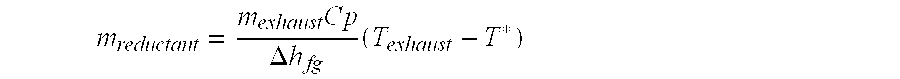Patents
Literature
82 results about "Maximum dose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medical Definition of maximum dose. : the largest dose of a medicine or drug consistent with safety.
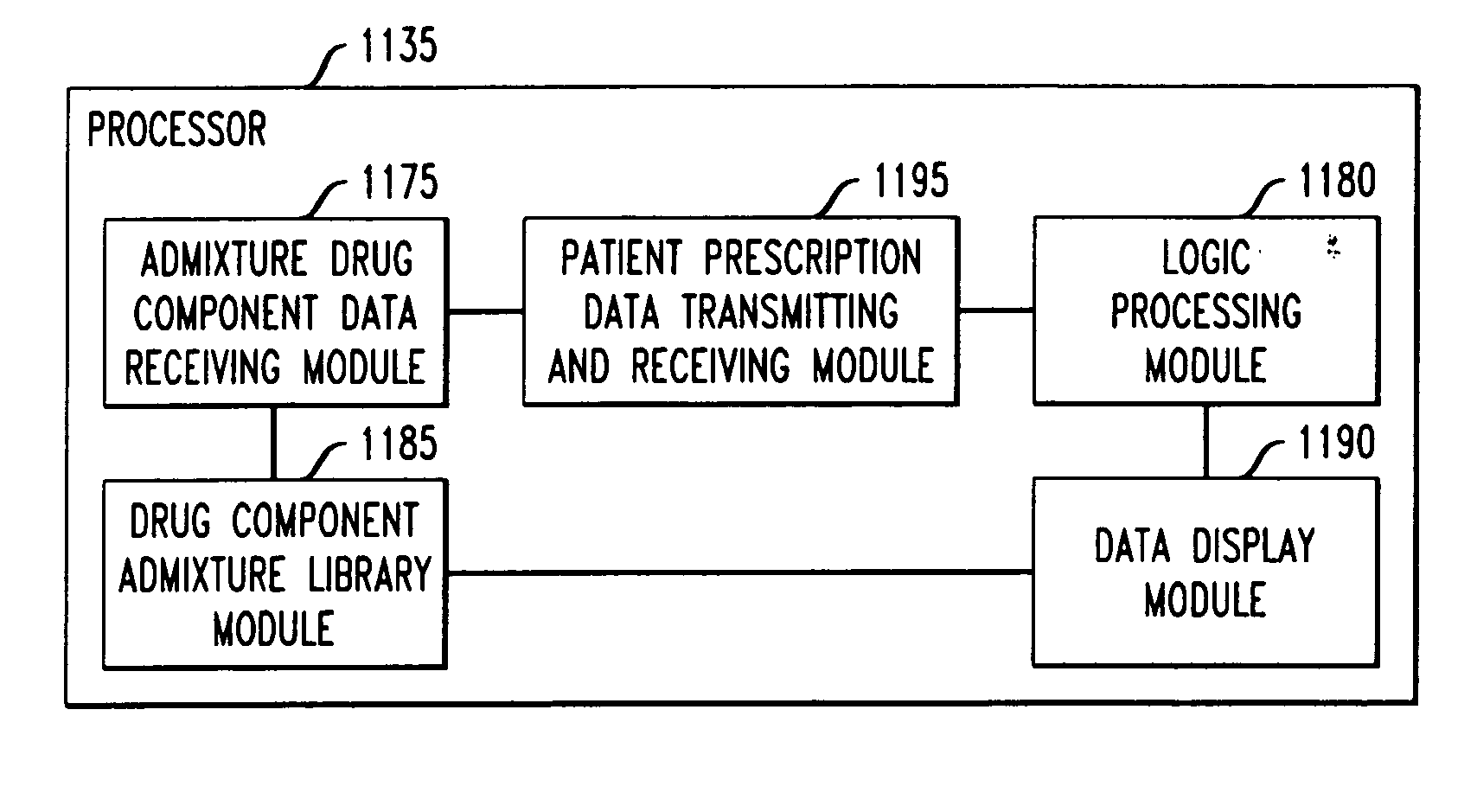
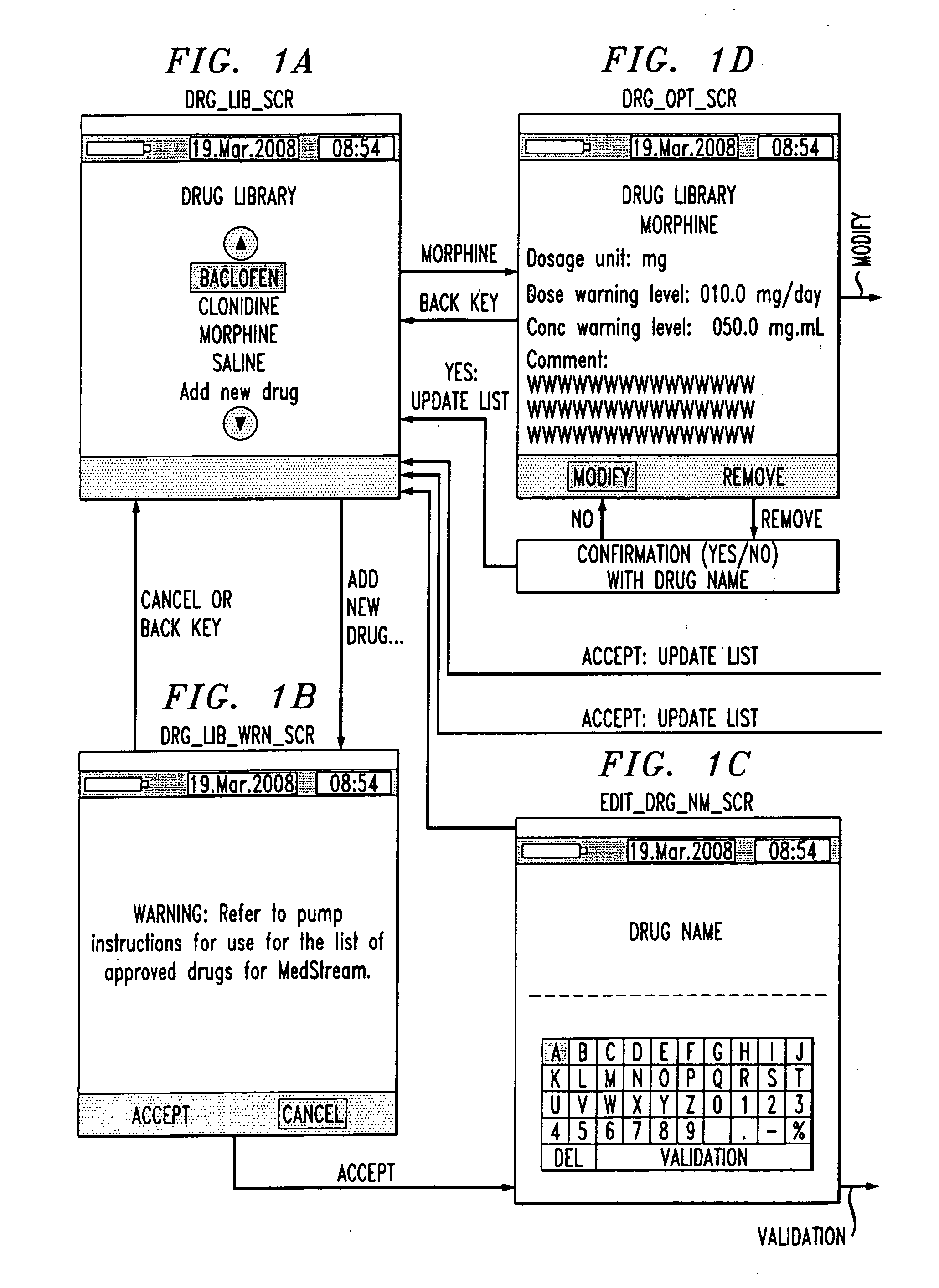
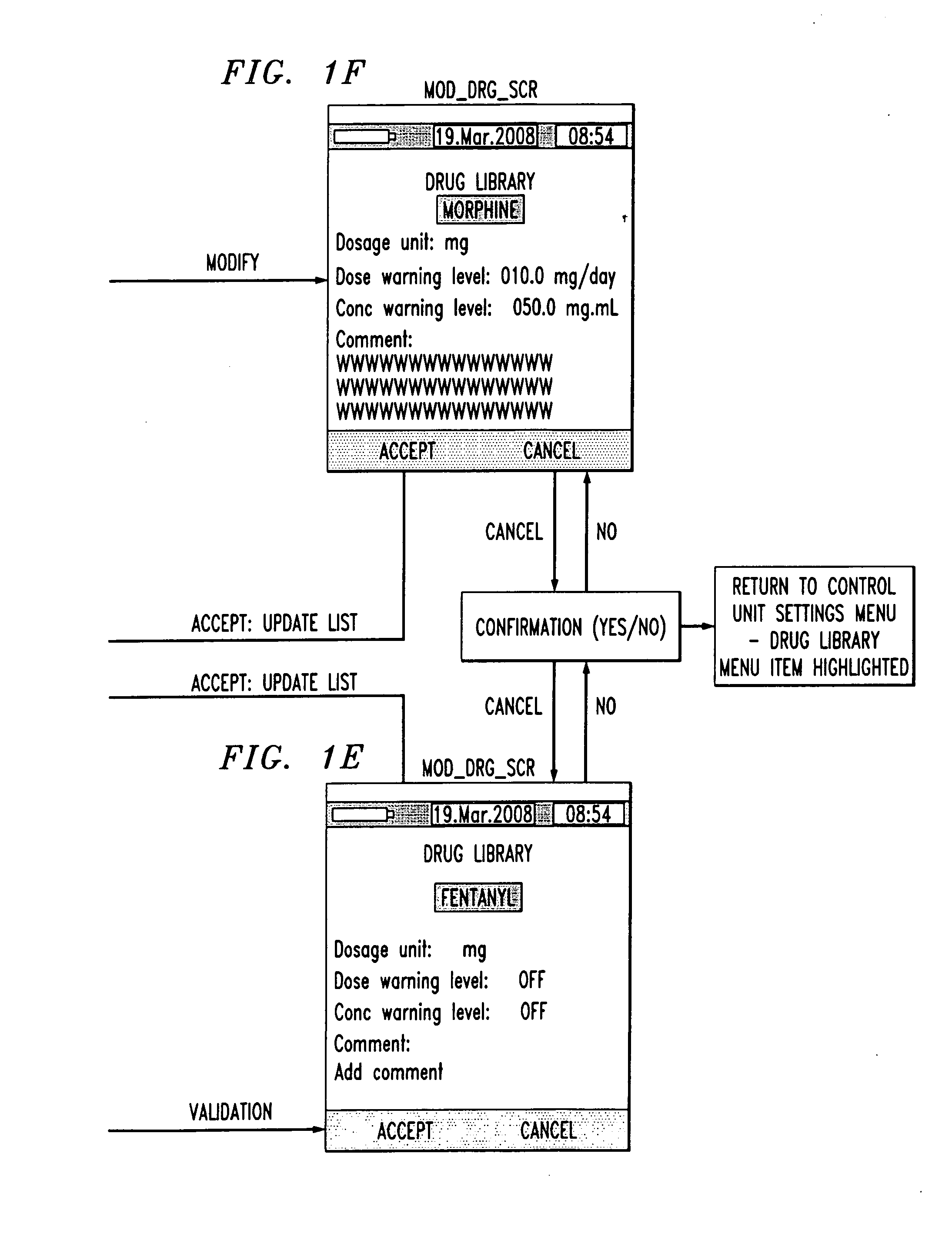
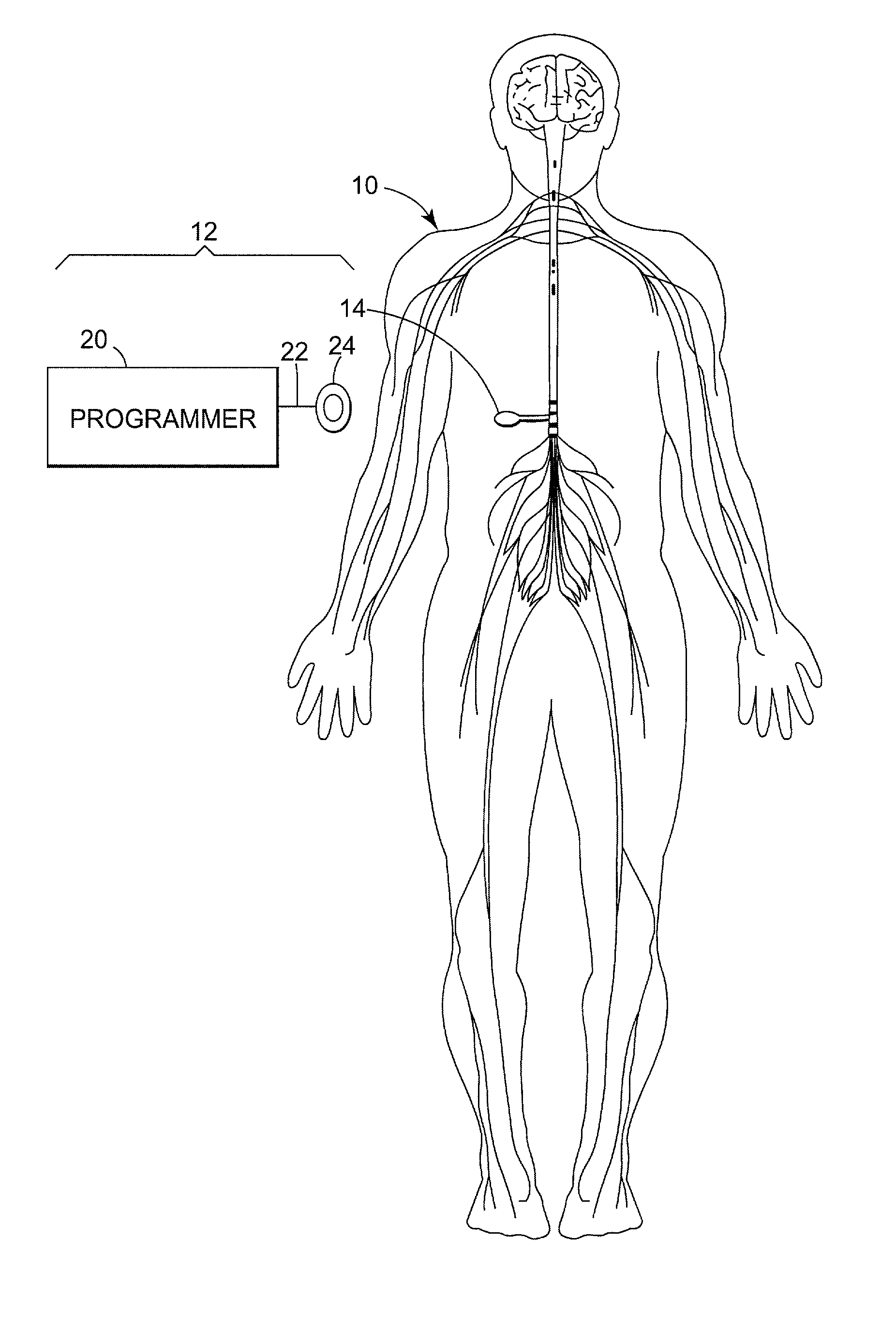
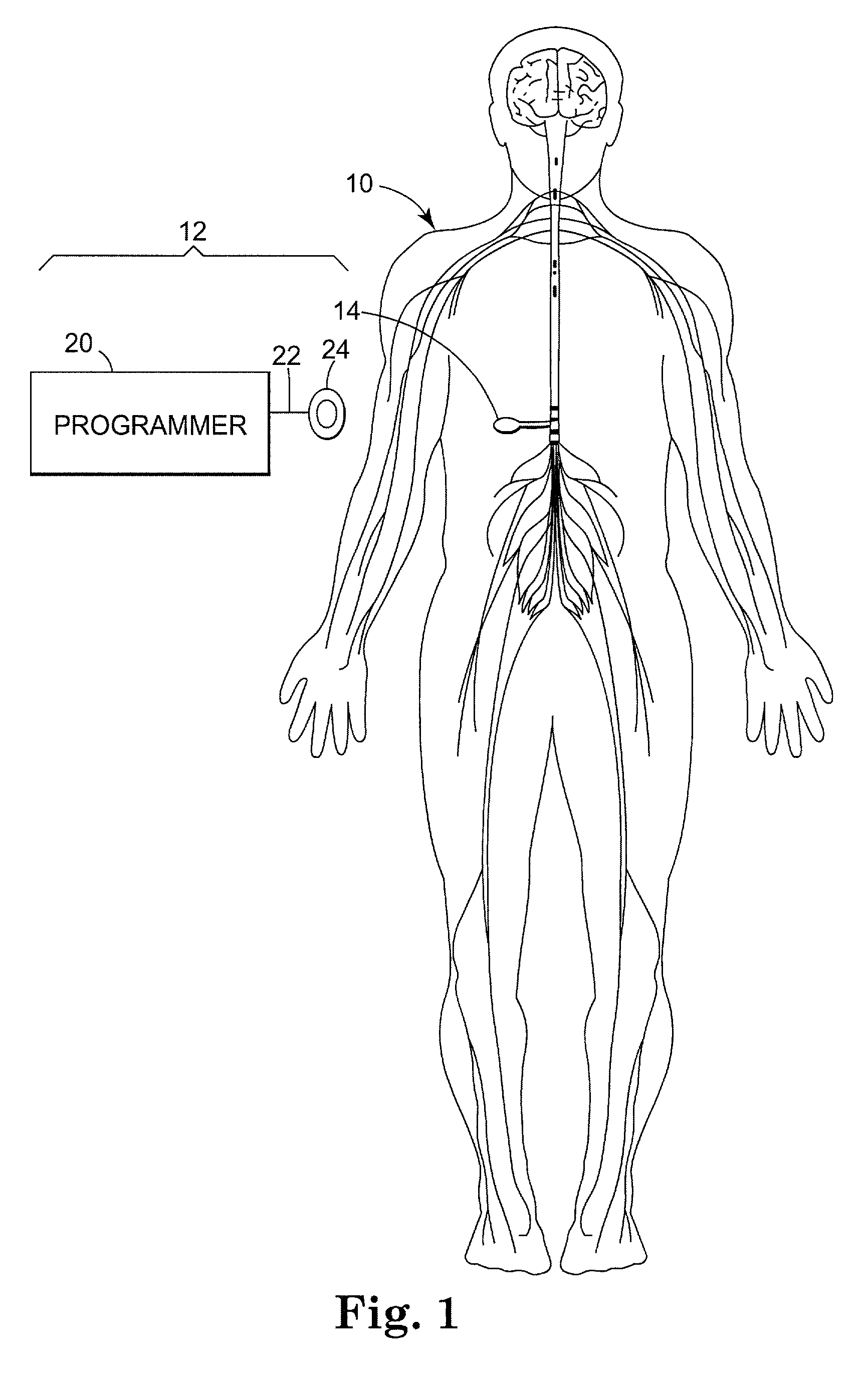
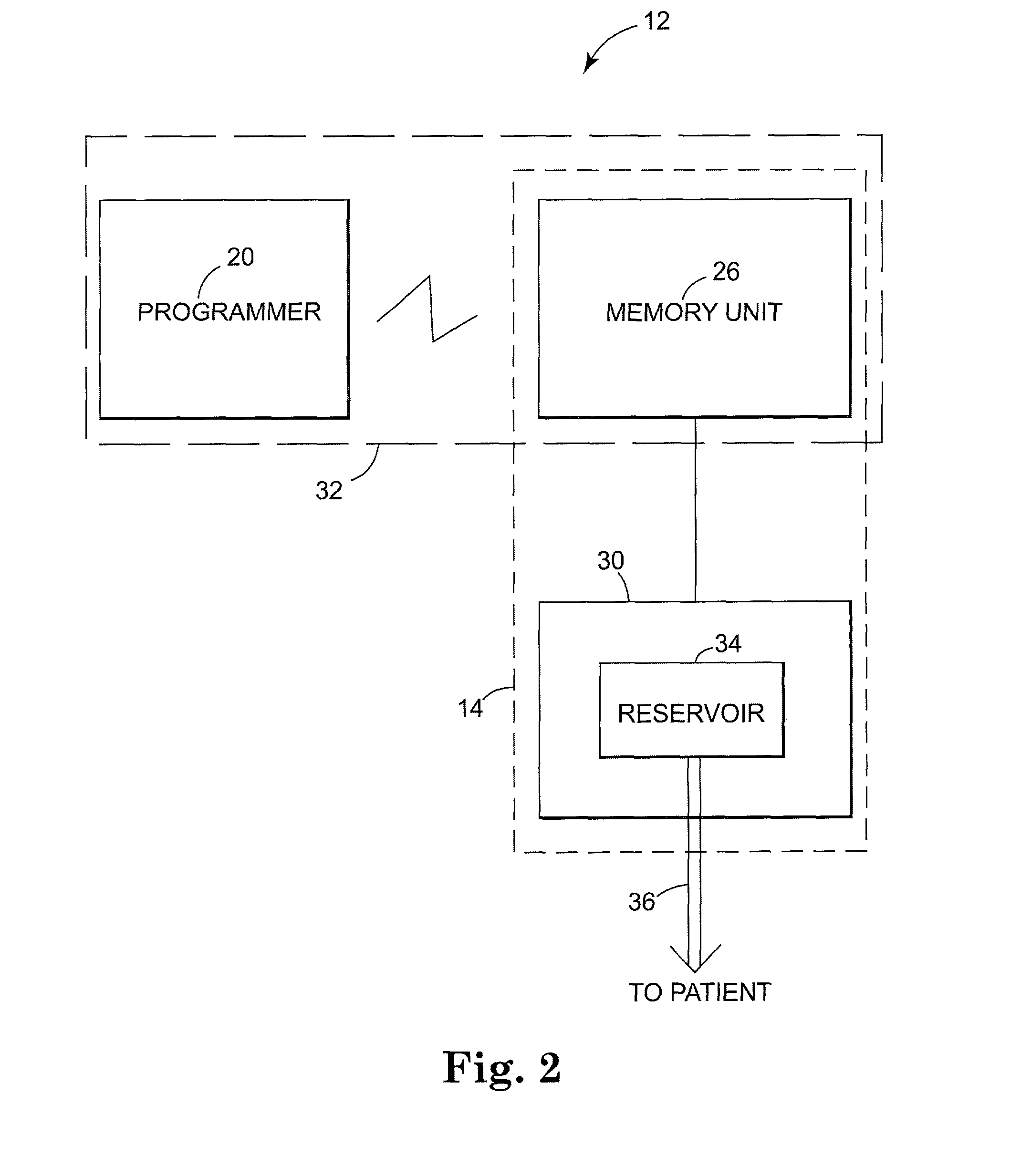
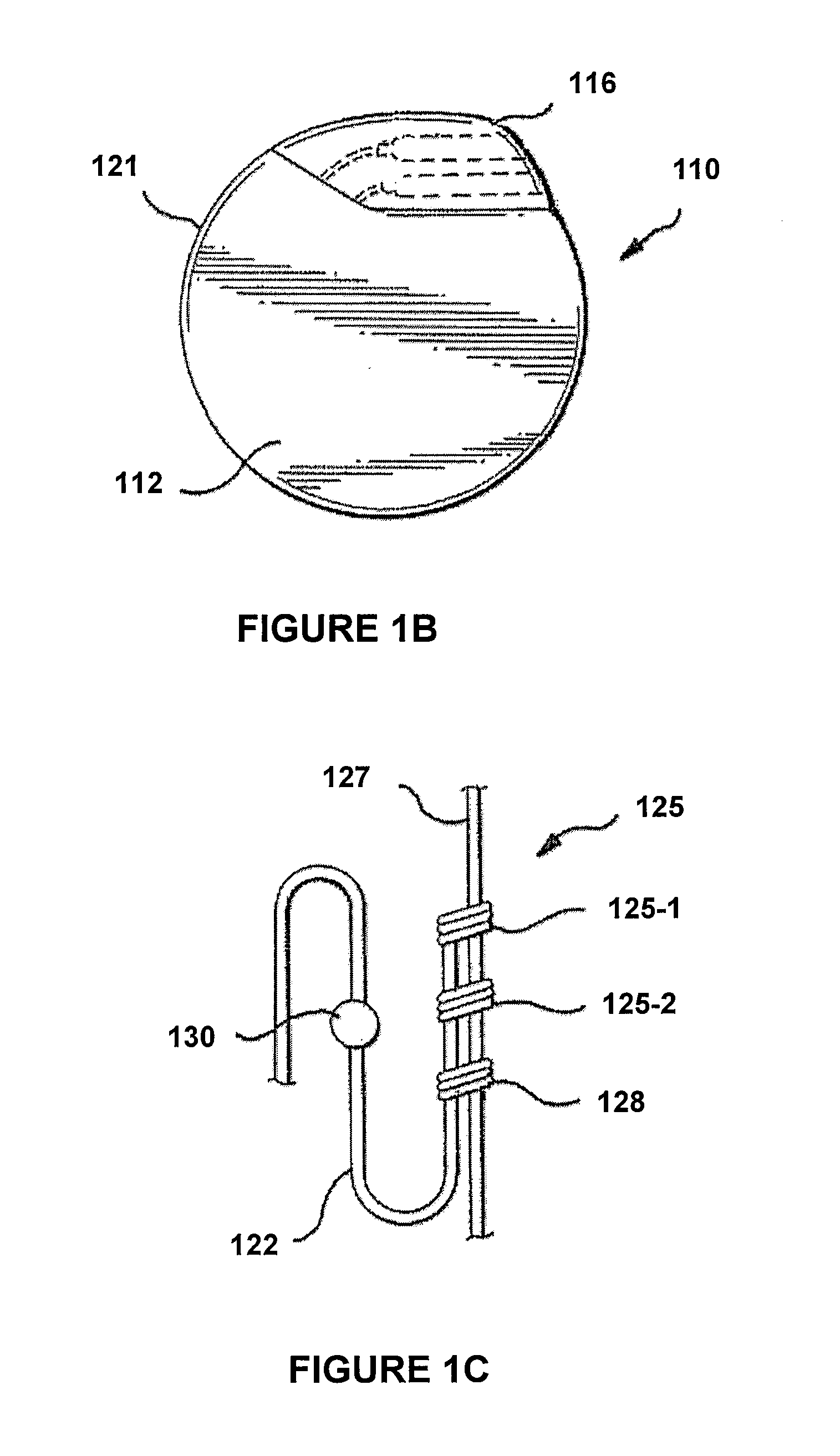
Drug component admixture library for a drug infusion delivery system
InactiveUS20110320049A1Shorten the timeReduce generationLevel controlControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsDrugs infusionDelivery system
Minimizing improper dosage of a drug admixture (including a single primary drug component and at least one second drug component). For each drug component in the drug admixture, receiving a name of the drug component along with its dosage unit, a maximum dose warning level and a maximum concentration warning level. Receiving a concentration for each of the single primary drug component and the at least one secondary drug component; and a dose setting of only the primary drug component. Automatically calculating a dose of each of the at least one secondary drug component. Generating an alert when: (i) the received dose setting of the primary drug component or calculated dose setting of the at least one secondary drug component exceeds the dose warning level; or (ii) the received concentration of the primary drug component or the at least one secondary drug component exceeds the concentration warning level.
