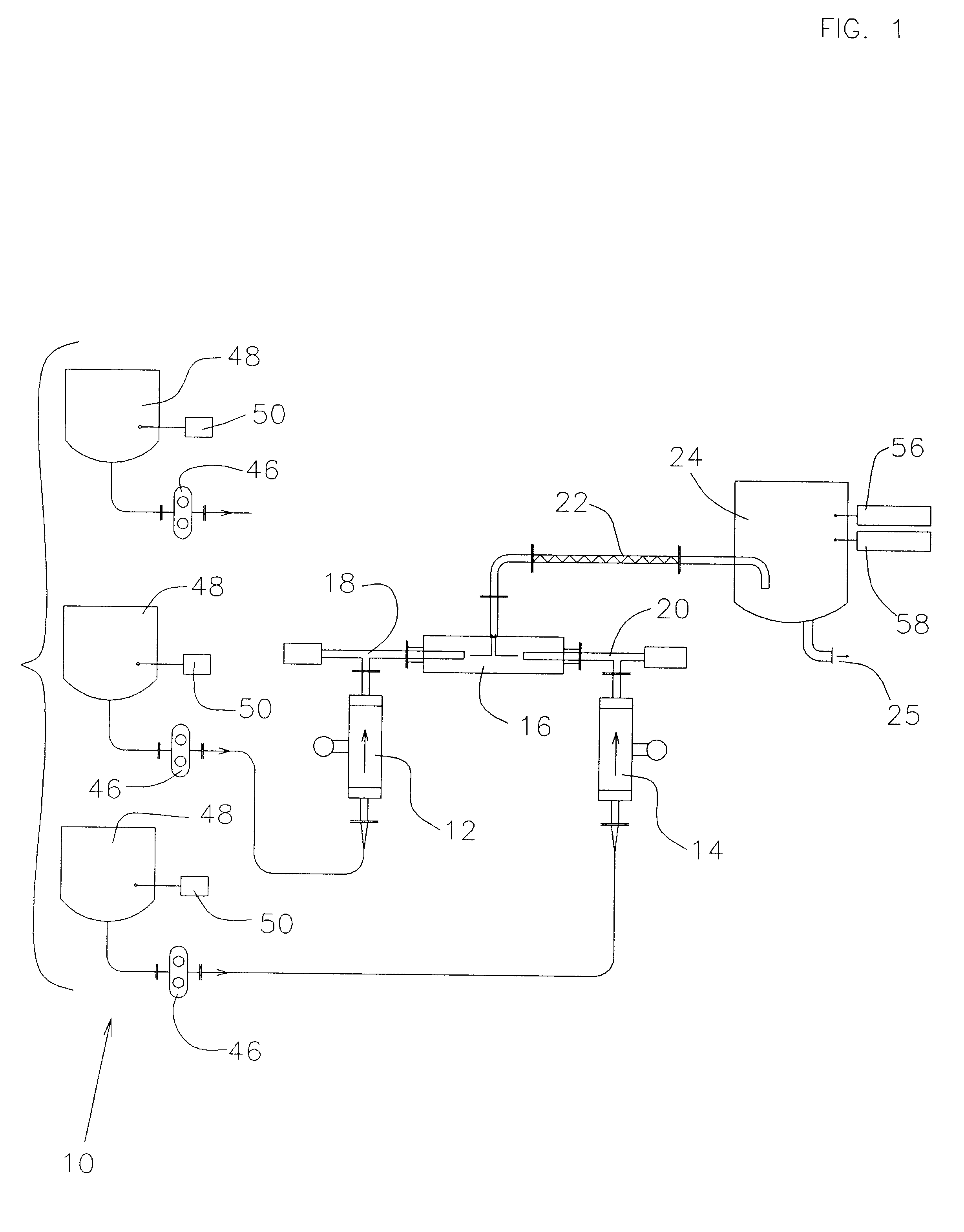Patents
Literature
2258results about "Controlling ratio of multiple fluid flows" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
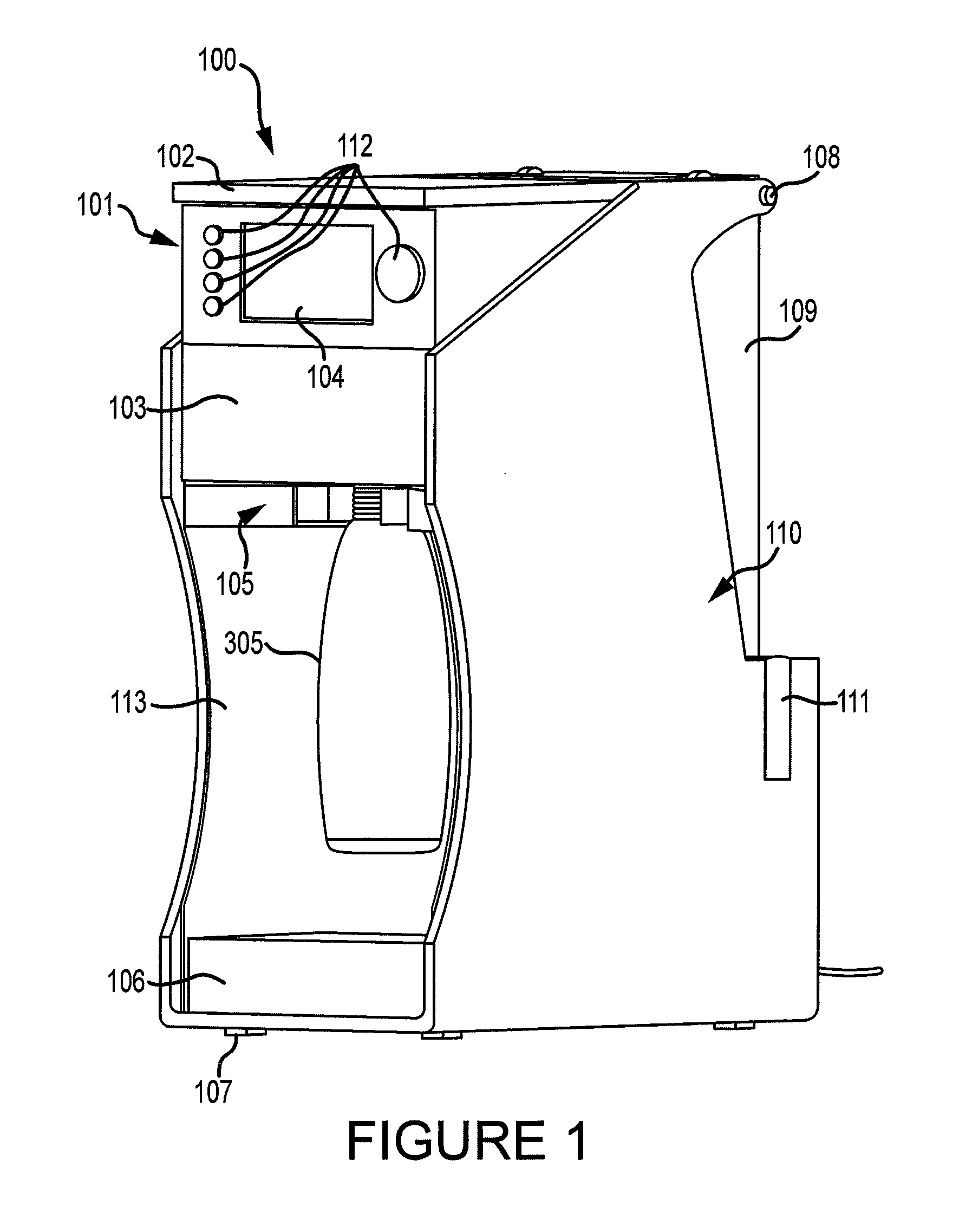
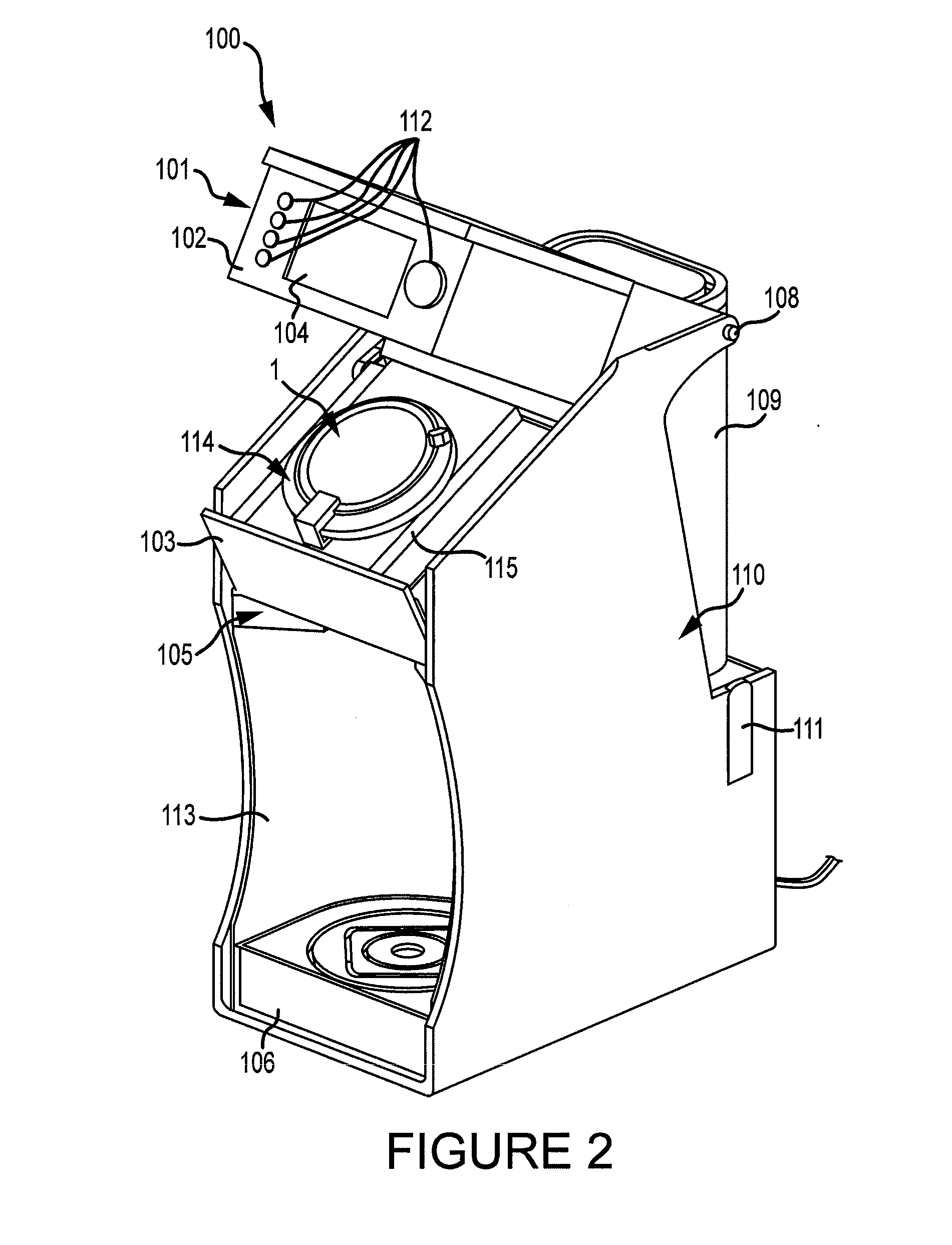
Aerosol generator and methods of making and using an aerosol generator
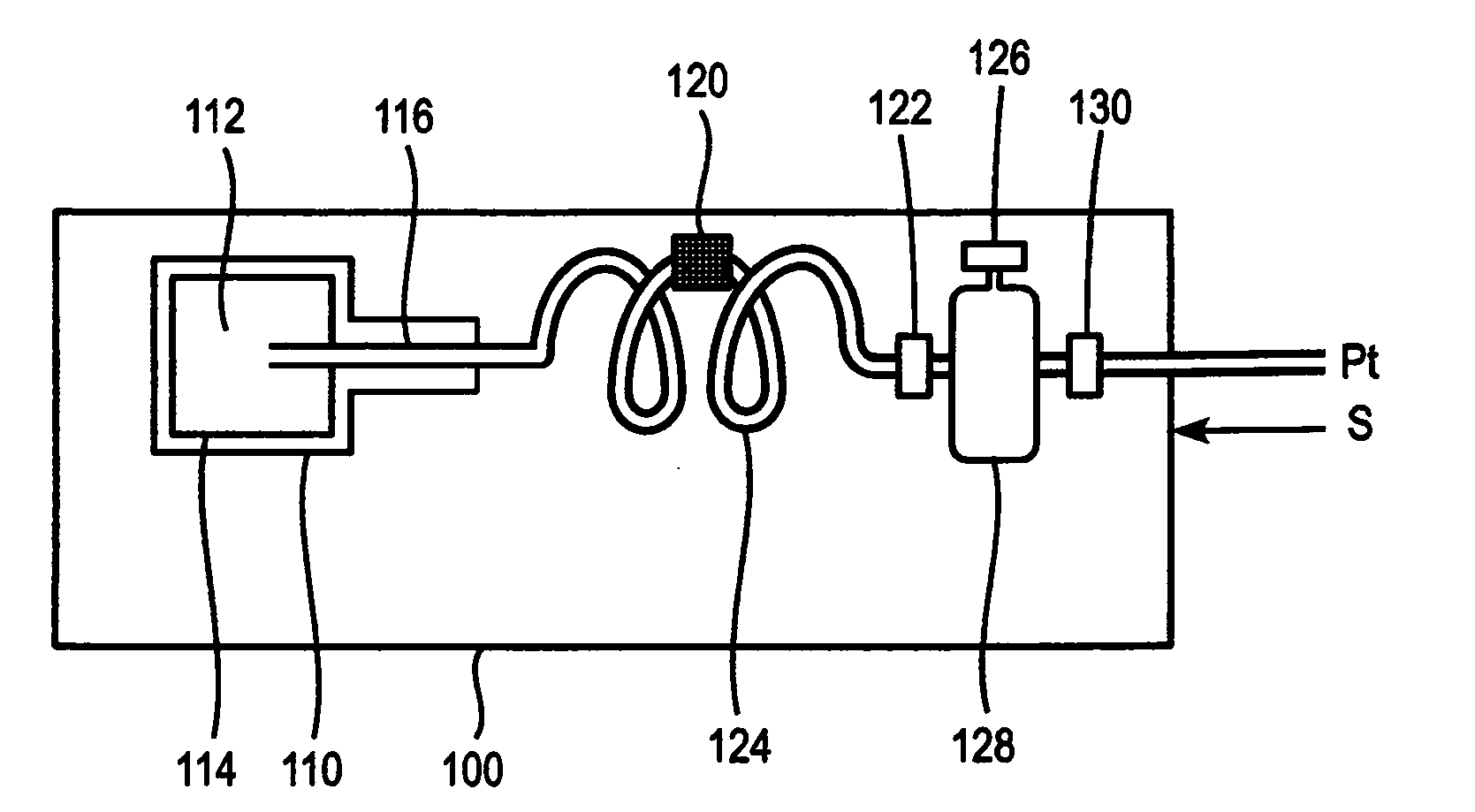
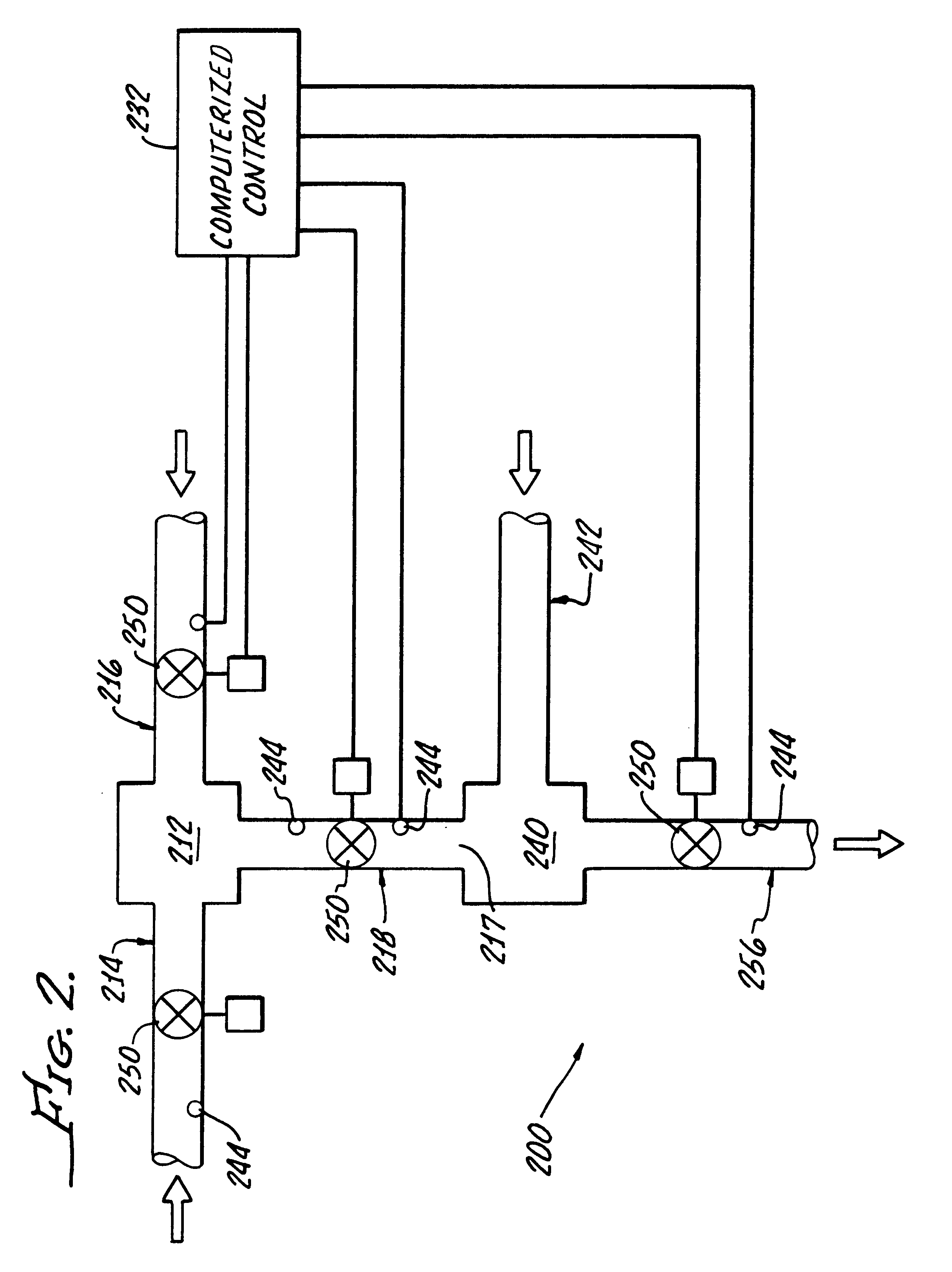
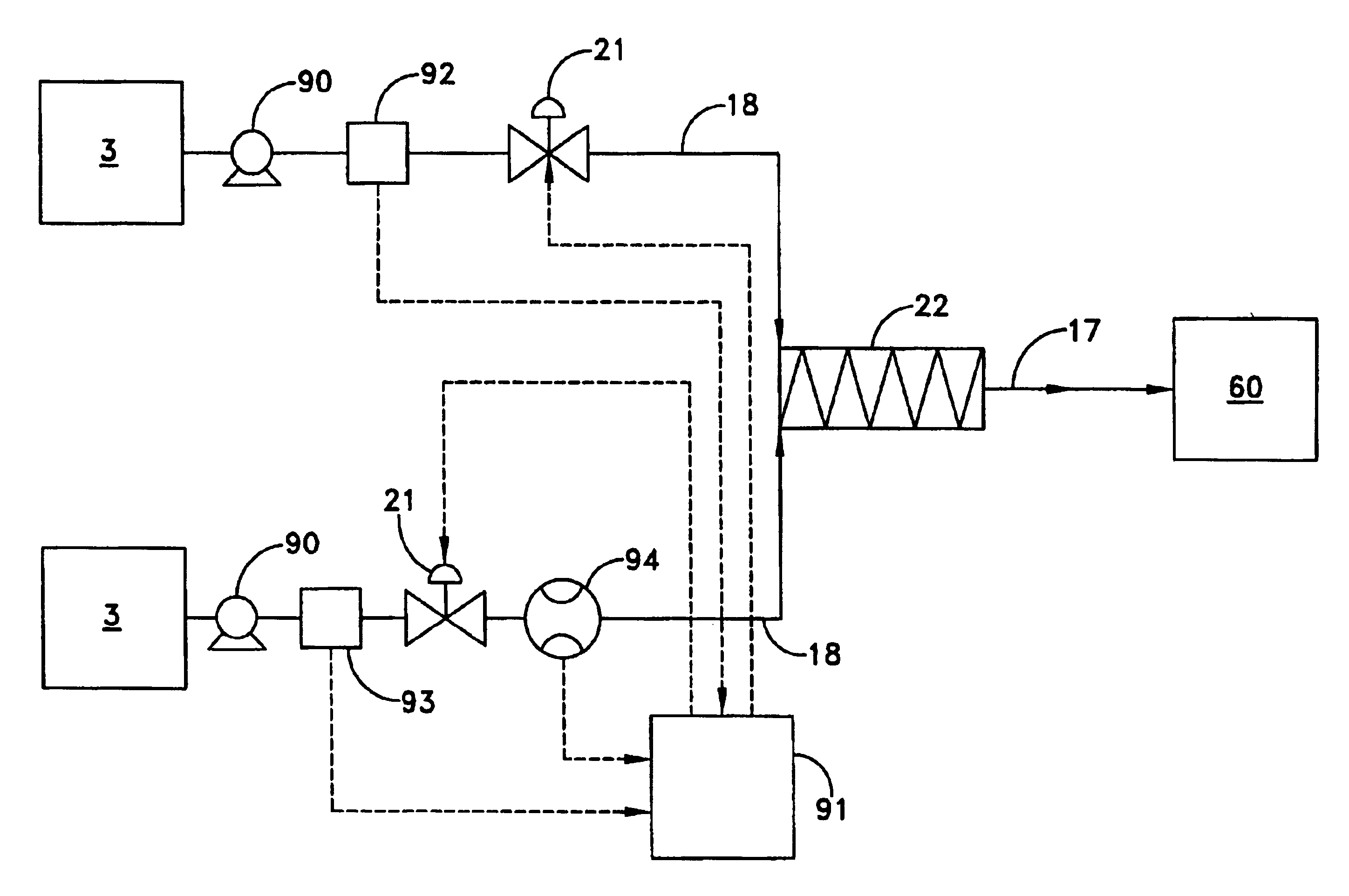
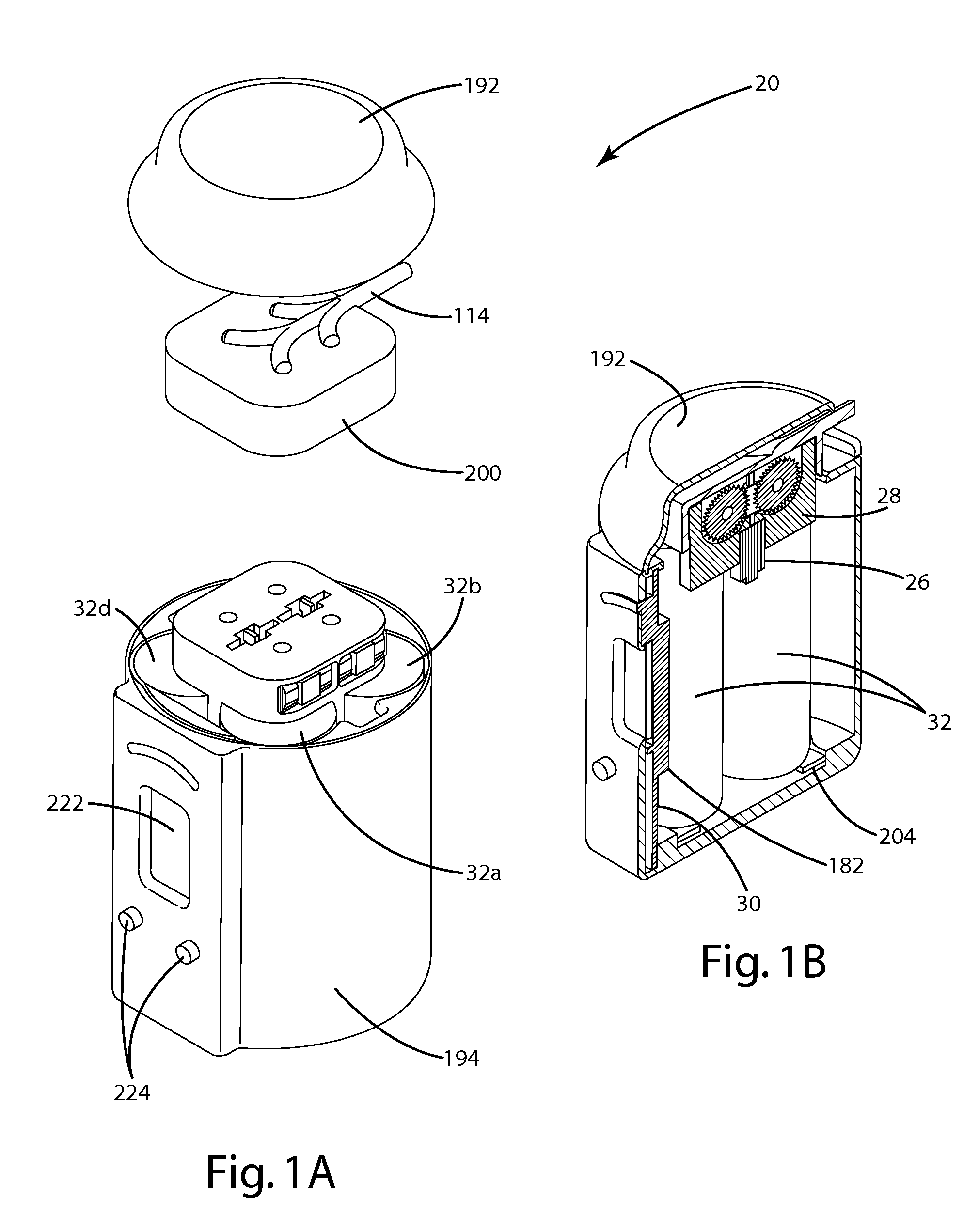
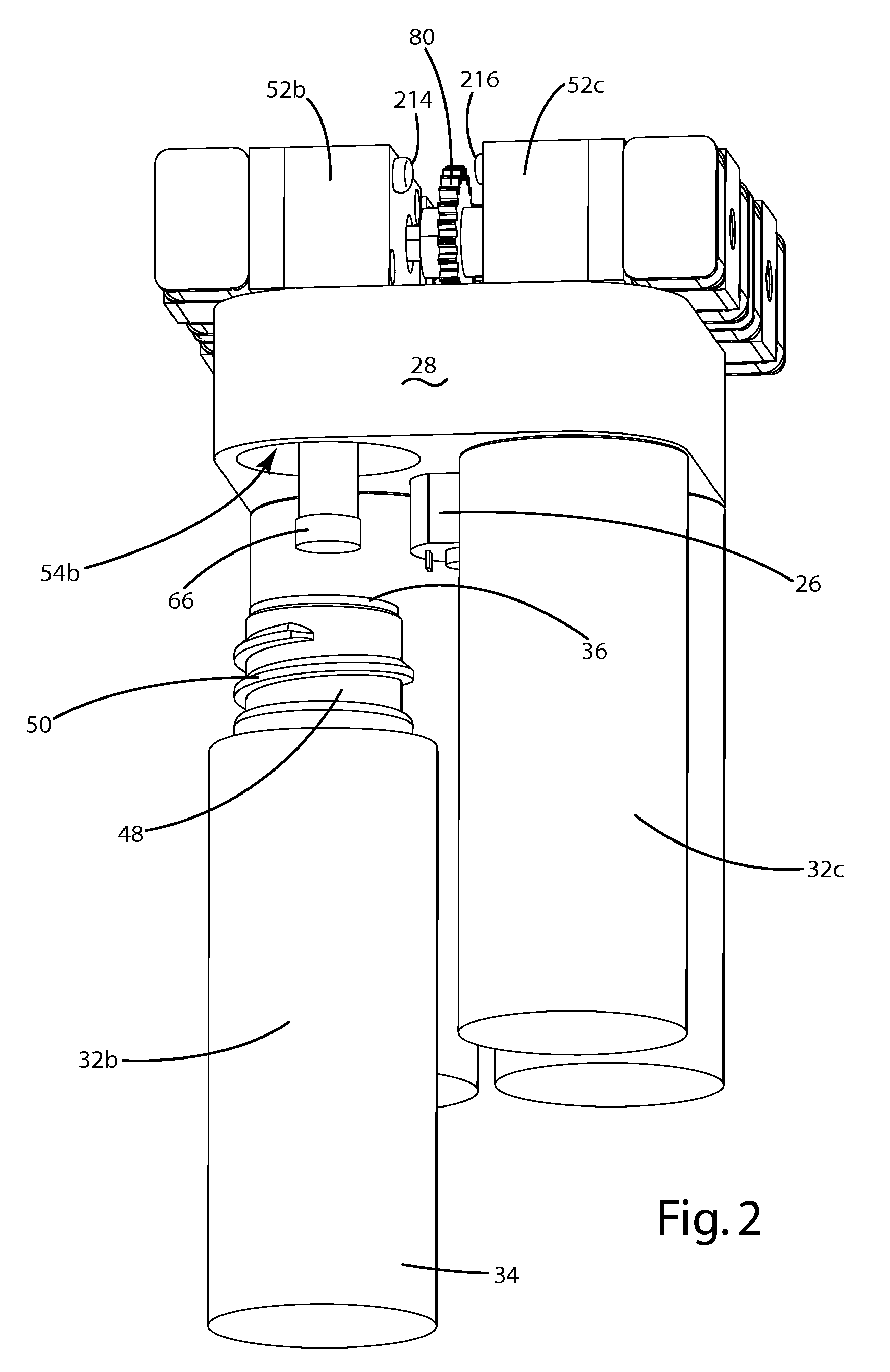
InactiveUS7117867B2Easy to useEasy to moveRespiratorsControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsRotary valveEngineering
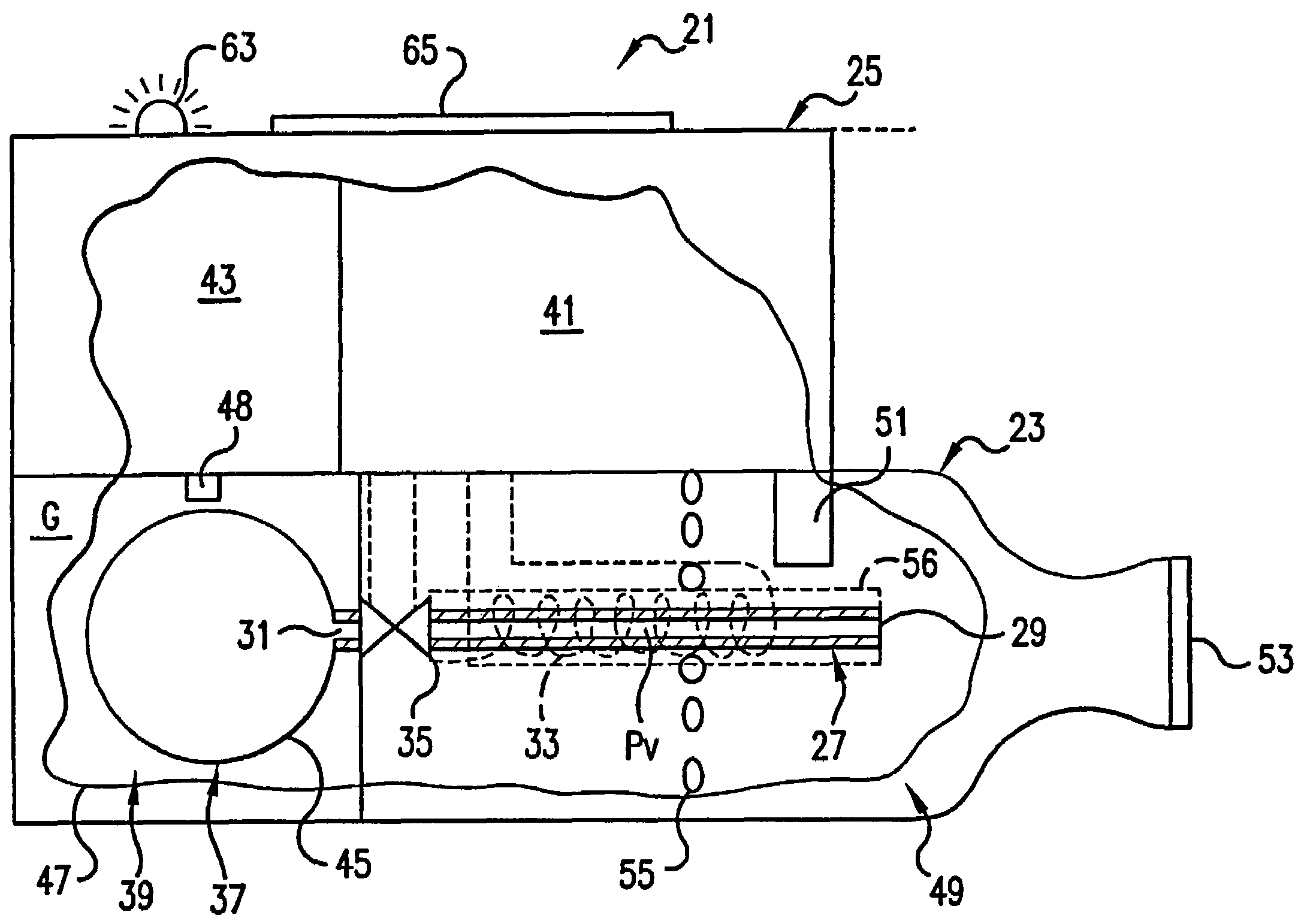
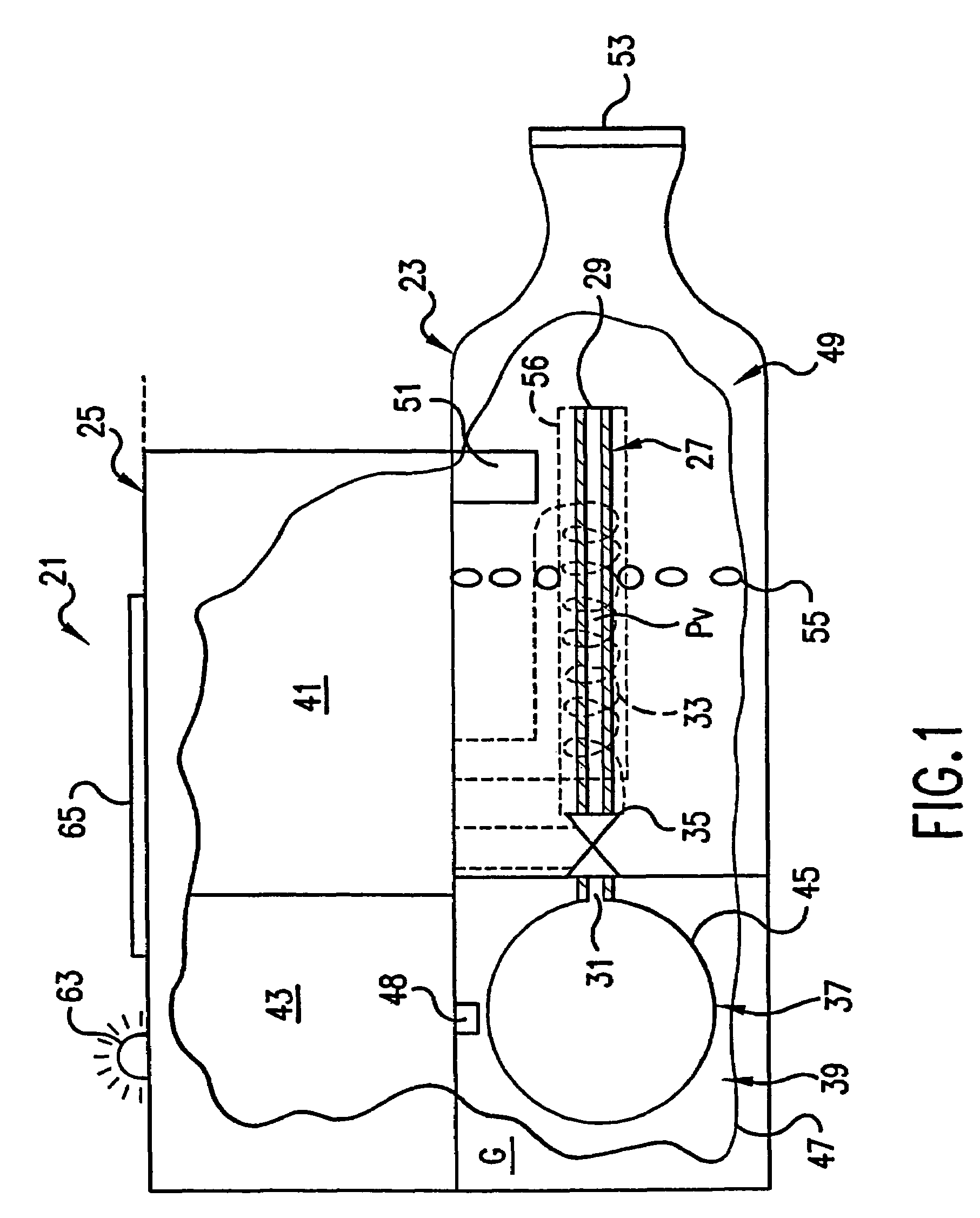
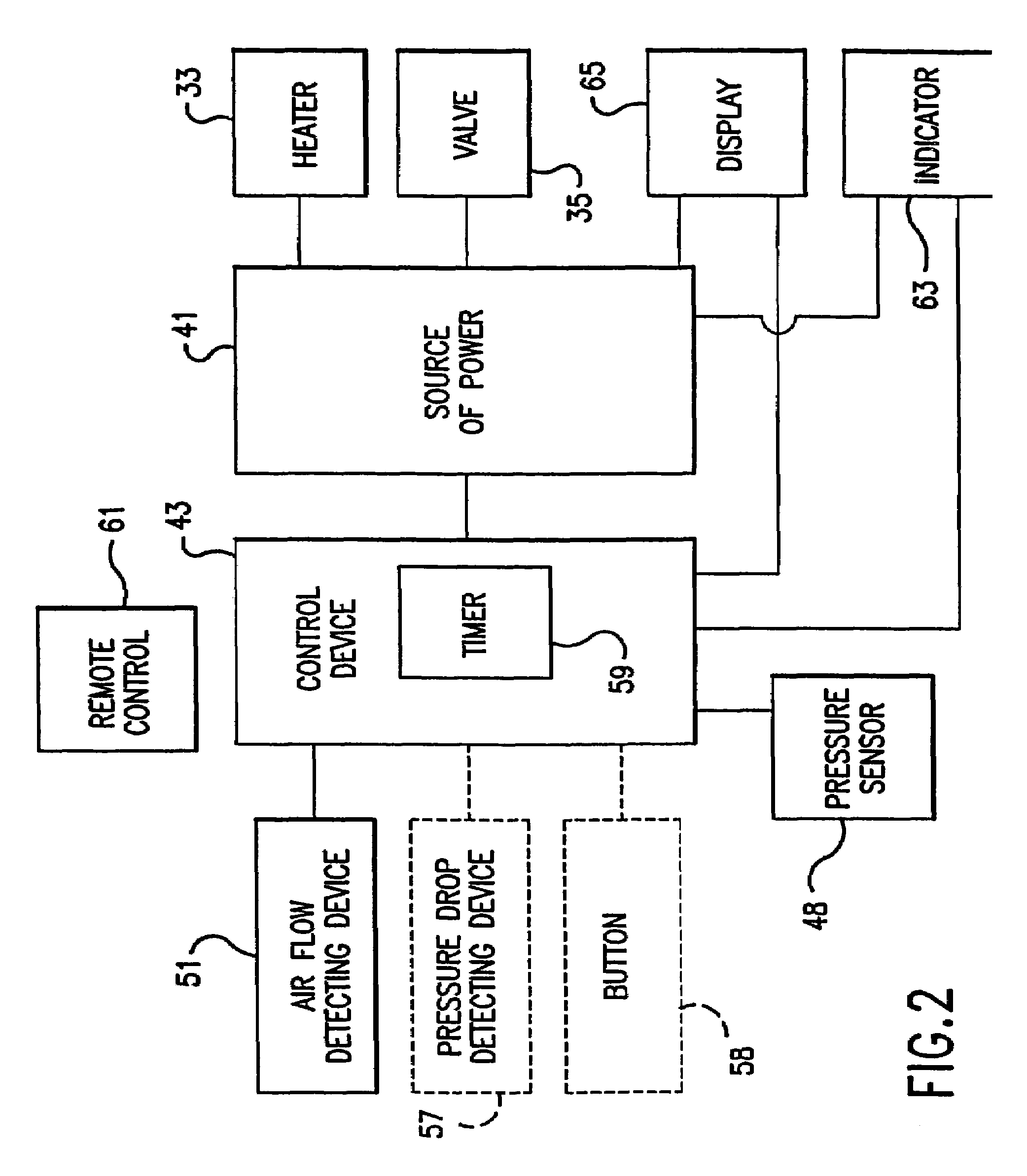
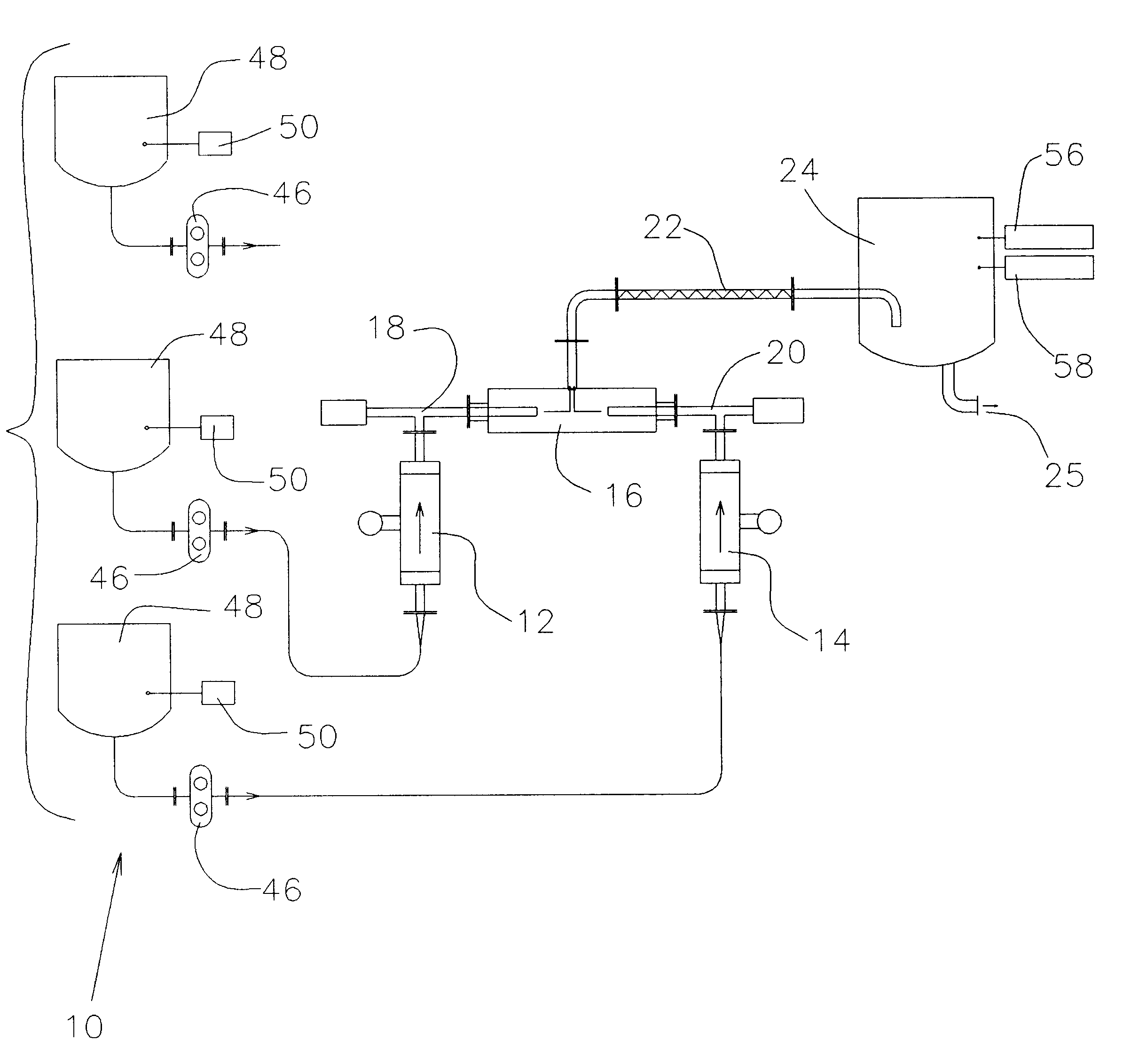
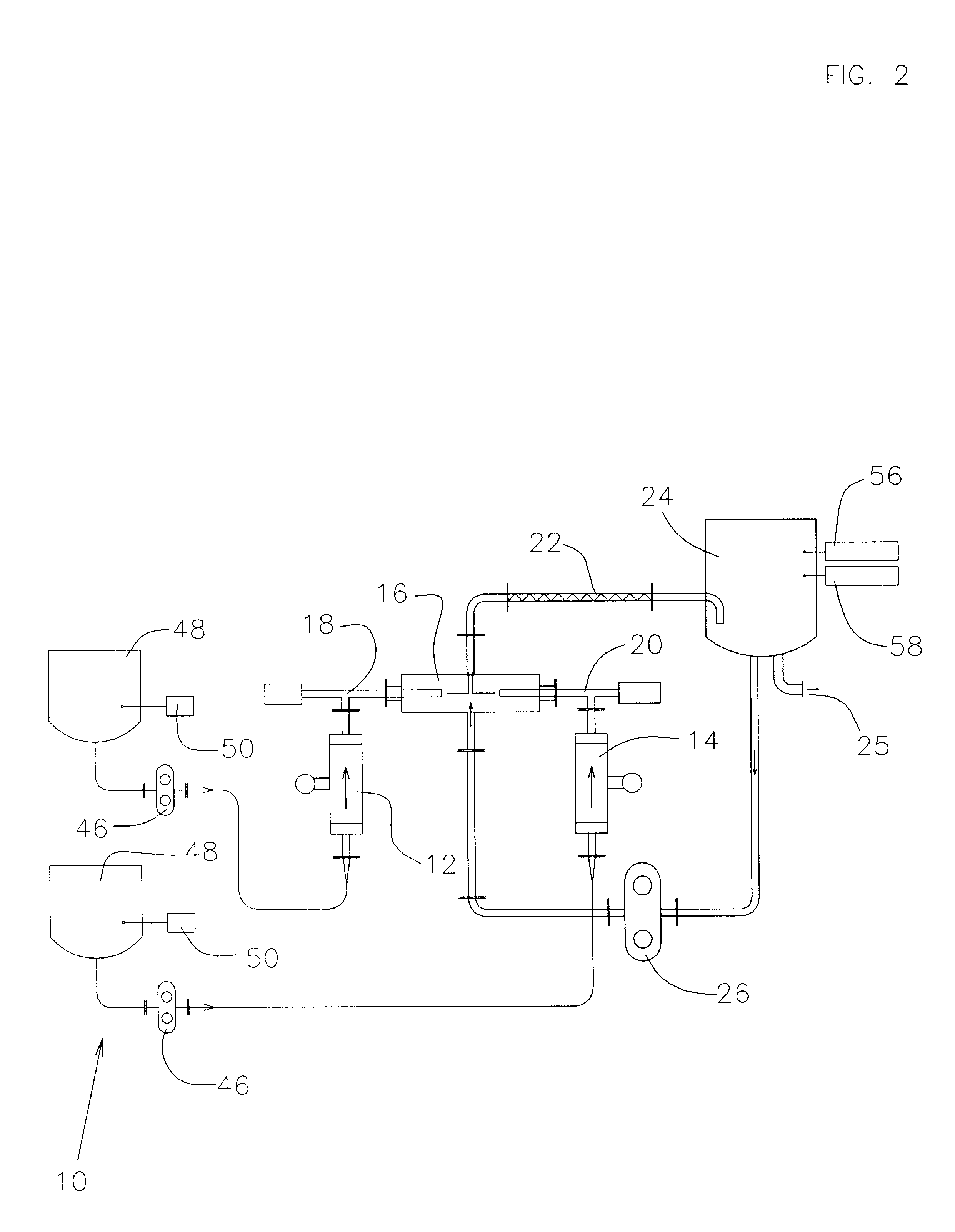
An aerosol generator includes a flow passage having an inlet and an outlet, a heater arranged relative to the flow passage for heating the flow passage, a source of material to be volatilized in communication with the inlet of the flow passage, a valve to open and close communication between the source of material and the inlet of the flow passage, and a pressurization arrangement for causing material in the source of material to be introduced into the flow passage when the valve is in an open position. The aerosol generator further includes a source of power for operating the heater and the valve, and a control device for controlling supply of power from the source of power to the heater and the valve. A metering device in an inhaler includes a pressurized source of medicated fluid and a metering chamber configured to deliver a predetermined volume of fluid to a heated flow passage in the inhaler. The metering chamber can be part of a rotary valve having a bore and a displacement member moveable within the bore from a first position where the fluid is loaded into the bore to a second position where the predetermined volume is ejected out of the bore. Another metering chamber has an elastic portion of a delivery passage in fluid communication with the pressurized source of liquid and the elastic portion of the delivery passage is deformed to eject the predetermined volume.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS USA INC
Methods and devices for minimally invasive respiratory support
ActiveUS20080135044A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAssisted ventilationCatheter
Modes, methods, systems and devices are described for providing assisted ventilation to a patient, including wearable ventilation systems with integral gas supplies, special gas supply features, ventilation catheters and access devices, and breath sensing techniques.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Double loop technology
InactiveUS20050272891A1Constant levelLimited wayControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsExhaust apparatusPolymer sciencePolyolefin
The present invention relates to an apparatus and process for polymerizing olefins. One embodiment comprises polymerizing at least one monomer in a first loop reactor in the presence of a catalyst to produce a first polyolefin fraction. A portion of the first polyolefin fraction is transferred to a second loop reactor, connected in series with the first loop reactor. The process further comprises polymerizing in the second loop reactor at least one monomer in the presence of a catalyst to produce a second polyolefin fraction in addition to the first polyolefin fraction. The combination of the first and second polyolefin fractions can produce a polymer resin fluff having bimodal molecular weight distribution.
Owner:TOTAL RES & TECH FELUY
