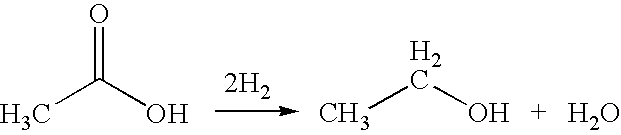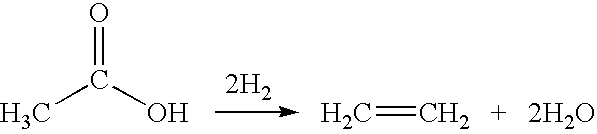Patents
Literature
6279 results about "Reaction zone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Reaction zone. [rē′ak·shən ‚zōn] (chemical engineering) In a catalytic reactor vessel, the location or zone within the vessel where the bulk of the chemical reaction takes place.
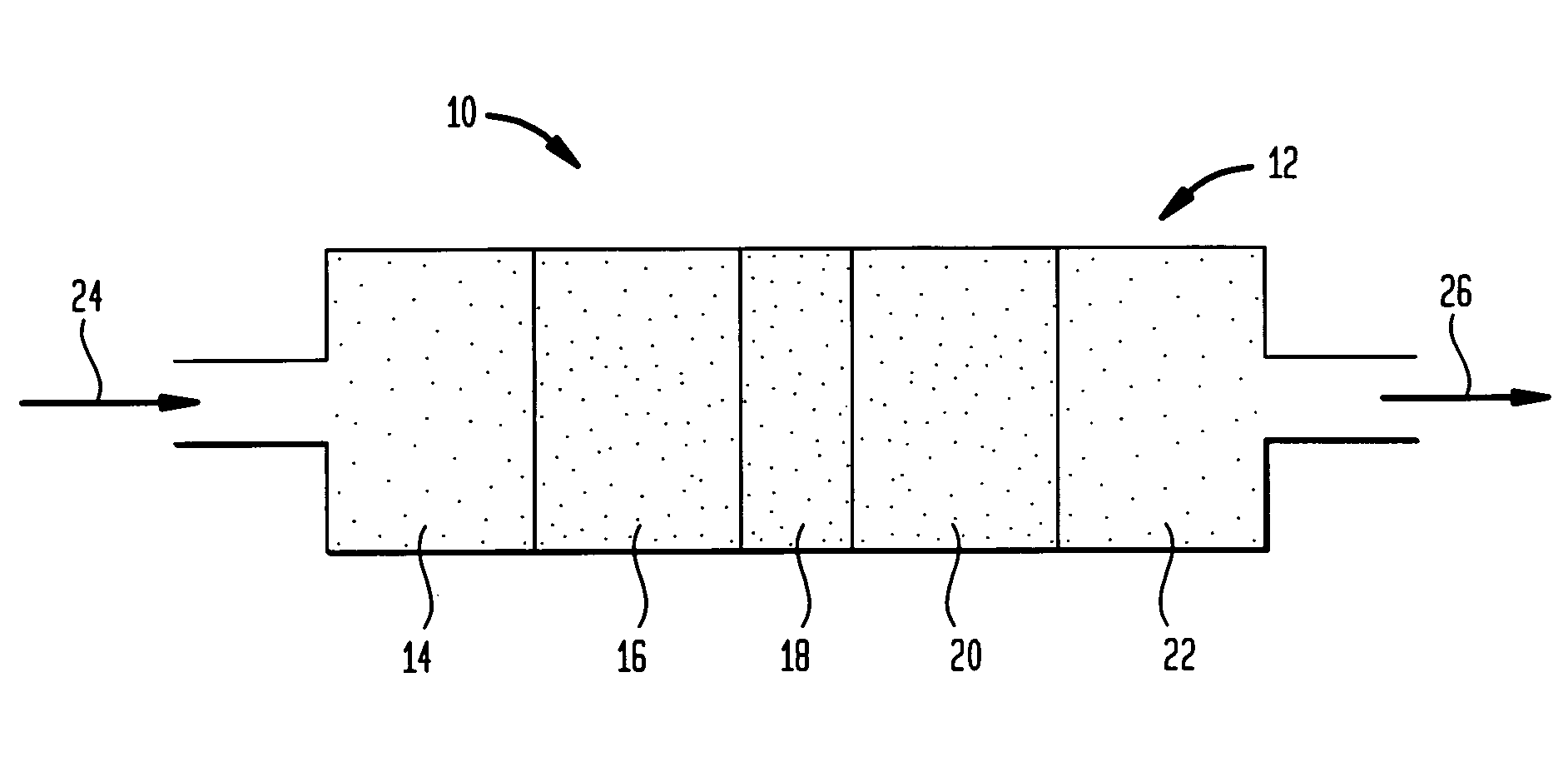
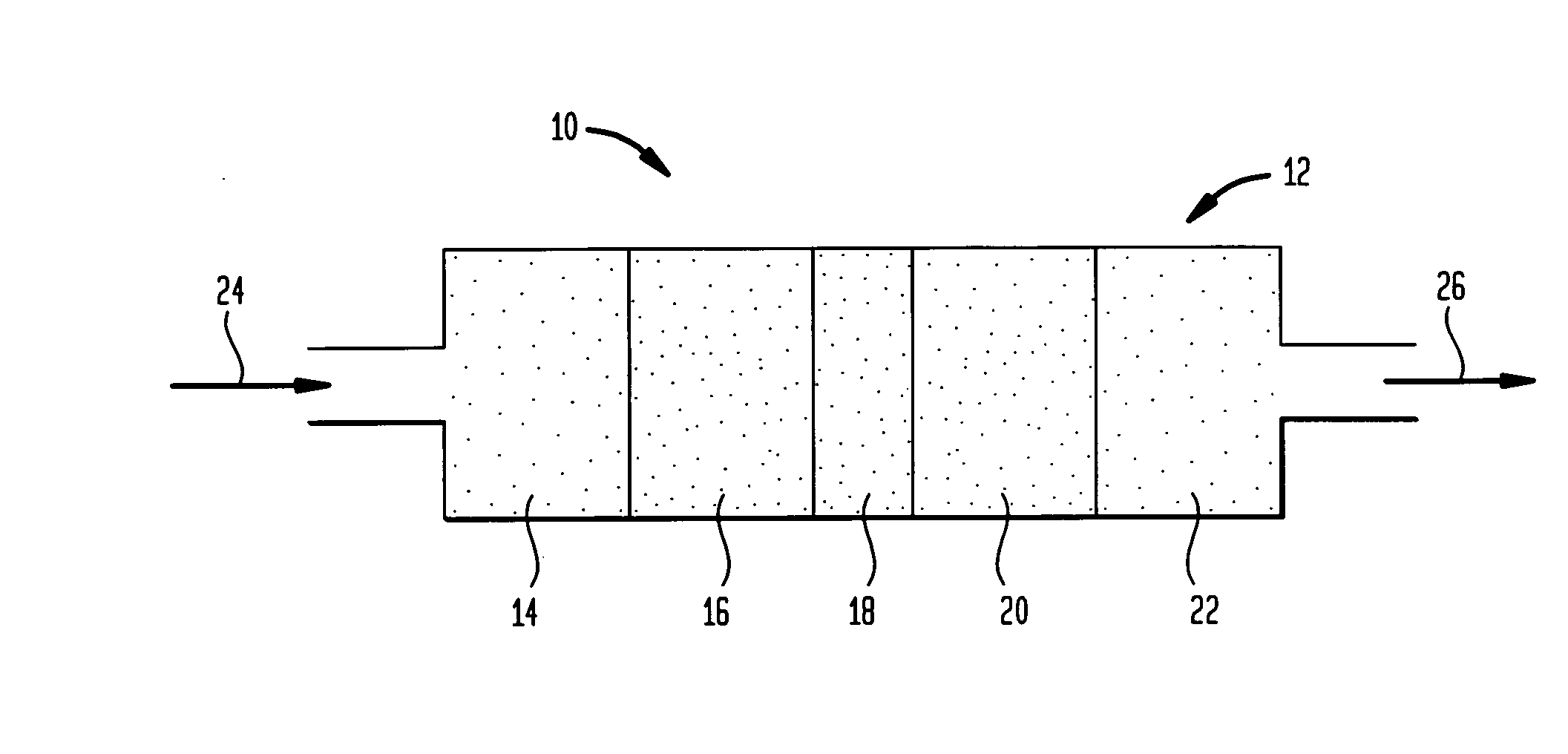
Ethylene production from acetic acid utilizing dual reaction zone process
A process for selective formation of ethylene from acetic acid includes contacting a feed stream containing acetic acid and hydrogen at an elevated temperature with a first catalytic composition including a suitable hydrogenating catalyst in a first reaction zone to form an intermediate mixture including ethanol and ethyl acetate; and subsequently reacting the intermediate mixture over a suitable dehydrating and / or cracking catalyst in a second reaction zone to form ethylene. Selectivities of ethylene of over 80% are achieved.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Process for catalytically producing ethylene directly from acetic acid in a single reaction zone
InactiveUS20100030001A1High selectivityHigh yieldHydrocarbonsBulk chemical productionAcetic acidHydrogen
A process for the selective production of ethylene by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethylene in a single reaction zone is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over either a copper supported on iron oxide, copper-aluminum catalyst, cobalt supported on H-ZSM-5, ruthenium-cobalt supported on silica or cobalt supported on carbon selectively produces ethylene in a vapor phase at a temperature in the range of about 250° C. to 350° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
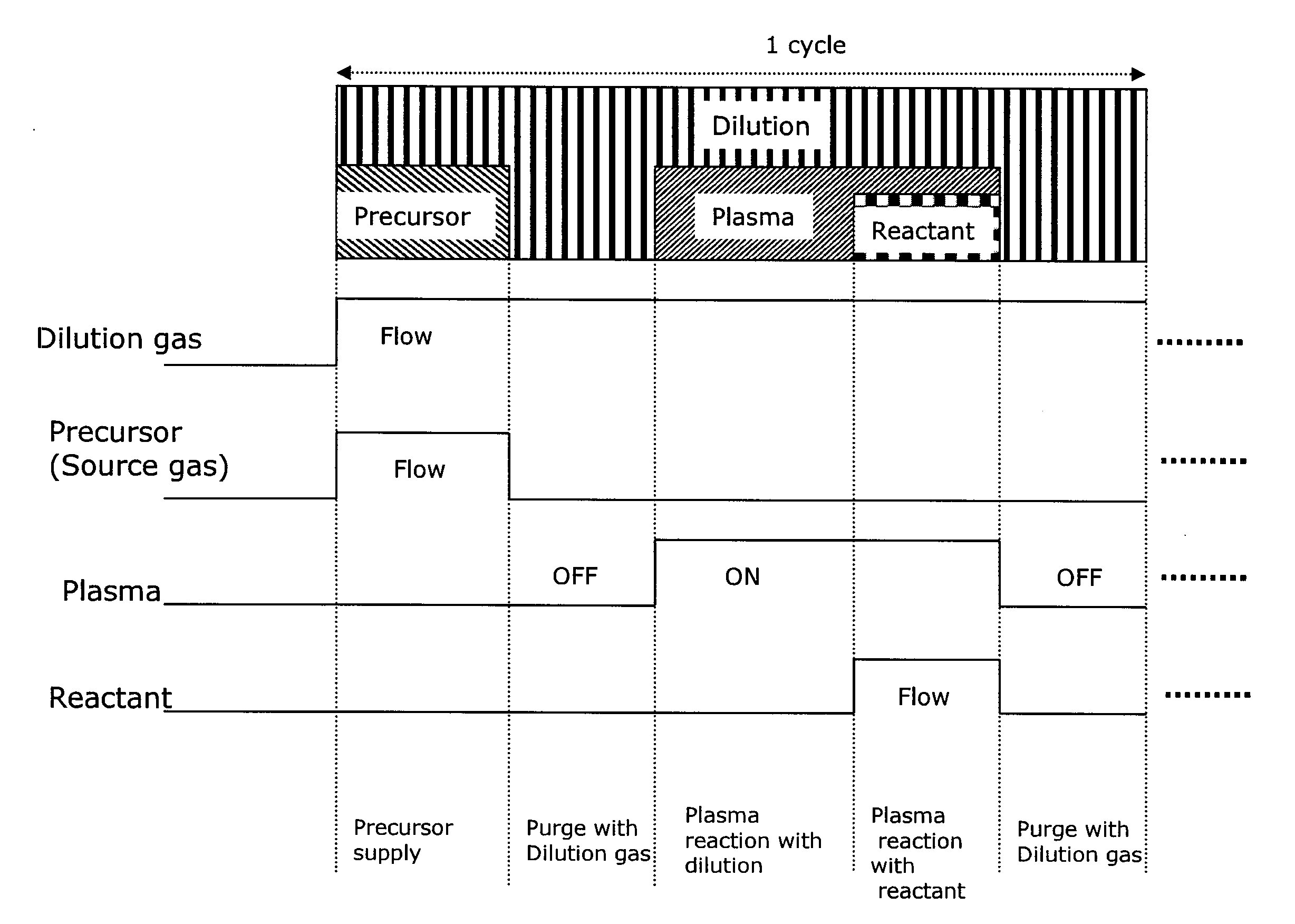
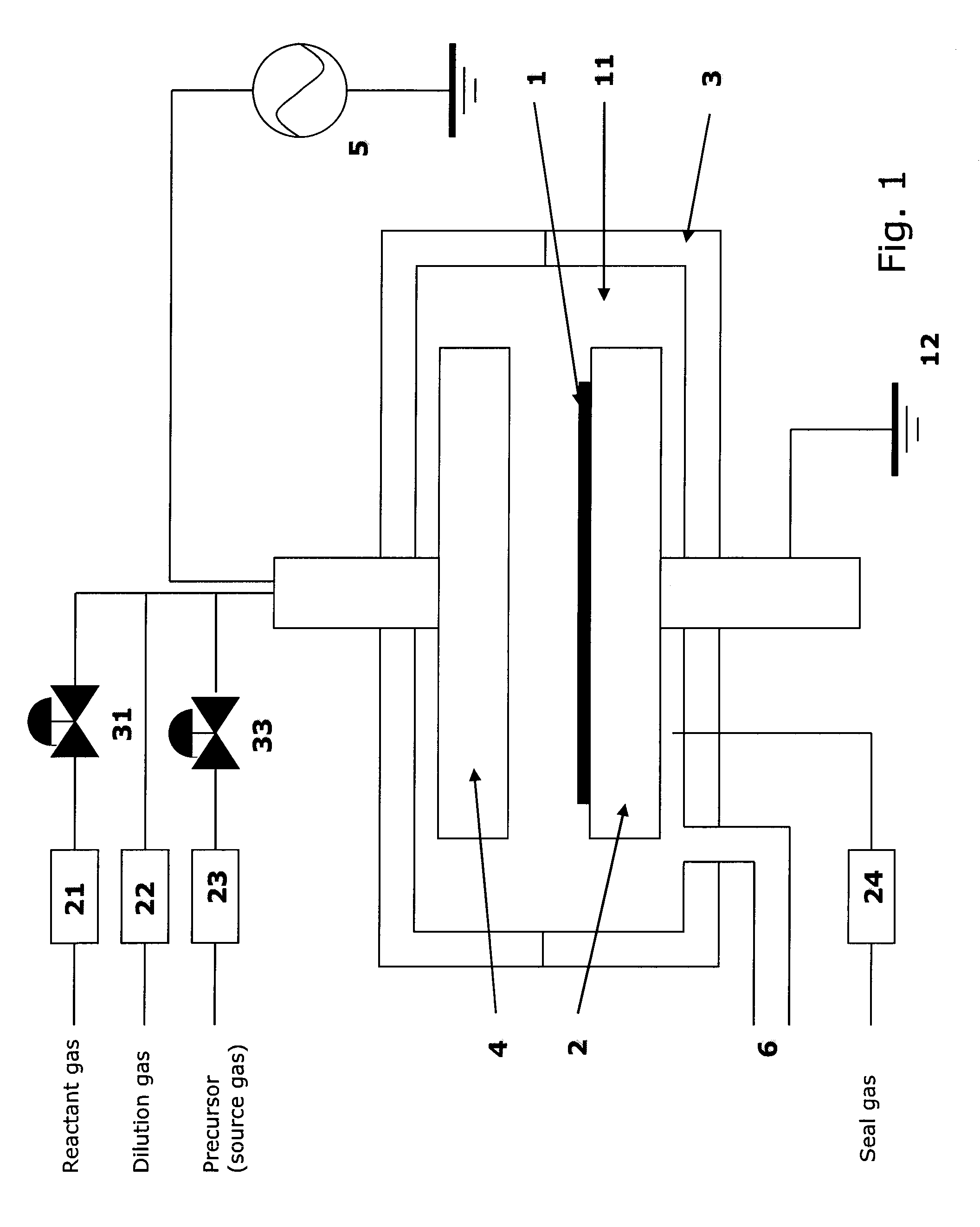
Method for Forming Single-Phase Multi-Element Film by PEALD
ActiveUS20130084714A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingReaction zoneGas plasma
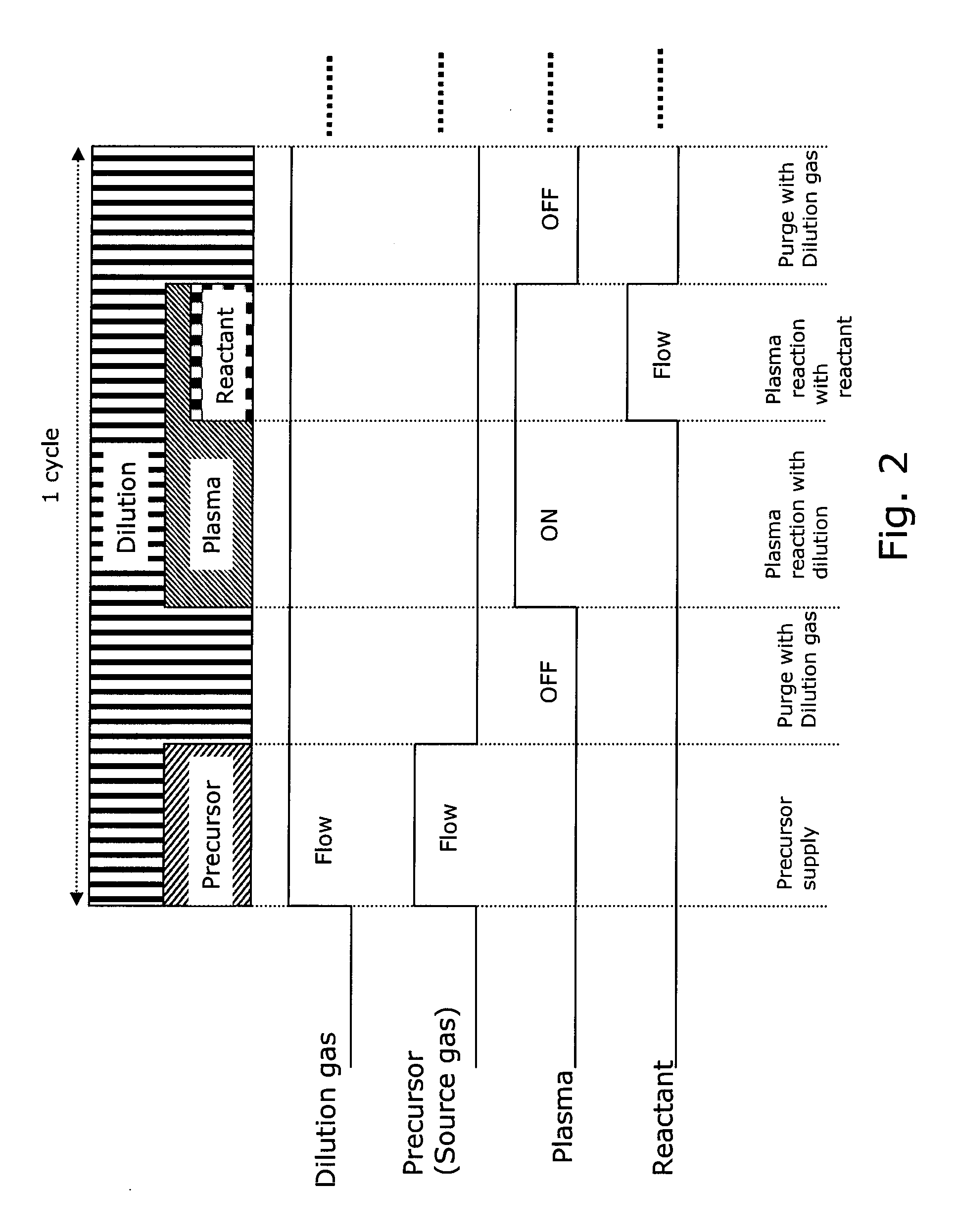
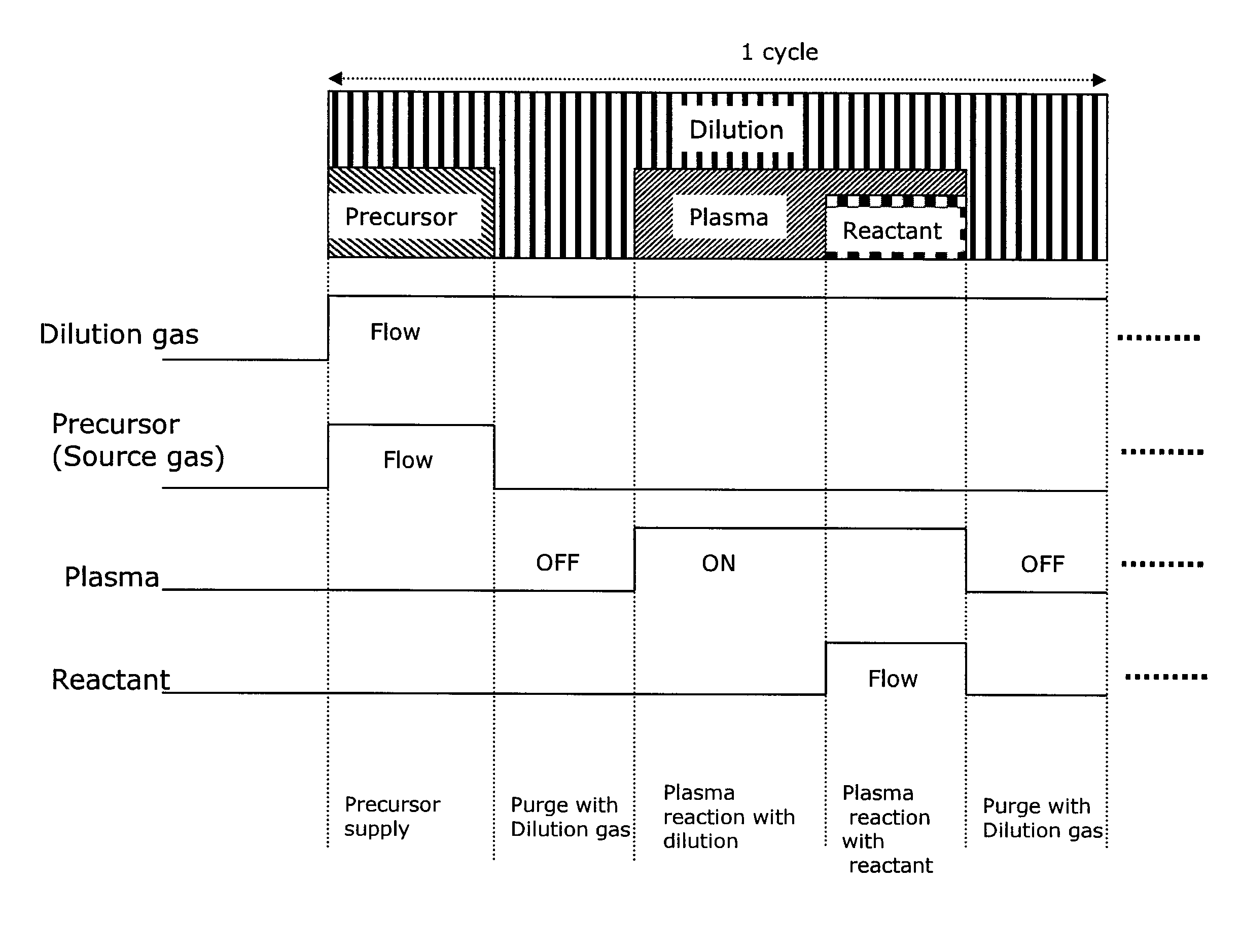
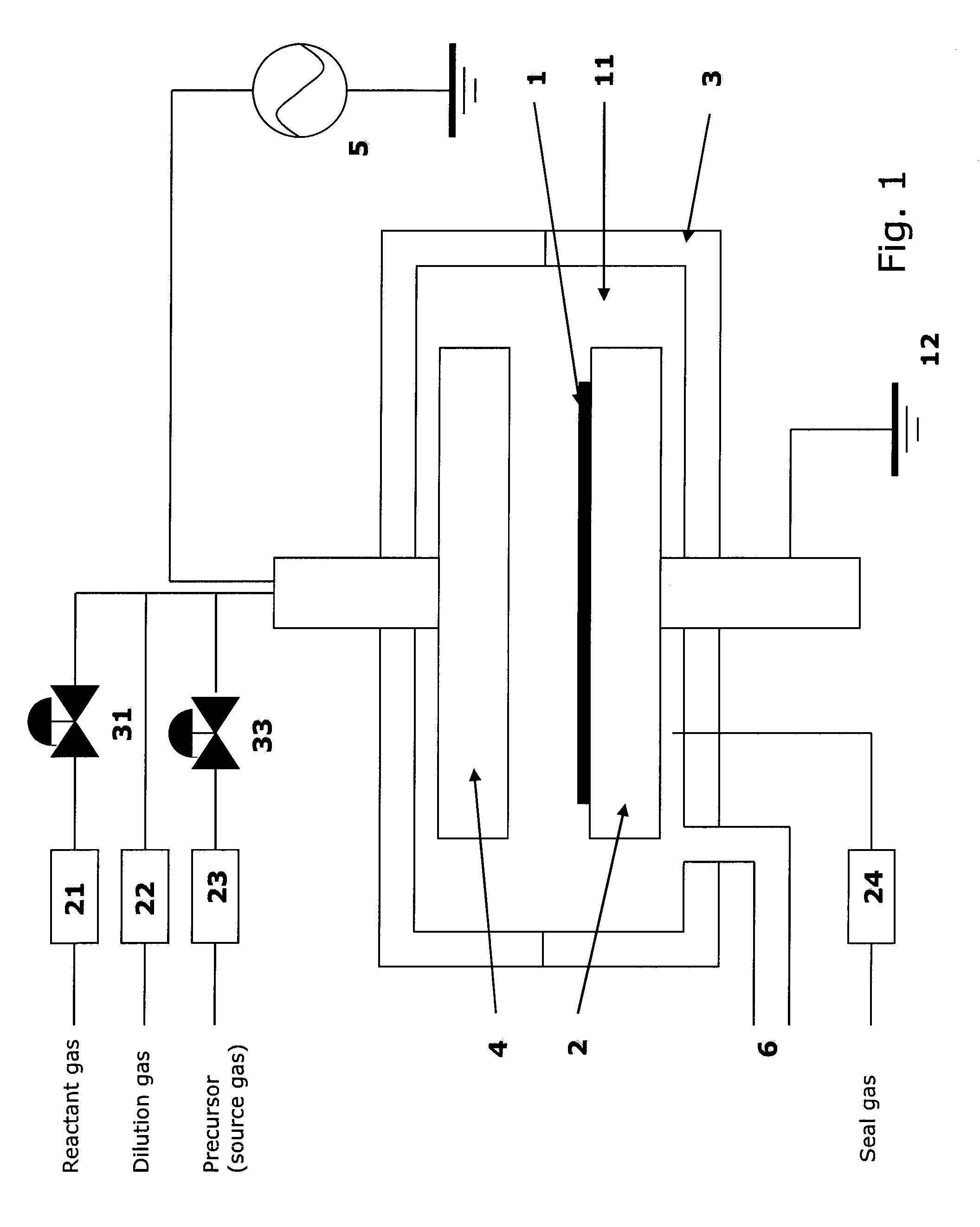
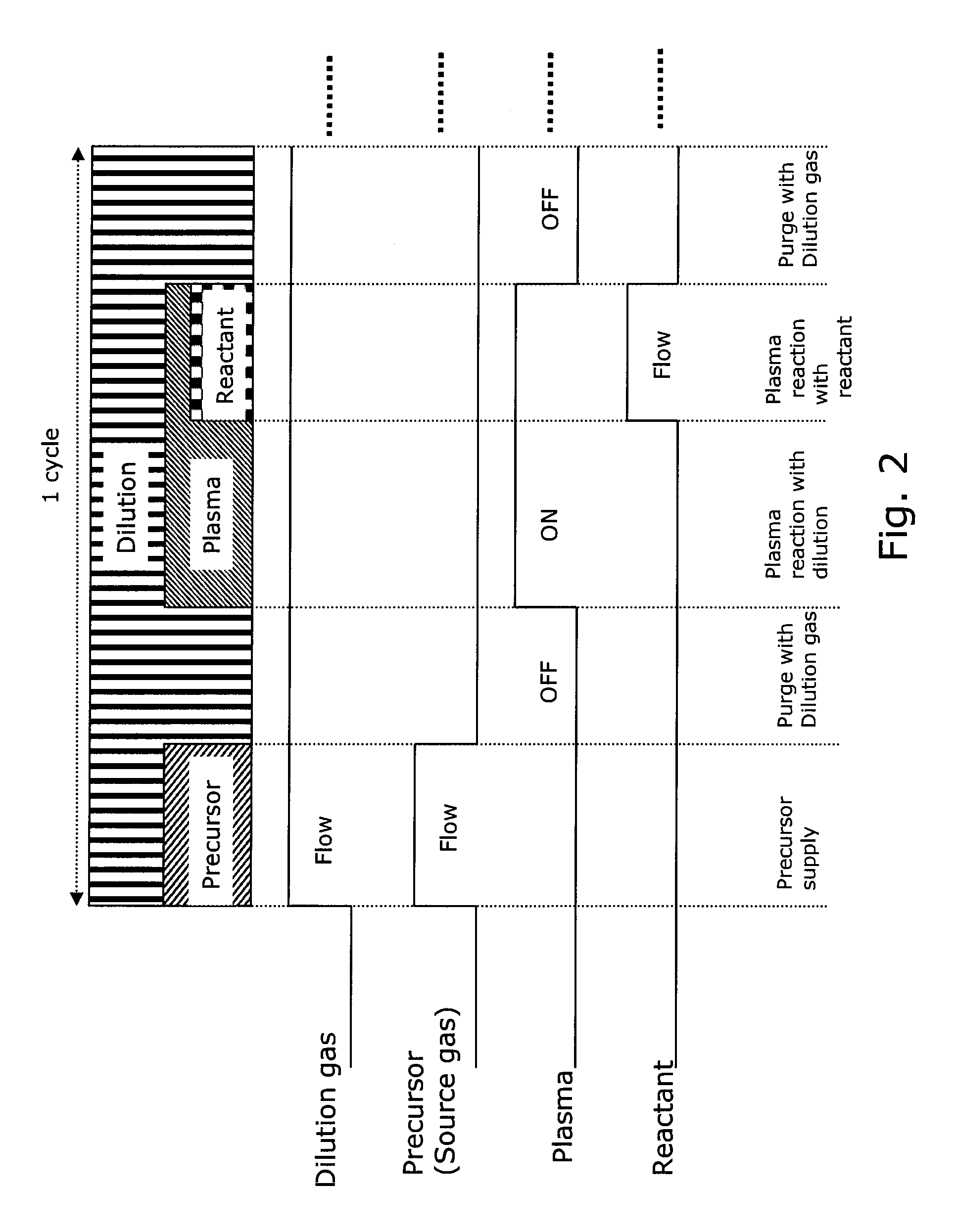
A method for forming a single-phase multi-element film on a substrate in a reaction zone by PEALD repeating a single deposition cycle. The single deposition cycle includes: adsorbing a precursor on the substrate in the absence of reactant and plasma; decomposing the precursor adsorbed on the substrate by an inert gas plasma; and reacting the decomposed precursor with a reactant gas plasma in the presence of the inert gas plasma. The multi-element film contains silicon and at least two non-metal elements constituting a matrix of the film, the precursor contains silicon and optionally at least one non-metal element to be incorporated in the matrix, and the reactant gas contains at least one non-metal element to be incorporated in the matrix.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Method for forming single-phase multi-element film by PEALD
