Patents
Literature
3159results about "Chemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
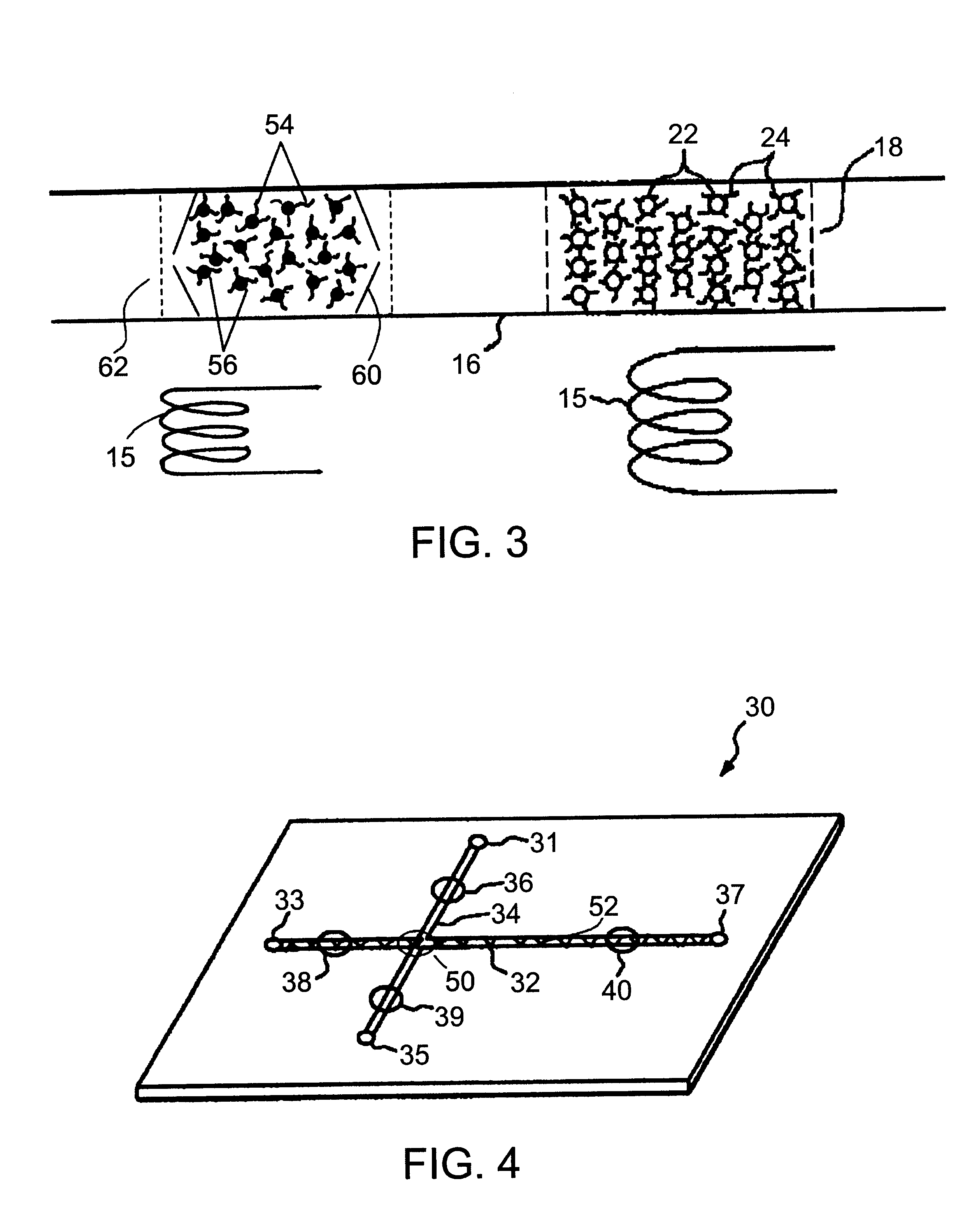
Microfluidic devices and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20080014589A1Eliminates surface wettingDielectrophoresisLiquid separation by electricityComputer moduleBiomedical engineering
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Microfluidic devices
InactiveUS20080003142A1Quickly and effectively and inexpensivelyDielectrophoresisHeating or cooling apparatusEngineering
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Non-planar microstructures for manipulation of fluid samples
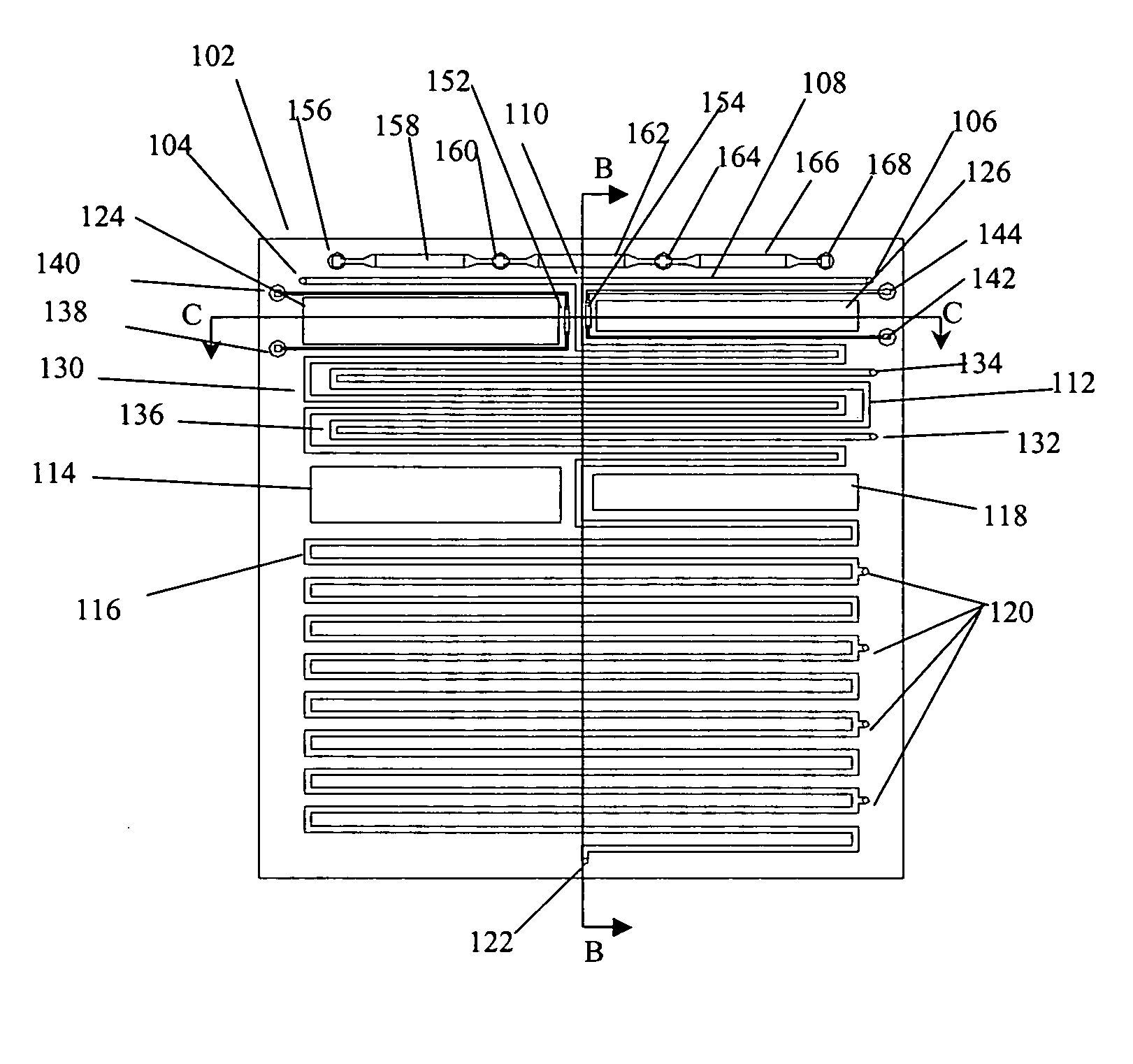
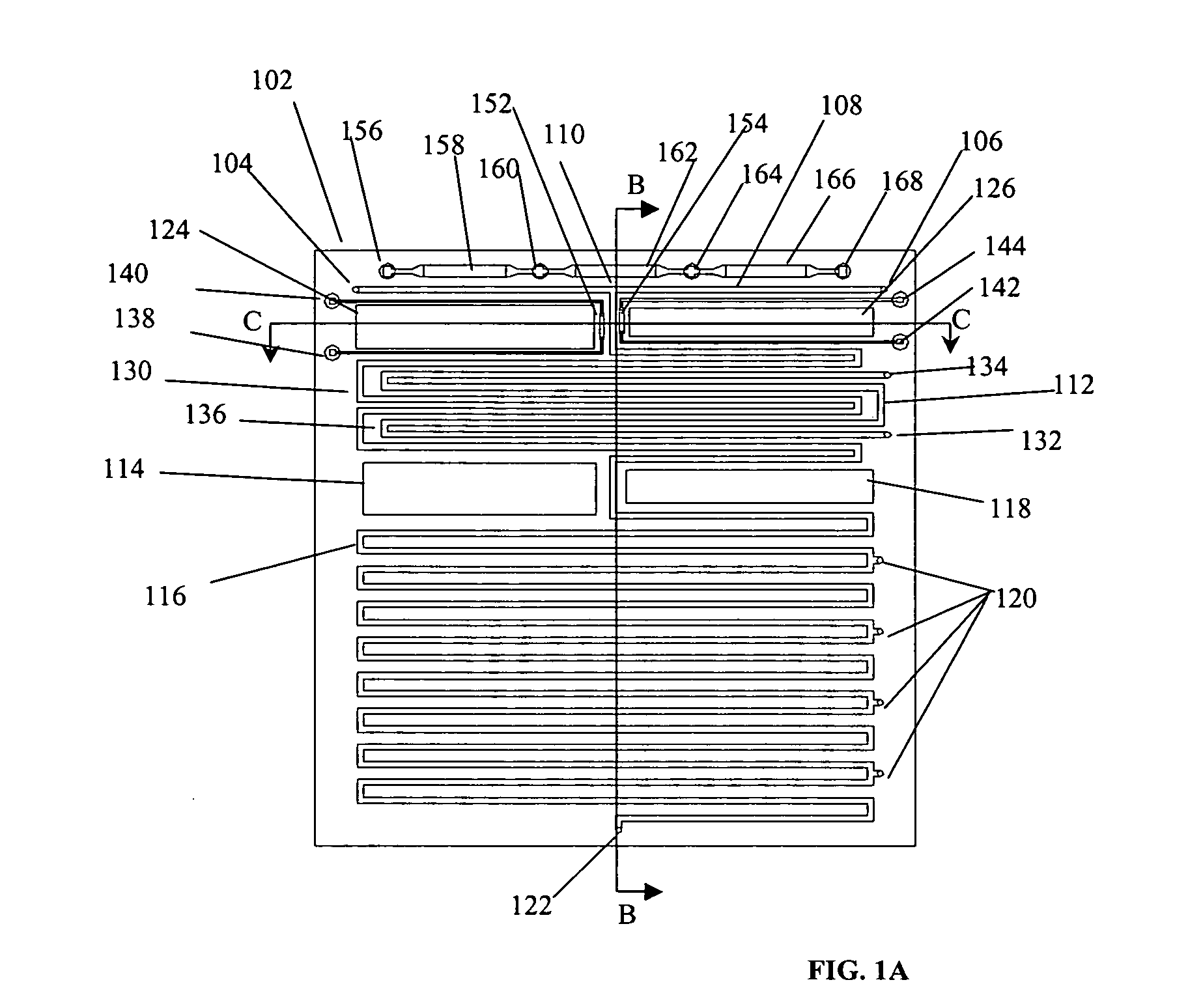
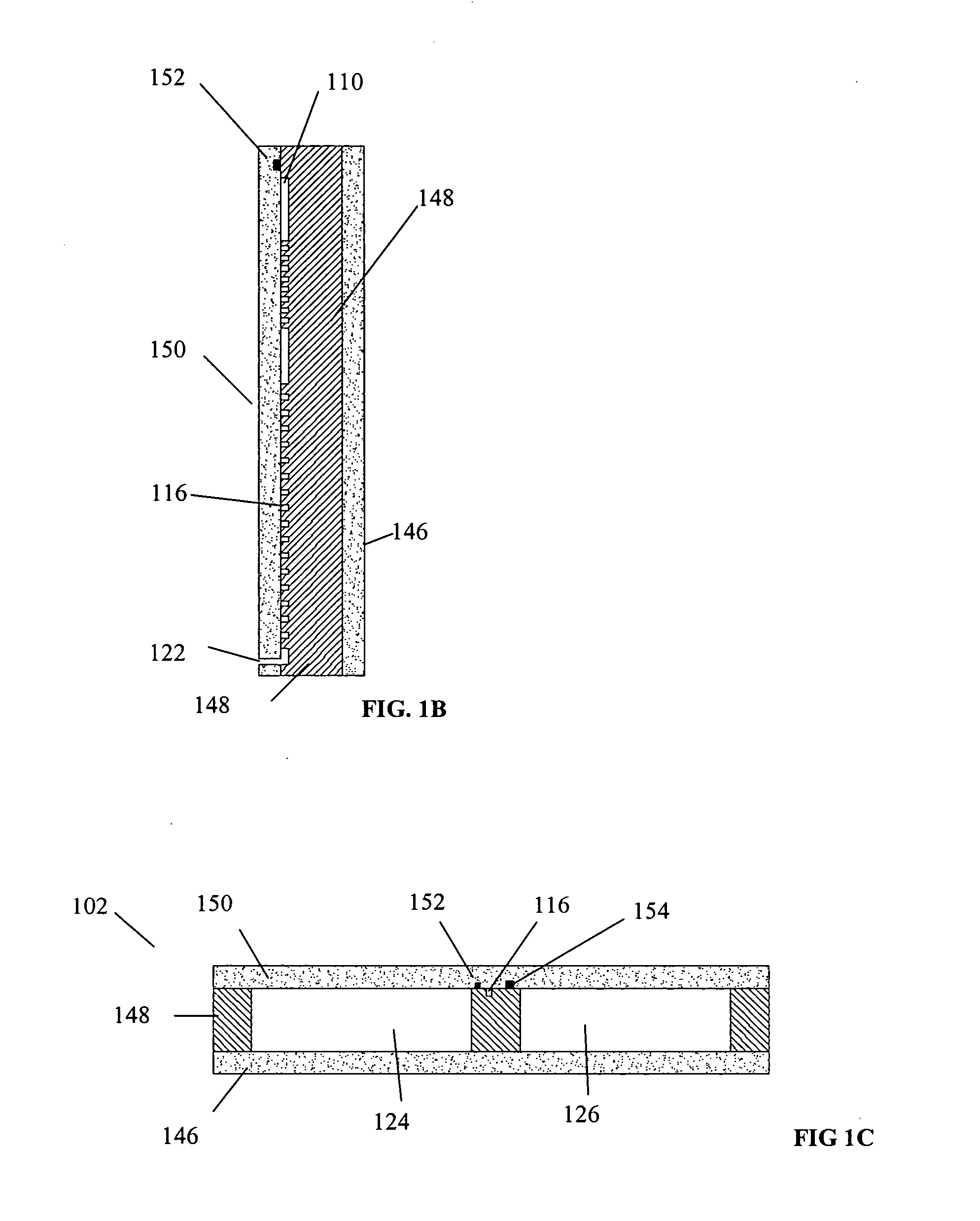
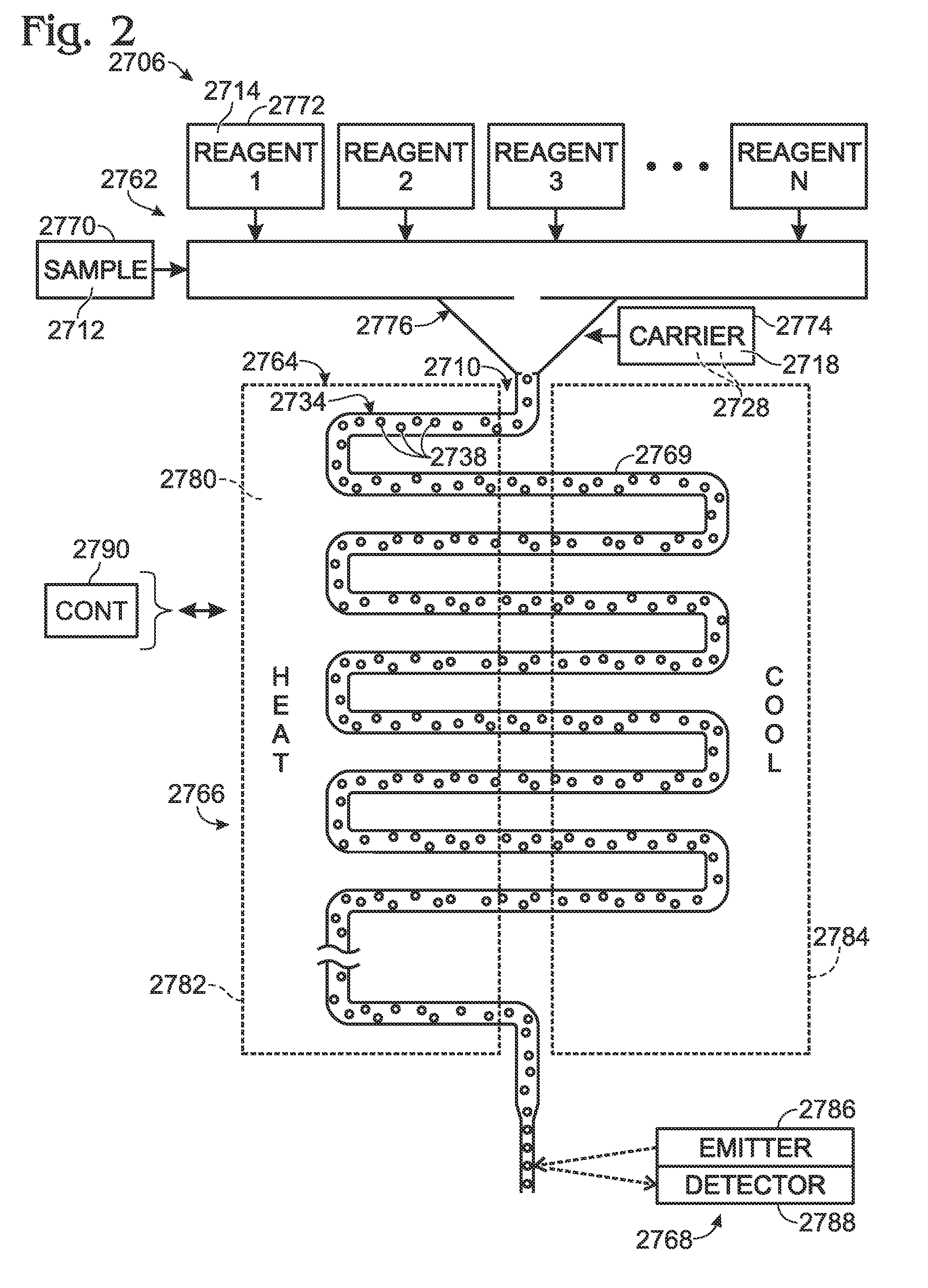
This invention comprises an apparatus and method for the manipulation of materials, including particles, cells, macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids and other moieties, in fluid samples. The apparatus comprises an enclosed chamber on a chip having an internal microstructure with surface area substantially greater than the facial surface area of the internal structure. Generally the internal microstructure comprises a continuous network of channels, each of which has a depth substantially greater than its width. The network may comprise a single channel, a single channel with multiple branches, multiple channels, multiple channels with multiple branches, and any combination thereof. The internal structure may present an inert, non-reactive surface, or be coated with a reactive ligand, or be electrically conductive and optionally be coated with an electrical insulator. Discrete portions of the internal structure may differ in structural and surface properties. Multiple chips may be linked together to create a multiplexed array of chambers, optionally linked to other analytical devices.