Decision information system for drug delivery devices
ActiveUS6928338B1Sampled-variable control systemsControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsDoses rateGeneral purpose computer
Decision information systems, methods, and computer programs for better informing decisions to use multiple drugs in drug delivery devices, including implantable devices, for drug administration. Executable computer programs and logic embodying methods of the invention can calculate consistent multiple drug mixture amounts and drug delivery flow rates. One program accepts user input indicating a desired first drug dose rate, an initial first drug concentration, a desired second drug dose rate, an initial second drug concentration, and the reservoir size of the drug delivery device. The program method calculates a first drug amount and a second drug amount to combine in a mixture as well as a first drug true concentration in the mixture. The drugs can be mixed consistent with the physician's instructions using the program output. The first drug true concentration can be entered into a programmer device as the only drug concentration entered. Another program calculates a consistent first drug, second drug, and diluent amount to be added to a mixture for injection into a fixed flow rate, implantable drug delivery device. Methods preferably output true concentrations and dose rates for all drugs to be added and most preferably show all calculations used to arrive at the flow rate and mixture amount calculations. Yet another program receives a new desired drug dose rate for a previously filled device. The program accepts the existing mixture volume and true drug concentrations for a partially depleted device and calculates a new mixture flow rate to achieve the desired dose rate using the existing mixture. The methods can be implemented as executable computer programs in programmer devices, general purpose computers, servers, handheld computers, and personal digital assistants.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Continuous liquid stream digital blending system
InactiveUS6186193B1More disadvantageSimplifies software and set-up computationLiquid fillingControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsHybrid systemDigital clock
The present invention consists of a method and apparatus providing for the continuous stream blending, preferably on a mass ratio basis, of two or more liquids. Each individual liquid stream is synchronously dosed in precise mass ratio to a common mixing point. The flow of each stream is on-off or digital. Repeated mass ratio doses of defined and matching flow interval, referred to as synchronous digital flow, interspersed with a defined interval of no flow, constitutes digital flow at a net rate sufficient to meet or exceed some required take-away of the blended liquids. In one preferred embodiment, each dose stream flow is produced and measured by a four element apparatus preferably consisting of a servo motor and controller, a precision positive displacement pump, a Coriolis mass meter and a precision flow stream shut-off device. The servo motor and controller establish and control a periodic and intermittent flow rate necessary to displace a defined mass dose in a precisely defined flow interval. The flow interval is measured against a precision millisecond digital clock. The Coriolis mass meter is used only to totalize mass flow to define the desired mass dose during the defined digital flow interval. The flow stream shut-off device ensures precise delivery of the mass dose to the common mixing point. The flow rate of a stream is automatically adjusted by the control electronics until the required mass dose is delivered in the defined flow interval.