ActiveUS8569184B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingReaction zoneGas plasma
Owner:ASM JAPAN
High Flow GaCl3 Delivery
InactiveUS20080018004A1Avoid insufficient heatingCarburetting airPolycrystalline material growthGas phaseReaction zone
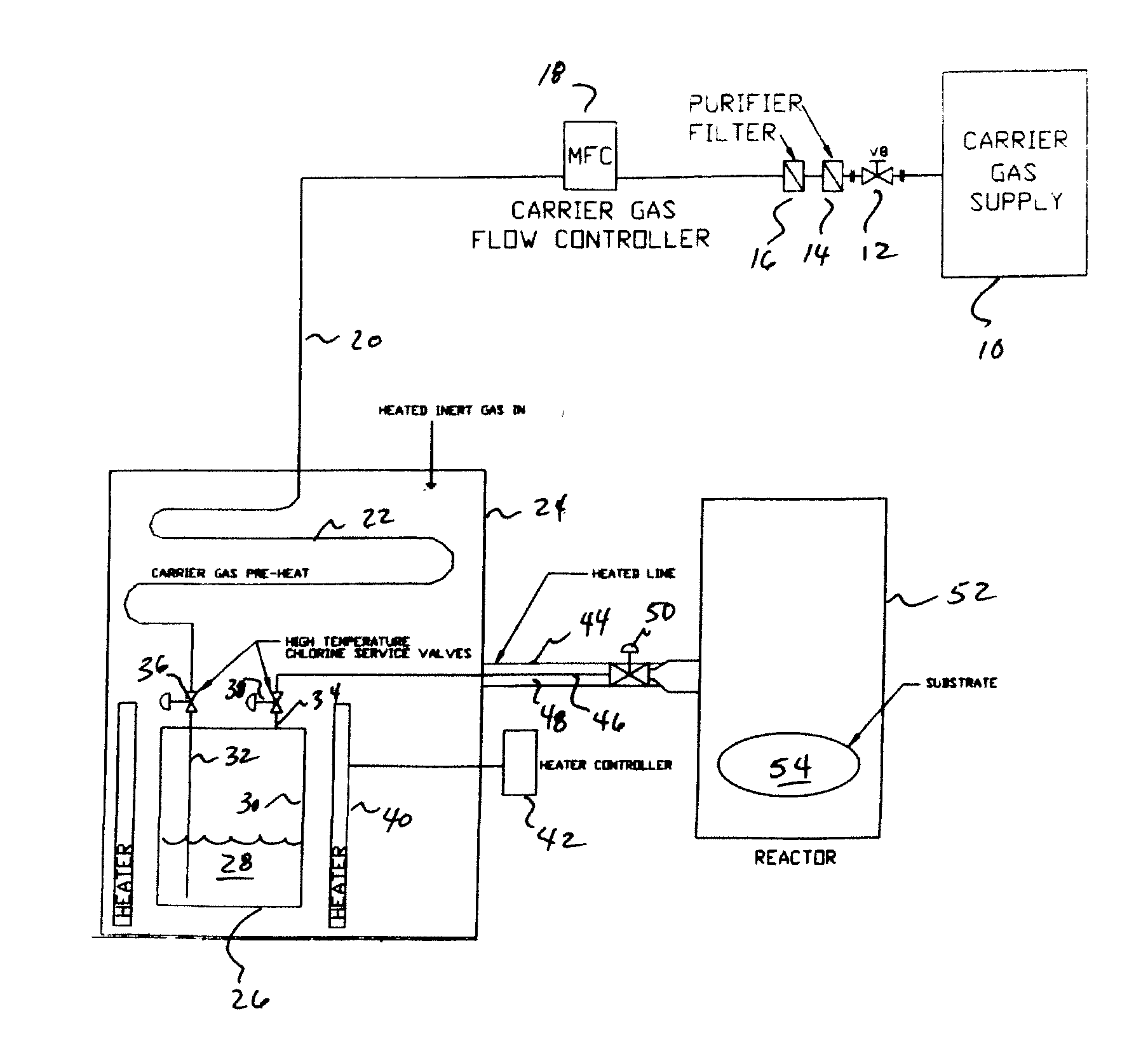
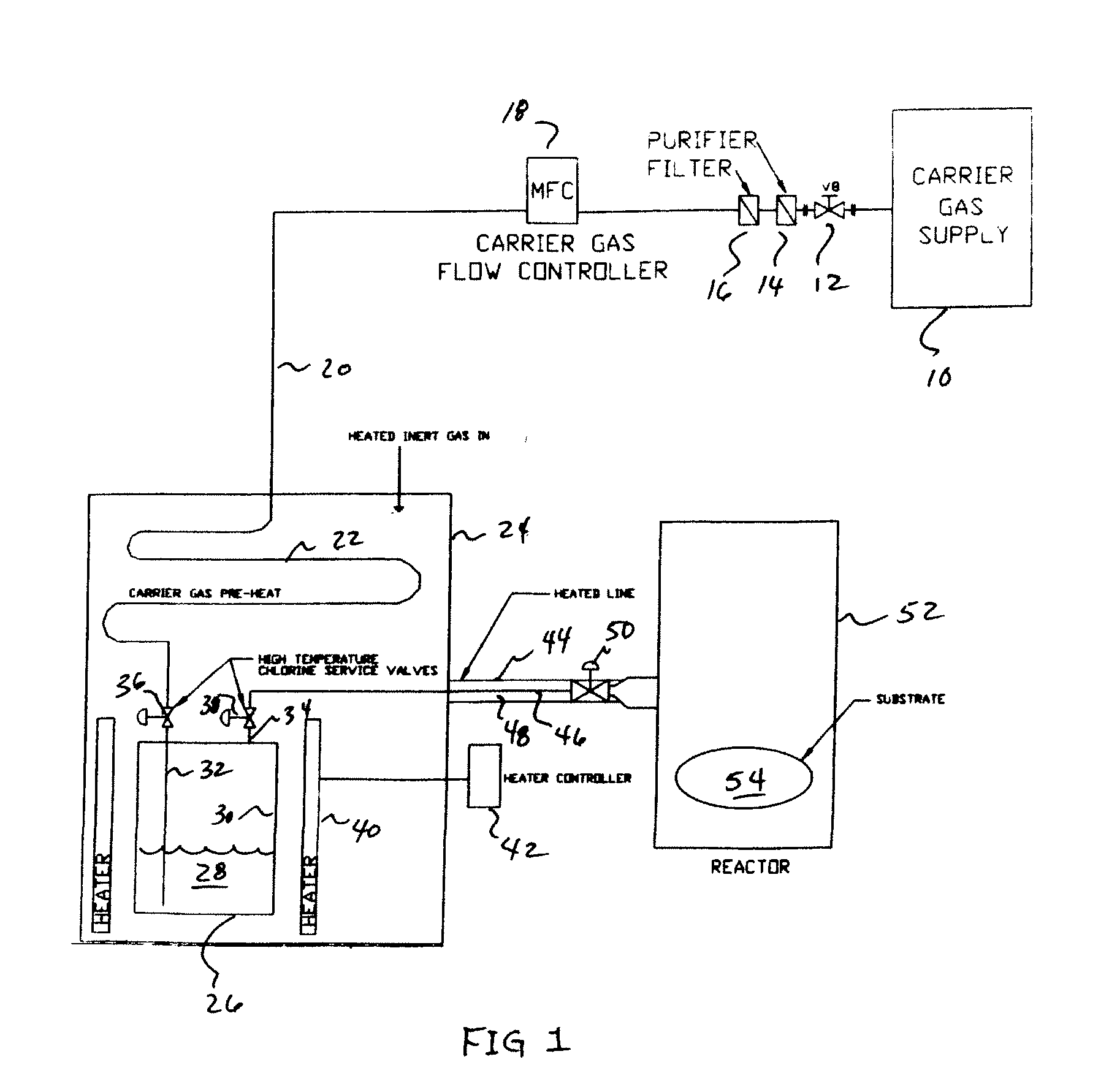
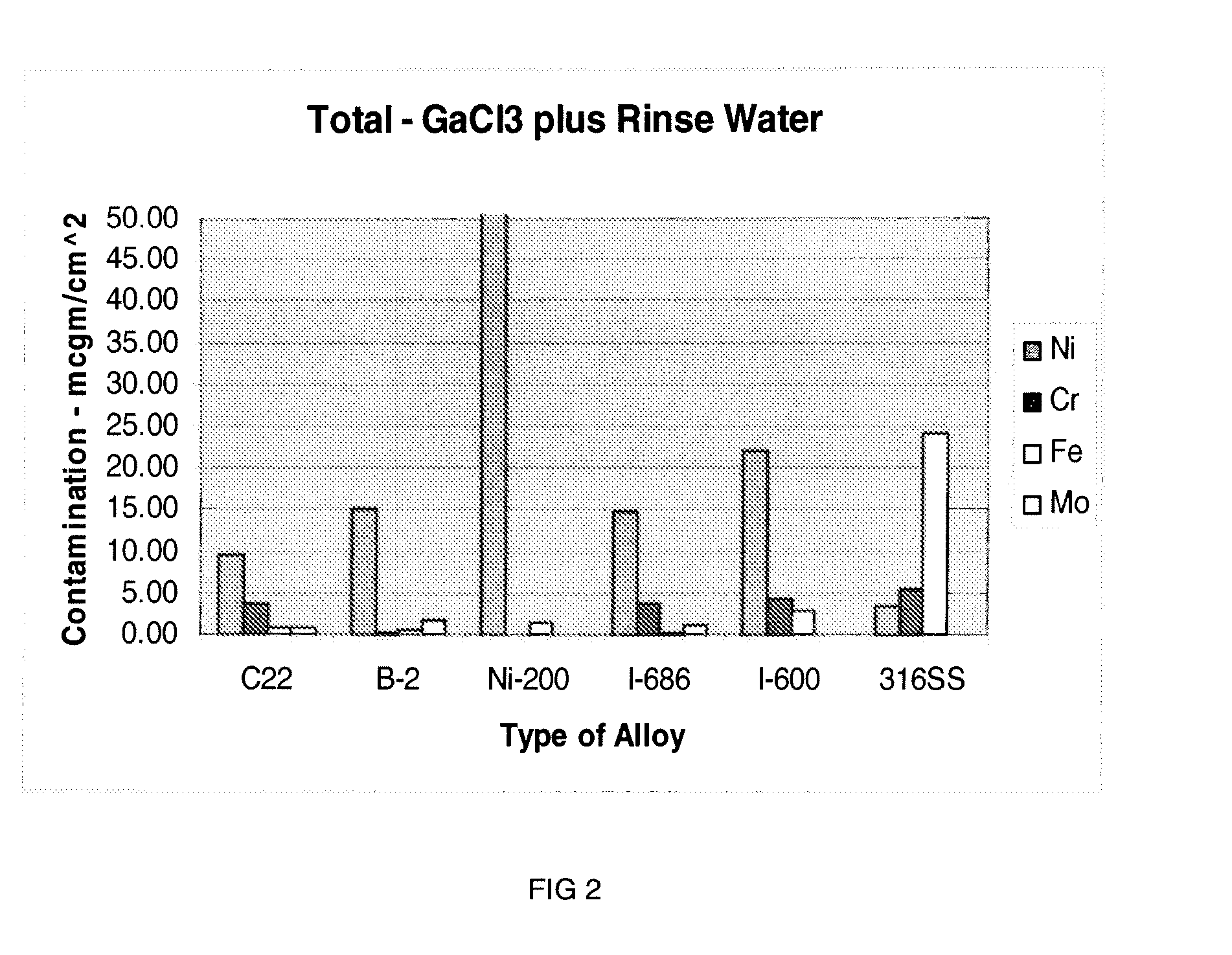
The present invention is an apparatus for deliverying high purity gallium trichloride in the vapor phase to a gallium nitride reactor, comprising; a source of carrier gas at an elevated pressure; a purifier to remove moisture from the carrier gas; a heater capable of heating the carrier gas to at least 80° C.; a container having a supply of gallium trichloride, a valve controlled inlet for the carrier gas having a dip tube with an outlet below the level of the gallium trichloride, a valve controlled outlet for removing the carrier gas and entrained gallium trichloride; a heater capable of heating sufficient to melt the gallium trichloride; a delivery line connected to the valve controlled outlet for carrying the entrained gallium trichloride to a reaction zone for gallium nitride. A process is also described for the apparatus.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Multi-zone reactor, system including the reactor, and method of using the same
ActiveUS20160268107A1Electric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingReaction zoneProcess engineering
Multi-zone reactors, systems including a multi-zone reactor, and methods of using the systems and reactors are disclosed. Exemplary multi-zone reactors include a movable susceptor assembly and a moveable plate. The movable susceptor assembly and movable plate can move vertically between reaction zones of a reactor to expose a substrate to multiple processes or reactants.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Pyrolytic reactor
A pyrolytic reactor comprising a fuel injection zone, a combustion zone adjacent to the fuel injections zone, an expansion zone adjacent to the combustion zone, a feedstock injection zone comprising a plurality of injection nozzles and disposed adjacent to the expansion zone, a mixing zone configured to mix a carrier stream and feed material and disposed adjacent to the feedstock injection zone, and a reaction zone adjacent to the mixing zone. The plurality of injection nozzles are radially distributed in a first assembly defining a first plane transverse to the feedstock injection zone and in a second assembly transverse to the feedstock injection zone.
