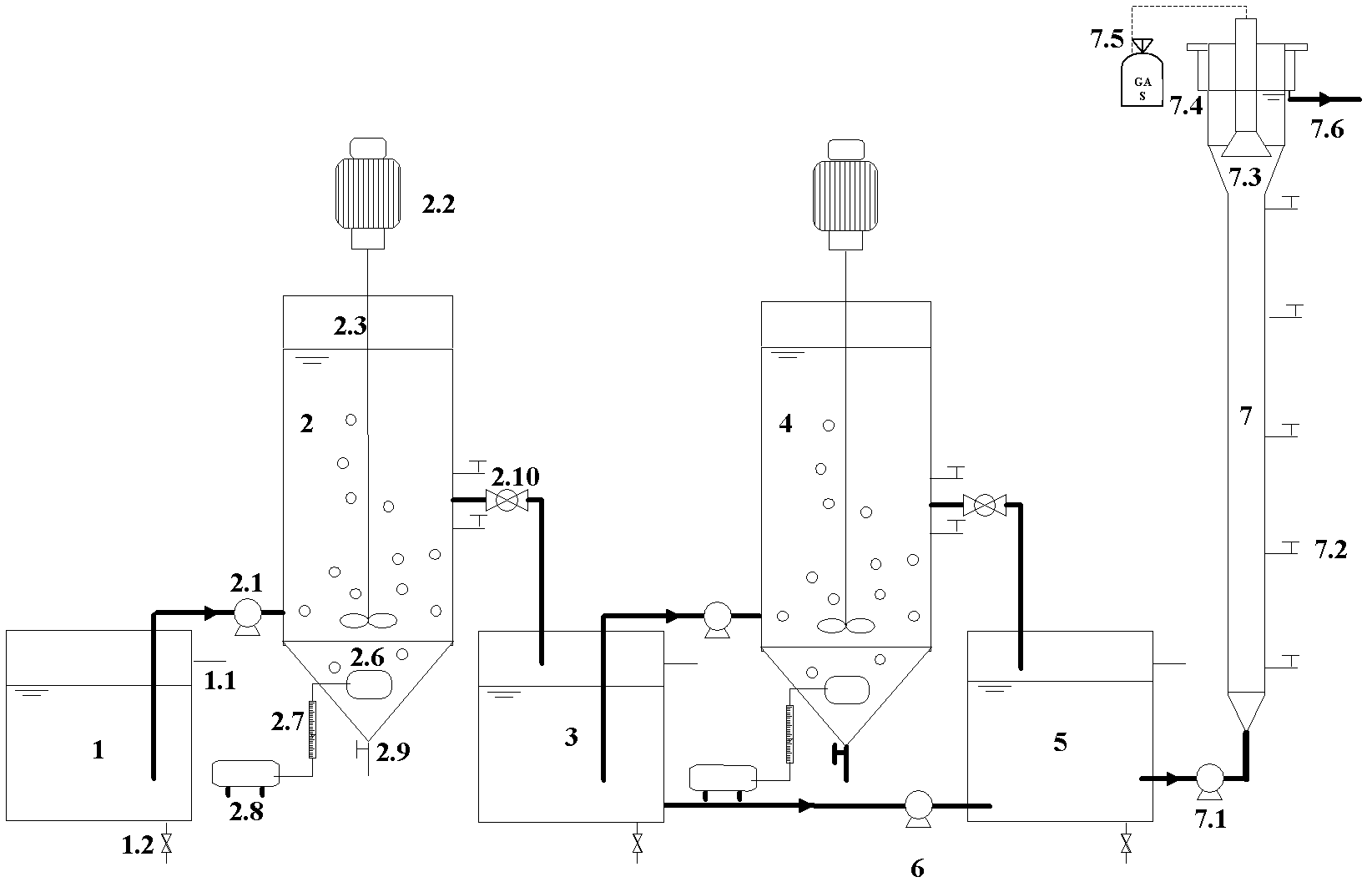
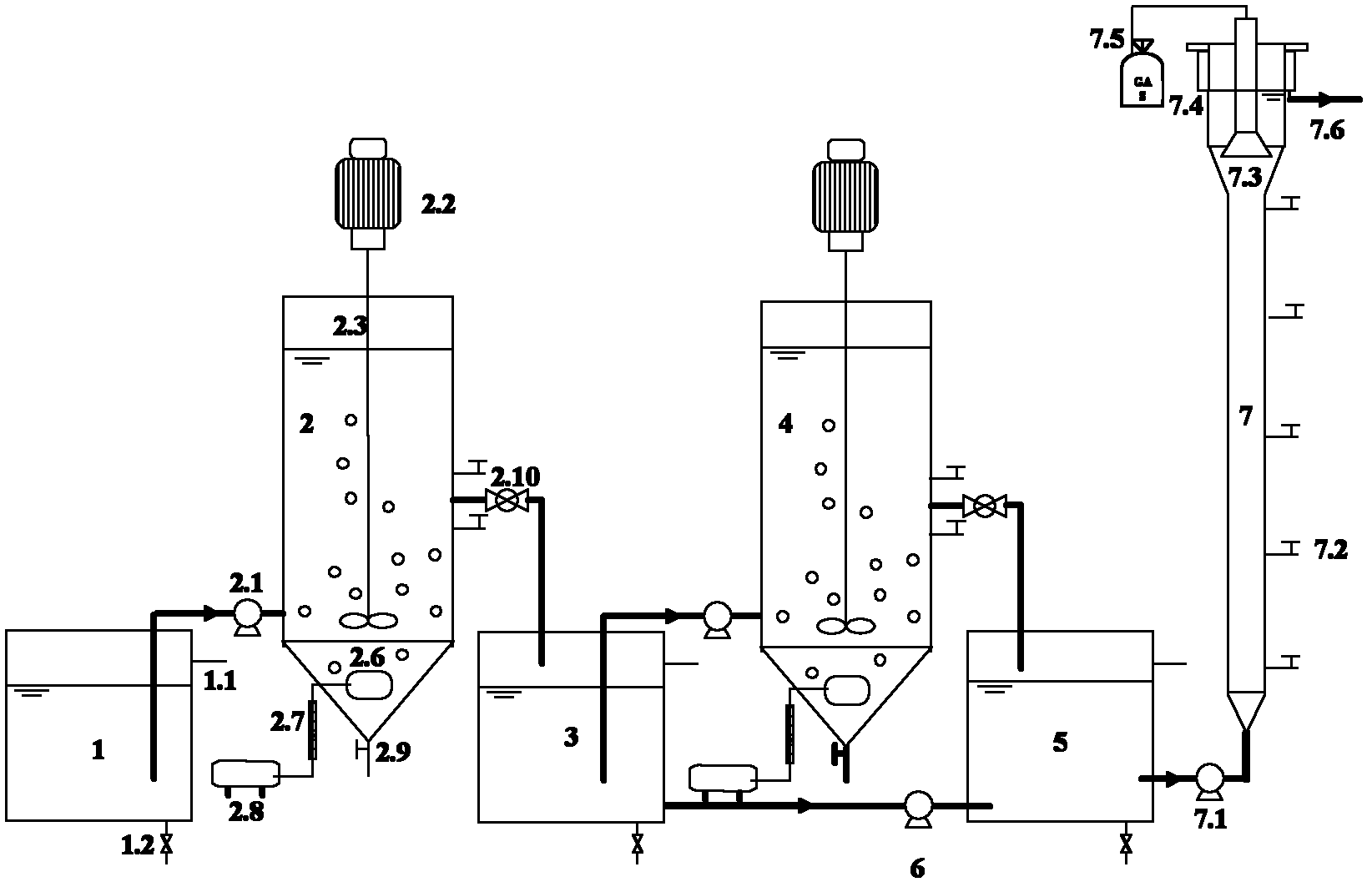
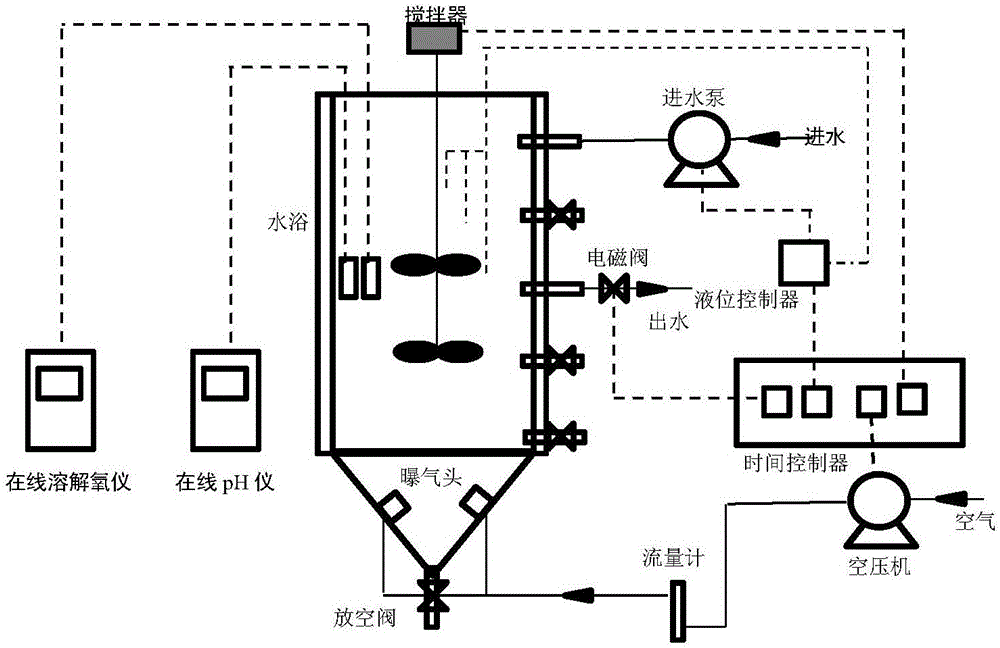
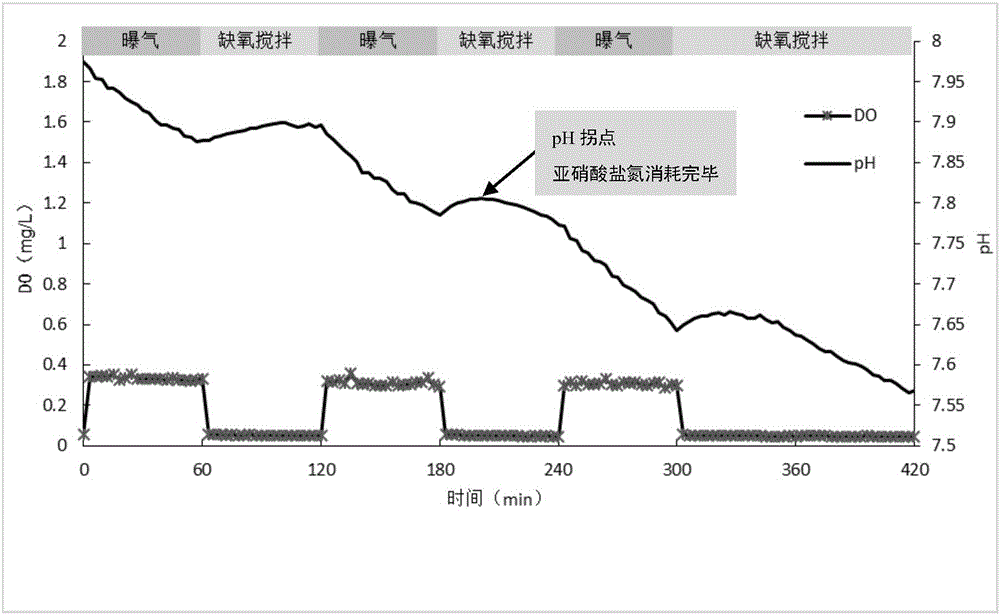
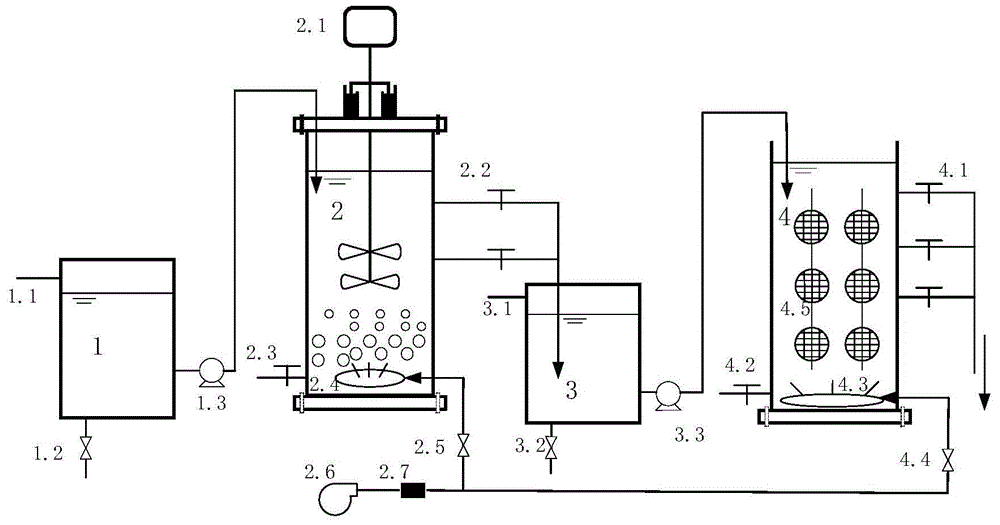
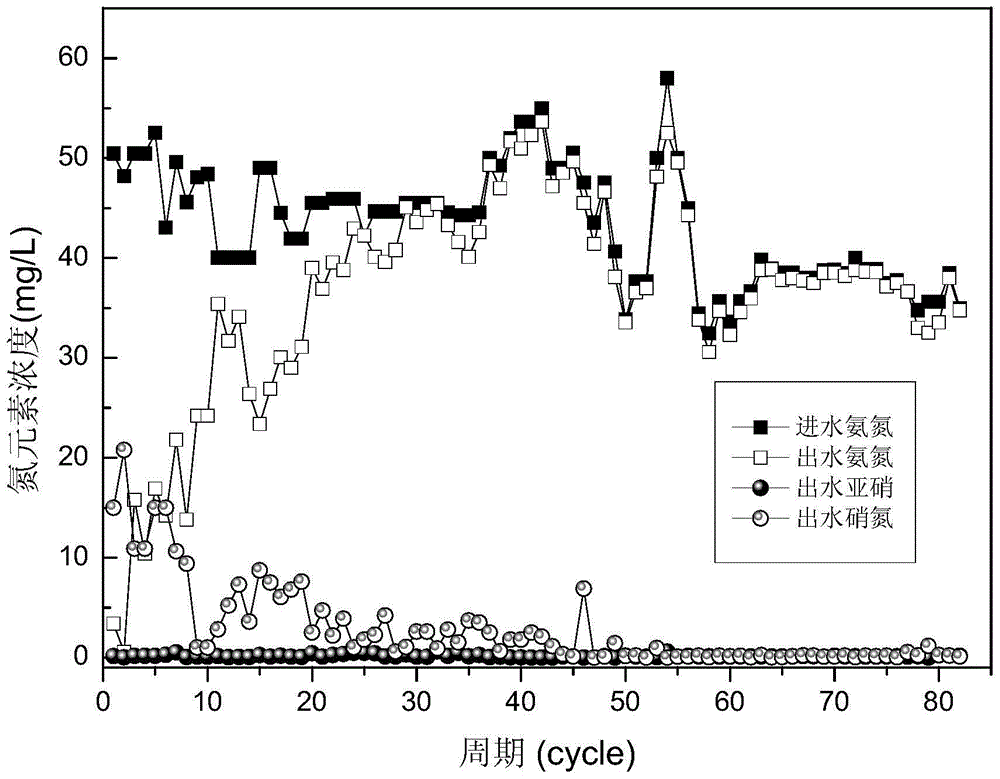
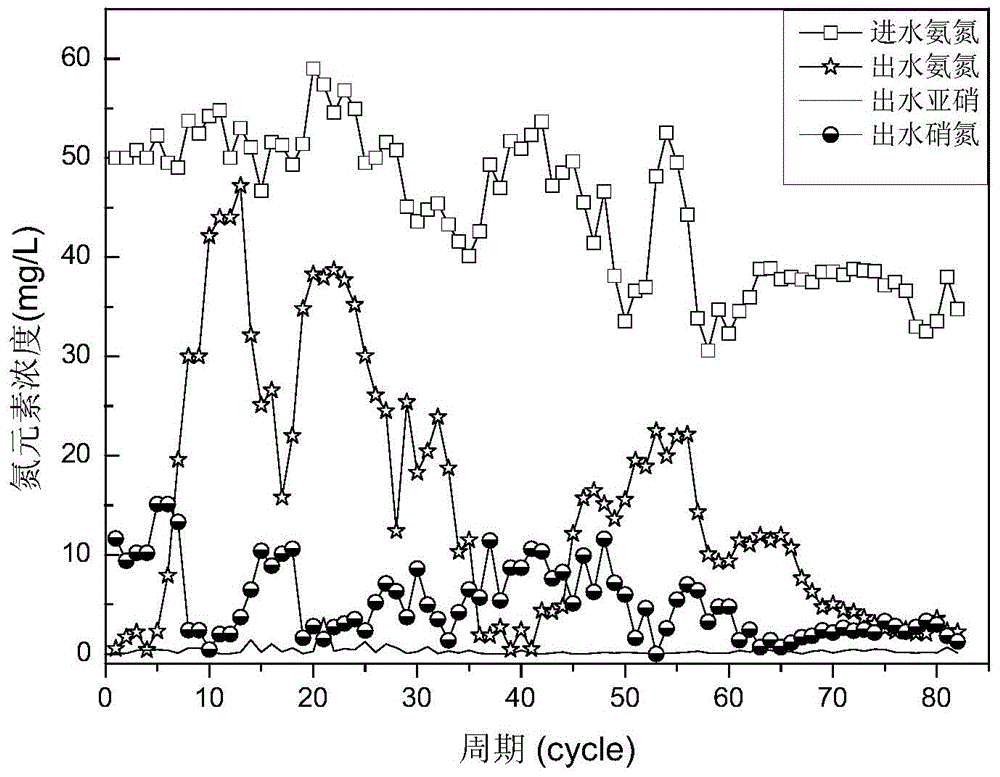
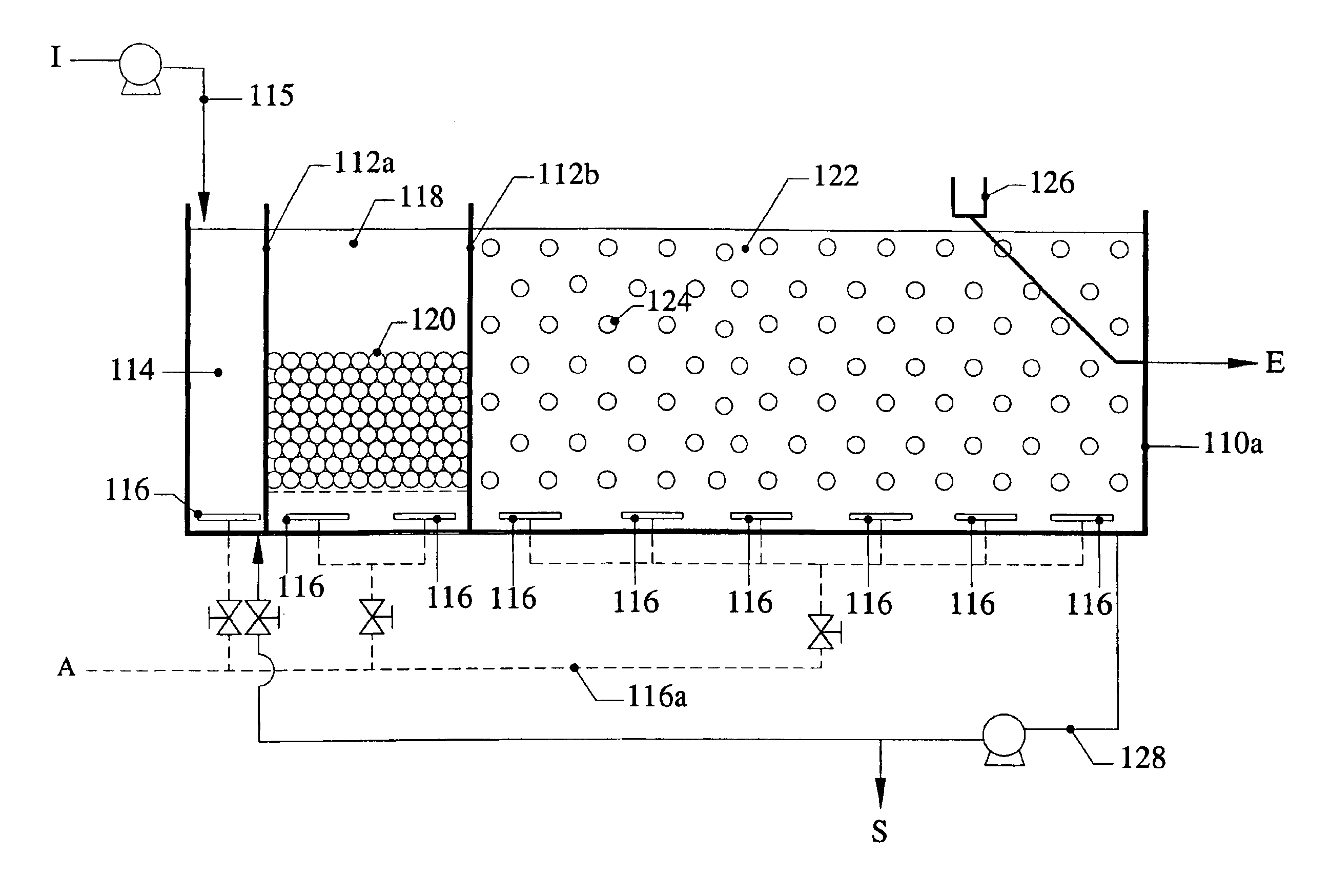
Patents
Literature
705 results about "Sequencing batch reactor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sequencing batch reactors (SBR) or sequential batch reactors are a type of activated sludge process for the treatment of wastewater. SBR reactors treat wastewater such as sewage or output from anaerobic digesters or mechanical biological treatment facilities in batches. Oxygen is bubbled through the mixture of wastewater and activated sludge to reduce the organic matter (measured as biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD)). The treated effluent may be suitable for discharge to surface waters or possibly for use on land.
