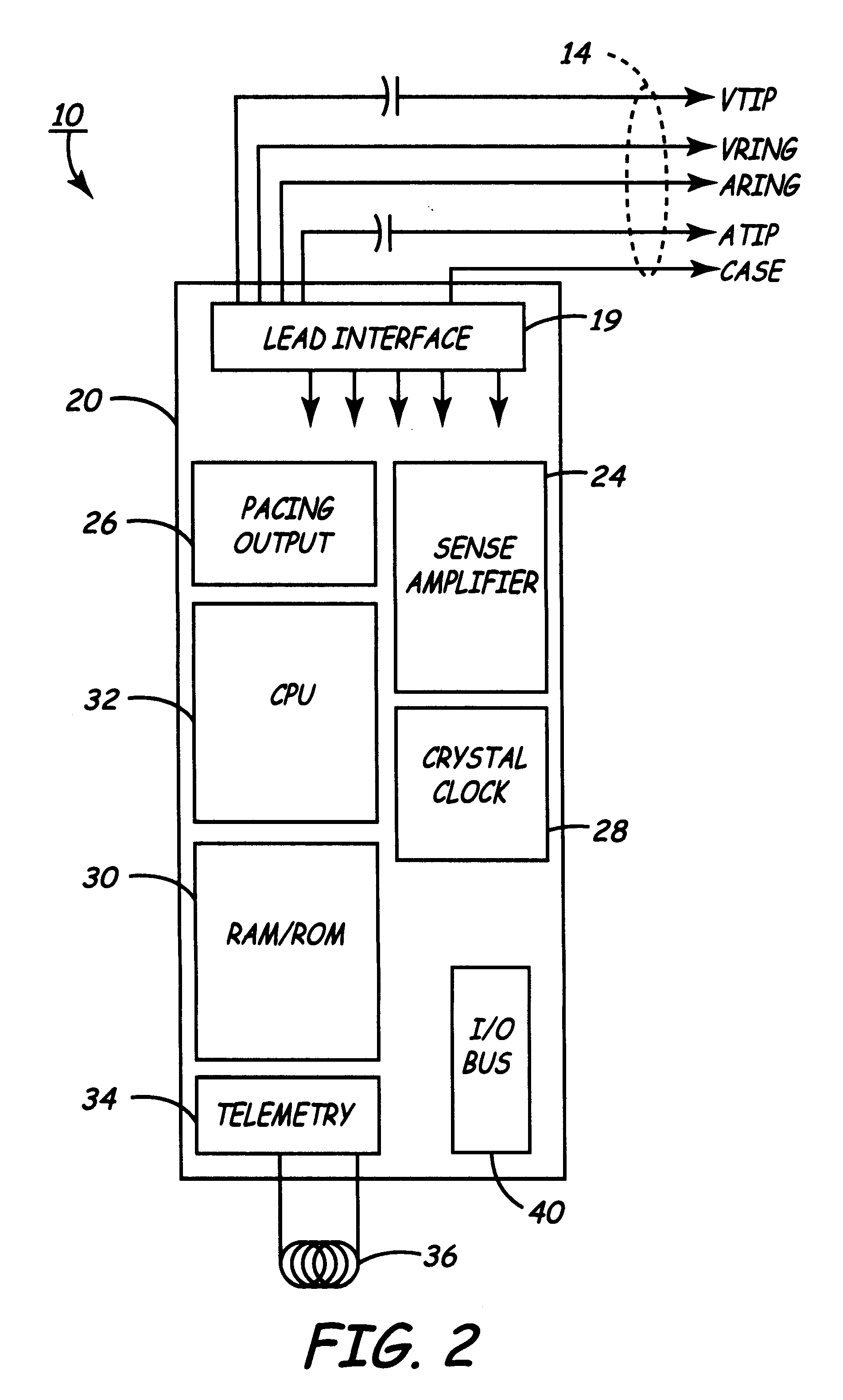
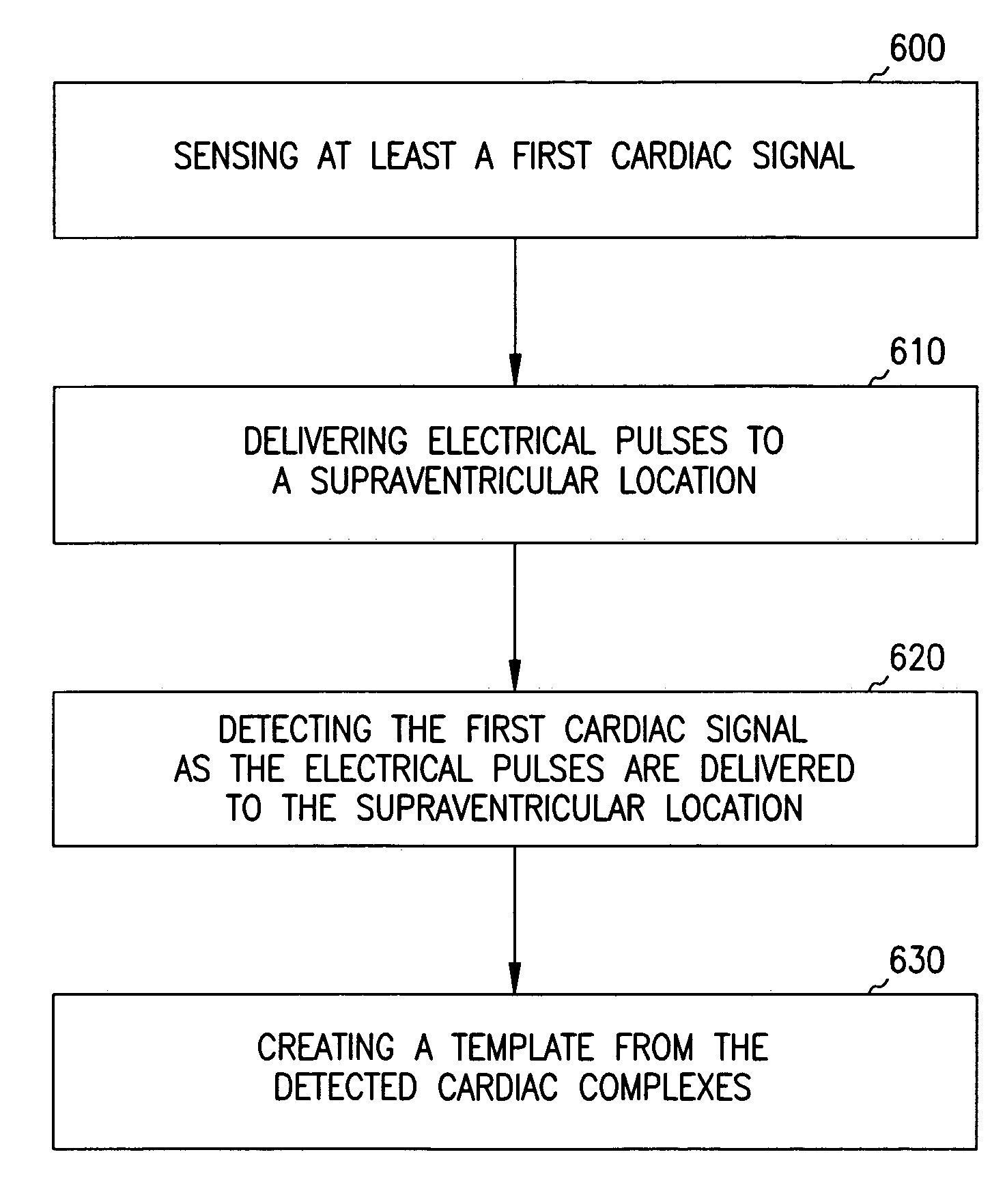
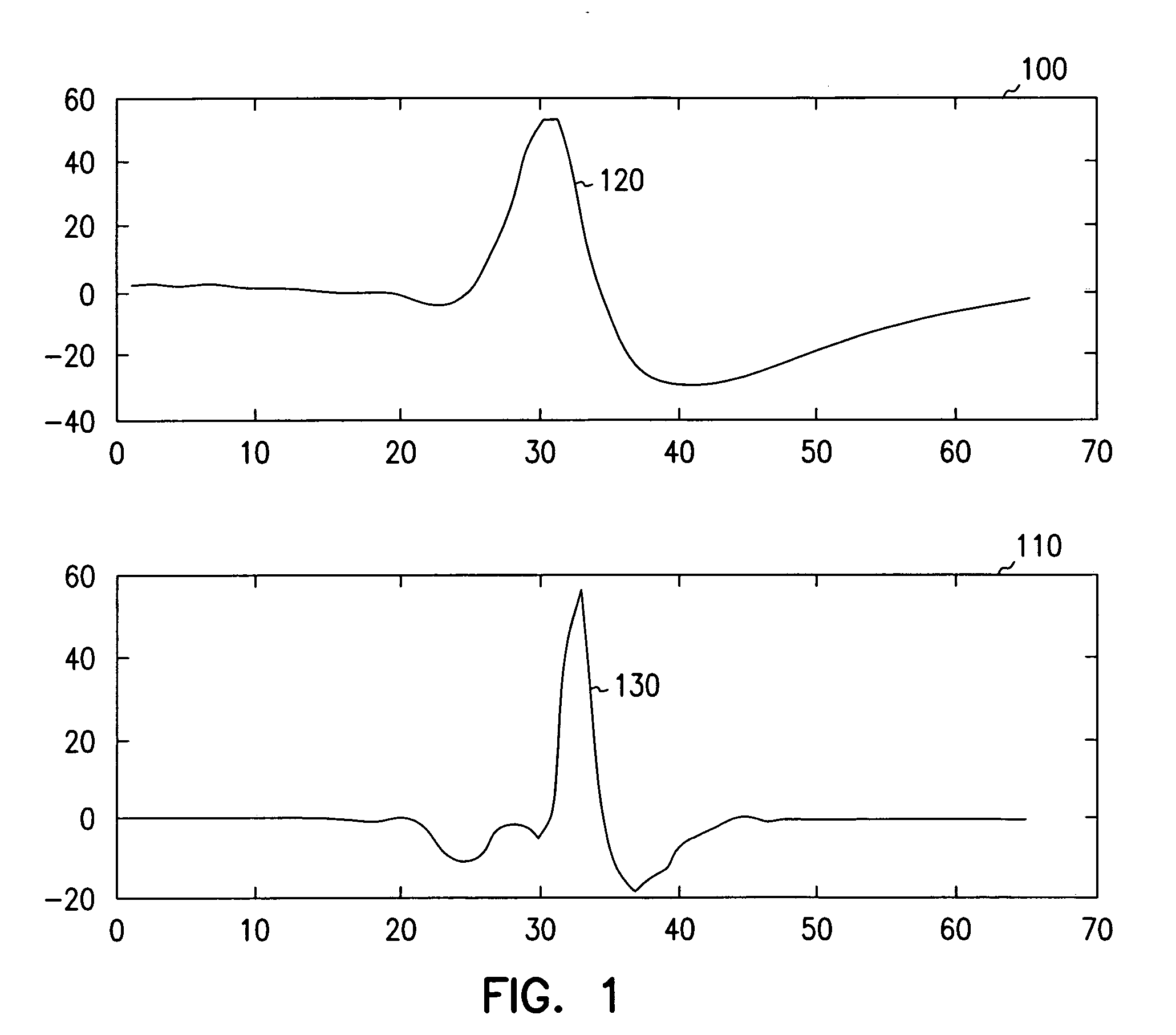
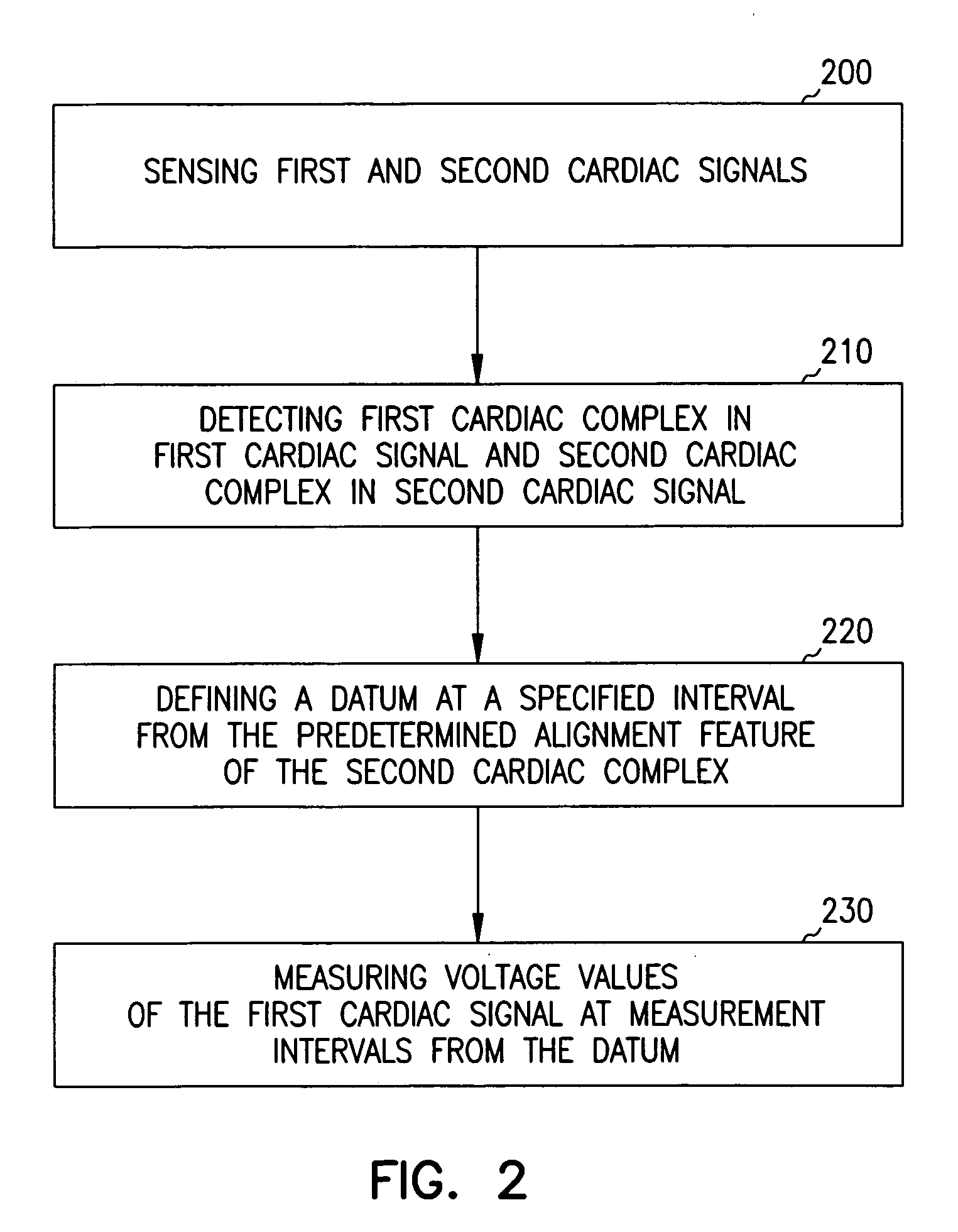
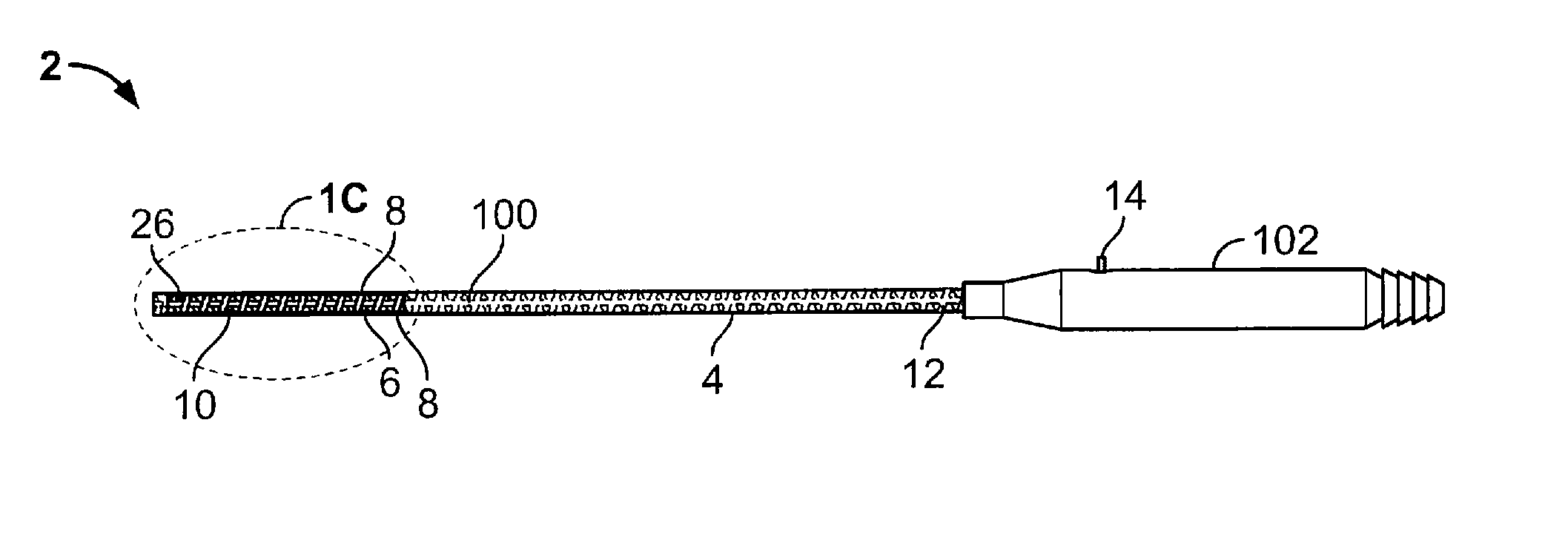
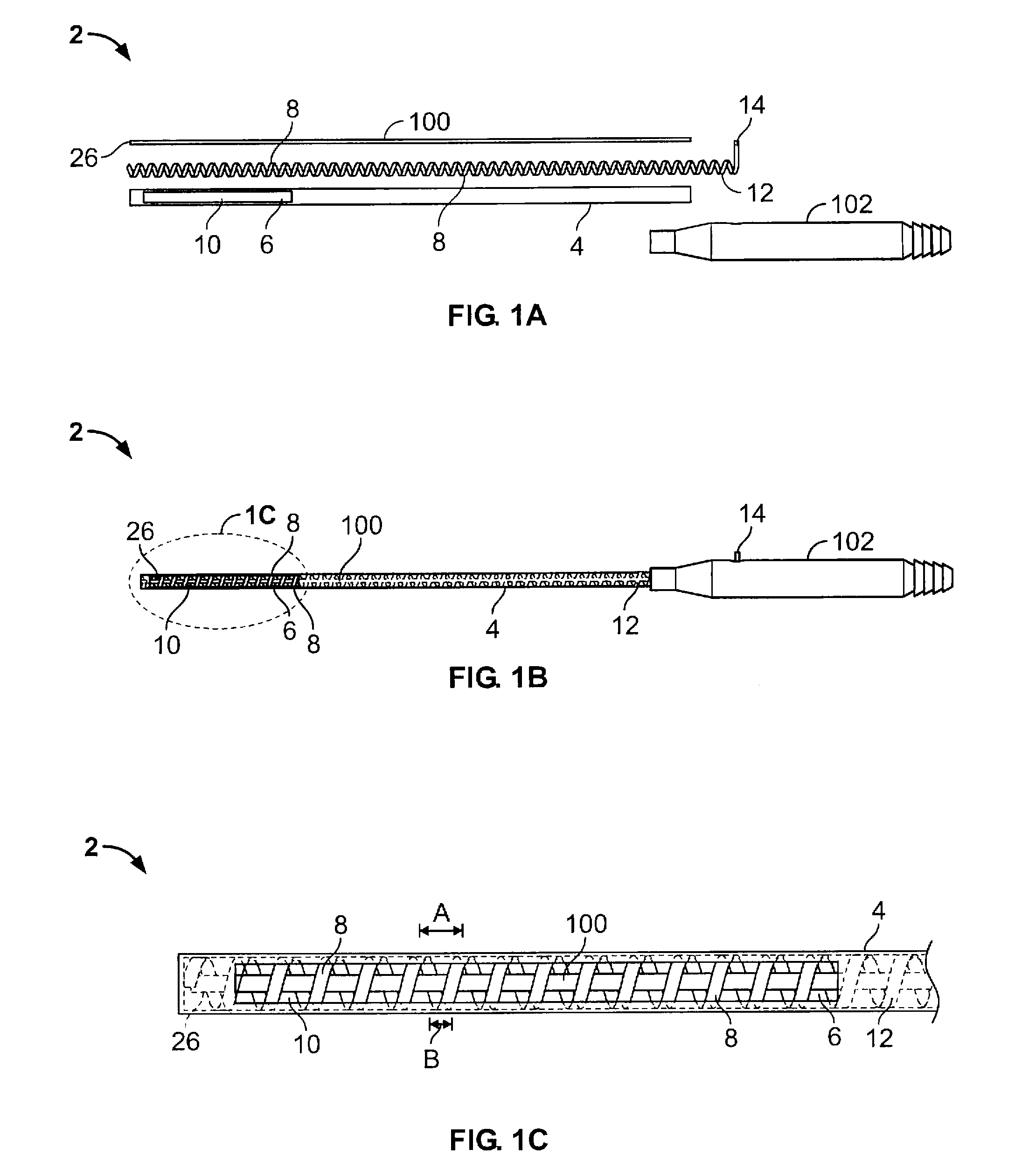
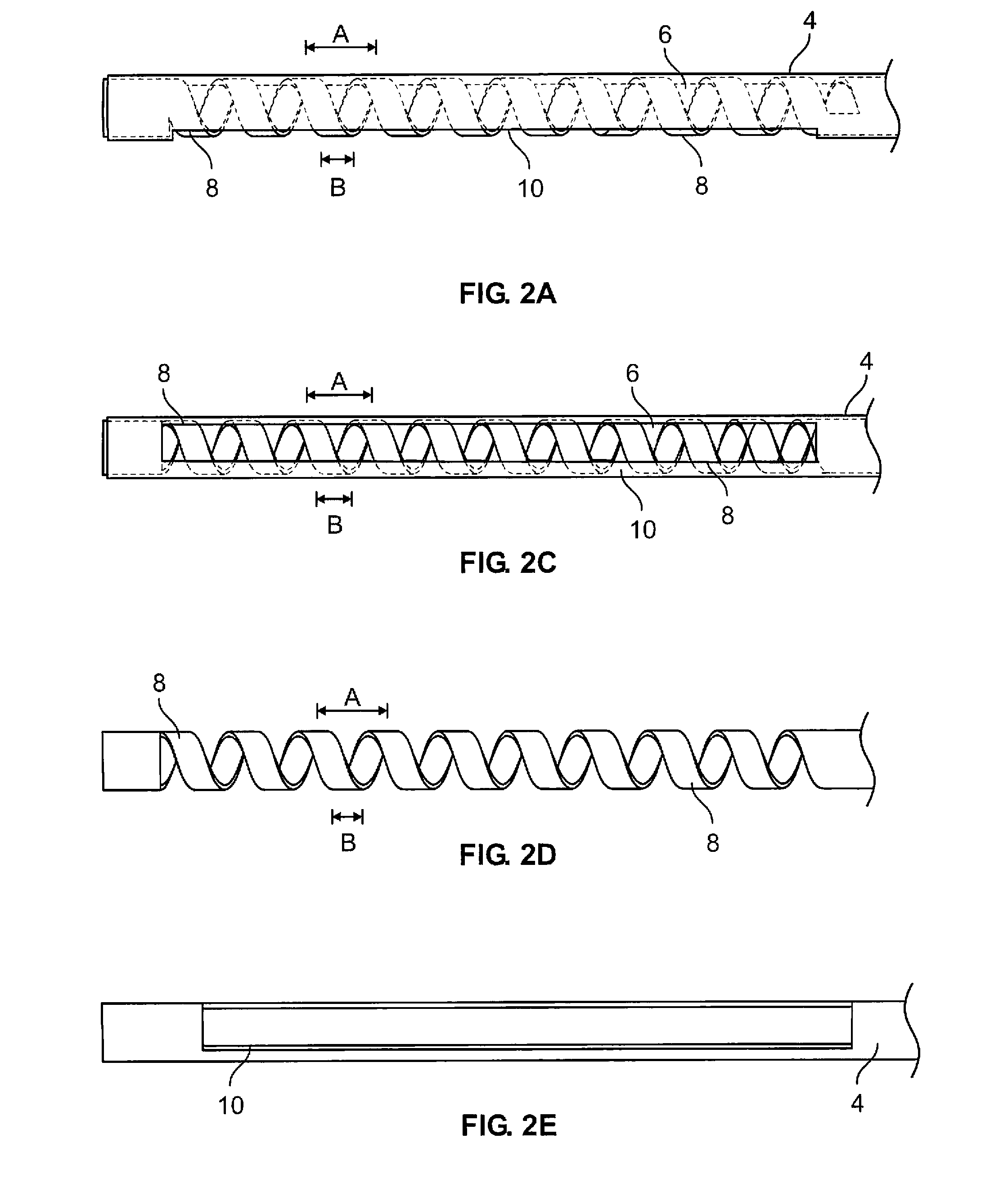
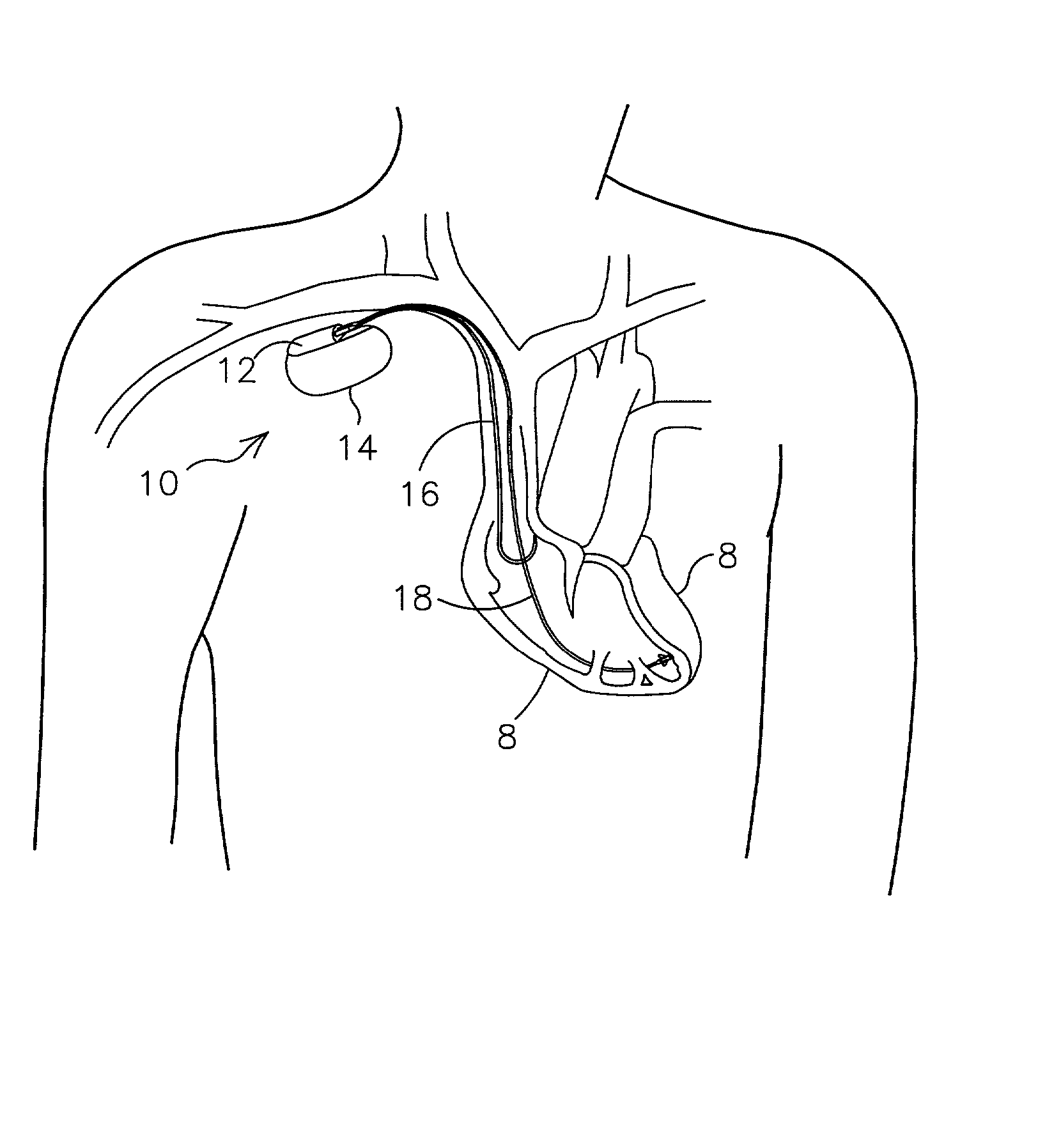
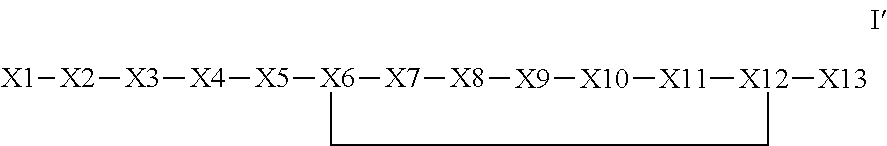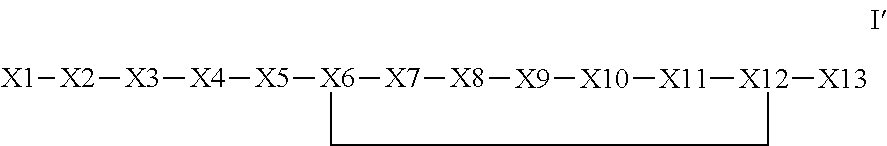Patents
Literature
341 results about "Tachycardia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
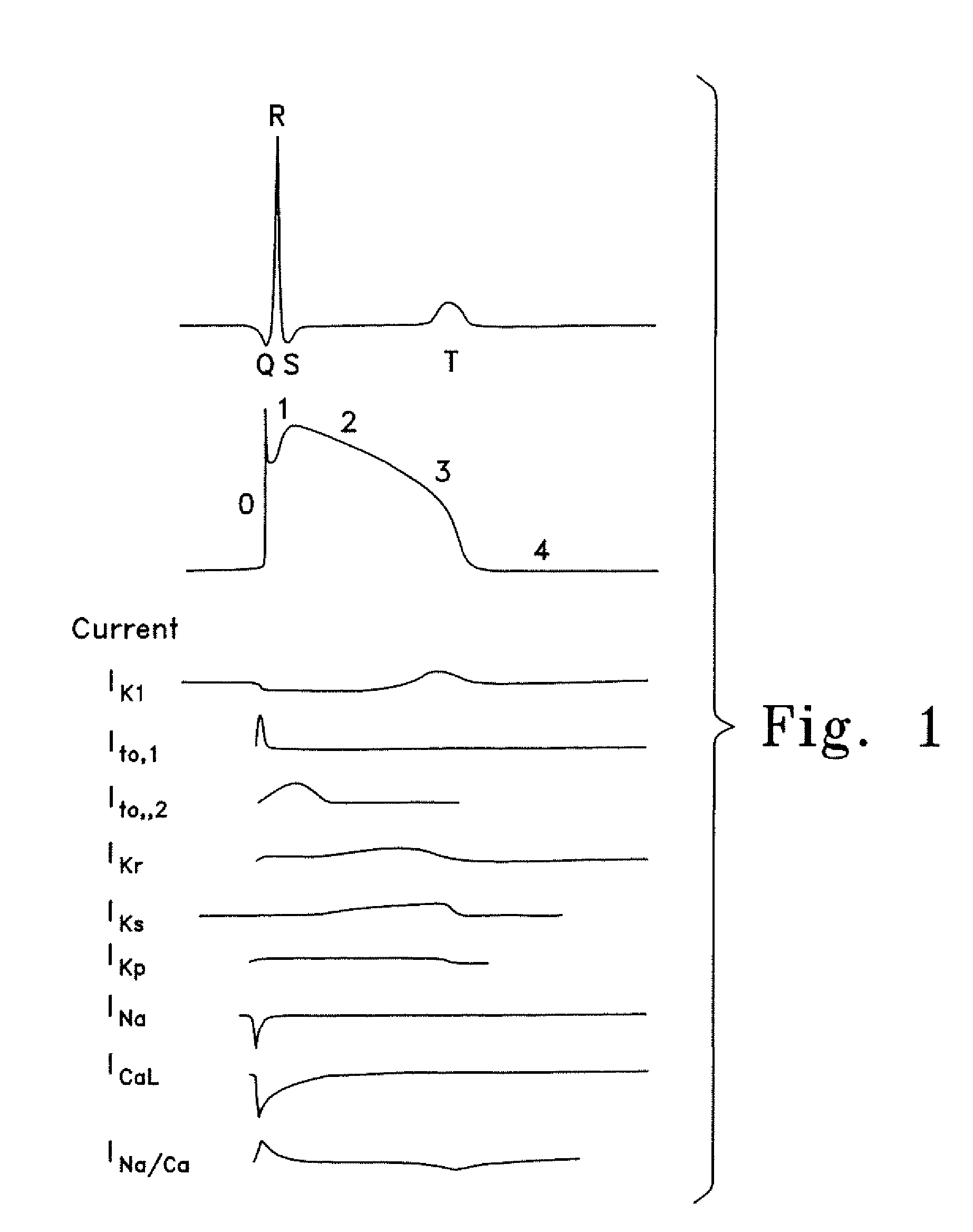
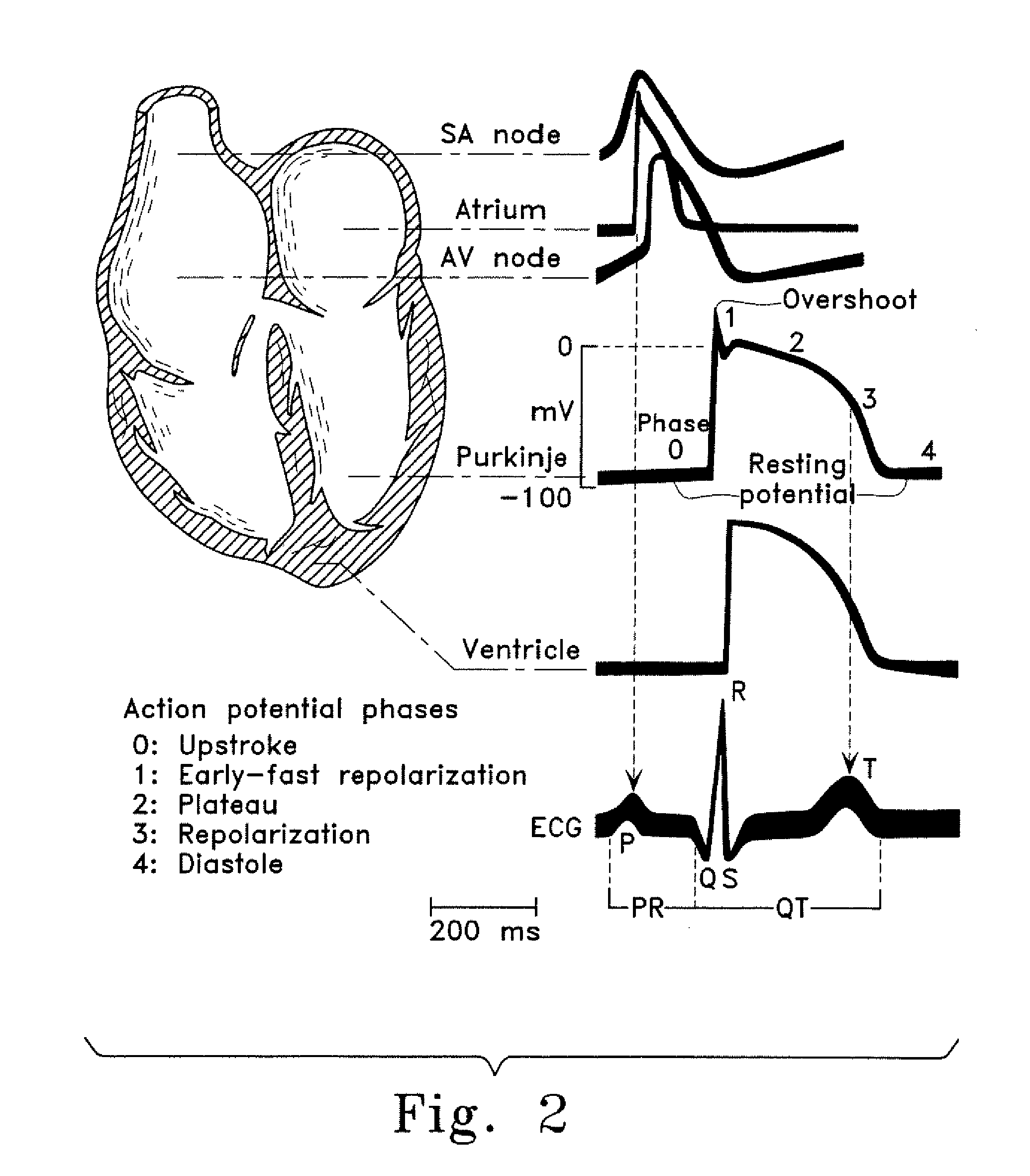
A heart rhythm disorder with heartbeats faster than usual, greater than 100 beats per minute.