Owner:CEPHEID INC
Miniaturized cell array methods and apparatus for cell-based screening
InactiveUS6103479AImprove throughputIncrease contentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyTemporal informationHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The present invention discloses devices and methods of performing high throughput screening of the physiological response of cells to biologically active compounds and methods of combining high-throughput with high-content spatial information at the cellular and subcellular level as well as temporal information about changes in physiological, biochemical and molecular activities. The present invention allows multiple types of cell interactions to be studied simultaneously by combining multicolor luminescence reading, microfluidic delivery, and environmental control of living cells in non-uniform micro-patterned arrays.
Owner:CELLOMICS
Capillary electroflow apparatus and method
The present invention concerns an apparatus for conducting a microfluidic process. The apparatus comprises integral first and second plates. The first plate comprises an array of sample receiving elements for receiving a plurality of samples from an array of sample containers and dispensing the samples. The second plate comprises a planar array of microfluidic networks of cavity structures and channels for conducting a microfluidic process. Also disclosed is a method for processing an array of samples. At least a portion of each sample in an array of sample wells is simultaneously transferred to a corresponding array of microfluidic networks of cavity structures and channels by means of a corresponding array of sample receiving elements that is in integral fluid communication with the array of microfluidic networks. The samples are then processed. Also disclosed is a device for conducting a microfluidic process wherein the device comprising a planar substrate having a planar array of microfluidic networks of cavity structures and channels for conducting a microfluidic process. A plurality of such devices may be present on a continuous sheet. The invention further includes kits for carrying out microfluidic processes comprising an apparatus as described above.
Owner:ACLARA BIOSCIENCES INC