Owner:ODEN MACHINERY
Bezel assembly for pneumatic control
ActiveUS20050095154A1Reducing pump strokeReducing the pump strokeFlow mixersOther blood circulation devicesPositive pressureEngineering
A bezel and bezel assembly in which the bezel is a rigid block with a plurality of cavities. A depression in the block has ribs extending up therefrom to form an elevated contour. The depression includes at least one cavity therein for the application of air pressure into the depression and over the elevated contour. A gasket fits over the bezel so that positive pressure applied through the at least one cavity in the depression forces a gasket membrane to expand away from the pumping side and negative pressure applied through the at least one cavity in the depression pulls the gasket membrane against the elevated contour of the ribs. The bezel may include solvent bondable tubing connections for making pneumatic connections to the bezel.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
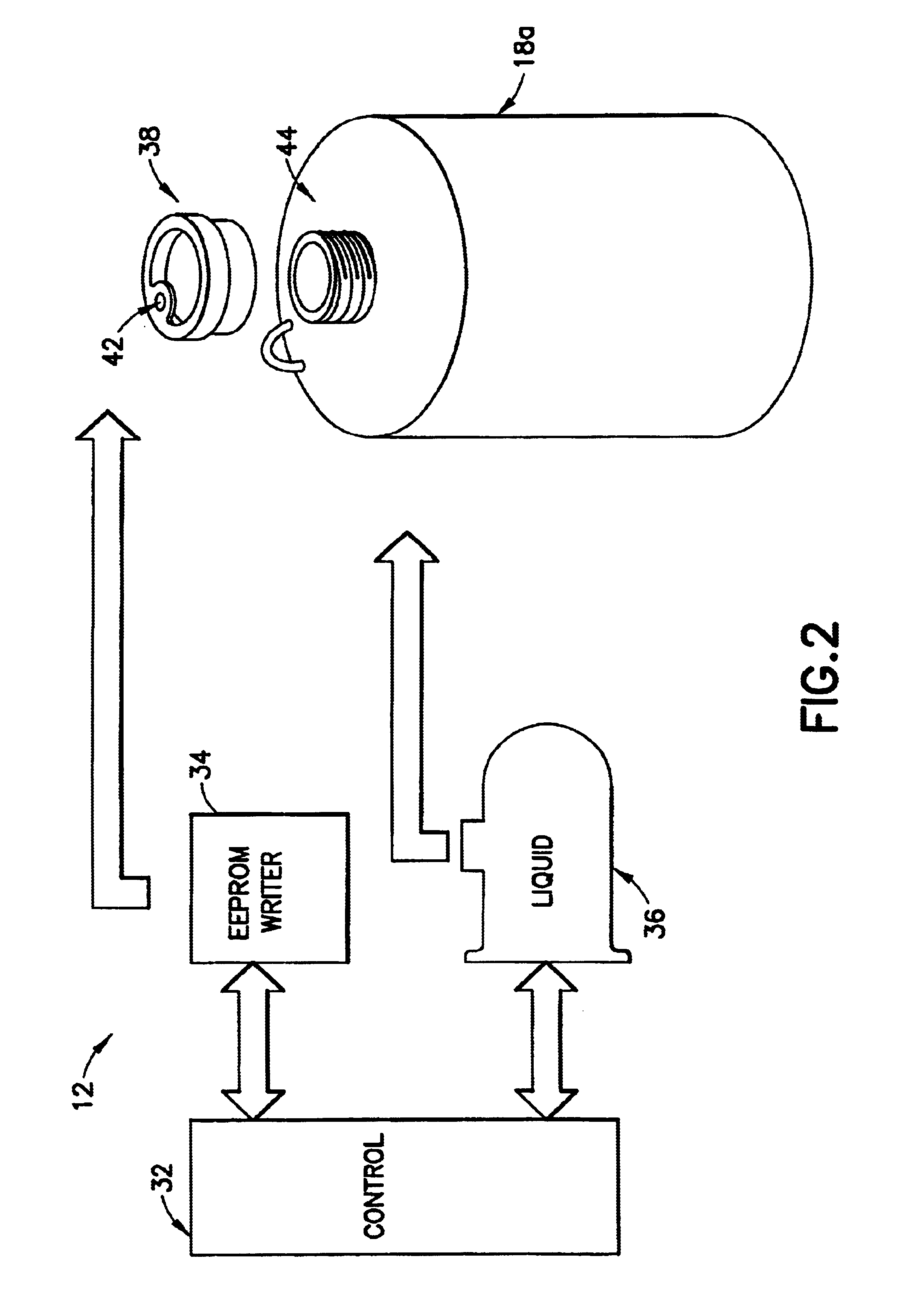
Liquid handling system with electronic information storage
The present invention is a system for handling liquid and a method for the same. The system has a container capable of holding a liquid. An electronic storage device is coupled with the container for electronically storing information relating to the liquid stored in the container. The system also has an antenna, for storing information to and reading information from the electronic storage device. Finally, the system has a microprocessor-based controller, coupled with the antenna, for controlling processing of the liquid based on information read from the electronic storage device by the antenna.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Patient interface systems
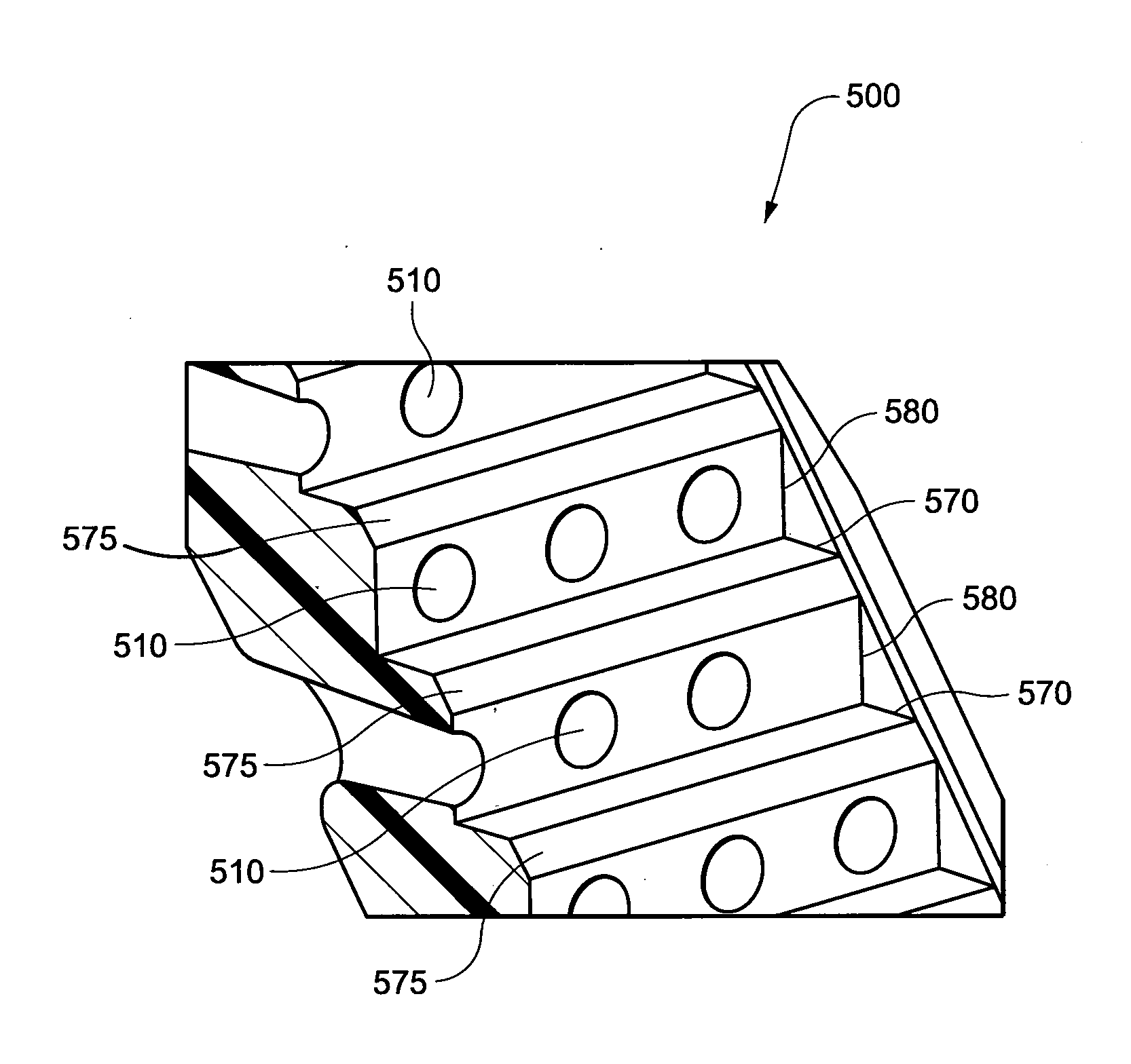
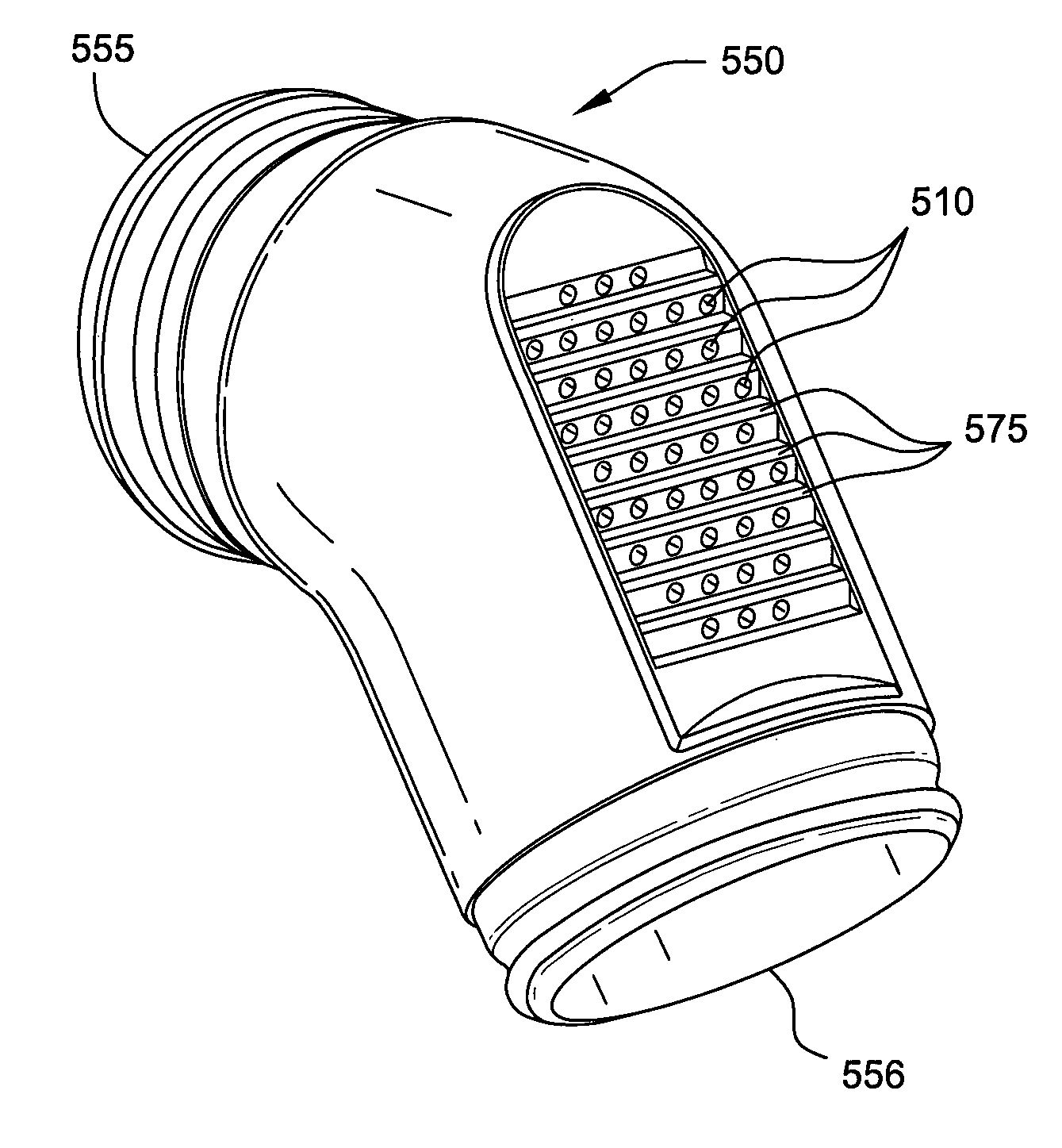
ActiveUS20120132209A1Easy to useEasy to appreciateControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsBreathing masksElastomerEngineering
A headgear for use with a patient interface for delivering a flow of breathable gas to a patient includes at least a strap (741) adapted to position the patient interface in sealing engagement with the patient's airways. The strap is constructed from an elastomer and a first side of the strap includes a first region (215) on a portion of its surface that is textured to reduce friction with objects contacting the strap. A textured surface coating for a portion of an elastomer strap included in a headgear system is adapted to contact the skin of a patient, when in use, and the coating has a Ra value greater than zero. A vent (500) for use with a patient interface for delivering a flow of breathable gas to a patient includes a plurality of rises (580) and runs (570) in a stepped arrangement; and a plurality of holes (510) in the stepped arrangement for the venting of gas.
Owner:RESMED LTD
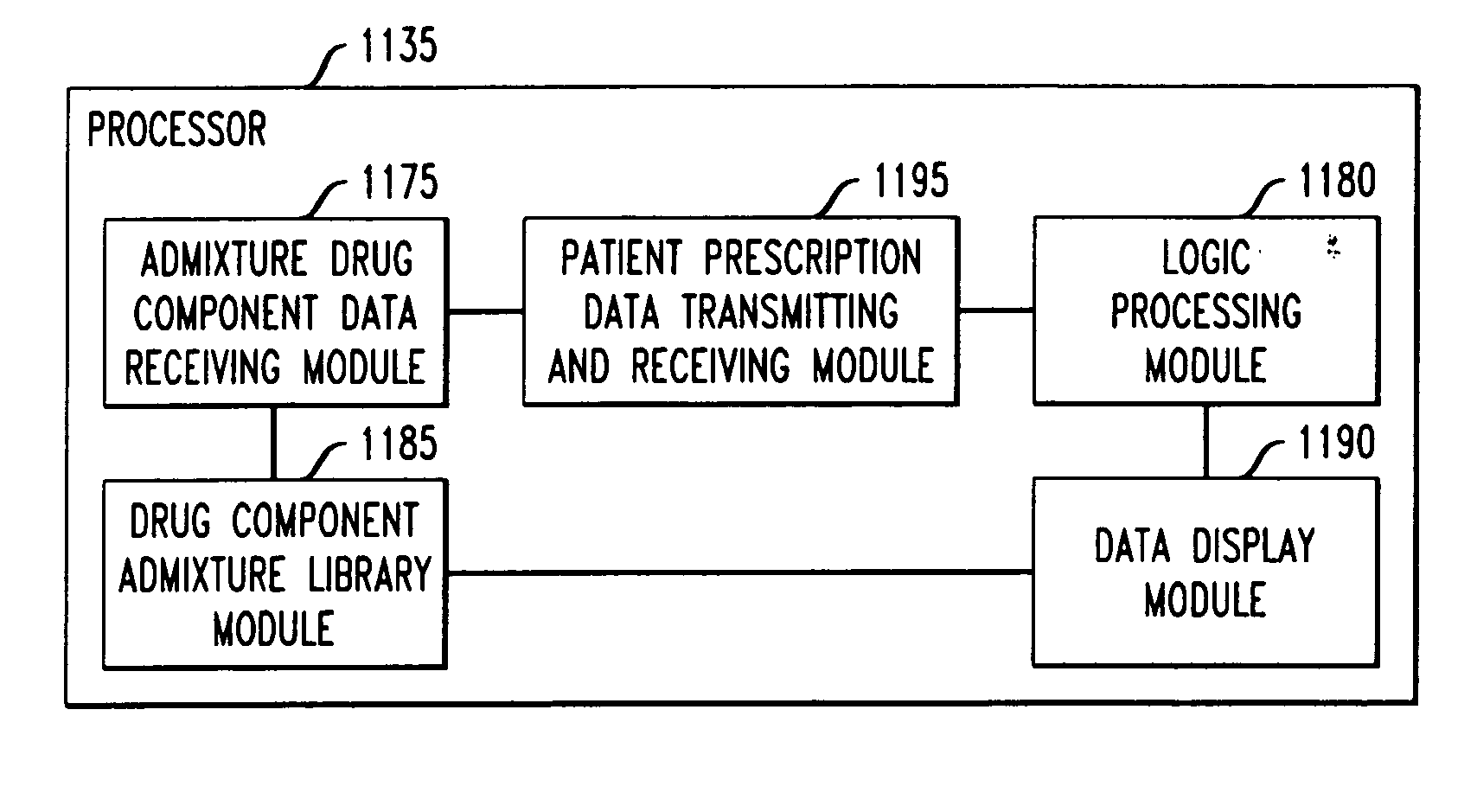
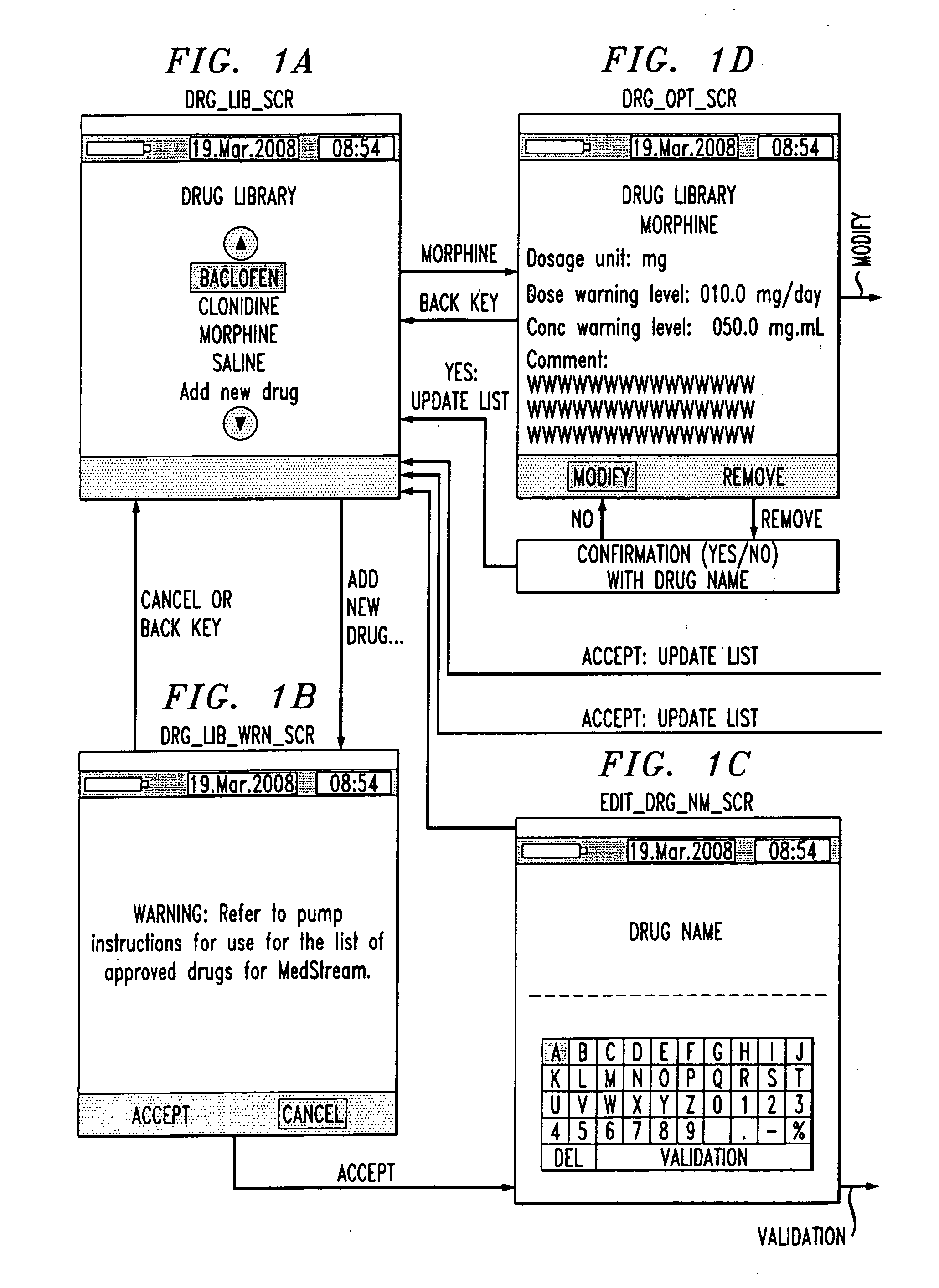
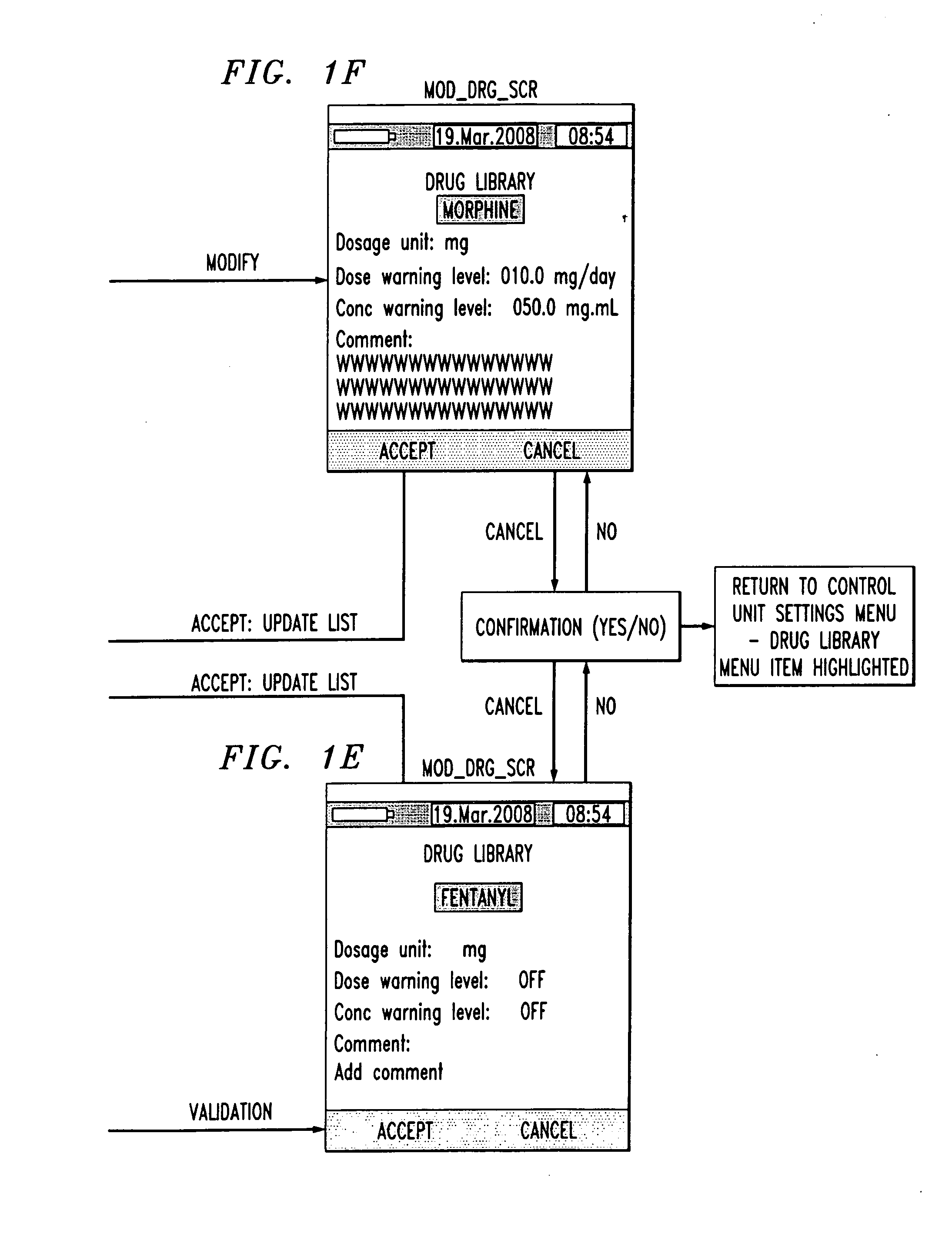
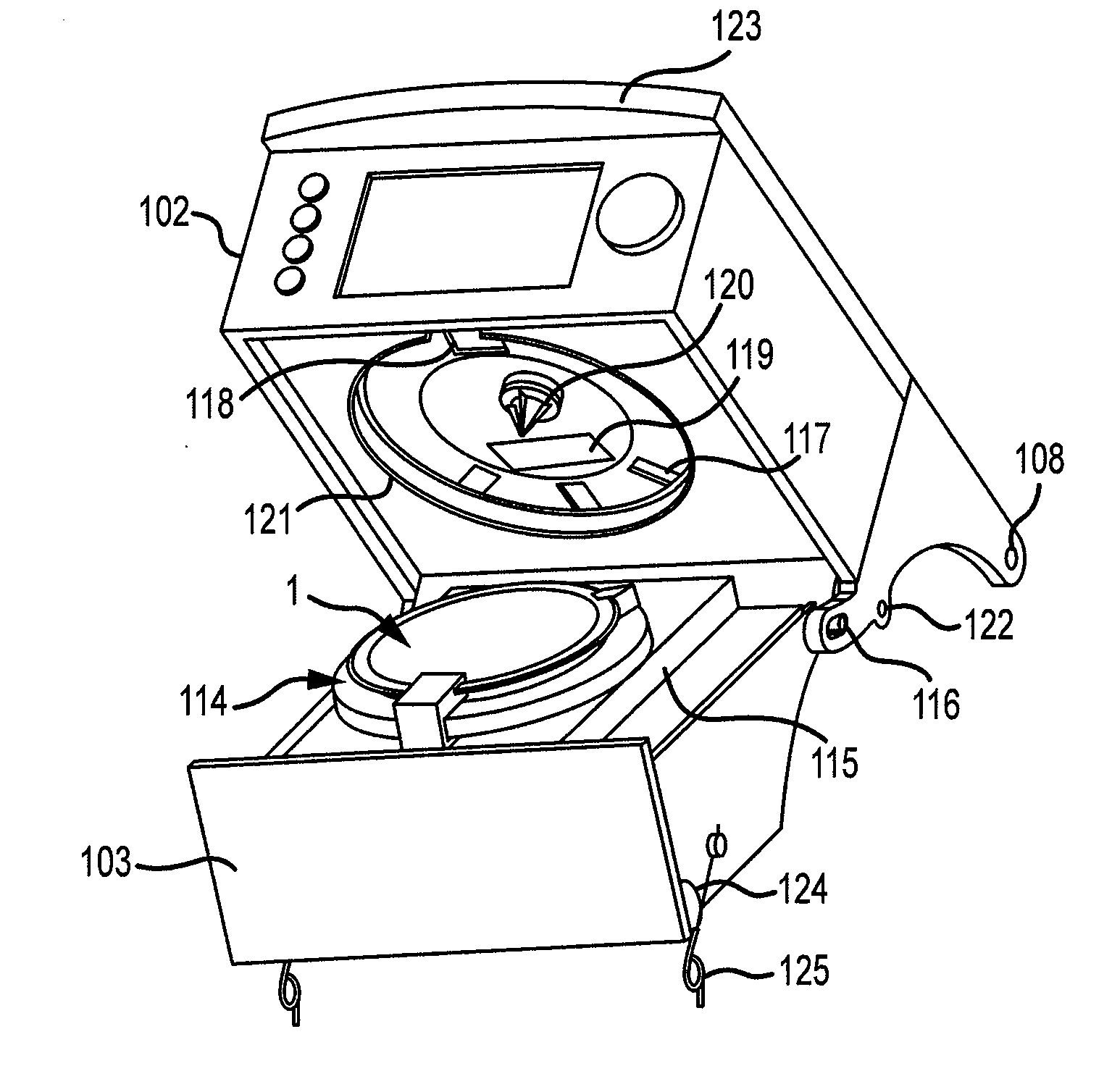
Drug component admixture library for a drug infusion delivery system
InactiveUS20110320049A1Shorten the timeReduce generationLevel controlControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsDrugs infusionDelivery system
Minimizing improper dosage of a drug admixture (including a single primary drug component and at least one second drug component). For each drug component in the drug admixture, receiving a name of the drug component along with its dosage unit, a maximum dose warning level and a maximum concentration warning level. Receiving a concentration for each of the single primary drug component and the at least one secondary drug component; and a dose setting of only the primary drug component. Automatically calculating a dose of each of the at least one secondary drug component. Generating an alert when: (i) the received dose setting of the primary drug component or calculated dose setting of the at least one secondary drug component exceeds the dose warning level; or (ii) the received concentration of the primary drug component or the at least one secondary drug component exceeds the concentration warning level.
Owner:MEDOS INT SARL
Apparatus and method for preparing a liquid mixture
A mixing apparatus, puncturing mechanism, and cartridge are disclosed. The mixing apparatus has a housing and a drawer with a recess. Corresponding cartridges may be inserted into the drawer and slid into the housing to facilitate mixing a liquid with contents of the cartridge. The liquid may originate from a reservoir in the mixing apparatus or a direct line. Also inside the housing of the mixing apparatus is the puncturing mechanism. The puncturing mechanism has a nozzle configured to puncture a lid of a cartridge and inject liquid to mix with the contents of the cartridge. The puncturing mechanism is further configured to drive an internal puncturing unit inside of the cartridge through a lower portion of the cartridge to allow liquid from the nozzle and contents of the cartridge to be dispensed into a receptacle.
