Patents
Literature
242 results about "Lead system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lead System is a site that’s devoted to sharing with you and training you on how to get lots of leads for your MLM, Affiliate or Network Marketing business.
Photography methods and systems
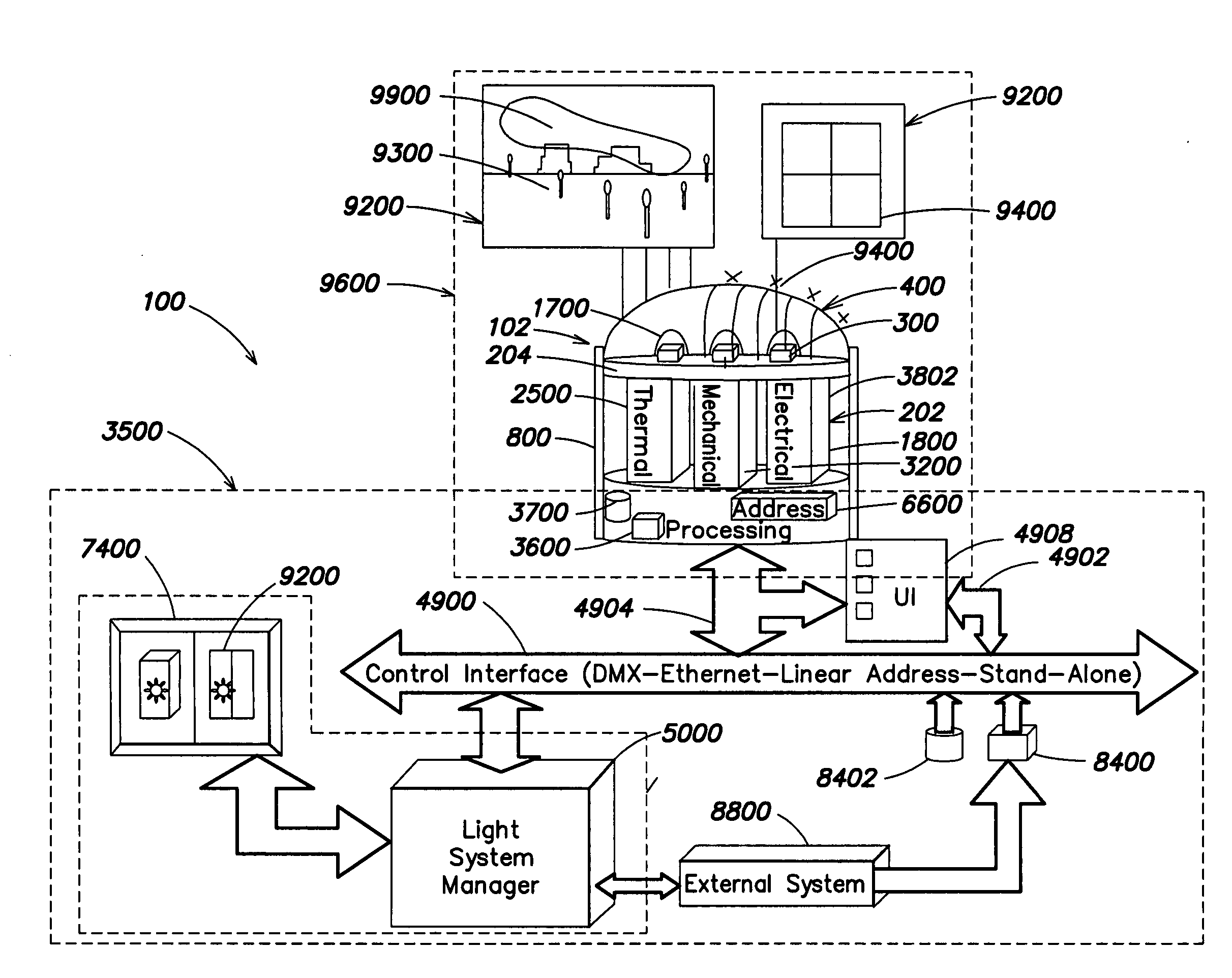
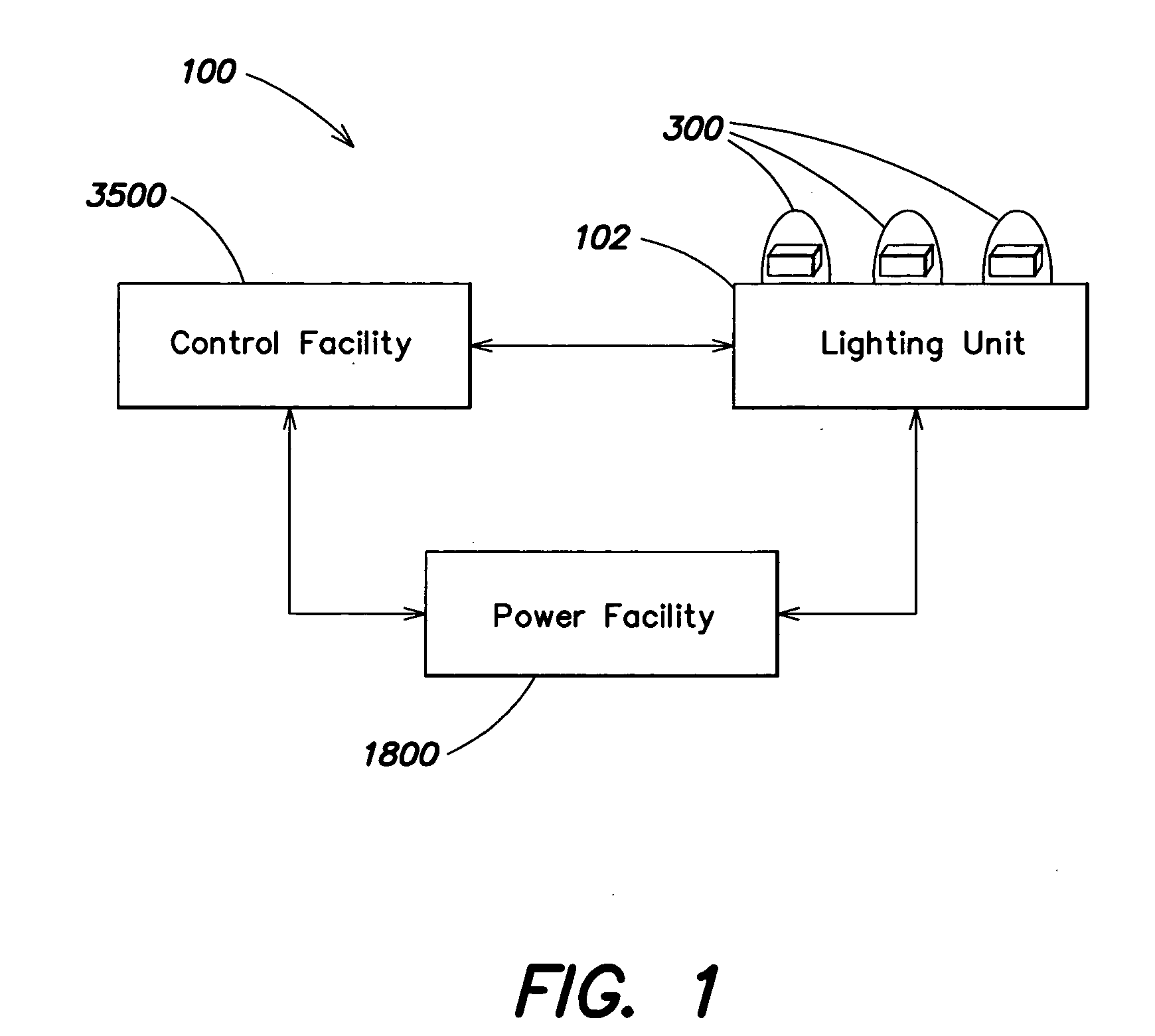
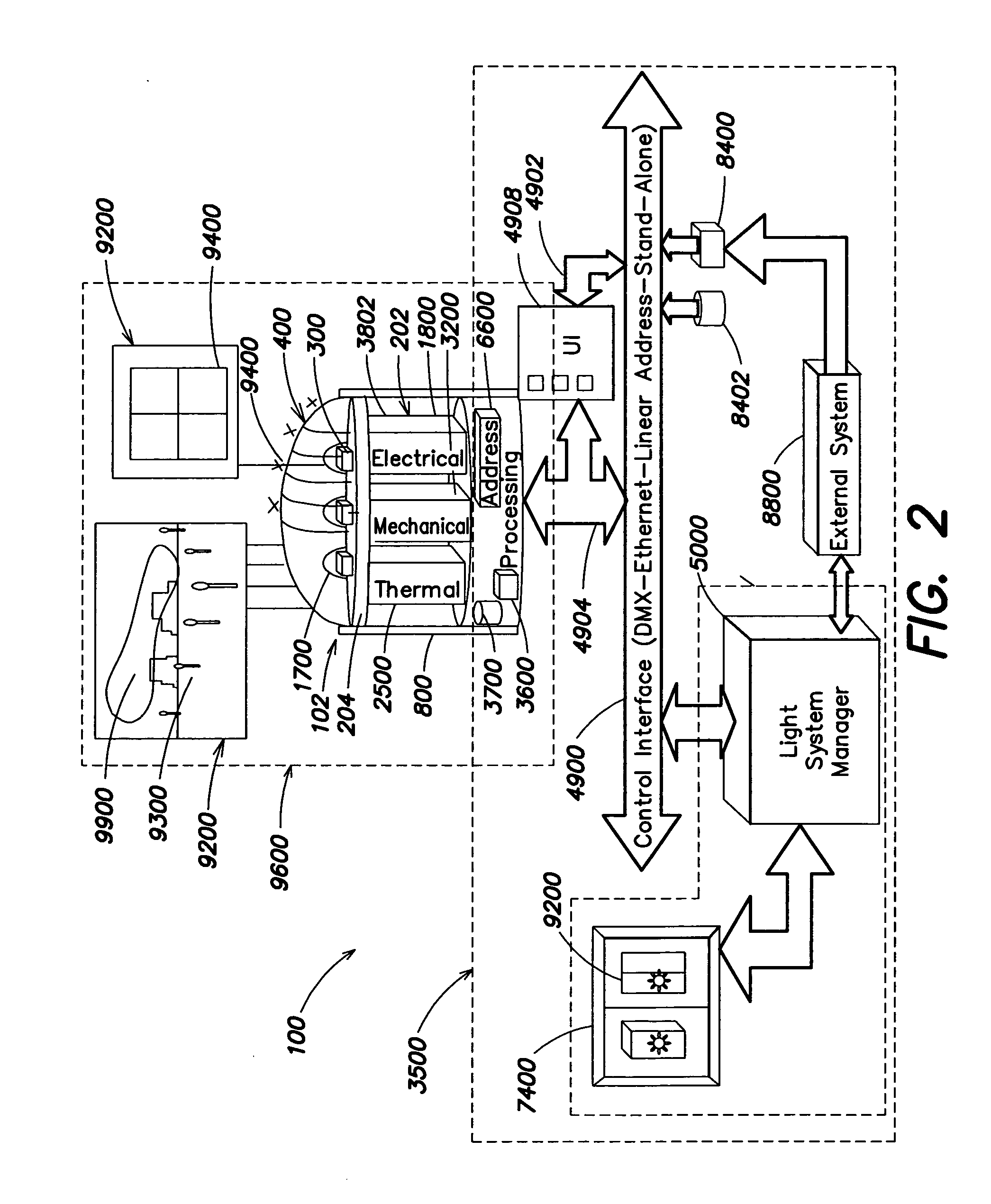
InactiveUS20050174473A1Reduce light outputEasy to customizeLighting applicationsTelevision system detailsEngineeringHue
The embodiments disclosed herein show how such LED methods and systems, especially intelligent LED systems, can be used for photographic and cinematography applications and provide many benefits. Controlled LED illumination allows easy customization of these features to create a particular mood and can be used to create light of desired saturation and hue.
Owner:COLOR KINETICS
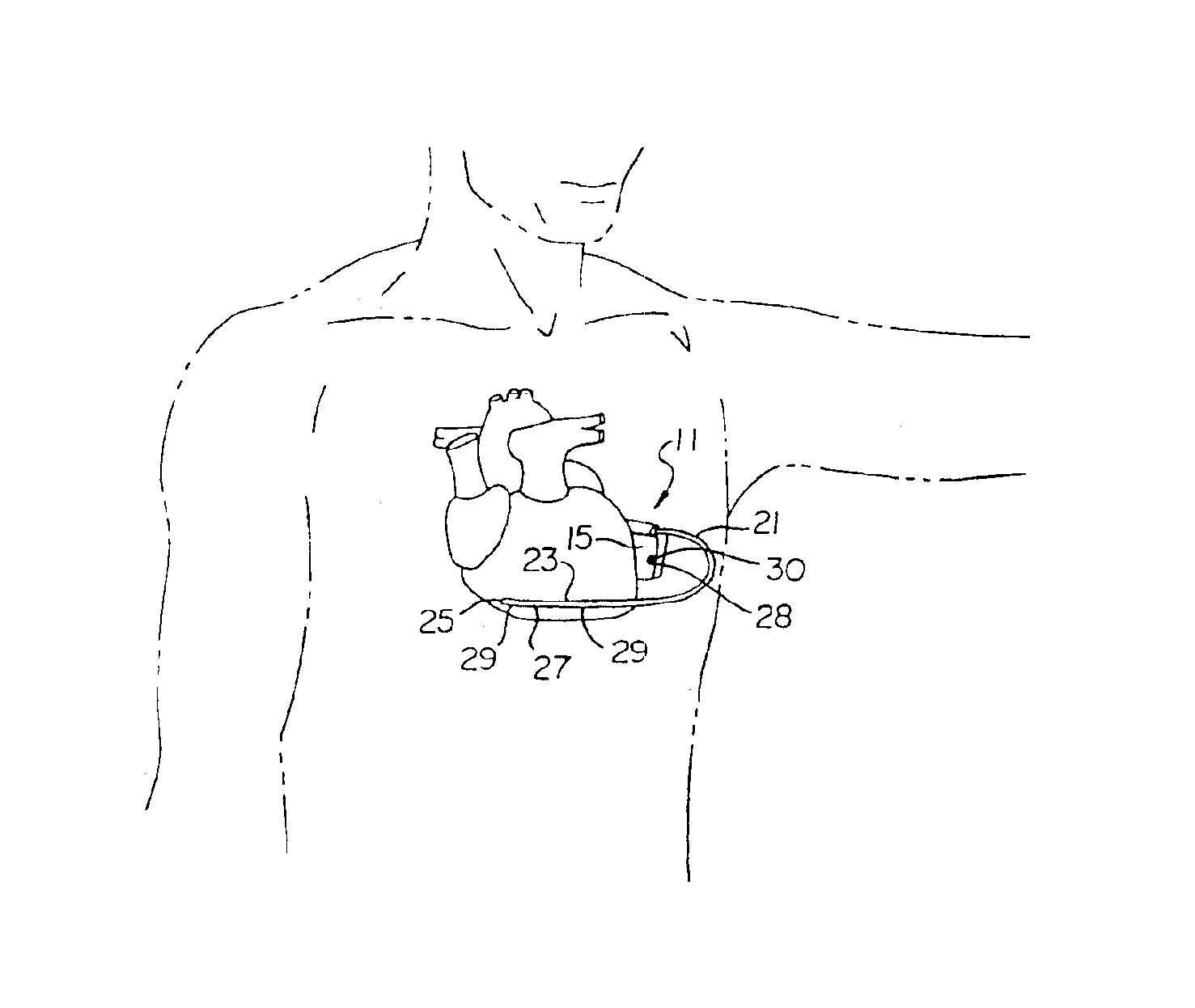
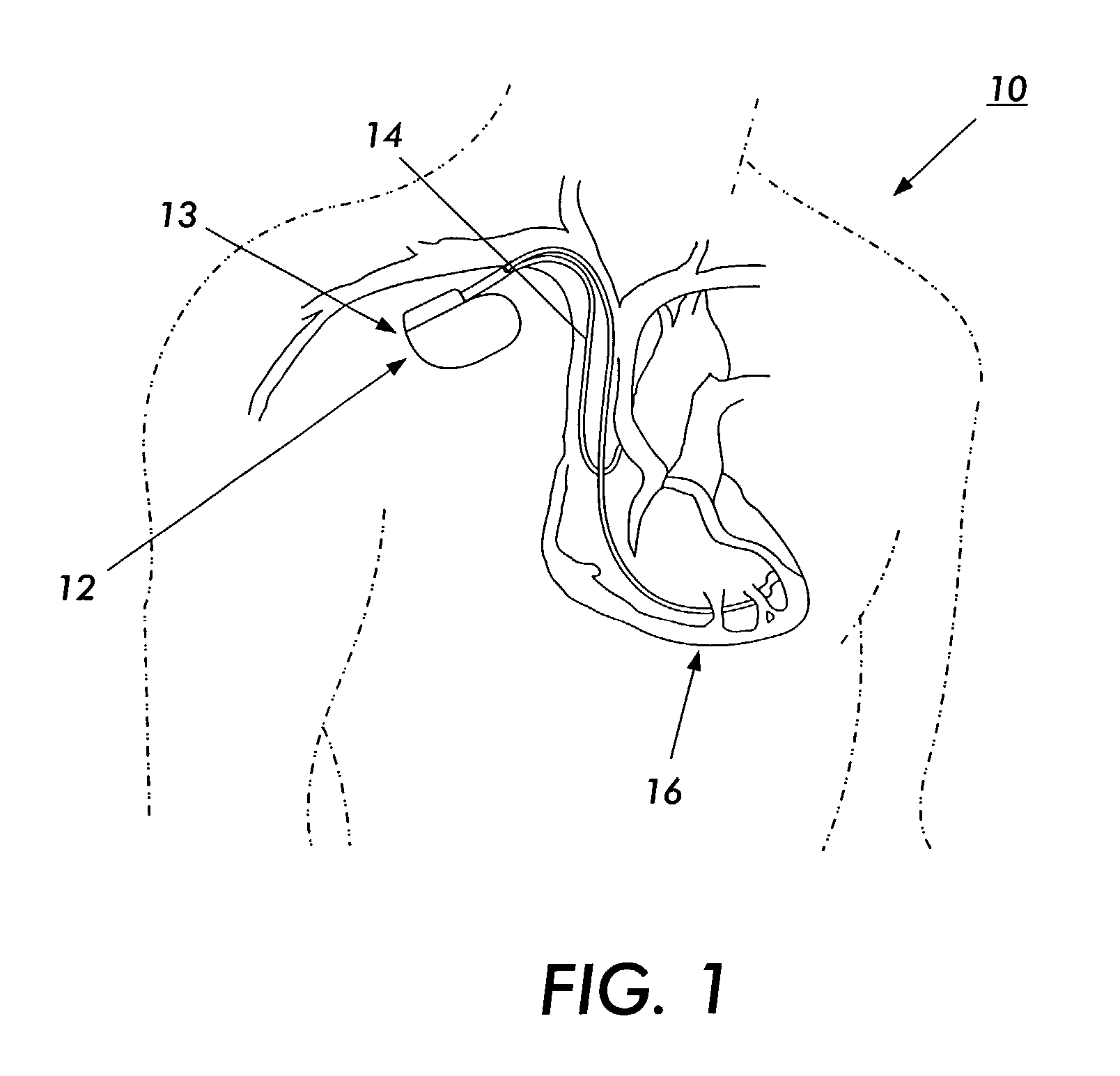
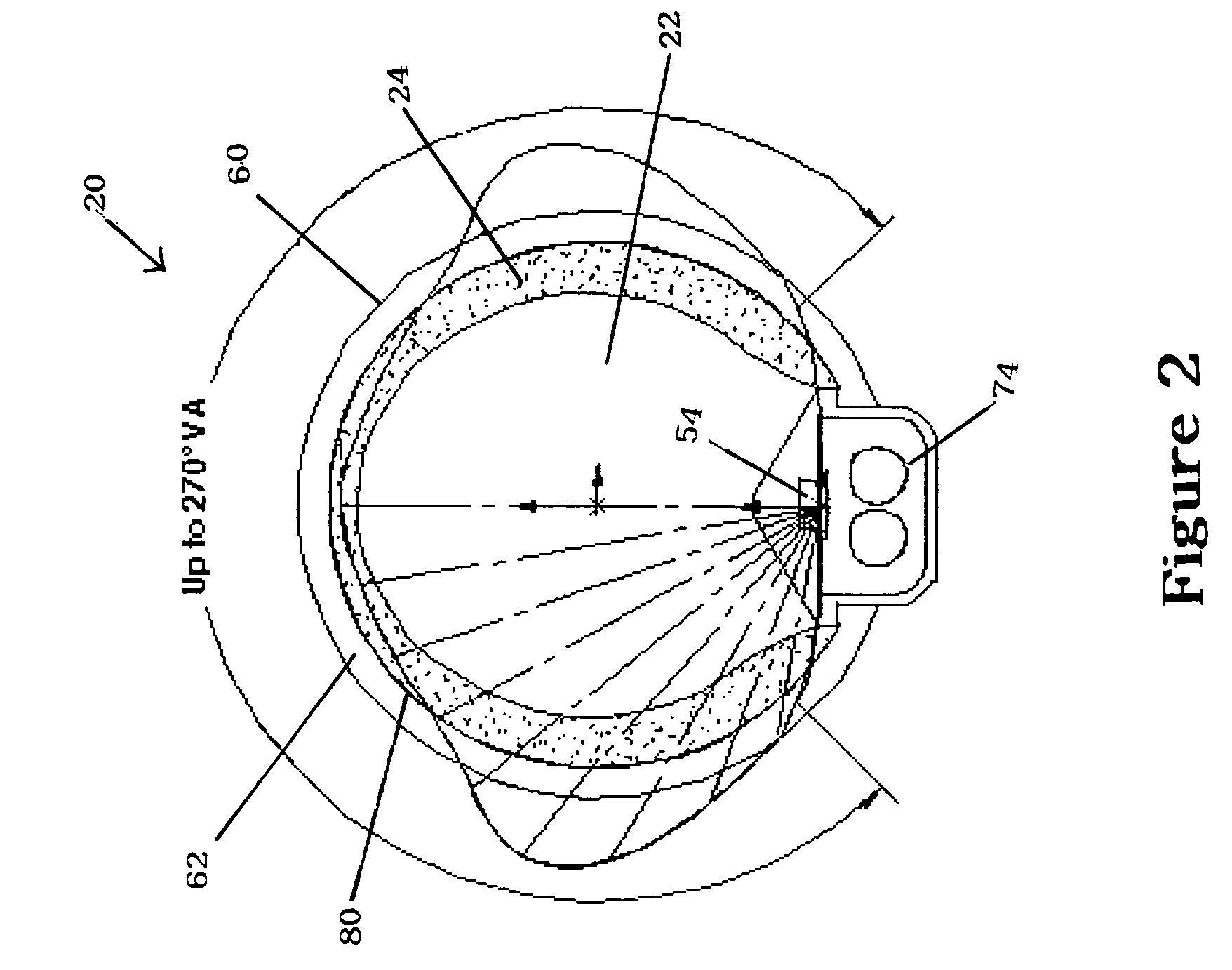
Biphasic waveform for anti-tachycardia pacing for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
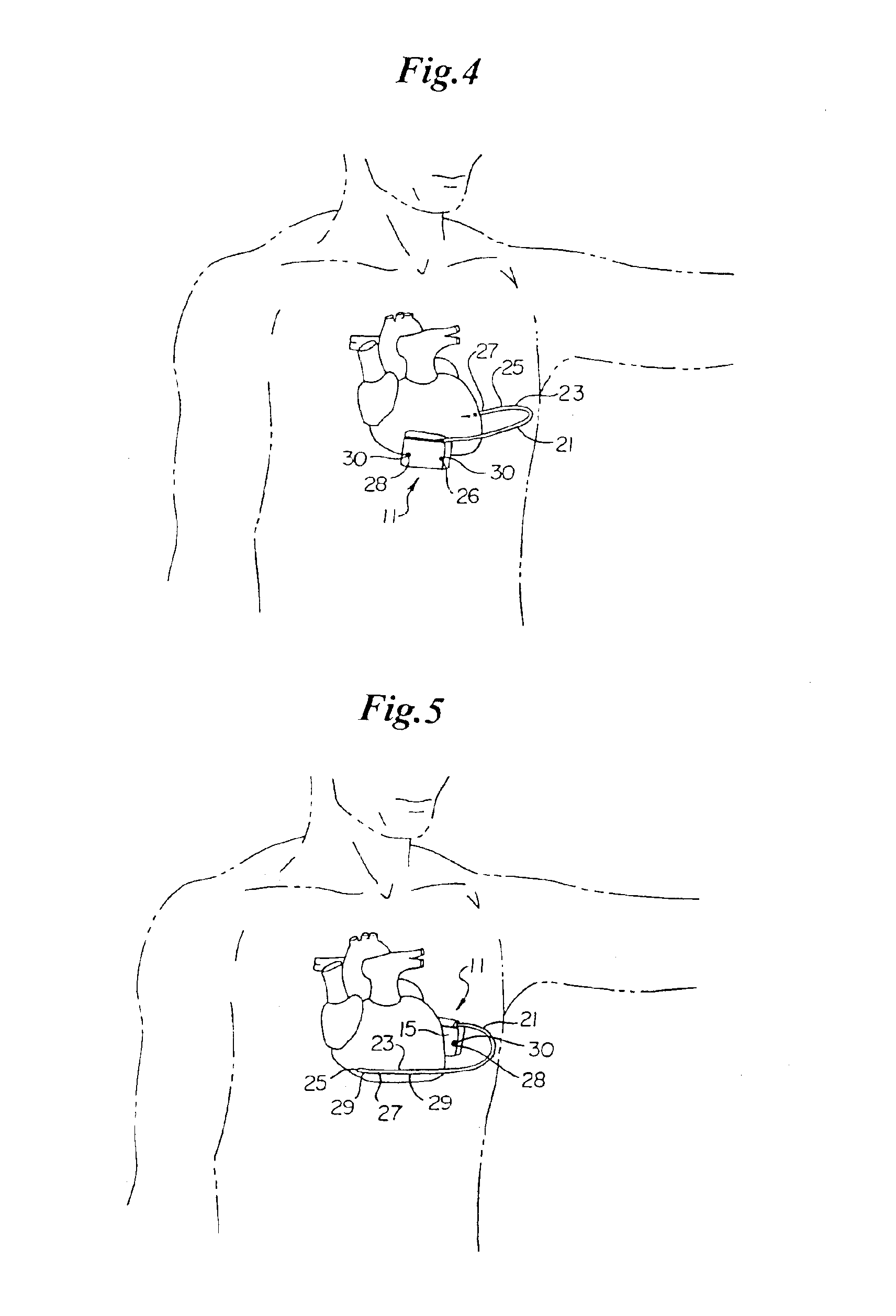
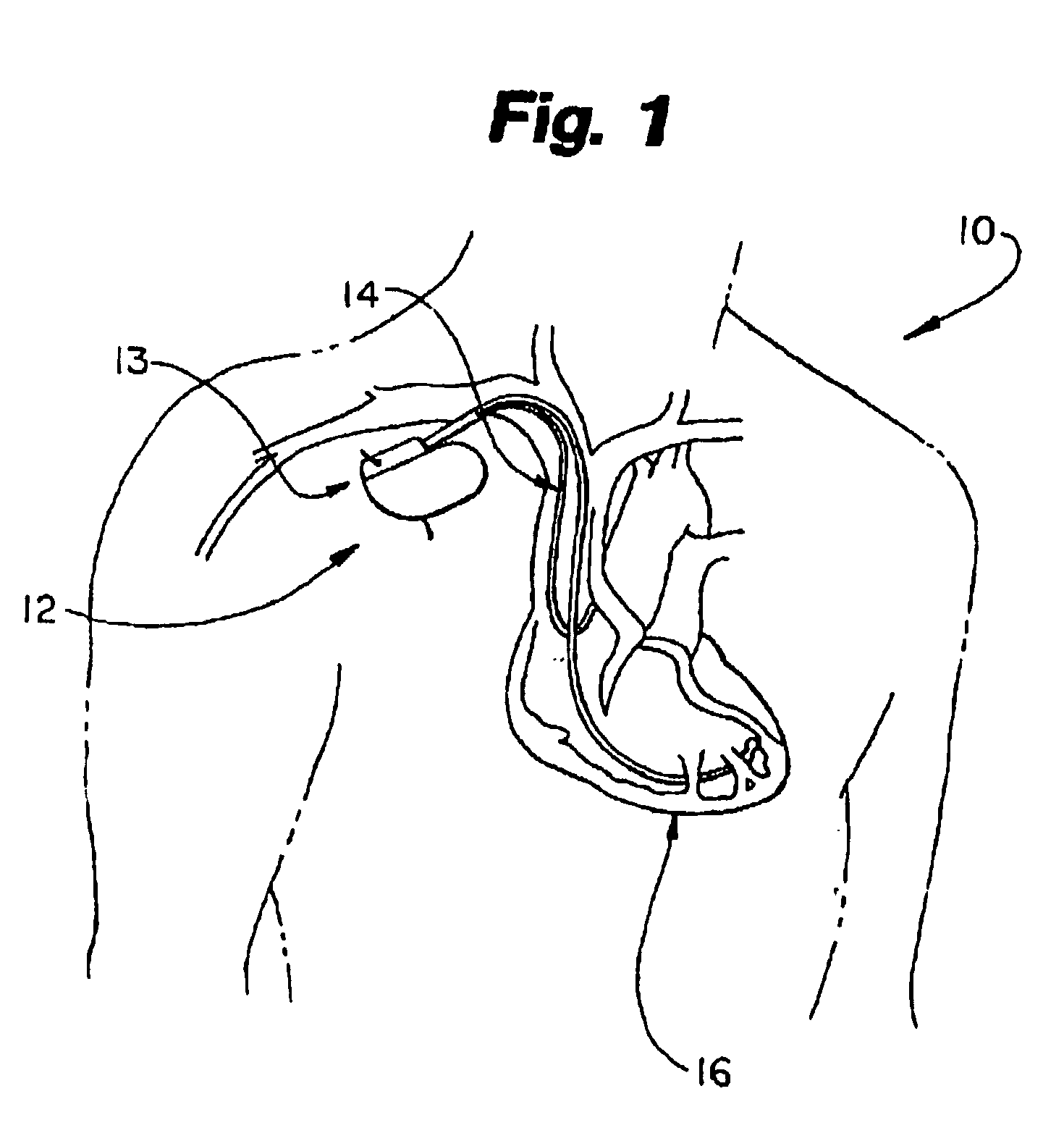
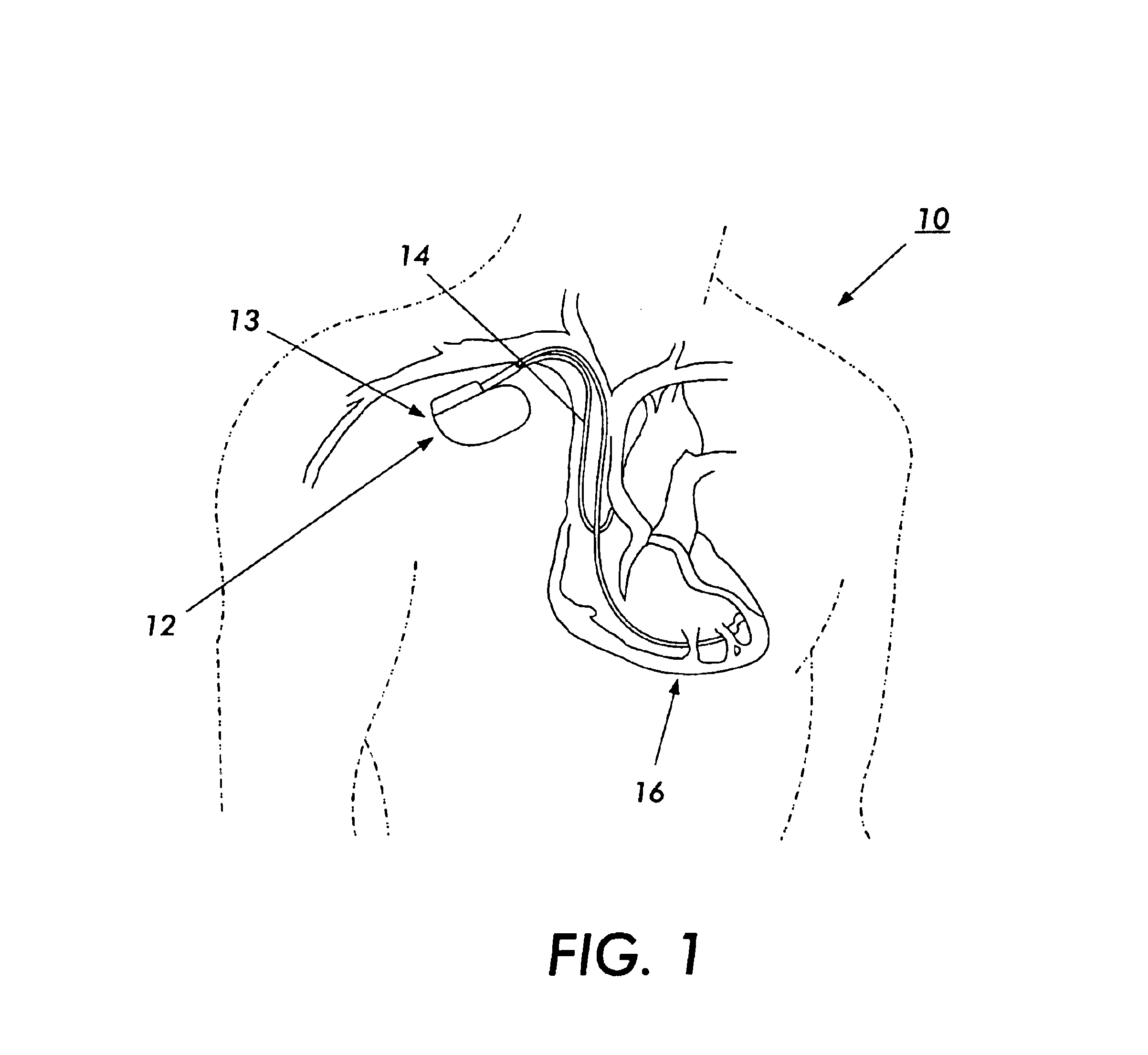
A power supply for an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for subcutaneous positioning between the third rib and the twelfth rib and using a lead system that does not directly contact a patient's heart or reside in the intrathorasic blood vessels and for providing anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the heart, comprising a capacitor subsystem for storing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy for delivery to the patient's heart; and a battery subsystem electrically coupled to the capacitor subsystem for providing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the capacitor subsystem.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
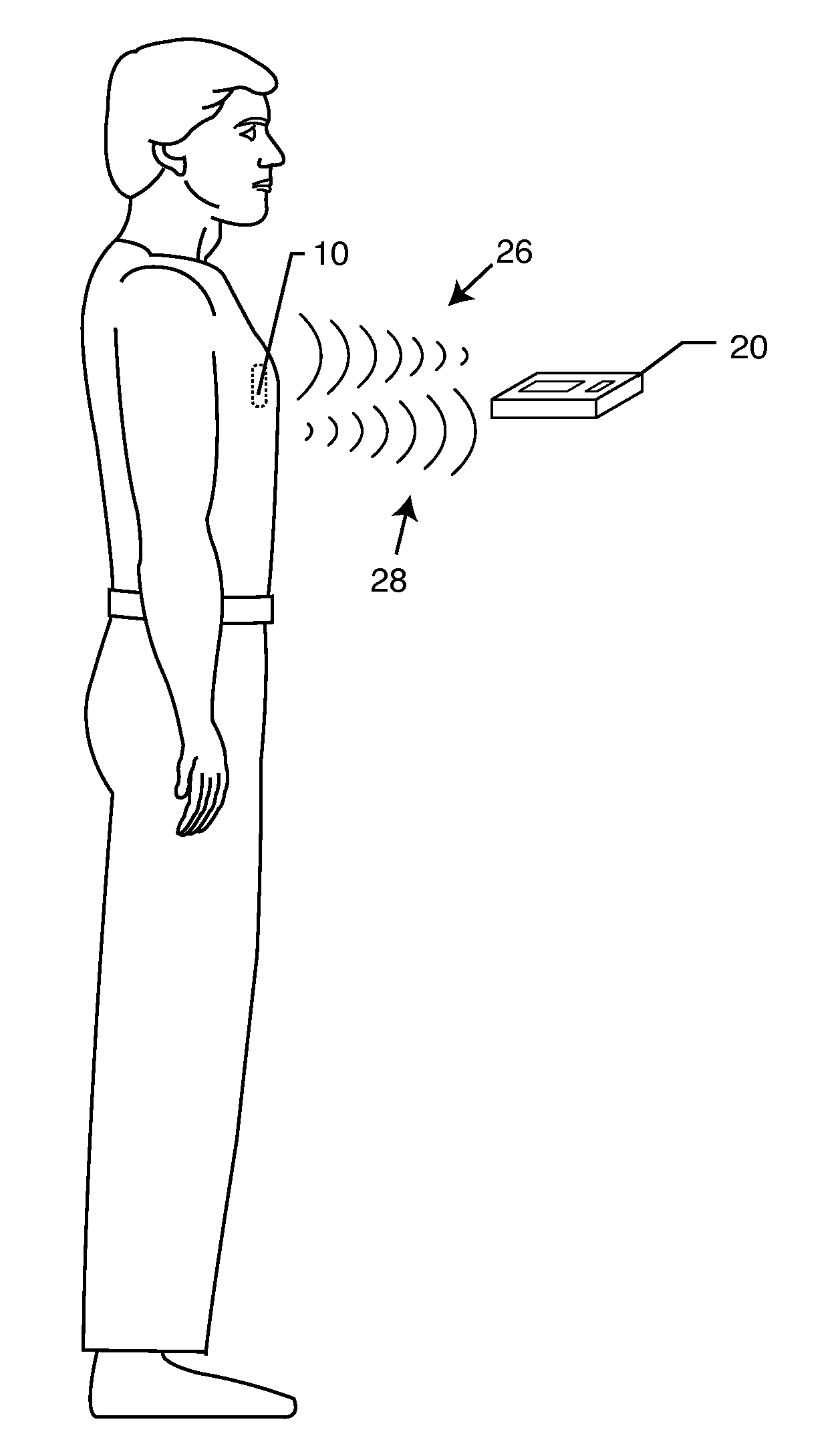
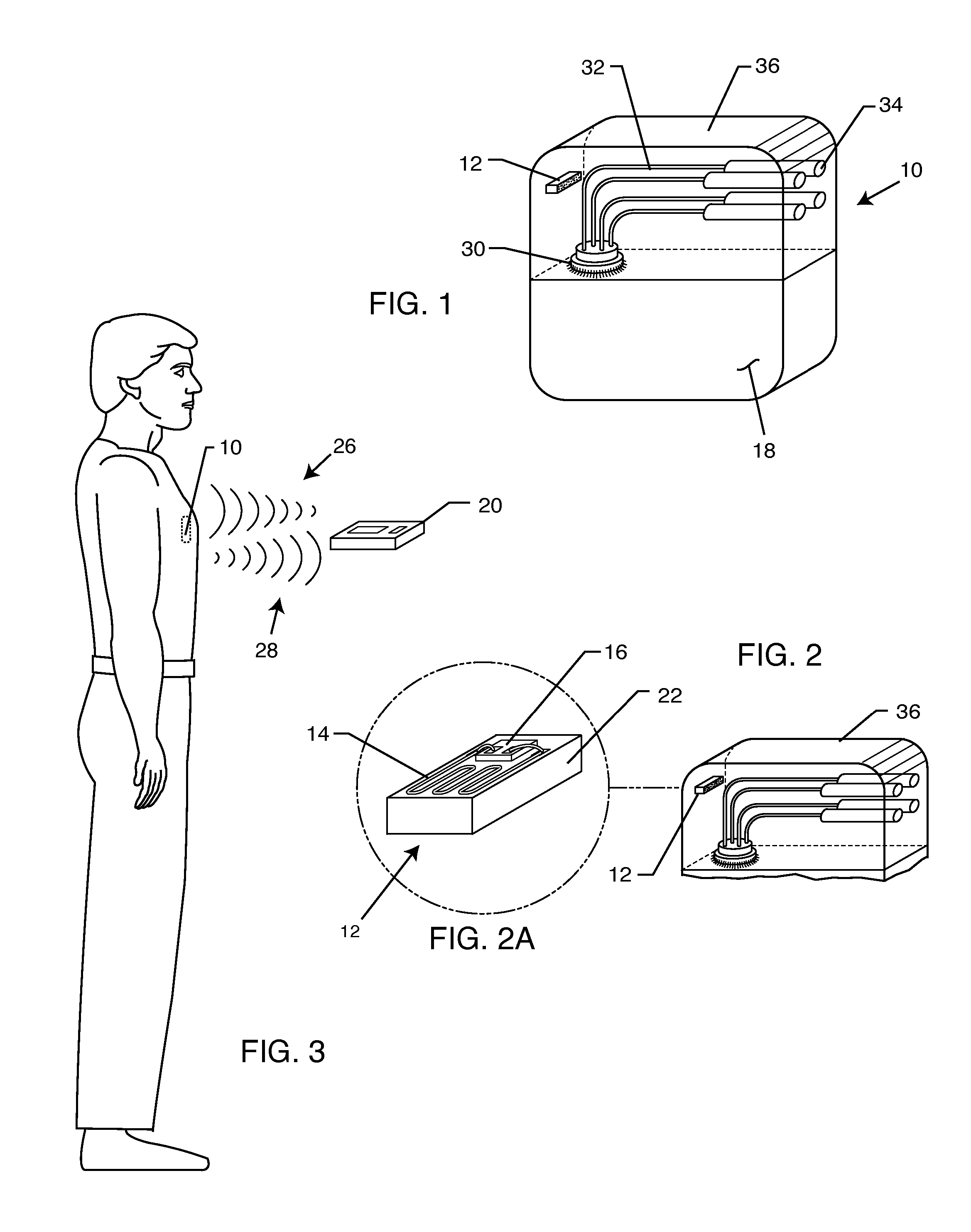
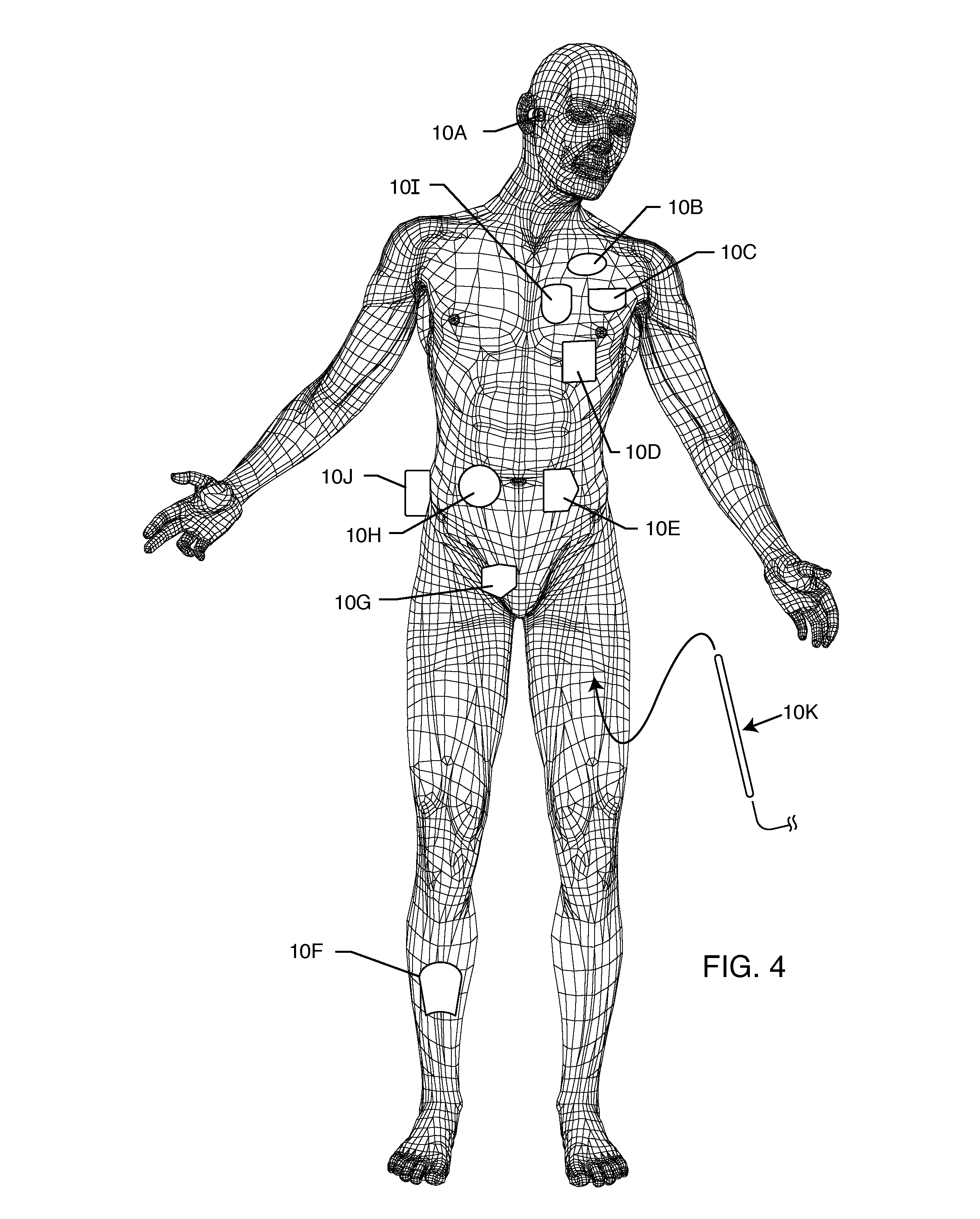
RFID detection and identification system for implantable medical lead systems
