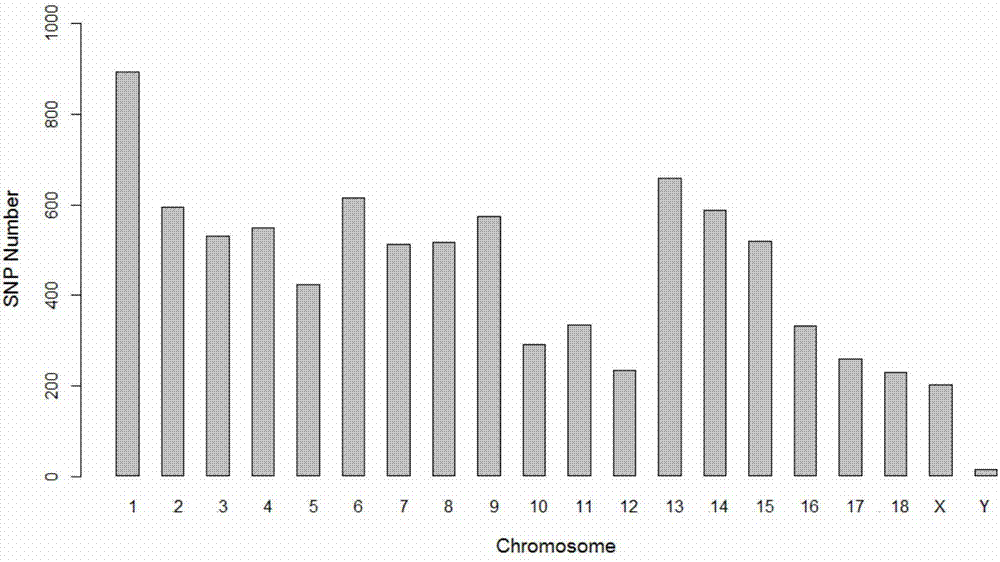
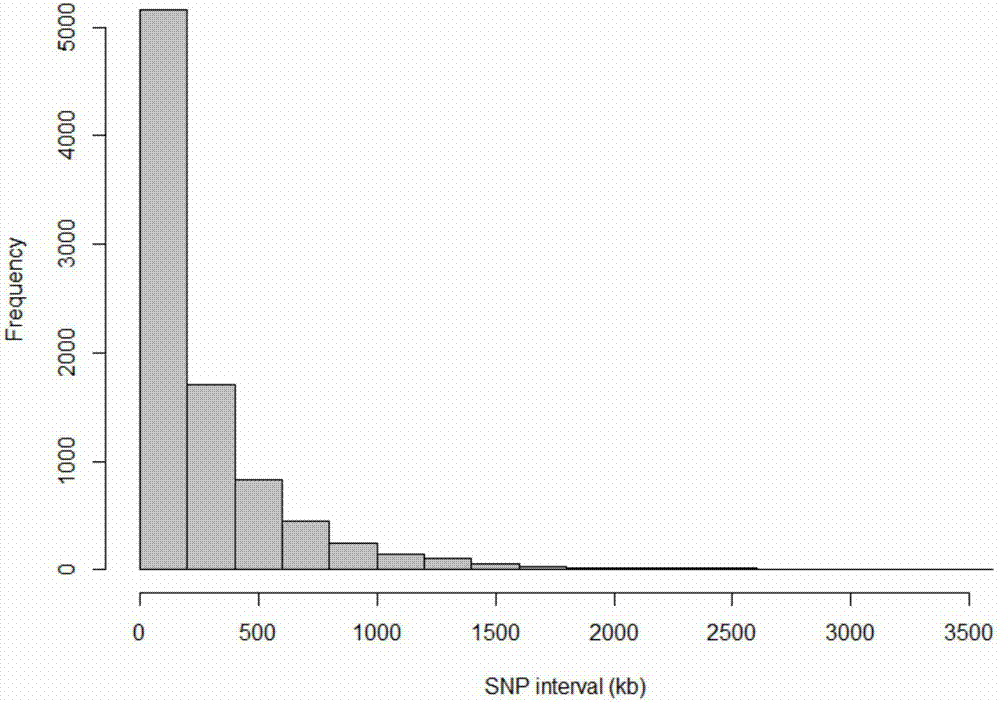
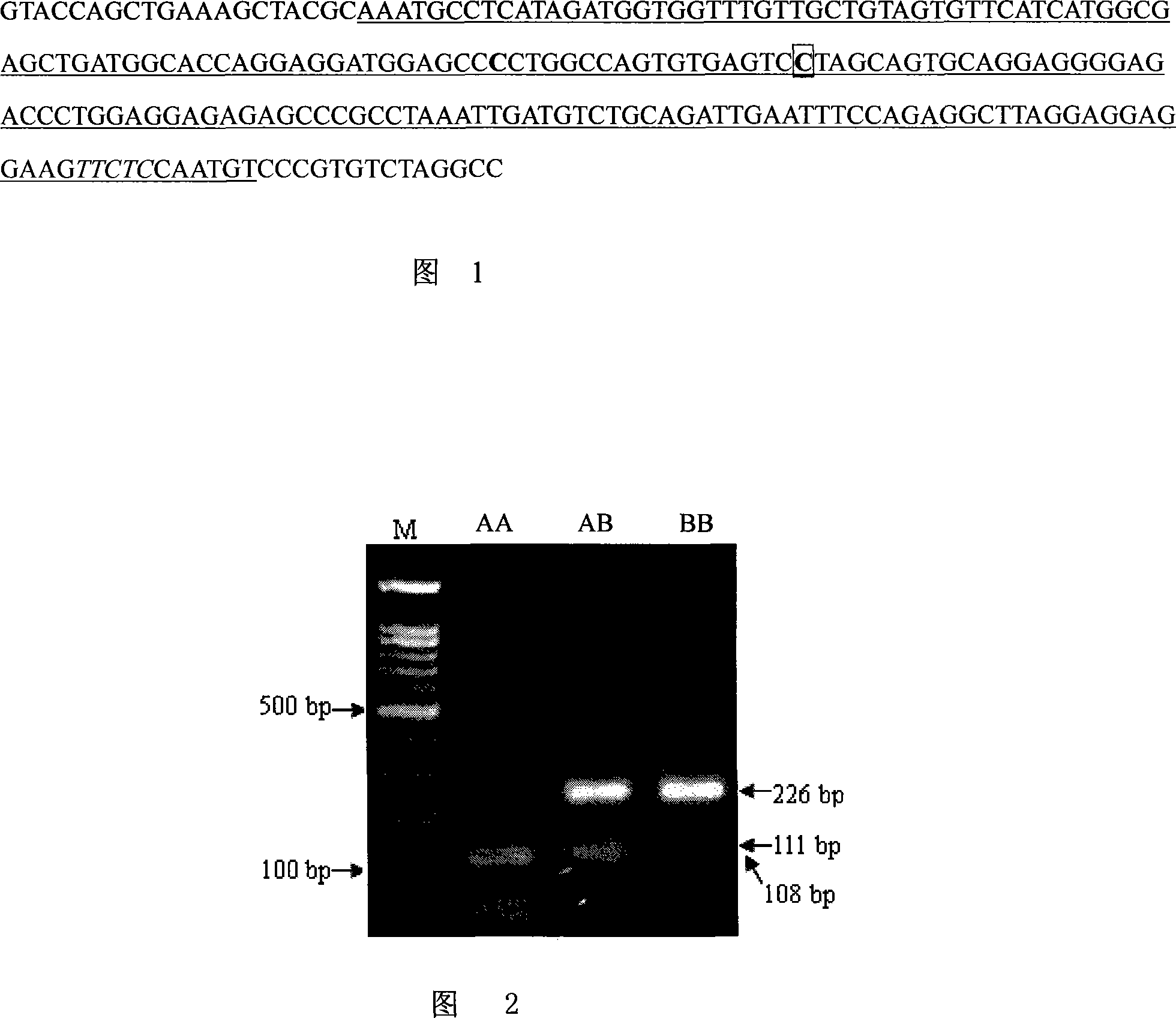
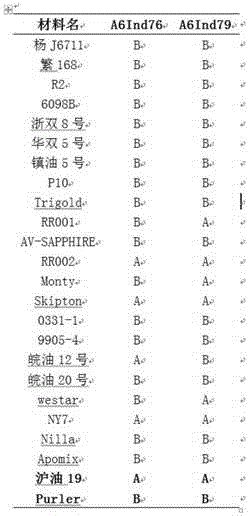
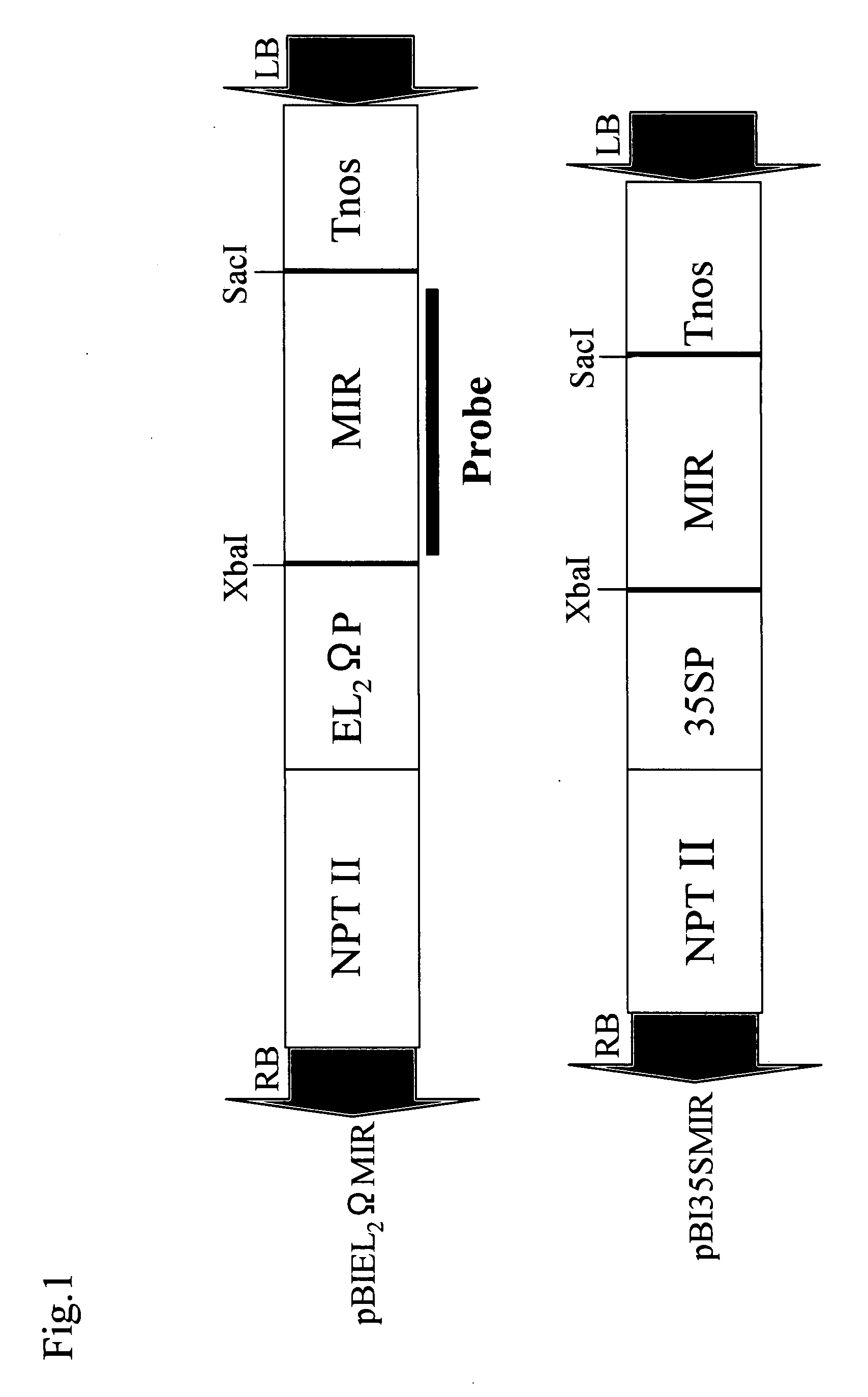
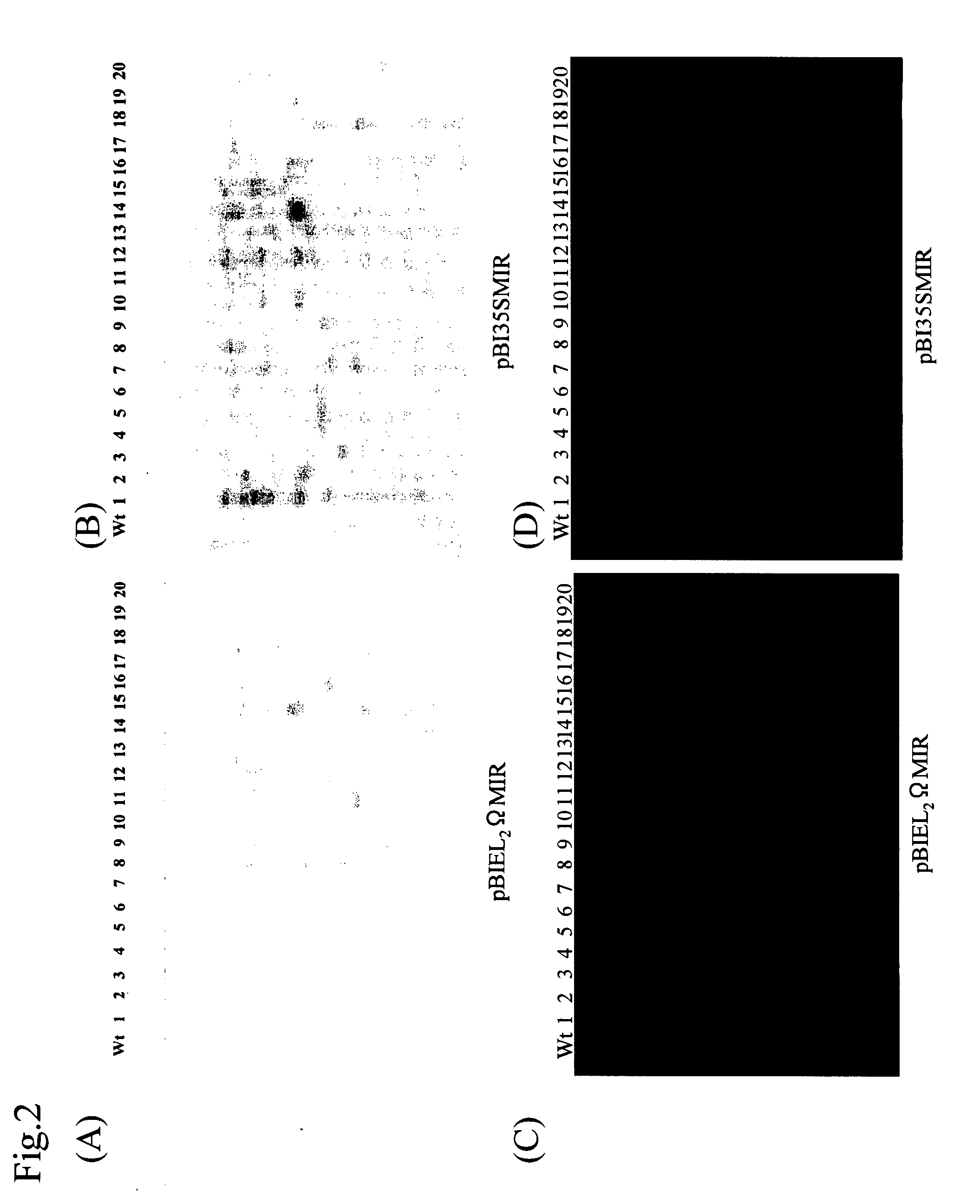
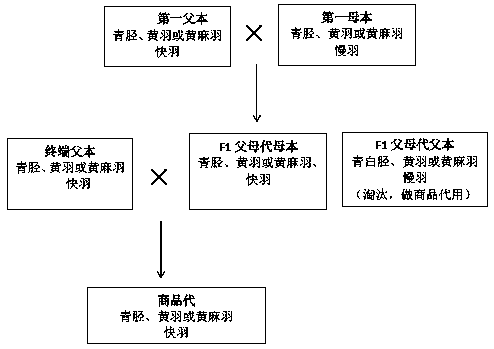
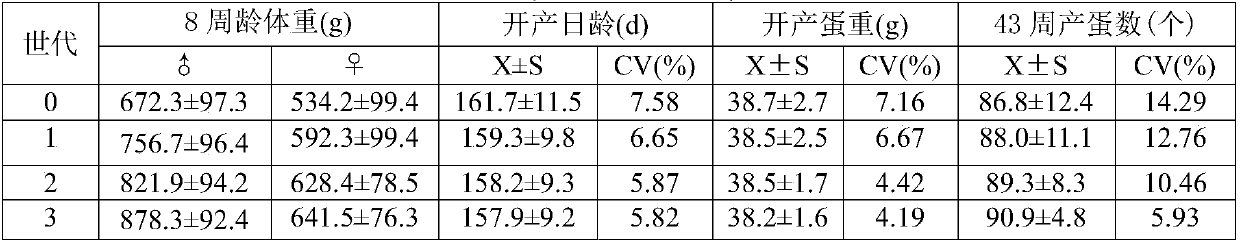
Patents
Literature
1624 results about "Molecular breeding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Molecular breeding is the application of molecular biology tools, often in plant breeding and animal breeding...
