Patents
Literature
1458 results about "Nanopore" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
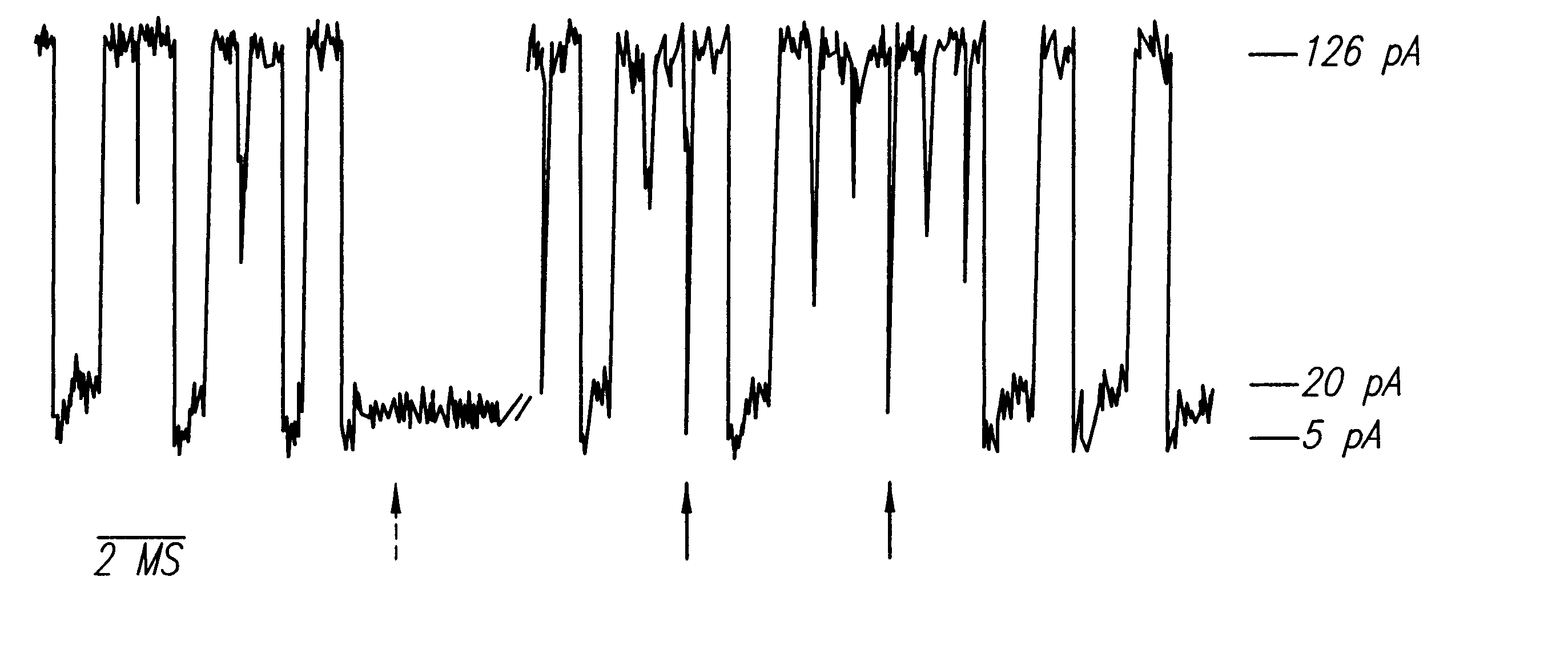
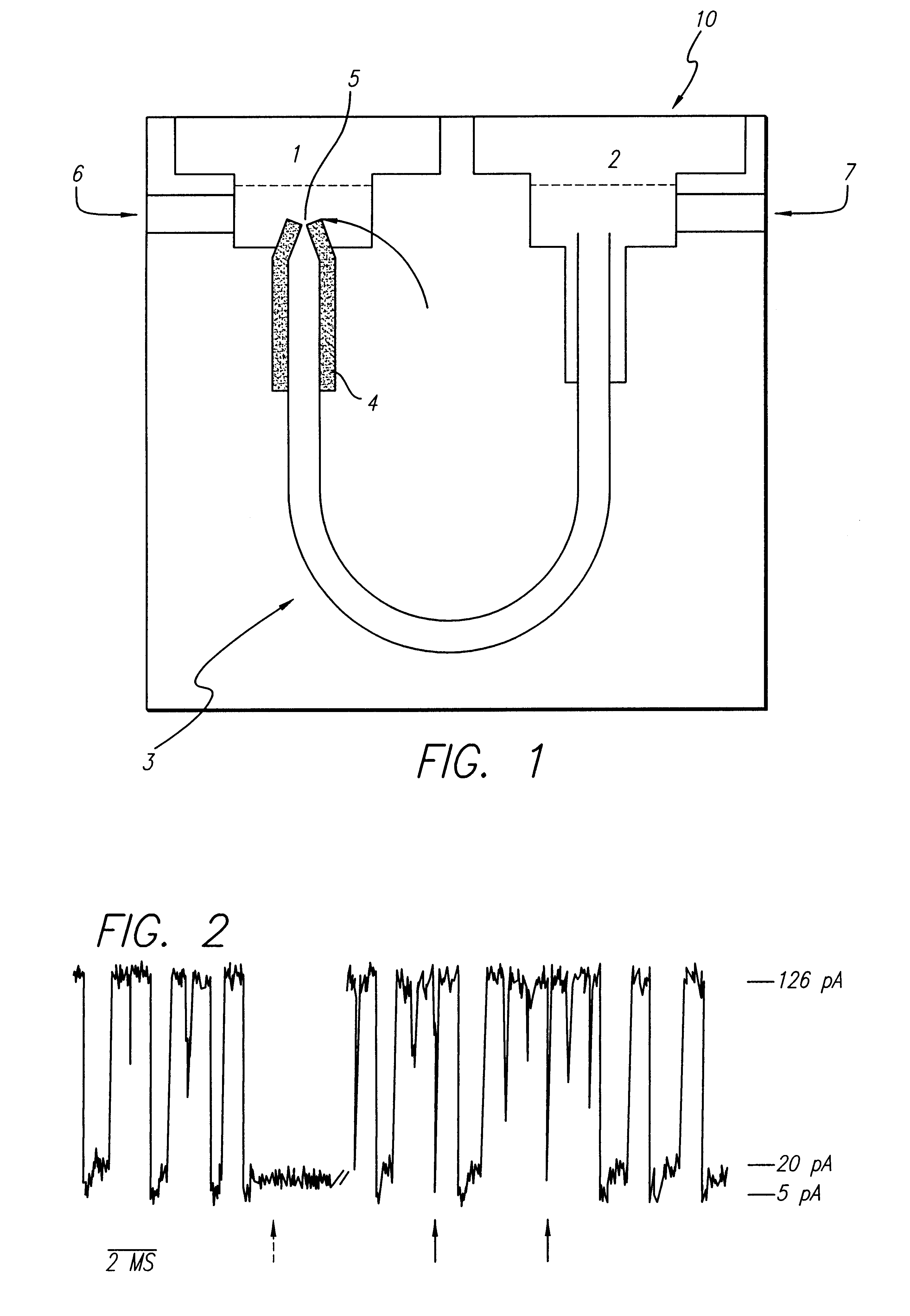
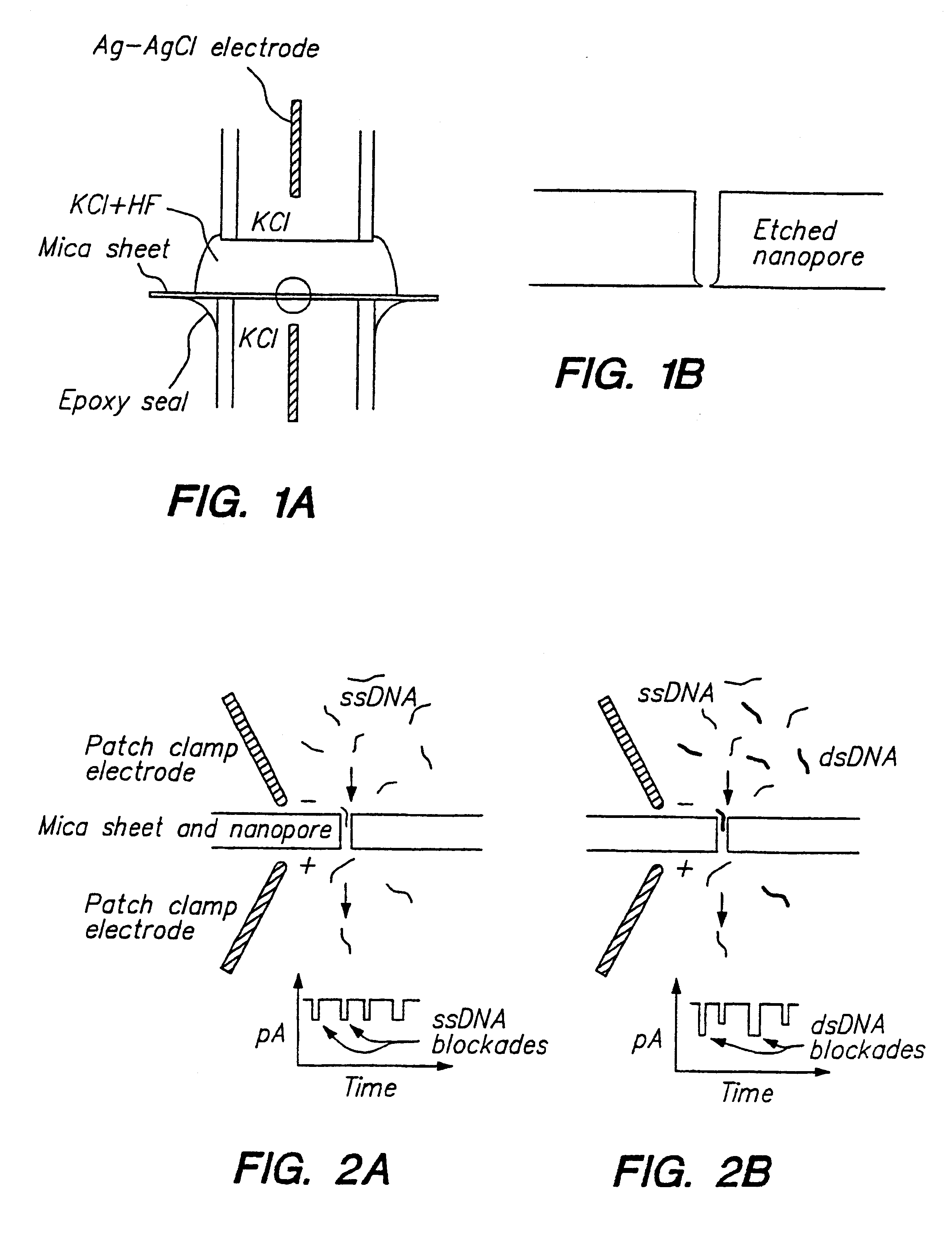
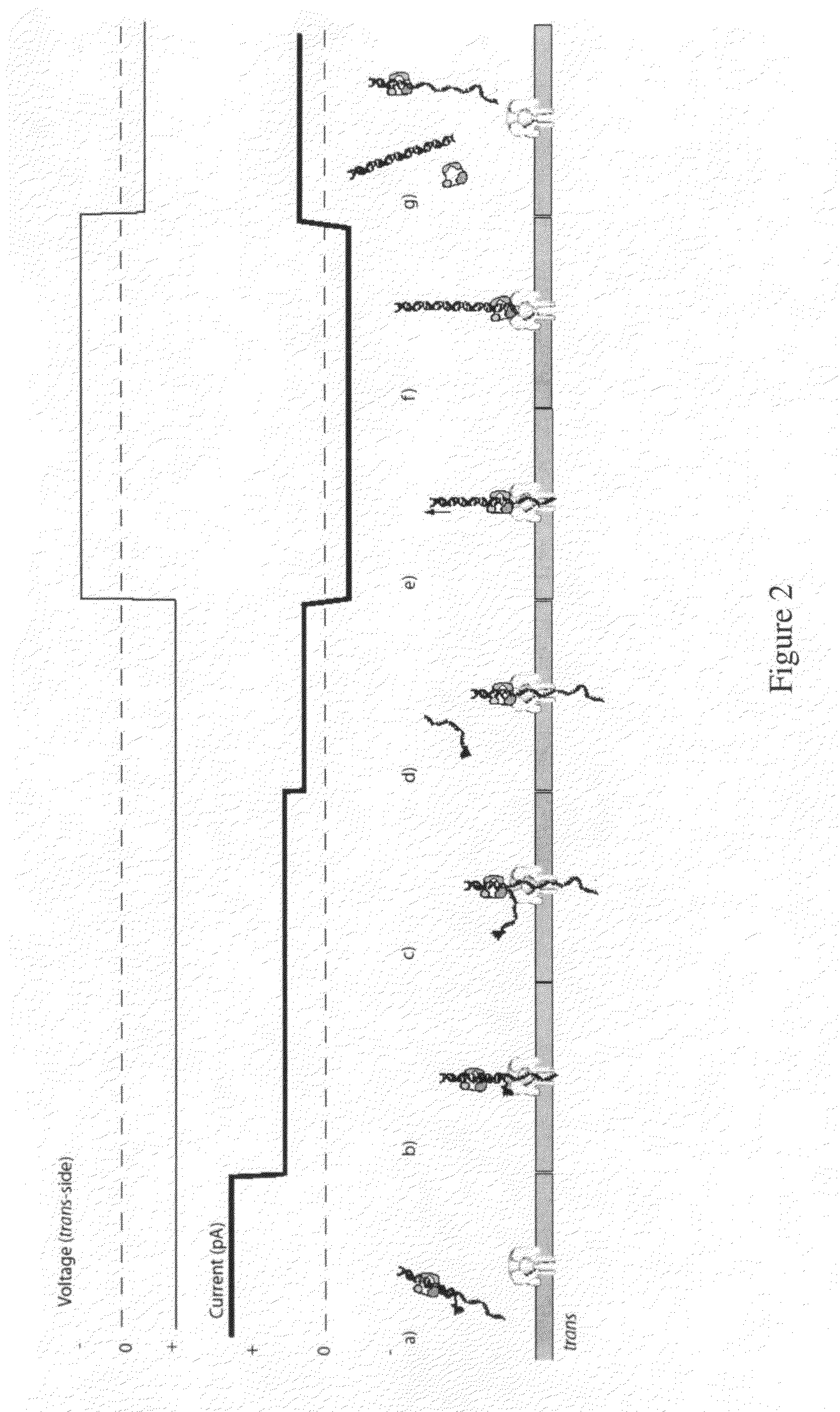
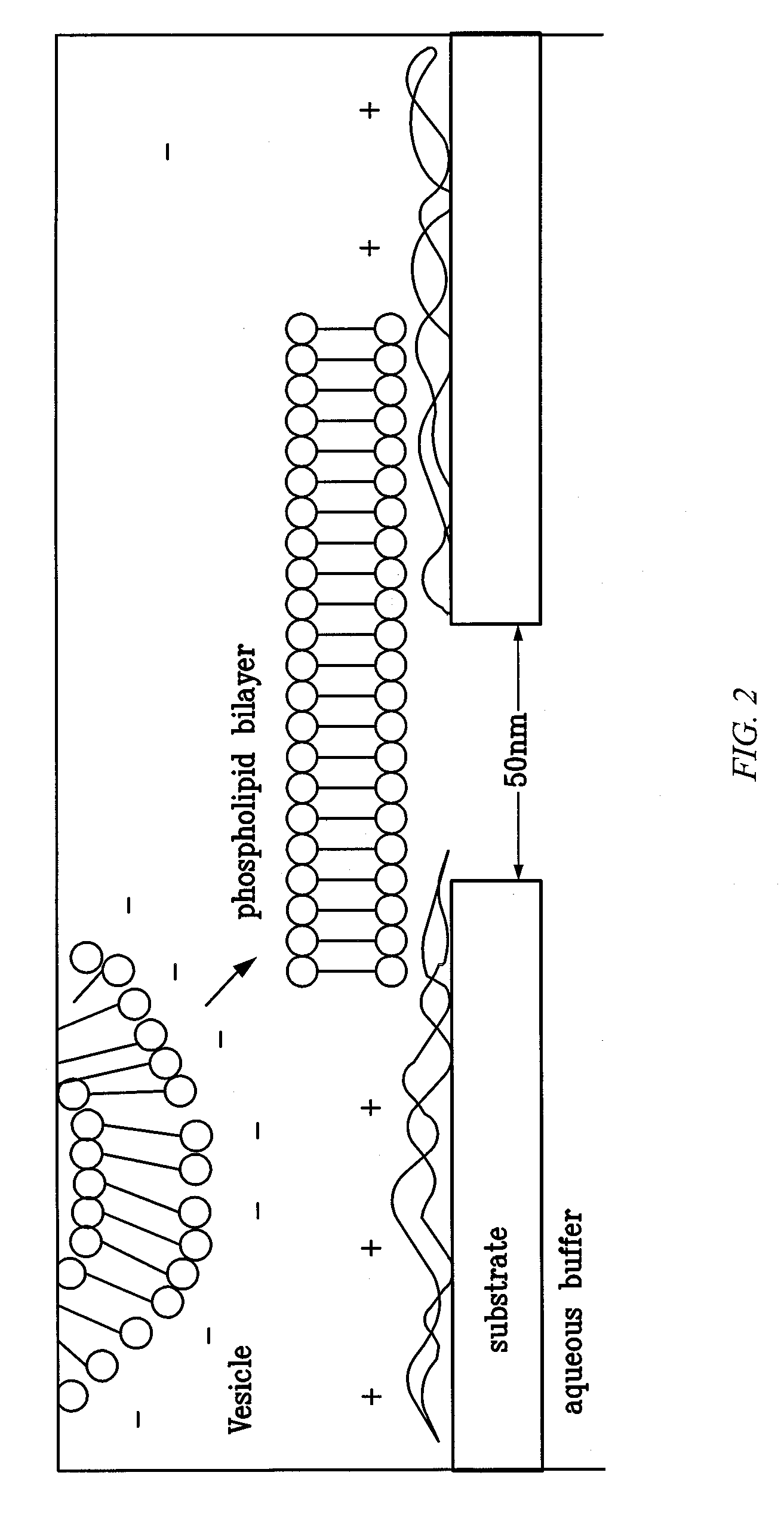
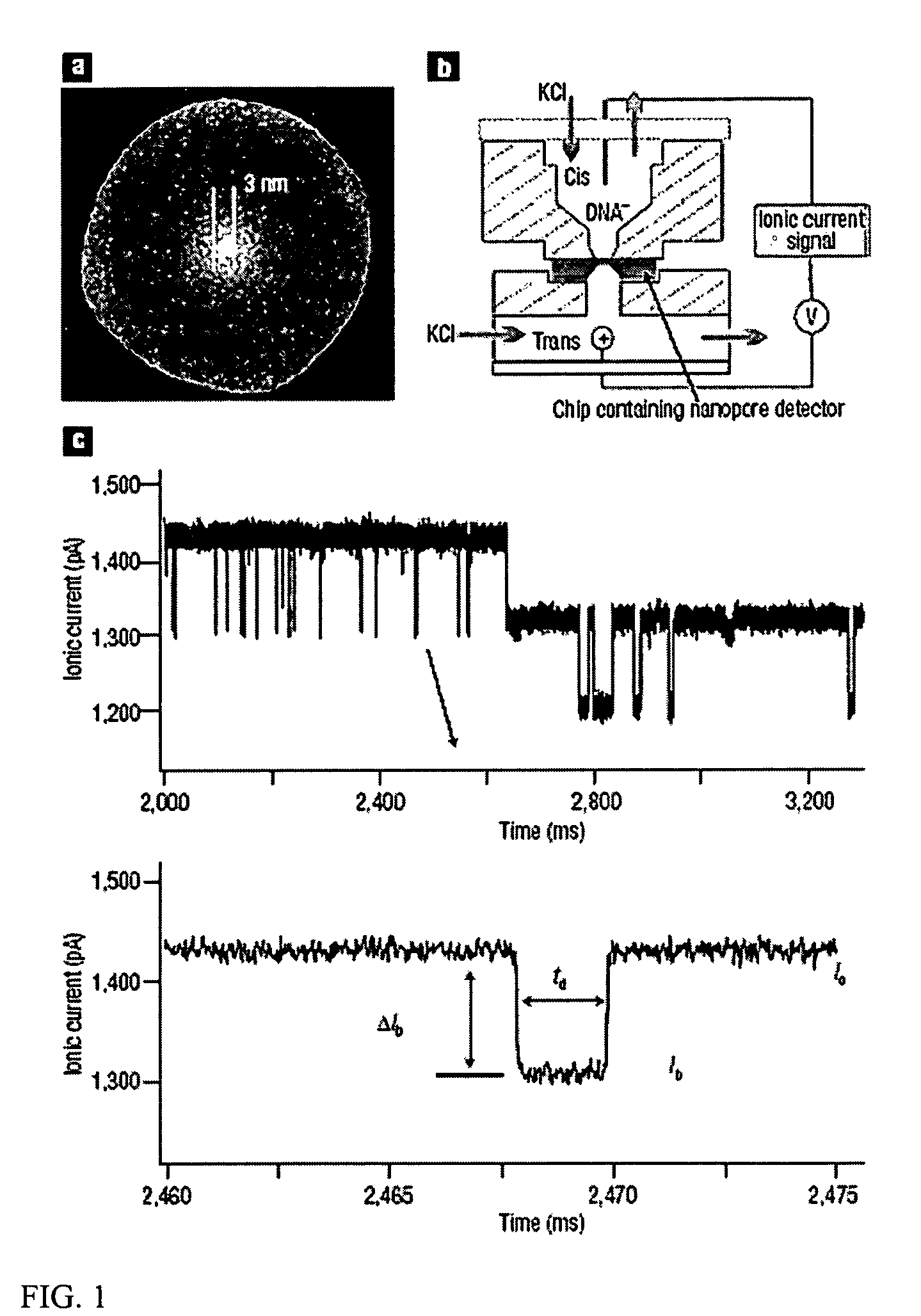
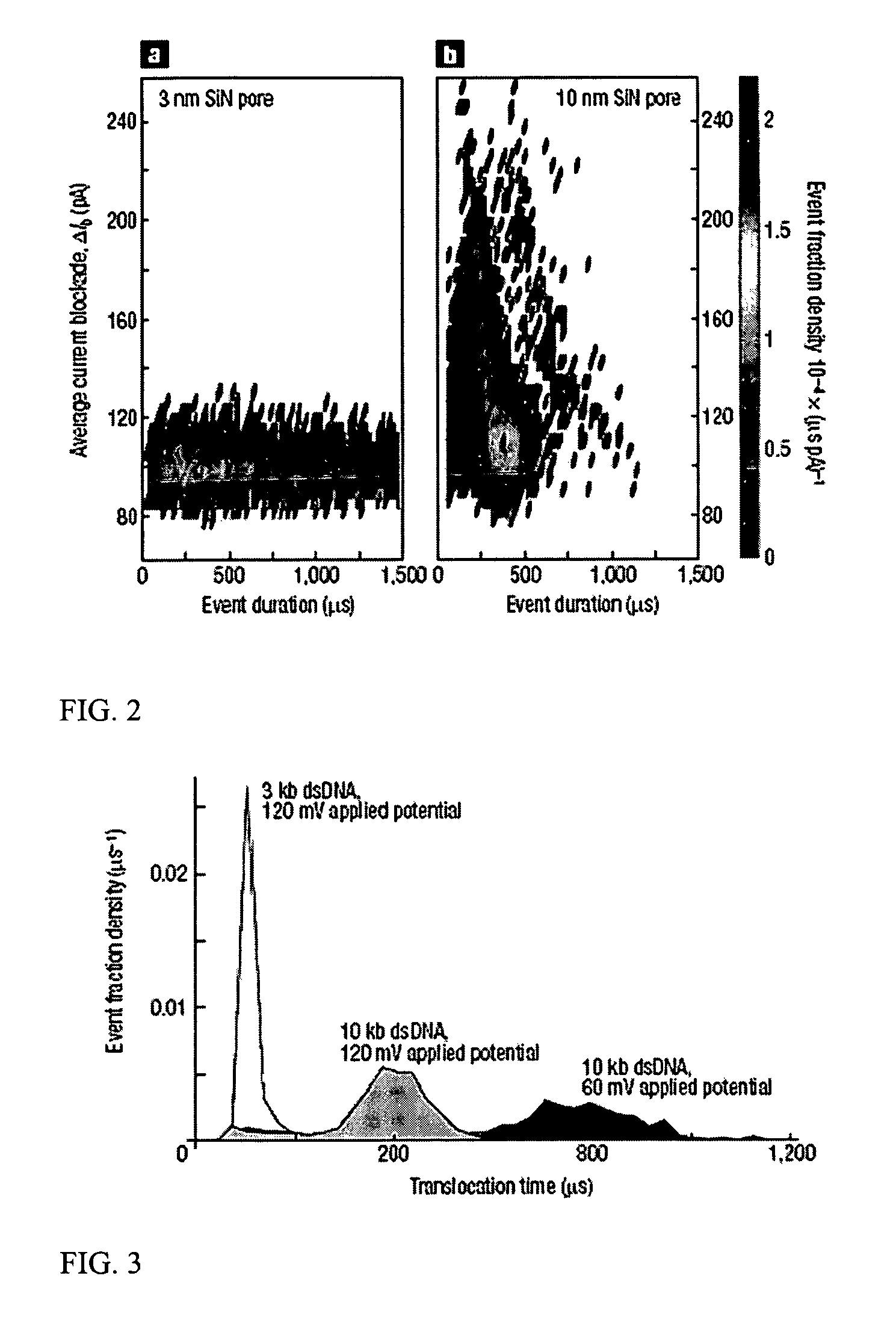
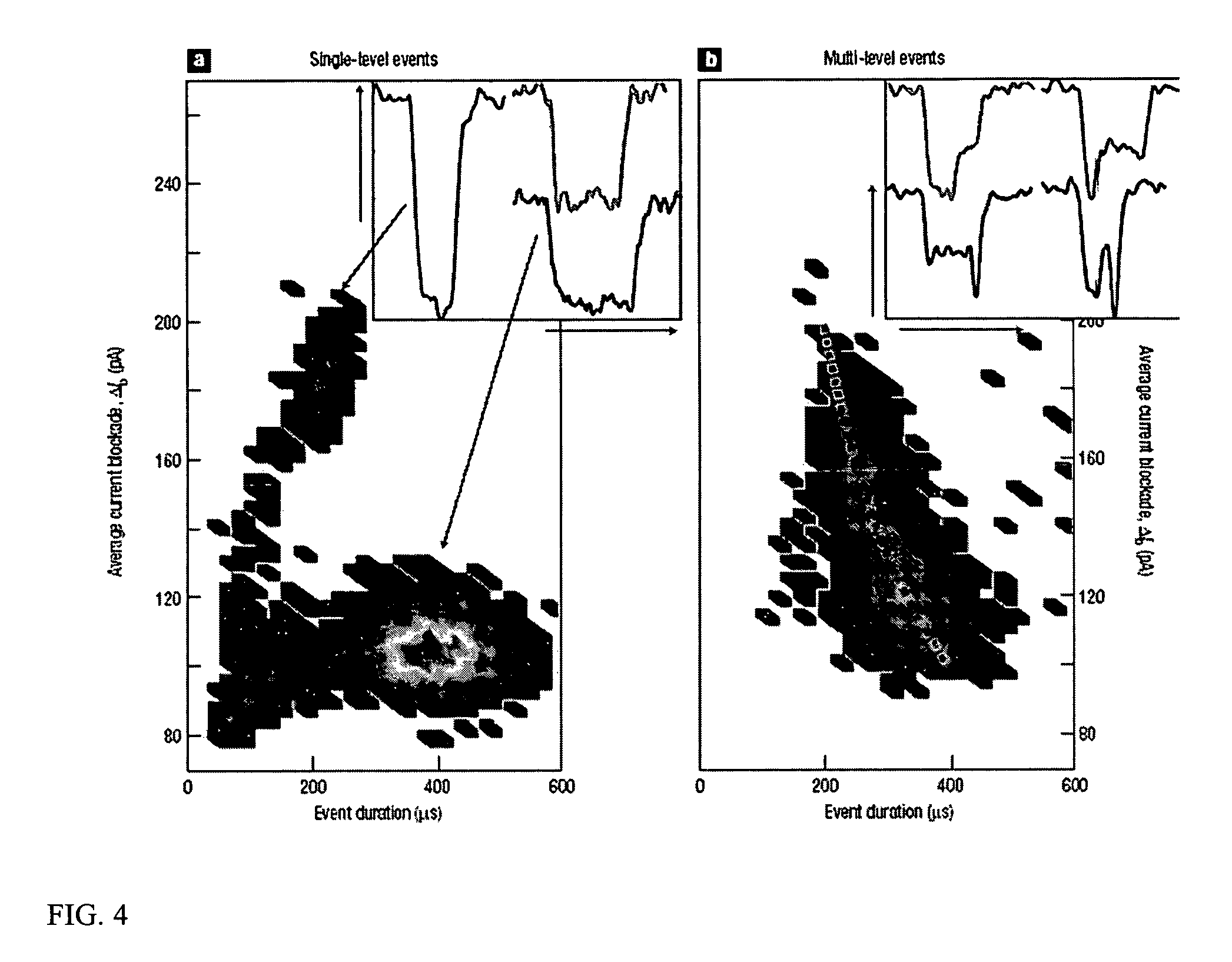
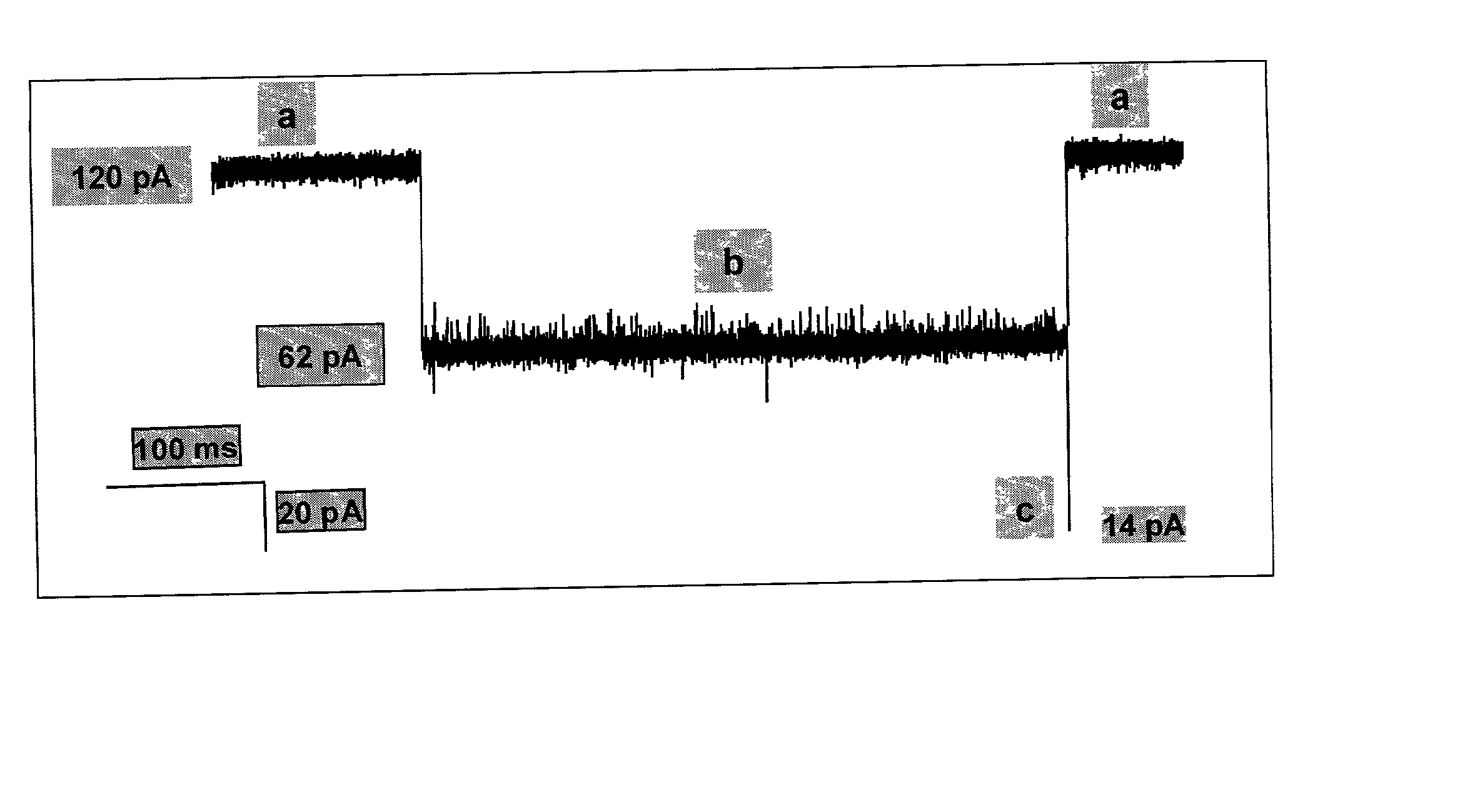
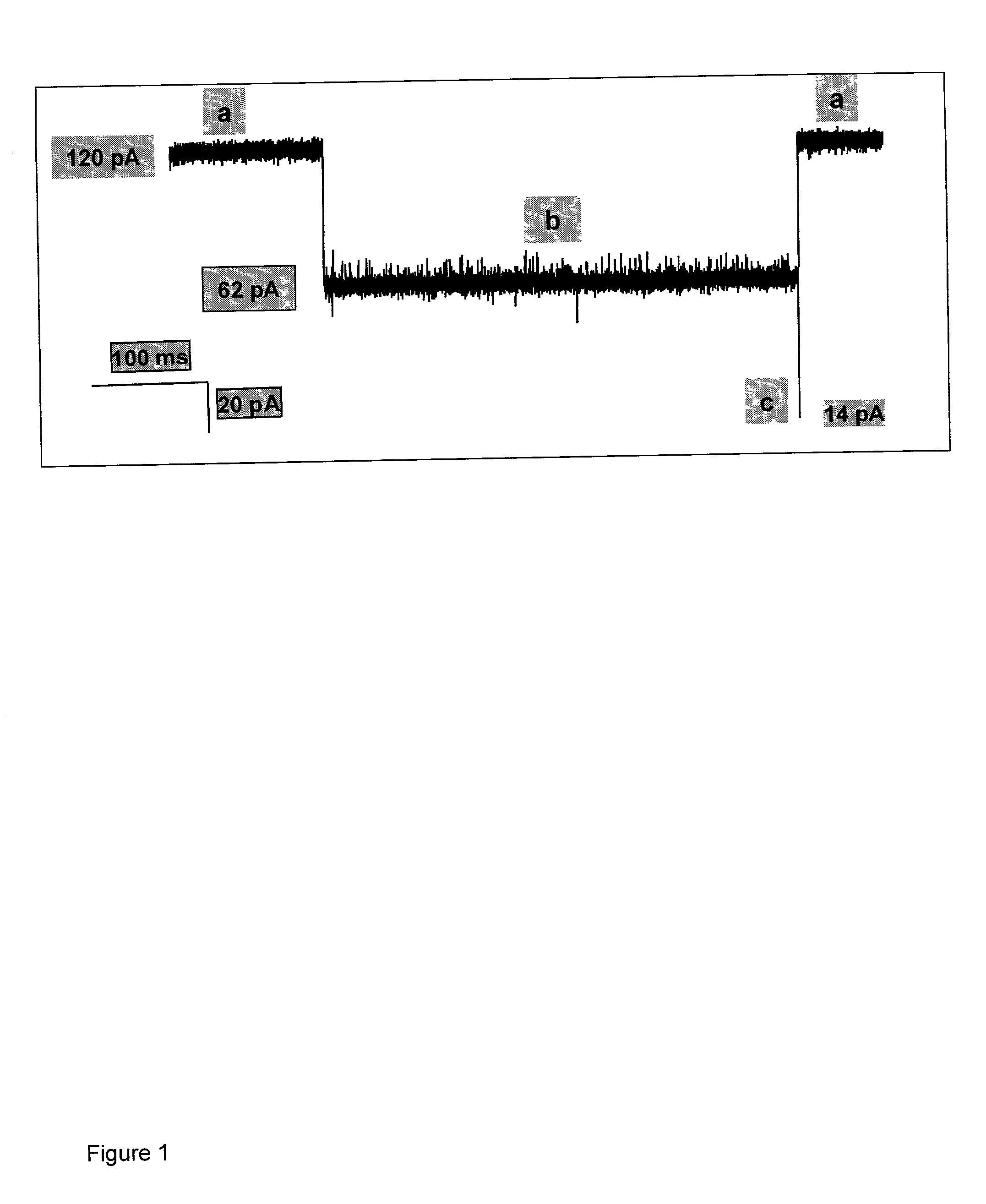
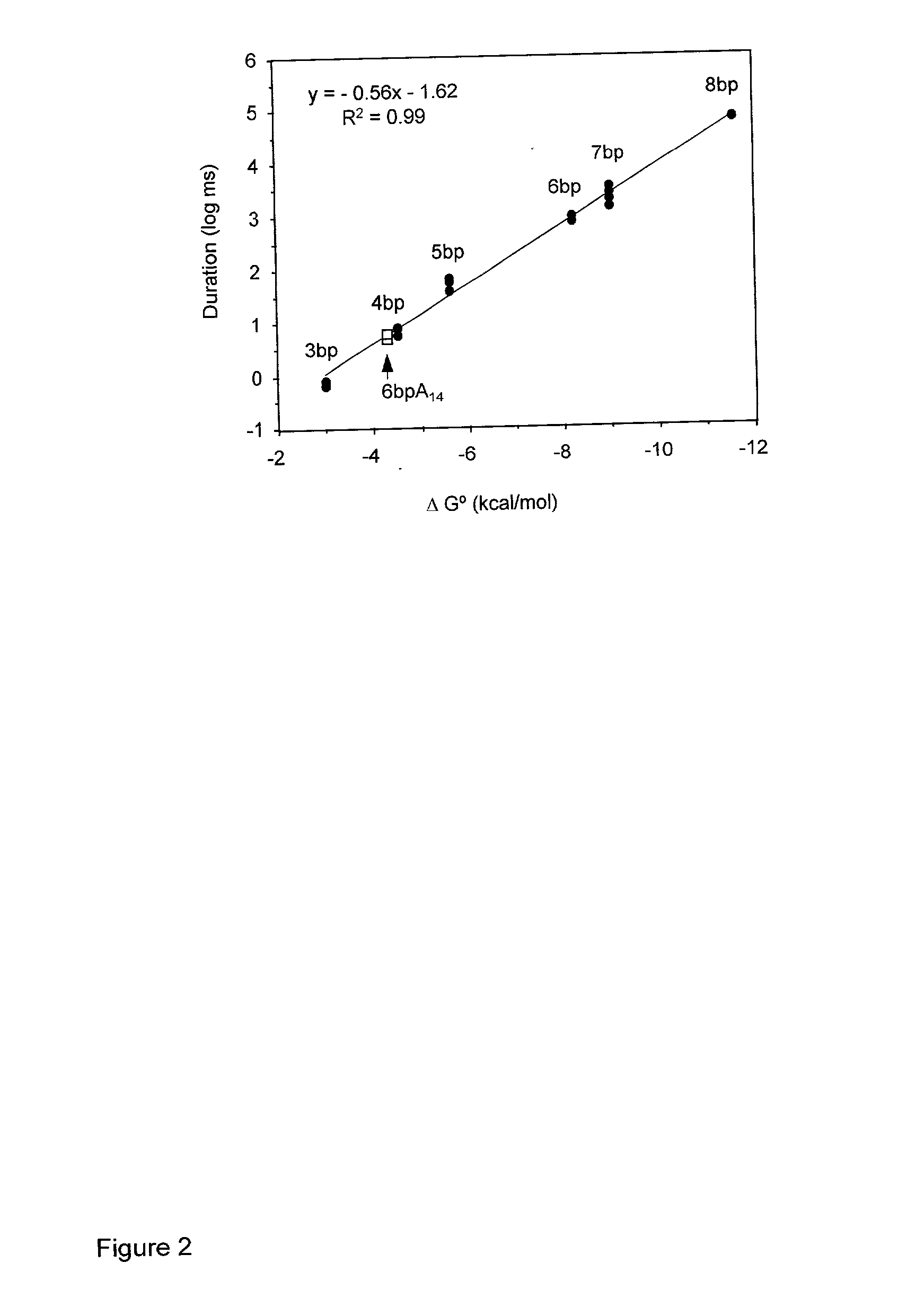
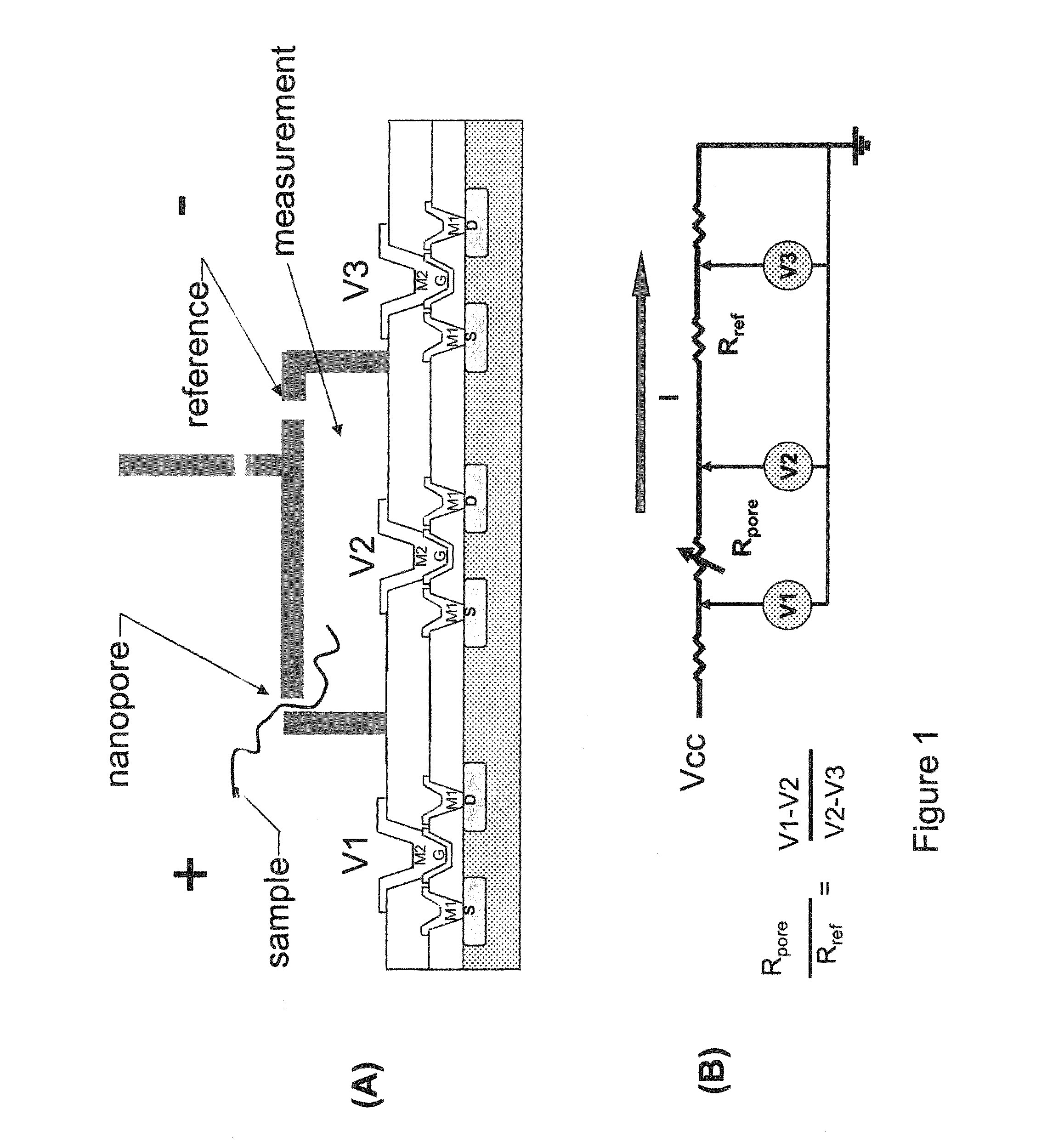
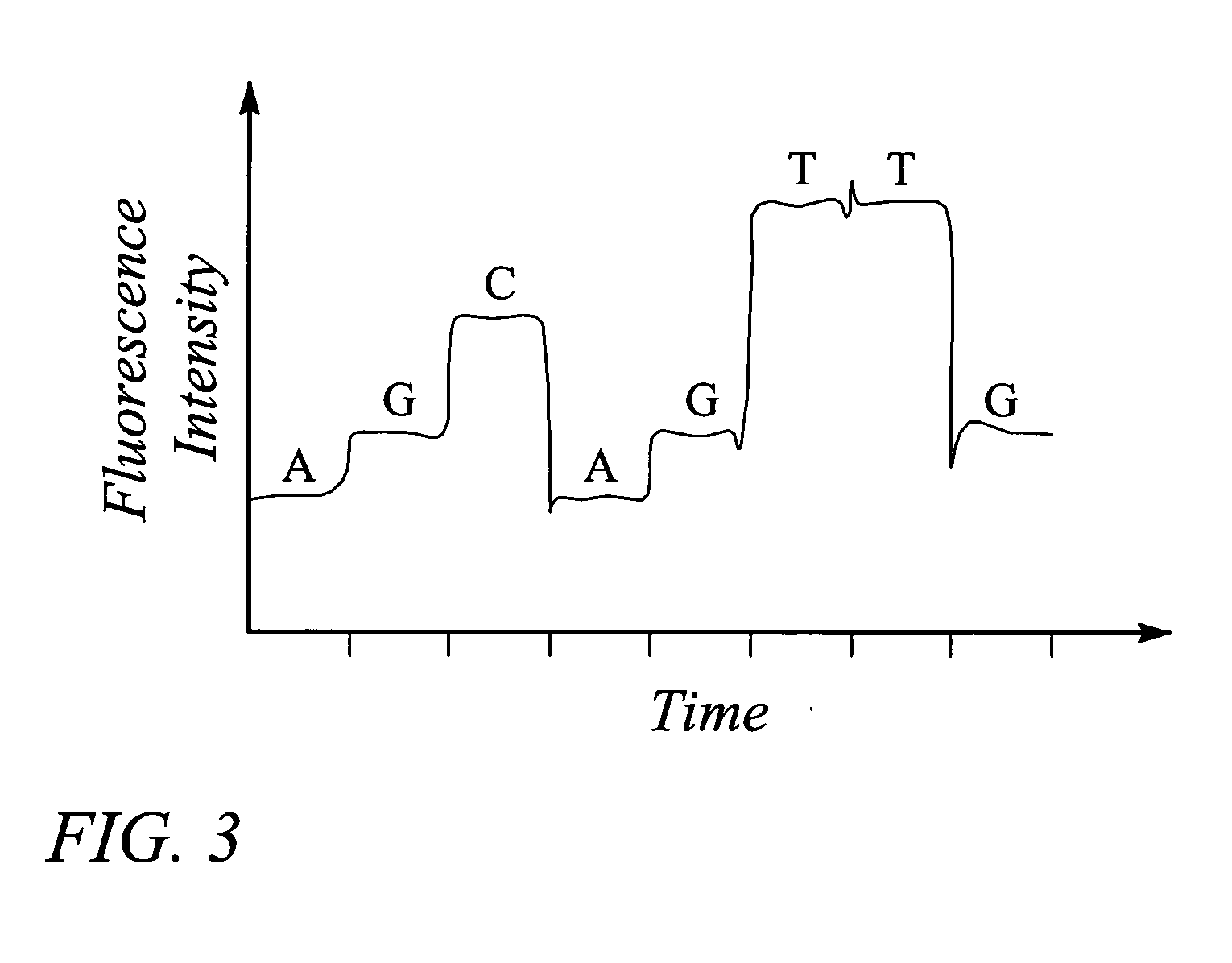
A nanopore is a pore of nanometer size. It may, for example, be created by a pore-forming protein or as a hole in synthetic materials such as silicon or graphene. When a nanopore is present in an electrically insulating membrane, it can be used as a single-molecule detector. It can be a biological protein channel in a high electrical resistance lipid bilayer, a pore in a solid-state membrane or a hybrid of these – a protein channel set in a synthetic membrane. The detection principle is based on monitoring the ionic current passing through the nanopore as a voltage is applied across the membrane. When the nanopore is of molecular dimensions, passage of molecules (e.g., DNA) cause interruptions of the "open" current level, leading to a "translocation event" signal. The passage of RNA or single-stranded DNA molecules through the membrane-embedded alpha-hemolysin channel (1.5 nm diameter), for example, causes a ~90% blockage of the current (measured at 1 M KCl solution).
Nanopore sequencing devices and methods
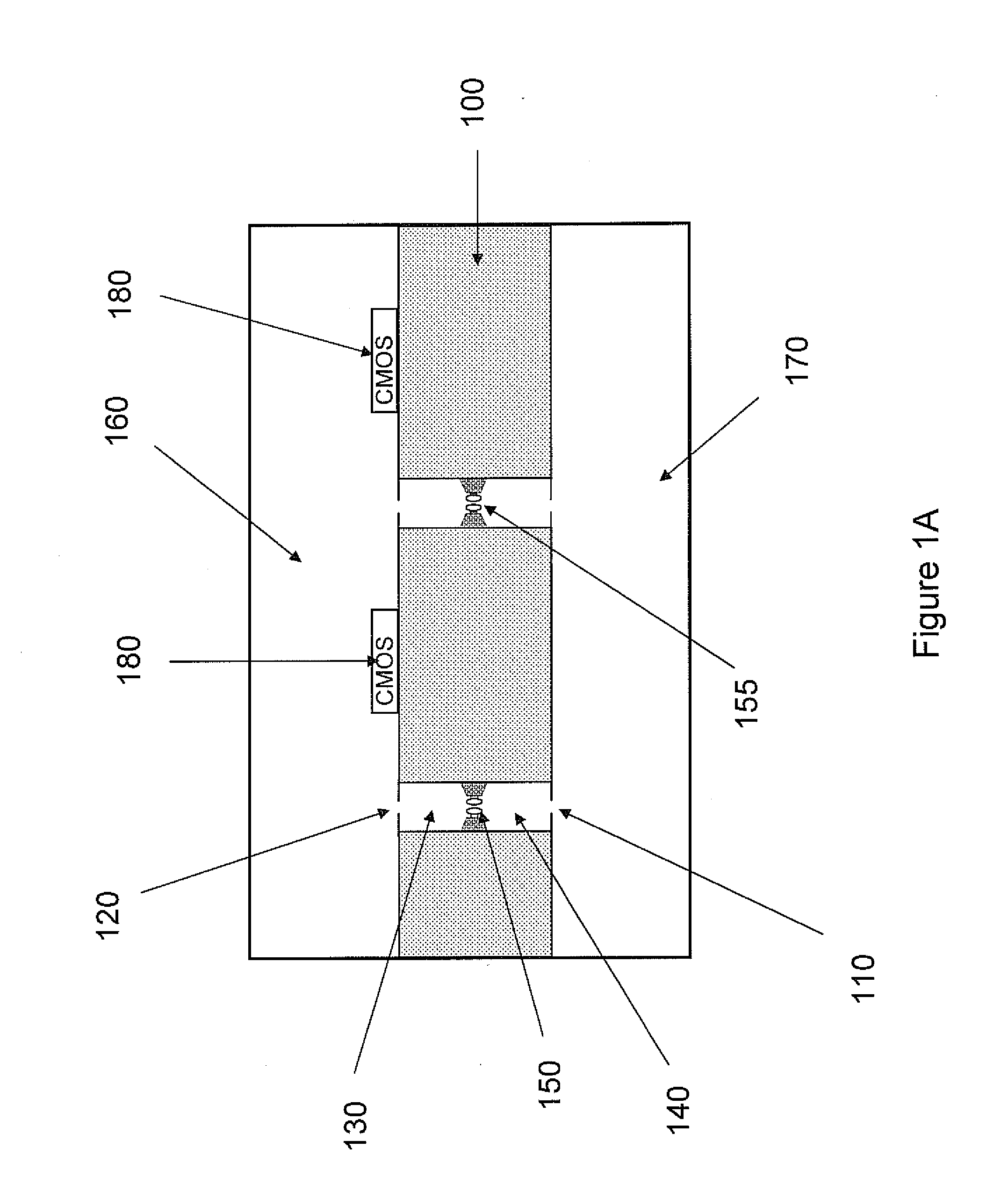
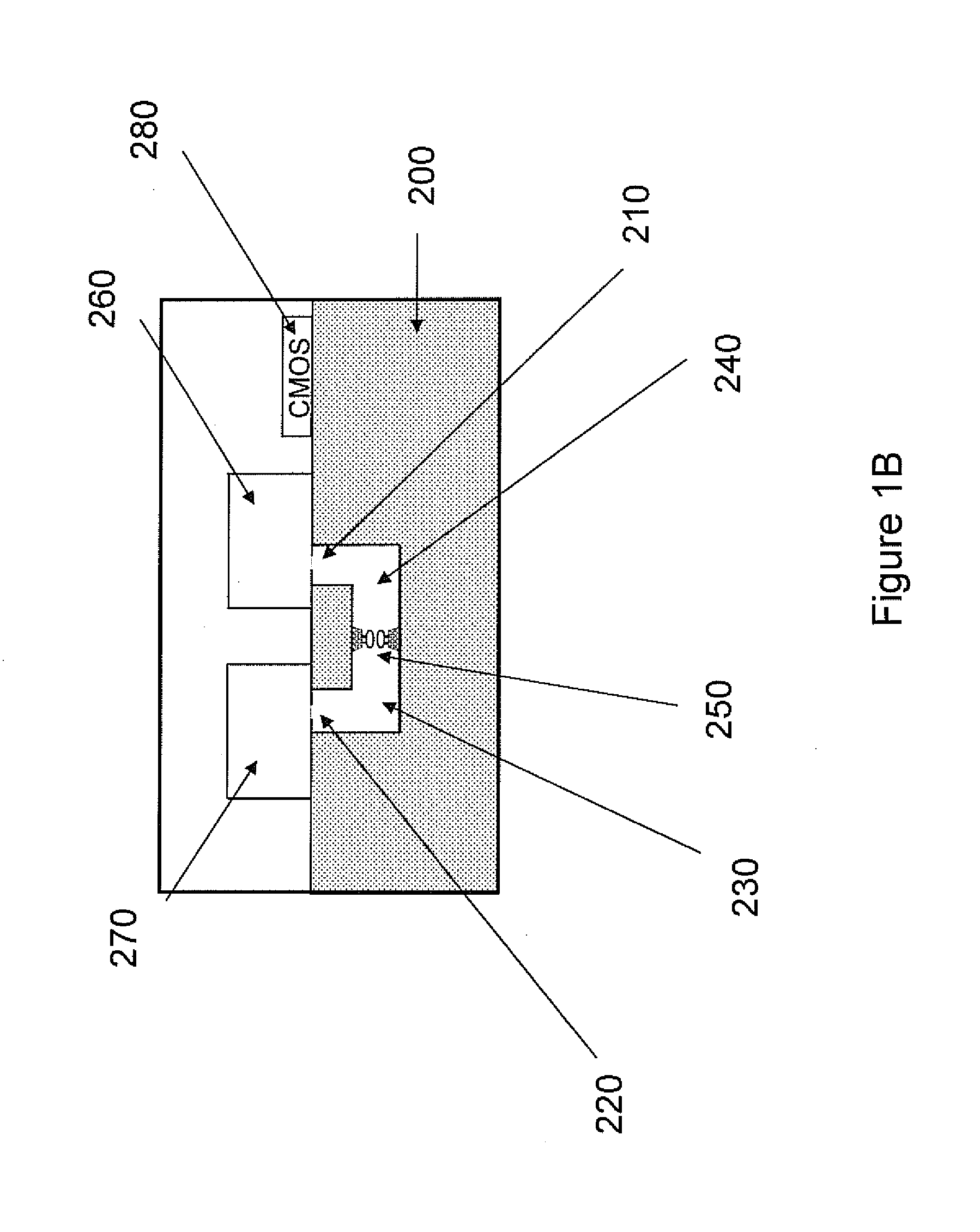
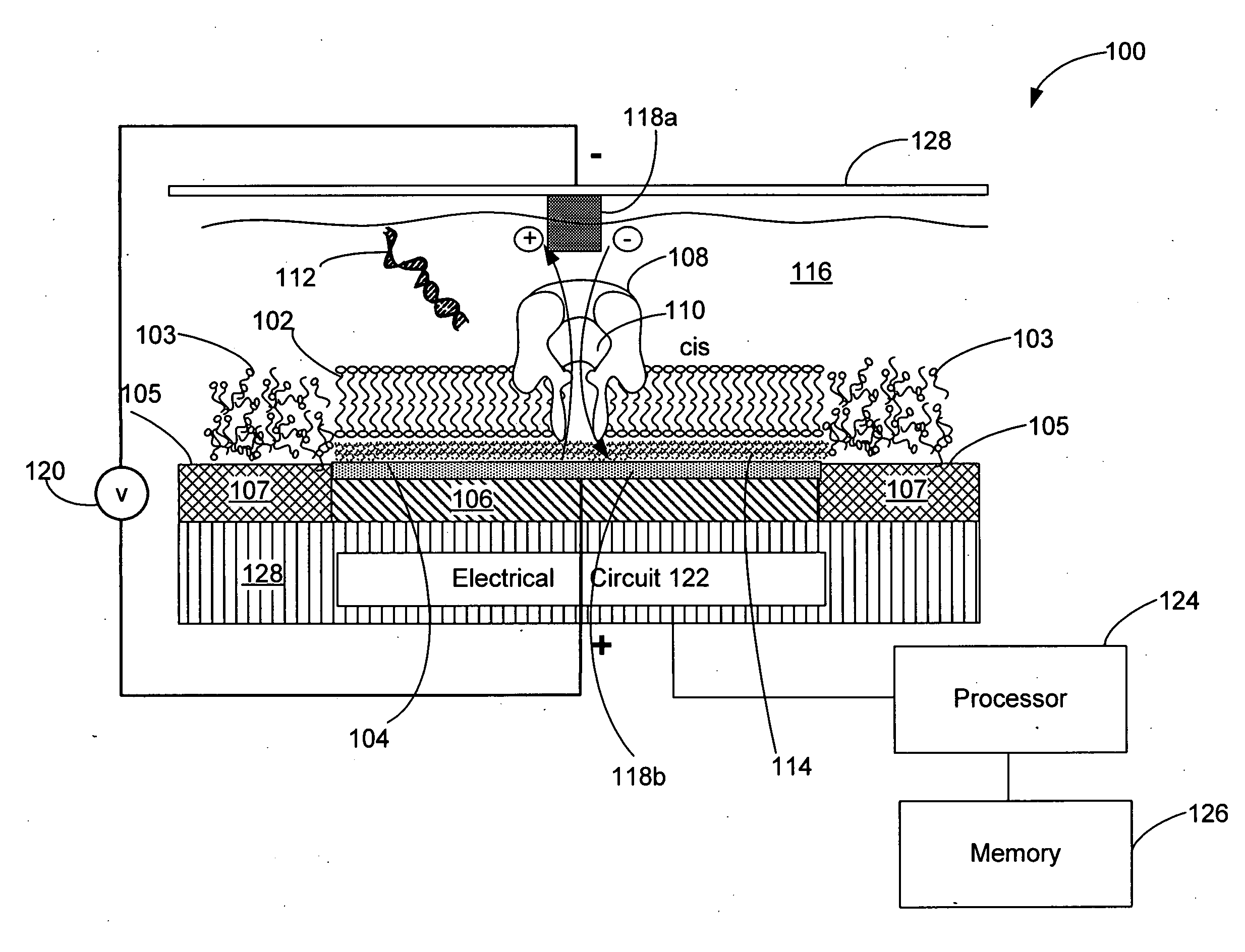
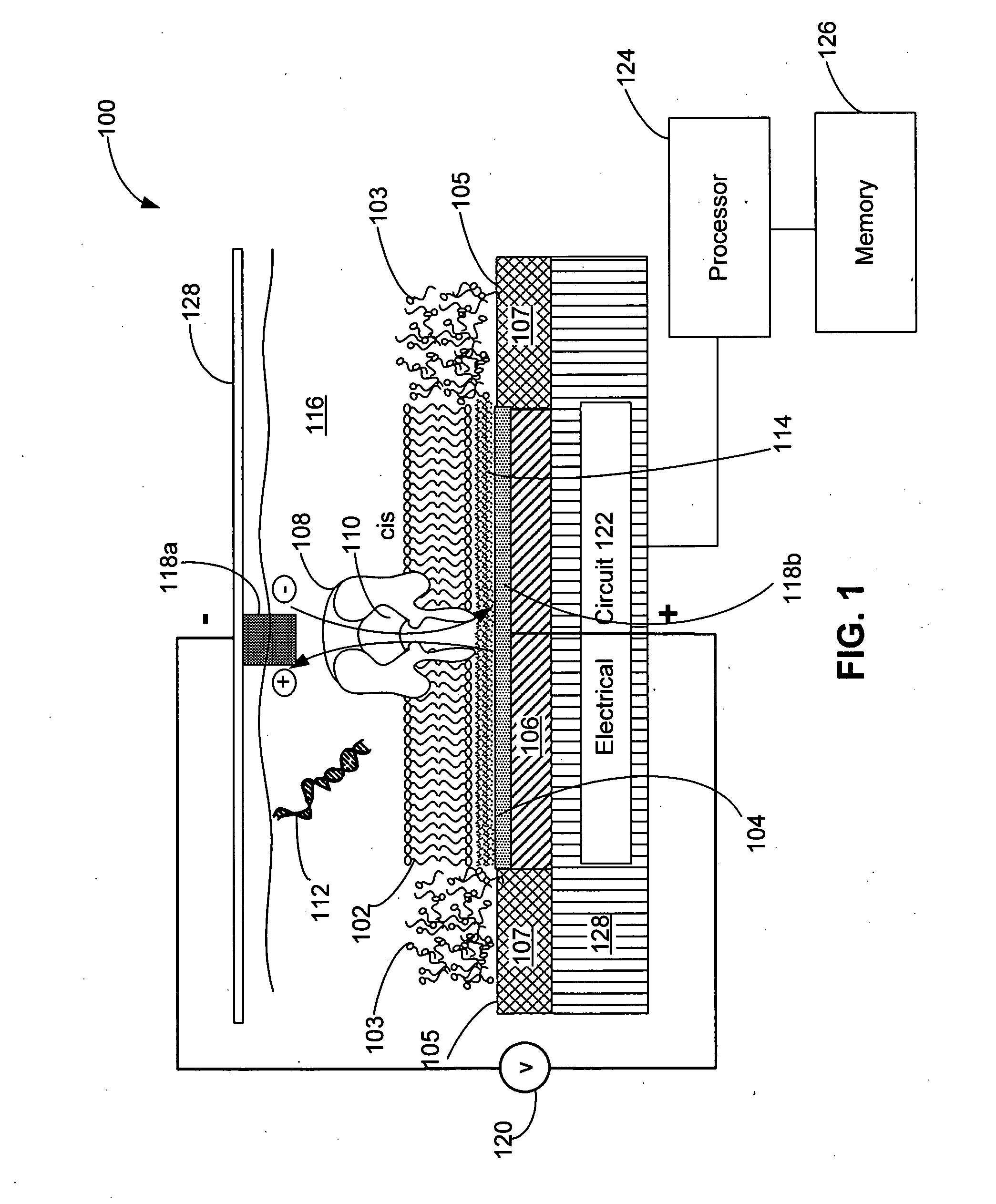
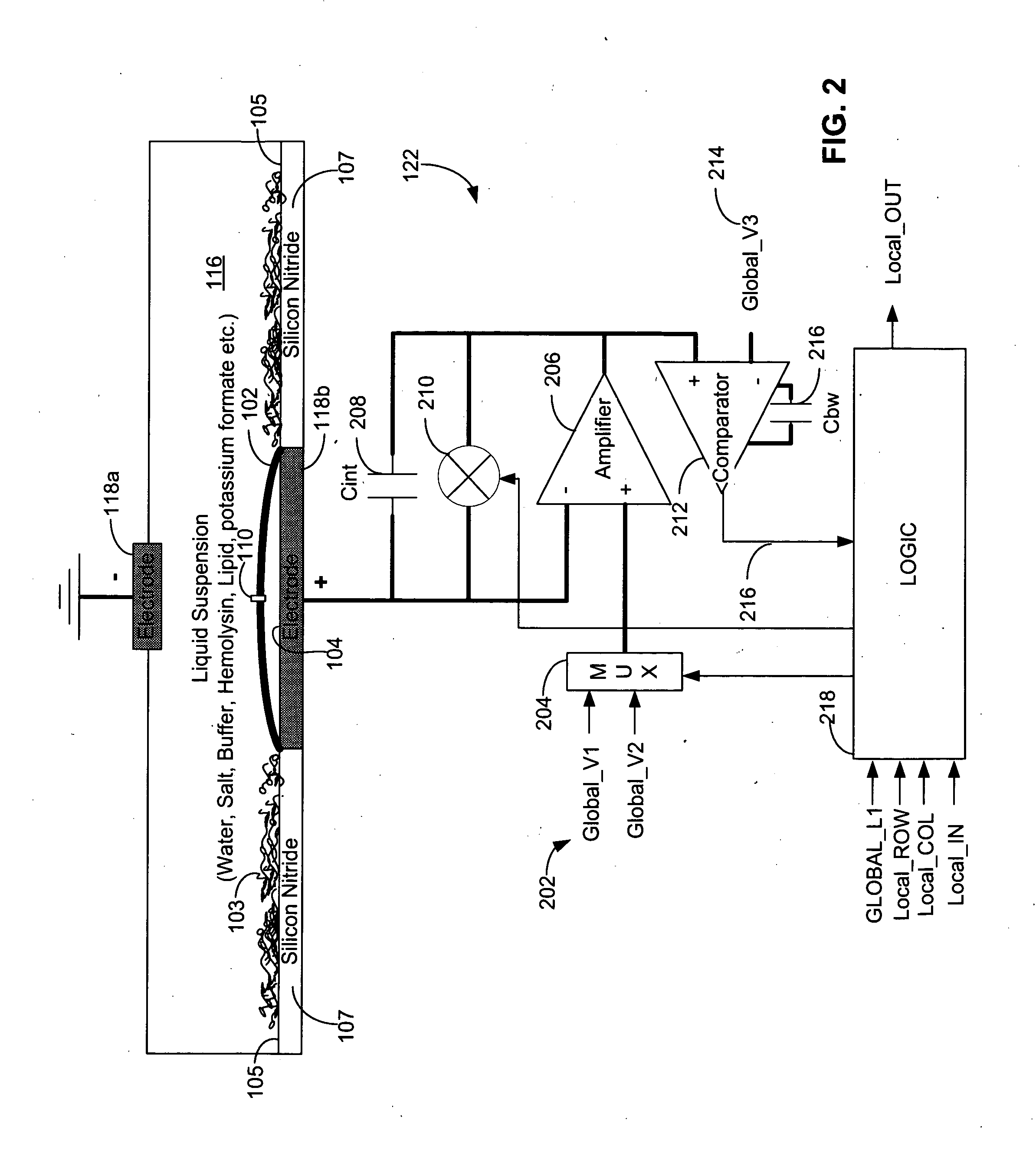
ActiveUS20100331194A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention relates to devices and methods for nanopore sequencing. The invention includes arrays of nanopores having incorporated electronic circuits, for example, in CMOS. In some cases, the arrays of nanopores comprise resistive openings for isolating the electronic signals for improved sequencing. Methods for controlling translocation of through the nanopore are disclosed.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