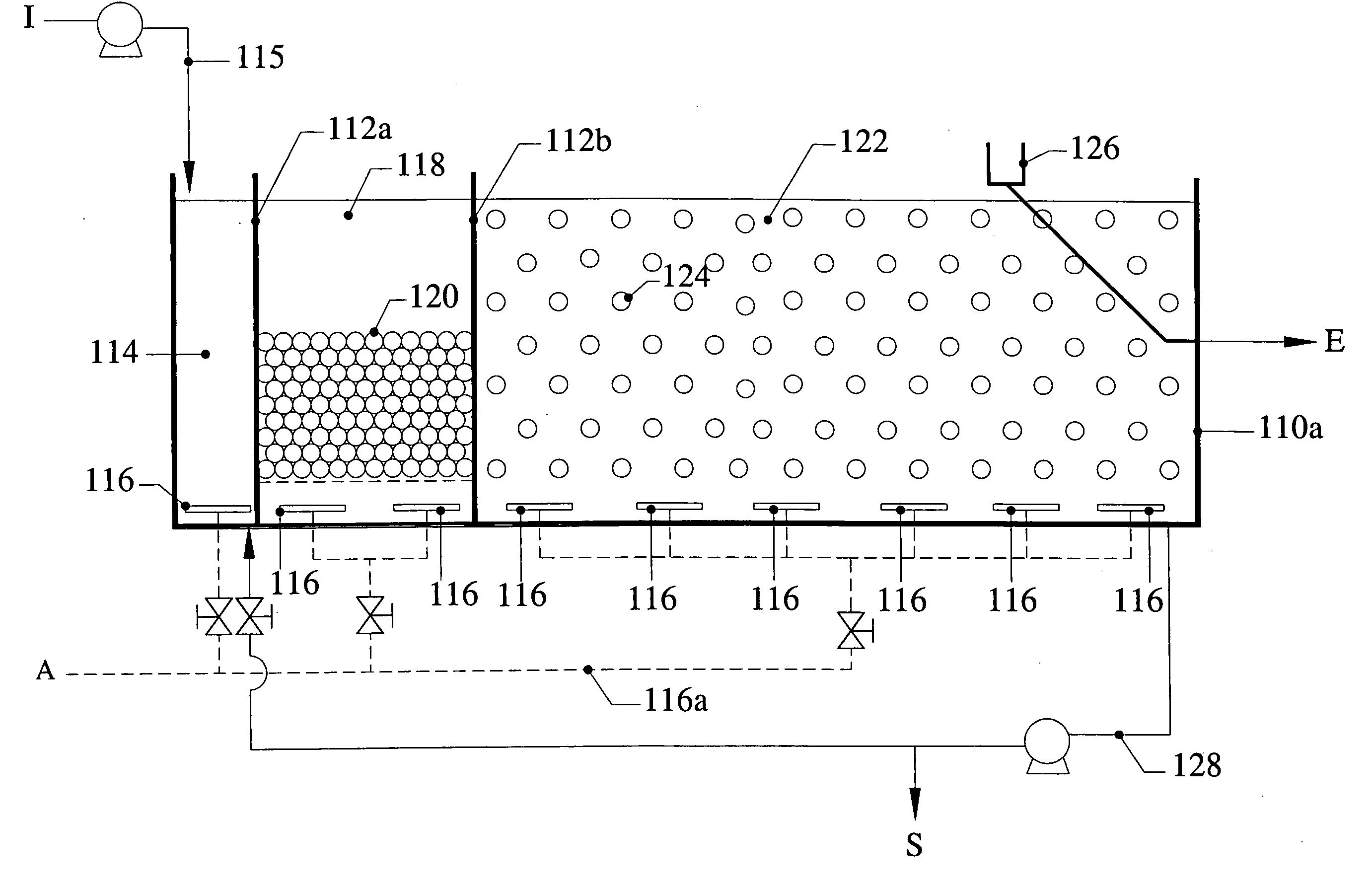
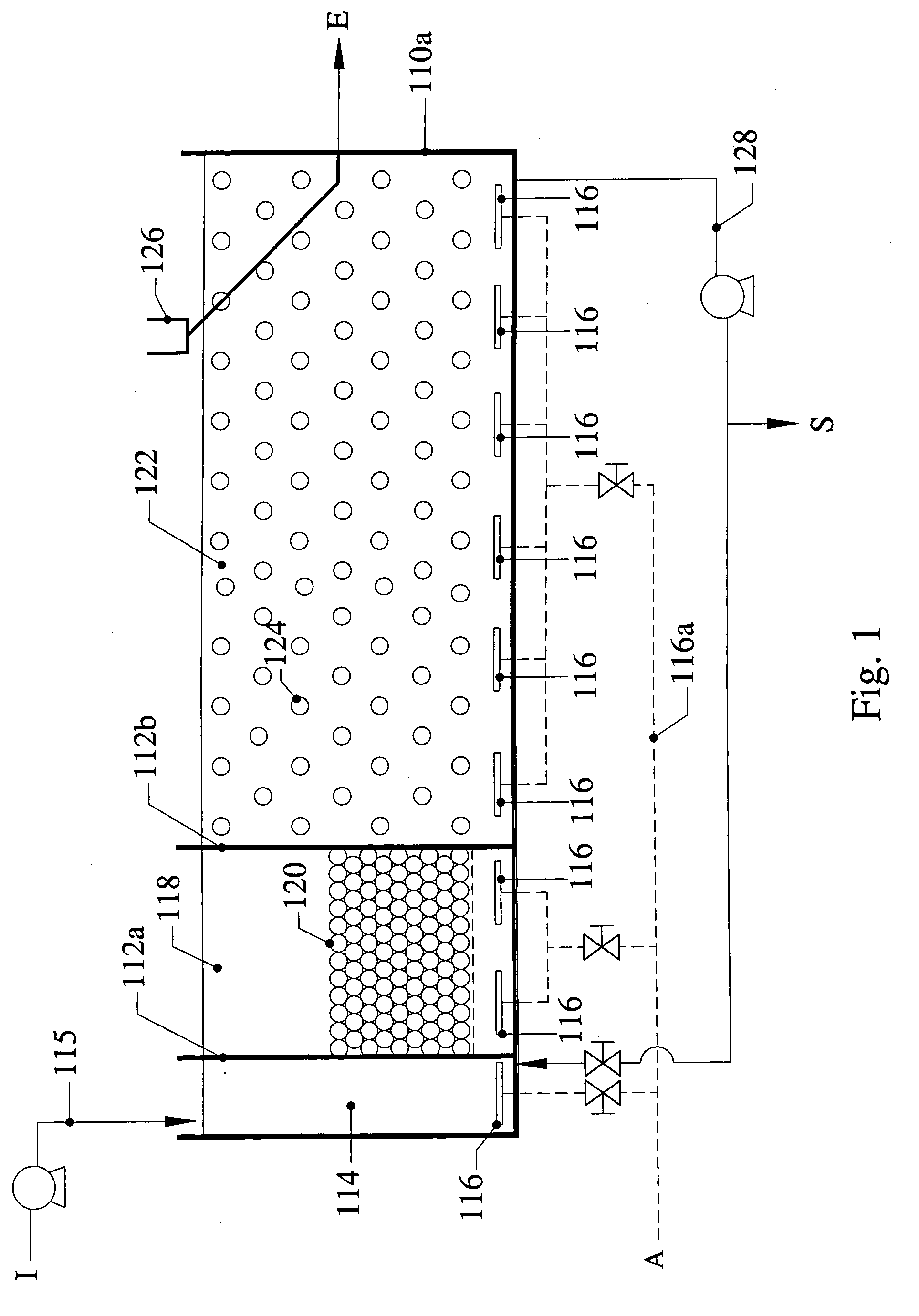
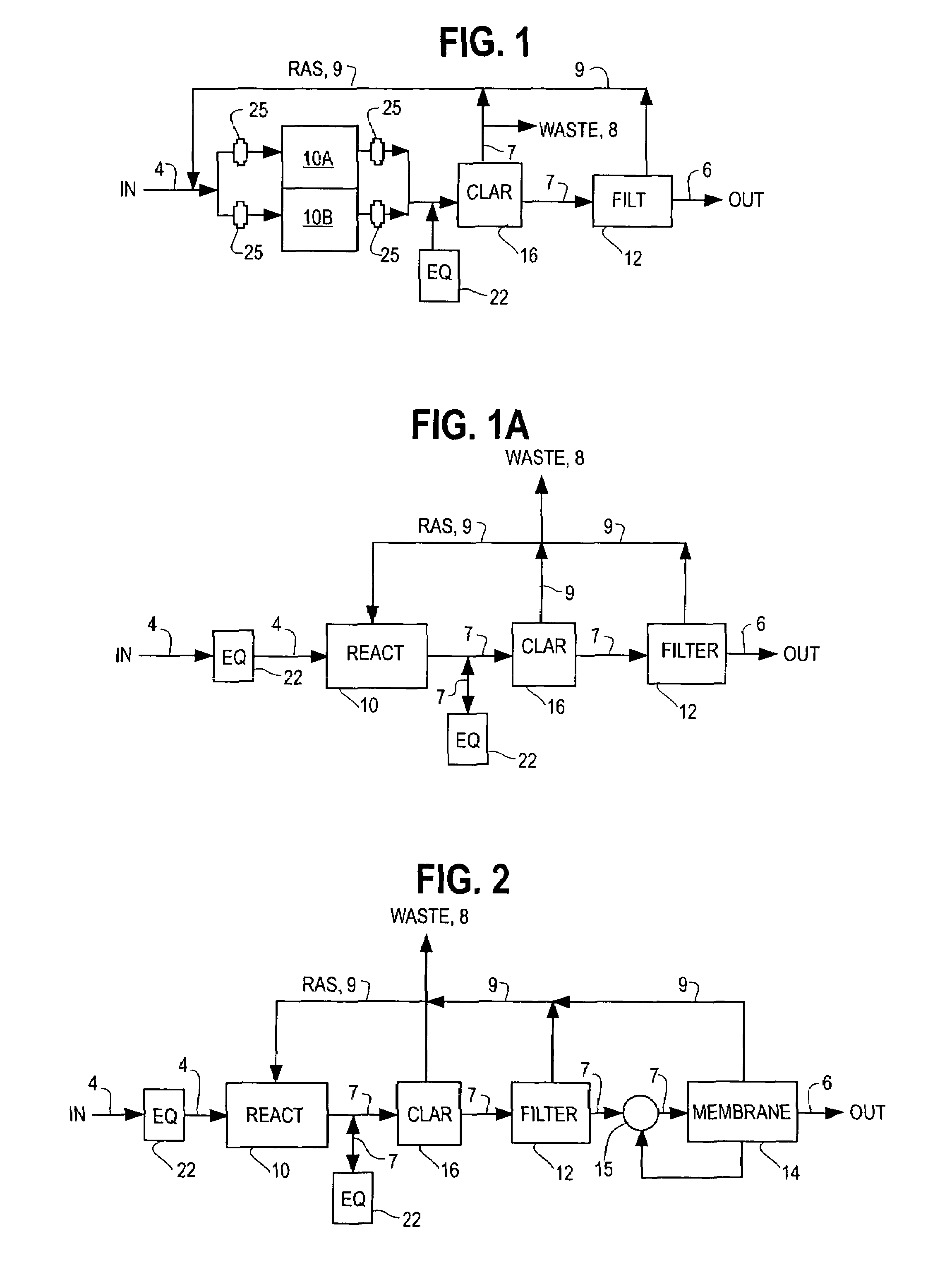
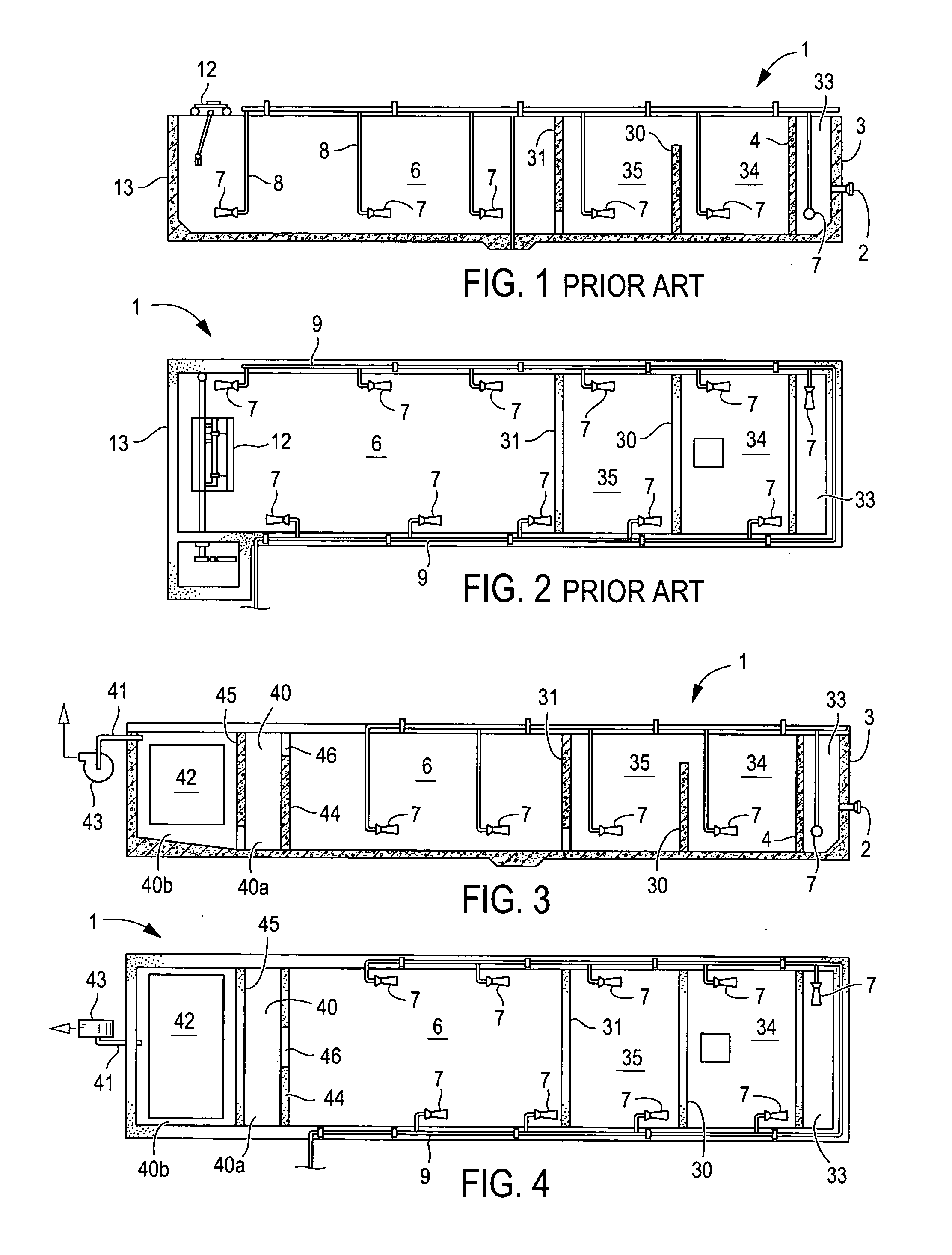
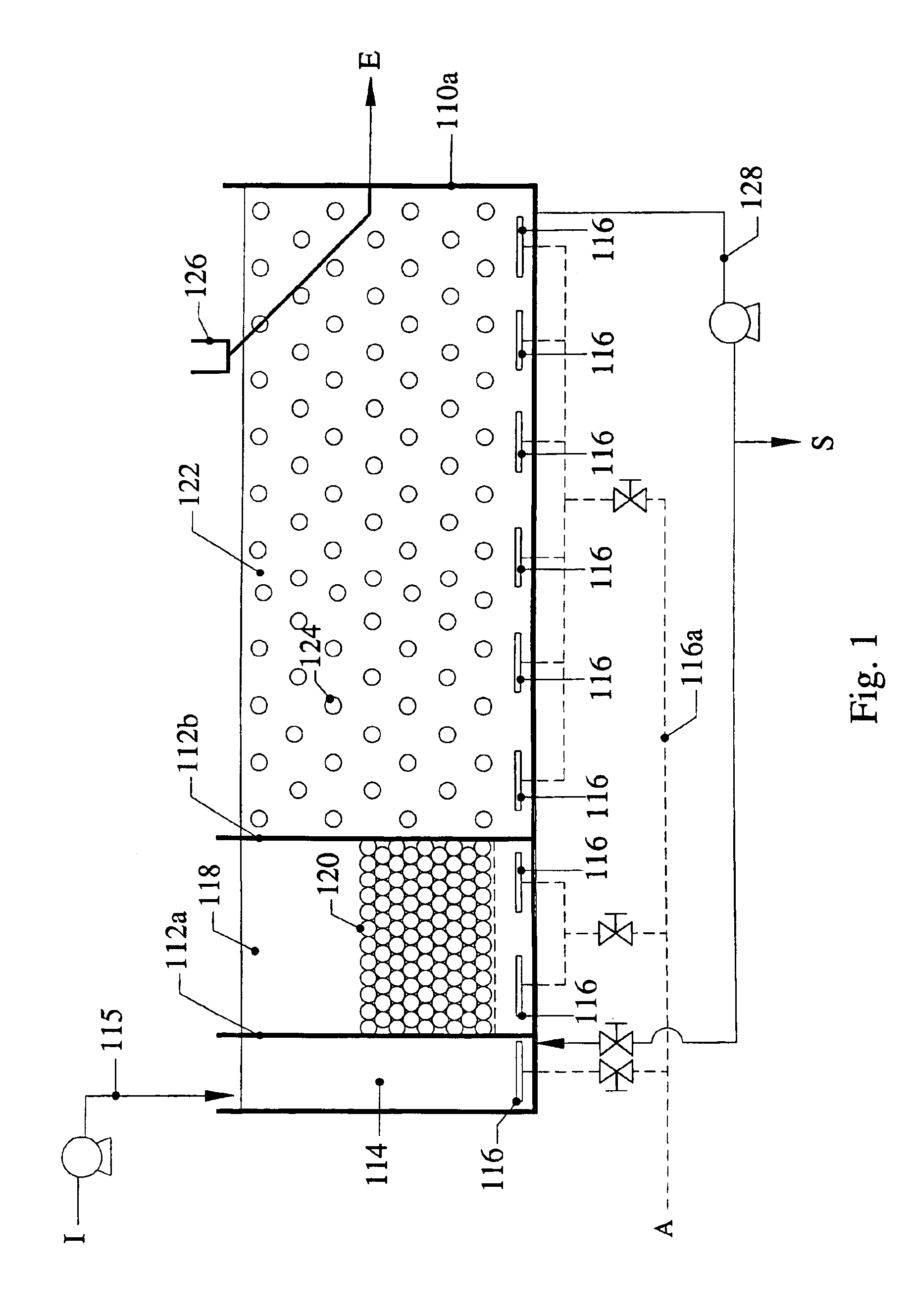
Combined activated sludge-biofilm sequencing batch reactor and process
InactiveUS20040206699A1Similar oxygen transfer efficiencyRemoval can be promoted and increasedTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesSequencing batch reactorActivated sludge
A new biofilm-activated sludge Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) treatment process for sewage or wastewater has successfully been developed as the third generation SBR (SBR3). This new SBR3 process utilizes a multi-stage and multi-sludge SBR configuration receiving either continuous or intermittent inflow of wastewater. Each stage has individually controlled continuous or alternating anaerobic / anoxic / aerobic operation, with or without mixing and recycling from the other stage(s). The configuration and operation is dependent upon the treatment objectives and effluent discharge requirements. In the preferred embodiment, carriers are used to facilitate control of operating conditions.