Fish breeding method for improving CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing and passage efficiency through fish roe preserving fluid
ActiveCN106191124AHigh target shooting efficiencyImproving gene editing passaging efficiencyMicroinjection basedAnimal husbandryFisheryMicroinjection
The invention belongs to the field of fish molecular breeding, and particularly relates to a fish breeding method for improving CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing and passage efficiency through fish roe preserving fluid. According to the method, the fish roe preserving fluid technology, the microinjection technology an the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology are ingeniously combined, the targeting efficiency of the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology and gene editing passage efficiency are greatly improved, the screening time needed by a gene editing method for fish breeding is obviously saved, and the method is of great significance in promoting rapid development of gene editing fish breeding.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Core SNP sites combination maizeSNP384 for building of maize DNA fingerprint database and molecular identification of varieties
ActiveCN104532359AImprove stabilityGood repeatabilityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular identificationAgricultural science
The invention discloses a core SNP sites combination maizeSNP384 for building of a maize DNA fingerprint database and molecular identification of varieties, and an application of the core SNP sites combination. The invention provides applications of 384 SNP sites in any one of the following conditions: (1) building of the maize DNA fingerprint database; (2) detecting of the authenticity of maize varieties; (3) genetic analysis of corn germplasm resources; and (4) molecular breeding of maize, wherein the physical positions of the 384 SNP sites are determined by comparison on the basis of a whole genome sequence of the maize variety B73; the version number of the whole genome sequence of the maize variety B73 is B73 RefGen V1; and the 384 SNP sites are MG001-MG384. An experiment proves that the 384 SNP sites can be applied to building of the maize variety DNA fingerprint database, identification of the variety authenticity, dividing of germplasm resource groups, and other related researches.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Plant stress tolerance correlative protein, coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a plant stress tolerance correlative protein, a coding gene and an application thereof. The plant stress tolerance correlative protein is the protein of the following (a) or (b): (a), a protein formed by an amino acid sequence shown in a sequence 1 in a sequence table; (b), a protein which is formed in a way that the amino acid sequence of the sequence 1 in the sequence table is substituted and / or lost and / or added by one or a plurality of amino acid residues, is correlative to plant stress tolerance and is derived from the sequence 1. The invention also provides the coding gene of the protein. The coding gene of the plant stress tolerance correlative protein is introduced into plant cells, and a transgenic plant variety with reinforced adverse circumstance stress tolerance to abiotic substances, such as salt, and the like can be obtained. The invention has very important theoretical and practical meanings for improving and reinforcing the stress tolerance of plants, increasing the yield, quickening the breeding process of stress tolerance molecules and effectively saving water resources.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
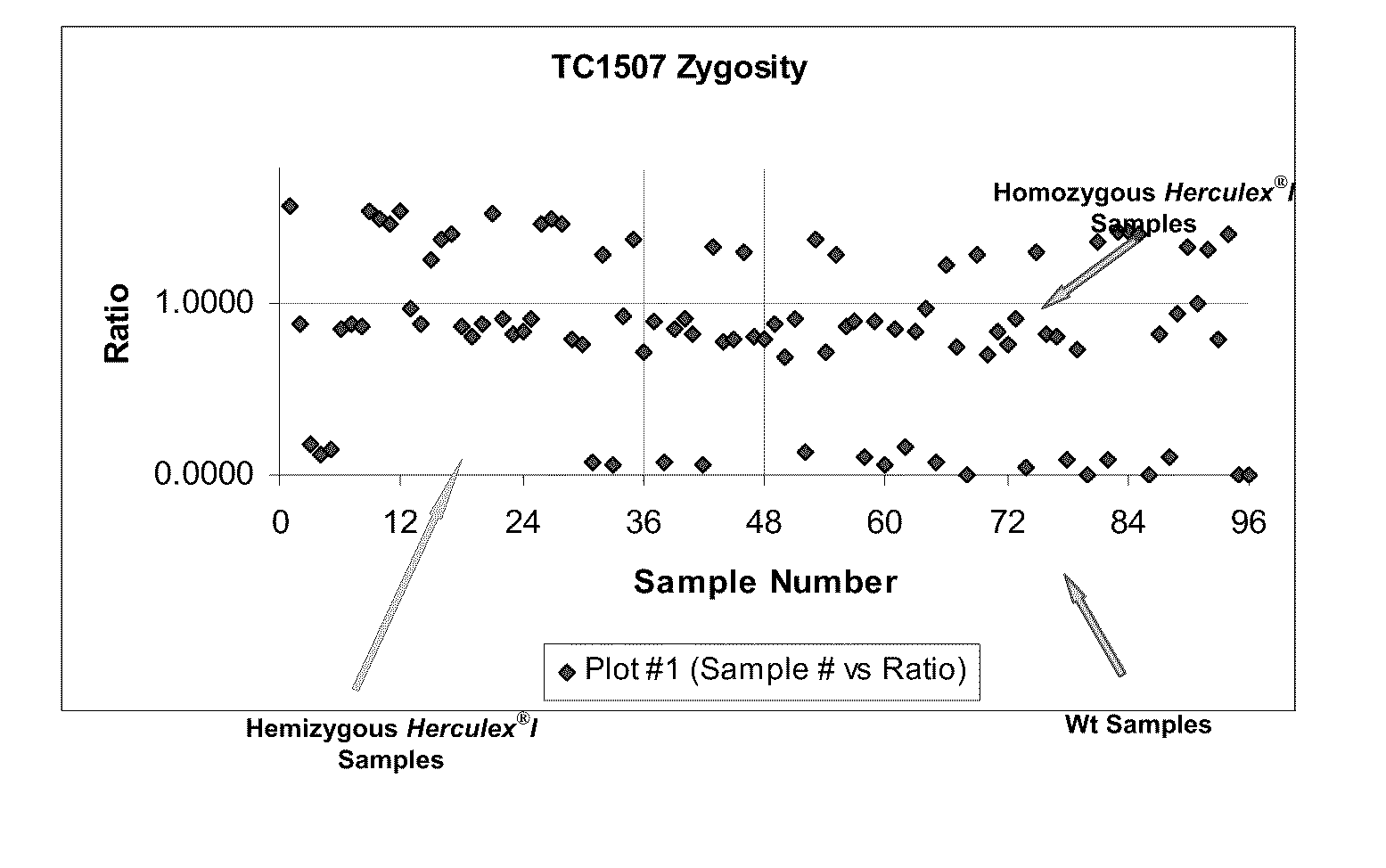
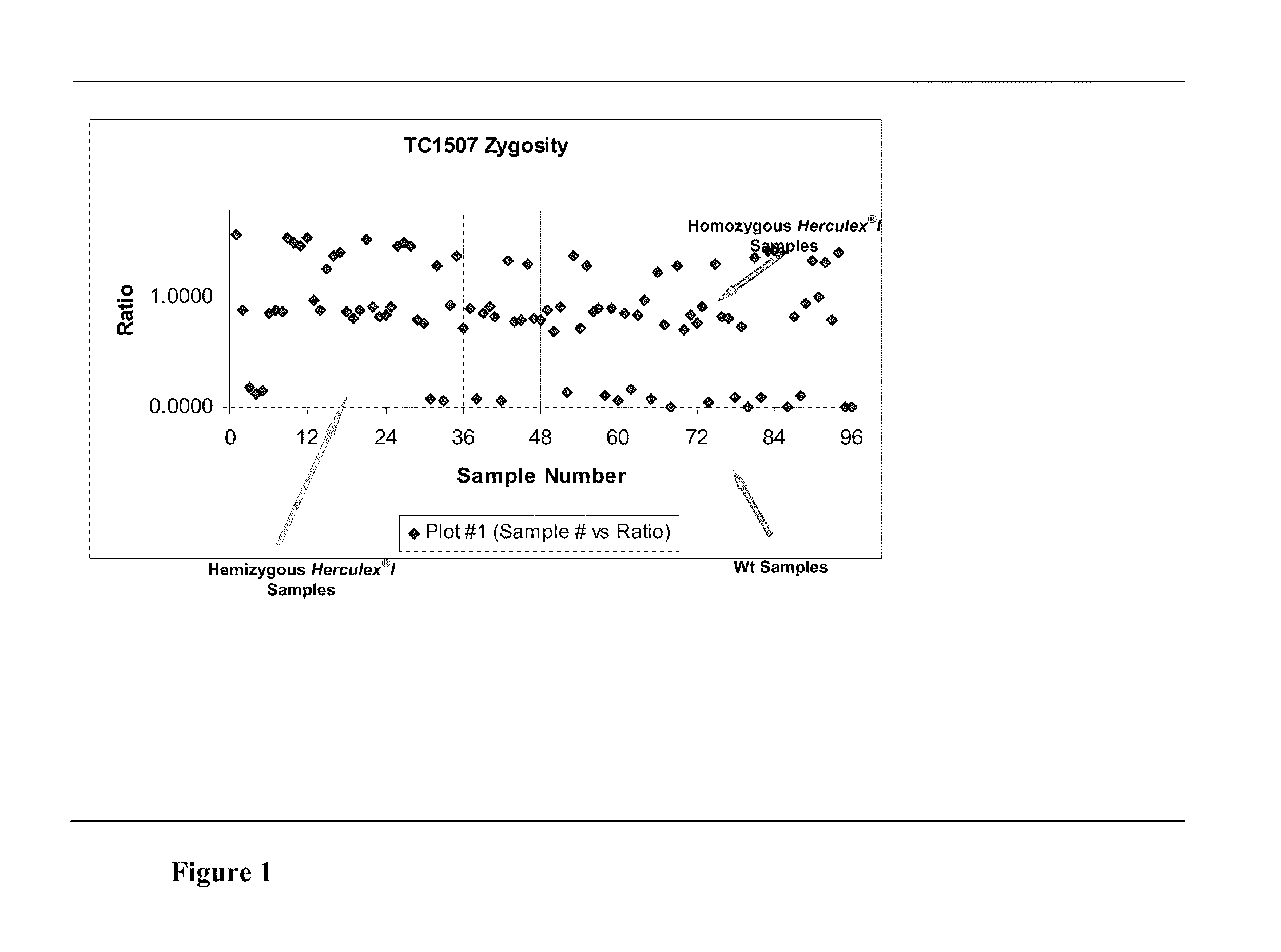
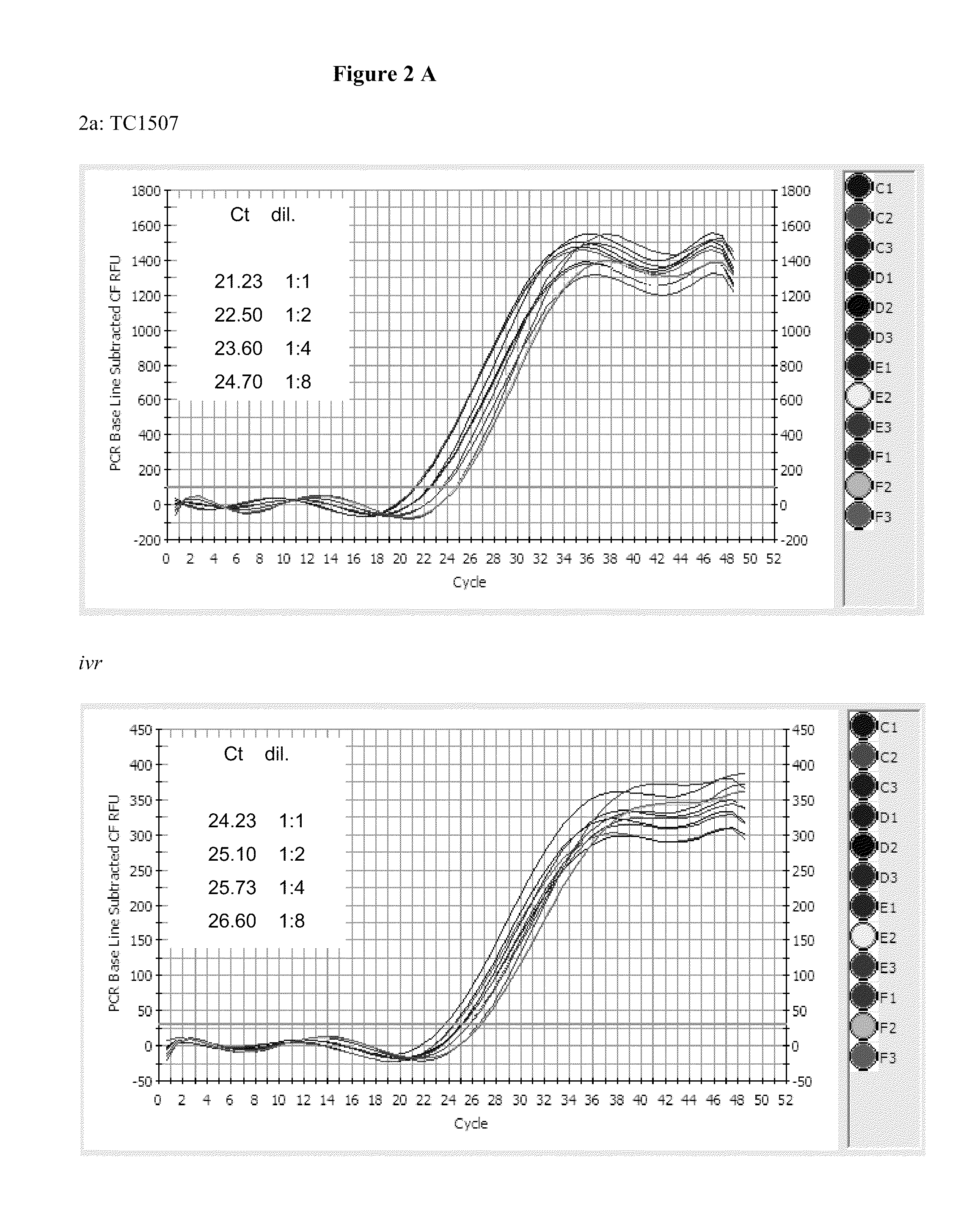
Endpoint taqman methods for determining zygosity of corn comprising tc1507 events
InactiveUS20110151441A1High throughput zygosity analysisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesPcr assay
A method for zygosity analysis of the maize Cry1F event TC1507 is provided. The method provides TC1507 event-specific and maize endogenous reference gene-specific primers and TaqMan probe combinations for use in an endpoint biplex TaqMan PCR assay capable of producing robust genotype calls for assisting in molecular breeding of TC1507.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
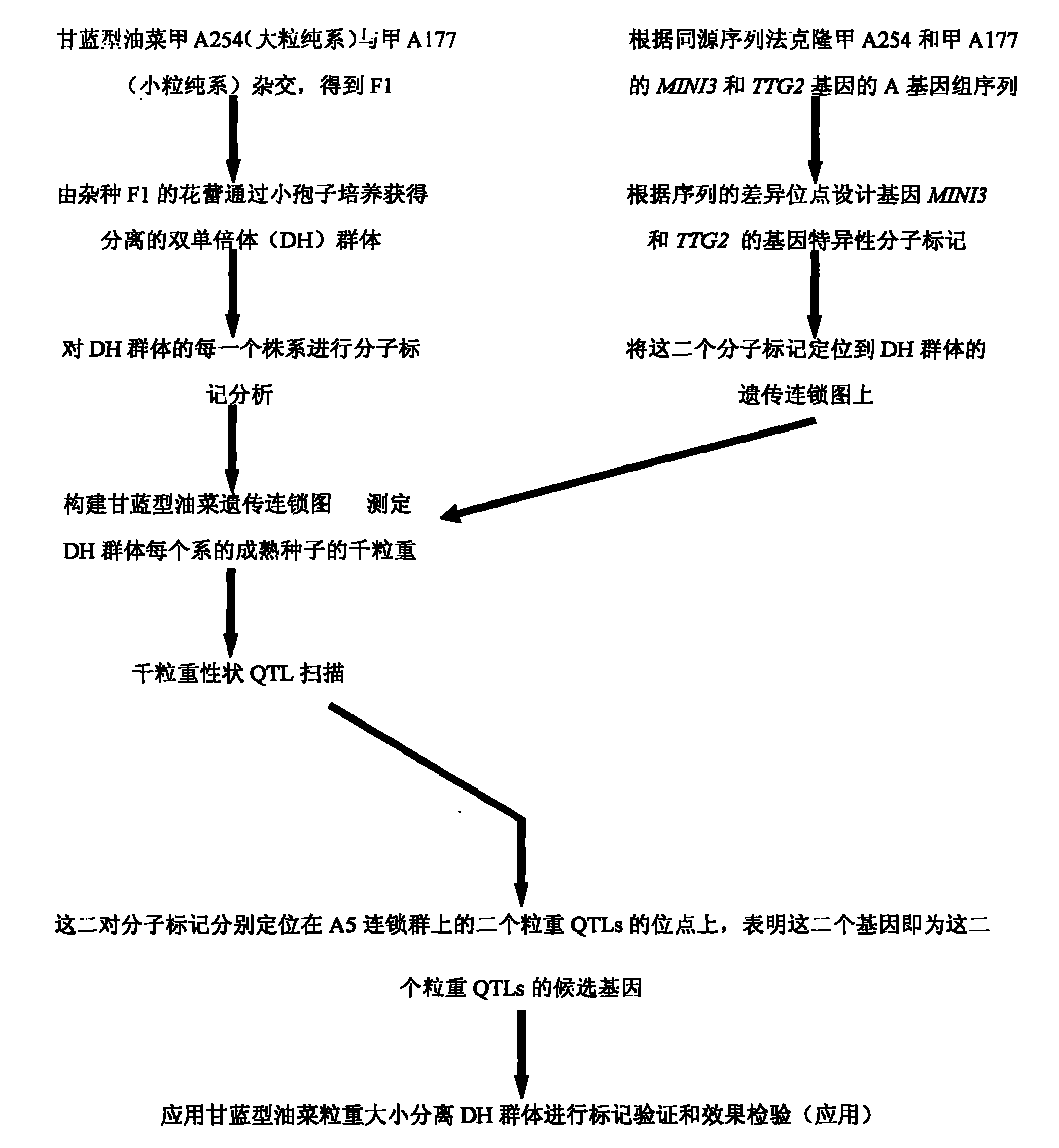
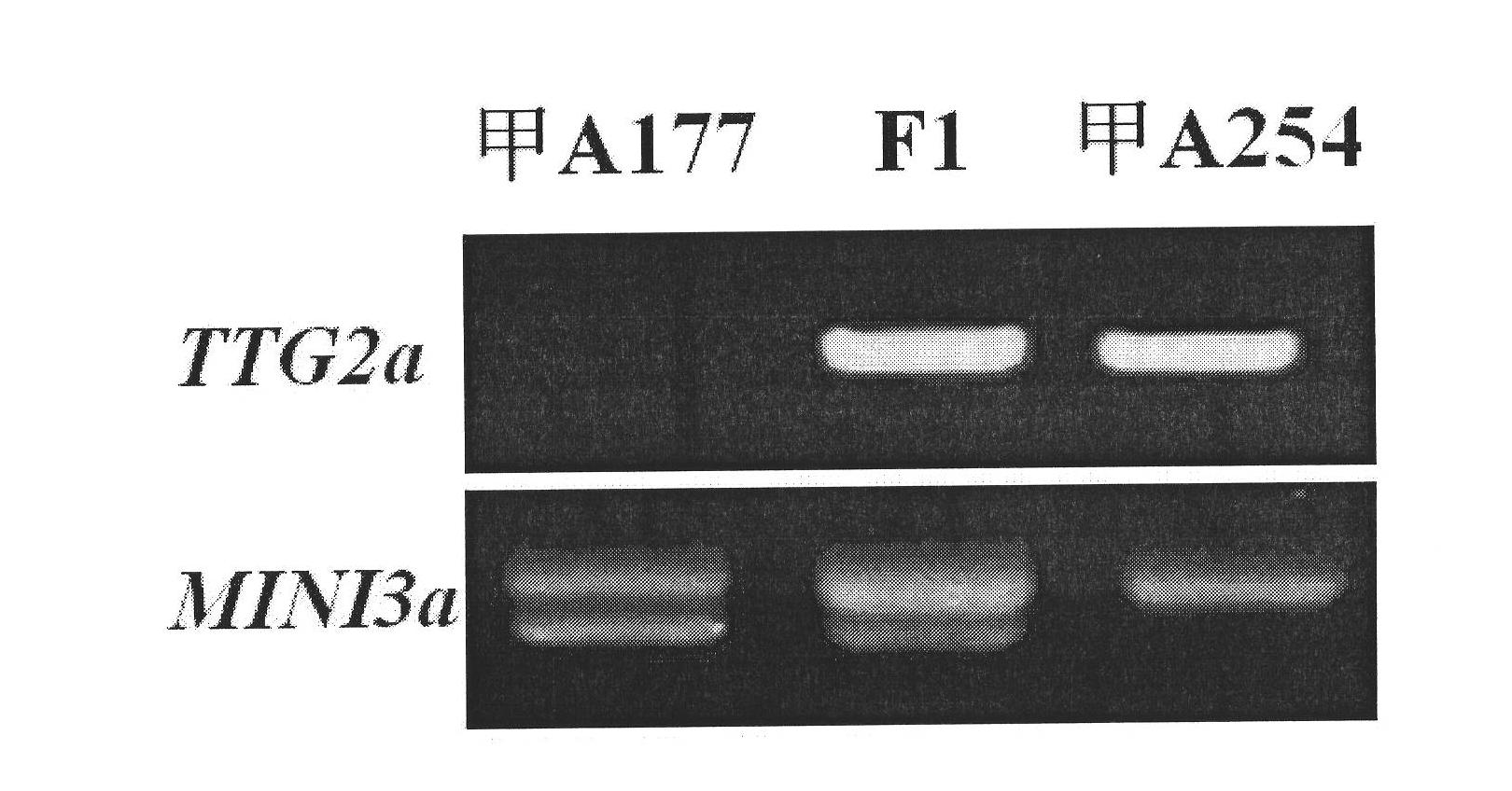
Specific molecular markers of related genes of brassica napus grain weight and application thereof
InactiveCN101962640ASpeed up the processOvercome the downside of choosingMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAgricultural scienceCandidate Gene Association Study
The invention belongs to the field of rape molecular breeding, and relates to preparation of specific molecular markers of related genes MINI3 and TTG2 of the brassica napus grain weight. Double haploid colony (DH) is constructed with brassica napus I A 254 as a female parent and a brassica napus I A 177 as a male parent through hybridization, and the DH colony genotype and the thousand seed weight data are analyzed to obtain a QTLs locus of grain weight character. The MINI3 and the TTG2 genes of the IA254 and the IA177 are cloned by using a homology based candidate gene method, specific molecular markers MINI3a and TTG2a of the MINI3 and the TTG2 genes are designed according to sequence different locuses, and the molecular markers MINI3a and TTG2a are located on two grain weight QTLs locus of an A5 linkage colony for related verification and application, which proves that the molecular marker prepared by the invention is a novel genetic marker. The gene sequence is obtained firstly. The invention provides a novel marker for the molecular breeding of the brassica napus grain weight, and also provides useful information for candidate gene clone and marker auxiliary selection of thethousand seed weight character locuses of the brassica napus.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
