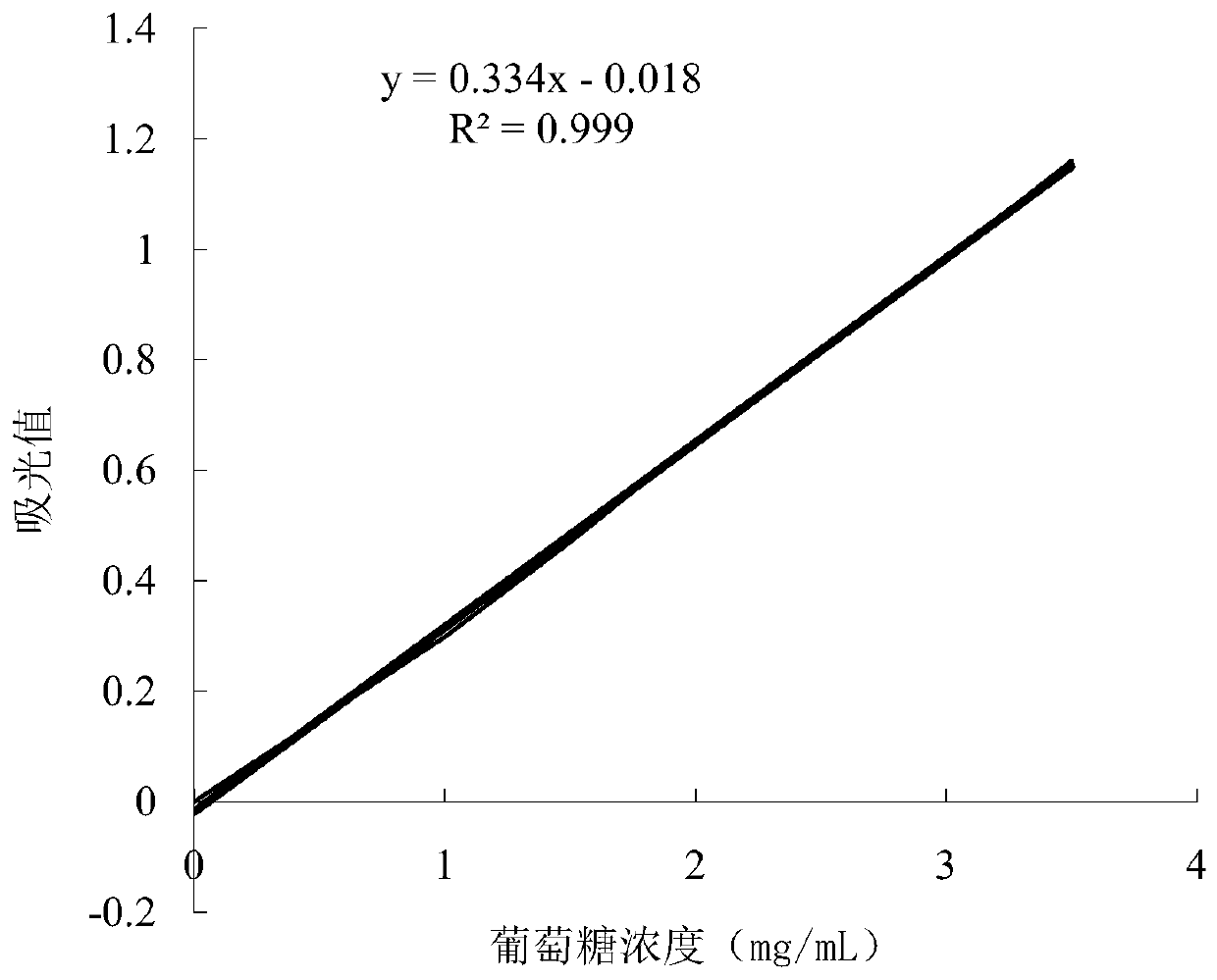
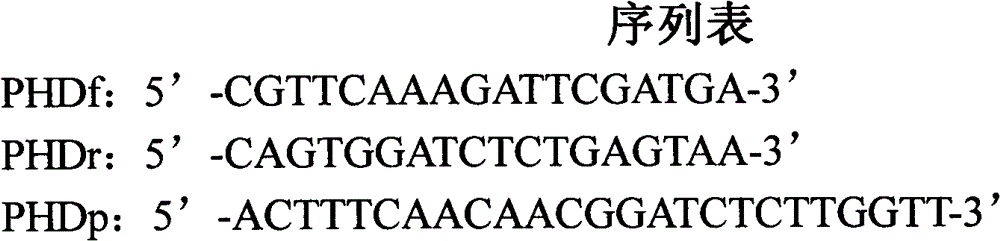Patents
Literature
69 results about "Phomopsis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phomopsis is a genus of ascomycete fungi in the family Valsaceae.
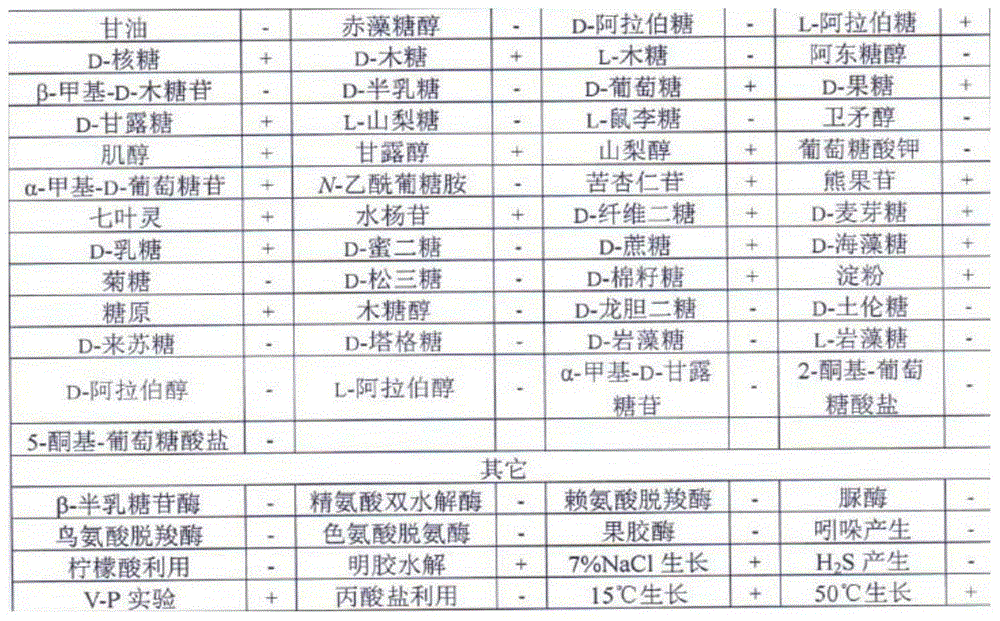
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum ZFH-3 and application thereof
ActiveCN104694430AImprove fertilityReduce usageFruit and vegetables preservationBacteriaBiotechnologyBacillus amyloliquefaciens
The invention discloses a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum ZFH-3 and application thereof. The classification designation of the strain is Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum, and the collection number is CGMCC No.9884. The strain has obvious inhibiting actions on multiple crop pathogens, especially can effectively control postharvest diseases of fruits, is well used for biological control of contact mold of citrus fruit, olive green mould of ditrus fruit, citrus phomopsis stem end rot, sour rot of citrus, anthracnose of citrus, anthracnose of banana, spike rot of banana, gray mold of strawberry, soft rot of strawberry and other pathogen fungi, obviously lowers the possibility of postharvest diseases of fruits, prolongs the storage life and shelf life, and reduces the consumption of chemical reagents. The strain has the advantages of simple culture conditions and high reproduction speed, can easily implement industrial production, popularization and application, and has favorable development and application prospects.
Owner:珠海真绿色技术有限公司
Lilium regale antifungal gene Lr14-3-3 and application thereof
InactiveCN103194456AIncreased fungal resistanceIncrease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyAntifungal
The invention discloses a lilium regale gene Lr14-3-3 with antifungal activity. The gene Lr14-3-3 has the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:1 and encodes protein 14-3-3. A relevant technology of functional genomics proves that the gene Lr14-3-3 has a function of improving the plant antifungal activity. The antifungal gene Lr14-3-3 is constructed to a plant expression vector and is transferred into tobacco to perform overexpression; the transgenic tobacco plant has strong in vitro antifungal activity; and the transgenic tobacco expressing the Lr14-3-3 has obvious inhibition effects on the growth of botryosphaeria dothidea, phomopsis fungi, fusarium oxysporum and alternaria.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Denitrifying phosphorus accumulation organism (DPAO) with function of efficiently removing nitrogen and phosphorus and application of DPAO
ActiveCN104726366ANo pollution in the processThorough denitrificationBacteriaTreatment using aerobic processesBacterial strainNitrogen gas
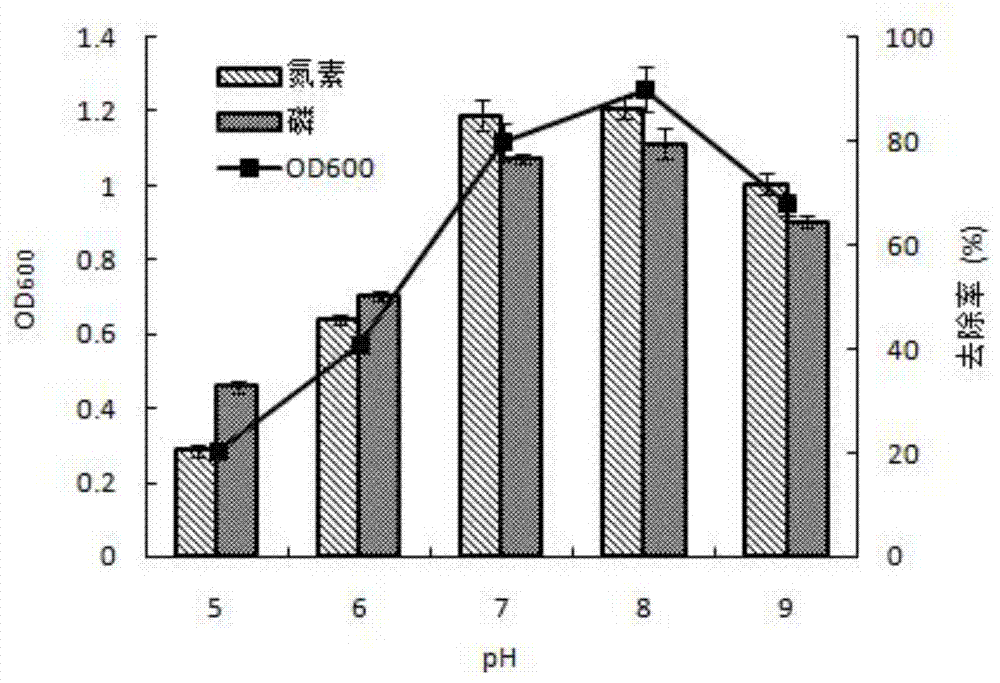
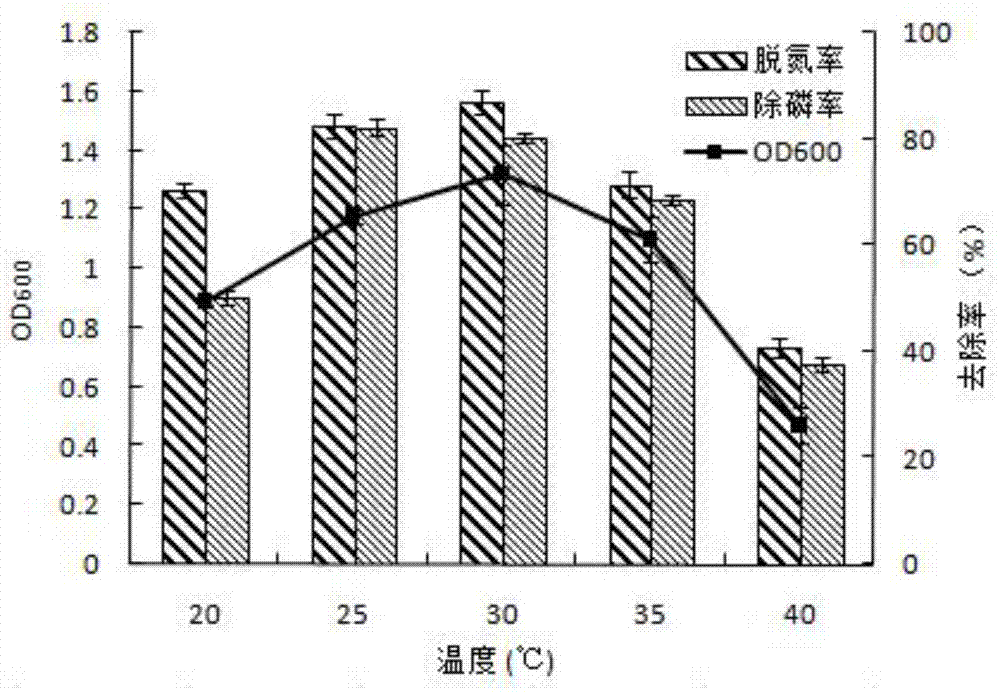
The invention relates to denitrifying phosphorus accumulation organism (DPAO) with a function of efficiently removing nitrogen and phosphorus and application of the DPAO, and belongs to the field of environmental microbiology. The bacterial strain is named Klebsiella sp. N14, belongs to Klebsiella species, and is preserved in China general microbiological culture center (CGMCC), the preservation number of the bacterial strain is CGMCC No. 10290. The bacterial strain is a Gram negative bacteria without spore and has thick capsule in a thick and short rod shape; the bacterial colony is milky white, the center of the bacteria is protruded, the edge is regular, and the surface is wet, transparent and glossy. The bacterial strain has a function of synchronously removing the nitrogen and the phosphorus, and can be applied to sewage biological sewage treatment process; after the bacterial strain is aerobically cultivated in nitrogen and phosphorus containing sewage for 24 hours, the phosphorous removal rate is 81.79%, and the nitrogen removal rate is 85.94%. The denitrifying final product of the bacteria strain is identified to be N2 with the full denitrifying capability; when the bacterial strain is used for treating the nitrogen and phosphorus containing sewage, inorganic nitrogen, such as nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen, in a water body is directly reduced to be harmless nitrogen gas to be discharged out of the water body; the effect is remarkable, the cost is low, and no secondary pollution exists.