Owner:UOP LLC
Industrial Wastewater Microwave Electrodeless UV Photocatalysis-Double Membrane Separation Coupling Treatment Device
InactiveCN102260003AAchieve coolingShort wavelengthWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWaste water treatment from animal husbandryIndustrial waste waterDecomposition
The present invention is an industrial waste water microwave electrodeless ultraviolet photocatalysis-dual membrane separation coupling treatment device, the device mainly consists of a reactor (1), a membrane separation system (2), a microwave electrodeless ultraviolet light source system (4), an aeration system, and an ozone tail gas decomposition device (7) connected to the reactor, and an inlet and outlet water system, wherein: the upper and lower parts of the reactor are respectively the reaction zone and the aeration zone, which are separated by a water distribution plate (5); the membrane separation system The microwave electrodeless ultraviolet light source system is located in the reaction zone and is separated by a corrugated partition (3); the aeration system is composed of a microporous aeration head (6) and a blower (8), and the microporous aeration head is located in the aeration At the bottom of the zone, the blower sends air to the aeration zone through the air duct. The invention has the characteristics of high reaction rate, complete degradation of organic matter, long-term operation and the like, and has strong operability and high safety. It is suitable for the treatment of refractory organic industrial wastewater, and it is also suitable for sterilization and disinfection in the field of water supply.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
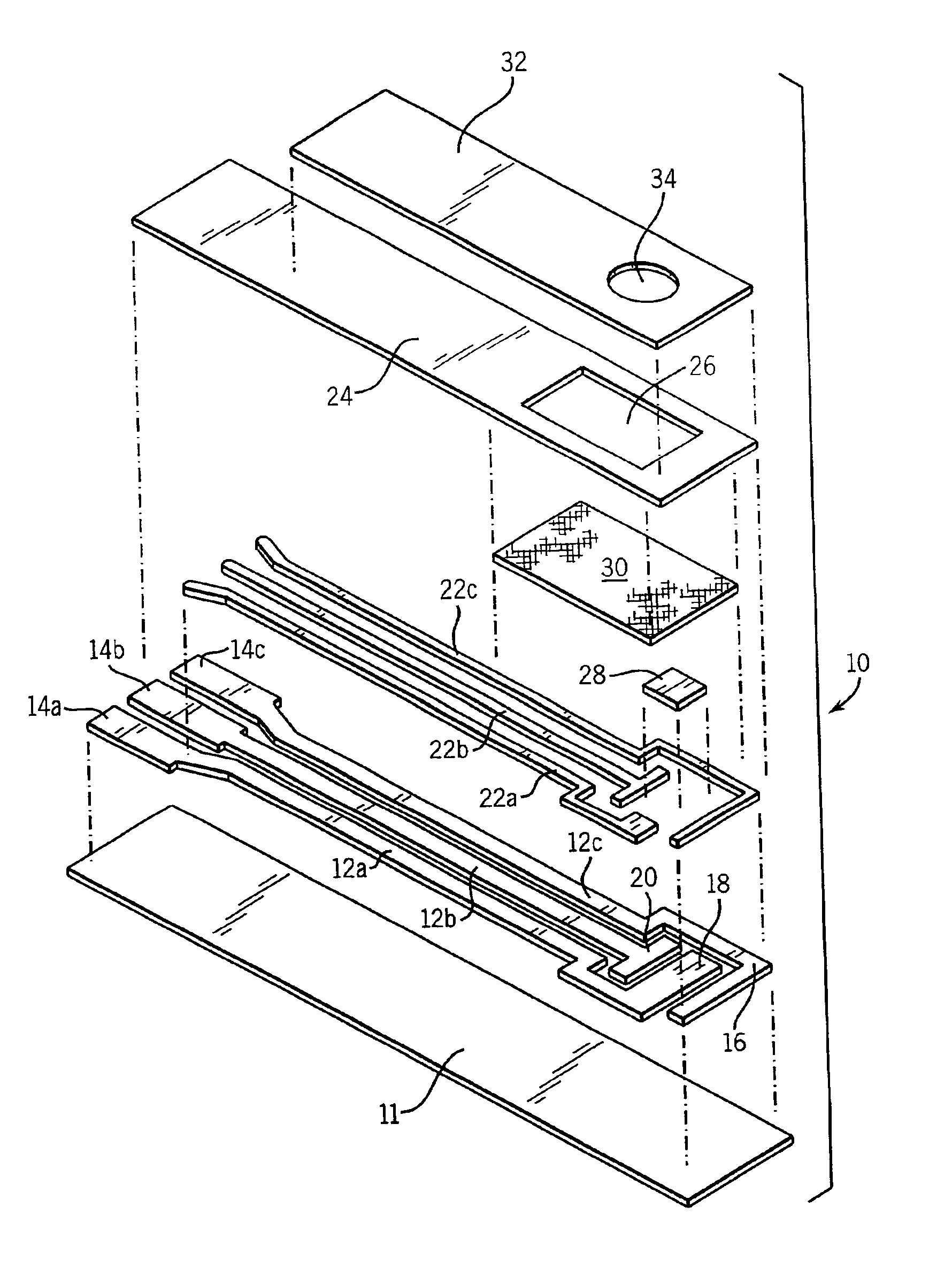
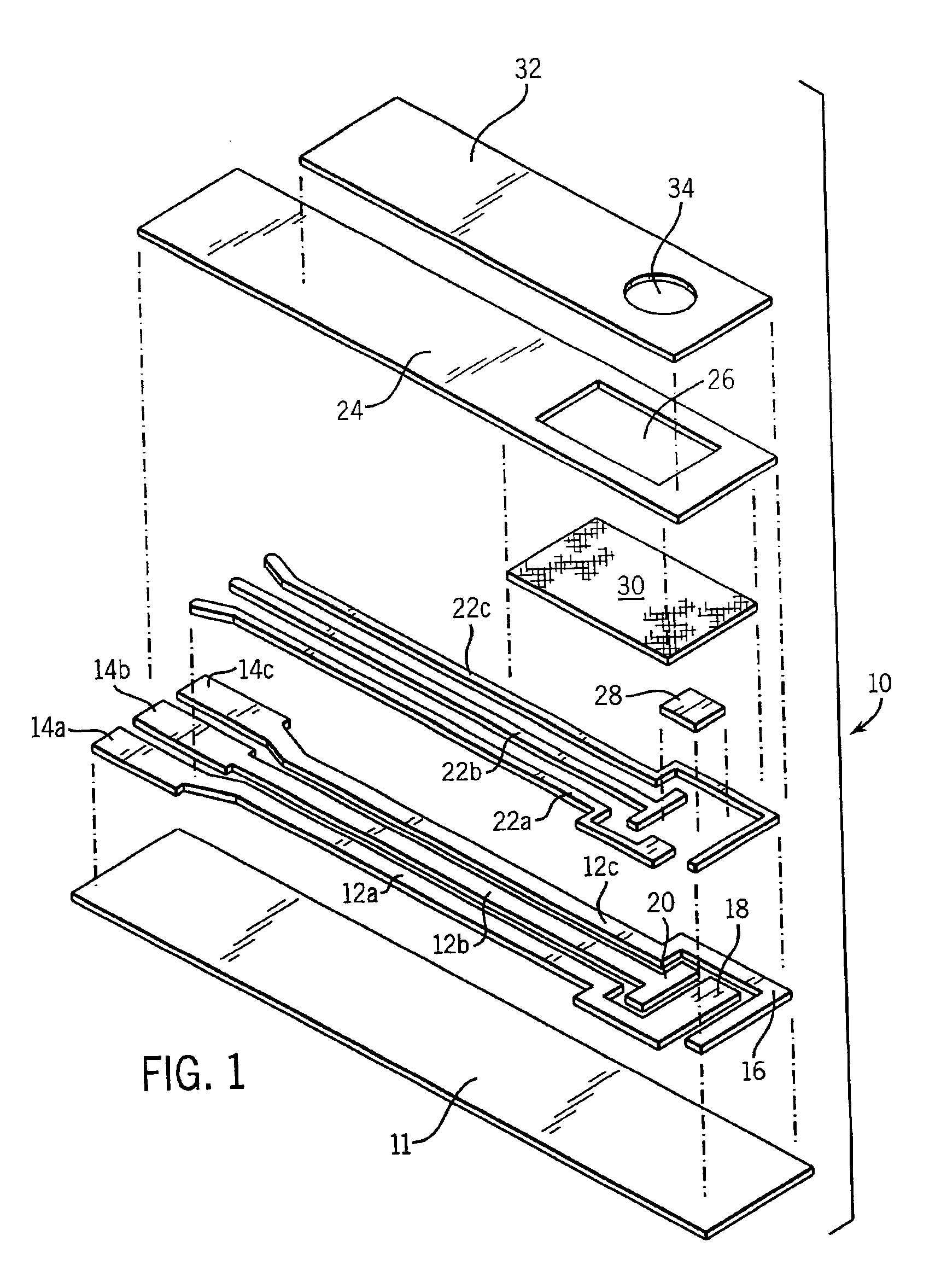
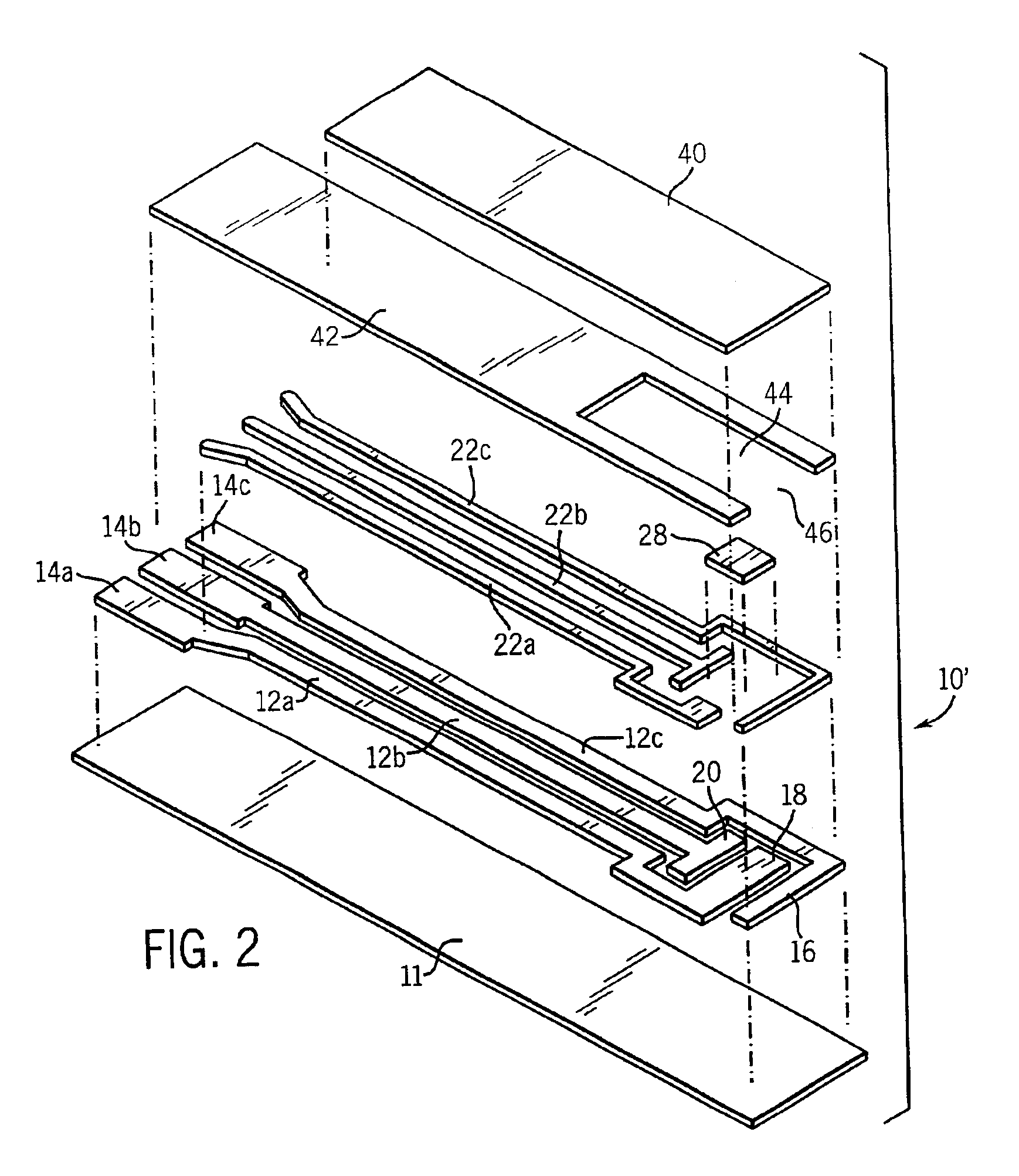
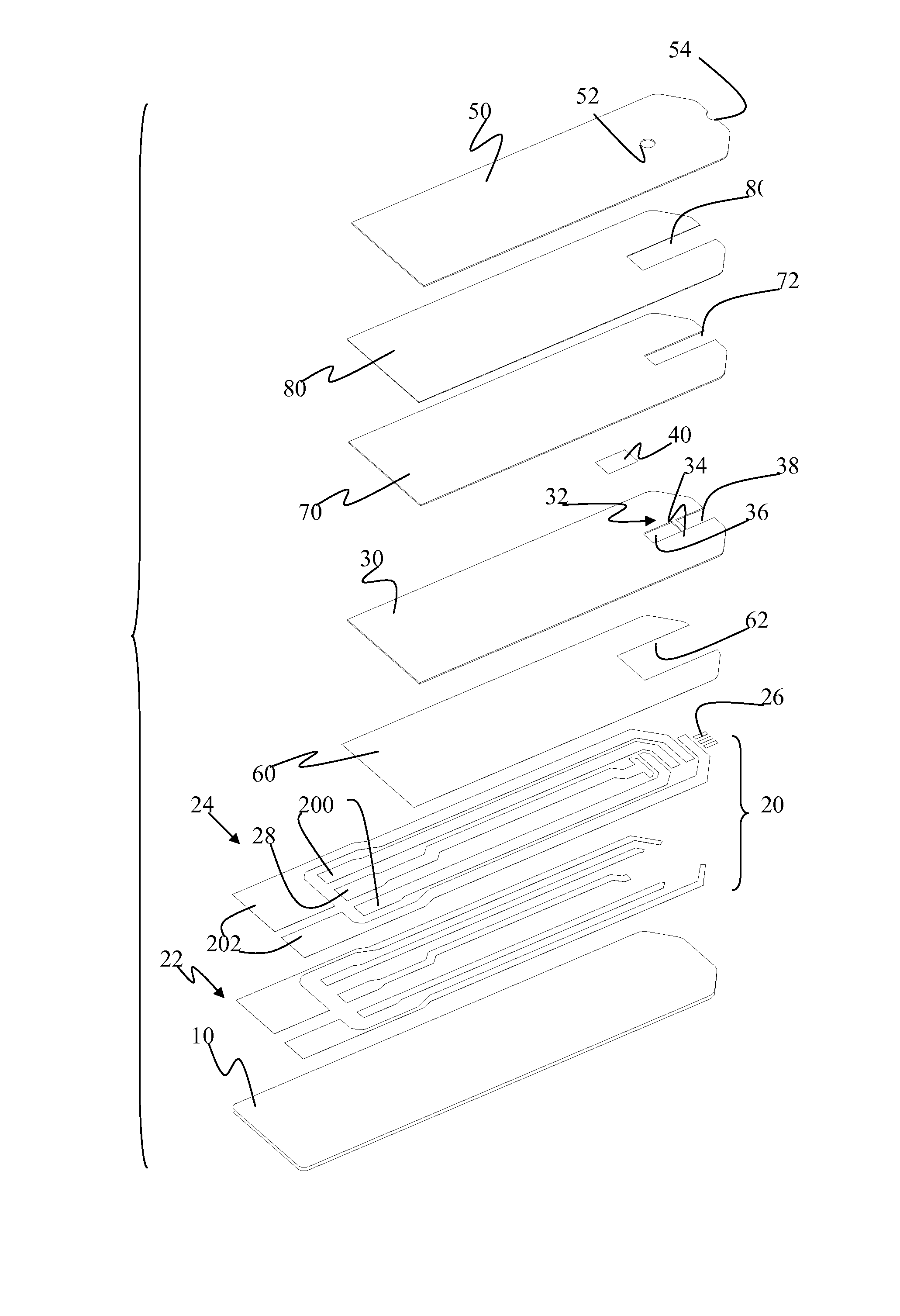
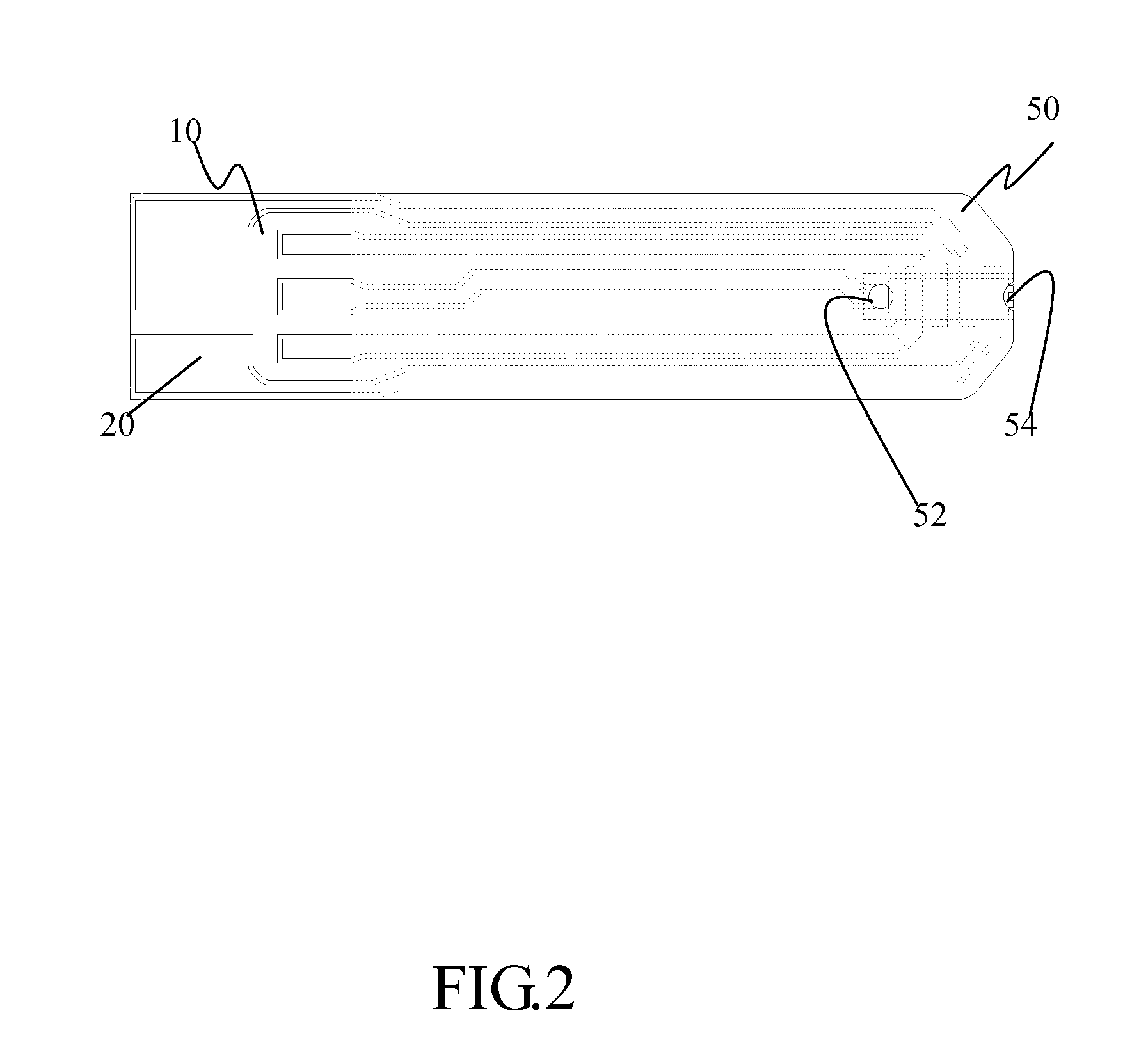
Electrochemical biosensor strip for analysis of liquid samples
InactiveUS6863800B2Easy to transportImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical biosensorConcentrations glucose
A biosensor in the form of a strip. In one embodiment, the biosensor strip comprises an electrode support, a first electrode, i.e., a working electrode, a second electrode, i.e., a counter electrode, and a third electrode, i.e., a reference electrode. Each of the electrodes is disposed on and supported by the electrode support. Each of the electrodes is spaced apart from the other two electrodes. The biosensor strip can include a covering layer, which defines an enclosed space over the electrodes. This enclosed space includes a zone where an analyte in the sample reacts with reagent(s) deposited at the working electrode. This zone is referred to as the reaction zone. The covering layer has an aperture for receiving a sample for introduction into the reaction zone. The biosensor strip can also include at least one layer of mesh interposed in the enclosed space between the covering layer and the electrodes in the reaction zone. This layer of mesh facilitates transporting of the sample to the electrodes in the reaction zone. In another embodiment, a biosensor strip can be constructed to provide a configuration that will allow the sample to be introduced to the reaction zone by action of capillary force. In this embodiment, the layer of mesh can be omitted. The invention also provides a method for determining the concentration of glucose in a sample of whole blood by using the biosensor of this invention.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Pumping System for Atomic Layer Deposition
InactiveUS20070095283A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPipeline systemsEngineeringReaction zone
A pumping apparatus for evacuating a reactant from a reactive region includes a vacuum able chamber, a hearth for supporting a workpiece, one or more gas introduction valves, one or more exhaust evacuation valves, and an adjustable valve providing one or more pathways there through formed by alignment of separate components of the valve, the components perforated with two or more openings to form the pathways.
