Patents
Literature
1304 results about "Steam reforming" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
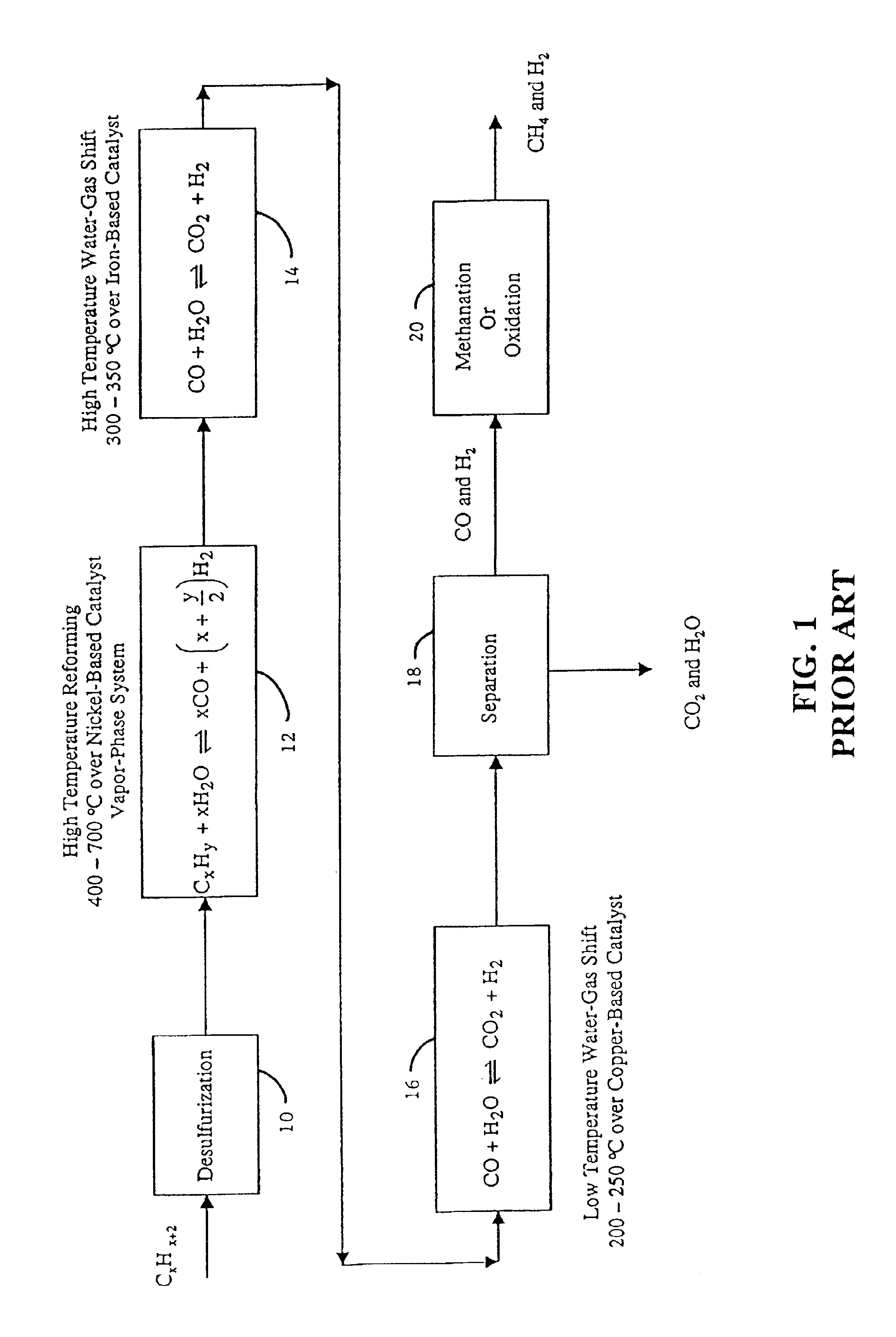
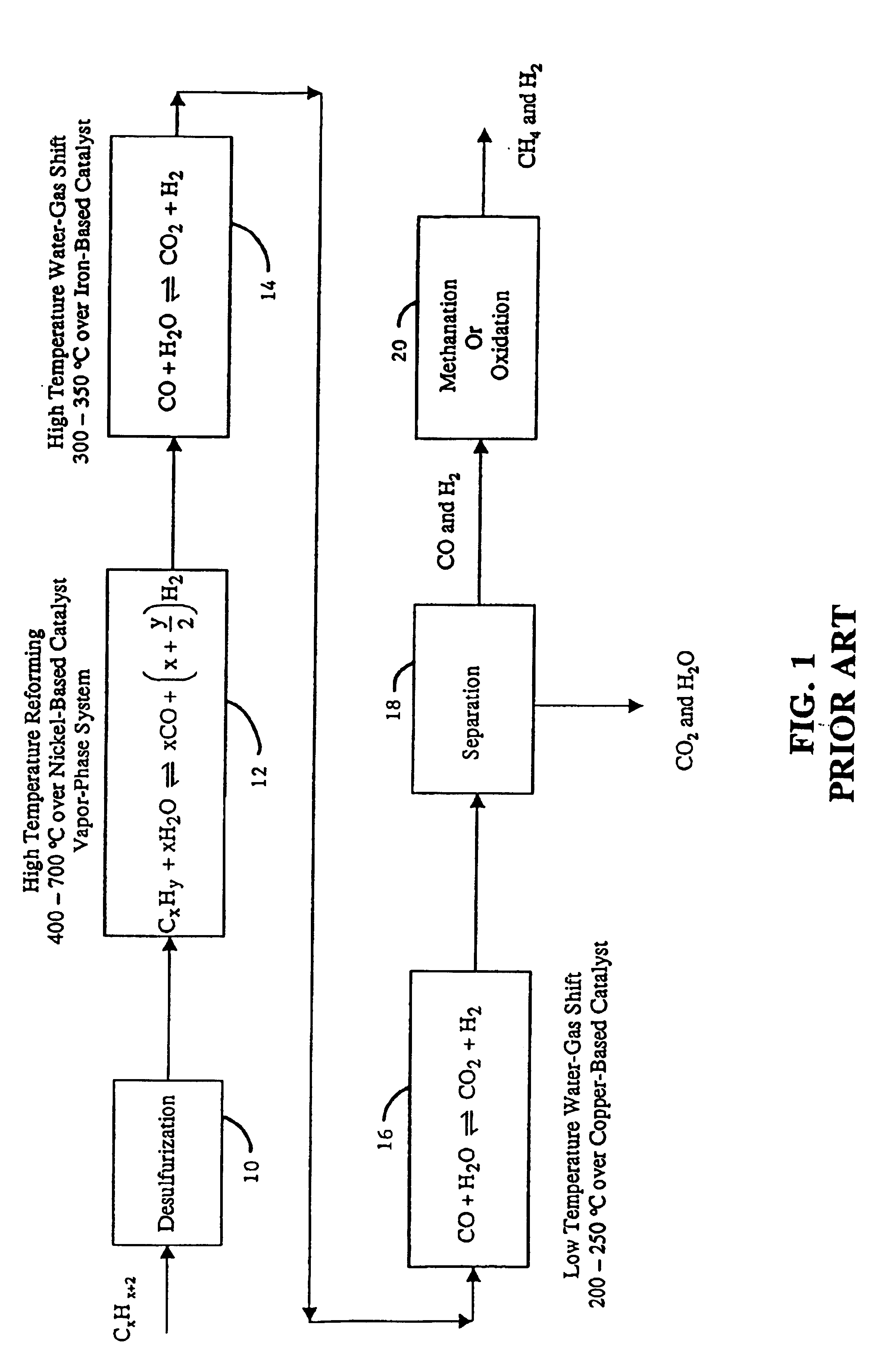
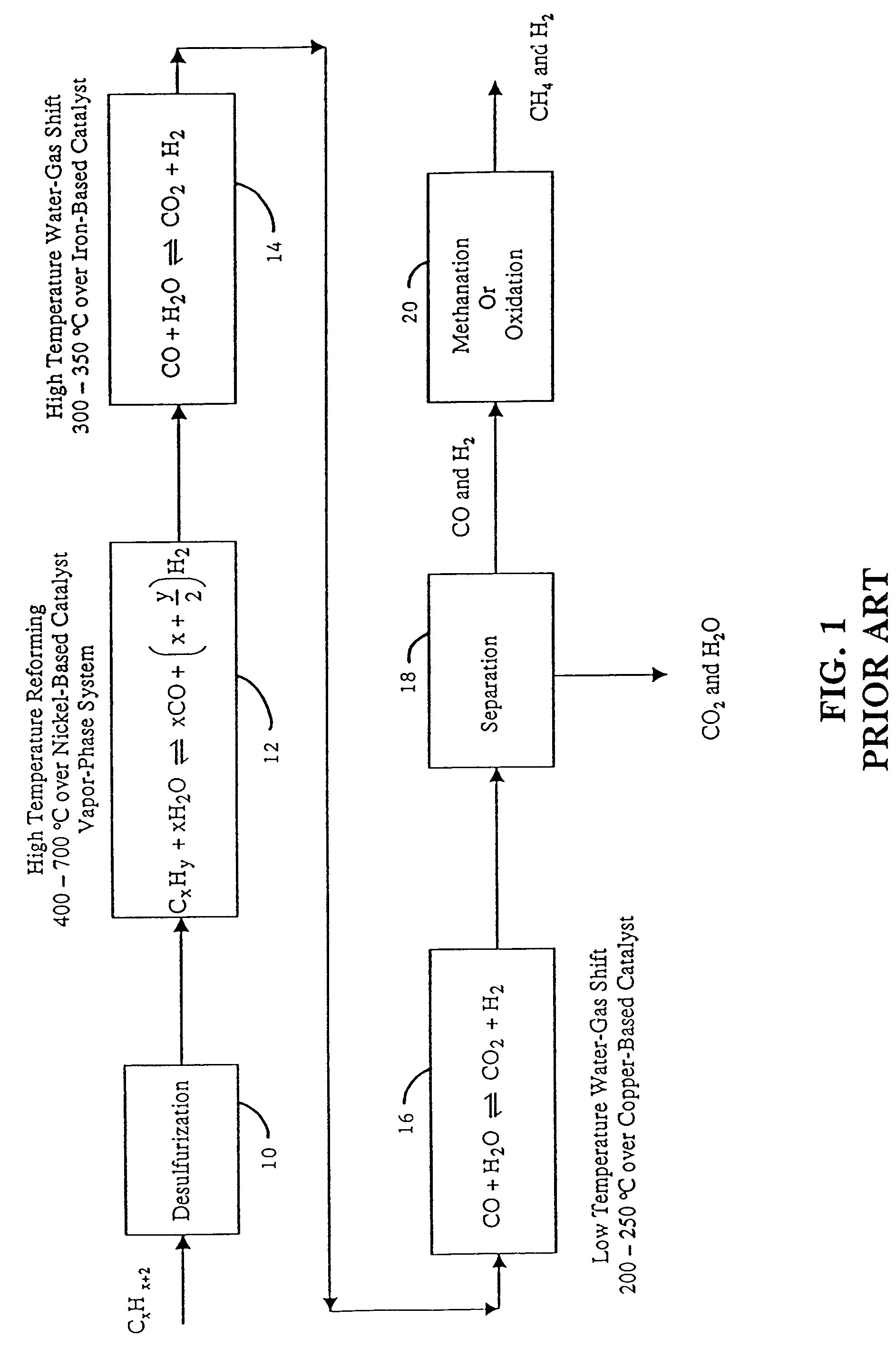
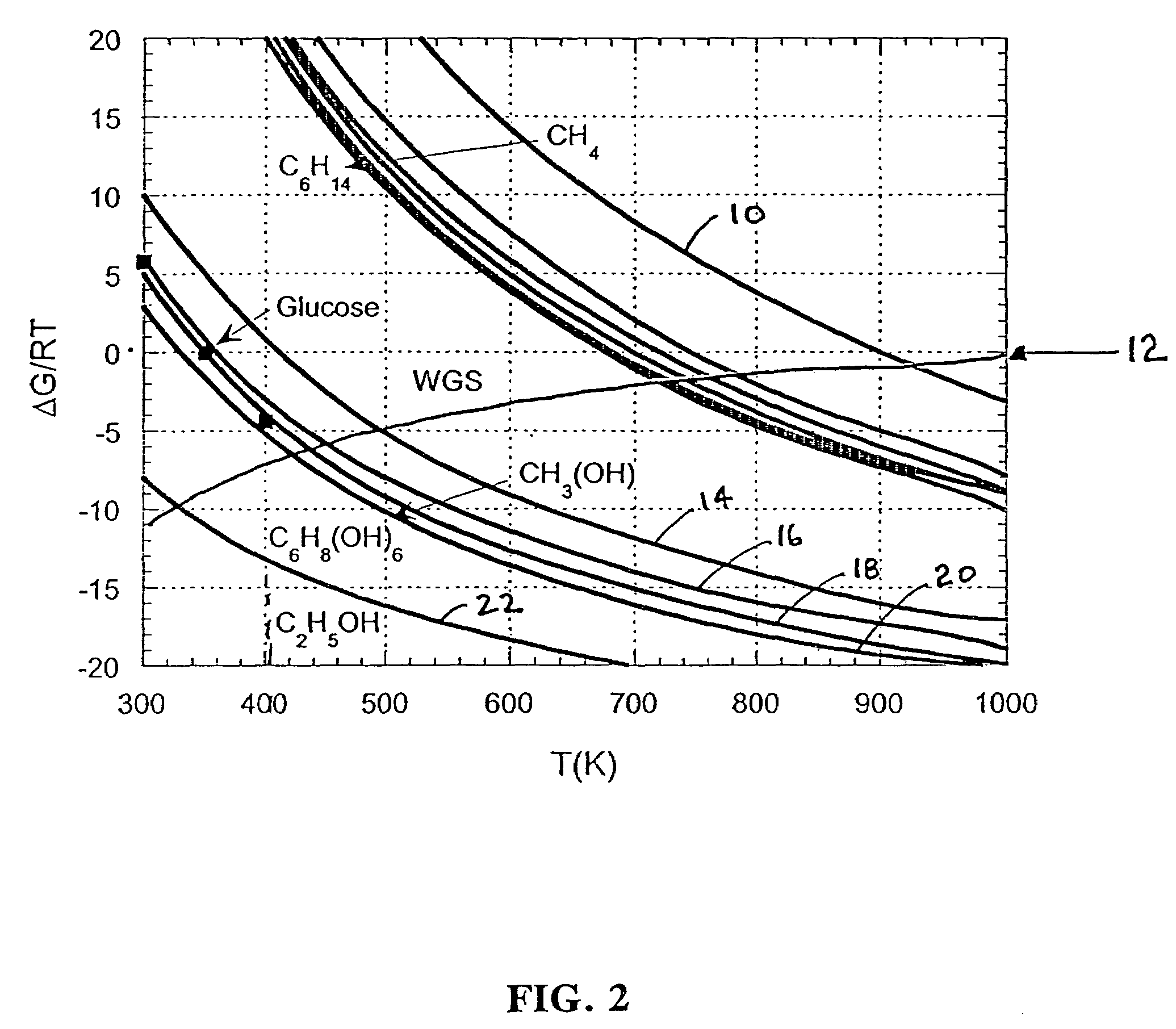
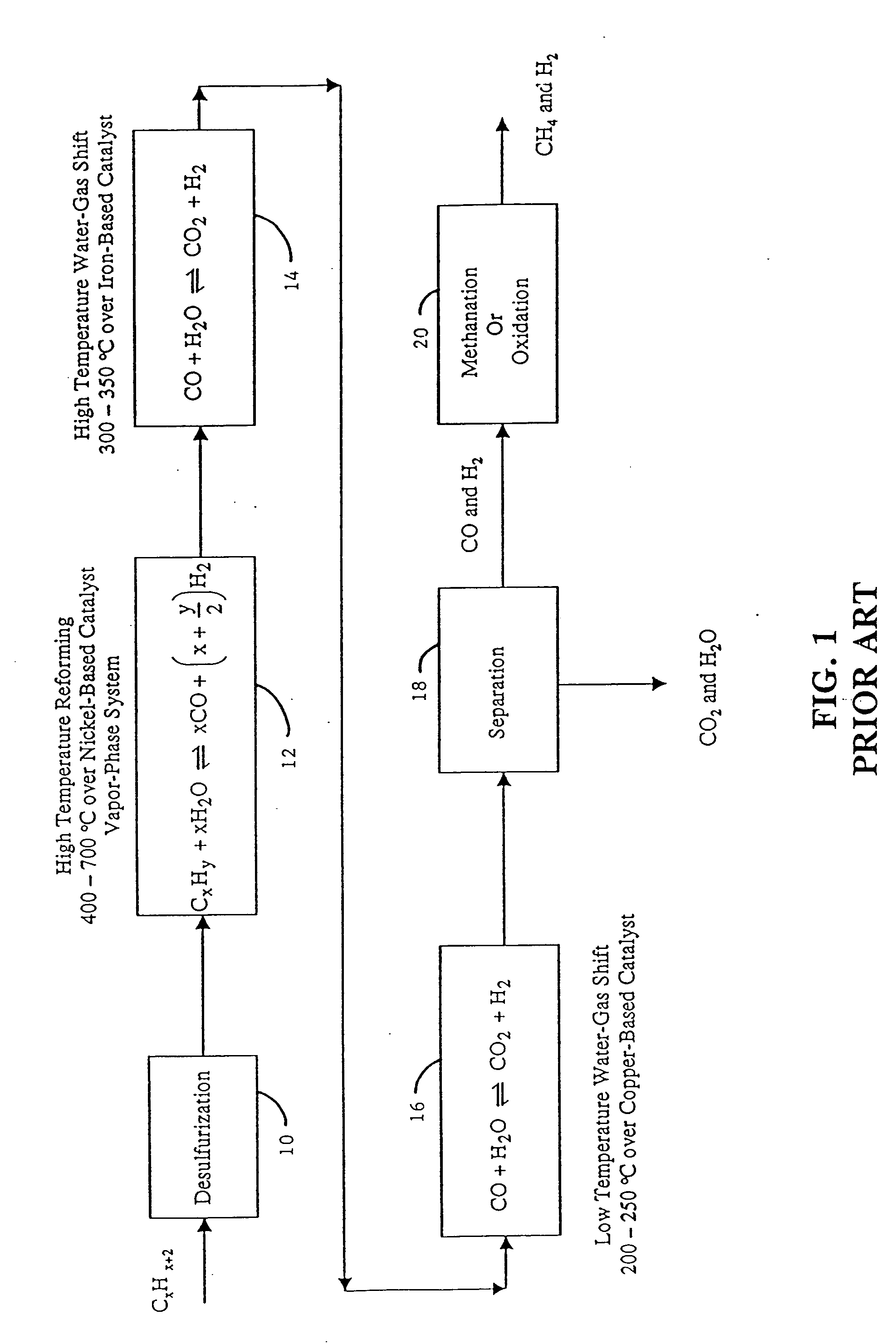
Steam reforming or steam methane reforming is a chemical synthesis for producing syngas (hydrogen and carbon monoxide) from hydrocarbons such as natural gas. This is achieved in a reformer which reacts steam at high temperature and pressure with methane in the presence of a nickel catalyst. The steam methane reformer is widely used in industry to make hydrogen.
Low-temperature hydrogen production from oxygenated hydrocarbons
InactiveUS6964757B2Reduce riskWeaken energyHydrogen productionHydrogen/synthetic gas productionSteam reformingAlkane
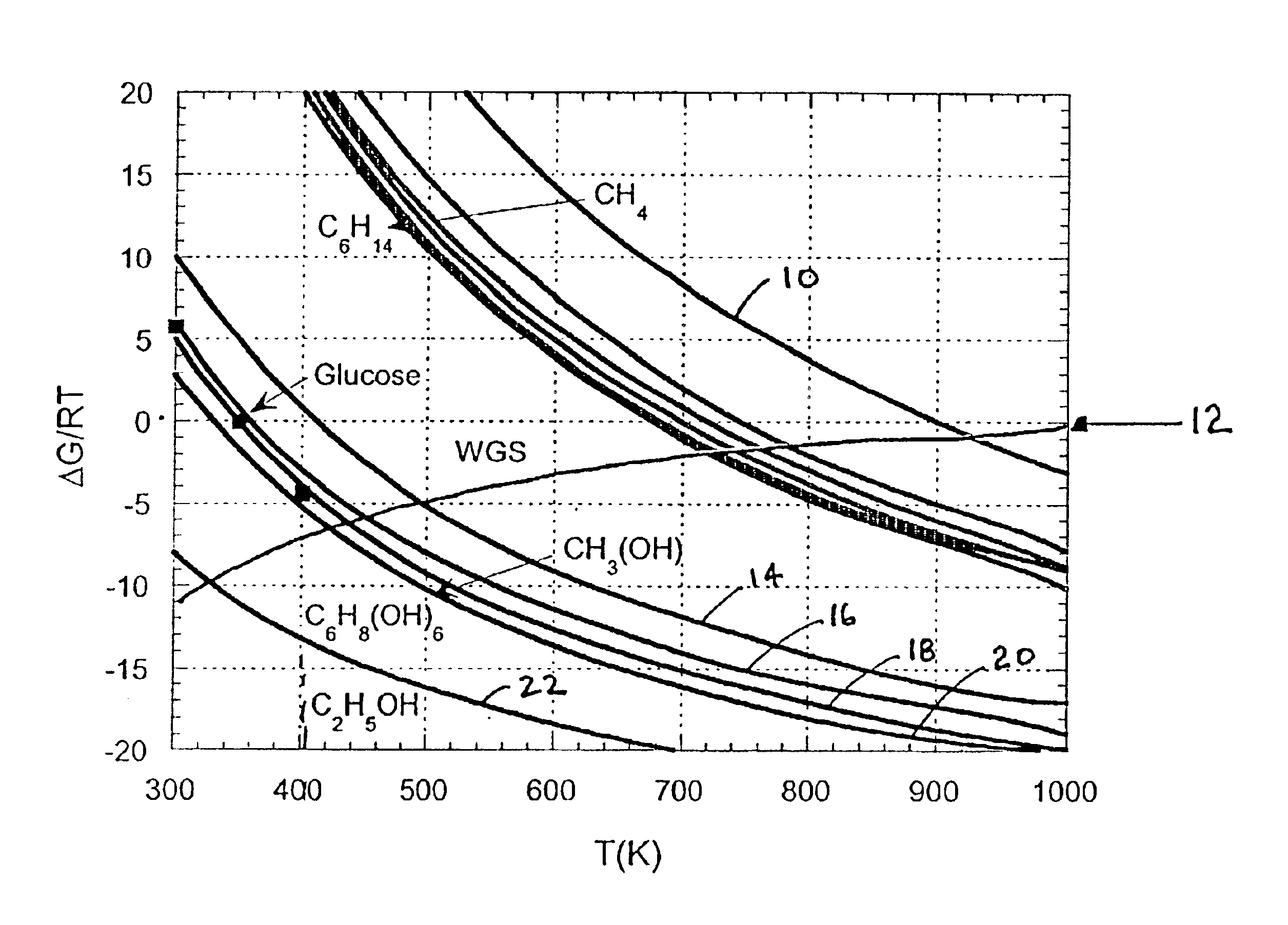
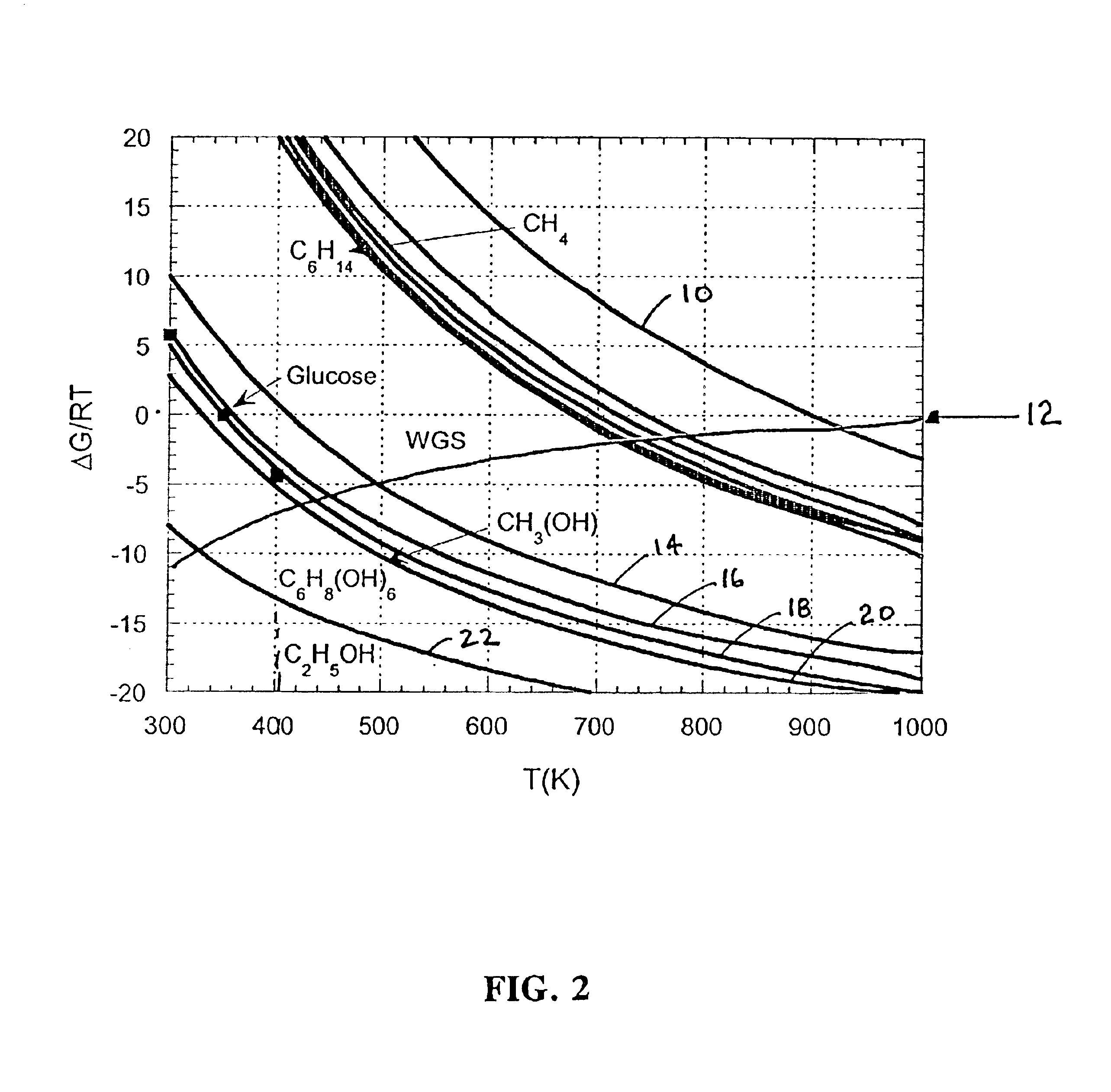
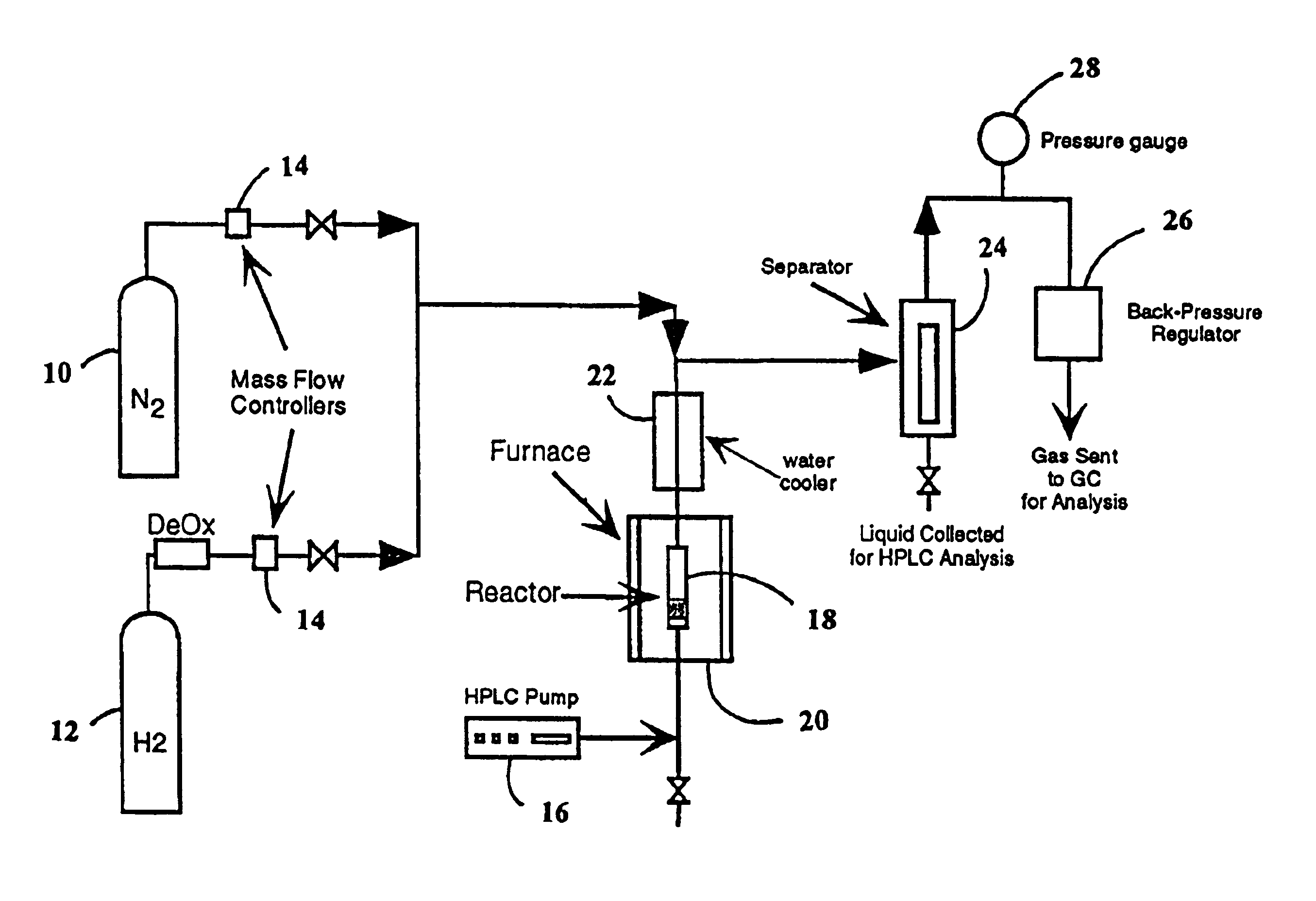
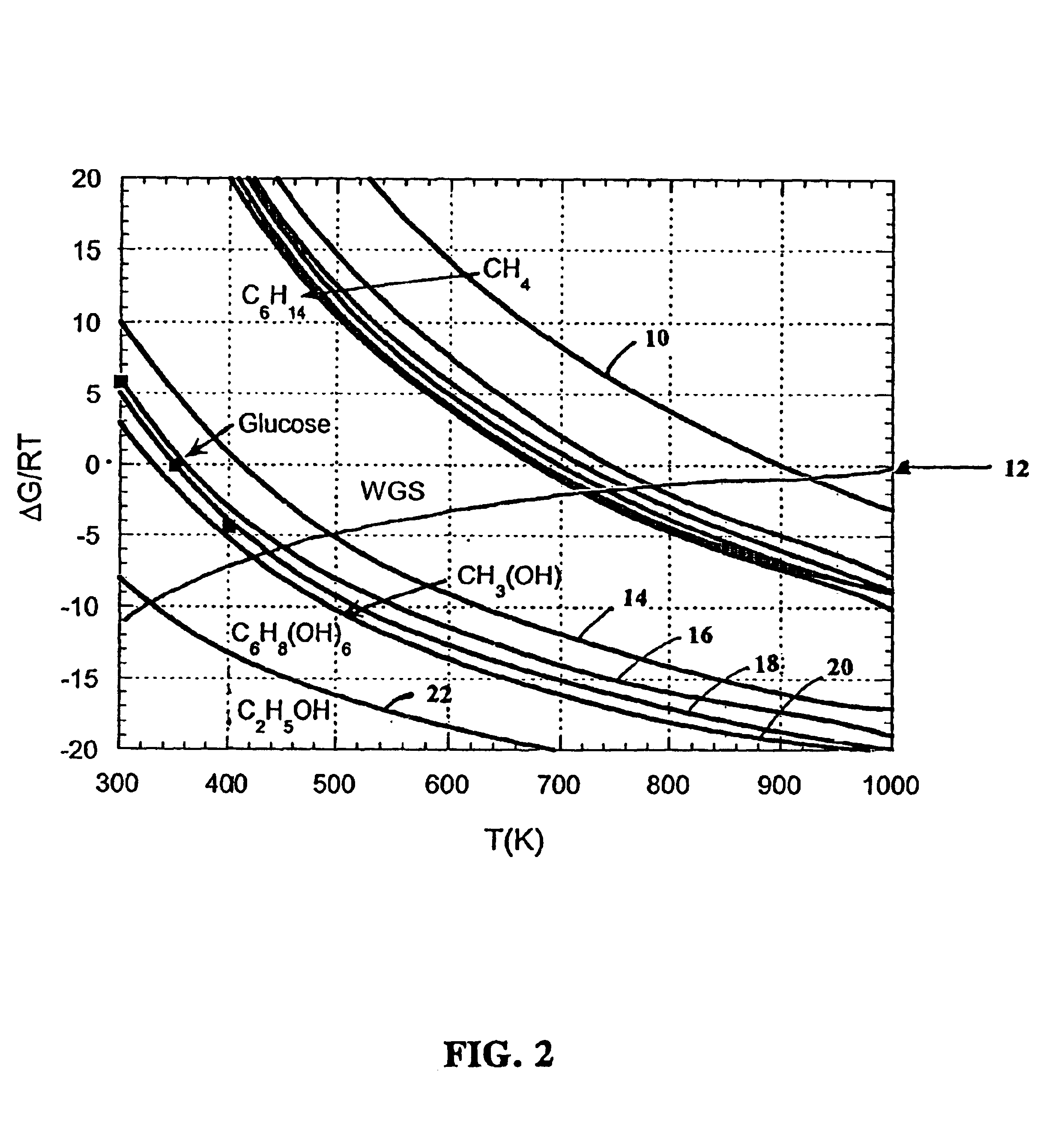
Disclosed is a method of producing hydrogen from oxygenated hydrocarbon reactants, such as methanol, glycerol, sugars (e.g. glucose and xylose), or sugar alcohols (e.g. sorbitol). The method takes place in the condensed liquid phase. The method includes the steps of reacting water and a water-soluble oxygenated hydrocarbon in the presence of a metal-containing catalyst. The catalyst contains a metal selected from the group consisting of Group VIIIB transitional metals, alloys thereof, and mixtures thereof. The disclosed method can be run at lower temperatures than those used in the conventional steam reforming of alkanes.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Low-temperature hydrogen production from oxygenated hydrocarbons
InactiveUS6964758B2High energy costWeaken energyHydrogen productionHydrogen/synthetic gas productionSteam reformingAlkane
