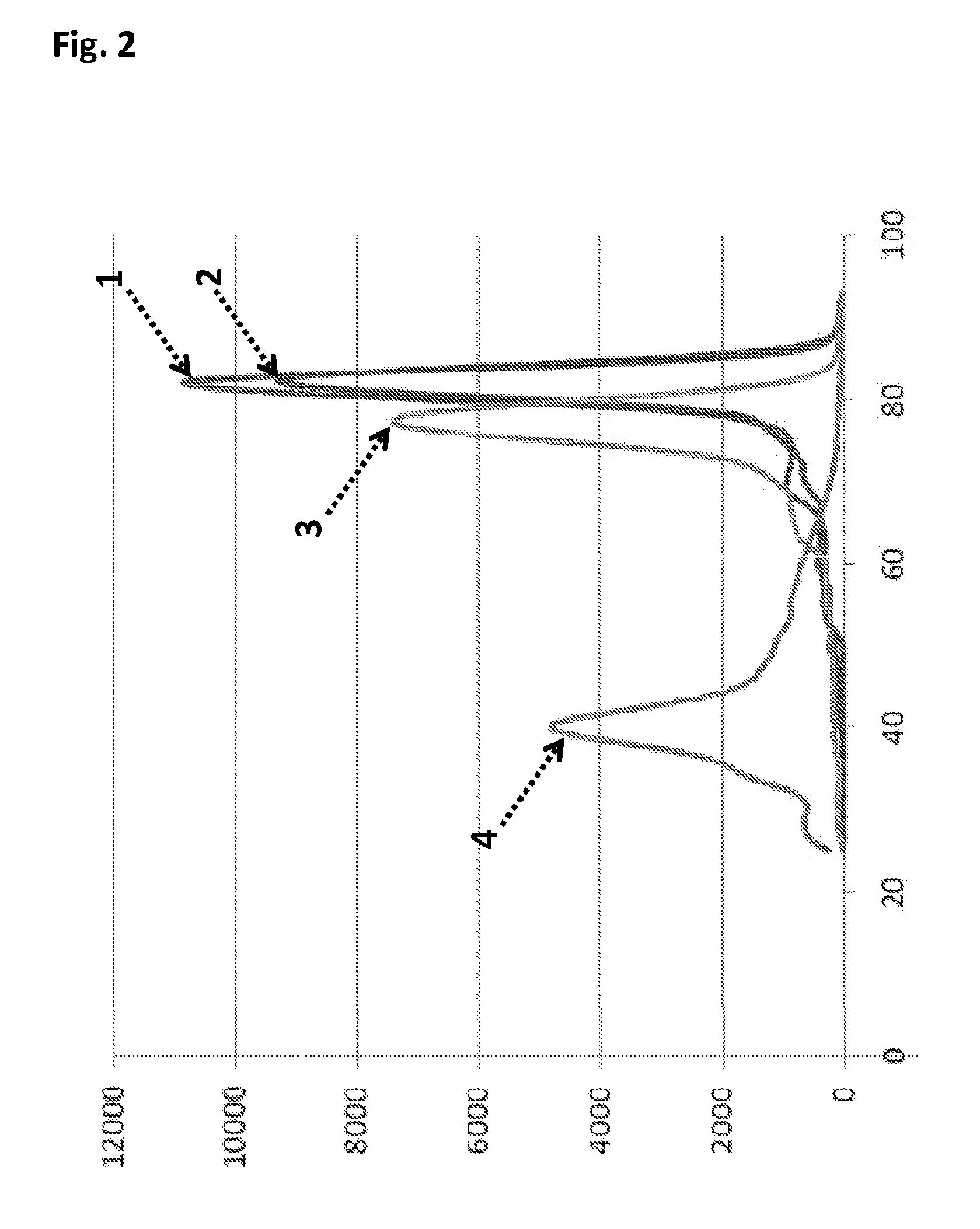
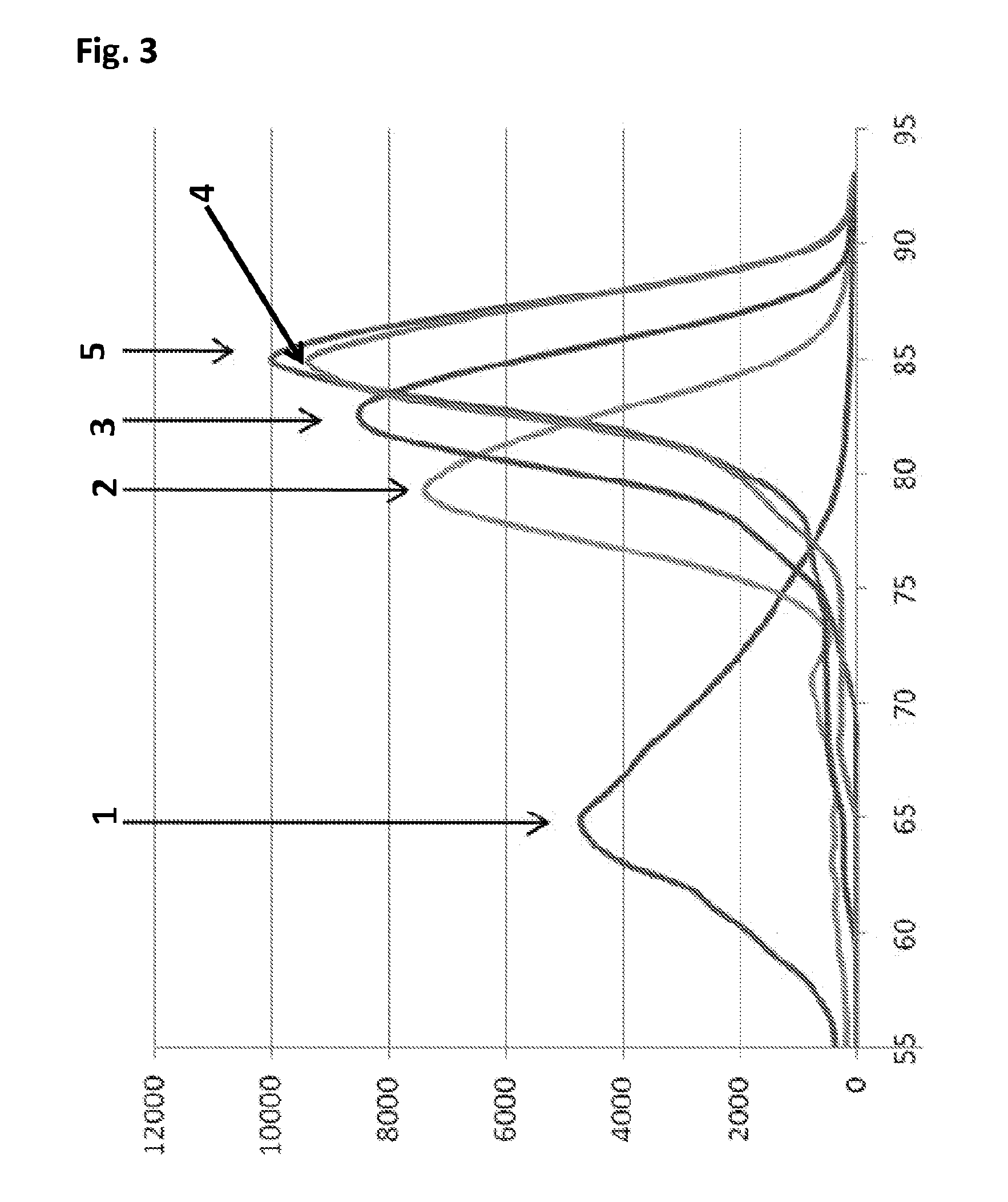
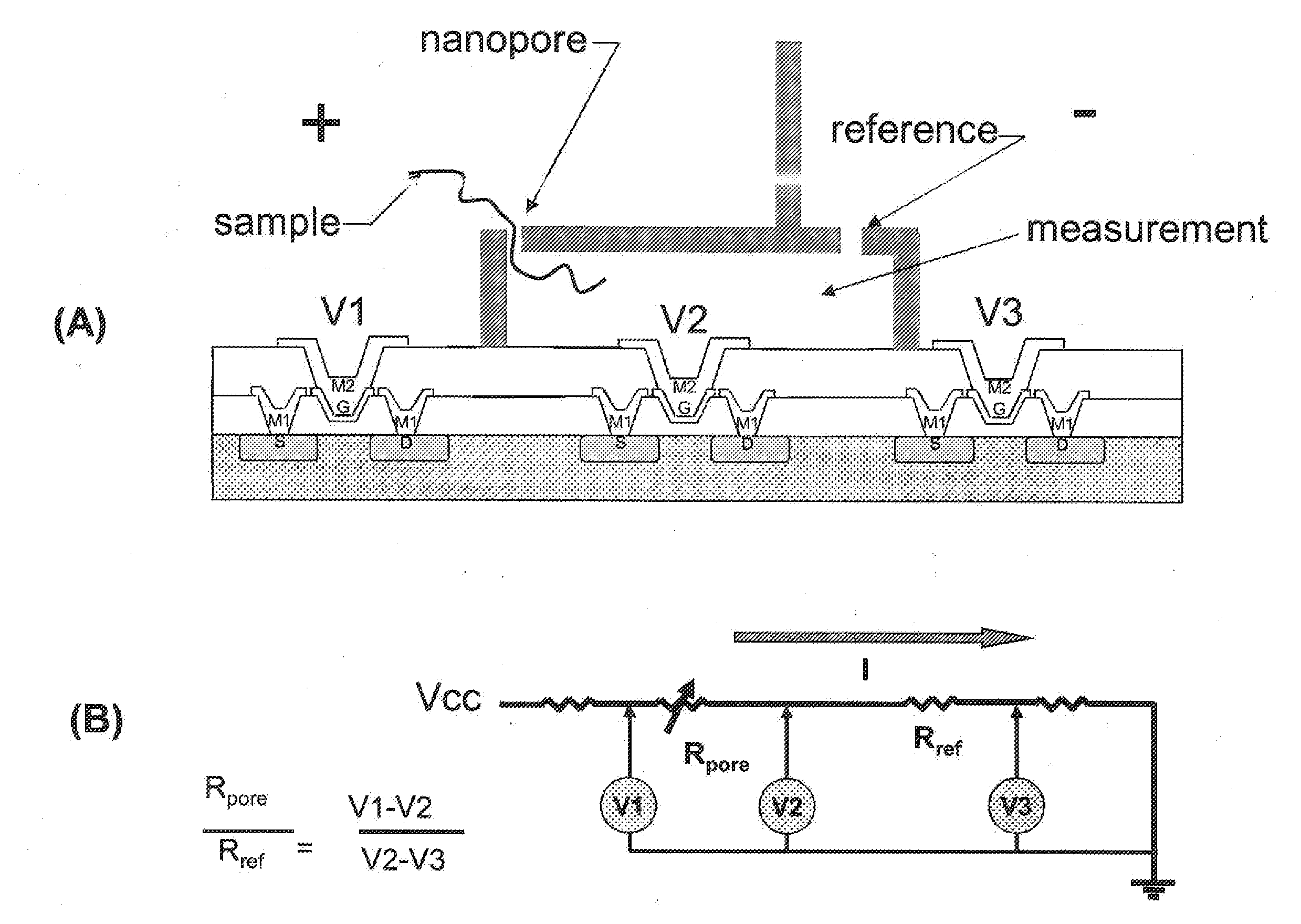
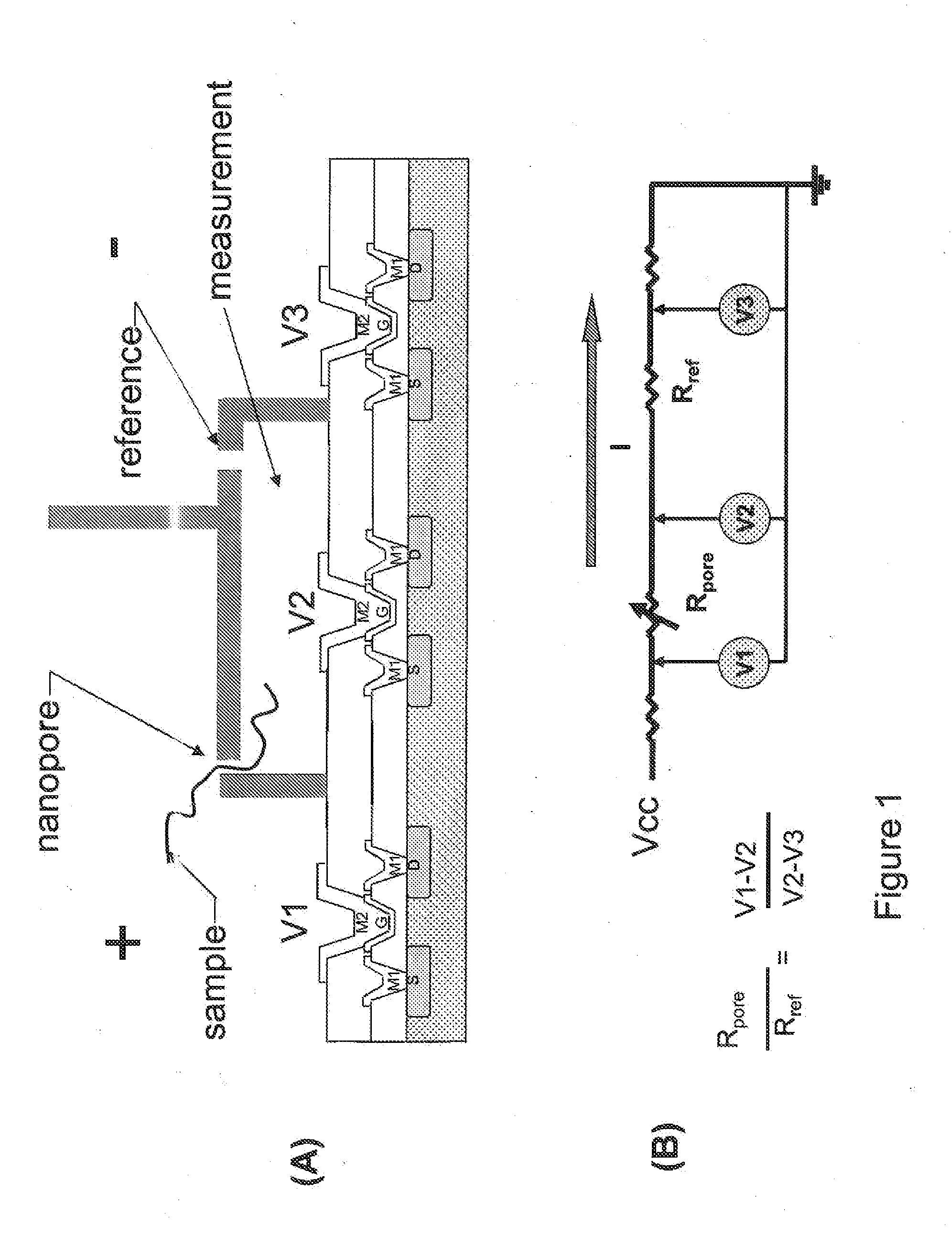
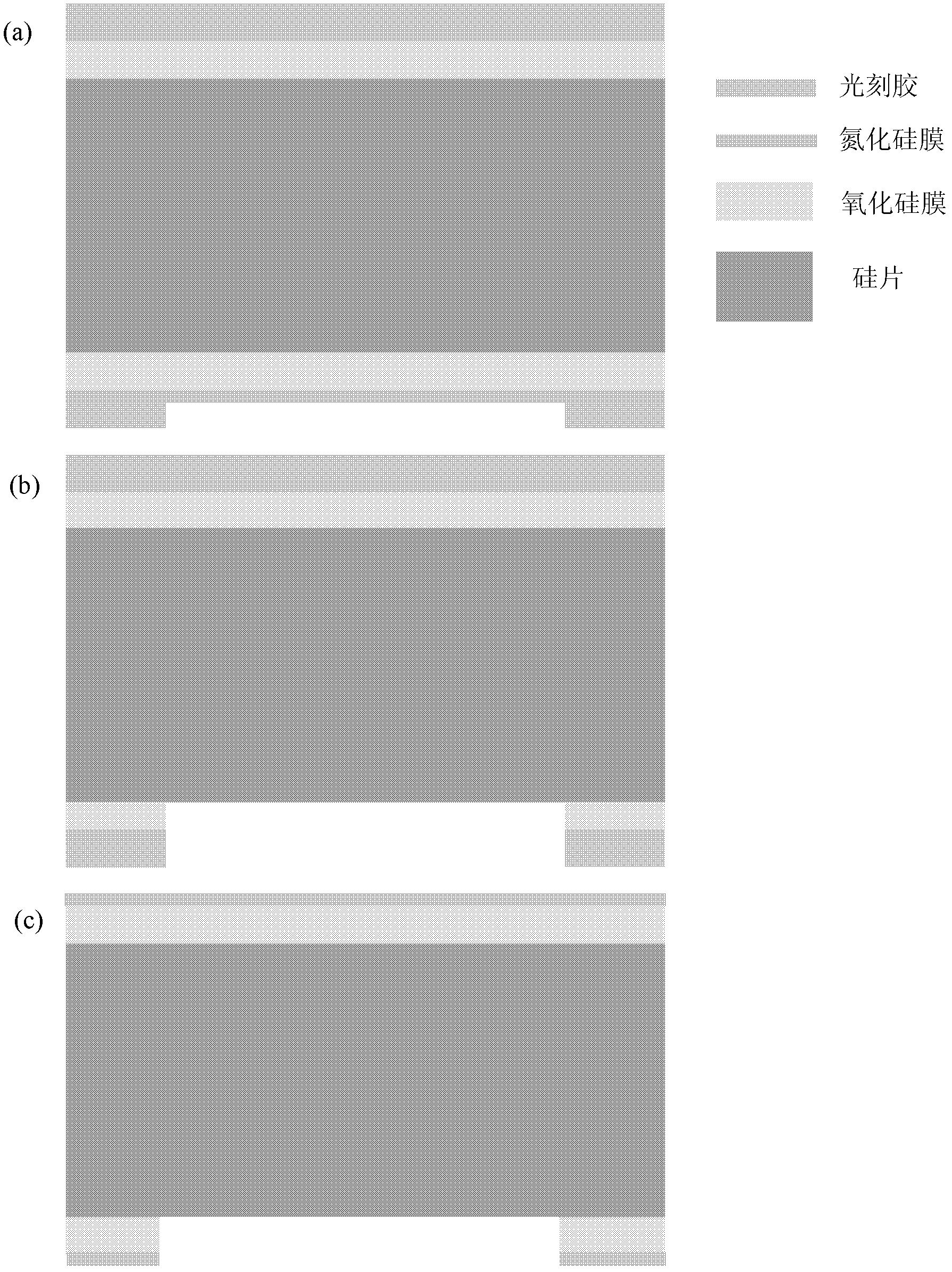Patents
Literature
185 results about "Nanopore sequencing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
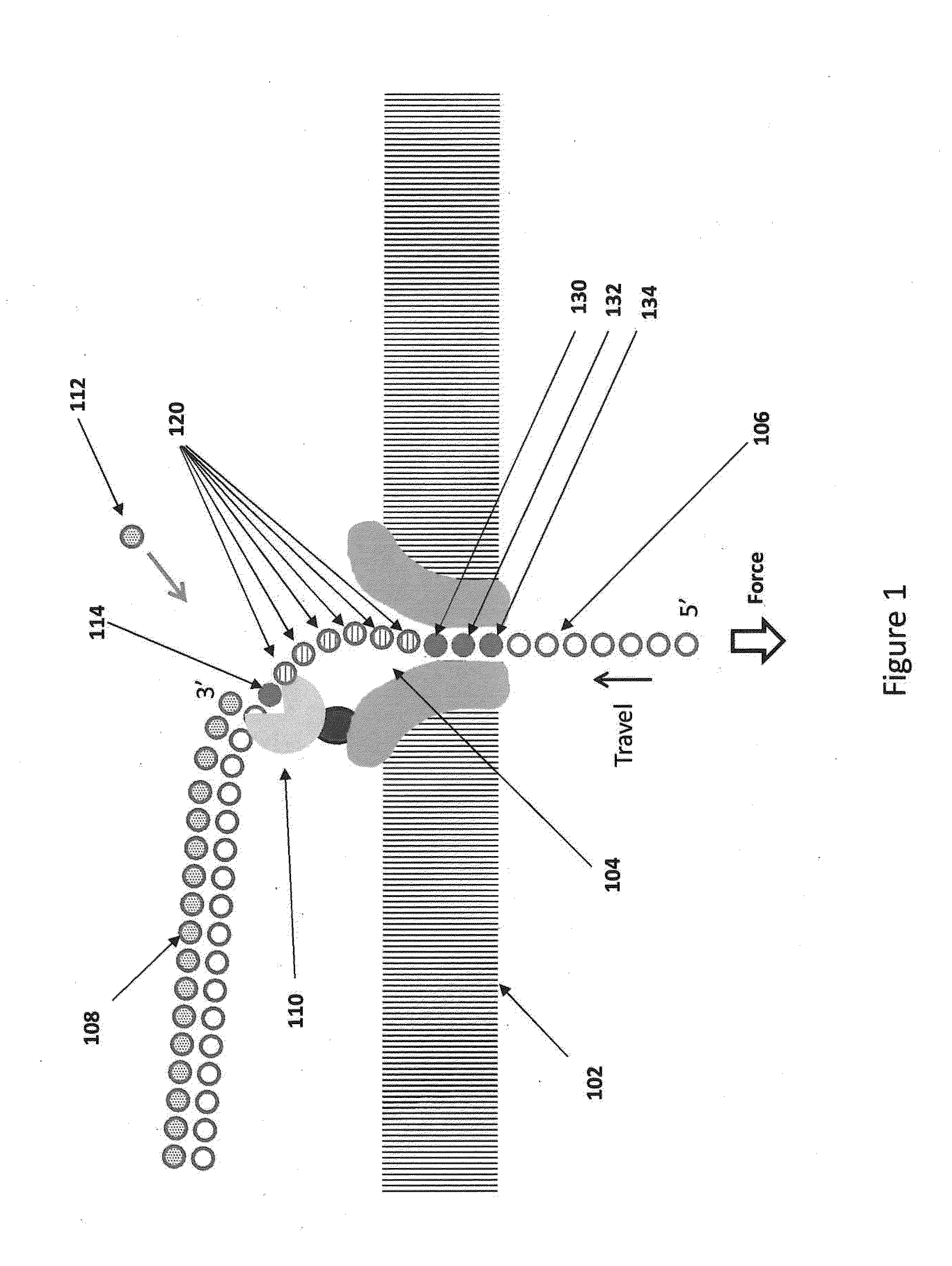
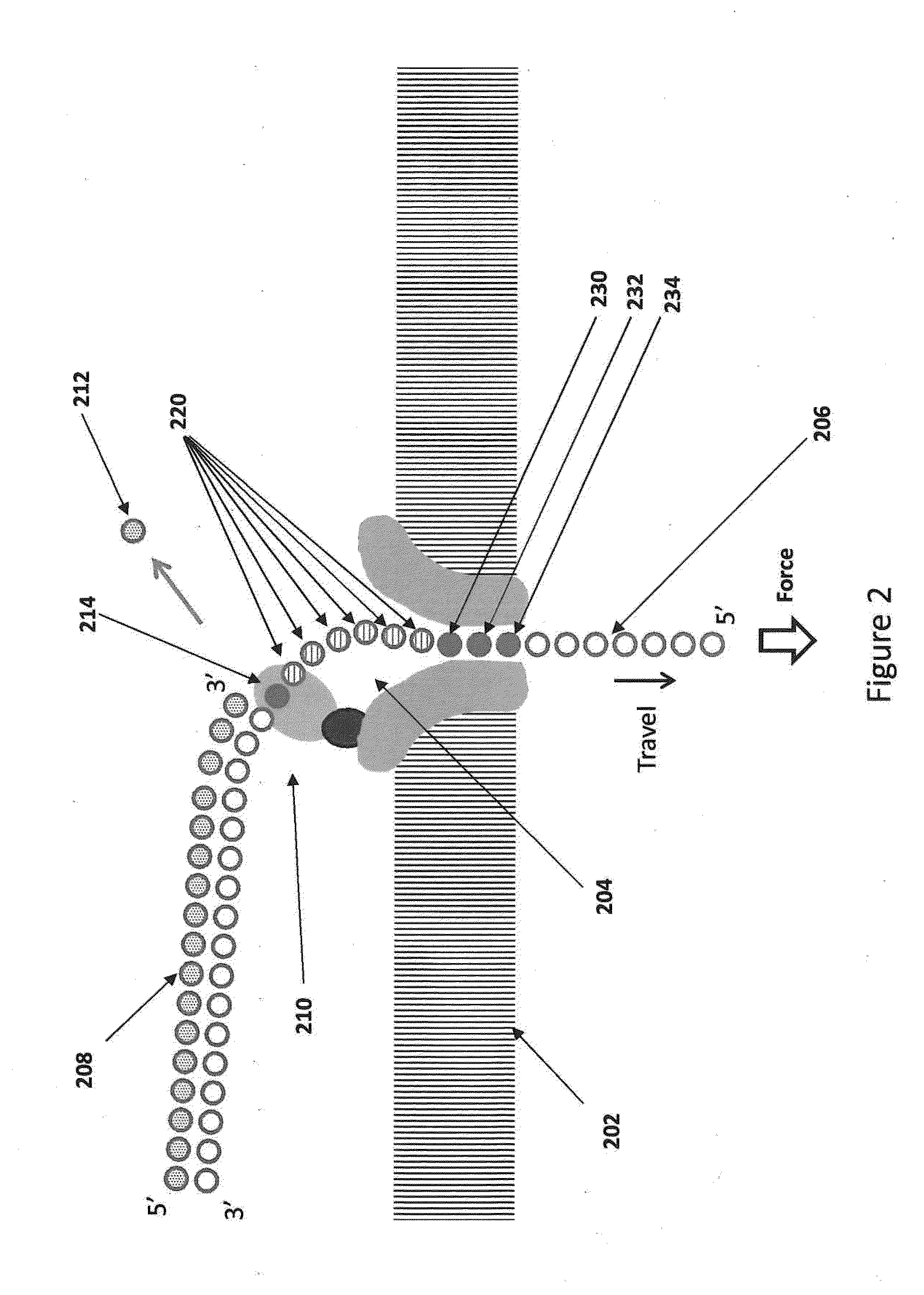
Nanopore sequencing is a third generation approach used in the sequencing of biopolymers- specifically, polynucleotides in the form of DNA or RNA. Using nanopore sequencing, a single molecule of DNA or RNA can be sequenced without the need for PCR amplification or chemical labeling of the sample. At least one of these aforementioned steps is necessary in the procedure of any previously developed sequencing approach. Nanopore sequencing has the potential to offer relatively low-cost genotyping, high mobility for testing, and rapid processing of samples with the ability to display results in real-time. Publications on the method outline its use in rapid identification of viral pathogens, monitoring ebola, environmental monitoring, food safety monitoring, human genome sequencing, plant genome sequencing, monitoring of antibiotic resistance, haplotyping and other applications.