A system for identifying active implantable medical devices (AIMD) and lead systems implanted in a patient using a radio frequency identification (RFID) tag having retrievable information relating to the AIMD, lead system and / or patient. The RFID tag may store information about the AIMD manufacturer, model number, serial number; lead wire system placement information and manufacturer information; MRI compatibility due to the incorporation of bandstop filters; patient information, and physician and / or hospital information and other relevant information. The RFID tag may be affixed or disposed within the AIMD or lead wires of the lead system, or surgically implanted within a patient adjacent to the AIMD or lead wire system.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
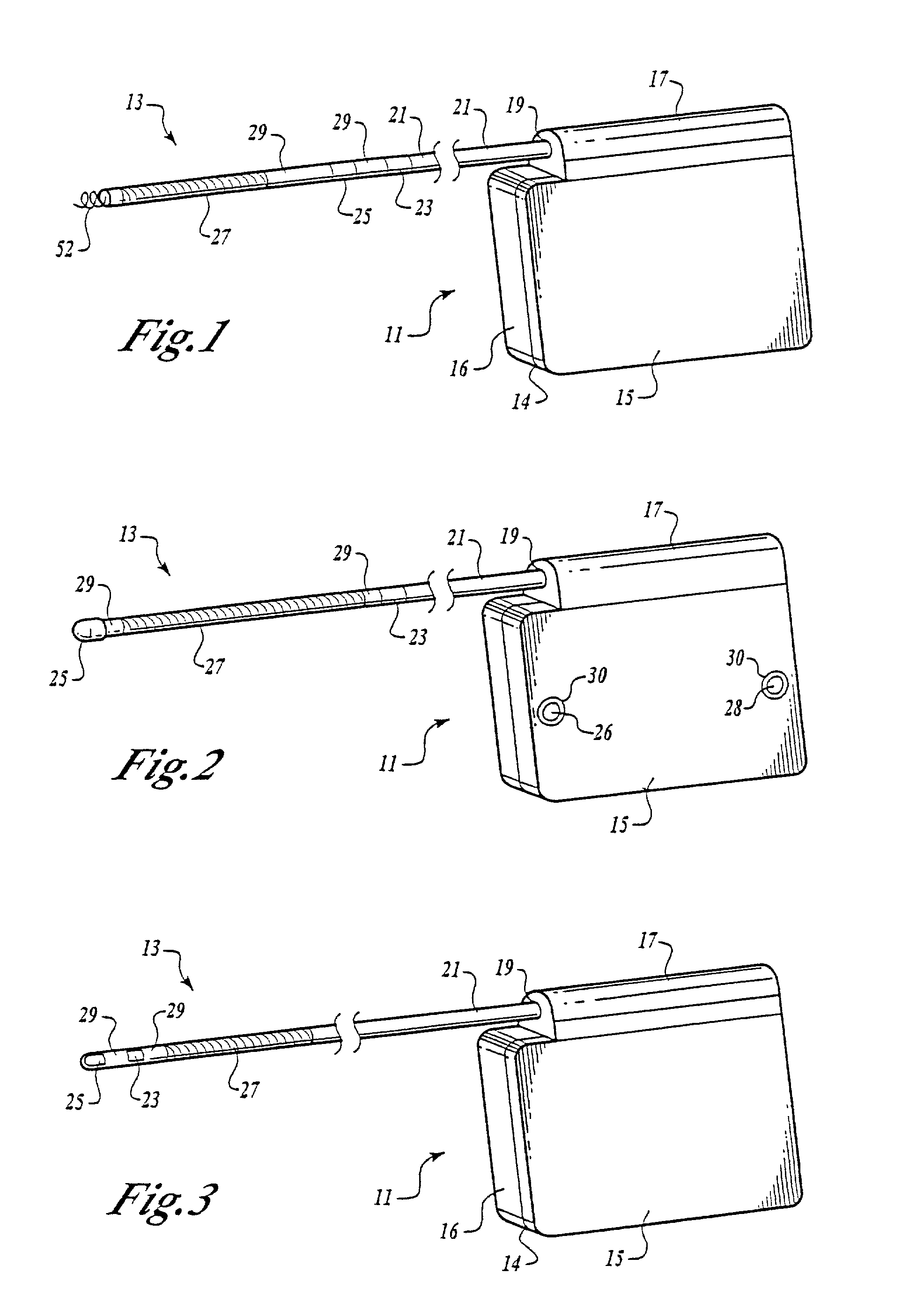
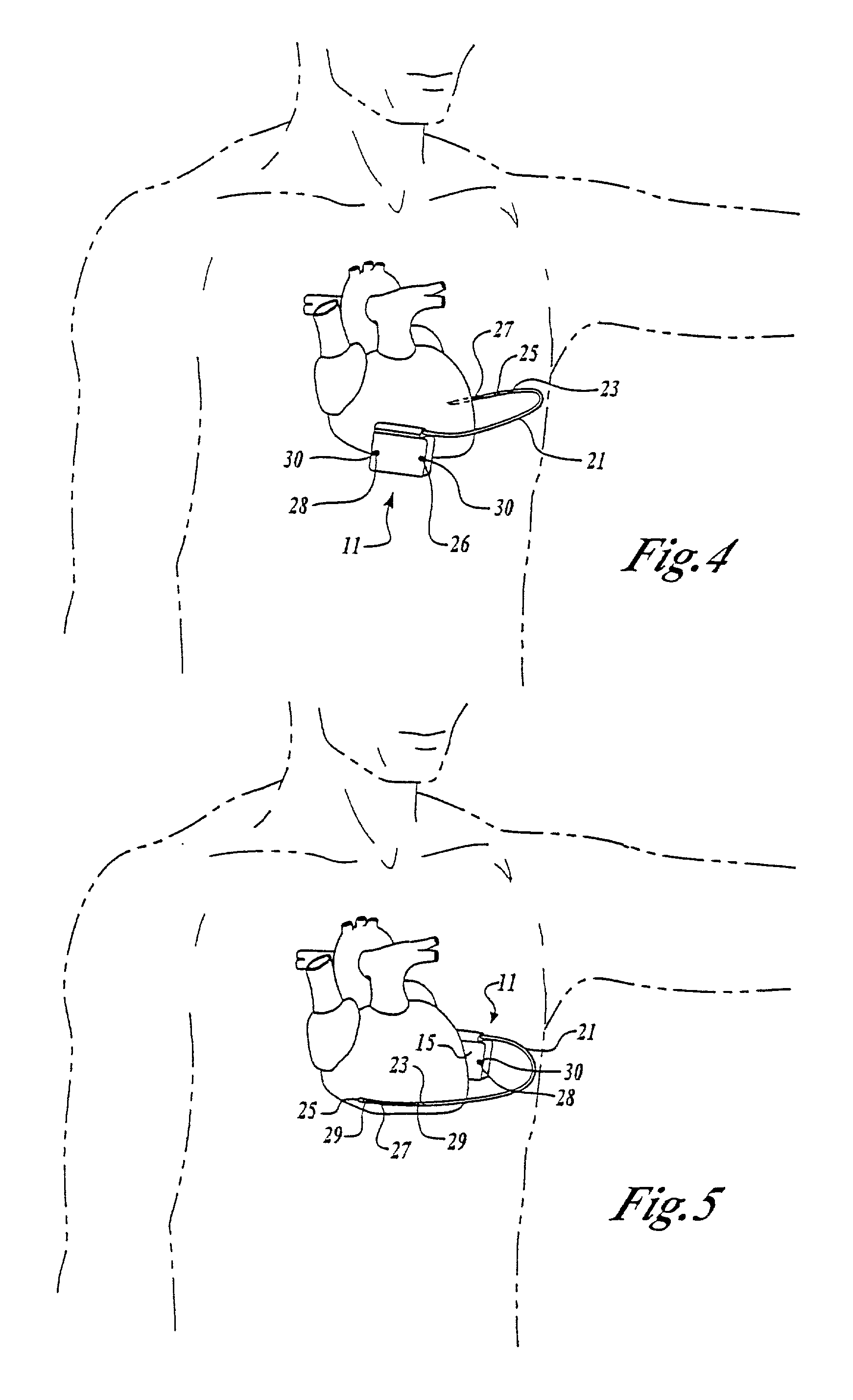
Delivery of active fixation implatable lead systems
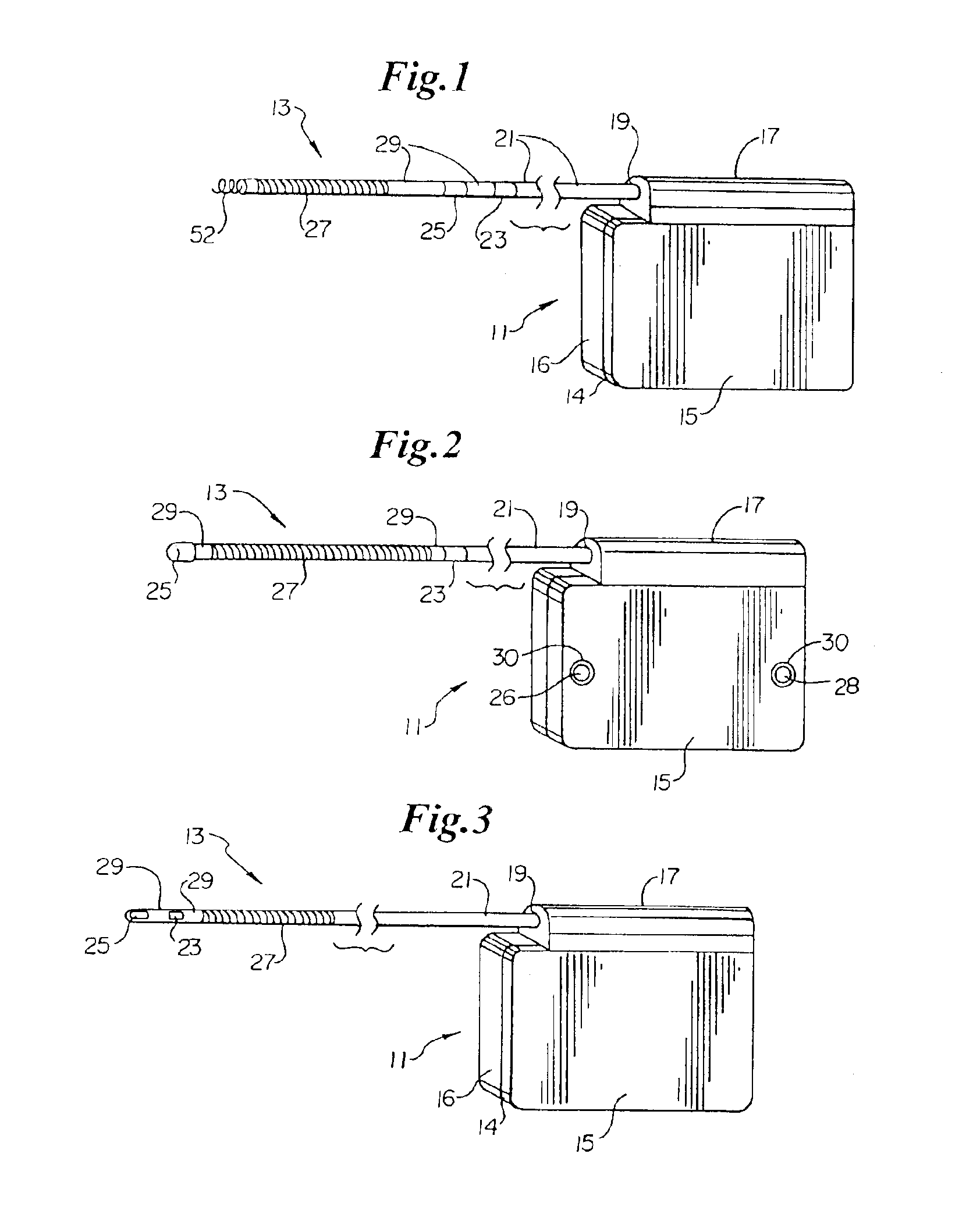
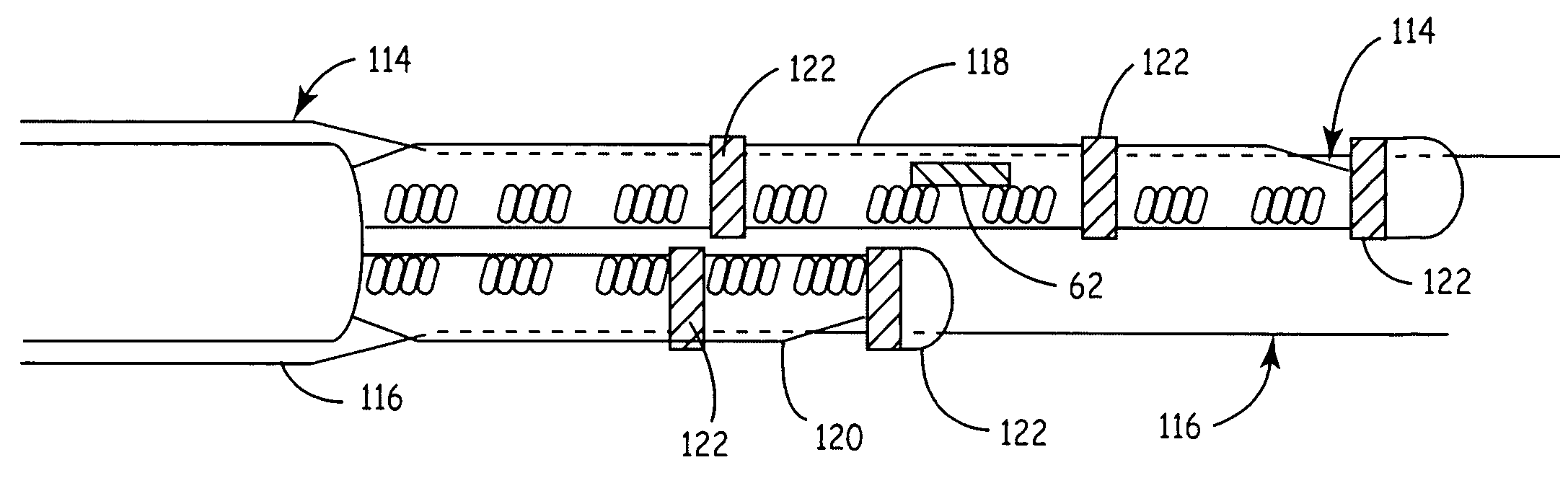
An implantable lead system includes an elongated device slideably engaged within a lumen of a lead body. A distal portion of the elongated device is slidable through a helix tip coupled to a distal end of the lead body by passing through a pierceable fluid-tight seal disposed in proximity to the distal end of the lead body; the seal prevents ingress of bodily fluid into the lumen of the lead body.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
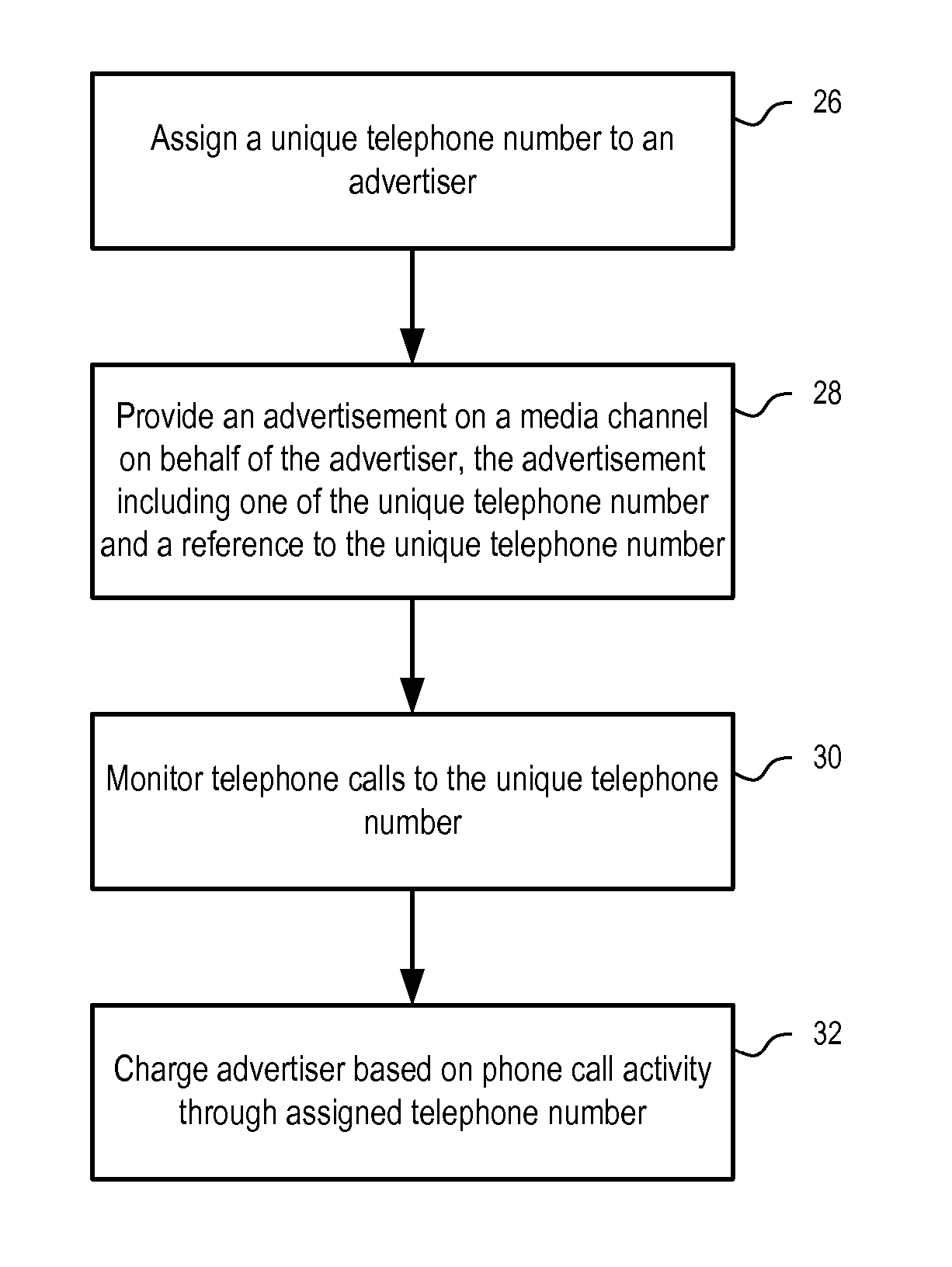
Methods and apparatuses to determine prices of communication leads
Systems and methods to determine prices for communication leads generated from pay for performance advertisements. In one embodiment, a method includes: providing an advertisement with a reference to customers on behalf of a specific party; facilitating communications between the party and a customer via the reference; and charging the party according to a price bid specified by the party in response to a lead to communications between the party and the customer facilitated via the reference. In one embodiment, a fee for the communication leads is determined according to the price bid specified by the party for the advertisement and at least one predetermined rule, which may be based on the geographic area of the advertisement, the categories of the advertisement, the price bids of a selected set of advertisements, and / or the query that causes the advertisement to be presented.