Owner:龙岩水发环境发展有限公司
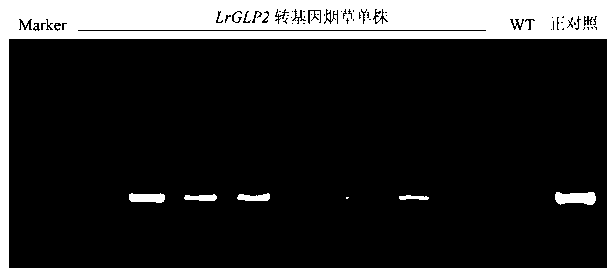
Lilium regale germin-like protein gene LrGLP2 and application thereof
InactiveCN103194457AIncrease resistanceReduce usagePlant peptidesFermentationNicotiana tabacumFungus
The invention discloses a lilium regale germin-like protein gene LrGLP2 with antifungal activity. The gene LrGLP2 has the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID:1 and encodes germin-like protein. A relevant technology of functional genomics proves that the gene LrGLP2 has a function of improving the plant antifungal activity. The antifungal gene LrGLP2 is constructed to a plant expression vector and is transferred into tobacco to perform overexpression; and the transgenic tobacco plant has strong in vitro antifungal activity. The LrGLP2 transgenic tobacco protein has different degrees of inhibition effects on the growth of botryosphaeria dothidea, phomopsis fungi, fusarium oxysporum and botrytis cinerea.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
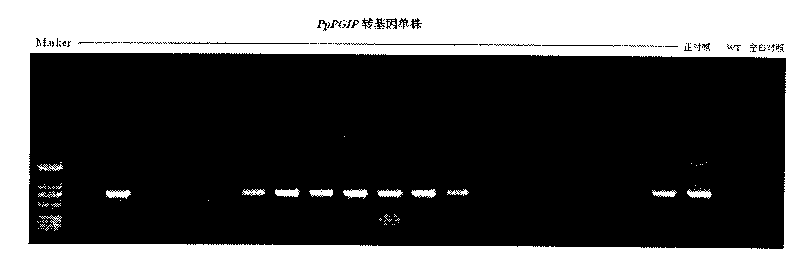
Red skinned pear polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein gene (PpPGIP) and application
InactiveCN101736015AIncrease resistanceReduce usageFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenomicsPentagalacturonic acid
This invention relates to a fungal resistance gene of red skinned pear, namely a polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein gene (PpPGIP), and application. The PpPGIP gene has a base sequence which is stated in a sequence-list SEQ ID; the length of the PpPGIP gene is 1,032bp, wherein 990bp is an open reading frame; and the PpPGIP gene codes polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins containing 330 amino acids. Functional genomics related technology prove that the PpPGIP gene has the function of improving antifungal function of plants. The antifungal PpPGIP gene is constructed on a plant expression vector and is excessively expressed after being transferred into tobacco, the transgenic tobacco for expressing PpPGIP has strong in vitro antifungal activity and the obvious inhibition effect on a plurality of funguses like Aspergillus niger, Phomopsis funguses, Alternaria alternata, penicillium, and the like.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Quick induced spore production method and application of Phomopsis
The invention discloses a quick induced spore production method and application of Phomopsis, belonging to the field of phytopathogen induced spore production. According to the method, Phomopsis mycelia cultured by a PDA (potato dextrose agar) solid culture medium, which is used as a spore production base, is subjected to lawn brooming, sterilized water flushing, drying and constant-temperature lighting culture to induce the mycelia to quickly produce abundant conidiomata within 4 days. Nine different strains of Phomopsis are respectively utilized to quickly produce spores in the mycelia in the dryly-stored activated state. When being used for quick simple induced spore production of Phomopsis, the method can greatly enhance the spore production efficiency, shortens the identification period, effectively saves the human and material resources and the abundant precious time of researchers, and thus, has great application potential and higher economic value.
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Restoration method special for oryza sativa L. polluted by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon phenanthrene
InactiveCN105921510AShorten the production cycleSimple production processFungiContaminated soil reclamationAgricultural pollutionRestoration method
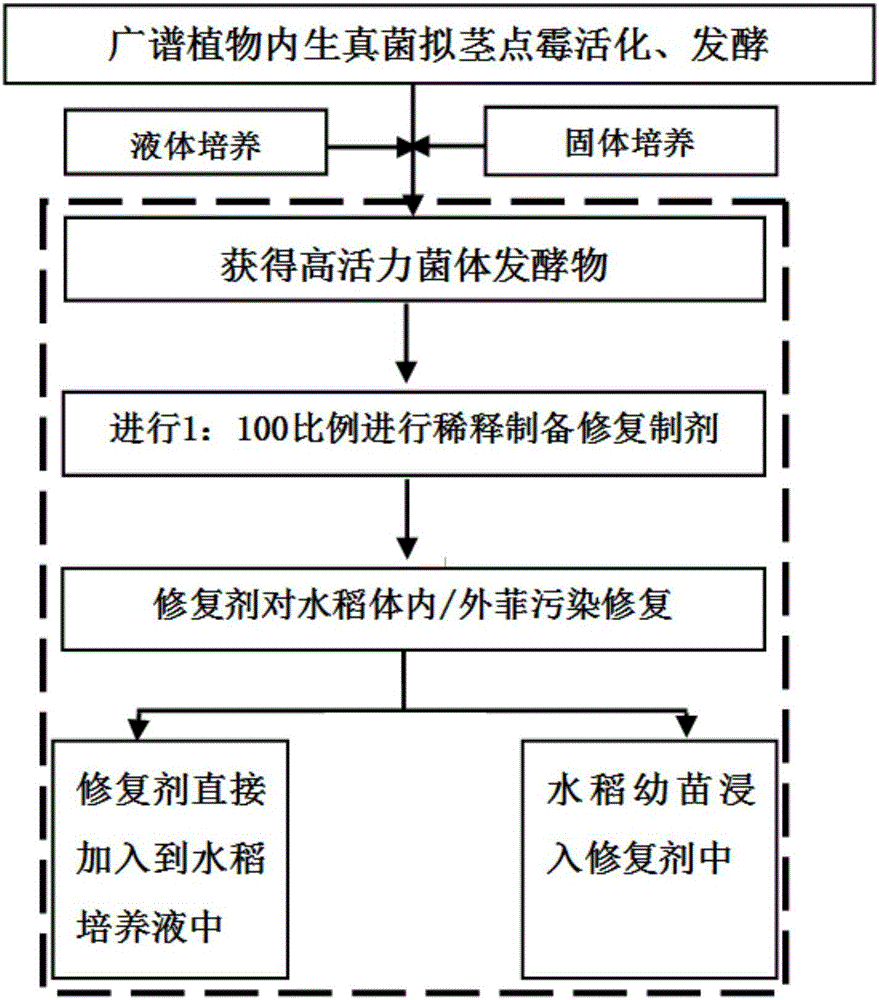
The invention relates to the field of agricultural pollution restoration, in particular to a restoration method special for oryza sativa L. polluted by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon phenanthrene. The method specifically relates to application of phomopsis liquidambari HQ285146 in preparation of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon phenanthrene degradation restoration agent special for oryza sativa L. The phomopsis liquidambari HQ285146 is activated and cultivated on a fluid nutrient medium or a solid medium containing potato dipping juice to obtain the oryza sativa L. restoration agent. Afterwards, the restoration agent is used for seedling dipping and is directly added into rhizosphere soil during transplant of oryza sativa L., and phenanthrene inside / outside oryza sativa L. bodies is effectively removed. Production of the agricultural phenanthrene pollution restoration agent is not affected by environment, the production period is short, the production process is simple, production time and yield are easy to control, and the effect is obvious. The method of plant dipping and direct agent adding into soil is adopted, the agent can act on polluted soil and plants, the method is simple and easy to operate, dosage is small, the cost is low, and the good effect can be achieved.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Indoor identification method for anti-phomopsis blight
ActiveCN104164472AEasy to controlUnified standardFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial resourcesBiology
The invention belongs to the technical field of gardening crop disease resistance identification, and concretely relates to an indoor identification method for anti-phomopsis blight. The method comprises the steps of seedling growing and colonization of eggplant, preparation of a fluid suspension for phomopsis blight pathogen, pathogen invasion treatment and pathogenesis investigation. According to the invention, eggplant fruit is selected as an identification material indoor, a self made cross-shaped cutter is used for making cross wound on the eggplant, a filter paper sheet containing the fluid suspension for phomopsis blight pathogen spore is used for invasion treatment, and then pathogenesis investigation is carried out, and thereby the appropriate concentration of the fluid suspension for phomopsis blight pathogen spore as well as the length and depth of the cross wound can be cleared. Compared with large land inoculation, factors such as inappropriate climate condition and other insect disease influence in environment can be avoided, and the method has the advantages of easy control of disease resistance screening condition, consistent standard, rapid pathogenesis, simple operation and reliable result, a lot of manpower and material resources can be saved, and the method is especially suitable for identification of large batch of phomopsis blight resistance for eggplant breeding material.
