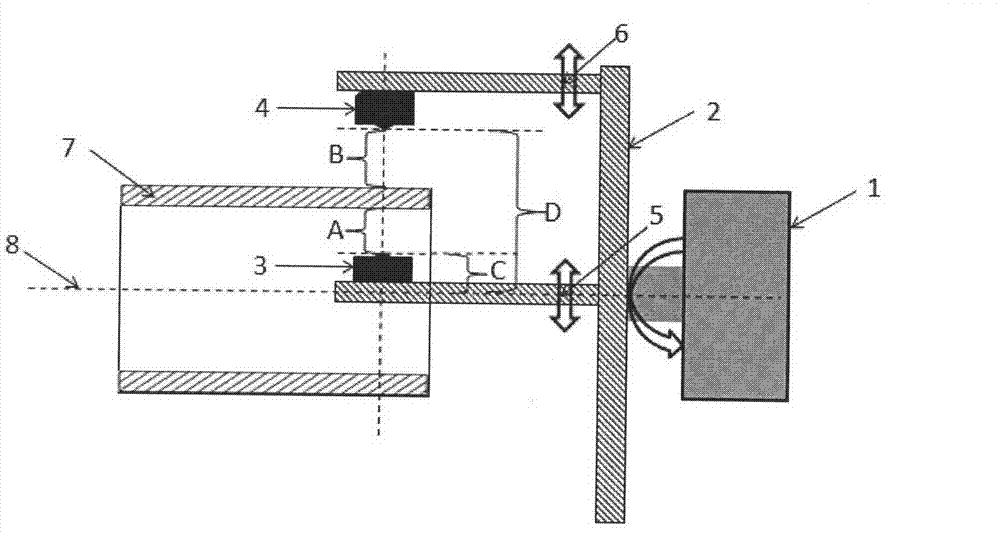
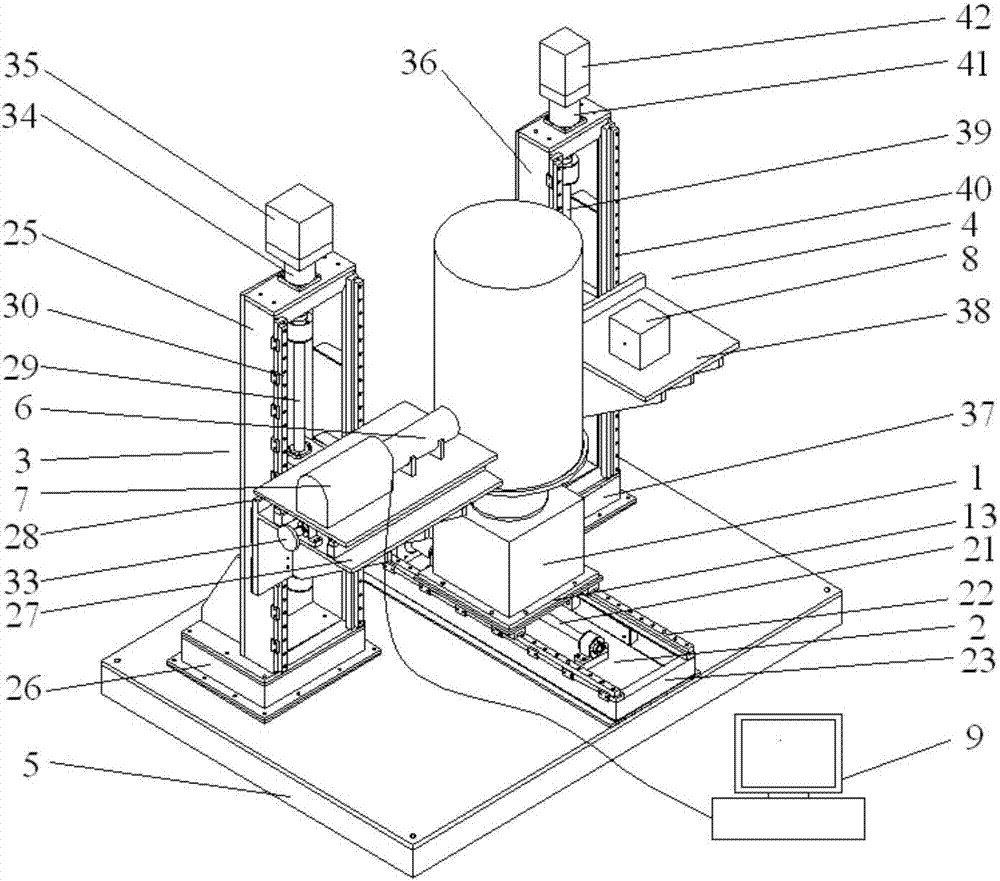
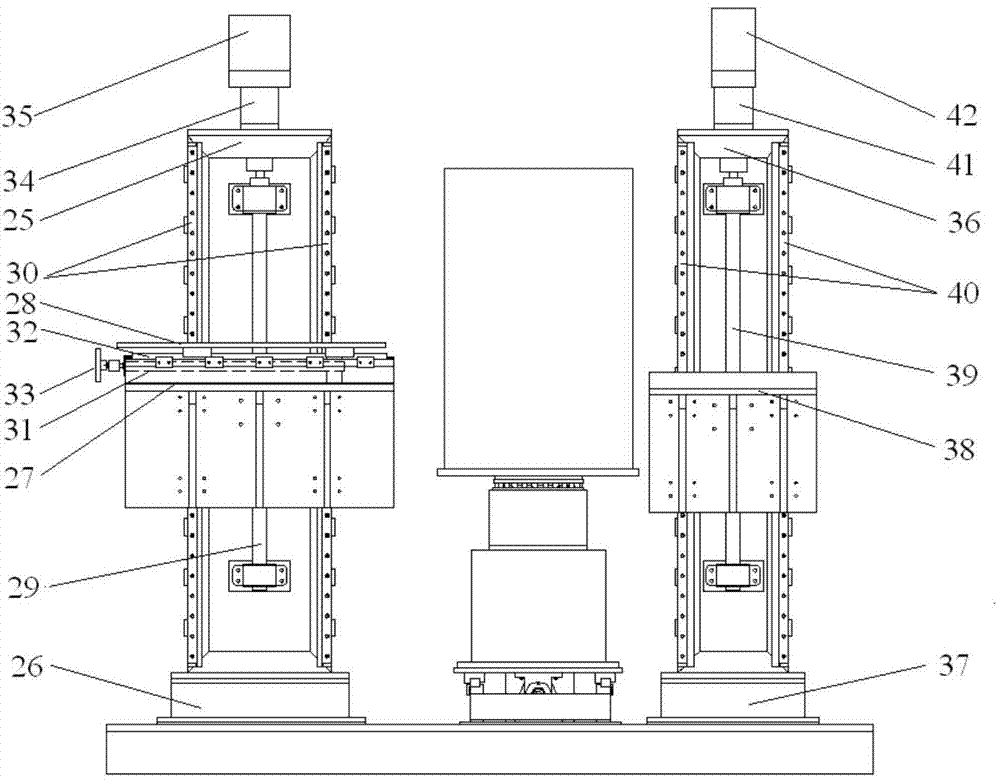
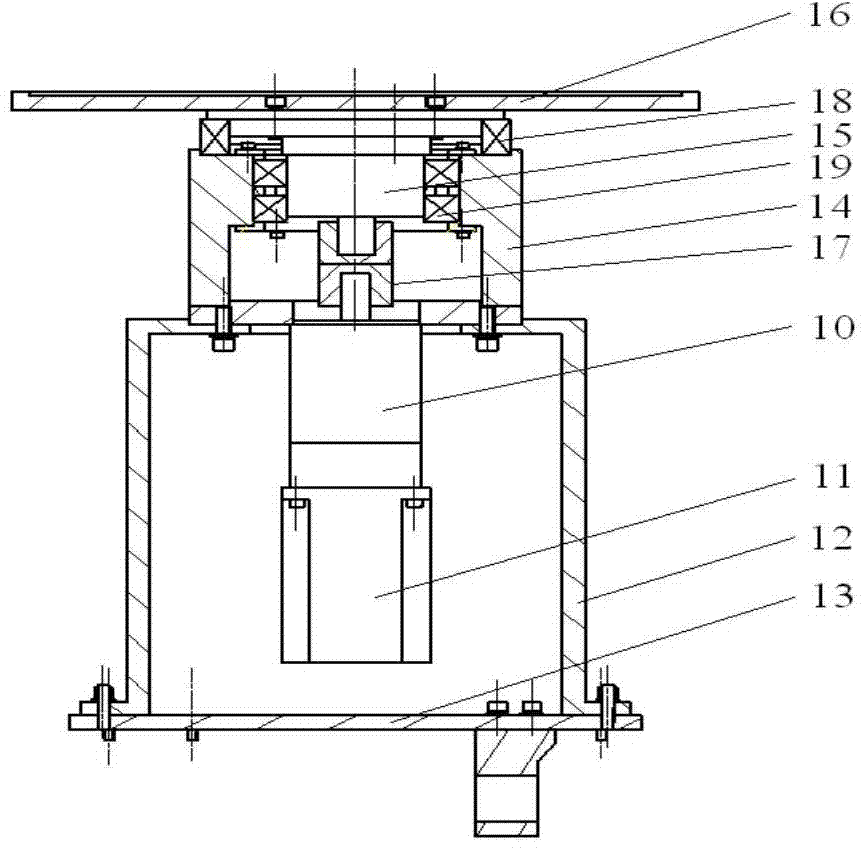
Patents
Literature
104results about How to "Long measurement time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
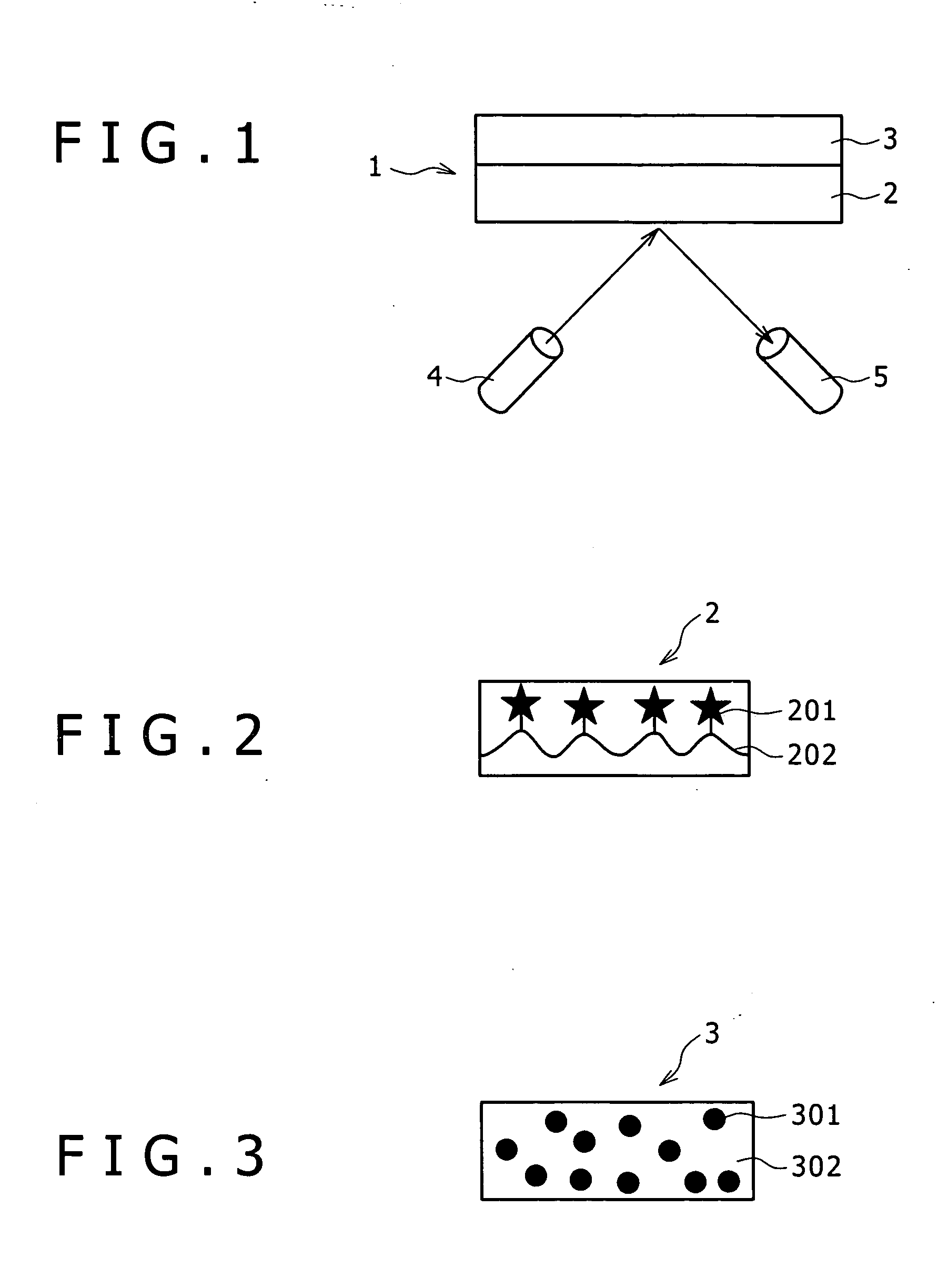
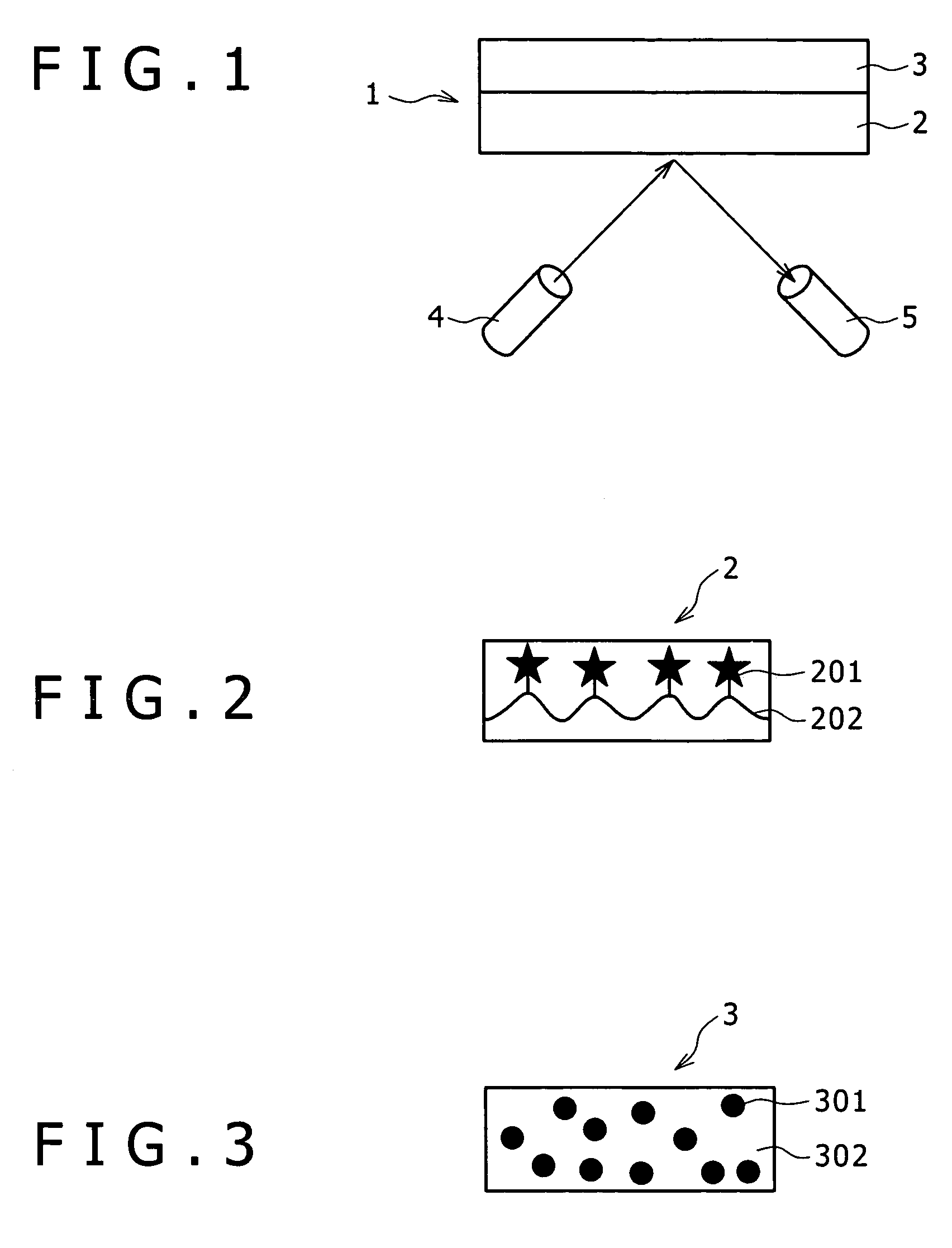
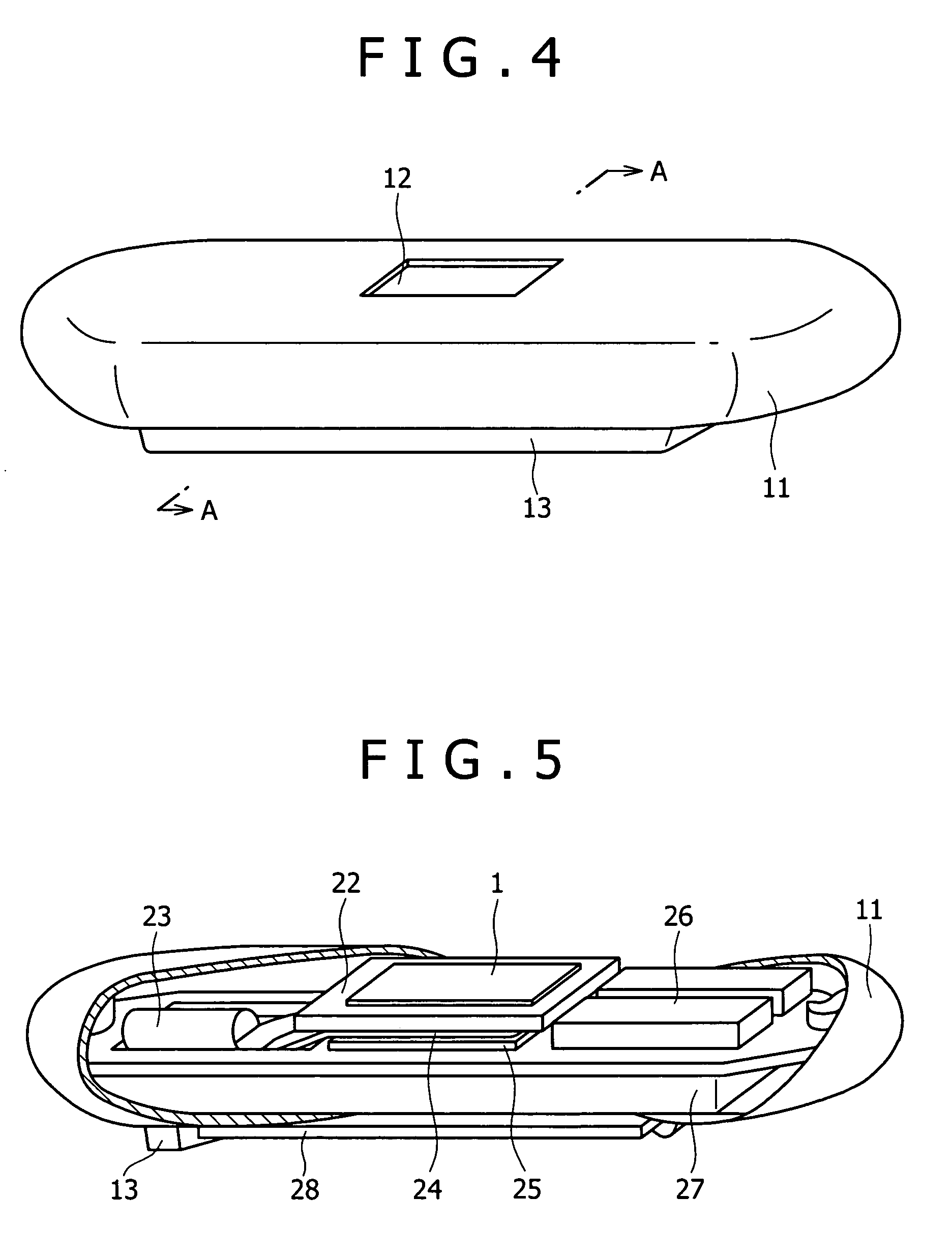
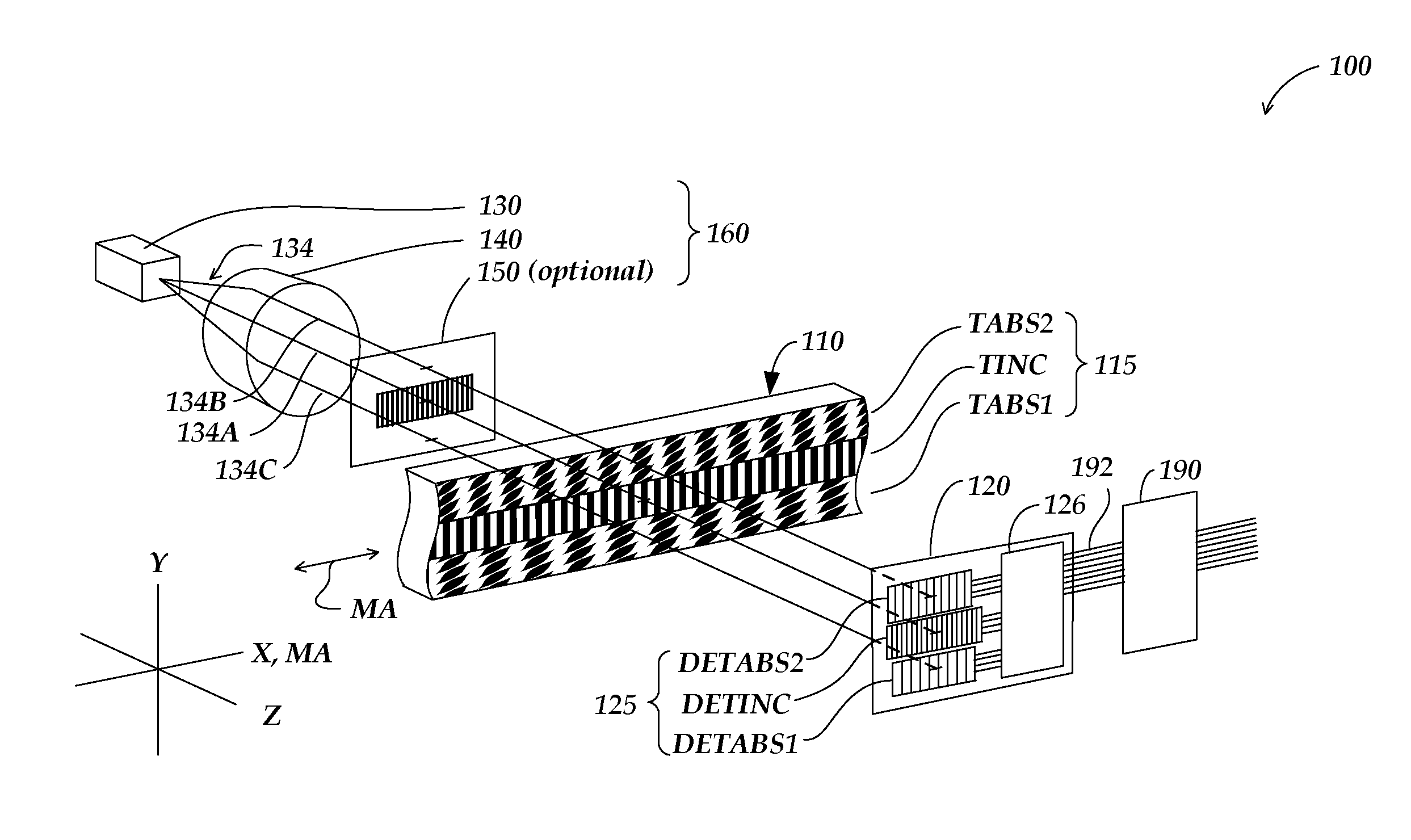
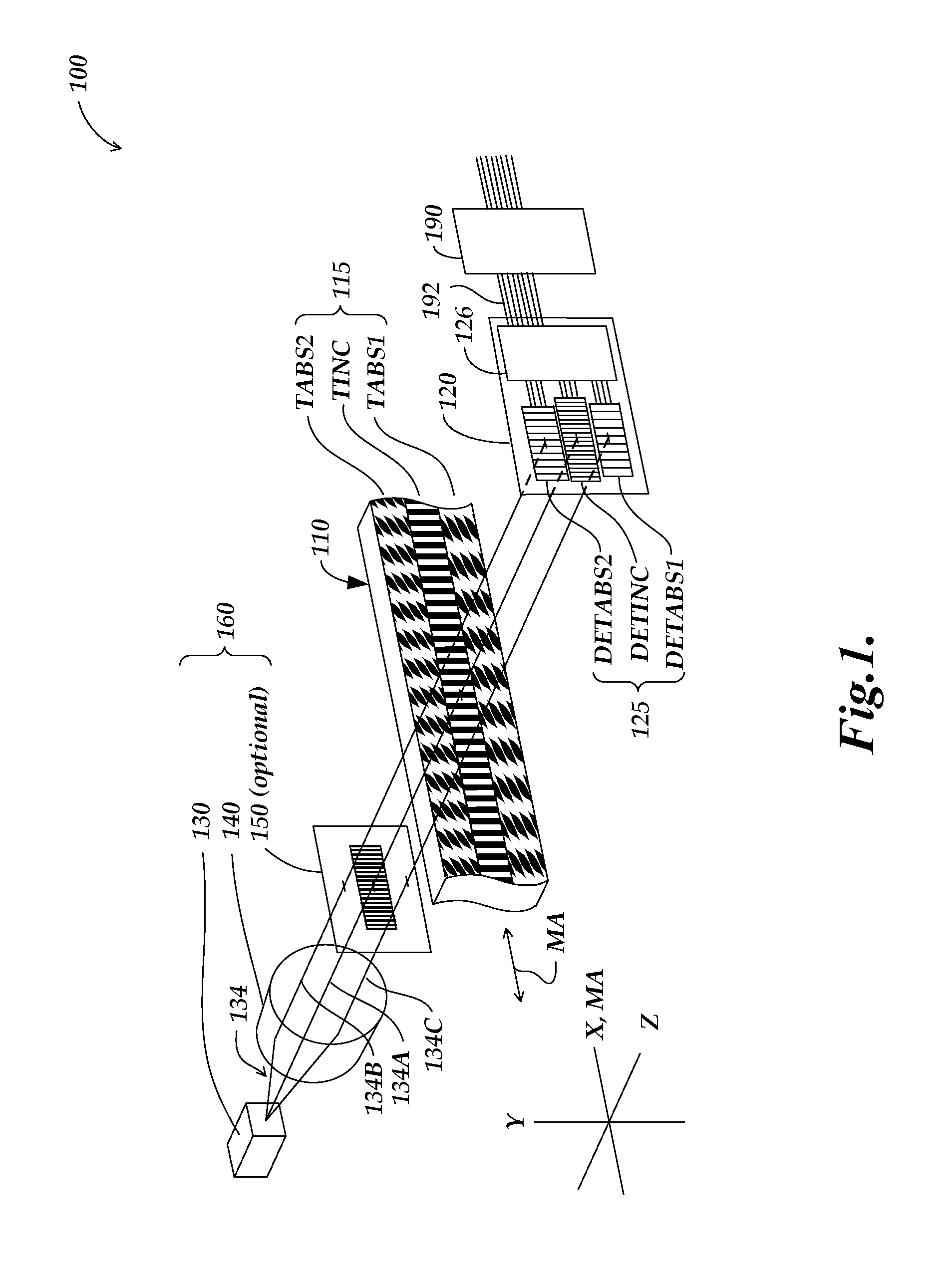
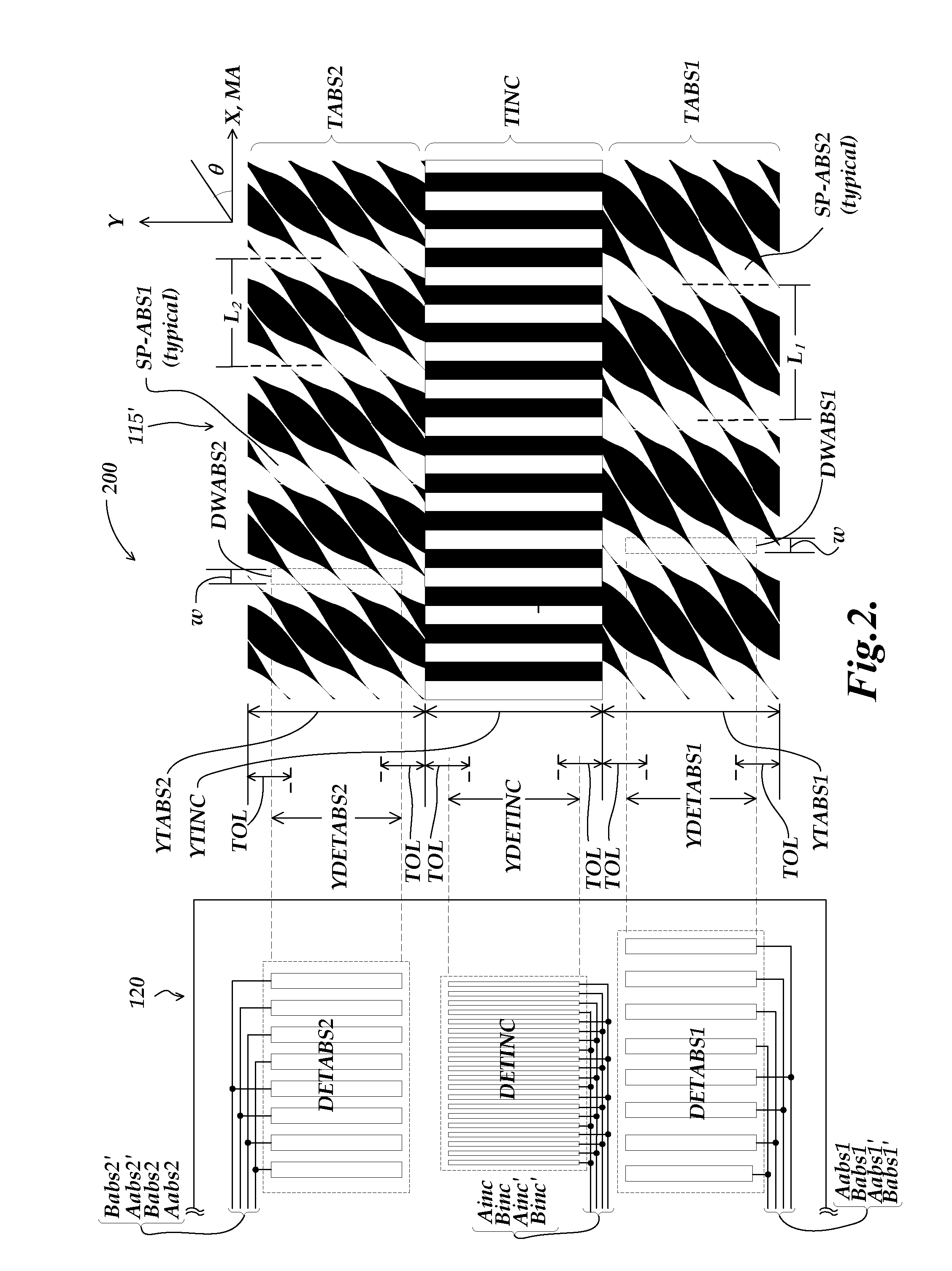
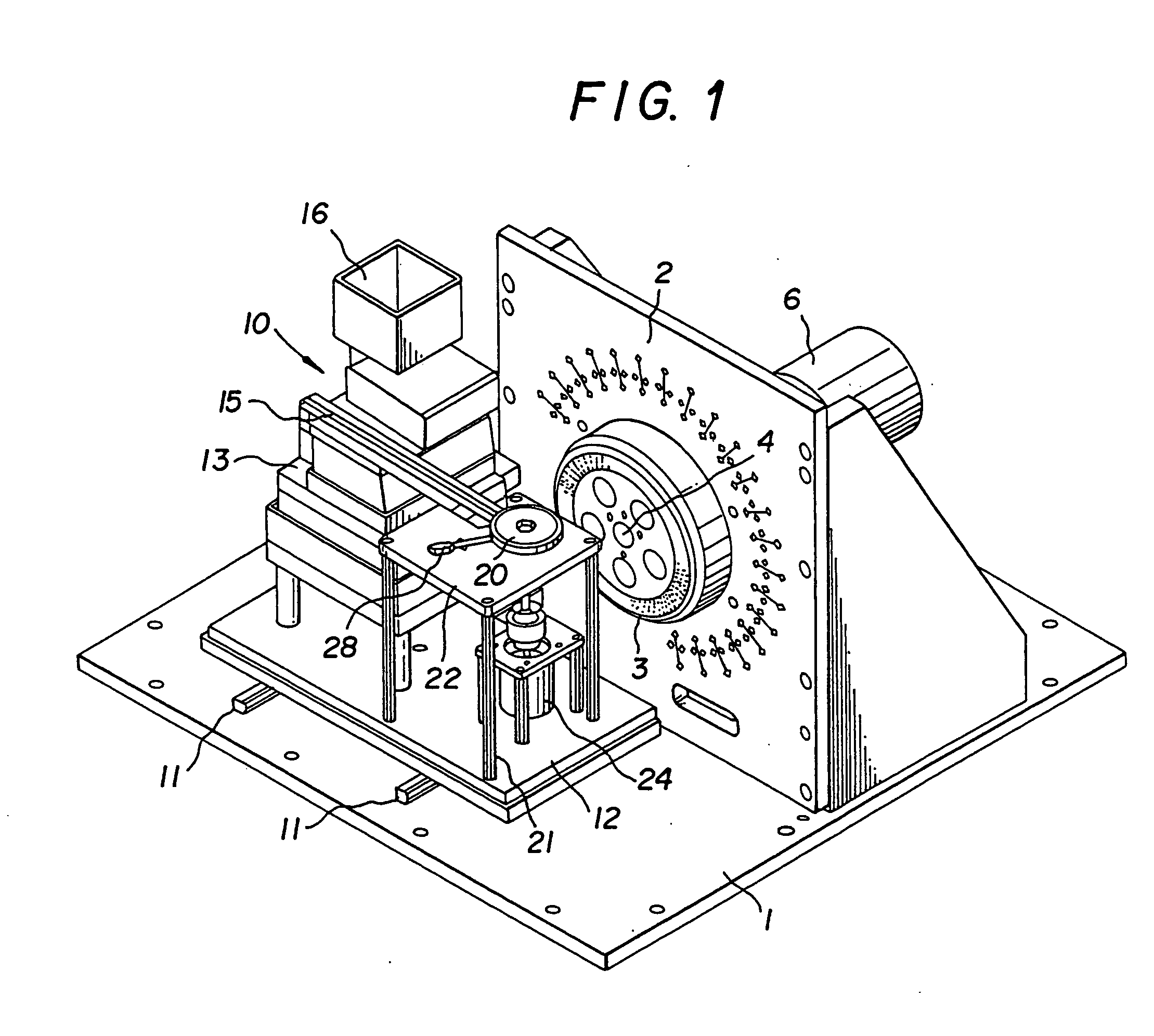
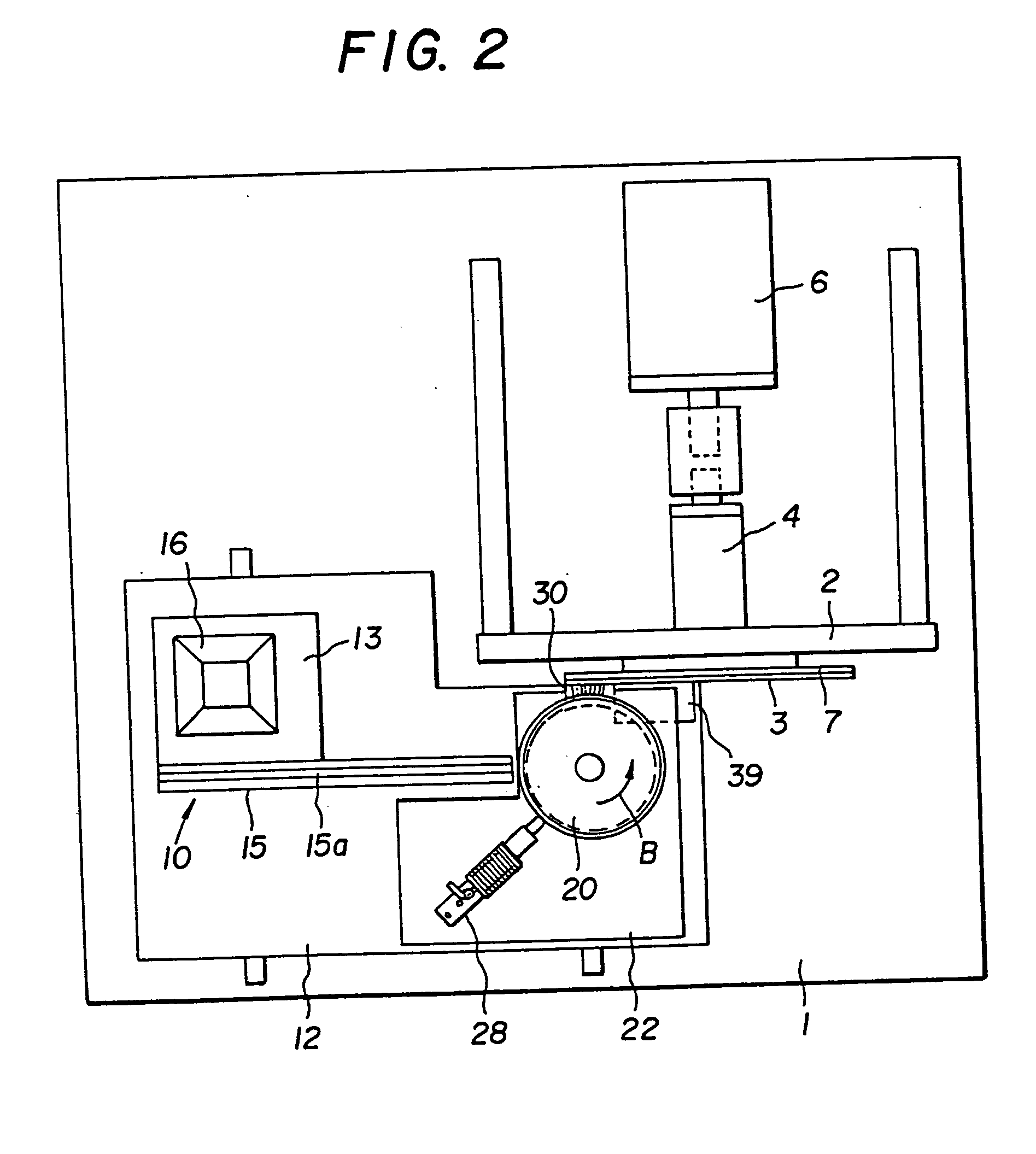
Absolute optical encoder with long range intensity modulation on scale
ActiveUS8309906B2Improved absolute encoderRaise the ratioElectric signal transmission systemsMaterial analysis by optical meansModulation functionOptical density
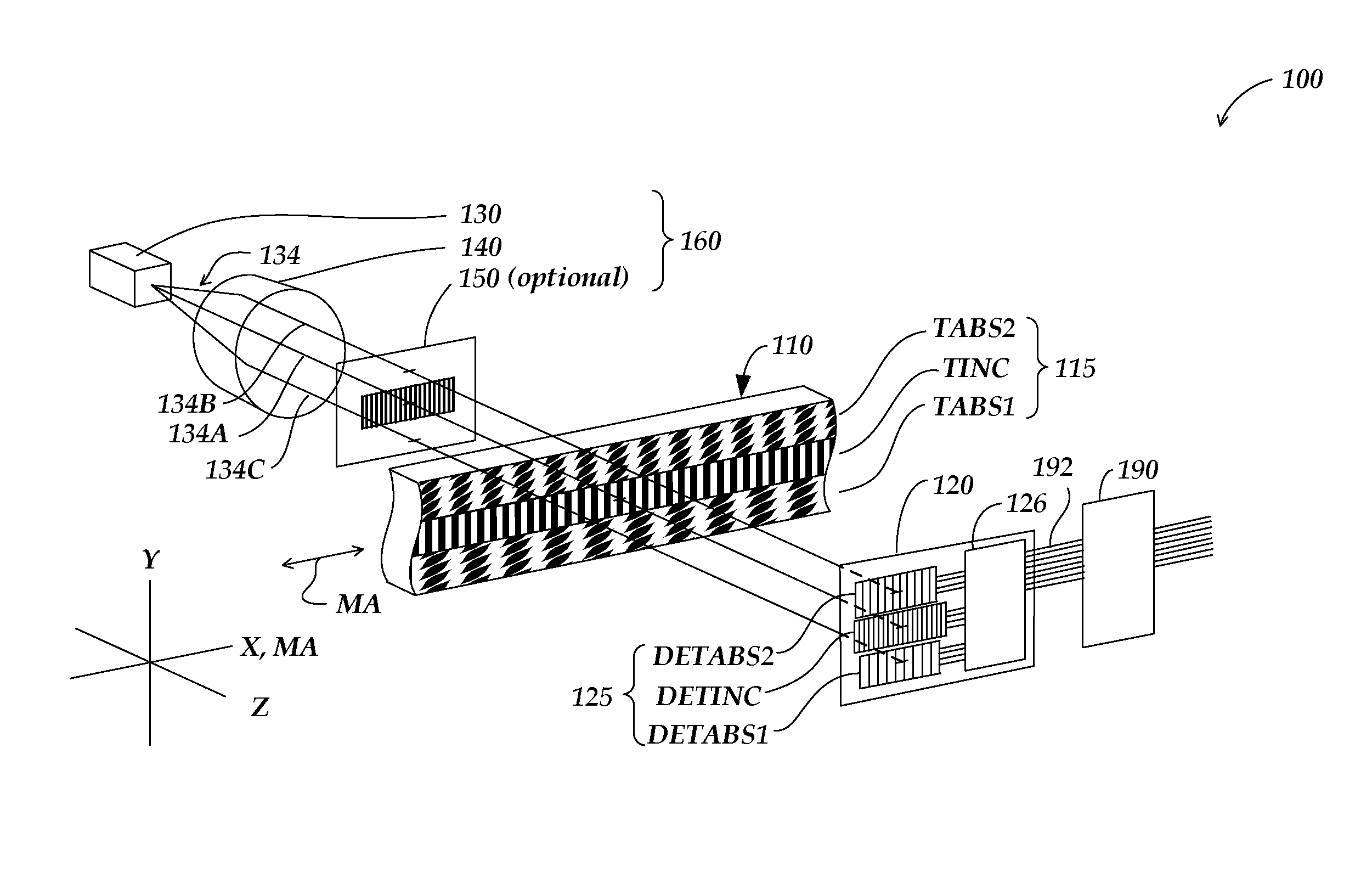
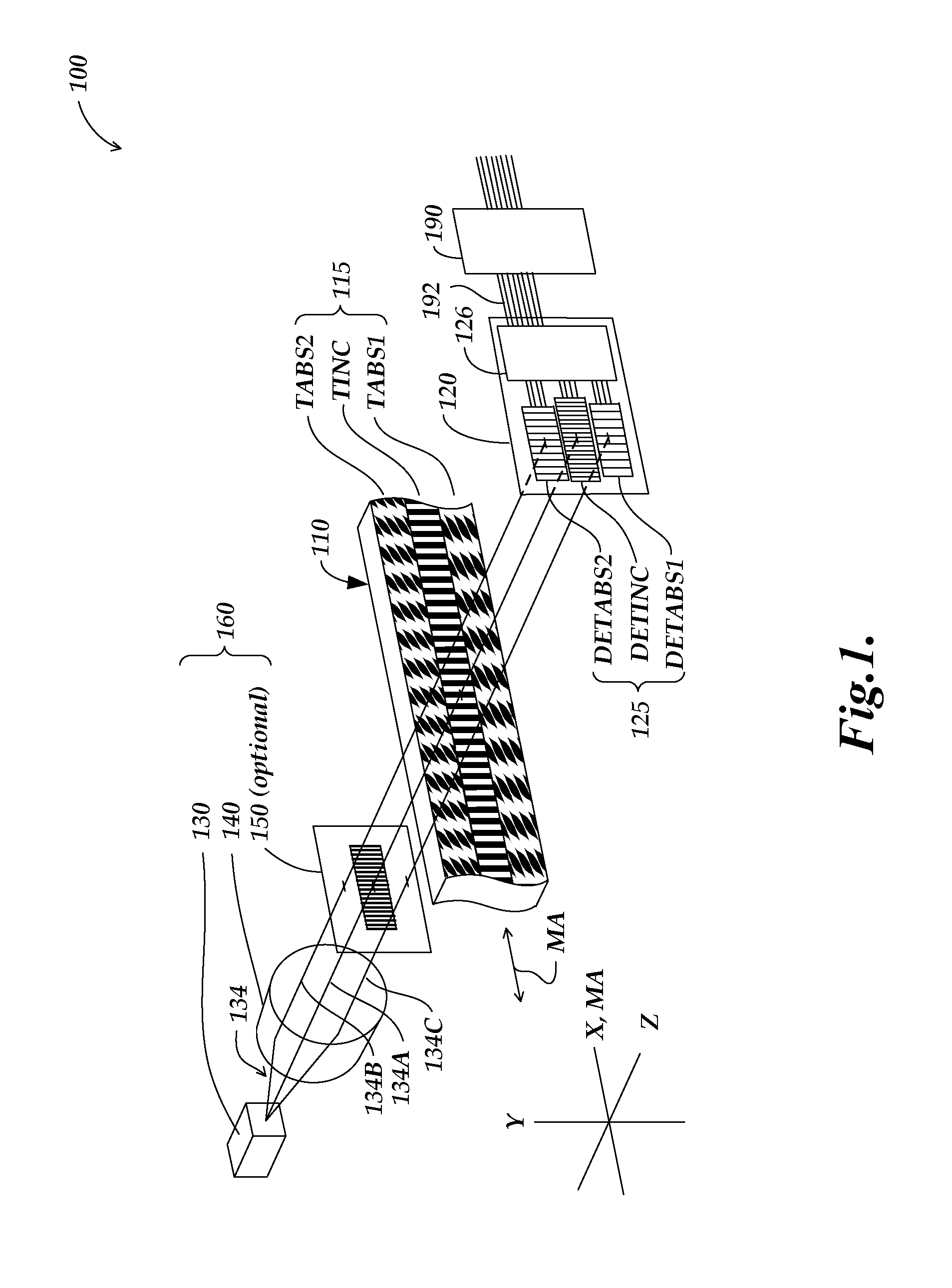
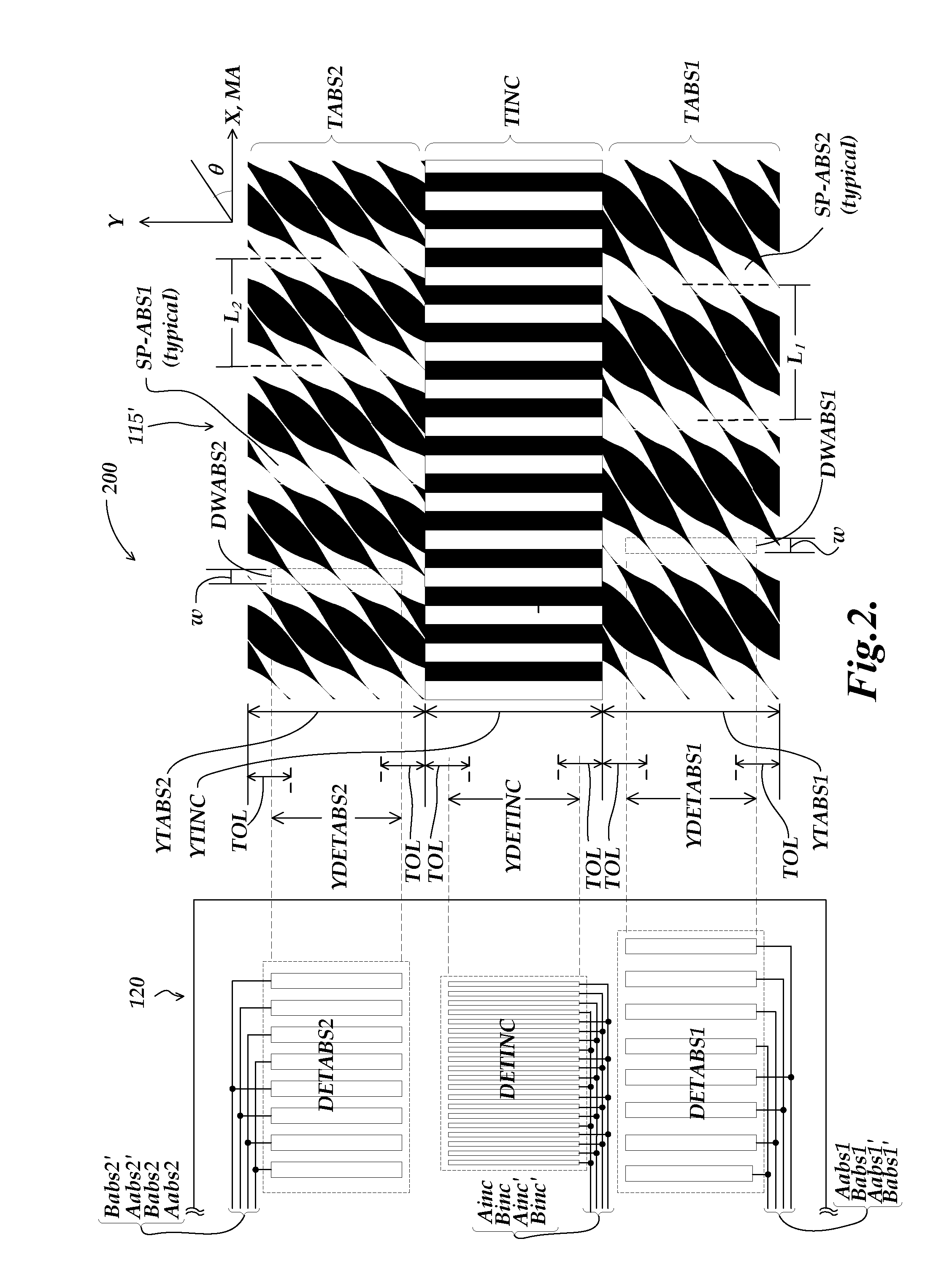
An encoder configuration comprises a dual-modulation scale track pattern that provides a first intensity modulation component for producing periodic signals, and a second intensity modulation component for producing a long-range absolute signal. The dual-modulation scale track pattern increases the range-to-resolution ratio of the encoder without the use of additional scale tracks that would increase the width of the encoder components. The long-range signal may be encoded in the dual-modulation scale track pattern either by varying certain dimensions of pattern elements included in the scale track or by superimposing a layer including an optical density variation along on the track on pattern elements of similar areas. In either case, the net offset and / or amplitude levels of the associated signals are modified along the scale track. These modified offset and / or amplitude levels provide the basis for the long-range absolute signal.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
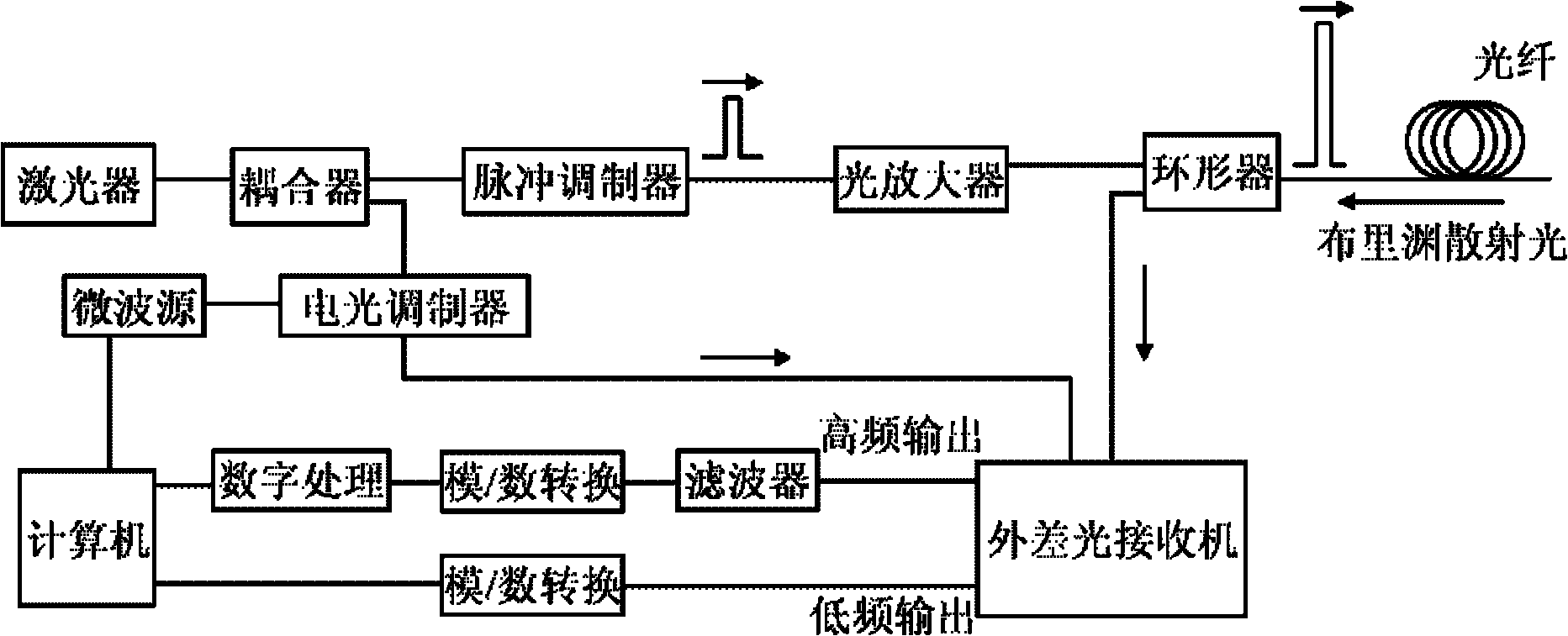
BOTDR (Brillouin Optical Time Domain Reflectometer) for calibrating optical power of reference light and calibrating method thereof
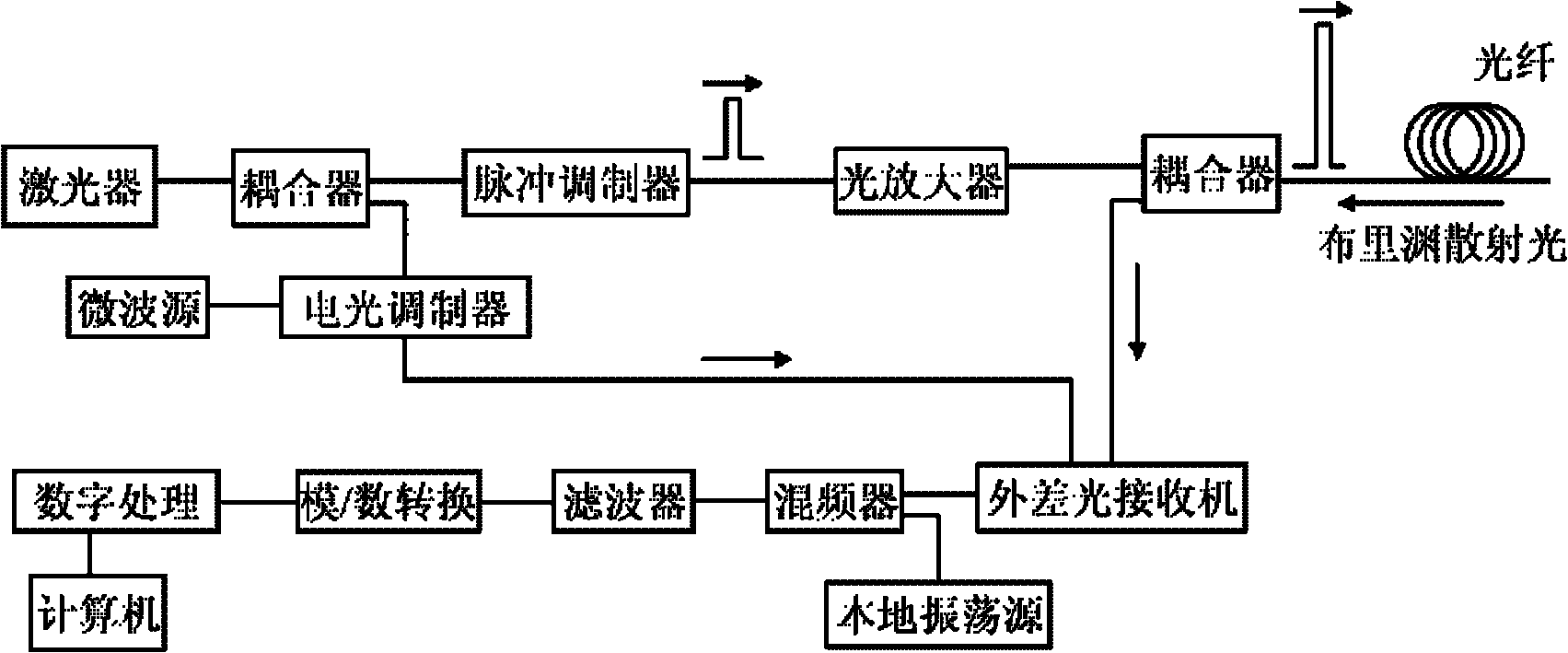
InactiveCN101839698AAccurate measurementHigh measurement accuracyThermometers using physical/chemical changesThermometer testing/calibrationTime domainOptical power
Owner:NANJING UNIV
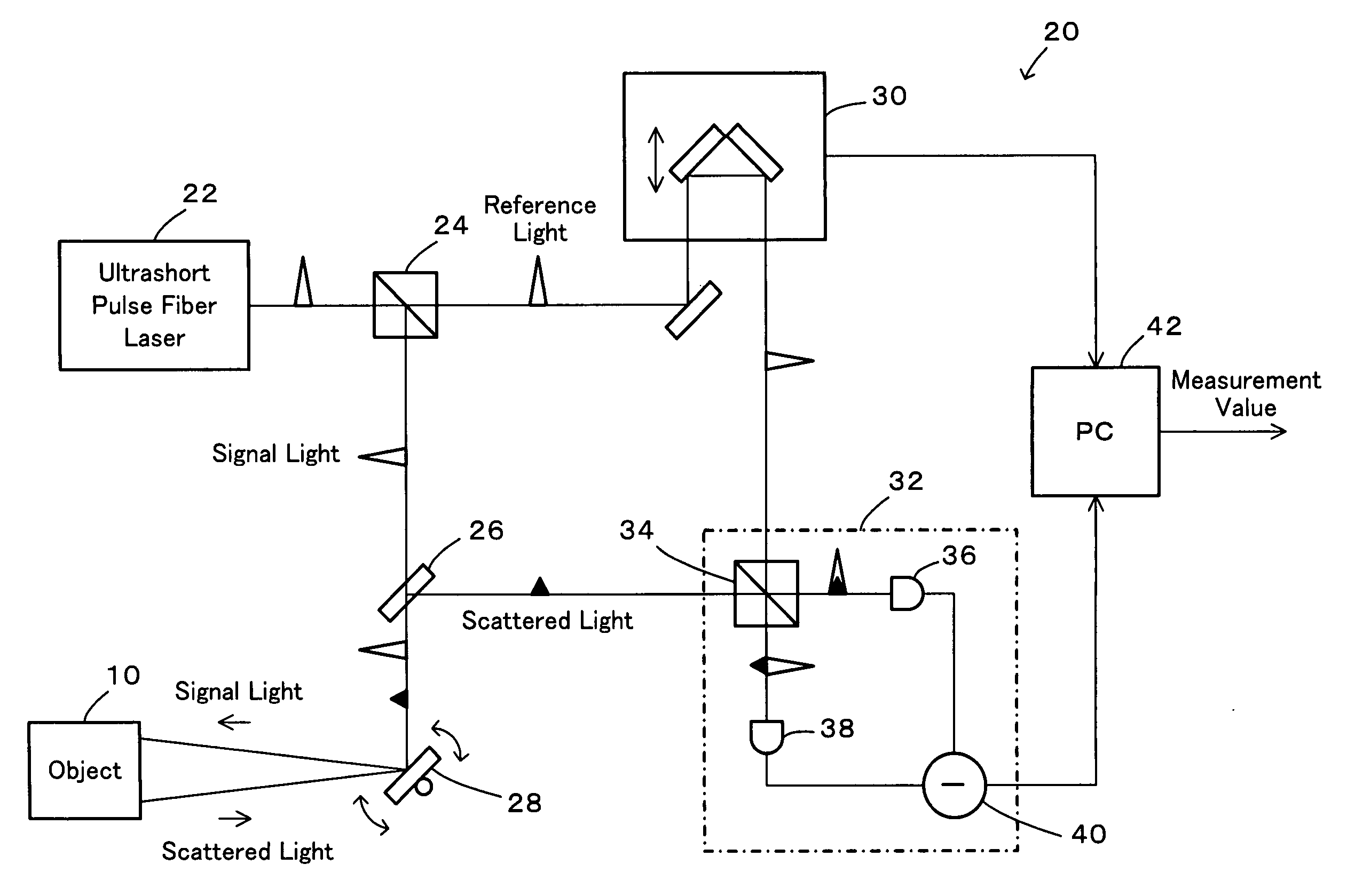
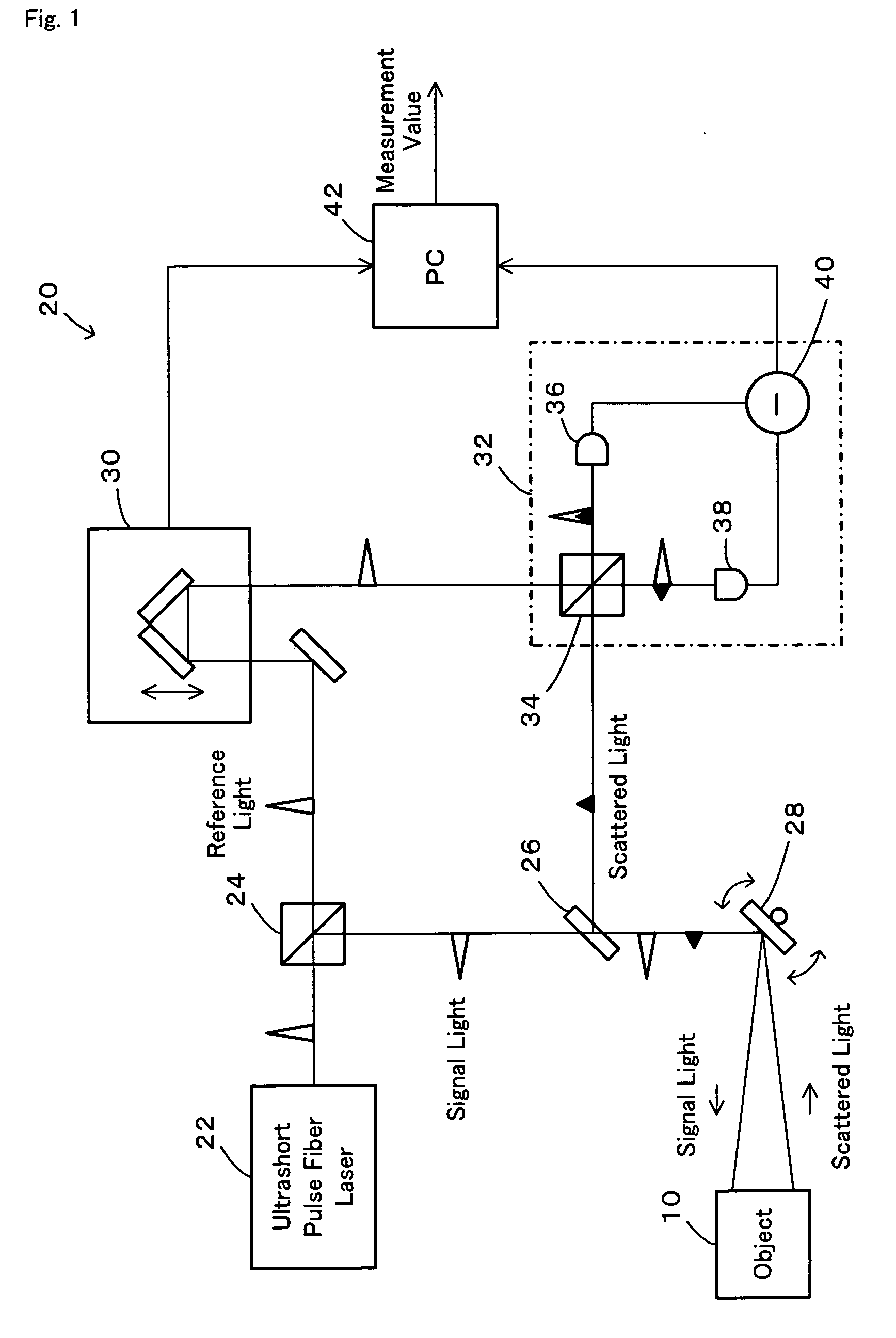
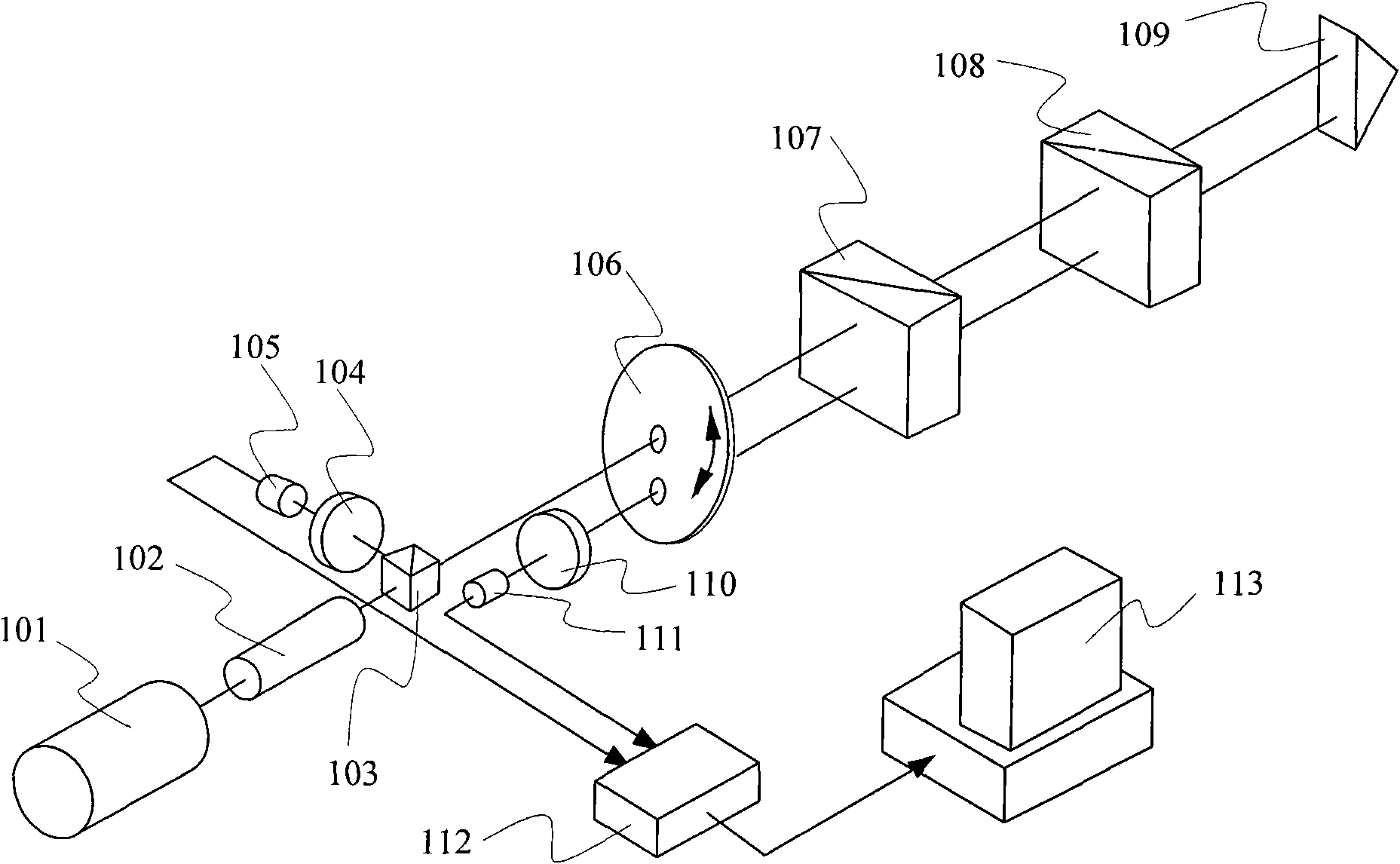
Distance measurement device and distance measurement method
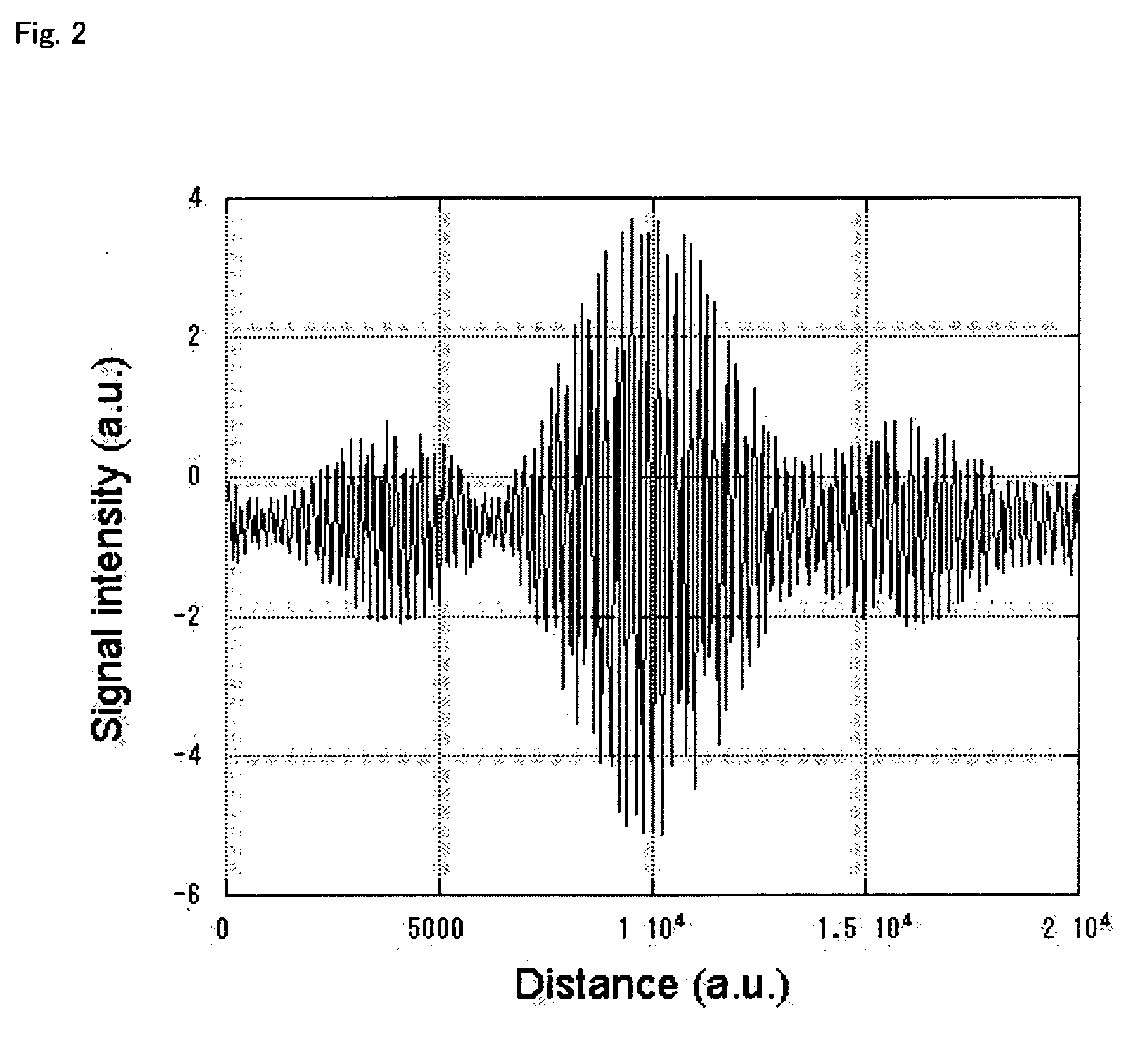
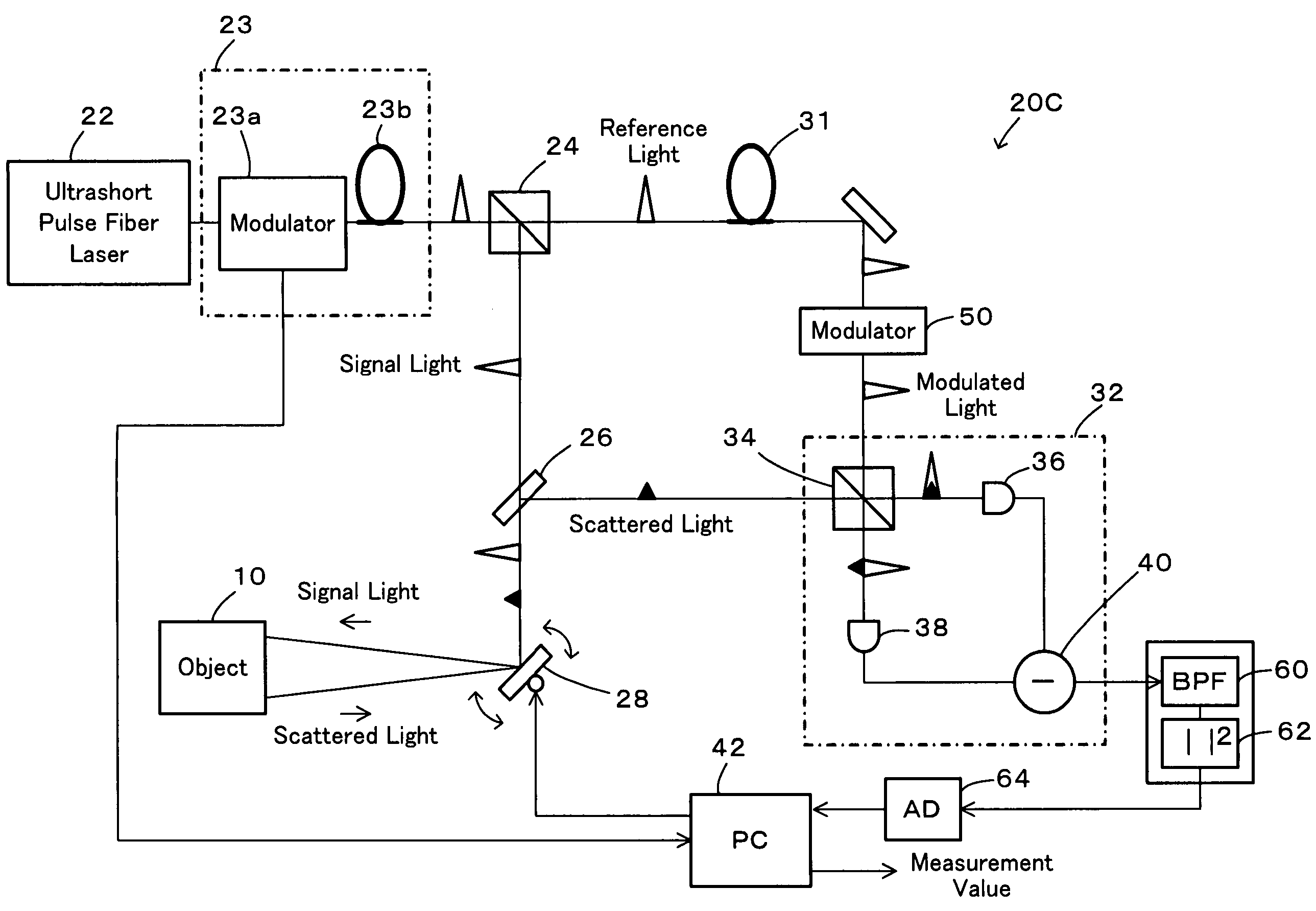
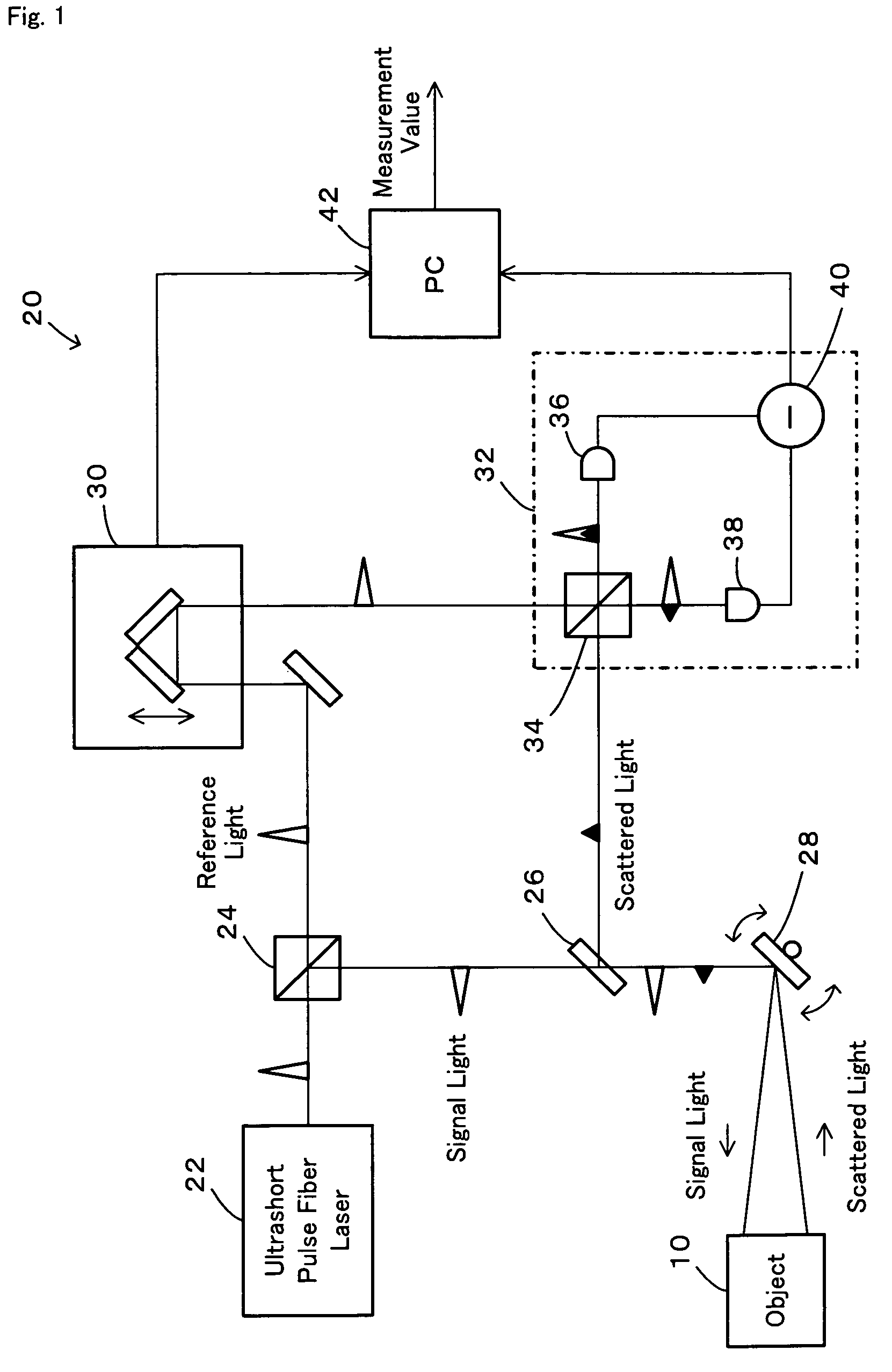
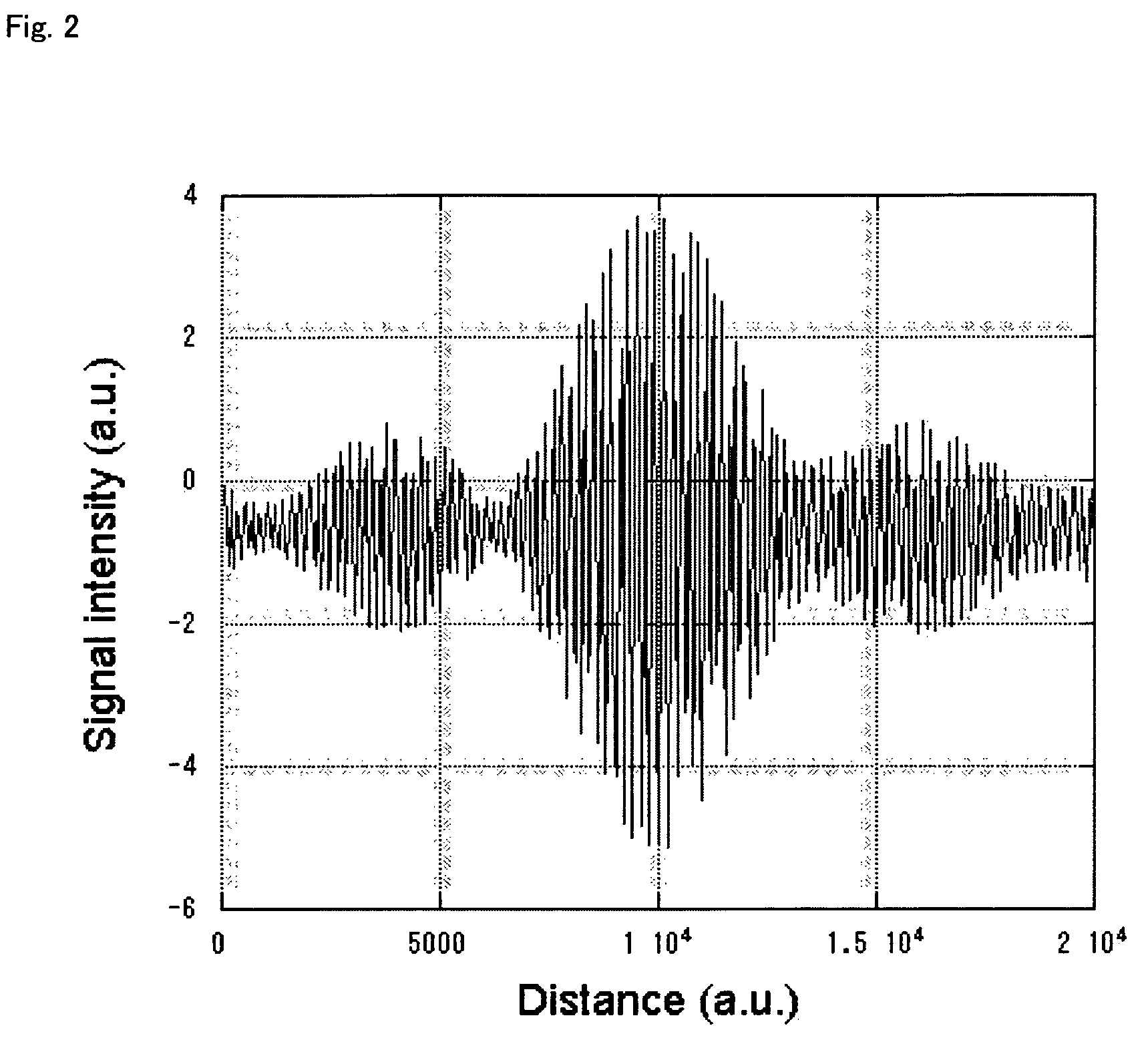