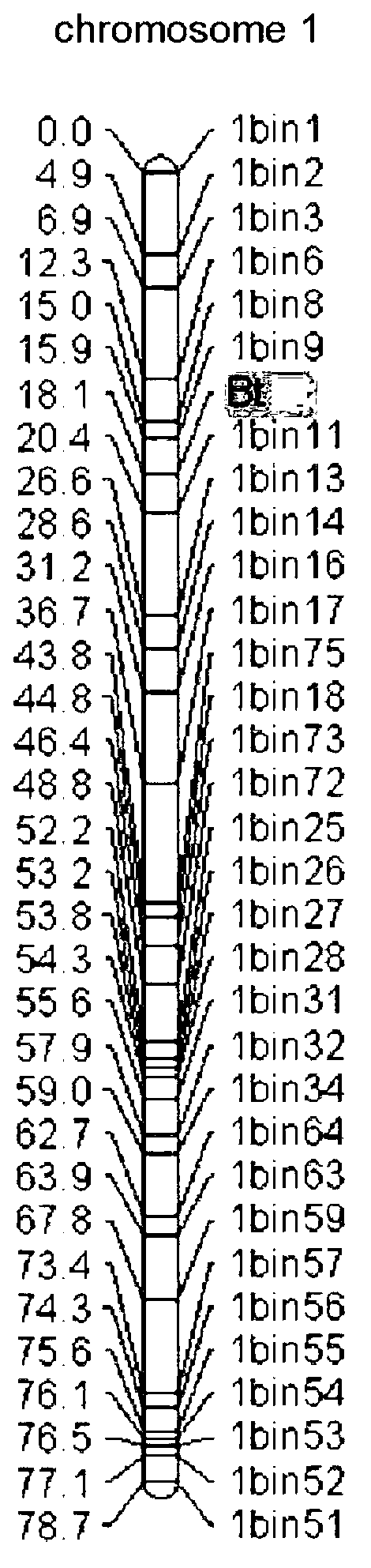
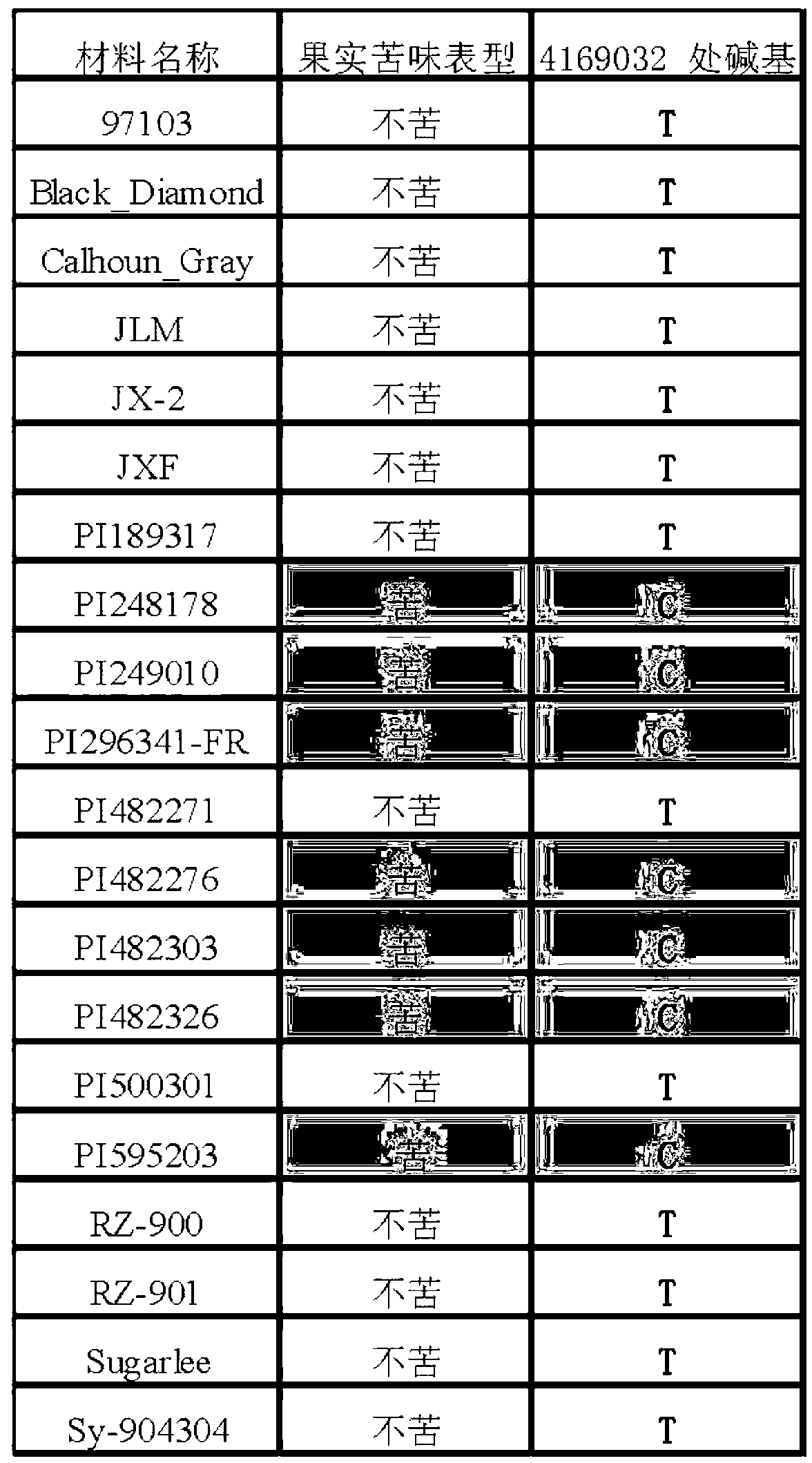
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) site and CAPS (cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence) mark interlocked with citrullus lanatus fruit bitter taste gene Bt (bitterness)
ActiveCN103194444AShorten the timeShorten the breeding cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationHigh densityMolecular breeding
The invention belongs to the fields of a gene sequence and an obtaining method of the gene sequence, and particularly relates to an obtaining method of an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) site and a CAPS (cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence) mark interlocked with a citrullus lanatus fruit bitter taste gene Bt (bitterness). The SNP site and the CAPS mark interlocked with the citrullus lanatus fruit bitter taste have nucleotide base sequences in SEQ ID NO:1-2 in a sequence table. The citrullus lanatus fruit bitter taste gene is primarily positioned by screening a bitter taste single plant in an RILs colony and combining with the high-density genetic map information of the citrullus lanatus; the candidate SNP site interlocked with the character is combined with separate colony verification analysis and natural colony verification analysis; the mark tightly interlocked with a target character is obtained; the SNP site and the CAPS mark can be applied to improvement of citrullus lanatus variety and molecular assisted breeding; a technical support is provided for molecular breeding of the citrullus lanatus quality; and meanwhile, the traditional gene positioning time is greatly shortened.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES +1
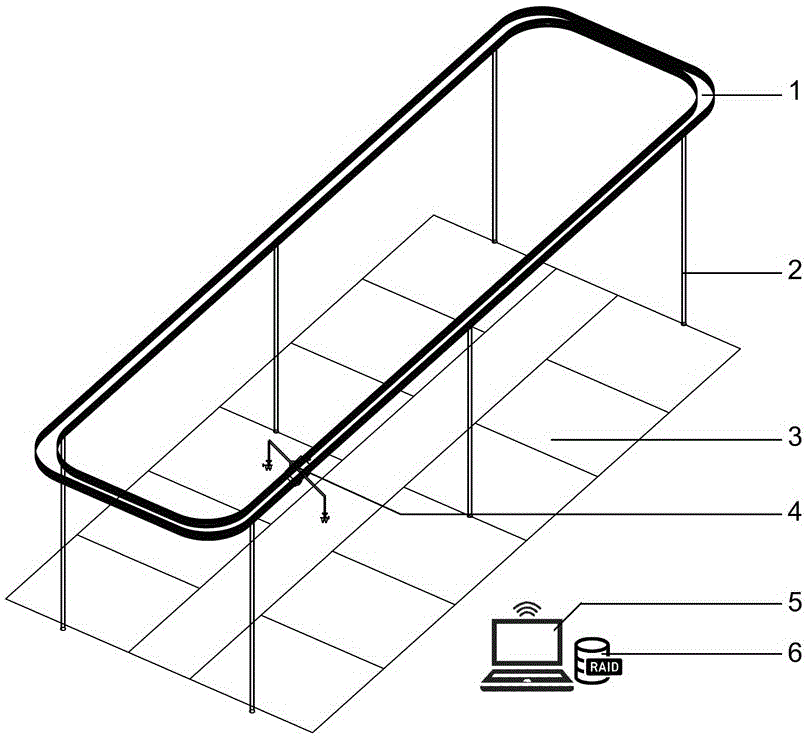
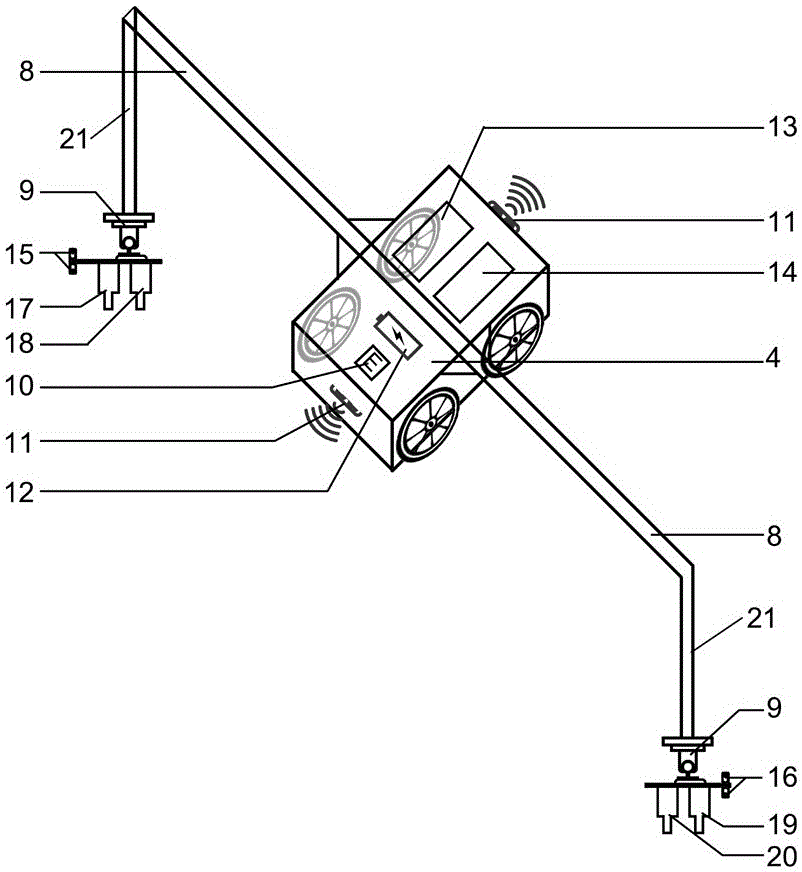
Field crop phenotypic information high-pass peer monitoring device and monitoring method
ActiveCN106441442AHigh return visit rateHighly integratedMeasurement devicesMeasuring instrumentMolecular breeding
The invention relates to a field crop phenotypic information high-pass peer monitoring device. An electric mobile trolley (4) carrying a sensor / camera / measurer moves on a test area (3) for testing, and test data is processed and analyzed. The invention further relates to a monitoring method for the field crop phenotypic information high-pass peer monitoring device. Phenotypic information of field crops can be quickly acquired, and tested crops do not need to be moved during testing, so that the natural growth state of the crops is kept, and the influence on the crops in the test process is greatly reduced. Thus, on the one hand, the designed field crop phenotypic information high-pass peer monitoring device can remarkably promote molecular breeding of crops and development of plant functional genomics; and on the other hand, the device can guide people to optimize field management measures and crop planting structures.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Whole-genome-selection-based method for breeding improved disease-resistant fish varieties
ActiveCN106480189ABreed fastEfficient cultivationMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBreed typeMolecular breeding
The invention aims at providing a whole-genome-selection-based method for breeding improved disease-resistant fish varieties, thereby overcoming defects in the traditional breeding technology, providing a molecular breeding method for cultivation of improved disease-resistant high-yield fish varieties, solving a problem of lack of a whole-genome selection method in the existing fish breeding industry, providing a technical means for improved disease-resistant fish variety breeding of the fish breeding industry, realizing upgrading of the fish breeding technique, and promoting rapid development of the fish breeding industry. The disease-resistant fish offspring obtained by using the method provided by the invention has the enhanced disease-resistant capability. An experiment result demonstrates that the survival rate from infection and breeding survival rate of a disease-resistant fish offspring that is bred based on the whole genome selection method are higher than those of the control group by 20% to 30%. Using the method provided by the invention, the improved disease-resistant fish breed can be bred rapidly and efficiently; and the disease-resistant capability and breeding survival rate of fish can be enhanced. Therefore, the method provided by the invention has the great application value and broad promotion prospects in the fish breeding industry.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
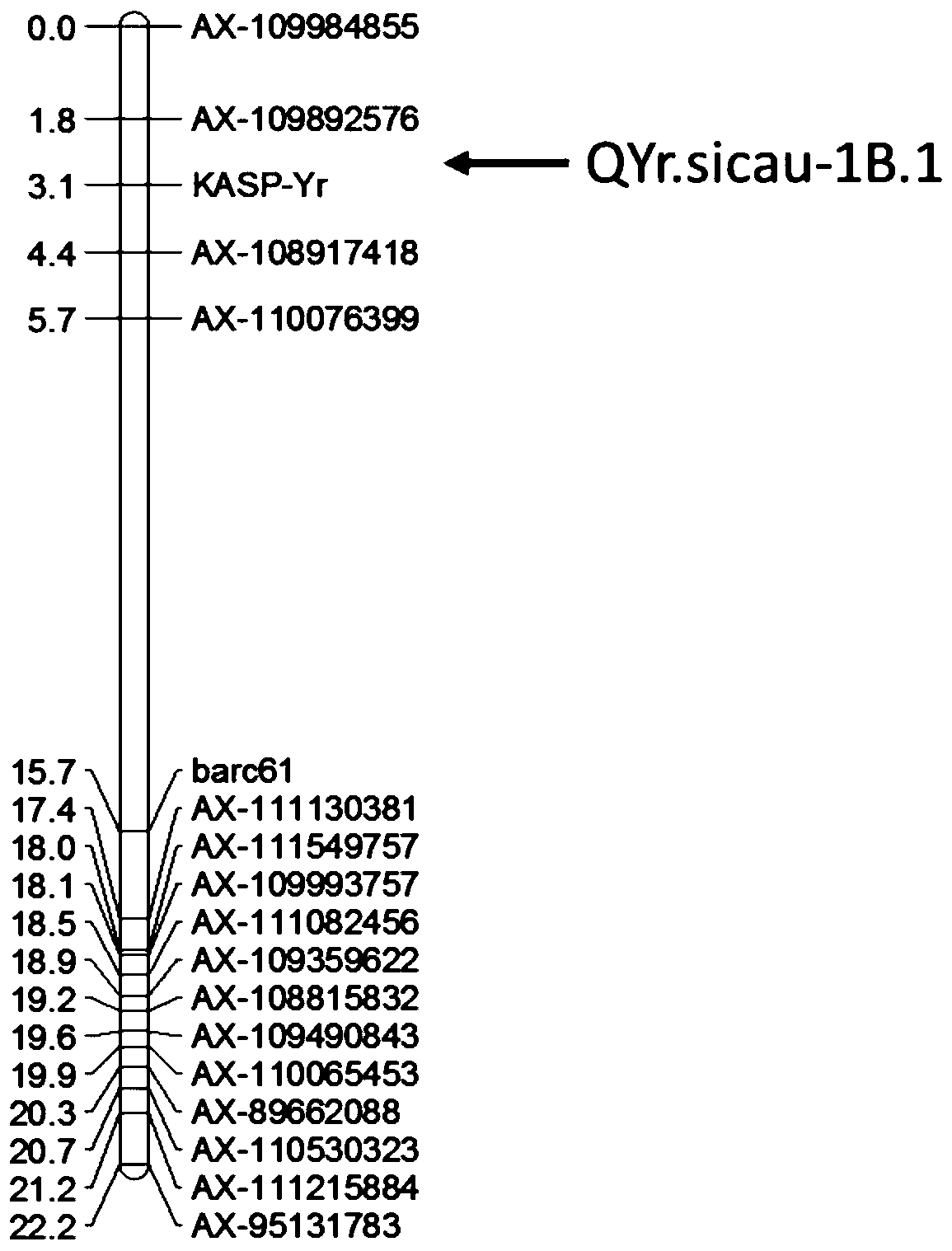
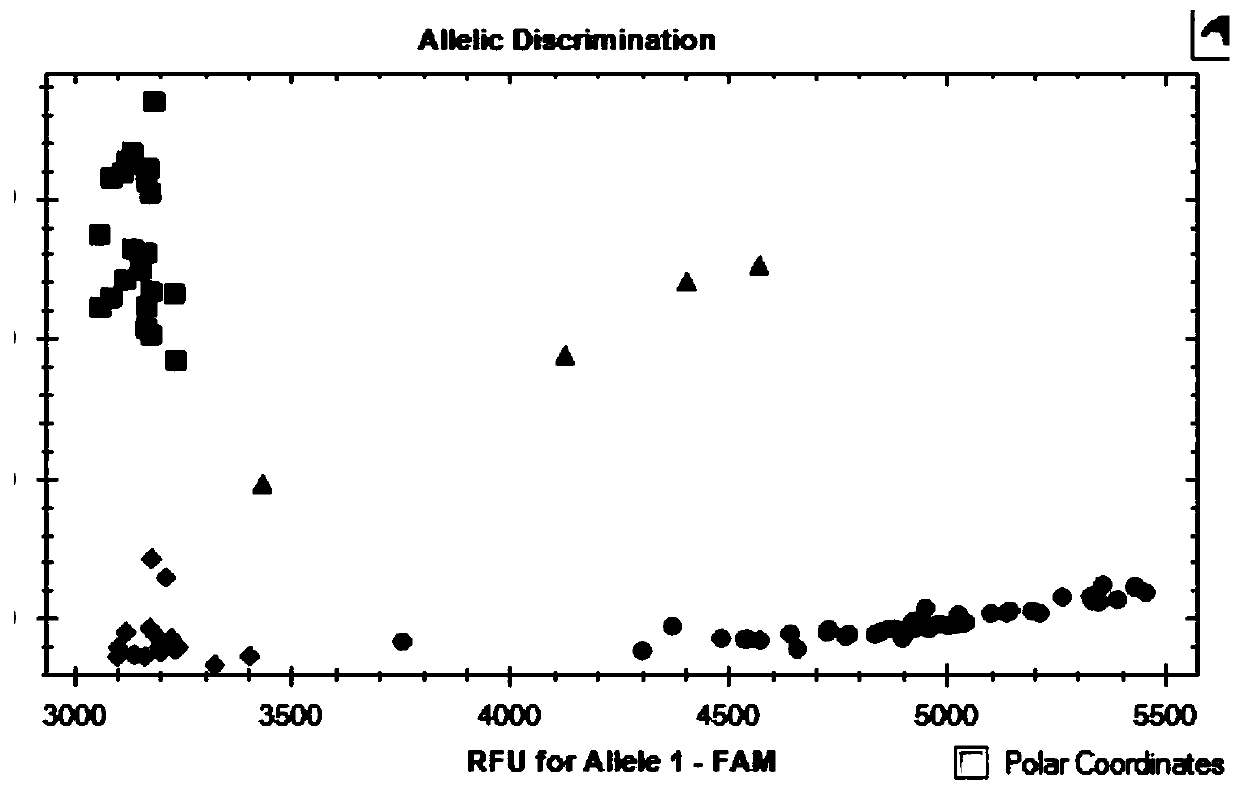
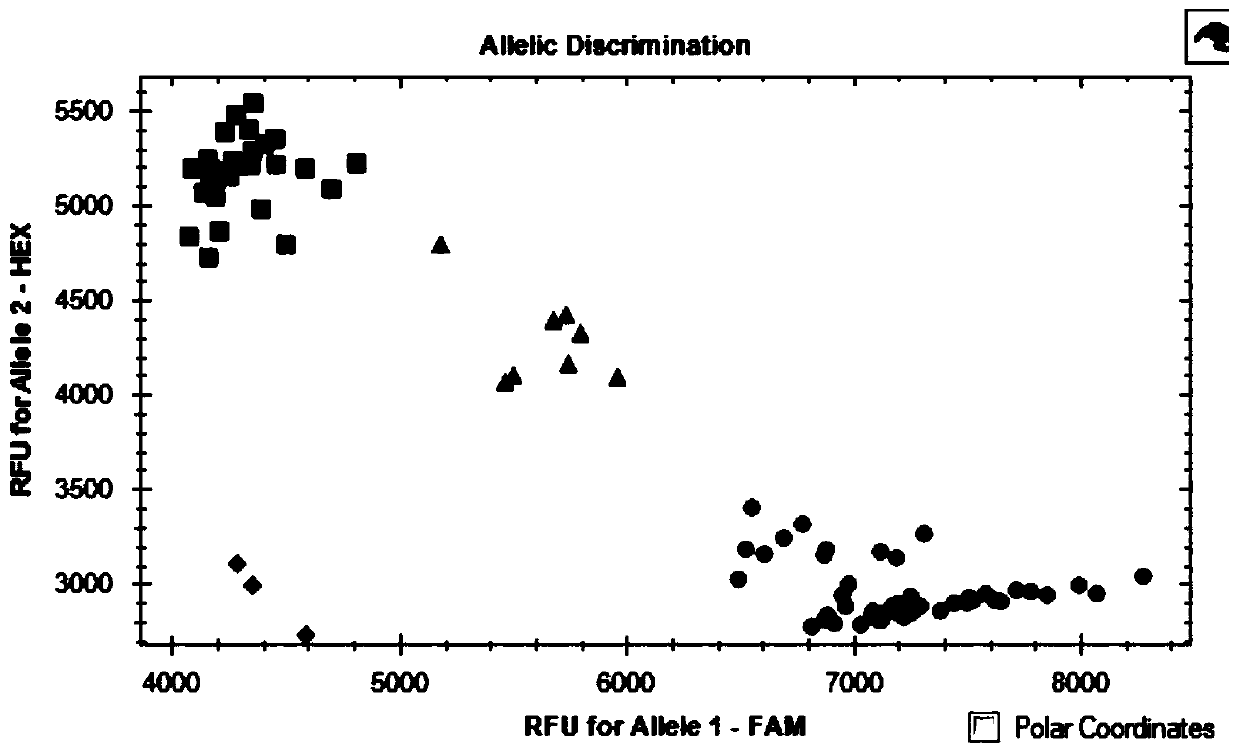
SNP molecular marker linked with wheat stripe rust resistance gene QYr.sicau-1B-1 and application thereof
ActiveCN109706263AQuick filterConvenient Assisted BreedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMolecular breeding
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular breeding, and provides an SNP molecular marker linked with a wheat stripe rust resistance gene QYr.sicau-1B.1 and application thereof. The SNPmolecular marker is KASP-Yr, which can be obtained by amplifying a primer having a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1-3. Detection analysis indicates that the molecular marker can be used for accurately tracking wheat stripe rust resistant QTL QYr.sicau-1B.1 and predicting the stripe rust resistance characteristics of wheat, so that molecular designed breeding can be performance conveniently. The invention further discloses a method for identifying the molecular marker linked with wheat stripe rust resistance QTL QYr.sicau-1B.1. By utilizing the method, the stripe rust resistance prediction accuracy can be reinforced to quickly screen wheat variety or strain with stripe rust resistance for breeding, the breeding process for high-yield variety of wheat can be greatly accelerated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Protein ErNAC7 related to drought and salt resistance of plants and coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN101906155AImprove salt toleranceImprove drought resistanceClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesBiotechnologySalt resistance