Owner:KINGSFORD ENVIRONMENTAL H K
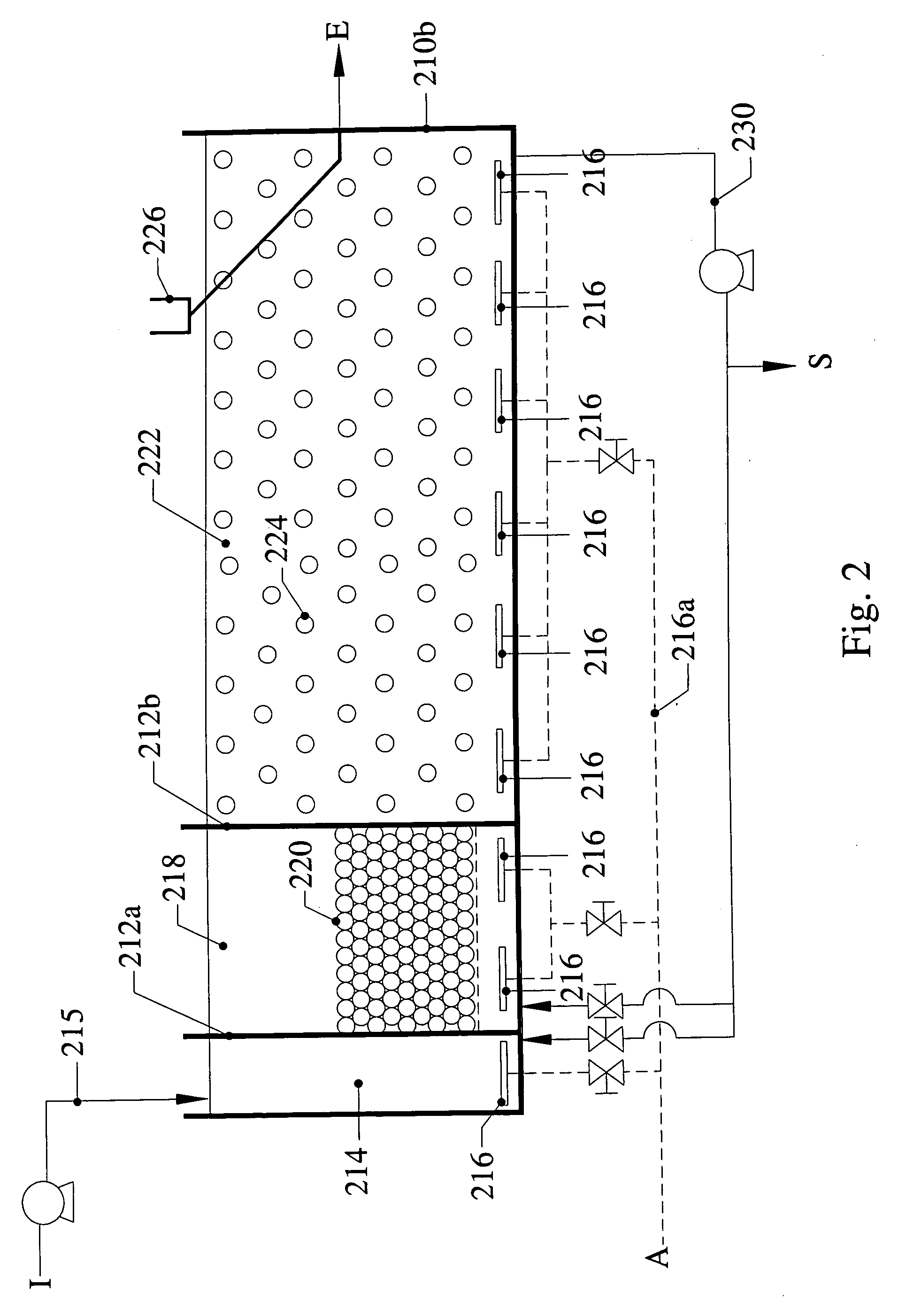
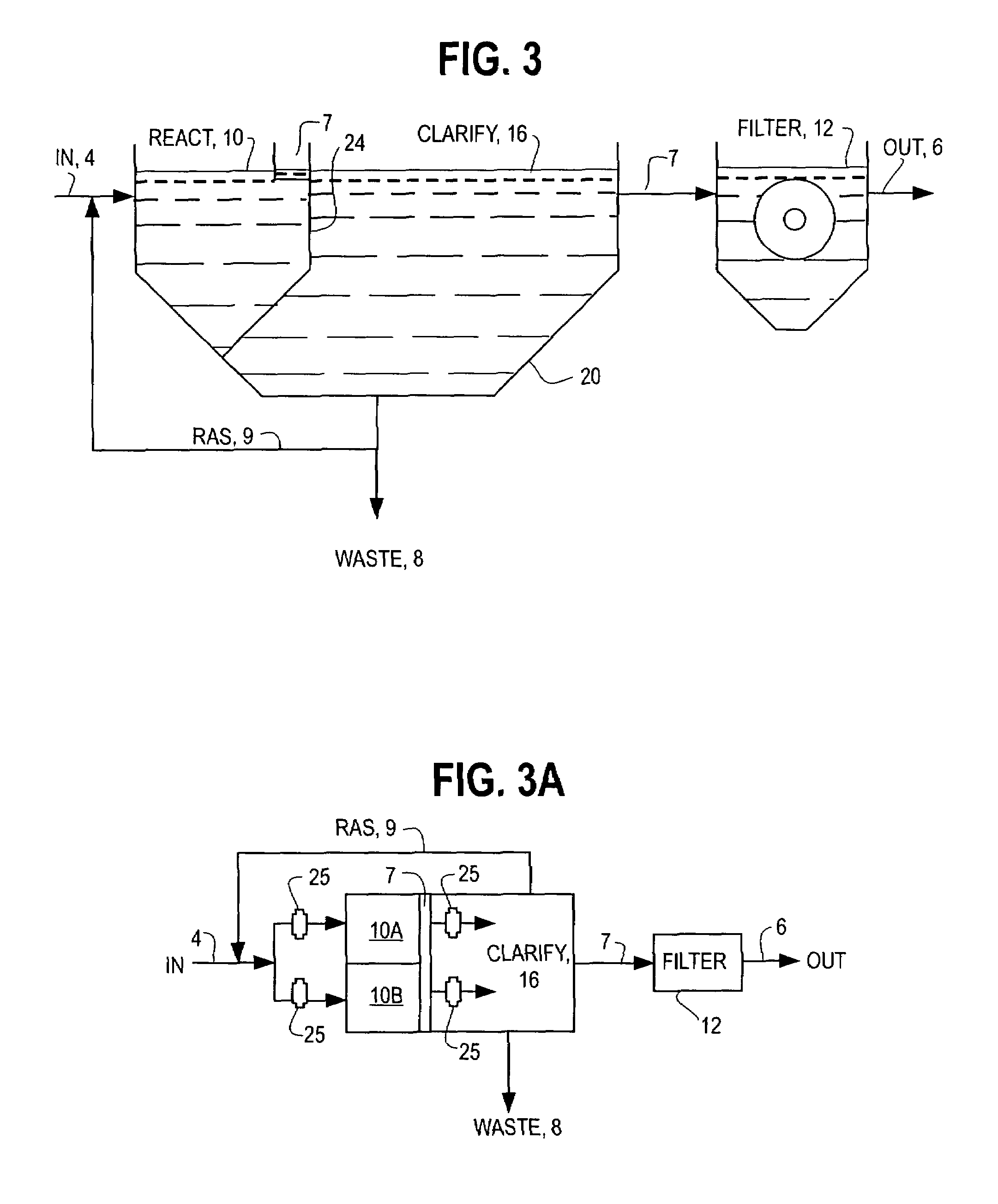
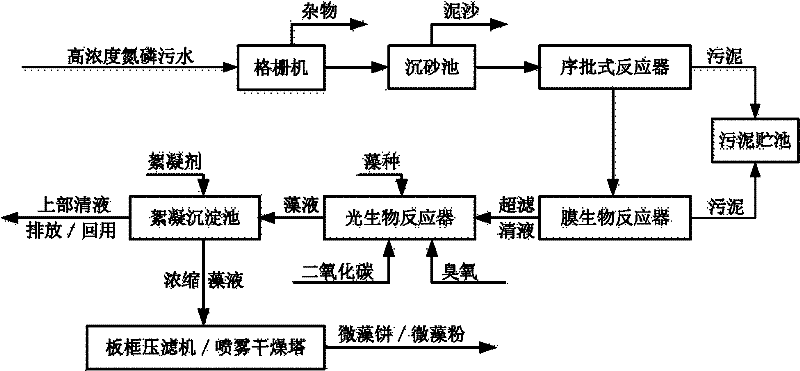
Multiple barrier biological treatment systems
InactiveUS7014763B2Small footprintReduce construction costsTreatment using aerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentSequencing batch reactorSingle vessel
The inventions separate the activated sludge, biochemical reaction stages of the batch treatment process of a sequencing batch reactor from the clarification and sedimentation stages by separating the locations where each process takes place. The separation may be accomplished in a variety of ways including constructing separate basins for each process, installing baffles or other partitions in a single vessel to isolate the areas where each process takes place, or other methods of process separation as are known in the art. In each process, treatment occurs through the performance of a series of operations. The operations are repeated for each batch of wastewater processed by the SBR. In a conventional SBR process, the cycle of operations for clarification and sedimentation are dependent on a preceding biochemical reaction step. However, in the present invention the clarification and sedimentation operations are independent of the biochemical reaction operations. It remains possible to coordinate operations so that the process cycles are coincident, however the benefits of the invention are more readily realized by the practice of independent operation.
Owner:AQUA AEROBIC SYST
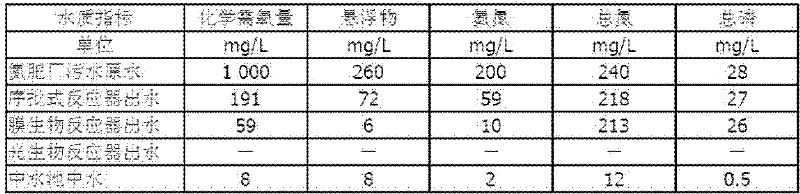
Nitrogen-phosphorus wastewater treating method by sequencing batch reactor coupled photobioreactor
ActiveCN102336498AWater quality varies widelyMultistage water/sewage treatmentSequencing batch reactorHigh concentration
The invention relates to the field of environmental wastewater treatment, specifically to a nitrogen-phosphorus wastewater treating method by a sequencing batch reactor coupled photobioreactor. The method provided by the invention is characterized in that it comprises the following steps of: removing impurities and sediments of high concentration nitrogen-phosphorus wastewater and then treating the wastewater by using active sludge in the sequencing batch reactor, decanting a supernatant from the sequencing batch reactor, adding the supernatant into a membrane bioreactor for further aerobic treatment, filtering by ultrafiltration membrane in the membrane bioreactor to remove micro-suspension and bacteria, adding a generated ultrafiltration supernatant into a photobioreactor, disinfecting by ozone and adding algae filament as well as a few necessary nutrient salt, filling with carbon dioxide waste gas to perform microalgae cultivation, discharging a algae liquid after a microalgae growth cycle and adding the algae liquid into a flocculating settling pool for sedimentation, standardly discharging or reusing a supernatant liquor, compressing the concentrate algae liquid at the bottominto a microalgae cake by a plate and frame filter press. The invention has advantages of wide range of treated nitrogen-phosphorus wastewater water quality variation and production of economical microalgae with the utilization of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients in wastewater as more as possible.
Owner:DALIAN DAKAI SEWAGE TREATMENT
Highly efficient treatment process for waster water with high content of salt
InactiveCN101054232AEasy to handleImprove settlement performanceWater contaminantsSustainable biological treatmentSequencing batch reactorSalinity
A high efficient processing technique for hypersaline waste water generates aerobic granular sludge in a sequencing batch reactor and adopts certain startup method and sluge domestication method, in condition of without halophilic bacteria, sludge in the reactor realize aggregating growth and form composite microecology, so hypersaline waste water can be processed effectively and resistance to salinity shock of the system can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for treating high-salinity high-concentration ammonia-nitrogen wastewater
InactiveCN102849857AOvercoming processingOvercome the shortcomings of wastewater resistant to high ammonia nitrogenBacteriaBiological water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationActivated sludge
The invention discloses a method for treating high-salinity high-concentration ammonia-nitrogen wastewater, characterized by: adopting sequencing batch reactor, accumulating nitrification sludge by alternately increasing the concentration of a nutrient solution or ammonia-nitrogen concentration, and domesticating to obtain high salinity-resisting high ammonia nitrogen-resisting nitrobacteria. According to the invention, the nitrobacteria can treat high-salinity wastewater having ammonia-nitrogen concentration of 500mg / L and having the salt content of no larger than 35g / L to make the effluent have the ammonia-nitrogen concentration of no larger than 10mg / L, thus the effluent achieve national level of discharging standard; the method has good effect on treating high-salinity high ammonia-nitrogen wastewater in chemical plant, leather factory, oil refinery and the like, can overcome the shortage that the nitrobacteria cannot simultaneously treat high-salinity and high ammonia-nitrogen wastewater existing in the prior art, and has important economic benefits and social benefits.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Process and method for denitrification and phosphorus removal of municipal sewage by half shortcut nitrification and anaerobic ammonium oxidation
ActiveCN102557356AAvoid inhibitionImprove efficiencyTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentSequencing batch reactorChemistry
The invention provides a process and method for denitrification and phosphorus removal of municipal sewage by half shortcut nitrification and anaerobic ammonium oxidation, which belongs to the technical field of sewage biological treatment. The process comprises an untreated water tank, a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) for removing organic matters, a first regulating water tank, a half shortcut nitrification SBR, a second regulating water tank and an autotrophic denitrification upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor sequentially connected in series. Sludge is separated according to sludge age, which avoids an influence of rapid propagation of heterotrophic bacteria to autotrophic denitrification flora; and a nitrification system adopts half shortcut nitrification, which stably maintains shortcut more easily, ensures the nitrosification rate of the nitrification system, and provides guarantee for denitrification stability of the system. The anaerobic ammonium oxidation technique is applied to deep denitrification treatment of domestic sewage, which reduces the oxygen consumption by 60% compared with the conventional denitrification method, is free of additional carbon sources and neutralizers, and realizes high-efficiency low-energy consumption municipal sewage treatment.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Rapid start method for integrated autotrophic denitrification system
ActiveCN106673205AExtend the aeration timeReduce hypoxic timeWater treatment parameter controlTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSequencing batch reactorMass ratio
The invention relates to a rapid start method for an integrated autotrophic denitrification system and belongs to the technical field of treatment of sewage with high ammonia nitrogen. An SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor) is inoculated with short-cut nitrification sludge and anammox sludge according to the mass ratio of (1: 3) to (1: 1), and the concentration of mixed sludge is 3,000mg / L to 4,000mg / L. The dissolved oxygen is controlled to be 0.3mg / L to 0.5mg / L by adopting an intermittent aeration operating mode, and the accumulation amount of nitrite nitrogen at the end of aeration is 20mg / L to 30mg / L; in each cycle, three aeration and hypoxic stages are set at intervals; each cycle has six stages, i.e., water inlet, aeration / hypoxic reaction, stirred degassing, precipitating, water outlet and standing. In a starting process, the concentration of dissolved oxygen is controlled unchanged, the balance of supply and consumption of nitrite nitrogen is maintained through a method of stagewise prolonging aeration stage time and shortening hypoxic stage time, and the rapid increase of denitrification load is achieved. When the initial ammonia nitrogen concentration in the reactor reaches 300mg / L, the balance of supply and consumption of nitrite nitrogen is maintained by means of shortening the hypoxic stage time. According to the method, the starting speed is high, the total-nitrogen removal load is high, and the operation is stable.
Owner:SHANGHAI YIKE ENVIRONMENT TECH CO LTD
Technology and method for treating urban sewage by three-section short-cut nitrification/ anaerobic ammonia oxidation
ActiveCN102583885AReduce oxygen consumptionImprove efficiencyTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentSequencing batch reactorConcentration ratio
The invention provides a technology and a method for treating urban sewage by three-section short-cut nitrification / anaerobic ammonia oxidation, and belongs to the technical field of biological treatment of sewage. A raw water tank, an organic substance removal sequencing batch reactor (SBR), a first regulating water tank, a short-cut nitrification SBR (provided with an on-line monitoring and feedback control system), a second regulating water tank and an autotrophic nitrogen removal up-flow anaerobic sludge bed / blanket (UASB) reactor are sequentially connected in series in the technology; and the sludge is separated according to the sludge age, so that the contradiction between denitrification and phosphorus removal sludge age is solved. By applying the real-time control technology of the short-cut nitrification SBR to the autotrophic nitrogen removal technology, the problems that the half short-cut of low ammonia nitrogen short-cut nitrification in continuous flow is difficult to maintain, the concentration ratio of ammonia nitrogen to nitrous in the effluent is difficult to control and the like are solved. By successfully applying the anaerobic ammonia oxidation technology todeep denitrification treatment of the domestic sewage, urban sewage treatment with high efficiency and low energy consumption is realized.