Owner:GALEWSKI CARL JOHAN
Method and apparatus of growing a thin film onto a substrate
InactiveUS20020108570A1Good film uniformitySimple and efficientPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInlet channelGas phase
A method and an apparatus for growing a thin film onto a substrate by the ALD process. The apparatus comprises a reaction chamber into which the substrate can be disposed; a plurality of inlet channels communicating with said reaction chamber, said inlet channels being suited for feeding the reactants employed in a thin-film growth process in the form of vapor-phase pulses into said reaction chamber; at least one outlet channel communicating with said reaction chamber, said outlet channel being suited for the outflow of reaction products and excess amounts of reactants from said reaction space; and a pre-reaction chamber arranged immediately upstream of the reaction chamber, said pre-reaction chamber forming a first reaction zone, in which the reactants of successive vapor-phase pulses can be reacted with each other in the vapor phase to form a solid product, whereas said reaction chamber forming a second reaction zone can be operated under conditions conducive to ALD growth of a thin film.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Multi-zone reactor, system including the reactor, and method of using the same
Multi-zone reactors, systems including a multi-zone reactor, and methods of using the systems and reactors are disclosed. Exemplary multi-zone reactors include a movable susceptor assembly and a moveable plate. The movable susceptor assembly and movable plate can move vertically between reaction zones of a reactor to expose a substrate to multiple processes or reactants.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Hydrogen production from carbonaceous material
InactiveUS6790430B1Avoid the needCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesGas turbine plantsCalcinationExothermic reaction
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE +1
Method and apparatus for producing methane from carbonaceous material
