Patents
Literature
75 results about "Wearable cardioverter defibrillator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
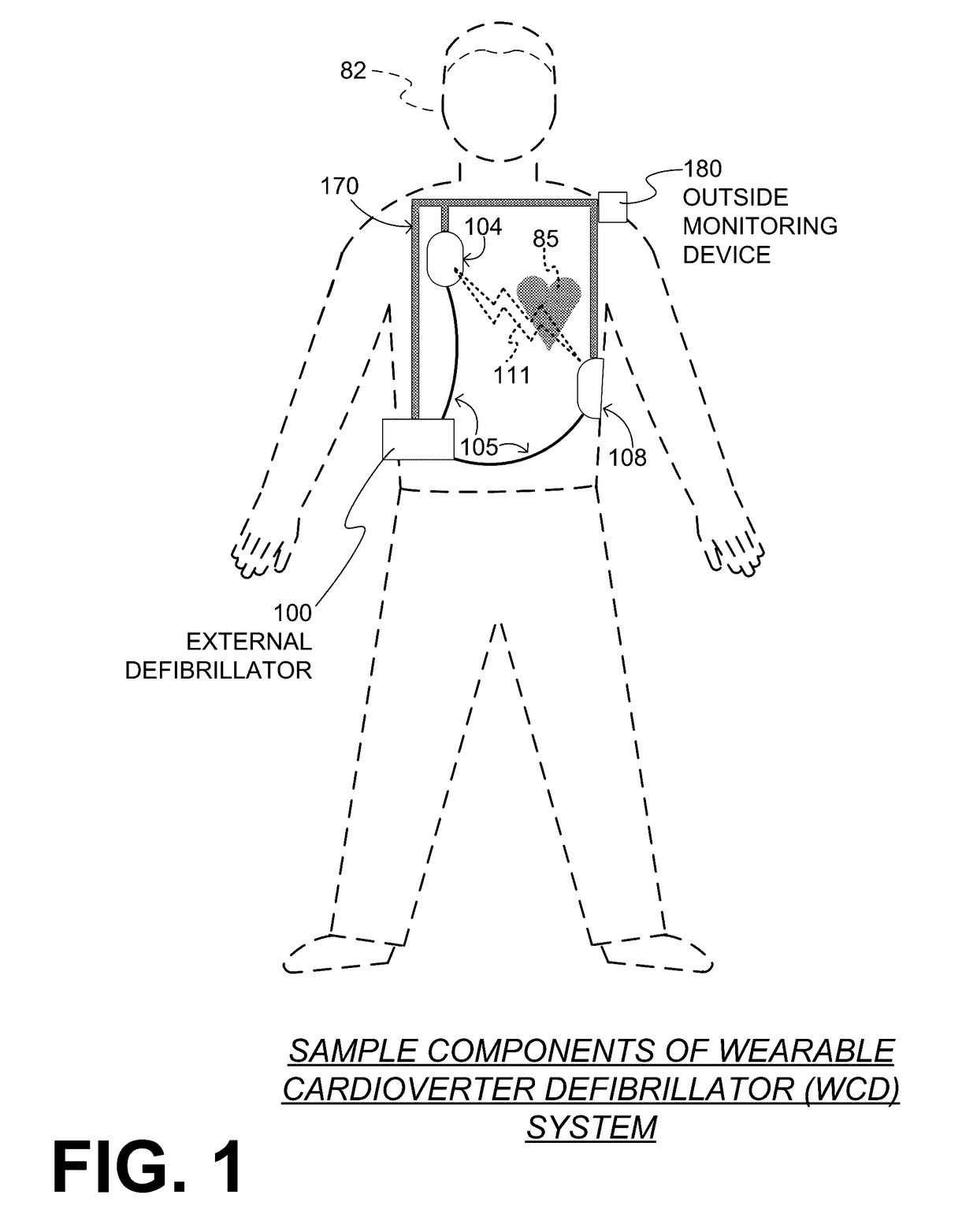
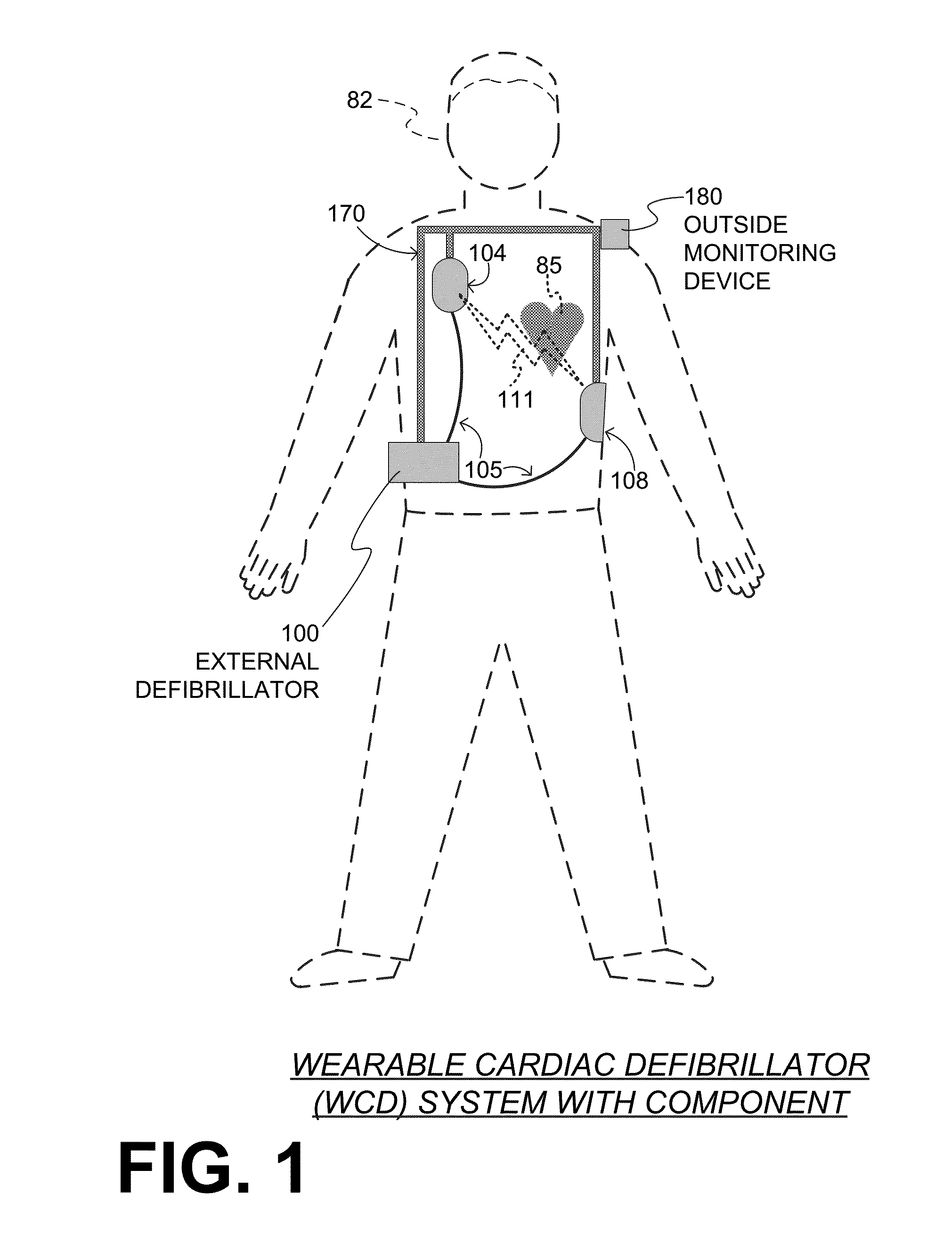
