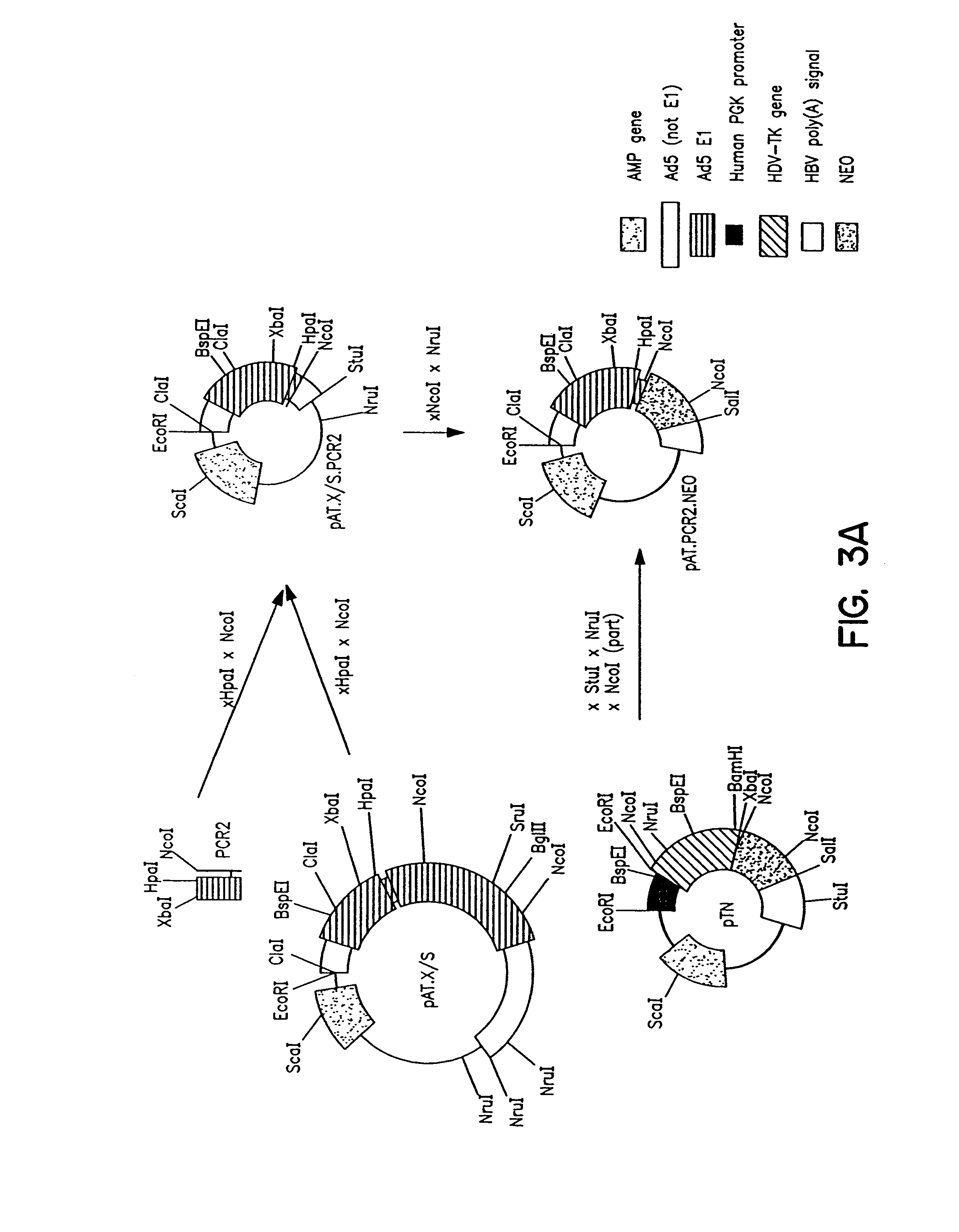
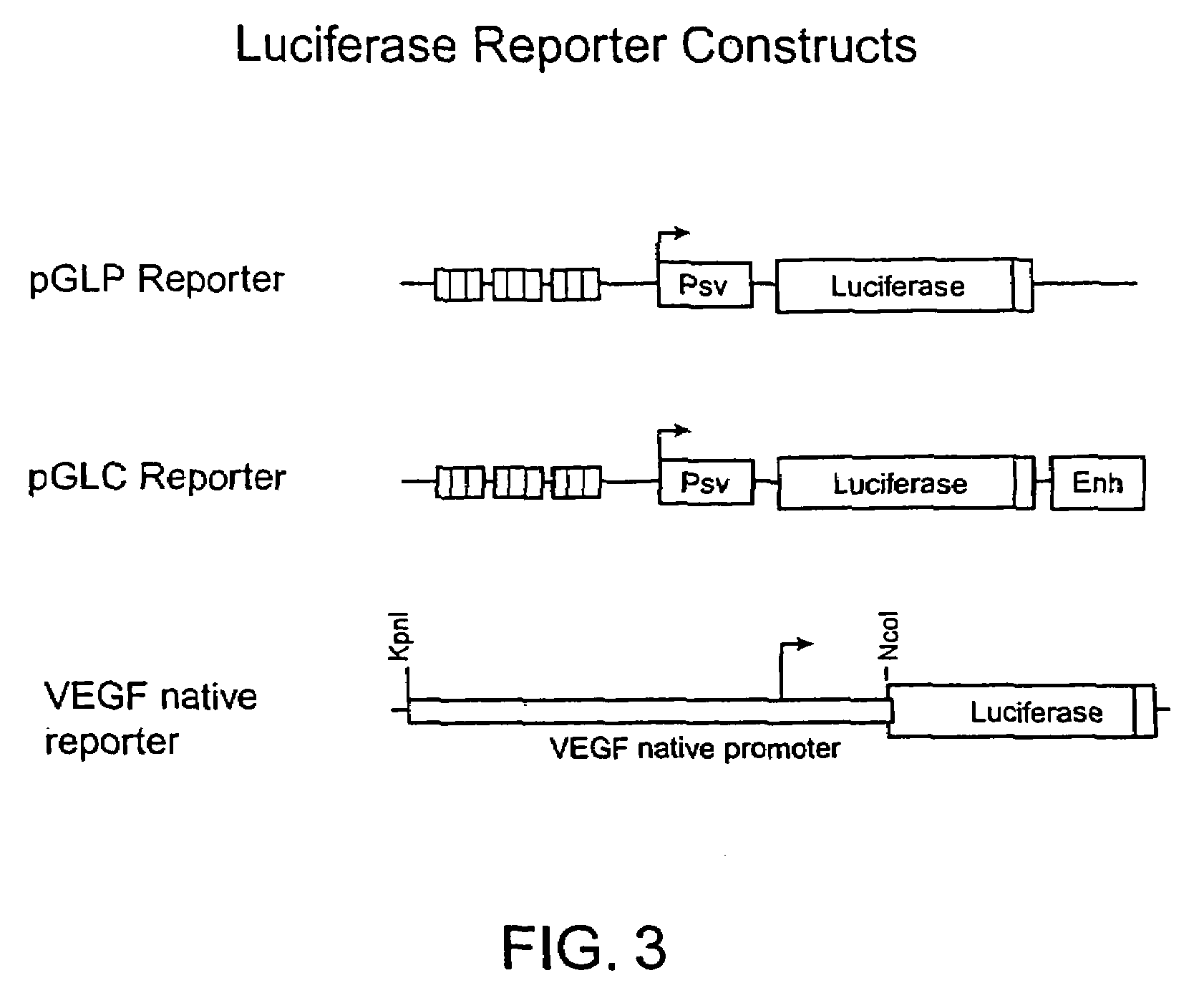
Patents
Literature
241 results about "Functional genomics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Functional genomics is a field of molecular biology that attempts to describe gene (and protein) functions and interactions. Functional genomics make use of the vast data generated by genomic and transcriptomic projects (such as genome sequencing projects and RNA sequencing). Functional genomics focuses on the dynamic aspects such as gene transcription, translation, regulation of gene expression and protein–protein interactions, as opposed to the static aspects of the genomic information such as DNA sequence or structures. A key characteristic of functional genomics studies is their genome-wide approach to these questions, generally involving high-throughput methods rather than a more traditional “gene-by-gene” approach.
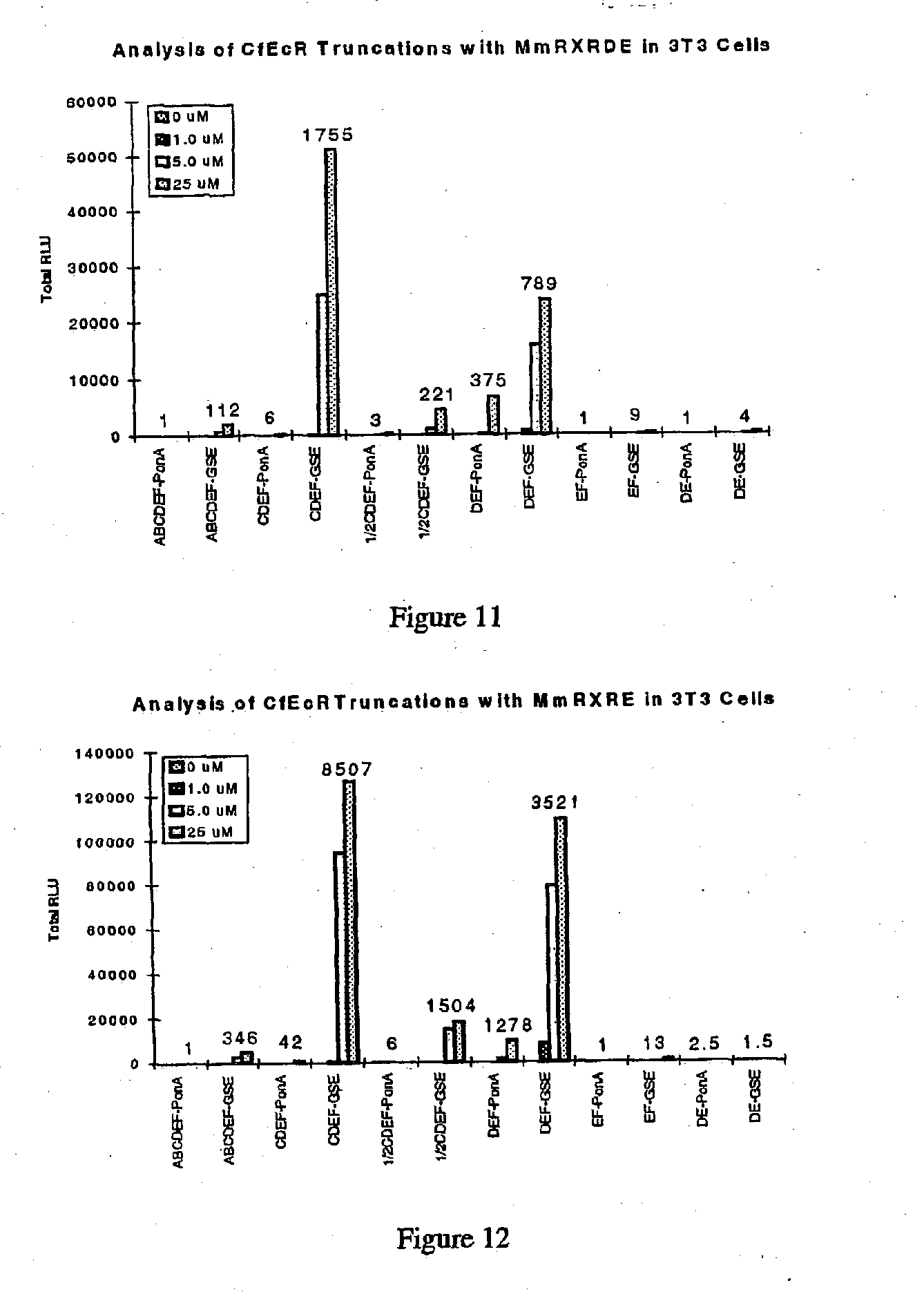
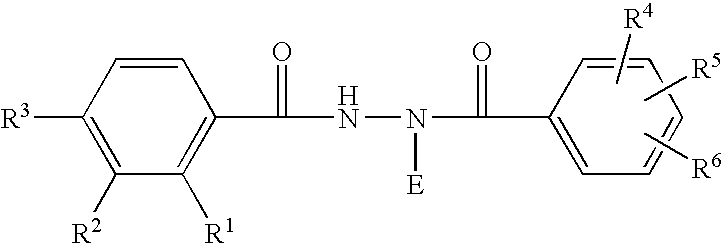
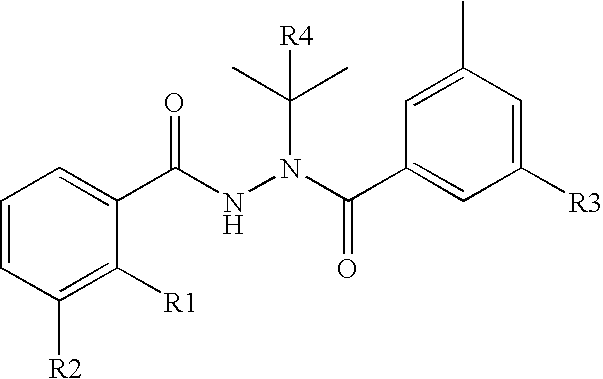
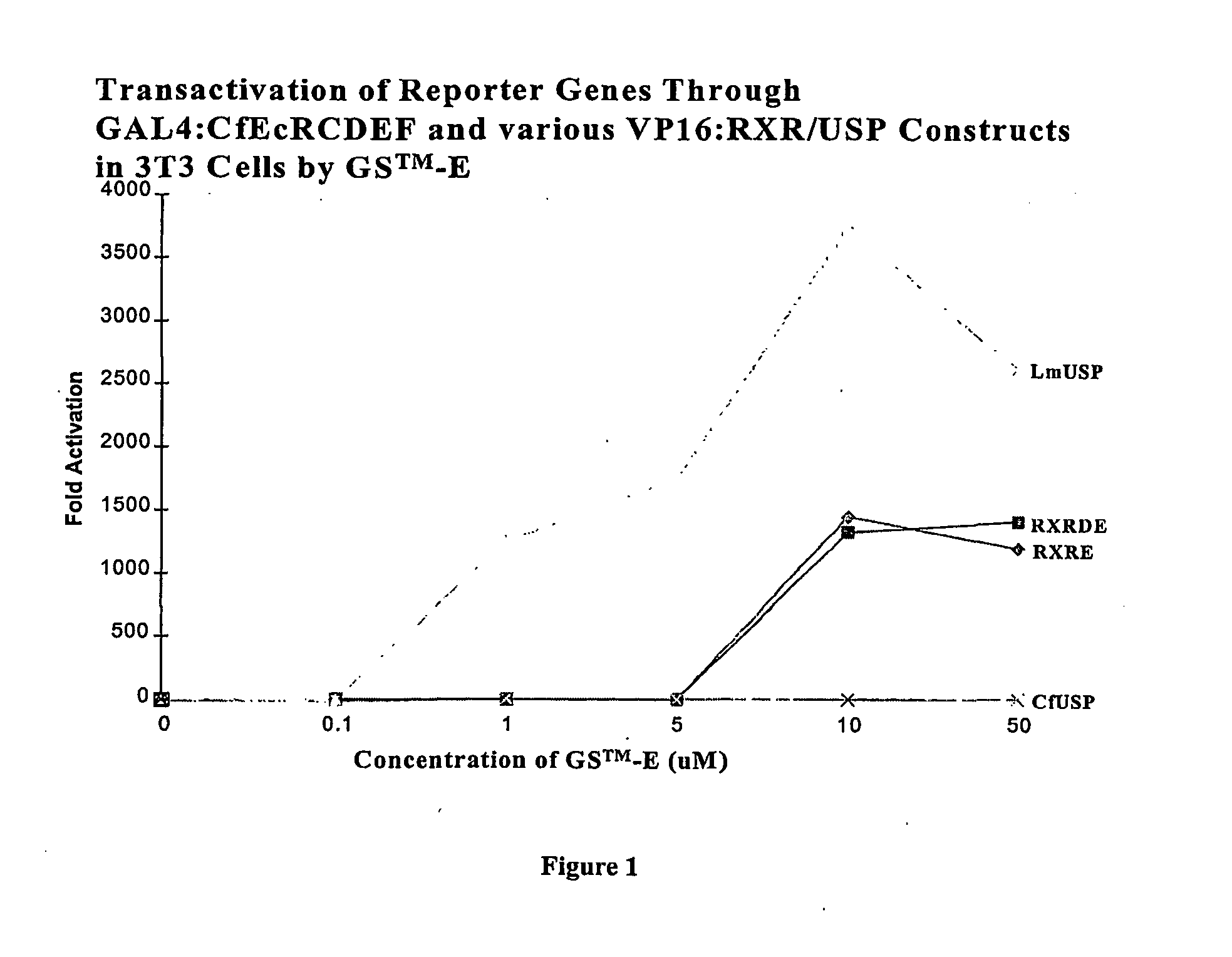
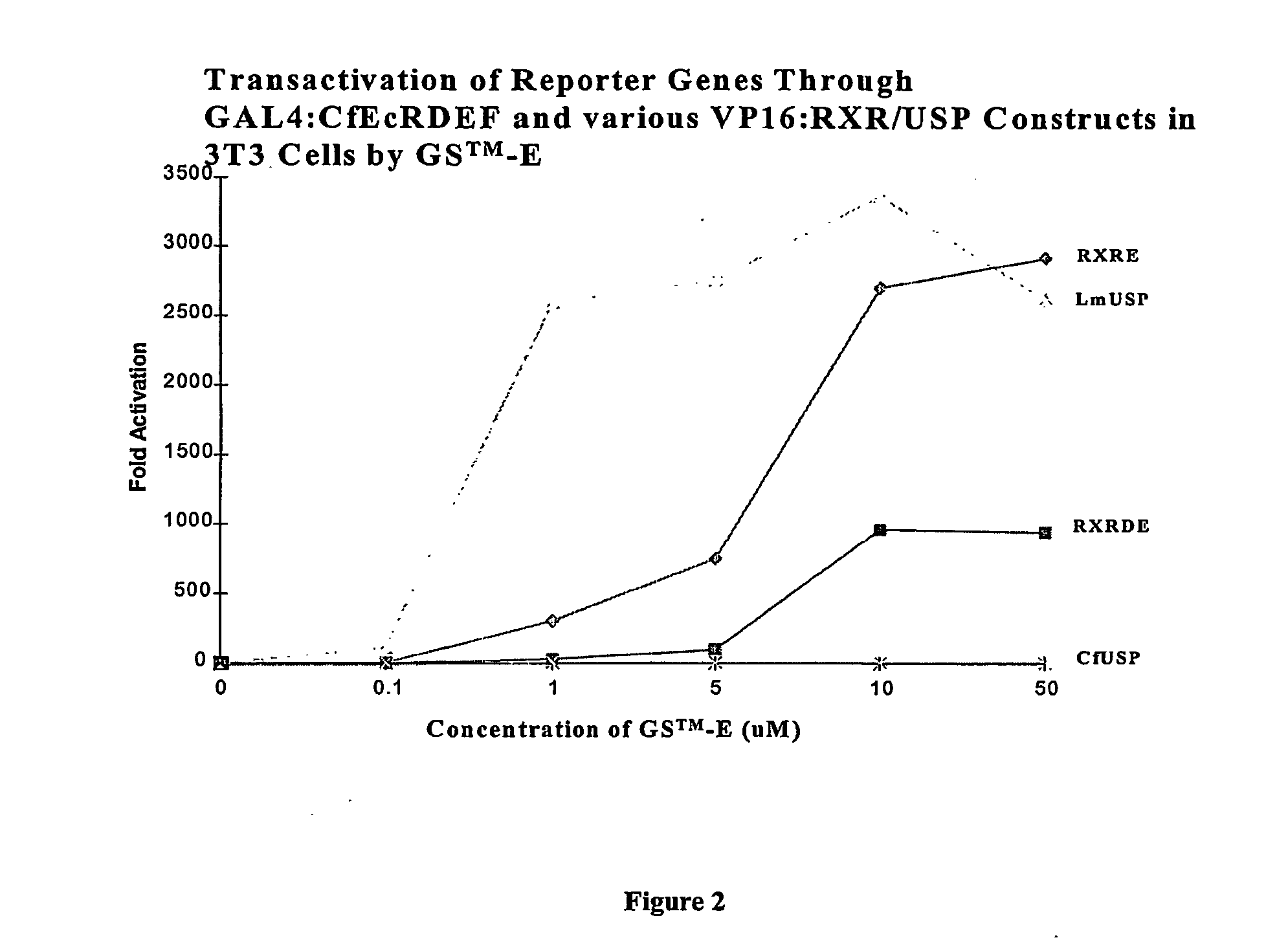
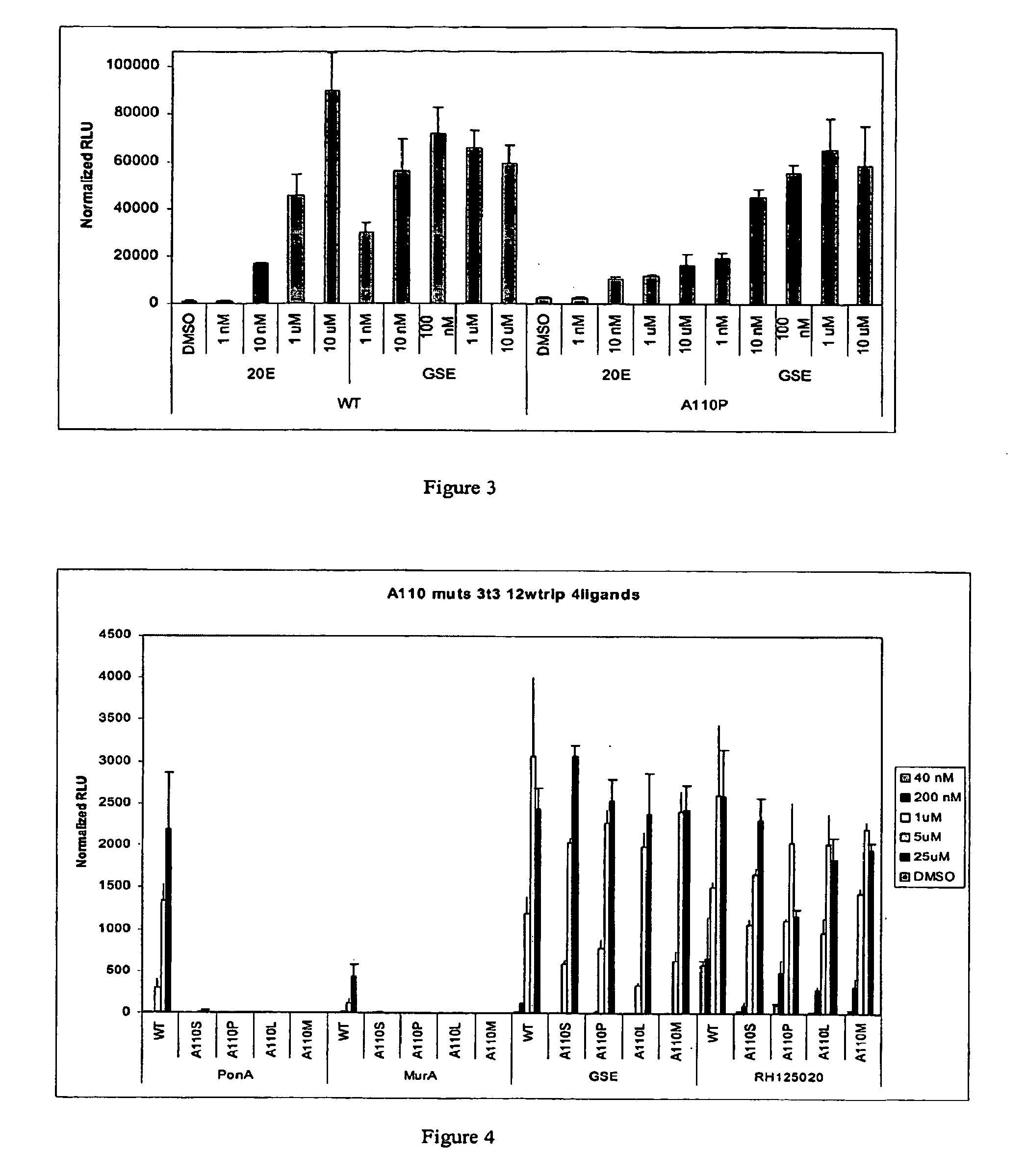
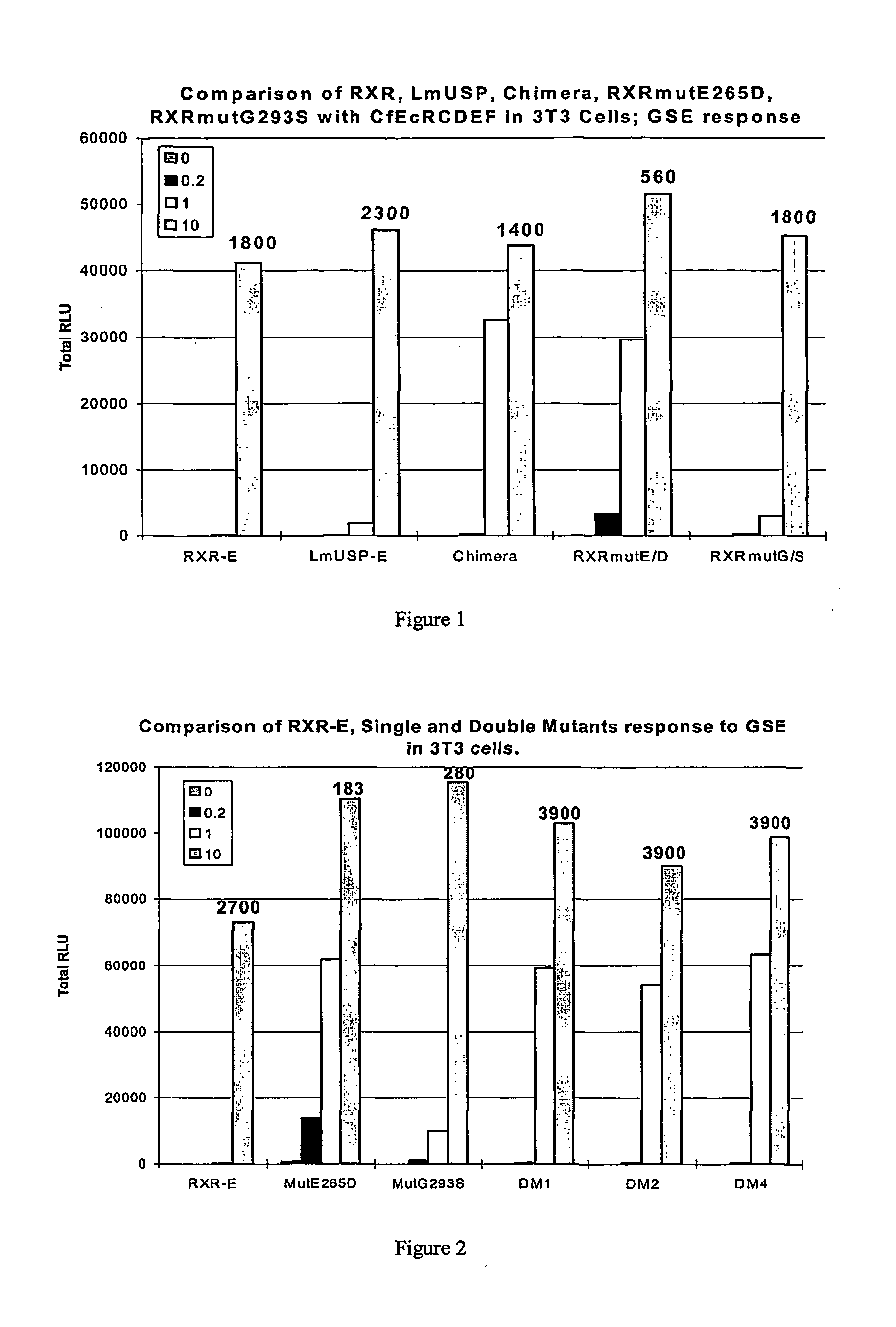
Novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in an nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in a Group H nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating the expression of a gene in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Mutant receptors and their use in a nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system
InactiveUS20050266457A1Improve efficiencyGreat degree of sequence similarityBiocideBacteriaHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysGenomics
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in a nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating the expression of a gene in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Novel ecdysone receptor-based induicible gene expression system
InactiveUS20070161086A1Fusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysBiotechnology
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to a novel inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating gene expression in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic plants and animals.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Functional genomics using crispr-cas systems, compositions, methods, screens and applications thereof