InactiveUS20070024842A1High precision measurementShorten the timeOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationOptical pathScattered light
In a distance measurement device of the invention, a light divider separates pulsed light emitted from an ultrashort pulse fiber laser into reference light A and signal light. A scanning mirror unit irradiates an object with the signal light as a division of the pulsed light and receives scattered light B, which is reflected from the object irradiated with the signal light. An optical path length adjustment unit adjusts an optical path length of the reference light A as a division of the pulsed light. A differential detector included in an interference signal generator detects the degree of interference of the reference light A having the adjusted optical path length with the scattered light B and outputs the detected degree of interference as an interference signal. A computer specifies an adjustment value set in the optical path length adjustment unit to attain a specific optical path length maximizing the interference signal and uses the specified adjustment value to compute a distance from a reference position of the scanning mirror unit to the object. The distance measurement device of the invention thus enables high-speed and highly-accurate measurement of the object.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY
Distance measurement device and distance measurement method
InactiveUS7535555B2Shorten the timeConvenient and accurateOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationSignal lightOptical pathlength
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY
Method capable of automatically adjusting rotation radius and measuring inner diameter and outer diameter of pipe end of steel pipe
InactiveCN104729416AReduce alignment precision requirementsReduced alignment requirementsUsing optical meansLaser rangingEngineering
Provided is a method capable of automatically adjusting a rotation radius and measuring an inner diameter and an outer diameter of a pipe end of a steel pipe. The method is a measuring method which aims at a measuring device for the inner diameter and the outer diameter of the pipe end, wherein laser ranging probes rotate around the pipe end. According to the measuring method, by using the mode that the rotation radius is automatically adjusted during the rotation measuring process, the defect that a laser triangulation method ranging probe is limited in the measuring range is compensated, the requirement for the aligning precision between a rotating central axis and a steel pipe central axis of a rotating platform is greatly lowered, a dynamic range capable of measuring changes on a pipe diameter is enlarged, the equipment cost of an auxiliary machine is lowered, and the stability and the practicality of equipment are improved. Meanwhile, during the operation, aiming at steel pipes with different sizes, the positions of probe fixed arms do not need to be adjusted in advance, the operation procedure is reduced, and the maintenance cost is lowered.