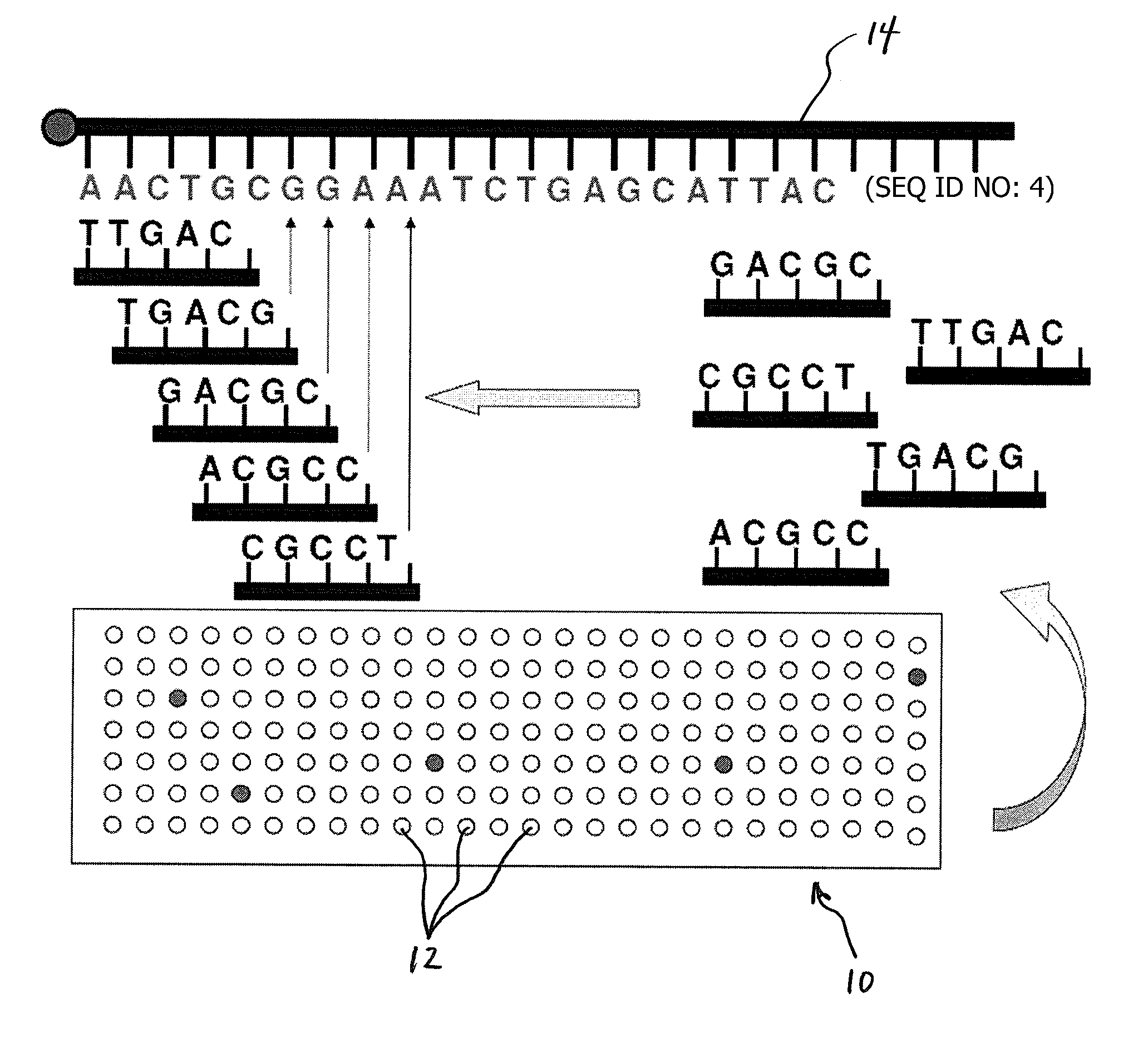
Nanopore sequencing devices and methods
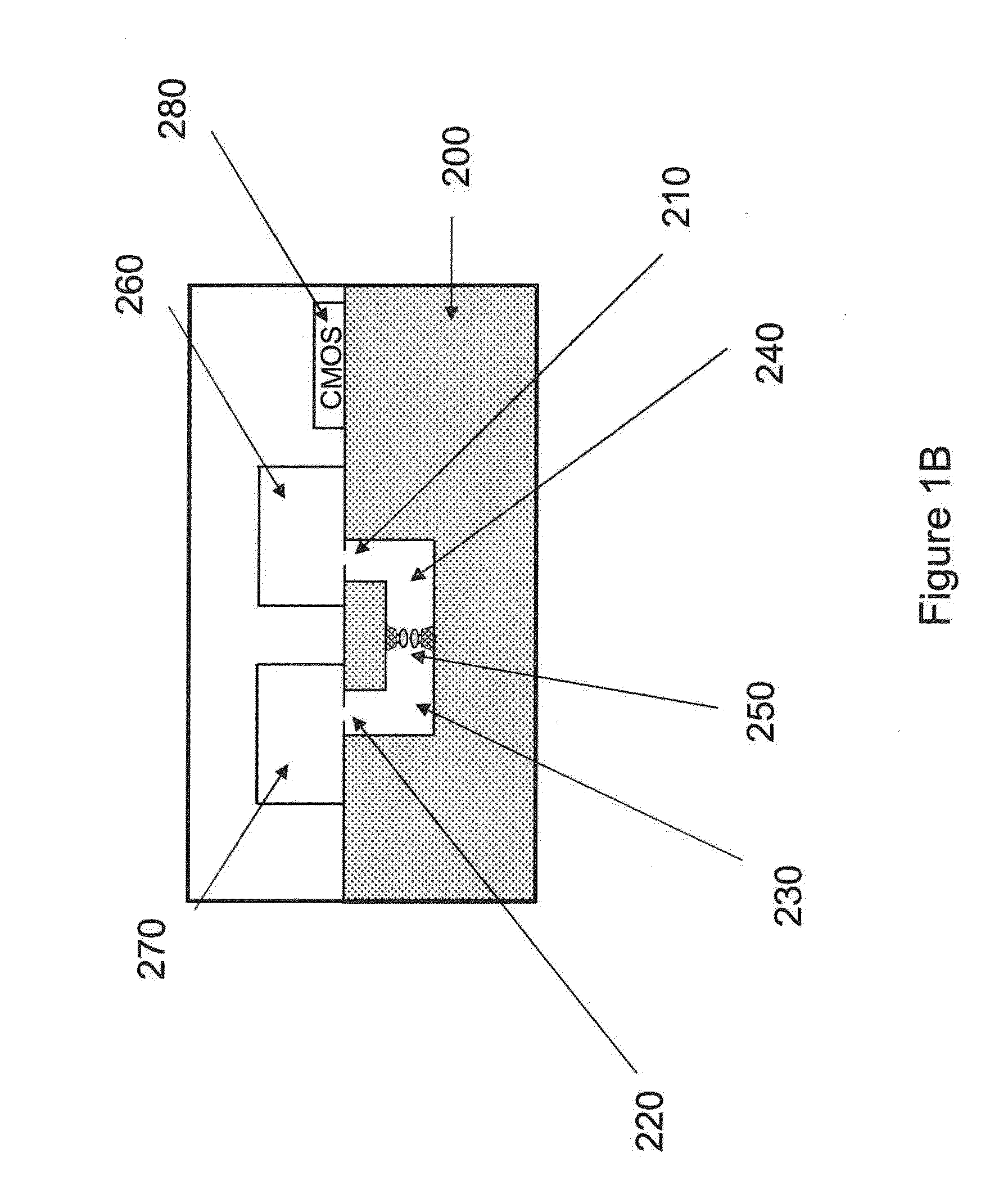
ActiveUS20100331194A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
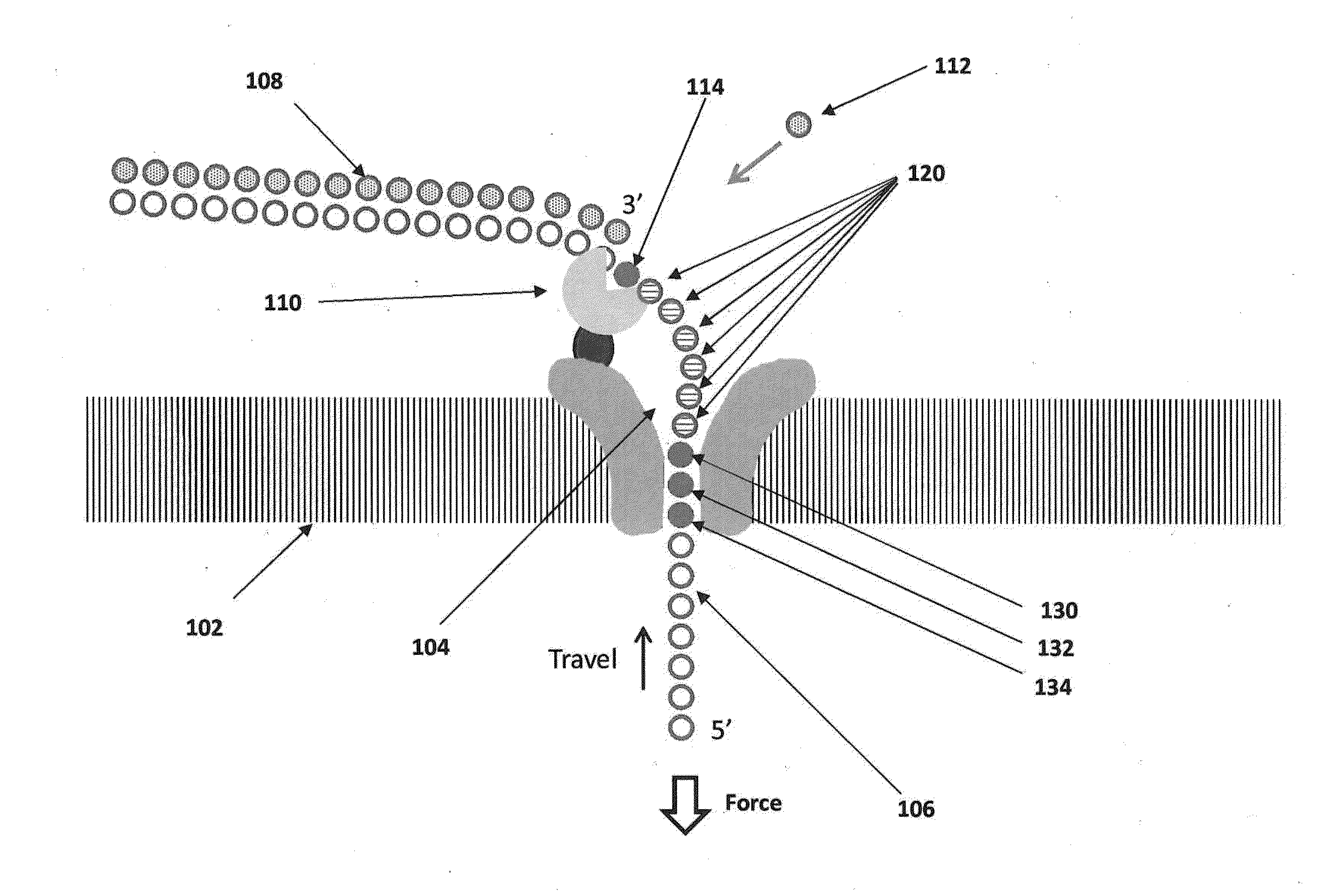
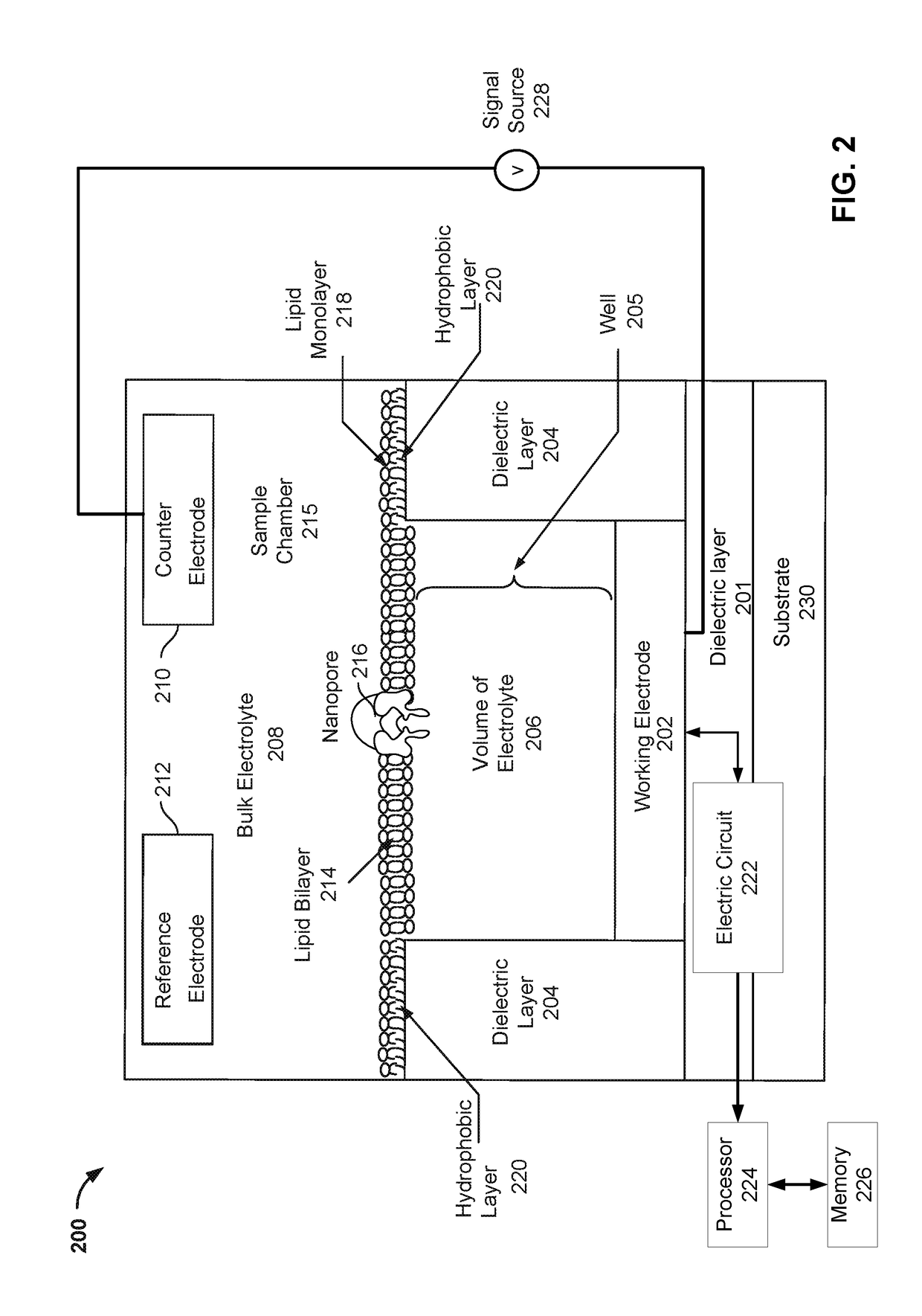
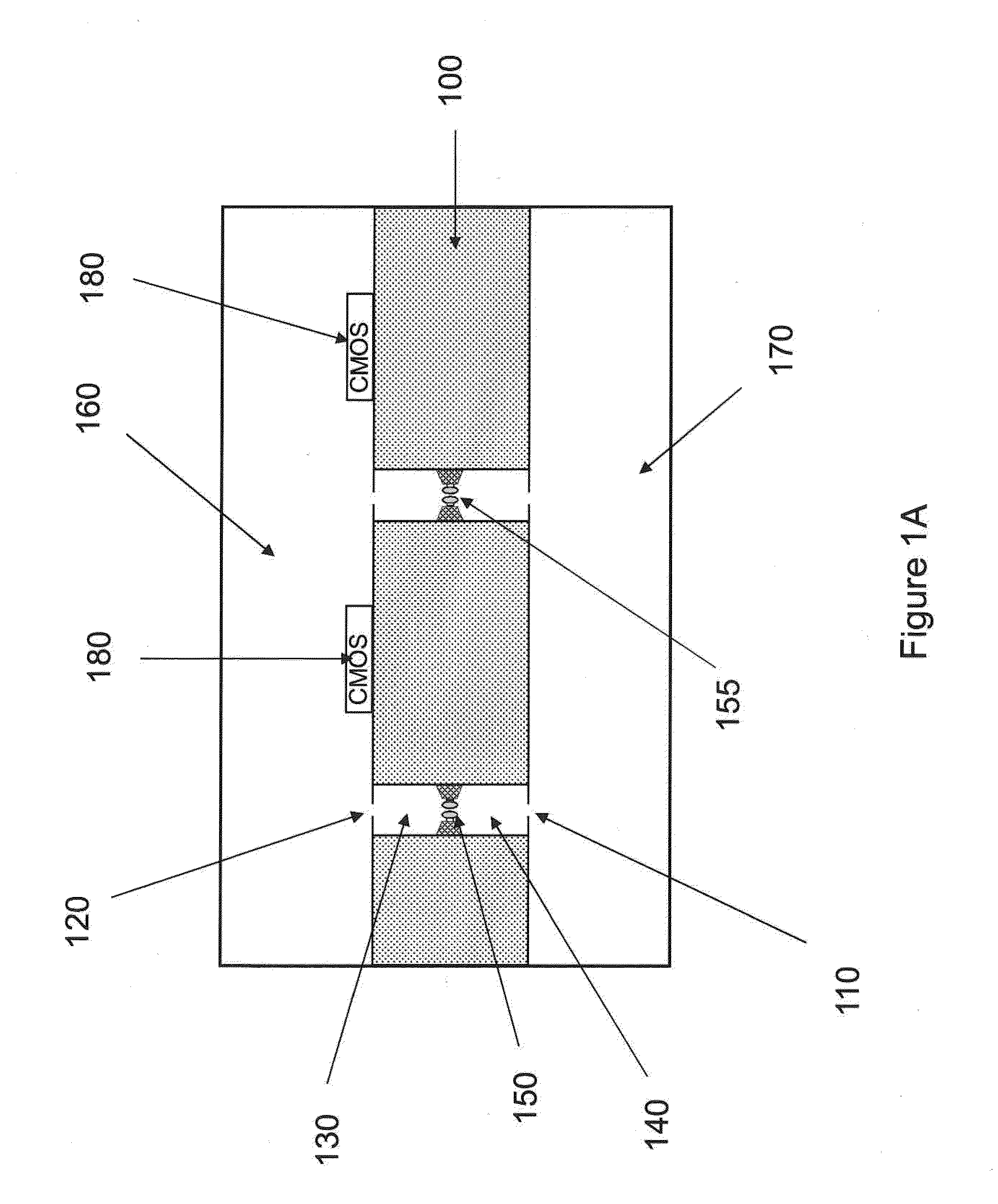
The invention relates to devices and methods for nanopore sequencing. The invention includes arrays of nanopores having incorporated electronic circuits, for example, in CMOS. In some cases, the arrays of nanopores comprise resistive openings for isolating the electronic signals for improved sequencing. Methods for controlling translocation of through the nanopore are disclosed.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Hybridization assisted nanopore sequencing
InactiveUS20070190542A1Eliminate needEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresHybridization probeNucleic Acid Probes
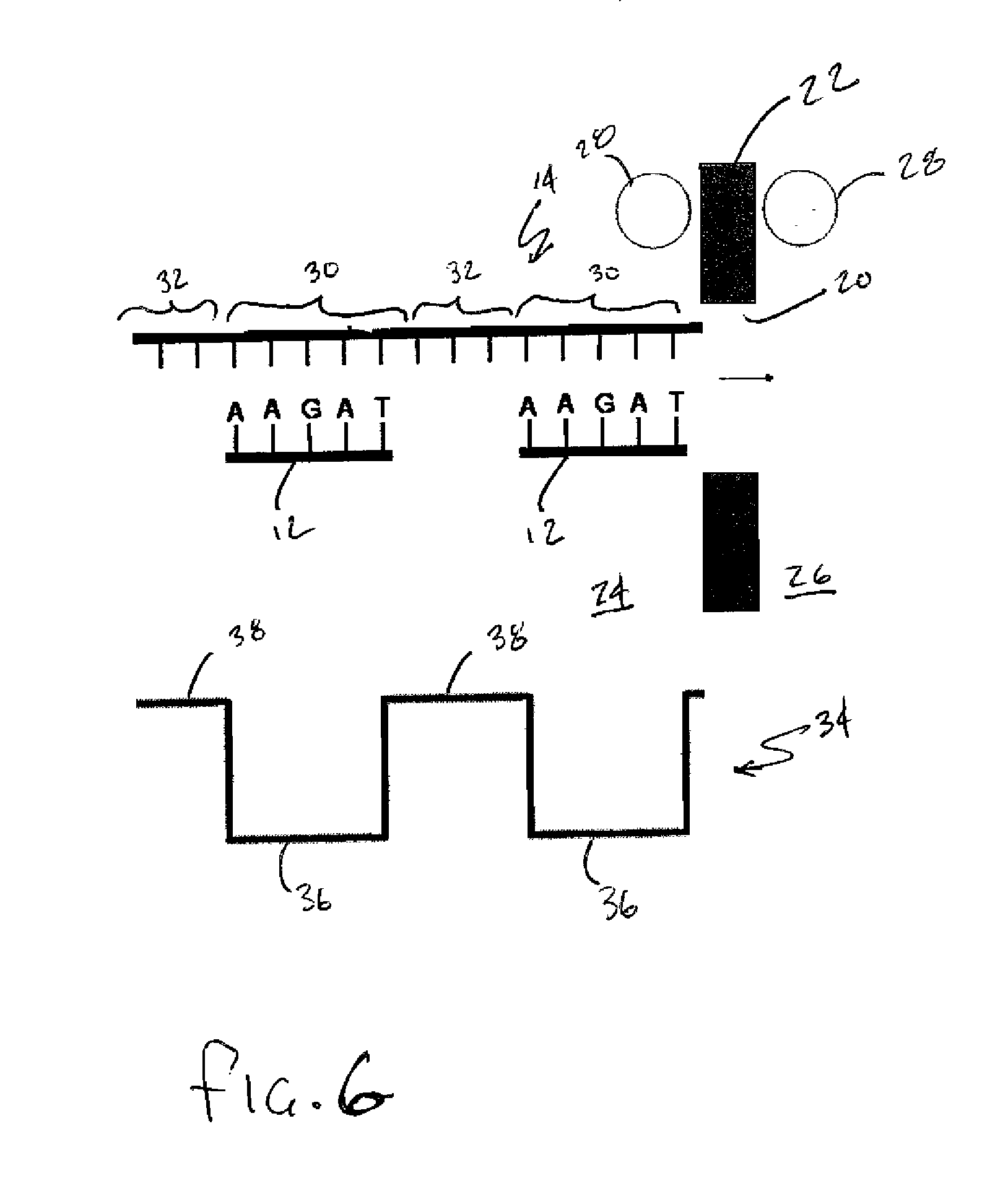
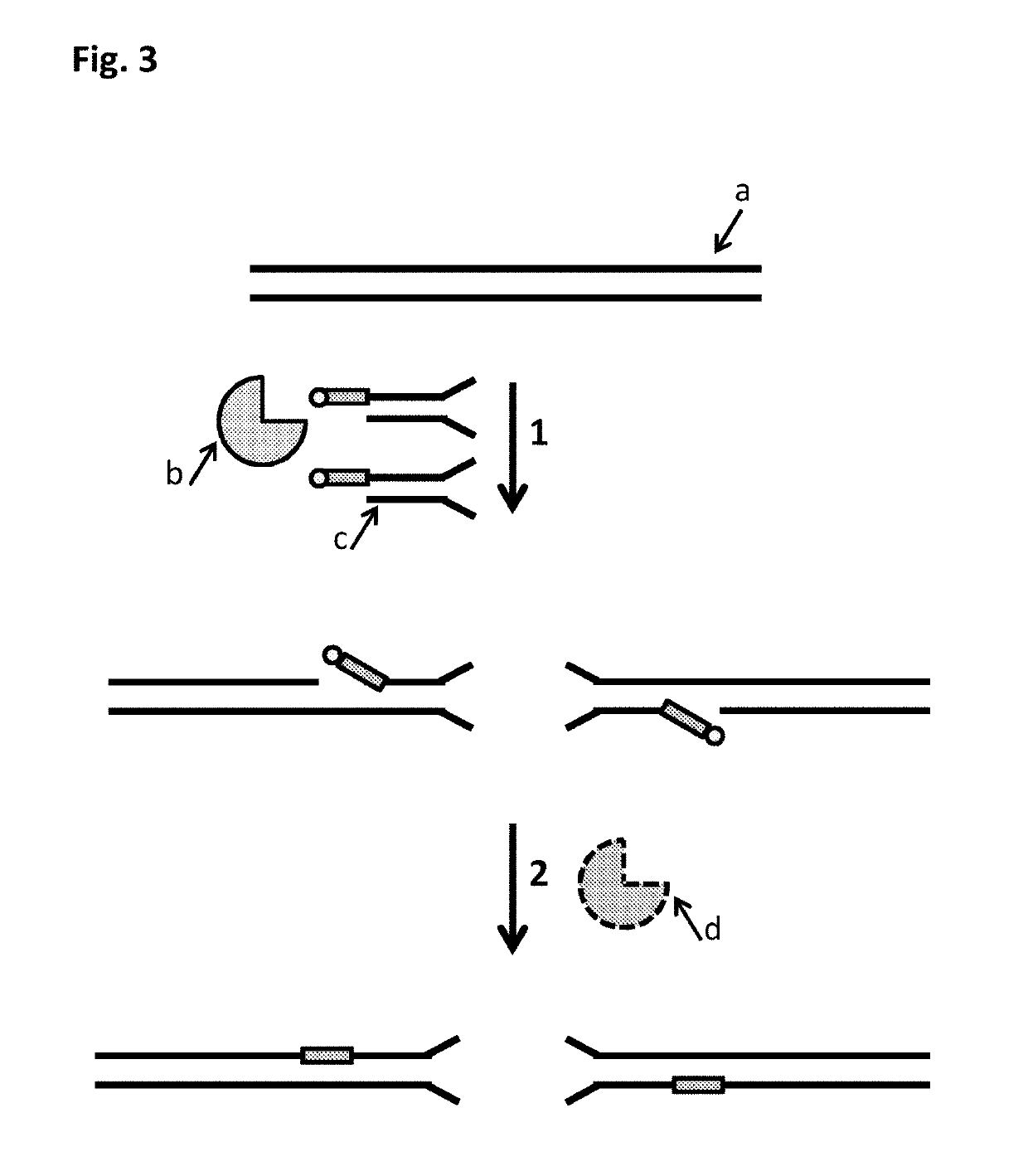
A method of employing a nanopore structure in a manner that allows the detection of the positions (relative and / or absolute) of nucleic acid probes that are hybridized onto a single-stranded nucleic acid molecule. In accordance with the method the strand of interest is hybridized with a probe having a known sequence. The strand and hybridized probes are translocated through a nanopore. The fluctuations in current measured across the nanopore will vary as a function of time corresponding to the passing of a probe attachment point along the strand. These fluctuations in current are then used to determine the attachment positions of the probes along the strand of interest. This probe position data is then fed into a computer algorithm that returns the sequence of the strand of interest.