System for performing and monitoring minimally invasive interventions
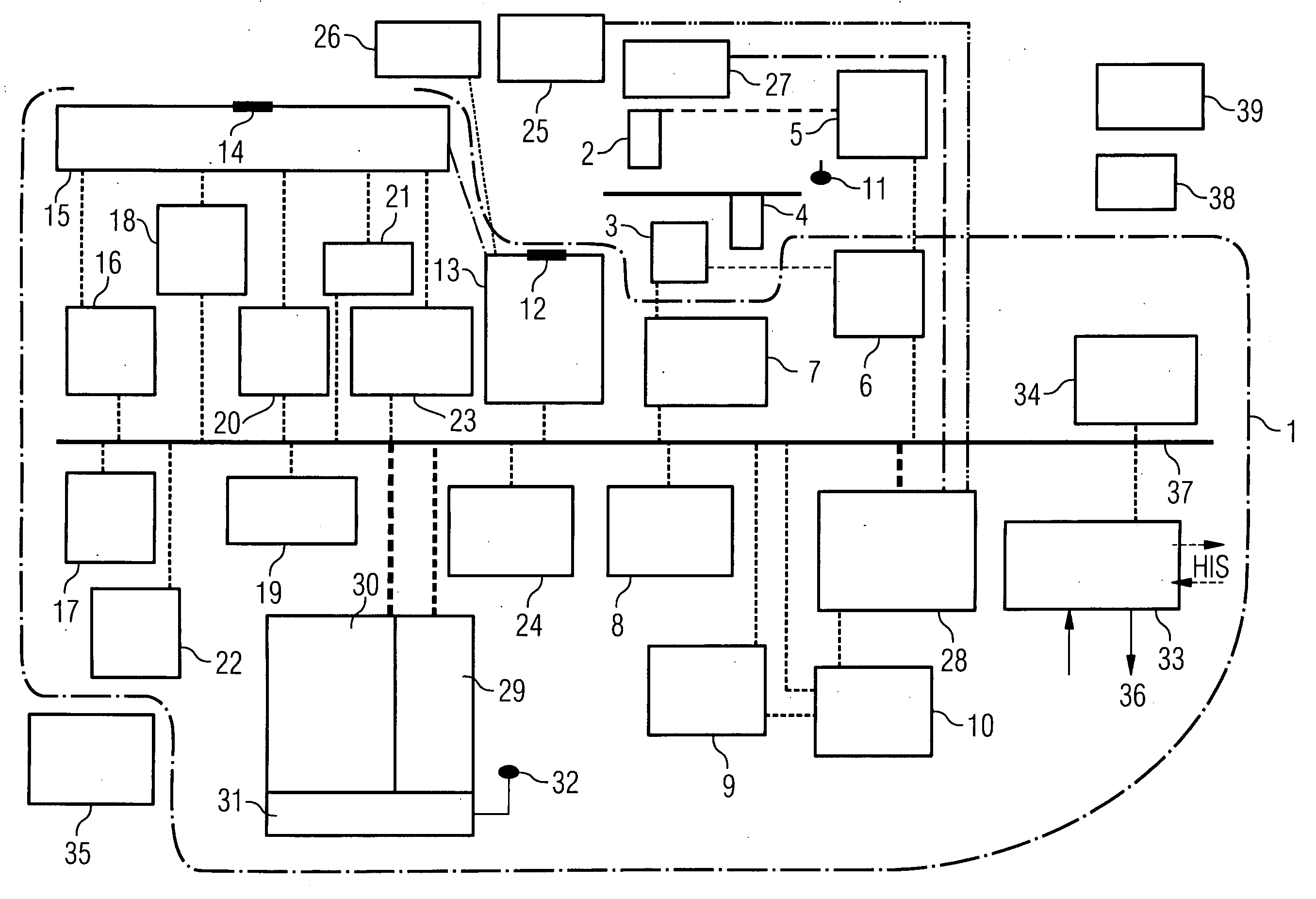
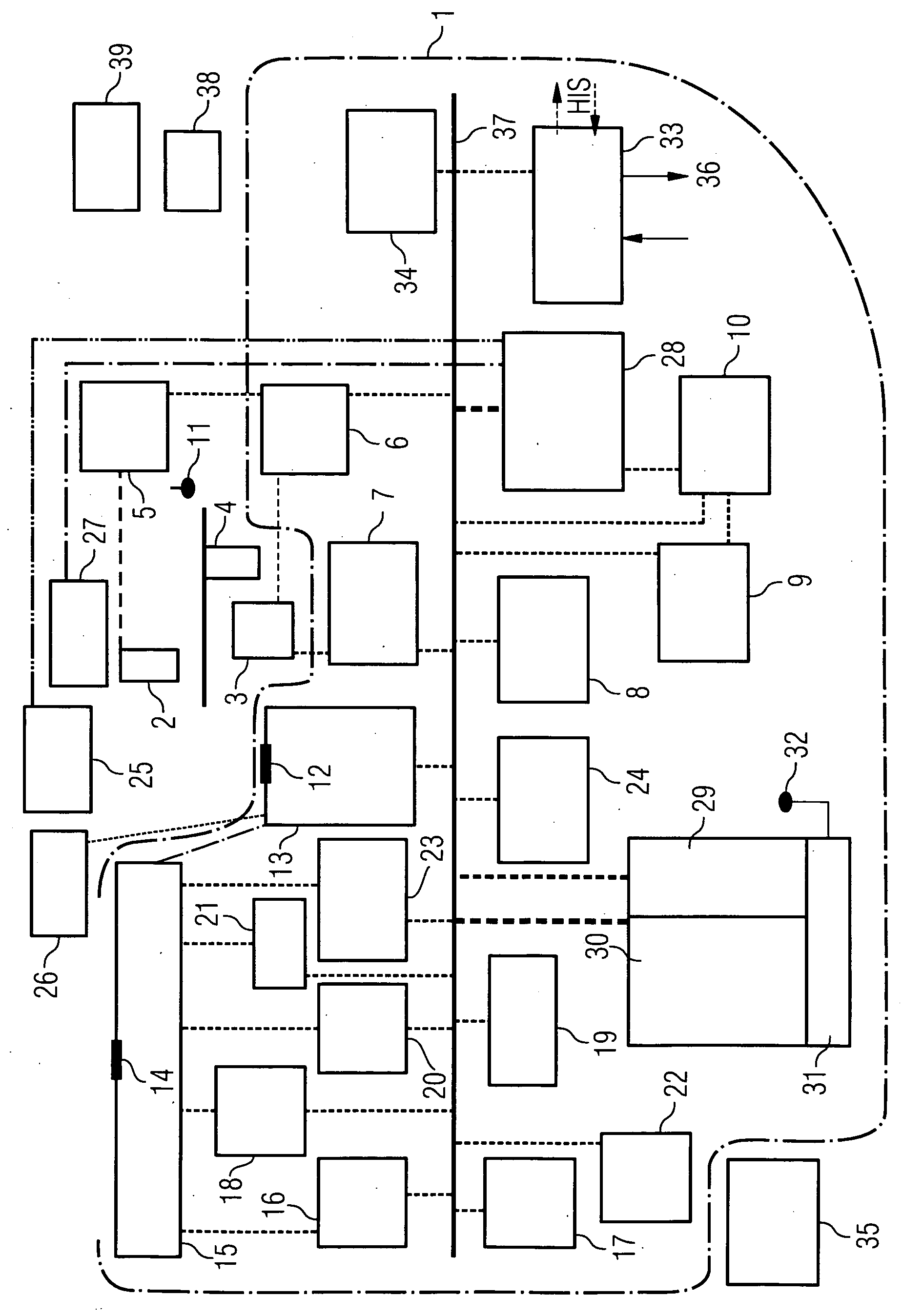
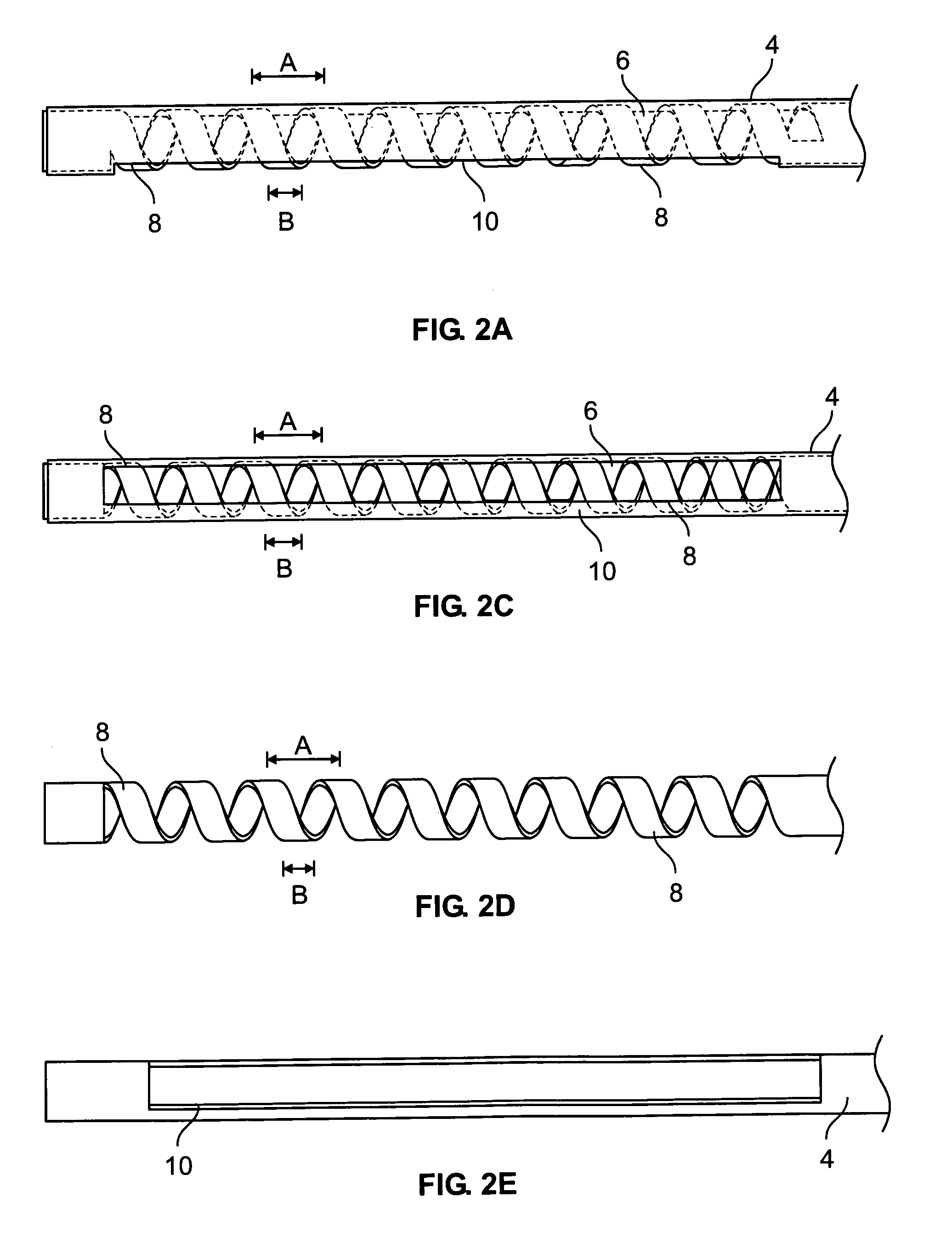
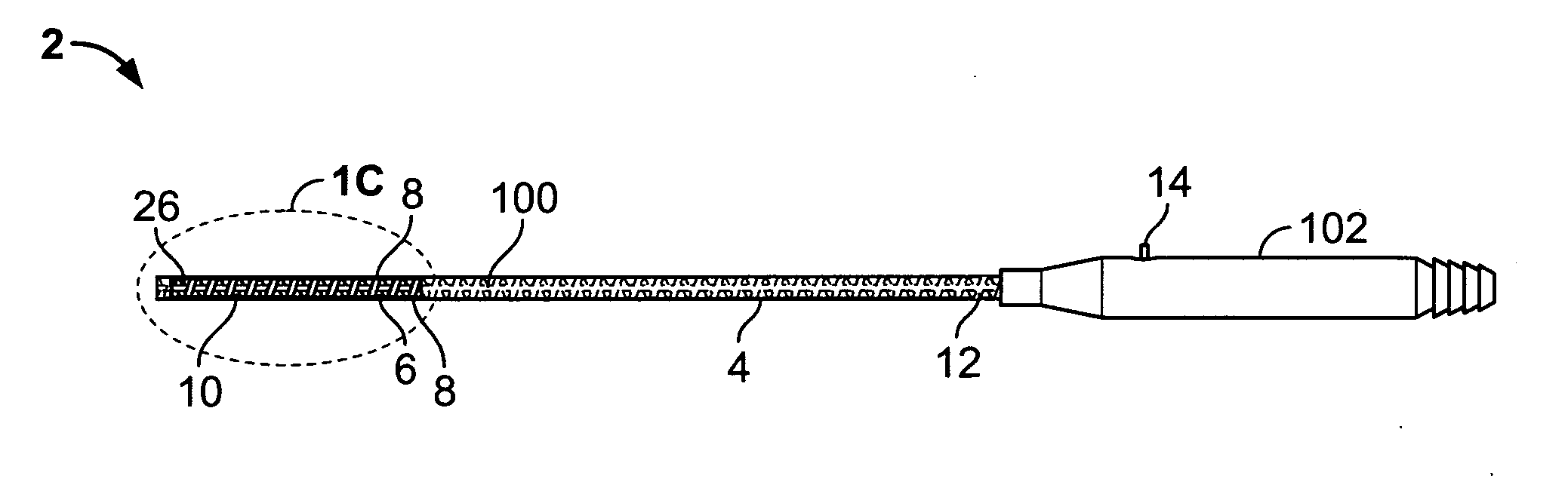
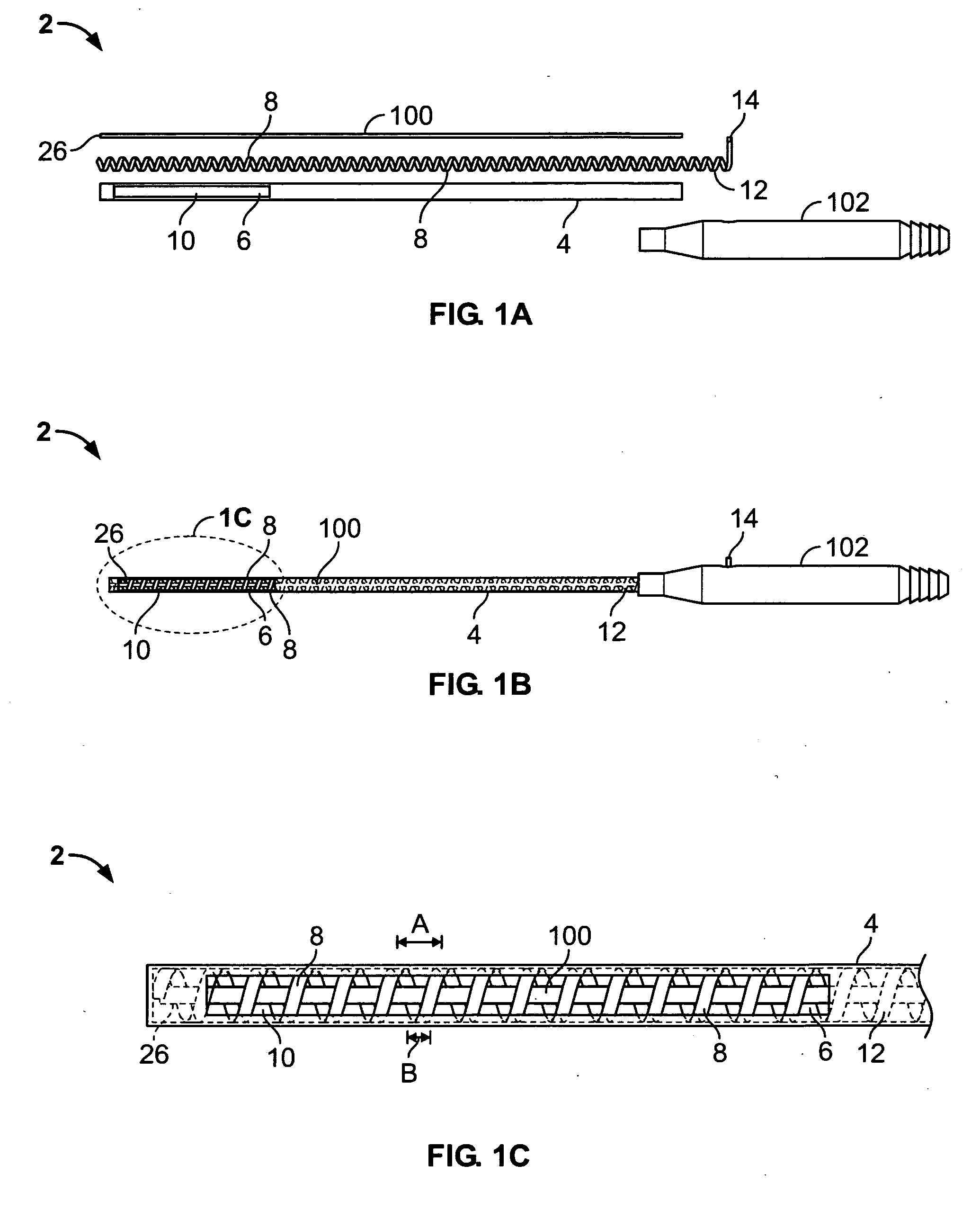
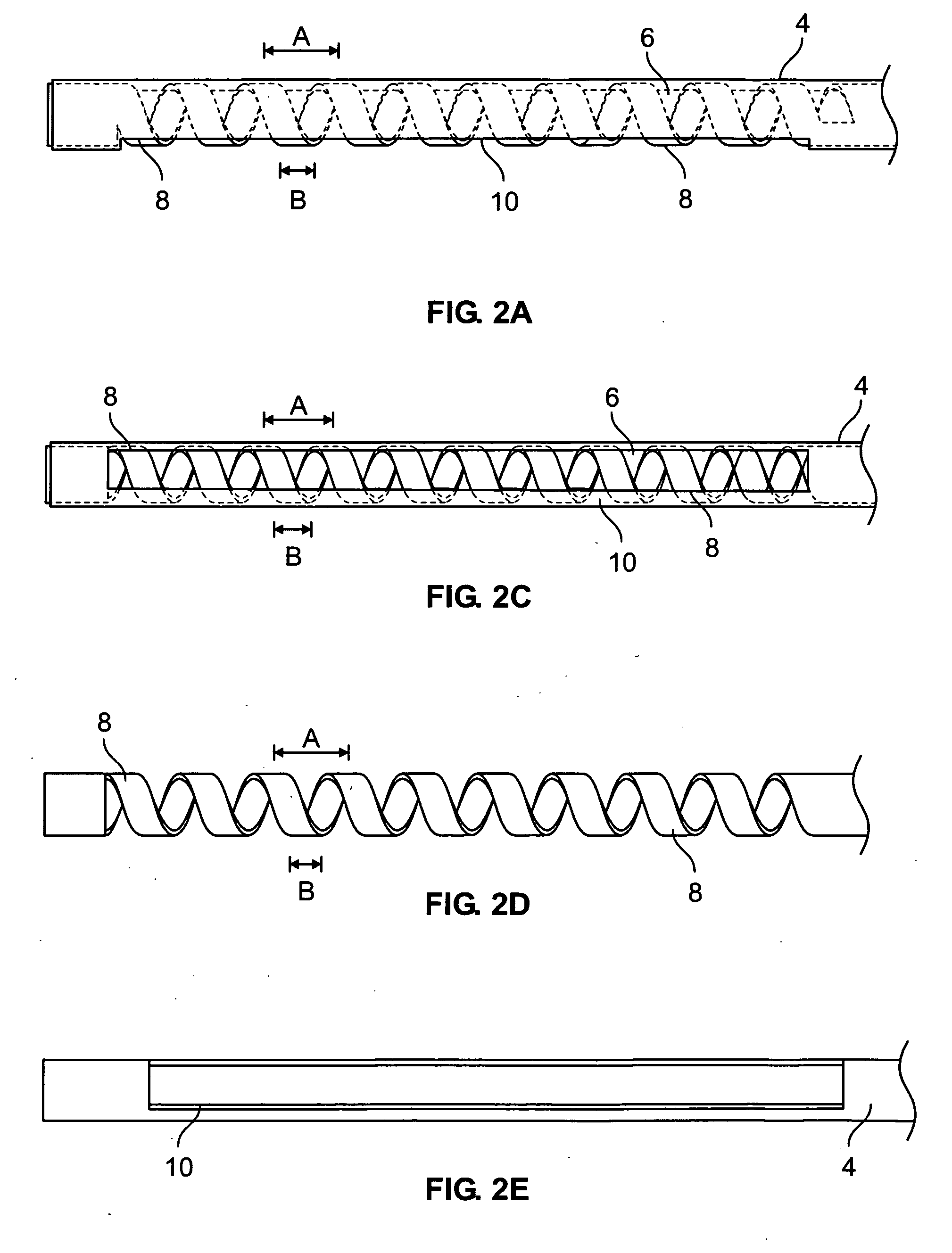
InactiveUS20070027390A1Reliable eliminationQuality improvementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyX-rayProcess measurement
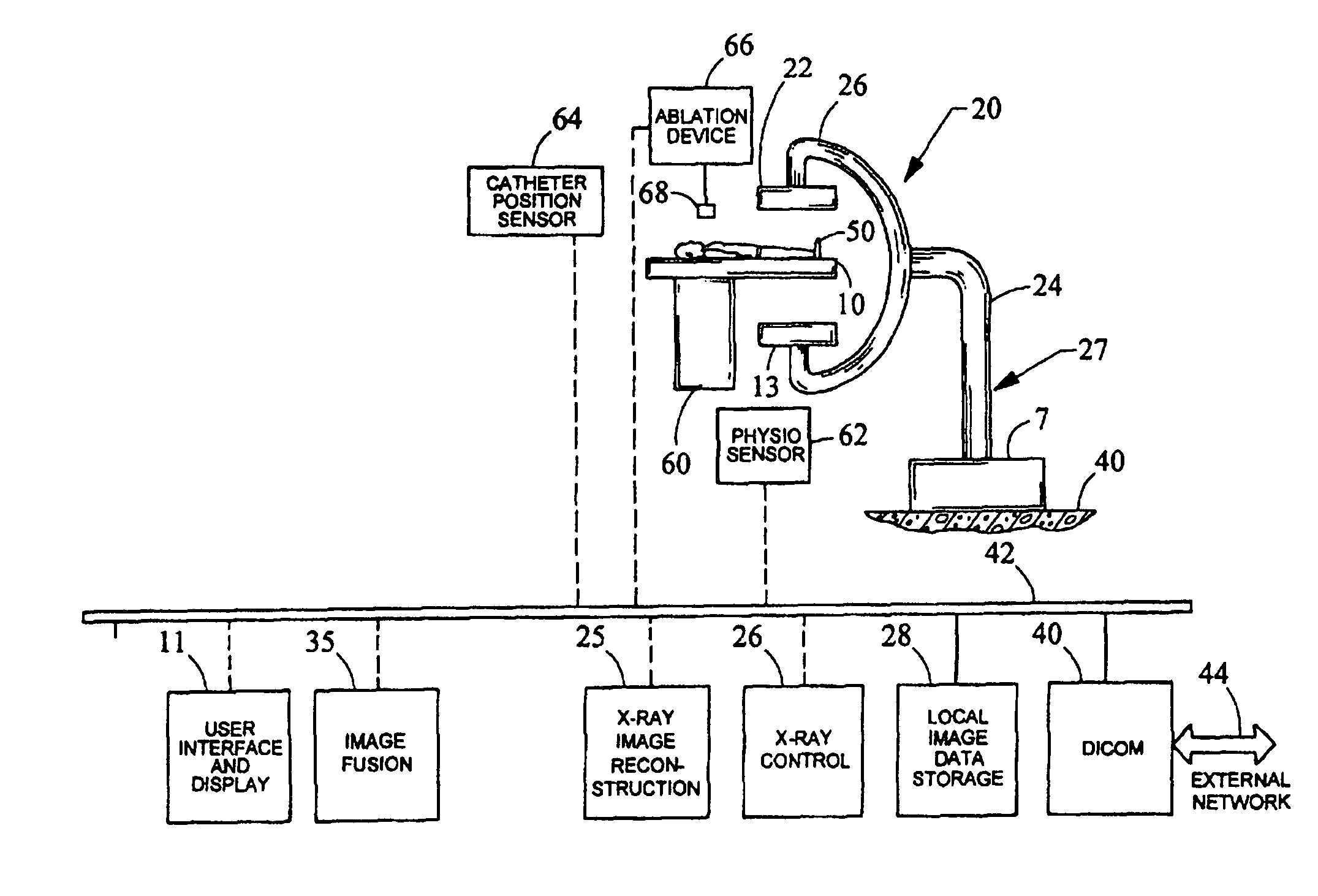
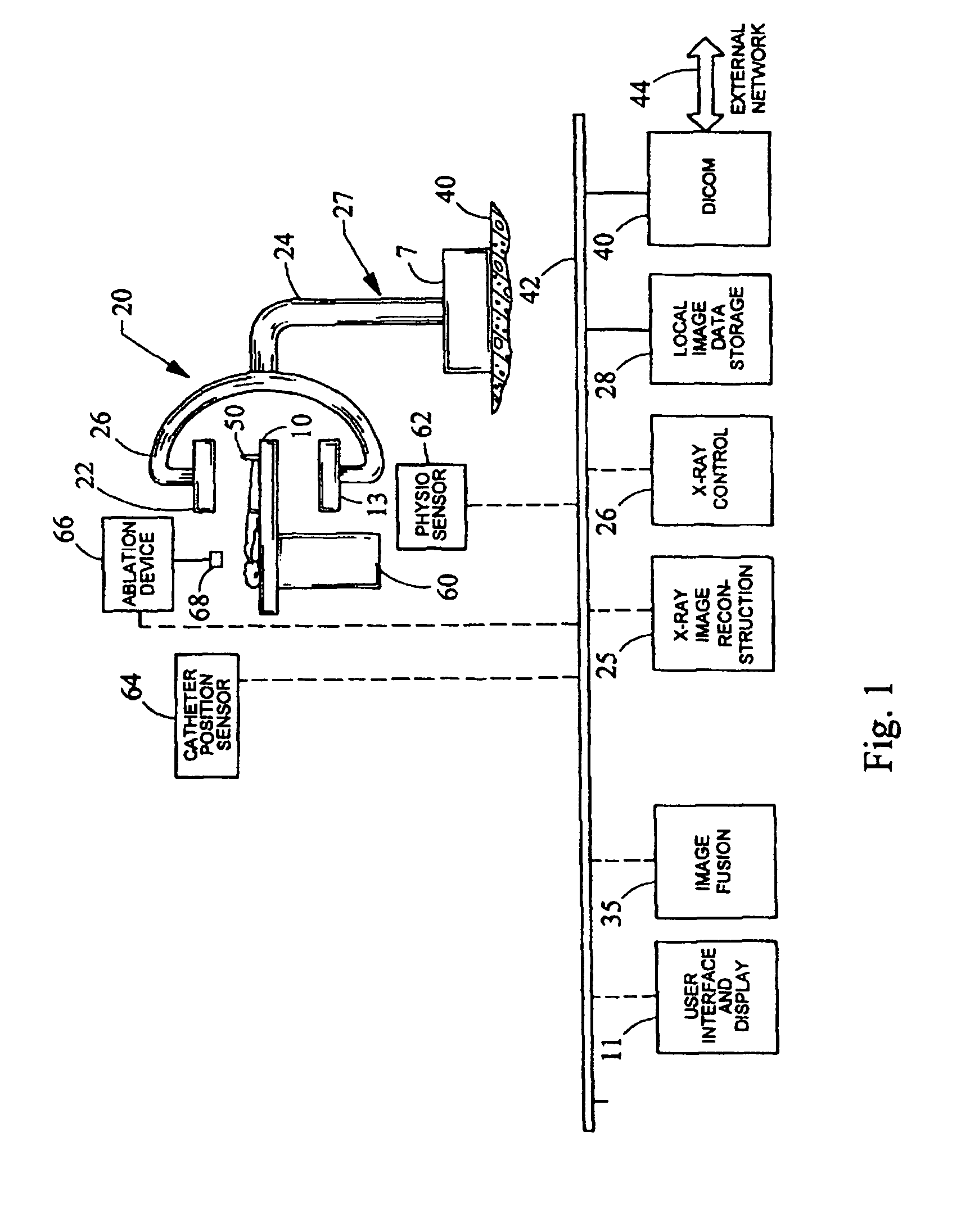
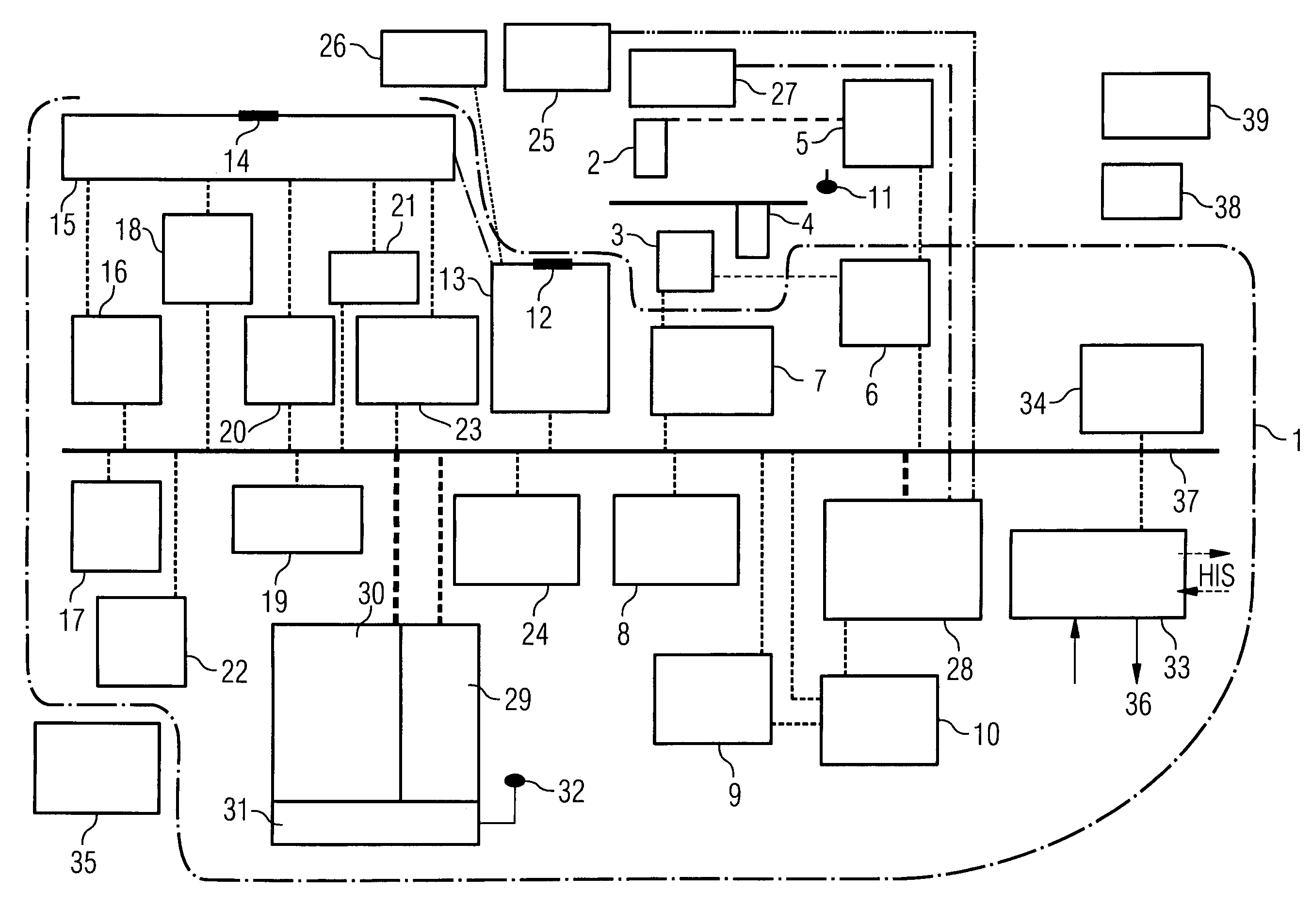
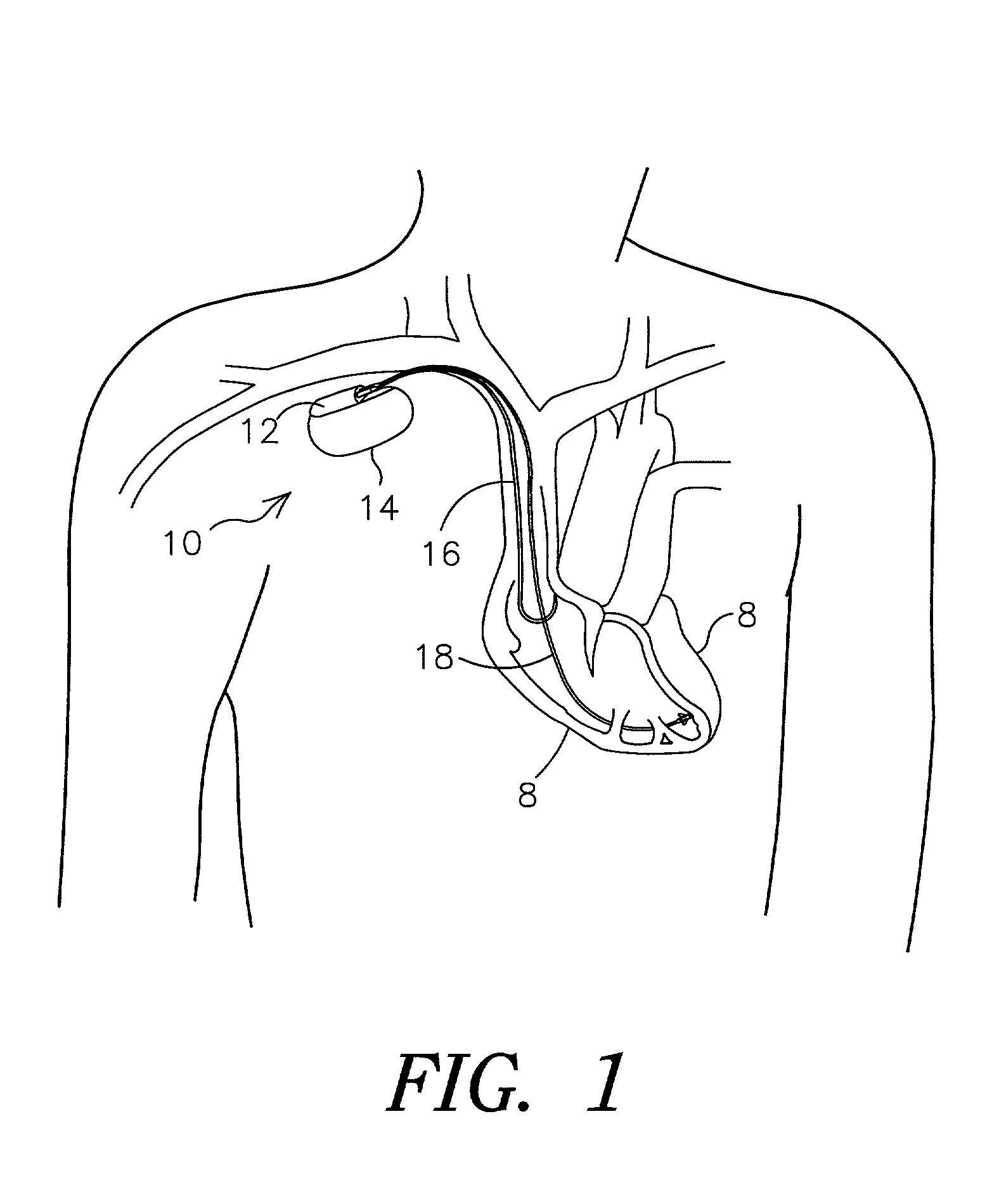
The present invention relates to a system for performing and monitoring minimally invasive interventions with an x-ray unit, in which at least one x-ray source and one x-ray detector can traverse a circular track through an angle range, an ECG recording unit, an imaging catheter, a mapping unit with a mapping catheter and an ablation unit with an ablation catheter. The system comprises a control and evaluation unit with interfaces for the units and catheters, which enable an exchange of data with the control and evaluation unit. The control and evaluation unit is designed for processing measurement or image data which it receives from the catheters and units, and for controlling the catheters and units for the capture of the measurement or image data. The workflow from the examination through to the therapy, particularly with regard to the treatment of tachycardial arrhythmias, is covered completely and continuously by the proposed system.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
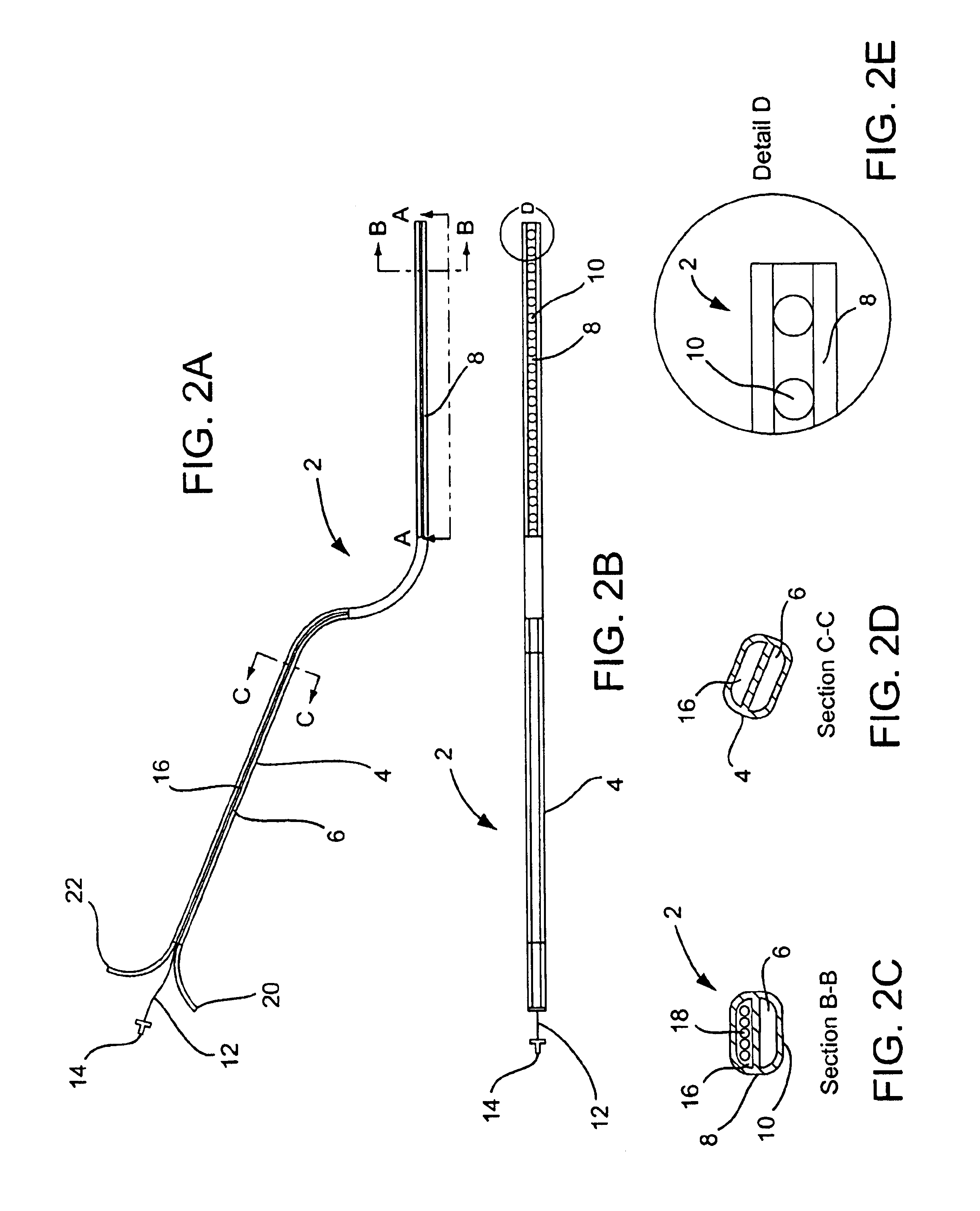
Vacuum coagulation probes
InactiveUS7063698B2Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesRadio frequencyArticular cartilage
An embodiment of the invention includes a surgical device for coagulating soft tissue such as atrial tissue in the treatment of atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and atrial tachycardia; tendon or ligament shrinkage; or articular cartilage removal. The surgical device integrates a suction mechanism with the coagulation mechanism improving the lesion creation capabilities of the device. The surgical device comprises an elongate member having an insulative covering