Owner:FORMULANOW
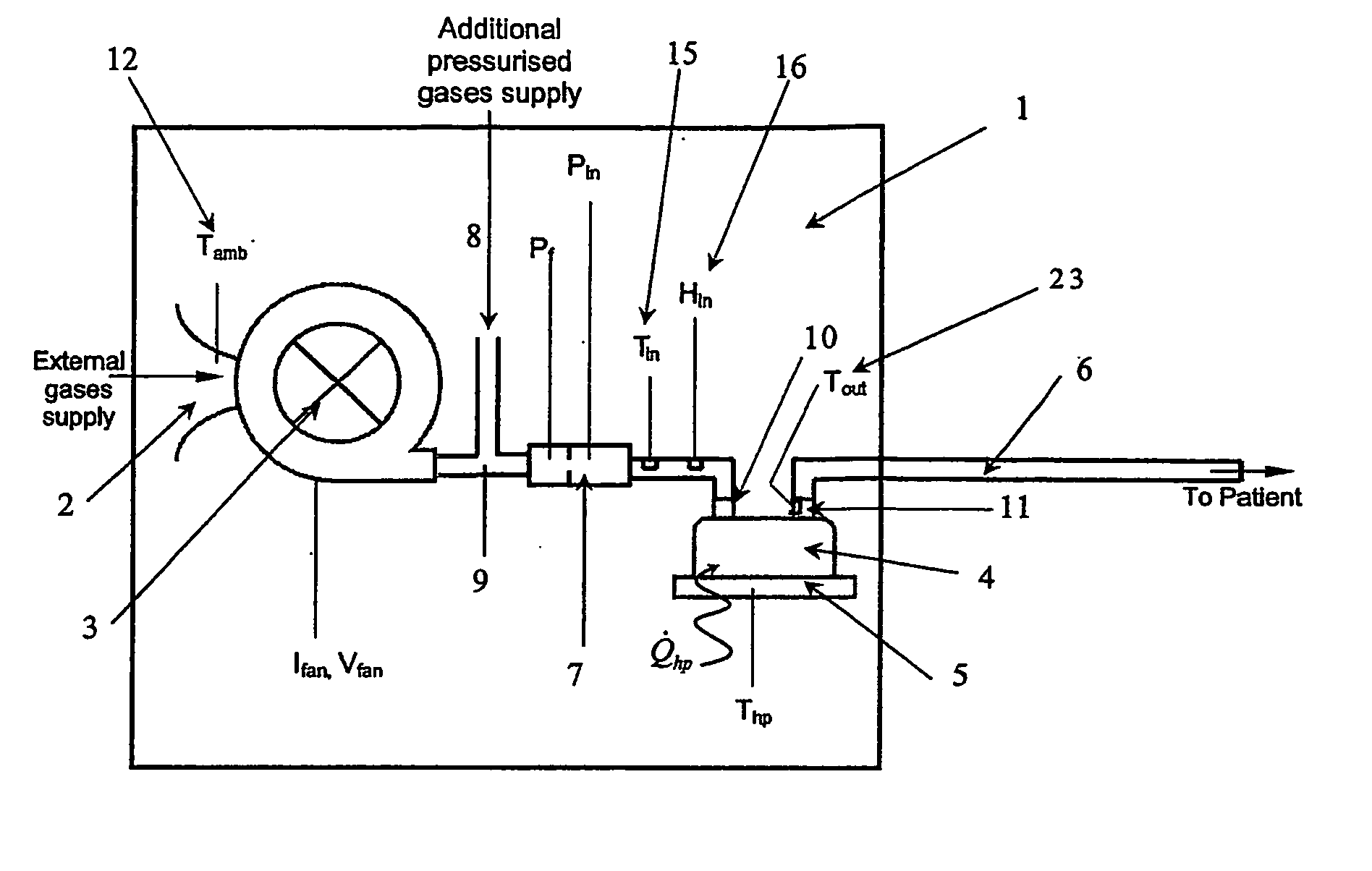
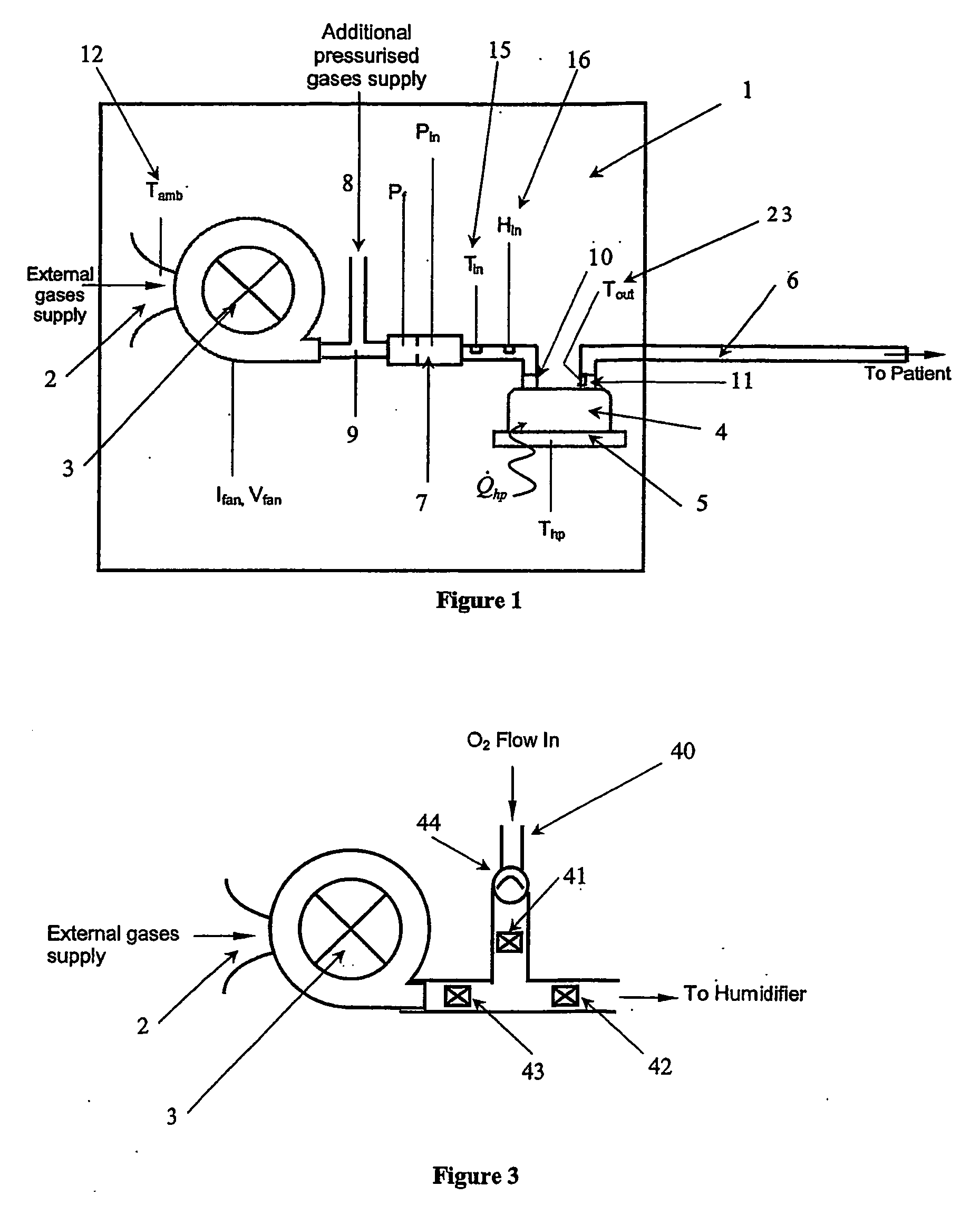
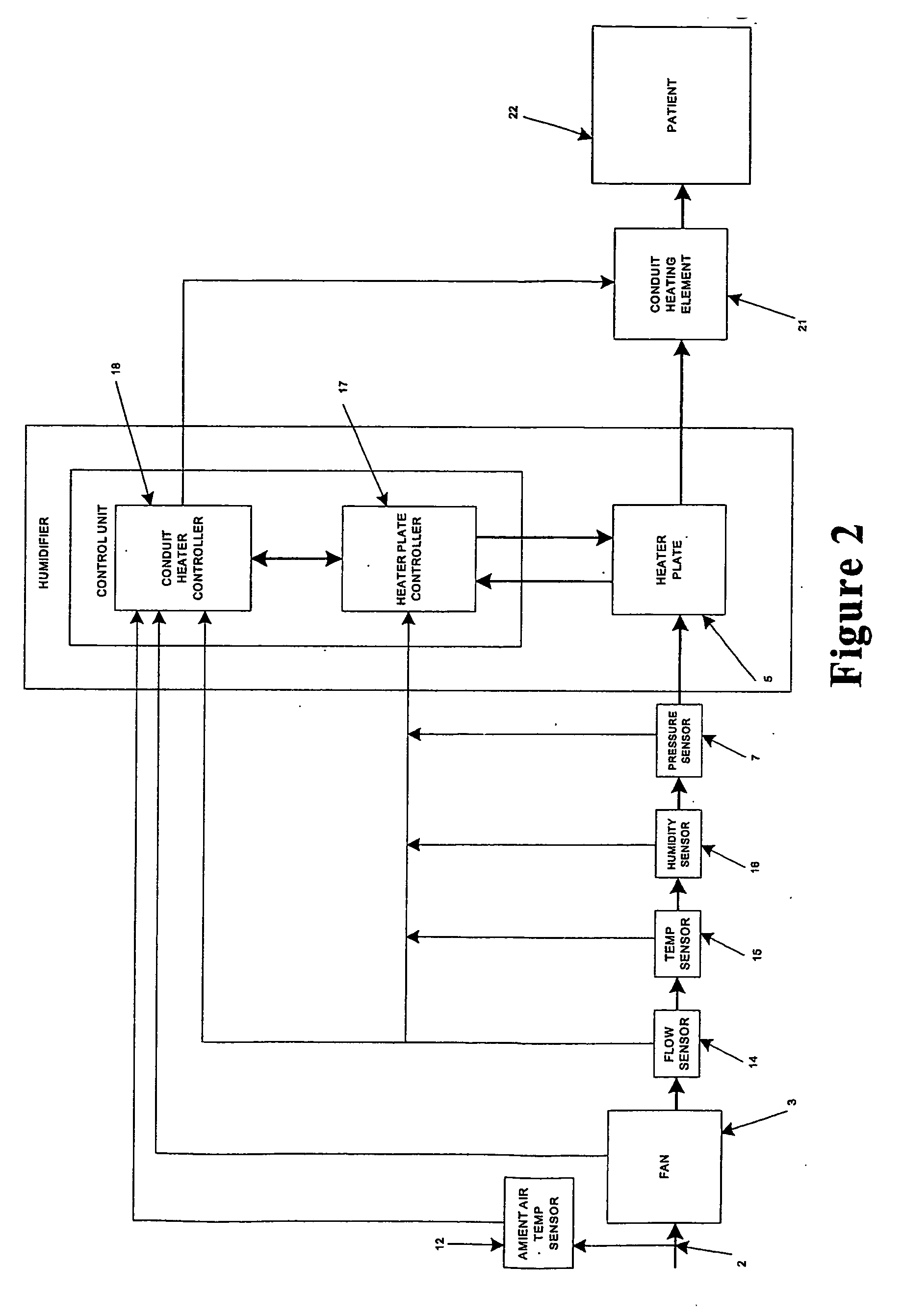
Humidification system
ActiveUS20060113690A1Eliminate needUsing liquid separation agentMedical devicesMarine engineeringHumidity
Breathing assistance apparatus including humidifier (4) and heated conduit (6) adapted to deliver humidified gases at desired and accurate level of humidity to patient. Humidifier includes controller (18) that delivers flow rate, temperature and humidity of gases and then determines required power input to deliver gases as required. Need for external sensors is dispensed with providing simple and less bulky apparatus.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL HEALTHCARE LTD
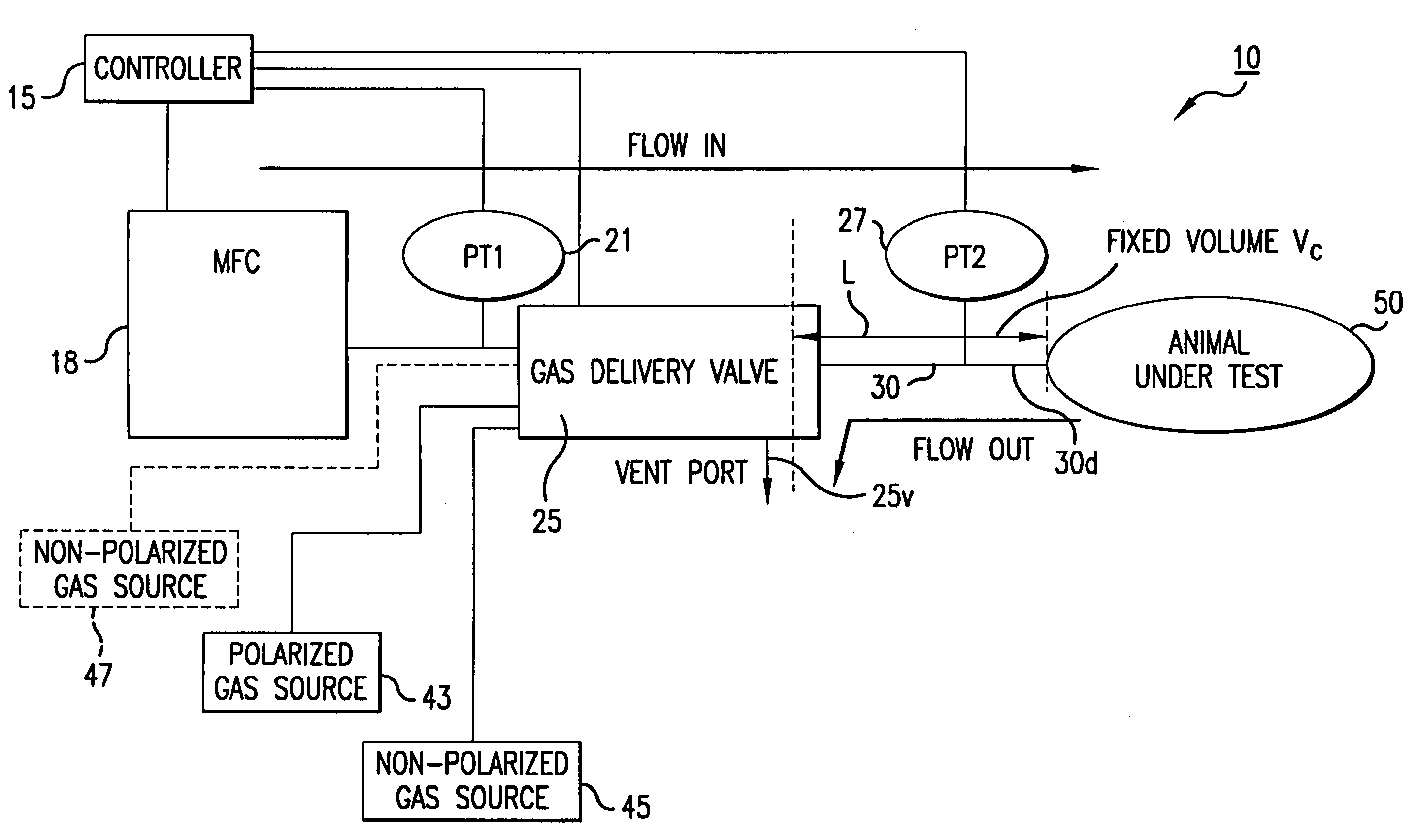
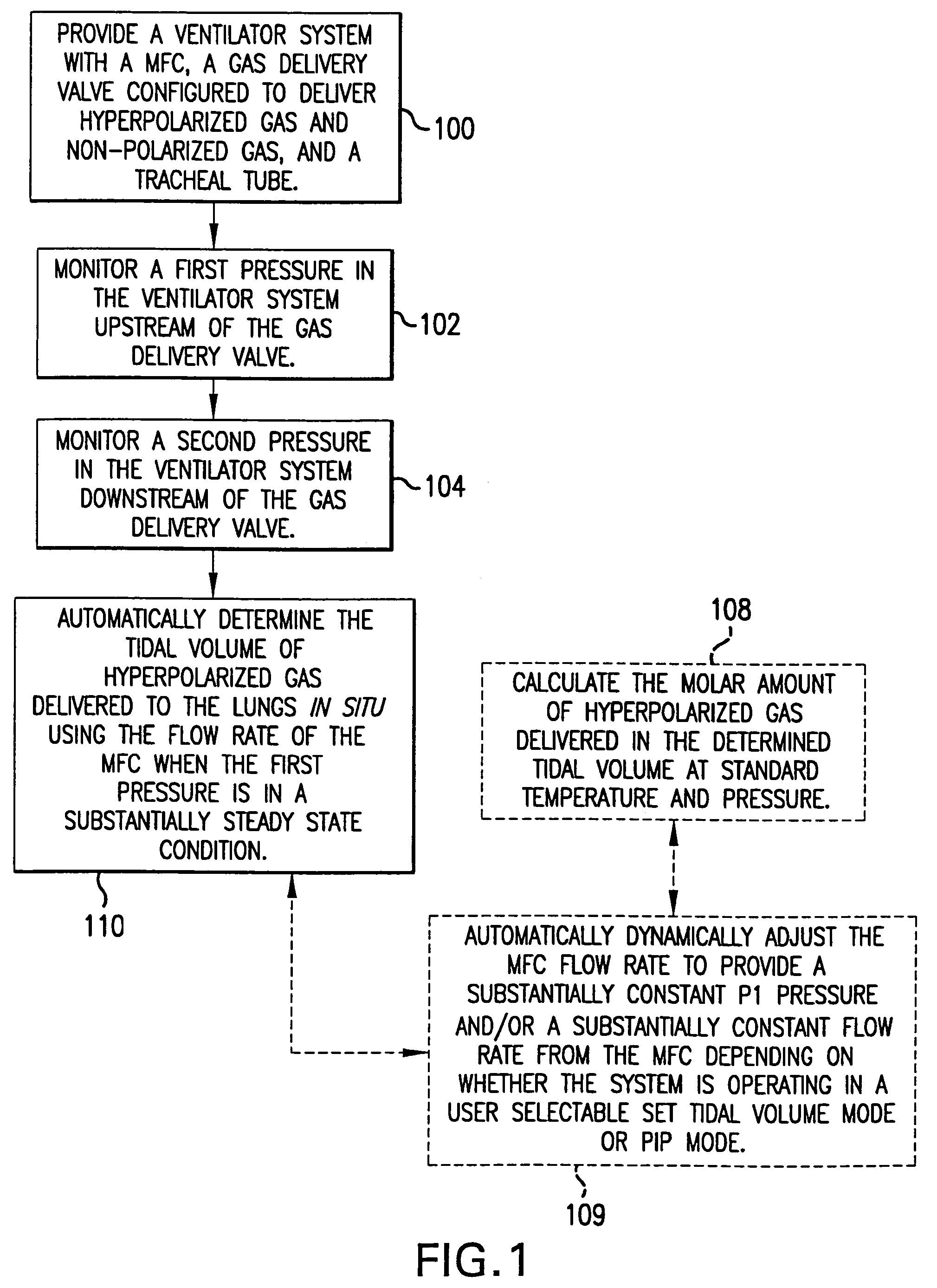
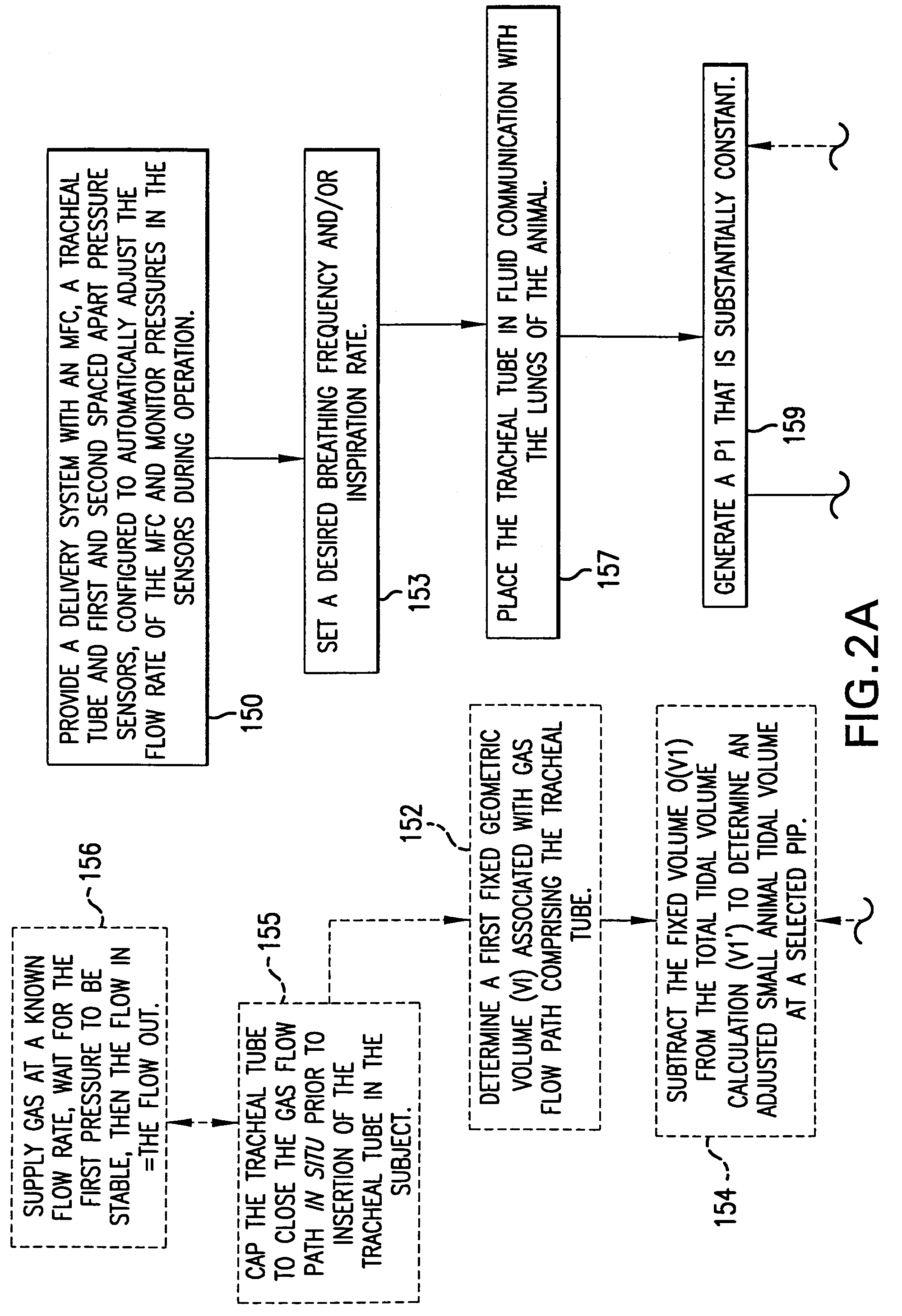
MRI/NMR-compatible, tidal volume control and measurement systems, methods, and devices for respiratory and hyperpolarized gas delivery
Ventilator systems include: (a) a mass flow controller; (b) a gas delivery valve in communication with the mass flow controller and configured to selectively dispense a plurality of different gases to a subject; (c) a first gas source in fluid communication with the gas delivery valve; (d) a second gas source in fluid communication with the gas delivery valve; (e) a first pressure sensor located upstream of the gas delivery valve; (f) a second pressure sensor located downstream of the gas delivery valve; and (g) a controller operatively associated with the first and second pressure sensors and the mass flow controller, the controller comprising computer program code that monitors the pressures measured by the first and second pressure sensors and automatically dynamically adjusts the flow rate of the mass flow controller.
Owner:POLAREAN
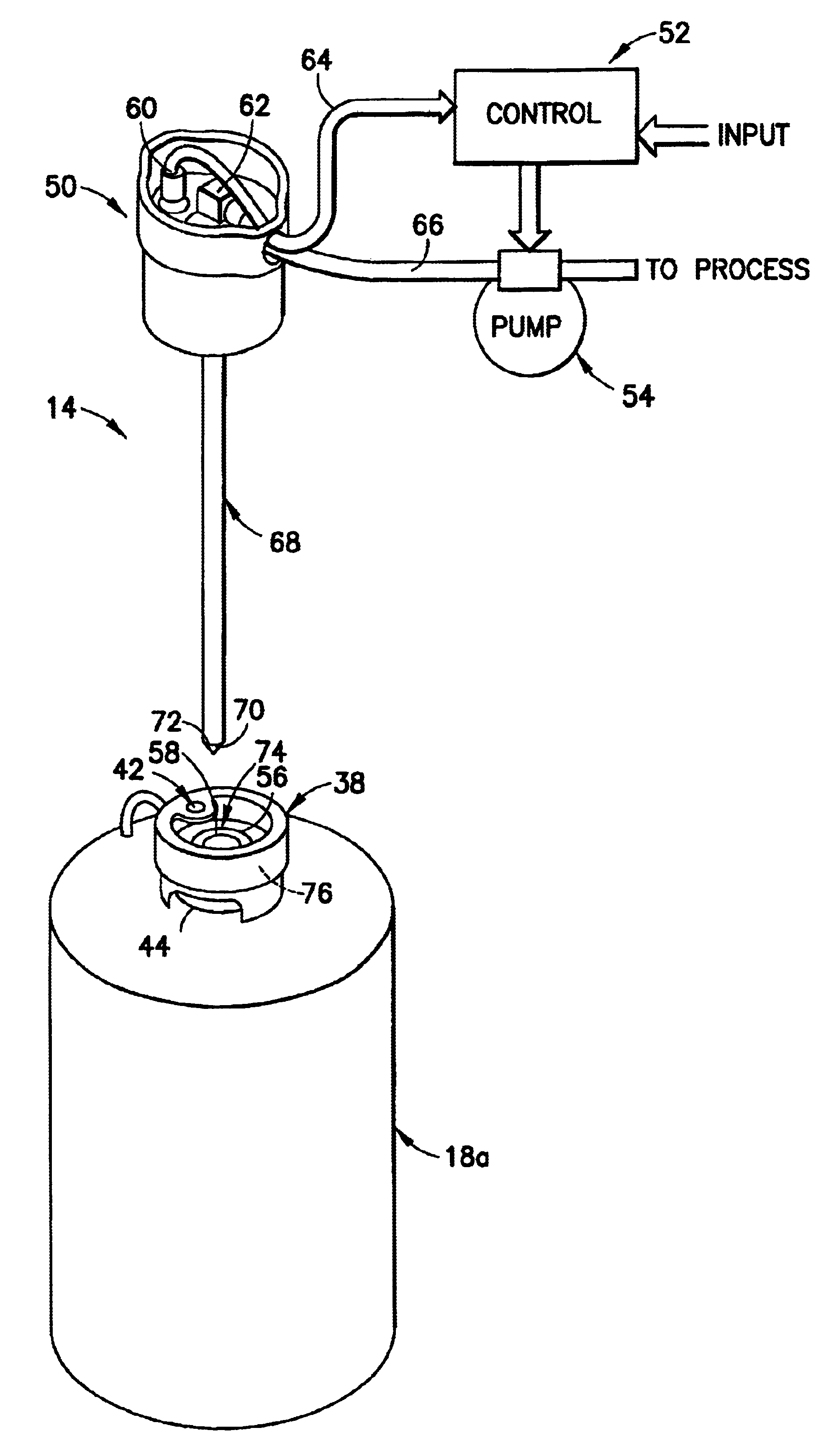
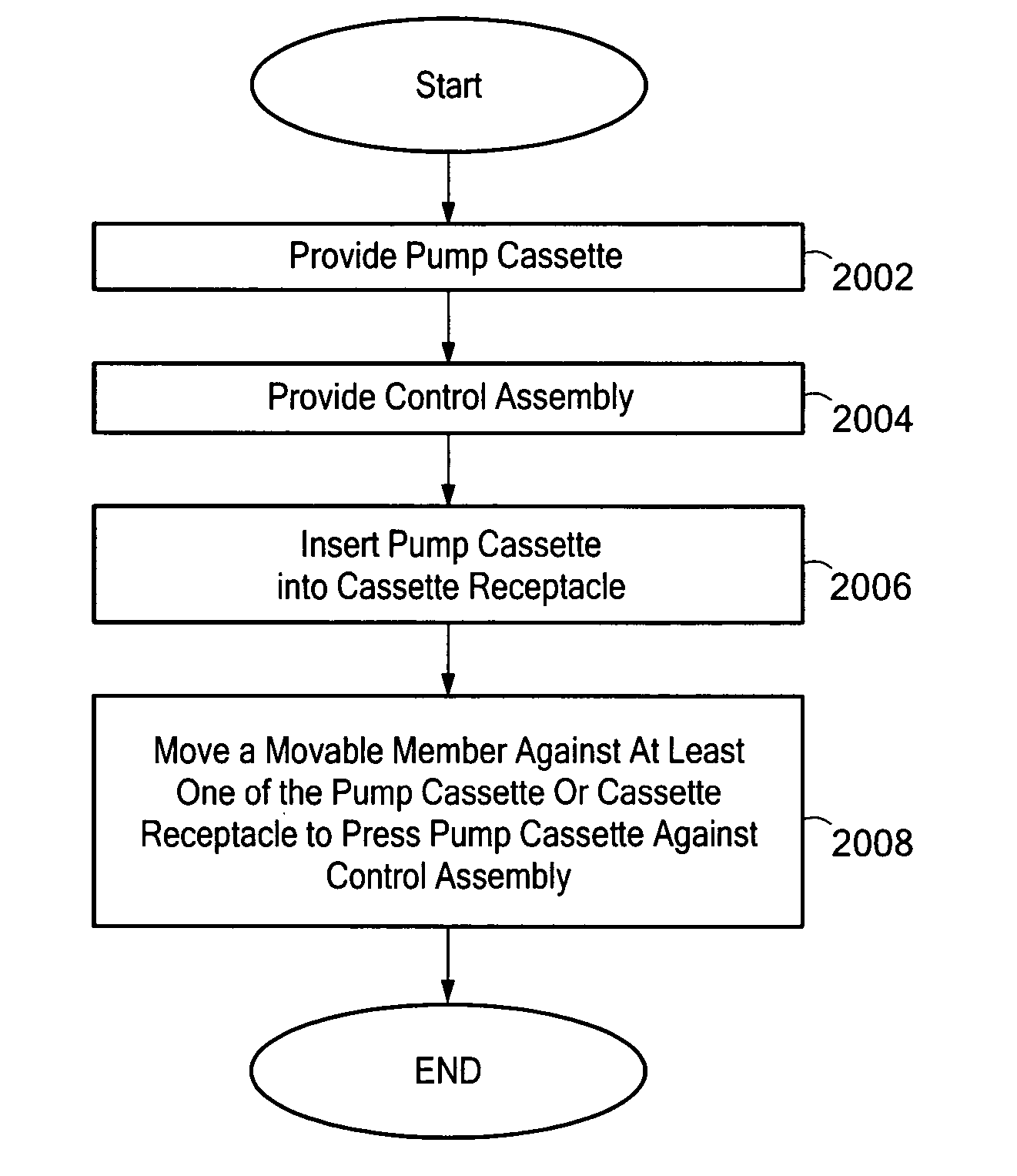
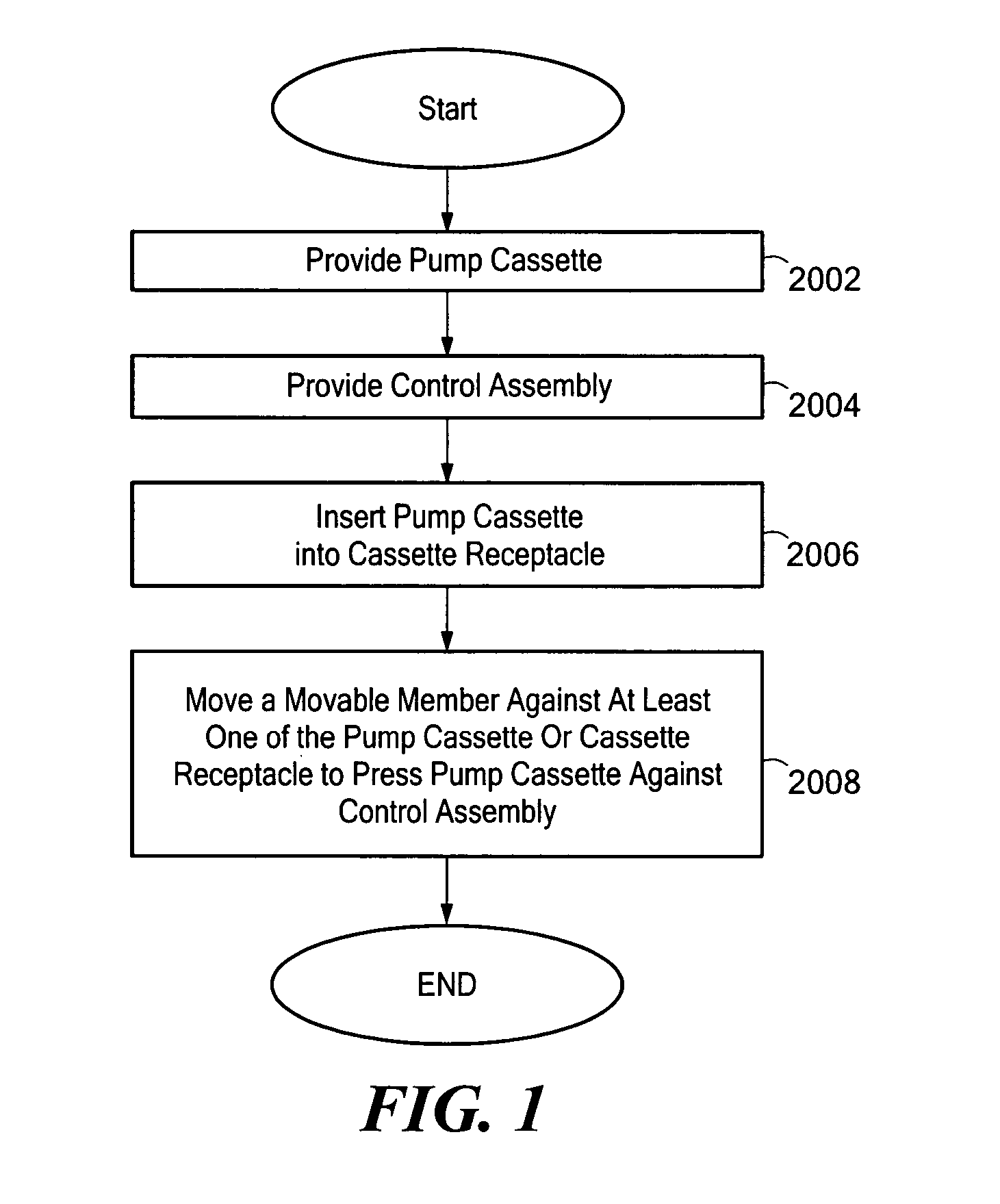
System and method for pumping fluid using a pump cassette
A system and method for pumping fluid using a pump cassette. The system includes a control assembly for operating the pump cassette. A force assembly having a movable member is capable of applying force to the pump cassette to press the pump cassette against the control assembly. The movable member may be an expandable member, such as a bladder.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Remote monitoring system for water
InactiveUS20050009192A1Minimal disruptionFunction increaseWater treatment parameter controlControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsControl signalMonitoring system
A water quality detection system for distributed water supply network. The system, 1, comprises a multiplicity of detectors, 5, wherein each detector of the detectors is capable of monitoring at least one attribute of water and providing a signal related to the attribute. A controller, 7, is provided which is capable of receiving each signal and comparing the signal to a control signal for the attribute. A response mechanism, 9, is responsive to the controller and activated when at least one signal matches the control signal. An access gate, 10, limits access to at least one of the detector, the controller or the response mechanism. An access key, 13, is provided for comparing a user attribute with a stored attribute wherein when the user attribute matches the stored attribute access is provided into the access gate.