Owner:NABSYS 2 0 +1
Nanopore sequencing using charge blockade labels
ActiveUS8652779B2Different levelDifferent modulus propertySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementNucleotidePolymerase L
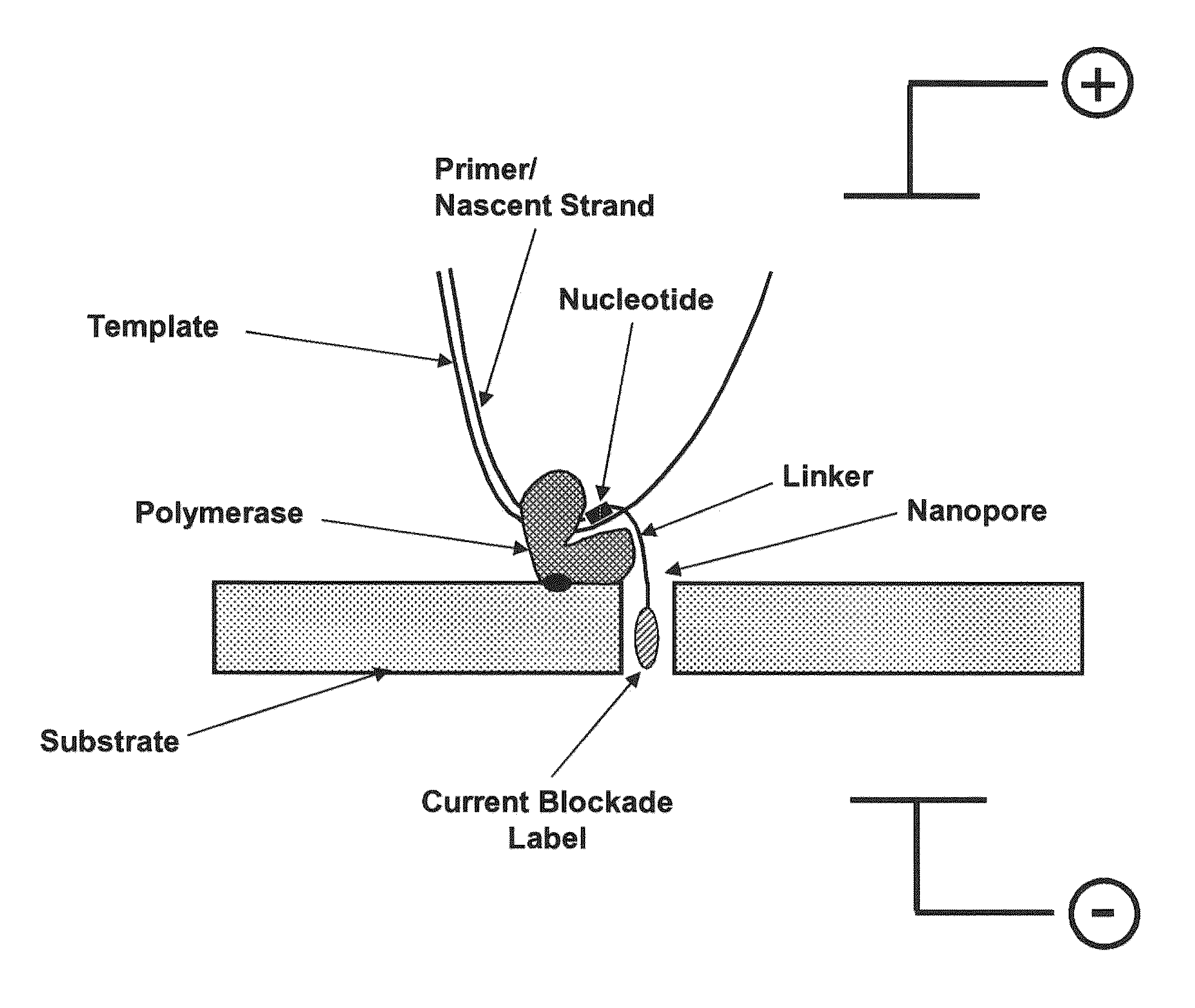
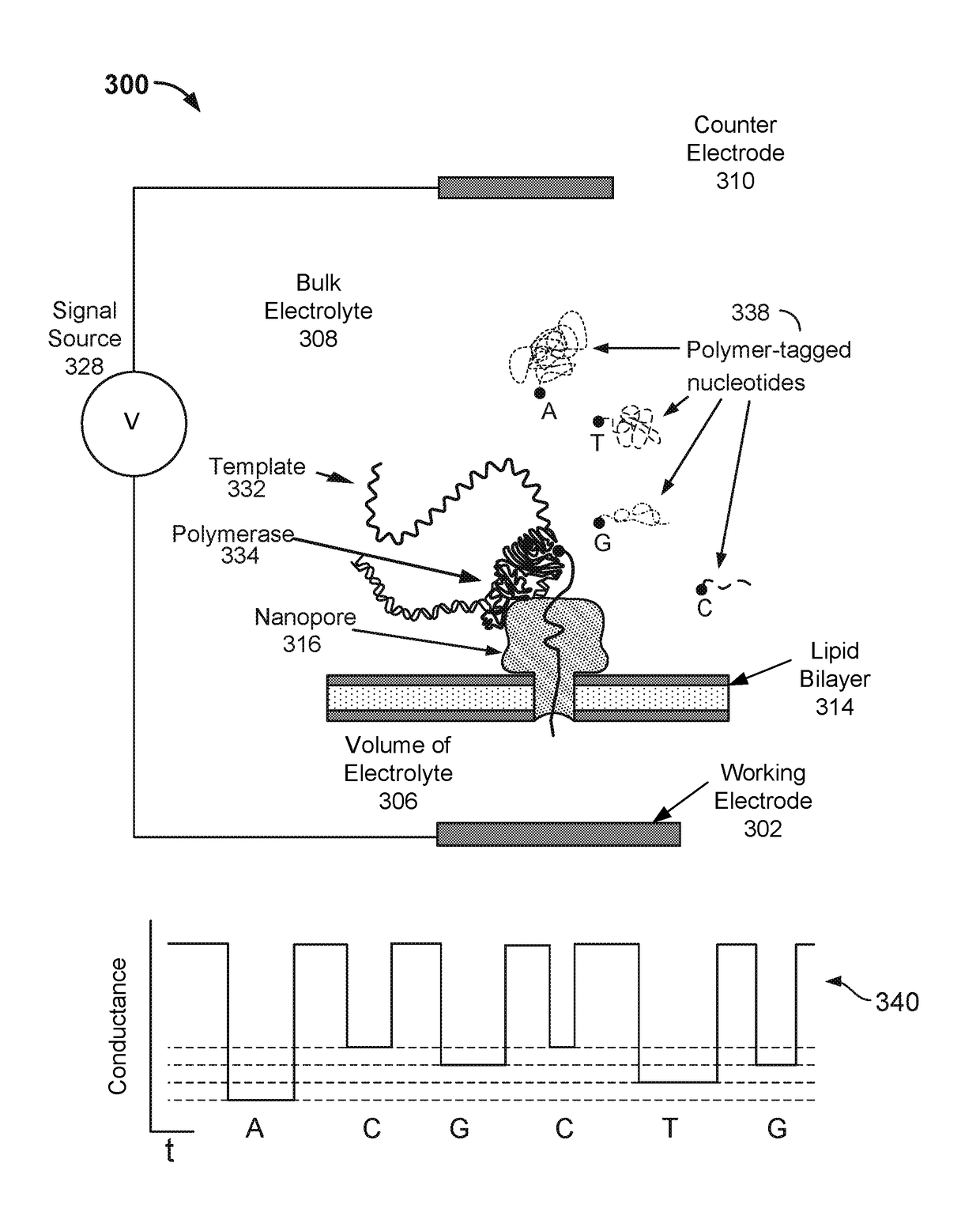
The invention relates to devices and methods for nanopore sequencing. The invention includes compositions and methods of nucleic acid sequencing using a single polymerase enzyme complex comprising a polymerase enzyme and a template nucleic acid attached proximal to a nanopore, and nucleotide analogs in solution comprising charge blockade label that are attached to the polyphosphate portion of the nucleotide analog such that the charge blockade labels are cleaved when the nucleotide analog is incorporated into a growing nucleic acid and the charge blockade label is detected by the nanopore to determine the presence and identity of the incorporated nucleotide and thereby determine the sequence of a template nucleic acid.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Nanopore sequencing using charge blockade labels
ActiveUS20130240359A1Different levelDifferent modulus propertySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementNucleotidePolymerase L
The invention relates to devices and methods for nanopore sequencing. The invention includes compositions and methods of nucleic acid sequencing using a single polymerase enzyme complex comprising a polymerase enzyme and a template nucleic acid attached proximal to a nanopore, and nucleotide analogs in solution comprising charge blockade label that are attached to the polyphosphate portion of the nucleotide analog such that the charge blockade labels are cleaved when the nucleotide analog is incorporated into a growing nucleic acid and the charge blockade label is detected by the nanopore to determine the presence and identity of the incorporated nucleotide and thereby determine the sequence of a template nucleic acid.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Modified base detection with nanopore sequencing
ActiveUS20130327644A1Reduce error rateReduce errorsElectrolysis componentsSugar derivativesGenomic DNASingle strand