Acrylic microchannels and their use in electrophoretic applications
Microchannels having at least an acrylic inner surface and methods of their use in electrophoretic applications are provided. The subject microchannels may be in the form of a variety of configurations suitable for holding an electrophoretic medium. The subject microchannels give rise to substantially reduced EOF and / or adsorption as compared to fused silica under conditions of electrophoresis and find use in a variety of electrophoretic applications in which charged entities are moved through a medium under the influence of the an applied electric field.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
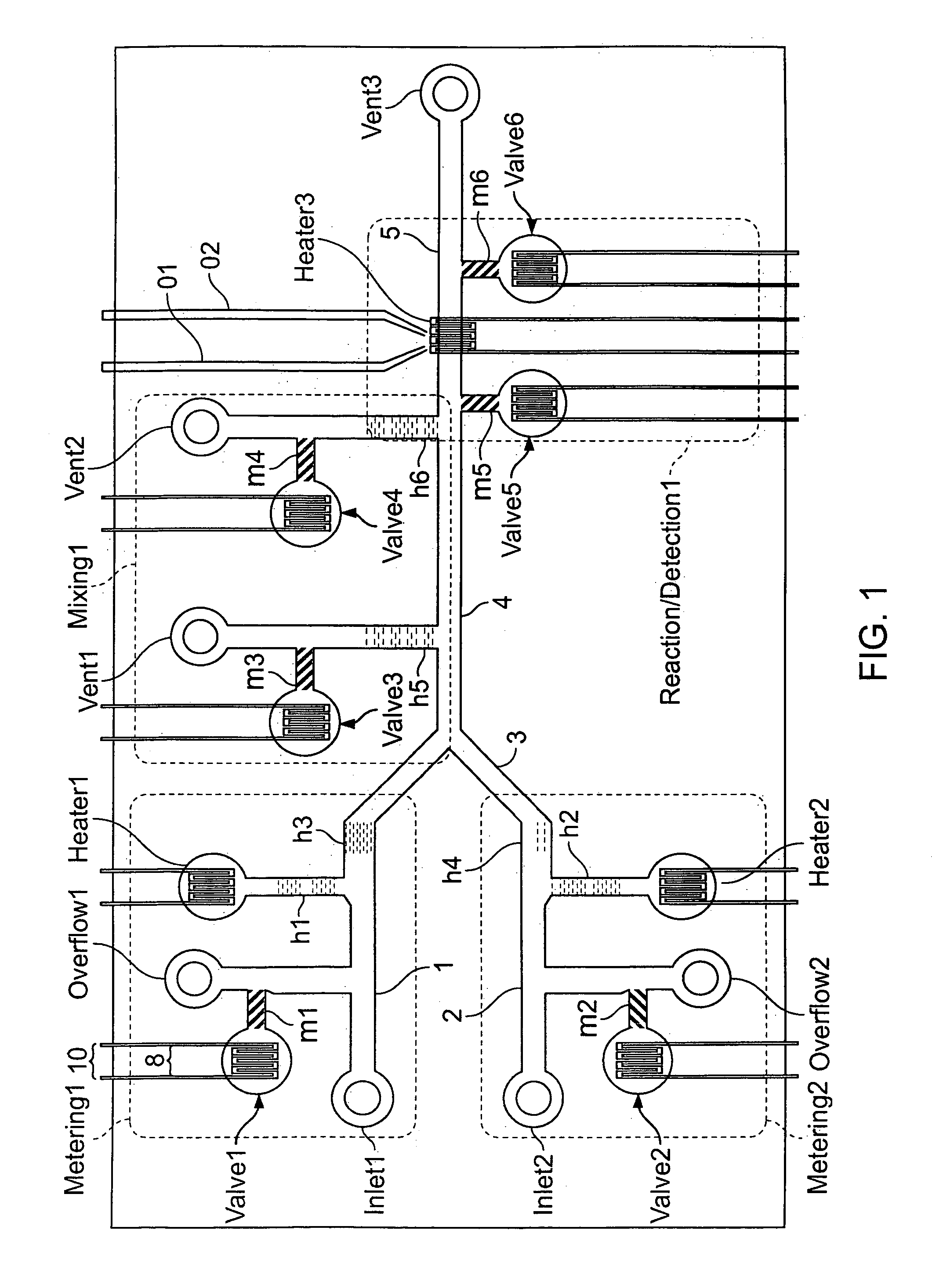
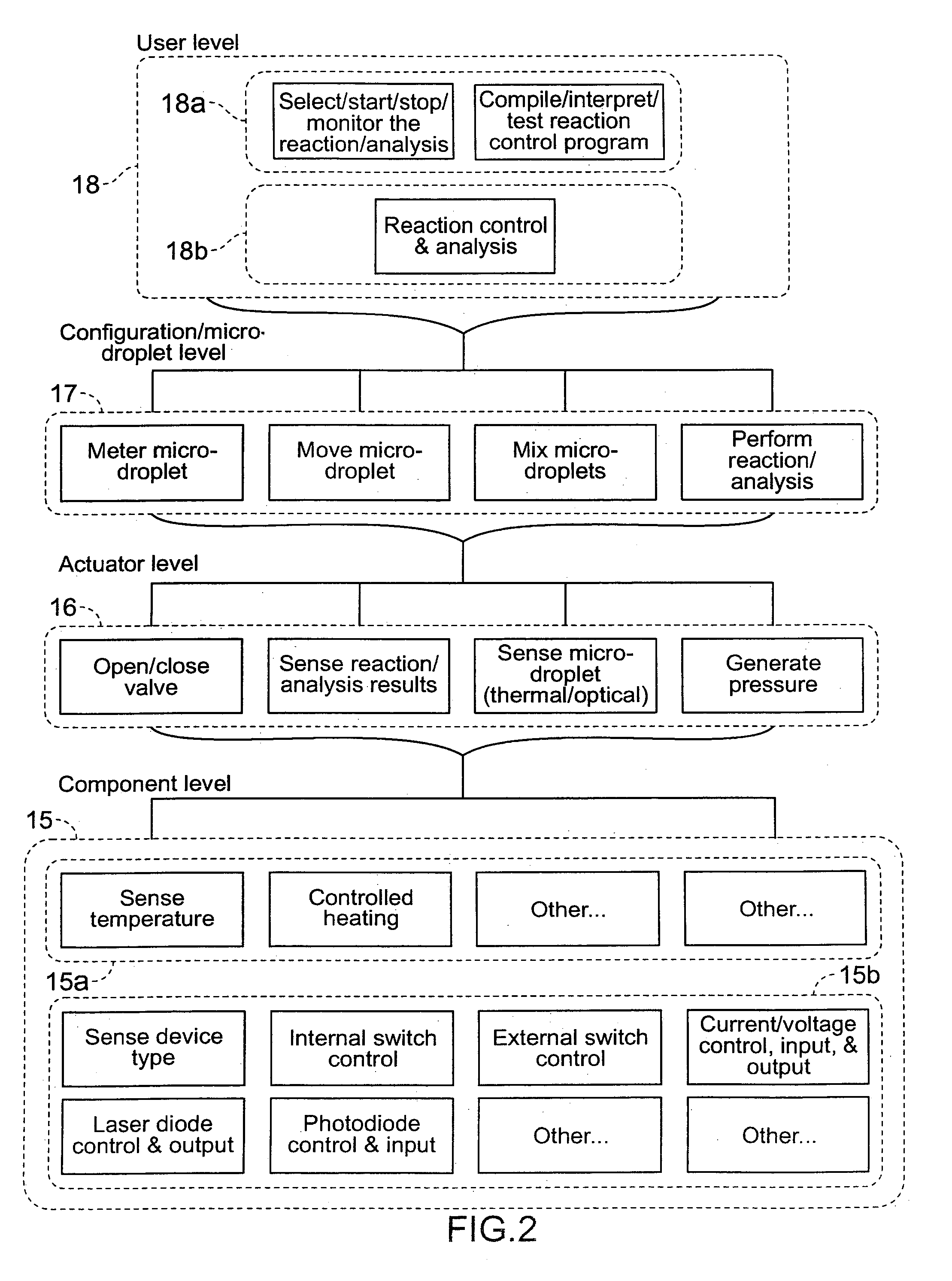
Methods and systems for control of microfluidic devices
InactiveUS20020143437A1Overcome deficienciesFixed microstructural devicesVolume/mass flow measurementControl systemLow voltage
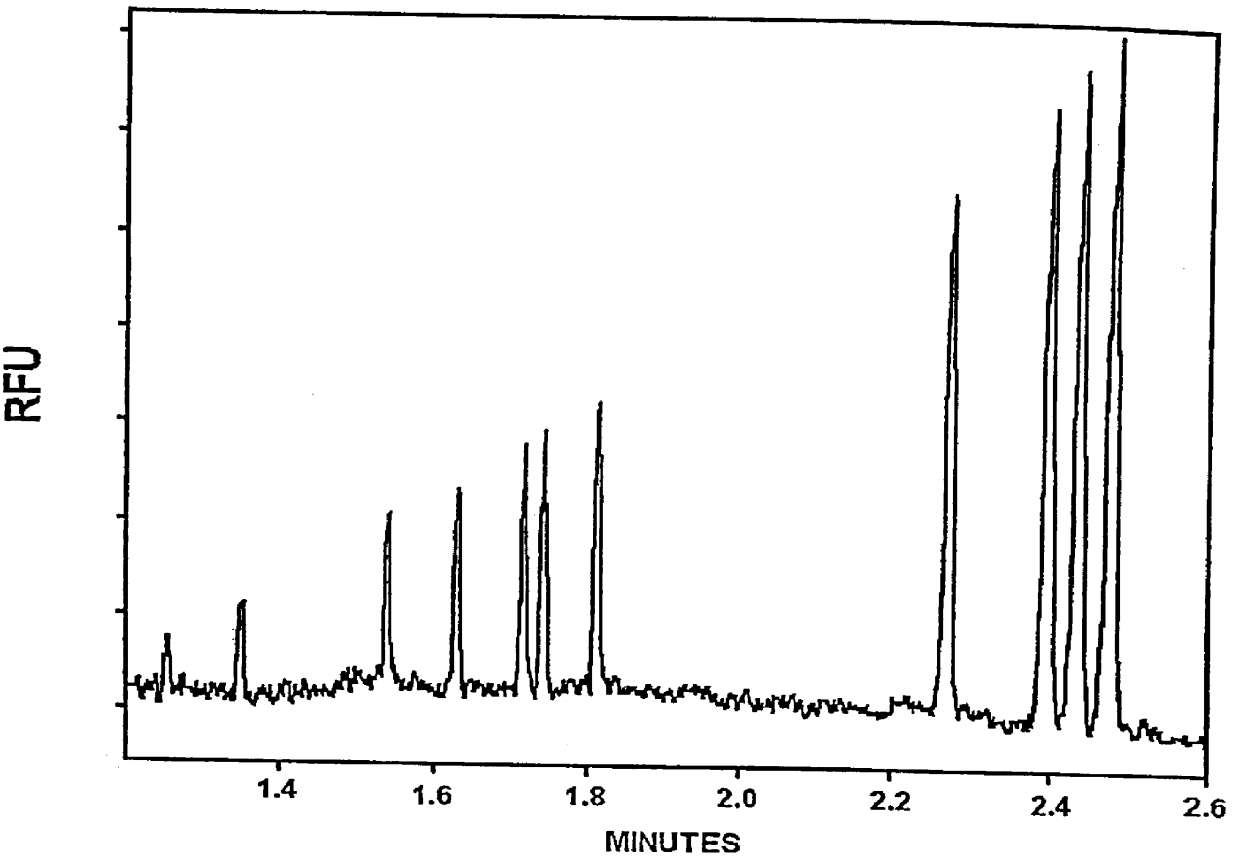
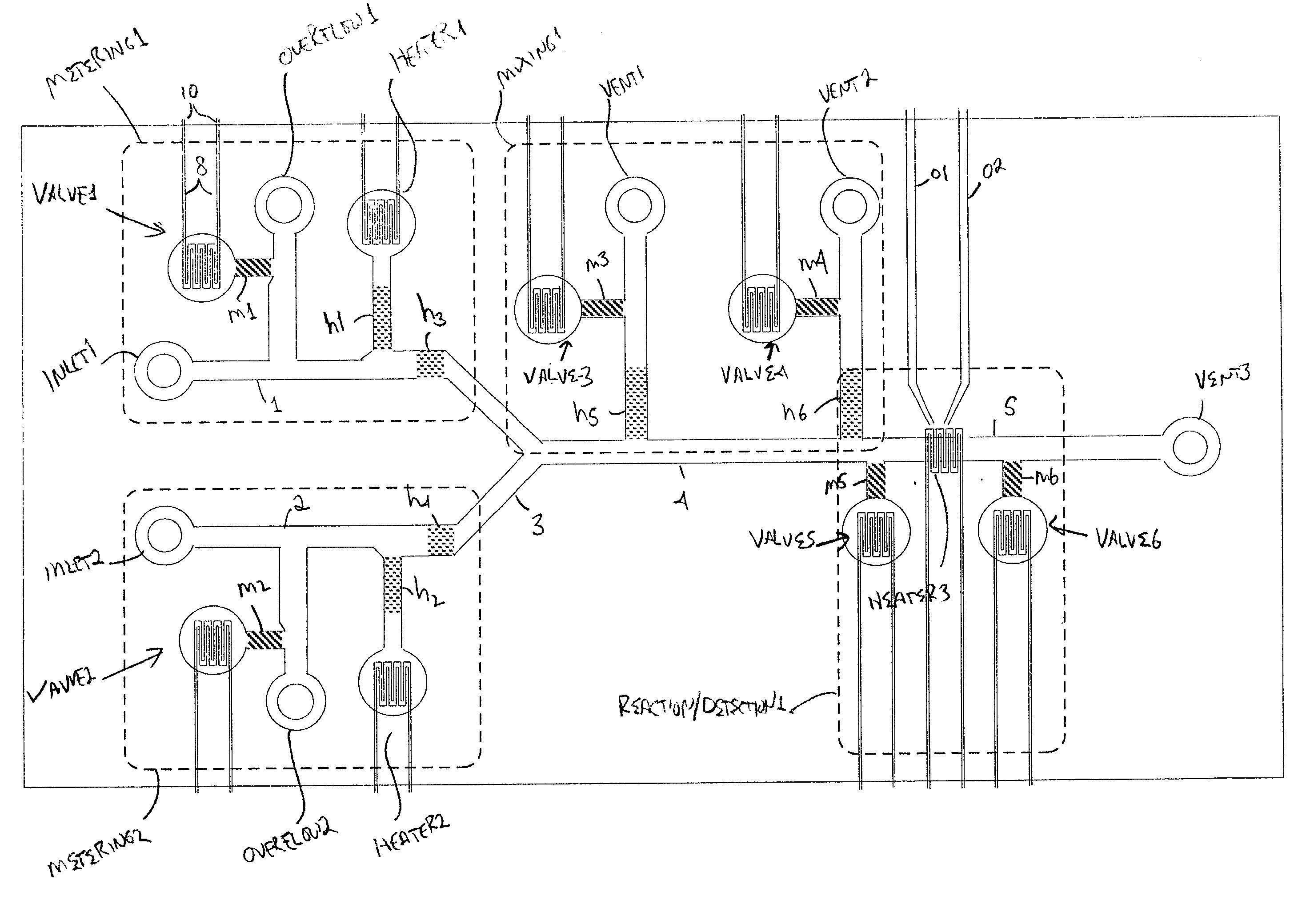
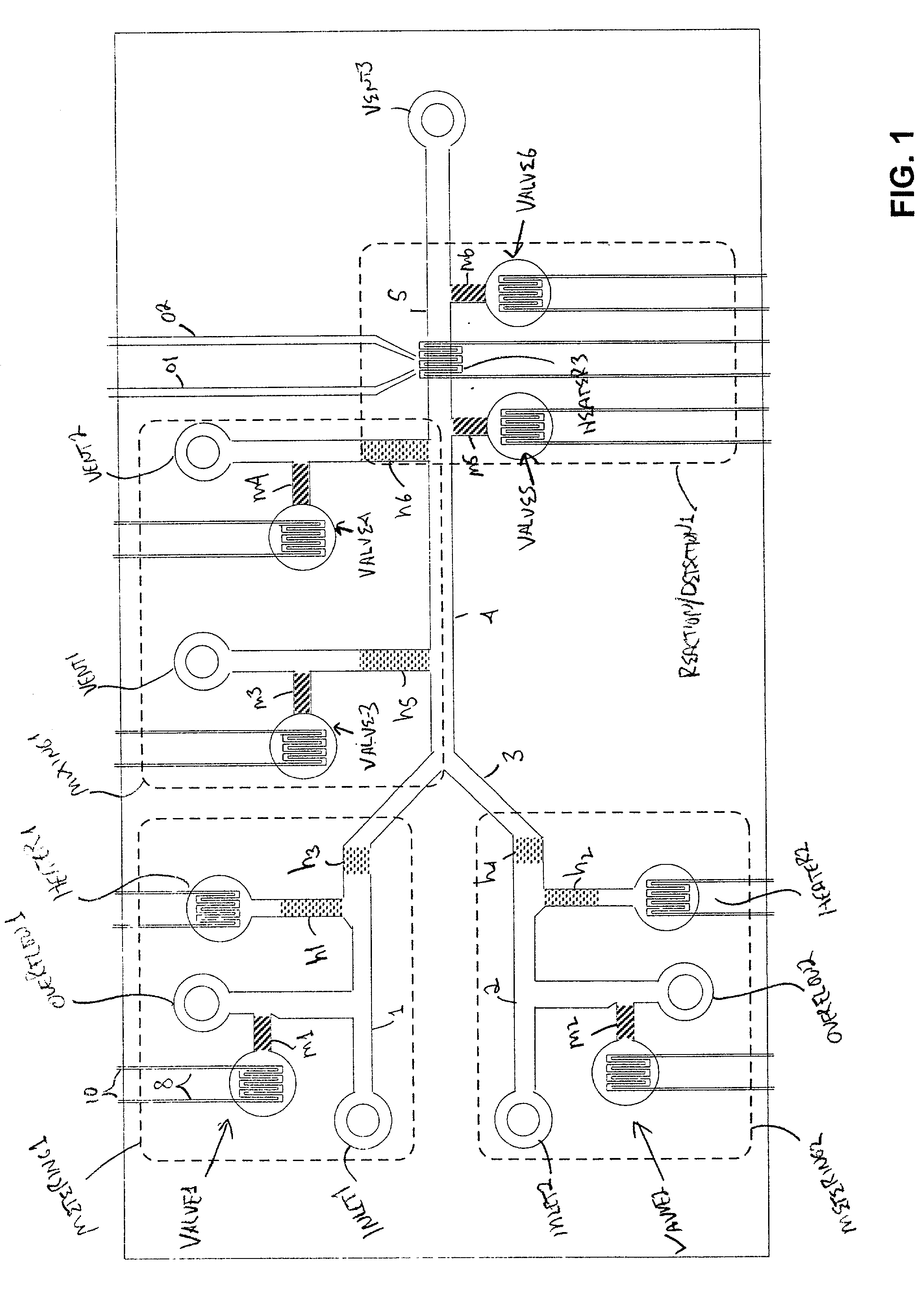
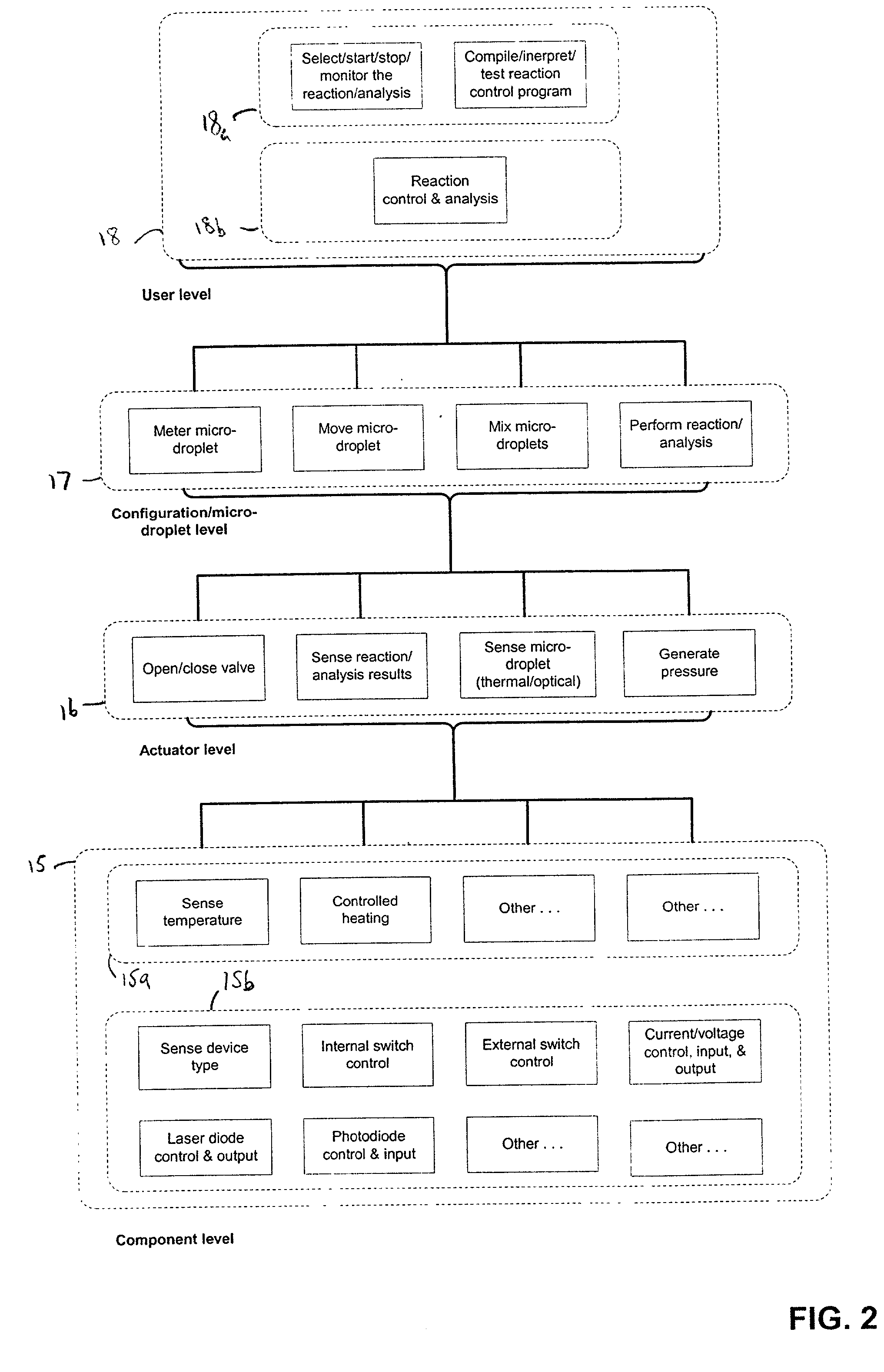
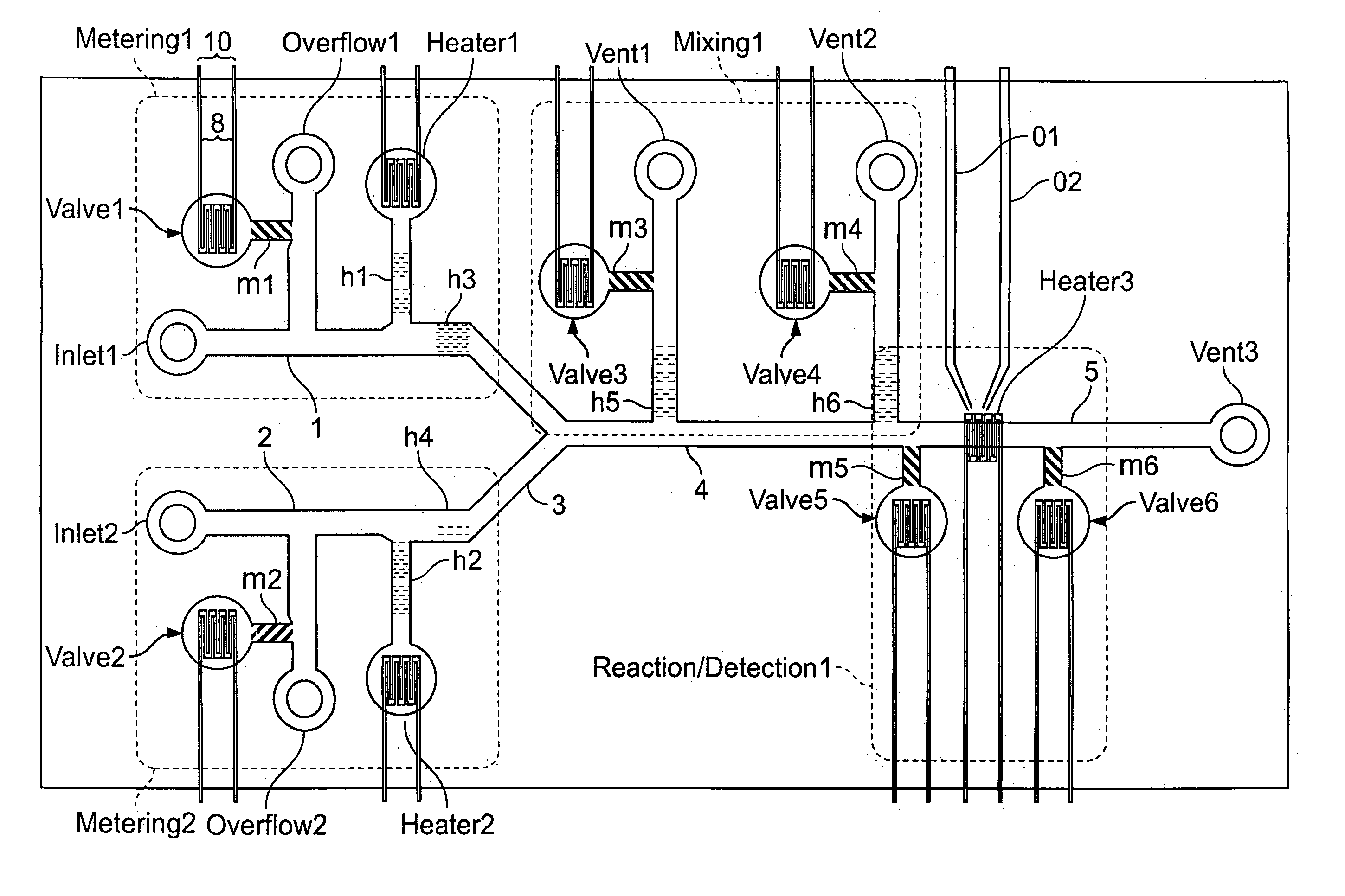
The present invention provides control methods, control systems, and control software for microfluidic devices that operate by moving discrete micro-droplets through a sequence of determined configurations. Such microfluidic devices are preferably constructed in a hierarchical and modular fashion which is reflected in the preferred structure of the provided methods and systems. In particular, the methods are structured into low-level device component control functions, middle-level actuator control functions, and high-level micro-droplet control functions. Advantageously, a microfluidic device may thereby be instructed to perform an intended reaction or analysis by invoking micro-droplet control function that perform intuitive tasks like measuring, mixing, heating, and so forth. The systems are preferably programmable and capable of accommodating microfluidic devices controlled by low voltages and constructed in standardized configurations. Advantageously, a single control system can thereby control numerous different reactions in numerous different microfluidic devices simply by loading different easily understood micro-droplet programs.