attached about conductive elements capable of coagulating soft tissue when radiofrequency or direct current energy is transmitted to the conductive elements. Openings through the insulative covering expose regions of the conductive elements and are coupled to lumens in the elongate member which are routed to a vacuum source. Suction causes the soft tissue to actively engage the opening thus the integrated, exposed conductive elements to facilitate the coagulation process and ensure the lesions created are consistent, continuous, and transmural. The embodiments of the invention can also incorporate cooling mechanisms associated with the conductive elements and coupled to a fluid source to passively transport fluid along the contacted soft tissue surface to cool thus pushing the maximum temperature deeper into tissue.
Owner:ATRICURE
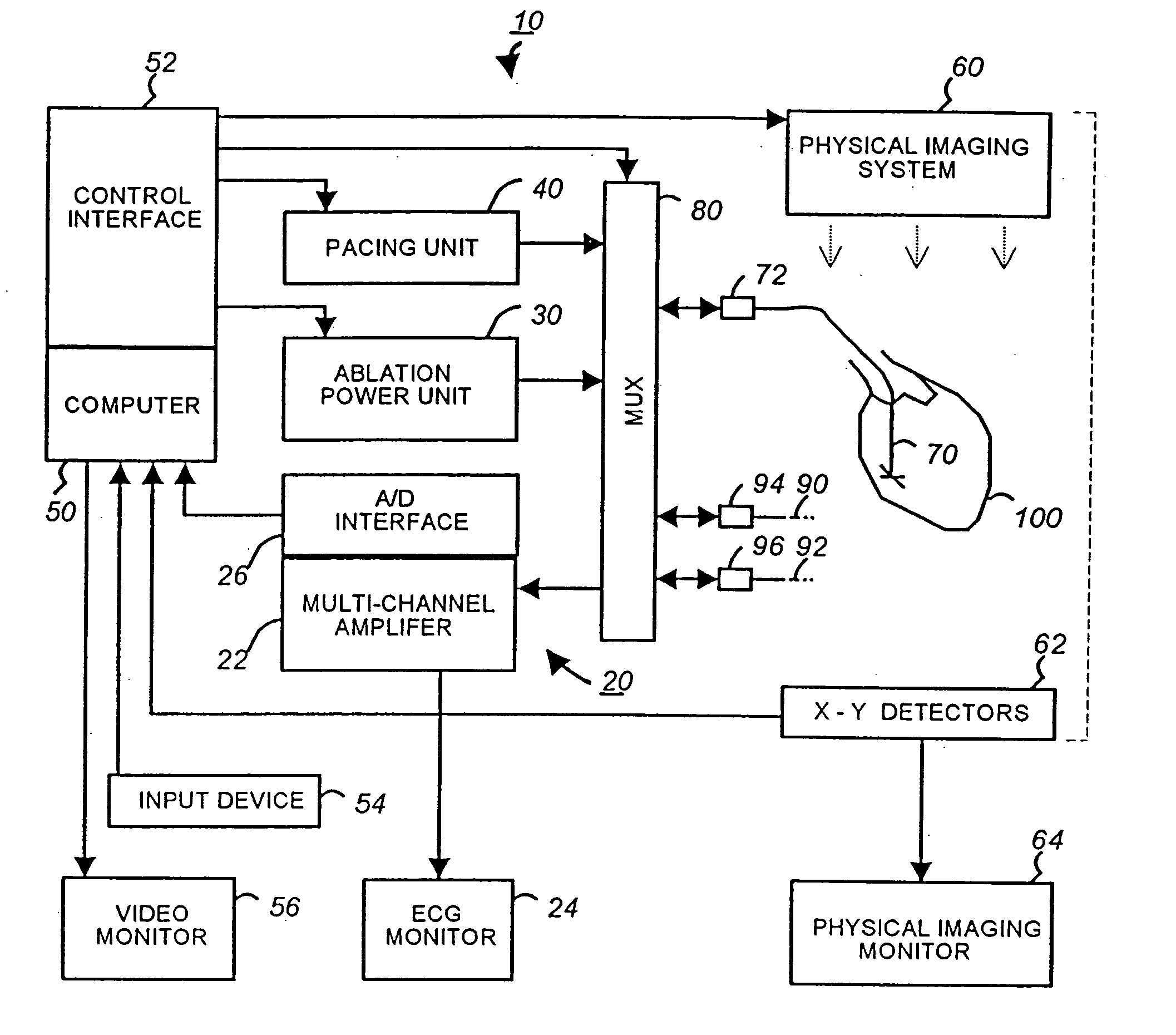
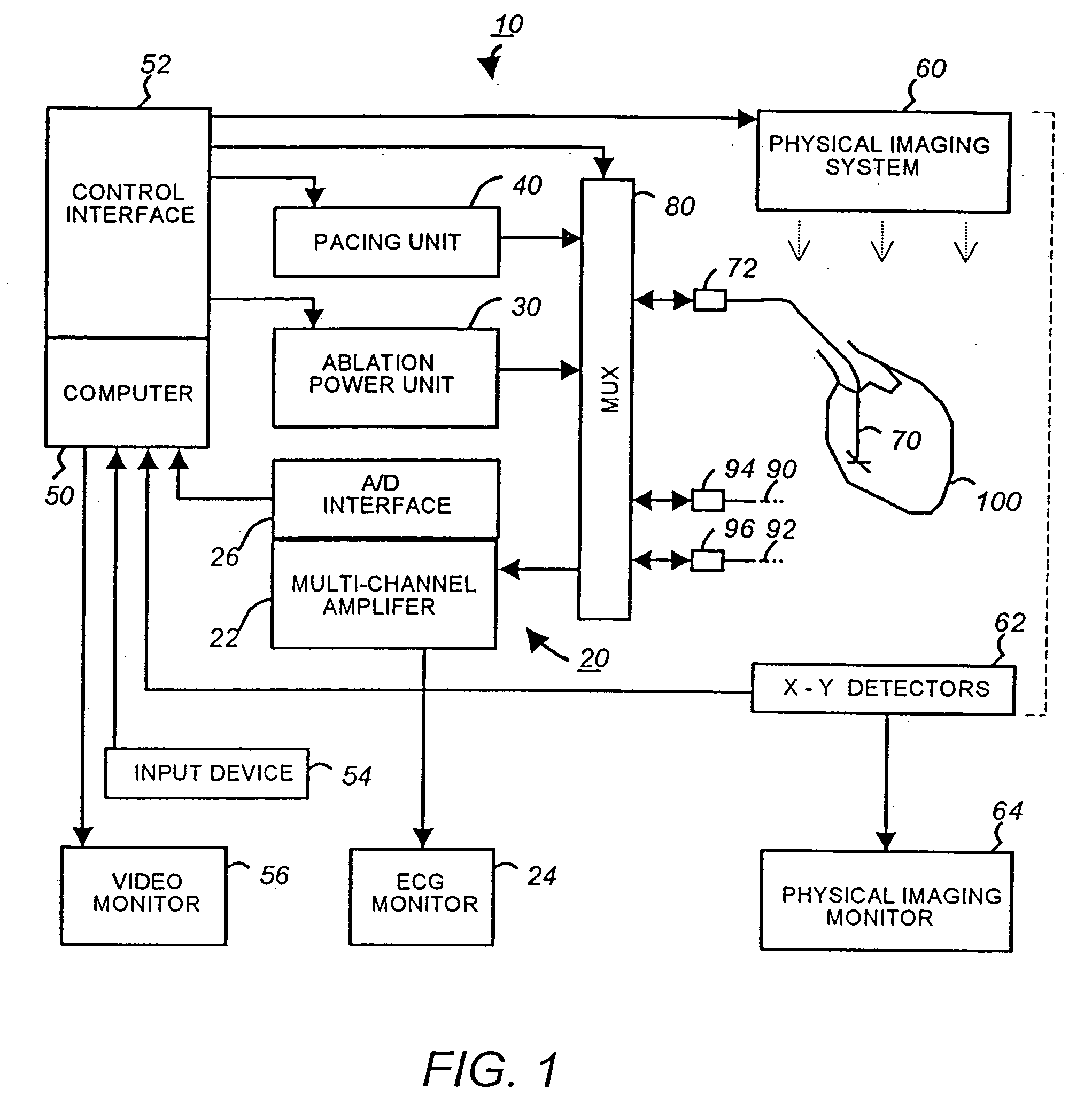
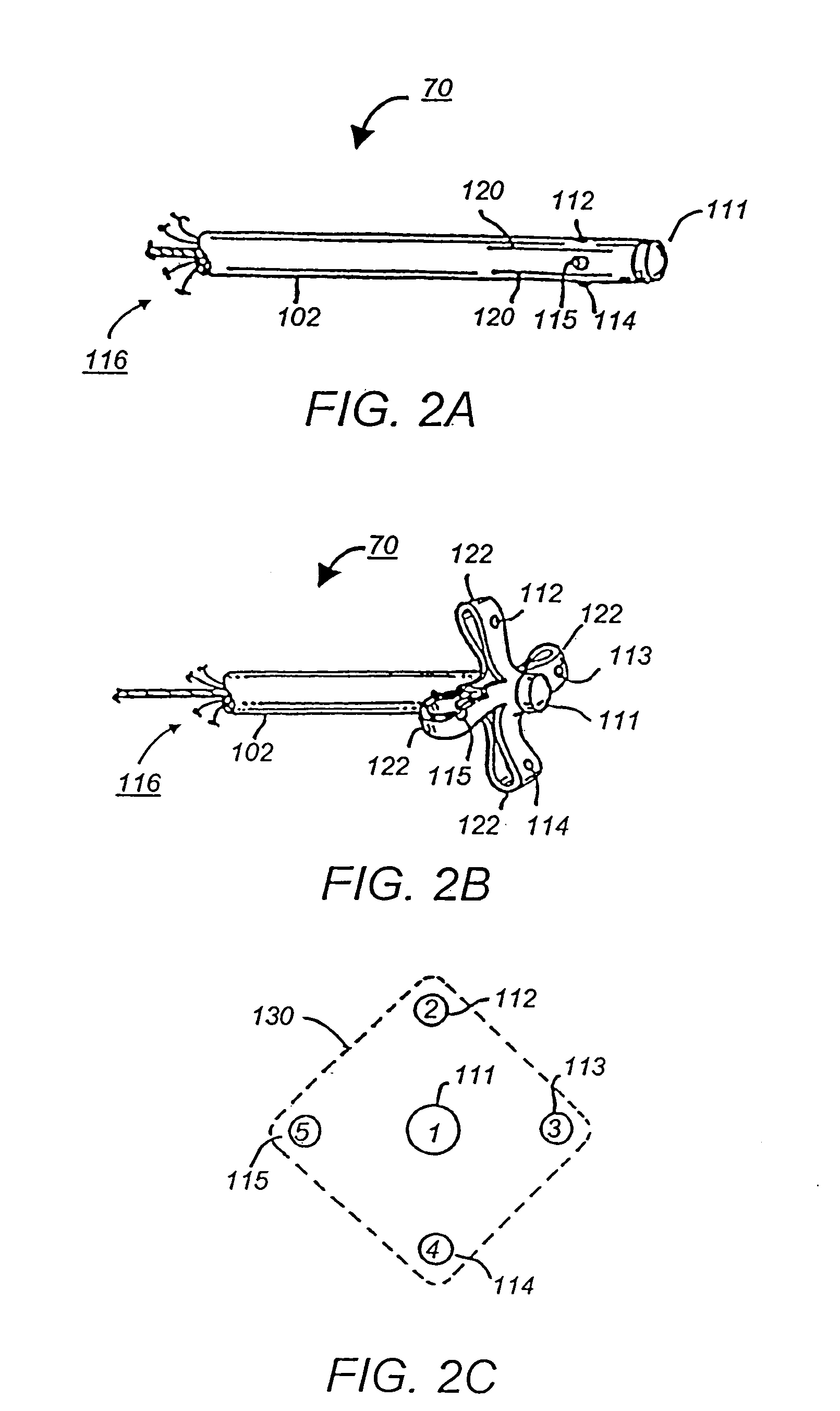
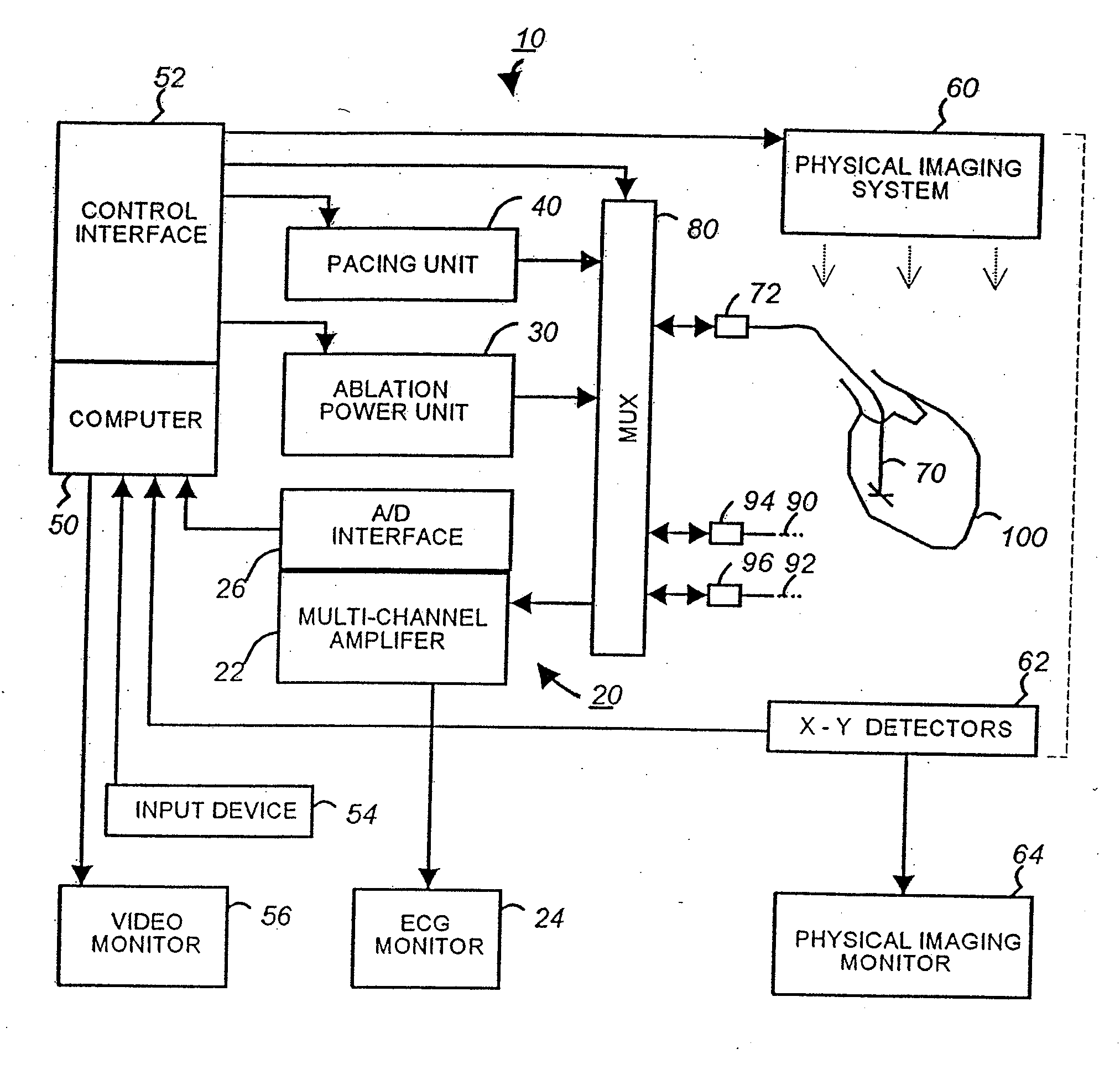
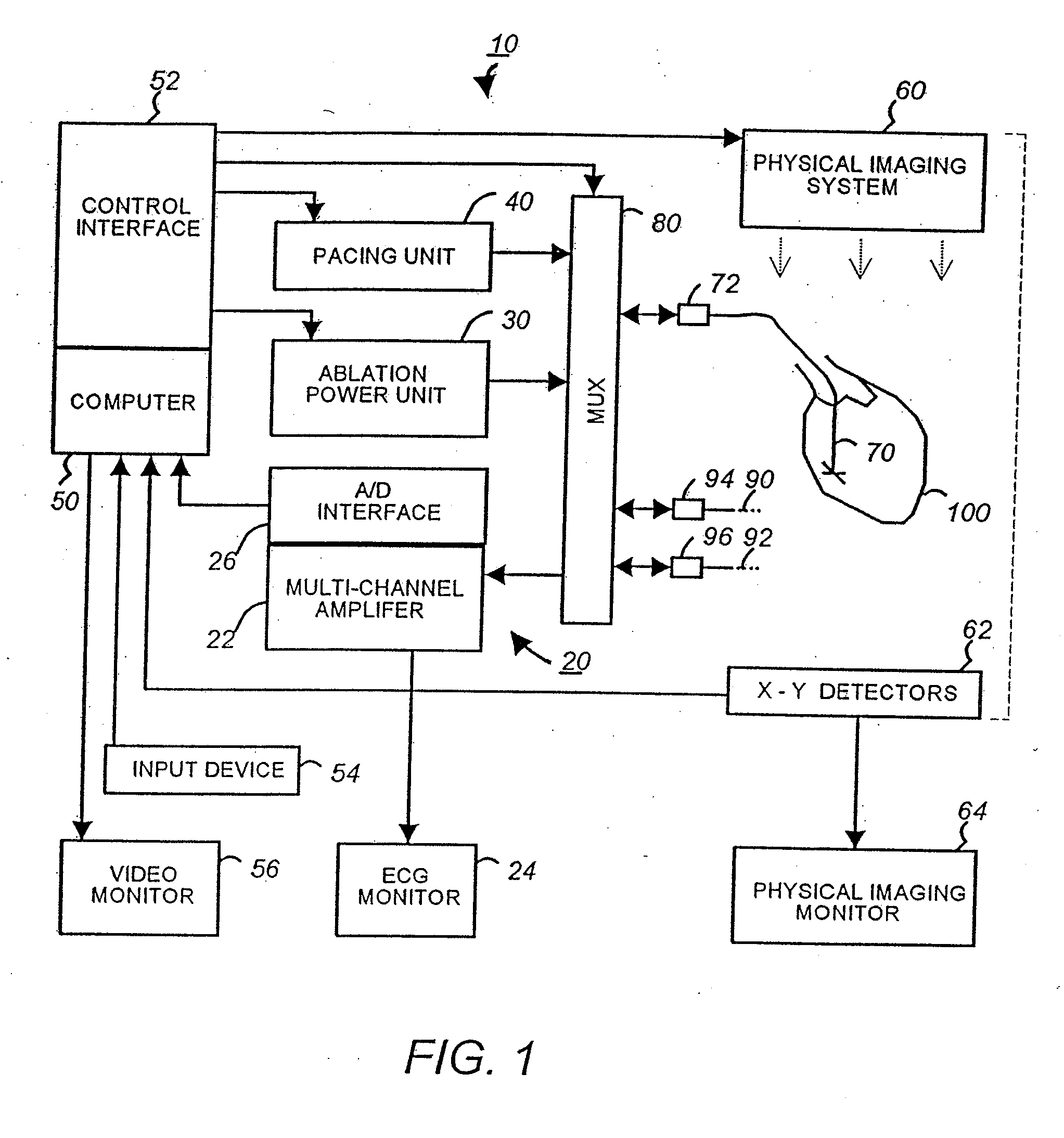
Apparatus and method for cardiac ablation
InactiveUS20050148892A1ElectrocardiographyControlling energy of instrumentVisual perceptionIntracardiac Electrogram
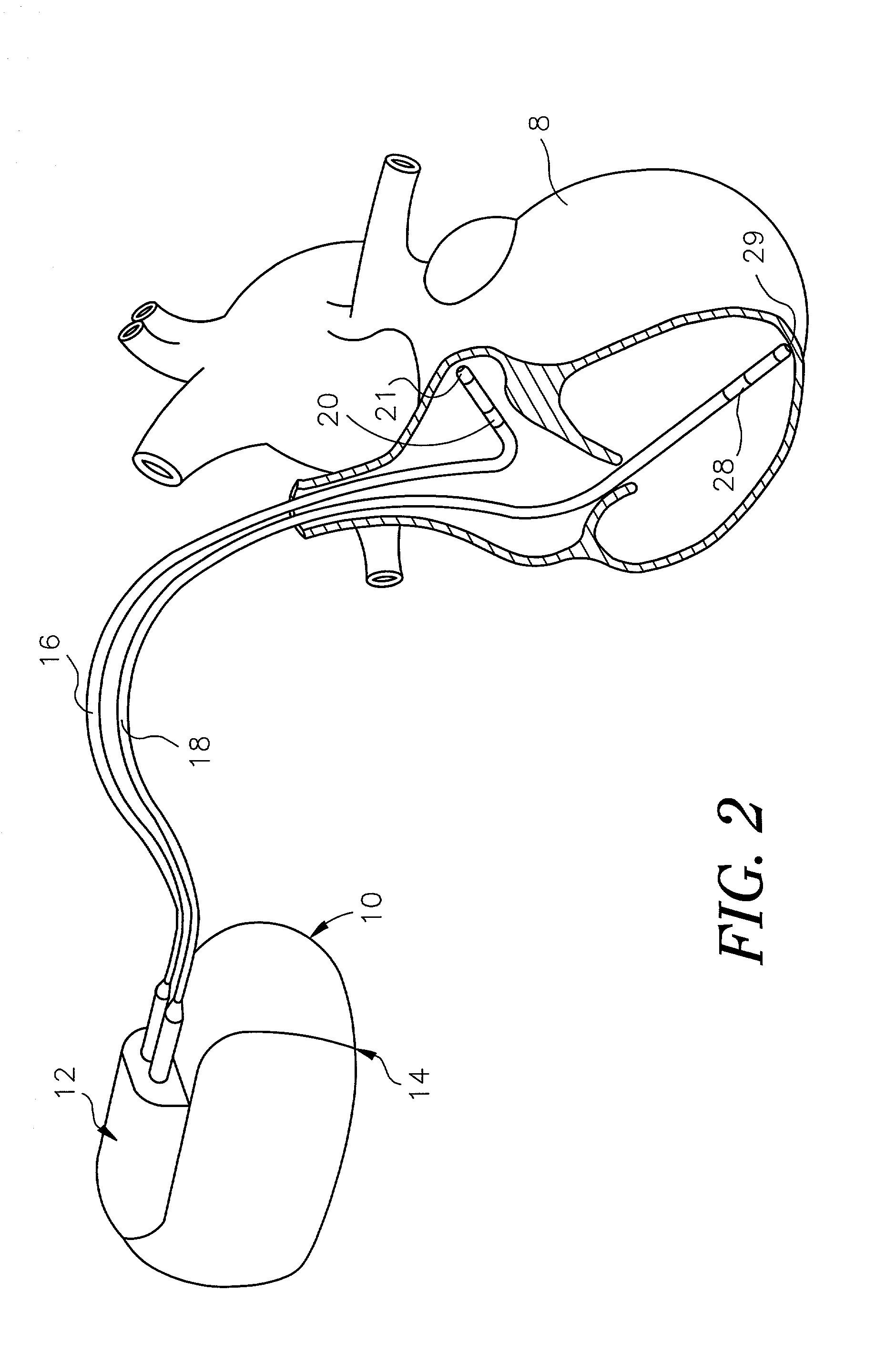
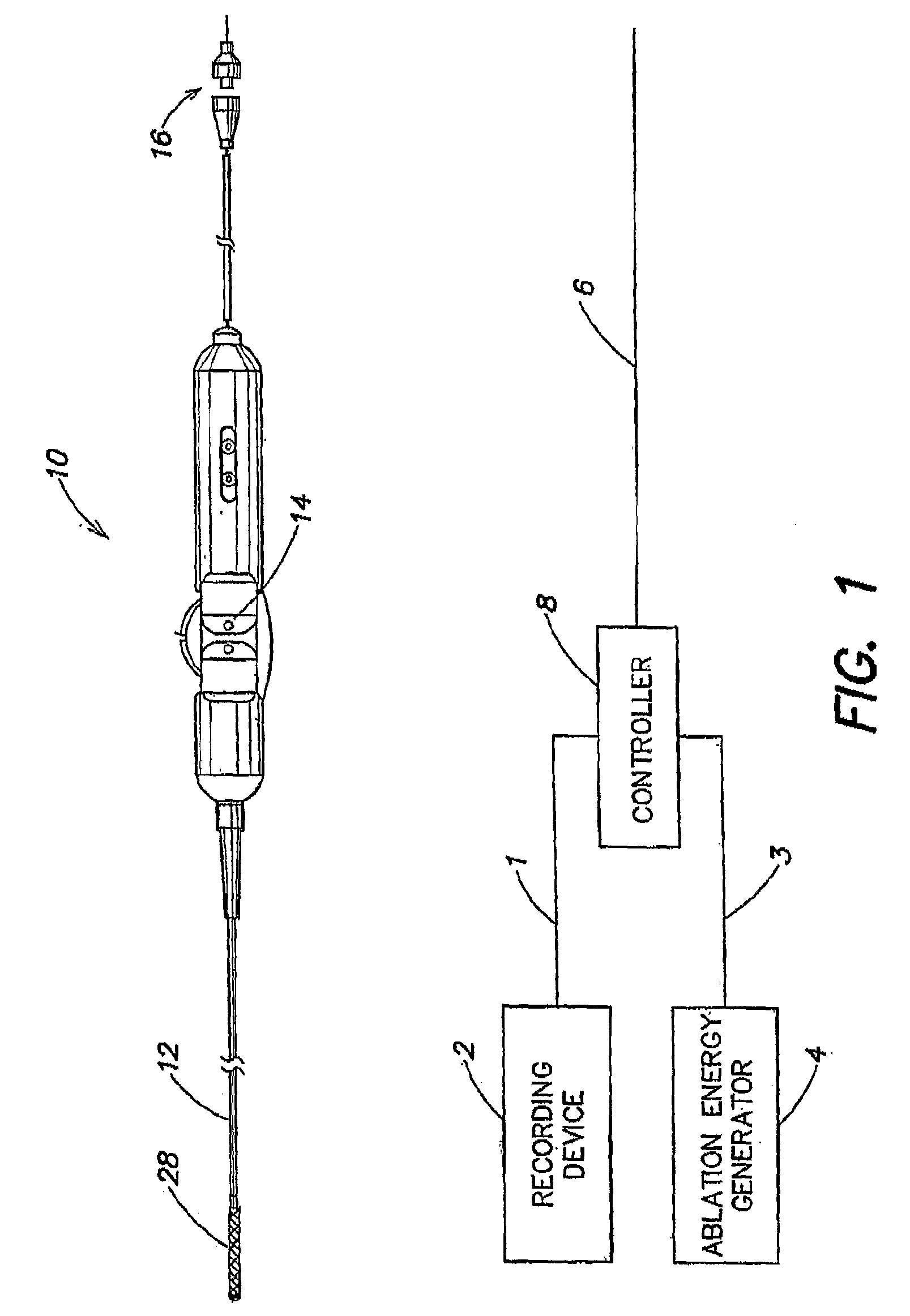
A system and method for cardiac mapping and ablation include a multi-electrode catheter introduced percutaneously into a subject's heart and deployable adjacent to various endocardial sites. The electrodes are connectable to a mapping unit, an ablation power unit a pacing unit, all of which are under computer control. Intracardiac electrogram signals emanated from a tachycardia site of origin are detectable by the electrodes. Their arrival times are processed to generate various visual maps to provide real-time guidance for steering the catheter to the tachycardia site of origin. In another aspect, the system also include a physical imaging system which is capable of providing different imaged physical views of the catheter and the heart. These physical views are incorporated into the various visual maps to provide a more physical representation. Once the electrodes are on top of the tachycardia site of origin, electrical energy is supplied by the ablation power unit to effect ablation.