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Semi-chromatography gamma scanning method for low-medium radioactive waste barrel measurement
ActiveCN104714245AHigh measurement accuracyTomoscanX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentCounting rateLow-level waste
The invention provides a semi-chromatography gamma scanning method for low-medium radioactive waste barrel measurement. A rotary platform, a detector platform, a detector with a collimator, a transmission source platform, a transmission source, a shielding part of the transmission source and an analysis module are adopted in the method. A waste barrel is divided into multiple section layers in the height direction, the waste barrel is rotated, surface distribution of radioactive point sources on the section layers is changed into linear distribution of ring sources in the radius direction, the detector conducts measurement at different section layer heights and different eccentric positions in the section layers, an equation set reflecting the mutual relation between the detector counting rate and the activity of nuclide in annular grids is established, the equation set is solved, distribution of the activity of the radioactive nuclide in the waste barrel in the diameter direction and the height direction of the barrel is acquired, and the total activity of the radioactive nuclide in the waste barrel is acquired through summation. The method is high in measurement accuracy, short in measurement time and high in practical value and application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Endoscopic image pickup method and magnetic resonance imaging device using the same
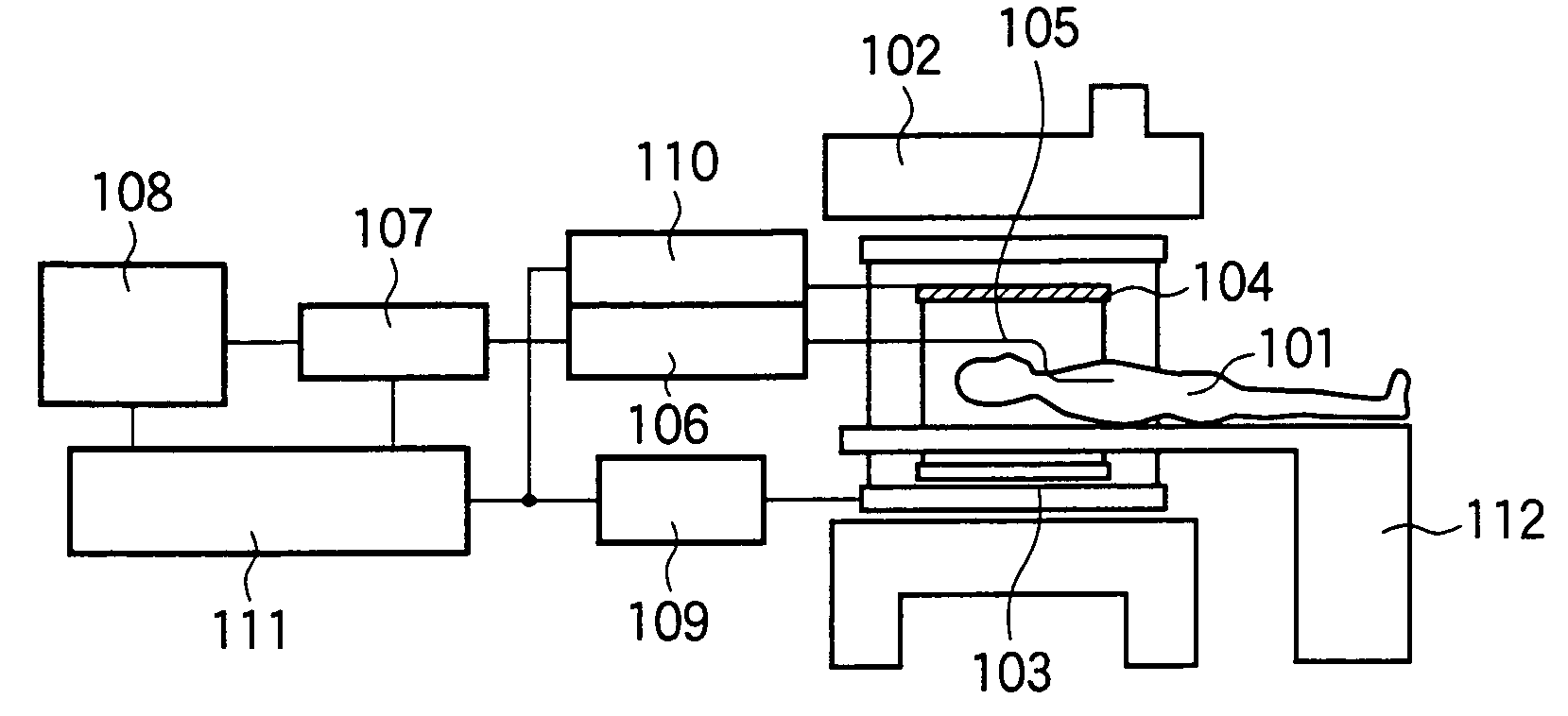
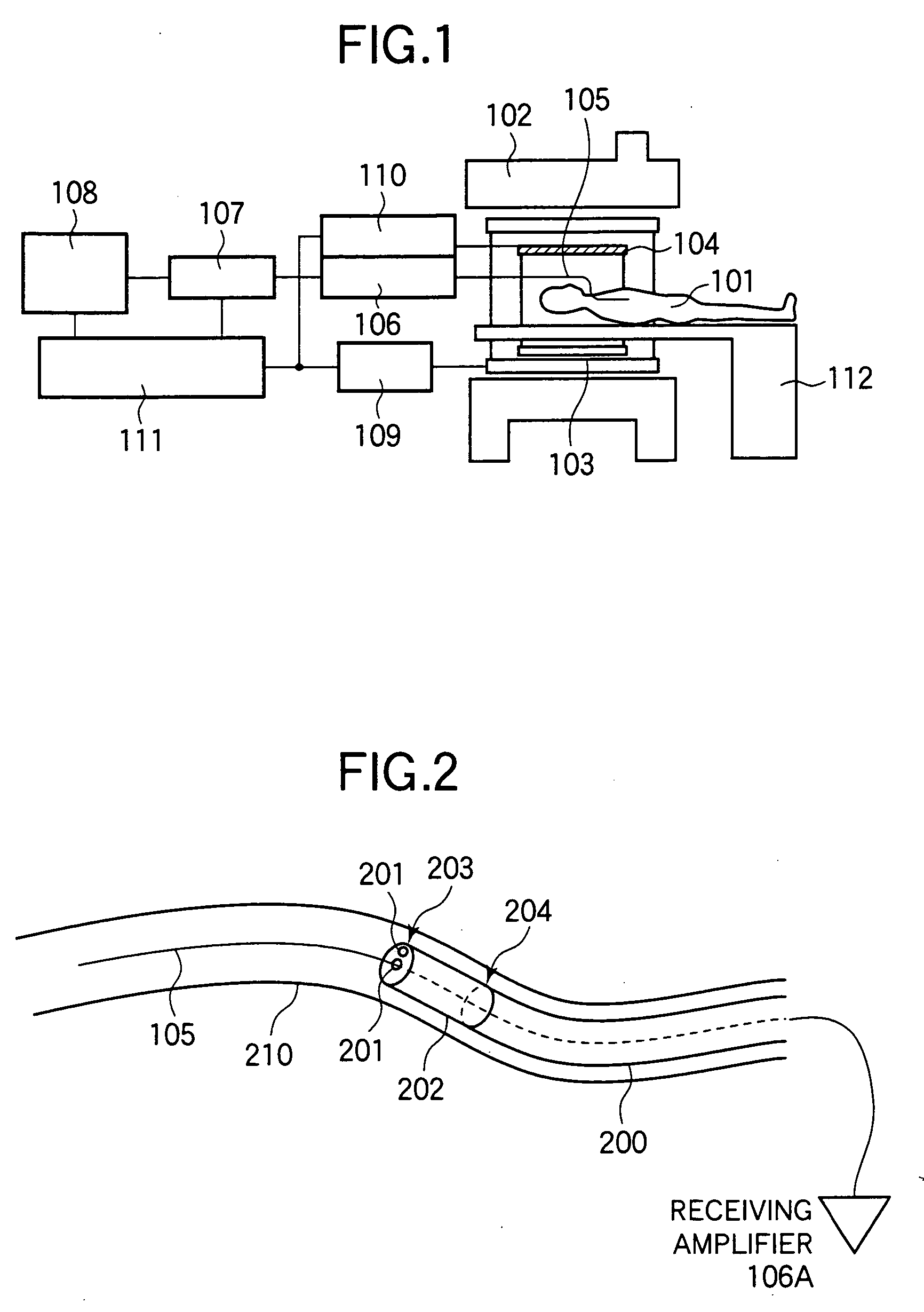
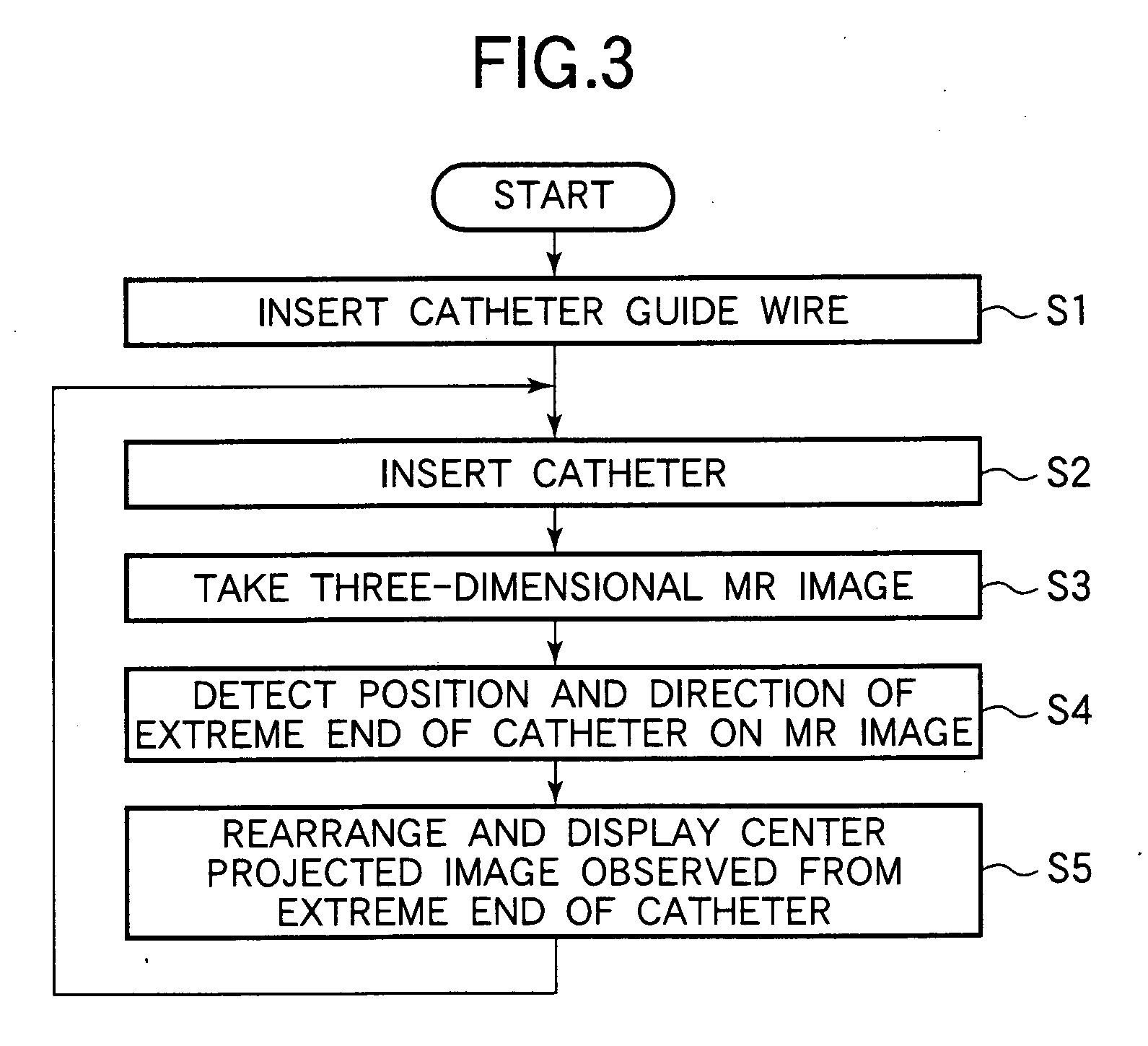
InactiveUS20050033164A1Short measurement timeLong measurement timeImage enhancementElectrotherapyTip positionGuide tube
An endoscope-like image taking method of the present invention includes a preparation step of providing at least one peculiar index, which can be discriminated from other portions on an MR image, at the tip of a catheter, a first step (S1) of previously inserting a metal guide wire for guiding the catheter into a body cavity of a patient into which the catheter is inserted, a second step (S2) of inserting the catheter into the body