ActiveUS20160251648A1Simplify methodologyImprove abilitiesStable introduction of DNAScreening processGenome scaleGenomics
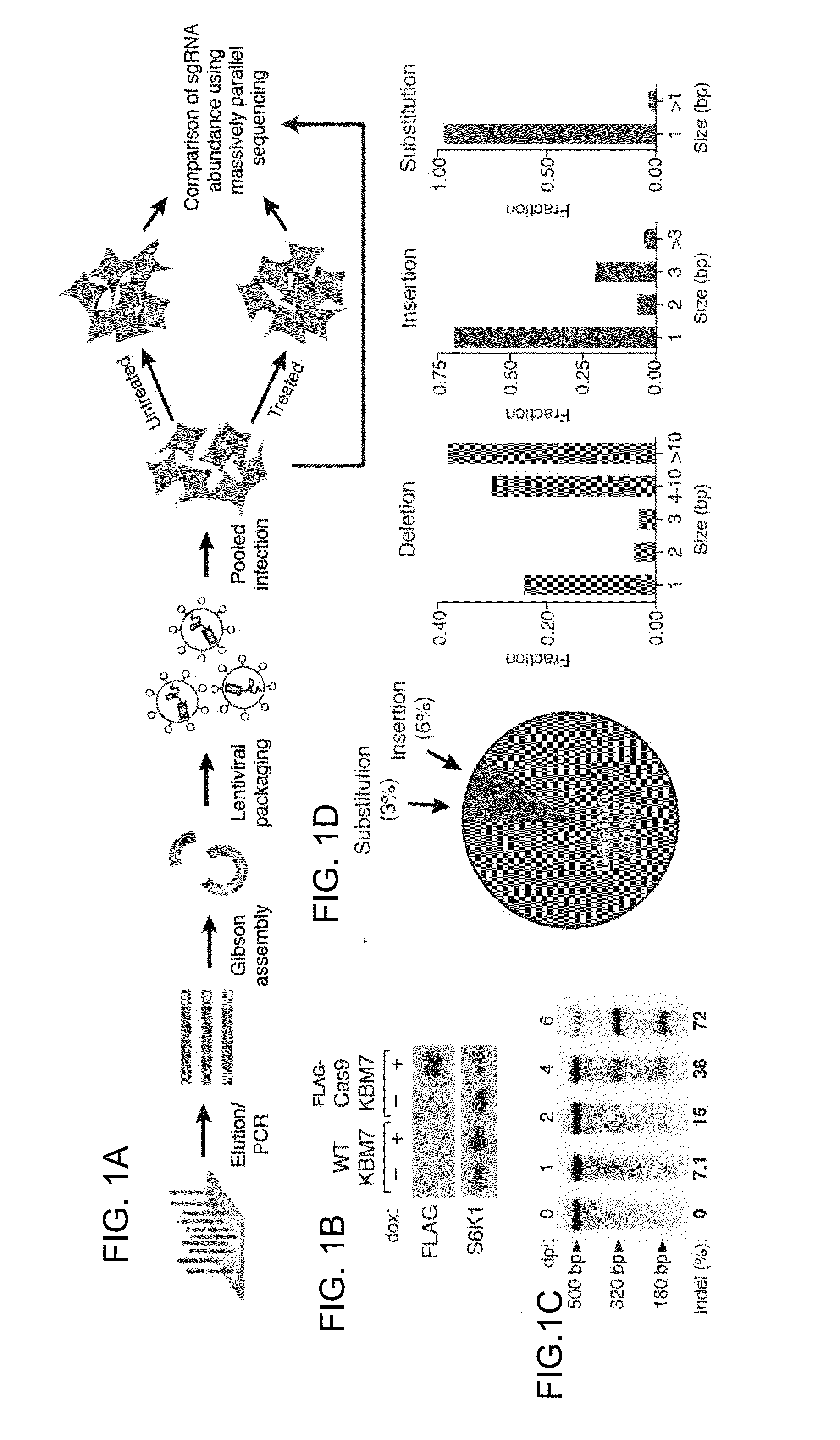
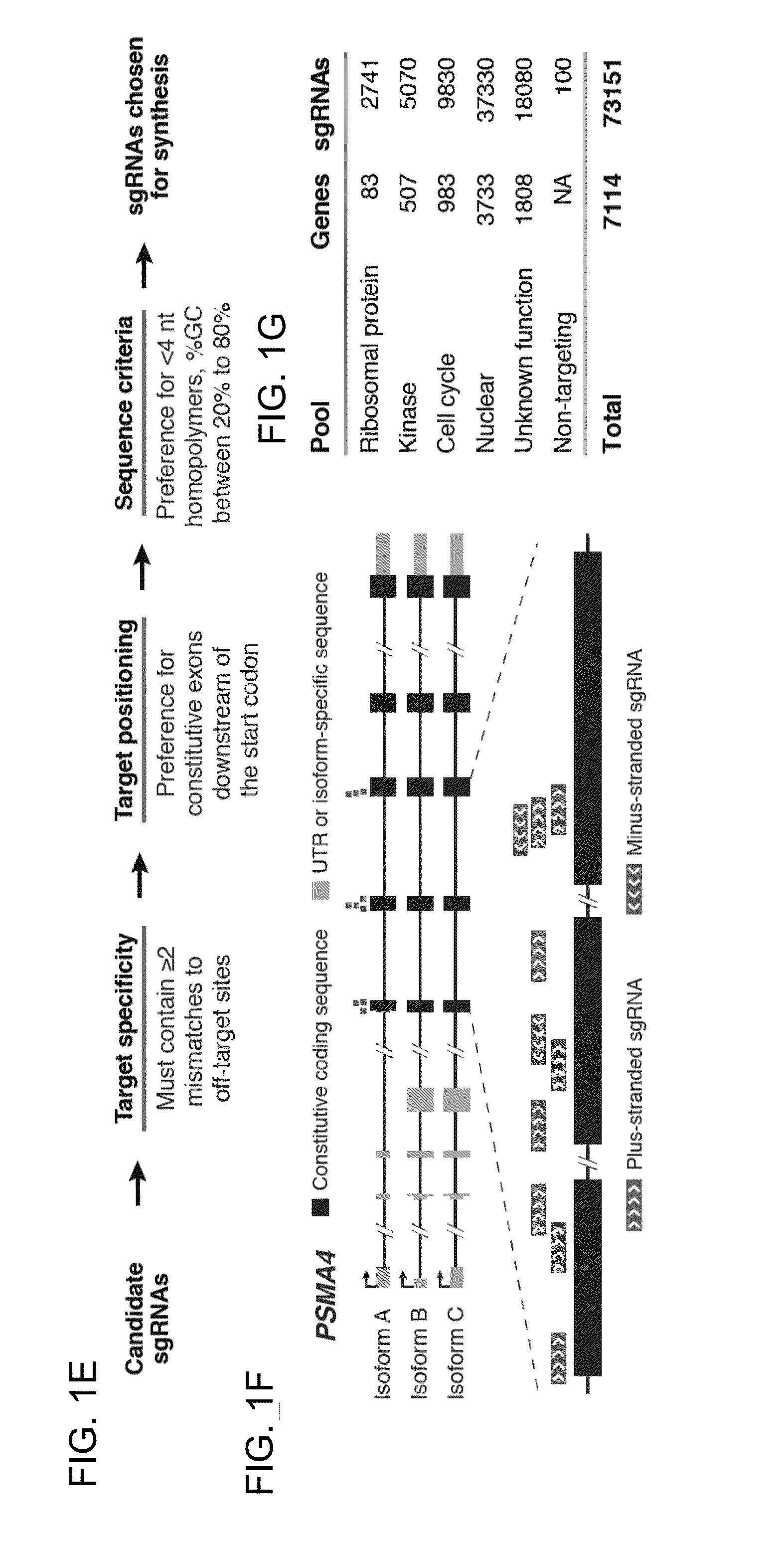
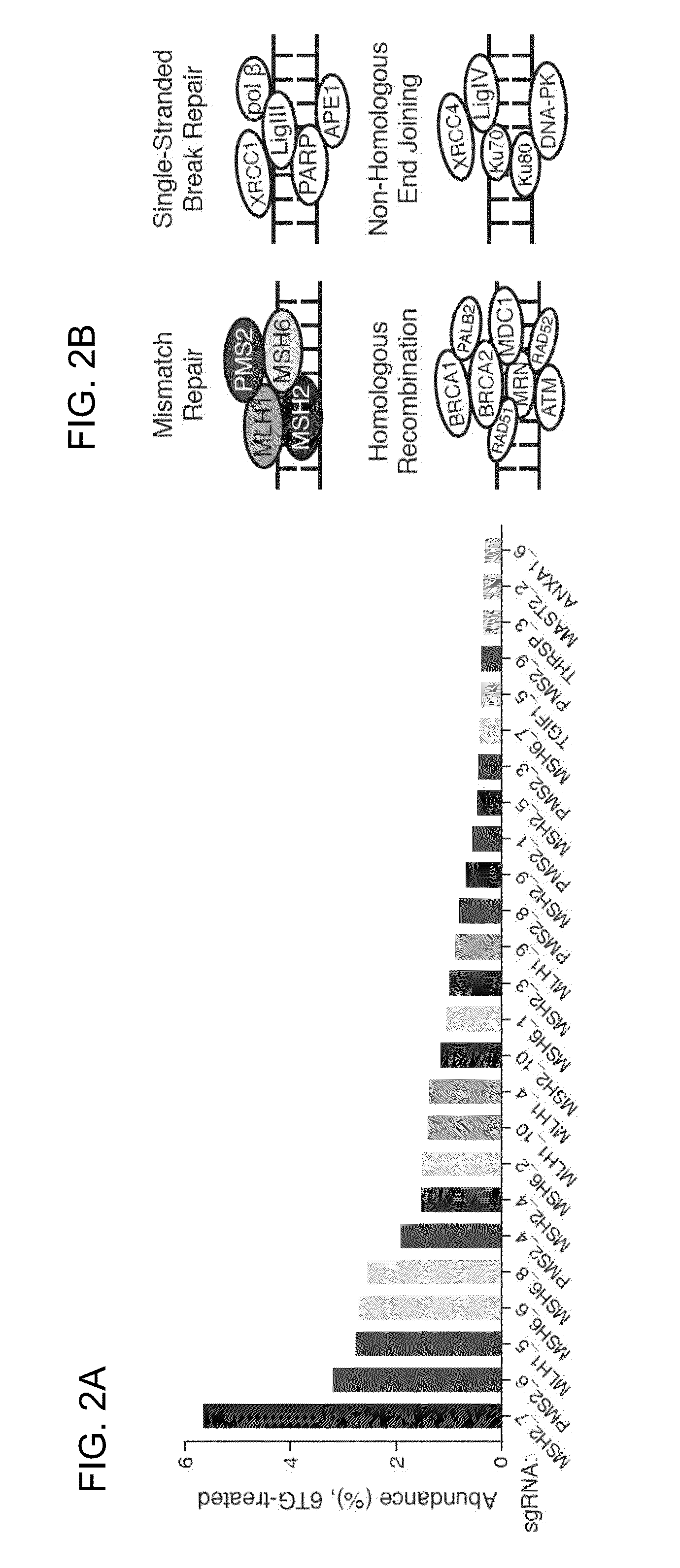
The present invention generally relates to libraries, kits, methods, applications and screens used in functional genomics that focus on gene function in a cell and that may use vector systems and other aspects related to Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)-Cas systems and components thereof. The present invention also relates to rules for making potent single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) for use in CRISPR-Cas systems. Provided are genomic libraries and genome wide libraries, kits, methods of knocking out in parallel every gene in the genome, methods of selecting individual cell knock outs that survive under a selective pressure, methods of identifying the genetic basis of one or more medical symptoms exhibited by a patient, and methods for designing a genome-scale sgRNA library.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
Chimeric retinoid x receptors and their use in a novel ecdysone receptor-based inducible gene expression system
InactiveUS20080263687A1FungiFusion with DNA-binding domainHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysBiotechnology
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to a novel ecdysone receptor / chimeric retinoid X receptor-based inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating gene expression in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large-scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms.
Owner:RHEOGENE INC DE
Novel ecdysone receptor-based inducible gene expression system
Owner:RHEOGENE INC DE
Mutant receptors and their use in a nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system
ActiveUS20080145935A1Improve efficiencyGreat degree of sequence similarityPeptide/protein ingredientsTissue cultureHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysGenomics
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in a nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating the expression of a gene in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Chimeric retinoid x receptors and their use in a novel ecdysone receptor-based inducible gene expression system