Owner:WUHAN SHUBO AGRI TECH CO LTD
Solanum melongena phomopsis rot resistance rapid identification method
InactiveCN104126432AAccurate identificationRapid identificationHorticulture methodsRapid identificationRoom temperature
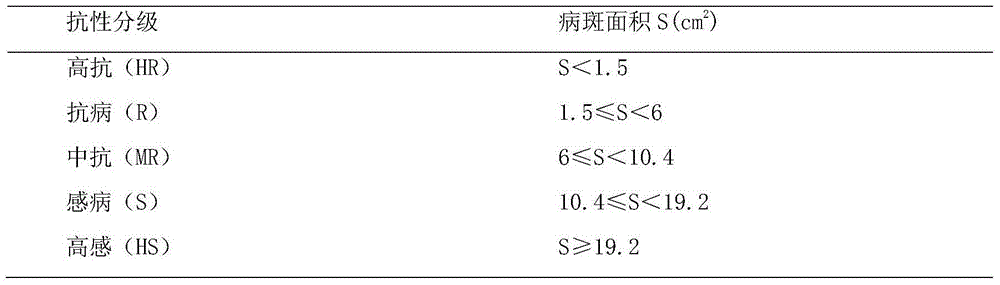
The invention discloses an solanum melongena phomopsis rot resistance rapid identification method comprising the following steps: (1) solanum melongena phomopsis rot strains are inoculated on a culture medium and are activated; the solanum melongena phomopsis rot strains are inoculated on a new culture medium; and well-cultured bacterial masses are selected for inoculation; (2) a wound is cut on a solanum melongena fruit sample to be tested; inoculation is carried out wherein a bacterial mass is flatly placed under solanum melongena fruit epidermis from the wound; the surface of the wound is covered by using a sterile absorbent cotton ball; sterile water is sprayed on the surface of the solanum melongena fruit; and the solanum melongena fruit is sealed by using a plastic wrap, such that the solanum melongena fruit is kept hydrate; (3) the solanum melongena fruit is placed under room temperature, and solanum melongena fruit epidermis lesion diameters d1 and d2 are counted with a decussation method; a lesion area is calculated; and the resistance level of the solanum melongena against phomopsis rot is divided according to the lesion area size. With the method provided by the invention, solanum melongena phomopsis rot resistance identification can be rapidly completed indoor. The method has the advantages of simple operation and short period. The operation is carried out indoor, such that inoculation environmental conditions are easy to control.
Owner:WUHAN VEGETABLE RES INST
Pesticide composition containing clothianidin and fluazinam and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN103891754AReduce dosageLow toxicityBiocideAnimal repellantsClothianidinPhyllocoptruta oleivora
The invention discloses a pesticide composition containing clothianidin and fluazinam. The pesticide composition comprises active components and additives, wherein the active components are clothianidin and fluazinam; the active components comprise 1-30 parts of clothianidin and 1-60 parts of fluazinam in parts by weight. A preparation method of the pesticide composition comprises the following steps: mixing the active components and the additives in parts by weight, and preparing according to ordinary preparation modes of preparations. The pesticide composition can be applied to prevention and control on orange tree phylloxerae, red spider, phyllocoptruta oleivora, aphid, phomopsis citri and anthracnose. The pesticide composition disclosed by the invention is relatively good in synergism, overcomes and delays pest resistance to pesticide, is superior to a single preparation in the prevention effect, resisting in rain wash, good in fast-acting property and long in lasting period, the time and the labor are saved, various pests and diseases can be simultaneously prevented and controlled, and the application cost is lowered.
Owner:LIUZHOU HUINONG CHEM
Method for preventing and treating diseases and insect pests of eggplants
