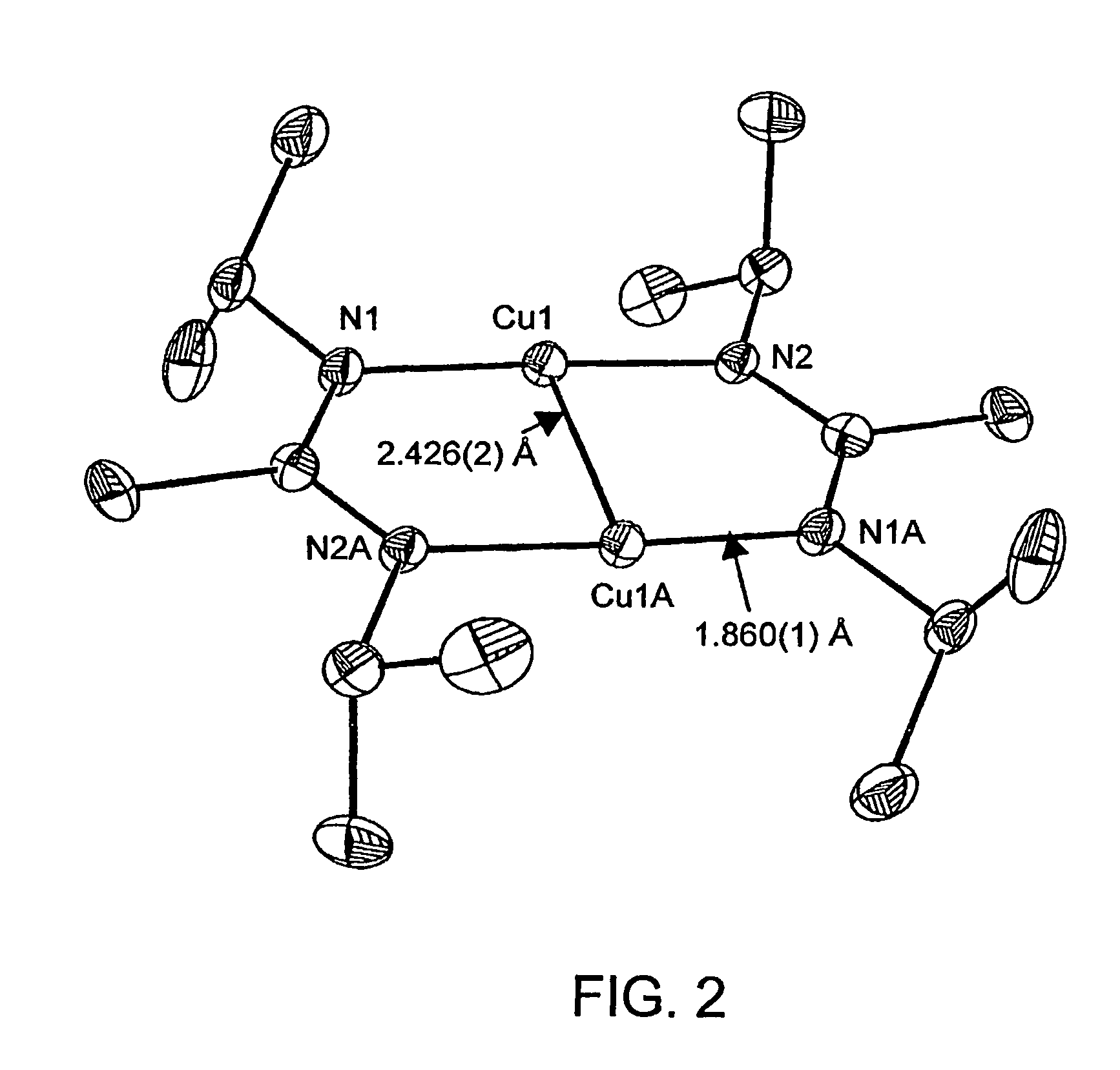
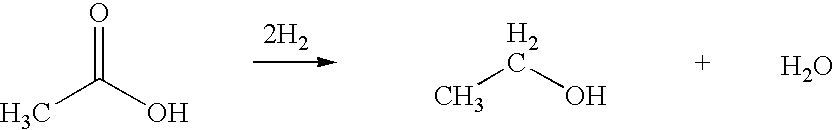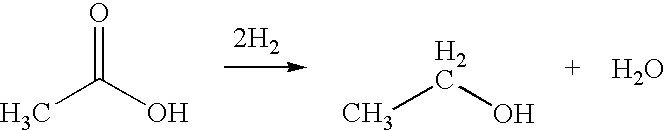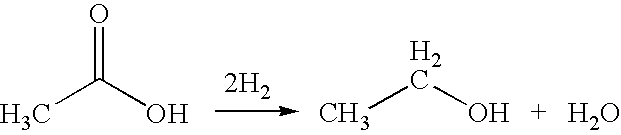Patents
Literature
69982 results about "Hydrogen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. With a standard atomic weight of 1.008, hydrogen is the lightest element in the periodic table. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the Universe, constituting roughly 75% of all baryonic mass. Non-remnant stars are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. The most common isotope of hydrogen, termed protium (name rarely used, symbol ¹H), has one proton and no neutrons.
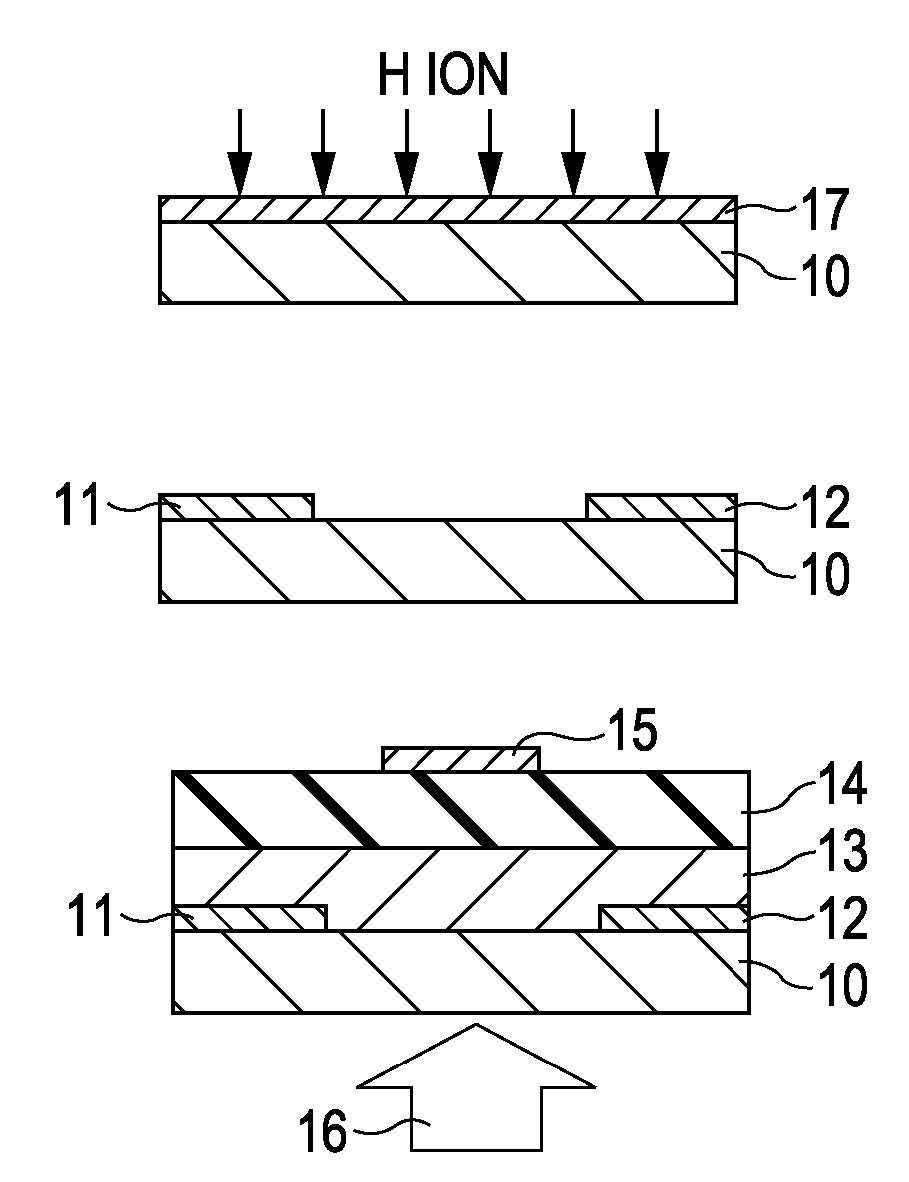
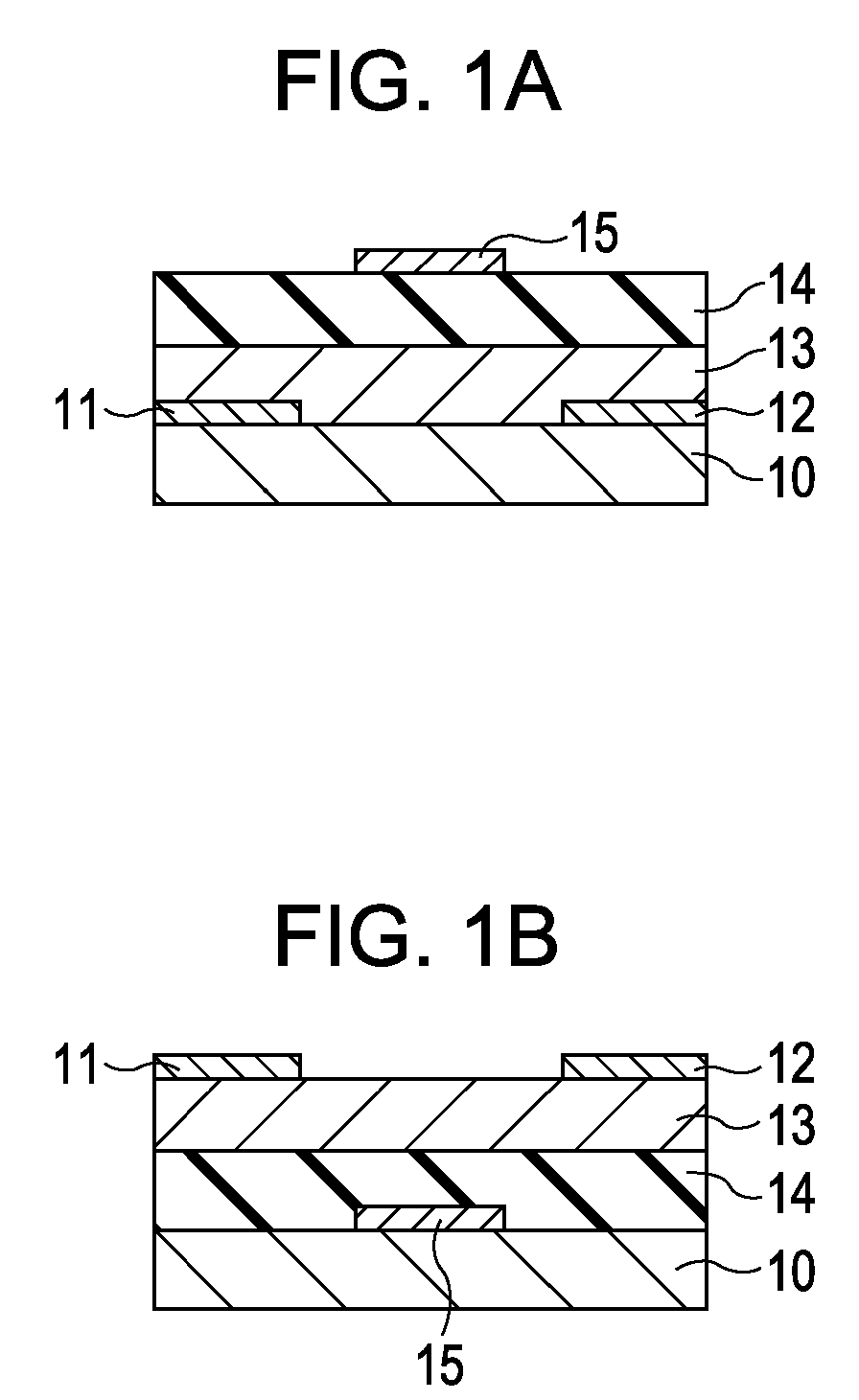
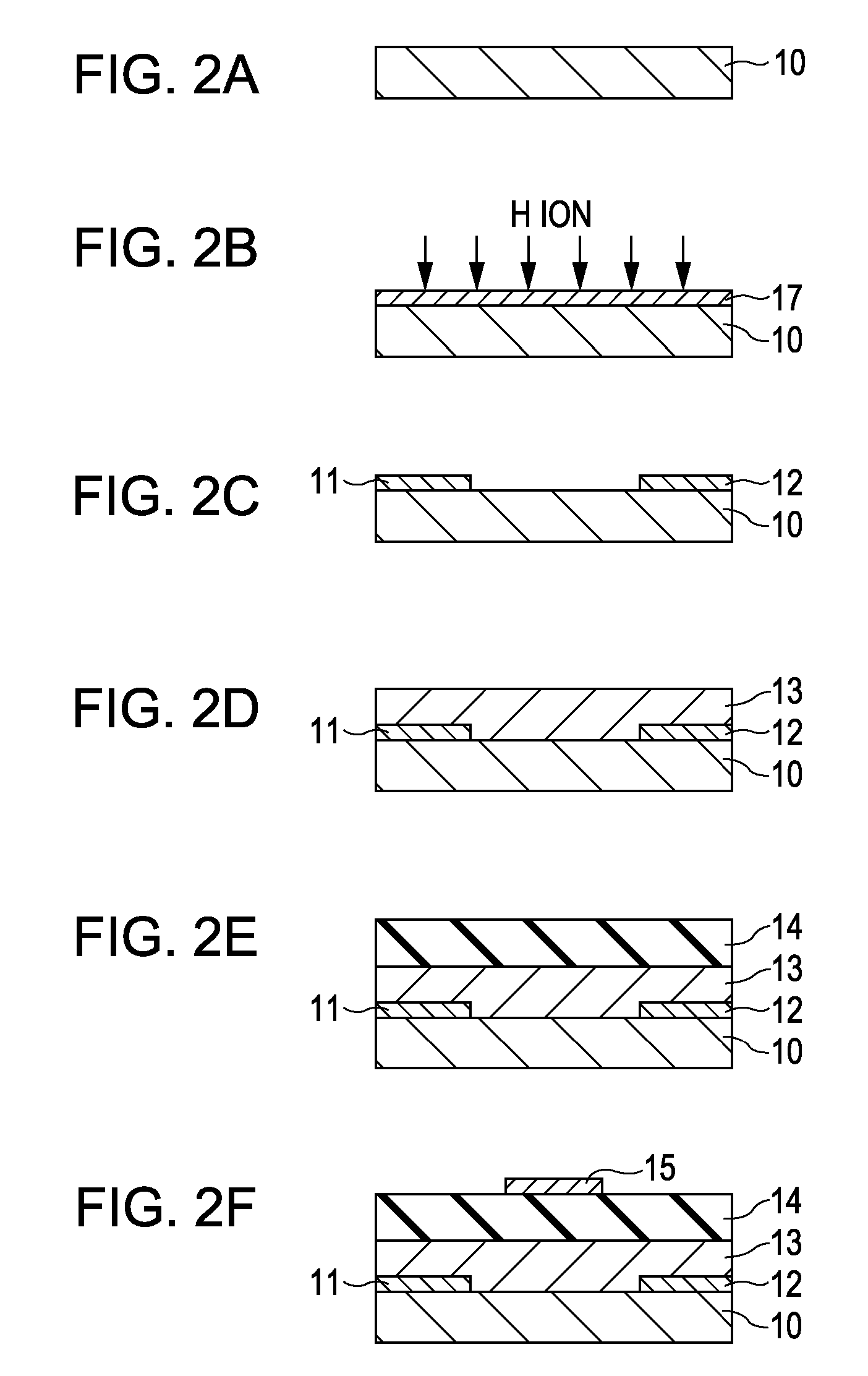
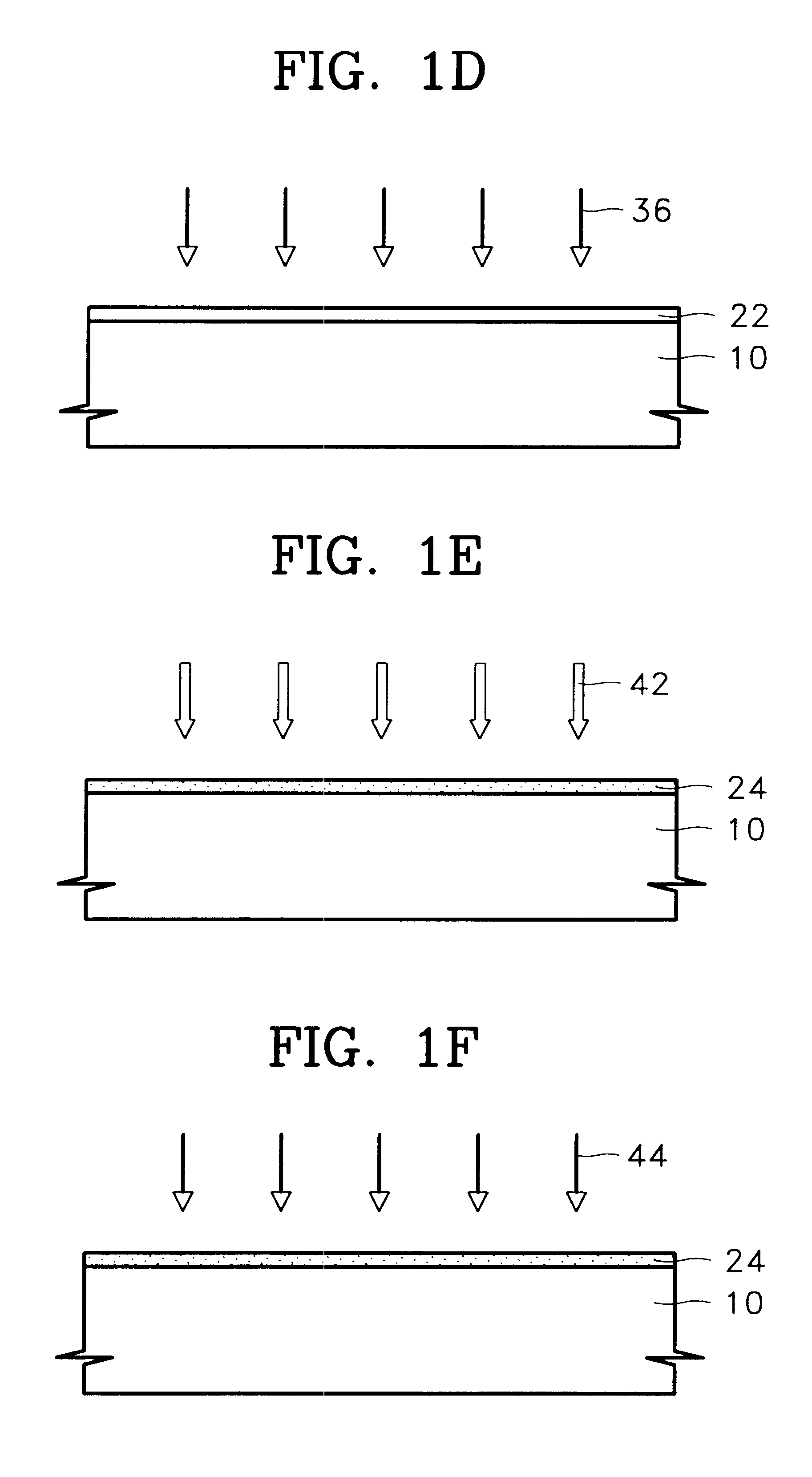
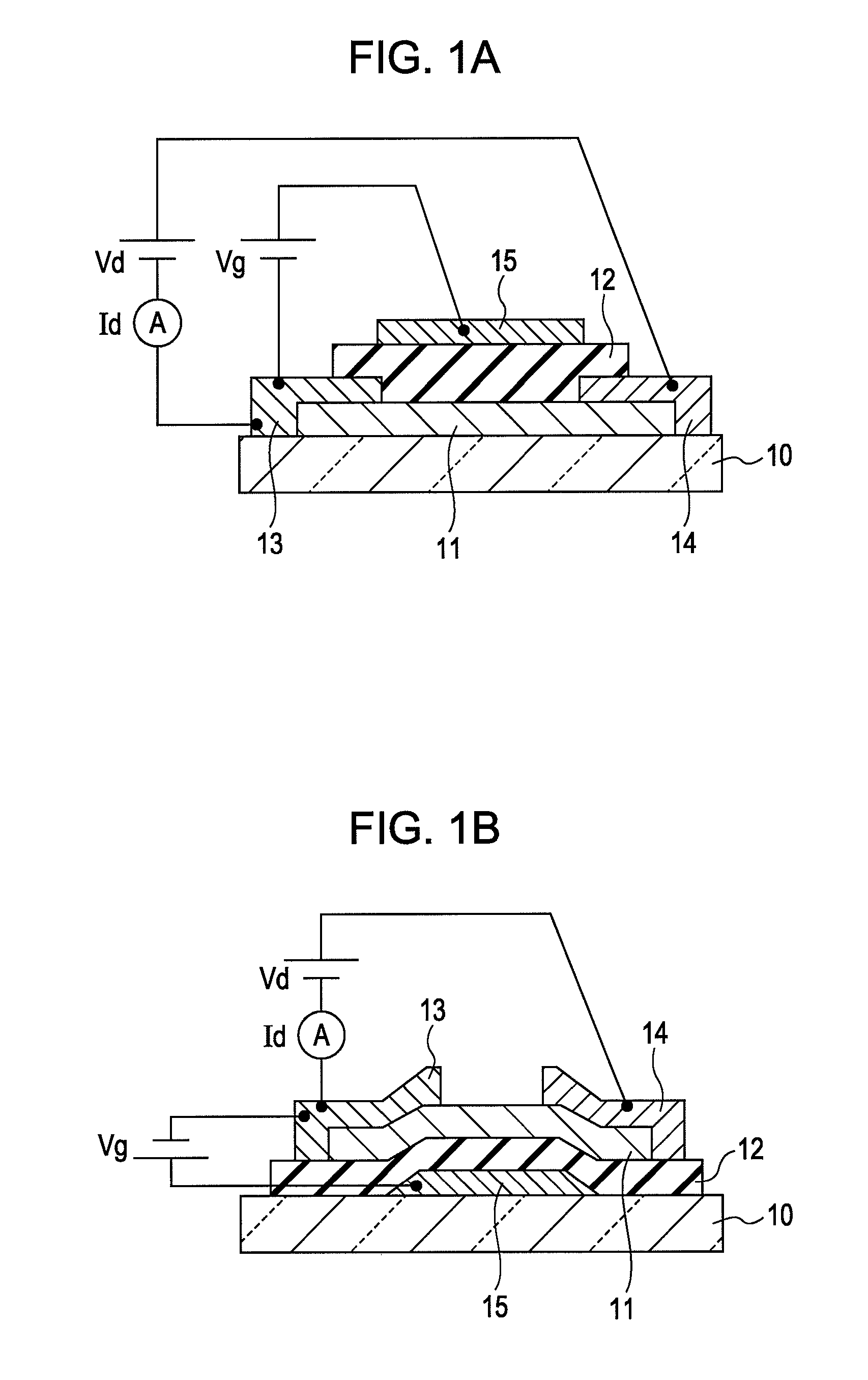
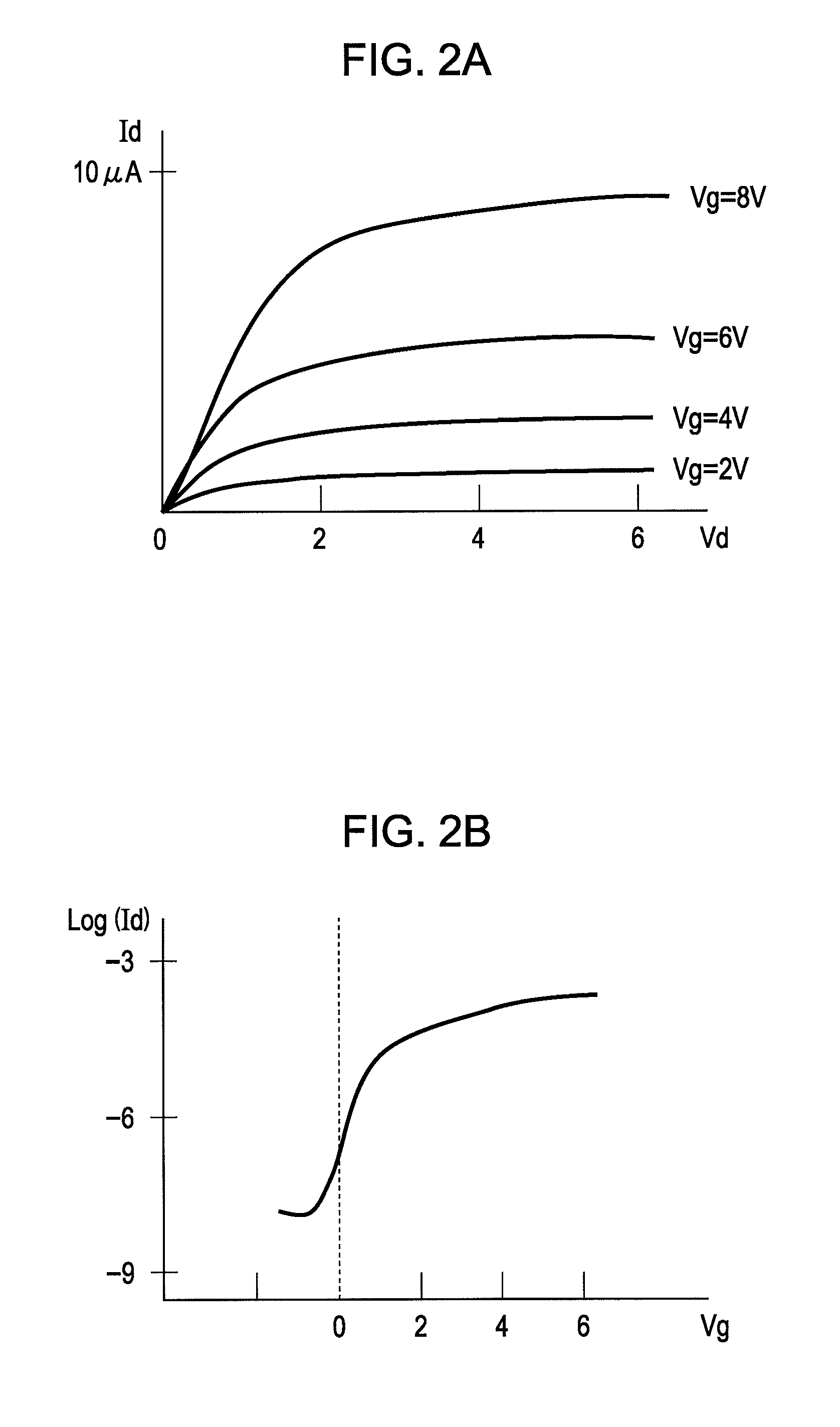
Field-effect transistor and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7411209B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenField-effect transistor
A method for manufacturing a field-effect transistor includes the steps of forming a source electrode and a drain electrode each containing hydrogen or deuterium; forming an oxide semiconductor layer in which the electrical resistance is decreased if hydrogen or deuterium is added; and, causing hydrogen or deuterium to diffuse from the source electrode and the drain electrode to the oxide semiconductor layer.
Owner:CANON KK
Hemostatic compositions for arresting blood flow from an open wound or surgical site
A hemostatic composition for stopping or decreasing blood flow from an open wound or medical or surgical procedure. Compositions of the invention comprise a mixture of a cationic polymer and a cation exchange material. In one embodiment, the composition comprises a mixture: (1) a high molecular weight copolymer of diallyl dimethyl ammonium chloride (DADMAC) and acrylamide [DADMAC copolymer], and (2) the hydrogen form of a crosslinked, sulfonated polystyrene (hydrogen resin). In an exemplified embodiment, a composition of the invention comprises the mixture of DADMAC copolymer and hydrogen resin provided in a dry powdered form. The compositions of the invention may be applied directly to a wound or treatment site, or they may be incorporated into a wound dressing, such as a bandage. The seal formed at a wound or treatment site treated with the present invention is adhesive and exhibits considerable toughness.