Disclosed is a method of producing hydrogen from oxygenated hydrocarbon reactants, such as glycerol, glucose, or sorbitol. The method can take place in the vapor phase or in the condensed liquid phase. The method includes the steps of reacting water and a water-soluble oxygenated hydrocarbon having at least two carbon atoms, in the presence of a metal-containing catalyst. The catalyst contains a metal selected from the group consisting of Group VIII transitional metals, alloys thereof, and mixtures thereof. The disclosed method can be run at lower temperatures than those used in the conventional steam reforming of alkanes.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
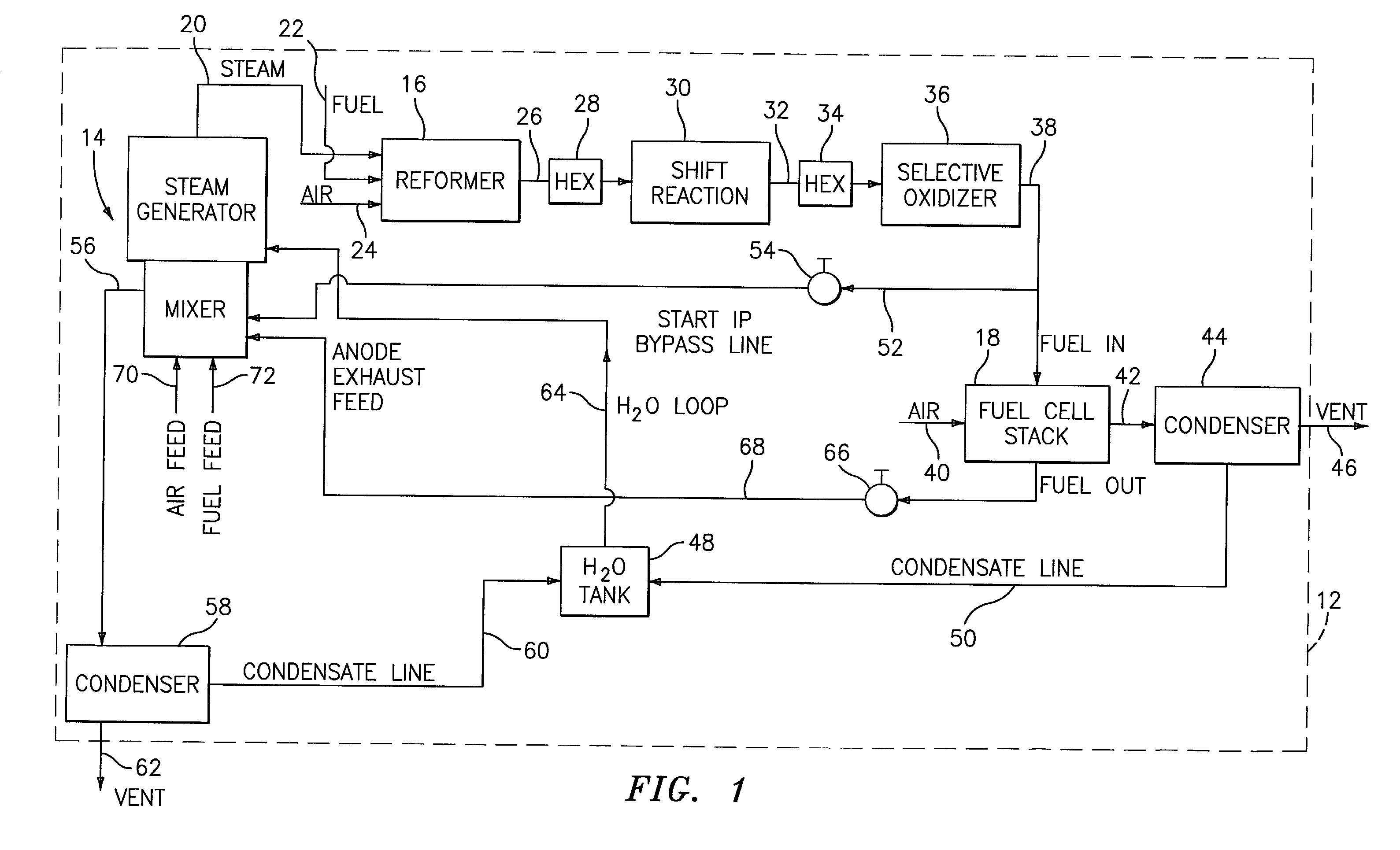
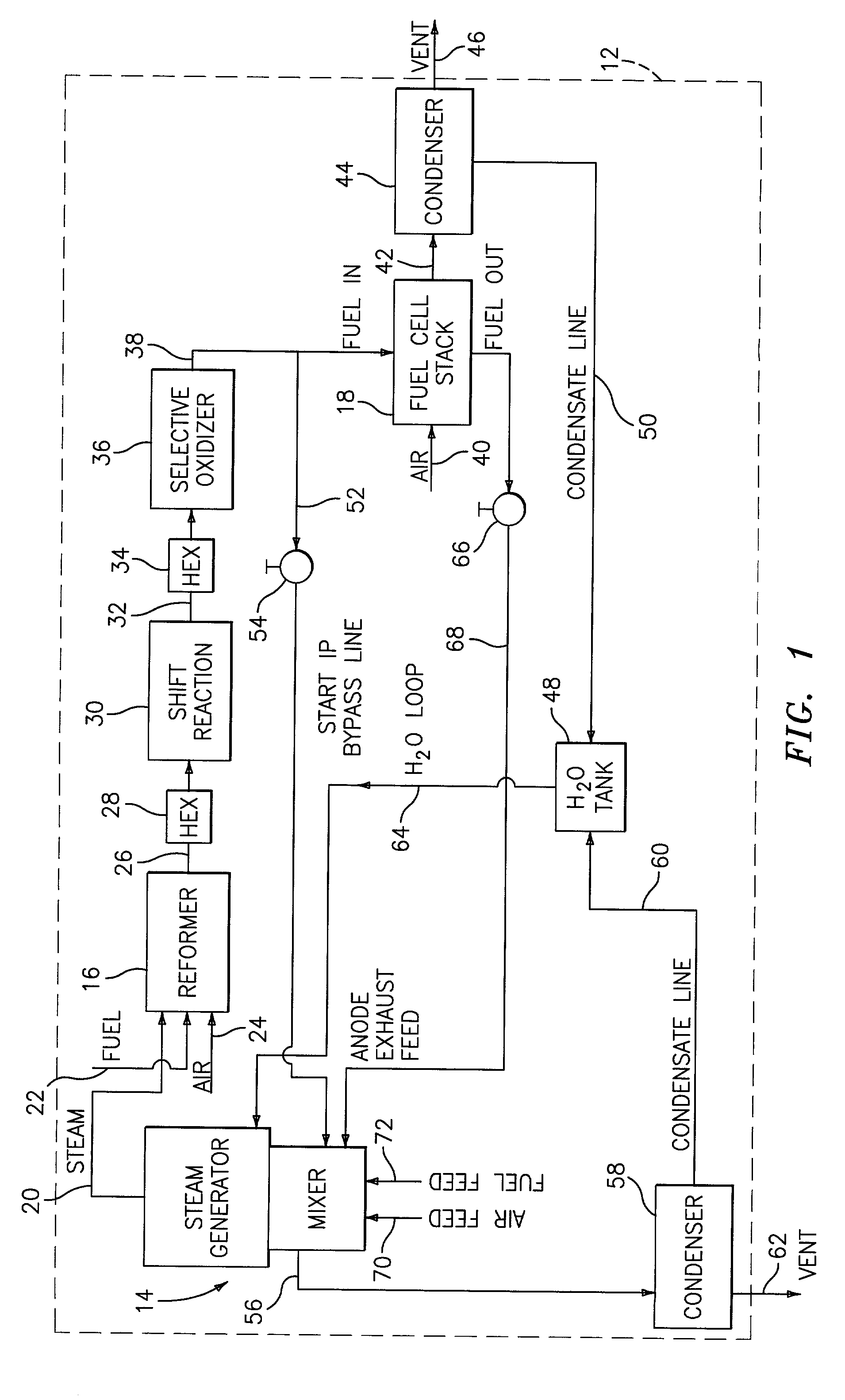
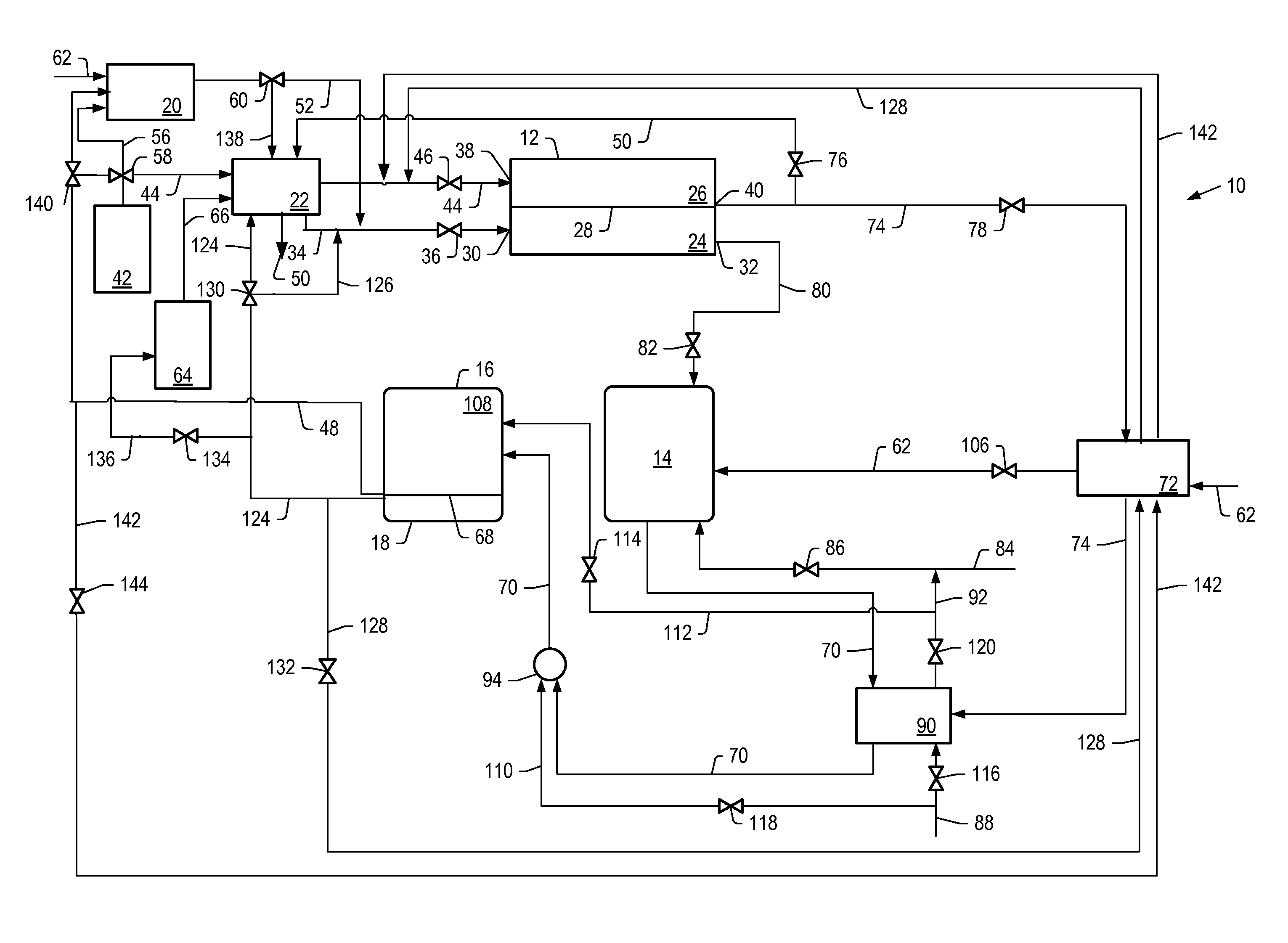
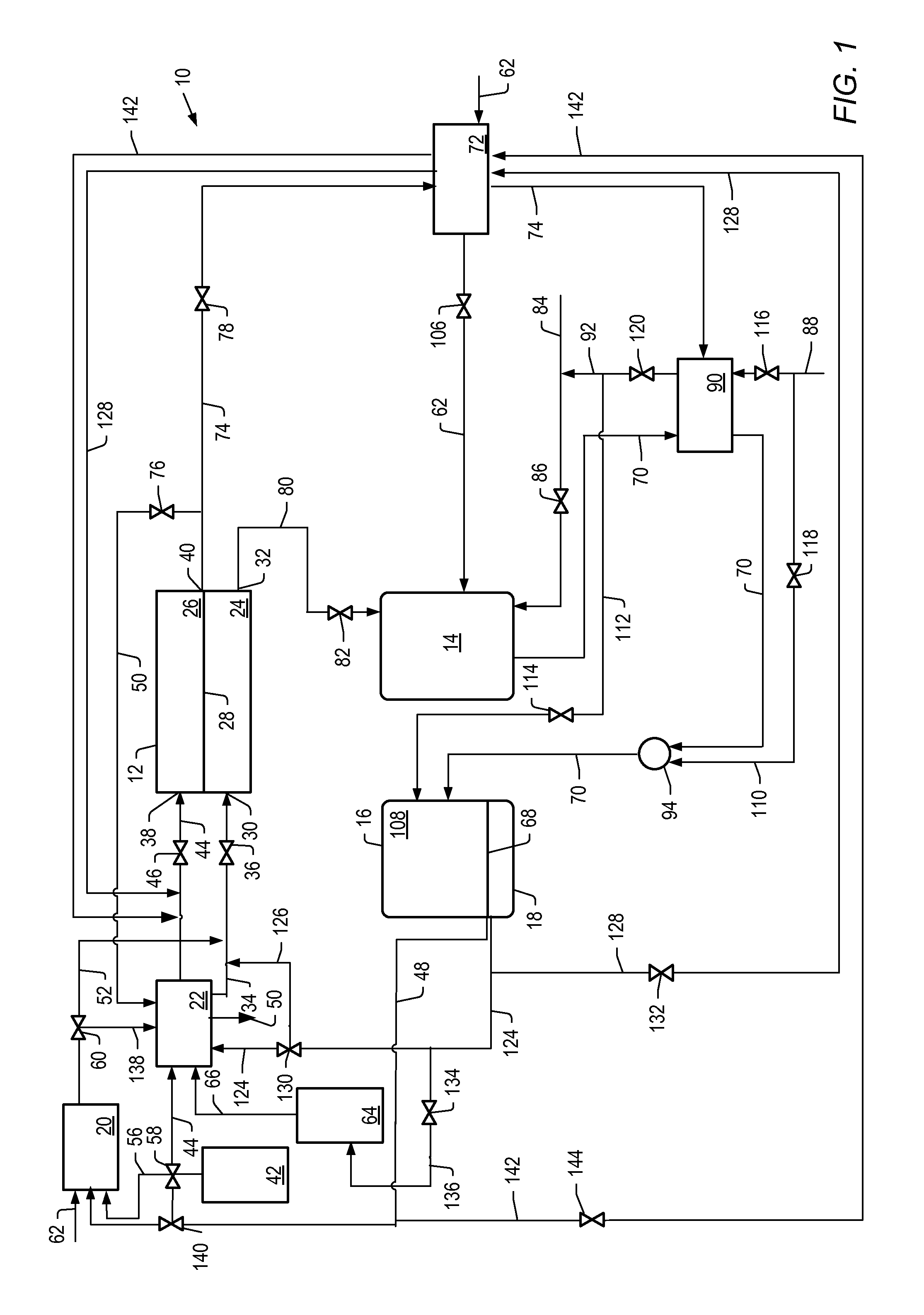
Steam generator for a PEM fuel cell power plant
A burner assembly includes a catalyzed burner for combusting an anode exhaust stream from a polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cell power plant. The catalysts coated onto the burner can be platinum, rhodium, or mixtures thereof. The burner includes open cells which are formed by a lattice, which cells communicate with each other throughout the entire catalyzed burner. Heat produced by combustion of hydrogen in the anode exhaust stream is used to produce steam for use in a steam reformer in the PEM fuel cell assembly. The catalyzed burner has a high surface area wherein about 70-90% of the volume of the burner is preferably open cells, and the burner has a low pressure drop of about two to three inches water from the anode exhaust stream inlet to the anode exhaust stream outlet . The burner assembly operates at essentially ambient pressure and at a temperature of up to about 1,700° F. (646° C.). The burner assembly can combust anode exhaust during normal operation of the fuel cell assembly. The burner assembly also includes an adjunct burner which can combust gasoline or anode bypass gas (the latter of which is a reformed fuel gas which is tapped off of the fuel cell stack fuel inlet line) during startup of the fuel cell power plant. Once start up of the fuel cell power plant is achieved, the burner assembly will need only combustion of the anode exhaust by the catalytic burner to produce steam for the reformer.