The invention discloses a method for preventing and treating diseases and insect pests of eggplants, and relates to the technical field of crop disease and insect pest prevention and treatment. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of preventing and treating eggplant phomopsis rot, preventing and treating cotton blight, preventing and treating verticillium wilt and preventing and treating yellow tea mite and red spiders. The method is reasonable, convenient to operate and good in effect.
Owner:ANHUI HUABO FOIL IND SCI & TECH
Method for controlling fungal pathogen with bacterial metabolite
ActiveUS8609083B1Increase agricultural productionOvercome disadvantagesBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesSnow mold
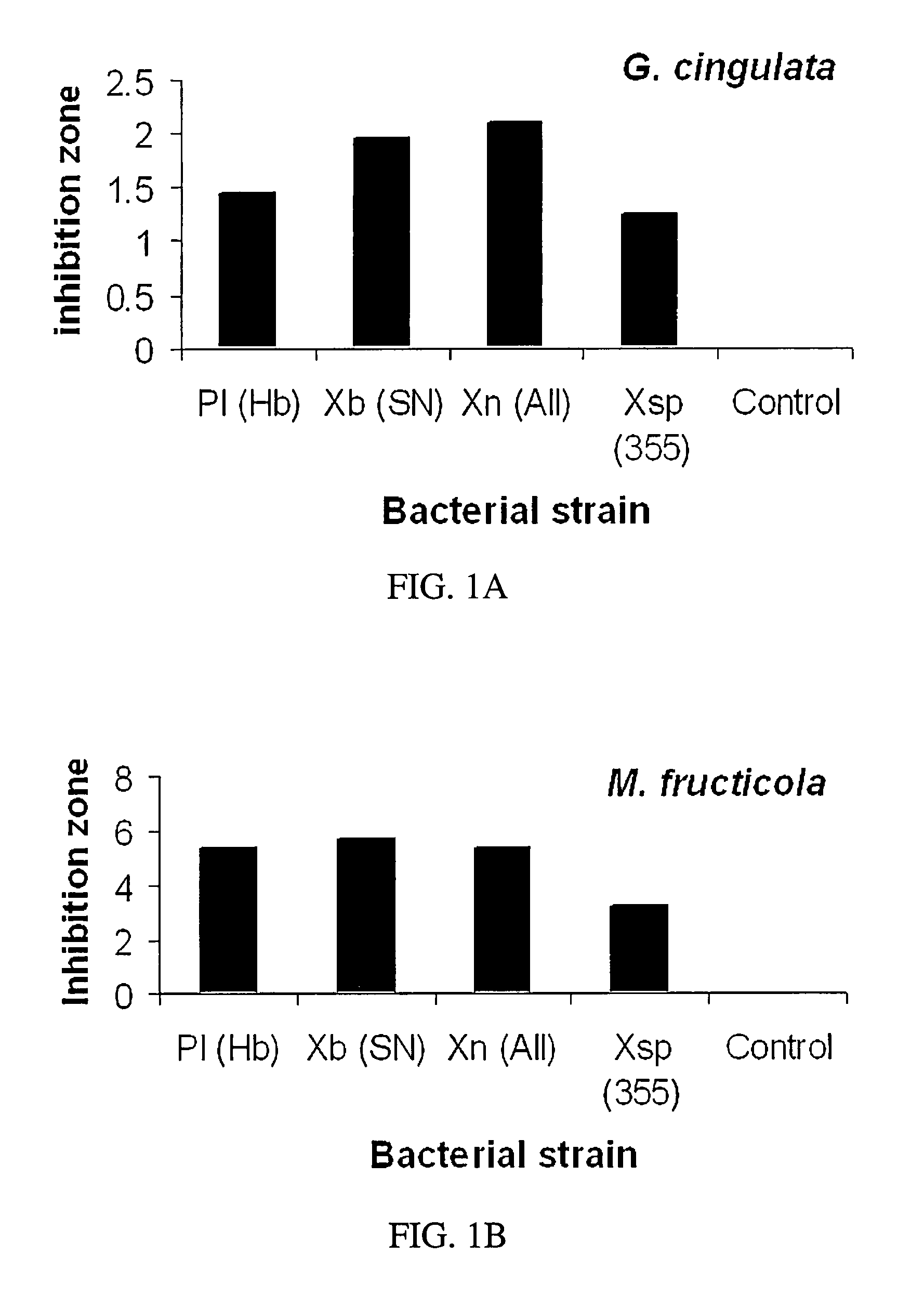
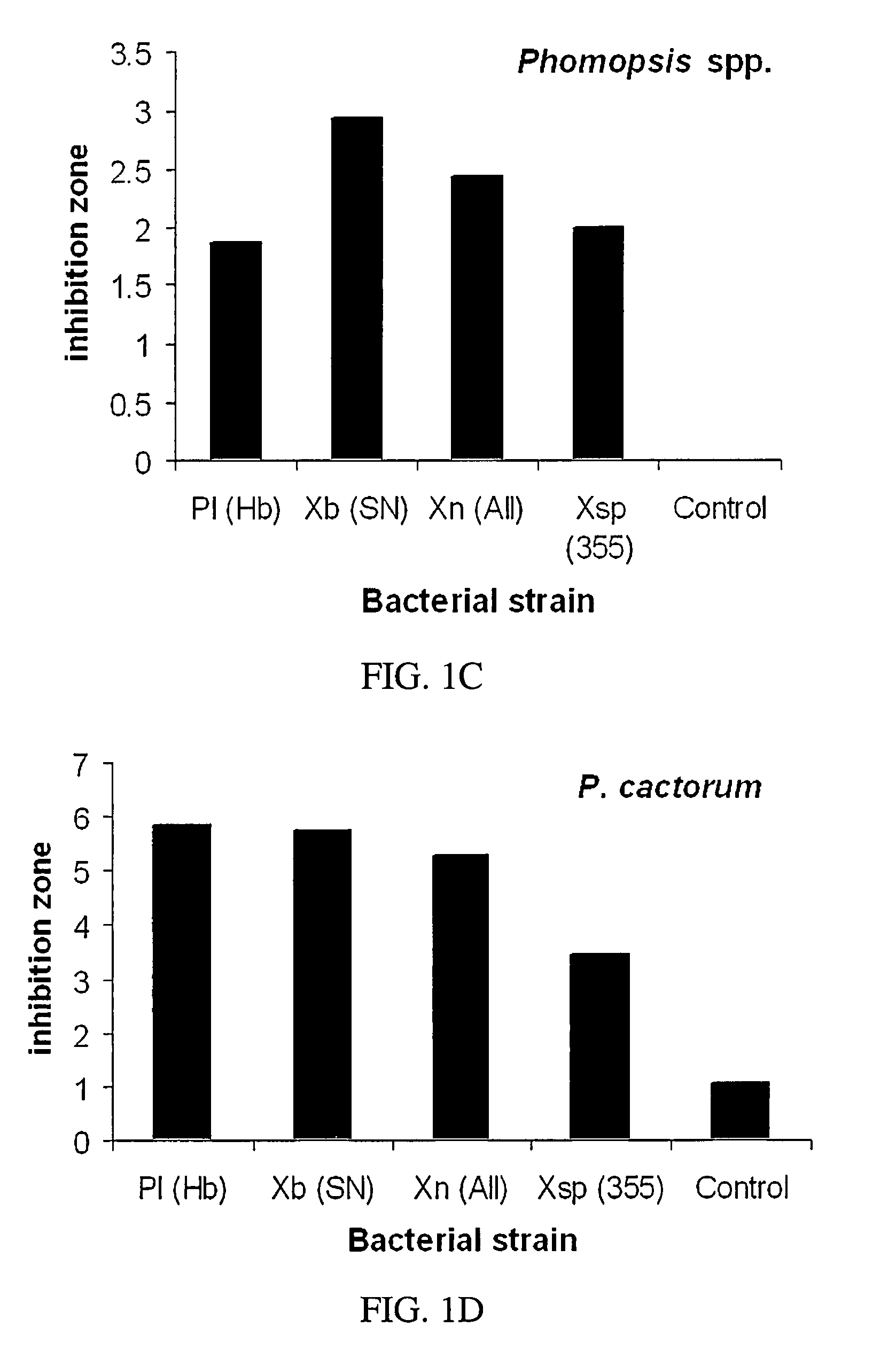
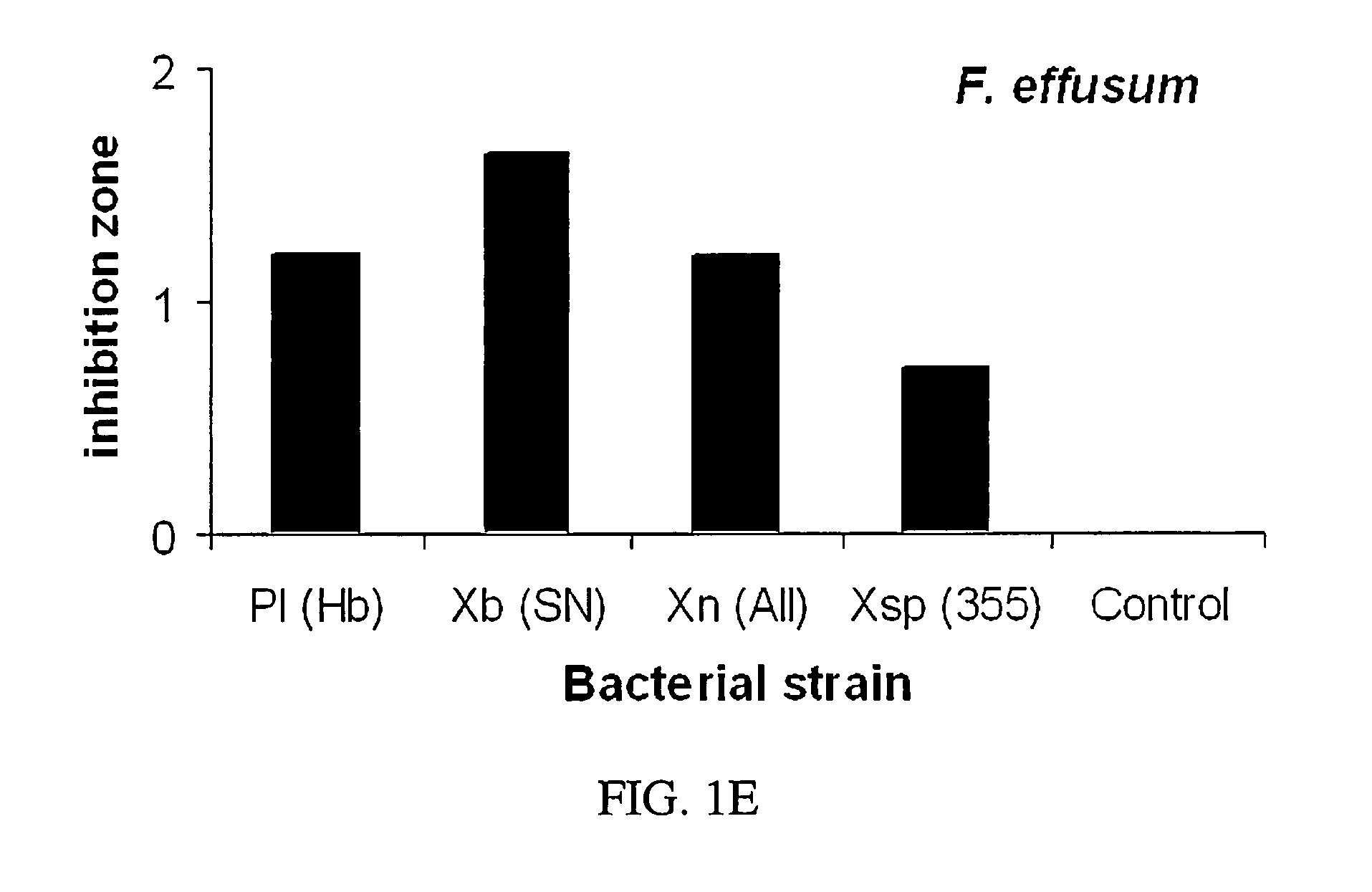
This invention relates to using bacterial metabolites to suppress phytopathogens, more particularly this invention relates to bacterial metabolites applied to Carya illinoensis and Prunus persica as a fungicide to suppress and inhibit Glomerella cingulata, Phomopsis sp., Phytophthora cactorum, Fusicladosporium effusum, and Monilinia fructicola.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Compound, preparation method and antibacterial application thereof
InactiveCN105418594AGood inhibitory effectEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideOrganic chemistryColletotrichumCarbendazim
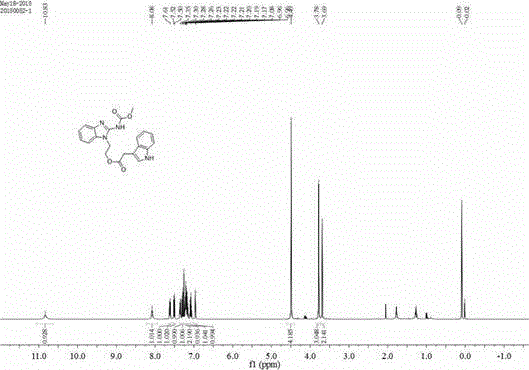
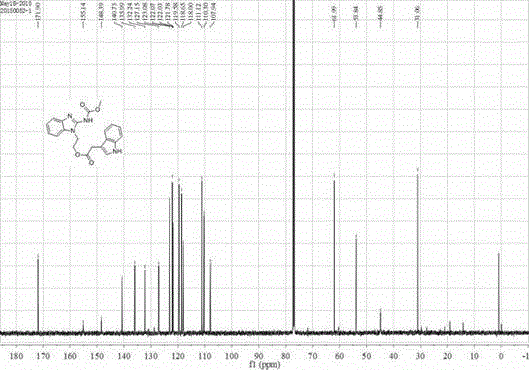
The invention relates to a preparation method of a novel medicine for inhibiting Cylindrocladium parasiticum, Colletotrichum corda and Phomopsis(Sacc.)Bubak. Indoleacetic acid, bromoethanol and carbendazim active compounds are used as synthetic raw materials to prepare an indoleacetic acid-carbendazim conjugate, which is the finish product, through a reaction. The invention also discloses nuclear magnetic resonance structure data, a hydrogen spectrogram and a carbon spectrogram of the novel compound. The compound has excellent antibacterial effects on the Cylindrocladium parasiticum, the Colletotrichum corda and the Phomopsis(Sacc.)Bubak.
Owner:ZHONGKAI UNIV OF AGRI & ENG
Phomopsis RNA (ribonucleic acid) polymerase (RPB1) gene amplification primer, as well as design method and application thereof
InactiveCN104195262ARapid Genetic Background AnalysisAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPolymerase LPhomopsis
The invention discloses a phomopsis RNA polymerase (RPB1) gene amplification primer, as well as a design method and application thereof. The primer is designed to aim at a universal primer of phomopsis funguses. An upstream primer PhR1-F has 43 basic groups: CGCCAGGGTTTTCCCAGTCACGACTGCAGCAAGGTGTTGGCTG, and a downstream primer PhR1-R has 43 basic groups: AGCGGATAACAATTTCACACAGGAGCGATGTCGTTGTCCATGTA. The primer can rapidly perform large-scaled genetic background analysis on the phomopsis funguses, and provides an important tool for species identification, geographical population identification or inspection and quarantine works of phomopsis in the country of China.
