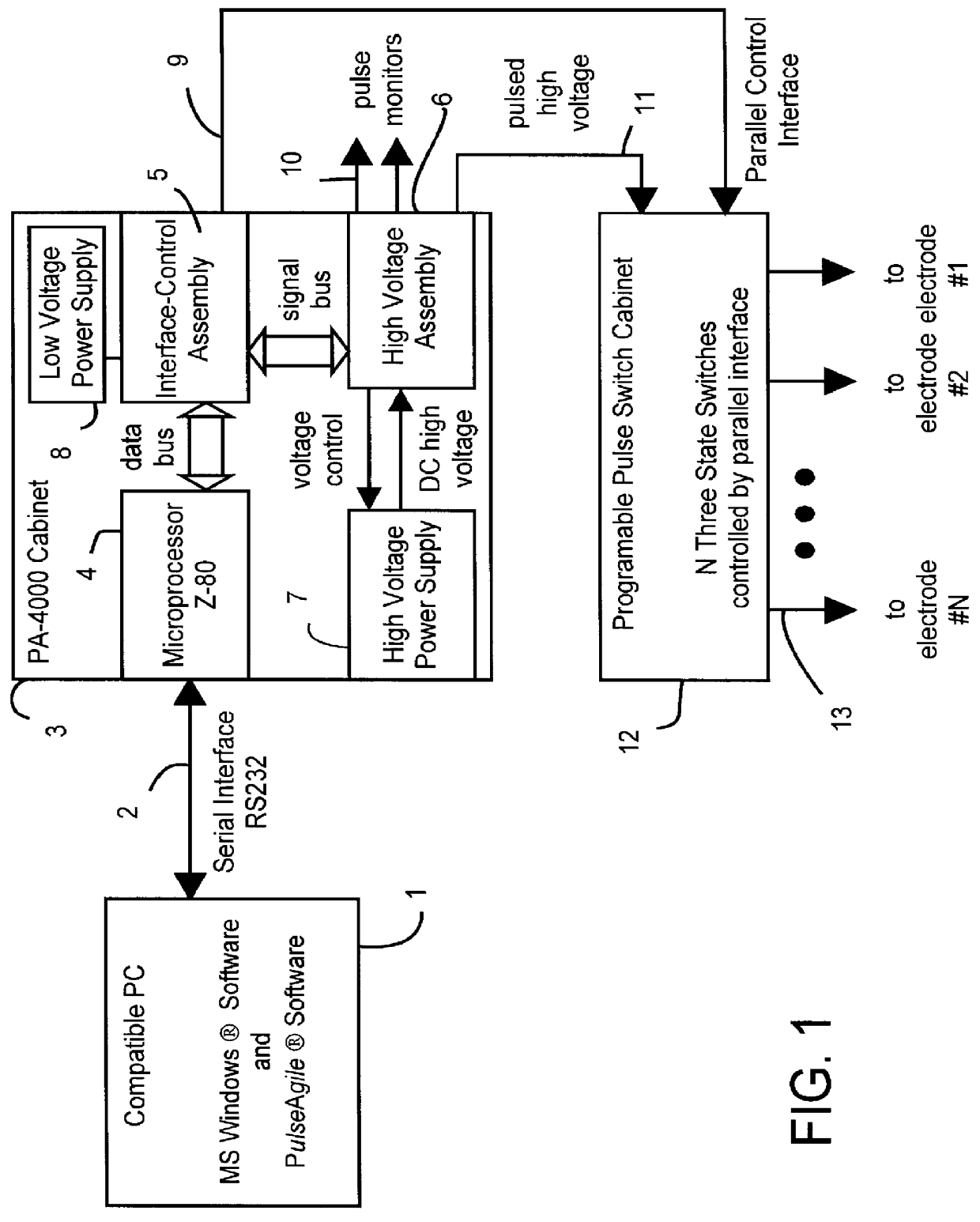
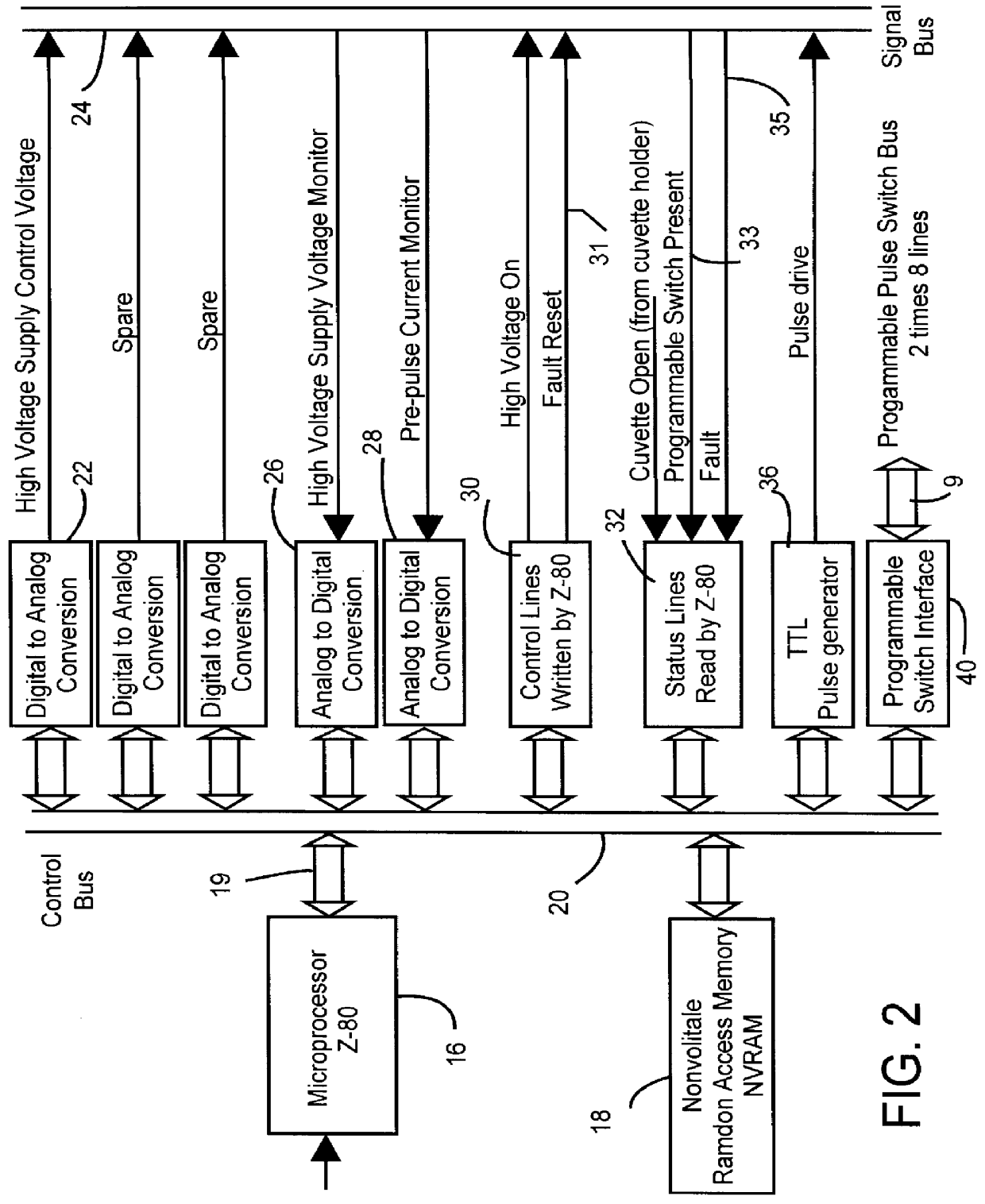
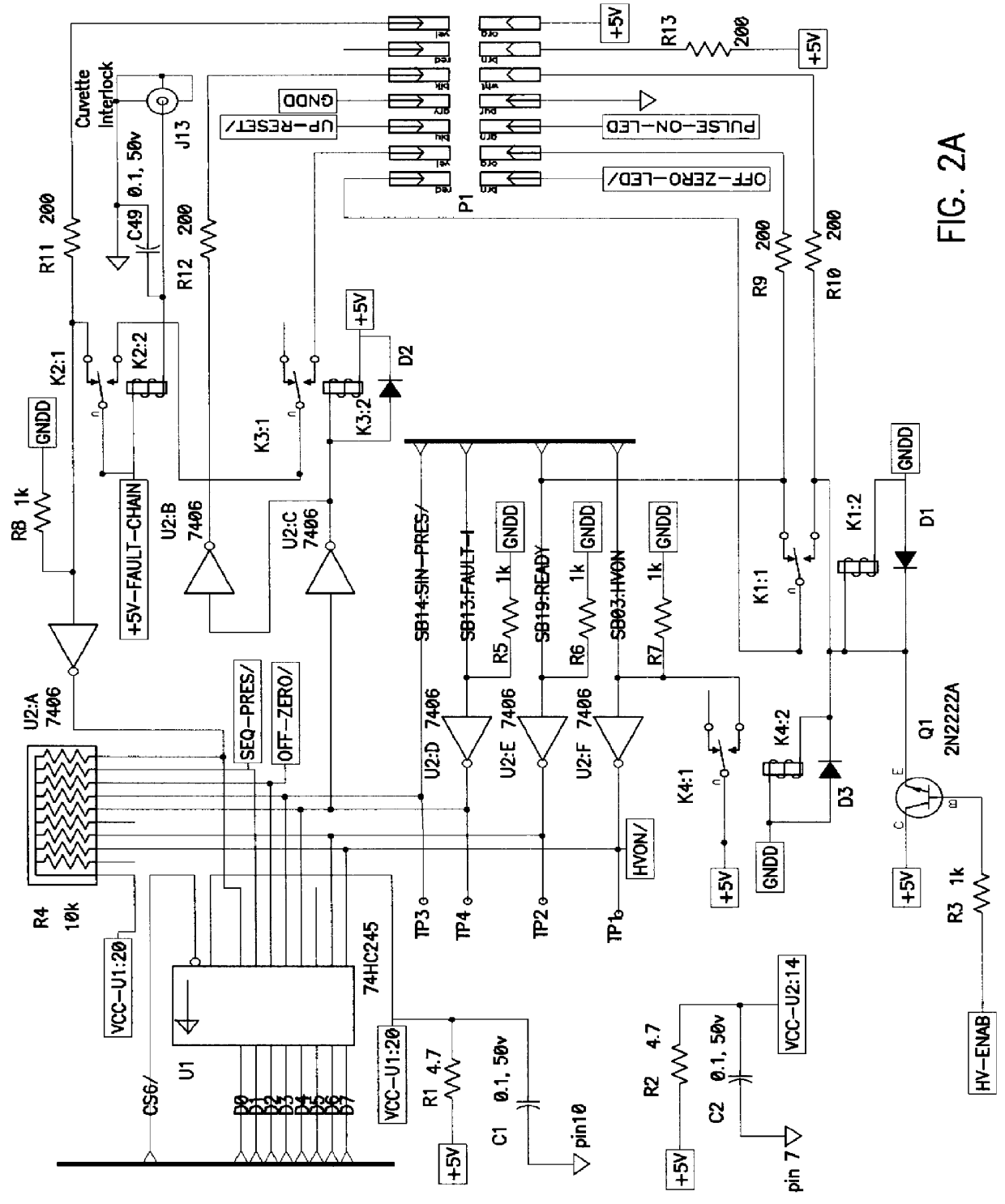
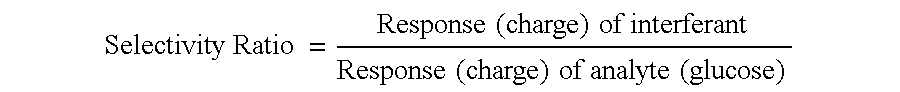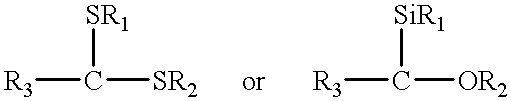Patents
Literature
1315results about "Liquid separation by electricity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
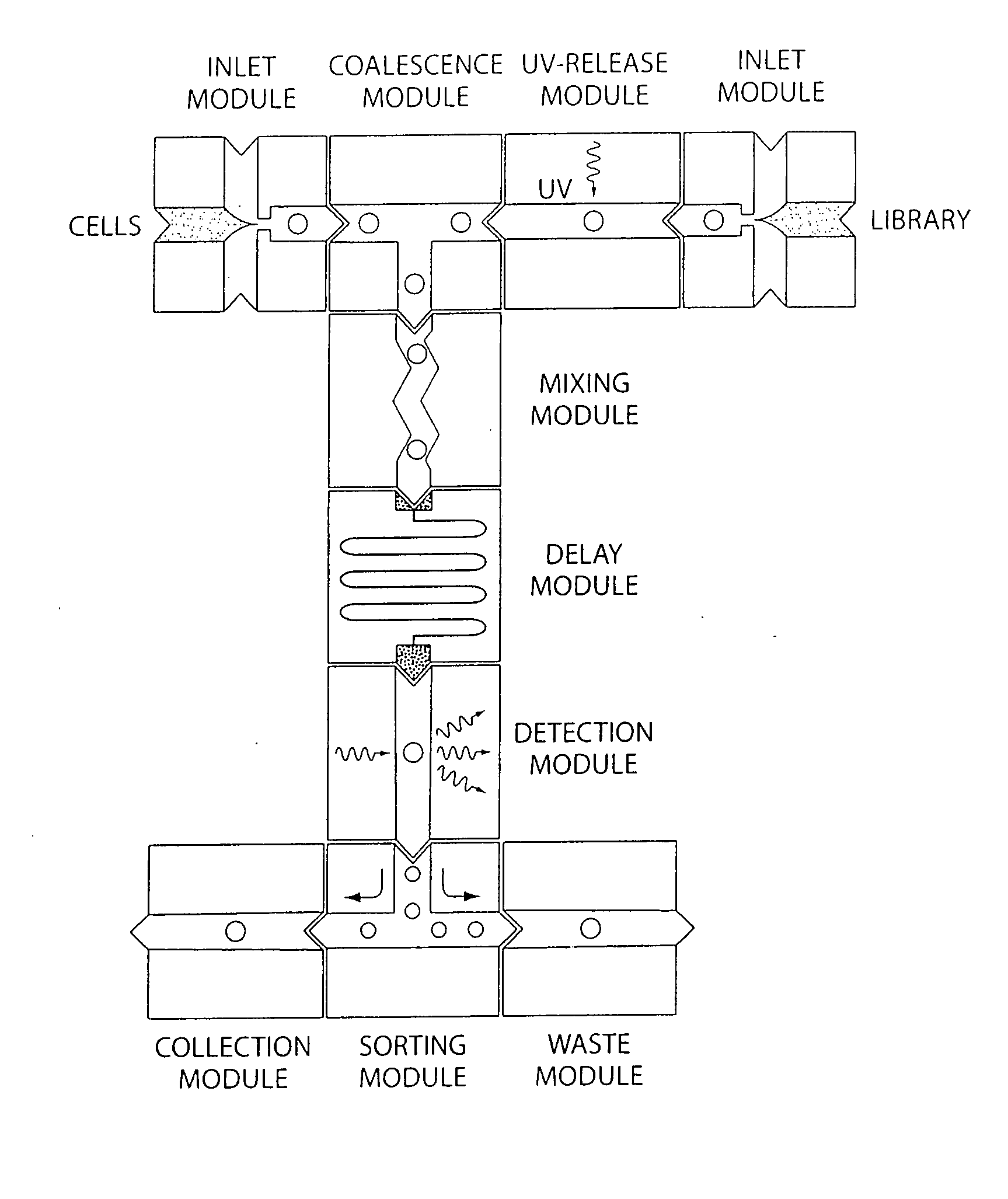
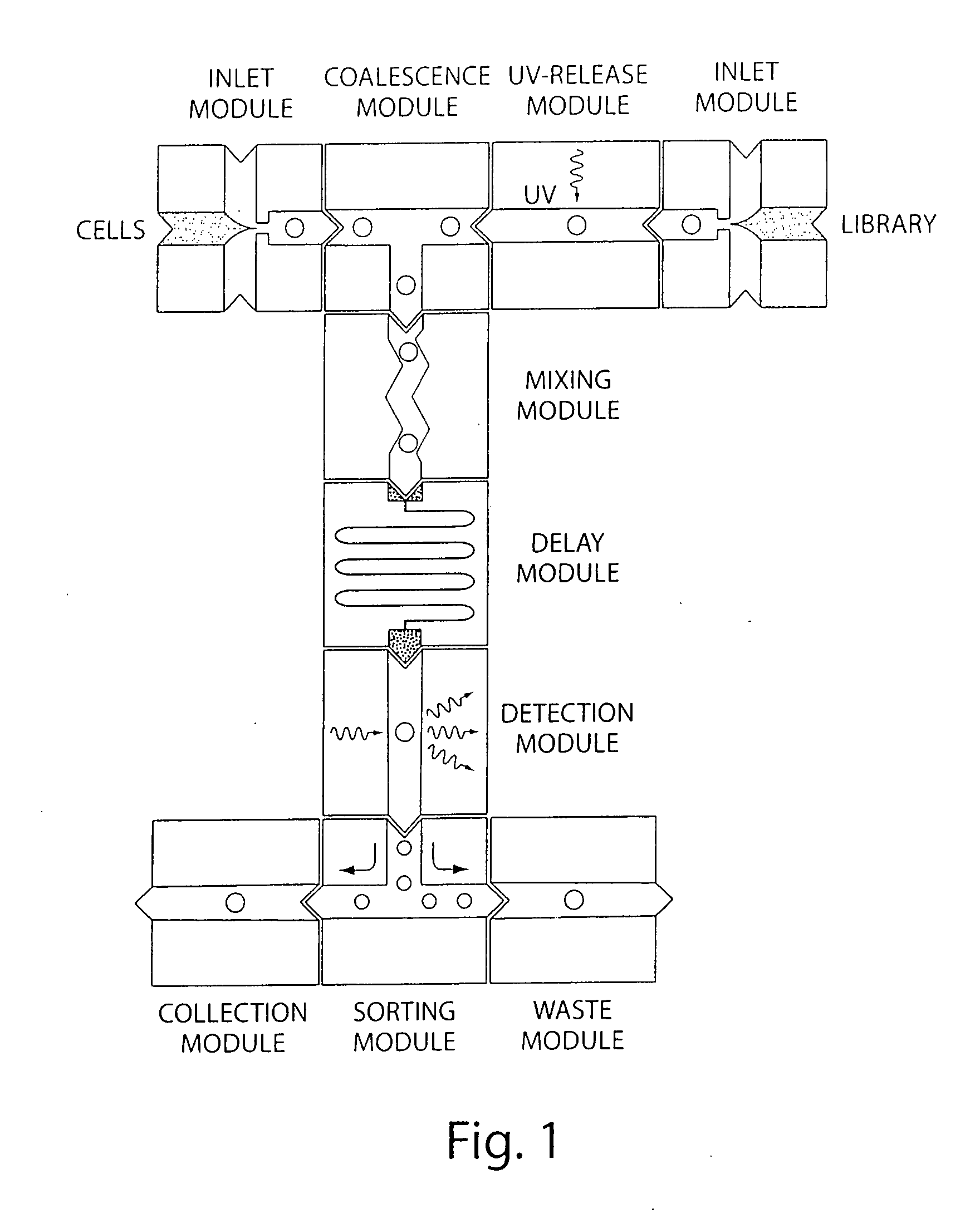
Microfluidic devices and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20080014589A1Eliminates surface wettingDielectrophoresisLiquid separation by electricityComputer moduleBiomedical engineering
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
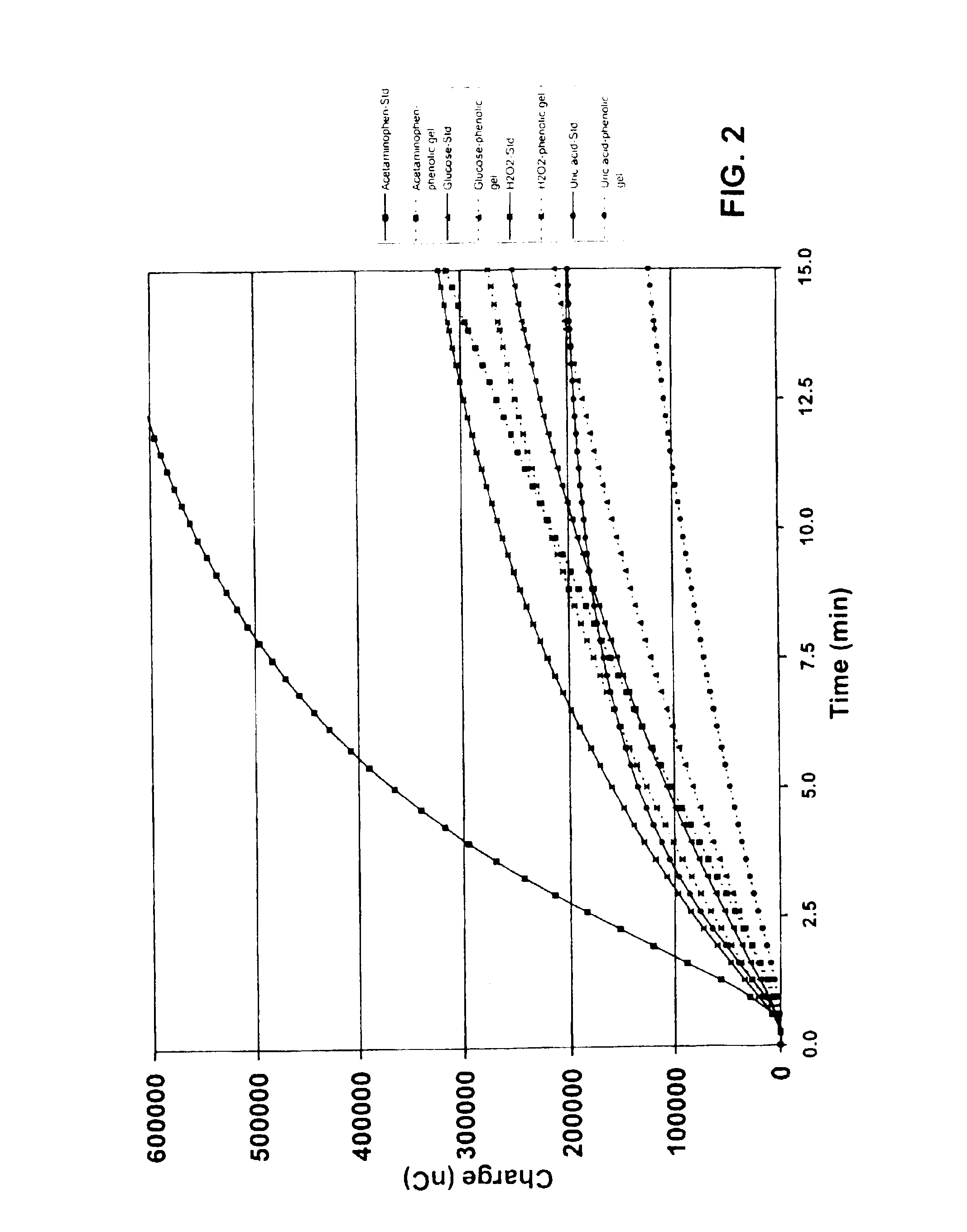
Glucose measuring assembly with a hydrogel
InactiveUS6902905B2Reduce presenceIncrease percentagePowder deliveryElectrotherapyIontophoresis therapyAnalyte
This invention relates to methods for reducing the presence of a compound in an ionically conductive material, e.g., for use in iontophoretic devices, wherein the presence of the compound interferes with detecting a selected analyte. Removal of the compound can typically take place either during or after the manufacture of the ionically conductive material or an assembly comprising this material. Also disclosed are methods for generating selectively permeable barriers on the reactive faces of electrodes. Further, this invention relates to hydrogels comprising one or more biocides, as well as assemblies containing such hydrogels.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC +1
Method for using magnetic particles in droplet microfluidics
ActiveUS20090283407A1Increasing concentration of targetReduce concentrationElectrostatic separatorsLiquid separation by electricityEngineeringDroplet microfluidics
Methods of utilizing magnetic particles or beads (MBs) in droplet-based (or digital) microfluidics are disclosed. The methods may be used in enrichment or separation processes. A first method employs the droplet meniscus to assist in the magnetic collection and positioning of MBs during droplet microfluidic operations. The sweeping movement of the meniscus lifts the MBs off the solid surface and frees them from