Owner:PDA SECURITY SOLUTIONS
Method for manufacturing a system for mixing fluids
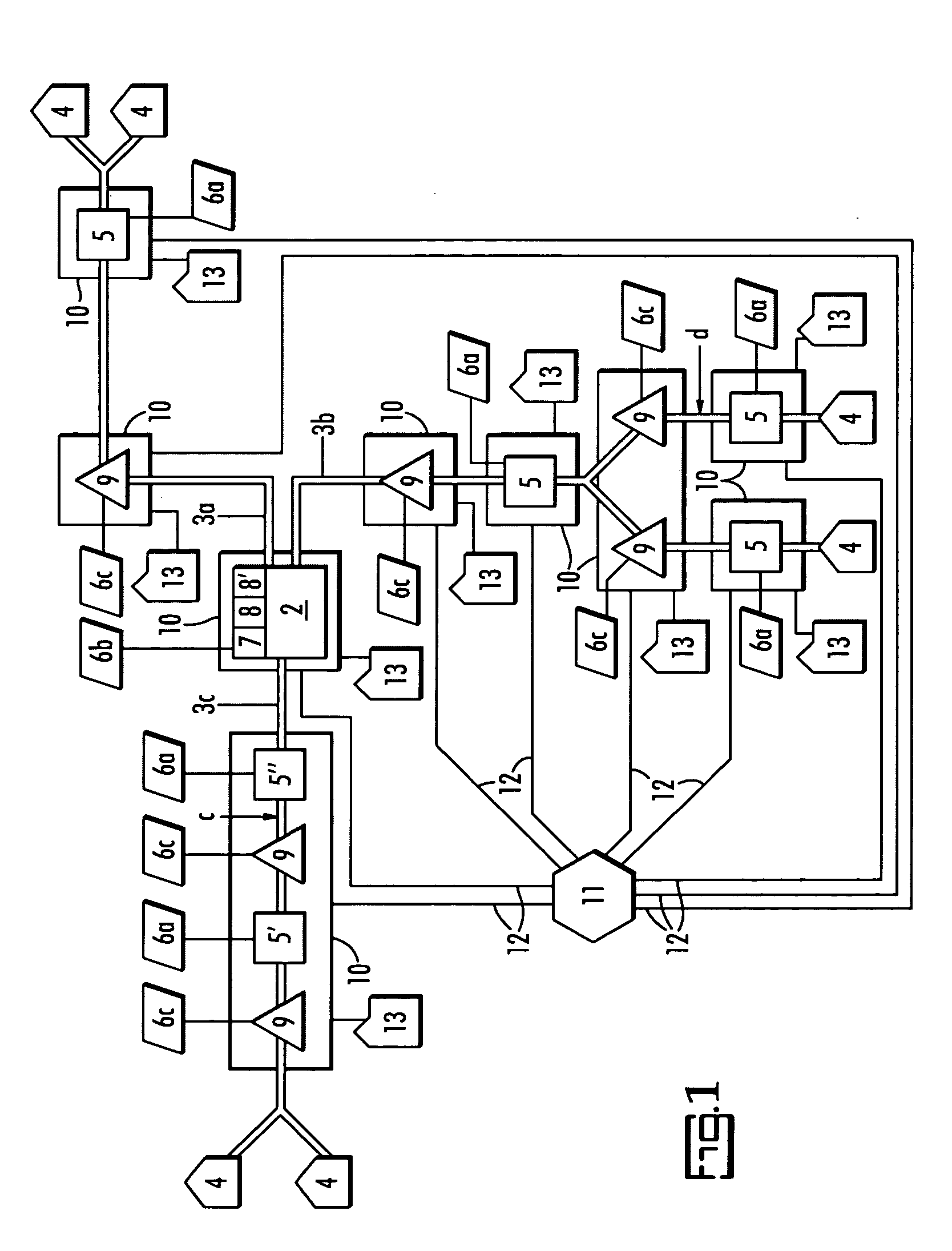
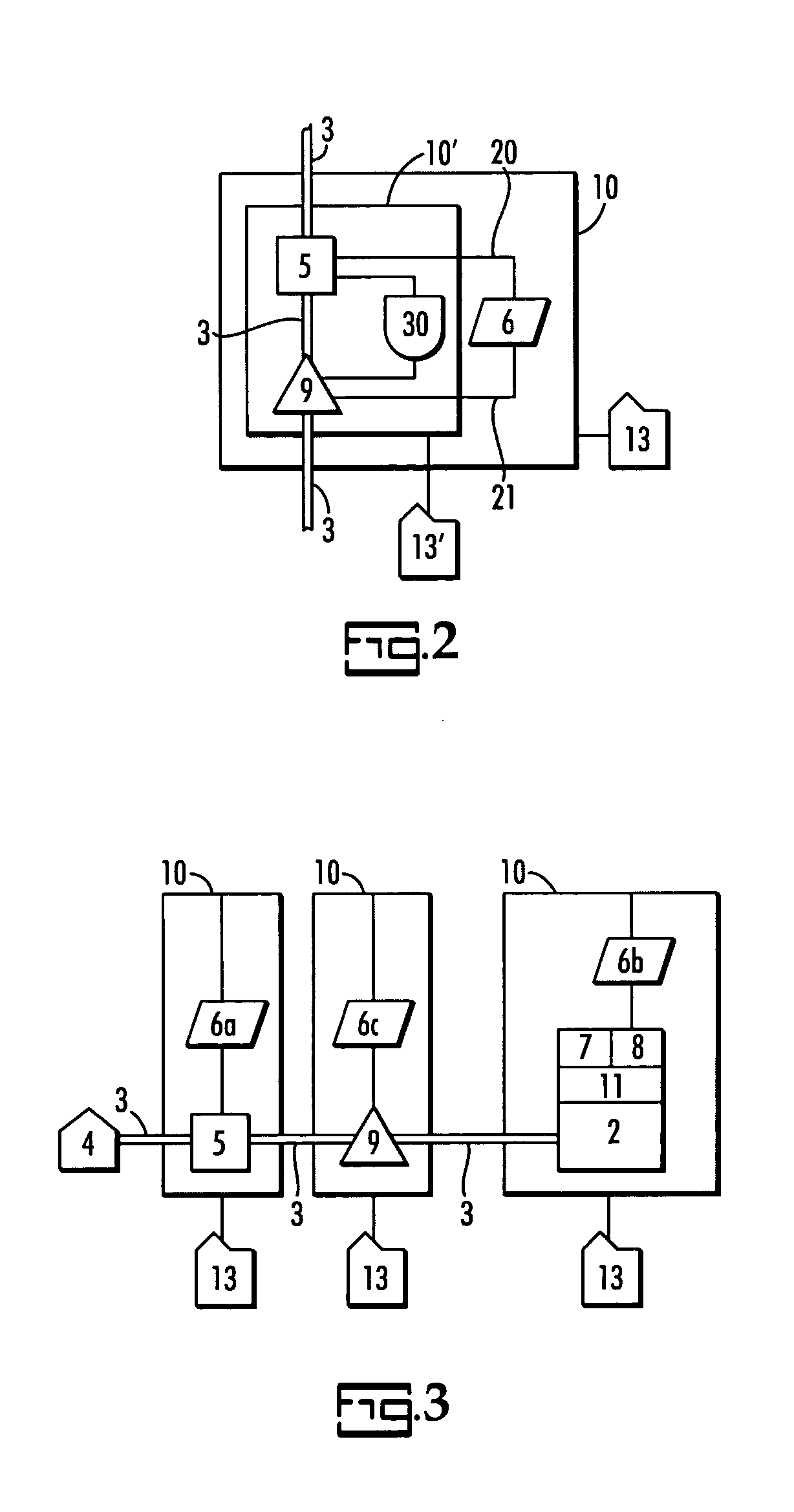
InactiveUS6224778B1Quality improvementLiquid separation auxillary apparatusIon-exchanger regenerationStream flowProcess engineering
A method of manufacturing a system for mixing fluids for providing a flow of a fluid product having a certain pre-established quality or characteristic, from a flow of a first fluid component and a flow of a second fluid component, wherein the fluid components do not meet the pre-established quality standards of the fluid product. The system includes a mixing reservoir; first and second fluid conduits connected to the mixing reservoir for flowing the first fluid component and the second fluid component, respectively into the reservoir; and a third fluid conduit connected to the mixing reservoir for discharging a flow of fluid product from the mixing reservoir, and sensors connected for sensing the flow rates and qualities of the first and second fluid components, flowing into the mixing reservoir and of the fluid product discharged from the mixing reservoir. Signals, associated with the sensors indicate the sensed flow rates and qualities, and controls responsive to the signals regulate the flows of fluid components into the mixing reservoir through controlled flow valves in the first and second conduits so as to cause the quality of the fluid product discharged from the mixing reservoir to at least meet the pre-established quality standards.
Owner:PELTZER CHARLES T
Systems and methods for aerosol delivery of agents
InactiveUS20040134494A1Effective treatmentAvoid pollutionControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsRespiratory masksUltrasonic nebulizersAerosol delivery
Aerosol delivery systems and methods for delivering an agent to a patient are described herein. The present invention includes embodiments comprising an insulated receptacle connected to a body to hold a vial of an agent to be delivered to a patient. The vial is located in an inverted position within the receptacle and connected to the housing. One or more reusable thermal packs can be located on the inner sides of the receptacle, to maintain a selected temperature surrounding the vial. The agent is administered to a patient by placing a prong into one of the patient's orifices and then activating an aerosol delivery system. Such systems comprise jet aerosolization and pneumatic and ultrasonic nebulizers and preferably are portable.
Owner:CREARE INC +1
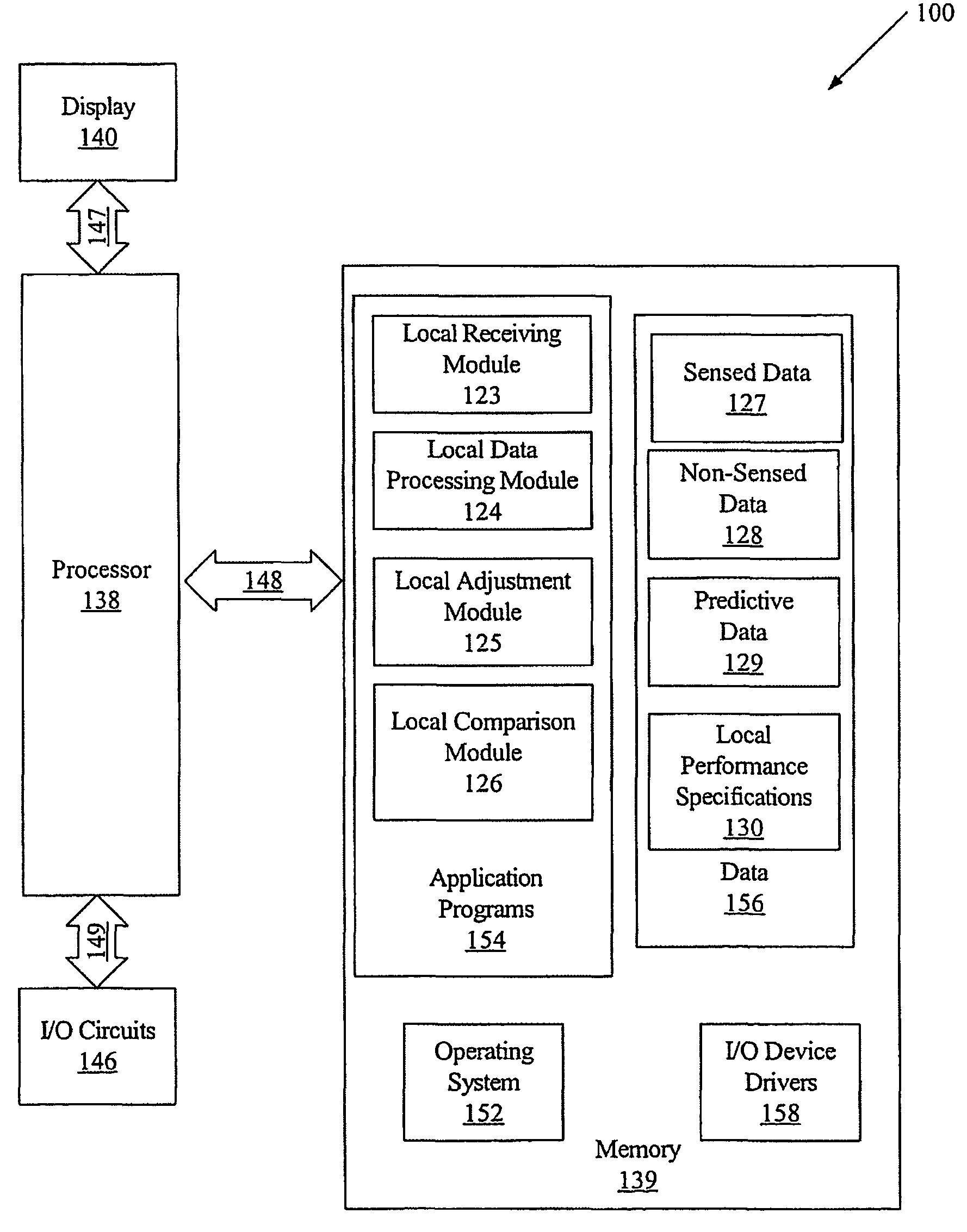
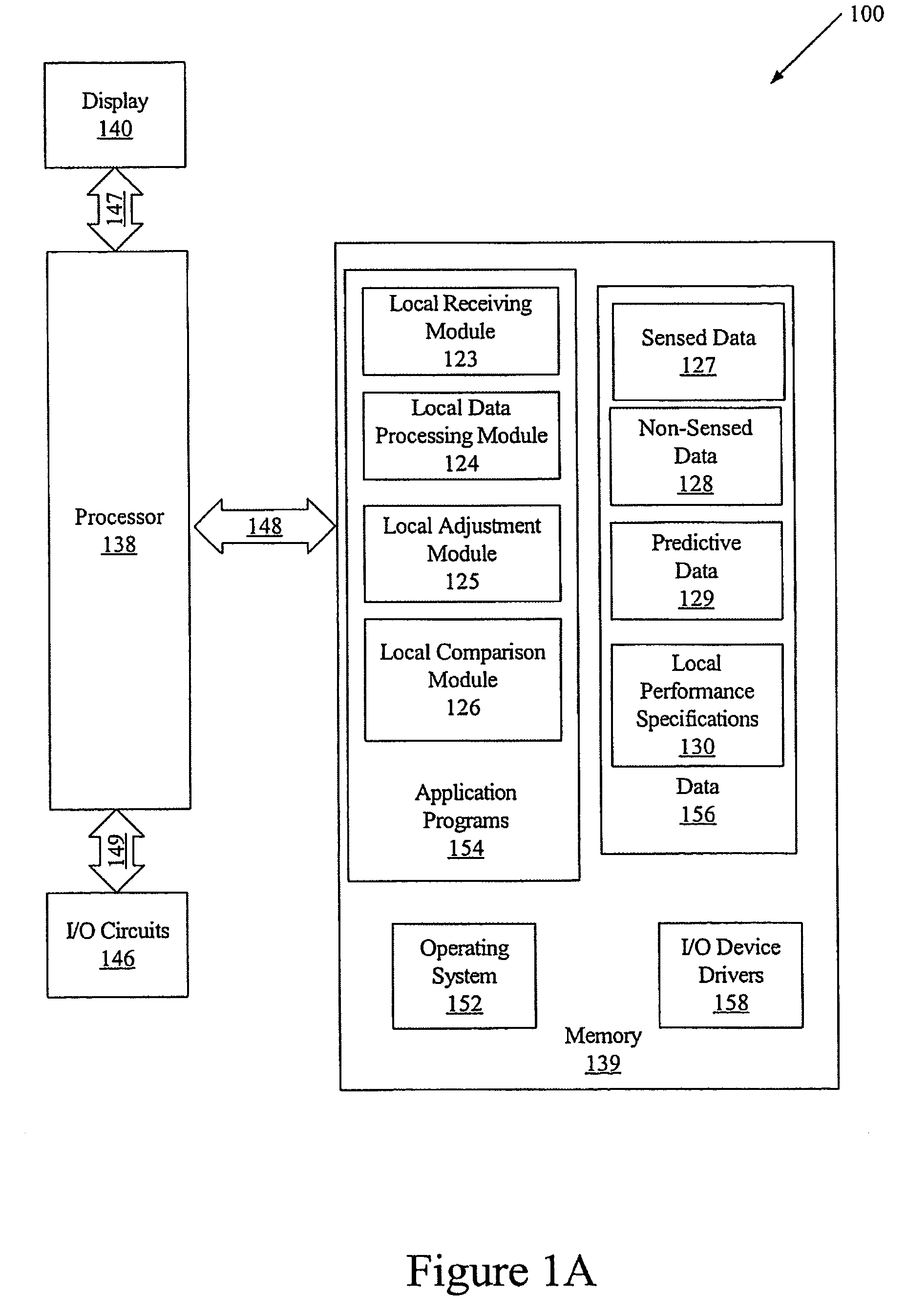
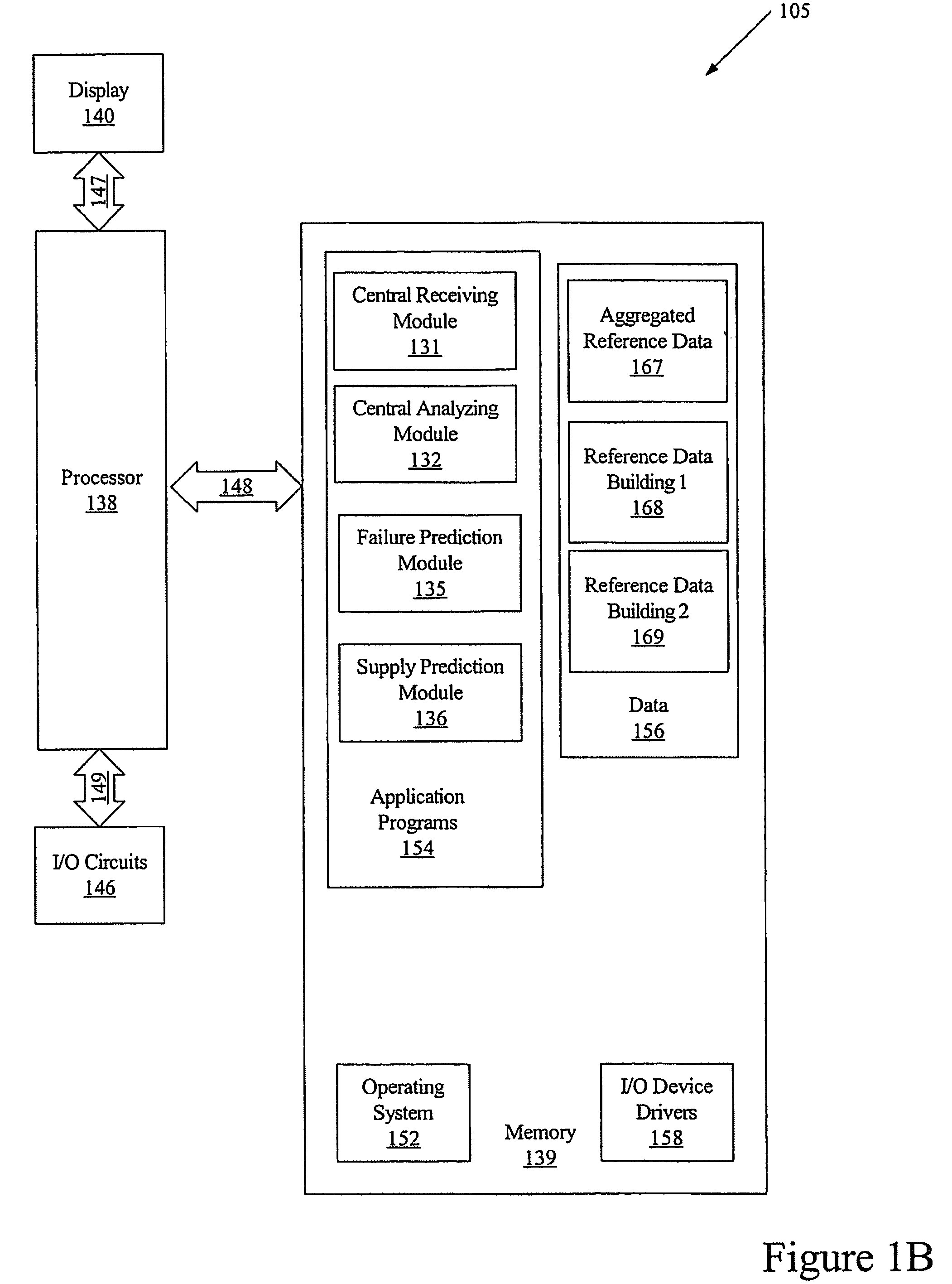
Methods, systems and computer program products for controlling a climate in a building
Methods, systems and computer program products are provided for controlling a climate in a building. Sensed data is received at a local processor in the building. The sensed data is associated with the climate in the building, weather outside the building and / or occupants of the building. The received sensed data is compared at the local processor with corresponding predictive data associated with the climate in the building, weather outside the building and / or occupants of the building. One or more parameters associated with the climate of the building is adjusted at the local processor based on a result of the comparison of the received sensed data and the predictive data.