cavity along the guide wire, a third step (S3) of executing an MR imaging sequence of a plurality of sliced images intersecting the guide wire, a fourth step (S4) of reconstructing three-dimensional image data based upon the nuclear magnetic resonance signals, which are generated from the patient when the sequence is executed and are received by the guide wire, and determining the tip position and the inserting direction of the catheter by detecting the peculiar index provided at the tip of the catheter based upon the three-dimensional image data, and a fifth step (S5) of reconstructing the center projected image using the three-dimensional image data and setting the tip position and the inserting direction of the catheter as a view point and a line-of-sight direction and displaying the center projected image on a display means, thereby an endoscope-like image, which is observed from the catheter in the body cavity of the patient, is taken and displayed in real time or semi-real time so that the insertion of the catheter is supported.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
Intracorporeal substance measuring assembly
ActiveUS20050221277A1Stably measure for longLong measurement timeMicrobiological testing/measurementCatheterAnalyteFluorescence
An intracorporeal substance measuring assembly to be provided in an embedded-type substance sensor for detecting and measuring an intercorporeal analyte includes: a detection layer containing at least one fluorescent indicator for generating fluorescence according to the concentration of the analyte; and an optical separation layer which is provided on the detection layer, is optically opaque, permits the analyte to penetrate therethrough, and prevents the penetration therethrough of at least one of living body substances possibly deteriorating the detection layer and / or obstructing the fluorescence.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Intracorporeal substance measuring assembly
ActiveUS7450980B2Stably measure for longLong measurement timeCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalyteFluorescence
An intracorporeal substance measuring assembly to be provided in an embedded-type substance sensor for detecting and measuring an intercorporeal analyte includes: a detection layer containing at least one fluorescent indicator for generating fluorescence according to the concentration of the analyte; and an optical separation layer which is provided on the detection layer, is optically opaque, permits the analyte to penetrate therethrough, and prevents the penetration therethrough of at least one of living body substances possibly deteriorating the detection layer and / or obstructing the fluorescence.