Owner:BALLARD POWER SYSTEMS
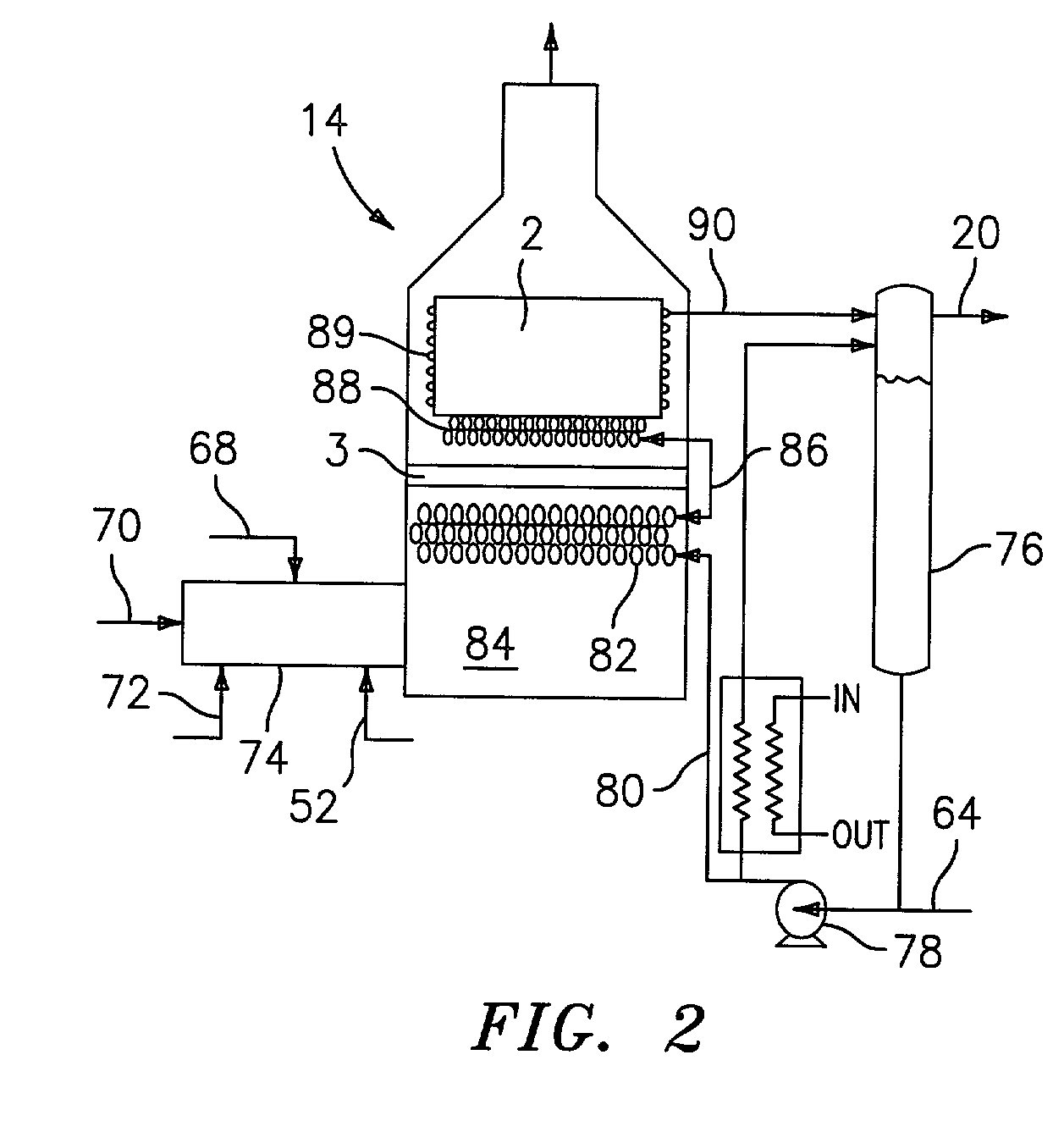
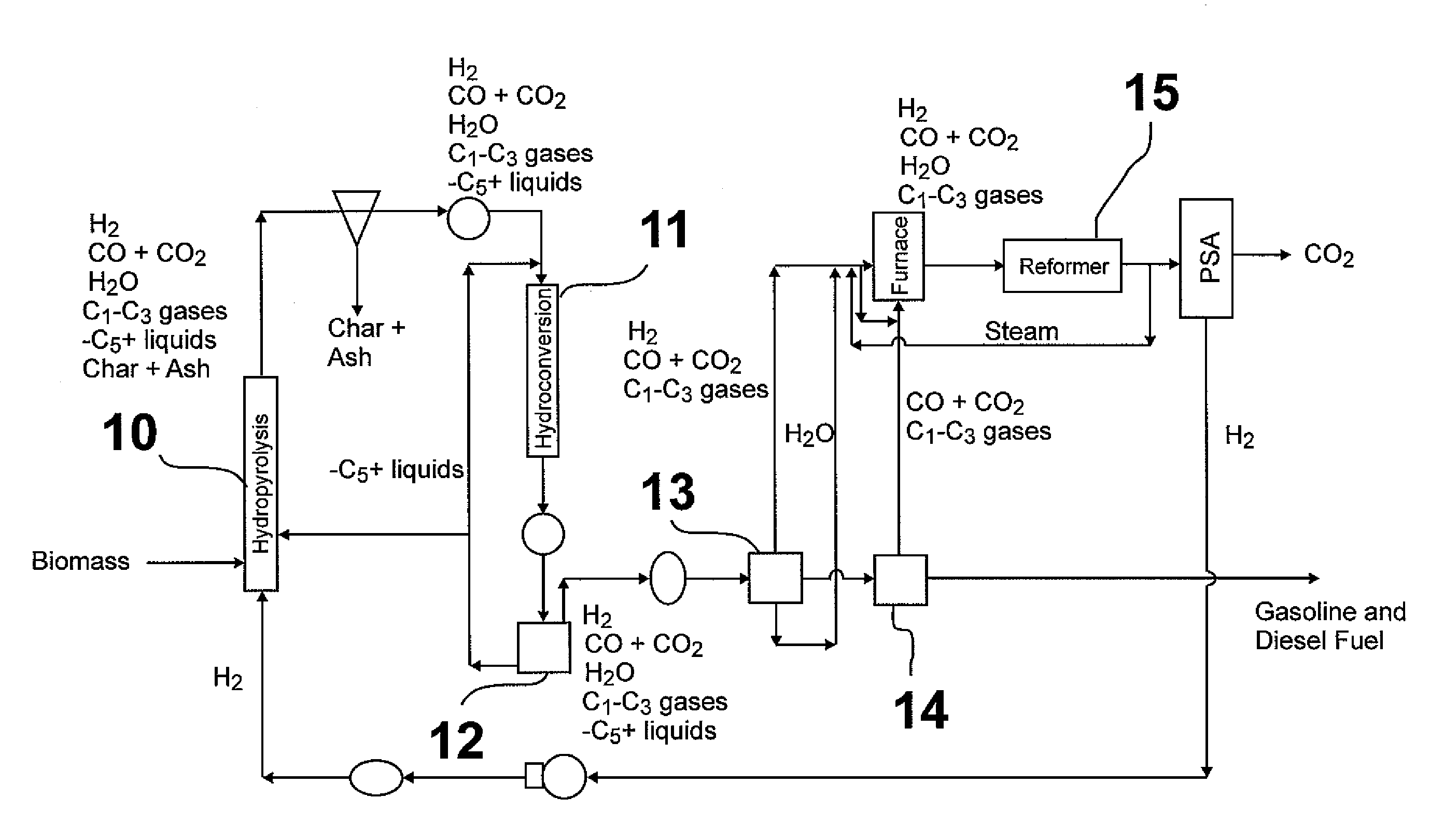
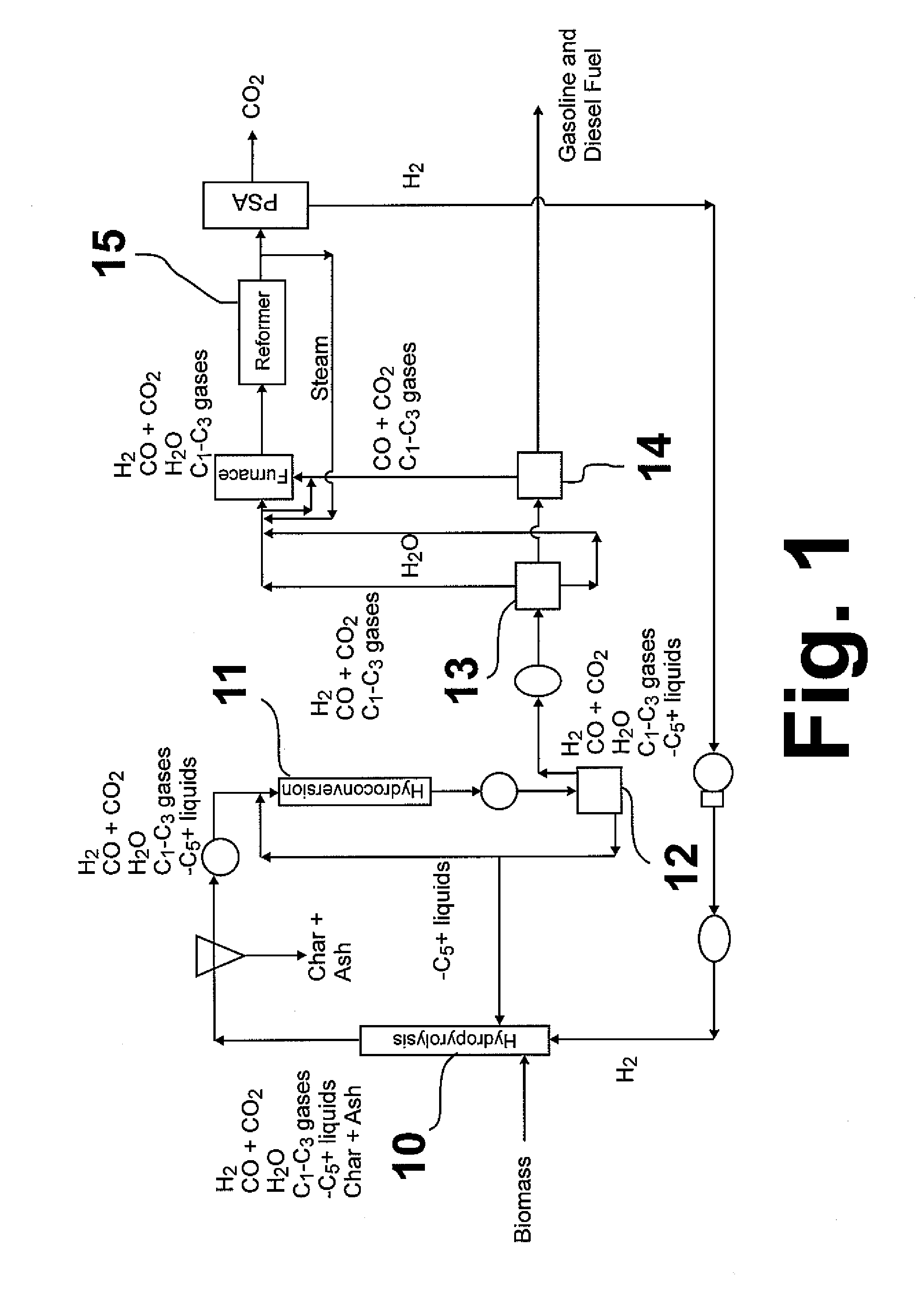
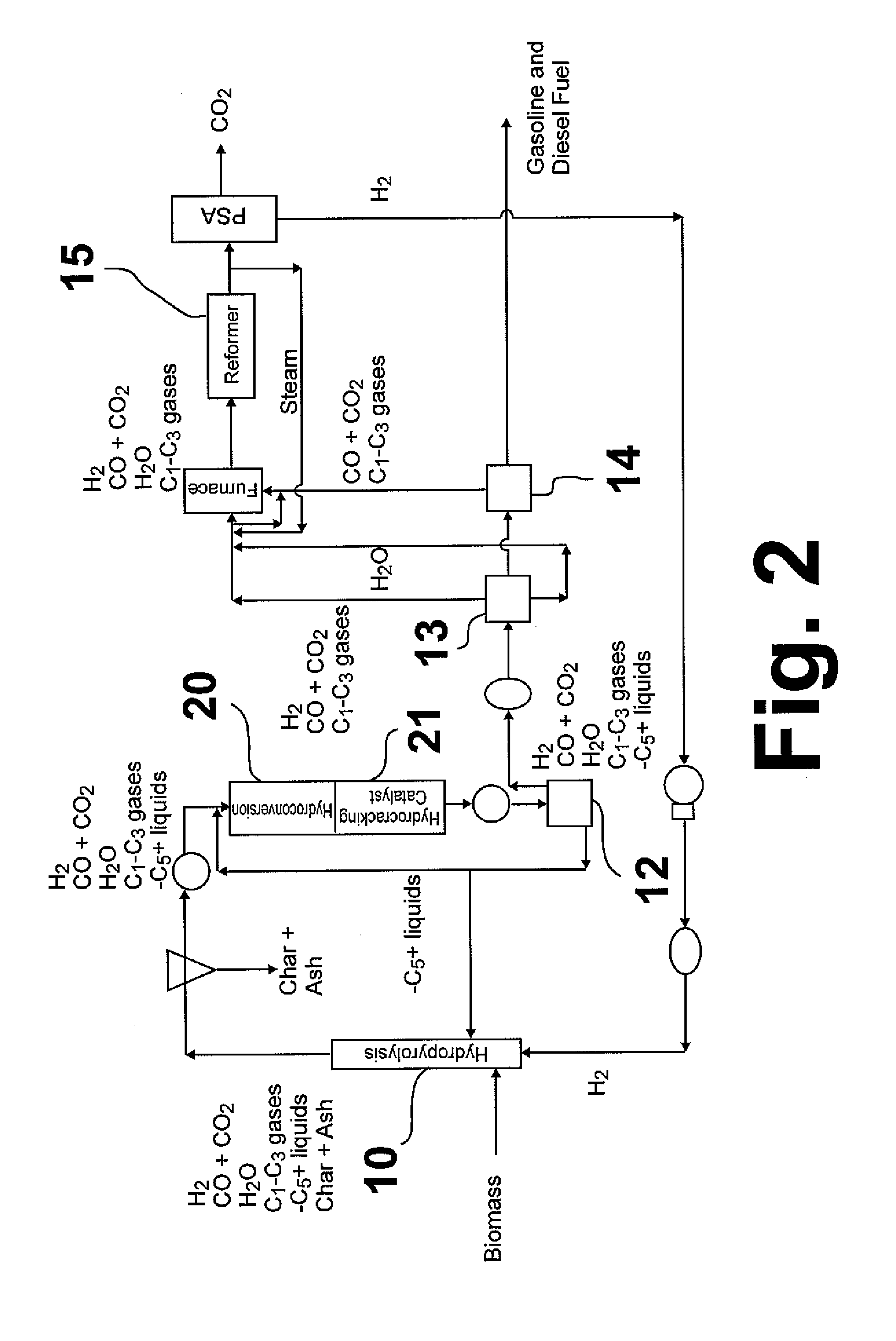
Hydropyrolysis of biomass for producing high quality liquid fuels
A self-sustaining process for producing high quality liquid fuels from biomass in which the biomass is hydropyrolyzed in a reactor vessel containing molecular hydrogen and a deoxygenating catalyst, producing a partially deoxygenated hydropyrolysis liquid, which is hydrogenated using a hydroconversion catalyst, producing a substantially fully deoxygenated hydrocarbon liquid and a gaseous mixture comprising CO and light hydrocarbon gases (C1-C3). The gaseous mixture is reformed in a steam reformer, producing reformed molecular hydrogen, which is then introduced into the reactor vessel for hydropyrolizing the biomass. The deoxygenated hydrocarbon liquid product is further separated to produce diesel fuel, gasoline, or blending components for gasoline and diesel fuel.
Owner:GAS TECH INST
Systems and processes of operating fuel cell systems
InactiveUS20110111315A1Well mixedFuel cell auxillariesFused electrolyte fuel cellsSteam reformingFuel cells
The present invention is directed to systems and processes for operating molten carbonate fuel cell systems. A process for operating the molten carbonate fuel cell includes providing a hydrogen-containing stream comprising molecular hydrogen to a molten carbonate fuel cell anode; heating a hydrocarbon stream, at least a majority of which is comprised of hydrocarbons that are liquid at 20° C. and atmospheric pressure, with a heat source comprising an anode exhaust from the molten carbonate fuel cell anode; contacting at least a portion of the heated hydrocarbon stream with a catalyst to produce a steam reforming feed comprising gaseous hydrocarbons, hydrogen, and at least one carbon oxide; separating at least a portion of the molecular hydrogen from the steam reforming feed; and providing at least a portion of the separated molecular hydrogen to the molten carbonate fuel cell anode as at least a portion of the stream comprising molecular hydrogen.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Methods and apparatus for producing syngas and alcohols
The present invention features methods and apparatus for the pyrolysis or torrefaction of a carbon-containing feedstock before it is converted to syngas. In some embodiments, biomass is first pretreated by torrefaction and / or pyrolysis, followed by devolatilization and / or steam reforming to produce syngas. Various mixtures of such pretreated biomass, combined with fresh biomass, can be employed to produce syngas. The syngas can be converted to alcohols, such as ethanol, or to other products.
Owner:RANGE FUELS INC
Apparatus and process for production of high purity hydrogen
InactiveUS20060248800A1High purityEnhanced overall recoveryCarbon compoundsIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationSteam reformingCombustion chamber
The invention relates to a new and improved process and apparatus for the production of high purity hydrogen by steam reforming. The apparatus is an integrated flameless distributed combustion-membrane steam reforming (FDC-MSR) or reactor for steam reforming of a vaporizable hydrocarbon to produce H2 and CO2, with minimal CO, and minimal CO in the H2 stream. The flameless distributed combustion drives the steam reforming reaction which pro-vides great improvements in heat exchange efficiency and load following capabilities. The reactor may contain multiple flameless distributed combustion chambers and multiple hydrogen-selective, hydrogen-permeable, membrane tubes. The feed and reaction gases may flow through the reactor either radially or axially. A further embodiment of the invention involves producing high purity hydrogen by dehydrogenation using an integrated FDC-membrane de-hydrogenation reactor. A still further embodiment of the invention involves a zero emission hybrid power system wherein the produced hydrogen is used to power a high-pressure internally manifolded molten carbonate fuel cell. In addition, the design of the FDC-SMR powered fuel cell makes it possible to capture good concentrations of CO2 for sequestration or use in other processes.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
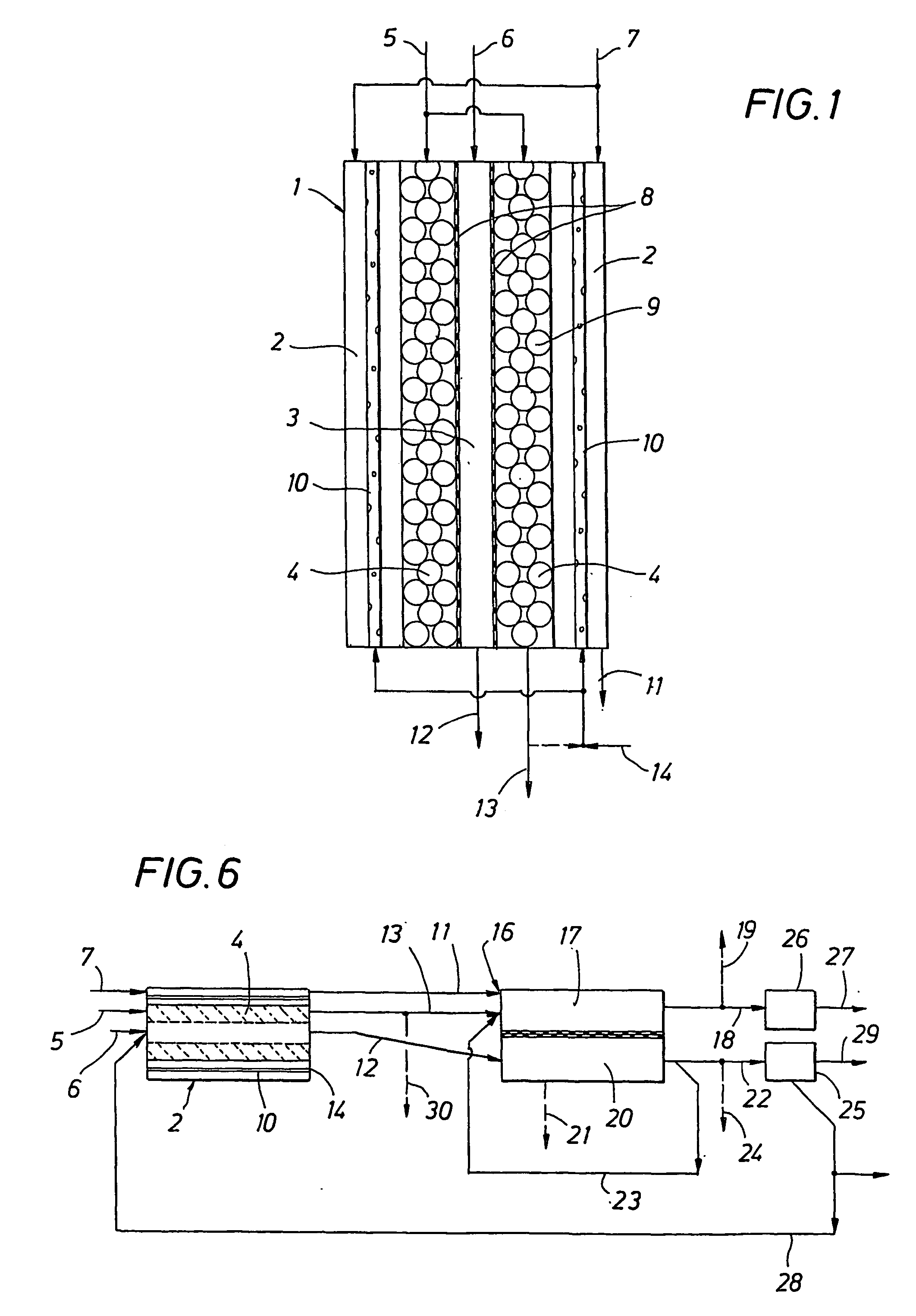
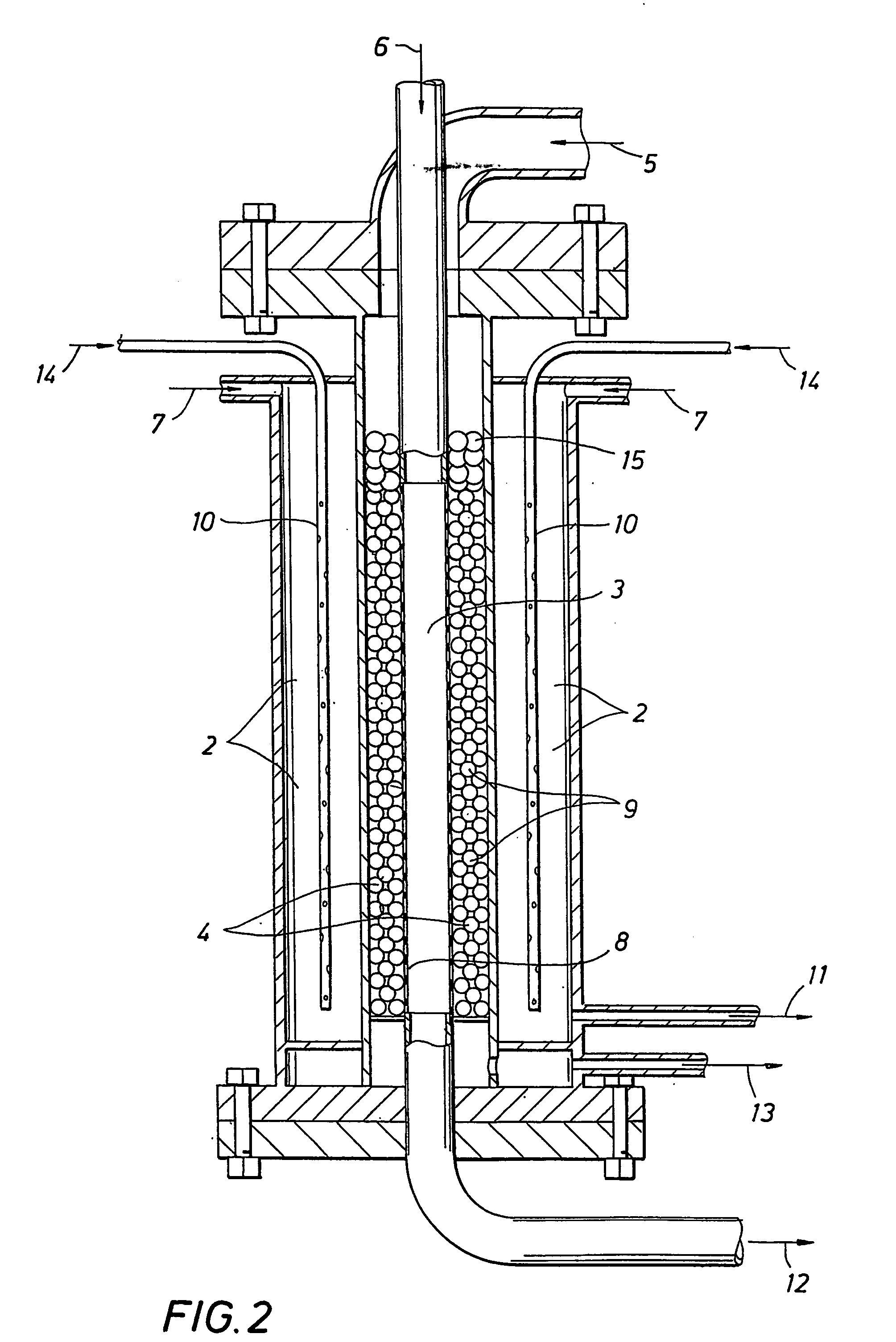
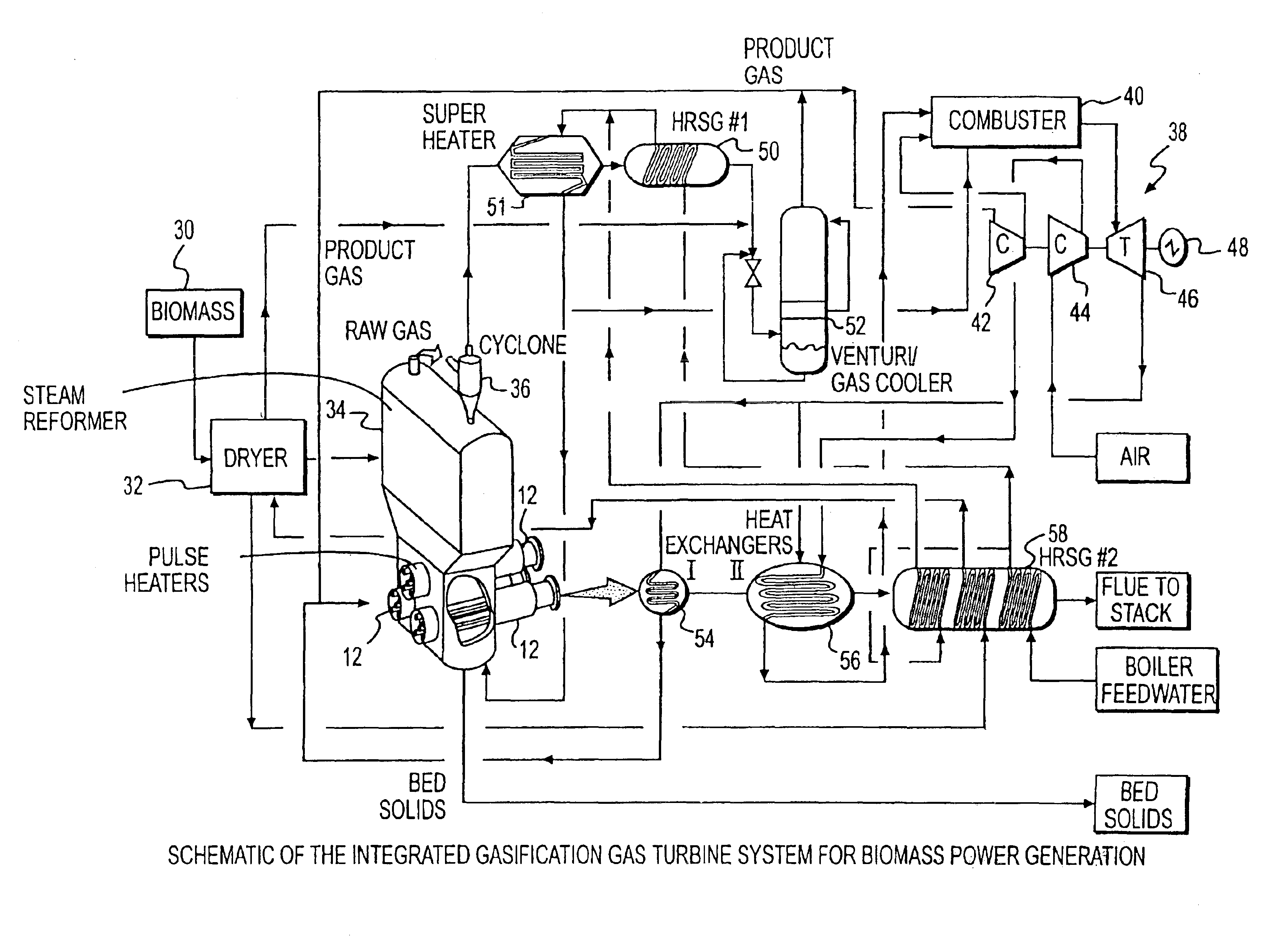
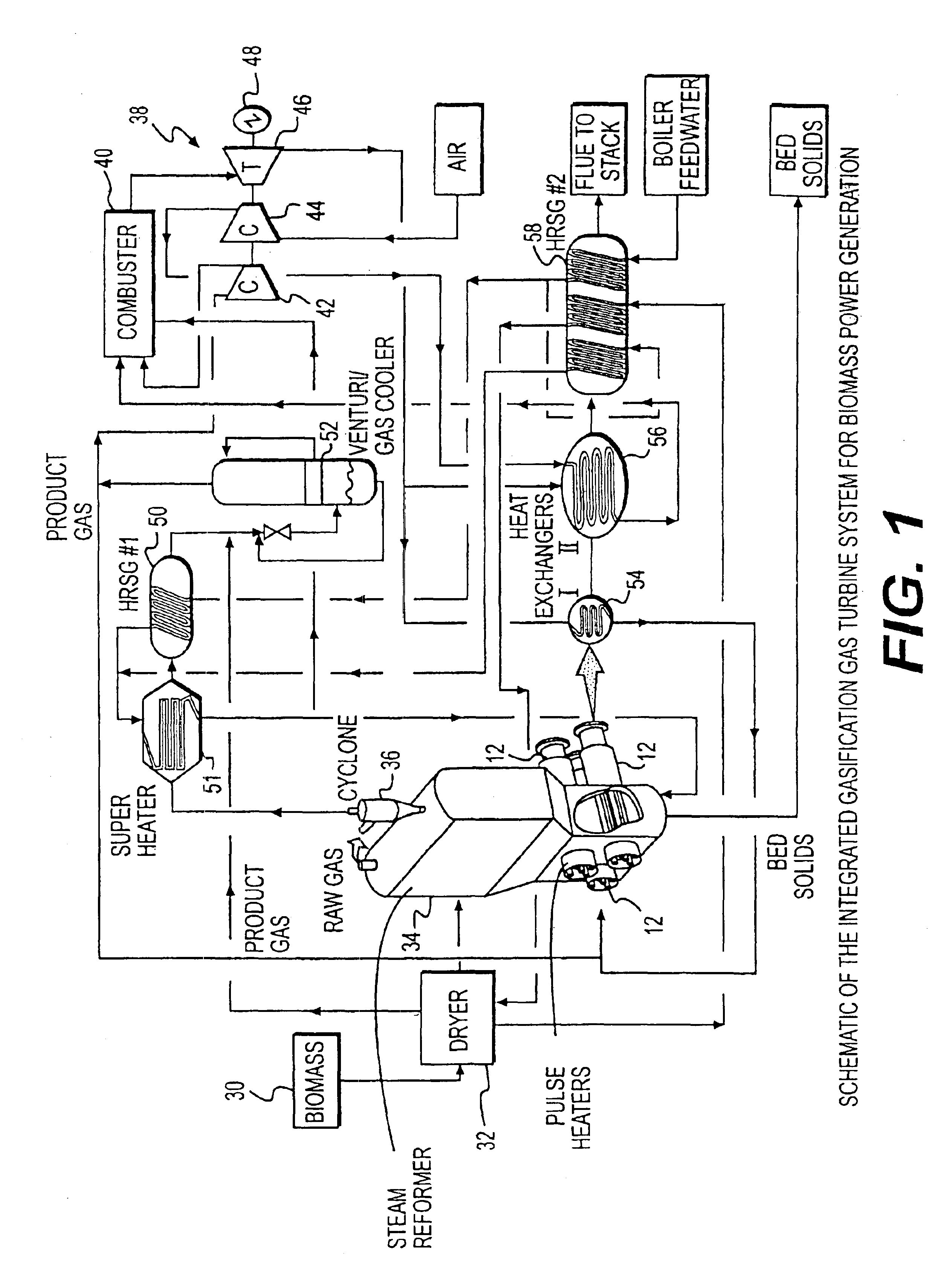
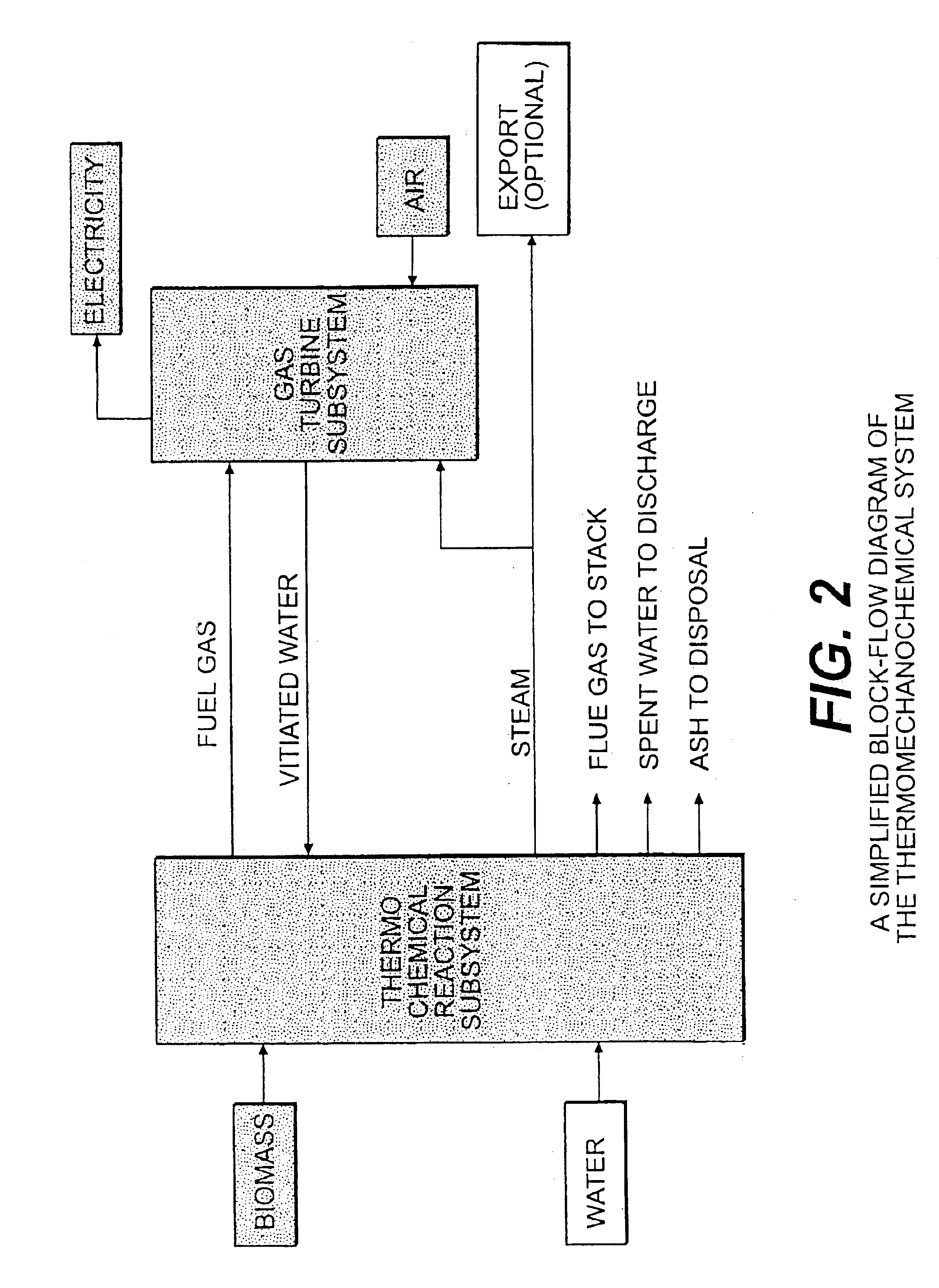
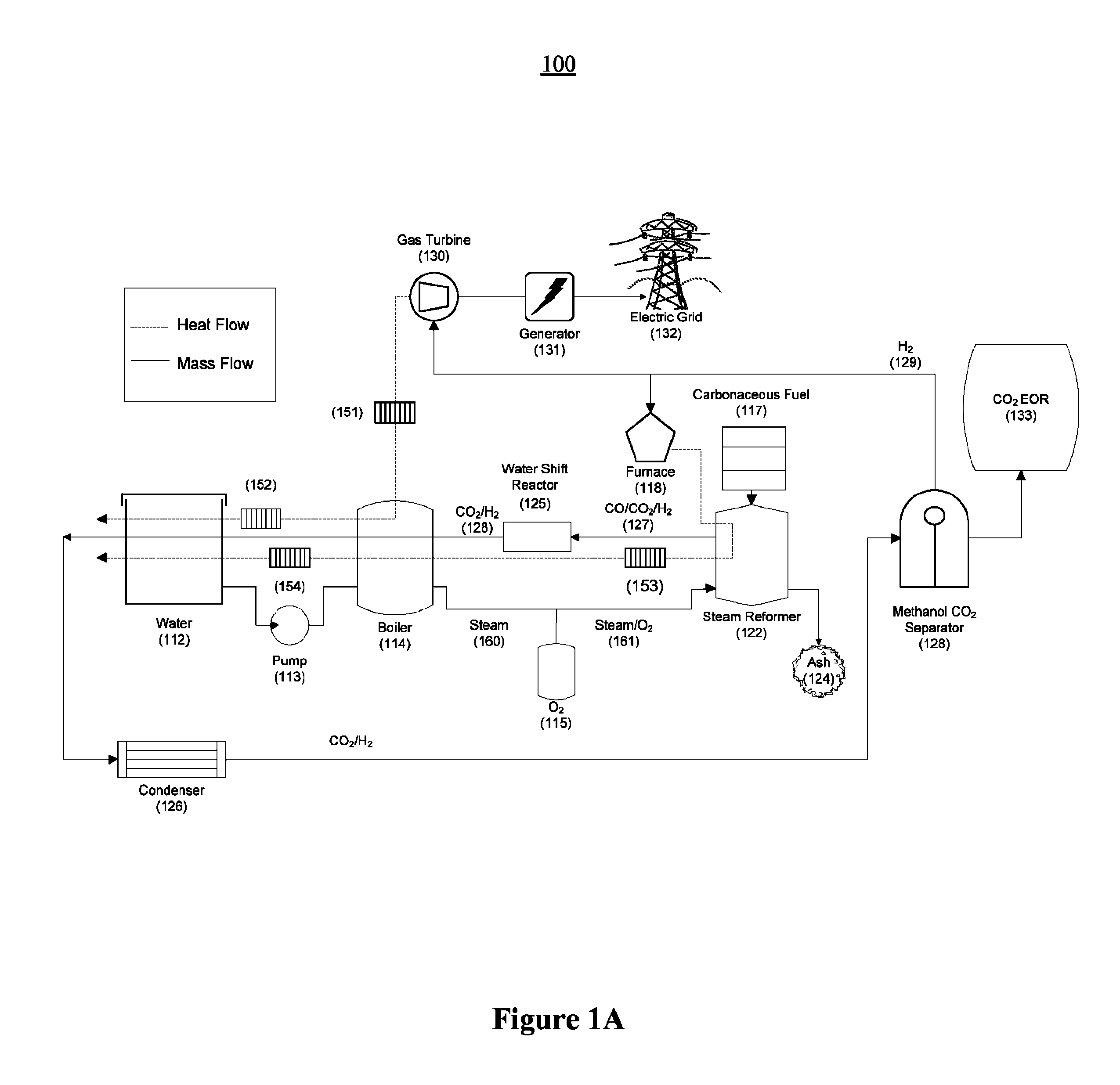
System integration of a steam reformer and gas turbine