Owner:上海立源生态工程有限公司
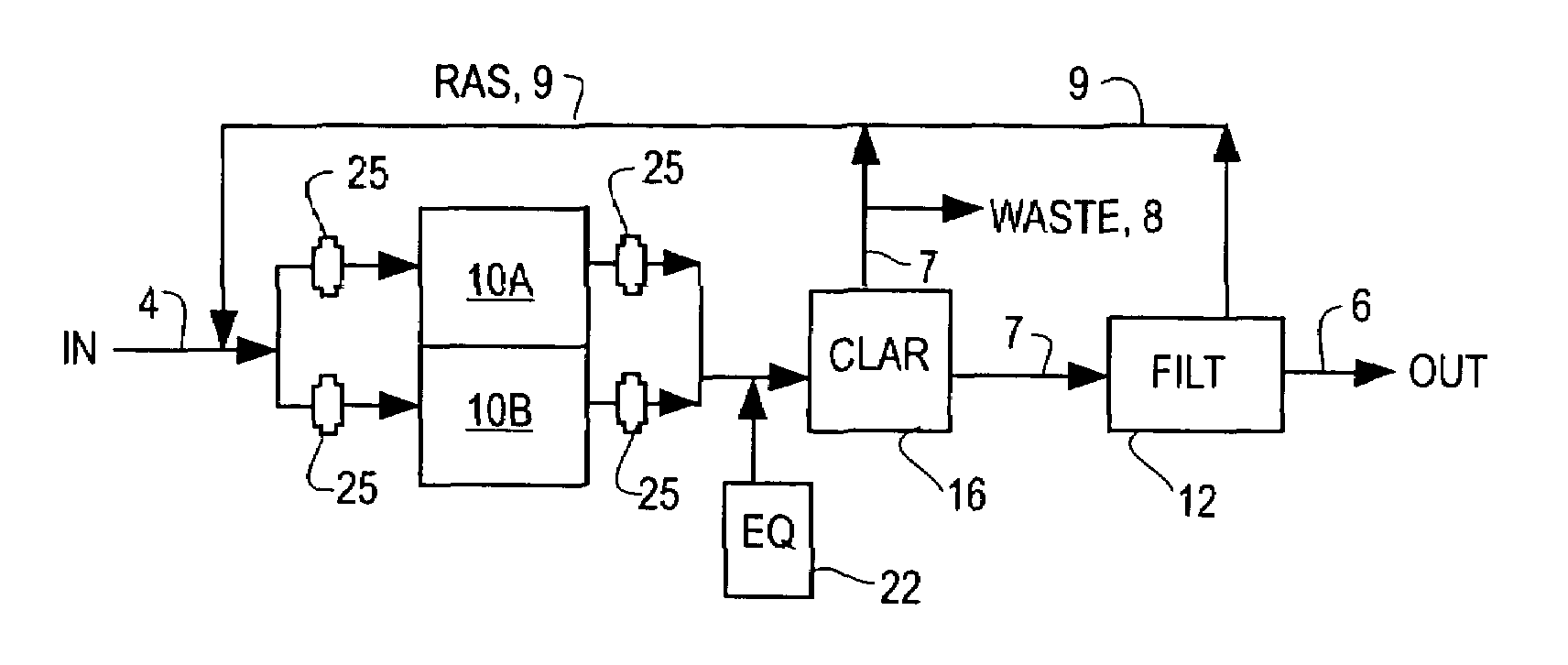
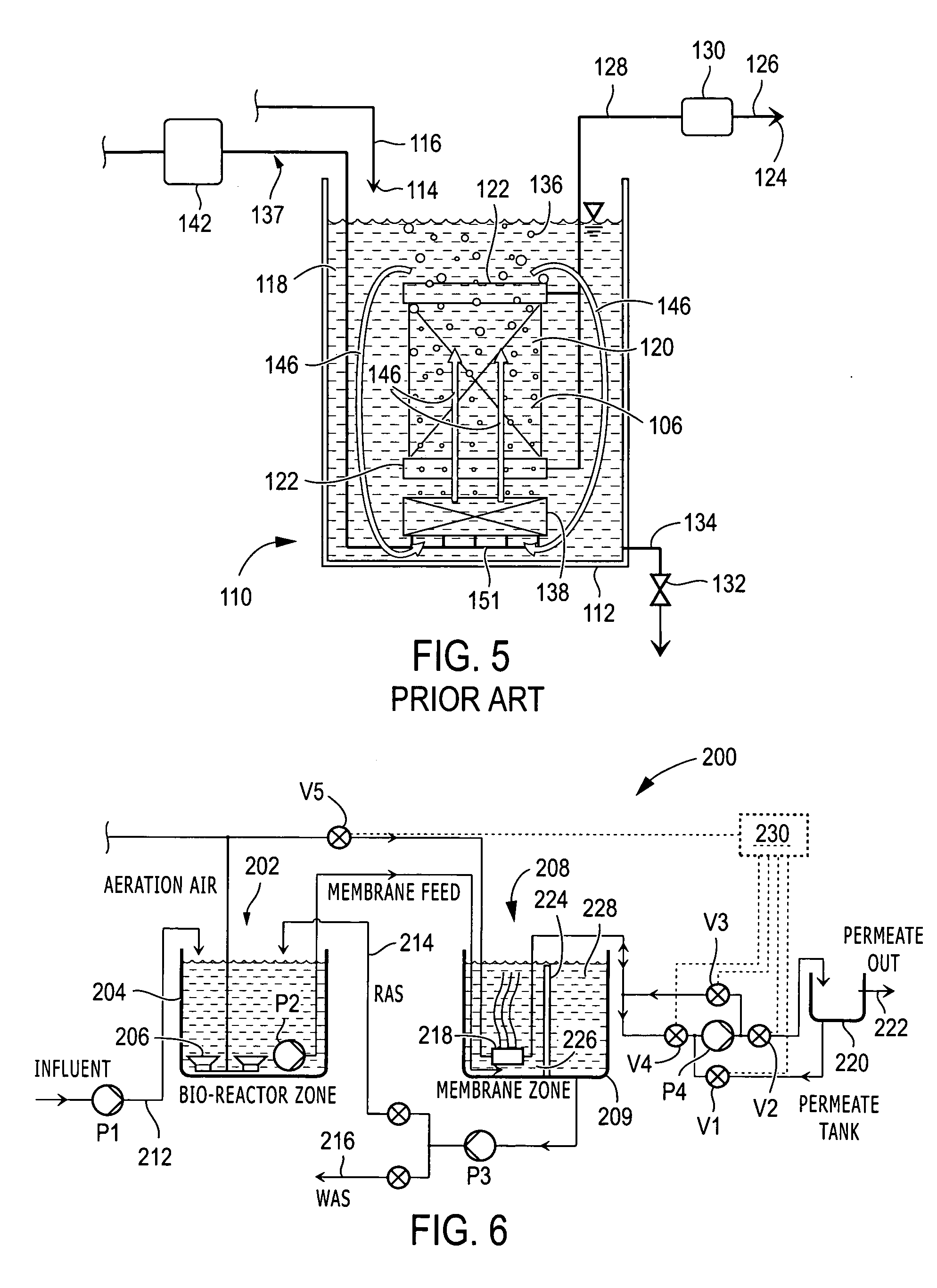
Energy-efficient biological treatment with membrane filtration
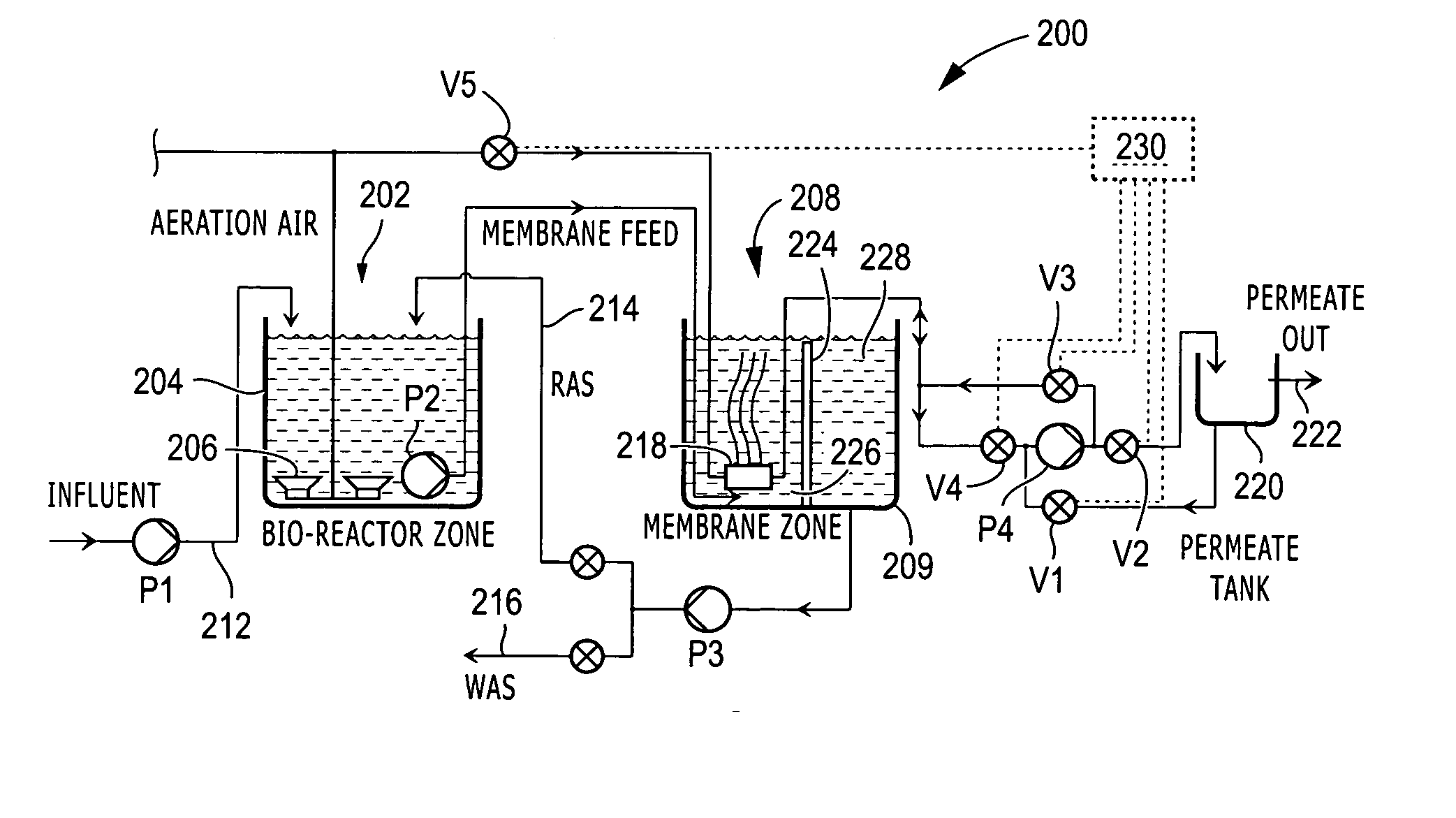
ActiveUS20060081534A1Easy to operateLiquid separation auxillary apparatusTreatment using aerobic processesSequencing batch reactorUltrafiltration
A membrane filtration system comprising one or more submerged ultrafiltration or microfiltration membrane assemblies at ambient pressure, each membrane assembly positioned 100-240 mm from a nearest wall, baffle, or adjacent membrane assembly and no more than 1 meter above a floor and at least 150 mm below the liquid level. Mixed liquor is discharged underneath each membrane assembly to create a vertical flow velocity in a range of 1-8 mm / second along an entire length of the membrane assembly. In a sequenced batch reactor system, a coarse bubble air diffuser for scouring each membrane assembly is supplied with air only during the backwash cycle of the filtration system and not during the filtration cycle. In a membrane bioreactor system, the biological treatment section is physically separated from the filtration section and fine bubble air diffusion is used in the biological treatment section.
Owner:ITT MFG ENTERPRISES LLC
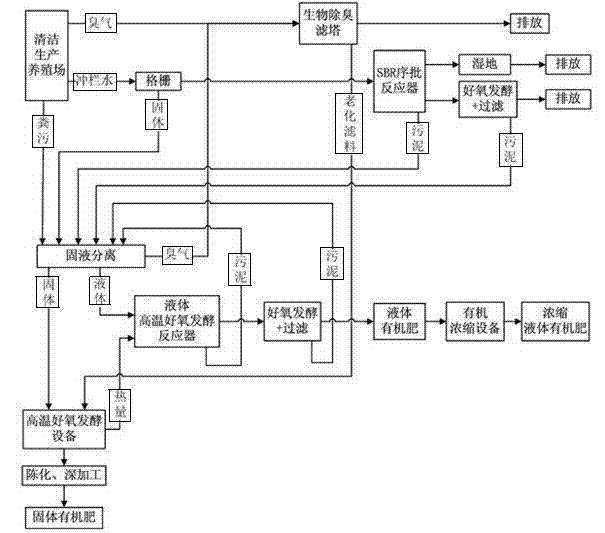
Pollution abatement method for livestock and poultry farm
ActiveCN102964149ALow costLow miniaturizationBio-organic fraction processingClimate change adaptationSequencing batch reactorActivated sludge
The invention discloses a pollution abatement method for a livestock and poultry farm. The method comprises the following steps of: separating feces from fence washing water and rain water at the source; carrying out solid-liquid separation on the feces and the sludge generated in each treatment procedure; conveying the separated liquid part to a plug flow anaerobic fermentation reactor or a liquid high-temperature aerobic fermentation reactor for liquid biological treatment, carrying out aerobic fermentation and filtration to get a liquid organic fertilizer; and conveying the separated solid part to a high temperature aerobic fermentation device, after fermentation, aging and deeply processing the solid part to get a solid organic fertilizer. Bad smell is exhausted after being processed in a biological deodorization filtering tower, and the filter material replaced from the biological deodorization filtering tower is considered as carbon source and conveyed to the solid aerobic fermentation device so as to be treated. Firstly, the fence washing water is treated by a grid impurity removal facility, after being treated by an SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor Activated Sludge Process) biological reactor and medicated for flocculation and sedimentation, the fence washing water is drained after being purified by a wet land, or drained after being treated by aerobic fermentation reaction and filtering, and the sedimentary sludge and the solid substances under the grid fence are conveyed into a solid-liquid separation procedure so as to be treated. The method can be used for managing or beneficially using all the pollutants, and contributing the effort for establishing the resource-saving and environmentally-friendly society.
Owner:HUNAN SAKAL ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
Two phase anaerobic contact sequencing batch reactor (ACSBR) system for treating wastewater containing simple and complex organic constituents
InactiveUS20060175252A1Improve efficiencyEfficient digestionWaste based fuelTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesSequencing batch reactorSuspended solids
A two-phase anaerobic treatment system and method for the treatment of wastewaters containing simple and complex organic constituents is provided wherein the complex organic constituents are broken down into simple organic constituents by acidogenic bacteria in a Phase One reactor and the simple organic constituents from the Phase One reactor are converted into biogas, mainly methane, in a Phase Two reactor by methanogenic bacteria. The method includes the steps of feeding wastewater to the Phase One reactor either in an intermittent batch mode or semi-continuous mode, and withdrawing effluent from the Phase One reactor preferably in a batch mode. Effluent from the Phase One reactor is fed to the Phase Two reactor in an intermittent batch mode while effluent from the Phase Two reactor is withdrawn in a batch mode. The method minimizes the transfer of suspended solids from the Phase One reactor to the Phase Two reactor.