Owner:THRYV INC
Field steerable electrical stimulation paddle, lead system, and medical device incorporating the same
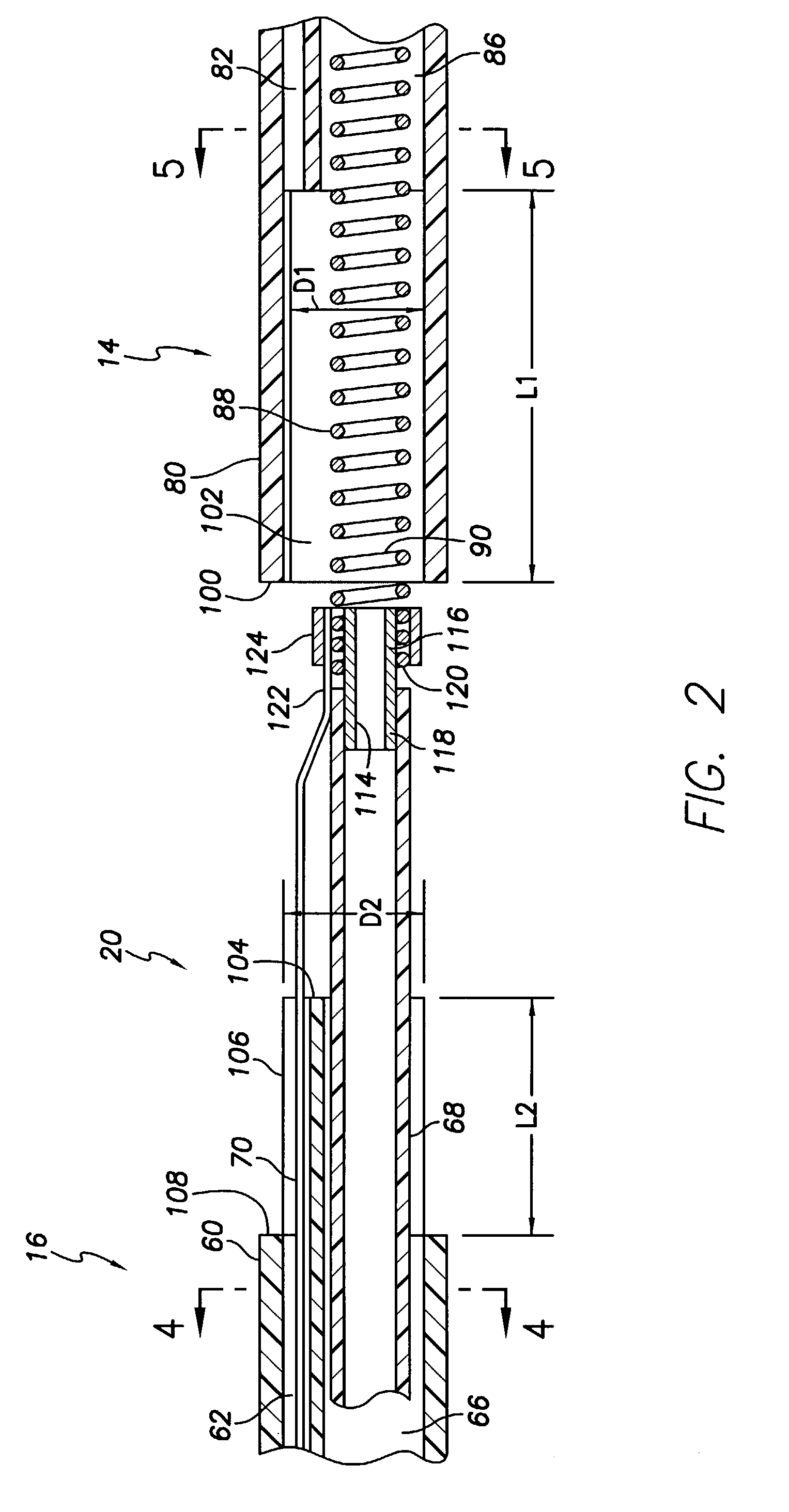
An implantable electrode paddle is adapted to receive an electrical signal from a medical device and generate an electrical field to stimulate selected body tissue. The paddle includes a housing including walls that define an interior space and a plurality of windows formed through at least a first one of the walls for transmitting the electrical field to the body tissue, an electrode array including a plurality of electrode groups, each electrode group including at least two electrodes individually secured in a respective window and spaced between about 0.1 mm and about 10 mm apart, and a plurality of wires, each of the wires being coupled to a respective electrode and routed within the interior space to receive the electrical signal. A lead assembly and an implantable medical device can include the paddle.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
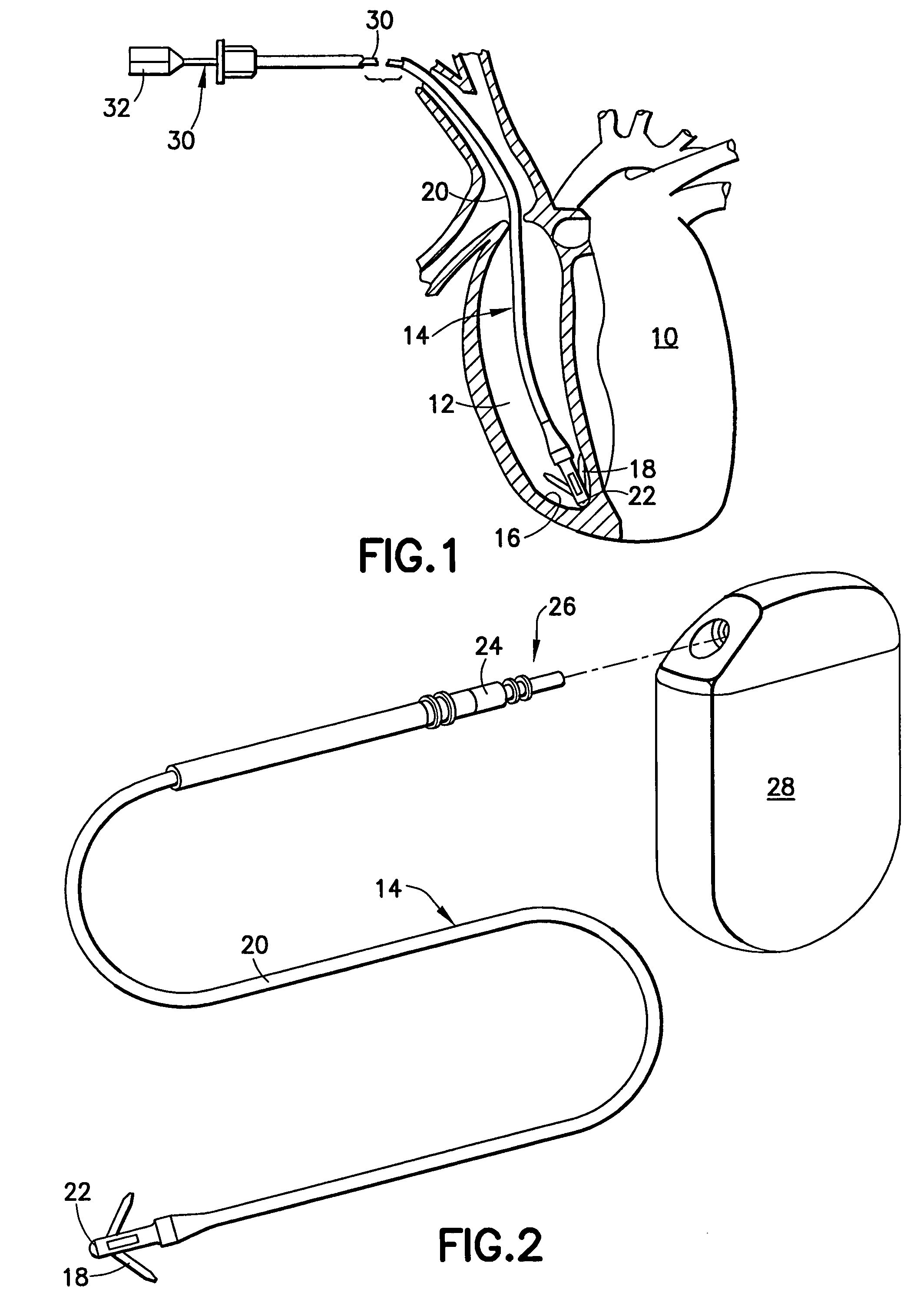
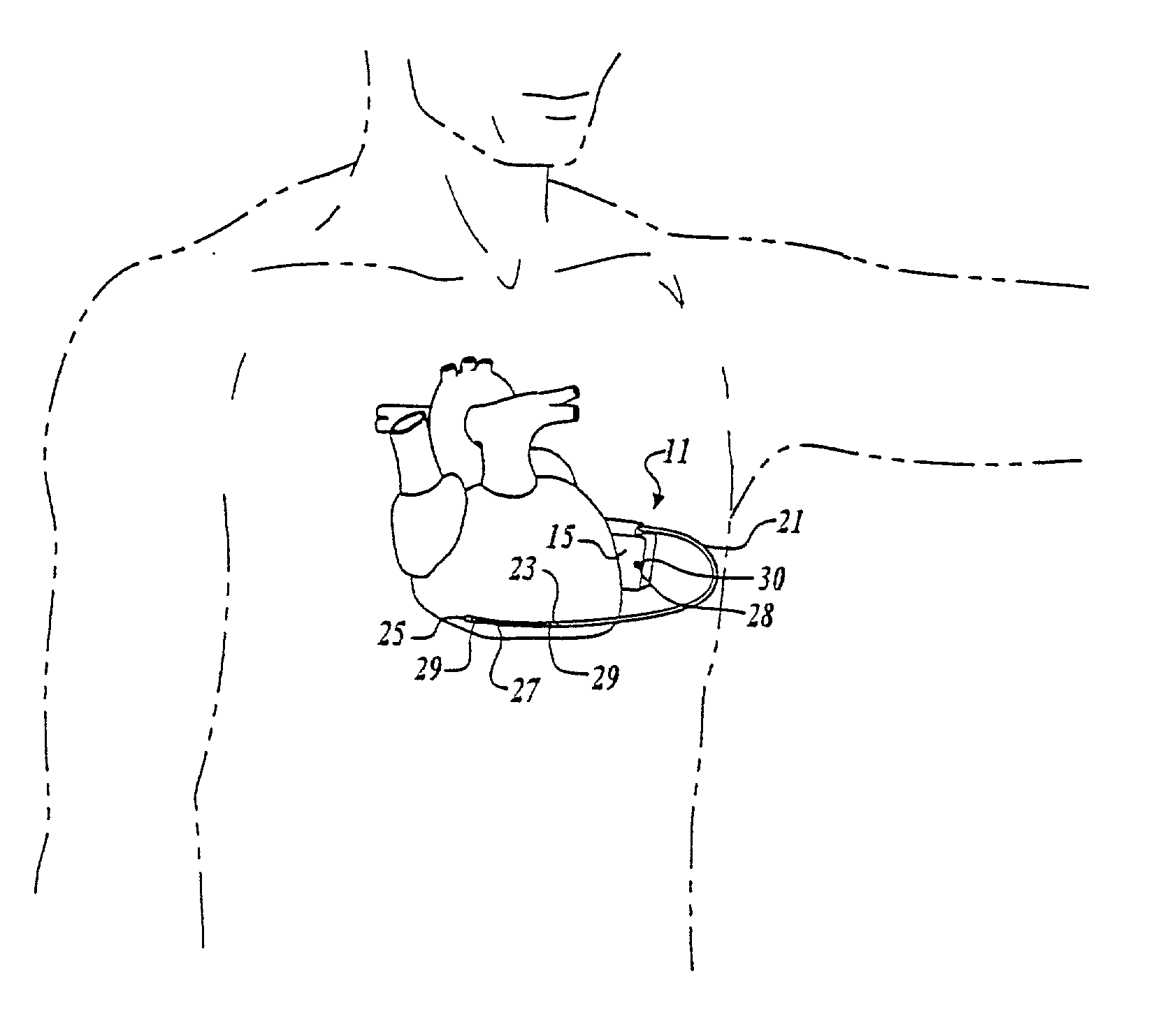
Implantable coronary sinus lead and lead system
InactiveUS6968237B2Increase flexibilitySmall diameterTransvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesElectrical conductorCoronary sinus
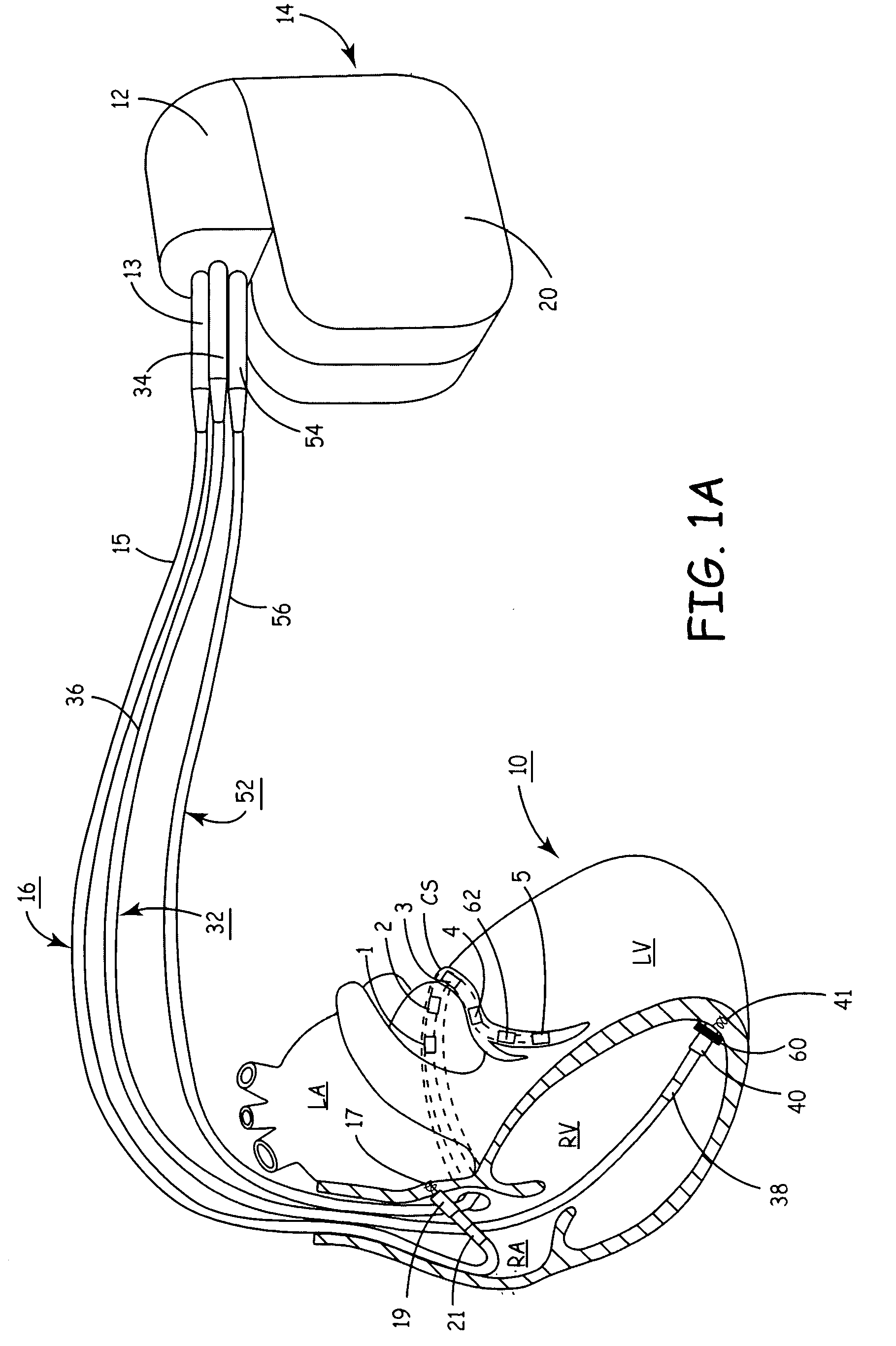
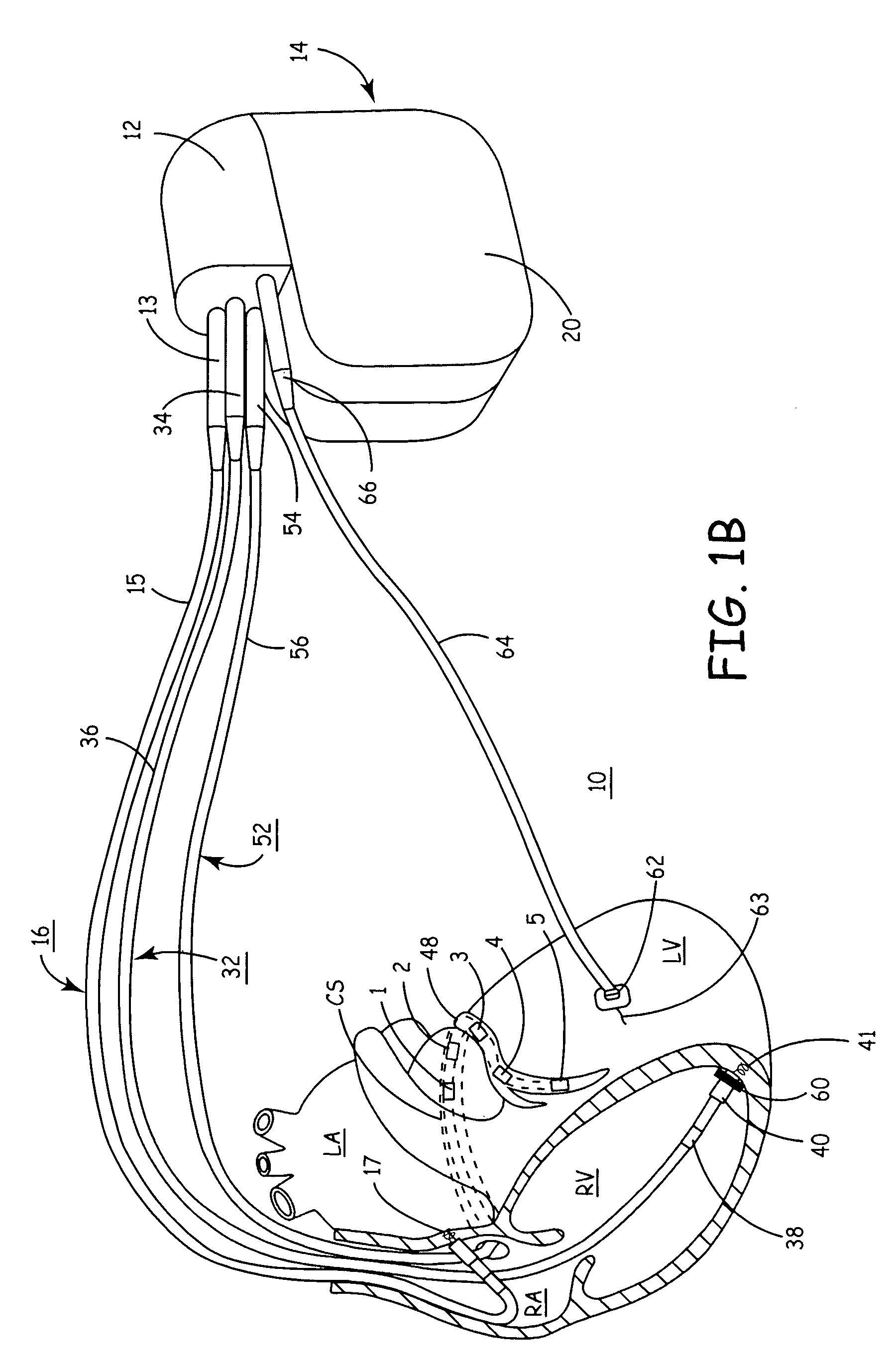
An implantable stimulation lead is disclosed for placement in the coronary sinus region and its associated coronary vessels overlying the left side of a patient's heart. The lead comprises at least one proximal connector; at least one tissue stimulation electrode; at least one conductor coupled between the at least one proximal connector and the at least one stimulation electrode; and a lead body including a housing of insulating material enclosing the at least one conductor, the lead body having a relatively flexible distal portion of, for example, silicone rubber, having a length corresponding to the coronary sinus region of the heart, and a stiffer proximal portion of, for example, polyurethane. A robust transition joint comprising telescoped sections of the distal and proximal portions of the lead body couples the two portions of the lead body.Also provided is a versatile lead delivery system including a stylet stop disposed within the distal portion of the lead body. The stylet stop defines an aperture dimensioned to pass a guide wire but not the enlarged distal tip of a stylet. The lead includes a tip electrode having a longitudinally extending bore dimensioned to permit passage of the guide wire through the tip electrode.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Curvilinear LED light source
ActiveUS20060028837A1Avoid easy installationEasily brokenLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceMulti materialLight guide
An LED system that simulates bare or exposed neon in appearance. The curvilinear LED light source comprises a rigid, formable light guide having a generally circular cross-section and a flexible LED light engine. The light guide is made of a material or materials that can be heated and formed into a desired shape. The light guide retains the desired shape upon cooling. The flexible light engine is inserted into a groove in the light engine.