A novel process and apparatus for power generation from biomass and other carbonaceous feedstocks are provided. The process integrates a pulse combustor steam reformer with a gas turbine to generate electricity such that (i) efficiency is higher than those of conventional and current advanced power systems, (ii) emissions are lower than those proposed in the new environmental regulations, and (iii) performance is comparable to that of combined cycle, even though a bottoming cycle is not included here. The pulse combustor steam reformer generates a hydrogen-rich, medium-Btu fuel gas that is fired in a gas turbine to generate electricity. The apparatus may be configured to produce only power or combined heat and power.
Owner:THERMOCHEM RECOVERY INT
Chemical microreactor and method thereof
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Process for the production of synthesis gas with conversion of CO2 into hydrogen
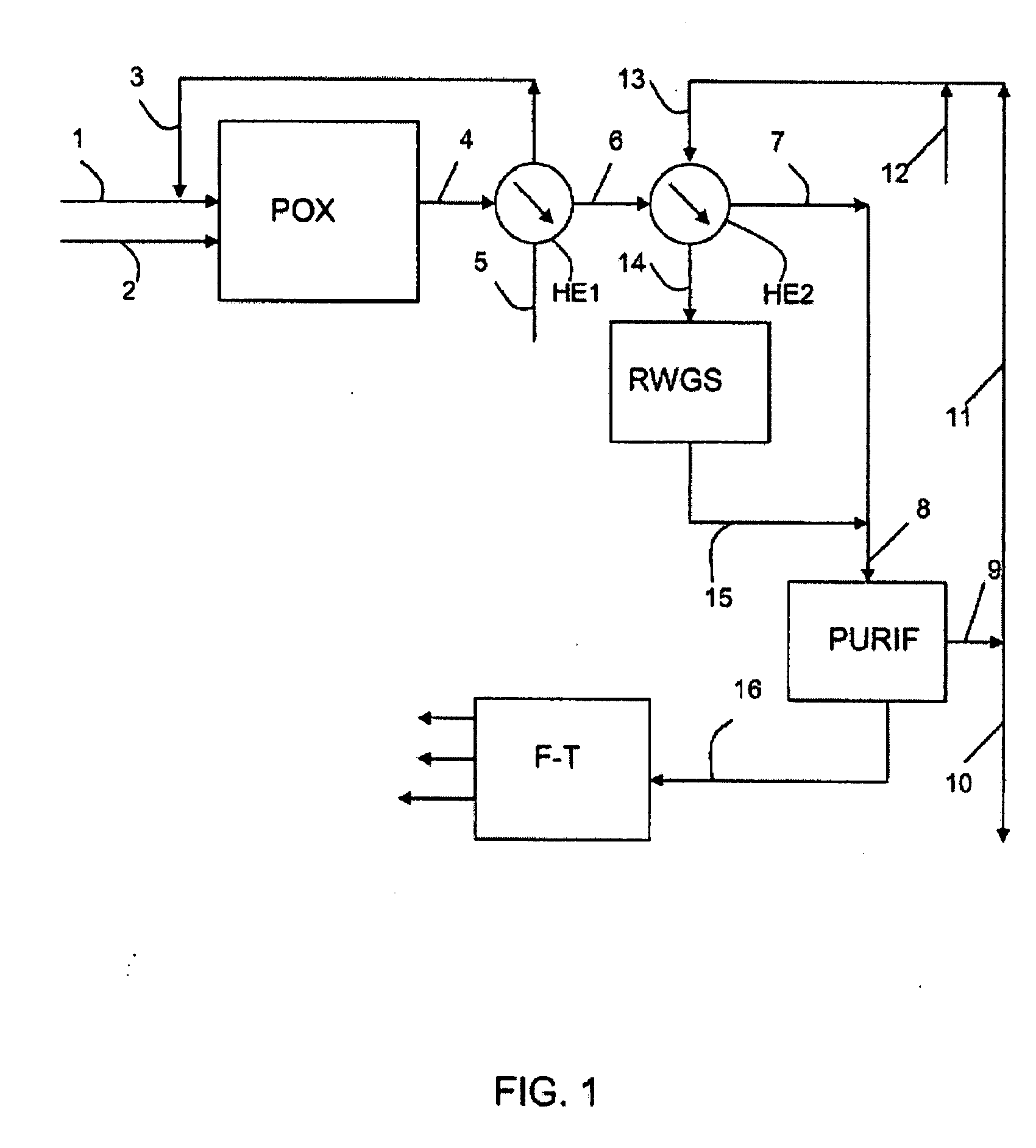
ActiveUS7846979B2Useful thermal recovery on the gasification effluentCombustible gas chemical modificationProductsSteam reformingPartial oxidation
Process for the production of liquid hydrocarbons from a feedstock that comprises at least one elementary feedstock from the group of biomass, coal, lignite, petroleum residues, methane, and natural gas, comprising: at least one stage a) for gasification of the feedstock by partial oxidation and / or steam reforming to produce a synthesis gas SG; a stage b) for separating CO2 from SG and a portion of the effluent of the subsequent stage c); the mixing of a portion of the CO2 that is separated with a gas of an H2 / CO ratio of more than 3; a stage c) for partial conversion with hydrogen, thermal or thermocatalytic, of the CO2 that is present in said first mixture according to the reaction: CO2+H2→CO+H2O in a specific reaction zone that is separated from said gasification zone or zones; a stage d) for Fisher-Tropsch synthesis on a synthesis gas that comprises at least a portion of SG and at least a portion of the CO that is produced by the conversion of CO2 into hydrogen.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Conversion of carbonaceous materials to synthetic natural gas by pyrolysis, reforming, and methanation
InactiveUS20080016769A1Reduce the temperatureCombustible gas chemical modificationProductsSyngasSteam reforming
The production of synthetic natural gas from a carbonaceous material, preferably a biomass material, such as wood. The carbonaceous material is first pyrolyzed, then subjected to steam reforming to produce a syngas, which is then passed to several clean-up steps then to a methanation zone to produce synthetic natural gas.
Owner:CLEAN ENERGY LLC
Integrated fuel processor subsystem with quasi-autothermal reforming
InactiveUS20050188615A1Provide flexibilitySufficient flexibilityReciprocating combination enginesExhaust apparatusSteam reformingFuel treatment
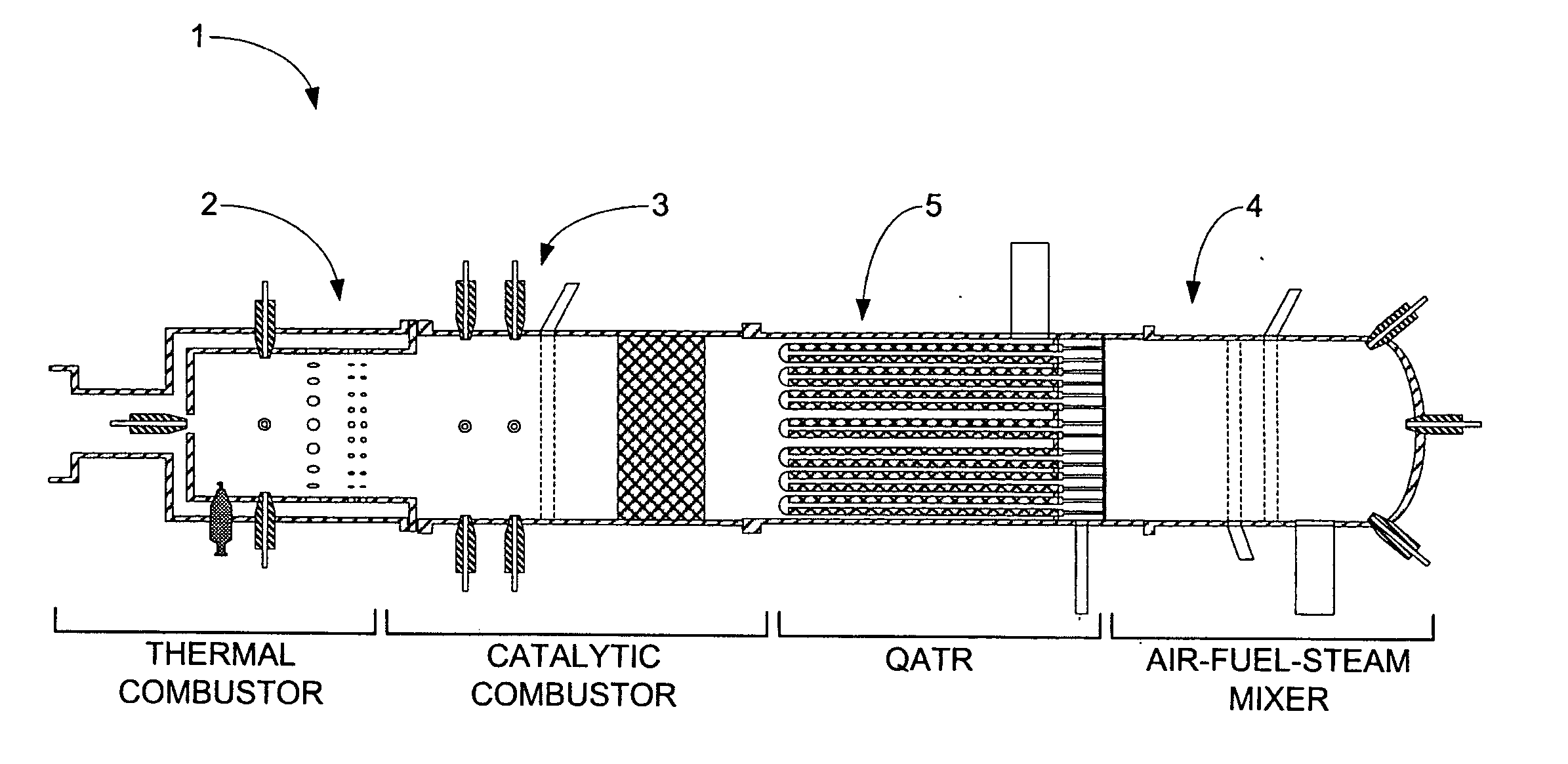
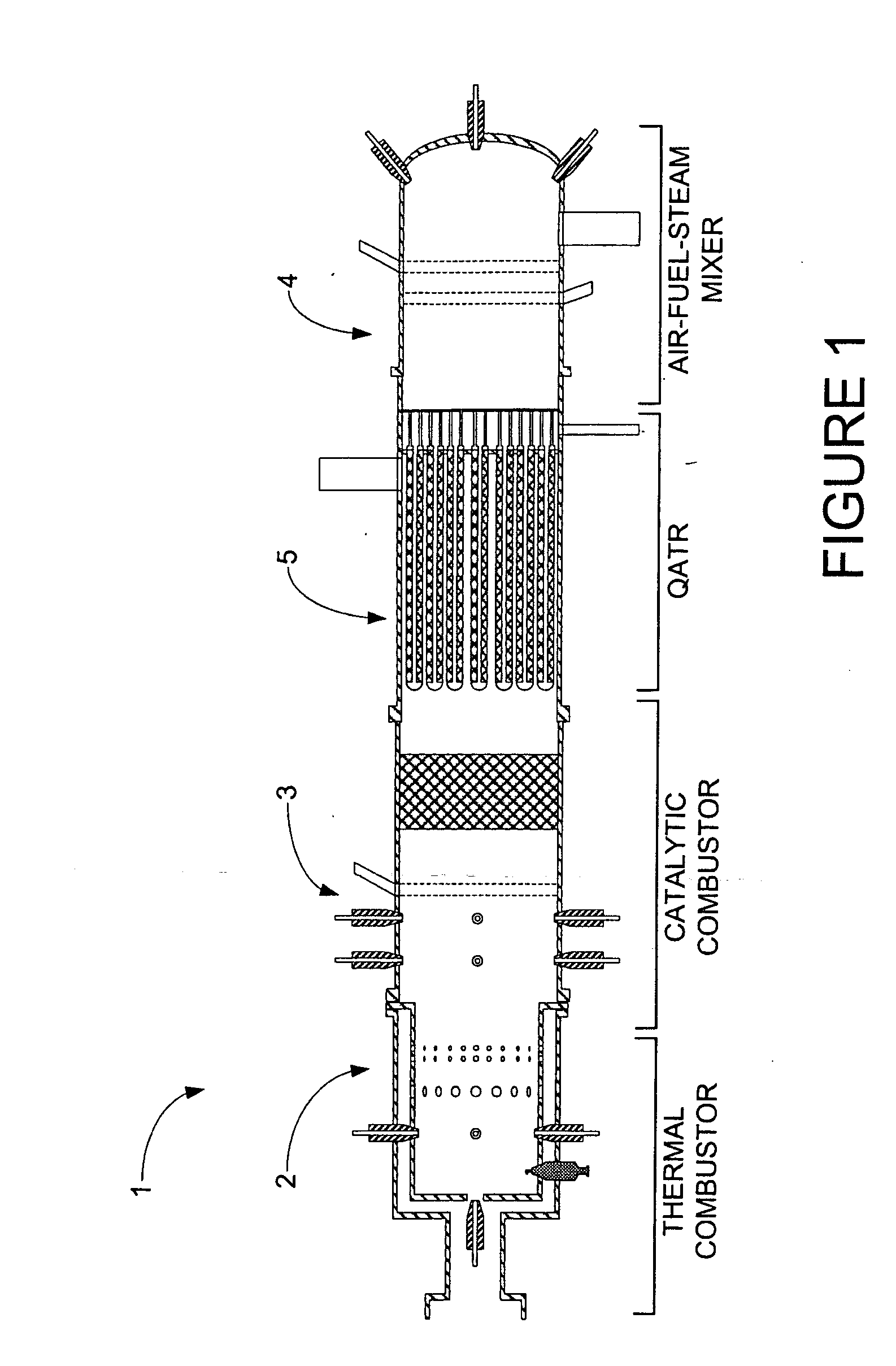
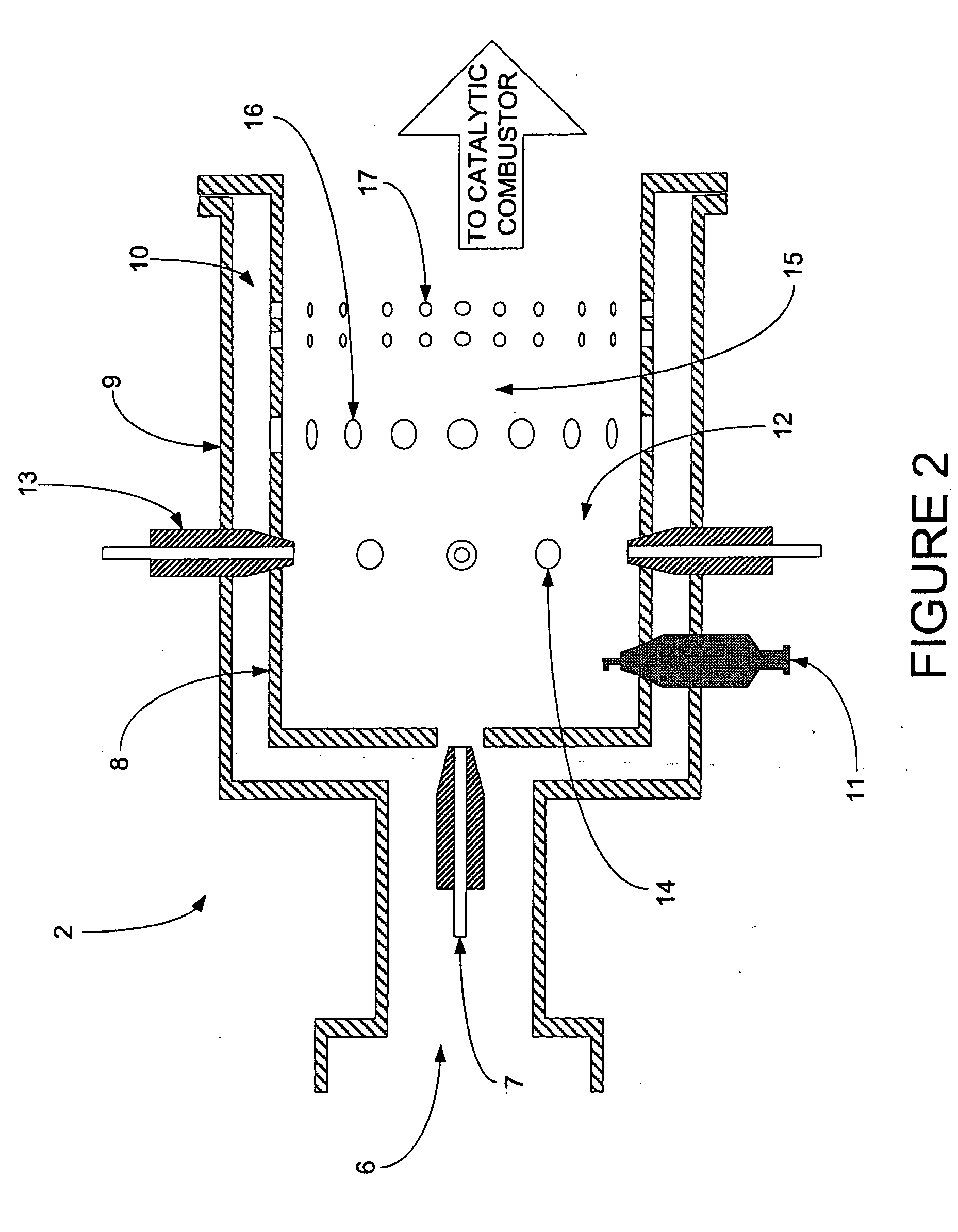
The present invention includes an integrated fuel processor subsystem incorporating a thermal combustor, a catalytic combustor, a quasi-autothermal reactor (QATR) and a air-fuel-steam (AFS) mixer to provide a range of operating modes exhibiting performance between that of a pure steam reformer and a pure autothermal reformer to increase the flexibility of the fuel processor to handle transient system demands such as cold starts, suppress emissions and carbon formation and improve efficiency.
Owner:FLARION TECH +1
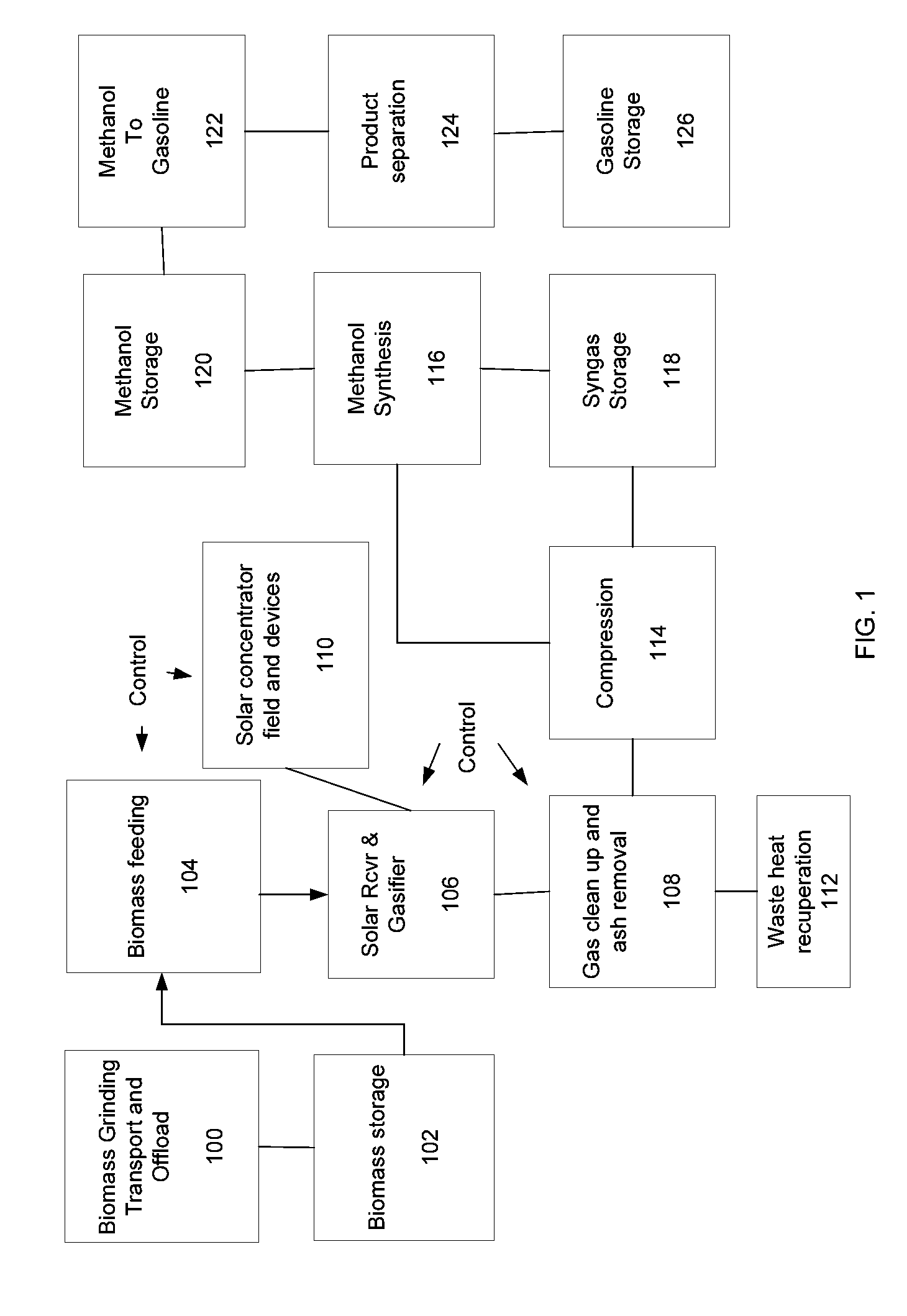
Systems and methods for solar-thermal gasification of biomass
InactiveUS20100237291A1Process control/regulationSolar heating energySteam reformingChemical reaction
A method, apparatus, and system for a solar-driven chemical plant that may include a solar thermal receiver having a cavity with an inner wall, where the solar thermal receiver is aligned to absorb concentrated solar energy from one or more of 1) an array of heliostats, 2) solar concentrating dishes, and 3) any combination of the two. Some embodiments may include a solar-driven chemical reactor having multiple reactor tubes located inside the cavity of solar thermal receiver, wherein a chemical reaction driven by radiant heat occurs in the multiple reactor tubes, and wherein particles of biomass are gasified in the presence of a steam (H2O) carrier gas and methane (CH4) in a simultaneous steam reformation and steam biomass gasification reaction to produce reaction products that include hydrogen and carbon monoxide gas using the solar thermal energy from the absorbed concentrated solar energy in the multiple reactor tubes.