Owner:TERUMO KK
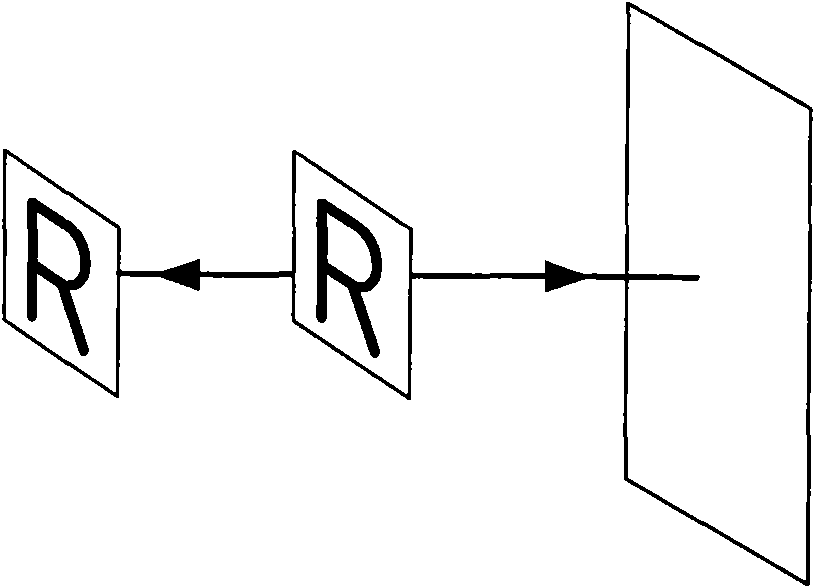
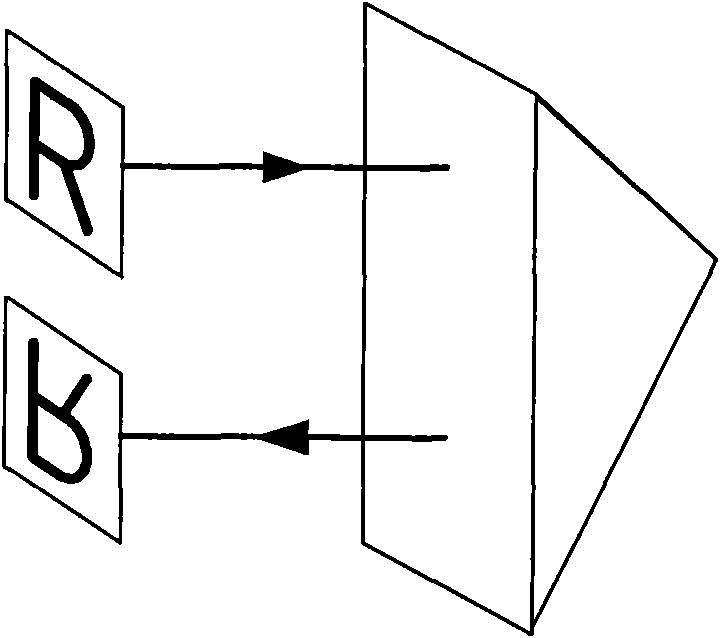
Device for measuring straightness/coaxiality by applying laser
ActiveCN101915560AFeature orientation does not changeWill not affect the measurementUsing optical meansWollaston prismMeasurement device
The invention discloses a device for measuring straightness / coaxiality by applying laser, comprising a first Wollaston prism, a second Wollaston prism and a transitional reflector which are arranged on the measuring light path in sequence, wherein the second Wollaston prism and the first Wollaston prism are positioned on the path of the light which returns after being reflected by the transitional reflector in sequence; the transitional reflector is of plane mirror structure with light path drift adaptation functions in the two mutually vertical directions; and when the incident light enters along the characteristic direction of the transitional reflector, the light which returns after being reflected by the transitional reflector is opposite and parallel to the incident light, and the distance between the light which returns and the incident light is constant. The device ensures the datum to be invariant during measuring the straightness in the horizontal and vertical directions, thus greatly simplifying the adjustment process, shortening the adjustment time and improving the adjustment efficiency.
Owner:北京市普锐科创科技有限责任公司
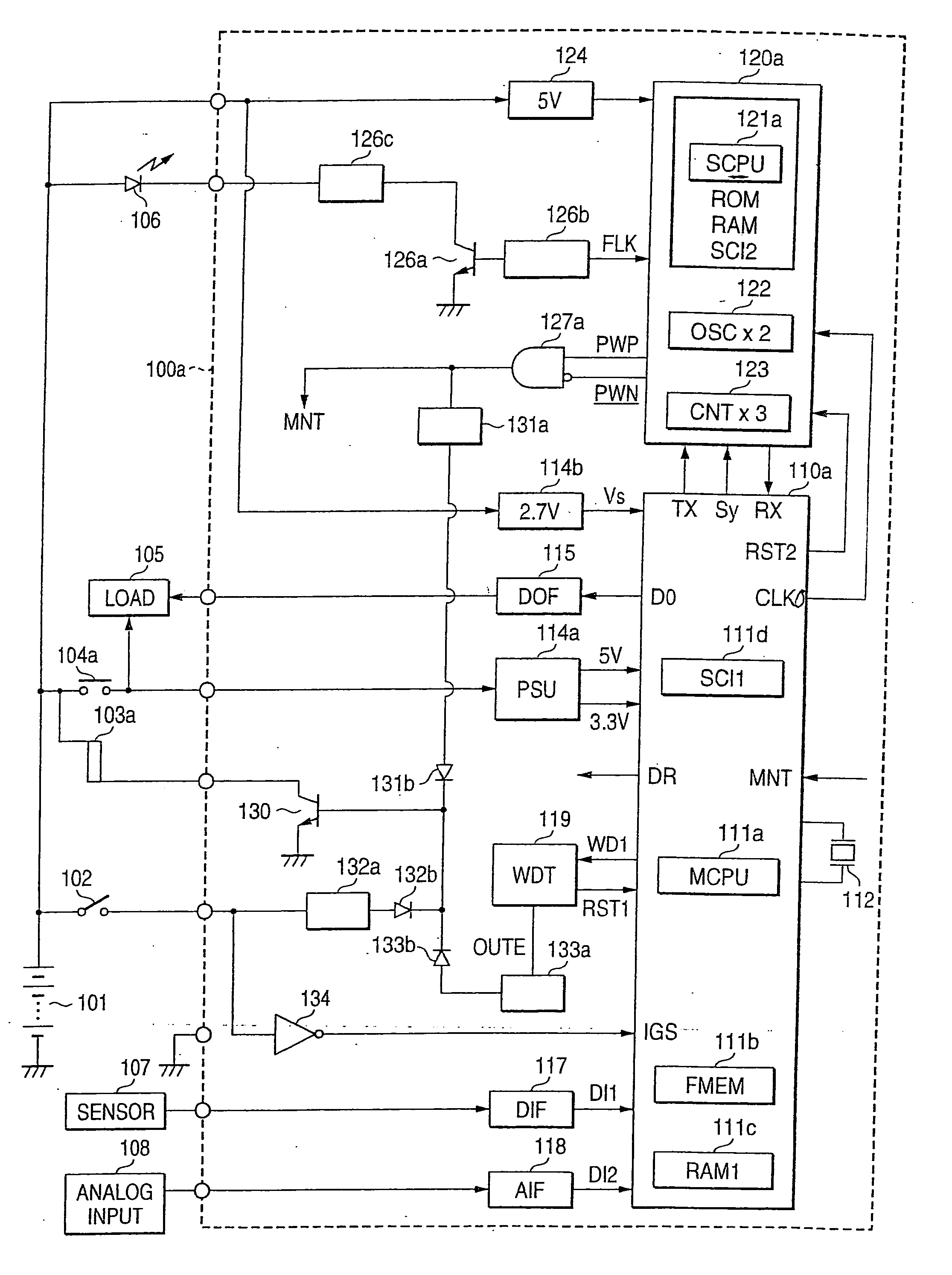
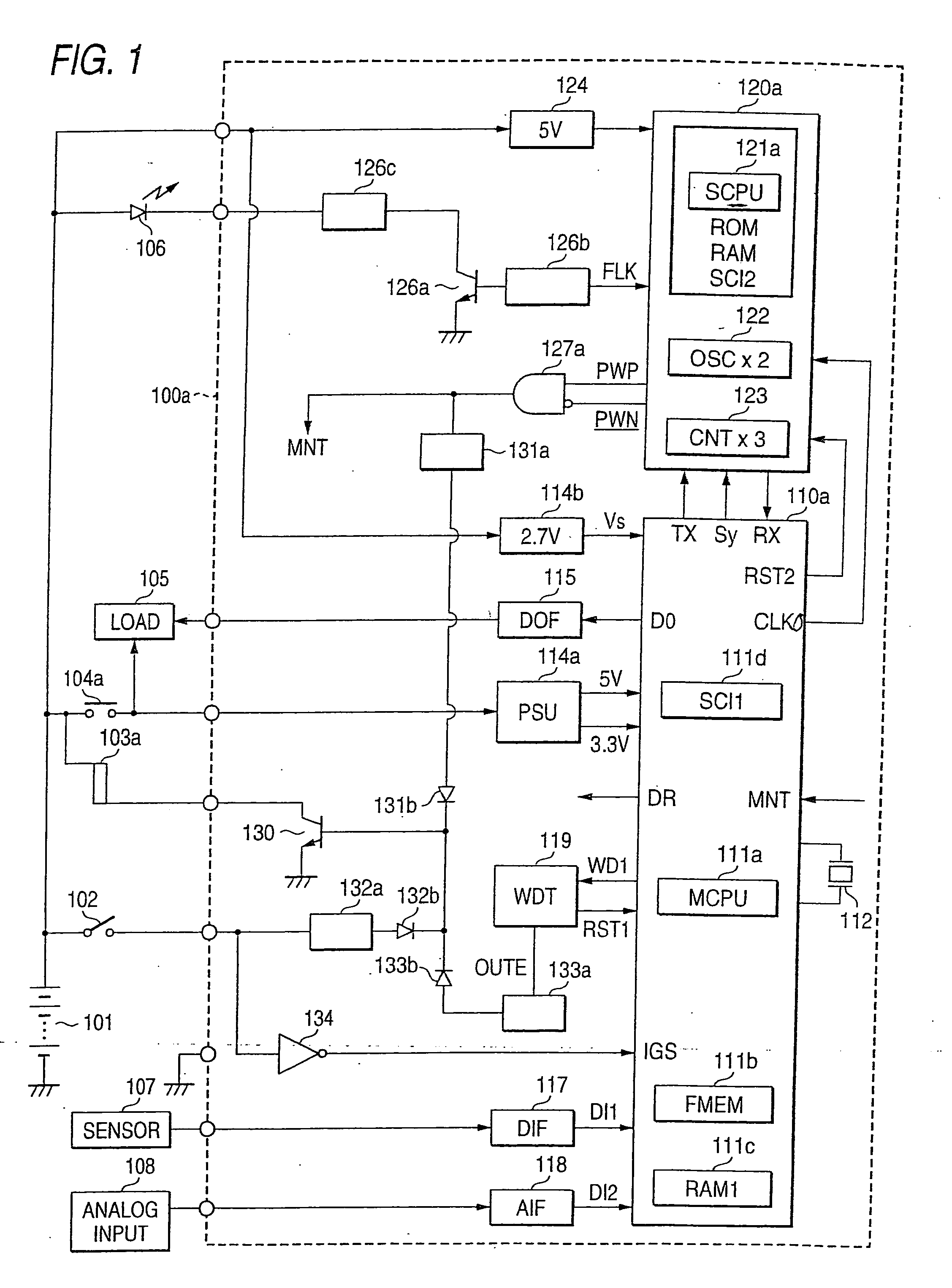
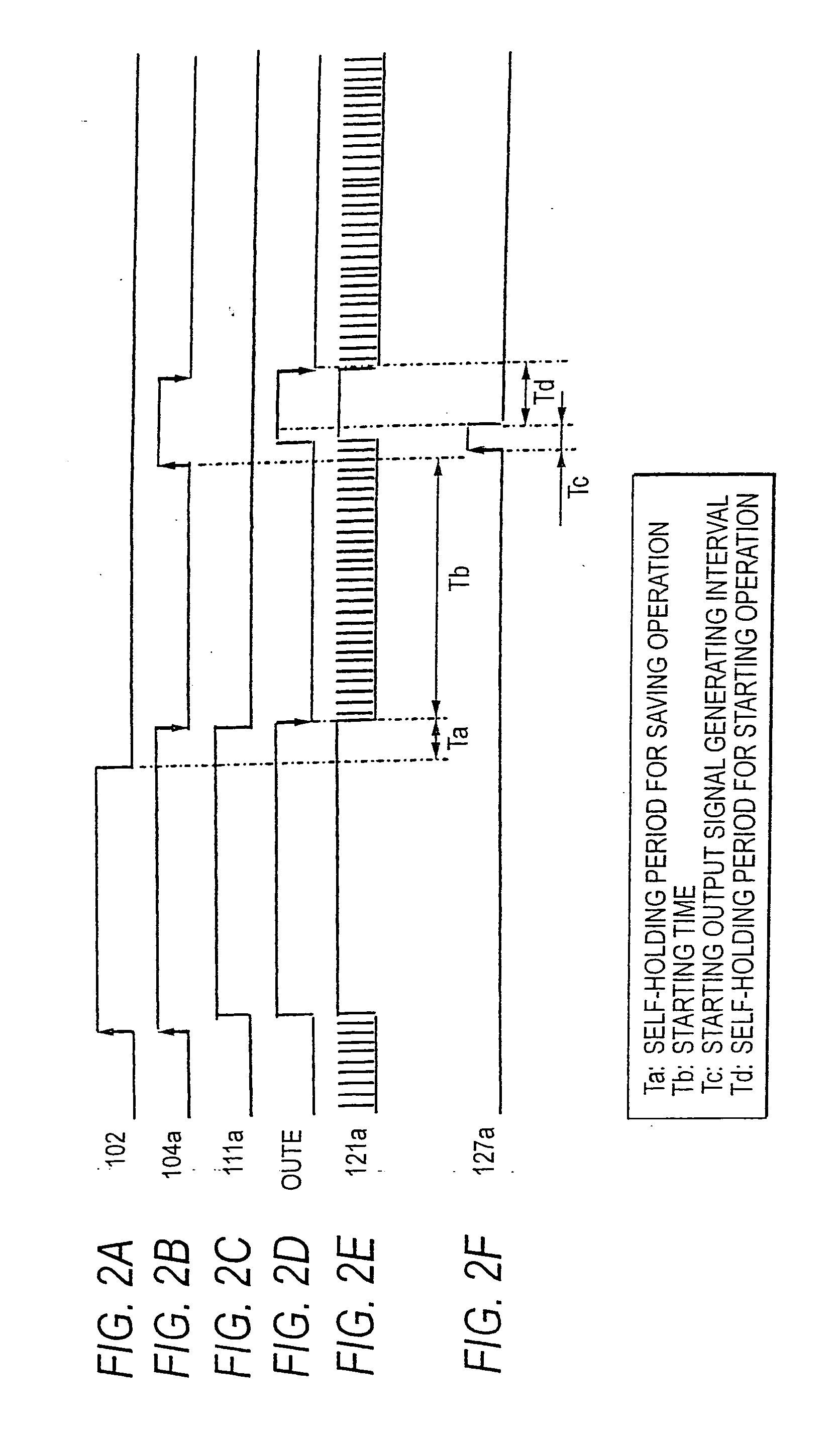
Car-mounted electronic control device
ActiveUS20050228562A1Exclude influenceImprove accuracyTime indicationElectrical controlElectricityLow speed
The car-mounted electronic control device is constructed to include a main control circuit unit to be powered with a car-mounted battery through a switching element and a main power source circuit, and a starting timer circuit unit powered at all times through an auxiliary power source circuit. The timer circuit unit is provided with a sub CPU for acting in synchronism with a high-speed clock signal, and a timing counter for counting the frequency-divided signal of a low-speed clock signal. When a power source switch is opened to interrupt a switching element, the timer circuit unit measures a target awakening time periodically by contrasting the period of the low-speed clock signal to the period of the high-speed clock signal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Absolute optical encoder with long range intensity modulation on scale
ActiveUS20110304482A1Improved absolute encoderRaise the ratioElectric signal transmission systemsMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical densityOrbit
An encoder configuration comprises a dual-modulation scale track pattern that provides a first intensity modulation component for producing periodic signals, and a second intensity modulation component for producing a long-range absolute signal. The dual-modulation scale track pattern increases the range-to-resolution ratio of the encoder without the use of additional scale tracks that would increase the width of the encoder components. The long-range signal may be encoded in the dual-modulation scale track pattern either by varying certain dimensions of pattern elements included in the scale track or by superimposing a layer including an optical density variation along on the track on pattern elements of similar areas. In either case, the net offset and / or amplitude levels of the associated signals are modified along the scale track. These modified offset and / or amplitude levels provide the basis for the long-range absolute signal.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Method for analysis of expired gas
InactiveUS6555821B1Good chanceLong measurement timeRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryAnalysis methodSpectrometer
A method for detecting and measuring volatile components in expired gas by sampling the expired gas containing the volatile components; passing infrared radiation from an interferometer through the sample; detecting infrared radiation transmitted from the sample to produce a signal characteristic for the volatile components in the sample; and processing the signal and a set of single component reference library spectra of pure molecular gases in order to detect and calculate the amount of the volatile components in the blood of an individual expiring the gas, including the use of a low resolution FT-IR spectrometer in the detecting and processing.
Owner:WALLAC
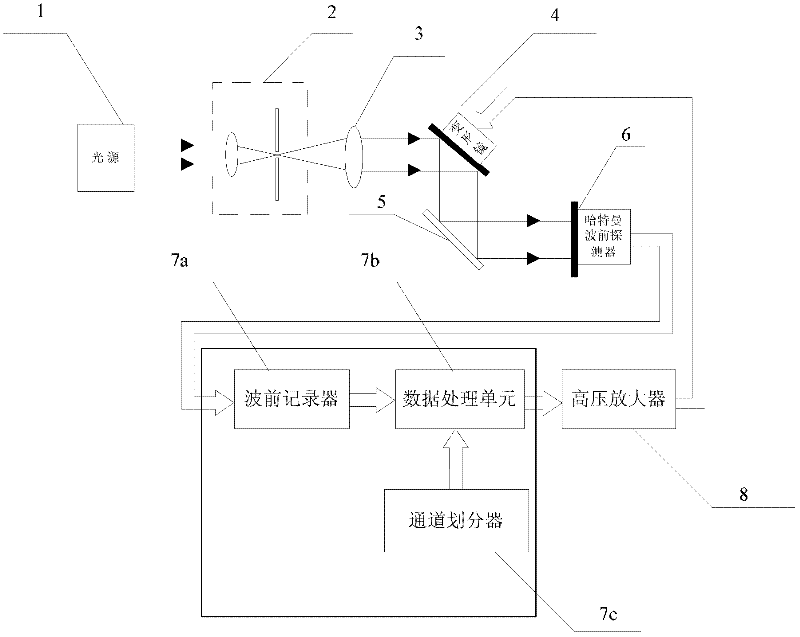
Device and method for measuring transfer matrix of adaptive optics system based on Hadamard matrix multi-channel method
ActiveCN102494785AReduce measurement cycle timeImprove noise immunityOptical measurementsAerodynamic testingWavefrontTransfer matrix
The invention provides a device and a method for measuring a transfer matrix of an adaptive optics system based on a Hadamard matrix multi-channel method. The device comprises an adaptive optics system, a channel divider, a wavefront recorder and a data processing unit, wherein the channel divider divides channels for a driver of a wavefront corrector of the adaptive optics system; the data processing unit applies voltage to the divided channels according to a Hadamard matrix, so that planar waves generate wavefront change after passing through the adaptive optics system; the wavefront recorder calculates and stores a wavefront slope curve; and the data processing unit performs matrix operation on a wavefront slope curve matrix so as to calculate the transfer matrix. The device for measuring the transfer matrix of the adaptive optics system based on the Hadamard matrix multi-channel method has high measuring precision and high speed; and an effective novel method is supplied to measurement of the transfer matrixes of a large adaptive optics system.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Measuring tape holding tool
A holder and guide for a measuring tape and a process of making and using the holder. The holder is made up of a hollow tube having a rectangular cross section. The tube has a slit or gap running the length of the tube to enable a measuring tape to be inserted. A magnet is attached to an exterior portion of the tube. The holder enables a user to insert any portion of a measuring tape inside the tube without having to insert the end of the tape measure therein. The holder facilitates in making measurements using a measuring tape, especially when a long distance is being measured and it is inconvenient to insert an end of the measuring tape through the guide to secure a middle portion of the measuring tape during measurement. The holder also has a magnet that attaches the holder to metallic objects enabling a single user to more easily make measurements using a measuring tape.
Owner:GRAHAM BRAXTON B
Method and device for identifying radionuclide Sr-89 and analyzing nuclear purity
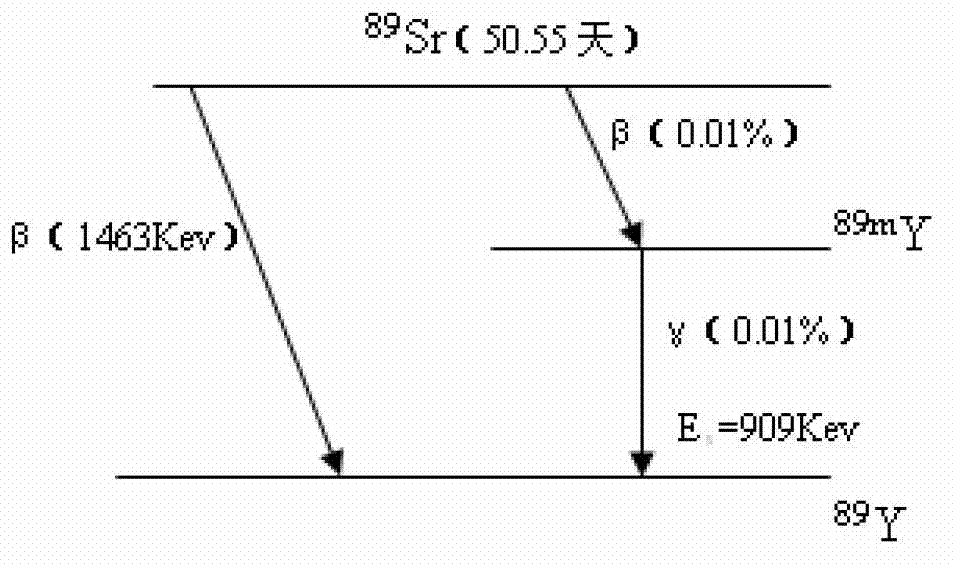
InactiveCN102736098ARapid identificationLow technical requirementsX-ray spectral distribution measurementRadiation intensity measurementGamma energyRadioactive waste
The invention relates to a method and a device for identifying a radionuclide Sr-89 and analyzing a nuclear purity. The method comprises the following steps of: (1), calibrating the activity of a sample and measuring the gamma radioactive source detection efficiency of a NaI gamma energy spectrometer; (3), calculating to obtain the emissivity of a gamma ray; (4), acquiring that the energy of the gamma ray is 909 Kev by the position of a gamma peak, obtaining that an energy specific value is approximately equal to 0.01% by the emissivity of the gamma ray and the activity of the sample, and determining that a nuclide is the Sr-89; and calculating to acquire the purity. The device comprises a lead chamber, a NaI crystal and photomultiplier, a lead tank, a plastic container, a penicillin bottle and a plastic cup. By using the method and the device, the strontium-89 nuclide and the nuclear purity are quickly and highly sensitively identified; by using the method and the device, the difficulty of a technical requirement on an operator is low; compared with the utilization of scintillating liquid, the amount of a radioactive waste can be reduced to improve the environment; meanwhile, the investment through which an enterprise needs to establish new equipment and an instrument is reduced; and the method and the device have a favorable application prospect.