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to a novel ecdysone receptor / chimeric retinoid X receptor-based inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating gene expression in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large-scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms.
Owner:RHEOGENE INC DE
Novel ecdysone receptor/invertebrate retinoid X receptor-based inducible gene expression system
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to a novel ecdysone receptor / invertebrate retinoid X receptor-based inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating gene expression in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large-scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in a nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in a Group H nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating the expression of a gene in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms.
Owner:RHEOGENE INC DE
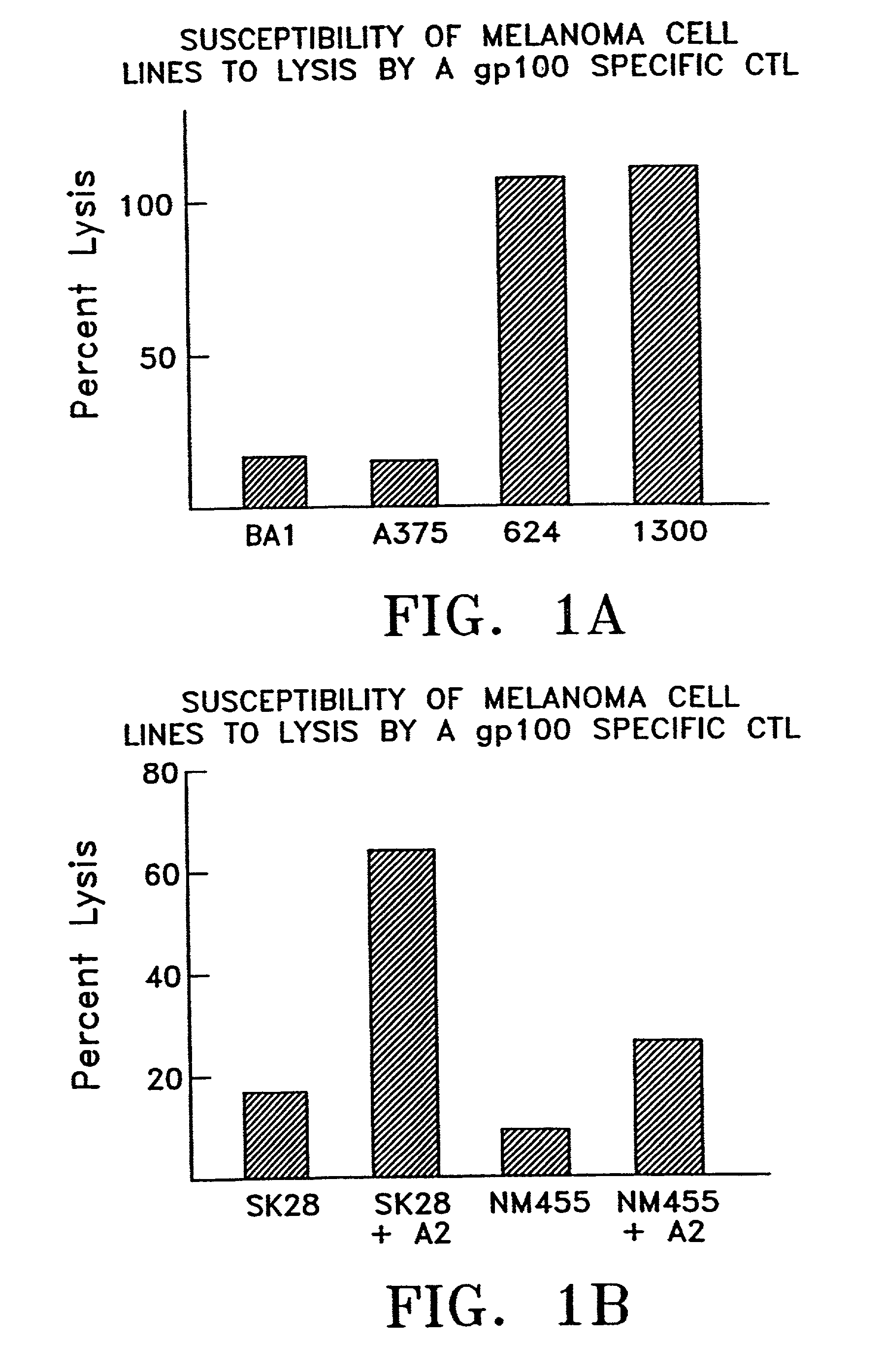
Genes differentially expressed in cancer cells to design cancer vaccines
Owner:GENZYME CORP
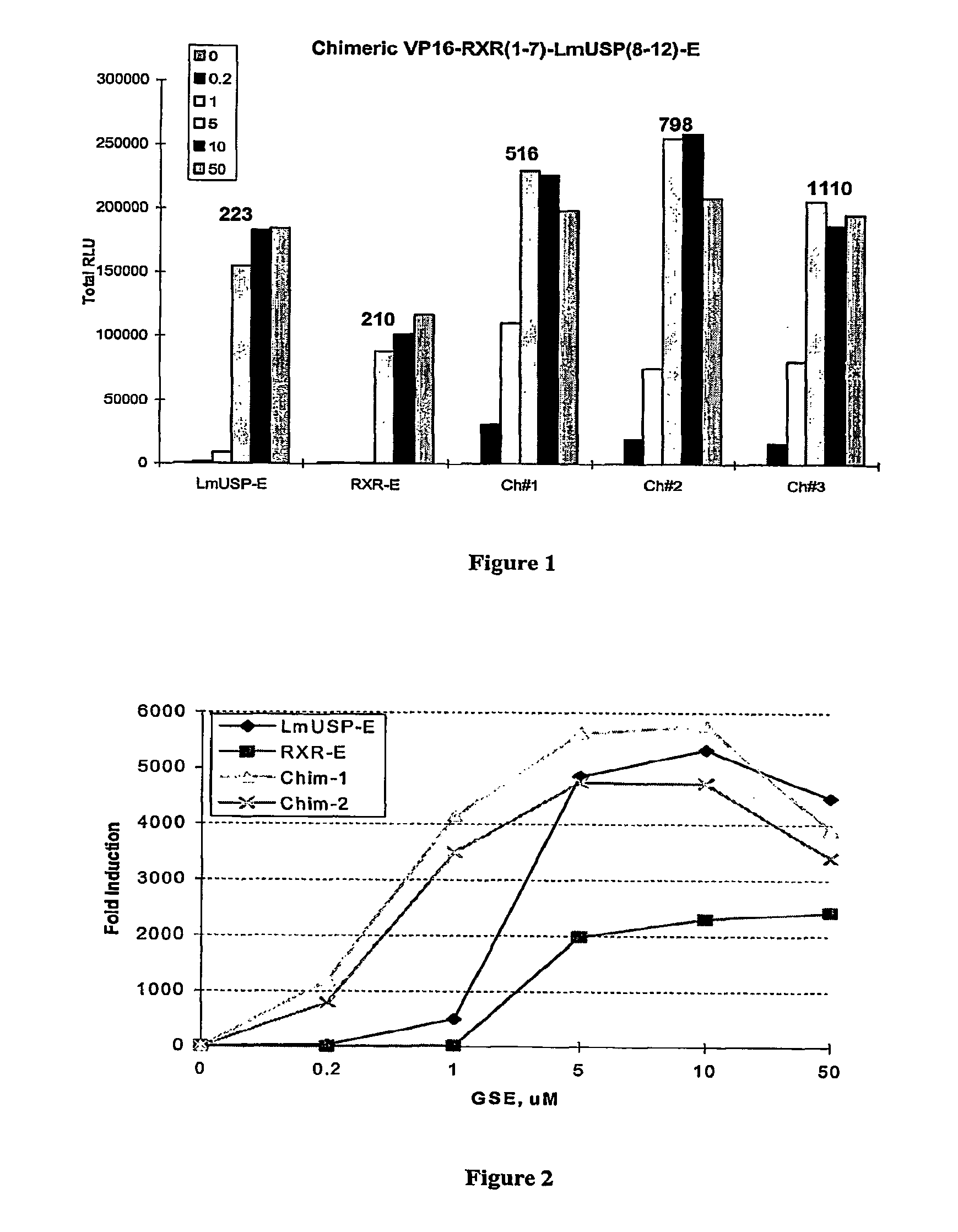
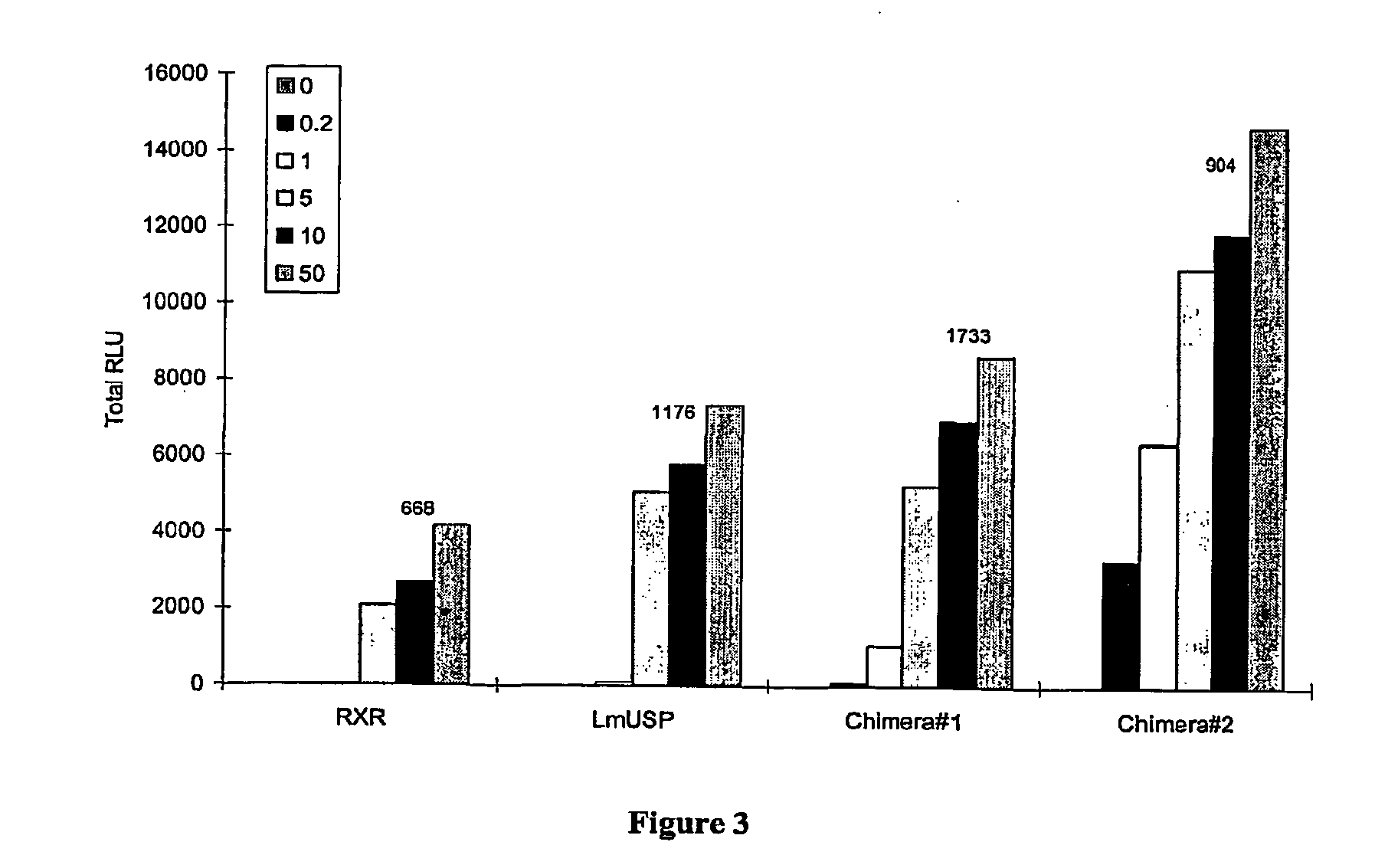
High throughput screening of gene function using libraries for functional genomics applications
InactiveUS7029848B2Altered phenotypeIncrease capacityFungiBacteriaGenomicsHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
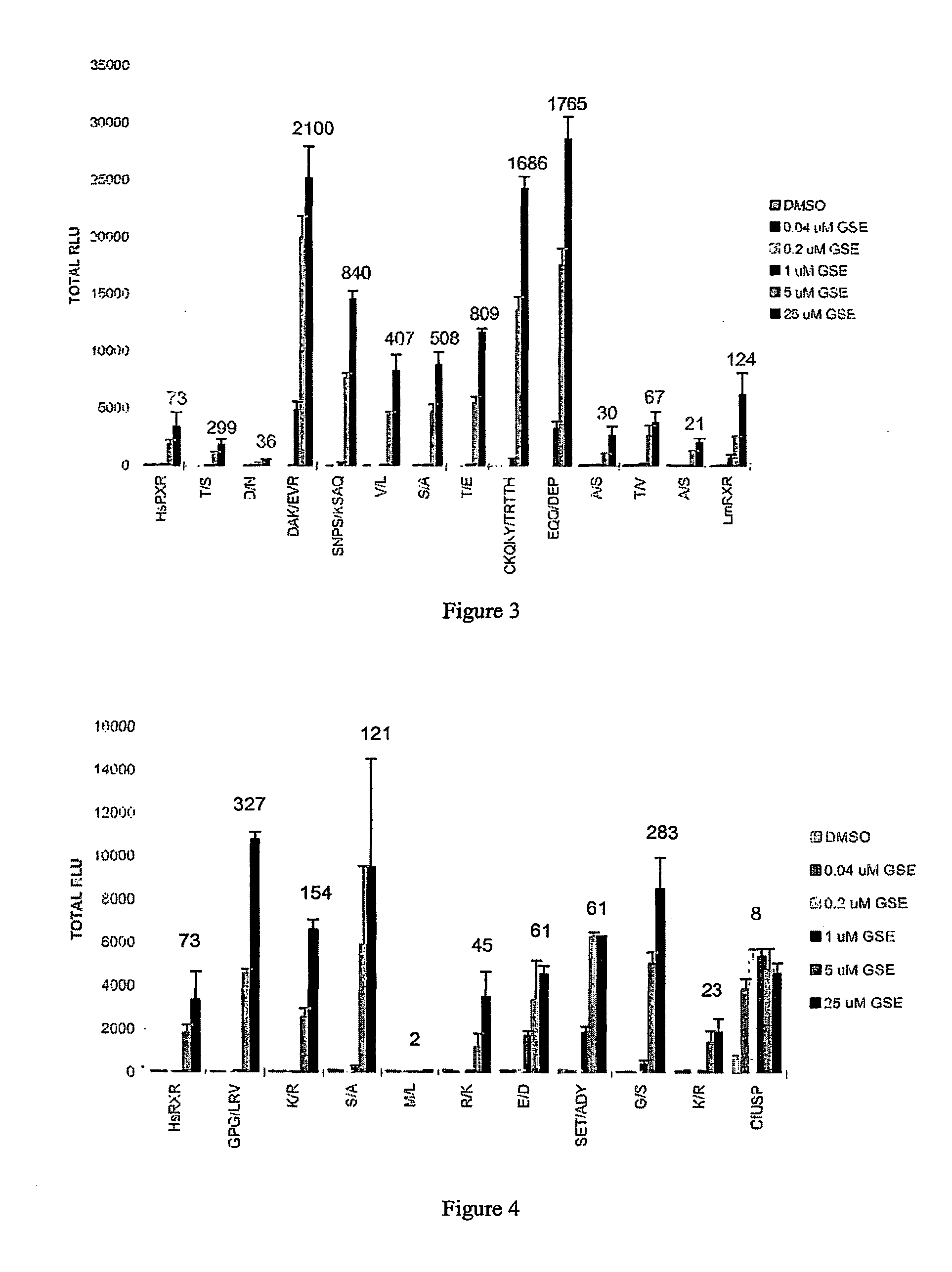
Novel means and methods for their use are provided to determine the function of the product(s) of one or more sample nucleic acids. The sample nucleic acids are synthetic oligonucleotides, DNA, or cDNA and encode polypeptides, antisense nucleic acids, or GSEs. The sample nucleic acids are expressed in a host by a vehicle to alter at least one phenotype of the host. The altered phenotype(s) is / are identified as a means to assign a biological function to the product(s) encoded by the sample nucleic acid(s).
Owner:GALAPAGOS GENOMICS
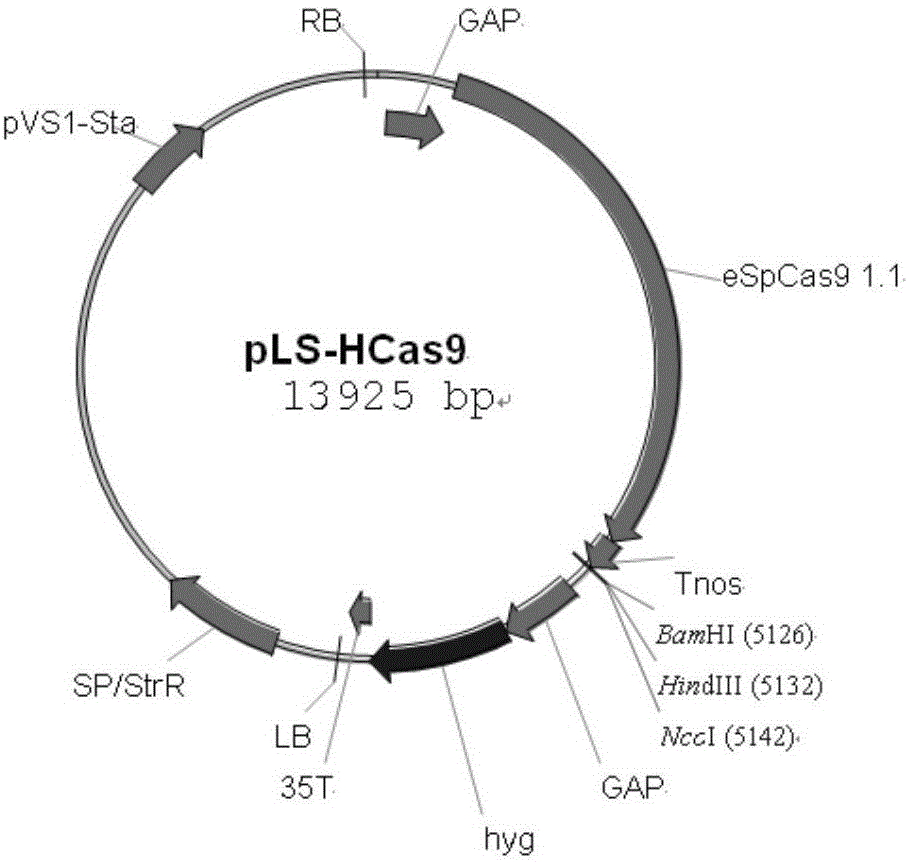
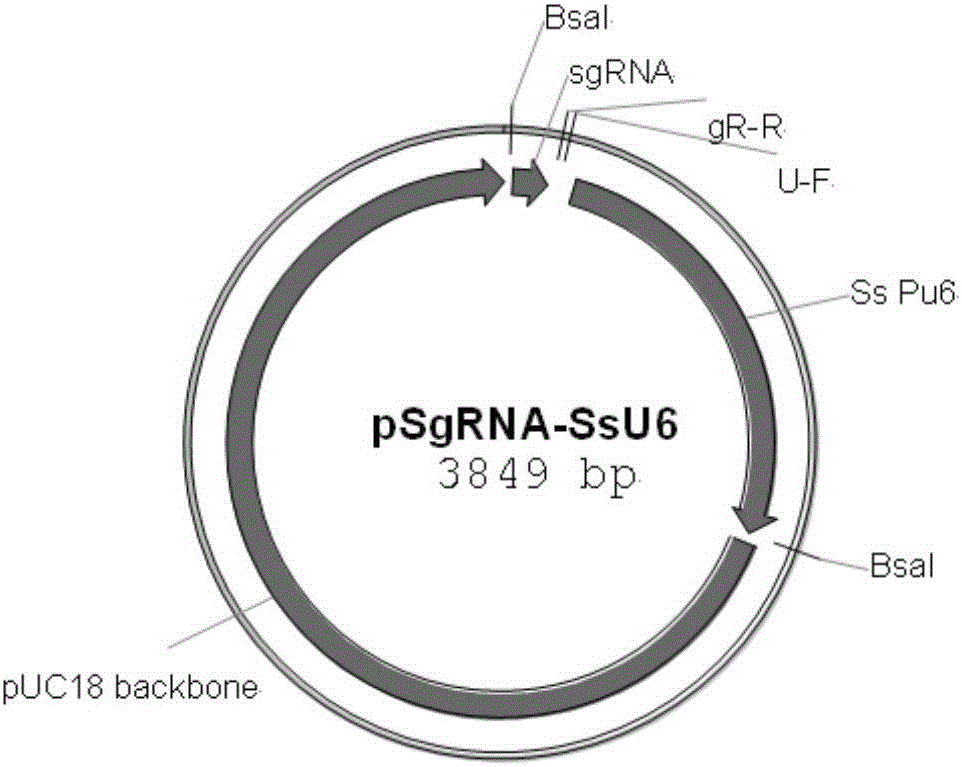
Site-specific insertional inactivation method and application mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens and CRISPR/Cas9
ActiveCN106434651ASpecify the direction of insertionRealize fixed-point insertionPeptidesNucleic acid vectorGenomicsMobile DNA