Owner:MEDOS INT SARL
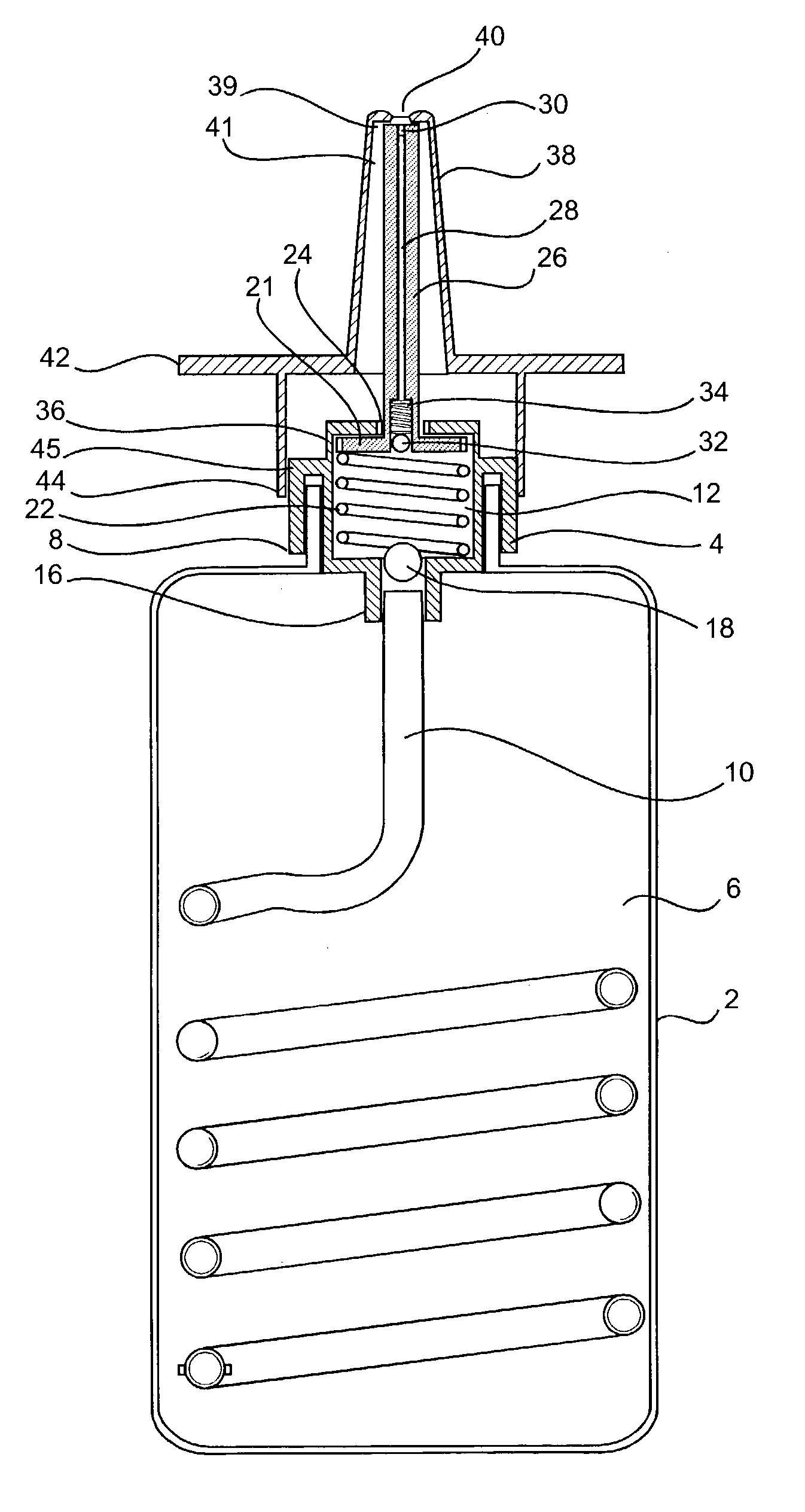
Patient controlled drug delivery device
InactiveUS20040068222A1Simple and inexpensive to manufactureSimple and inexpensive to and useInfusion devicesMedical devicesControlled drugsCatheter
A delivery device for patient-controlled infusion of a medicament, the delivery device comprising a reservoir for the medicament and a pump having a predetermined delivery dose which is capable of displacing the medicament from the reservoir and delivering it to a patient, wherein the pump comprises a pumping means, a first conduit, capable of restricting flow rate, chosen in conjunction with the delivery dose of the pumping means to define a predetermined maximum dosage rate, said conduit connecting the reservoir to a pumping means, a one-way valve in fluid communication with the first conduit and the pumping means which permits medicament flow into the pumping means but prevents reverse flow, a controlling means, and a second conduit extending from the pumping means and having a distal end through which the medicament may be released, wherein the controlling means: (a) is in fluid communication with the pumping means and the second conduit; (b) opens when pressured within the dose chamber exceeds a predetermined minimum opening pressure for the controlling means; and, (c) is adapted to prevent the reverse flow of medicament and air into the pumping means.
Owner:ONEIL ALEXANDER GEORGE BRIAN & ONEIL CHRISTINE JOINTLY
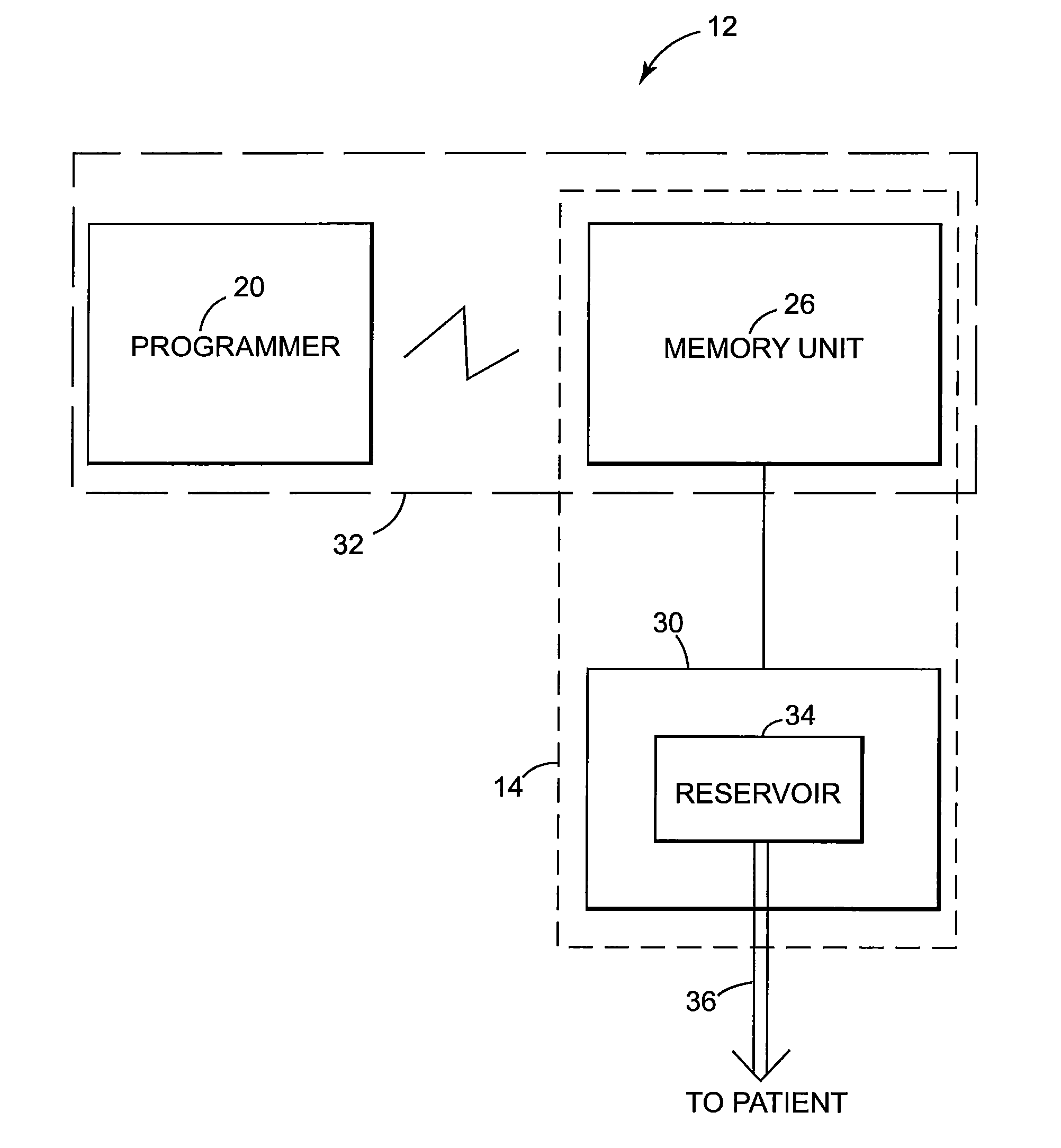
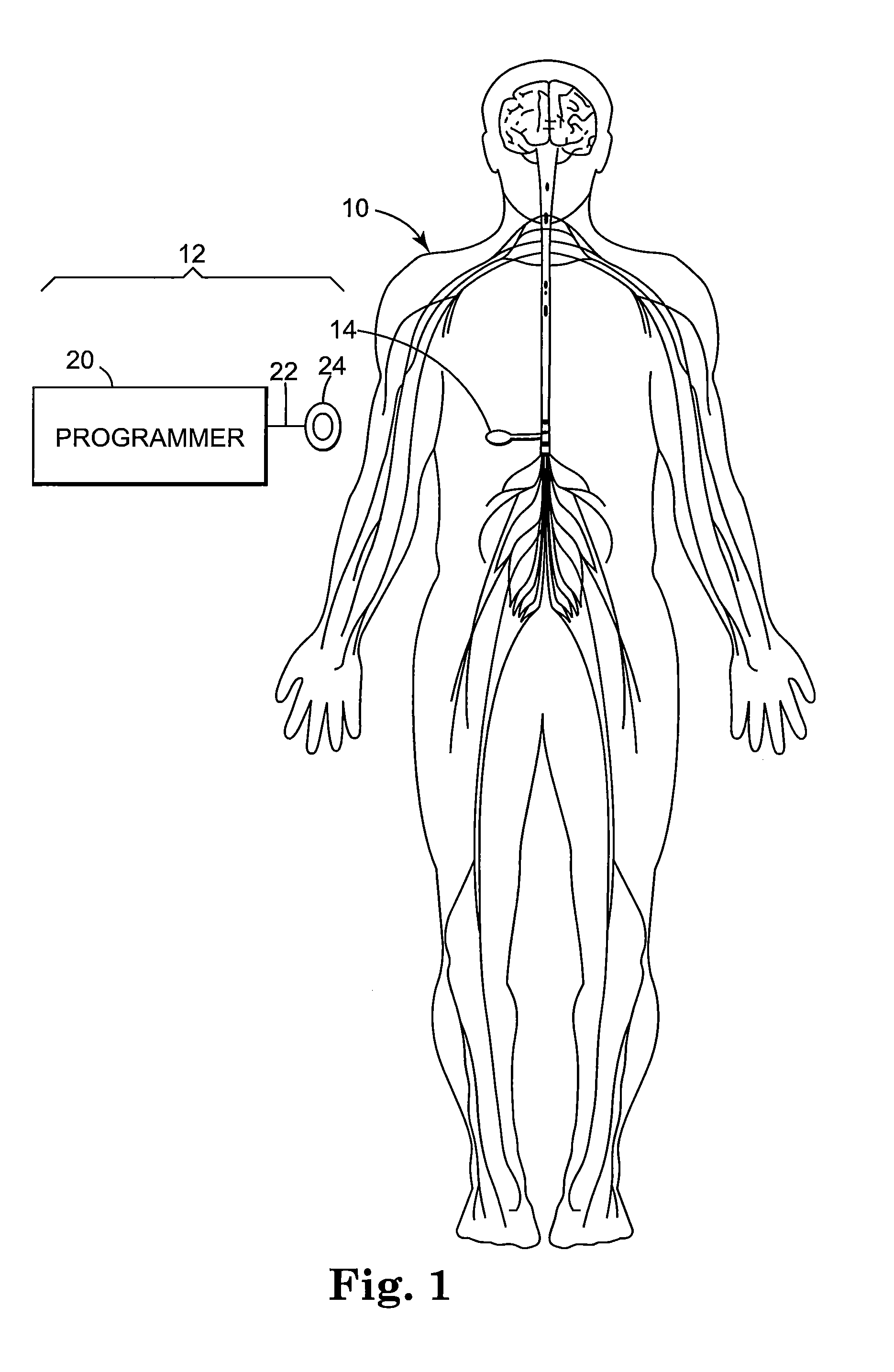
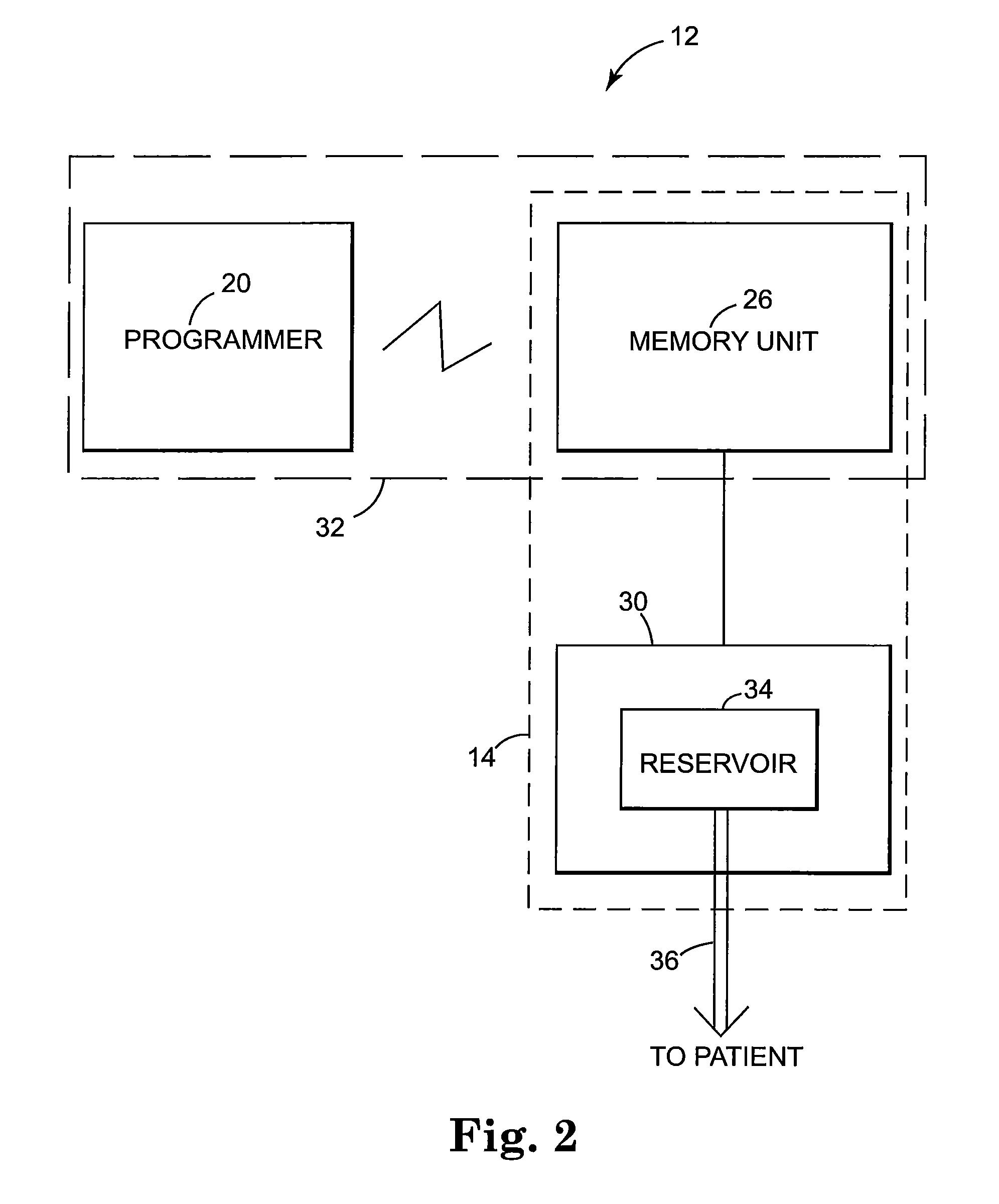
Dosing limitation for an implantable medical device
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
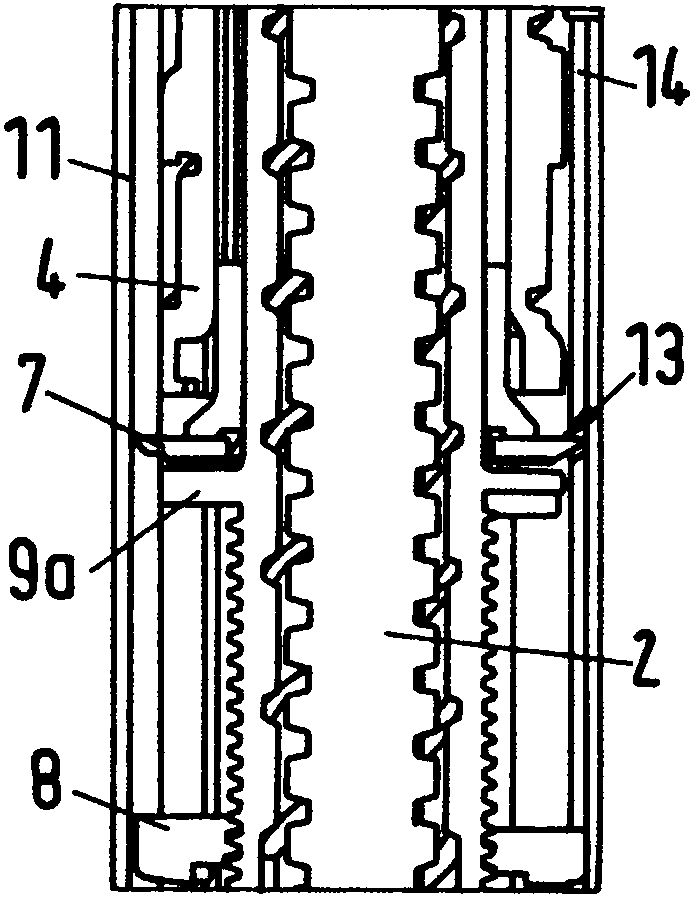
Dose setting mechanism with maximum dose limiting element
InactiveCN102655899APerformance is not affectedLower cost of goodsInfusion syringesIntravenous devicesBiomedical engineeringMaximum dose
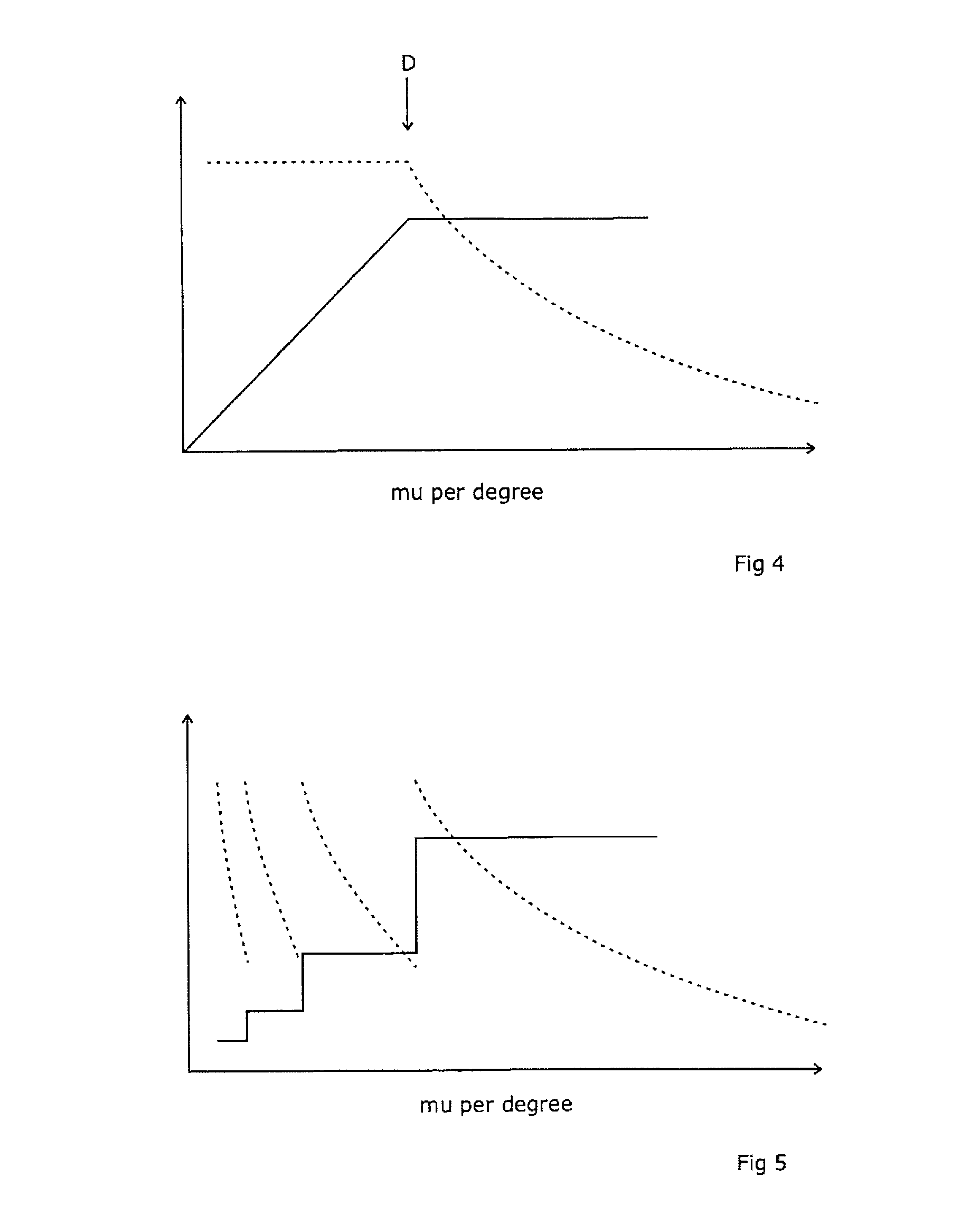
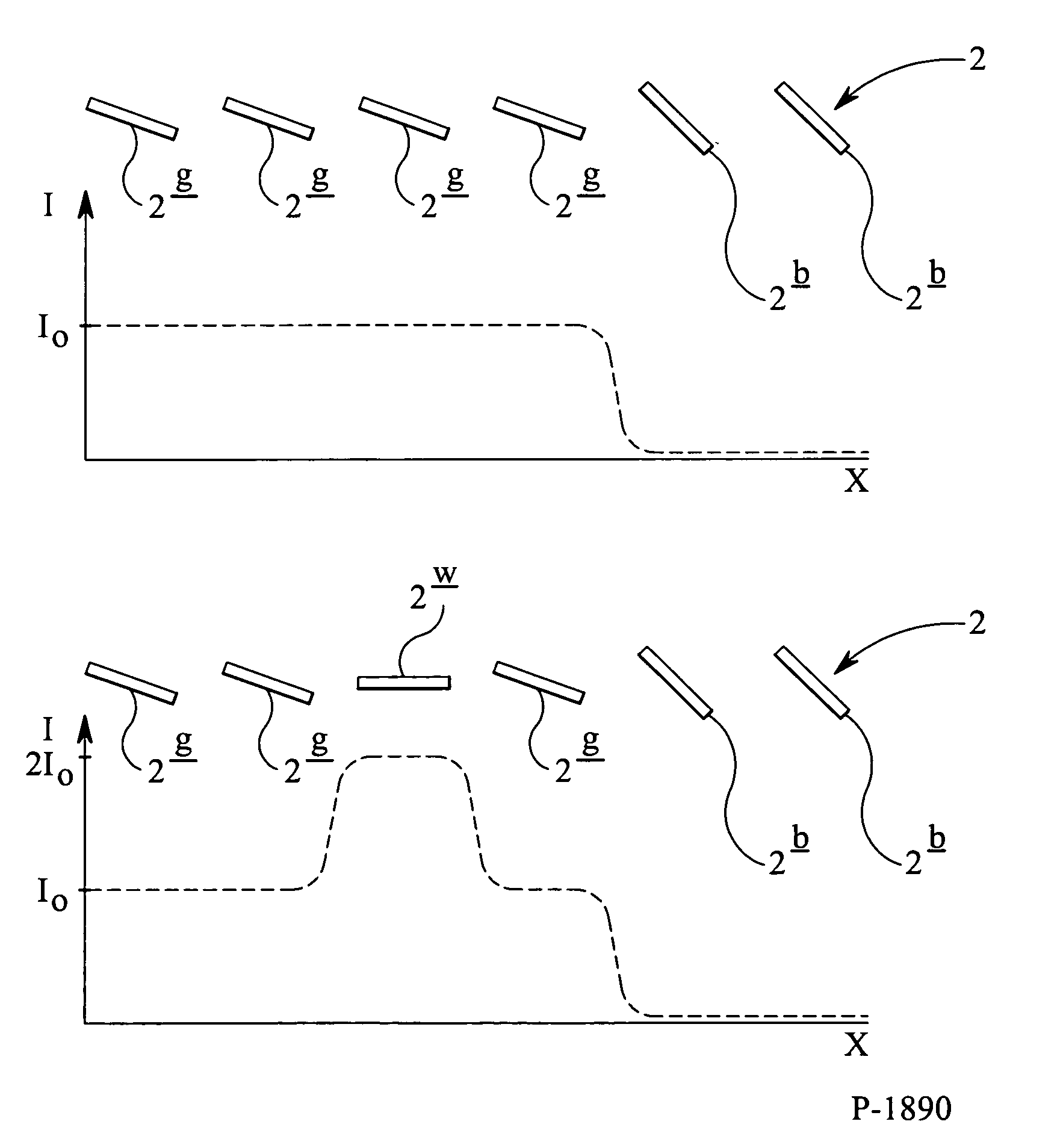
A dose setting mechanism for a drug delivery device is provided comprising first maximum dose stop features (1) on a first component part (2) of the drug delivery device and corresponding second maximum dose stop features (3) on a second component part (4) of the drug delivery device, with the first and second maximum dose stop features (1, 3) being designed to limit a relative movement between the first and second component parts (2, 4). To limit the maximum dose which can be chosen, a maximum dose limiting device (5, 10, 10', 10", 10"') is provided interposed on the first component part (2) between the first and second maximum dose stop features (1, 3).