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to protein ErNAC7 related to drought and salt resistance of plants and a coding gene and application thereof. The protein has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1 and a gene sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The protein related to the drought and salt resistance and the coding gene thereof have important theoretical and actual meanings for improving and enhancing the stress resistance of tobacco, improving yield, accelerating the breeding process of stress-resisting molecules and effectively saving water resources.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
SNP molecular marker associated with chromosome 6 and fiber strength of upland cotton
ActiveCN106868131AShorten the breeding cycleImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMolecular breeding
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular breeding of cotton and discloses an SNP molecular marker associated with fiber strength of upland cotton as well as detection and application thereof. The SNP molecular marker is obtained by taking stable RIL group of cotton as the material through a genome resequencing method. When the SNP markers are used for carrying out molecular marker-assisted breeding selection, the breeding period can be greatly shortened; the breeding efficiency of the cotton can be improved; the cotton fiber strength can be improved.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cabbage type rape high oleic acid molecular marker, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101824472ASpeed up the breeding processReduce breeding workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMarker-assisted selectionHigh oleic acid
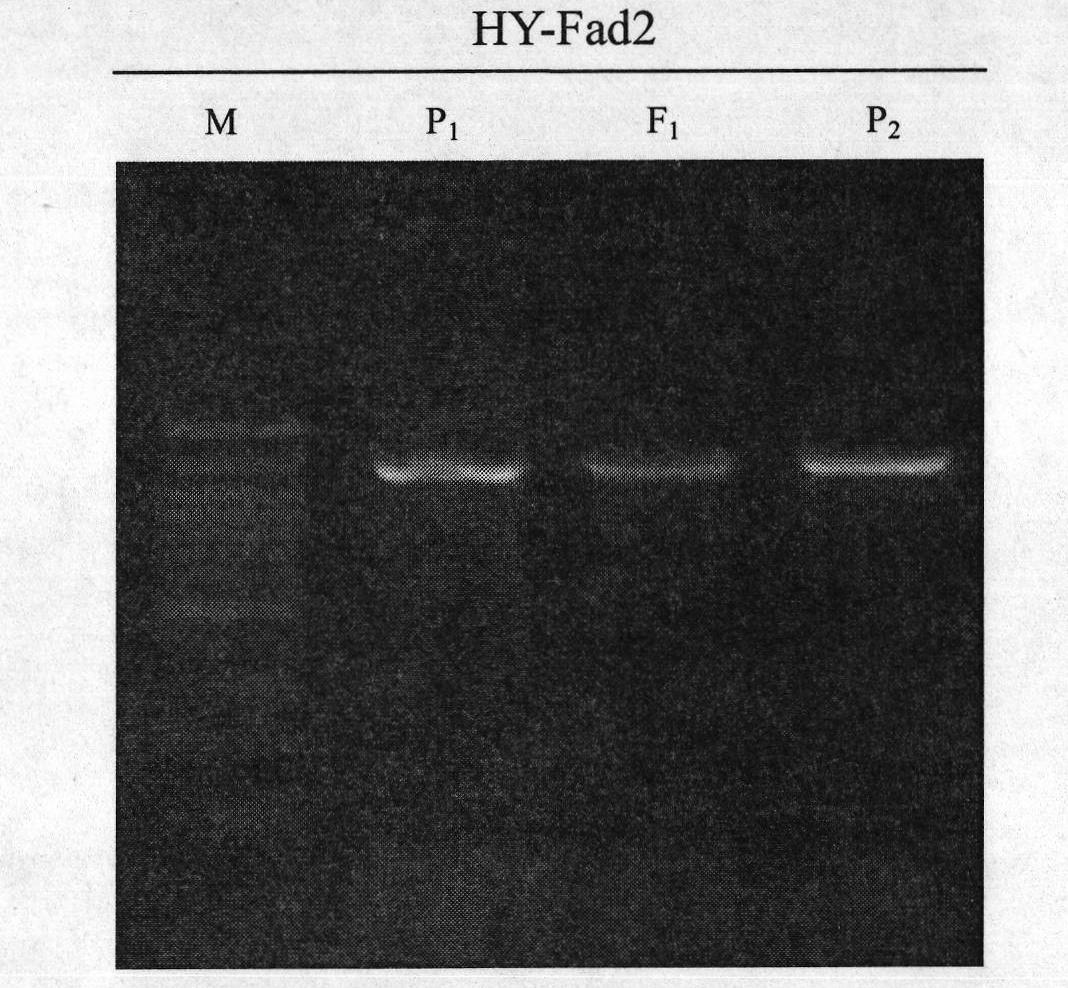
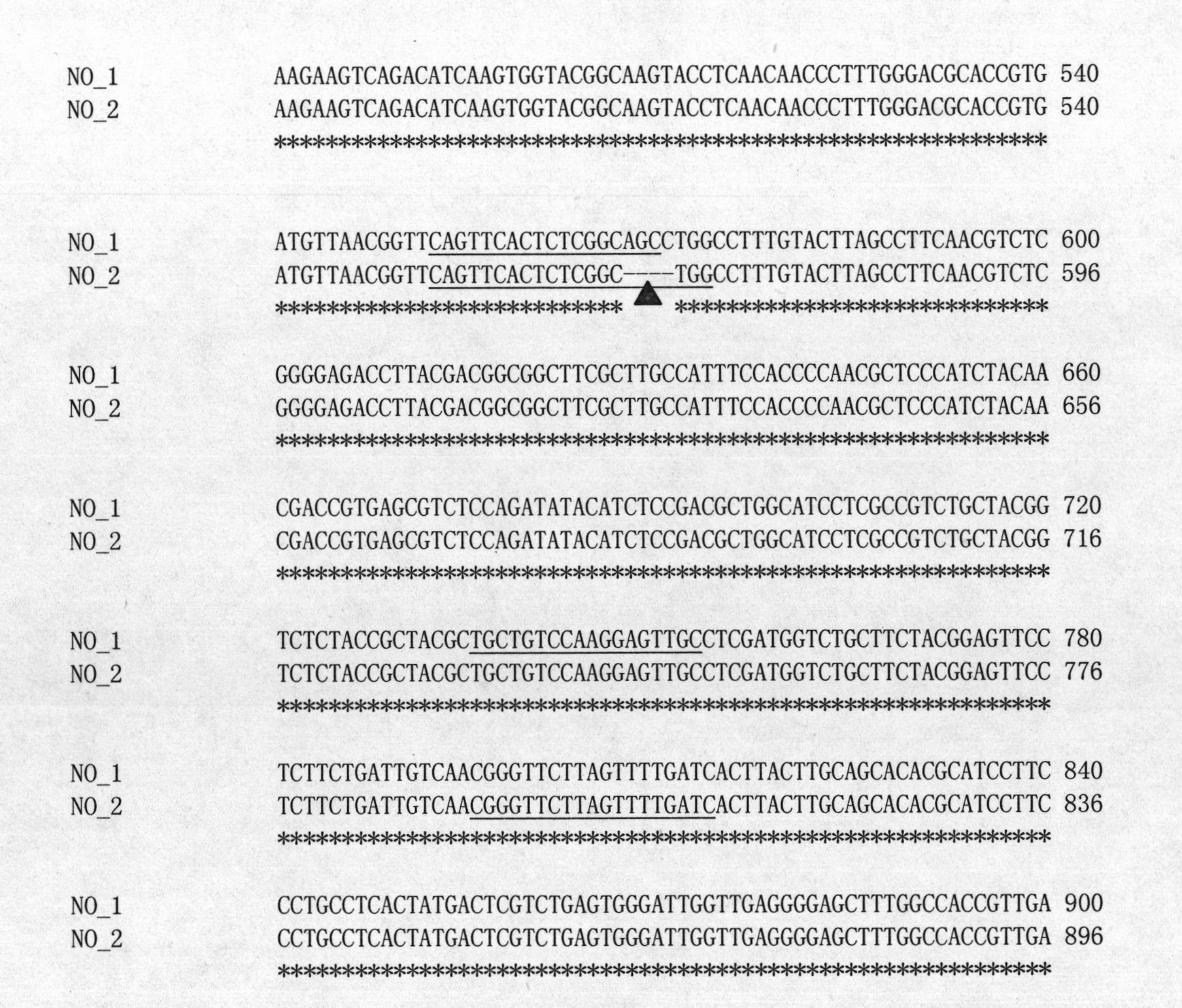
The invention belongs to the technical field of rape molecular breeding, in particular relates to a preparation method for a cabbage type rape high oleic acid codominant SCAR molecular marker and application as marker assisted selection in breeding high oleic acid cabbage type rape new products. The difference of nucleotide sequences of AA254 and AA177 is identified by cloning and checking sequences on DNA segments of fad2 gene of genomes of high oleic acid cabbage type rape strain AA254 and low oleic acid cabbage type rape strain AA177, primers YQ-Fad2a-1 and YQ-Fad2a-2 are developed by utilizing the difference of the nucleotide sequences provided by the invention, and then the codominant SCAR molecular marker which can distinguish cabbage type rape high oleic acid and low oleic acid is obtained. The invention provides a new marker for the rape molecular breeding. The invention also discloses the preparation method and the application of the molecular marker.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Plant drought-resistance and salt-tolerance associated protein TaNAC, and encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN101899103AImprove salt toleranceSpeed up the breeding processPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, in particular to a plant drought-resistance and salt-tolerance associated protein TaNAC, an encoding gene thereof and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the protein is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 and the gene sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The plant drought-resistance and salt-tolerance associated protein and the encoding gene thereof of the invention has very important theoretical and practical significance for improving and enhancing the stress resistance of tobacco, increasing the yield, promoting the breeding process of stress resistant molecules and effectively saving water resources.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Non-transgenic genome directed molecule improvement method and application of main crops
InactiveCN103555711AImprove qualityIncrease resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyBiotechnologyMolecular breeding
The present invention provides a non-transgenic directed molecule breeding method for crops, an application of a method containing genome directed modification in crop agronomy characteristic improvement, and a non-transgenic progeny screening method, and further relates to an application of the methods in crop conventional breeding. With the method, the sequence structure of the important characteristic determination gene of the crop can be controllably changed so as to directedly obtain the required favorable characteristic, and the filial generation plant with an improvement effect and with no transgenic component can be obtained with genetic segregation so as to accelerate breeding and avoid transgenic safety problem. The breeding method combines advantages of traditional breeding and transgenic breeding.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Pig-whole-genome low-density SNP chip and manufacturing method and application thereof