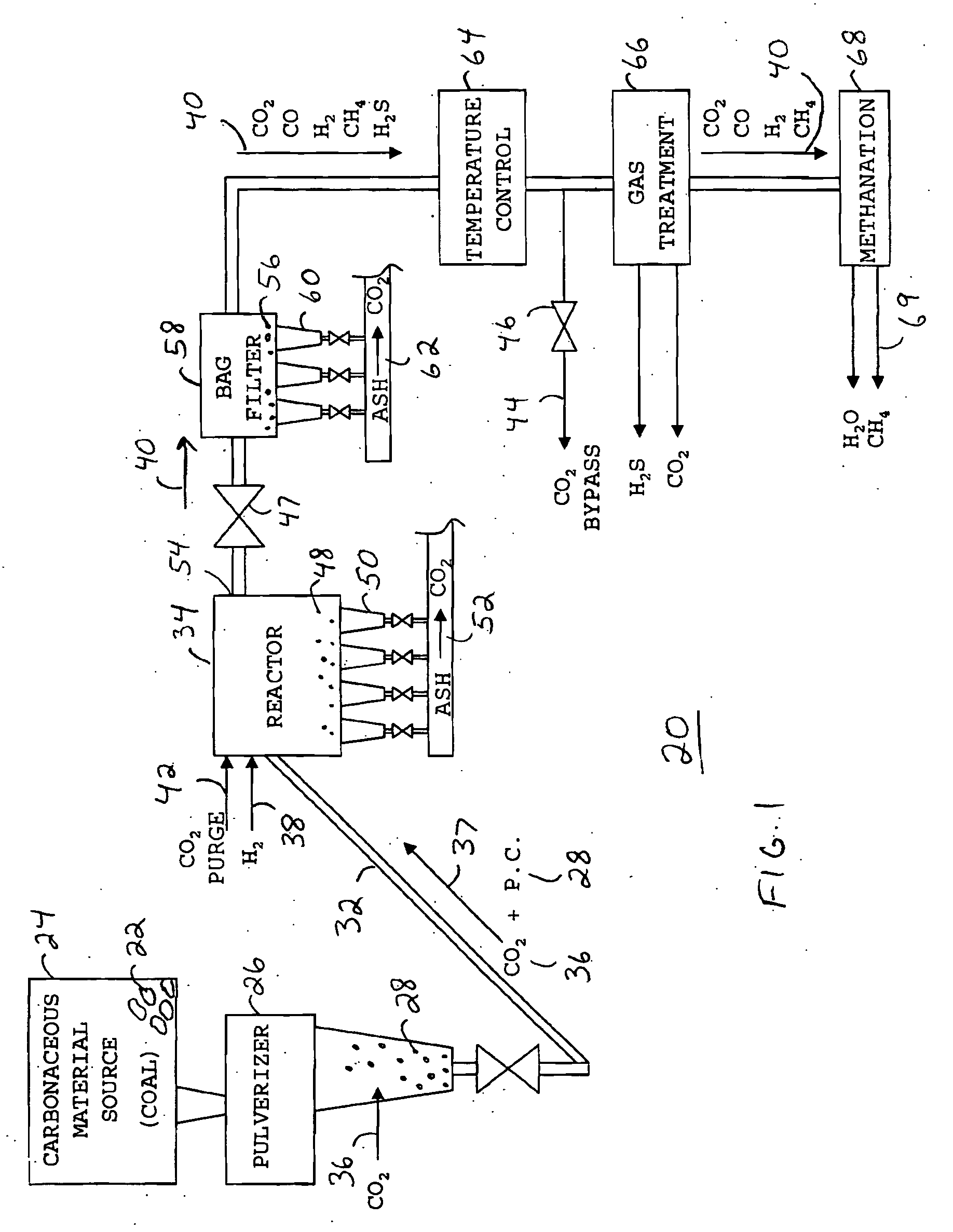
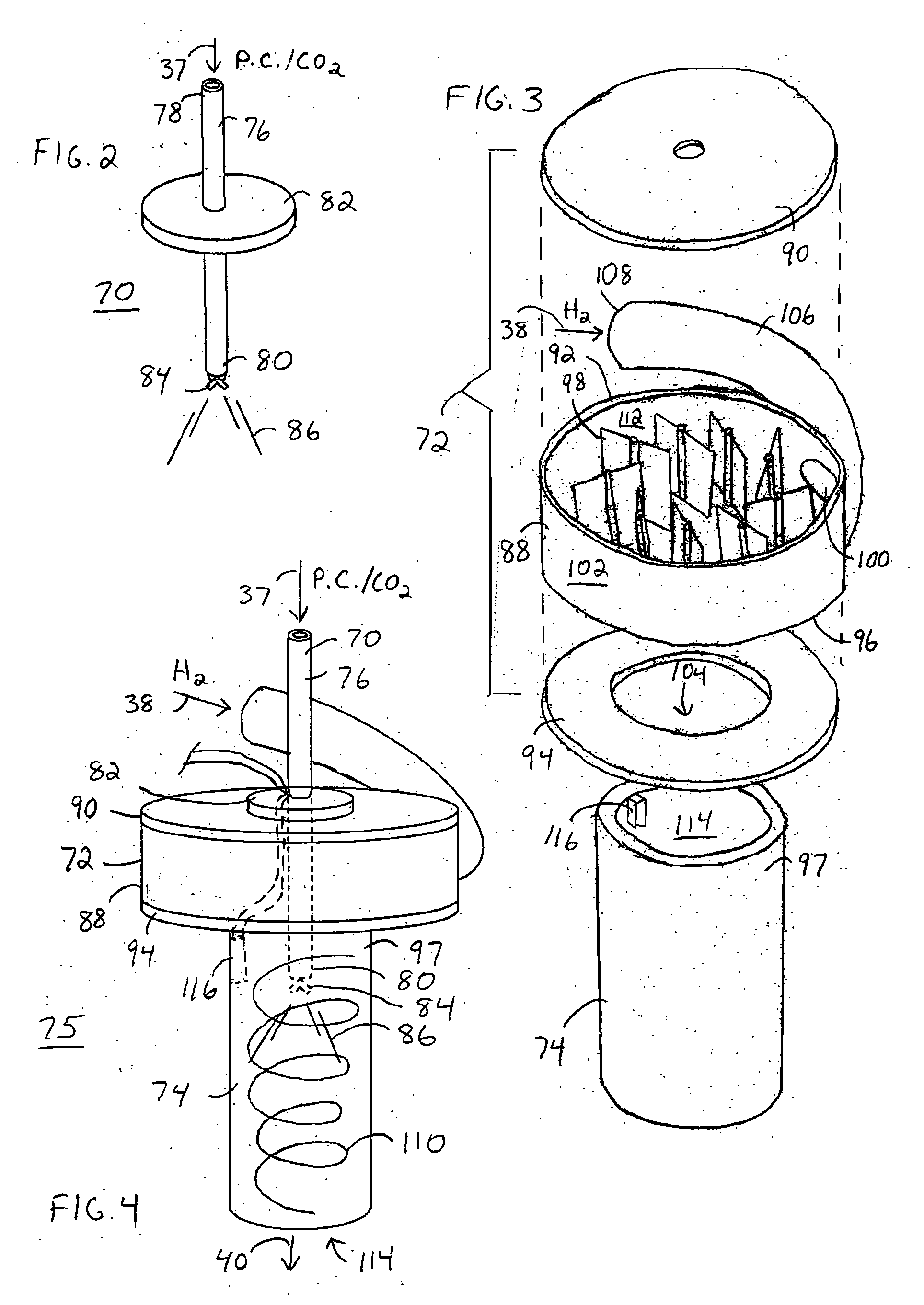
InactiveUS20060265953A1Efficient productionEfficient deliveryHydrogen separationGaseous fuelsHydrogenReaction zone
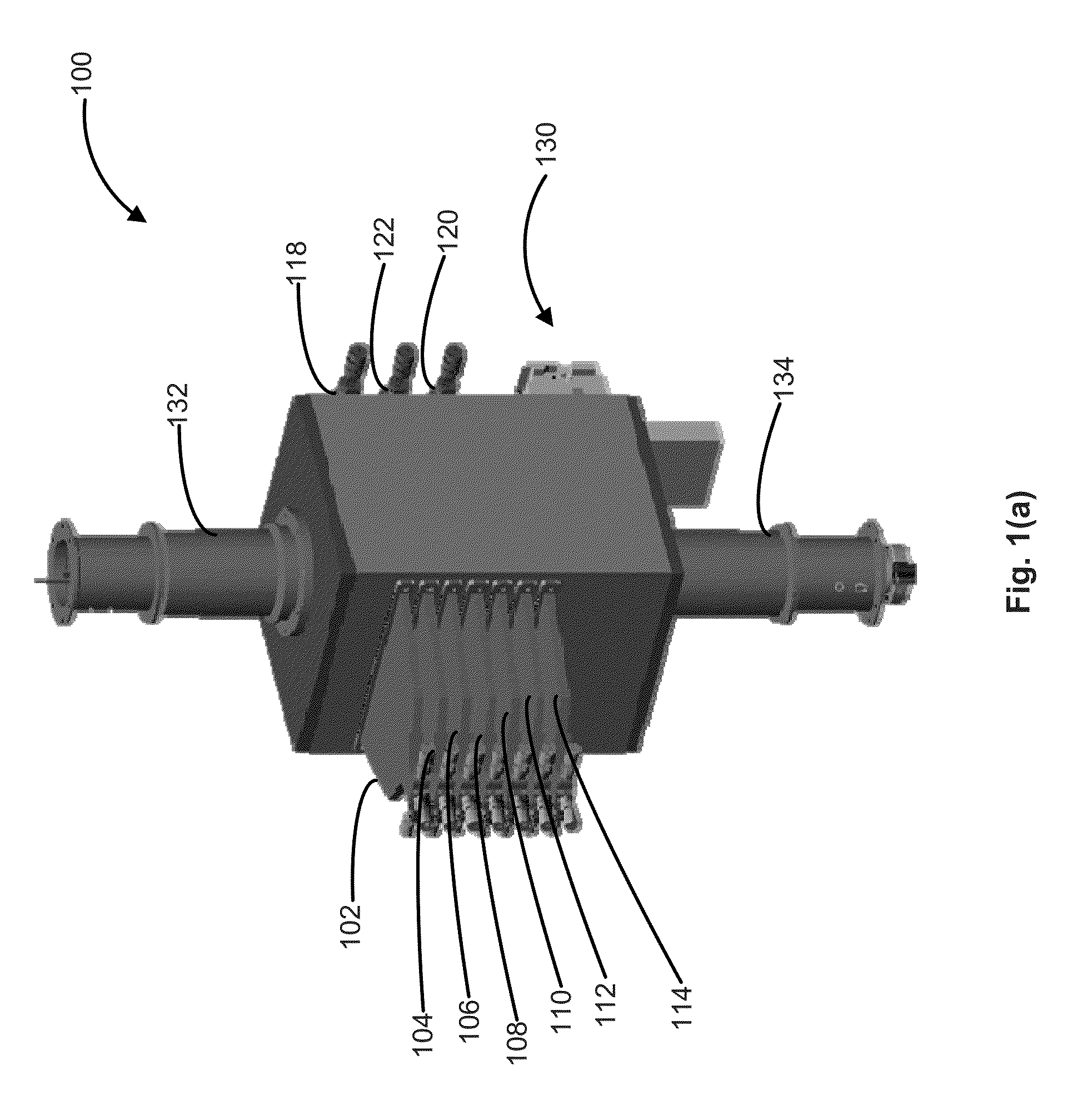
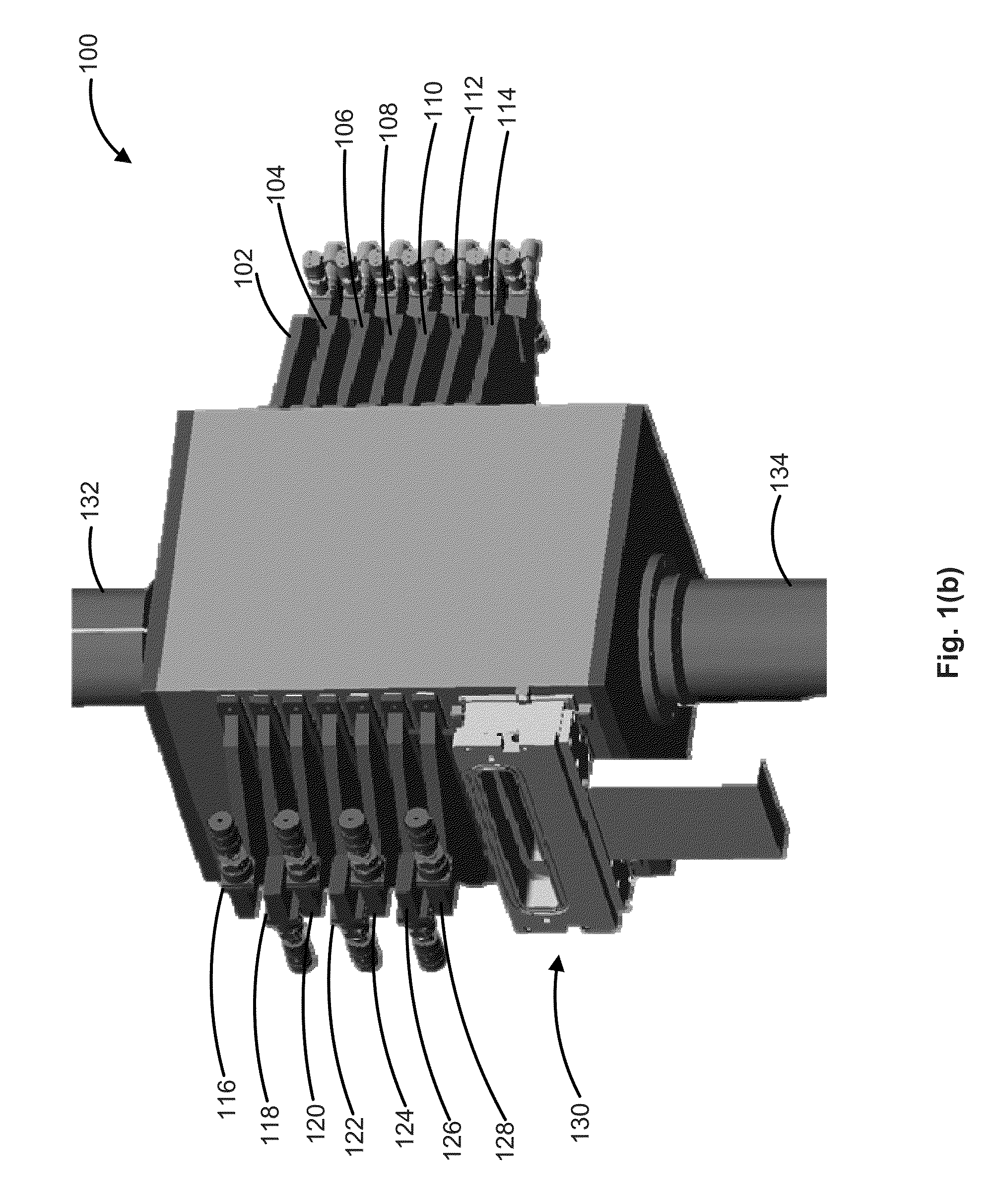
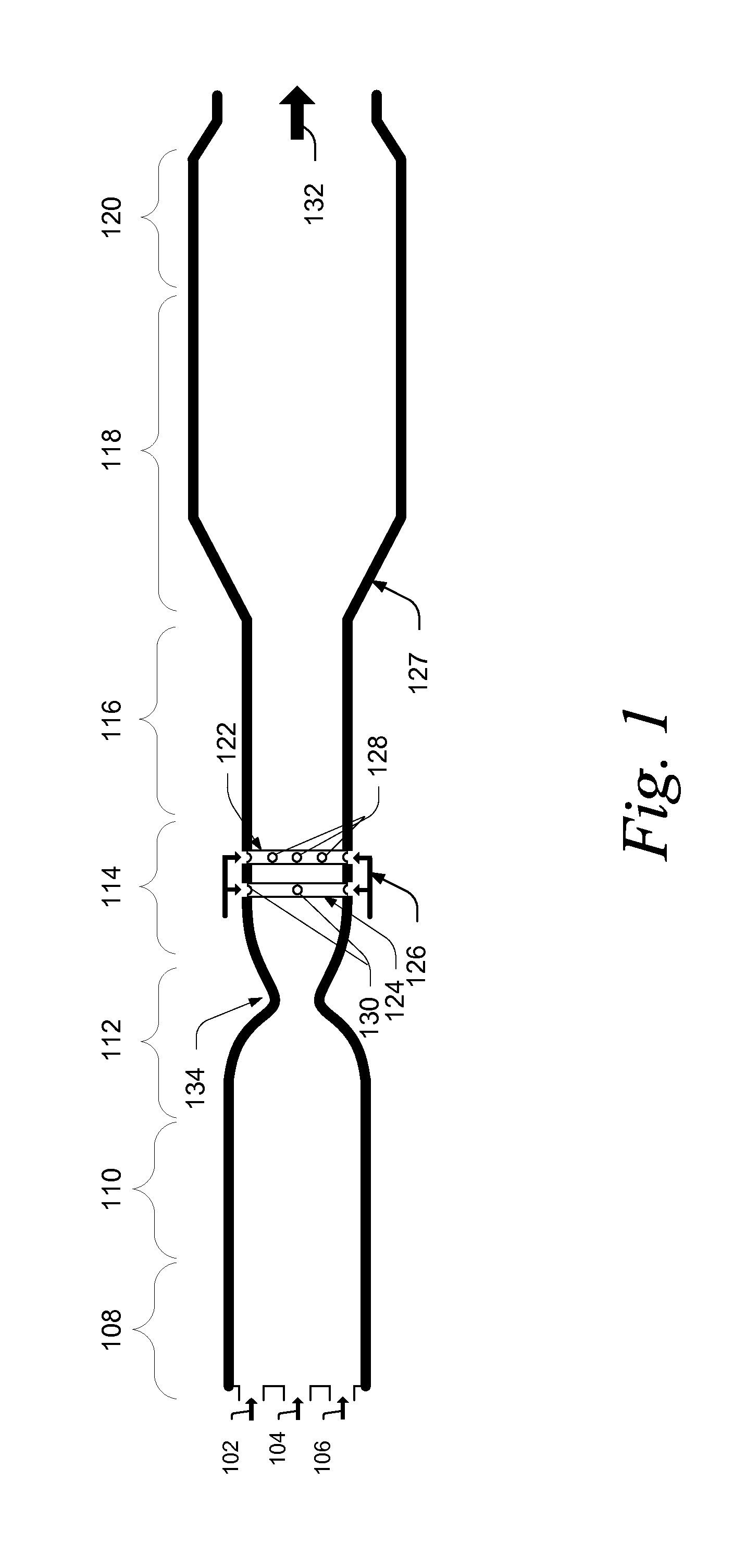
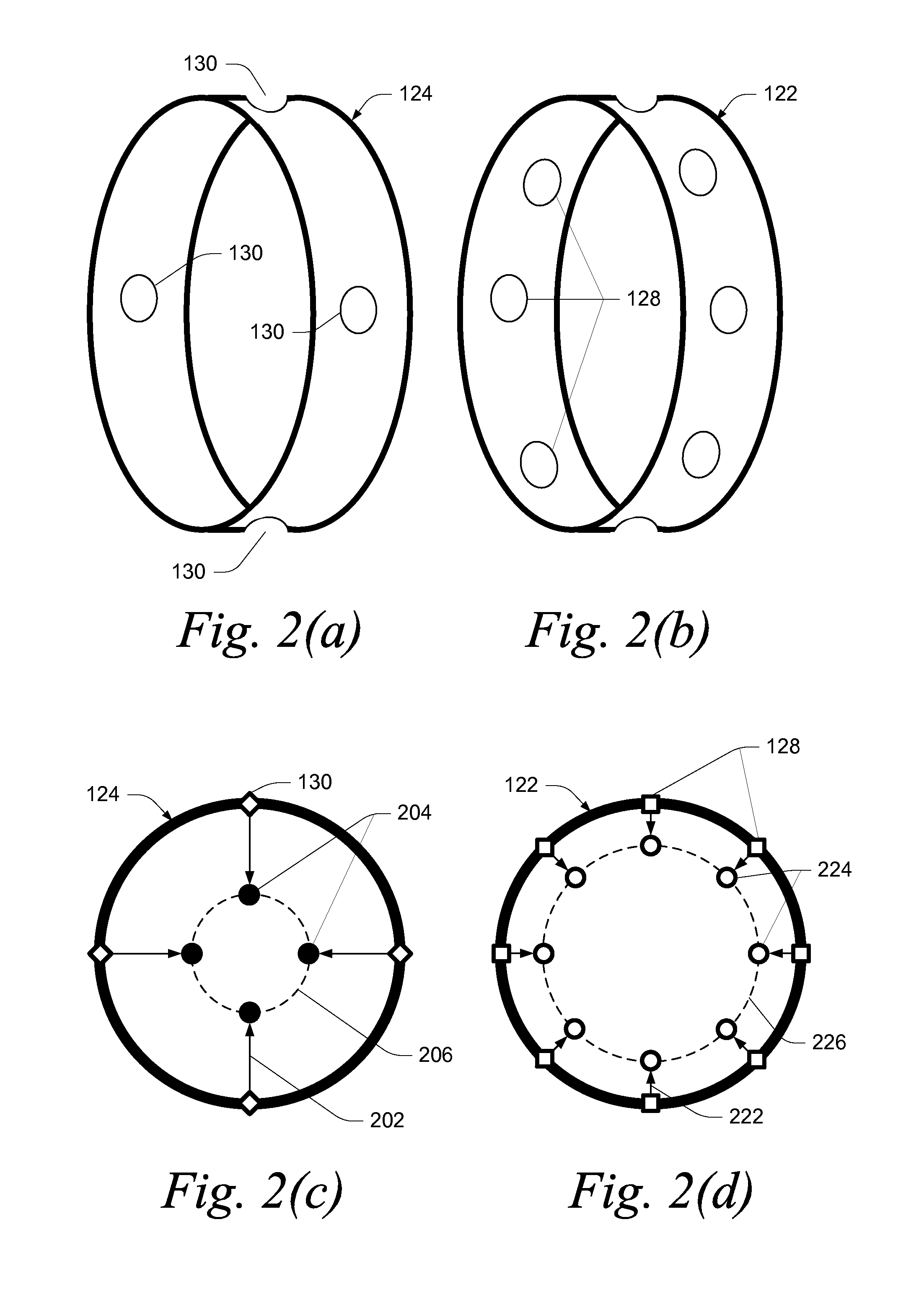
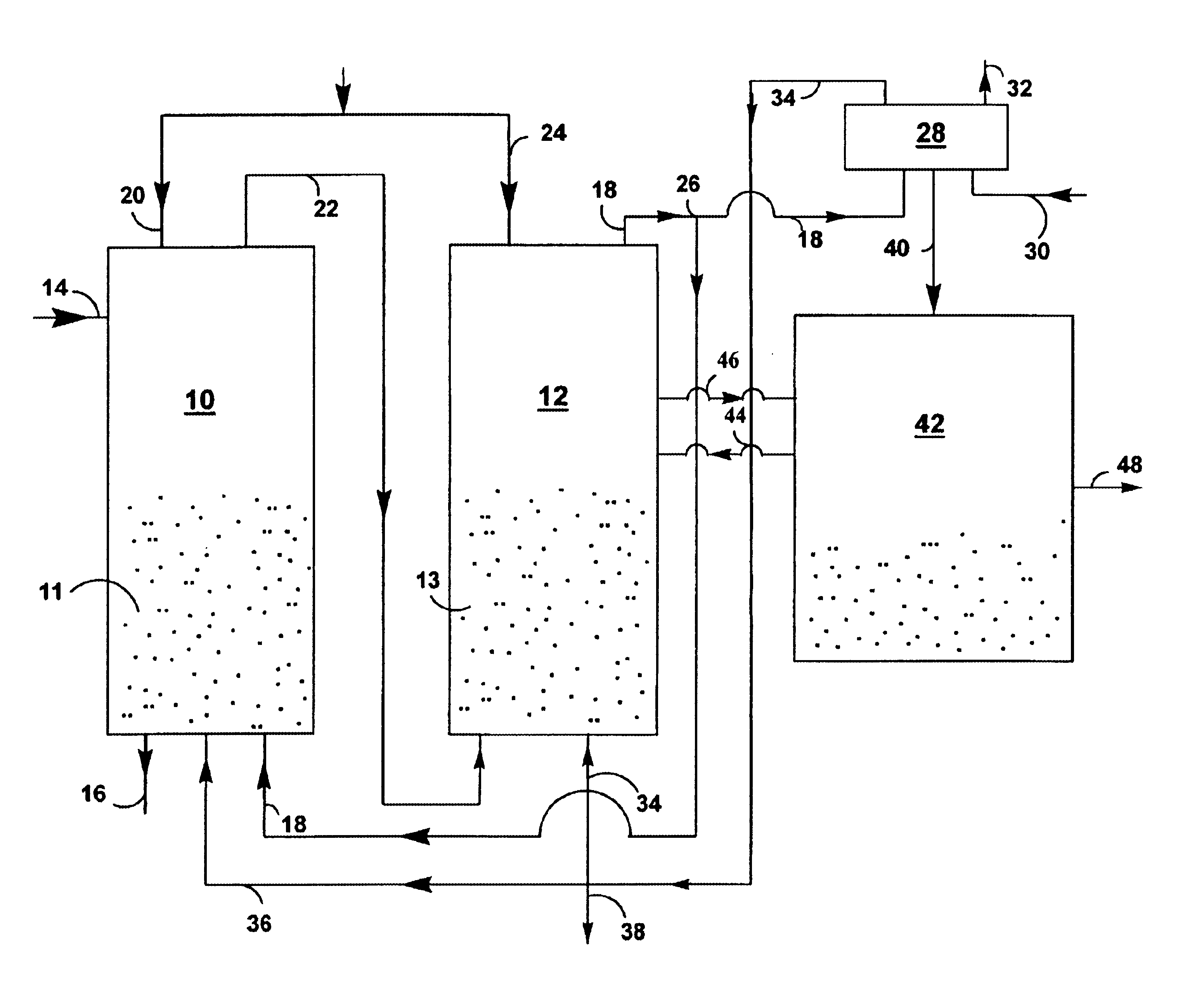
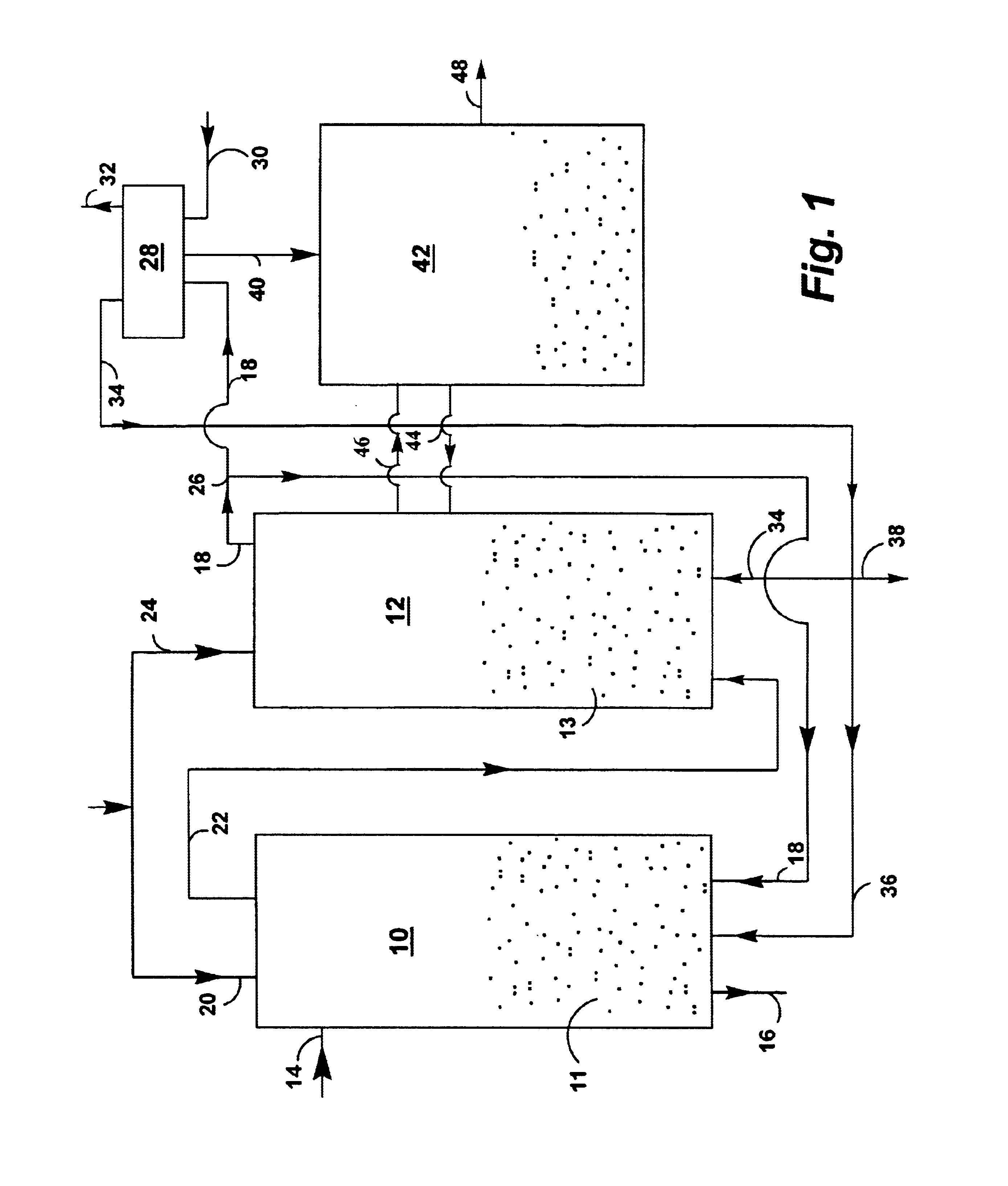
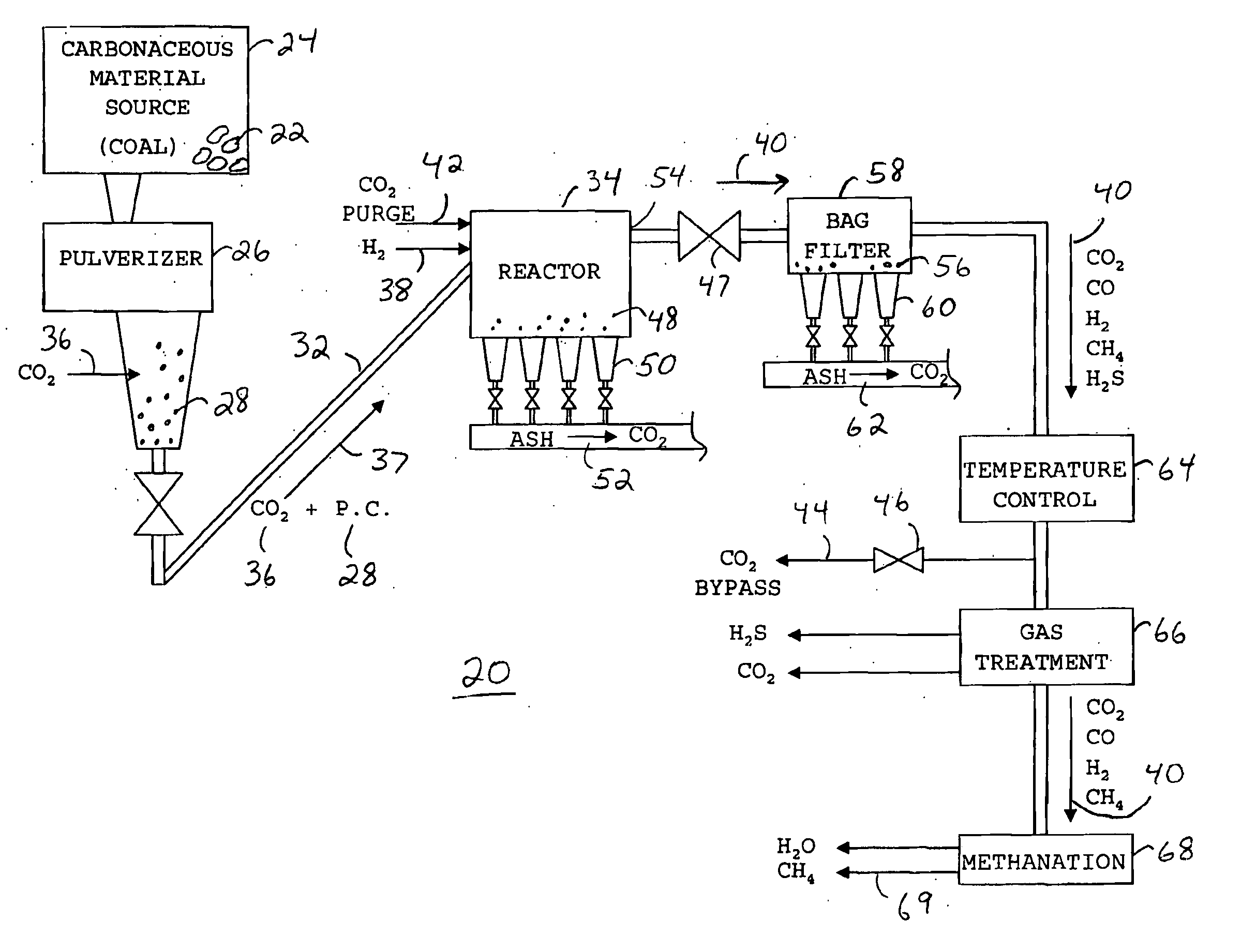
A method for producing methane (69) from a carbonaceous (22) material includes conveying pulverized carbonaceous material (28) entrained in an inert carrier fluid, such as carbon dioxide (36), into a reactor (34). The reactor (34) includes a vortex region (72) for receiving hydrogen gas (38) and imparting a swirling motion to the hydrogen gas (38). The pulverized carbonaceous material (28) is exposed to the swirling stream of hydrogen gas (38) in a first reaction zone (114) within the reactor (34) to form an exit gas (40) that includes methane (69). Remaining unreacted carbonaceous material (28) is further exposed to the hydrogen gas (38) in a second, low velocity, reaction zone (120). The methane rich exit gas (40) is subsequently extracted from the reactor (34) for further processing.
Owner:ARIZONA PUBLIC SERVICE
Method and apparatus of time and space co-divided atomic layer deposition
InactiveUS20070215036A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringAtomic layer deposition
Space and time co-divided atomic layer deposition (ALD) apparatuses and methods are provided. Substrates are moved (e.g., rotated) among multiple reaction zones, each of which is exposed to only one ALD reactant. At the same time, reactants are pulsed in each reaction zone, with purging or other gas removal methods between pulses. Separate exhaust passages for each reactant and purging during wafer movement minimizes particle contamination. Additionally, preferred embodiments permit different pulsing times in each reaction space, thus permitting flexibility in pulsing.