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Drug infusion system programmable in flex mode
A drug infusion system capable of delivering a fluid medication to a patient under direction of a medical professional continually at a basal rate and at an interval rate in each of a plurality of time slots over a specified period of time. The total dose of the fluid medication to be delivered to the patient over the period of time based on the basal rate and the interval rate for each of the plurality of time slots is determined, compared the total dose against a maximum dose. The basal rate is adjusted, if necessary, so that the total dose does not exceed the maximum dose.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
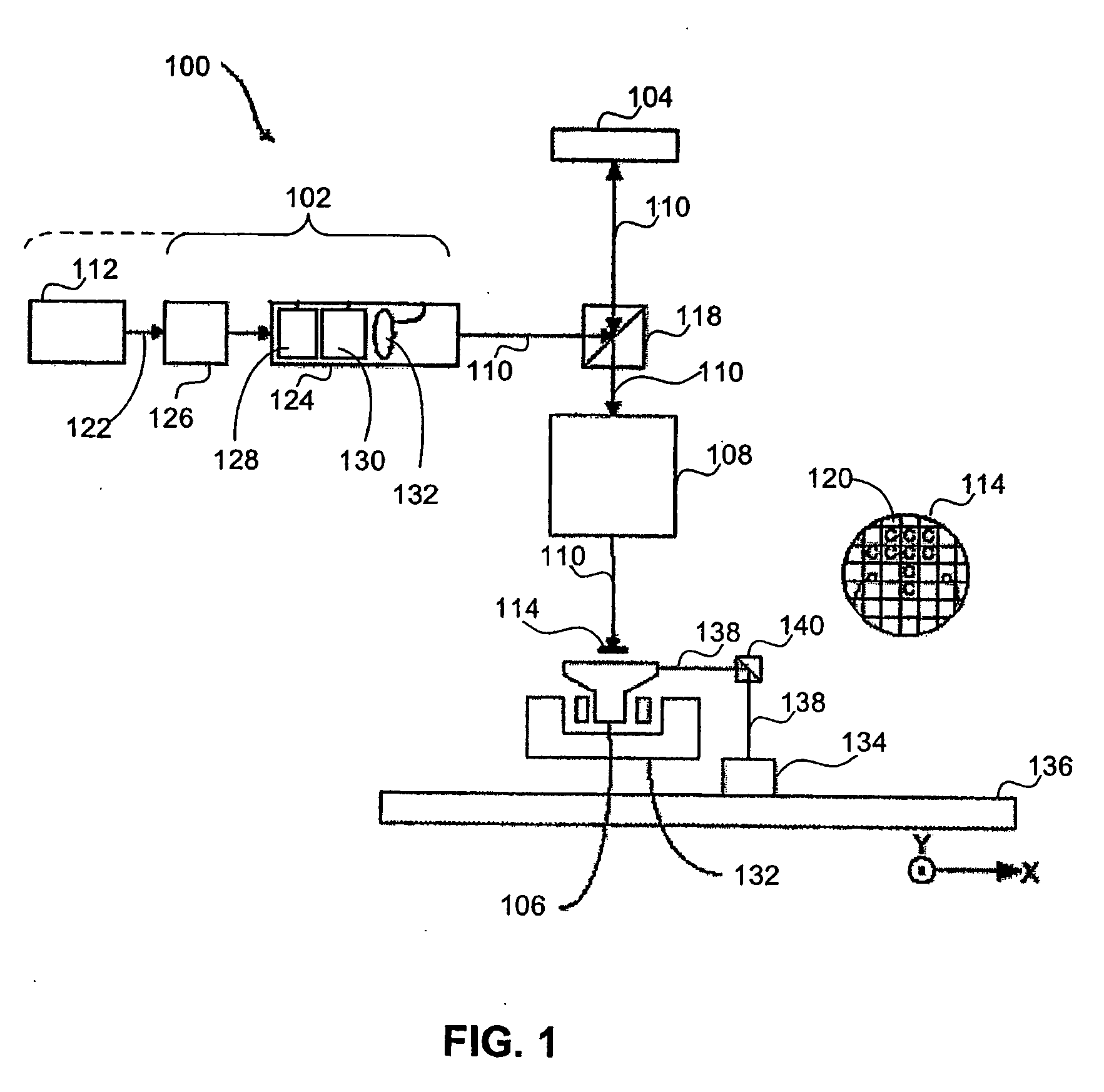
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
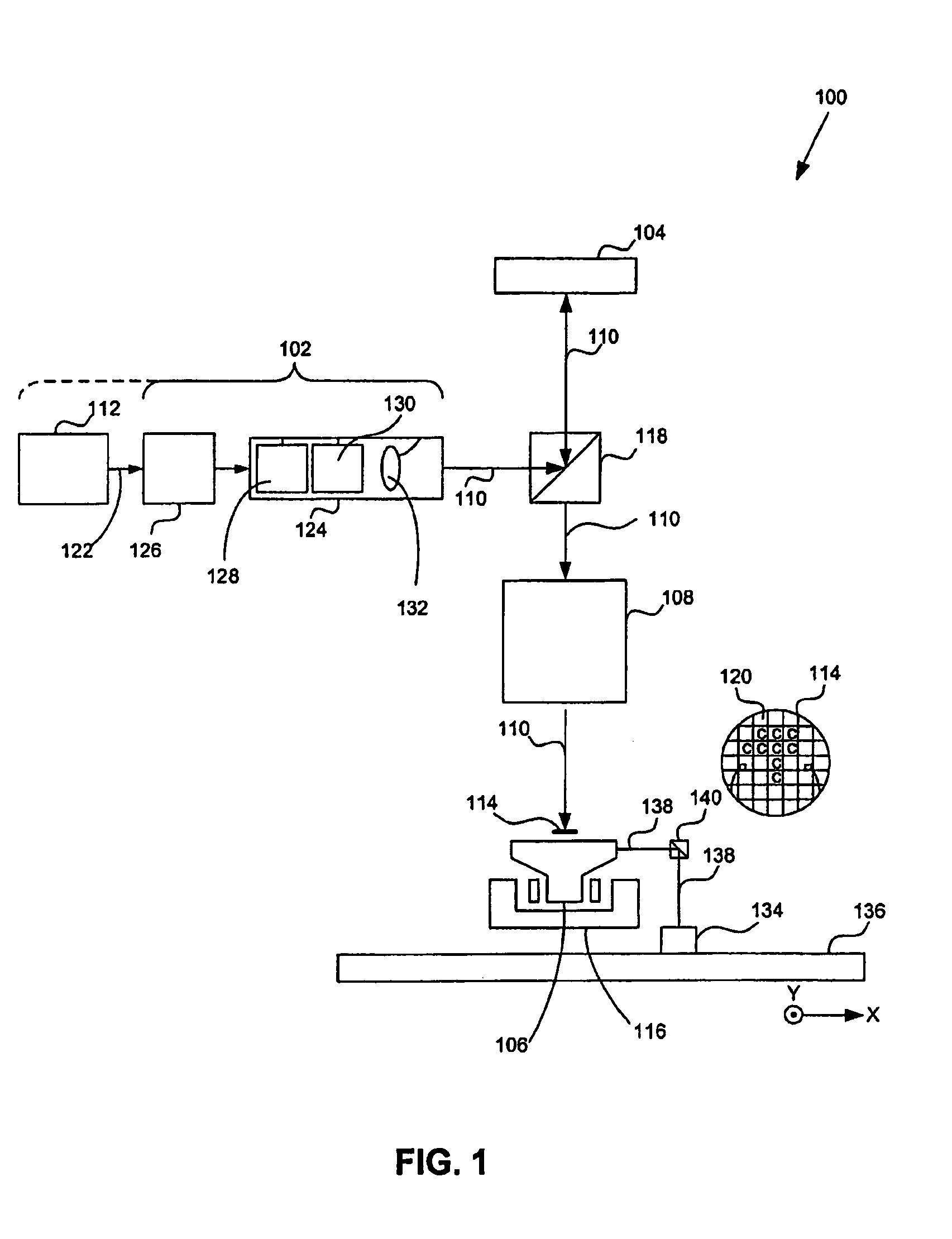
ActiveUS20050270515A1Increase radiation doseReduce the amount of compensationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLight beamMaximum dose
A system and method to manufacturing a device provide a substrate and perform at least one exposure step. Each exposure step projects a patterned beam of radiation, which was patterned using an individually controllable elements, onto a target portion of the substrate. The projected patterned beam includes a plurality of pixels. Each exposure step also: (a) ordinarily controls the elements, such that each pixel delivers a radiation dose no greater than a predetermined normal maximum dose to the target portion in the exposure step; and (b) exceptionally controls the elements, such that at least one selected pixel delivers an increased radiation dose, greater than the normal maximum dose. The increased dose may be delivered to compensate for the effect of a defective element at a known position in the array on a pixel adjacent a selected pixel. Alternatively, it may compensate for underexposure of the target portion at the location of a selected pixel resulting from exposure of that location to a pixel affected by a known defective element in another exposure step. The invention uses doses up to the predetermined normal maximum for normal printing, but reserves at least one increased dose for compensation purposes. Accordingly, even when a dead black pixel falls in the middle of a group of surrounding white pixels it can be compensated for by increasing the radiation dose delivered by one or more of those neighboring white pixels, above the normal fully white value.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
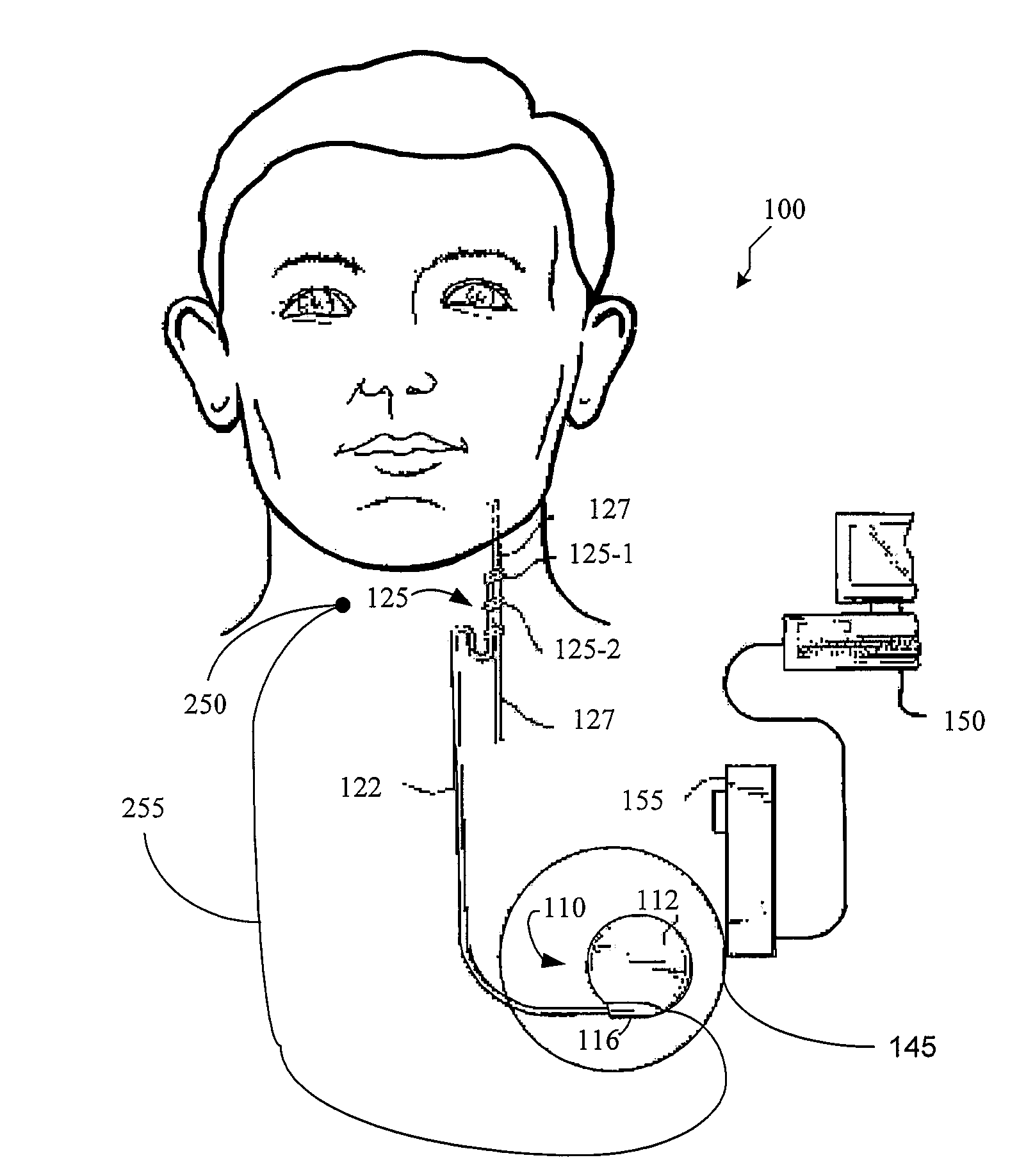
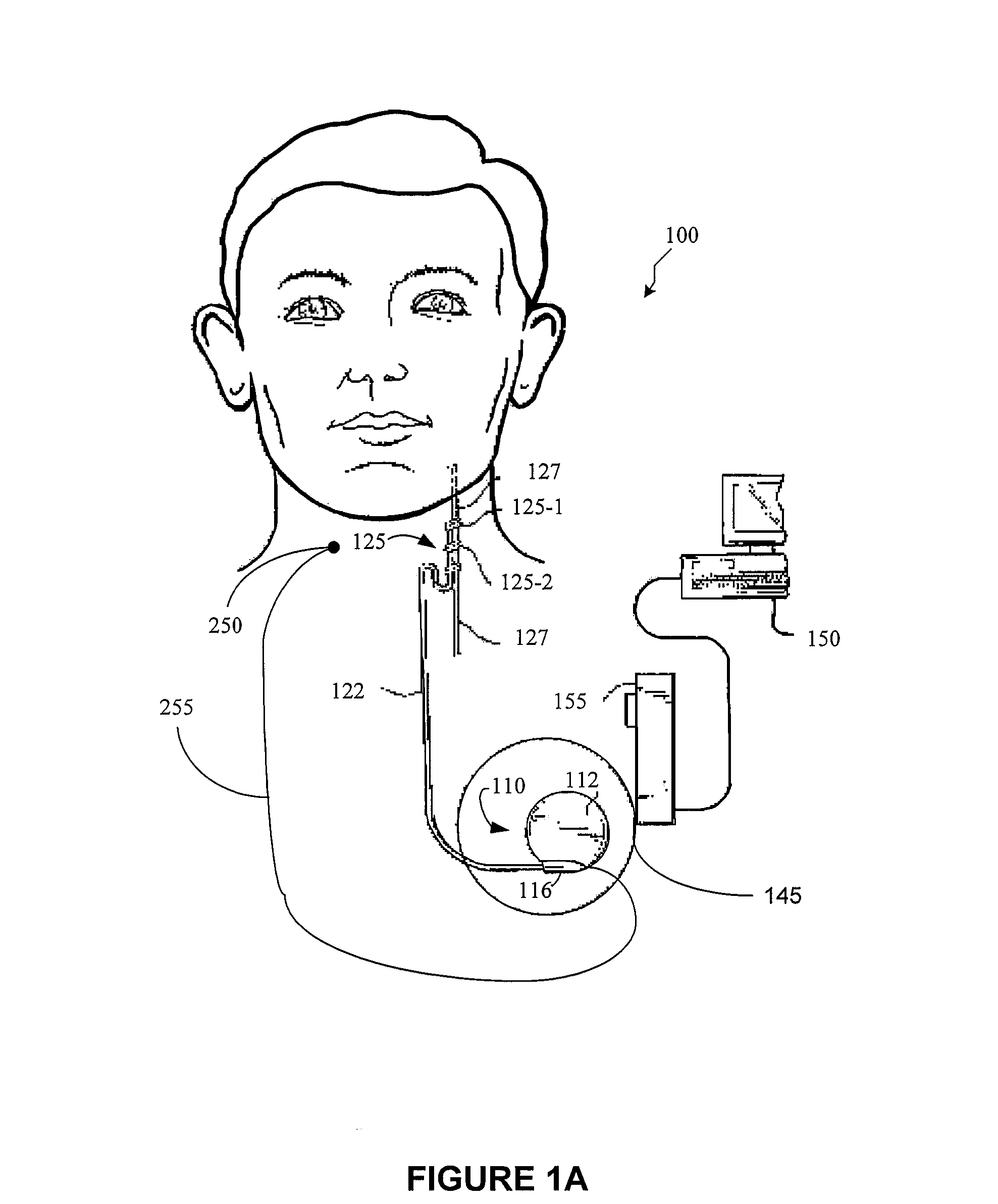
Dosing Limitation for an Implantable Medical Device
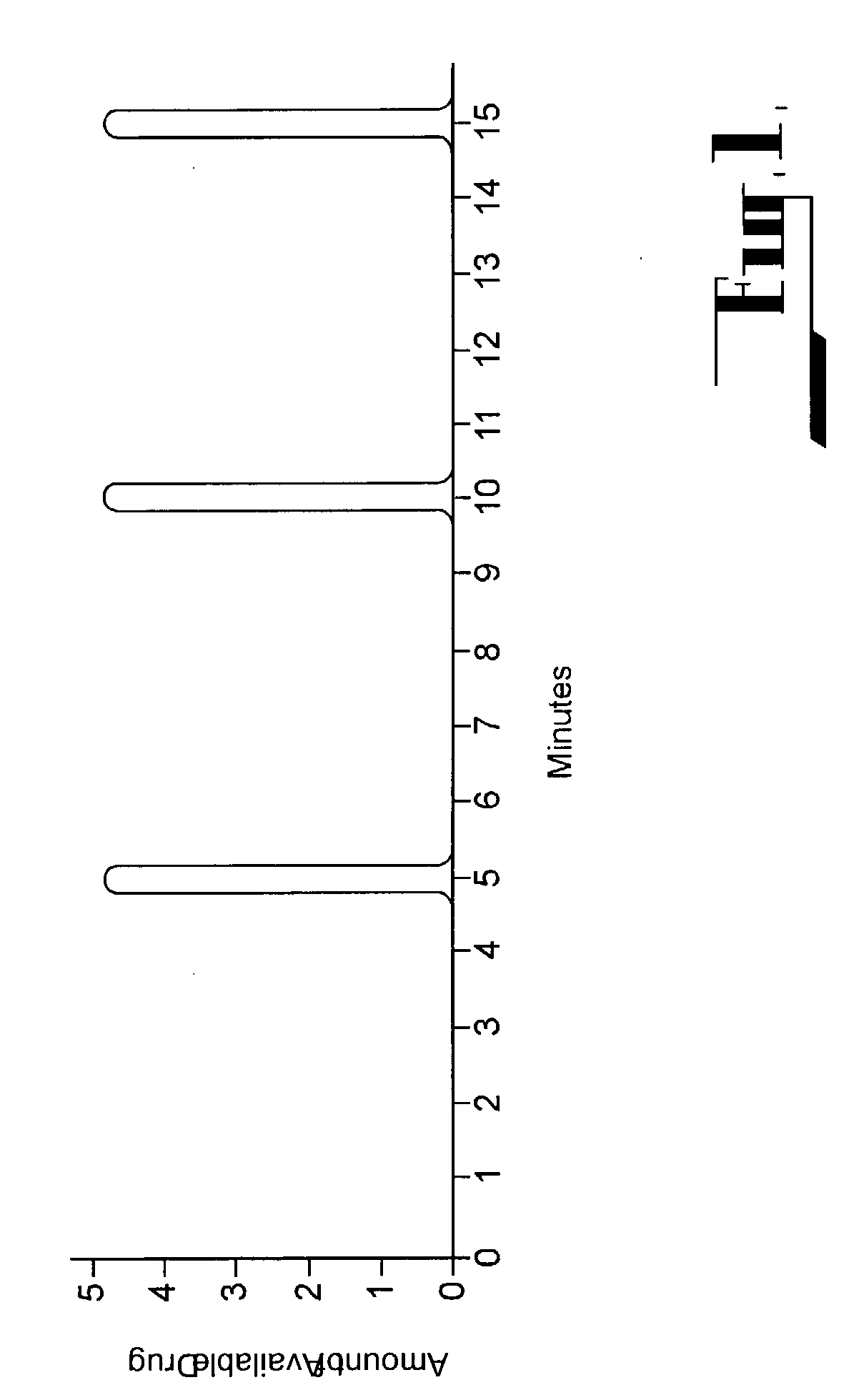
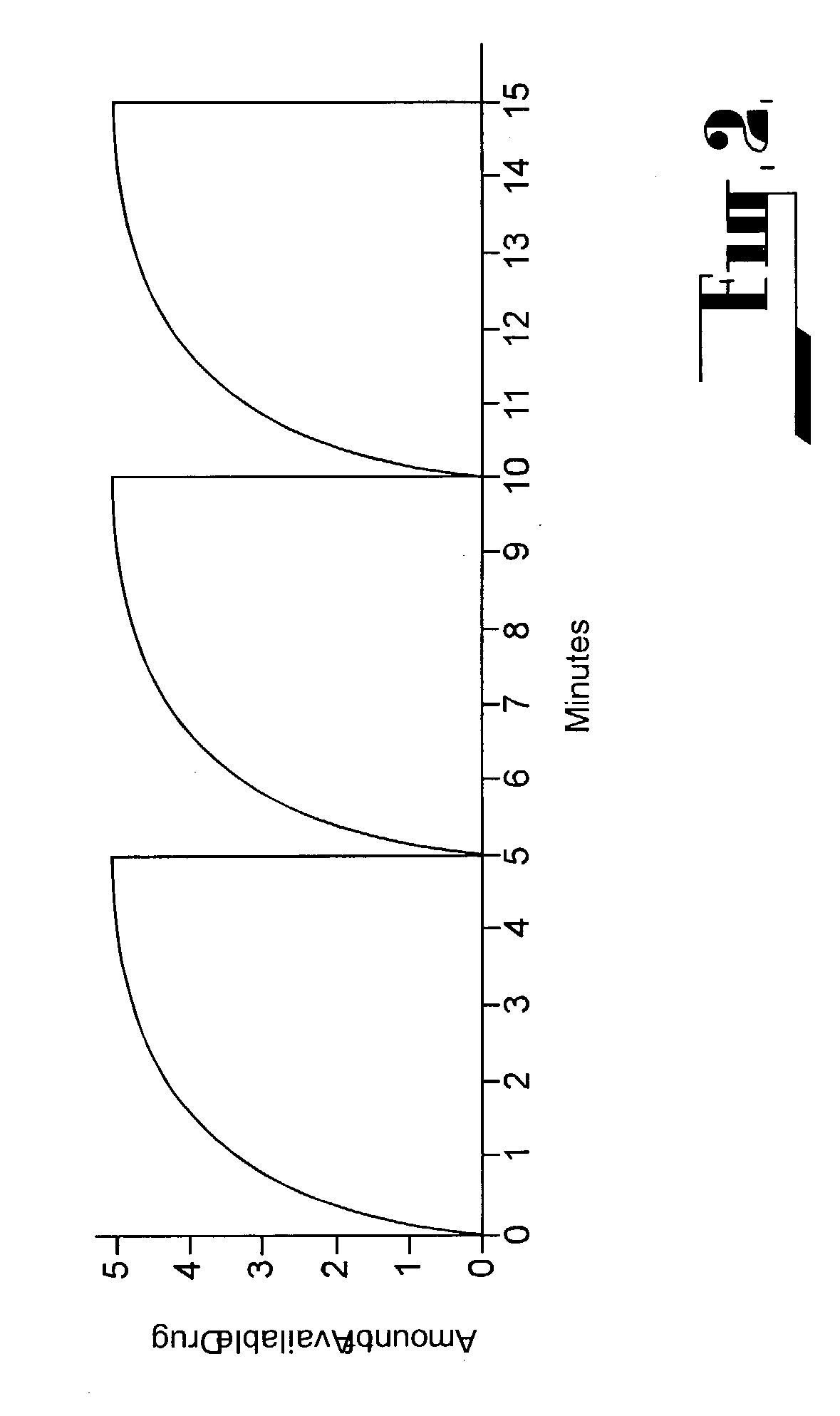
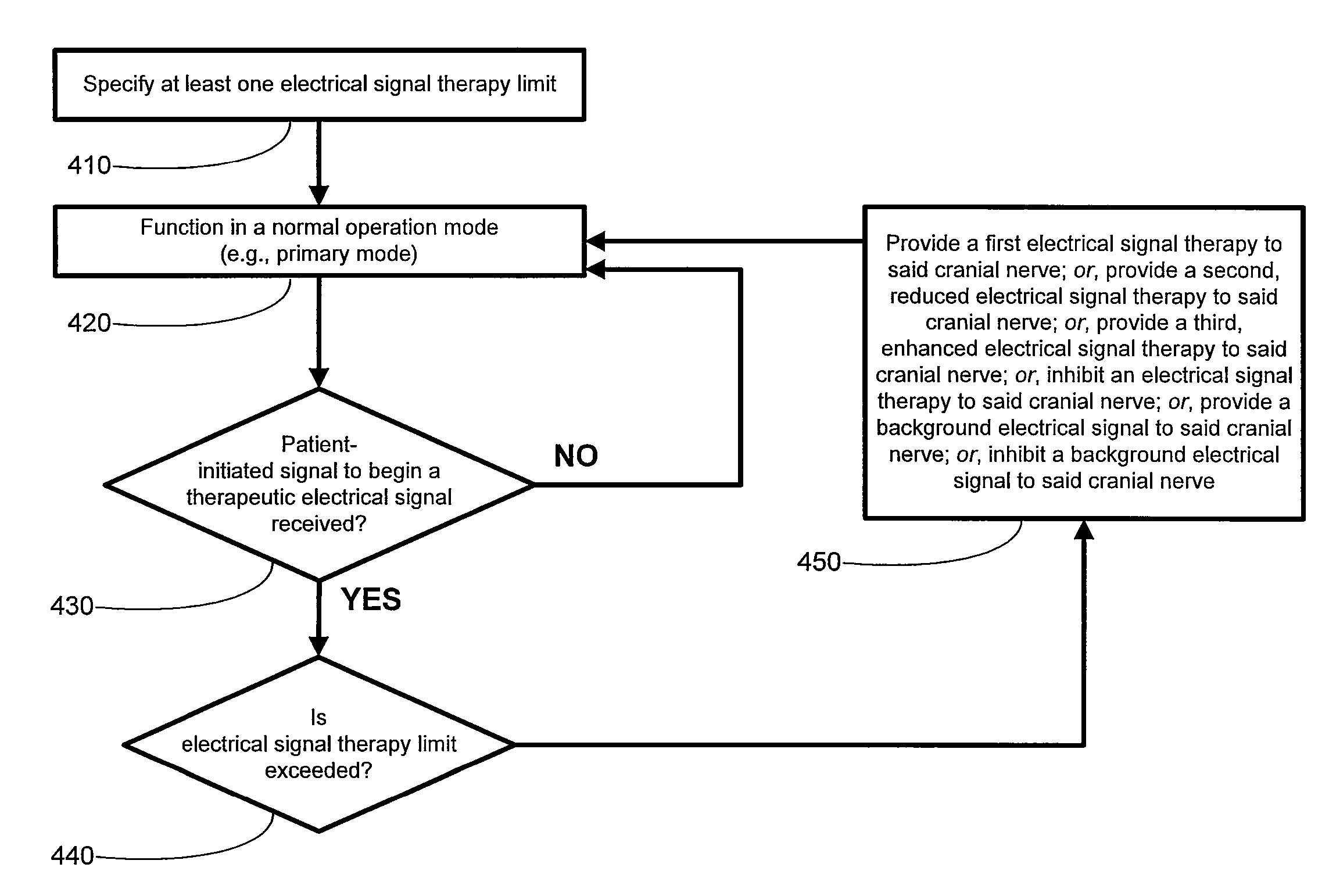
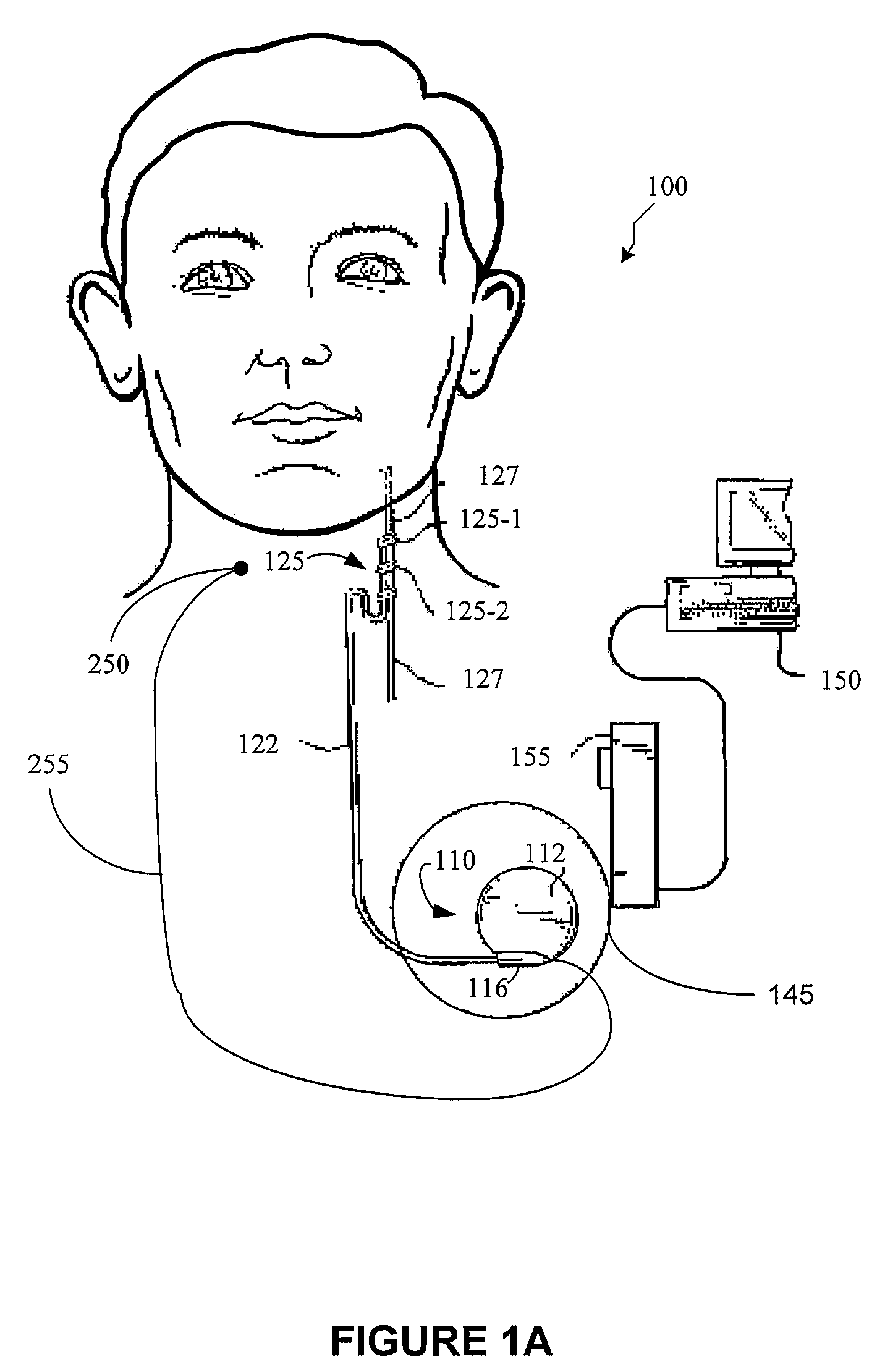
A method for limiting patient-initiated electrical signal therapy provided by an implantable medical device (IMD) to a cranial nerve of a patient. At least one electrical signal therapy limit selected from the group consisting of a maximum number of patient-initiated signals to provide a therapeutic electrical signal per a time period, a maximum dose of the therapeutic electrical signal per a time period, a maximum duration of the therapeutic electrical signal per a time period, a maximum rate of change of the number of patient-initiated signals to provide a therapeutic electrical signal per a time period, a maximum rate of change of the dose of the therapeutic electrical signal per a time period, and a maximum rate of change of the duration of the electrical signal therapy per a time period is specified. A patient-initiated signal to begin a therapeutic electrical signal is received. Whether or not said electrical signal therapy limit is exceeded by said step of detecting a patient-initiated signal is determined. An action in response to said step of determining whether or not said limit is exceeded is performed, said action selected from the group consisting of providing a first electrical signal therapy to said cranial nerve, providing a second, reduced electrical signal therapy to said cranial nerve, providing a third, enhanced electrical signal therapy to said cranial nerve, inhibiting an electrical signal therapy to said cranial nerve, providing a background electrical signal to said cranial nerve, and inhibiting a background electrical signal to said cranial nerve.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Infusion system programmable in flex mode
A drug infusion system capable of delivering a fluid medication to a patient under direction of a medical professional continually at a basal rate and at an interval rate in each of a plurality of time slots over a specified period of time. The total dose of the fluid medication to be delivered to the patient over the period of time based on the basal rate and the interval rate for each of the plurality of time slots is determined, compared the total dose against a maximum dose. The basal rate is adjusted, if necessary, so that the total dose does not exceed the maximum dose.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Radiotherapeutic apparatus