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
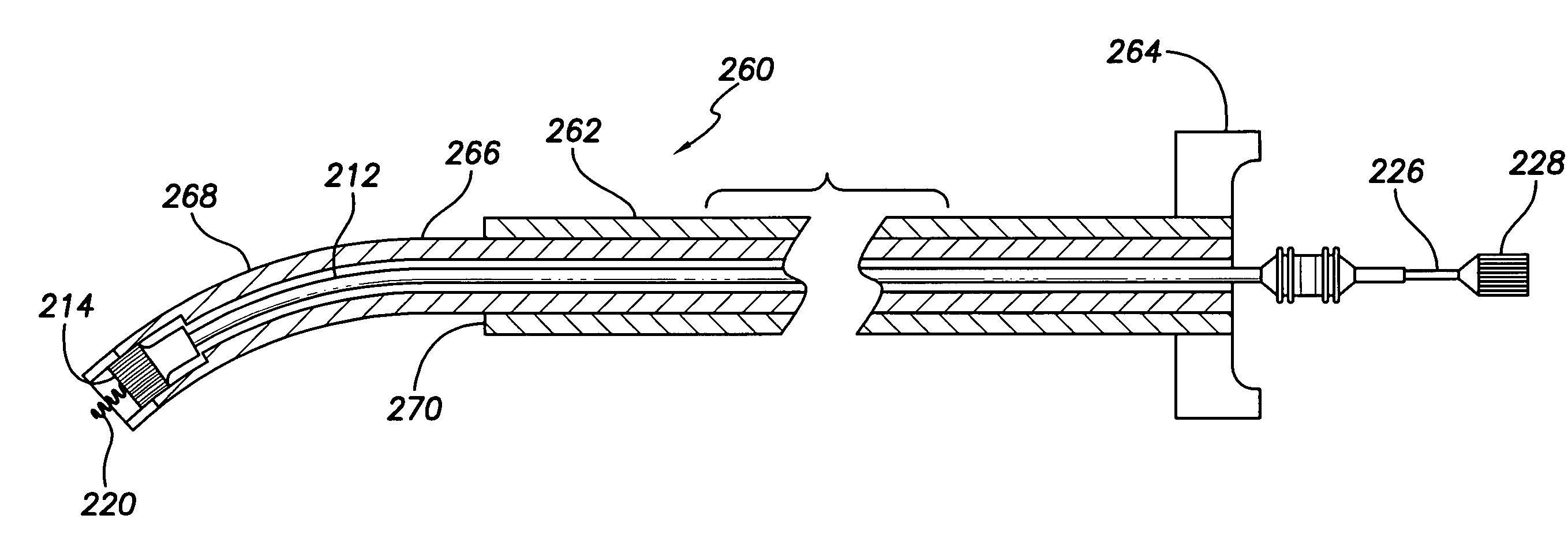
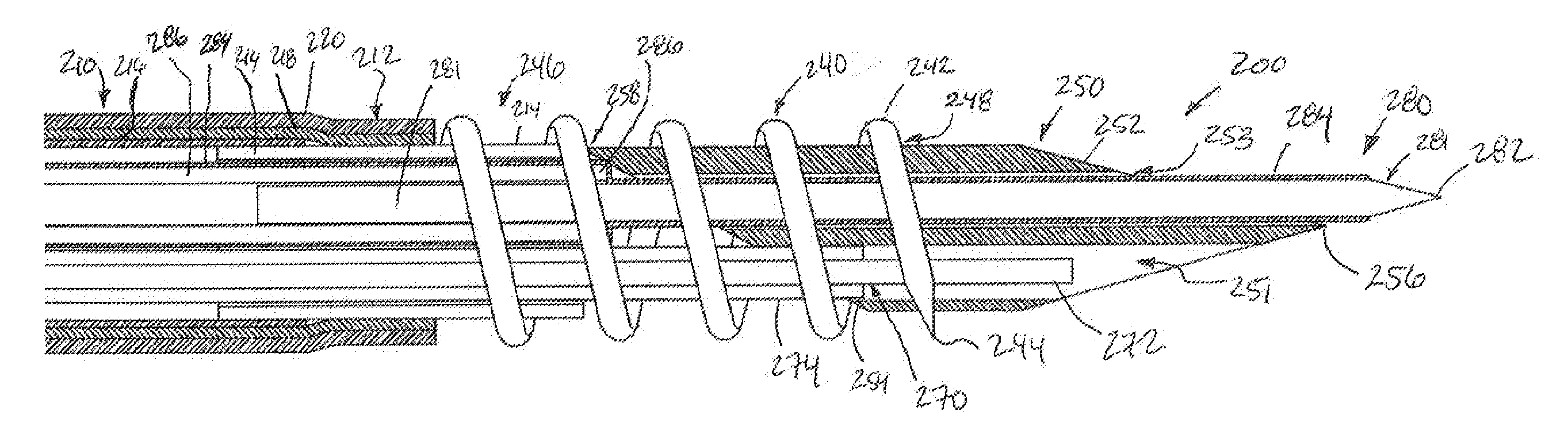
Myocardial lead and lead system
ActiveUS7369901B1Minimizes junctionAvoid packagingEpicardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsCardiac muscleLead system
An implantable myocardial stimulation lead comprises a lead body having a distal end and a proximal end, and an electrical connector carried by the proximal end of the lead body. An electrode header carried by the distal end of the lead body has an axis and includes a helical fixation element extending along the axis, the electrode header having a surface configured to receive a driver for rotating the electrode header to screw the helical fixation element into the tissue of the heart. The lead body carries along its length a strain relief member resisting excessive bending of the lead body.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
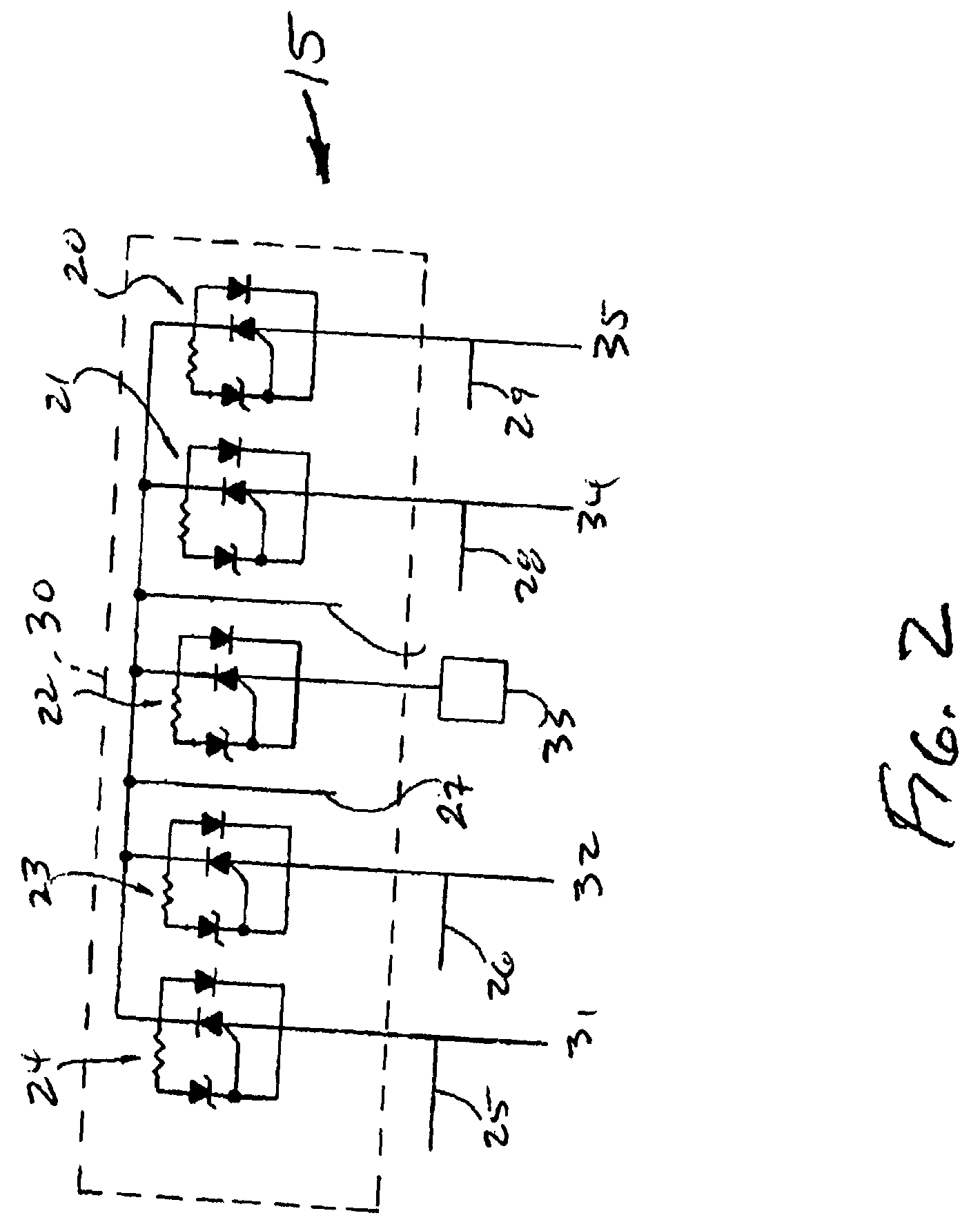
Reconfigurable, fault tolerant multiple-electrode cardiac lead systems
InactiveUS20050090870A1Easy to detectEfficient deliveryElectrocardiographyEpicardial electrodesLead systemVentricular tissue
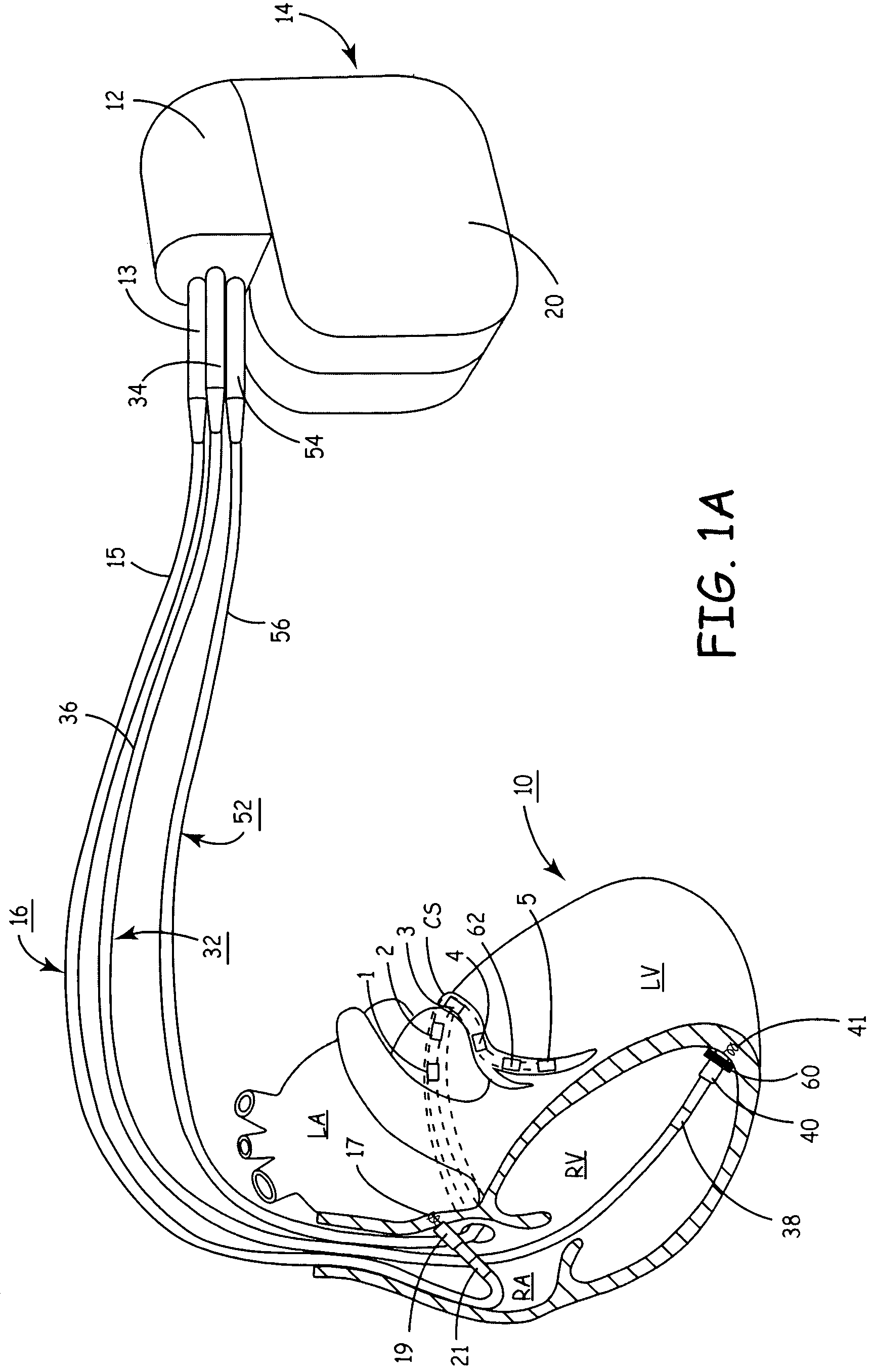
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for assessing ventricular function on a chronic basis using a plurality of electrodes disposed on or about a left ventricle and / or a right ventricle—and optionally, at least one mechanical or metabolic sensor—all operatively electrically coupled to an implantable medical device. The plurality of electrodes are preferably spaced-apart so that at least one electrode is disposed electrical communication with a discrete volume of ventricular tissue. In one embodiment, the discrete volume of tissue is defined by multiple longitudinal and axial planes as known and used in the medical arts. Thus, according to the present invention, at least one electrode couples to appropriate sensing circuitry and essentially provides a localized electrogram (EGM) that, when compared to other EGMs, provides for configurable, localized delivery of therapeutic pacing stimulus, diverse impedance-sensing vectors, various diagnostic information regarding myocardial function and / or anti-tachycardia pacing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
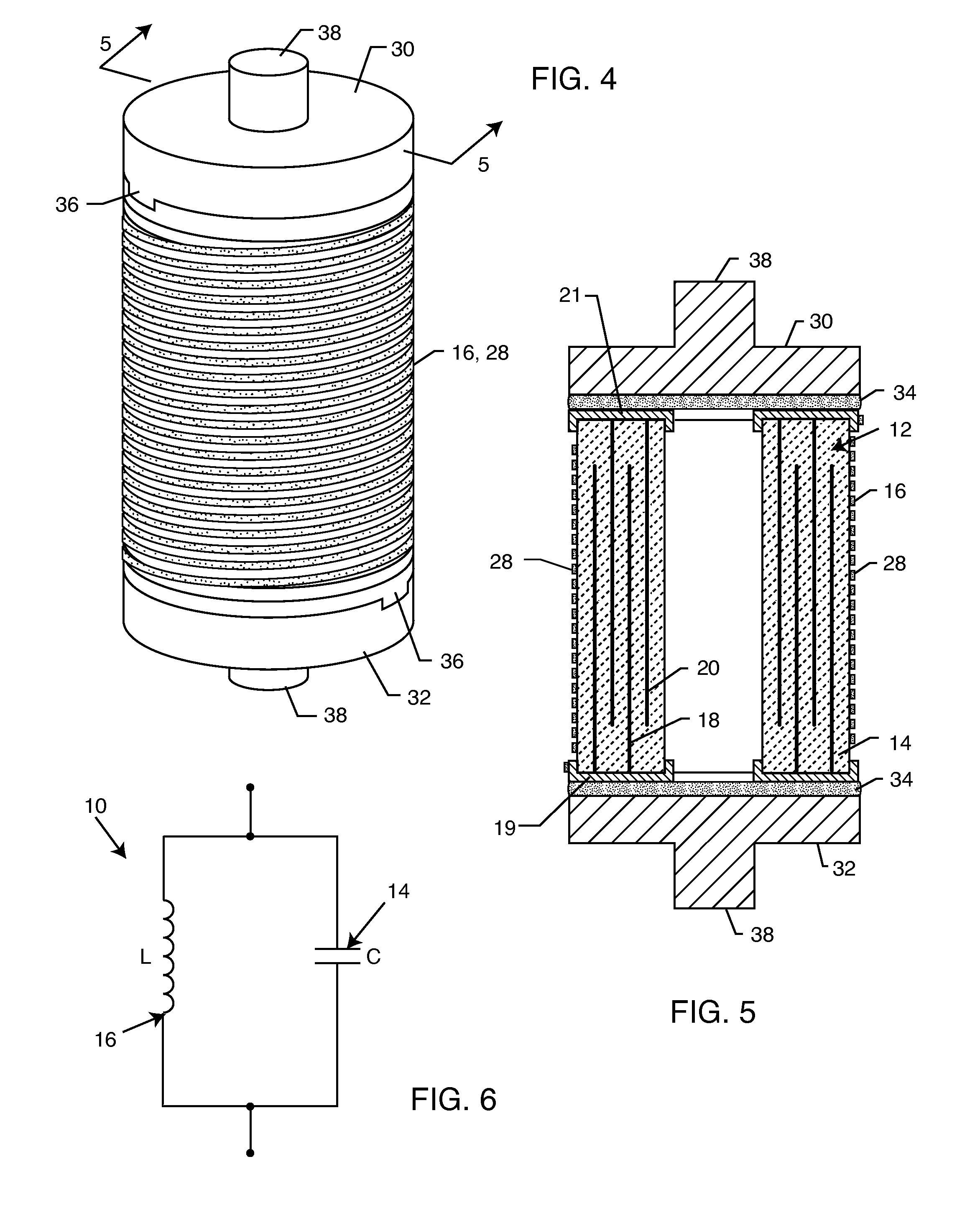
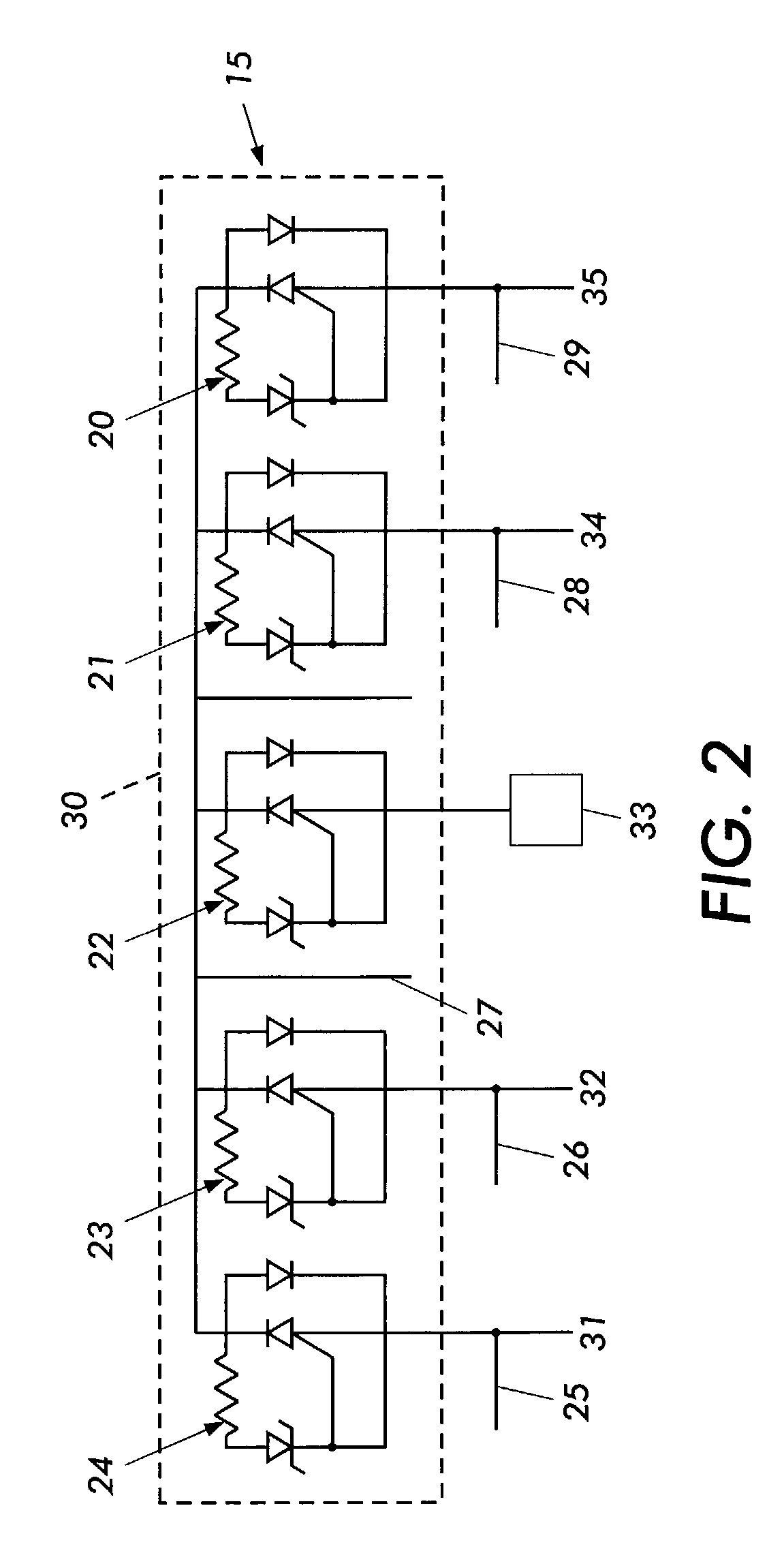
Cylindrical bandstop filters for medical lead systems
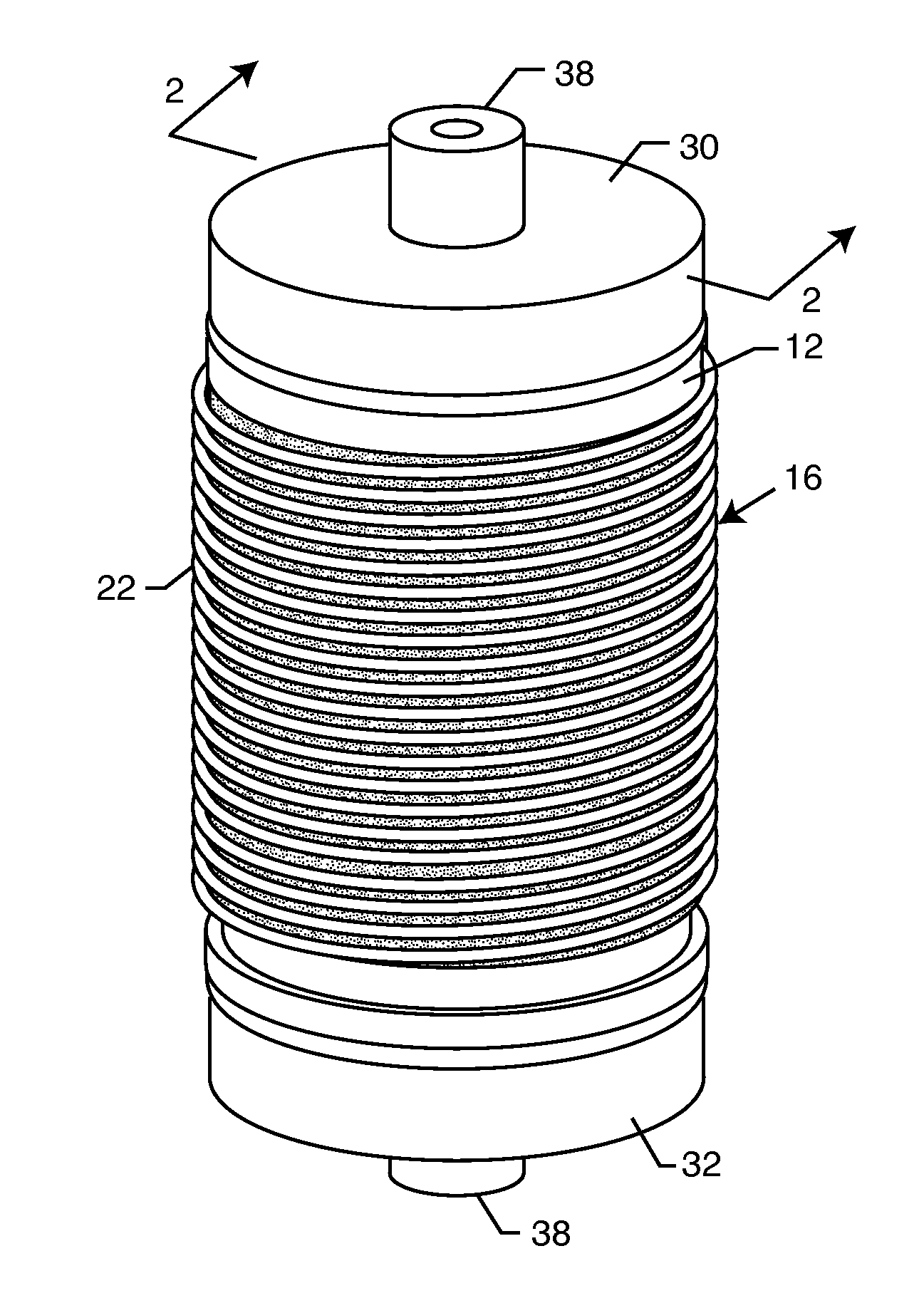
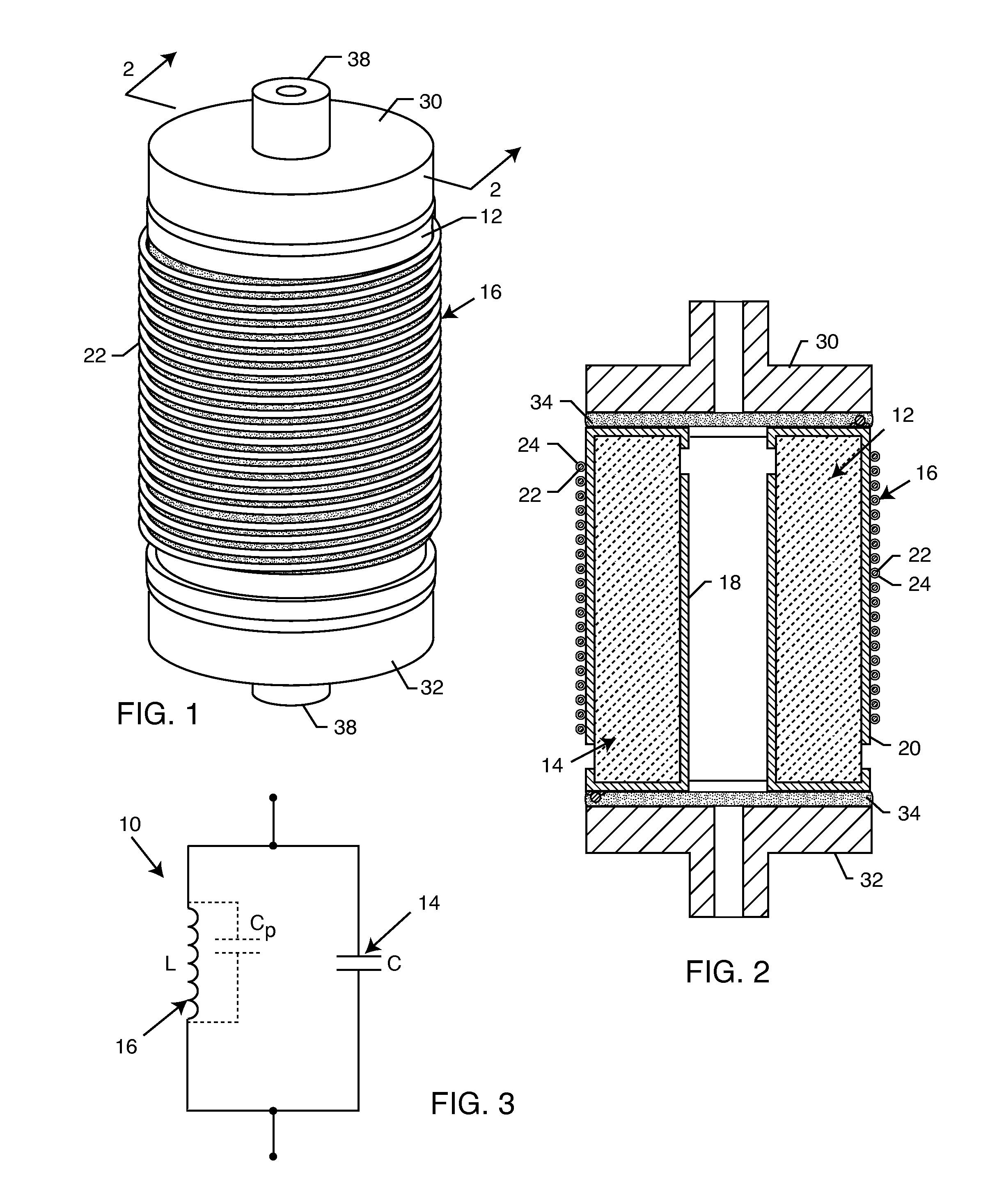
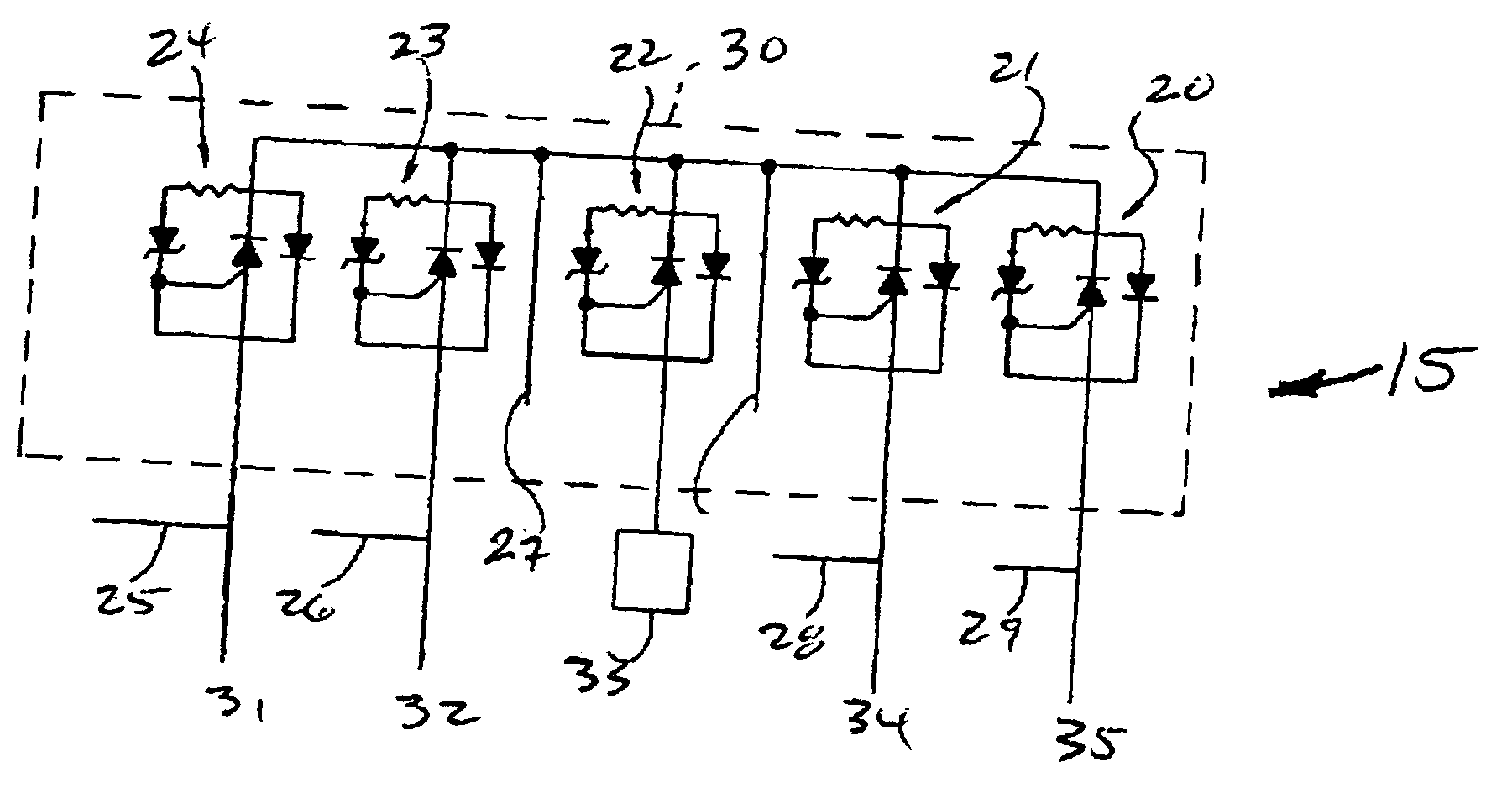
InactiveUS20080116997A1Avoid enteringMultiple-port networksAnti-noise capacitorsCapacitanceBand-stop filter
