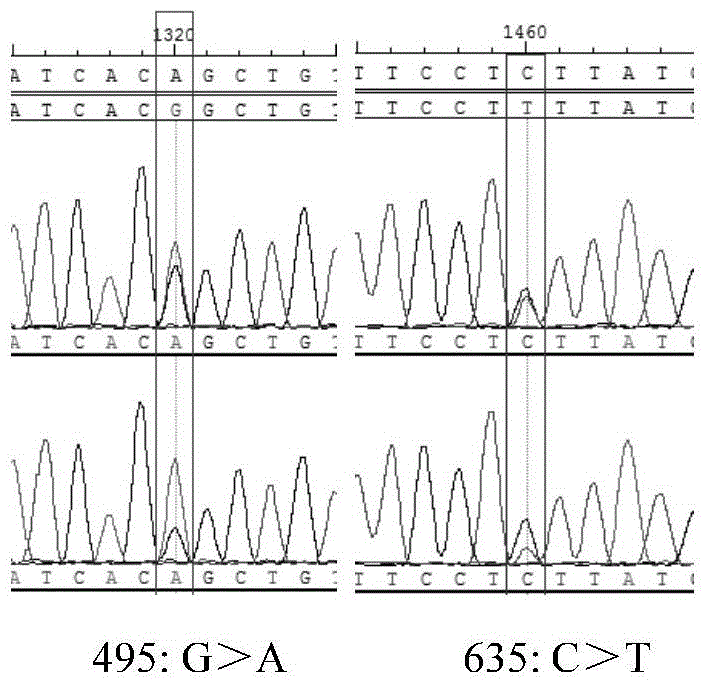
Molecular marker related to pH (Potential of Hydrogen) value character of pig muscle
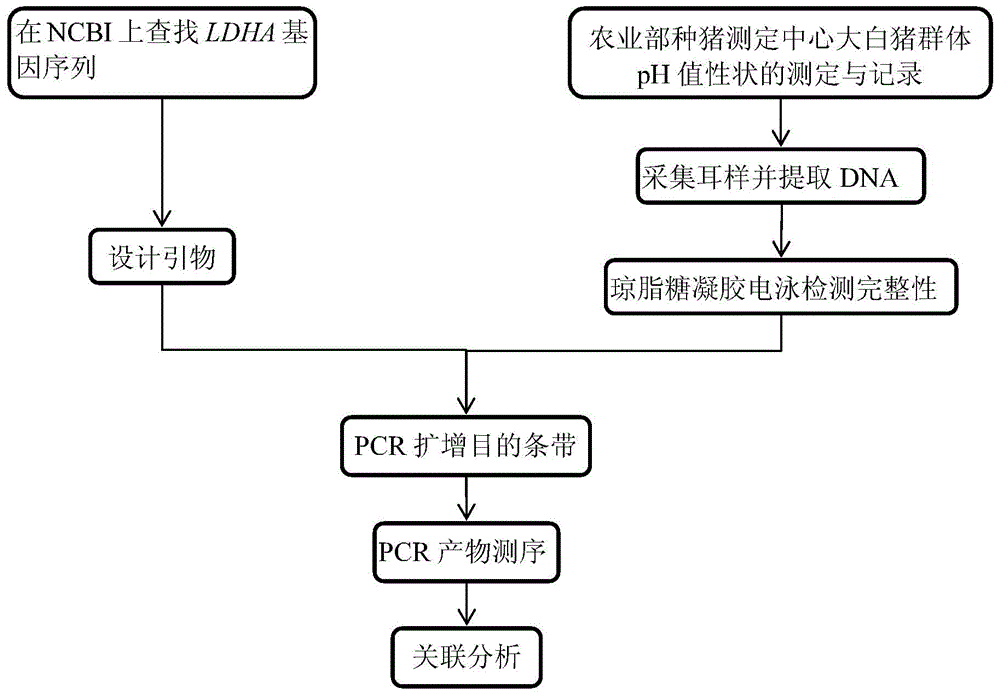
InactiveCN104480216AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHydrogenMarker-assisted selection
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of livestock molecular markers, and particularly relates to an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker related to a pH (Potential of Hydrogen) value character of pig muscle. The molecular marker is obtained by LDHA (Lactate DehydrogenaseHydroxyacyl) gene cloning and has a nucleotide sequence as shown in Figure 4.In the sequence as shown in Figure 4, the 495th position has allele G or A base substitution, and the 635th position of the sequence has allele C or T base substitution. The new molecular marker is provided for assistant selection of pig markers.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
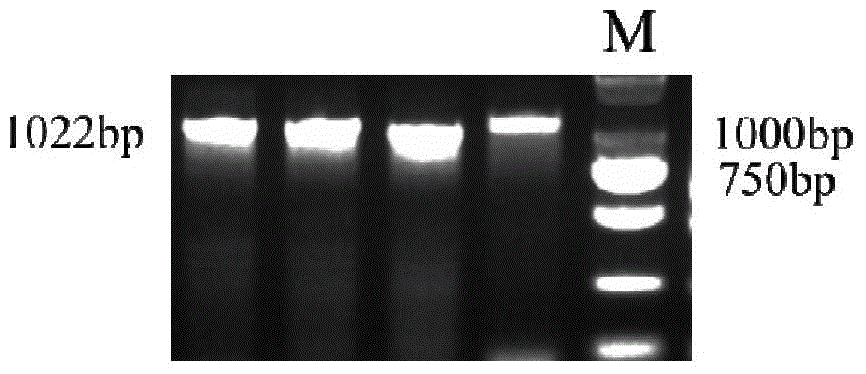
Pig muscle quality correlated numerator mark CSRP3 clone and application thereof
InactiveCN101319252AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMarker-assisted selectionEnzyme digestion
The invention belongs to the livestock gene engineering technical field, in particular relating to a molecular marker GSRP3 and an application thereof, wherein, the molecular marker GSRP3 is applied as porcine marker-assisted selection and relates to quality properties of porcine muscle. The molecular marker is produced by cloning a CSRP3 gene, and a cDNA sequence of the molecular marker is shown in a sequence table SEQ ID NO: 1. A base substitution of C1924-T1924 exists at 1924bpth of a sequence table SEQ ID NO: 2, and leads to the enzyme digestion polymorphism of TaqI PCR-RFLP. The invention also discloses a primer used for amplifying an intact cDNA sequence and a partial DNA sequence of the CSRP3 gene and a method for polymorphic detection, and provides a novel molecular marker for the porcine marker-assisted selection.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
South China Sea conotoxin coding sequence as well as preparation method and application of South China Sea conotoxin
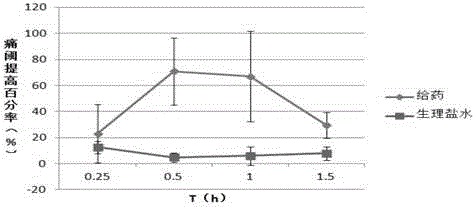
The invention discloses a South China Sea conotoxin coding sequence as well as a preparation method and application of the South China Sea conotoxin. A new O-super family toxin gene Cq1.0 is discovered from the venom canal of South China Sea conotoxin through a method for constructing a cDNA library and is obtained by utilizing a high-throughput sequencing method. A mouse hot plate experiment and a zebrafish muscle injection experiment discover that the conotoxin Cq1.0 has the effects of central analgesia and nerve anesthesia, can be taken as a probe for the classification and the identification of ion channel types and subtypes or for the research and the development of tool drugs and the preparation of analgesic drugs.
