Patents
Literature
10383results about "Treatment using aerobic processes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
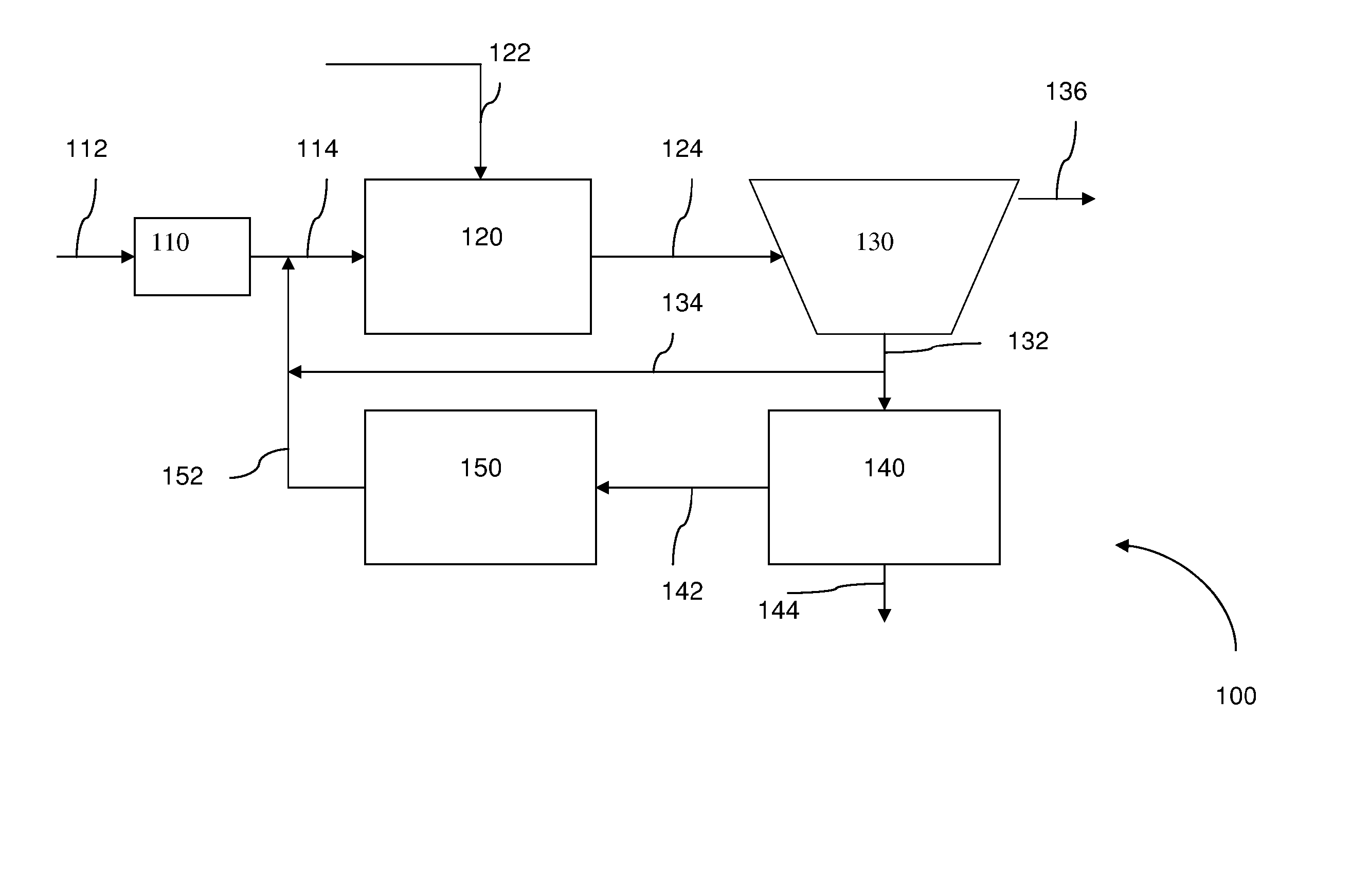
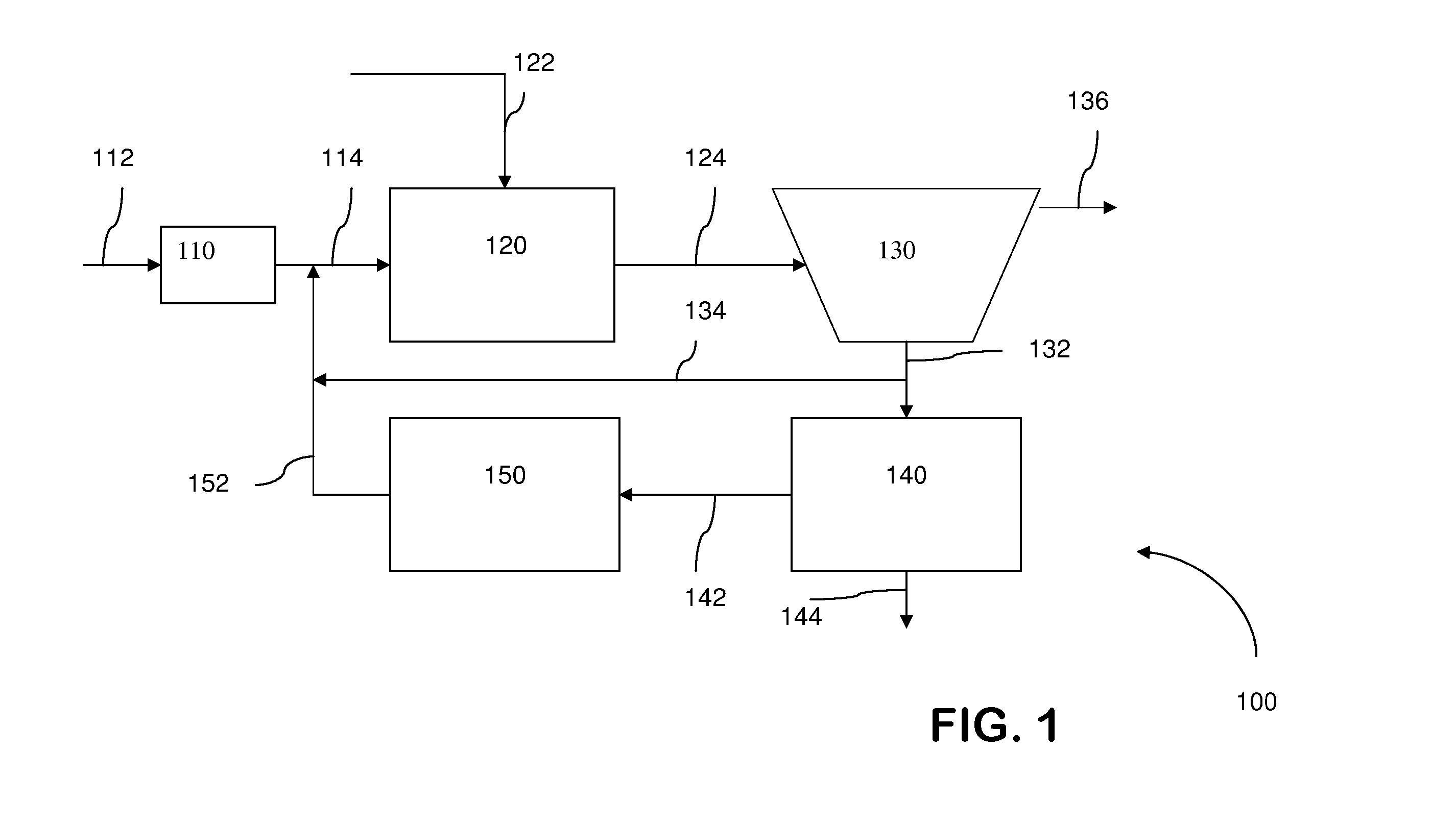
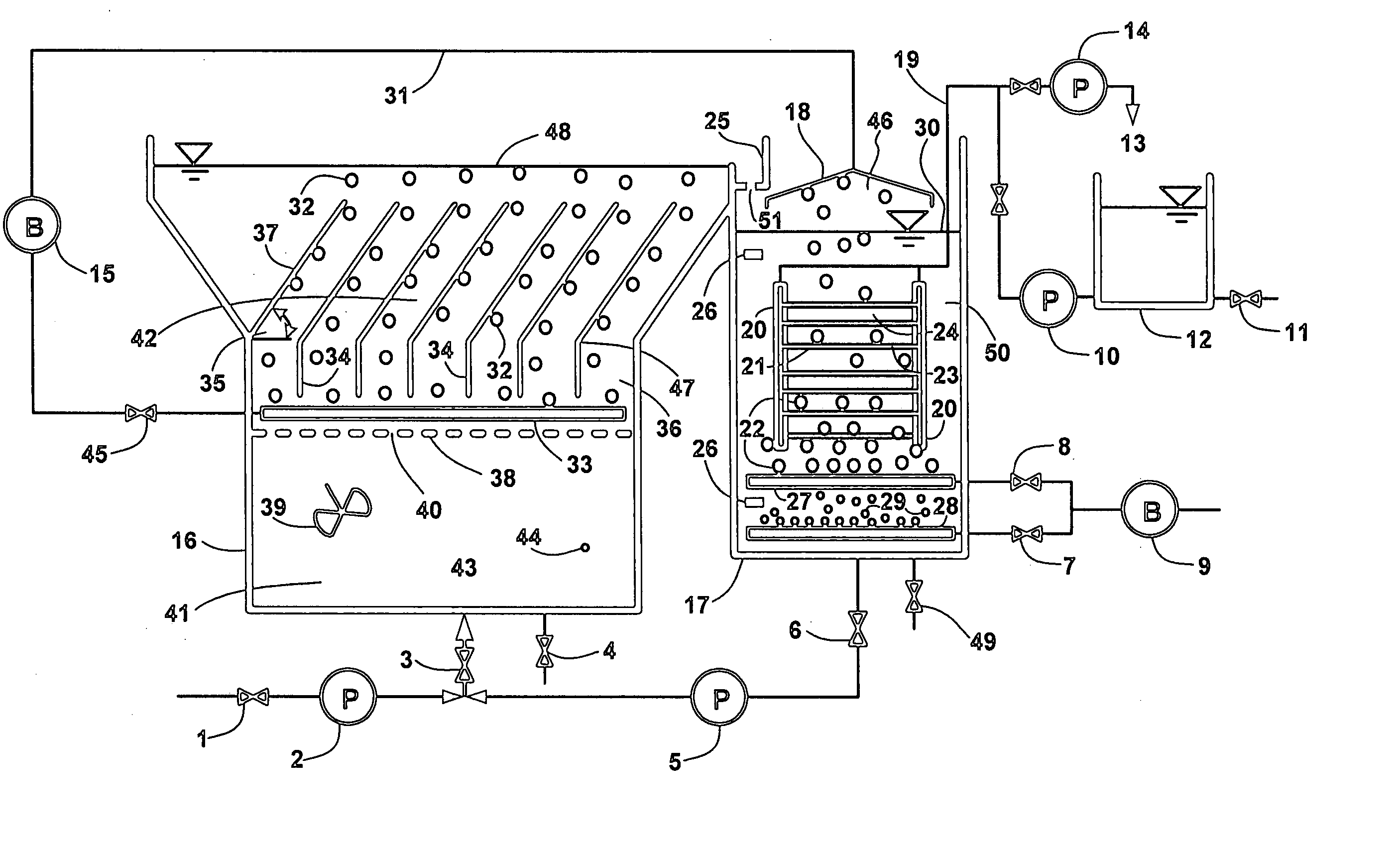
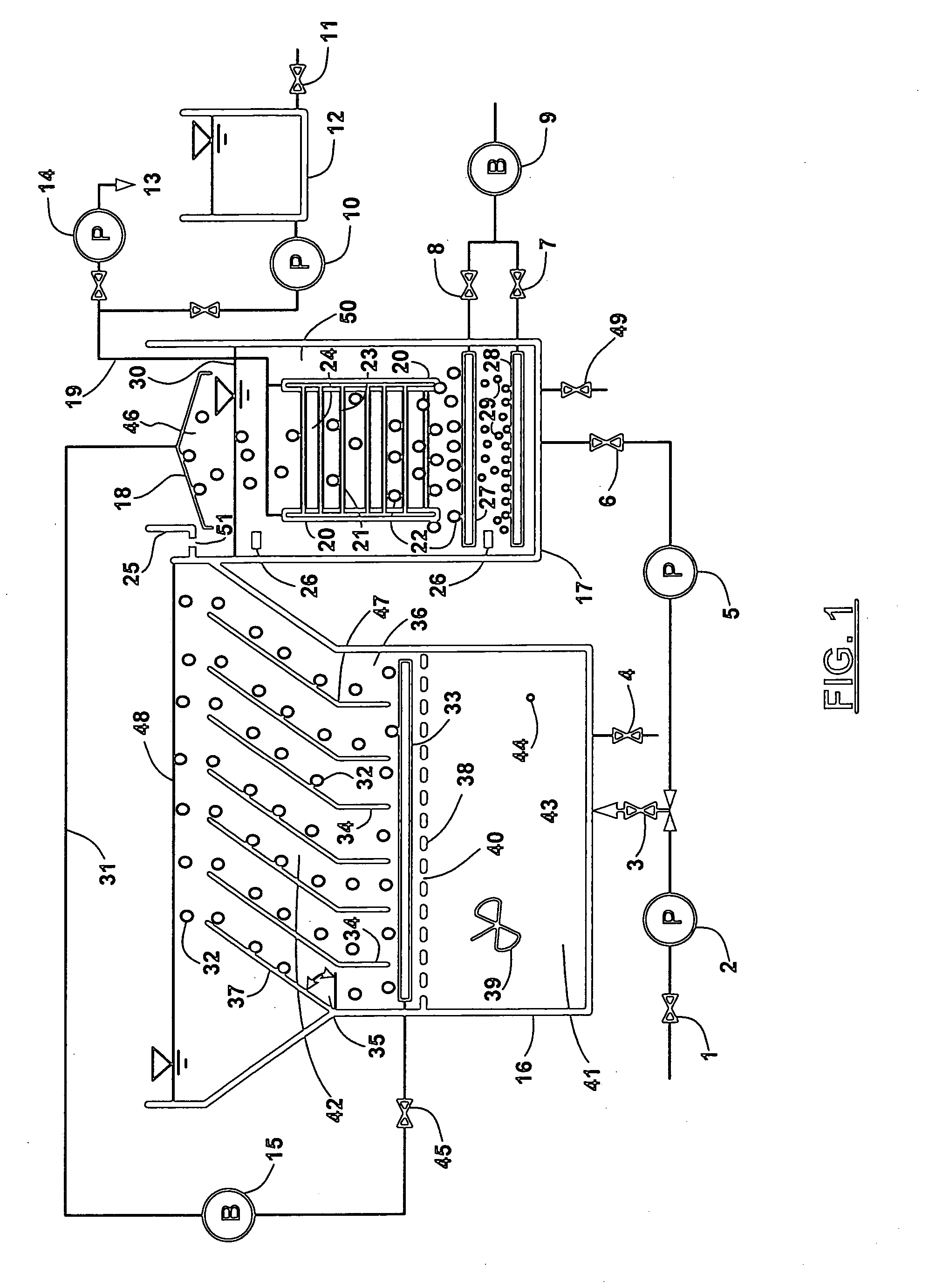
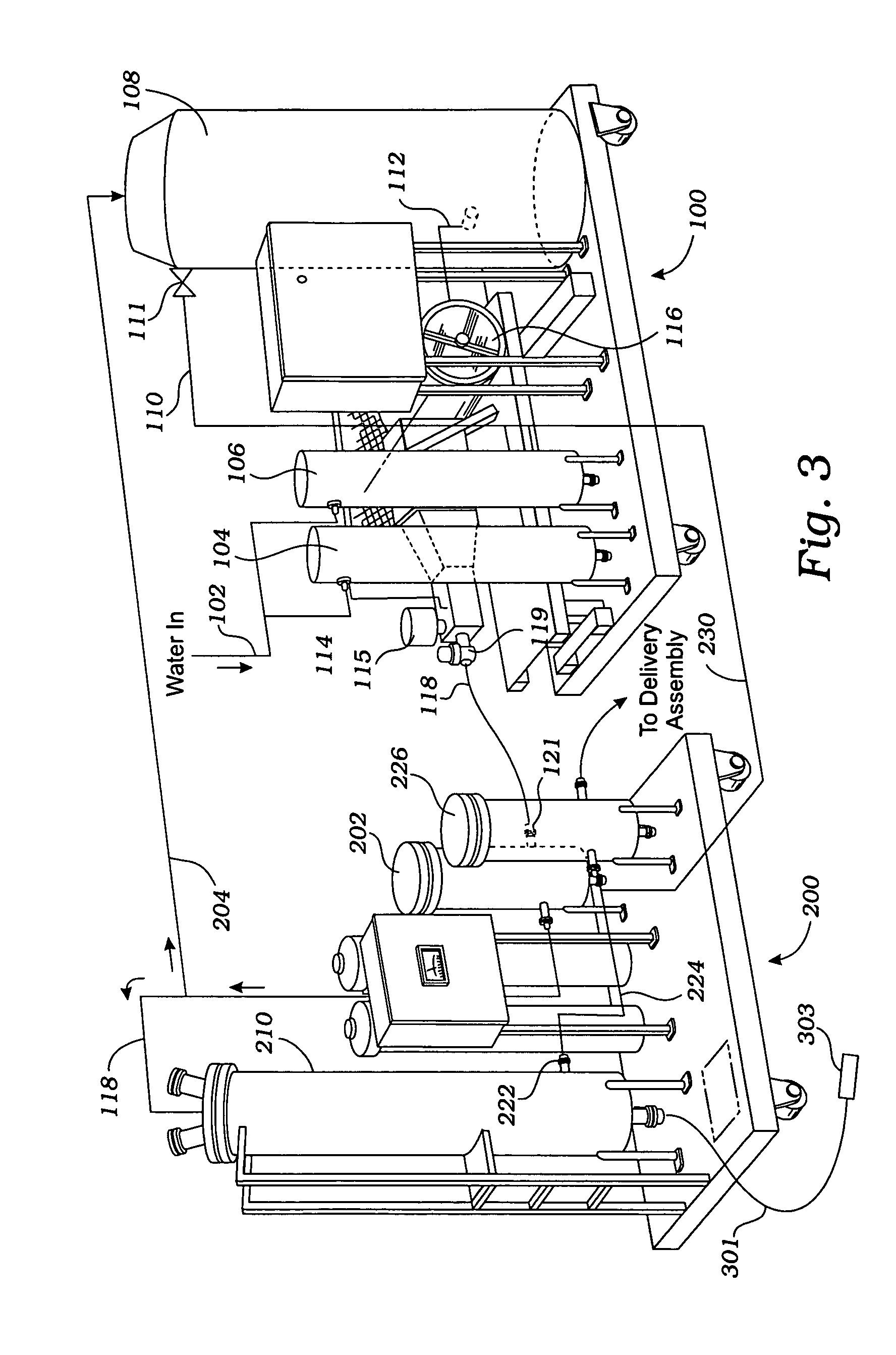
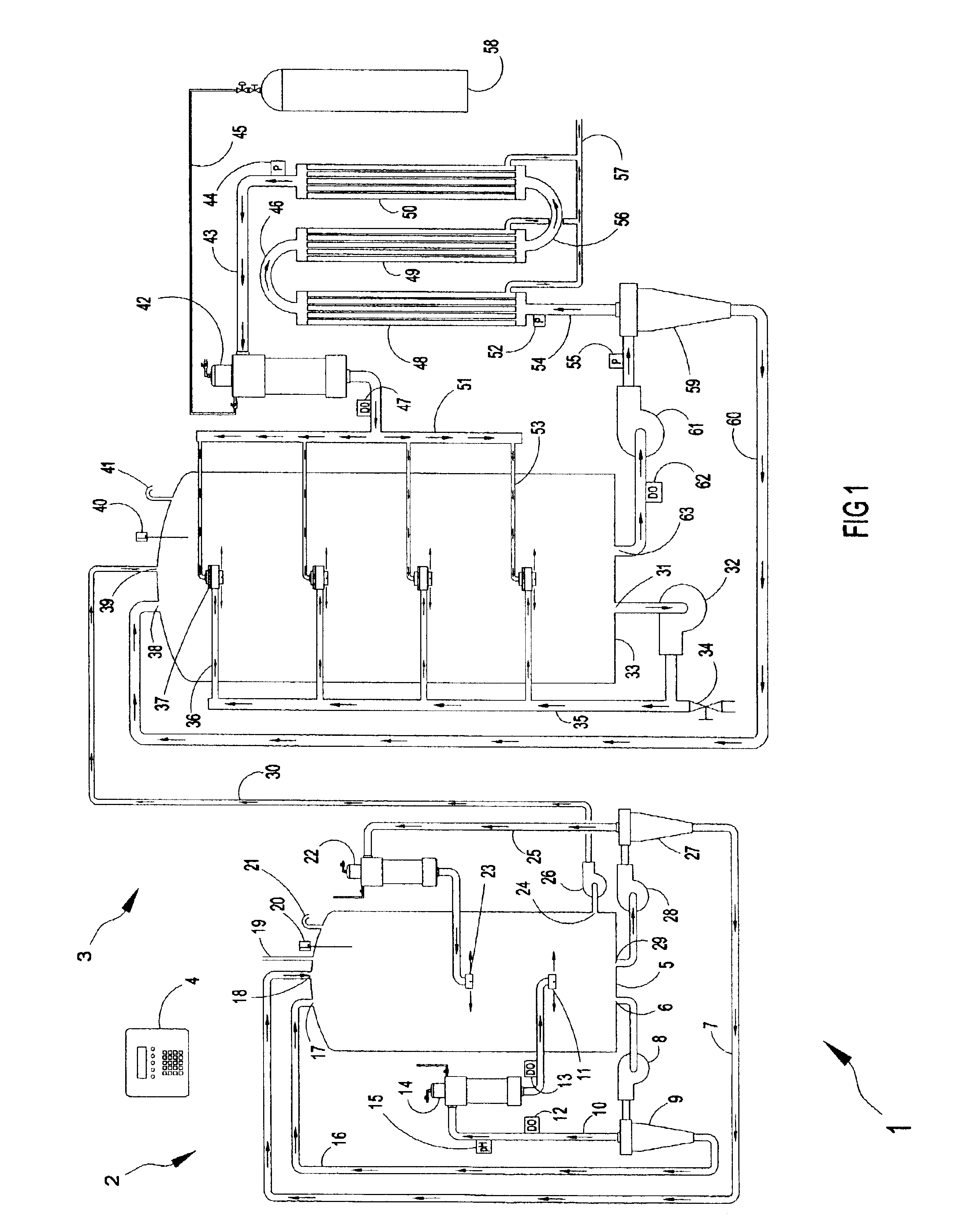
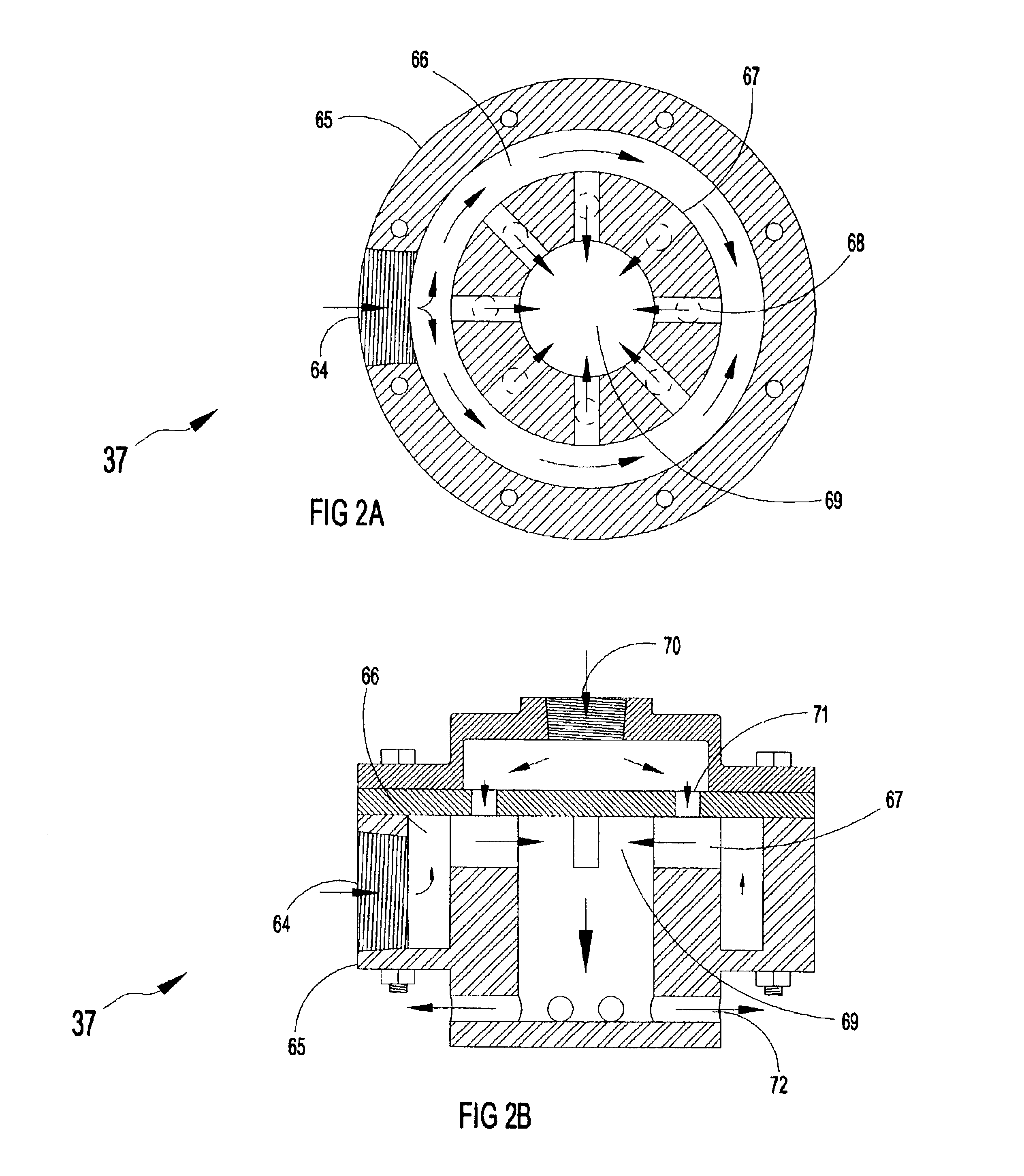
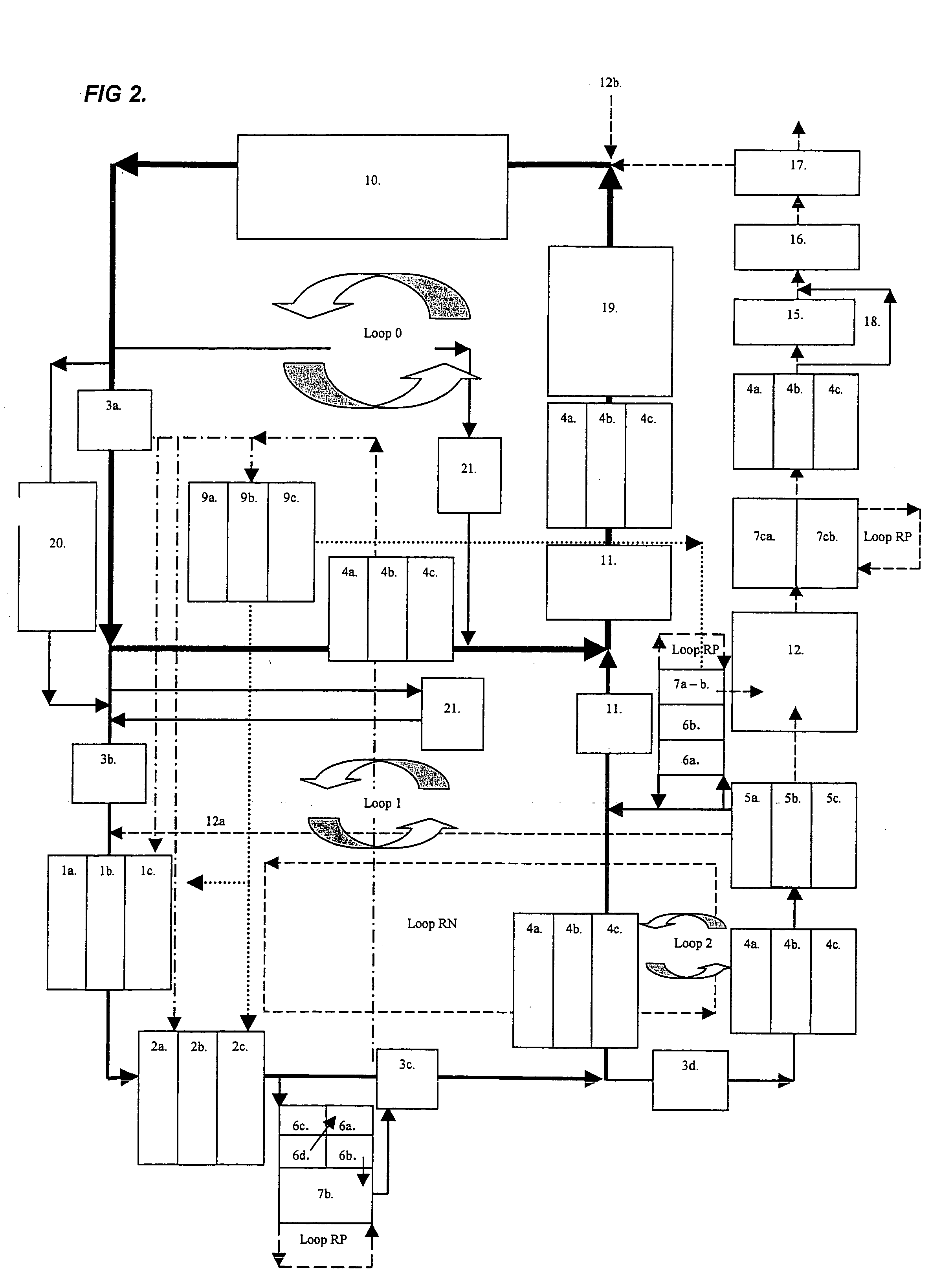
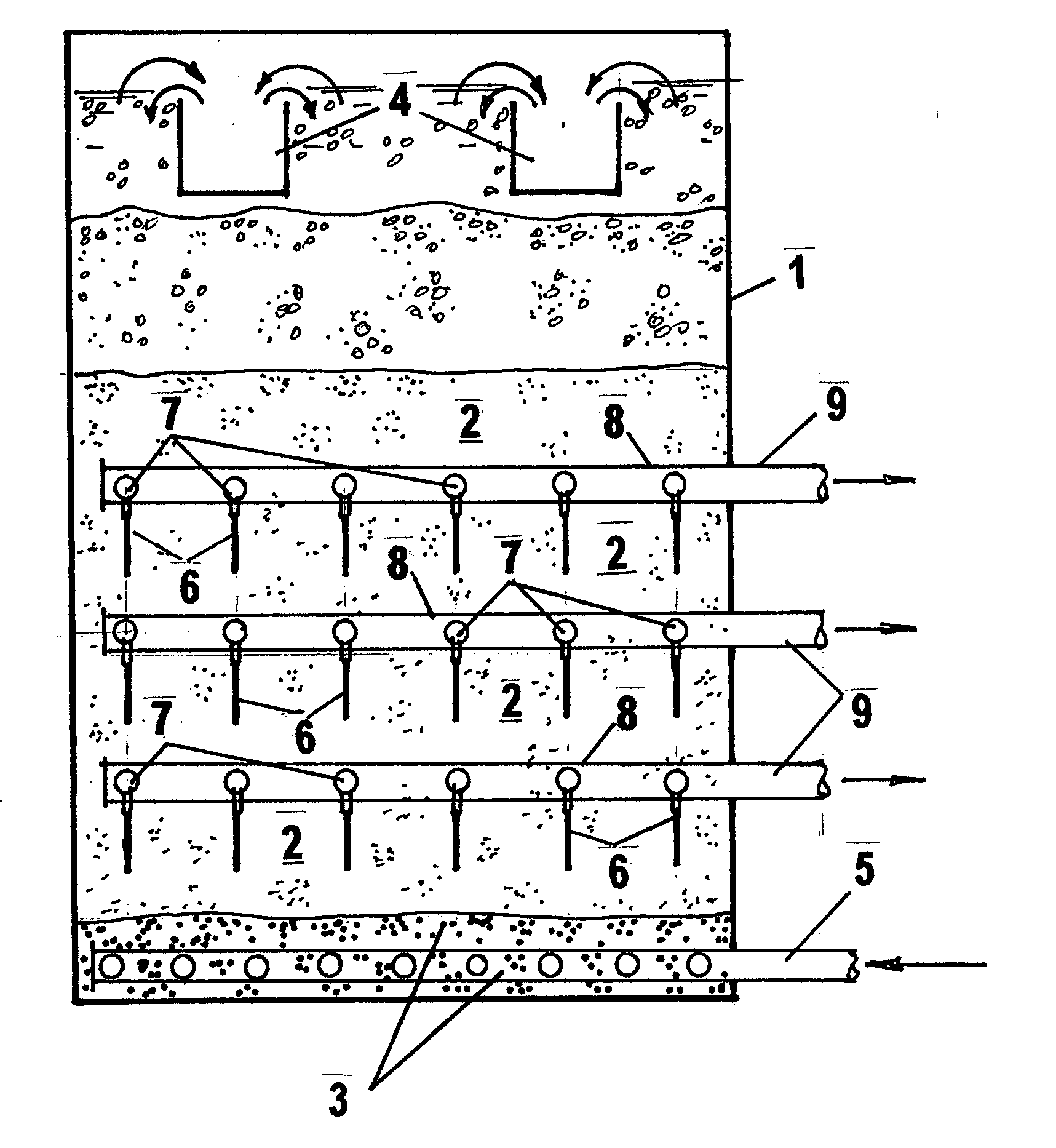
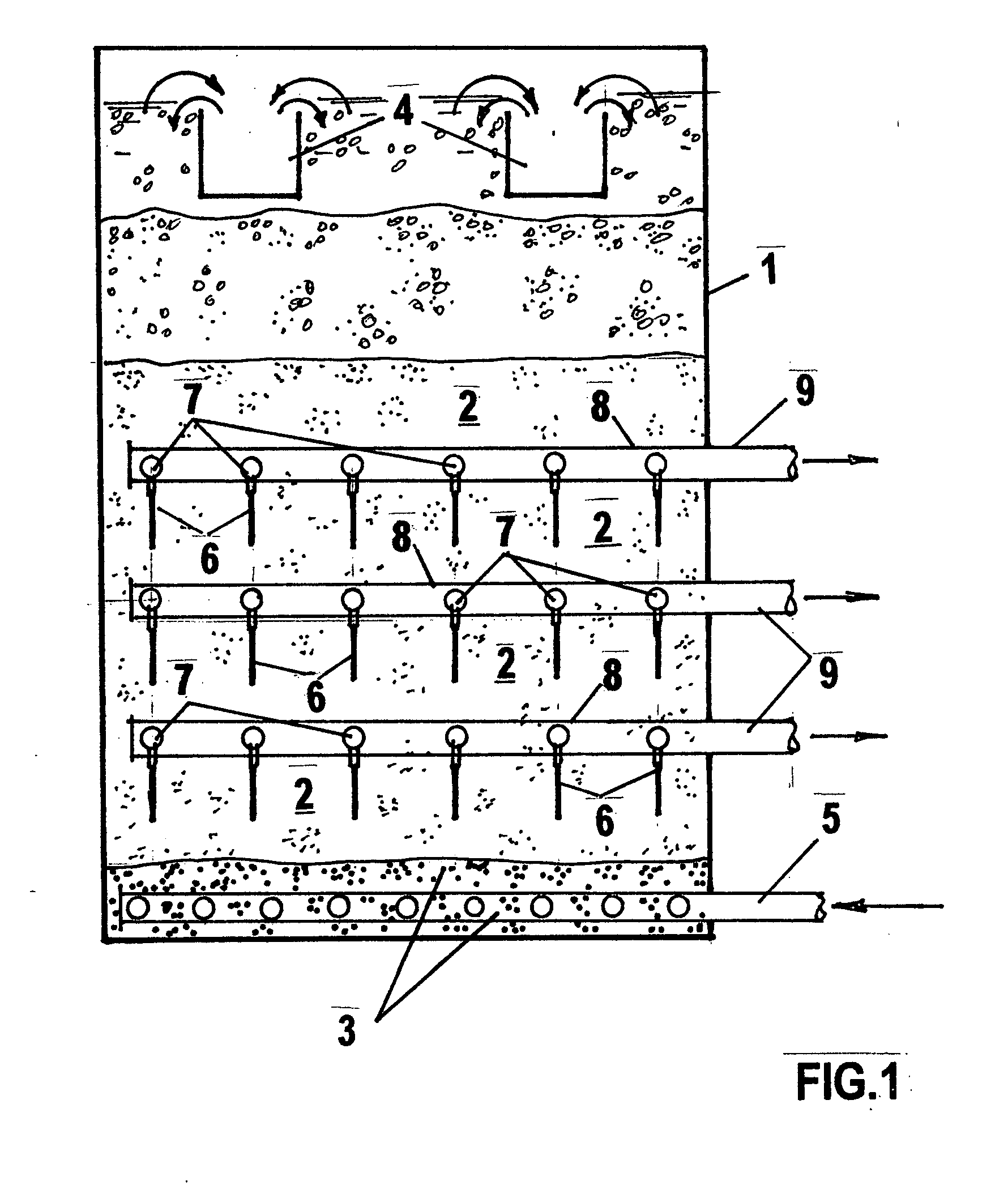
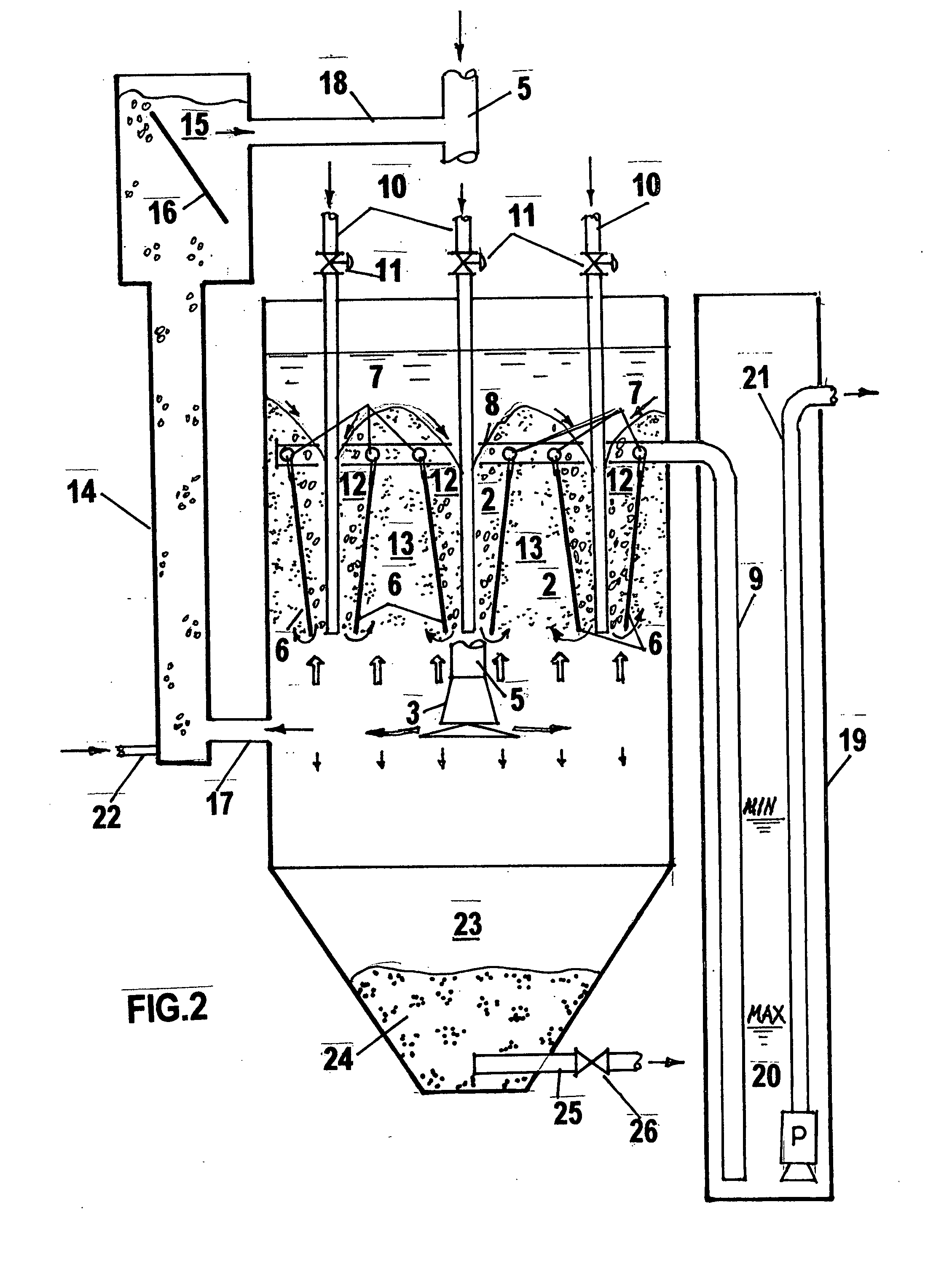
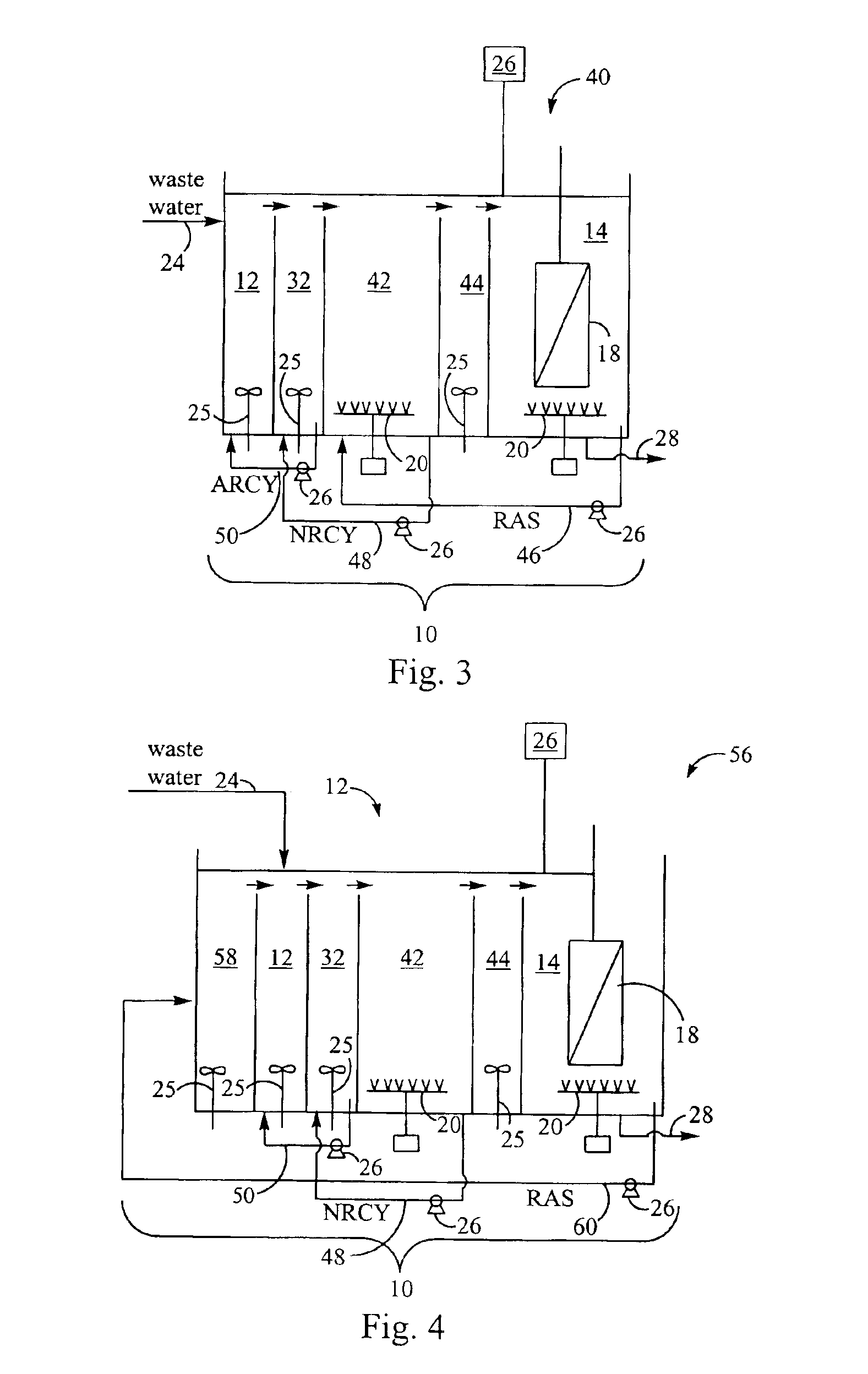
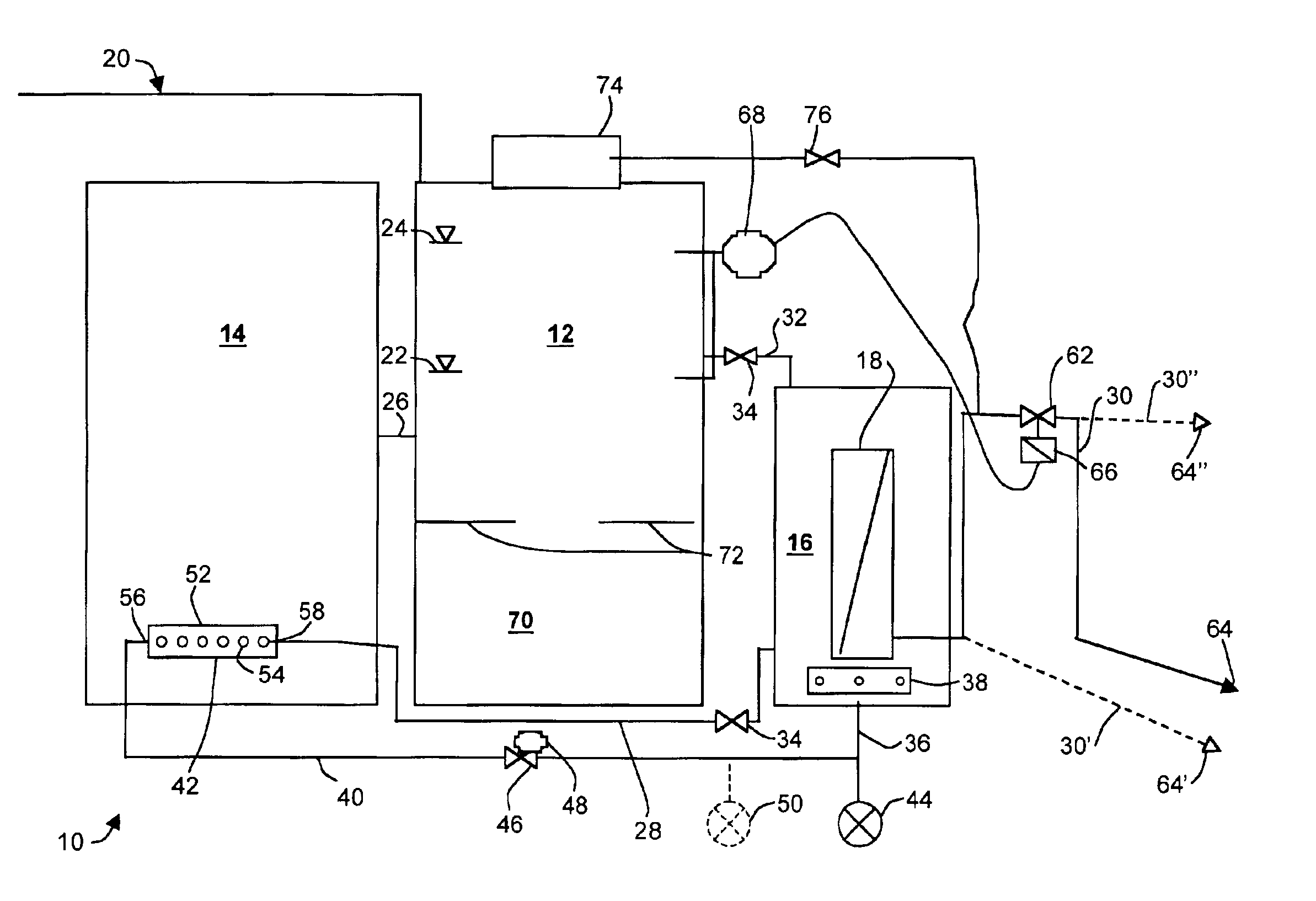
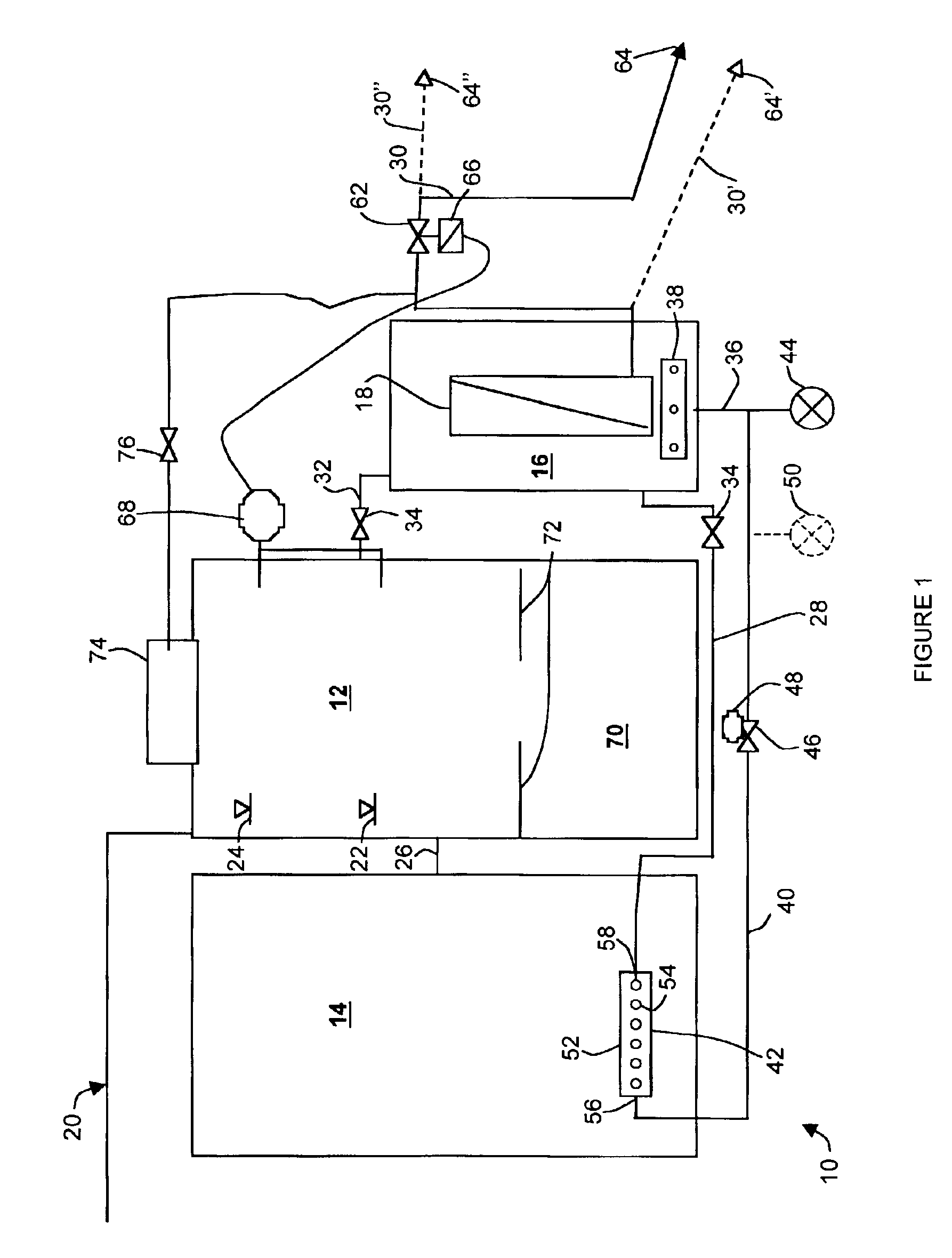
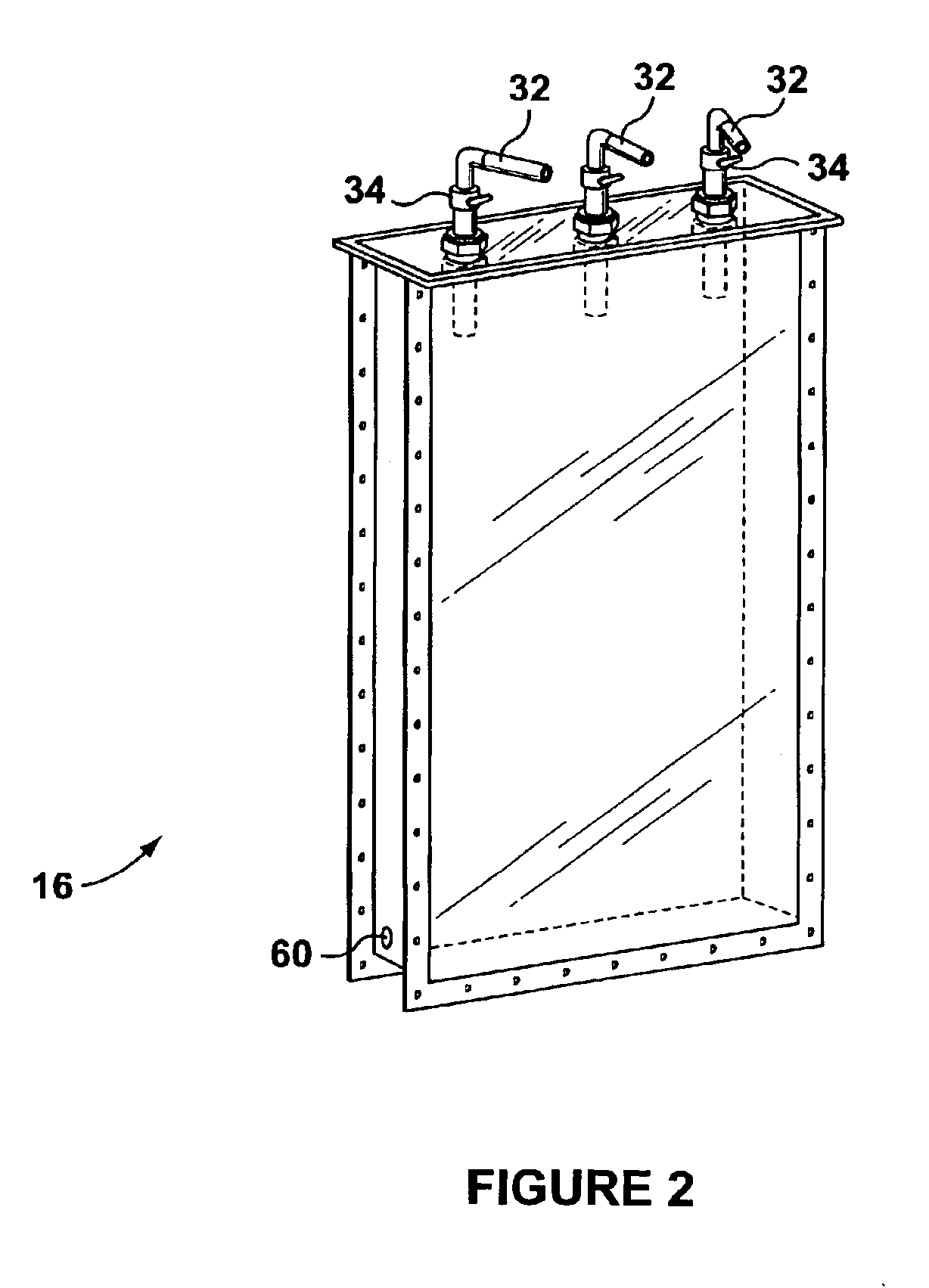
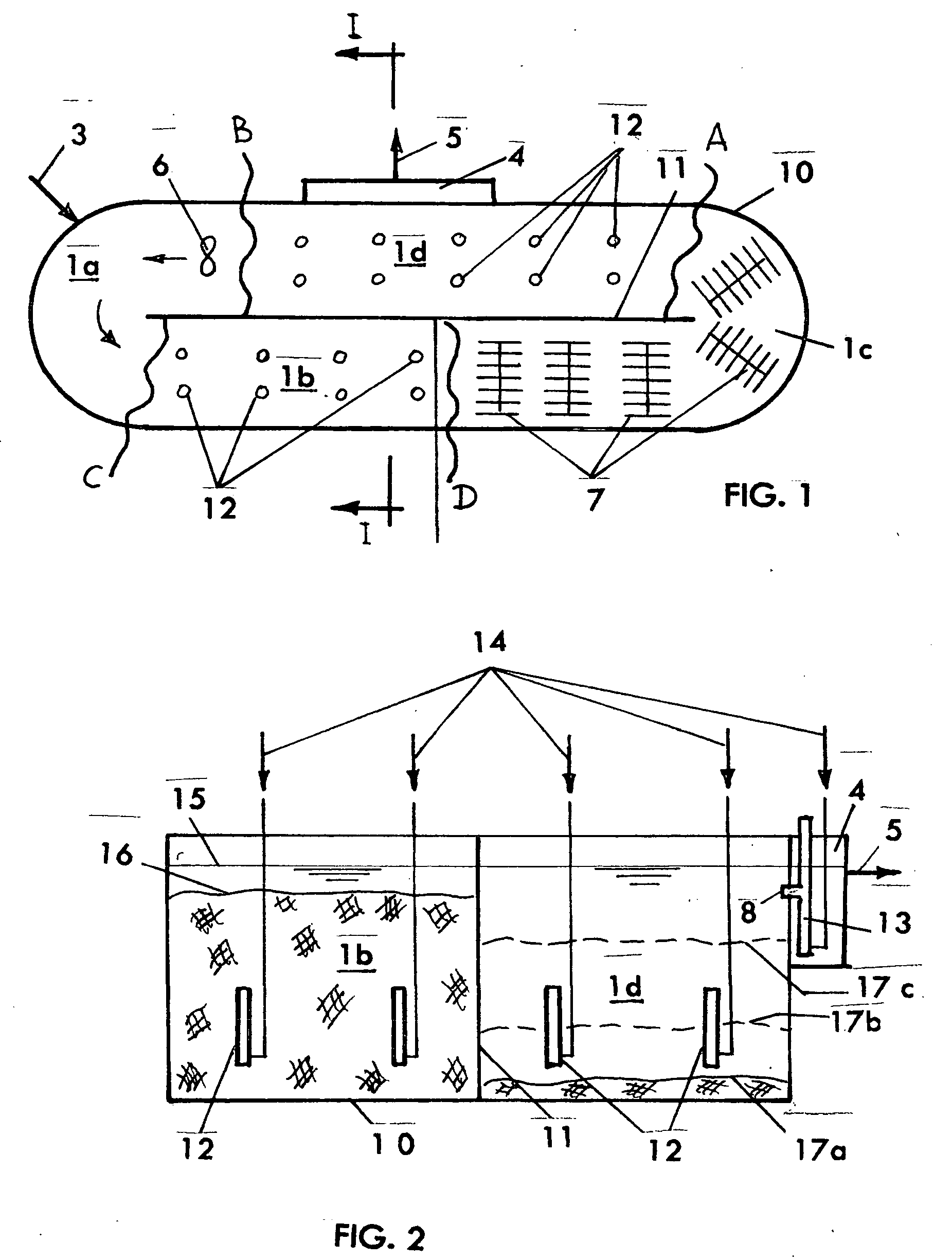
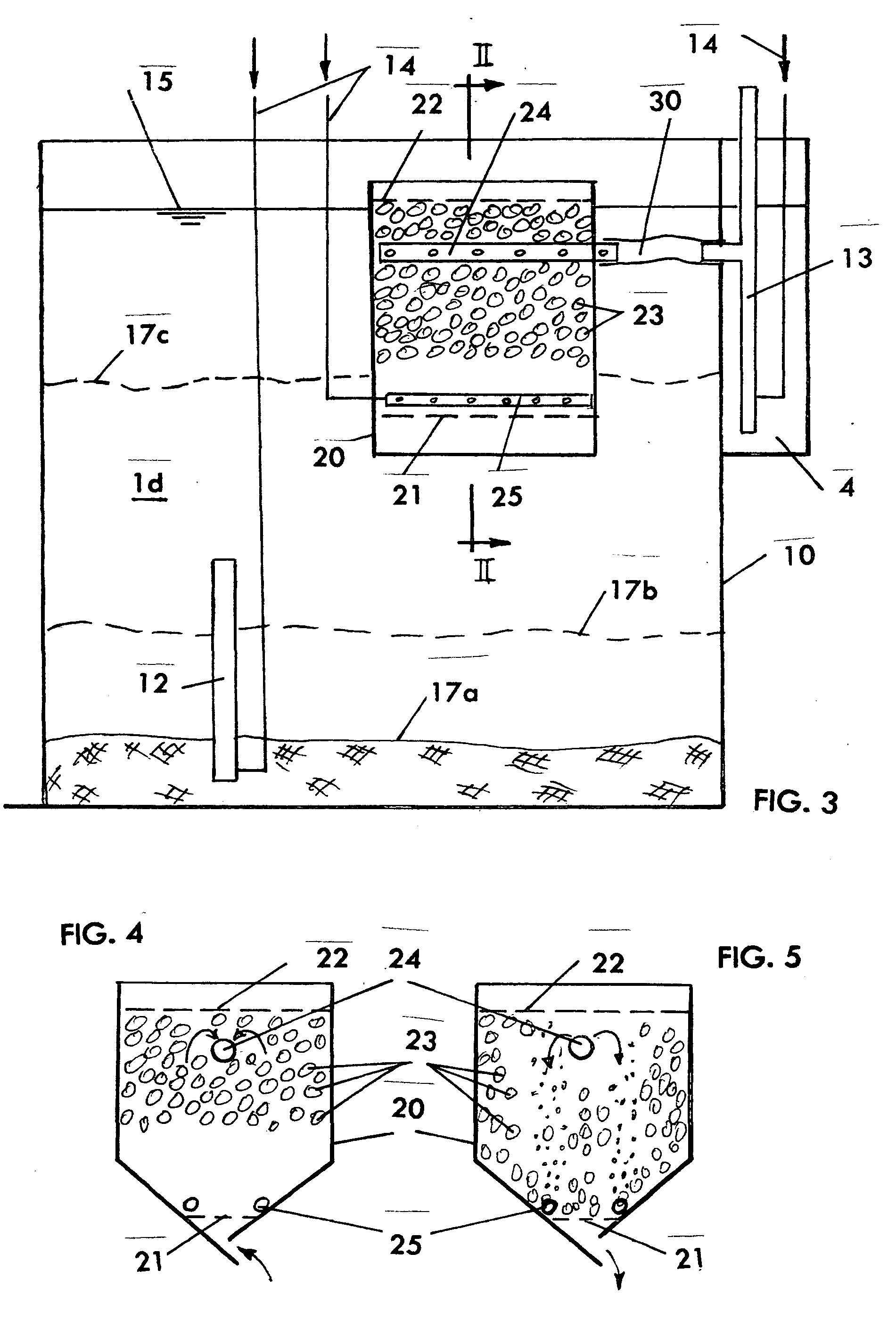
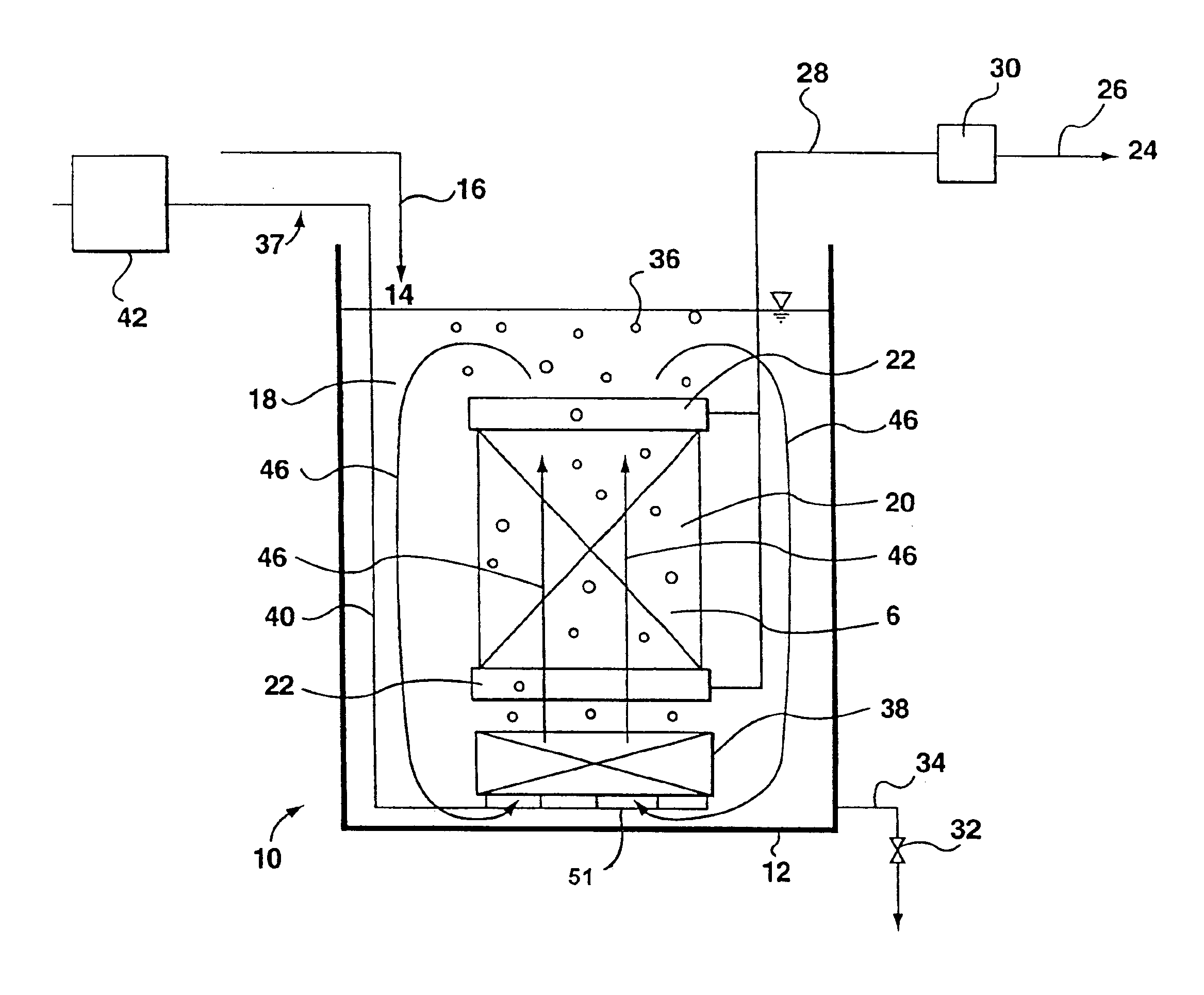
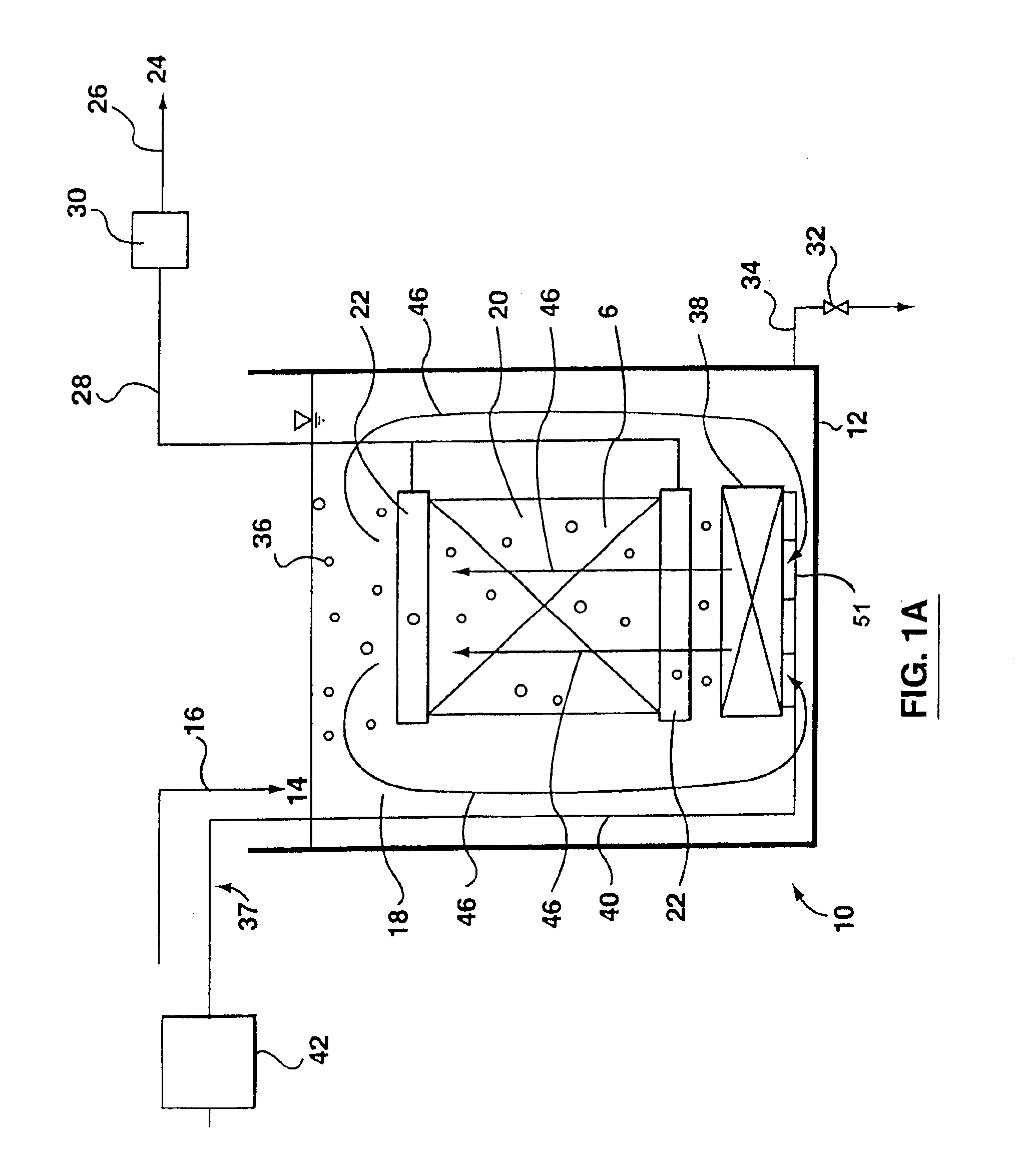
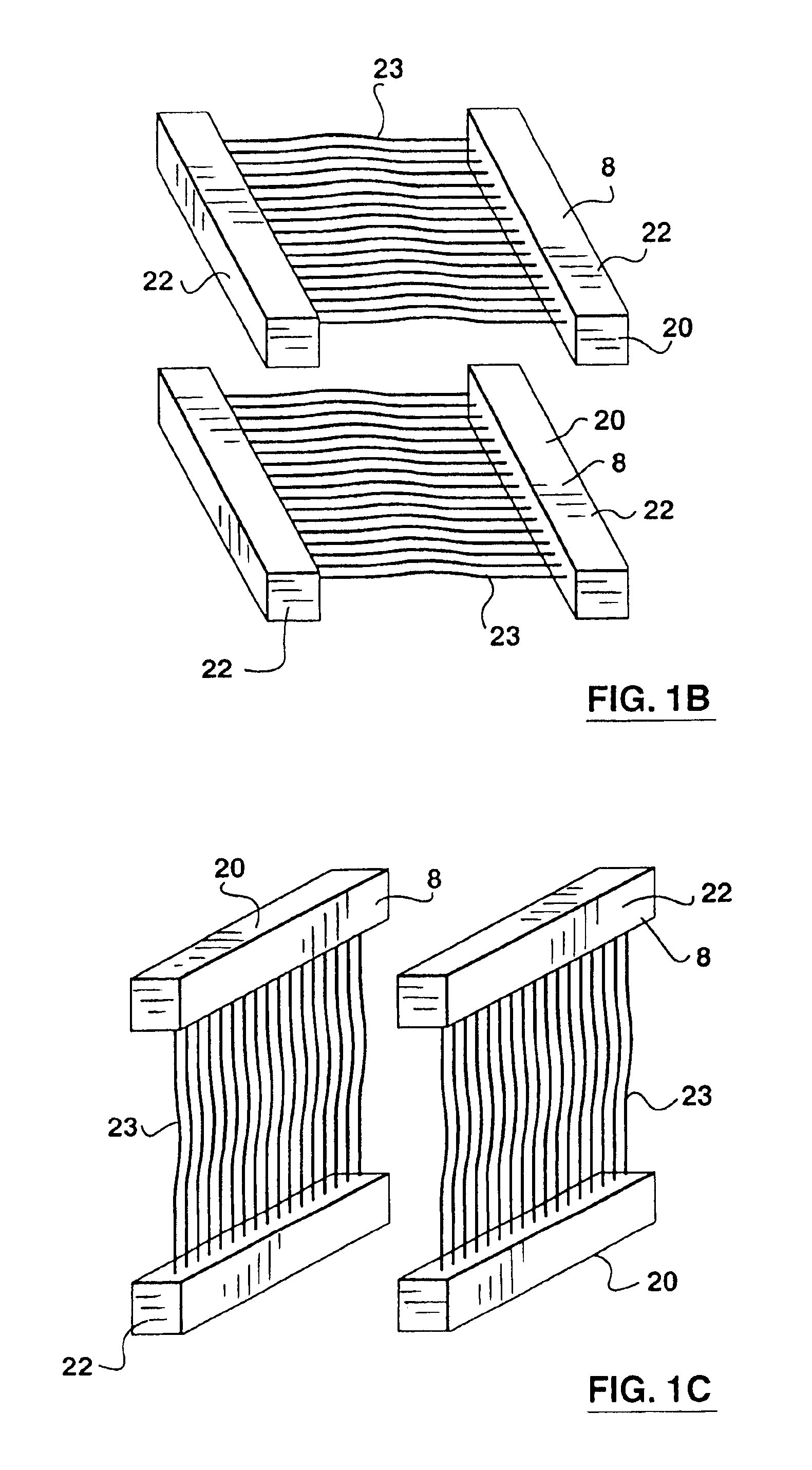
Wastewater treatment system and method
ActiveUS20070209999A1Treatment using aerobic processesTreatment involving filtrationActivated carbonWater treatment system
The invention is directed to a method and apparatus for treating wastewater. The wastewater treatment system includes a bioreactor including activated carbon and a first biological population. The wastewater treatment system may also include a membrane bioreactor and / or a wet oxidation unit.