Owner:SUNDROP IP HLDG LLC
Low-temperature hydrogen production from oxygenated hydrocarbons
InactiveUS7618612B2Reduce riskWeaken energyHydrogen productionHydrogen/synthetic gas productionSteam reformingAlkane
Disclosed is a method of producing hydrogen from oxygenated hydrocarbon reactants, such as methanol, glycerol, sugars (e.g. glucose and xylose), or sugar alcohols (e.g. sorbitol). The method takes place in the condensed liquid phase. The method includes the steps of reacting water and a water-soluble oxygenated hydrocarbon in the presence of a metal-containing catalyst. The catalyst contains a metal selected from the group consisting of Group VIIIB transitional metals, alloys thereof, and mixtures thereof. The disclosed method can be run at lower temperatures than those used in the conventional steam reforming of alkanes.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
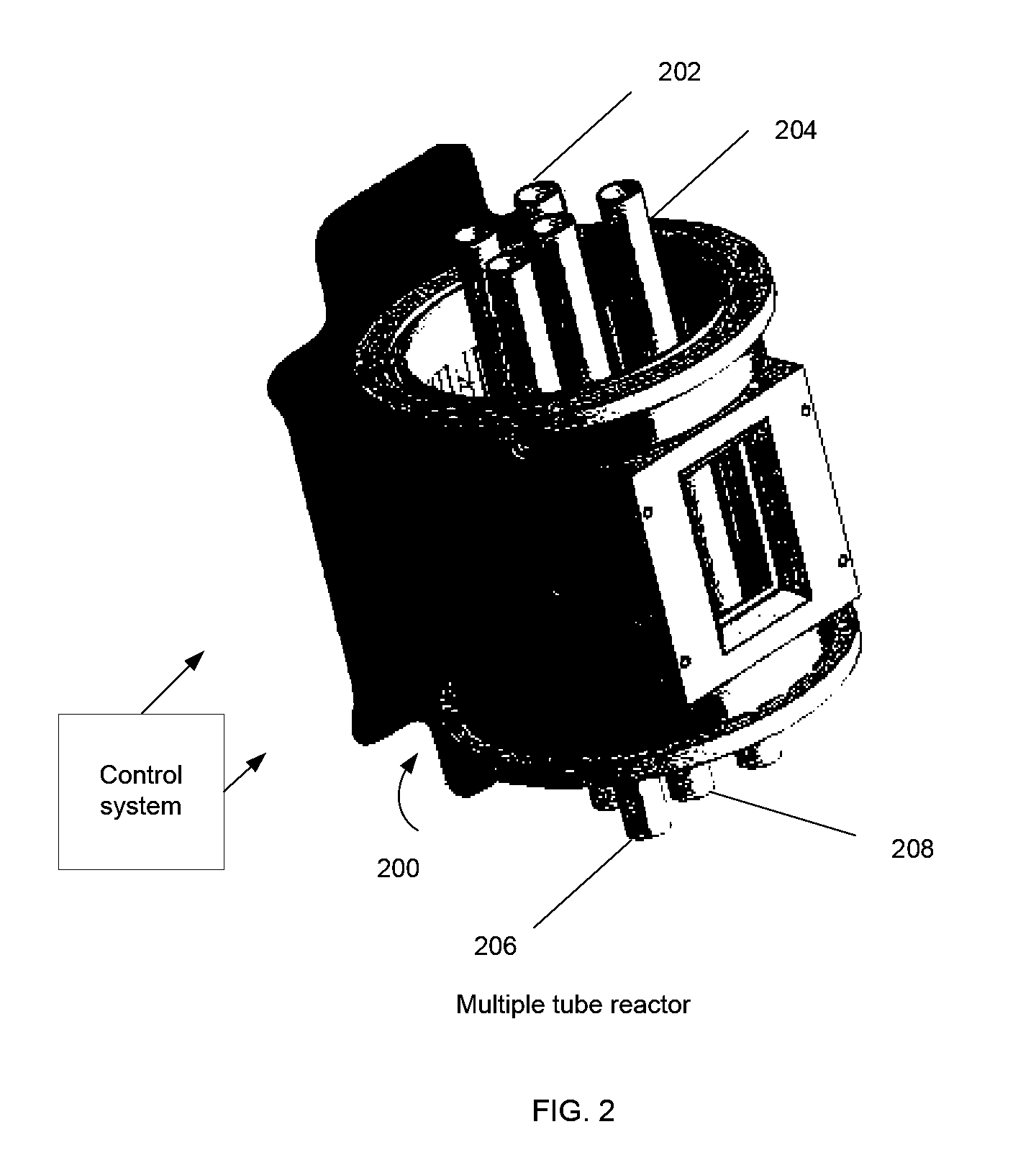
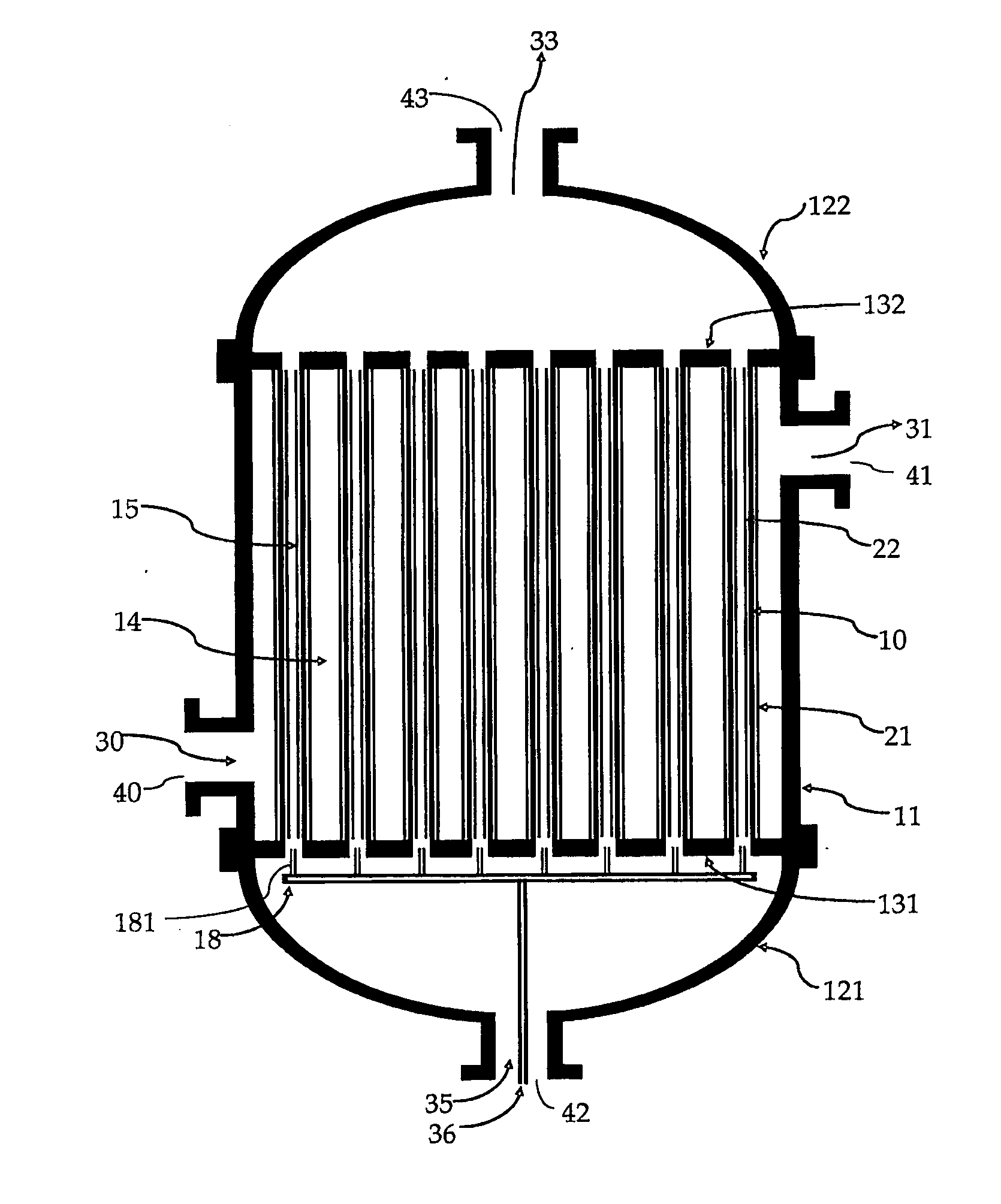
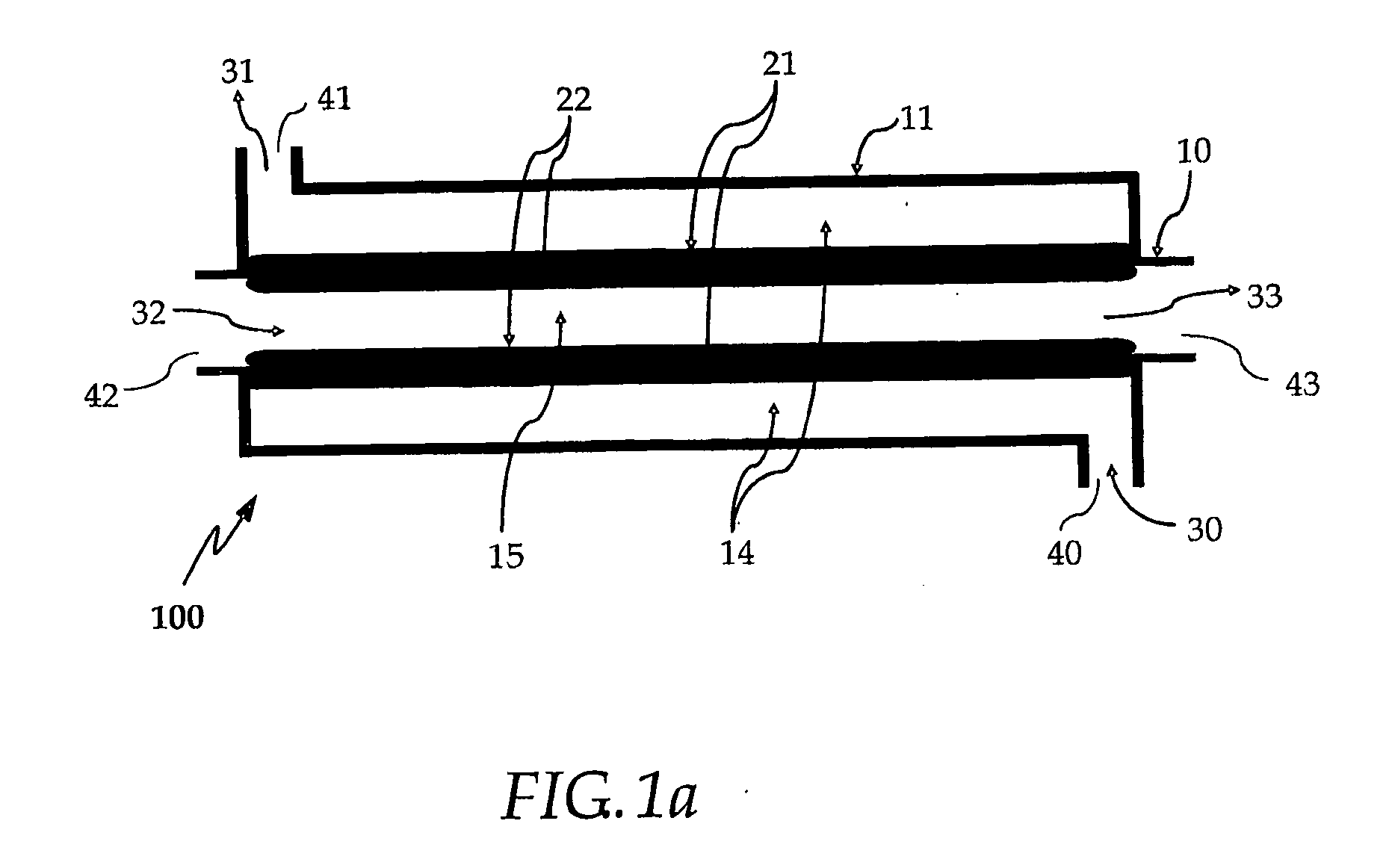
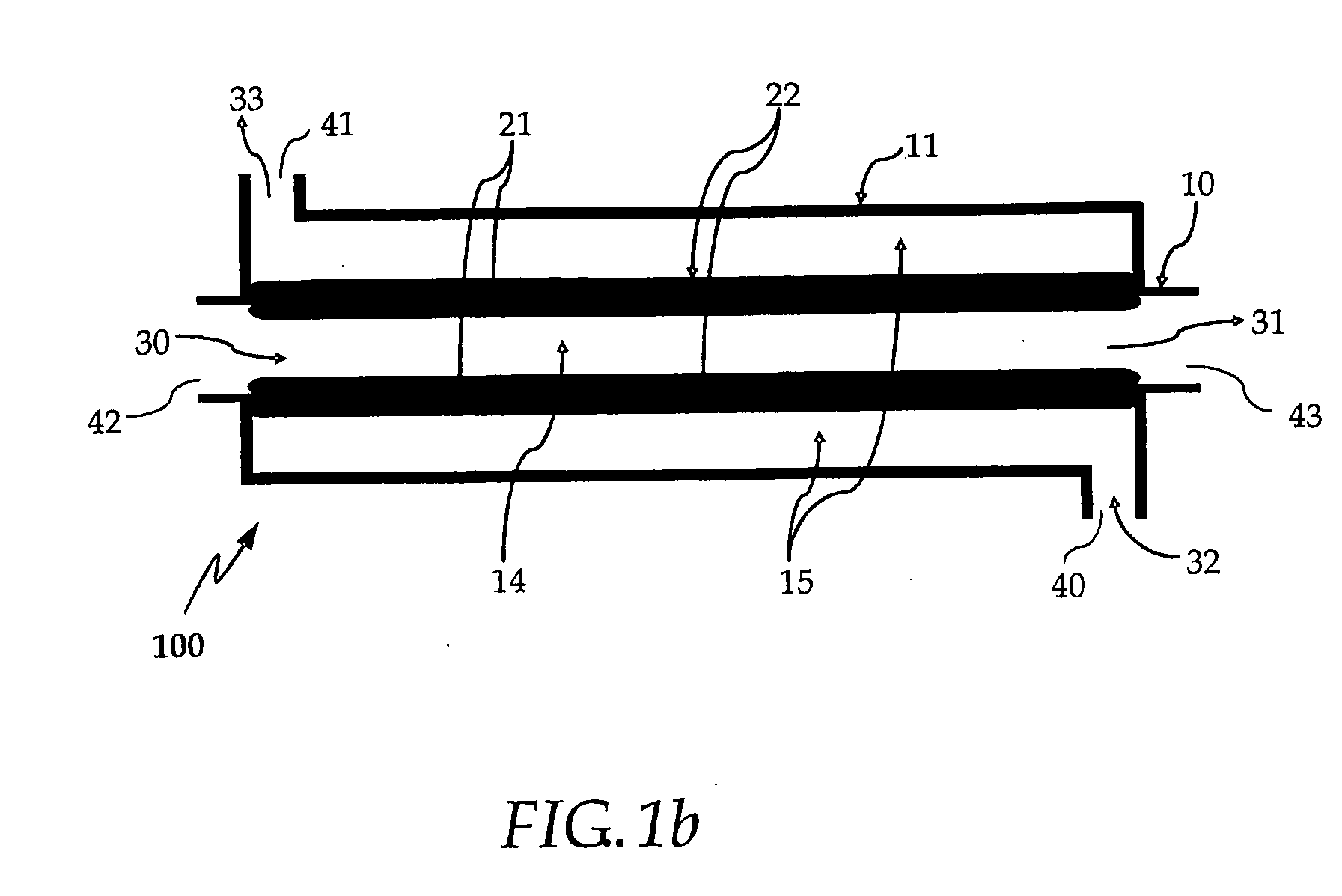
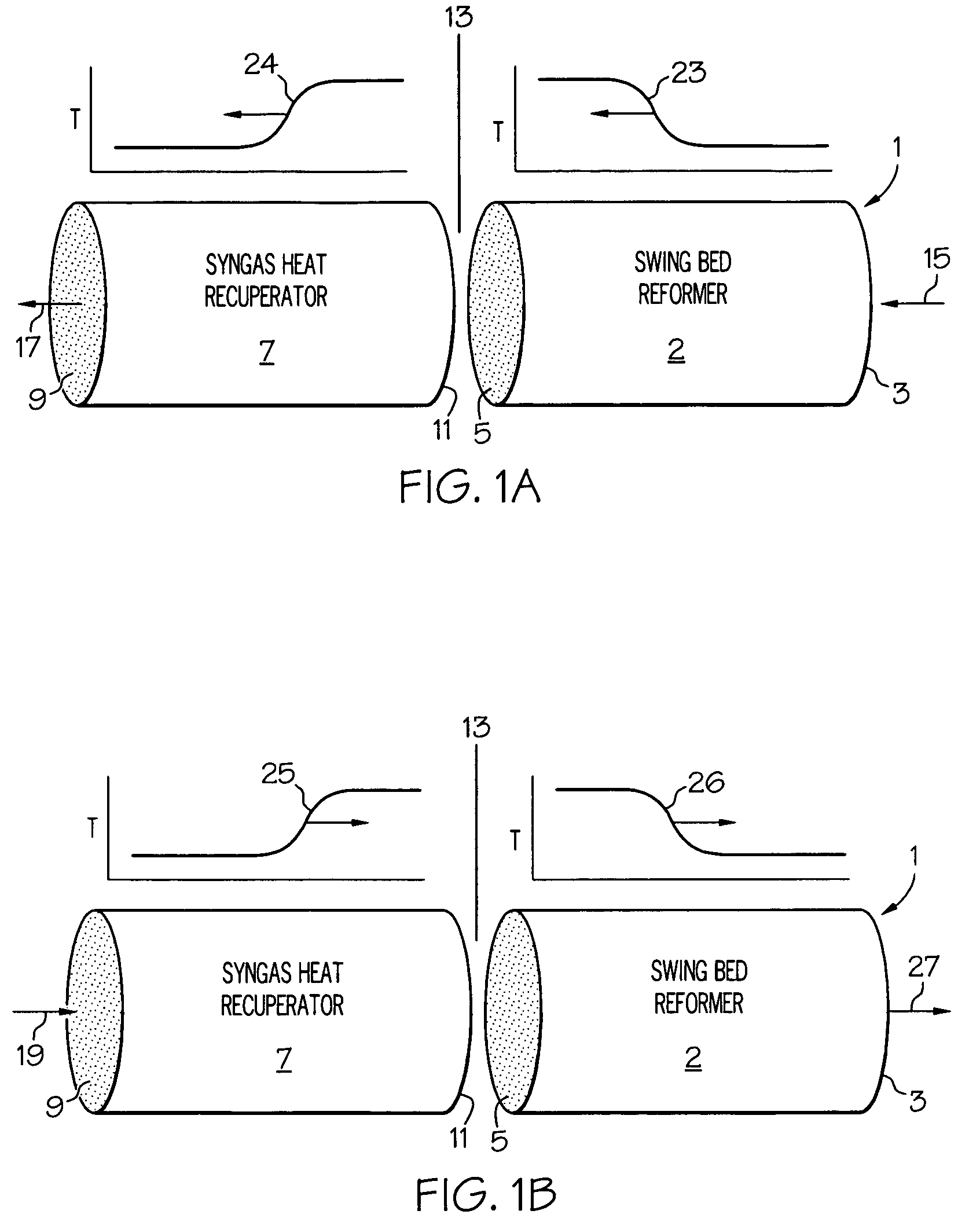
Highly heat integrated reformer for hydrogen production
InactiveUS20100178219A1Improve distributionEasy to introduceCatalytic gas-gas reactionHydrogenCatalytic reformingSteam reforming
Described herein is a highly heat integrated steam reformer / combustor assembly that can be used in a fuel processor for hydrogen production from a fuel source. The assembly comprises a reforming section and a combustion section separated by a wall. Catalyst able to induce the reforming reactions is coated on the wall facing the reforming section. Catalyst able to induce the combustion reactions is coated on the wall facing the combustion section. A steam and fuel mixture is supplied to the reforming section where it is reformed to product hydrogen. A fuel and air mixture is supplied to the combustion section where it is combusted to supply the heat for the reformer. Catalytic combustion takes place on the combustion catalyst coated on one side of the wall while catalytic reforming takes place on the reforming catalyst coated on the other side of the wall. Heat transfer is very facile and efficient across the wall. Multiple such assemblies can be bundled to form reactors of any size.