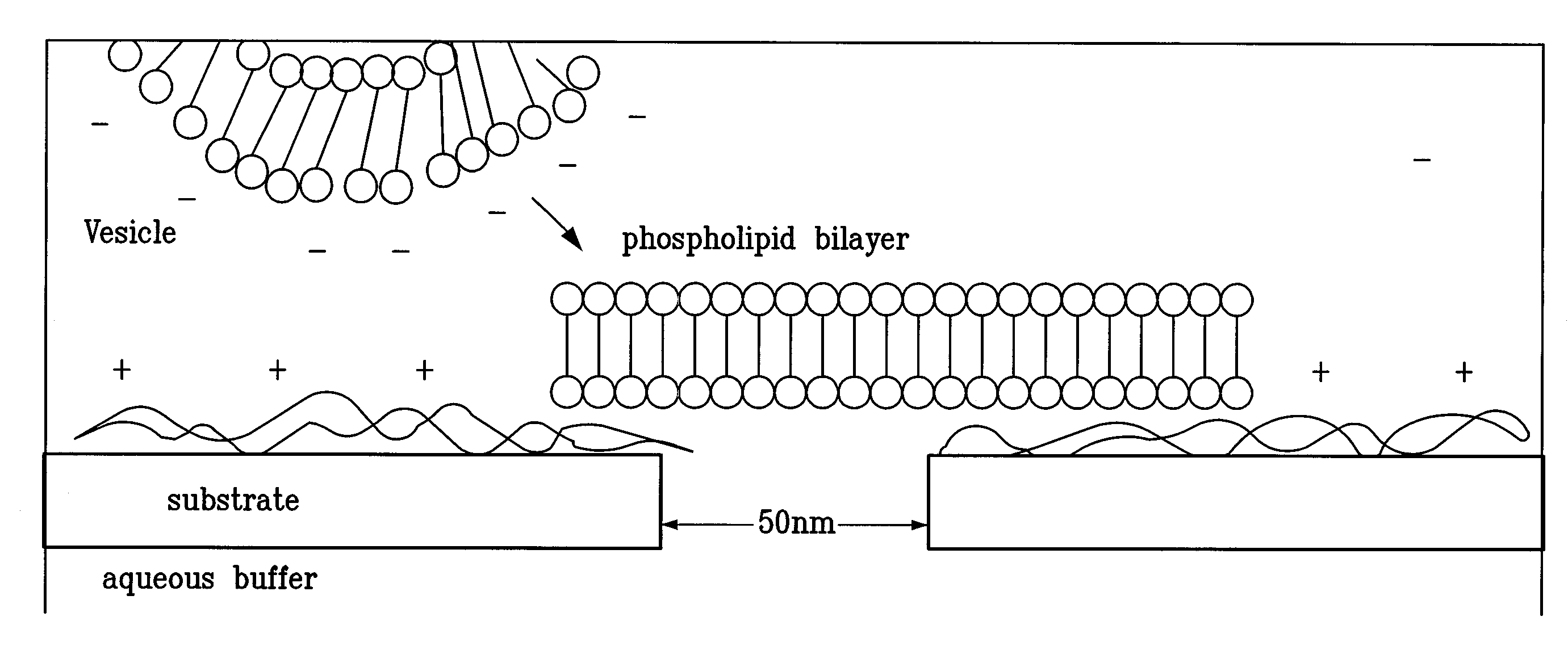
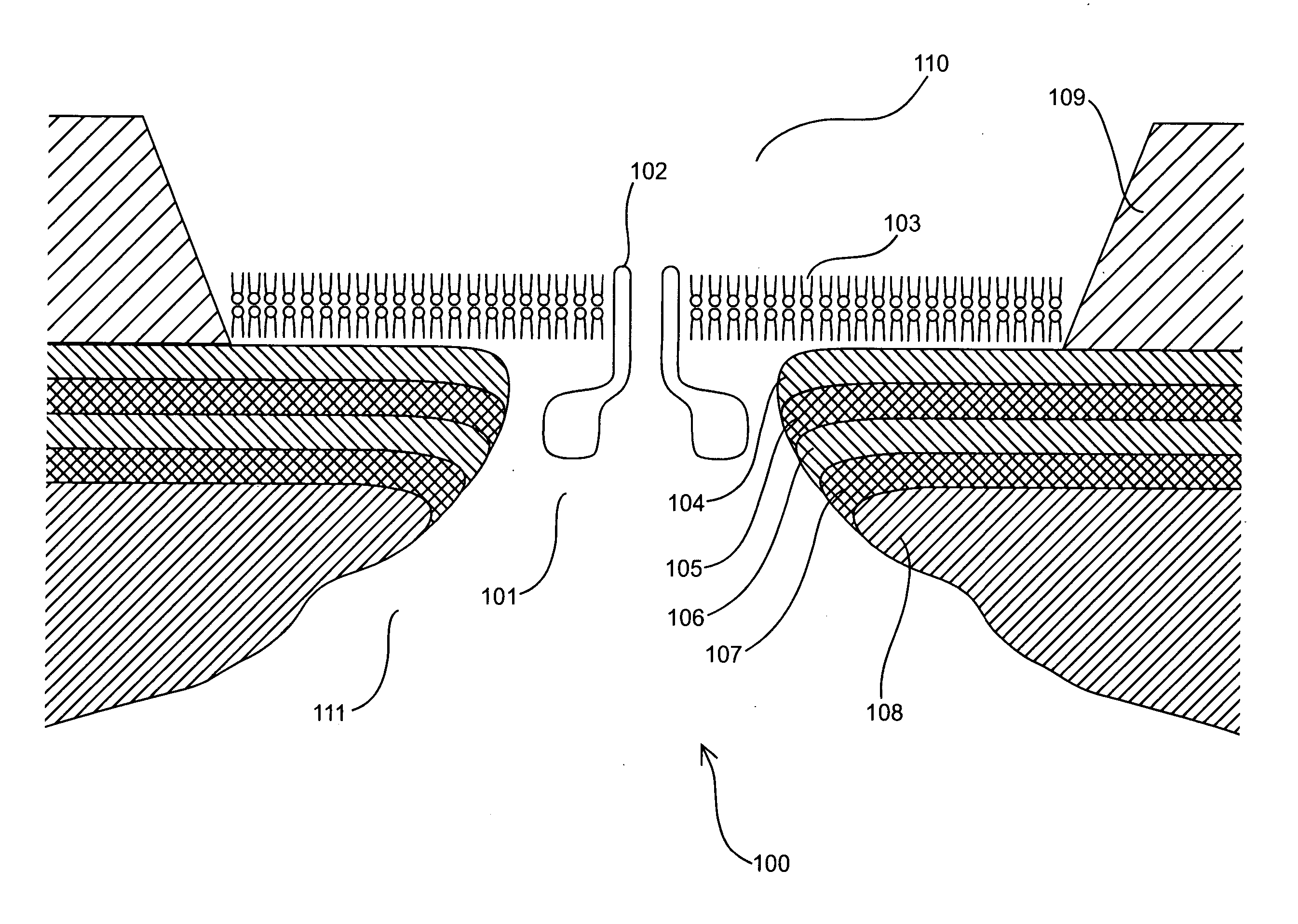
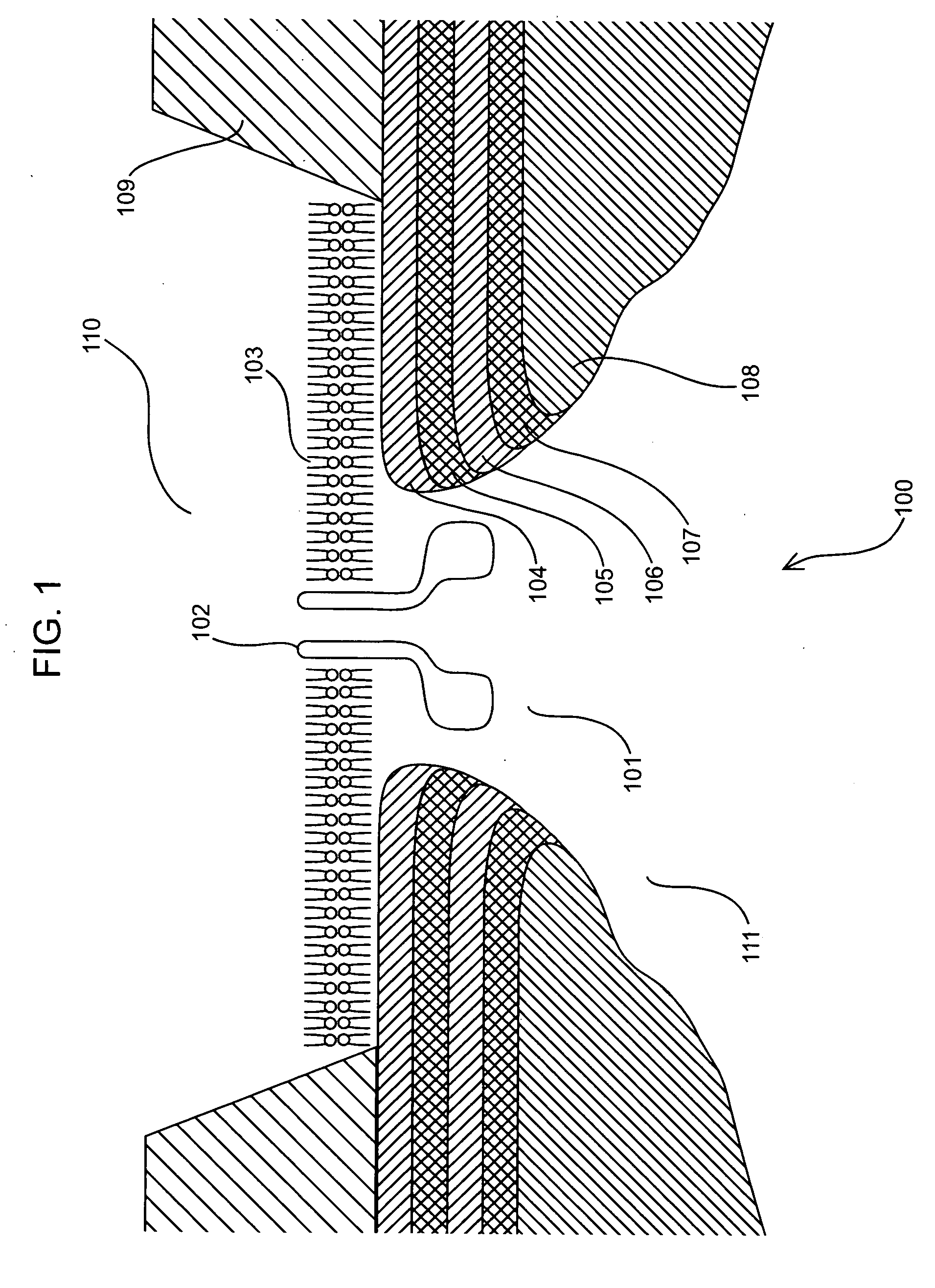
Miniature support for thin films containing single channels or nanopores and methods for using same
Single-channel thin film devices and methods for using the same are provided. The subject devices comprise cis and trans chambers connected by an electrical communication means. At the cis end of the electrical communication means is a horizontal conical aperture sealed with a thin film that includes a single nanopore or channel. The devices further include a means for applying an electric field between the cis and trans chambers. The subject devices find use in applications in which the ionic current through a nanopore or channel is monitored where such applications include the characterization of naturally occurring ion channels, the characterization of polymeric compounds, and the like.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Hybridization assisted nanopore sequencing
InactiveUS20070190542A1Eliminate needEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresHybridization probeNucleic Acid Probes
A method of employing a nanopore structure in a manner that allows the detection of the positions (relative and / or absolute) of nucleic acid probes that are hybridized onto a single-stranded nucleic acid molecule. In accordance with the method the strand of interest is hybridized with a probe having a known sequence. The strand and hybridized probes are translocated through a nanopore. The fluctuations in current measured across the nanopore will vary as a function of time corresponding to the passing of a probe attachment point along the strand. These fluctuations in current are then used to determine the attachment positions of the probes along the strand of interest. This probe position data is then fed into a computer algorithm that returns the sequence of the strand of interest.