Owner:DESAI JAWAHAR M
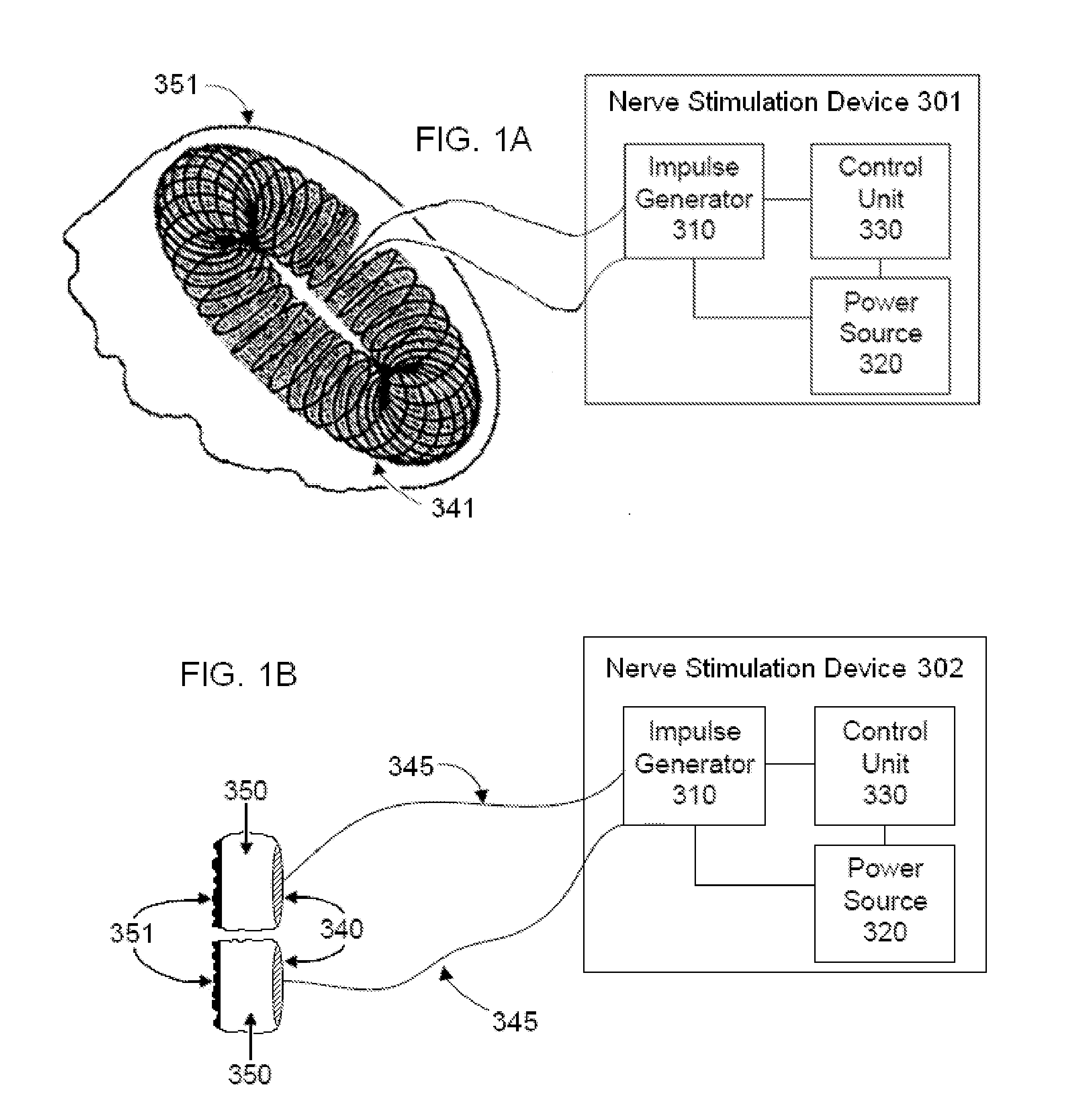
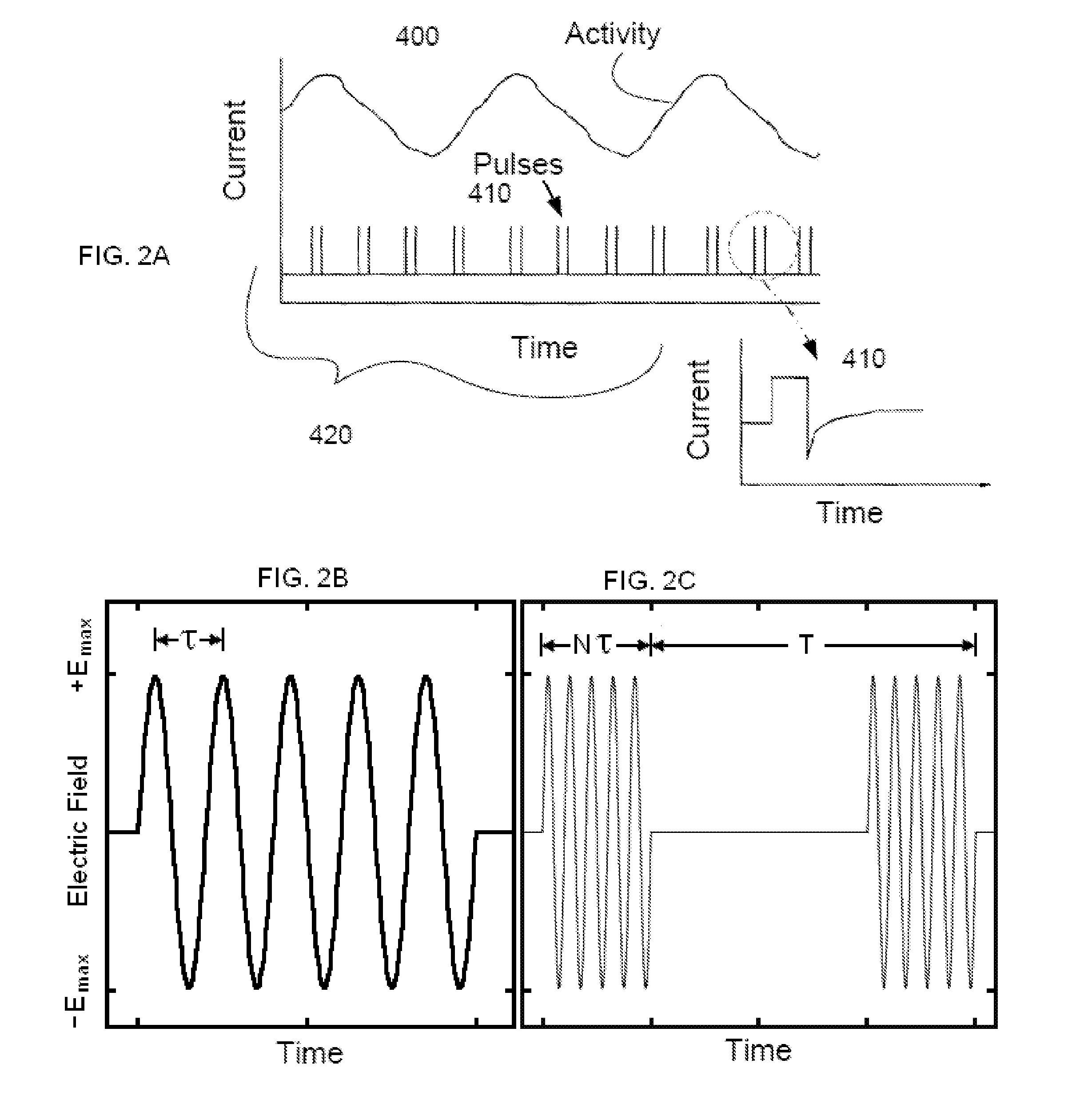
Nerve stimulation methods for averting imminent onset or episode of a disease
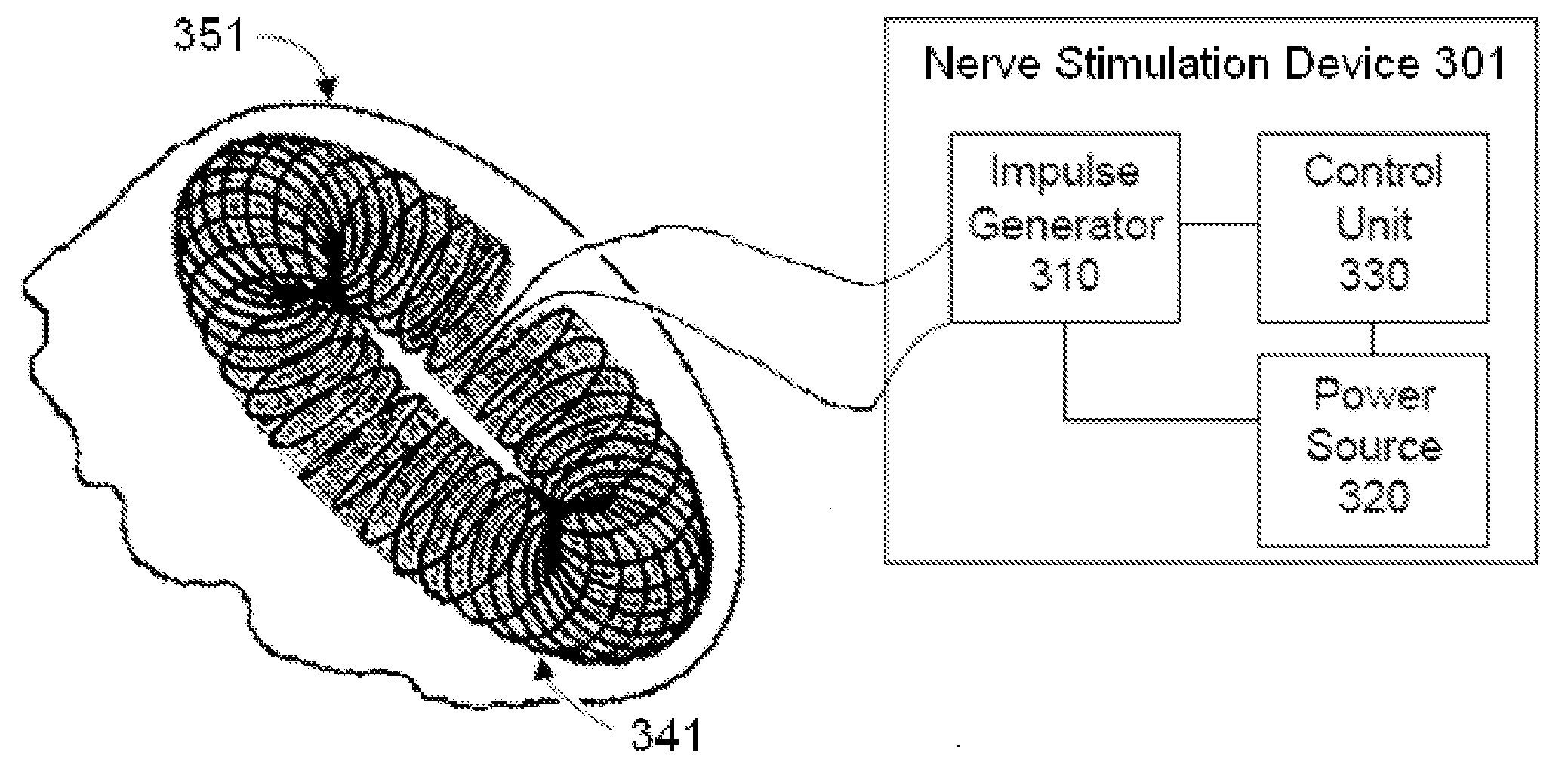
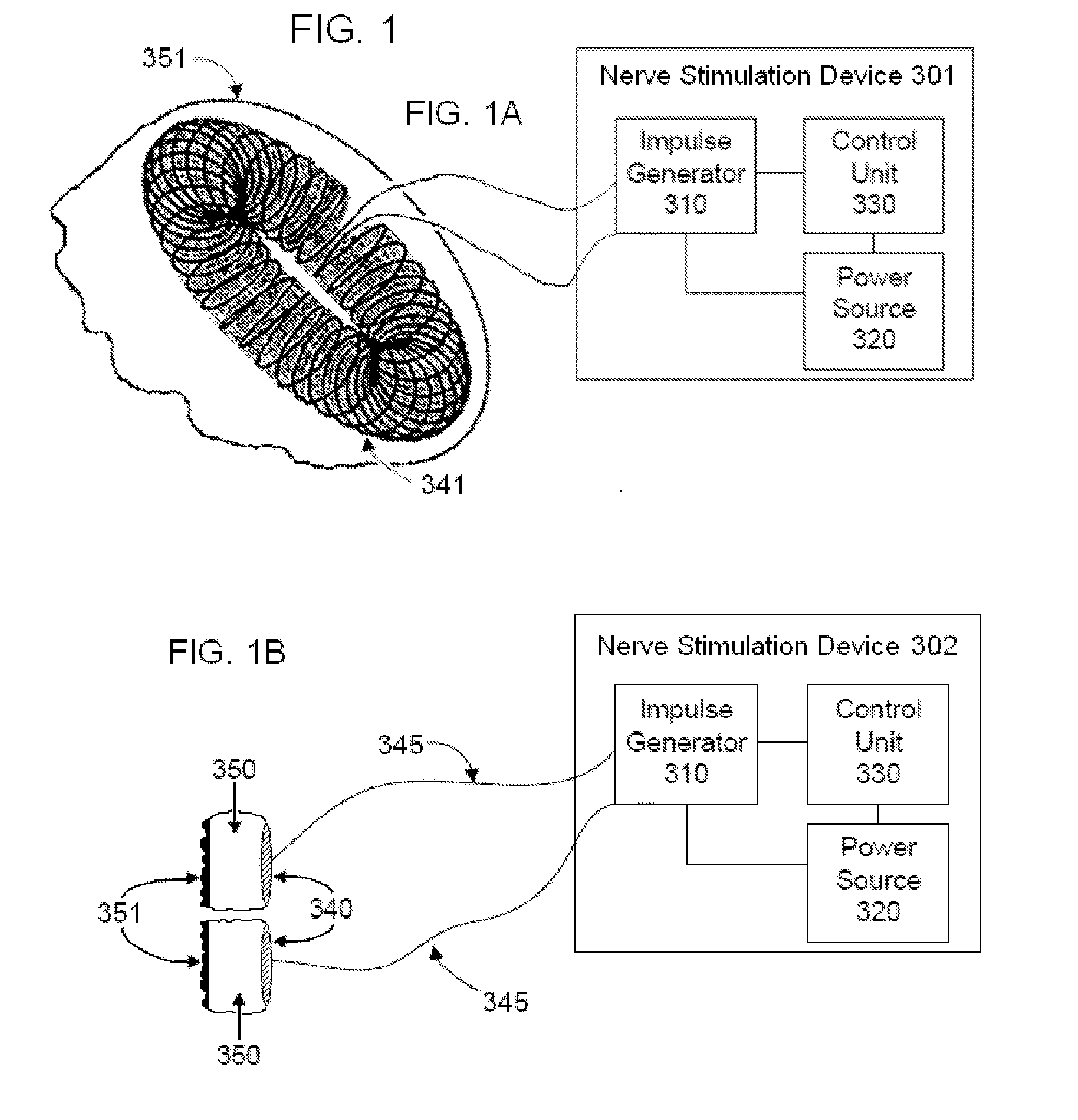
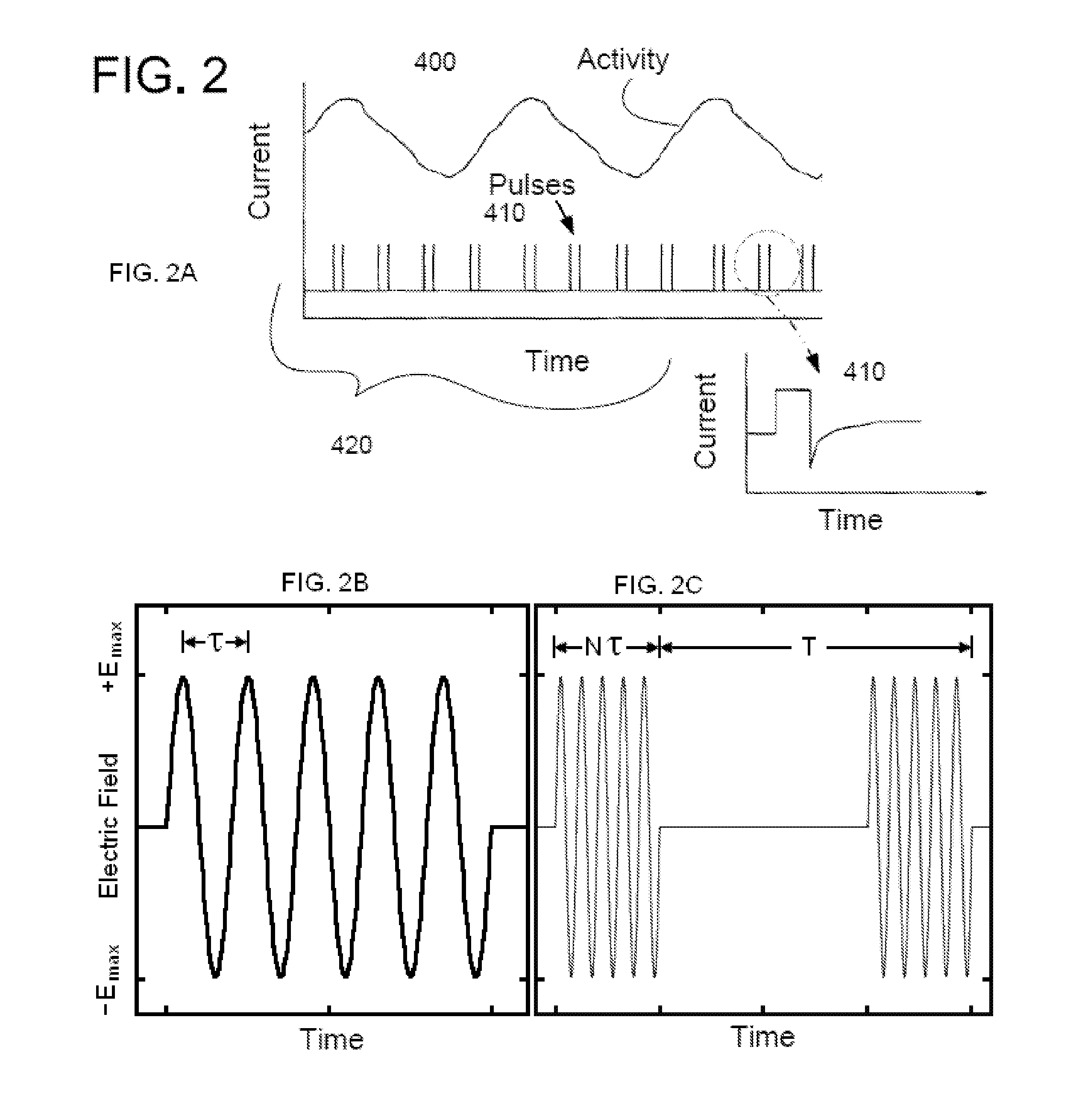
Transcutaneous electrical and magnetic nerve stimulation devices are disclosed, along with methods of averting imminent medical attacks using energy that is delivered noninvasively by the devices. The attacks comprise asthma attack, epileptic seizure, attacks of migraine headache, transient ischemic attack or stroke, onset of atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, onset of ventricular fibrillation or tachycardia, panic attack, and attacks of acute depression. The imminence of an attack is forecasted using grey-box or black-box models as used in control theory. In preferred embodiments of the disclosed methods, a vagus nerve in the neck of a patient is stimulated noninvasively to avert the attack.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
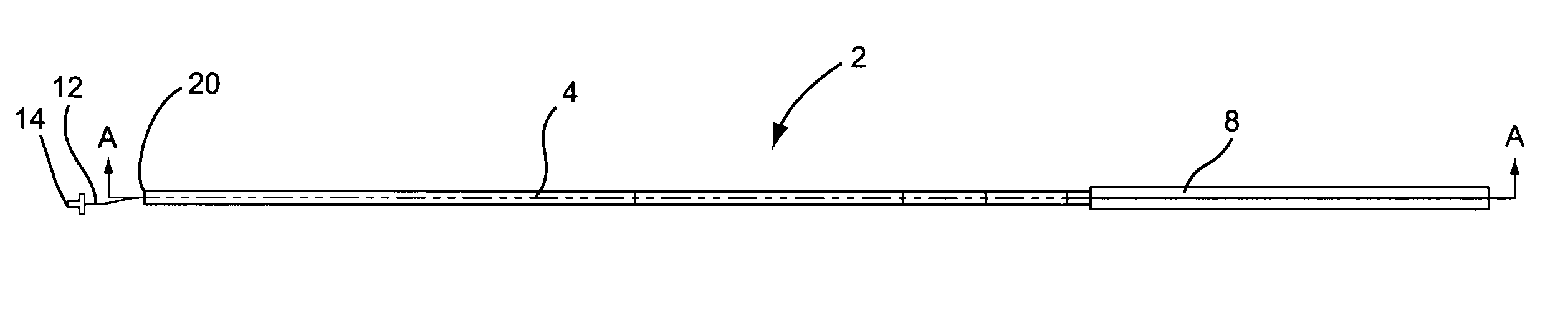
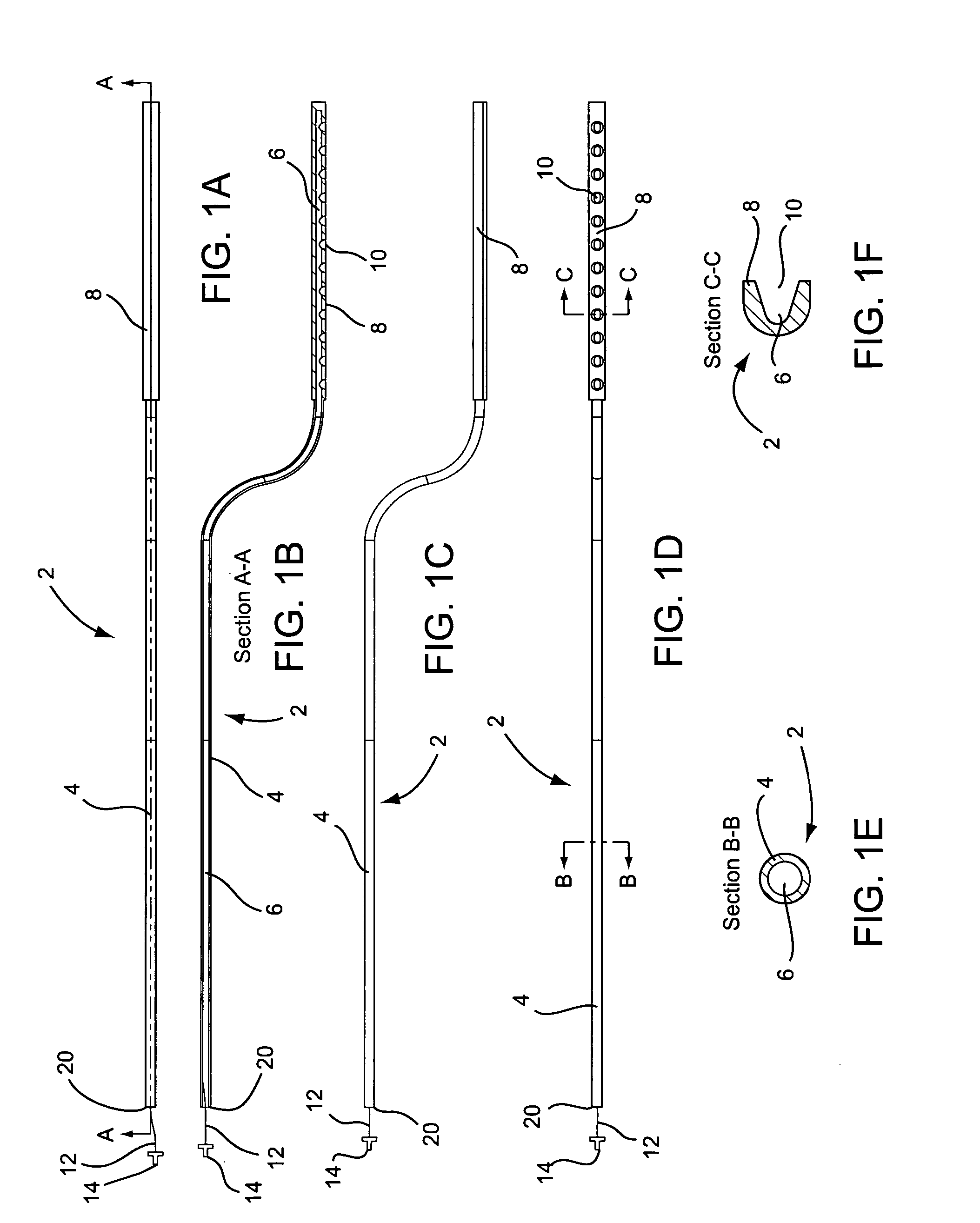
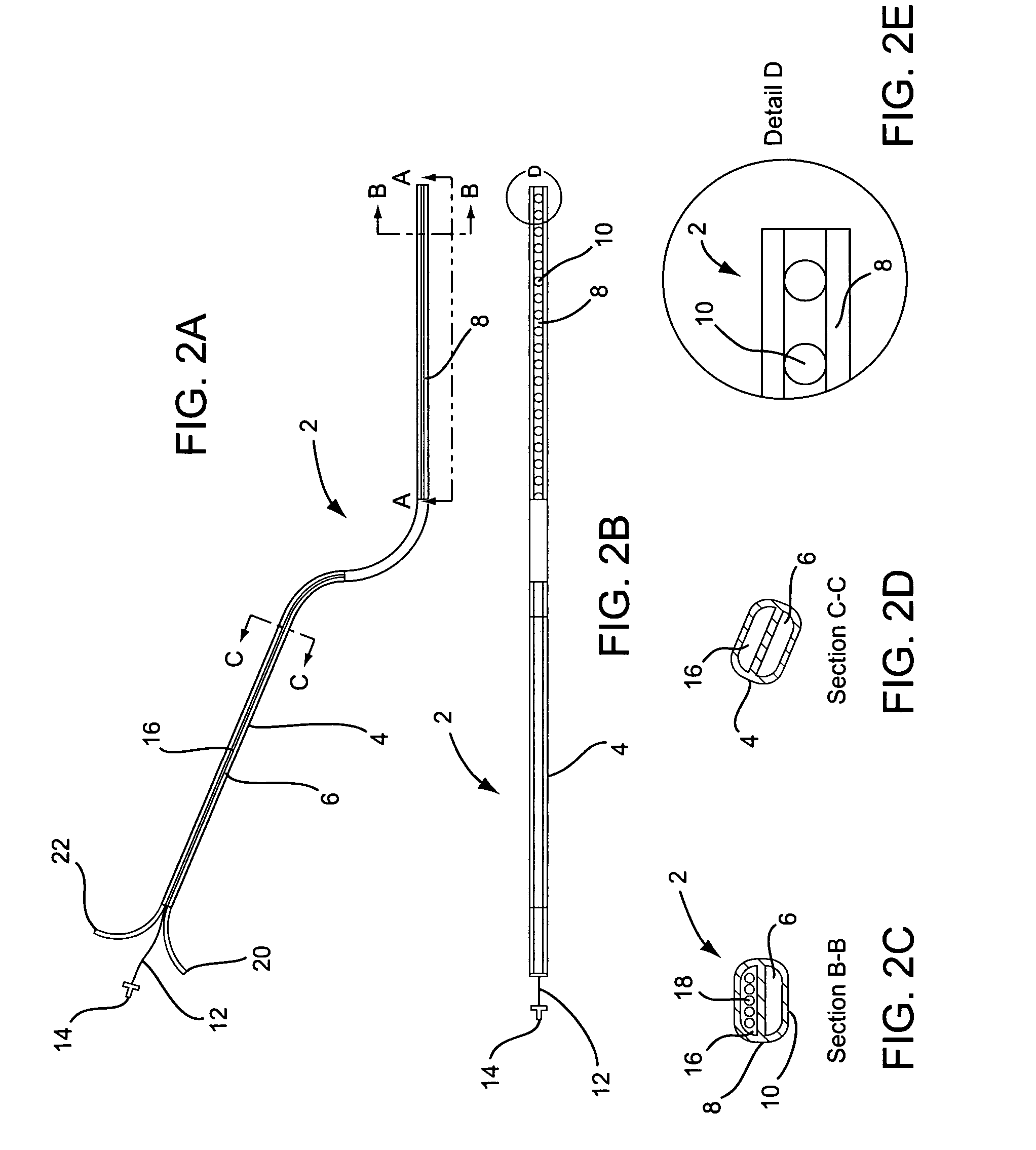
Classification of supraventricular and ventricular cardiac rhythms using cross channel timing algorithm
InactiveUS6889081B2ElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisCardiac cycleVentricular tachycardia
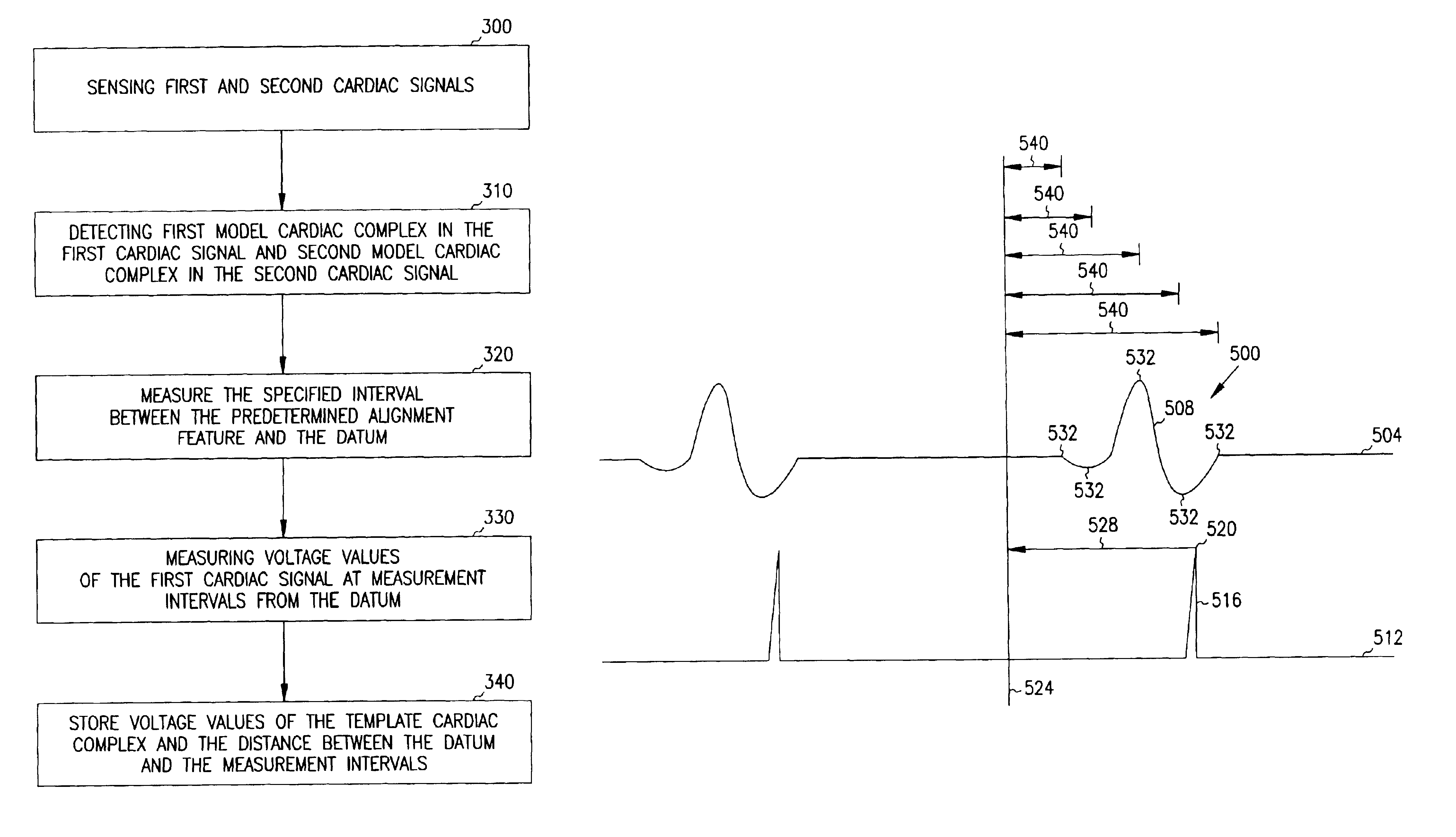
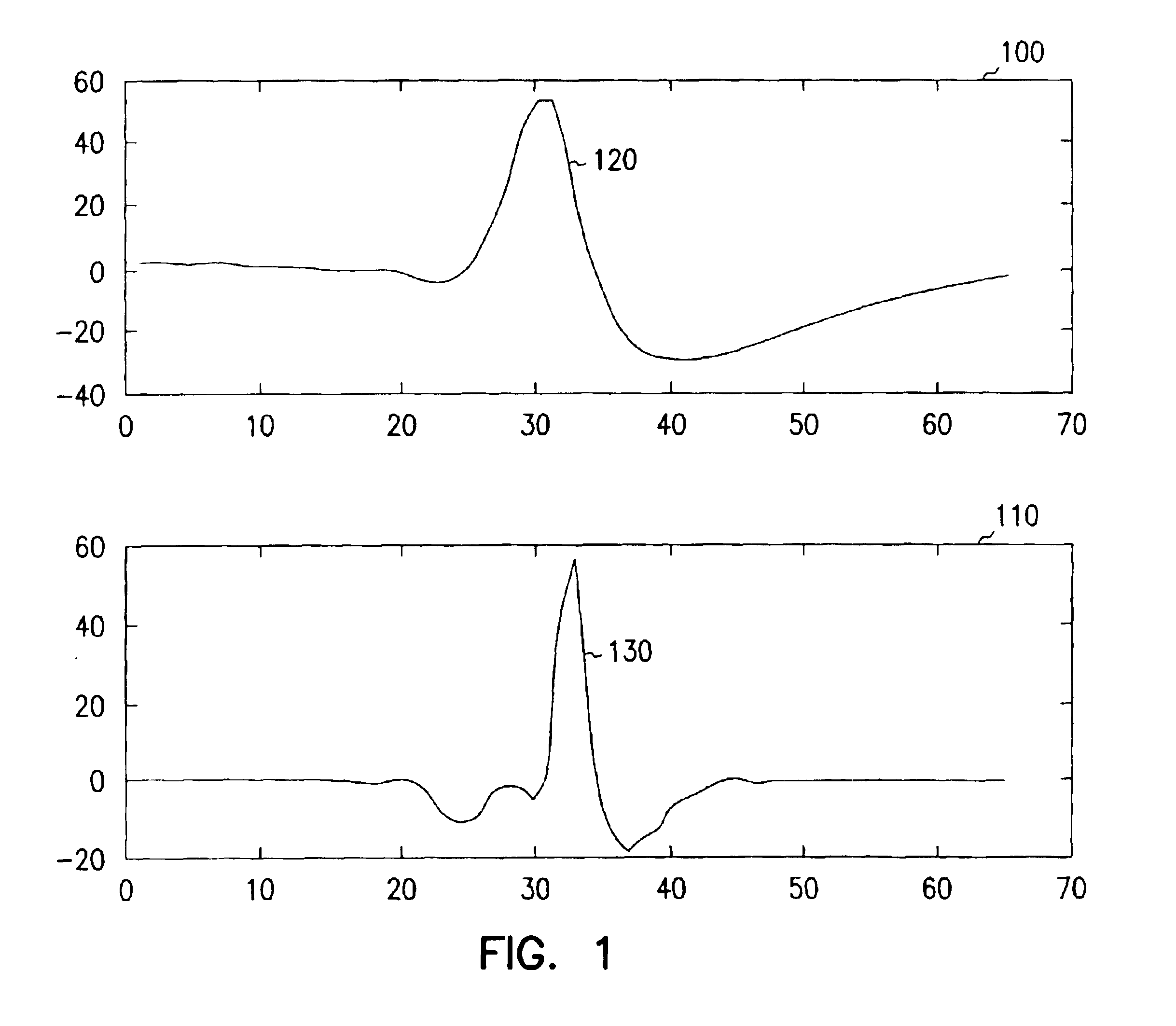
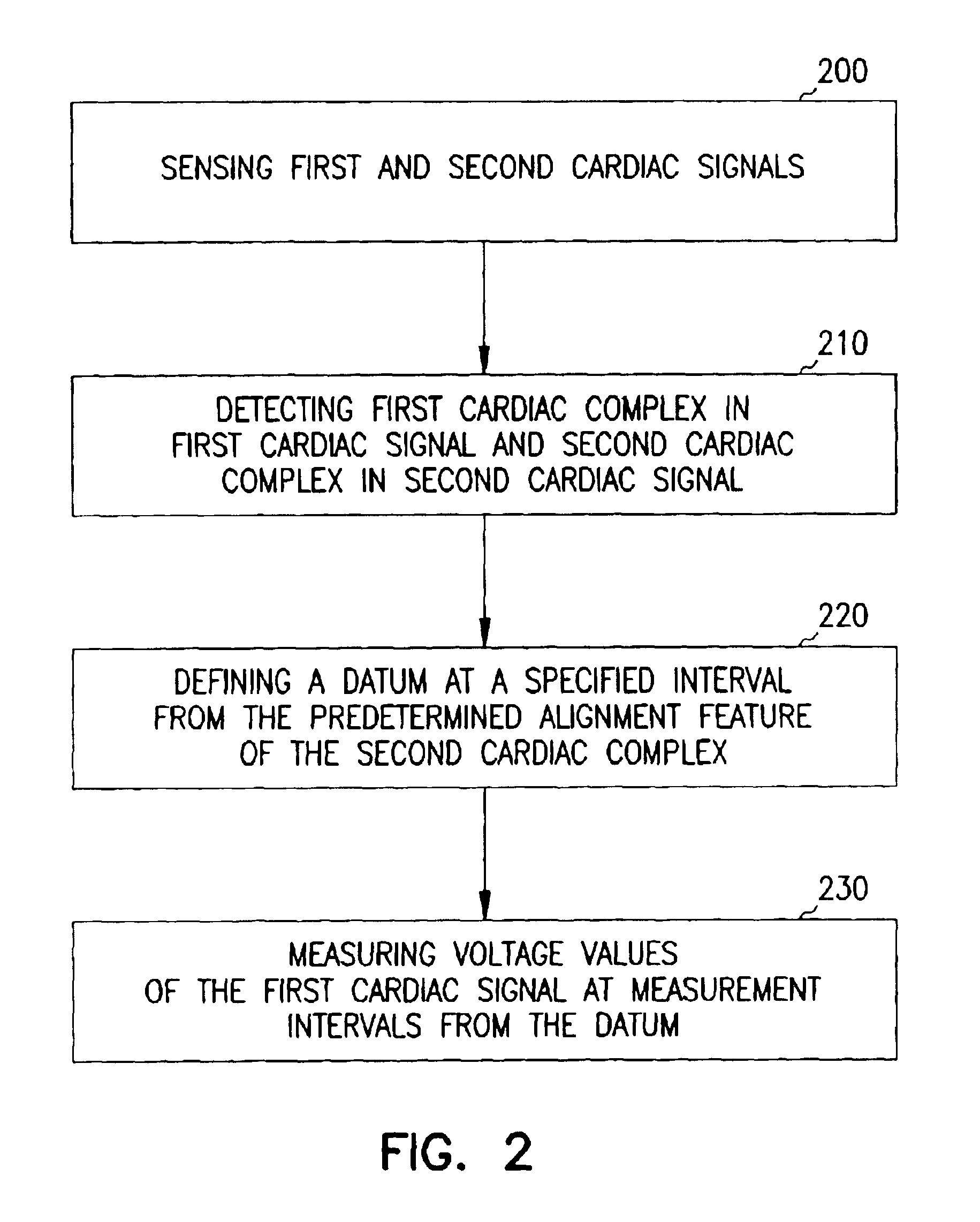
A system and method for classifying cardiac complexes sensed during a tachycardia episode. A first cardiac signal and a second cardiac signal are sensed, where the first cardiac signal has a voltage. A first cardiac complex and a second cardiac complex of a cardiac cycle are detected in the first and second cardiac signal, respectively. A predetermined alignment feature is identified in the second cardiac complex. A datum is defined, or positioned, at a specified interval from the predetermined alignment feature of the second cardiac complex. Voltage values are then measured from the first cardiac complex at each of two or more measurement intervals from the datum. The voltage values are then compared voltage values measured from NSR cardiac complexes to classify the first cardiac complex is either a ventricular tachycardia complex or a supraventricular tachycardiac complex.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Vacuum coagulation probe for atrial fibrillation treatment
InactiveUS6893442B2Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesLess invasiveRadio frequency
An embodiment of the invention includes a surgical device for coagulating soft tissue such as atrial tissue in the treatment of atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and atrial tachycardia. The surgical device can include at least one elongate member comprising conductive elements adapted to coagulate soft tissue when radiofrequency or direct current energy is transmitted to the conductive elements. Openings through said conductive elements are routed through lumens in the elongate member to a vacuum source to actively engage the soft tissue surface intended to coagulate into intimate contact with the conductive elements to facilitate the coagulation process and ensure the lesions created are consistent, contiguous, and transmural. The embodiments of the invention can also incorporate cooling openings positioned near the conductive elements and coupled with a vacuum source or an injection source to transport fluid through the cooling openings causing the soft tissue surface to cool thus pushing the maximum temperature deeper into tissue. The embodiments of the invention can also incorporate features to tunnel between anatomic structures or dissect around the desired tissue surface to coagulate thereby enabling less invasive positioning of the soft tissue coagulating device and ensuring reliable and consistent heating of the soft tissue.
Owner:ATRICURE
Heart disease detection patch
InactiveUS20060030782A1Inexpensive and simple to useSuitable for self-administrationElectrocardiographySensorsFibrillationNon invasive