Owner:RES INST OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV & SHENZHEN
Specific primer for detecting mRNA expression levels of MSTN genes of cows and fluorescent quantitative detecting kit
InactiveCN104894266AConvenient and fast quantitative detectionMonitor growth and development statusMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPhysiologyNucleotide
The invention provides a specific primer for detecting the mRNA expression levels of MSTN genes of cows. The specific primer is characterized by having the nucleotide sequence as follows: an upstream primer has the sequence: 5'-AACCAGGAGAAGATGGAC-3'; and a downstream primer has the sequence: 5'-TTAGAGGGTAACGACAGC-3'. The invention also provides a corresponding fluorescent quantitative PCR detecting kit. The specific primer can be used for achieving the aims of conveniently, rapidly and quantitatively detecting the mRNA transcriptional levels of MSTN genes, monitoring the muscle growth and development states of different cows (including milk cows, cattle and yaks), different tissues and different periods and also identifying diseases related to cow muscle dysplasia. The specific primer has the advantages of high sensitivity, good stability and low experimental cost on the aspect of detecting the transcriptional levels of the genes.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
RT-LAMP detection kit and detection method of infectious myonecrosis viruses
InactiveCN106086233AAccurate identificationSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementWater bathsInfectious bronchitis virus
The invention discloses an RT-LAMP detection kit and a detection method of infectious myonecrosis viruses, wherein the kit consists of a mixed solution of outer primers F3 and B3 and inner primers FIP and BIP; and nucleotide sequences of the primers F3, B3, FIP and BIP are separately shown as SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2, SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.4. According to the detection method, an RT-LAMP detection system is used for detecting whether a sample contains the infectious myonecrosis viruses or not. The method is simple and convenient to operate and is relatively low in requirement on experimental instruments, and the method can be completed in a normal constant-temperature water bath kettle within 60min; moreover, by virtue of a method of adding a dye to a final product and by directly observing a result with naked eyes, the method can rapidly and accurately identify the infectious myonecrosis viruses; and the method has a broad popularization and application prospect in prawn aquaculture.