Owner:ASM GENITECH KOREA
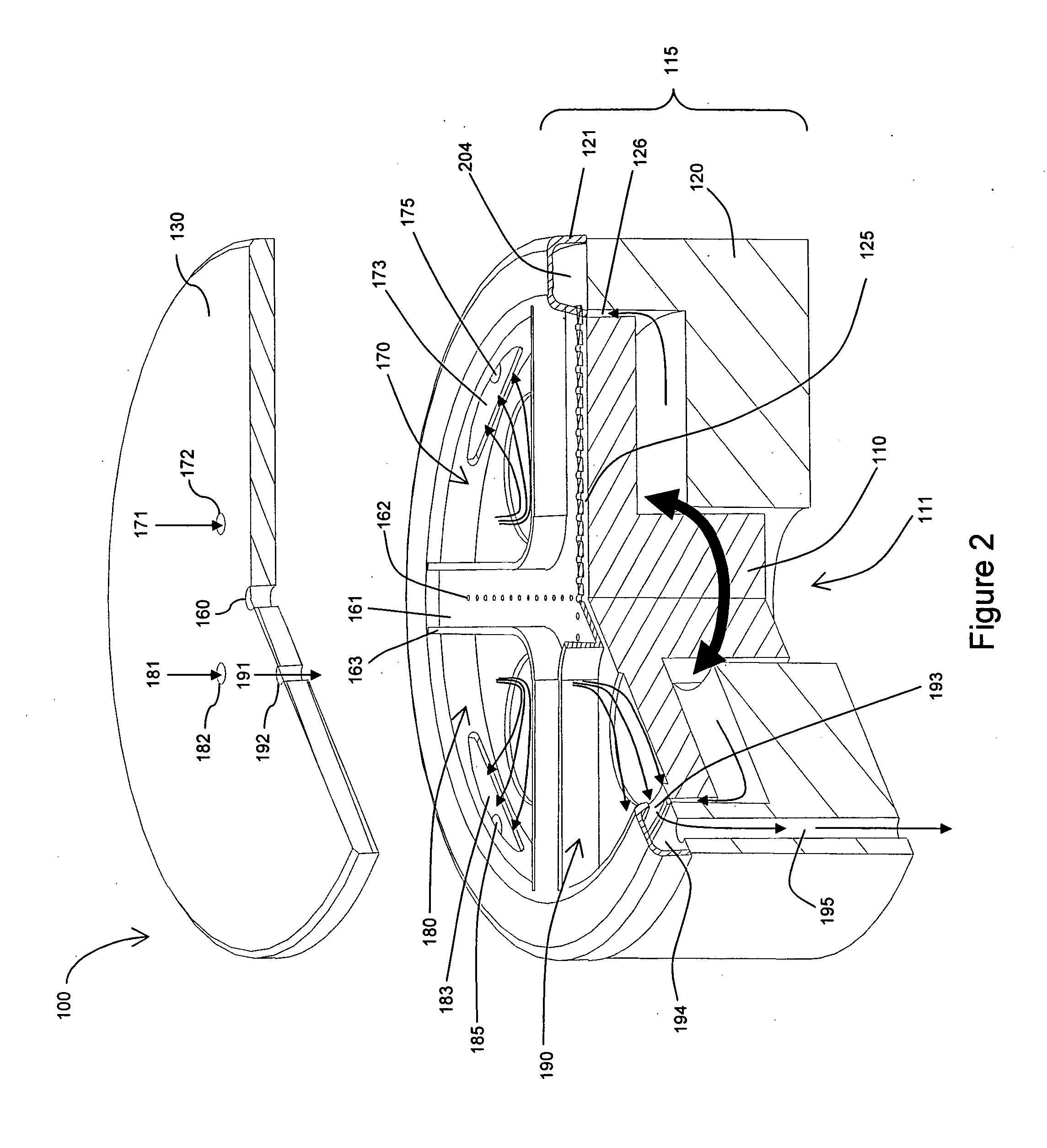
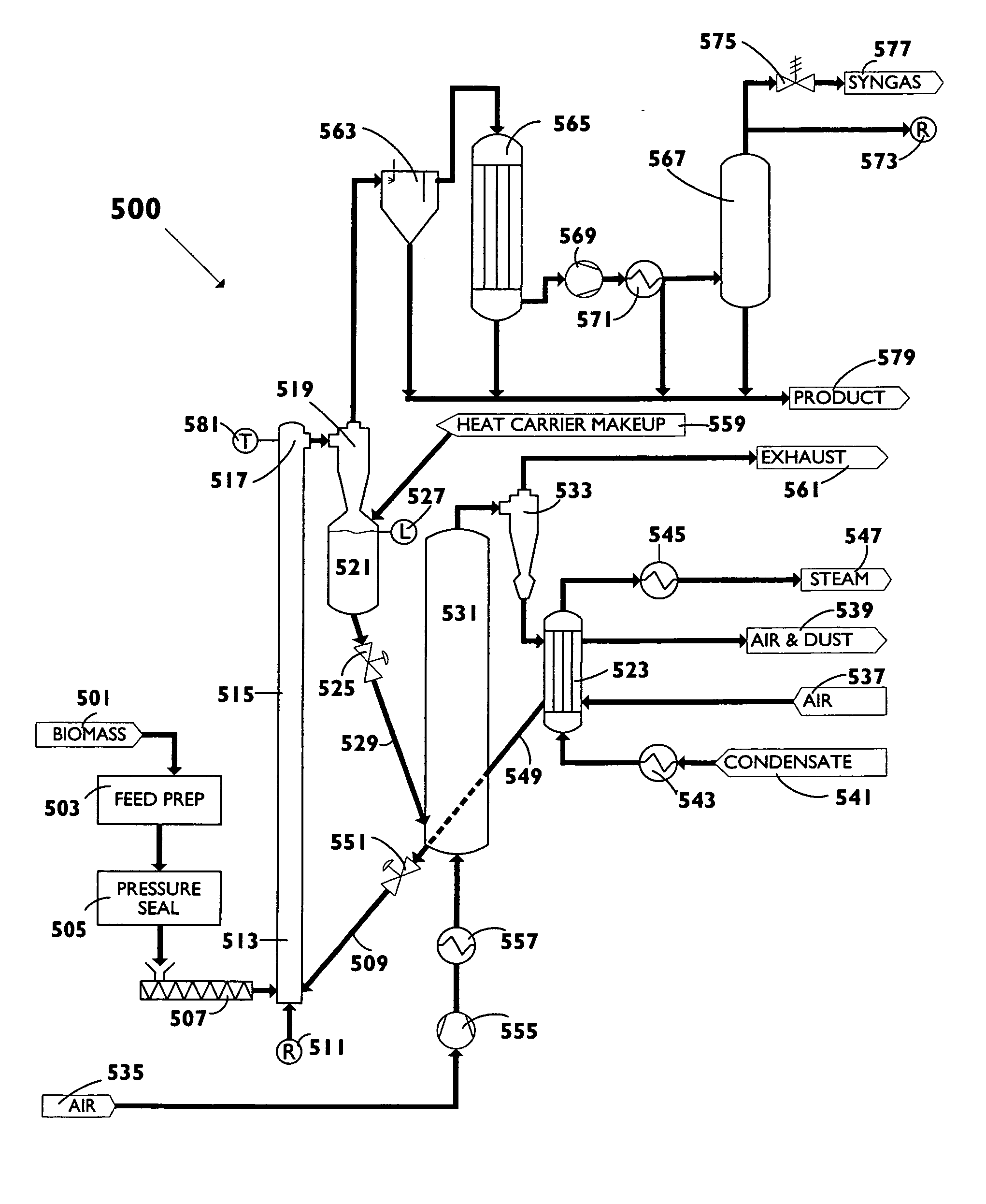
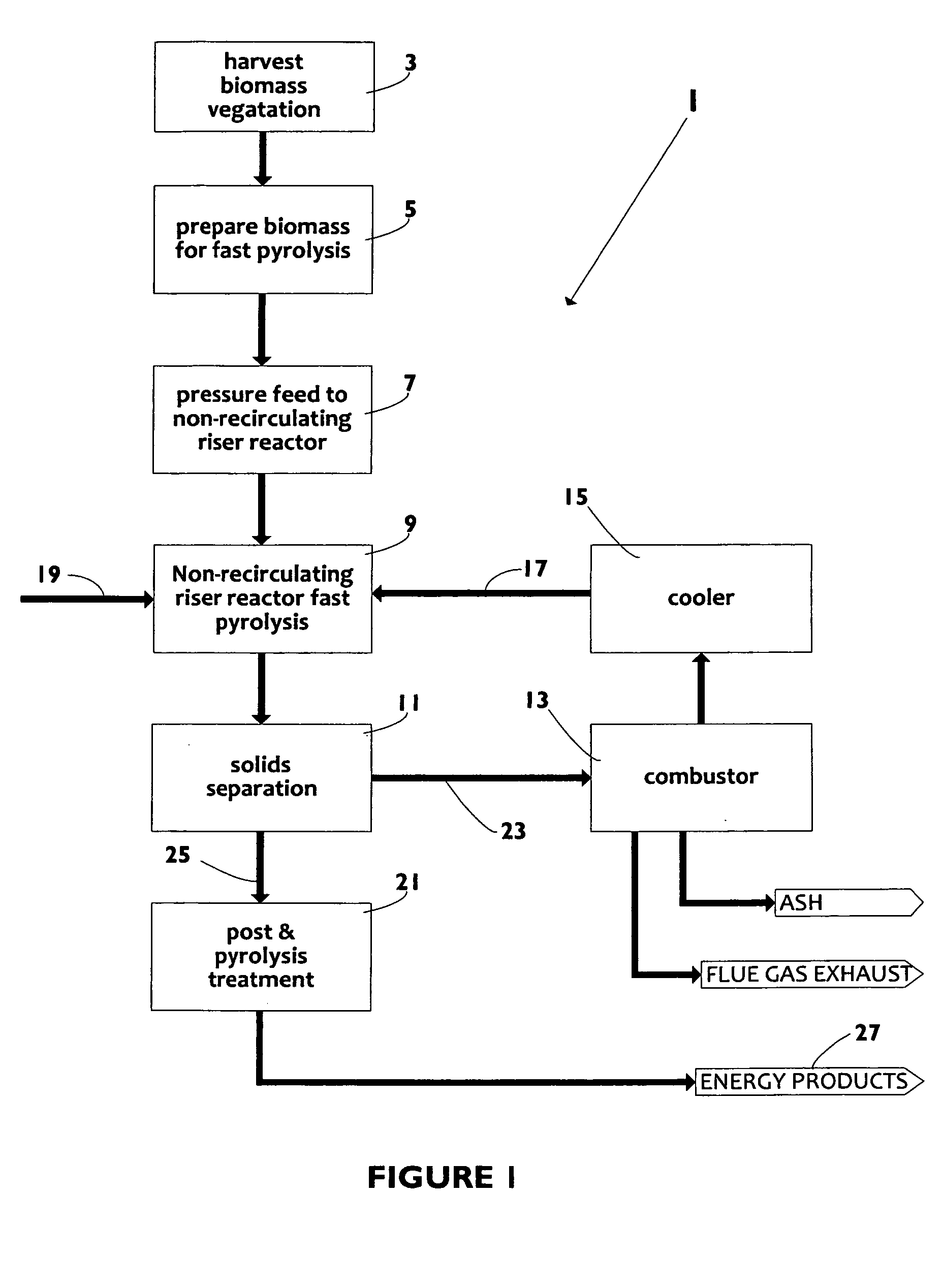
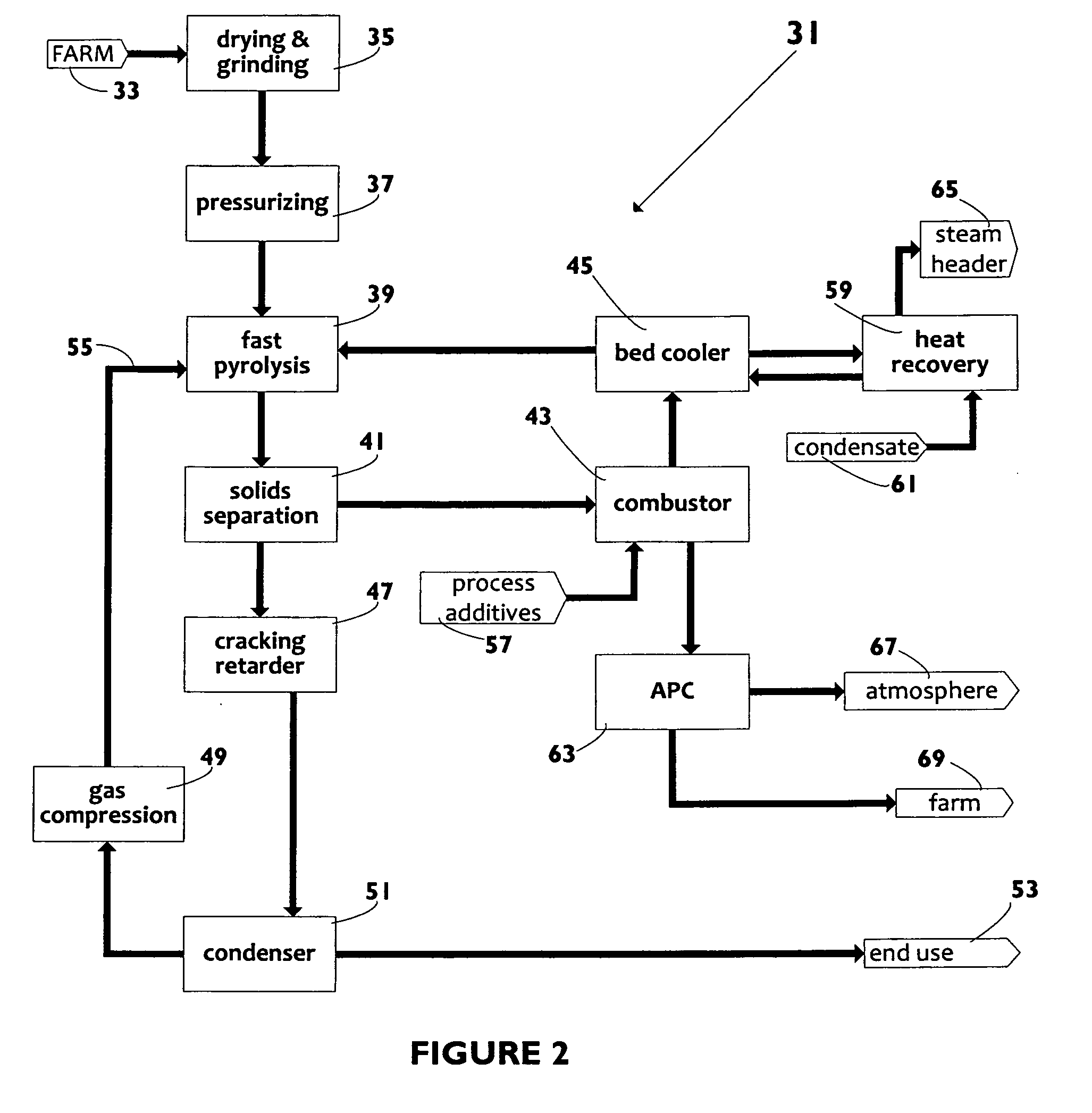
Biomass fast pyrolysis system utilizing non-circulating riser reactor
A biomass fast pyrolysis system for conversion of biomass vegetation to synthetic gas and liquid fuels includes: a) a non-circulating riser reactor for pyrolysis of biomass vegetation feedstock utilizing a heat carrier, the non-circulating riser reactor being physically structured and adapted to have a rate of reaction of at least 8,000 biomass vegetation feedstock lbs / hr / ft2, utilizing a ratio of heat carrier to biomass vegetation feedstock of about 7:1 to about 11.5:1, the riser reactor having a base input region at its bottom, a central reaction region and an output region at its top, the riser reactor including a cyclone disengager at its output region for separation of pyrolysis resulting char and heat carrier from the pyrolysis product gases, the cyclone disengager having an output downcomer and an output upcomer, the cyclone disengager output downcomer being connected to and feeding into a side combustor unit, the riser reactor being a non-circulating riser reactor in that the heat carrier is not returned directly to the riser reactor from the cyclone disengager and travels first down the cyclone disengager output downcomer to the side combustor unit; and, b) the side combustor unit for combusting pyrolysis resultant char and reheating the heat carrier the side combustor having a heat carrier downcomer connected to the base input region of the riser reactor.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ENERGY GLOBAL
Two stage process for hydrodesulfurizing distillates using bulk multimetallic catalyst
InactiveUS6929738B1Preparation by oxo-reaction and reductionOrganic compound preparationLiquid productHydrogen
A two stage hydrodesulfurizing process for producing low sulfur distillates. A distillate boiling range feedstock containing in excess of about 3,000 wppm sulfur is hydrodesulfurized in a first hydrodesulfurizing stage containing one or more reaction zones in the presence of hydrogen and a hydrodesulfurizing catalyst. The liquid product stream thereof is passed to a first separation stage wherein a vapor phase product stream and a liquid product stream are produced. The liquid product stream, which has a substantially lower sulfur and nitrogen content then the original feedstream is passed to a second hydrodesulfurizing stage also containing one or more reaction zones where it is reacted in the presence of hydrogen and a second hydrodesulfurizing catalyst at hydrodesulfurizing conditions. The catalyst in any one or more reaction zones is a bulk multimetallic catalyst comprised of at least one Group VIII non-noble metal and at least two Group VIB metals.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
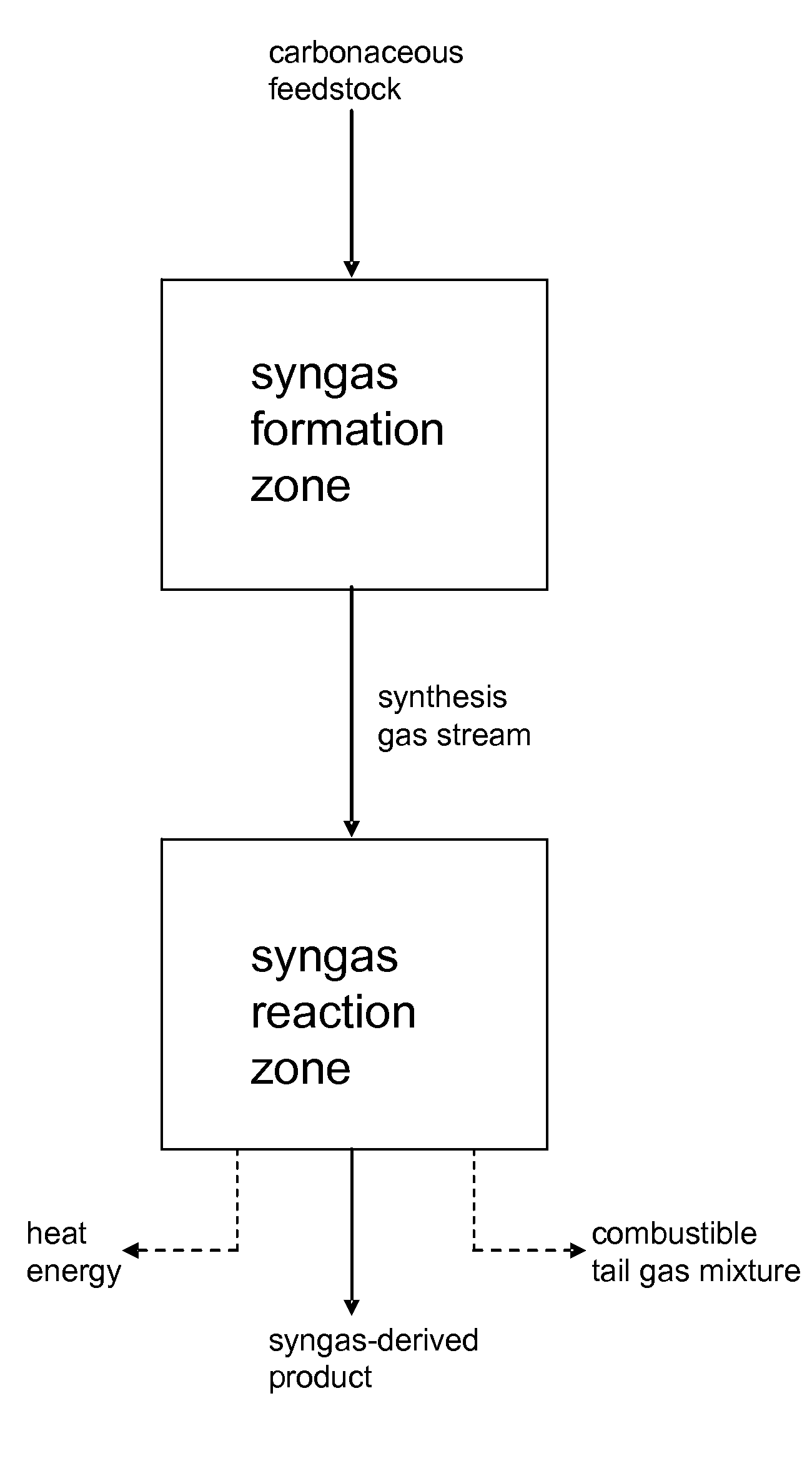
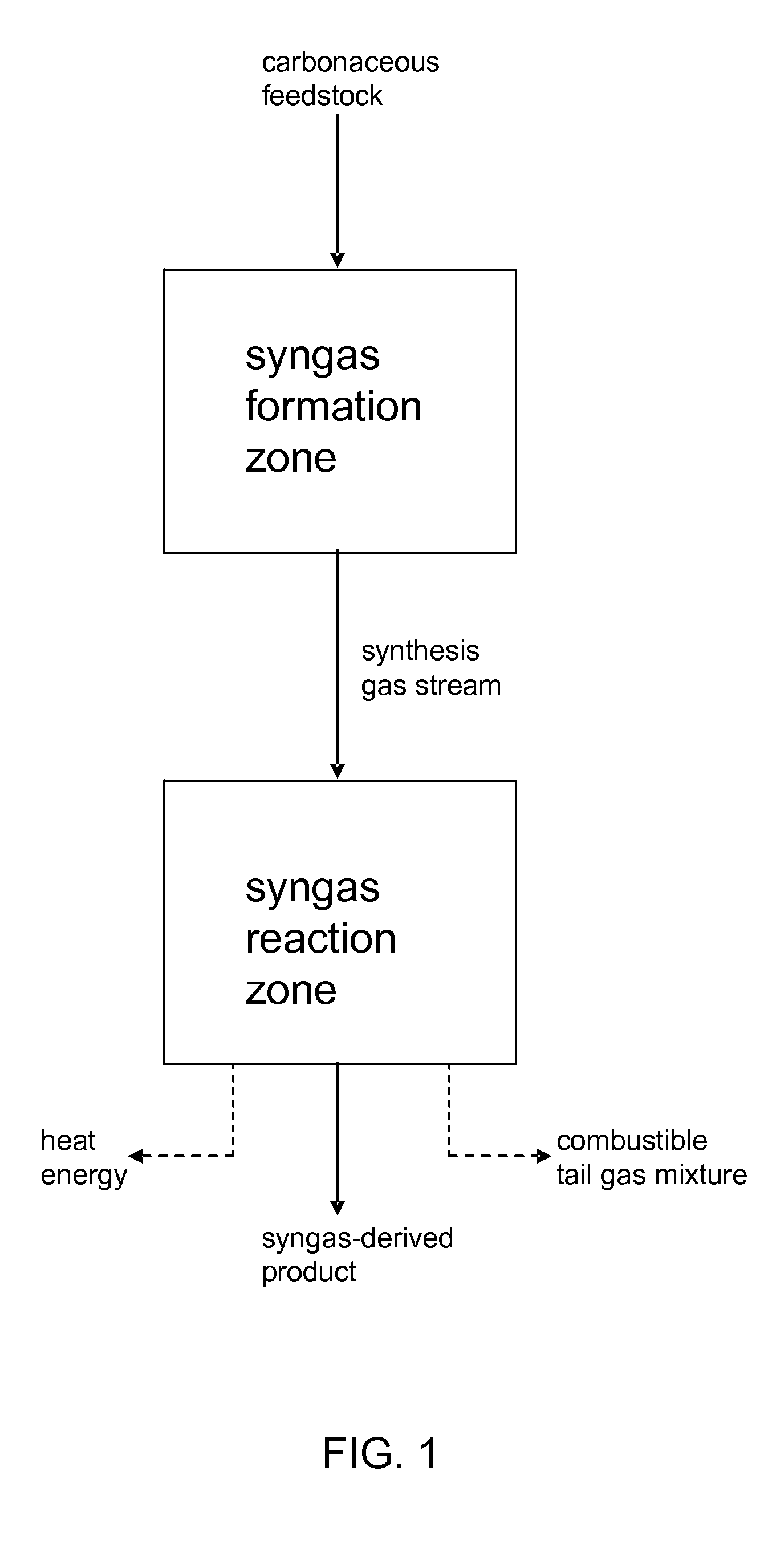
Processes for Making Syngas-Derived Products
The present invention provides processes for making syngas-derived products. For example, one aspect of the present invention provides a process for making a syngas-derived product, the process comprising (a) providing a carbonaceous feedstock; (b) converting the carbonaceous feedstock in a syngas formation zone at least in part to a synthesis gas stream comprising hydrogen and carbon monoxide; (c) conveying the synthesis gas stream to a syngas reaction zone; (d) reacting the synthesis gas stream in the syngas reaction zone to form the syngas-derived product and heat energy, a combustible tail gas mixture, or both; (e) recovering the syngas-derived product; and (f) recovering the heat energy formed from the reaction of the synthesis gas stream, burning the combustible tail gas mixture to form heat energy, or both.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Process to produce low viscosity poly-alpha-olefins
ActiveUS20070043248A1Hydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionPolyolefinAlpha-olefin
This invention relates to a process to produce a polyalpha-olefin comprising: 1) contacting one or more alpha-olefin monomers having 3 to 24 carbon atoms with an unbridged substituted bis cyclopentadienyl transition metal compound having: 1) at least one non-isoolefin substitution on both cyclopentadientyl rings, or 2) at least two substitutions on at least one cyclopentadienyl ring, a non-coordinating anion activator, and optionally an alkyl-aluminum compound, where the molar ratio of transition metal compound to activator is 10:1 to 0.1:1, and if the alkyl aluminum compound is present then the molar ratio of alkyl aluminum compound to transition metal compound is 1:4 to 4000:1, under polymerization conditions wherein: i) hydrogen is present at a partial pressure of 0.1 to 50 psi, based upon the total pressure of the reactor or the concentration of the hydrogen is from 1 to 10,000 ppm or less by weight; ii) wherein the alpha-olefin monomer(s) having 3 to 24 carbon atoms are present at 10 volume % or more based upon the total volume of the catalyst / activator / alkylaluminum compound solutions, monomers, and any diluents or solvents present in the reaction; iii) the residence time of the reaction is at least 5 minutes; iv) the productivity of the process is at least 43,000 grams of total product per gram of transition metal compound; v) the process is continuous or semi-continuous, and vi) the temperature in the reaction zone does not rise by more than 10° C. during the reaction; and vii) ethylene is not present at more than 30 volume % of the monomers entering the reaction zone; and 2) obtaining a polyalpha-olefin (PAO), optionally hydrogenating the PAO, wherein the PAO comprises at least 50 mole % of a C3 to C24 alpha-olefin monomer, and wherein the PAO has a kinematic viscosity at 100° C. of 20 cSt or less.