The invention provides a disposable sensor patch for the non-invasive detection of heart disease. The patch is placed on a person's chest area for automatic analysis of ECG. The heart condition is indicated via an indicator integrated within the patch. The patch is inexpensive and simple for self-administration. In one embodiment, the status of the heart is indicated via multiple LEDs. The detection and indication typically occurs, within 24 hours or sooner if a condition is readily identifiable. The patch is thin, flexible, and incorporates a battery, ECG amplifier, and a processor for analyzing ECG waveform and indicating the heart condition. A software algorithm searches for a cardiac abnormality such as arrhythmia, bradycardia, tachycardia, fibrillation, mycocardial infarction, ischemia, long-QT syndrome, blocks, late potentials, and premature contractions. In another embodiment, results and relevant ECG data are stored in memory for later retrieval.
Owner:CARDIOVU
In vivo simulator for microwave treatment
InactiveUS6175768B1Reduce the possibilityWide bandwidthElectrotherapyLavatory sanitoryPeristaltic pumpVentricular tachycardia
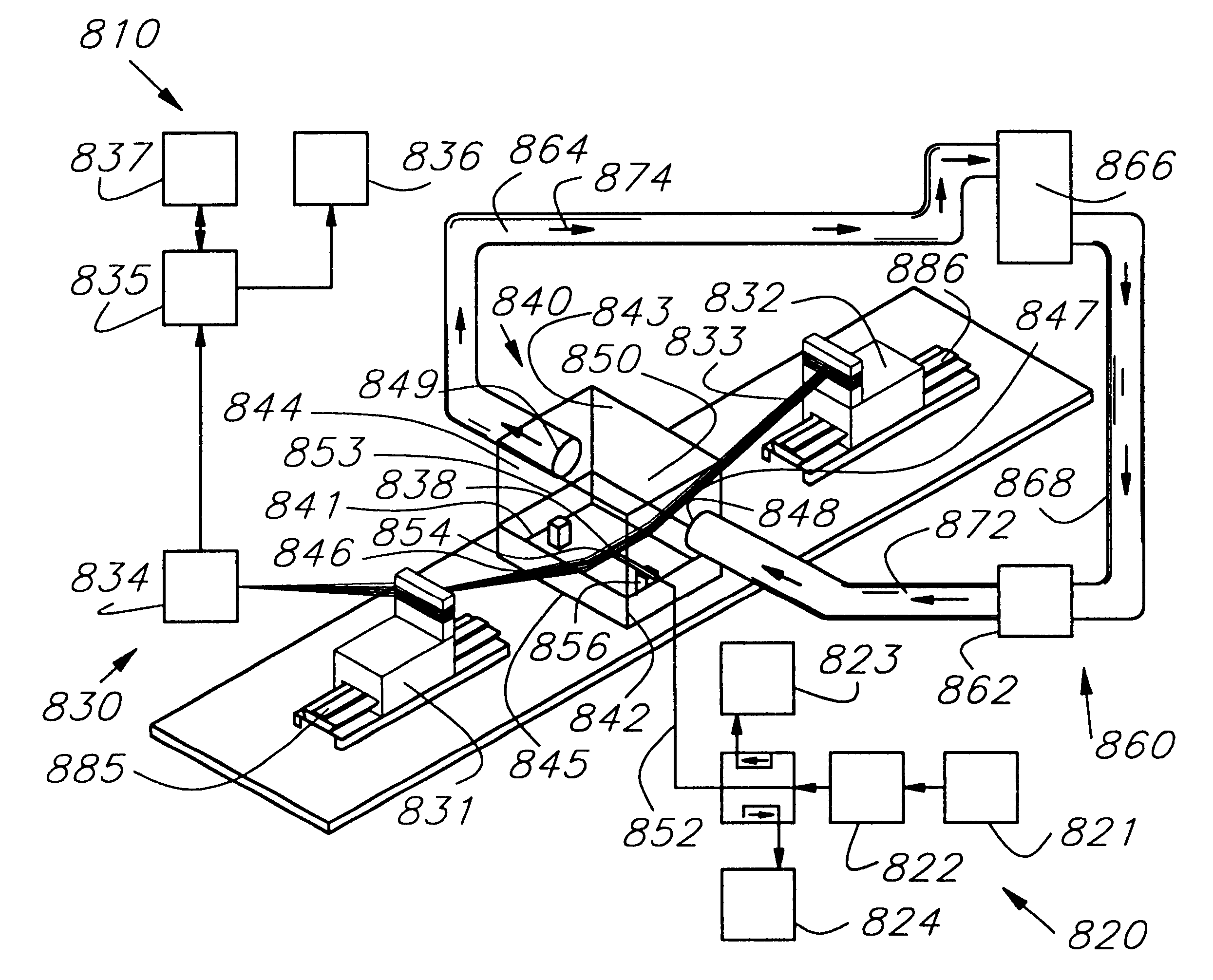
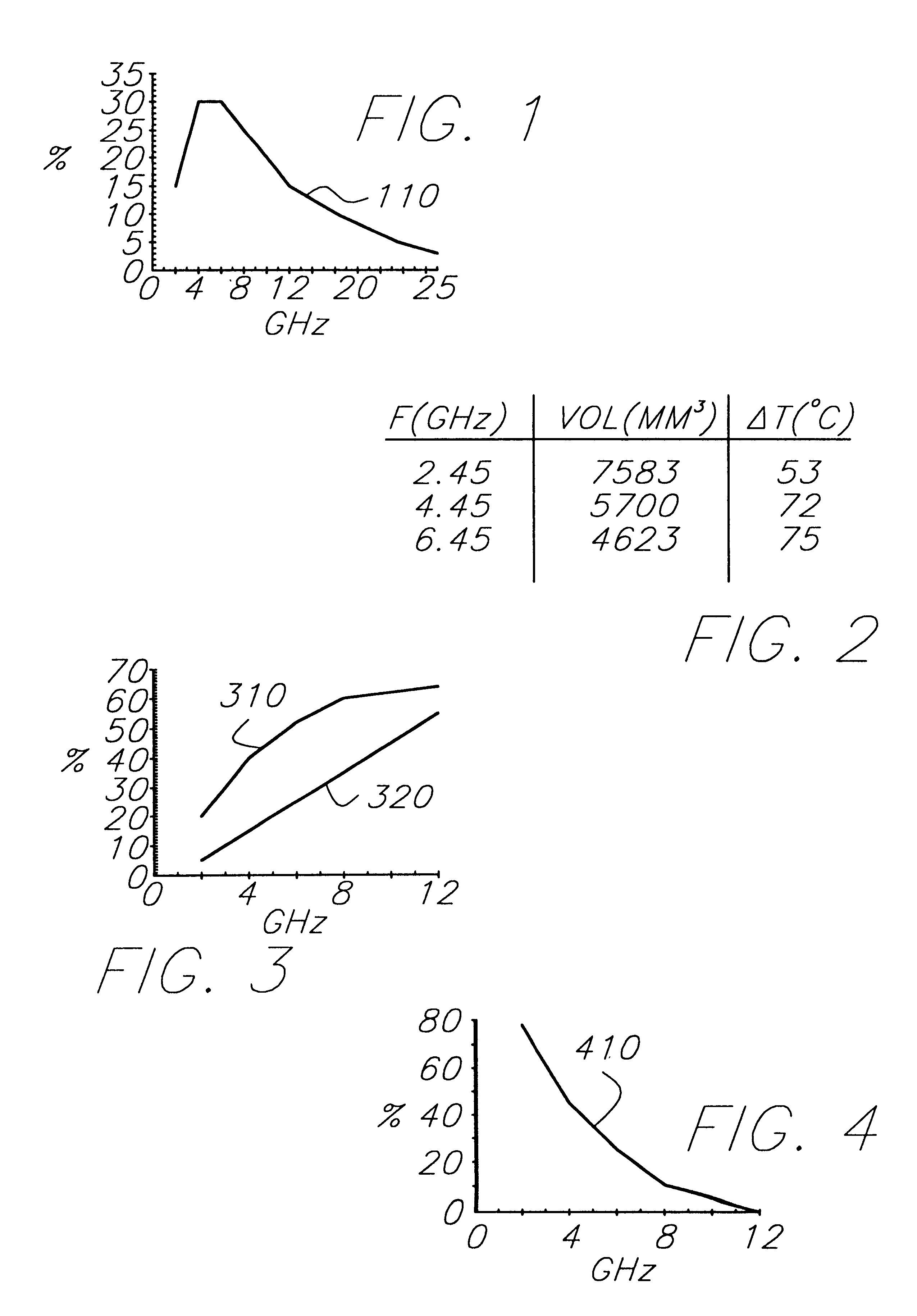
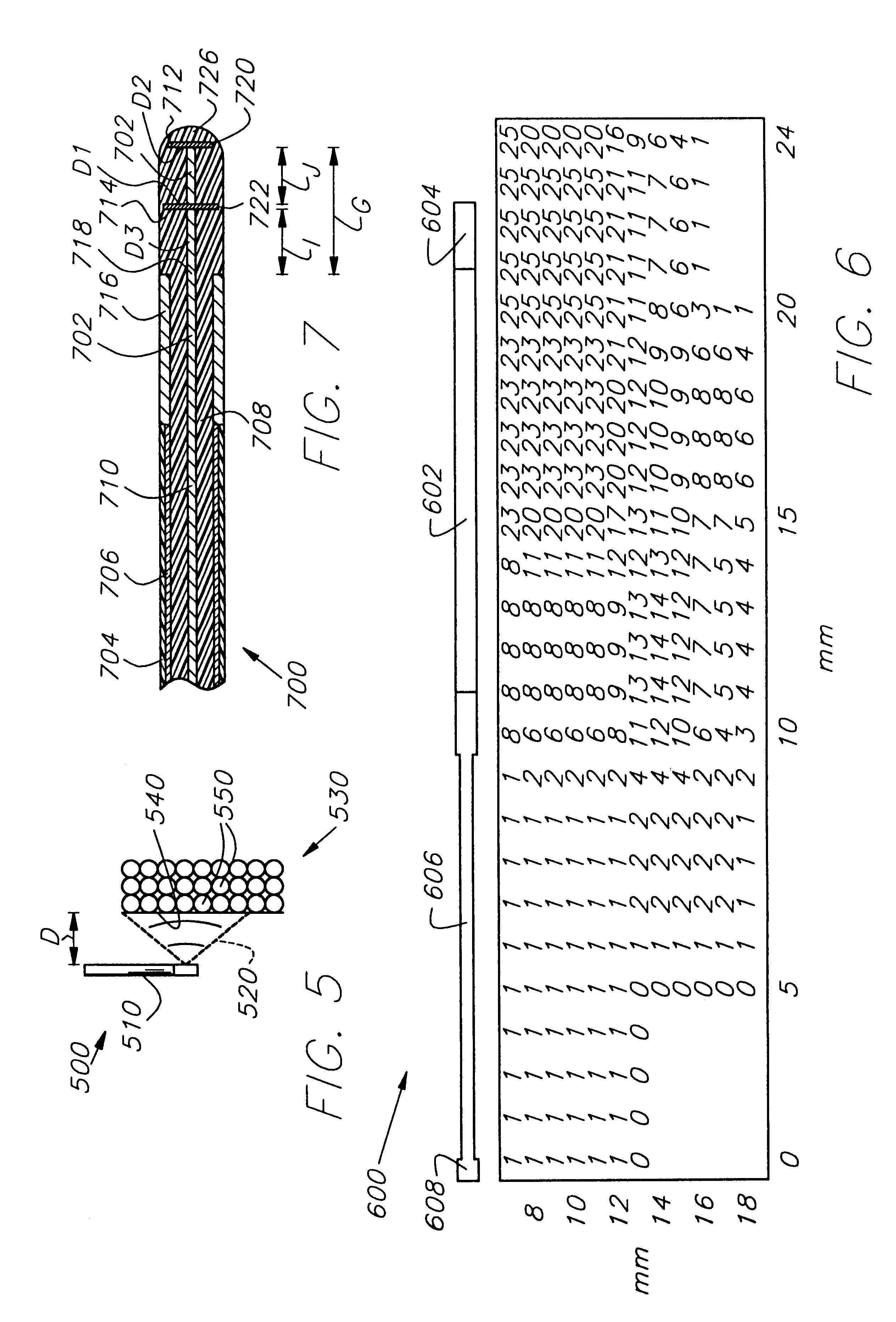
Method and apparatus are provided for propagating microwave energy into heart tissues to produce a desired temperature profile therein at tissue depths sufficient for thermally ablating arrhythmogenic cardiac tissue to treat ventricular tachycardia and other arrhythmias while preventing excessive heating of surrounding tissues, organs, and blood. A wide bandwidth double-disk antenna (700) is effective for this purpose over a bandwidth of about six gigahertz. A computer simulation provides initial screening capabilities for an antenna such as antenna, frequency, power level, and power application duration. The simulation also allows optimization of techniques for specific patients or conditions. In operation, microwave energy between about 1 Gigahertz and 12 Gigahertz is applied to monopole microwave radiator (600) having a surface wave limiter (606). A test setup provides physical testing of microwave radiators (854) to determine the temperature profile created in actual heart tissue or ersatz heart tissue (841). Saline solution (872) pumped over the heart tissue (841) with a peristaltic pump (862) simulates blood flow. Optical temperature sensors (838) disposed at various tissue depths within the heart tissue (841) detect the temperature profile without creating any electromagnetic interference. The method may be used to produce a desired temperature profile in other body tissues reachable by catheter (510) such as tumors and the like.
Owner:NASA
Nerve stimulation methods for averting imminent onset or episode of a disease
Transcutaneous electrical and magnetic nerve stimulation devices are disclosed, along with methods of averting imminent medical attacks using energy that is delivered noninvasively by the devices. The attacks comprise asthma attack, epileptic seizure, attacks of migraine headache, transient ischemic attack or stroke, onset of atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, onset of ventricular fibrillation or tachycardia, panic attack, and attacks of acute depression. The imminence of an attack is forecasted using grey-box or black-box models as used in control theory. In preferred embodiments of the disclosed methods, a vagus nerve in the neck of a patient is stimulated noninvasively to avert the attack.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Apparatus And Method For Cardiac Ablation
InactiveUS20070161915A1ElectrocardiographyControlling energy of instrumentVisual perceptionIntracardiac Electrogram
A system and method for cardiac mapping and ablation include a multi-electrode catheter introduced percutaneously into a subject's heart and deployable adjacent to various endocardial sites. The electrodes are connectable to a mapping unit, an ablation power unit a pacing unit, all of which are under computer control. Intracardiac electrogram signals emanated from a tachycardia site of origin are detectable by the electrodes. Their arrival times are processed to generate various visual maps to provide real-time guidance for steering the catheter to the tachycardia site of origin. In another aspect, the system also include a physical imaging system which is capable of providing different imaged physical views of the catheter and the heart. These physical views are incorporated into the various visual maps to provide a more physical representation. Once the electrodes are on top of the tachycardia site of origin, electrical energy is supplied by the ablation power unit to effect ablation.