Owner:NABSYS 2 0 +1
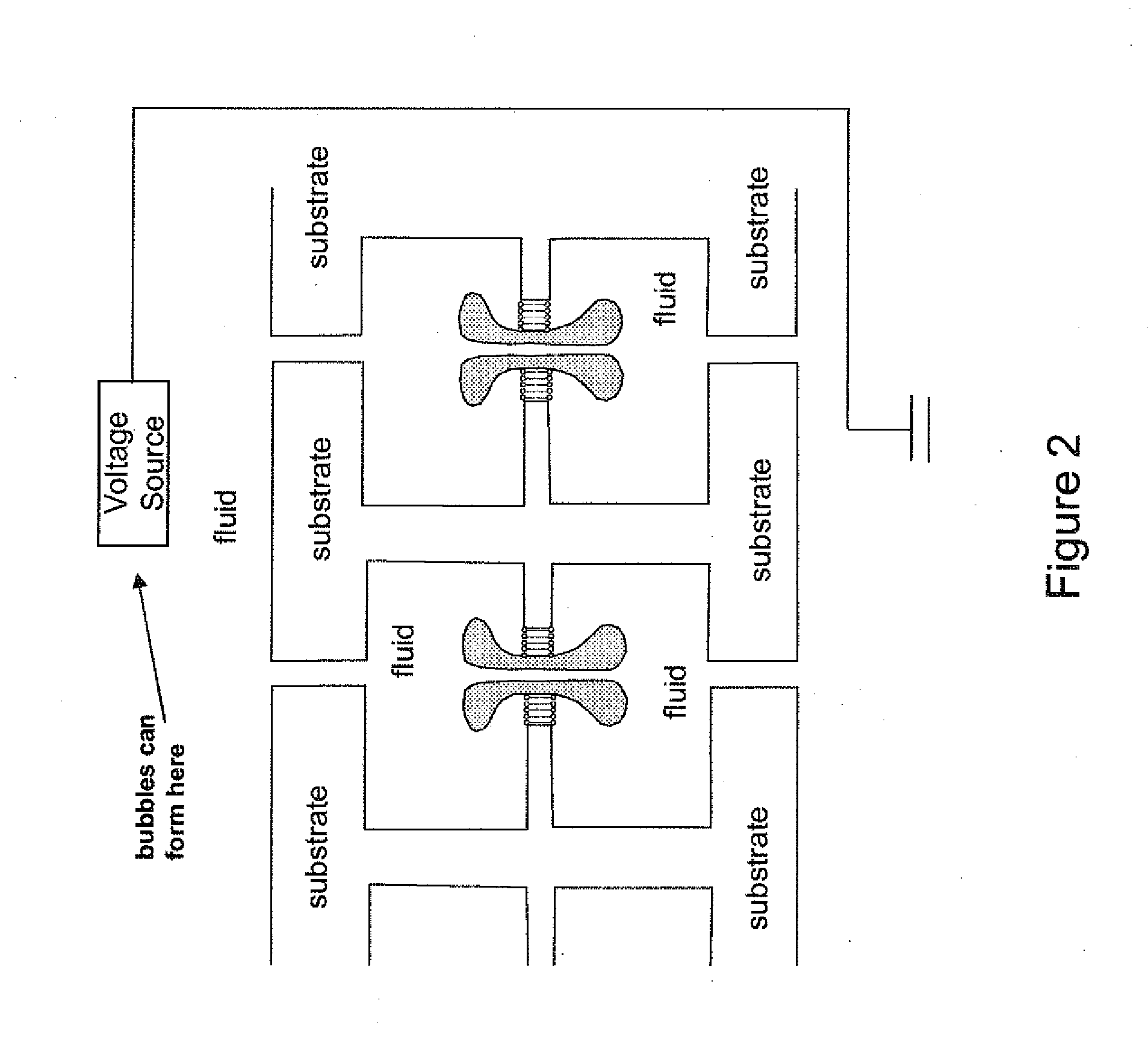
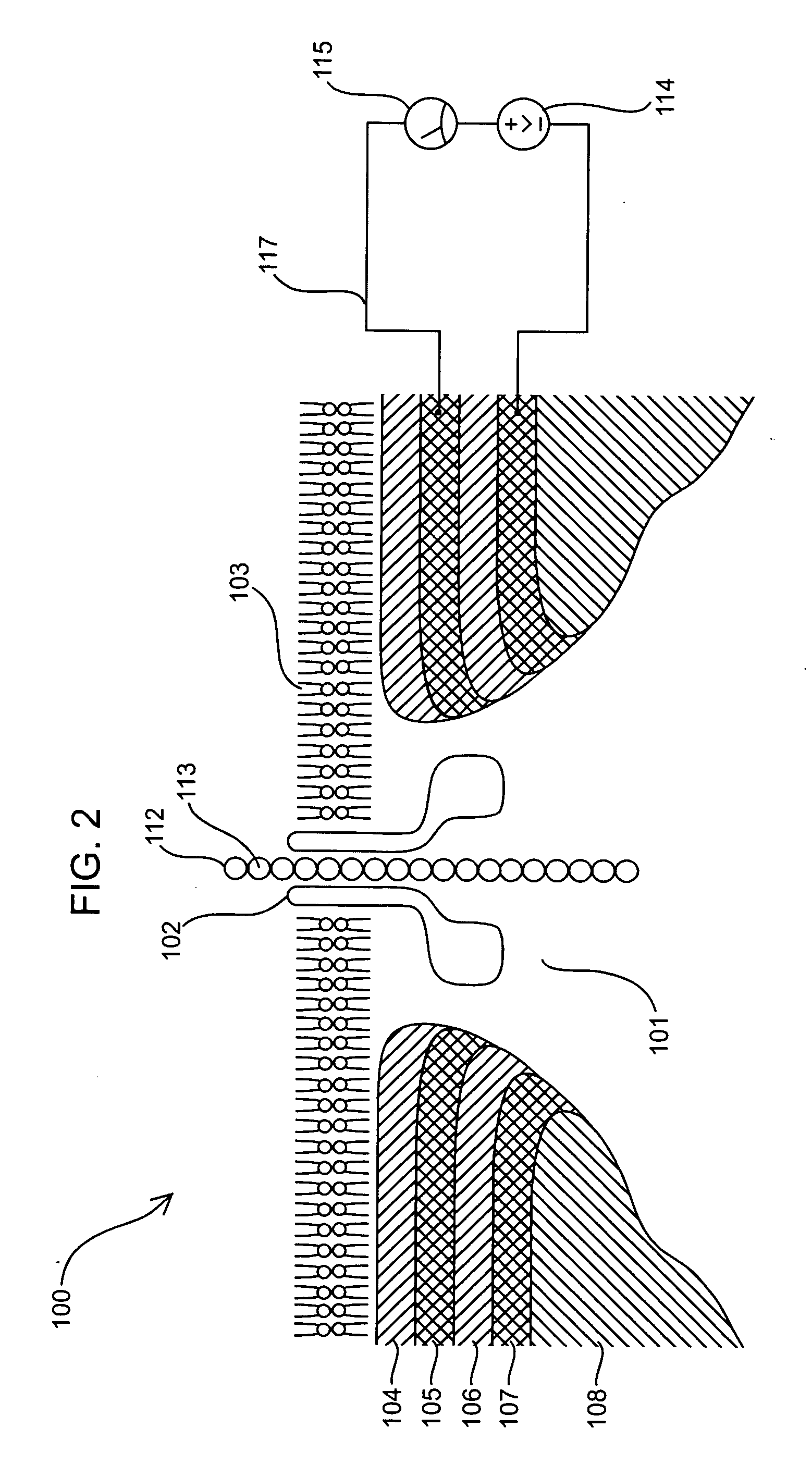
Nanopore with resonant tunneling electrodes
InactiveUS20070138132A1Paper/cardboard articlesDecorative surface effectsPotential differenceBiopolymer
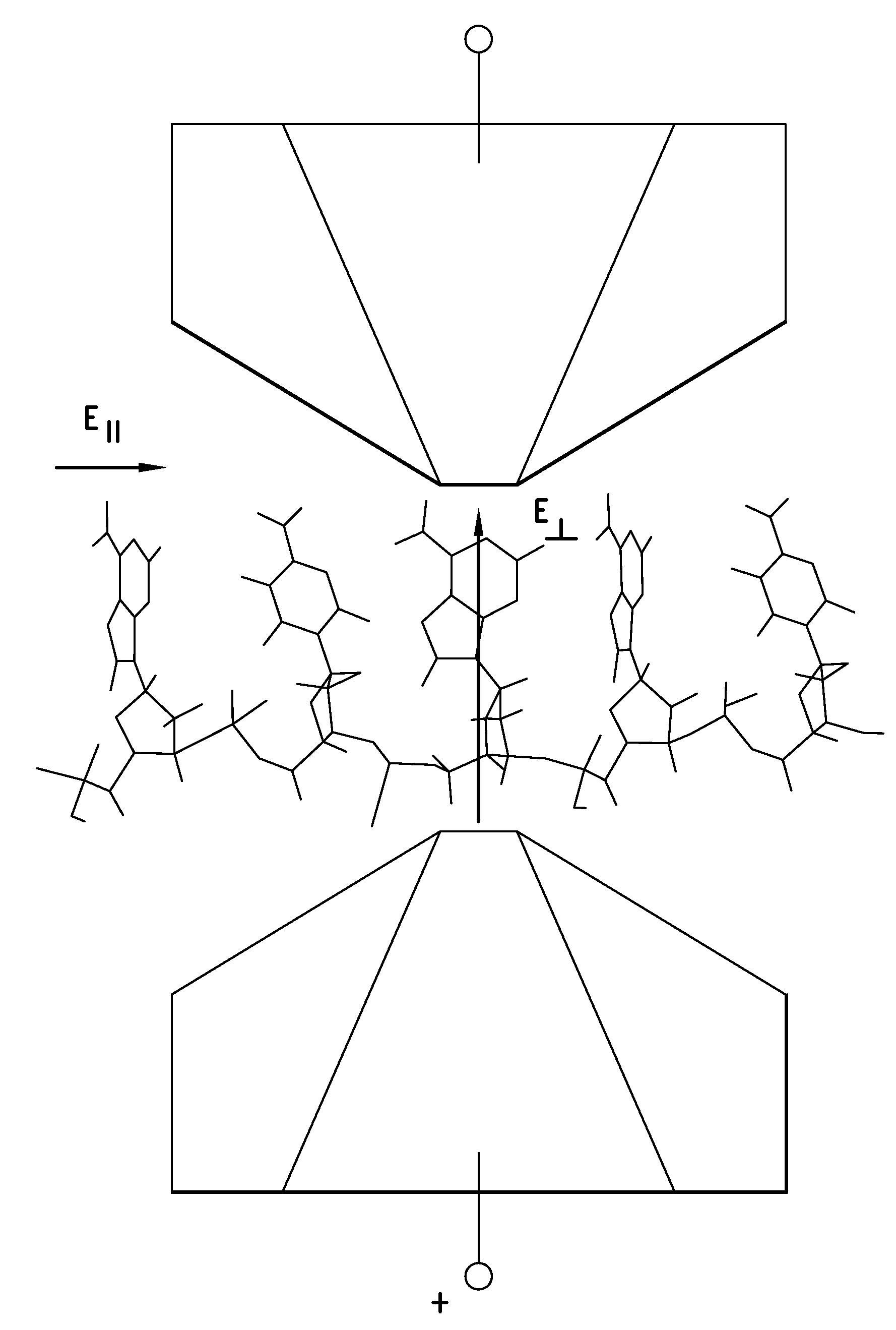
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for making an apparatus for sensing and / or characterizing a biopolymer translocating a nanopore. The apparatus of the present invention provides a first electrode, a first insulator, a second electrode, a optional insulator, a voltage source for applying a time varying potential difference between the electrodes, and a means of measuring the resulting current between the two electrodes. A method for making the apparatus is also disclosed.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Solid state molecular probe device
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
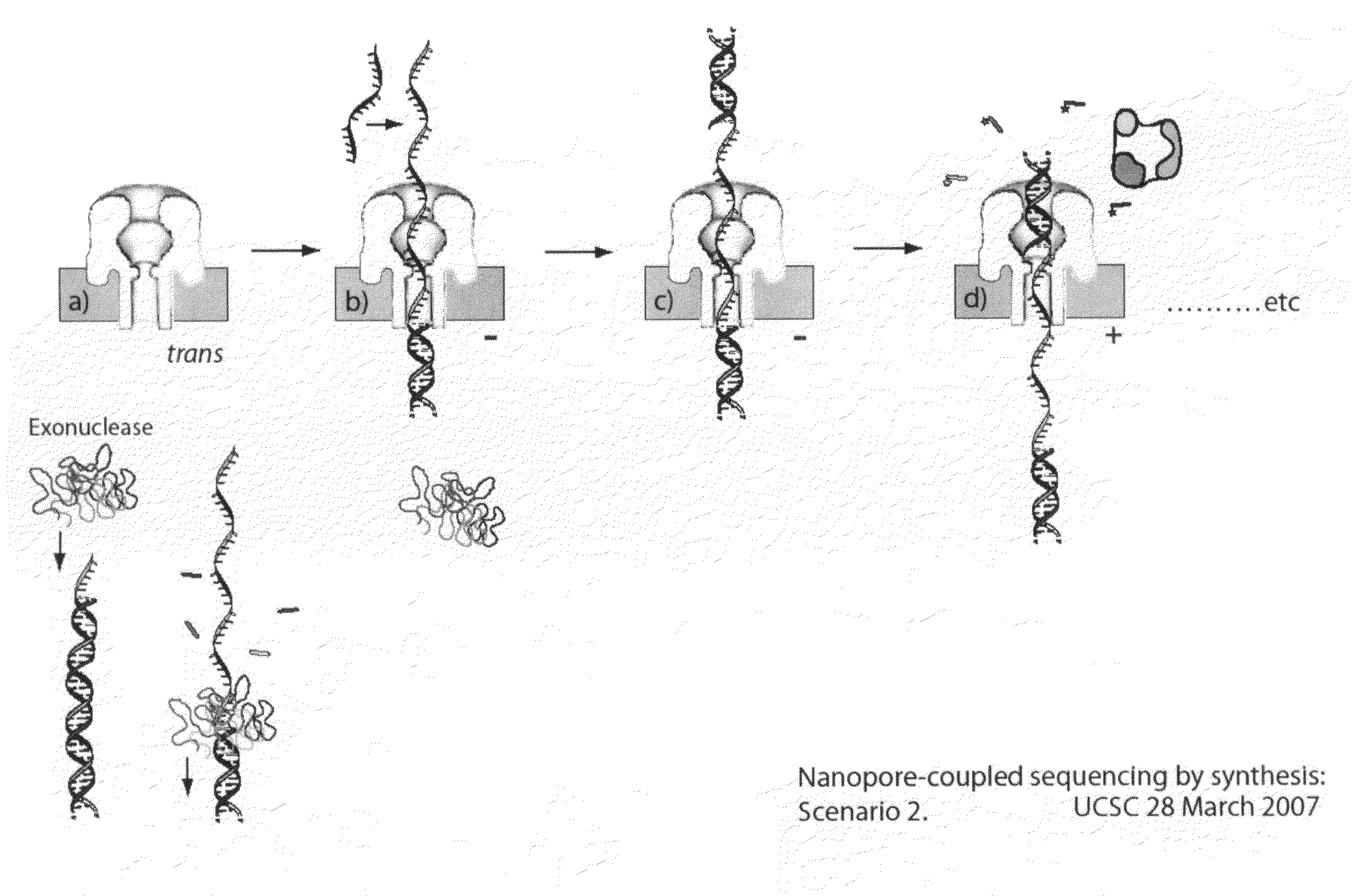
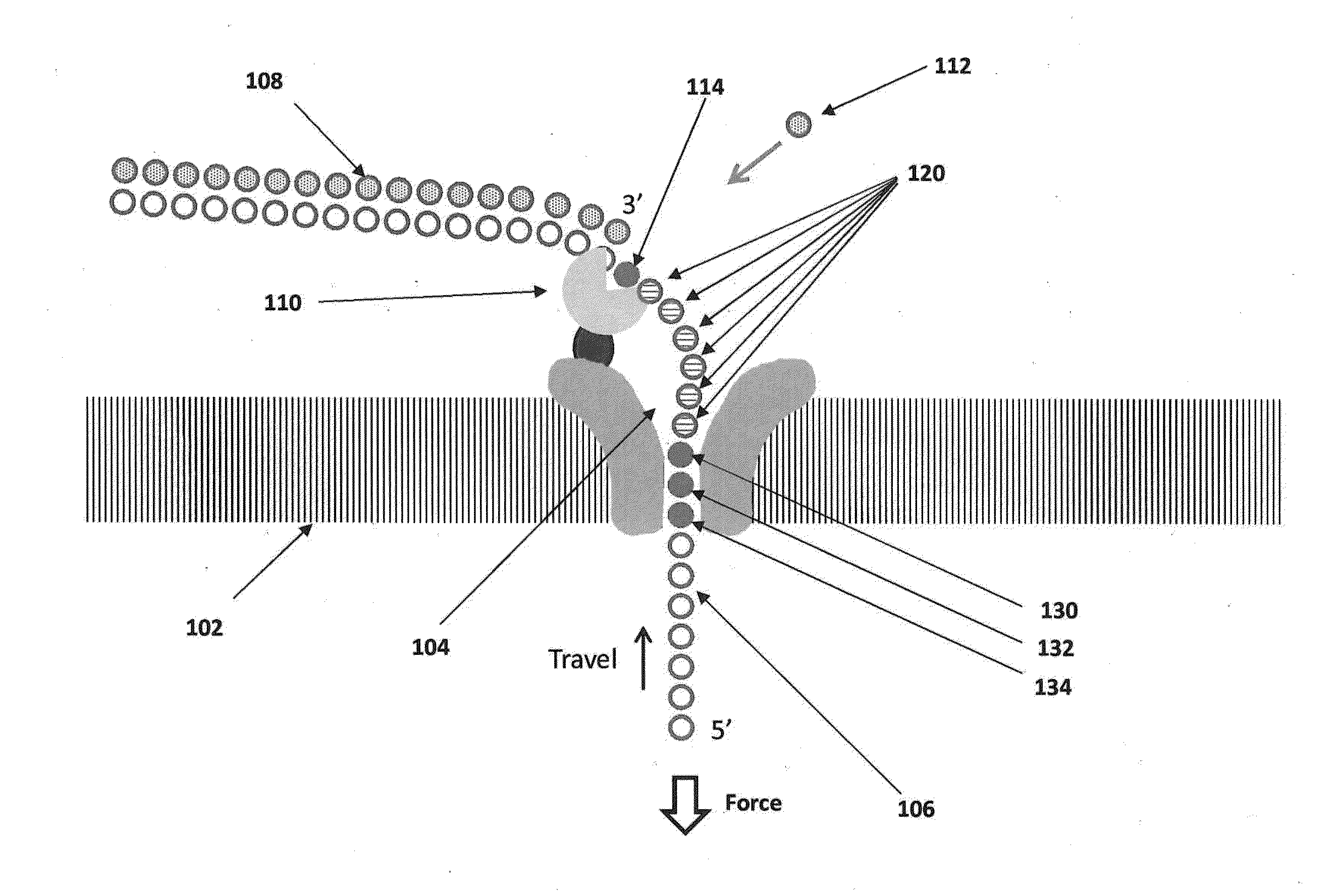
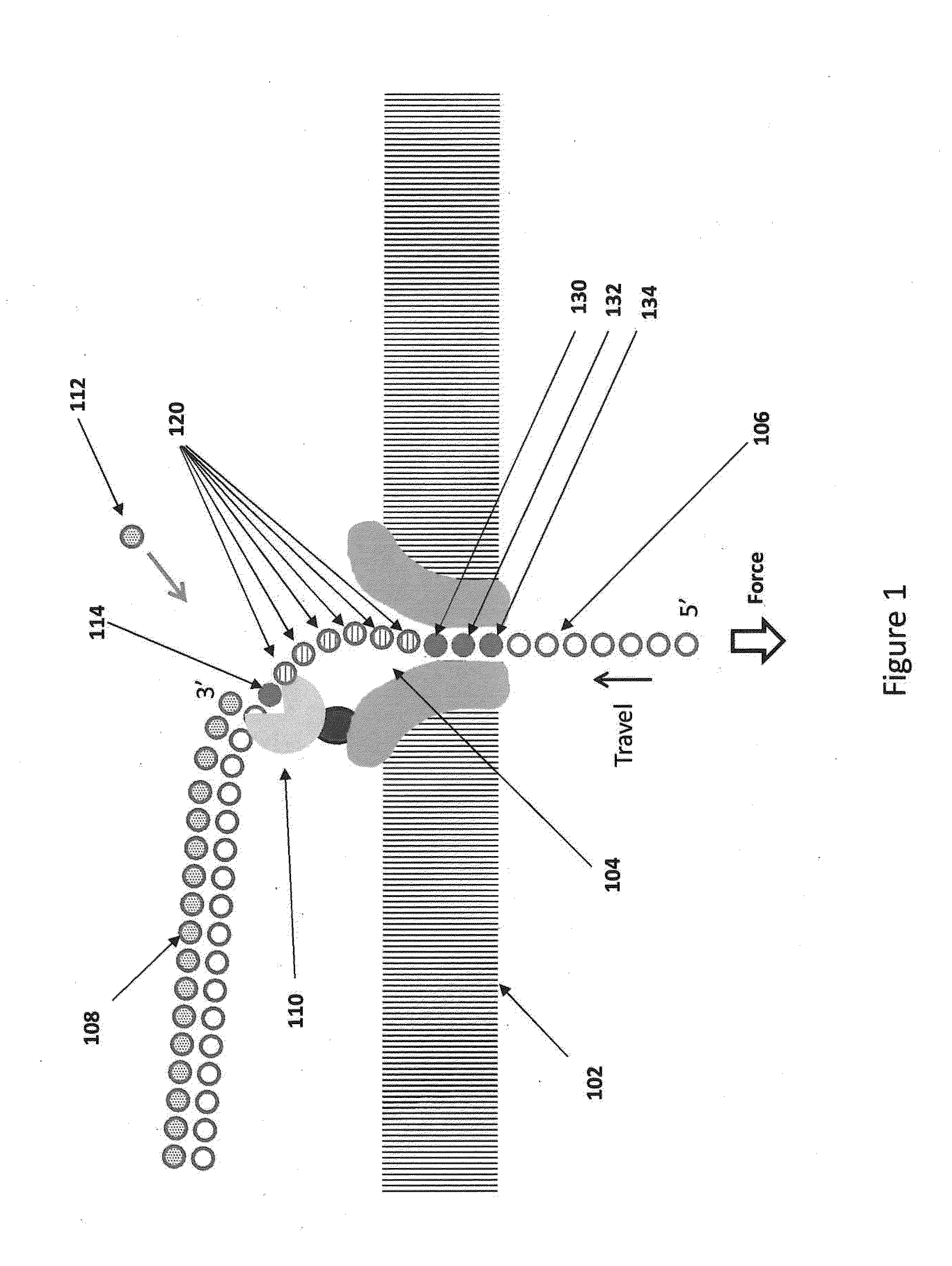
Method and apparatus for nucleic acid sequencing and identification
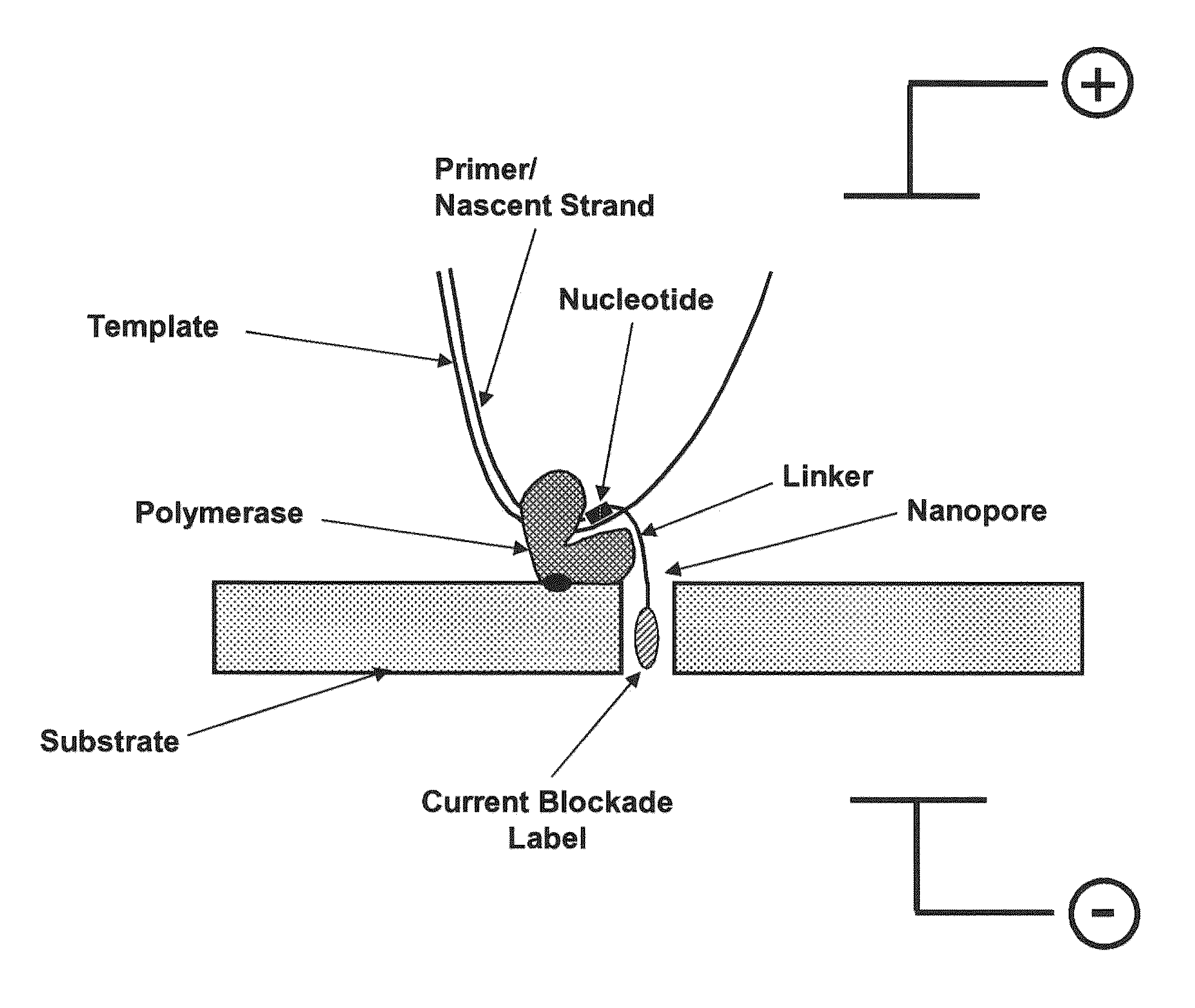
InactiveUS7005264B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyPhotodetectorNucleic acid sequencing
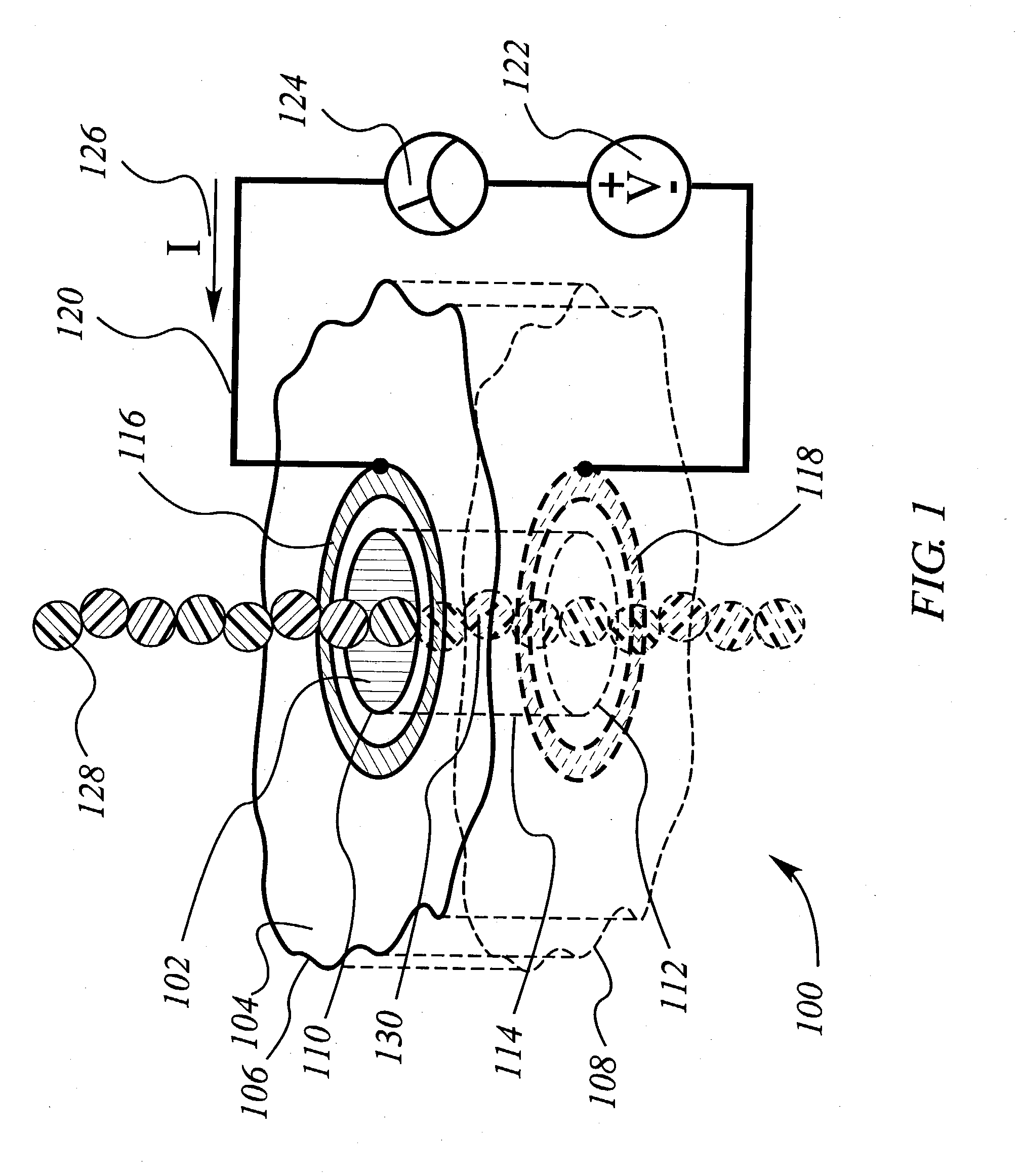
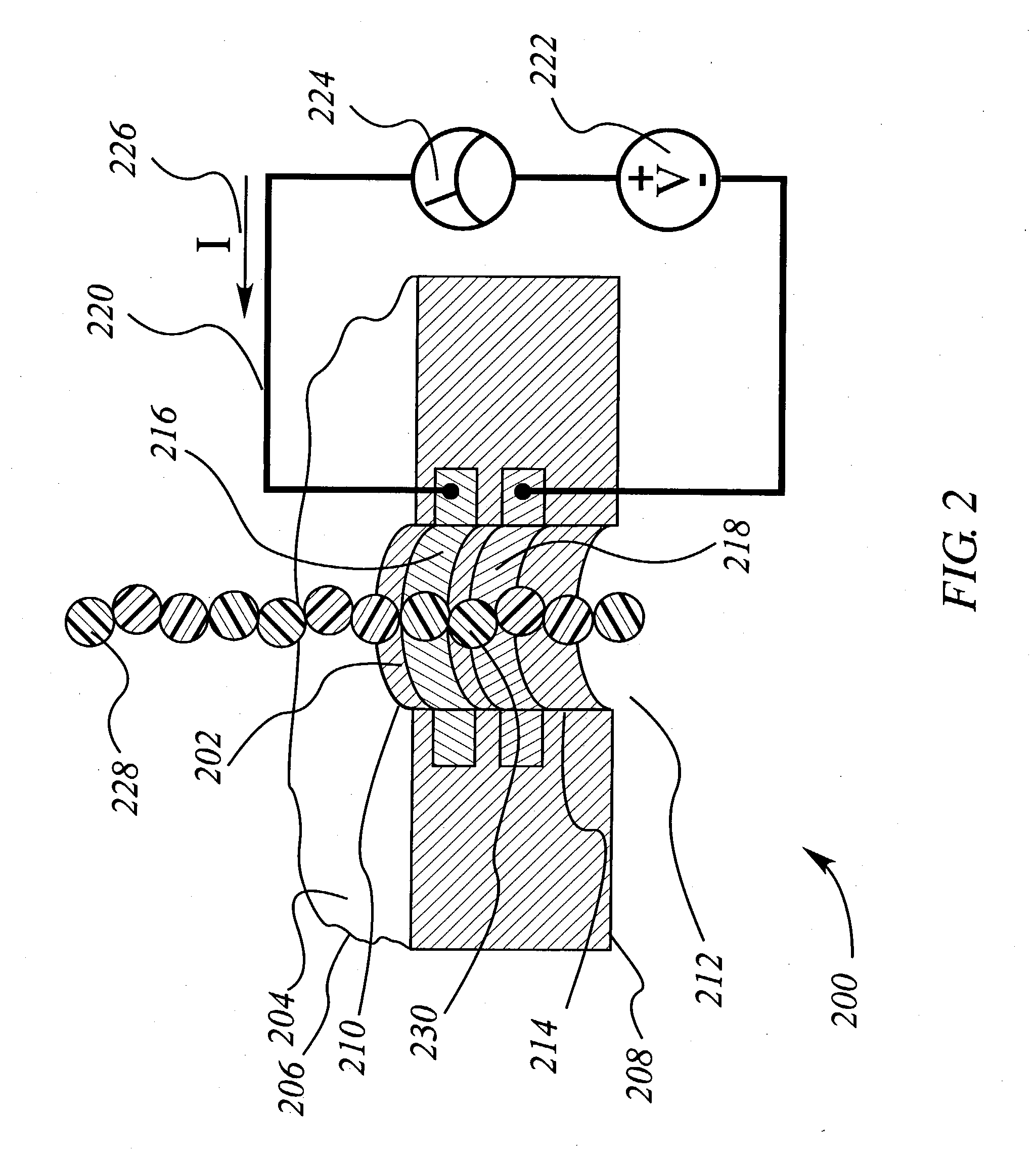
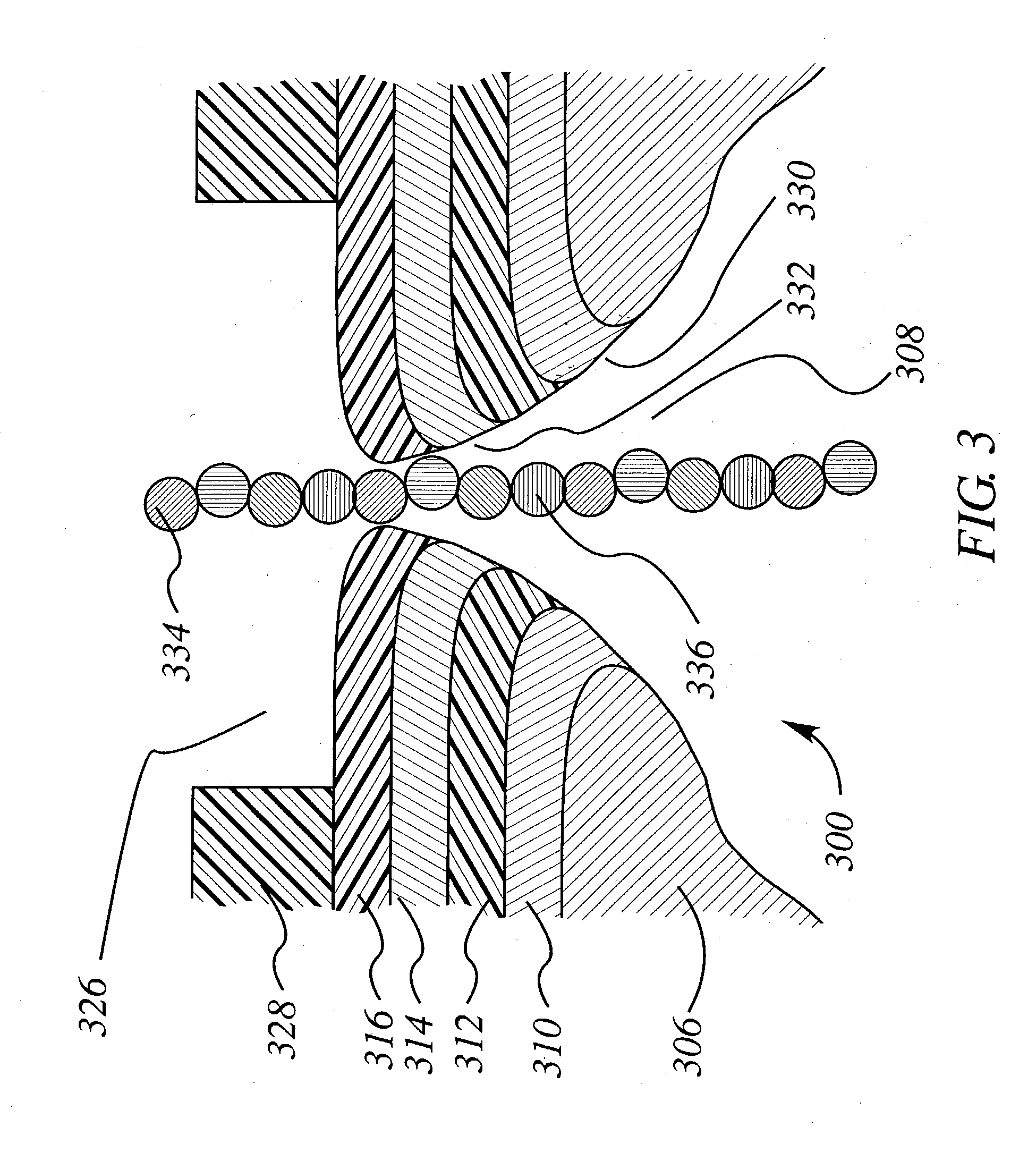
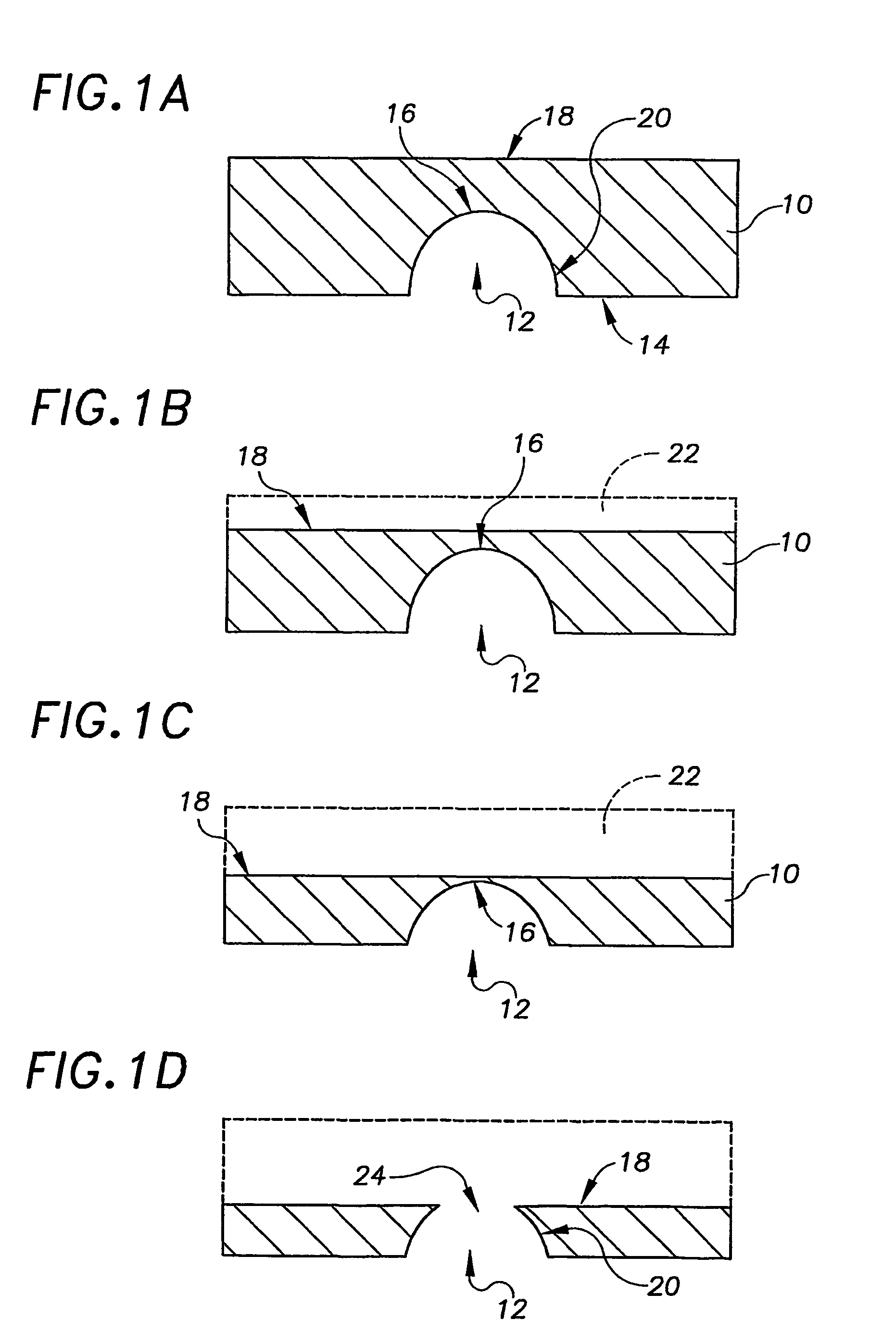
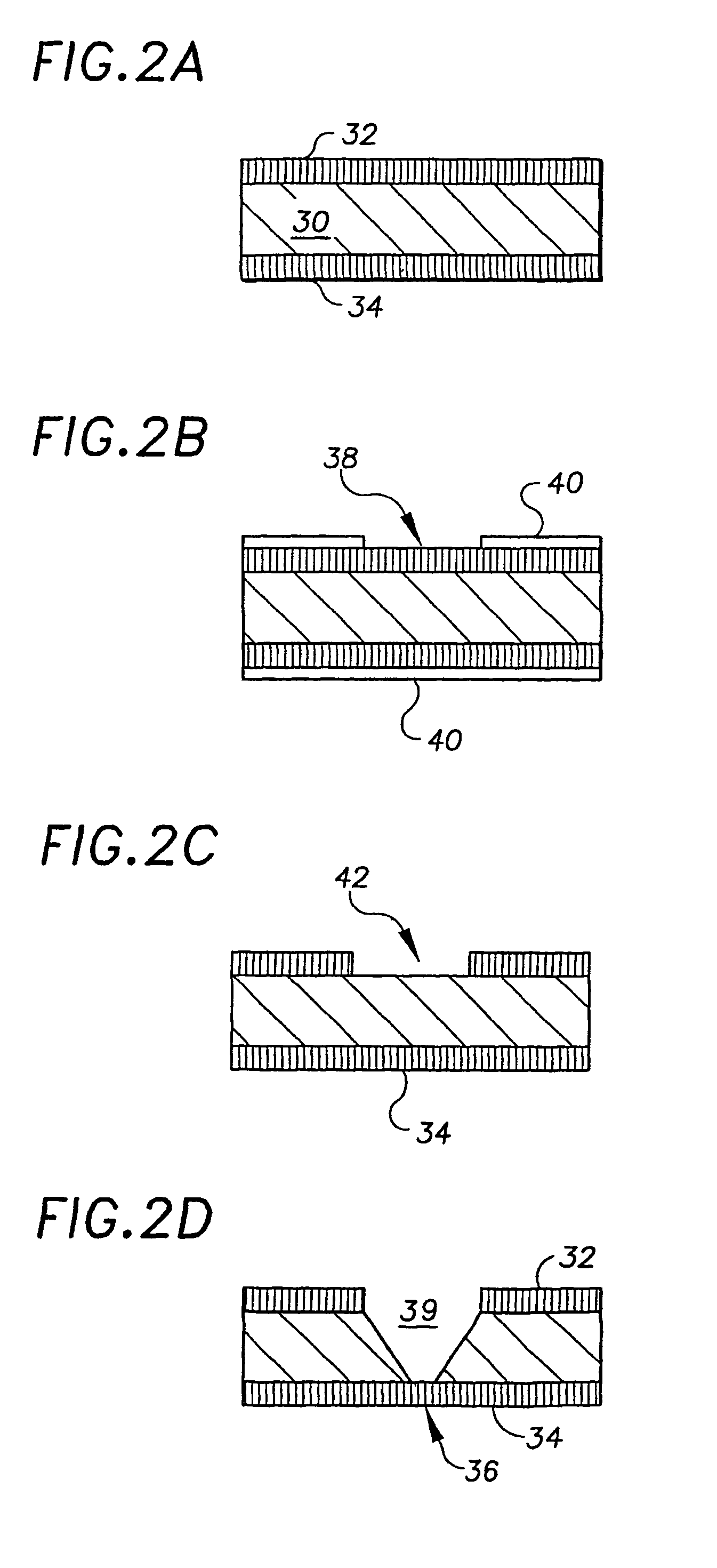
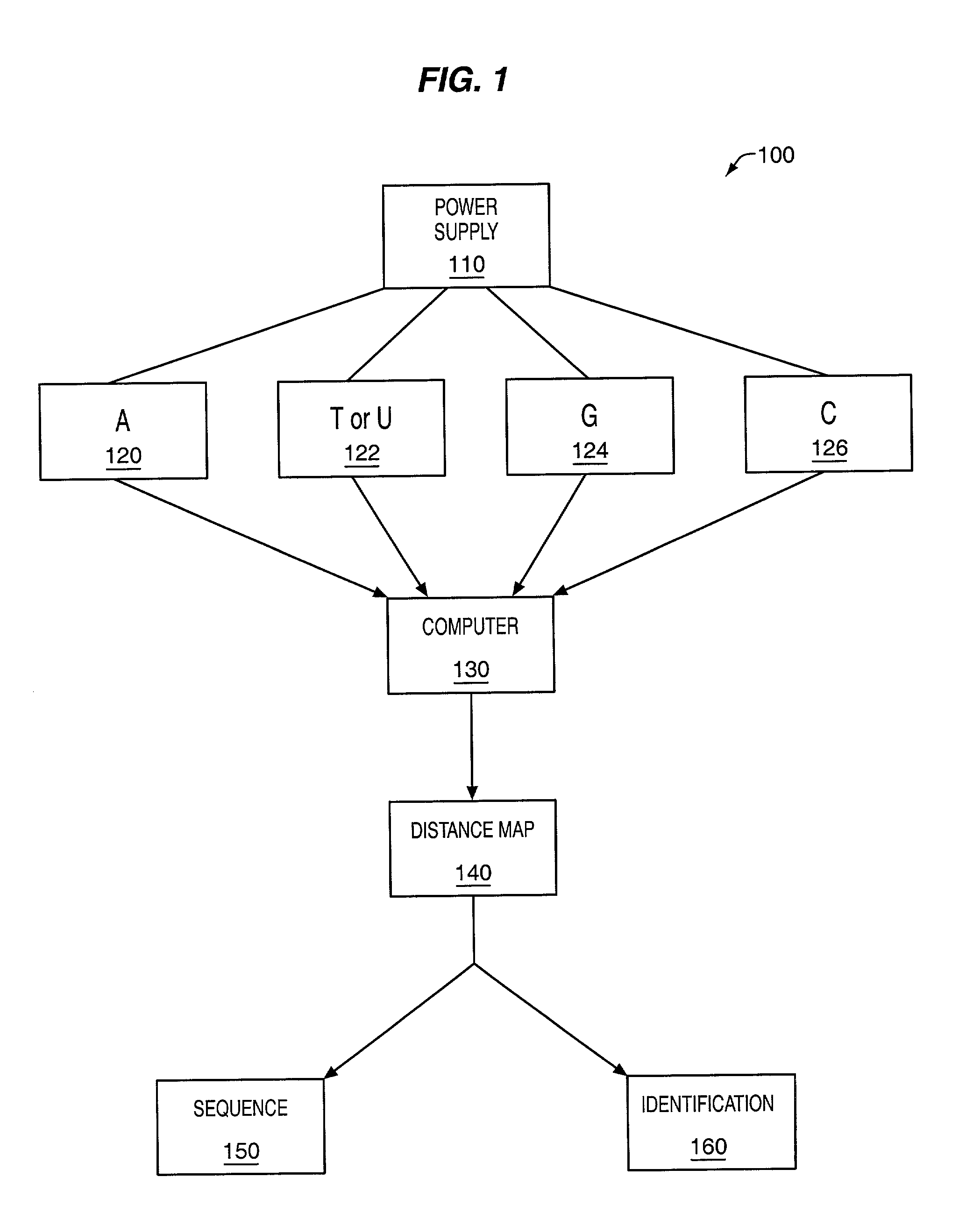
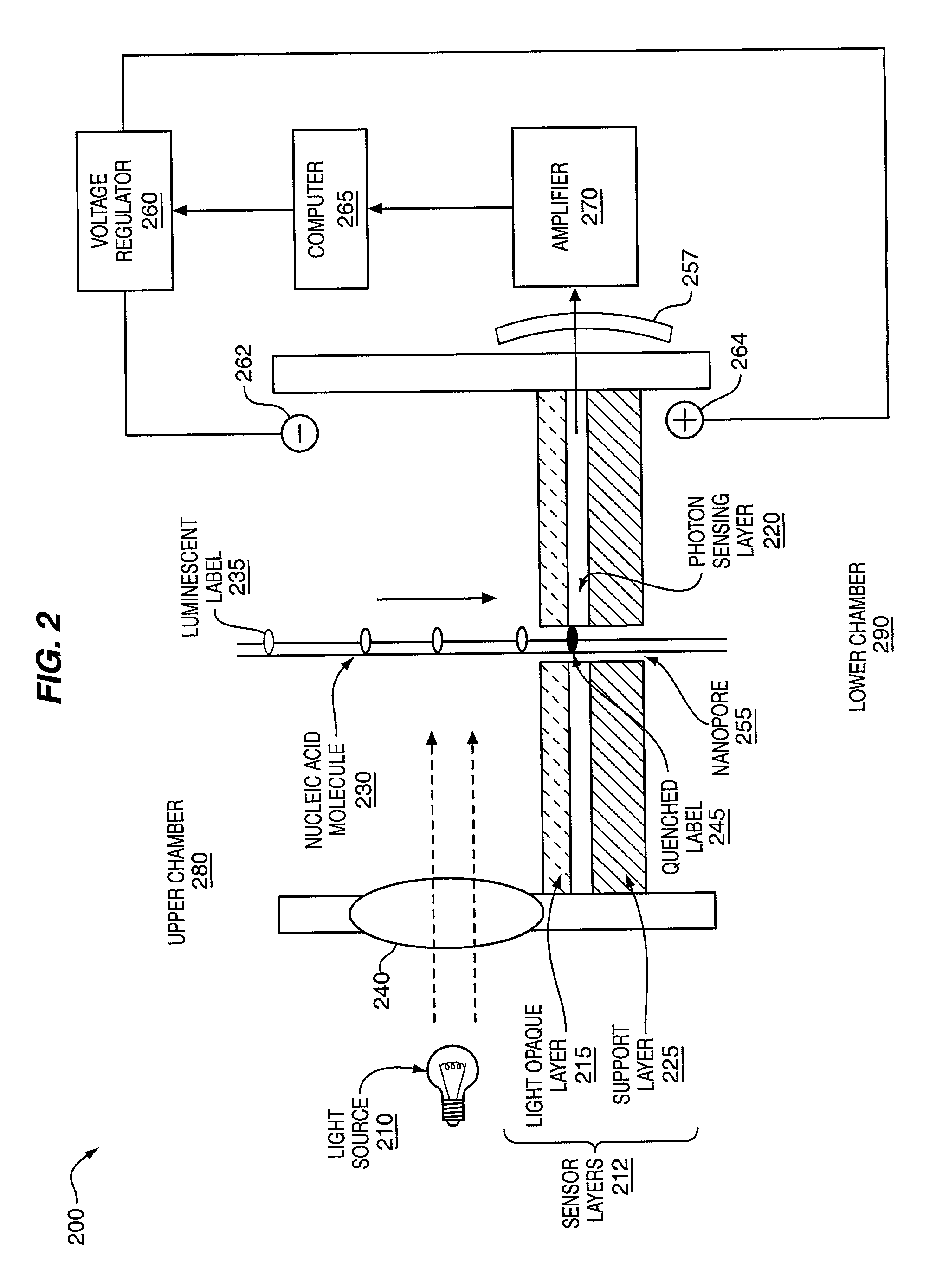
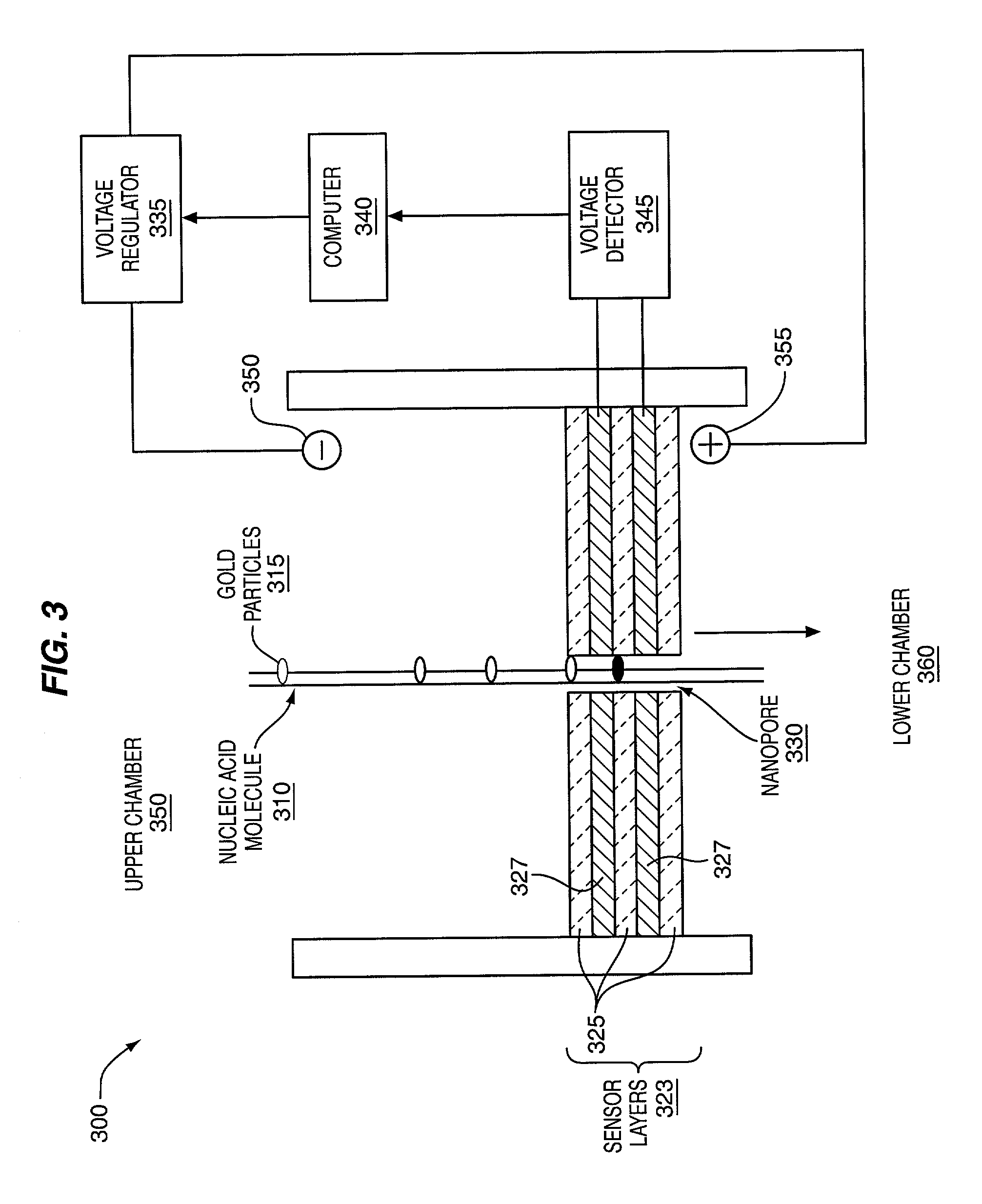
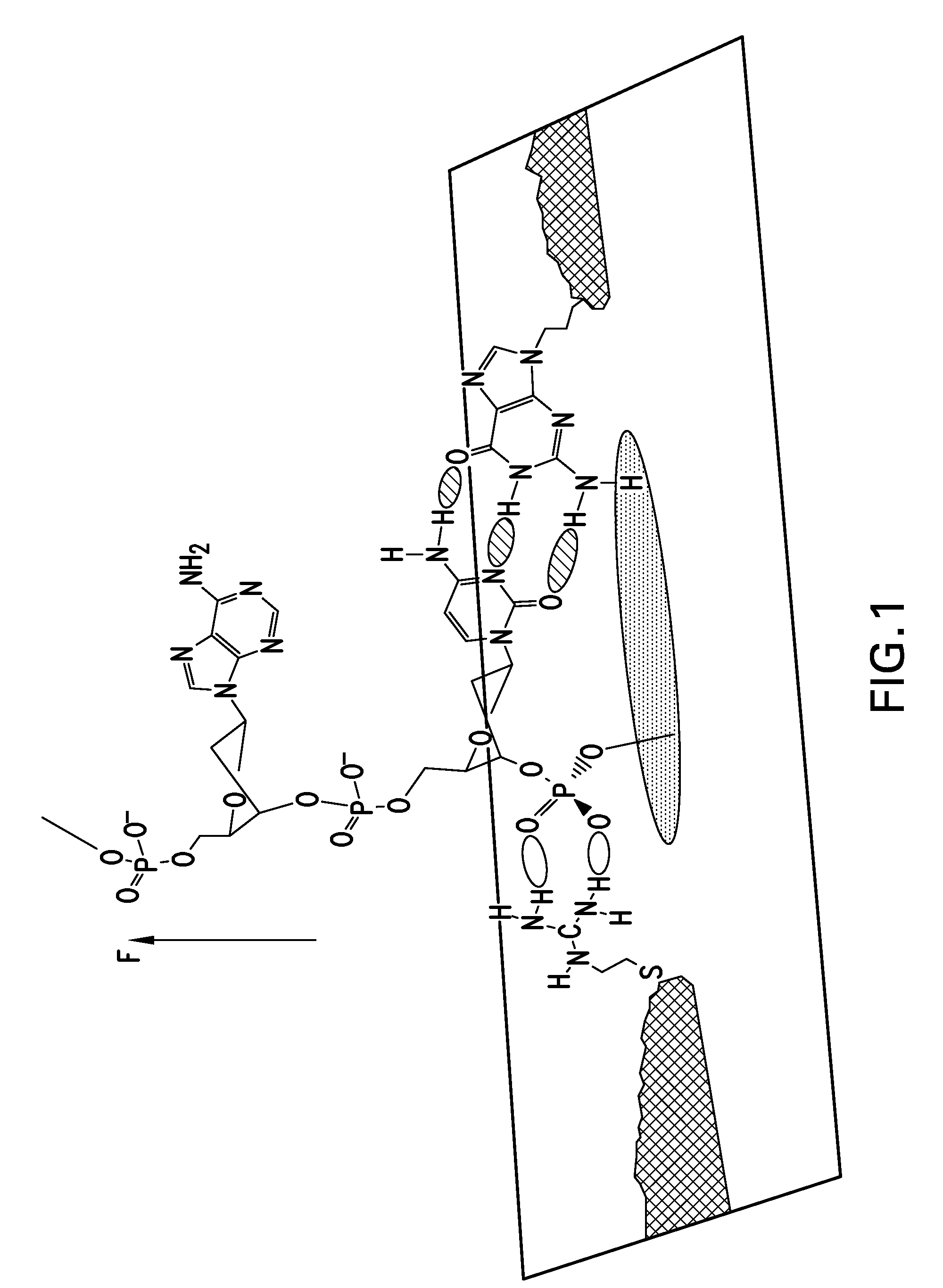
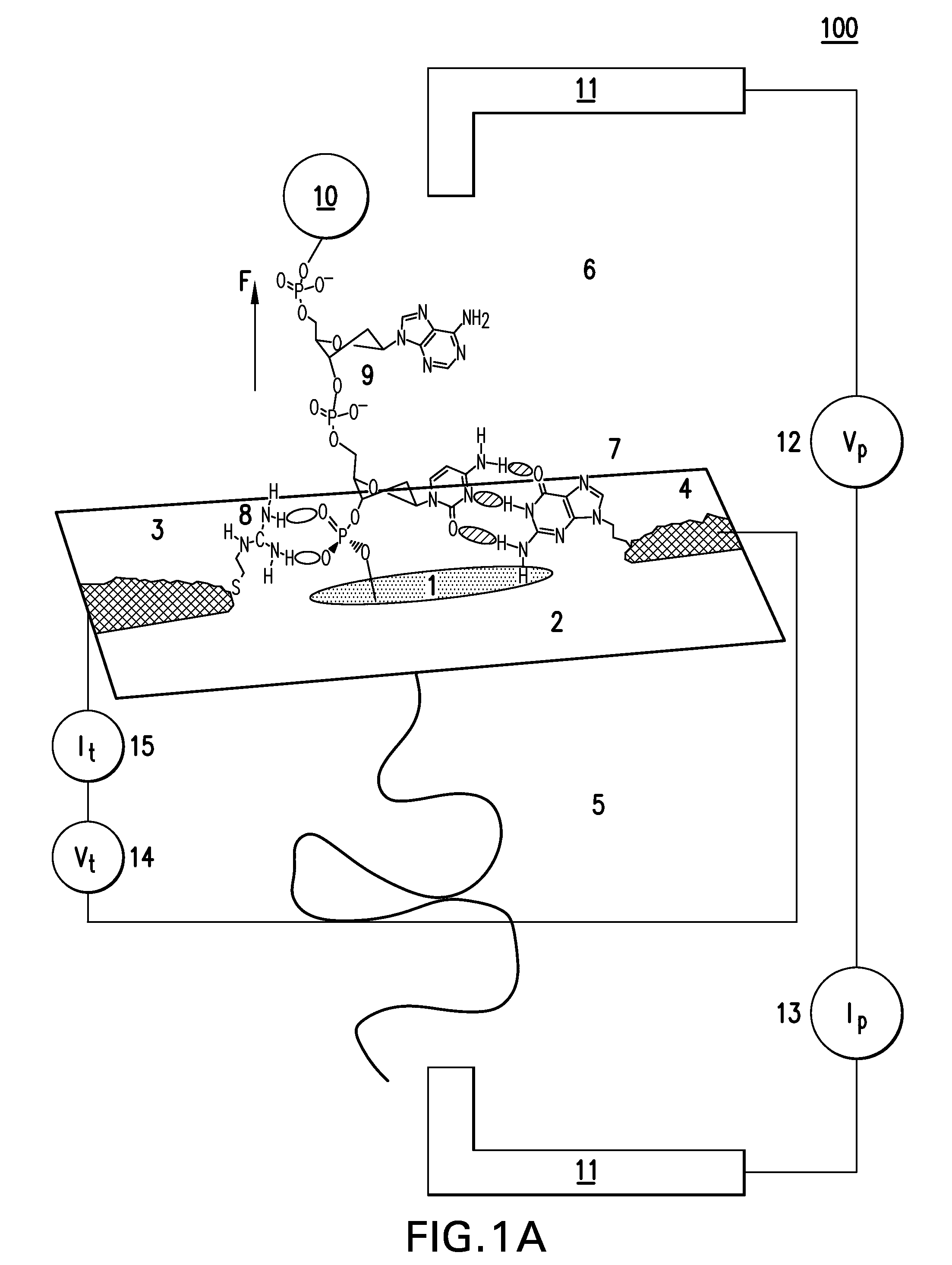
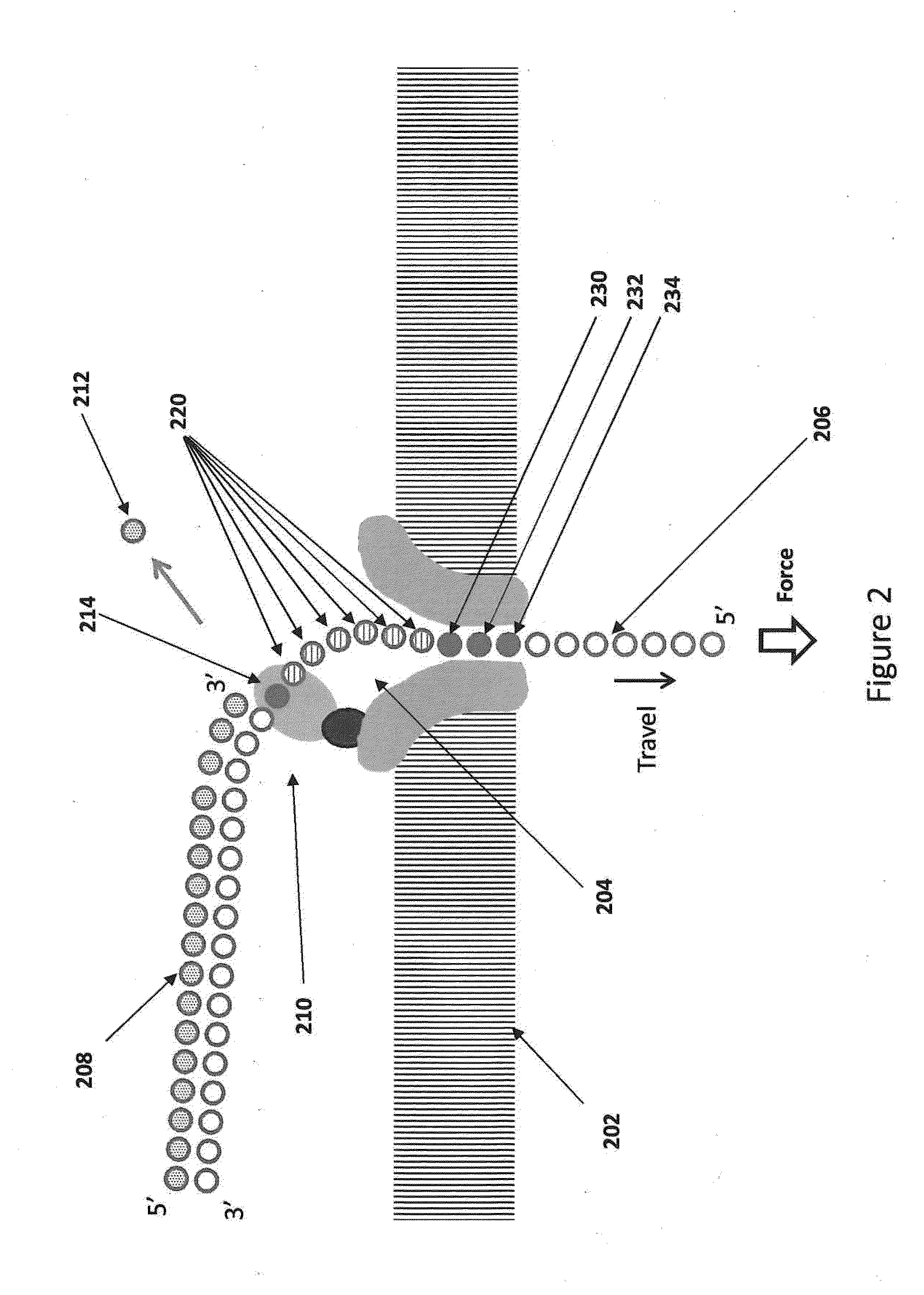
The methods and apparatus 100 disclosed herein are of use for sequencing and / or identifying nucleic acids 230, 310. Nucleic acids 230, 310 containing labeled nucleotides 235, 245, 315 may be synthesized and passed through nanopores 255, 310. Detectors 257, 345 operably coupled to the nanopores 255, 310 may detect the labeled nucleotides 235, 245, 315. By determining the time intervals at which labeled nucleotides 235, 245, 315 are detected, distance maps 140 for each type of labeled nucleotide 235, 245, 315 may be compiled. The distance maps 140 in turn may be used to sequence 150 and / or identify 160 the nucleic acid 230, 310. In different embodiments of the invention, luminescent nucleotides 235, 245 or nanoparticles 315 may be detected using photodetectors 257 or electrical detectors 310. Apparatus 100 and sub-devices 200, 300 of use for nucleic acid 230, 310 sequencing 150 and / or identification 160 are also disclosed herein.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Methods of determining the presence of double stranded nucleic acids in a sample
InactiveUS6428959B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRNA blottingAssay
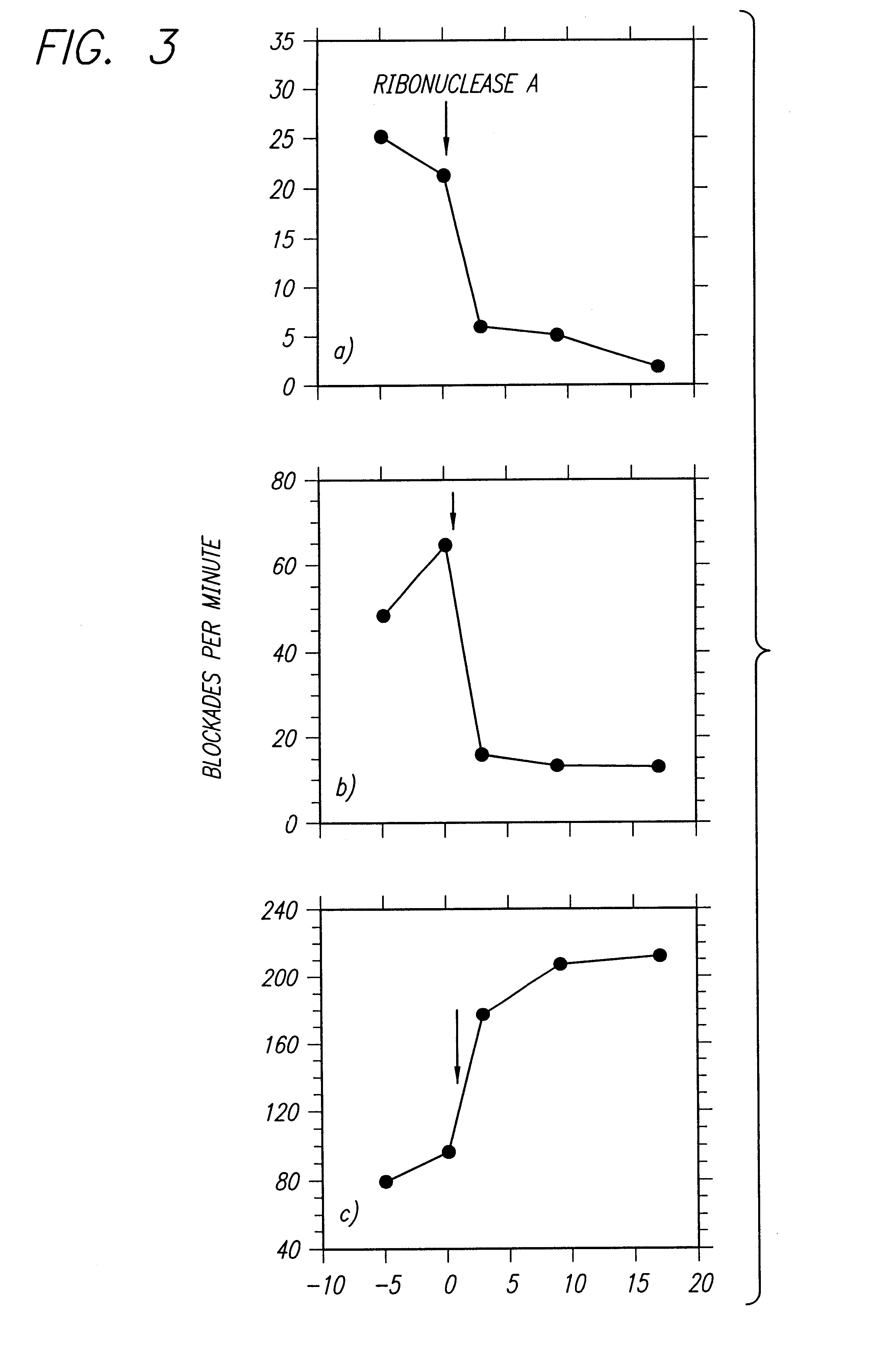
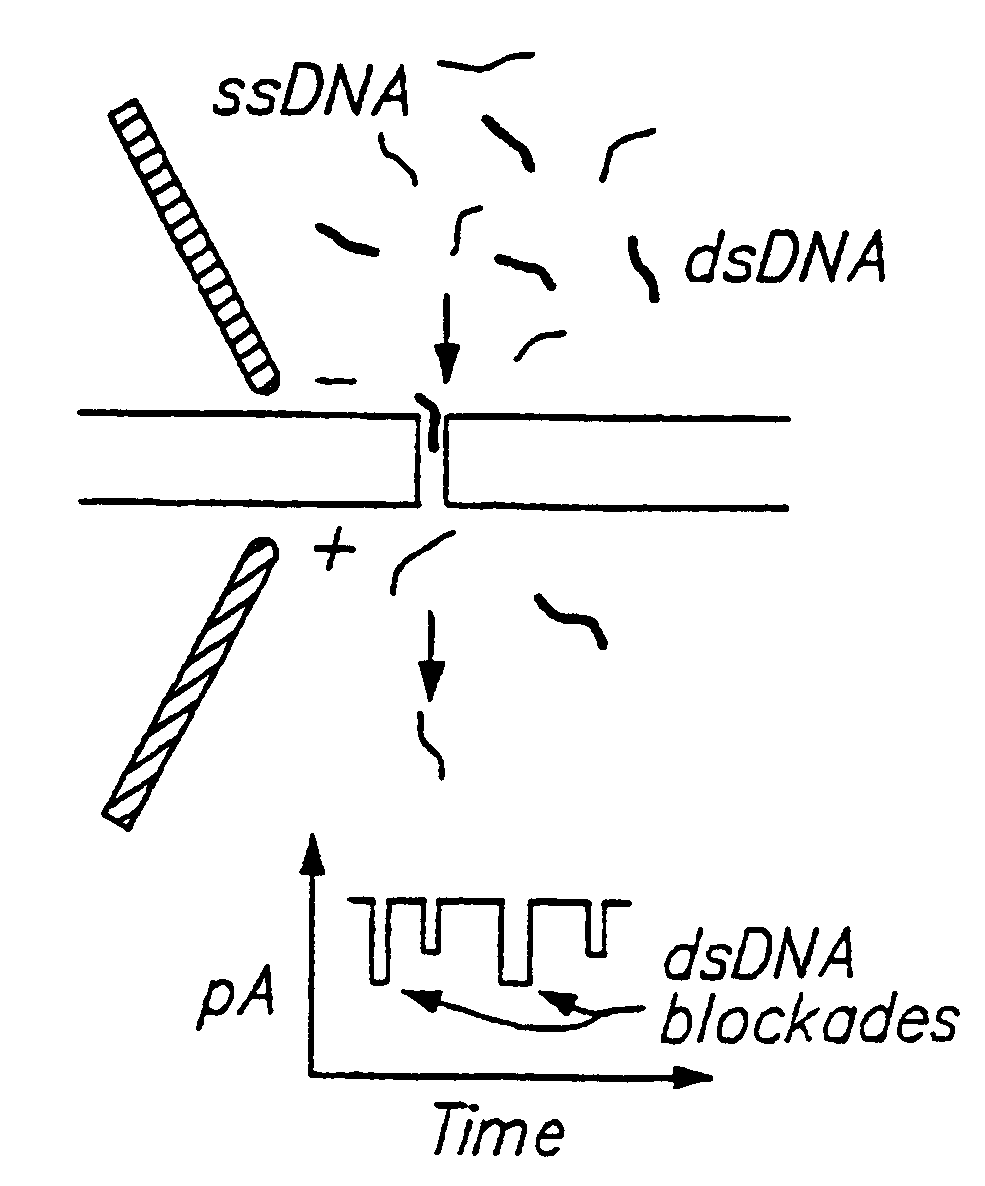
Methods for determining the presence of double stranded nucleic acids in a sample are provided. In the subject methods, nucleic acids present in a fluid sample are translocated through a nanopore, e.g. by application of an electric field to the fluid sample. The current amplitude through the nanopore is monitored during the translocation process and changes in the amplitude are related to the passage of single- or double-stranded molecules through the nanopore. The subject methods find use in a variety of applications in which the detection of the presence of double-stranded nucleic acids in a sample is desired, e.g. in hybridization assays, such as Northern blot assays, Southern blot assays, array based hybridization assays, etc.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