Owner:山东拜尔检测股份有限公司
Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) related to sheep eye muscle property and application thereof
InactiveCN101974514AThick eye musclesIncreasing the thicknessMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationLarge eyesBio engineering
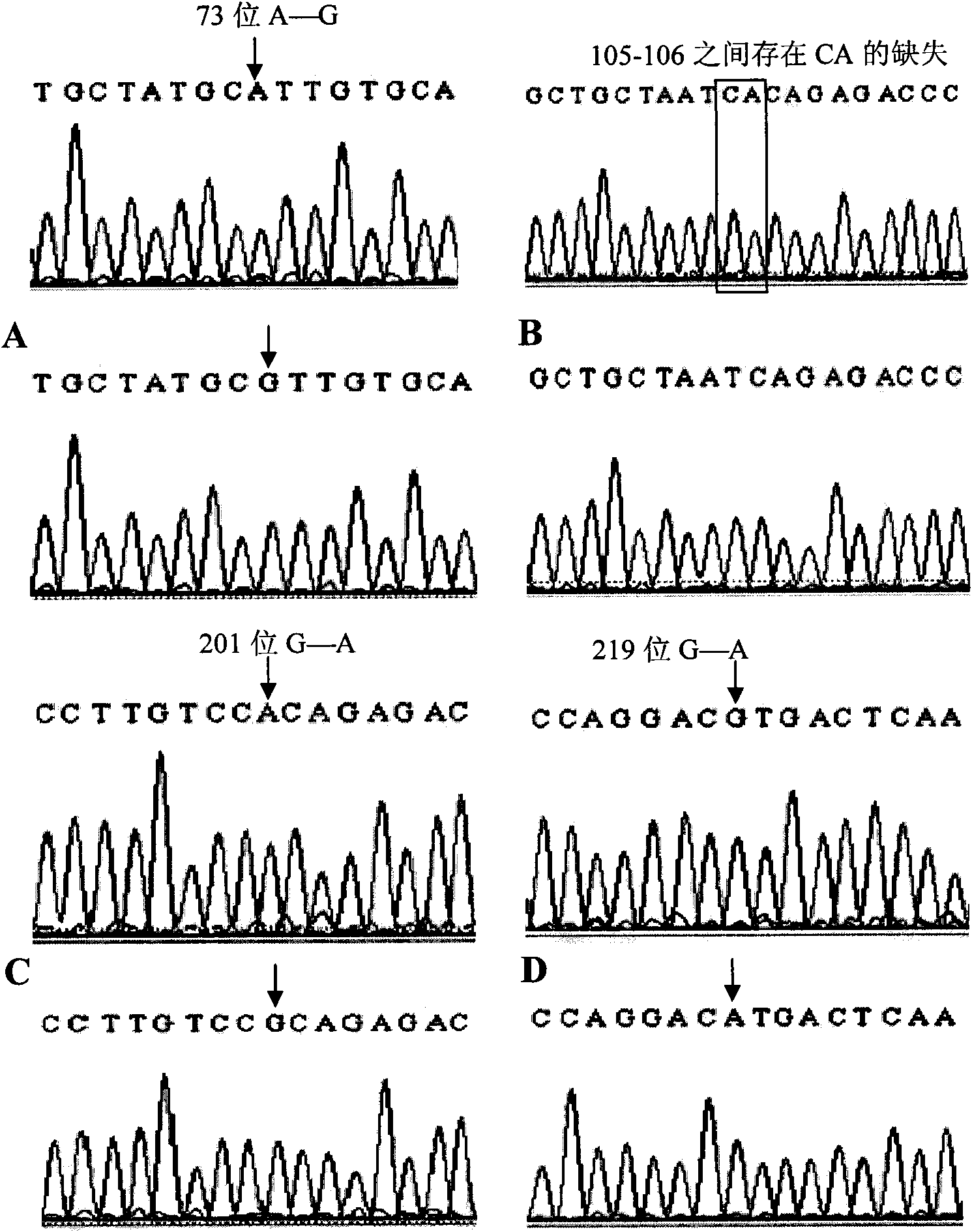
The invention relates to the field of biological engineering, in particular to a method for predicting a sheep eye muscle property by single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP). Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification is performed on the total deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of sheep by primers shown as SEQ ID No.2 and SEQ ID No.3, the SNP of a PCR amplification product is detected, the 73rd basic group at the 5' end of SEQ ID No.1 in a sequence table is determined as G or A and an individual with a G allelic gene has a large eye muscle area and a large eye muscle width. Due to the detection of a polymorphic site, a new material is provided for molecular breeding and scientific basis is provided for the marker-assisted selection of the sheep eye muscle property.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for increasing activity of myogenin (MyoG) gene promoter
InactiveCN103194450AImprove expression efficiencyHigh expression activityVector-based foreign material introductionDNA preparationPromoter activityNucleotide sequencing
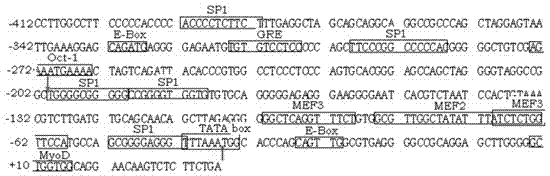
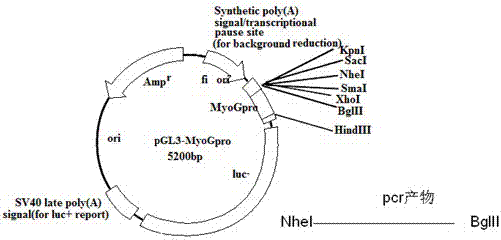
The invention relates to a method for increasing the activity of a myogenin (MyoG) gene promoter, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The method for increasing the activity of the myogenin (MyoG) gene promoter is characterized in that a deletion fragment