Methods, compositions, and systems are provided for characterization of modified nucleic acids. Nanopore sequencing is performed using a processive enzyme to control the rate of translation of a single strand of a nucleic acid through a nanopore. The presence and identity of a modified base can be determined by monitoring the kinetics of translation through the pore even though the events that lead to the kinetic changes are separated in time and space from the translation of the modified base or it's compliment through the nanopore. The invention also comprises the use of hemi-genomic DNA in nanopore sequencing.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
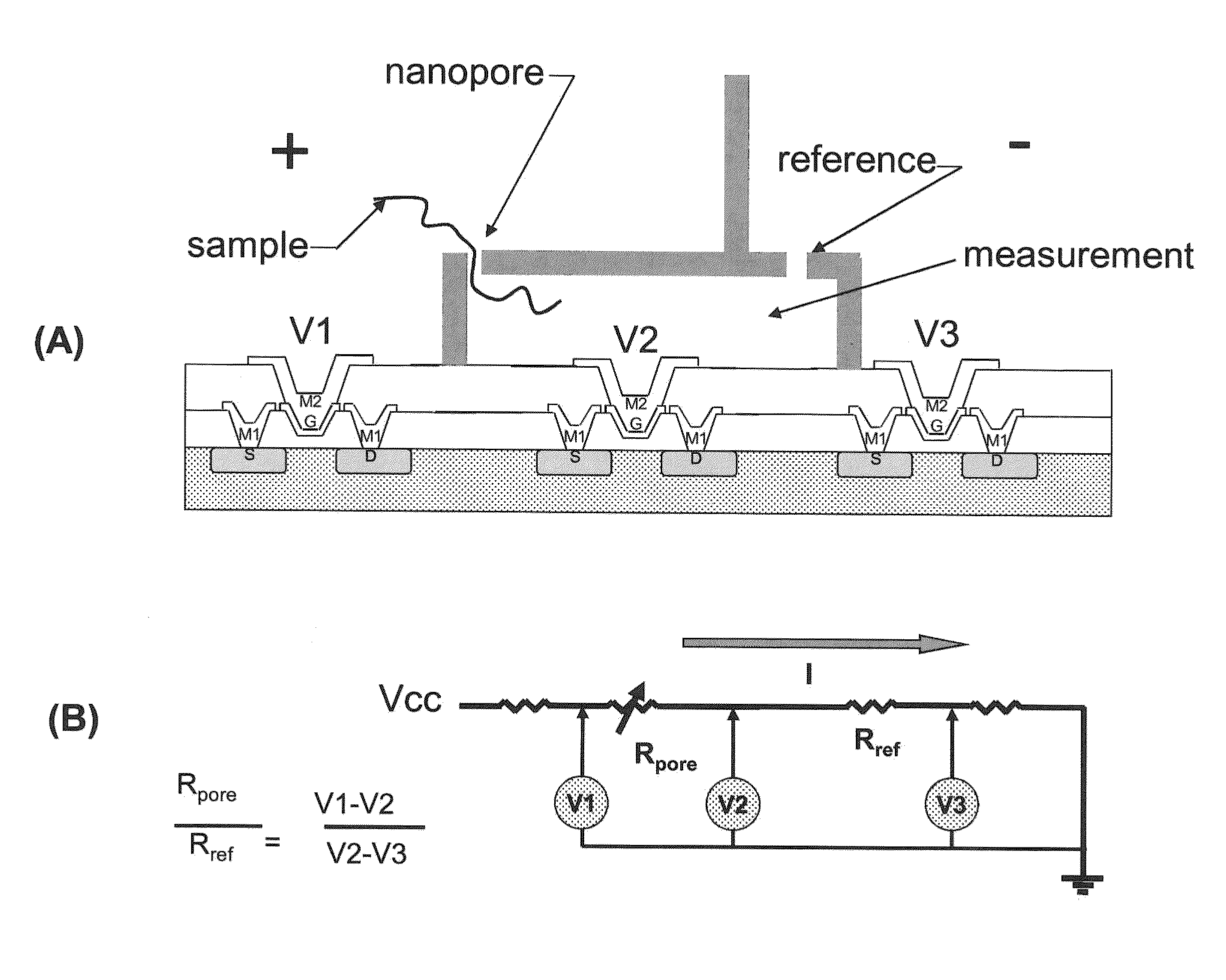
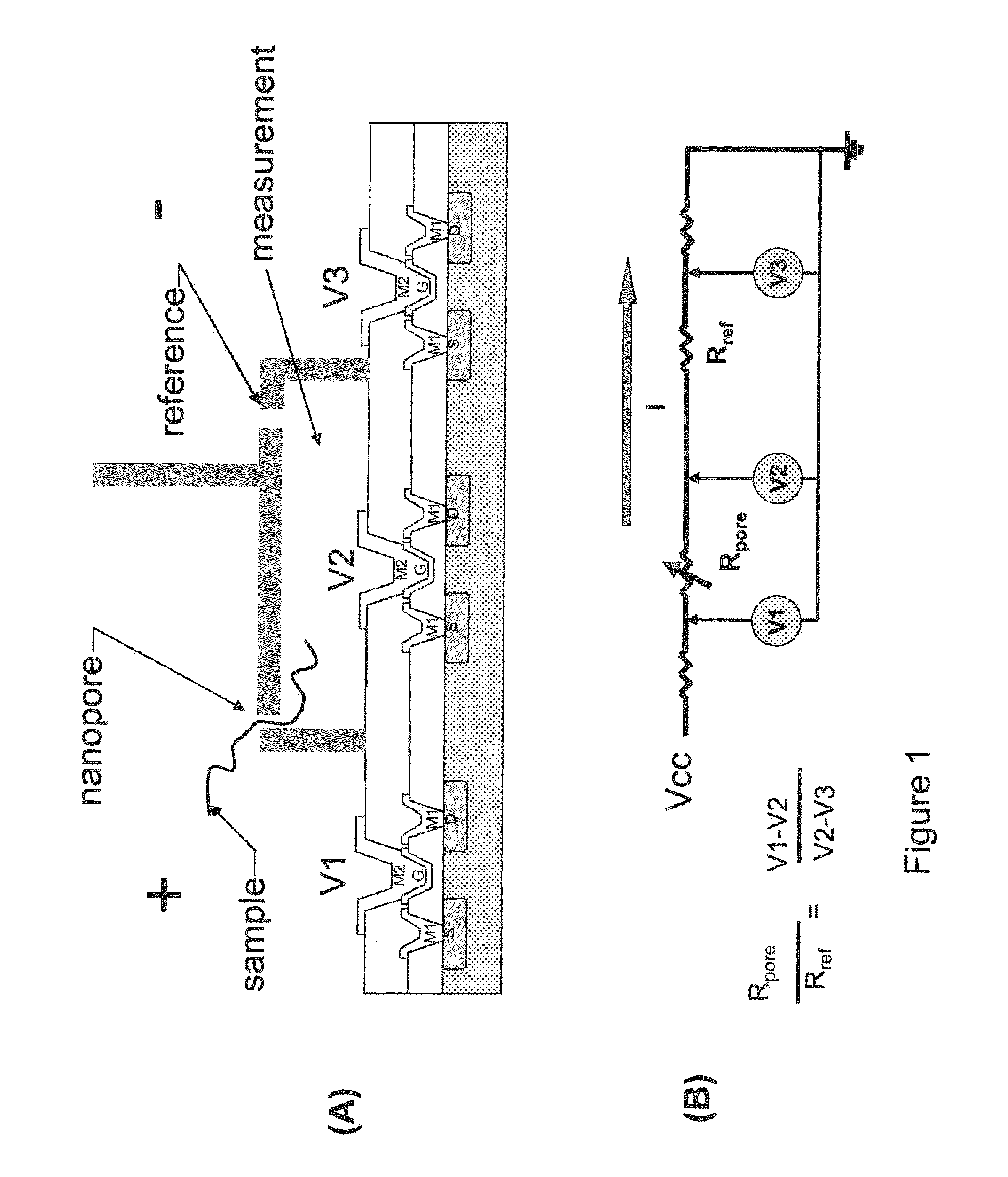
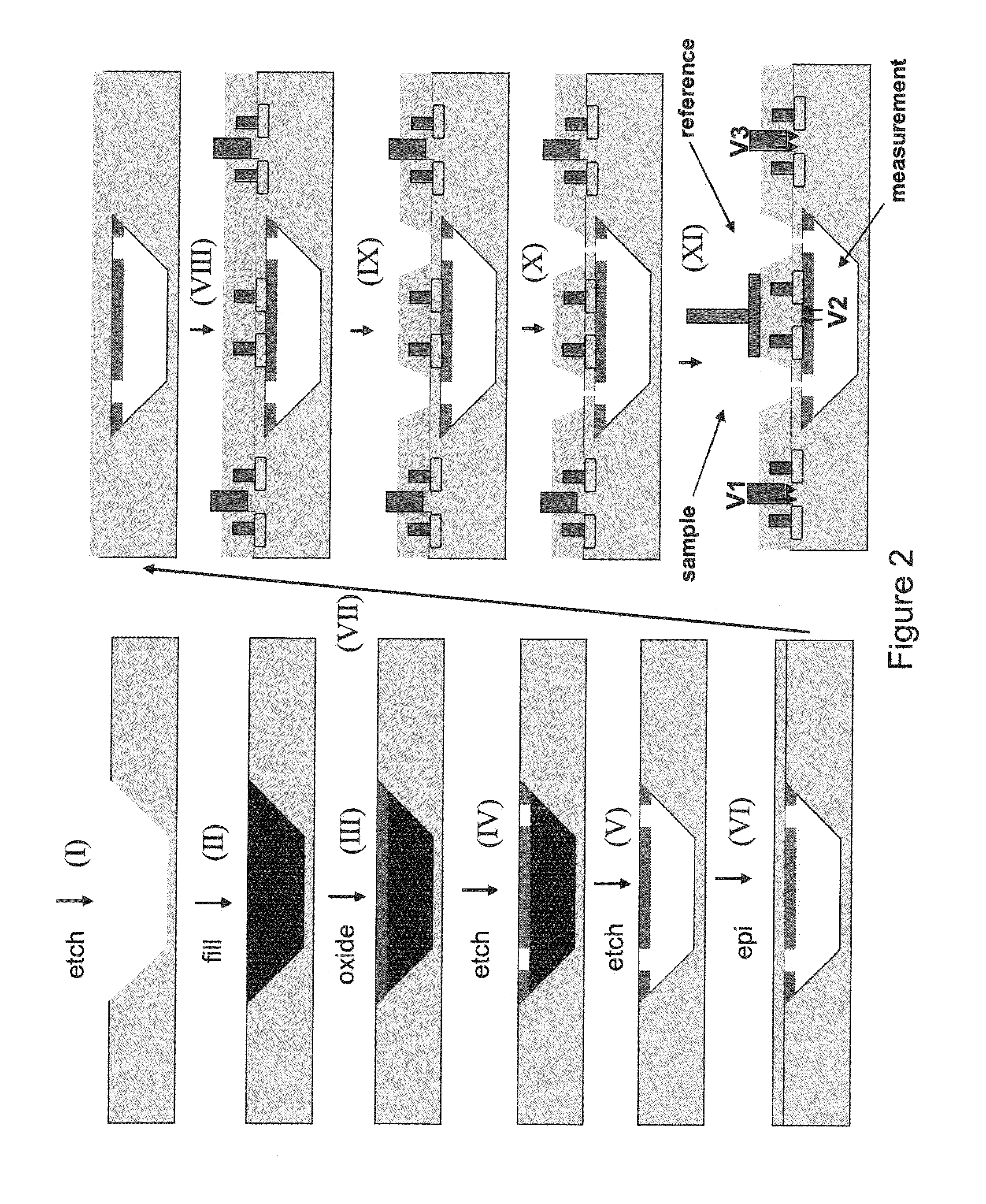
Nanopore sequencing using ratiometric impedance
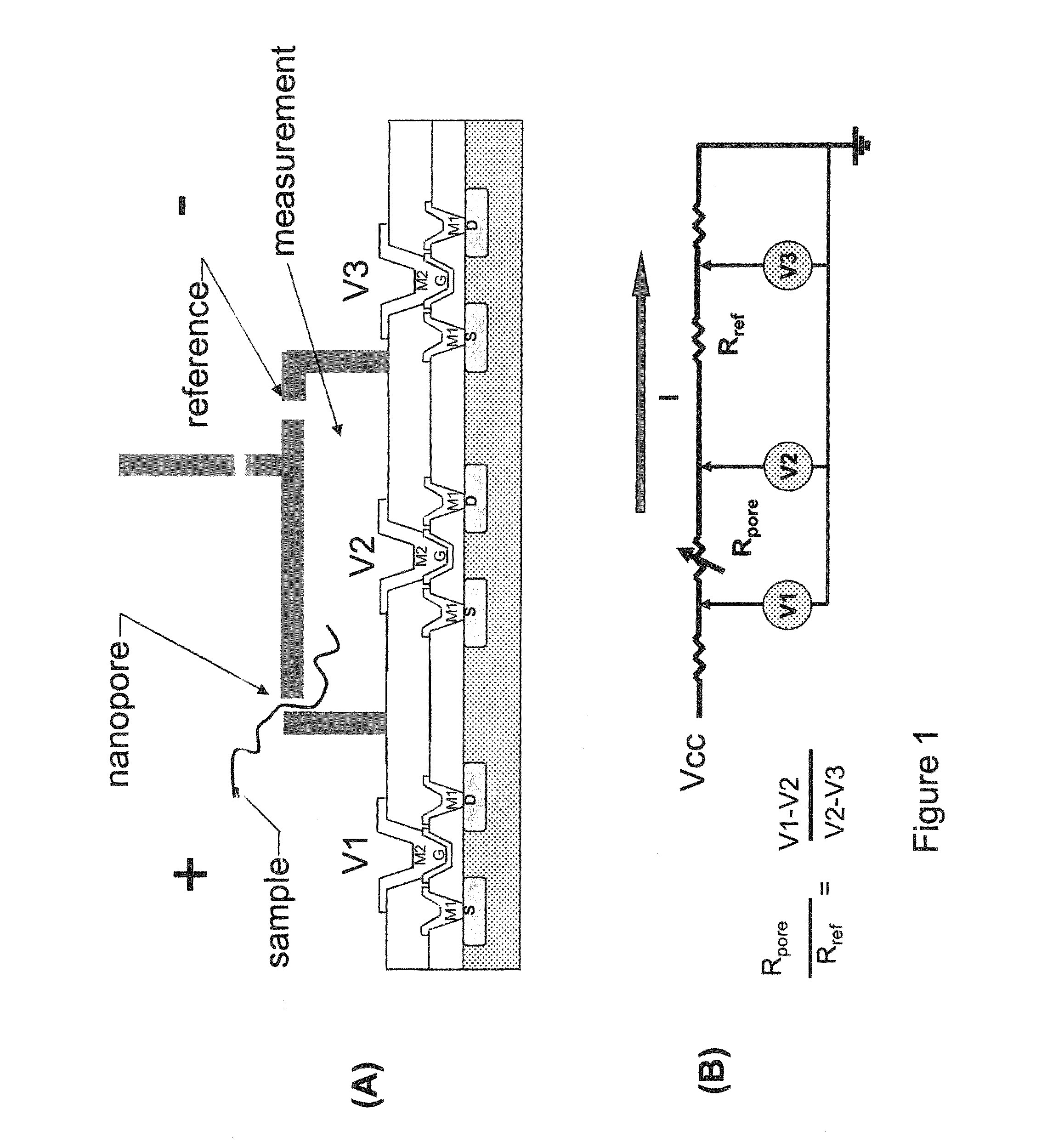
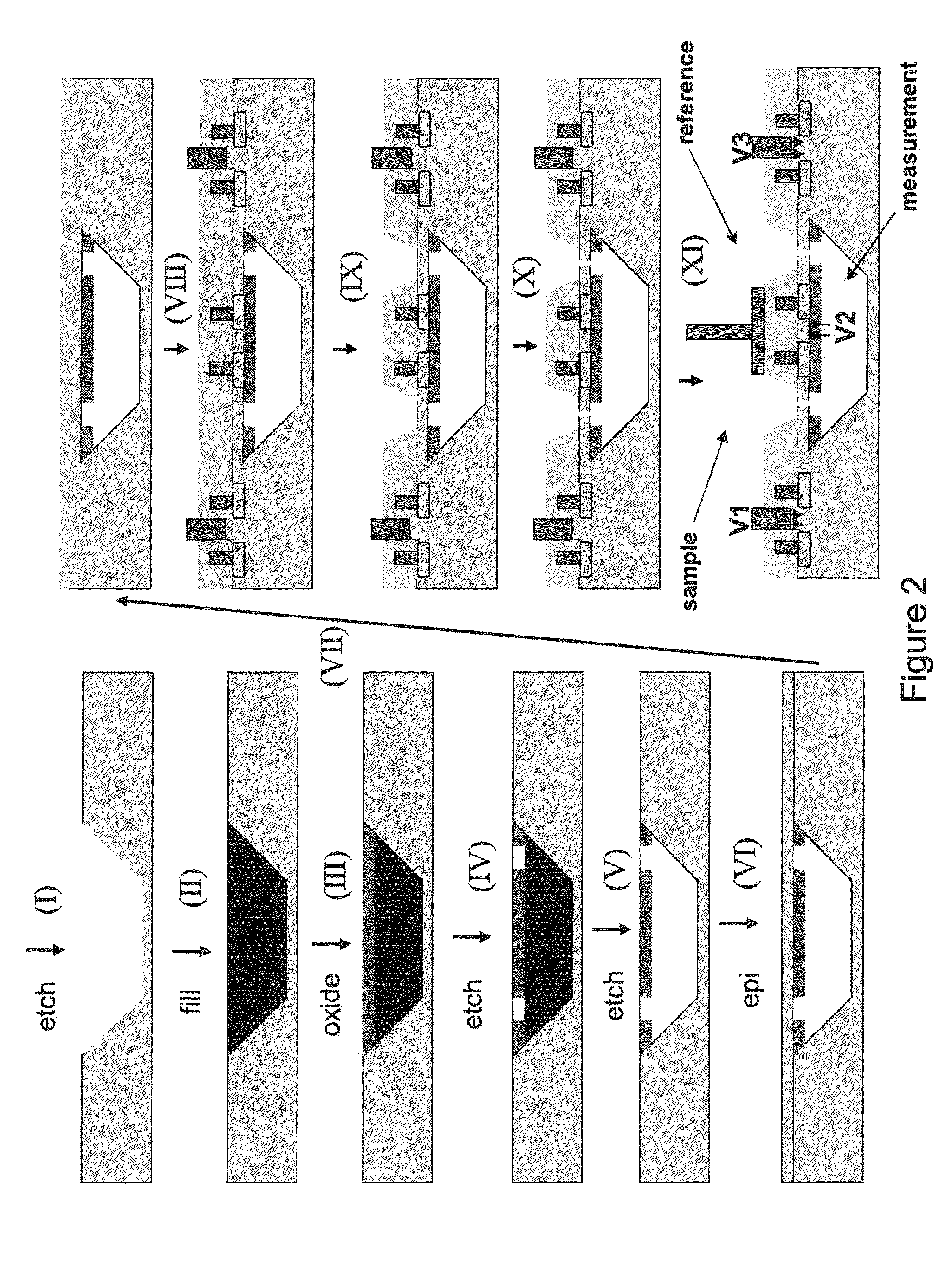
ActiveUS9017937B1Different levelDifferent modulus propertyMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisPotential measurementCMOS
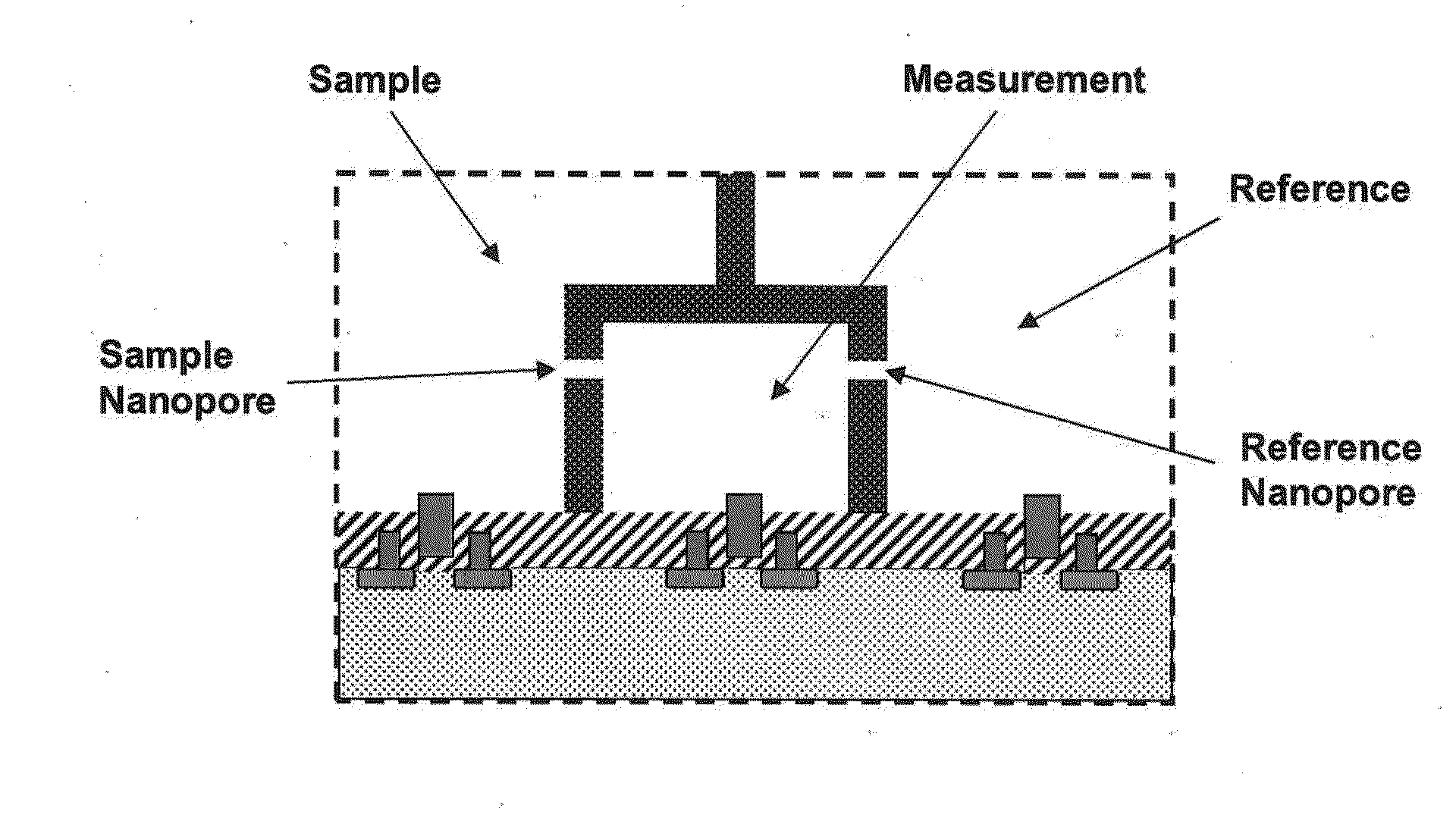
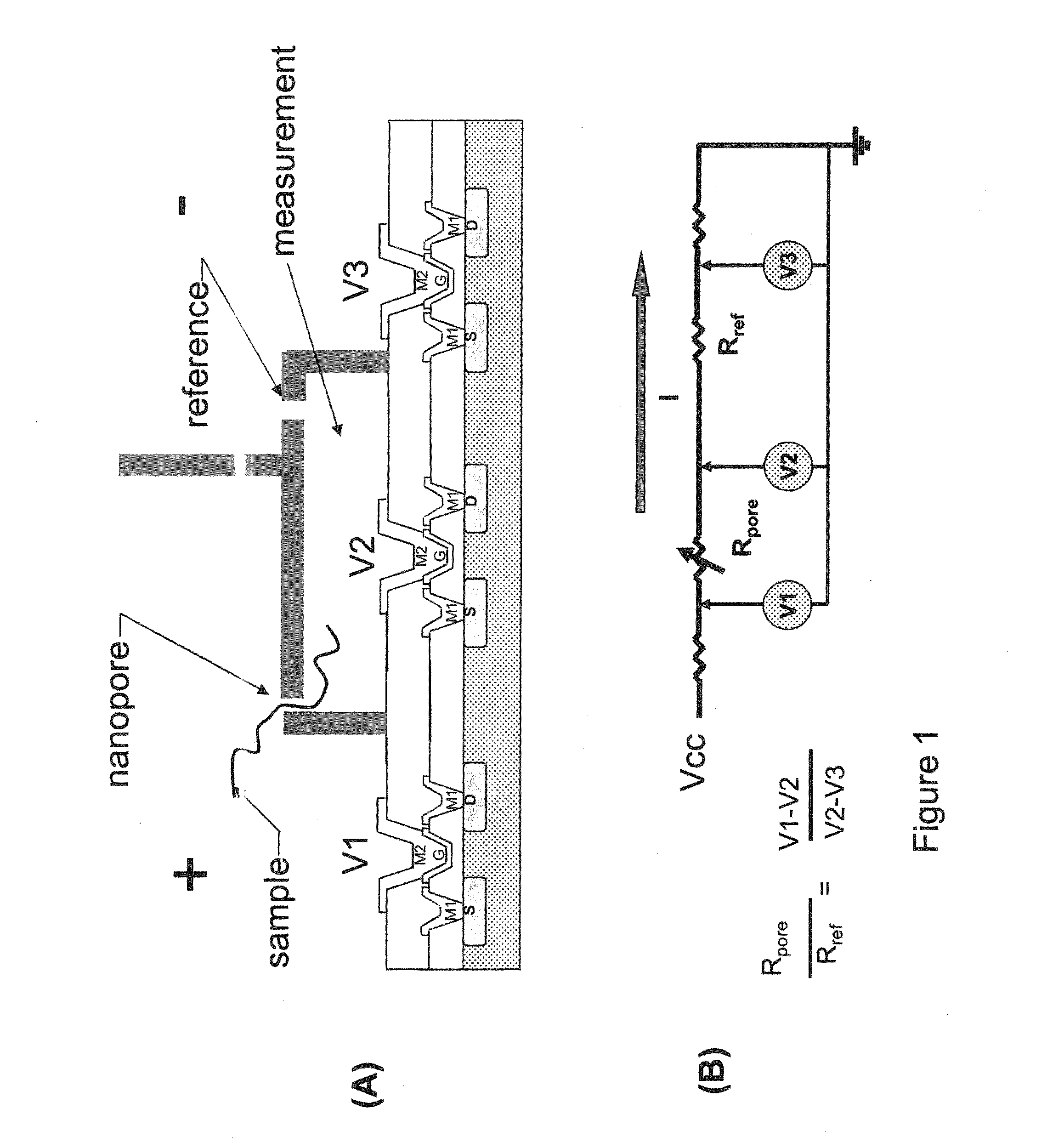
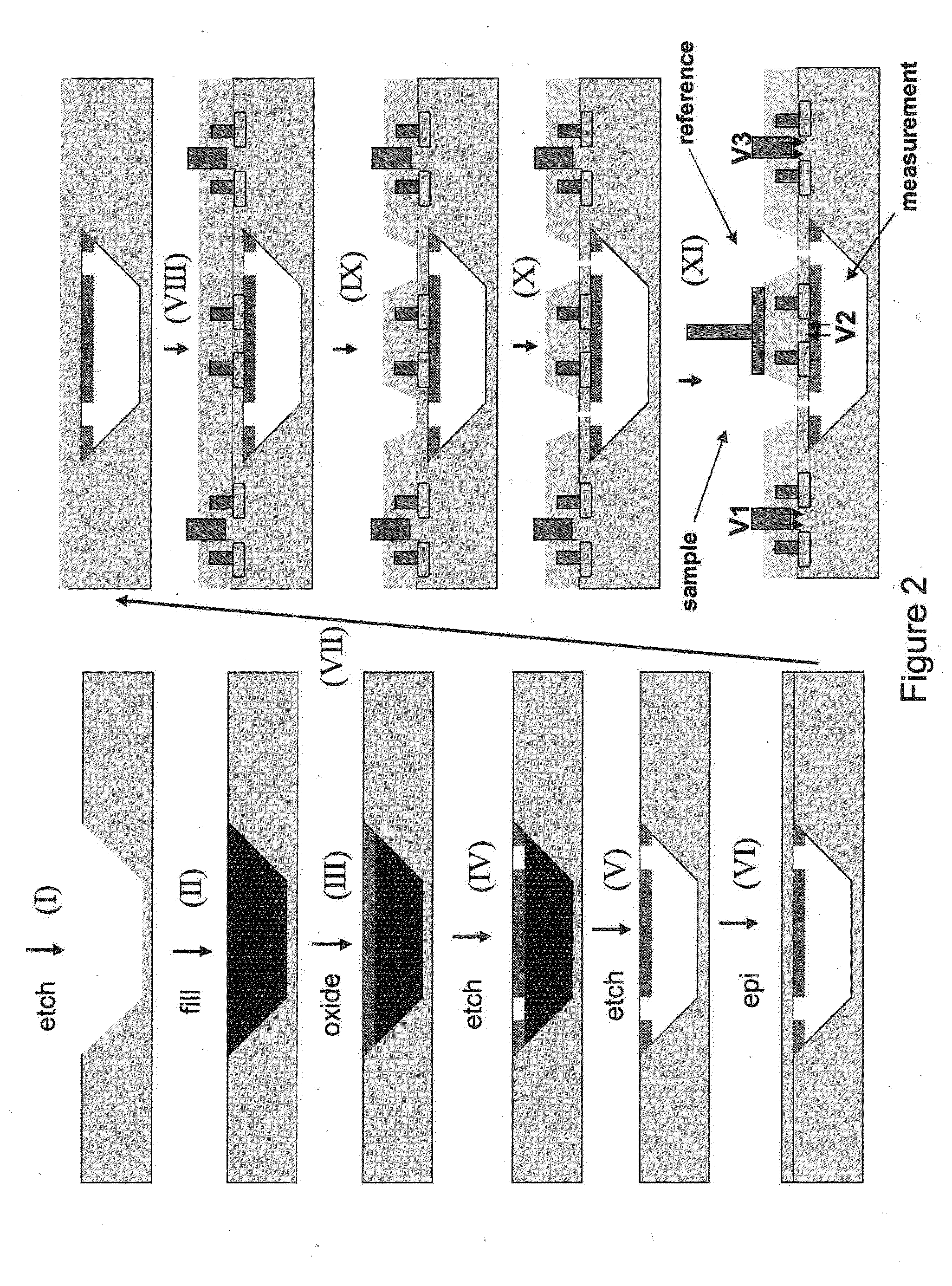
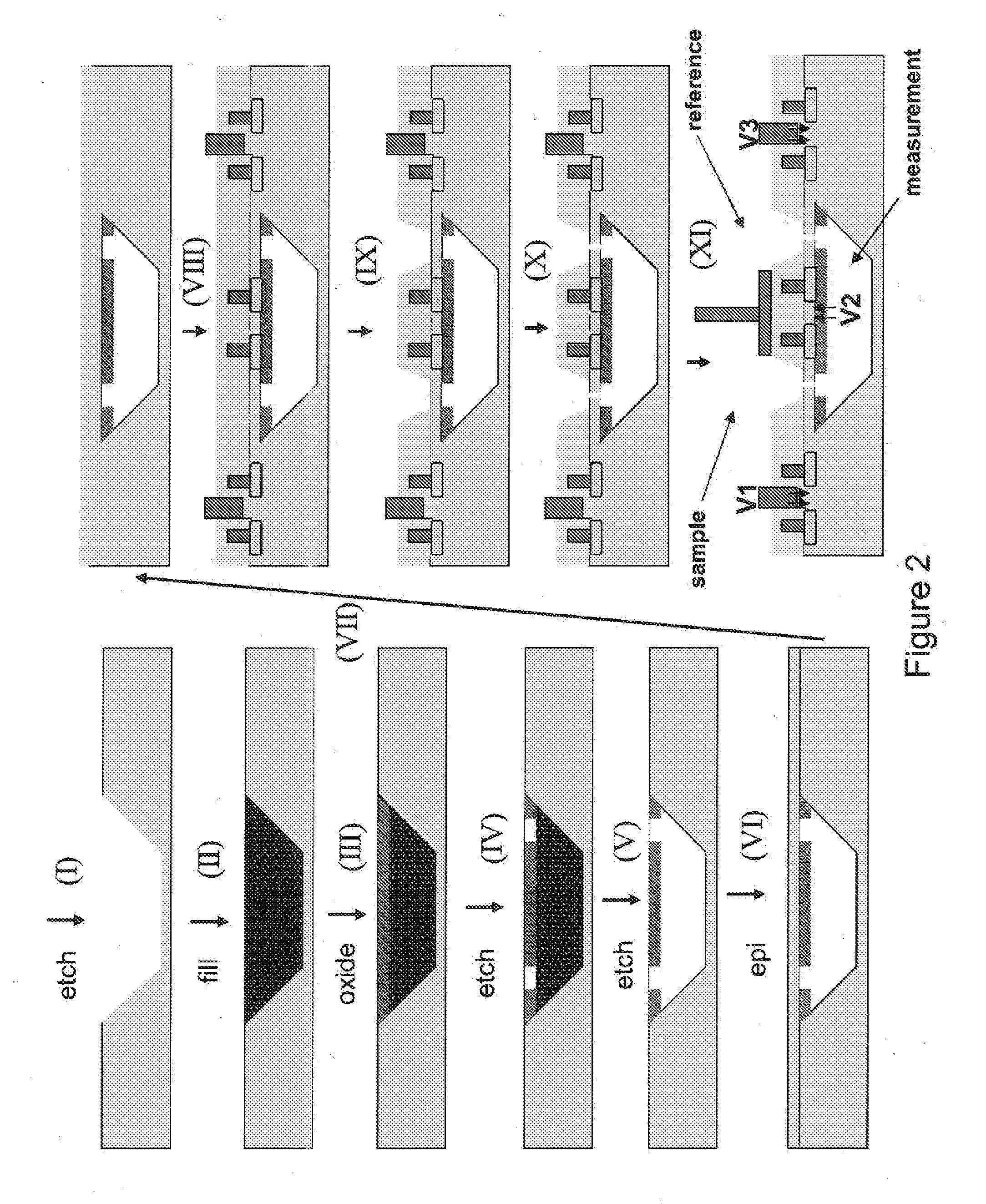
The invention relates to devices and methods for nanopore sequencing. The invention includes arrays of nanopores having incorporated electronic circuits, for example, in CMOS. The invention includes devices having sample and reference pores connecting sample, measurement and reference chambers, wherein potential measurements in each chamber is used to provide an accurate determination of current through a sample nanopore, improving nanopore sequencing.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
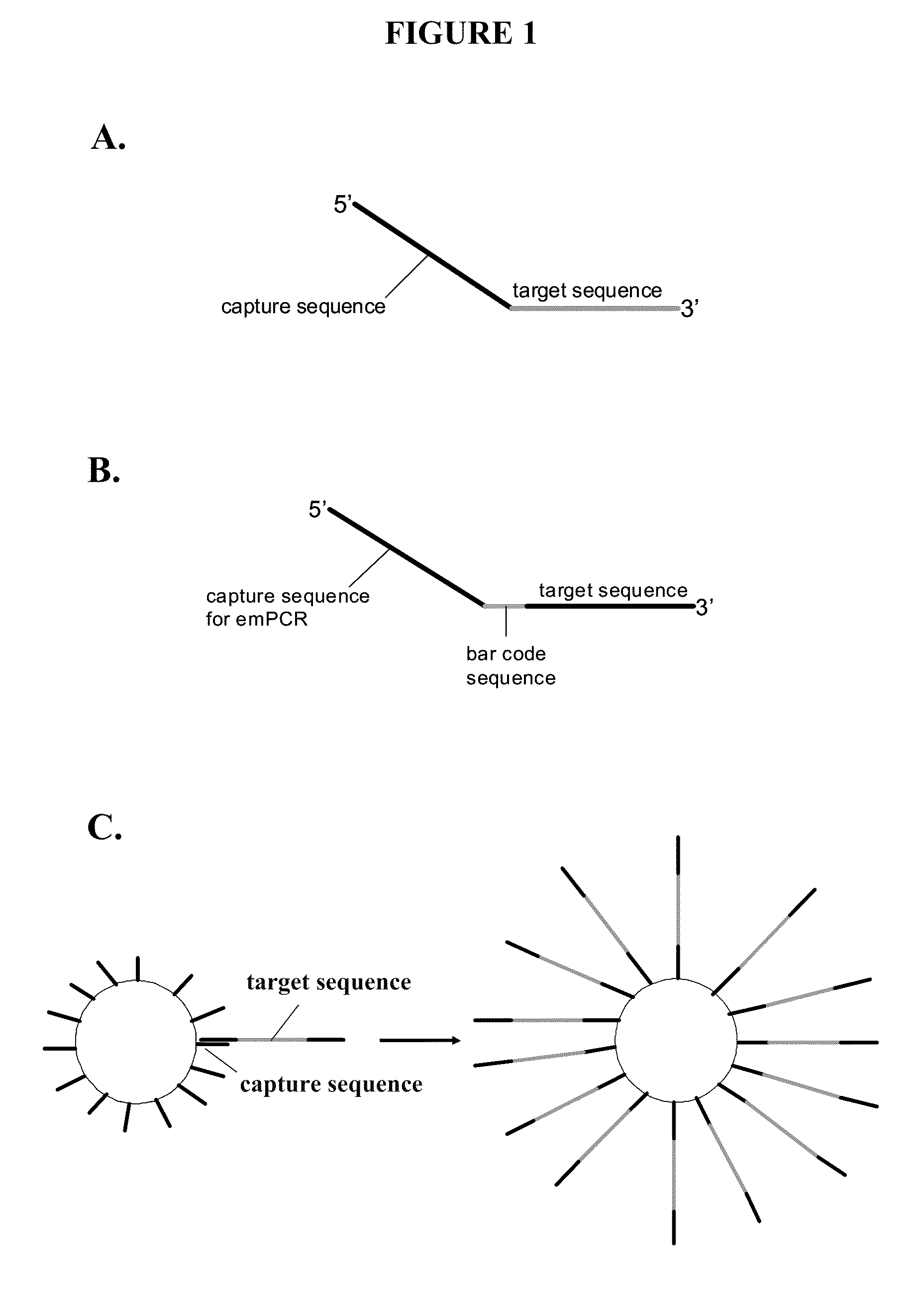
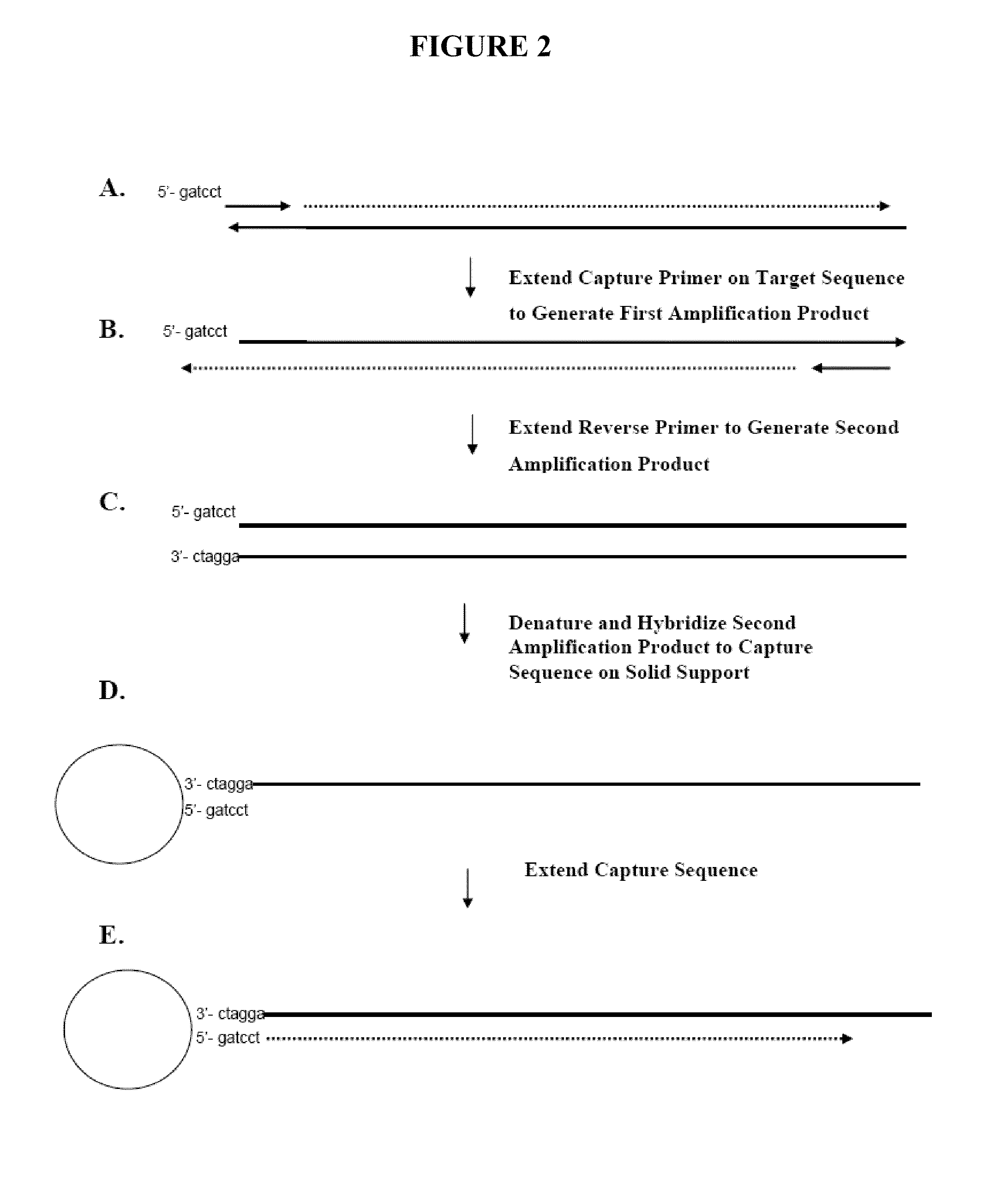
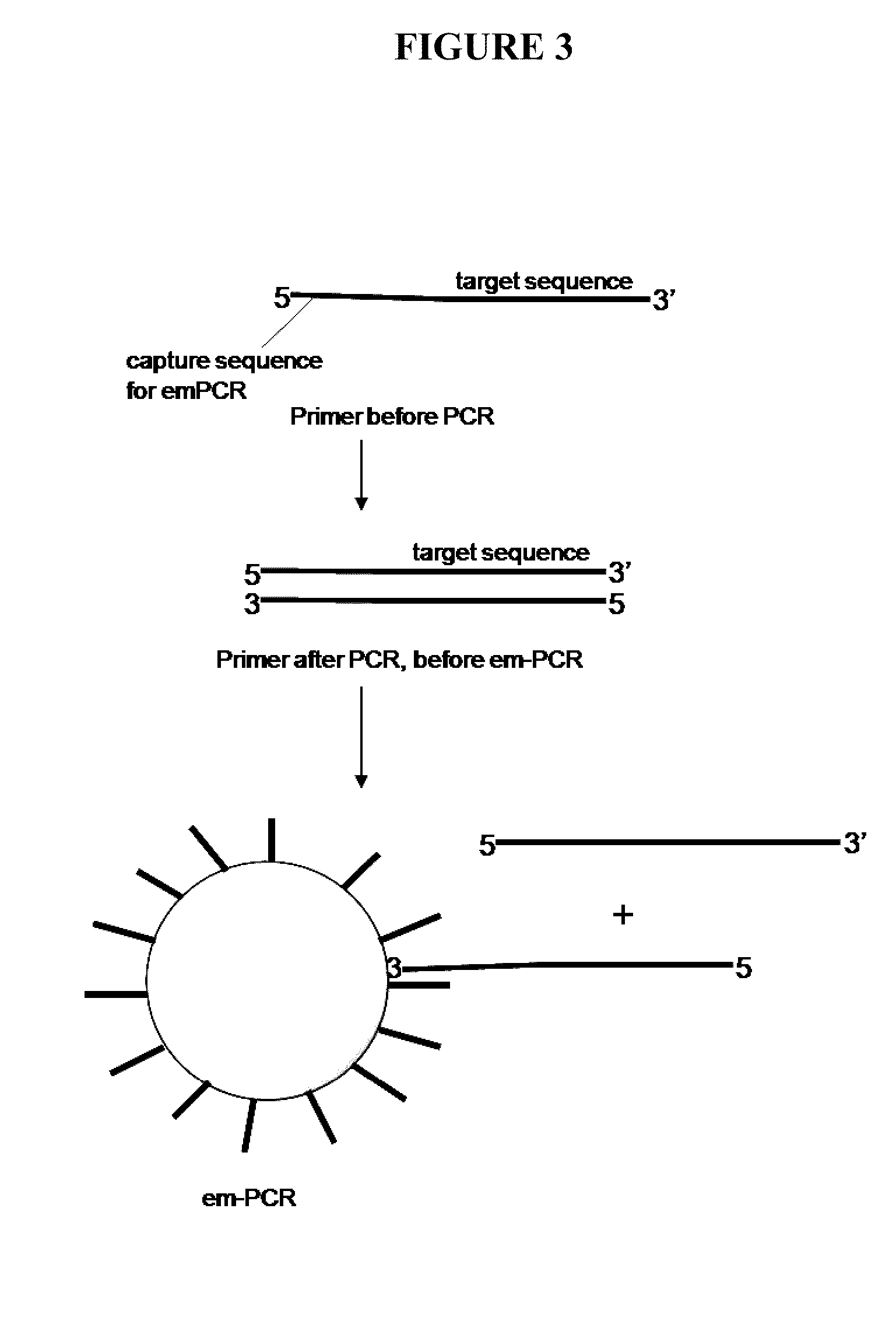
Capture primers and capture sequence linked solid supports for molecular diagnostic tests
InactiveUS9416409B2Microbiological testing/measurementSequence analysisMolecular diagnosticsMolecular Diagnostic Testing
The present invention provides systems, methods, and compositions for performing molecular tests. In particular, the present invention provides methods, compositions and systems for generating target sequence-linked solid supports (e.g., beads) using a solid support linked to a plurality of capture sequences and capture primers composed of a 3′ target-specific portion and a 5′ capture sequence portion. In certain embodiments, the target sequence linked solid support is used in sequencing methods (e.g., pyrosequencing, zero-mode waveguide type sequencing, nanopore sequencing, etc.) to determine the sequence of the target sequence (e.g., in order to detect the identity of a target nucleic acid in sample).