The invention relates to a pig-whole-genome low-density SNP chip. The chip is a DNA sequence which is shown in an SEQ ID NO.1-8846. The pig-whole-genome low-density SNP chip has the advantages that the pig-whole-genome low-density SNP chip is researched and analyzed from an existing 80 k chip, and under the situation that the selection accuracy is not remarkably lowered, unrelated SNP marks are creatively removed, and the number of the SNP marks is lowered to 8846. The pig-whole-genome low-density SNP chip has the innovative significance on pig breeding and selection, so that pig breeding is possibly popularized through the pig-whole-genome low-density SNP chip, and the Chinese pig breeding and selection progress can be greatly accelerated.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV +1
Method for detecting pork quality traits
InactiveCN101230391AThe method is accurate and simpleHigh-precision detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotype determinationGene type
The invention discloses a method of detecting the quality of pork. In the method, the gene type of the pig is determined by detecting that the ribonucleotide is C or G on the 451st site on the 51end of the sequence 1 or the 112th site on the 5 (1) end of the sequence 2; and the quality of pork is determined by the gene type; the method of determining the gene type of the pig is as follows: when the ribonucleotide is C on the 451st site on the 5 (1) end of the sequence 1, the homozygote gene type is AA; when the ribonucleotide is G on the 112th site on the 51 end of the sequence 2, the homozygote gene type is BB; the heterozygous gene type is AB; the method of determining the quality of pork via the gene type is as follows: the AA gene type pork tenderness and pH are higher than the AB gene type pork; the AB gene type AB gene type are higher than the BB gene type pork. The method of invention can be applied to detect the tenderness and pH value of the pig which indicate the quality of muscle, which provides a method of accurately and conveniently detecting the hereditary character for the molecular breeding of pig.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
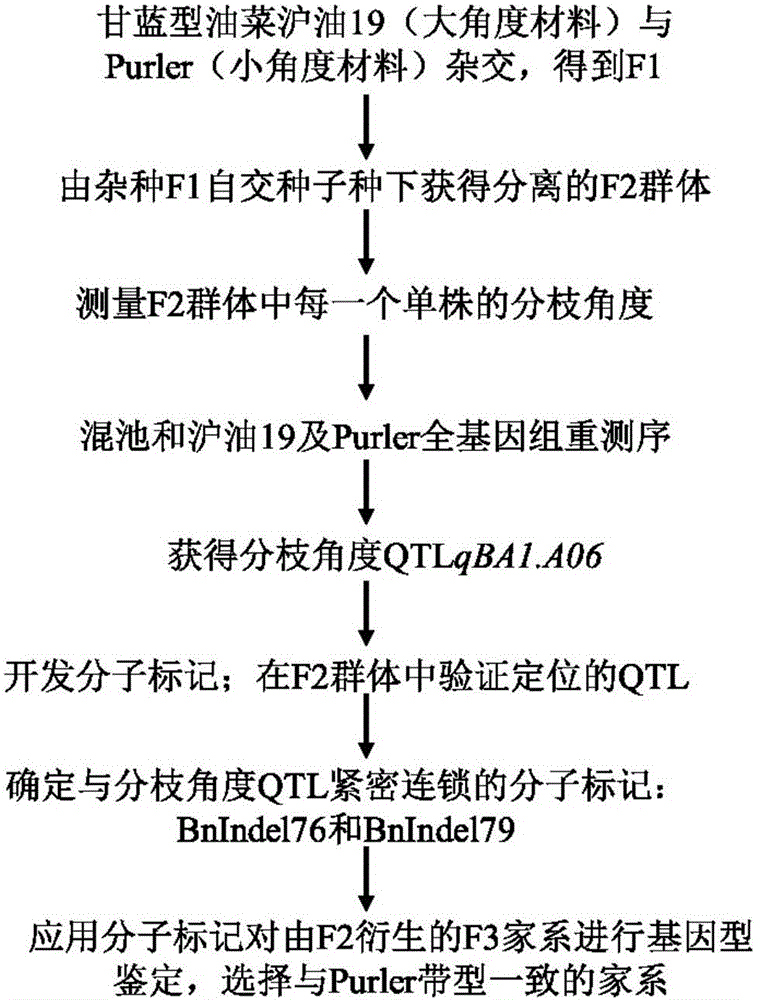
Molecular marker in close linkage with rape crotch angle character QTL (Quantitative Trait Loci) and application
ActiveCN105969852ANot affectedAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceF2 population
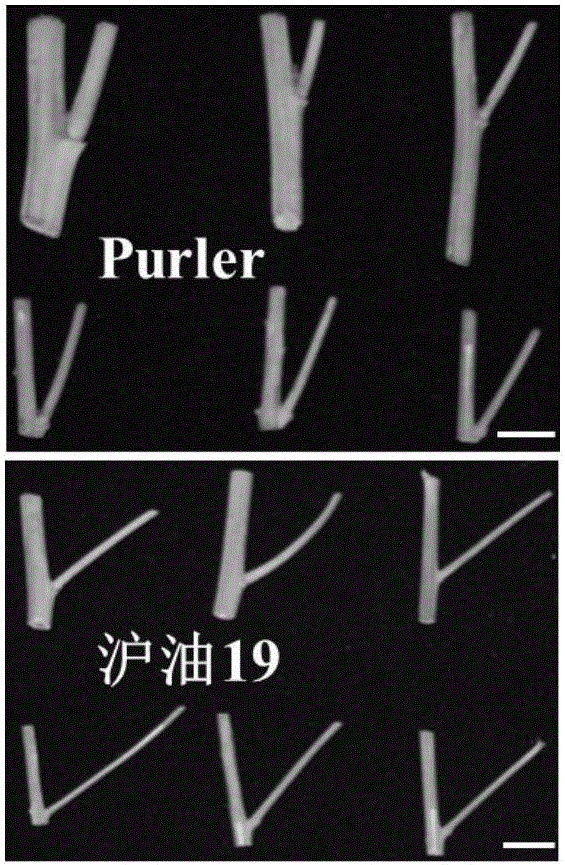
The invention discloses a molecular marker in close linkage with rape crotch angle character QTL (Quantitative Trait Loci) and application. The molecular marker is characterized by carrying out hybridization by taking cabbage type rape variety Shanghai oil 19 as a female parent and Purler as a male parent, establishing F2 segregation population through selfing of hybrid F1, and analyzing, thus obtaining a crotch angle locus qBA1.A06; designing a primer by utilizing an Indel marker at the boundary of the crotch angle locus qBA1.A06 so as to detect the parents and the F2 population, thus obtaining a molecular marker BAIndel76 and a molecular marker BAIdenl79 which are in close linkage with the crotch angle character QTL; identifying a rape gene type formed after hybridization of the two parents by utilizing a marker primer, and carrying out auxiliary selection by utilizing the marker, thus greatly increasing the selection efficiency. According to the molecular marker disclosed by the invention, a novel genetic marker is provided for molecular breeding of the rape plant type, and useful information is also provided for accurate positioning on the crotch angle character QTL of the cabbage type rape and map-based cloning on related genes.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for selecting and breeding green-shin dominant white-feather broiler chicken strain
ActiveCN103583469AAvoid the tediousness of test cross breedingShorten the generation intervalAnimal husbandryMarker-assisted selectionDominant white
The invention discloses a method for selecting and breeding a green-shin dominant white-feather broiler chicken strain and belongs to the technical field of molecular breeding. The marker-assisted selection method is adopted for identifying the genotype of the locus of dominant white feathers of chicken, the genotype of the locus can be quickly figured out, and the defects that test cross is complex, generation intervals are long and the like in conventional breeding are overcome. According to the green-shin dominant white-feather broiler chicken strain with the genotype II is produced by adopting the method, the complexity of test cross selecting and breeding is avoided, the generation intervals are shortened, the process of breeding is accelerated, and breeding cost is lowered. Moreover, the meat quality of the chicken strain is fine and tender, the taste of the meat is delicious, production performance is high, carcasses of the chicken do not have colored feather vestiges, and therefore the carcasses look better. Besides, the strain is used as a male parent to hybridize and match a high-yield laying hen breed or a fast-growth broiler chicken breed, and high-yield green-shin dominant white-feather broiler chicken or fast-growth green-shin dominant white-feather broiler chicken can be produced.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
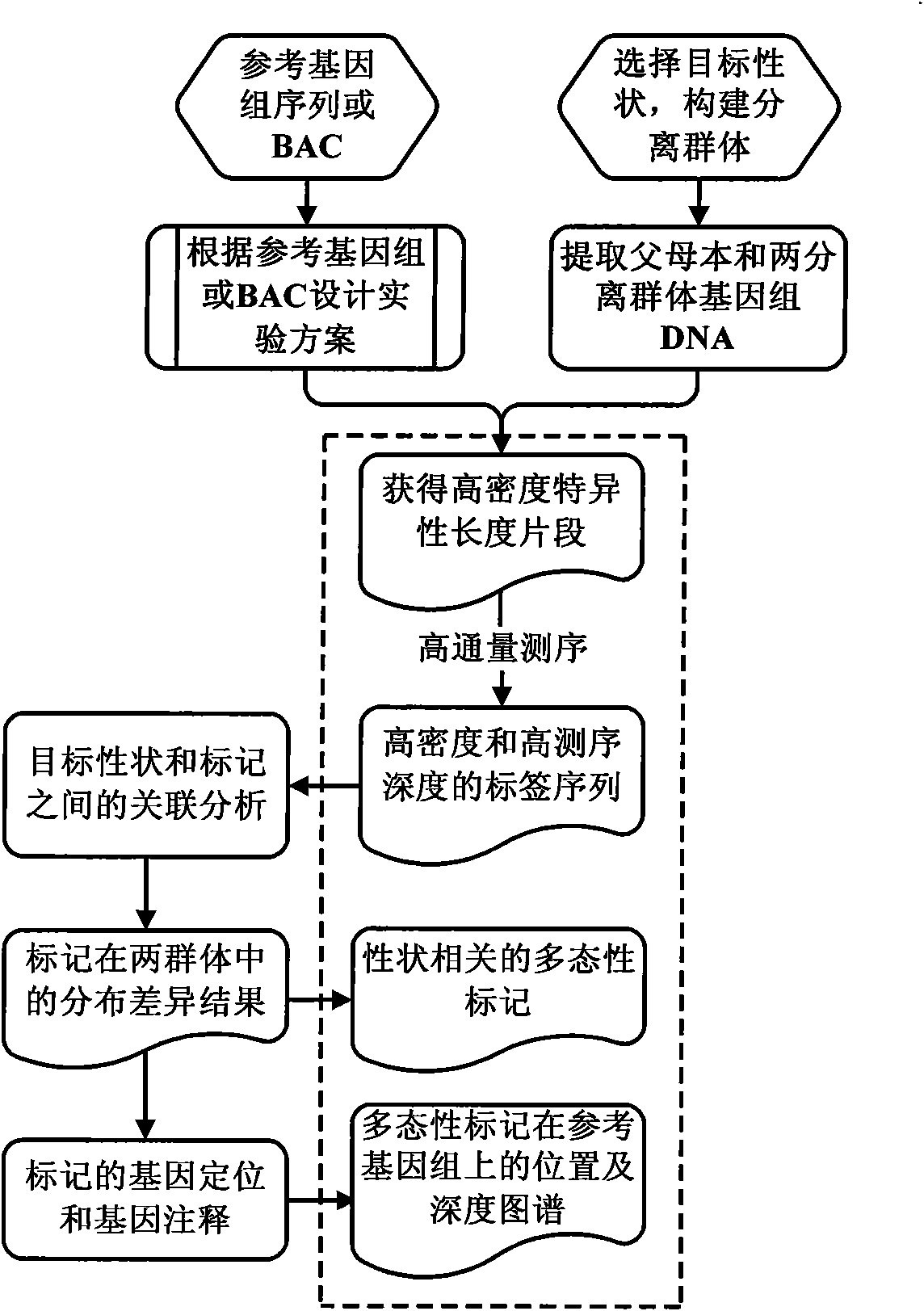
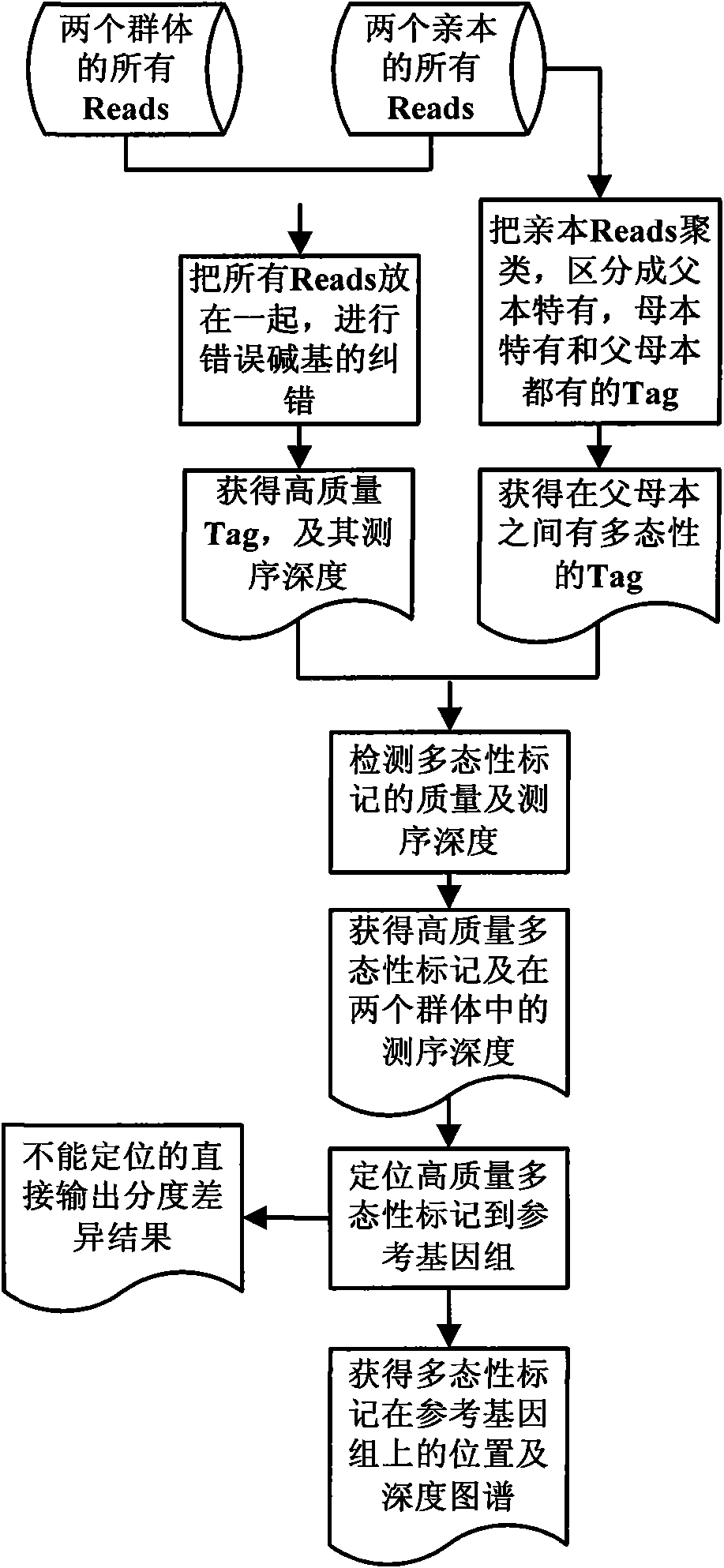
Method for screening molecular markers correlative with properties based on sequencing technique and BSA (Bulked Segregant Analysis) technique
ActiveCN101886132AIncreased development throughputIncrease the number ofMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular breedingLinkage concept