which is 373 bp in length and has higher muscle specific promoter activity, namely pGL3-MyoGpro373, is obtained by adopting a method for analyzing the activity of a promoter deletion fragment by means of cloning a nucleotide sequence, which is at the 5' end control region of the MyoG gene and is 2125 bp in length; a promoter element therein having the SP1 positive regulation effect is cloned; the two fragments are connected in series, so that an expression carrier containing two copying numbers of promoter regulatory elements is constructed; the expression carrier is called as pGL3-MyoGpro373-double, namely a promoter sequence having double characteristics; and the base composition of the expression carrier is represented by Seq ID No:2.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker related to muscle drip loss character of meat rabbit and application of SNP molecular marker
ActiveCN113718041AImportant benefitsImportant social valueMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPhysiologyNucleotide
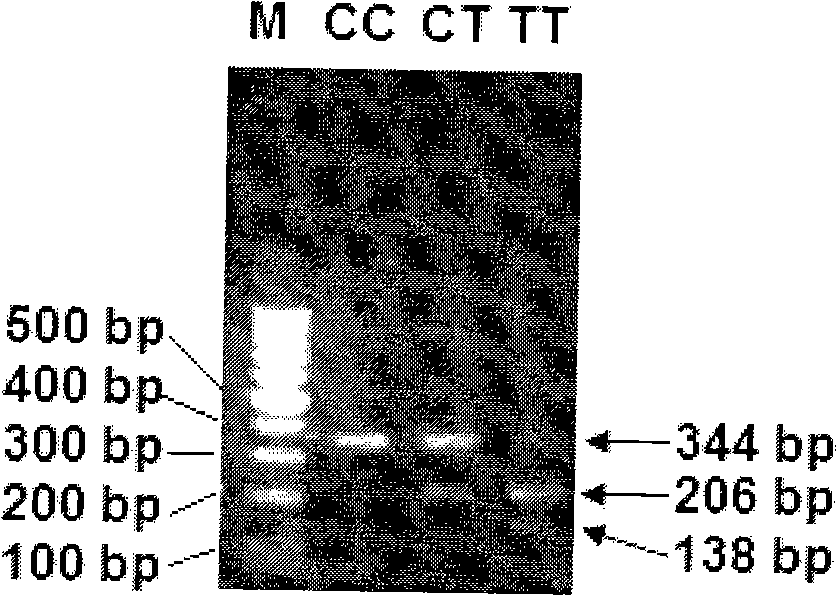
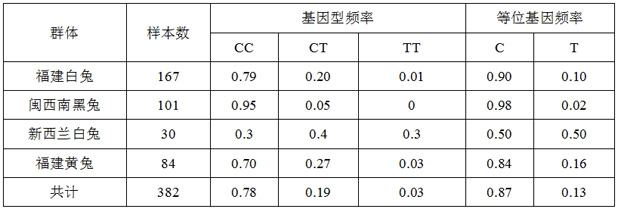
The invention relates to an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker related to a muscle drip loss character of a meat rabbit and application of the SNP molecular marker. The SNP molecular marker is located in a 3' end non-coding region of a meat rabbit FABP4 gene, the nucleotide sequence of the SNP molecular marker is shown as SEQ ID No.1, a C / T mutation exists at the 101th basic group of the sequence, the mutation causes the nucleotide of the sequence to generate polymorphism, and when the genotype of the locus is TT, the meat rabbit to be detected belongs to an individual with low muscle drip loss.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com