Owner:UPENDRAKUMAR K C +2
Technology for treating domestic sewage by realizing partial short-cut nitrification, sludge fermentation coupling denitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation in sequencing batch reactor
ActiveCN108585202AEasy to upgradeAchieve reductionTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSustainable biological treatmentSequencing batch reactorNitration
The invention discloses a technology for treating domestic sewage by realizing partial short-cut nitrification, sludge fermentation coupling denitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation in a sequencing batch reactor, and belongs to the field of the sewage sludge biological treatment. The technology comprises an inlet water tank, a partial short-cut nitrification reactor (PN-SBR), an intermediate water tank, an anaerobic ammonia oxidation coupling sludge fermentation and denitrification reactor (ASFD-SBR), and an outlet water tank. The partial short-cut nitrification is performed in the partial short-cut nitrification reactor (PN-SBR), and a part of ammonia nitrogen in raw water is converted to nitrite nitrogen. The influent ammonia nitrogen and the nitrite nitrogen are converted to a nitrogen gas and a little of nitrate nitrogen by anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria in the anaerobic ammonia oxidation coupling sludge fermentation and denitrification reactor (ASFD-SBR), and the generated nitrate nitrogen is reduced to the nitrogen gas by a carbon source generated by sludge fermentation, wherein static bed filler is used for retaining the anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria, and denitrification and sludge fermentation processes are performed in floc sludge. The technology is capable of saving energy consumption, and simultaneously realizing the deep denitrification of theurban domestic sewage in a low carbon nitrogen ratio (C / N) and the recycling of the sludge.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
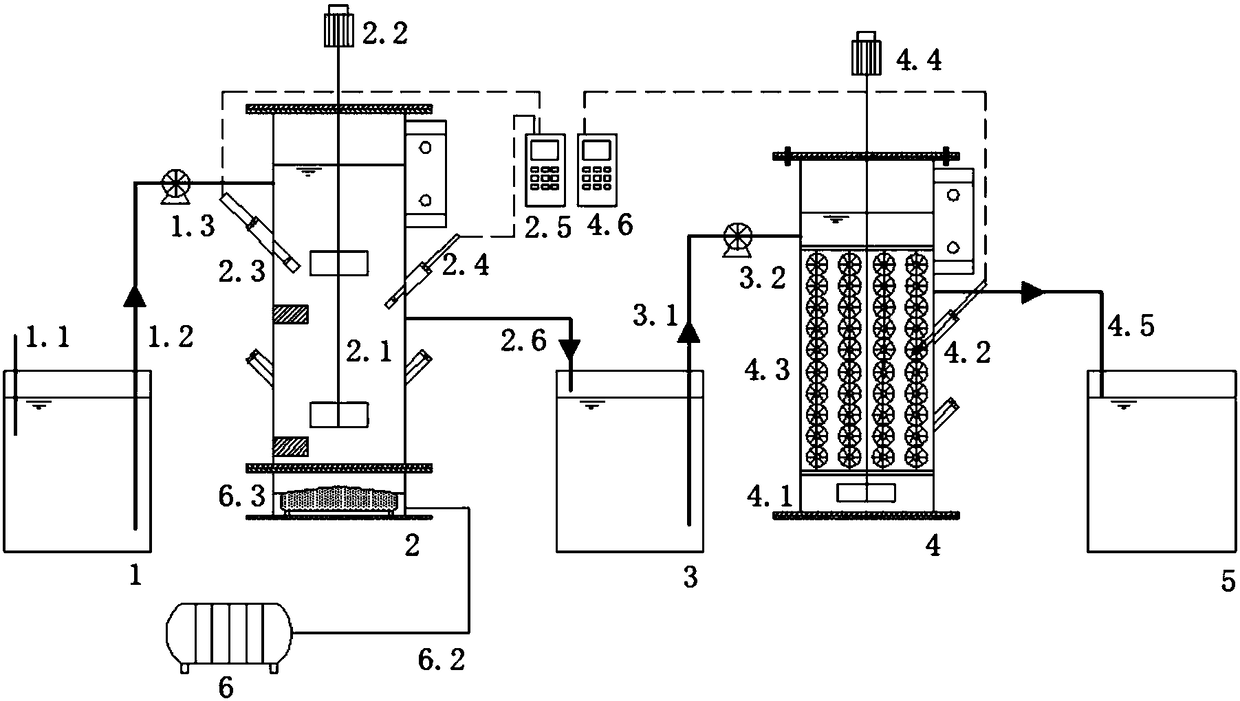
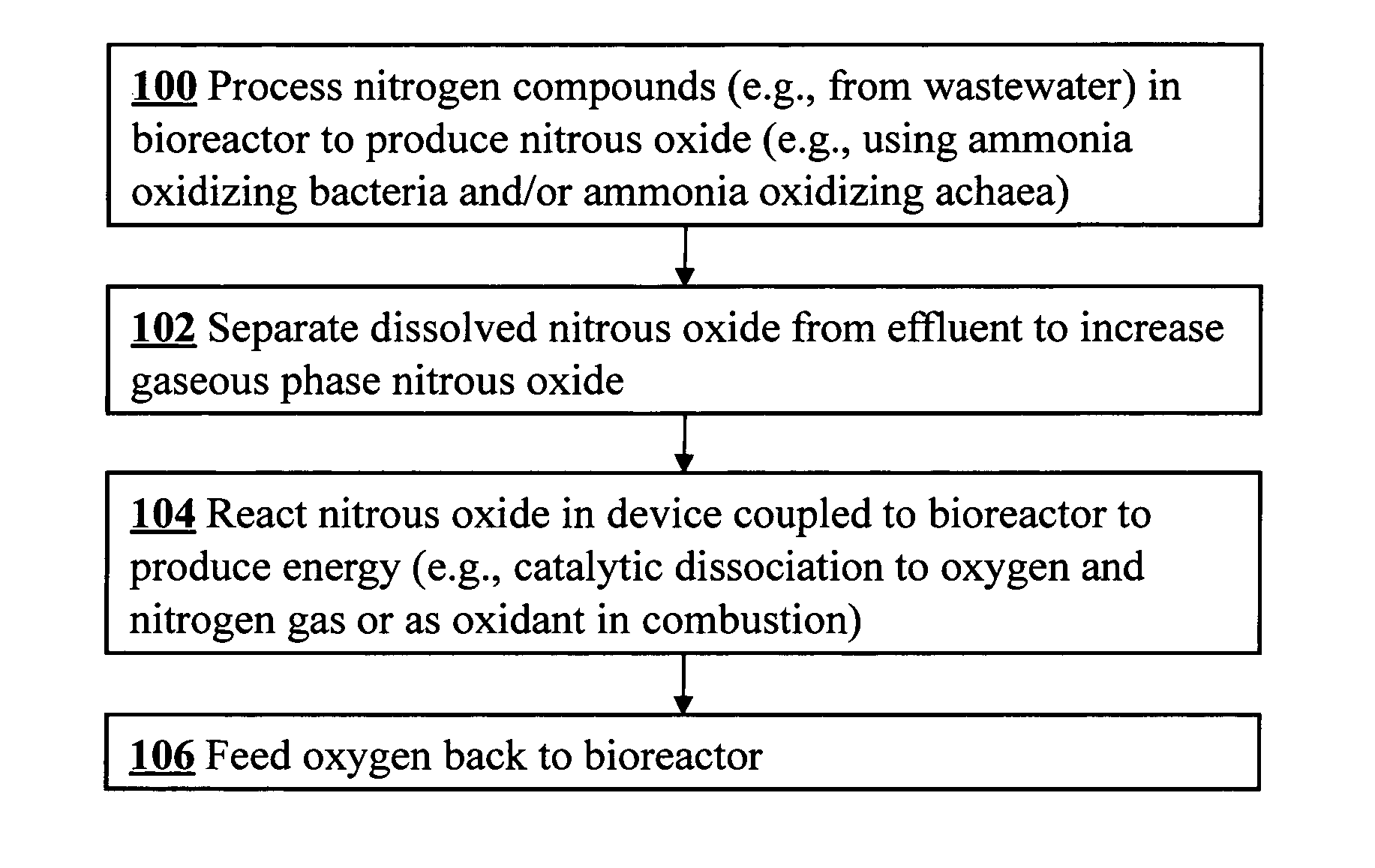
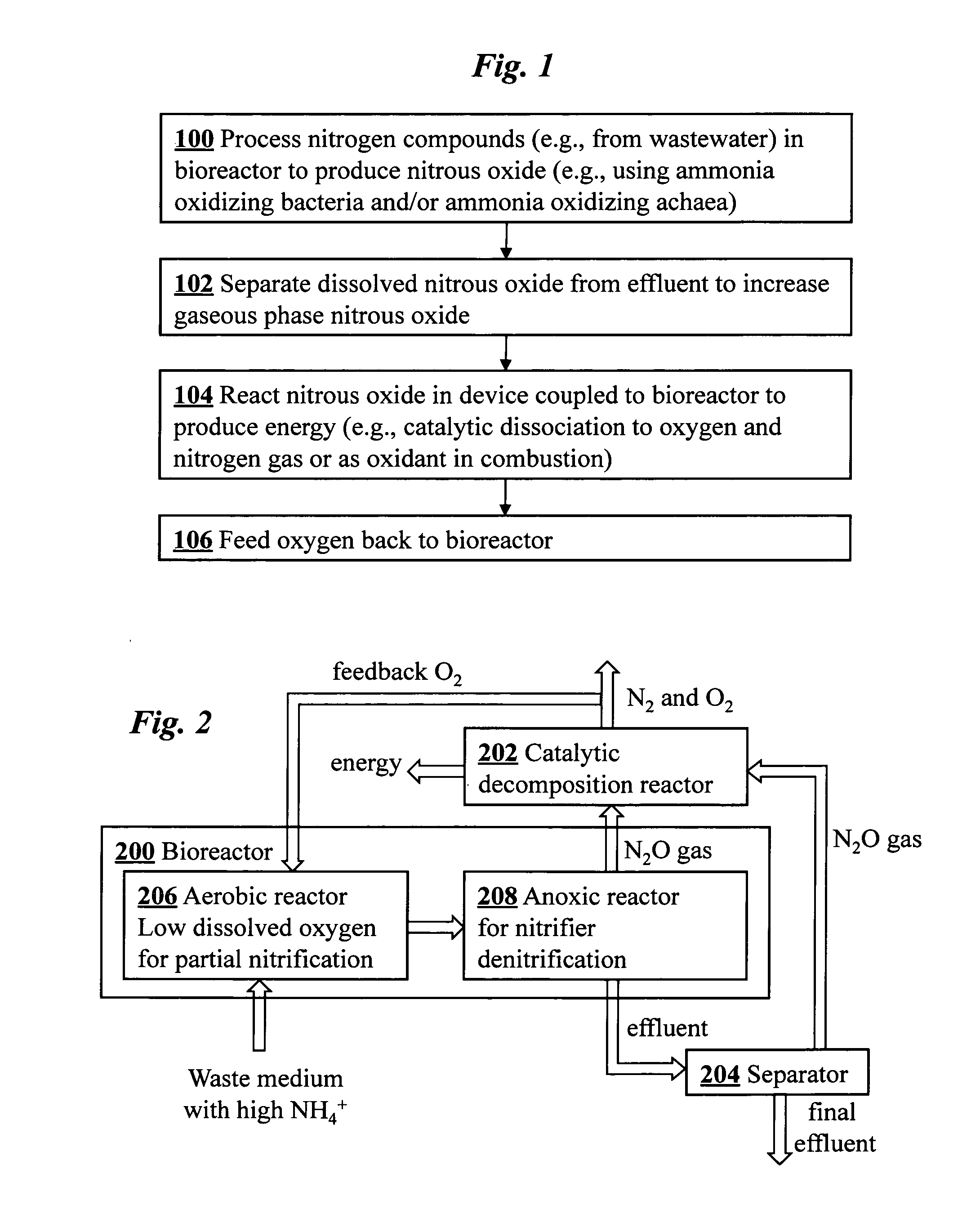
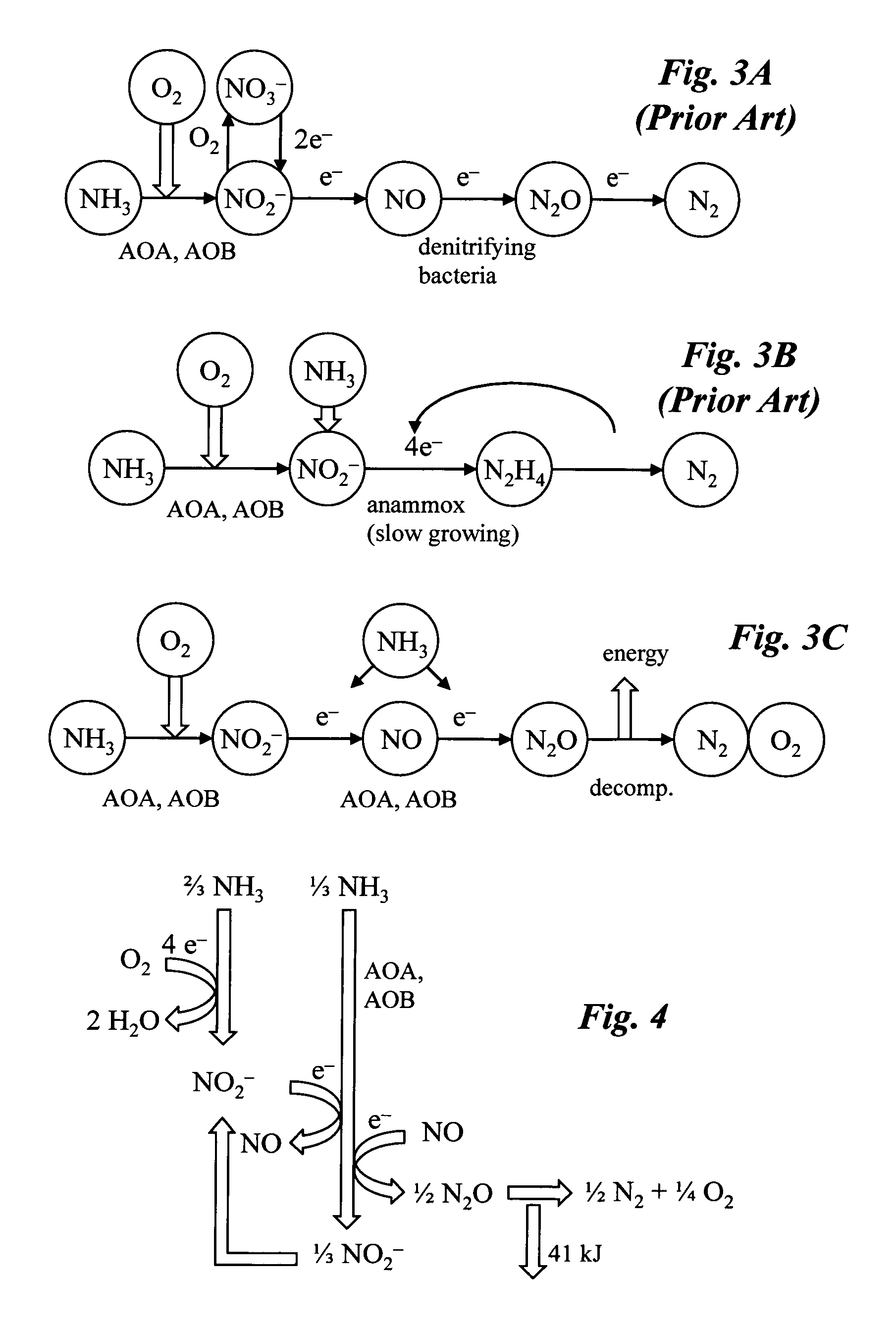
Microbial production of nitrous oxide coupled with chemical reaction of gaseous nitrous oxide
InactiveUS20110207061A1Treatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSustainable biological treatmentSequencing batch reactorFiber
A bioreactor designed to produce N2O from organic nitrogen and / or reactive nitrogen in waste is coupled to a hardware reactor device in which the N2O is consumed in a gas phase chemical reaction, e.g., catalytic decomposition to form oxygen and nitrogen gas.Heat from the exothermic reaction may be used to generate power. The N2O may alternatively be used as an oxidant or co-oxidant in a combustion reaction, e.g., in the combustion of methane. The bioreactor may have various designs including a two-stage bioreactor, a hollow-fiber membrane bioreactor, or a sequencing batch reactor. The bioreactor may involve Fe(II)-mediated reduction of nitrite to nitrous oxide.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Control method for partial nitrification-anaerobic ammonia oxidation integrated denitrification process