The invention provides a method for screening DNA molecular markers closely correlative with properties, which is mainly used for identifying DNA molecular markers correlative with properties by combining super bulked segregant analysis (BSA) with a high throughput sequencing technique. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out parameter training to data comprising different species genomes or BAC (Bacterial Artificial Chromosome) sequences and the like by utilizing a bioinformatics method to find out an optimal marker sequencing scheme for improving the development efficiencyof the markers; carrying out correlative analysis to bulked segregant sequencing results to detect the molecular markers correlative with the properties and position back to the genomes or BAC, and then precisely positioning candidate functional genes through the high-density property-correlative molecular markers. Compared with the traditional method, the method has the advantages of greatly improving throughput and greatly reducing cost. The method can be used for carrying out marker positioning to large groups and directly determining the linkage between the markers and the target properties, has high reliability and accuracy of correlative analysis, and is mainly applied to the aspects of marker development and gene positioning, such as crop molecular breeding and the like.
Owner:BIOMARKER TECH
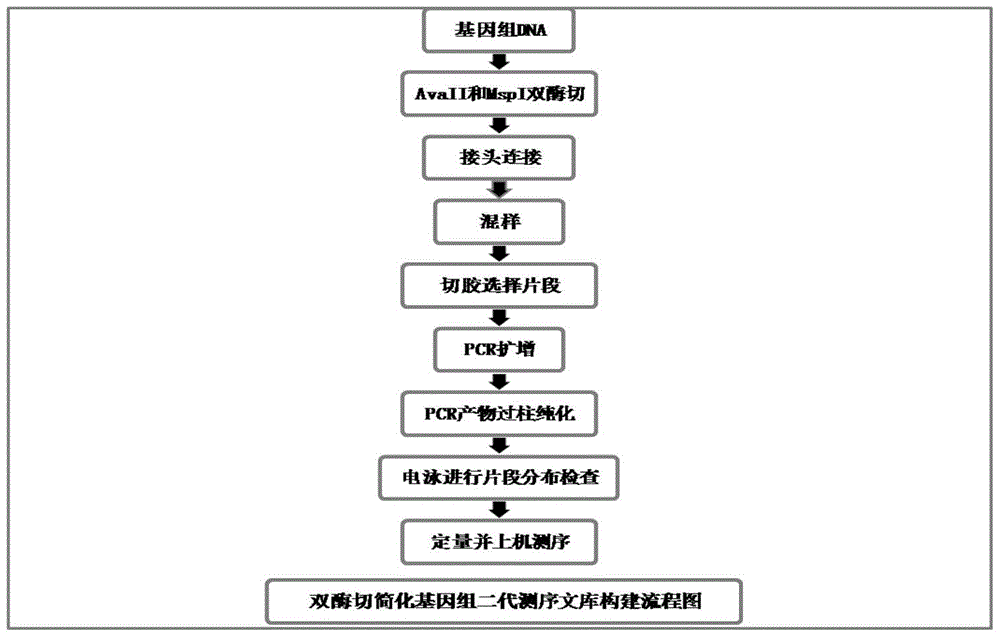
Construction method for double enzyme digestion simplified genome next generation sequencing library and matched kit
InactiveCN105696088AGet rid of dependenceSimplify the library building processMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGenomic sequencingEnzyme digestion
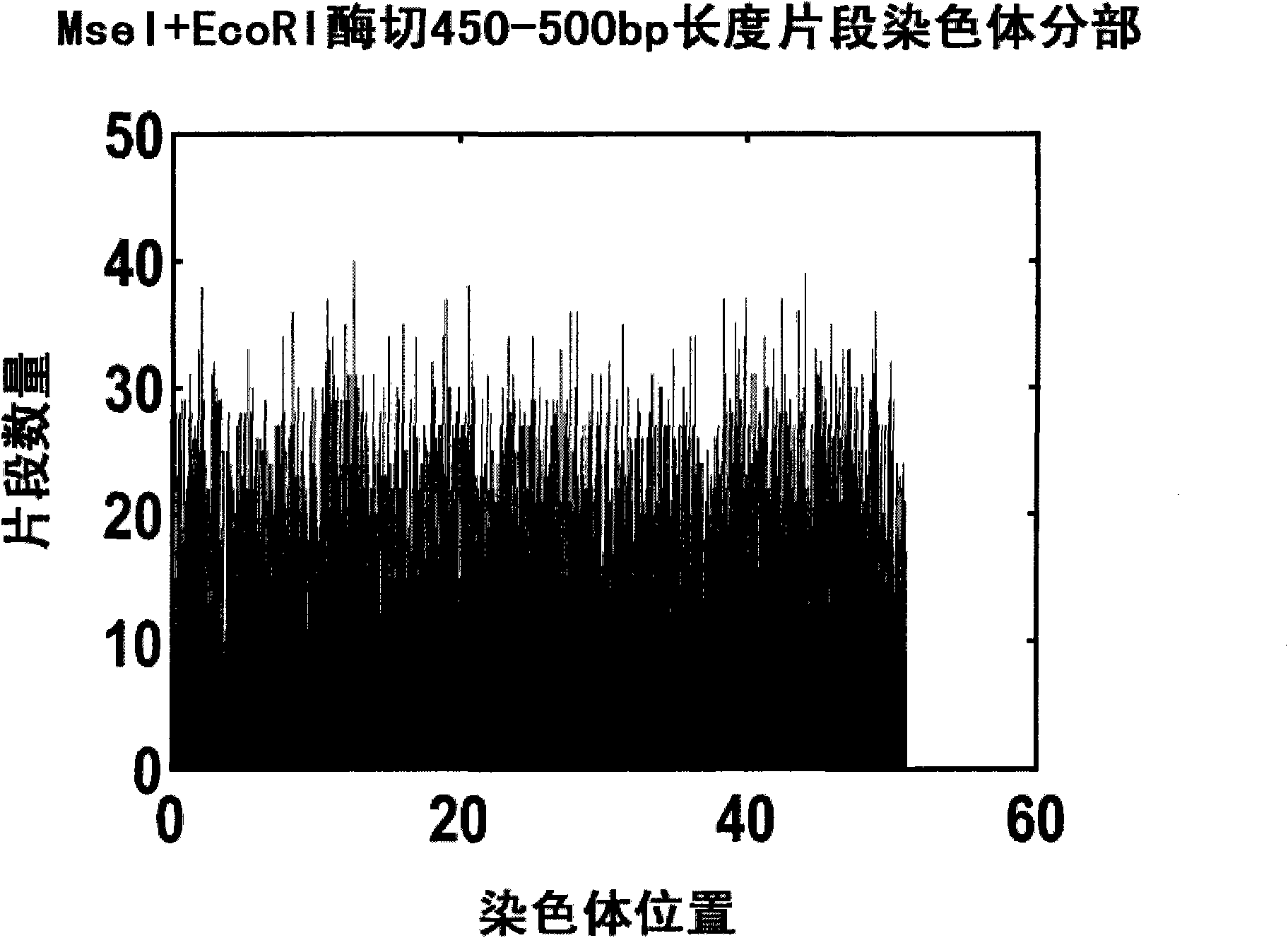
The invention provides a construction method for a simplified genome next generation sequencing library based on double enzyme digestion and a kit. Aiming at defects of an existing construction method for the double enzyme digestion simplified genome next generation sequencing library, the double enzyme digestion combined range is expanded, and excessive dependence on expensive instruments of constructing the simplified genome library is reduced, the library construction flow path is simplified, library construction cost is reduced, the sequencing efficiency is improved, and meanwhile the technology is easy and flexible to operate and easier for researchers to master and can be realized in a common molecule lab. The construction method is particularly suitable for miniature or medium-scale labs needing to conduct SNP molecular marker development, genetic map construction, population genetics research, phylogeny biological research and the like on a great number of species with incomplete reference genomes. The construction method has good practical application value and application prospects in the fields of molecular breeding of agriculture, conservation biology and evolutionary biology.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for Producing Genetically Modified Plant Expressing Miraculin
InactiveUS20090205068A1Keep levelSuppressing excessive sugar intakePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderFood additiveBiotechnology
The present invention relates to: a method for producing a transgenic plant expressing miraculin, comprising introducing a miraculin gene into a useful plant that can be easily produced and cultivated throughout the year using plant molecular breeding technology; a transgenic plant expressing miraculin, which is produced by the method; and the use thereof. The present invention also relates to a food additive, a food or drink, or an antidiabetic drug, which contains miraculin that is produced by the transgenic plant.
Owner:HIROSHI EZURA +1
Hybrid seed production method of high uniformity yellow chicken complete set line suitable for chilled marketing
ActiveCN108029634AProtect intellectual propertyImprove survival rateAnimal husbandryHybrid seedAnimal science
The invention belongs to the technical field of poultry genetic breeding, and particularly relates to a hybrid seed production method of high uniformity yellow chicken three-line combination suitablefor chilled marketing. According to the method, a slow-feathering, yellow-feathering and green-shank chicken line is adopted as a first male parent, a fast-feathering, yellow-feathering, yellow-shank,high-yield and high-quality chicken line is adopted as a first female parent, and hybridization is conducted to obtain an F1 female parent; a local chicken line which is fast-feathering, and yellow-feathering, jute-feathering, sexual precocity and big cockscomb in appearance with the weight within + / -10% of the average weight is selected as a terminal sire, and hybridization is conducted betweenthe terminal sire and the F1 female parent to obtain commercial generation with high uniformity. According to the method, by means of regular and molecular breeding, selections of physical conformation, sexual precocity, weight uniformity and slaughter traits and comprehensive selection of meat quality traits are focused on and carried out, the bred yellow chicken commercial generation is high inuniformity and survival rate, and significant in heterosis; and the chicken has big cockscomb, green shank, fine pores and firm skin.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF POULTRY SCI +1
Molecular markers from sea island cotton Hai 1 and related to cotton fiber strength and application of molecular markers
InactiveCN103497949AHelps to filterImprove qualityMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceMolecular breeding
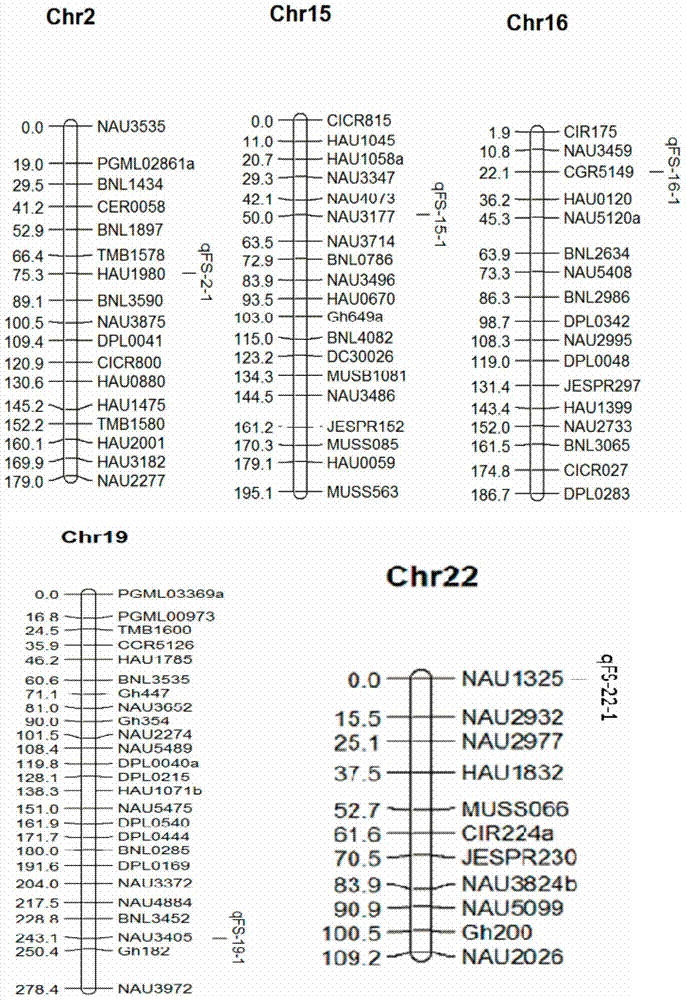
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular breeding, in particular to molecular markers from sea island cotton Hai 1 and related to cotton fiber strength and application of the molecular markers. The molecular markers includes HAU1980240, NAU3177160, CGR5149280, NAU3405220 and NAU1325210. By the molecular markers, defects of current breeding techniques in fiber quality identification are overcome, fiber strength selection efficiency can be increased, and breeding process of new varieties of high-quality fibers can be accelerated.