Owner:BIOLIFE
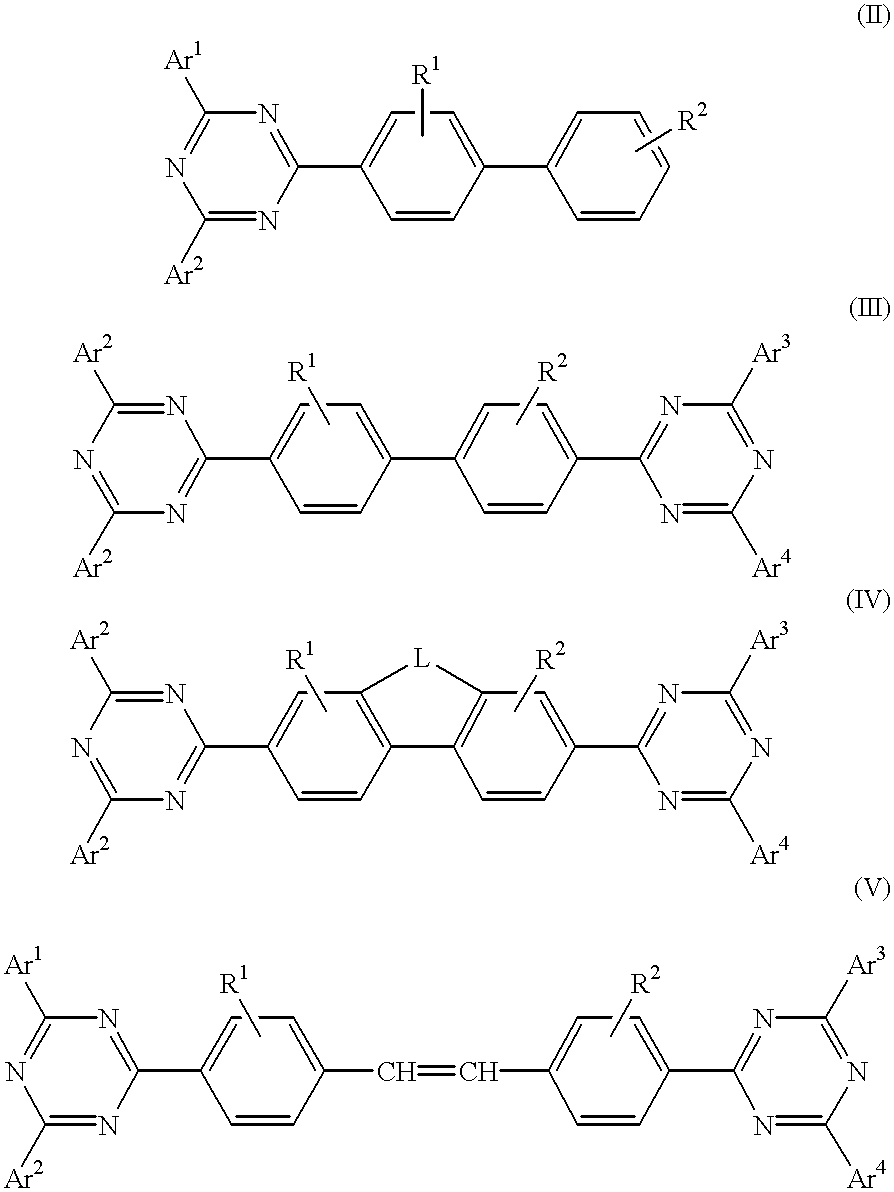
Electroluminescent (EL) devices
InactiveUS6225467B1Improve efficiencyIncreased durabilitySilicon organic compoundsElectroluminescent light sourcesArylHalogen
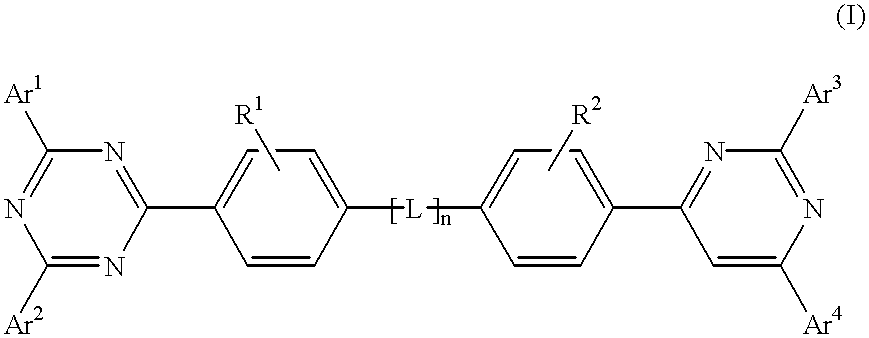
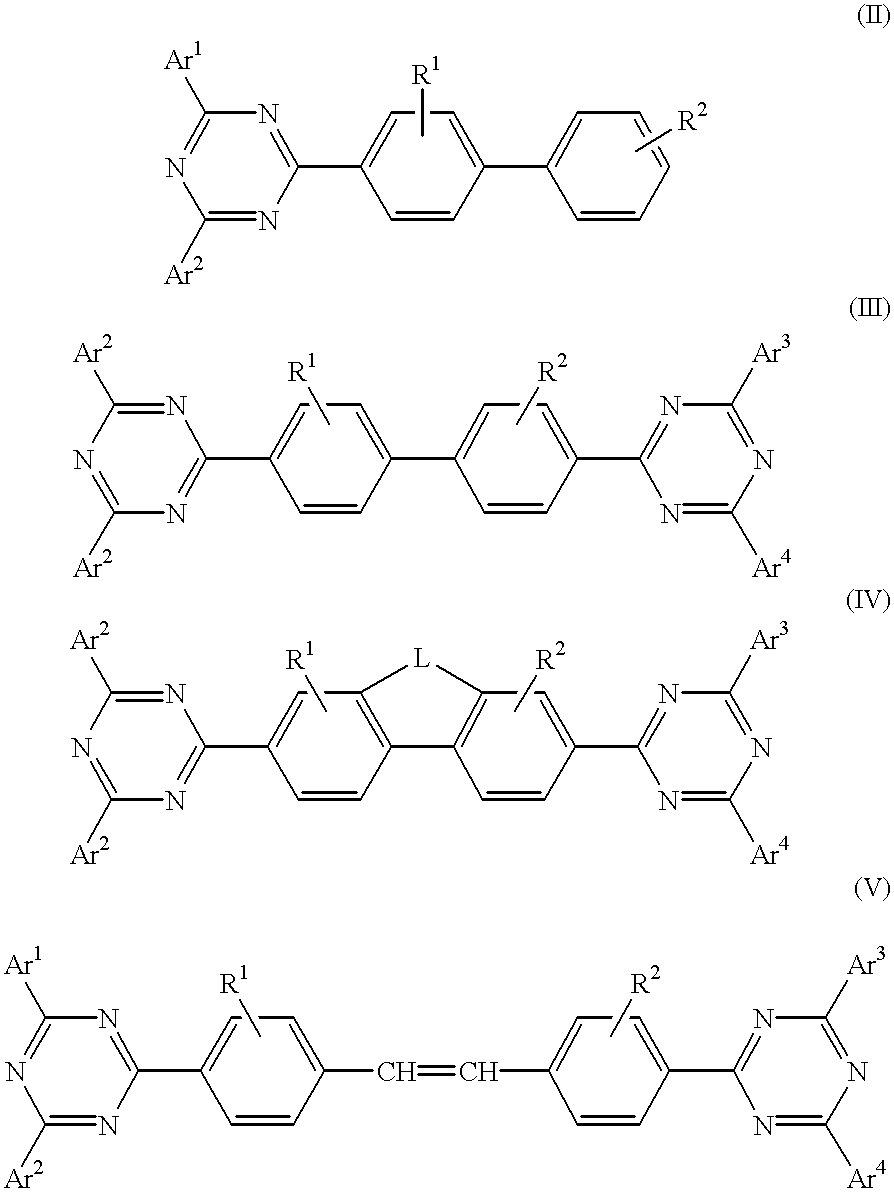
The triazinewherein Ar1, Ar2, Ar3, and Ar4 are each independently an aryl; R1 and R2 are substituents selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, an alkyl, an aryl, an alkoxy, a halogen atom, and a cyano; R3 and R4 are each a divalent group L selected from the group consisting of -C(R'R'')-, alkylene, an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom, and -Si(R'R'')-, wherein R' and R'' are selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, and aryl.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
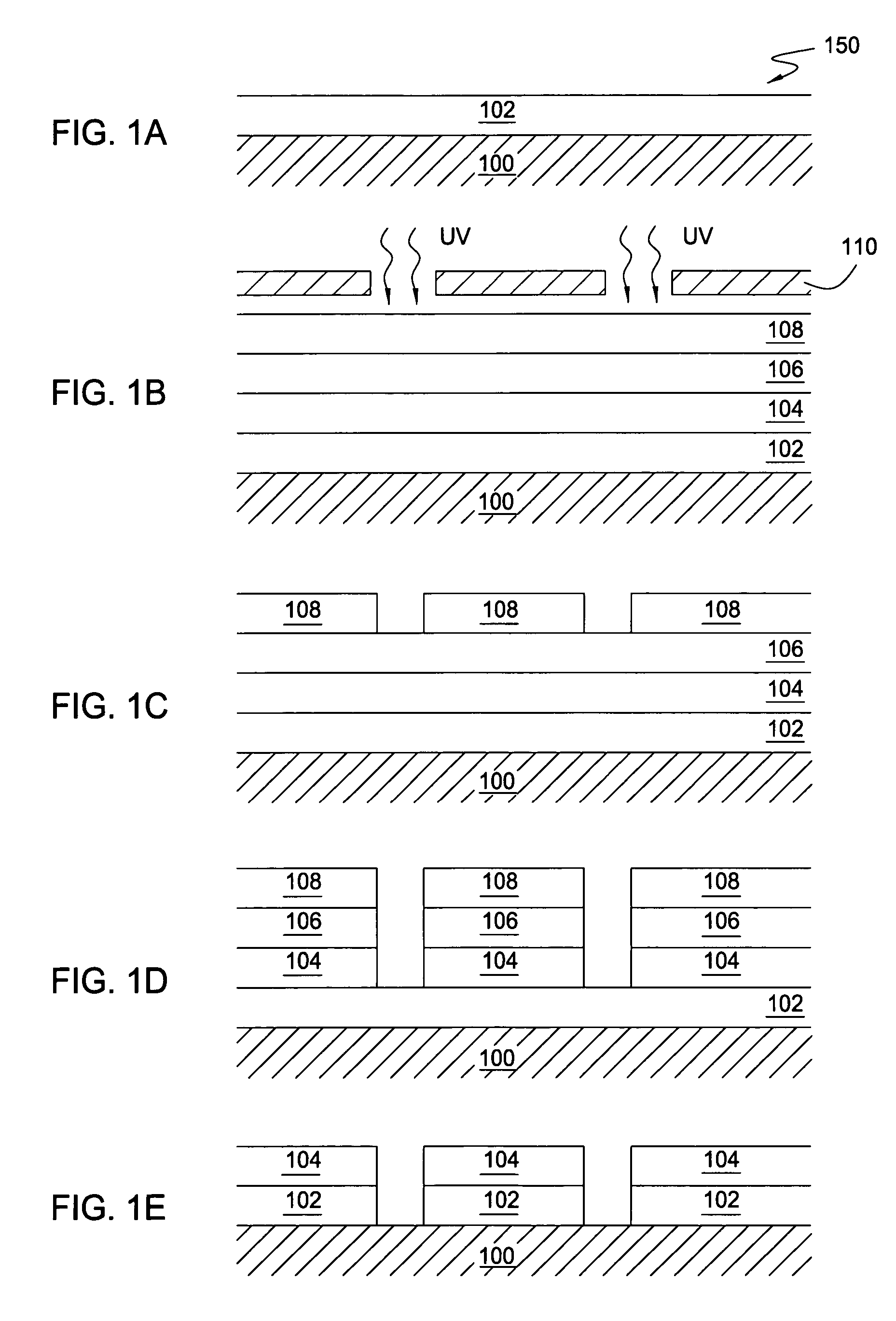
Methods of forming thin films by atomic layer deposition
InactiveUS6468924B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenProduct gas
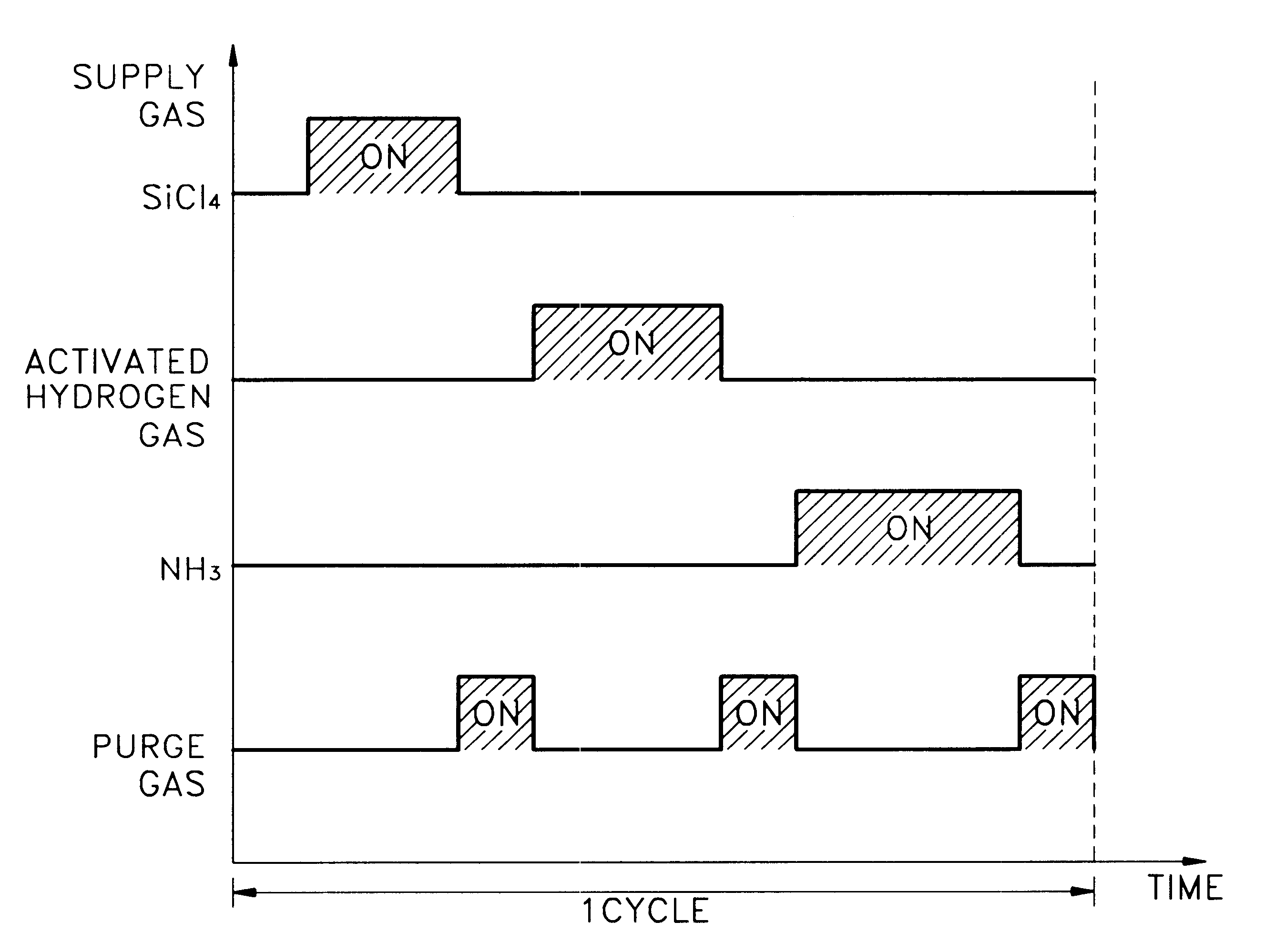
Methods of forming thin films include forming a first layer comprising a first element that is chemisorbed to a surface of a substrate, by exposing the surface to a first source gas having molecules therein that comprise the first element and a halogen. A step is then performed to expose the first layer to an activated hydrogen gas so that halogens associated with the first layer become bound to hydrogen provided by the activated hydrogen gas. The first layer may then be converted to a thin film comprising the first element and a second element, by exposing a surface of the first layer to a second source gas having molecules therein that comprise the second element.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Liquid precursors for the CVD deposition of amorphous carbon films
ActiveUS20050287771A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDual frequencyHydrogen
Methods are provided for depositing amorphous carbon materials. In one aspect, the invention provides a method for processing a substrate including positioning the substrate in a processing chamber, introducing a processing gas into the processing chamber, wherein the processing gas comprises a carrier gas, hydrogen, and one or more precursor compounds, generating a plasma of the processing gas by applying power from a dual-frequency RF source, and depositing an amorphous carbon layer on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
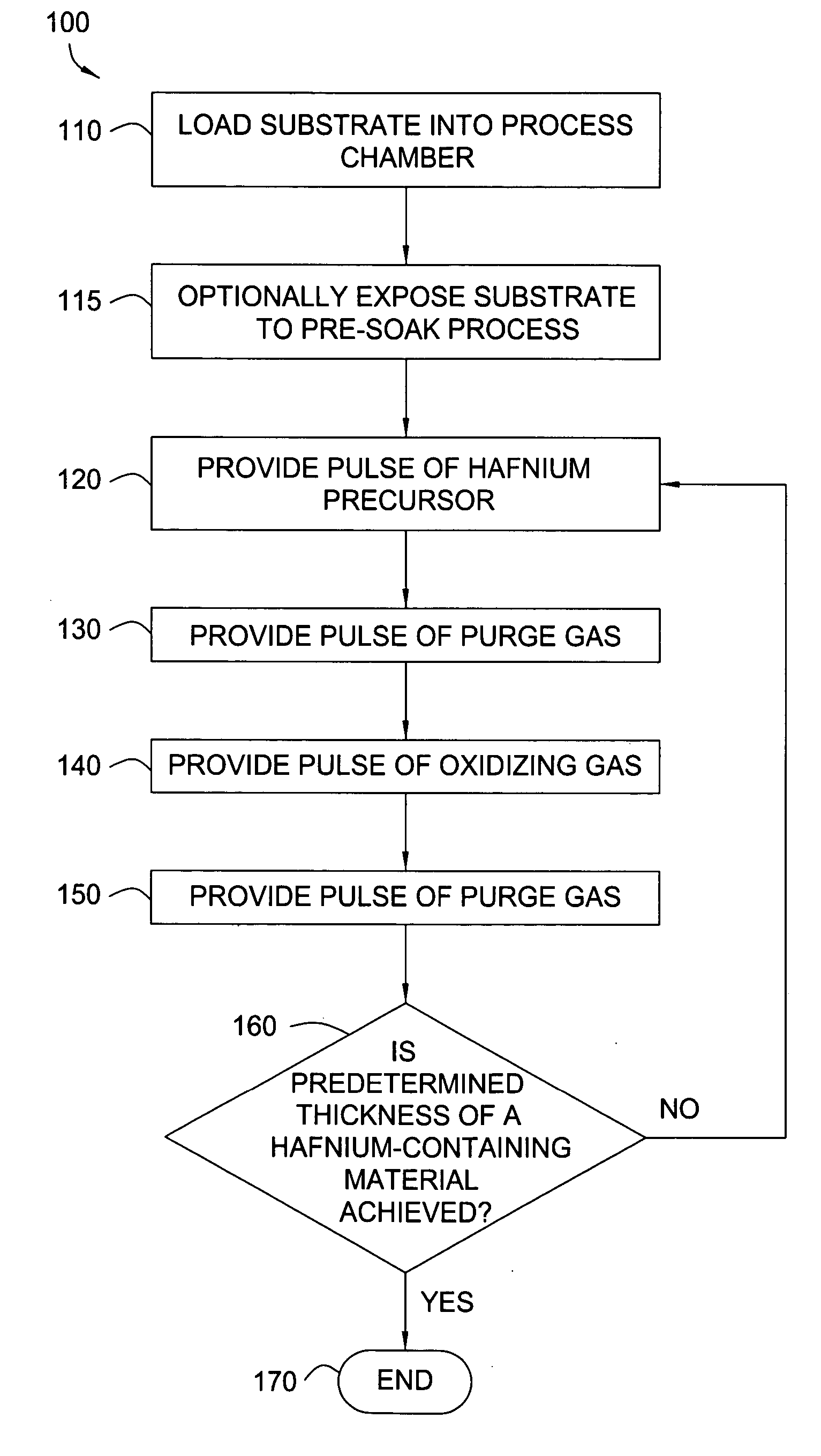
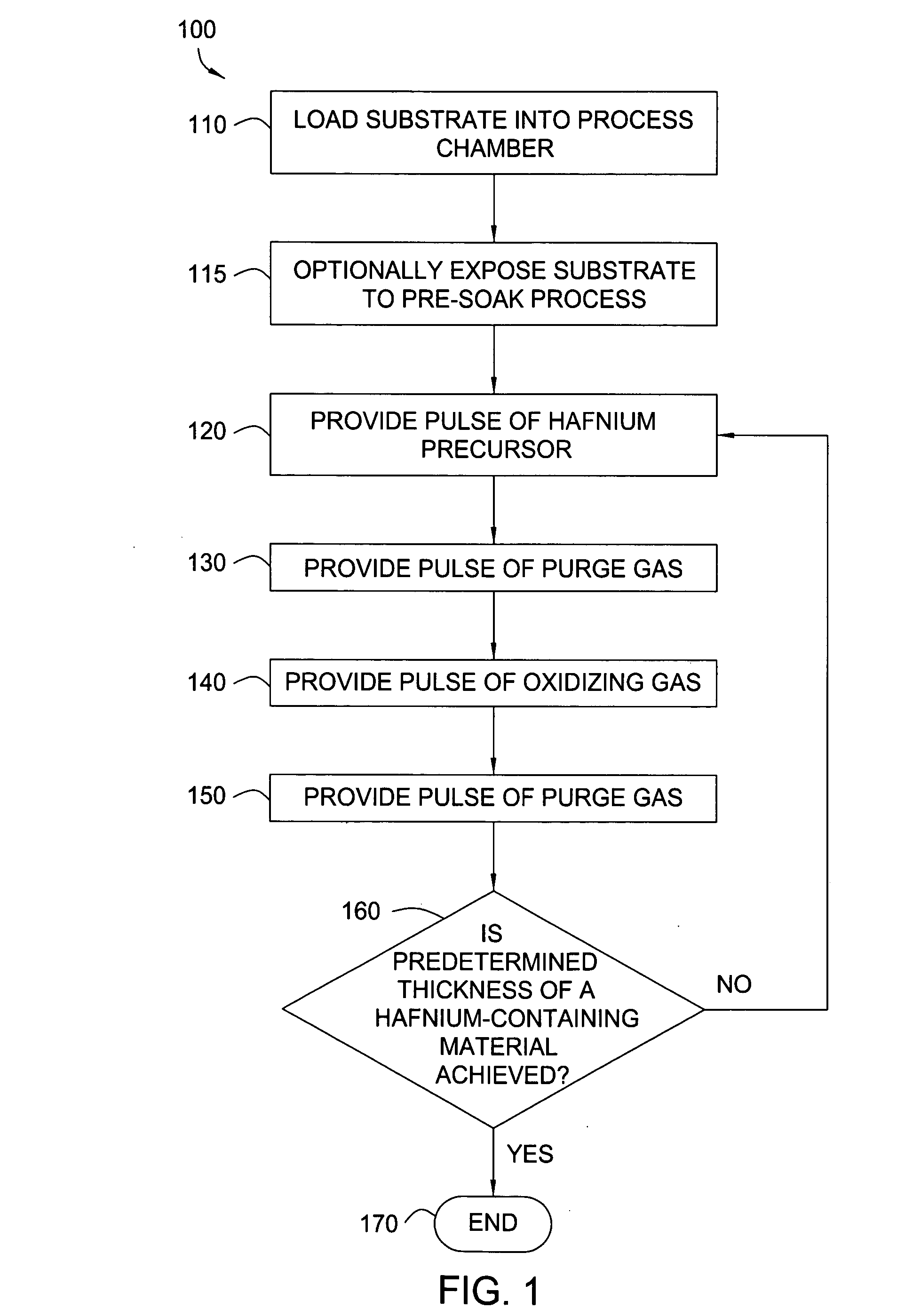
Apparatuses and methods for atomic layer deposition of hafnium-containing high-k dielectric materials
InactiveUS20050271813A1Steam generation heating methodsDecorative surface effectsGas phaseWater vapor
Embodiments of the invention provide methods for depositing dielectric materials on substrates during vapor deposition processes, such as atomic layer deposition (ALD). In one example, a method includes sequentially exposing a substrate to a hafnium precursor and an oxidizing gas to deposit a hafnium oxide material thereon. In another example, a hafnium silicate material is deposited by sequentially exposing a substrate to the oxidizing gas and a process gas containing a hafnium precursor and a silicon precursor. The oxidizing gas usually contains water vapor formed by flowing a hydrogen source gas and an oxygen source gas through a water vapor generator. In another example, a method includes sequentially exposing a substrate to the oxidizing gas and at least one precursor to deposit hafnium oxide, zirconium oxide, lanthanum oxide, tantalum oxide, titanium oxide, aluminum oxide, silicon oxide, aluminates thereof, silicates thereof, derivatives thereof or combinations thereof.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Field effect transistor using amorphous oxide film as channel layer, manufacturing method of field effect transistor using amorphous oxide film as channel layer, and manufacturing method of amorphous oxide film
InactiveUS7791074B2Easy to controlSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHysteresisHydrogen
An amorphous oxide containing hydrogen (or deuterium) is applied to a channel layer of a transistor. Accordingly, a thin film transistor having superior TFT properties can be realized, the superior TFT properties including a small hysteresis, normally OFF operation, a high ON / OFF ratio, a high saturated current, and the like. Furthermore, as a method for manufacturing a channel layer made of an amorphous oxide, film formation is performed in an atmosphere containing a hydrogen gas and an oxygen gas, so that the carrier concentration of the amorphous oxide can be controlled.