Owner:HANDYLAB
Systems and methods of forming particles
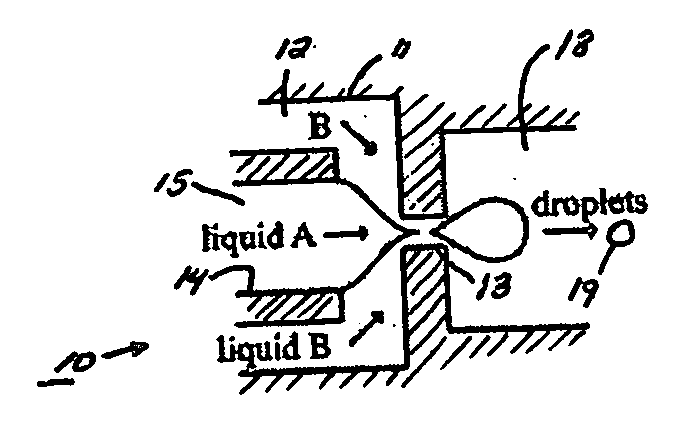
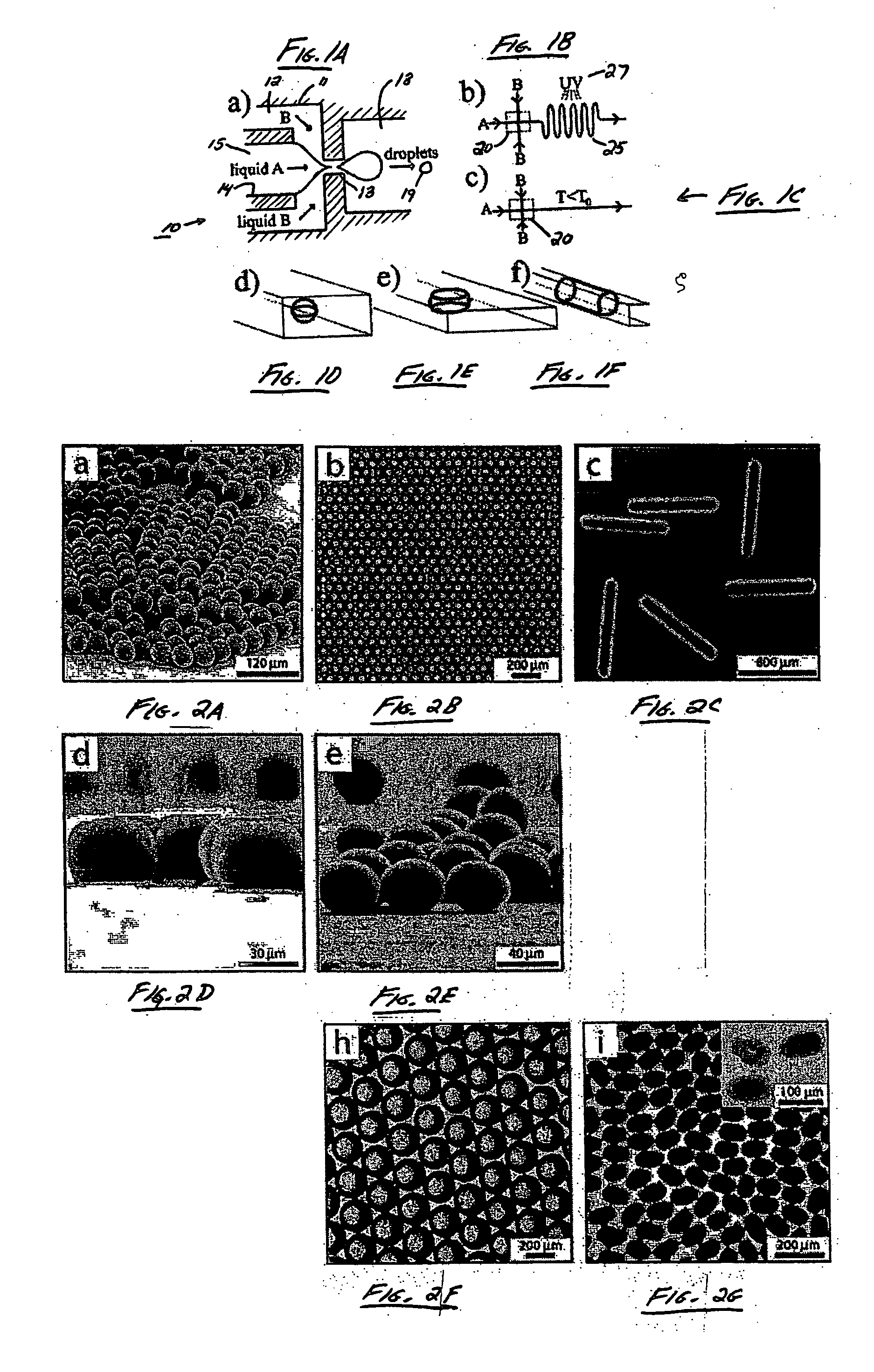
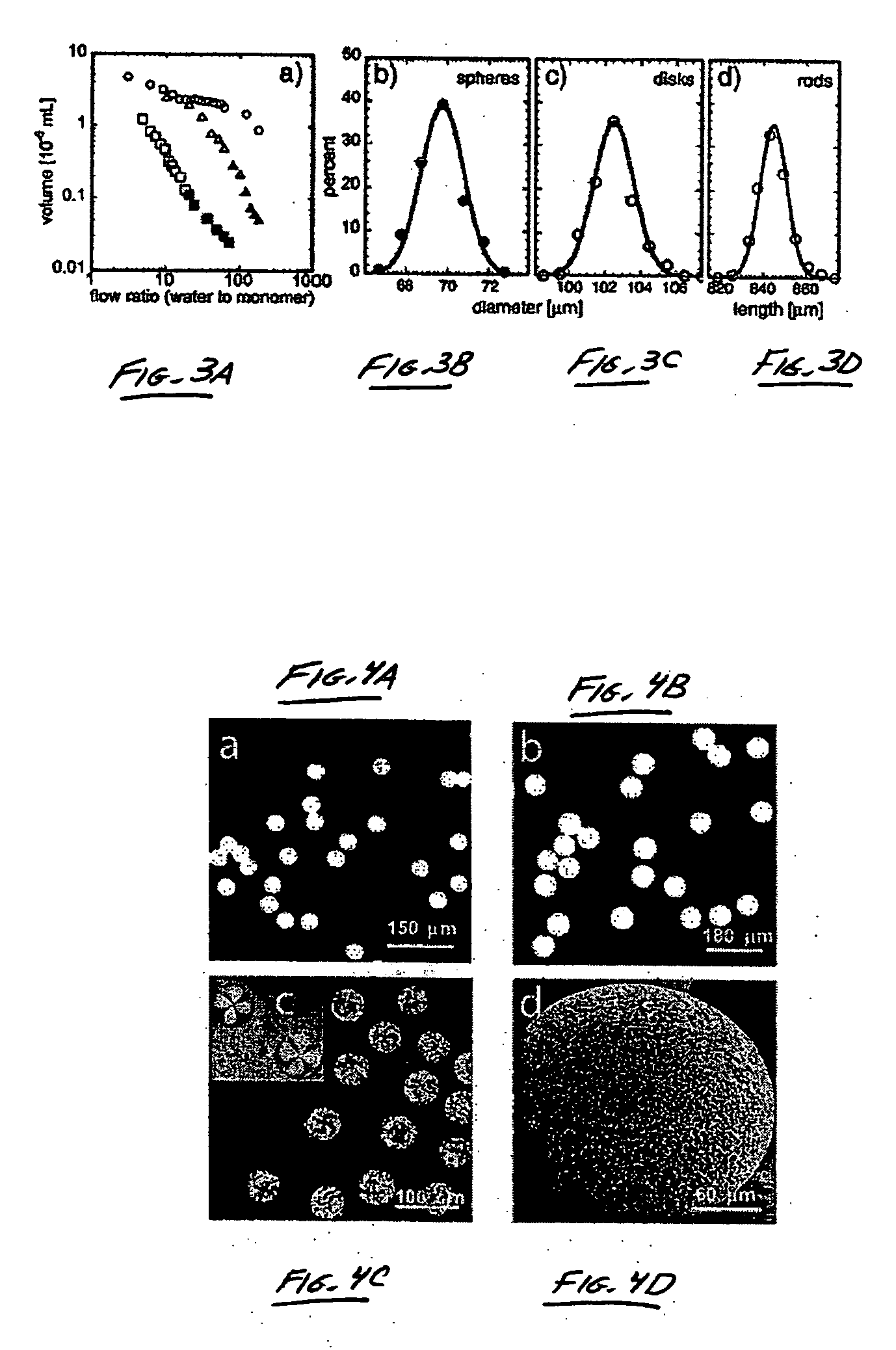
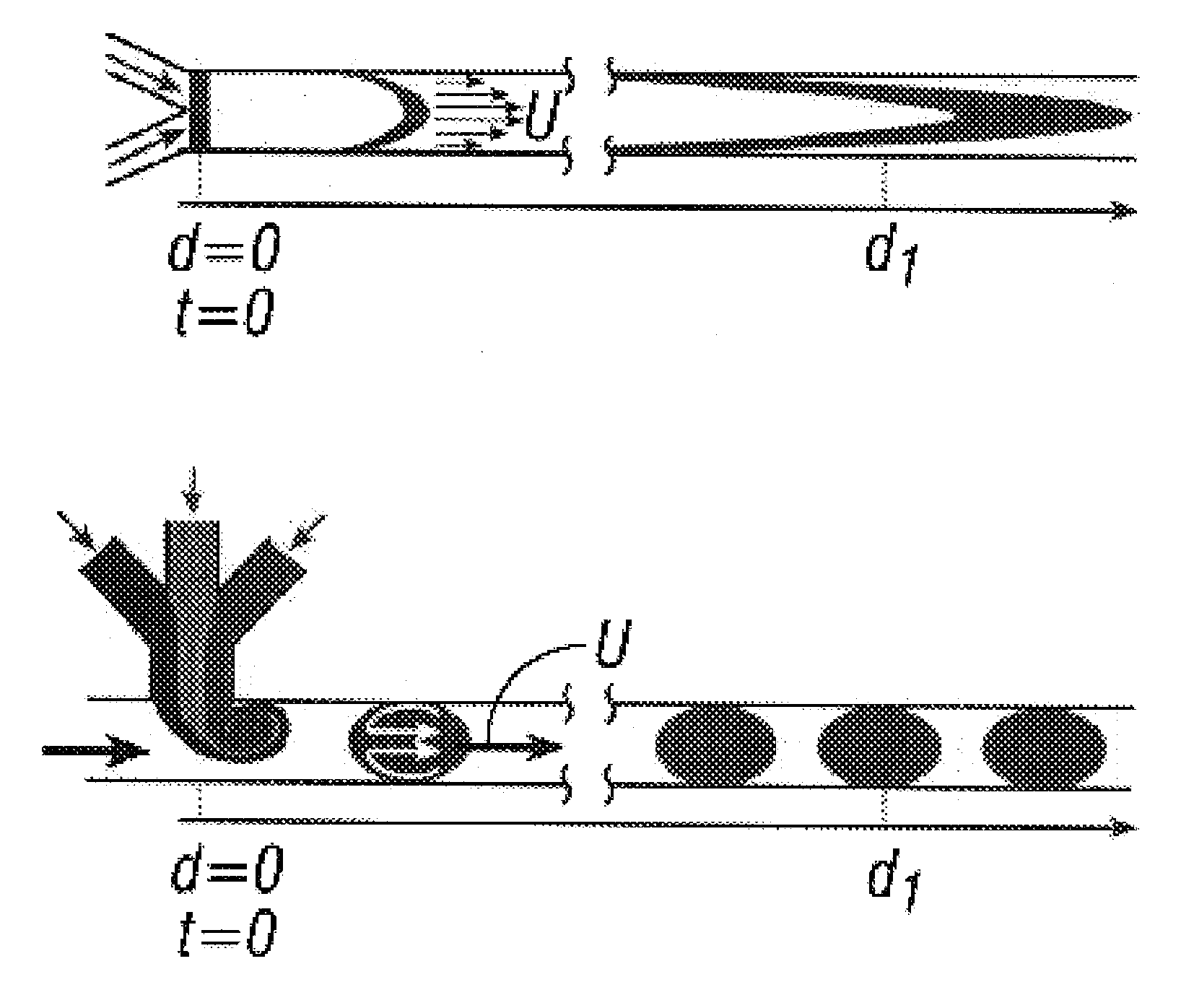
InactiveUS20070054119A1Synthetic resin layered productsChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsChemical reactionMicrometer
The present invention generally relates to systems and methods of forming particles and, in certain aspects, to systems and methods of forming particles that are substantially monodisperse. Microfluidic systems and techniques for forming such particles are provided, for instance, particles may be formed using gellation, solidification, and / or chemical reactions such as cross-linking, polymerization, and / or interfacial polymerization reactions. In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a plurality of particles having an average dimension of less than about 500 micrometers and a distribution of dimensions such that no more than about 5% of the particles have a dimension greater than about 10% of the average dimension, which can be made via microfluidic systems. In one set of embodiments, at least some of the particles may comprise a metal, and in certain embodiments, at least some of the particles may comprise a magnetizable material. In another set of embodiments, at least some of the particles may be porous. In some embodiments, the invention includes non-spherical particles. Non-spherical particles may be formed, for example, by urging a fluidic droplet into a channel having a smallest dimension that is smaller than the diameter of a perfect mathematical sphere having a volume of the droplet, and solidifying the droplet, and / or by exposing at least a portion of a plurality of particles to an agent able to remove at least a portion of the particles.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Device and method for pressure-driven plug transport and reaction
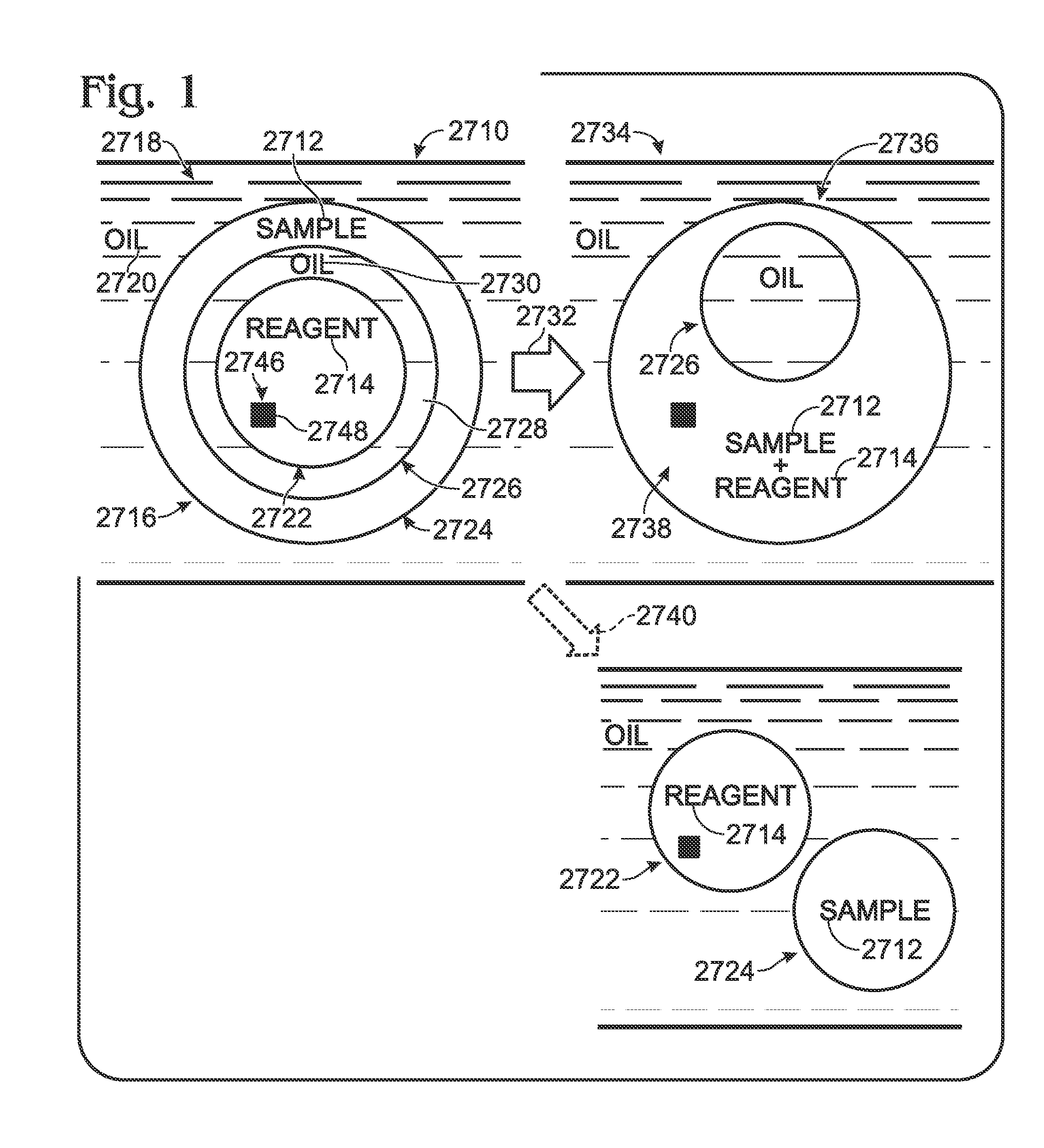
InactiveUS7129091B2Well mixedQuick mixMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsPressure.driveCarrier fluid