various surface forces acting on the MBs. A second method uses chemical additives to reduce the adhesion of MBs to surfaces. Both methods allow the MBs on a solid surface to be effectively moved by magnetic force. Droplets may be driven by various methods or techniques including, for example, electrowetting, electrostatic, electromechanical, electrophoretic, dielectrophoretic, electroosmotic, thermocapillary, surface acoustic, and pressure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
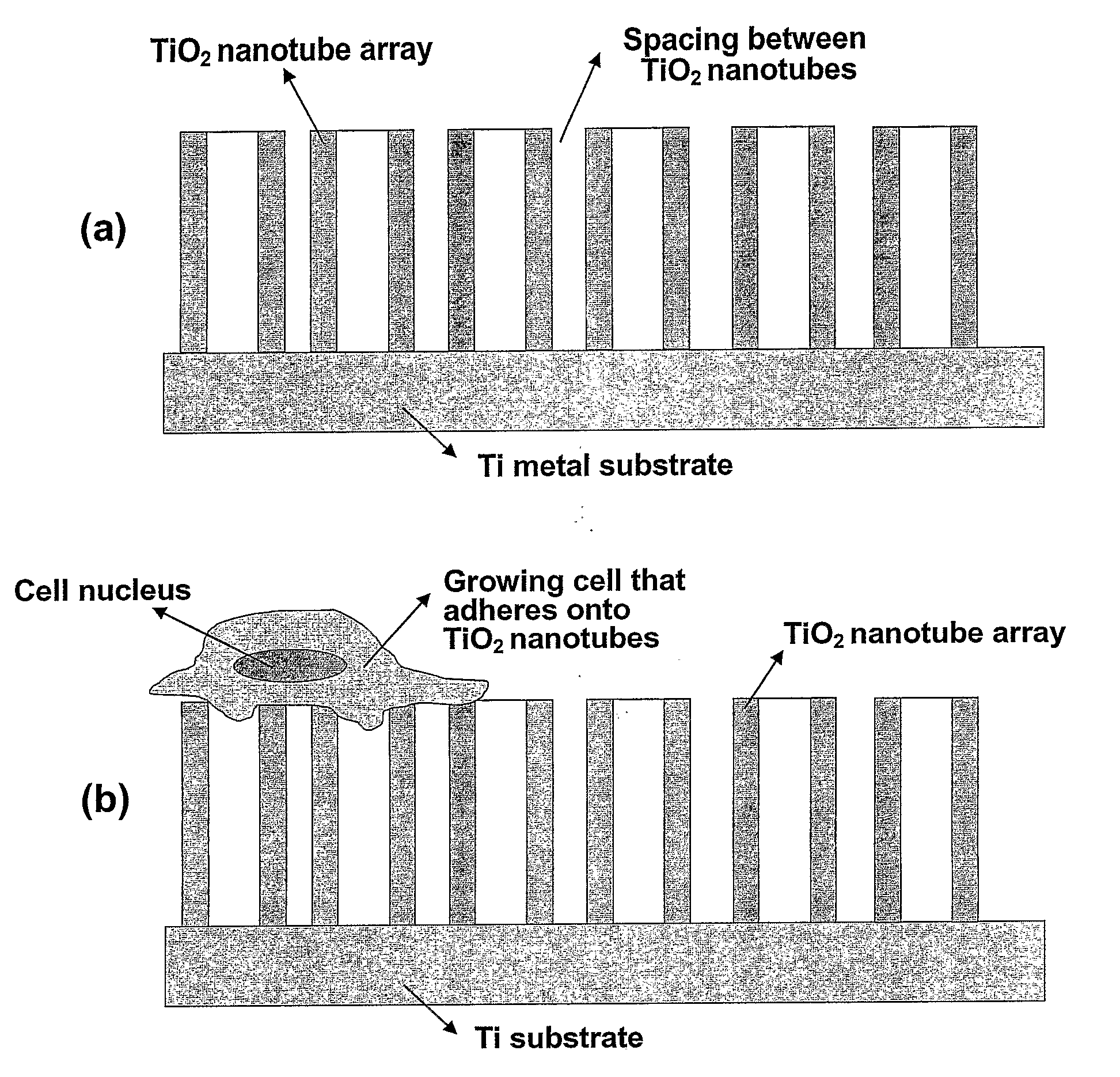
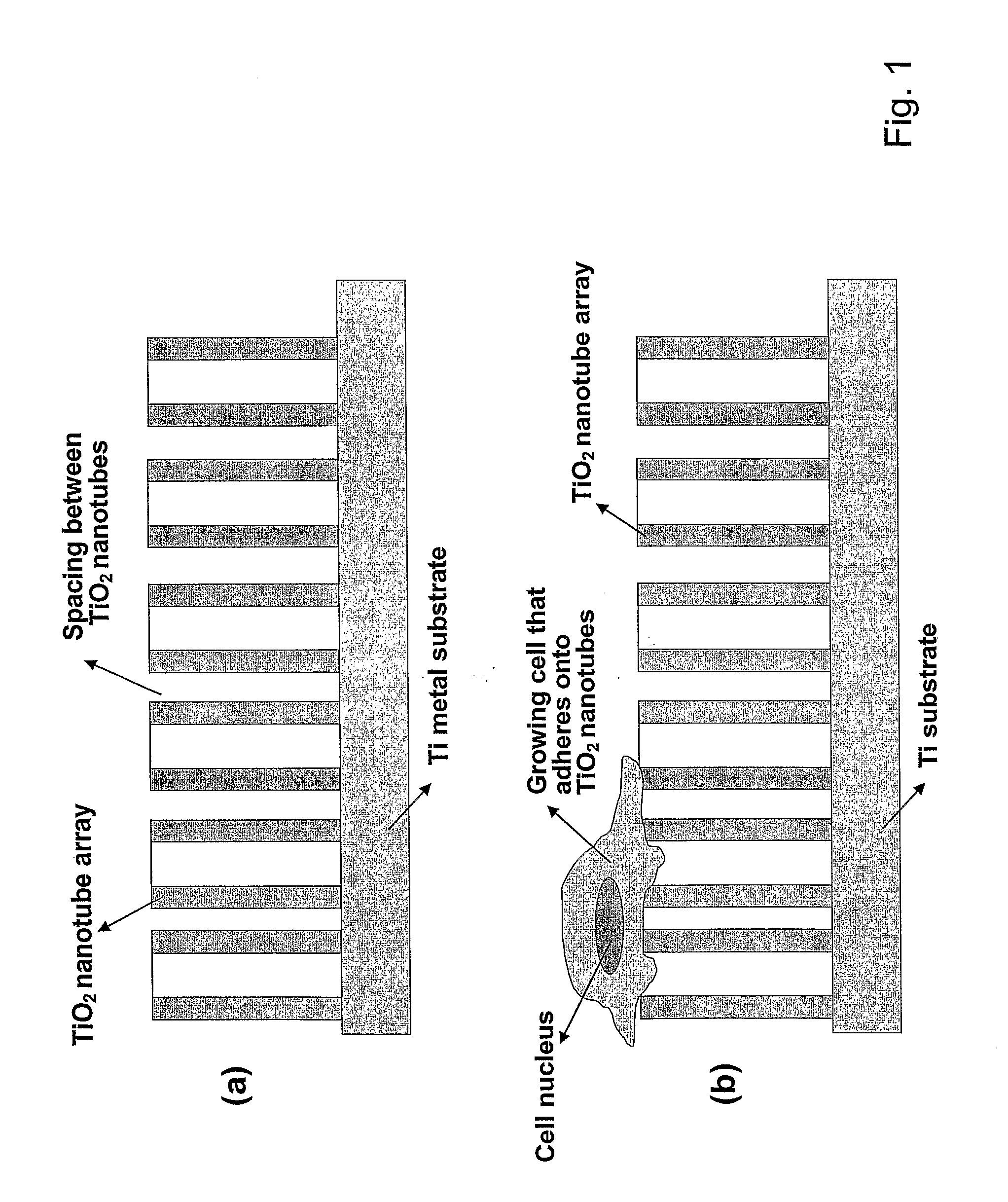
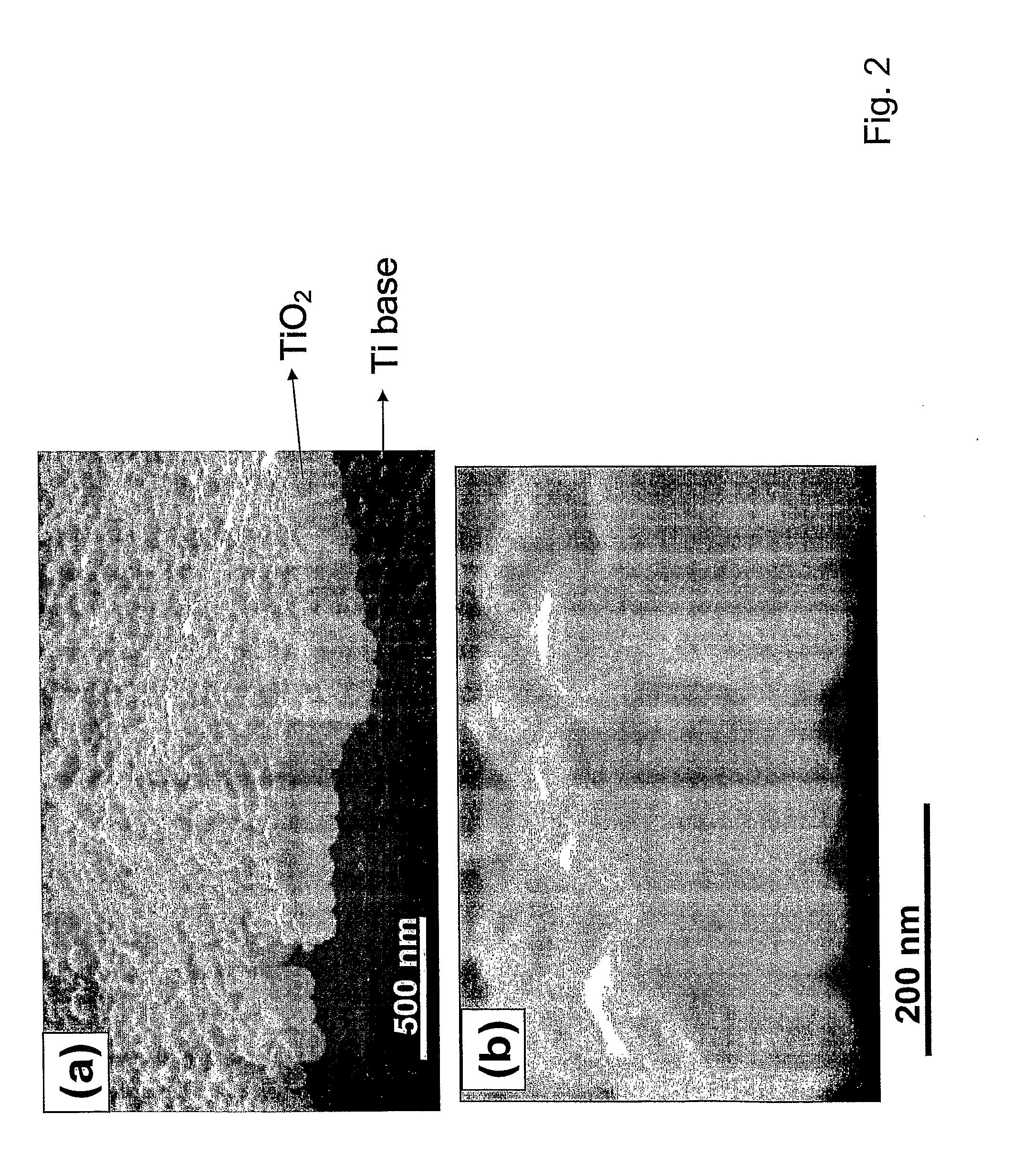
Compositions comprising nanostructures for cell, tissue and artificial organ growth, and methods for making and using same
ActiveUS20090220561A1Improve bone formationIncreased durabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsIn vivoNanostructure
The invention provides articles of manufacture comprising biocompatible nanostructures comprising nanotubes and nanopores for, e.g., organ, tissue and / or cell growth, e.g., for bone, kidney or liver growth, and uses thereof, e.g., for in vitro testing, in vivo implants, including their use in making and using artificial organs, and related therapeutics. The invention provides lock-in nanostructures comprising a plurality of nanopores or nanotubes, wherein the nanopore or nanotube entrance has a smaller diameter or size than the rest (the interior) of the nanopore or nanotube. The invention also provides dual structured biomaterial comprising micro- or macro-pores and nanopores. The invention provides biomaterials having a surface comprising a plurality of enlarged diameter nanopores and / or nanotubes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
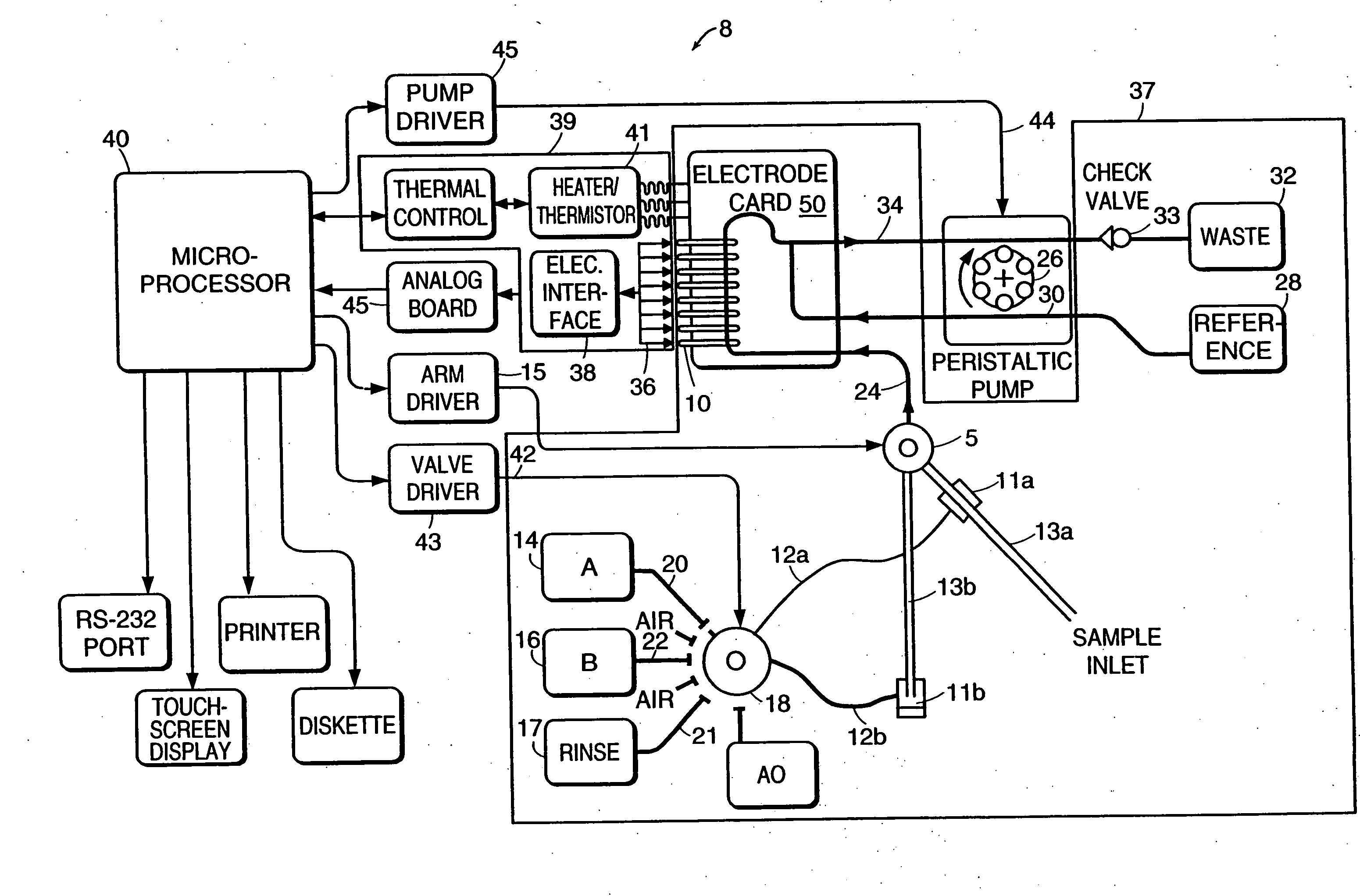
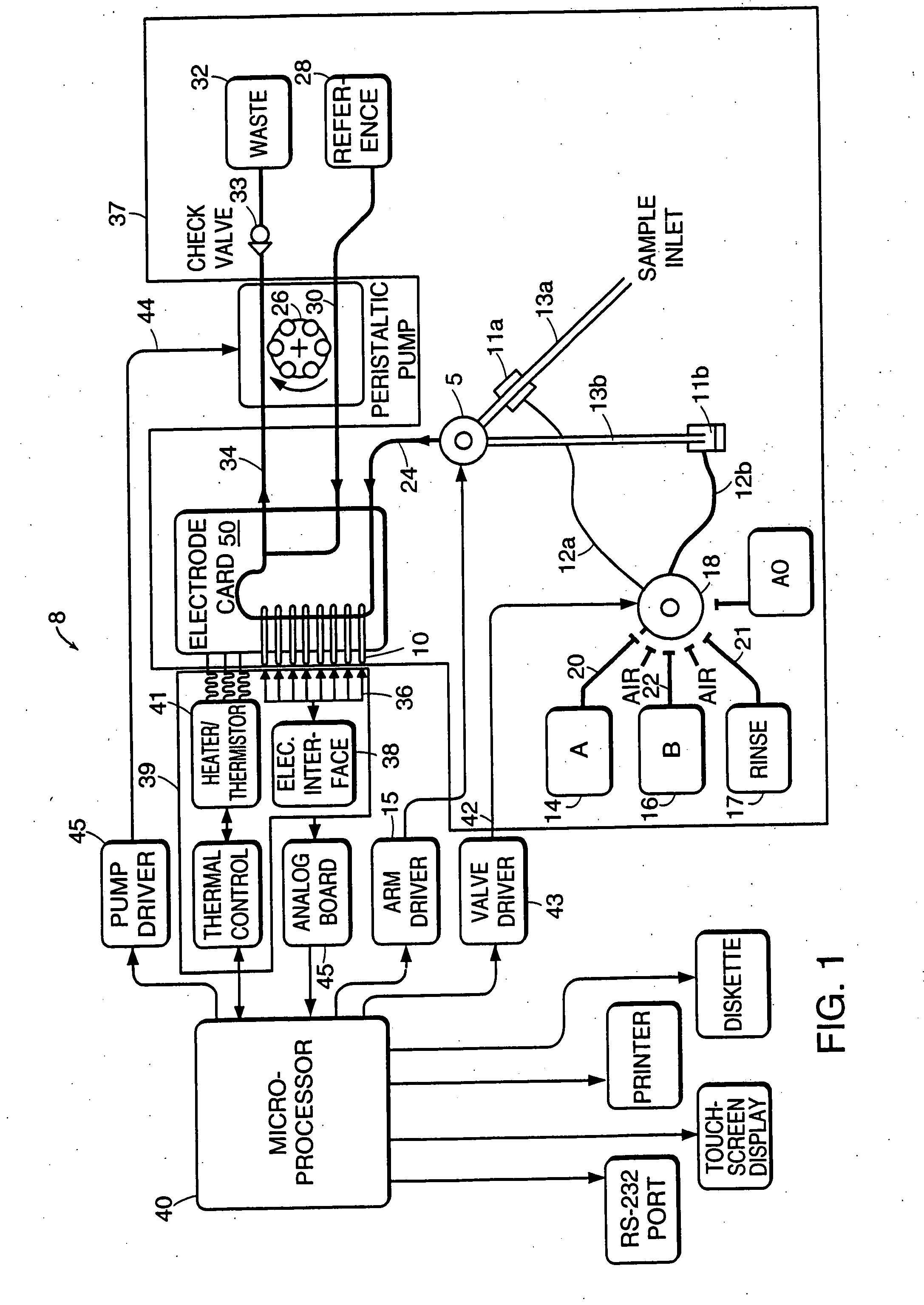
Universal sample preparation system and use in an integrated analysis system
The invention provides for devices and methods for interfacing microchips to cartridges and pneumatic manifolds. The cartridges, microchips, and pneumatic manifolds can be integrated with downstream preparation devices, such as thermal regulating devices and separation and analysis devices.