Owner:TRUVEON CORP
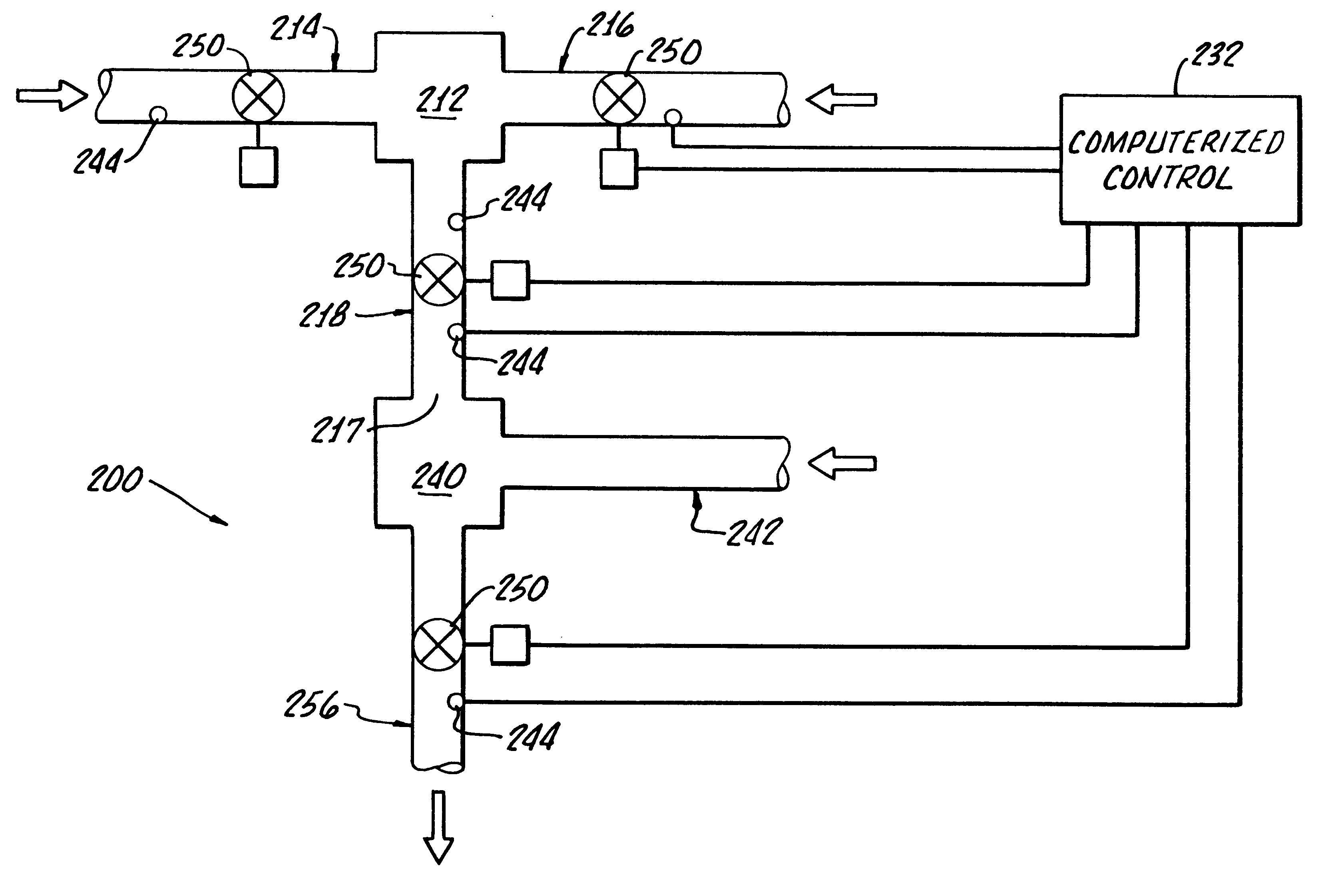
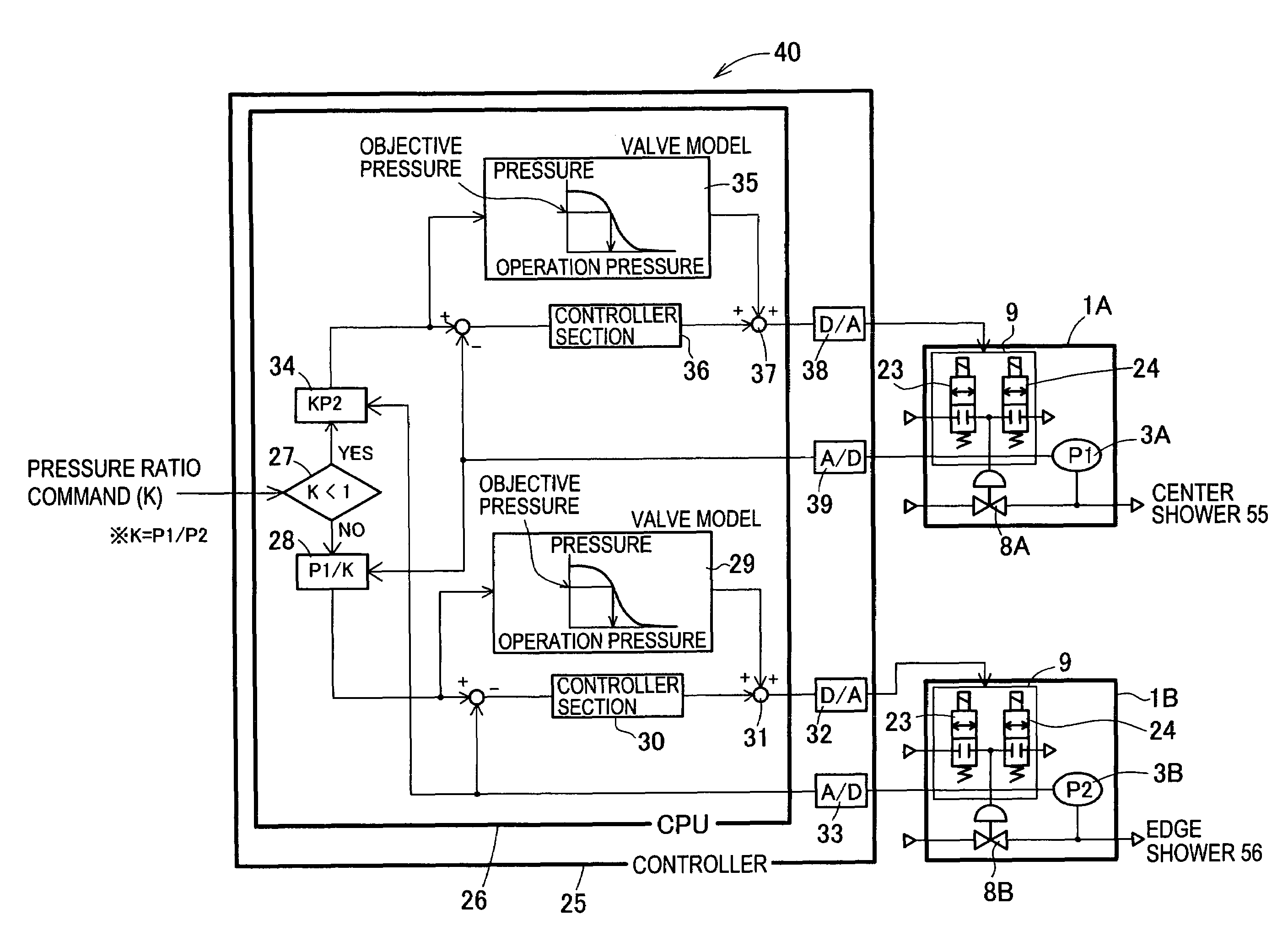
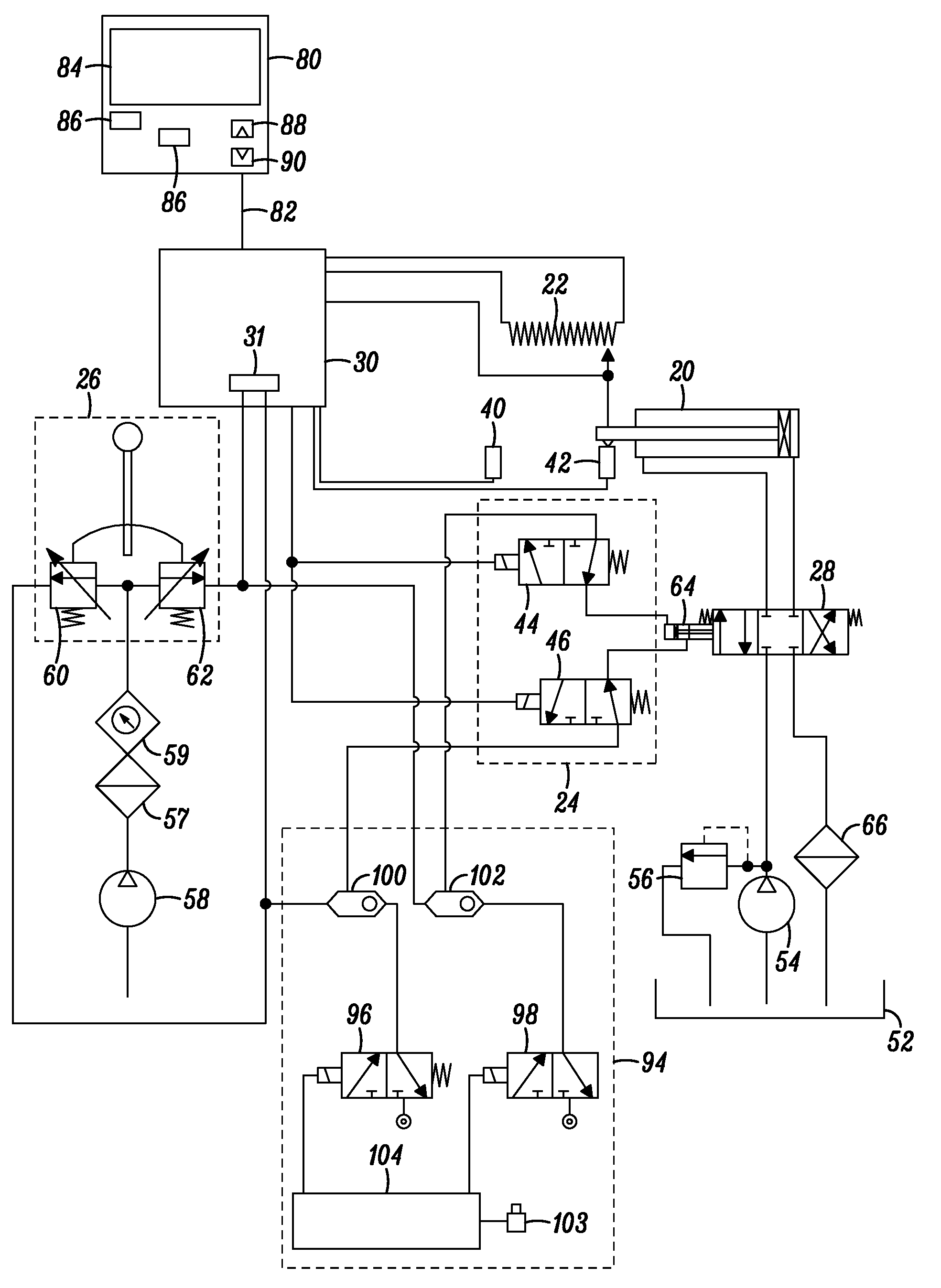
Relative pressure control system and relative flow control system
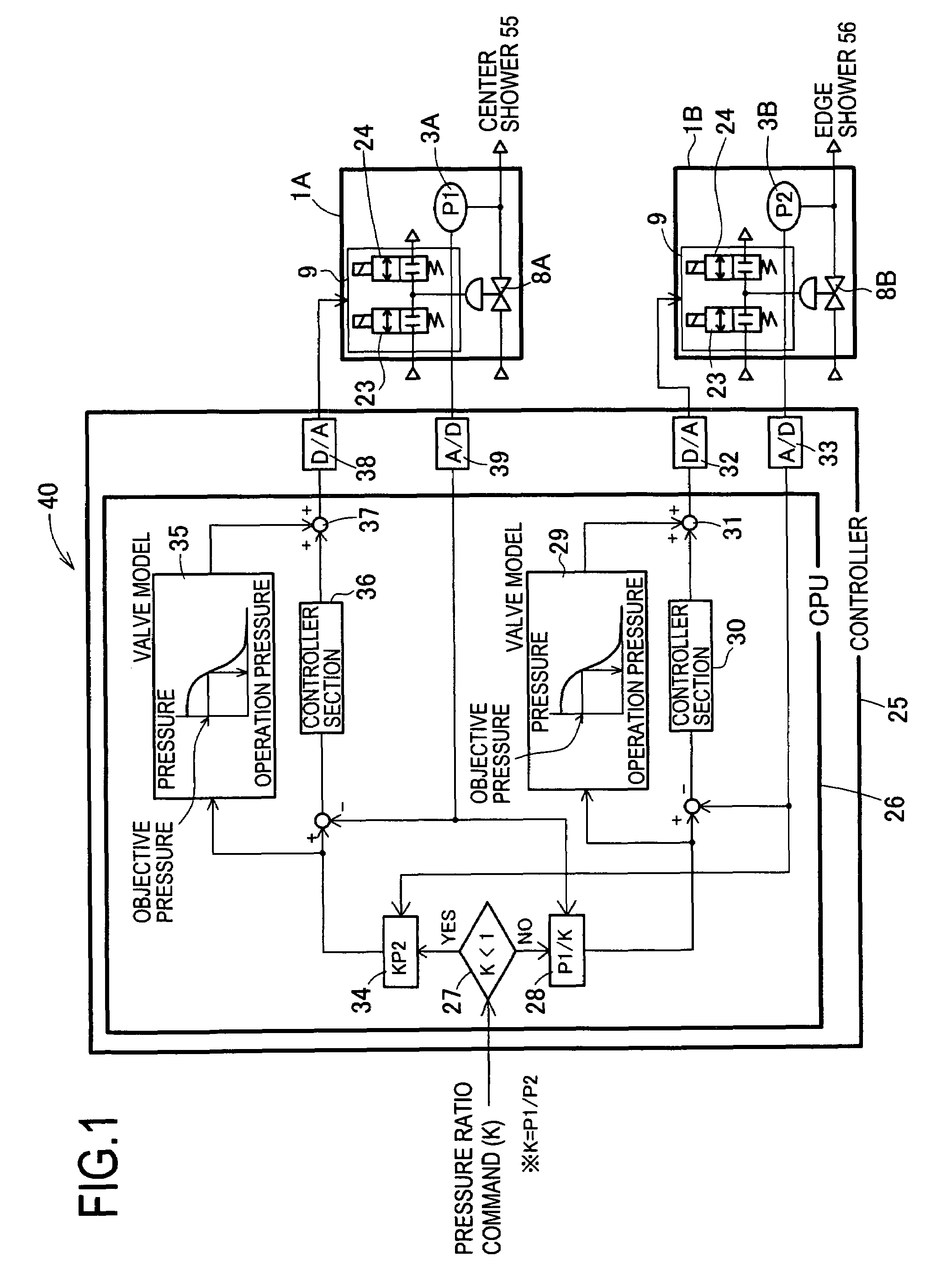
ActiveUS7353841B2Accurate supervisionReduce the amount of controlOperating means/releasing devices for valvesControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsRelative pressureSolenoid valve
Provided is a relative pressure control system has a simple configuration, but enables accurate regulation of a division ratio of an operation gas, and concurrently makes it possible to securely drain the operation gas from an operation gas pipeline in case of emergency. The system includes a plurality of air operated valves of a normally open type that are connected to an operation gas pipeline supplied with an operation gas; pressure sensors that are series connected to the respective air operated valves and that detect output pressures of the respective air operated valves; a controller that controls operation pressures of the respective air operated valves in accordance with the pressures detected by the pressure sensors; and a hard interlock solenoid valve that correlates the plurality of air operated valves to one another so that at least one of the plurality of air operated valves is normally opened. In the configuration, an opening of a specified one of the plurality of air operated valves is regulated, the operation gas is output at a predetermined division ratio.
Owner:CKD +1
System and method for dividing flow
InactiveUS6418954B1Controlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsFlow control using electric meansEngineeringAirflow
A system for dividing a single flow of gas into two or more secondary flows of known, precise values, without requiring a high upstream pressure. The system includes an inlet for receiving the single gas flow, and first and second flow lines connected to the inlet. A mass flow meter measures gas flow through the first line and provides a signal indicative of the measured flow rate. A restrictor restricts gas flow through the first line to a desired flow rate, and has a smallest cross-sectional flow area selected to provide an upstream pressure high enough to allow the mass flow meter to operate properly and lower than a predetermined upper pressure limit. A mass flow controller receives the signal indicative of the measured flow rate from the mass flow meter and maintains a flow rate through the second line based on the signal.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
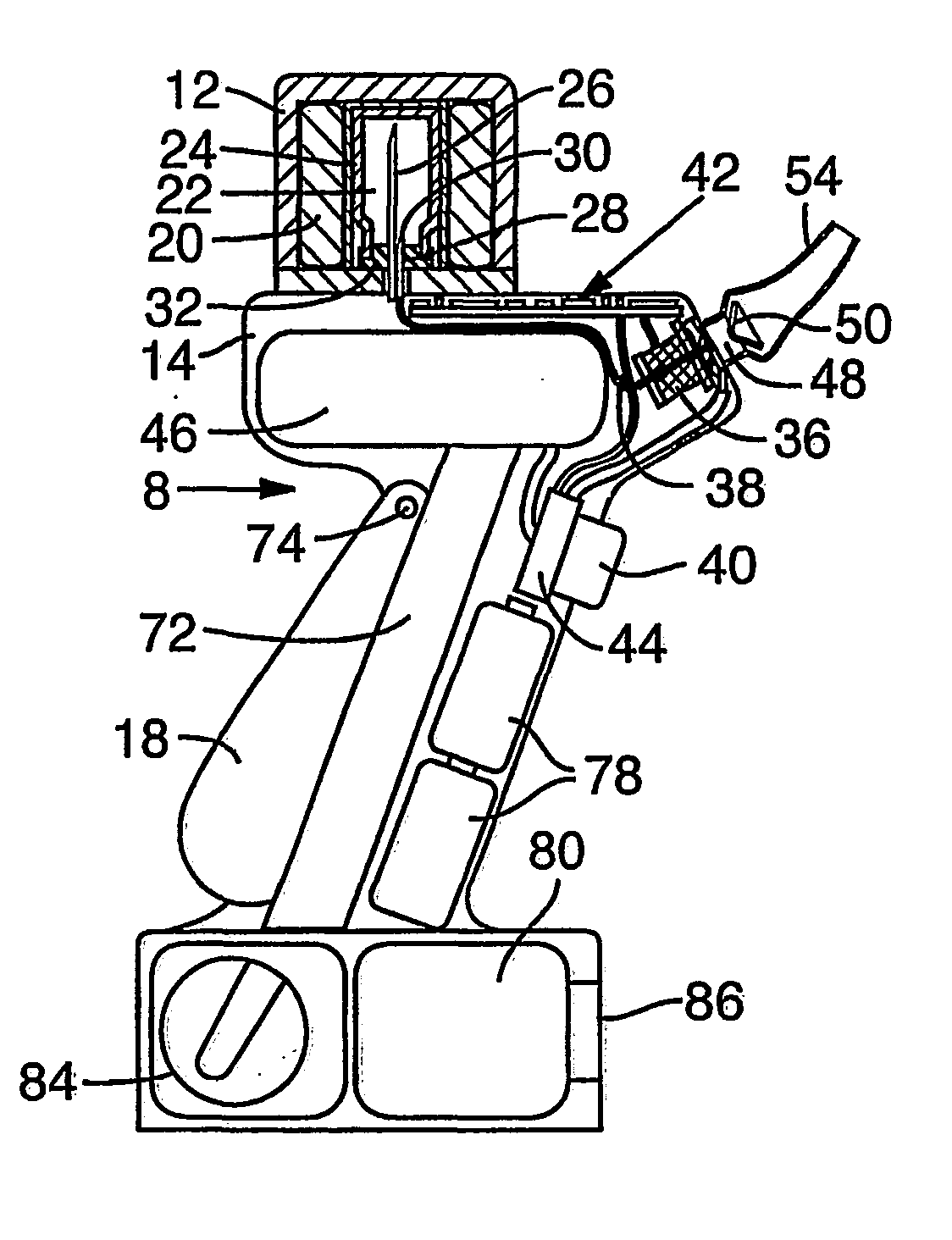
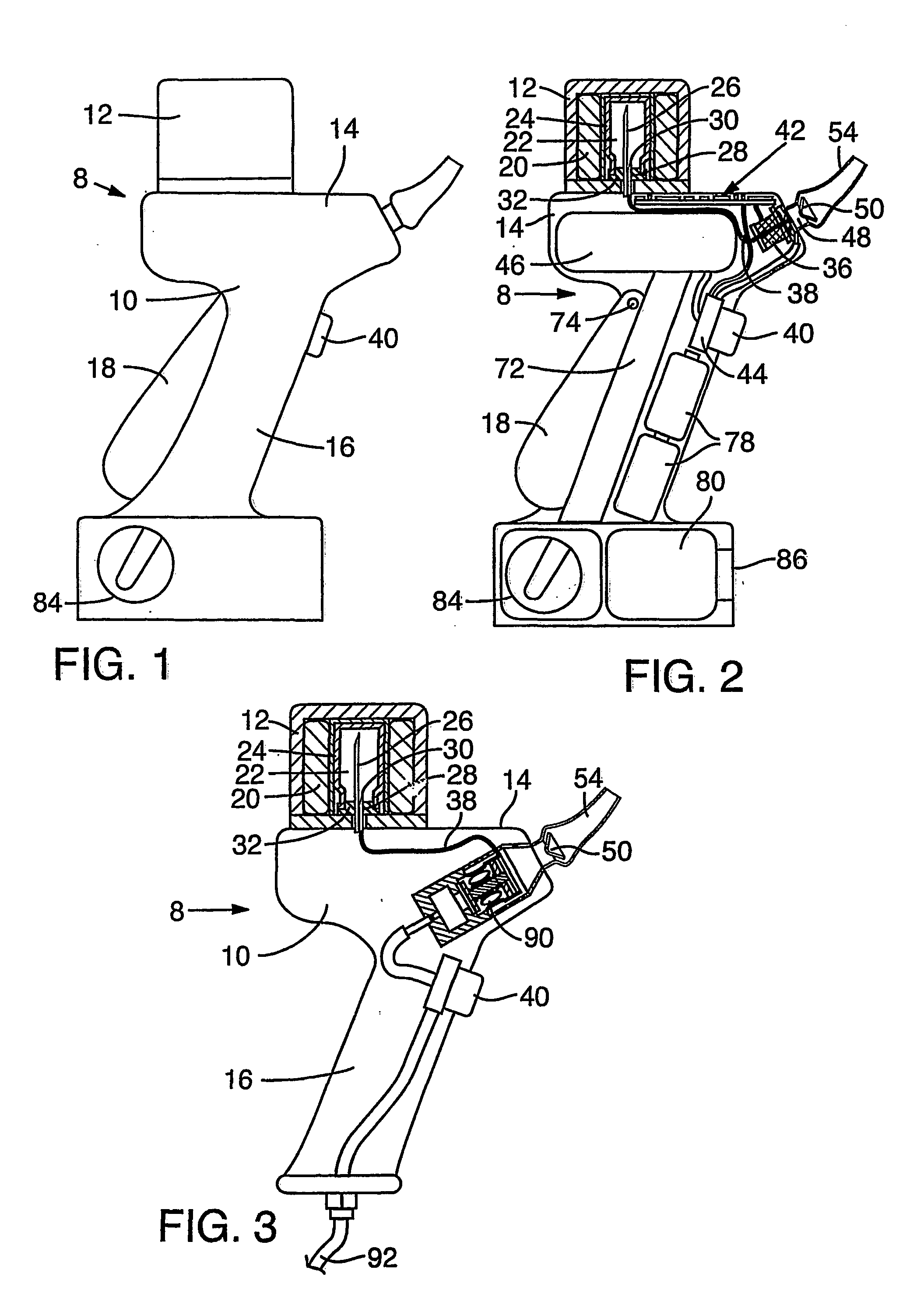
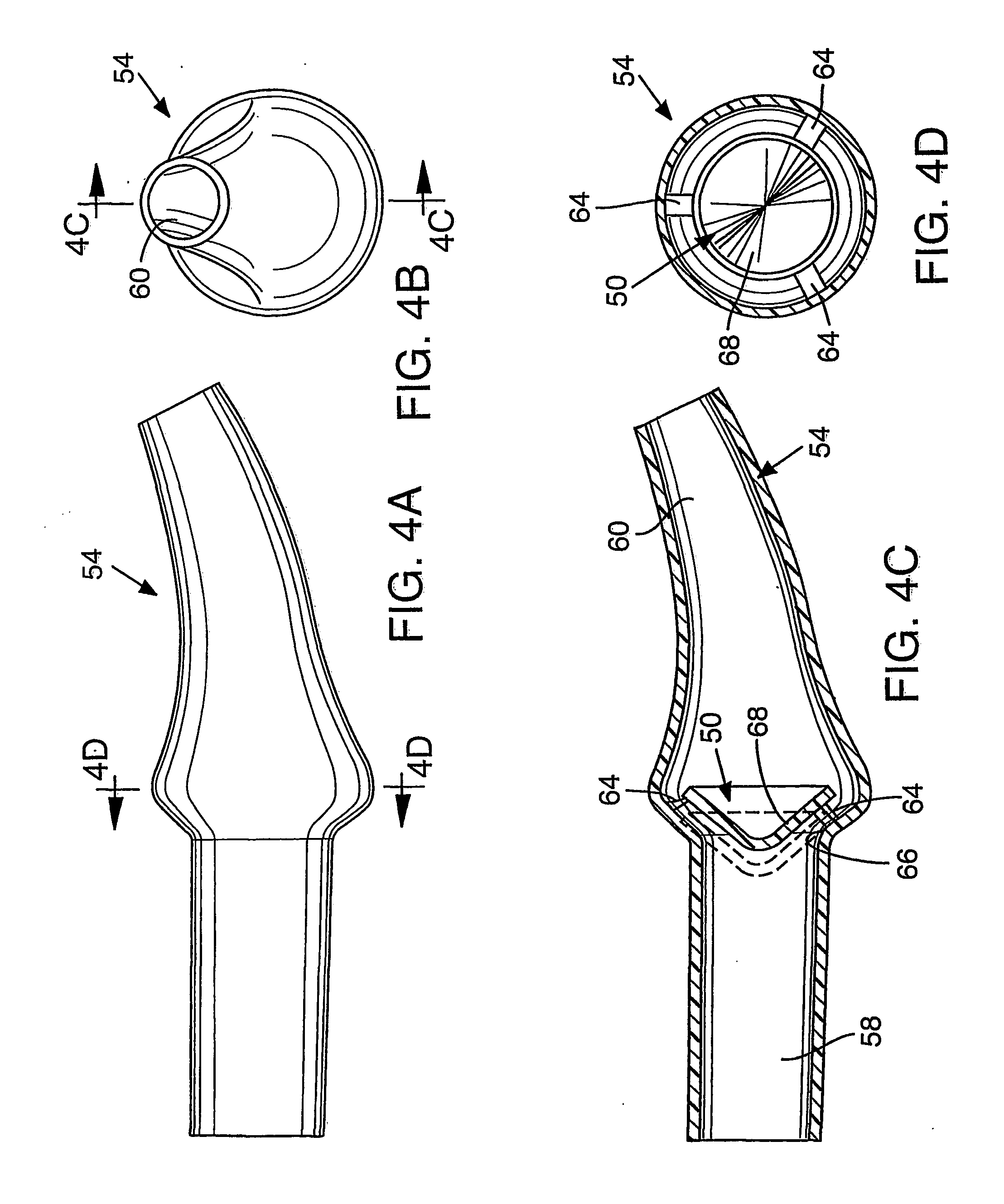
Patient interface assemblies for use in ventilator systems to deliver medication to a patient
InactiveUS7870857B2Weight optimizationTracheal tubesControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsInhalationCatheter
According to one aspect of the present invention, a ventilator system includes (a) a ventilator device having an inhalation port and exhalation port; (b) a patient conduit for delivering to and removing gas from the patient; (c) an exhalation conduit fluidly connected to the exhalation port and the patient conduit; (d) an inhalation conduit fluidly connected to the inhalation port and the patient conduit; and (e) a device for generating aerosolized medication, the device being fluidly connected to the inhalation conduit so that the aerosolized medication is delivered to the patient as the patient inhales. According to the present invention, at least the inhalation conduit has a variable length to position the device for generating aerosolized medication a predetermined distance from the patient conduit.
Owner:AEON RES & TECH INC
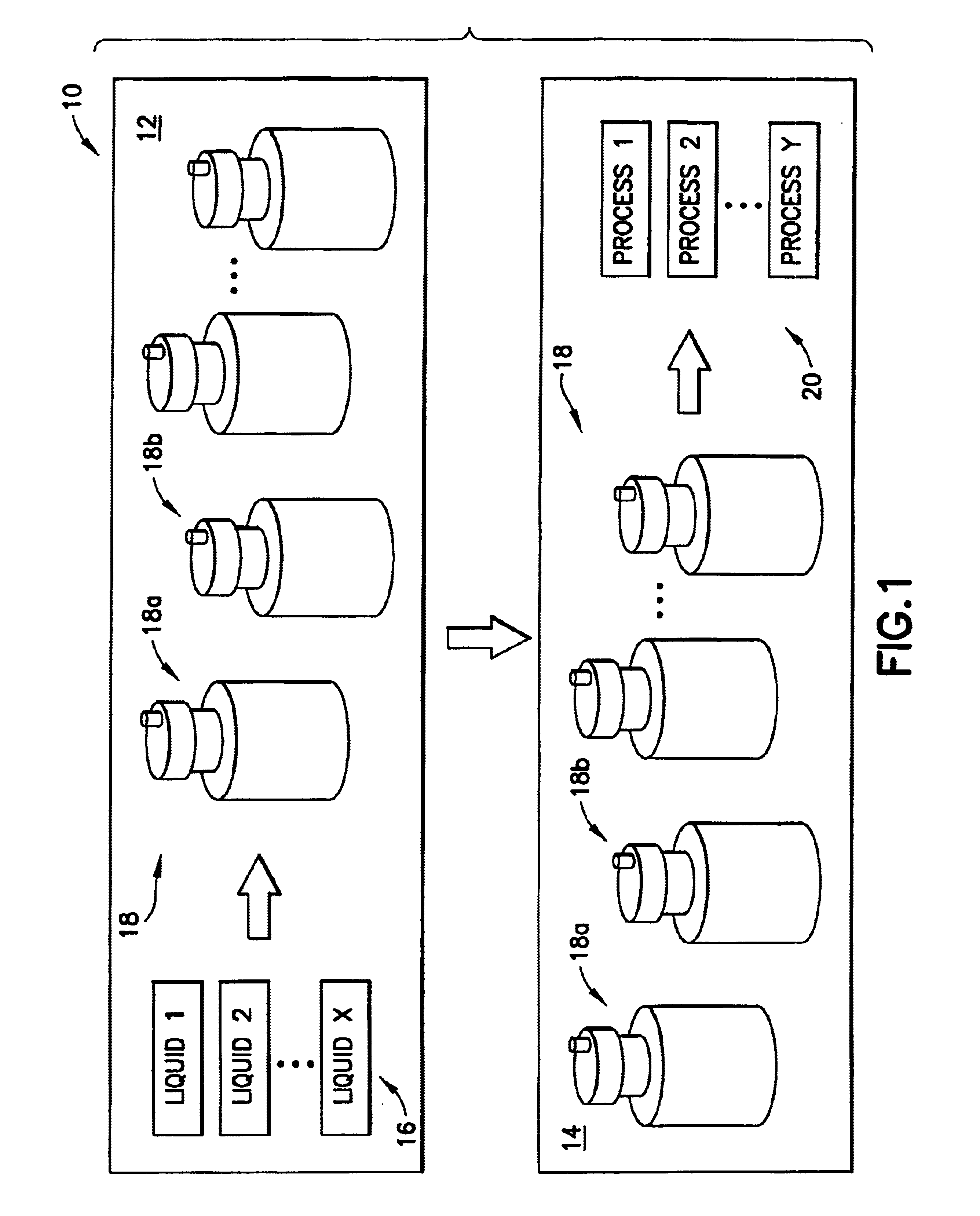
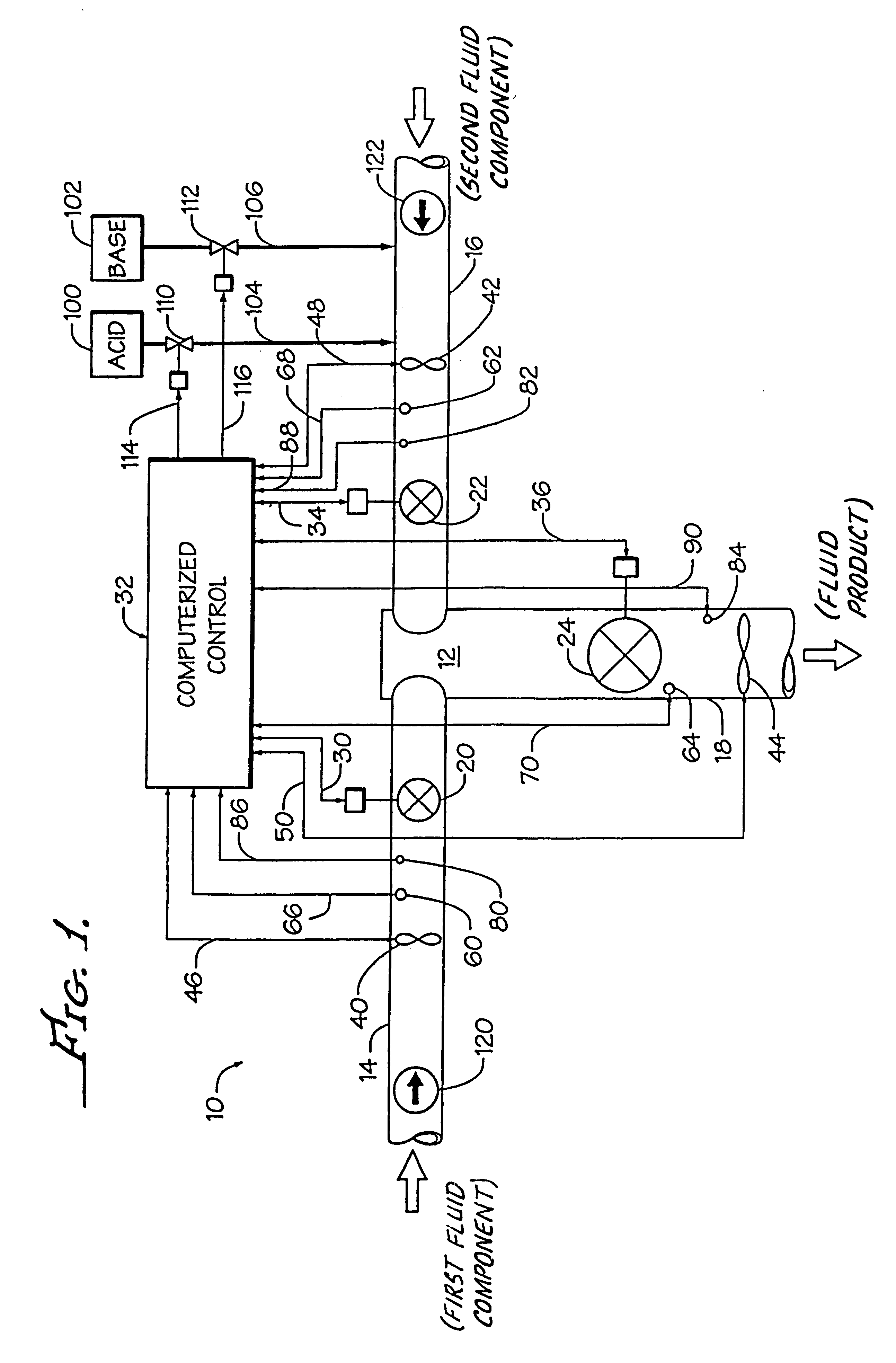
Method and apparatus for blending process materials
A method and apparatus for blending and supplying process materials. The method and apparatus are particularly applicable to the blending of ultra-high purity chemicals, the blending of abrasive slurries with other chemicals for the polishing of semiconductor wafers, and high-accuracy blending of chemicals. The apparatus may include a dispensing subsystem that supplies process materials to a mixing subsystem where they are blended with a static mixer. The method may include supplying process materials with a dispensing subsystem and blending the process materials in a static mixer.