Owner:CANON KK
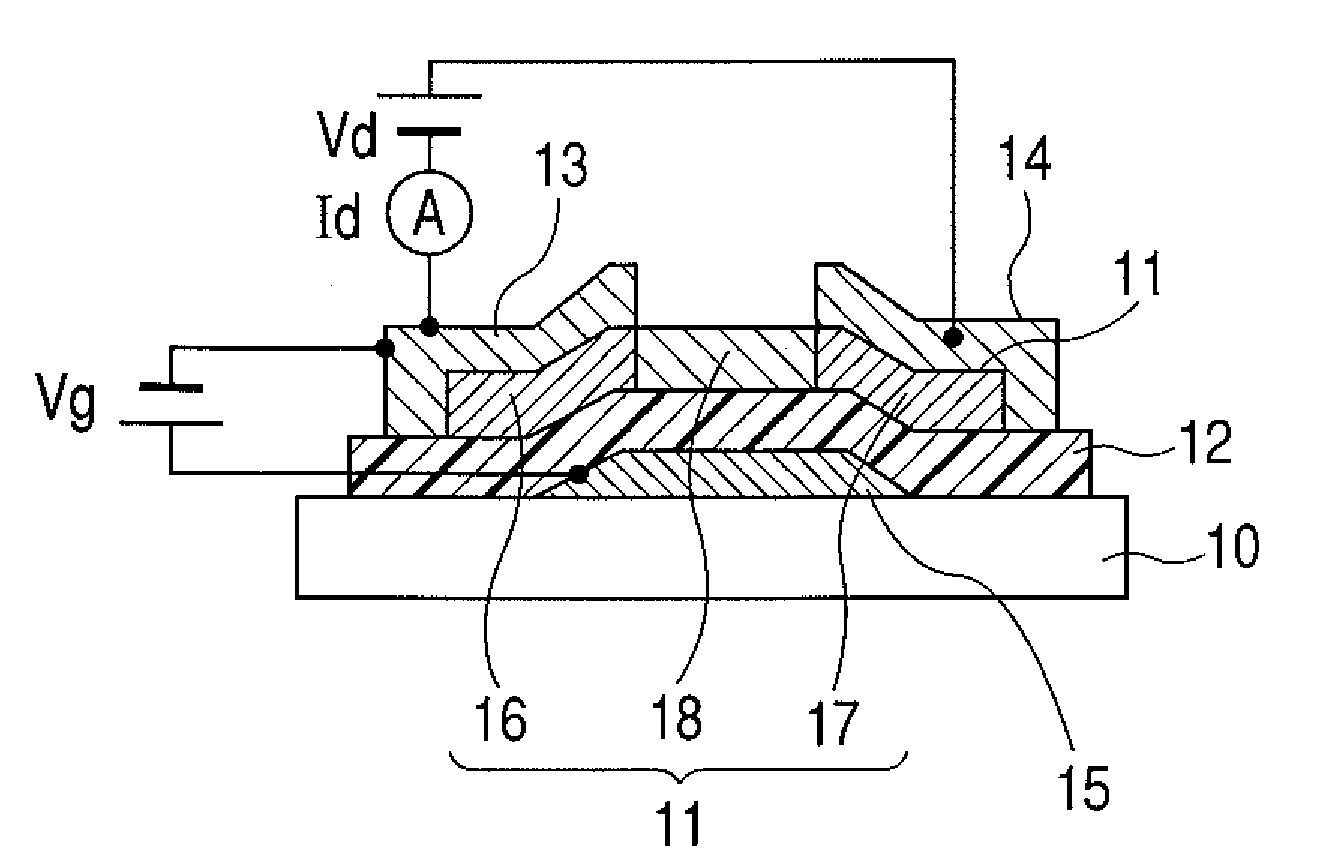
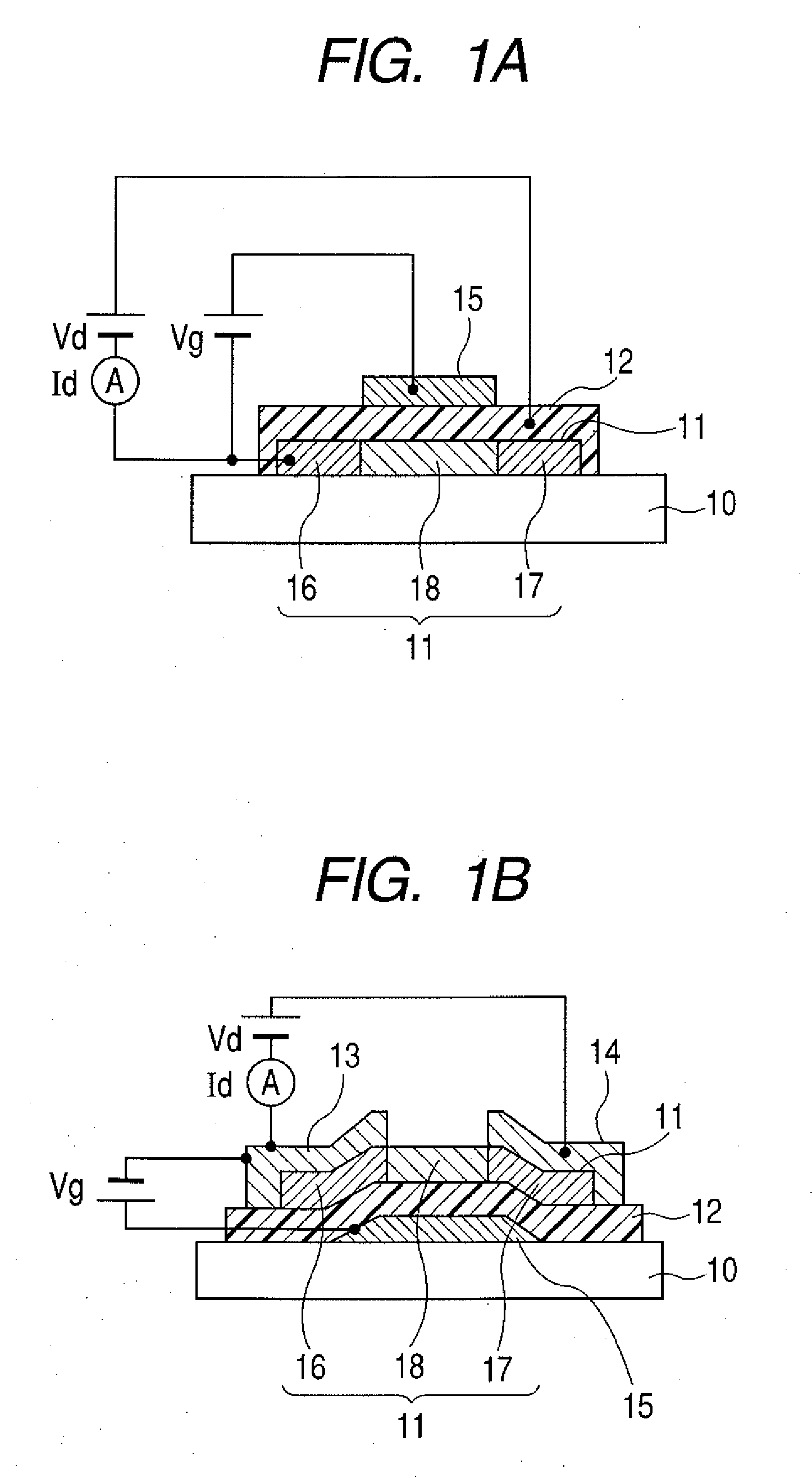
Field effect transistor using oxide film for channel and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090065771A1Reduce variationImprove accuracyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenField-effect transistor
Owner:CANON KK
Integrated low K dielectrics and etch stops
InactiveUS6340435B1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHydrogenFluorocarbon
A method of depositing and etching dielectric layers having low dielectric constants and etch rates that vary by at least 3:1 for formation of horizontal interconnects. The amount of carbon or hydrogen in the dielectric layer is varied by changes in deposition conditions to provide low k dielectric layers that can replace etch stop layers or conventional dielectric layers in damascene applications. A dual damascene structure having two or more dielectric layers with dielectric constants lower than about 4 can be deposited in a single reactor and then etched to form vertical and horizontal interconnects by varying the concentration of a carbon:oxygen gas such as carbon monoxide. The etch gases for forming vertical interconnects preferably comprises CO and a fluorocarbon, and CO is preferably excluded from etch gases for forming horizontal interconnects.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Ethanol production from acetic acid utilizing a cobalt catalyst
InactiveUS7608744B1High selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionAcetic acidPlatinum
A process for the selective production of ethanol by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethanol is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over either cobalt and palladium supported on graphite or cobalt and platinum supported on silica selectively produces ethanol in a vapor phase at a temperature of about 250° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
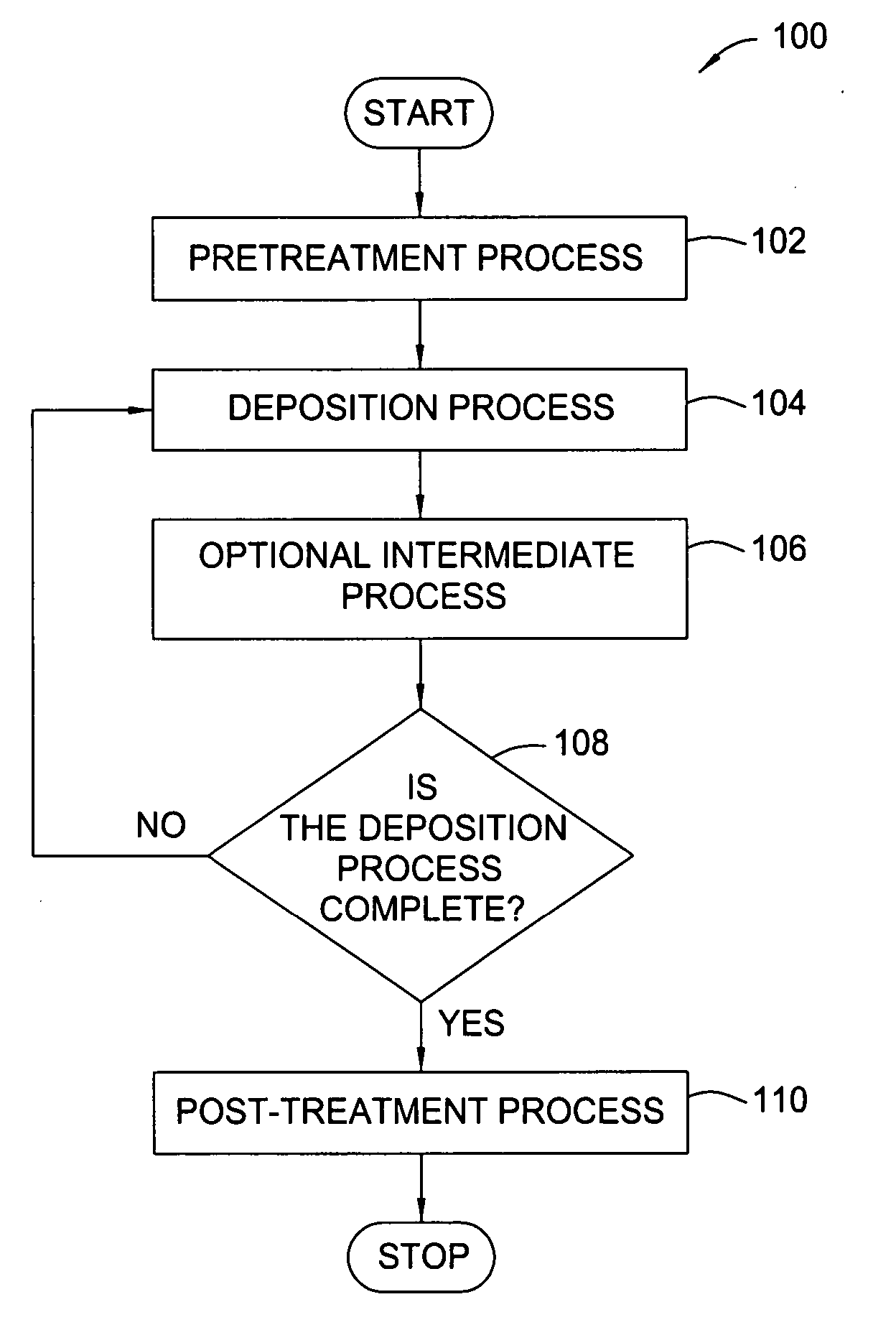
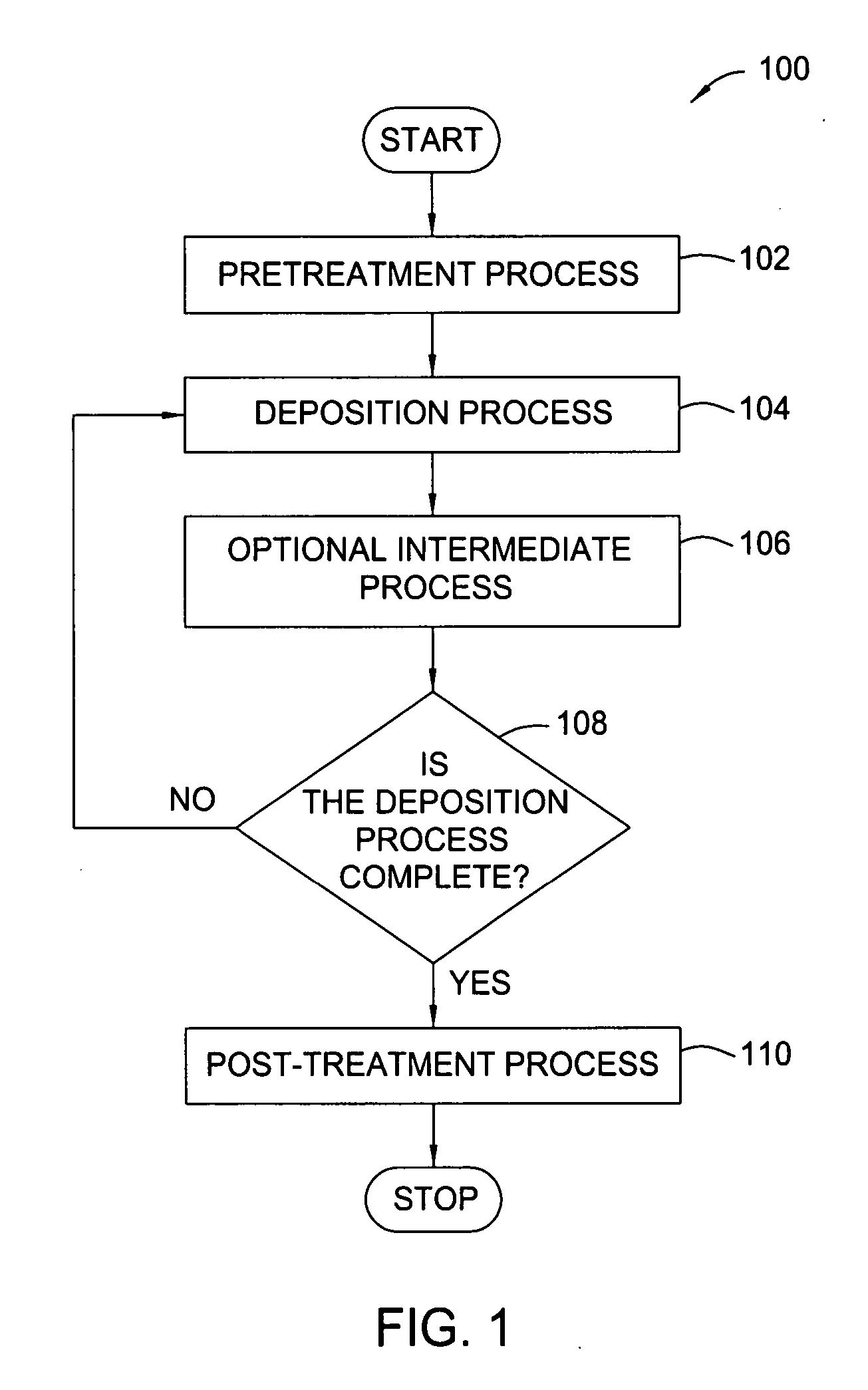
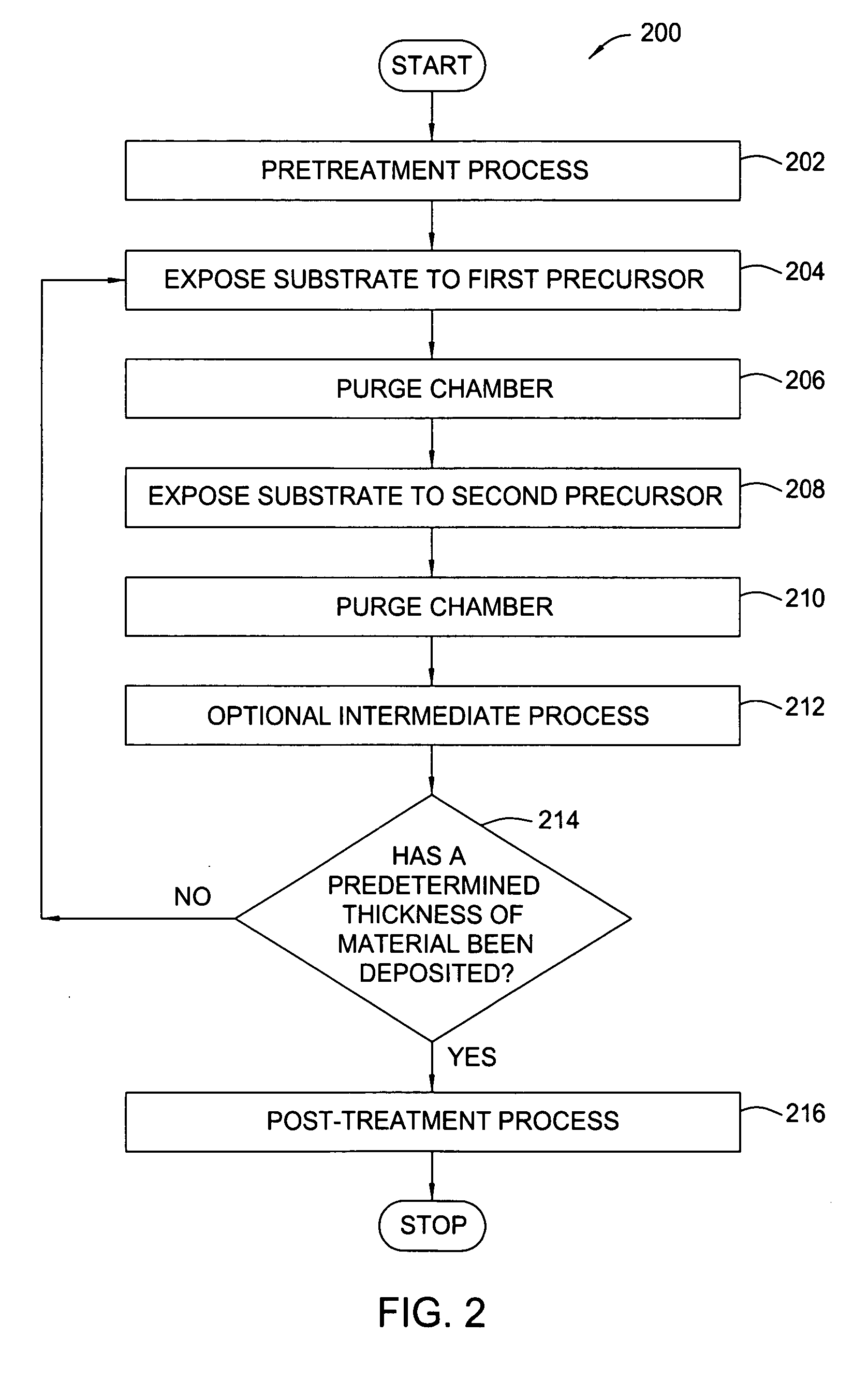
Treatment processes for a batch ALD reactor
Embodiments of the invention provide treatment processes to reduce substrate contamination during a fabrication process within a vapor deposition chamber. A treatment process may be conducted before, during or after a vapor deposition process, such as an atomic layer deposition (ALD) process. In one example of an ALD process, a process cycle, containing an intermediate treatment step and a predetermined number of ALD cycles, is repeated until the deposited material has a desired thickness. The chamber and substrates may be exposed to an inert gas, an oxidizing gas, a nitriding gas, a reducing gas or plasmas thereof during the treatment processes. In some examples, the treatment gas contains ozone, water, ammonia, nitrogen, argon or hydrogen. In one example, a process for depositing a hafnium oxide material within a batch process chamber includes a pretreatment step, an intermediate step during an ALD process and a post-treatment step.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
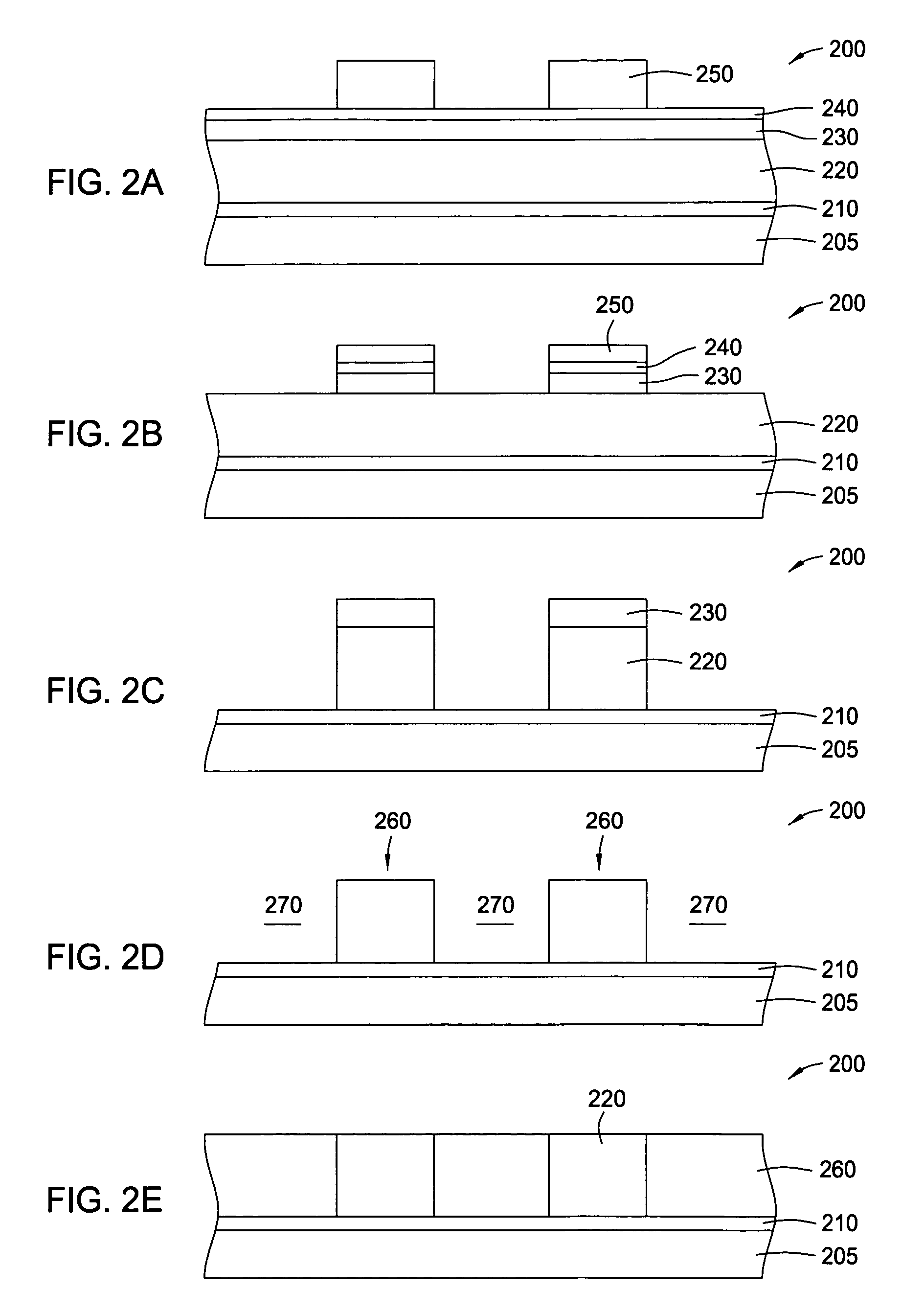
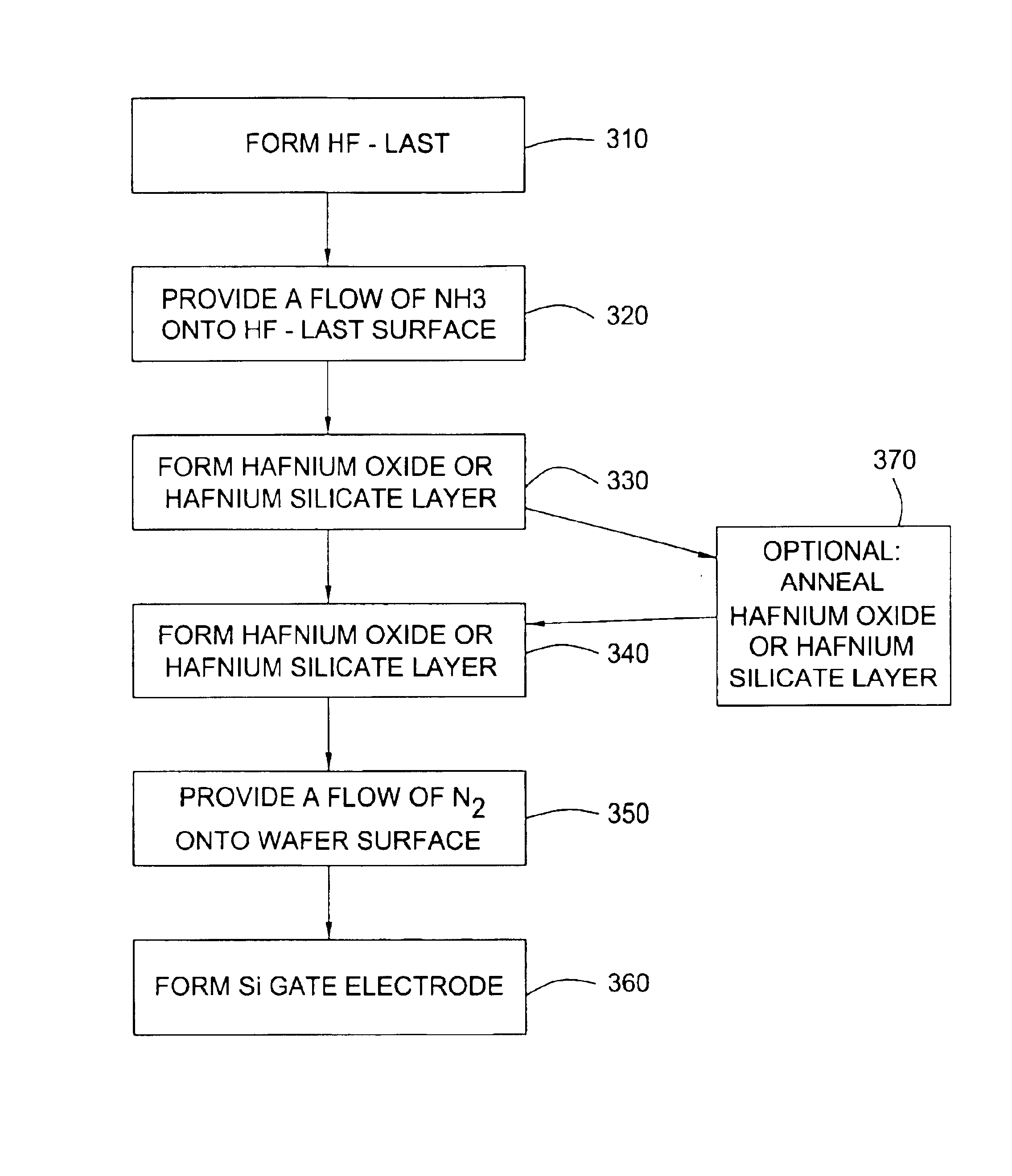
System and method for forming a gate dielectric
InactiveUS6858547B2Vacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrofluoric acidGate dielectric
A method of forming a dielectric stack on a pre-treated surface. The method comprises pre-cleaning a semiconductor wafer to remove native oxide, such as by applying hydroflouric acid to form an HF-last surface, pre-treating the HF-last surface with ozonated deionized water, forming a dielectric stack on the pre-treated surface and providing a flow of NH3 in a process zone surrounding the wafer. Alternately, the method includes pre-treating the HF-last surface with NH3, forming the stack after the pre-treating, and providing a flow of N2 in a process zone surrounding the wafer after the forming. The method also includes pre-treating the HF-last surface using an in-situ steam generation process, forming the stack on the pre-treated surface, and annealing the wafer after the forming. The pre-treating includes providing an inert gas flow in a process zone surrounding the HF-last surface, reacting hydrogen with an oxidizer in the process zone for a very short duration, and providing an inert gas flew in the process zone after the reacting.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Direct and selective production of ethanol from acetic acid utilizing a platinum/tin catalyst