ActiveUS20090213991A1Avoid less flexibilityReduce doseX-ray apparatusX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose rateClassical mechanics
A radiotherapeutic apparatus comprises a source able to emit a beam of therapeutic radiation along a beam axis, a multi-leaf collimator arranged to collimate the beam to a desired shape, wherein the source is rotateable about a rotation axis that is substantially orthogonal and intersects with the beam axis thereby to describe an arc around that axis, and further comprises a control means able to control the dose / time rate of the source, the rotation speed of the source, and the multi-leaf collimator position. The control means is arranged to receive a treatment plan in which the arc is divided into a plurality of notional arc-segments, and specifying the total dose for the arc-segment and a start and end MLC position. It then controls the source in accordance with that plan over an first arc-segment such that at least one of the rotation speed and dose rate are constant and the multi-leaf collimator changes shape, and a second arc segment such that at least one of the rotation speed and dose rate are constant at a level different to the constant level adopted during the first arc-segment. It achieves this by calculating the total time required for the arc segment for a plurality of factors including an MLC leaf movement from a prescribed position at the start of the arc-segment to a prescribed position at the end of the arc-segment, at a maximum leaf speed, rotation of the source from the start to the end of the arc-segment at a maximum source rotation speed, delivery of the dose at a maximum dose rate per time, selecting the factor dictating the longest time, and controlling the apparatus so that the selected factor operates at its respective maximum and the remaining factors are operated at a reduced rate selected to match that longest time.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
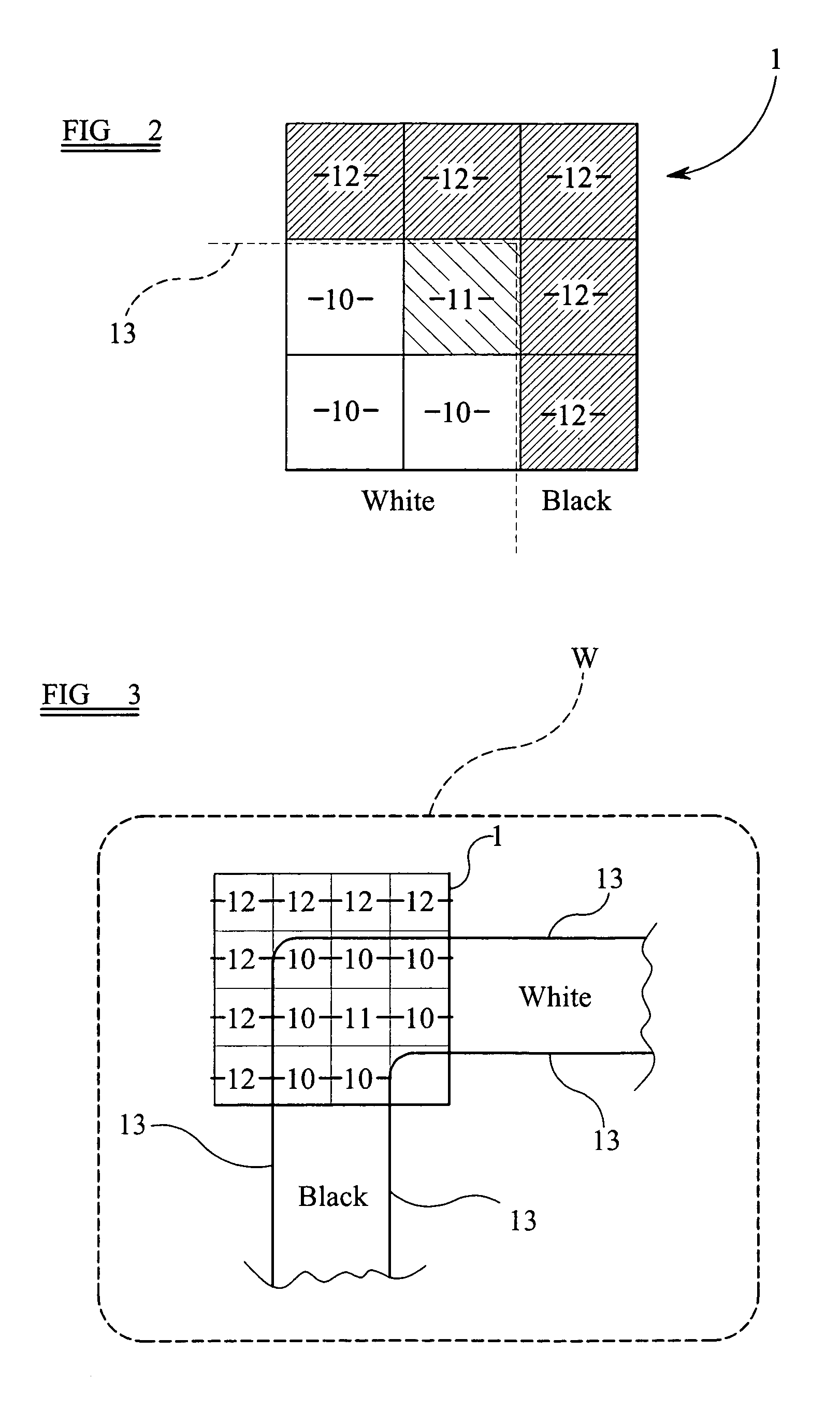
Enhanced stitching by overlap dose and feature reduction
ActiveUS20150242563A1Improve critical dimension uniformityIncrease exposureElectric discharge tubesPhotomechanical apparatusMedicineMaximum dose
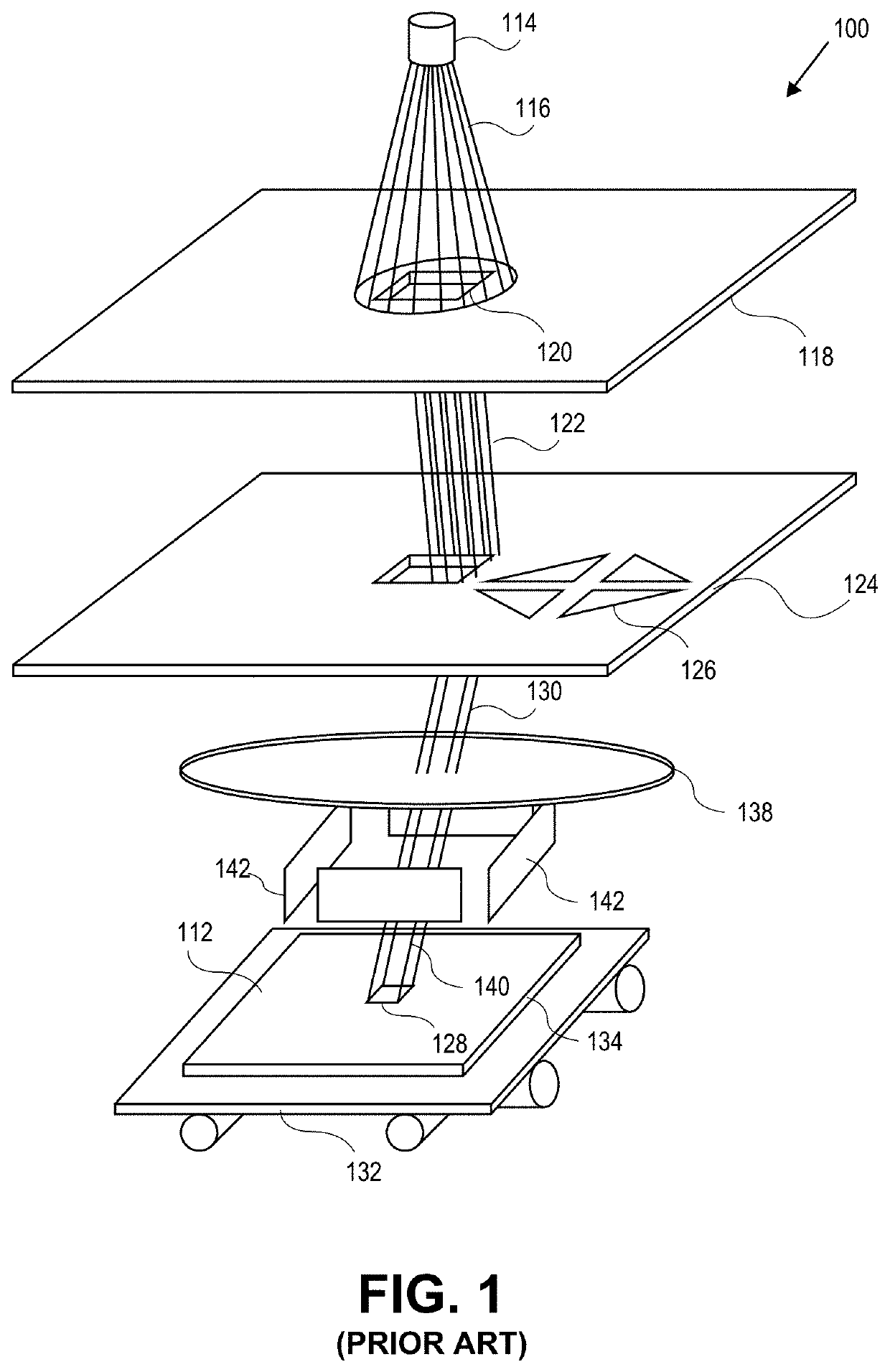
A method for processing exposure data (40) for exposing a pattern on a target (30) using a plurality of charged particle beams (24), the exposure data comprising pattern data (42) representing one or more features (60) to be written on the target (30) and exposure dose data (52) describing exposure dose of the charged particle beams. The method comprises setting one or more dose values of the exposure dose data (52) such that a sum of dose values corresponding to a position in an overlap area (36) of the target exceeds a maximum dose value for the non-overlap areas (38) of the target where adjacent sub-areas (34) do not overlap, and dividing the pattern data (42) into a plurality of sub-sections (44), each of the sub-sections comprising pattern data describing a part of the pattern to be written in a corresponding sub-area (34) of the target (30), wherein the pattern data (42) comprises overlap pattern data (46) describing a part of the pattern to be written in a corresponding overlap area (36) of the target where adjacent sub-areas (34) overlap, and processing the overlap pattern data (46) to reduce a size of one or more features described by the overlap pattern data.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method of delivering a fluid medication to a patient in flex mode
A method of delivering a fluid medication to a patient under direction of a medical professional continually at a basal rate and at an interval rate in each of a plurality of time slots over a specified period of time. The total dose of the fluid medication to be delivered to the patient over the period of time based on the basal rate and the interval rate for each of the plurality of time slots is determined, compared the total dose against a maximum dose. The basal rate is adjusted, if necessary, so that the total dose does not exceed the maximum dose.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
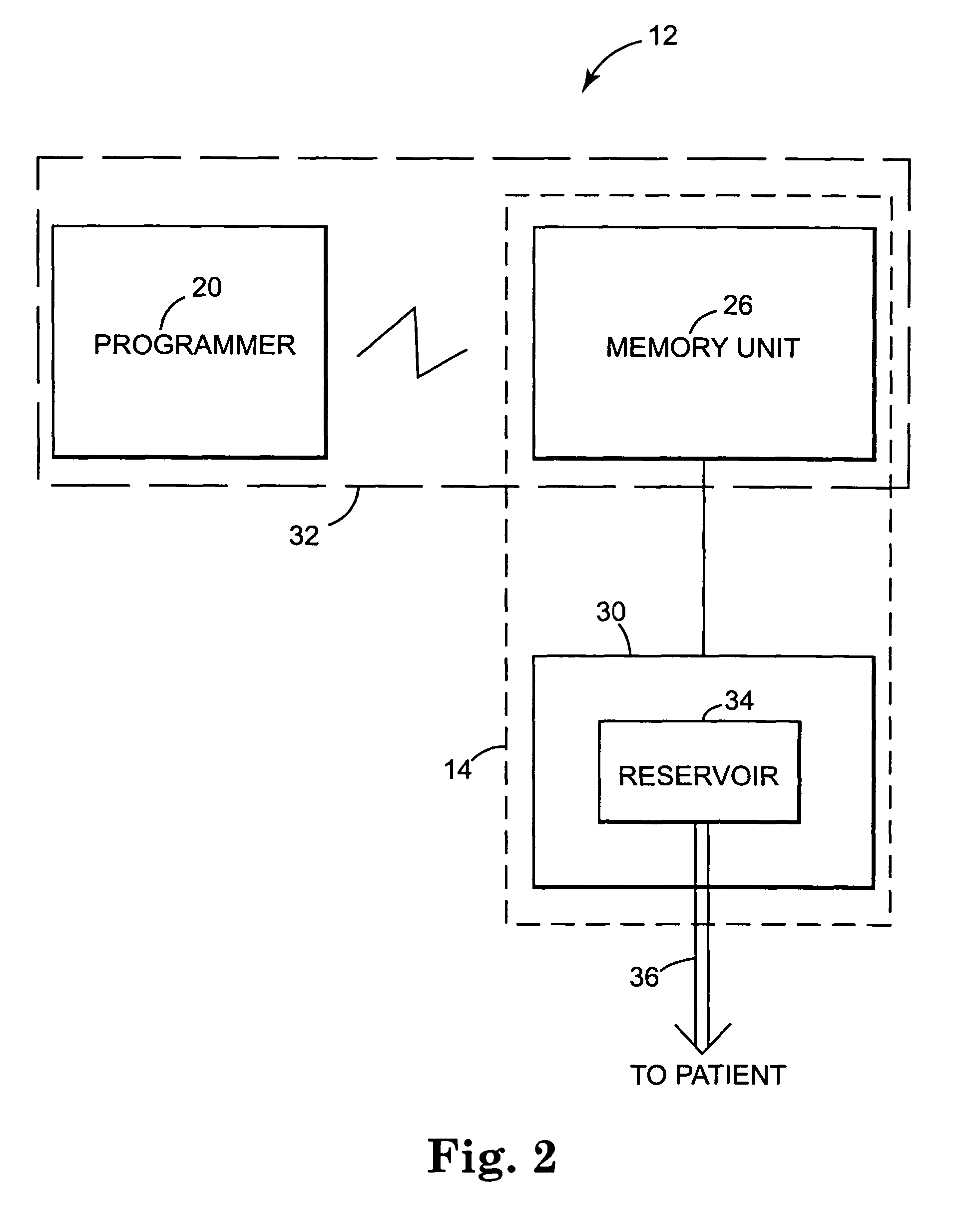
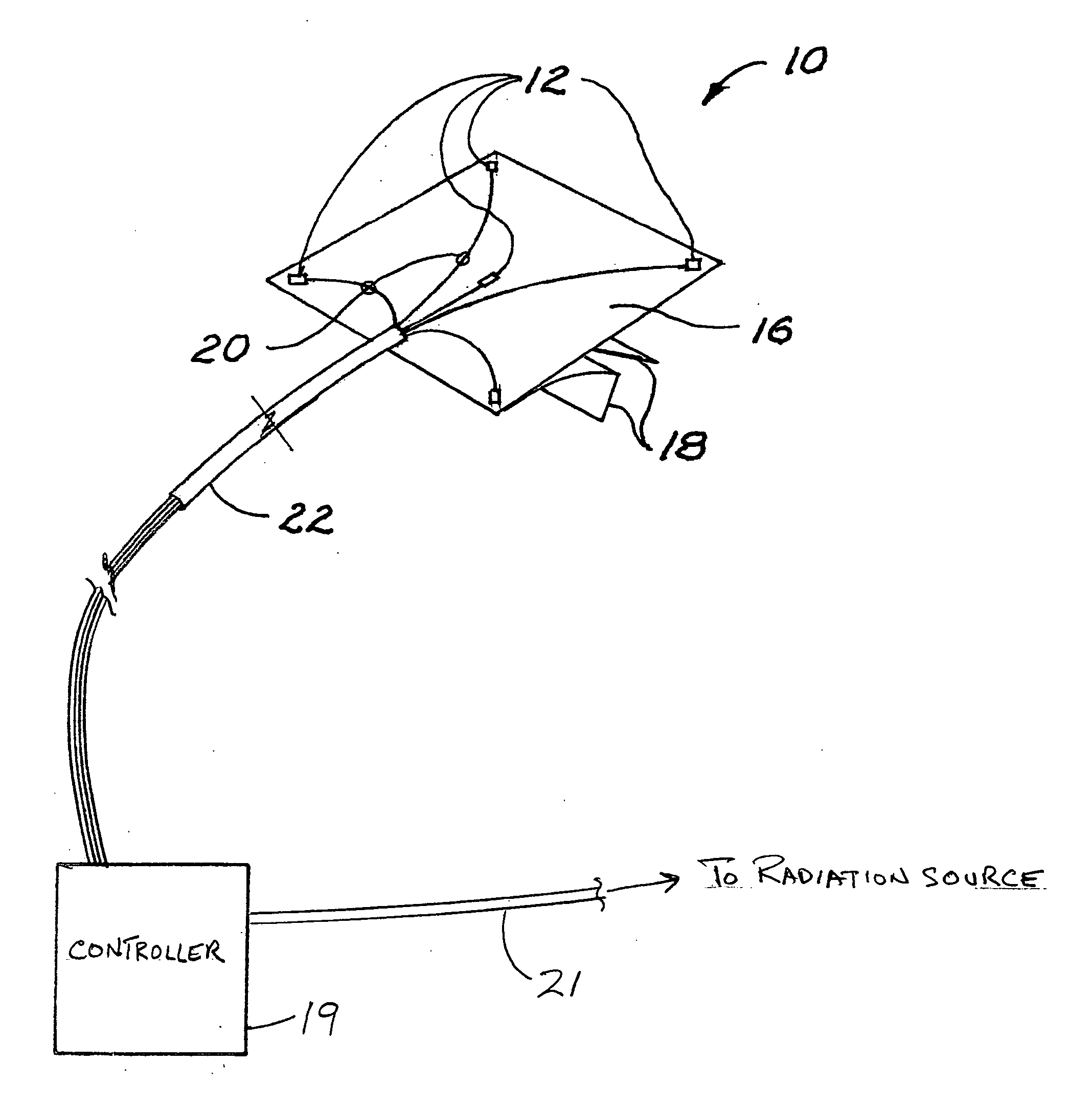
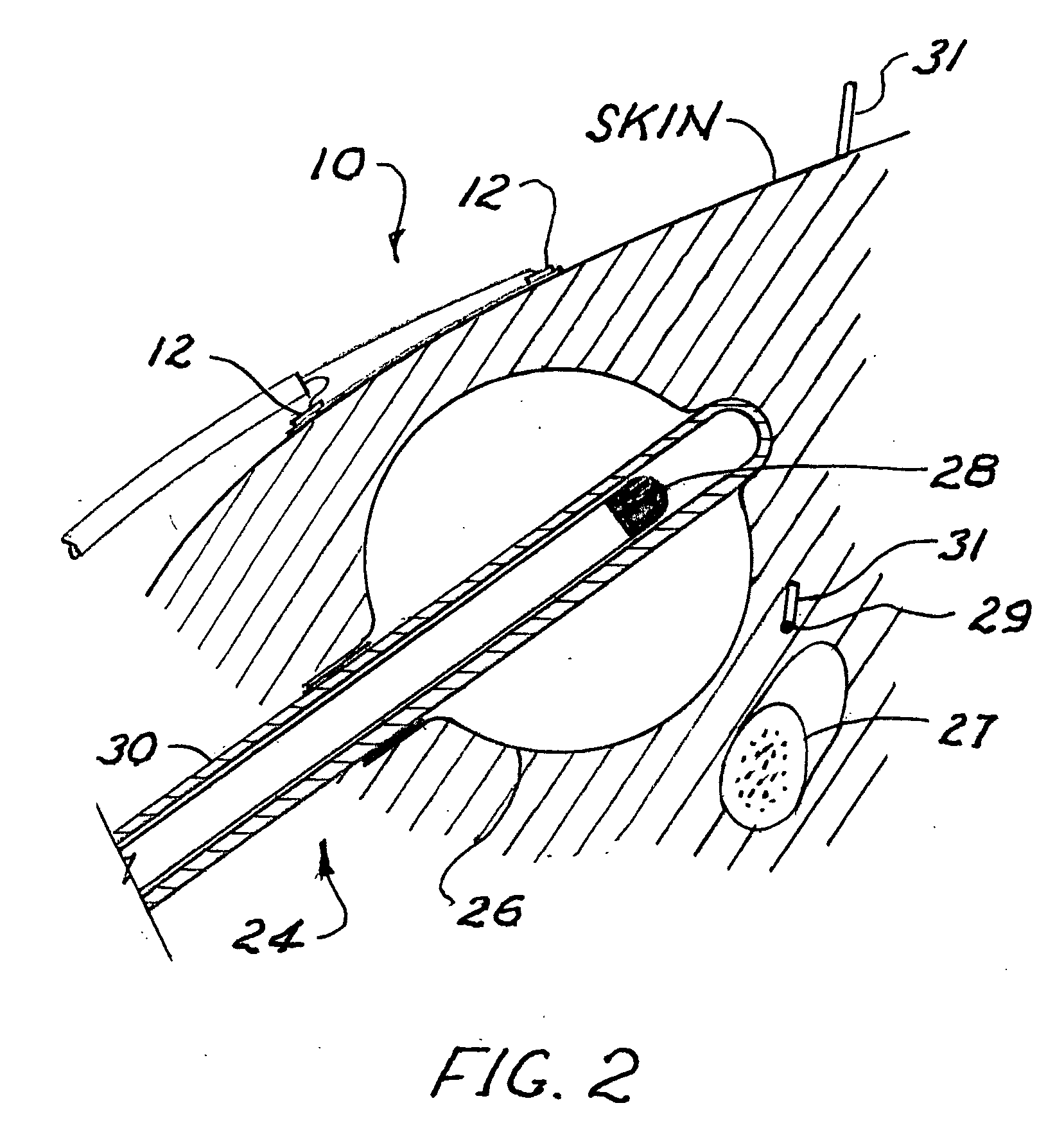
Radiation sensor arrays for use with brachytherapy
InactiveUS20100127181A1Precise positioningDosage controlDosimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansSensor arrayRadiation sensor
A radiation sensor array is carried on a flexible sheet of film, for placement on the skin of a patient adjacent to a brachytherapy location beneath the skin. With the array approximately centered on a position where radiation source to skin distance is estimated to be minimum, the array of sensors is used to monitor radiation dose received at the skin. With a controller connected to the array and preferably also to the radiation source in the applicator, the radiation dose received at all skin points of interest can be monitored, a point of maximum dose and a projected approach to limit dose can be calculated, and in response the system can warn the operator or control a brachytherapy procedure so as to discontinue radiation or control the radiation level or source position in real time. The system can also include percutaneous sensors.