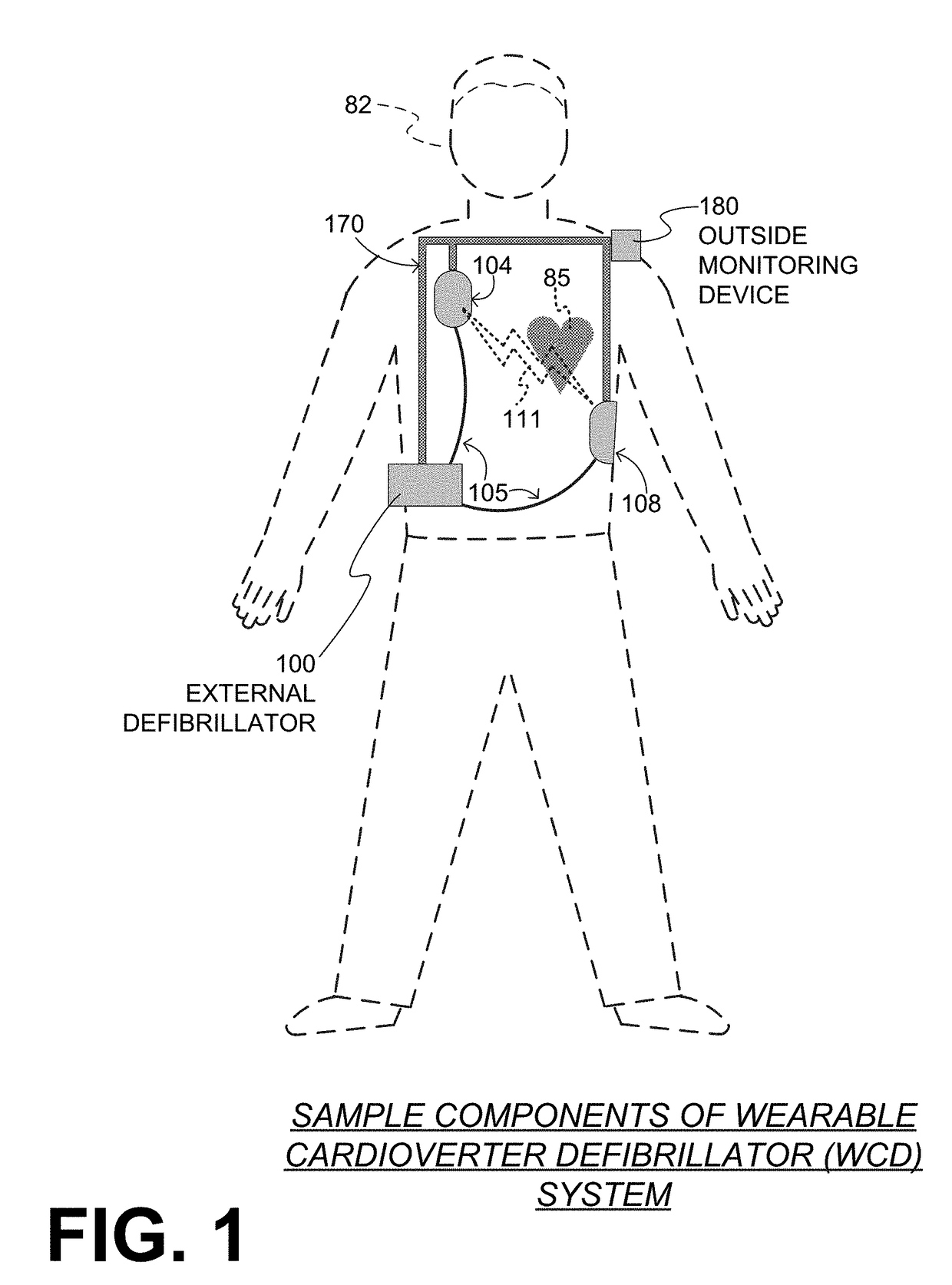
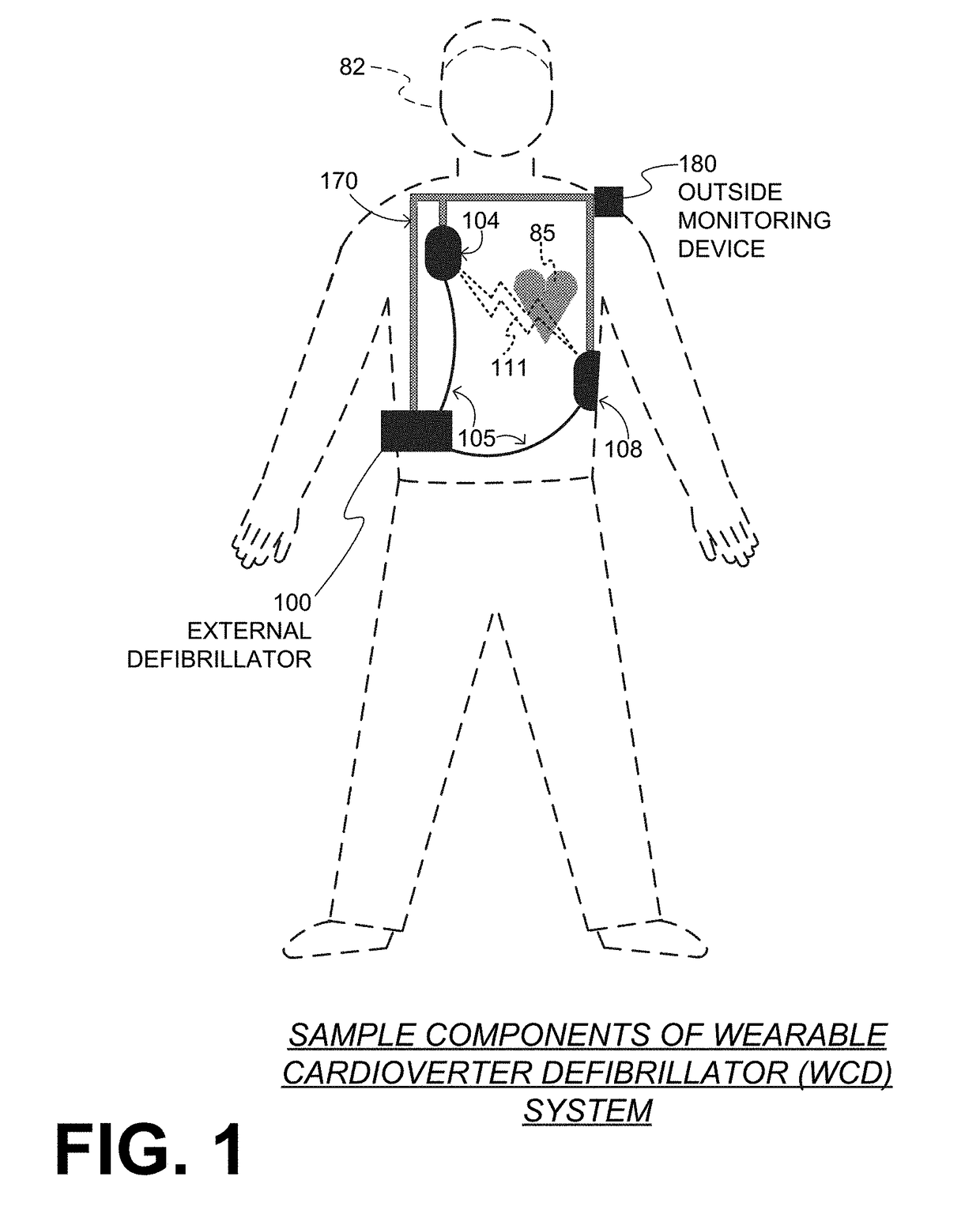