InactiveUS7863489B2High selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionCalcium silicateAcetic acid
A process for the selective production of ethanol by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethanol is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over a platinum and tin supported on silica, graphite, calcium silicate or silica-alumina selectively produces ethanol in a vapor phase at a temperature of about 250° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
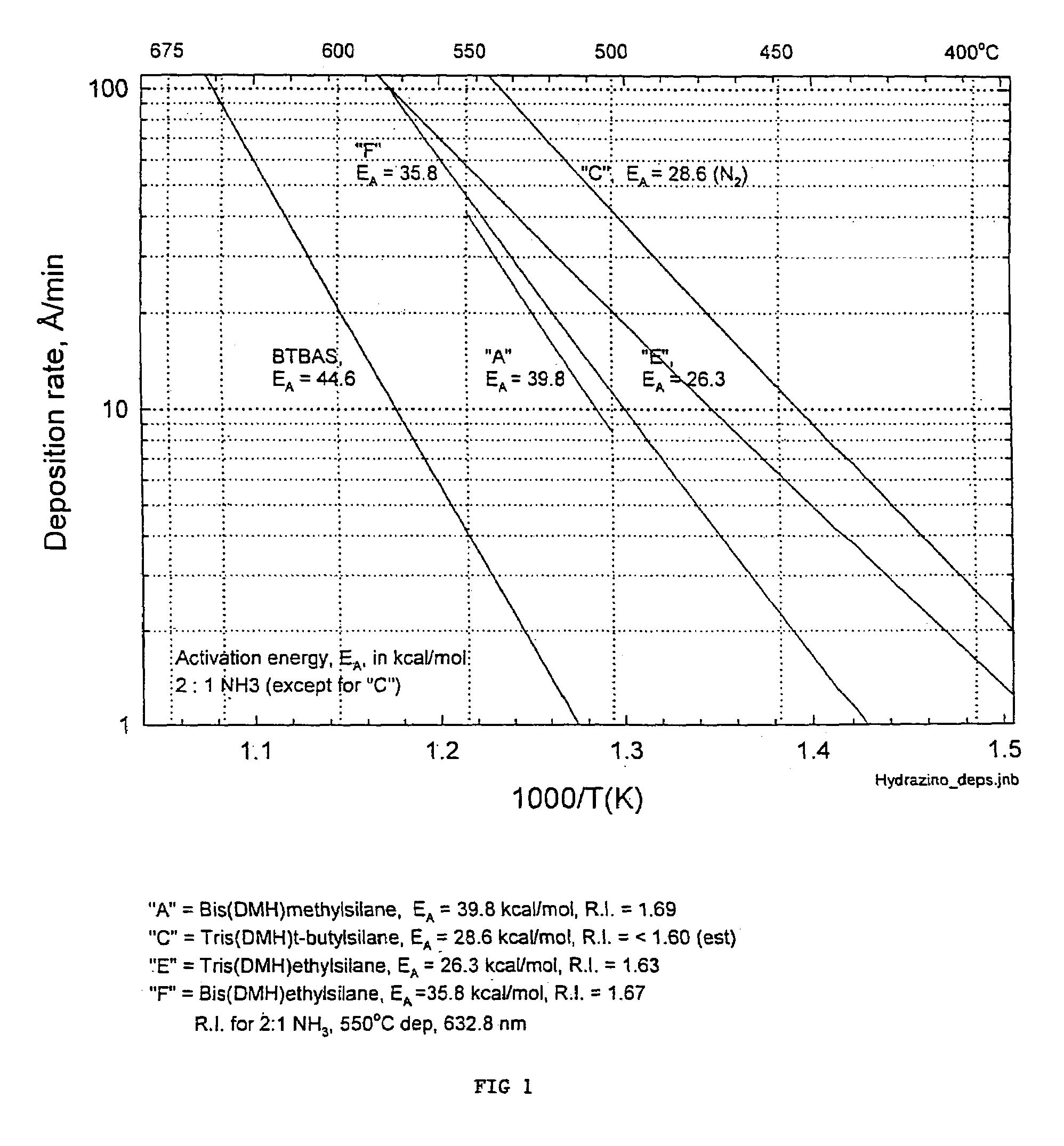
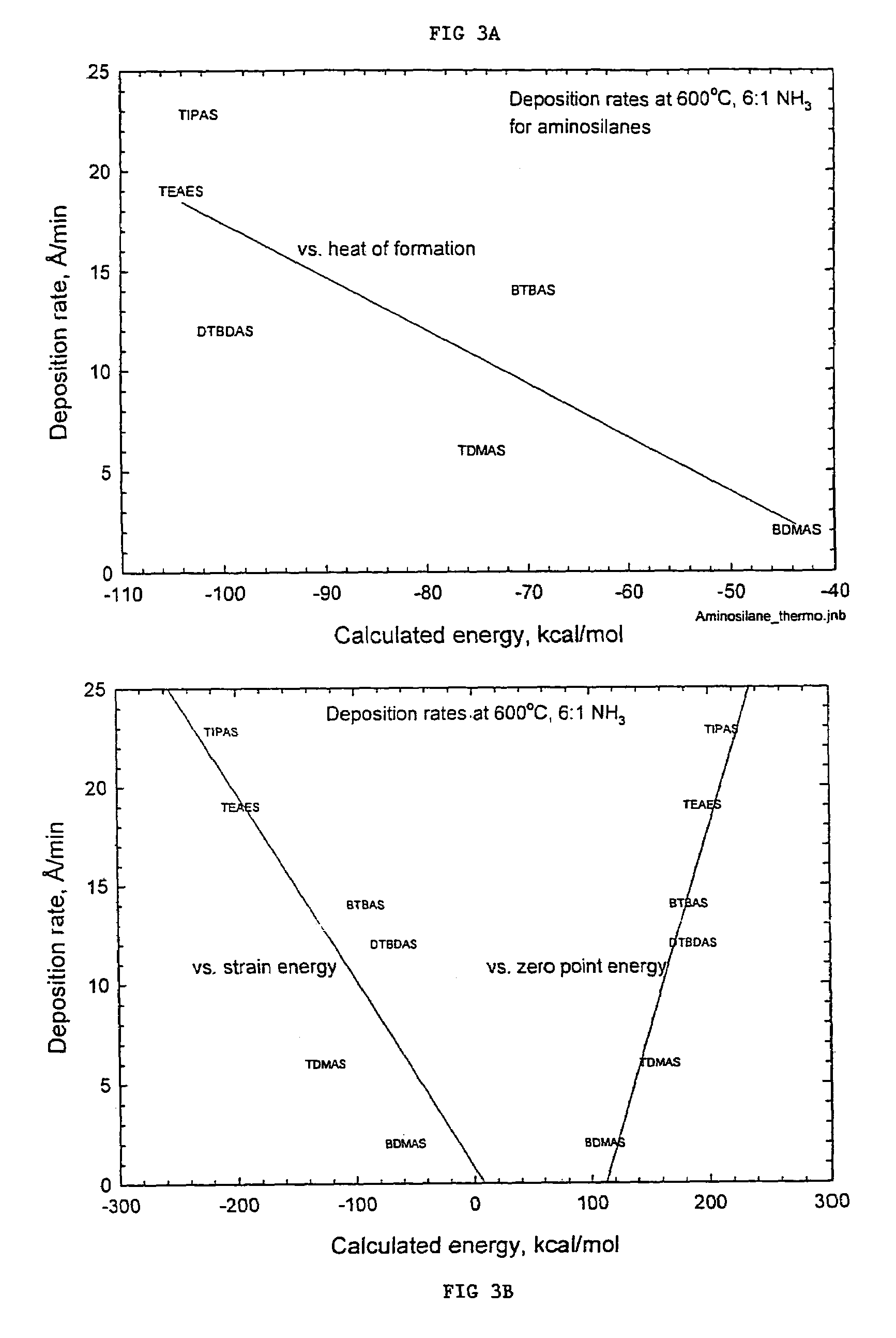
Precursors for depositing silicon containing films and processes thereof
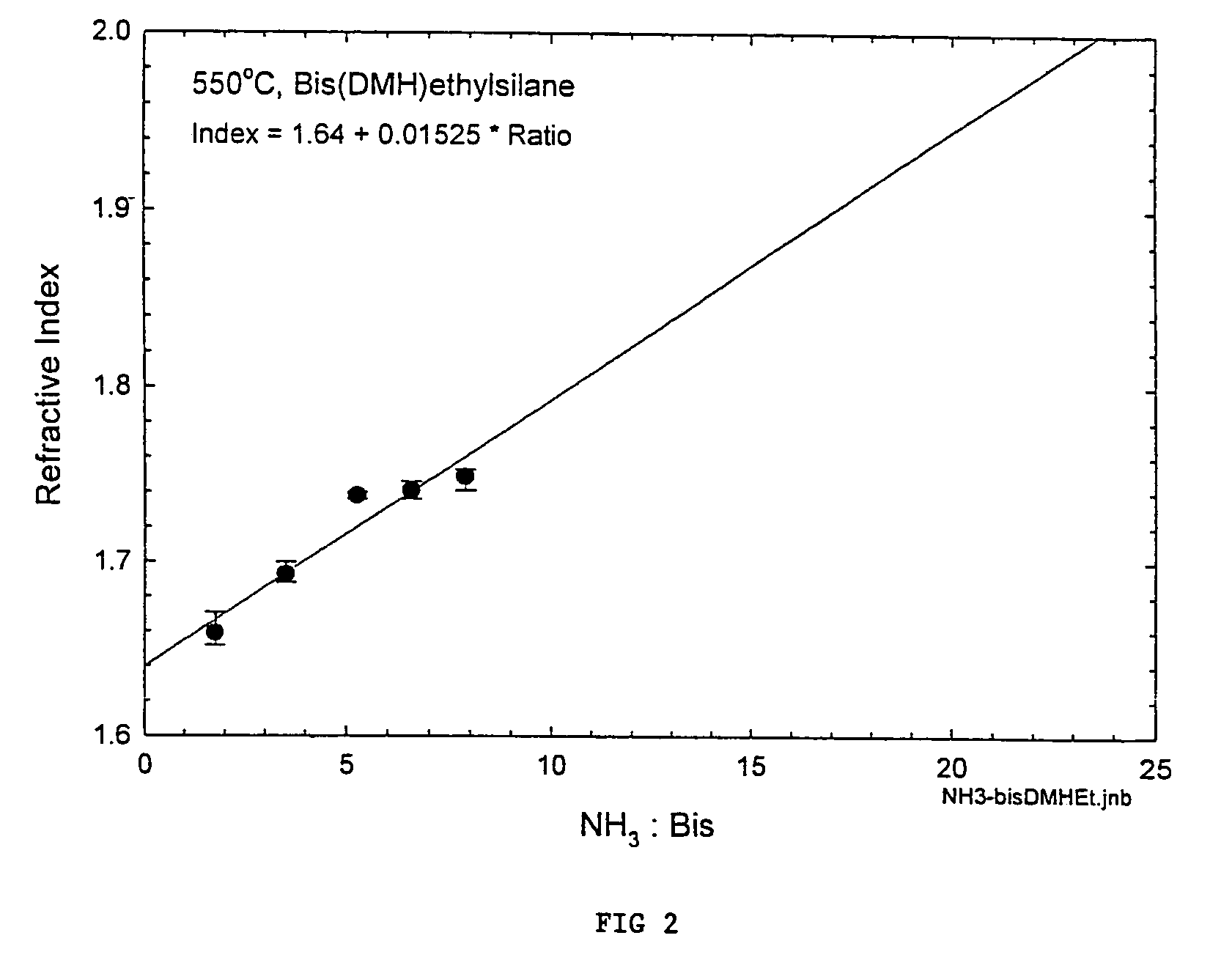
Processes for precursors for silicon dielectric depositions of silicon nitride, silicon oxide and silicon oxynitride on a substrate using a hydrazinosilane of the formula:[R12N—NH]nSi(R2)4−nwhere each R1 is independently selected from alkyl groups of C1 to C6; each R2 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, vinyl, allyl, and phenyl; and n=1–4. Some of the hydrazinosilanes are novel precursors.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
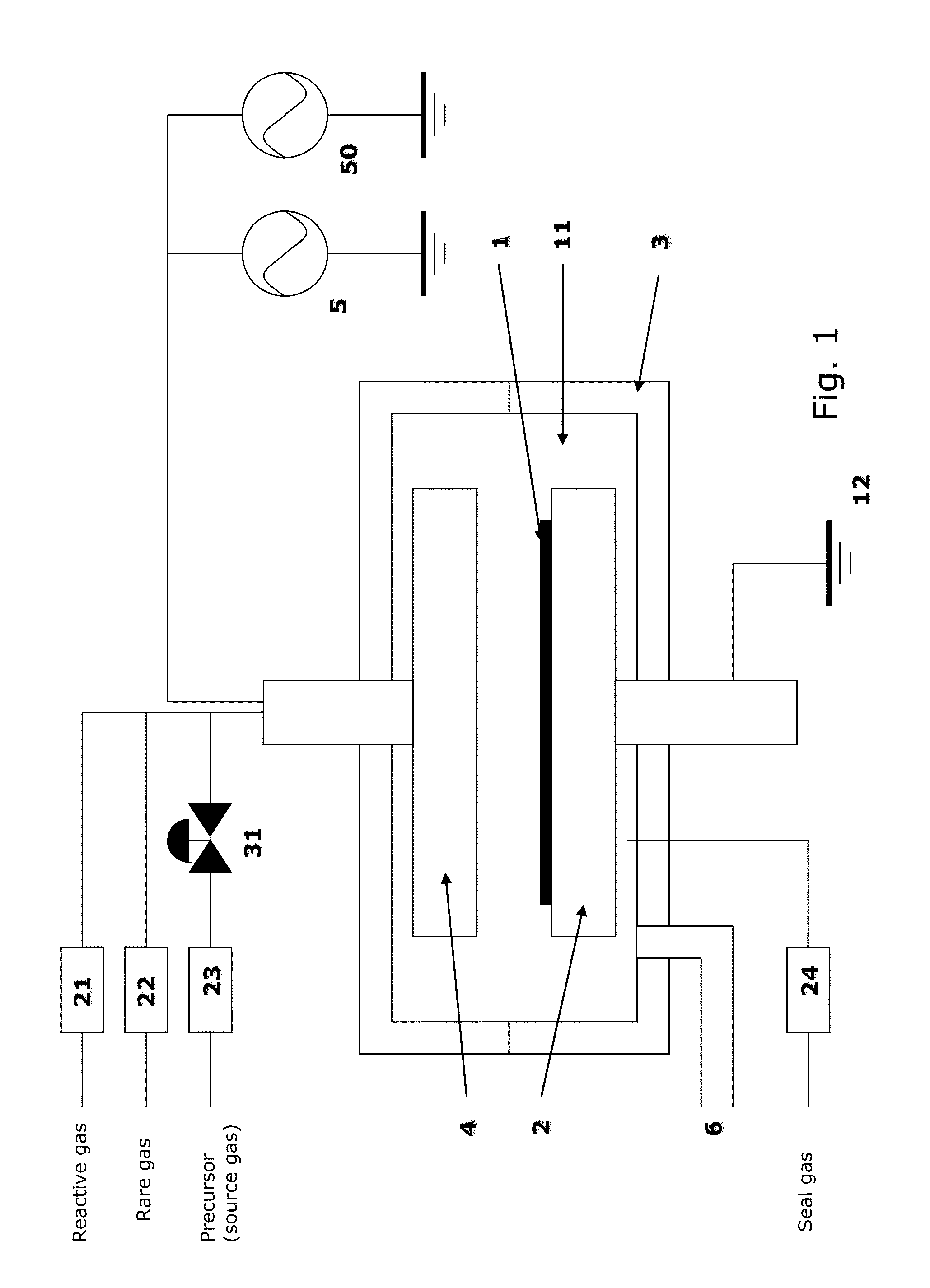
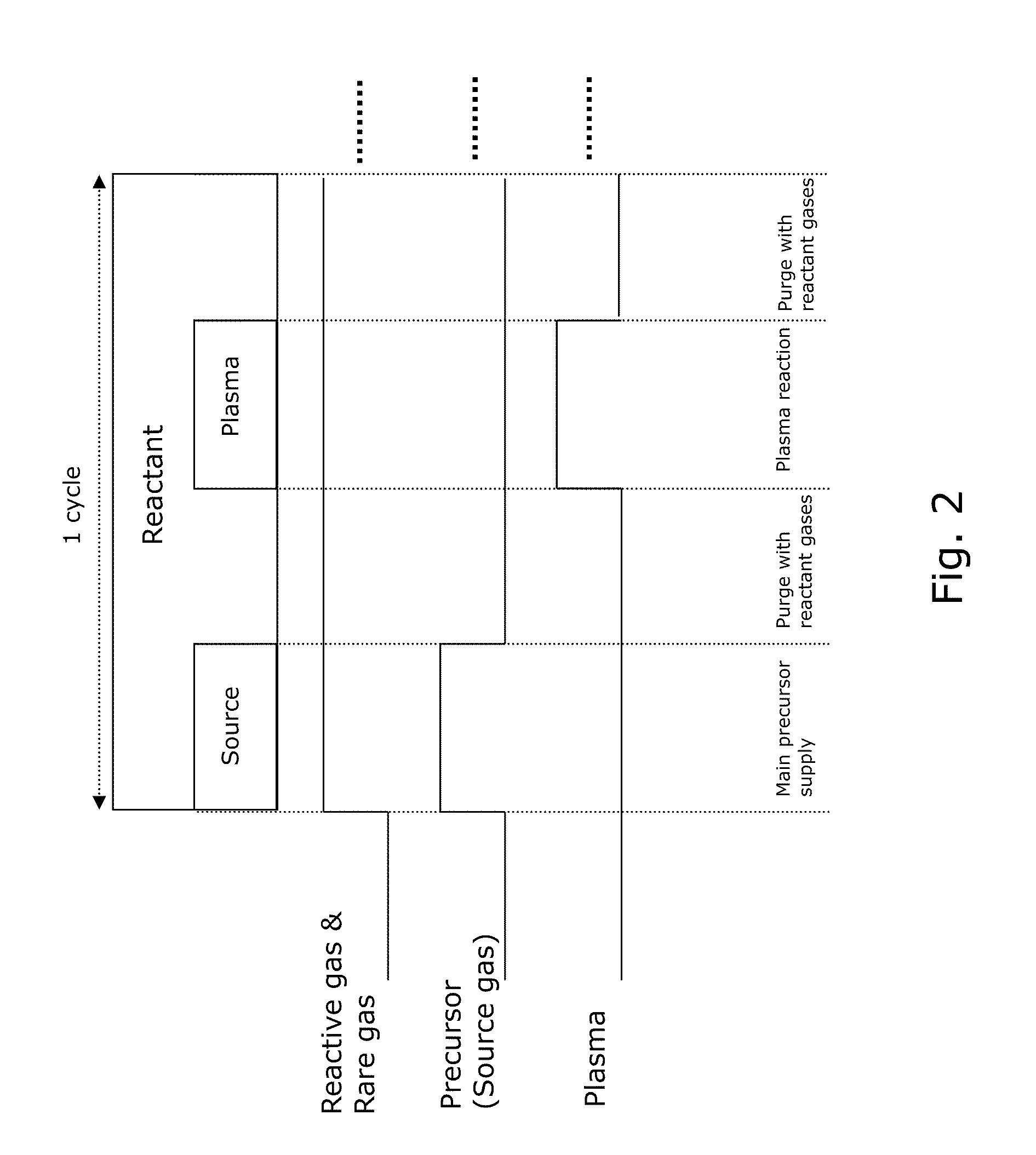
METHOD OF DEPOSITING DIELECTRIC FILM HAVING Si-N BONDS BY MODIFIED PEALD METHOD
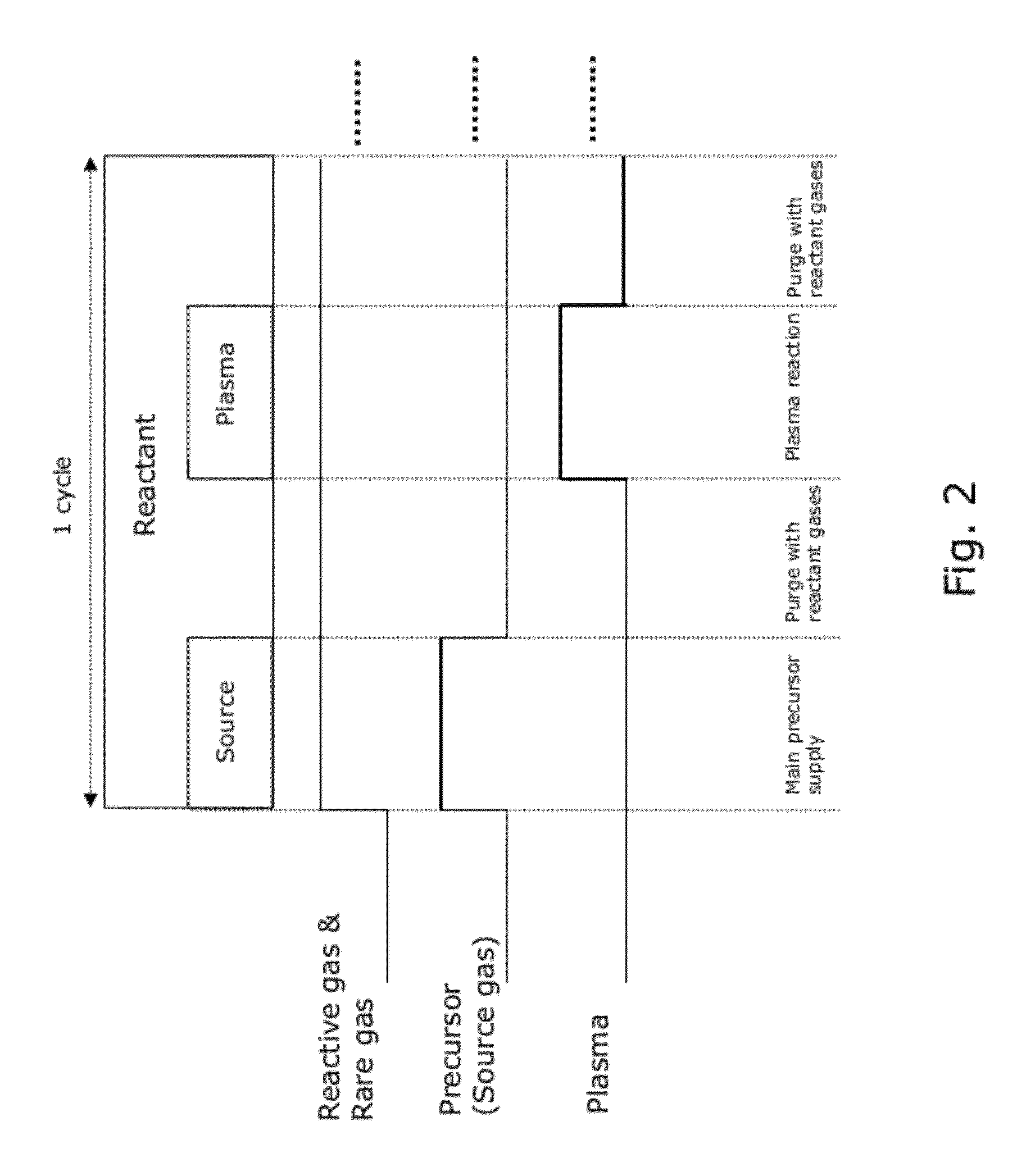
ActiveUS20110086516A1High conformalityIncrease deposition rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricNoble gas
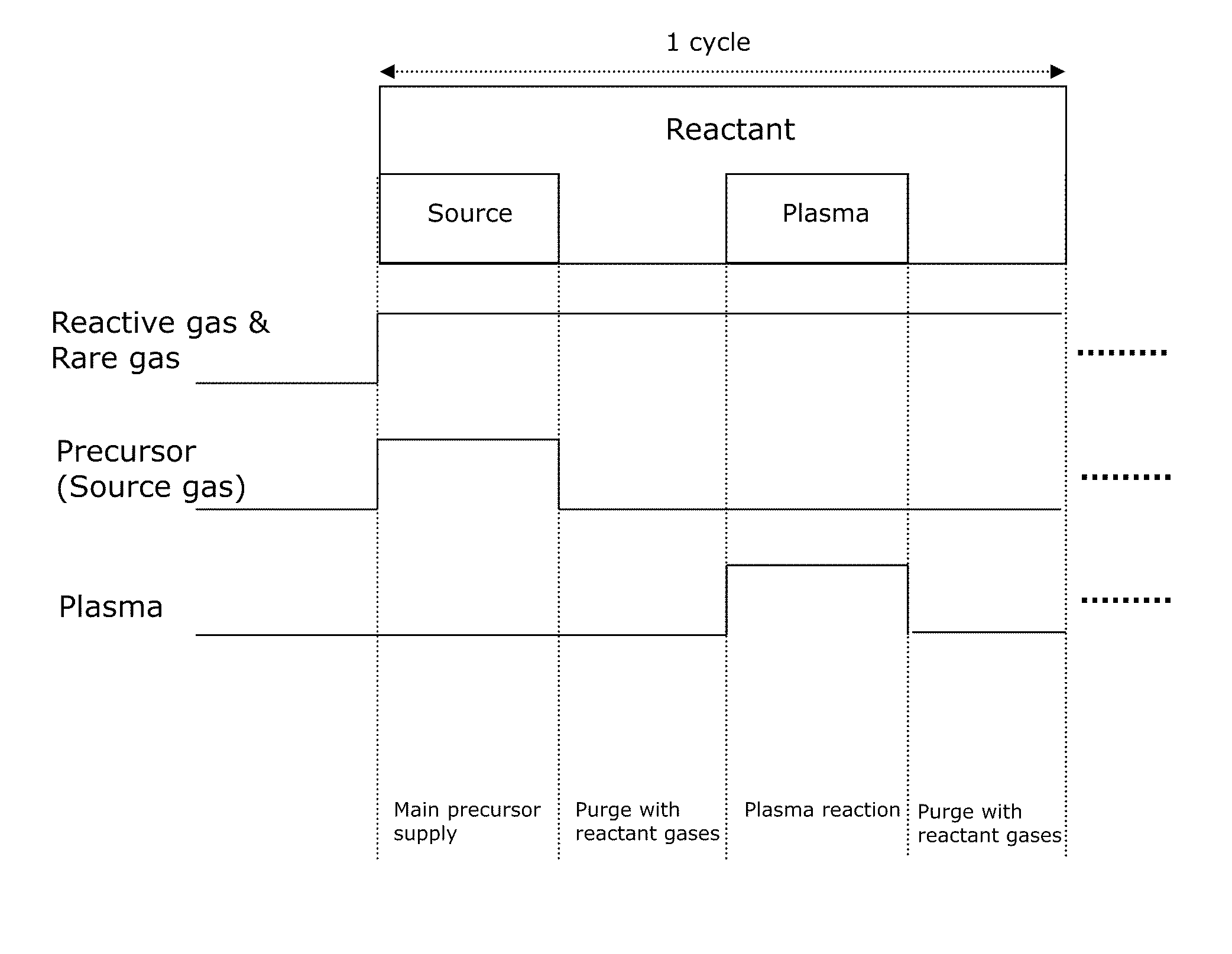
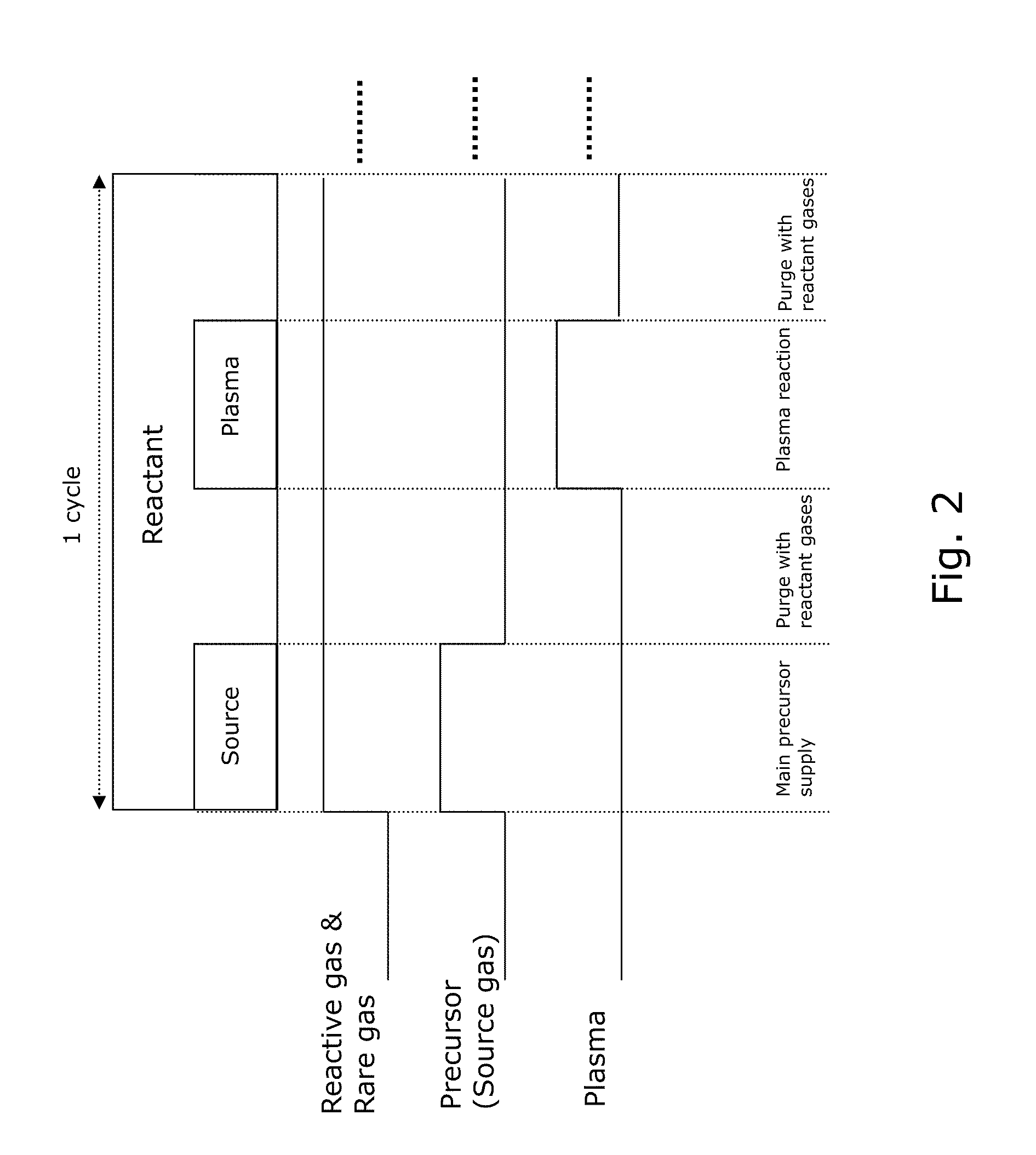
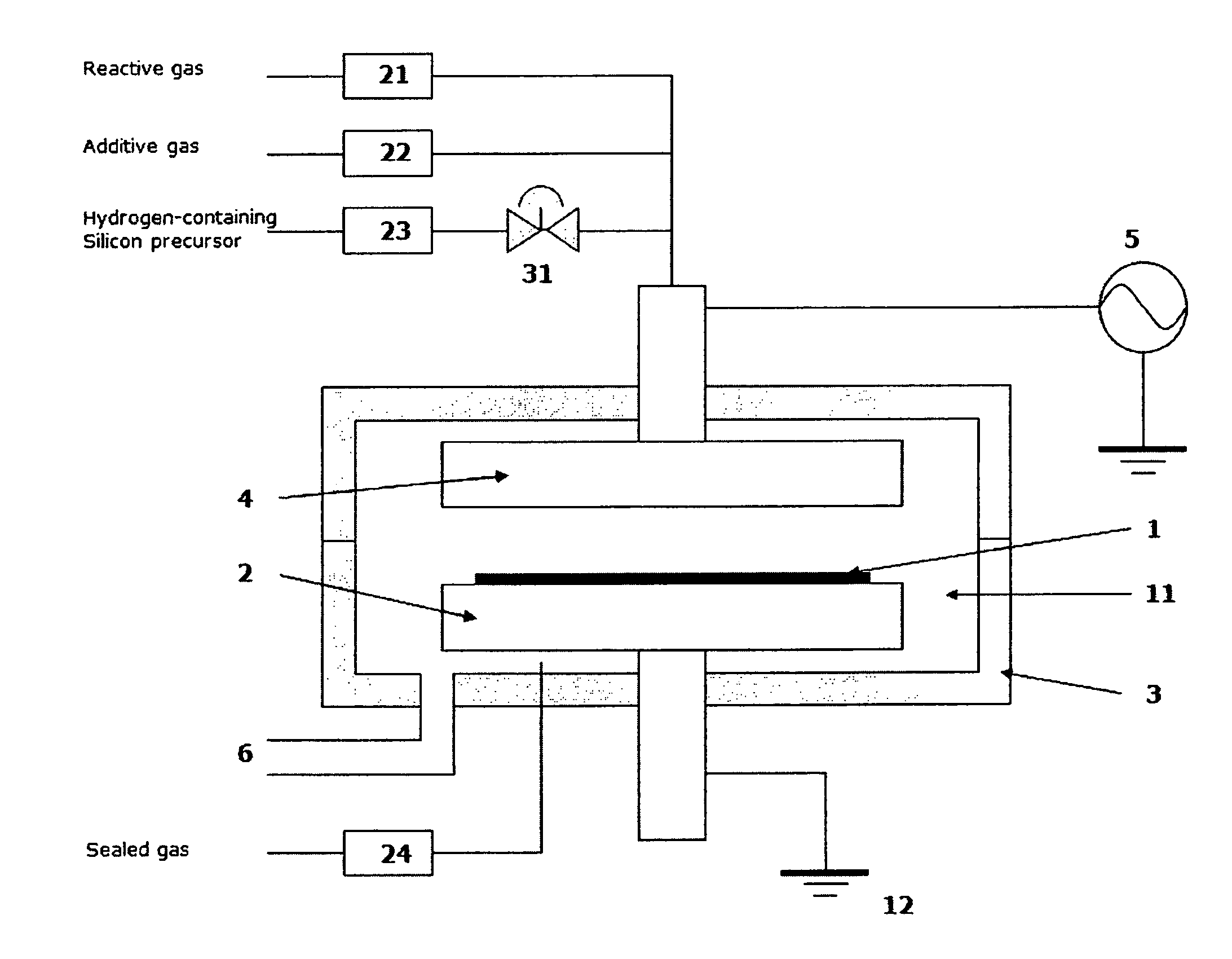
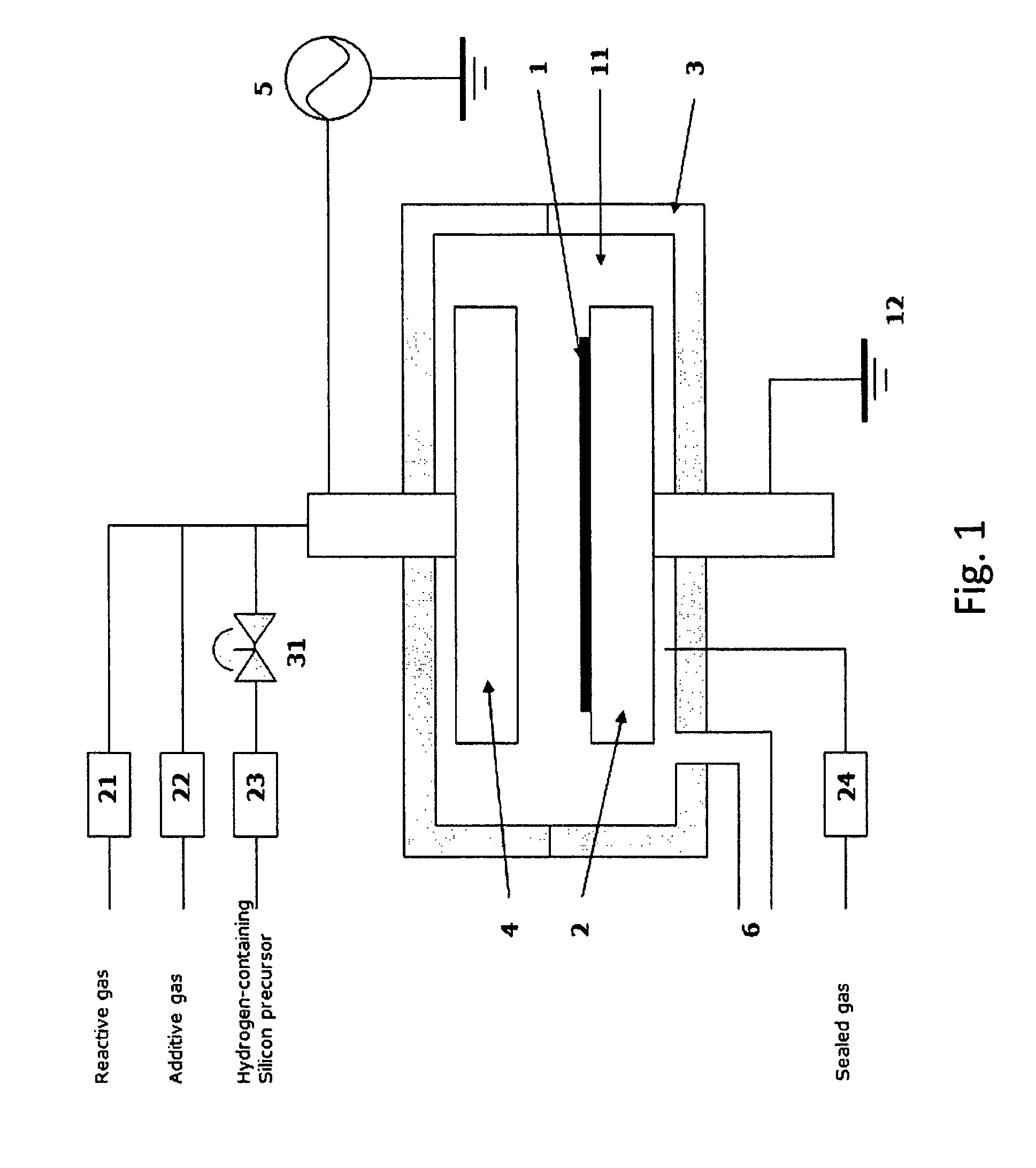
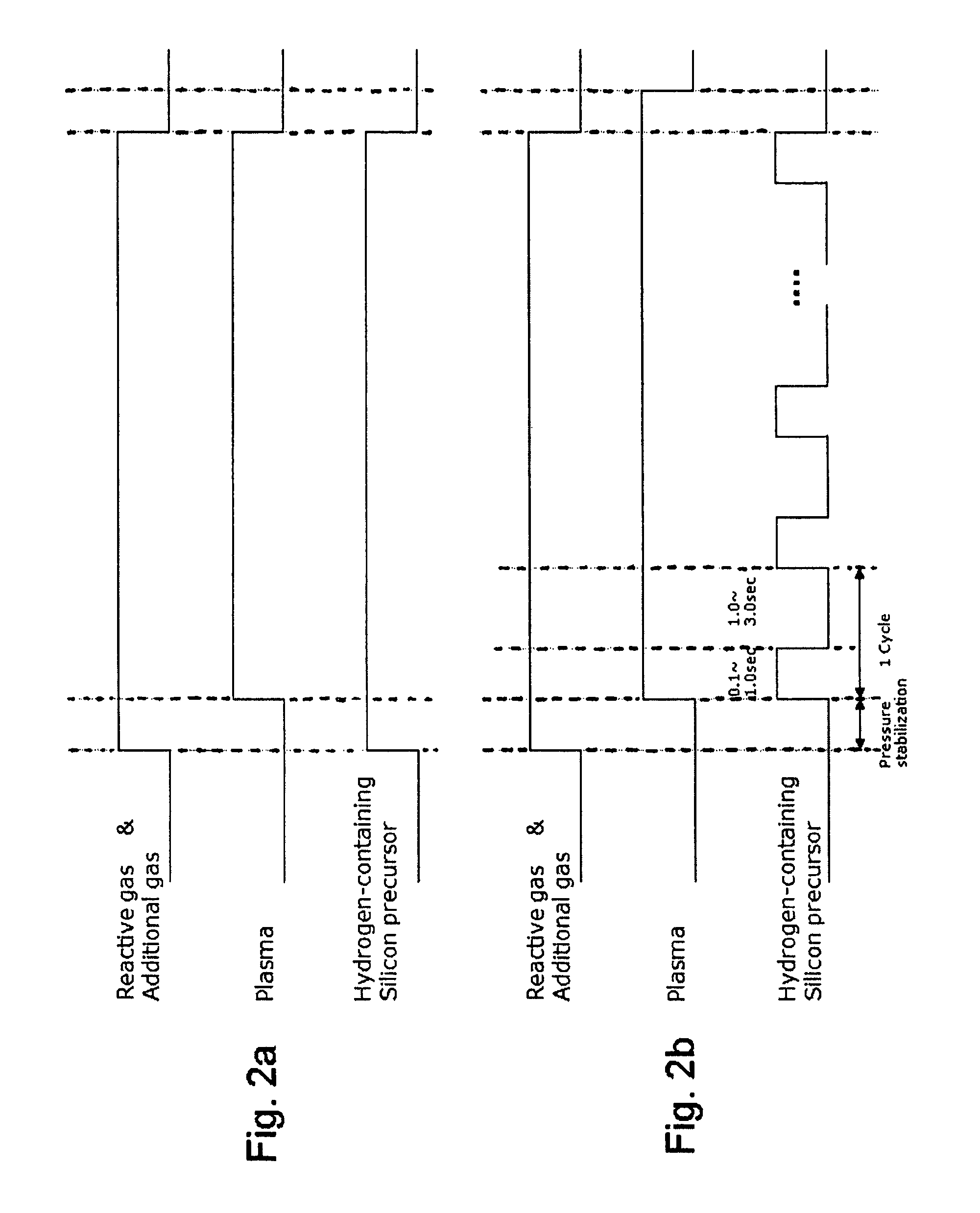
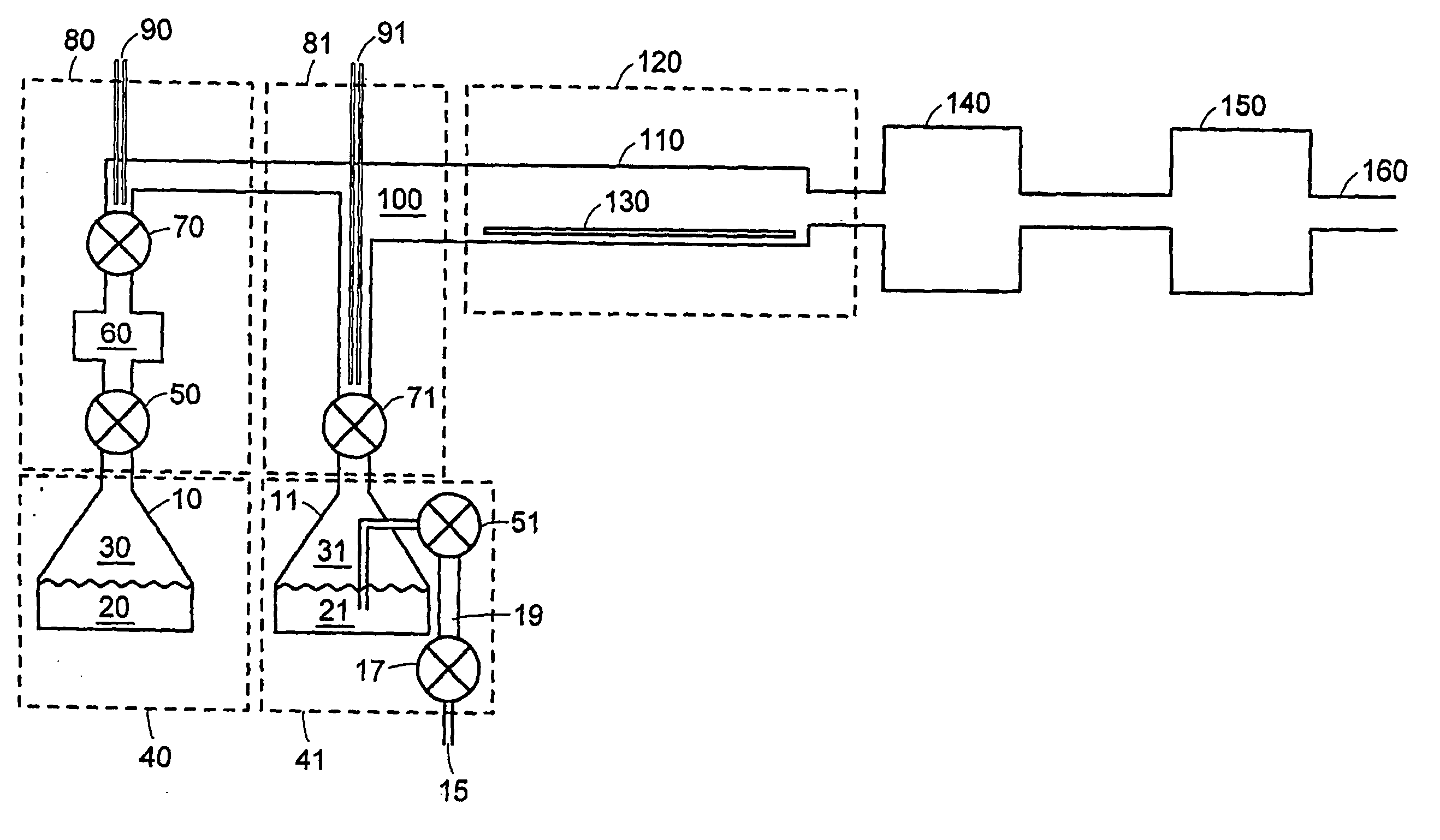
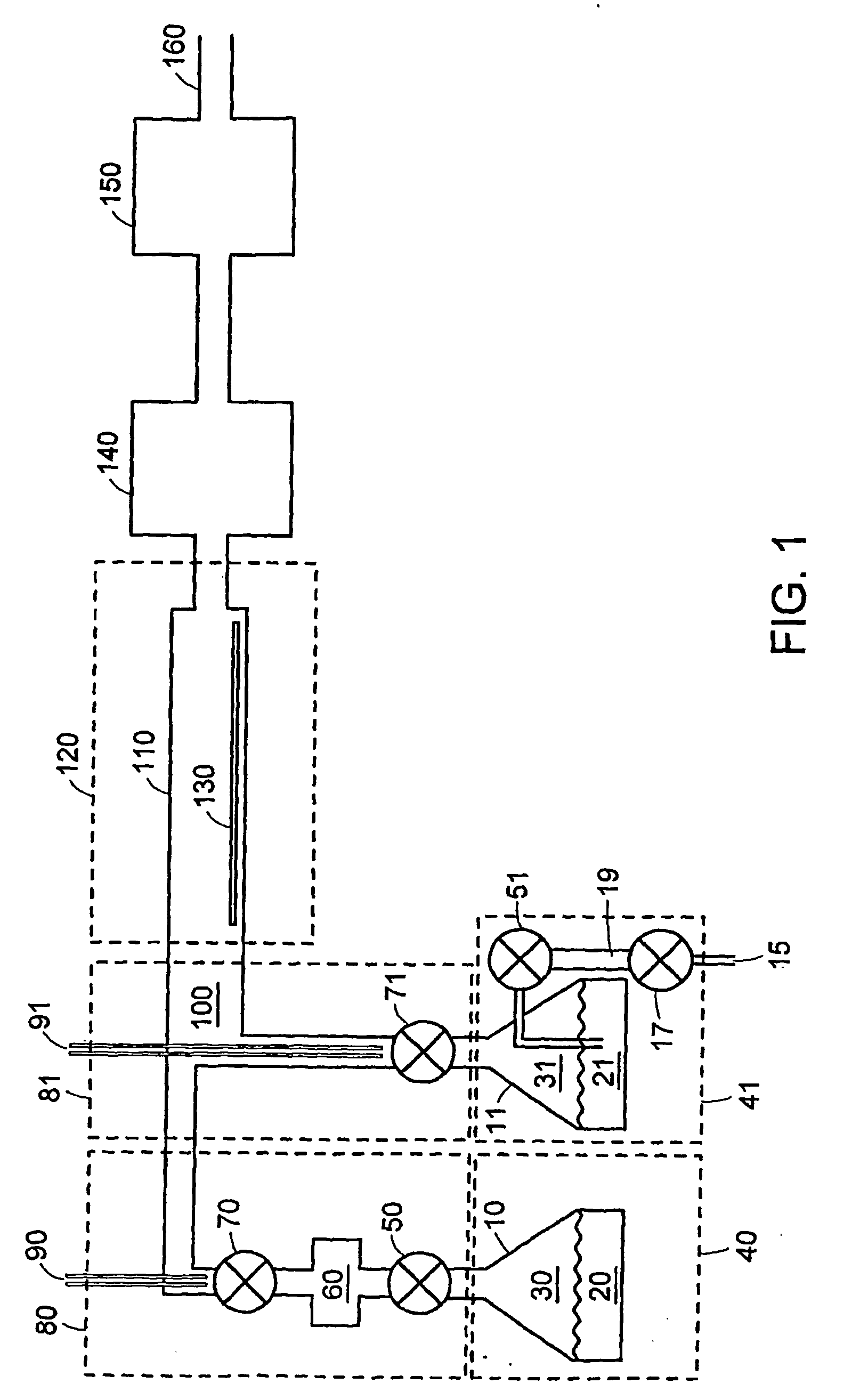
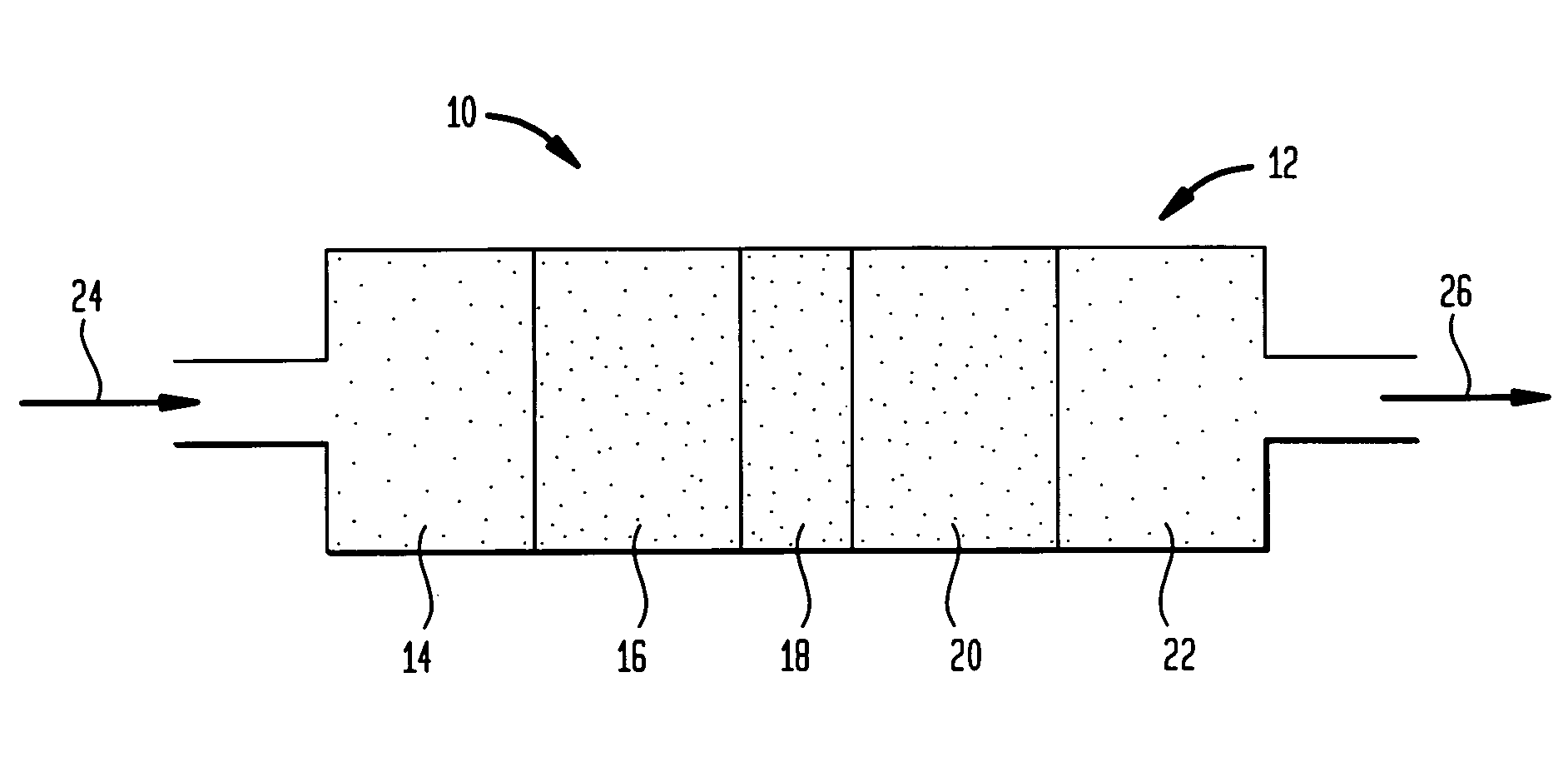
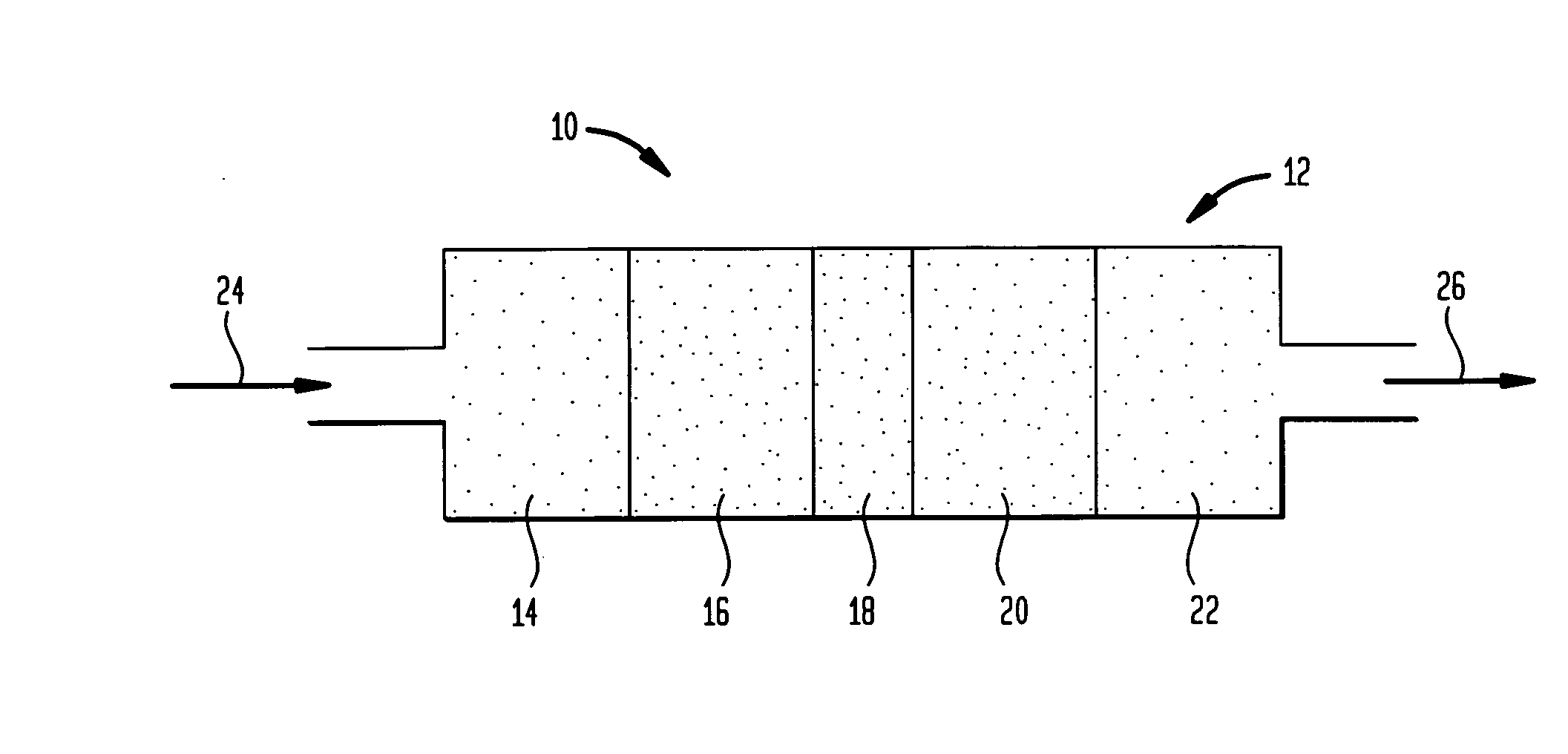
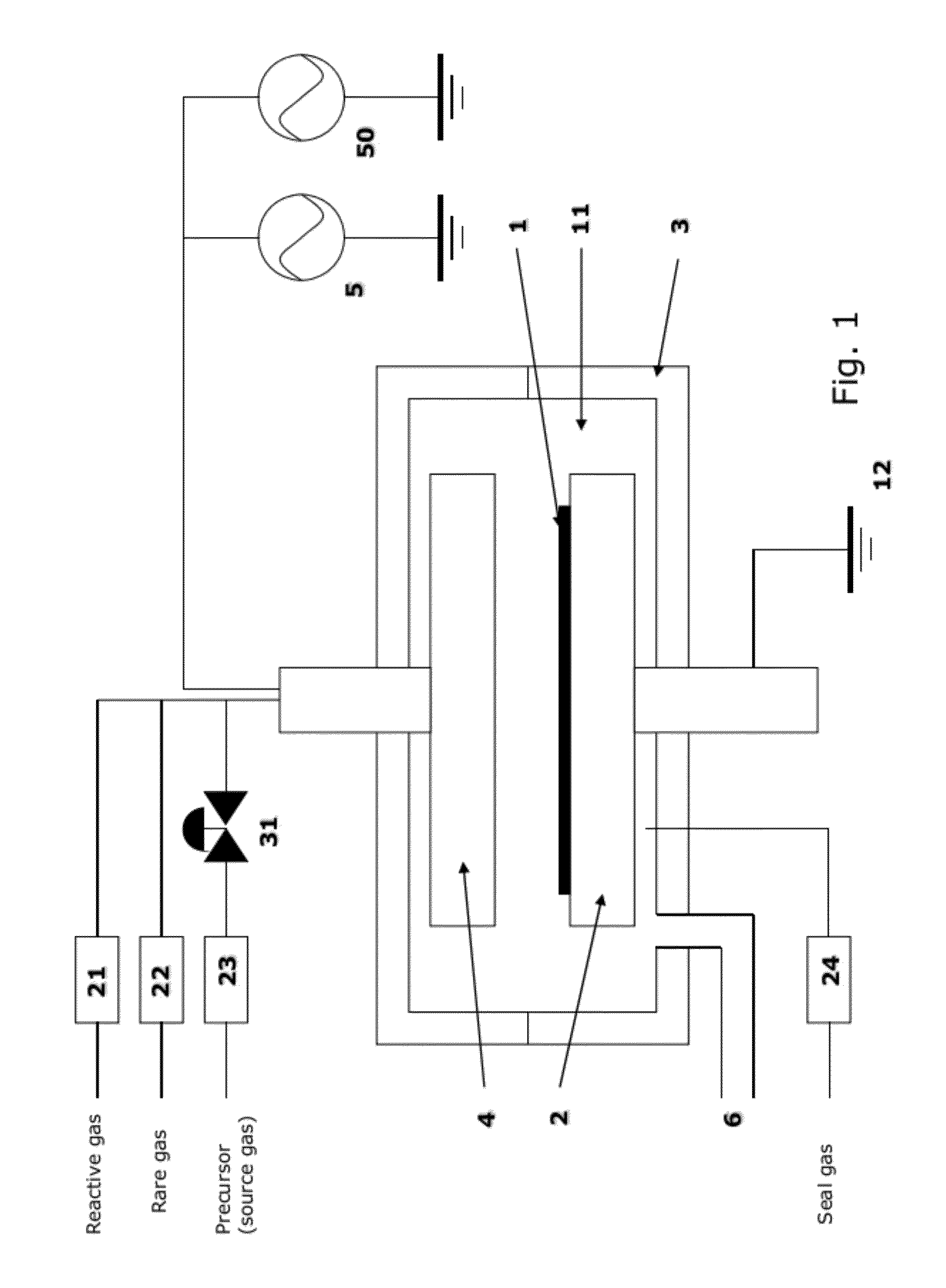
A method of forming dielectric film having Si—N bonds on a semiconductor substrate by plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD), includes: introducing a nitrogen- and hydrogen-containing reactive gas and a rare gas into a reaction space inside which the semiconductor substrate is placed; introducing a hydrogen-containing silicon precursor in pulses of less than 1.0-second duration into the reaction space wherein the reactive gas and the rare gas are introduced; exiting a plasma in pulses of less than 1.0-second duration immediately after the silicon precursor is shut off; and maintaining the reactive gas and the rare gas as a purge of less than 2.0-second duration.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Method of depositing dielectric film having Si-N bonds by modified peald method
ActiveUS8173554B2Increase deposition rateHigh conformalitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricHydrogen
A method of forming dielectric film having Si—N bonds on a semiconductor substrate by plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD), includes: introducing a nitrogen- and hydrogen-containing reactive gas and a rare gas into a reaction space inside which the semiconductor substrate is placed; introducing a hydrogen-containing silicon precursor in pulses of less than 1.0-second duration into the reaction space wherein the reactive gas and the rare gas are introduced; exiting a plasma in pulses of less than 1.0-second duration immediately after the silicon precursor is shut off; and maintaining the reactive gas and the rare gas as a purge of less than 2.0-second duration.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
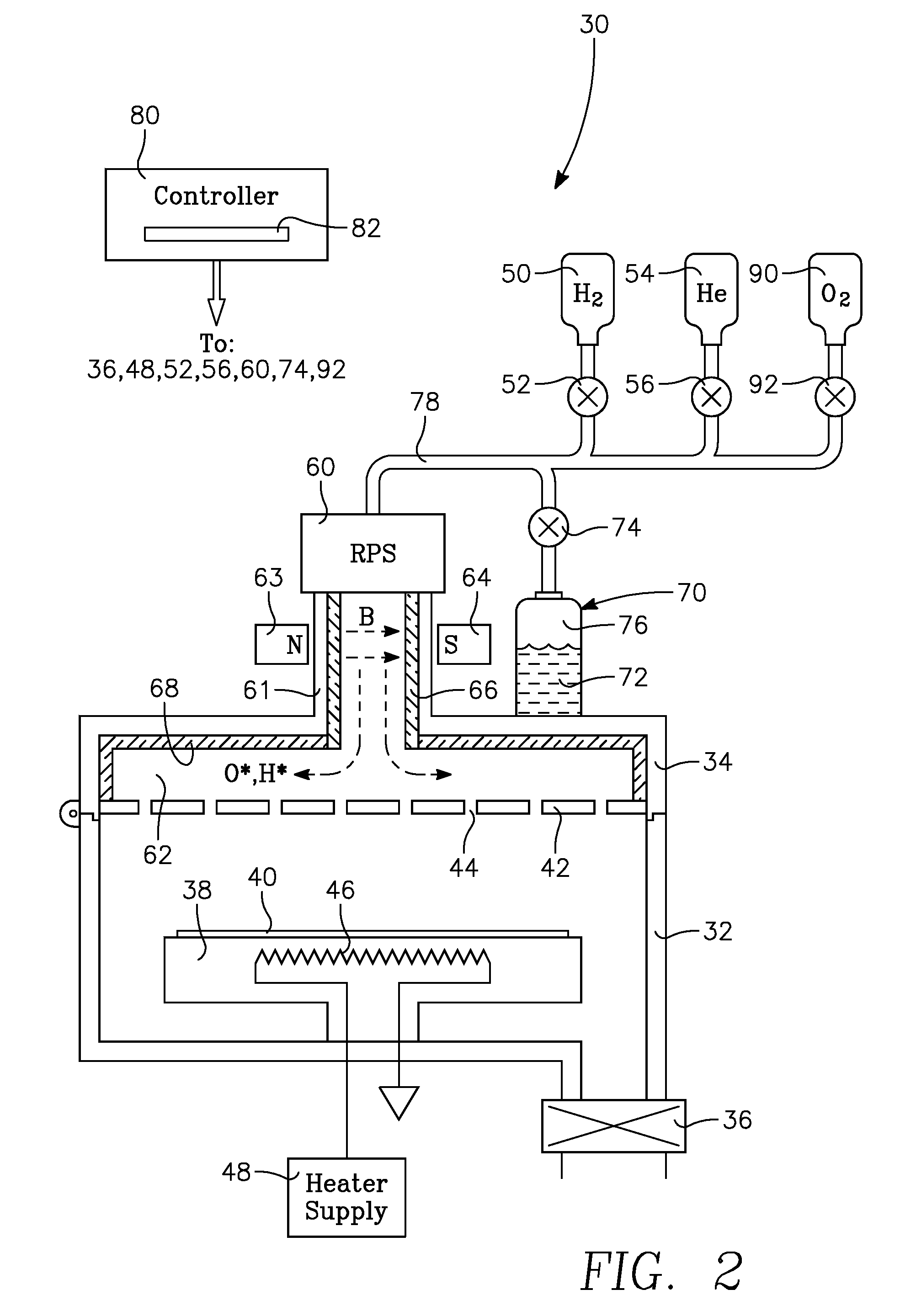