Owner:HELBIO HYDROGEN & ENERGY PRODN SYST
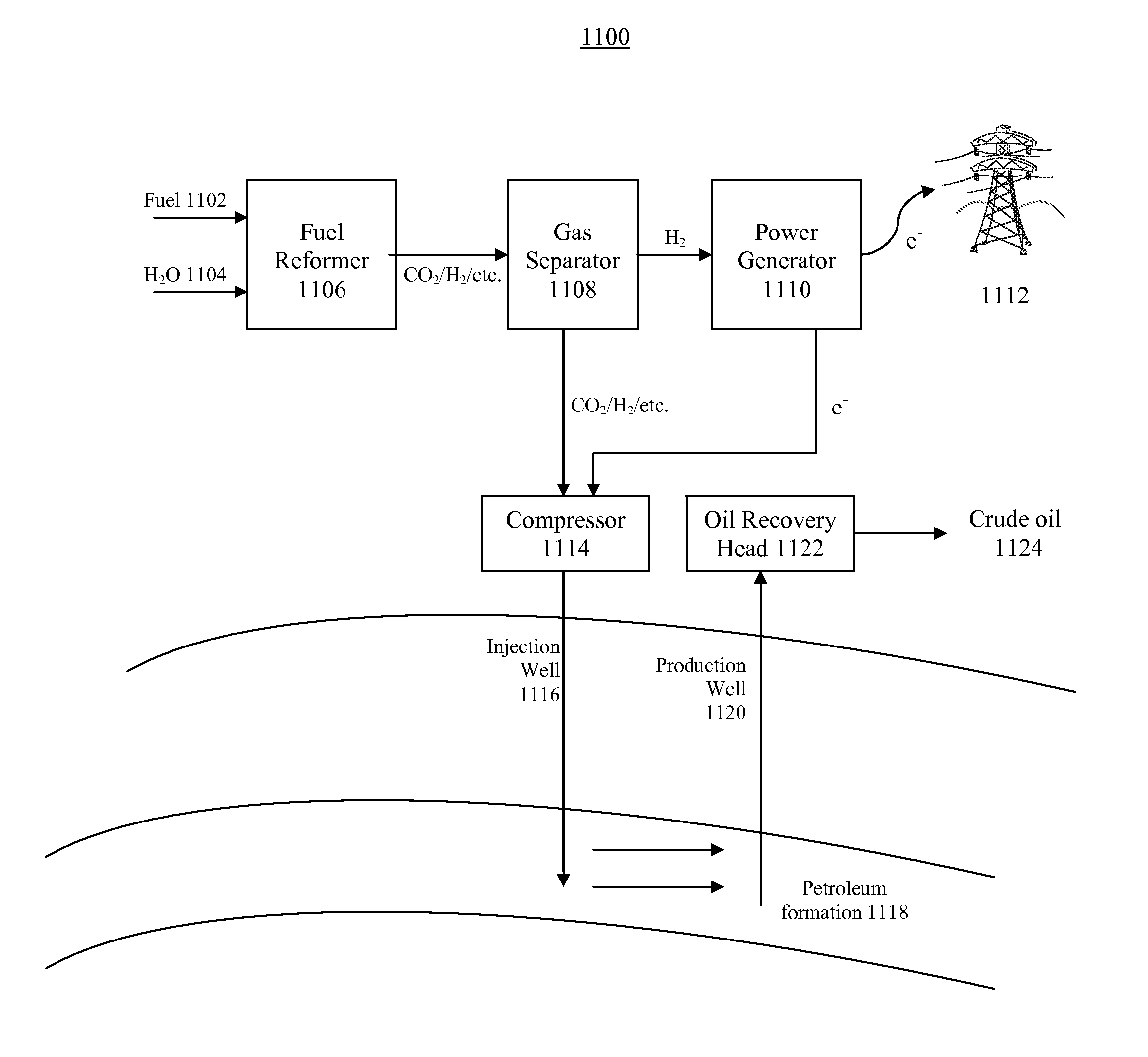
Systems and methods for generating in-situ carbon dioxide driver gas for use in enhanced oil recovery
InactiveUS8616294B2Drilling rodsOther gas emission reduction technologiesSteam reformingSuperheated steam
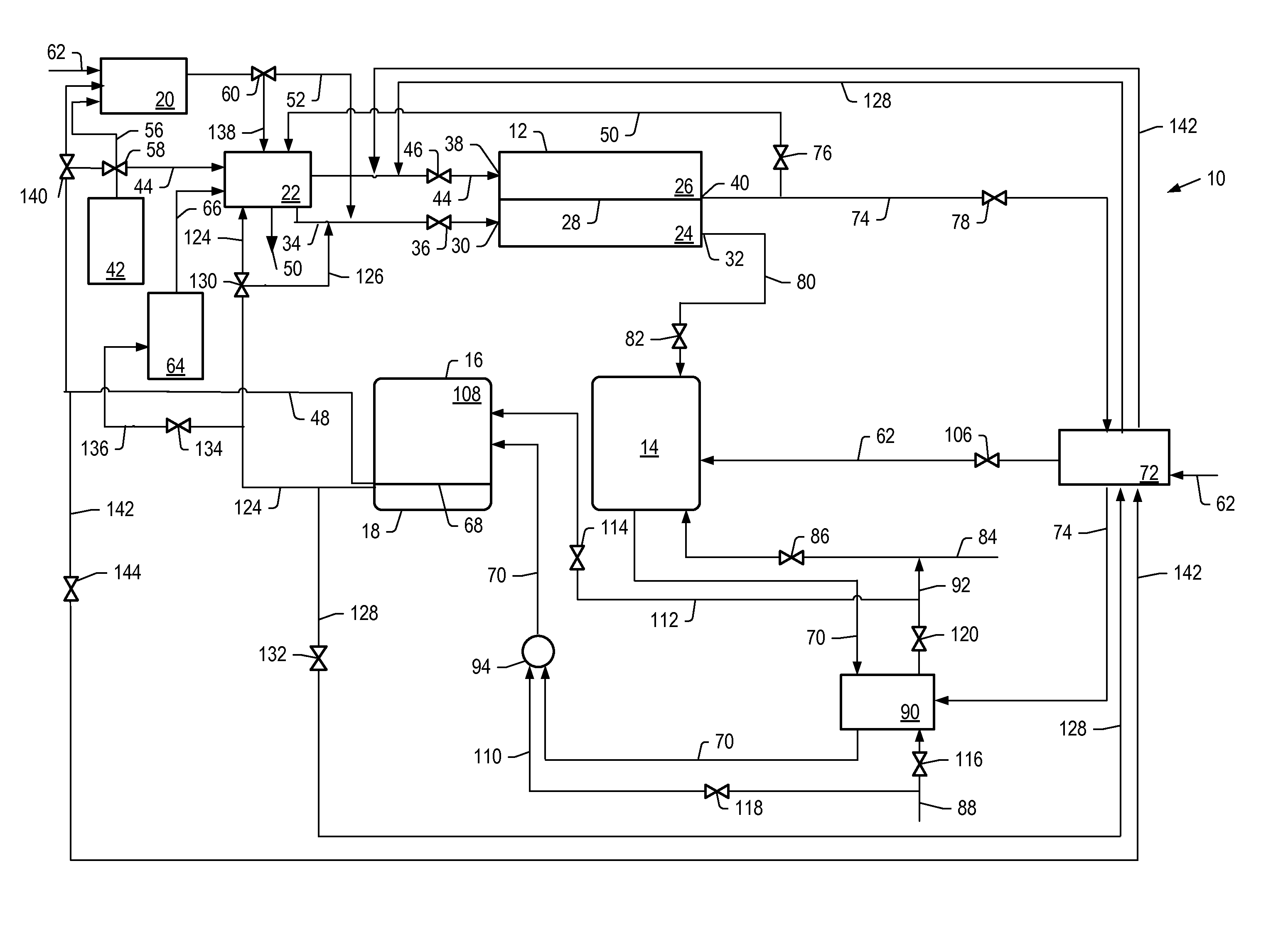
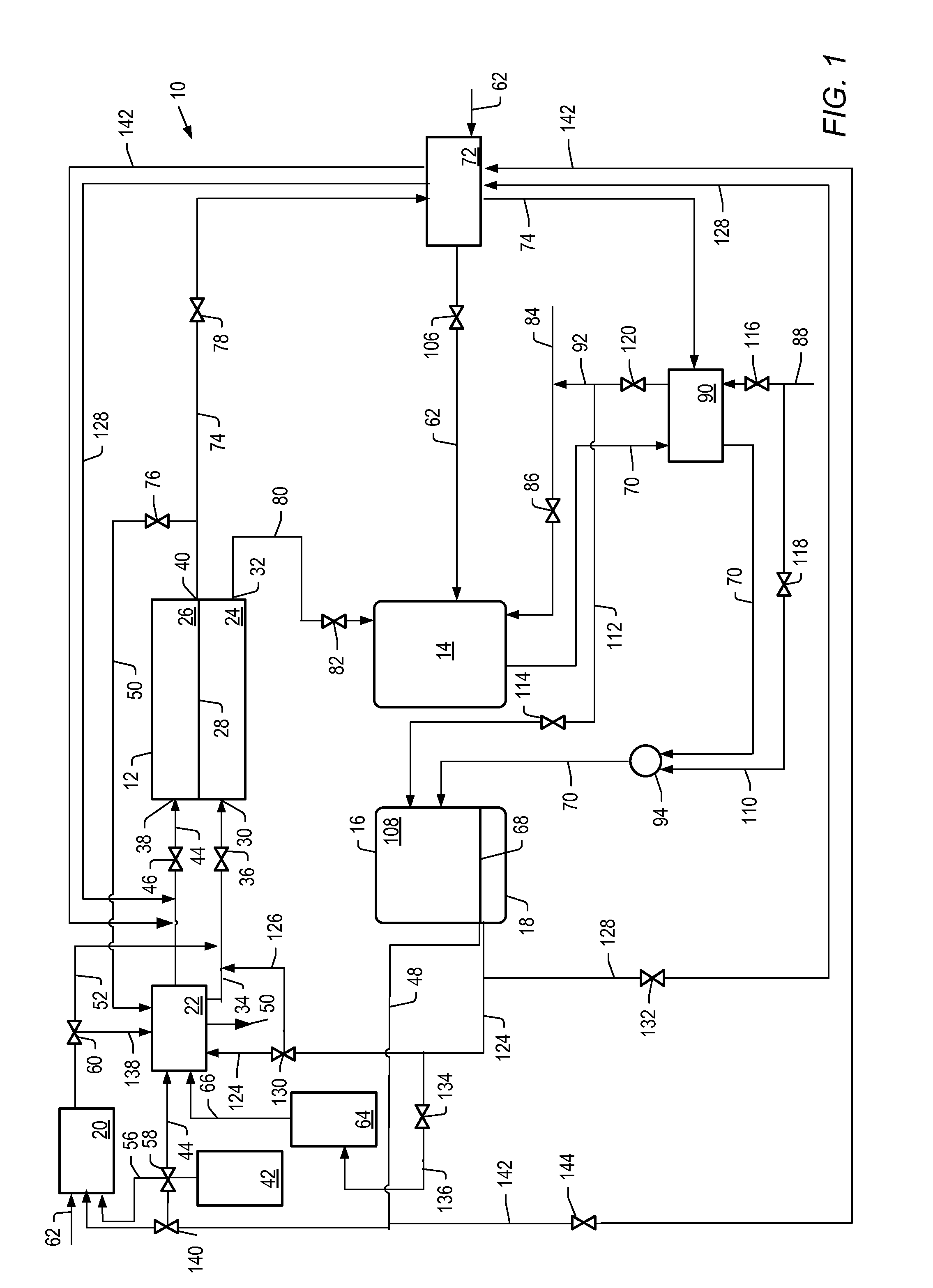
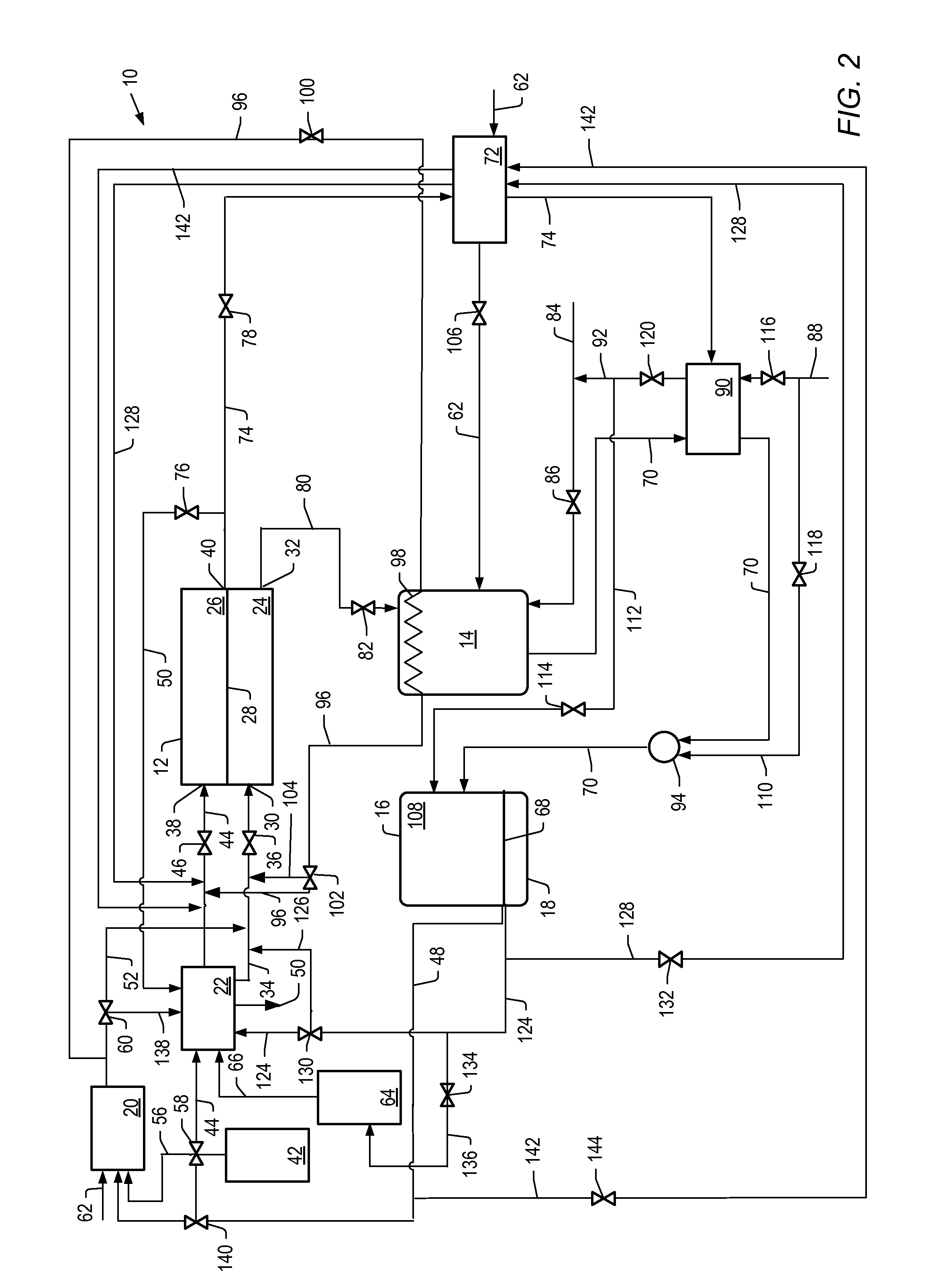
The present invention is an in-situ apparatus for generating carbon dioxide gas at an oil site for use in enhanced oil recovery (EOR). The apparatus includes a steam generator adapted to boil and superheat water to generate a source of superheated steam, as well as a source of essentially pure oxygen. The apparatus also includes a steam reformer adapted to react a carbonaceous material with the superheated steam and the pure oxygen, in an absence of air, to generate a driver gas comprising primarily carbon dioxide gas and hydrogen gas. A separator is adapted to separate at least a portion of the carbon dioxide gas from the rest of the driver gas to generate a carbon dioxide-rich driver gas and a hydrogen-rich fuel gas. A compressor is used for compressing the carbon dioxide-rich driver gas for use in enhanced oil recovery, and the compressed carbon dioxide-rich driver gas, with substantially no oxygen, is injected to a predetermined depth in order to enhance oil recovery at the oil site. Unlike traditional CO2-EOR, which requires large power plants stationed near metropolitan areas and expensive pipeline networks, the in-situ apparatus can be placed or constructed at the site of the oil field, while a portion of the carbonaceous material may be obtained from a site outside the oil field.
Owner:PIONEER ENERGY
Methanol manufacture using pressure swing reforming
ActiveUS7148261B2Easy to produceIncrease pressureOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionSteam reformingHydrogen
A process for producing methanol is described in which a hydrocarbon is steam reformed in a reforming zone, and during the reforming stage, of a cyclic steam reformer having a reforming stage and a regeneration stage, the steam reforming being conducted under conditions effective to produce a first effluent stream containing synthesis gas. Fuel and an oxygen-containing gas are combusted in the regeneration stage of the reformer so as to reheat the reforming zone to a temperature sufficient for the reforming stage and generate a flue gas. At least part of the first effluent stream is contacted with a methanol synthesis catalyst under conditions effective to convert synthesis gas to methanol and form a methanol-containing stream and a tail gas stream comprising unreacted carbon monoxide and hydrogen. At least part of the tail gas stream is recycled as fuel for the regeneration stage of the cyclic steam reformer.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Oxygen transport membrane system and method for transferring heat to catalytic/process reactors
A method and apparatus for producing heat used in a synthesis gas production process is provided. The disclosed method and apparatus include a plurality of tubular oxygen transport membrane elements adapted to separate oxygen from an oxygen containing stream contacting the retentate side of the membrane elements. The permeated oxygen is combusted with a hydrogen containing synthesis gas stream contacting the permeate side of the tubular oxygen transport membrane elements thereby generating a reaction product stream and radiant heat. The present method and apparatus also includes at least one catalytic reactor containing a catalyst to promote the steam reforming reaction wherein the catalytic reactor is surrounded by the plurality of tubular oxygen transport membrane elements. The view factor between the catalytic reactor and the plurality of tubular oxygen transport membrane elements radiating heat to the catalytic reactor is greater than or equal to 0.5.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Optimum integration of Fischer-Tropsch synthesis and syngas production
InactiveUS6696501B2High synthetic yieldImprove efficiencyHydrogenHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesSyngasSteam reforming
A method is described for conversion of natural gas or other fossil fuels to higher hydrocarbons, comprising the following steps: a) reaction of natural gas with steam and oxygenic gas in at least one reforming zone in order to produce a synthesis gas consisting primarily of hydrogen and CO, in addition to some carbon dioxide; b) passing said synthesis gas to a Fisher-Tropsch reactor in order to produce a crude synthesis stream consisting of lower hydrocarbons, water and non-converted synthesis gas; c) separation of said crude synthesis stream in a recovery zone, into a crude product stream mainly containing heavier hydrocarbons, a water stream and a tail gas stream mainly containing the remaining constituents; which is charaterized in that the method also comprises the following steps; d) stream reformation of at least part of the tail gas in a separate steam reformer; e) introduction of the reformed tail gas into the gas stream before this is led into the Fischer-Tropsch reactor.