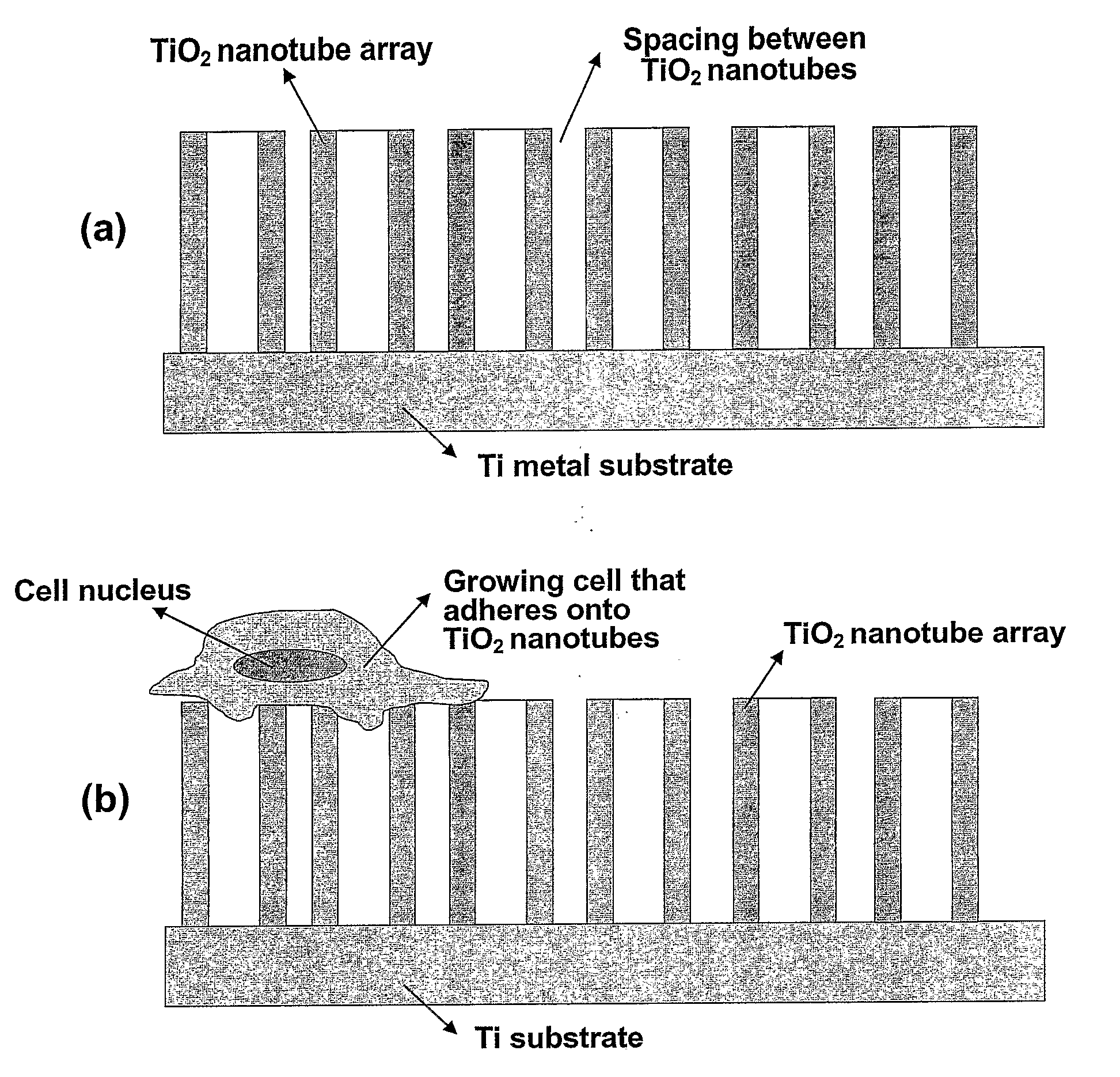
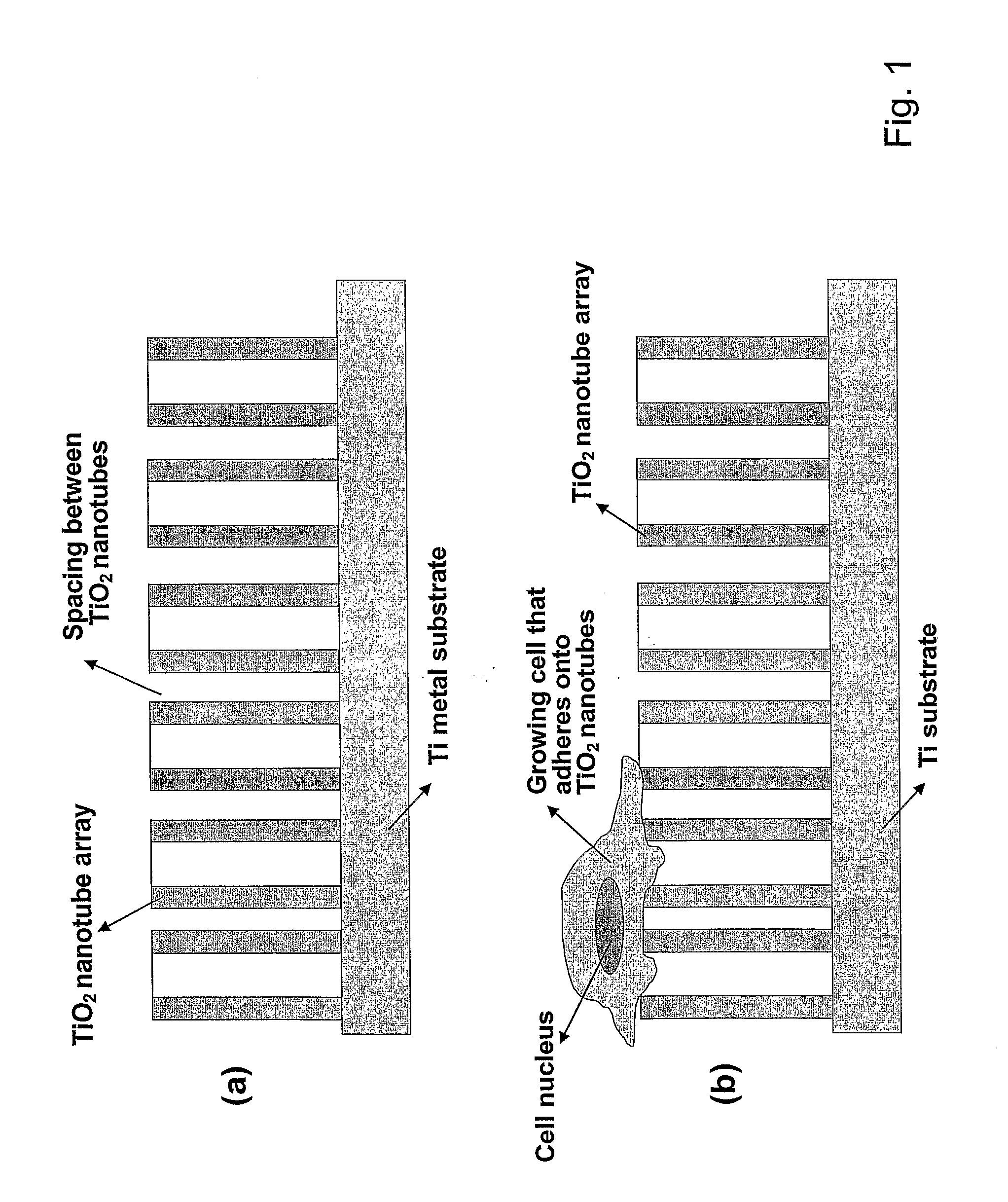
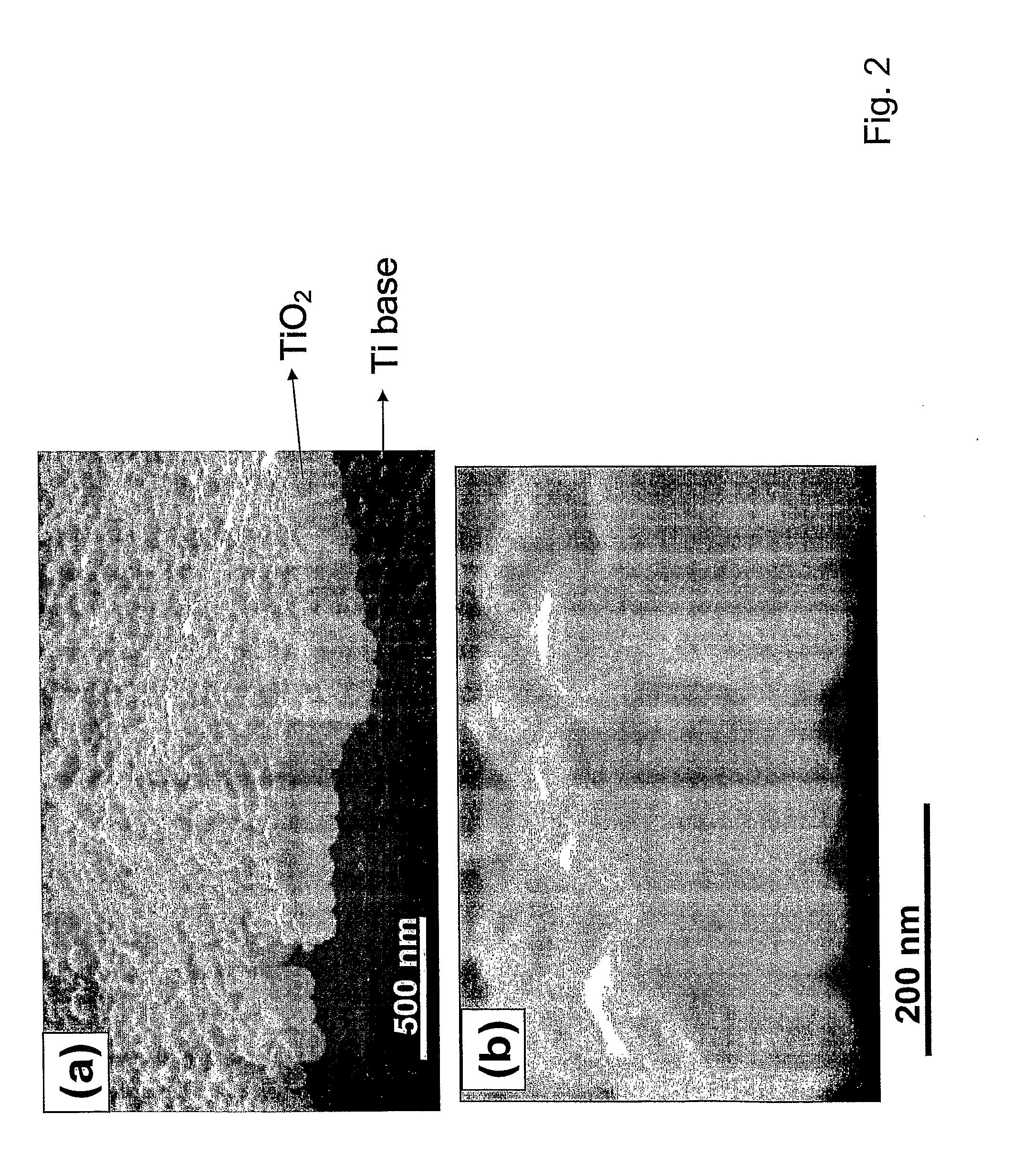
Compositions comprising nanostructures for cell, tissue and artificial organ growth, and methods for making and using same
ActiveUS20090220561A1Improve bone formationIncreased durabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsIn vivoNanostructure
The invention provides articles of manufacture comprising biocompatible nanostructures comprising nanotubes and nanopores for, e.g., organ, tissue and / or cell growth, e.g., for bone, kidney or liver growth, and uses thereof, e.g., for in vitro testing, in vivo implants, including their use in making and using artificial organs, and related therapeutics. The invention provides lock-in nanostructures comprising a plurality of nanopores or nanotubes, wherein the nanopore or nanotube entrance has a smaller diameter or size than the rest (the interior) of the nanopore or nanotube. The invention also provides dual structured biomaterial comprising micro- or macro-pores and nanopores. The invention provides biomaterials having a surface comprising a plurality of enlarged diameter nanopores and / or nanotubes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions, devices, systems, for using a Nanopore
ActiveUS20100035260A1Low costRapidityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsStructural biologyMolecular switch
The invention herein disclosed provides for devices and methods that can detect and control an individual polymer in a mixture is acted upon by another compound, for example, an enzyme, in a nanopore in the absence of requiring a terminating nucleotide. The devices and methods are also used to determine rapidly (˜>50 Hz) the nucleotide base sequence of a polynucleotide under feedback control or using signals generated by the interactions between the polynucleotide and the nanopore. The invention is of particular use in the fields of drug discovery, molecular biology, structural biology, cell biology, molecular switches, molecular circuits, and molecular computational devices, and the manufacture thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Chemical functionalization of solid-state nanopores and nanopore arrays and applications thereof
ActiveUS20110053284A1Avoid stickingChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiopolymerElectron
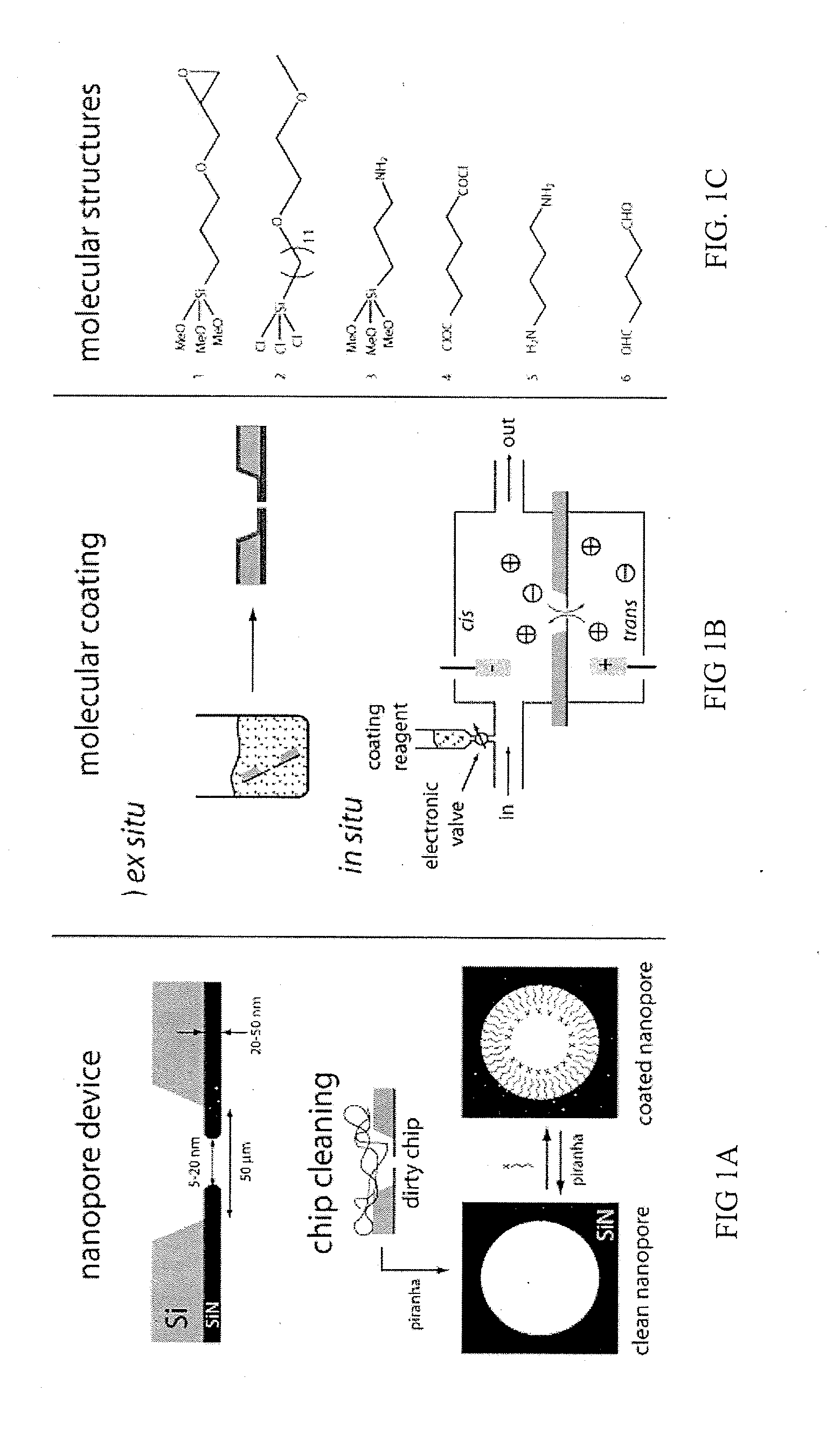
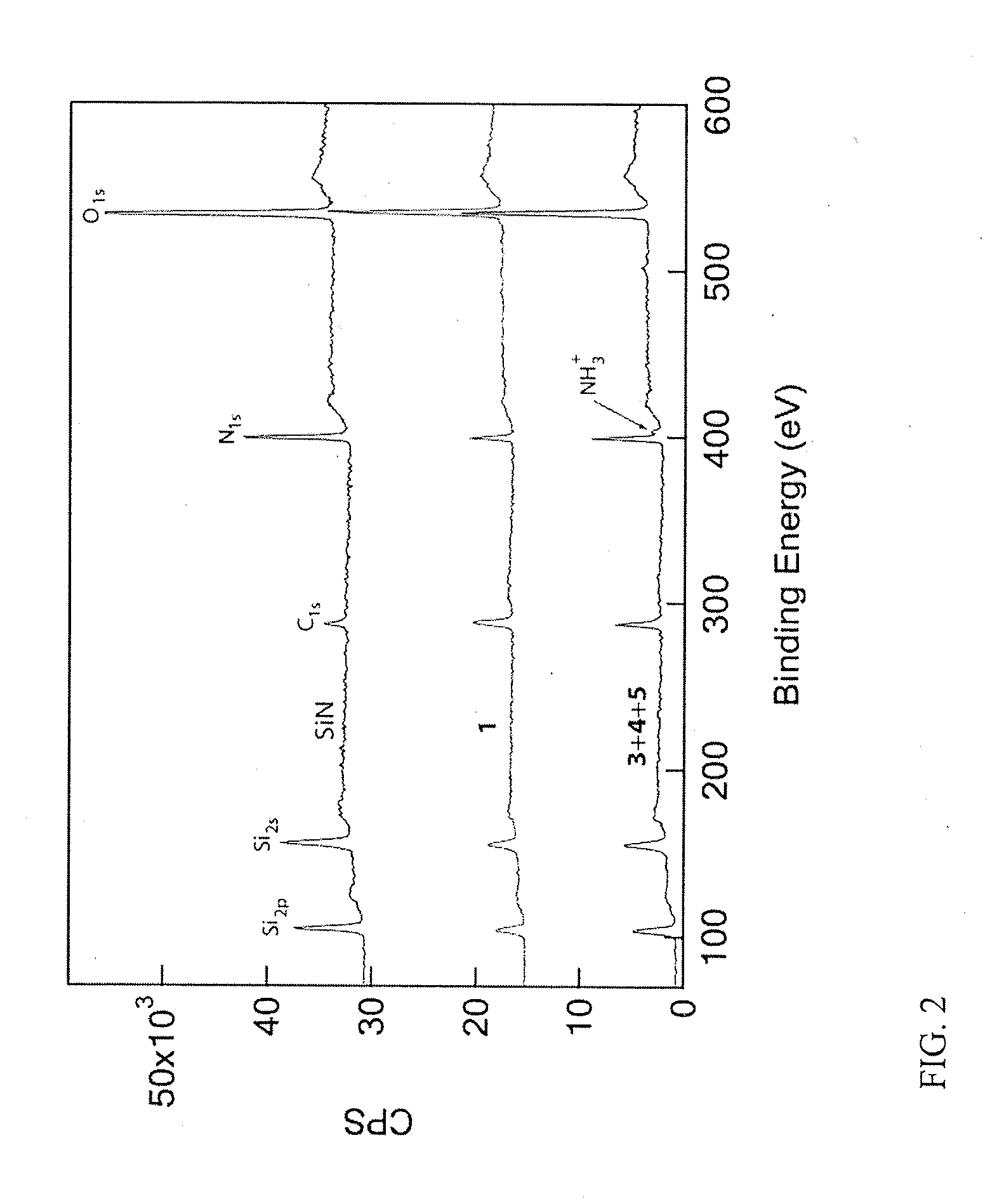
Chemical functionalization of solid-state nanopores and nanopore arrays and applications thereof. Nanopores are extremely sensitive single-molecule sensors. Recently, electron beams have been used to fabricate synthetic nanopores in thin solid-state membranes with sub-nanometer resolution. A new class of chemically modified nanopore sensors are provided with two approaches for monolayer coating of nanopores by: (1) self-assembly from solution, in which nanopores −10 nm diameter can be reproducibly coated, and (2) self-assembly under voltage-driven electrolyte flow, in which 5 nm nanopores may be coated. Applications of chemically modified nanopore are provided including: the detection of biopolymers such as DNA and RNA; immobilizing enzymes or other proteins for detection or for generating chemical gradients; and localized pH sensing.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Devices and Methods for Target Molecule Characterization