Owner:ANIMAL & PLANT & FOOD INSPECTION CENT OF TIANJIN ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
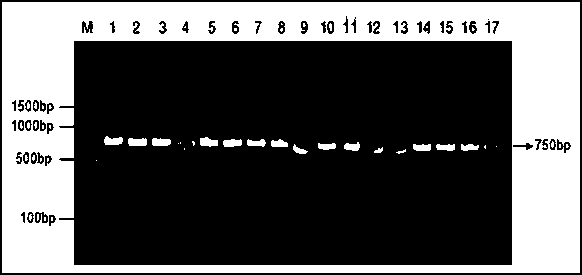
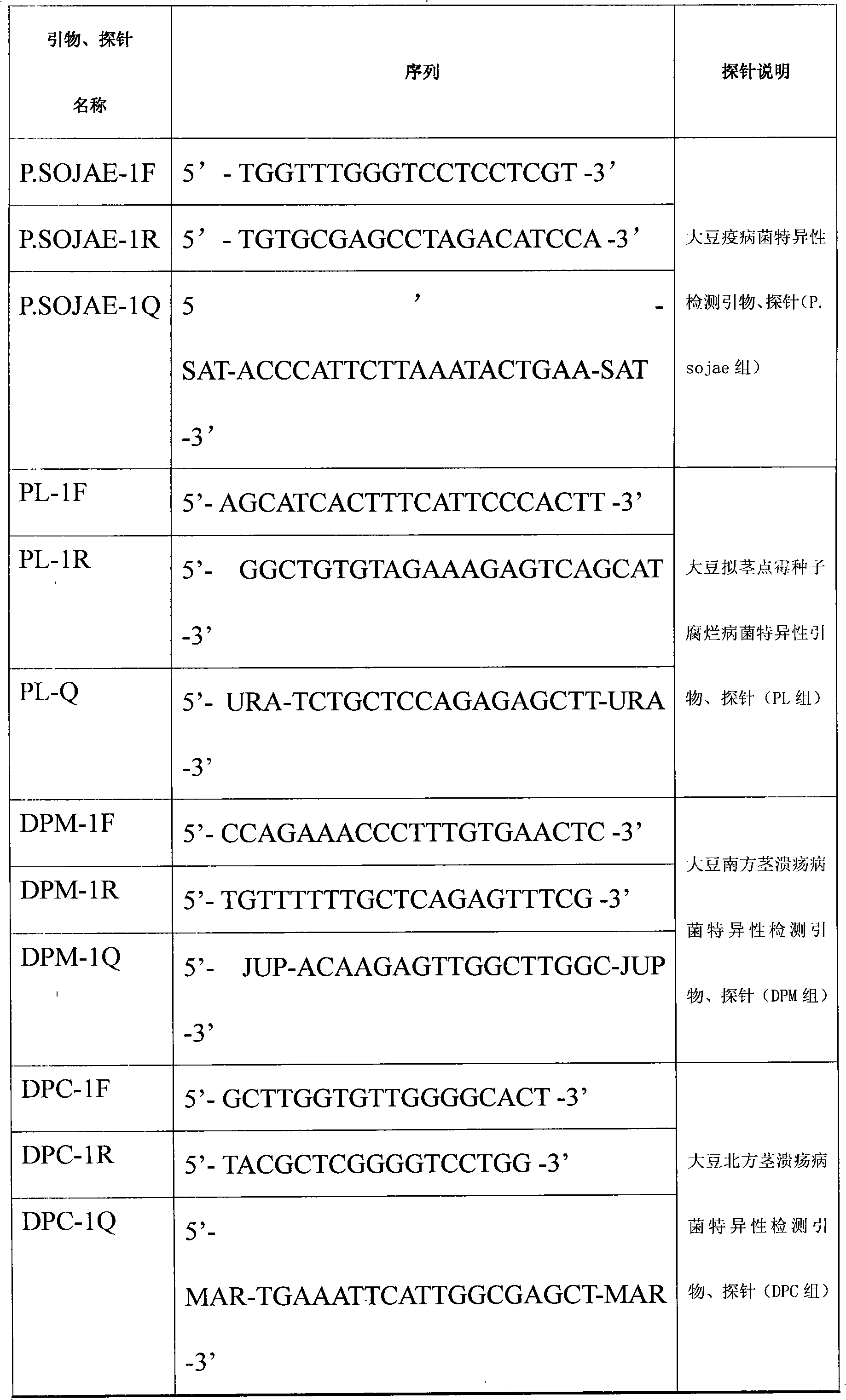
Multiple real-time fluorescence PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection method and kit of soybean quarantine virus diseases
InactiveCN101857905AStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFungal diseaseFluorescence
The invention relates to a simple, quick, specific and sensitive real-time fluorescence PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection method and a kit thereof for simultaneously detecting one or more soybean fungal diseases of soybean phytophthora parasitica, soybean phomopsis seed rot germs, soybean south stem ulcer germs and soybean north stem ulcer germs. The real-time fluorescence PCR detection method and the kit are suitable for departments of port inspection and quarantine, agricultural production, plant protection, and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
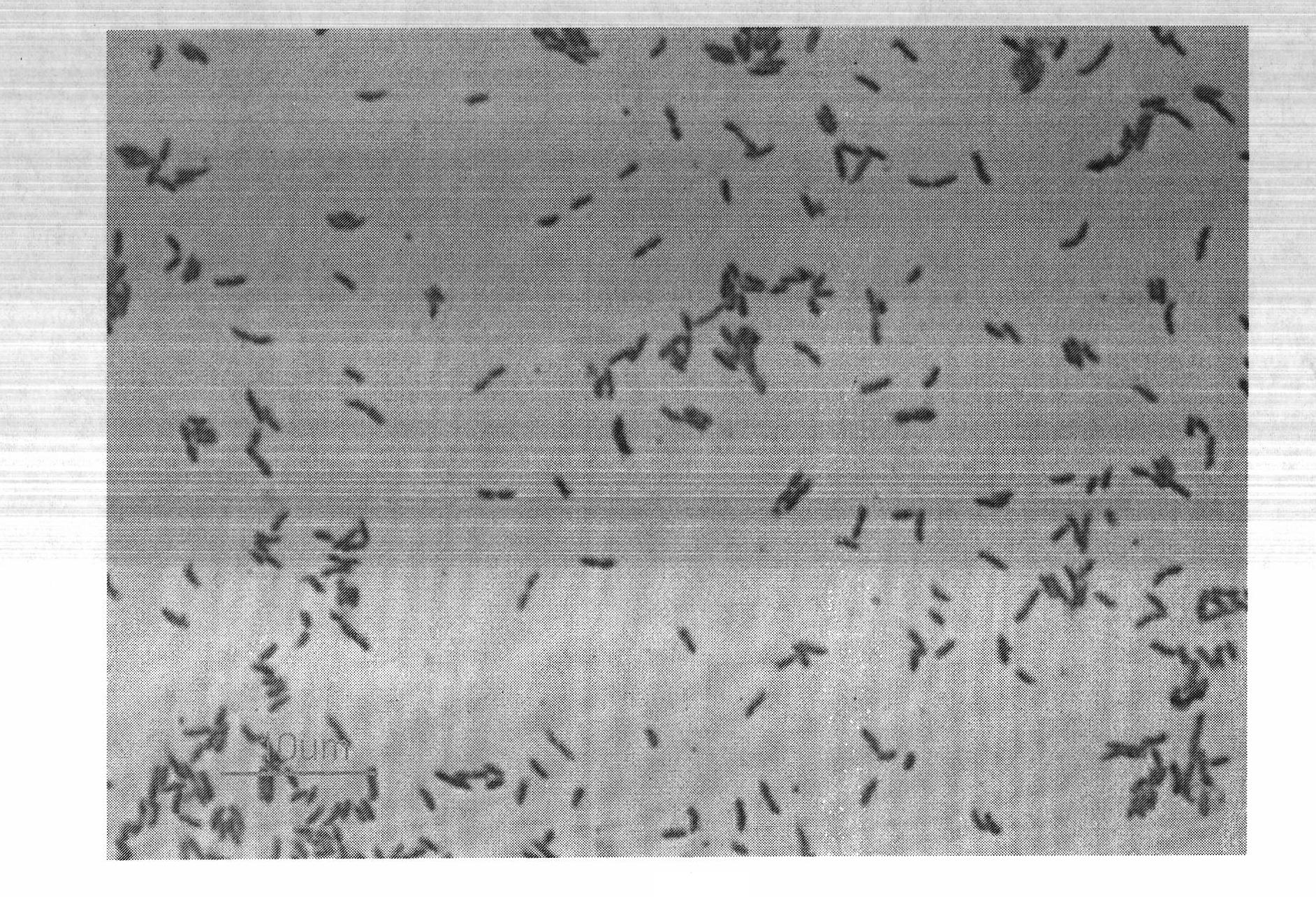
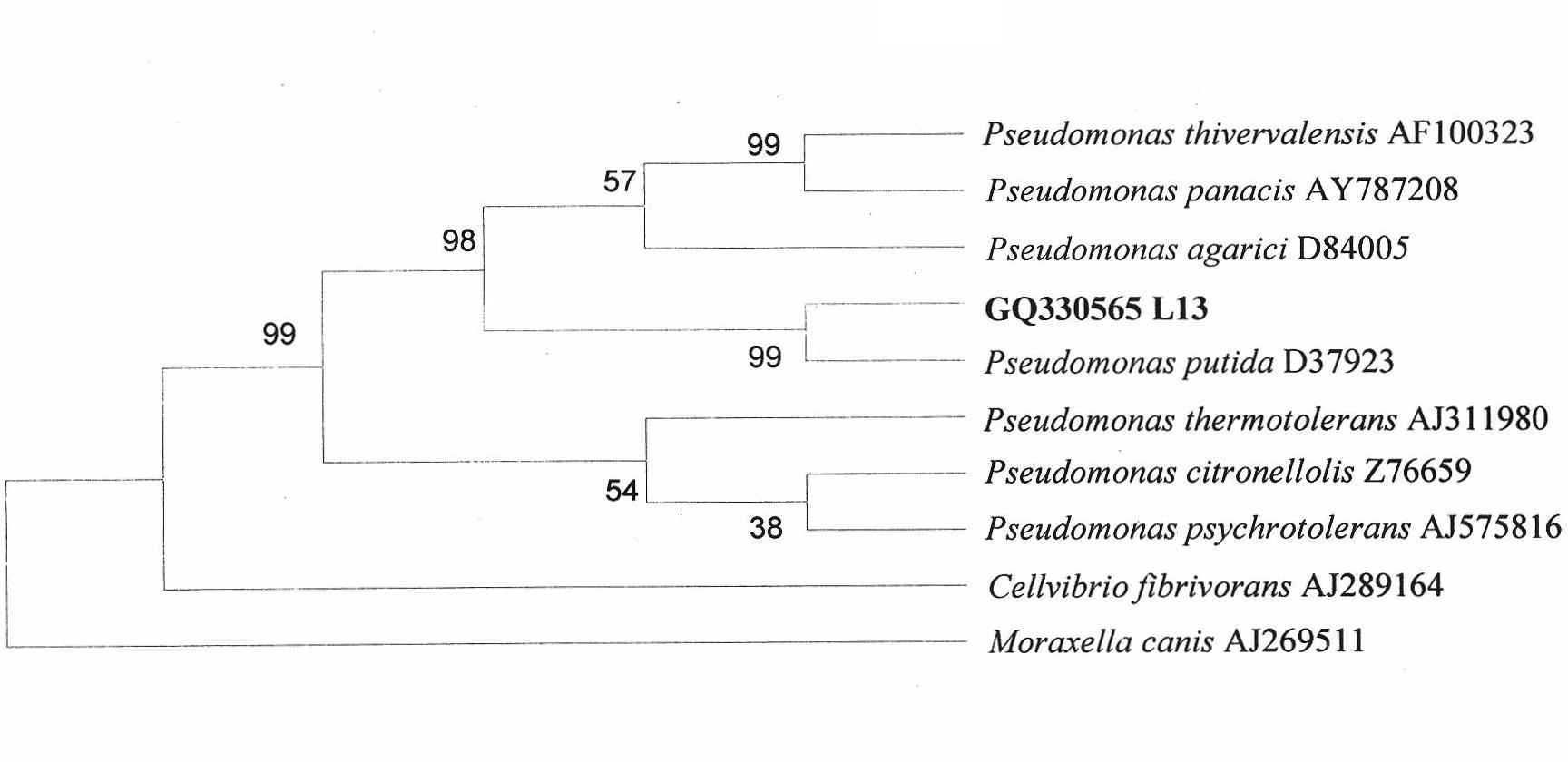
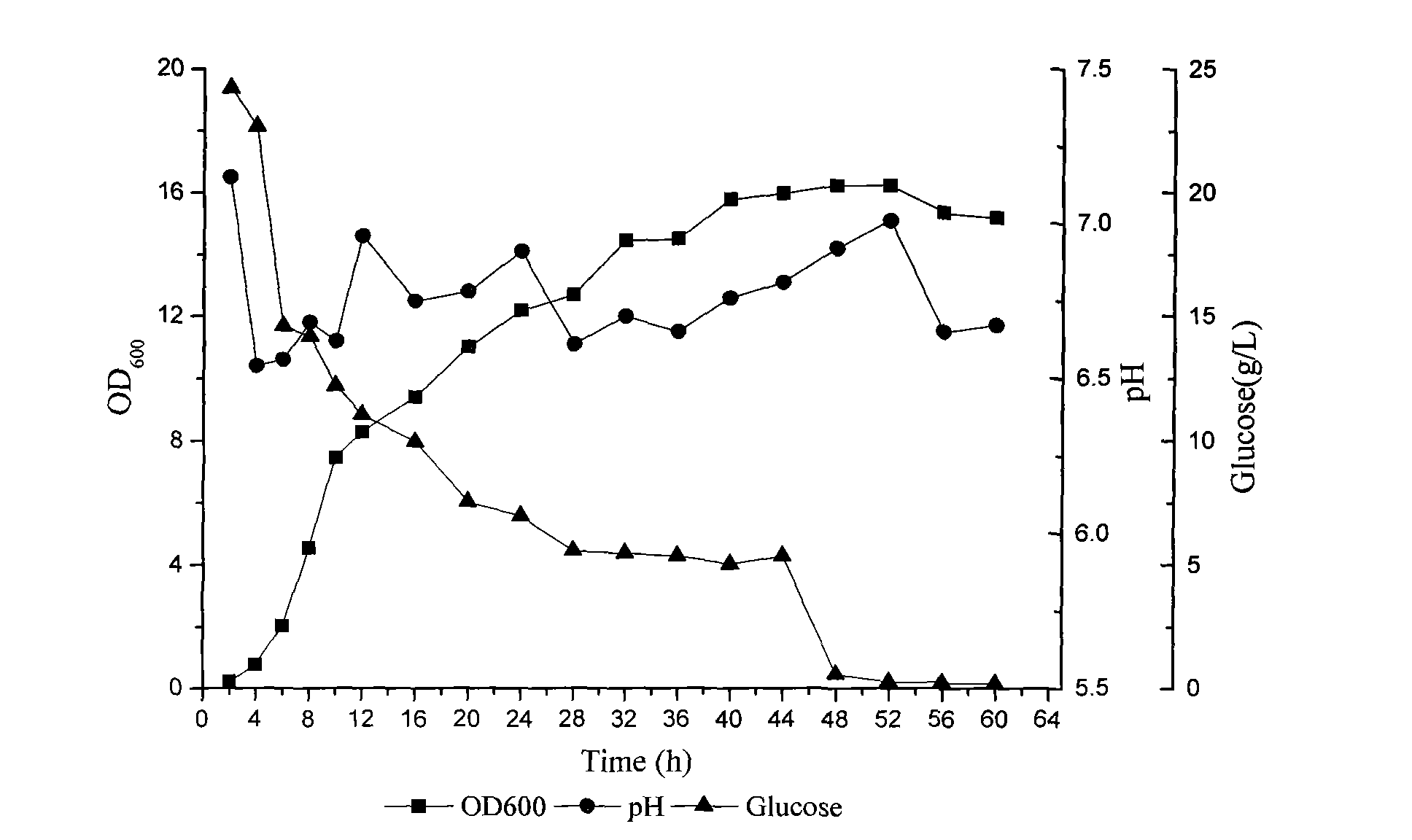
Phosphorus-dissolving pseudomonas putida L13 and fermentation process thereof
InactiveCN102649941APromote growthImprove micro-ecological environmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphatePseudomonas putida
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural microbiology, and particularly relates to the separation screening and fermentation cultivation of phosphorus-dissolving pseudomonas putida L13. A phosphorus-dissolving pseudomonas putida L13 strain with the capacity of dissolving phosphorus is obtained through separation, and the preservation No. is CCTCC No.2010342. The fermentation process comprises the following steps of: (1) taking L13 bacterial strain slope seeds for streak cultivation on an LB (lysogeny broth) culture medium flat plate to obtain first-level seeds; (2) inoculating a first-level seed single bacterial colony into an LB culture medium shake flask to make OD (optical density) 600 be 2.0 to obtain second-level seeds; (3) inoculating the second-level seeds into a shake flask for fermentation cultivation to obtain the pseudomonas putida; or inoculating the second-level seeds into a fermentation tank so as to obtain the pseudomonas putida through optimized cultivation. The pseudomonas putida strain disclosed by the invention grows rapidly, the yield of the pseudomonas putida is high, and the viable count can reach more than 10 billions. The phosphorus-dissolving amount of the phosphorus-dissolving pseudomonas putida in a PKO (Pikovskaya') culture medium in which 1-3g / L of calcium phytate is the unique phosphorus source can reach 120-220mg / L, and the phosphorus-dissolving amount of the phosphorus-dissolving pseudomonas putida in a PKO culture medium in which 4-6g / L of tricalcium phosphate is the unique phosphorus source can reach 300-500mg / L.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST OF HUBEI PROVINCE +2
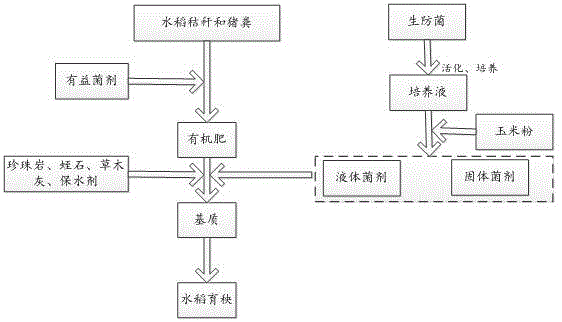
Preparation method of mechanical transplanting rice seedling raising substrate
ActiveCN106518401AHigh nutrient content of the substrateImprove water retentionExcrement fertilisersGrowth substratesPeatPaddy soils
The invention discloses a preparation method of a mechanical transplanting rice seedling raising substrate, and especially relates to applications of a biological agent. According to the preparation method, straw waste is taken as a raw material, fermentation with a plurality of beneficial microorganisms is carried out for 40 to 60 days, an obtained microbial organic fertilizer is mixed with perlite, vermiculite, peat, and a water-retaining agent at a certain ratio so as to prepare a rice seedling raising substrate, and the biological agent phomopsis HQ285146 prepared from corn flour is added. The obtained mechanical transplanting rice seedling raising substrate is light in volume-weight, is convenient to carry, is excellent in water-retaining property, is capable of reducing irrigation times, saving water, and is abundant in nutrients; no extra topdressing is needed in the whole rice seedling raising process; obtain seedlings are uniform; root system activity coefficient is high; cost is low; compatibility with mechanical transplanting technology is high; using amount of paddy soil is reduced; and environment pollution caused by improper treatment of straw is avoided.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
Specificity PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) identifying method of phomopsis amygdali
InactiveCN102229985ARapid identificationSensitive methodMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAgricultural sciencePhomopsis