The invention discloses a site-specific insertional inactivation method mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens and CRISPR / Cas9. Endogenous snRNA promoter of Ustilago scitaminea (u6 promoter of Ustilago scitaminea) is used to drive sgRNA expression cassette. CRISPR / Cas9 system integrates with Ti plasmid of agrobacterium tumefaciens to construct the Ustilago scitaminea site-specific insertional inactivation system mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens with hygromycin as a selection marker. Specific sequence of the objective gene is cloned into sgRNA expression cassette for transformation of Ustilago scitaminea basidiospores, thus the mobile DNA fragment is exactly inserted into the objective gene sequence of Ustilago scitaminea, achieving the goal of damage to gene function. The invention provides an important tool for study of Ustilago scitaminea functional genomics. The system has the advantages of high efficiency and accuracy, and is convenient to use to conduct gene function researches in Ustilago scitaminea.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
High throughput functional genomics
InactiveUS20030065452A1High impedance sealReduce lateral flowMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsBiotechnology
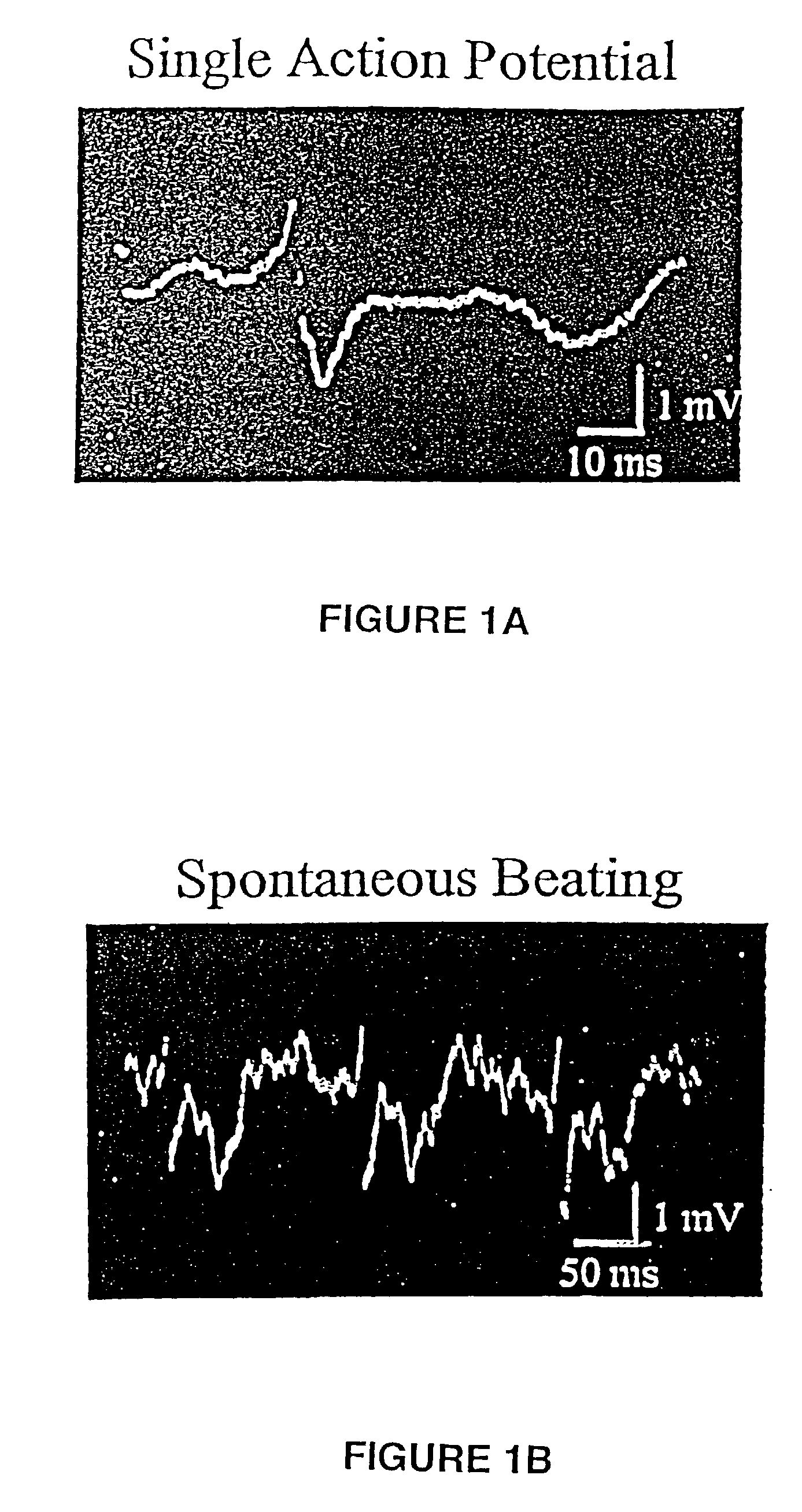
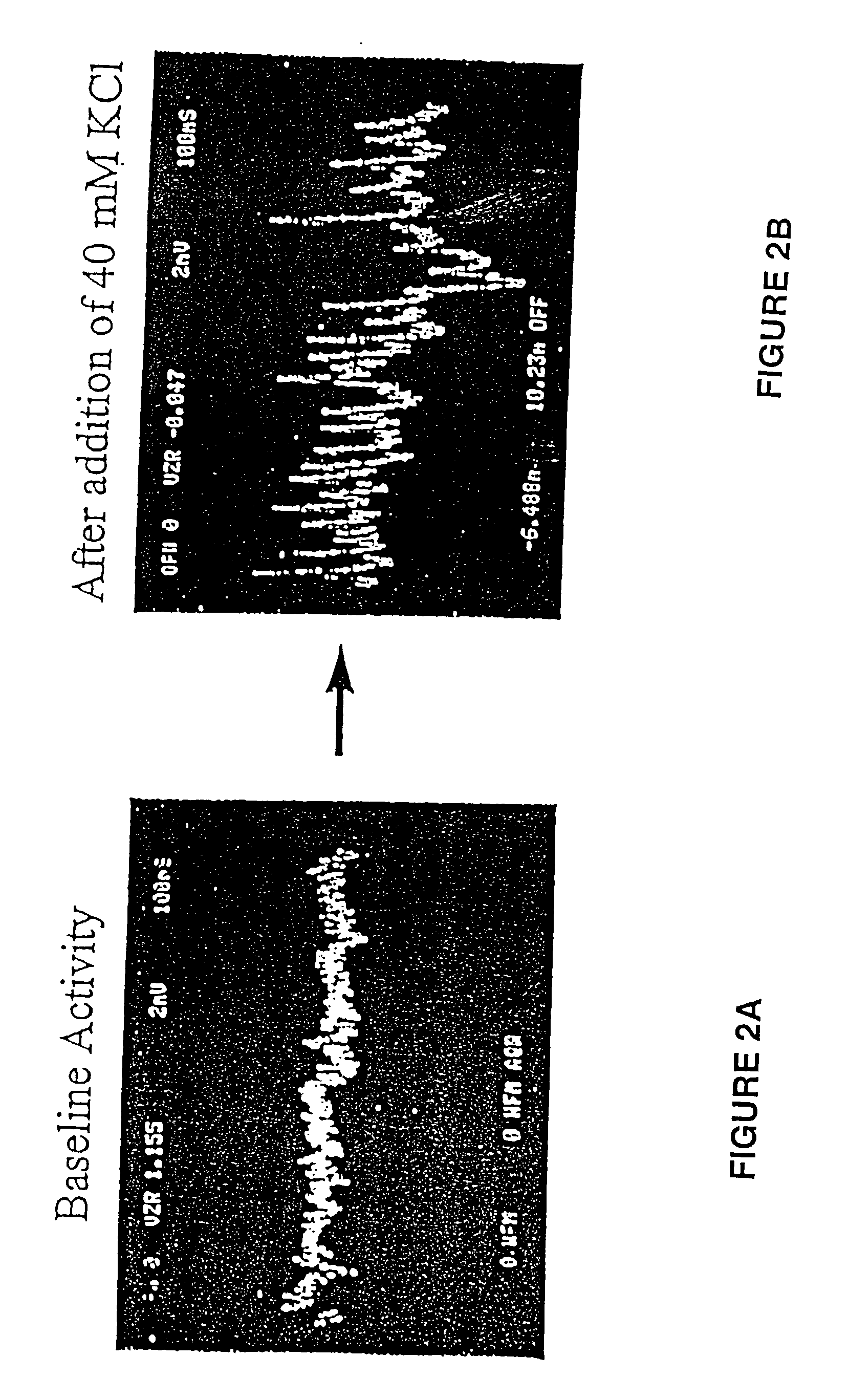
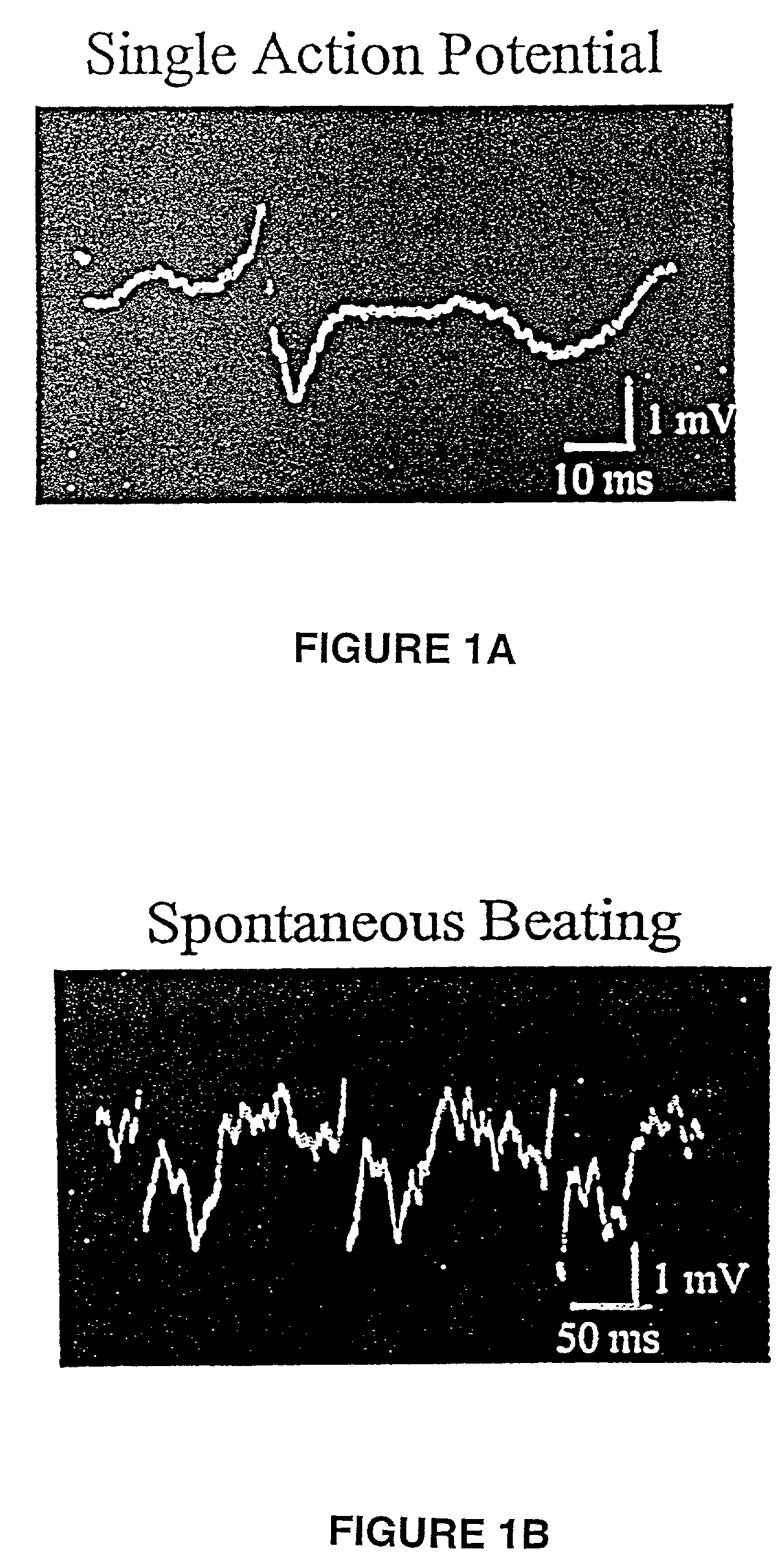
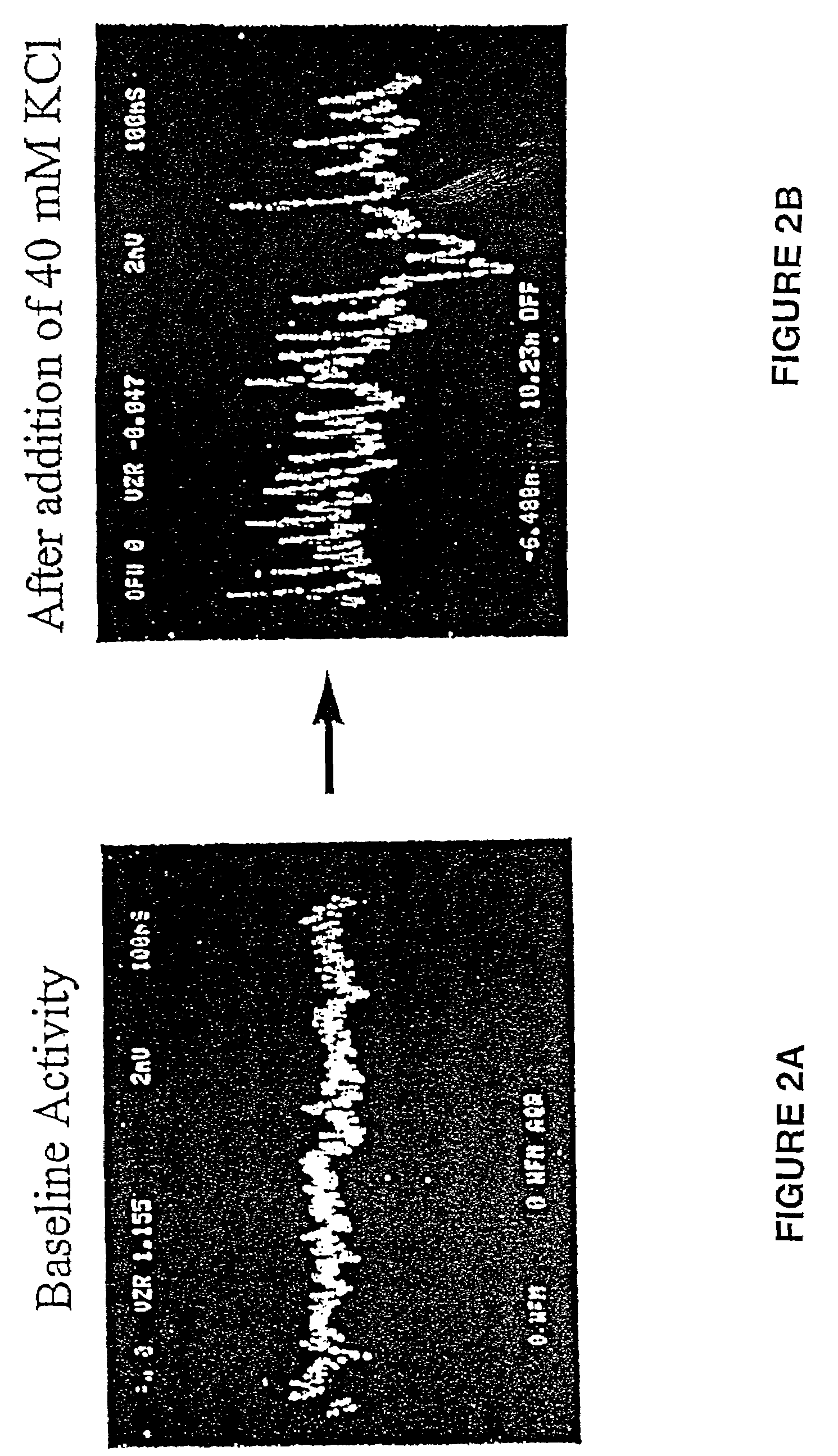
This invention focuses on the marriage of solid-state electronics and neuronal function to create a new high-throughput electrophysiological assay to determine a compound's acute and chronic effect on cellular function. Electronics, surface chemistry, biotechnology, and fundamental neuroscience are integrated to provide an assay where the reporter element is an array of electrically active cells. This innovative technology can be applied to neurotoxicity, and to screening compounds from combinatorial chemistry, gene function analysis, and basic neuroscience applications. The system of the invention analyzes how the action potential is interrupted by drugs or toxins. Differences in the action potentials are due to individual toxins acting on different biochemical pathways, which in turn affects different ion channels, thereby changing the peak shape of the action potential differently for each toxin. Algorithms to analyze the action potential peak shape differences are used to indicate the pathway(s) affected by the presence of a new drug or compound; from that, aspects of its function in that cell are deduced. This observation can be exploited to determine the functional category of biochemical action of an unknown compound. An important aspect of the invention is surface chemistry