Owner:INTEGENX
Aqueous treatment apparatus utilizing precursor materials and ultrasonics to generate customized oxidation-reduction-reactant chemistry environments in electrochemical cells and/or similar devices
ActiveUS20110024361A1Prevent precipitationReduce maintenance costsFrom normal temperature solutionsLiquid separation by electricityEnvironmental chemistrySet point
An electrochlorination and electrochemical system for the on-site generation and treatment of municipal water supplies and other reservoirs of water, by using a custom mixed oxidant and mixed reductant generating system for the enhanced destruction of water borne contaminants by creating custom oxidation-reduction-reactant chemistries with real time monitoring. A range of chemical precursors are provided that when acted upon in an electrochemical cell either create an enhanced oxidation, or reduction environment for the destruction or control of contaminants. Chemical agents that can be used to control standard water quality parameters such as total hardness, total alkalinity, pH, total dissolved solids, and the like are introduced via the chemical precursor injection subsystem infrequently or in real time based on sensor inputs and controller set points.
Owner:GLOBAL WATER INVESTMENTS LLC
Method and apparatus for sustainable energy and materials
A process for the production of hydrogen from anaerobically decomposed organic materials by applying an electric potential to the anaerobically decomposed organic materials, including landfill materials and sewage, to form hydrogen, and for decreasing the time required to treat these anaerobically decomposed organic materials. The organic materials decompose to volatile acids such as acetic acid, which may be hydrolyzed by electric current to form hydrogen. The process may be continuously run in sewage digestion tanks with the continuous feed of sewage, at landfill sites, or at any site having a supply of anaerobically decomposed or decomposable organic materials.
Owner:MCALISTER TECH LLC +1
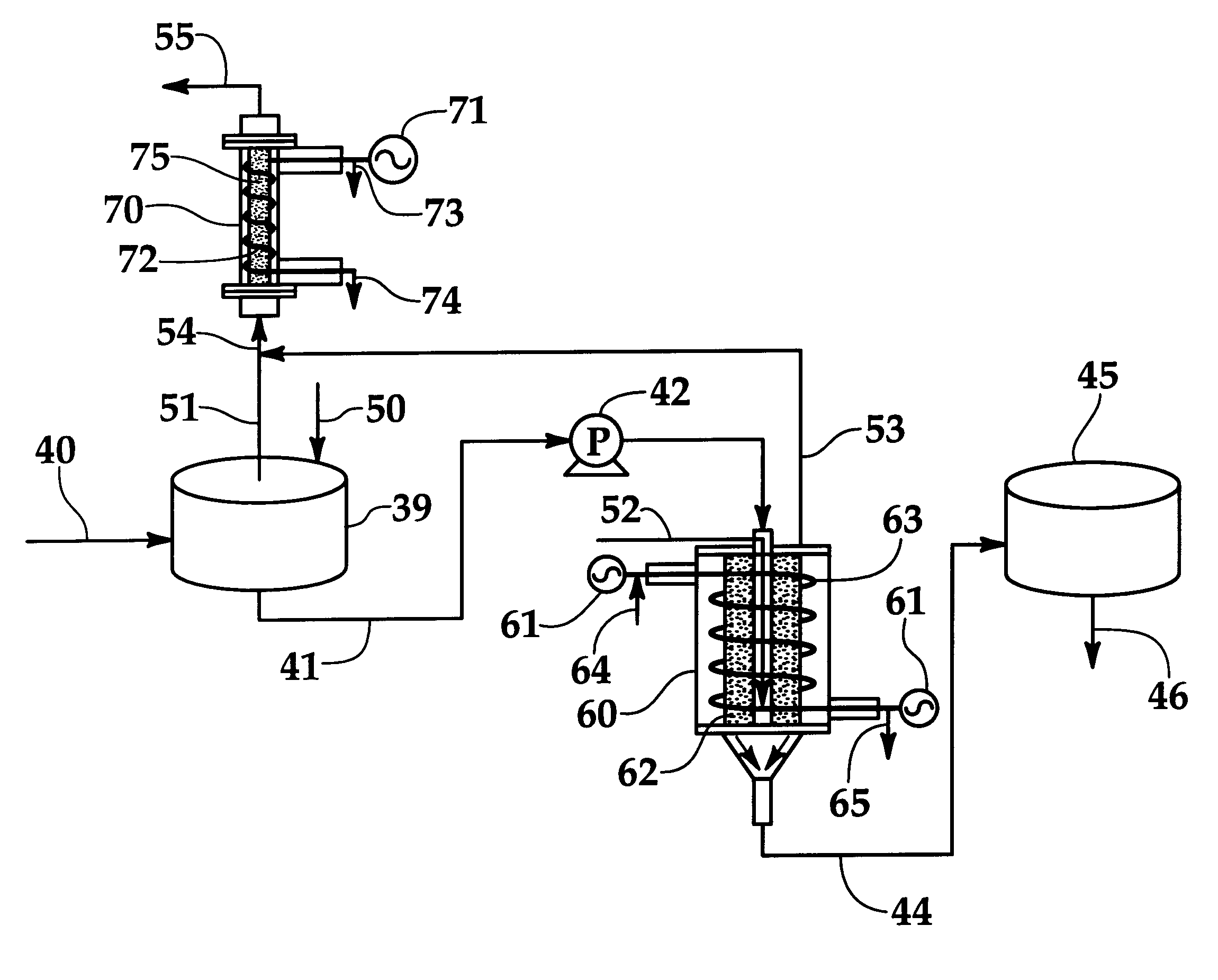
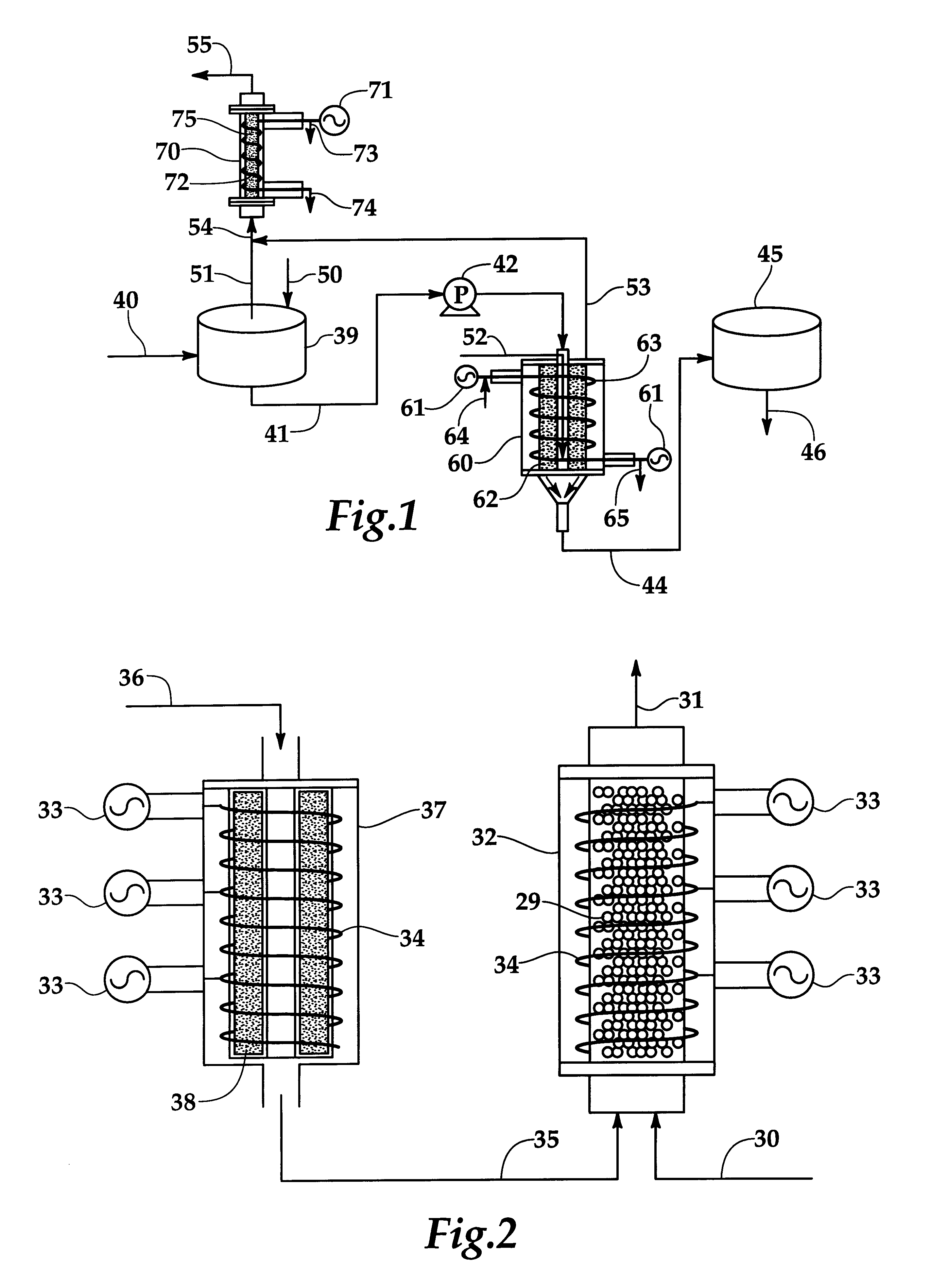
Apparatus and method for separation of particles suspended in a liquid from the liquid in which they are suspended
InactiveUS20100078384A1Improve concentrationAvoid turbulenceSemi-permeable membranesLiquid separation by electricityUltrasonic sensorCompressibility
A method for separating, or removing, particulate material, e.g., blood cells, from a sample of fluid, e.g., whole blood of a patient, in which the particulate material is suspended. In the case of separating blood cells from blood plasma or blood serum, the resulting samples of blood plasma or blood serum can be used for in vitro diagnostic applications. In normal practice, a whole blood sample of a patient are provided and then introduced into an apparatus that contains a flow channel. An acoustic field, which contains acoustic standing waves from external ultrasonic transducers, is located within the flow channel. Laminar flow is maintained in the flow channel. Blood cells and platelets are separated from blood plasma or blood serum at the end of the flow channel and collected. The method described herein allows fluid components to differentially migrate to areas of preferred acoustic interaction. The parameters that affect separation of particles are size, density, compressibility of the particles, and the fluid surrounding the particles.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Alignment of carbon nanotubes using magnetic particles