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI
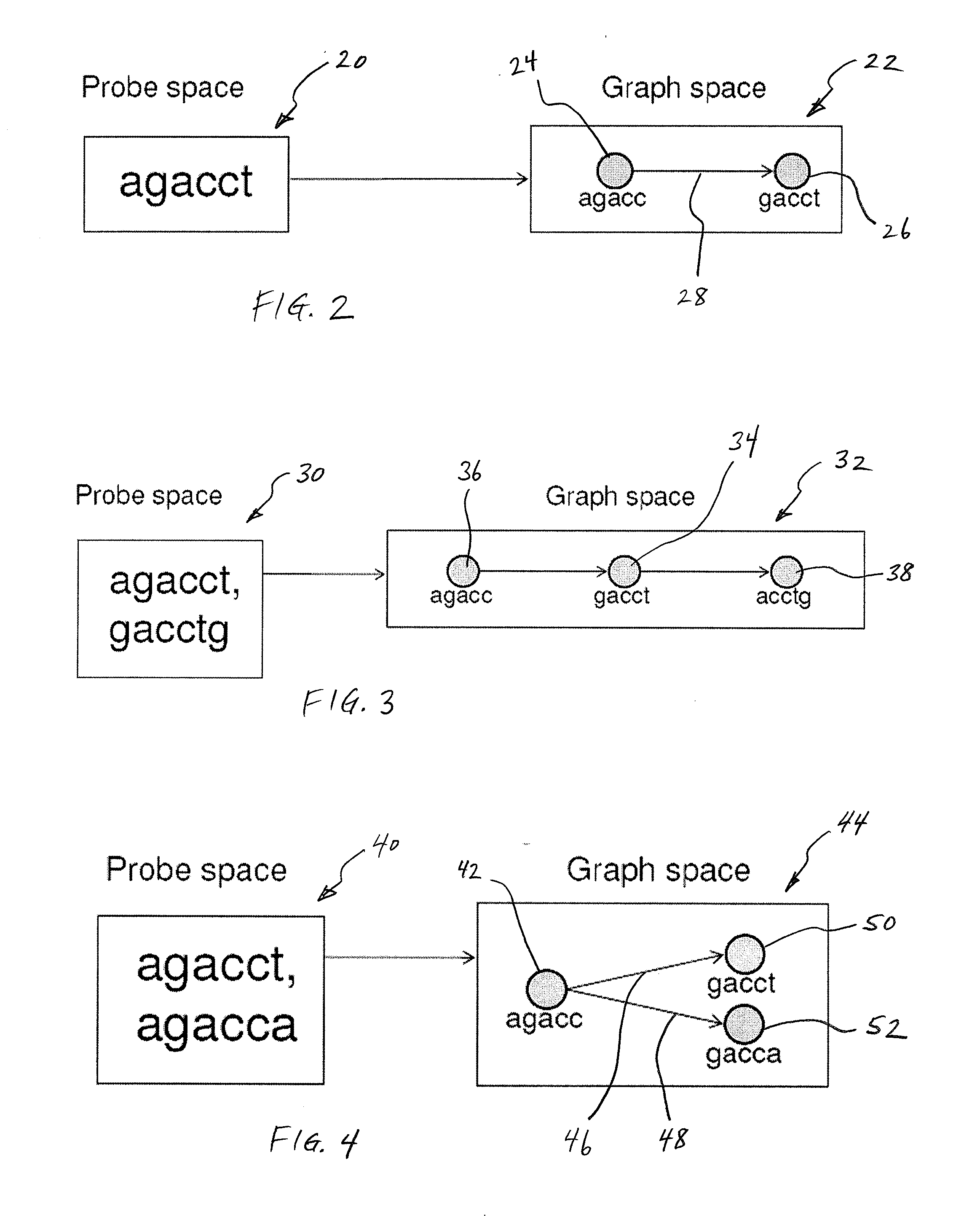
Methods for Sequencing a Biomolecule by Detecting Relative Positions of Hybridized Probes
ActiveUS20120122712A1Eliminate and greatly reduce ambiguityIncreases ambiguityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningProbe typeAmbiguity
A sequencing method is presented in which a biomolecule is hybridized with a specially chosen pool of different probes of known sequence which can be electrically distinguished. The different probe types are tagged such that they can be distinguished from each other in a Hybridization Assisted Nanopore Sequencing (HANS) detection system, and their relative positions on the biomolecule can be determined as the biomolecule passes through a pore or channel. The methods eliminate, resolve, or greatly reduce ambiguities encountered in previous sequencing methods.
Owner:NABSYS 2 0
Sample preparation method
ActiveUS9551023B2Well representedSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolynucleotide
The invention relates to a method for modifying a template polynucleotide for characterization, especially for nanopore sequencing. The method produces a modified polynucleotide which is complementary to the template polynucleotide at some positions and which contains universal or abasic nucleotides at the other, and in some instances predicable, positions. The resulting modified polynucleotide can then be characterized.
Owner:OXFORD NANOPORE TECH LTD
Nanopore sequencing using charge blockade labels
ActiveUS20140309144A1Different levelDifferent modulus propertyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolymerase L
The invention relates to devices and methods for nanopore sequencing. The invention includes compositions and methods of nucleic acid sequencing using a single polymerase enzyme complex comprising a polymerase enzyme and a template nucleic acid attached proximal to a nanopore, and nucleotide analogs in solution comprising charge blockade label that are attached to the polyphosphate portion of the nucleotide analog such that the charge blockade labels are cleaved when the nucleotide analog is incorporated into a growing nucleic acid and the charge blockade label is detected by the nanopore to determine the presence and identity of the incorporated nucleotide and thereby determine the sequence of a template nucleic acid.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Formation and calibration of nanopore sequencing cells
ActiveUS20170370903A1Improved base detection capabilityEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNanoporeStandardization
Improved multi-cell nanopore-based sequencing chips and methods can employ formation, characterization, calibration, and / or normalization techniques. For example, various methods may include one or more steps of performing physical checks of cell circuitry, forming and characterizing a lipid layer on the cells, performing a zero point calibration of the cells, forming and characterizing nanopores on the lipid layers of each cell, performing a sequencing operation to accumulate sequencing signals from the cells, normalizing those sequencing signals, and determining bases based on the normalized sequencing signals.
Owner:ROCHE SEQUENCING SOLUTIONS INC
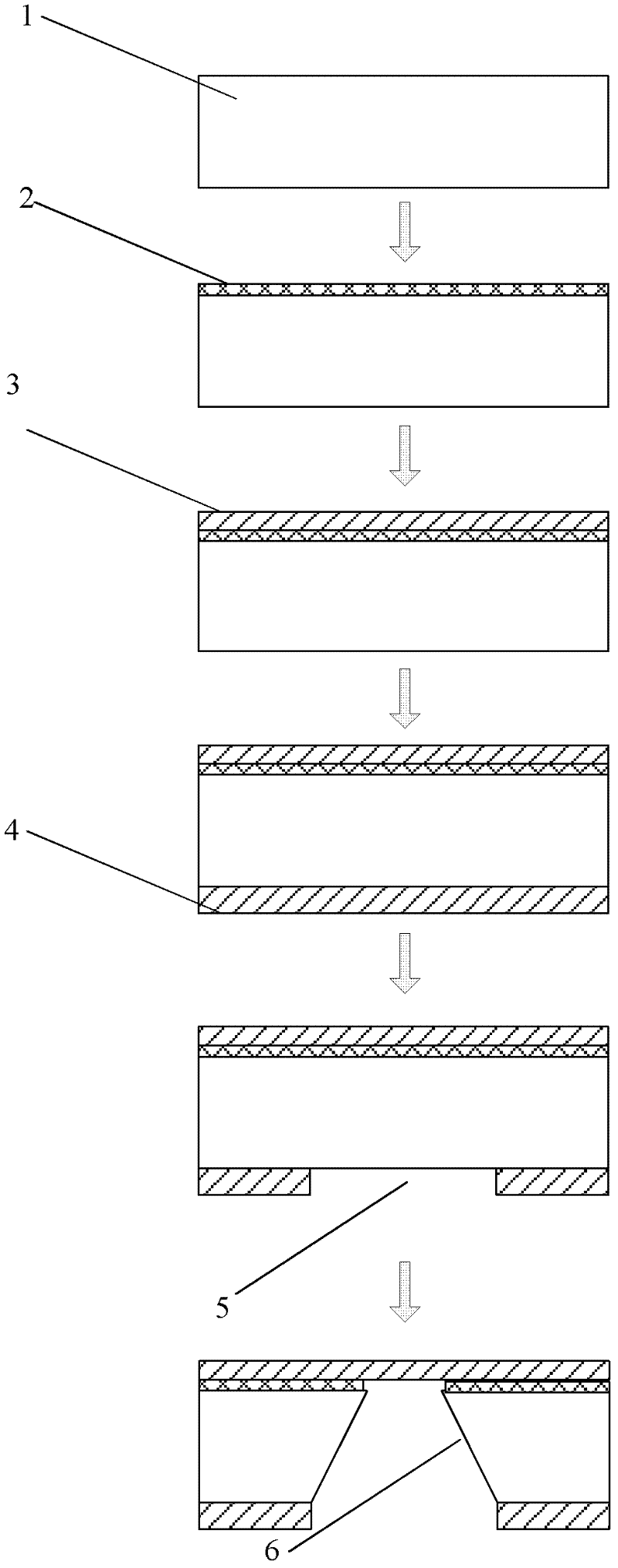
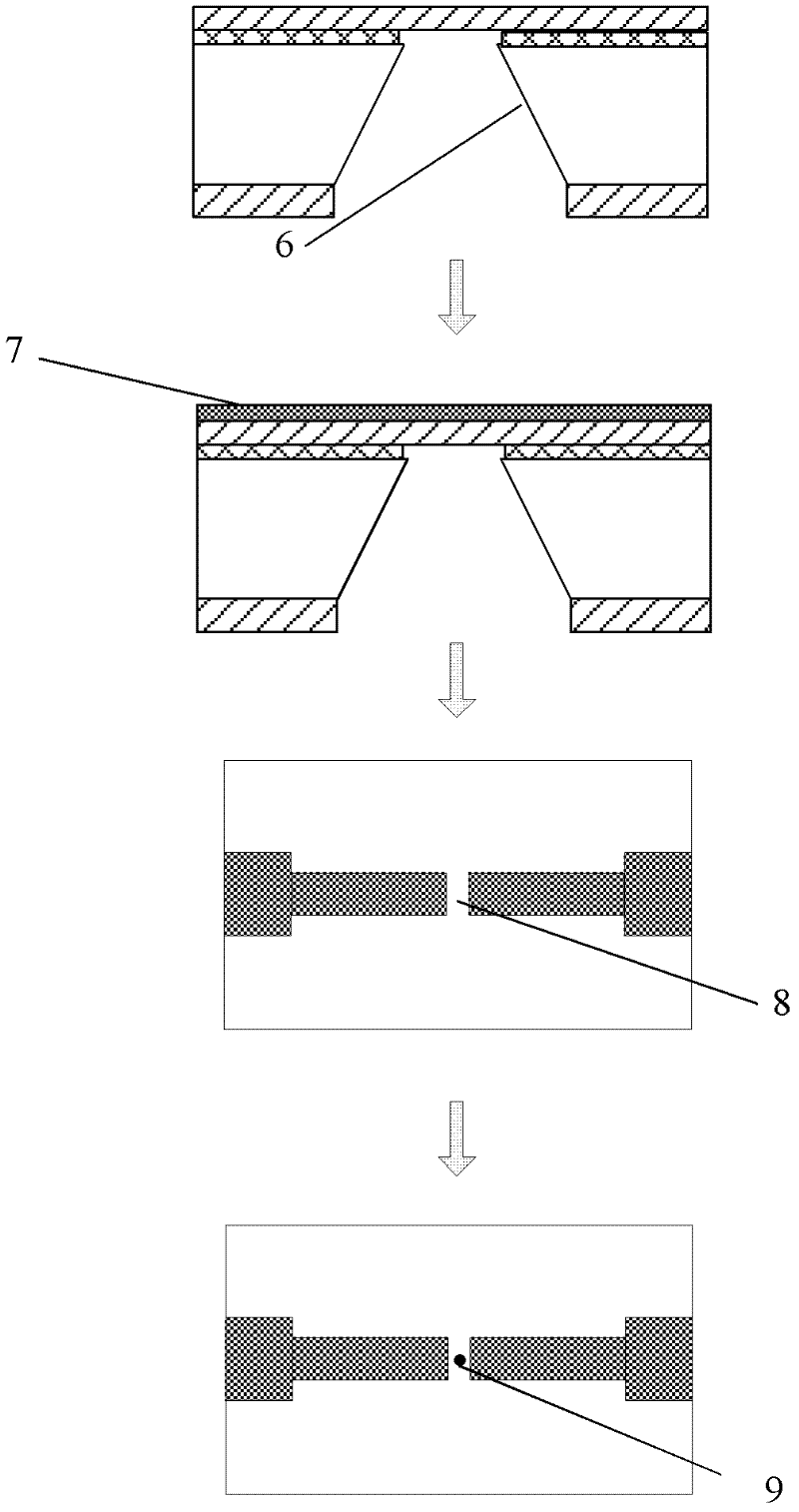
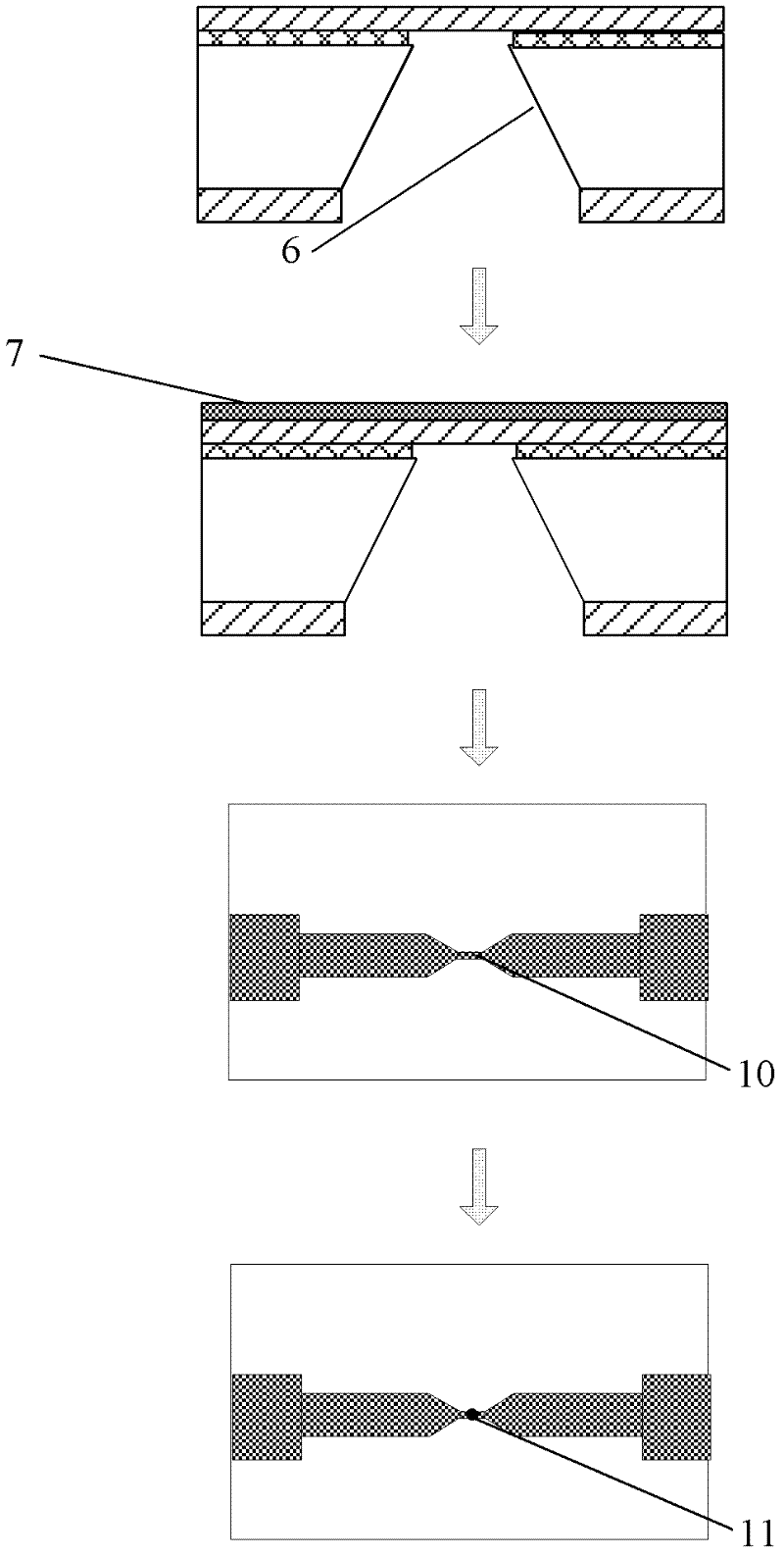
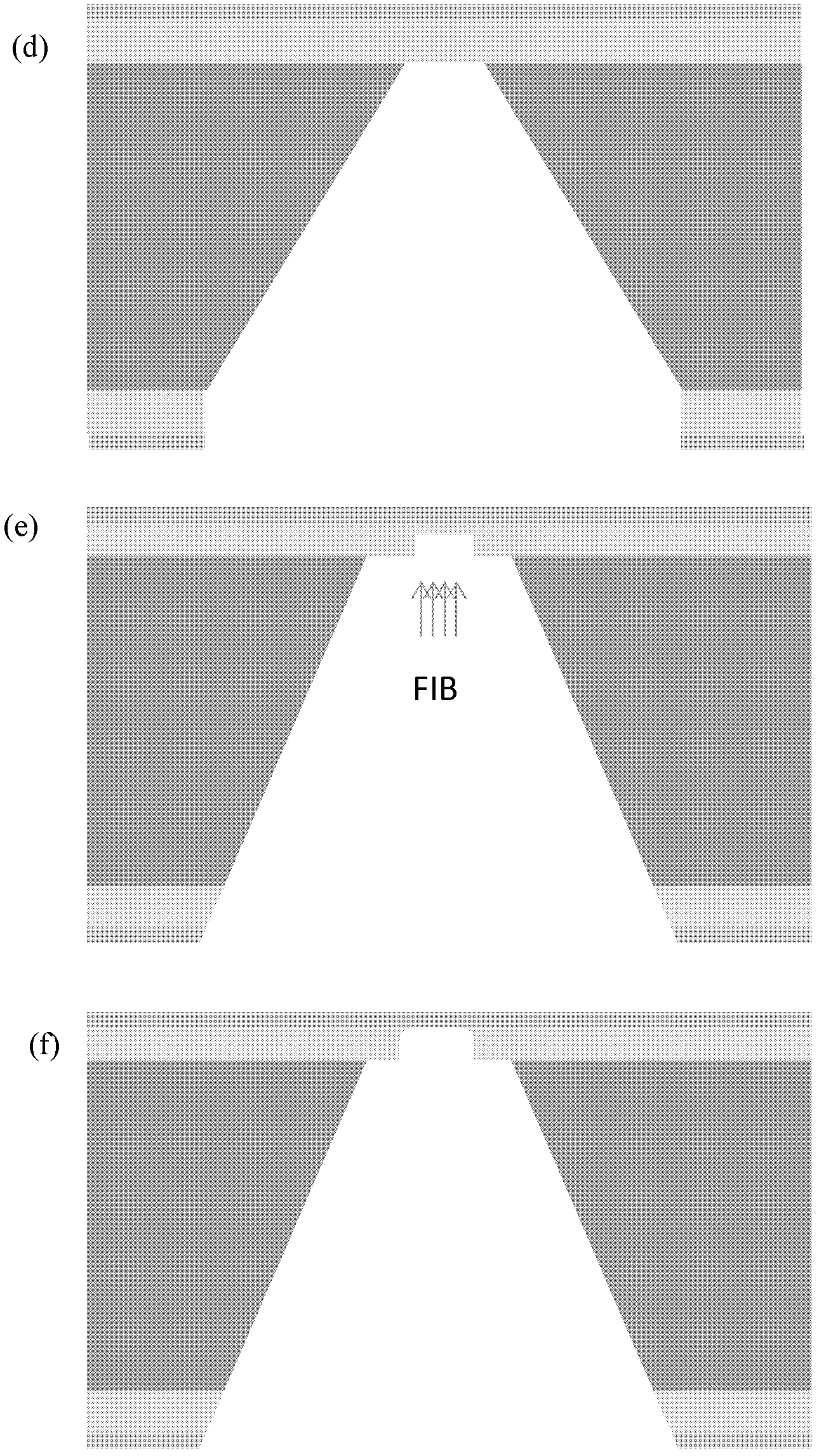
Method for preparing nano-gap electrodes on surface of nano-pore and in nano-pore
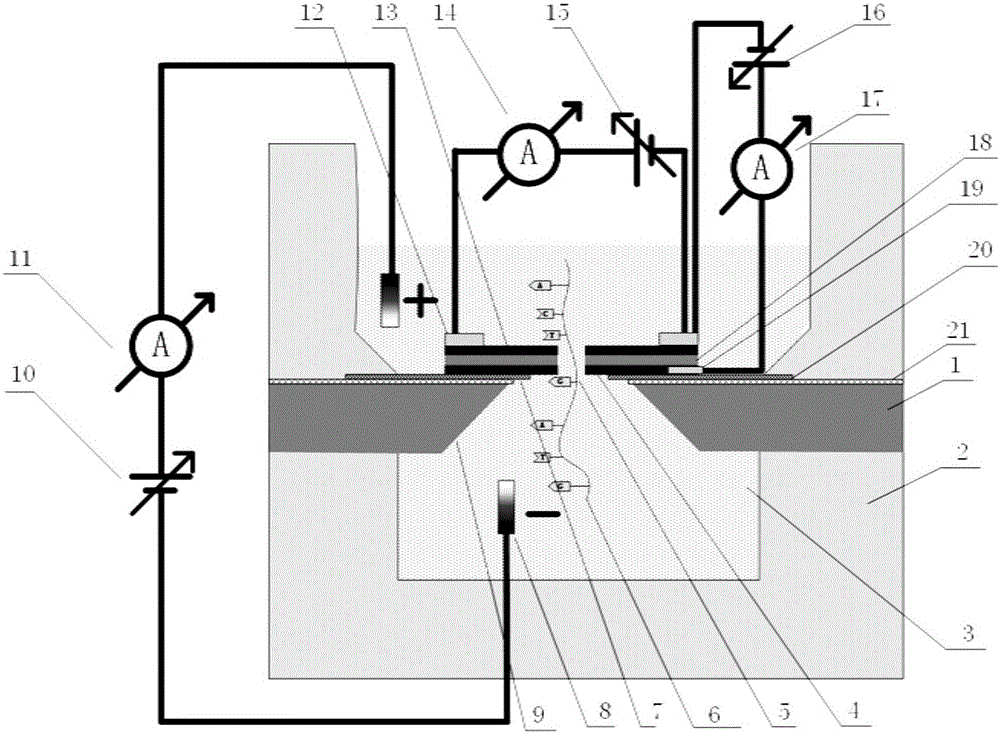
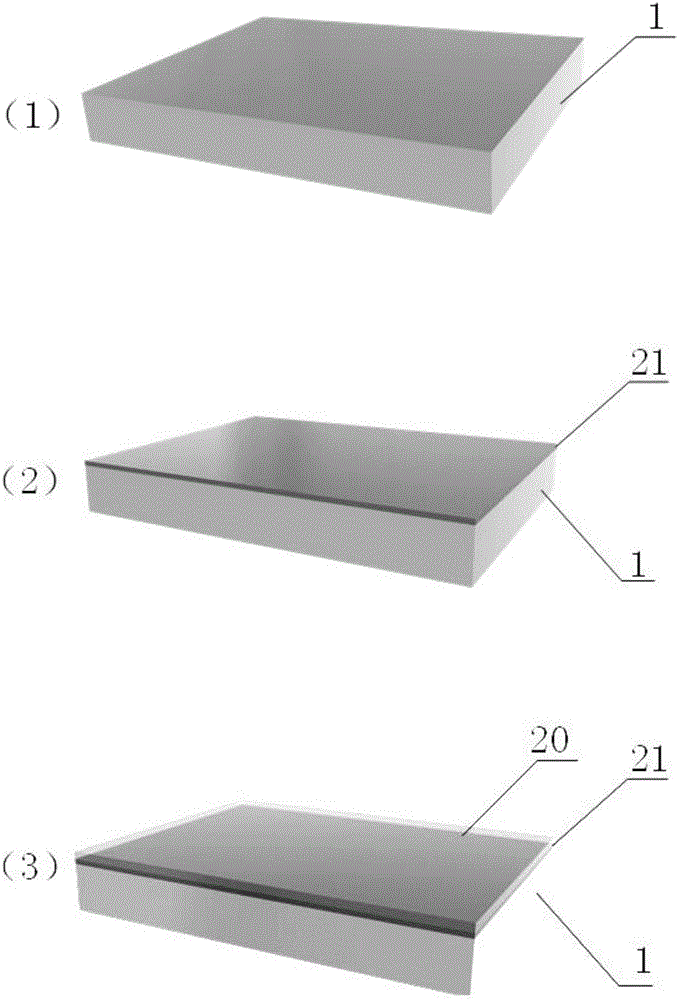
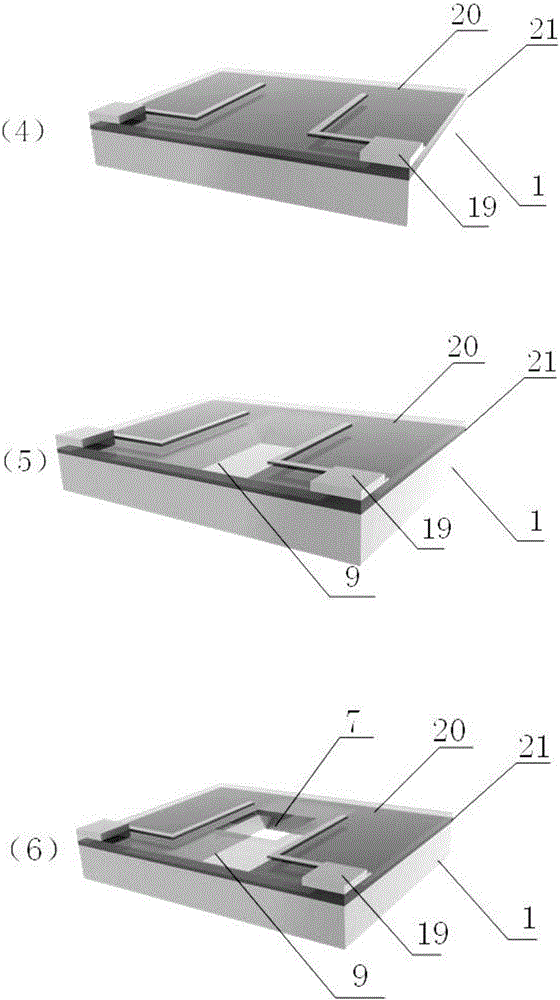
The invention relates to a method for preparing nano-gap electrodes on the surface of a nano-pore and in the nano-pore. The method enables two-dimensional two-channel simultaneous detection of signal changes in a molecular through hole to be realized and accuracy of sequencing of a nano-pore to be improved. The method for preparing a nano-gap electrode on the surface of a nano-pore comprises the following steps: forming a micron-sized metal line on the surface of a substrate, etching the micron-sized metal line into a metal line with line width at a nanometer level, etching a through nano-pore in the substrate at a position corresponding to the nanometer metal line, and cutting the metal line through corrosion so as to directly form a surface nano-gap electrode at the opening of the nano-pore. To improve the invention, a micron-sized metal line is formed on the surface of the substrate and etched until the line width of the metal line is 10 to 50 nm, then etching is carried out on themetal line so as to form opposite electrodes, a through nano-pore is etched in the substrate at a position corresponding to a nano-gap, the metal line is allowed to grow towards the edge of the nano-pore, and therefore, a surface nano-gap electrode is formed at the opening of the nano-pore.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for carrying out deceleration and monomolecular capture on nucleic acid molecule based on solid-state nano hole
ActiveCN102621214AReduced velocity across nanopore devicesShorten speedMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresElectrolyteElectric field
The invention discloses a method for carrying out deceleration and monomolecular capture on a nucleic acid molecule based on a solid-state nano hole. The method comprises the following steps of: adding the nucleic acid molecule to be measured into a nano hole sequencing device filled with an electrolyte, wherein the nano hole sequencing device comprises an electrolytic bath provided with an anode and a cathode, and a solid-state nano hole thin film for separating the anode of the electrolytic bath from the cathode of the electrolytic bath; placing the nucleic acid molecule in a positive chamber of the electrolytic bath; during measurement, introducing a pressure external field into the positive chamber as a driving external field for the perforation of the nucleic acid molecule; applying a voltage between the anode and the cathode as an electric field external field reverse to the pressure external field; and in a measurement process, enabling the acting force of the pressure external field, from which the nucleic acid molecule is suffered in the nano hole to be more than or approximately equal to electric field force according to a deceleration purpose or a capture purpose to be realized by the method. By using the method, on the premise that the signal-to-noise ratio of a measurement signal is not decreased, the speed at which a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule penetrates through a nano hole device can be effectively decreased, and a perforation speed can be slowed down for above one order of magnitude.