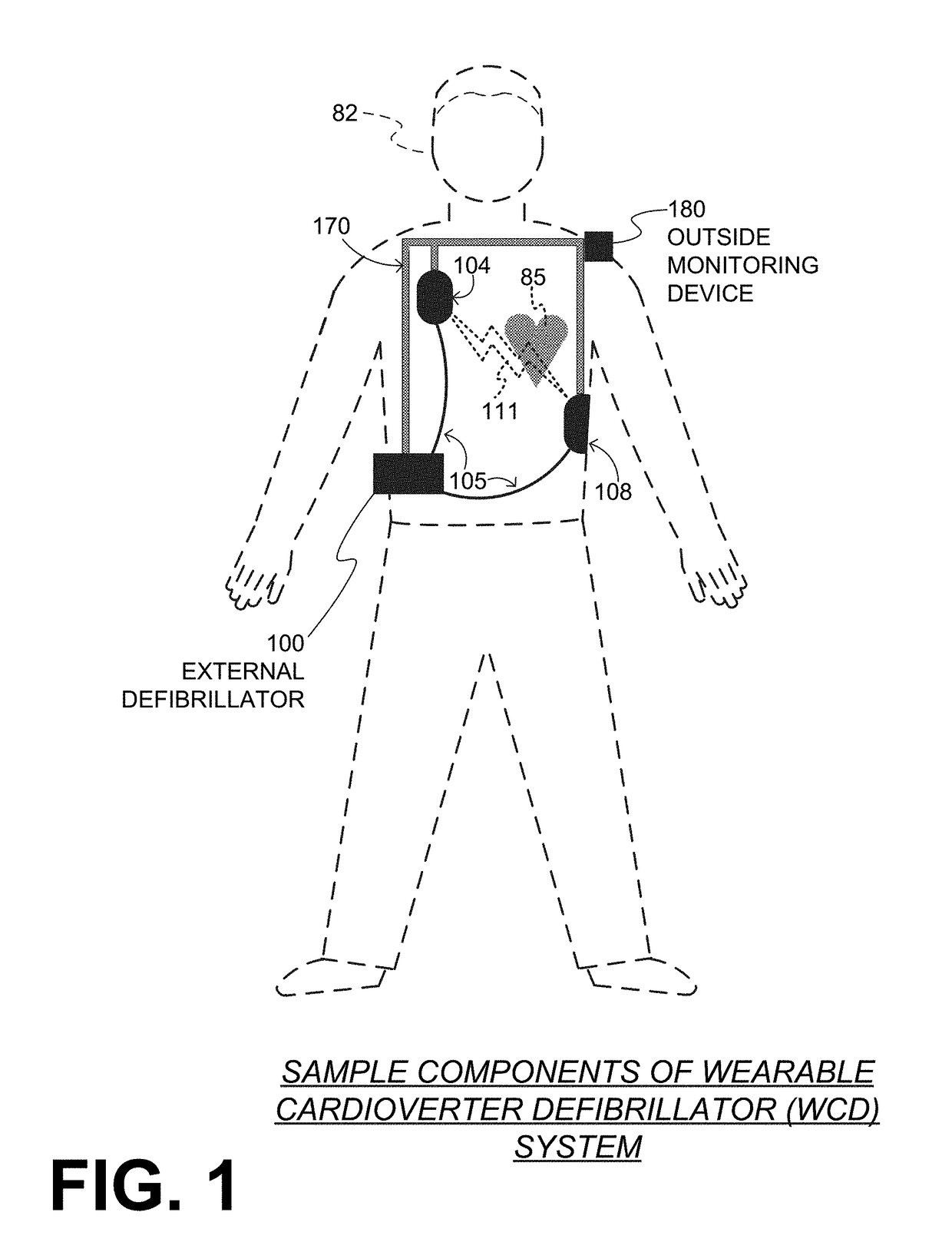
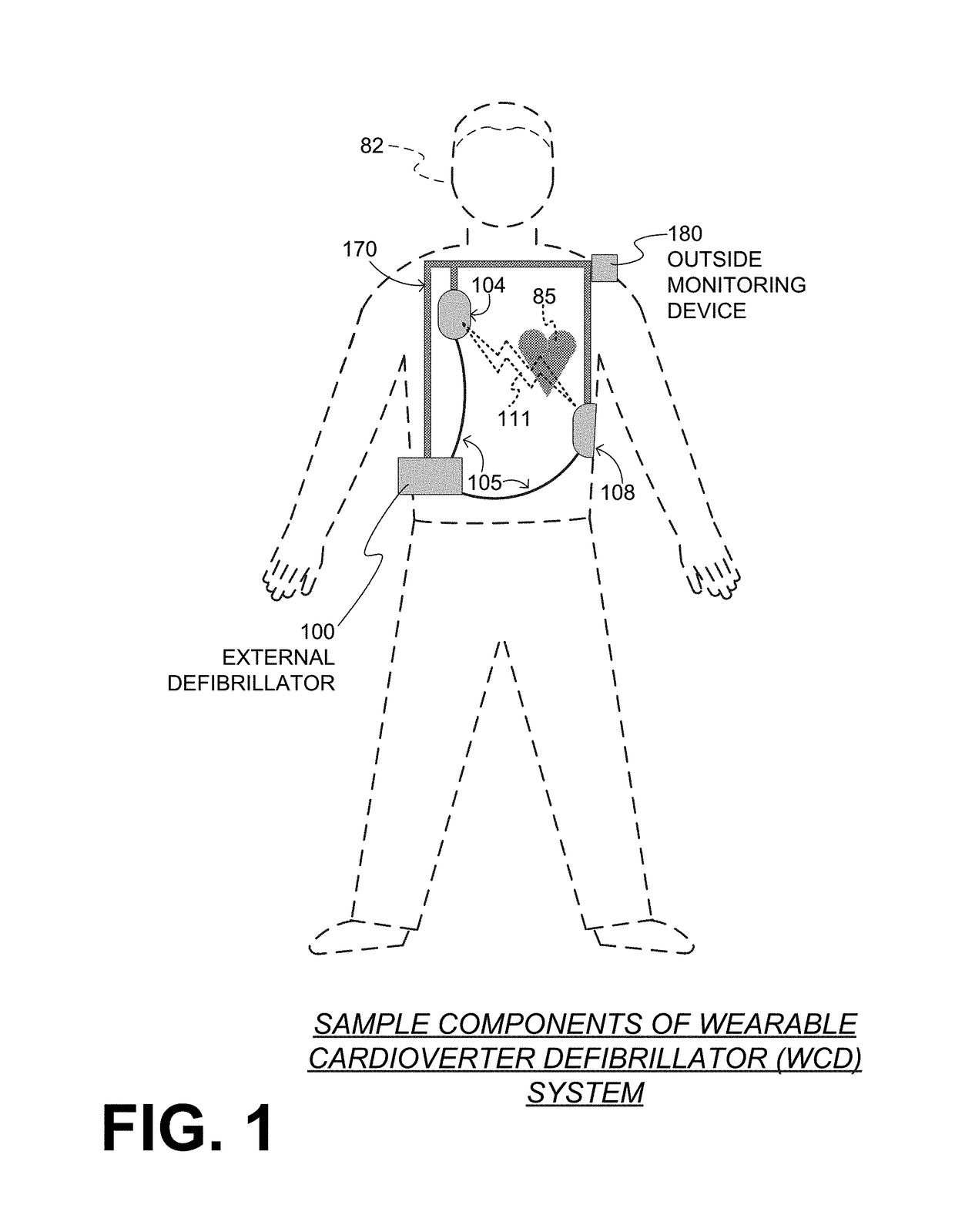