Owner:CATHEFFECTS
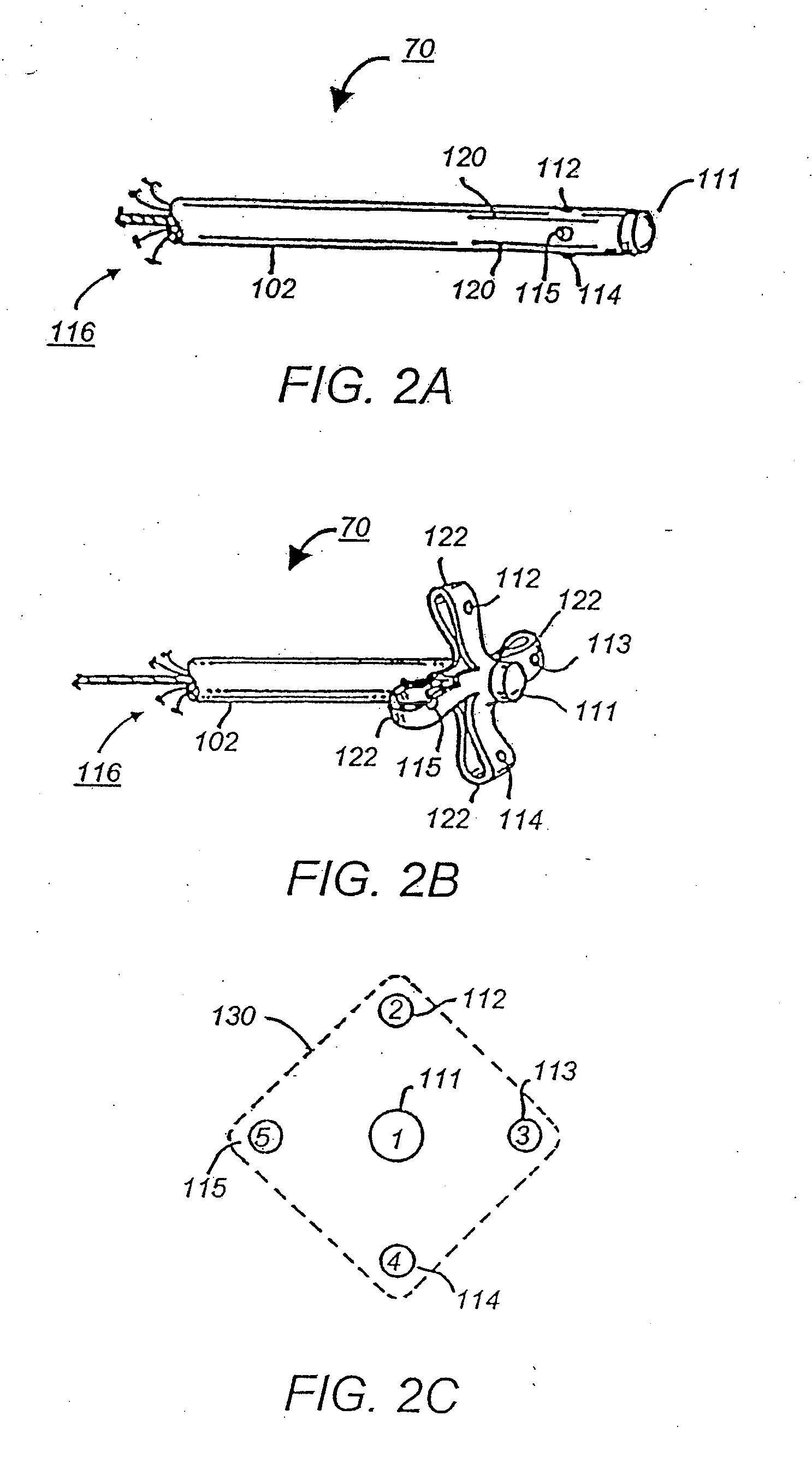
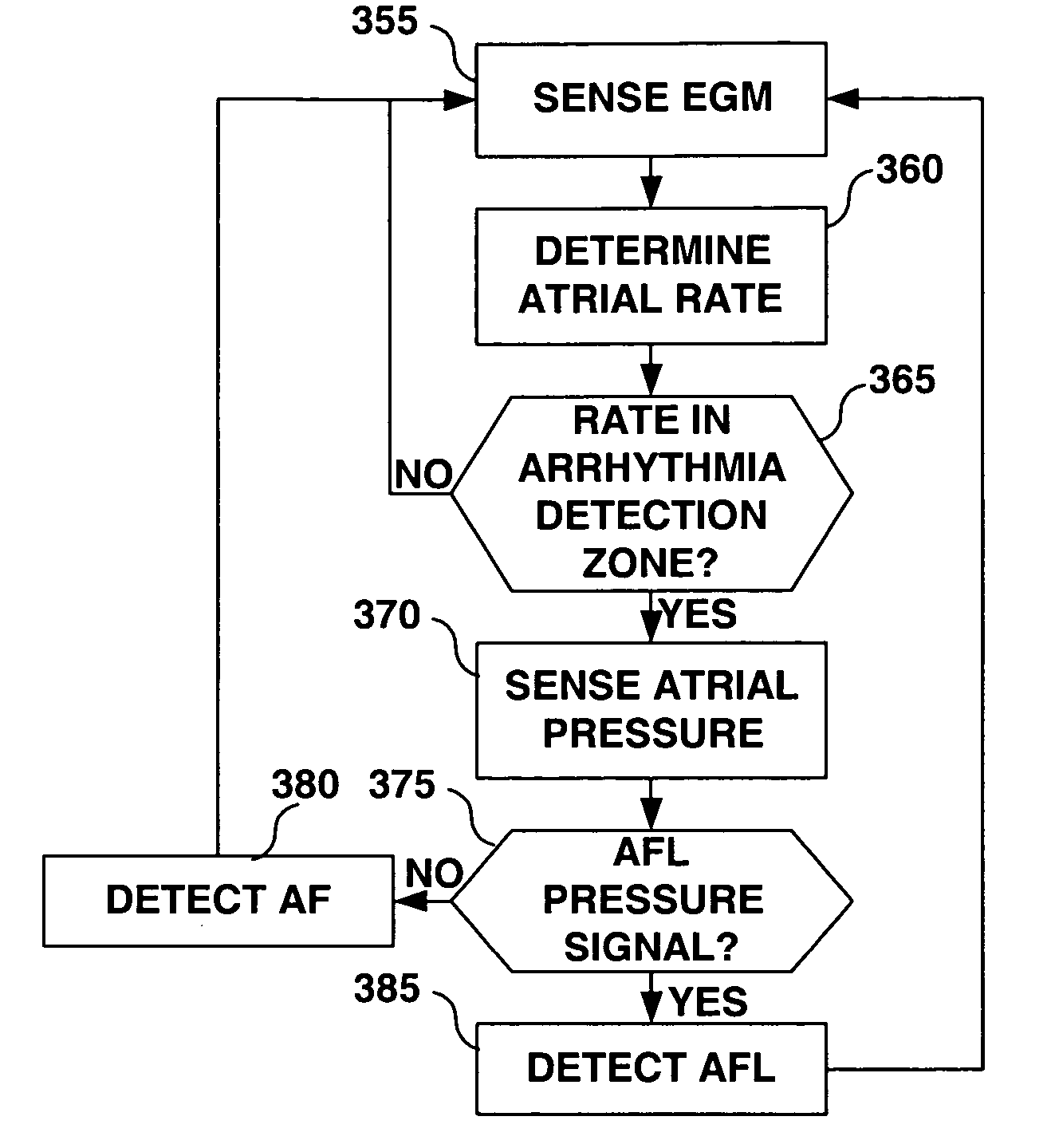
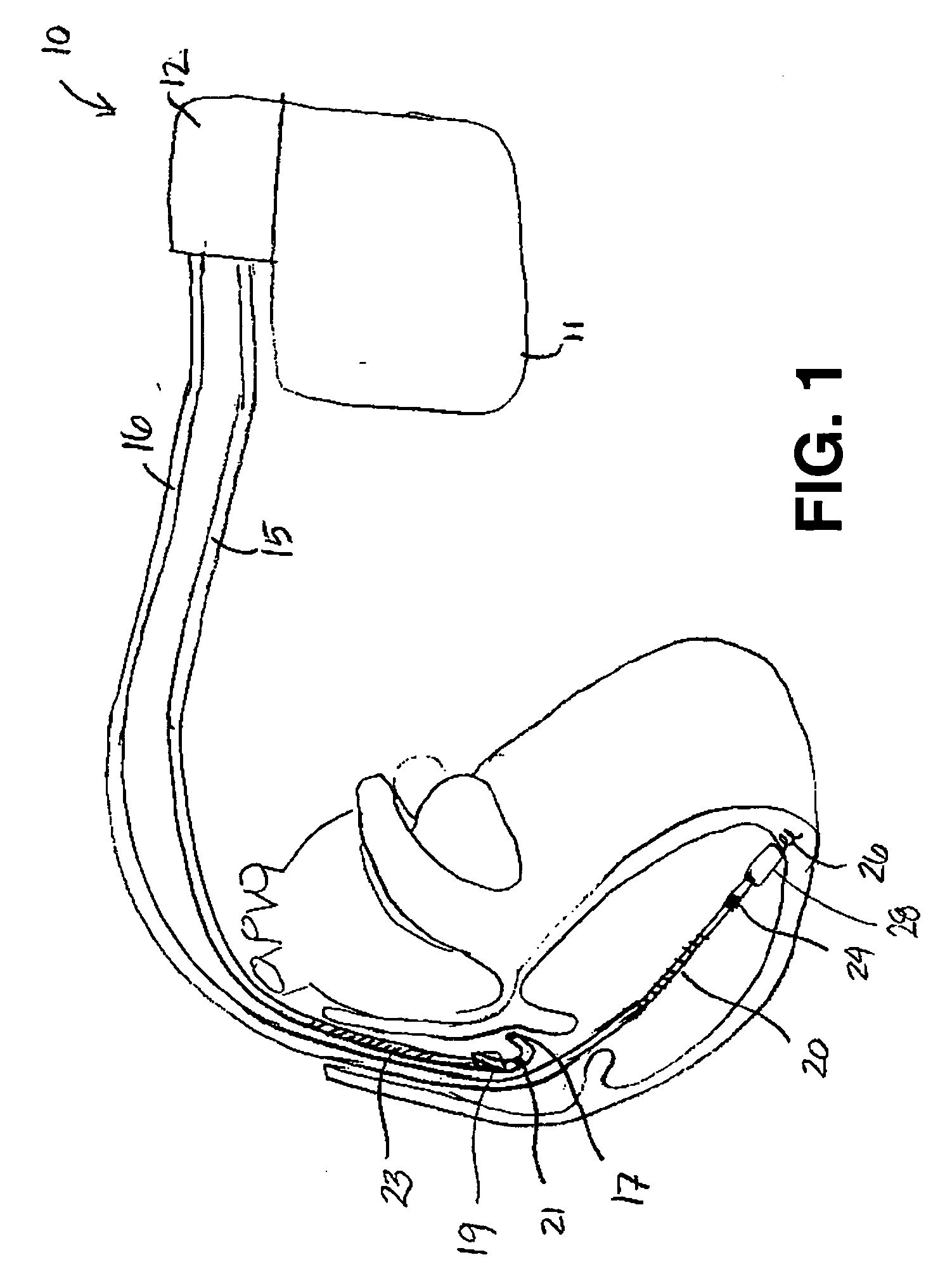
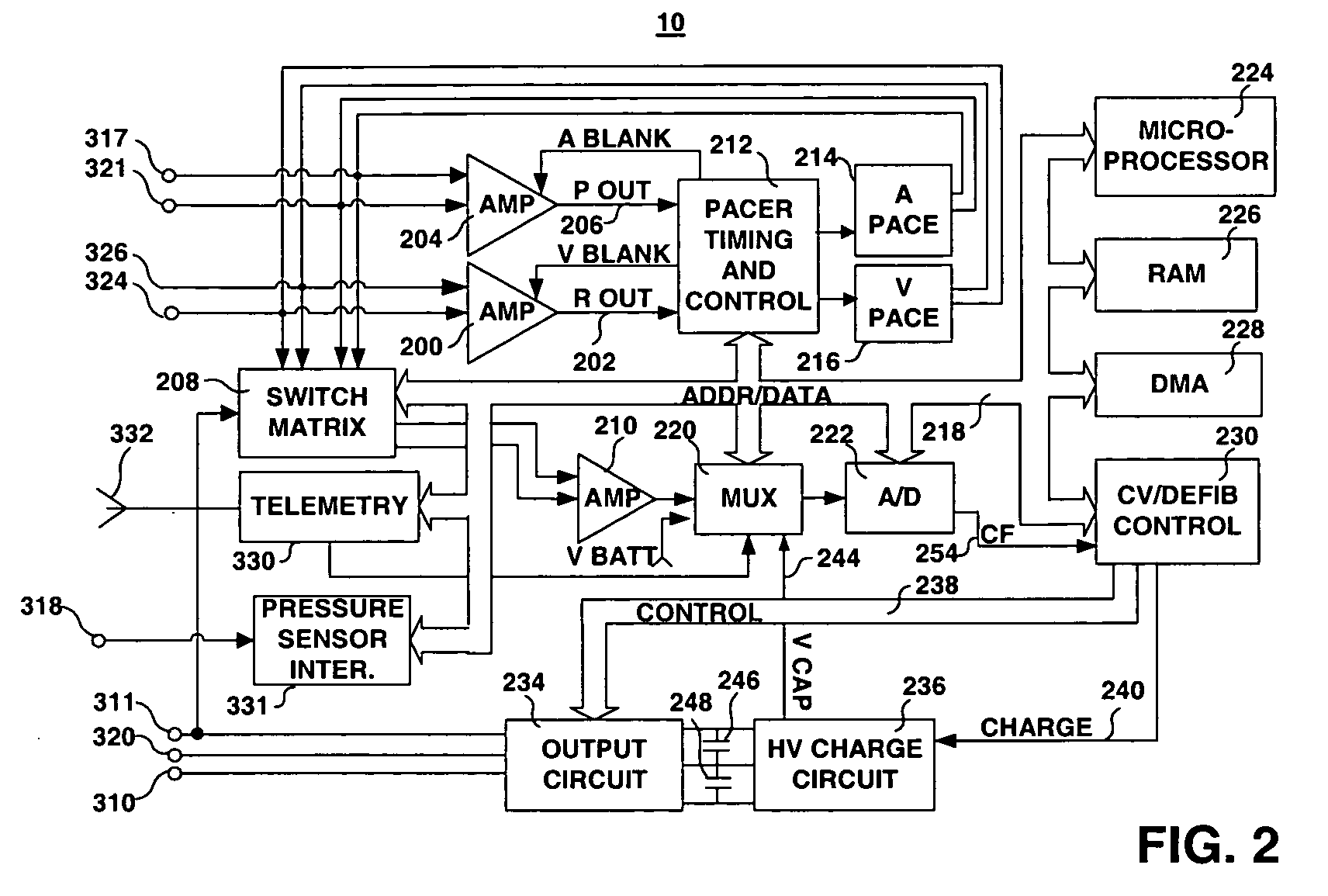
Combination of electrogram and intra-cardiac pressure to discriminate between fibrillation and tachycardia
A system and method for detecting and classifying cardiac arrhythmias based on cardiac pressure signals or the combination of cardiac electrical and cardiac pressure signals. A cardiac electrogram signal is sensed to derive a cardiac rate from which an arrhythmia detection is made when the cardiac rate meets arrhythmia detection criteria. An intracardiac pressure signal is sensed to derive an indicator of tachycardia based on an analysis of the pressure signal in either the time domain or frequency domain. The detected arrhythmia is classified as tachycardia or fibrillation based on the tachycardia indicator wherein the tachycardia indicator is compared to tachycardia detection criteria and the arrhythmia is classified as tachycardia if tachycardia detection criteria are met and the arrhythmia is classified as fibrillation if the tachycardia detection criteria are not met.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Vacuum coagulation probe for atrial fibrillation treatment
InactiveUS20060009762A1Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesAnatomical structuresLess invasive
An embodiment of the invention includes a surgical device for coagulating soft tissue such as atrial tissue in the treatment of atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and atrial tachycardia. The surgical device can include at least one elongate member comprising conductive elements adapted to coagulate soft tissue when radiofrequency or direct current energy is transmitted to the conductive elements. Openings through said conductive elements are routed through lumens in the elongate member to a vacuum source to actively engage the soft tissue surface intended to coagulate into intimate contact with the conductive elements to facilitate the coagulation process and ensure the lesions created are consistent, contiguous, and transmural. The embodiments of the invention can also incorporate cooling openings positioned near the conductive elements and coupled with a vacuum source or an injection source to transport fluid through the cooling openings causing the soft tissue surface to cool thus pushing the maximum temperature deeper into tissue. The embodiments of the invention can also incorporate features to tunnel between anatomic structures or dissect around the desired tissue surface to coagulate thereby enabling less invasive positioning of the soft tissue coagulating device and ensuring reliable and consistent heating of the soft tissue.
Owner:ATRICURE
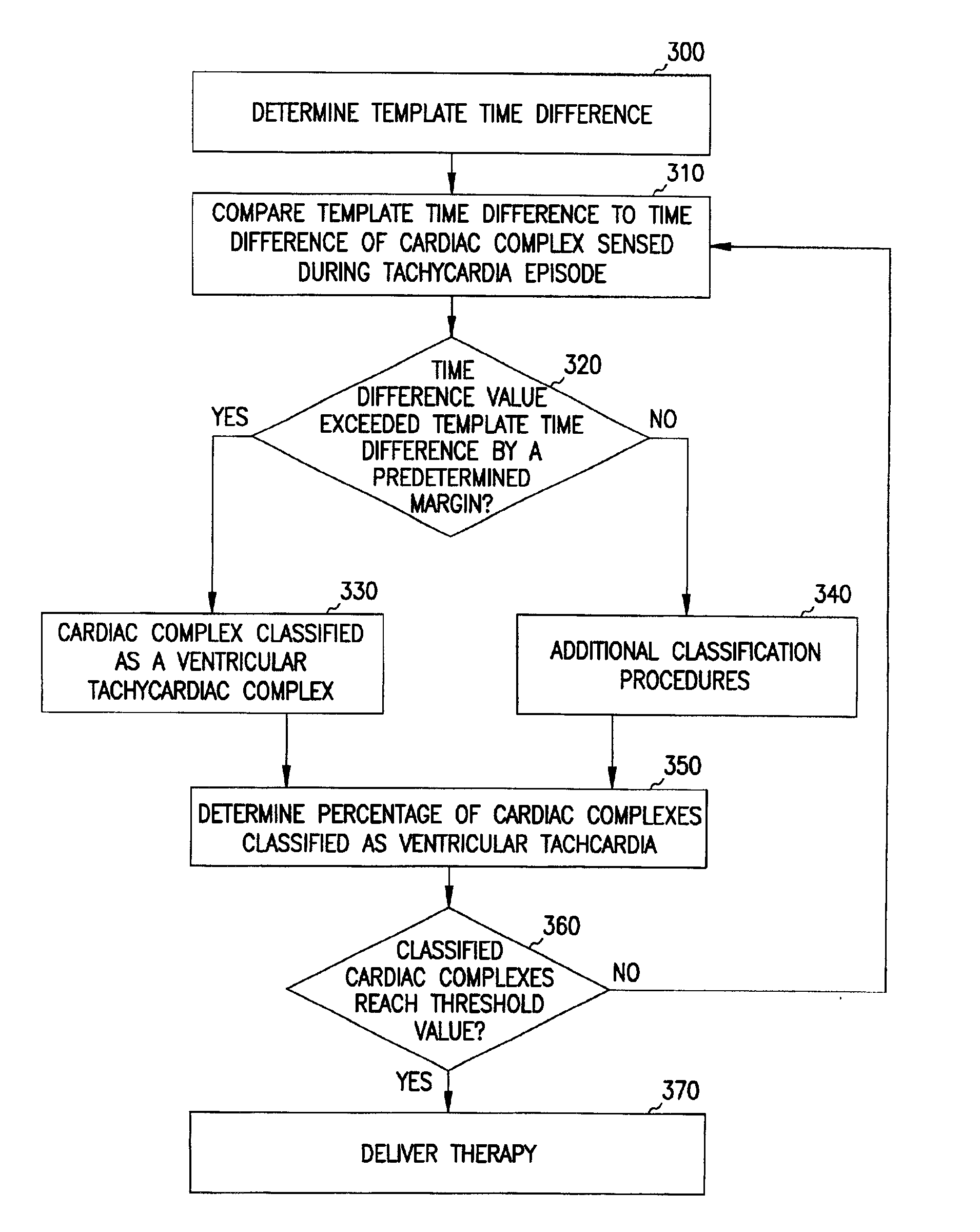
System and method for arrhythmia discrimination
InactiveUS6959212B2Effective treatmentHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringVentricular dysrhythmiaVentricular tachycardia
The present invention provides a system and a method for discriminating supraventricular tachyarrhythmias from ventricular arrhythmias during a tachycardia episode. First cardiac signals and second cardiac signals are sampled for cardiac complexes. A first feature on the first cardiac signal and a second feature on the second cardiac signal are utilized to determine an average time difference for a plurality of normal sinus rhythm complexes. A time difference between the first feature and the second feature is then determined for each cardiac complex of a tachycardiac rhythm. The cardiac complex is characterized as a ventricular tachycardia complex if the time difference exceeds the average time difference by a predetermined amount. Otherwise, it is classified as VT if its morphology after alignment is different from that during normal sinus rhythm.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
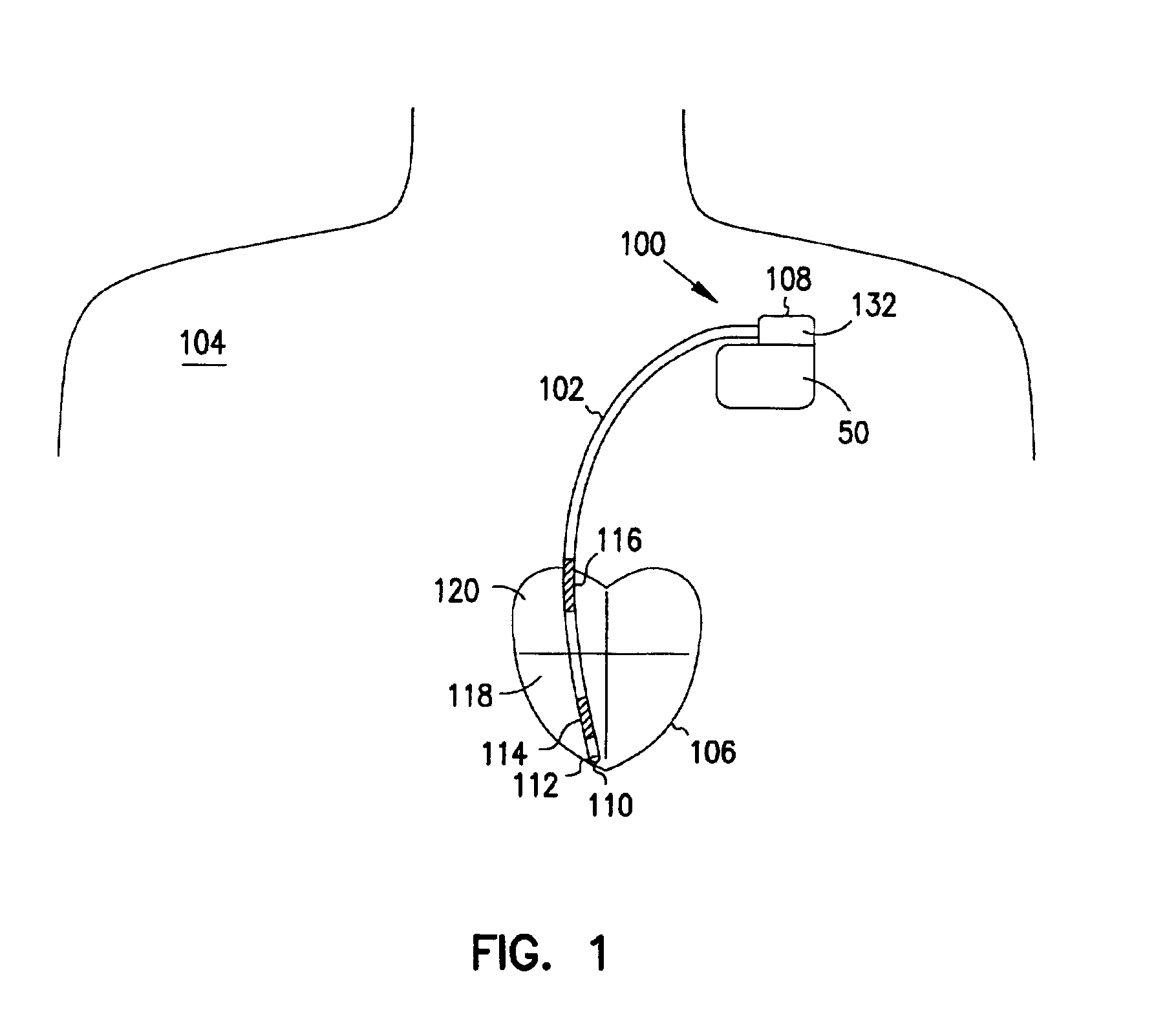
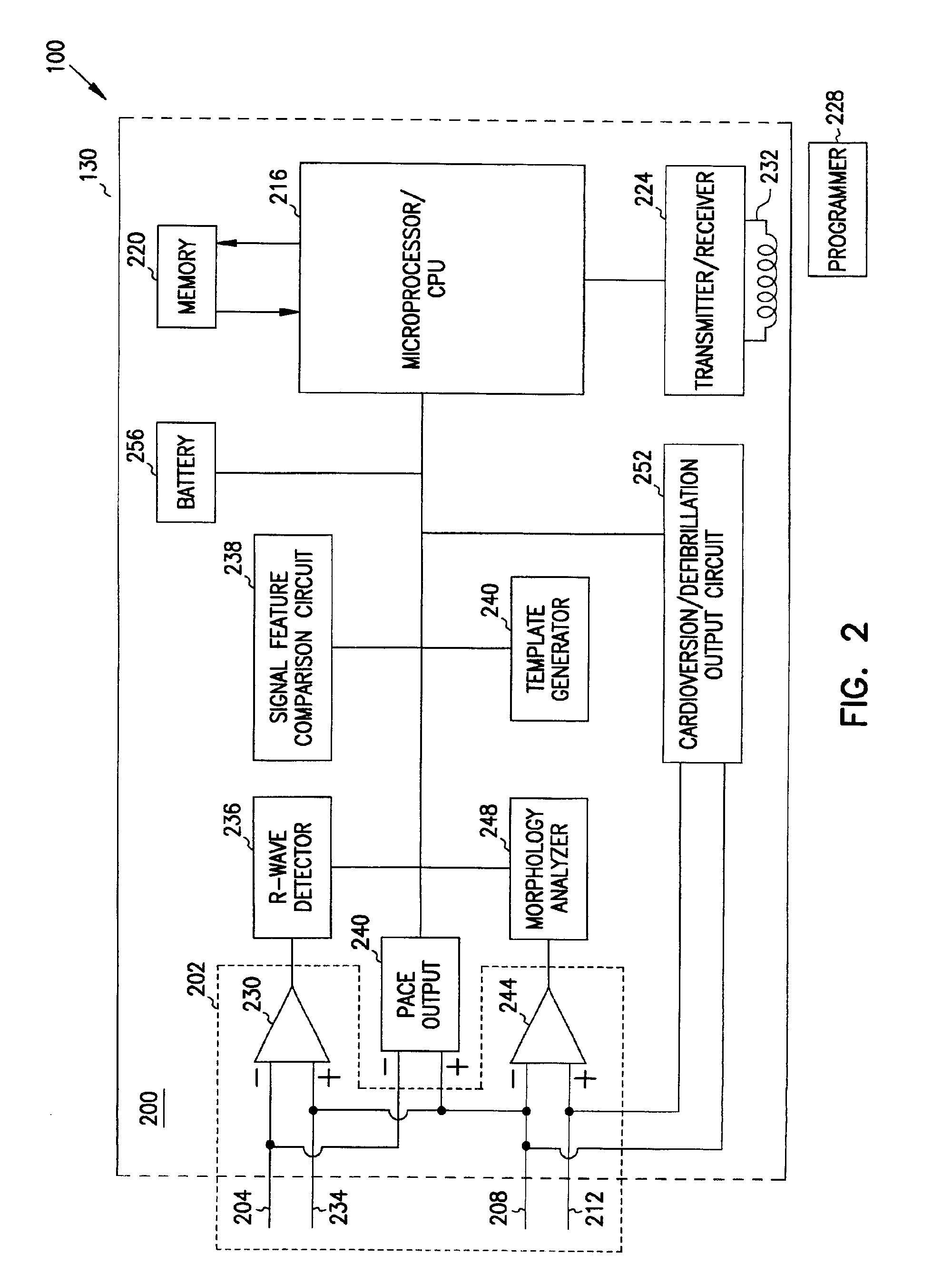
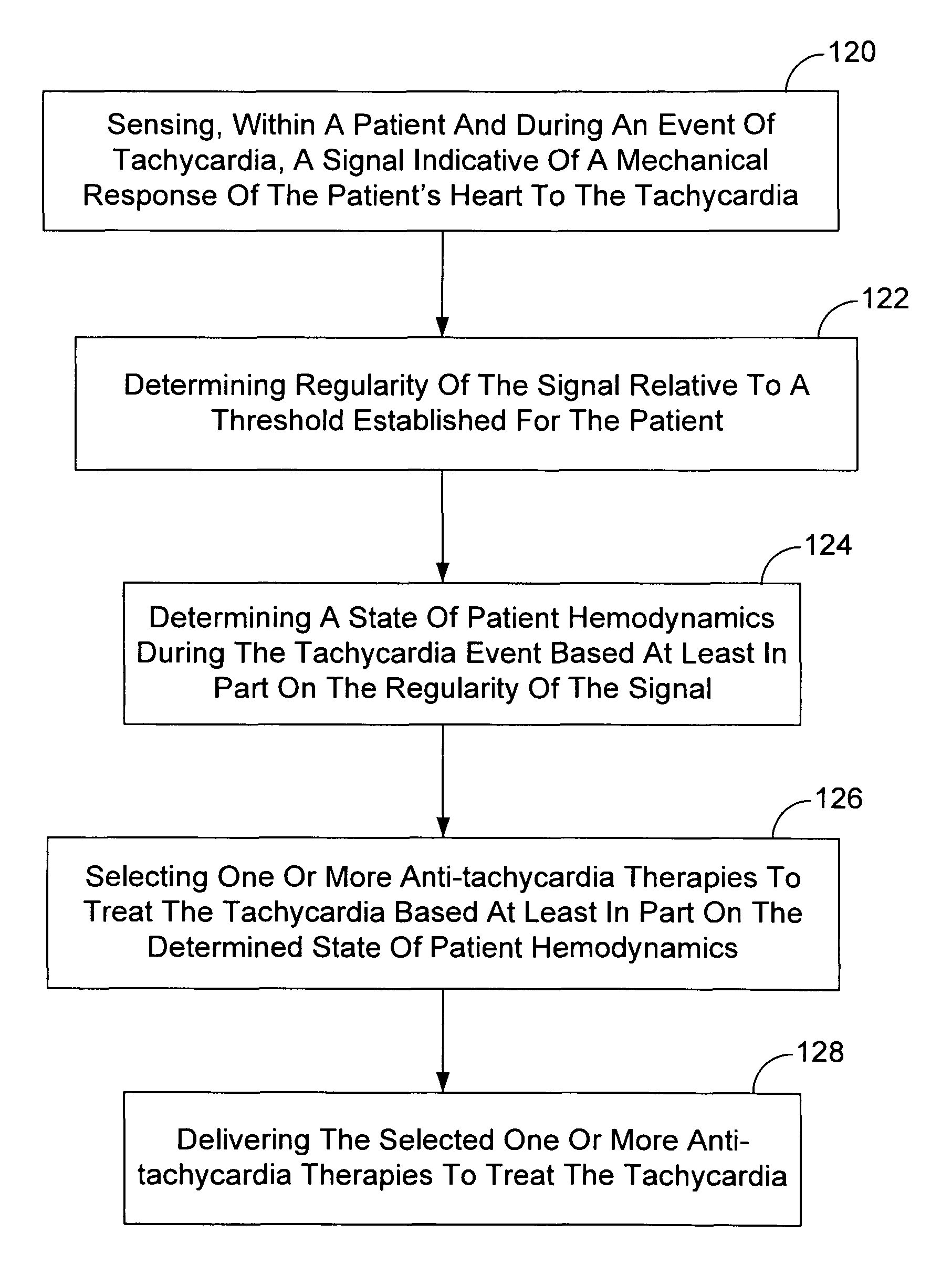
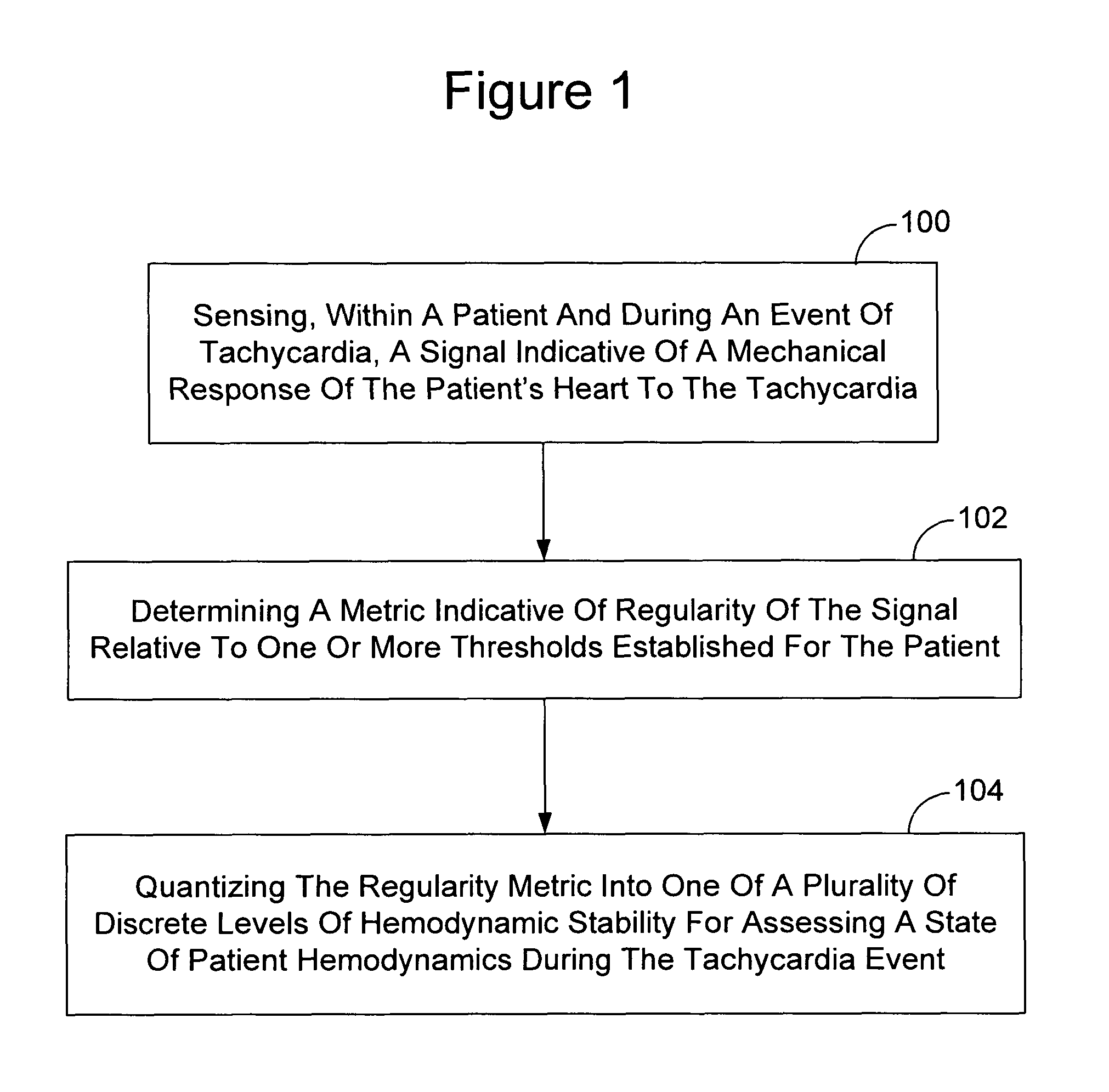
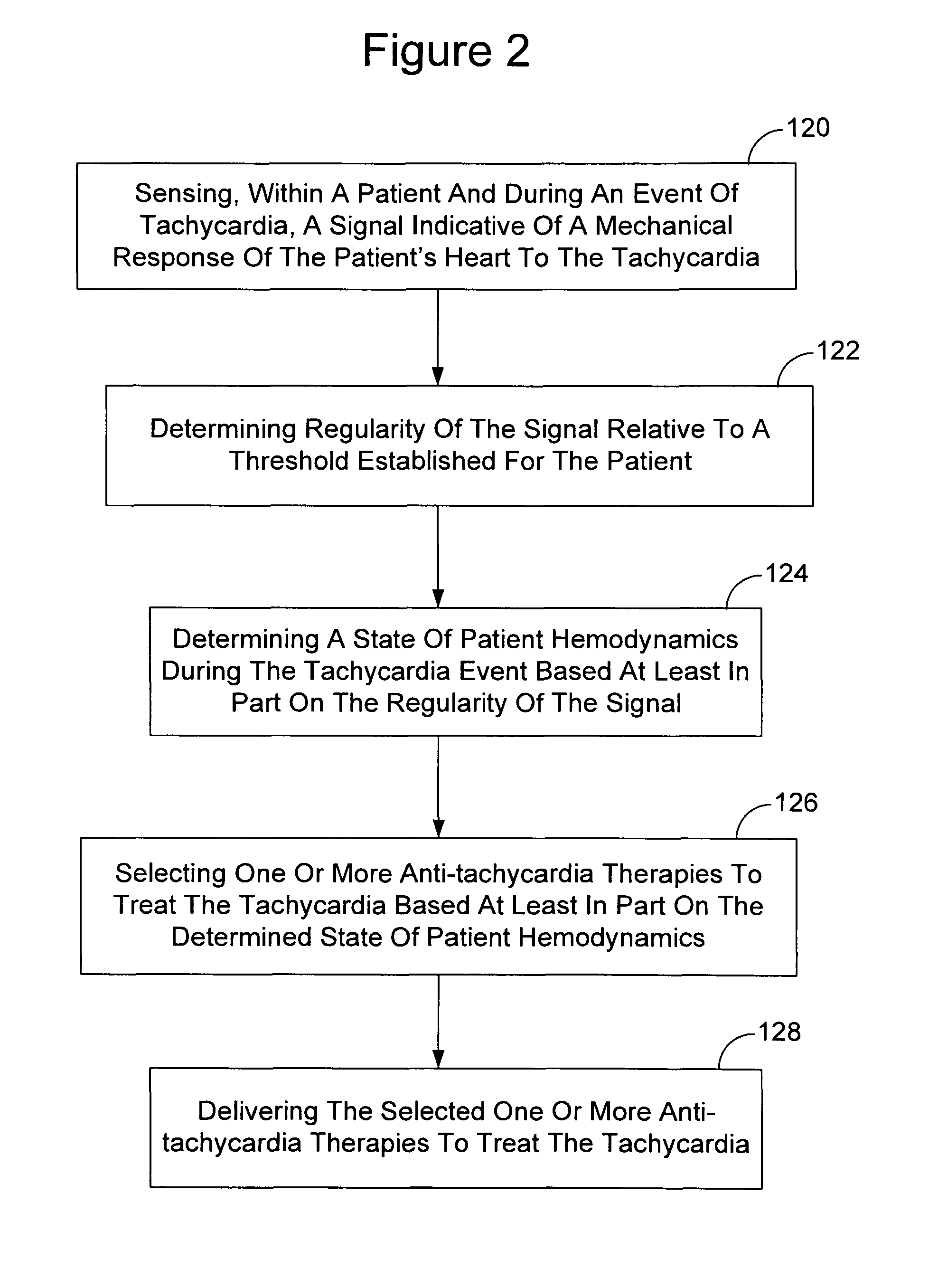
Tachycardia hemodynamics detection based on cardiac mechanical sensor signal regularity
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Synthetic apelin mimetics for the treatment of heart failure
ActiveUS8673848B2Extended half-lifeIncrease constraintsNervous disorderSkeletal disorderCardiac fibrosisVentricular tachycardia
The invention provides a synthetic polypeptide of Formula I′:or an amide, an ester or a salt thereof, wherein X1, X2, X3, X4, X5, X6, X7, X8, X9, X10, X11, X12 and X13 are defined herein. The polypeptides are agonist of the APJ receptor. The invention also relates to a method for manufacturing the polypeptides of the invention, and its therapeutic uses such as treatment or prevention of acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF), chronic heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, atrial fibrillation, Brugada syndrome, ventricular tachycardia, atherosclerosis, hypertension, restenosis, ischemic cardiovascular diseases, cardiomyopathy, cardiac fibrosis, arrhythmia, water retention, diabetes (including gestational diabetes), obesity, peripheral arterial disease, cerebrovascular accidents, transient ischemic attacks, traumatic brain injuries, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, burn injuries (including sunburn) and preeclampsia. The present invention further provides a combination of pharmacologically active agents and a pharmaceutical composition.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
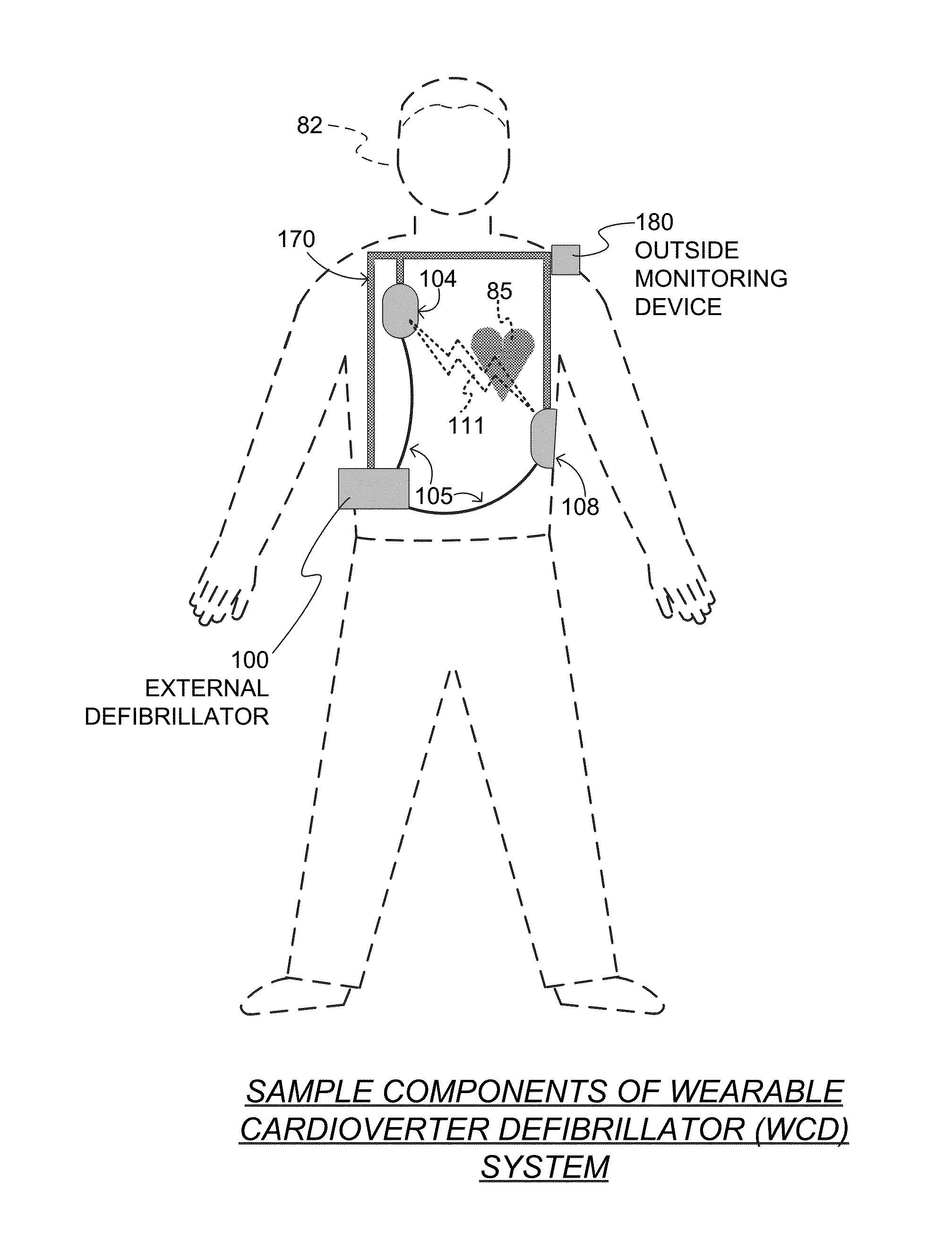
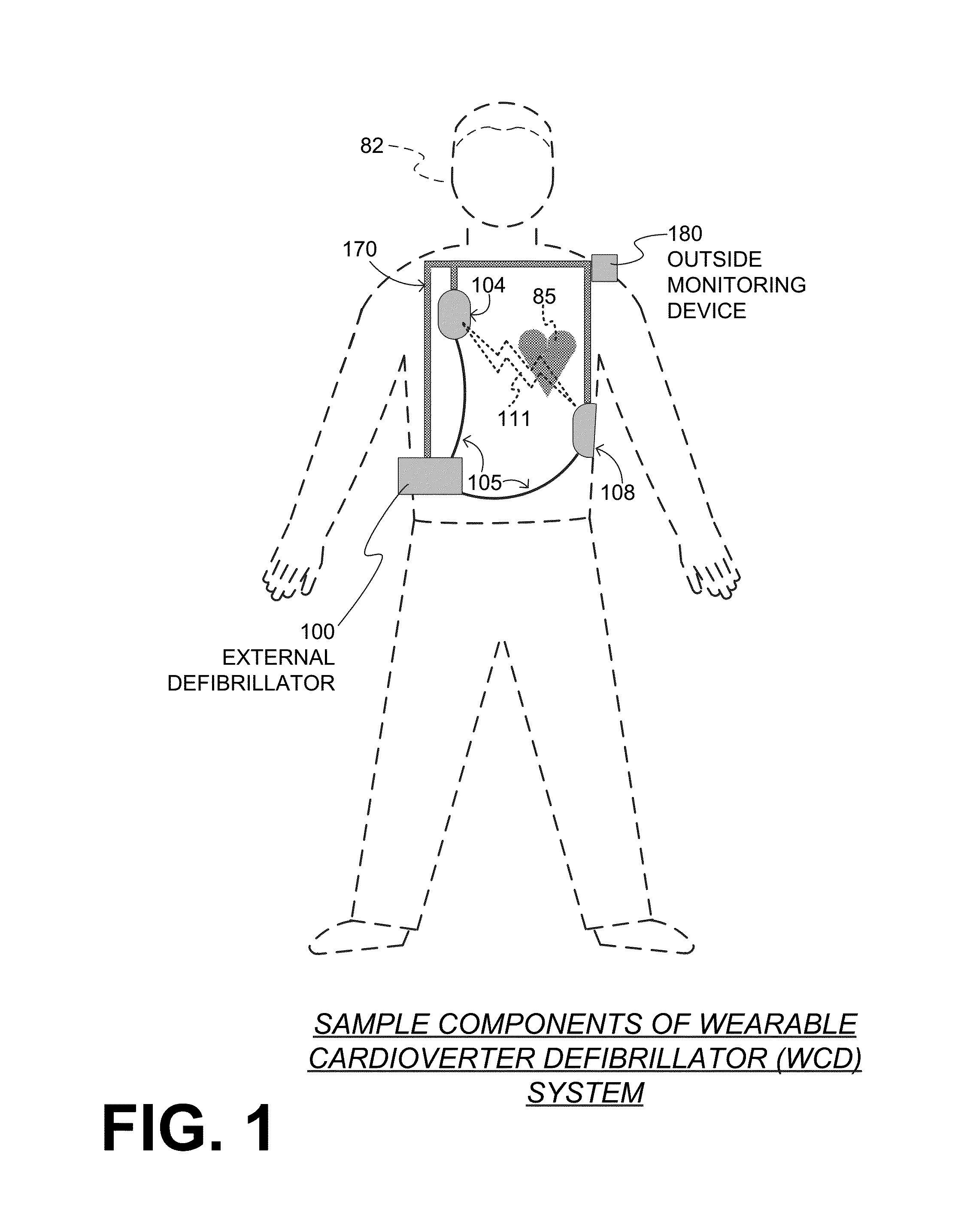
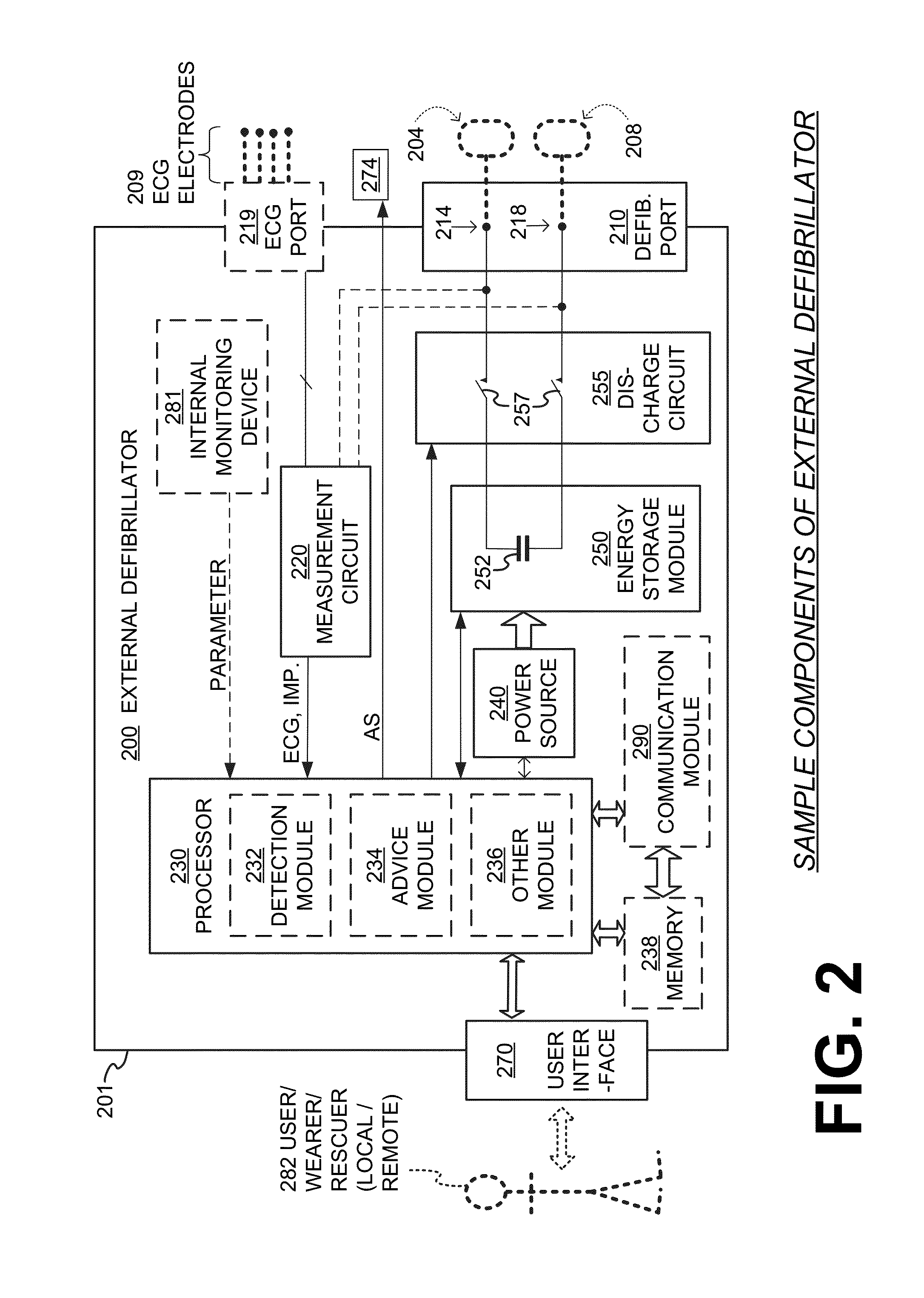
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system informing patient that it is validating just-detected cardiac arrhythmia
ActiveUS20160082277A1Reduce morbidityHeart defibrillatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringVentricular tachycardiaWearable cardioverter defibrillator
In some embodiments, a wearable cardioverter defibrillator (“WCD”) system may output an opening human-perceptible indication, after detecting a shockable cardiac arrhythmia but before validating it. This may succeed in informing the patient that the WCD system is working, and in particular analyzing a just-detected cardiac arrhythmia. The information may give comfort and confidence to the patient who may be conscious, and be experiencing only ventricular tachycardia but not ventricular fibrillation.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
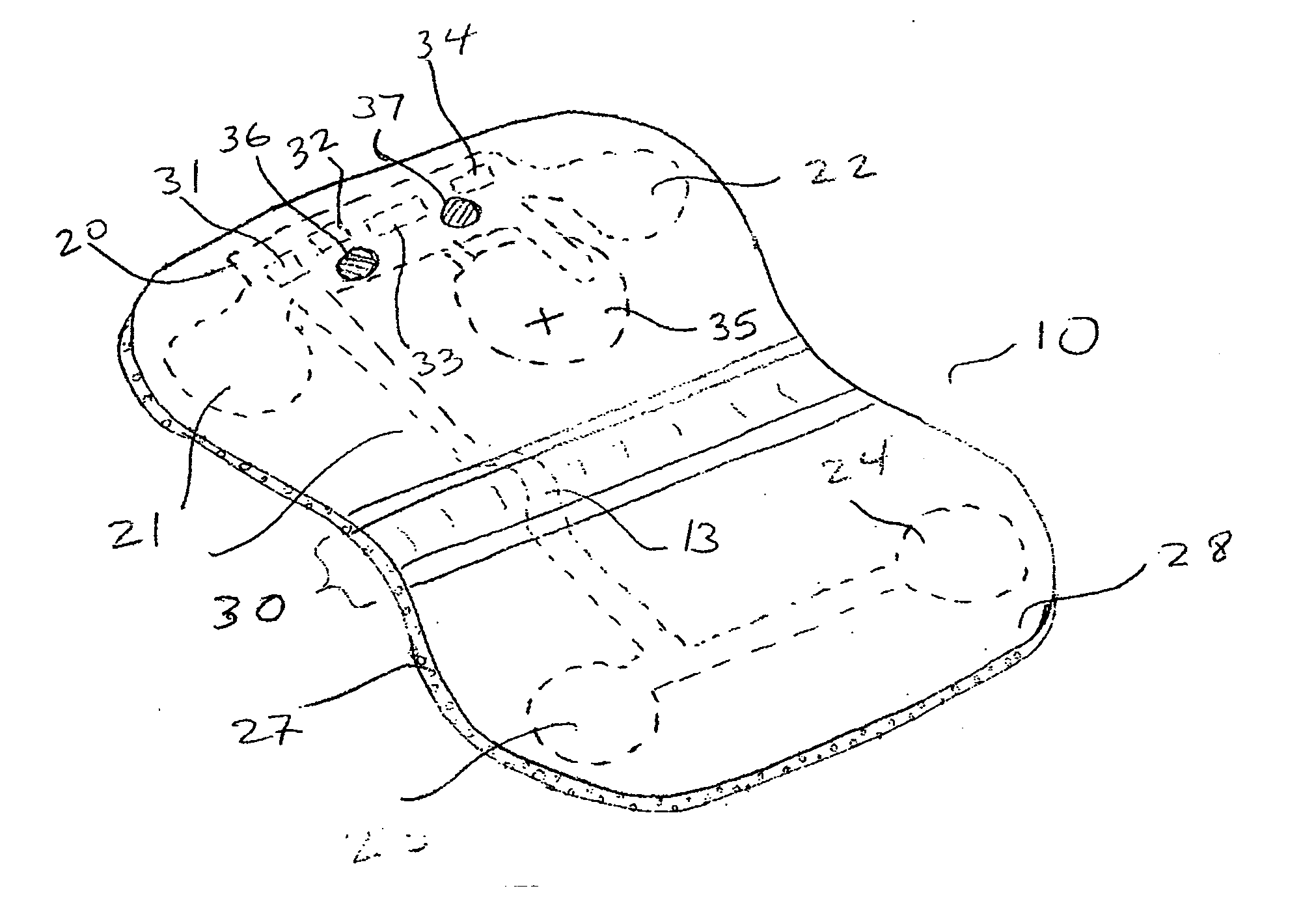
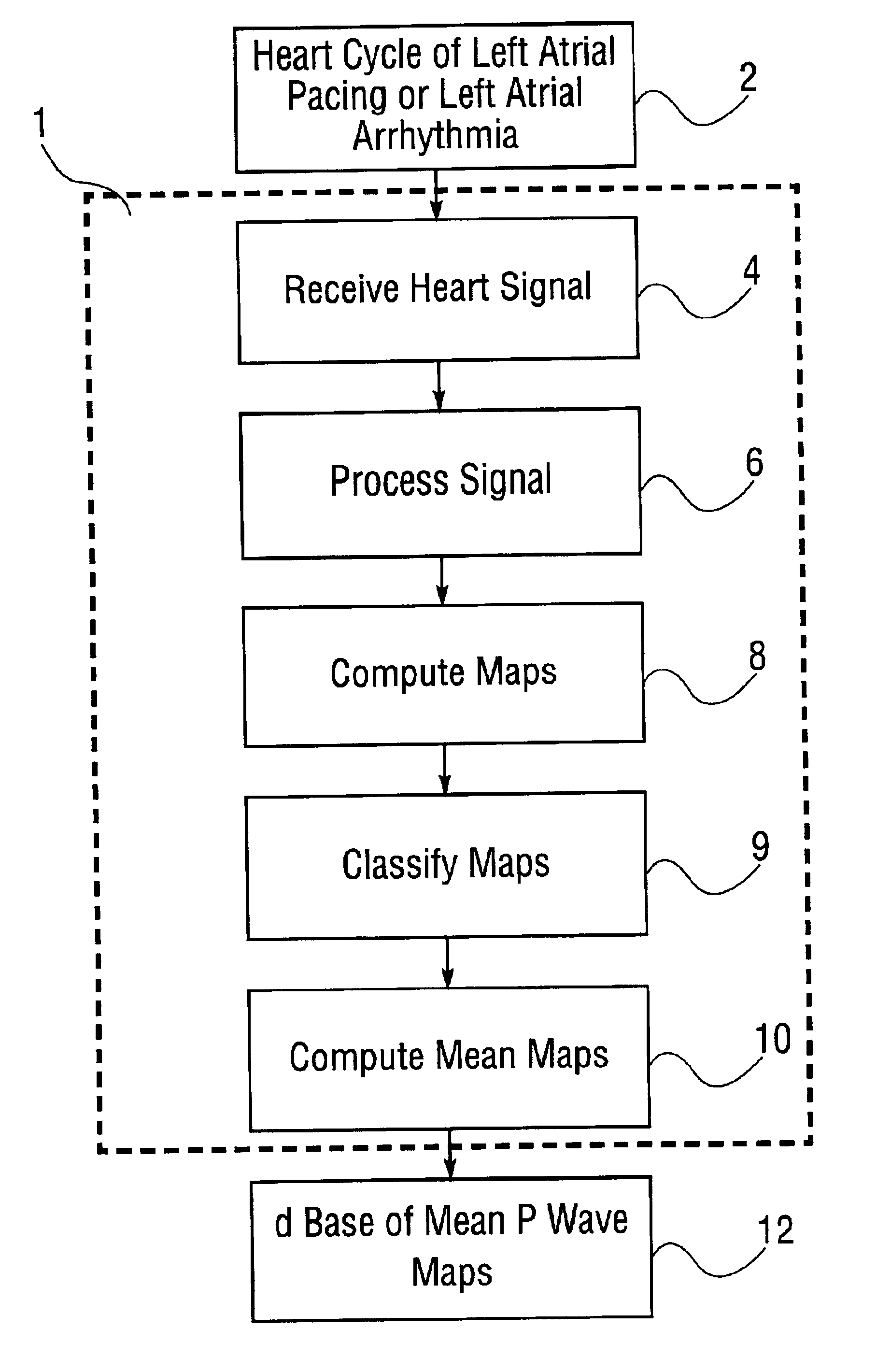