Owner:MEGA FLUID SYST
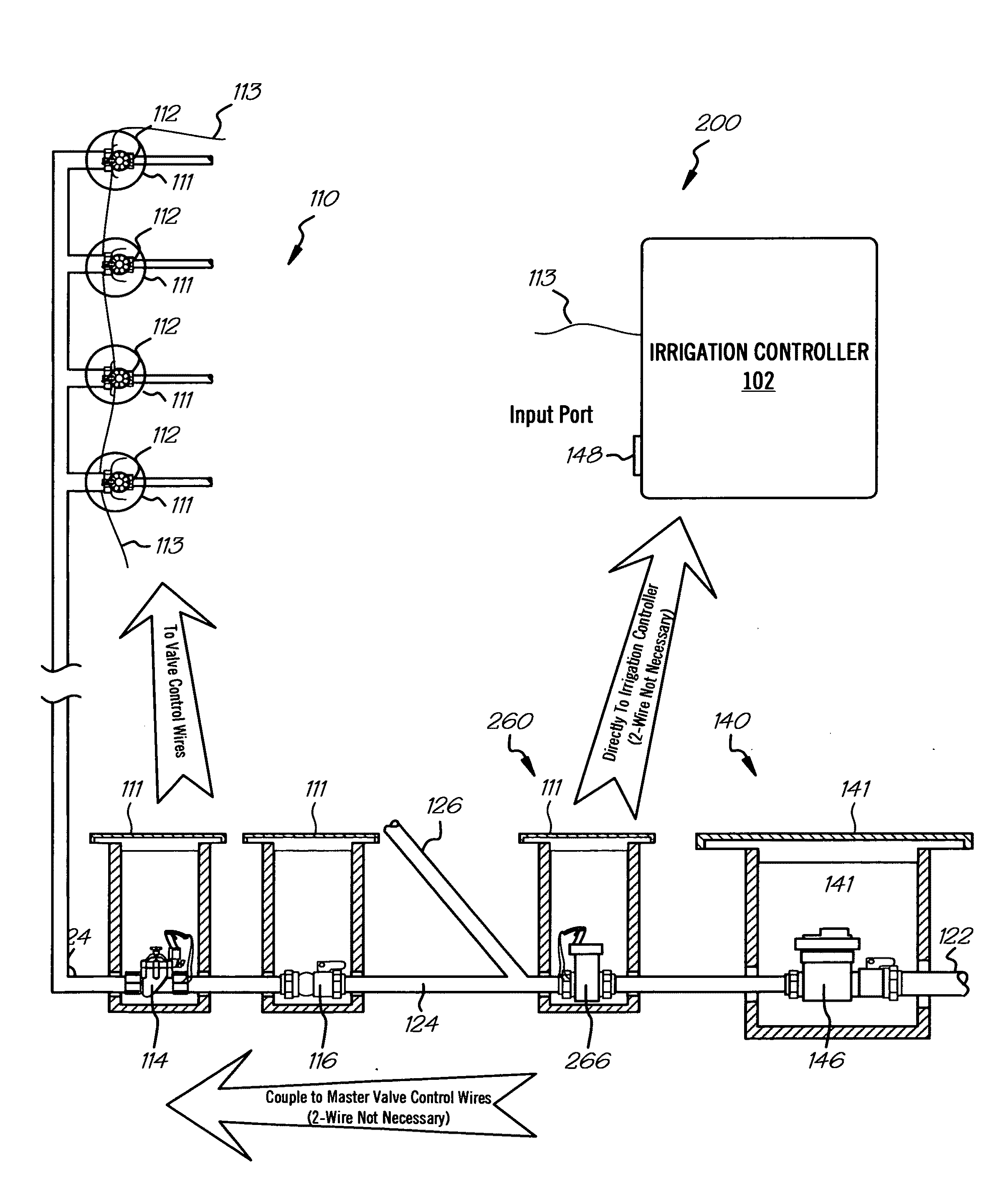
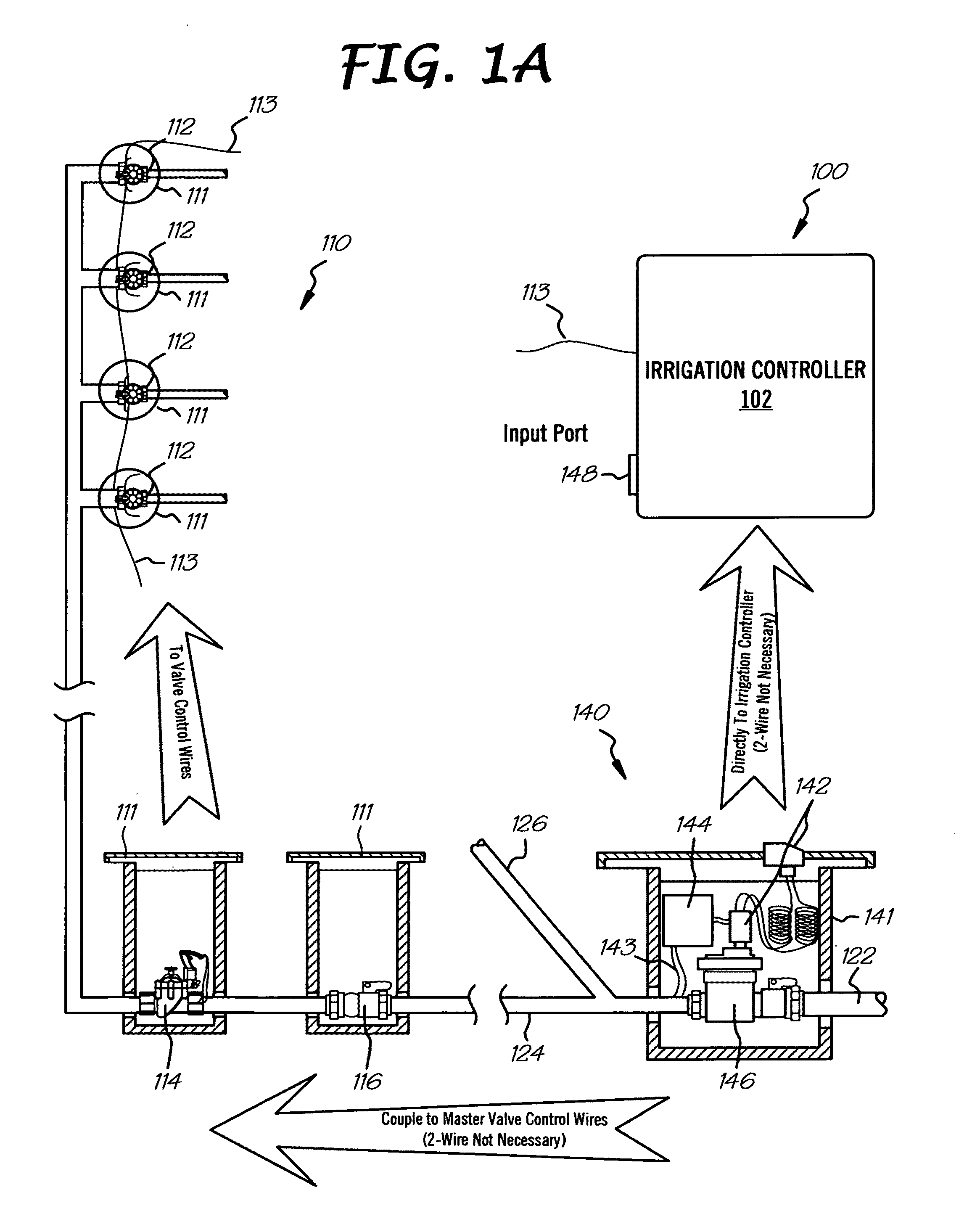
Irrigation flow converter, monitoring system and intelligent water management system
InactiveUS20110190947A1Reduce the amount requiredLess waterControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsWatering devicesWater useMonitoring system
The present invention is directed to an intelligent water management irrigation system for monitoring the total water usage for a billing site and preventing cumulative water usage from exceeding a water budget by adjusting the amount of water used for irrigation. Irrigation zone priority values are selected for each irrigation zone that specify a percentage of the full water need that the foliage in the zone can survive and are saved in an intelligent water management irrigation (IWMI) controller. The IWMI controller receives water usage information originating from a property's water meter and compares the measured water usage with the allowable water budget. Water usage is tracked separately for the household use and landscape use (irrigation). Prior to each irrigation cycle, the IWMI controller estimates the amount of water that will be needed by the landscape and for household use during the remainder of a billing cycle; household use is given precedence over landscape use. If the water budget will support both, irrigation can proceed normally. If the budget will not support both, the IWMI controller estimates the amount of water needed for the remainder of the billing cycle if only a priority watering amount is allocated for each landscape zone. If the water budget will support priority irrigation, landscape watering can proceed in priority irrigation mode. If the water budget will not support priority irrigation watering, the irrigation cycle is skipped and the water usage estimations are recalculated prior to the next irrigation cycle.
Owner:TELSCO INDS
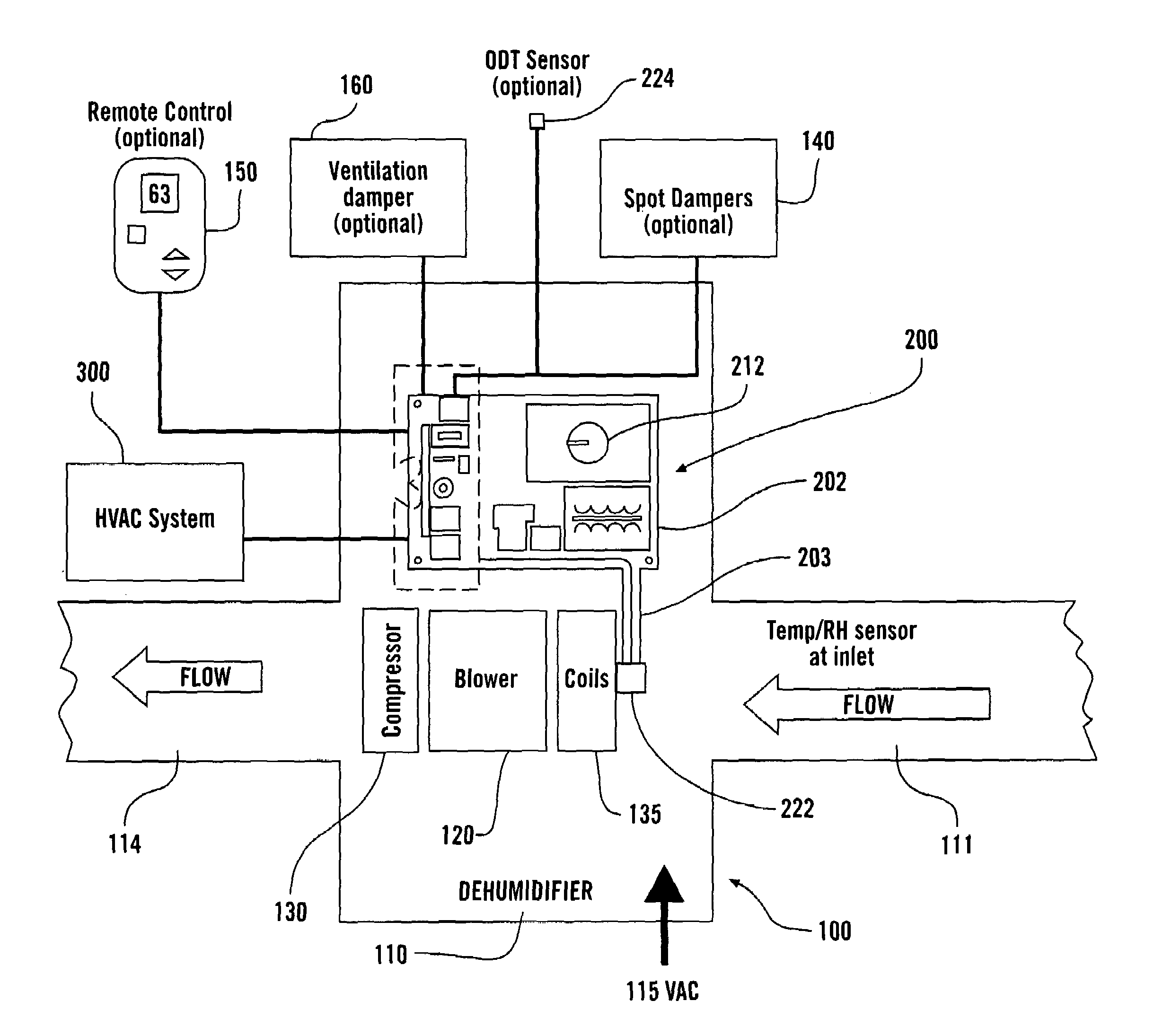
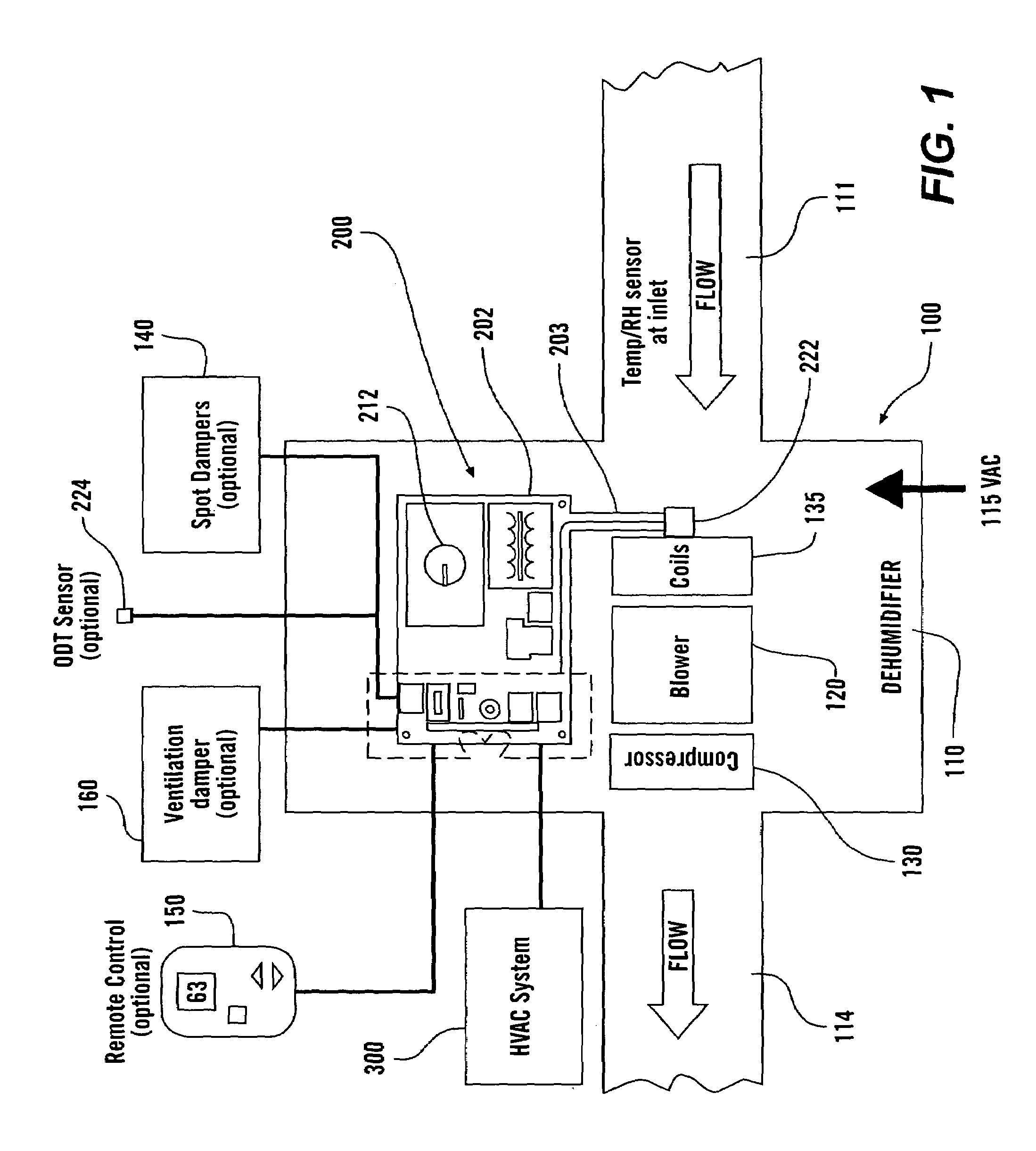
Systems and methods for whole-house dehumidification based on dew point measurements
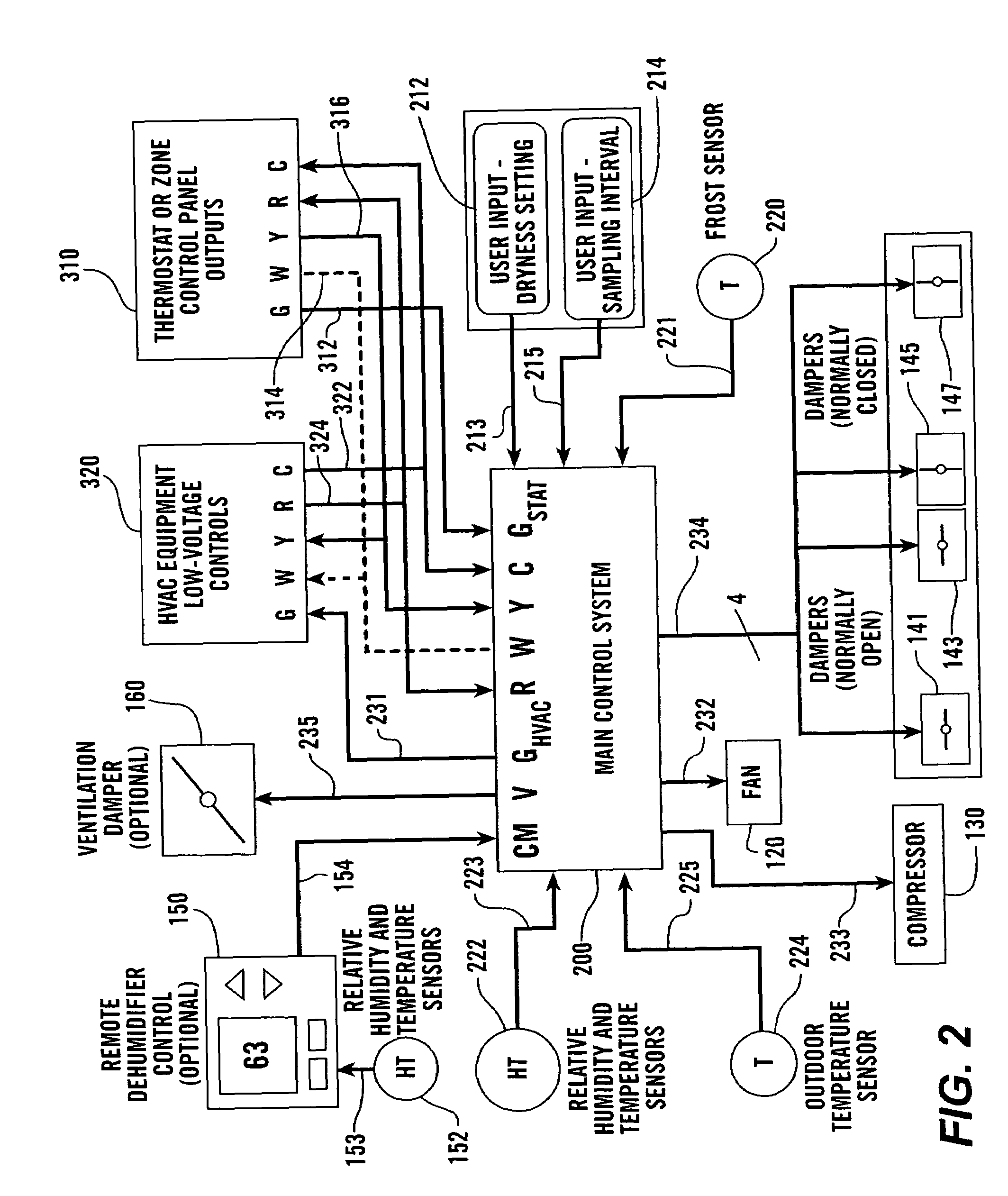
ActiveUS7574871B2Speed up evaporationEfficient dehumidificationMechanical apparatusControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsInterior spaceEngineering
A dehumidifier system is connected to an interior space of a building through supply and return ducts, either directly and / or through an HVAC system. Controllable dampers can be used to select how the dehumidifier system is connected to the interior space and the HVAC system. The dehumidifier determines the dew point of the ambient air from temperature and relative humidity measurements taken at location(s) of relative humidity and temperature sensors. Based on the determined dew point, the dehumidifier system determines whether to operate. The temperature and relative humidity sensors can be located in the interior space or within the dehumidifier, where they project into the air stream flowing through the dehumidifier. The dehumidifier system operates in response in part to blower calls to the HVAC system and controls the HVAC system and a ventilation system to distribute the dehumidified air and outside air throughout the building.
Owner:RES PRODS
Ventilation system with humidity responsive ventilation controller
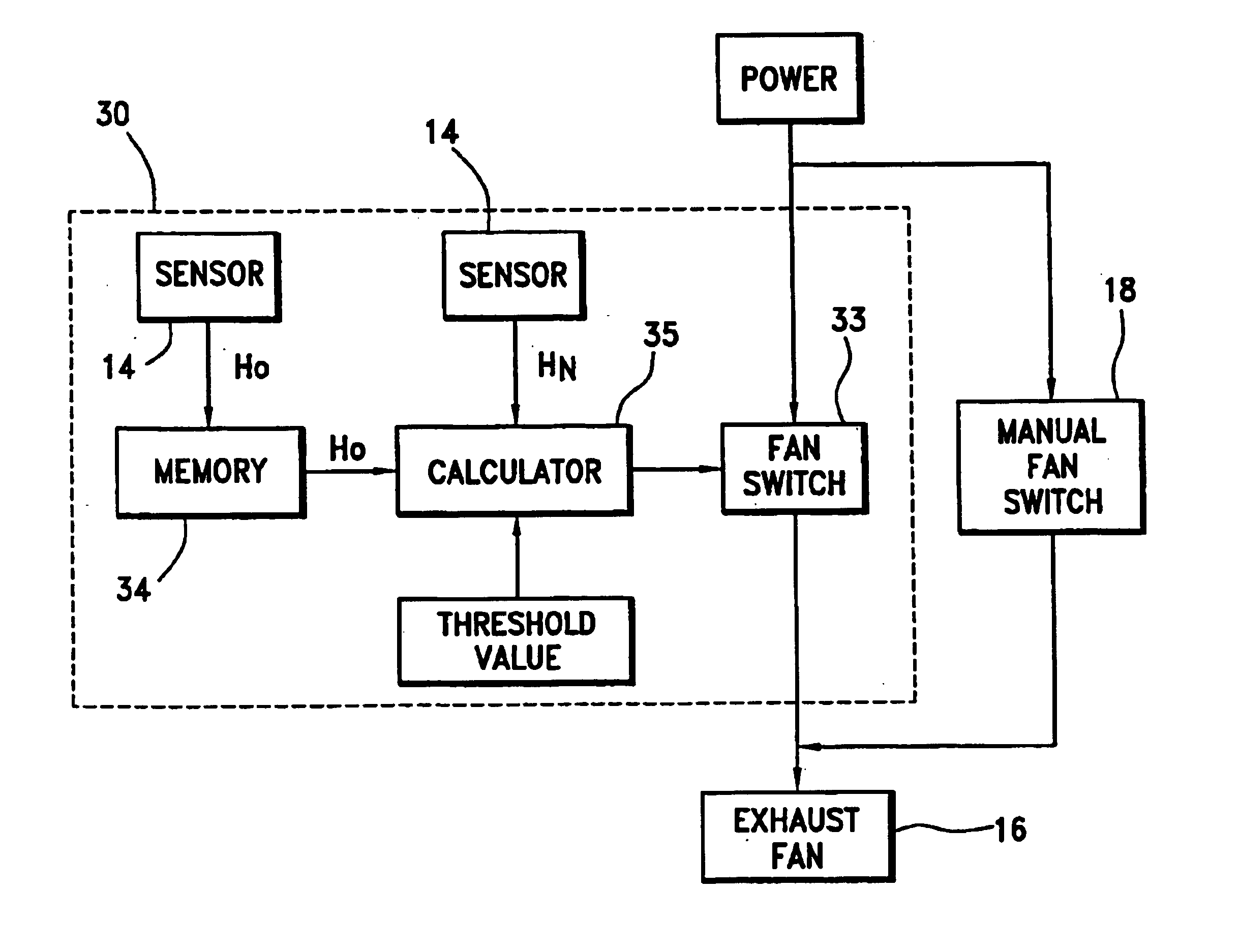
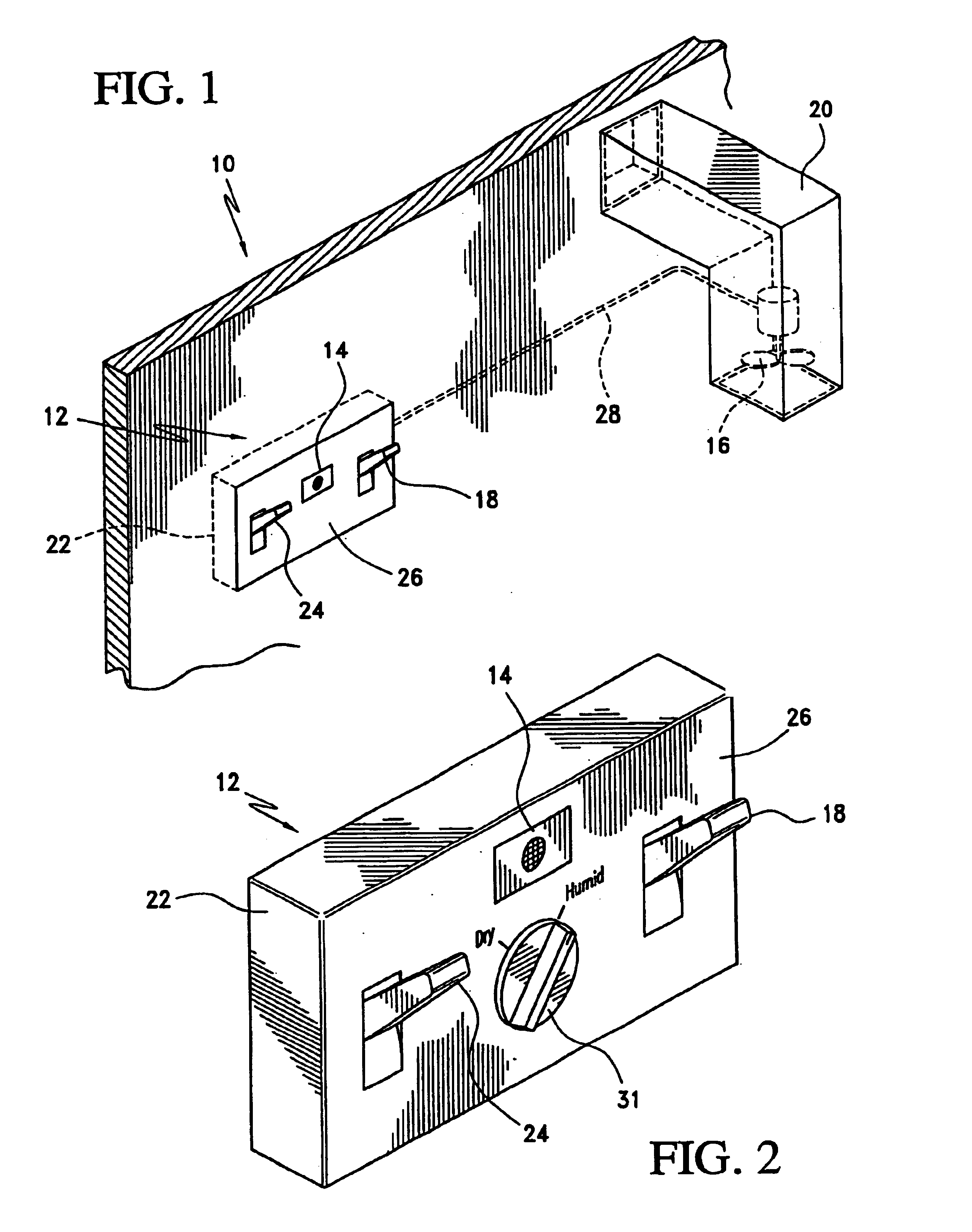
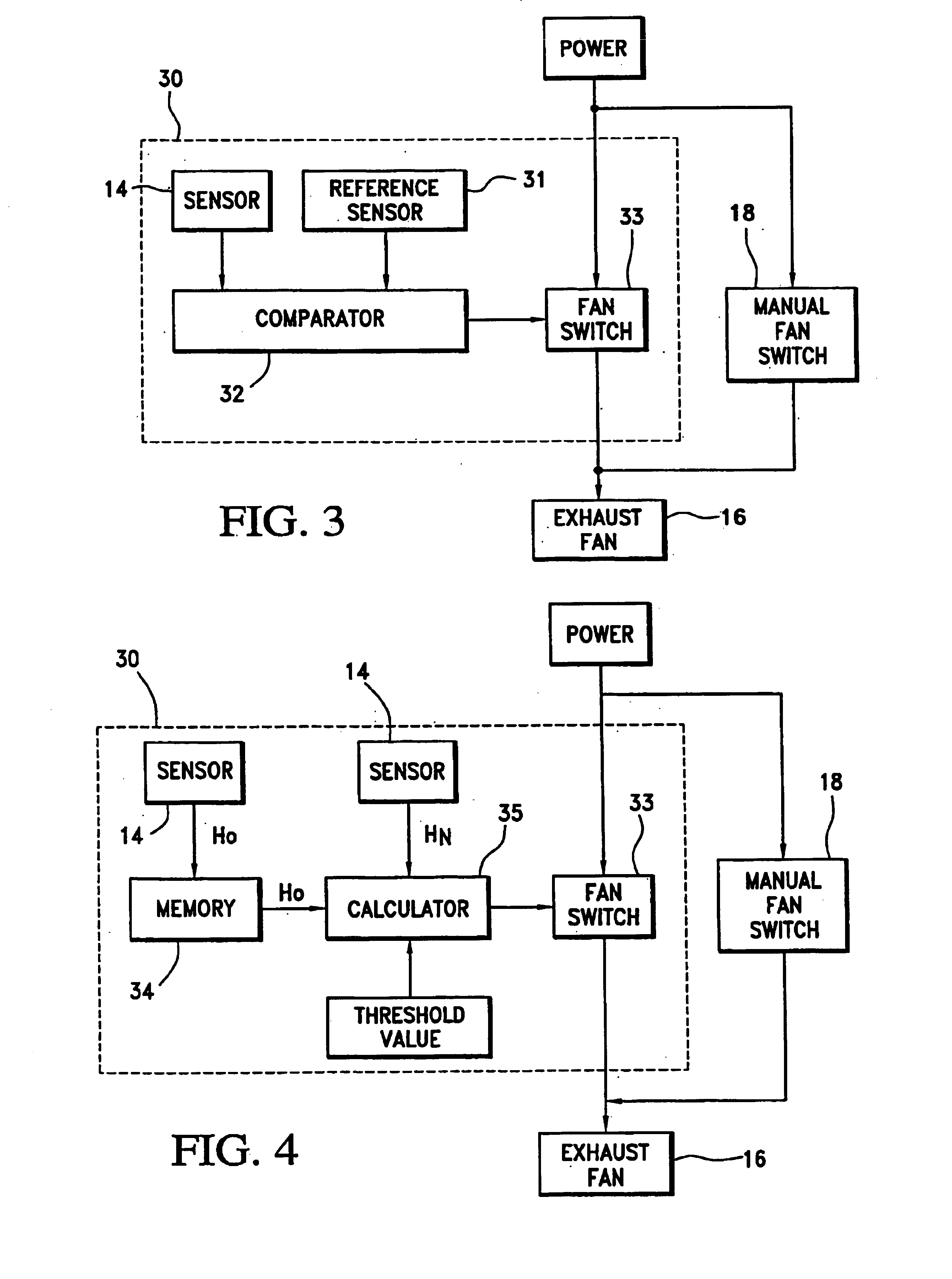
InactiveUS6935570B2Reduce humiditySatisfactory humidity levelMechanical apparatusControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsElectrical junctionEngineering
A ventilation controller including at least one humidity sensor for controlling the humidity of a room. The ventilation controller incorporates a housing sized and shaped to replace, or be placed in, a standard electrical junction box. Circuitry in the controller receives data from the sensor(s). The controller automatically switches on power to an exhaust fan when either the humidity exceeds a manually set humidity level and / or a rapid increase in humidity is observed. When a plurality of sensors is employed, the humidity level from a first sensor is compared by logic circuitry to the humidity levels detected at a reference sensor(s). When the humidity at the first sensor exceeds the humidity at the reference sensor(s), the ventilation controller switches on power to the exhaust fan.