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
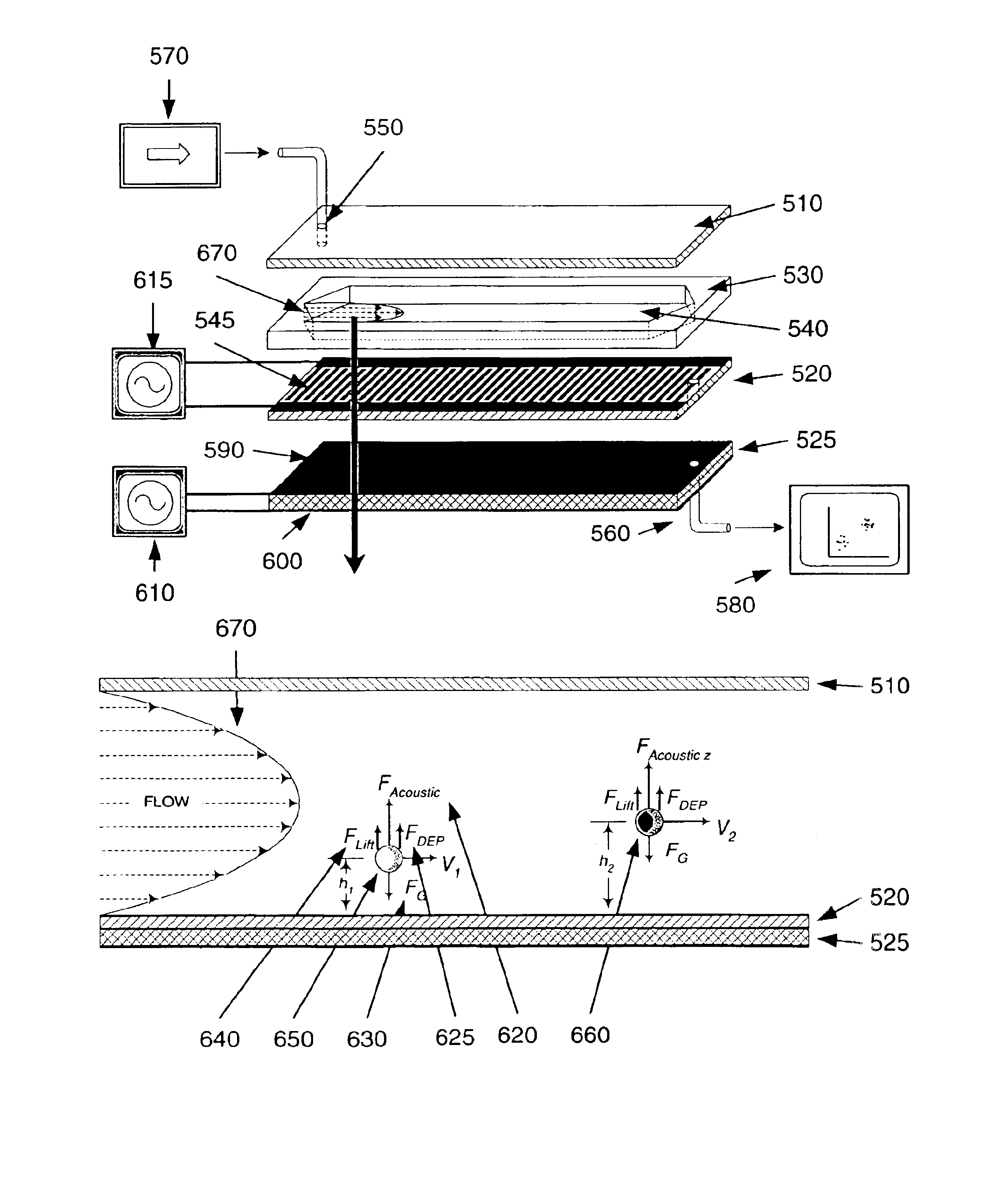
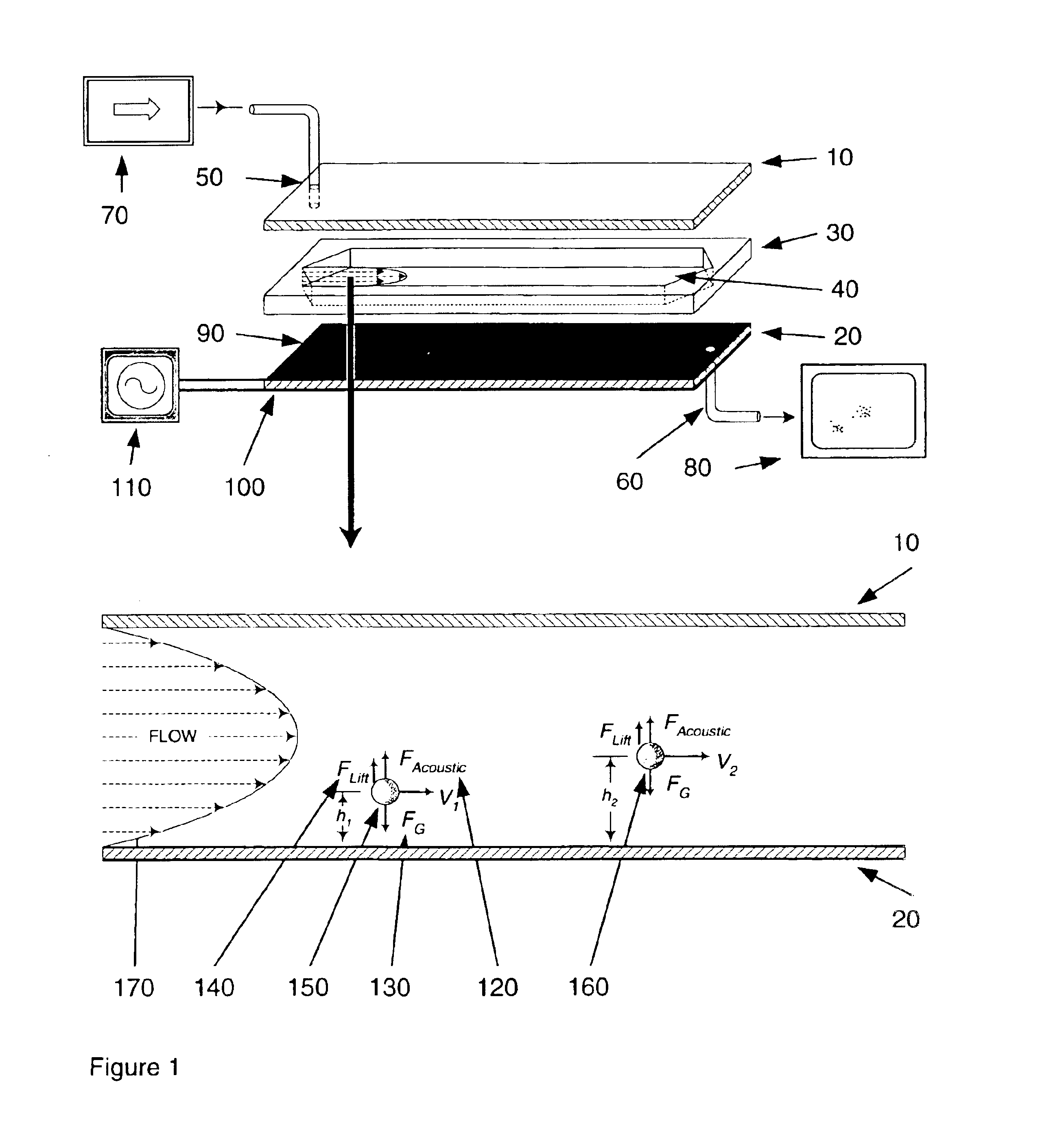
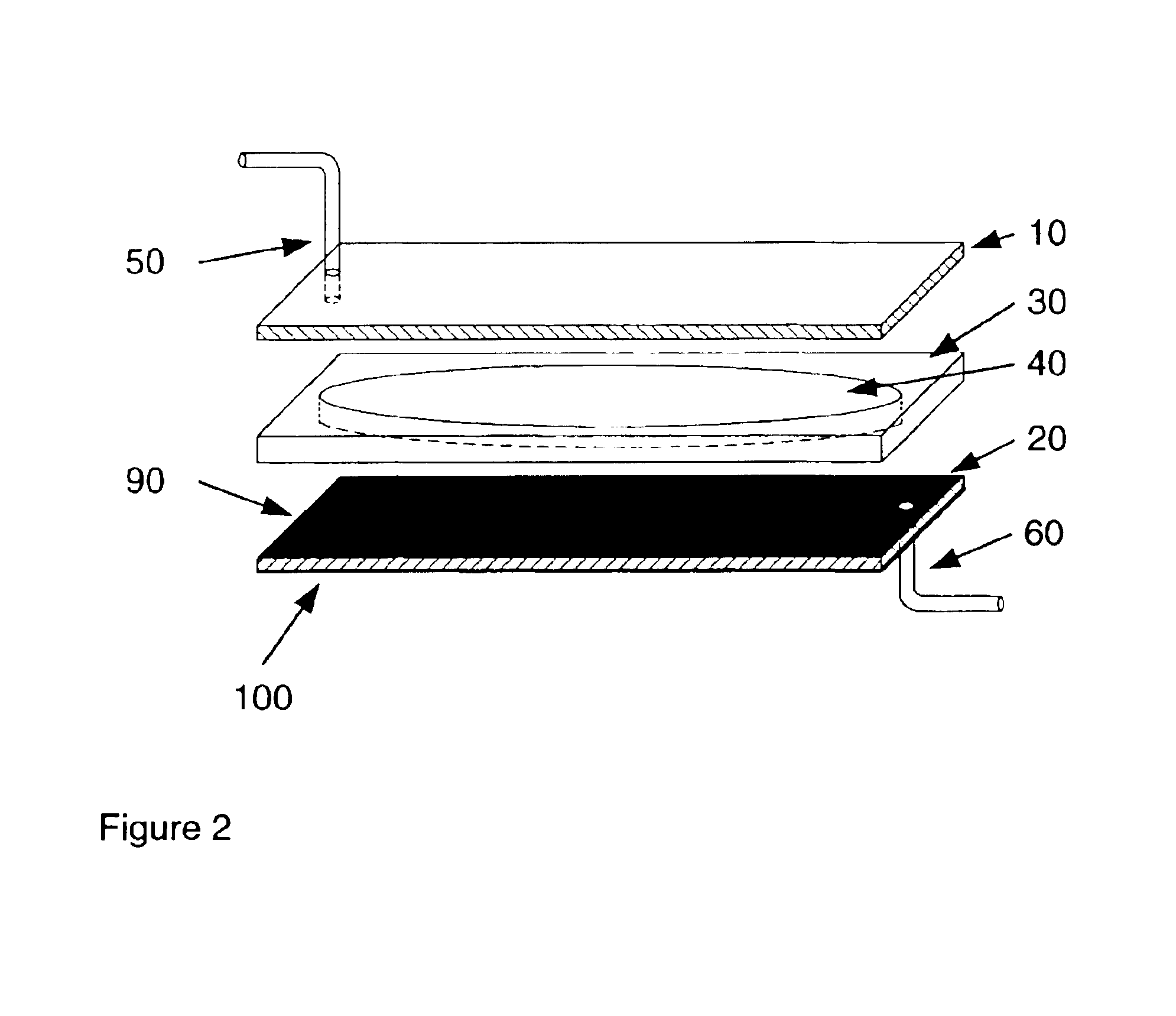
Method and apparatus for acoustically controlling liquid solutions in microfluidic devices
InactiveUS6948843B2Improve reaction speedAccelerating molecular interactionSequential/parallel process reactionsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersSound sourcesAcoustic energy
Acoustic energy is used to control motion in a fluid. According to one embodiment, the invention directs acoustic energy at selected naturally occurring nucleation features to control motion in the fluid. In another embodiment, the invention provides focussed or unfocussed acoustic energy to selectively placed nucleation features to control fluid motion. According to one embodiment, the invention includes an acoustic source, a controller for controlling operation of the acoustic source, and one or more nucleation features located proximate to or in the fluid to be controlled.
Owner:COVARIS INC
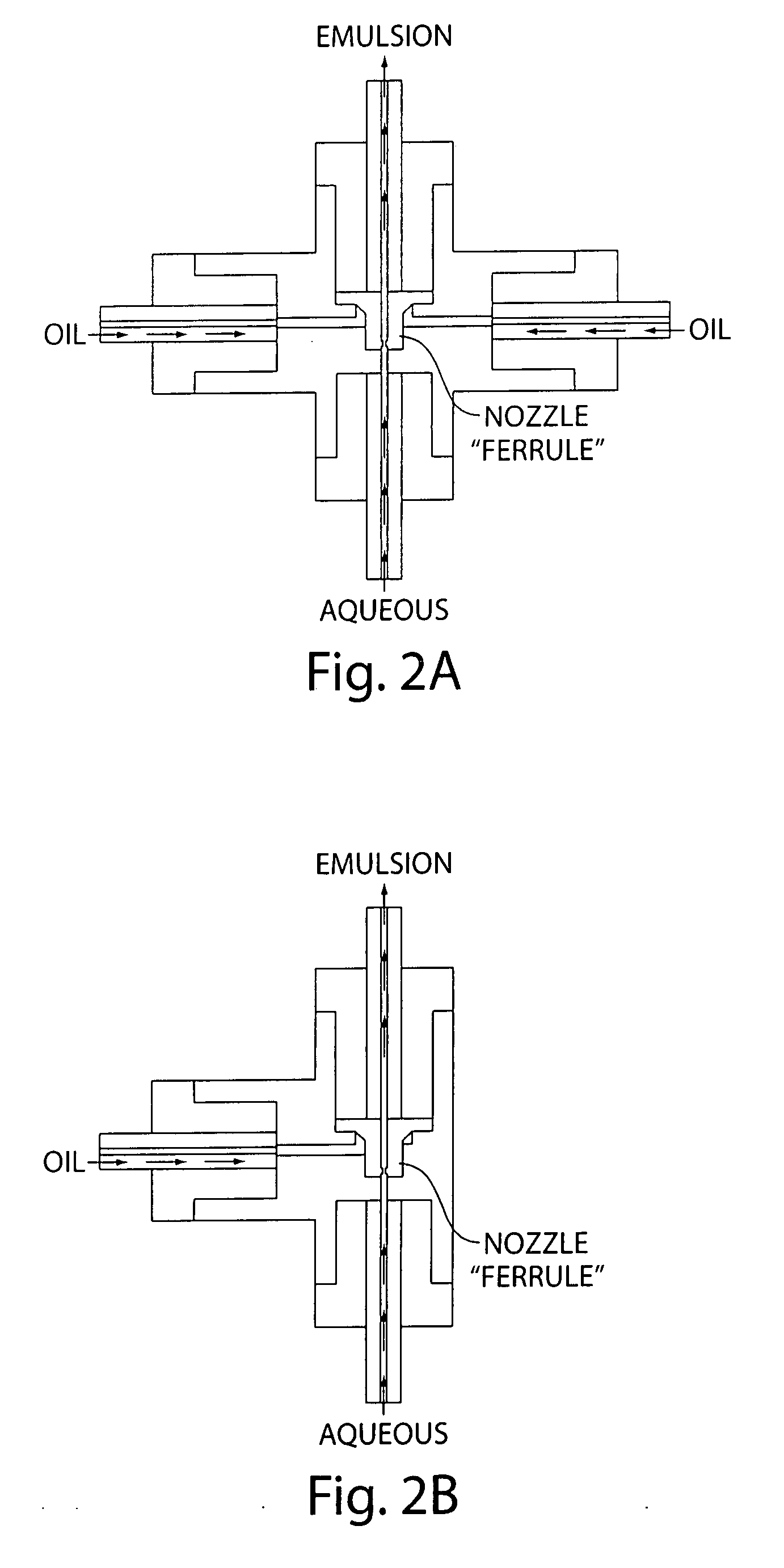
Process for producing emulsion and microcapsules and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS7268167B2Rapid productionSimple wayFlow mixersMixing methodsEmulsionMechanical engineering
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Three-dimensional microfluidics incorporating passive fluid control structures
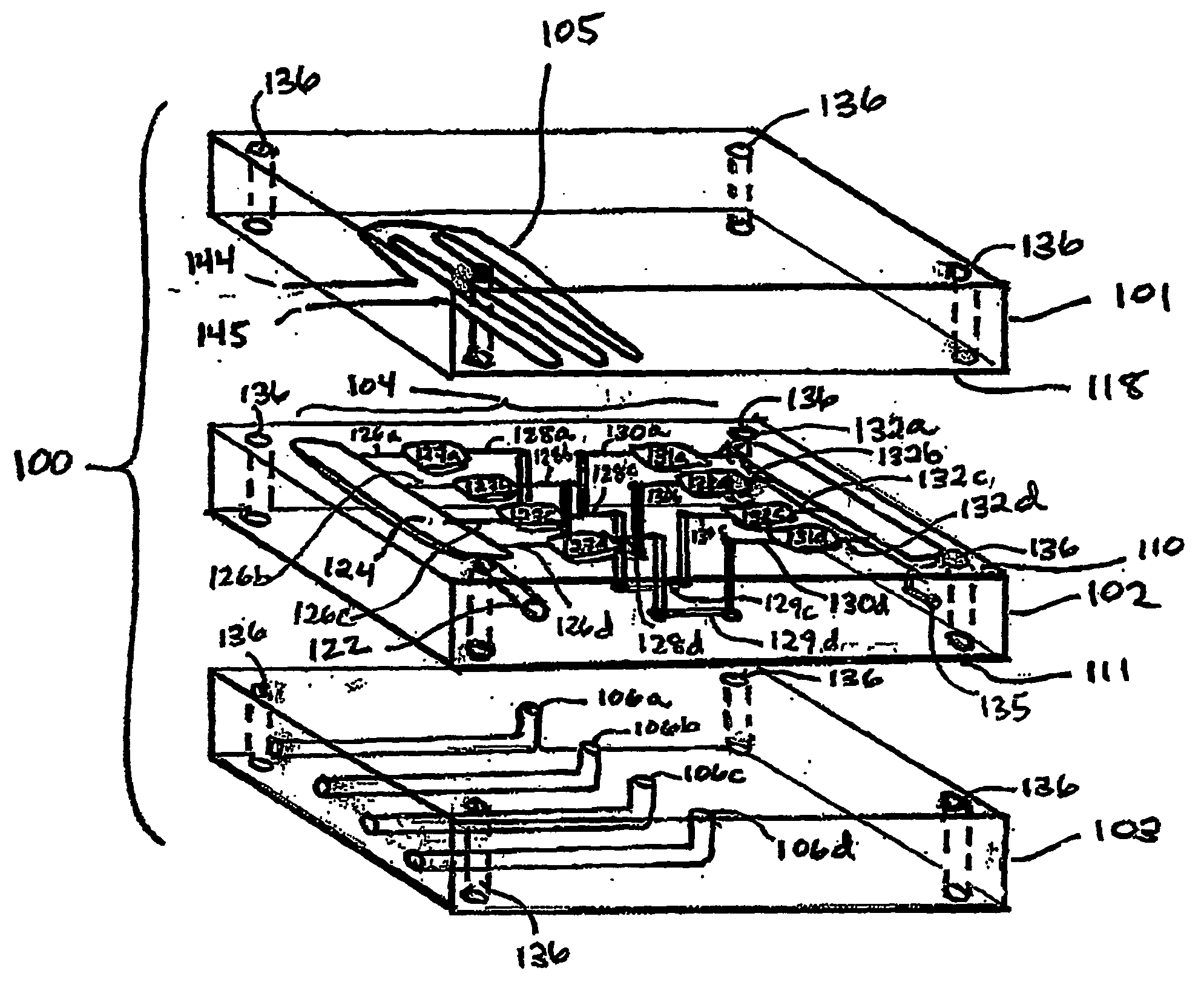
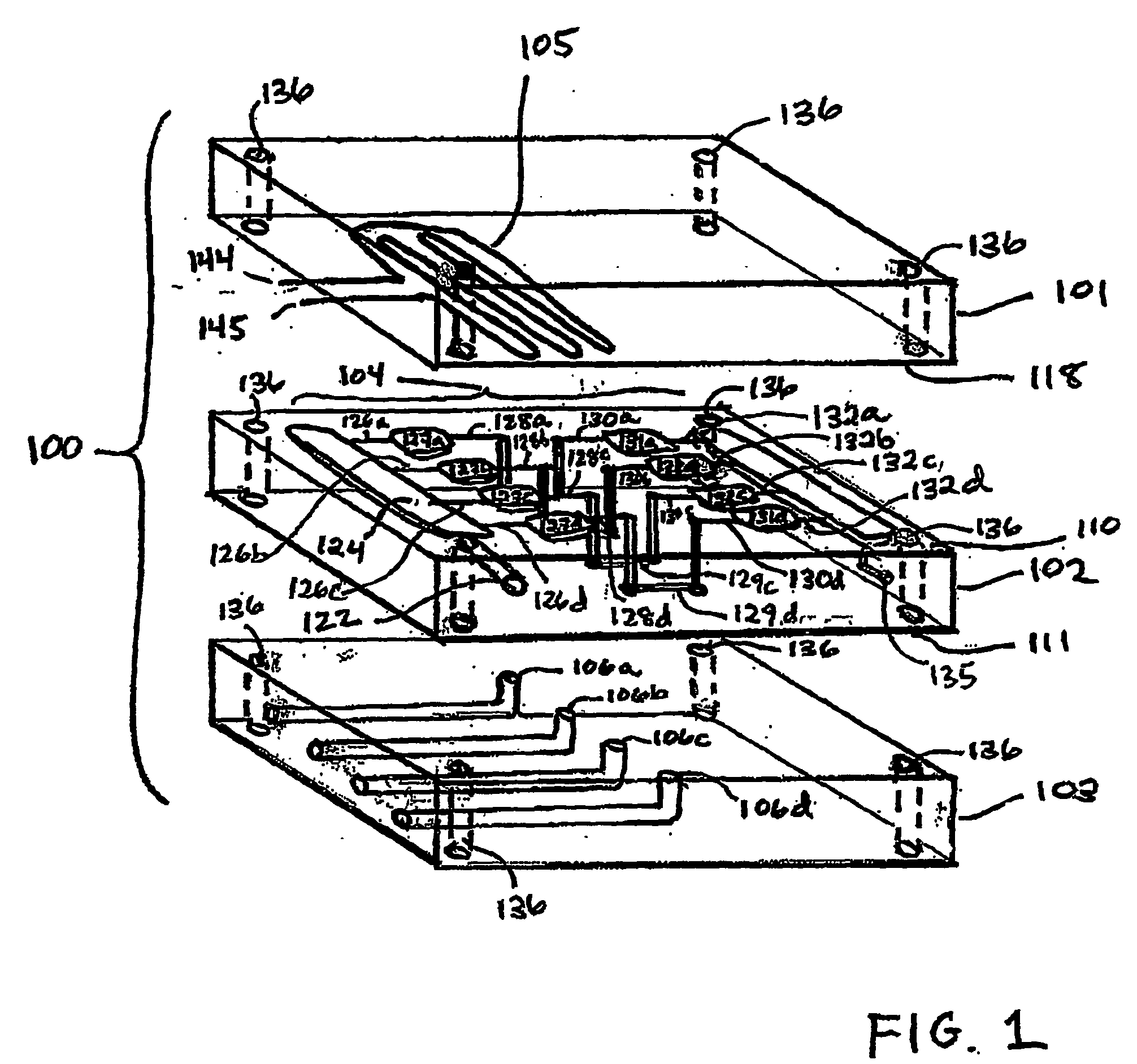
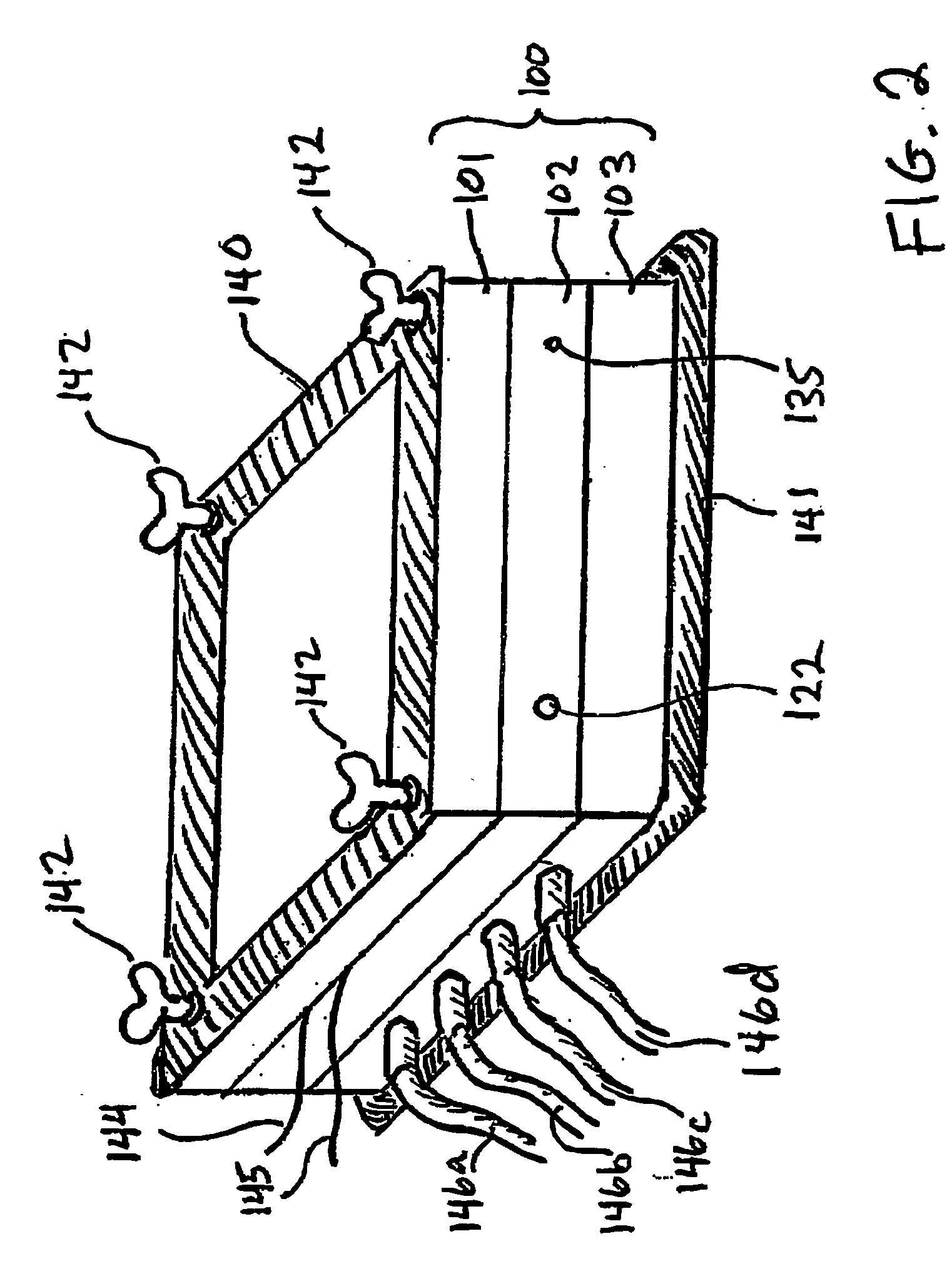
InactiveUS20040109793A1Simple and effective and versatile controlShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersHeating or cooling apparatusFluid controlMicrofluidics
A three-dimensional microfluidic device (100) formed from a plurality of substantially planar layers (101, 102, 103) sealed together is disclosed
Owner:BIOMICRO SYST
Droplet Microreactor
InactiveUS20080124252A1Improve purification effectInexpensive to fabricateChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMicroreactorLab-on-a-chip