A one-piece cylindrical bandstop filter for medical lead systems incorporates parallel capacitive and inductive elements in a compact cylindrical configuration. The compact cylindrical configuration of the bandstop filter does not add significantly to the size or weight of the medical lead system. Preferably, the bandstop filters are of biocompatible materials or hermetically sealed in biocompatible containers. The parallel capacitive and inductive elements are placed in series with the medical lead system, and are selected so as to resonate at one or more selected frequencies, typically MRI pulsed frequencies.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
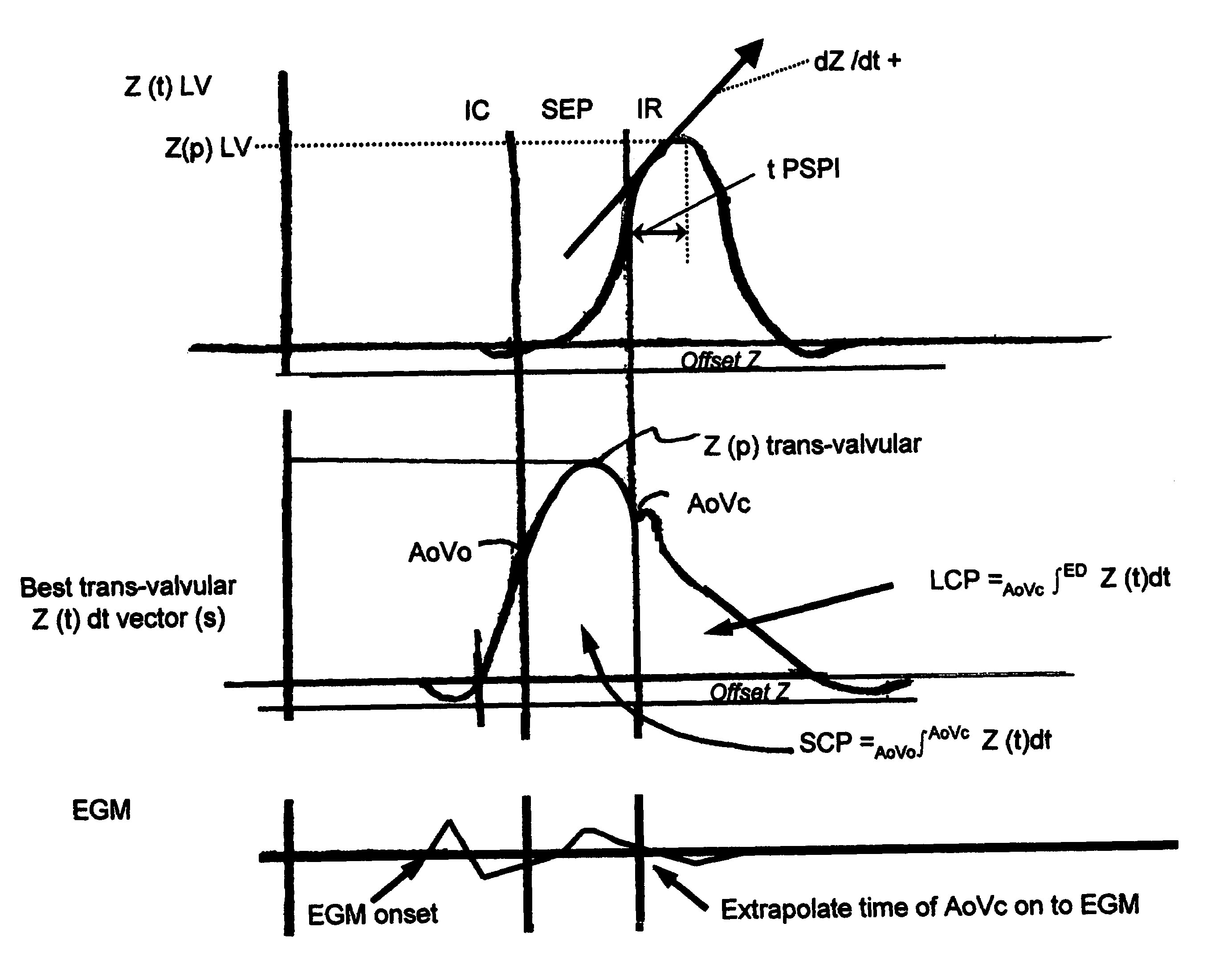
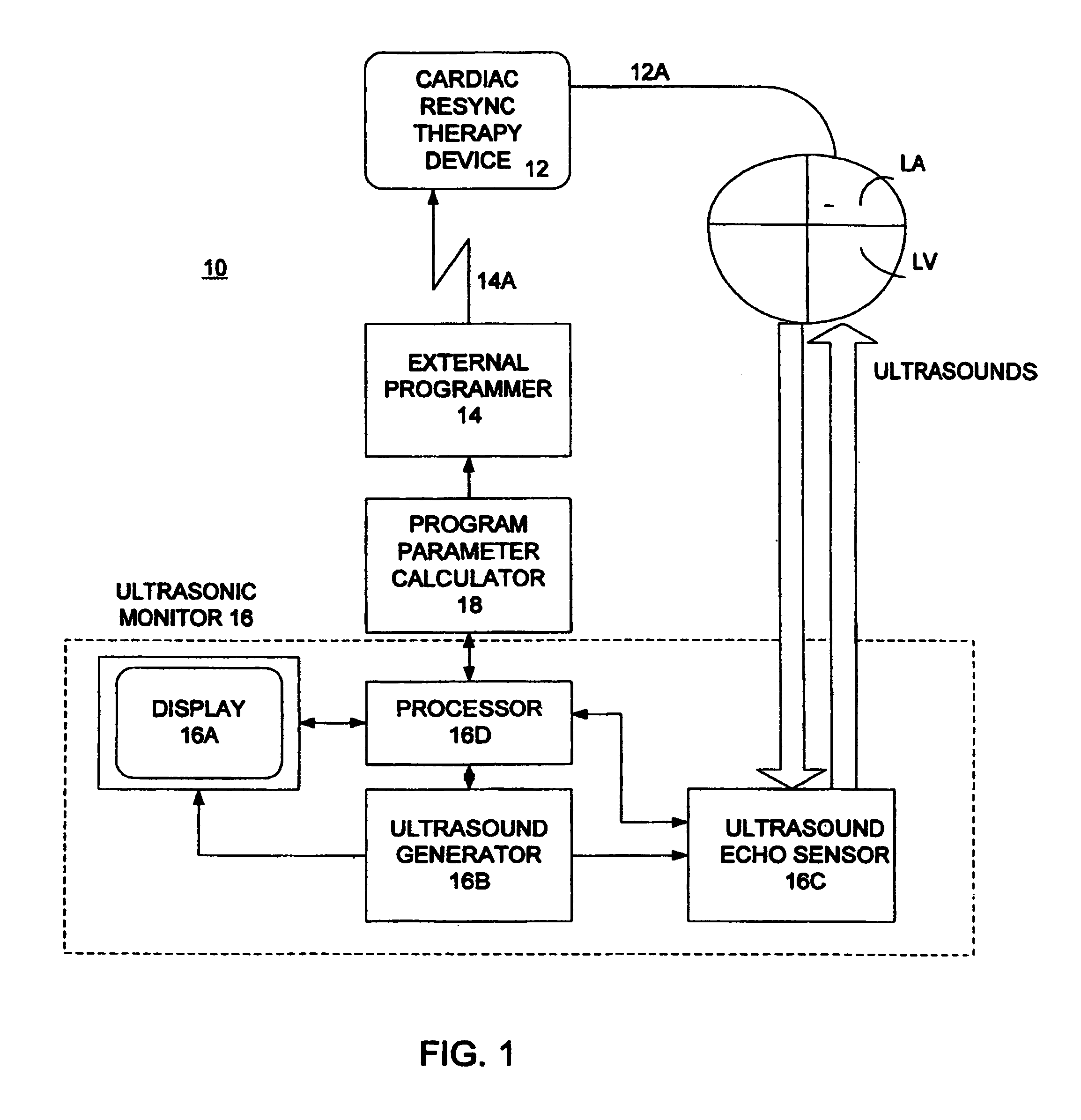
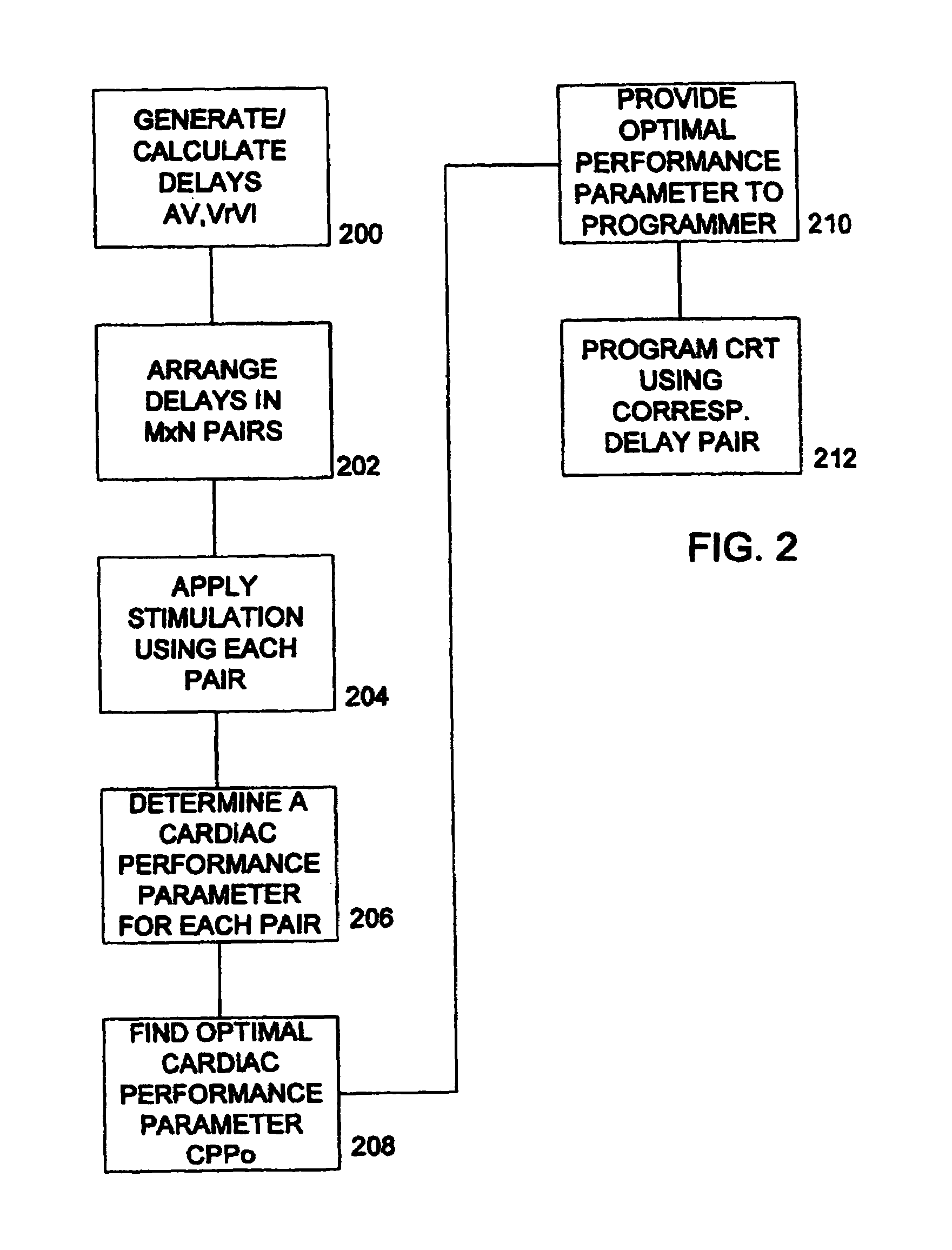
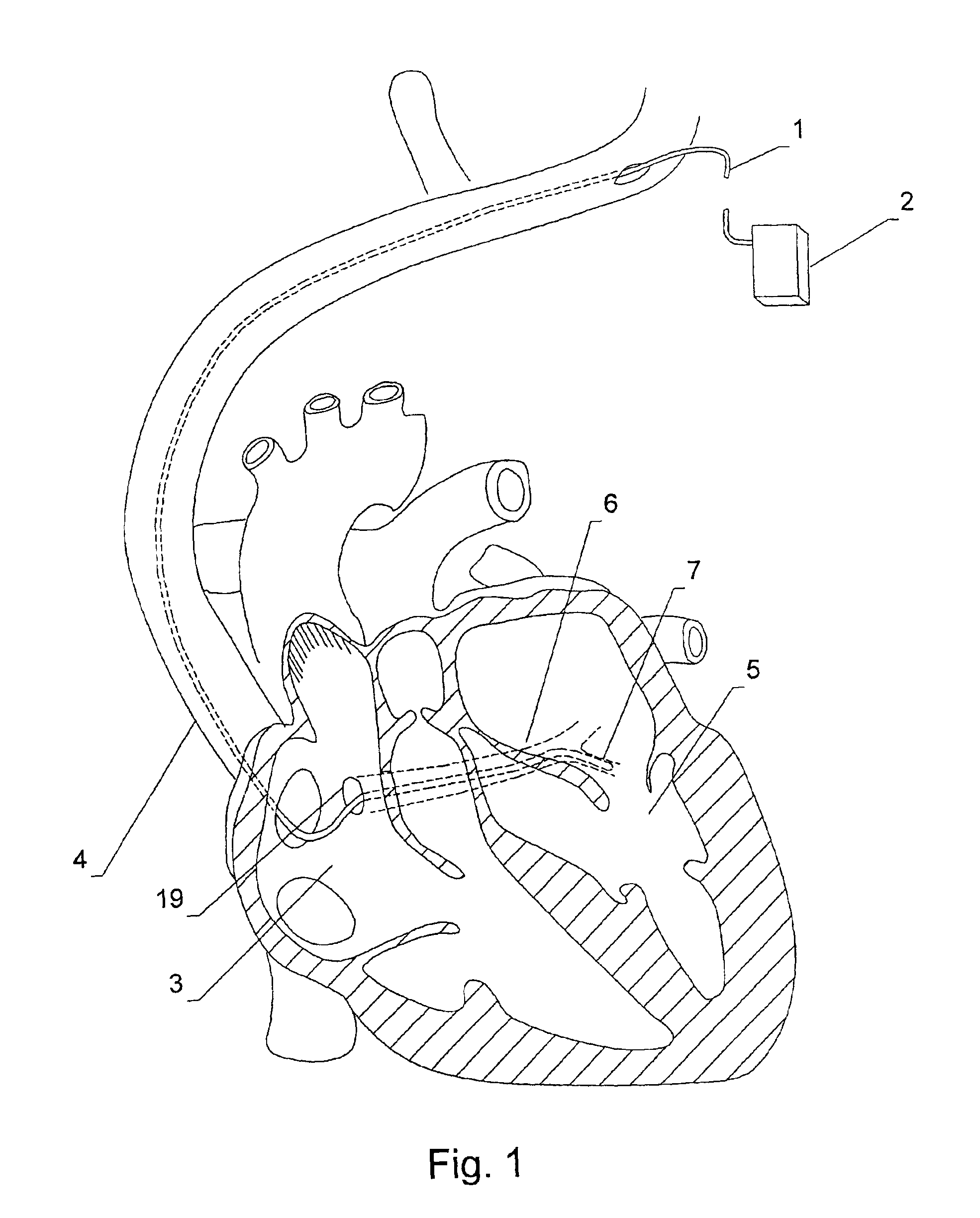
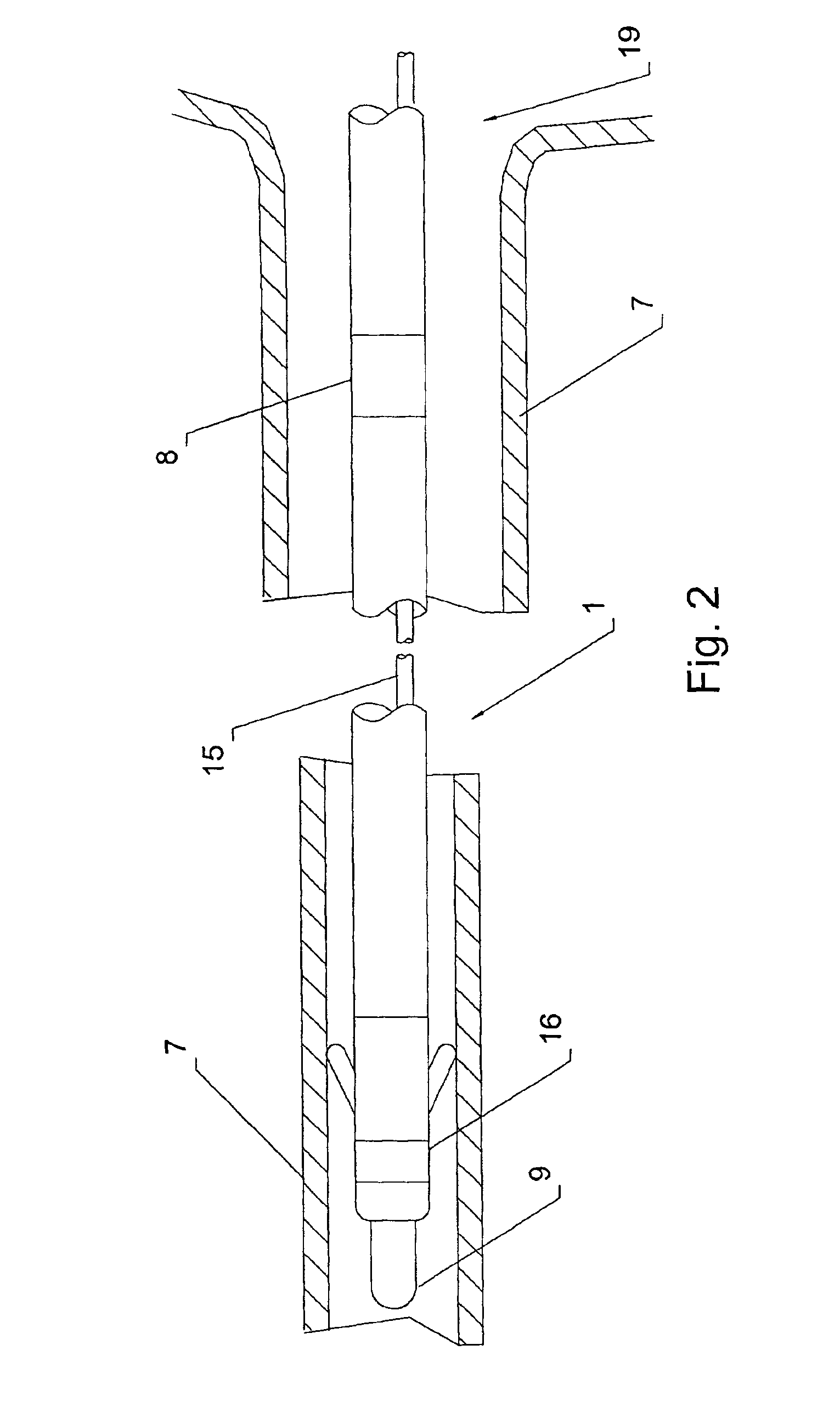
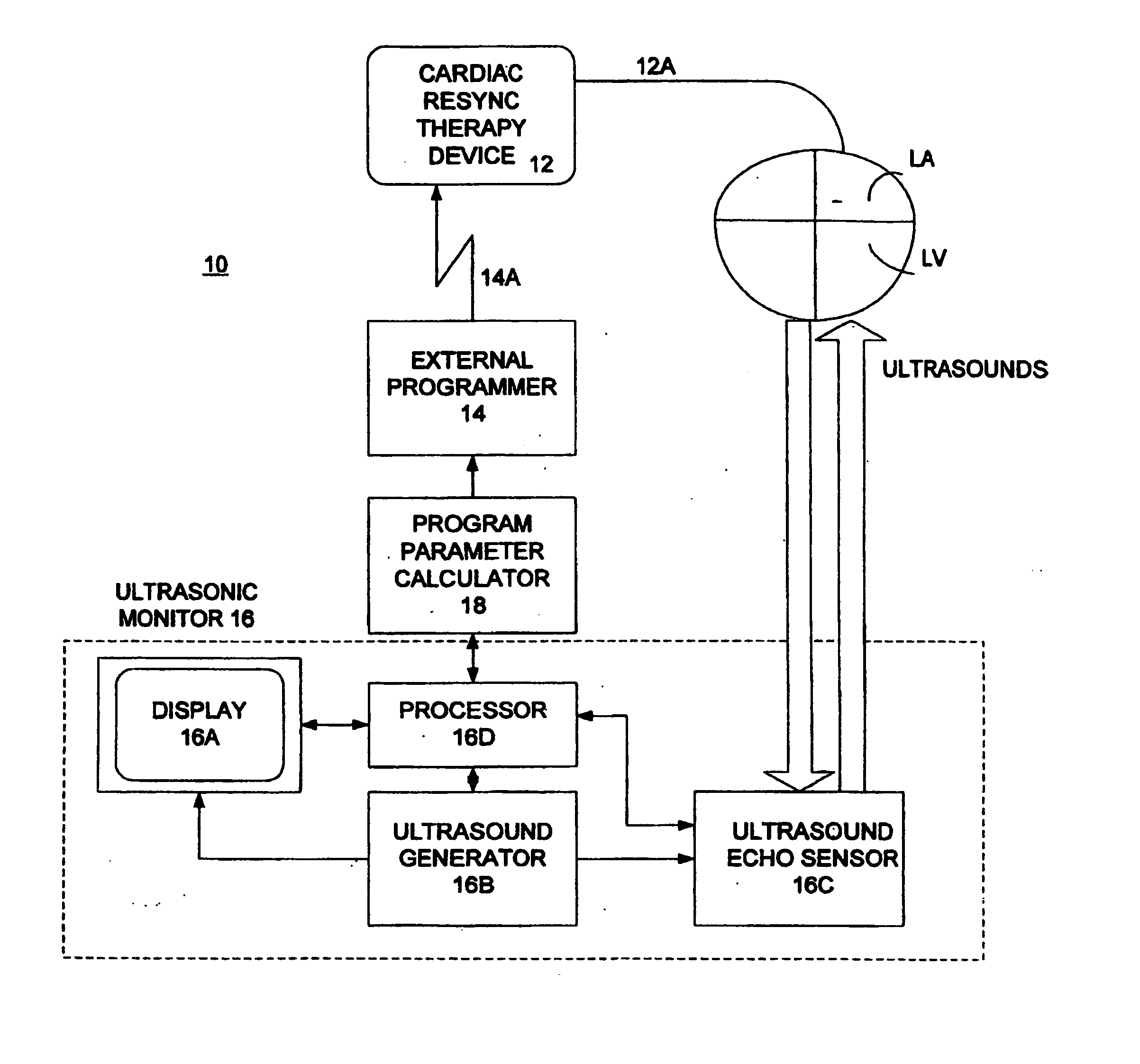
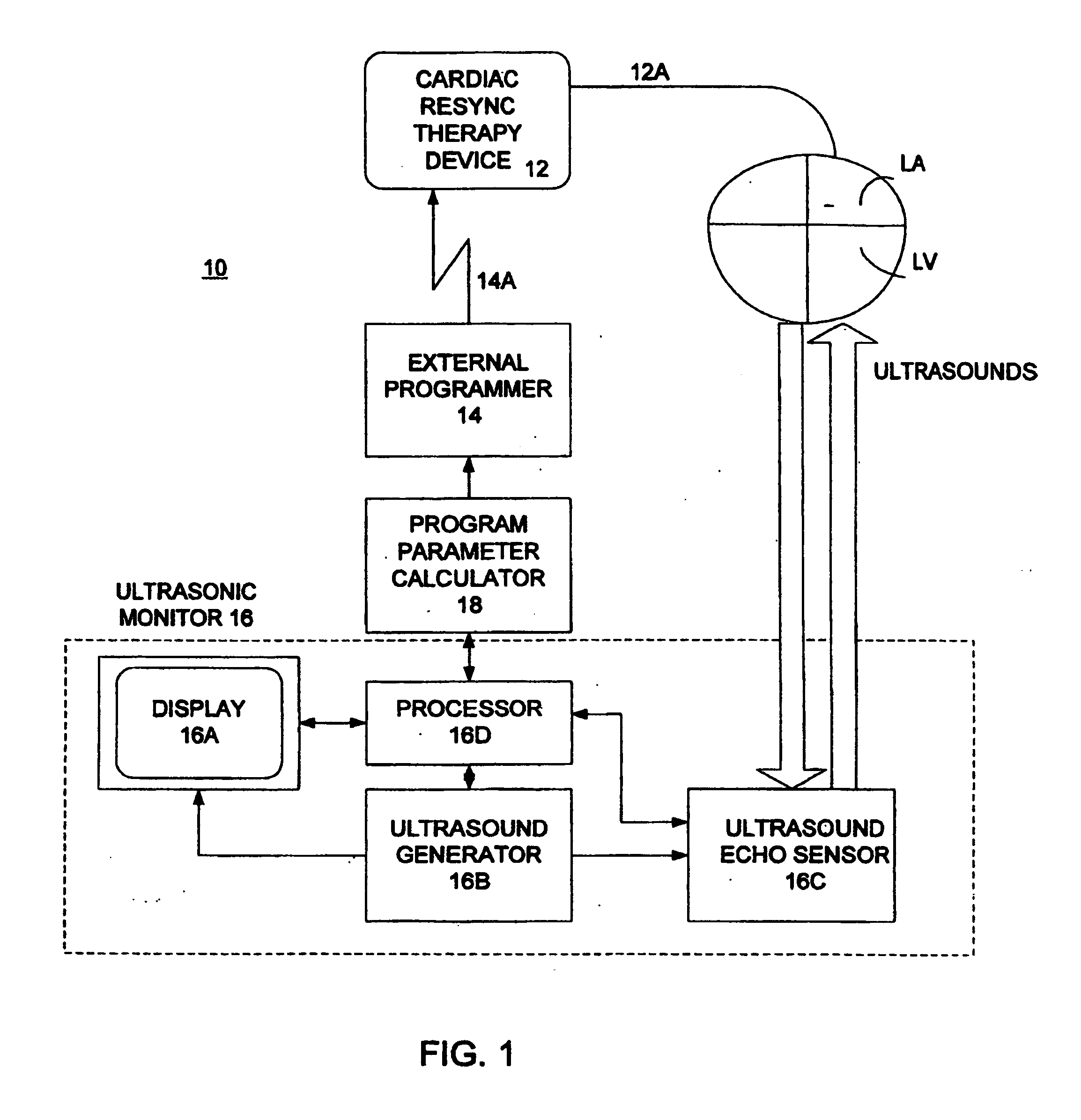
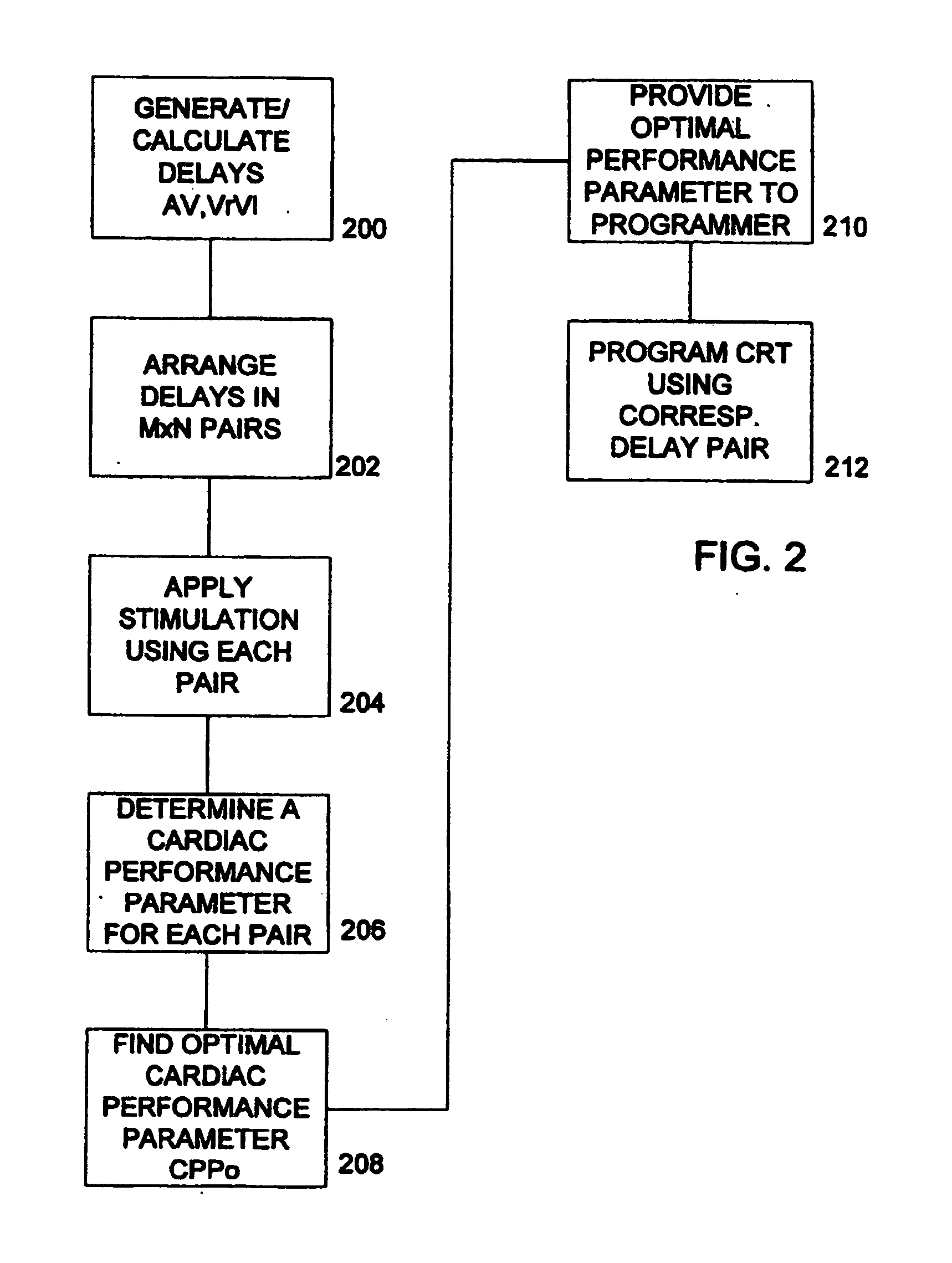
Optimization of impedance signals for closed loop programming of cardiac resynchronization therapy devices
What are described herein are implantable cardiac devices such as pacemakers and defibrillators that deliver cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), and to a method of optimizing acquisition of impedance signals between electrodes present on implanted lead systems. This system then automatically determines which electrodes or electrode combinations acquire impedance waveforms that have the best signal to noise ratio (highest fidelity) and characterize data most representative of dysynchronous electro-mechanical events. Using closed loop algorithms which provide electrograms and a variety of impedance data reflective of the patient's clinical status, the system autonomously modifies interval timing within the CRT device.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
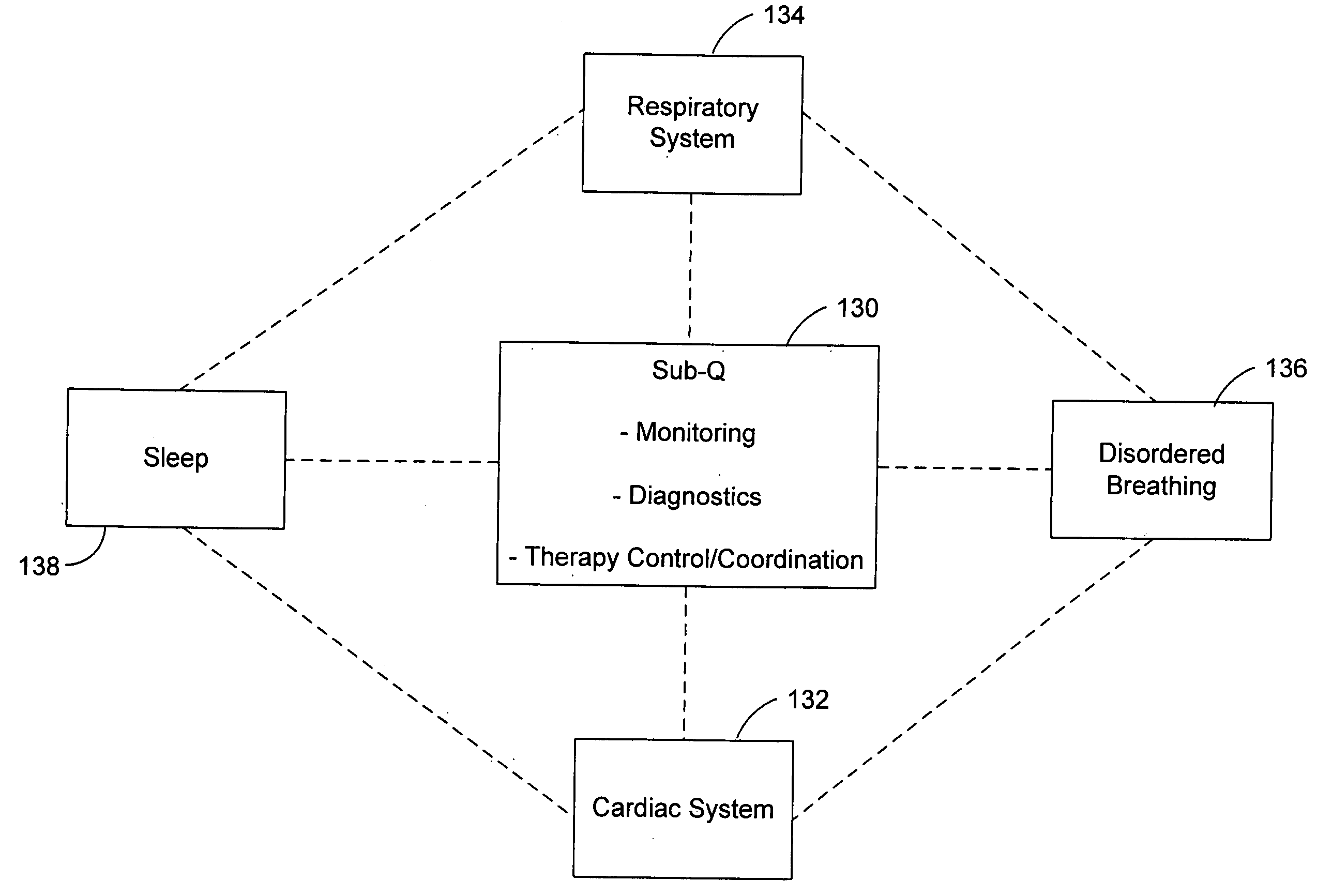
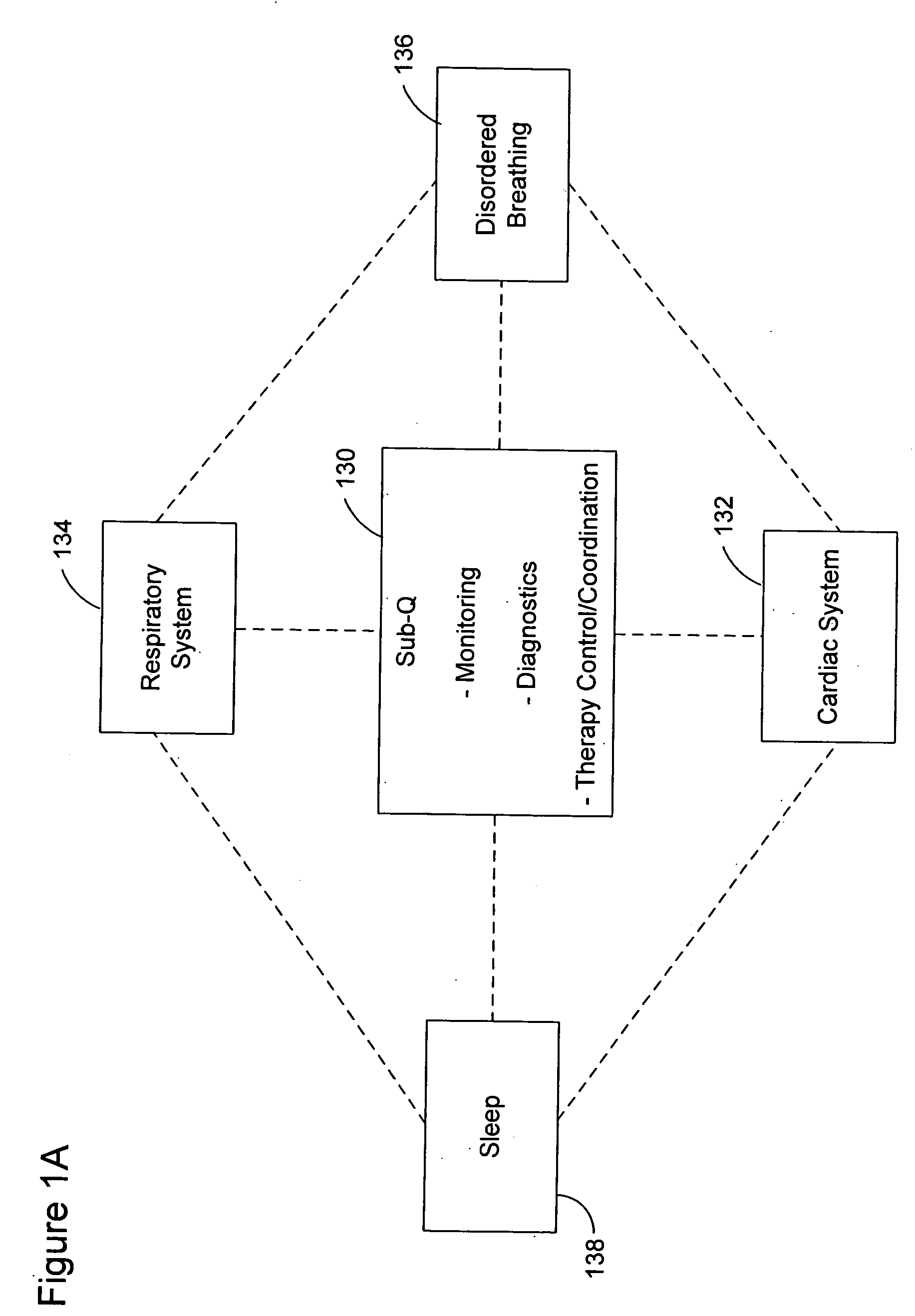
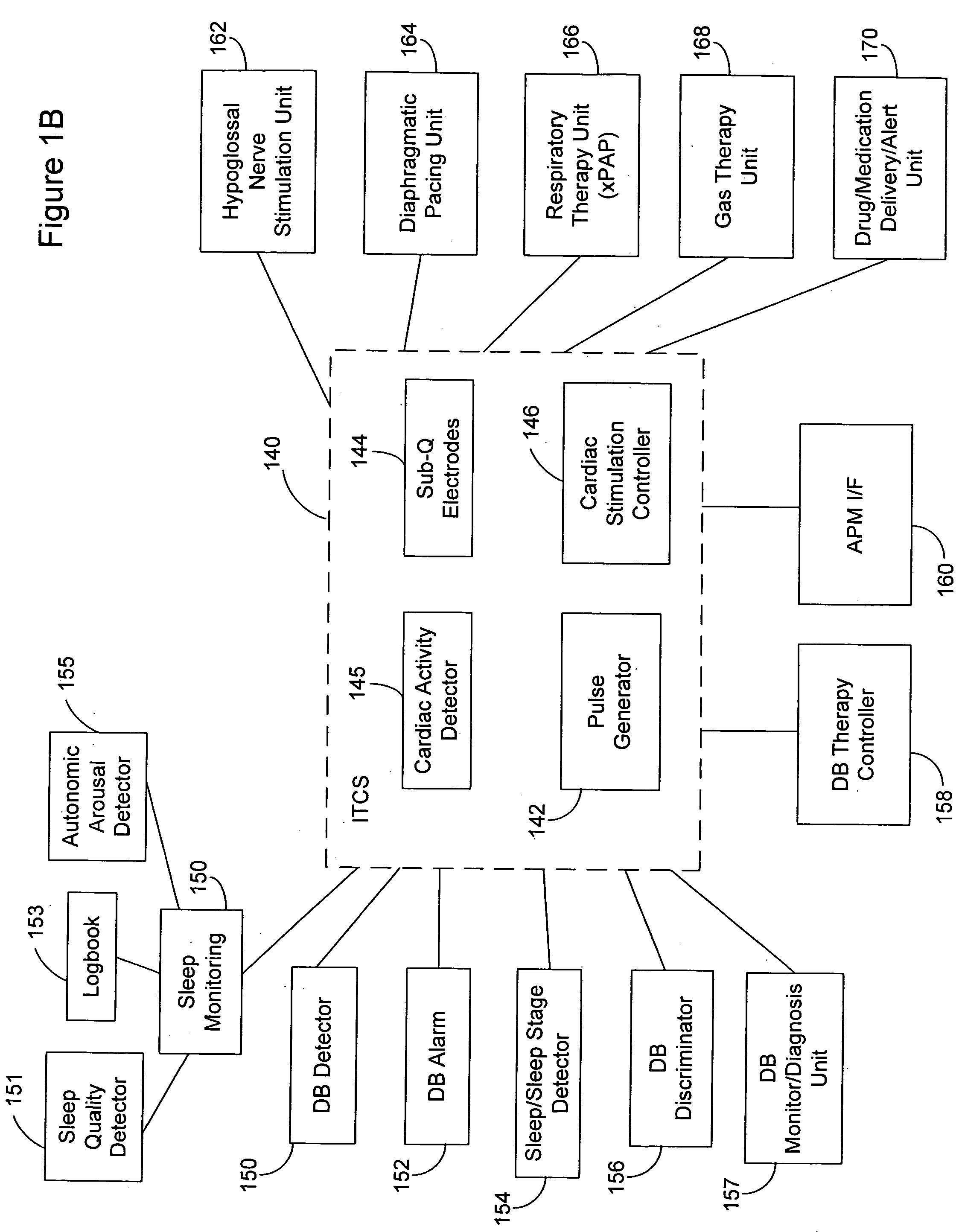
Subcutaneous cardiac rhythm management with disordered breathing detection and treatment
InactiveUS20050107838A1Heart defibrillatorsInertial sensorsPositive airway pressure deviceCardiac activity
A lead system, coupled to an implantable device, is configured for subcutaneous, non-intrathoracic placement relative to a patient's heart. Cardiac activity detection circuitry is coupled to the lead system and configured to detect cardiac rhythms. Disordered breathing detection circuitry is coupled to the lead system and configured to detect disordered breathing. One or both of cardiac therapy circuitry and disordered breathing therapy circuitry may be coupled to the lead system and configured to delivery therapies to treat disordered breathing. Such therapies include cardiac pacing, diaphragmatic pacing, and hypoglossal nerve stimulation therapies. A patient-external respiratory device, such as a positive airway pressure device, may be configured to deliver a disordered breathing therapy. One or more of a patient-internal drug delivery device, a patient-external drug delivery device, or a gas therapy device may be employed to treat disordered breathing.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
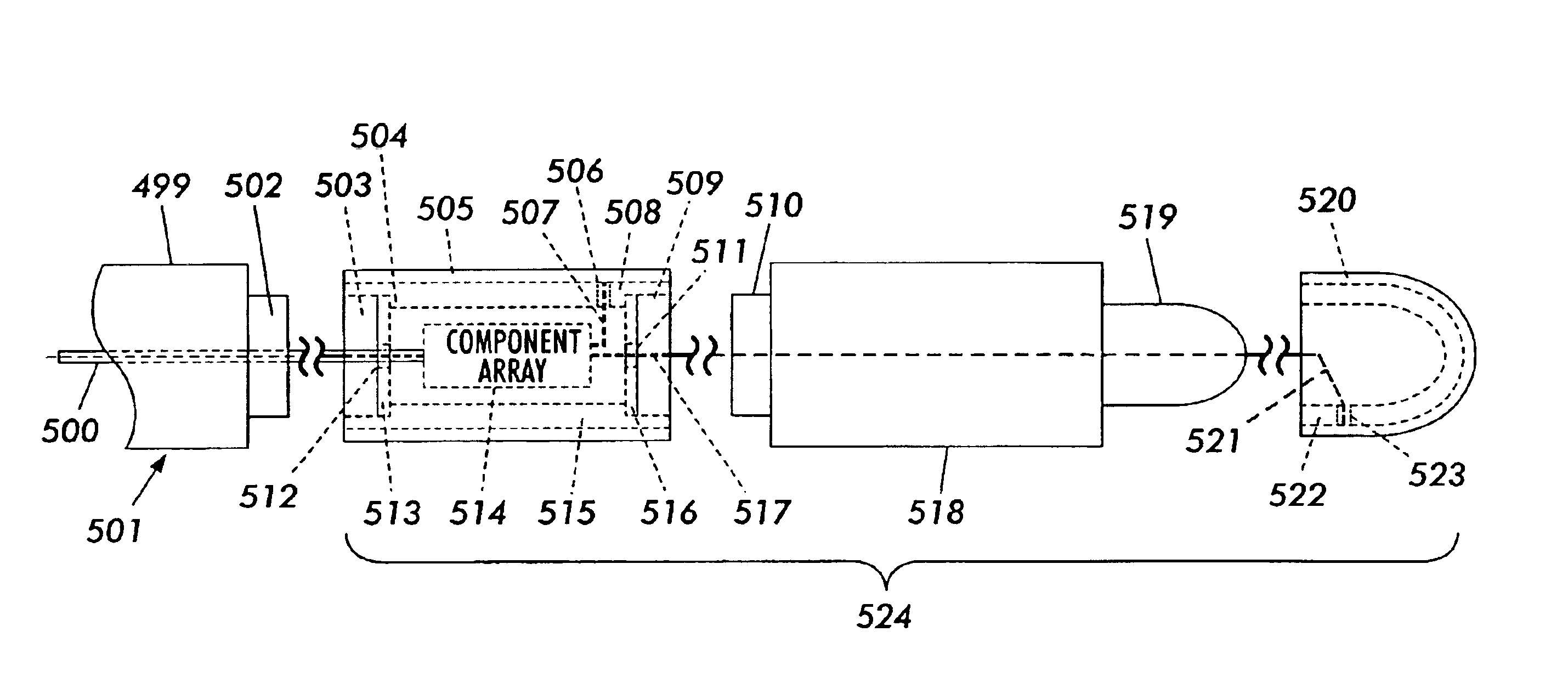
Electromagnetic interference immune tissue invasive system