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Production of agglomerates from gas phase
ActiveUS20050006801A1Avoid enteringImprove mechanical propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyMulti-walled nanotubesGas phaseReaction zone
A process for production of an agglomerate comprises the steps of: passing a flow of one or more gaseous reactants into a reactor; reacting the one or more gaseous reactants within a reaction zone of the reactor to form product particles; agglomerating the product particles into an agglomerate; and applying a force to the agglomerate to displace it continuously away from the reaction zone.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
Radiation-heated fluidized-bed reactor
InactiveUS7029632B1Low levelHigh puritySiliconFluidised-bed furnacesFluidized bedReaction temperature
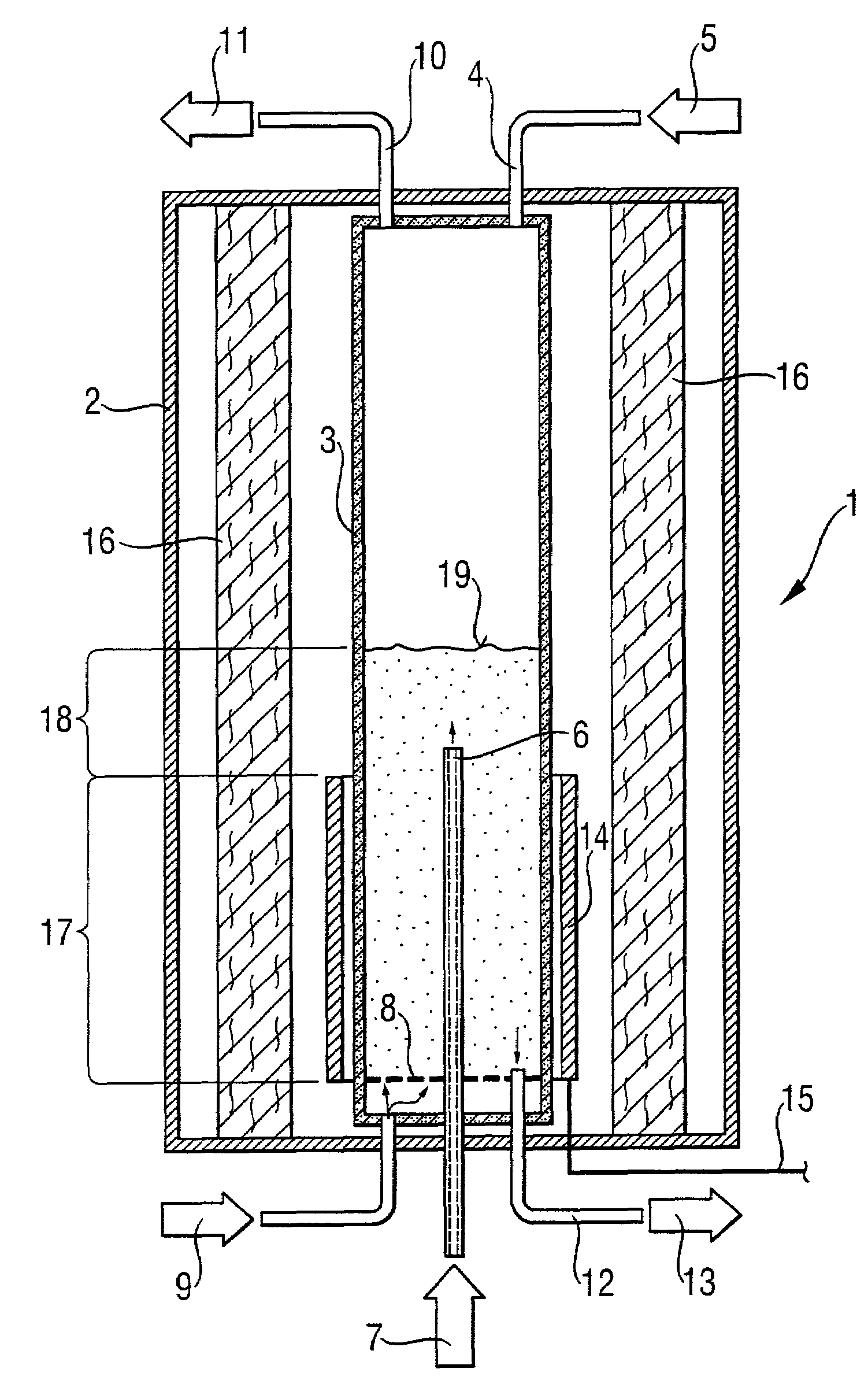
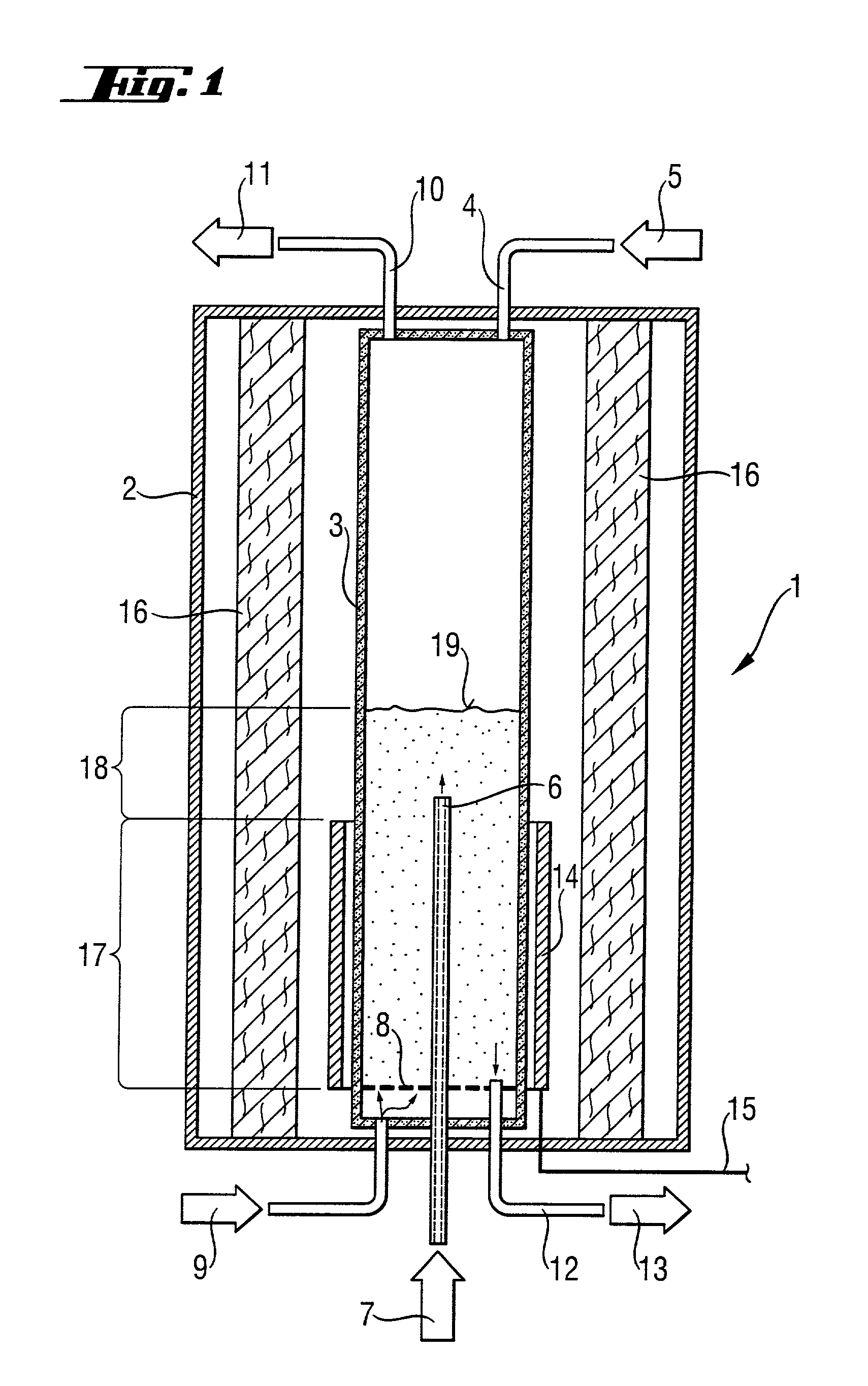
A radiation-heated fluidized-bed reactor and a process for producing high-purity polycrystalline silicon by using this reactor are provided. In this reactor, a heater device (14) is a radiation source for thermal radiation which is arranged outside the inner reactor tube and as a cylinder around the heater zone, without being in direct contact with the inner reactor tube. The inner reactor tube is designed in such a manner that it uses thermal radiation to heat the silicon particles in the heating zone to a temperature which is such that the reaction temperature is established in the reaction zone.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
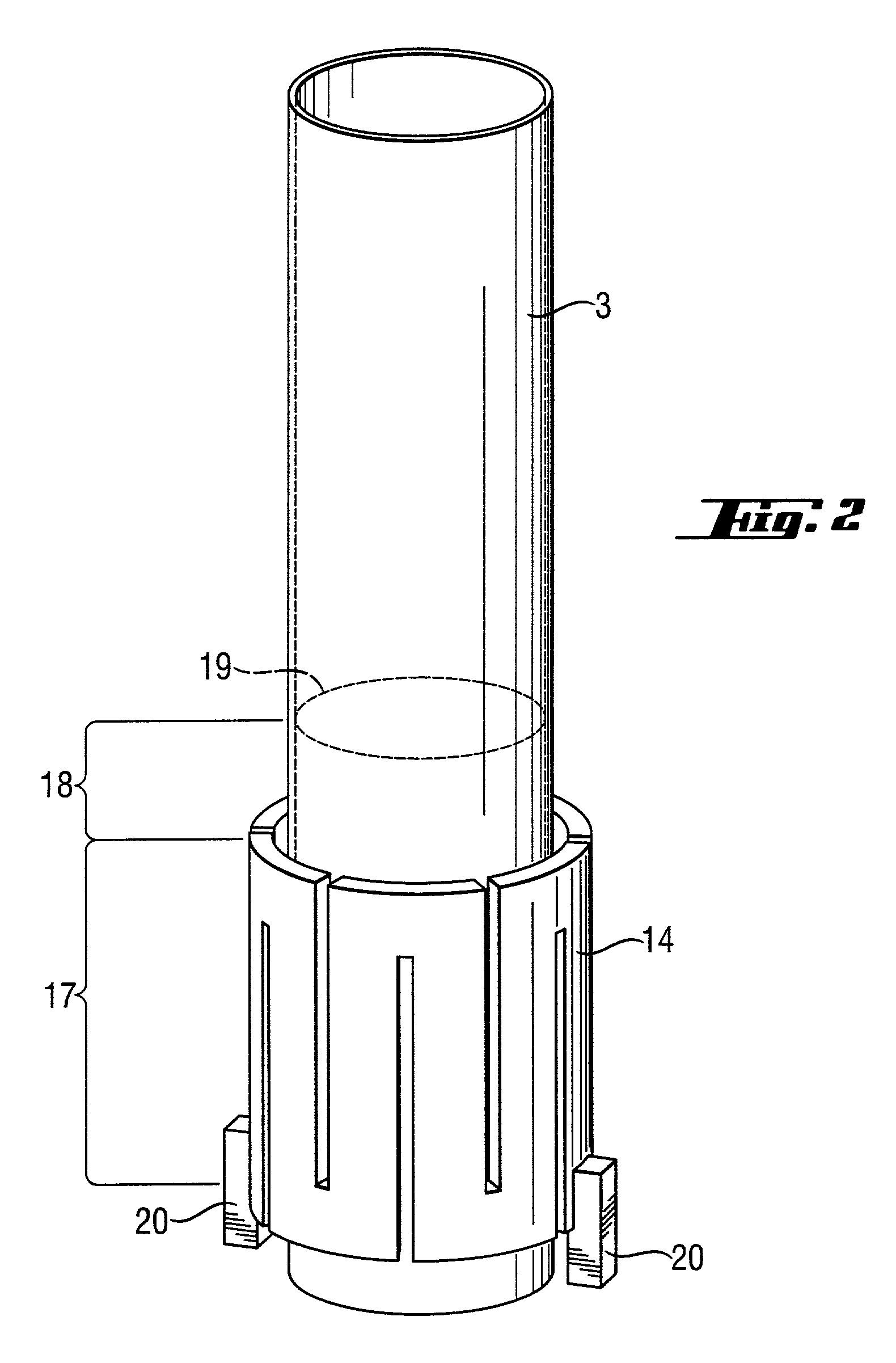
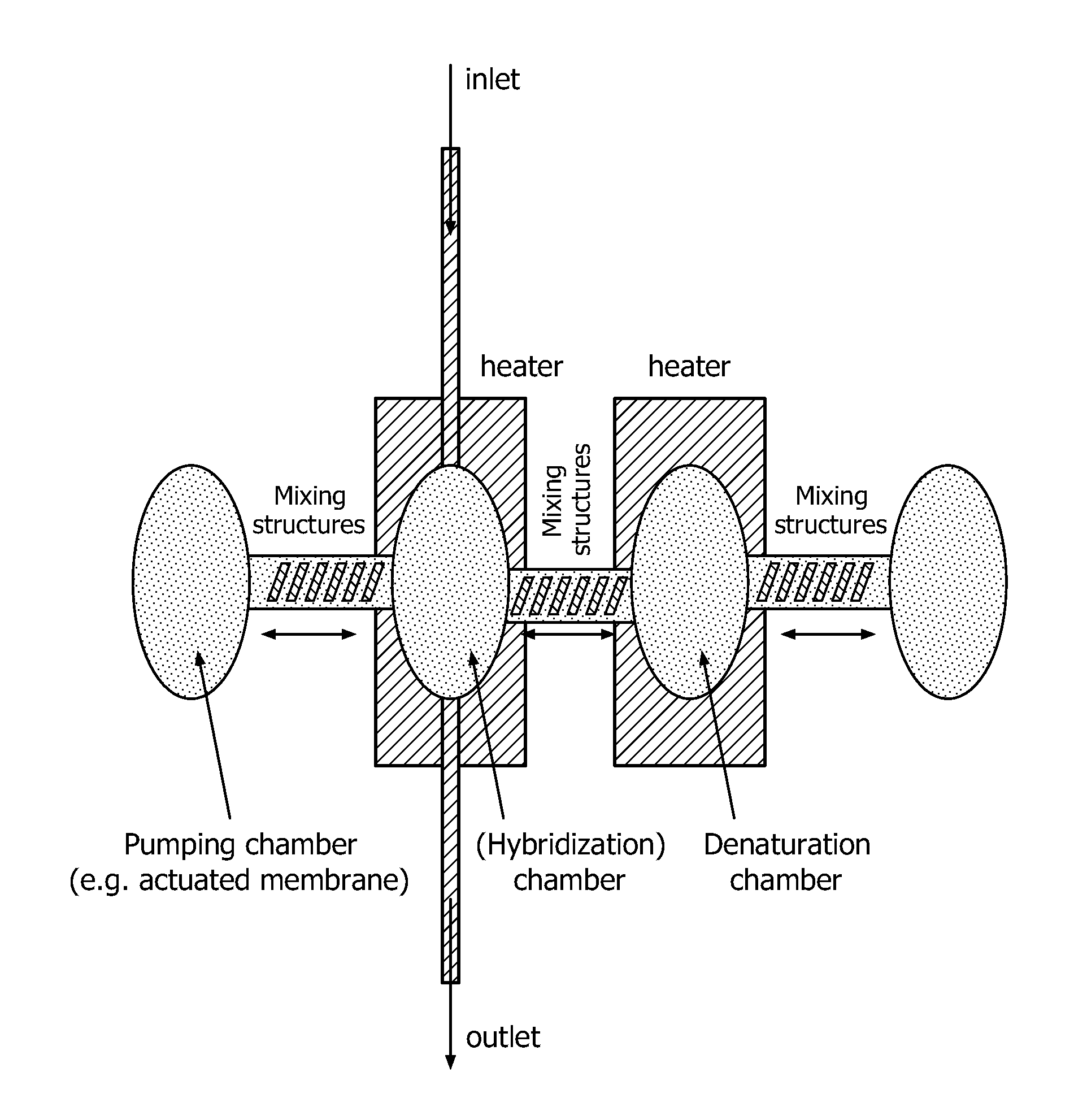
Devices and methods for microarray selection
ActiveUS20120165219A1Avoidance of long hybridization timeImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningTemperature controlTarget enrichment
The present invention relates to a device for the specific selection of target molecules, comprising: (a) at least one reaction zone comprising a microarray, wherein the microarray comprises a substrate, on which one or more species of capture molecules are immobilized, comprising one or more temperature control and / or regulating units for controlling and / or regulating the temperature within the zone; (b) at least one non-reaction zone comprising one or more temperature control and / or regulating units for controlling and / or regulating the temperature within the zone, which is in fluid connection with the reaction zone; and (c) at least one transportation means capable of generating and / or regulating a fluid flow between said reaction zone (a) and said non-reaction zone comprising one or more temperature control and / or regulating units (b). The present invention further relates to a device for the specific selection of target molecules wherein the immobilized capture molecules are organized in the microarray in the form of spots, elongated spots and / or lines. In a further aspect the present invention relates to a method of specifically selecting target molecules, comprising the introducing a medium to such a device, performing interaction reactions in a reaction zone, transporting not interacted or not bound target molecules to a zone allowing reactivation of the target molecules and performing additional interaction reactions with the reactivated target molecules at the reaction zone, as well as the use of such a device for specifically selecting target molecules, e.g. for target enrichment also referred to as microarray based genome selection (MGS) in the literature.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method of making sensor
InactiveUS6849216B2Improve performanceRelieve pressureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectron transfer mediatorReaction zone
A sensor is provided for the determination of various concentrations of one or more components within a fluid sample. The sensor includes an injection molded body, at least two electrodes, an enzyme, and if desired, an electron transfer mediator. The body includes a reaction zone for receiving a fluid sample. The electrodes are at least partially embedded within the plastic body and extend into the reaction zone. Also contained within the reaction zone is an enzyme capable of catalyzing a reaction involving a compound within the fluid sample. Additionally, the sensor incorporates fill detection which activates a meter, attached to the sensor, for measuring the electrochemical changes occurring in the reaction zone.