InactiveUS20050239948A1Material nanotechnologyLiquid separation by electricityMagnetite NanoparticlesNanometre
Methods are provided for aligning carbon nanotubes and for making a composite material comprising aligned carbon nanotubes. The method for aligning carbon nanotubes comprises adsorbing magnetic nanoparticles to carbon nanotubes dispersed in a fluid medium to form a magnetic particle-carbon nanotube composite in the fluid medium; and exposing the composite to a magnetic field effective to align the nanotubes in the fluid medium. The method for making a composite material comprising aligned carbon nanotubes comprises (1) adsorbing magnetic nanoparticles to carbon nanotubes to form a magnetic particle-carbon nanotube composite; (2) dispersing the magnetic particle-carbon nanotube composite in a fluid matrix material to form a mixture; (3) exposing the mixture to a magnetic field effective to align the nanotubes in the mixture; and (4) solidifying the fluid matrix material to form a nanotube / matrix material composite comprising the aligned nanotubes which remain aligned in the absence of said magnetic field.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE RES FOUND +1
Electroporation electrode configuration and methods
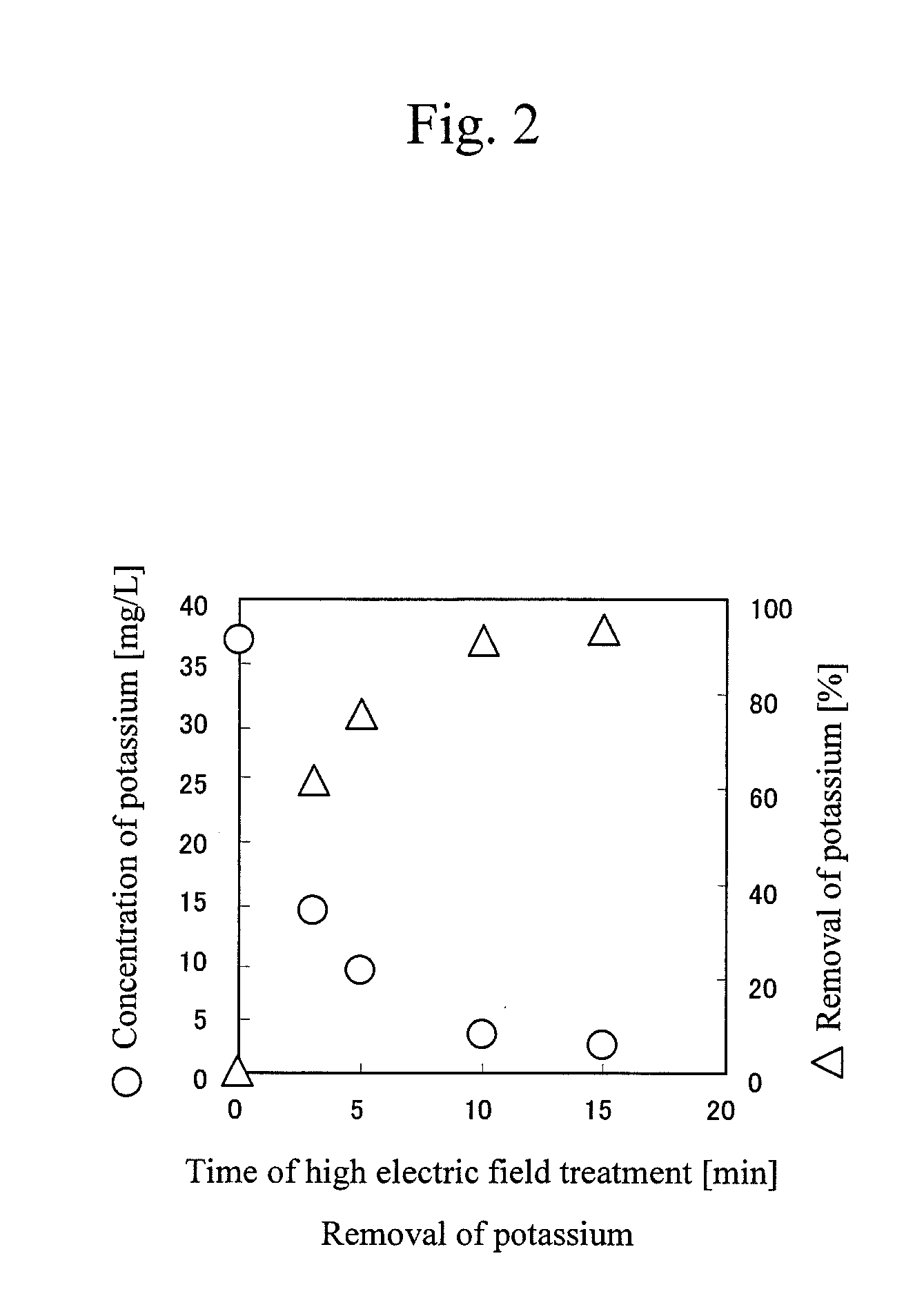
InactiveUS20130196441A1High electric fieldReduce potential differenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsLiquid separation by electricityPotential differenceElectroporation
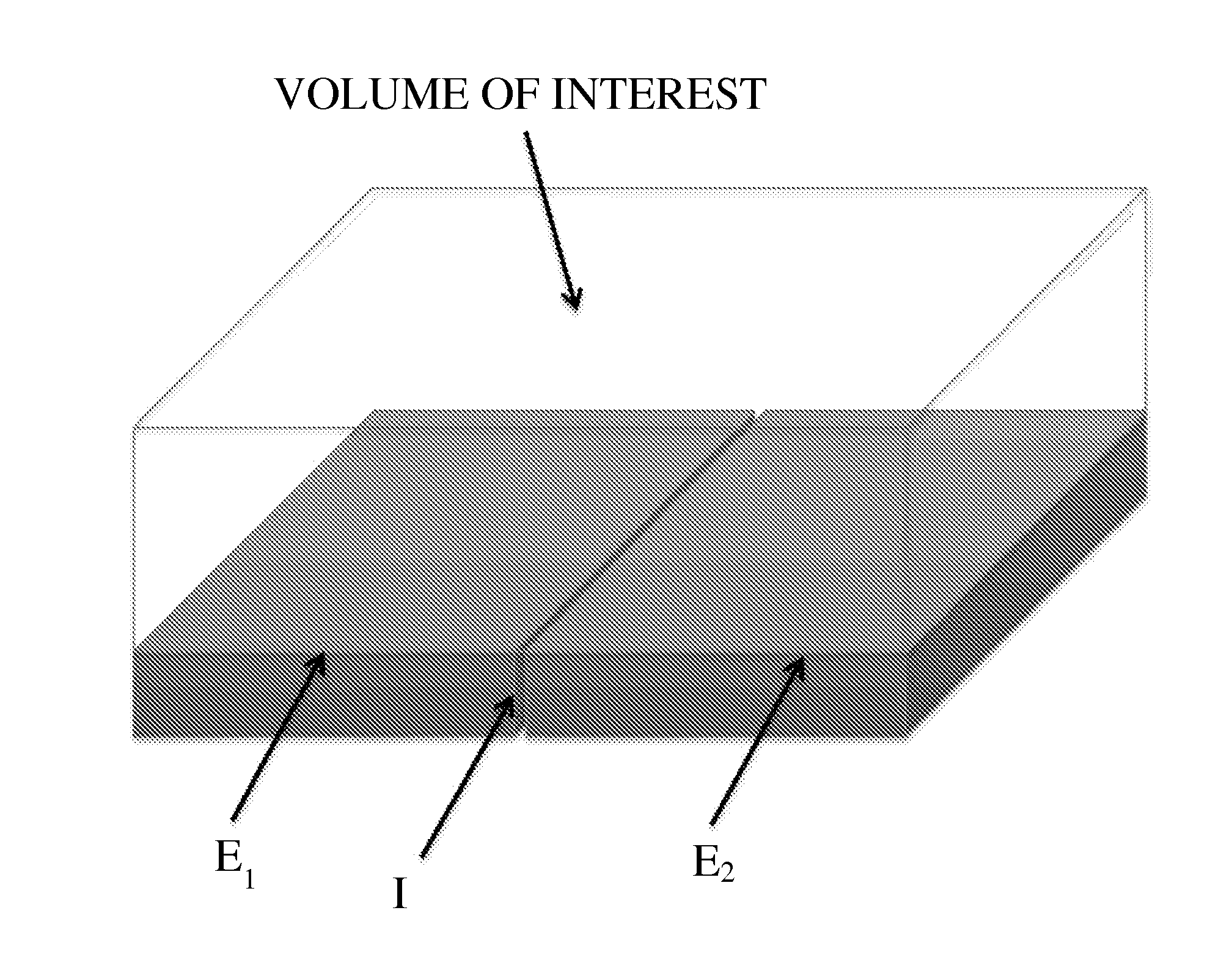
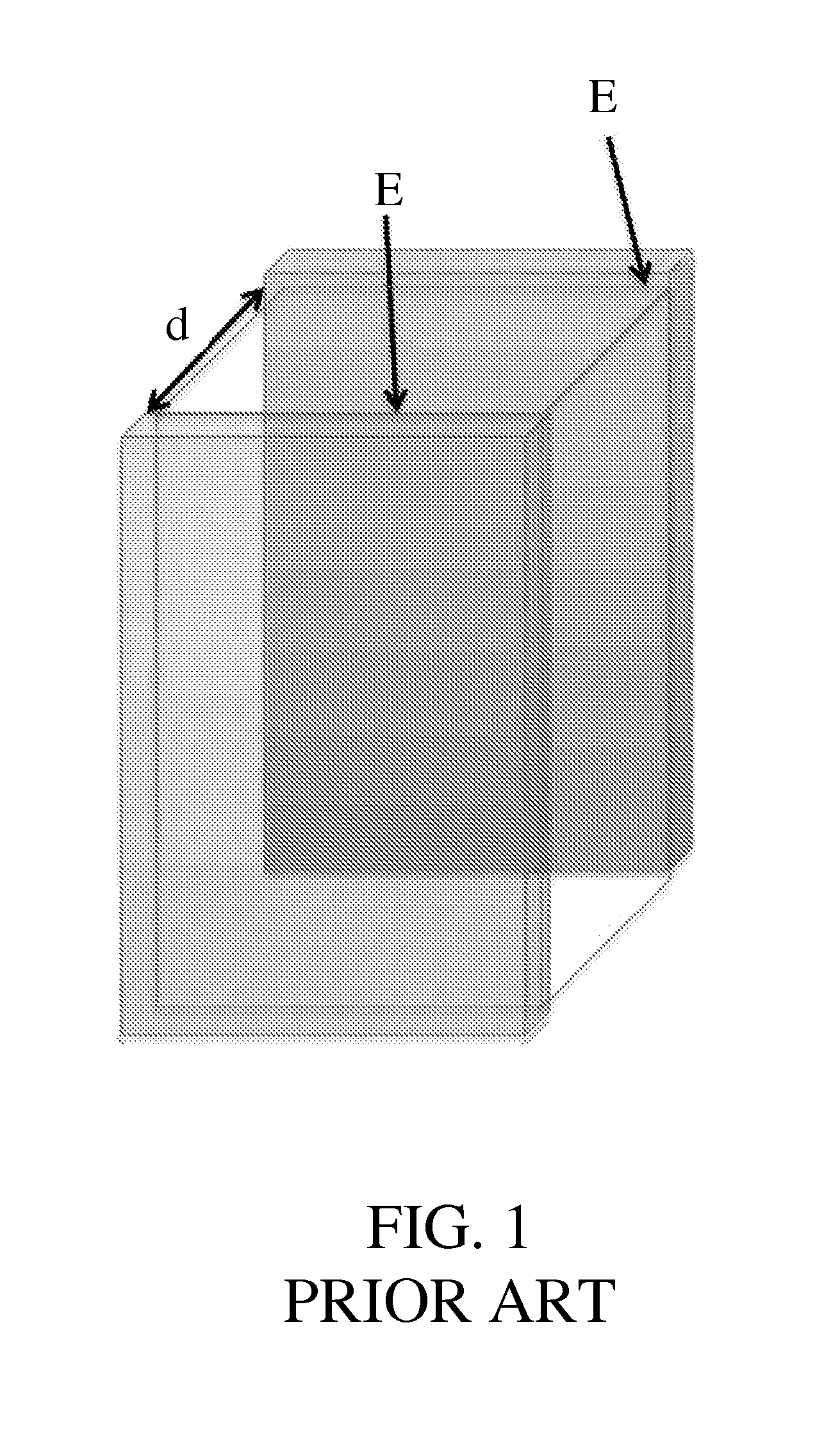
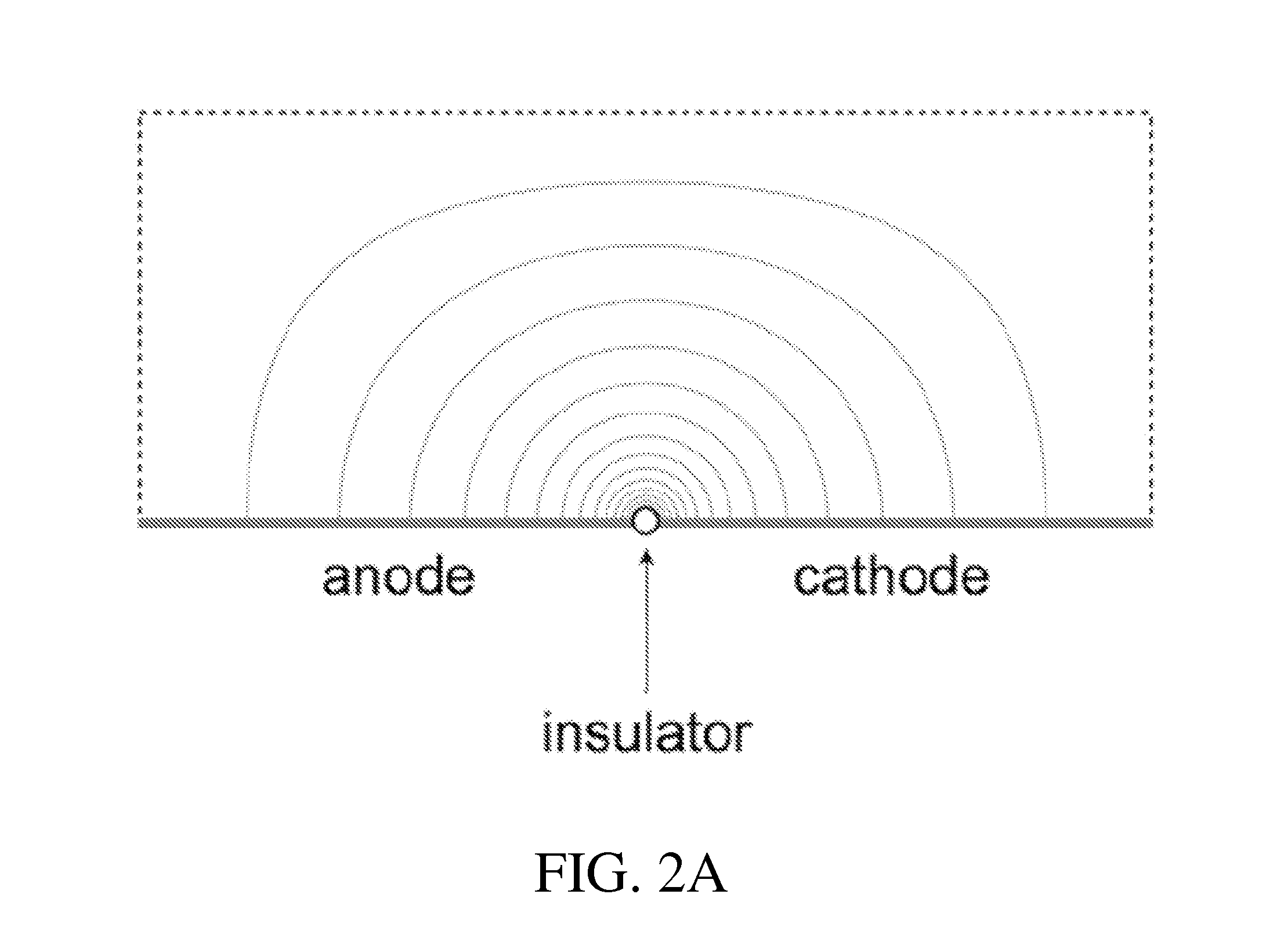
Provided herein are the concept that “singularity-based configuration” electrodes design and method can produce in an ionic substance local high electric fields with low potential differences between electrodes. The singularity-based configuration described here includes: an anode electrode; a cathode electrode; and an insulator disposed between the anode electrode and the cathode electrode. The singularity-based electrode design concept refers to electrodes in which the anode and cathode are adjacent to each other, placed essentially co-planar and are separated by an insulator. The essentially co-planar anode / insulator / cathode configuration bound one surface of the volume of interest and produce desired electric fields locally, i.e., in the vicinity of the interface between the anode and cathode. In an ideal configuration, the interface dimension between the anode and the cathode tends to zero and becomes a point of singularity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for determining the state of fouling/cleaning of membrane modules
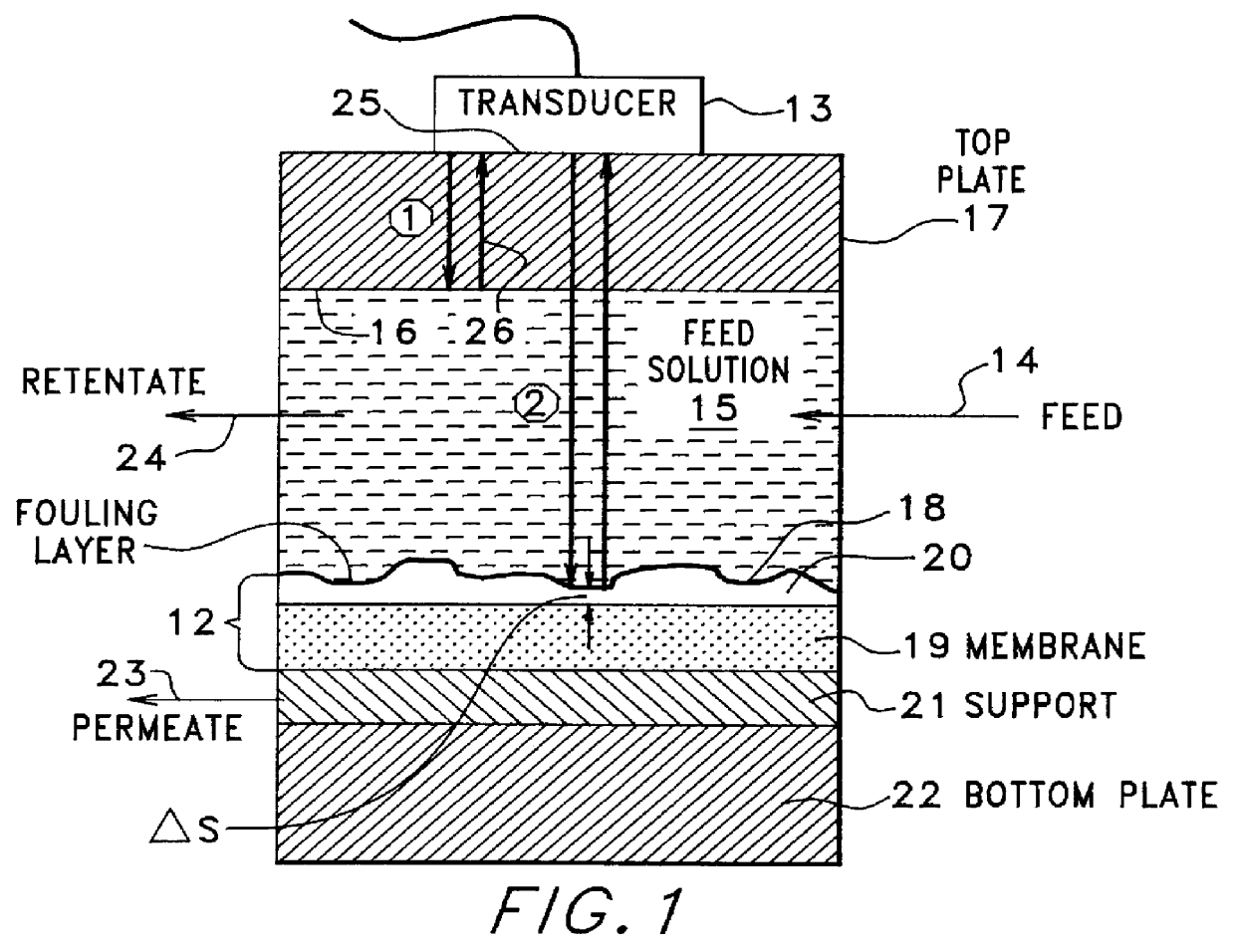
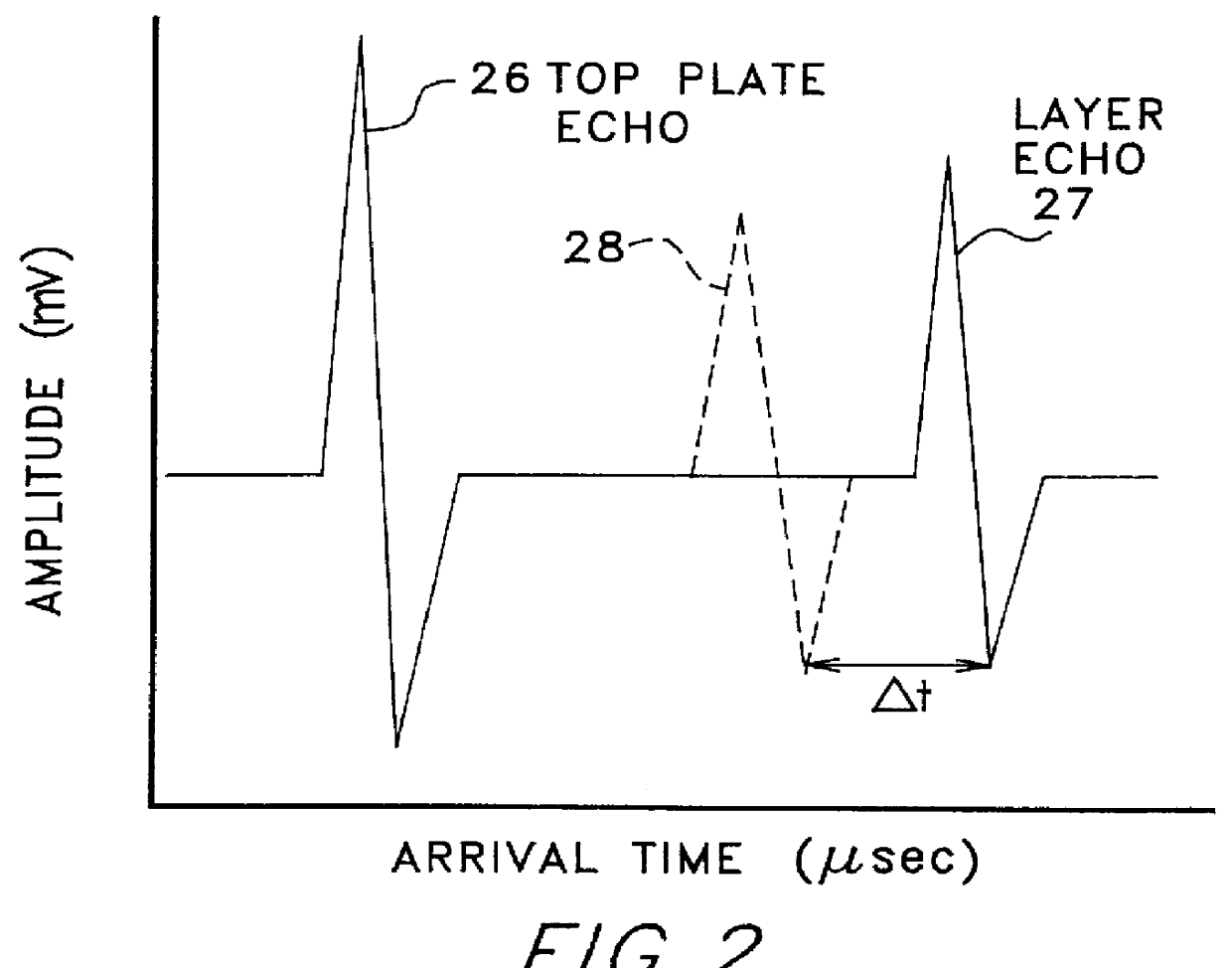
InactiveUS6161435AVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTime domainSpiral wound
The fouling state of a polymeric membrane within the high pressure housing of a spiral wound or a hollow fiber membrane module is determined. An ultra sonic transducer positioned with its emitting face in physical engagement with the outer surface of the housing is pulse energized by a pulser / receiver device. A membrane echo signal is detected by a receiver of the pulser / receiver device. A reference echo signal indicative of a fouled or an unfouled state of the membrane is compared to the echo signal to determine the membrane fouling state. The echo to reference comparing step can