Owner:XOFT INC
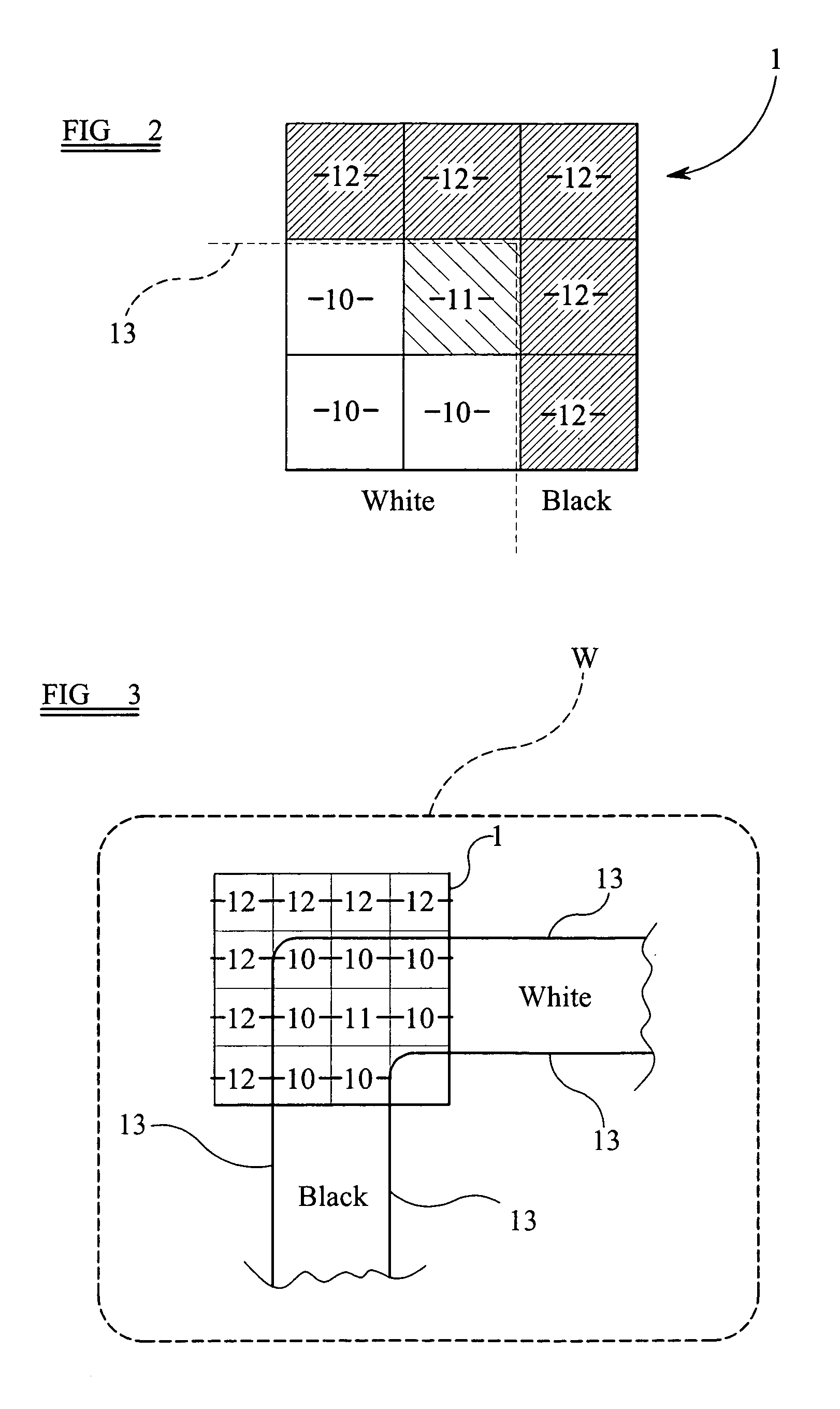
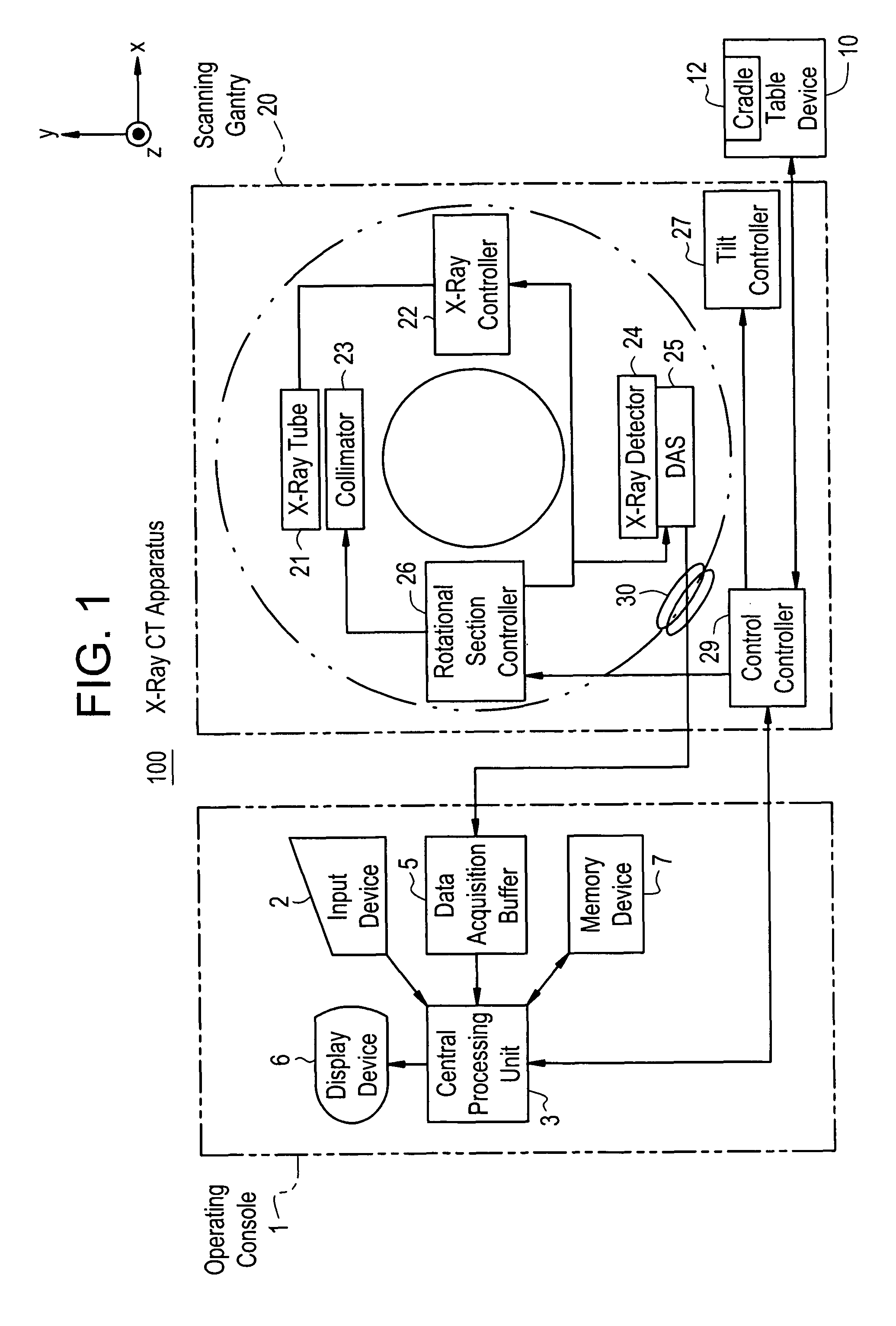
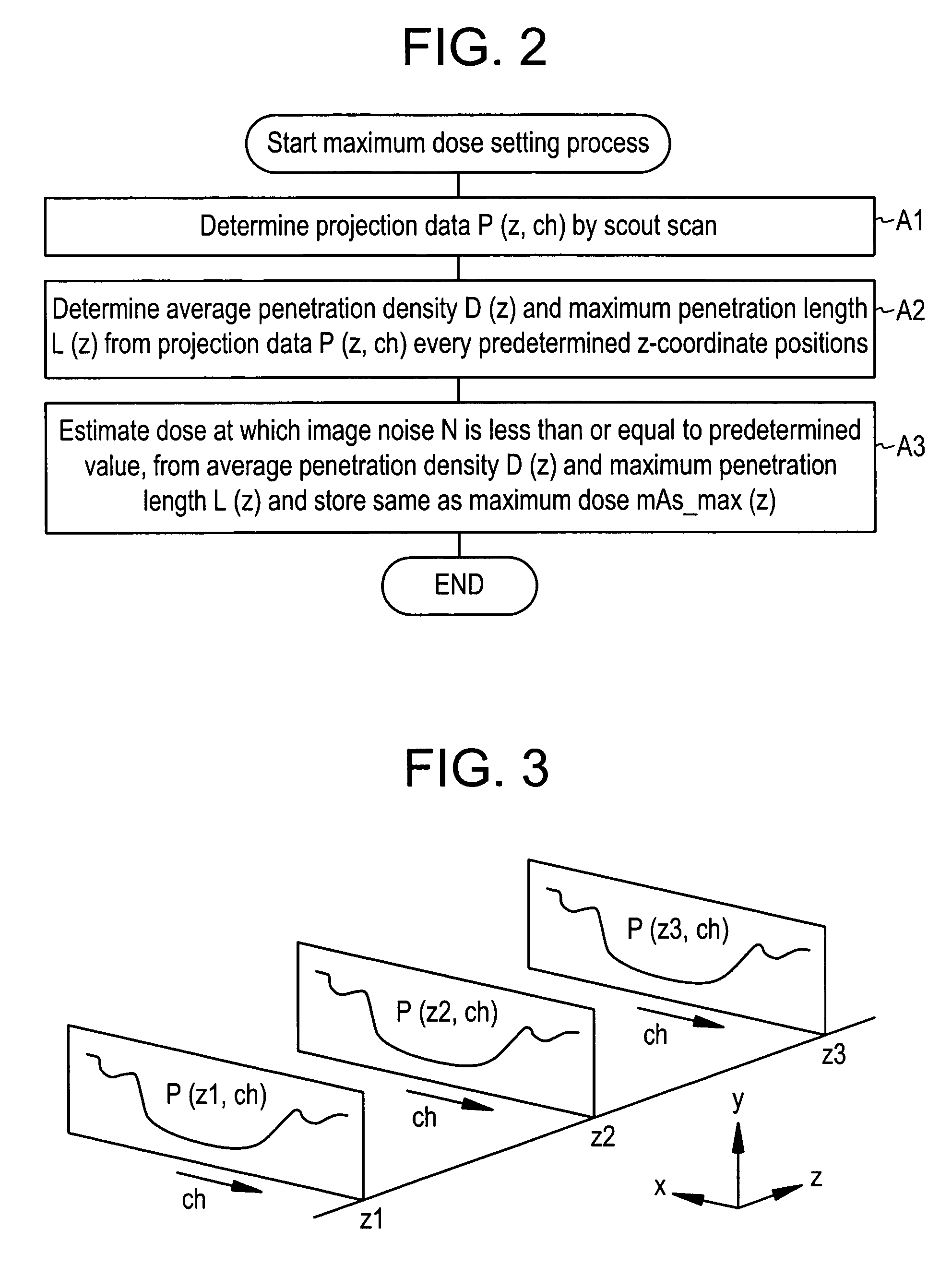
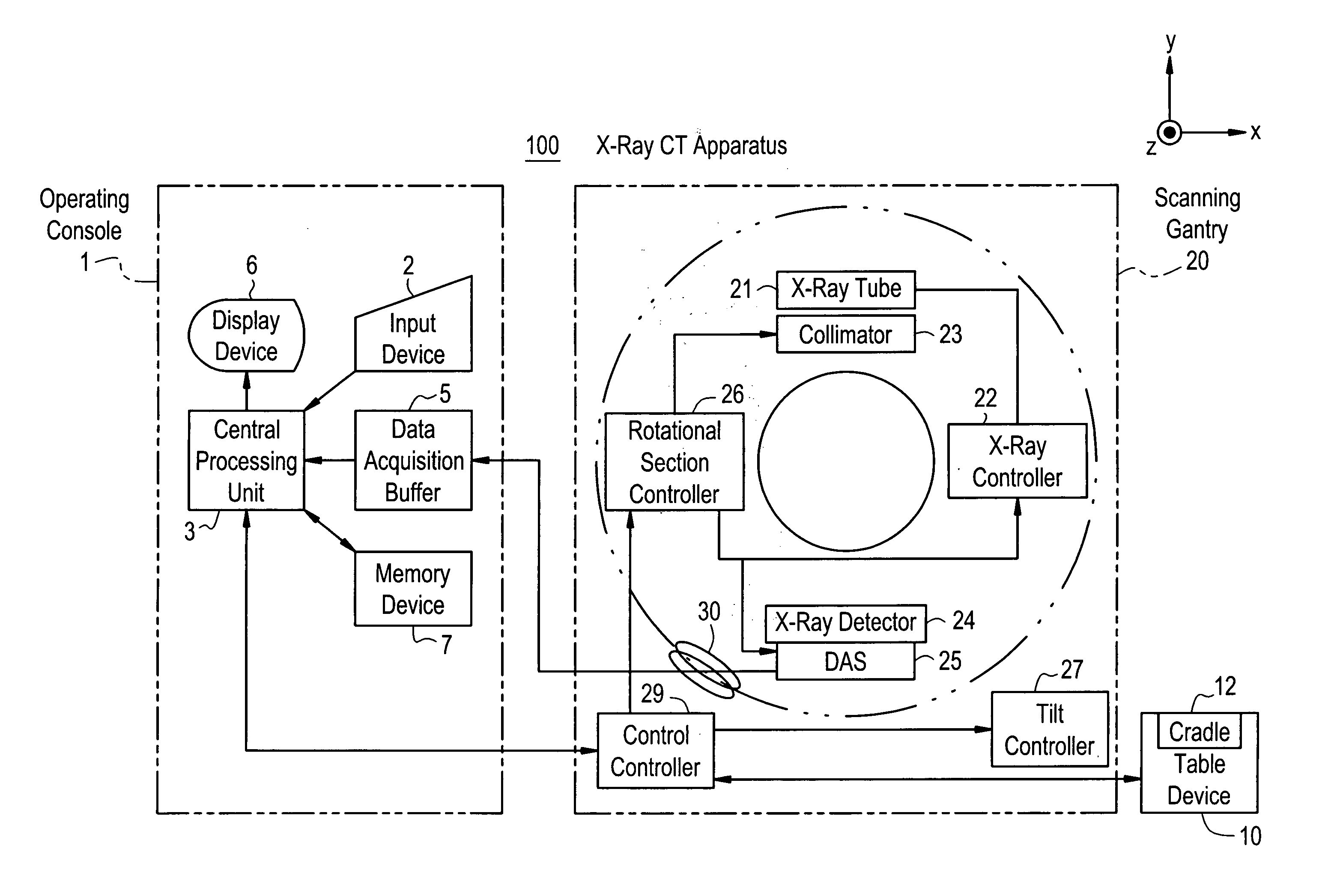
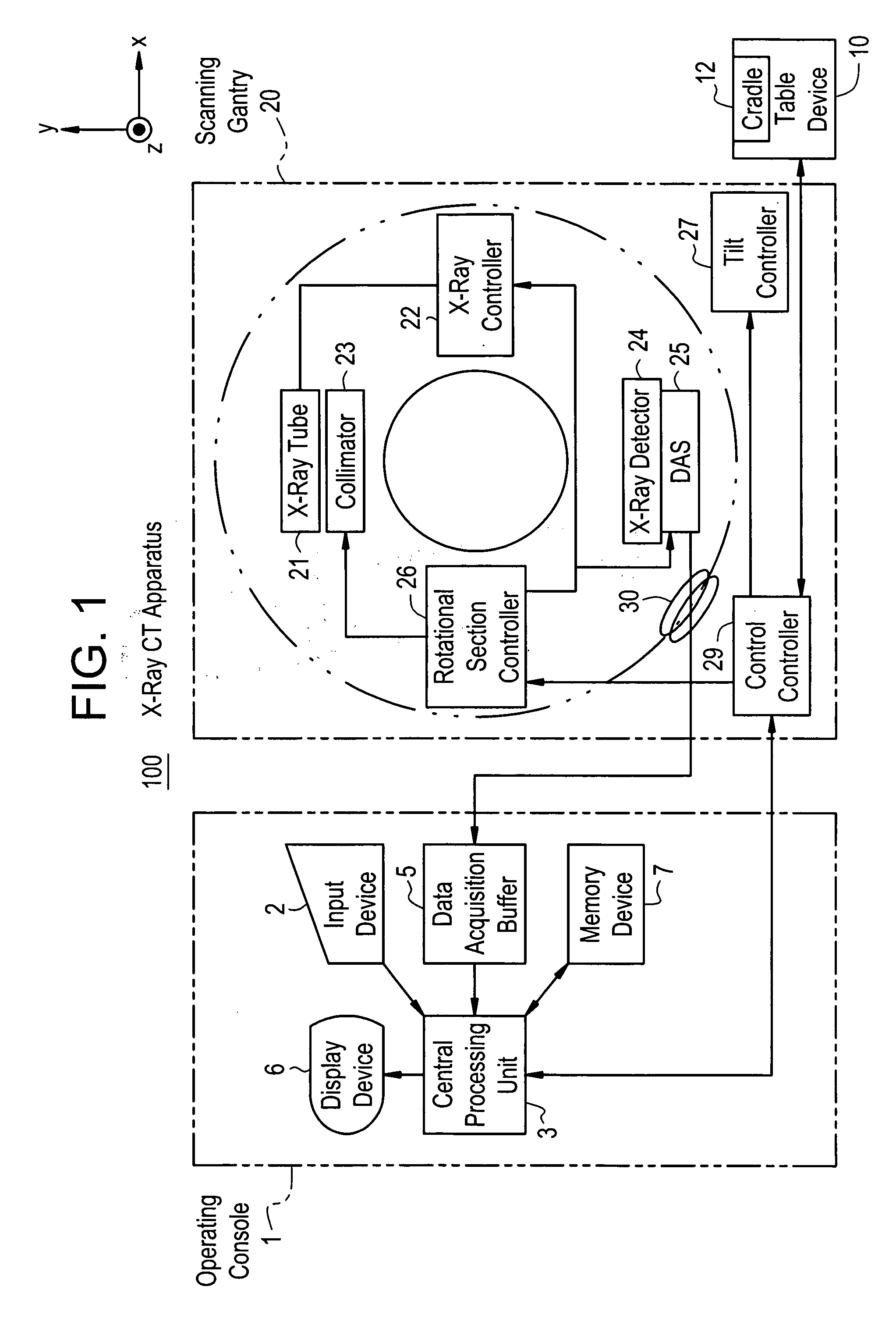
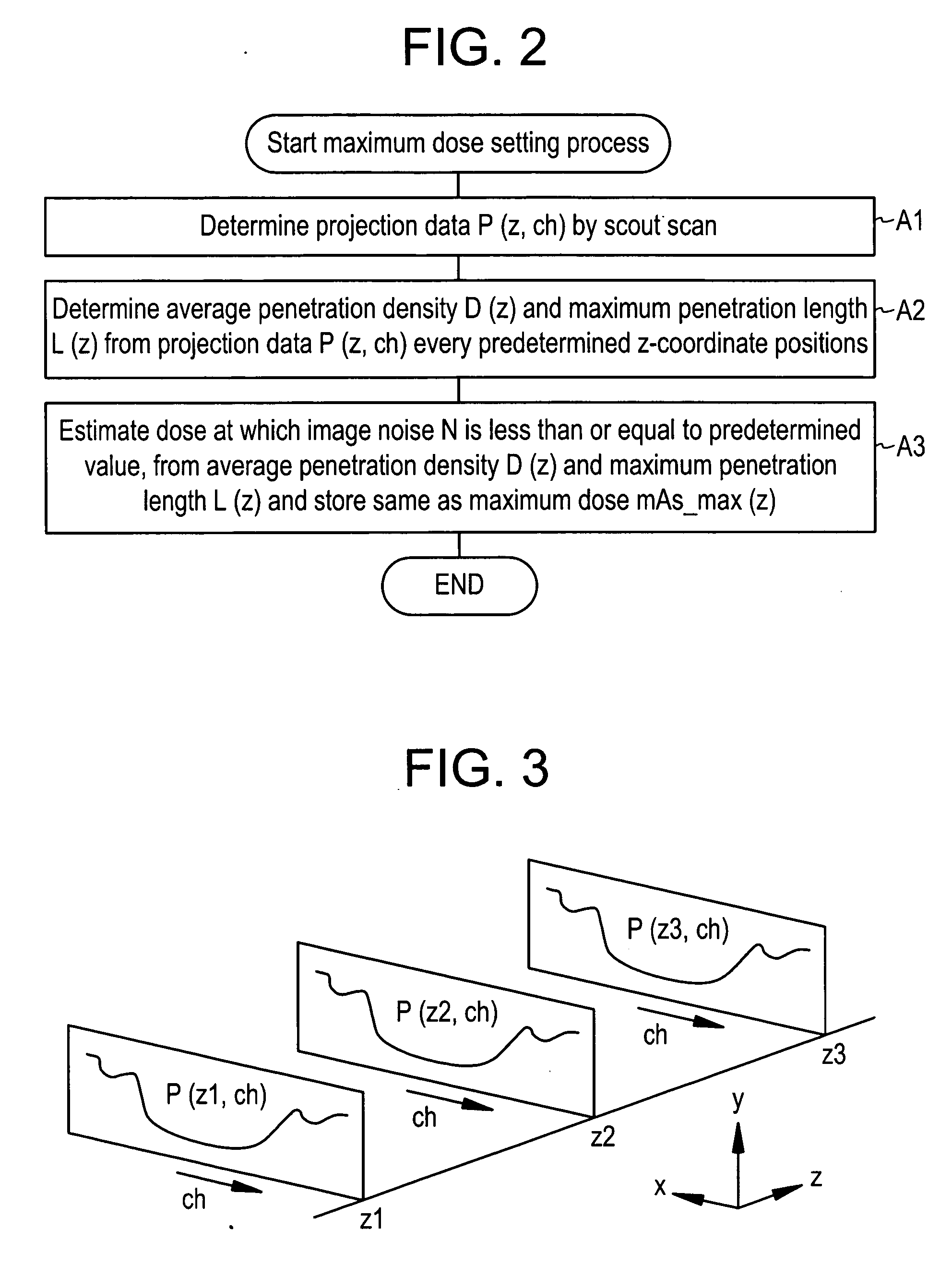
Dose evaluating method and X-ray CT apparatus
InactiveUS7756243B2Preventing doseDose can be prevented from becoming excessiveMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayMaximum dose
With the objective of evaluating whether a dose is excessive for a subject, such a dose that image noise reaches less than or equal to a predetermined value is estimated upon an axial scan on the basis of projection data acquired by a scout scan. The dose is set as a maximum dose. An area other than air, of an image obtained by the axial scan is partitioned into a plurality of small areas i. Image noises N(i) at the respective small areas i are calculated. A warning image G1 in which all of pixel values of pixels in small areas in which the image noises N(i) are less than or equal to a predetermined value, are substituted with pixel values expressed in black level, is created and displayed.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Radiotherapeutic apparatus
ActiveUS8503608B2Avoid less flexibilityReduce doseX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose rateMulti leaf collimator
Owner:ELEKTA AB
New application of scutellarin
InactiveCN104940187AReduce proteinuriaReduce direct damageOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticHypercoagulable statesHypoproteinemia
The invention relates to the technical field of medicine, in particular to a new application of scutellarin, and provides the application of the scutellarin in preparing medicine for reducing pathological changes of kidney tissue and the application of the scutellarin in preparing medicine for treating nephritis. The new application of the scutellarin is proved by experiments to show that the intragastric administration is continuously performed on nephritis model rats with the scutellarin in the dose of 20 mg / kg and 40 mg / kg for eight weeks, the proteinuria of the model animals can be obviously reduced, hypoproteinemia, hyperlipidemia and the hypercoagulable state of blood can be corrected, the serum lipid peroxidation product content of the model rats can be lowered, the expression of TNF-alpha in the kidney tissue can be inhibited, and a protection effect on the kidney tissue and a good improvement effect on the kidney function are achieved; in addition, the maximum dose of intragastric administration on the rats is equal to and more than 18 g / kg, and obvious acute toxicity reaction and death do not occur on the animals.