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Integrated closed loop system for industrial water purification
InactiveUS7001519B2Improve purification efficiencyTreatment using aerobic processesWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic matterIndustrial water
The present invention relates to an integrated closed loop system for aquaculture in at least one culturing tank and using continuous bioreactor technology for the biological treatment and removal of organic material, nitrogen and phosphorous, comprising: an integrated, partially or wholly closed loop system for waste water treatment, where the water contains nitrogen containing compounds and / or substances, comprising at least one production unit of such nitrogen containing compounds and / or substances and using continuous bioreactor technology for the biological treatment and removal of organic matter, nitrogen and phosphorous from the said water at continuous flow, comprising: a) at least one suspended carrier bioreactor for bacterial growth under anoxic conditions to cause anaerobic denitrification, with one or several compartments, preceding b) at least one suspended-carrier bioreactor for bacterial growth under oxic conditions to cause aerobic nitrification, c) the denitrification taking place after the production unit, and d) the nitrification taking place prior to the production unit in a by-pass mode as part of the continuous flow.
Owner:GREENFISH
Method for treating wastewater in a membrane bioreactor to produce a low phosphorus effluent
ActiveUS20050045557A1Minimizing space requirementMinimizing attendant costTreatment using aerobic processesOther chemical processesActivated sludgeMembrane bioreactor
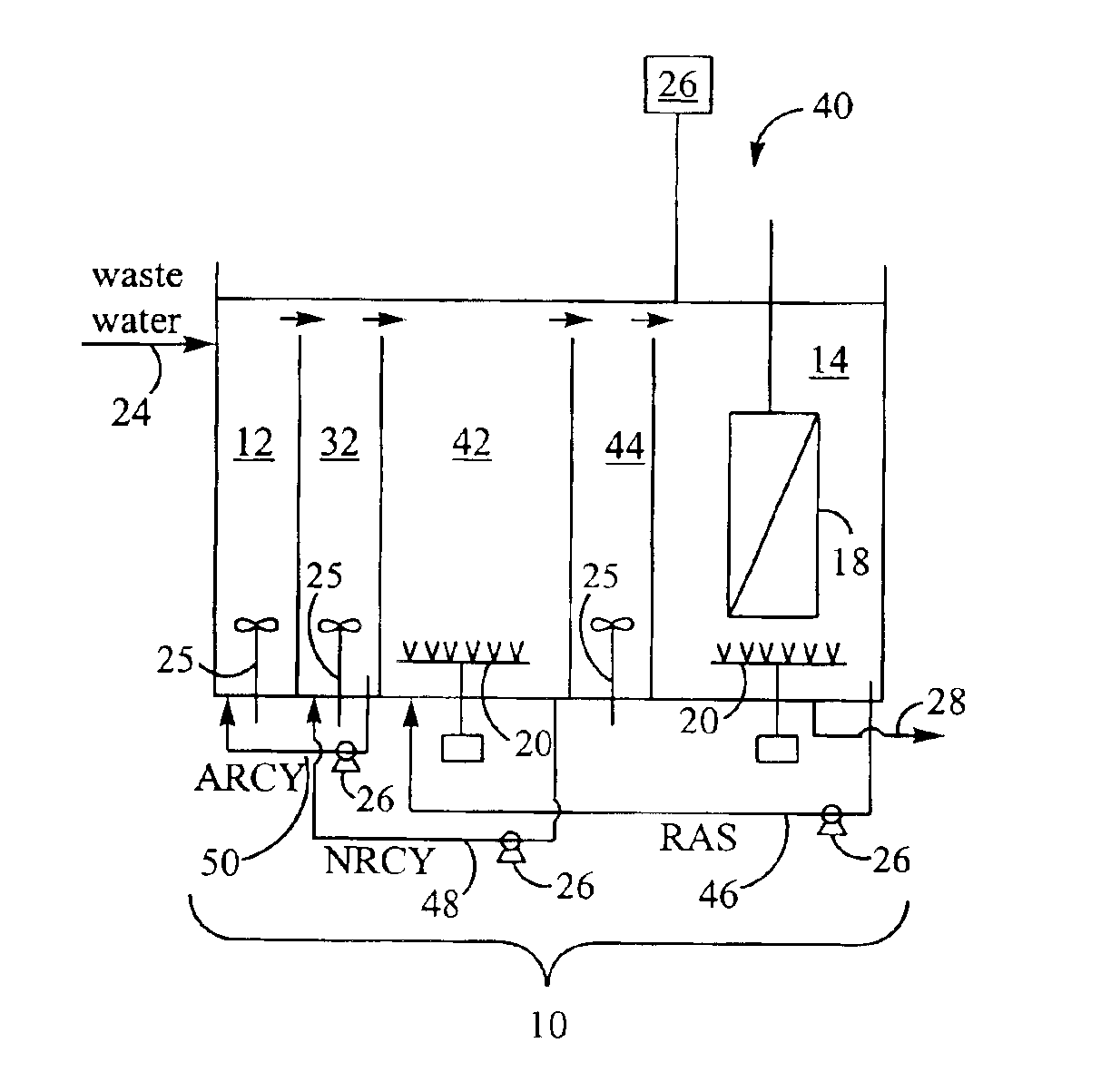
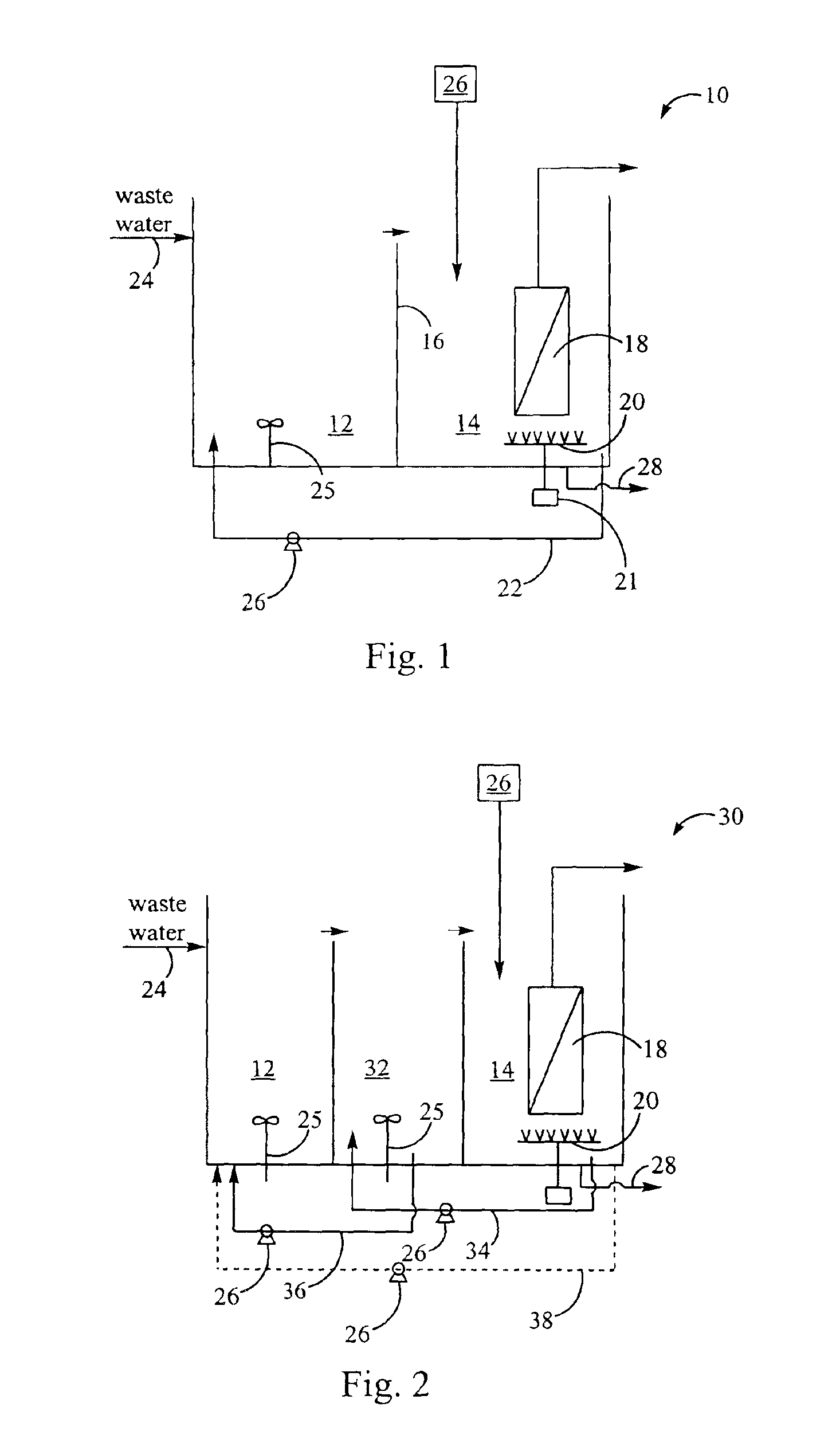
Removal of biological nutrients from a wastewater yielding a low phosphorous (e.g., less than 0.25 mg / L) output includes providing a serial multistage bioreactor containing activated sludge having in hydraulic series an anaerobic zone and a downstream aerobic zone, with each zone having an upstream inlet and a downstream outlet. The wastewater is provided to the anaerobic zone inlet. A quantity of chemical sufficient to precipitate soluble and particulate phosphorous is added to the downstream aerobic zone in an amount sufficient to yield a low phosphorous output. Treated water is separated from the activated sludge and precipitated phosphorous and a return activated sludge separated from the treated water is recycled to the anaerobic zone.