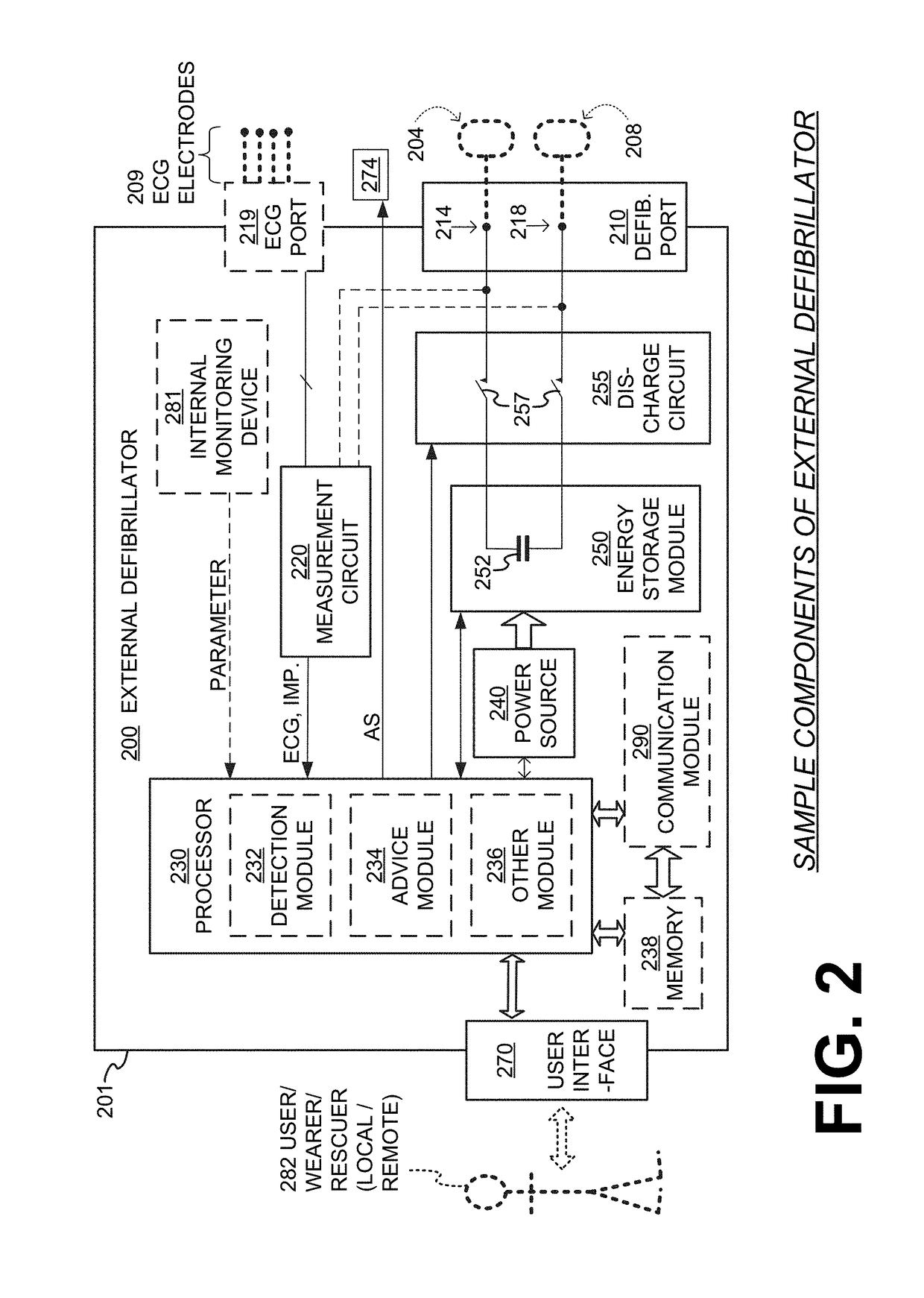
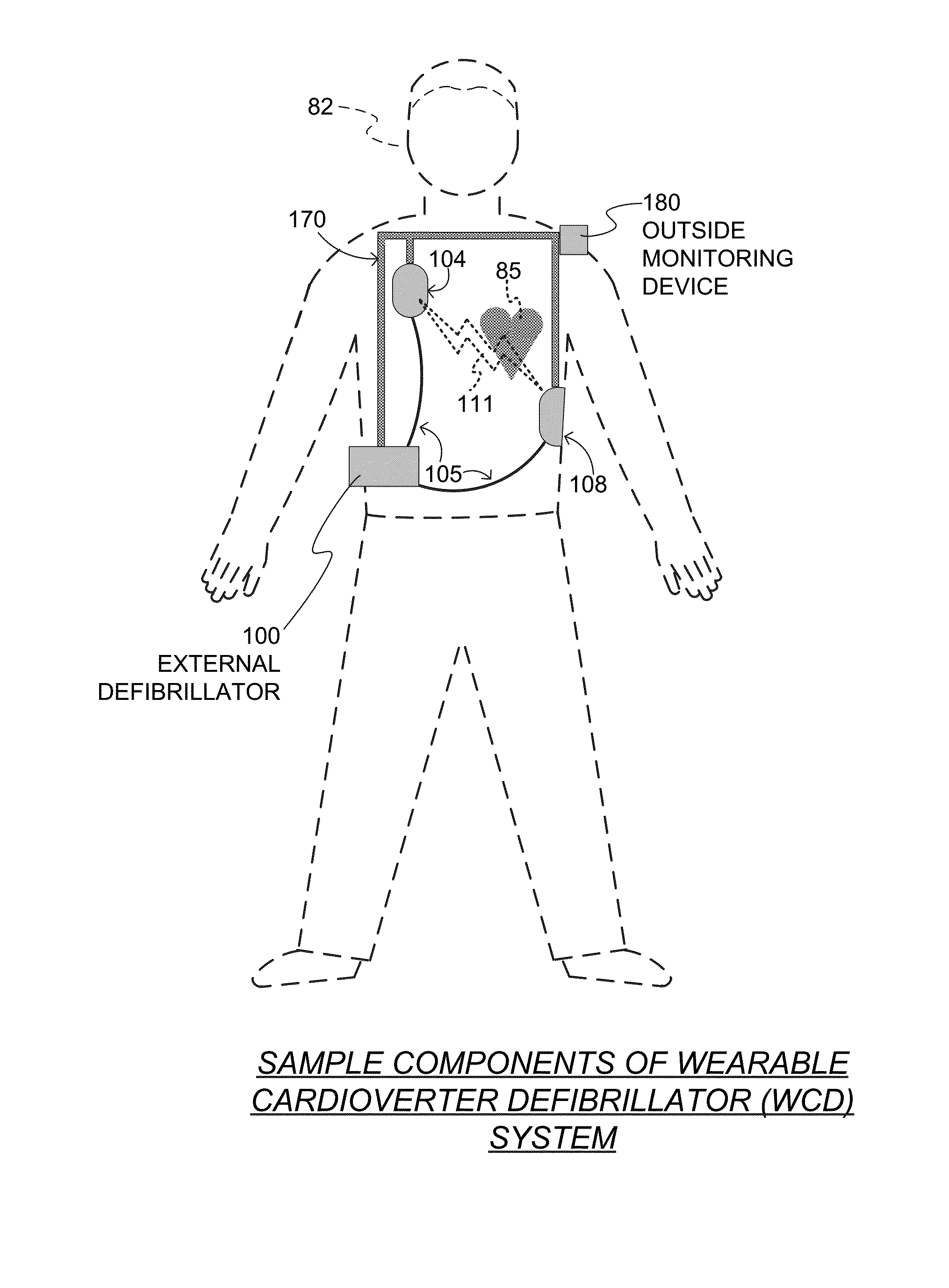
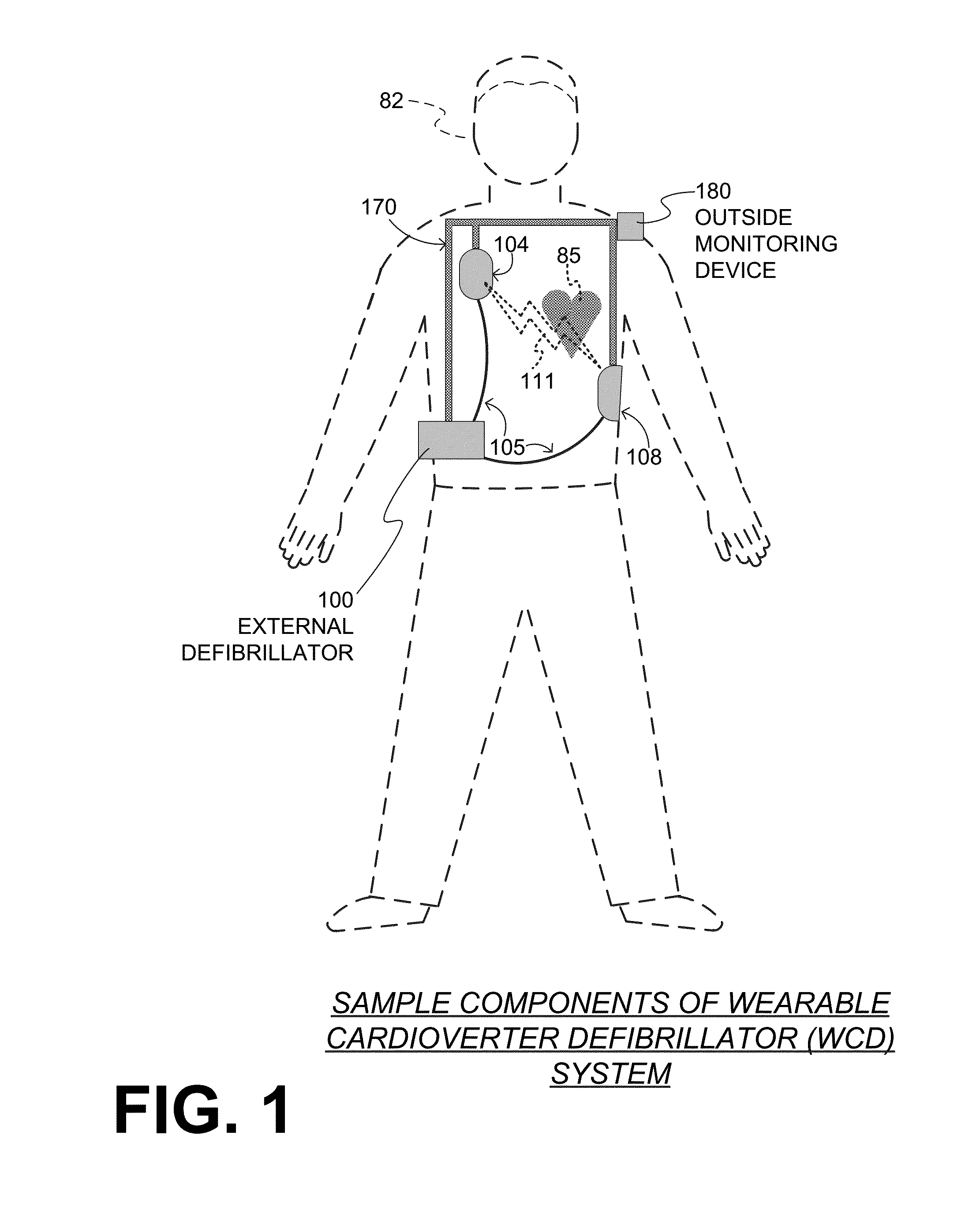