ActiveCN103226366AReal-time monitoring of process parametersHigh degree of automationControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsChemical variable controlSequencing batch reactorAeration rate
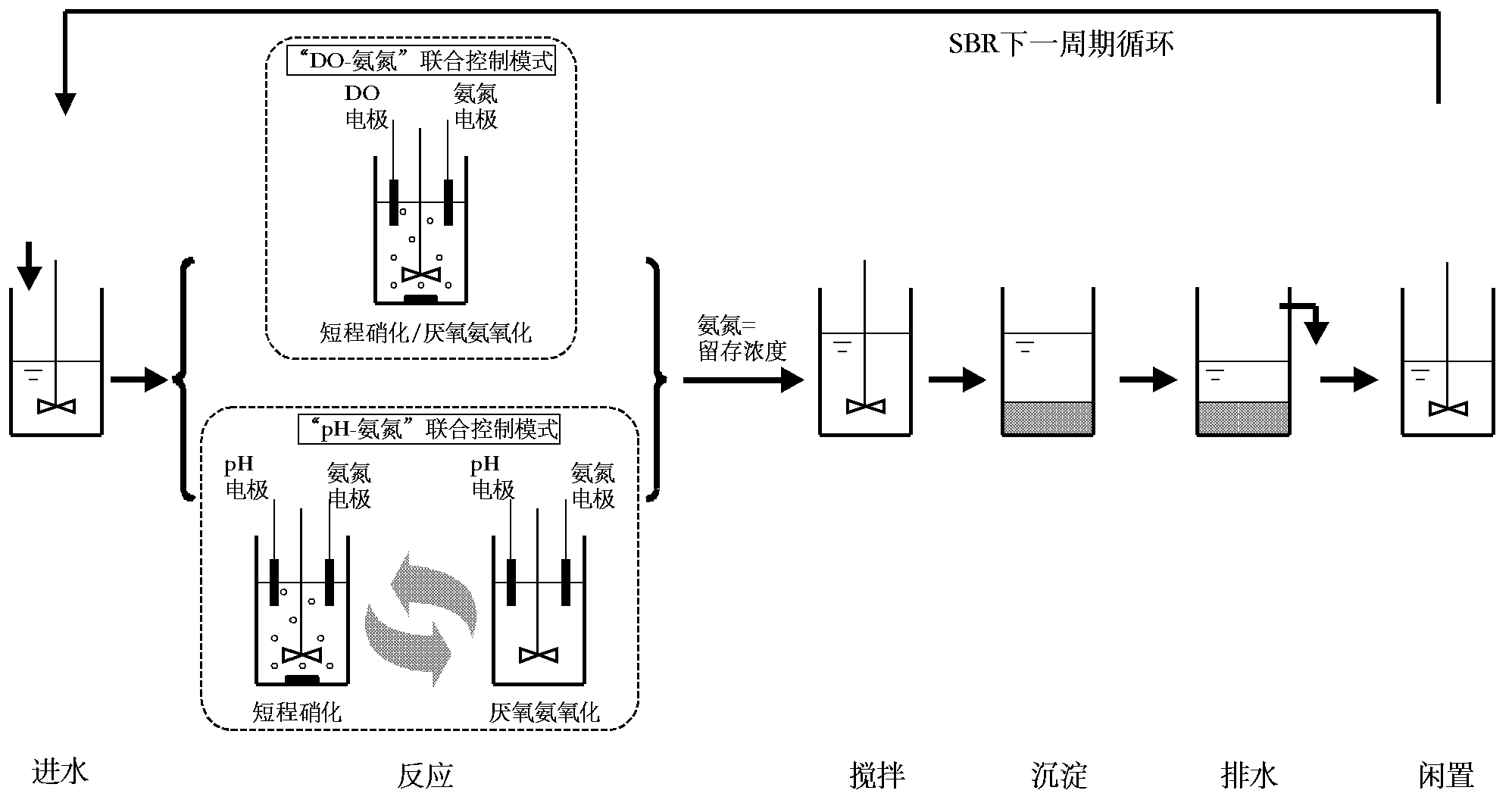
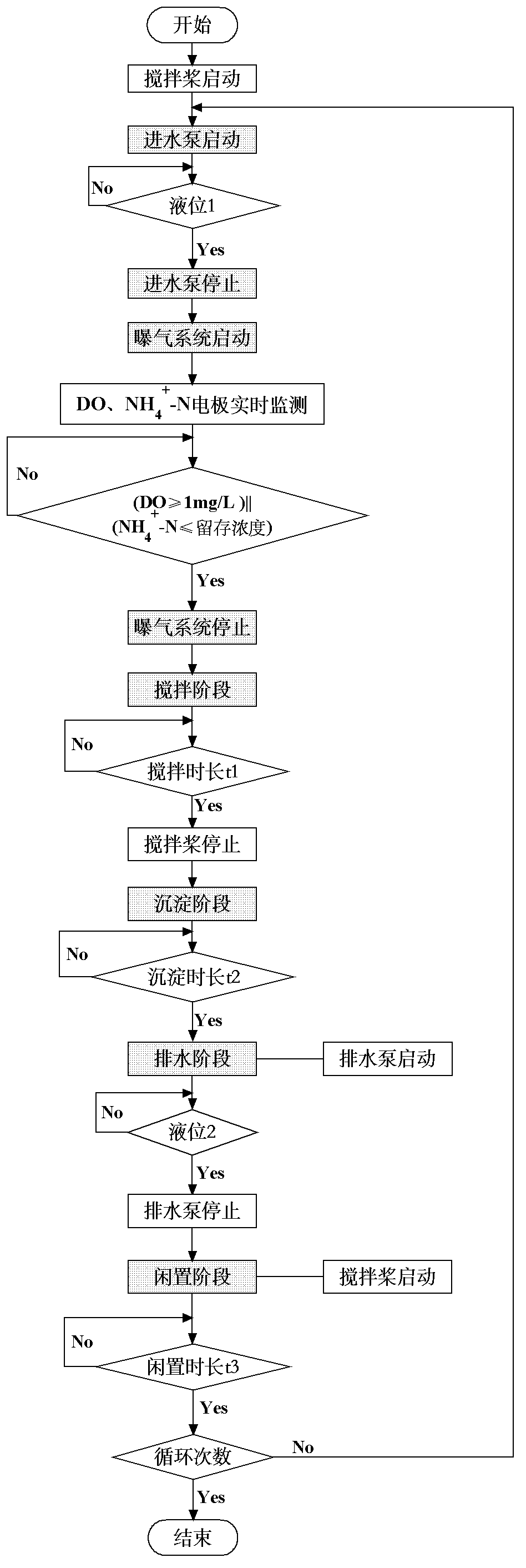
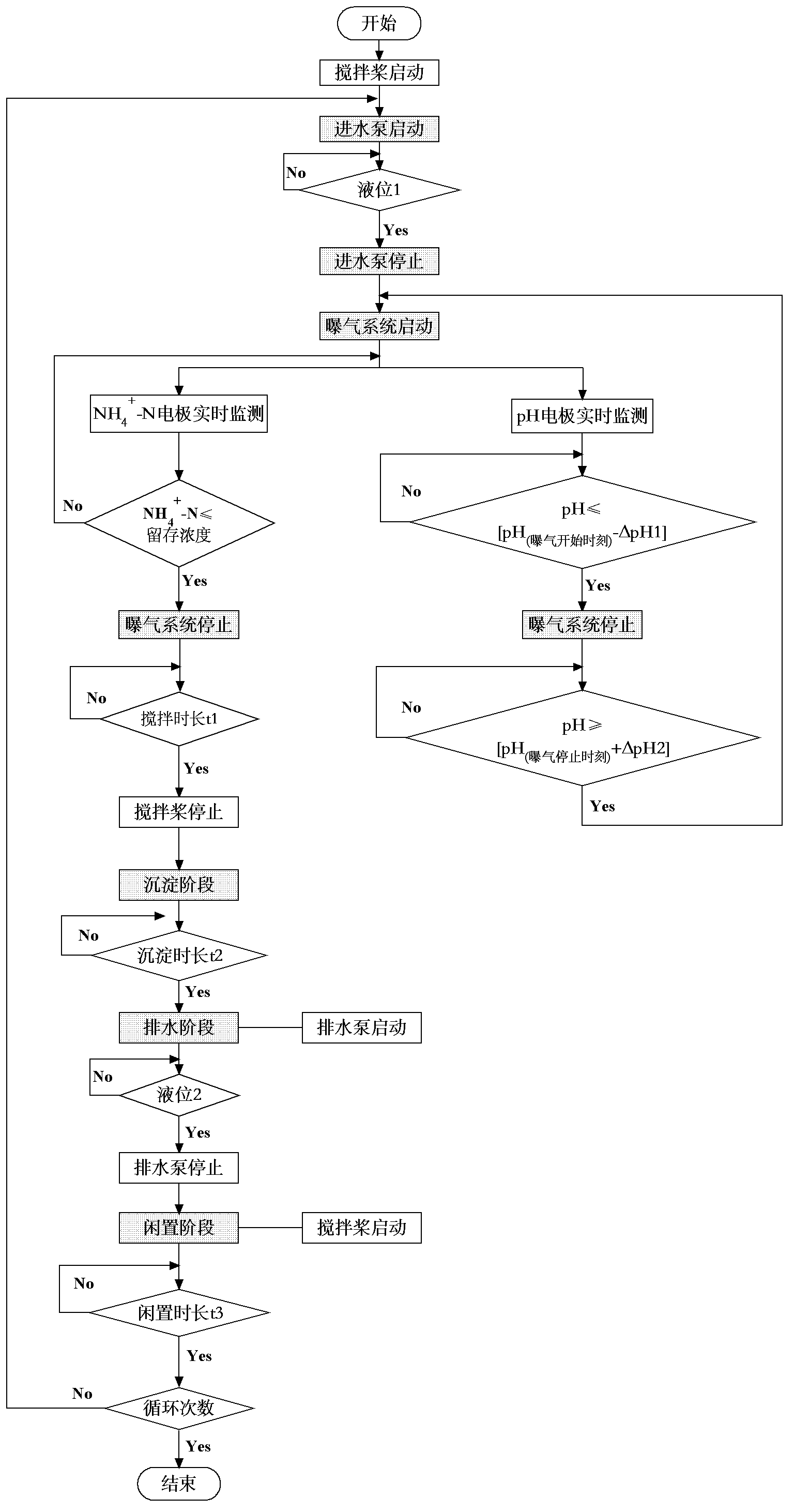
The invention discloses a control method for a partial nitrification-anaerobic ammonia oxidation integrated SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor) denitrification process. The method consists of a dissolved oxygen-ammonia nitrogen control method and a pH-ammonia nitrogen control method respectively, wherein the dissolved oxygen-ammonia nitrogen control method comprises the steps that a dissolved oxygen on-line electrode and an ammonia nitrogen on-line electrode are utilized, the aeration rate is controlled through the dissolved oxygen on-line electrode, furthermore the concentration level of NO2-N in an SBR is controlled so as to synchronously carry out the partial nitrification and the anaerobic ammonia oxidation reaction in one same SBR, and the ammonia nitrogen residual concentration in the SBR is controlled through the ammonia nitrogen on-line electrode; and the pH-ammonia nitrogen control method comprises the steps that a pH on-line electrode and the ammonia nitrogen on-line electrode are utilized, an aeration system is controlled to stop through the decreasing amplitude delta pH1 of the pH at the nitration period, the aeration system is controlled to start through the increasing amplitude delta pH2 of the pH in the anaerobic ammonia oxidation period, the partial nitrification and the anaerobic ammonia oxidation reaction are carried out in one same SBR alternatively, and the ammonia nitrogen residual concentration in the SBR is controlled through the ammonia nitrogen on-line electrode.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for Treating Municiple Wastewater Employing Two Sequencing Biofilm Batch Reactors
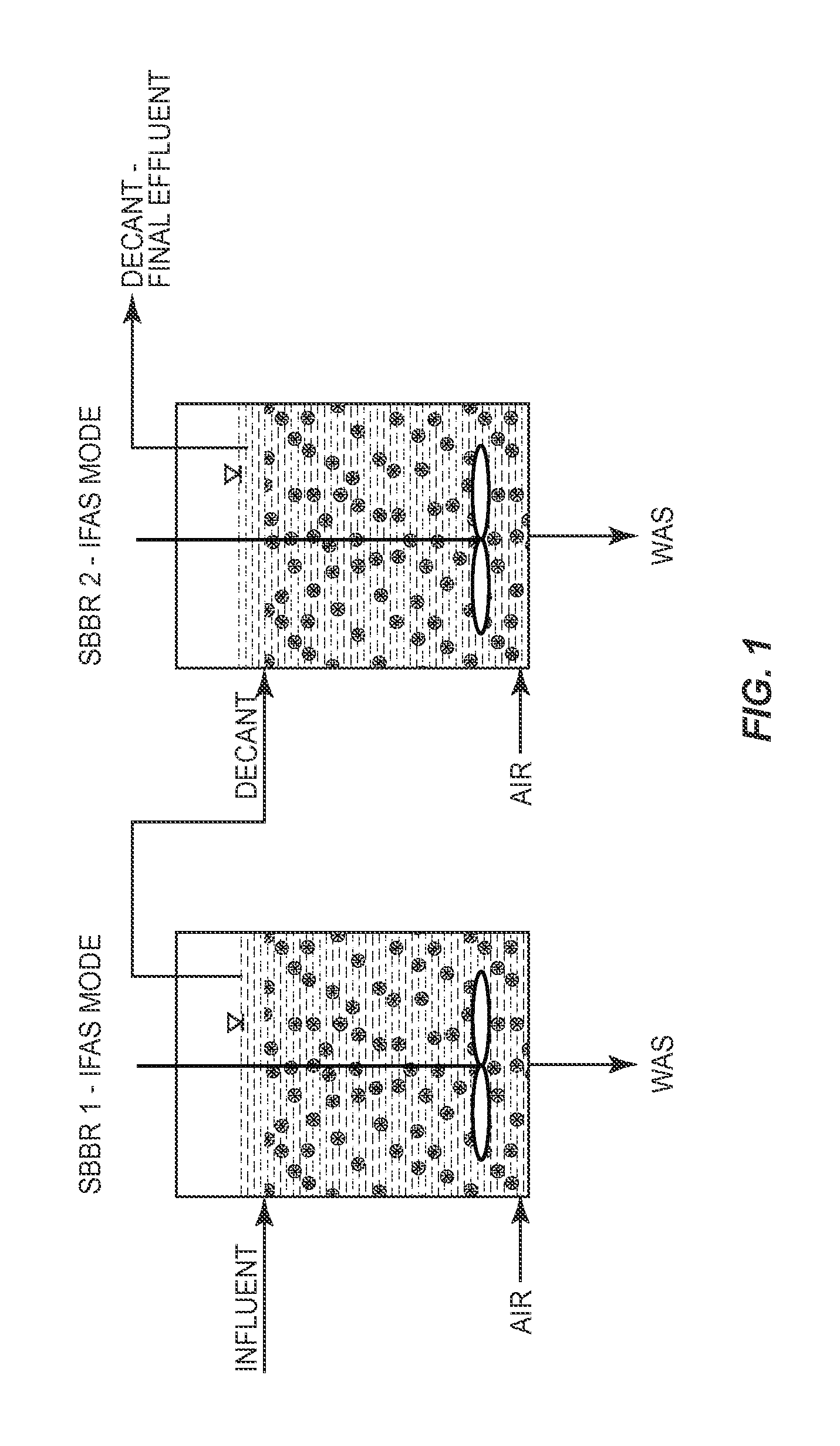
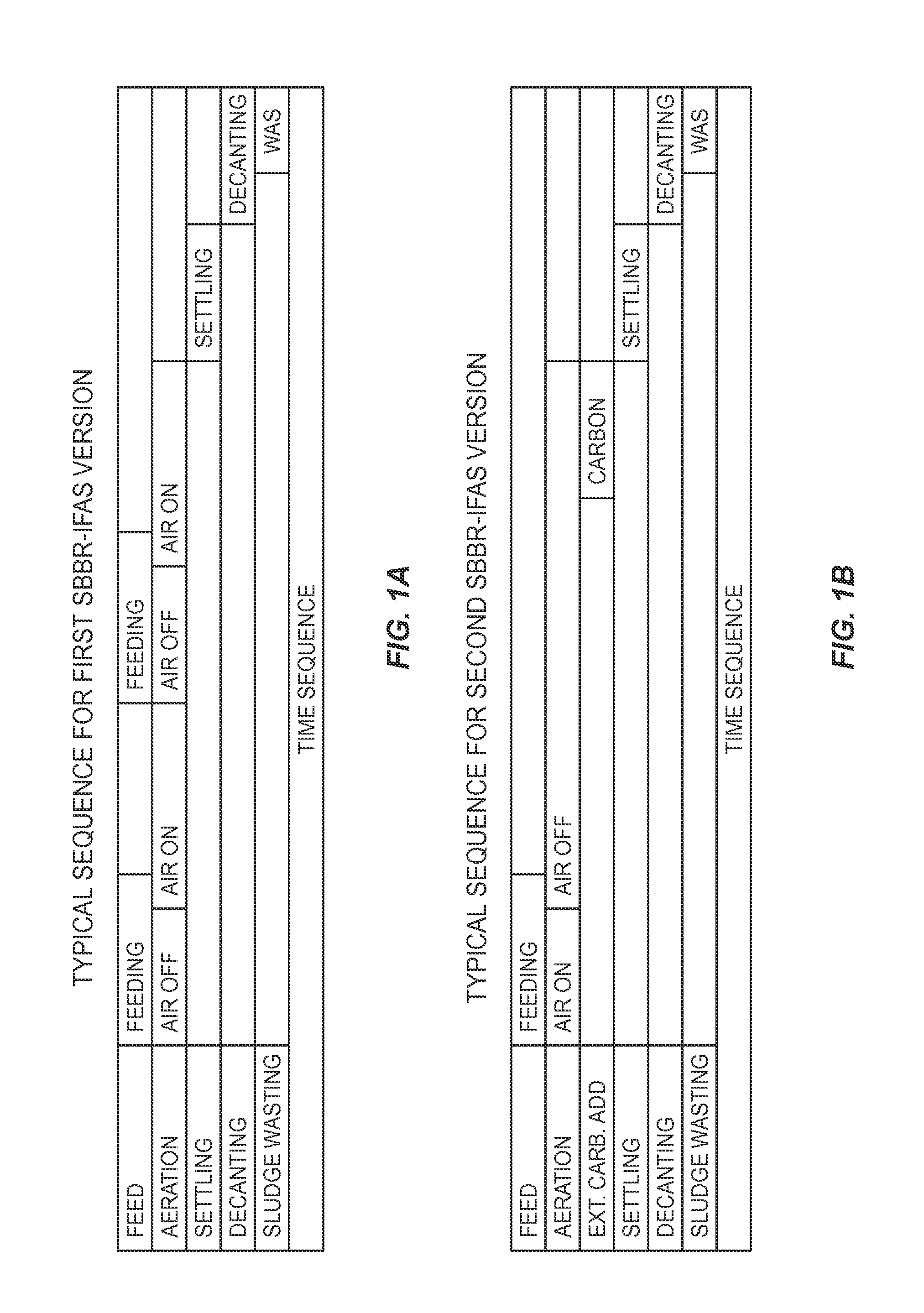
InactiveUS20140238931A1Reduce concentrationPromote growthTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesSustainable biological treatmentSequencing batch reactorSewage
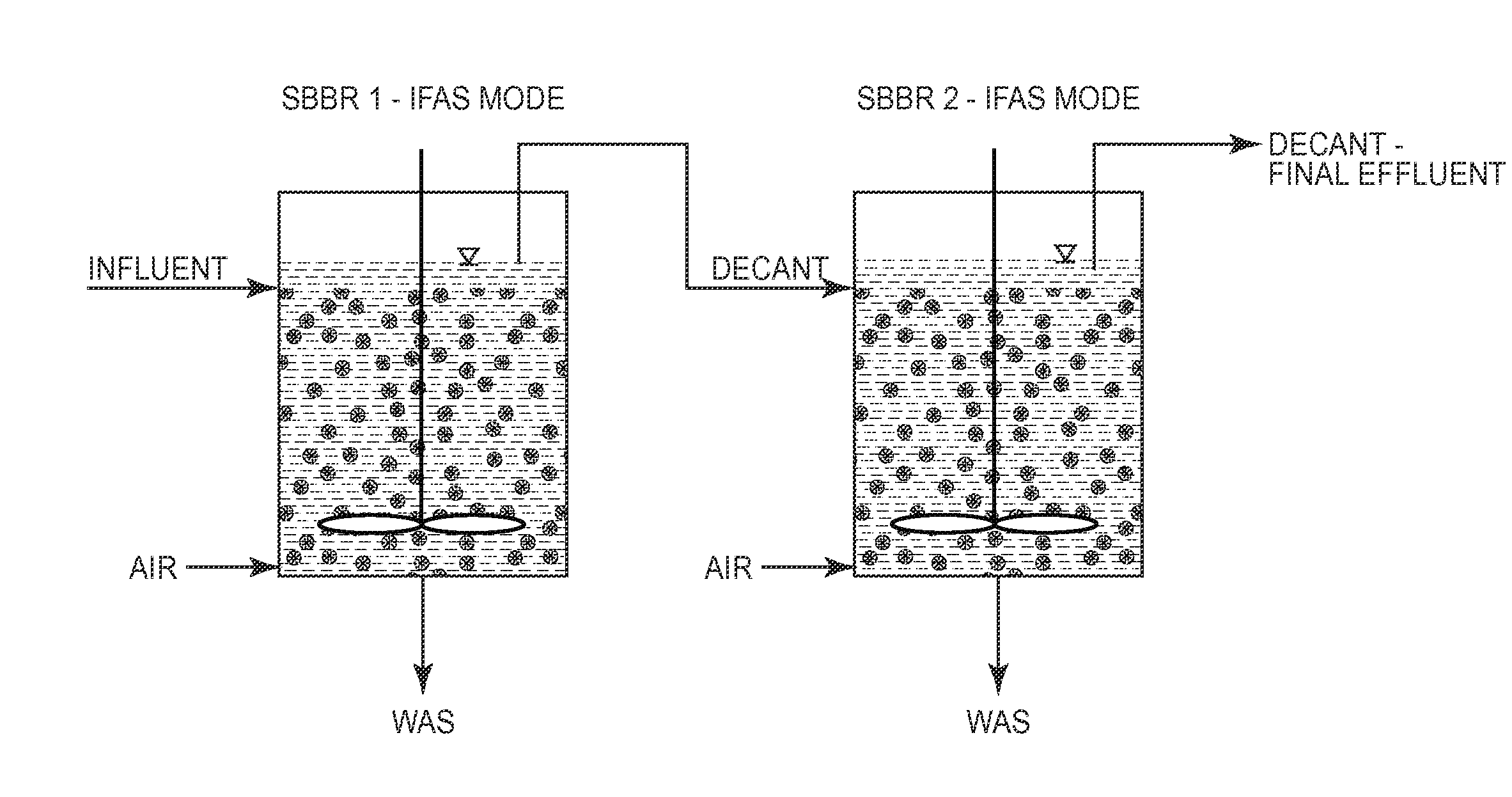
A method is provided for removing BOD and ammonium from wastewater in a mainstream process that includes deammonification. Wastewater including BOD and ammonium is directed to a first sequence batch reactor (SBBR). The wastewater is treated in the first SBBR and in the process nitrite is accumulated such that the wastewater includes a nitrite-to-ammonium stoichiometric ratio that enables anammox bacteria to effectively remove ammonium and nitrite from the wastewater. Thereafter the wastewater is directed the wastewater from the first SBBR to a second SBBR. The second SBBR is operated under anoxic conditions and employs anammox bacteria to remove ammonium and nitrite from the wastewater. In certain embodiments, a pre-denitrification step or process is employed in the first SBBR to remove BOD. In addition, in certain embodiments, the second SBBR includes an oxic phase for converting some ammonium to nitrite and, in some cases, an external carbon source is added to the wastewater under anoxic conditions to reduce the concentration of the nitrate in the wastewater.