Owner:STATOIL ASA PETRO SA (NO)
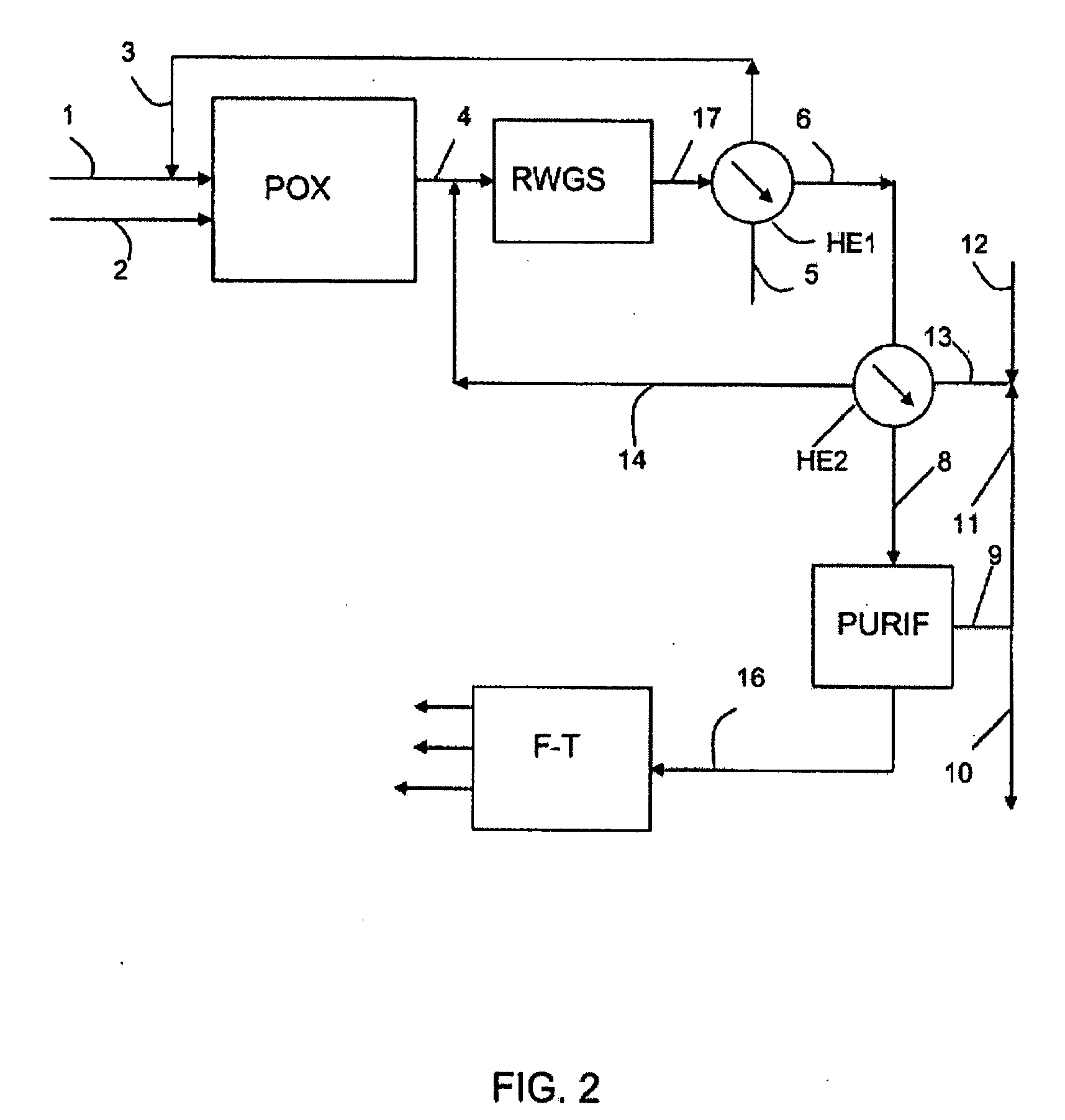
Process for the production of synthesis gas with conversion of CO2 into hydrogen
ActiveUS20090012188A1High carbon yieldImproved energy integrationCombustible gas chemical modificationProductsSteam reformingPartial oxidation
Process for the production of liquid hydrocarbons from a feedstock that comprises at least one elementary feedstock from the group of biomass, coal, lignite, petroleum residues, methane, and natural gas, comprising: at least one stage a) for gasification of the feedstock by partial oxidation and / or steam reforming to produce a synthesis gas SG; a stage b) for separating CO2 from SG and a portion of the effluent of the subsequent stage c); the mixing of a portion of the CO2 that is separated with a gas of an H2 / CO ratio of more than 3; a stage c) for partial conversion with hydrogen, thermal or thermocatalytic, of the CO2 that is present in said first mixture according to the reaction: CO2+H2→CO+H2O in a specific reaction zone that is separated from said gasification zone or zones; a stage d) for Fisher-Tropsch synthesis on a synthesis gas that comprises at least a portion of SG and at least a portion of the CO that is produced by the conversion of CO2 into hydrogen.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
System and method for producing synthesis gas
ActiveUS20070124997A1Hydrogen separation using solid contactCatalyst regeneration/reactivationSteam reformingFluidized bed
A system for producing synthesis gas includes a regeneration zone. The regeneration zone includes a first fluidized bed configured to receive an oxidant for producing a regenerated oxygen transfer material. The system further includes a mixed reforming zone comprising a second fluidized bed configured to receive a first fuel and the regenerated oxygen transfer material to produce a first reformate stream and a steam reforming zone comprising a third fluidized bed configured to receive the first reformate stream, a second fuel and steam to produce the synthesis gas. The regeneration zone, mixed reforming zone and steam-reforming zone are in fluid communication with each other.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
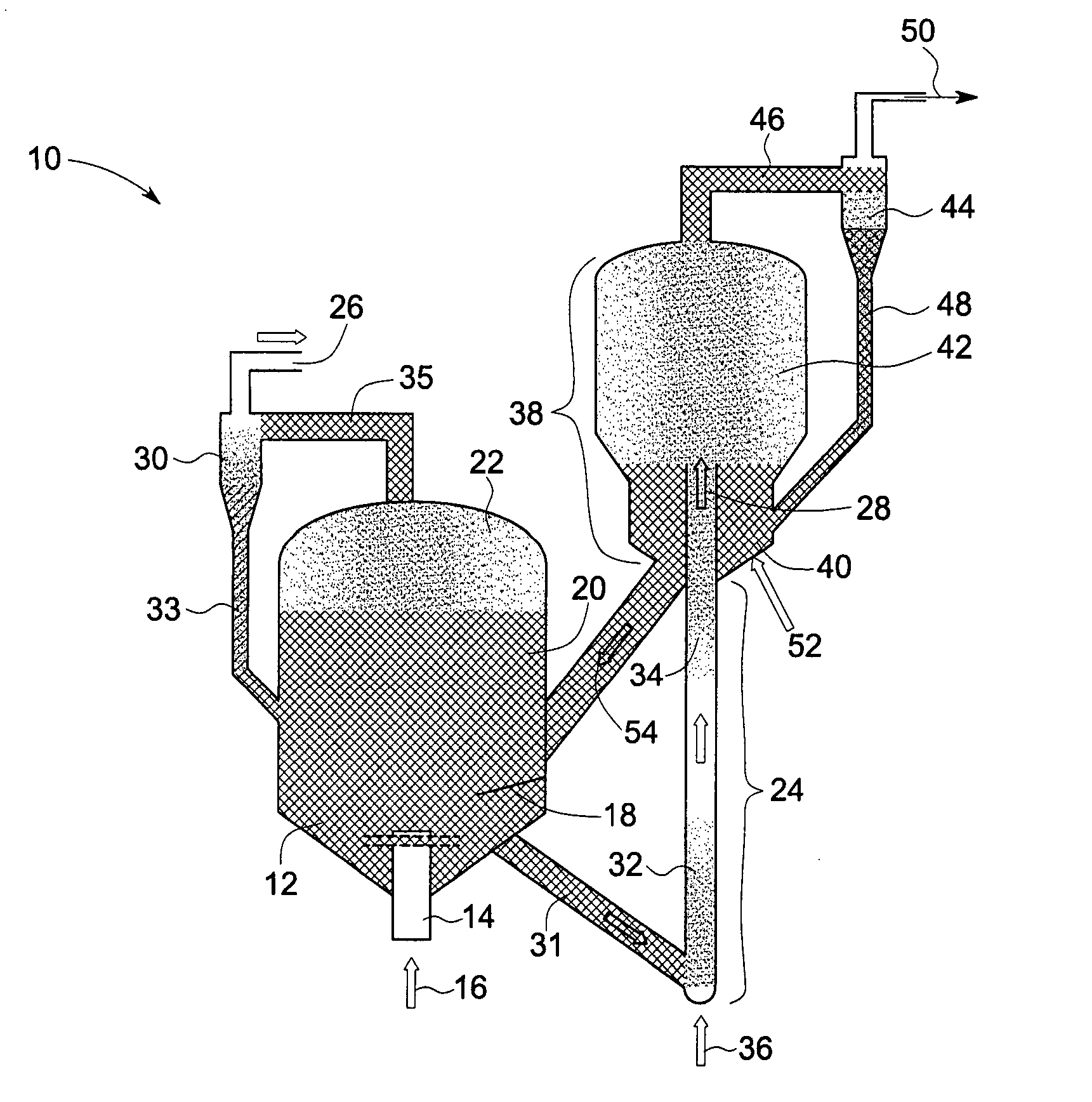
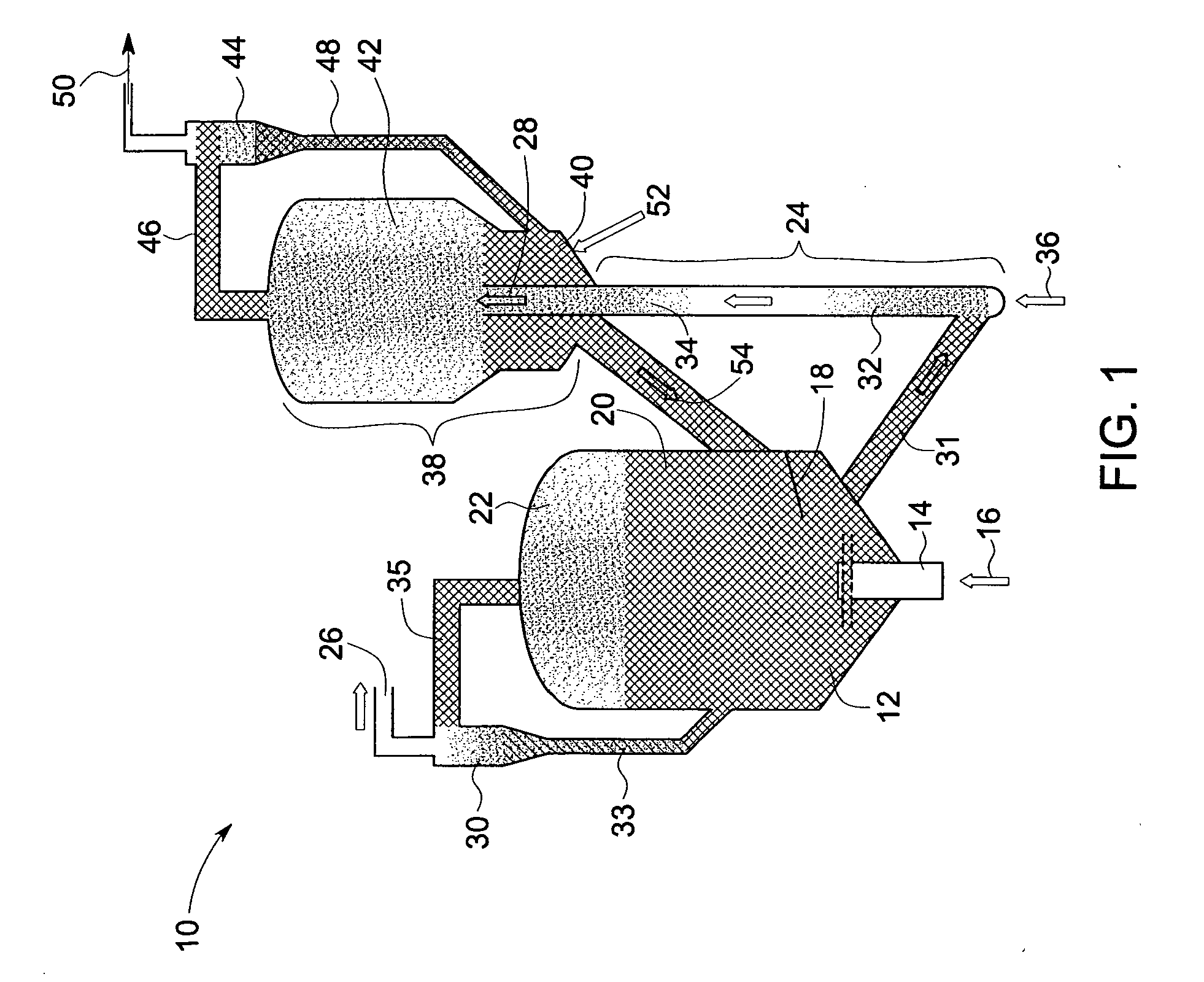
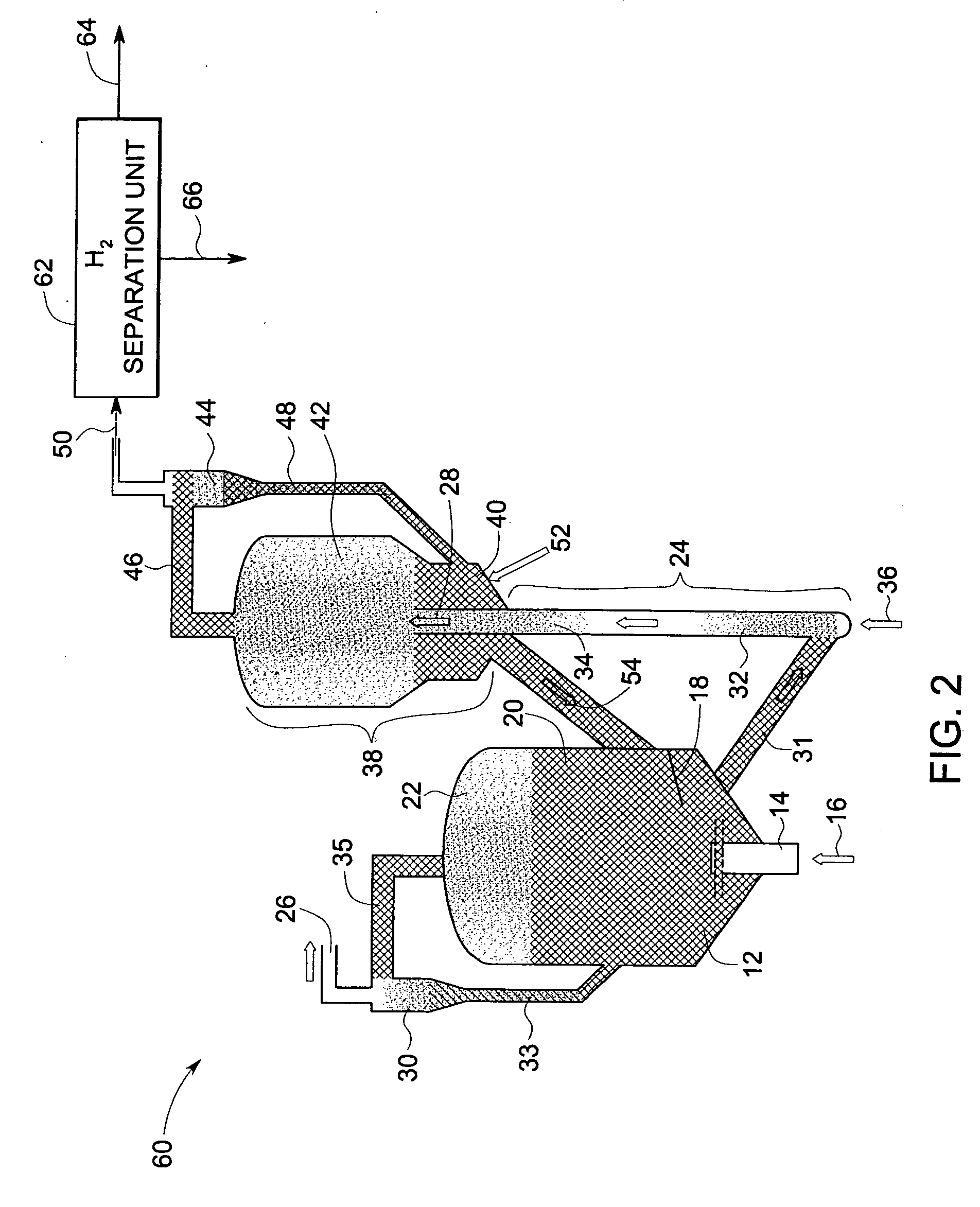
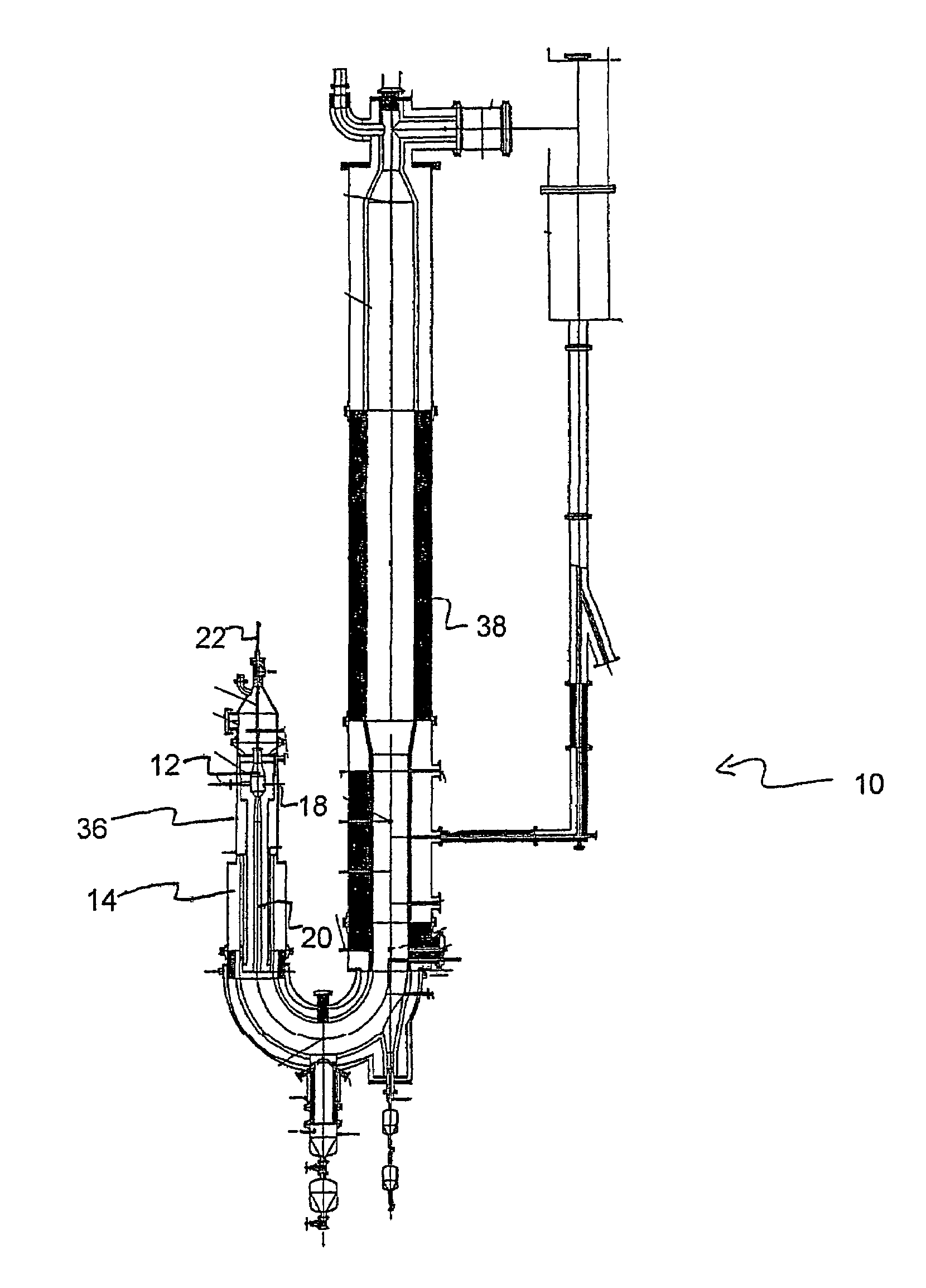
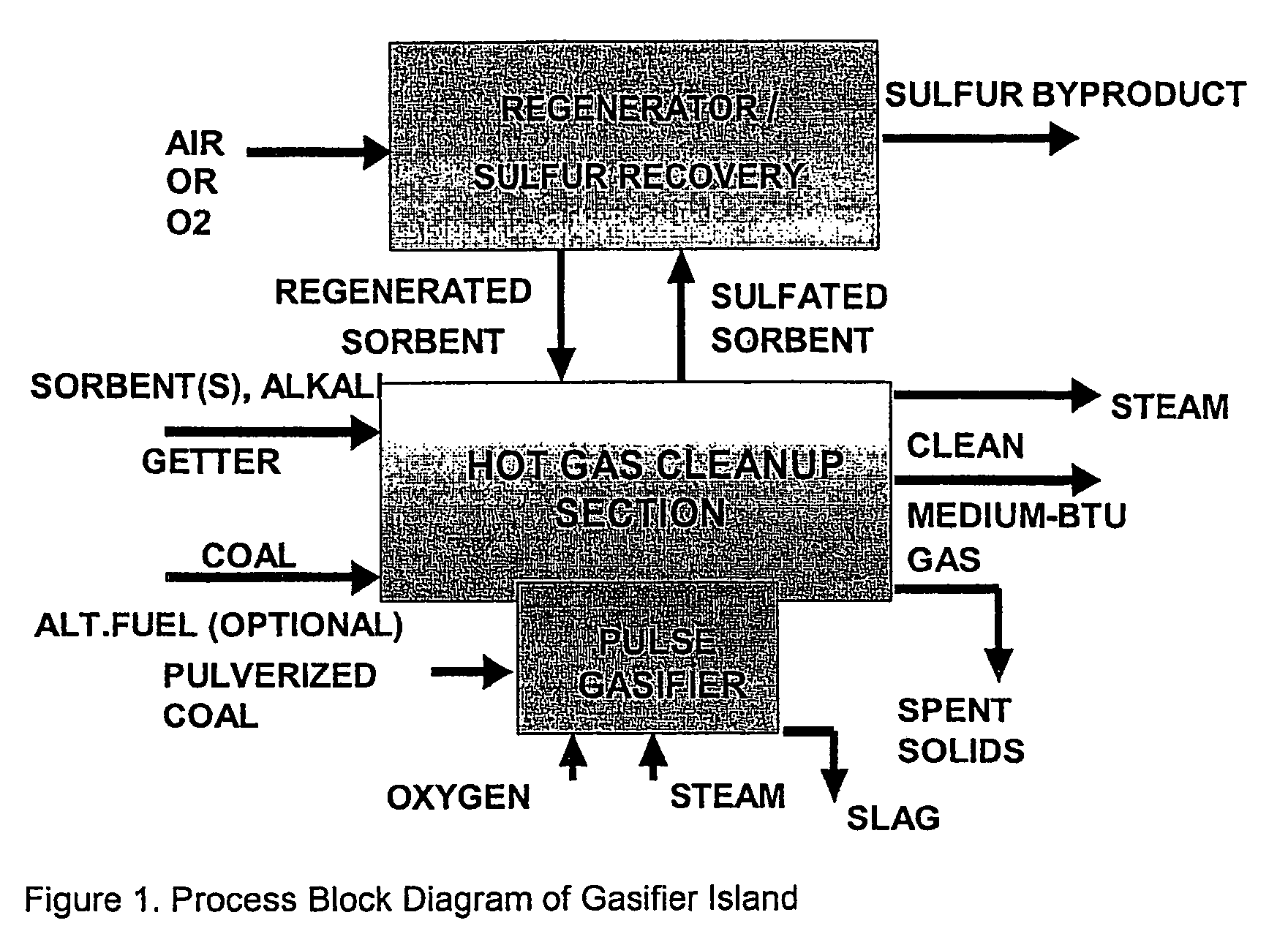
Pulse gasification and hot gas cleanup apparatus and process
InactiveUS6997118B2Easy to useConducive to agglomerationAuxillary pretreatmentGasifier mechanical detailsSteam reformingElectricity
A gasifier system and process comprises a pulse combustion device in communication with a fluid channel for producing a gas stream having heat or fuel value. The pulse combustion device is operated under sub-stoichiometric conditions such that combustion and steam reforming both occur in the fluid channel. The pulse combustion device also produces a pulsating combustion product stream and an acoustic pressure wave. The acoustic pressure wave serves to cause agglomeration of particles contained within the combustion stream for easy removal. In one embodiment, a sulfur capturing agent is injected into the fluid channel for not only removing sulfur from the combustion product stream but for also facilitating particle agglomeration. Ultimately, a gas stream containing hydrogen is produced that may be used in various processes, such as in the production of electricity.
Owner:MFG & TECH CONVERSION INT
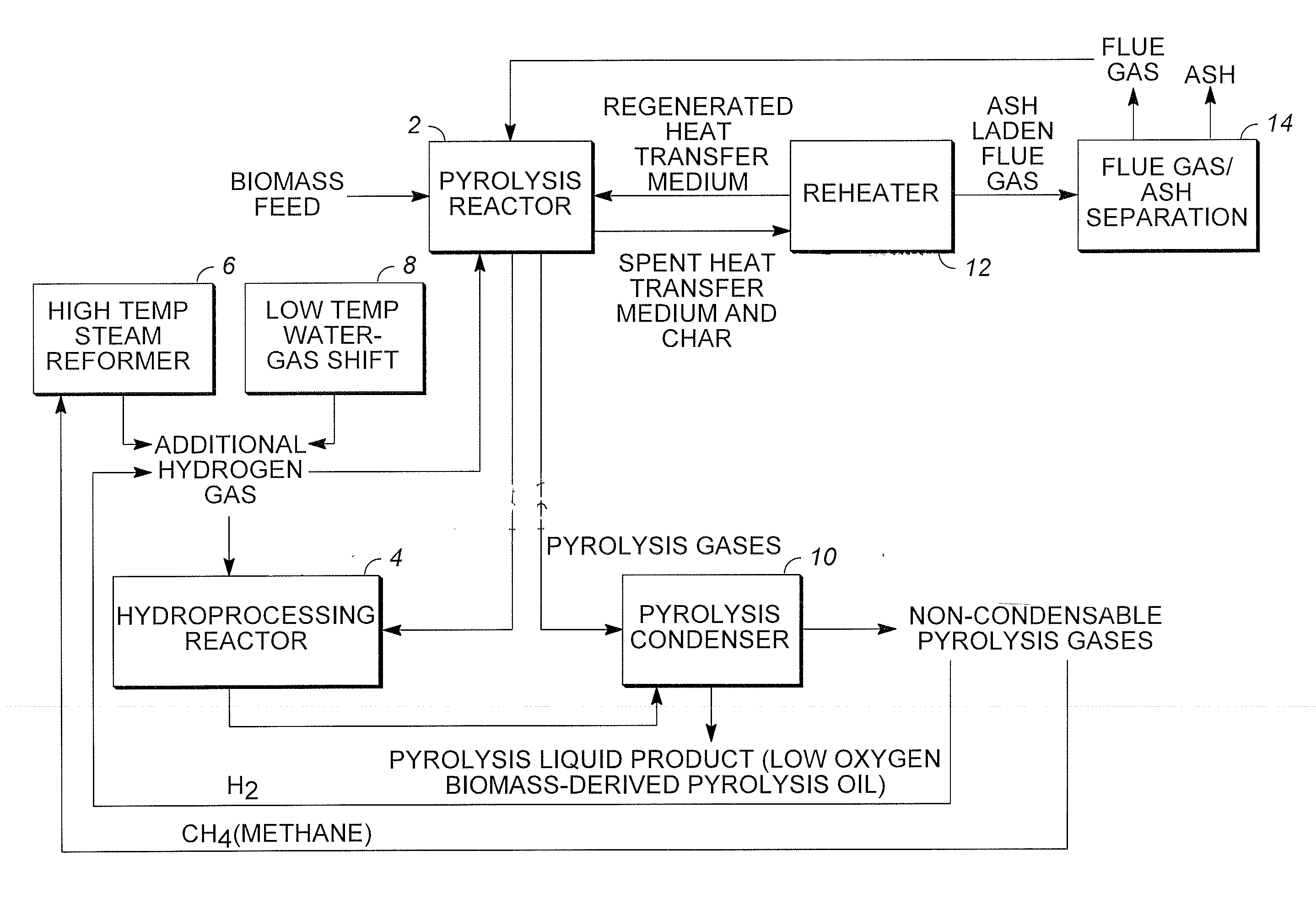
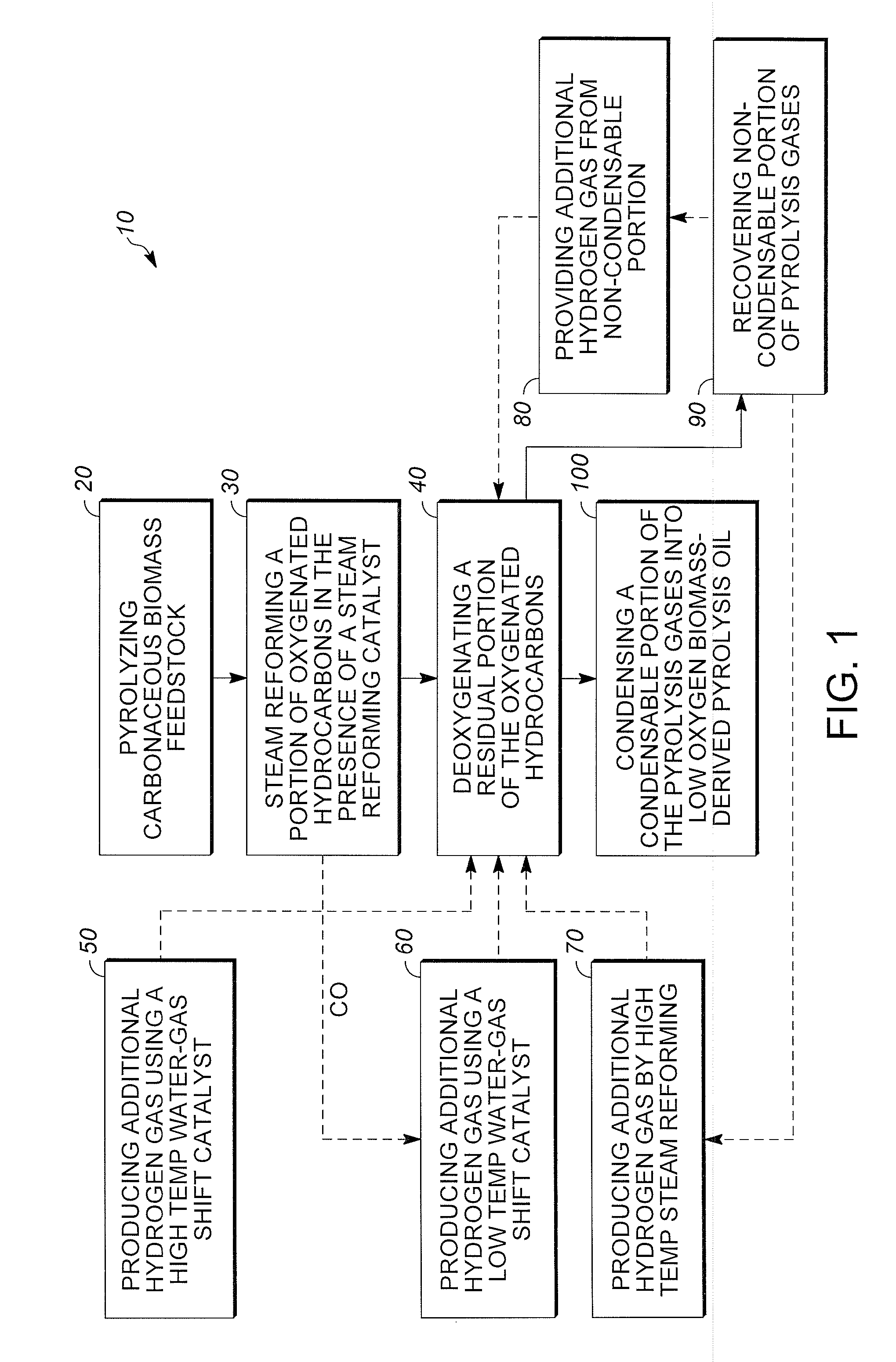
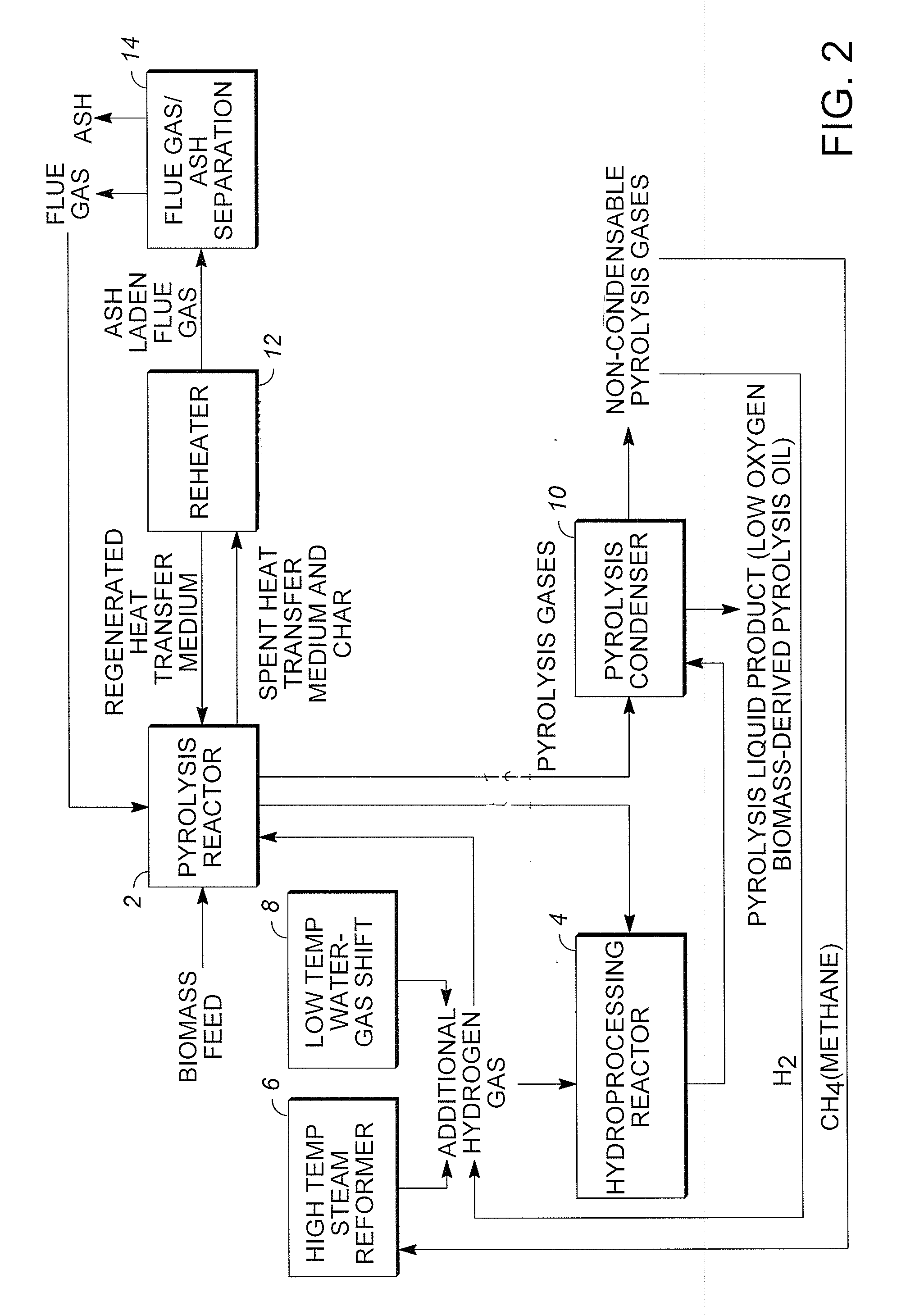
Low oxygen biomass-derived pyrolysis oils and methods for producing the same
InactiveUS20110201854A1Direct heating destructive distillationBiofuelsSteam reformingPartial oxidation
Methods are provided for producing low oxygen biomass-derived pyrolysis oil from carbonaceous biomass feedstock. The carbonaceous biomass feedstock is pyrolyzed in the presence of a steam reforming catalyst to produce char and pyrolysis gases. During pyrolysis, a portion of the oxygenated hydrocarbons in the pyrolysis gases is converted into hydrocarbons by steam reforming also yielding carbon oxides and hydrogen gas. The hydrogen gas at least partially deoxygenates a residual portion of the oxygenated hydrocarbons. Additional hydrogen gas may also be produced by water-gas shift reactions to deoxygenate the residual portion of the oxygenated hydrocarbons in the pyrolysis gases. Deoxygenation may occur in the presence of a hydroprocessing catalyst. A condensable portion of the pyrolysis gases is condensed to form low oxygen biomass-derived pyrolysis oil.