InactiveUS20020128689A1Avoid failureAvoid interferenceMagnetic measurementsTransvascular endocardial electrodesFiberElectricity
An electromagnetic immune tissue invasive system includes a primary device housing. The primary device housing having a control circuit therein. A shielding is formed around the primary device housing to shield the primary device housing and any circuits therein from electromagnetic interference. A lead system transmits and receives signals between the primary device housing. The lead system is either a fiber optic system or an electrically shielded electrical lead system.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Curvilinear LED light source
An LED system that simulates bare or exposed neon in appearance. The curvilinear LED light source comprises a rigid, formable light guide having a generally circular cross-section and a flexible LED light engine. The light guide is made of a material or materials that can be heated and formed into a desired shape. The light guide retains the desired shape upon cooling. The flexible light engine is inserted into a groove in the light engine.
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
Current waveforms for anti-tachycardia pacing for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter- defibrillator
A power supply for an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for subcutaneous positioning between the third rib and the twelfth rib and using a lead system that does not directly contact a patient's heart or reside in the intrathoracic blood vessels and for providing anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the heart, comprising a capacitor subsystem for storing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy for delivery to the patient's heart; and a battery subsystem electrically coupled to the capacitor subsystem for providing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the capacitor subsystem.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Non-invasively maneuverable lead system
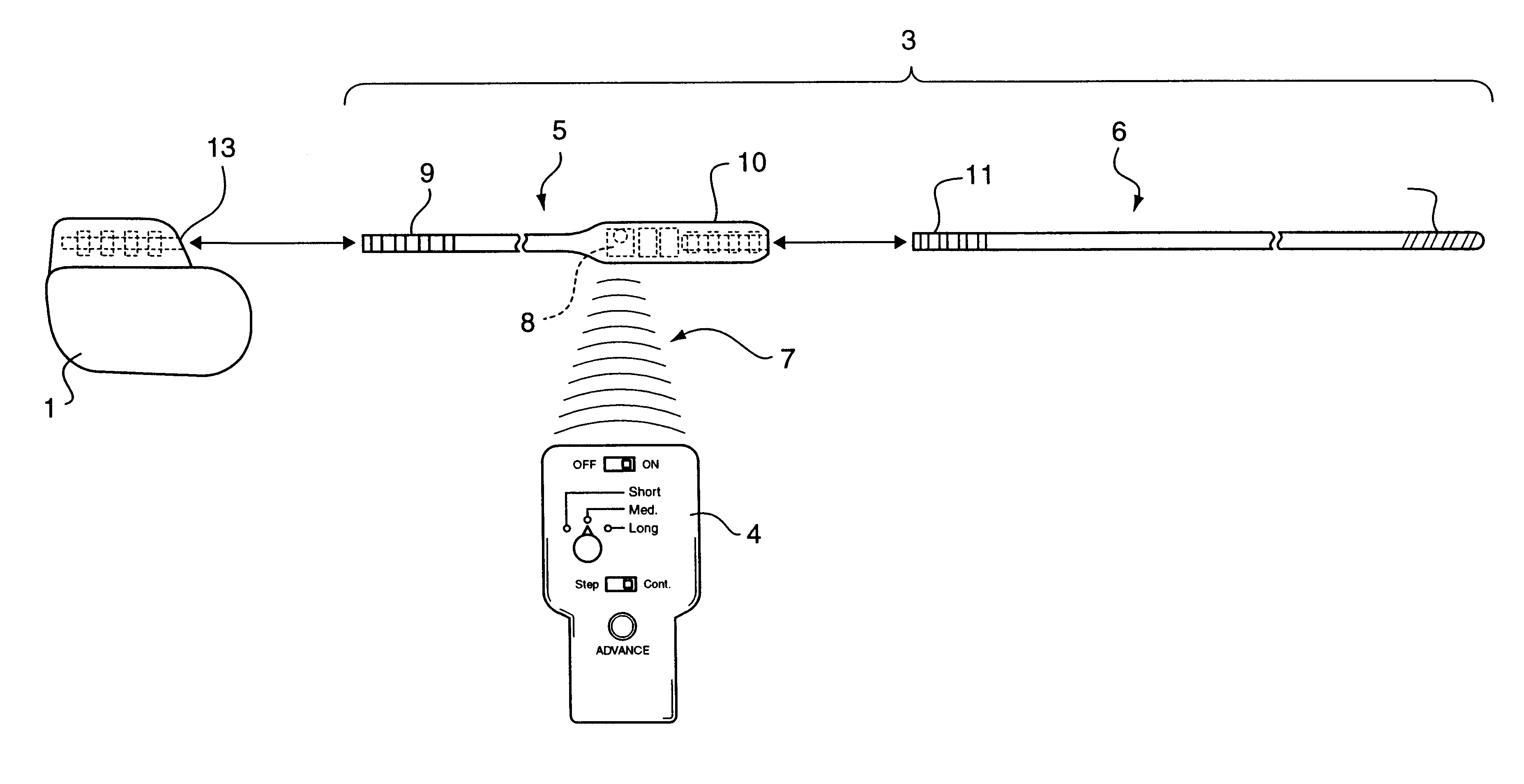
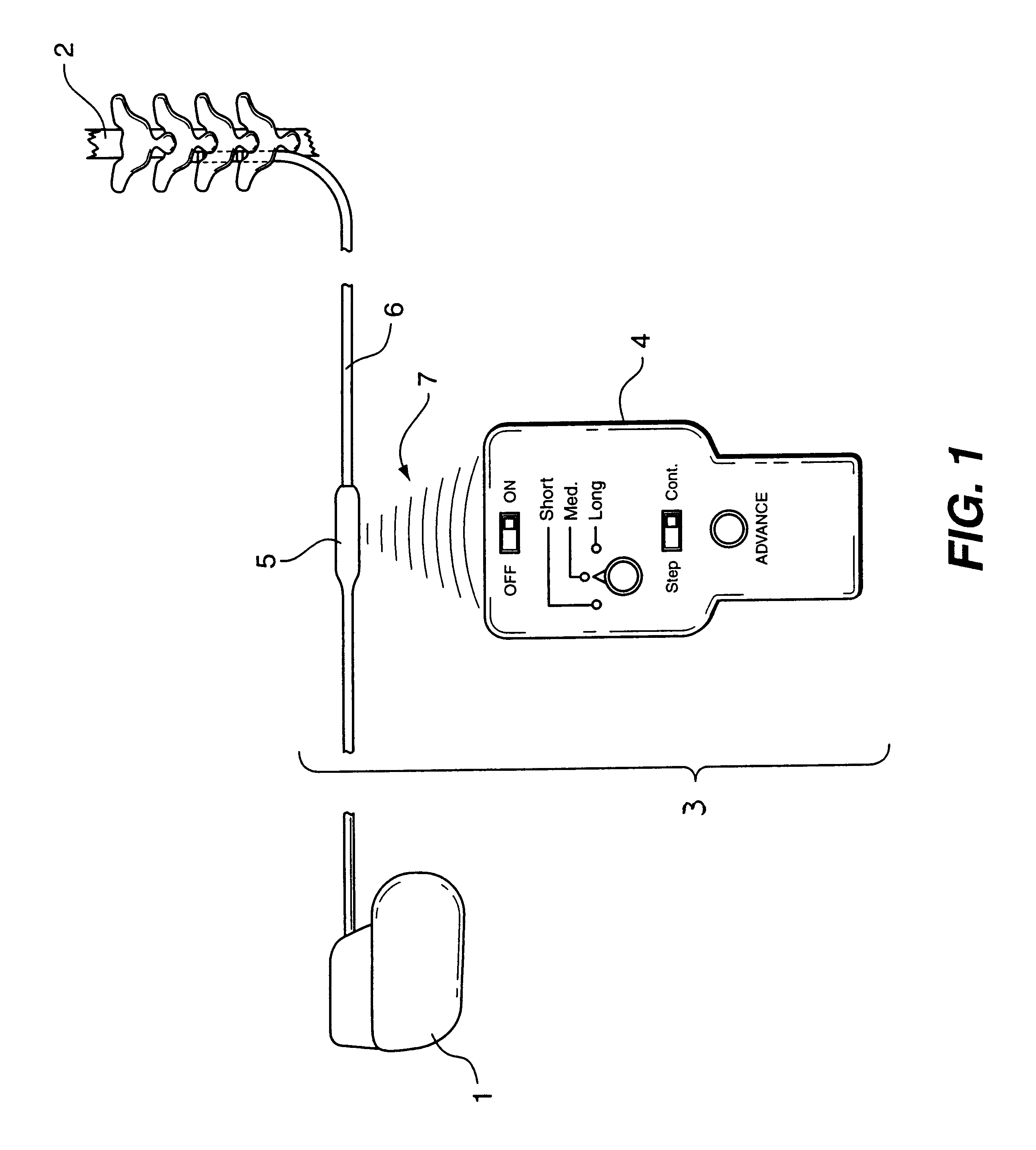
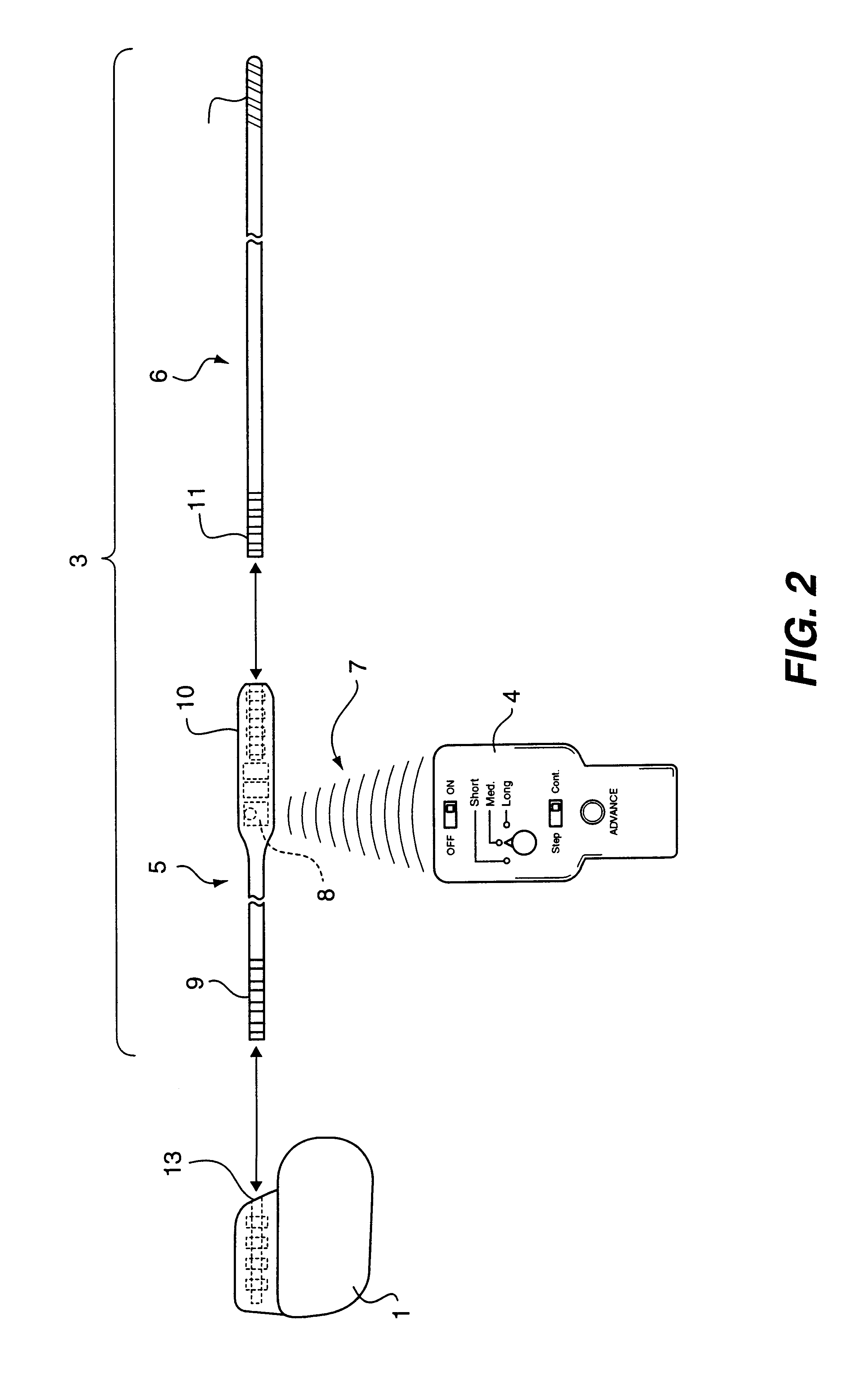
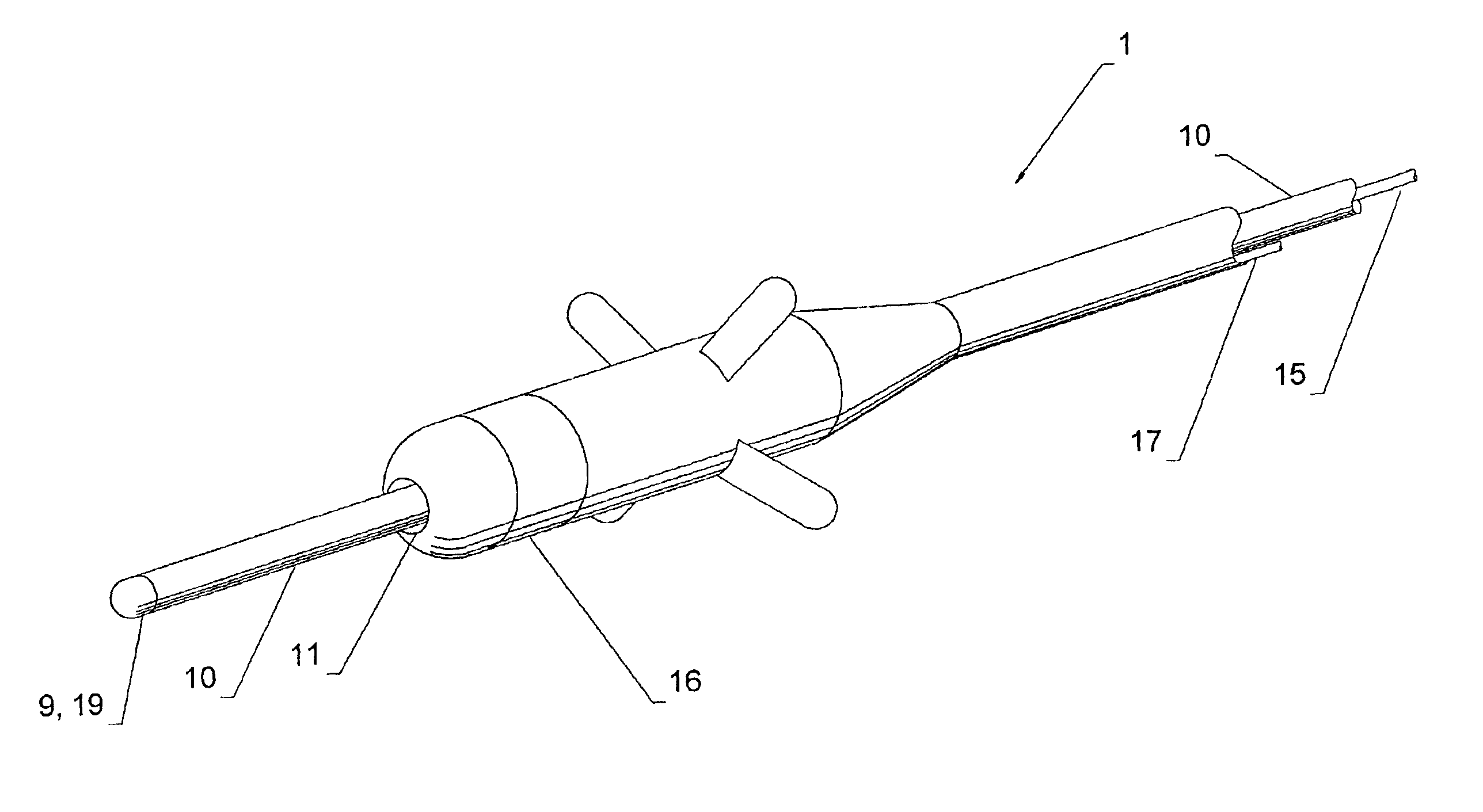
The method and system for non-invasively repositioning at least one stimulating electrode on a lead relative to tissue, such as nerve tissue, in a body includes elements for carrying out the method and the steps of: providing a lead having at least one stimulating electrode thereon which is located skew to an elongate axis of the lead; implanting the lead in a body; implanting in the body a drive mechanism having structure for engaging and rotating the lead; and, providing an exterior signal generating and transmitting mechanism for transmitting electromagnetic signals from outside the body to the drive mechanism implanted in the body for causing the drive mechanism to rotate the lead thereby to adjust the position of the at least one stimulating electrode on the lead relative to tissue in the body.