Owner:ACKER PHILLIP F
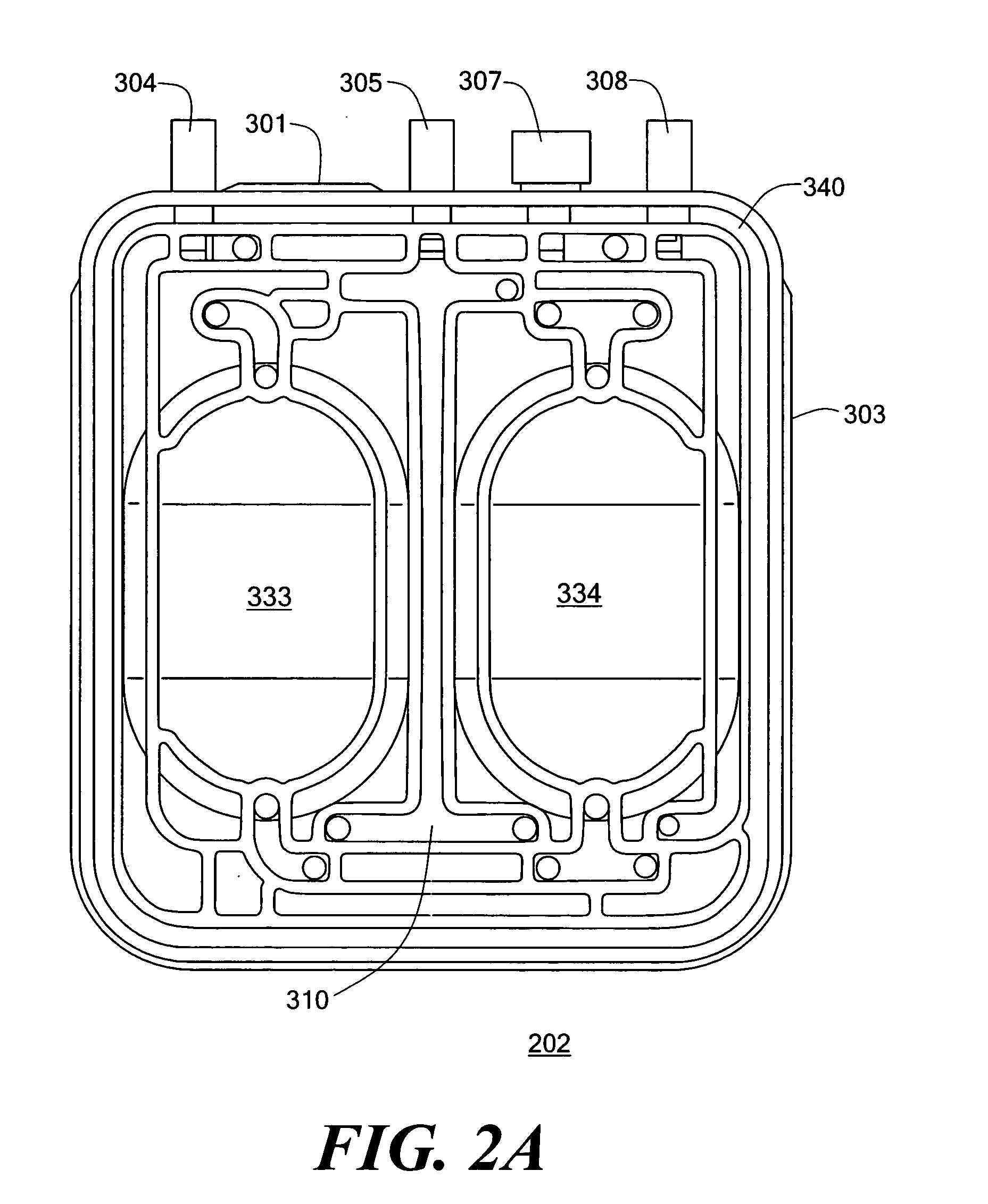
Pump cassette bank
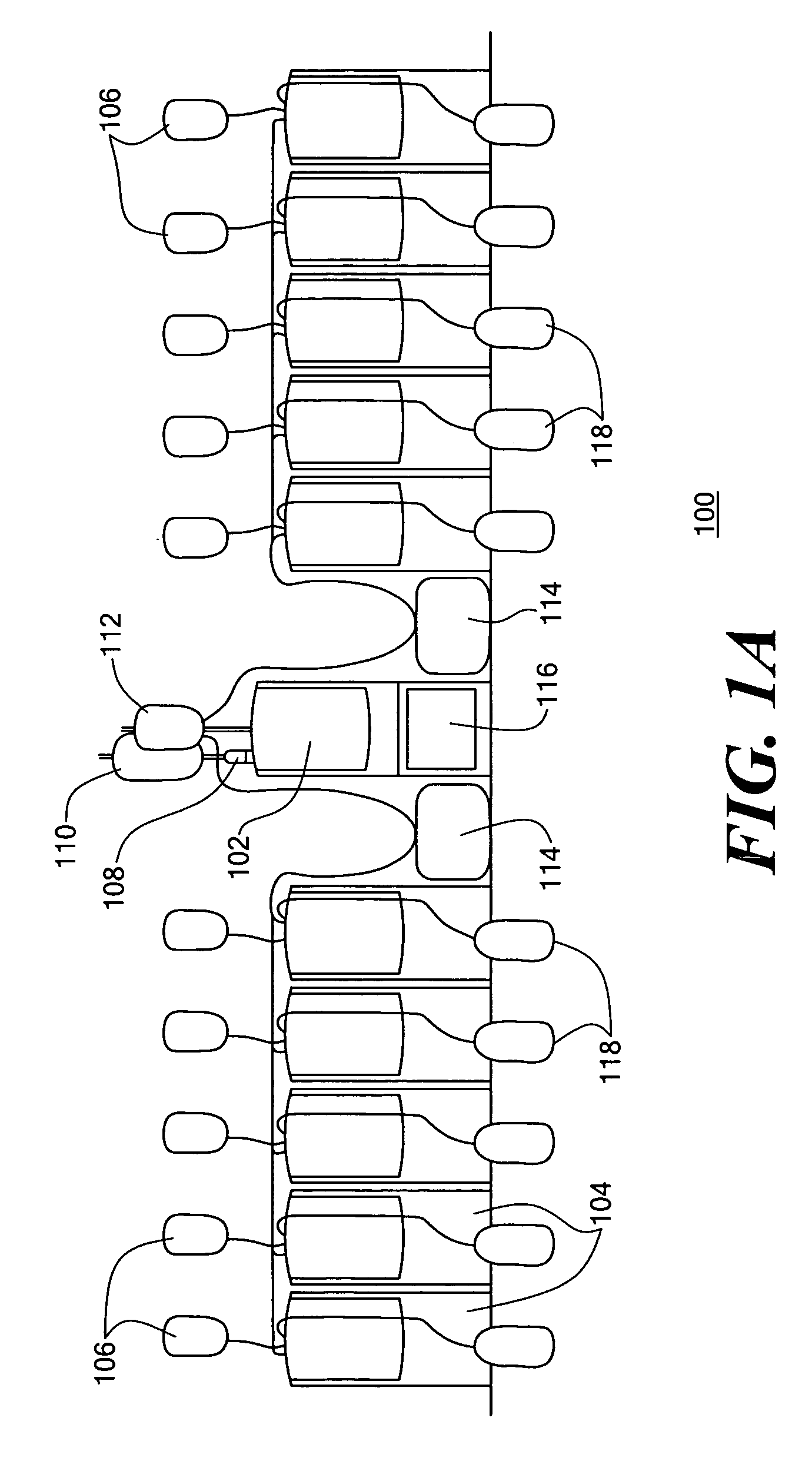
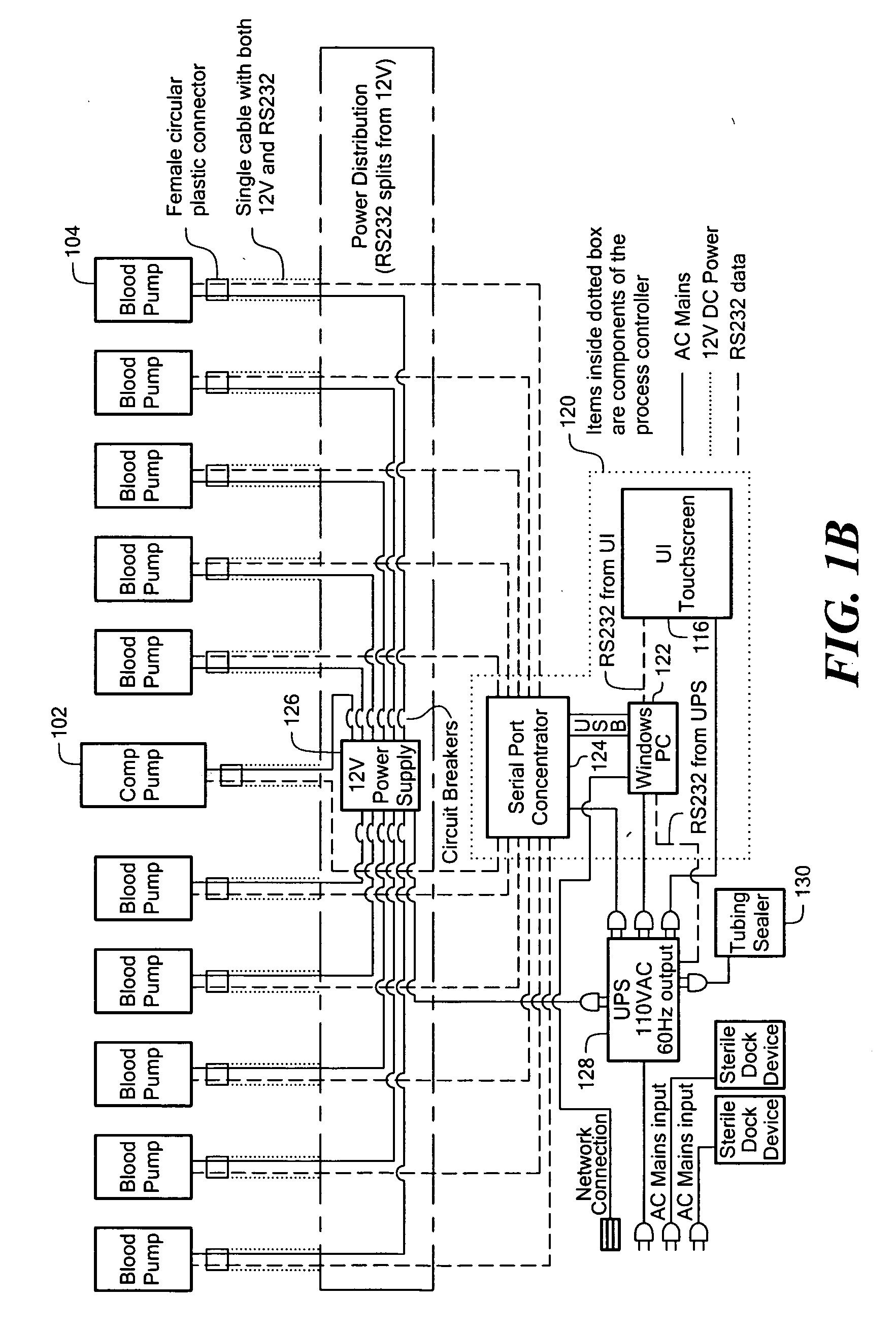
A plurality of pump cassettes are connected through distribution tubing to a single inlet tube such that the inlet tube is shared by the pump cassettes through the distribution tubing. The plurality of pump cassettes may be symmetrically attached to the distribution tubing. A four-port coupling may be inserted in the distribution tubing for making connection to the inlet tube and a middle one of the pump cassettes when the number of cassettes is an odd number.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Method and apparatus for dispensing fluid compositions
ActiveUS20100185322A1Combine accuratelySmall sizePump componentsMixer accessoriesRegimenControl system
A miniaturized fluid dispensing system for dispensing customized fluids. The dispenser may include first and second reservoirs containing constituent fluids; a drive motor; at least two pump assemblies commonly driven by the drive motor and in communication with the first and second reservoirs; first and second valve assembly in communication with the first and second pump assemblies; and a control system for selectively controlling the valve assemblies to blend and discharge a composition from the constituent fluids. The system may include a dispensing header to house the valves and to define ‘discharge’ and ‘recirculation’ flow paths for each constituent fluid. The present invention also provides a method for dispensing a fluid regimen (e.g. a plurality of compositions) by periodically blending and discharging varying compositions over time.
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
Patient interface systems
ActiveUS8573201B2Easy to useEasy to appreciateControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsBreathing masksElastomerEngineering
A headgear for use with a patient interface for delivering a flow of breathable gas to a patient includes at least a strap (741) adapted to position the patient interface in sealing engagement with the patient's airways. The strap is constructed from an elastomer and a first side of the strap includes a first region (215) on a portion of its surface that is textured to reduce friction with objects contacting the strap. A textured surface coating for a portion of an elastomer strap included in a headgear system is adapted to contact the skin of a patient, when in use, and the coating has a Ra value greater than zero. A vent (500) for use with a patient interface for delivering a flow of breathable gas to a patient includes a plurality of rises (580) and runs (570) in a stepped arrangement; and a plurality of holes (510) in the stepped arrangement for the venting of gas.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Gravimetric blender with operatively coupled bar code reader
InactiveUS6188936B1Accurate measurementEntered easily and accuratelyDigital data processing detailsRotary stirring mixersBarcodeMicroprocessor
A method for weight blending of granular materials comprises at a remote site generating a command for desired operation of granular material weight blending apparatus; encoding said command into transportable time-stable machine readable tangible storage media; transporting said media to a bar code reader operatively connected to said granular material weight blending apparatus; scanning the tangible media having the command encoded thereon to read the command; and providing the read command as input to a in microprocessor operatively connected to said granular material weight blending apparatus for regulating operation of the same.
Owner:MAGUIRE PROD
Hydraulic Actuator Control System
InactiveUS20080228323A1Slow motionFluid couplingsControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsElectronic controllerControl signal
A system for controlling motion of a hydraulic actuator during a portion of its range of motion is described, including a sensor on the hydraulic actuator for providing a signal indicating that the actuator is near a portion of its range of motion, and a pneumatic control valve that is configured to selectively modify a pressurized air control signal to in turn restrict flow of pressurized hydraulic fluid to the hydraulic actuator. The hydraulic actuator control system further includes an electronic controller for controlling the pneumatic control valve in response to a signal from the sensor. The hydraulic actuator control system thereby slows the motion of the hydraulic actuator near the portion of its range of motion.
Owner:HARTFIEL AUTOMATION
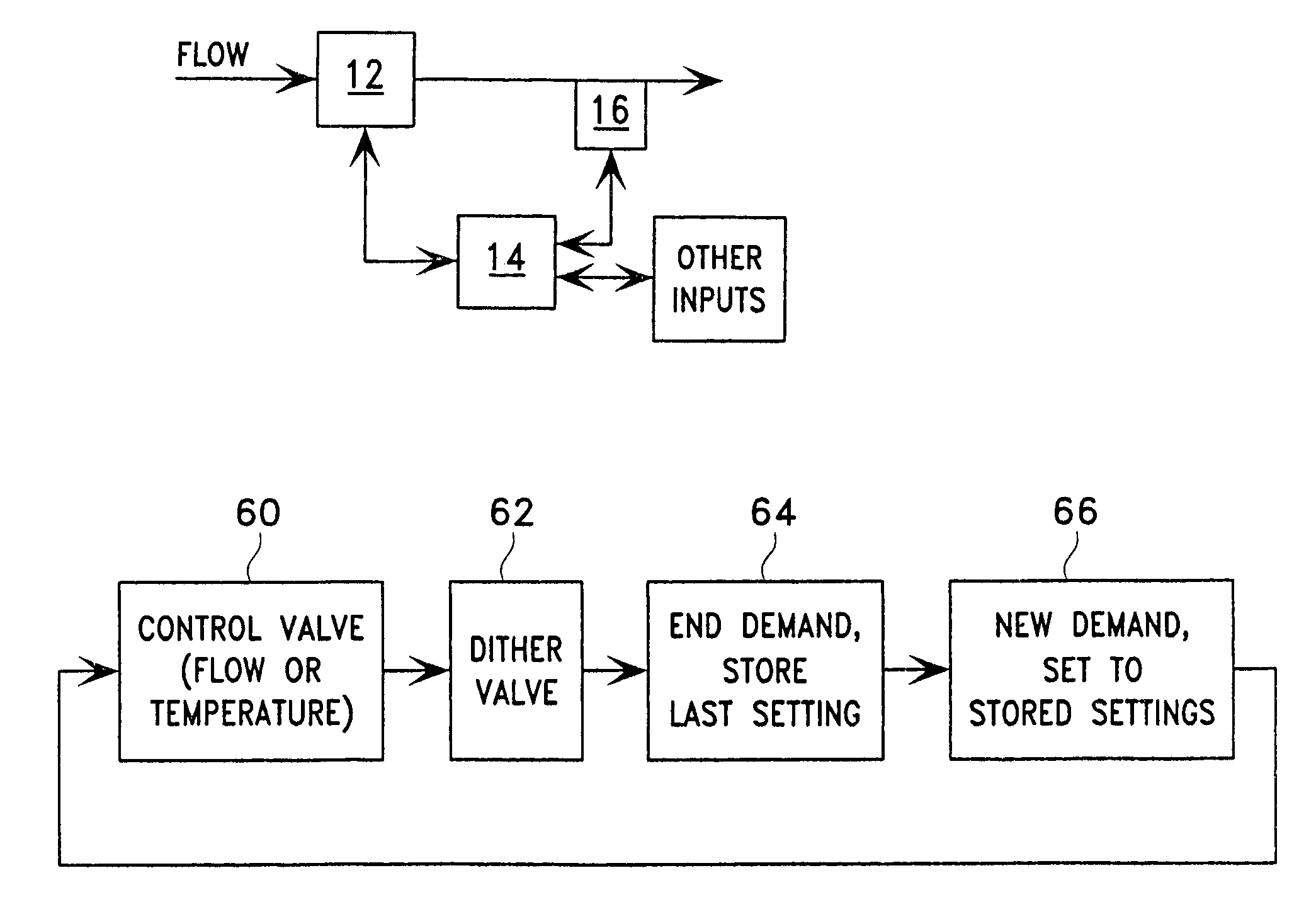
Method and apparatus for flow control
ActiveUS7156115B2Eliminate and substantially reduce problemControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsFlow control using electric meansControl systemControl valves
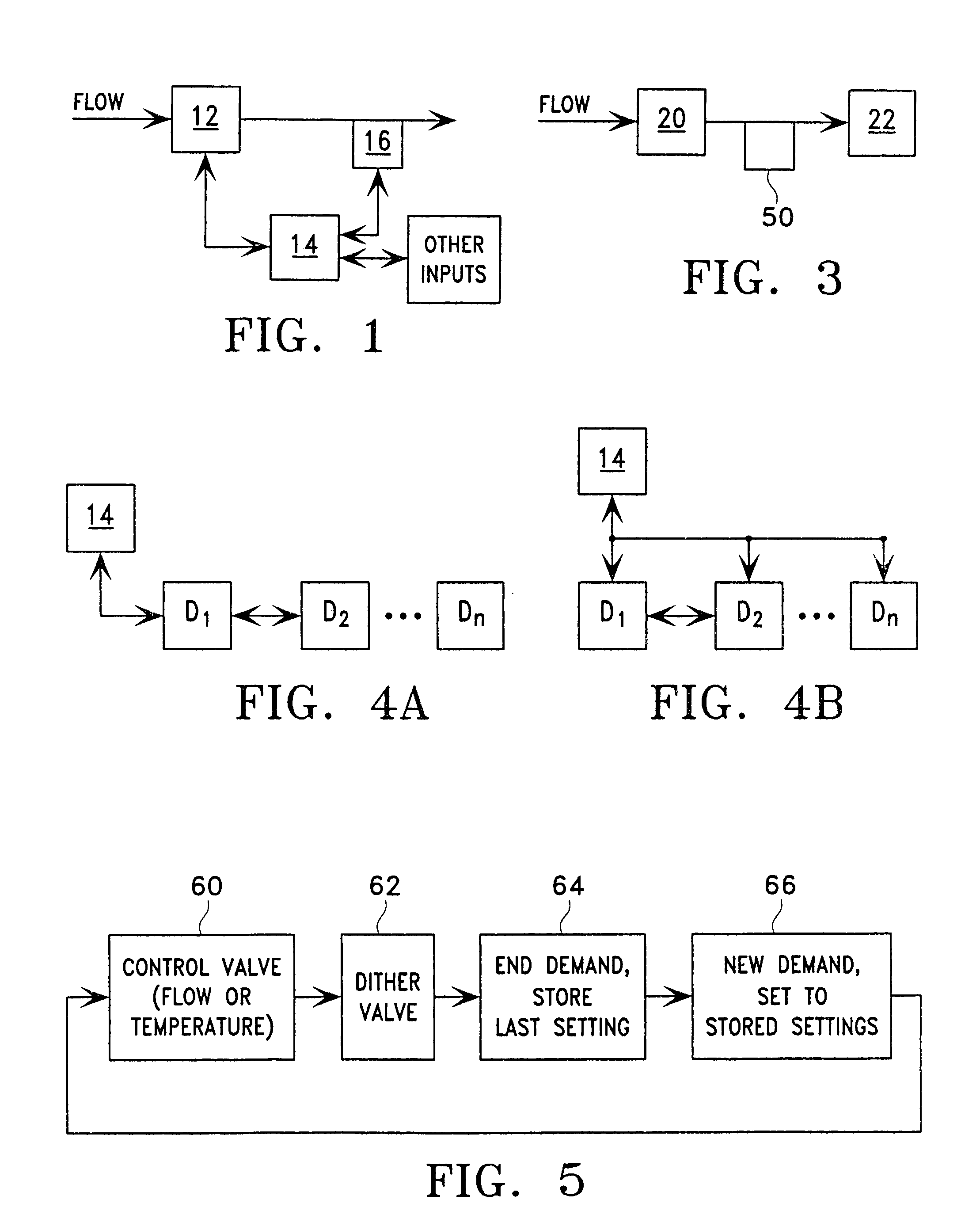
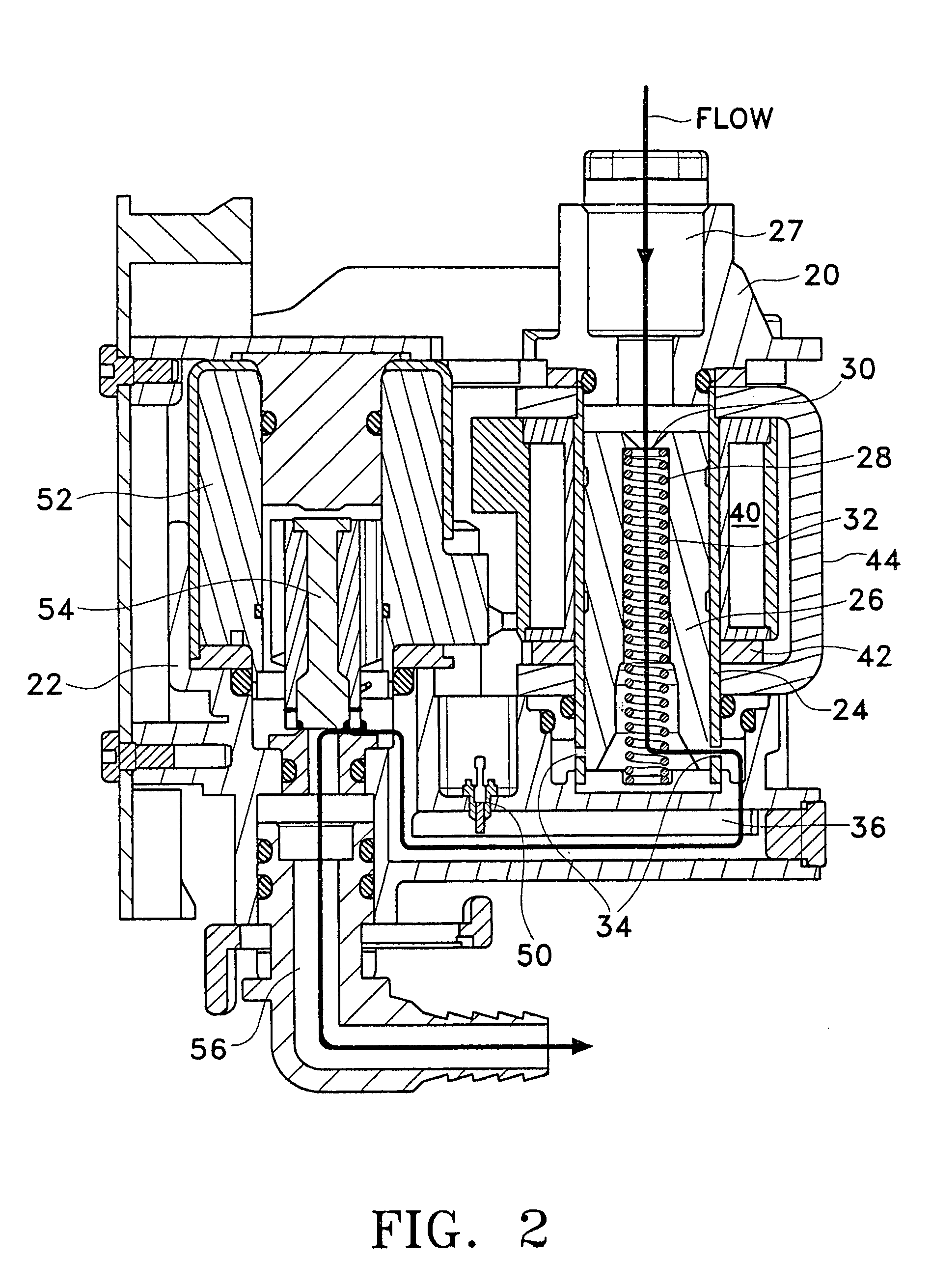
A flow control system (10) is provided in which a flow control valve (12) is controlled by a control system (14). The control system (14) measures a flow rate or temperature of a fluid flowing through the flow control valve (12) and adjusts the flow control valve (12) to achieve a desired flow rate. The flow control valve (12) includes an electromagnetically adjustable spool (26).
Owner:LANCER PARTNERSHIP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com