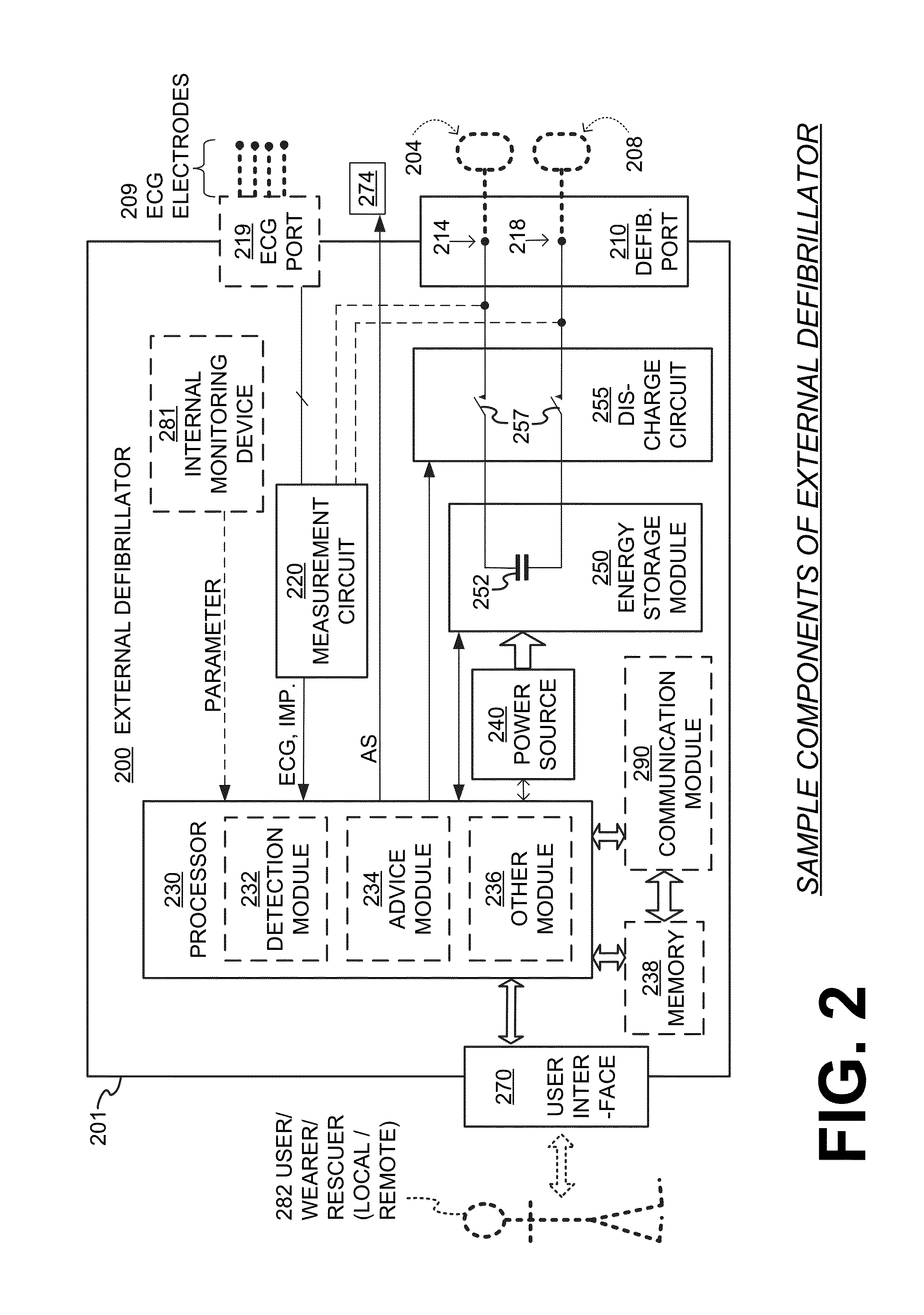
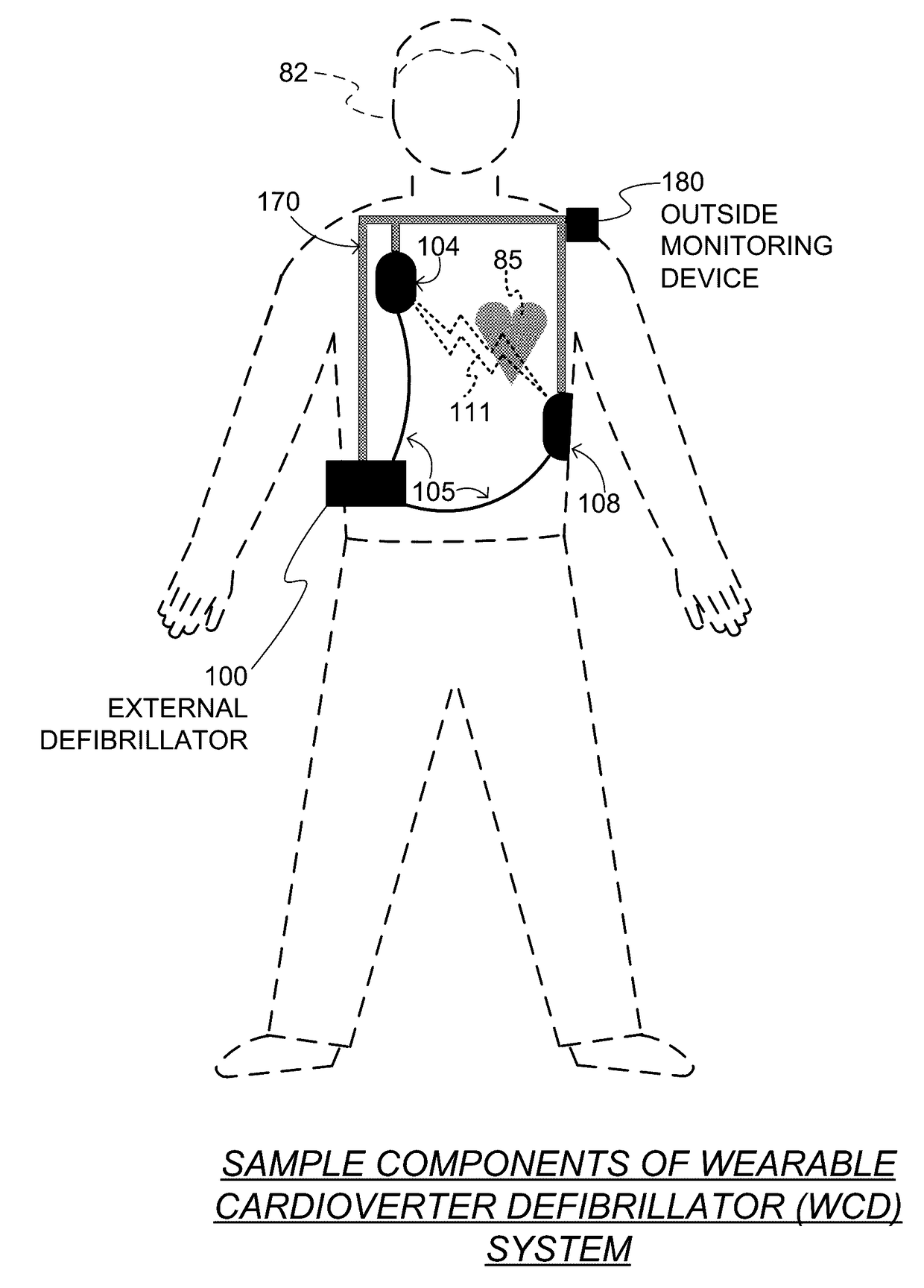