Owner:PLEXUS
Method and apparatus for monitoring left ventricular work or power
A body implantable system employs a lead system having at least one electrode and at least one thermal sensor at a distal end. The lead system is implanted within a patient's heart in a coronary vein of the left ventricle. The thermal sensor can be attached to a catheter that is disposed within an open lumen of the lead system. The thermal sensor senses a coronary vein temperature. The coronary vein temperature can be measured at a detector / energy delivery system and used as an activity indicator to adaptively control pacing rate. The measured coronary vein temperature can be also used with a left ventricular flow measurement to determine hemodynamic efficiency of the heart. A detected change in hemodynamic efficiency can be used by the detector / energy delivery system to modify the delivery of electrical pulses to the lead system.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Optimization of impedance signals for closed loop programming of cardiac resynchronization therapy devices
InactiveUS20050182447A1Reduce dysynchronyImprove congestive heart failure symptomElectrotherapyArtificial respirationCardiac pacemaker electrodeClosed loop
The present invention is related to implantable cardiac devices such as pacemakers and defibrillators that deliver cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), and to a method of optimizing acquisition of impedance signals between electrodes present on implanted lead systems. This system then automatically determines which electrodes or electrode combinations acquire impedance waveforms that have the best signal to noise ratio (highest fidelity) and characterize data most representative of dysynchronous electromechanical events. Using closed loop algorithms which provide electrograms and a variety of impedance data reflective of the patient's clinical status, the system autonomously modifies interval timing within the CRT device.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
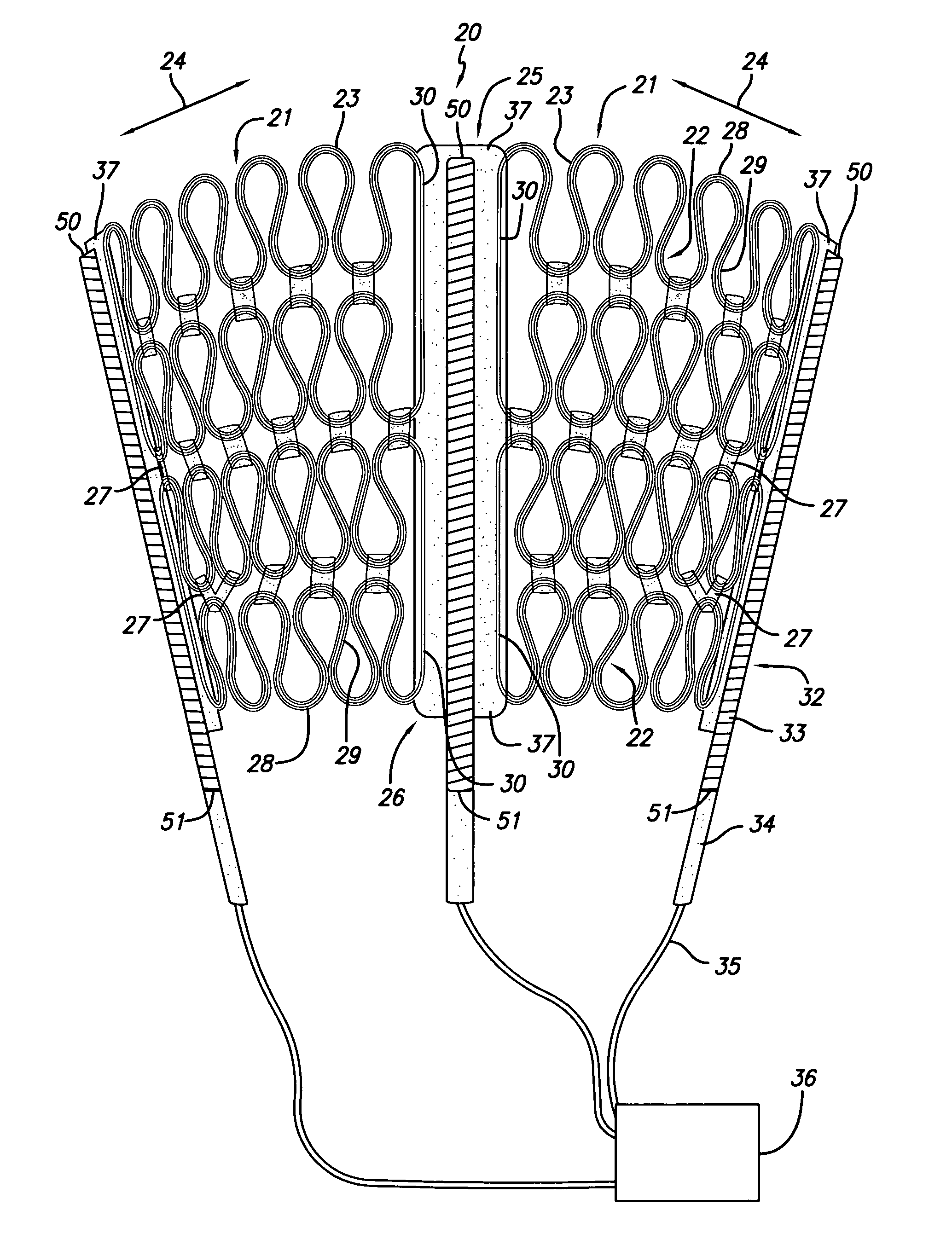
Cardiac harness for treating heart disease
InactiveUS7158839B2Limit cardiac functionFunction increaseEpicardial electrodesHeart valvesSystoleLead system
A system for treating the heart includes a cardiac harness associated with a cardiac rhythm management devise which does not have a lead system. The cardiac harness applies a compressive force on the heart during diastole and systole, and the cardiac rhythm management devise will deliver an electrical shock to the heart for defibrillation and / or can be used for pacing / sensing. The cardiac harness and cardiac rhythm management devise are both delivered and implanted by minimally invasive access.
Owner:PARACOR MEDICAL INC
Reconfigurable, fault tolerant multiple-electrode cardiac lead systems
InactiveUS7142919B2Easy to detectEfficient deliveryElectrocardiographyEpicardial electrodesLead systemVentricular tissue
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for assessing ventricular function on a chronic basis using a plurality of electrodes disposed on or about a left ventricle and / or a right ventricle—and optionally, at least one mechanical or metabolic sensor—all operatively electrically coupled to an implantable medical device. The plurality of electrodes are preferably spaced-apart so that at least one electrode is disposed electrical communication with a discrete volume of ventricular tissue. In one embodiment, the discrete volume of tissue is defined by multiple longitudinal and axial planes as known and used in the medical arts. Thus, according to the present invention, at least one electrode couples to appropriate sensing circuitry and essentially provides a localized electrogram (EGM) that, when compared to other EGMs, provides for configurable, localized delivery of therapeutic pacing stimulus, diverse impedance-sensing vectors, various diagnostic information regarding myocardial function and / or anti-tachycardia pacing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Electromagnetic interference immune tissue invasive system
InactiveUS20020133086A1Avoid failureAvoid interferenceMagnetic measurementsTransvascular endocardial electrodesFiberElectricity
An electromagnetic immune tissue invasive system includes a primary device housing. The primary device housing having a control circuit therein. A shielding is formed around the primary device housing to shield the primary device housing and any circuits therein from electromagnetic interference. A lead system transmits and receives signals between the primary device housing. The lead system is either a fiber optic system or an electrically shielded electrical lead system.
Owner:BIOPHAN TECH
Electromagnetic interference immune tissue invasive system
InactiveUS6829509B1Avoid failureAvoid interferenceCoupling for high frequencyTransvascular endocardial electrodesElectricityFiber
An electromagnetic immune tissue invasive system includes a primary device housing. The primary device housing having a control circuit therein. A shielding is formed around the primary device housing to shield the primary device housing and any circuits therein from electromagnetic interference. A lead system transmits and receives signals between the primary device housing. The lead system is either a fiber optic system or an electrically shielded electrical lead system.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
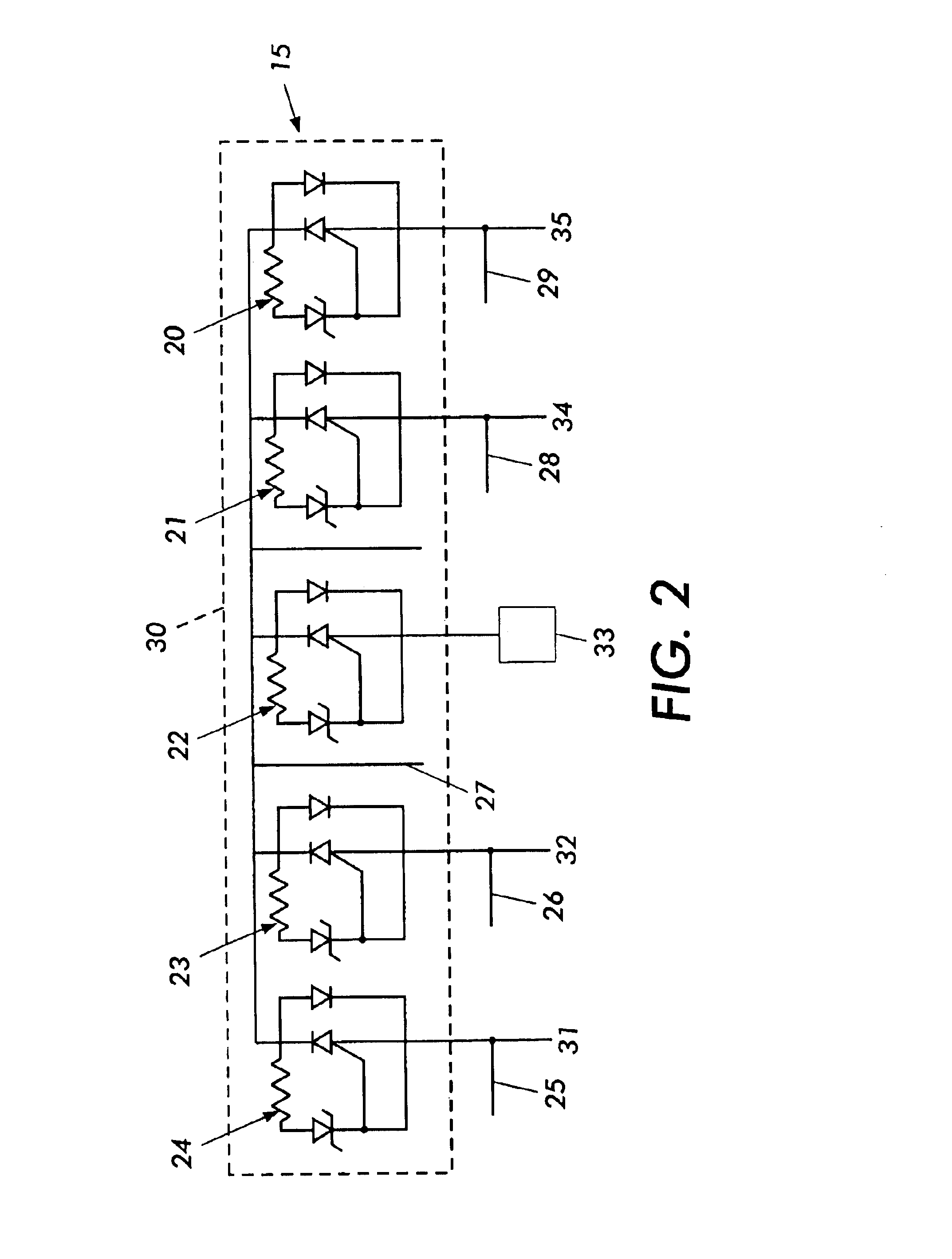
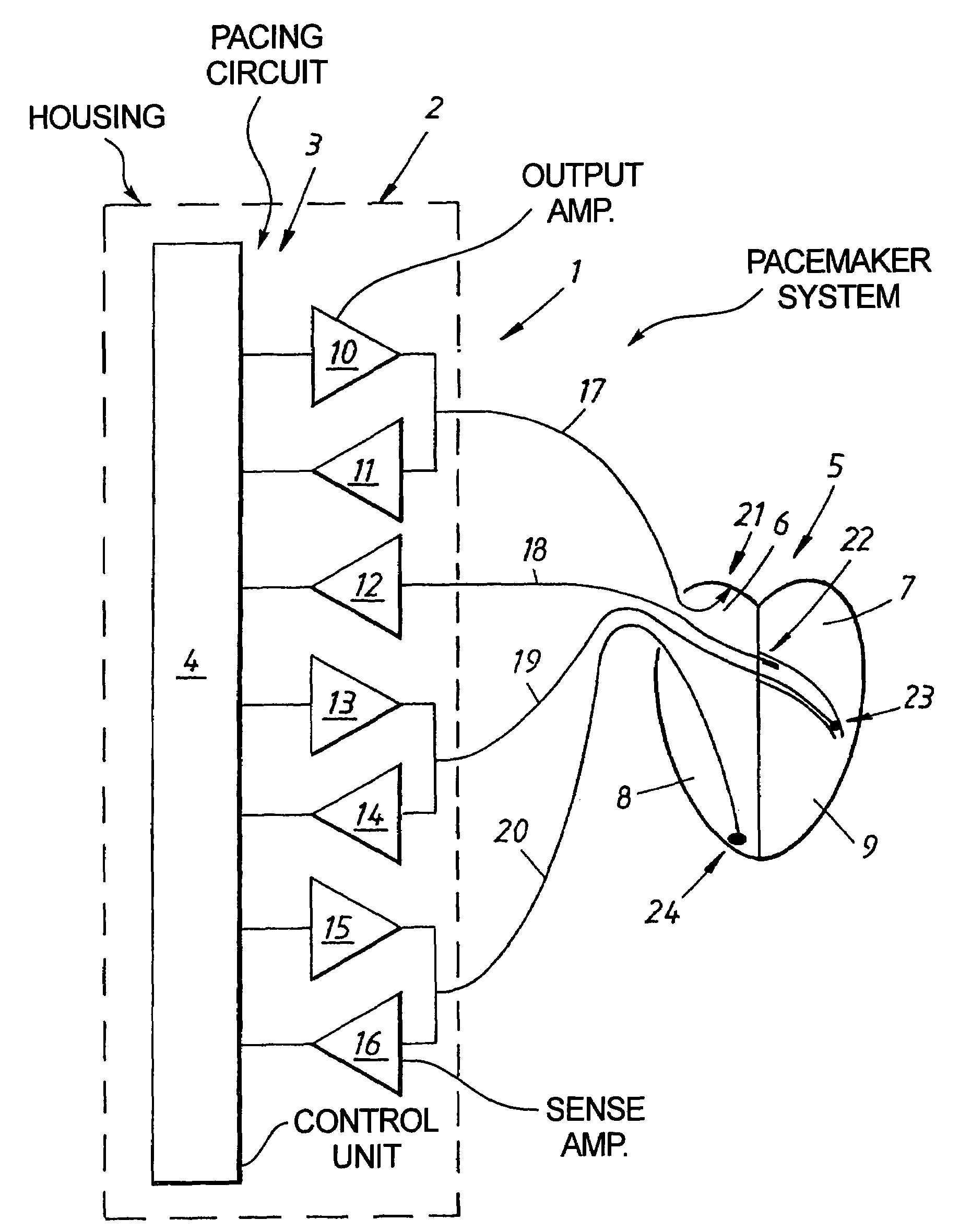
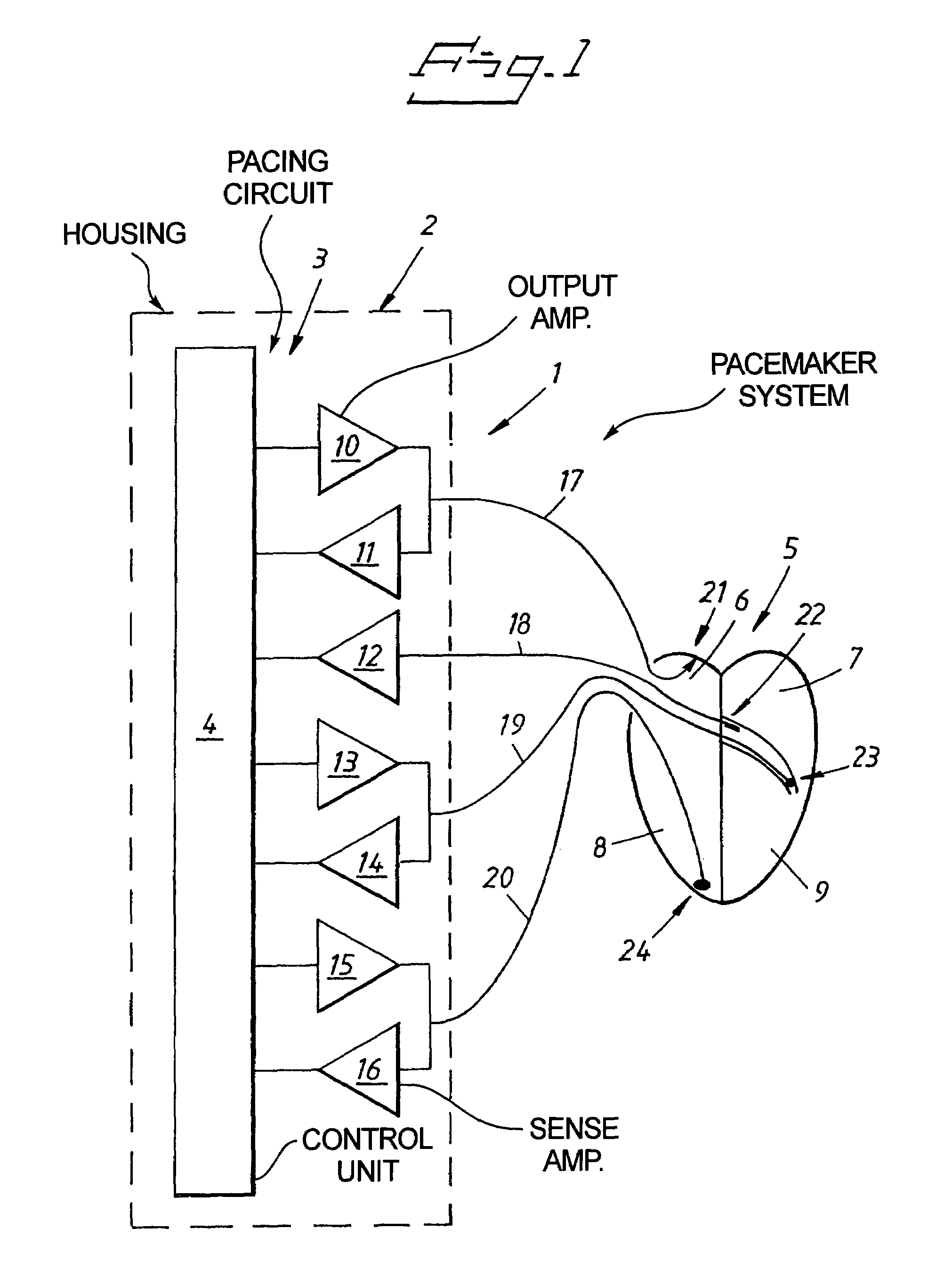
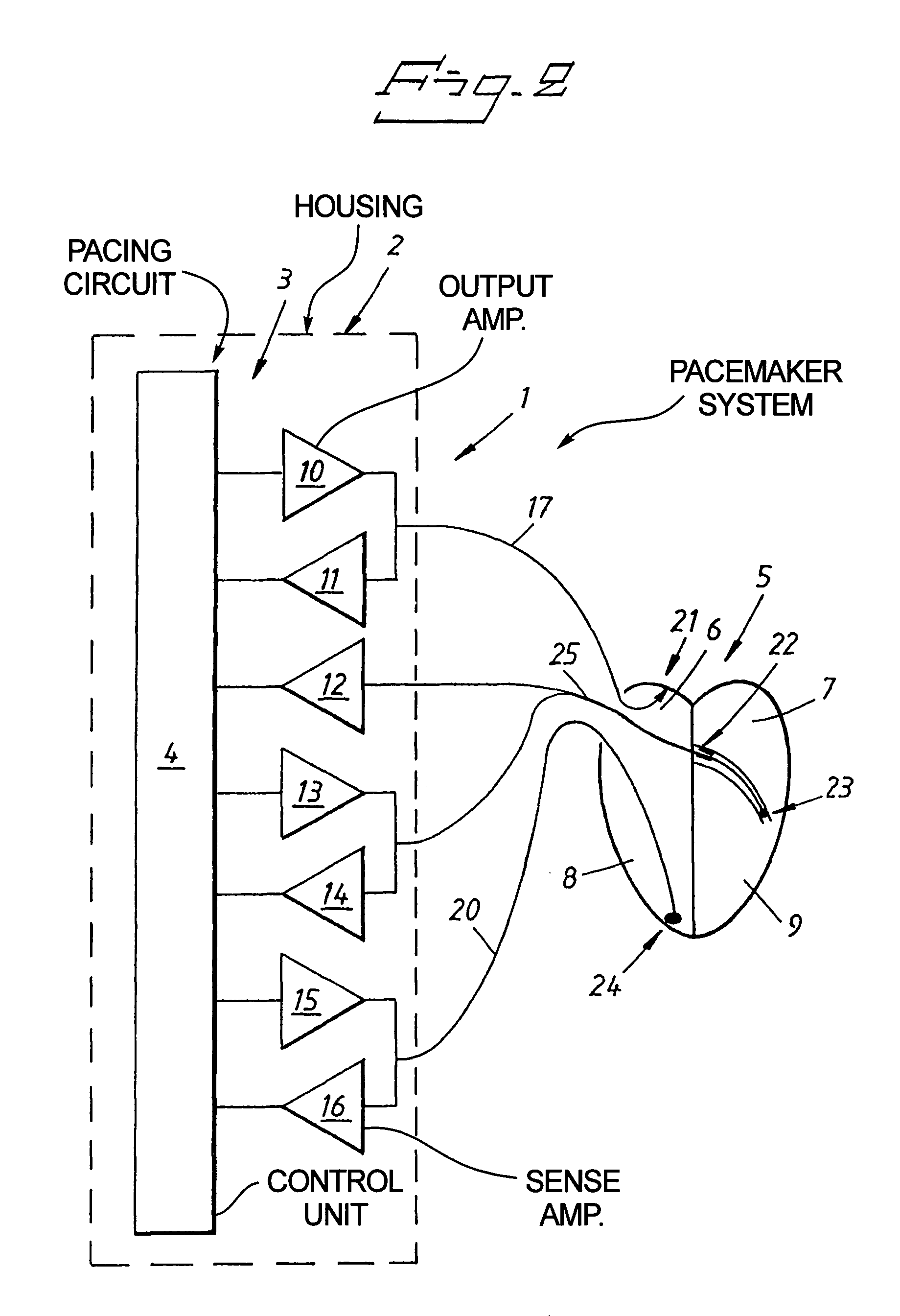
Cardiac stimulating device