The present invention relates to a droplet microreactor, i.e. a microreactor consisting of a droplet of a specific liquid, the microreactor being wall-less, wherein the interface of the specific liquid with the ambient environment and with the support on which the droplet is deposited defines the limits of the microreactor. The microreactor is characterized in that it consists of a droplet comprising at least one ionic liquid. The present invention also relates to methods for carrying out chemical or biochemical reactions and / or mixes using said droplet microreactor, and also to a lab-on-chip comprising a microreactor according to the invention.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Device and method for pressure-driven plug transport and reaction
InactiveUS20050272159A1Well mixedQuick mixMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsPressure.driveCarrier fluid
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Microfluidic devices comprising biochannels
InactiveUS6875619B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyAnalyteBiological organism
The present invention is directed to a variety of microfluidic devices with configurations including the use of biochannels or microchannels comprising arrays of capture binding ligands to capture target analytes in samples. The invention provides microfluidic cassettes or devices that can be used to effect a number of manipulations on a sample to ultimately result in target analyte detection or quantification.
Owner:CLINICAL MICRO SENSORS +1
Microfluidic chemical reactor for the manufacture of chemically-produced nanoparticles
InactiveUS20050129580A1Maintain propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthProcess functionNanoparticle
The present invention discloses microfluidic modules for making nanocrystalline materials in a continuous flow process. The microfluidic modules include one or more flow path with mixing structures and one or more controlled heat exchangers to process the nanocrystalline materials and reagents in the flow path. The microfluidic modules can be interconnected to form microfluidic reactors that incorporate one or more process functions such as nucleation, growth, and purification.