Owner:CH2M HILL
Polytopic multiplex holography
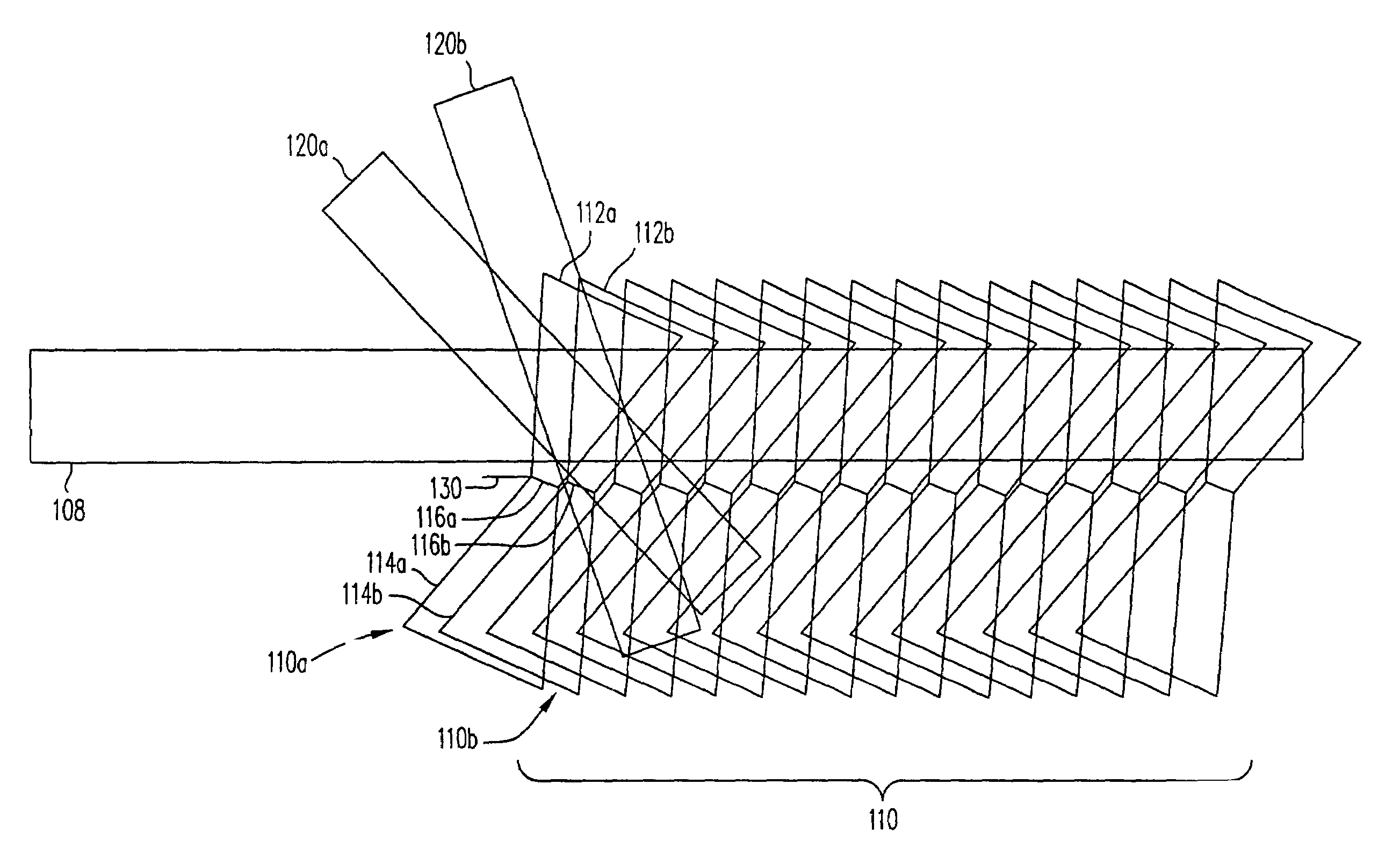
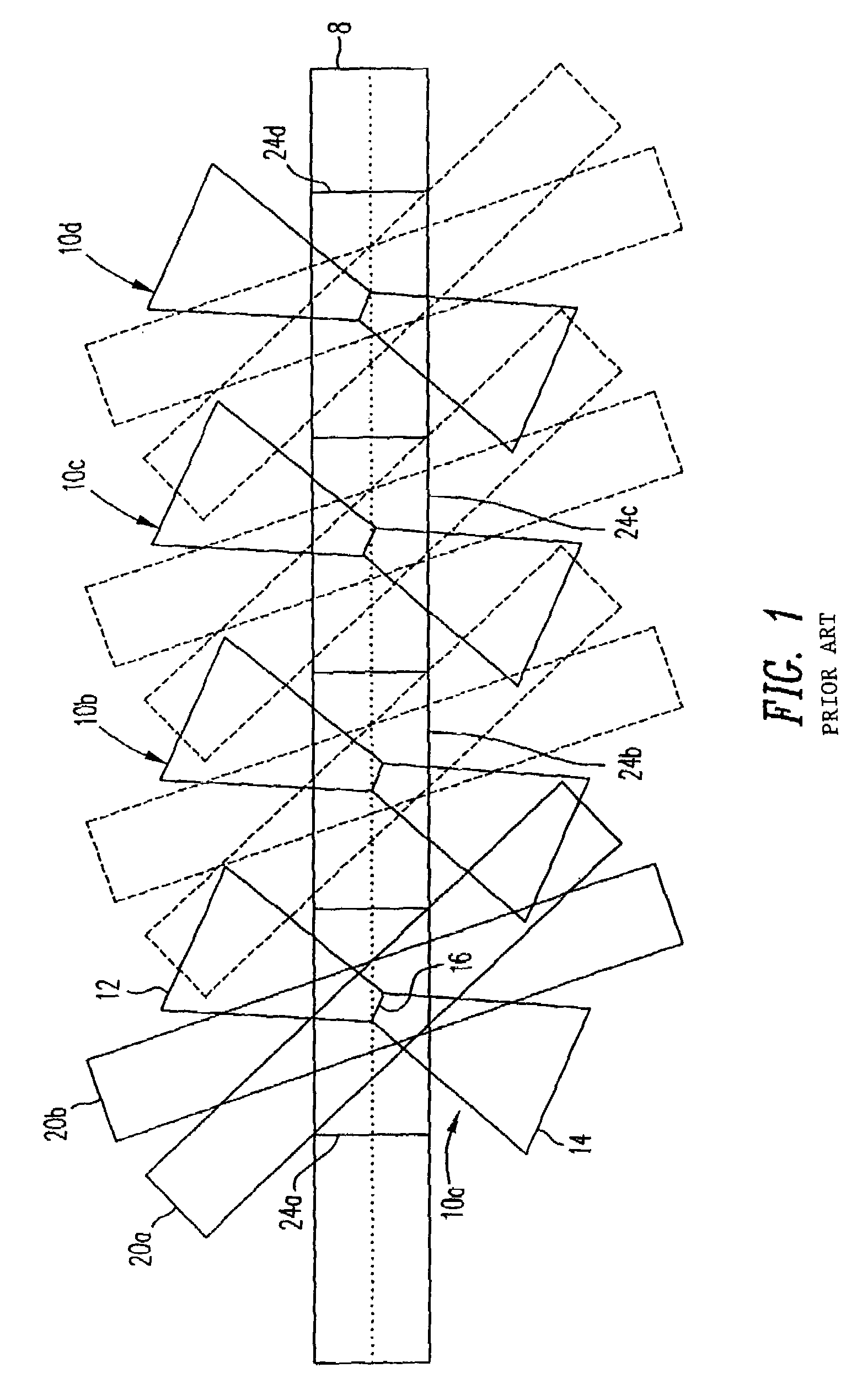
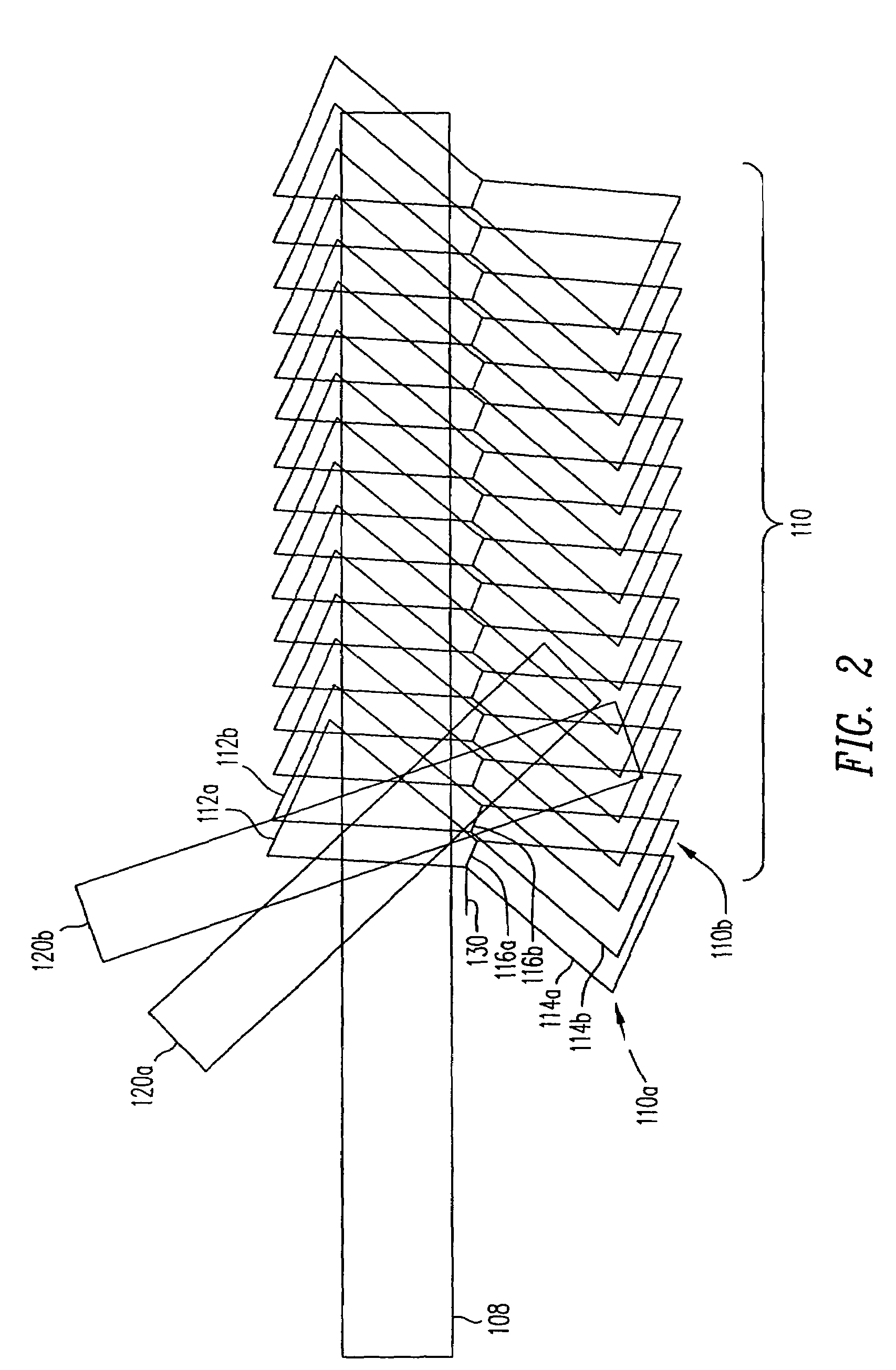
ActiveUS7092133B2Treatment using aerobic processesTransportation and packagingMultiplexingLight beam
Disclosed is a multiplexing method and apparatus that allows holograms to be spatially multiplexed with partial spatial overlap between neighboring stacks of holograms. Each individual stack can additionally take full advantage of an alternate multiplexing scheme such as angle, wavelength, phase code, peristrophic, or fractal multiplexing, for example. An amount equal to the beam waist of the signal beam writing a hologram separates individual stacks of holograms. Upon reconstruction, a hologram and its neighbors will all be readout simultaneously. An filter is placed at the beam waist of the reconstructed data such that the neighbors that are read out are not transmitted to the camera plane. Alternatively, these unwanted reconstructions can be filtered out with an angular filter at an intermediate plane in the optical system that has a limited angular passband.
Owner:AKONIA HOLOGRAPHICS
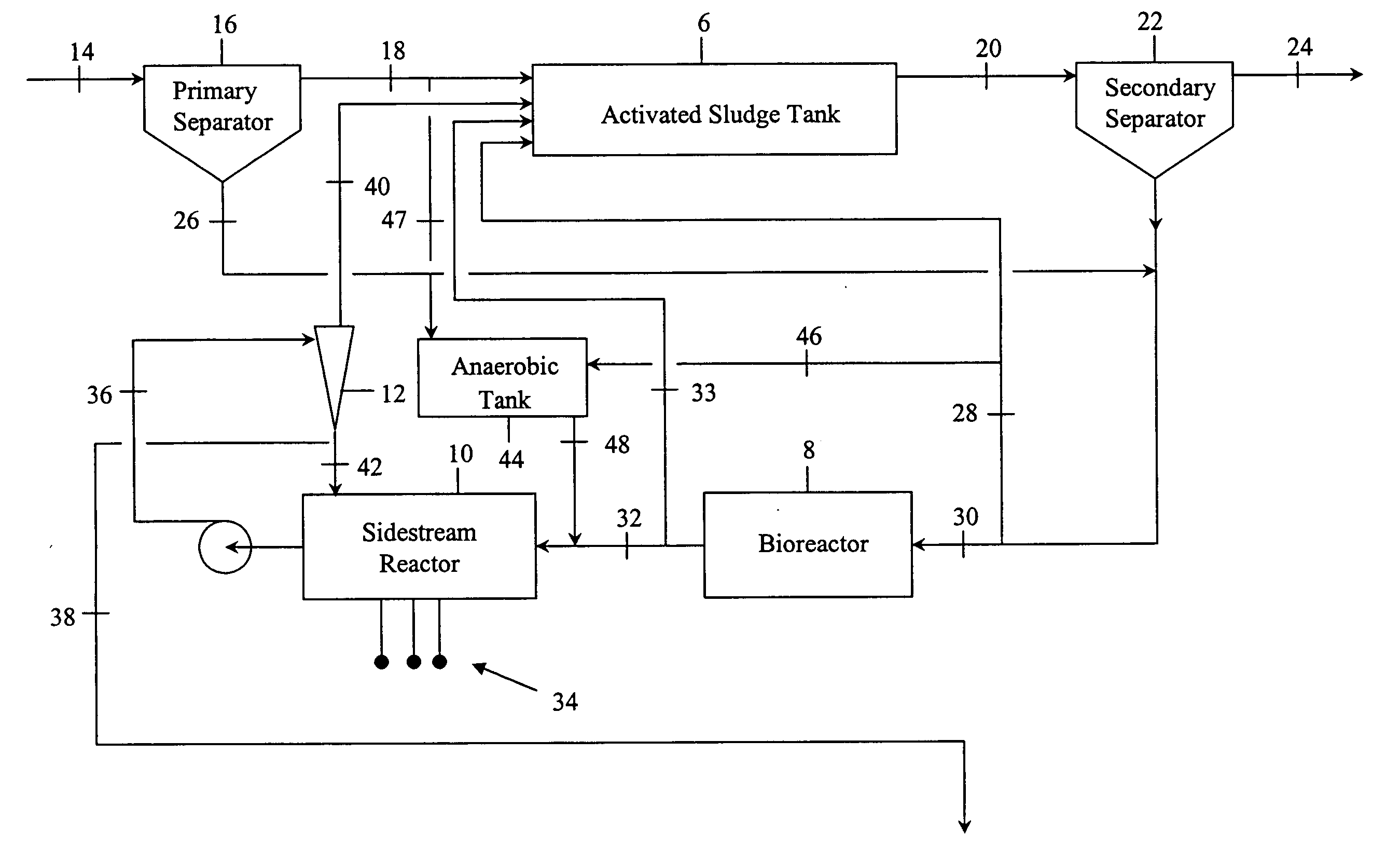
Process to enhance phosphorus removal for activated sludge wastewater treatment systems
InactiveUS20070000836A1Water/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationWater treatment parameter controlActivated sludgePhosphate
Contaminated wastewaters comprising biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), nitrogen and phosphorus are treated by an activated sludge process. The process utilizes an activated sludge tank, a solid-liquid separator, and a bioreactor to significantly reduce, or eliminate, waste activated sludge (WAS) within a sludge stream. A sidestream reactor is employed downstream from the bioreactor to remove soluble phosphates left in the sludge stream by the low WAS process. Within the sidestream reactor, a source of multivalent metal ions is added to a slightly alkaline sludge stream to precipitate the phosphates. The solid phosphates have a specific gravity higher than that of the organic matter in the sludge stream and may be separated from the sludge stream based upon differential settling velocity.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
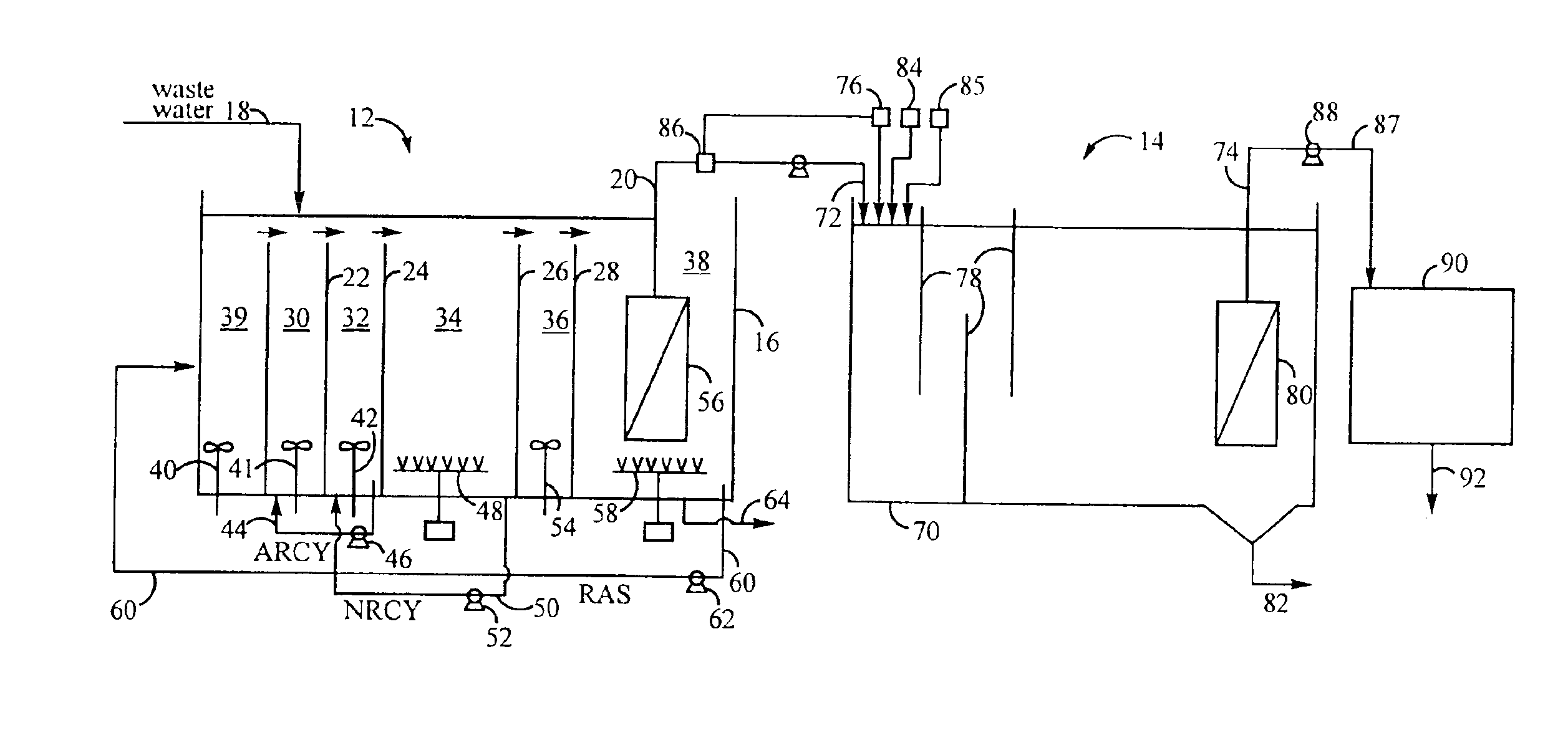
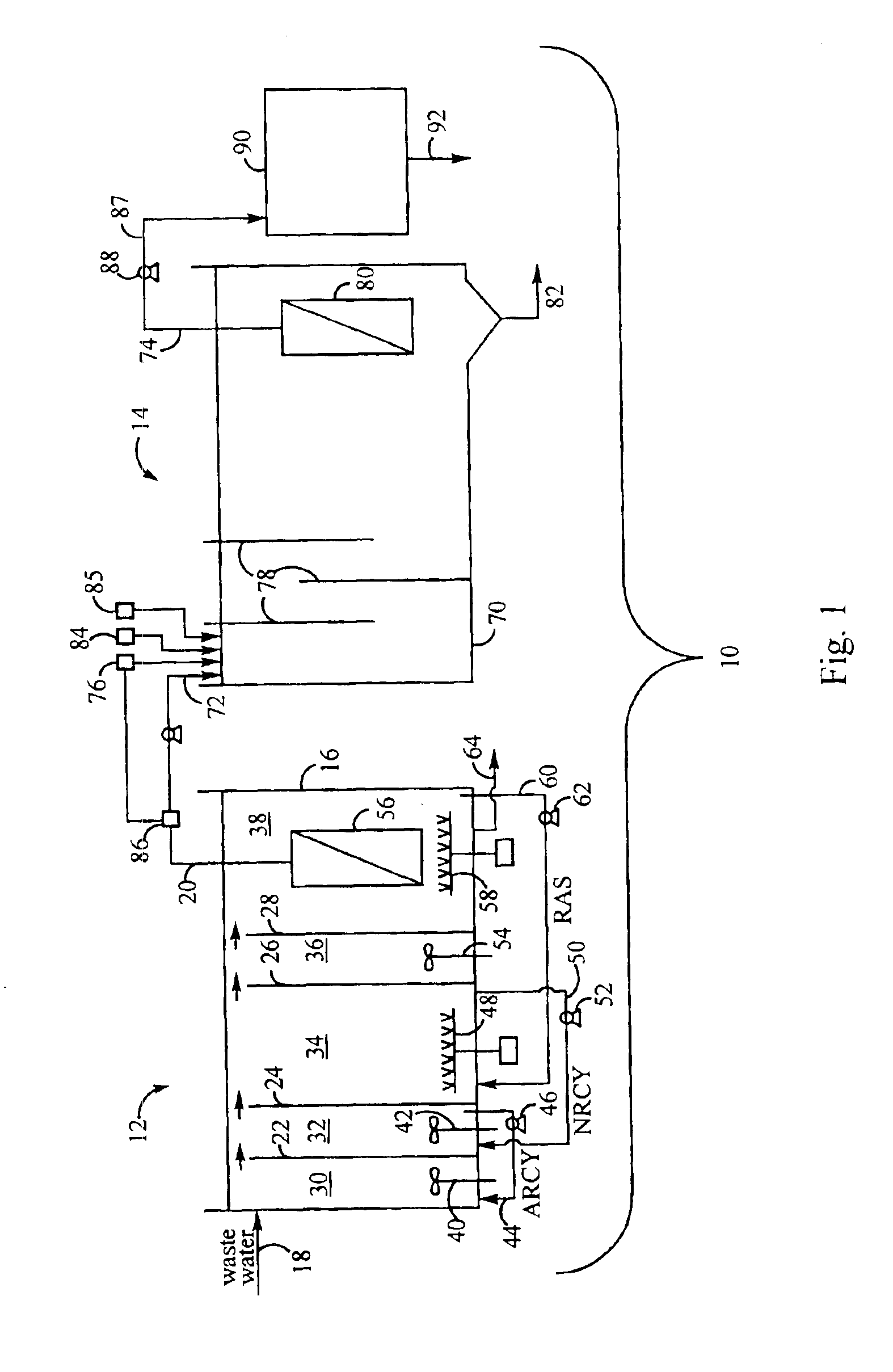
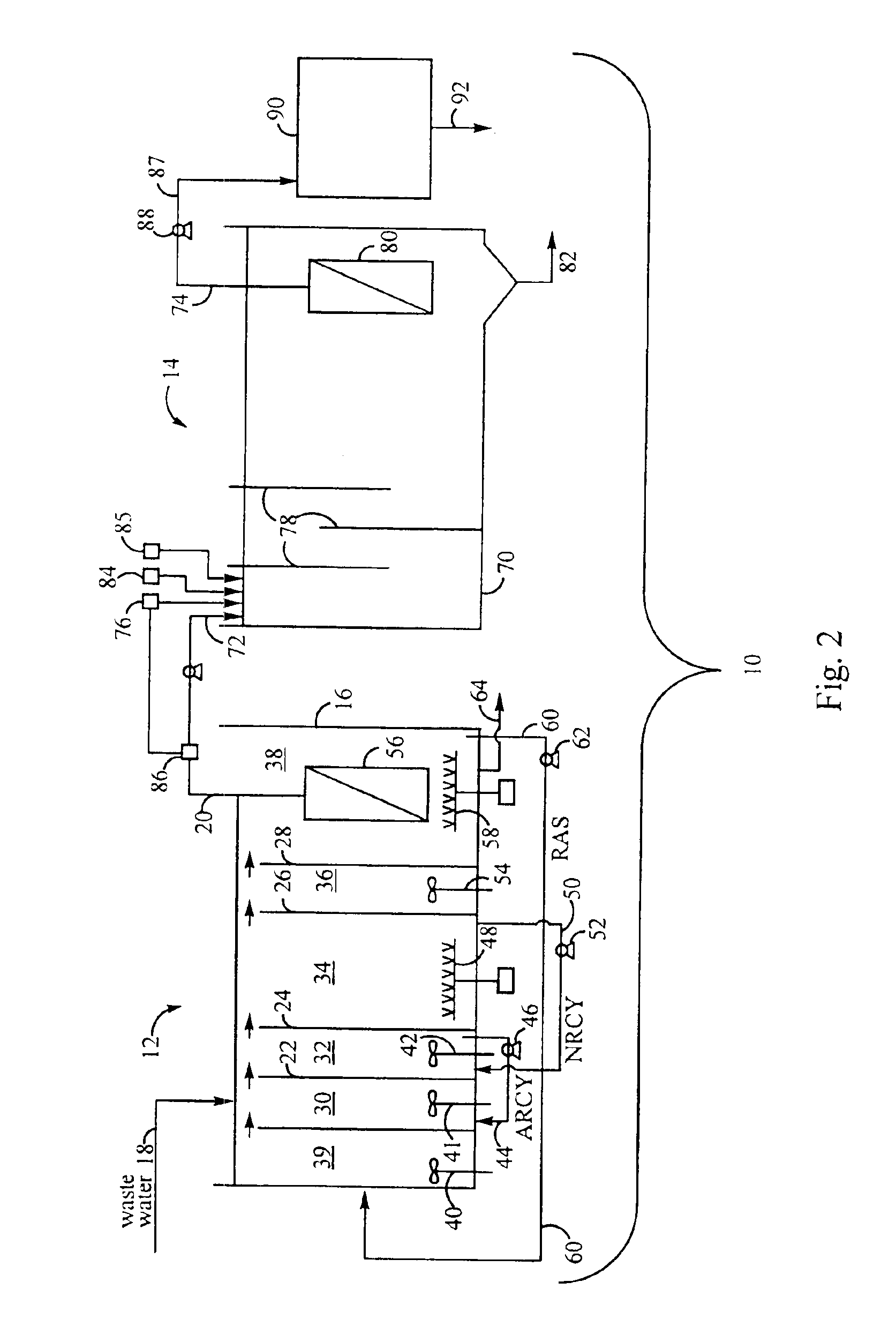
Treatment of wastewater containing phosphorous and nitrogen
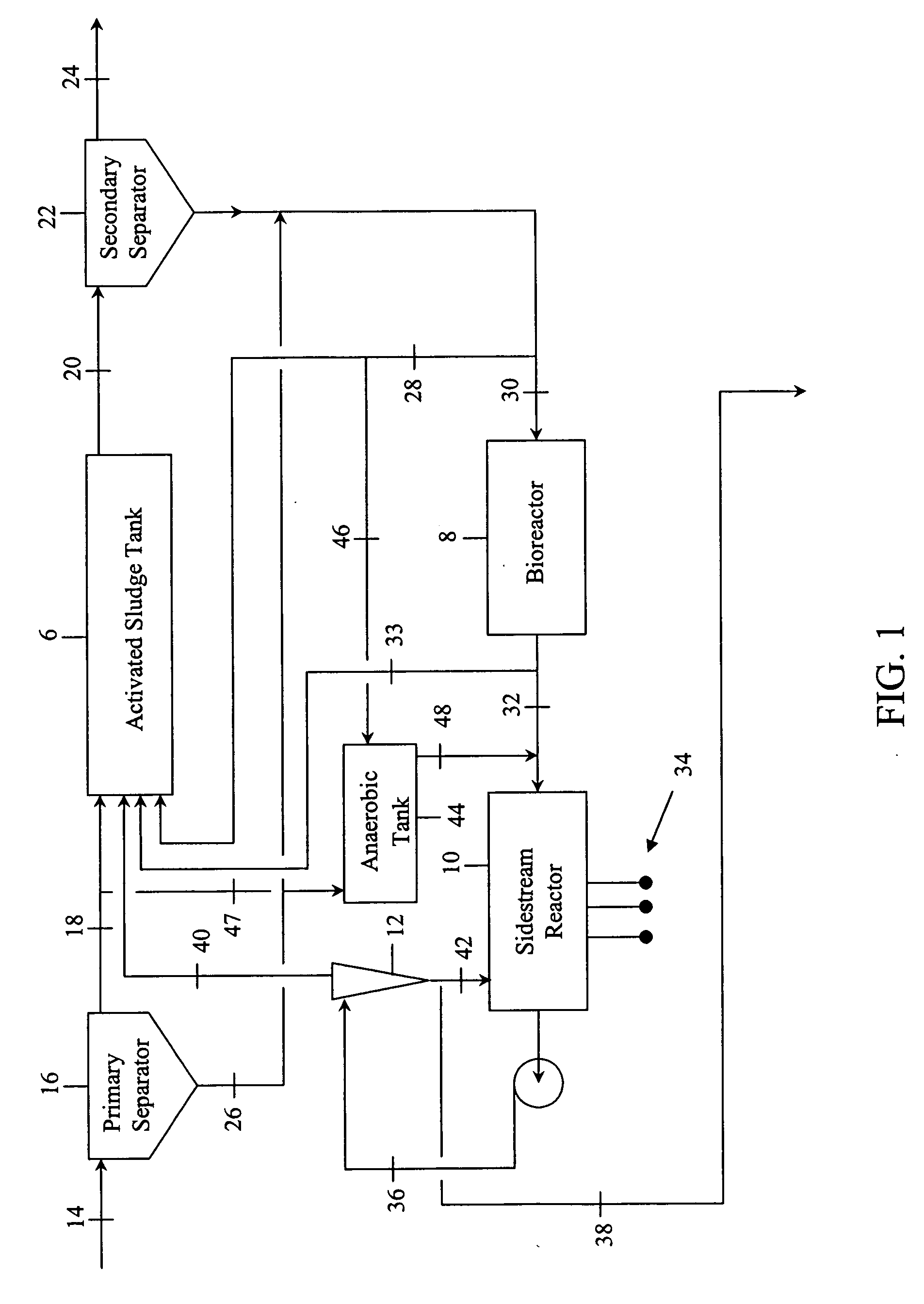
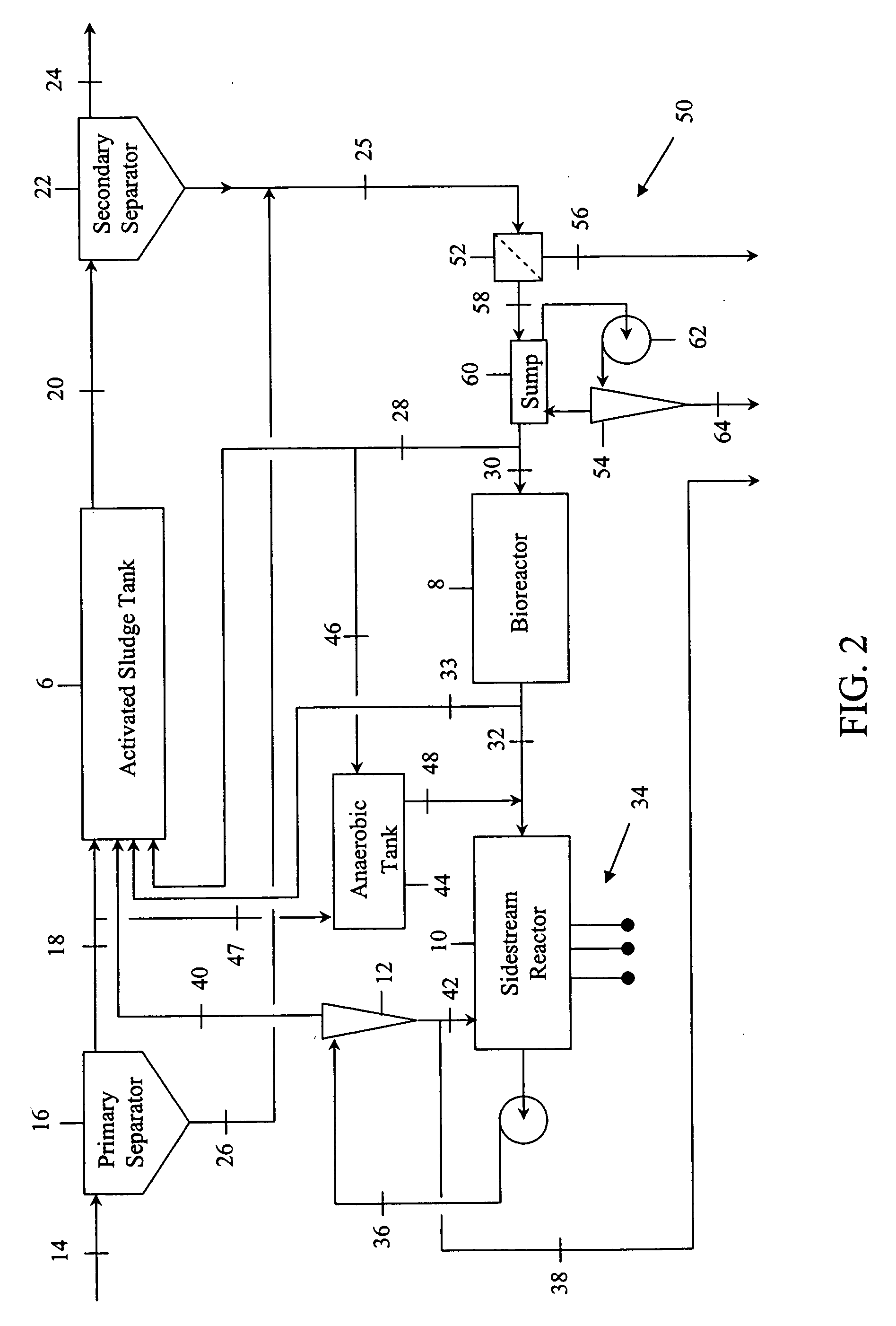
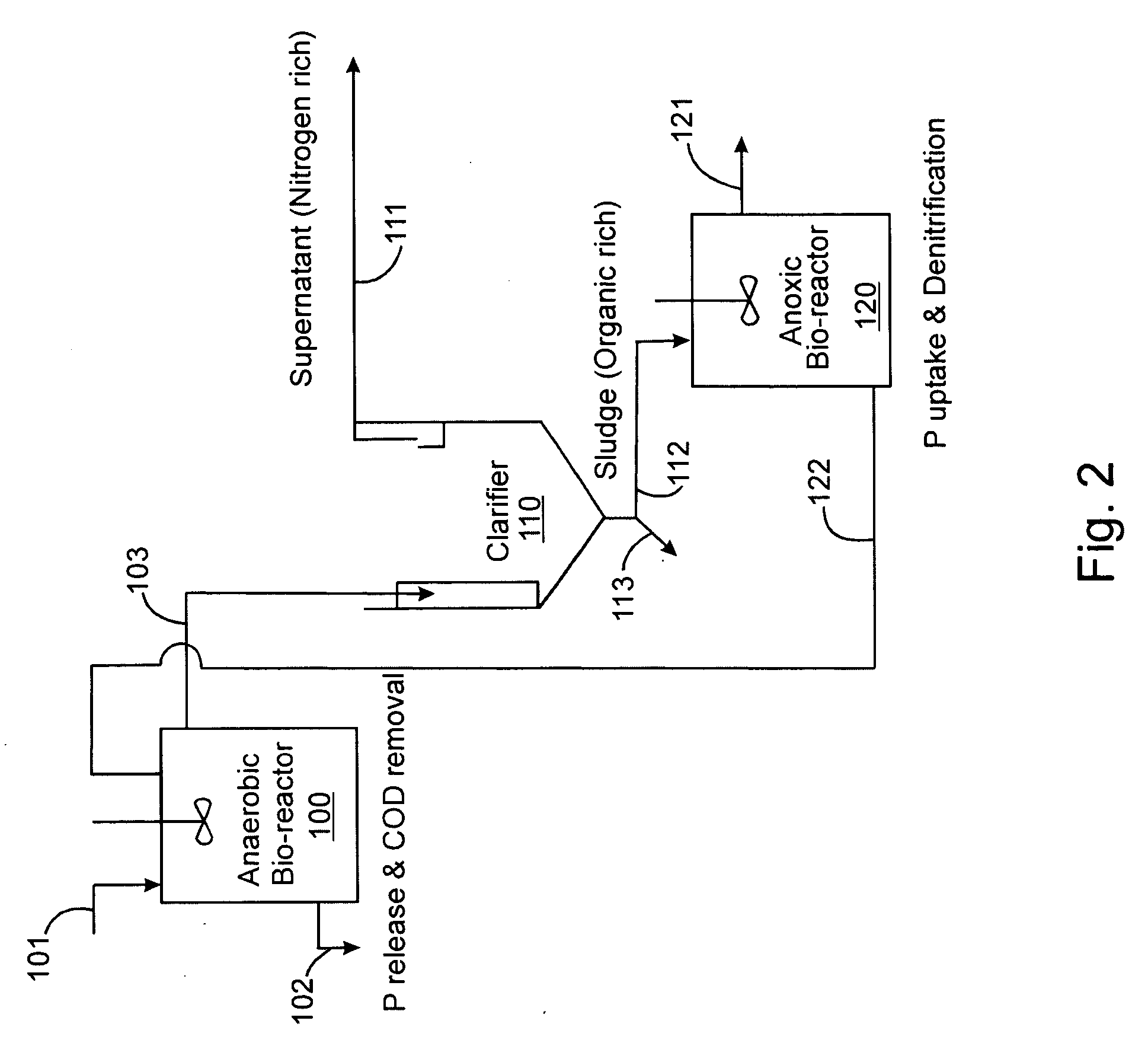
InactiveUS20060249449A1Great extent of P releaseHigh P uptakeTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesOxygenClarifier
A method and process for the treatment of wastewater containing phosphorous and nitrogen. The wastewater is first anaerobically treated to produce an anaerobic effluent from which insoluble organic carbon is separated to form a sludge rich in organic carbon that is used as a substrate during anoxic treatment of the wastewater by de-nitrifying phosphorous accumulating organisms (DPAO's) and ordinary de-nitrifying organisms. The separation of insoluble organic carbon is normally conducted using a clarifier located intermediate the anaerobic and anoxic bio-reactors. In one embodiment, the ammonia rich clarifier supernatant is directed to an aerobic reactor for nitrification and the nitrate produced is recycled to the anoxic bio-reactor. The final effluent may be membrane filtered to retain nitrifying biomass within the aerobic bio-reactor. The invention reduces overall hydraulic residence time and sludge volume, which results in a smaller, less expensive wastewater treatment system.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
Zero excess sludge membrane bioreactor
InactiveUS20050194310A1High yieldAcceptable levelTreatment using aerobic processesDialysis systemsChemical oxygen demandTotal nitrogen