be based upon comparing amplitude domain signals, comparing time-domain signals, comparing combinations of amplitude domain and time-domain signals, and comparing transformations of amplitude domain and time-domain signals. A clean or a fouled reference echo can be provided from a clean or a fouled membrane and then stored for use during a liquid separation process, or a clean reference echo signal can be obtained on-line from a second transducer whose echo signal is derived from an area of the membrane known to remain relatively unfouled during the liquid separation process, or a clean or fouled reference echo signal can be provided for later use during a cleaning process or during a liquid separation process. Multiple transducers and a switching network can sample the fouling state at different positions within the membrane module.
Owner:UNIV TECH
Temperature control in a ceramic membrane reactor
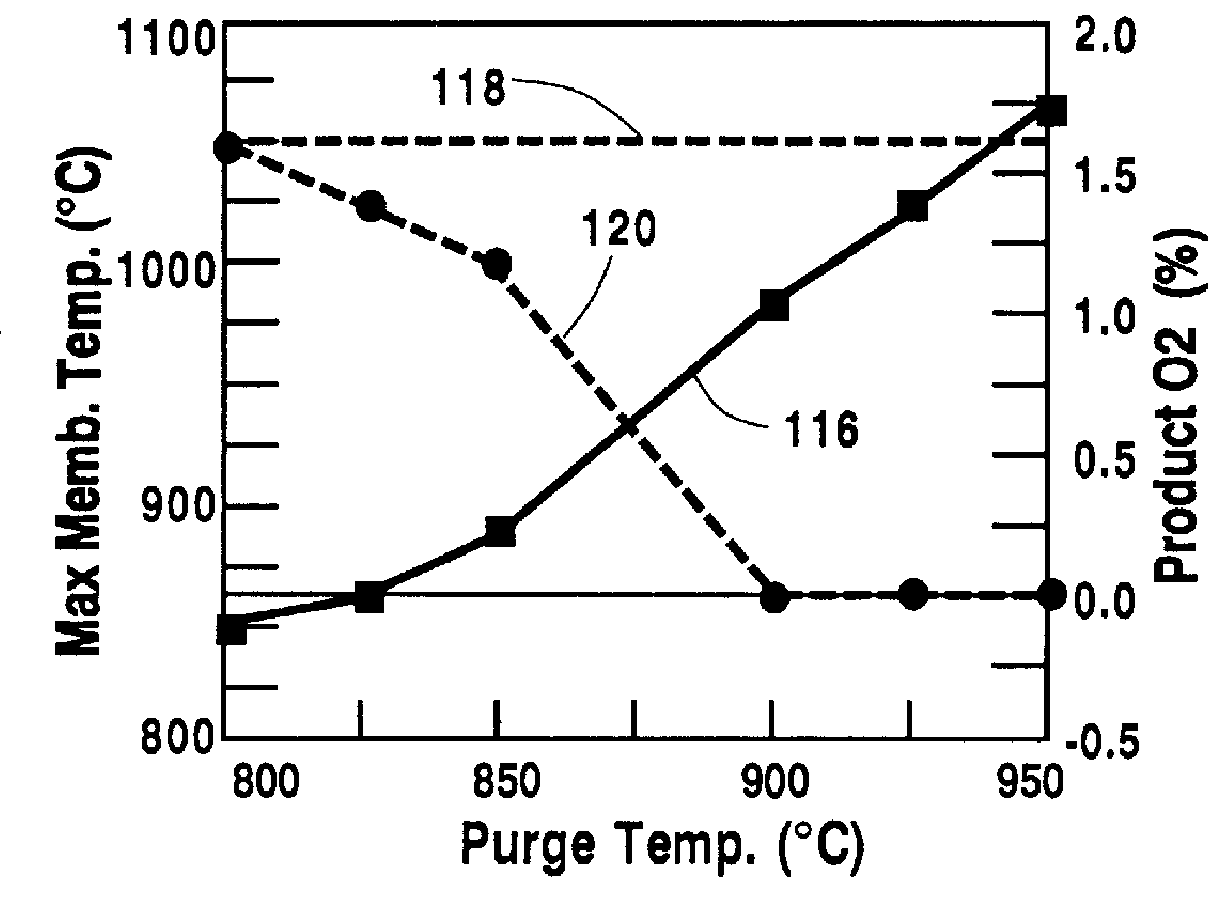
InactiveUS6010614AEnhance exchangeFine surfaceHydrogenLiquid separation by electricityTemperature controlOxygen ions
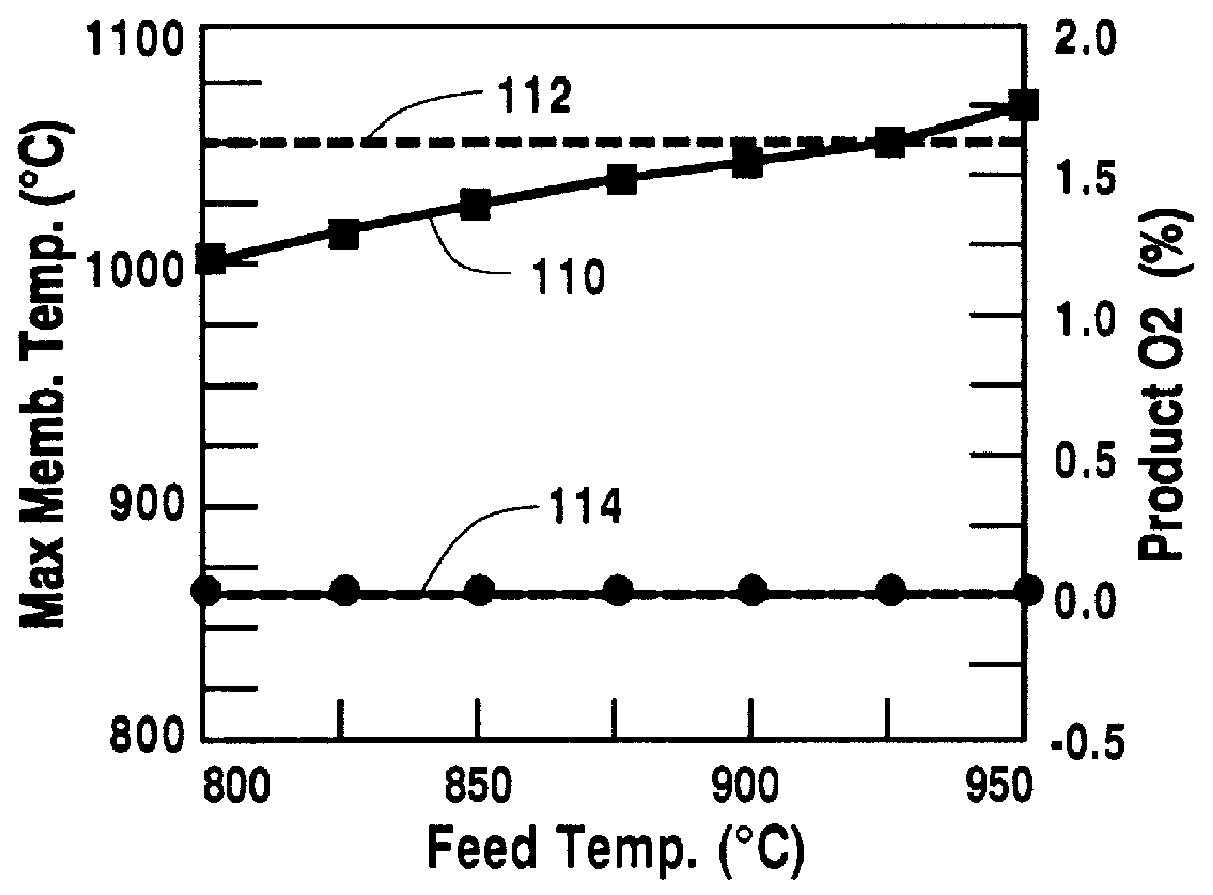
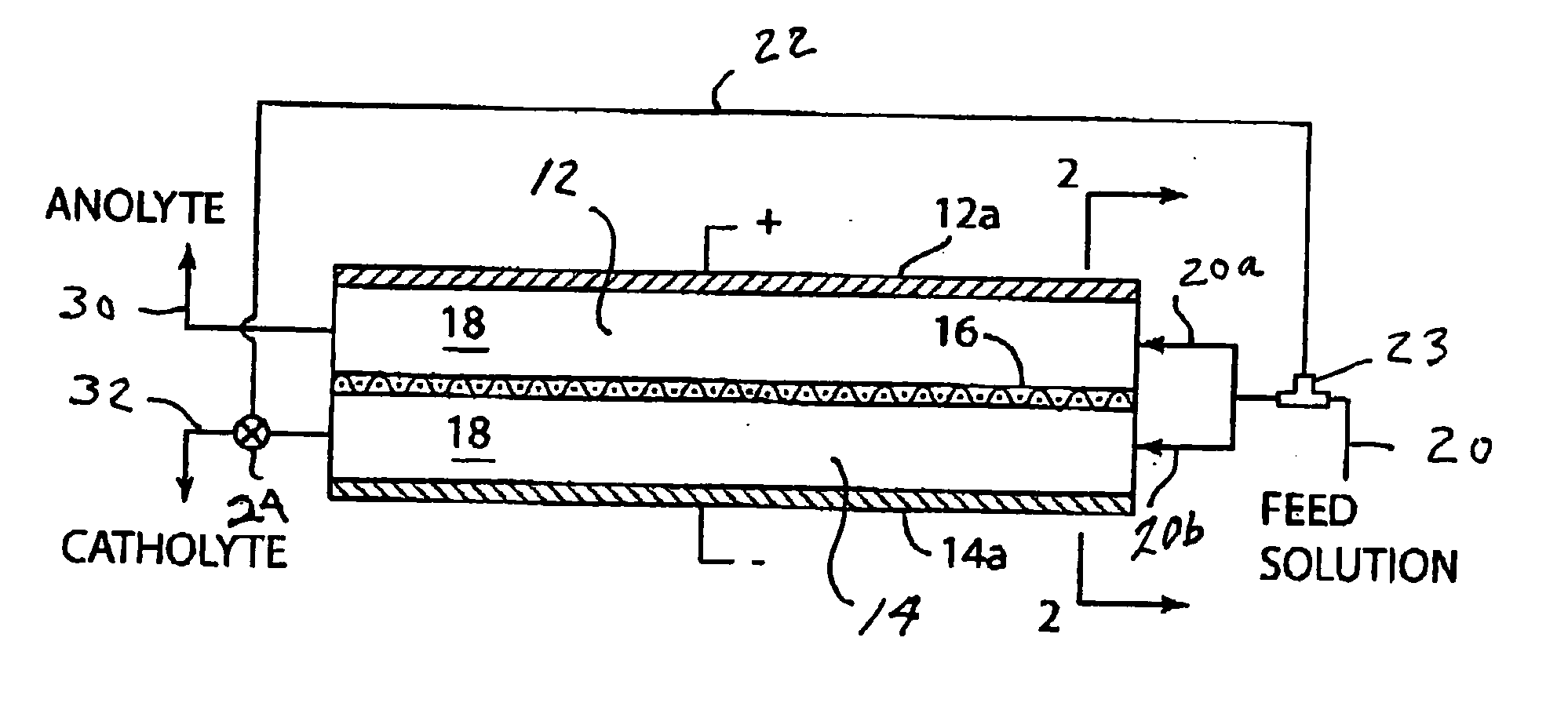
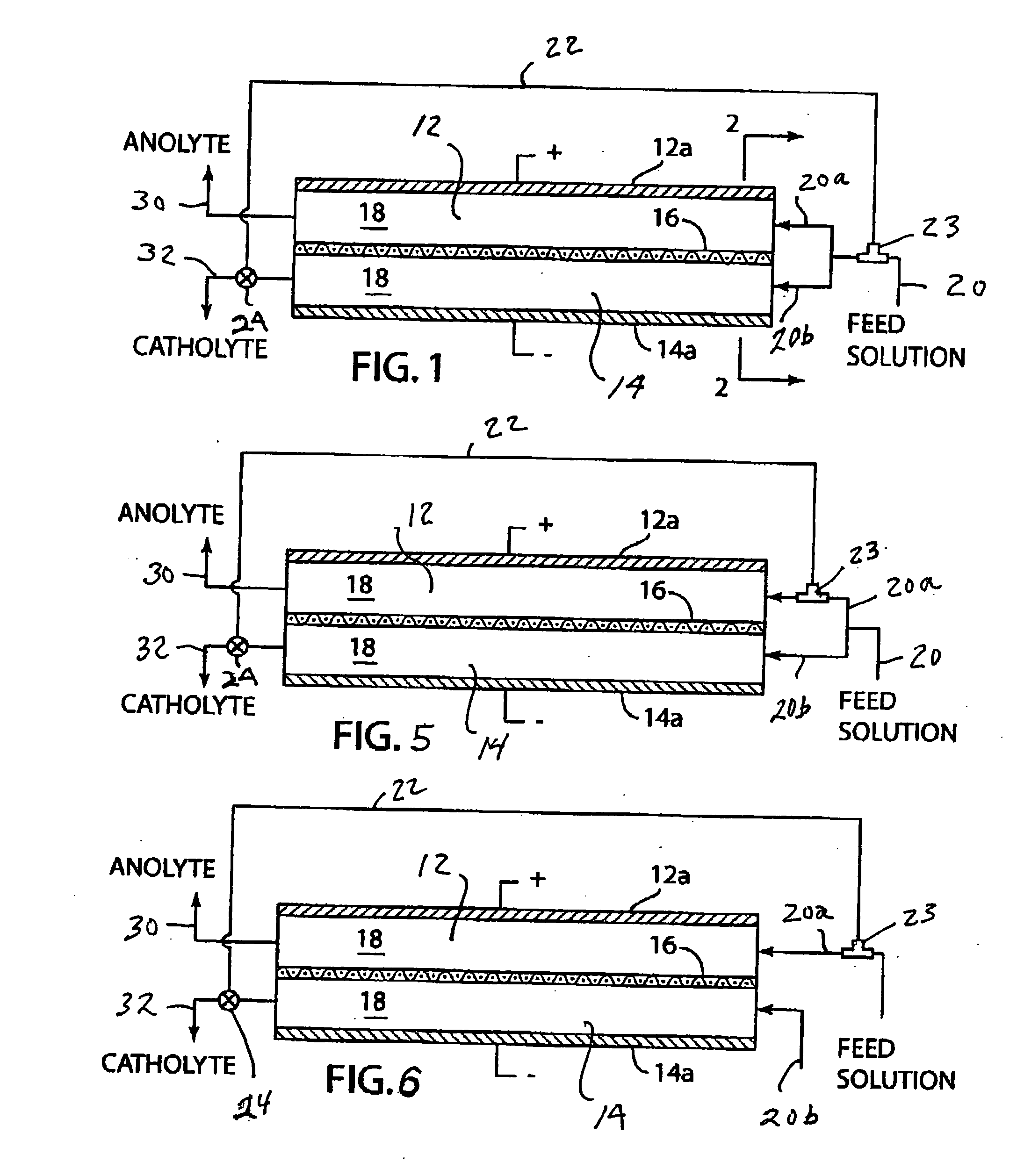
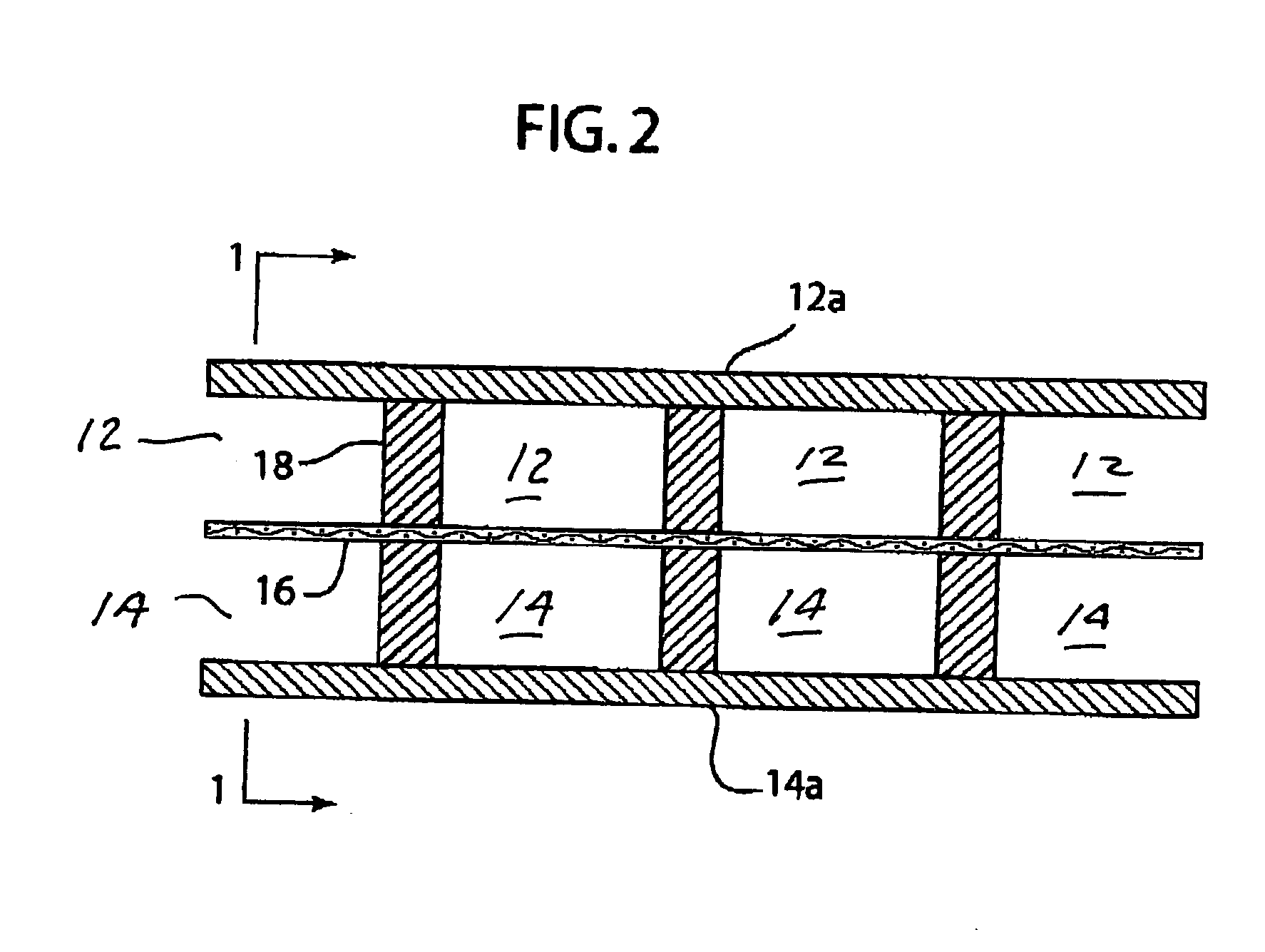
A method for maintaining the temperature of an oxygen-selective ion transport membrane within a desired temperature range includes providing an ion transport reactor with the oxygen-selective ion transport membrane. An oxygen-donating feed gas is delivered to a cathode side at a first temperature, at a first rate, and at a first oxygen partial pressure and a reactant gas is supplied to an anode side at a second temperature and a second rate. A physical condition is then established within the ion transport reactor that favors the transport of elemental oxygen through the oxygen selective ion transport membrane as oxygen ions. One or more process variables are then regulated to maintain the temperature of the oxygen selective ion transport membrane within the desired range.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Method and apparatus for electrolyzing water
InactiveUS20050126928A1Increase chanceCellsWater treatment parameter controlElectrolysed waterSalt solution
Feed water comprising an aqueous salt solution is supplied to an anode chamber and to a cathode chamber. The feed water is cathodically electrolyzed in the cathode chamber to produce alkaline electrolyzed water (catholyte) and is anodically electrolyzed in the anode chamber to produce electrolyzed water (anolyte) whose pH is modified. A portion of alkaline catholyte from the cathode chamber is recycled back to the feed water during continuous electrolysis to provide a blend of feed water and alkaline catholyte to the anode chamber to control pH of the anodically electrolyzed water therein to provide more stable bactericidal activity thereof over time.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
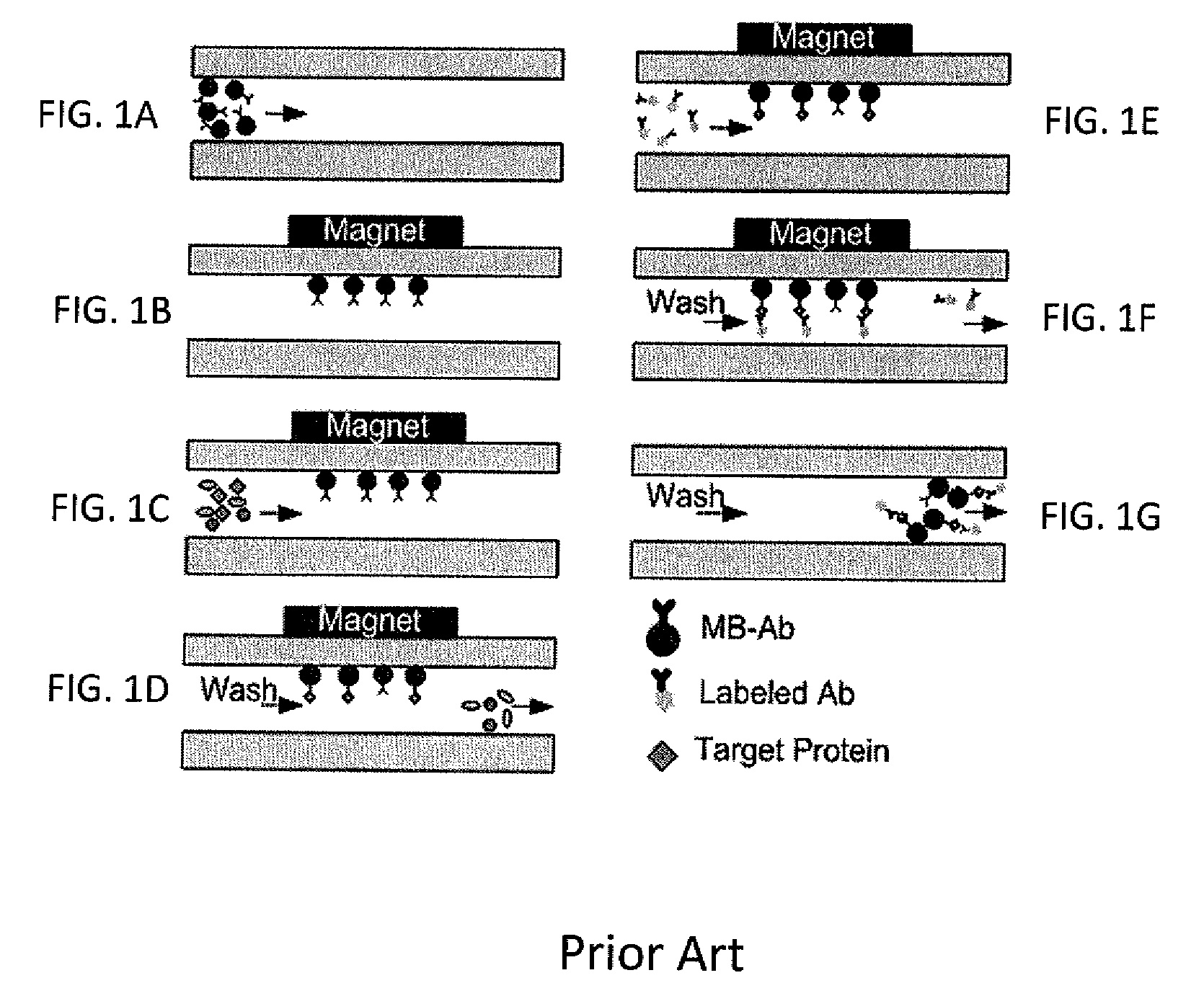
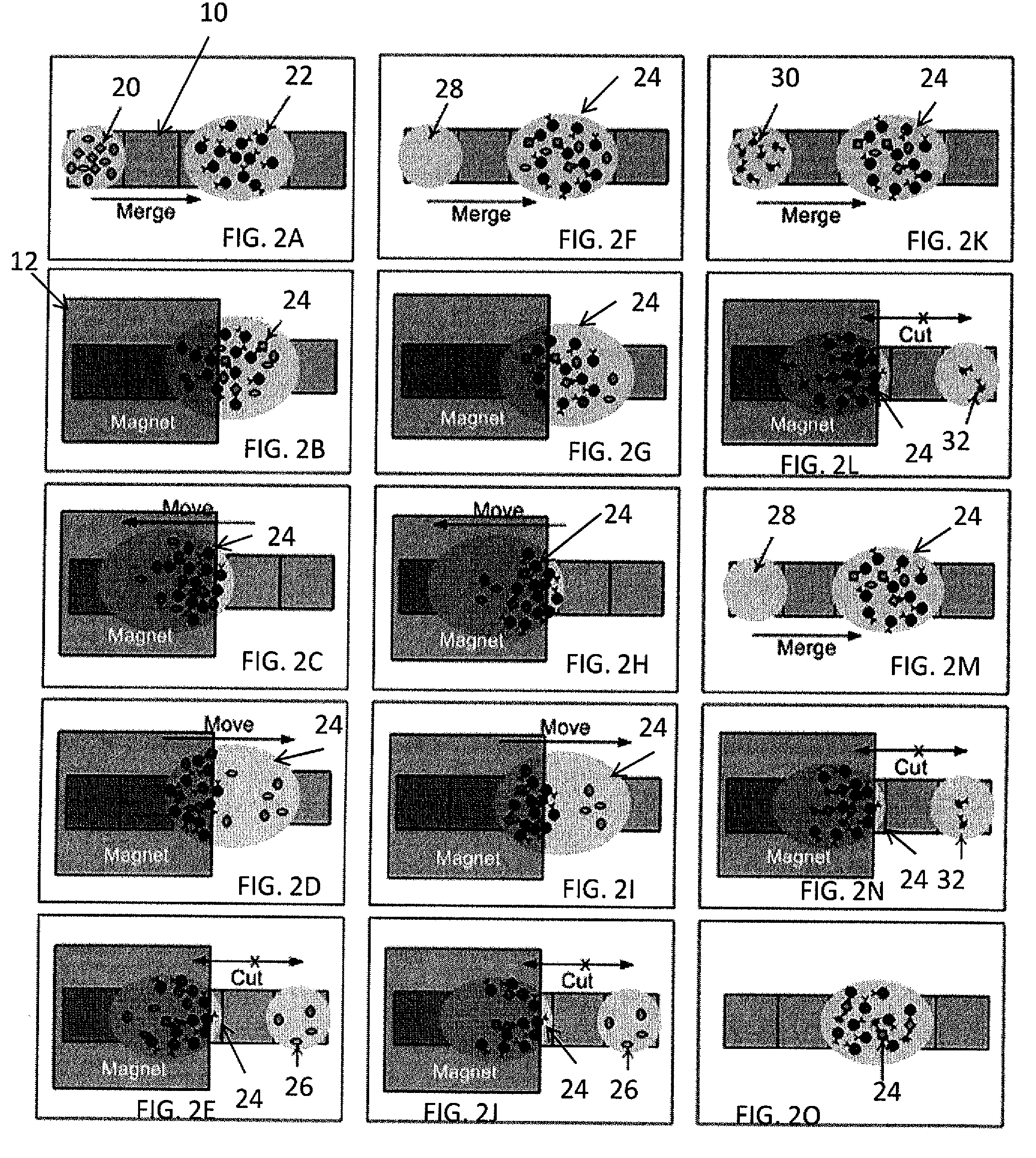
Bead Incubation and Washing on a Droplet Actuator
The present invention relates to bead incubating and washing on a droplet actuator. Methods for incubating magnetically responsive beads that are labeled with primary antibody, a sample (i.e., analyte), and secondary reporter antibodies on a magnet, on and off a magnet, and completely off a magnet are provided. Also provided are methods for washing magnetically responsive beads using shape-assisted merging of droplets. Also provided are methods for shape-mediated splitting, transporting, and dispensing of a sample droplet that contains magnetically responsive beads. The apparatuses and methods of the invention provide for rapid time to result and optimum detection of an analyte in an immunoassay.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