Owner:LAKE SHORE CRYOTRONICS INC
Methods and systems for control of microfluidic devices
InactiveUS7010391B2Easy programmingSludge treatmentFixed microstructural devicesControl systemLow voltage
Owner:HANDYLAB
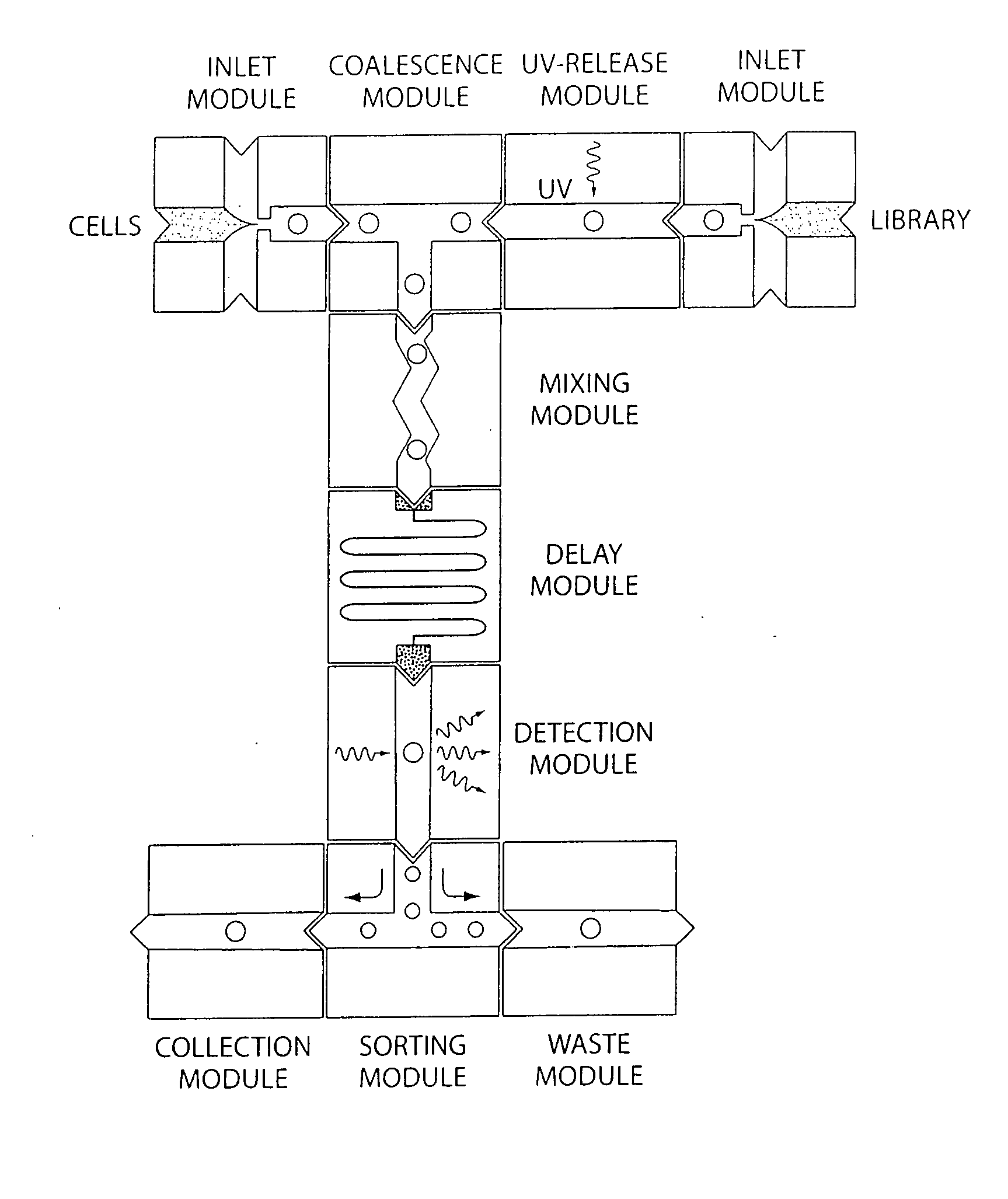
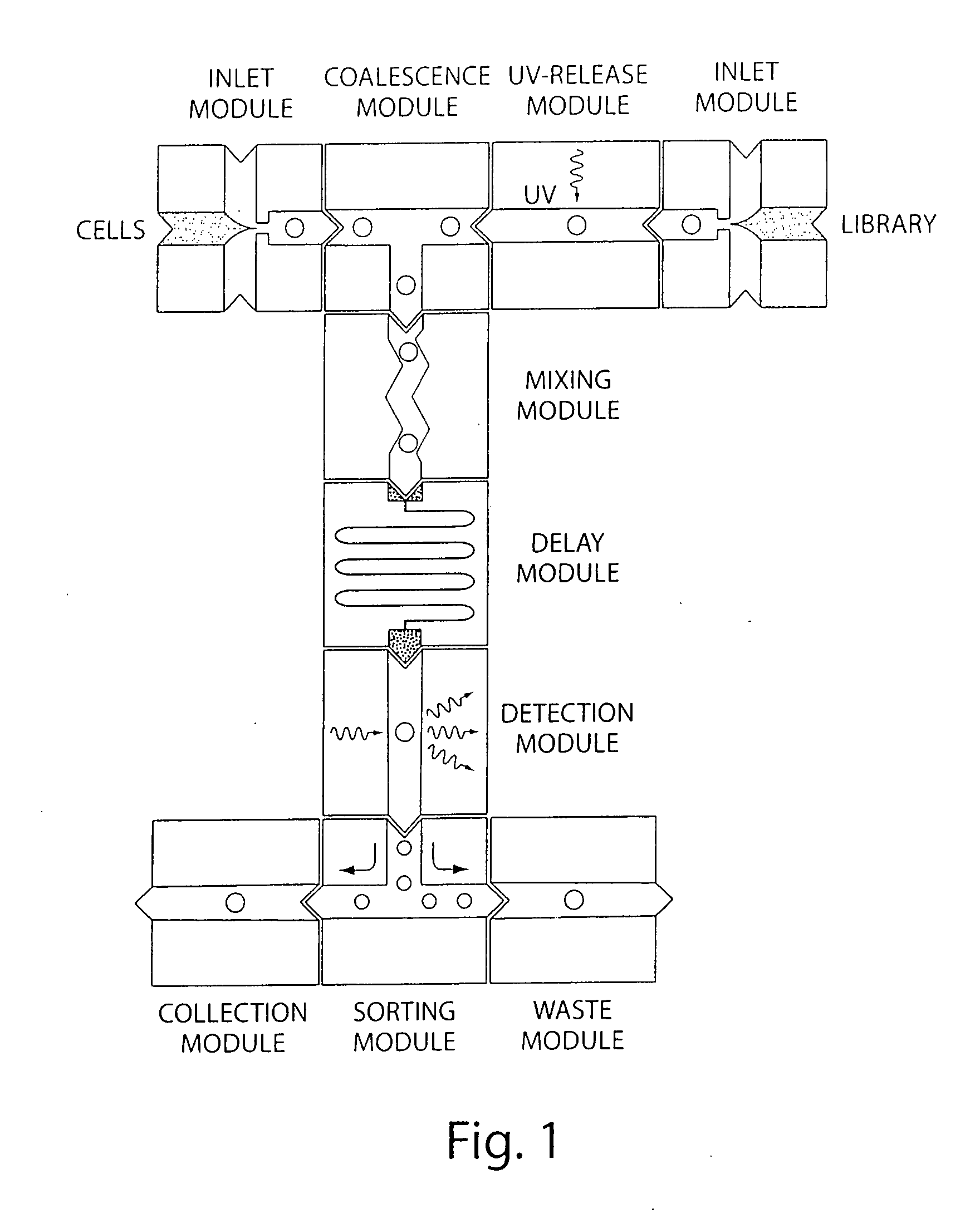
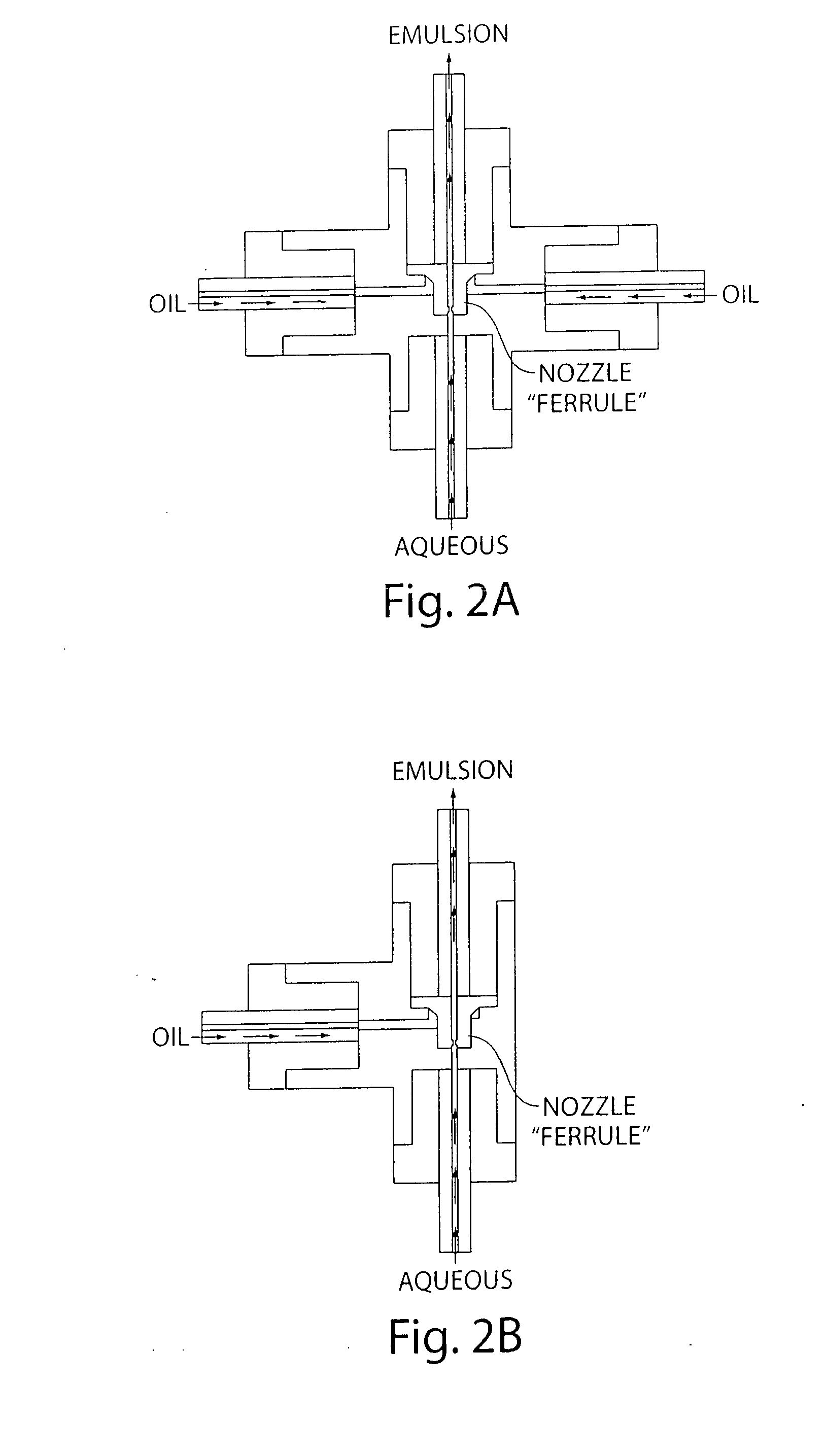
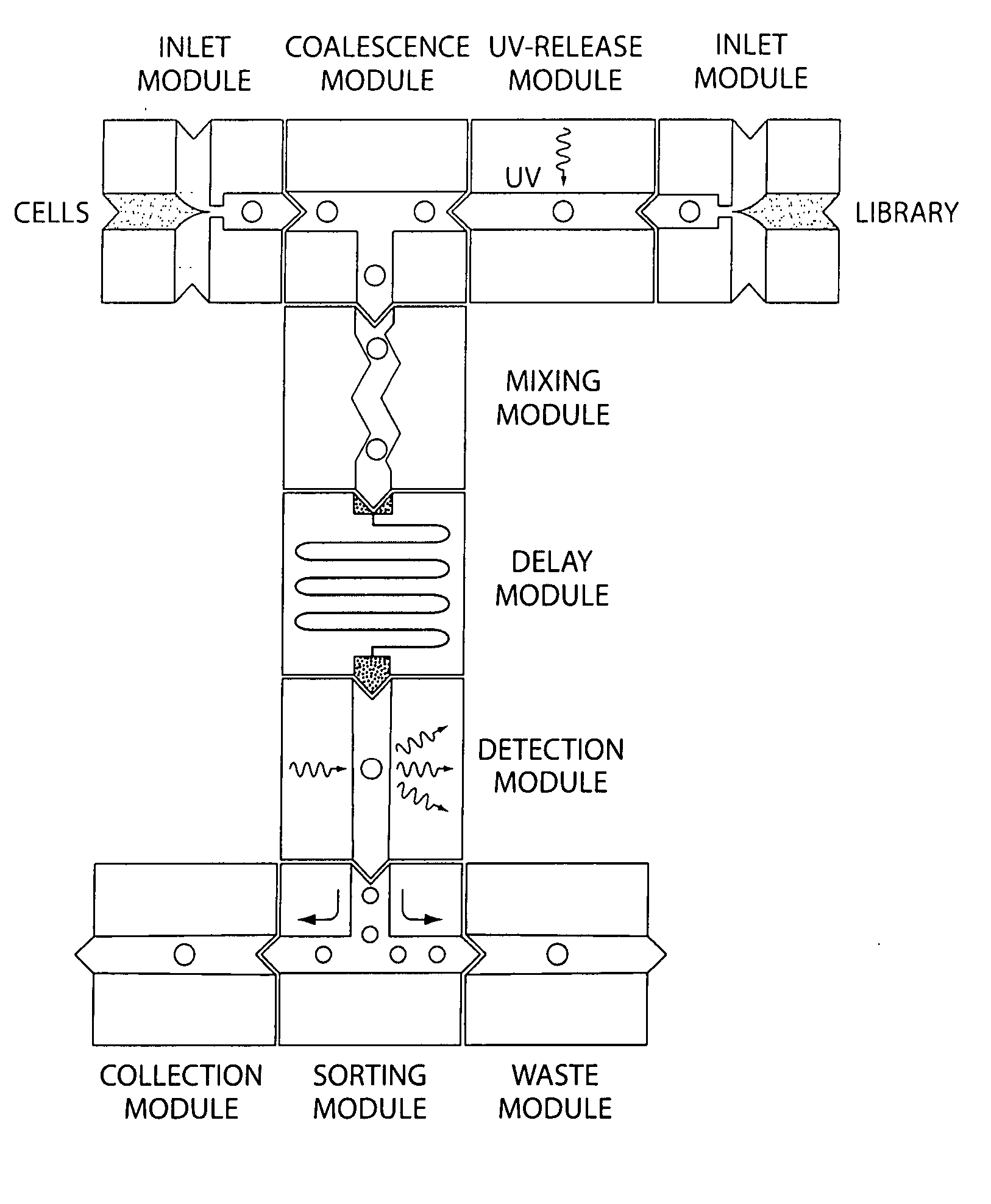
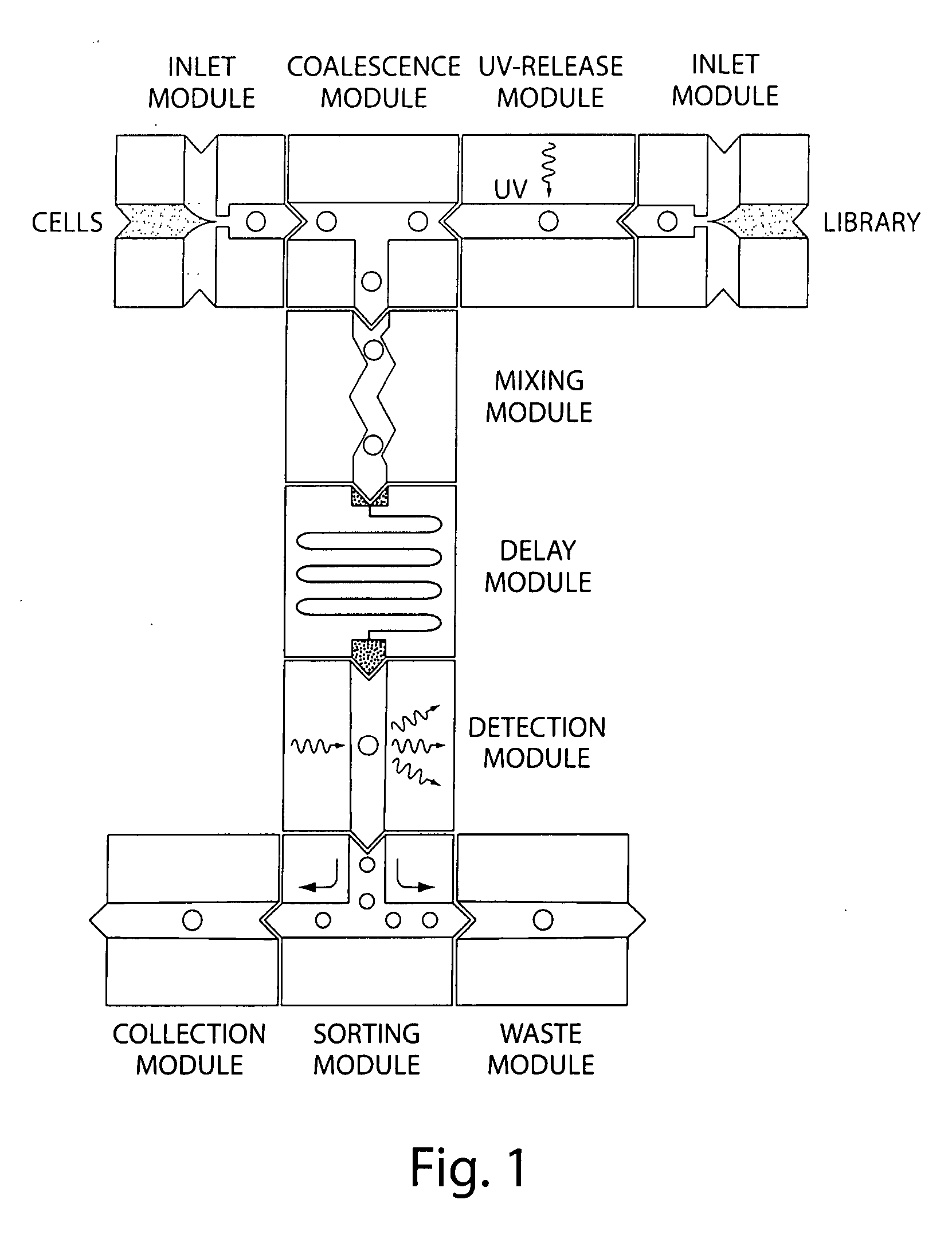
System for mixing fluids by coalescence of multiple emulsions
ActiveUS20110053798A1High-confidence resultLower the volumeSequential/parallel process reactionsHeating or cooling apparatusEmulsionChemistry
System, including methods, apparatus, compositions, and kits, for the mixing of small volumes of fluid by coalescence of multiple emulsions.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Compositions and methods for liquid metering in microchannels
InactiveUS20030070677A1Material nanotechnologyShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersElectrophoresisComputer module
The movement and mixing of microdroplets through microchannels is described employing microscale devices, comprising microdroplet transport channels, reaction regions, electrophoresis modules, and radiation detectors. Microdroplets are metered into defined volumes and are subsequently incorporated into a variety of biological assays. Electronic components are fabricated on the same substrate material, allowing sensors and controlling circuitry to be incorporated in the same device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Apparatuses and methods for field flow fractionation of particles using acoustic and other forces
InactiveUS6881314B1Easy to separateEfficient separationDielectrophoresisElectrostatic separatorsElectrophoresisDielectrophoretic force
This invention relates generally to the field of field-flow-fractionation. In particular, the invention provides apparatuses and methods for the discrimination of matters utilizing acoustic force, or utilizing acoustic force with electrophoretic or dielectrophoretic force, in field flow fractionation.