Owner:河南永安纺织有限公司
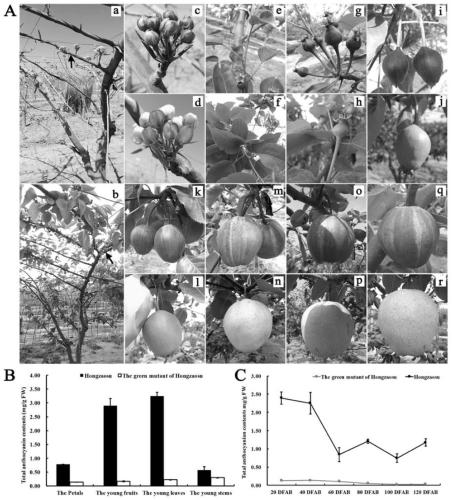
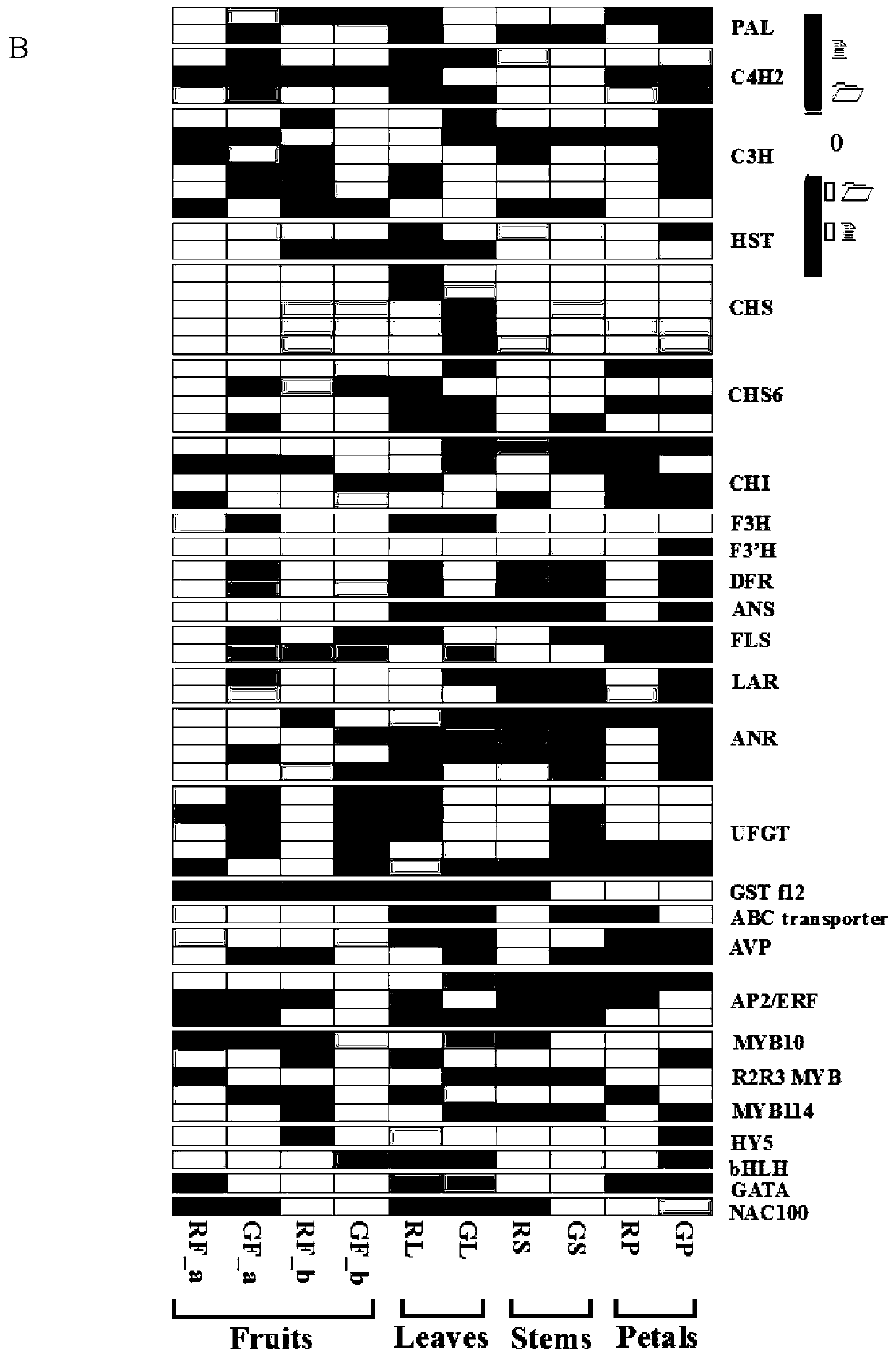
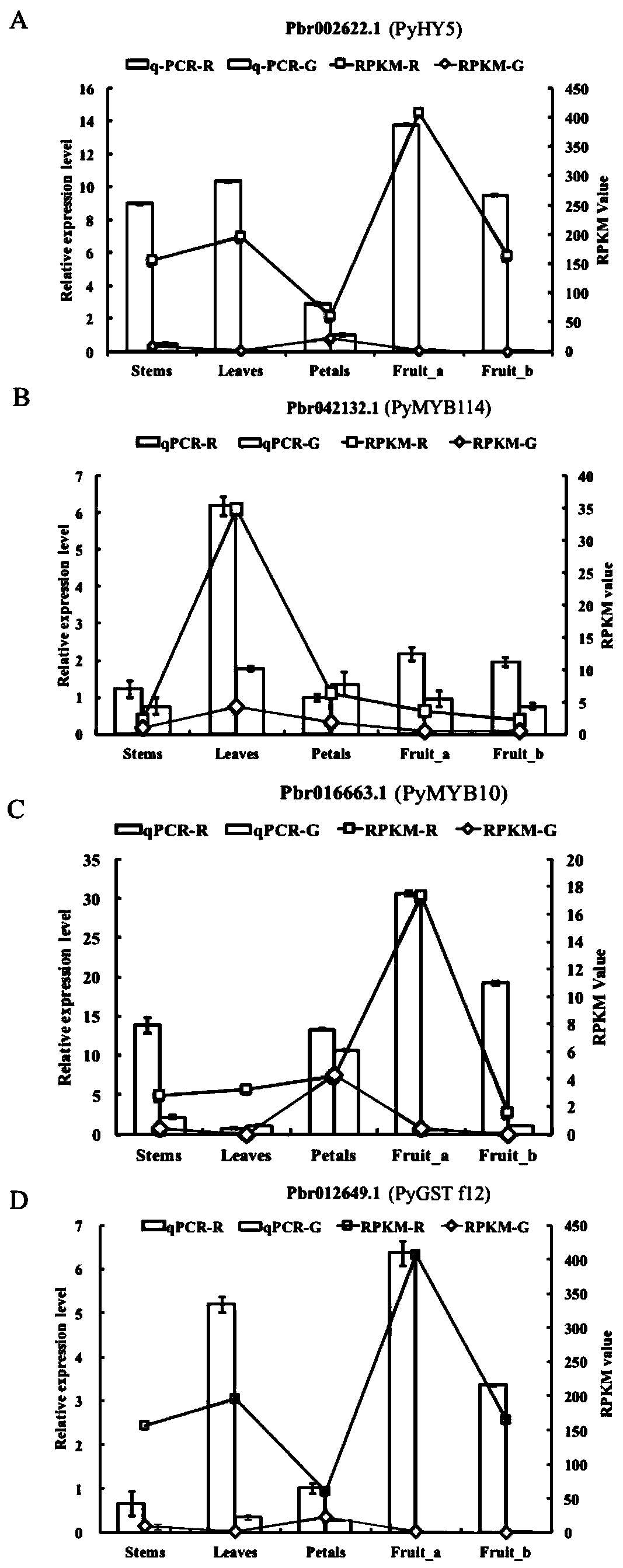
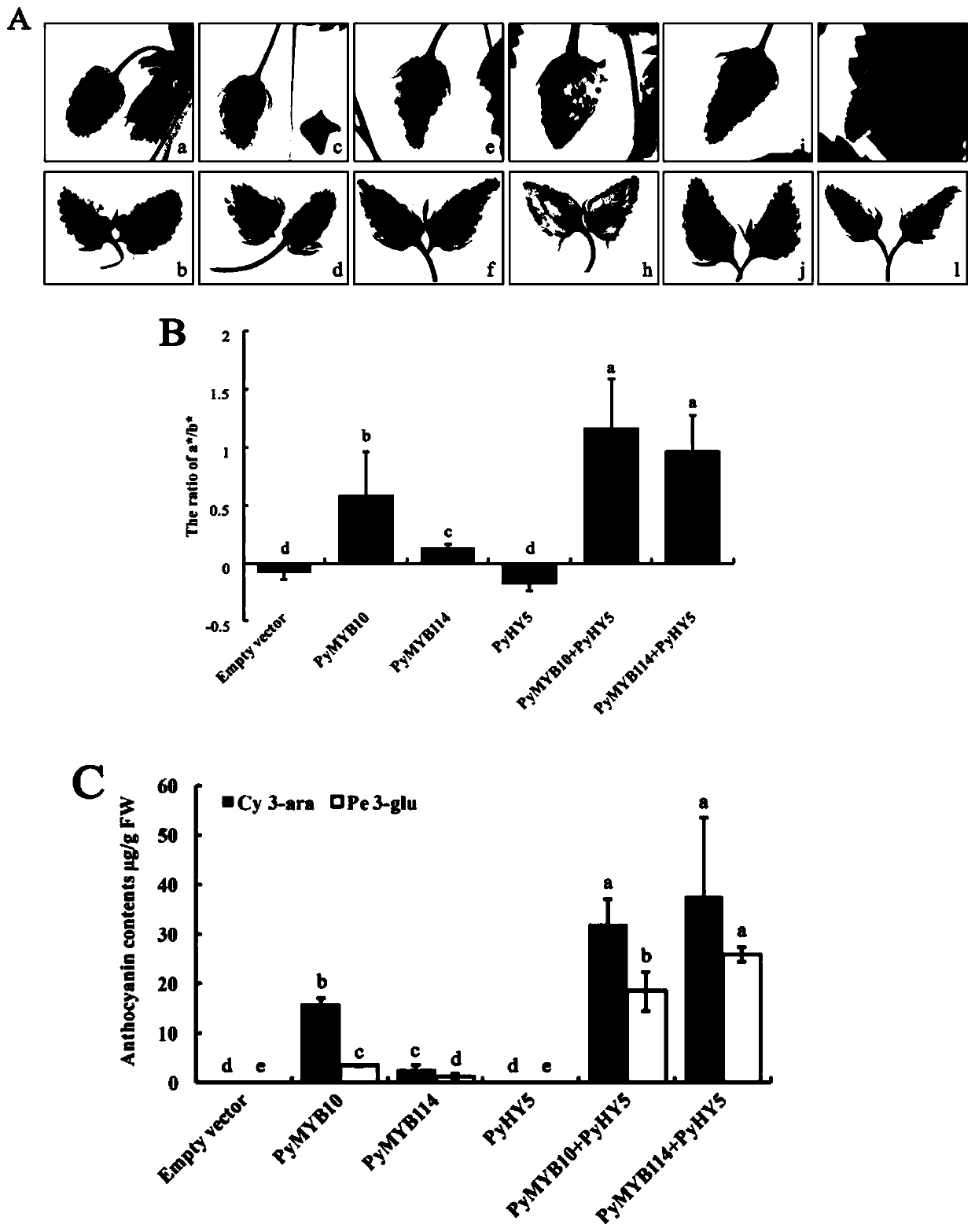
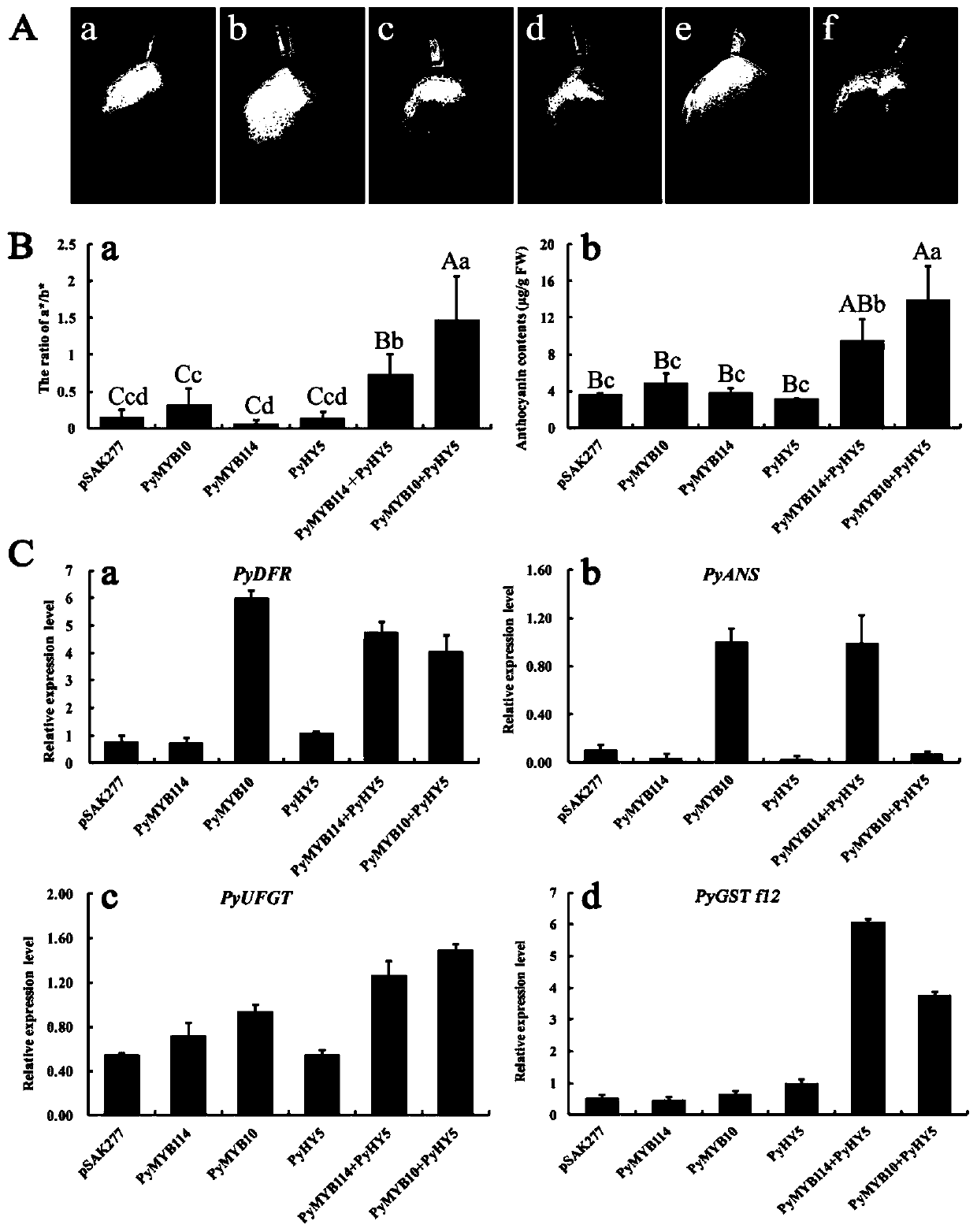
PyGSTf12 gene related to transport of anthocyanin in pear fruits, and recombinant expression vector and application of PyGSTf12 gene
InactiveCN109810990AAchieve friendlyReduce the cost of farmingBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementFragariaAgricultural science
The invention discloses a pear transcription factor PyGSTf12, and a recombinant expression vector and application thereof. The sequence difference between the PyGSTf12 and a promoter thereof is used as a molecular marker for identifying red and green peels, wherein the PyGSTf12 and the promoter are respectively separated from 'Red Zaosu' pears and yellow bud mutated fruits thereof, and the nucleotide sequences of the PyGSTf12 and the promoter are respectively as shown in SEQ ID No. 31 and SEQ ID No. 32. By a dual-luciferase report system, an agrobacterium-mediated instant genetic transformation method proves that the PyGSTf12 co-transformed by transcription factors PyHY5 and PyMYB114 promotes accumulation of anthocyanin in strawberry and pear fruits, and the PyGSTf12 promoter promotes thetransport function of the anthocyanin; through discovery of the PyGSTf12 gene, new genetic resources are provided for molecular breeding that promotes synthesis of the anthocyanin in pear peels, and new genetic resources are provided for the implementation of green agriculture; the development and utilization of the genetic resources is beneficial to agricultural cost reduction and environmental friendliness.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
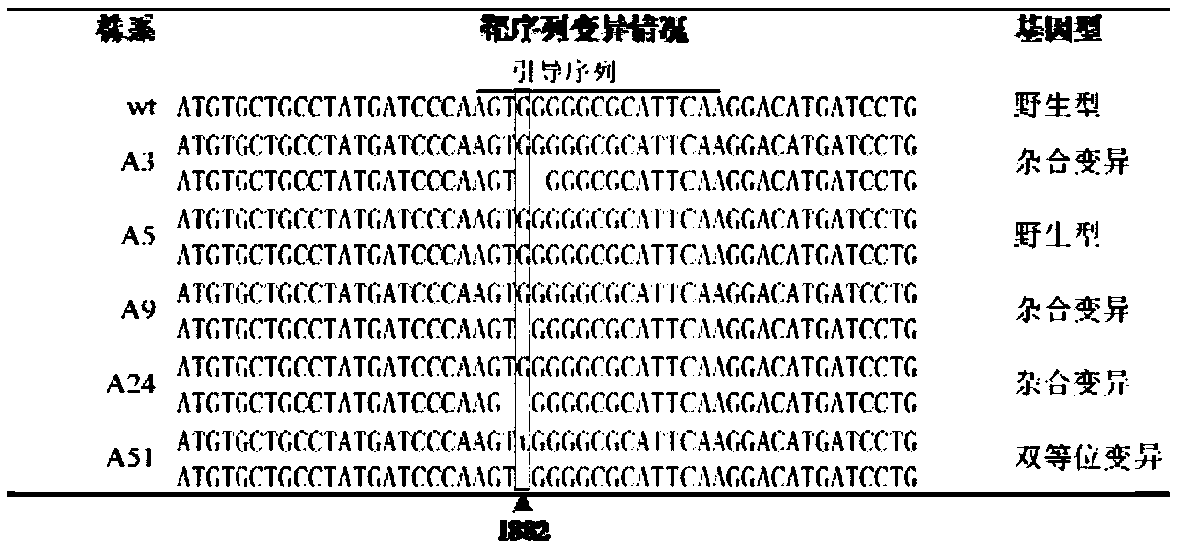
Applications of ALS (acetolactate synthase) mutant type protein based on gene editing technology and ALS mutant type protein gene in plant breeding
ActiveCN109097346ANo significant change in basic agronomic traitsImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesAgricultural scienceAcetolactate synthase
The invention discloses a rice ALS (acetolactate synthase) mutant type protein, a mutant type gene and applications of the rice ALS mutant type protein and the mutant type gene. The amino acid sequence of the ALS mutant type protein has following mutation: the 628-poisiton amino acid corresponding to the amino acid sequence of rice ALS has the mutation. The invention further discloses a breeding method of creating herbicide-resistant rice by gene editing. The CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology is used for editing the ALS gene for the first time, a T-DNA-knockout new material with the stably inherited herbicide resistant characteristic can be obtained in the T2 generation through offspring screening, and basic agronomic traits of the new material have no obvious change. Compared with breeding based on chemical mutagenesis, hybrid transform breeding and the like, the orderly improved molecular breeding technology based on gene editing has the advantages of being rapid, accurate, efficient and the like, and by means of combination with gene function marked genotype selection, breeding efficiency can be greatly increased and breeding progress is substantially accelerated.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
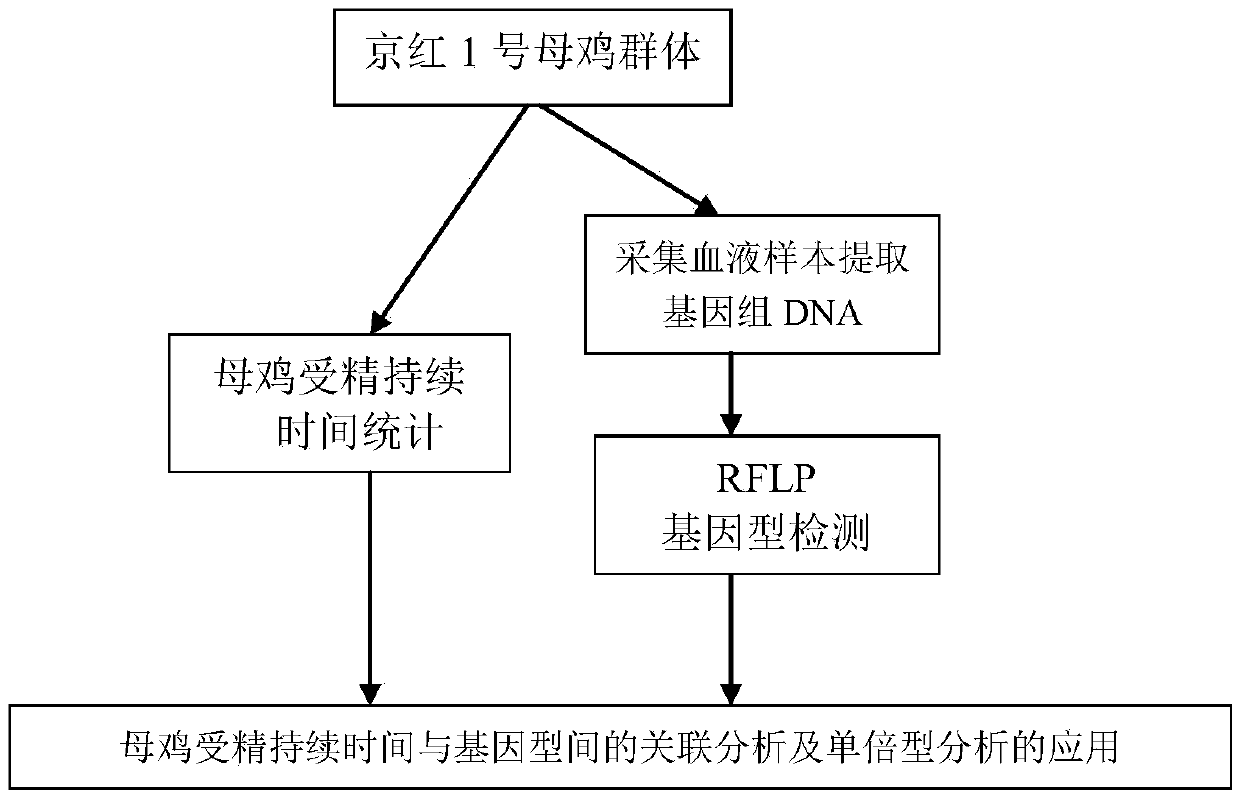
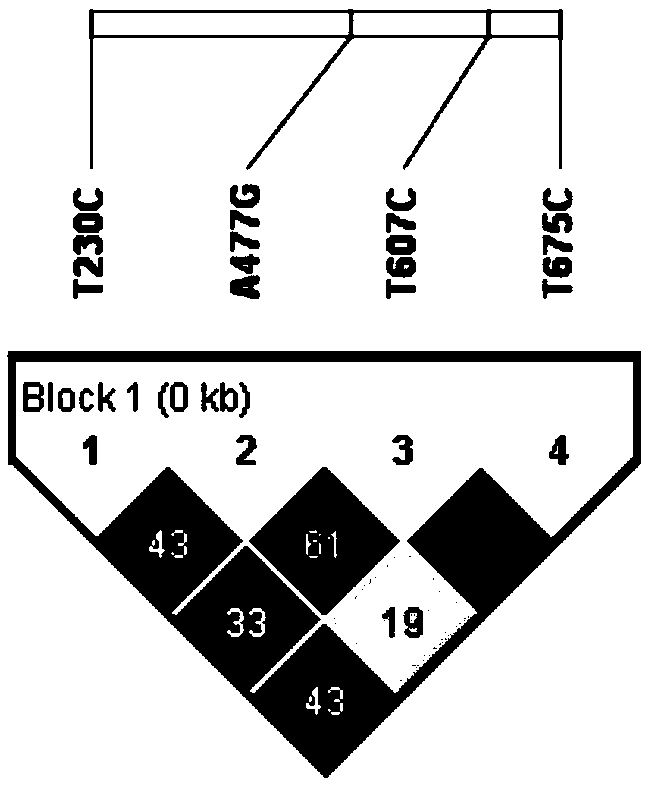
SNP molecular markers related to chicken-fertilization duration time characters and application thereof
ActiveCN105506086AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideMolecular breeding
The invention provides SNP molecular markers related to chicken-fertilization duration time characters and an application thereof. TGFB3 genes are subjected to polymorphic researching and association analysis with the association analysis method, and the SNP molecular markers related to the chicken-fertilization duration time characters are found from first introns of the chicken TGFB3 genes for the first time; the SNP molecular markers particularly relate to four SNP molecular markers related to hen-fertilization duration time characters and the positioning and the application of a haplotype formed by the four SNP molecular markers. The SNP molecular markers are obtained through association analysis, and the nucleotide sequences of the SNP molecular markers are shown as SEQ ID NO:1-4. The molecular markers and the haplotype can be used for molecular breeding of chicken-fertilization duration time.