An inclined plate coupled membrane bioreactor for treating feed water having excessive level of nutrients in particular chemical oxygen demand and total nitrogen and suspended solids has an aerobic bioreactor for nitrification and aerobic biodegradation in which membranes are submerged for permeate extraction, and an anoxic bioreactor for denitrification within which the inclined plates are outfitted to confine as much anoxic sludge as possible. An air oxygenating and an air scouring are continuously provided to the aerobic bioreactor to maintain a desired aerobic environment and to mitigate membrane fouling while an intermittent air blowing is provided to the anoxic bioreactor to blow out gaseous content generated through denitrification and to rectify the uniformed flow along the inclined plates. The aerobic sludge is recycled to the lower compartment of anoxic bioreactor and the supernatant of anoxic bioreactor is collected as weir effluent and delivered to the downstream aerobic bioreactor. Permeate is intermittently extracted from the membranes by a suction pump. There is no excess sludge withdrawn from the inclined plate coupled membrane bioreactor throughout the experiment.
Owner:YAMAMOTO KAZUO +1
Process to produce biofuels from biomass
Biofuels can be produced by: (i) providing a biomass containing celluloses, hemicelluloses, lignin, nitrogen compounds and sulfur compounds; (ii) removing sulfur compounds and nitrogen compounds from the biomass by contacting the biomass with a digestive solvent to form a pretreated biomass containing carbohydrates and having less than 35% of the sulfur content and less than 35% of the nitrogen content of untreated biomass on a dry mass basis; (iii) contacting the pretreated biomass directly with hydrogen in the presence of a hydrogenolysis catalyst to form a plurality of oxygenated intermediates, and (vi) processing at least a portion of the oxygenated intermediates to form a liquid fuel.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Method and system for nitrifying and denitrifying wastewater
ActiveUS7147778B1Reducing and minimizing dissolved oxygen concentrationReduces and minimizes dissolved oxygen concentrationTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesActivated sludgeOxygen
A wastewater treatment system is provided that includes first and second reactors, each operative to nitrify or denitrify wastewater contained therein. Downstream from the first and second reactors is a membrane reactor that operates under aerobic conditions and includes one or more submersed membranes for separating solids. Extending between the membrane reactor and each of the first and second reactors is a return activated sludge line with appropriate controls for permitting return activated sludge to be directed to one of the reactors at a time. To nitrify and denitrify wastewater, a wastewater influent stream is alternatively directed to the anoxic reactors which are alternatively operated under aerobic and anoxic conditions so as to nitrify or denitrify the wastewater contained therein. To reduce or minimize the dissolved oxygen return from the membrane reactor to the first and second reactors, the flow of return activated sludge is controlled such that generally return activated sludge is returned to the reactor operating under aerobic conditions.
Owner:KRUGER I INC
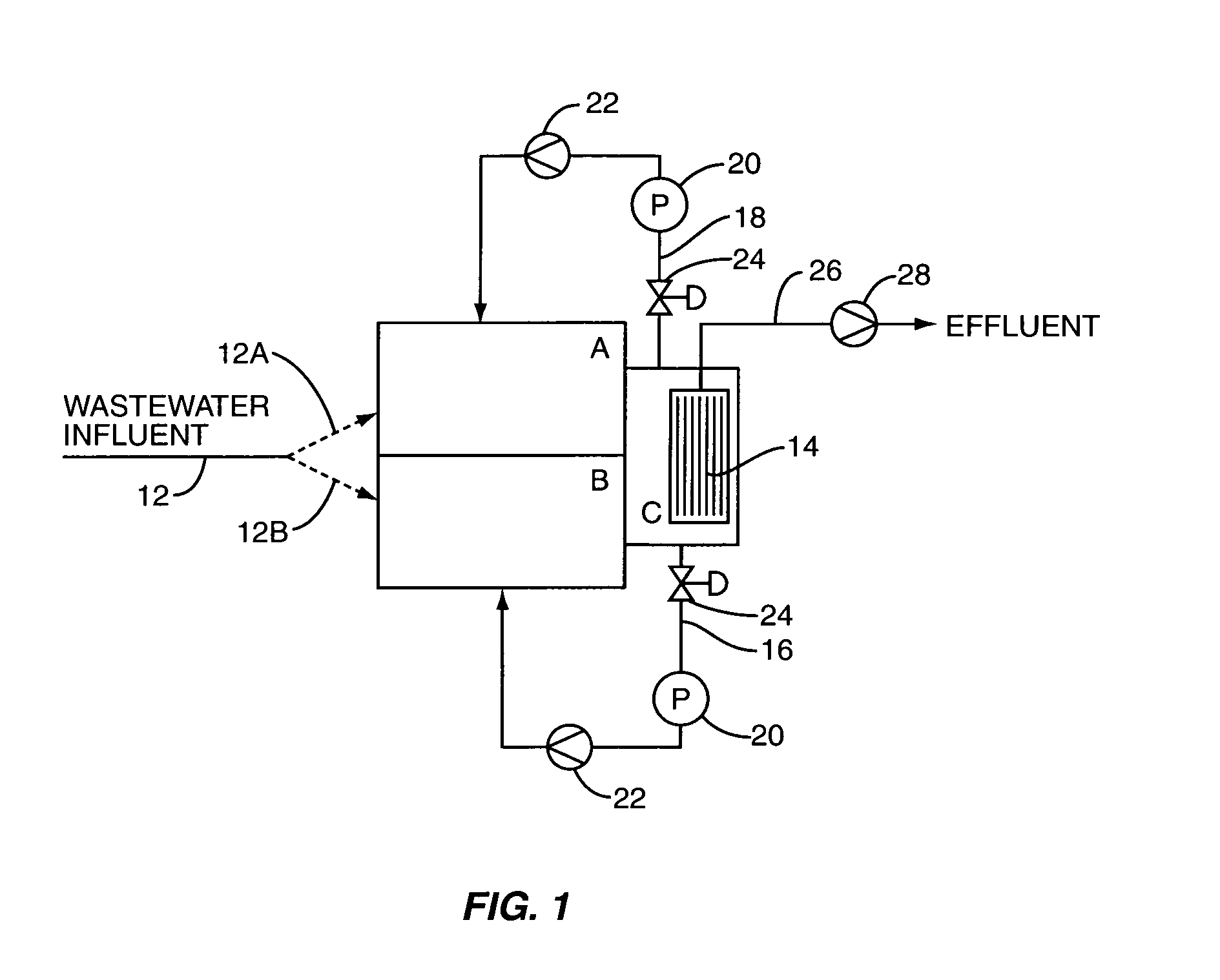
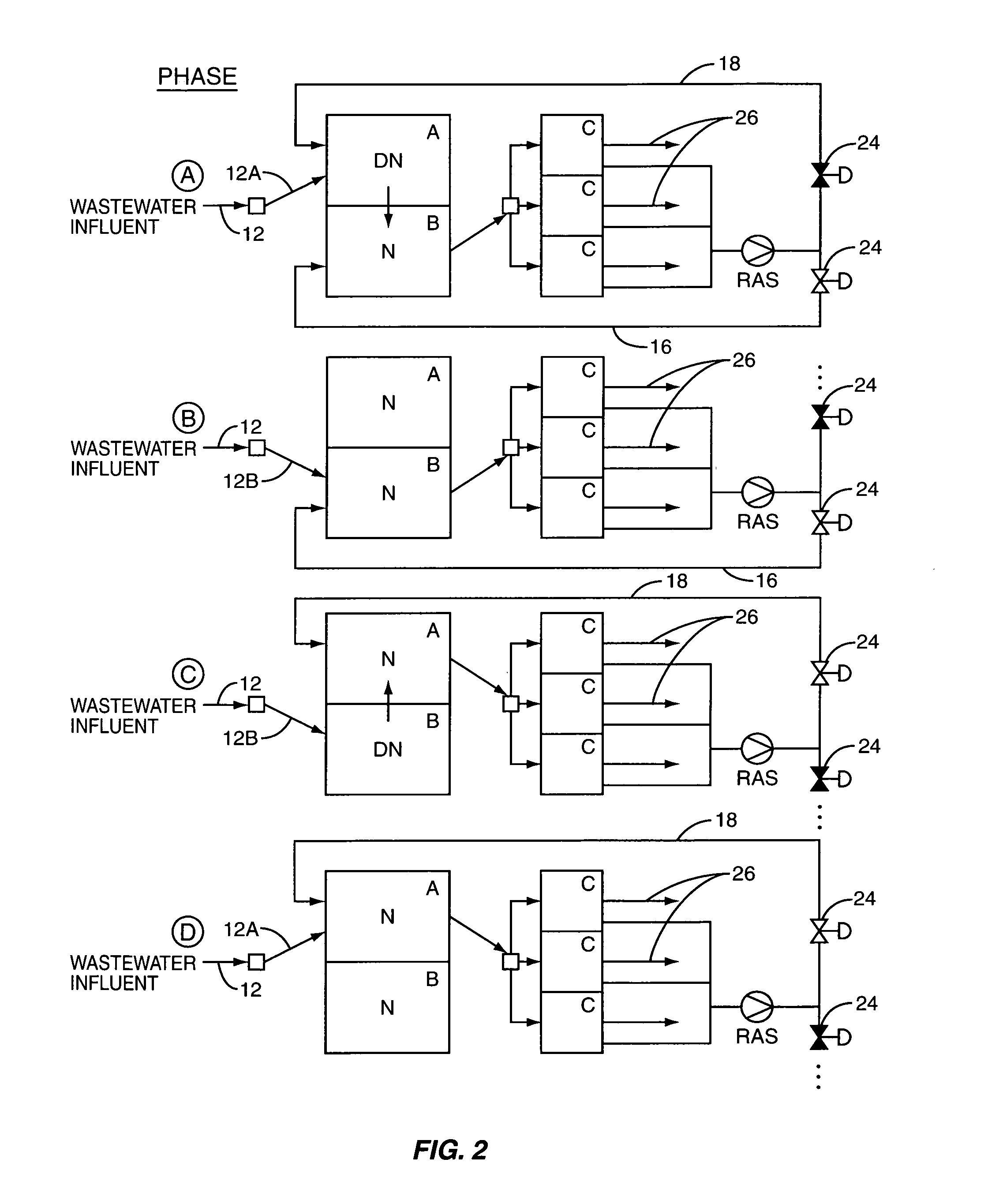
Apparatus for oxygenating wastewater
InactiveUS7008535B1Easy to assembleEasy to cleanTreatment using aerobic processesFlow mixersForming gasWastewater
A method and apparatus creates gas-enriched fluid that is used to treat wastewater. In one embodiment, the wastewater is withdrawn from a supply of wastewater to be treated, and the wastewater is delivered in an atomized manner to a vessel pressurized with gas to form gas-enriched wastewater. The gas-enriched wastewater is then delivered to the supply of wastewater to be treated.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV +1
Method and apparatus for treating wastewater using membrane filters
InactiveUS6863818B2Good removal effectEfficient workTreatment using aerobic processesBiological treatment regulationActivated sludgeBioreactor
An apparatus using activated sludge for the removal of biological nutrients from a wastewater includes a bioreactor for containing a mixture of wastewater under treatment and activated sludge. The bioreactor is divided into a plurality of serially connected treatment zones and includes a wastewater inlet, a downstream aerobic zone and an upstream aerobic zone between the wastewater inlet and the downstream aerobic zone, the upstream and downstream aerobic zones being separated by an anoxic zone. A method for removal of nutrients from a wastewater includes providing a wastewater to an inlet of a serial, multi-zone, activated sludge bioreactor containing an activated sludge. The bioreactor has a downstream aerobic zone from which water is removed and an upstream aerobic zone between the wastewater inlet and the downstream aerobic zone, the upstream and downstream aerobic zones being separated by an anoxic zone.