that permits establishment of a high impedance seal between cell and a metal microelectrode. This seal recreates the interface that enables functional patch-clamp electrophysiology with glass micropipettes, and allows extracellular electrophysiology on a microelectrode array. Thus, the invention teaches the feasibility of using living cells as diagnostics for high throughput real-time assays of cell function.
Owner:HICKMAN JAMES J
Lilium regale Wilson WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY1 and application
ActiveCN105441460AIncrease resistanceReduce usagePlant peptidesFermentationNicotiana tabacumNucleotide
The invention discloses a lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY1. The lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY1 has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and codes a protein with a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. According to the lilium regale Wilson WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY1, functional genomics related technical research verifies that the LrWRKY1 gene has the function of increasing the fungus resistance of plants; when the antifungal LrWRKY1 gene is constructed to a plant expression vector and is transferred to tobaccos for overexpression, transgenic tobacco plants have strong in-vitro antifungal activities, and experimental results show that the LrWRKY1 overexpressed transgenic tobaccos have obvious inhibiting effects on the growth of four fungi including botryosphaeria, sclerotinite, botrytis cinerea and fusarium oxysporum.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Chiral diacylhydrazine ligands for modulating the expression of exogenous genes via an ecdysone receptor complex
ActiveUS8076517B2Inhibit expressionUrea derivatives preparationOrganic active ingredientsGene expression levelOrganism
The present invention provides diacylhydrazine ligands and chiral diacylhydrazine ligands for use with ecdysone receptor-based inducible gene expression systems. Thus, the present invention is useful for applications such as gene therapy, large scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based screening assays, functional genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms, where control of gene expression levels is desirable. An advantage of the present invention is that it provides a means to regulate gene expression and to tailor expression levels to suit the user's requirements.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