Owner:VEOLIA WATER SOLUTIONS & TECH SUPPORT
Ballasted sequencing batch reactor system and method for treating wastewater
InactiveUS20100213123A1Water/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationTreatment using aerobic processesSequencing batch reactorEngineering
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
Method for treating wastewater generated by cyclohexanone ammoximation process
ActiveCN101734825AStrong resistance to water impactSimple processing methodMultistage water/sewage treatmentNature of treatment waterCyclohexanoneSequencing batch reactor
The invention provides a method for treating wastewater generated by a cyclohexanone ammoximation process, which comprises the following steps: performing advanced oxidation reaction on the wastewater to be treated; and then, adopting a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) to perform treatment. The method firstly adopts an advanced oxidation method to carry out oxidation reaction on organic matters in the wastewater generated by the cyclohexanone ammoximation process so as to improve the biodegradability of the wastewater and reduce the content of the organic matters in the wastewater simultaneously, and then adopts a treatment method of the SBR to further remove the organic matters in the wastewater and remove ammonia nitrogen in the wastewater, so that the treated wastewater meets the requirement of up-to-standard discharge.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Device and method for synchronously treating high-ammonia-nitrogen wastewater through sludge fermentation
ActiveCN103663879ASave dosingSave on processing costsMultistage water/sewage treatmentSequencing batch reactorNitrogen removal
The invention provides a device and a method for synchronously treating high-ammonia-nitrogen wastewater through sludge fermentation. A raw water pool in a system is connected with an SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor); the SBR is connected with a sludge fermentation coupled denitrification synchronous autotrophic nitrogen removal reactor through a middle water tank and a sludge storage pool. The method comprises the following steps: high-ammonia-nitrogen wastewater firstly enters the SBR through the raw water pool for partial nitrification, the SBR drains water into the middle water tank, and then the water and residual sludge together enter the sludge fermentation coupled denitrification synchronous autotrophic nitrogen removal reactor for synchronous residual sludge fermentation, anaerobic ammonia oxidation and nitrogen removal by denitrification. The device and the method which are disclosed by the invention are suitable for advanced high-ammonia-nitrogen wastewater treatment, so that low-carbon-consumption sewage denitrification is realized, and the yield of the residual sludge in the system can be reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for culturing shortcut nitrification granular sludge by combining dual inhibition of FA and FNA
InactiveCN102173504AEasy to separateIncrease concentrationSludge processingSustainable biological treatmentSequencing batch reactorChemical oxygen demand
The invention relates to a method for culturing shortcut nitrification granular sludge by combining the dual inhibition of free ammonia (FA) and free nitrous acid (FNA), and belongs to the technical field of the biological denitrification of wastewater. The method comprises the following steps of: inoculating flocculent active sludge to a sequencing batch reactor (SBR), and pumping wastewater which contains chemical oxygen demand (COD) and ammonia nitrogen and serves as inflow from the bottom of the reactor; after a liquid level is reached, starting a stirrer and a blast blower to perform aerobic nitration, degrading organic matters and oxidizing the ammonia nitrogen to form nitrites; after the nitration is finished, stopping aerating and stirring, precipitating to obtain supernatant containing the nitrites, and discharging sewage from a drainage valve, wherein in the culture conditions, the temperature of the reactor is between 25 and 30 DEG C, NaHCO3 solution is added after aeration is performed for 30 minutes, so that the pH value is kept between 7.5 and 8.0, dissolved oxygen is between 3 and 5 mg / L, upflow is provided at the speed of between 1.0 and 1.5 cm / s, and sludge age is between 12 and 15 days; and culturing for 30 to 50 days to obtain the shortcut nitrification granular sludge. By the method, the removal efficiency of a denitrification system can be improved effectively, oxygen supply and denitrification carbon sources can be saved, the yield of the sludge can be reduced, the volume of the reactor can be reduced, and the construction and operating cost can be saved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for accelerating aerobic sludge granulation by aid of charcoal
InactiveCN105417689AShorten the time of granulationImprove settlement performanceWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsSequencing batch reactorActivated sludge
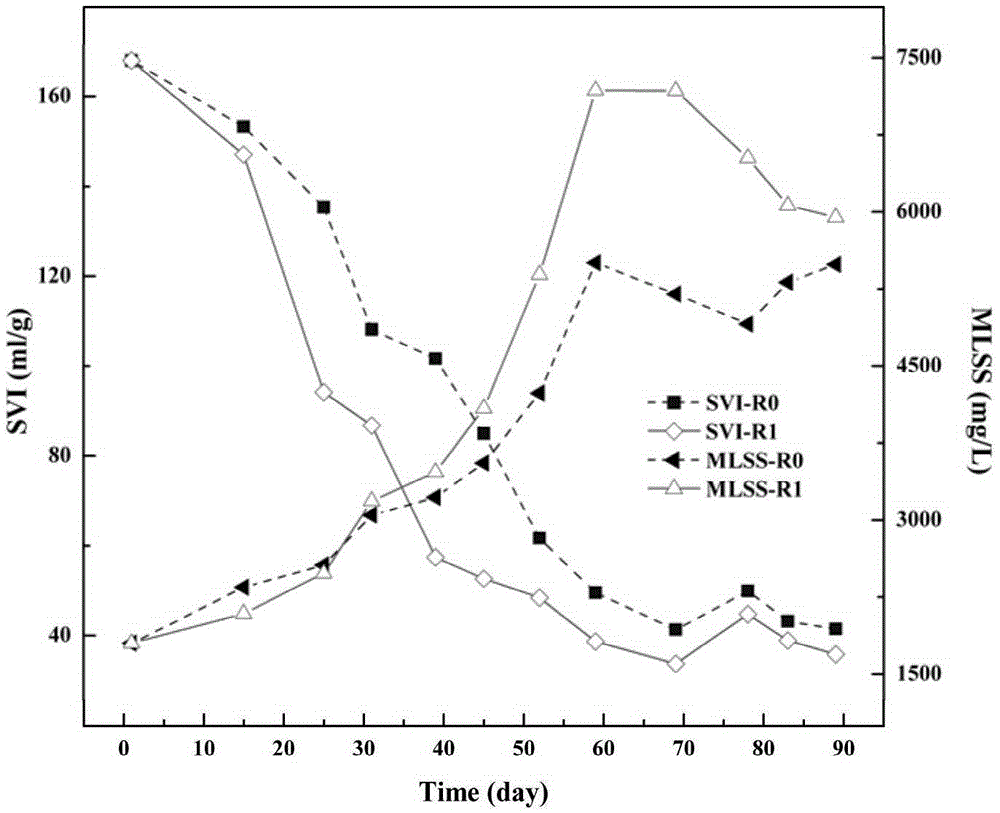
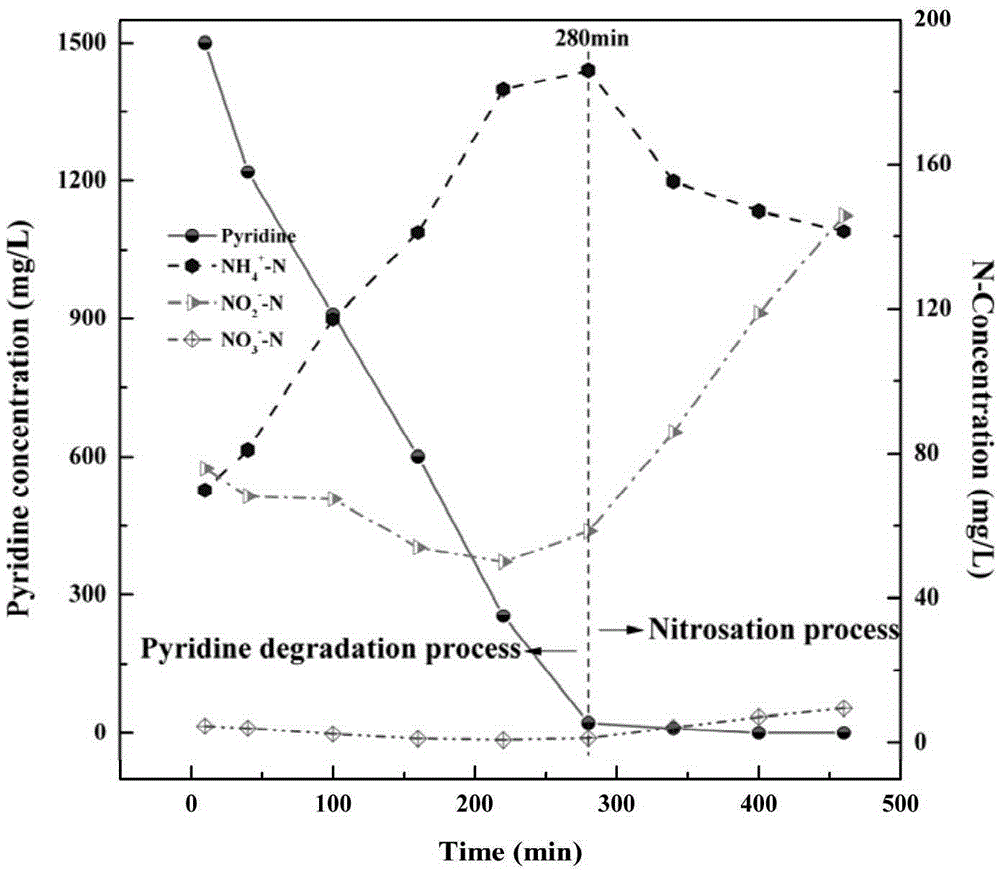
The invention discloses a method for accelerating aerobic sludge granulation by the aid of charcoal. The method includes that pyridine degradation bacteria Rhizobium sp. NJUST18 and ordinary activated sludge are used as compound inocula for the aerobic granular sludge, the charcoal is used as a crystal nucleus for the aerobic granular sludge in a sequencing batch reactor form, and quick forming of the pyridine degradation aerobic granular sludge can be promoted. The method has the advantages that the aerobic granular sludge with a pyridine degradation function can grow by the aid of pyridine which is a unique carbon source and a unique nitrogen source, granules have regular shapes and are good in sedimentation after the cultivated granular sludge is mature, reaction systems are high in sludge concentration, the high-concentration pyridine can be degraded and is subjected to synchronous nitrosation, and the cultivation time of the aerobic granular sludge for treating wastewater difficult to biodegrade can be effectively shortened.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Reduction control device and method for N2O produced in denitrification dephosphorization process
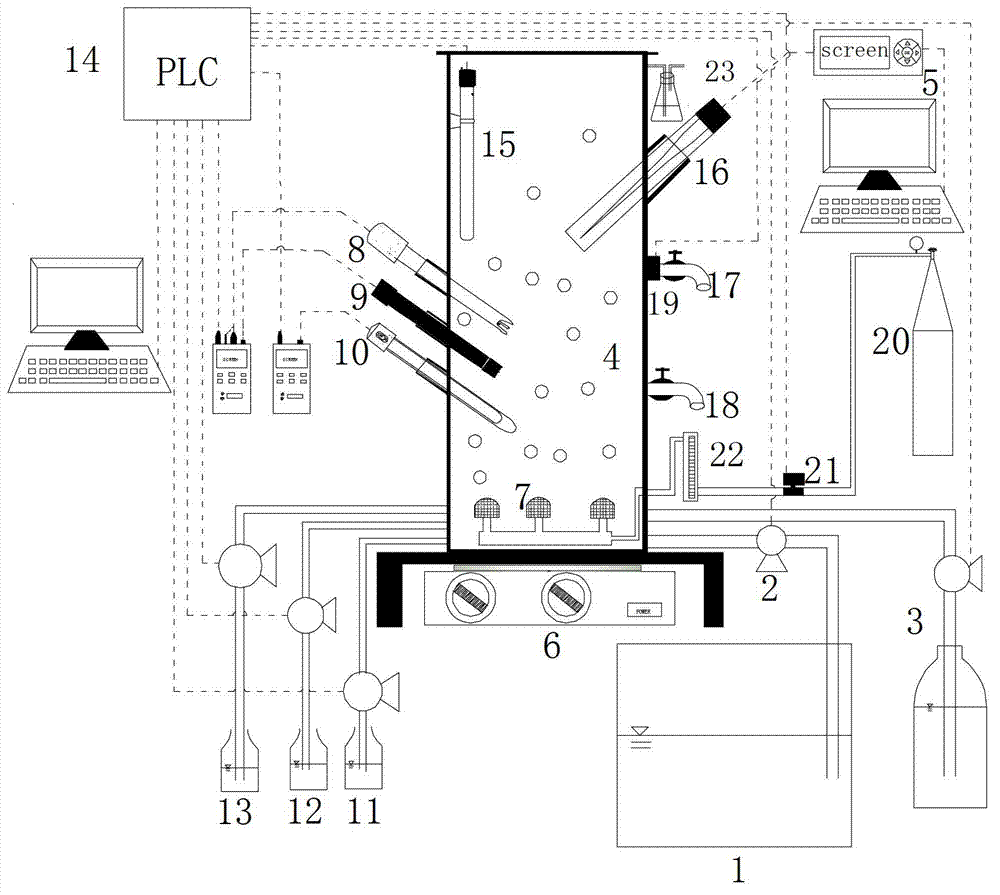
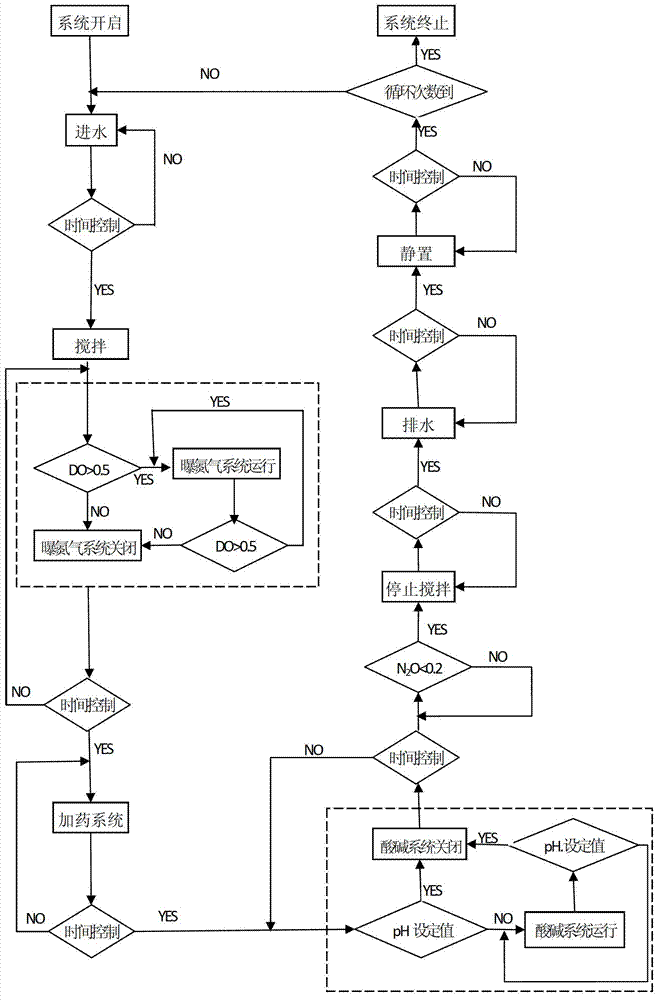
ActiveCN102849850AAutomatic control of online recording dataExcellent process parametersTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesTotal factory controlPeristaltic pumpActivated sludge
The invention provides a reduction control device and method for N2O produced in the denitrification dephosphorization process and belongs to the technical fields of automatic control of an activated sludge process treatment system and wastewater biological denitrification dephosphorization by means of a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) process. Aiming at solving the technical problem that sodium nitrite adopted to serve as an electron acceptor produces N2O in the denitrification dephosphorization process in the existing SBR process, the device uses an SBR as a main body and comprises a water distribution tank, a peristaltic pump, a magnetic stirring apparatus, an acid adding system, an alkali adding system, an on-line control system connected with a computer and a N2O on-line detecting system. The on-line control system is connected with a water inlet peristaltic pump, a mud discharging system, the acid adding system, the alkali adding system, a temperature control device, the stirring apparatus, a drain valve, a relay on a magnetic valve of a nitrogen aerating system, an oxidation reduction potential (ORP) sensor, a pH sensor and a dissolved oxygen sensor. The N2O on-line detecting system is connected with a N2O microelectrode. The whole process is automatically finished through a programmable logic controller (PLC) of the computer, and the N2O on-line detecting system performs quantitative analysis to the nitrogen conversion condition to confirm dominant mechanism and influencing factors for the N2O production in the denitrification dephosphorization process.