Owner:CH2M HILL
Membrane coupled activated sludge method and apparatus operating anoxic/anaerobic process alternately for removal of nitrogen and phosphorous
ActiveUS20070108125A1Quality improvementSimple processTreatment using aerobic processesMixing methodsActivated sludgeNitrogen
Disclosed are a membrane coupled activated sludge method and apparatus operating anoxic / anaerobic processes alternately for removal of nitrogen and phosporus, wherein nitrogen and phosphorous together with organics in the sewage, wastewater, filthy water etc. can be simultaneously removed with an economic and efficient manner, an operation thereof is easy and efficient, a capacity thereof is high and the method is economic due to the reduced operating costs with performing measurement and control of a recycle rate, a recycle time of alternate operation of the anoxic and anaerobic process, an amount of sludge, an amount of aeration and an operation of a blower for an intermittent membrane cleaning.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for treatment of wastewater employing membrane bioreactors
InactiveUS6805806B2Accelerates the biodegradation processAvoid cloggingLiquid separation auxillary apparatusTreatment using aerobic processesAeration systemFiltration
Methods and apparatus employing membrane filtration in biodegradation processes for treatment of wastewater are described. A bioreactor system is described having an equalization system, a membrane bioreactor system, and a controller. Aeration systems for a membrane bioreactor, such as a mixer, and an ultrafilter subsystem are also described, as is a rotary membrane ultrafilter.
Owner:HYDROTREAT
Integrated closed loop system for industrial water purification
InactiveUS20050061737A1Small surface areaIncreasing biofilm thicknessTreatment using aerobic processesWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic matterIndustrial water
The present invention relates to an integrated closed loop system for aquaculture in at least one culturing tank and using continuous bioreactor technology for the biological treatment and removal of organic material, nitrogen and phosphorous, comprising: an integrated, partially or wholly closed loop system for waste water treatment, where the water contains nitrogen containing compounds and / or substances, comprising at least one production unit of such nitrogen containing compounds and / or substances and using continuous bioreactor technology for the biological treatment and removal of organic matter, nitrogen and phosphorous from the said water at continuous flow, comprising: a) at least one suspended carrier bioreactor for bacterial growth under anoxic conditions to cause anaerobic denitrification, with one or several compartments, preceding b) at least one suspended-carrier bioreactor for bacterial growth under oxic conditions to cause aerobic nitrification, c) the denitrification taking place after the production unit, and d) the nitrification taking place prior to the production unit in a by-pass mode as part of the continuous flow.
Owner:GREENFISH
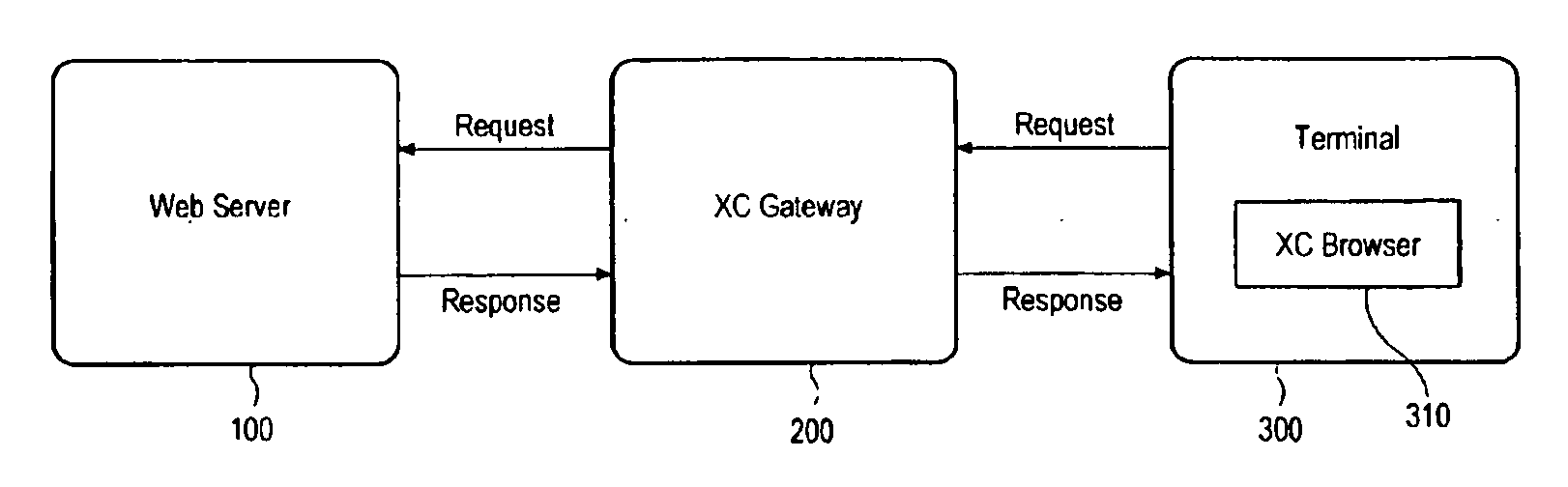
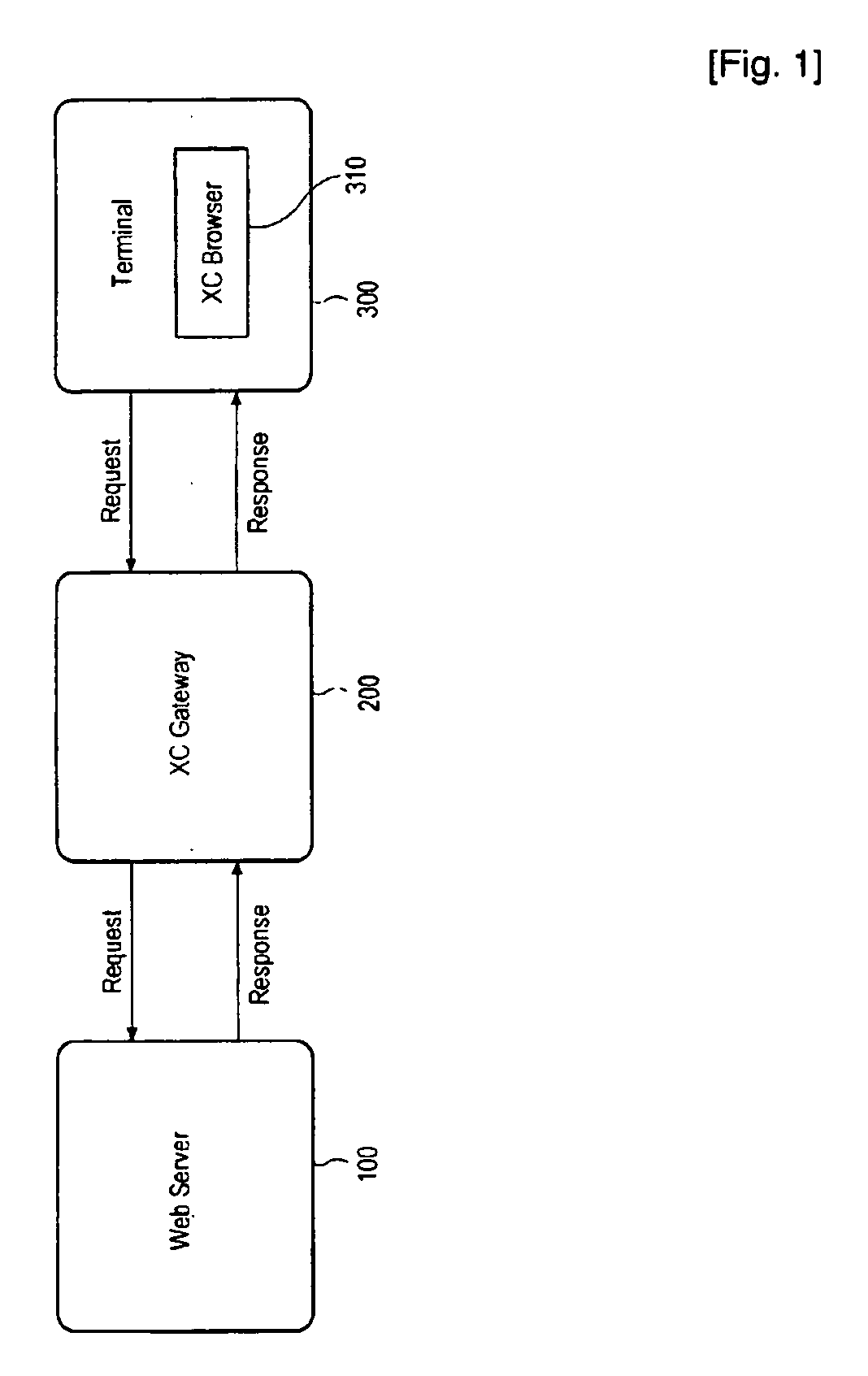
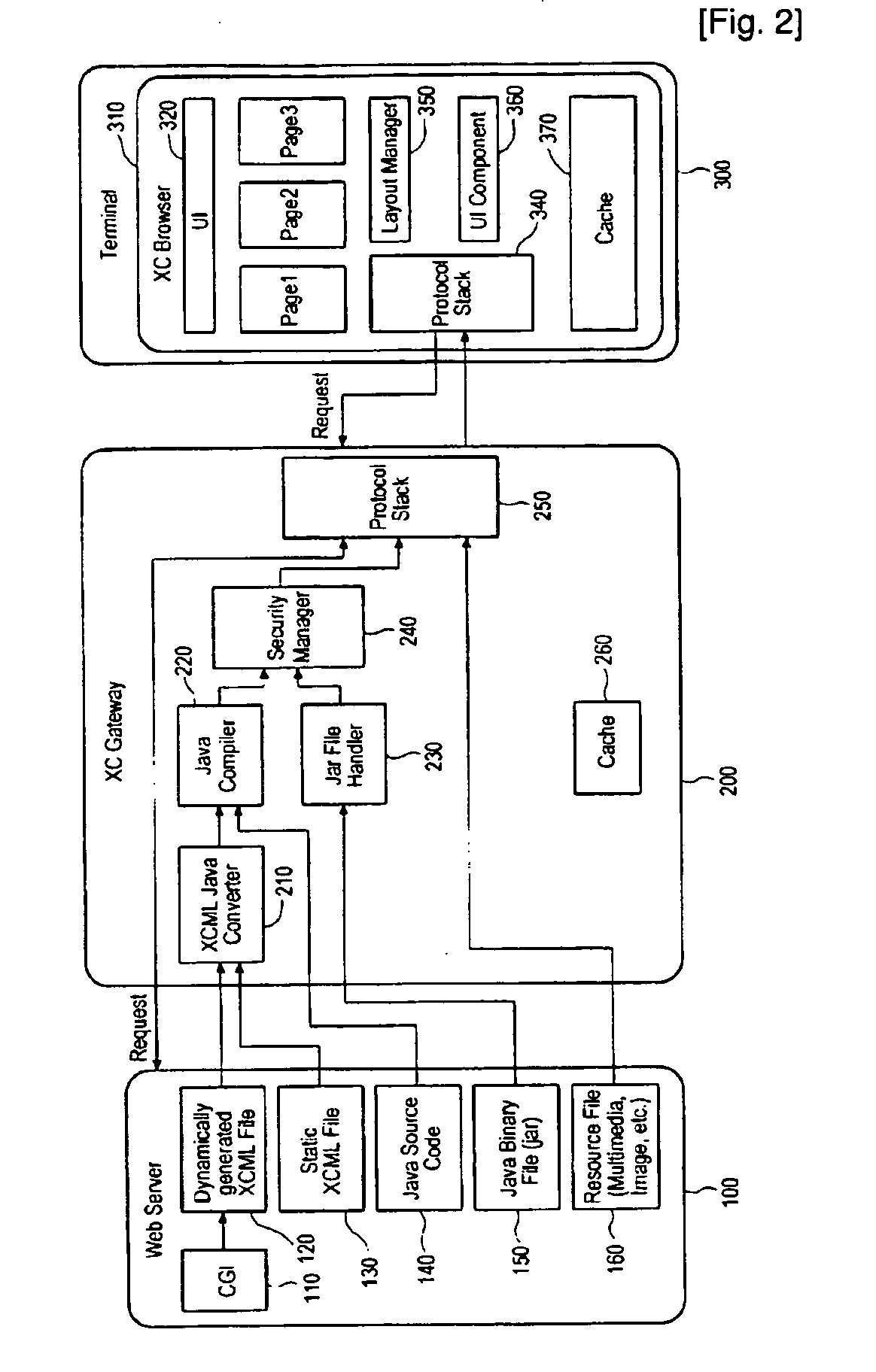
System and method for providing and handling executable web content
InactiveUS20100005527A1Low limitImprove efficiencyTreatment using aerobic processesTransportation and packagingWeb browserWorld Wide Web
The present invention relates to a system for providing executable web content to a terminal. The present invention provides a system comprising a server, which provides an executable web content comprising a declarative language part in declarative language and a non-declarative part, and a gateway, which receives the executable web content from the server, converts it into a format executable in a web browser of the terminal, and transmits the converted content to the terminal.
Owner:REALNETWORKS ASIAPACIFIC CO LTD
Method for water filtration
InactiveUS20090045135A1Great hydraulic resistancePromote circulationTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment involving filtrationNatural sourceSuspended particles
This is a method of filtration of a liquid comprising steps of sequential filtration of said liquid through at least one deep bed medium producing at least one first filtrate followed by at least one membrane medium filtration producing at least one second filtrate, wherein said membrane medium is at least periodically within said deep bed media Many types of deep bed and membrane media can be used. The domain of using contact clarification (direct filtration) can be expanded towards greater solids concentration. Operation and backwash, is simplified, continuous filtration becomes possible. Water can be water from natural source water, process water, wastewater, aqueous or non-aqueous suspensions, emulsions, solutions. Treatment can include mechanical interception of suspended particles, chemical, physical chemical, electrochemical, and biological processes. In water and wastewater processing, control over suspended solids, BOD, COD, nitrogen and phosphorus compounds, bacteria and viruses, heavy metals, color, and other constituents can be dramatically improved as compared to conventional processes. The method can be accommodated in new and modified existing treatment systems.
Owner:KHUDENKO ENG
Wastewater treatment system
InactiveUS6893567B1Expand the populationShorten treatment timeTreatment using aerobic processesMixing methodsEnteropathogenic bacteriaTreatment system
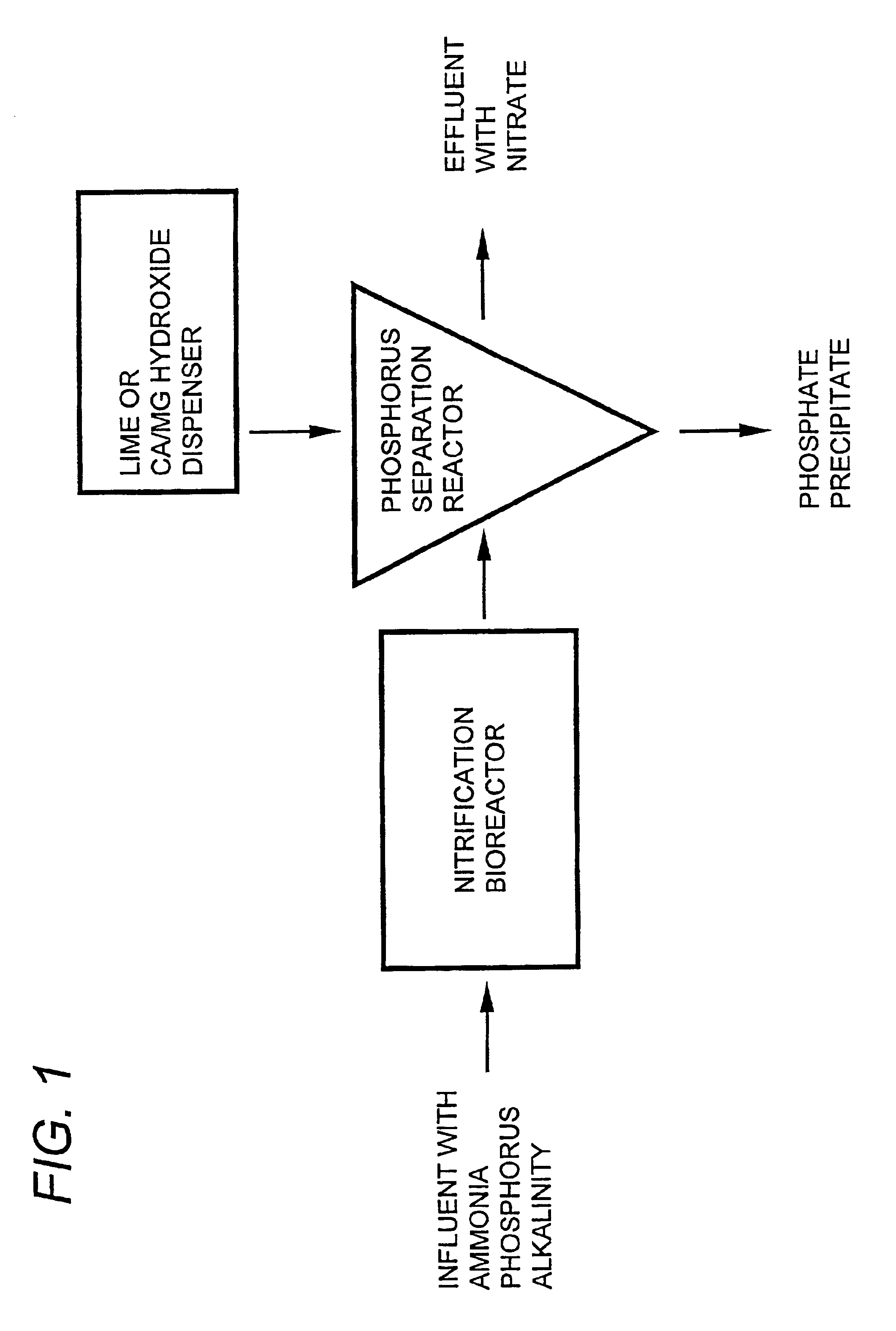
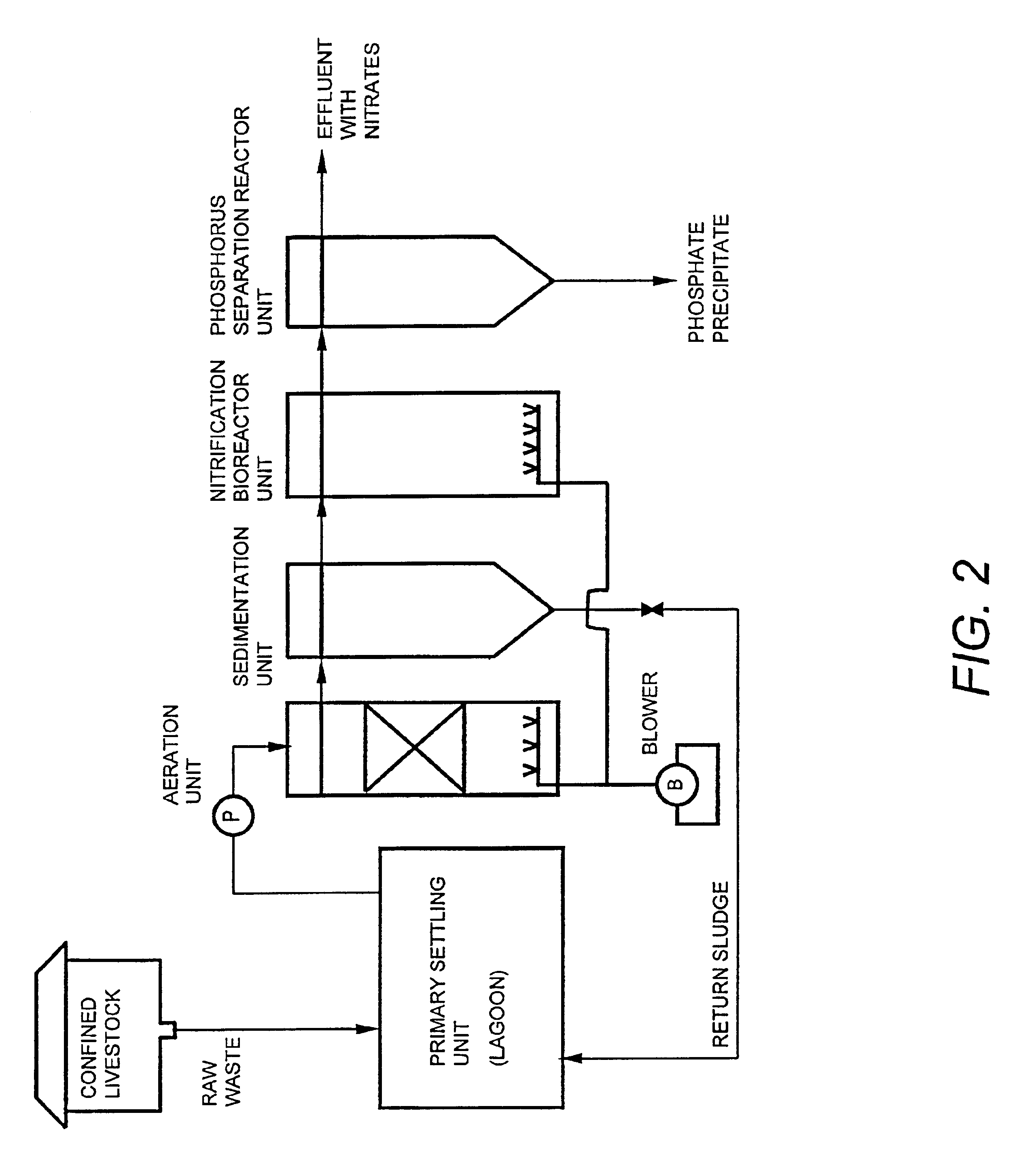
Wastewater treatment systems and processes for: removal of solids, pathogens, nitrogen, and phosphorus from municipal and agricultural wastewater include nitrification of wastewater and increasing the pH of the nitrified wastewater by adding a metallic-containing salt and hydroxide to precipitate phosphorus to form a useable effluent having a specified nitrogen:phosphorus ratio that is useful as a fertilizer or spray for remediation of contaminated soils. The presence of infectious microorganism such as enteropathogenic bacteria and picarnoviruses will be reduced in the useable effluent. The precipitated phosphorus is recovered and used to form useable phosphorus products.
Owner:AGRI UNTED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC +1
Method for treating wastewater in a membrane bioreactor to produce a low phosphorus effluent
InactiveUS6946073B2Reduce outputPromoting robust nutrient uptakeTreatment using aerobic processesOther chemical processesActivated sludgeMembrane bioreactor
Removal of biological nutrients from a wastewater yielding a low phosphorous (e.g., less than 0.25 mg / L) output includes providing a serial multistage bioreactor containing activated sludge having in hydraulic series an anaerobic zone and a downstream aerobic zone, with each zone having an upstream inlet and a downstream outlet. The wastewater is provided to the anaerobic zone inlet. A quantity of chemical sufficient to precipitate soluble and particulate phosphorous is added to the downstream aerobic zone in an amount sufficient to yield a low phosphorous output. Treated water is separated from the activated sludge and precipitated phosphorous and a return activated sludge separated from the treated water is recycled to the anaerobic zone.