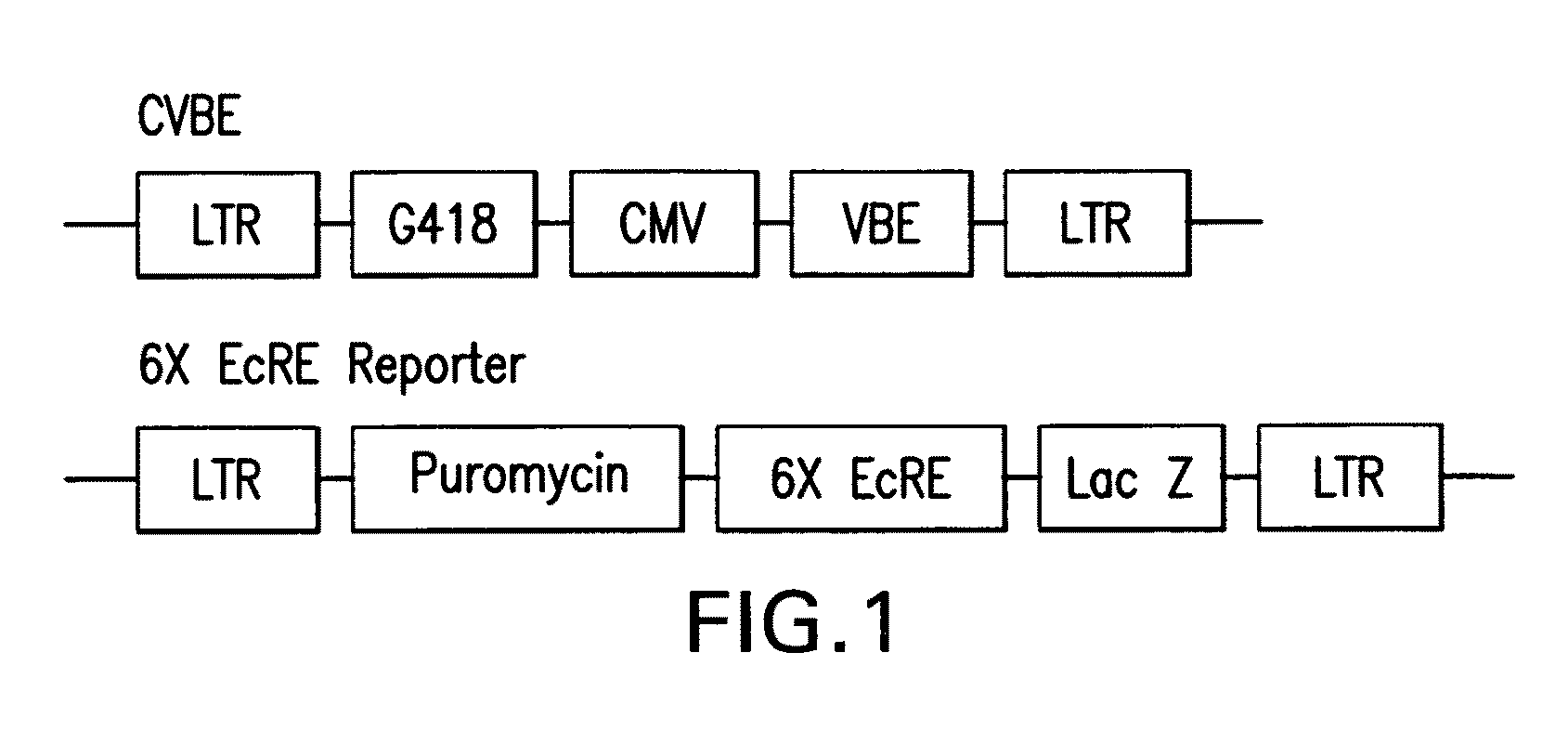
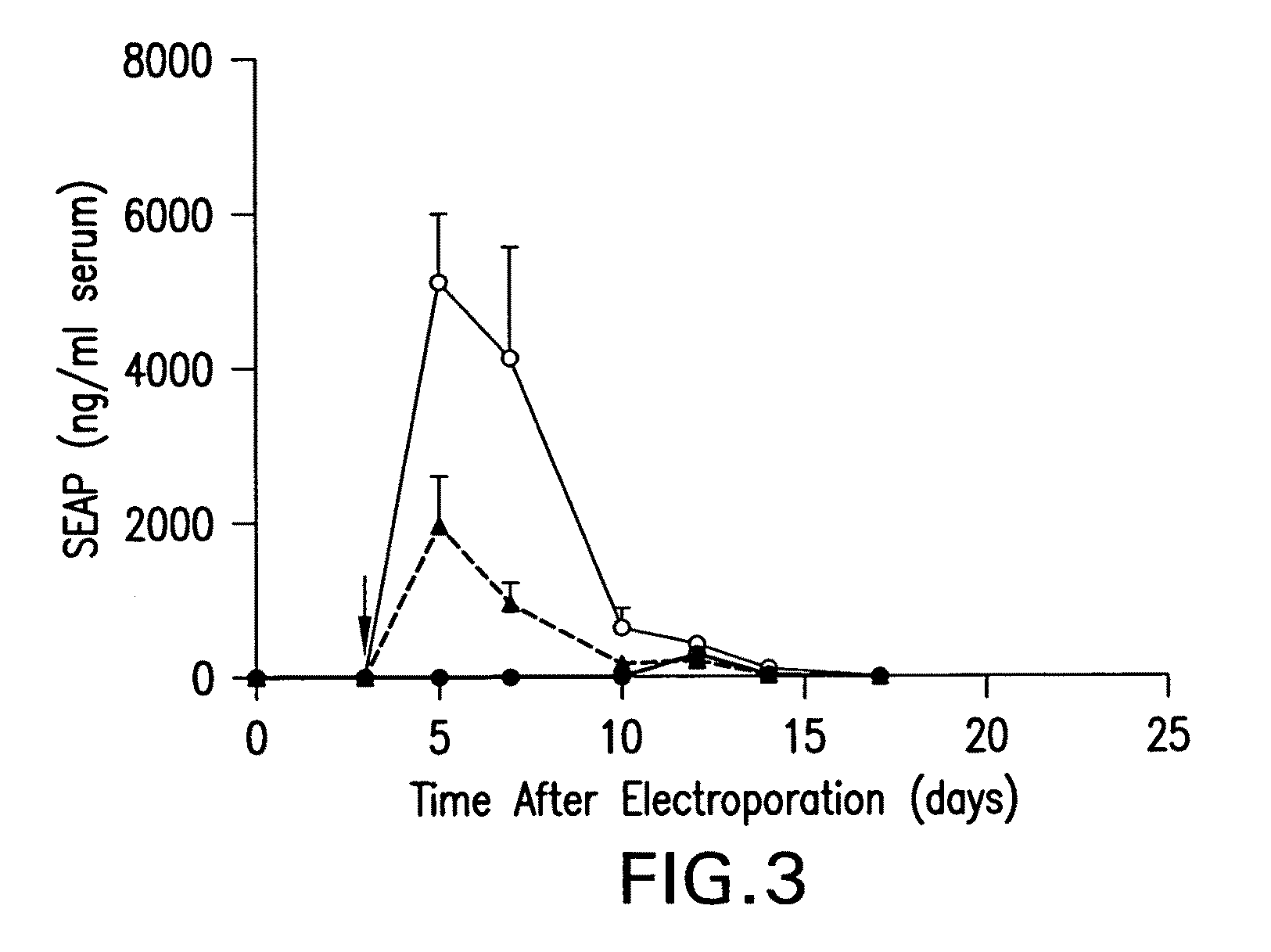
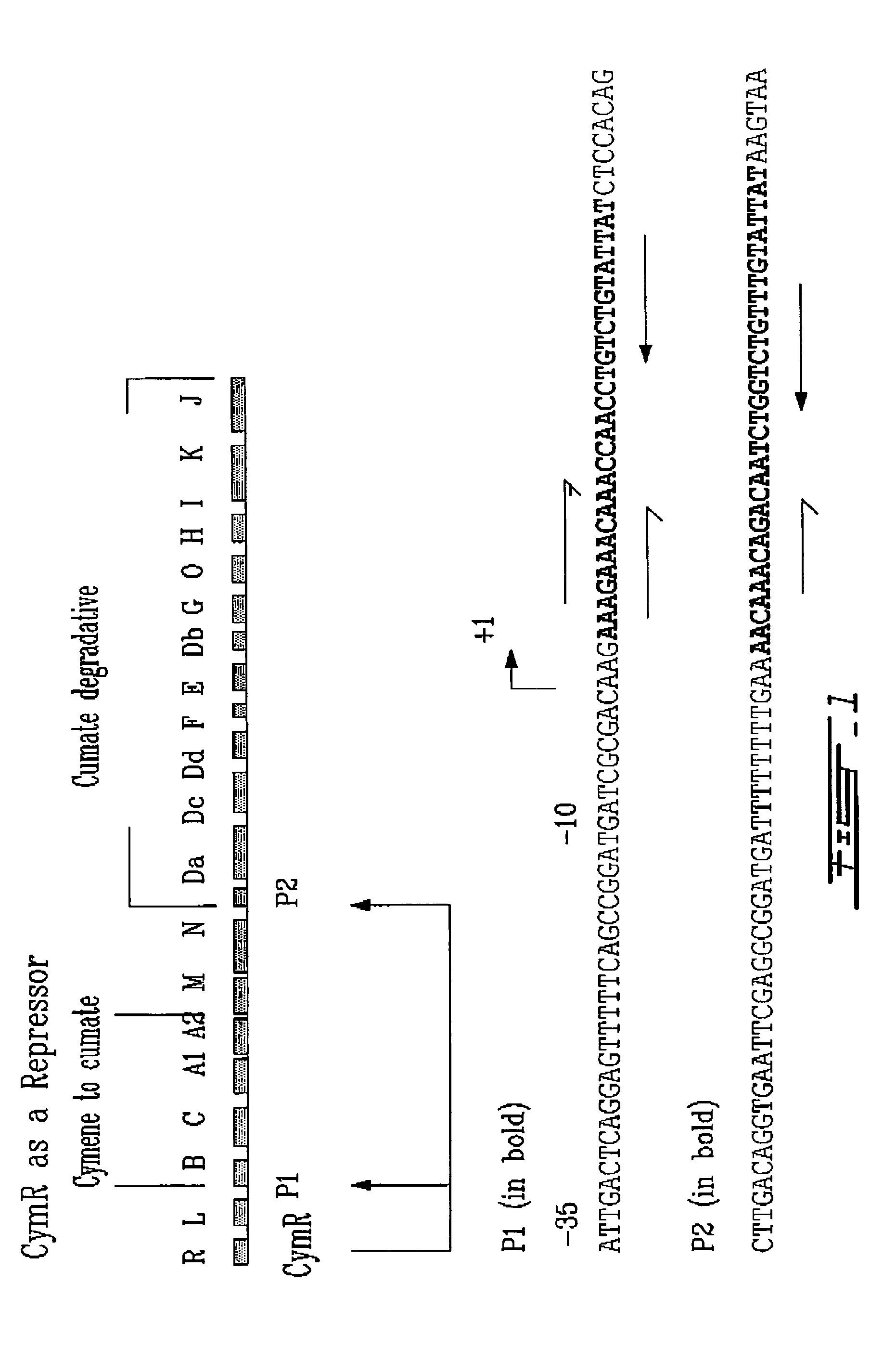
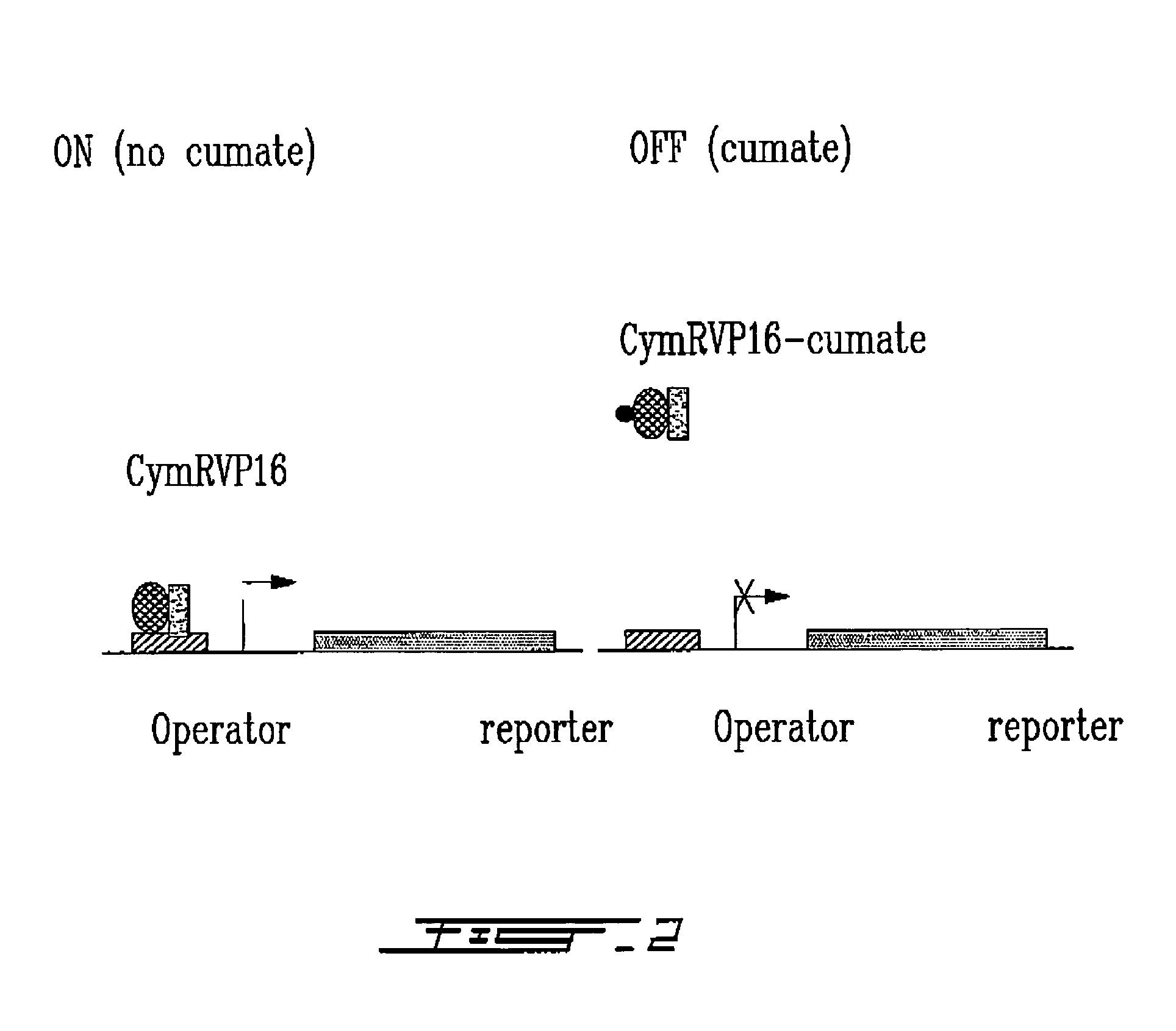
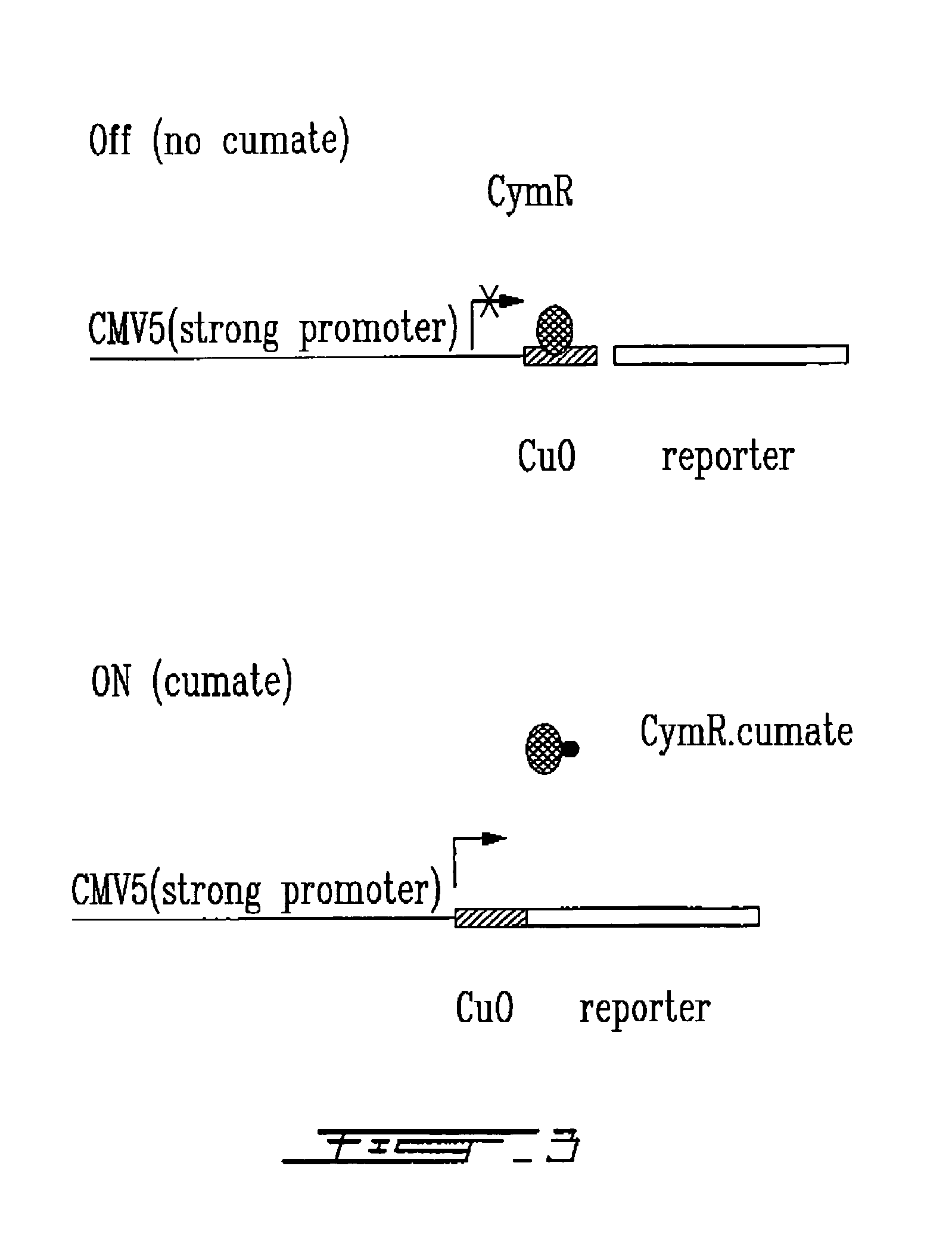
Cumate-inducible expression system for eukaryotic cells
The invention relates to a new “gene-switch” (cumate-inducible switch) for mammalian cells. This switch is as useful in the development of expression systems and cell-based assays for functional genomics as in the generation of viral vectors for gene therapy.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
High throughput functional genomics
InactiveUS7266457B1Reduce lateral flowImprove sealingMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiotechnologyGenomics
This invention focuses on the marriage of solid-state electronics and neuronal function to create a new high-throughput electrophysiological assay to determine a compound's acute and chronic effect on cellular function. Electronics, surface chemistry, biotechnology, and fundamental neuroscience are integrated to provide an assay where the reporter element is an array of electrically active cells. This innovative technology can be applied to neurotoxicity, and to screening compounds from combinatorial chemistry, gene function analysis, and basic neuroscience applications. The system of the invention analyzes how the action potential is interrupted by drugs or toxins. Differences in the action potentials are due to individual toxins acting on different biochemical pathways, which in turn affects different ion channels, thereby changing the peak shape of the action potential differently for each toxin. Algorithms to analyze the action potential peak shape differences are used to indicate the pathway(s) affected by the presence of a new drug or compound; from that, aspects of its function in that cell are deduced. This observation can be exploited to determine the functional category of biochemical action of an unknown compound. An important aspect of the invention is surface chemistry that permits establishment of a high impedance seal between cell and a metal microelectrode. This seal recreates the interface that enables functional patch-clamp electrophysiology with glass micropipettes, and allows extracellular electrophysiology on a microelectrode array. Thus, the invention teaches the feasibility of using living cells as diagnostics for high throughput real-time assays of cell function.