Owner:湖北欣华生态畜禽开发有限公司
Pear transcription factor PyHY5, and recombinant expression vector and application thereof
The invention discloses a pear transcription factor PyHY5 and application of a recombinant expression vector of the pear transcription factor PyHY5. The nucleotide sequence of a transcription factor PyHY5 gene which is separated from 'Red Zaosu' pears and has a function of promoting anthocyanin biosynthesis of pear peels is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, and the encoded amino acid sequence of the transcription factor PyHY5 gene is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2. Transcription factors PyHY5 and PyMYB114 are co-transformed into strawberry and pear fruits by an agrobacterium-mediated transformation method;according to biological function verification, the cloned PyHY5 gene and a cofactor PyMYB114 thereof interact to promote the transport function of anthocyanin in the pear peels; through discovery of new functions of the PyHY5, new genetic resources are provided for molecular breeding that promotes accumulation of the anthocyanin in the pear peels, and new genetic resources are provided for the implementation of green agriculture; the development and utilization of the genetic resources is beneficial to agricultural cost reduction and environmental friendliness.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
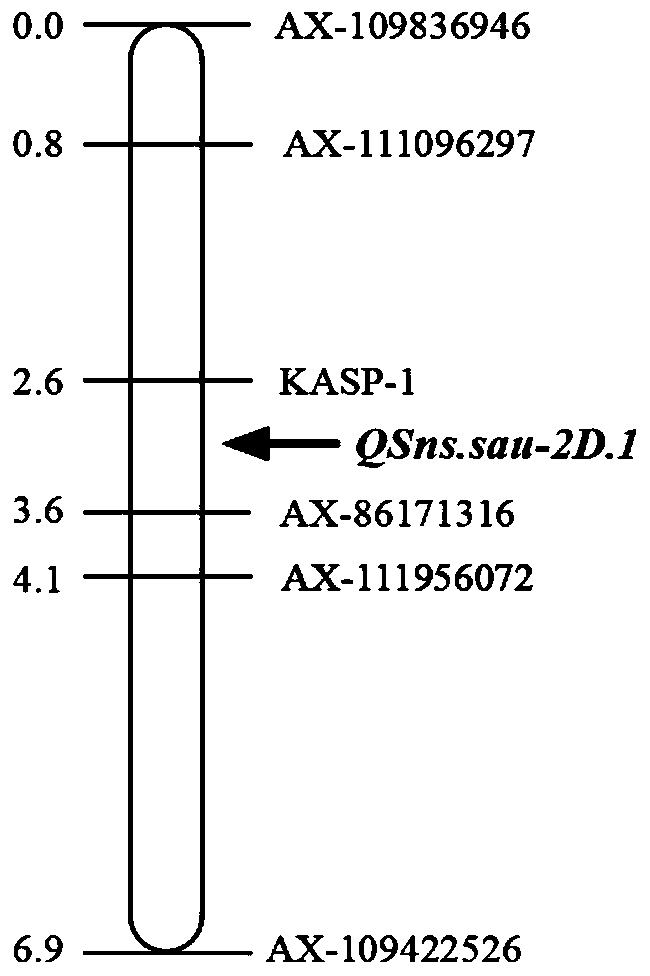
Wheat spikelet number QTL linked SNP molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN109825621AImprove use valueImprove selection identification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMolecular breeding
The invention discloses a wheat spikelet number QTL linked SNP molecular marker and application thereof. The SNP molecular marker KASP-1 is located on the short arm of a 2D chromosome of the RefSeqv1.0 genome version, and the 100 bp sequence before and after is shown as SEQ ID NO.46, the polymorphism is C / T and can be obtained by primer amplification shown in SEQ ID NO.1-3. The molecular marker can accurately track the wheat spikelet number QTL QSns.sau-2D.1 to predict the wheat spikelet number and facilitate molecular breeding. The invention also discloses a method for identifying the wheat spikelet number QTL QSns.sau-2D.1 molecular marker. By means of the method, the wheat spikelet number prediction accuracy can be enhanced, so as to quickly screen out wheat varieties or lines with increased spikelet number for breeding, and the breeding process of the wheat high yield varieties can be accelerated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Method for detecting chicken fatty character
InactiveCN1900316AEasy to breedImprove conversion rateMicrobiological testing/measurementMarker-assisted selectionMolecular breeding
The method of detecting chicken fatty character is to detect whether the 646-th base from the 5' end of chicken PGC-1alpha gene cDNA is A or G. The present invention provides one effective, accurate, simple and feasible molecular genetic marker for the auxiliary molecular mark selection of meat chicken breeding and the improvement of chicken's abdomen fatty character. The detection method is simple, low in cost and accurate.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
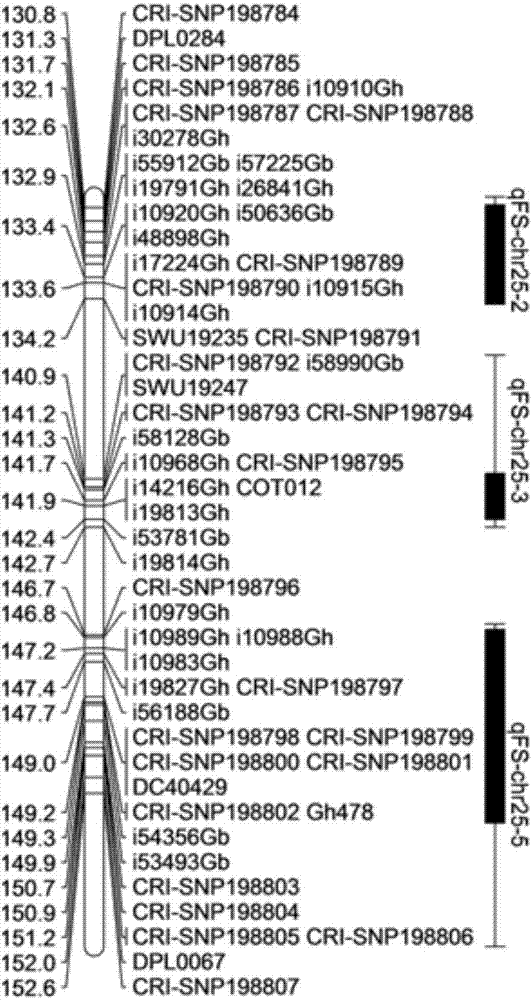
SNP molecular markers related to fiber strength of upland cotton 25# chromosome
ActiveCN107043813AShorten the breeding cycleImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRe sequencingAgricultural science
The invention relates to SNP molecular markers related to fiber strength of an upland cotton 25# chromosome. The invention belongs to the technical field of cotton molecular breeding and discloses the SNP molecular markers related to fiber strength of the upland cotton and detection and application thereof. The SNP molecular markers are obtained by taking a stable RIL group of cotton as a material by means of a genome re-sequencing method. The SNP markers disclosed by the invention are used for molecular marker-assisted selection, so that the breeding period can be greatly shortened, and the breeding efficiency of the cotton fiber strength can be increased.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com