Owner:NINGBO JUNAN PHARMA TECH
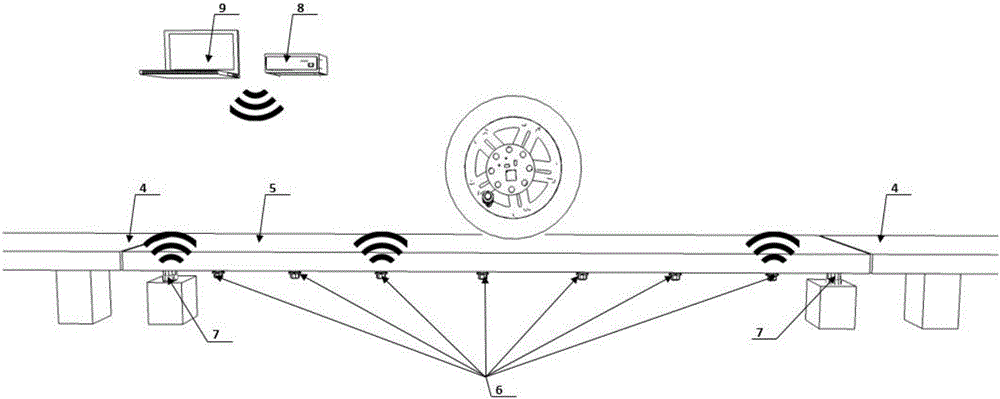
Real-time vertical wheel impact force measurement method based on tire pressure monitoring
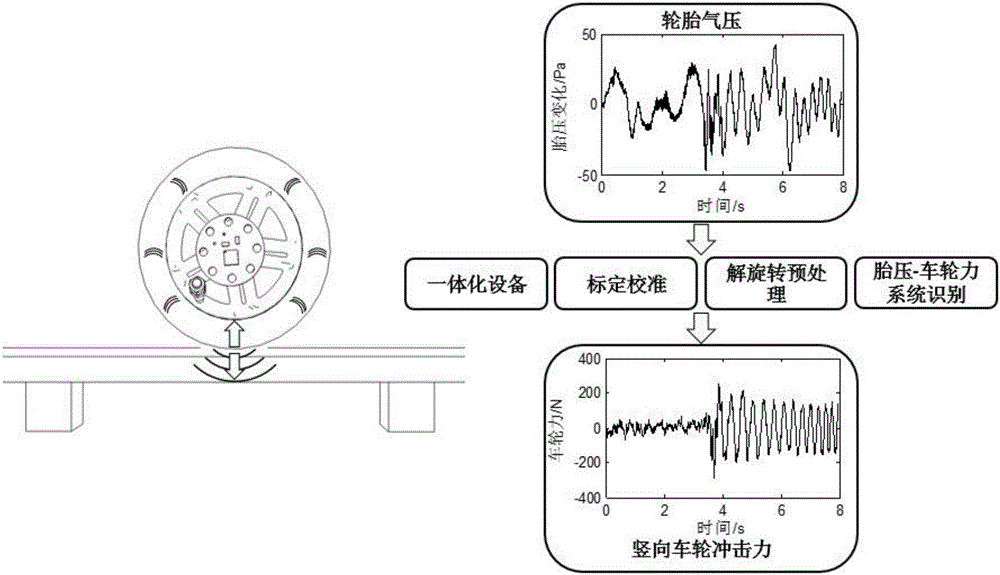
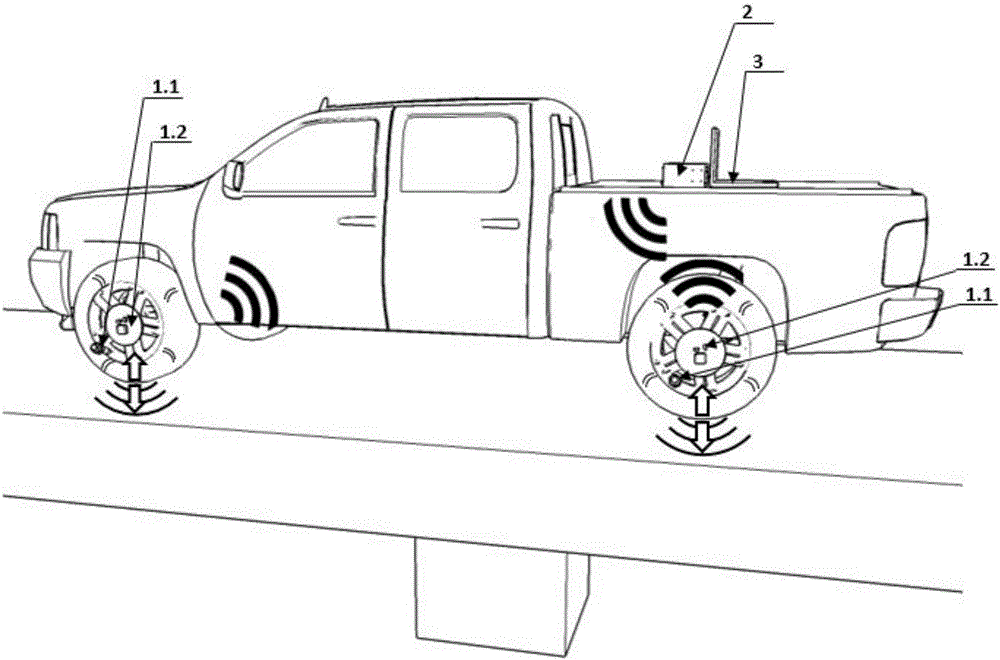
ActiveCN106198058AAccurate measurementSignificant progressInflated body pressure measurementTyre measurementsEngineeringHealth condition
The invention discloses a real-time vertical wheel impact force measurement method based on tire pressure monitoring. Integrated equipment with a tire pressure derotation preprocessing module, a tire pressure-wheel force system identifying module, a calibrating and correcting method module and a tire pressure-wheel force measuring module is mainly included. Real-time tire pressure data is collected through the integrated equipment, corresponding vertical wheel impact force is obtained through the derotation preprocessing module and the tire pressure-wheel force system identifying module, and correction can be conduced according to a calibrating method. Accordingly, a wheel force measurement solving scheme which is efficient, accurate and high in adaptability is provided from the theory layer and the equipment layer, the quick assessment requirement on vast bridge health condition is met, and meanwhile the method has the great potential in the fields of road safety diagnosis, vehicle performance design and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
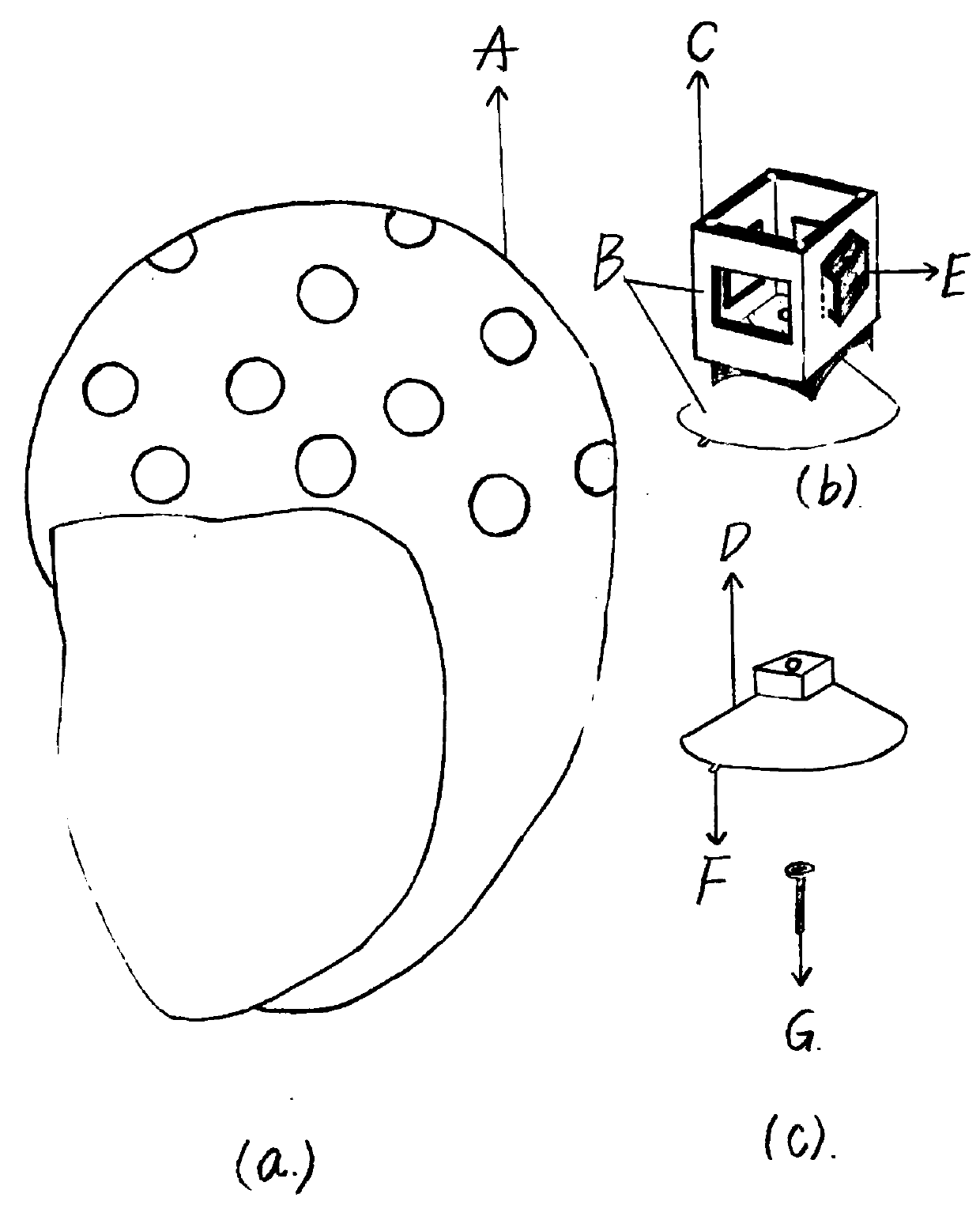
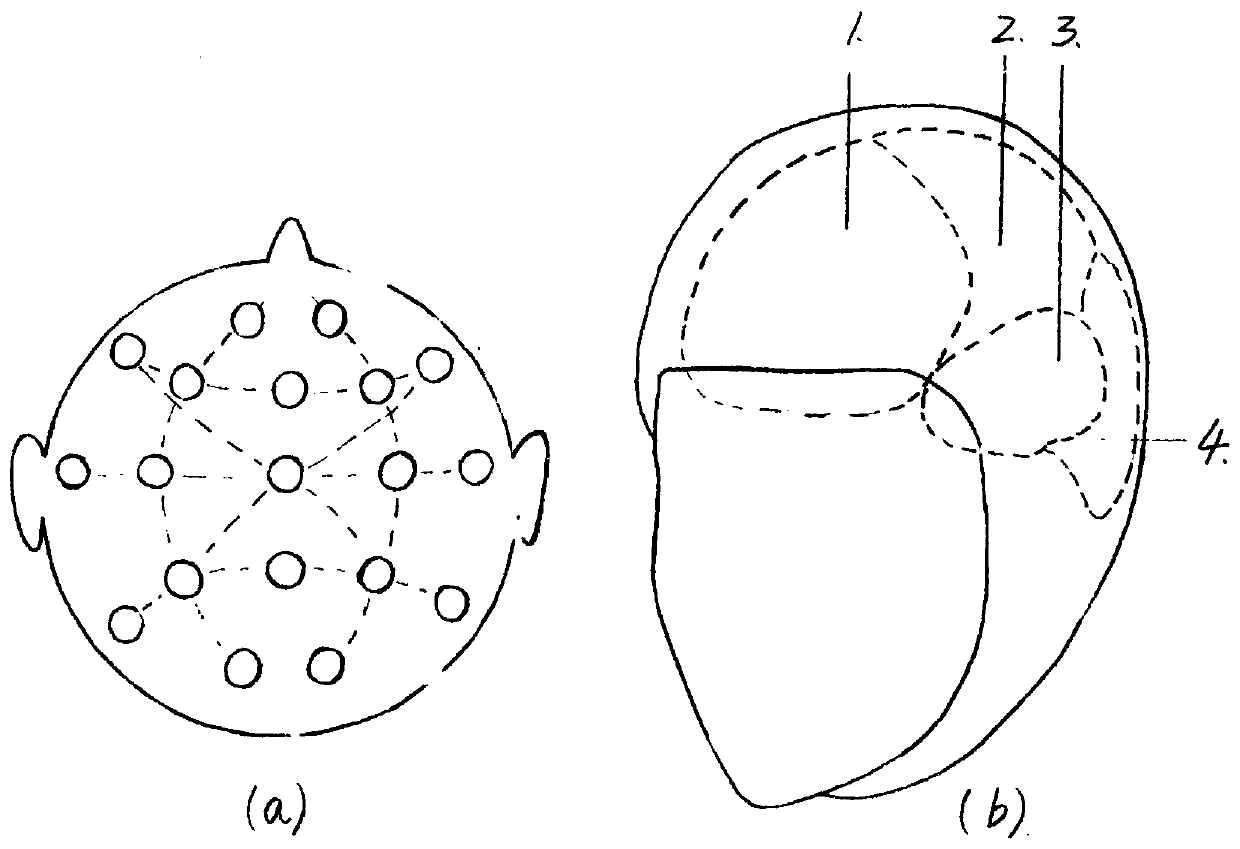
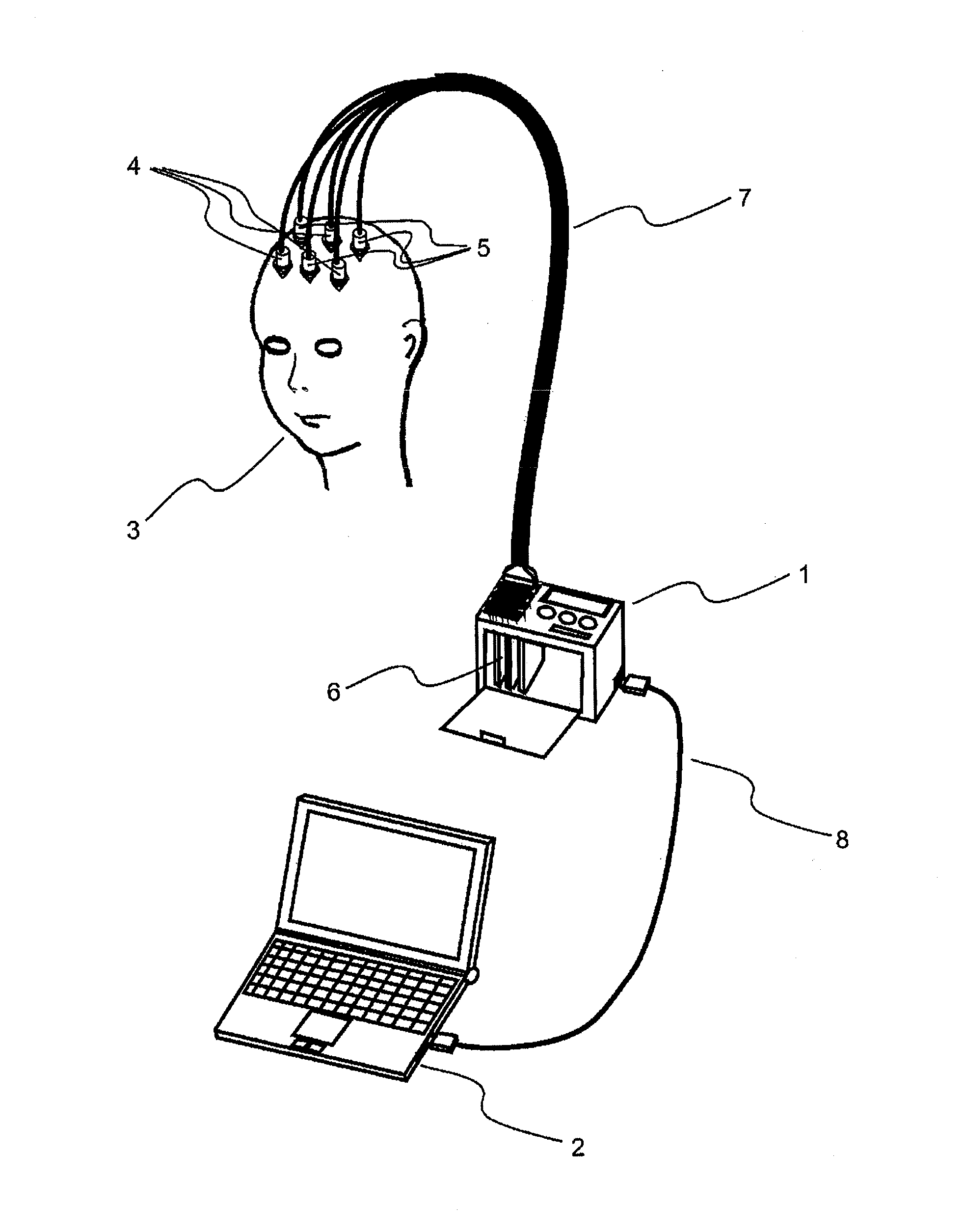
Sucked type wearable flexible MEG cap for measuring human brain magnetic field signals
ActiveCN110710966ANo shakingInsert smoothlyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsThermal insulationSilica gel
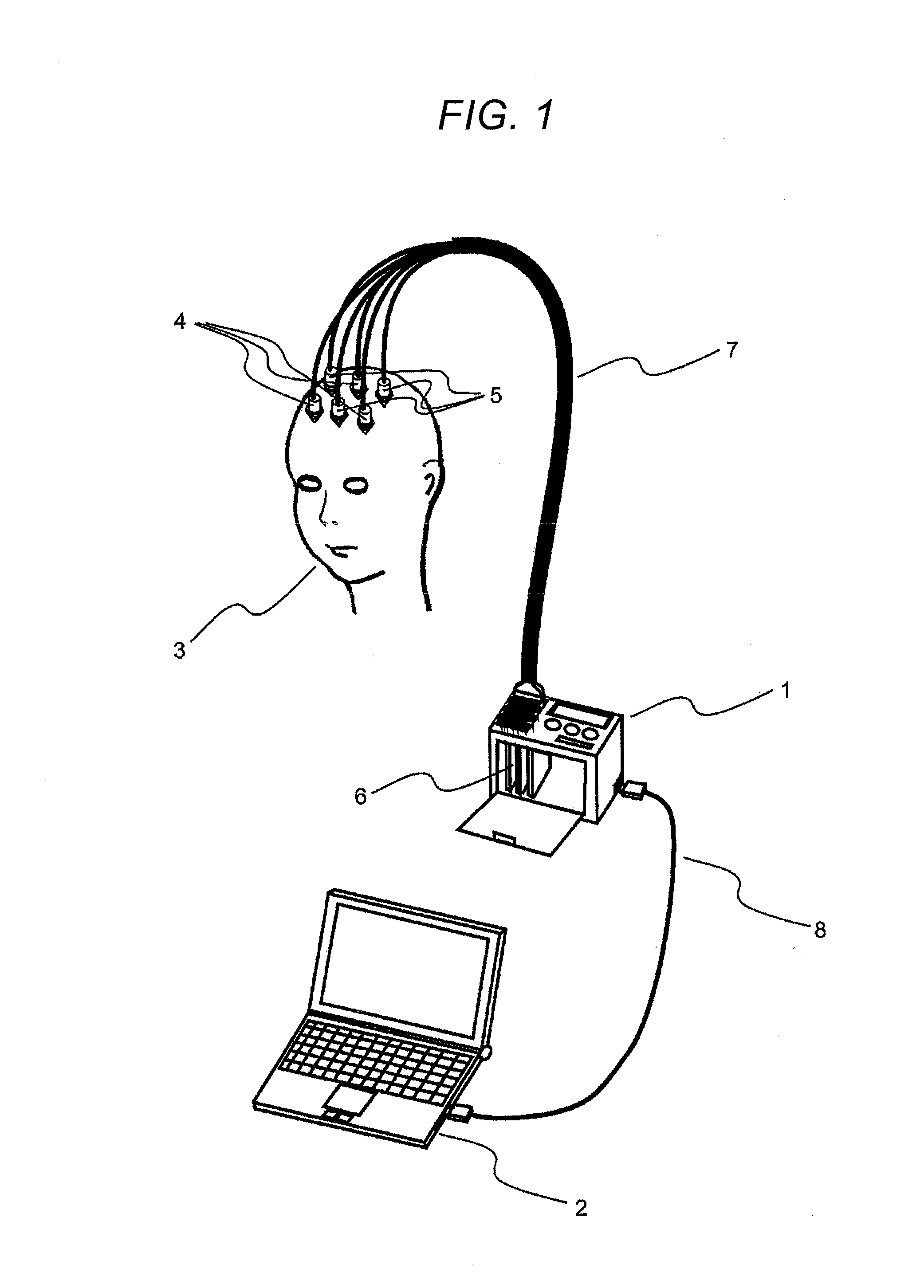
The invention discloses a sucked type wearable flexible MEG cap for measuring human brain magnetic field signals, belongs to the field of biomedical engineering, and relates to a medical instrument. The MEG cap consists of a flexible cap body and sucked type clamping grooves, wherein each sucked type clamping groove comprises a clamping groove, a sucker and a fixing bolt for connecting the clamping groove and the sucker; a grid MEG capable of arranging the sucked type clamping grooves in array is drawn on the surface of the flexible cap body in reference of an internationally general 10-20 standard EEG acquisition lead system and physiological construction and functional division of human brains; the flexible cap is made of a thermal insulation silicone material, can be attached to scalp of a testee closely, and guarantees the distance between low-intensity field measuring sensors inserted into the sucked type clamping grooves and the real scalp of the testee is the minimum as far as possible; and the flexible cap cooperates with the sucked type clamping grooves, can adapt any measurement positions of complex human head curved surfaces. The sucked type wearable flexible MEG cap isan MEG detection tool with higher universality, very low detection cost and reliability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
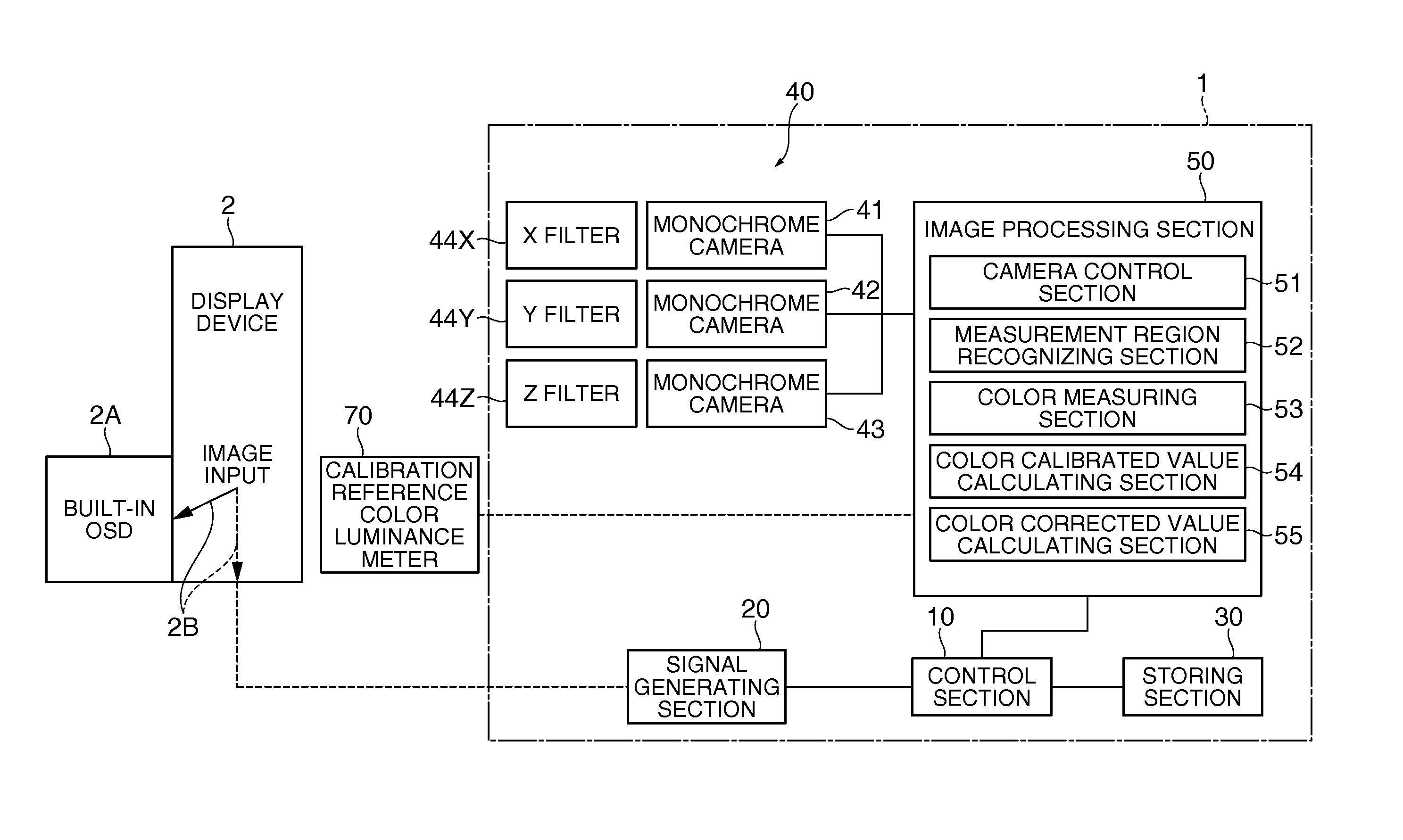
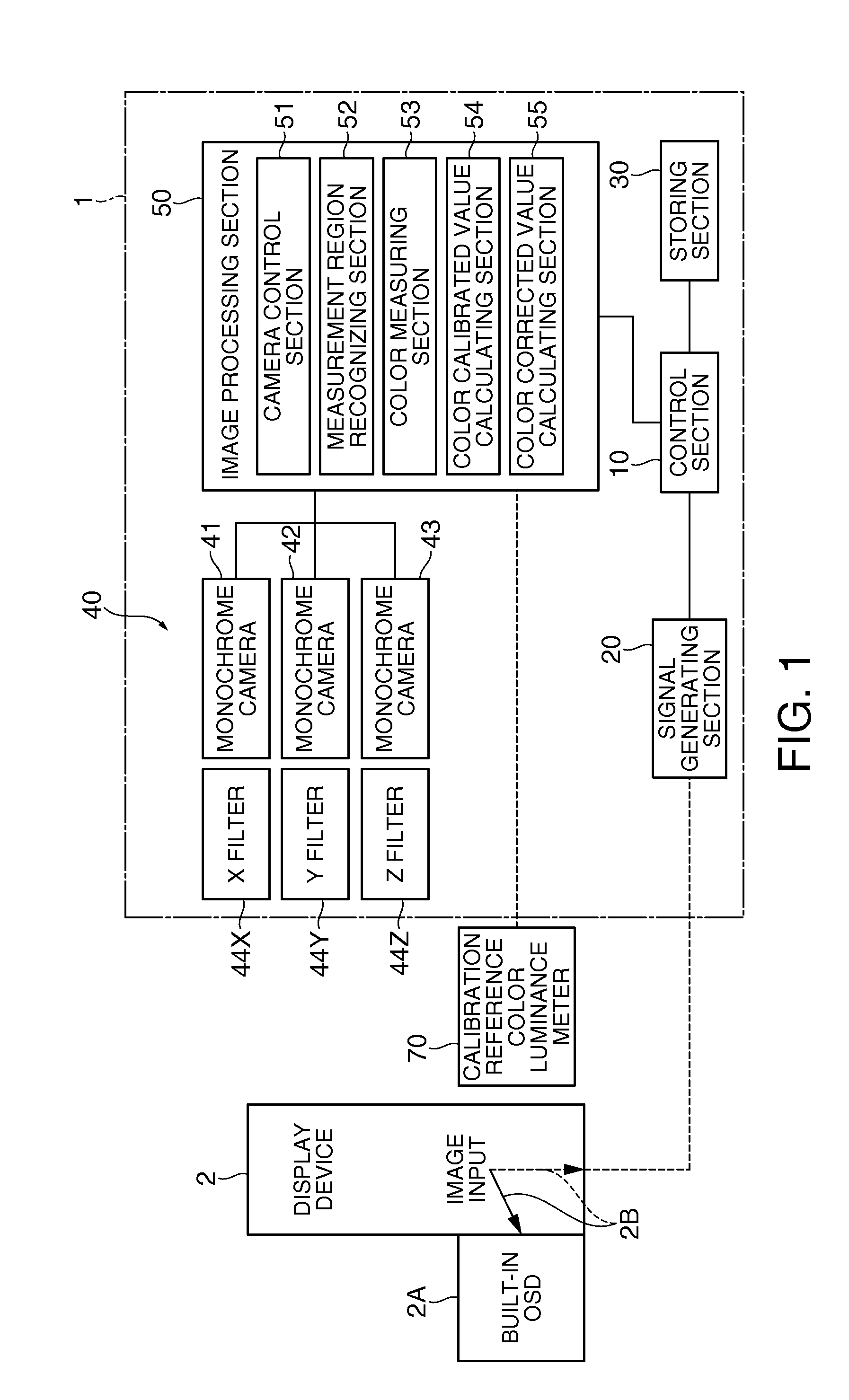
Color measuring apparatus and color measuring method
InactiveUS20110249116A1High precisionShort timeColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsCamera controlImaging processing
A color measuring apparatus includes an image taking section; a signal generating section selecting a teach image in which a plurality of measurement regions are set or a measurement image for color measurement and making a display device display the selected image; a camera control section controlling the image taking section to make the image taking section take an image of the image displayed on the display device; a measurement region recognizing section recognizing the measurement regions by performing image processing on the teach image whose image was taken by the image taking section; and a color measuring section measuring the color of each of measured regions corresponding to the measurement regions recognized by the measurement region recognizing section, the measured regions in the measurement image whose image was taken by the image taking section.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Electronic salt meter
ActiveUS20110140704A1Improve accuracyLong measurement timeSemi-permeable membranesResistance/reactance/impedenceElectricityThermal equilibrium state
An electronic salt meter including a sensor rod, salt meter body and receiving components to measure a temperature and salinity. The electronic salt meter includes a first and sensor electrode and a temperature sensor to detect a temperature of the measurement object. A measurement monitoring unit detects whether the first and second sensor electrodes are electrically connected to each other. A salinity measurement unit applies an AC power to the first and second sensor electrodes to measure salinity of the measurement object. A temperature measurement unit applies a power to the temperature sensor to measure the temperature of the measurement object. A thermal equilibrium detection unit stores the temperature value previously measured, and when the temperature variation is less than a predetermined threshold, it is determined as a thermal equilibrium state. A room-temperature salinity conversion unit converts the salinity value into a salinity value at room temperature.