The present invention provides a device having at least one constriction that is sized to permit translocation of only a single copy of the molecule. The device has a pair of spaced apart sensing electrodes that border the constriction, which may be a nanopore. The first electrode is connected to a first affinity element and the second electrode is connected to a second affinity element. The first and second affinity elements are configured to temporarily form hydrogen bonds with first and second portions of the target molecule as the latter passes through the constriction.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
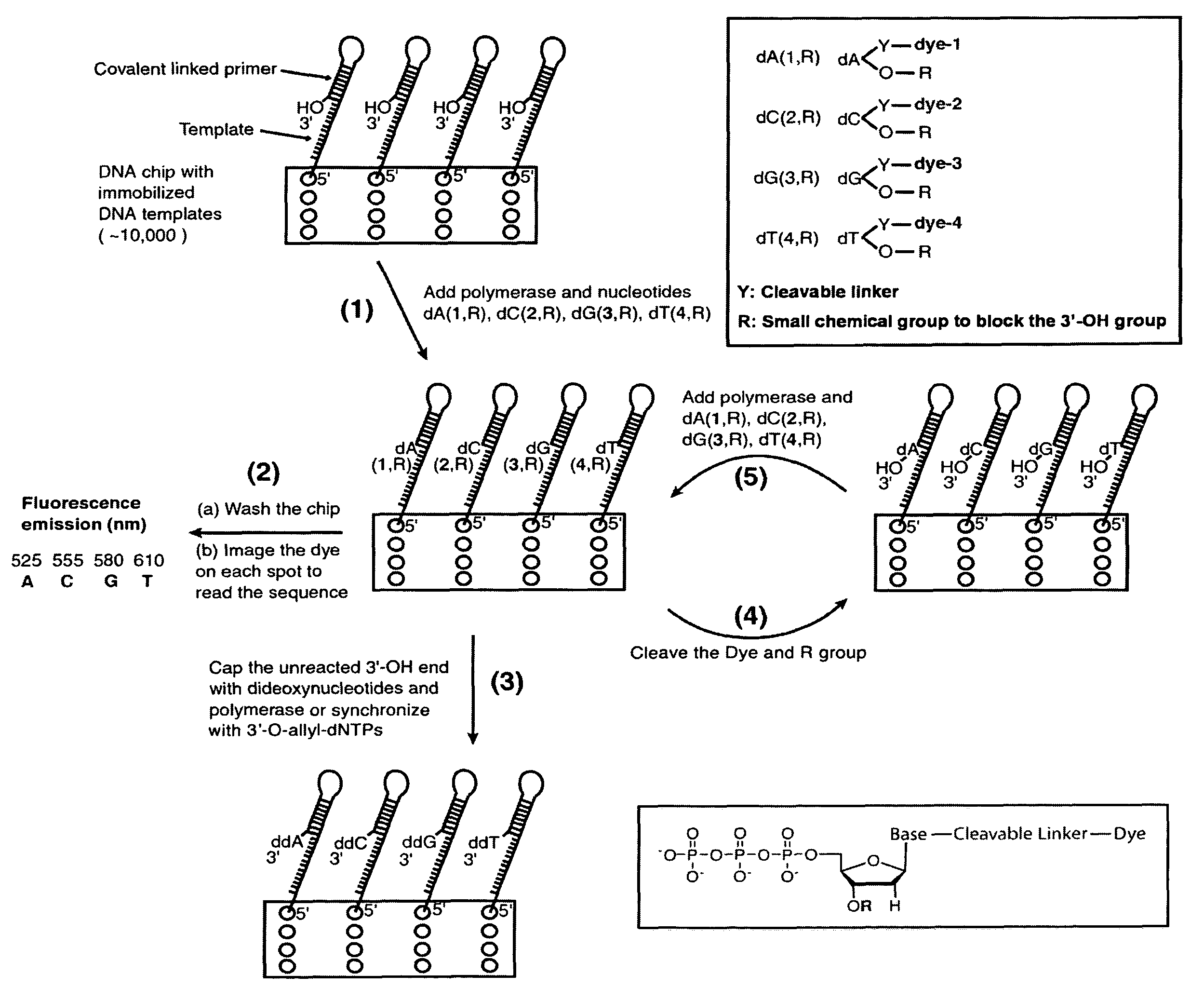
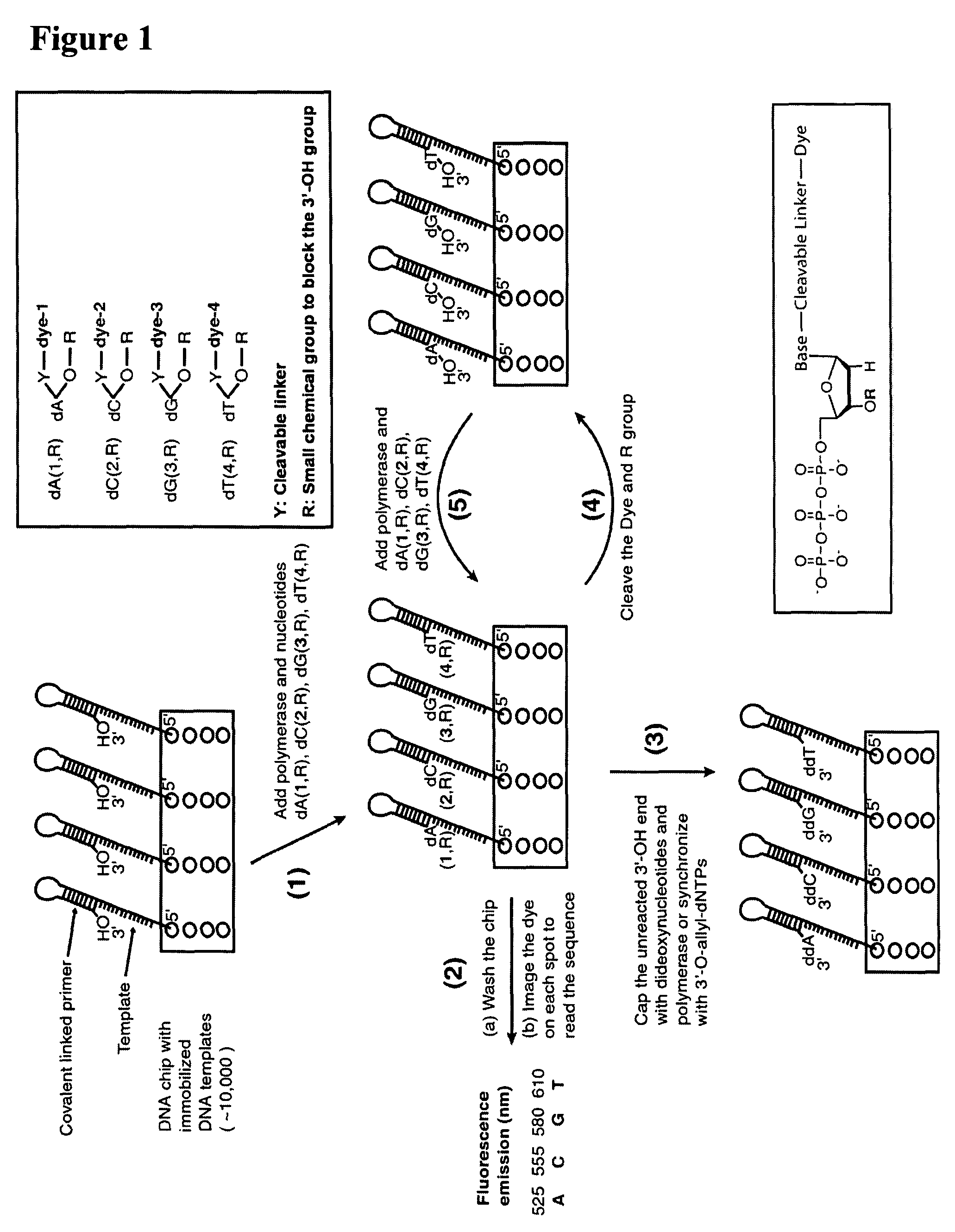
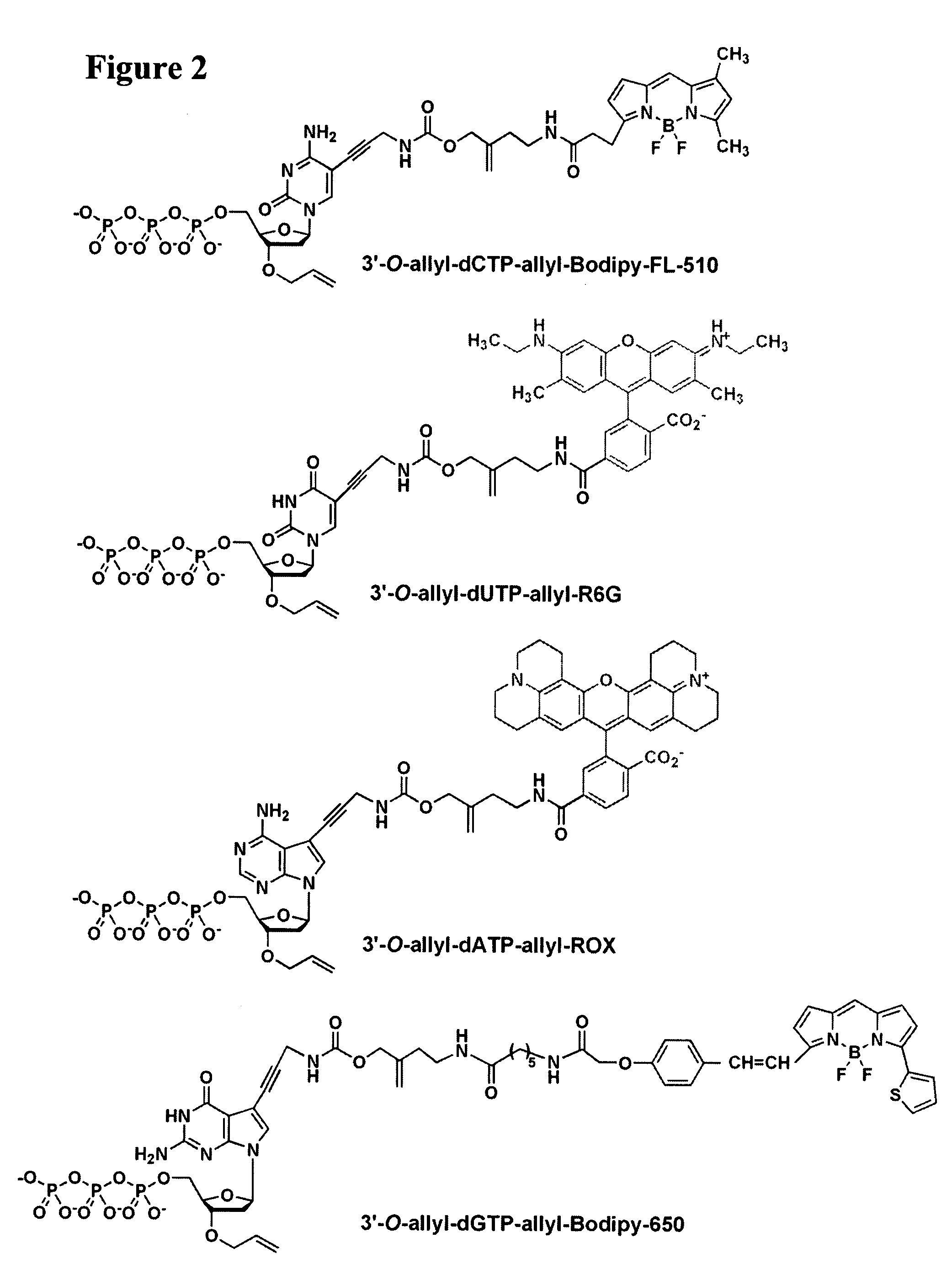
Four-color DNA sequencing by synthesis using cleavable fluorescent nucleotide reversible terminators
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Micro-array evanescent wave fluorescence detection device
InactiveUS7175811B2Quench emissionAvoid disadvantagesOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsWaveguidePolymer
Novel nanowell microarrays are disclosed in optical contact with polymer waveguides wherein evanescent field associated with lightwaves propagated in the waveguide excite target substances in the nanowells either by a common waveguide or by individual waveguides. Fluid samples are conveyed to the nanowells by means of microfluidics. The presence of the target substances in fluid samples is detected by sensing fluorescent radiation generated by fluorescent tag bound to the target substances. The fluorescent tags generate fluorescent radiation as a result of their excitation by the evanescent field. One or more PMT detectors or a CCD detector are located at the side of the waveguide opposite to the nanowells. Fluorescent radiation is detected due to its coupling with the waveguide or its emission through the waveguide.
Owner:EDGELIGHT BIOSCI
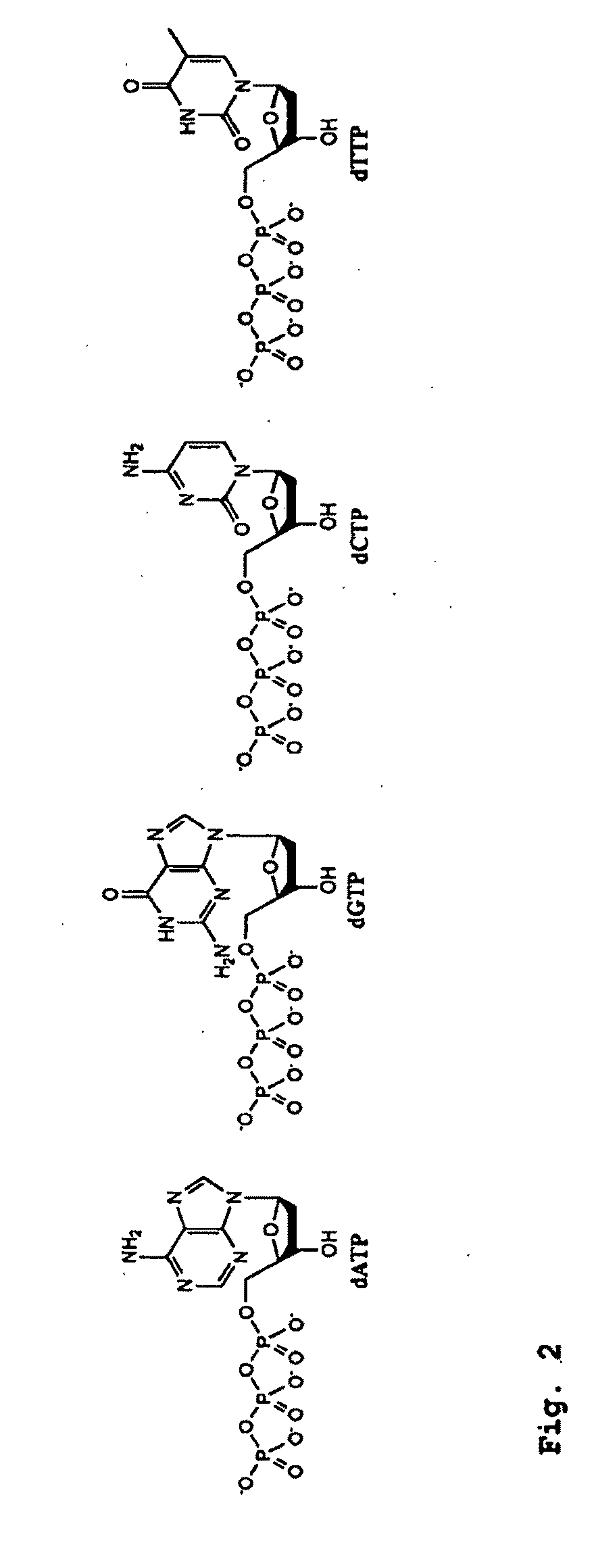
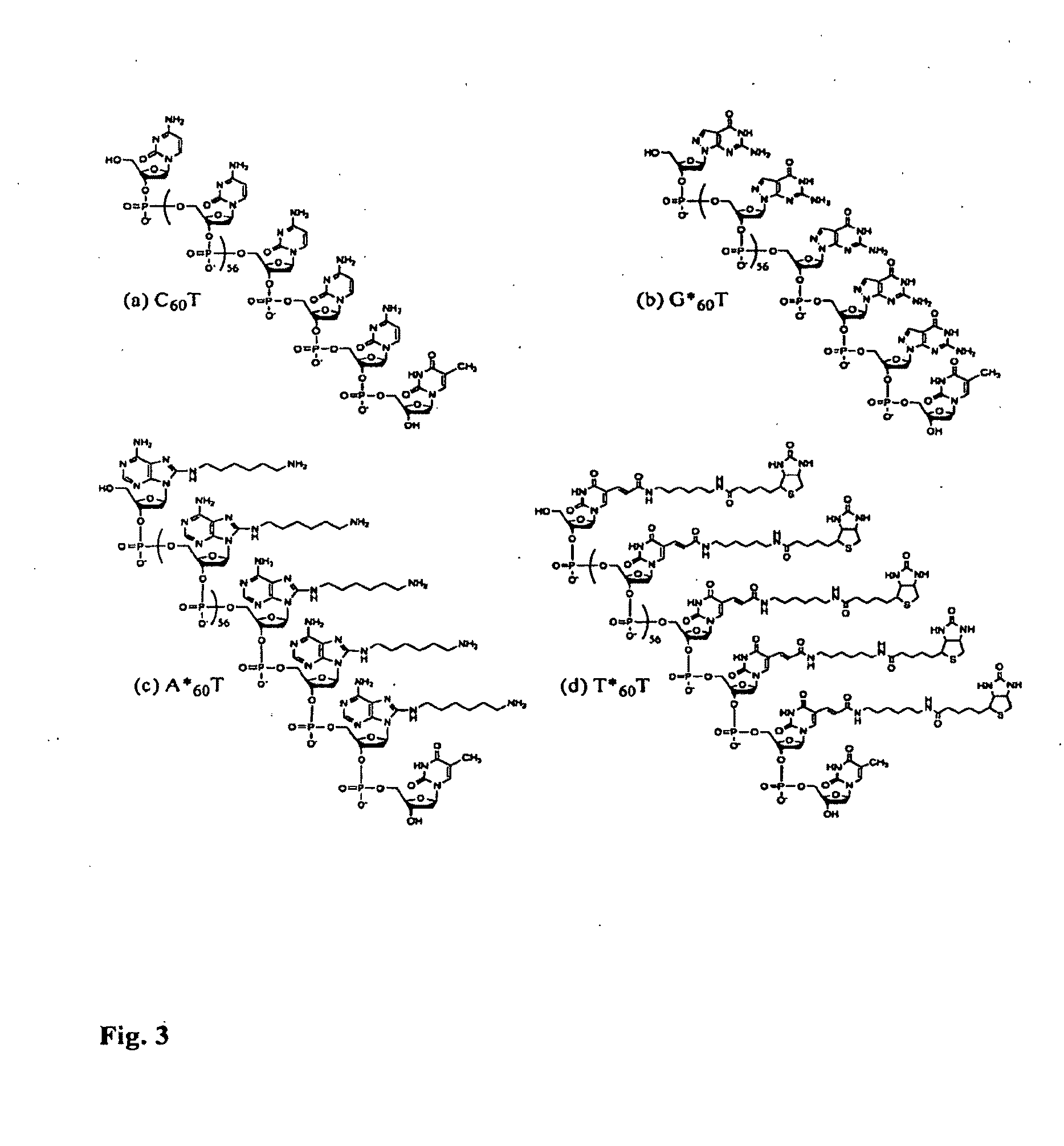
DNA Sequencing by Nanopore Using Modified Nucleotides
ActiveUS20090298072A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideSingle strand dna
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Nanopore arrays and sequencing devices and methods thereof
Provided are devices comprising one or more nanoscale pores for use in, inter alia, analyzing various biological molecules. Also provided are methods for the fabrication of nanoscale pores in solid-state substrates, methods for functionalizing nanopores in solid-state substrates, and methods for sequencing polymers using devices containing nanoscale pores.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Study of polymer molecules and conformations with a nanopore
The invention features methods for evaluating the conformation of a polymer, for example, for determining the conformational distribution of a plurality of polymers and to detect binding or denaturation events. The methods employ a nanopore which the polymer, e.g., a nucleic acid, traverses. As the polymer traverses the nanopore, measurements of transport properties of the nanopore yield data on the conformation of the polymer.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods and devices for characterizing duplex nucleic acid molecules