Owner:APPL BIOMEDICAL LLC
Thermal synthesis apparatus and process
InactiveUS6821500B2Improve efficiencyHigh yieldCarbon monoxideIndirect heat exchangersNuclear engineeringReaction zone
An apparatus for thermal conversion of one or more reactants to desired end products includes an insulated reactor chamber having a high temperature heater such as a plasma torch at its inlet end and, optionally, a restrictive convergent-divergent nozzle at its outlet end. In a thermal conversion method, reactants are injected upstream from the reactor chamber and thoroughly mixed with the plasma stream before entering the reactor chamber. The reactor chamber has a reaction zone that is maintained at a substantially uniform temperature. The resulting heated gaseous stream is then rapidly cooled by passage through the nozzle, which "freezes" the desired end product(s) in the heated equilibrium reaction stage, or is discharged through an outlet pipe without the convergent-divergent nozzle. The desired end products are then separated from the gaseous stream.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Process For The Continuous Production Of Polycrystalline High-Purity Silicon Granules
ActiveUS20080299291A1Efficient heatingLong operating campaignPolycrystalline material growthLiquid surface applicatorsFluidized bedReaction zone
High-purity polysilicon granules are prepared by depositing reaction gas on silicon granules in a fluidized bed reactor having:a reactor space comprising at least two zones lying one above the other, the lower zone weakly fluidized by introduction of a silicon-free gas into silicon granules in the lower zone by a plurality of individual dilution gas nozzles, and a second, reaction zone directly abutting the lower zone,the reaction zone heated via its outwardly bounding wall,introducing silicon-containing reaction gas as a vertical high speed gas jet into the reaction zone by reaction gas nozzle(s), forming local reaction gas jets surrounded by bubble-forming fluidized bed, gas decomposing leading to particle growth,wherein the reaction gas has fully or almost fully reacted to chemical equilibrium conversion before reaching the wall or bed surface.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
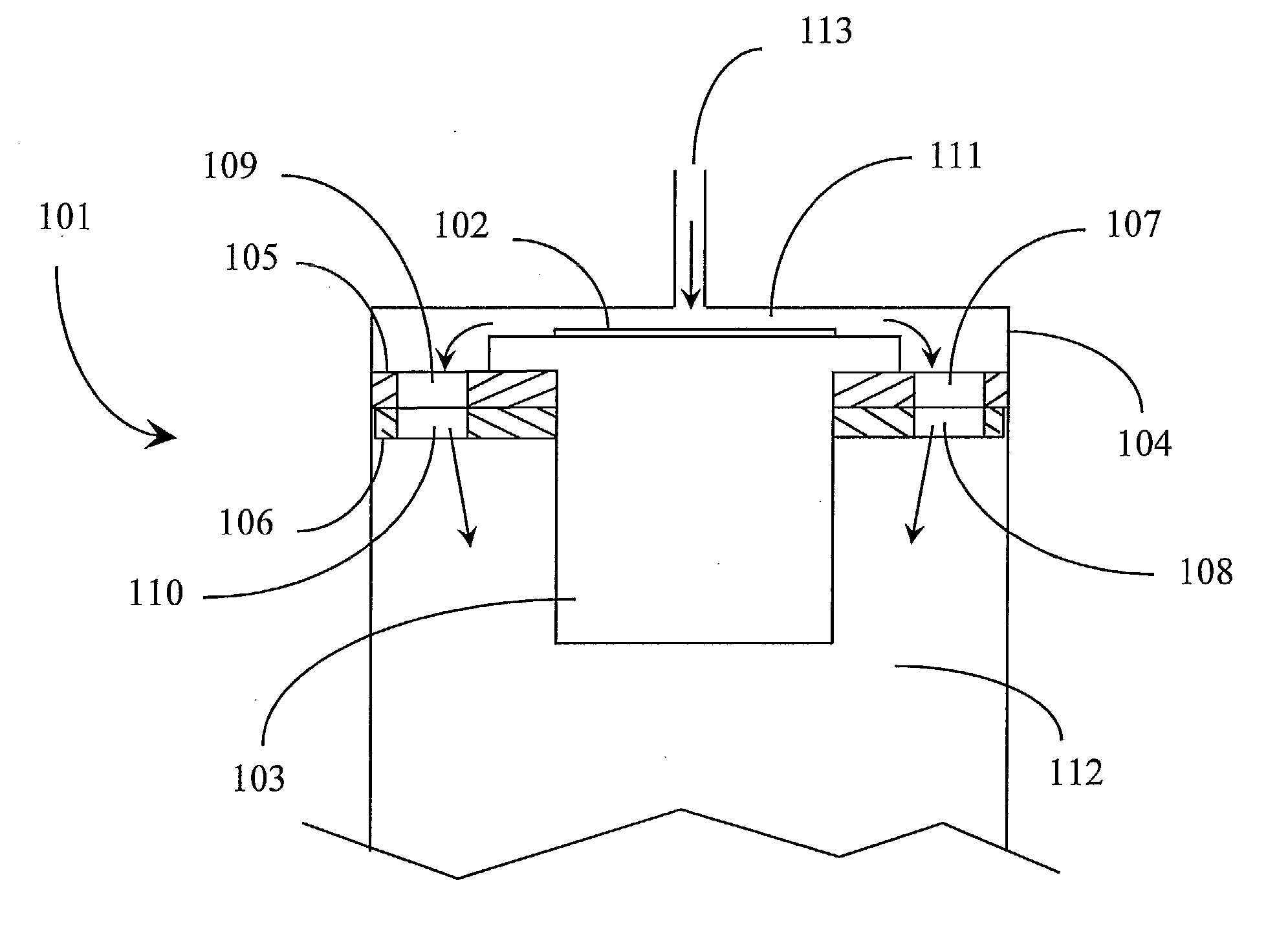
Method and apparatus for ALD on a rotary susceptor
InactiveUS6869641B2Minimize cross-contaminationFrom chemically reactive gasesChemical vapor deposition coatingSusceptorGas phase
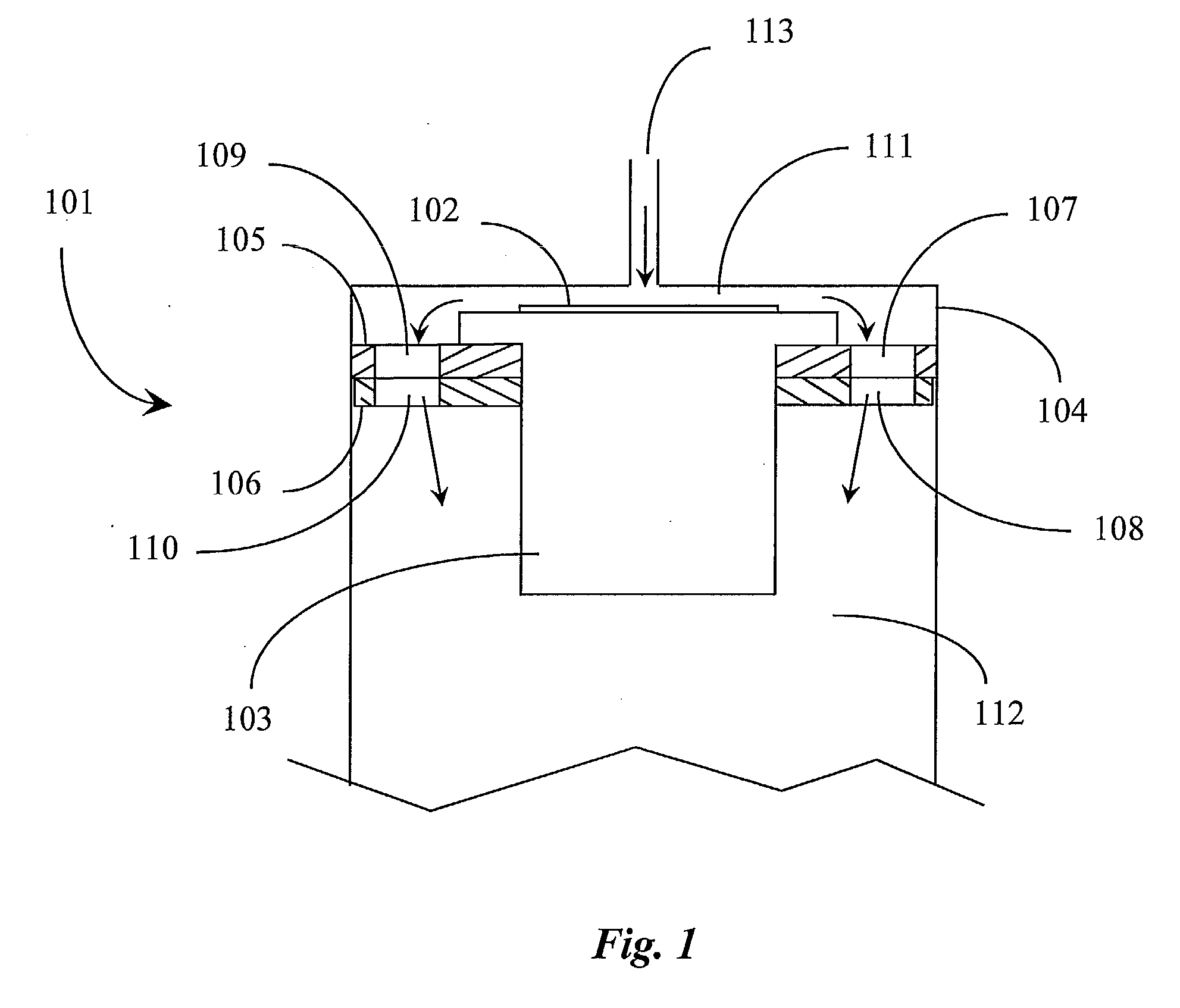
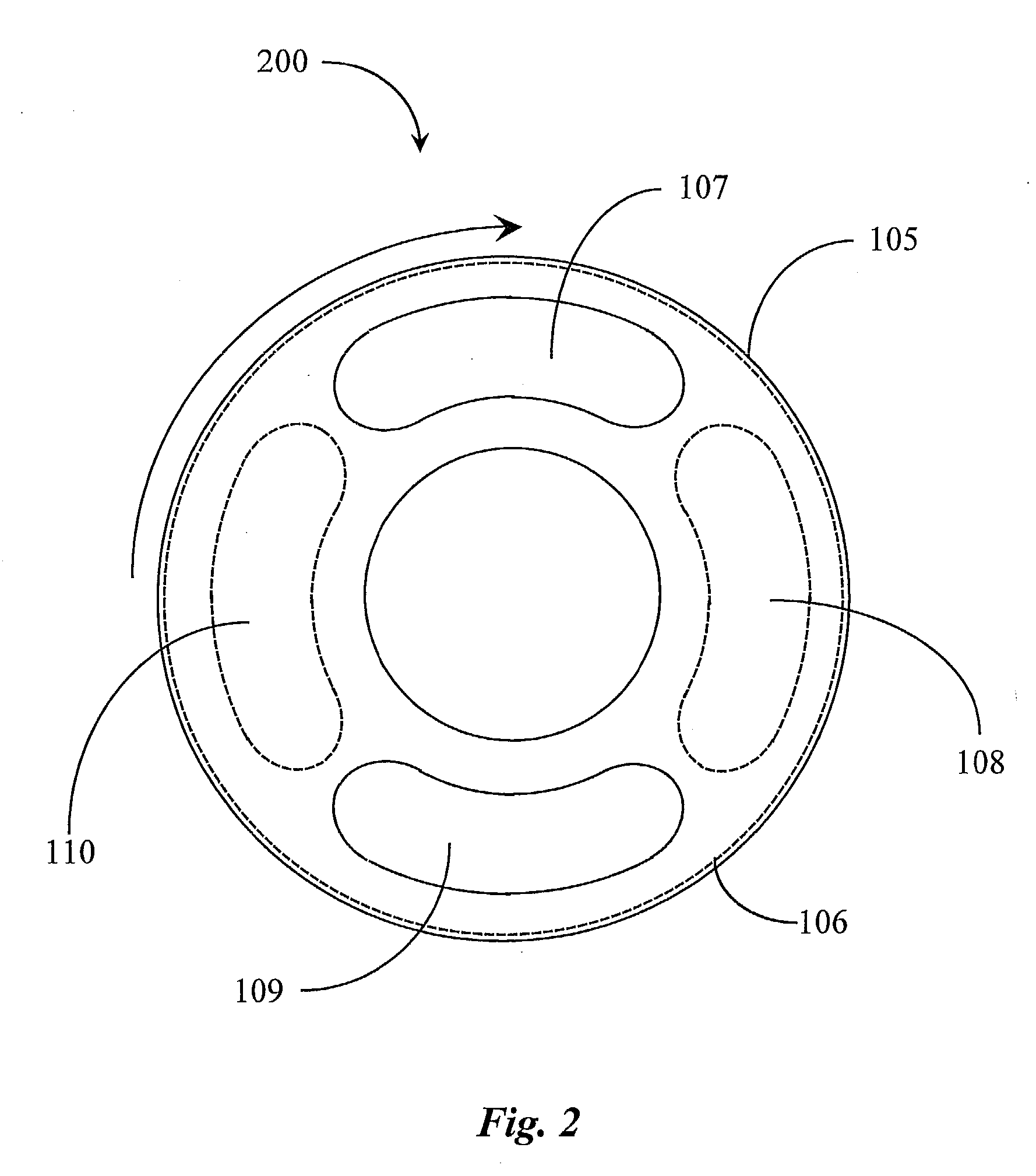
A chemical vapor deposition method and apparatus is disclosed. The process is carried out in an apparatus having a number reactive zones, each surrounded by a corresponding exhaust zone, all of which are both contained within a buffer zone. Pressure relationships are controlled such that buffer gas from the buffer zone flows into the exhaust zones and reactive gas from the reactive zones flow into the exhaust zones. As a result, cross-contamination of gases between the reactive zones is avoided.
Owner:OERLIKON ADVANCED TECH +2
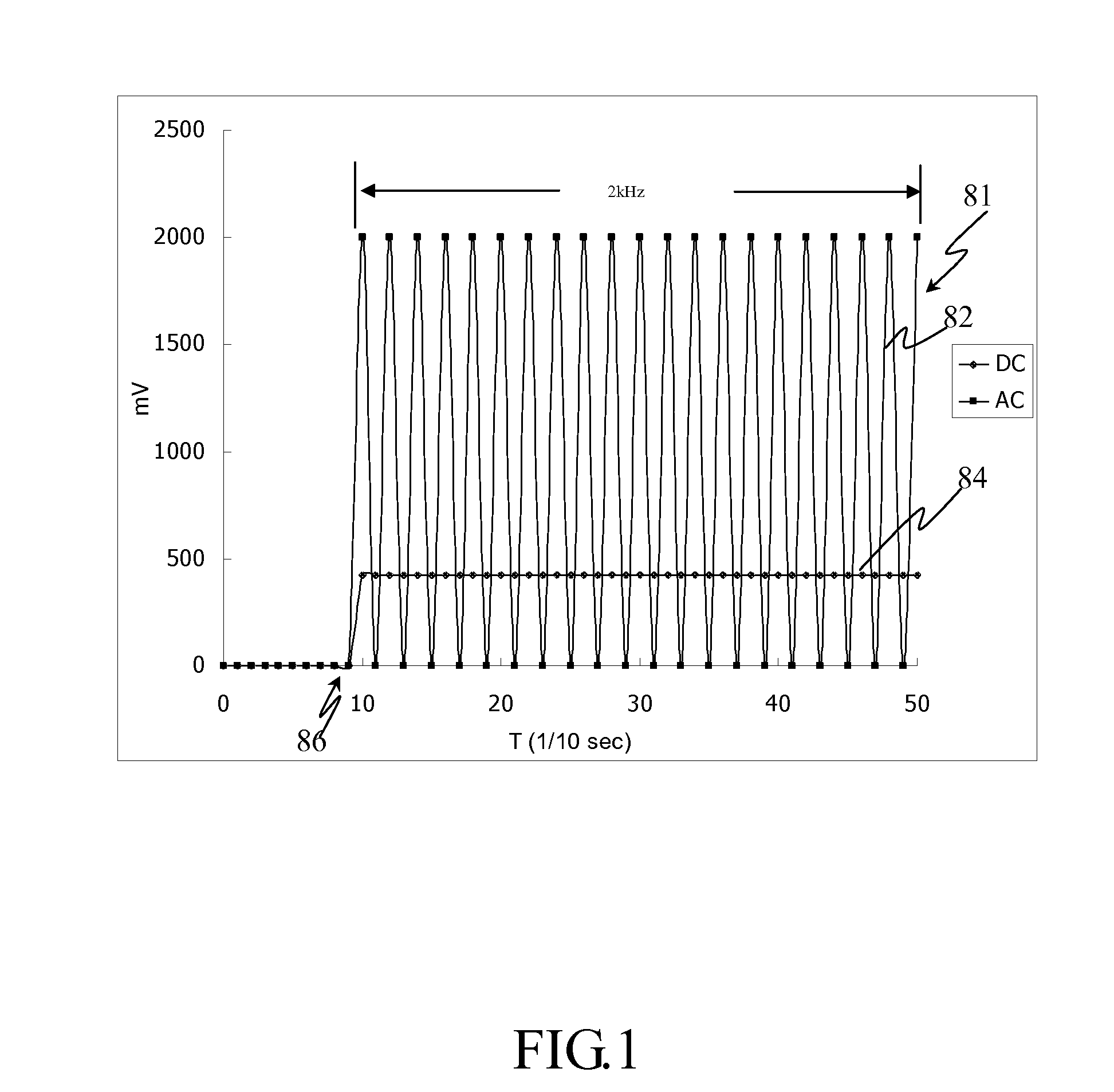
System and method for measuring analyte concentration with interferant correction
InactiveUS20110139634A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsConstant frequencyAnalyte
The present invention is related to an electrochemical biosensing test strip, biosensing meter, system and method for analyte measurement incorporating a hematocrit correction. The biosensor strip comprises a first and a second electrode sets respectively for detecting analyte concentration and hematocrit level. The first and second electrode sets are respectively corresponding to different reaction zones and a reaction reagent is only formed on the first electrode set corresponding reaction zone. Applying a first signal comprising a DC component and a second signal comprising an AC component that has a constant frequency respectively to the first and second electrode sets can respectively detect an uncorrected analyte concentration and hematocrit level. Therefore, the corrected analyte concentration is more accurate by incorporating the hematocrit correction.
Owner:TAIDOC TECH CORP
Catalytic oxidation process
InactiveUS6447745B1Hydrocarbon from carbon oxidesCatalyst activation/preparationElemental compositionPartial oxidation
A process for the partial catalytic oxidation of a hydrocarbon containing feed comprising contacting the feed with an oxygen-containing gas in the presence of a catalyst retained within a reaction zone in a fixed arrangement, wherein the catalyst comprises at least one catalytically active metal selected from the group consisting of silver and Group VIII elements supported on a porous ceramic carrier. The porous ceramic carrier has a distribution of total pores wherein about 70% of the total pores (1) have a volume-to-surface area (V / S) ration that is within about 20% of the mean V / S value for the total pores and no pores have a V / S ration that is greater than twice the mean V / S value for the total pores; (2) have a pore-to-pore distance between neighboring pores that is within about 25% of the mean pore-to-pore distance between neighboring pores; and (3) have a pore throat area that is within about 50% of the mean pore throat are for the pores. Additionally, about 50% of the total pores have a coordination number between neighboring pores that is within about 25% of the mean coordination number between neighboring pores. Preferably, the oxidation process comprises a multistage, staged oxygen, catalytic partial oxidation process having fewer than or equal to about five stages and including a first stage preheat temperature of greater than about 550° C., and wherein the temperature of the product mixture in each stage following the first stage is at least about 700° C.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Production of Aviation Fuel from Renewable Feedstocks
ActiveUS20090283442A1Improve solubilityMinimize severityTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonIsomerizationBoiling point
A hydrocarbon product stream having hydrocarbons with boiling points in the aviation fuel range is produced from renewable feedstocks such as plant and animal oils. The process involves treating a renewable feedstock by hydrogenating, deoxygenating, isomerization, and selectively hydrocracking the feedstock to produce paraffinic hydrocarbons having from about 9 to about 16 carbon atoms and a high iso / normal ratio in a single reaction zone containing a multifunctional catalyst, or set of catalysts, having hydrogenation, deoxygenation, isomerization and selective hydrocracking functions.
Owner:UOP LLC
Process for the production of synthesis gas with conversion of CO2 into hydrogen
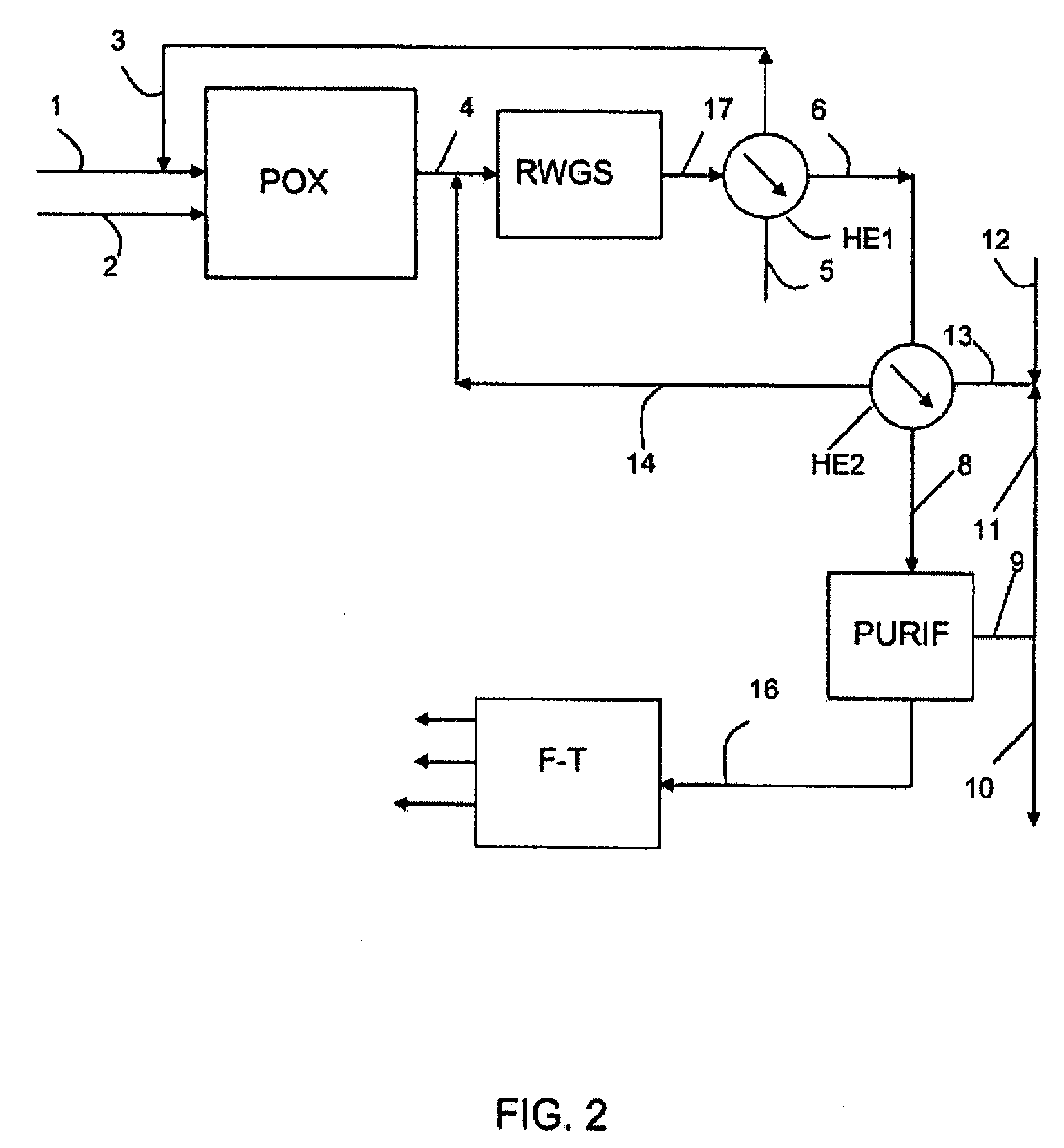
ActiveUS7846979B2Useful thermal recovery on the gasification effluentCombustible gas chemical modificationProductsSteam reformingPartial oxidation
Process for the production of liquid hydrocarbons from a feedstock that comprises at least one elementary feedstock from the group of biomass, coal, lignite, petroleum residues, methane, and natural gas, comprising: at least one stage a) for gasification of the feedstock by partial oxidation and / or steam reforming to produce a synthesis gas SG; a stage b) for separating CO2 from SG and a portion of the effluent of the subsequent stage c); the mixing of a portion of the CO2 that is separated with a gas of an H2 / CO ratio of more than 3; a stage c) for partial conversion with hydrogen, thermal or thermocatalytic, of the CO2 that is present in said first mixture according to the reaction: CO2+H2→CO+H2O in a specific reaction zone that is separated from said gasification zone or zones; a stage d) for Fisher-Tropsch synthesis on a synthesis gas that comprises at least a portion of SG and at least a portion of the CO that is produced by the conversion of CO2 into hydrogen.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com