Owner:HESPEROS
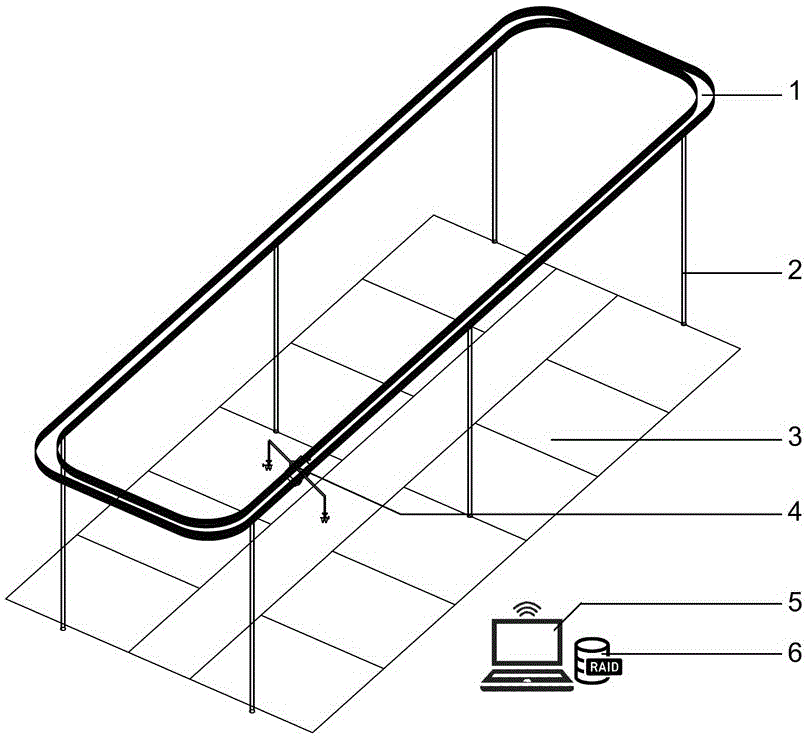
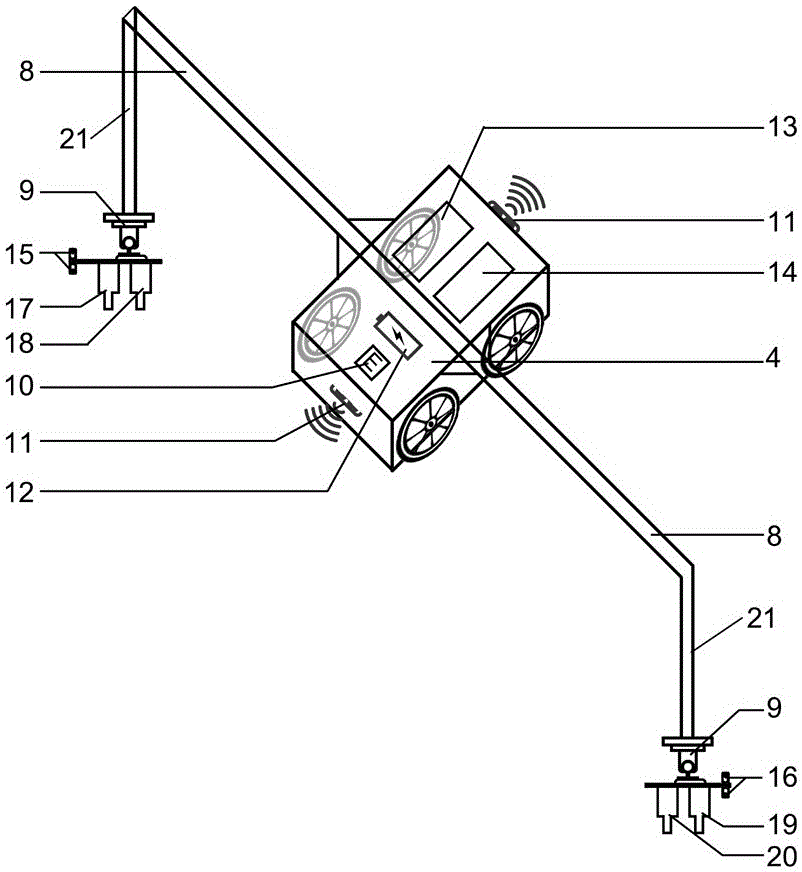
Field crop phenotypic information high-pass peer monitoring device and monitoring method
ActiveCN106441442AHigh return visit rateHighly integratedMeasurement devicesMeasuring instrumentMolecular breeding
The invention relates to a field crop phenotypic information high-pass peer monitoring device. An electric mobile trolley (4) carrying a sensor / camera / measurer moves on a test area (3) for testing, and test data is processed and analyzed. The invention further relates to a monitoring method for the field crop phenotypic information high-pass peer monitoring device. Phenotypic information of field crops can be quickly acquired, and tested crops do not need to be moved during testing, so that the natural growth state of the crops is kept, and the influence on the crops in the test process is greatly reduced. Thus, on the one hand, the designed field crop phenotypic information high-pass peer monitoring device can remarkably promote molecular breeding of crops and development of plant functional genomics; and on the other hand, the device can guide people to optimize field management measures and crop planting structures.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
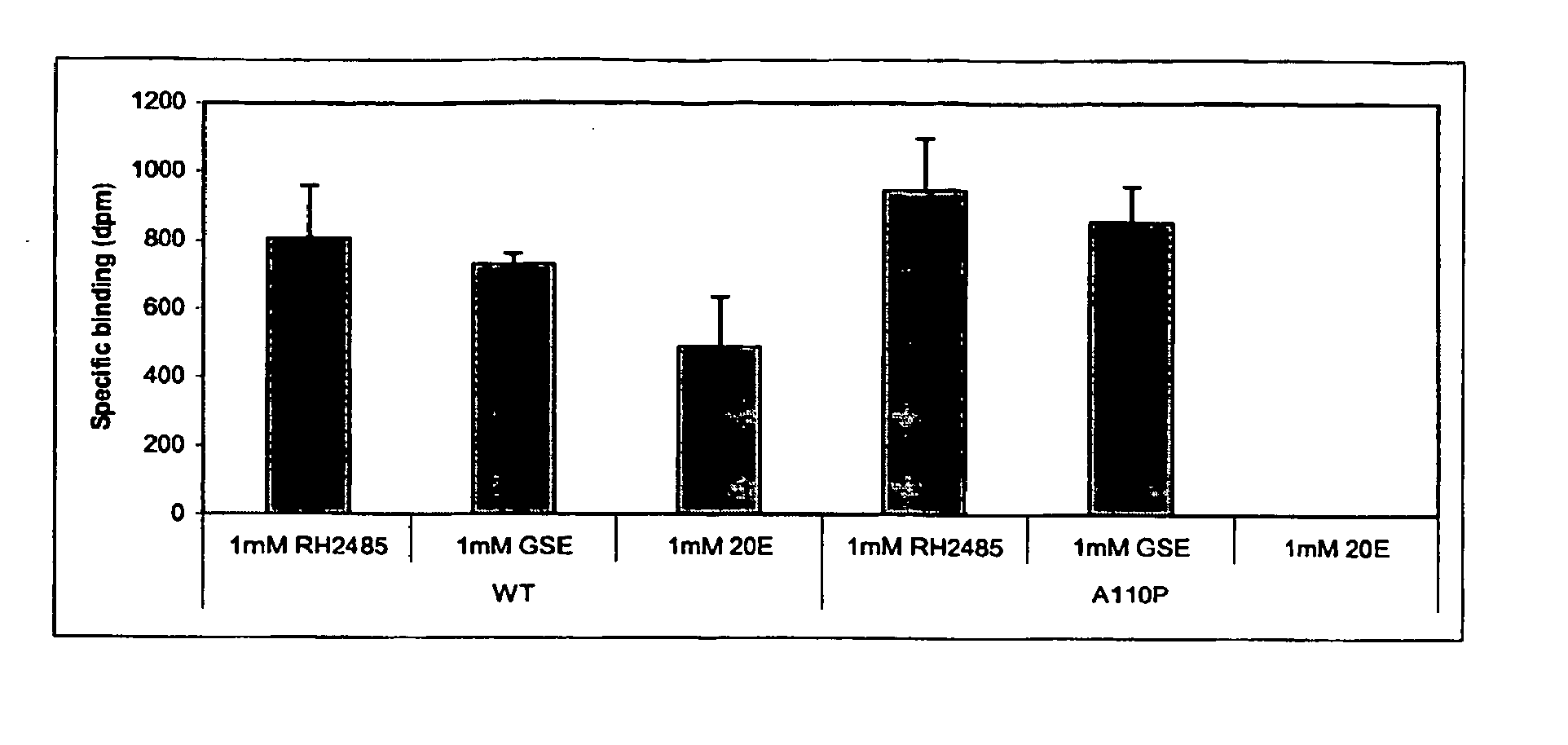
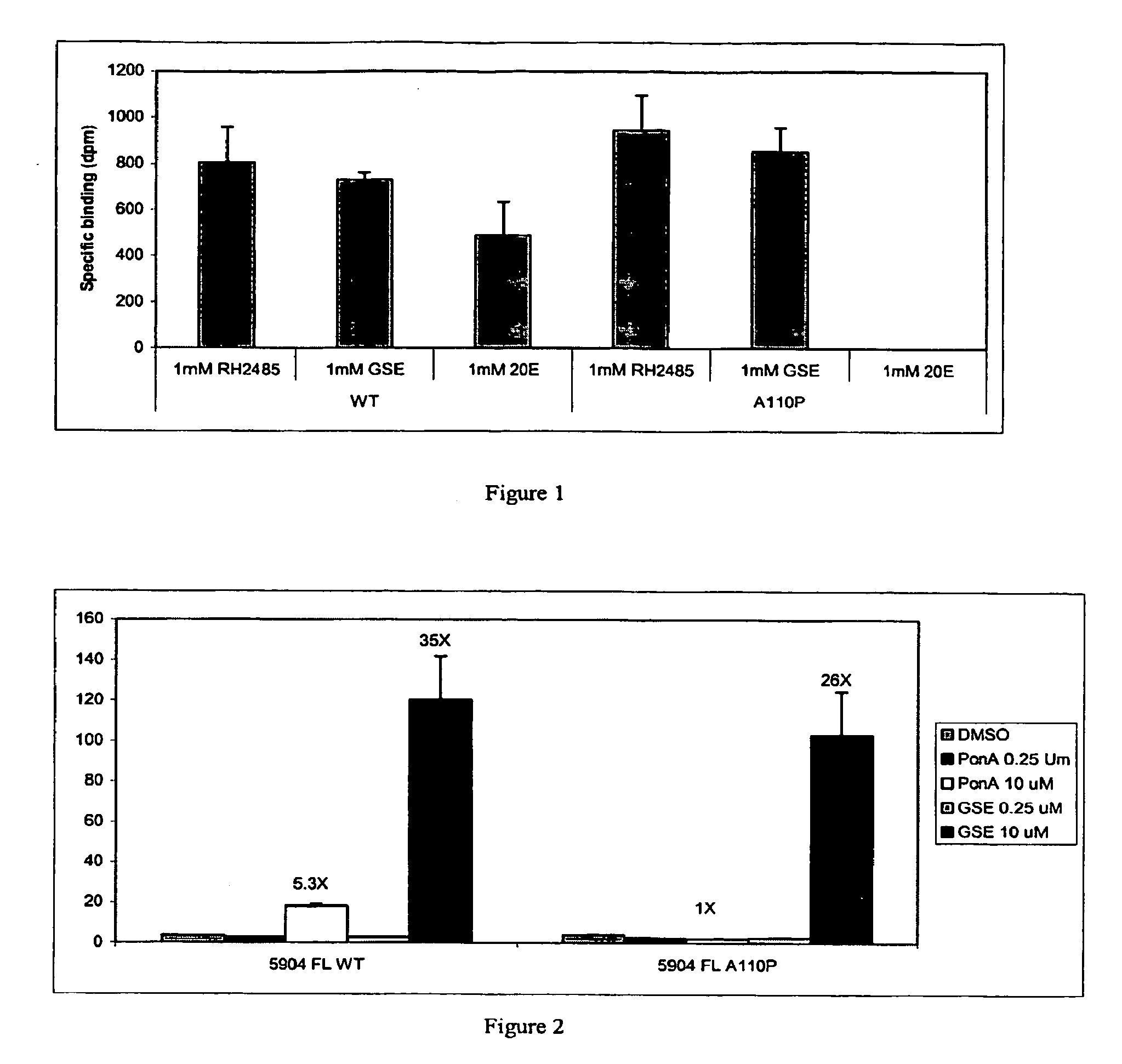
Novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in an ecdysone receptor-based inducible gene expression system
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in a nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating the expression of a gene in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
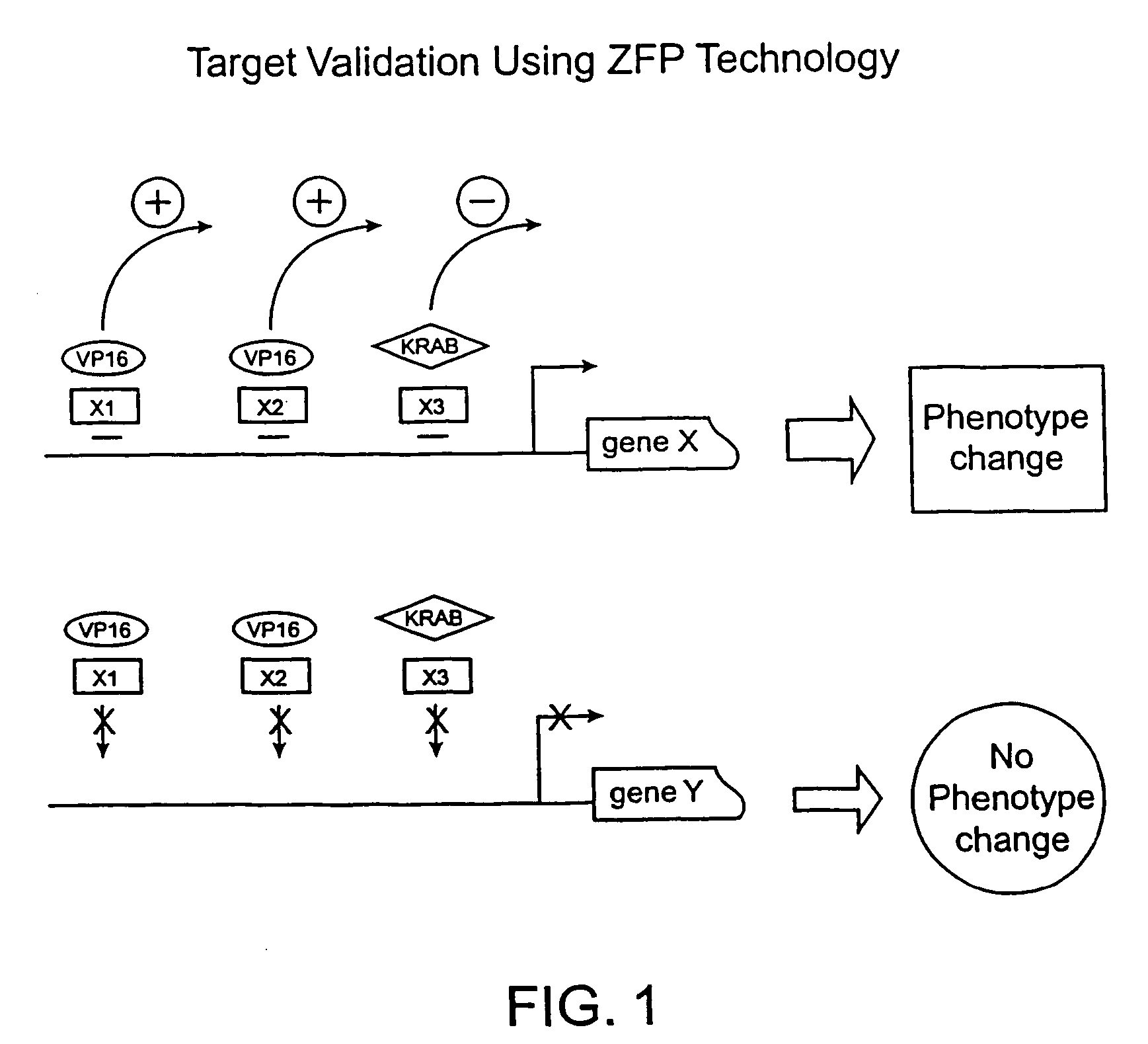
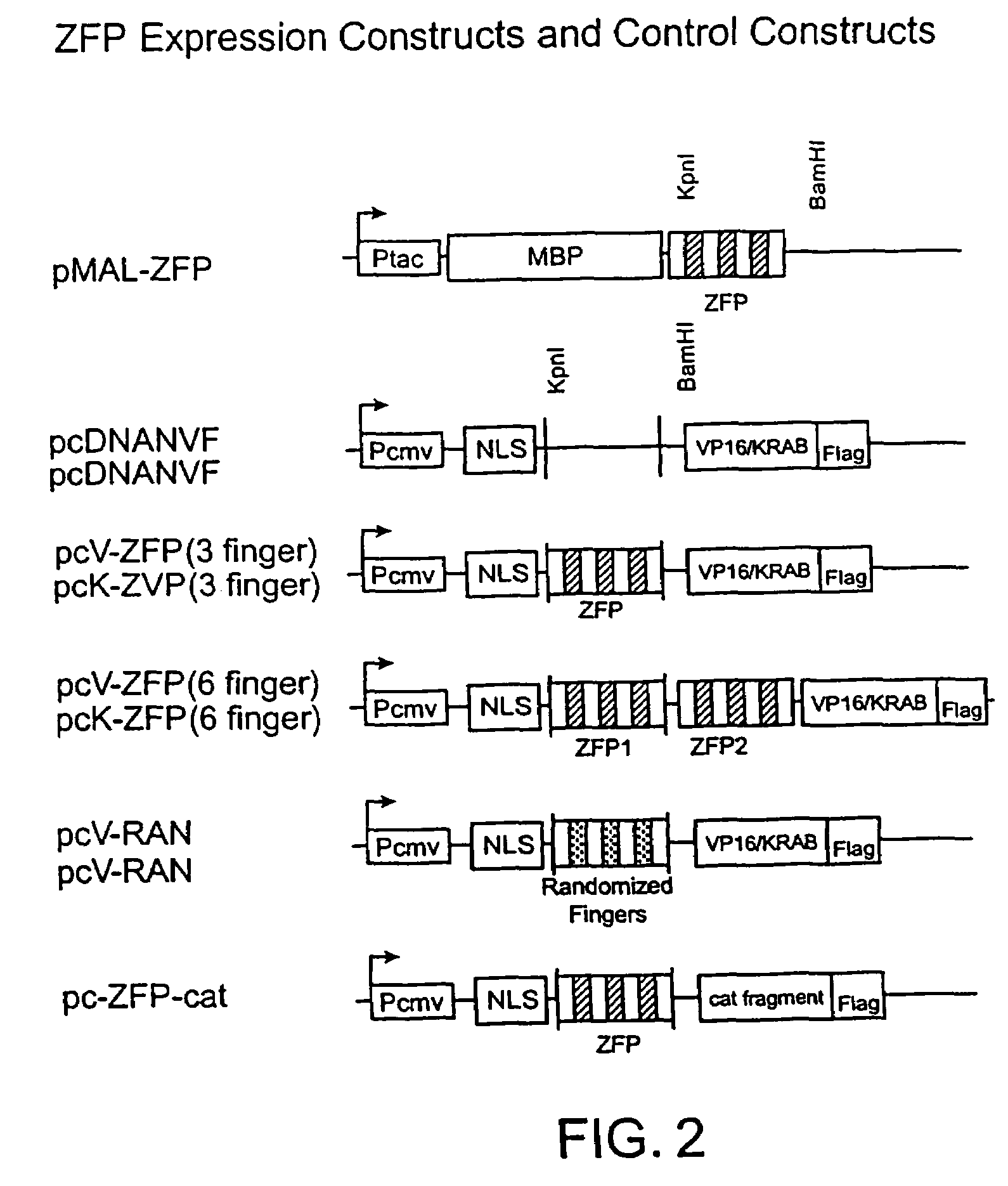
Functional genomics using zinc finger proteins
InactiveUS7235354B2Prevents repressionInhibition of activationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsZinc
The present invention provides methods of regulating gene expression using recombinant zinc finger proteins, for functional genomics and target validation applications.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Application of panax japonicus transcription factor gene PjWRKY1
ActiveCN105087601AIncrease contentHigh expressionGenetic engineeringFermentationBiotechnologyGenomics
The invention discloses application of panax japonicus transcription factor gene PjWRKY1, namely, application in improving the expression quantity of key enzyme genes in the biological synthesis of panax japonicus saponins, and increasing the content of saponins in panax japonicus callus. The nucleotide sequence of the PjWRKY1 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and WRKY transcription factors are coded. Through the adoption of functional genomics and techniques related to metabolic engineering, a panax japonicus PjWRKY1 transcription factor is proved to have the effect of positively regulating the biological synthesis of panax japonicus saponins; when the panax japonicus PjWRKY1 transcription factor gene disclosed by the invention is established on a plant expression vector and transferred into the panax japonicus callus for over expression, the expression quantity of the key enzyme genes in the synthetic route of panax japonicus saponins is increased, and the yield of panax japonicus saponins is increased.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Reagent kit for quantitatively assessing long-term recurrence risks of breast cancer
InactiveCN102586410AEasy to operateTest results are stableMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceGenomicsBreast cancer metastasis
The invention relates to the functional genomic and gene expression detection technology and the analysis technology, and discloses a reagent kit for quantitatively assessing long-term recurrence risks of breast cancer. Particularly, a type of genes capable of being used for breast cancer metastasis and prognostic molecular classification is screened within a human functional genome expression profile range, the detection technology is created, and the reagent kit is prepared and applied to breast cancer metastasis and prognostic assessment for a patient. The reagent kit for quantitatively assessing long-term recurrence risks of breast cancer comprises 21 pairs of primers, 21 specific taqman fluorescent probes, 10XRT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) buffer solution, 2.5mM of dNTP (diethyl-nitrophenyl thiophosphate) mixed liquor, reverse transcriptase, DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) polymerase, 10XPCR buffer solution and RNA (ribonucleic acid) enzyme inhibitor. The reverse transcription PCR technology is combined with the taqman fluorescent quantitative PCR technology, reverse transcription primers, real-time PCR primers and the taqman fluorescent probes are self-designed and optimized, reverse transcription PCR reagent and taqman fluorescent quantitative PCR reagent are integrated to prepare the detection reagent kit, operation is simple and fast, detection results are more stable, and detection cost is lower.