Owner:美国哈佛大学 +1
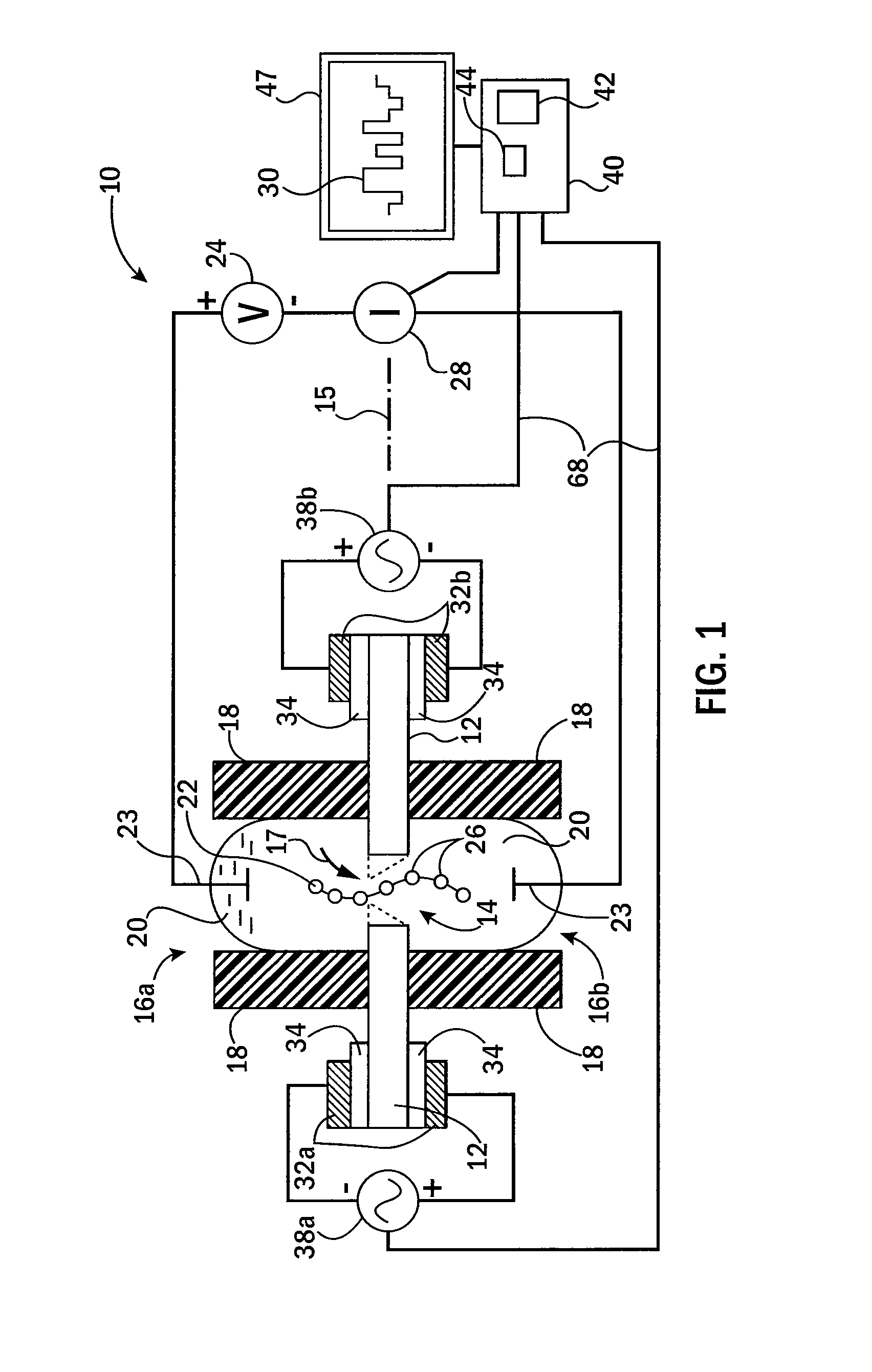
System and Apparatus for Nanopore Sequencing
ActiveUS20140266147A1Long measurement timeFast transition timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansControl systemEngineering
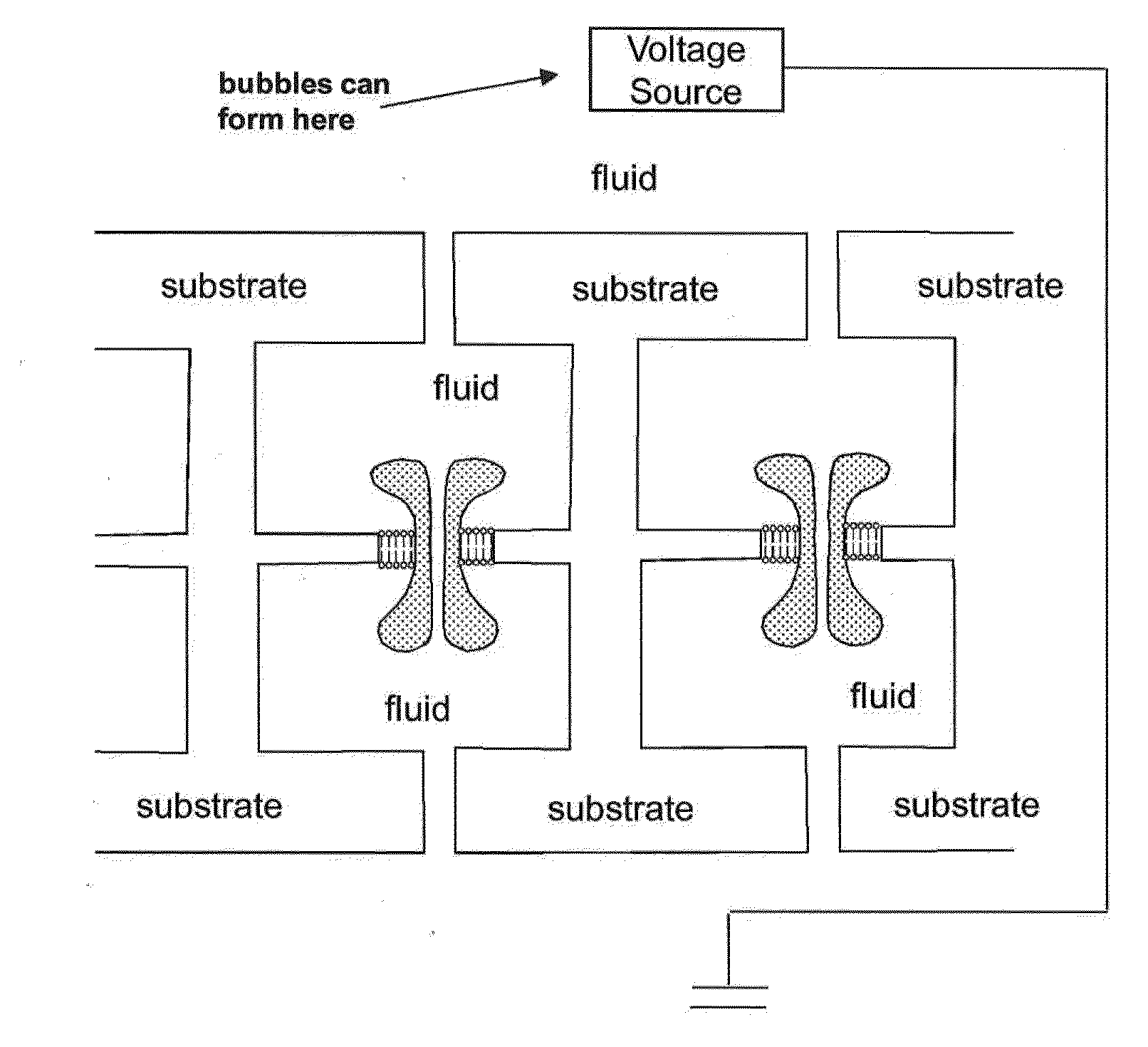
A piezoelectric substrate having a nanopore opening that separates two reservoirs of conductive fluid may provide for sensitive biological measurements by allowing control of the size of the nanopore according to piezoelectric stimulation of the substrate. Multiple embodiments are provided of monolithic piezoelectric substrates and nanopores for this purpose as well as a control system for controlling the nanopore dimensions electrically using AC or DC waveforms.
Owner:UNIV OF HAMBURG +1
Method
ActiveUS20160194677A1Well representedNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolynucleotide
The invention relates to a method for modifying a template double stranded polynucleotide, especially for characterisation using nanopore sequencing. The method produces from the template a plurality of modified double stranded polynucleotides. These modified polynucleotides can then be characterised.
Owner:OXFORD NANOPORE TECH LTD
Method
ActiveUS20170240955A1Well representedMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisNucleotidePolynucleotide
The invention relates to a method for modifying a template double stranded polynucleotide, especially for characterisation using nanopore sequencing. The method produces from the template a plurality of modified double stranded polynucleotides. These modified polynucleotides can then be characterised.
Owner:OXFORD NANOPORE TECH LTD
Method for detecting genomic structure variation based on nanopore sequencing
ActiveCN110600078ARealize detectionDeepen understandingSequence analysisInstrumentsNatural resourceLarge fragment
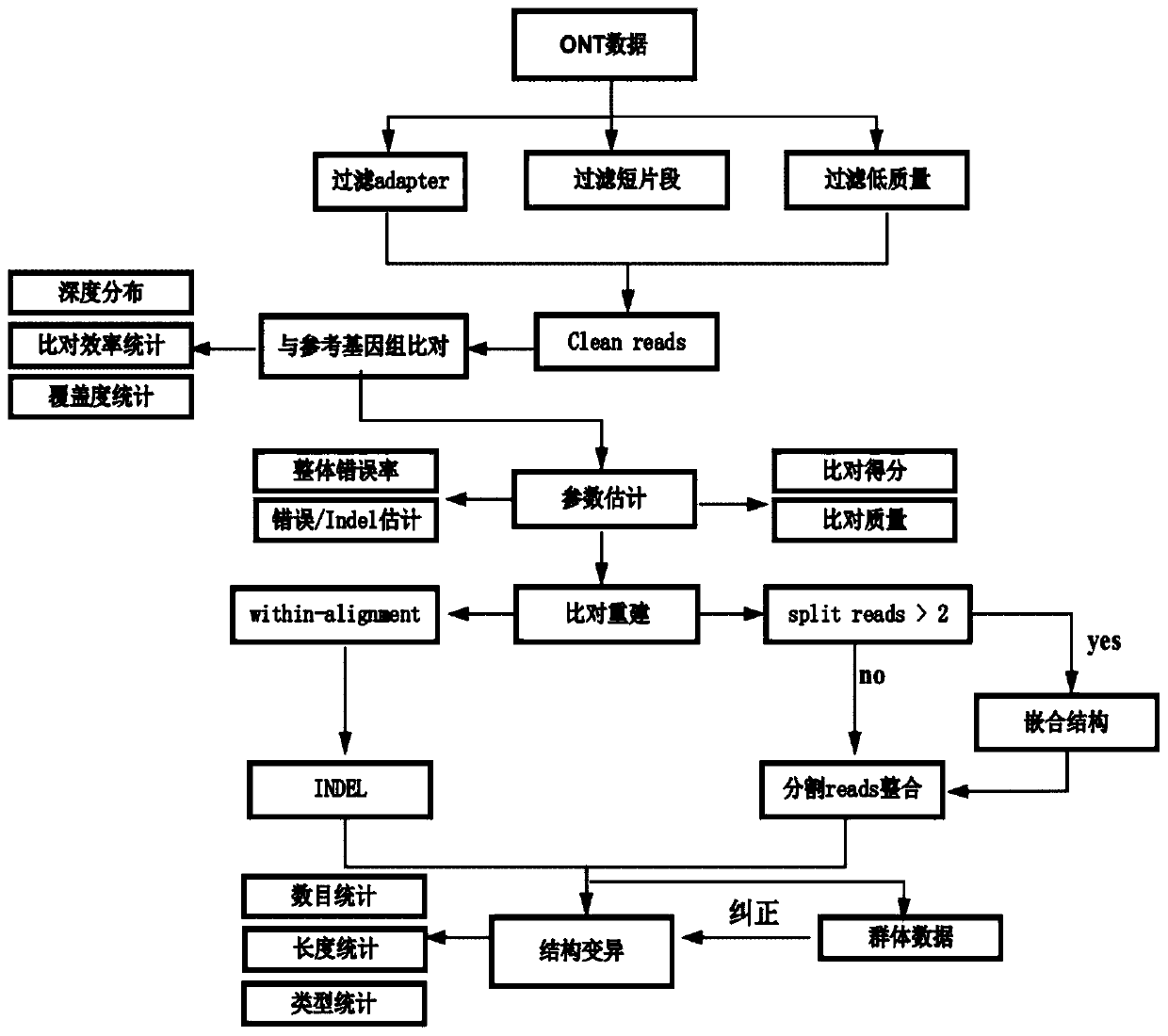
The present invention provides a method for detecting genomic structure variation based on nanopore sequencing, which includes performing nanopore sequencing data quality control and genomic mapping;excavating within-alignment reads and split reads information; defining structural variation and typing; and performing multi-sample data variation type integration. The method of the invention can detect the variation of mutants and wild-type materials, the variation between extremely resistant materials, transgenic events and the location of inserted fragments; can also organically integrate theresults of a large number of samples and assist in the correction of variation sites; provide rich structural variation data for natural resource groups for subsequent GWAS analysis; not only can detect common large fragment structural variations, but also have high accuracy and precision in the detection of chimeric mutations, and clusters the reads of the typed structural mutations to determinehomozygous and heterozygous structural variations.
Owner:BIOMARKER TECH
Polymerase variants
ActiveUS20180245147A1Easy to processIncrease read lengthMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesPolymerase LBiology
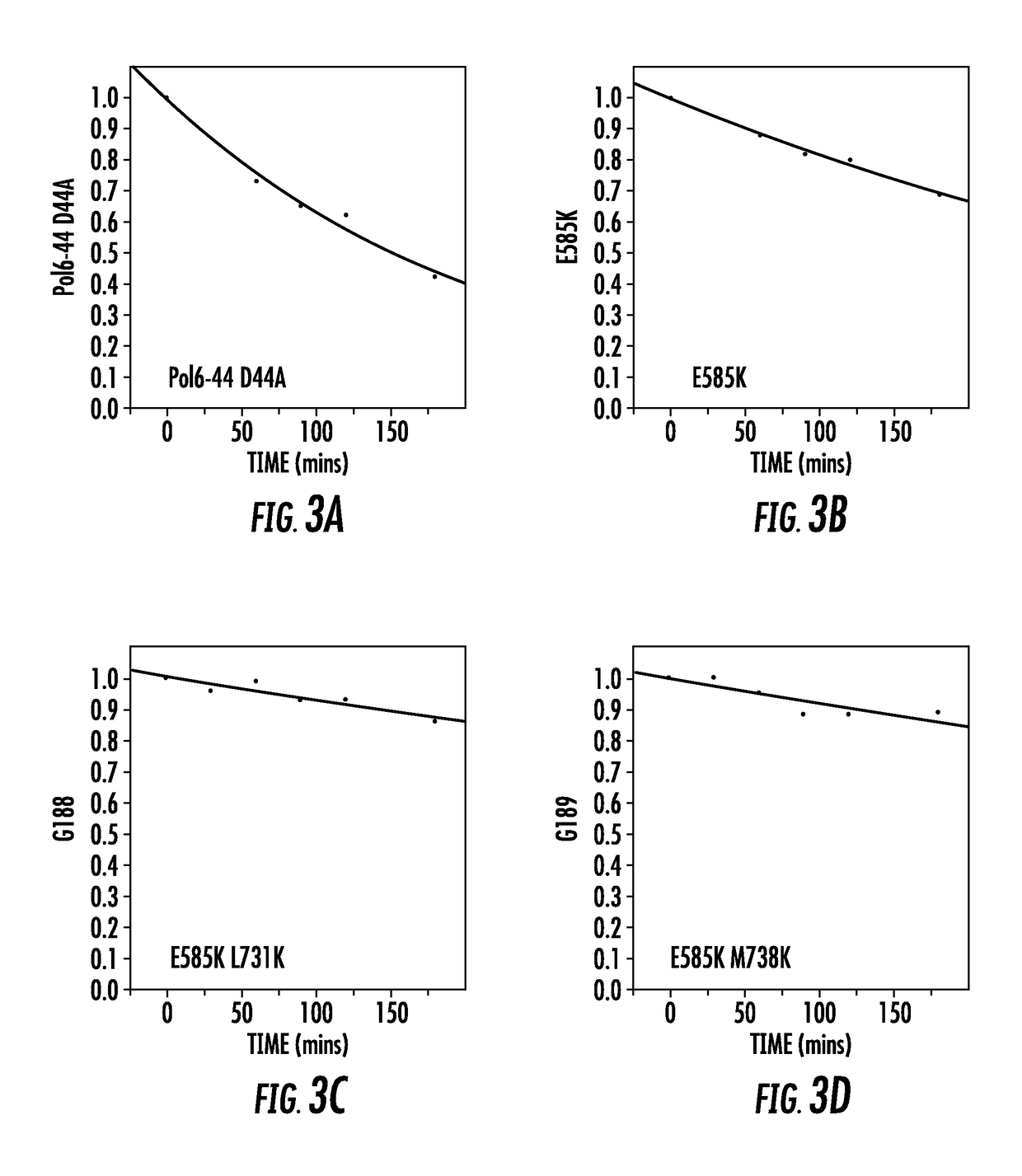
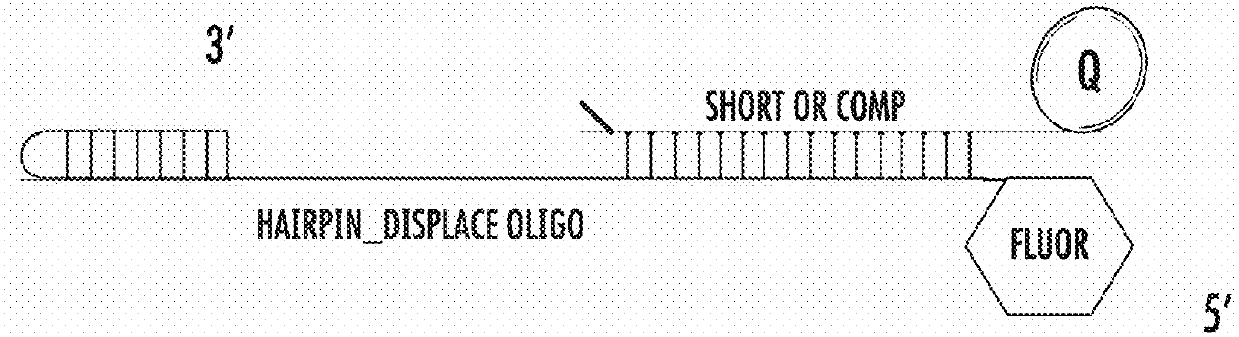
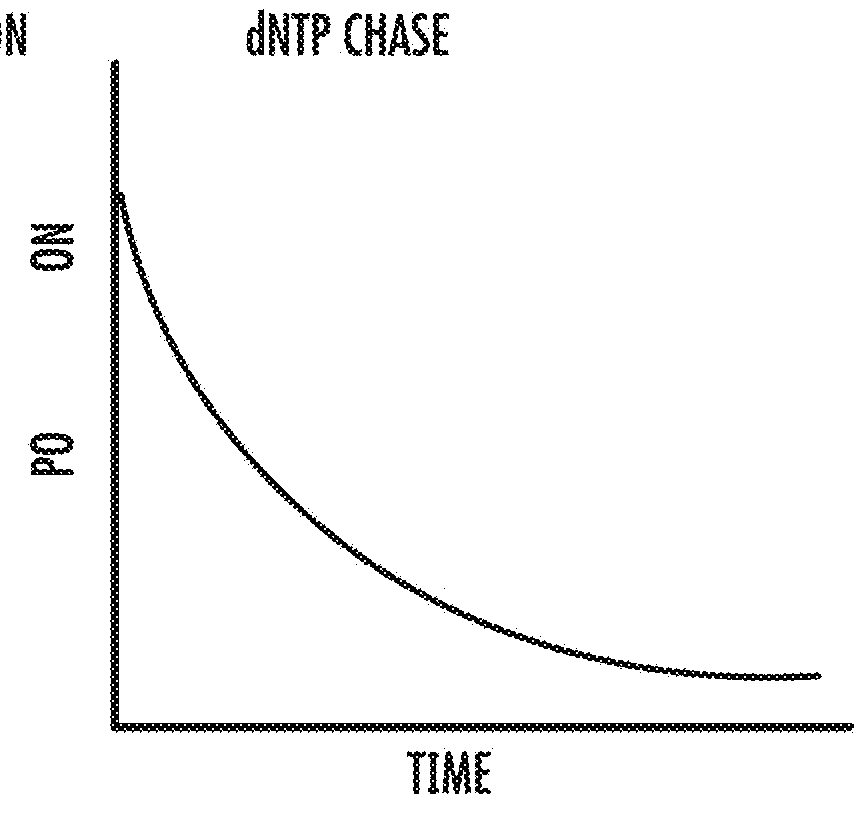
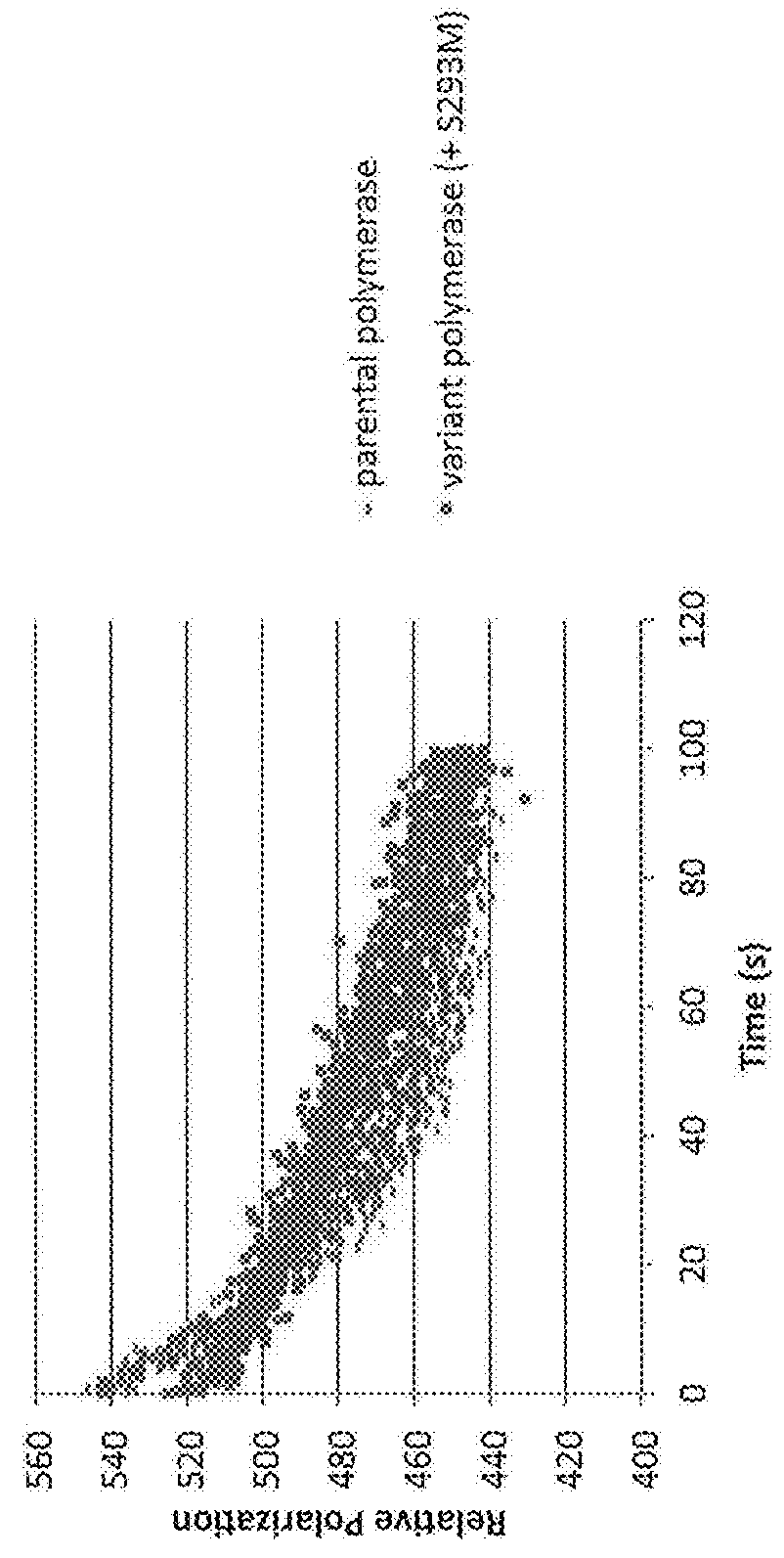
The present of disclosure provides variant Pol6 polymerase polypeptide, compositions comprising the Pol6 variant polypeptides, and methods for using the variant Pol6 polypeptides for determining the sequencing of nucleic acids, for example, by nanopore sequencing. The variant Pol6 polymerases possess decreased rates of dissociation of template from the polymerase-template complex, which result n increased processivity relative to the parental Pol6 polypeptides from which they are derived.