The invention relates to a special PCR indentifying method of phomopsis amygdali. According to the method provided by the invention, PCR amplification is carried out by utilizing a primer pair 4, wherein a positive primer sequence is Pa-F2: 5'GCCGGCCCCCTTCTG3'; a negative primer sequence is Pa-R2: 5'GCCTGCCTCGTTTTTACACA3'. The specificity PCR identifying method of phomopsis amygdali, provided by the invention, can be used as an efficient way for identifying the phomopsis amygdali and other strains in and out of the genus of the phomopsis. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of high speed, high flexibility, good specificity, simpleness and convenience for operation and low needed experiment conditions, thereby extremely high practical value.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
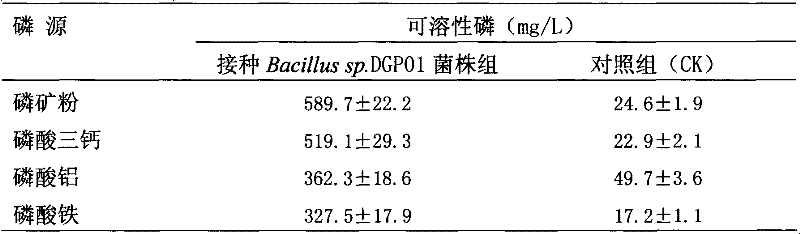
Angelica root rhizosphere efficient phosphate-solubilizing bacterium and microbial inoculum prepared from same and application thereof
InactiveCN102250784AIncrease productionImprove qualityAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaPhosphateInorganic phosphorus
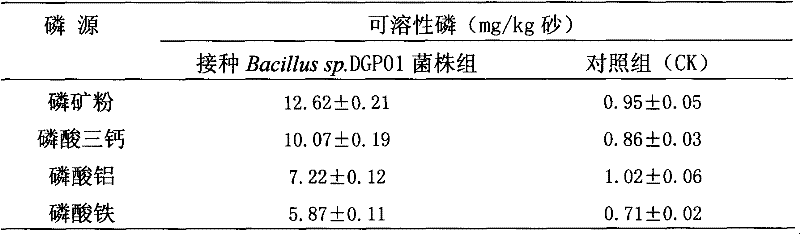
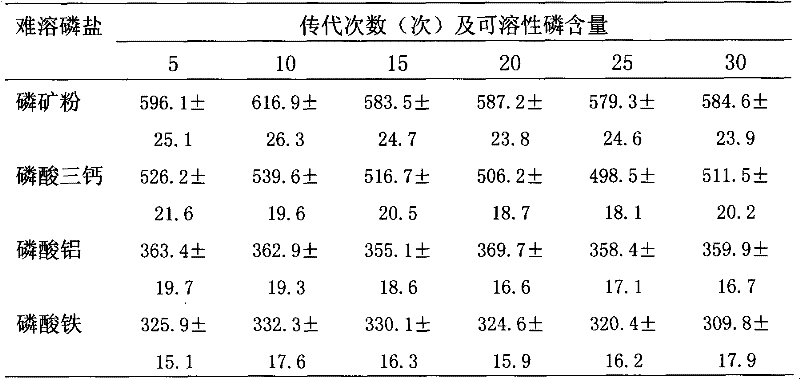
The invention discloses an angelica root rhizosphere efficient phosphate-solubilizing bacterium and a microbial inoculum prepared from the same and application thereof. The phosphate-solubilizing bacterium is bacillus sp.DGP01 which is collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (Address: Datun Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, 100101) with the collection number CGMCCNo.4755 on April 7, 2011. The microbial inoculum of the phosphate-solubilizing bacterium is prepared by the following steps of: inoculating a bacillus sp.DGP01 strain into a seed culture medium shakeflask and performing shaking culturing for an exponential growth phase; inoculating the cultured strain into a seeding tank which is filled with a fermentation culture medium and culturing for an exponential growth phase; and inoculating the fermentation liquor into a production tank which is filled with a fermentation culture medium for culturing. By adopting the phosphate-solubilizing bacterium, slightly-soluble inorganic phosphorus can be transformed into high-quality phosphorus compounds which can be directly absorbed and utilized by plants, the biological effectiveness of slightly-soluble phosphorus in soil can be enhanced, the utilization efficiency of a phosphorus fertilizer is increased, the fertilizer is saved, and the yield is increased; and moreover, the phosphate-solubilizing bacterium plays an important role in culturing and utilizing the ecological fertility of soil and keeping the ecological balance of agriculture, and has an application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Nucleic acid compositions conferring disease resistance
InactiveUS20050019767A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyHeterologous
This invention encompasses the identification and isolation of genes that confer disease control properties in plants, as well as plants comprising such genes. These genes are derived from the following sources: Nicotiana benthamiana, Oryzae sativa (var. Indica IR7), Papaver rhoeas, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Trichoderma harzianum (Rifai 1295-22). The control conferred is against the one or more of the following phytopathogens: Aspergillus flavus, Cercospora zeae-maydis, Fusarium monilforme, Fusarium graminearum, Helminthosporium maydis, Phoma lingam, Phomopsis helianthi, Phytopthera infestans, Pyricularia oryzae, Pythium ultimum, Rhizoctonia solani, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Ustilago maydis, and Verticillium dahliae. Further, this invention encompasses other homologous and heterologous sequences with a high degree of functional similarity.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Cinnamomum longipaniculatum leaf essential oil antibacterial method
ActiveCN110150333AGood antibacterial effectEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideFungicidesFusarium oxysporumCinnamomum longipaniculatum
The invention discloses a cinnamomum longipaniculatum leaf essential oil antibacterial method. An essential oil is extracted by using a vapor distillation method or a simultaneous distillation and extraction method, a distilled liquid is subjected to oil-water separation, an oil part is dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate to prepare a cinnamomum longipaniculatum leaf essential oil, and the obtained cinnamomum longipaniculatum leaf essential oil is adopted as an effective component for inhibiting plant pathogenic fungi. When the volume ratio of the cinnamomum longipaniculatum leaf essential oilis 7:25, the antibacterial rates of the cinnamomum longipaniculatum leaf essential oil upon fusarium oxysporum, fusicoccum aesculi and phomopsis are respectively not less than 80%, 90% and 61%.