Methods and devices are provided for characterizing a duplex nucleic acid, e.g., a duplex DNA molecule. In the subject methods, a fluid conducting medium that includes a duplex nucleic acid molecule is contacted with a nanopore under the influence of an applied electric field and the resulting changes in current through the nanopore caused by the duplex nucleic acid molecule are monitored. The observed changes in current through the nanopore are then employed as a set of data values to characterize the duplex nucleic acid, where the set of data values may be employed in raw form or manipulated, e.g., into a current blockade profile. Also provided are nanopore devices for practicing the subject methods, where the subject nanopore devices are characterized by the presence of an algorithm which directs a processing means to employ monitored changes in current through a nanopore to characterize a duplex nucleic acid molecule responsible for the current changes. The subject methods and devices find use in a variety of applications, including, among other applications, the identification of an analyte duplex DNA molecule in a sample, the specific base sequence at a single nulceotide polymorphism (SNP), and the sequencing of duplex DNA molecules.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Systems and methods for characterizing a molecule
Techniques for characterizing a molecule are described herein. In one example, a portion of the molecule is trapped in a nanopore, a variable voltage is applied across the nanopore until the trapped portion of molecule is moved within the nanopore, and the molecule is characterized based on the electrical stimulus required to affect movement of at least a portion of the trapped portion of the molecule within the nanopore.
Owner:GENIA TECH
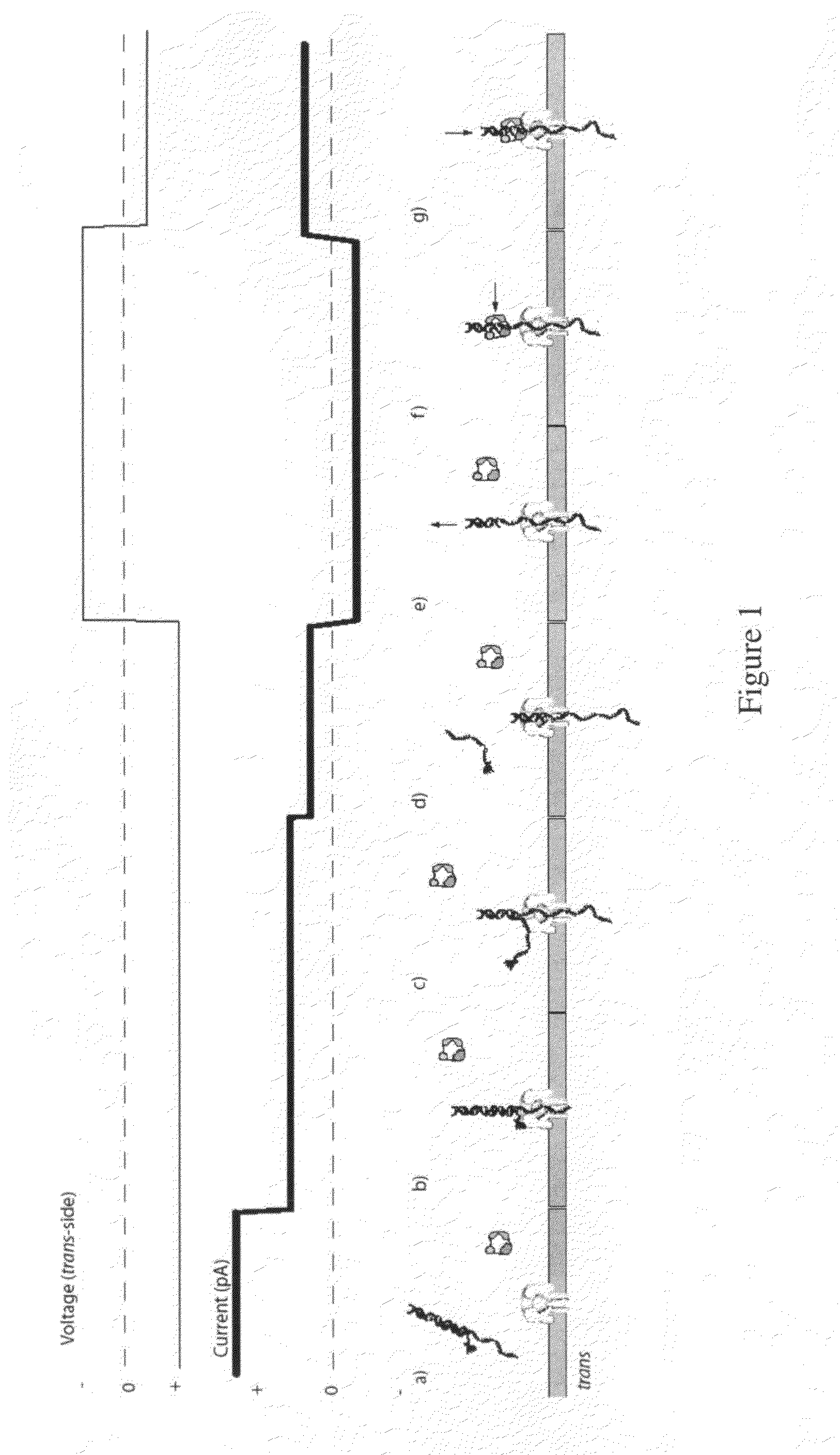
Nanopore sequencing using charge blockade labels
ActiveUS8652779B2Different levelDifferent modulus propertySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementNucleotidePolymerase L
The invention relates to devices and methods for nanopore sequencing. The invention includes compositions and methods of nucleic acid sequencing using a single polymerase enzyme complex comprising a polymerase enzyme and a template nucleic acid attached proximal to a nanopore, and nucleotide analogs in solution comprising charge blockade label that are attached to the polyphosphate portion of the nucleotide analog such that the charge blockade labels are cleaved when the nucleotide analog is incorporated into a growing nucleic acid and the charge blockade label is detected by the nanopore to determine the presence and identity of the incorporated nucleotide and thereby determine the sequence of a template nucleic acid.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
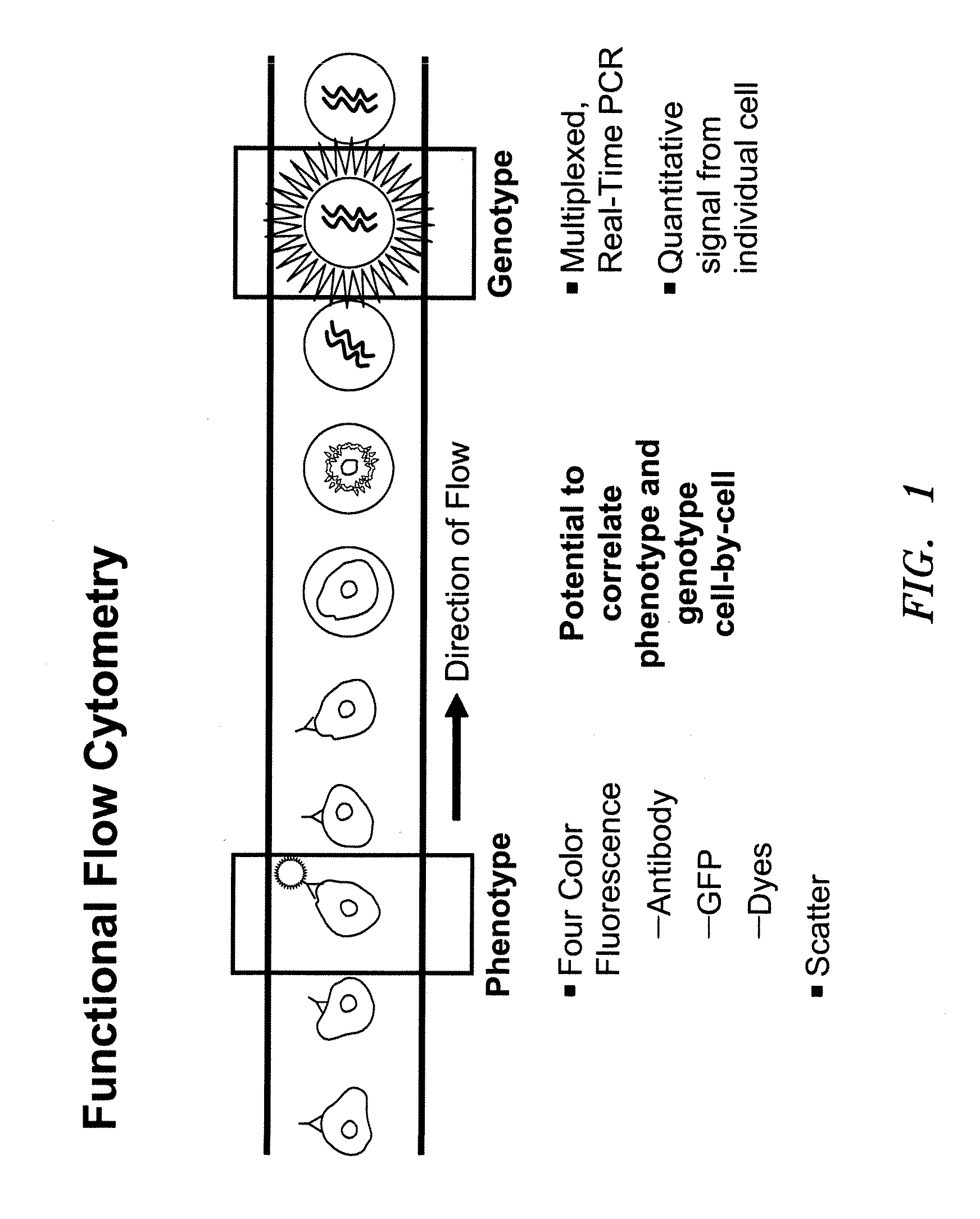
Methods and Devices for Correlated, Multi-Parameter Single Cell Measurements and Recovery of Remnant Biological Material
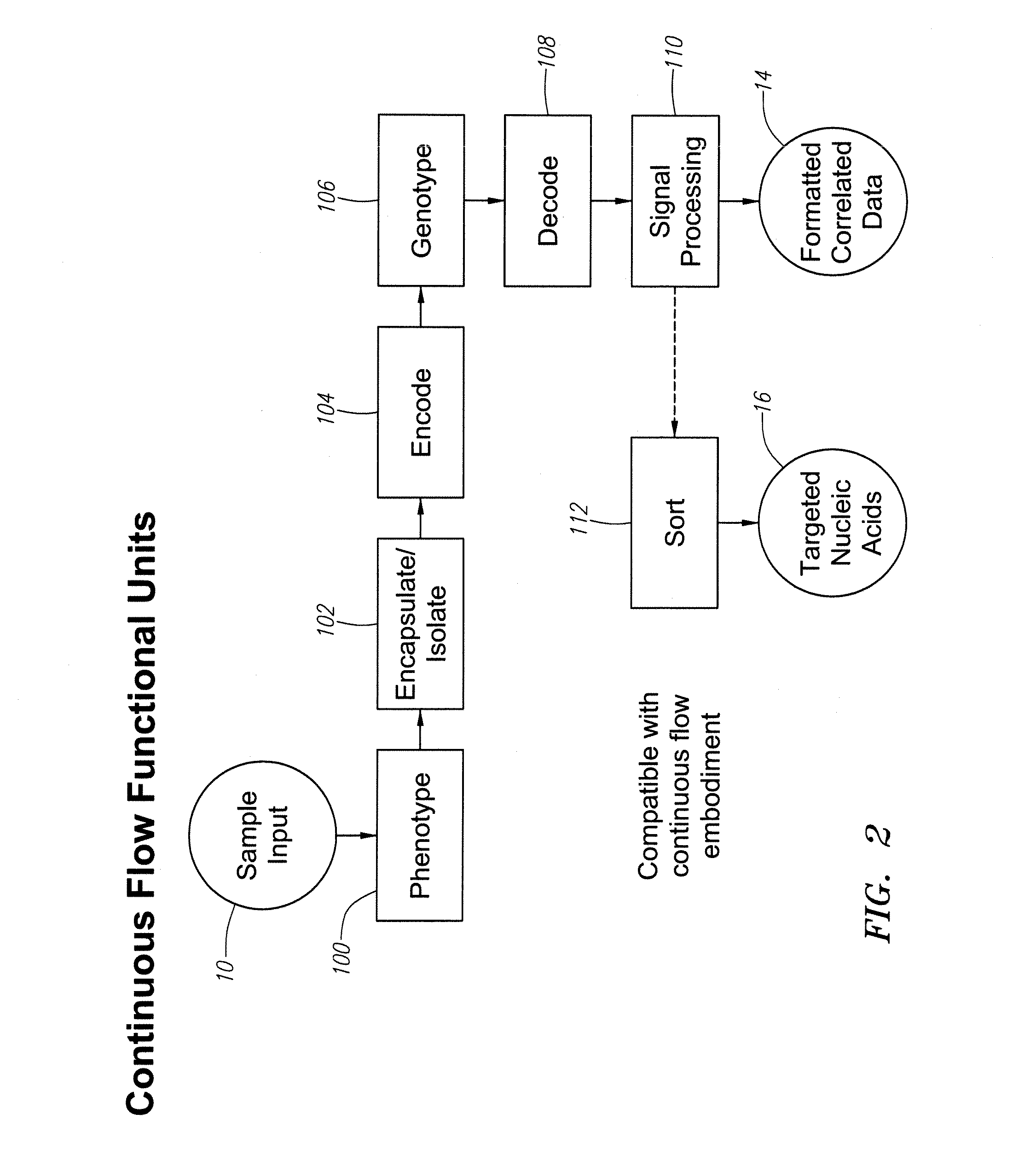
InactiveUS20090042737A1Reduces number of point of interrogationHeating or cooling apparatusLibrary screeningPhenotype genotypeGenotype Analysis
Methods and apparatus are provided for analysis and correlation of phenotypic and genotypic information for a high throughput sample on a cell by cell basis. Cells are isolated and sequentially analyzed for phenotypic information and genotypic information which is then correlated. Methods for correlating the phenotype-genotype information of a sample population can be performed on a continuous flow sample within a microfluidic channel network or alternatively on a sample preloaded into a nano-well array chip. The methods for performing the phenotype-genotype analysis and correlation are scalable for samples numbering in the hundreds of cells to thousands of cells up to the tens and hundreds of thousand cells.