Owner:CH2M HILL
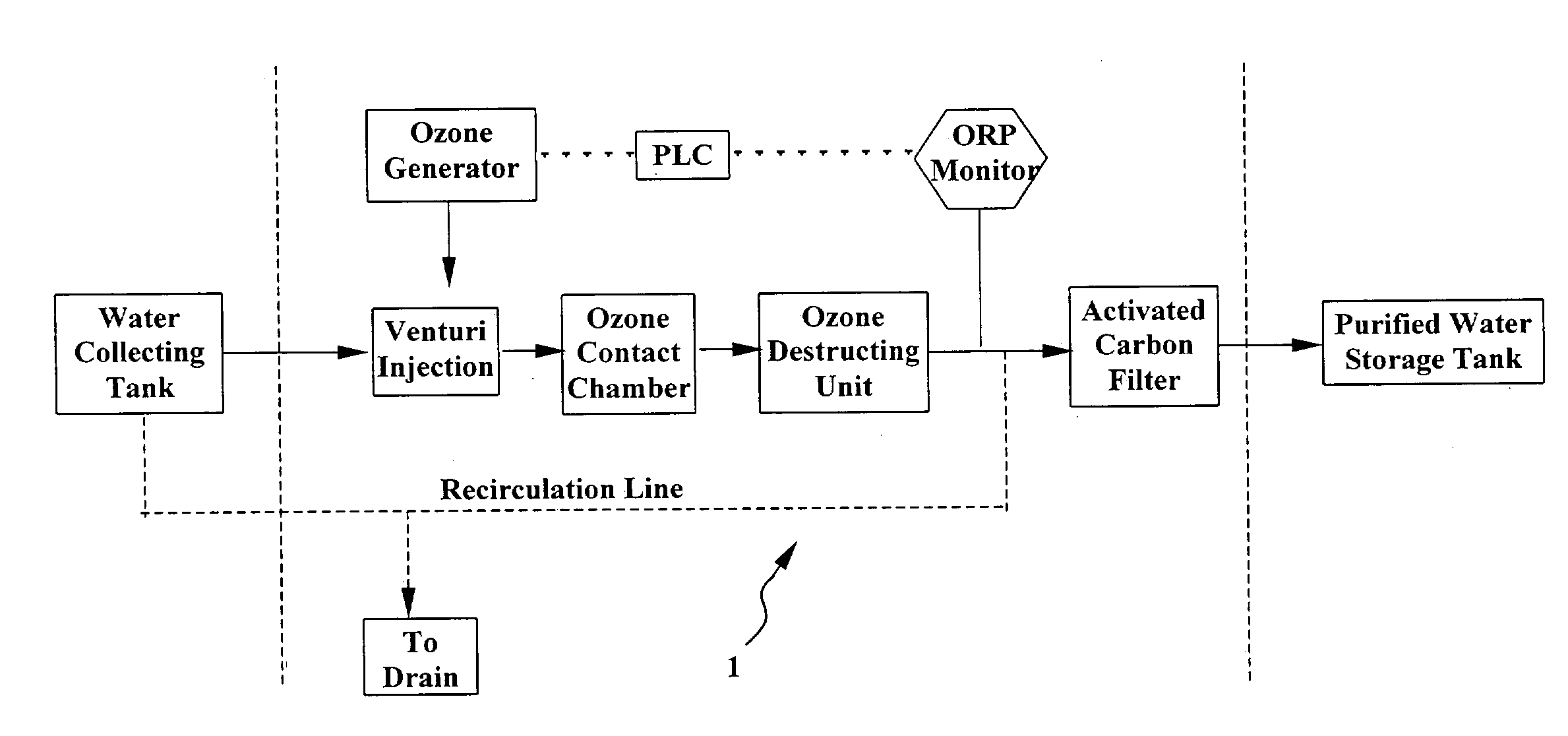
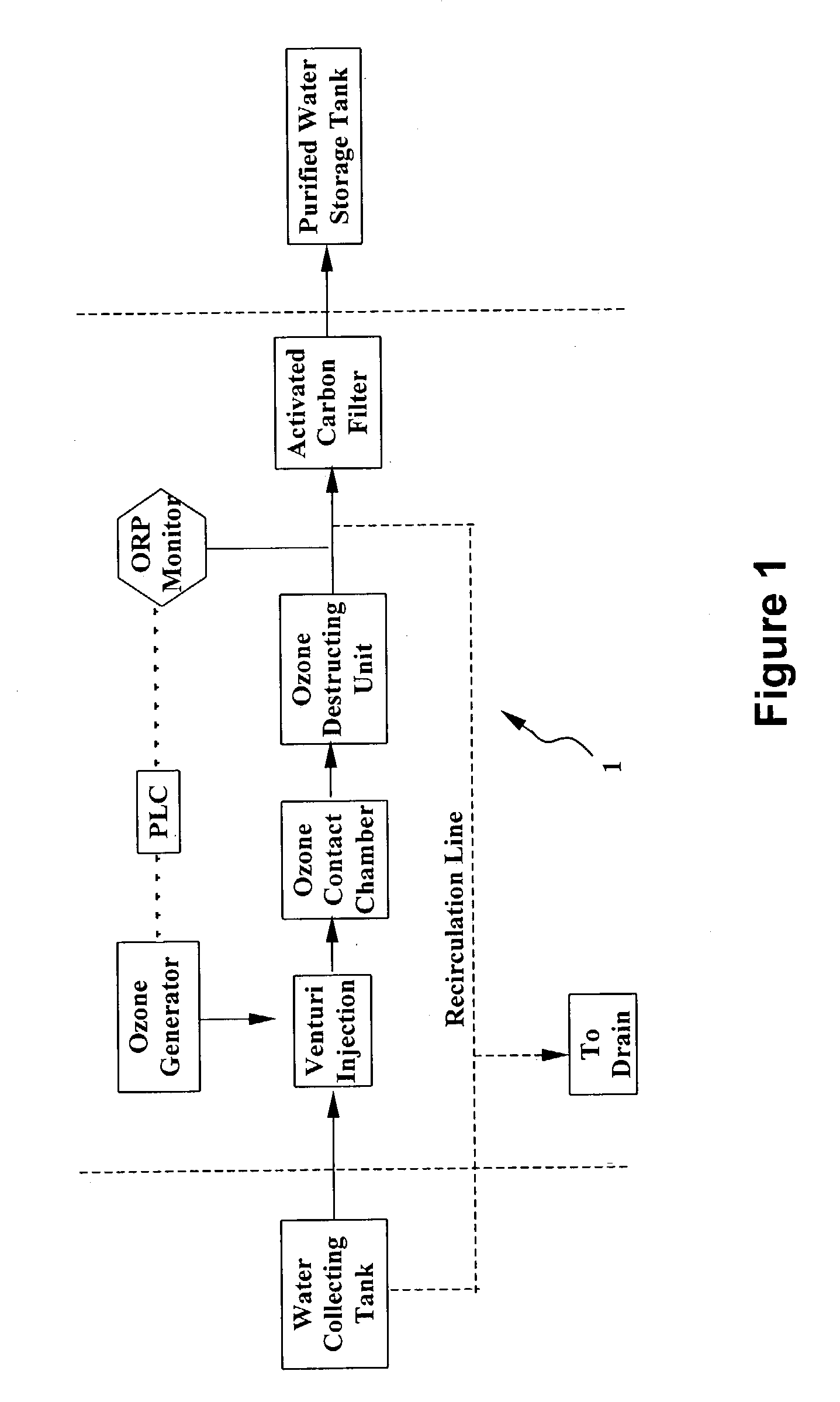
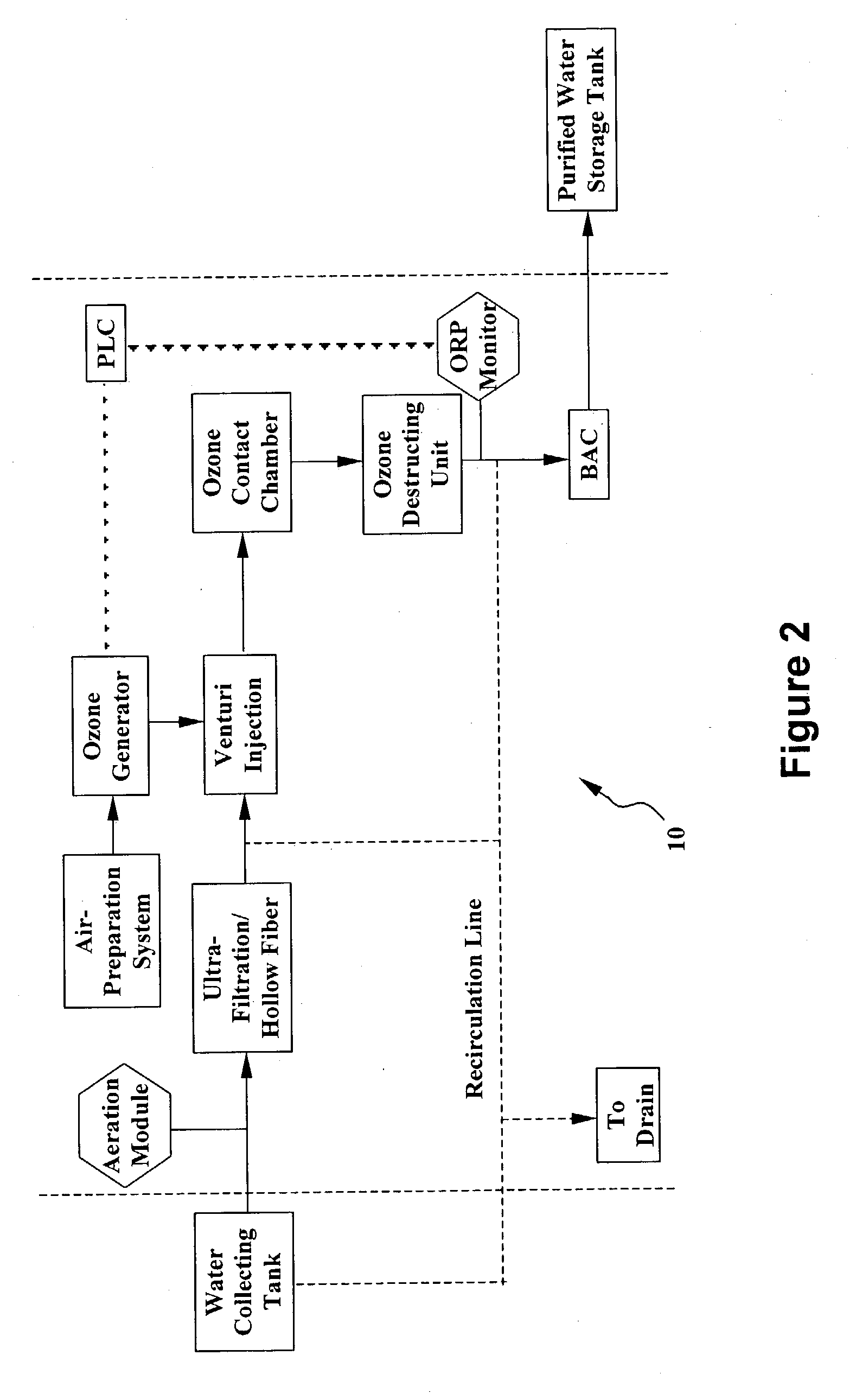
System and method for water purification
InactiveUS20040168989A1Treatment using aerobic processesSedimentation separationBiological activated carbonActivated carbon filtration
A self-contained, portable water purification system, including (a) an ozone supply, (b) an ozone contact chamber for mixing a contaminated or potentially contaminated water stream with ozone generated by such ozone supply, (c) an ozone destruction unit for destructing ozone contained in the water stream and converting said water stream into an oxygen-rich and ozone-depleted water stream, and (d) a downstream biologically active carbon filter, for receiving such oxygen-rich and ozone-depleted water stream and biologically destructing at least a portion of contaminants contained therein.
Owner:TEMPEST ENVIRONMENTAL SYST
Membrane bioreactor, process and aerator
InactiveUS6863817B2Increase pressureEasy to moveTreatment using aerobic processesUsing liquid separation agentSiphonGravity flow
A reactor has an aerobic tank, an anoxic tank and a sealed membrane tank with conduits for circulating mixed liquor between them. Permeation starts when the mixed liquor reaches a high level and stops when the mixed liquor reaches a low level. A sensor, for detecting the mixed liquor level, may stop and start permeation. Pressure builds in the membrane tank when membrane air is on. Transmembrane pressure is also provided by gravity flow or siphon. Membrane air generates an air lift which drives the mixed liquor circulation. The total amount of air provided by an air source is divided and varied in time between the membrane aerator and the process aerator. The process aerator acts as a screening inlet to the conduit to the membrane tank. Chemical maintenance cleaning is provided by gravity flow.
Owner:ZENON TECH PARTNESHIP
High performance, energy efficient system and method for wastewater treatment with resource recovery and reduced residual solids generation
ActiveUS20080223783A1Treatment with anaerobic baffled reactorsWater treatment parameter controlRetention timeCell mass
A wastewater treatment system is provided including an aerobic membrane bioreactor and an anaerobic digester system connected to receive wasted solids continuously from the aerobic membrane bioreactor and also connected to return effluent from the anaerobic digester system continuously to the aerobic membrane bioreactor. Further, a process is provided for treating wastewater including the step of wasting a volume fraction of organic cell mass from an aerobic membrane bioreactor to an anaerobic digester system and maintaining a solids retention time (SRT) in the bioreactor that is (1) greater than a time needed to achieve growth of organisms suitable for converting carbonaceous biochemical oxygen demand (CBOD) into cell mass and (2) less than a time at which substantial decay of the organisms occurs. The system and process may further include optional pretreatment and / or phosphorus and / or nitrogen removal downstream of the membrane bioreactor system.
Owner:HSBC BANK
Black-odor river pollution treatment method
InactiveCN101417840AEfficient removalControl and reduce the total amount receivedTreatment using aerobic processesWater aerationMicrobial agentSelf purification
The invention discloses a method for managing town black and olid river pollution in situ by utilizing biological repair technology, which takes the steps and measures of aerating and oxygenizing in riverway, adding a complex microbial agent, biologically repairing bottom sediment, arranging a bio-nest system and the like, so as to control and eliminate the exogenous and endogenous pollution of the river, purify the water quality of the river, improve the self-purification ability of the water body and achieve the purpose of eliminating black and olid. The method does not need to build structures in the riverway or lead the river water out of the riverway to be treated, or dredge the bottom sediment in the river, therefore the method is generally applicable to incomplete sewage interception and dredging or the rivers which can not be intercepted sewage or dredged temporarily, and the in situ treatment to the riverway which is affected by tide and has complicated fluid variation. Therefore, the method which can lead the water body to recover normal ecological function provides the practical, economic and convenient treatment method for various town black and olid rivers.
Owner:黎赓桓 +1
Process for the production of purified water and hydrocarbons from fossil resources
InactiveUS6462097B1Reduce adsorbate contentTreatment using aerobic processesIon-exchanger regenerationSorbentPurified water
A process for the production of purified water and hydrocarbons comprising at least one stage of separation of the water and hydrocarbons formed during a Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, at least one stage of purification of the separated water by bringing it into contact with at least one adsorbent selected from the group consisting of: the active carbons, clays which are hydrophobic or rendered hydrophobic, and zeolites which are hydrophobic or rendered hydrophobic. This process may optionally include a stripping stage before the adsorption step.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE +2
Inverted air box aerator and aeration method for immersed membrane
InactiveUS6863823B2Reduce air volumeLower the volumeTreatment using aerobic processesIon-exchanger regenerationFiltrationAir space
An aerator for immersed filtering membranes has an aerator shell with openings for discharging bubbles from its upper surface and a shape capable of temporarily containing a volume of air in fluid communication with the openings. The shell is open to tank water below it and located so that discharged bubbles will rise through an assembly of the filtering membranes. The shell may be wholly or partially made of parts of the assemblies of filtering membranes. A supply of air is provided to the air space in the aerators alternating between a high flow rate and a low flow rate in short cycles of between about 10 seconds and 100 seconds. A filtration system has an inlet for adding substrate and an outlet for retentate are located so as to create a horizontal flow of substrate through the tank. Membrane assemblies are located within the horizontal flow of substrate. Aerators as described above are provided and operated as described above.
Owner:ZENON TECH PARTNERSHIP
Combined activated sludge-biofilm sequencing batch reactor and process
InactiveUS20040206699A1Similar oxygen transfer efficiencyRemoval can be promoted and increasedTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesSequencing batch reactorActivated sludge
A new biofilm-activated sludge Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) treatment process for sewage or wastewater has successfully been developed as the third generation SBR (SBR3). This new SBR3 process utilizes a multi-stage and multi-sludge SBR configuration receiving either continuous or intermittent inflow of wastewater. Each stage has individually controlled continuous or alternating anaerobic / anoxic / aerobic operation, with or without mixing and recycling from the other stage(s). The configuration and operation is dependent upon the treatment objectives and effluent discharge requirements. In the preferred embodiment, carriers are used to facilitate control of operating conditions.
Owner:KINGSFORD ENVIRONMENTAL H K
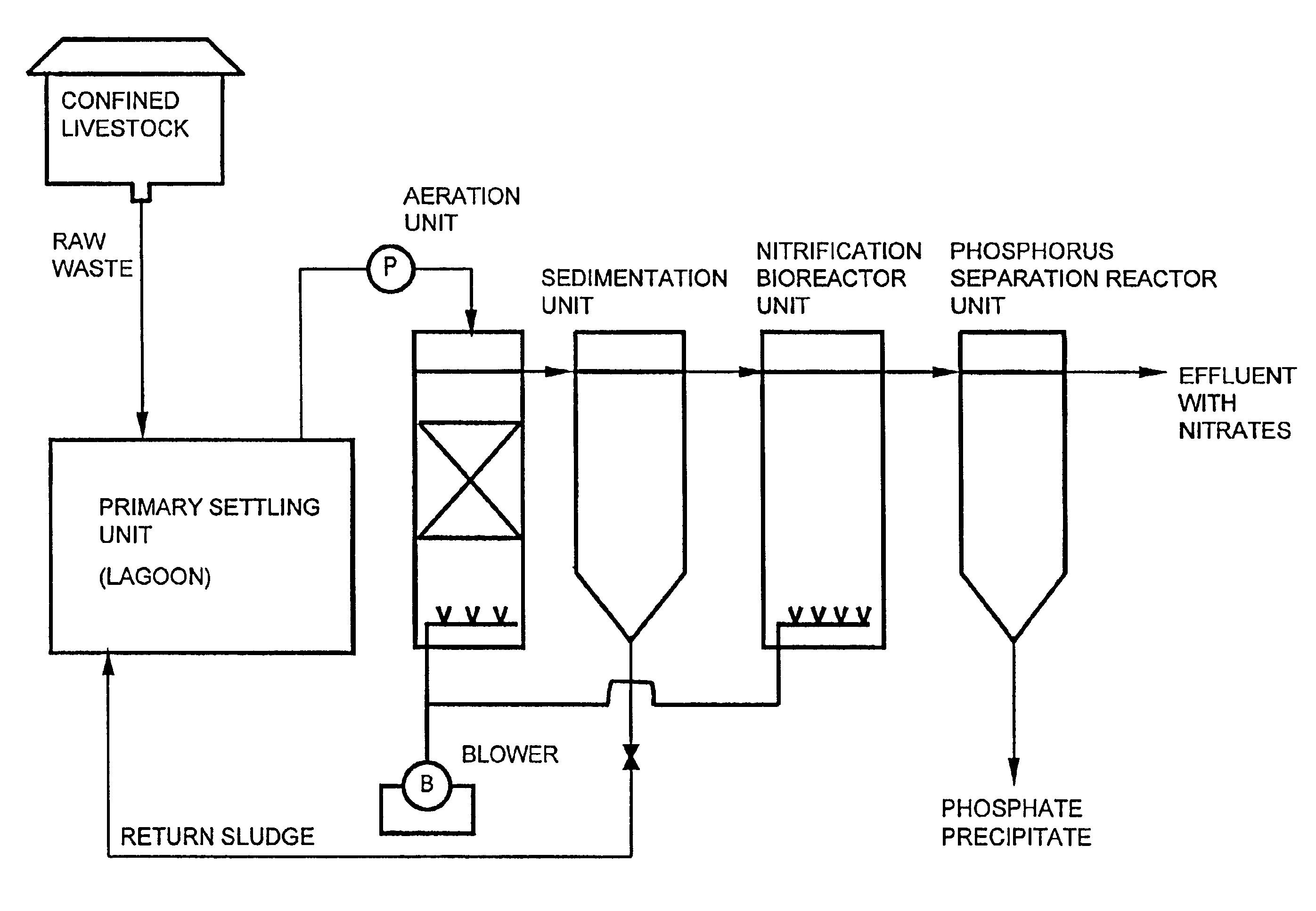
Apparatus and method for purification of agricultural animal waste
InactiveUS6039874AEffective treatment of wastewaterReducing fertilizer nutrientTreatment using aerobic processesOther chemical processesAbove groundFiltration
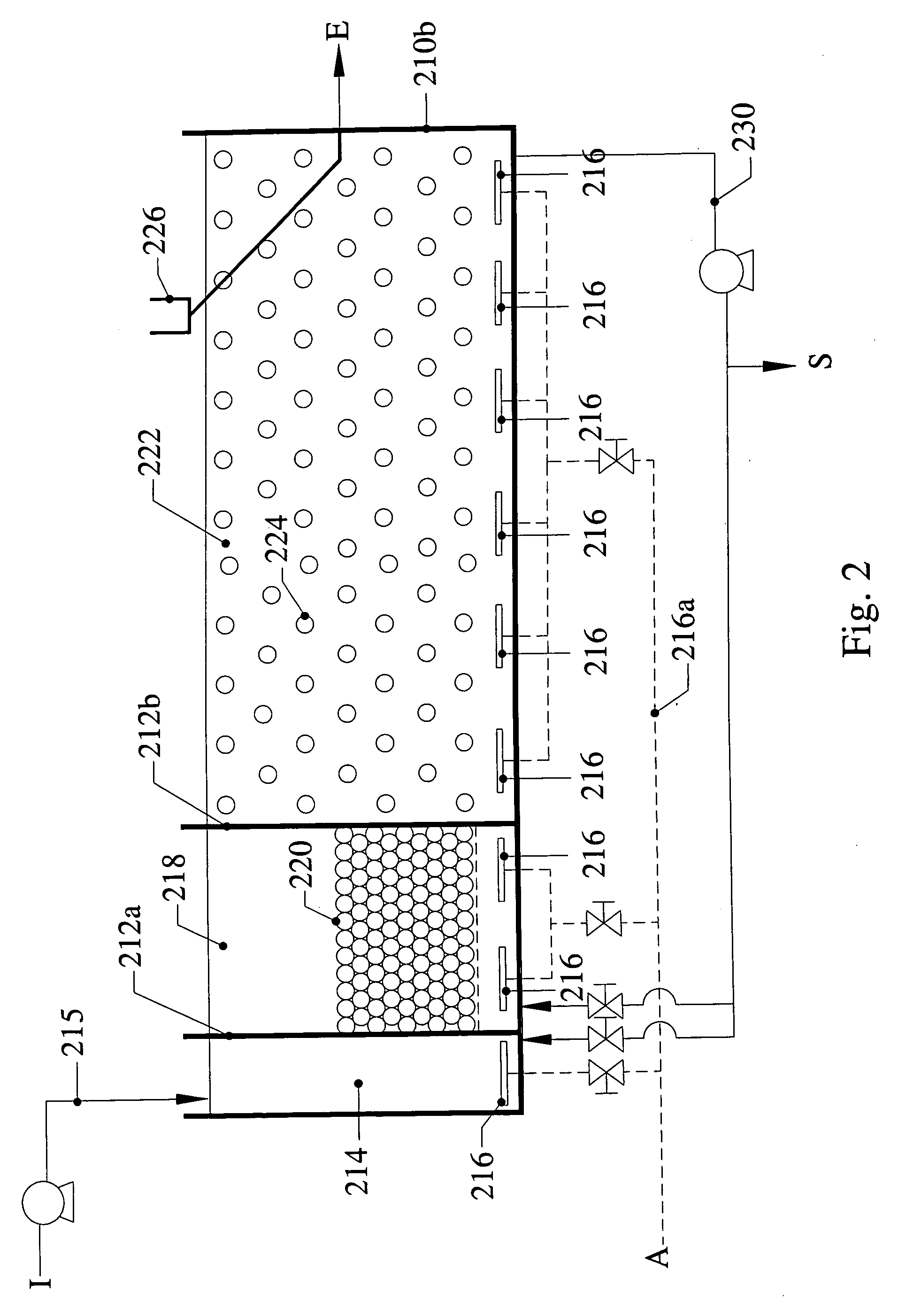
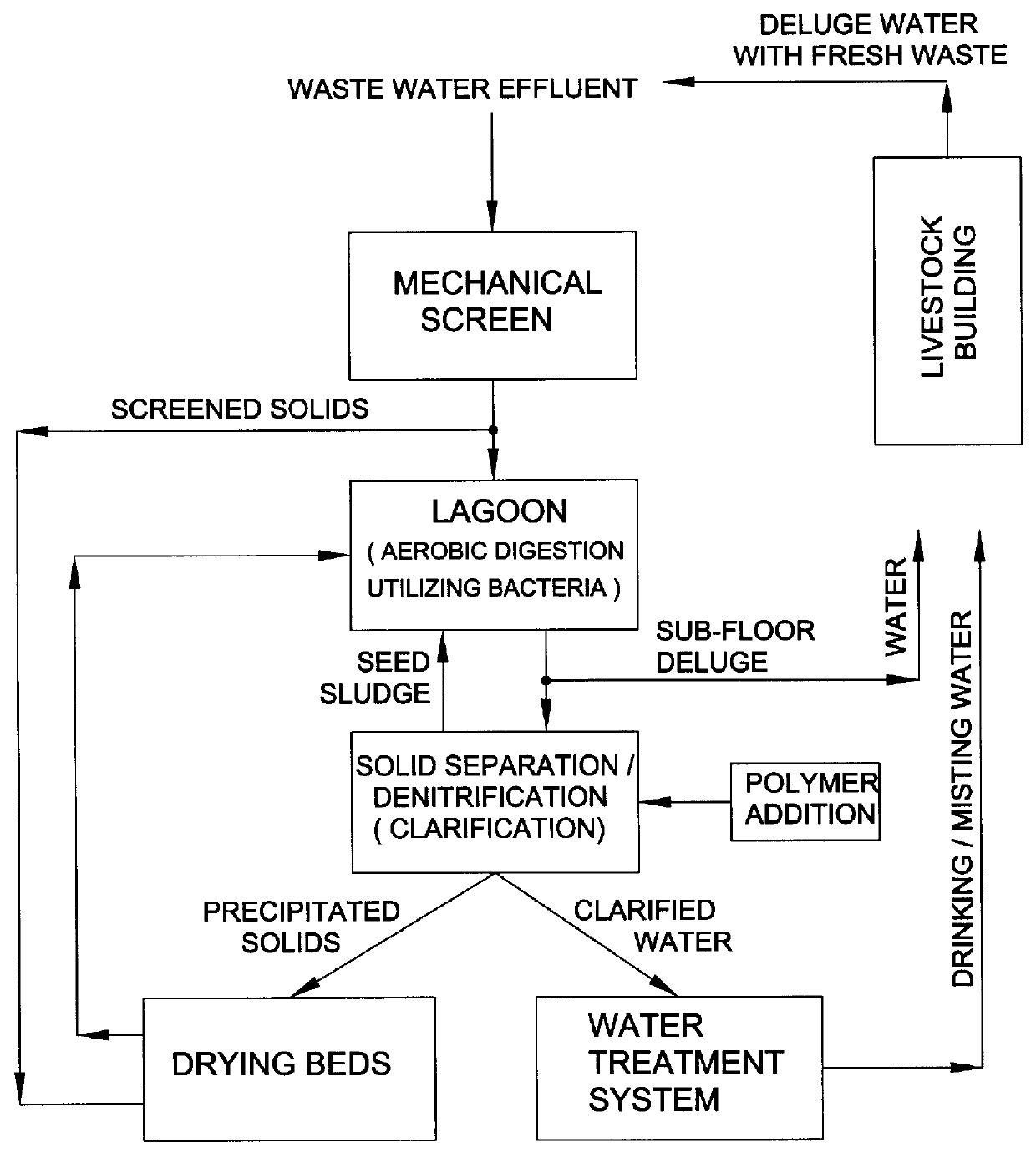
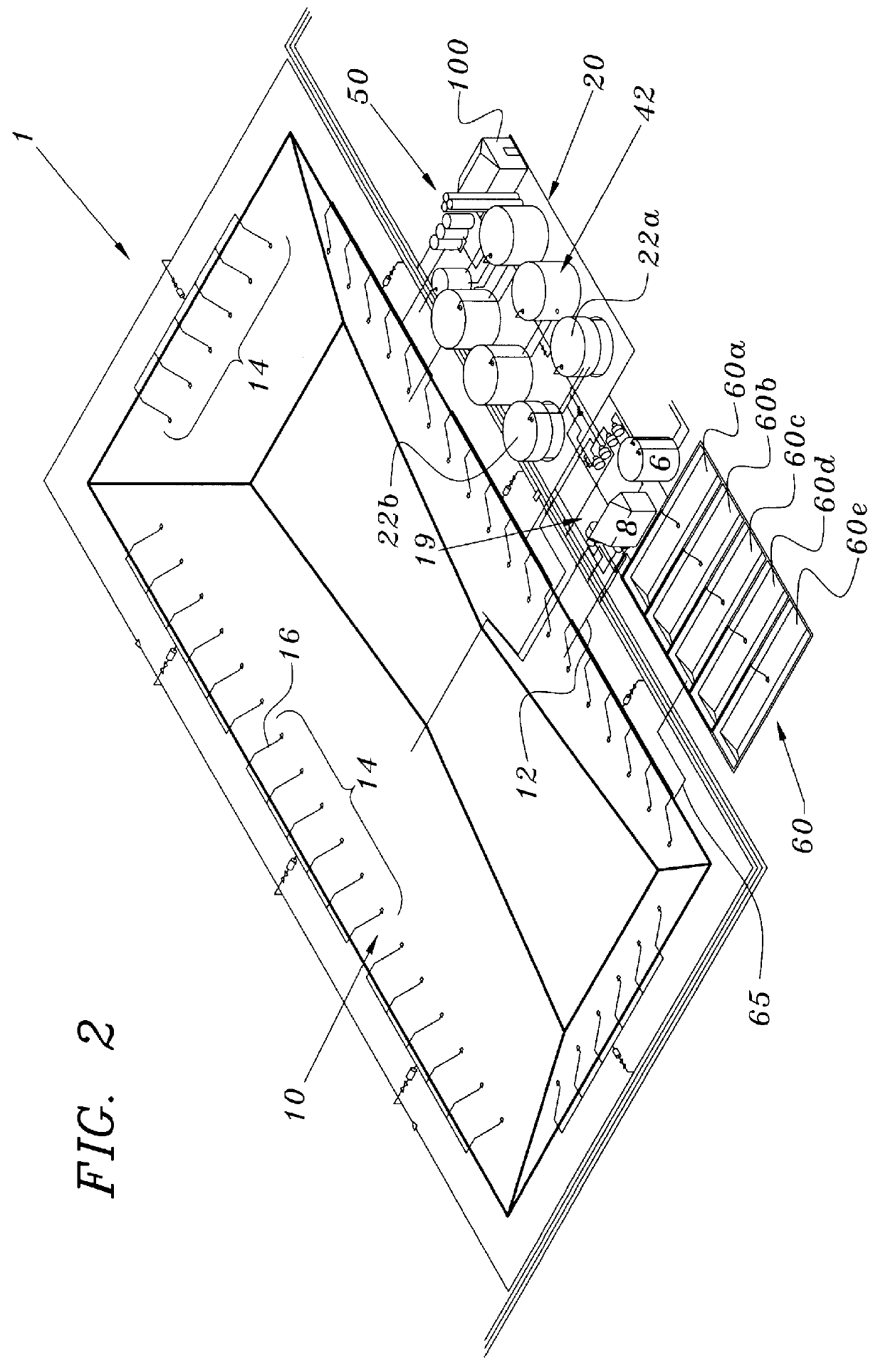
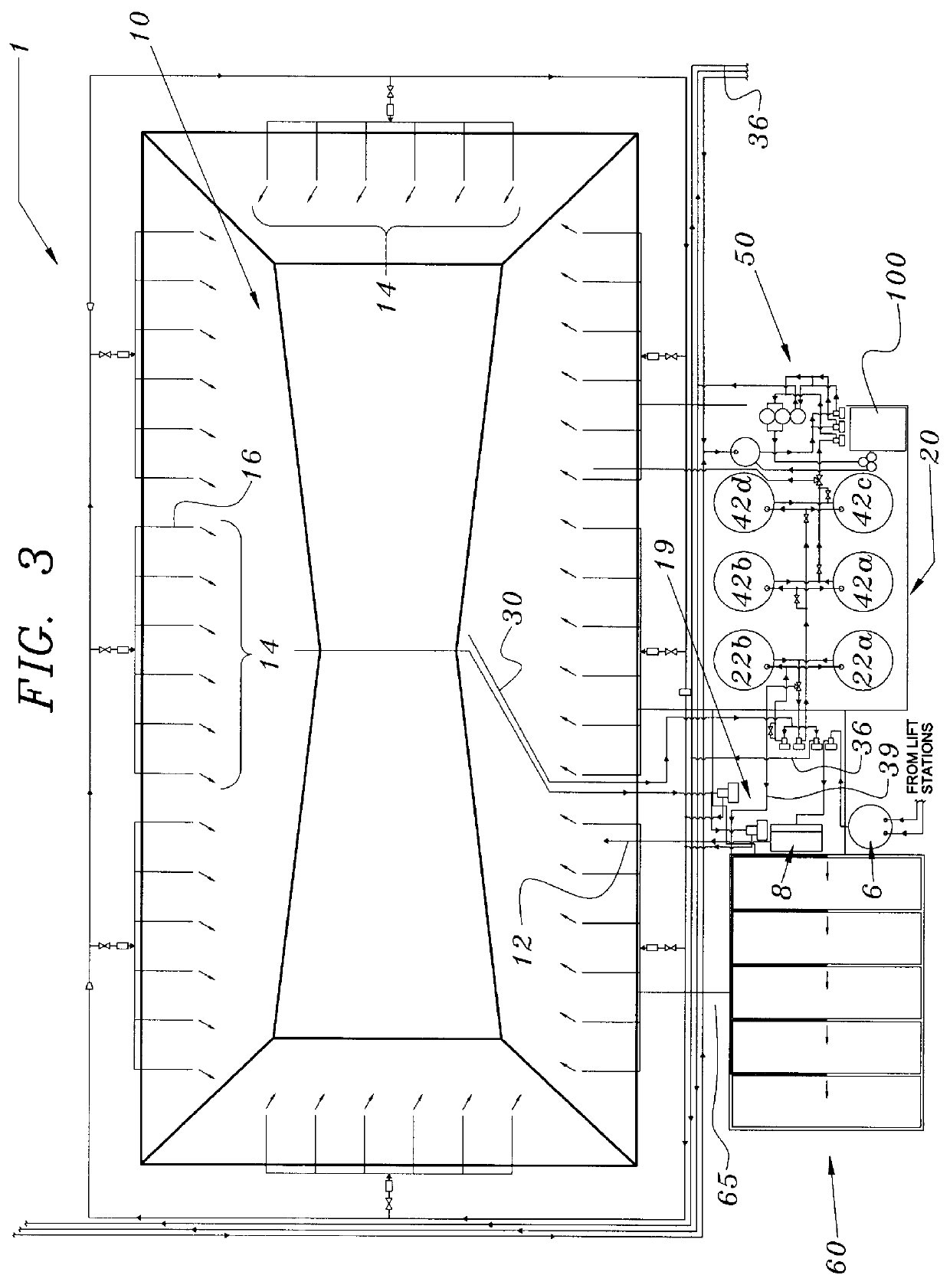
An apparatus and method for treating and reusing the wastewater discharged from agricultural animal farms. The apparatus and method of the present invention is designed to be a zero discharge system in which no wastewater will be discharged or spray irrigated. The wastewater effluent is first passed through a mechanical screen were bulk solids are separated and partially de-watered. The screened effluent is then directed to a primary plastic-lined earthen lagoon where it undergoes aerobic digestion utilizing specially selected bacteria. After treatment in the primary lagoon, the wastewater effluent is used to wash the floors of the hog houses or undergoes a purification phase including solids separation / denitrification, filtration and sterilization. The solids separation / denitrification phase (clarification) preferably takes place in an anoxic environment in preferably above-ground tanks where suspended solids removal will occur as well as denitrification for nitrate reduction. The clarification process may be facilitated through use of polymer addition. The majority of solids will be sent to a plurality of drying beds for de-watering and subsequent removal.