An implantable cardiac stimulating device has a pacing circuit connected via an electrode lead system to a first electrode which stimulates and detects activity in the left ventricle, a second electrode to stimulate and detect activity in the right atrium, and to a third electrode to detect activity in the left atrium. Upon the occurrence of a paced or sensed depolarization of the right atrium, a first AV-delay is started. When the subsequent left atrial depolarization is detected, a new AV-interval is started that is optimized for the left side of the heart. Either the left ventricle only, or both ventricles, is paced at the optimized left side AV-interval.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
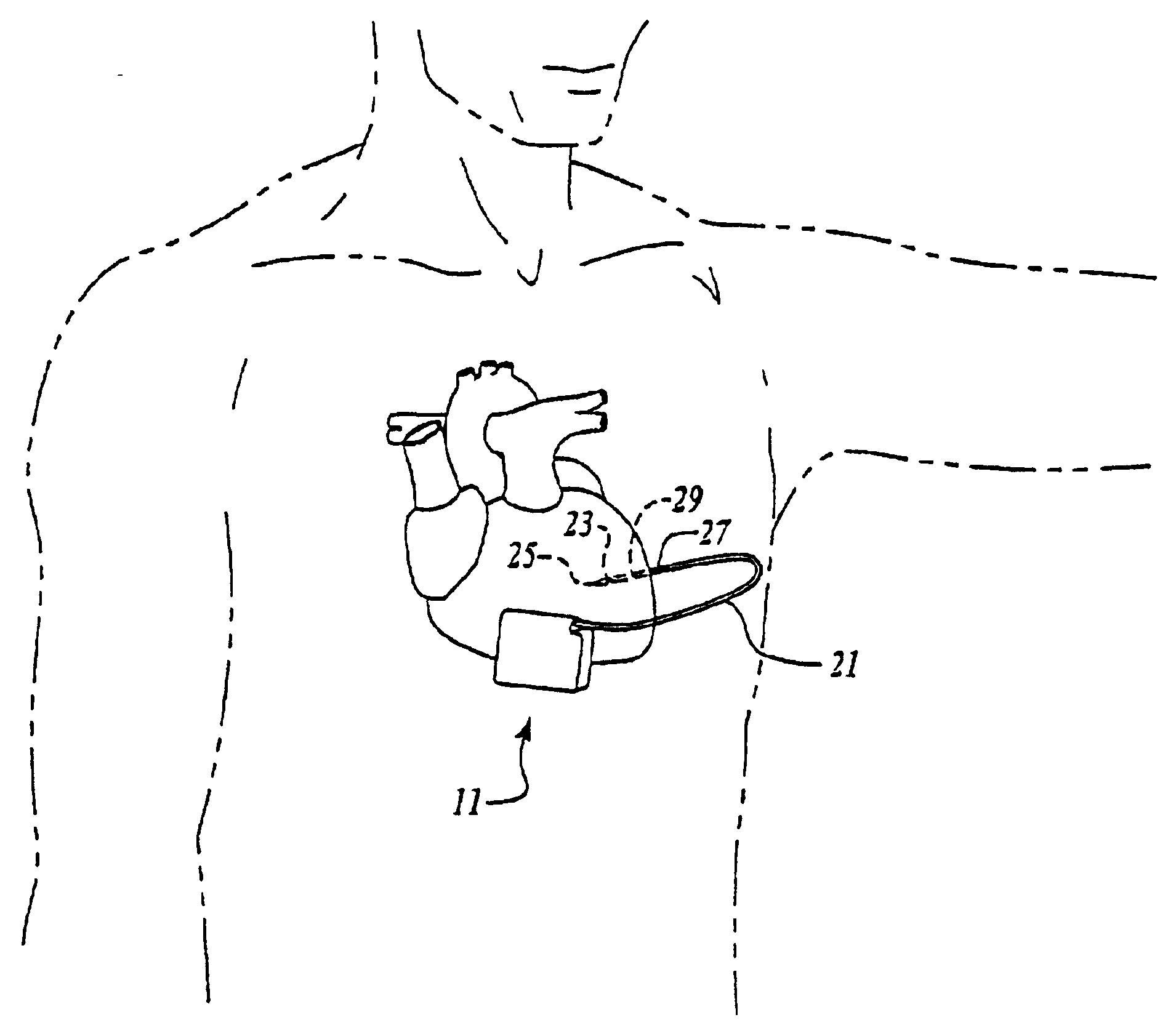
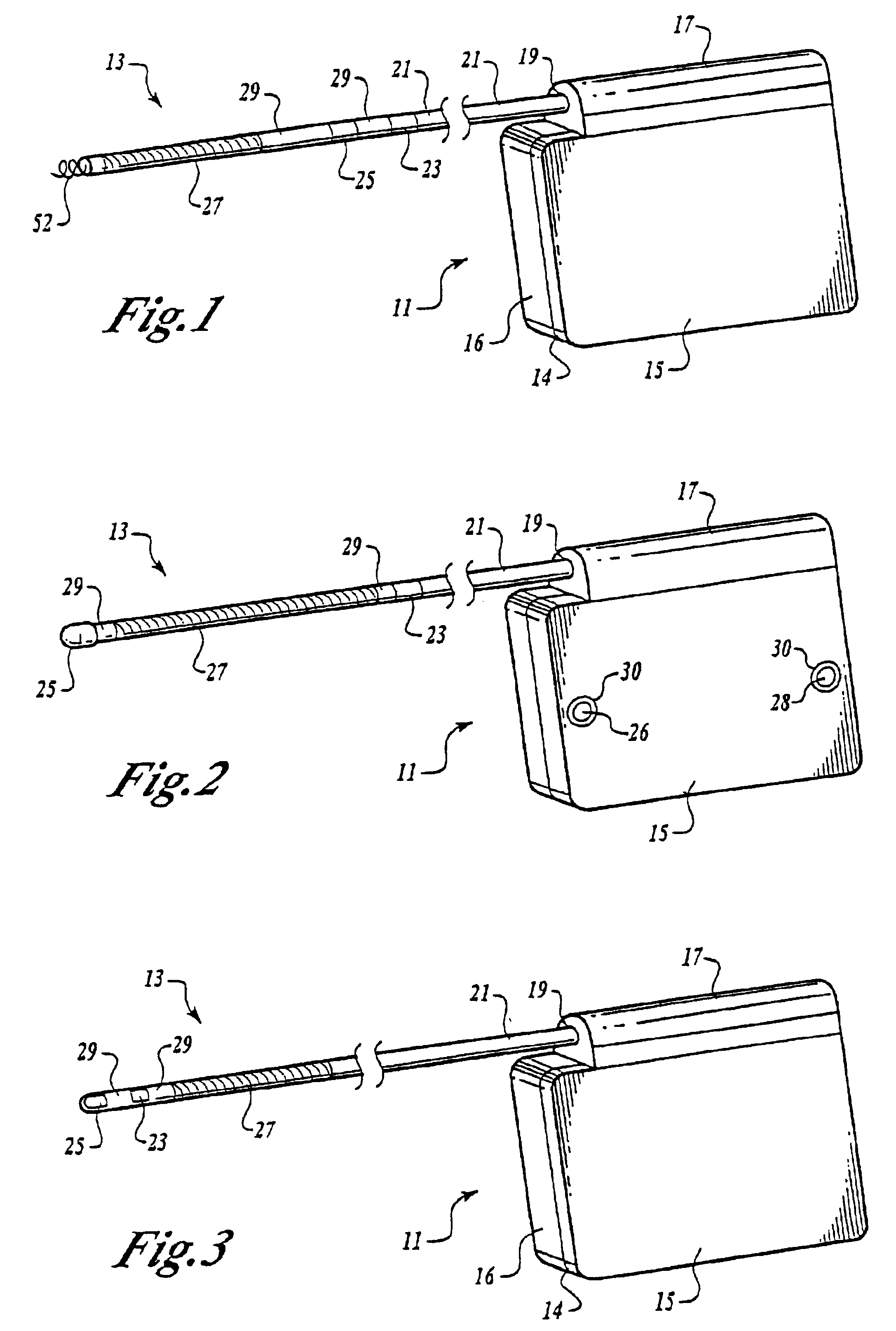
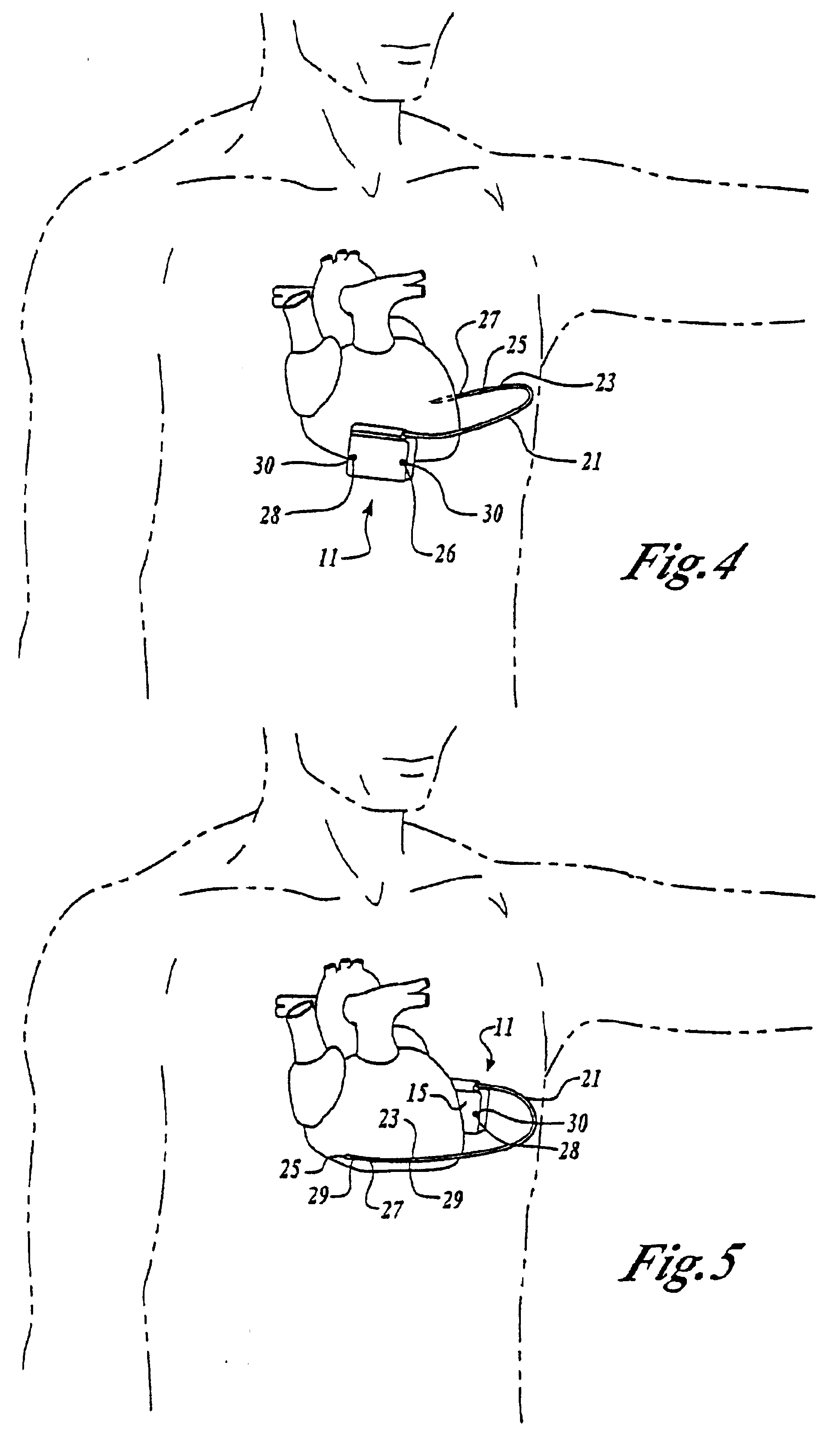
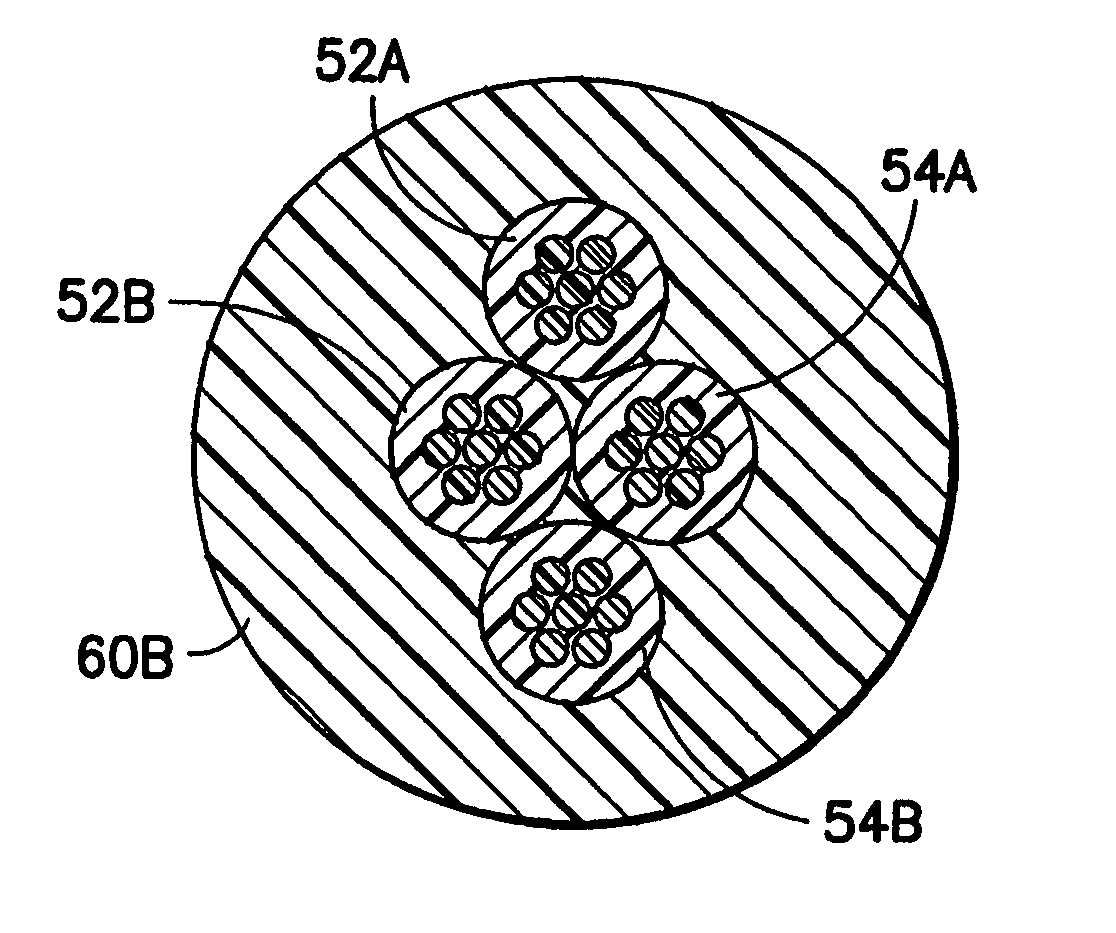
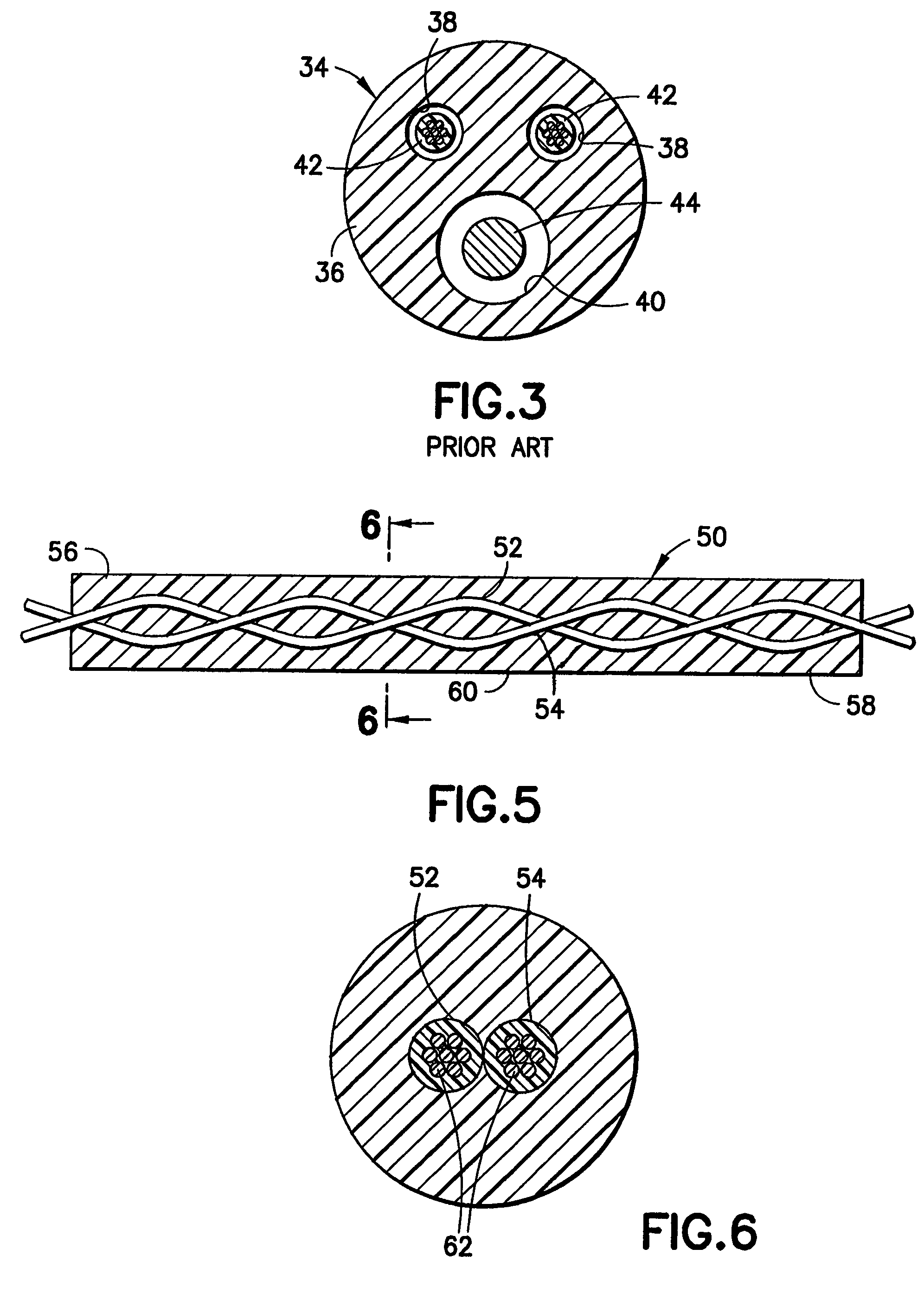
Construction of a medical electrical lead
ActiveUS7174220B1Reduce processing stepsShorten cycle timeTransvascular endocardial electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityElectrical conductor
An implantable cardiac stimulation lead system for use with an implantable stimulation device includes at least a pair of conductors, braided together and extending between proximal and distal ends and co-extruded with flexible resilient insulation material. Each conductor may be a multi-strand cable composed of MP35N or DFT and have its outer peripheral surfaces coated with insulative material. An electrical connector is coupled to the proximal end of the lead system for connection with a stimulation device and includes terminals electrically connected to the conductors. The proximal connector is thereby electrically coupled to a distal tip electrode and to at least one electrode proximally spaced from the distal tip electrode. The lead system may include an elongated tubular lead body of flexible resilient insulative material having a longitudinally extending lumen for receiving a stylet for aid in implanting the lead system. Alternatively, an introducer sheath may be employed for implantation.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Monophasic waveform for anti-bradycardia pacing for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
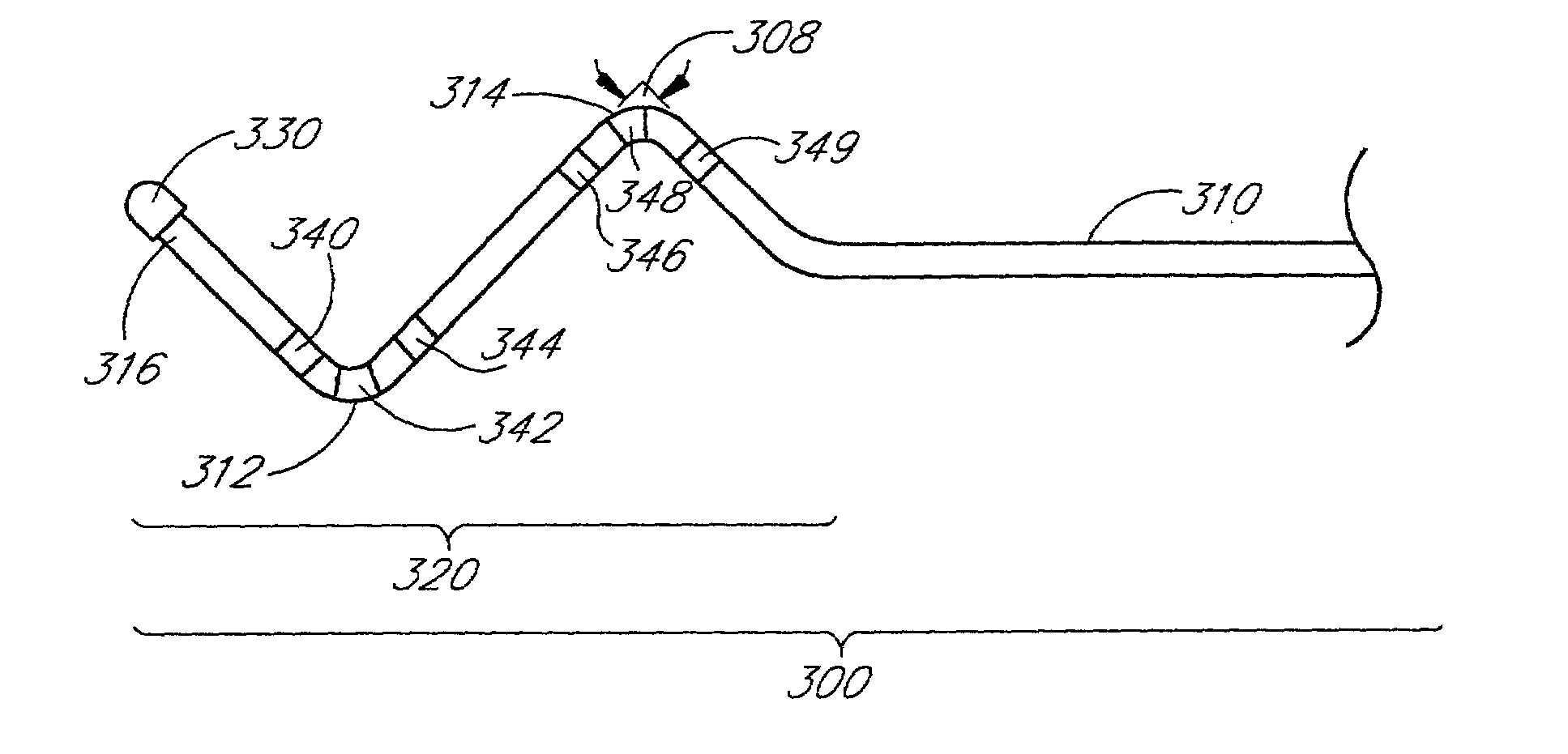
Self-anchoring coronary sinus lead
InactiveUS7313444B2Easily traverse bendTransvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesLeft marginal veinVein
An implantable cardiac lead system suitable for placement in the coronary sinus region of the heart. The lead system comprises a lead having two or more non-helical bends in its distal portion. The two or more non-helical bends cooperate to prevent the lead from dislodgment or displacement inside the coronary sinus. The lead system may further comprise a stylet suitable for steering the lead into at least one of the coronary sinus vein, great cardiac vein, left marginal vein, left posterior ventricular vein, and small cardiac vein. The stylet is tapered in its distal portion to provide enhanced maneuverability and steerability inside the coronary sinus region. The lead system may also comprise an introducer which aids in introducing the lead into the heart.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Electromagnetic interference immune tissue invasive system
InactiveUS20020128691A1Avoid failureAvoid interferenceMagnetic measurementsTransvascular endocardial electrodesFiberElectricity
An electromagnetic immune tissue invasive system includes a primary device housing. The primary device housing having a control circuit therein. A shielding is formed around the primary device housing to shield the primary device housing and any circuits therein from electromagnetic interference. A lead system transmits and receives signals between the primary device housing. The lead system is either a fiber optic system or an electrically shielded electrical lead system.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Transmuscular left ventricular cardiac stimulation leads and related systems and methods
InactiveUS20100069983A1Increase contractilityTransvascular endocardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsLeft ventricular sizeCardiac pacemaker electrode
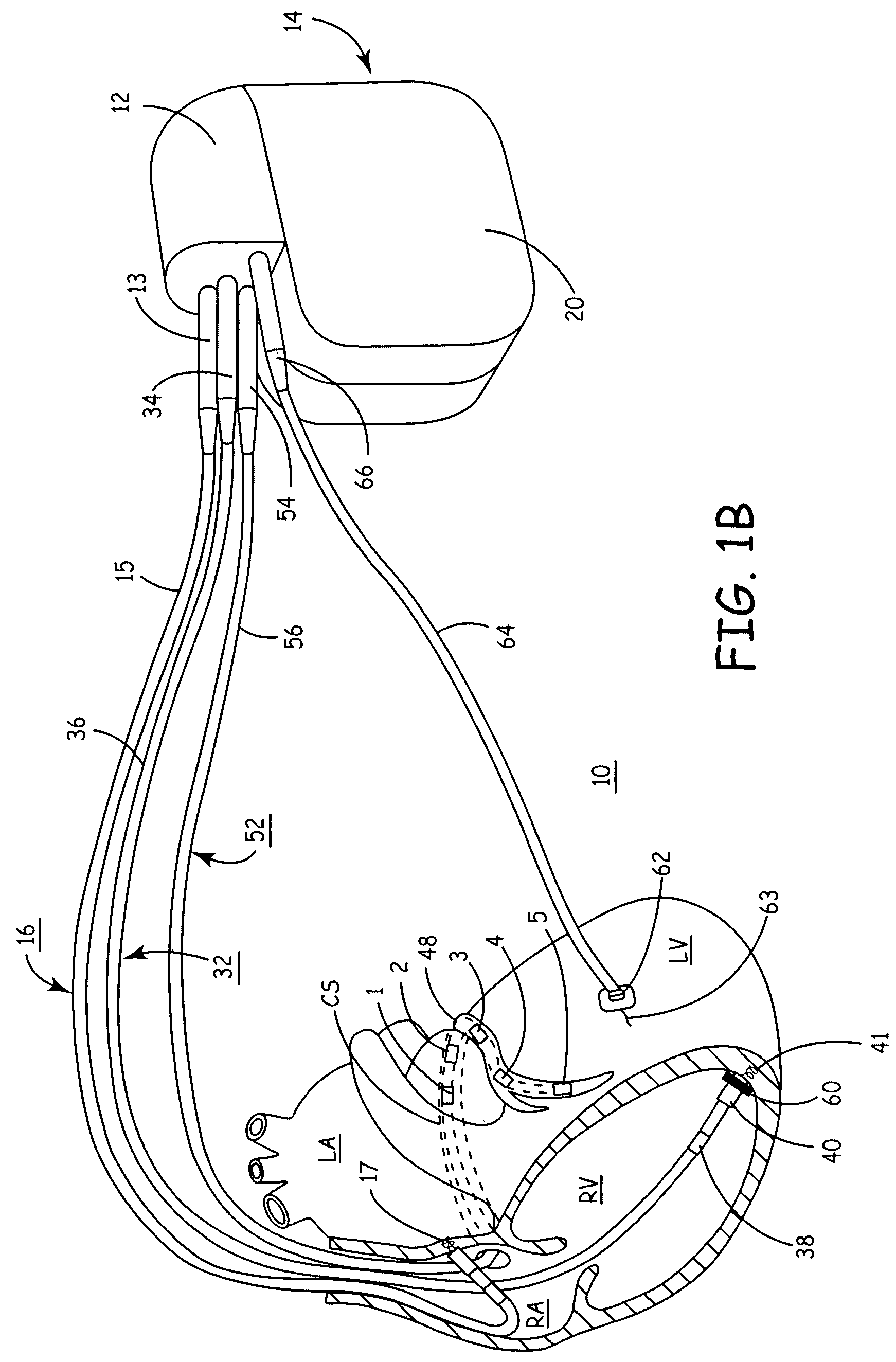
A cardiac stimulation system and method delivers a left ventricle stimulator from a right ventricle lead system in the right ventricle chamber, into a right side of an interventricular septum at a first location, and transmuscularly from the first location to a second location along the left side of the septum. The left ventricle stimulator is affixed at the second location for transmuscular stimulation of the left ventricle conduction system. A biventricular stimulation system further includes a right ventricle stimulator also delivered by the right ventricle lead system to the first location along the right side of the septum for right ventricular stimulation. An energy source is coupled to the transmuscular stimulation system, i.e., a pacemaker, and / or defibrillator, or to enhance contractility, and may be coupled directly or via “leadless” system(s). Various highly beneficial particular arrangements of stimulators and leads are further described.
Owner:EMERGE MEDSYST
RFID detection and identification system for implantable medical lead systems
A system for identifying active implantable medical devices (AIMD) and lead systems implanted in a patient using a radio frequency identification (RFID) tag having retrievable information relating to the AIMD, lead system and / or patient. The RFID tag may store information about the AIMD manufacturer, model number, serial number; lead wire system placement information and manufacturer information; MRI compatibility due to the incorporation of bandstop filters; patient information, and physician and / or hospital information and other relevant information. The RFID tag may be affixed or disposed within the AIMD or lead wires of the lead system, or surgically implanted within a patient adjacent to the AIMD or lead wire system.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com