Owner:SDIC XINKAI WATER ENVIRONMENT INVESTMENT CO LTD
Quick starting method of SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor) for synchronously denitrifying and removing phosphor
InactiveCN103588300AReduce startup timeEffective proliferationBacteriaTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSequencing batch reactorFungicide
The invention discloses a quick starting method of an SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor) for synchronously denitrifying and removing phosphor, and belongs to the field of sewage treatment. The quick starting method using a batch-injection chronological sequencing batch reactor comprises the following steps: (1), operating the SBR system under an anaerobic / aerobiotic alternation condition, and domesticating and enriching phosphorus-accumulating bacteria, so that the phosphorus-accumulating bacteria intake phosphor under the aerobiotic condition and release phosphor under the anaerobic condition; removing phosphate in water by removing mud; (2), changing an operating way of the system, and enriching denitrifying phosphate-accumulating organisms; increasing an anoxic zone and shortening the aeration time, so that the denitrifying phosphate-accumulating organisms utilize an intracellular carbon source and use nitrate / nitrite as an electron acceptor to intake phosphor; (3), adding a compound fungicide into the reaction, so that biological enhancement is repeatedly coupled with anaerobic / aerobiotic / anoxic / aerobiotic starting method, DPB (Denitrifying Phosphorus-removal Bacteria) are effectively proliferated, glycogen accumulating organisms are restrained, the starting time of the reactor is shortened, and the water outlet effect is improved. The starting way disclosed by the invention operates about 50 days in total, can be used for saving about 30 days and saving the aeration time by about 30% in comparison with an anaerobic / aerobiotic / anoxic starting method.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor) and SBBR (Sequencing Biofilm Batch Reactor) municipal sewage high-efficiency biological treatment method and device based on anaerobic ammonia oxidation
ActiveCN103601341AEasy to trainAvoid sludge ageMultistage water/sewage treatmentSequencing batch reactorMembrane reactor
The invention provides a SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor) and SBBR (Sequencing Biofilm Batch Reactor) municipal sewage high-efficiency biological treatment method and device based on anaerobic ammonia oxidation, and belongs to the technical field of sewage biological treatment. The device is provided with an SBR and an SBBR and is characterized in that sewage enters the SBR firstly, so that the biological phosphorus removal is realized through anaerobic-aerobiotic alternate operation, and meanwhile, organic matters in water are removed through heterotrophic bacteria; by controlling the short sludge age and no occurrence of nitrification, the surplus sludge quantity is large, and the phosphorous and organic matter removal effect is good; and yielding water of the SBR enters the SBBR, so that the partial nitrification-anaerobic ammonia oxidation autotrophic nitrogen removal is realized through low-oxygen aeration operation. The process operation method comprises the following steps: (1) sludge inoculation and initialization phase; and (2) operational phase. The method and the device are suitable for the treatment of municipal sewage with low carbon nitrogen ratio, are energy-saving and have good nitrogen and phosphorous removal effects and high removal rate of pollutants; and the system control is flexible.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
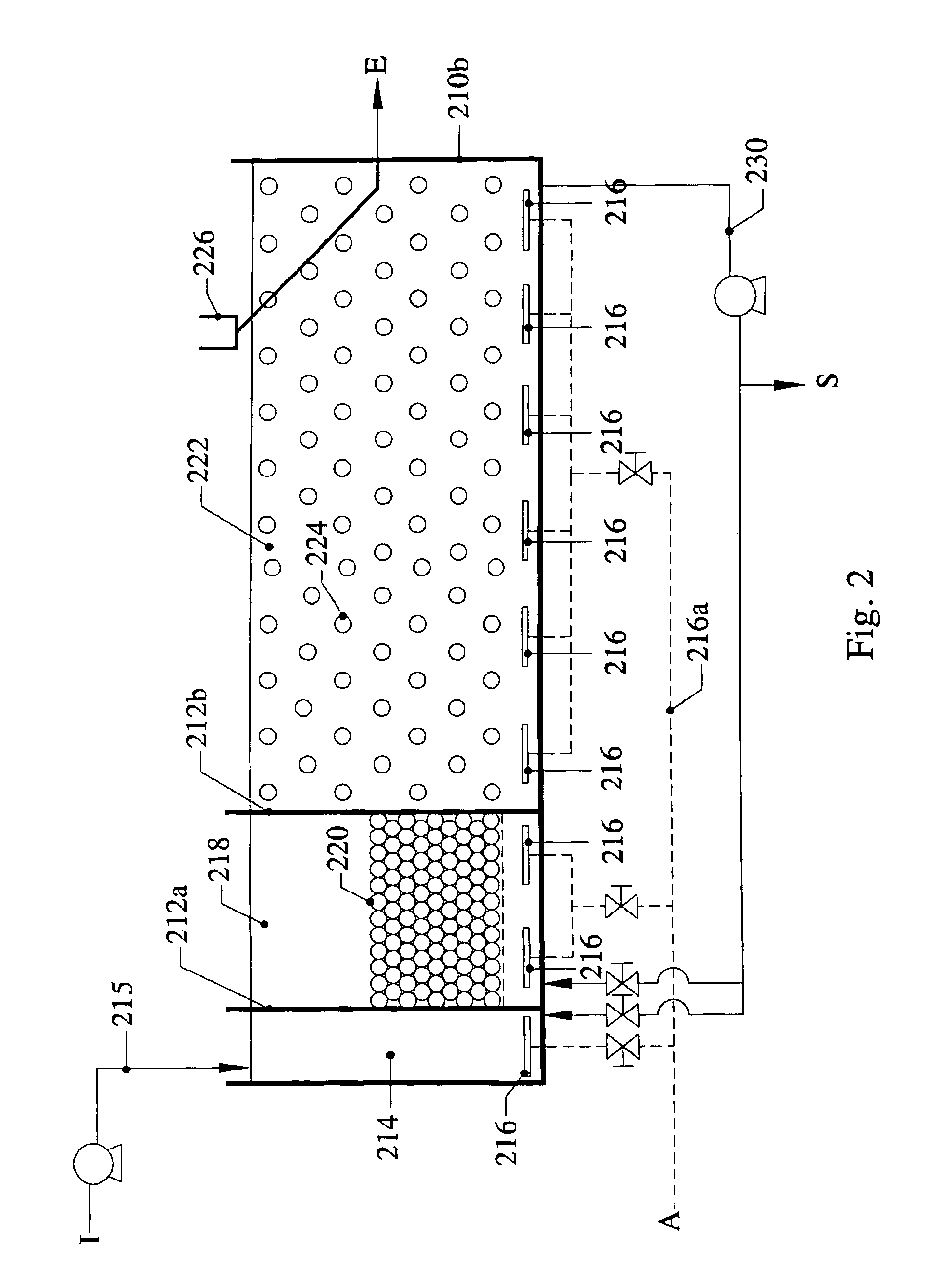
Combined activated sludge-biofilm sequencing batch reactor and process
InactiveUS6926830B2Improve efficiencyEasy to operateTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesSequencing batch reactorActivated sludge
Owner:KINGSFORD ENVIRONMENTAL H K
Rapid culture method of aerobic granular sludge
InactiveCN102219297AGuaranteed uptimeStable particle characteristicsSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentSequencing batch reactorActivated sludge
Belonging to the technical field of biological wastewater treatment, the invention specifically relates to a rapid culture method of aerobic granular sludge. The method comprises the steps of: inoculating activated sludge in a sequencing batch reactor; pumping waste water into the reactor through a water inlet at the bottom of the reactor; conducting an aeration operation through an aeration device located at the bottom of the reactor; setting a precipitation time and bringing the reactor into a precipitation process; discharging the waste water above a water outlet out of the reactor by a drainage pump. Wherein, with a precipitation time longer than 0 but shorter than 15 minutes and an organic loading higher than 1.5g 1<-1> d<-1>, the steps between water inletting and water discharging repeat periodically in the reactor. The operation period may range from 0.5-12 hours, the time for water inletting and water discharging may be in a range of from 1 to 120 minutes, and the aeration intensity can be 0.1-5vvm. The method of the invention can effectively shorten the culture time of granular sludge, and the aerobic granular sludge generated by the rapid culture method enjoys a capability to maintain long-term stable operation.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method and device for quickly enriching ammonia oxidizing bacteria
ActiveCN102559489AGrowth inhibitionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologySequencing batch reactor
The invention provides a method and a device for quickly enriching ammonia oxidizing bacteria. The ammonia oxidizing bacteria are enriched by a sequencing batch reactor, a method of gradually increasing ammonia nitrogen concentration in a culture solution and a pH process controlling method; and the adopted culture solution for enriching comprises the inorganic salt used as a main component, and a trace element culture solution, a buffer solution and ammonia carbonate; and the concentration of dissolved oxygen in the culture process is maintained more than 5mg / L by a process controlling device, pH is maintained 7.0 to 8.5, and temperature is maintained 20 to 25 DEG C. By the scheme, the growth of heterotrophic bacteria in activated sludge can be inhibited obviously, and the enriched ammonia oxidizing bacteria are 60 to 65 percent of the total number of microorganism bacteria in the activated sludge, and are tolerant to high ammonia nitrogen concentration; and finally high-ammonia-nitrogen wastewater of which the concentration can reach 500mg / L can be treated, and high-concentration ammonia nitrogen in the wastewater can be reduced to less than 1.0mg / L.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for rapidly forming anammox granule sludge
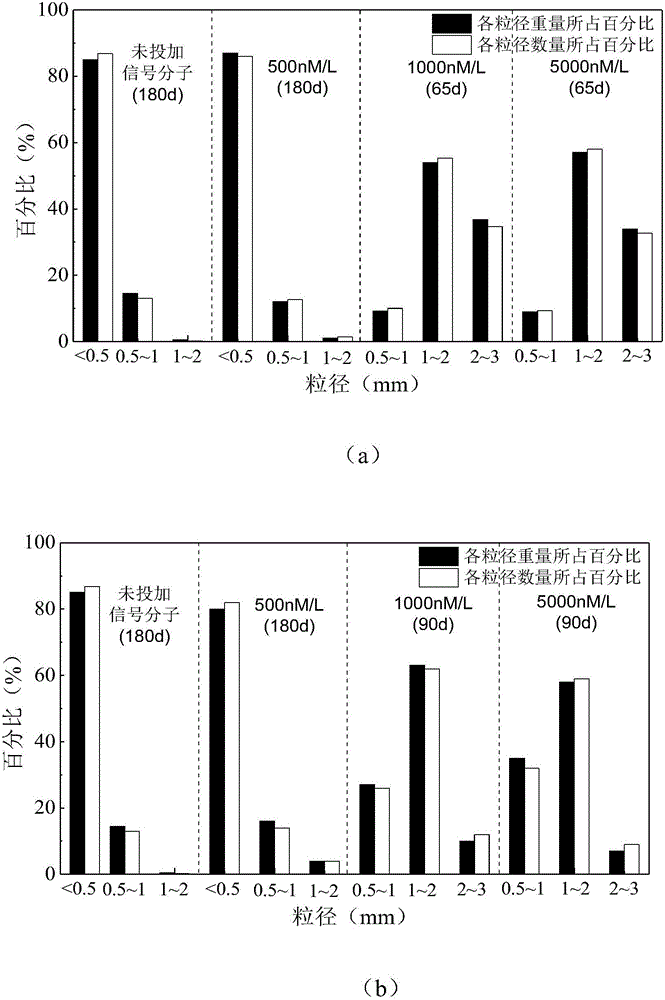
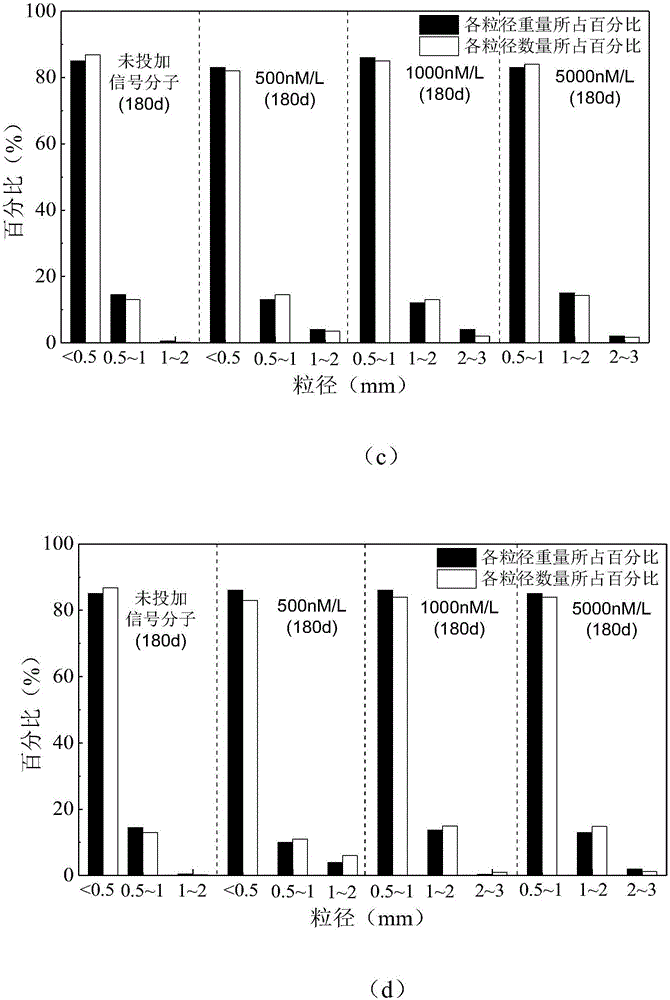
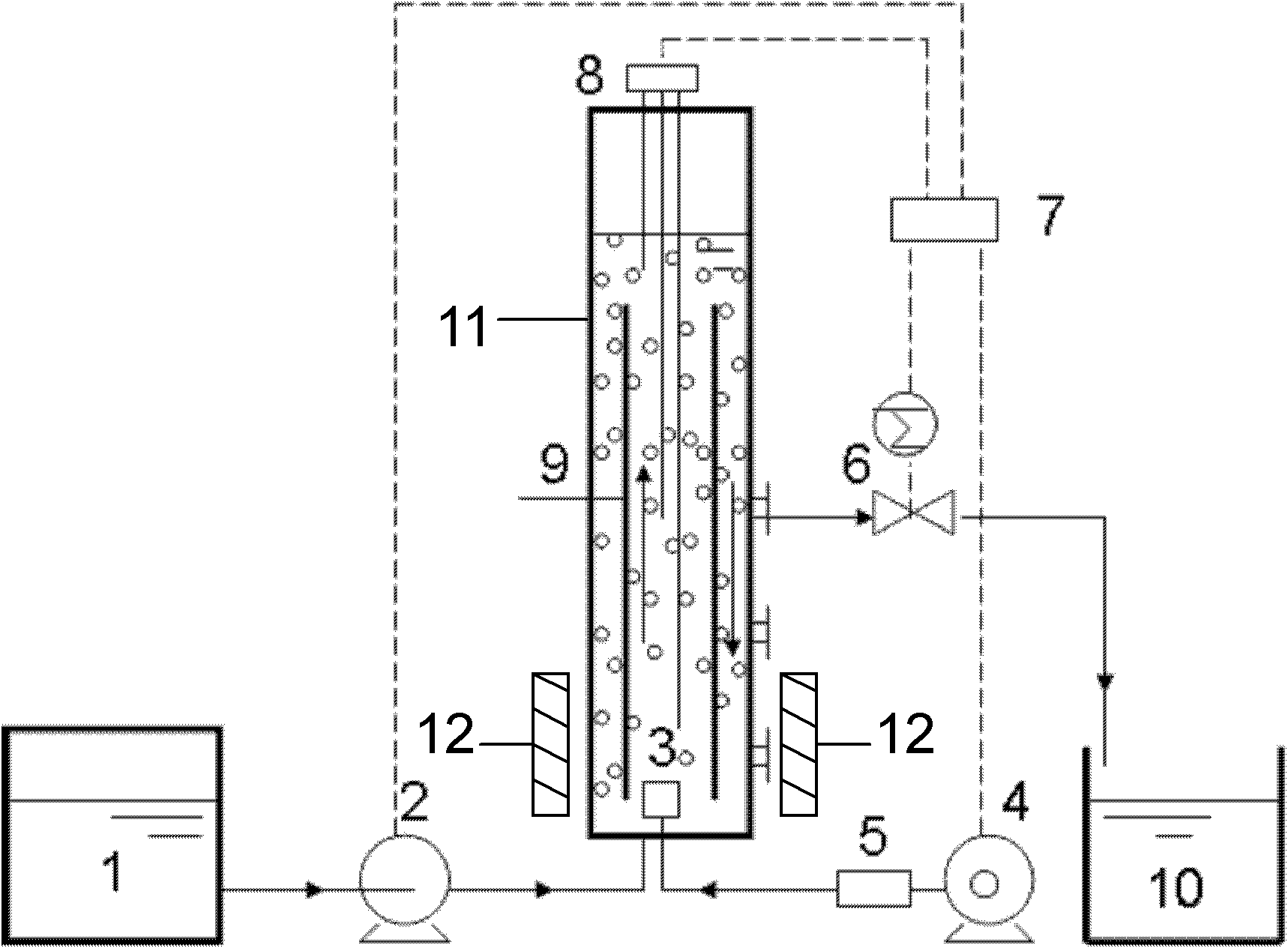
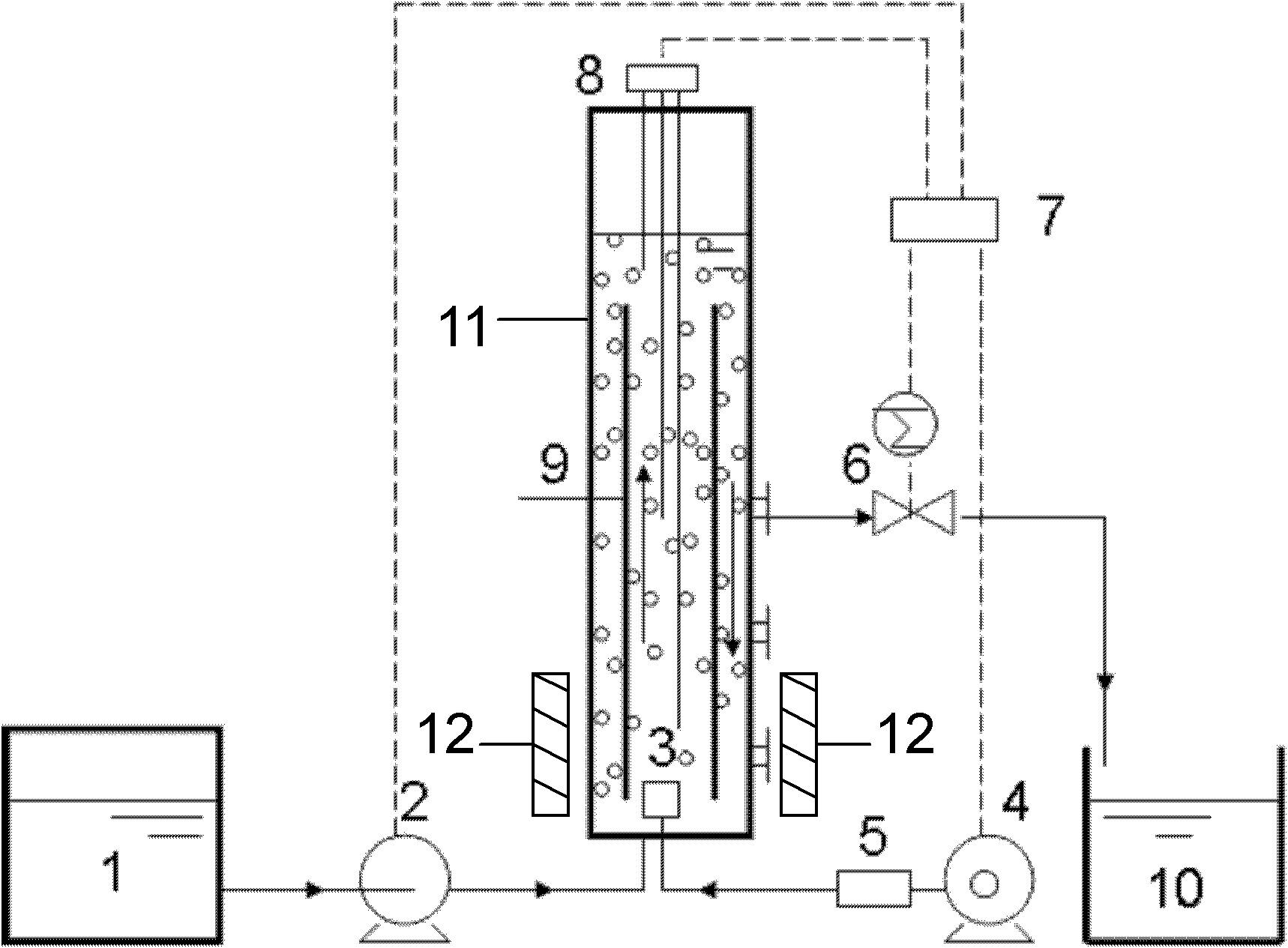
ActiveCN106698658AShorten the formation timeImprove hydrophobicityTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesSequencing batch reactorSignalling molecules
The invention discloses a method for rapidly forming an anammox granule sludge, and belongs to the field of wastewater treatment. Proper amount of an inoculated sludge is added to an SBR (Sequencing Batch reactor), a nutrient solution containing ammonia nitrogen and nitrite is added, the concentrations of both ammonia nitrogen and nitrite in the nutrient solution are both 50 mg / L, an AHLs quorum sensing signal molecule at certain concentration is added into the nutrient solution in the SBR each day, the environment temperature is 32-33 DEG C, the pH value is 7.8-8.3, the DO concentration is 0.15 mg / L or lower, and batch cultivation is conducted. The time for forming the anammox granule sludge is short, and the effect of the granule sludge is good.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Reinforced aerobic granular sludge culture method
InactiveCN102153192AGuaranteed normal growthCompact structureSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentSequencing batch reactorChemical oxygen demand
The invention discloses a reinforced aerobic granular sludge culture method, and belongs to the field of sewage treatment. The method comprises the following steps of: arranging symmetrical permanent magnets at the outer side of the bottom of a sequencing batch airlift reactor (SBAR), so that stable static magnetic fields are generated in the reactor; simultaneously adding flocculent aerobic active sludge serving as seed sludge into the SBAR, and performing aerobic granular sludge culture; and operating the SBAR in a mode of water inlet, aeration, settlement and drainage. By the method, the formation of the aerobic granular sludge can be accelerated, the complete granulation time of the flocculent active sludge is shortened to 3 to 4 weeks, and the problem of overlong culture time of the conventional aerobic granular sludge is solved. The aerobic granular sludge obtained by the method has good stability, and the chemical oxygen demand (COD) and the ammonia nitrogen removal effect can be remarkably improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Advanced treatment process for gas field produced water
ActiveCN103601348AEasy to separateReduce odorMultistage water/sewage treatmentSequencing batch reactorEvaporation
The invention discloses an advanced treatment process for gas field produced water, which solves the problem that in existing wastewater treatment processes, foam cannot be well controlled, calcium and magnesium ions cannot be well removed, and resources cannot be utilized. The process comprises the following treatment processes: a foam separating process; an absorption-coagulation integrated process; a two-effect evaporation process; a catalytic oxidation treatment process; and an SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor) biochemical treatment. Through the treatment process, existing produced water with high content of slat and organic matters reaches the standards, and the treatment process disclosed by the invention is reasonable in flow, compact in equipment installation, small in occupied area and can be conveniently used together with other processes. In addition, the treatment process is low in investment expense, low in operating cost and low in comprehensive energy consumption, and the environment-friendly and social benefits are remarkably superior to those of other technical schemes.
Owner:四川光隆环保科技有限公司
Biological treatment method of waste water from printing and dying
InactiveCN1544351AEasy to handleImprove running stabilitySludge processingWater/sewage treatmentBenzeneSequencing batch reactor
The invention provides a biological treatment process for printing and dyeing waste water, in particular printing and dyeing wastewater containing amino-benzene, wherein an anaerobic baffle reactor (ABR) and a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) are combined for water treatment, the treatment process comprises the steps of, pumping the printing and dyeing wastewater into anaerobic baffle reactor, the printing and dyeing wastewater being treated by the sludge layer of the anaerobic baffle reactor and fed in batch into the sequencing batch rector for active sludge treatment, the ABR process according to the invention realizes both decoloration and partial degradation of amino-benzene.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com