Owner:AGRIMOND USA CORP
Wastewater treatment system with membrane separators and provision for storm flow conditions
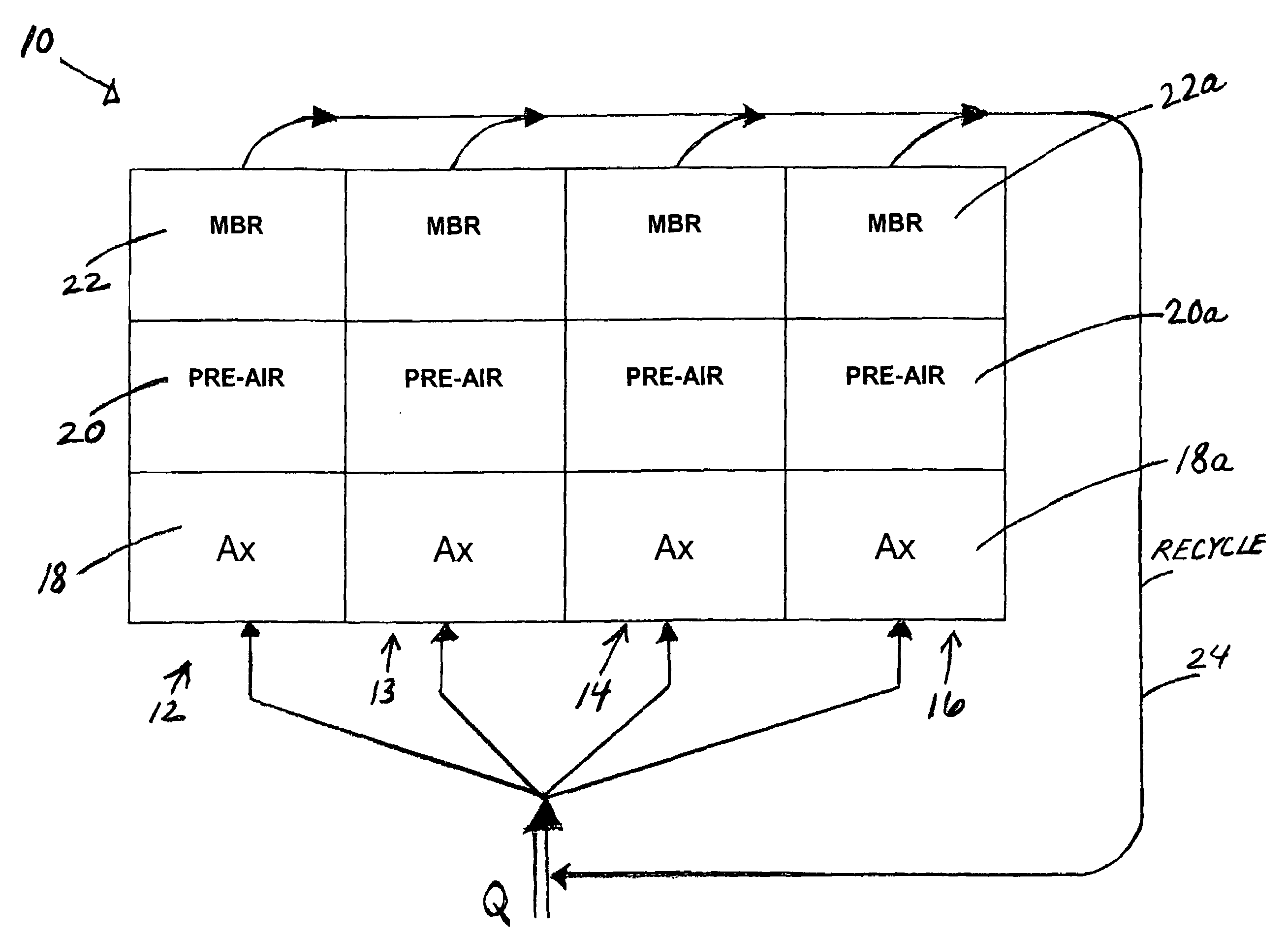
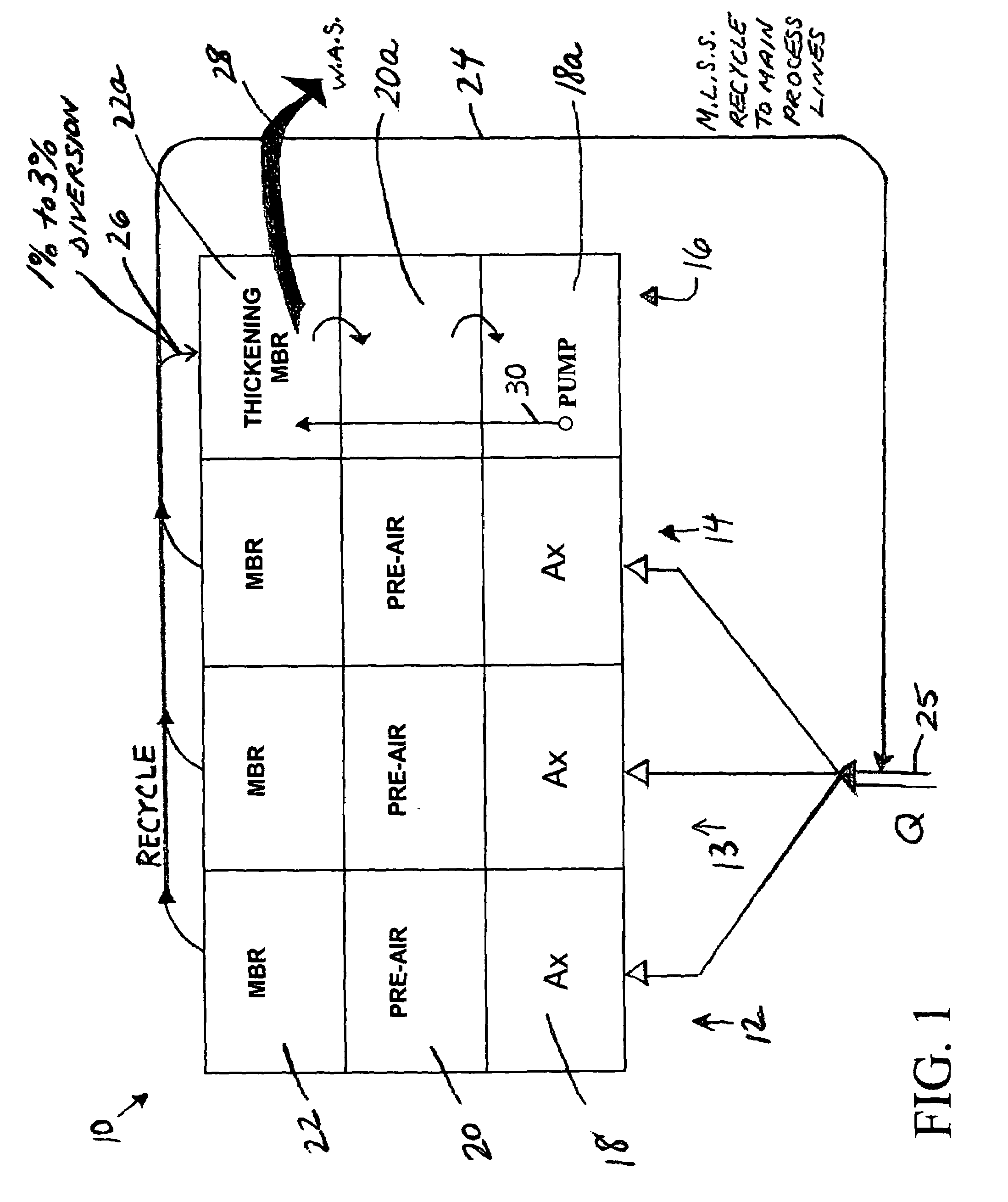
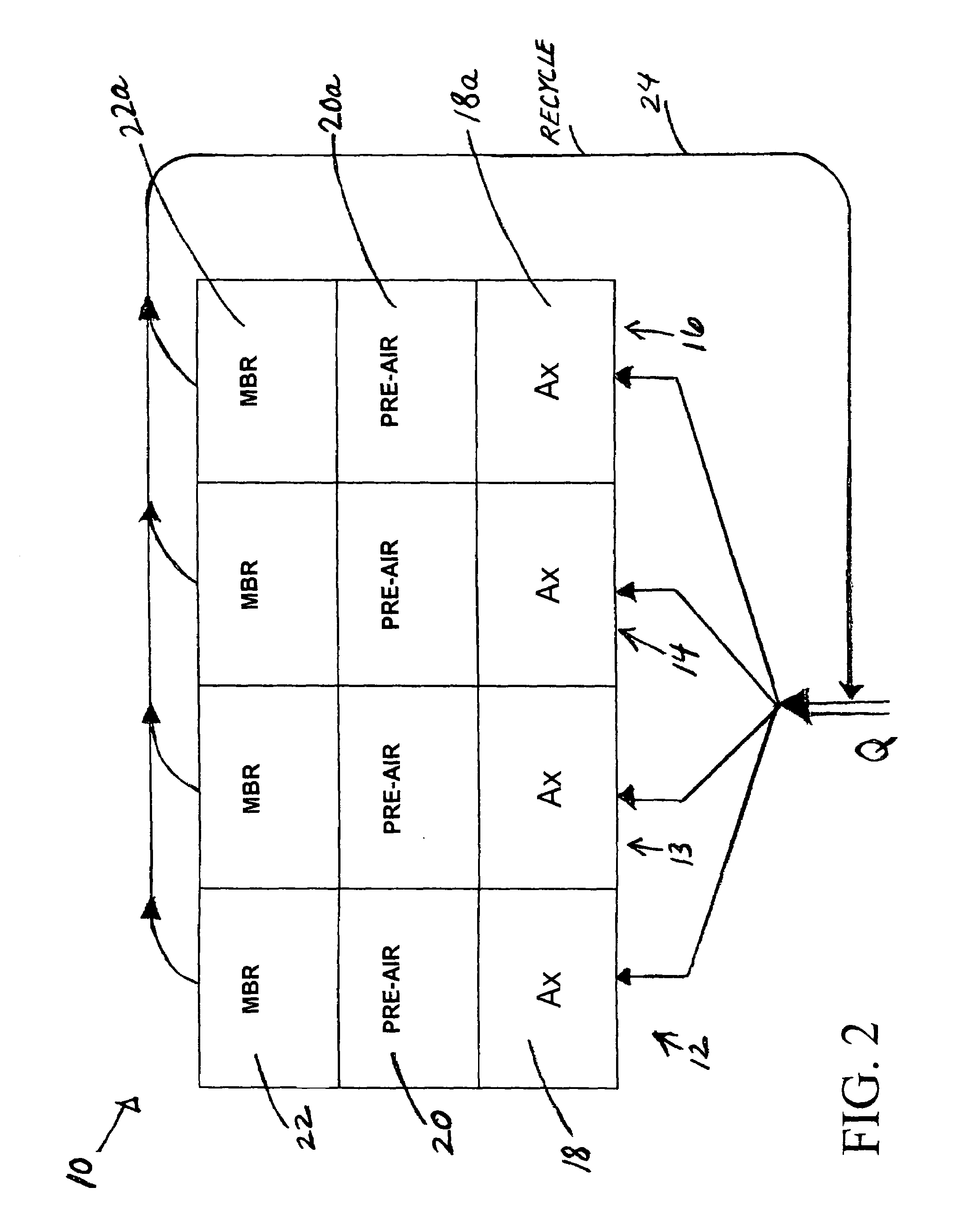
ActiveUS7147777B1Increase biomassTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesStreamflowTreatment system
In a wastewater treatment system and process utilizing membrane bioreactors (MBRs), multiple, parallel series of tanks or stages each include, an MBR stage. Under conditions of normal flow volume into the system, influent passes through several parallel series of stages or process lines, which might be, for example, an anoxic stage, an aeration stage and an MBR stage. From the MBR stages a portion of M.L.S.S. is cycled through one or more thickening MBRs of similar process lines, for further thickening and further processing and digesting of the sludge, while a majority portion of the M.L.S.S. is recycled back into the main process lines. During peak flow conditions, such as storm conditions in a combined storm water / wastewater system, all of the series of stages with their thickening MBRs are operated in parallel to accept the peak flow, which is more than twice normal flow. M.L.S.S. is recycled from all MBR stages to the upstream end of each of all the parallel process lines, mixing with influent wastewater, and the last one or several process lines no longer act to digest the sludge. Another advantage is that with the thickened sludge in the last process line of basins, which ordinally act to digest the sludge, there is always sufficient biomass in the system to handle peak flow, the biomass being available if needed for a sudden heavy flow or an event that might bring a toxic condition into the main basins.
Owner:OVIVO INC
Batch-continuous process and reactor
InactiveUS20060081533A1Precise positioningTreatment using aerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentRetention timeWastewater
This is a method of batch-continuous operation for treatment and separation of liquid-solid mixtures in a reactor with reactive solids comprising steps of continuously feeding the liquid in the reactor, contacting (possibly, mixing) liquid with the solids in at least a portion of the reactor, periodically separating the liquid from the solids in unmixed, or predominantly unmixed, portion of the reactor, discharging at least a portion of the separated liquid from the reactor, and retaining the separated solids in the unmixed portion of the reactor, and periodically resuspending the solids in the unmixed portion of the reactor and transferring the resuspended soilds into the portion of the reactor for contacting liquid with the solids. The contacting and / or mixing of the liquid with the solids in the mixed portion of the reactor can be continuous or periodic mixing. The unmixed zone differs from the quiescent zone in conventional clarifiers. It is a flow-through zone with a noticeably high velocity of flow as in aeration tanks of biological treatment systems. The retention time in unmixed zones is much shorter than in clarifiers. The method and apparatus can be used to treat water and wastewater, and in various chemical, biochemical, and pharmaceutical processing operations.
Owner:KHUDENKO BORIS M
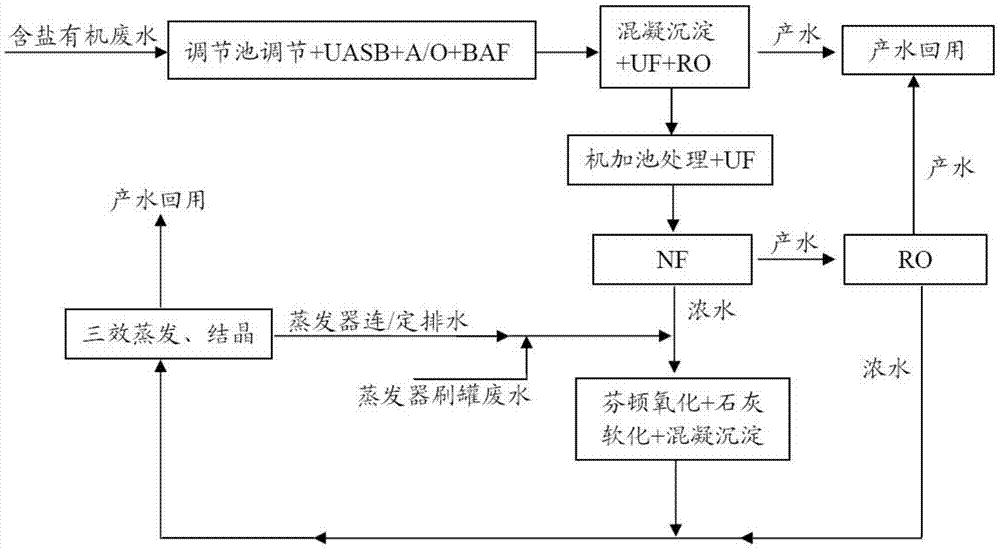
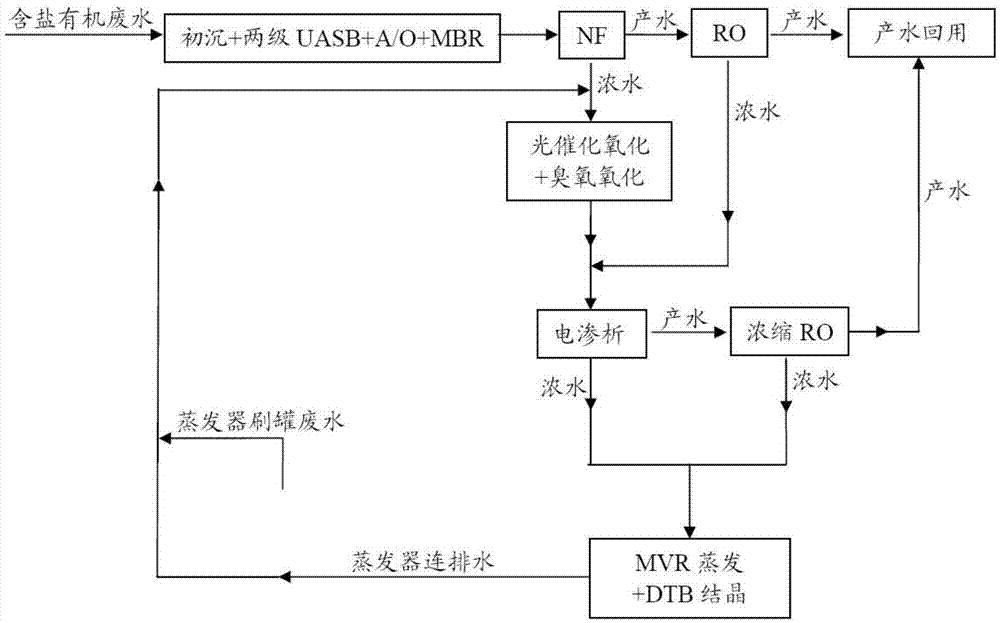
Zero-discharge treatment method of salt-containing organic wastewater
InactiveCN105439395AEasy to handleEfficient reuseTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment involving filtrationEvaporationOrganic matter
The invention provides a zero-discharge treatment method of salt-containing organic wastewater. The method comprises the following steps that biochemical treatment and filtering treatment are performed on wastewater; then, membrane concentration is performed; pure-water-producing high-organic-matter-content membrane concentration concentrated water and optional low-organic-matter-content membrane concentration concentrated water are obtained; the high-organic-matter-content membrane concentration concentrated water is used for high-grade oxidation treatment; high-grade oxidation produced water is used for regulation treatment to obtain high-grade oxidation outlet water; the obtained high-grade oxidation outlet water is subjected to evaporation treatment; or the obtained high-grade oxidation outlet water and the low-organic-matter-content membrane concentration concentrated water are mixed under the condition that the low-organic-matter-content membrane concentration concentrated water exists in the step, and then, the evaporation treatment is carried out; external discharge concentration liquid of an evaporator and / or high-salt-content high-organic-matter-content wastewater discharged during the tank brushing of the evaporator are conveyed back into a high-grade oxidation treatment unit; after the liquid is mixed with the high-organic-matter-content membrane concentration concentrated water, the high-grade oxidation treatment is carried out. The wastewater treatment method is stable and reliable; the long-period and stable operation of an evaporation system can be ensured; the zero discharge of the industrial wastewater is realized.
Owner:DATANG INT CHEM TECH RESINST
Cyclic aeration system for submerged membrane modules
InactiveUS6881343B2Easy illustrationSmall sizeTreatment using aerobic processesLighting and heating apparatusAeration systemEnvironmental engineering
An aeration system for a submerged membrane module has a set of aerators connected to an air blower, valves and a controller adapted to alternately provide a higher rate or air flow and a lower rate of air flow in repeated cycles. In an embodiment, the air blower, valves and controller, simultaneously provide the alternating air flow to two or more sets of aerators such that the total air flow is constant, allowing the blower to be operated at a constant speed. In another embodiment, the repeated cycles are of short duration. Transient flow conditions result in the tank water which helps avoid dead spaces and assists in agitating the membranes.
Owner:ZENON TECH PARTNERSHIP
Popular searches
Sustainable biological treatment Steroscopic systems Sludge treatment by oxidation Specific water treatment objectives Electrical measurement instrument details Water contaminants Water/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysis Water/sewage treatment by sorption Pisciculture and aquaria Energy based wastewater treatment
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com