Method of manufacture of a heart valve support frame
InactiveUS20050150775A1Eliminate unevennessIncrease flexibilityElectrolysis componentsFrom normal temperature solutionsEngineeringReady to use
Methods for forming a support frame for flexible leaflet heart valves from a starting blank include converting a two-dimensional starting blank into the three-dimensional support frame. The material may be superelastic, such as NITINOL, and the method may include bending the 2-D blank into the 3-D form and shape setting it. A merely elastic material such as ELGILOY may be used and plastically deformed in stages, possibly accompanied by annealing, to obtain the 3-D shape. Alternatively, a tubular blank could be formed to define a non-tubular shape, typically conical. A method for calculating the precise 2-D blank shape is also disclosed. A mandrel assembly includes a mandrel and ring elements for pressing the blank against the external surface of the mandrel prior to shape setting.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
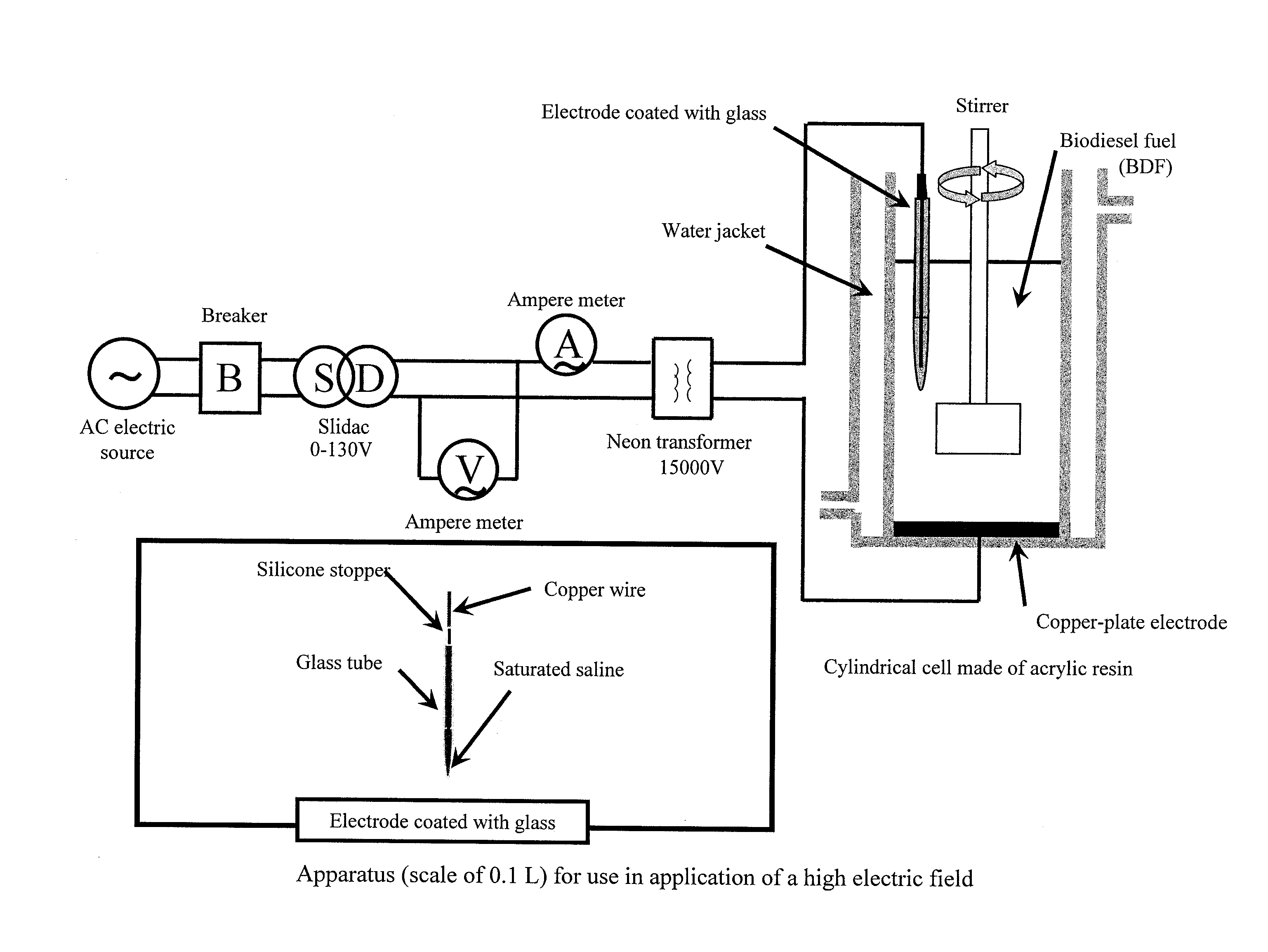
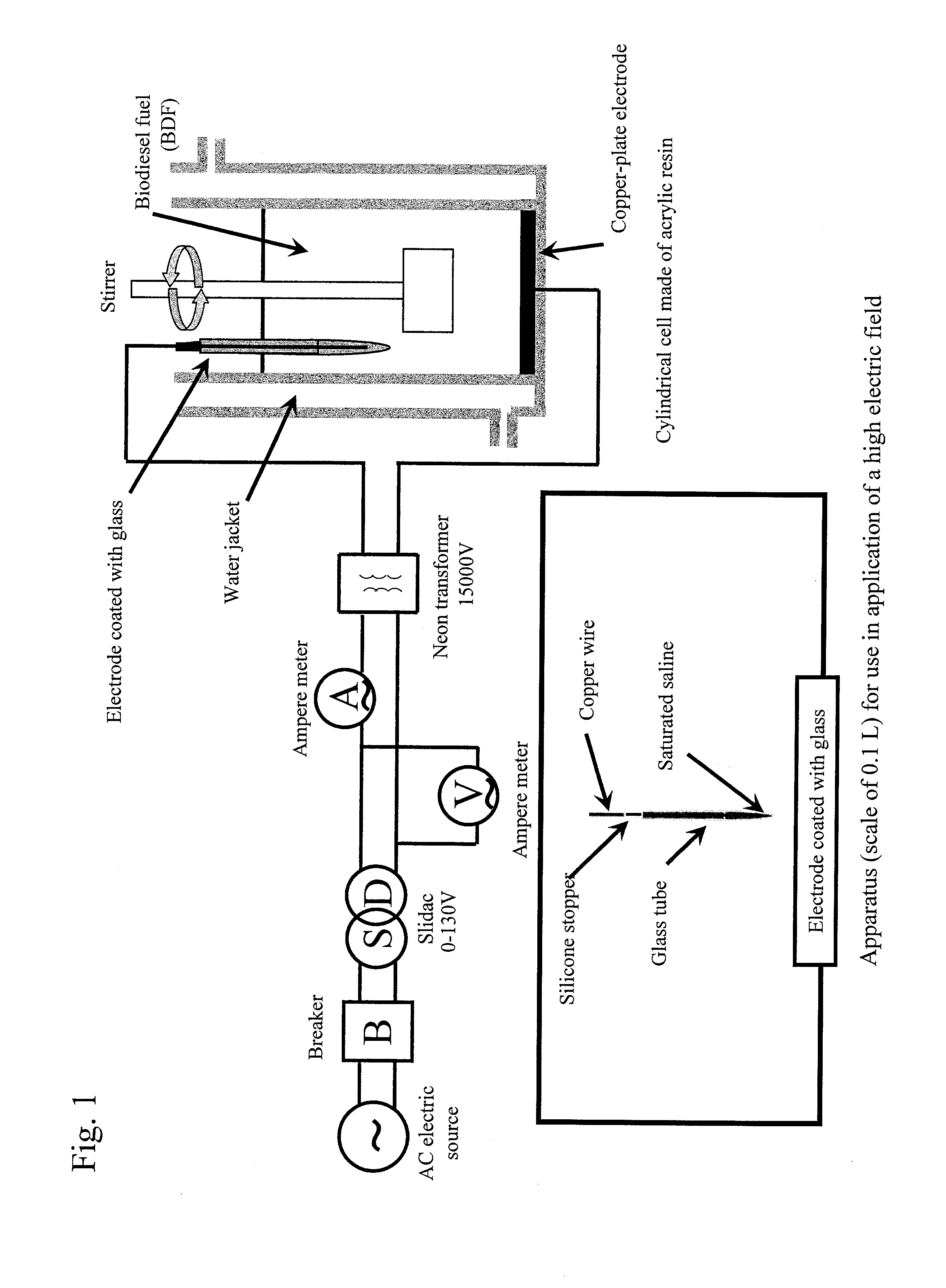
Method for purifying biodiesel fuel
InactiveUS20090025277A1Preventing and greatly reducing generationWater/sewage treatment by irradiationLiquid separation by electricityDemulsifierBiodiesel
Provided is a method for purifying a biodiesel fuel while completely preventing or greatly reducing generation of waste water. The present invention relates to a method for purifying a biodiesel fuel characterized by applying an electric field to or heating a crude biodiesel fuel and a method for purifying a biodiesel fuel characterized by adding water (preferably containing a demulsifier such as an inorganic calcium salt or a magnesium salt) to a crude biodiesel fuel to form W / O emulsion, and breaking the emulsion by application of an electric field or heating, etc.
Owner:KAGOSHIMA UNIV
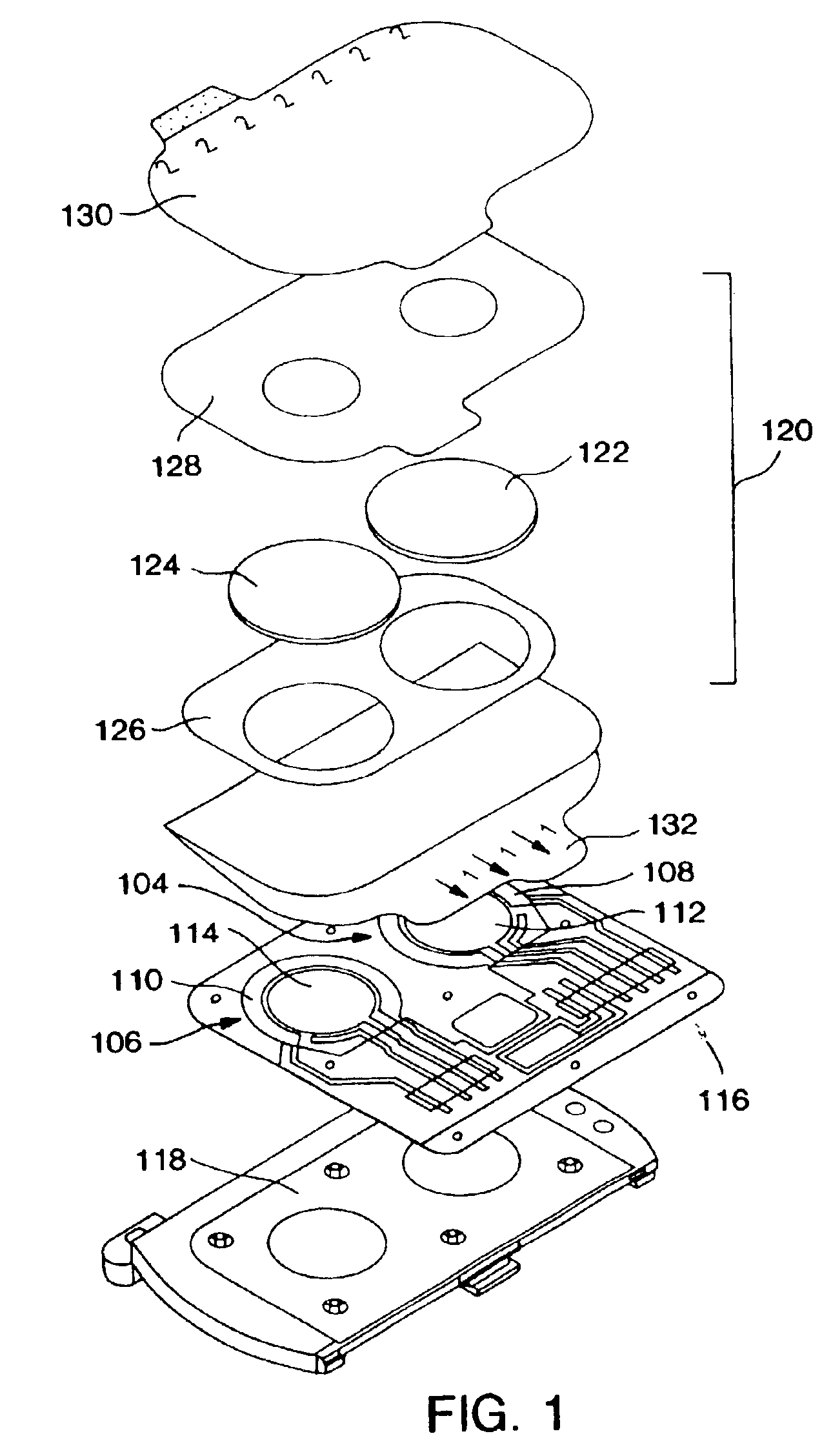
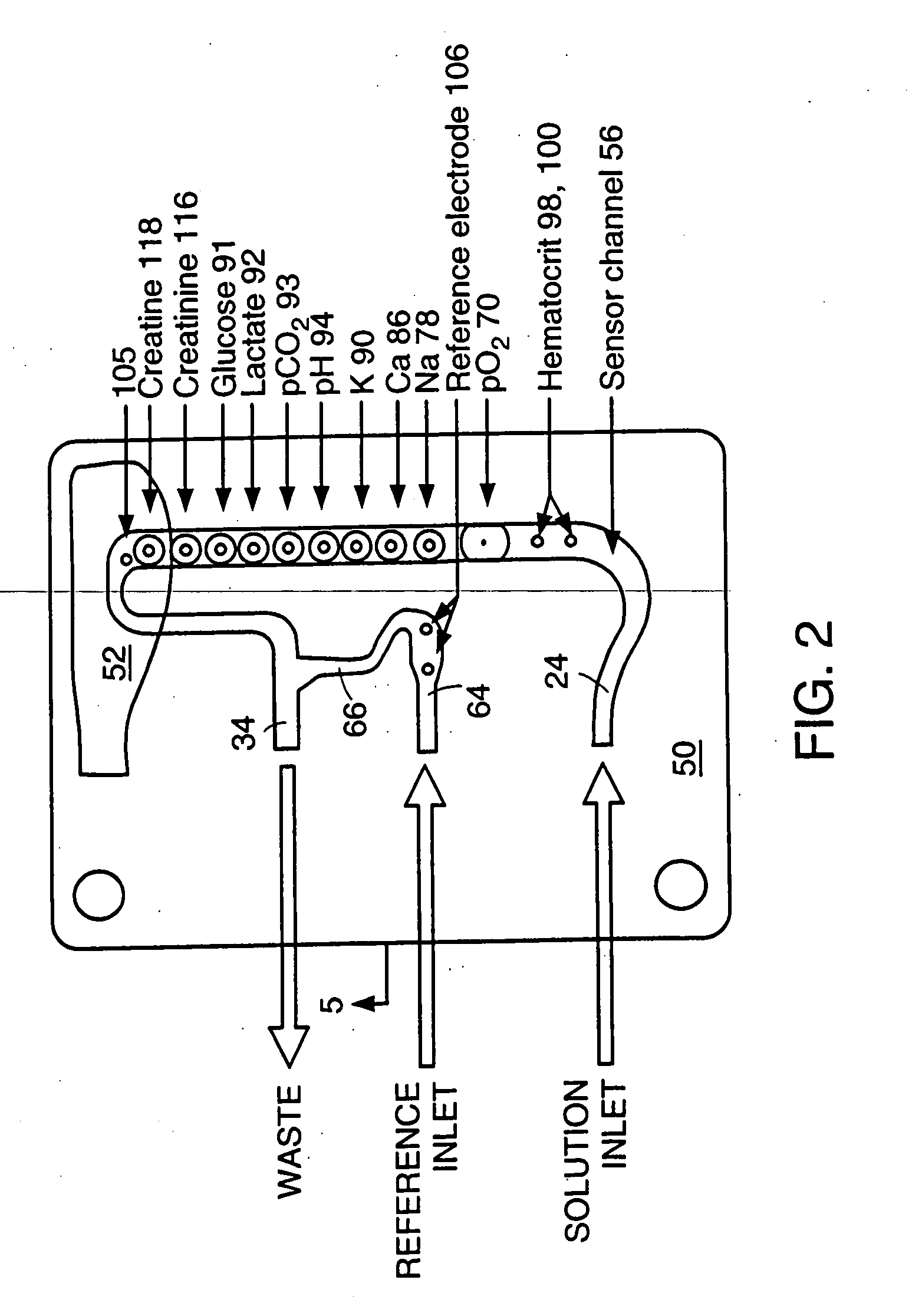
Analytical instruments, biosensors and methods thereof
InactiveUS20050126929A1Improve accuracyIncreasing lifetimeElectrolysis componentsLiquid separation by electricitySensor systemEnzyme
An electrochemical sensor system and membrane and method thereof for increased accuracy and effective life of electrochemical and enzyme sensors.
Owner:INSTR LAB
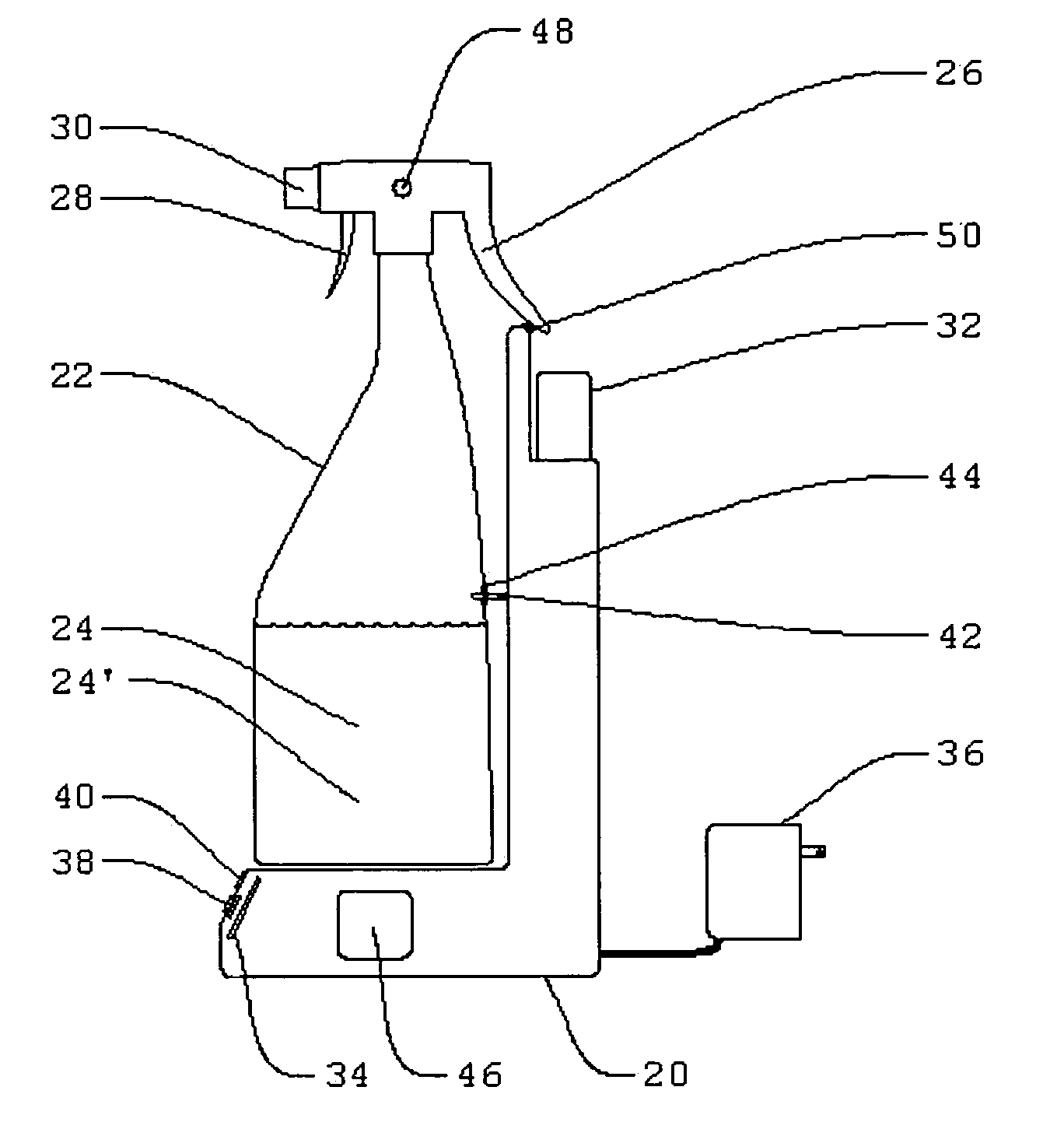
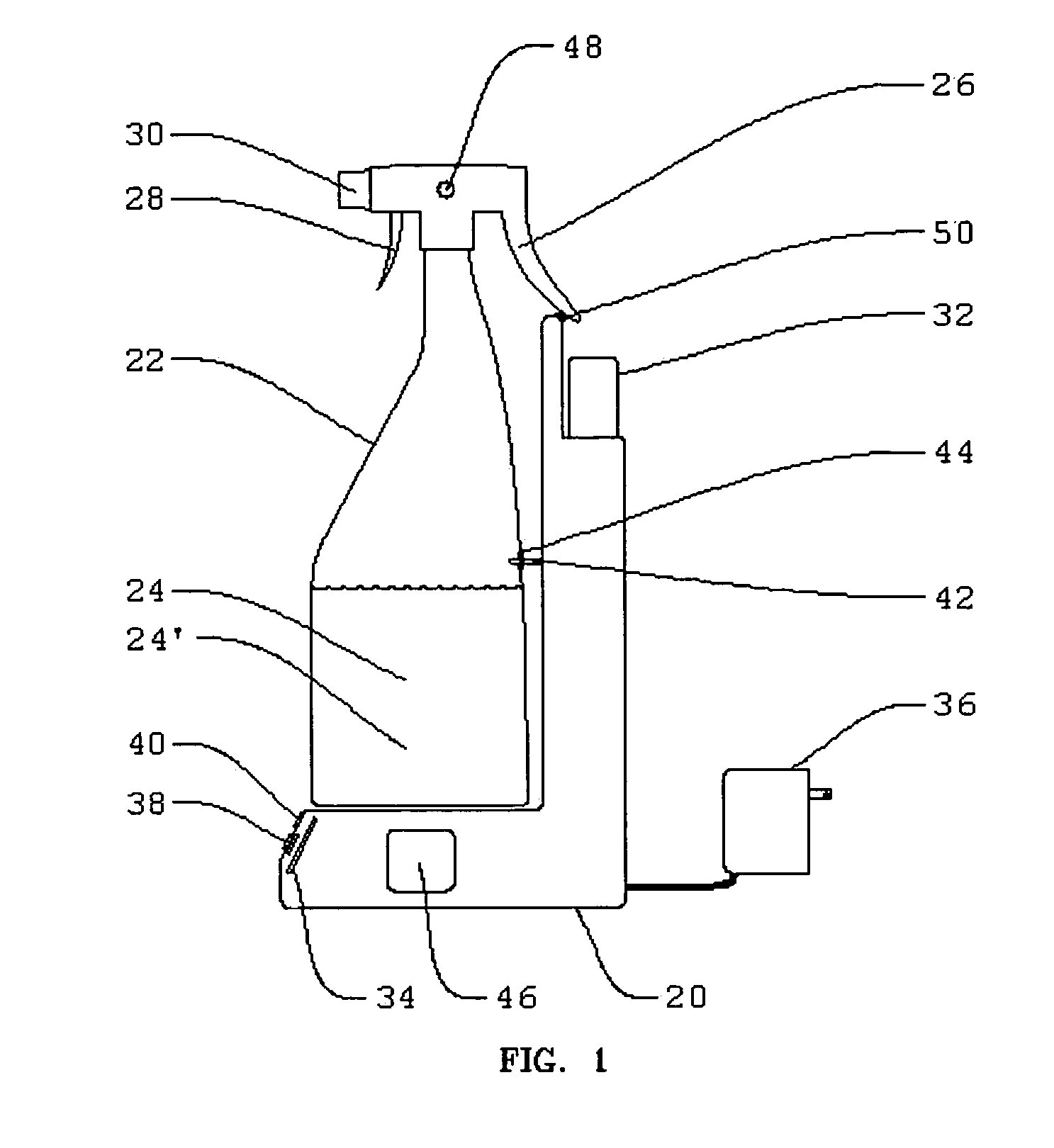
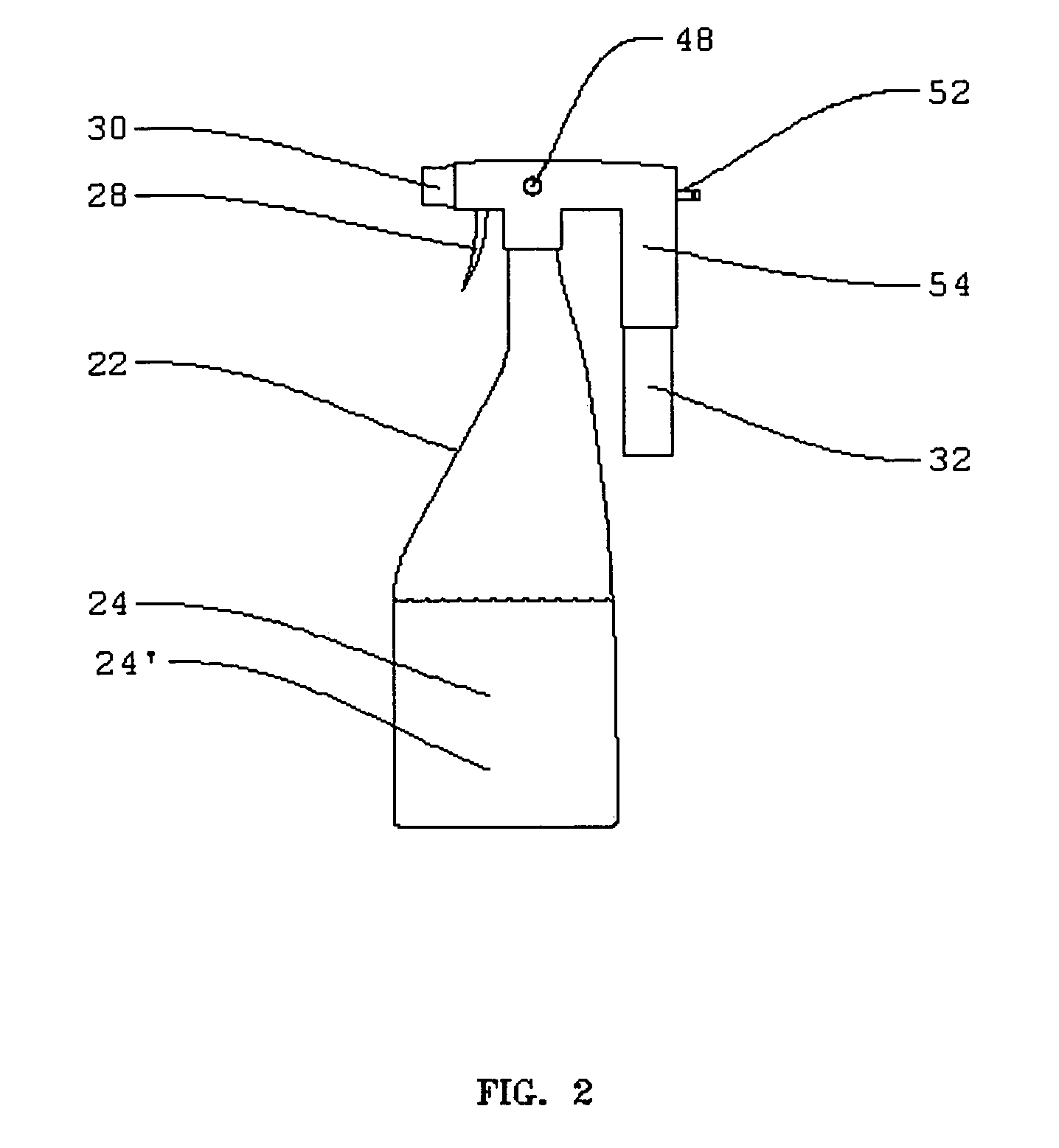
Electrolytic cell for surface and point of use disinfection
InactiveUS7008523B2Suitable for useCellsWater treatment parameter controlDisinfectantElectrical battery
The present invention is an apparatus and method for disinfecting or sanitizing a desired object. The apparatus includes a container for an aqueous solution; the container may be a spray bottle. The apparatus includes an electrolytic cell, containing an electrolyte, an electrical power source, a control circuit for providing an electric charge to the electrolyte to create an oxidant, and a fluid connection between the cell and container to permit introduction of the oxidant into the aqueous solution to create a disinfectant.