Owner:JINGGANGSHAN UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing cytochalasin H by using endophytic fungi in mangrove forest
InactiveCN105925646AIncrease contentEasy to prepareMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsBiotechnologyMangrove
The invention relates to the technical field of medicinal chemistry and particularly discloses a method for preparing cytochalasin H by using endophytic fungi in a mangrove forest. The preparation method includes the following steps that S1, phomopsis liquidambari B3 strains of the endophytic fungi in the mangrove forest are inoculated to a sterilized culture medium; S2, culture is performed under the condition of the temperature of 25-35 DEG C for 5-30 days; S3, fermentation liquid and mycelium are separated; S4, separation and purification are conducted on the fermentation liquid and / or the mycelium to obtain the cytochalasin H. The preparation method is simple and convenient, and the prepared cytochalasin H is high in content and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEDICAL UNIV
Application of tenuazonic acid in preparation of microbial source fungicide
The invention discloses application of tenuazonic acid in preparation of microbial source fungicide. The tenuazonic acid has a structural formula as described in the specification and a molecular formula of C10H15NO3 with a molecular weight of 197. The tenuazonic acid has inhibition activity to phytopathogens. According to identification results and biological activity experiment results, the tenuazonic acid has substantial bacteriostatic activity to Valsa mali, Phomopsis vexan and Venturia nashicola. When the tenuazonic acid with a concentration of 100 [mu]g / mL is applied, the inhibition rates of Valsa mali, Phomopsis vexan and Venturia nashicola are 95.9%, 77.6% and 100.0%, respectively; thus, it is proved that the tenuazonic acid has potential in development of the microbial source fungicide.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bacillus subtilis for inhibiting phomopsis and application thereof
ActiveCN109929782APromote degradationStrong endoglucosidase activityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsKiwi fruitStaphylococcus aureus
The invention provides a bacillus subtilis for inhibiting phomopsis which is bacillus subtilis T8 deposited in China Center for Type Culture Collection on December 5, 2018 with the preservation numberof CCTCC NO: M 2018860. The bacillus subtilis T8 has good cellulose degradation capability, can produce cellulase, and has strong endoglucanase activity, filter paper enzymatic activity, exonucleaseactivity and beta-glucosidase activity. The bacillus subtilis T8 can inhibit phomopsis, and an ethanol supernatant and a protein have inhibitory effects on the phomopsis. In addition, the bacillus subtilis T8 can inhibit the growth of escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus, candida albicans, shigella dysenteriae and enterobacter faecalis, and has a development and utilization value in inhibitinghuman pathogenic bacteria. The invention also provides application of the bacillus subtilis T8 in producing cellulase and preventing kiwi fruit soft rot.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI
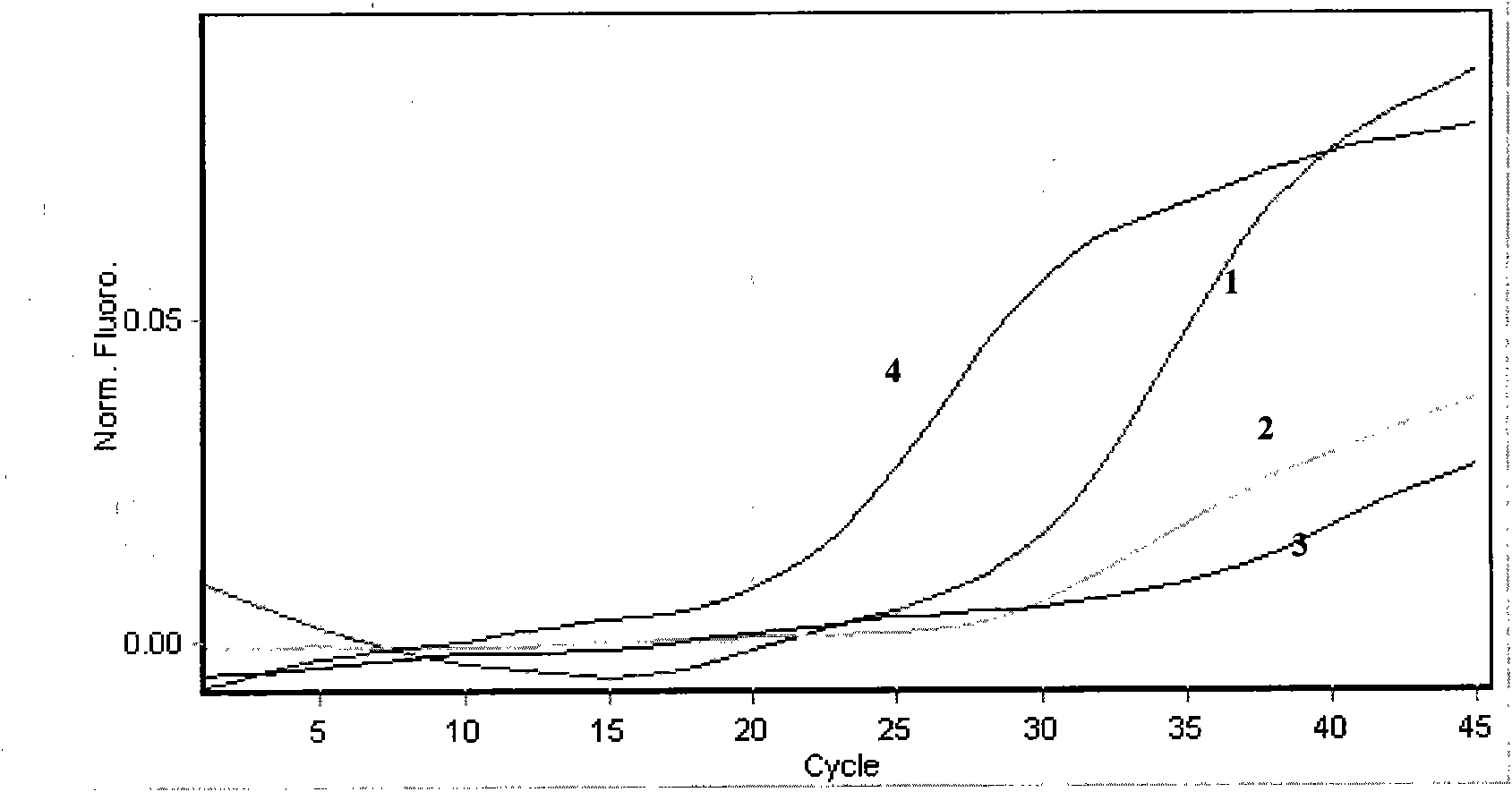
Real-time fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit for Phomopsis helianthi M.Muntanola-Cvetkovic et al.
InactiveCN103060436AImprove featuresImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleotideFluorescence
The invention provides a real-time fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit for Phomopsis helianthi M.Muntanola-Cvetkovic et al. Nucleotide sequences of primers adopted by the kit are shown in a sequence table PHDf&PHDr and a nucleotide sequence of probes is shown in a sequence table PHDp. The kit takes the total DNA of samples as a template, utilizes the primers and the probes to carry out real-time fluorescent PCR amplification, collects data after each cycle ends and judges the results according to the amplification curve after reaction ends. The kit has very good specificity and stability, and the detection method is quick and simple and has high accuracy and flexibility, thus providing guarantees for import and export safety of plant materials possibly carrying Phomopsis helianthi M.Muntanola-Cvetkovic et al.
Owner:新疆出入境检验检疫局检验检疫技术中心
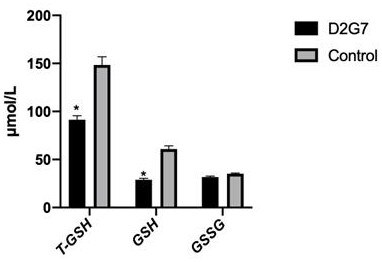
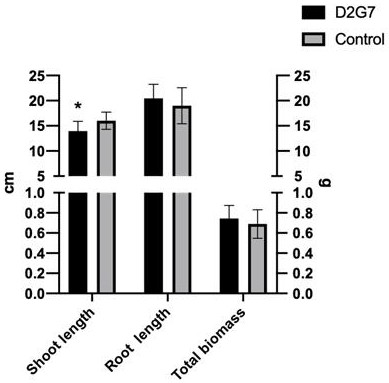
Plant endophytic fungus phomopsis D2G7 and application thereof
ActiveCN112280694ALow costStrong toleranceBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBioremediationEndophytic fungus
The invention discloses a plant endophytic fungus phomopsis (Phomopsis columnaris) D2G7. The preservation number of the plant endophytic fungus phomopsis cloumnaris D2G7 in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center is CGMCC No. 21044. The strain is applied to bioremediation of heavy metals lead, zinc and cadmium; under the stress of heavy metal pollution, the strain can promote plant growth, promote the transfer capacity of plants to heavy metals, has strong accumulation capacity to heavy metals cadmium and zinc, and is suitable for in-situ remediation of large-area heavy metal cadmium and zinc pollution.
Owner:云南省生态环境科学研究院
Liquid fertilizer for preventing and treating eggplant phomopsis rot
InactiveCN109020647AIncrease antibacterial substancesImprove immunityBio-organic fraction processingAnimal corpse fertilisersMicrobial agentAllium sativum
The invention discloses a liquid fertilizer for preventing and treating eggplant phomopsis rot, which includes, by weight, 10-20 parts of beef extract, 6-10 parts of euphorbia pekinensis, 5-10 parts of hawthorn flowers, 10-12 parts of tea bran, 6-8 parts of acorus calamus, 6-8 parts of folium eriobotryae, 4-6 parts of garlic, 13-18 parts of a microbial agent, 3-4 parts of shell powder, 4-6 parts of composite vitamins, 8-12 parts of composite amino acid, 4-8 parts of brassinosteroids, 6-9 parts of azadirachtin, 10-15 parts of veratrine, 20-30 parts of weak acidic electrolytic water, and 80-120parts of distilled water. The liquid fertilizer not only can effectively prevent the burst of the eggplant phomopsis rot but also can increases Mu-yield of the eggplants.