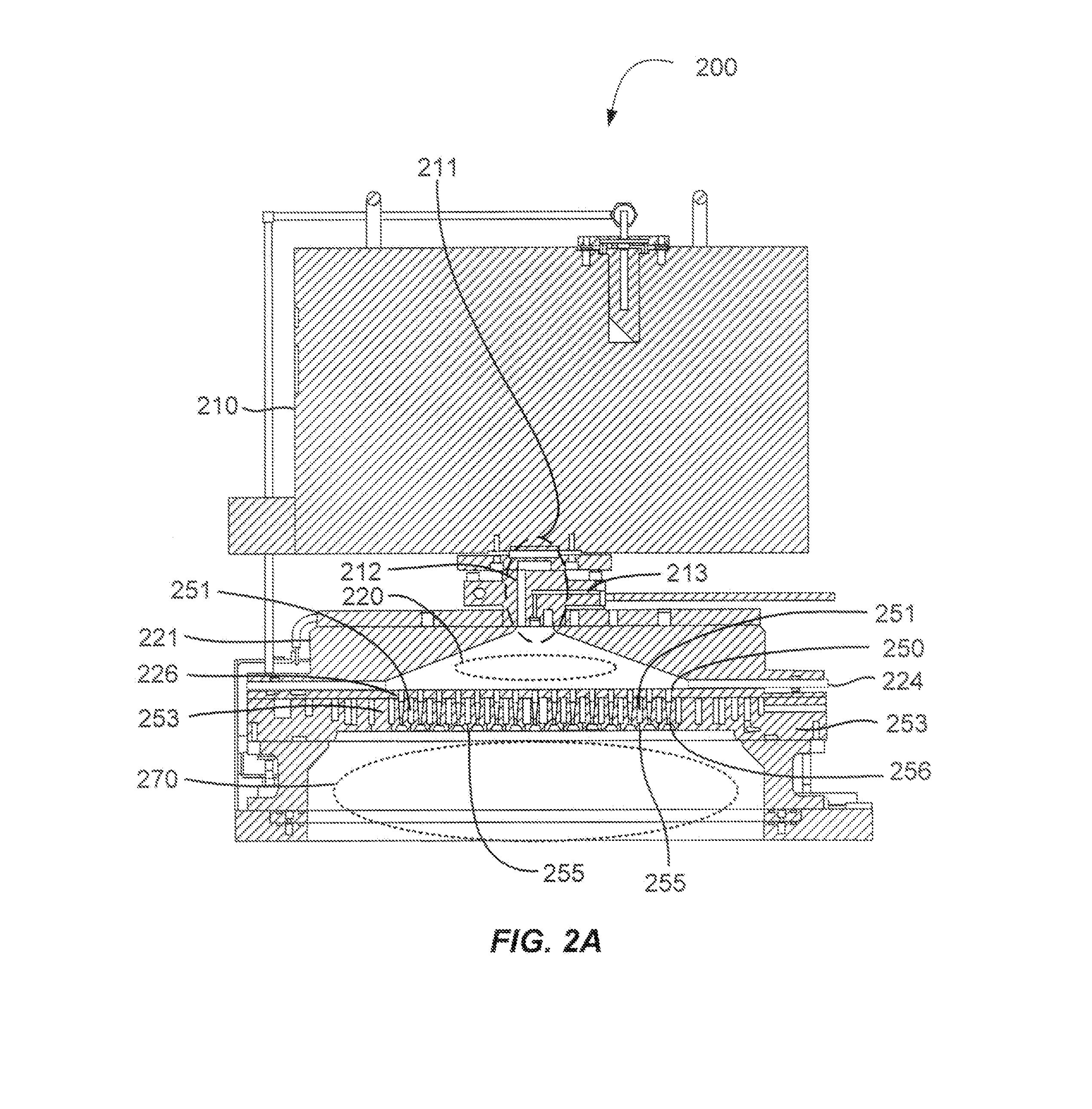
Remote Plasma Source for Pre-Treatment of Substrates Prior to Deposition
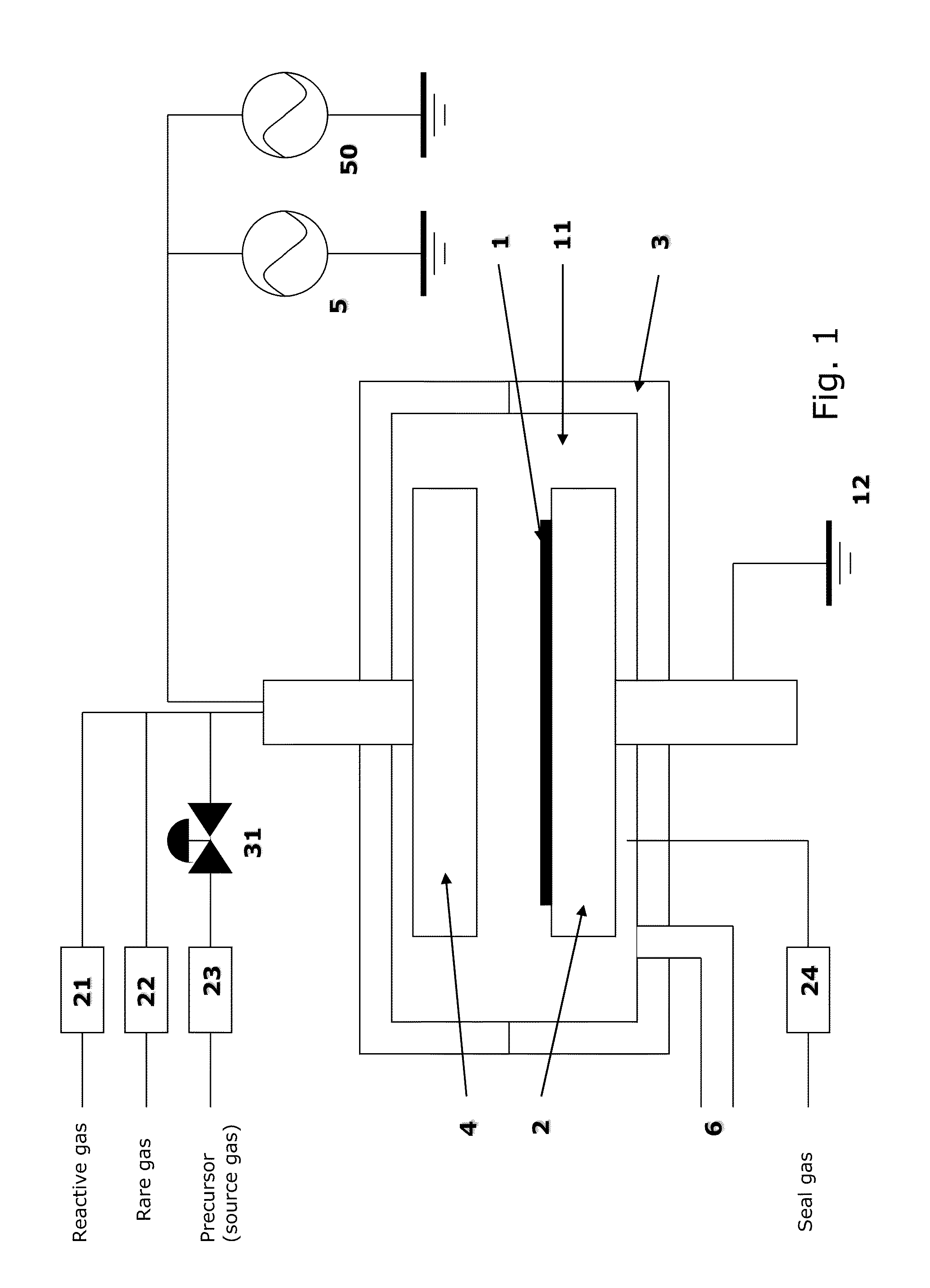
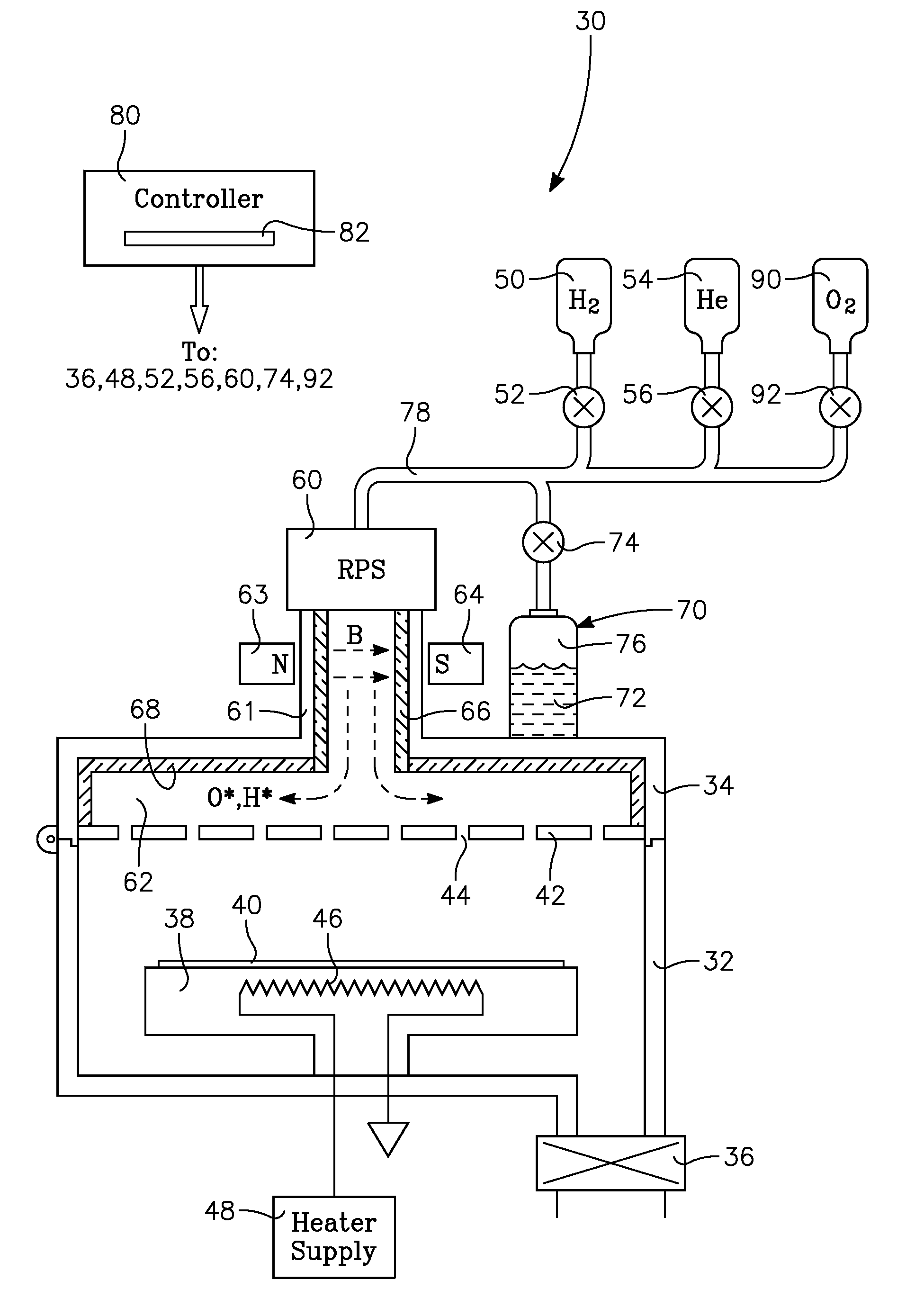
ActiveUS20090017227A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygenRefractory metals
A plasma processing chamber particularly useful for pre-treating low-k dielectric films and refractory metal films subject to oxidation prior to deposition of other layers. A remote plasma source (RPS) excites a processing gas into a plasma and delivers it through a supply tube to a manifold in back of a showerhead faceplate. The chamber is configured for oxidizing and reducing plasmas in the same or different processes when oxygen and hydrogen are selectively supplied to the RPS. The supply tube and showerhead may be formed of dielectric oxides which may be passivated by a water vapor plasma from the remote plasma source. In one novel process, a protective hydroxide coating is formed on refractory metals by alternating neutral plasmas of hydrogen and oxygen.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Organometallic Complex, Light-Emitting Element, Light-Emitting Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device
InactiveUS20140246656A1Improve efficiencyHigh sublimabilityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesHydrogenEmission efficiency
As a novel substance having a novel skeleton, an organometallic complex having high emission efficiency and improved color purity is provided. The color purity is improved by reducing the half width of an emission spectrum. The organometallic complex is represented by General Formula (G1). In General Formula (G1), at least one of R1 to R4 represents a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, and the others each independently represent hydrogen or a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms. Note that the case where all of R1 to R4 represent alkyl groups each having 1 carbon atom is excluded. Further, R5 to R9 each independently represent hydrogen or a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method to increase silicon nitride tensile stress using nitrogen plasma in-situ treatment and ex-situ UV cure
ActiveUS20080020591A1Improve performanceFilm stress is increasedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogen plasmaUV curing
Stress of a silicon nitride layer may be enhanced by deposition at higher temperatures. Employing an apparatus that allows heating of a substrate to substantially greater than 400° C. (for example a heater made from ceramic rather than aluminum), the silicon nitride film as-deposited may exhibit enhanced stress allowing for improved performance of the underlying MOS transistor device. In accordance with alternative embodiments, a deposited silicon nitride film is exposed to curing with ultraviolet (UV) radiation at an elevated temperature, thereby helping remove hydrogen from the film and increasing film stress. In accordance with still other embodiments, a silicon nitride film is formed utilizing an integrated process employing a number of deposition / curing cycles to preserve integrity of the film at the sharp corner of the underlying raised feature. Adhesion between successive layers may be promoted by inclusion of a post-UV cure plasma treatment in each cycle.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Red phosphorescent compounds and organic electroluminescent devices using the same
ActiveUS20070104980A1High color purityLong life-timeIndium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensDopantHydrogen
Disclosed herein are red phosphorescent compounds of the following Formulas 1 to 4: wherein is R1, R2 and R3 are independently a C1-C4 alkyl group, R4, R5, R6 and R7 are independently selected from hydrogen, C1-C4 alkyl groups and C1-C4 alkoxy groups, and is selected from 2,4-pentanedione, 2,2,6,6,-tetramethylheptane-3,5-dione, 1,3-propanedione, 1,3-butanedione, 3,5-heptanedione, 1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentanedione, 1,1,1,5,5,5-hexafluoro-2,4-pentanedione, and 2,2-dimethyl-3,5-hexanedione; wherein is R1 and R2 are independently selected from C1-C4 alkyl groups and C1-C4 alkoxy groups, R3, R4, R5 and R6 are independently selected from hydrogen, C1-C4 alkyl groups and C1-C4 alkoxy groups, and is selected from 2,4-pentanedione, 2,2,6,6,-tetramethylheptane-3,5-dione, 1,3-propanedione, 1,3-butanedione, 3,5-heptanedione, 1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentanedione, 1,1,1,5,5,5-hexafluoro-2,4-pentanedione and 2,2-dimethyl-3,5-hexanedione; wherein is R1 and R2 are independently selected from C1-C4 alkyl groups and C1-C4 alkoxy groups, R3, R4, R5 and R6 are independently selected from hydrogen, C1-C4 alkyl groups and C1-C4 alkoxy groups, and is selected from 2,4-pentanedione, 2,2,6,6,-tetramethylheptane-3,5-dione, 1,3-propanedione, 1,3-butanedione, 3,5-heptanedione, 1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentanedione, 1,1,1,5,5,5-hexafluoro-2,4-pentanedione and 2,2-dimethyl-3,5-hexanedione; and wherein is R1 and R2 are independently selected from C1-C4 alkyl groups and C1-C4 alkoxy groups, R3, R4, R5 and R6 are independently selected from hydrogen, C1-C4 alkyl groups and C1-C4 alkoxy groups, and is selected from 2,4-pentanedione, 2,2,6,6,-tetramethylheptane-3,5-dione, 1,3-propanedione, 1,3-butanedione, 3,5-heptanedione, 1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentanedione, 1,1,1,5,5,5-hexafluoro-2,4-pentanedione and 2,2-dimethyl-3,5-hexanedione. Further disclosed herein is an organic electroluminescent (EL) device comprising an anode, a hole injecting layer, a hole transport layer, a light-emitting layer, an electron transport layer, an electron injecting layer, and a cathode laminated in this order wherein one of the red phosphorescent compounds is used as a dopant of the light-emitting layer.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method of forming conformal dielectric film having Si-N bonds by PECVD
A method of forming a conformal dielectric film having Si—N bonds on a semiconductor substrate by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) includes: introducing a nitrogen- and hydrogen-containing reactive gas and an additive gas into a reaction space inside which a semiconductor substrate is placed; applying RF power to the reaction space; and introducing a hydrogen-containing silicon precursor in pulses into the reaction space wherein a plasma is excited, thereby forming a conformal dielectric film having Si—N bonds on the substrate.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Atomic layer deposition using metal amidinates
ActiveUS20060141155A1Improve conductivityReduce the temperatureGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsHydrogenWater vapor
Metal films are deposited with uniform thickness and excellent step coverage. Copper metal films were deposited on heated substrates by the reaction of alternating doses of copper(I) NN′-diisopropylacetamidinate vapor and hydrogen gas. Cobalt metal films were deposited on heated substrates by the reaction of alternating doses of cobalt(II) bis(N,N′-diisopropylacetamidinate) vapor and hydrogen gas. Nitrides and oxides of these metals can be formed by replacing the hydrogen with ammonia or water vapor, respectively. The films have very uniform thickness and excellent step coverage in narrow holes. Suitable applications include electrical interconnects in microelectronics and magnetoresistant layers in magnetic information storage devices.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
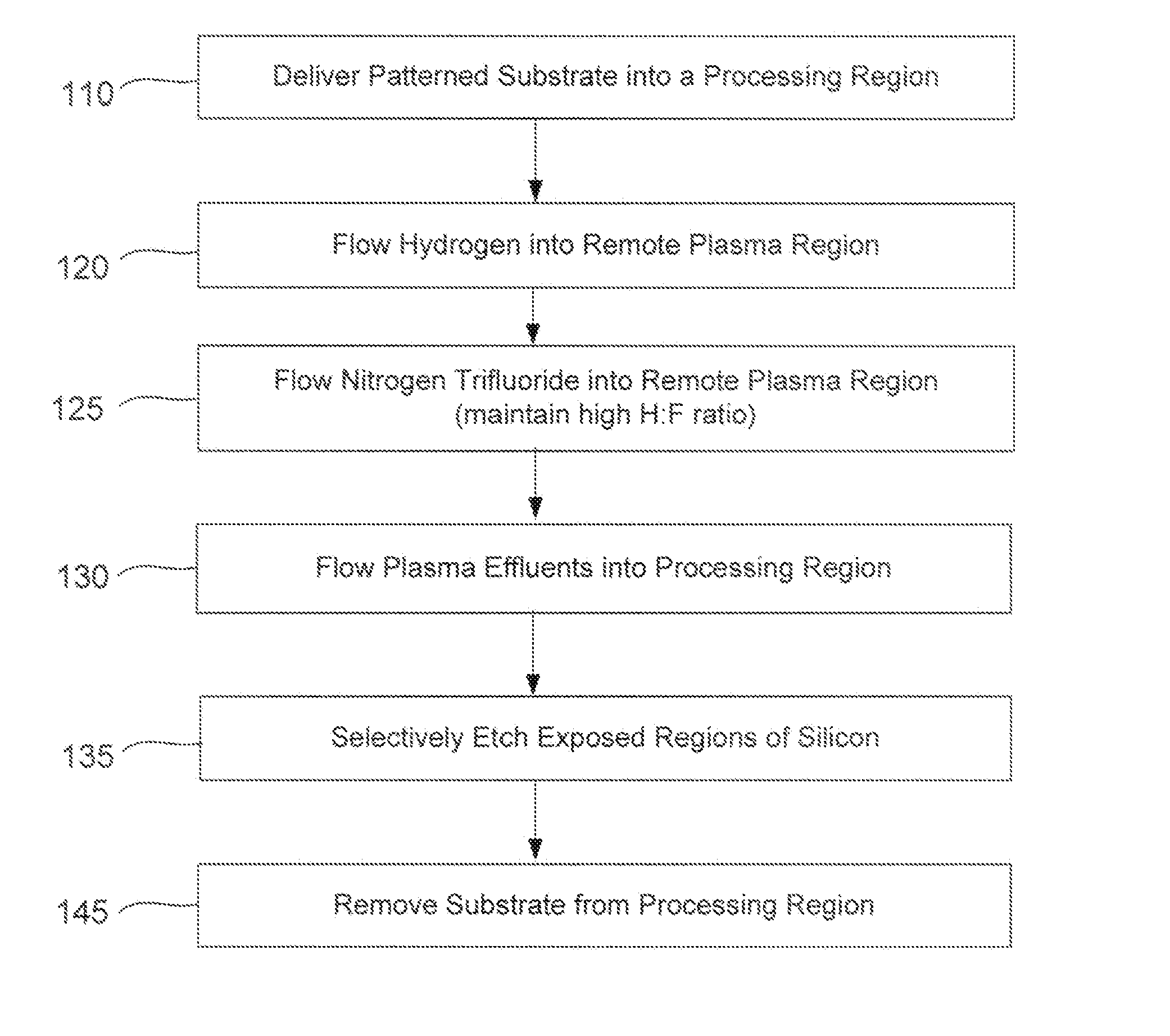
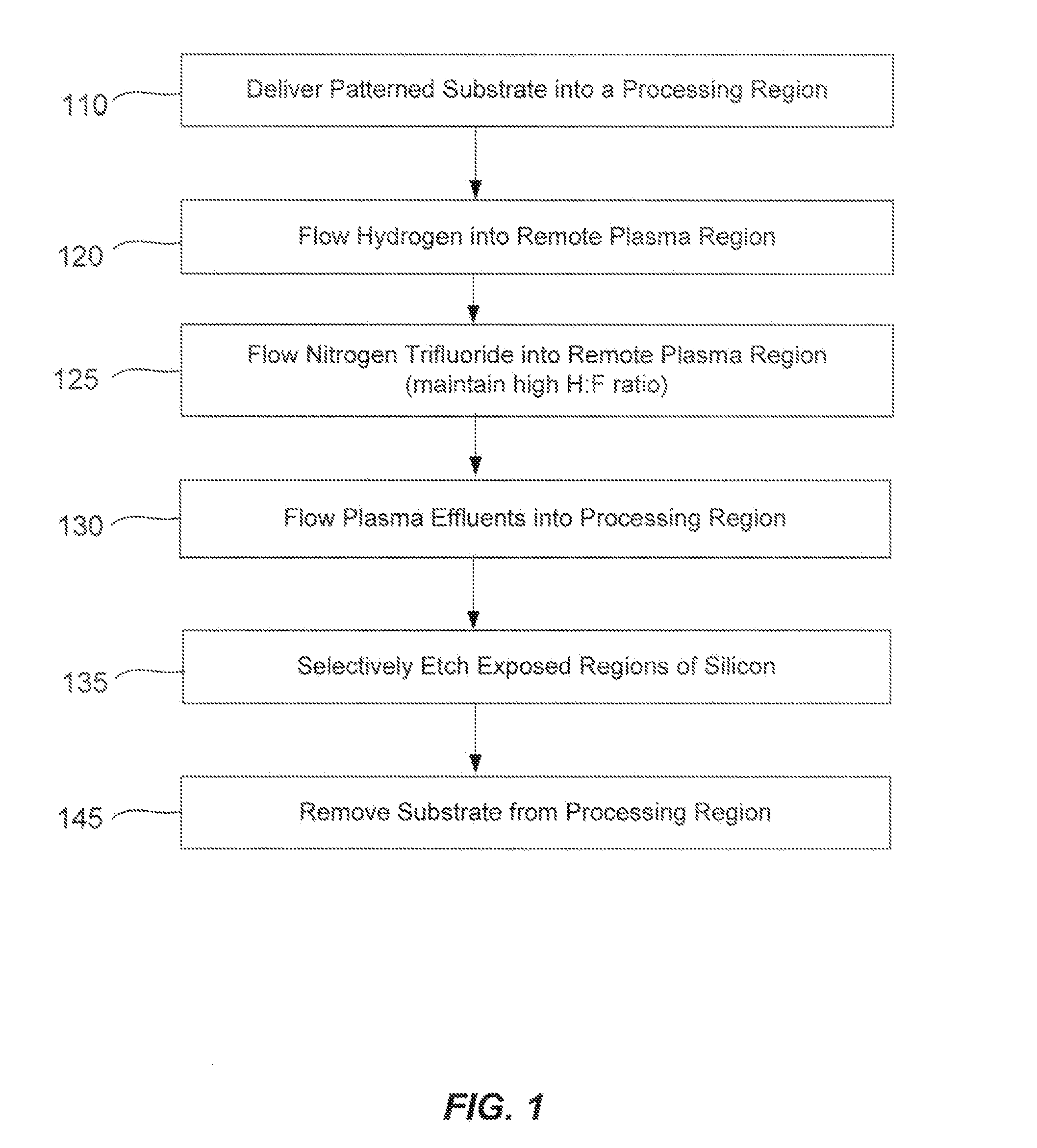
Selective etch of silicon by way of metastable hydrogen termination
ActiveUS20130089988A1Easy to disassembleReduces and substantially eliminates numberElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaHydrogen
Methods of etching exposed silicon on patterned heterogeneous structures is described and includes a remote plasma etch formed from a fluorine-containing precursor and a hydrogen-containing precursor. Plasma effluents from the remote plasma are flowed into a substrate processing region where the plasma effluents react with the exposed regions of silicon. The plasmas effluents react with the patterned heterogeneous structures to selectively remove silicon while very slowly removing other exposed materials. The silicon selectivity results, in part, from a preponderance of hydrogen-containing precursor in the remote plasma which hydrogen terminates surfaces on the patterned heterogeneous structures. A much lower flow of the fluorine-containing precursor progressively substitutes fluorine for hydrogen on the hydrogen-terminated silicon thereby selectively removing silicon from exposed regions of silicon. The methods may be used to selectively remove silicon far faster than silicon oxide, silicon nitride and a variety of metal-containing materials.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for Depositing Conformal Amorphous Carbon Film by Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD)
ActiveUS20100093187A1Good shape retentionHighly conformalSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon layerNitrogen gas
Methods and apparatus for depositing an amorphous carbon layer on a substrate are provided. In one embodiment, a deposition process includes positioning a substrate in a substrate processing chamber, introducing a hydrocarbon source having a carbon to hydrogen atom ratio of greater than 1:2 into the processing chamber, introducing a plasma initiating gas selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, helium, argon, nitrogen, and combinations thereof into the processing chamber, with the hydrocarbon source having a volumetric flow rate to plasma initiating gas volumetric flow rate ratio of 1:2 or greater, generating a plasma in the processing chamber, and forming a conformal amorphous carbon layer on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method to increase the compressive stress of PECVD silicon nitride films
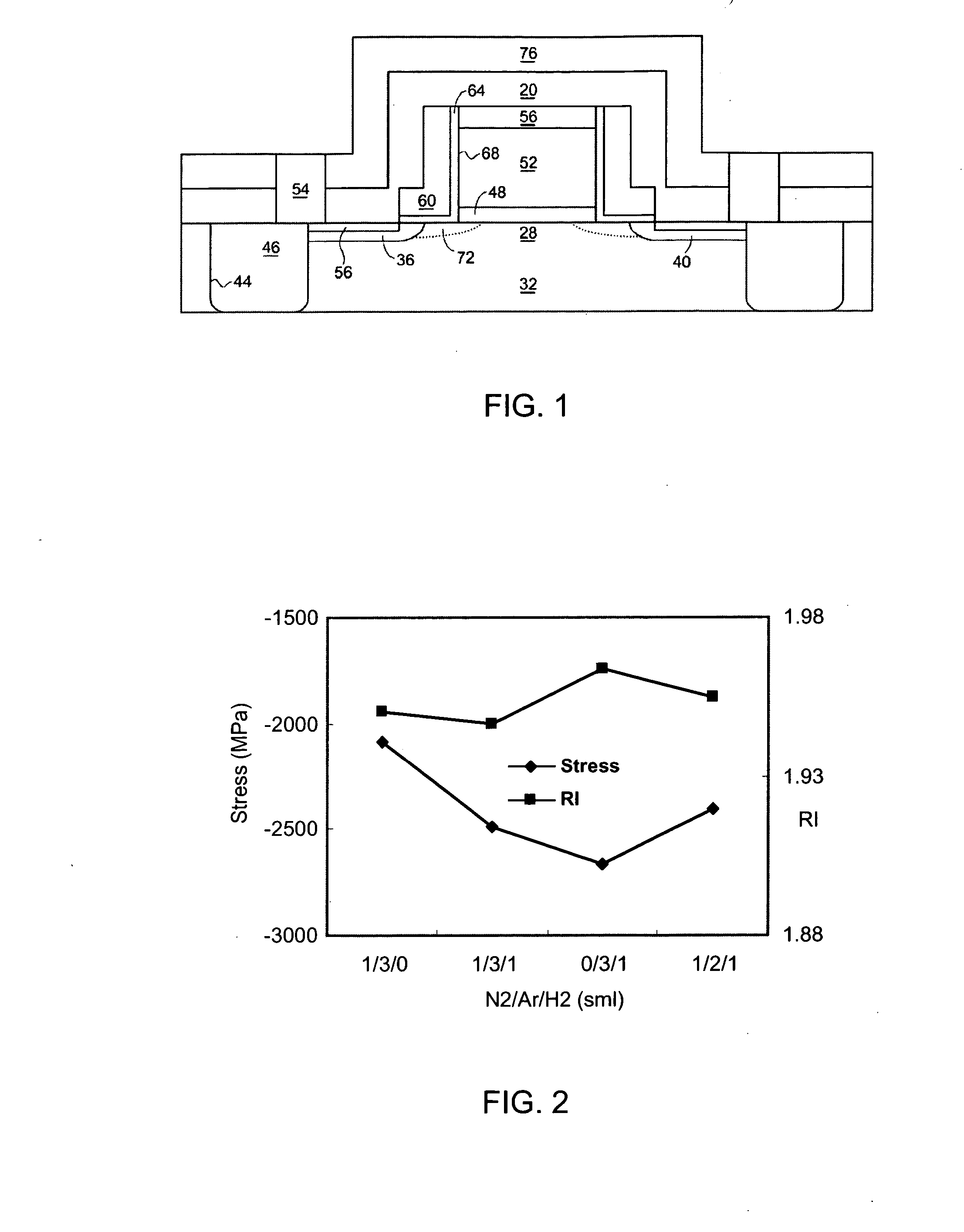
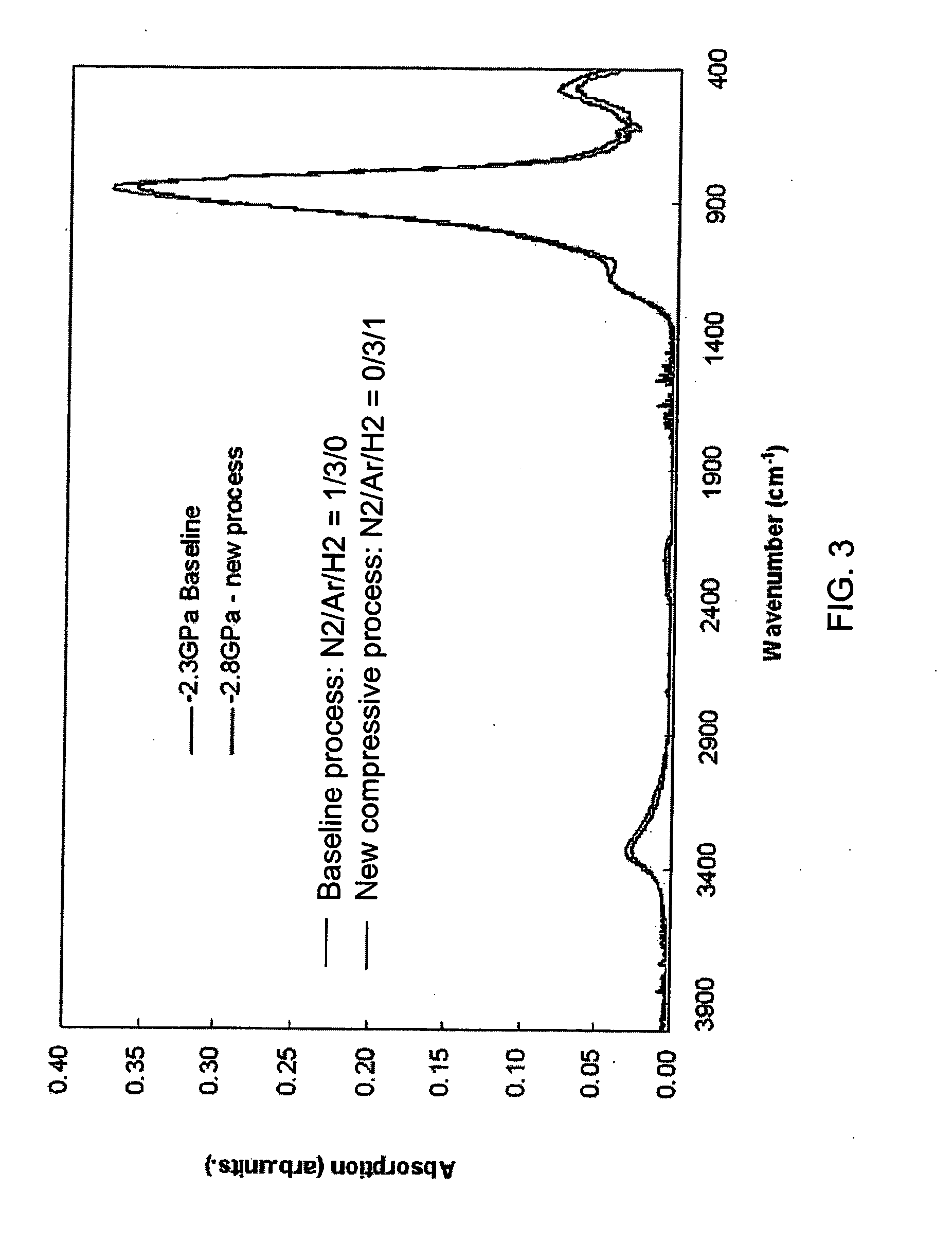
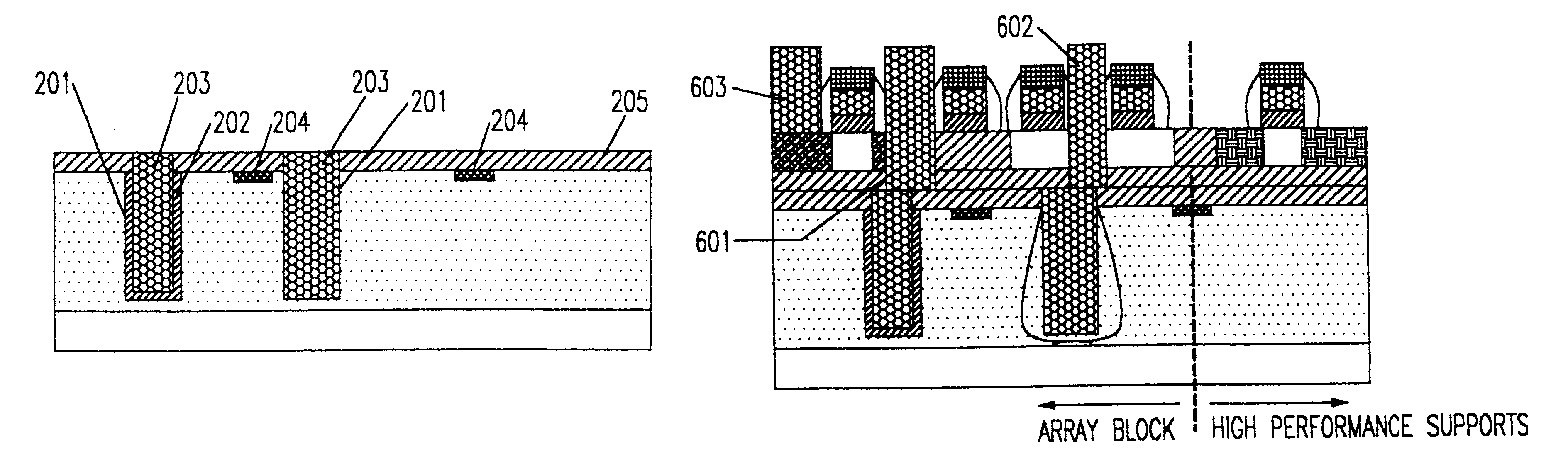
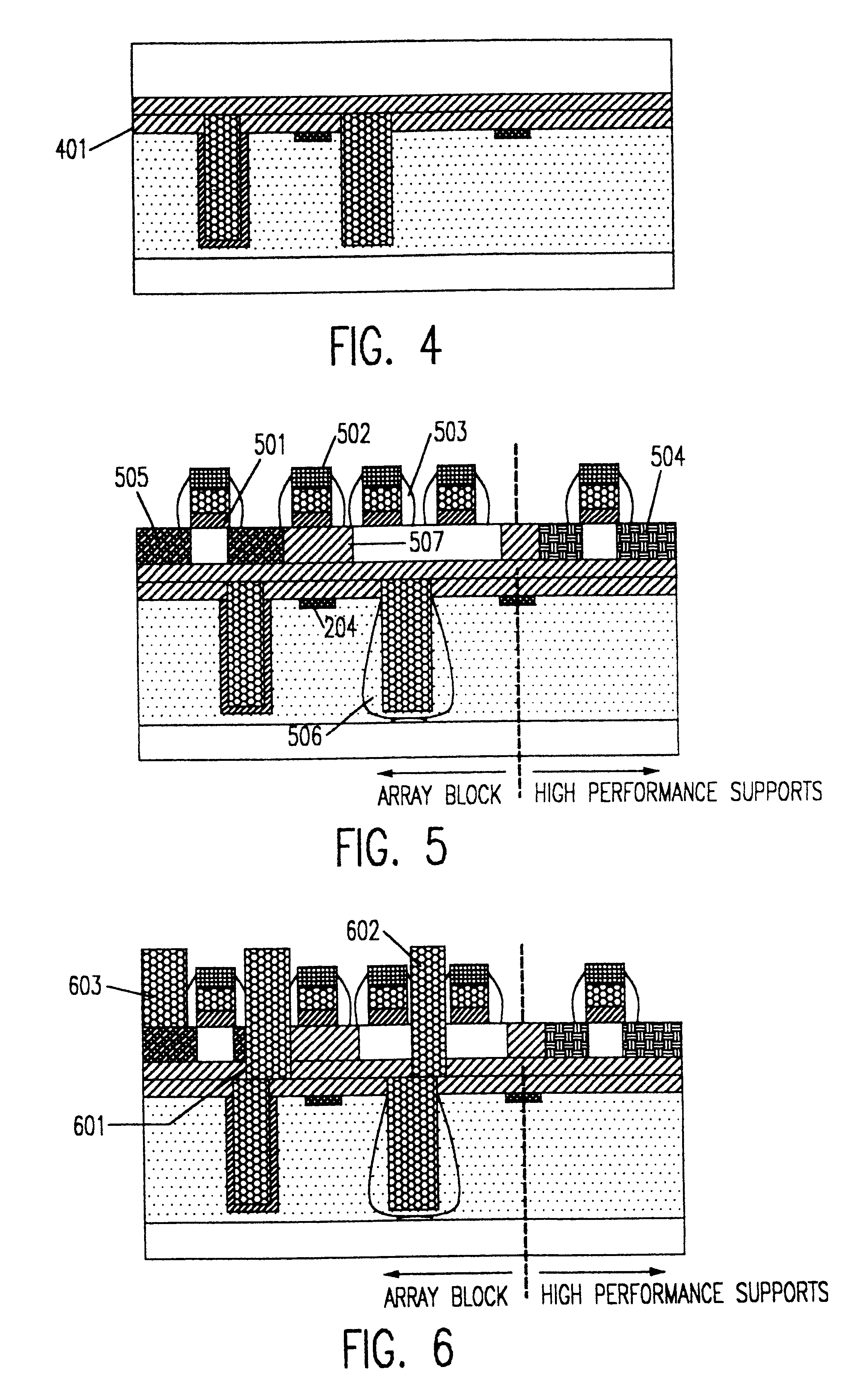
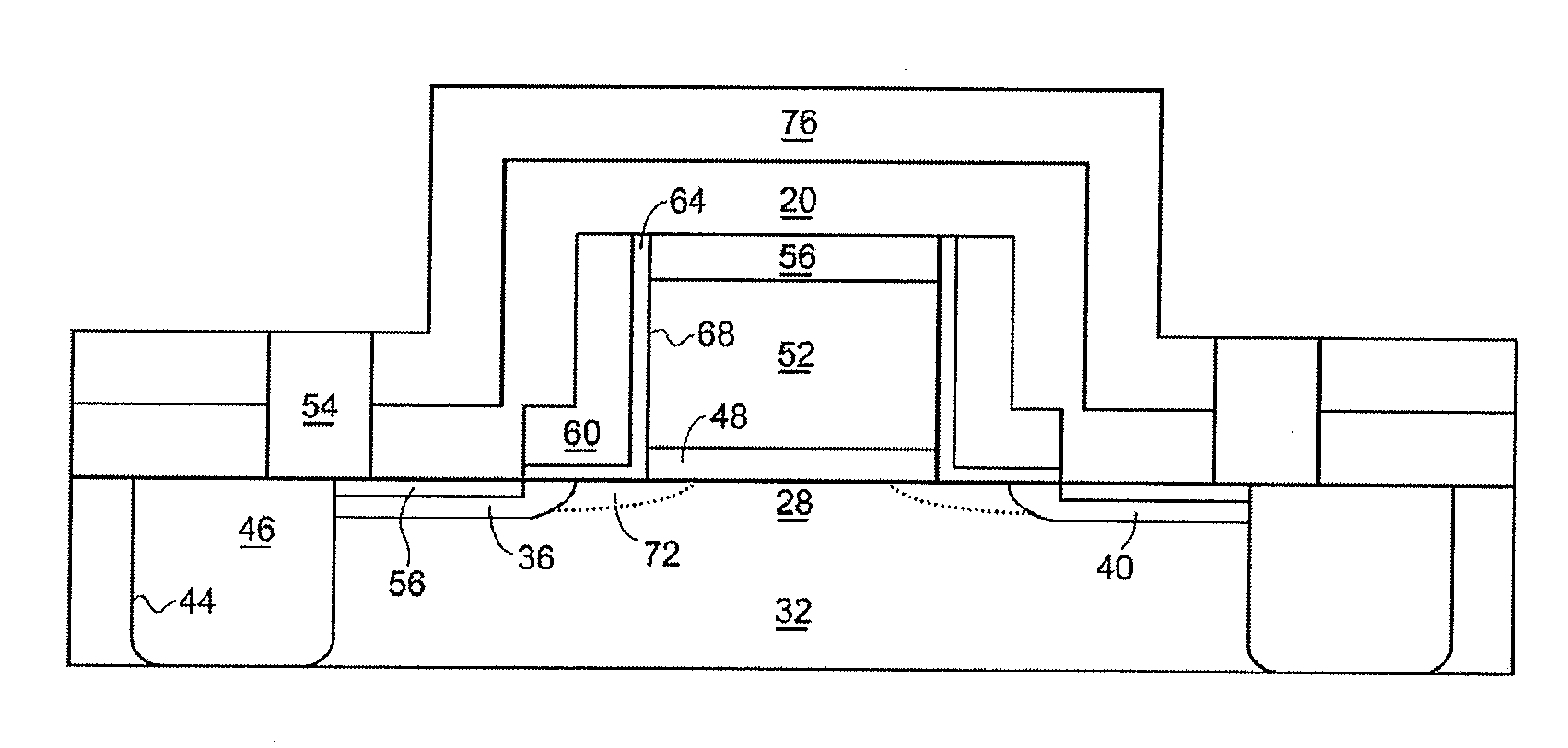
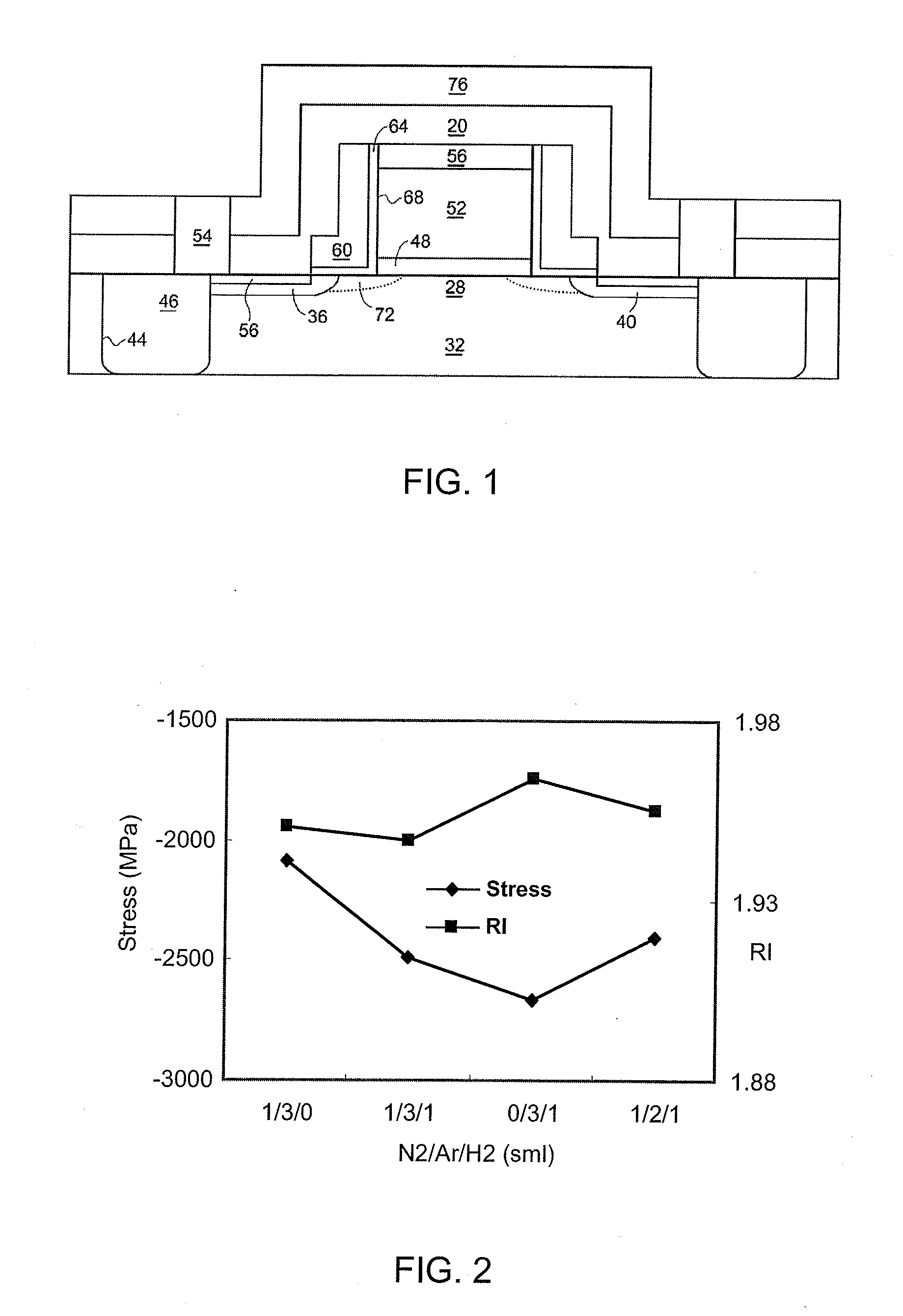
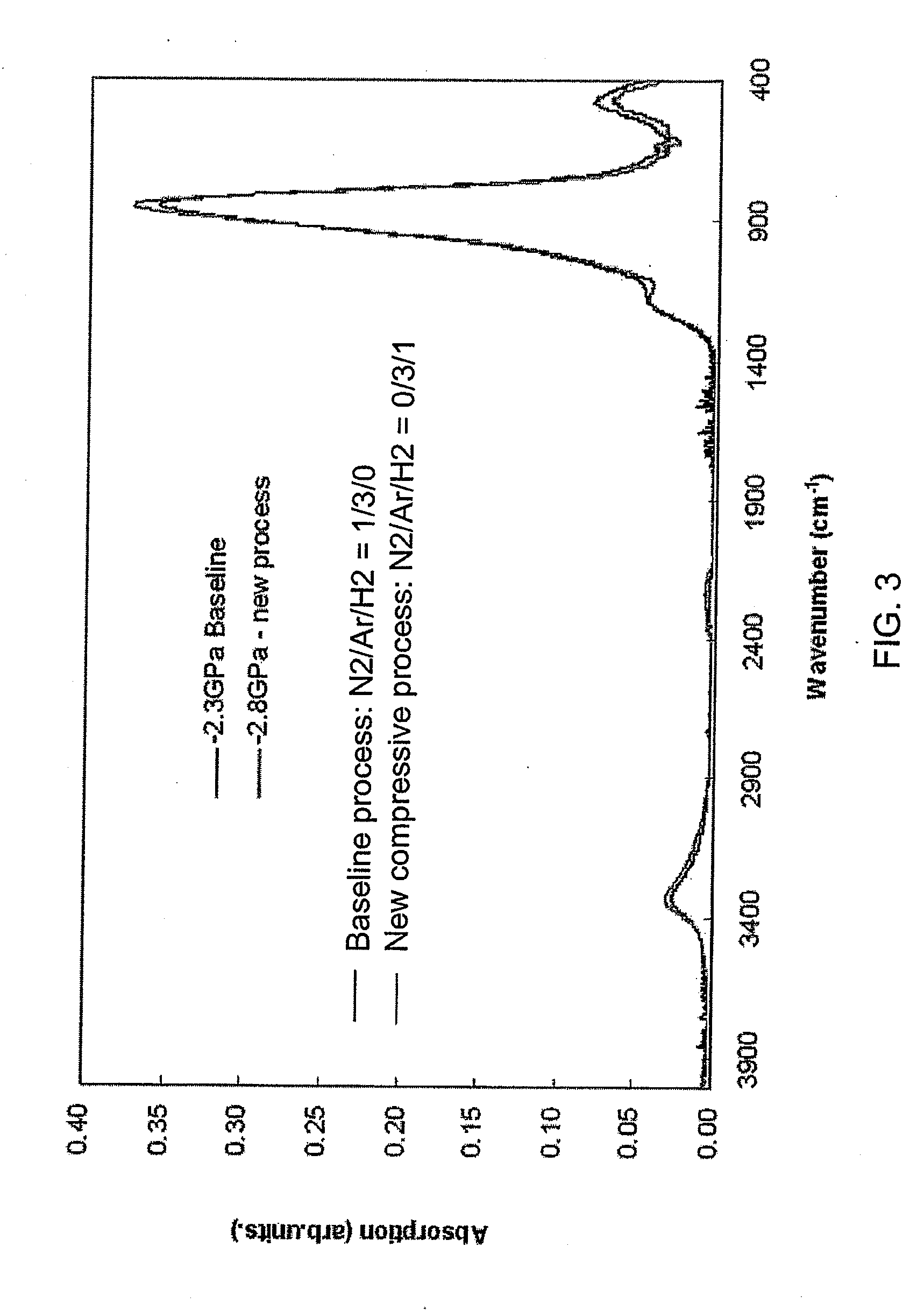
ActiveUS20060269692A1Increase silicon nitride compressive stressReduce defectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic cleaningHydrogenDevice material
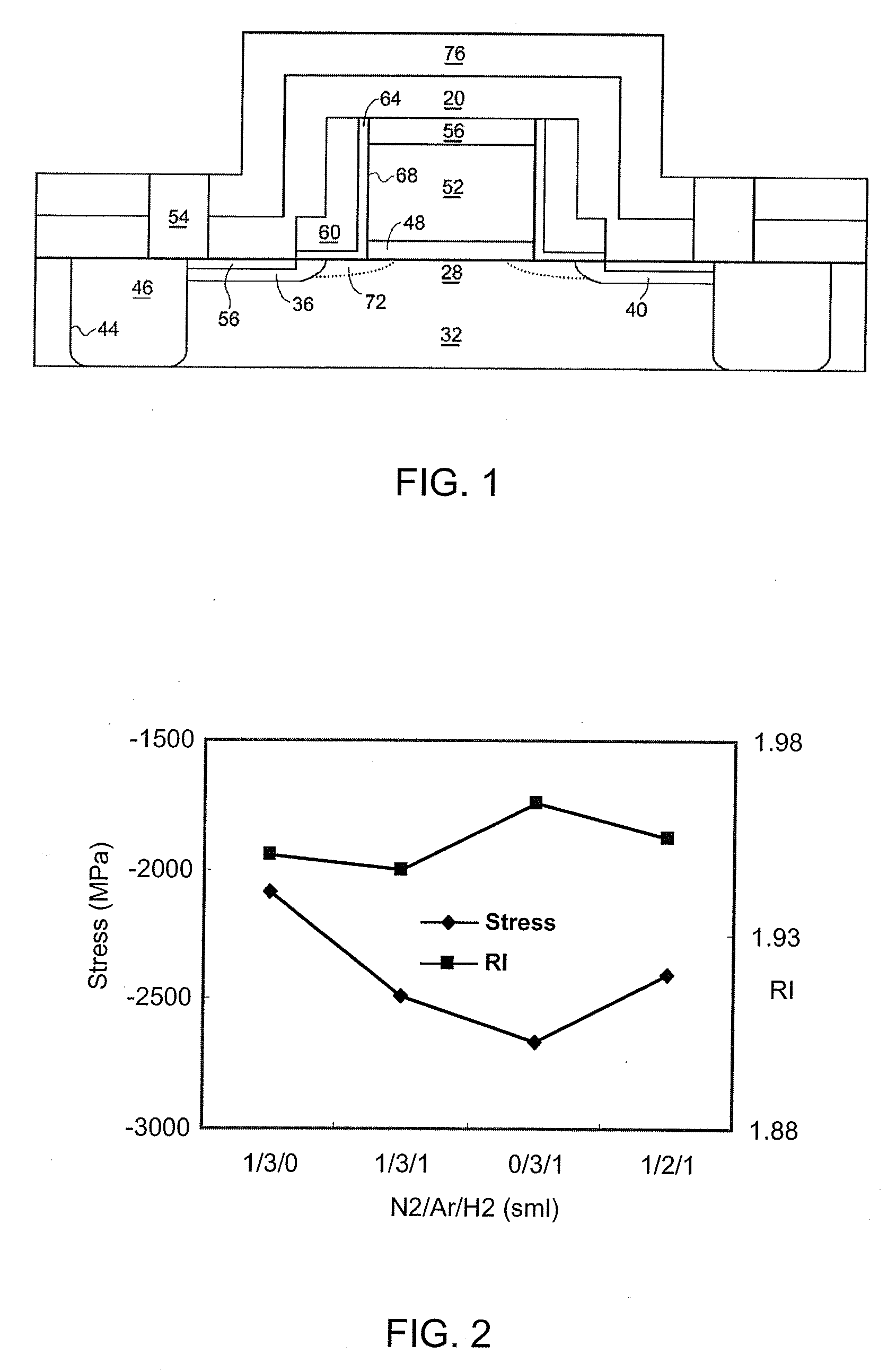
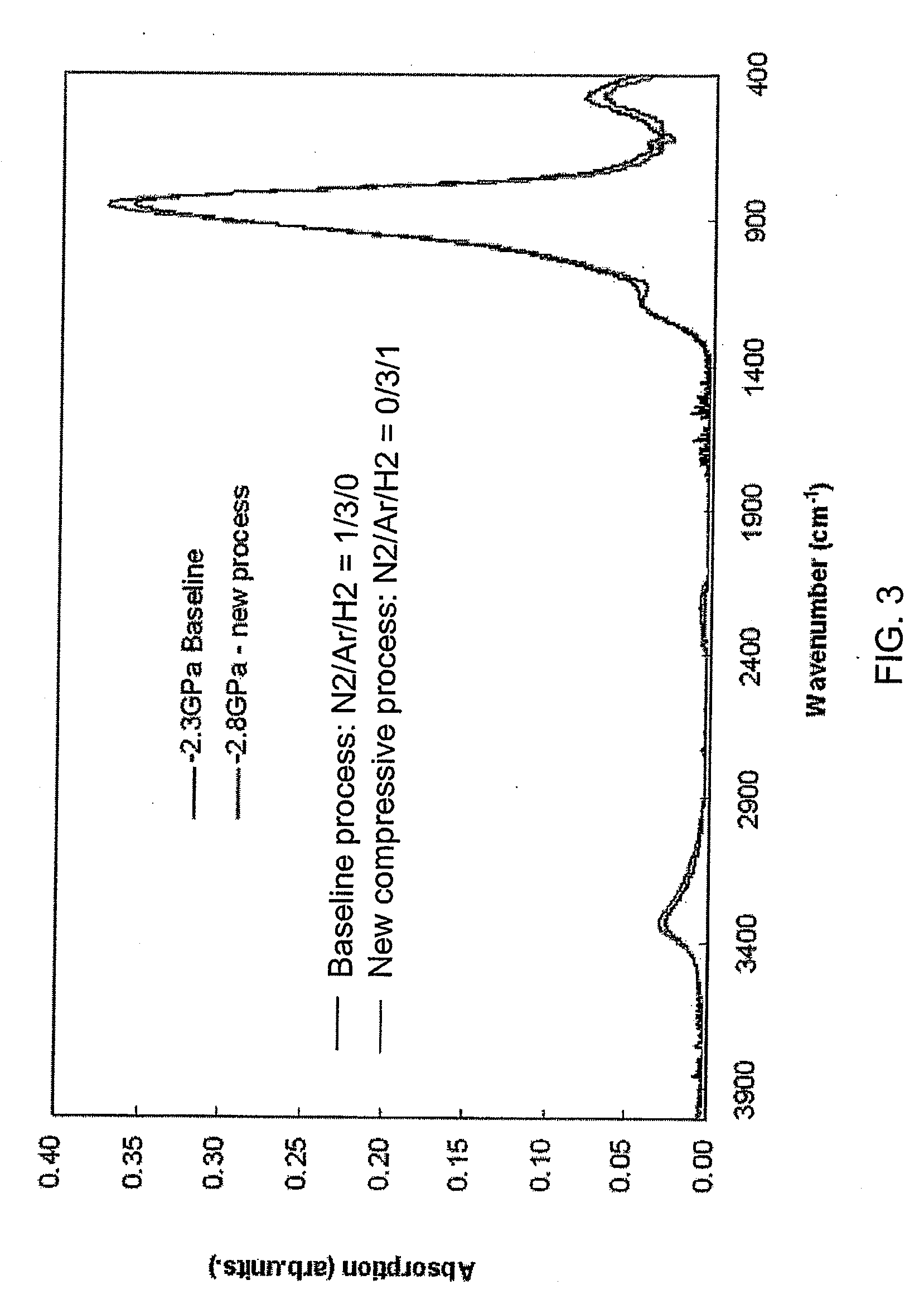
Compressive stress in a film of a semiconductor device may be controlled utilizing one or more techniques, employed alone or in combination. A first set of embodiments increase silicon nitride compressive stress by adding hydrogen to the deposition chemistry, and reduce defects in a device fabricated with a high compressive stress silicon nitride film formed in the presence of hydrogen gas. A silicon nitride film may comprise an initiation layer formed in the absence of a hydrogen gas flow, underlying a high stress nitride layer formed in the presence of a hydrogen gas flow. A silicon nitride film formed in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention may exhibit a compressive stress of 2.8 GPa or higher.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
SOI stacked DRAM logic
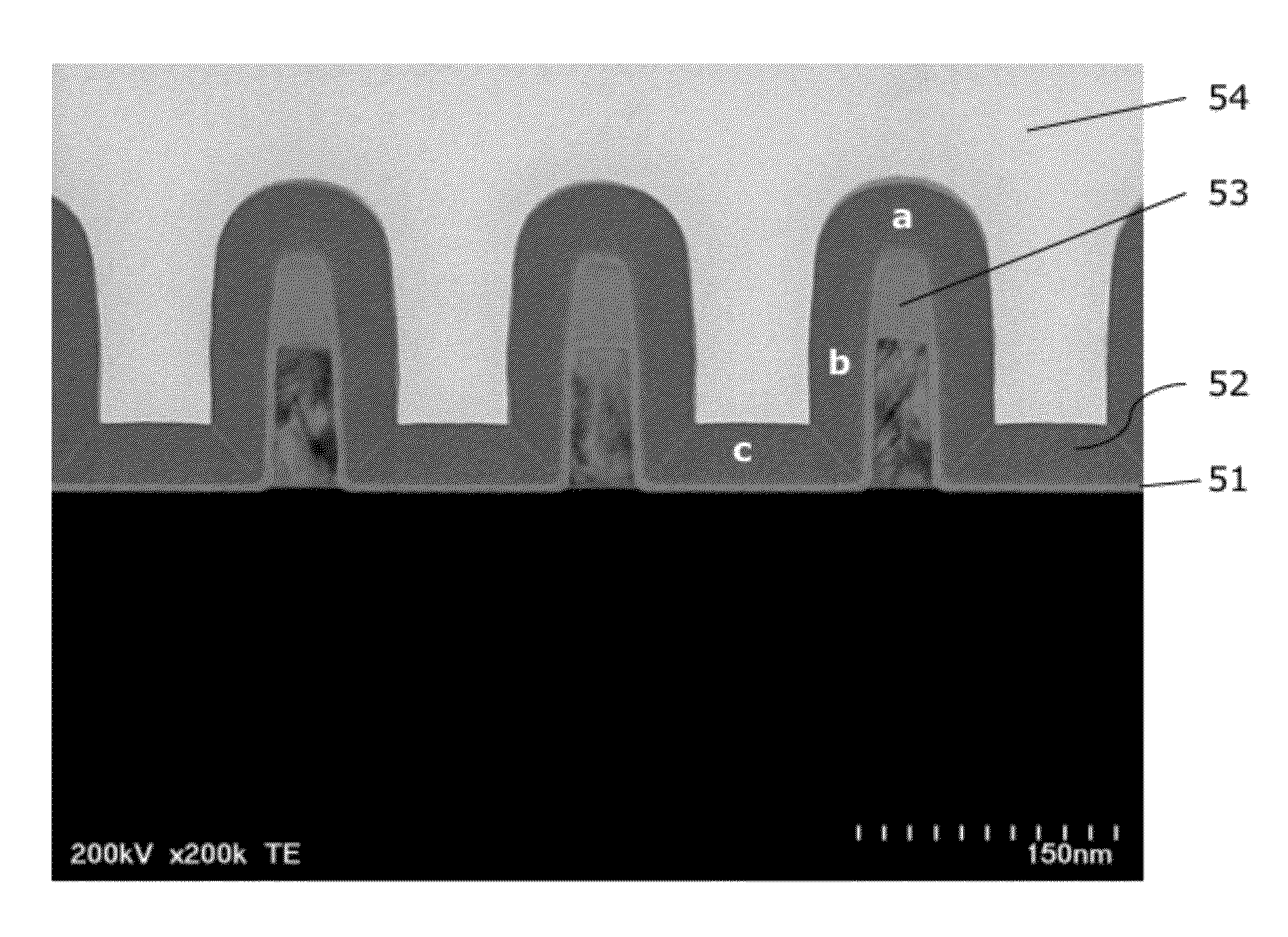
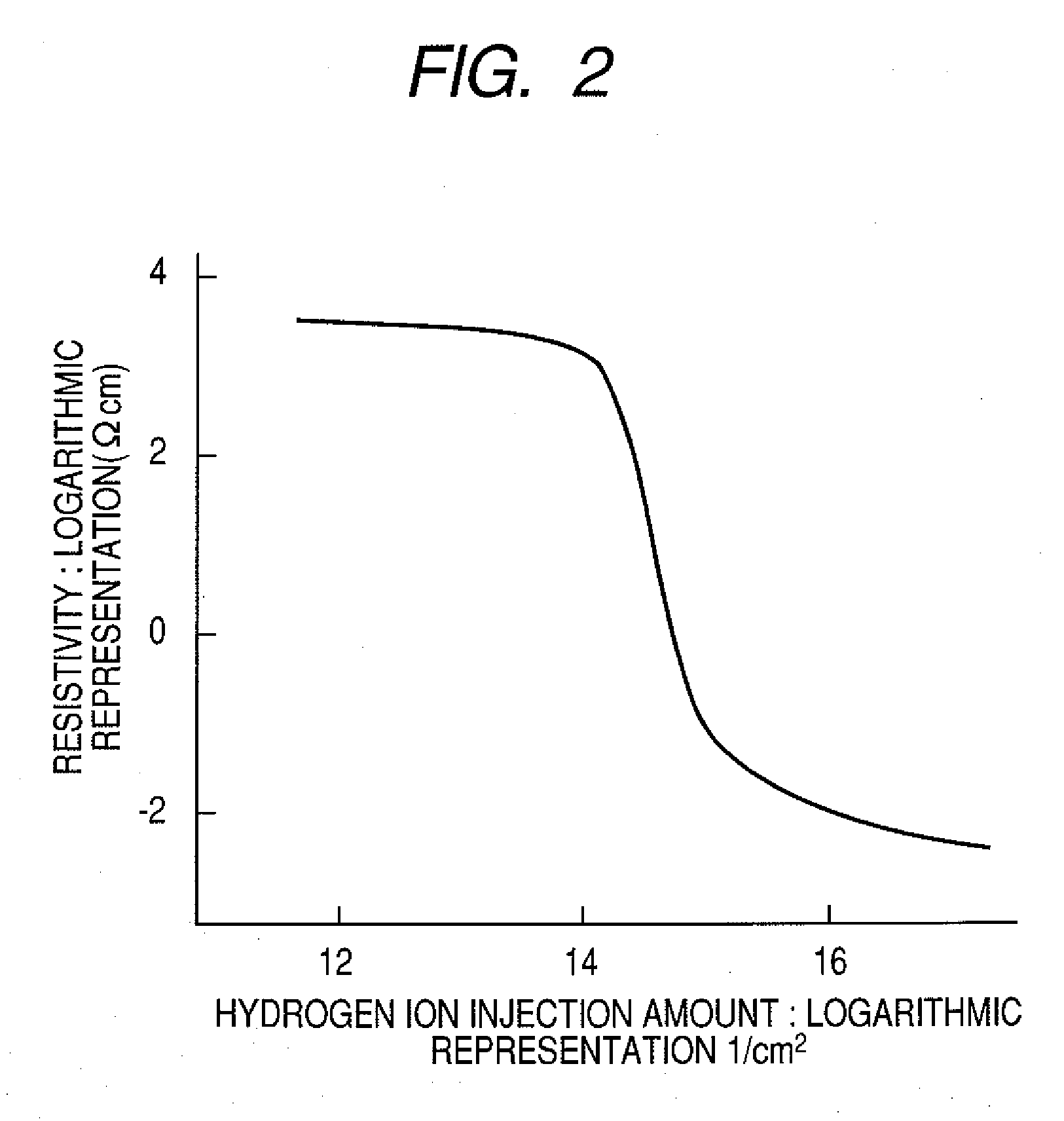
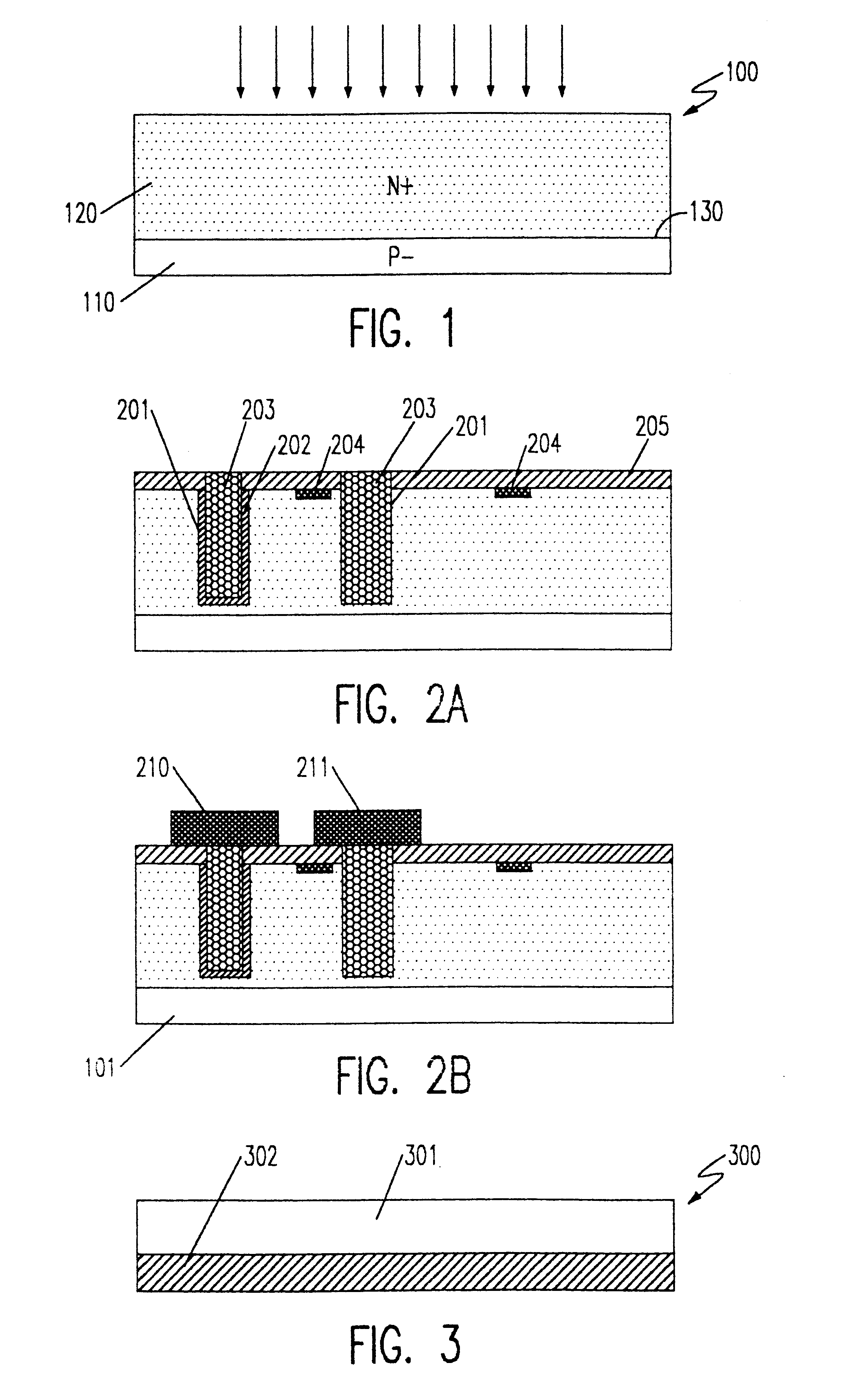
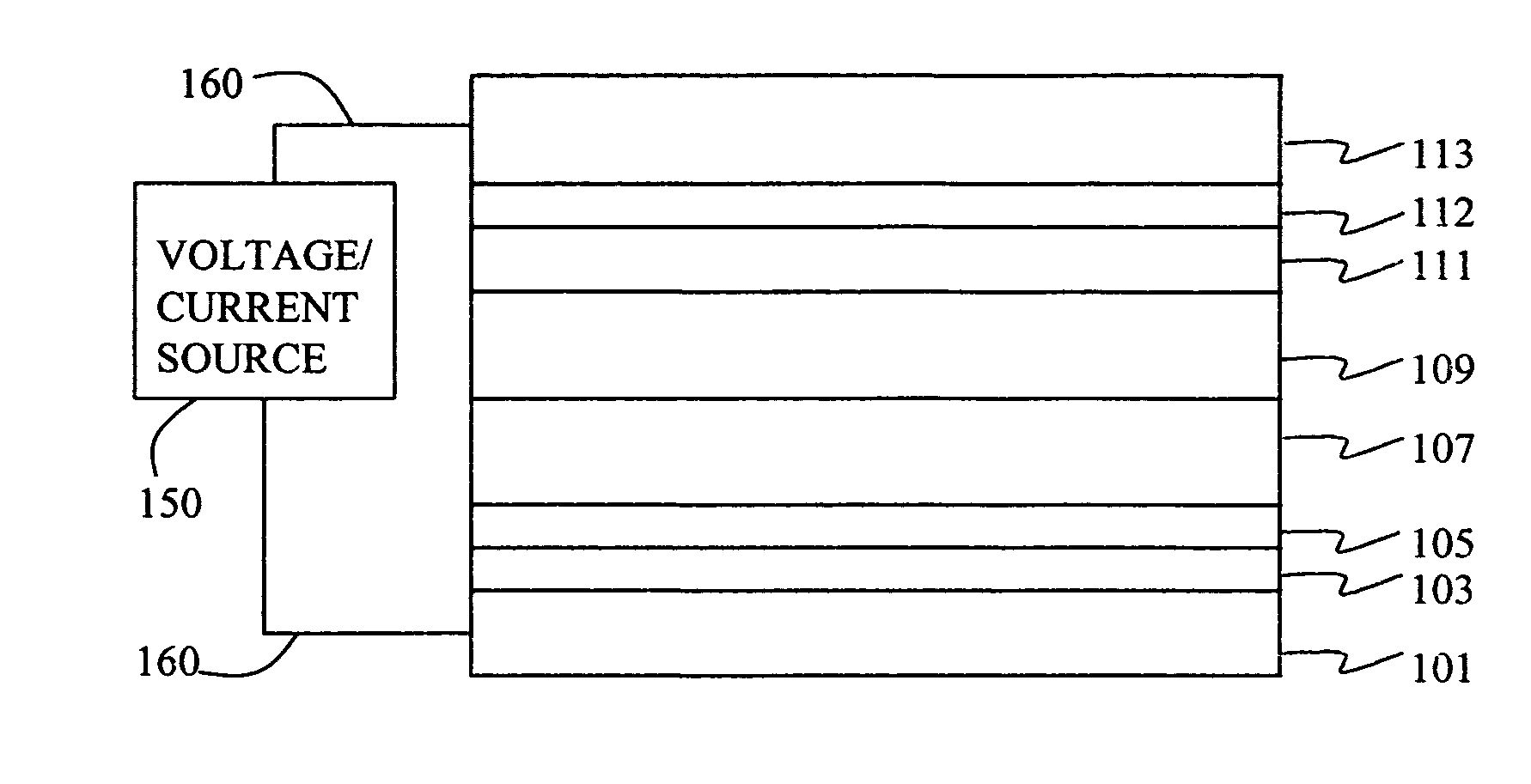
A composite, layered, integrated circuit formed by bonding of insulator layers on wafers provides for combination of otherwise incompatible technologies such as trench capacitor DRAM arrays and high performance, low power, low voltage silicon on insulator (SOI) switching transistors and short signal propagation paths between devices formed on respective wafer layers of a chip. In preferred embodiments, an SOI wafer is formed by hydrophilic bonding of a wafer over an integrated circuit device and then cleaving a layer of the second wafer away using implanted hydrogen and low temperature heat treatment. Further wafers of various structures and compositions may be bonded thereover and connections between circuit elements and connection pads in respective wafers made using short vias that provide fast signal propagation as well as providing more numerous connections than can be provided on chip edges.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method to increase silicon nitride tensile stress using nitrogen plasma in-situ treatment and ex-situ UV cure