Owner:DE NORA HLDG US INC
Surface-coating method
ActiveUS20060141156A1Improve adhesionShorten the timePhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsMaterials scienceSurface coating
The invention relates to the deposition or attachment of materials to surfaces. It relates to a process for coating a surface with a first material and a second material, comprising the following steps: placing the first material on the said surface, inserting into the first material placed on the said surface precursor molecules of the second material, converting the said precursor molecules of the second material inserted into the first material into the said second material such that this second material becomes formed on the said surface to be coated and within the said first material placed on the said surface. The object of the process of the invention is to allow the deposition of materials of any type onto surfaces of any type.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
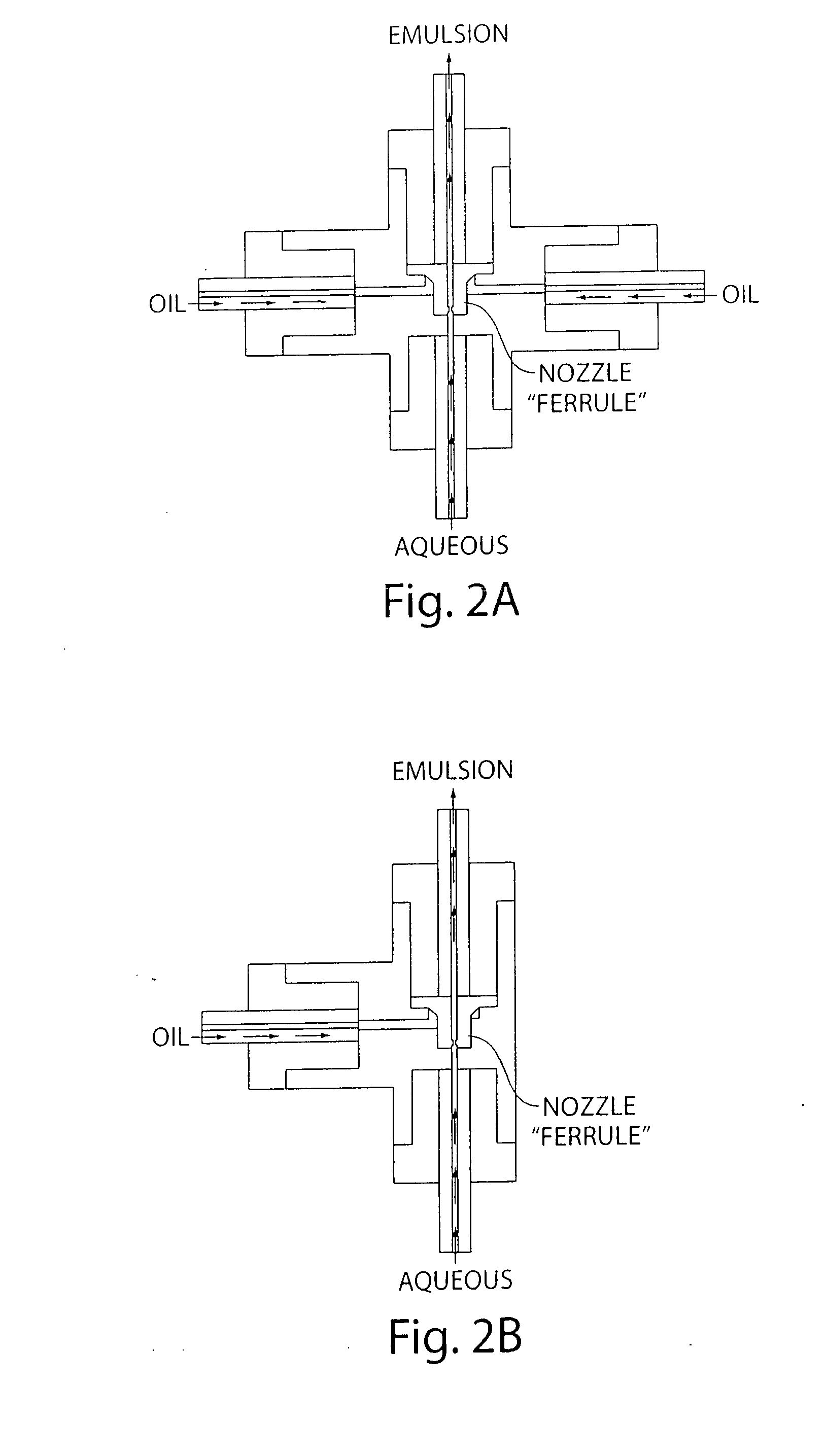
Continuous flow, electrohydrodynamic micromixing apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20010050881A1Increase chanceRapid and thorough mixing of fluidElectrostatic separatorsLiquid separation by electricityHigh rateDissolution
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus that employ electrohydrodynamic flows in miscible, partially miscible and immiscible multiphase systems to induce mixing for dissolution and / or reaction processes. The apparatus and methods of the present invention allow micromixing of two or more components and can advantageously be used to conduct liquid-phase reactions uniformly and at high rates
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
Systems and Methods for Separating Particles and/or Substances from a Sample Fluid
ActiveUS20090194420A1Liquid separation auxillary apparatusSludge treatmentFluid systemAmount of substance
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Method and Apparatus for Demulsifying an Oil-Water Emulsion Via Ultrasonic
ActiveUS20070272618A1Good effectExtension of timeDewatering/demulsification with mechanical meansLiquid separation by electricityUltrasound - actionOil water emulsion
A method for demulsifying water-oil emulsions through ultrasonic action, comprises a step of making the water-oil emulsions flow through at least one ultrasonic acting region in a flow direction, wherein: within the ultrasonic acting region, a concurrent ultrasonic wave whose traveling direction is the same as the flow direction of the water-oil emulsions is generated by at least a one first ultrasonic transducer provided at the upstream end of the ultrasonic acting region, and at same time, a countercurrent ultrasonic wave whose traveling direction is opposite to the flow direction of the water-oil emulsions is generated by at least a one second ultrasonic transducer provided at the downstream end of the ultrasonic acting region; and the concurrent ultrasonic wave and the countercurrent ultrasonic wave act simultaneously on the water-oil emulsions which flow through the ultrasonic acting region, so as to demulsify the water-oil emulsions. After being demulsified, the water-oil emulsions gravity settle and separate, or settle and separate under an electric field, so as to be dewatered. The present invention can apply to various water-oil separating technologies in the procedures from mining to processing of crude oil.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP
Systems and Methods of Urea Processing to Reduce Sorbent Load
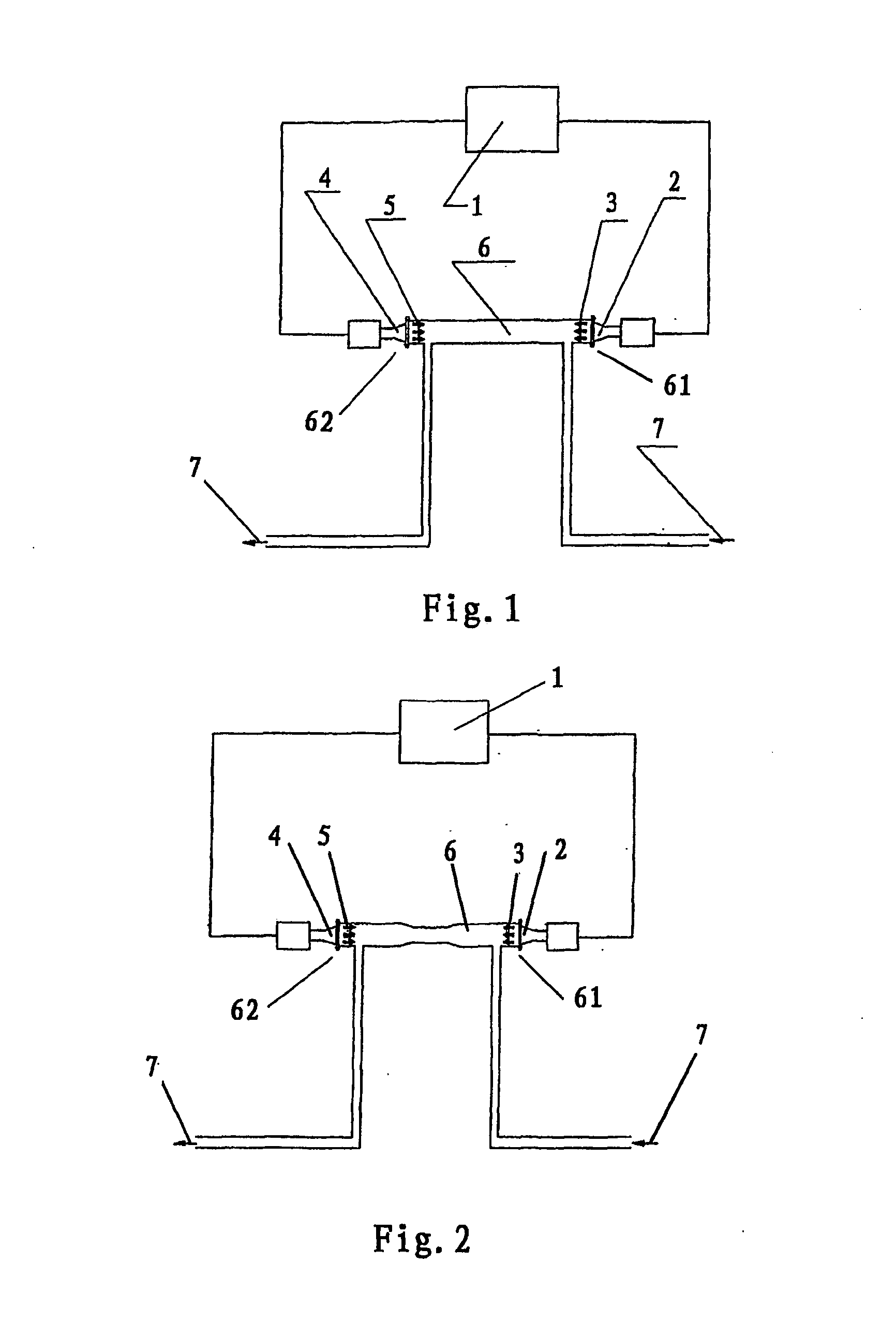
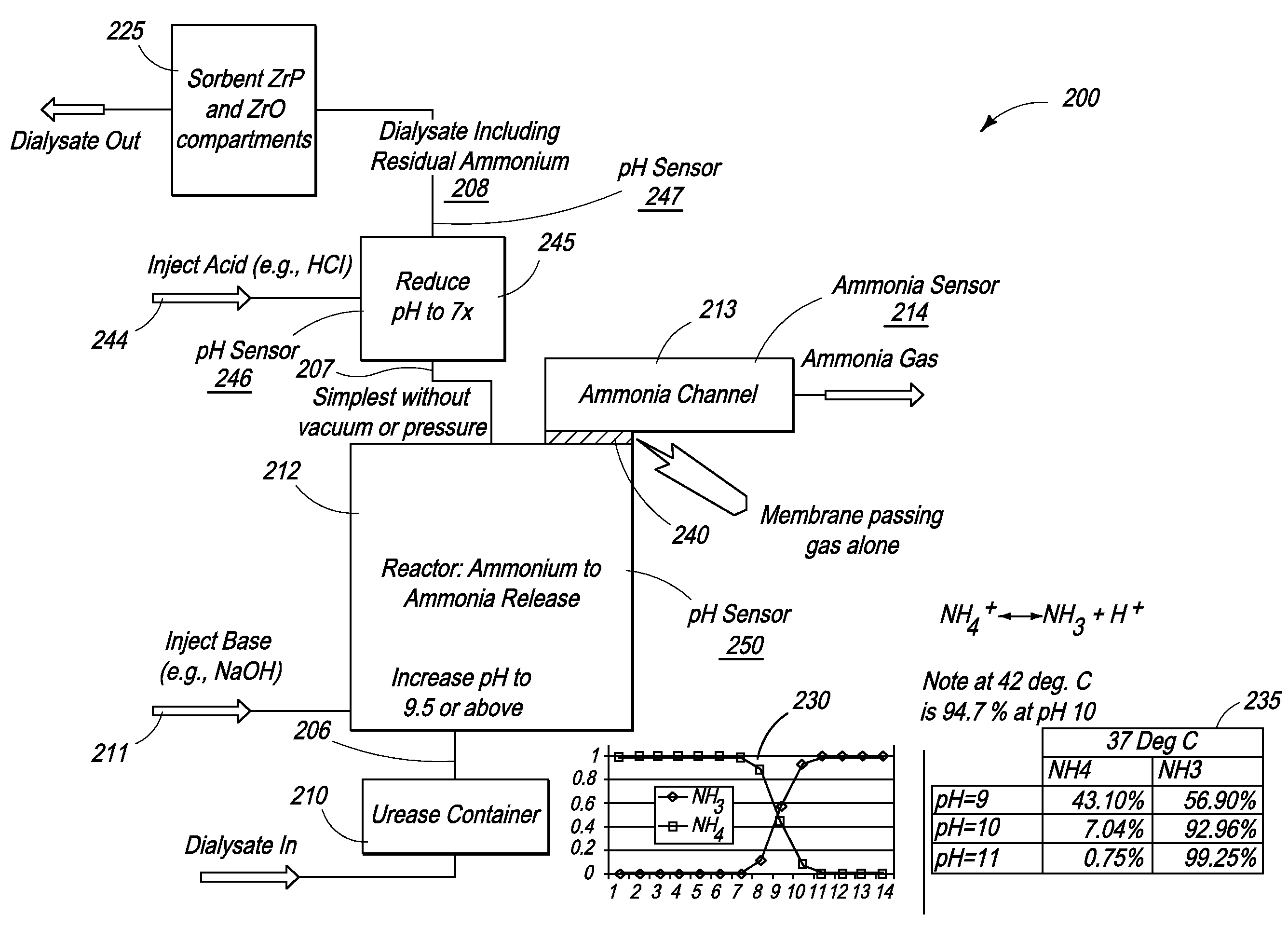
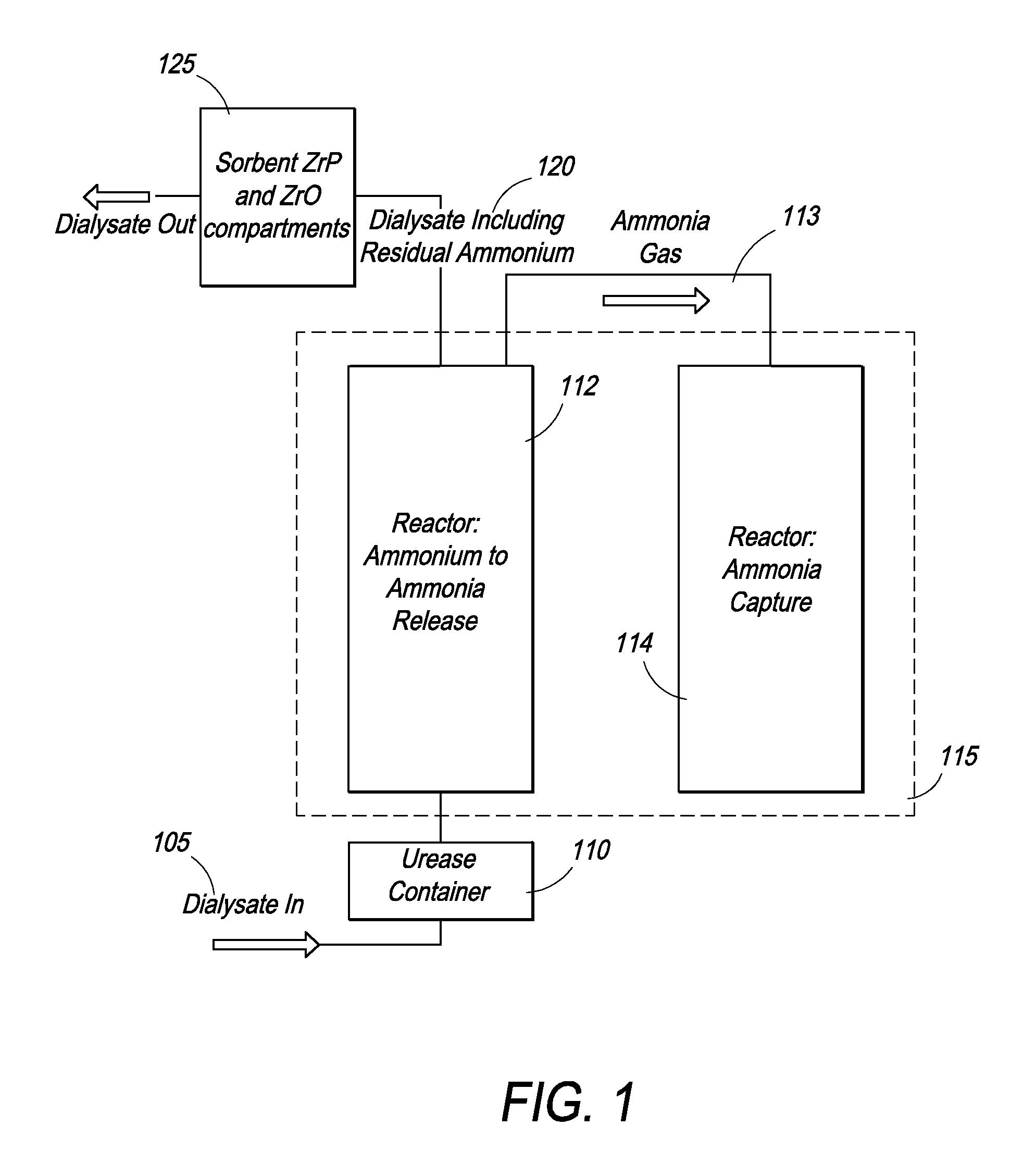
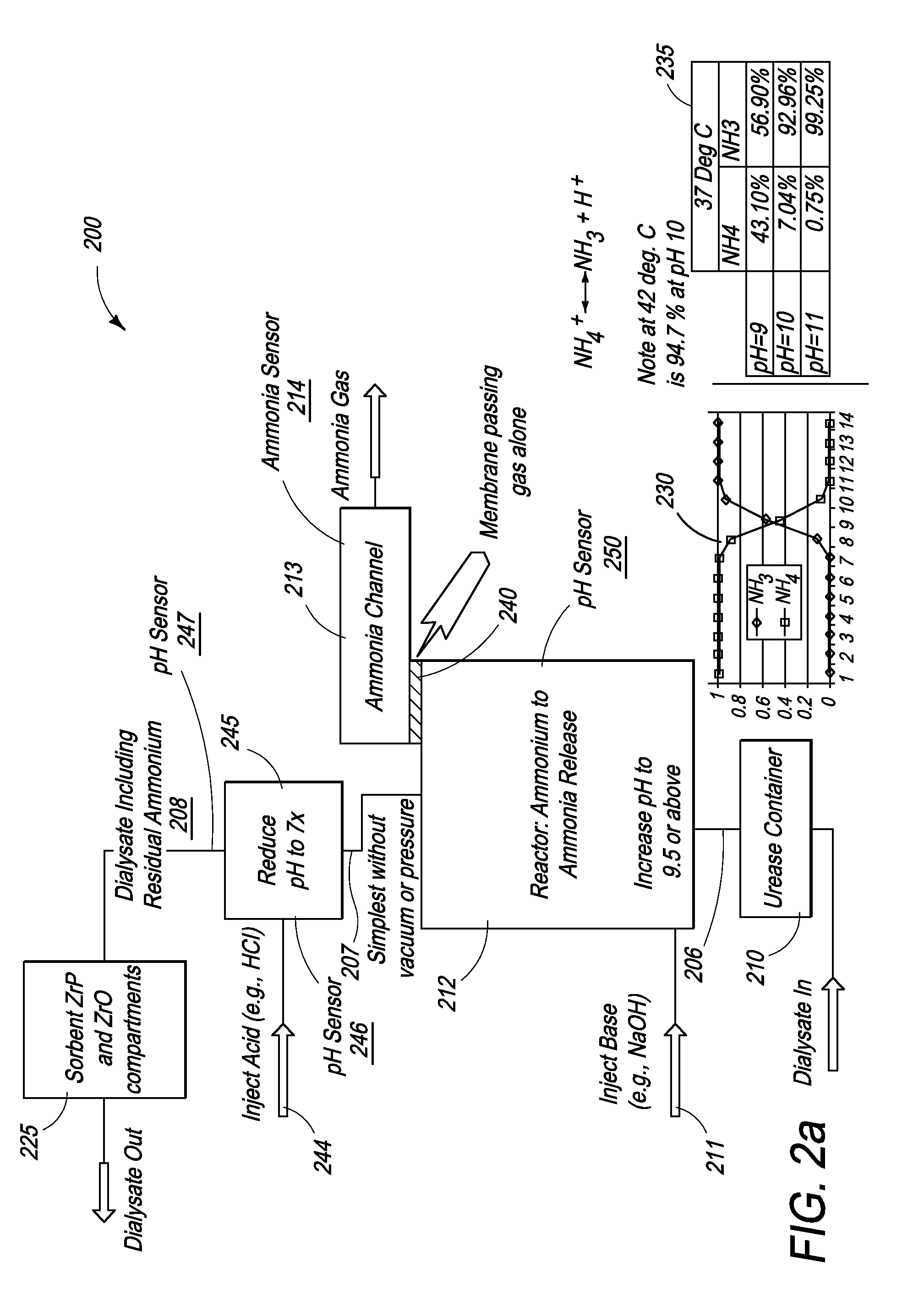
InactiveUS20100184198A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAmmonium compoundsSorbent
The present invention provides novel methods for removal and disposal of ammonia from spent dialysate in a dialysis system. Ammonium ions present in spent dialysate are converted into gaseous ammonia by raising the pH of the spent dialysate solution in a first reactor. Gaseous ammonia diffuses through a semi-permeable hydrophobic membrane at the outlet of the first reactor and into a second reactor via a gas channel. The second reactor converts gaseous ammonia into an ammonium compound for easy disposal.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Systems, apparatuses, and methods for extracting non-polar lipids from an aqueous algae slurry and lipids produced therefrom
InactiveUS20110095225A1Increase volume flowEasy extractionLiquid separation by electricityMicroorganism lysisLipid formationPhospholipid
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for extracting non-polar lipids from microalgae are achieved using a lipid extraction device having an anode and a cathode that forms a channel and defines a fluid flow path through which an aqueous slurry is passed. An electromotive force is applied across the channel at a gap distance in a range from 0.5 mm to 200 mm to cause the non-polar lipids to be released from the algae cells. The non-polar lipids can be extracted at a high throughput rate and with low concentrations of polar lipids such as phospholipids and chlorophyll.