Owner:KPC PHARM INC
Dose evaluating method and X-ray CT apparatus
InactiveUS20060115039A1Prevent dosePreventing doseMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayMaximum dose
With the objective of evaluating whether a dose is excessive for a subject, such a dose that image noise reaches less than or equal to a predetermined value is estimated upon an axial scan on the basis of projection data acquired by a scout scan. The dose is set as a maximum dose. An area other than air, of an image obtained by the axial scan is partitioned into a plurality of small areas i. Image noises N(i) at the respective small areas i are calculated. A warning image G1 in which all of pixel values of pixels in small areas in which the image noises N(i) are less than or equal to a predetermined value, are substituted with pixel values expressed in black level, is created and displayed.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Dosing mechanism for a drug deliver device
A maximum settable dose feature is disclosed that is set by a user or health care professional one time that prevents future injections from exceeding the desired maximum dose. The feature includes a locking band initially in an unlocked configuration, which transforms to a locked configuration when activated after setting a desired maximum dose. The feature can include a trigger mechanism to transform the locking band to the locked configuration.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
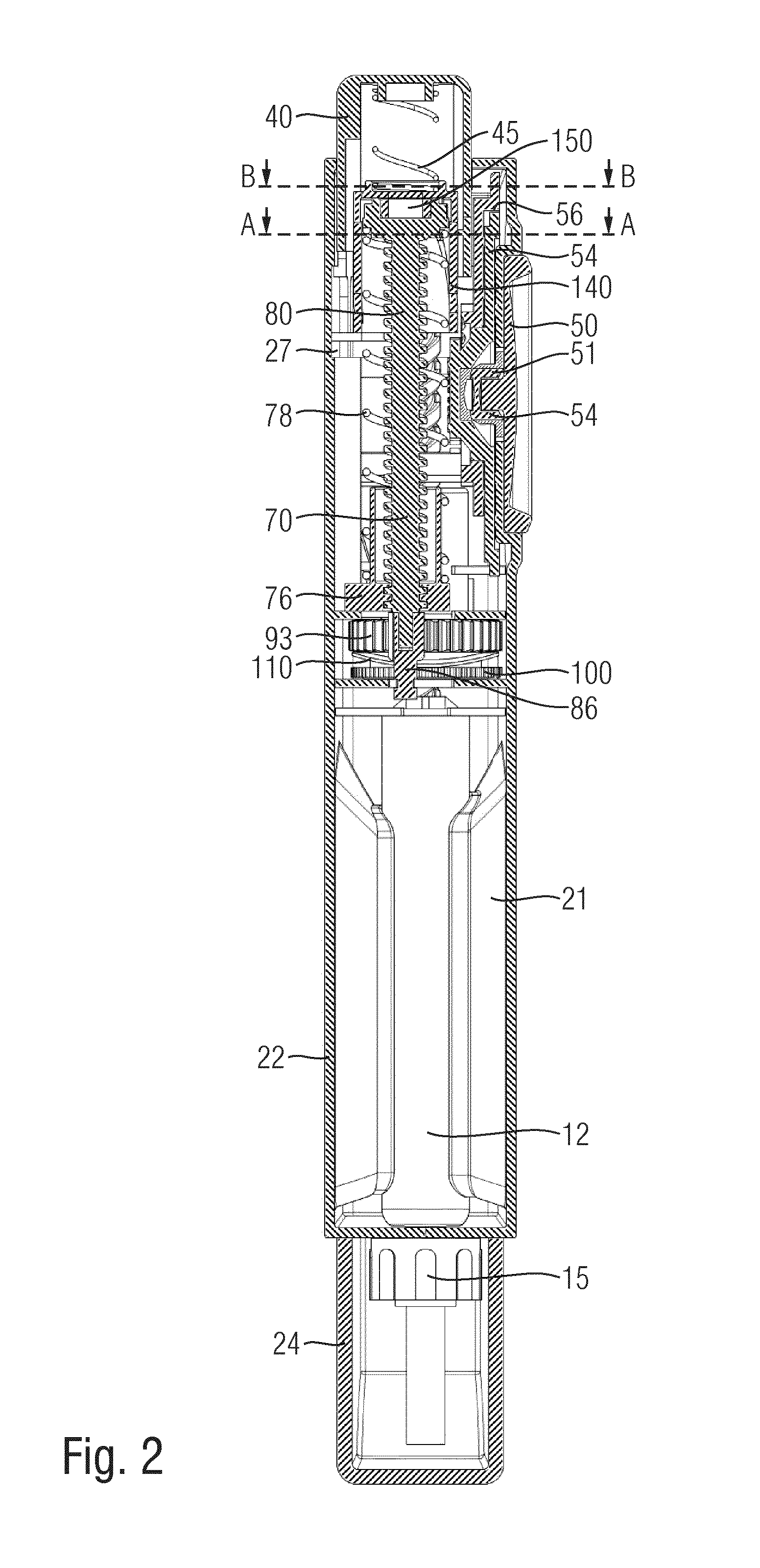
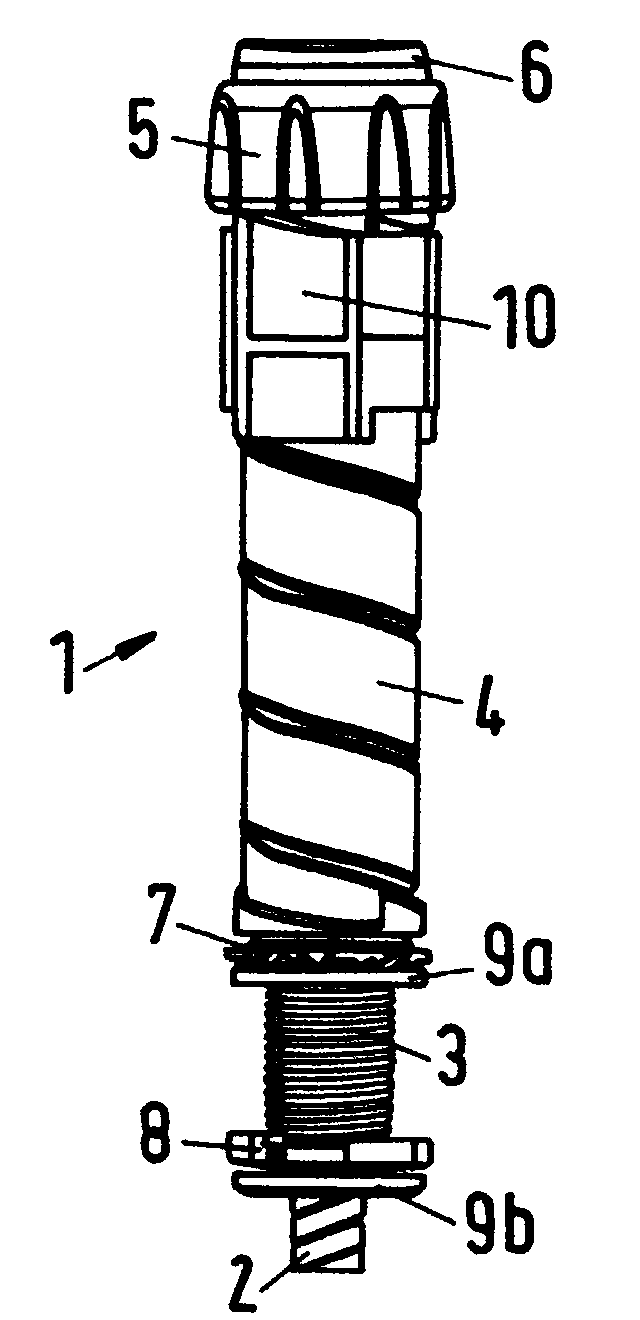
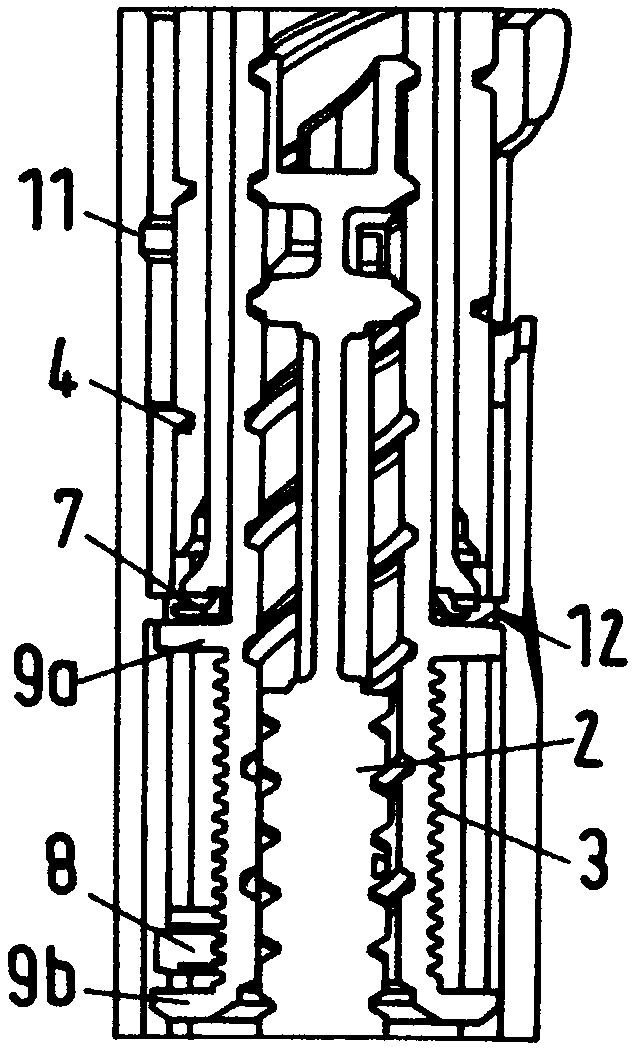
Hand-held drug injection device and dose setting limiter mechanism therefor
InactiveUS20160045673A1Easy and unequivocal to readAvoid disadvantagesAutomatic syringesMedical devicesDrug injectionDose limit
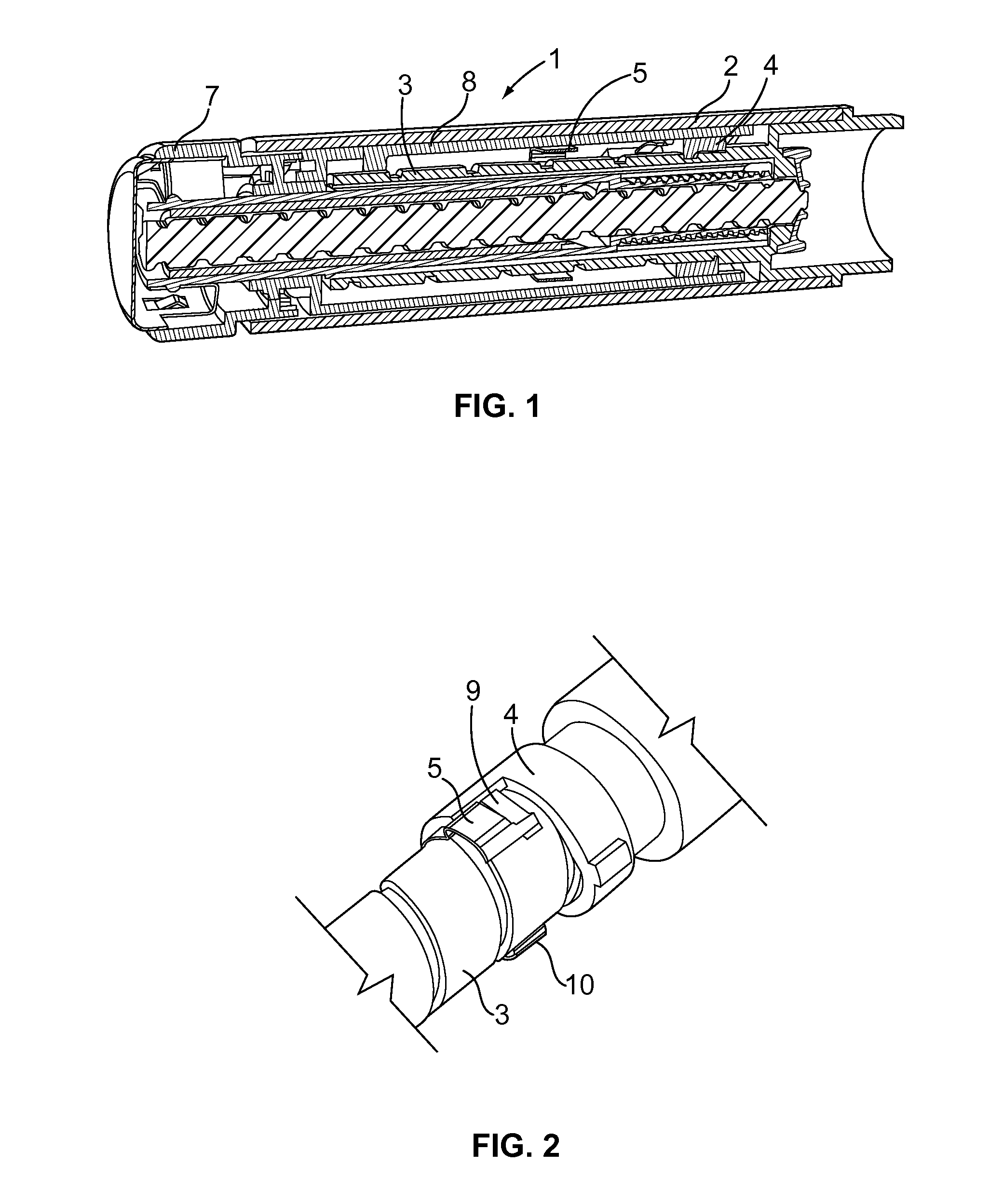
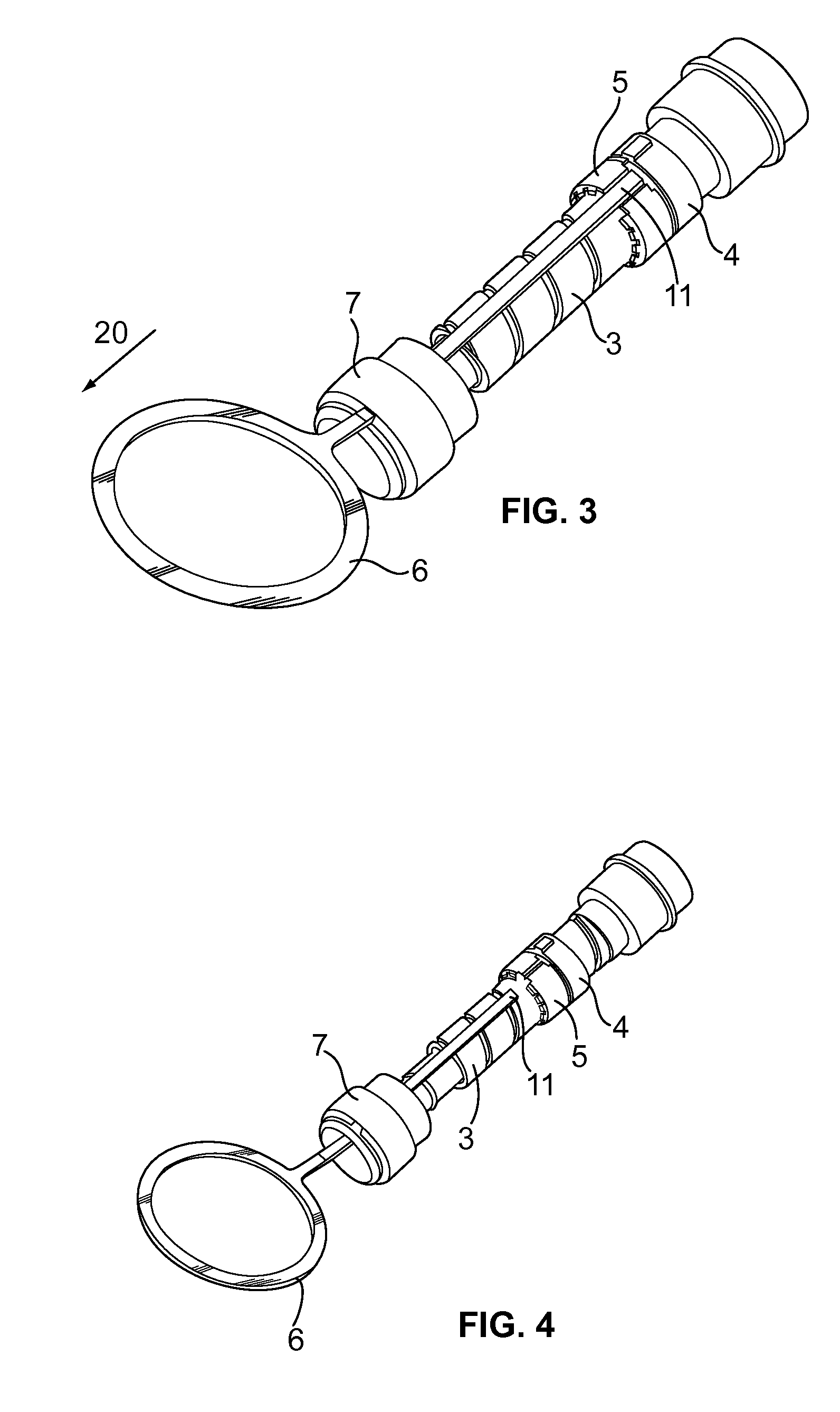
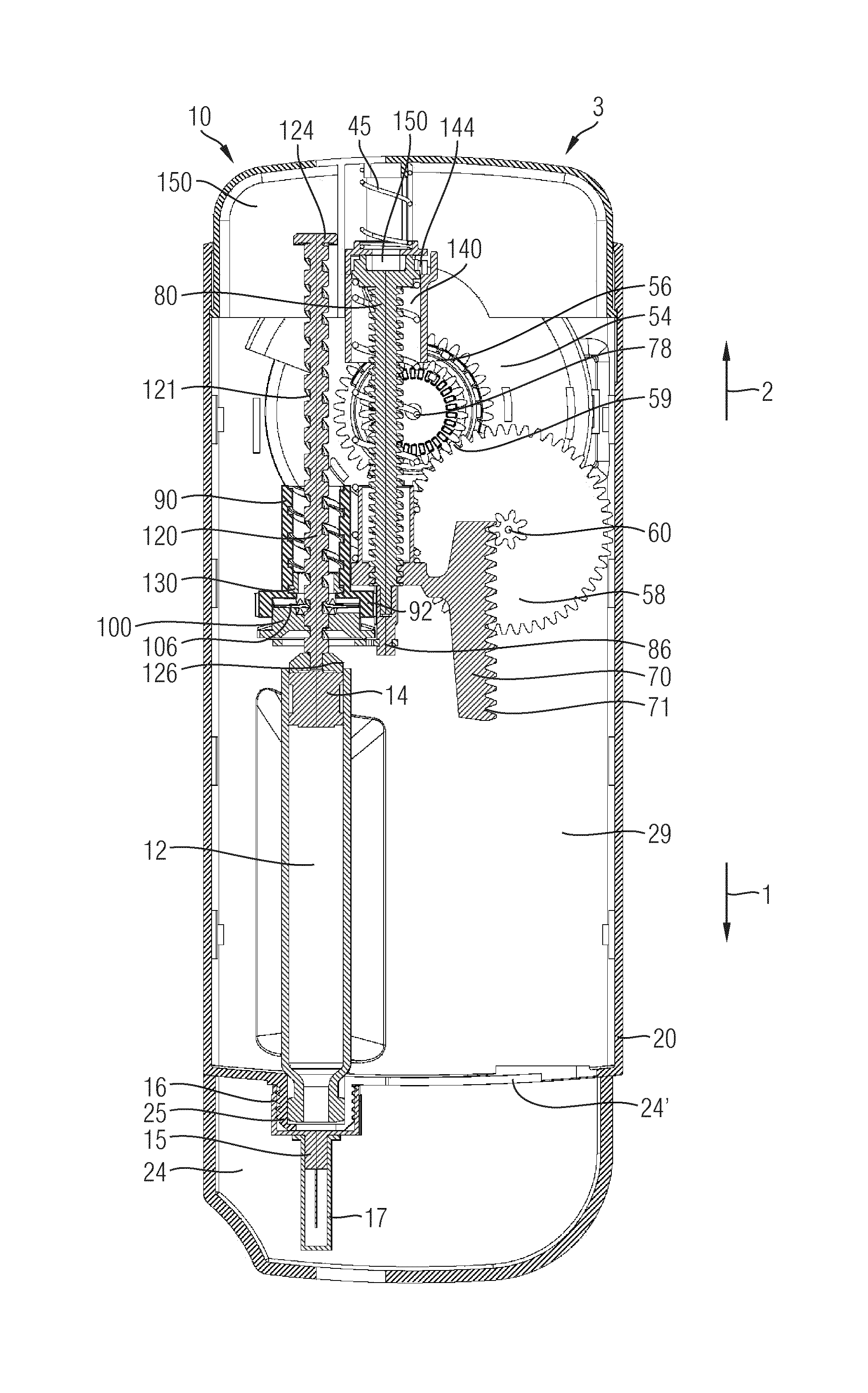
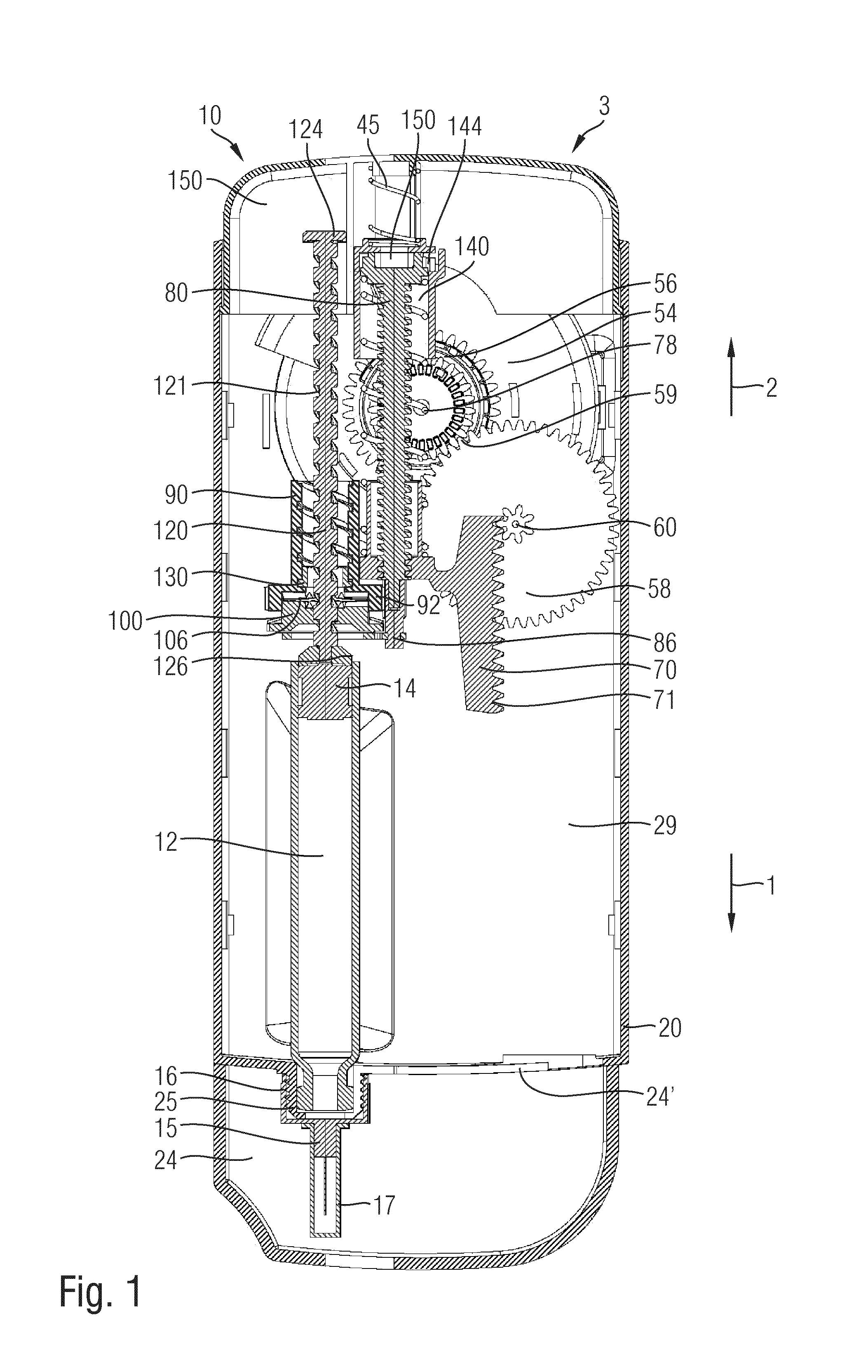
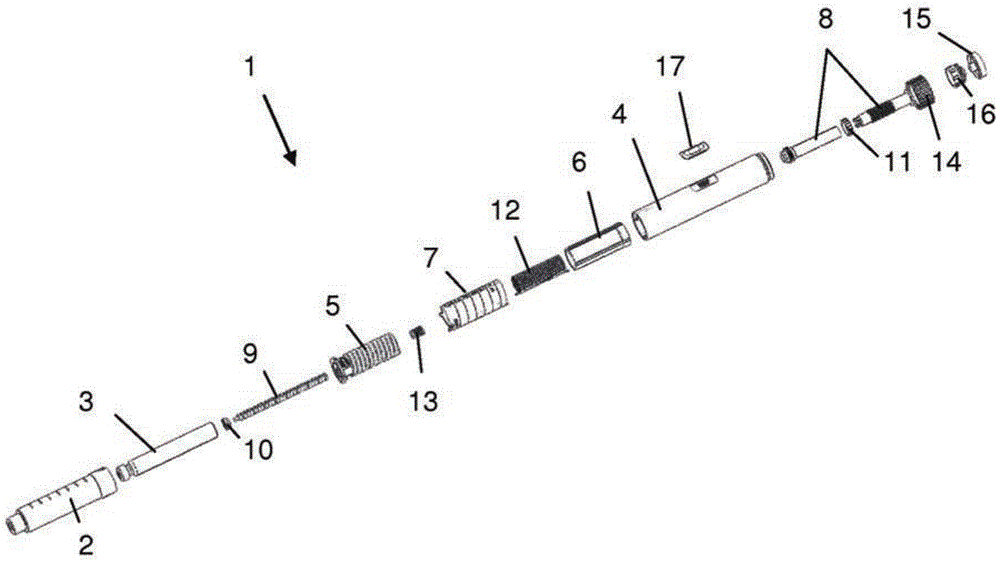
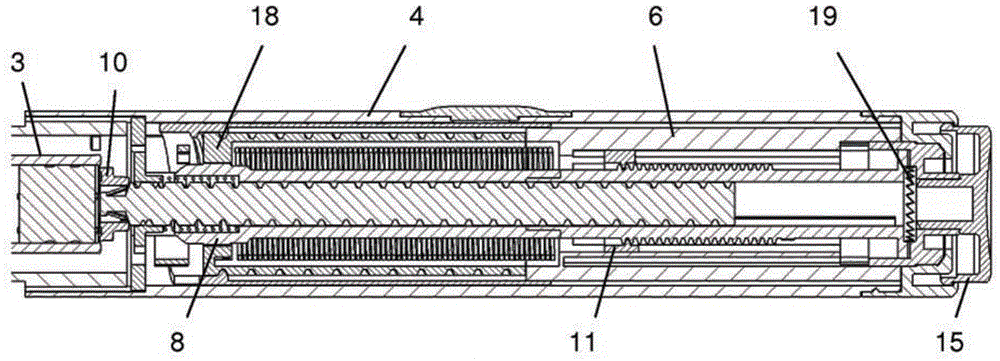
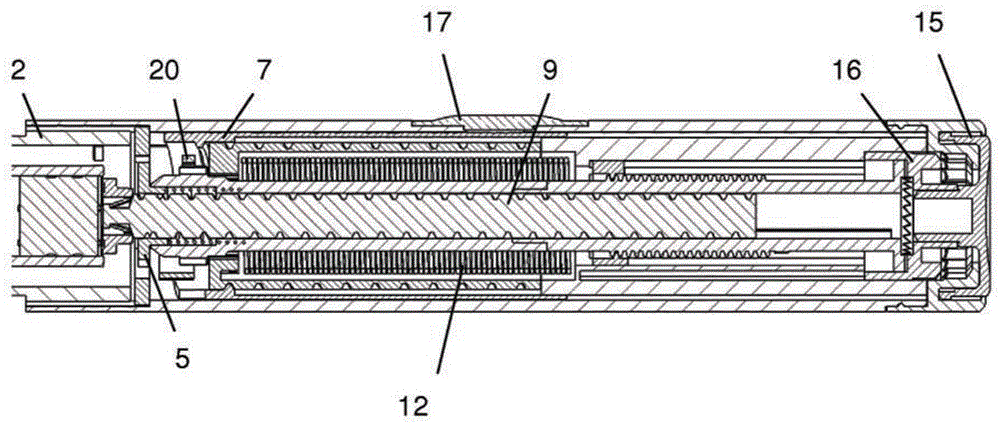
The present invention relates to a drive mechanism of a drug delivery device for dispensing of a dose of a medicament, the mechanism comprising: —a housing (20), —a piston rod (120) extending in an axial direction (1, 2) to operably engage with a piston (14) of a cartridge (12), —a drive sleeve (90) rotatably supported in the housing (20), at least partially enclosing the piston rod (120), the drive sleeve (90) is operably releasable from the piston rod (120) for setting of a dose and the drive sleeve (90) is operably engageable with the piston rod (120) for dispensing of the dose, —a dose limiting member (130) threadedly engaged with the drive sleeve (90), rotatably locked to the housing (20) and being displaceable in axial direction (1, 2) in response to a rotation of the drive sleeve (90) relative to the piston rod (120), —at least one stop member (124) provided on the piston rod (120) to engage with the dose limiting member (130) for impeding a further displacement of the drive sleeve (90) relative to the piston rod (120), when a maximum dose configuration has been reached.