Owner:ROCHE SEQUENCING SOLUTIONS INC
Nano-pore sensing device based on two-dimensional layer materials and configuring method thereof
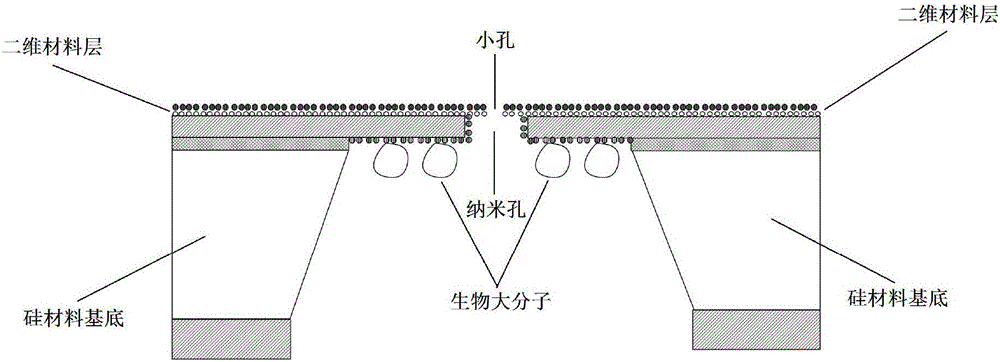
InactiveCN105779279AHigh precisionMeet the needs of readingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsInformation deviceBiological macromolecule
The invention discloses a nano-pore sensing device based on two-dimensional layer materials and a configuring method and application thereof.The sensing device comprises a silicon material substrate, a two-dimensional material layer, a nano-pore and biomacromolecules.The two-dimensional material layer is attached to the surface of the silicon material substrate, the nano-pore in the silicon material substrate is communicated with a small hole in the two-dimensional material layer, and the biomacromolecules are anchored to the other end of the nano-pore.Compared with the prior art, the nano-pore sensing device has the advantages that the characteristic of control over the DNA hole passing speed of the biological nano-pore and the advantages of stability, easy design and array processing of the solid nano-pore are combined, the advantage that the space resolution in nano-pore sequencing is broken through through the nano-pore manufactured through the two-dimensional layer materials is adopted, and the nanometer device capable of directly conducting efficient information reading on an analyte is developed so that the requirement for reading DNA encoding information in current medical and future information devices can be met, and the accuracy of nano-pore sequencing is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Polymerase Variants
ActiveUS20180094249A1Improved strand displacementCharacteristic can be alteredMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesBiotechnologyPolymerase L
The present disclosure provides variant Pol6 polymerase polypeptides, compositions comprising the Pol6 variant polypeptides, and methods for using the variant Pol6 polypeptides for determining the sequencing of nucleic acids, for example, by nanopore sequencing. The variant Pol6 polymerases possess decreased rates of dissociation of template from the polymerase-template complex, which result in increased processivity relative to the parental Pol6 polypeptides from which they are derived.
Owner:ROCHE SEQUENCING SOLUTIONS INC +1
Method for modifying a template double stranded polynucleotide using a MuA transposase
ActiveUS10570440B2Well representedSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolynucleotide
The invention relates to a method for modifying a template double stranded polynucleotide, especially for characterisation using nanopore sequencing. The method produces from the template a plurality of modified double stranded polynucleotides. These modified polynucleotides can then be characterised.
Owner:OXFORD NANOPORE TECH LTD
Nanopore sequencing using n-mers
The invention relates to devices and methods for nanopore sequencing. The invention provides for using the signals from n-mers to provide sequence information, for example where the system has less than single base resolution. The invention includes arrays of nanopores having incorporated electronic circuits, for example, in CMOS. In some cases, the arrays of nanopores comprise resistive openings for isolating the electronic signals for improved sequencing. Methods for controlling translocation of through the nanopore are disclosed.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
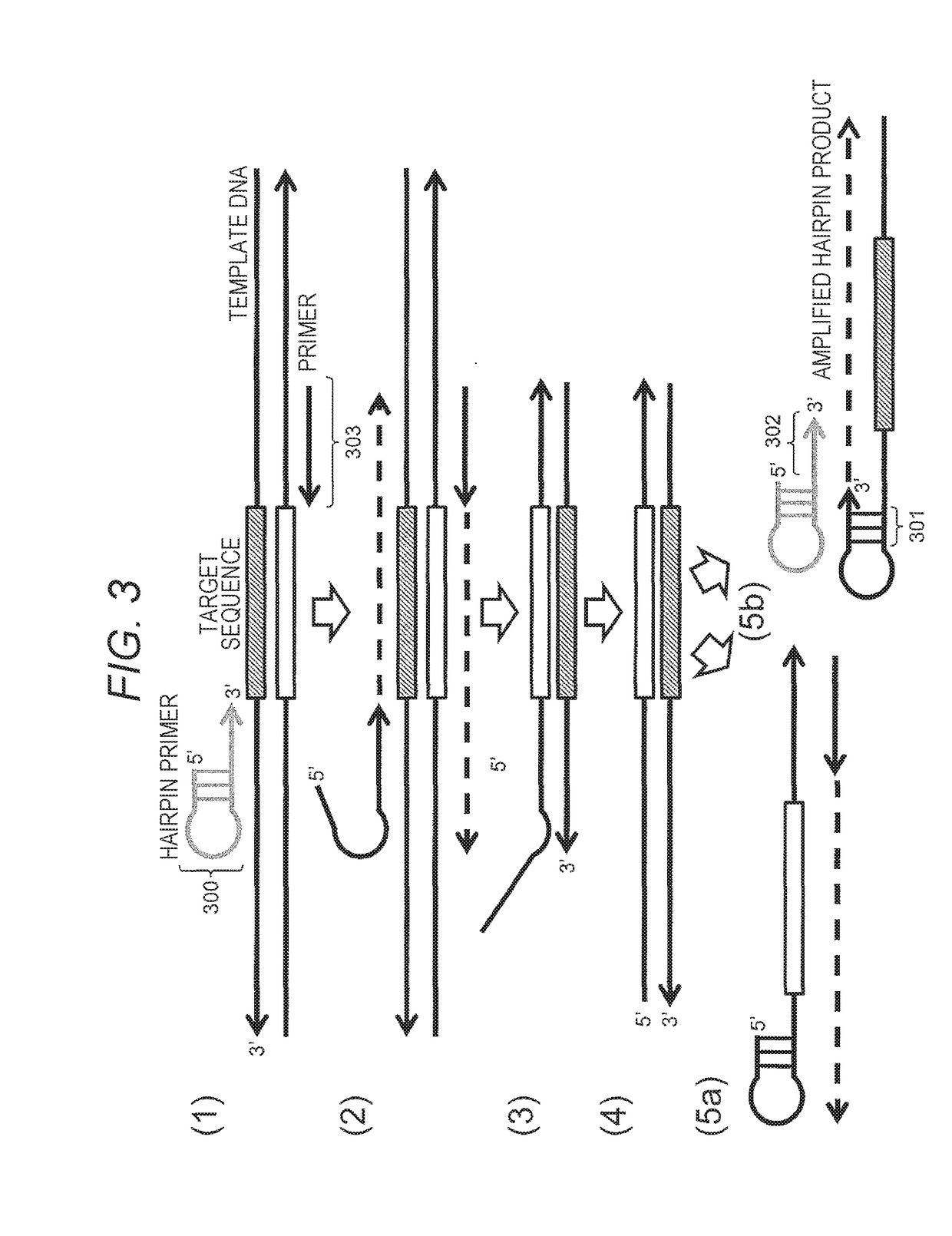
Method for Constructing Nucleic Acid Molecule
ActiveUS20180030506A1High precision analysisImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologySingle strandNucleic acid sequencing
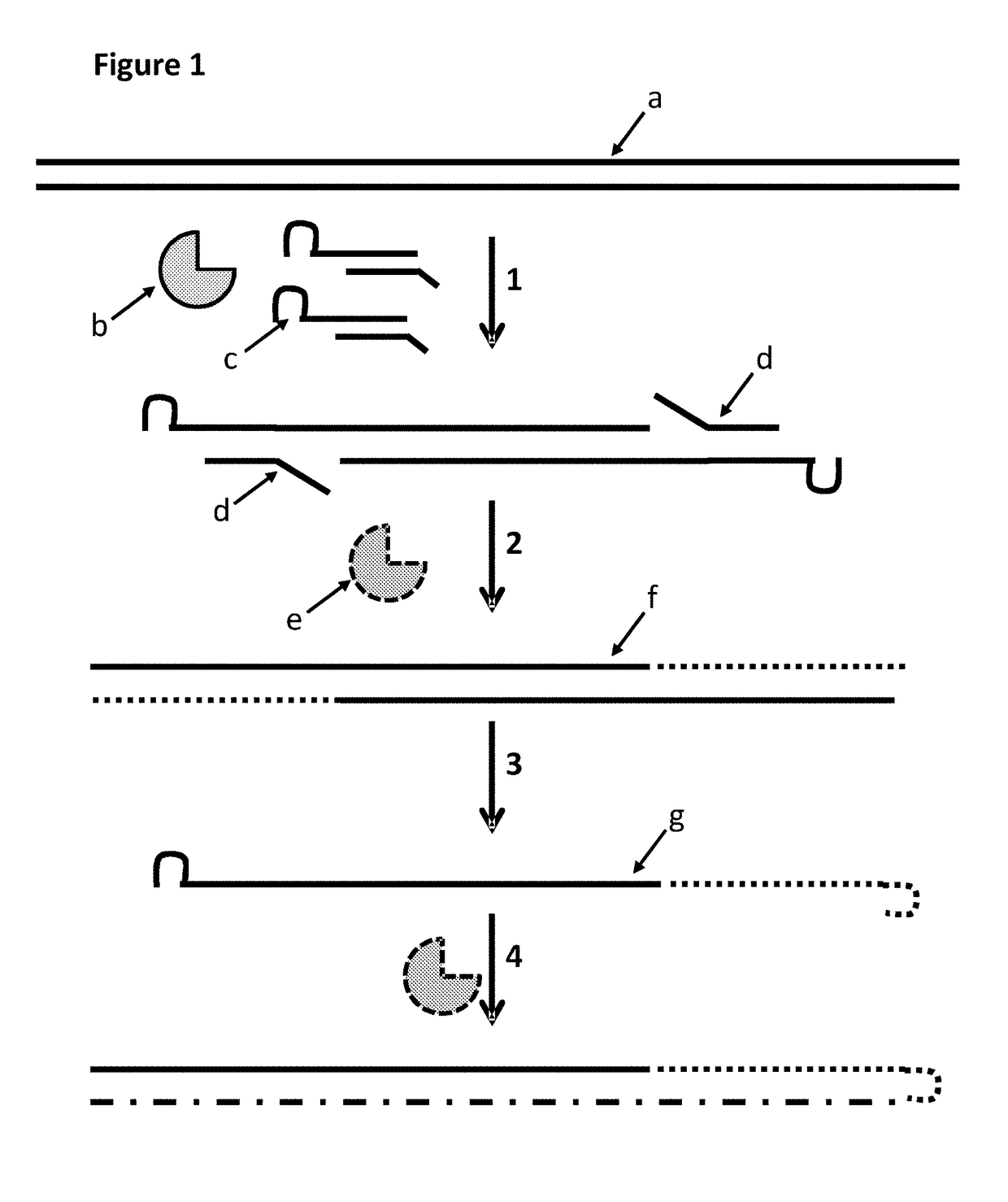
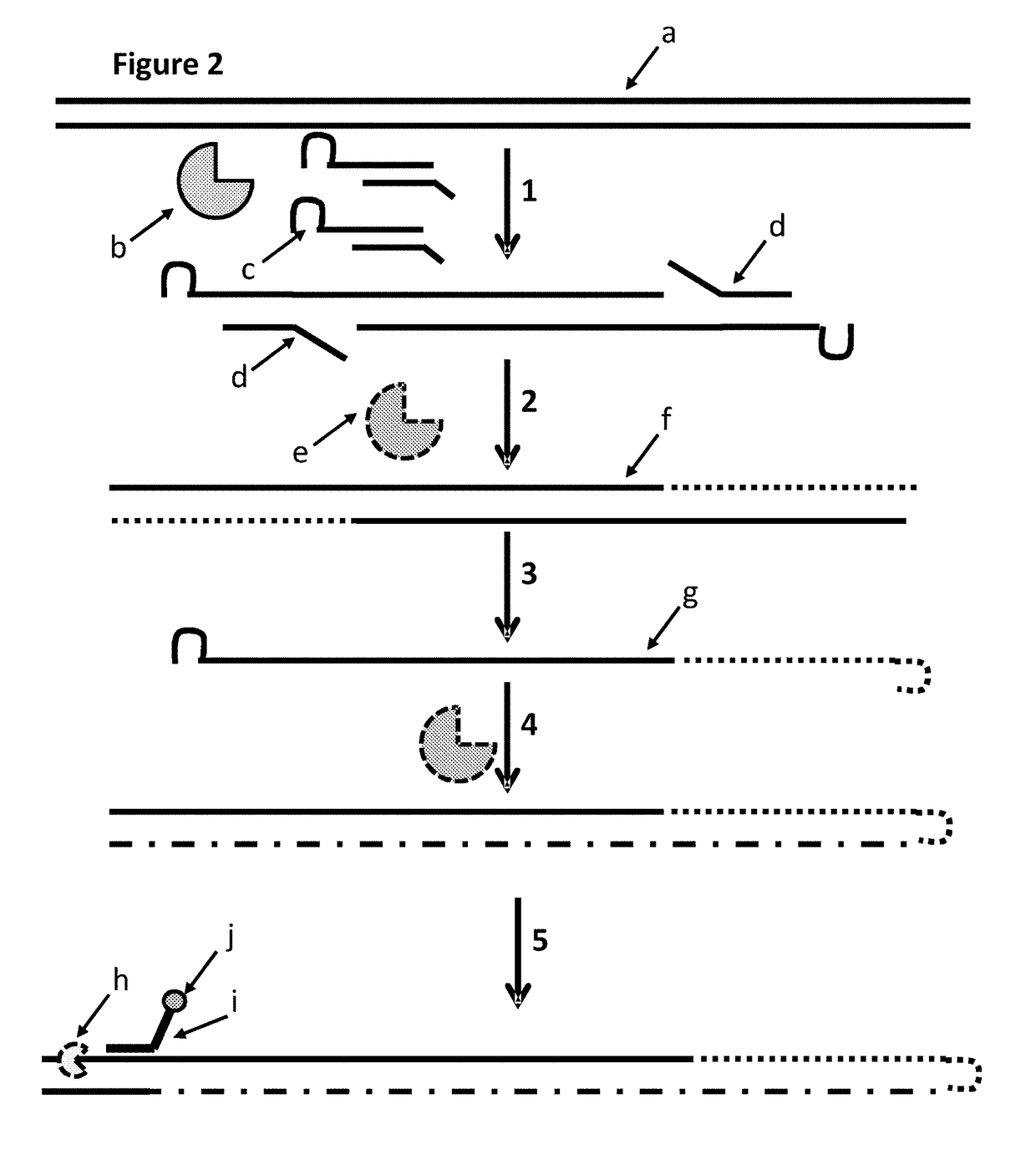
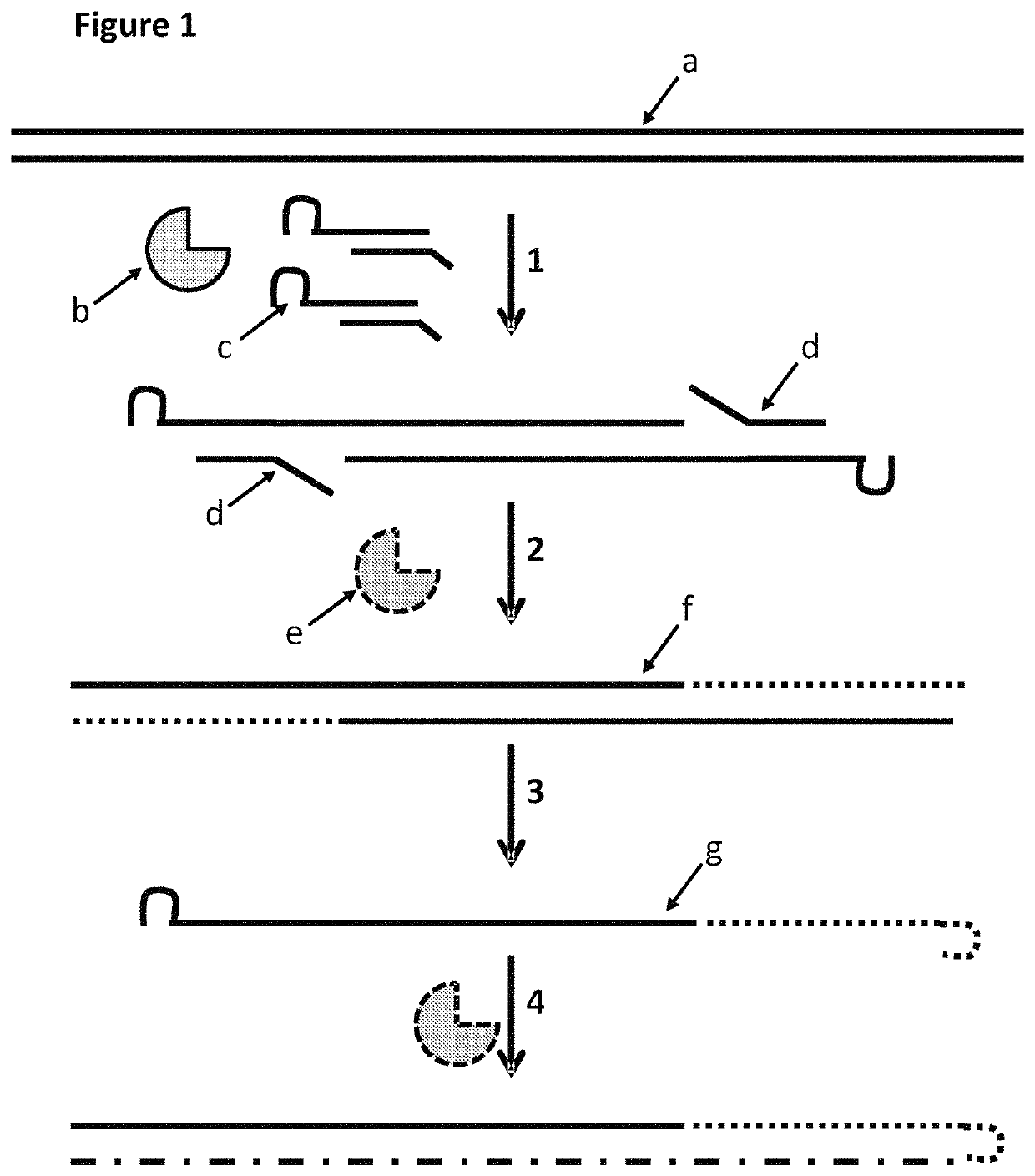
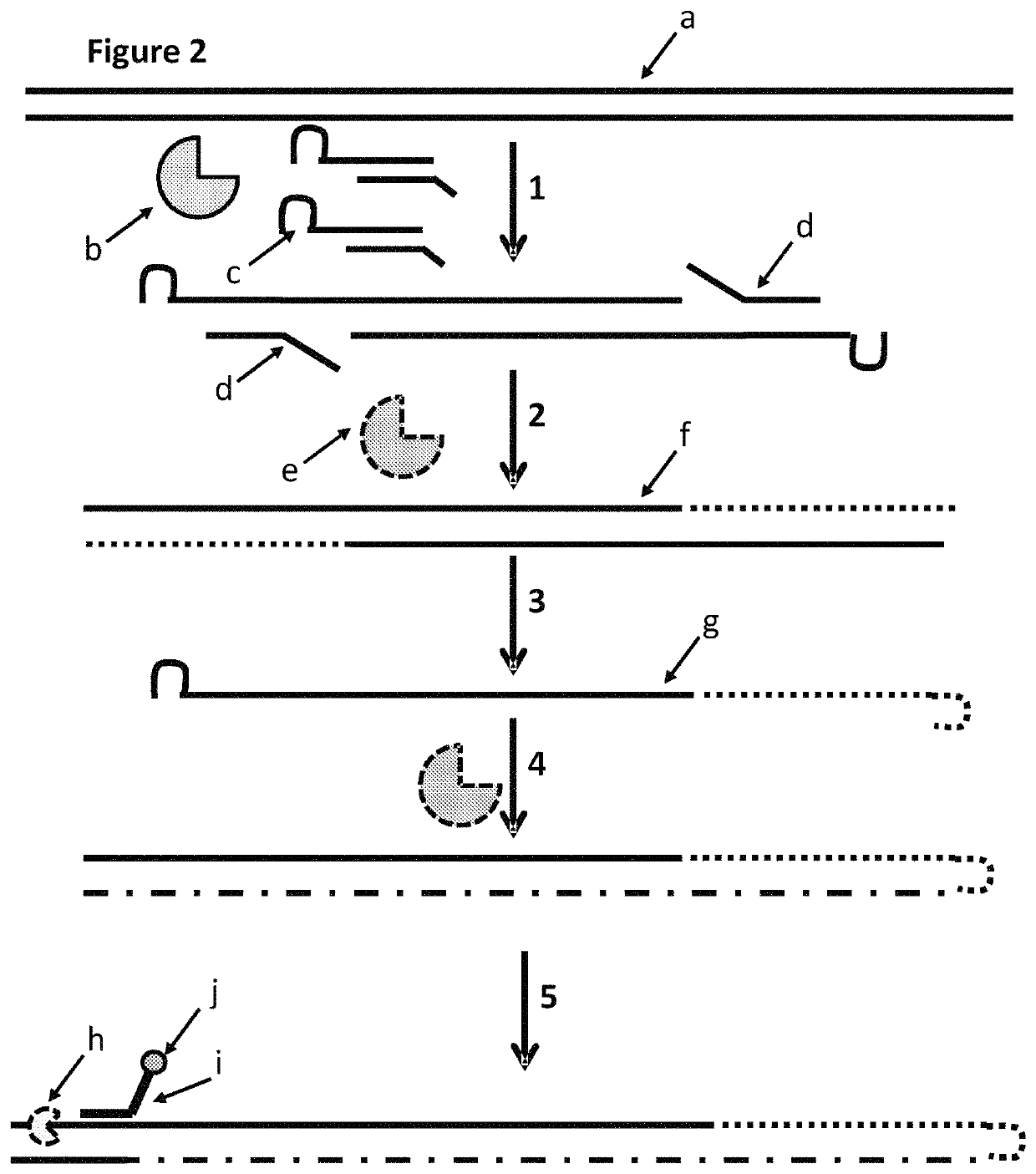
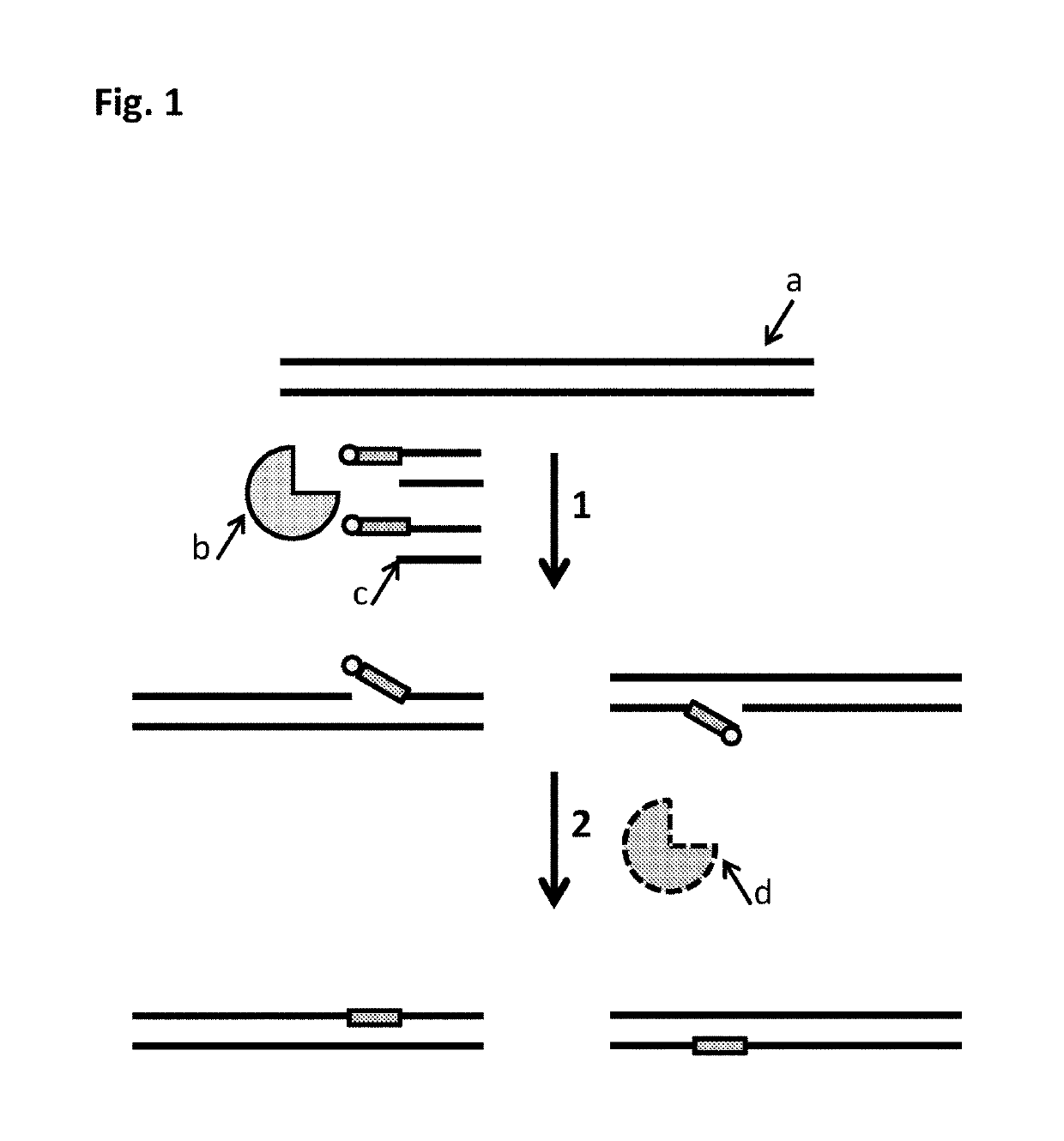
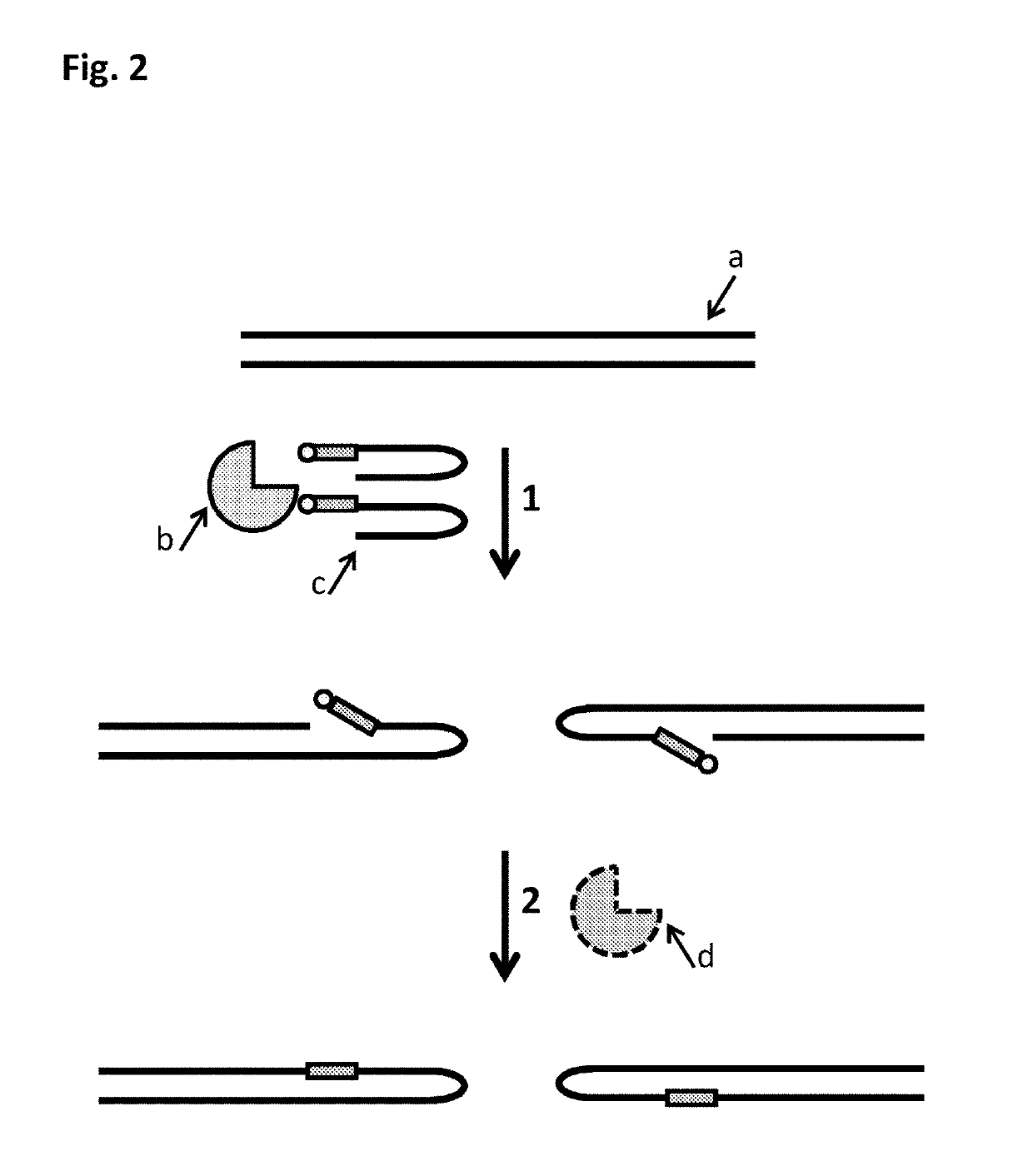
The present invention provides a method for constructing a single-stranded nucleic acid molecule for nucleic acid sequencing by means of a nanopore sequencer, said method including: a step in which at least one hairpin primer including a single-stranded region on the 3′ side and a pair of primers are used to synthesize a complementary strand of template DNA that includes the target sequence; and a step in which the synthesized complementary strand forms a hairpin structure inside a molecule and a template extension reaction is carried out. The obtained nucleic acid molecule includes both the target sequence and the complementary strand thereof in the sequence. Single strand construction enables analysis by nanopore sequencing, and the sequence of only the target nucleic acid, which does not include information of the complementary strand, is repeatedly analyzed, thus enabling analysis to be conducted with greater precision by addressing the problem of sequence errors.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Metagenome sample library construction method and identification method based on nanopore sequencing platform and kit
ActiveCN109487345AShorten the timeTrue reflection compositionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationComputational biologyBuilding construction
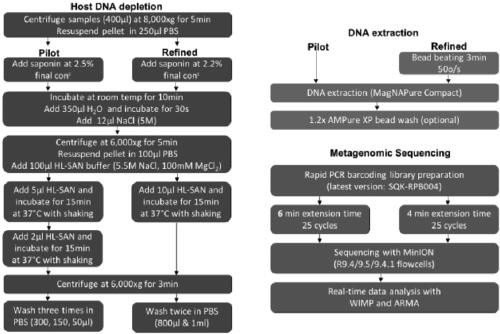
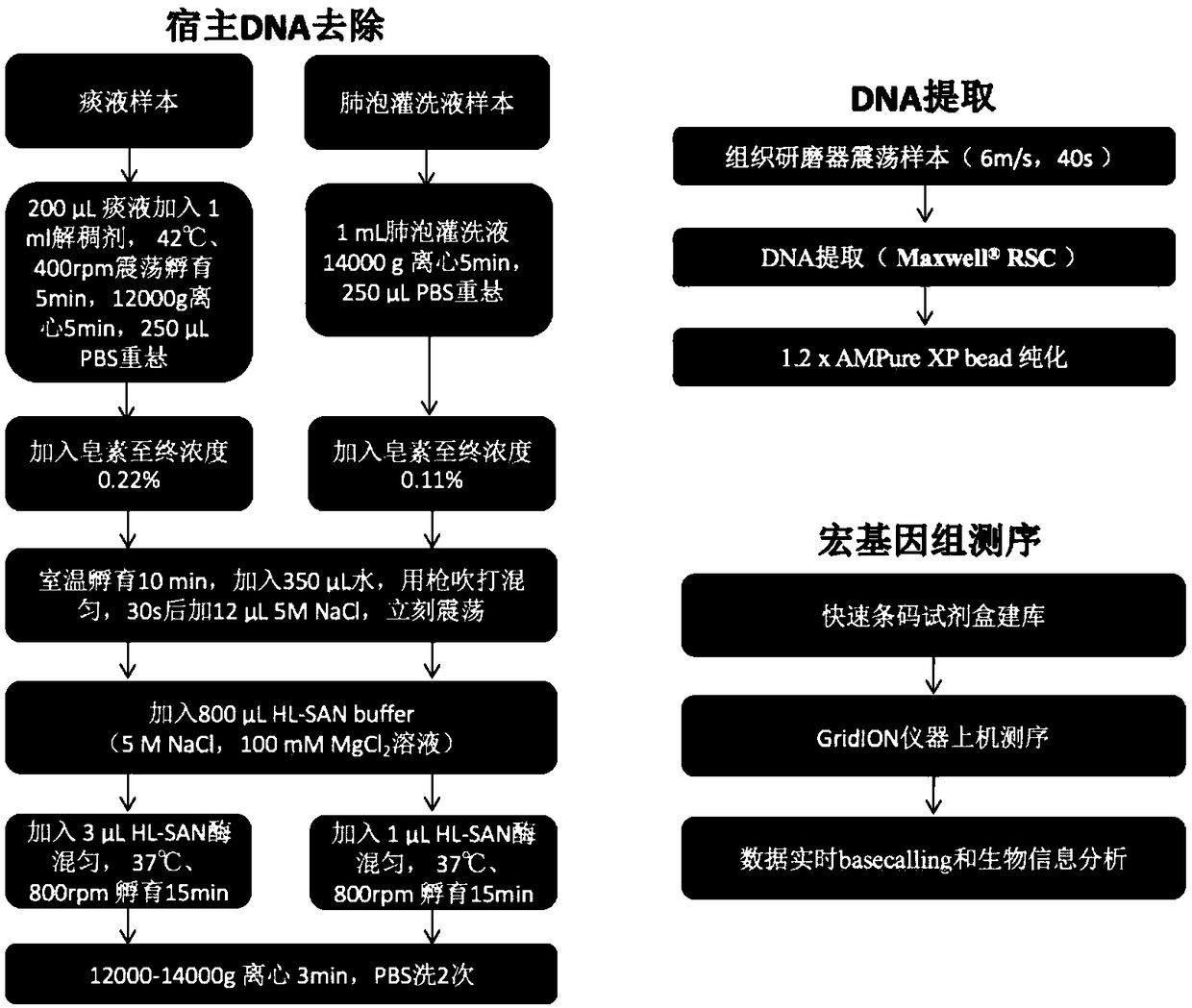
The invention relates to a metagenome sample library construction method and an identification method based on a nanopore sequencing platform and a kit. The method comprises host removal pre-treatmentand sample library construction on human and animal metagenome samples by combining incomplete host removal based on the nanopore sequencing platform so as to sequence and identify the metagenomes. Compared with a conventional process flow, the method is simpler and rapider, meets the reasonable detection demands, omits flows such as library construction PCR in the identifying process, extrudes deviation caused by PCR amplification, and can be used for identifying metagenome microorganisms more truly and accurately.