Owner:ORGINOIL INC
Process for electrocoagulating waste fluids
An electrocoagulation process for removing organic and metal contaminants from a pressurized waste fluid is disclosed in which a clarified waste fluid is produced when the pressure is released.
Owner:GAVREL TOM G +1
Method and apparatus for treating materials with electrical fields having varying orientations
InactiveUS6117660AMany timesImprove cell survivalElectrolysis componentsLiquid separation by electricityEngineeringPulse sequence
PCT No. PCT / US97 / 09300 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 10, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 10, 1999 PCT Filed Jun. 10, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 56893 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 17, 1998The object of the invention is to provide a method and apparatus for treating membrane containing material with electrical fields and with an added treating substance. With the method, a plurality of electrodes (121-128) are arrayed around the material to be treated and are connected to outputs of an electrode selection apparatus (110). Inputs of the electrode selection apparatus are connected to outputs of an agile pulse sequence generator. A treating substance is added to the membrane-containing material. Electrical pulses are applied to the electrode selection apparatus and are routed through the electrode selection apparatus in a predetermined, computer-controlled sequence to selected electrodes in the array of electrodes, whereby the membrane containing material is treated with the added treating substance and with electrical fields of sequentially varying directions. The routing of applied pulses through the electrode selection apparatus (110) to selected electrodes (121-128) can be done in an enormous number of ways.
Owner:ICHOR MEDICAL SYST
Micro-circuit system with array of functionalized micro-electrodes
InactiveUS6203758B1Immobilised enzymesSequential/parallel process reactionsCombinatorial chemistryElectron
A micro-circuit for performing analyses of multimolecular interactions and for performing molecular syntheses, comprising: (a) a support; (b) at least one micro-electrode attached to the support, the micro-electrode being selectively electronically activated and the micro-electrode having a protective layer which is removable; (c) a binding entity for attachment to the at least one micro-electrode, the binding entity being capable of attachment to at least one micro-electrode when the protective layer has been removed; and (d) a power source being operatively connected to at least one micro-electrode for electronically activating at least one micro-electrode. The micro-circuit of the present invention also includes embodiments featuring a micro-circuit reader for detecting the interaction of the binding entity to a complementary probe, as well as methods for making and using the micro-circuit of the present invention.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
Method and apparatus for treatment of organic matter-containing wastewater
InactiveUS6547951B1Improve efficiencyImprove abilitiesCellsLiquid separation by electricitySurface layerWave form
Disclosed is a novel method for treatment of wastewater containing organic contaminant materials by oxidatively decomposing the contaminant materials by a radical reaction involving hydroxyl radicals. The method comprises passing the wastewater through a wastewater treatment conduit (6) comprising a straightly tubular member (6) and a radical generating part consisting of a truncated pyramidal or conical tubular member (1) having an inner surface layer of titanium dioxide to serve as a positive electrode and connected to the upstream end of the straightly tubular member and a negative electrode rod (4) coaxially held relative to the truncated tubular member and applying a pulsed DC voltage having a rectangular wave form at a specified frequency. The efficiency of wastewater treatment can be improved by providing an ultrasonic part consisting of a truncated tubular member similar (7) to the above and connected to the downstream end of the straightly tubular member and an ultrasonic vibrator (8) mounted thereon to emit pulsed ultrasonic waves.
Owner:DAISHIN DESIGN CORP
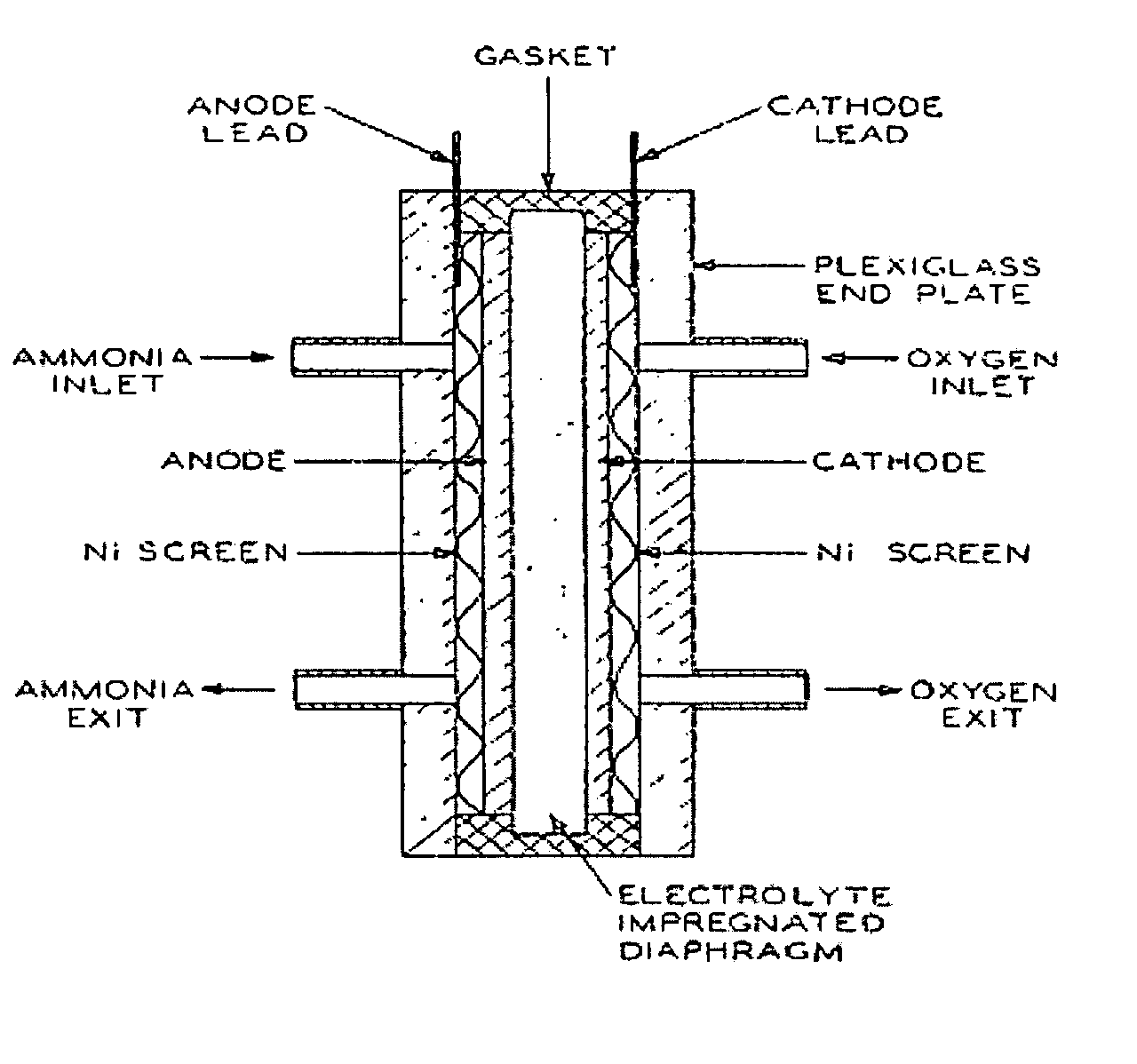
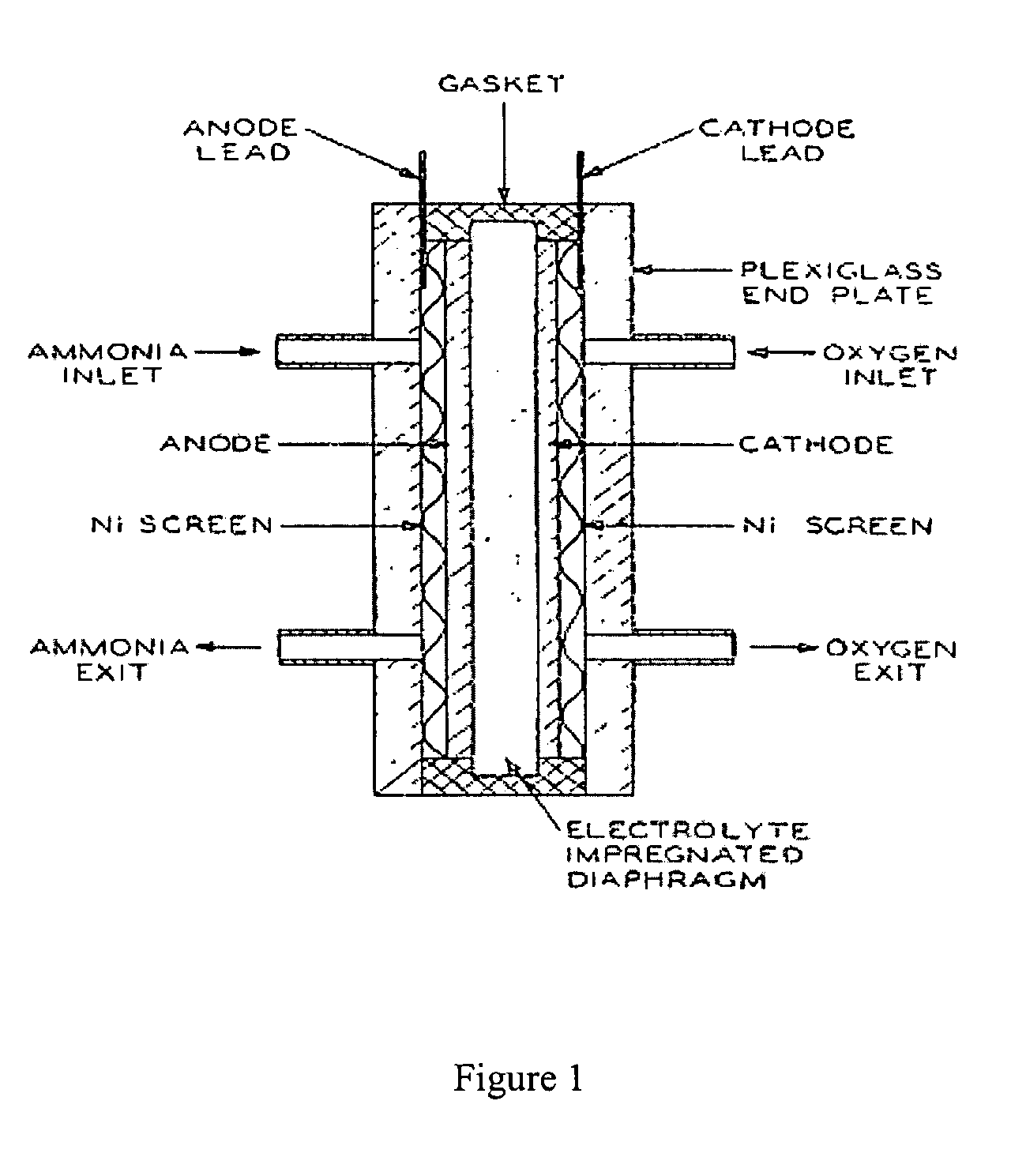
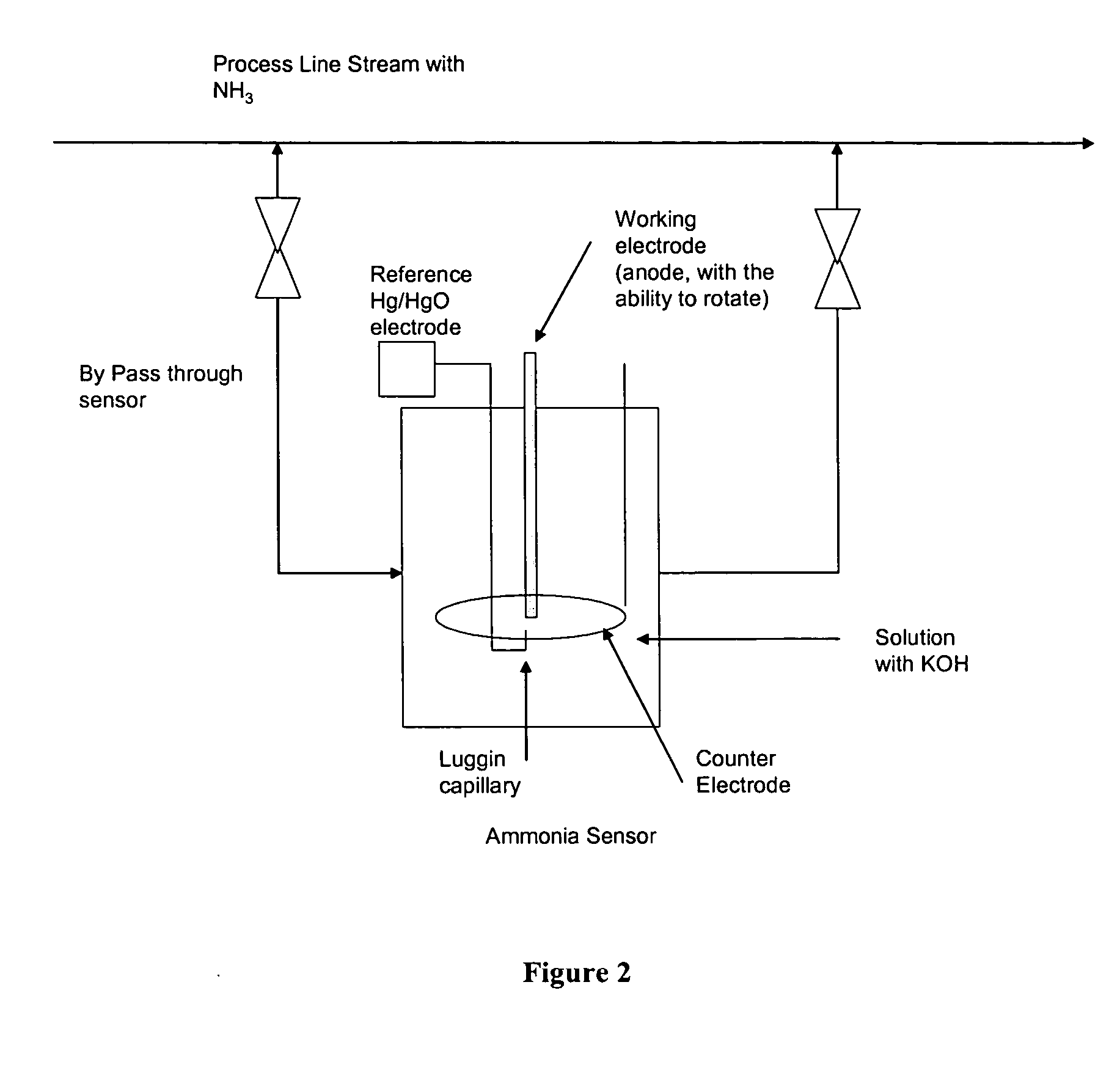
Electro-catalysts for the oxidation of ammonia in alkaline media
InactiveUS20050211569A1From normal temperature solutionsLiquid separation by electricityChemistryIridium
An electro-catalyst for the oxidation of ammonia in alkaline media; the electrocatalyst being a noble metal co-deposited on a support with one or more other metals that are active to ammonia oxidation. In some embodiments, the support is platinum, gold, tantalum, or iridium. In some embodiments, the support has a layer of Raney metal deposited thereon prior to the deposition of the catalyst. Also provided are electrodes having the electro-catalyst deposited thereon, ammonia electrolytic cells, ammonia fuel cells, ammonia sensors, and a method for removing ammonia contaminants from a contaminated effluent.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
Process for microwave decomposition of hazardous matter
InactiveUS6187988B1Promote oxidationNitrogen compoundsLiquid separation by electricityActivated carbonHydrazine compound
This process occurs in the presence of activated carbon or its equivalent by decomposing adsorbed hazardous materials, such as hydrazine and microorganisms, on the carbon surface by radiofrequency energy in the microwave range at near ambient conditions of temperature and pressure. Further microwave oxidation to nonhazardous gases occurs in the presence of a microwaves enhanced oxidation catalyst.
Owner:CHA CHANG YUL
Popular searches
Flow mixers Volume/mass flow measurement Chemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactors Fluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elements Isotope separation Biomass after-treatment Fluid speed measurement Optical light guides DNA preparation Water/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fields
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com