Owner:SON YUN HO
Resistive particle sensors having measuring electrodes
InactiveUS7872466B2High measurement sensitivityHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFault locationSoot particlesElectric field
A sensor for determining the concentration of particles in gases, in particular of soot particles, has at least one substrate element, and a measuring area between at least one first and one second measuring electrode, the two measuring electrodes being configured so that by applying a voltage between the measuring electrodes, an asymmetric electric field is formed on the measuring area. The sides of the first and second measuring electrodes, facing one another, may not be parallel to one another, for example. Furthermore, at least one measuring electrode may have a structure along the side facing the other measuring electrode or along the finger electrodes.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Seismic sensor array devices and methods of data collection
InactiveUS20110305112A1Quick measurementImprove detection efficiencySeismic signal receiversElastomerSensor array
A sensor vehicle of the present invention has one or more rotatable track means (parallel if two or more) spaced apart by a support frame and adapted to be towed or otherwise moved in a forward direction parallel to a forward axis of said track means. Rotatable track means have two or more supporting wheels aligned on a vertical plane along the forward axis, which axis is generally parallel to a ground surface upon which said sensor vehicle travels. Tracked vehicles are well known in the art of ground and earth moving equipment having flexible, elastomer-based tracks or segmented metal tracks with associated support frames and wheels, most of which may be adapted to achieve the objects of the invention.
Owner:LIAO YI
Electronic part transport device and inspection apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20050062466A1Long measurement timeMeasurement time be increaseElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingTransport engineeringTransport medium
An electronic part transport device includes a transport medium having a plurality of lines of cavities. The lines are concentric with respect to the rotation axis. A driving device rotationally drives the transport medium. A supply device separately supplies a plurality of randomly introduced electronic parts one by one. A delivery device feeds the electronic parts separately supplied by the supply device into the cavities of the transport medium. A removal device takes the electronic parts out of the cavities of the transport medium.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Nucleic acid analysis apparatus
InactiveUS20050196778A1High measurement accuracyLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFailure rateFluorescence
An apparatus measures individual measurement sites on a DNA chip in a short period of time. The DNA chip is irradiated by light-emitting diodes (LEDs) so as to excite fluorescent dye at each measurement site, and fluorescence emitted from the individual measurement sites is detected all at once. Since substantially uniform measurement conditions can be obtained for each measurement site, measurement accuracy increases. The read mechanism requires less space and is less costly, thereby decreasing the failure rate and virtually eliminating the need for maintenance of the apparatus.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
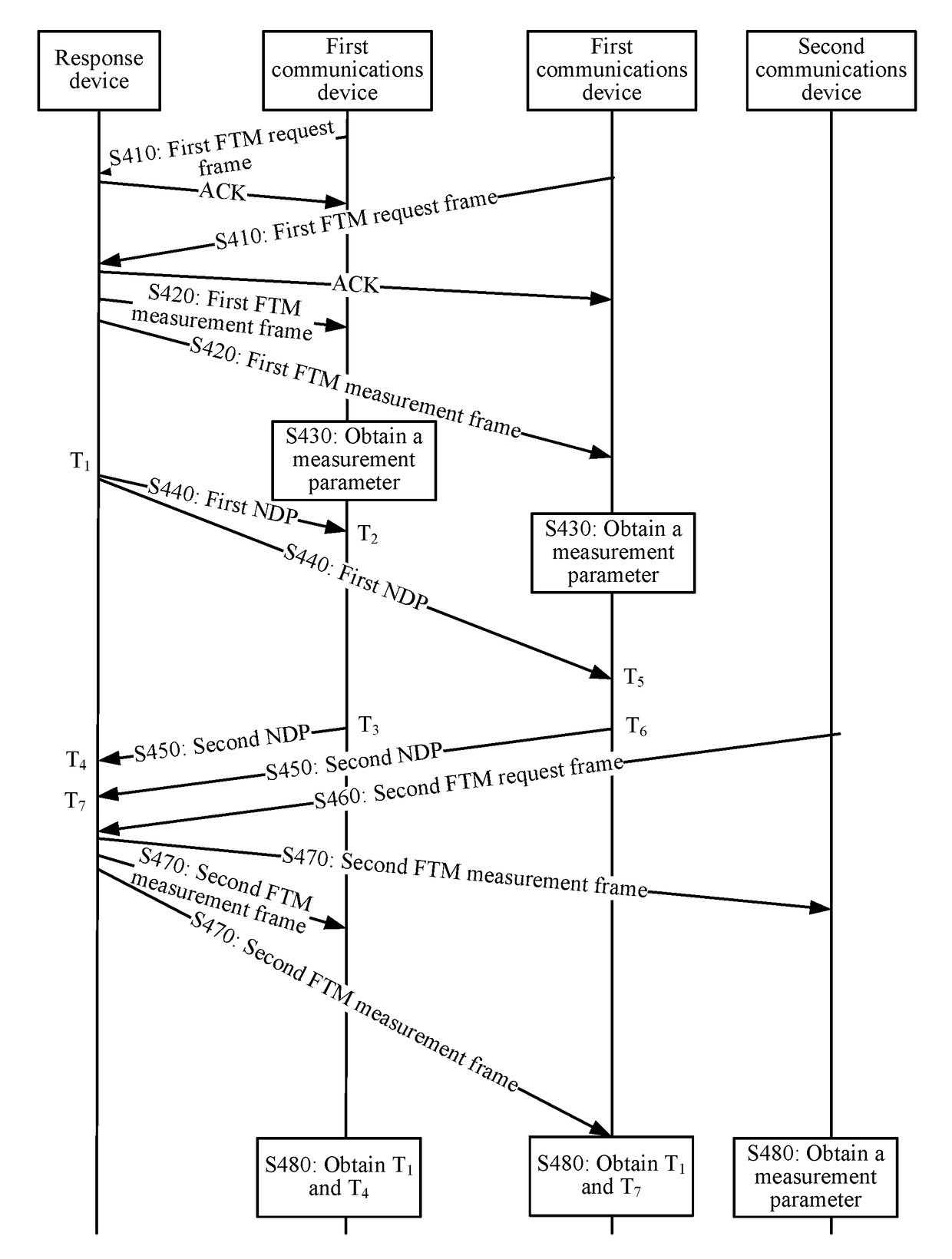
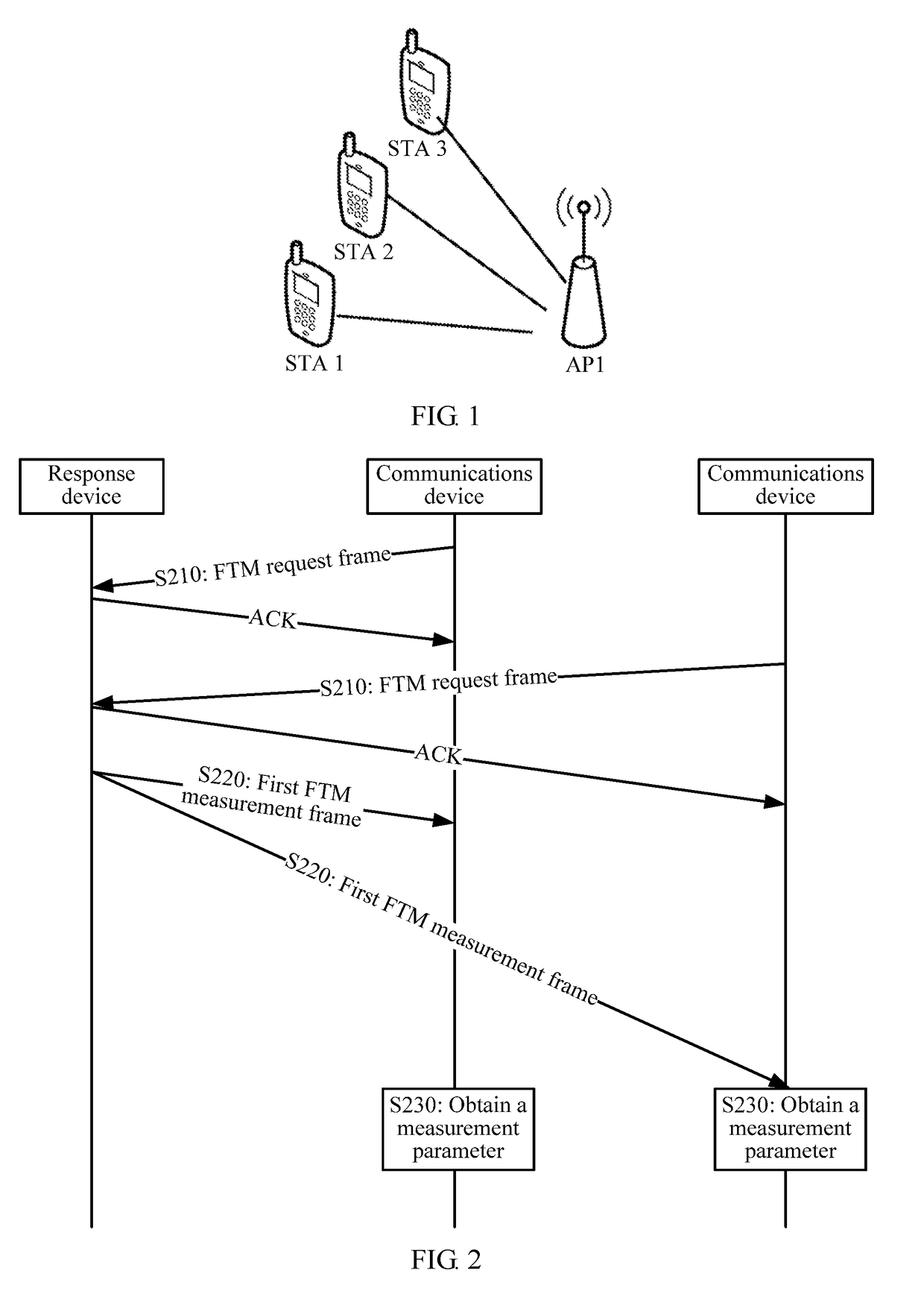
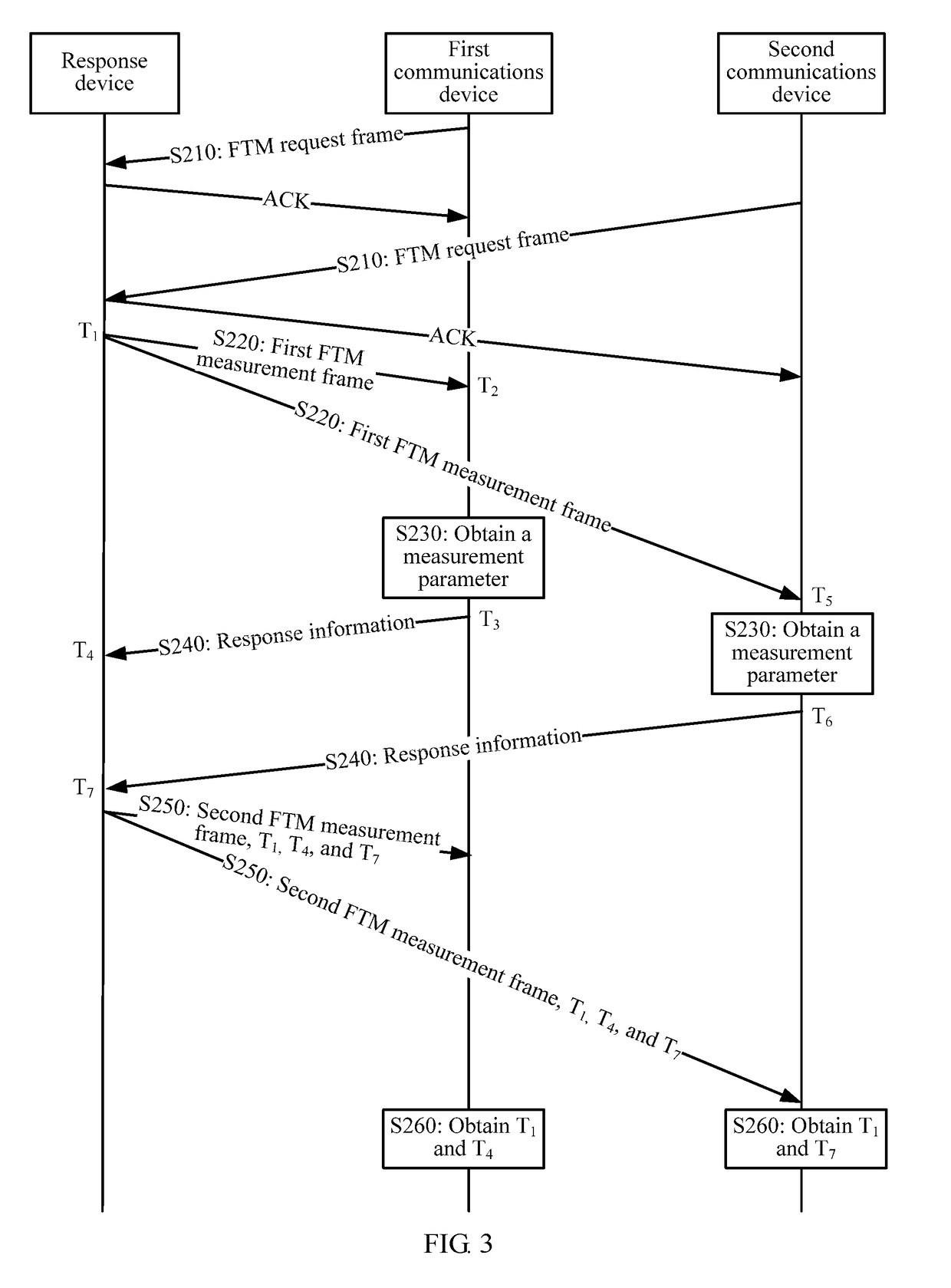
Fine timing measurement ftm method and communications device
ActiveUS20180310194A1Long measurement timeReduce measurement efficiencySynchronisation arrangementSynchronisation information channelsCommunication deviceReal-time computing
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Lipid membrane, method for measuring membrane permeability, and method for screening
InactiveUS6861260B2Quick measurementEfficient preparationImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMembrane permeabilityLipid formation
The object of the present invention is to provide a lipid membrane whose permeability to substances is high and strongly correlated with the permeability of biomembranes to drugs and which therefore is suitable for rapid measurement. The present invention provides a membrane comprising an unsaturated C7-C9 hydrocarbon and a lipid.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Wave and sea level measuring method for deep sea and high sea based on satellite-based differential enhanced technology
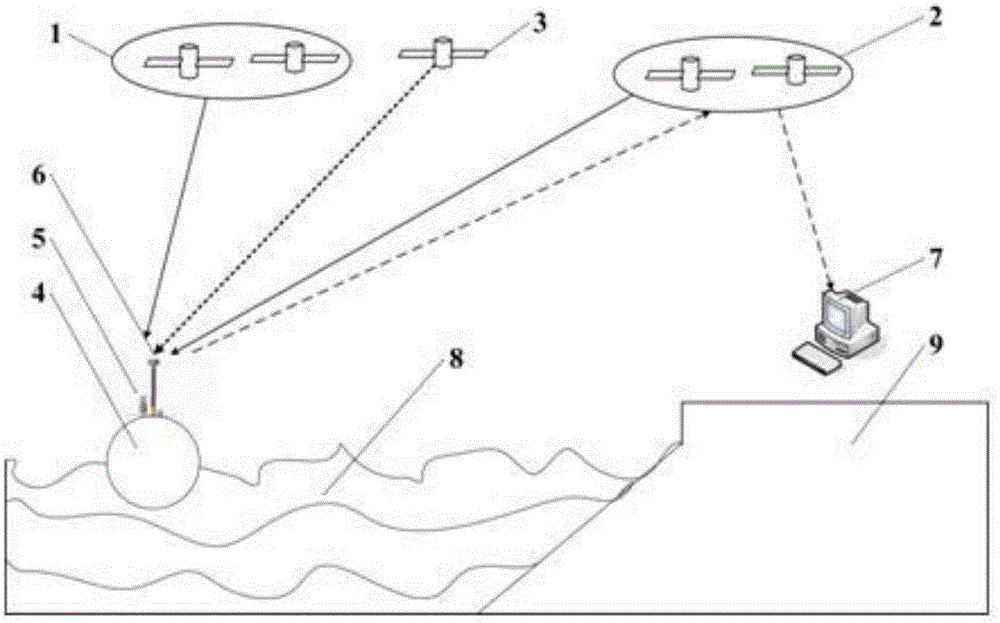
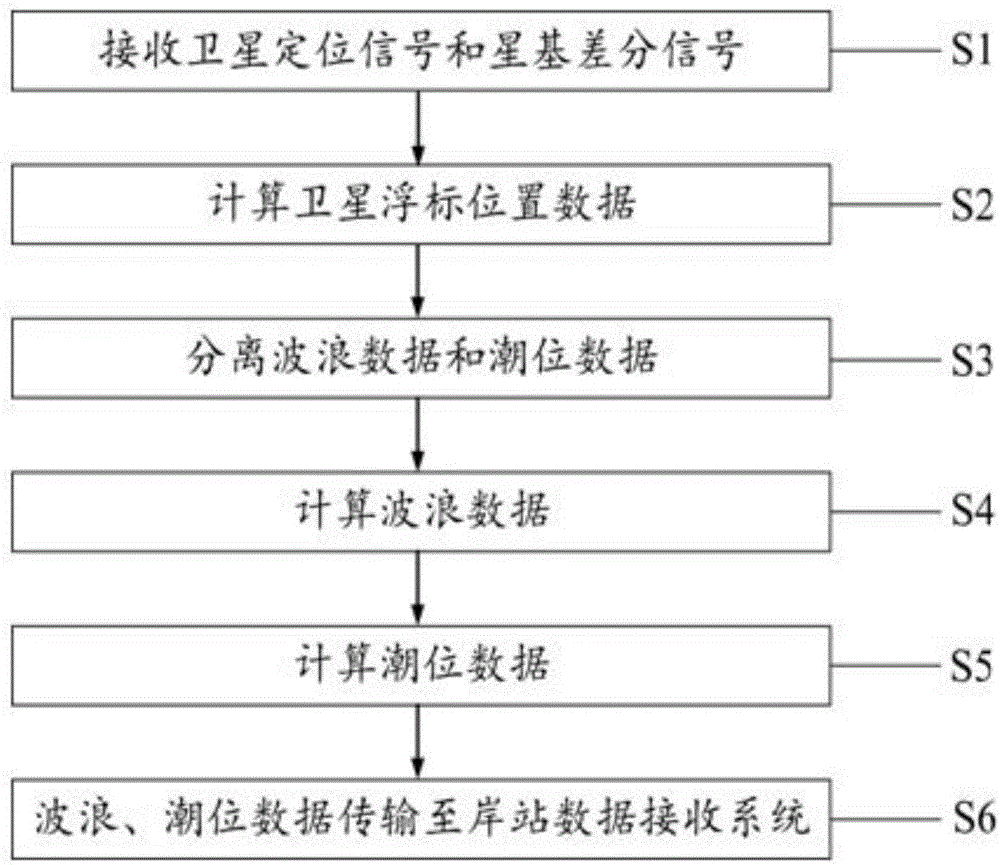
InactiveCN106840113AEasy to useReliable measurementMeasuring open water depthLevel indicators by floatsDifferential signalingShore station
The invention discloses a wave and sea level measuring method for deep sea and high sea based on a satellite-based differential enhanced technology. By taking a Beidou system as a primary platform which is matched with a GPS (Global Positioning System), a fused localization method is formed by adopting the satellite-based differential enhanced technology, so that wave and sea level measuring work of deep sea and high sea in a global range is realized. The method comprises the following technical steps of: receiving a satellite positioning signal and a satellite-based differential signal; calculating three-dimensional position data of a satellite float; separating wave data and sea level data; calculating the wave data; calculating the sea level data; and transmitting the wave data and sea level data to a shore station data receiving system. By mounting a Beidou / GPS satellite positioning receiving card board and a satellite-based differential signal receiving module, waves and sea levels in the deep sea and high sea in the global range can be measured. The method has the characteristics of being high in measuring precision, far in working distance, wide in coverage, long in cruising duration and the like.