Owner:SANOFI SA
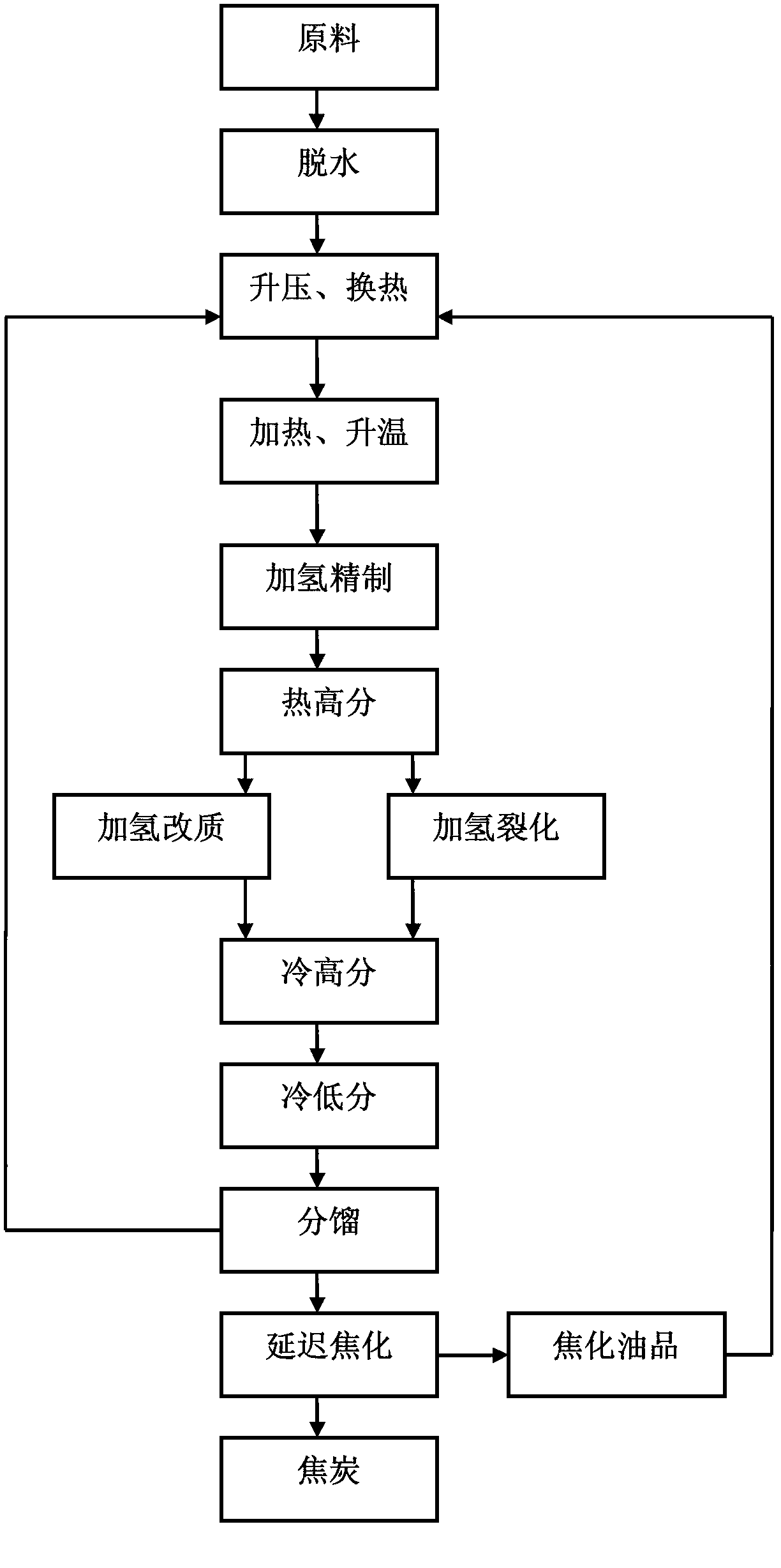
Heavy oil full-fraction hydrotreatment method and system thereof
ActiveCN103275758AHigh yieldReliable hydrogenation production processTreatment with hydrotreatment processesHydrogenFixed bed
The invention discloses a heavy oil full-fraction hydrotreatment method and a system thereof. the method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: a heavier component raw oil is mixed with hydrogen after undergoing dehydration and booster heat exchange treatments; the mixed heavier component raw oil and hydrogen are heated and then enter a boiling bed hydrofinishing reactor for a hydrofinishing reaction; products obtained after the hydrofinishing reaction enter a thermal high-pressure separator for separation of light and heavier components; light components enter a fixed bed hydro-upgrading reactor for a hydro-upgrading reaction, and heavier components enter a boiling bed hydrocracking reactor for a hydrocracking reaction; an effluent obtained after the hydro-upgrading reaction and an effluent obtained after the hydrocracking reaction are mixed and cooled by heat exchange and undergo gas-oil-water separation; after temperature of separated oil rises by heat exchange, a qualified oil product is obtained by fractionation; and fractionized tail oil undergoes boost heat exchange treatment to be used as raw oil for hydrogenation feeding. The system provided by the invention has advantages of large technological handling capacity and long running period. In addition, the maximum dose of the light components can be produced; and the yield of the oil product is high and reaches more than 90%.
Owner:HUADIAN HEAVY IND CO LTD
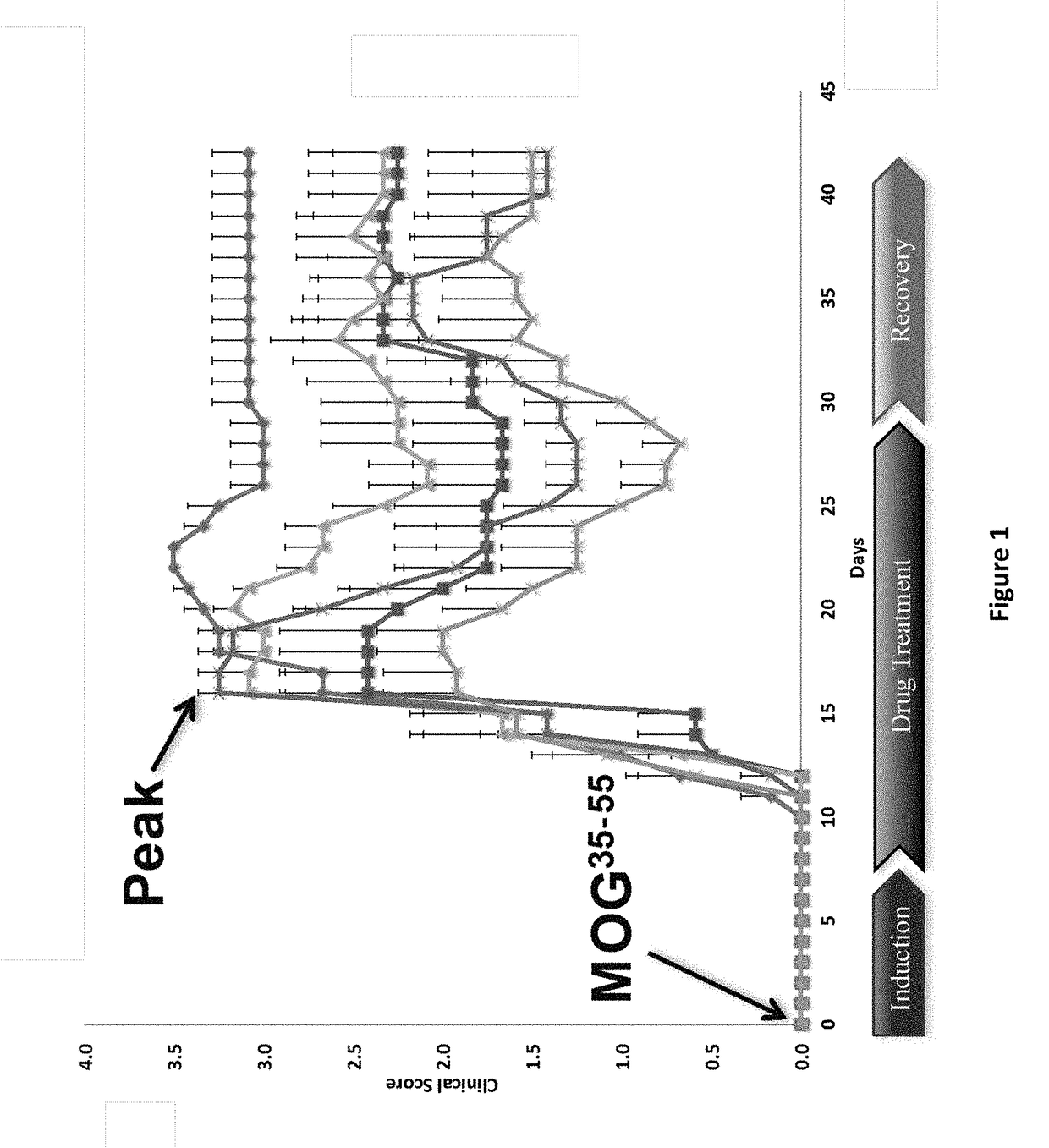
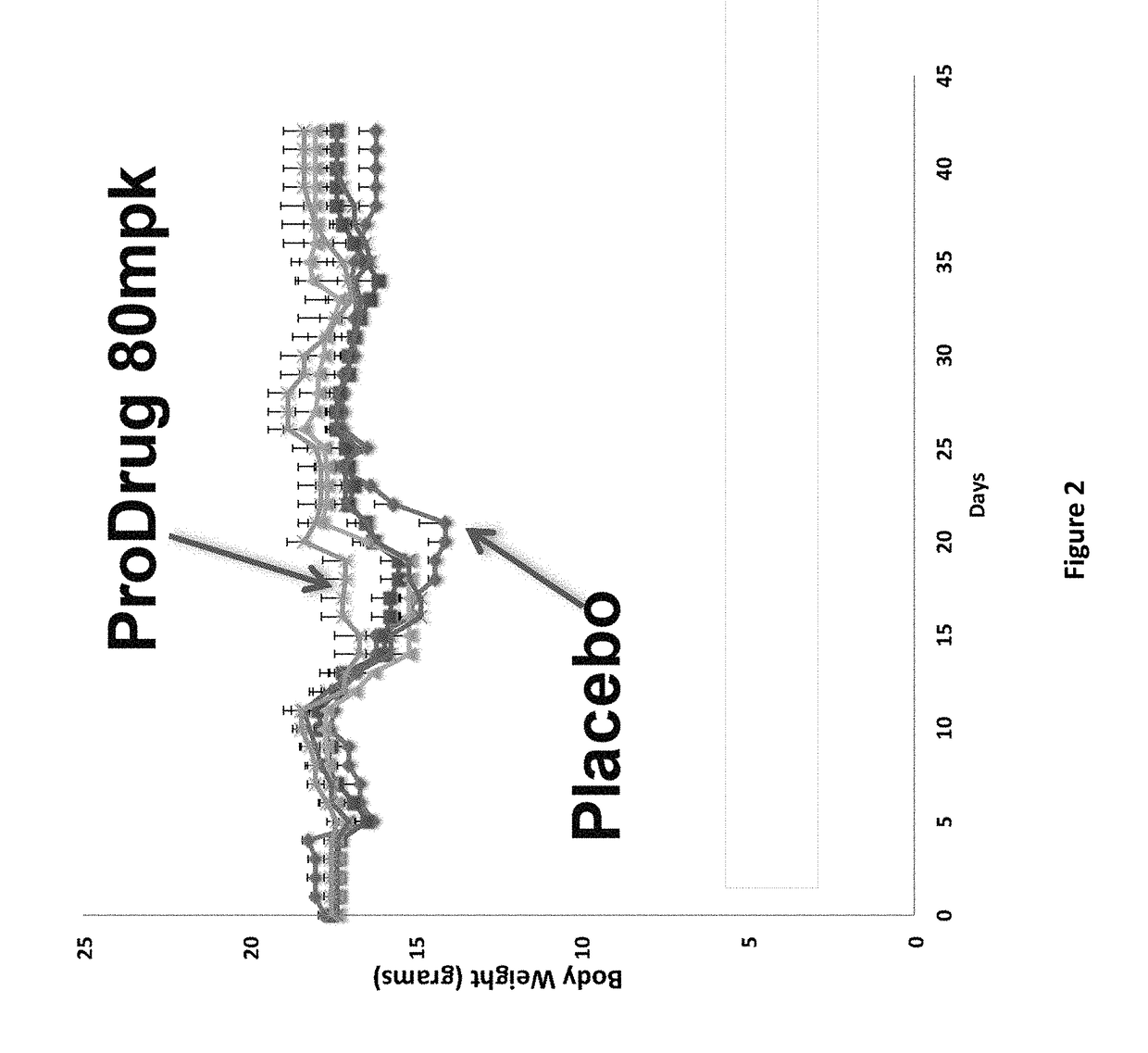
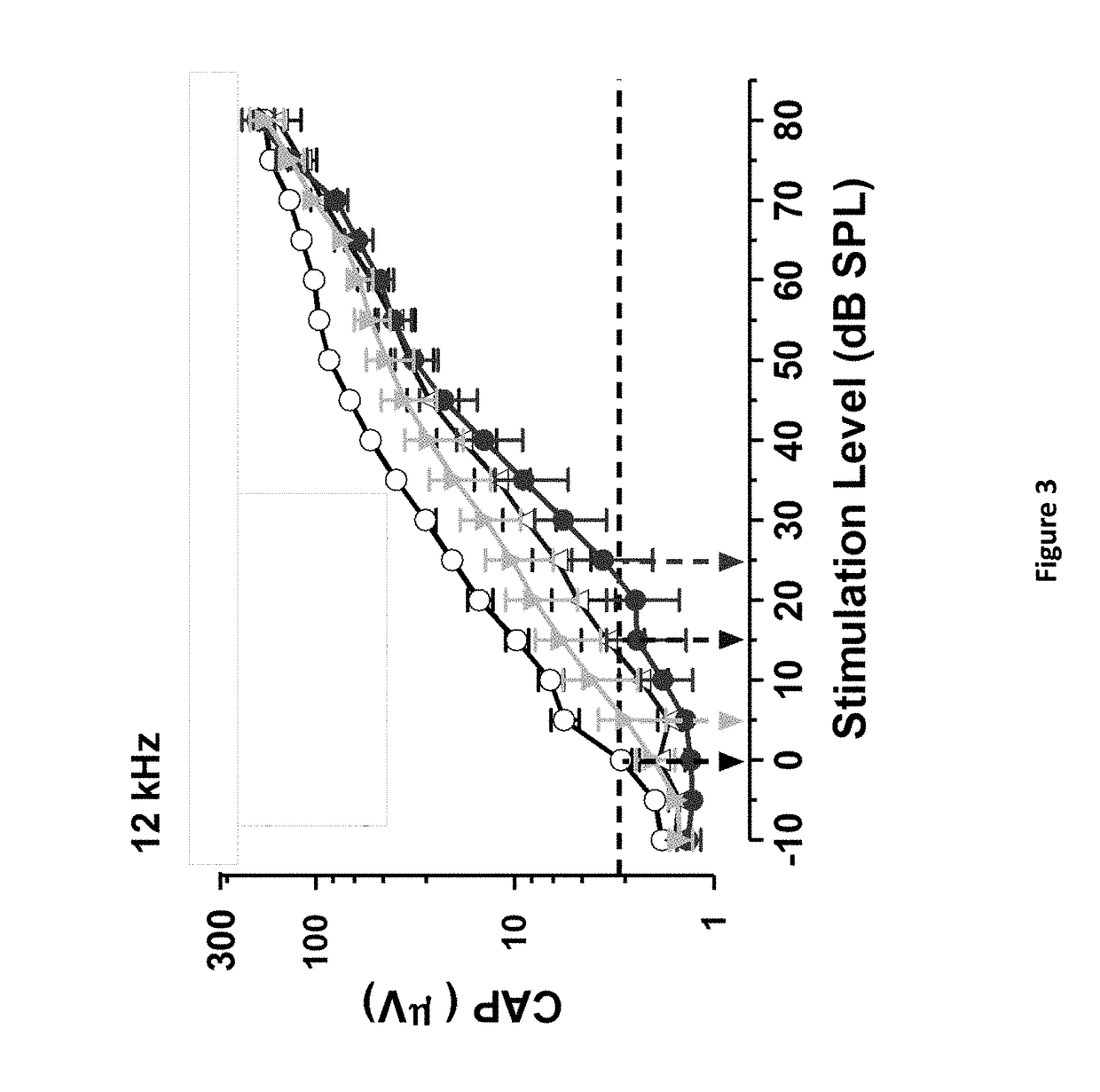
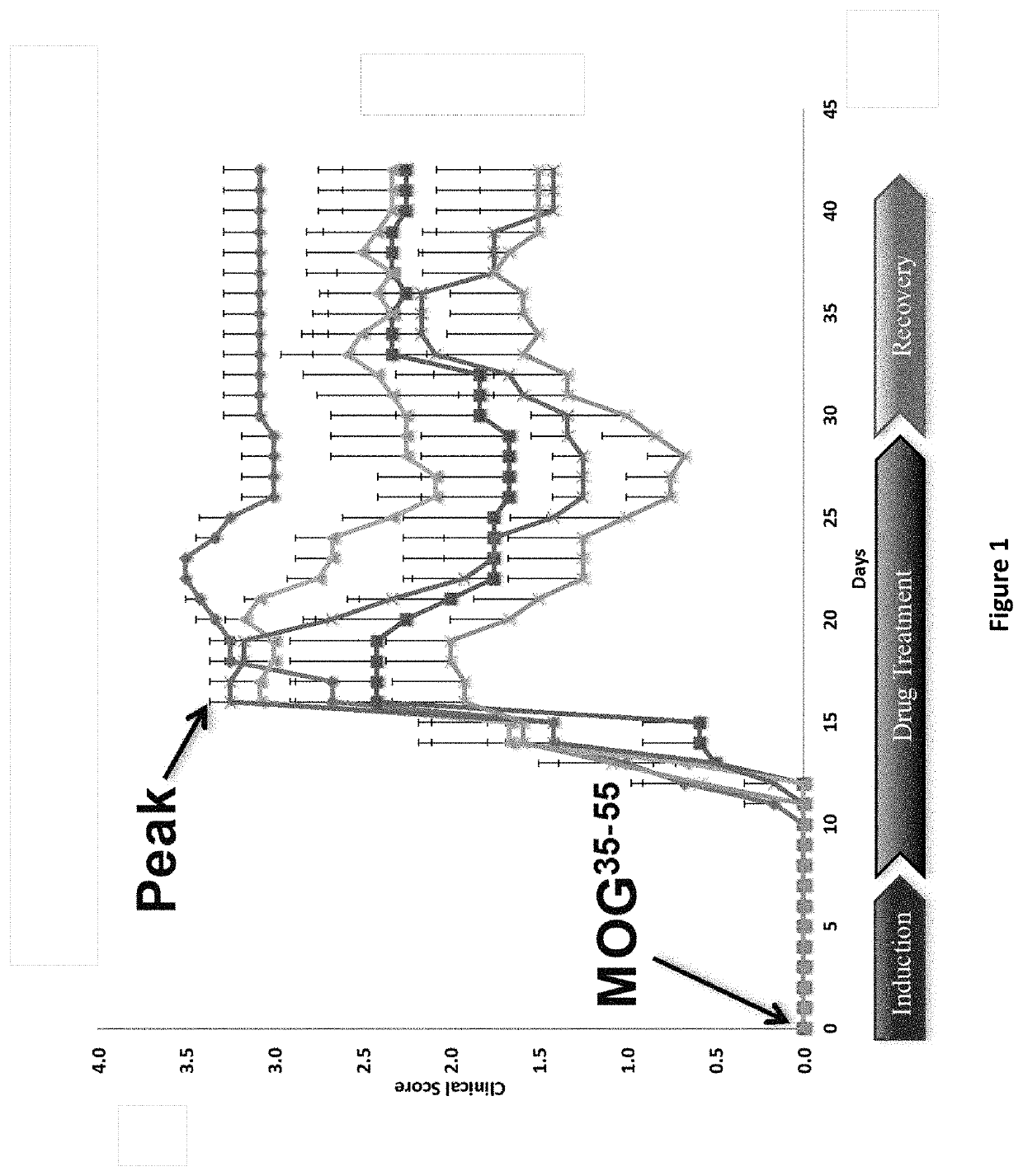
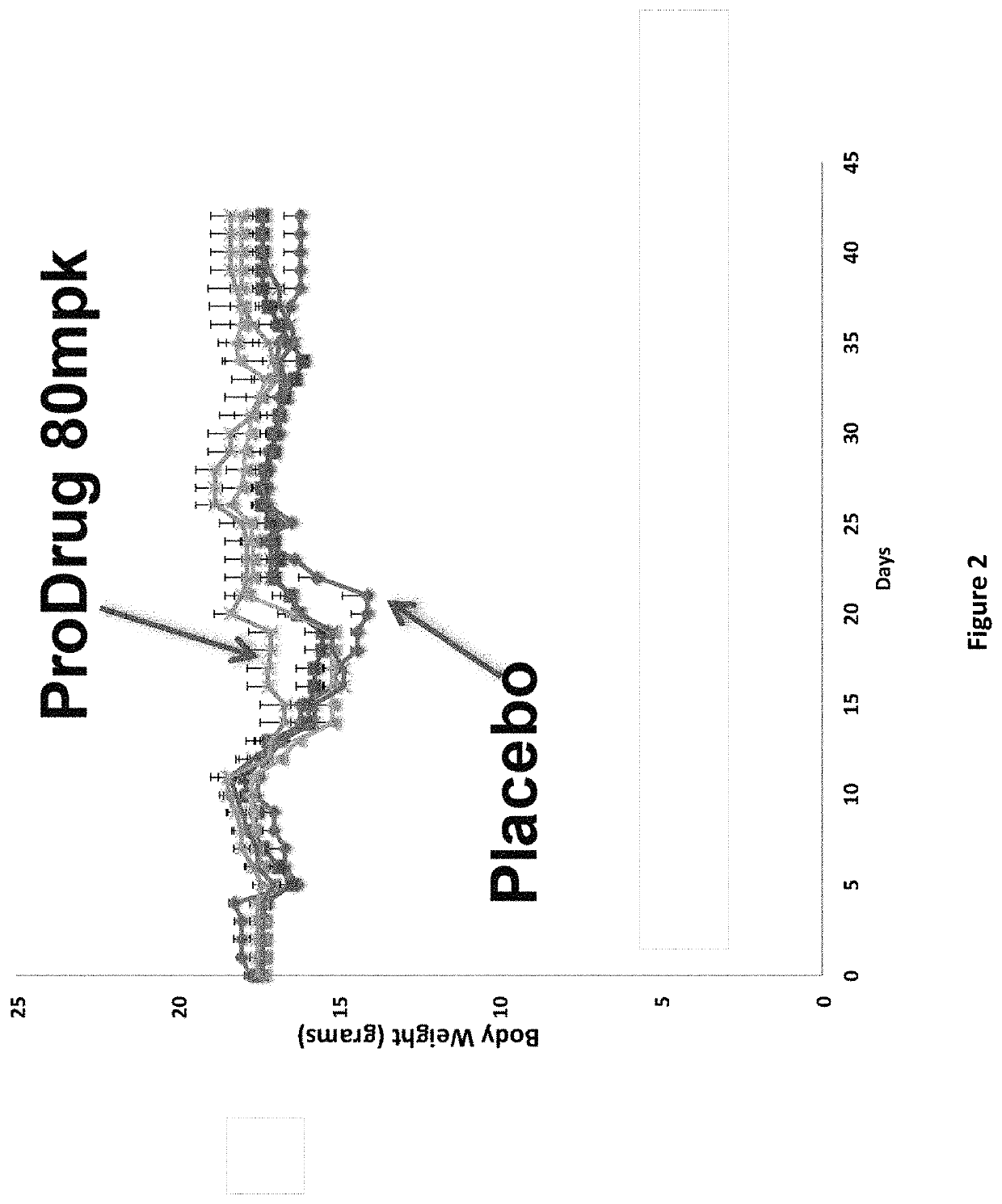
DNP and DNP Prodrug Treatment of Neuromuscular, Neurodegenerative, Autoimmune, Developmental, Traumatic Brain Injury, Concussion, Dry Eye Disease, Hearing Loss and/or Metabolic Diseases
ActiveUS20170252347A1Good blood pressureImprove blood sugar levelsSenses disorderNervous disorderHL - Hearing lossDepressant
A composition and method of treatment of neuromuscular, neuromuscular degenerative, neurodegenerative, autoimmune, developmental, traumatic, hearing loss related, and / or metabolic diseases, including spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) syndrome (SMA1, SMA2, SMA3, and SMA4, also called Type I, II, III and IV), traumatic brain injury (TBI), concussion, keratoconjunctivitis sicca (Dry Eye Disease), glaucoma, Sjogren's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, post-LASIK surgery, anti-depressants use, Wolfram Syndrome, and Wolcott-Rallison syndrome. The composition is selected from the group consisting of 2,3-DNP, 2,4-DNP, 2,5-DNP, 2,6-DNP, 3,4-DNP, or 3,5-DNP, bipartite 2,3-dinitrophenol, 2,4-dinitrophenol, 2,5-dinitrophenol, 2,6-dinitrophenol, 3,4-dinitrophenol, or 3,5-dinitrophenol (2,3-DNP, 2,4-DNP, 2,5-DNP, 2,6-DNP, 3,4-DNP, or 3,5-DNP) prodrugs; Gemini prodrugs, bioprecursor molecules, and combinations thereof. A dose of the composition for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases may be from about 0.01 mg / kg of body weight to about 50 mg / kg of body weight of the patient in need of treatment. A dose of the composition for treatment of metabolic diseases may be from about 1 mg / 70 kg of body weight to about 100 mg / 70 kg of body weight of the patient in need of treatment, and a maximum dose per day is about 200 mg / 70 kg of body weight of the patient in need of treatment.