Owner:PROGENITY INC
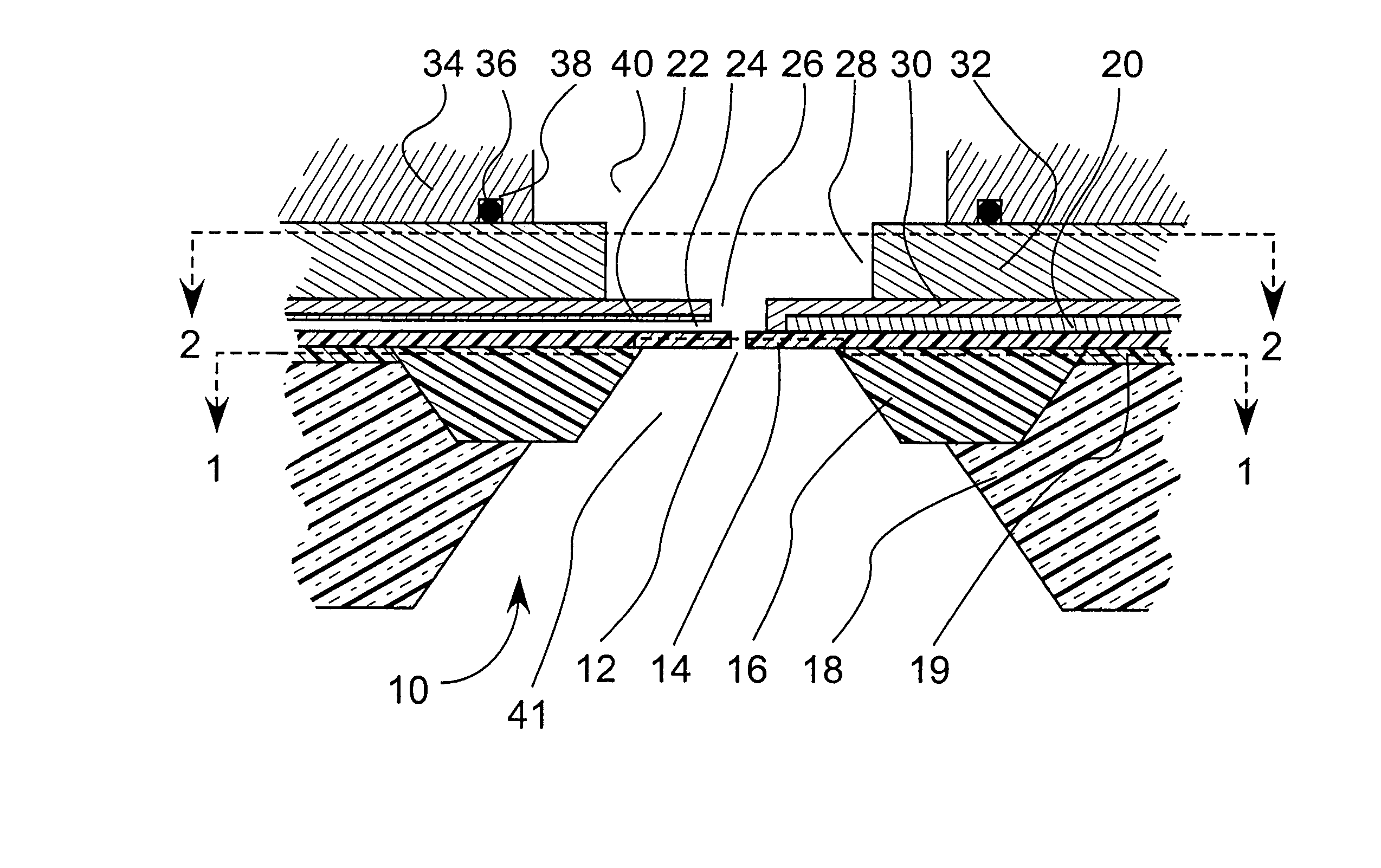
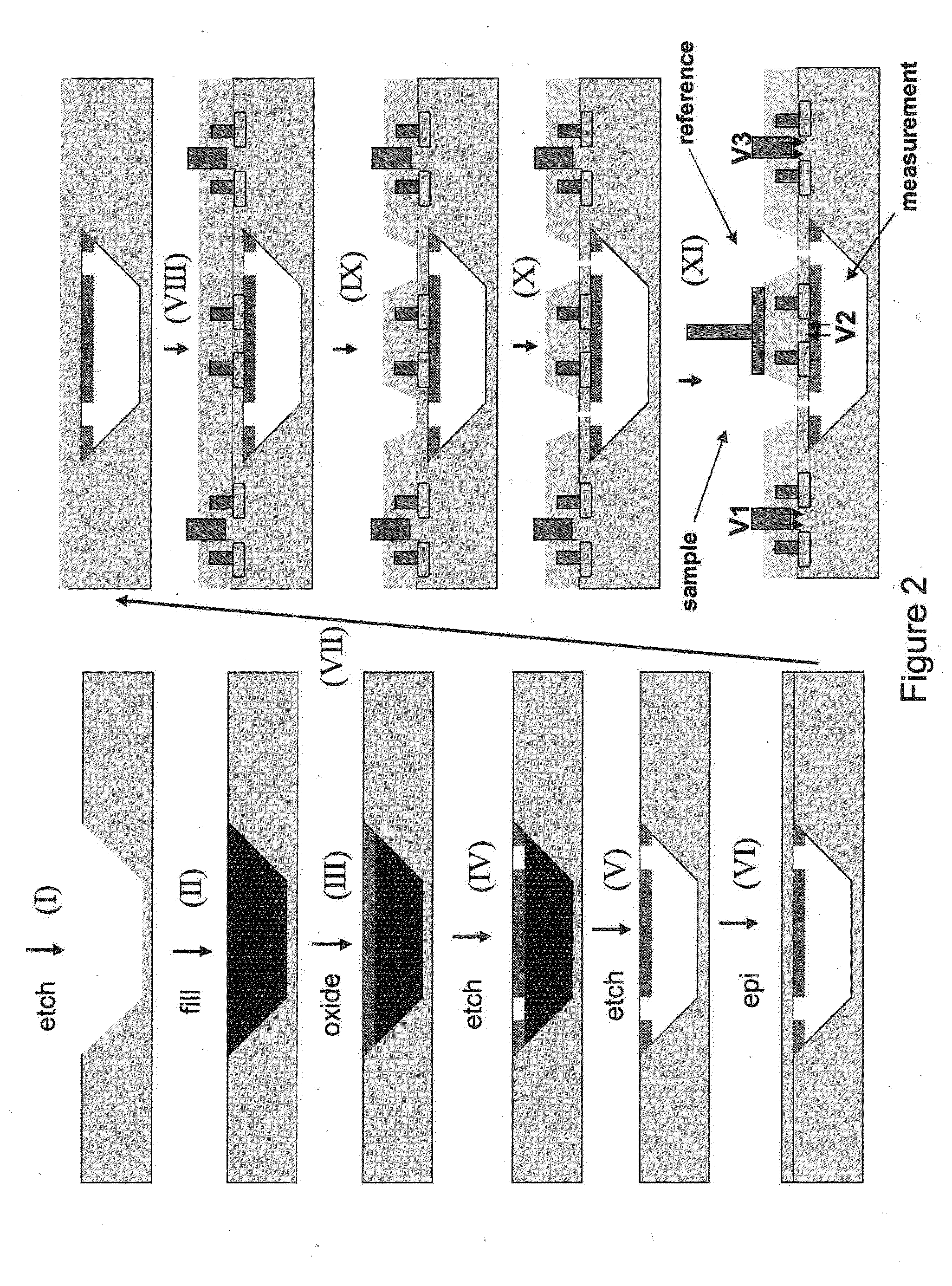
Addressable nanopores and micropores including methods for making and using same
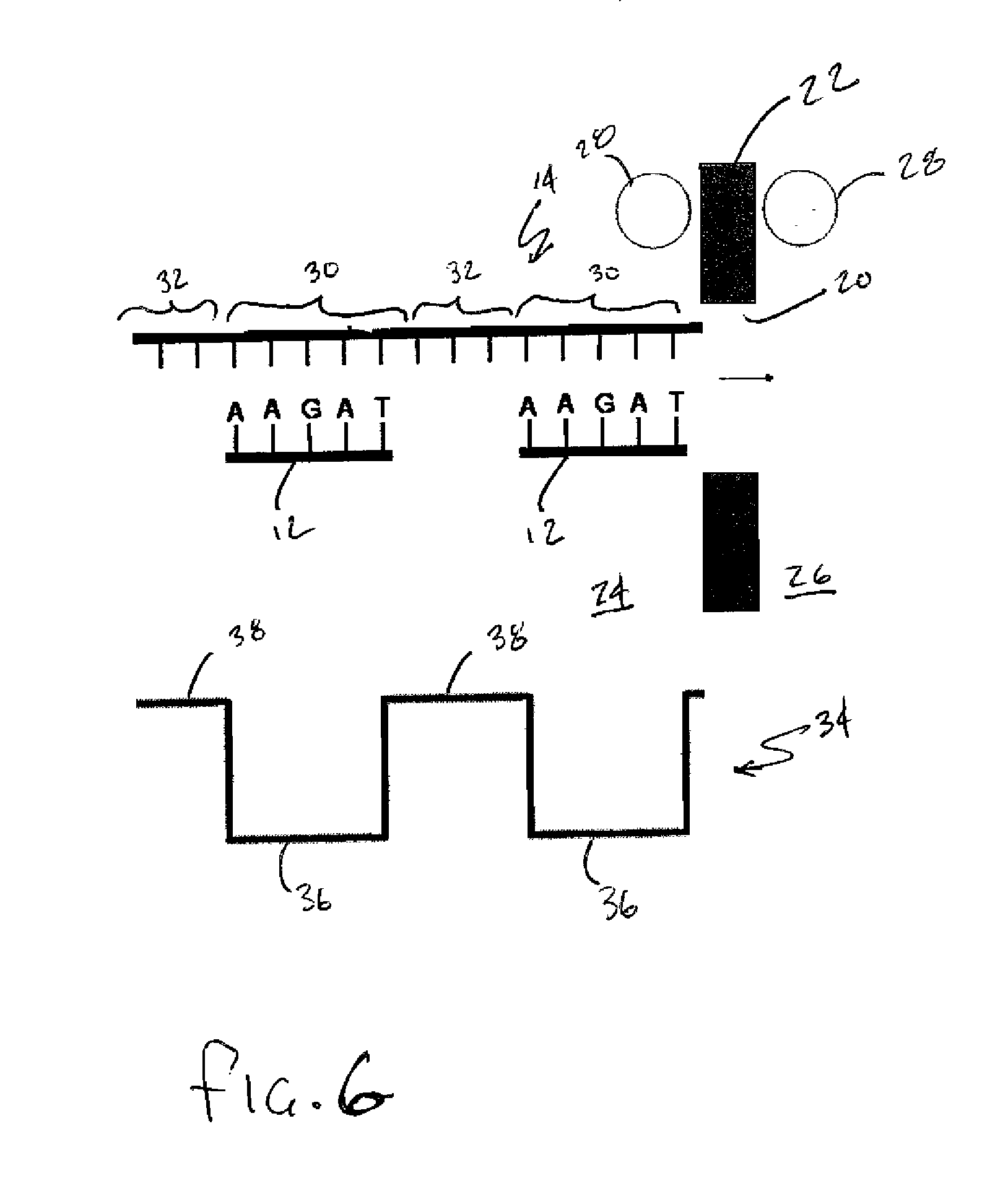
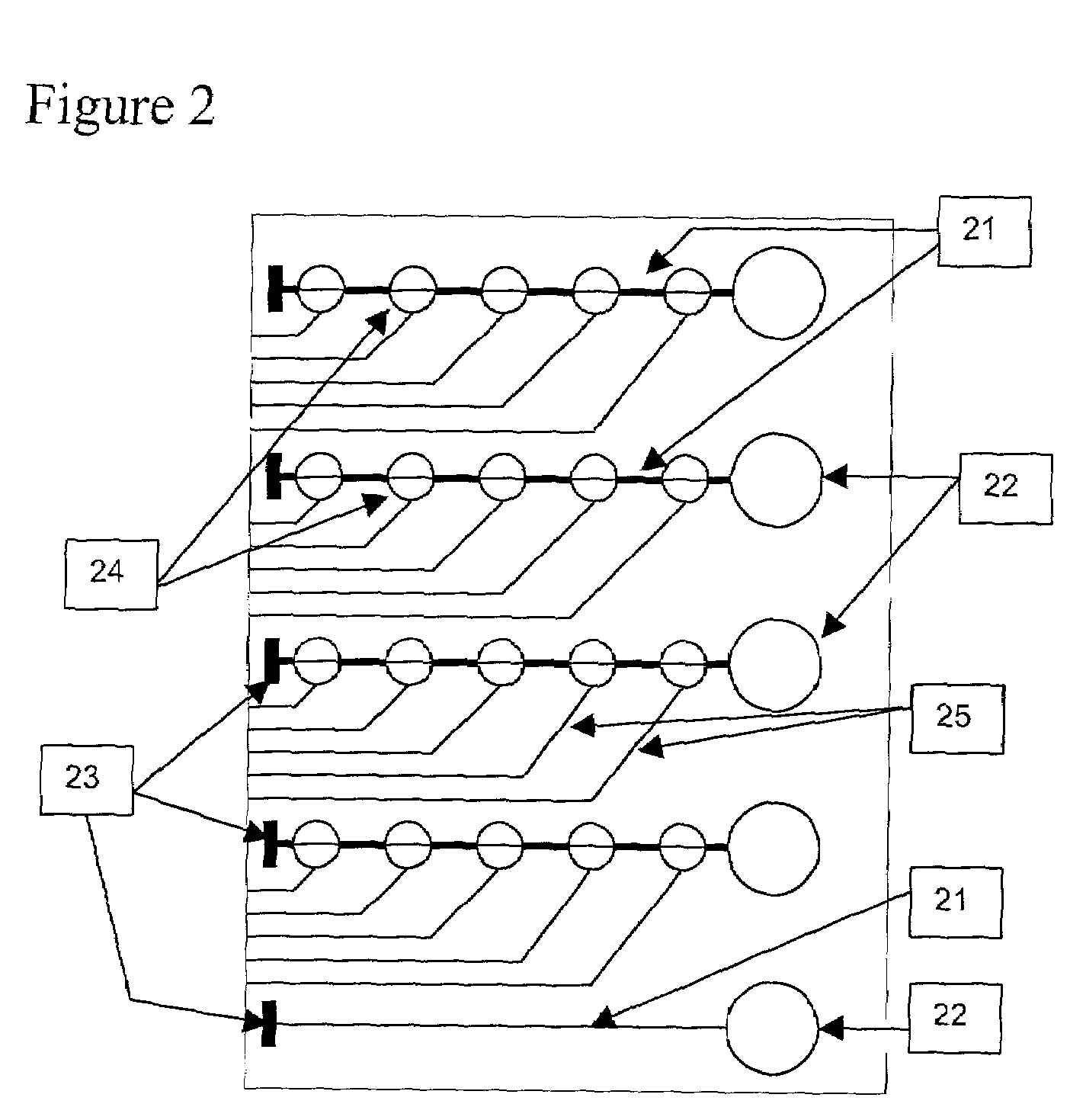
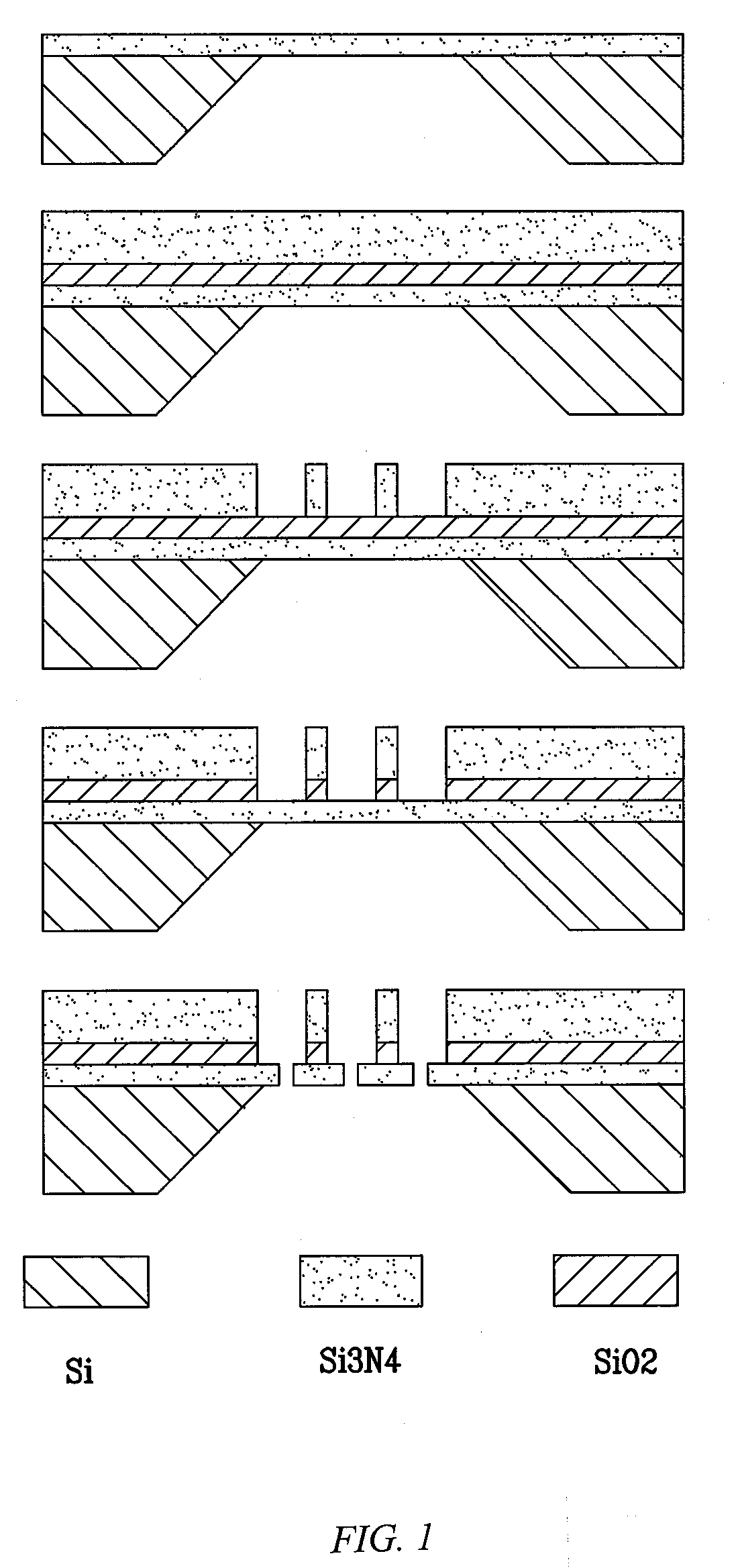
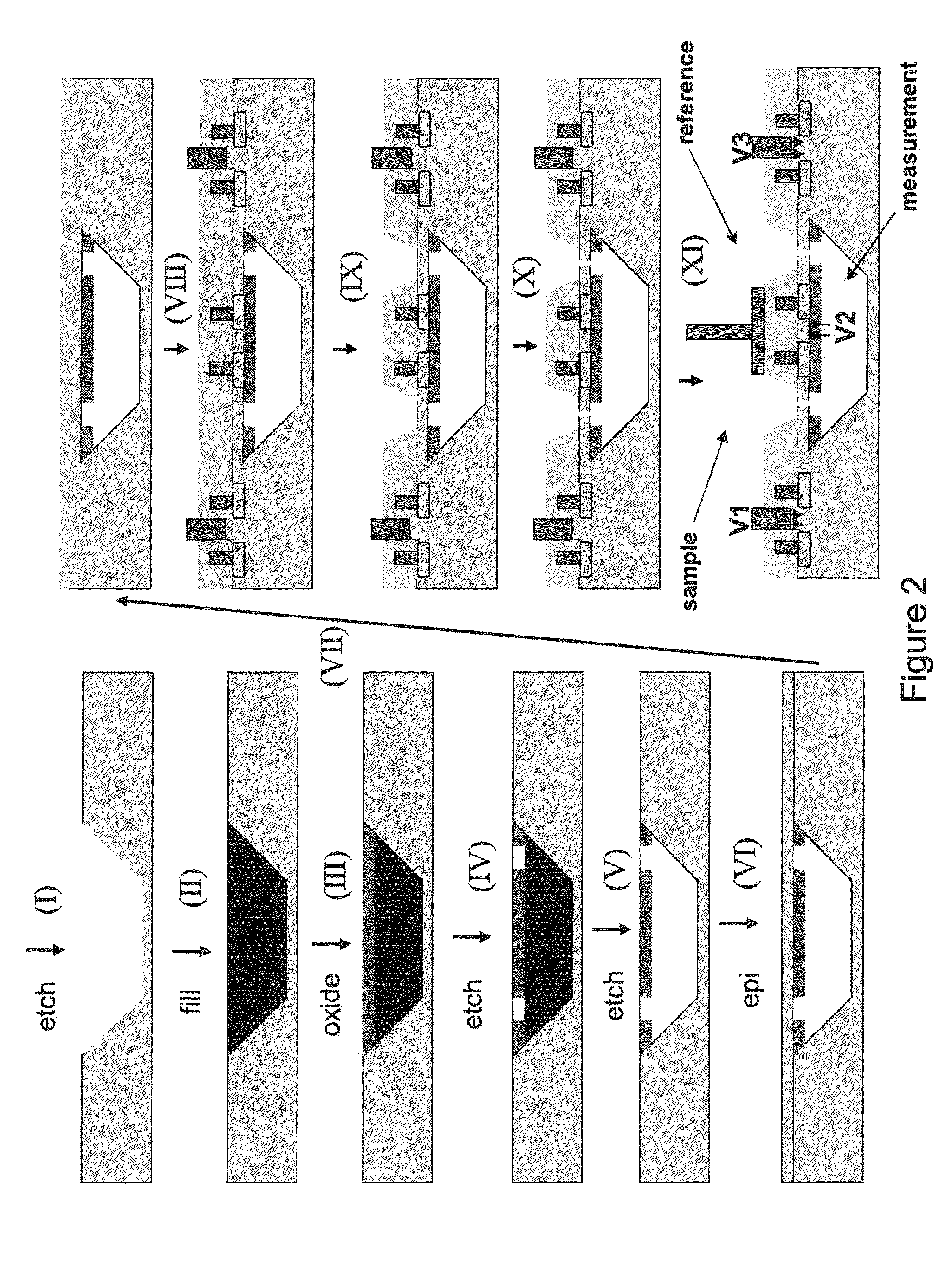
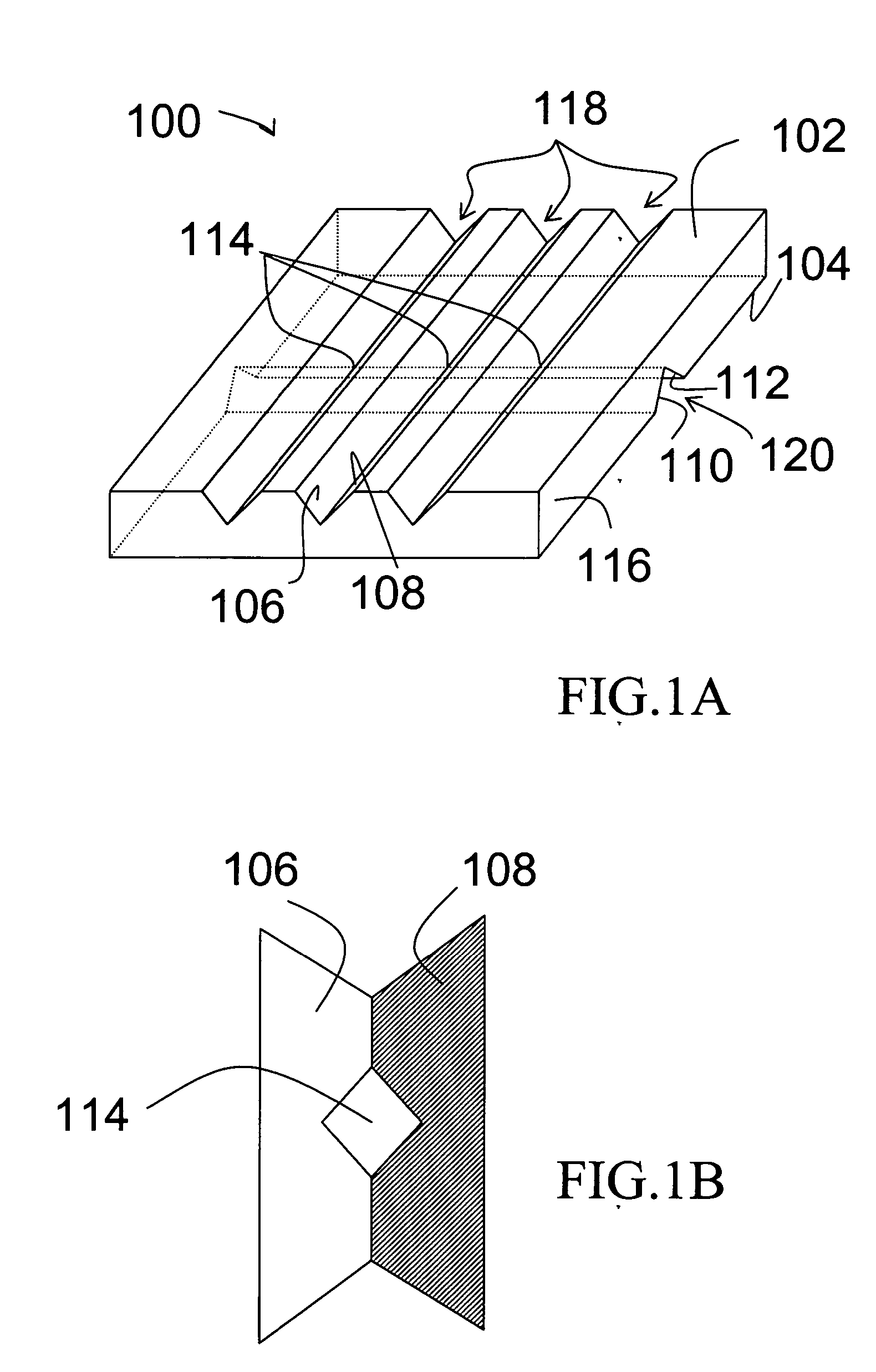
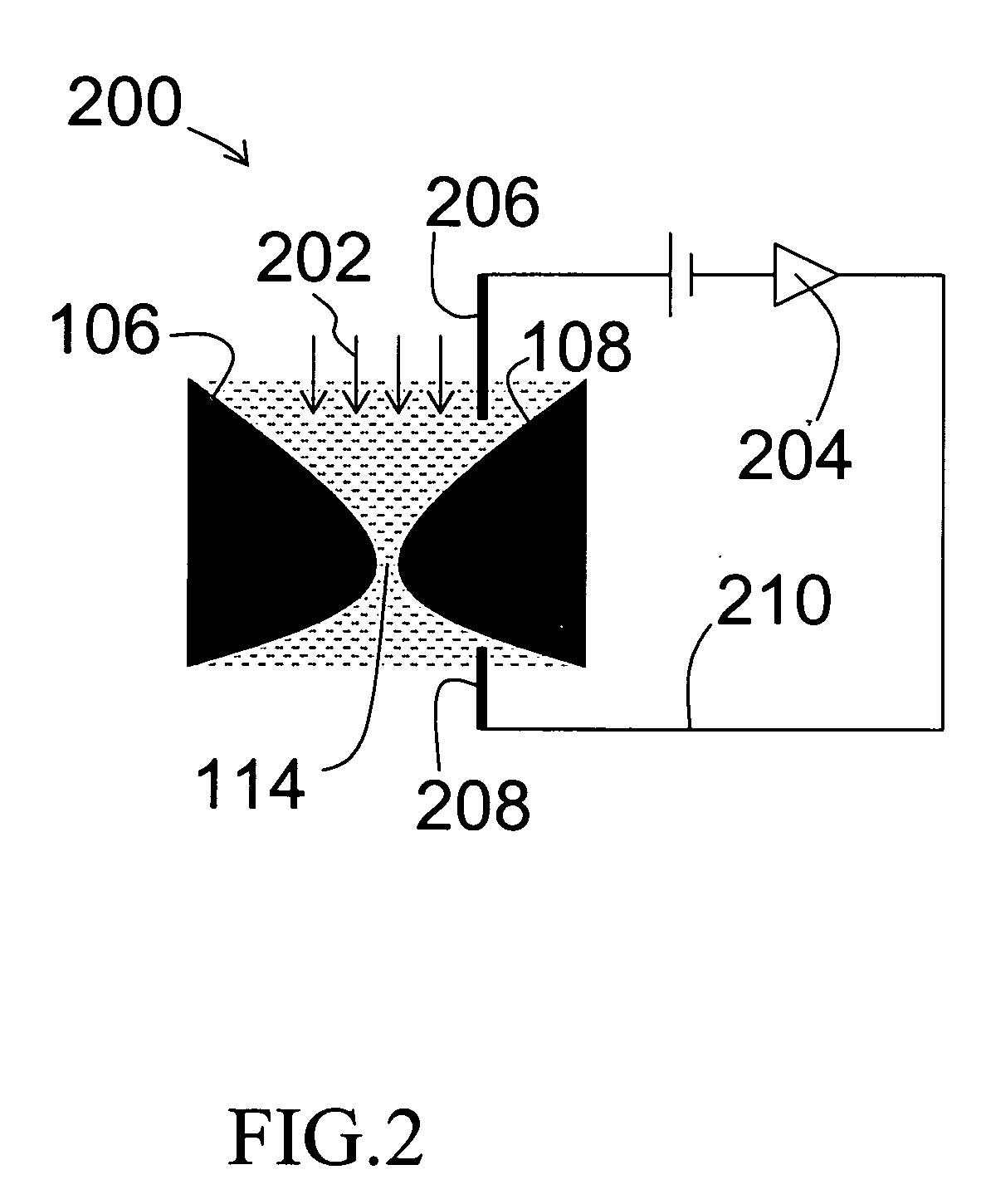
ActiveUS20050127035A1Reduce the overall diameterEasy to controlBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringNanopore
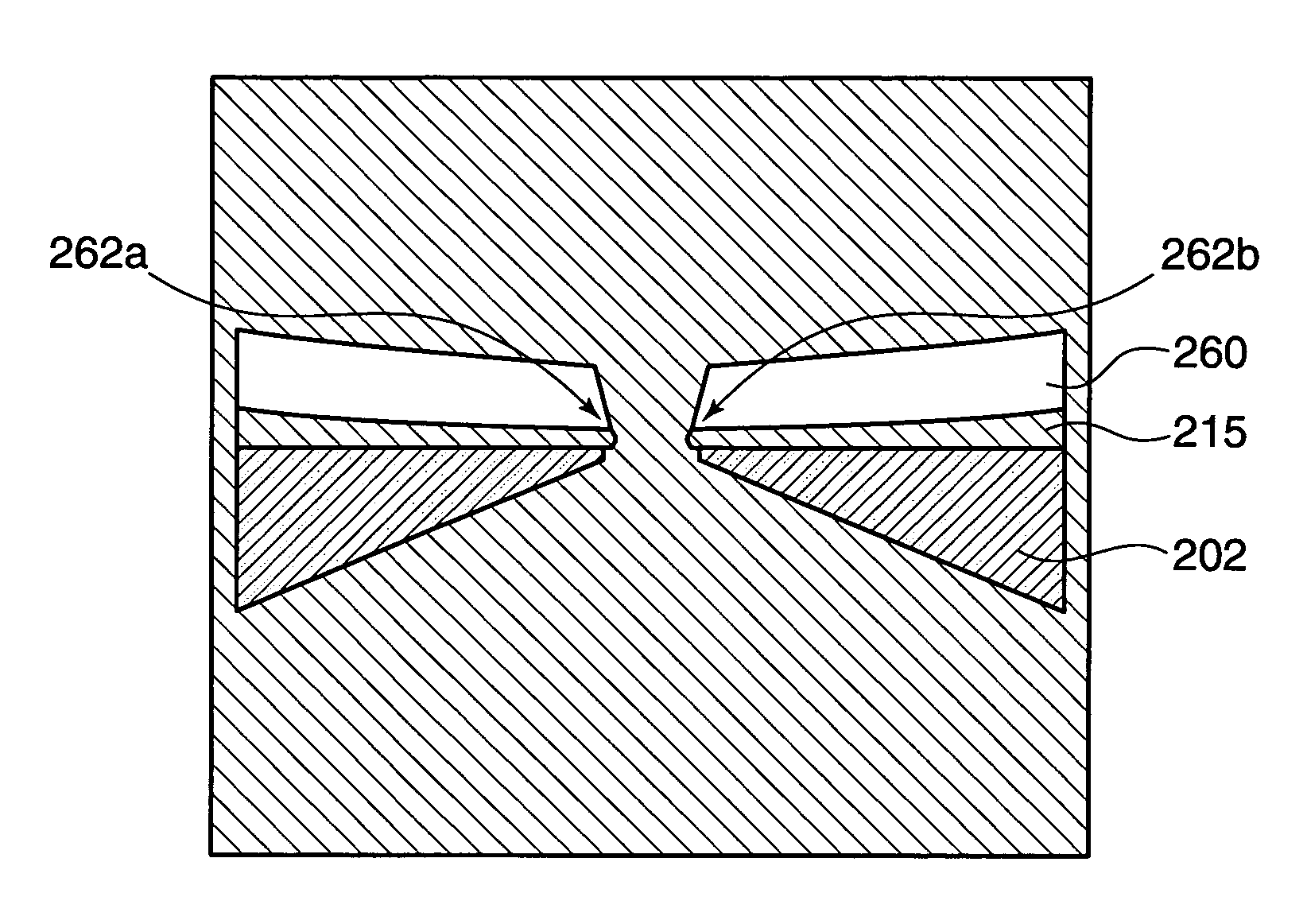
Featured are devices and systems embodying one or more electrically-addressable-solid-state nanopores useful for sensing and / or characterizing single macromolecules as well as sequencing DNA or RNA. In one aspect of the present invention, there is featured a linear or 2-D electrically-addressable array of nanopores, where the nanopores are located at points of intersections between V-shaped grooves formed in an upper surface of the insulating member and a V-shaped groove formed in a lower surface of the insulating member. In another aspect of the present invention the solid-state nanopore of the present invention the width and / or length of the nanopore is defined or established by sharp edges of cleaved crystals that are maintained in fixed relation during the formation of the insulating member including the nanopore.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY +1
Molecular resonant tunneling sensor and methods of fabricating and using the same
InactiveUS20060231419A1Easy to detectImproved characterizationWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementEngineeringNanopore
Resonant tunneling devices and methods of using and fabricating the same are provided. The subject devices include a first and second fluid containment members separated by a fluid barrier having a single nanopore therein providing fluid communication between the first and second fluid containment members, wherein the nanopore has a top inner diameter that is smaller than a bottom inner diameter and includes first and second perimeter electrodes separated by an insulator element, and a proteinaceous channel positioned in the nanopore. Also provided are methods of fabricating such a device and methods of using such a device for improved detection and characterization of a sample.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
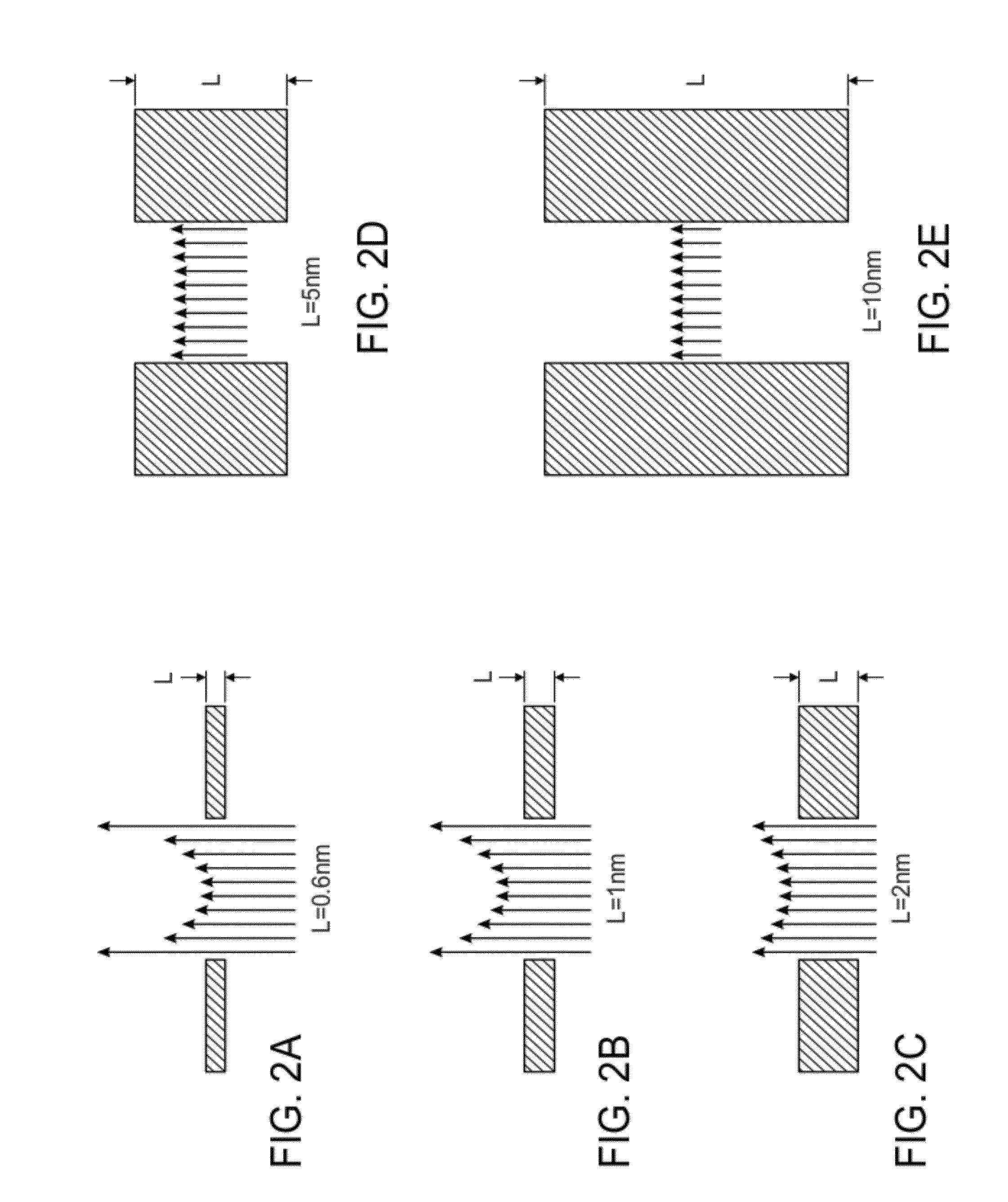
Apparatus and method for making a low capacitance artificial nanopore
An apparatus and method for making a nanopore chip exhibiting low capacitance. The apparatus provides a thin diaphragm on a rigid semiconductor frame suitable for nanopore fabrication, the diaphragm having associated thicker insulator regions to reduce capacitance. Also disclosed is a method of making the apparatus.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Nanoporous Drug Delivery System
Disclosed herein are controlled release drug delivery systems. The systems comprise a medical device at least one nonoporous surface, at least one bioactive agent and optionally a biodegradable polymer. The nanoporous surfaces of the medical devices contain nanopores capable of acting as reservoirs for drugs that are controllably released.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Detection and identification of biopolymers using fluorescence quenching
InactiveUS20050095599A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceBiopolymer
The present invention provides an apparatus for detecting a nanoscale moiety and a method for sensing a nanoscale moiety. The apparatus includes a substrate having a nanopore, at least one excitable molecule attached to the substrate adjacent to the nanopore, and a light source for exciting the excitable molecule attached to the substrate adjacent to the nanopore wherein the excitable molecule is quenched by the quencher molecule on the nanoscale moiety as it passes by the excitable molecule. The invention also includes a method for detecting the presence or identity of the nanoscale moiety.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Nanometric Material Having a Nanopore Enabling High-Sensitivity Molecular Detection and Analysis
ActiveUS20120234679A1Sludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementSingle layer grapheneProtein translocation
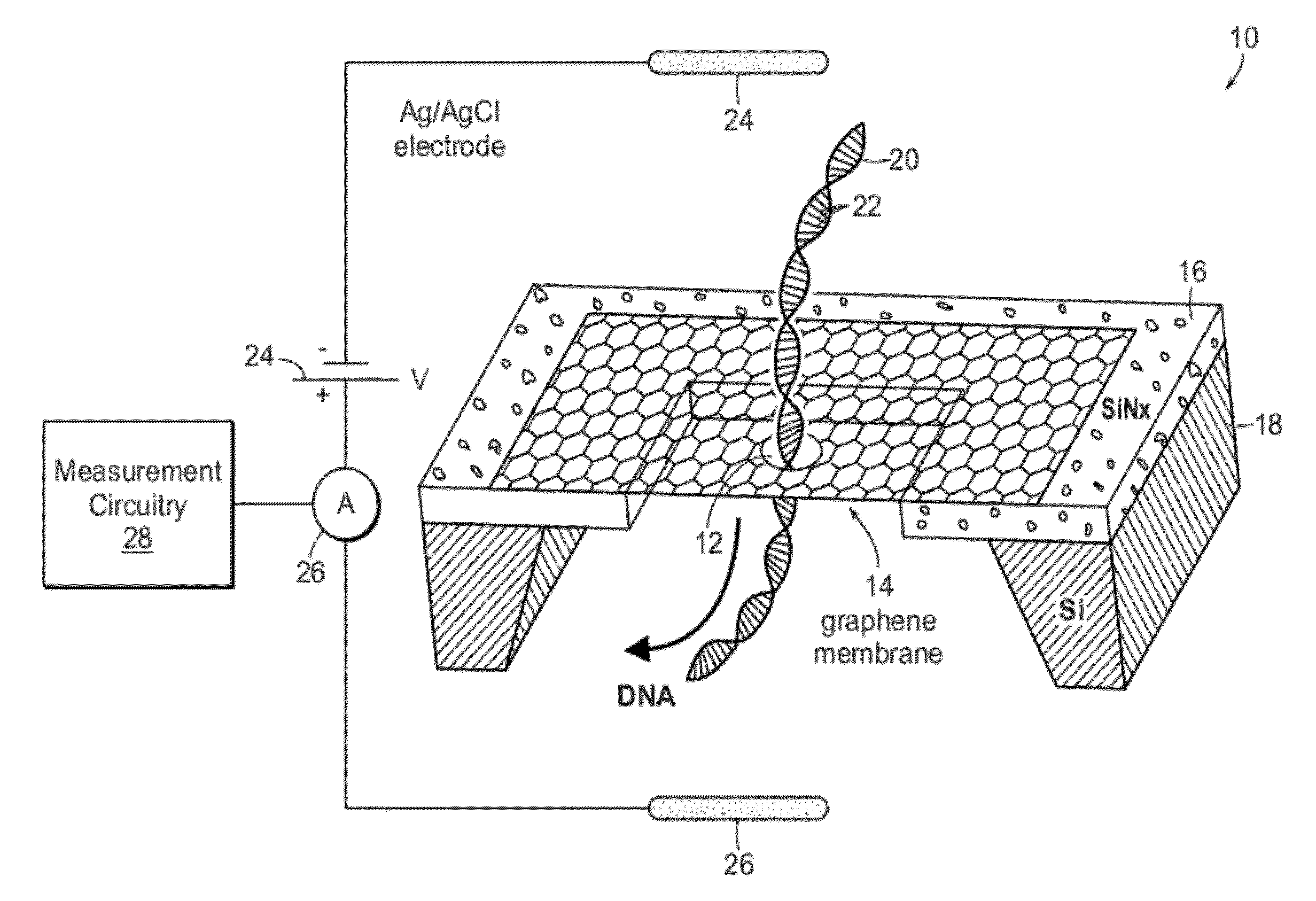
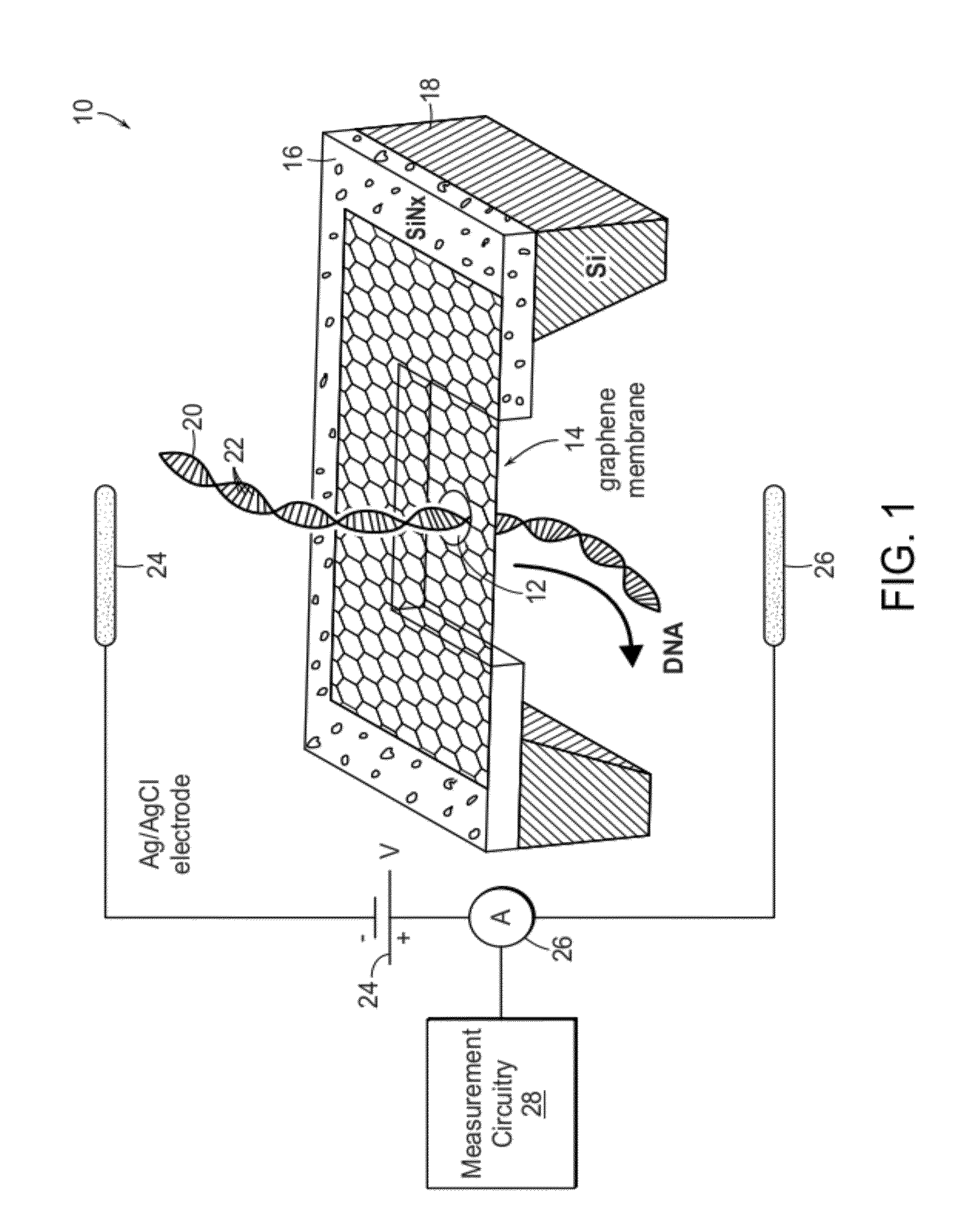