InactiveUS20120196450A1Increase pressureImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogen plasmaHydrogen
Stress of a silicon nitride layer may be enhanced by deposition at higher temperatures. Employing an apparatus that allows heating of a substrate to substantially greater than 400° C. (for example a heater made from ceramic rather than aluminum), the silicon nitride film as-deposited may exhibit enhanced stress allowing for improved performance of the underlying MOS transistor device. In accordance with some embodiments, a deposited silicon nitride film is exposed to curing with plasma and ultraviolet (UV) radiation, thereby helping remove hydrogen from the film and increasing film stress. In accordance with other embodiments, a silicon nitride film is formed utilizing an integrated process employing a number of deposition / curing cycles to preserve integrity of the film at the sharp corner of the underlying raised feature. Adhesion between successive layers may be promoted by inclusion of a post-UV cure plasma treatment in each cycle.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Ethylene production from acetic acid utilizing dual reaction zone process
A process for selective formation of ethylene from acetic acid includes contacting a feed stream containing acetic acid and hydrogen at an elevated temperature with a first catalytic composition including a suitable hydrogenating catalyst in a first reaction zone to form an intermediate mixture including ethanol and ethyl acetate; and subsequently reacting the intermediate mixture over a suitable dehydrating and / or cracking catalyst in a second reaction zone to form ethylene. Selectivities of ethylene of over 80% are achieved.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Method of depositing dielectric film by modified peald method
ActiveUS20120220139A1Increase deposition rateHigh conformalitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingNoble gasHydrogen
A method of forming a film on a semiconductor substrate by plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD), includes: introducing a nitrogen- and hydrogen-containing reactive gas and a rare gas into a reaction space inside which the semiconductor substrate is placed; introducing a precursor in pulses of less than 1.0-second duration into the reaction space wherein the reactive gas and the rare gas are introduced; exiting a plasma in pulses of less than 1.0-second duration immediately after the precursor is shut off; and maintaining the reactive gas and the rare gas as a purge of less than 2.0-second duration.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Organic element for low voltage electroluminescent devices
InactiveUS20070092753A1Reduce the driving voltageIncrease brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsAnthraceneHydrogen
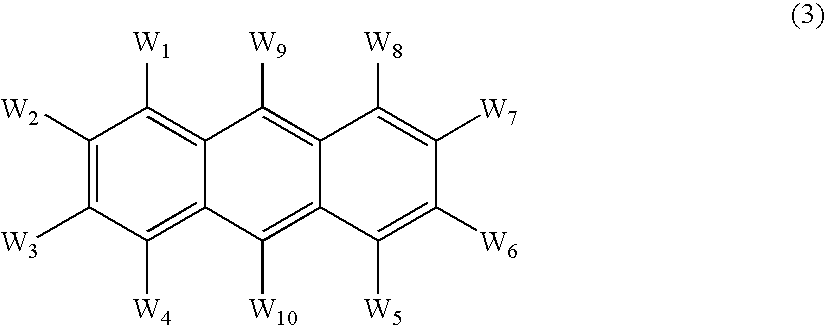
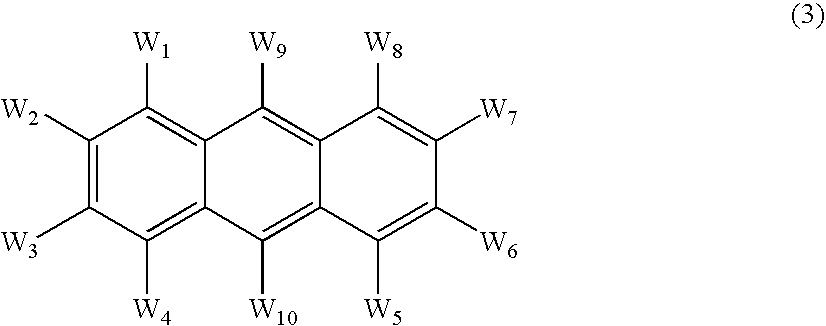
An OLED device comprises a cathode, a light emitting layer and an anode, in that order, wherein (i) the light-emitting layer comprises up to 10 volume % of a light emitting compound and at least one anthracene host compound of Formula (3): wherein W1-W10 independently represents hydrogen or an independently selected substituent, and (ii) a further layer located between the cathode and the light emitting layer, contains (a) 10-volume % or more of an anthracene compound of Formula (3) and (b) at least one salt or complex of an element selected from Group IA, IIA, IIIA and IIB of the Periodic Table. Such devices exhibit reduced drive voltage while maintaining good luminance.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com