Owner:MITOCHON PHARMA INC +1
Lithographic apparatus and method utilizing dose control
ActiveUS7123348B2Increase radiation doseReduce the amount of compensationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLight beamMaximum dose
A system and method are used to manufacture a device using at least one exposure step. Each exposure step projects a patterned beam of radiation onto a substrate. The patterned beam includes a plurality of pixels. Each pixel delivers a radiation dose no greater than a predetermined normal maximum dose to the target portion in the exposure step and / or at least one selected pixel delivers an increased radiation dose, greater than the normal maximum dose. The increased dose may be delivered to compensate for the effect of a defective element at a known position in the array on a pixel adjacent a selected pixel or compensate for underexposure of the target portion at the location of a selected pixel resulting from exposure of that location to a pixel affected by a known defective element in another exposure step.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Injection device with dose setting mechanism having maximum dose stop
A dose setting mechanism for a drug delivery device is provided comprising a dose setting member and a further element. Maximum dose stop features are provided on a housing and on the further element.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
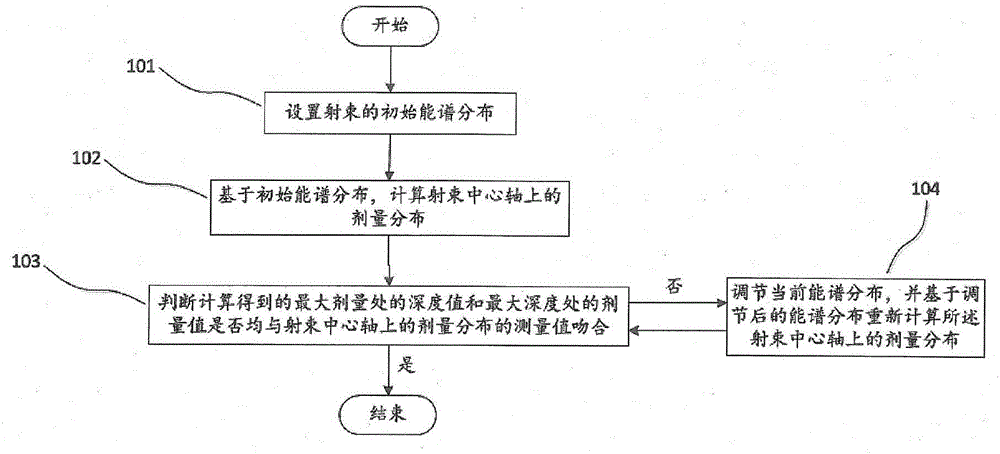
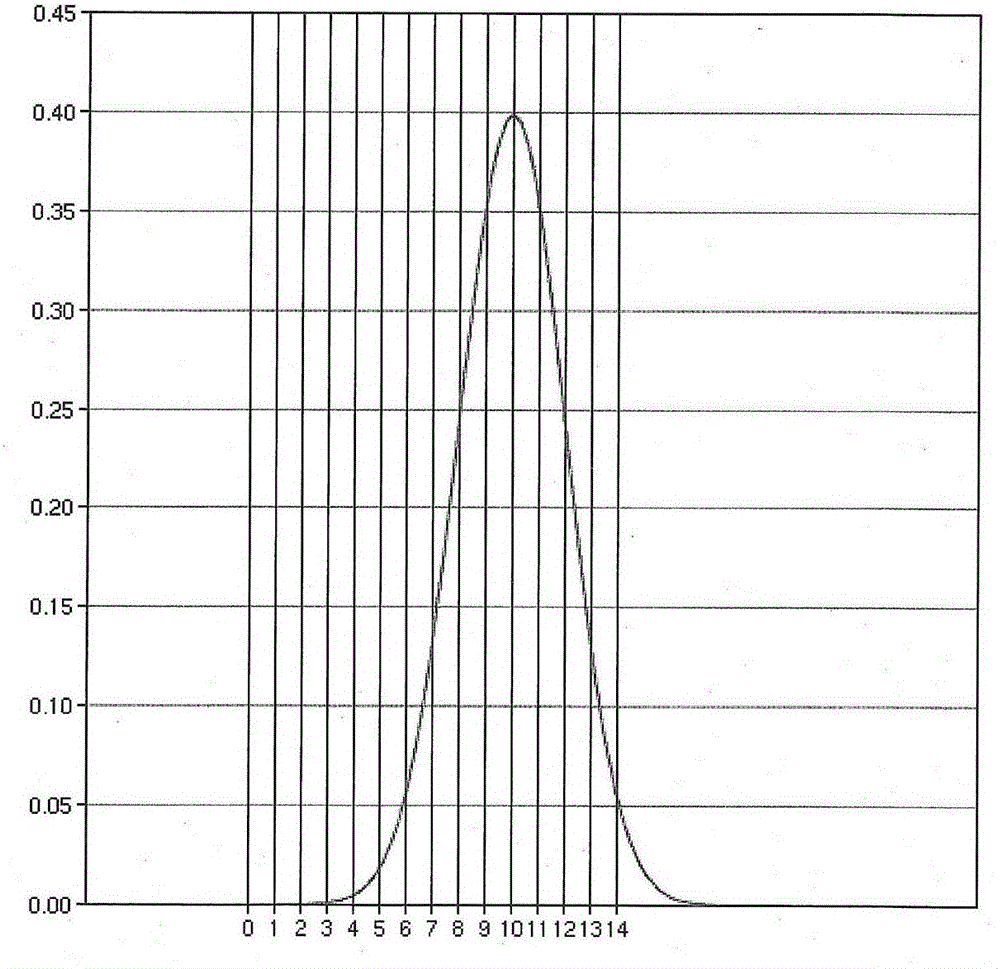
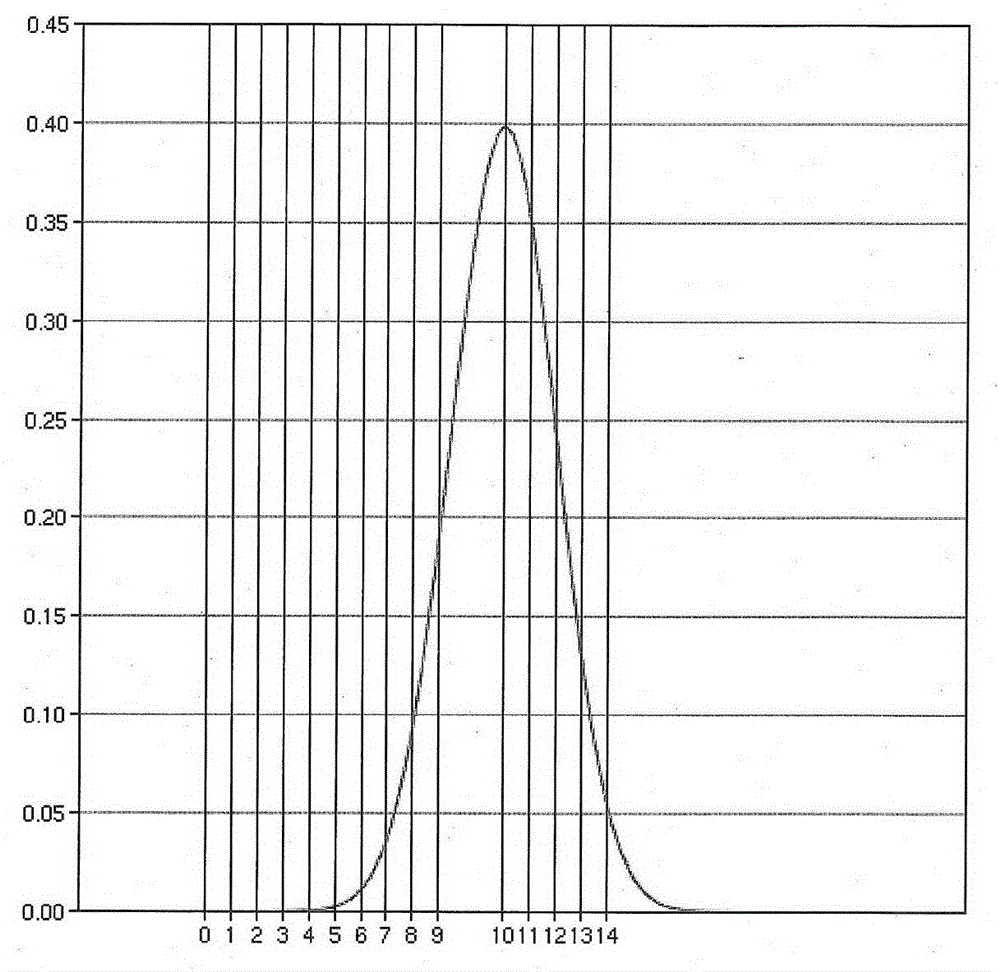
Method and device for obtaining beam energy spectrum, and dose distribution calculating method
ActiveCN105866821AHigh precisionSmall step sizeX-ray spectral distribution measurementBeam energyMedicine
The invention discloses a method for obtaining a beam energy spectrum, and the method comprises the steps: setting the initial energy spectrum distribution of a beam; calculating the dose distribution on a central axis of the beam based on the initial energy spectrum distribution; judging whether a calculated depth value of a maximum dose place and the dose value of the maximum dose place are matched with the measurement value of dose distribution on the central axis of the beam or not: enabling the current energy spectrum distribution to serve as the energy spectrum distribution of the beam if the calculated depth value and the dose value are matched with the measurement value, or else, adjusting the current energy spectrum distribution, and calculating the dose distribution on the central axis of the beam based on the adjusted energy spectrum distribution till the calculated depth value and the dose value are matched with the measurement value. The method is simple and effective.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
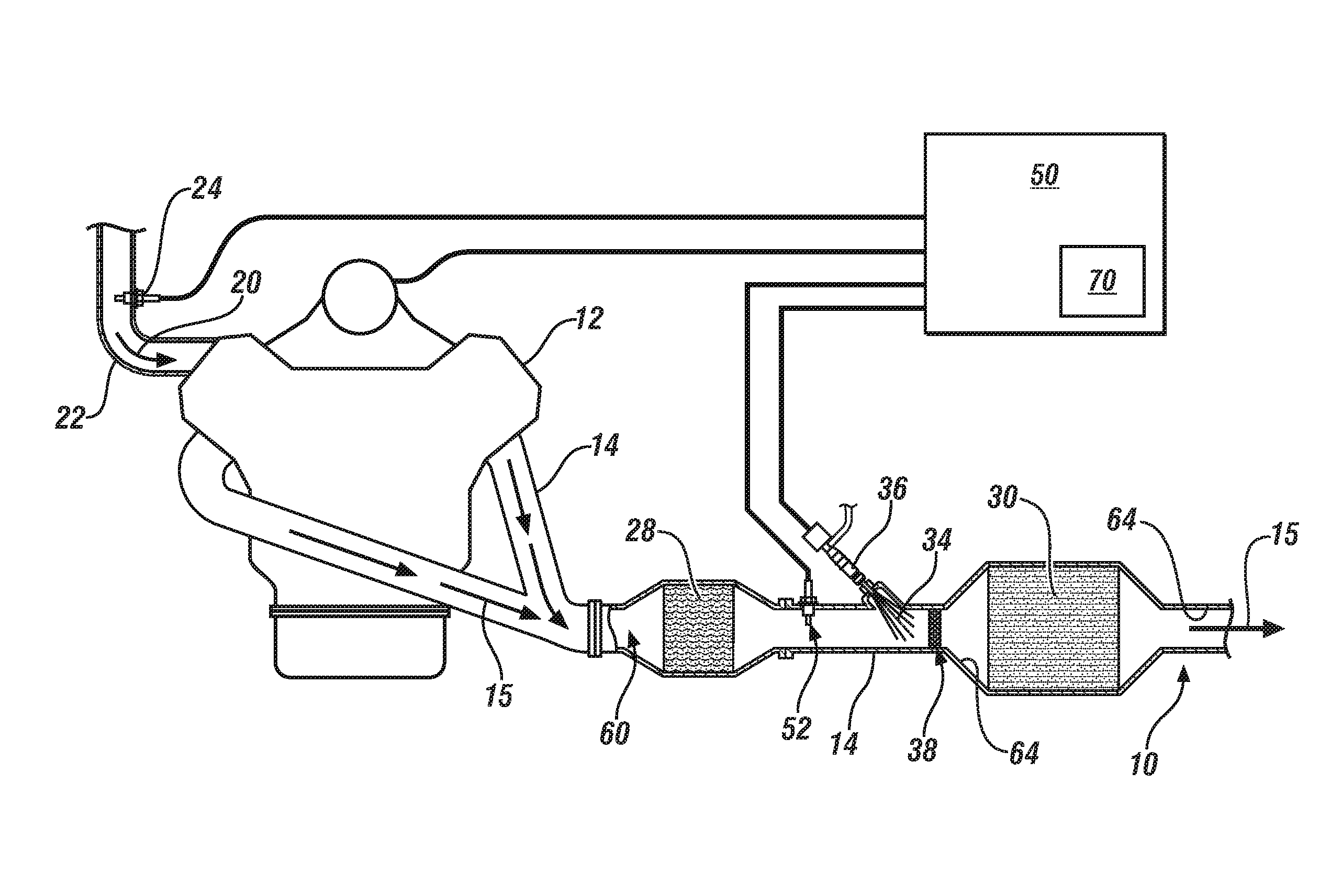
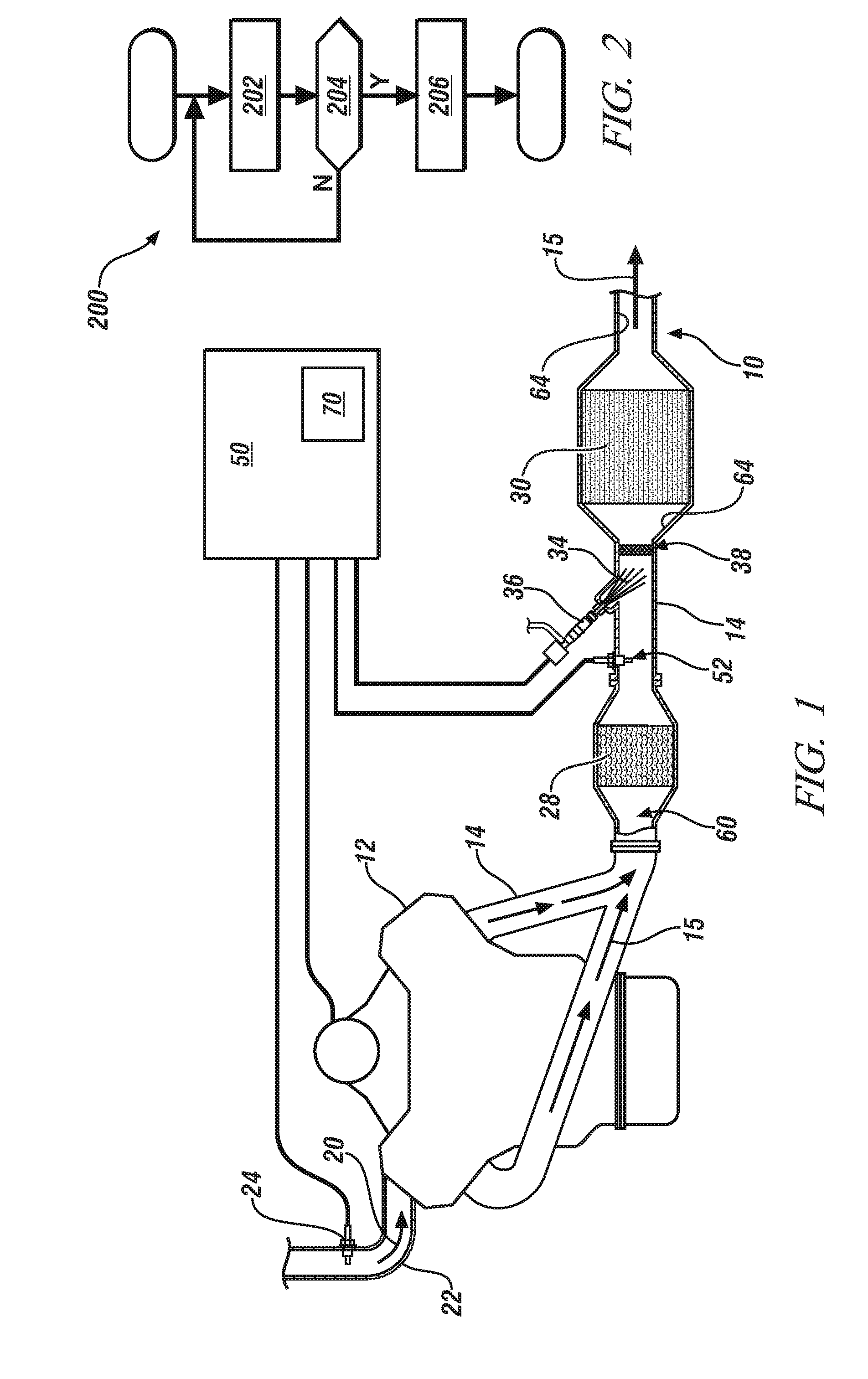
System and method for determining a maximum dose rate of reductant
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Radiotherapy system and treatment plan generation method thereof
PendingCN113797447AIncrease radiation doseRaise the minimum doseTomographyRadiation diagnosticsMedical imaging dataNormal tissue
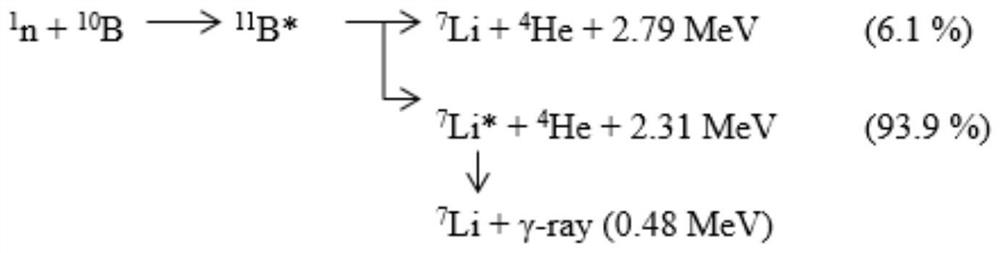
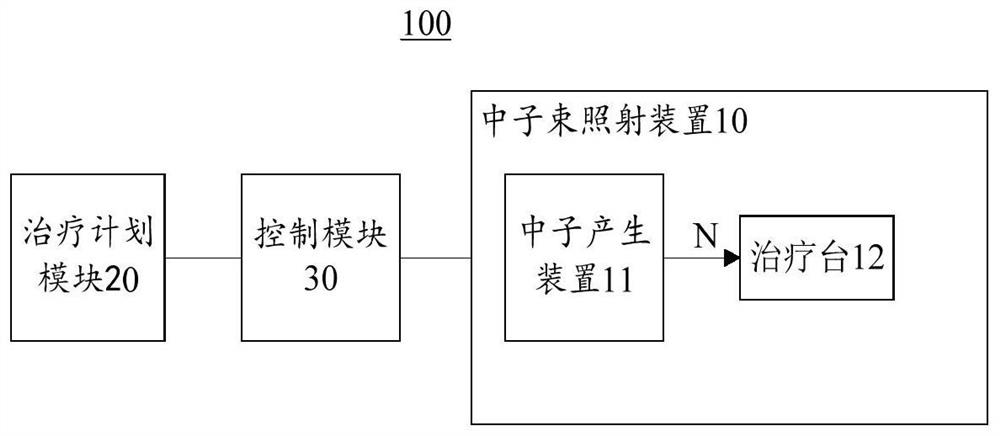
The invention discloses a radiotherapy system and a treatment plan generation method thereof. The radiotherapy system comprises a beam irradiation device, a treatment plan module and a control module. The beam irradiation device generates a treatment beam and irradiates an irradiated body to form an irradiated part, the treatment plan module generates a treatment plan according to parameters of the treatment beam and medical image data of the irradiated part, and the control module calls the treatment plan corresponding to the irradiated body from the treatment plan module, and controls the beam irradiation device to sequentially irradiate the irradiated body according to the at least two irradiation angles determined by the treatment plan generation method and the irradiation time corresponding to each irradiation angle. According to the radiotherapy system and the treatment plan generation method thereof, the radiation quantity of the shallow part of the irradiated part can be dispersed, and the radiation quantity of the deep part of a lesion tissue can be increased, so that the maximum dose of a normal tissue can be reduced, the minimum dose of the lesion tissue can be increased, and uniform distribution of the dose in the lesion tissue can be ensured.
Owner:NEUBORON THERAPY SYST LTD
Low-medium level radioactive waste barrel surface dose rate detection device and application thereof
ActiveCN111736197ASolve the problem that it is difficult to accurately obtain the maximum surface dose rateSolve the problem that the detector needs to be installed separately at a fixed position of 1mDosimetersRadioactive decontaminationDoses rateNuclear power
The invention discloses low-medium level radioactive waste barrel surface dose rate detection equipment and an application thereof, and relates to the technical field of nuclear power station solid waste treatment. The equipment comprises a waste bin rotating assembly, a waste bin surface dose rate detection device and a waste bin surface activity measurement device; the waste bin surface dosage rate detection device comprises a lifting support assembly, a lifting power assembly and a mechanical arm assembly. The mechanical arm assembly comprises a limiting transmission sliding block, a mechanical arm upper arm, an electric telescopic rod, a mechanical arm lower arm, an upper and lower arm torsional elastic piece, a detector assembly and a detector position adjusting elastic part. A dose rate detection device is arranged on one side, far away from the mechanical arm lower arm, of the detector assembly; rollers are respectively arranged at two ends of one side, far away from the mechanical arm lower arm, of the detector assembly; the dose rate distribution, maximum dose rate detection and activity detection of different heights and distances of the waste bin are implemented by adopting one detector assembly, so the use is very convenient.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method and system for determining a charged particle beam exposure for a local pattern density
ActiveUS10748744B1Electric discharge tubesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusParticle beamMaximum dose
A method for exposing a pattern in an area on a surface using a charged particle beam system is disclosed and includes inputting an original set of exposure information for the area and inputting a target post-proximity effect correction (PEC) maximum dose. A local pattern density is calculated for the area of the pattern based on the original set of exposure information. A pre-PEC maximum dose is determined for the area. The original set of exposure information is modified with the pre-PEC maximum dose.
Owner:D2S
Drive mechanism and injection device herewith
The present invention relates to a drive mechanism which is suitable for an injection device (1; 101; 201; 301; 401), especially a pen type drug delivery device. The mechanism comprises a housing (4; 104; 204; 304; 404), a dosing member (7; 107; 206; 306; 407), which during dose setting, dose resetting and dose dispensing rotates relative to the housing between a zero dose position and a maximum dose position, and an insert (5; 126; 205; 307; 431) which is rotationally constrained to the housing. The dosing member (7; 107; 206; 306; 407) and the insert (5; 126; 205; 307; 431) each comprise at least one abutment feature (22, 24; 122, 24; 222; 422, 424) contacting each other when the dosing member (7; 107; 206; 306; 407) reaches its zero dose position during dose dispensing, wherein an audible and / or tactile feedback is generated by the contact of the abutment features (22, 24; 122, 124; 222; 422, 424).
Owner:SANOFI SA
Method and system for determining a charged particle beam exposure for a local pattern density
ActiveUS11062878B2Electric discharge tubesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusNuclear engineeringParticle beam
A method for exposing a pattern in an area on a surface using a charged particle beam system is disclosed and includes determining a local pattern density for the area of the pattern based on an original set of exposure information. A pre-PEC maximum dose is determined for the area. The original set of exposure information is modified with the pre-PLC maximum dose.
Owner:D2S
DNP and DNP Prodrug Treatment of Neuromuscular, Neurodegenerative, Autoimmune, Developmental, Traumatic Brain Injury, Concussion, Dry Eye Disease, Hearing Loss and/or Metabolic Diseases
A composition and method of treatment of neuromuscular, neuromuscular degenerative, neurodegenerative, autoimmune, developmental, traumatic, hearing loss related, and / or metabolic diseases, including spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) syndrome (SMA1, SMA2, SMA3, and SMA4, also called Type I, II, III and IV), traumatic brain injury (TBI), concussion, keratoconjunctivitis sicca (Dry Eye Disease), glaucoma, Sjogren's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, post-LASIK surgery, anti-depressants use, Wolfram Syndrome, and Wolcott-Rallison syndrome. The composition is selected from the group consisting of 2,3-DNP, 2,4-DNP, 2,5-DNP, 2,6-DNP, 3,4-DNP, or 3,5-DNP, bipartite 2,3-dinitrophenol, 2,4-dinitrophenol, 2,5-dinitrophenol, 2,6-dinitrophenol, 3,4-dinitrophenol, or 3,5-dinitrophenol (2,3-DNP, 2,4-DNP, 2,5-DNP, 2,6-DNP, 3,4-DNP, or 3,5-DNP) prodrugs; Gemini prodrugs, bioprecursor molecules, and combinations thereof. A dose of the composition for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases may be from about 0.01 mg / kg of body weight to about 50 mg / kg of body weight of the patient in need of treatment. A dose of the composition for treatment of metabolic diseases may be from about 1 mg / 70 kg of body weight to about 100 mg / 70 kg of body weight of the patient in need of treatment, and a maximum dose per day is about 200 mg / 70 kg of body weight of the patient in need of treatment.
Owner:BIOVENTURES LLC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com