There is provided a substantially bare, self-supported single-layer graphene membrane including a nanopore extending through a thickness of the graphene membrane from a first to a second membrane surface opposite the first graphene membrane surface. A connection from the first graphene membrane surface to a first reservoir provides, at the first graphene membrane surface, a species in an ionic solution to the nanopore, and a connection from the second graphene membrane surface to a second reservoir is provided to collect the species and ionic solution after translocation of the species and ionic solution through the nanopore from the first graphene membrane surface to the second graphene membrane surface. An electrical circuit is connected on opposite sides of the nanopore to measure flow of ionic current through the nanopore in the graphene membrane.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Nanopore sequencing using charge blockade labels
ActiveUS20130240359A1Different levelDifferent modulus propertySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementNucleotidePolymerase L
The invention relates to devices and methods for nanopore sequencing. The invention includes compositions and methods of nucleic acid sequencing using a single polymerase enzyme complex comprising a polymerase enzyme and a template nucleic acid attached proximal to a nanopore, and nucleotide analogs in solution comprising charge blockade label that are attached to the polyphosphate portion of the nucleotide analog such that the charge blockade labels are cleaved when the nucleotide analog is incorporated into a growing nucleic acid and the charge blockade label is detected by the nanopore to determine the presence and identity of the incorporated nucleotide and thereby determine the sequence of a template nucleic acid.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
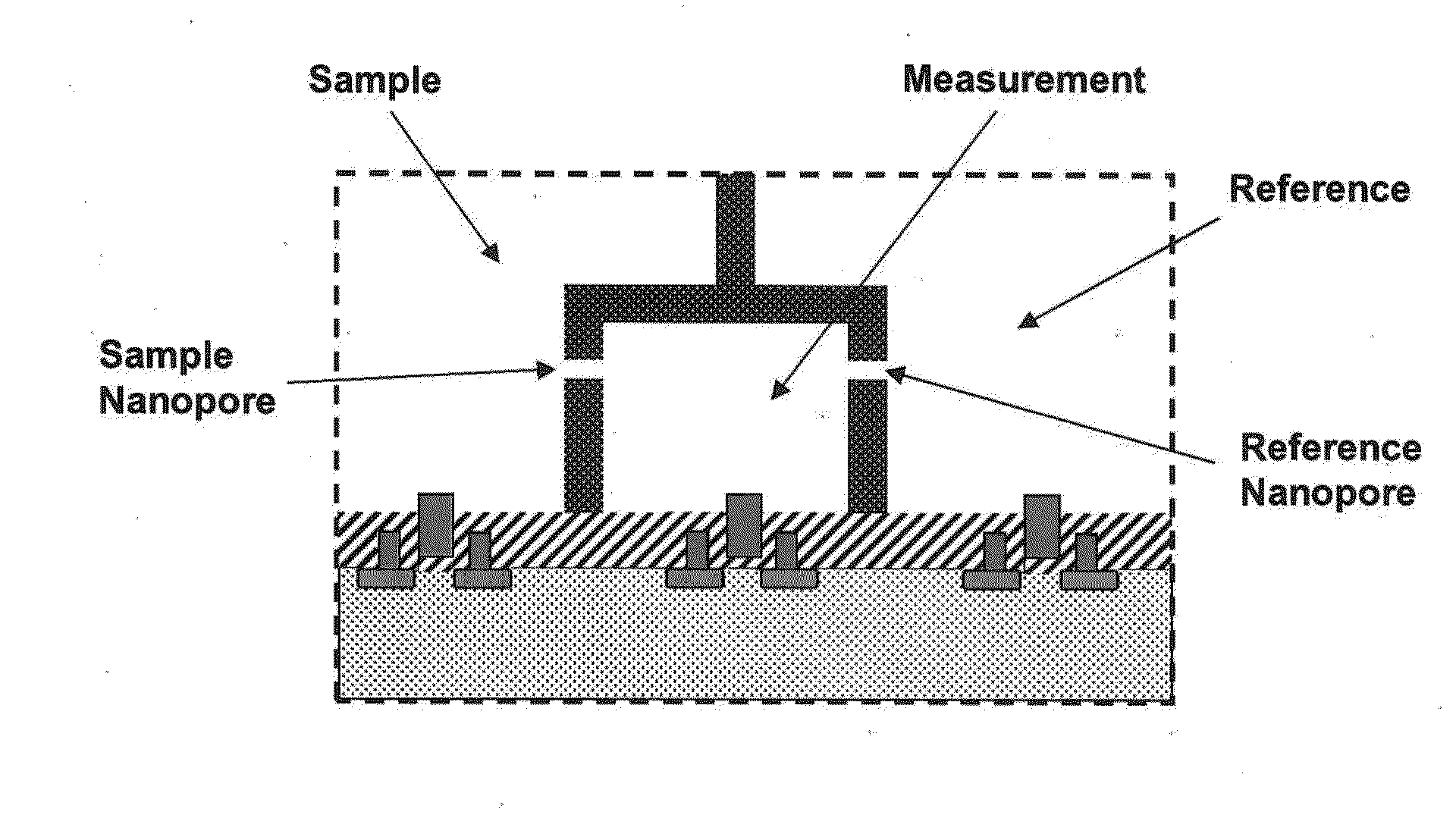
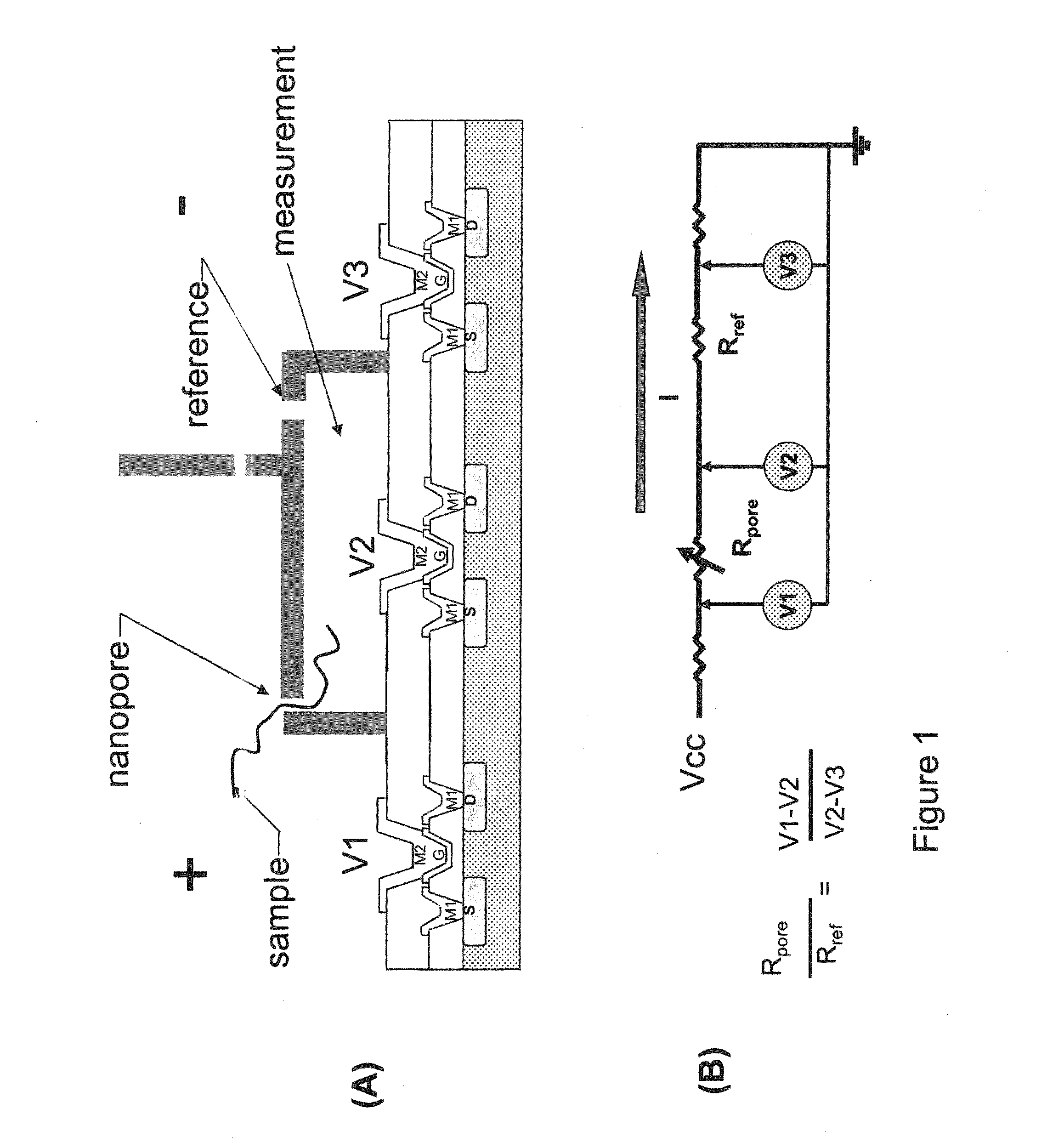
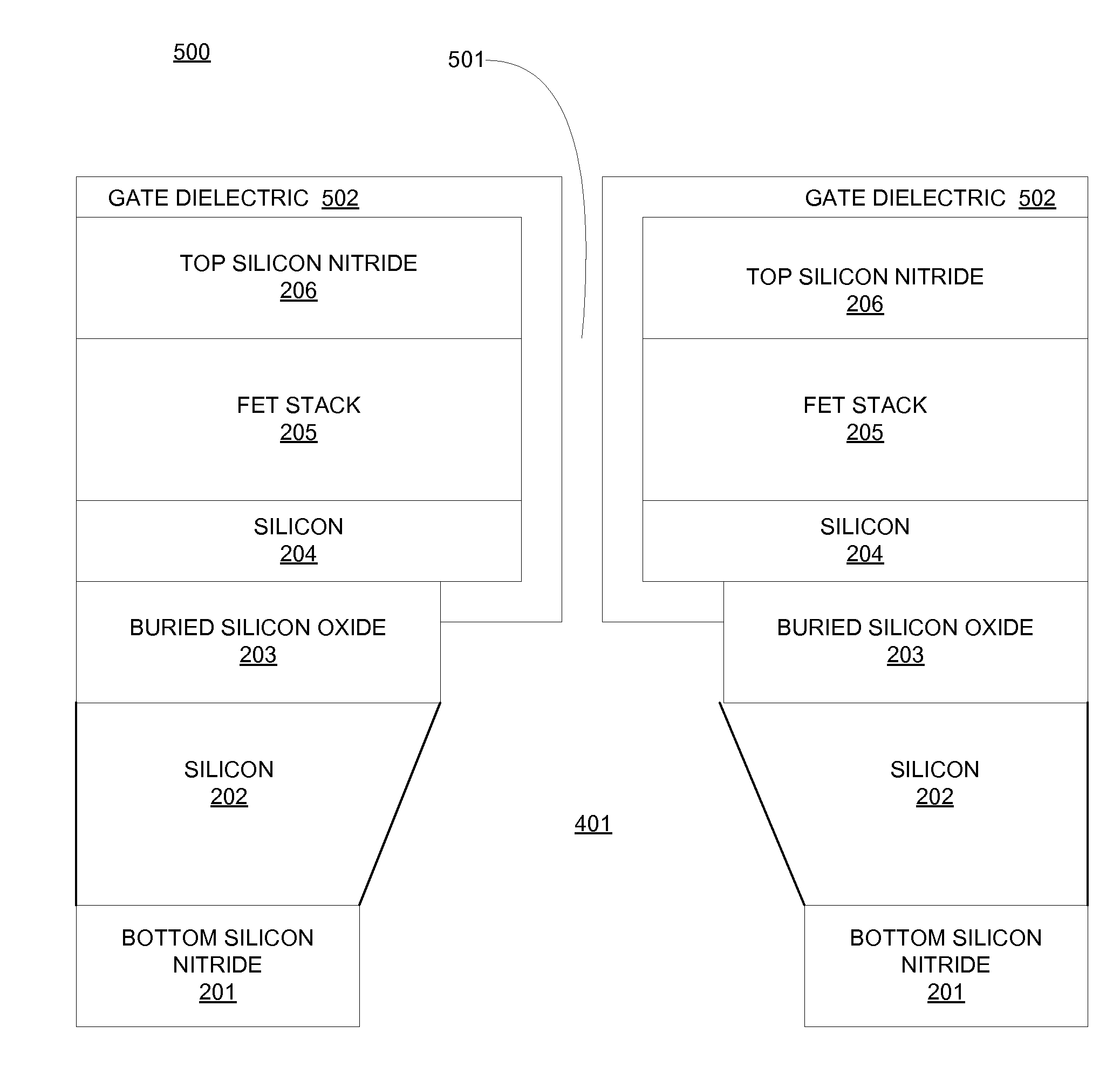
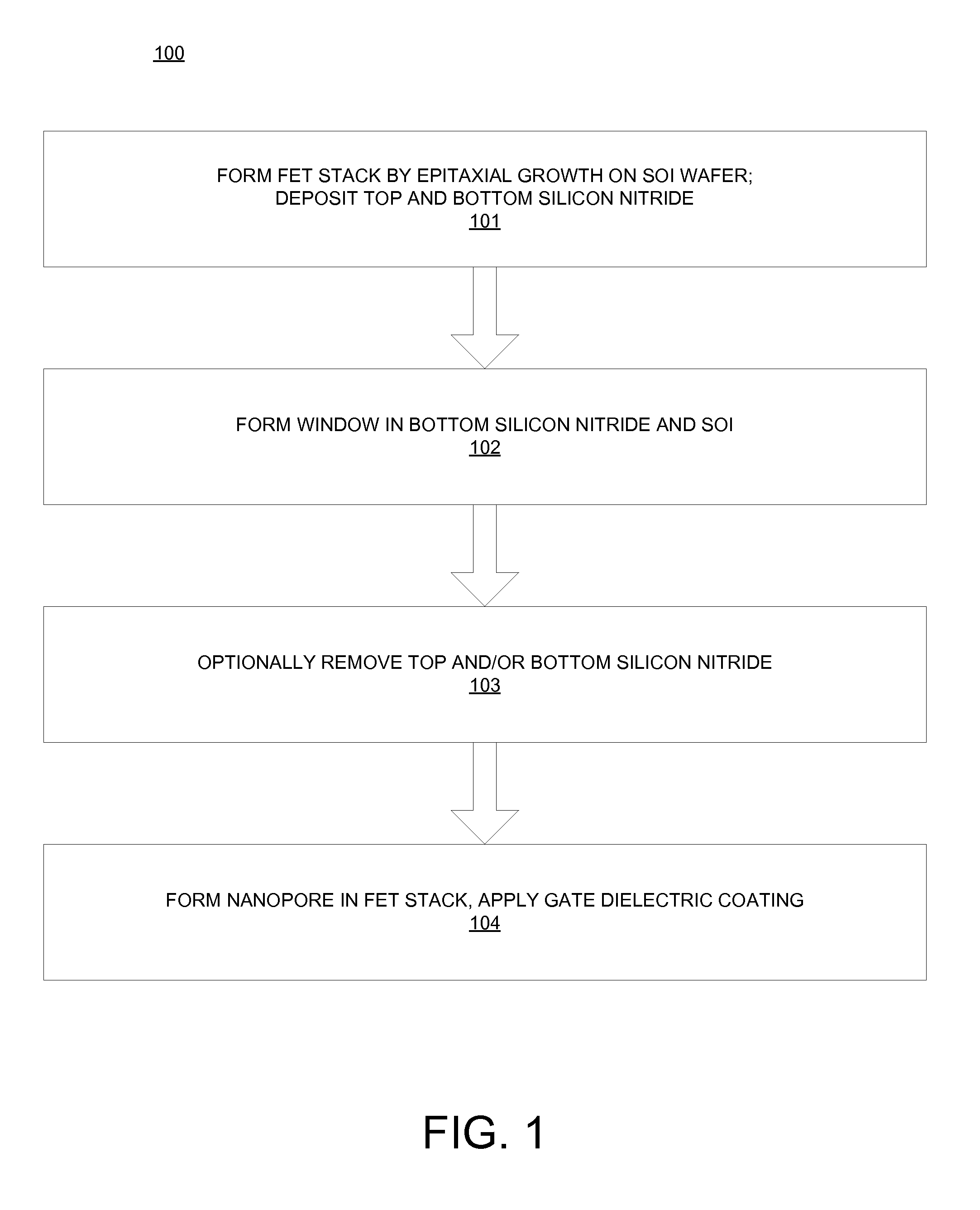
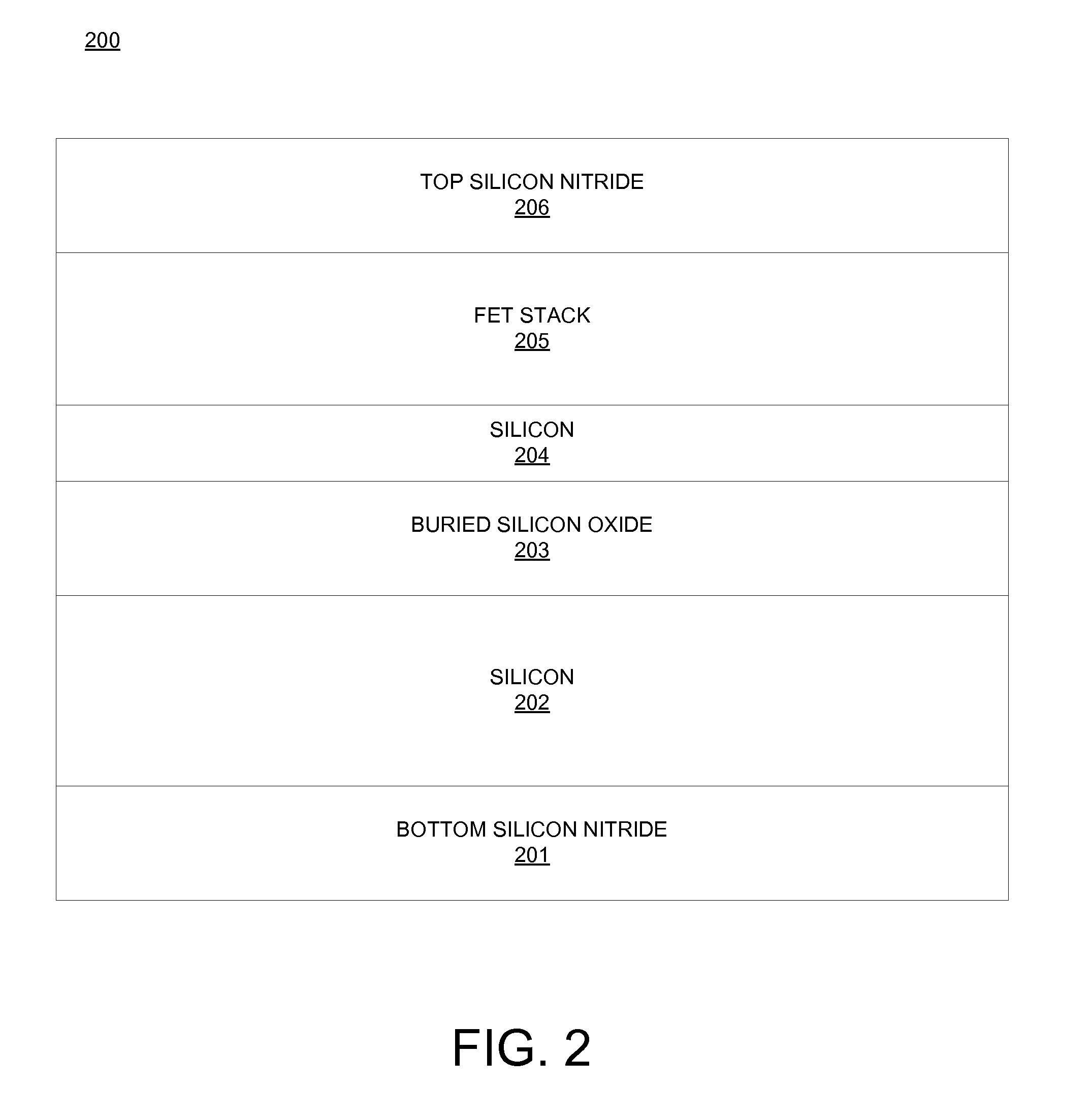
FET Nanopore Sensor
ActiveUS20110279125A1Microbiological testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSub thresholdDrain current
A method of using a sensor comprising a field effect transistor (FET) embedded in a nanopore includes placing the sensor in an electrolyte comprising at least one of biomolecules and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA); placing an electrode in the electrolyte; applying a gate voltage in the sub-threshold regime to the electrode; applying a drain voltage to a drain of the FET; applying a source voltage to a source of the FET; detecting a change in a drain current in the sensor in response to the at least one of biomolecules and DNA passing through the nanopore.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Modified base detection with nanopore sequencing
ActiveUS20130327644A1Reduce error rateReduce errorsElectrolysis componentsSugar derivativesGenomic DNASingle strand
Methods, compositions, and systems are provided for characterization of modified nucleic acids. Nanopore sequencing is performed using a processive enzyme to control the rate of translation of a single strand of a nucleic acid through a nanopore. The presence and identity of a modified base can be determined by monitoring the kinetics of translation through the pore even though the events that lead to the kinetic changes are separated in time and space from the translation of the modified base or it's compliment through the nanopore. The invention also comprises the use of hemi-genomic DNA in nanopore sequencing.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Reversed liquid crystalline phases with non-paraffin hydrophobes
Compounds which are otherwise difficult to solubilize, such as, for example, pharmaceutical actives difficult for the body to absorb, are solubilized into a composition using a solvent system that is a structured fluid. The structured fluid is a reversed cubic phase or reversed hexagonal phase material, or a combination thereof, which includes a polar solvent, a surfactant and a non-paraffinic liquid with a high octanol-water partition coefficient which does not qualify as a surfactant. The compositions thus formed are able to enhance absorption of drugs by the induction of local, transient nanopores in biomembrane absorption barriers and particularly those in which efflux mechanisms, such as those associated with P-glycoprotein and / or cytochrome 3A4, are active. The compositions and methods that are used for solubilizing pharmaceutical actives in structured fluids can simultaneously accomplish solubilization of difficultly soluble drugs and enhancement of absorption.
Owner:LYOTROPICS THERAPEUTICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com