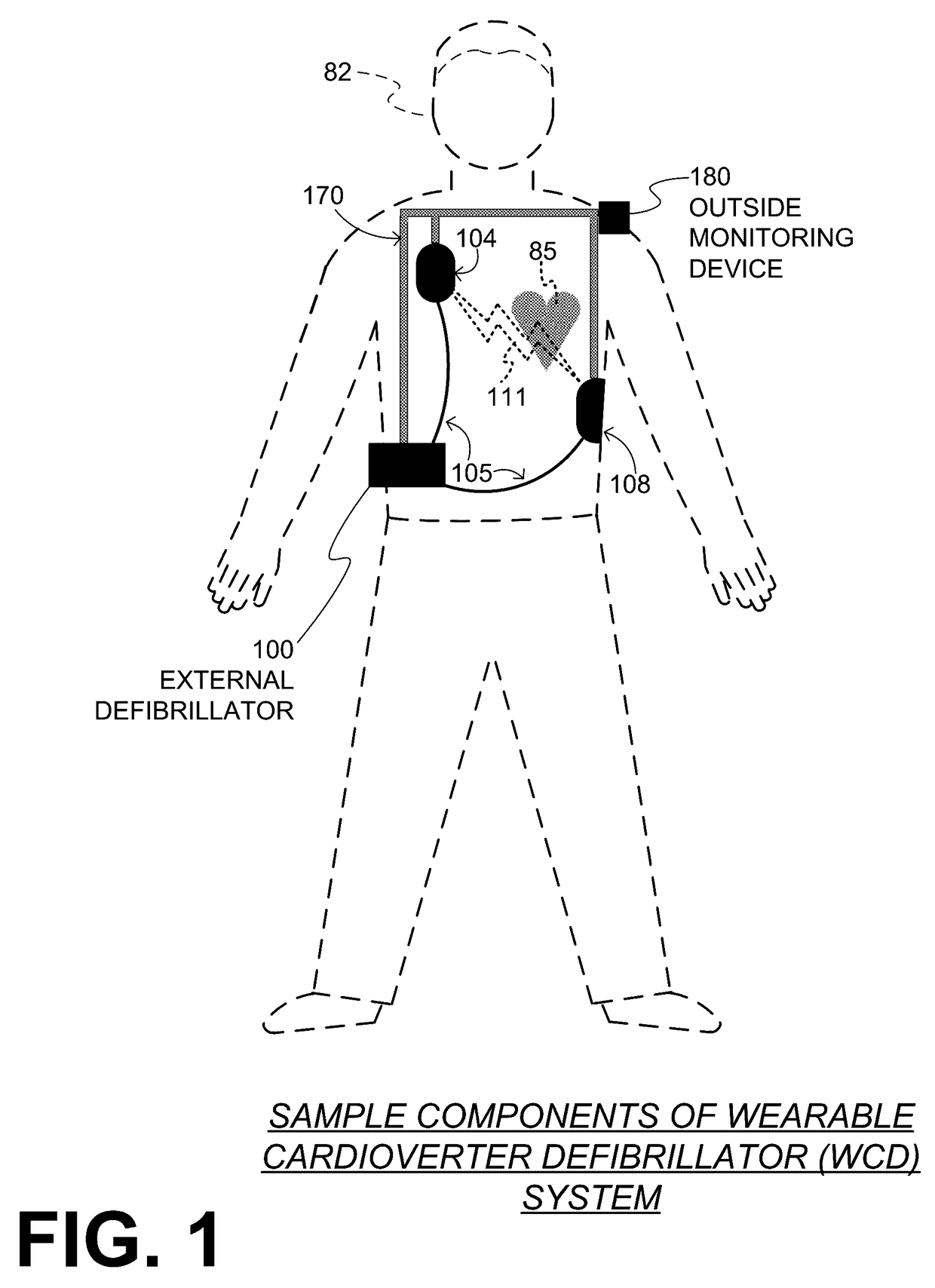
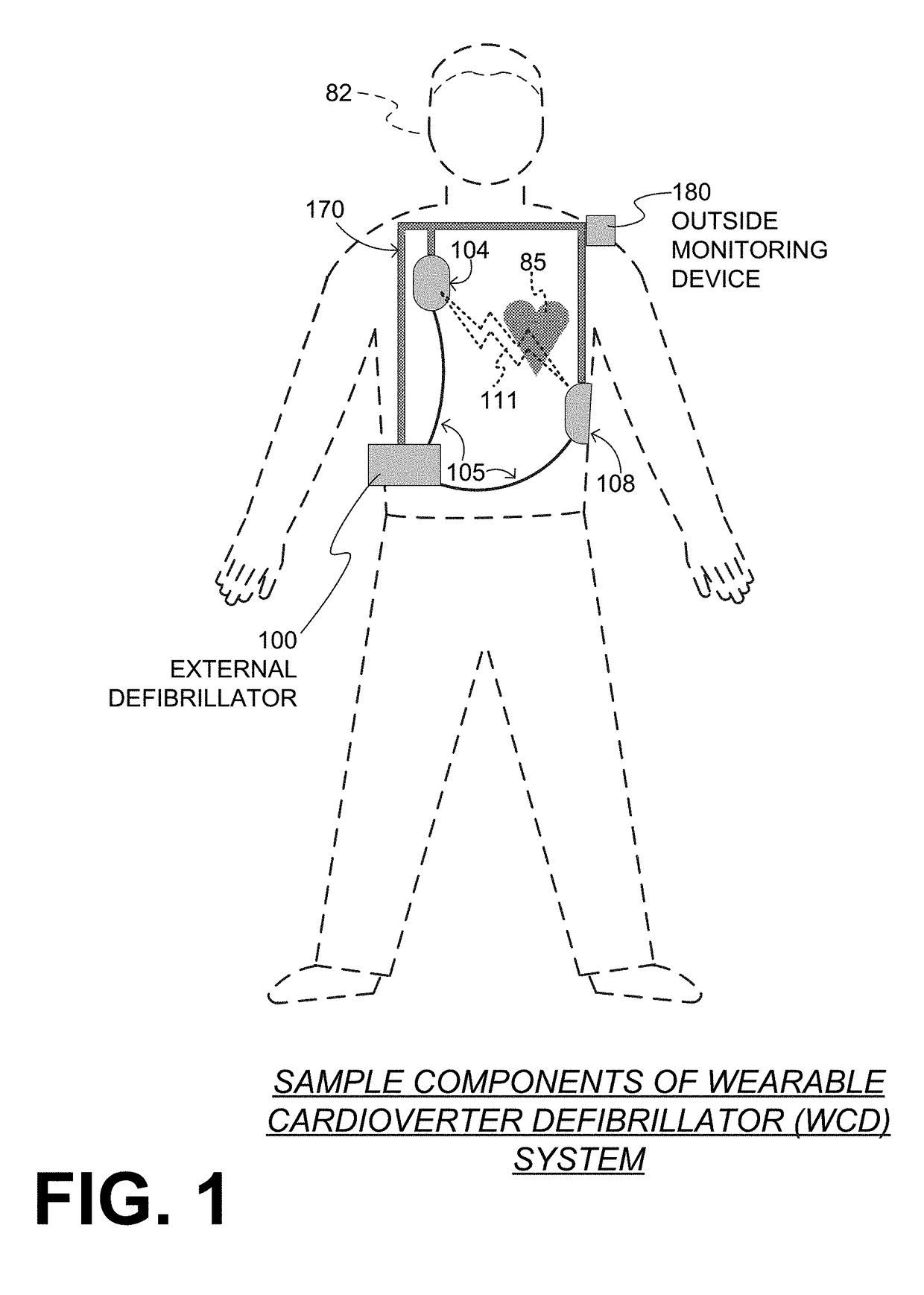
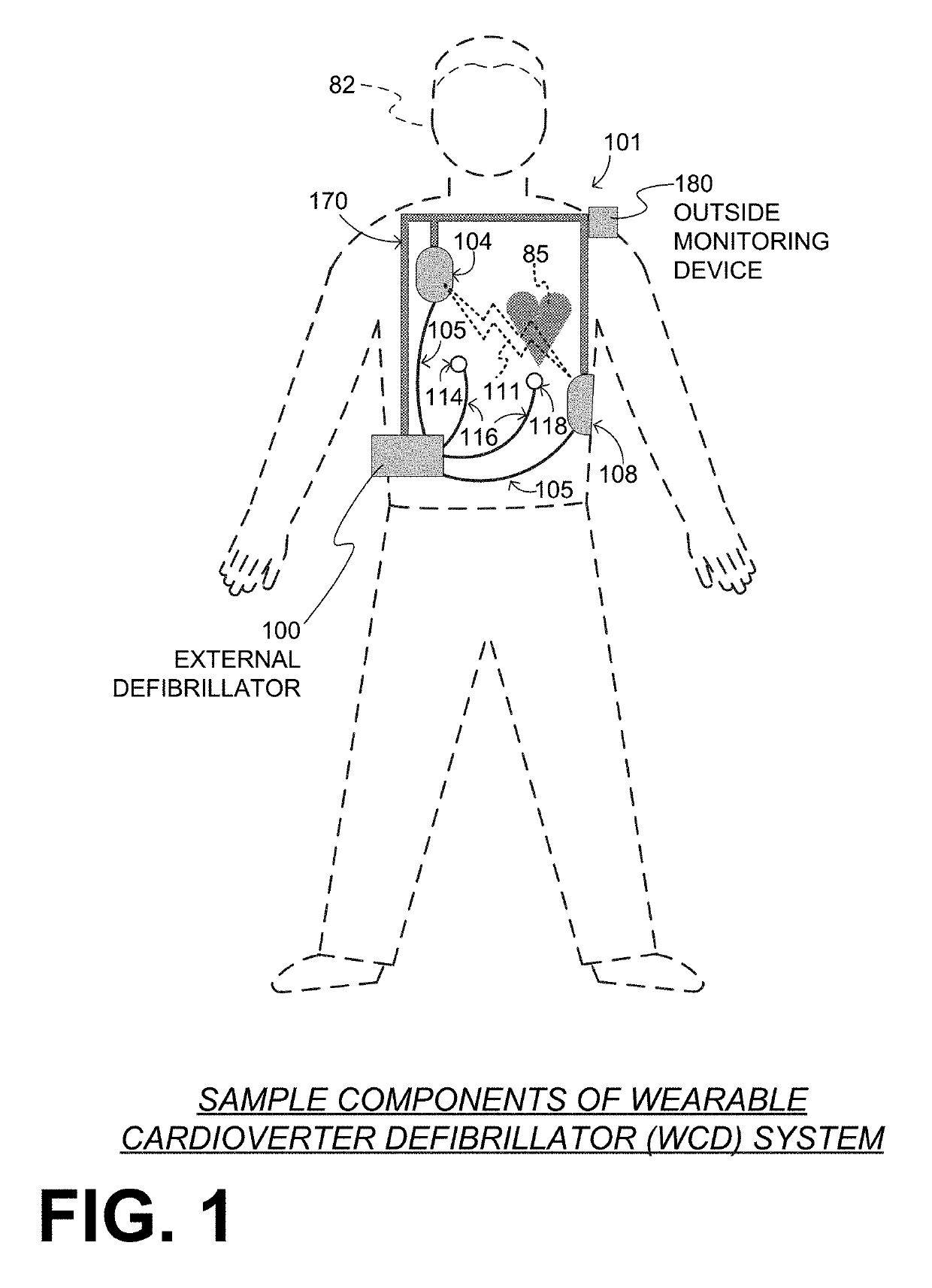