Owner:BEIJING SIMCERE MEDICAL LAB CO LTD +2
Multi-pass sequencing
ActiveCN107002130AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansData setConcatemer
Improved single molecule sequencing methods, compositions, and devices, are provided. In a first aspect, the present invention provides a multi-pass method of sequencing a target sequence using nanopore sequencing, the method comprising: i) providing a non-naturally occurring concatemer nucleic acid molecule comprising a plurality of copies of the target sequence; ii) nanopore sequencing at least three copies of the target sequence in the concatemer, thereby obtaining a multi-pass sequence dataset, wherein the multi-pass sequence dataset comprises target sequence datasets for the at least three copies of the target sequence; and iii) using the multi-pass sequence dataset to determine the target sequence.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST +1
Polynucleotide modification methods
ActiveUS10501767B2Well representedMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesNucleotidePolynucleotide
The invention relates to a method for modifying a template double stranded polynucleotide, especially for characterization using nanopore sequencing. The method produces from the template a plurality of modified double stranded polynucleotides. These modified polynucleotides can then be characterized.
Owner:OXFORD NANOPORE TECH LTD
DNA sequencing device and manufacturing method
InactiveCN105838592AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove interferenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHexagonal boron nitrideGraphene nanoribbons
The invention provides a DNA sequencing device and a manufacturing method. The device mainly comprises a silicon dioxide thin film arranged on a double-side polished monocrystalline silicon piece. A silicon nitride thin film grows on the top of the silicon dioxide thin film. A bottom layer contact electrode is prepared on the silicon nitride thin film and covered with a bottom layer graphene micro-strip. The bottom layer graphene micro-strip is covered with a hexagonal boron nitride micro-strip. The hexagonal boron nitride micro-strip is covered with a top layer graphene micro-strip. A graphene-hexagonal boron nitride-graphene heterostructure is formed by the bottom layer graphene micro-strip, the hexagonal boron nitride micro-strip and the top layer graphene micro-strip. Graphene-hexagonal boron nitride-graphene nano-pores are etched. According to the device, the problem that a conventional solid-state nano-pore channel is too long, so that the sequencing resolution ratio does not reach single base is solved, and the problem that a tunneling electrode is difficult to manufacture in a tunneling current DNA sequencing method is solved. The advantages lay a foundation for achieving single base resolution ratio and direct nano-pore sequencing.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
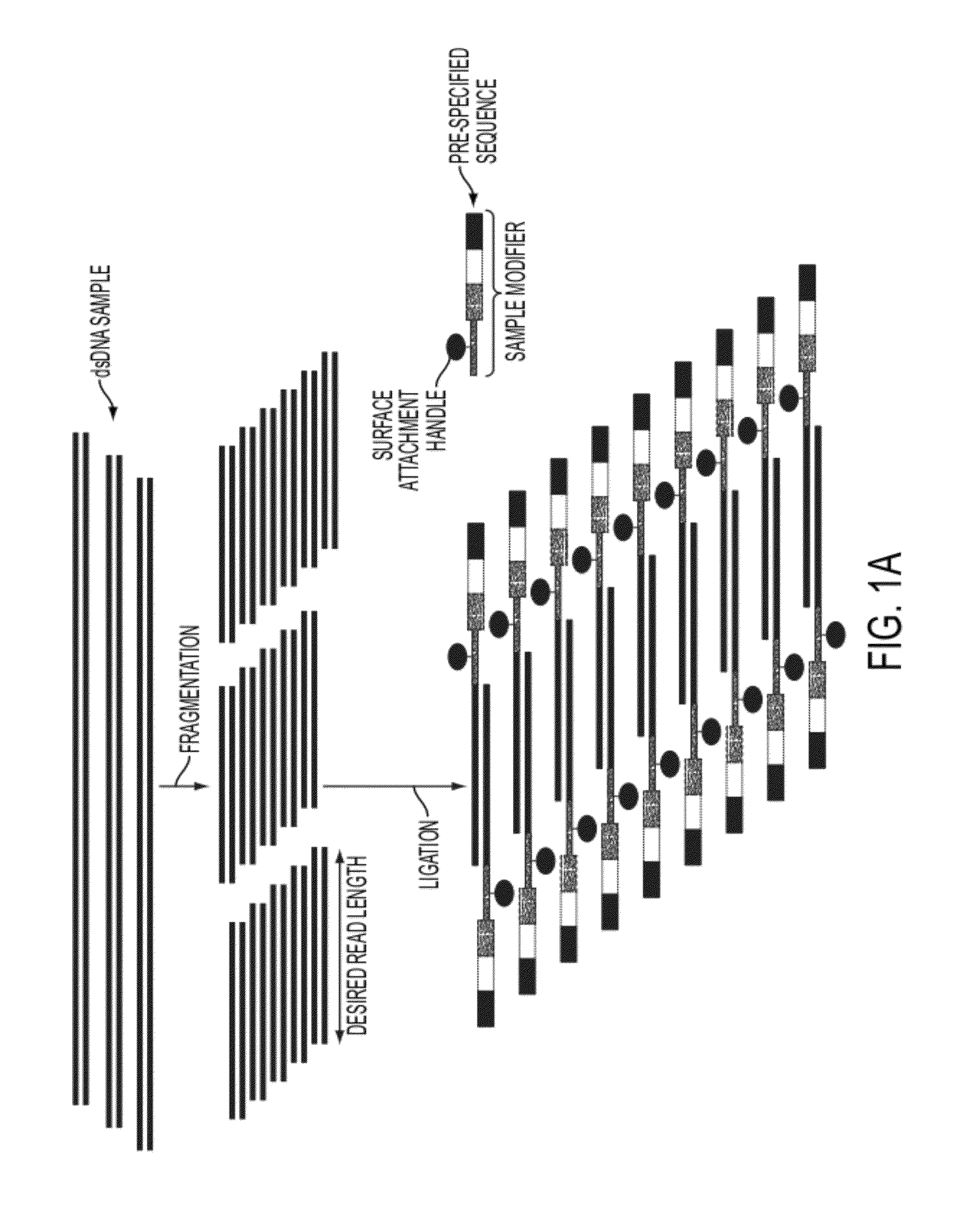
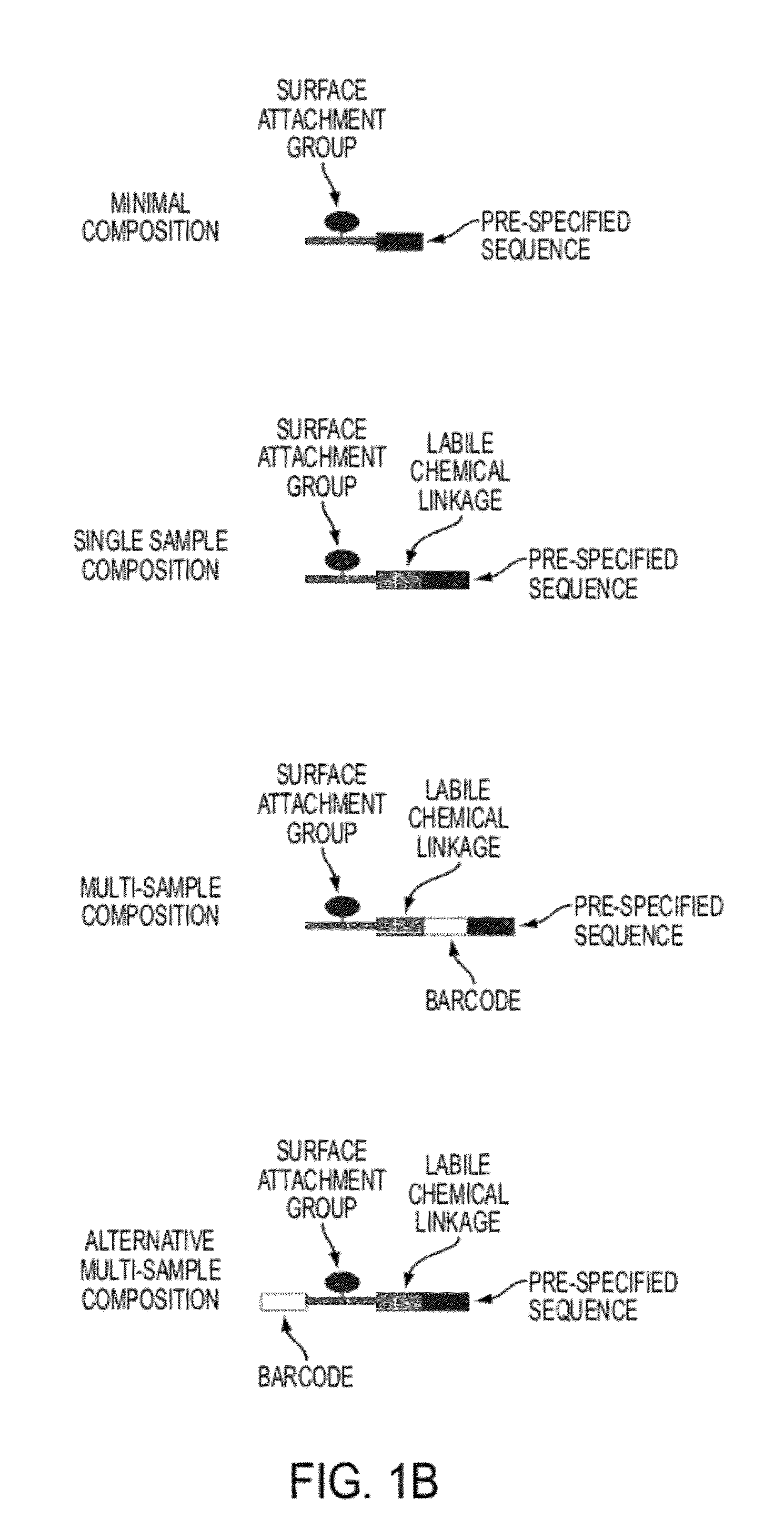
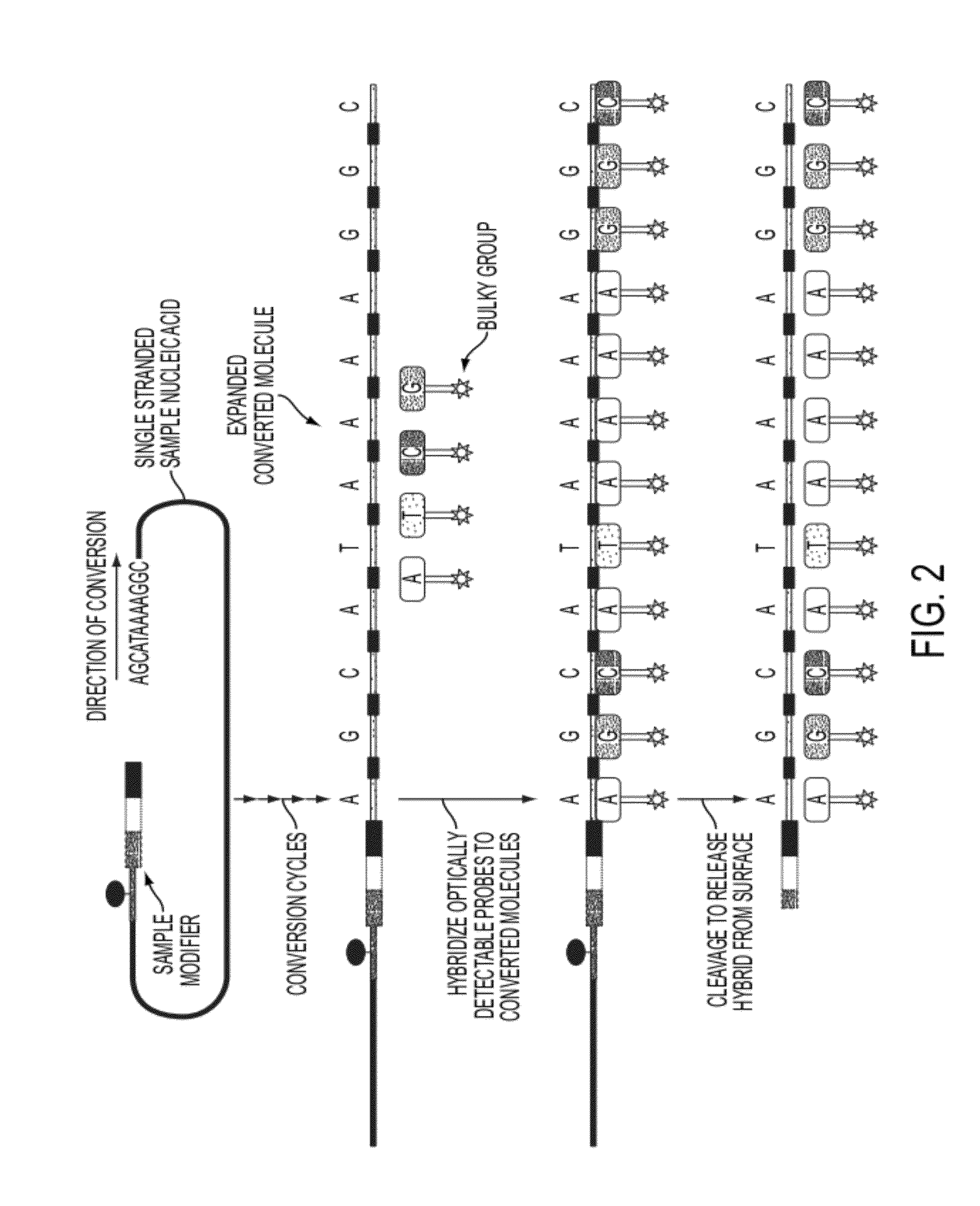
Sequence preserved DNA conversion for optical nanopore sequencing
InactiveUS20120316075A1Generate accuratelyMicrobiological testing/measurementNanosensorsNucleotide sequencingNanopore
The present invention relates to a method for conversion of a target nucleic acid molecule according to a predetermined nucleotide code into a converted nucleic acid molecule. The converted nucleic acid molecule has utility for determining the nucleotide sequence of the target nucleic acid molecule, for example, using a nanopore.
Owner:NOBLEGEN BIOSCI
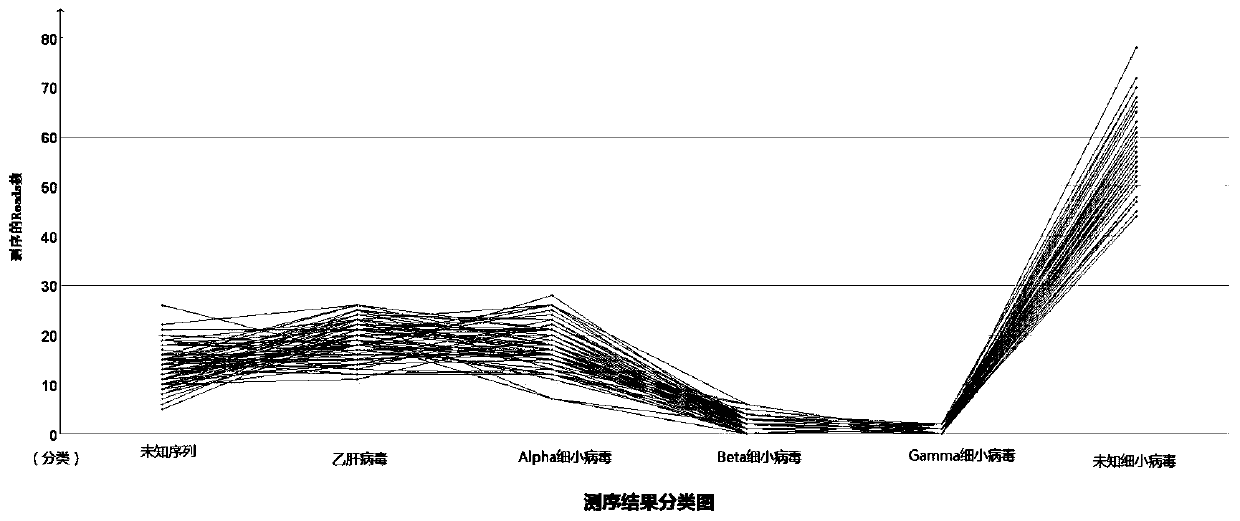
Nanopore three-generation sequencing detection method for plasma virology
ActiveCN111254190AReal-time detectionReal-time analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsBlood specimenViral nucleic acid
The invention provides a nanopore three-generation sequencing detection method for plasma virology. The method comprises the following steps: preparation of viral nucleic acid in blood samples and incorporation of standard nucleic acid internal reference, construction of nanopore sequencing library, real-time sequencing of nanopore and conversion of real-time fast file, bioinformatics analysis andthe like. The method not only can rapidly detect virus group of a blood sample, but also can improve coverage rate of a whole genome sequence of virus and achieve a purpose of rapidly detecting the virus of the blood sample.
Owner:INST OF PATHOGEN BIOLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Primer group and kit for rapidly identifying respiratory tract microorganisms based on nanopore sequencing and application of primer group
ActiveCN112501268APrecise positioningImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesPneumonitisEnterococcus
The invention discloses a primer group for detecting respiratory tract microorganisms based on a nanopore sequencing method. The nucleotide sequences of the primer group are as shown in SEQ ID NO:1-20. The microorganisms are streptococcus pneumoniae, staphylococcus aureus (resisting to methicillin), klebsiella pneumoniae, pseudomonas aeruginosa, acinetobacter baumannii, stenotrophomonas maltophilia, candida albicans, haemophilus influenzae, legionella pneumophila, enterococcus faecium, chlamydia psittaci, cryptococcus gattii, aspergillus fumigatus and pneumocystis jiroveci. According to the invention, sequencing optimization is carried out on different types of samples of the respiratory tract microorganisms, so that the detection method, the kit and the like are suitable for various typesof respiratory tract samples; and a targeted amplification method is adopted, so that the detection requirements of sputum, alveolar lavage and other sample types can be met. In addition, parallel sequencing can be performed, so that the flux of the detected samples is increased, the sequencing time is shortened, and the contradiction between the flux of detected pathogenic species and the cost and time is further relieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com