Owner:UOP LLC
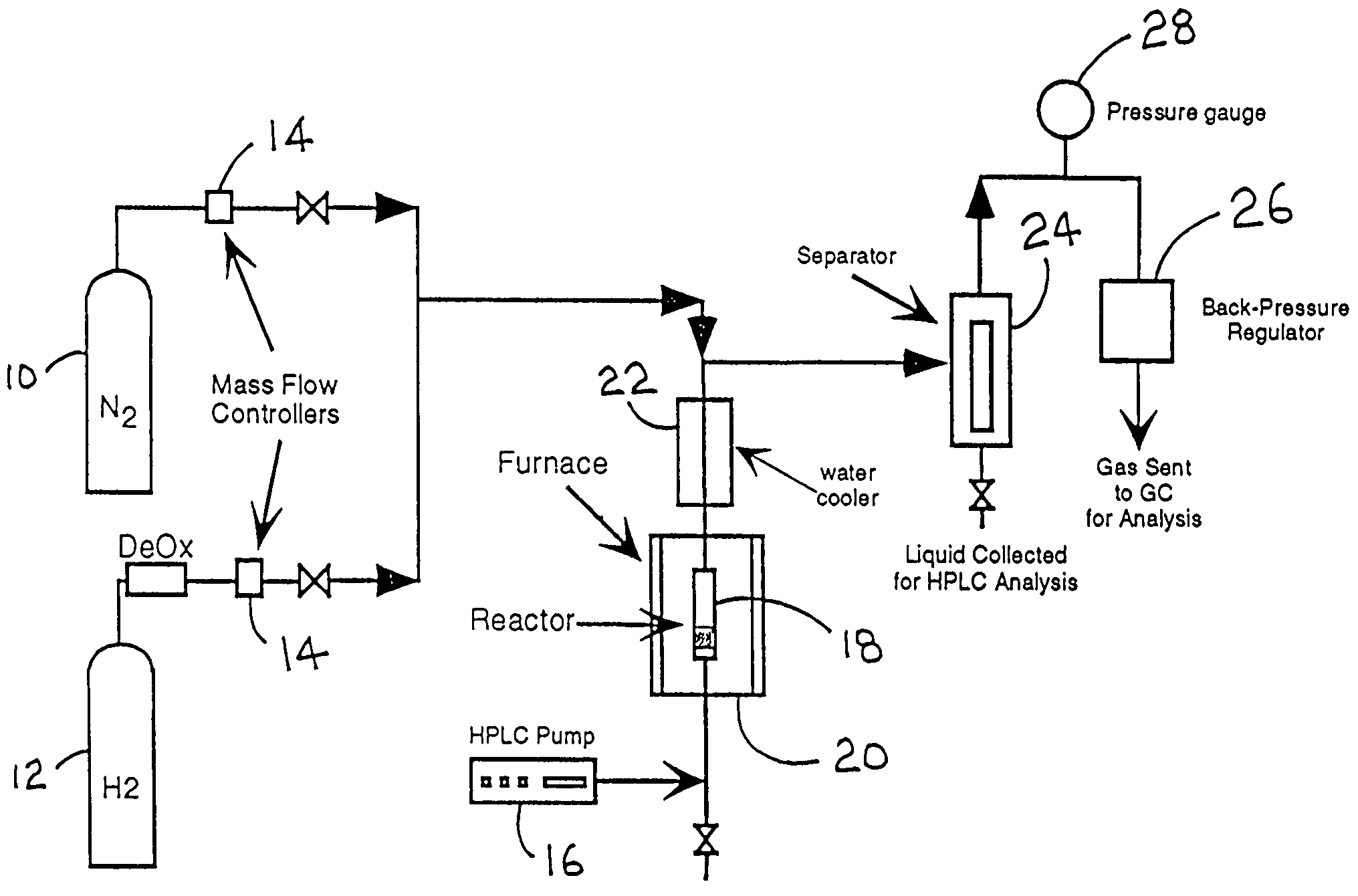
Method and apparatus for obtaining enhanced production rate of thermal chemical reactions
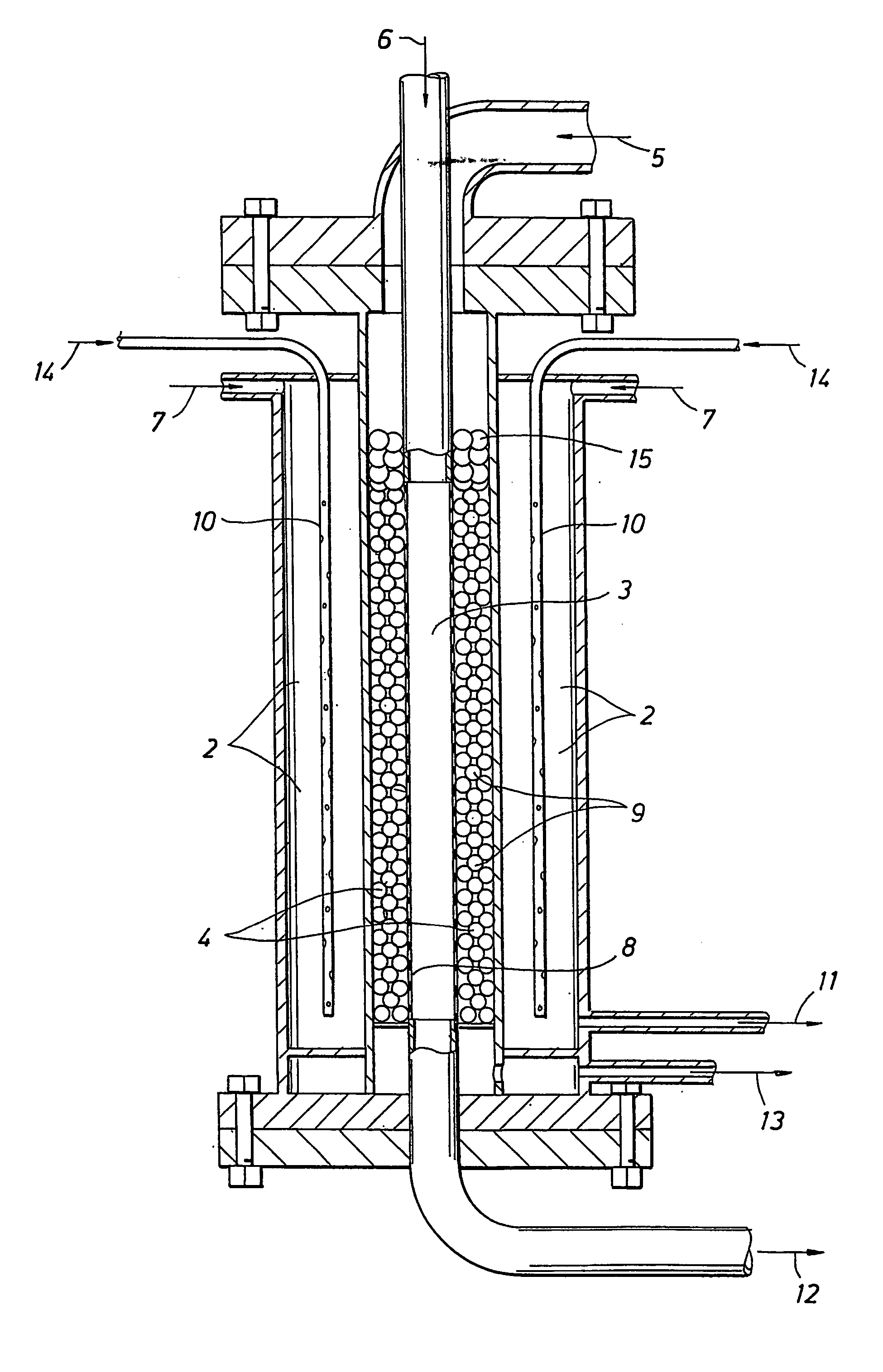
InactiveUS7045114B2Reduce formationReaction is slowOrganic chemistry methodsChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsSteam reformingChemical reaction
Reactors and processes are disclosed that can utilize high heat fluxes to obtain fast, steady-state reaction rates. Porous catalysts used in conjunction with microchannel reactors to obtain high rates of heat transfer are also disclosed. Reactors and processes that utilize short contact times, high heat flux and low pressure drop are described. Improved methods of steam reforming are also provided.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Chemical microreactor and method thereof
InactiveUS6960235B2Physical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen separationMicroreactorSteam reforming
A chemical microreactor suitable for generation of hydrogen fuel from liquid sources such as ammonia, methanol, and butane through steam reforming processes when mixed with an appropriate amount of water contains capillary microchannels with integrated resistive heaters to facilitate the occurrence of catalytic steam reforming reactions. One such microreactor employs a packed catalyst capillary microchannel and at least one porous membrane. Another employs a porous membrane with a large surface area or a porous membrane support structure containing a plurality of porous membranes having a large surface area in the aggregate, i.e., greater than about 1 m2 / cm3. The packed catalyst capillary microchannels, porous membranes and porous membrane support structures may be formed by a variety of methods.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Low-temperature hydrogen production from oxygenated hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20050207971A1Reduce riskHigh energy costHydrogen productionHydrogen/synthetic gas productionAlkaneSteam reforming
Disclosed is a method of producing hydrogen from oxygenated hydrocarbon reactants, such as methanol, glycerol, sugars (e.g. glucose and xylose), or sugar alcohols (e.g. sorbitol). The method takes place in the condensed liquid phase. The method includes the steps of reacting water and a water-soluble oxygenated hydrocarbon in the presence of a metal-containing catalyst. The catalyst contains a metal selected from the group consisting of Group VIIIB transitional metals, alloys thereof, and mixtures thereof. The disclosed method can be run at lower temperatures than those used in the conventional steam reforming of alkanes.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
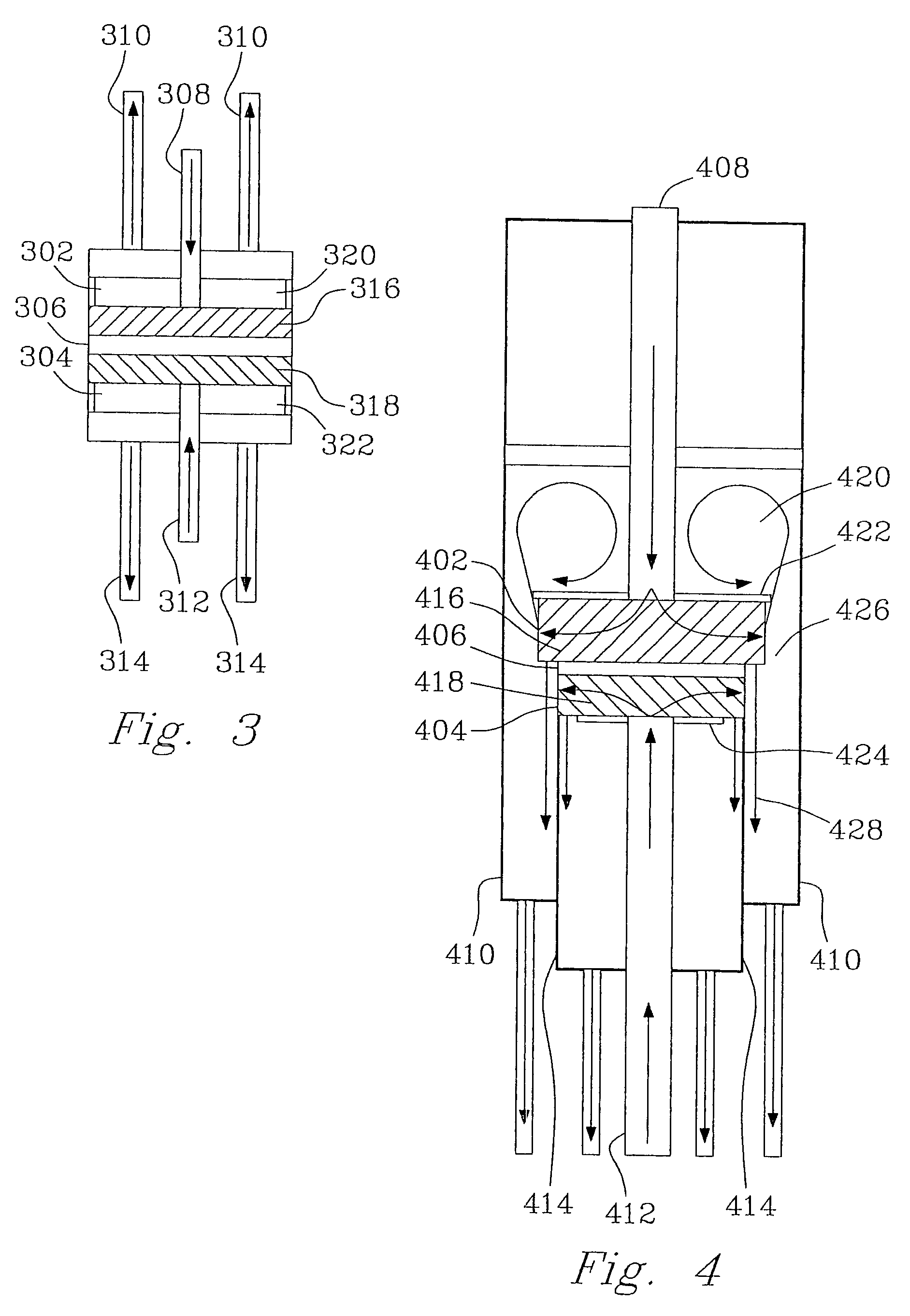
Microcombustors, microreformers, and methods for combusting and for reforming fluids
InactiveUS7077643B2Desirable performance capabilitySmall sizeHydrogenFurnace componentsSteam reformingCombustor
The present invention provides microcombustors, microreformers, and methods of steam reforming alcohols over a catalyst. The microcombustors can be manufactured with a very small size and can operate at very low temperature. Surprisingly superior results and properties obtained in methods of the present invention are also described.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Methods and apparatus for producing syngas and alcohols
The present invention features methods and apparatus for the pyrolysis or torrefaction of a carbon-containing feedstock before it is converted to syngas. In some embodiments, biomass is first pretreated by torrefaction and / or pyrolysis, followed by devolatilization and / or steam reforming to produce syngas. Various mixtures of such pretreated biomass, combined with fresh biomass, can be employed to produce syngas. The syngas can be converted to alcohols, such as ethanol, or to other products.
Owner:RANGE FUELS INC
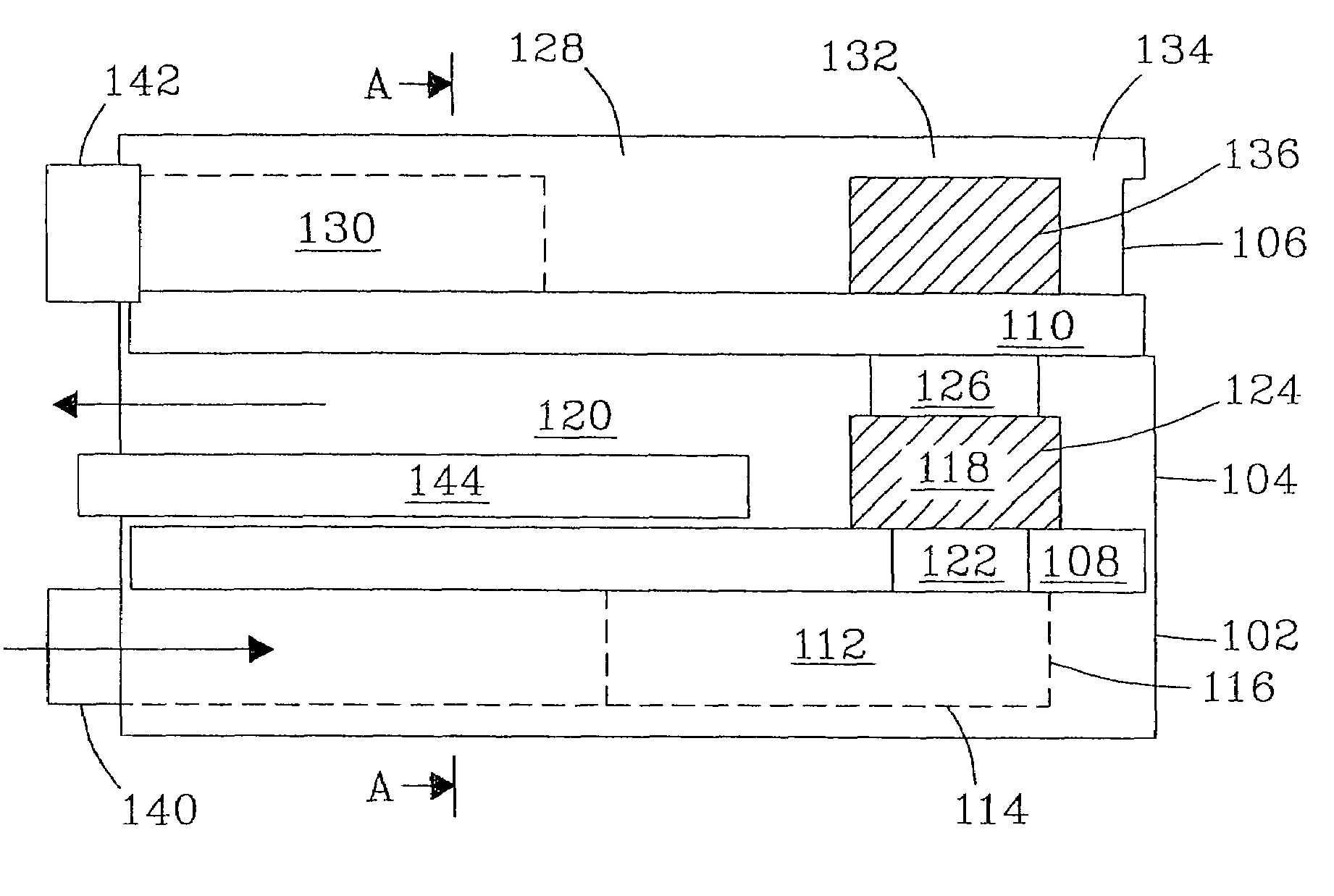
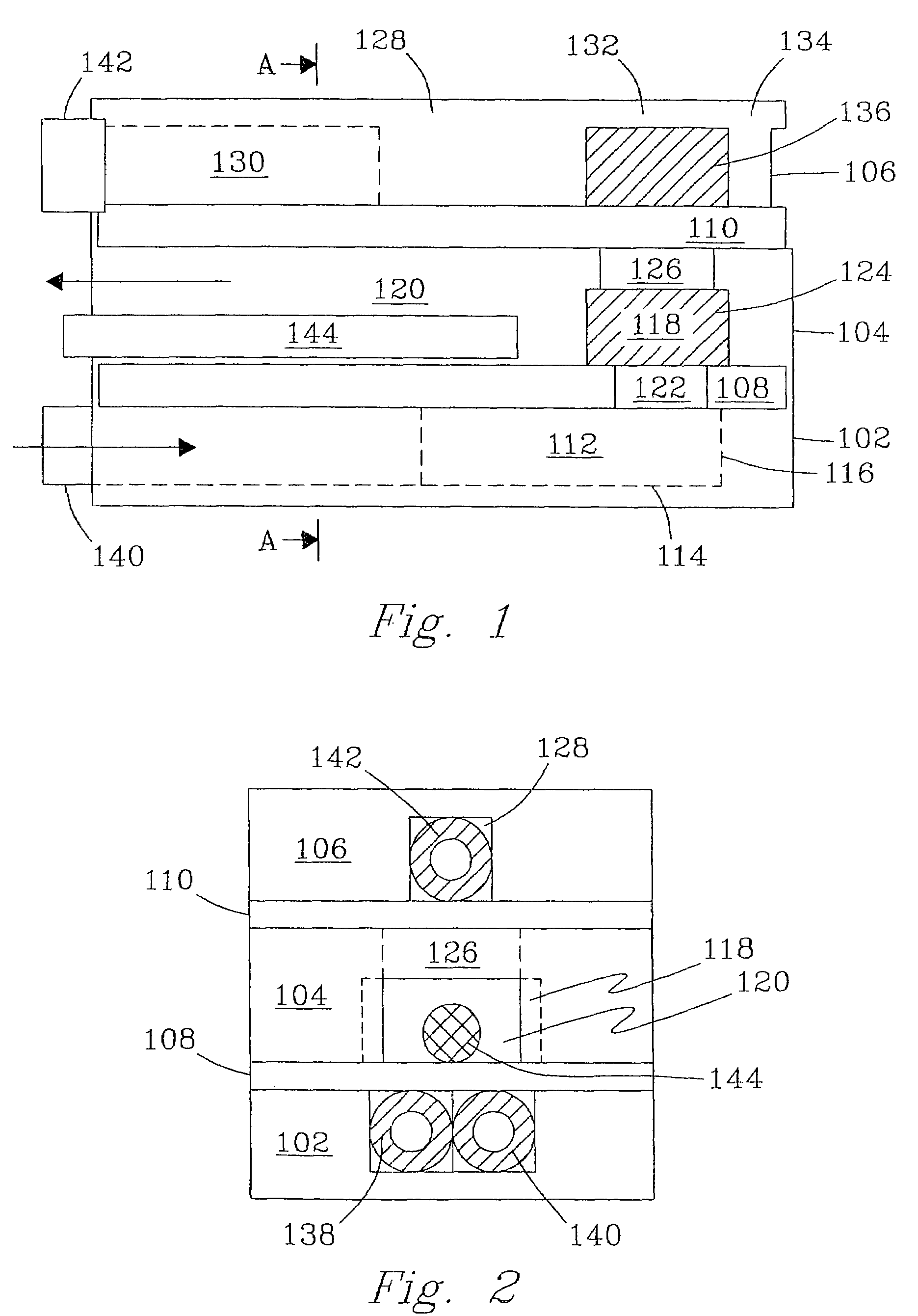
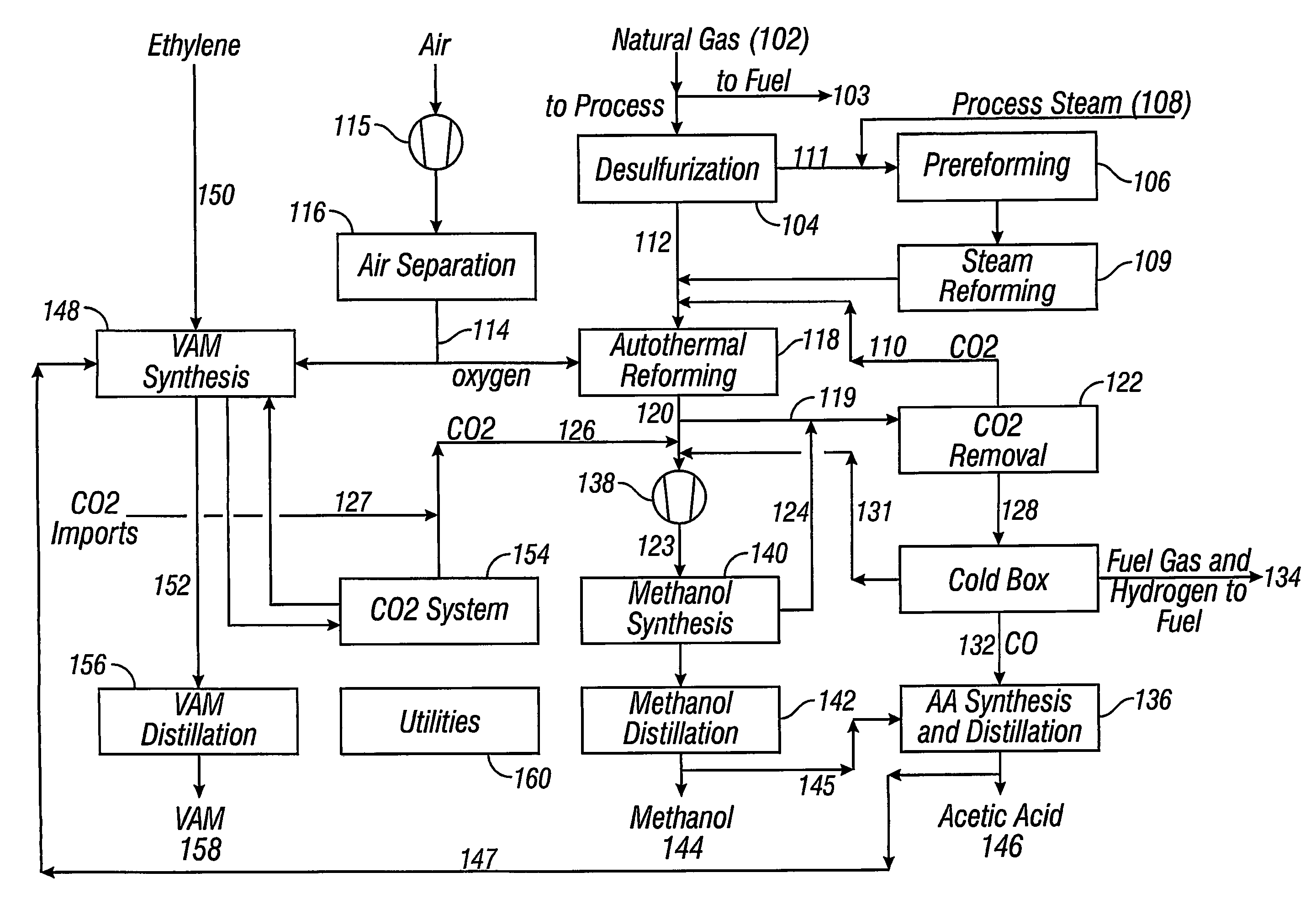
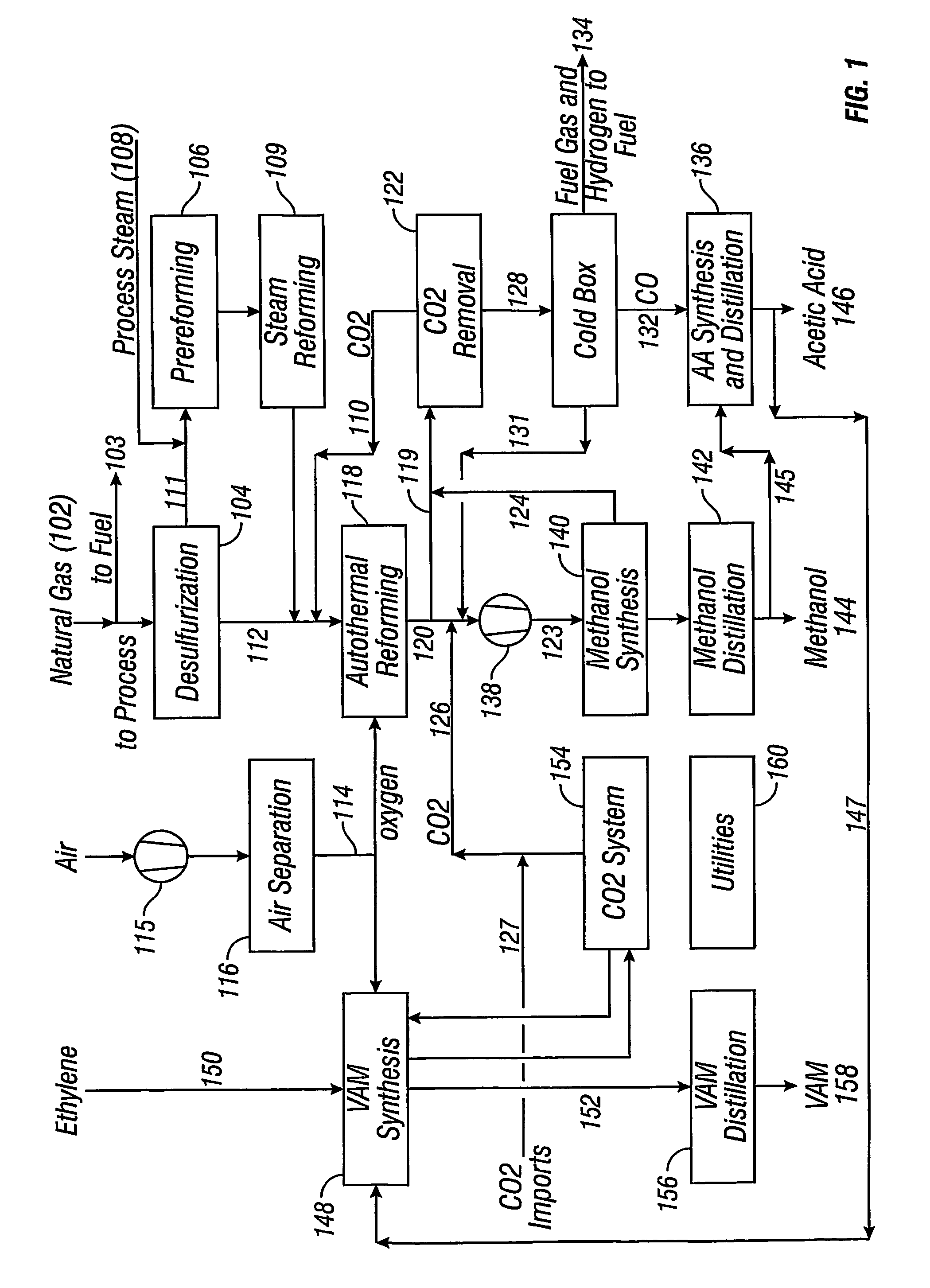
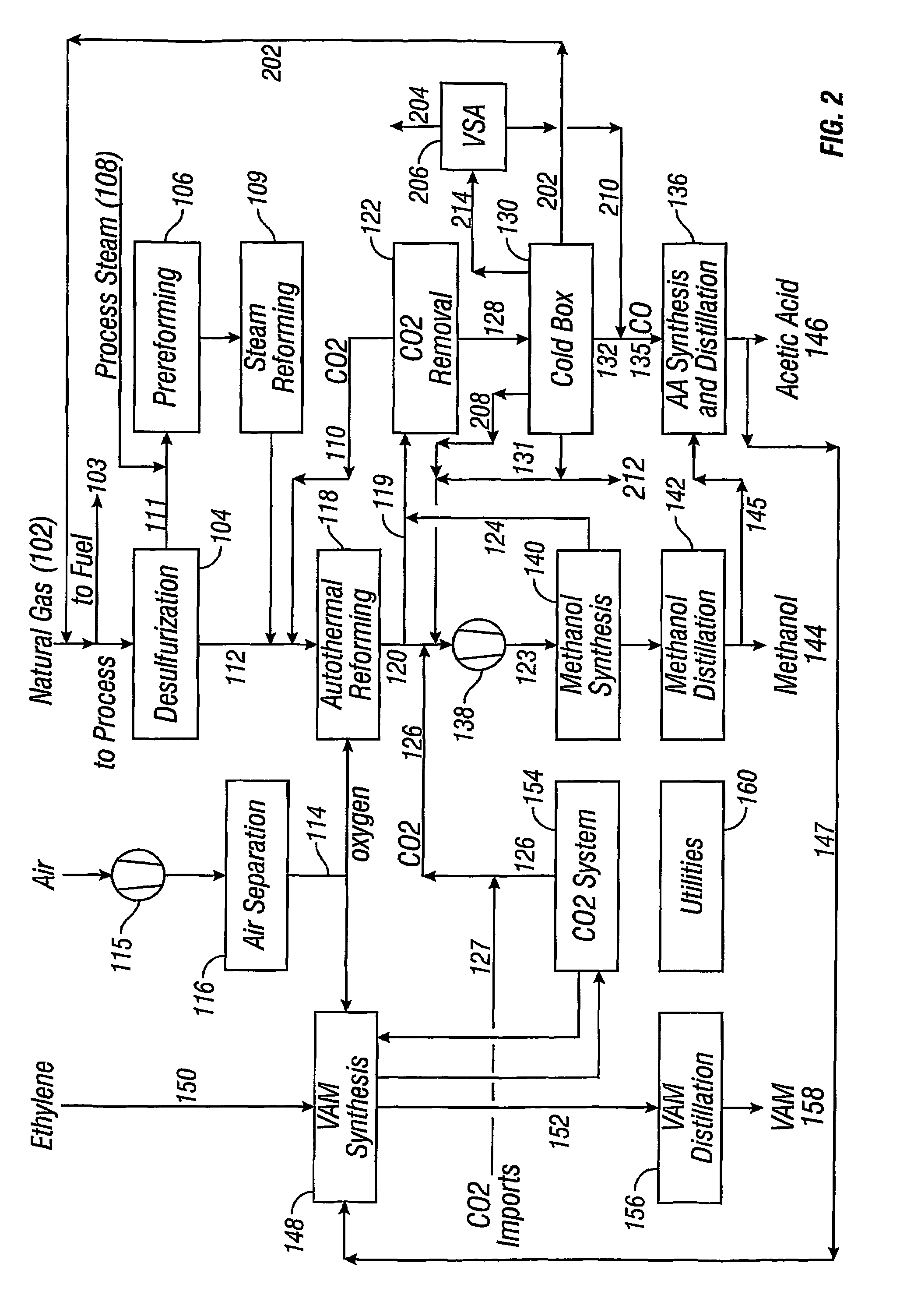
Integrated process for acetic acid and methanol
InactiveUS7470811B2Improve matchIncrease productionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationSteam reformingCo2 removal
Owner:ACETEX
Systems and processes for operating fuel cell systems
The present invention is directed to systems and processes of operating molten carbonate fuel cell systems. A process for operating the molten carbonate fuel cell includes providing a hydrogen-containing stream comprising molecular hydrogen from a high temperature hydrogen-separation device to a molten carbonate fuel cell, wherein the high temperature hydrogen-separation device comprises one or more high temperature hydrogen-separating membranes; mixing at least a portion of hydrocarbons to be provided to, or provided to, a first reformer with anode exhaust from the molten carbonate fuel cell; at least partially reforming some of the hydrocarbons in the first reformer to produce a steam reforming feed; and providing the steam reforming feed to a second reformer, wherein the second reformer comprises the high temperature hydrogen-separation device or the second reformer is operatively coupled to the high temperature hydrogen-separation device, and the high temperature hydrogen-separation device is configured to produce at least a portion of the stream comprising molecular hydrogen provided to the molten carbonate fuel cell.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com