Owner:NAT CENT OF OCEAN STANDARDS & METROLOGY
Biological Optical Measuring Apparatus
InactiveUS20140012136A1Eliminate noise componentsLong measurement timeDiagnostics using lightSensorsContact pressurePressure sensor
A biological optical measuring apparatus includes a light source probe and a light receiving probe, one of which is provided with a pressure sensor to detect a contact pressure of a skin of a subject. Pairs of plural values of the contact pressure and light detection signals are previously recorded as calibration data, an estimated value of a false signal is derived from a detection value of the pressure sensor at primary measurement and the calibration data, and a measurement signal waveform in which a noise component due to a movement of the subject is removed is acquired by subtracting the estimated value from a light measurement signal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Apparatus for determining total organic carbon
InactiveUS20100098588A1Rapid continuous measurementReduce the impact of interferenceChemical analysis using combustionBiological testingAdditive ingredientSample water
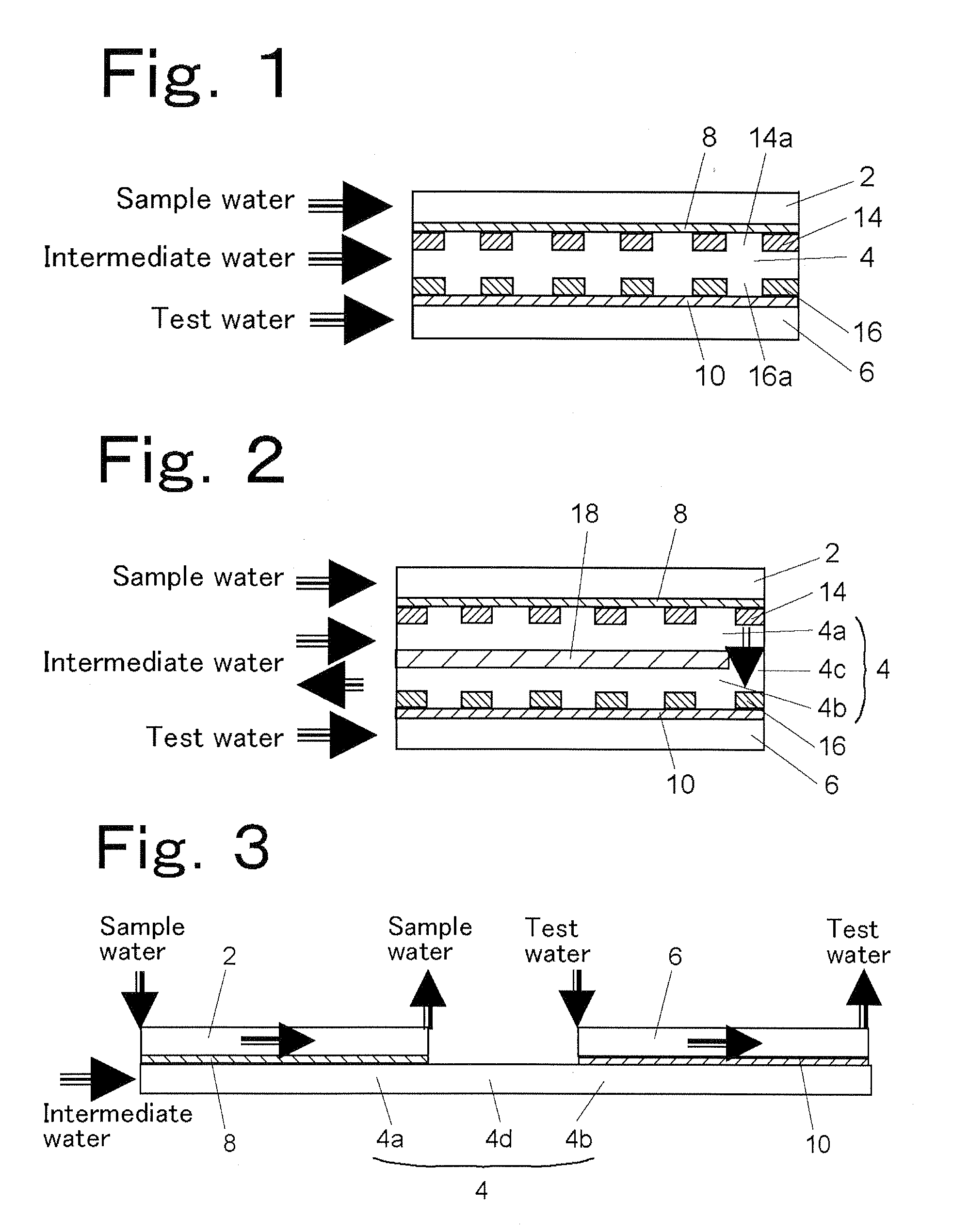
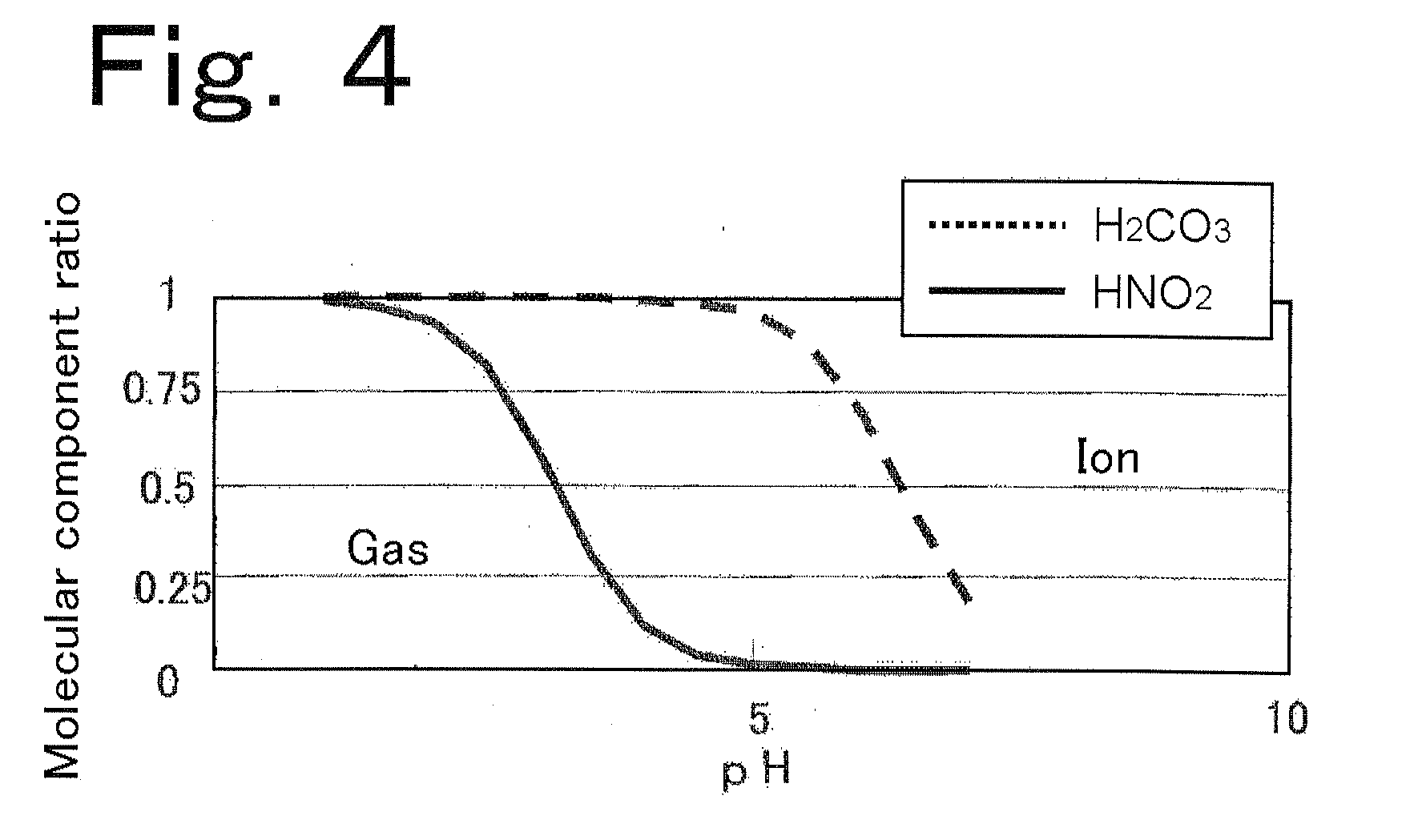
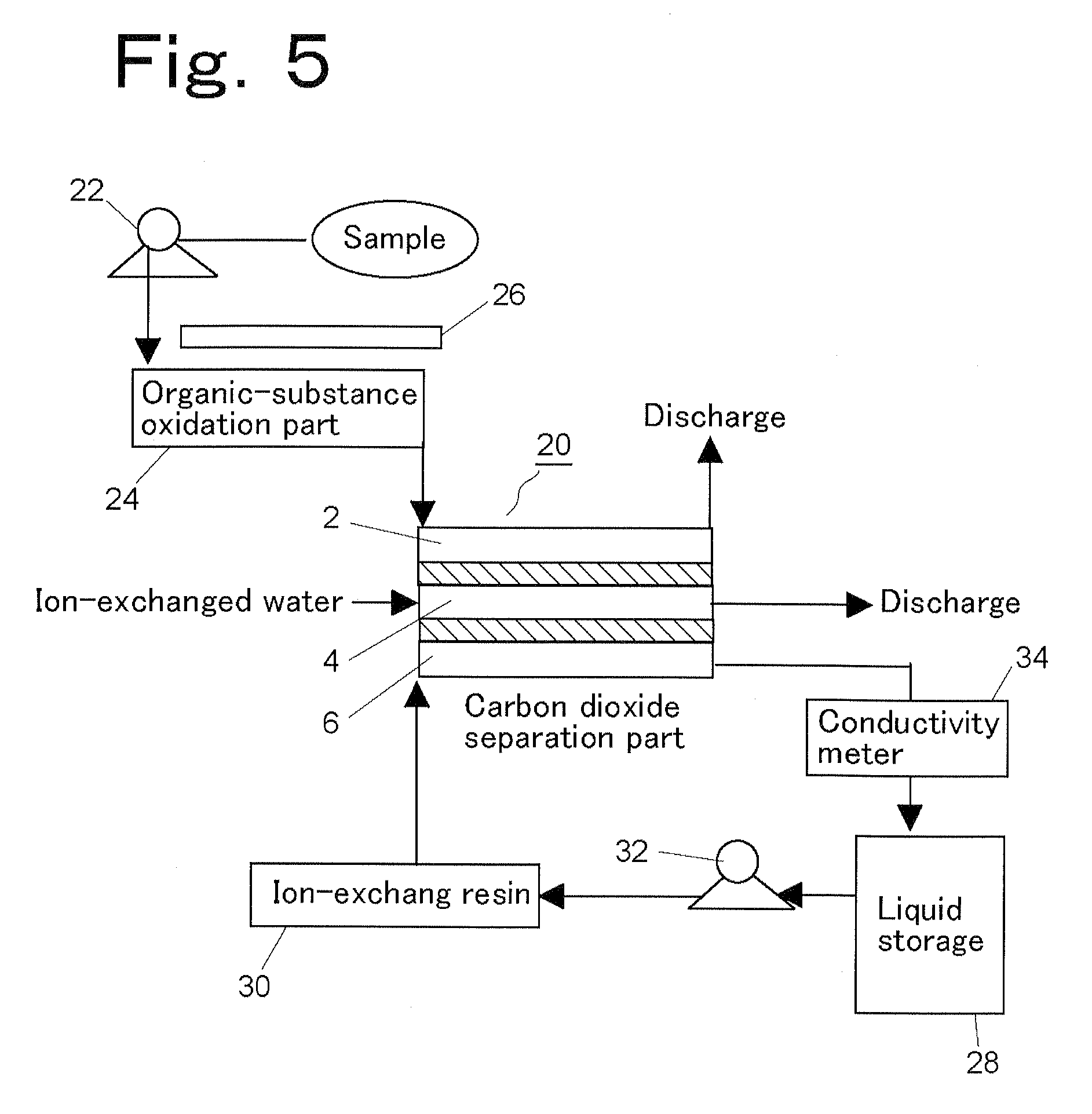
[PROBLEMS] To use in a carbon dioxide separation part a gas-permeable membrane capable of maintaining high-speed determination and to diminish the influence of interfering ingredients.[MEANS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMS] An apparatus which comprises: an organic-substance oxidation part in which organic substances contained in a sample water supplied are oxidized into carbon dioxide; a carbon dioxide separation part in which the carbon dioxide contained in the sample water treated with the organic-substance oxidation part is caused to permeate and come into a measurement water; and a conductivity measurement part in which the conductivity of the measurement water sent from the carbon dioxide separation part is measured. The carbon dioxide separation part comprises: a sample water channel in which the sample water treated with the organic-substance oxidation part flows; an intermediate water part in which an intermediate water having a higher pH value in a neutral region than the sample water flowing through the sample water channel is present; and a measurement water channel through which the measurement water comprising deionized water flows. The sample water channel is in contact with the intermediate water part through a gas-permeable membrane, and the intermediate water part is in contact with the measurement water channel through a gas-permeable membrane.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Method for monitoring the electrical energy quality in an electrical energy supply system, power quality field device and power quality system
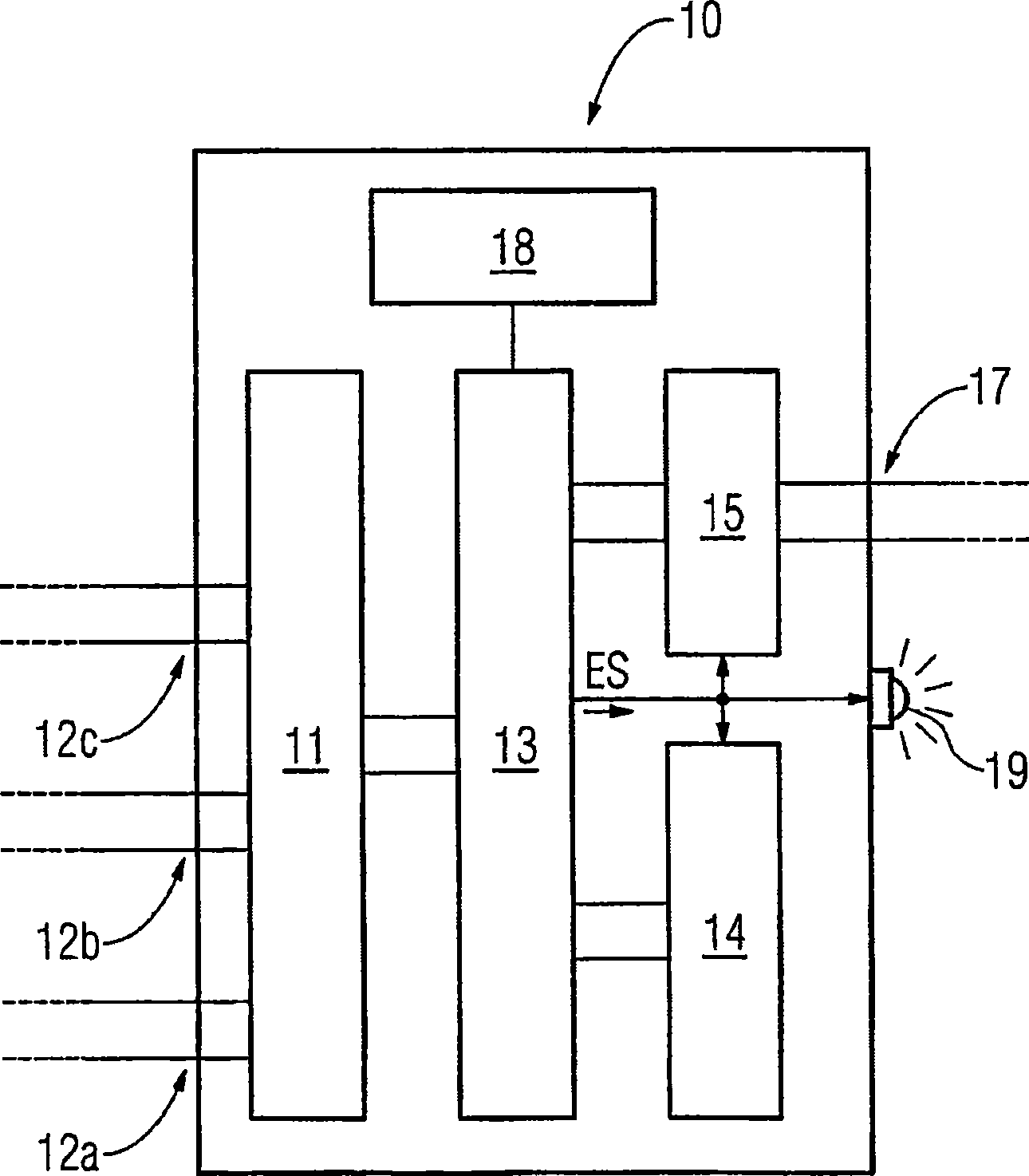
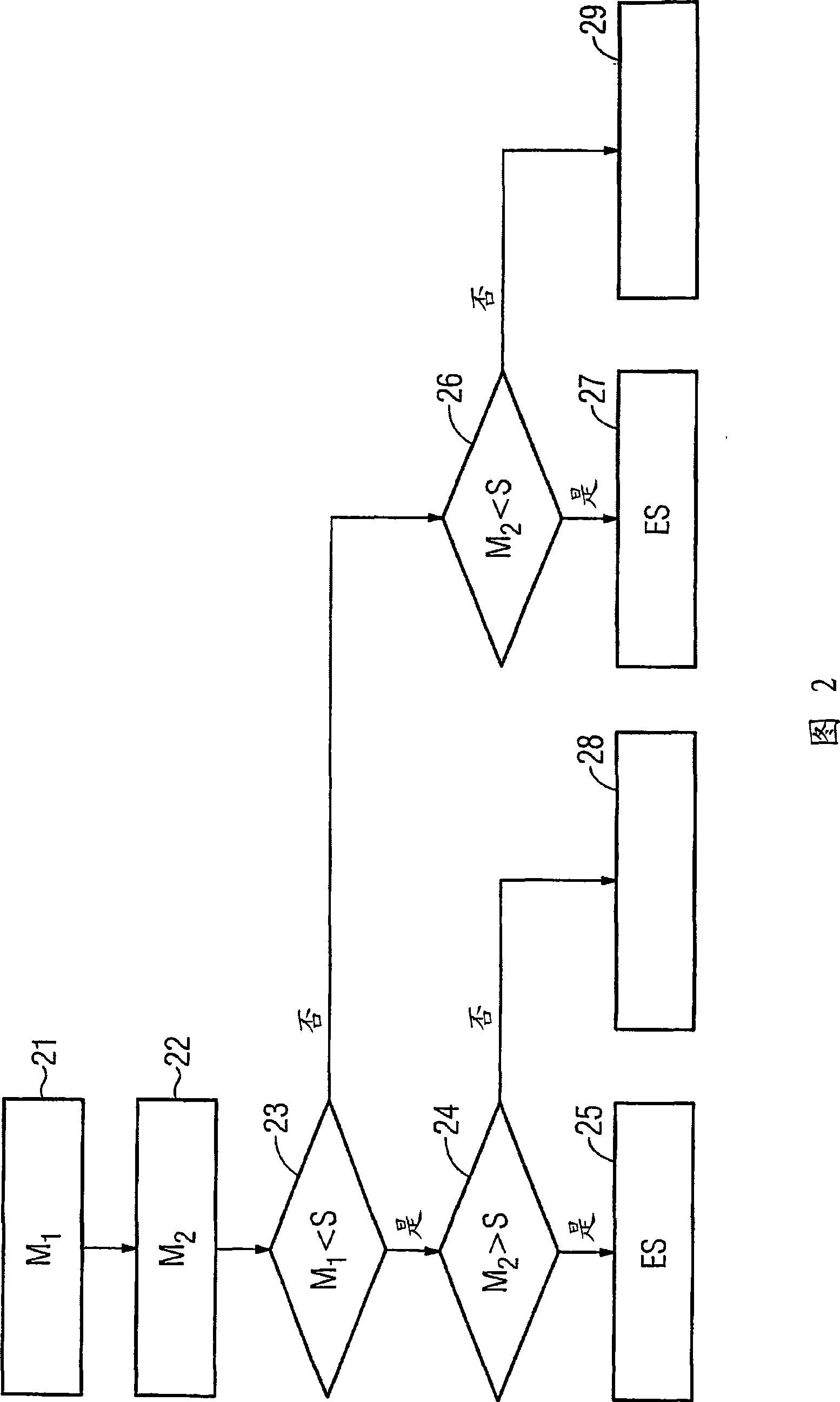
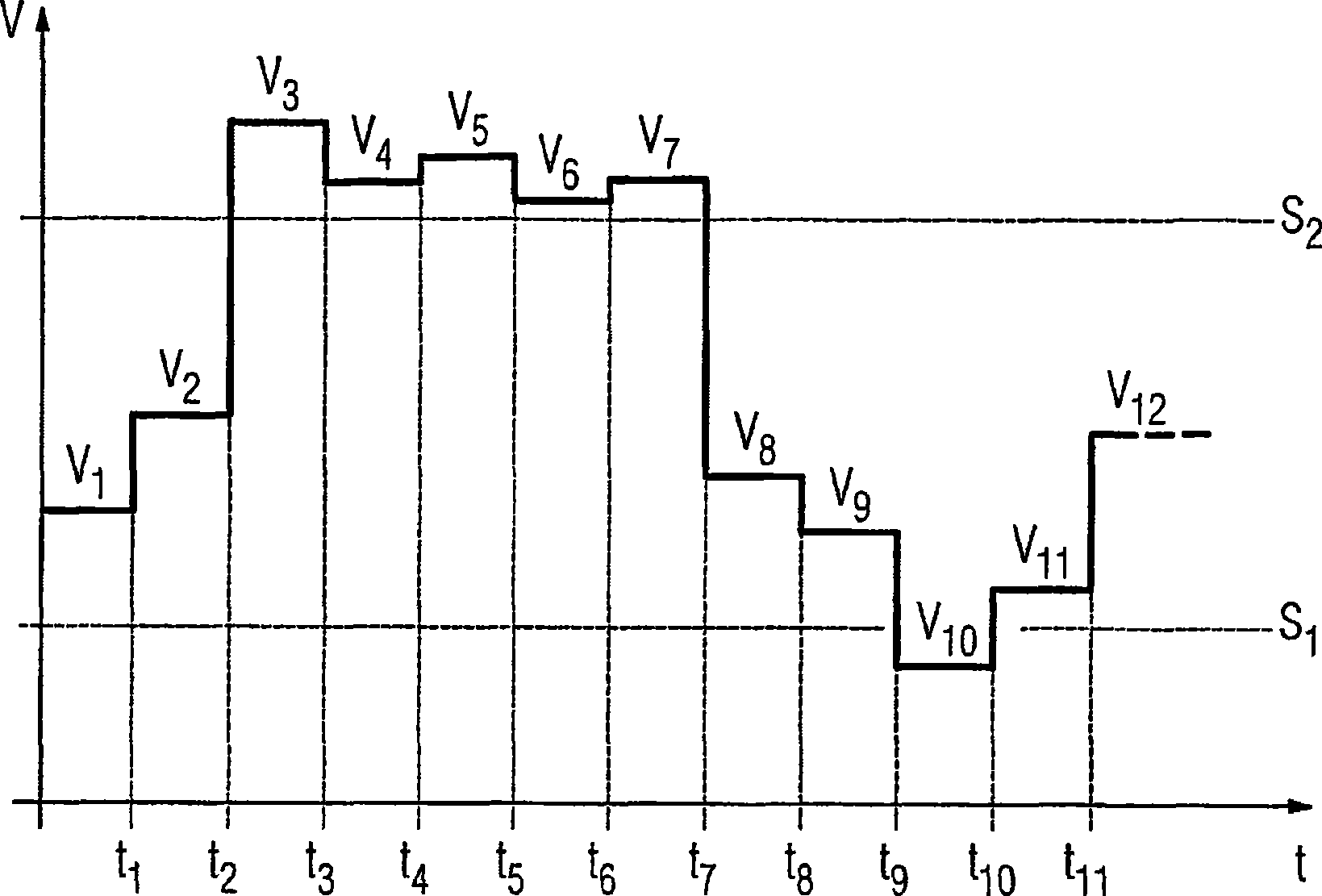
InactiveCN101427437AReduce storage capacityLow costCurrent/voltage measurementInformation technology support systemPower qualityMeasurement device
In order to be able to carry out monitoring of the electrical energy quality of an electrical energy supply system using an electrical power quality field device with comparatively little complexity, a method for monitoring the electrical energy quality of an electrical energy supply system is proposed in which the following steps are carried out: - detection of a first measured value of a first power quality characteristic by means of a measuring device (11) of a power quality field device (10, 50) arranged at a measurement point of the electrical energy supply system at a first measurement time; - detection of a second measured value of the first power quality characteristic by means of the measuring device (11) at a second measurement time, which directly follows the first measurement time; - comparison of the first and the second measured value with at least one predetermined threshold value, and - generation of an event signal, which indicates an infringement of the at least one threshold value, precisely when one of the two measured values is above and one of the two measured values is below the at least one threshold value. The invention also relates to a power quality field device in which such a method is carried out as well as to a power quality system.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com