Database of body surface ECG P wave integral maps for localization of left-sided atrial arrhythmias
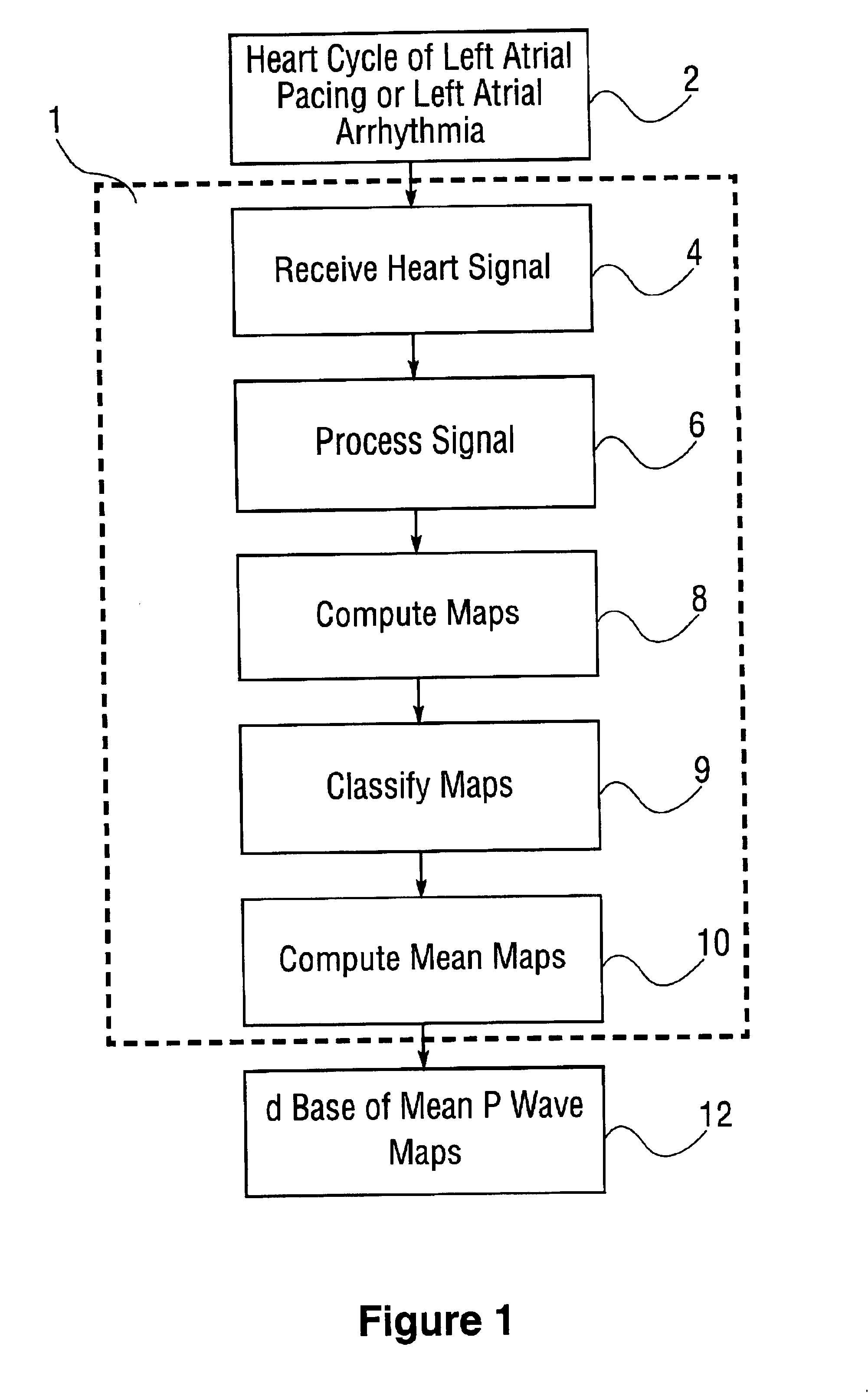
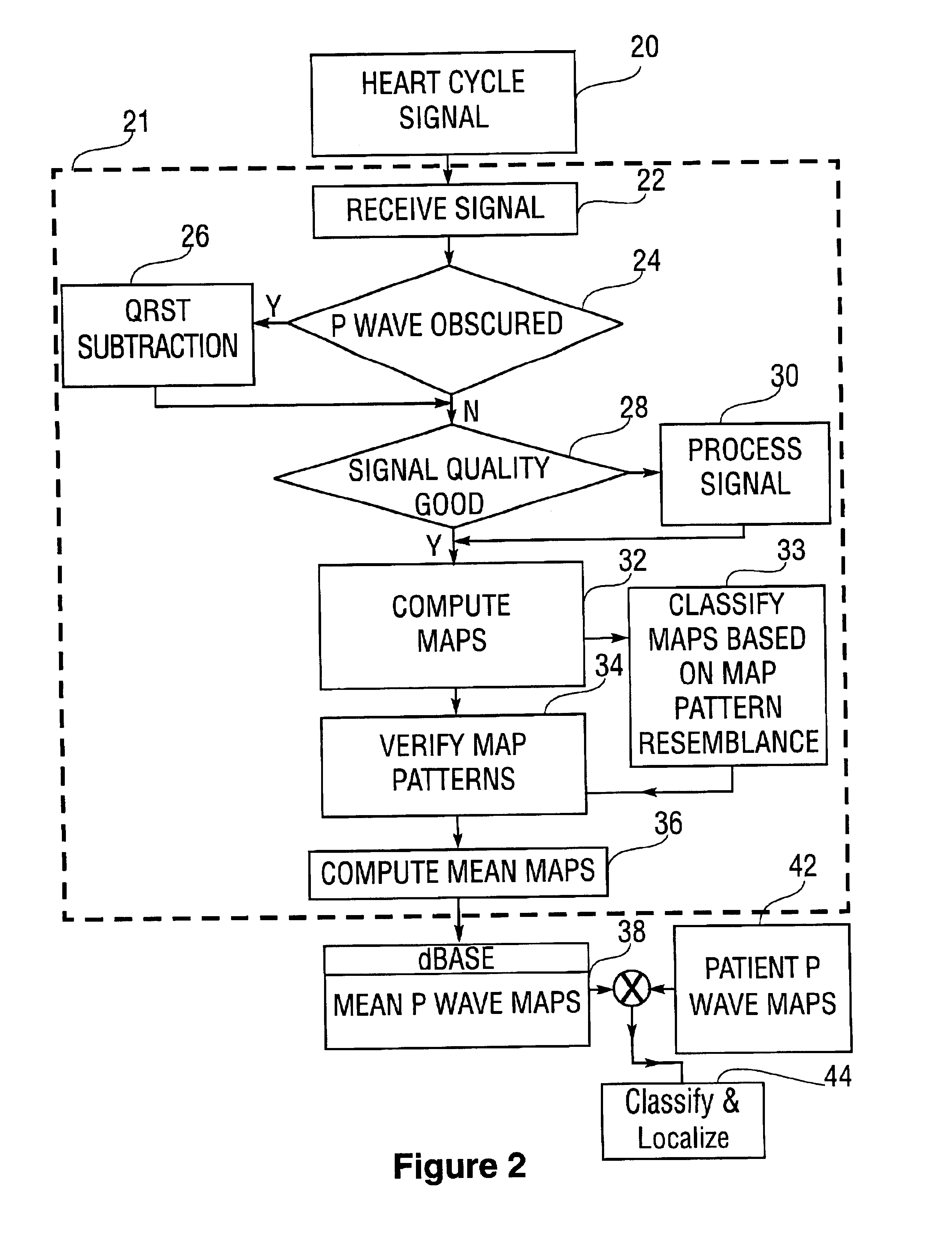
InactiveUS6931273B2ElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyIsorhythmic Atrioventricular DissociationHypsarrhythmia
A system and method are provided for developing a database of body surface ECG P-wave maps for classification and localization of left-sided atrial arrhythmias. The system and method include generating and receiving P-wave data in a subject by left atrial pacing or receiving P-wave data in a subject during spontaneously occurring or induced left atrial arrhythmias; computing (e.g. potential or integral) maps of the P-wave data; classifying the maps specific to a left atrial ectopic origin; verifying the classification procedure; averaging the classified maps into mean maps; and storing and accessing the mean maps in the database. The mean maps of the P-wave data in the database can be used to automatically classify and localize P-wave data from a patient obtained during a left atrial arrhythmia such as atrial tachycardia, focal atrial fibrillation, or orthodromic atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and system for performing ablation to treat ventricular tachycardia
ActiveUS8195271B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputed tomographyVentricular tachycardia
A system and method of treating tachycardias and similar syndromes by the use of catheter ablation of tissue is described. A computed tomography (CT)-like image of the heart is obtained and processed to segment the various types of tissue. Papillary muscle areas are identified and displayed differently from the other nearby tissues so that the muscles can be avoided during treatment to avoid or minimize damage to the muscles during ablation treatment. Electrophysical data and scar tissue may also be identified in the image, which may be of the endoscopic type. The position of the catheter may be displayed as a synthetic image on the endoscopic view.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
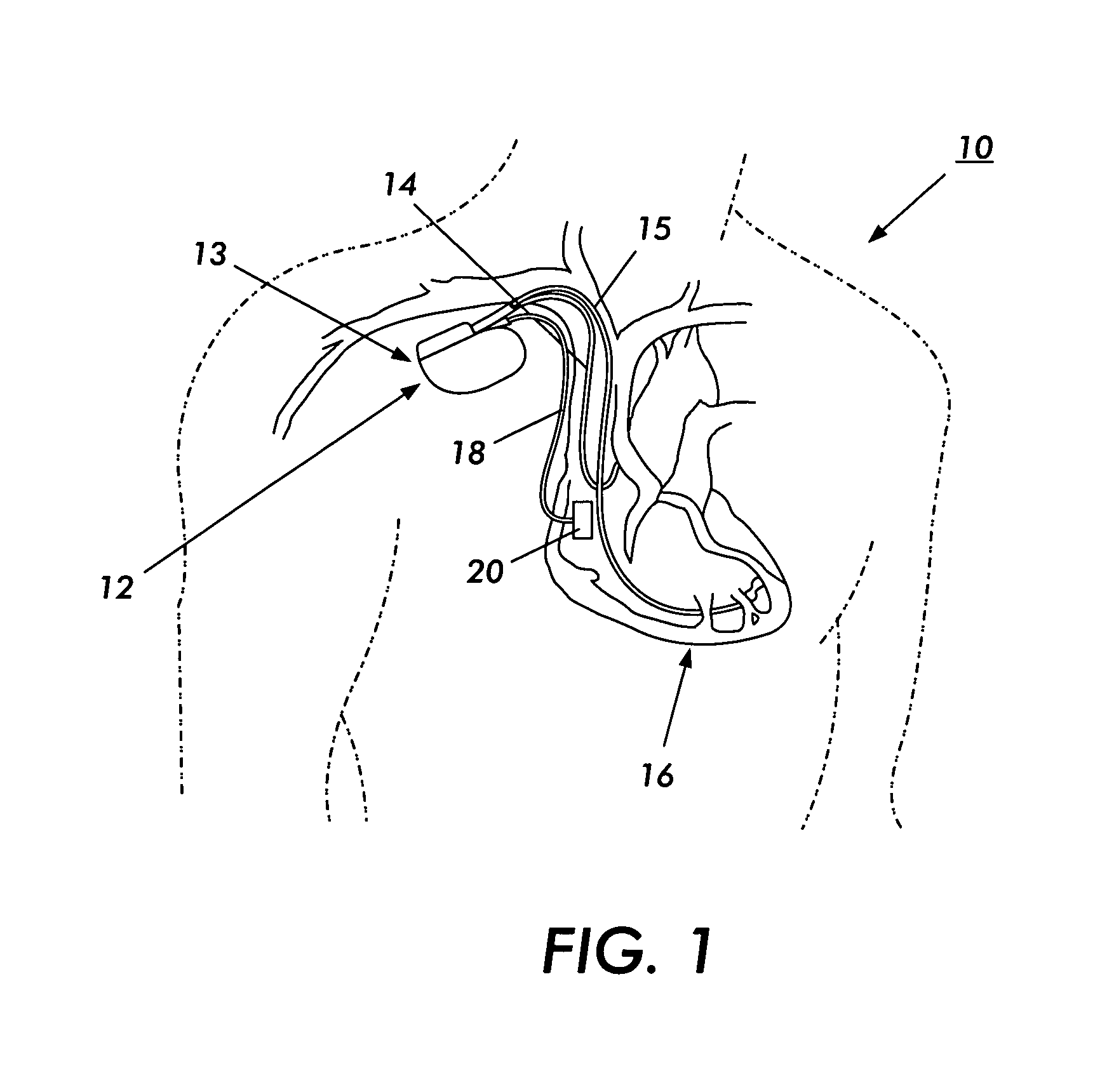
Subcutaneous defibrillation system and method using same
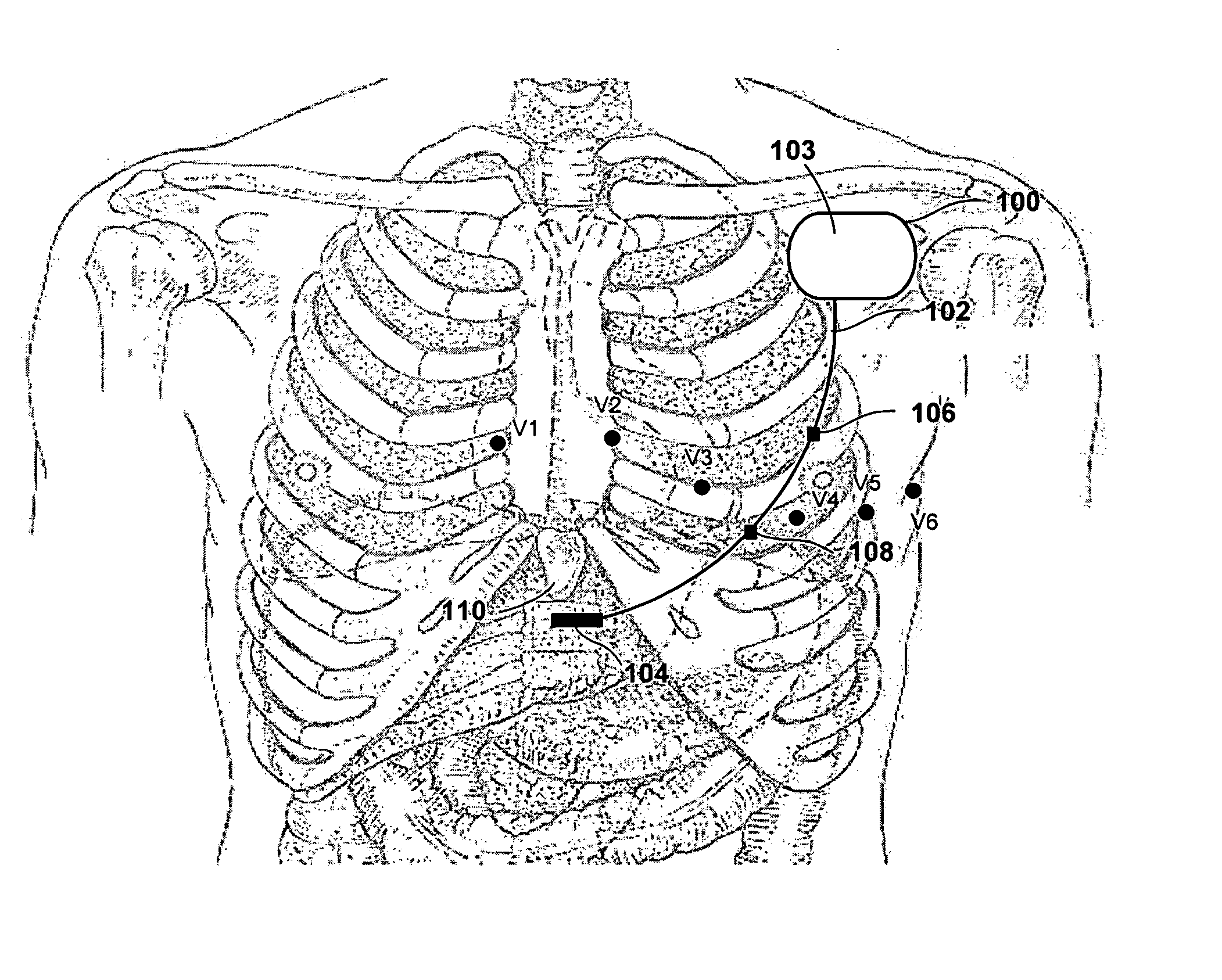
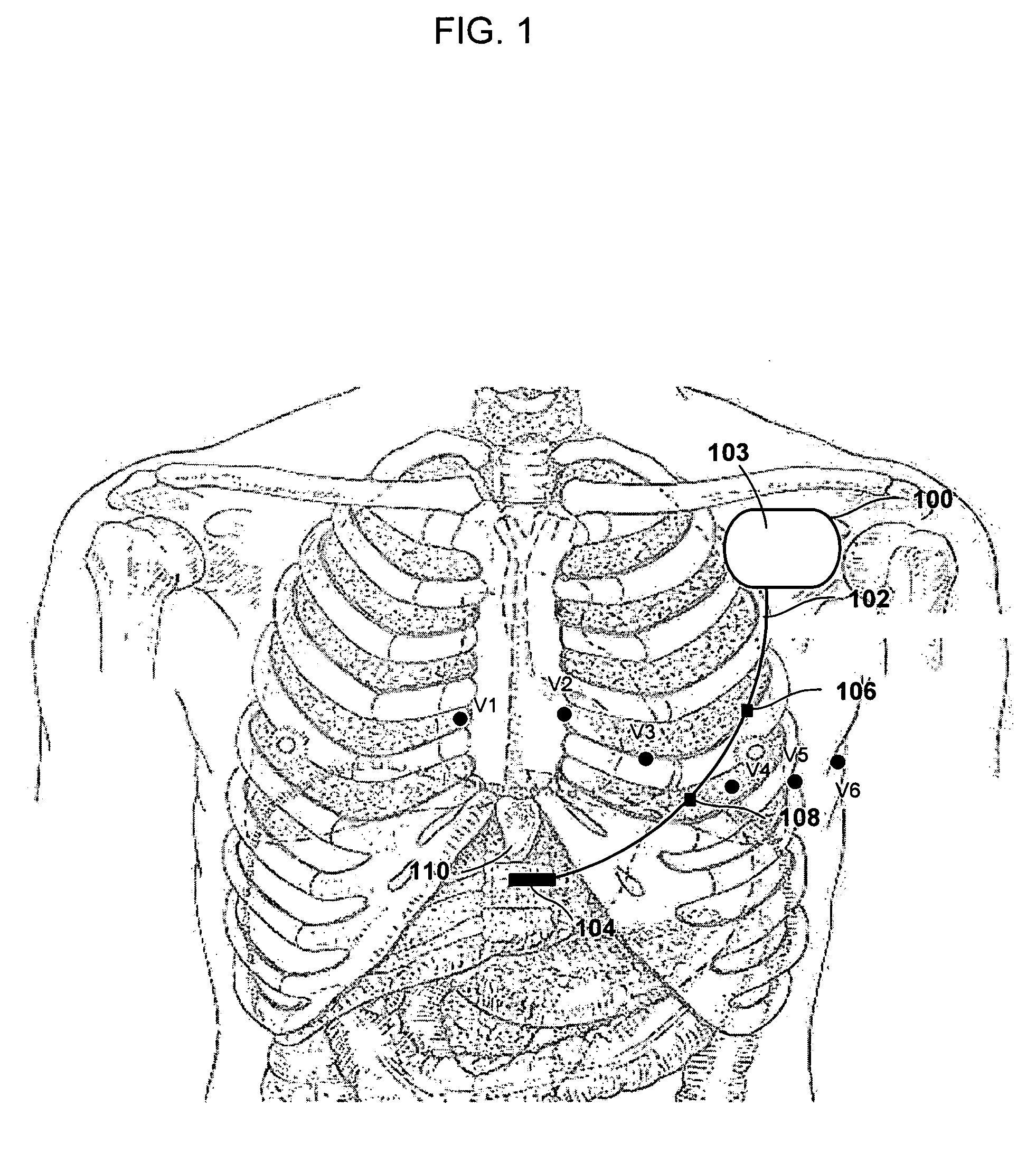
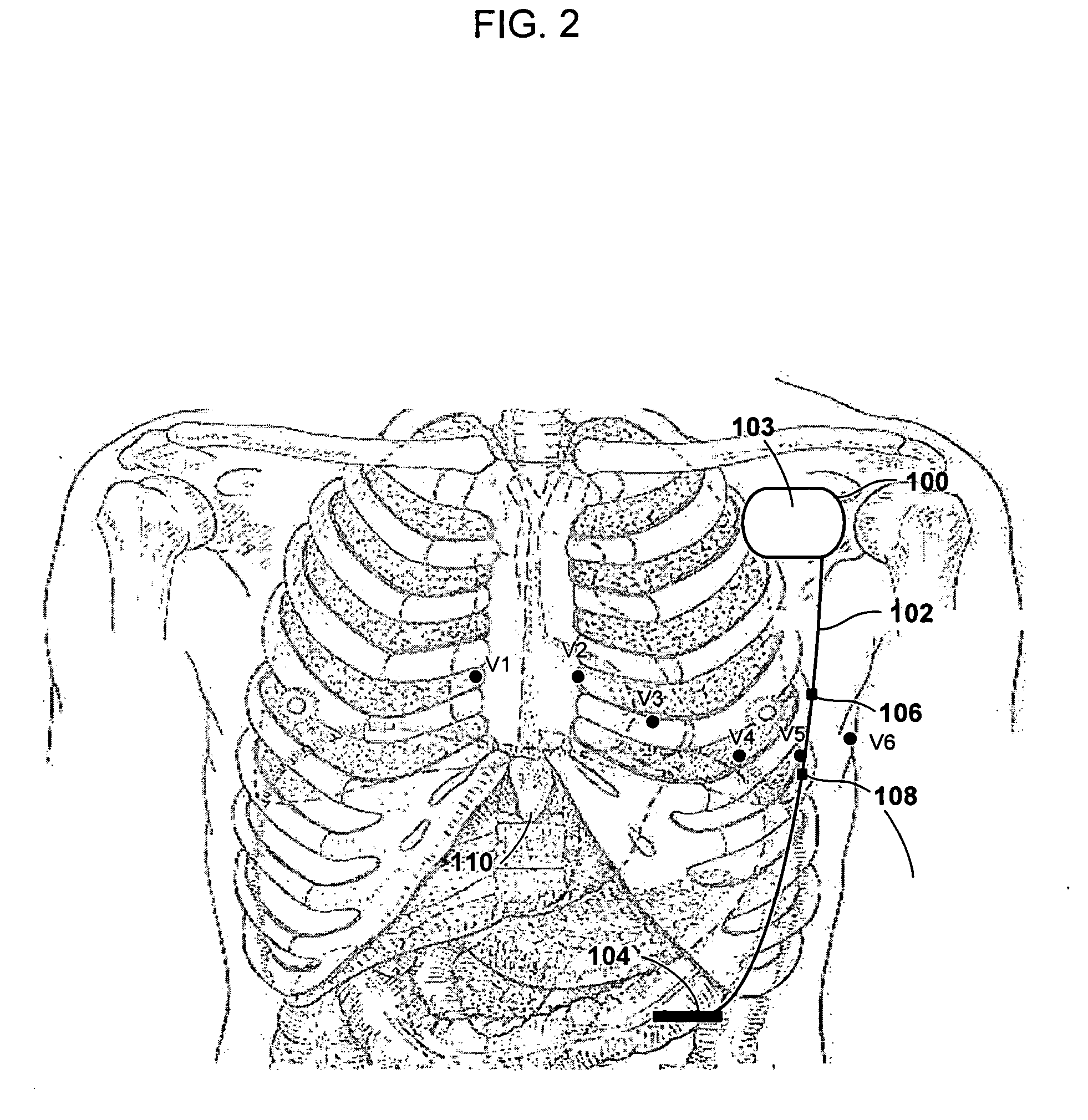
A medical system includes a housing configured for implantation within a patient's subclavicular region. Detection circuitry provided in the housing is configured to detect cardiac electrical activity. Energy delivery circuitry provided in the housing is configured to deliver therapy to treat a detected tachycardia or fibrillation episode. A lead is coupled to the housing, detection circuitry, and energy delivery circuitry. The lead is configured for subcutaneous, non-intrathoracic placement within the patient, and extends from the subclavicular region to just below the patient's ribs or the subxiphoid process. A defibrillation electrode is provided at a distal end of the lead body. A pair of sensing electrodes is provided on the lead body at locations consistent with positions V2-V5 of surface electrocardiogram electrodes.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Methods for adjusting cardiac detection criteria and implantable medical devices using same
InactiveUS6873870B2Quick checkAccurate identificationElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsHemodynamically stableHemodynamic measurements
Implantable medical devices and methods of tachycardia detection that provide adjustable detection criteria based upon a hemodynamic parameter. In some embodiments, the apparatus and methods provide for detection and delivery of therapy for hemodynamically stable and hemodynamically unstable tachycardias by varying a number of intervals detected (NID) threshold based on hemodynamic measurements.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for displaying information retrieved from an implanted medical device
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Classification of supraventricular and ventricular cardiac rhythms using cross channel timing algorithm
InactiveUS20050159781A1ElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisCardiac cycleVentricular tachycardia
A system and method for classifying cardiac complexes sensed during a tachycardia episode. A first cardiac signal and a second cardiac signal are sensed, where the first cardiac signal has a voltage. A first cardiac complex and a second cardiac complex of a cardiac cycle are detected in the first and second cardiac signal, respectively. A predetermined alignment feature is identified in the second cardiac complex. A datum is defined, or positioned, at a specified interval from the predetermined alignment feature of the second cardiac complex. Voltage values are then measured from the first cardiac complex at each of two or more measurement intervals from the datum. The voltage values are then compared voltage values measured from NSR cardiac complexes to classify the first cardiac complex is either a ventricular tachycardia complex or a supraventricular tachycardiac complex.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Methods of coagulating tissue
InactiveUS20060206113A1Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesRadio frequencyLesion
An embodiment of the invention includes a surgical device for coagulating soft tissue such as atrial tissue in the treatment of atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and atrial tachycardia; tendon or ligament shrinkage; or articular cartilage removal. The surgical device integrates a suction mechanism with the coagulation mechanism improving the lesion creation capabilities of the device. The surgical device comprises an elongate member having an insulative covering attached about conductive elements capable of coagulating soft tissue when radiofrequency or direct current energy is transmitted to the conductive elements. Openings through the insulative covering expose regions of the conductive elements and are coupled to lumens in the elongate member which are routed to a vacuum source. Suction causes the soft tissue to actively engage the opening thus the integrated, exposed conductive elements to facilitate the coagulation process and ensure the lesions created are consistent, continuous, and transmural. The embodiments of the invention can also incorporate cooling mechanisms associated with the conductive elements and coupled to a fluid source to passively transport fluid along the contacted soft tissue surface to cool thus pushing the maximum temperature deeper into tissue.
Owner:ATRICURE
System for performing and monitoring minimally invasive interventions