Owner:NANJING ZHIQIAO AGRI CO LTD
Naringenin production method based on phomopsis cell fermentation
PendingCN110283857AOvercoming selectivityOvercome purityVectorsTransferasesBiotechnologyChemical synthesis
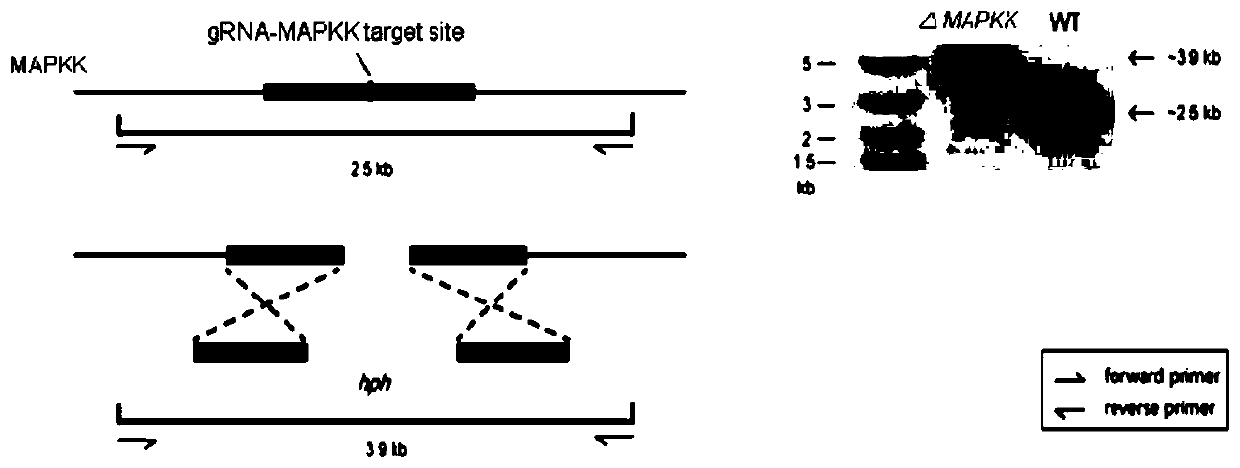
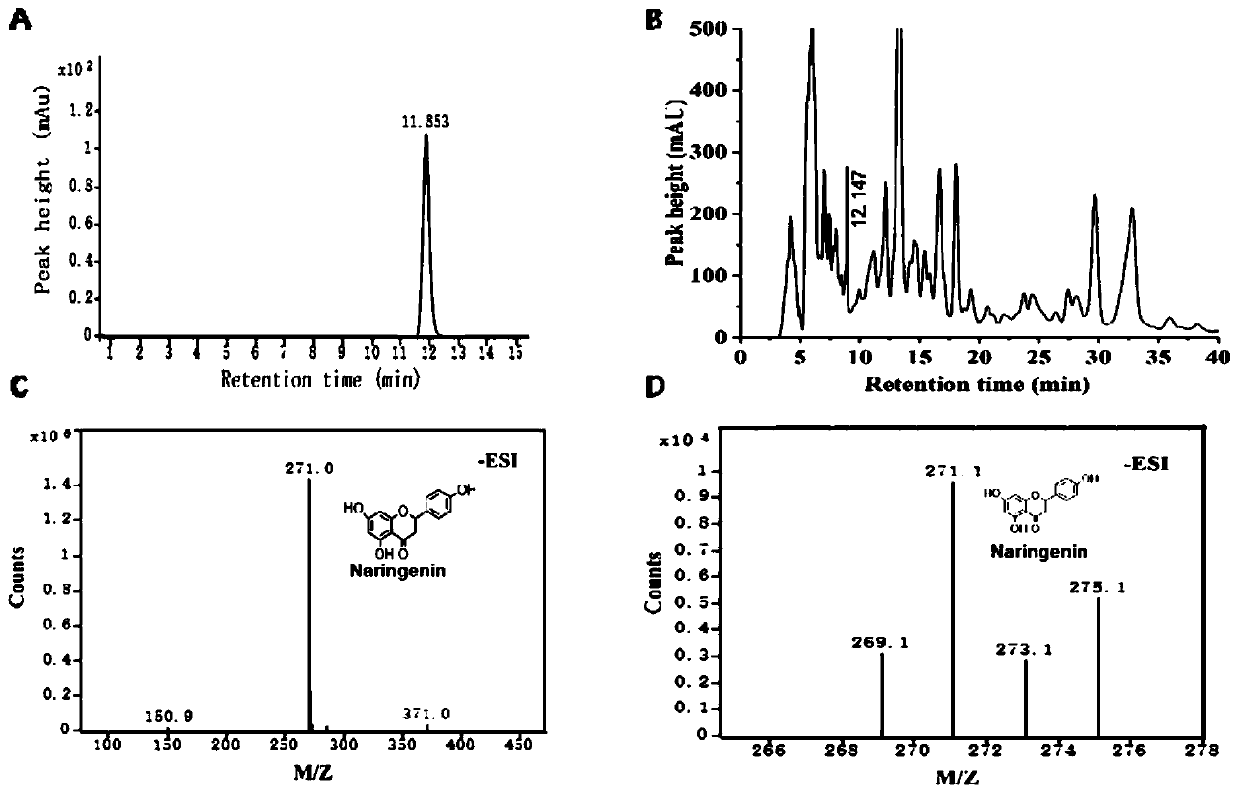
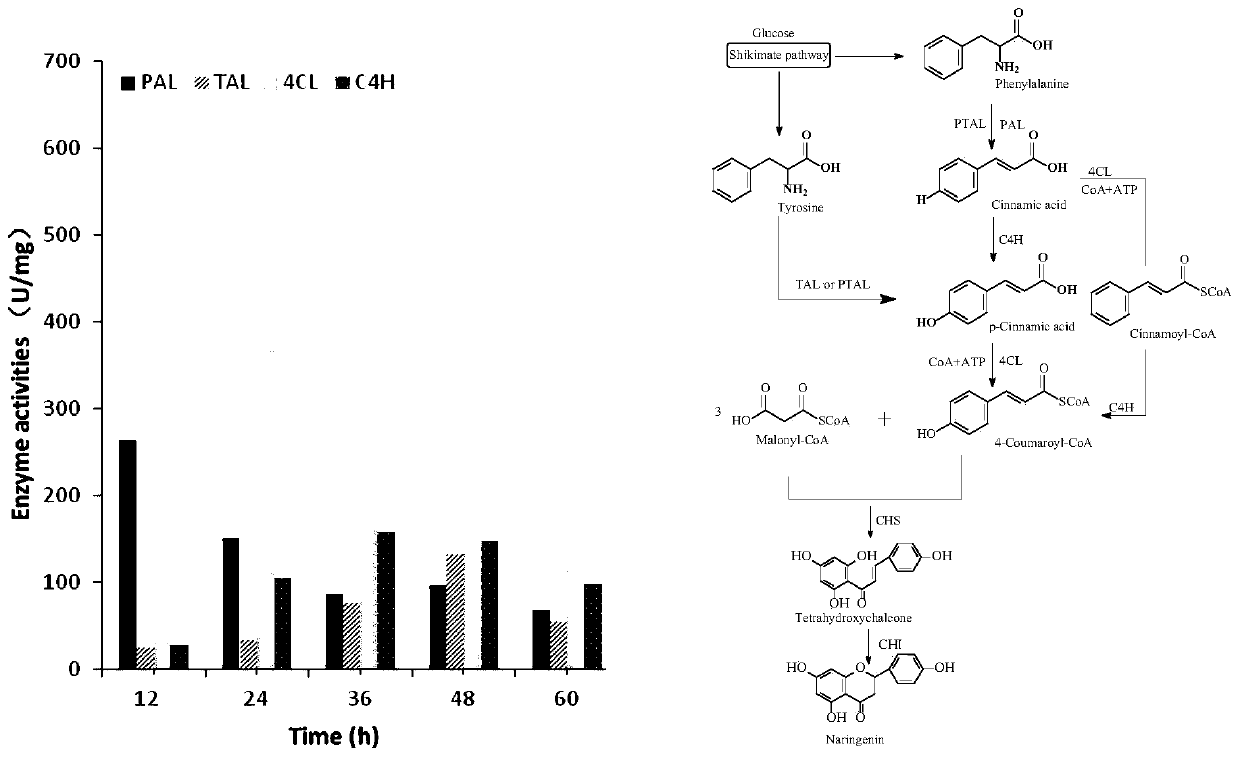
The invention discloses a naringenin production method based on phomopsis cell fermentation. After an MAPKK gene related to the endogenous fungus phomopsis global regulation factor signal transduction is knocked out by CRISPR-Cas9, biosynthesis of naringenin is activated, and naringenin can be obtained from fermentation broth and mycelia of mutant strains. Naringenin is produced in a microbial natural synthesis way for the first time, the rapid naringenin production method is provided, defects of long period and difficulty in extraction of a plant extraction method and defects of poor product selectivity, low product purity, harsh reaction conditions and serious environmental pollution of a chemical synthesis method are overcome, the method has the advantages of good selectivity, high product purity and mild reaction conditions, is simple and convenient to operate and has good application prospect in food and medicine production, and a new idea is provided for naringenin production.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preventing and treating eggplant diseases and insect pests
The invention discloses a method for preventing and treating eggplant diseases and insect pests, and relates to the technical field of crop plant disease and insect pest prevention and treatment. The method is characterized by including the steps of eggplant phomopsis rot prevention and treatment, phytophthora parasitica prevention and treatment, greensickness prevention and treatment, and polyphagotarsonemus latus and red spider prevention and treatment. The method is reasonable, convenient and rapid to operate and good in effect.
Owner:GUZHEN WANJIA ECOLOGICAL LIVESTOCK FARM
Biocontrol strain LS01 for preventing and controlling phomopasis asparagi and biocontrol inoculant of biocontrol strain
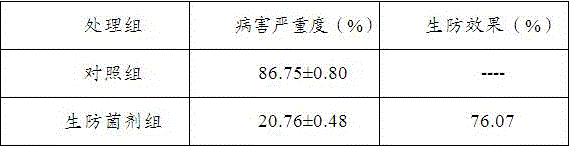
The invention relates to a biocontrol strain LS01 for preventing and controlling phomopasis asparagi and an application of the biocontrol strain to a biocontrol inoculant, and belongs to the technical field of plant protection. The invention provides the paenibacillus polymyxa LS01 and the application thereof as well as the biocontrol inoculant comprising the strain (the paenibacillus polymyxa) and an application of the biocontrol inoculant. The biocontrol strain LS01 provided by the invention is the paenibacillus polymyxa, which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, with strain preservation number of CGMCC NO. 11690. The biocontrol inoculant is prepared by conducting shaking culture on the strain in an LB culture solution at 28-37 DEG C at 180rpm for 20-48h, implementing centrifuging, collecting bacteria and processing the bacteria by virtue of a microbial freeze-drying method, wherein the total concentration of living bacteria in the finished inoculant product ranges from 1*10<6>CFU / g to 1*10<11>CFU / g; and in practical application, the finished inoculant product is applied in the form of a bacterium suspension which is obtained by diluting the finished inoculant product with sterile water at the ratio of 1: 20. Based upon tests, the biocontrol inoculant provided by the invention can achieve a bacteriostasis rate on asparagus phomopsis to 100%, and under a room-temperature condition (artificial inoculation), an effect of preventing the phomopasis asparagi can reach 76.07%.
Owner:CHINA NAT RES INST OF FOOD & FERMENTATION IND CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com