Owner:AVIVA BIOISCI CORP +2
Microfluidic devices for methods development
InactiveUS6880576B2Material nanotechnologySludge treatmentChromatographic separationFlow resistivity
Microfluidic devices with multiple fluid process regions for subjecting similar samples to different process conditions in parallel are provided. One or more common fluid inputs may be provided to minimize the number of external fluid supply components. Solid materials such as chromatographic separation media or catalyst media is preferably provided in each fluid process region. Solid materials may be supplied to the devices in the form of slurry, with particles retained by porous elements or frits. Different fluid process regions may having different effective lengths, different solid material types or amounts, or may receive different ratios of common fluids supplied to the device. The flow resistances of dissimilar fluid process regions may be balanced passively with the addition of impedance elements in series with each fluid process region.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Chemico-mechanical microvalve and devices comprising the same
InactiveUS6375901B1Fixed microstructural devicesVolume/mass flow measurementBiomedical engineeringMicro valve
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
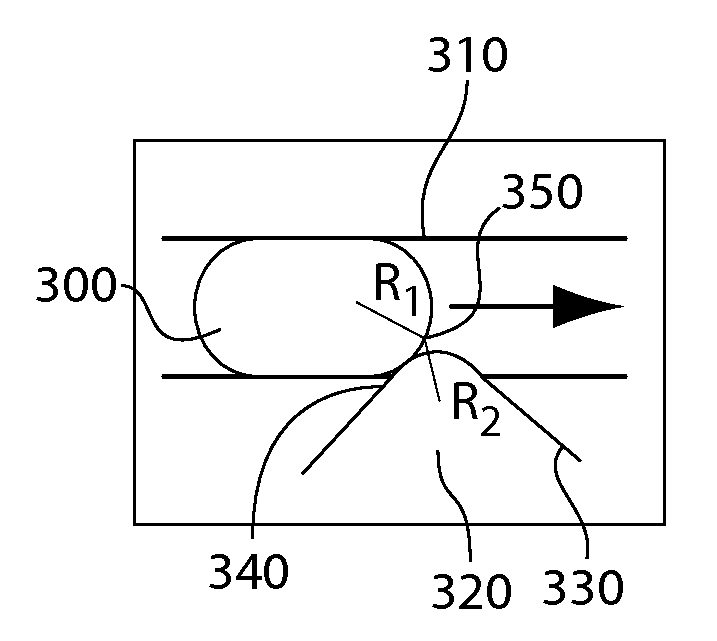
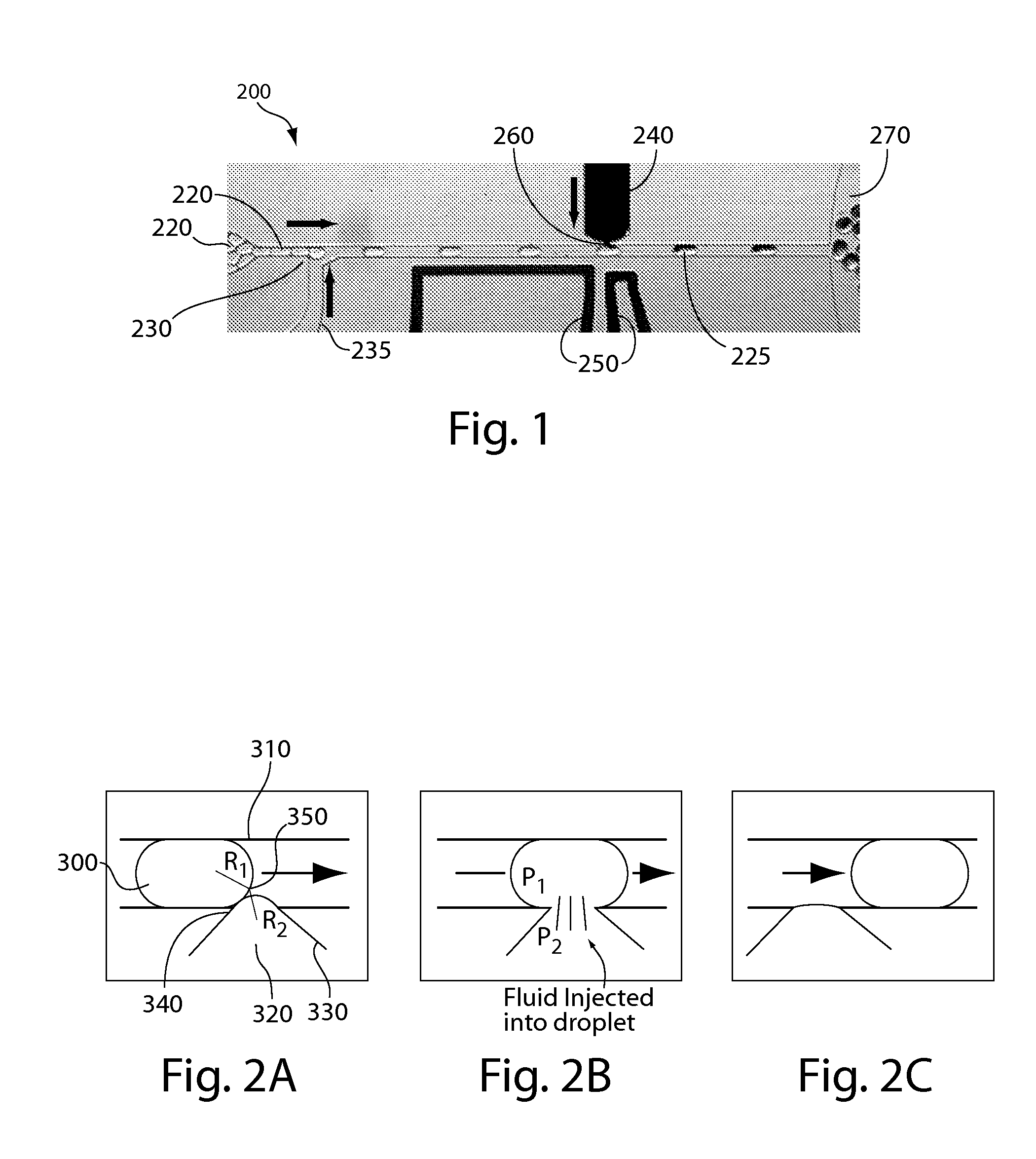
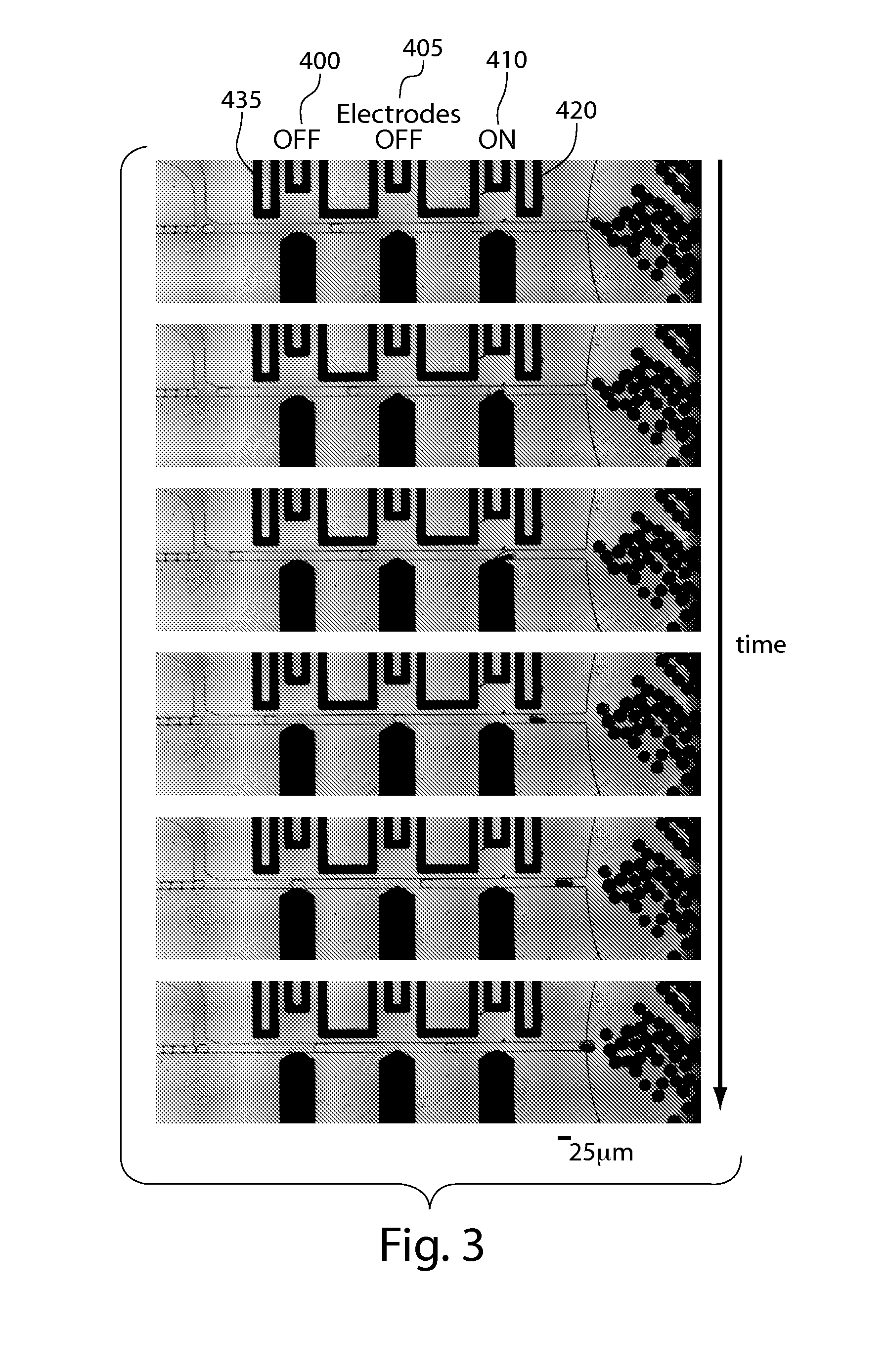
Fluid injection
ActiveUS20120132288A1Avoid enteringValve arrangementsFlow mixersBiomedical engineeringFluid injection
The present invention generally relates to systems and methods for the control of fluids and, in some cases, to systems and methods for flowing a fluid into and / or out of other fluids. As examples, fluid may be injected into a droplet contained within a fluidic channel, or a fluid may be injected into a fluidic channel to create a droplet. In some embodiments, electrodes may be used to apply an electric field to one or more fluidic channels, e.g., proximate an intersection of at least two fluidic channels. For instance, a first fluid may be urged into and / or out of a second fluid, facilitated by the electric field. The electric field, in some cases, may disrupt an interface between a first fluid and at least one other fluid. Properties such as the volume, flow rate, etc. of a first fluid being urged into and / or out of a second fluid can be controlled by controlling various properties of the fluid and / or a fluidic droplet, for example curvature of the fluidic droplet, and / or controlling the applied electric field.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Device and method for pressure-driven plug transport and reaction
ActiveUS20050087122A1Eliminate evaporationWell mixedMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsPressure.driveCarrier fluid
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Parallel flow process optimization reactors
InactiveUS20020048536A1Extreme flexibilityAdvantageously and flexibly employedProcess control/regulationSequential/parallel process reactionsProcess optimizationDistribution system
Owner:FREESLATE
Microfluidic Chemical Reaction Circuits
InactiveUS20080281090A1Shaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingChemical reactionCompound (substance)
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +3
Microfludic system (EDI)
InactiveUS6717136B2Minimal loss of precious materialCheap and disposableIon-exchange process apparatusMaterial nanotechnologyAnalyteEngineering
A microfluidic device comprising an MS-analyte presentation unit for a EDI-MS apparatus, said unit comprising an essentially planar support plate which on one side has one, two or more ports (MS-ports) comprising an area (EDI area) for presenting the MS-analyte to a mass spectrometer. The EDI area comprises a layer I of conducting material. The characteristic feature of the device is that layer (I) has a conductive connection and / or that there is a calibrator area in the proximity of the MS-port.
Owner:GYROS
Manifold designs, and flow control in multichannel microchannel devices
InactiveUS20050087767A1Equally distributedLow costChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineering
Owner:VELOCYS CORPORATION
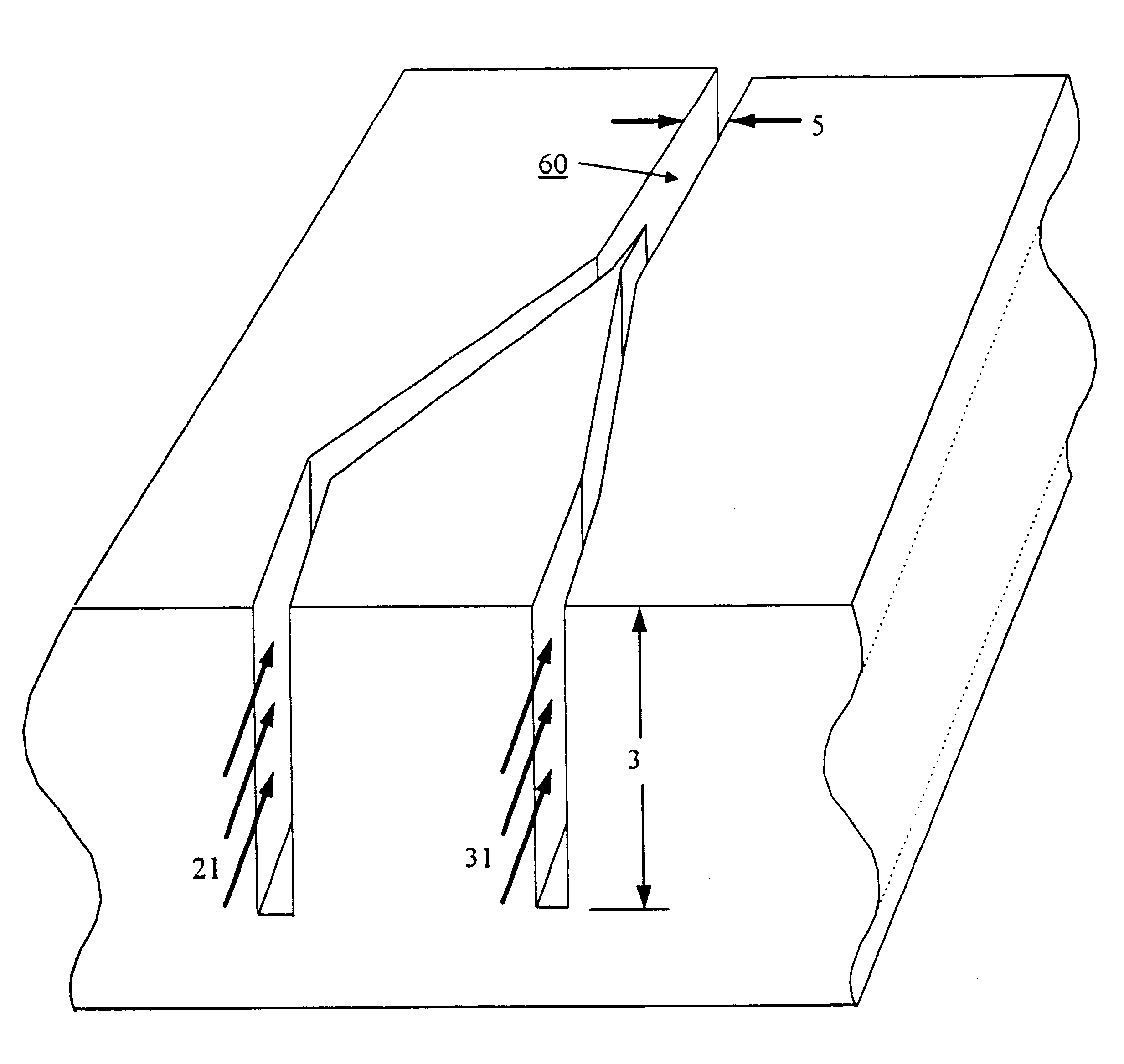
Device for parallel and synchronous injection for sequential injection of different reagents
InactiveUS20030082081A1Exhaust apparatusChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsInjection volumeBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a microfluidic device for injecting series of mobile reaction chambers (102, 103) having non-miscible segmenters (101) in microchannels (21 to 26), comprising: injection means (10) for injecting into microreaction channels alternatingly and in parallel liquid to form mobile reaction chambers and liquid for forming the segmenters; means for controlling the progression of one of the two liquids, applied to act on one zone (31) of each microchannel delimiting an injection volume of said liquid; the control means being able to cause stopping or slowing of the progression of said liquid over the zone of each microchannel by exerting an action based on a physico-chemical property of the liquid and said action not affecting the other liquid.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Microfluidic rotary flow reactor matrix
InactiveUS20050037471A1Economy of scale in reagent consumptionMinimizing pipetting stepBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusEngineeringMedical diagnosis
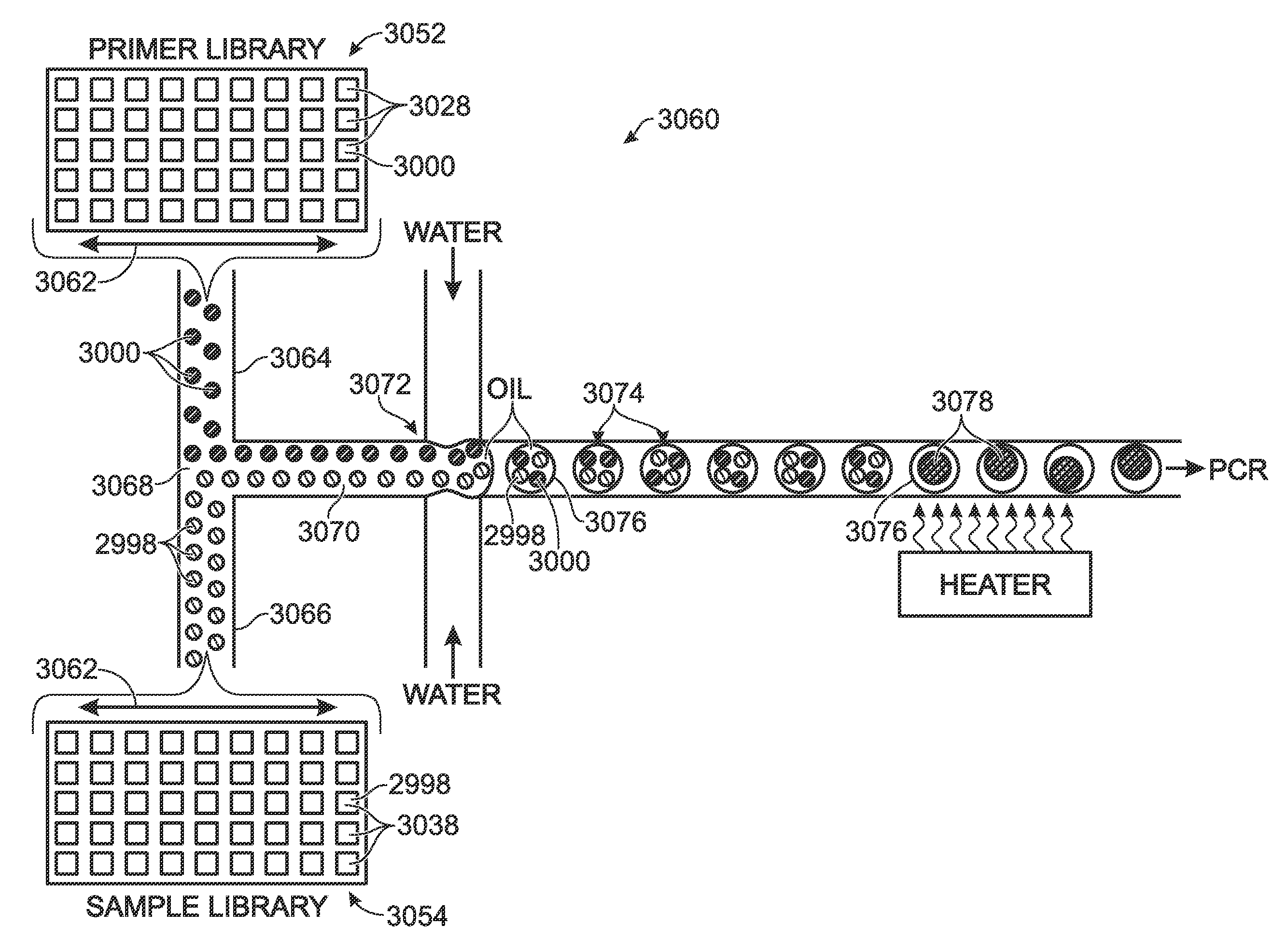
A microfluidic device comprises a matrix of rotary flow reactors. The microfluidic matrix device offers a solution to the “world-to-chip” interface problem by accomplishing two important goals simultaneously: an economy of scale in reagent consumption is achieved, while simultaneously minimizing pipetting steps. N2 independent assays can be performed with only 2N+1 pipetting steps, using a single aliquot of enzyme amortized over all reactors. The chip reduces labor relative to conventional fluid handling techniques by using an order of magnitude less pipetting steps, and reduces cost by consuming two to three orders of magnitude less reagents per reaction. A PCR format has immediate applications in medical diagnosis and gene testing. Beyond PCR, the microfluidic matrix chip provides a universal and flexible platform for biological and chemical assays requiring parsimonious use of precious reagents and highly automated processing.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com