InactiveUS8548567B2Reliable eliminationQuality improvementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyProcess measurementWork flow
The present invention relates to a system for performing and monitoring minimally invasive interventions with an x-ray unit, in which at least one x-ray source and one x-ray detector can traverse a circular track through an angle range, an ECG recording unit, an imaging catheter, a mapping unit with a mapping catheter and an ablation unit with an ablation catheter. The system comprises a control and evaluation unit with interfaces for the units and catheters, which enable an exchange of data with the control and evaluation unit. The control and evaluation unit is designed for processing measurement or image data which it receives from the catheters and units, and for controlling the catheters and units for the capture of the measurement or image data. The workflow from the examination through to the therapy, particularly with regard to the treatment of tachycardial arrhythmias, is covered completely and continuously by the proposed system.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for detection and treatment of tachycardia and fibrillation
InactiveUS6879856B2Precise deliveryQuickly and accurately classifyingHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsSoftware systemVentricular tachycardia
The invention relates to devices that detect and / or treat tachyarrhythmias. The invention includes software systems that distinguish among various tachyarrhythmias in order to provide treatment for specific tachyarrhythmias. One aspect of the invention employs a methodology to provisionally detect ventricular tachycardia and / or fibrillation and thereafter apply a discrimination function to a series of measured intervals preceding the provisional detection. Discrimination is accomplished by sorting the intervals preceding provisional detection into bins corresponding to interval ranges and examining the relative distribution of the intervals within the bins.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Vacuum coagulation probes
InactiveUS20060200124A1Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesArticular cartilageLesion
An embodiment of the invention includes a surgical device for coagulating soft tissue such as atrial tissue in the treatment of atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and atrial tachycardia; tendon or ligament shrinkage; or articular cartilage removal. The surgical device integrates a suction mechanism with the coagulation mechanism improving the lesion creation capabilities of the device. The surgical device comprises an elongate member having an insulative covering attached about conductive elements capable of coagulating soft tissue when radiofrequency or direct current energy is transmitted to the conductive elements. Openings through the insulative covering expose regions of the conductive elements and are coupled to lumens in the elongate member which are routed to a vacuum source. Suction causes the soft tissue to actively engage the opening thus the integrated, exposed conductive elements to facilitate the coagulation process and ensure the lesions created are consistent, continuous, and transmural. The embodiments of the invention can also incorporate cooling mechanisms associated with the conductive elements and coupled to a fluid source to passively transport fluid along the contacted soft tissue surface to cool thus pushing the maximum temperature deeper into tissue.
Owner:ATRICURE
Methods for adjusting cardiac detection criteria and implantable medical devices using same
InactiveUS20020188215A1ElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsHemodynamically stableHemodynamic measurements
Implantable medical devices and methods of tachycardia detection that provide adjustable detection criteria based upon a hemodynamic parameter. In some embodiments, the apparatus and methods provide for detection and delivery of therapy for hemodynamically stable and hemodynamically unstable tachycardias by varying a number of intervals detected (NID) threshold based on hemodynamic measurements.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Mapping and Ablation Method for the Treatment of Ventricular Tachycardia
ActiveUS20080281391A1ElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyVentricular outflow tractVentricular tachycardia
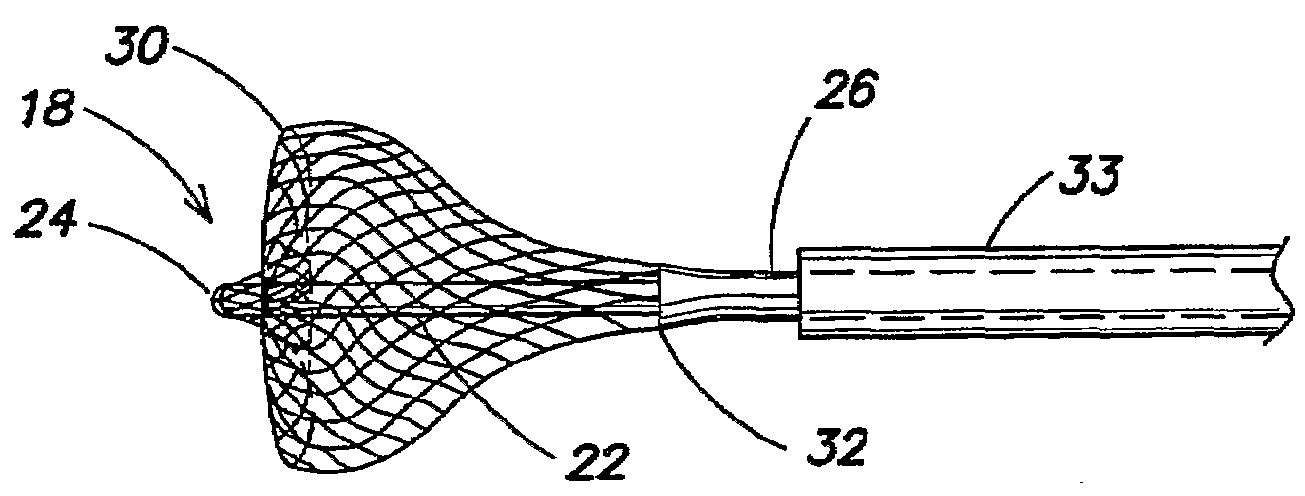
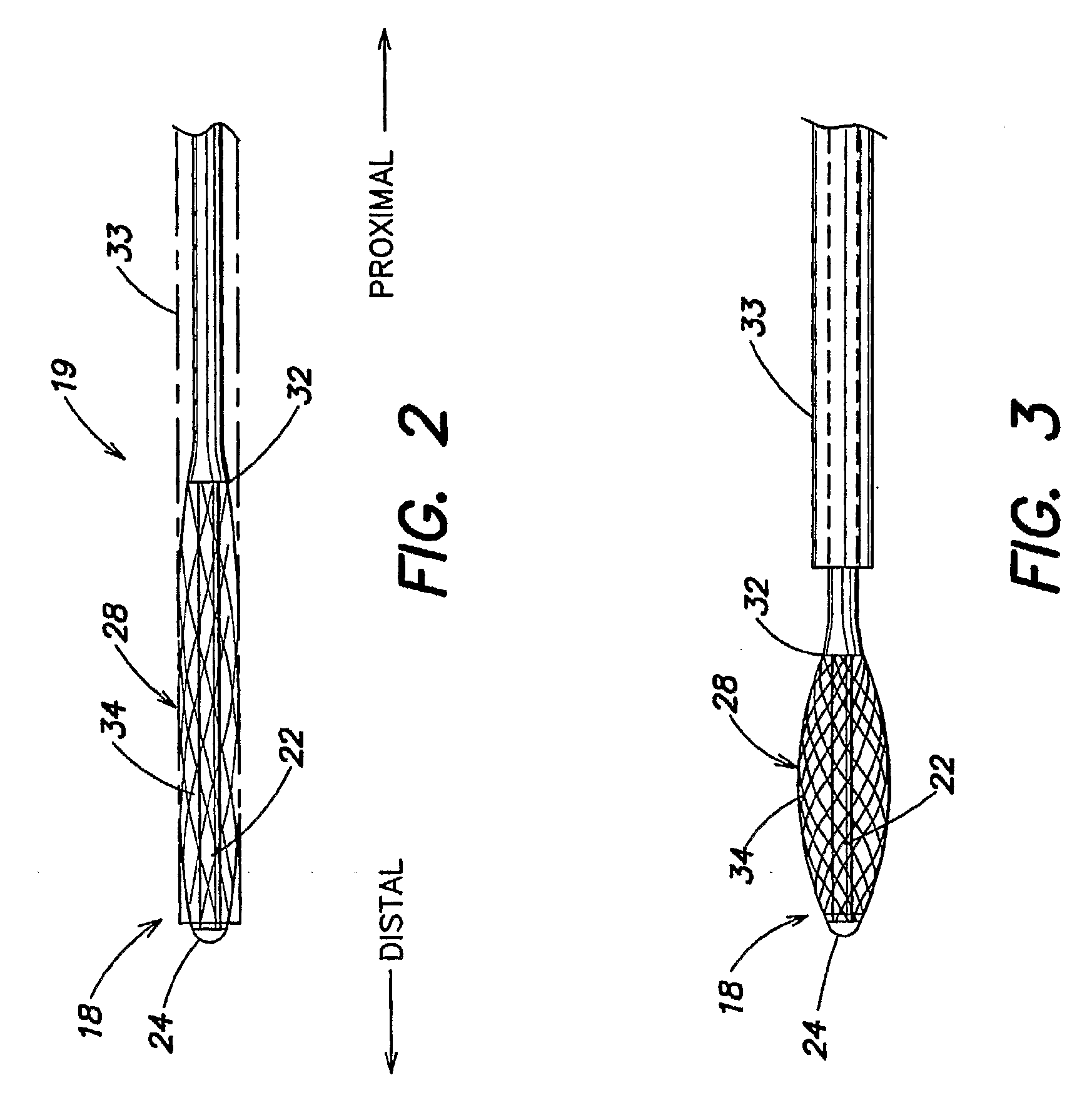
An apparatus for mapping and / or ablating tissue includes a braided conductive member that that may be inverted to provide a ring-shaped surface. When a distal tip of the braided conductive member is retracted within the braided conductive member, the lack of a protrusion allows the ring-shaped surface to contact a tissue wall such as a cardiac wall. In an alternative configuration, the braided conductive member may be configured with the distal portion forming a proboscis that can be used to stably position the braided conductive member relative to a blood vessel, such as a ventricular outflow tract. The braided conductive member has a plurality of electronically active sites that may be accessed individually for stable mapping over a broad area for stable mapping or ablation to form broad and deep lesions.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method of treating arrhythmias
InactiveUS20100004255A1Undesirable side-effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistrySide effectVentricular tachycardia
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
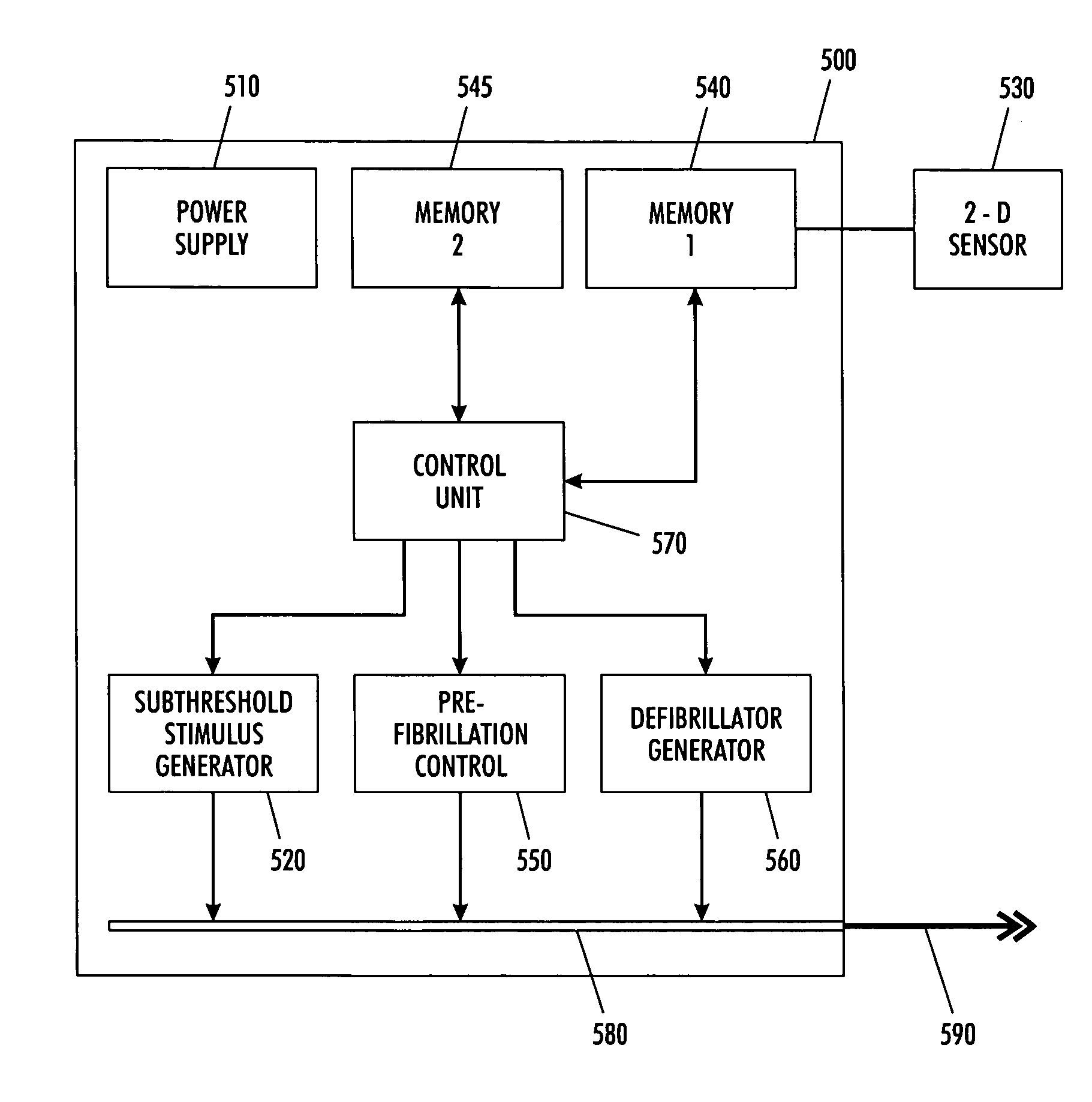
Fibrillation/tachycardia monitoring and preventive system and methodology
A cardiac assist device senses conditions of a heart and controls the generation of various electrical stimuli in response to sense conditions of the heart. The cardiac assist device generates a electrical pulse so as to defibrillate a fibrillated heart when the cardiac assist device determines from the sensed conditions a state of fibrillation. The cardiac assist device generates a chaos control electrical signal so as to bring a pre-fibrillated heart condition back into a normal beating condition when the cardiac assist device determines from the sensed conditions a pre-state of fibrillation. Lastly, the cardiac assist device generates an electrical enhancement signal that causes a threshold of pacing cells in the heart to be exceeded in response to a subthreshold stimulus when the cardiac assist device determines from the sensed conditions a subthreshold pacing signal.
Owner:ELECTROHEALING HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com