Owner:苏州科贝生物技术有限公司
Devices, Solutions and Methods for Sample Collection
ActiveUS20140120531A1Improve securityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsInterior spaceEpigenetics
The disclosure relates to devices, solutions and methods for collecting and processing samples of bodily fluids containing cells (as well as embodiments for the collection, and processing and / or analysis of other fluids including toxic and / or hazardous substances / fluids). In addition, the disclosure relates generally to function genomic studies and to the isolation and preservation of cells from saliva and other bodily fluids (e.g., urine), for cellular analysis. With respect to devices for collection of bodily fluids, some embodiments include two mating bodies, a cap and a tube (for example), where, in some embodiments, the cap includes a closed interior space for holding a sample preservative solution and mates with the tube to constitute the (closed) sample collection device. Upon mating, the preservation solution flows into the closed interior space to preserve cells in the bodily fluid. The tube is configured to receive a donor sample of bodily fluid (e.g., saliva, urine), which can then be subjected to processing to extract a plurality of cells. The plurality of cells can be further processed to isolate one and / or another cell type therefrom. The plurality of cells, as well as the isolated cell type(s), can be analyzed for functional genomic and epigenetic studies, as well as biomarker discovery.
Owner:DNA GENOTEK
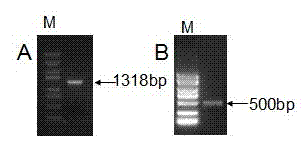
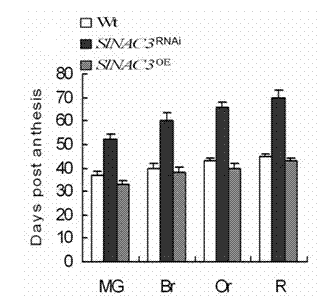
Tomato fruit ripening gene SINAC3 and application thereof
InactiveCN102787124ADelayed maturationRational regulation of the maturation processPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyGenomics
The invention discloses a tomato fruit ripening gene SINAC3 and application thereof. The tomato fruit ripening gene SINAC3 has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQIDNO.1 or protein of an amino acid sequence coded as SEQIDNO.2, a typical NAC homology domain and coded NAC protein. As proved by the relevant technology of functional genomics, the tomato fruit ripening gene SINAC3 plays an important role in tomato fruit ripening. The tomato fruit ripening gene SINAC3 is structured onto a plant expression vector and transferred into a tomato for interference expression, the transgenic tomato can show the capacity of delaying fruit ripening, and the tomato fruit ripening gene SINAC3 can be directly used for controlling the ripening progress of fruits in production.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
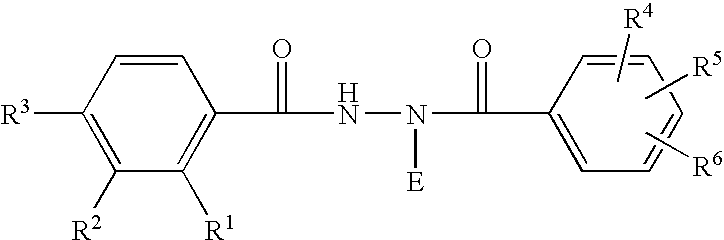
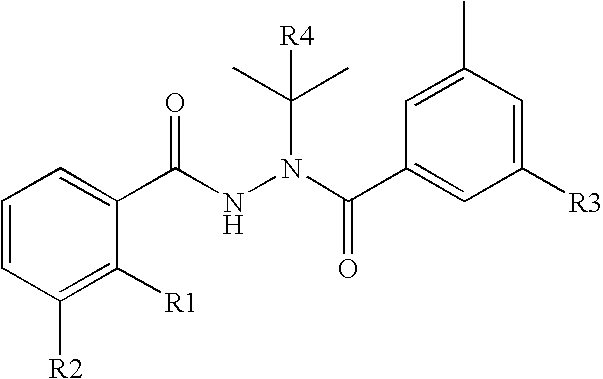
Boron-Containing Diacylhydrazines
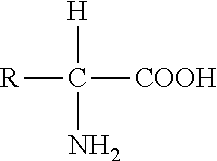
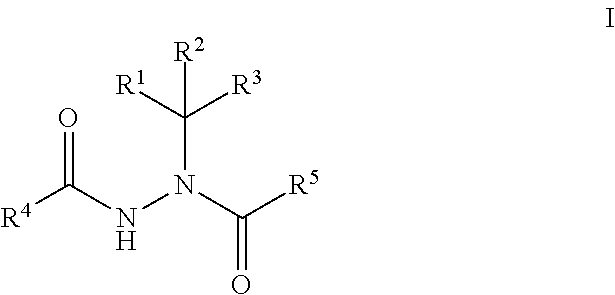
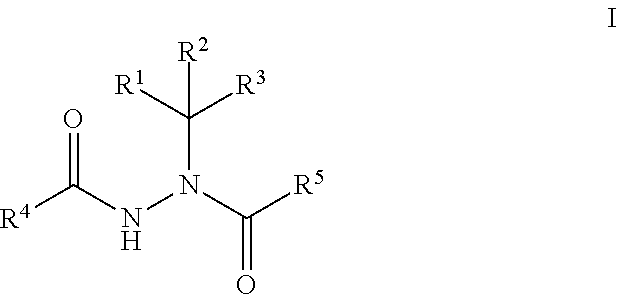
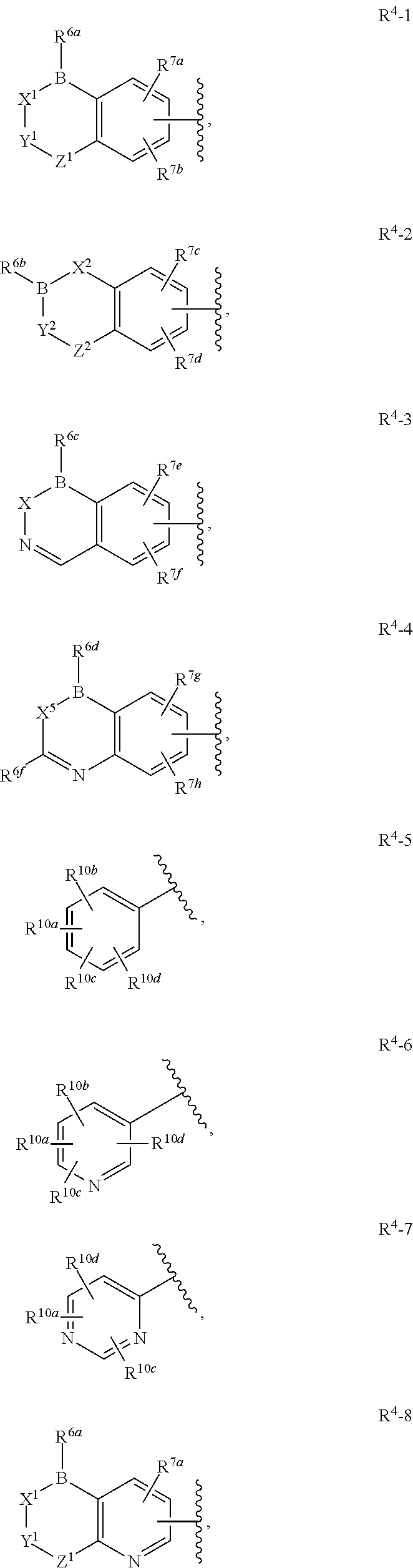
The present disclosure provides boron-containing diacylhydrazines having Formula I:and the pharmaceutically acceptable salts and solvates thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are defined as set forth in the specification. The present disclosure also provides the use of boron-containing diacylhydrazines is ecdysone receptor-based inducible gene expression systems. Thus, the present disclosure is useful for applications such as gene therapy, treatment of disease, large scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based screening assays, functional genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms, where control of gene expression levels is desirable.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Thaumatin-like protein gene PpTLP from pyrus pyrifolia nakai with antifungal activity and application
InactiveCN101736024AIncrease resistanceReduce usageFungicidesGenetic engineeringGenomicsNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to a thaumatin-like protein gene PpTLP from pyrus pyrifolia nakai with antifungal activity and application. The gene PpTLP has the base sequence shown in SEQID and coded thaumatin-like proteins. The invention verifies that the gene PpTLP has the function of improving the antifungal ability of the plants through correlation technique of functional genomics. When the antifungal gene PpTLP is constructed on a plant expression vector and is transformed into tobacco to be overexpressed, the transgenic tobacco has high antifungal activity. The protein from the transgenic tobacco expressing PpTLP has obvious inhibitory effects on various fungi such as sclerotinia sclerotiorum, phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae, phomopsis sp. and the like.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
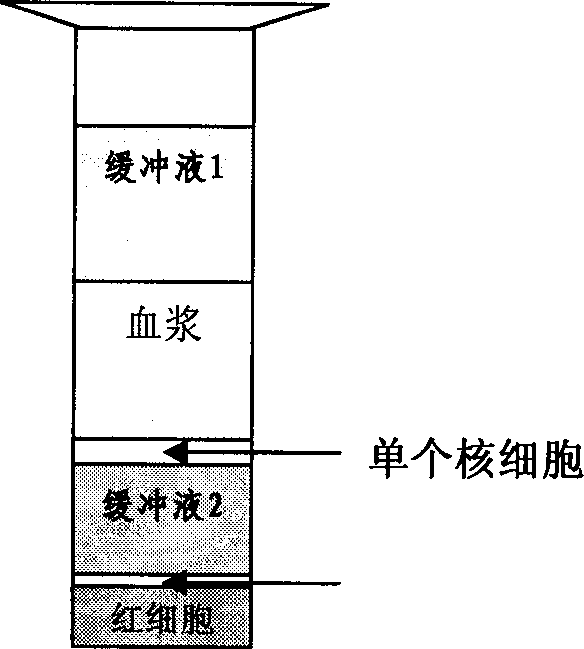
Method for separating cell and special separating liquid for cell
The invention discloses a cell separating method and special cell separating medium. The special cell separating medium gains is solvent gained by adding surface active agent into general cell separating medium. The cell separating method includes the following steps: mixing the surface active agent and current cell separating medium in given volumetric proportion; centrifuging to gain special cell separating medium; adding cell separating sample into the special cell separating medium; and centrifuging; colleting cloud layer cell and washing to gain purified cell. The invention greatly shortens sample adding and cell separating time, simplifies operation. And it is fit for large-scale separating. Its effect is stable and reliable. And high purity goal cell can be gained. The separating method is simple, and has strong operability. The invention has high practical application value and broad market prospect in cell biology, functional genome, and cell engineering fields.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY4 and application thereof
ActiveCN110734482AIncrease resistanceReduce usagePlant peptidesGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyAntifungal
The invention discloses a lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY4. The nucleotide sequence of the lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY4 is described as in the SEQ ID NO:1,and the coded protein of the lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY4 corresponds to the amino acid sequence described in the SEQ ID NO:2. According to the lilium regale WRKY transcriptionfactor gene LrWRKY4, it is proved that the LrWRKY4 gene has the function of improving the antifungal ability of plants through the technical research related to the functional genomics, the antifungal LrWRKY4 gene is constructed to a plant expression vector and transferred into tobacco for overexpression, the transgenic tobacco has very high antifungal activity, and the experimental result showsthat the tobacco with the LrWRKY4 gene overexpressed is highly resistant to infestation of nigrospora oryzae, fusarium graminearum, fusarium graminearum, botryosphaeria and fusarium solanum.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nonglutinous rice callus culture medium and genetic transformation method mediated by agrobacterium tumfaciens
ActiveCN101717749AQuality improvementEfficient inductionPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsMinor elementGenotype
The invention discloses a nonglutinous rice callus culture medium and a genetic transformation method mediated by agrobacterium tumfaciens. The culture medium contains major elements, minor elements, organic elements and hormone in different culture stages which are required for the growth of nonglutinous rice calluses. The genetic transformation method of nonglutinous rice based on the culture medium comprises the steps of induction, subculture, pre-culture, co-culture, sieving, aftersieving, differentiation, rooting of the calluses and the like. The method is widely suitable for nonglutinous rice genotypes, all genetic transformation of the tested 35 nonglutinous rice genotypes are successful, and the transformation rate is between 20% and 50%. The genetic transformation method solves the technical problem of low genotype reliance and transformation frequency existing in the nonglutinous rice callus culture and mediation of agrobacterium tumfaciens for a long time, and is widely applied to the research in the molecular biology, the functional genomics of the nonglutinous rice and the genetic improvement of varieties. The planting area of the nonglutinous rice accounts for more than 80% of the total production area of the nonglutinous rice, and the genetic transformation method has an important function on the research of the basic biology, the improvement of new varieties and the safety guarantee of future grain.
Owner:WUHAN BIORUN BIO TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com