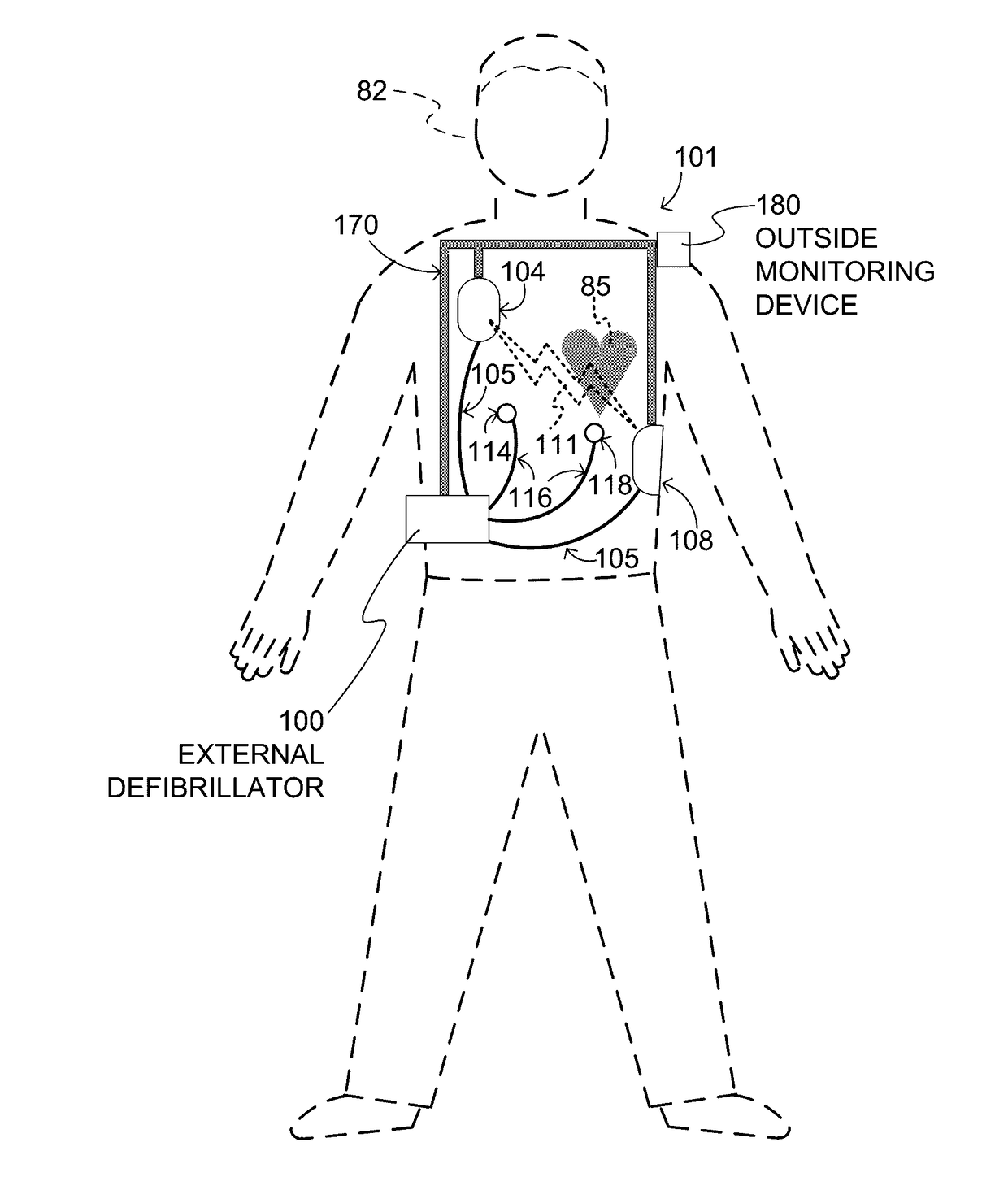
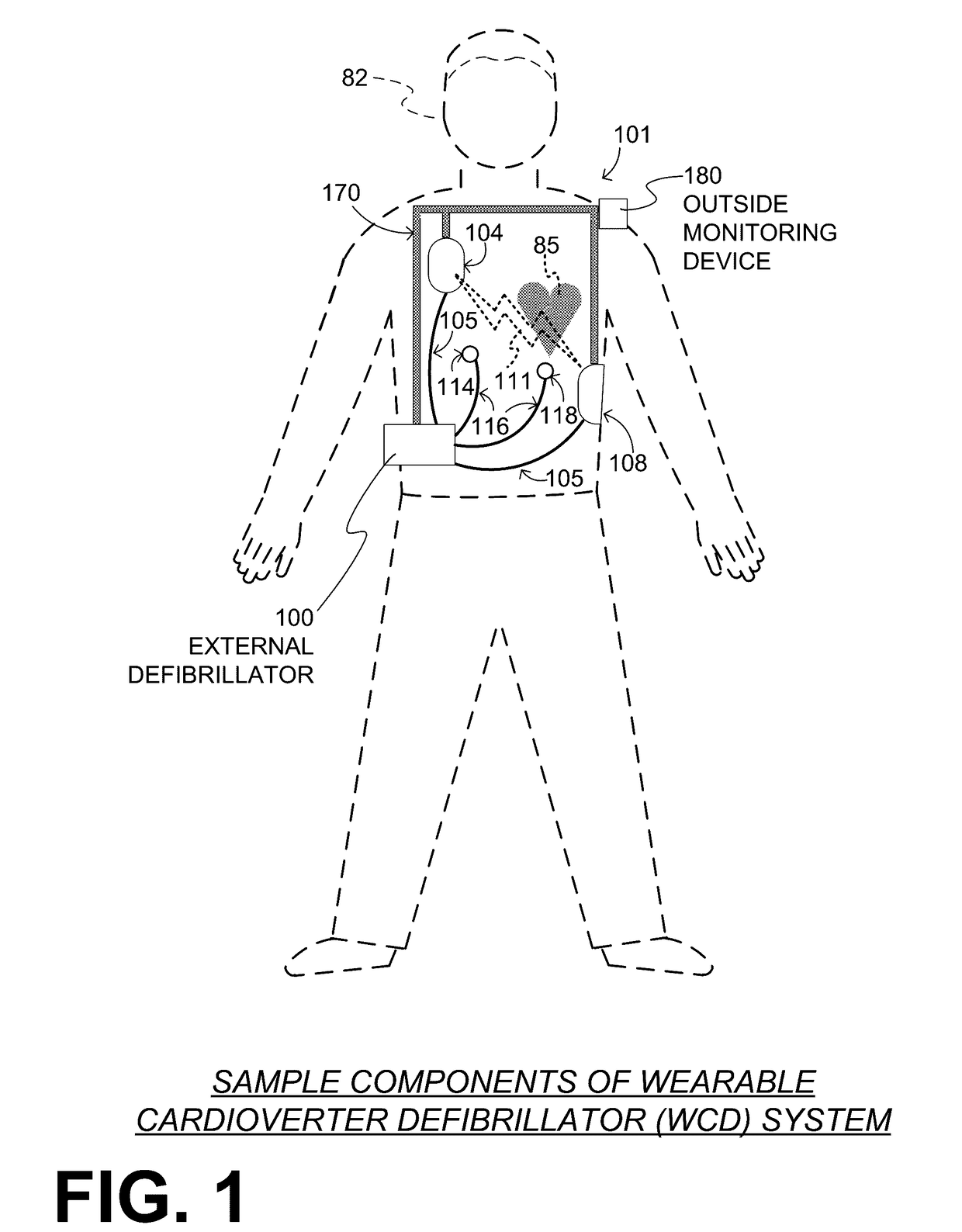
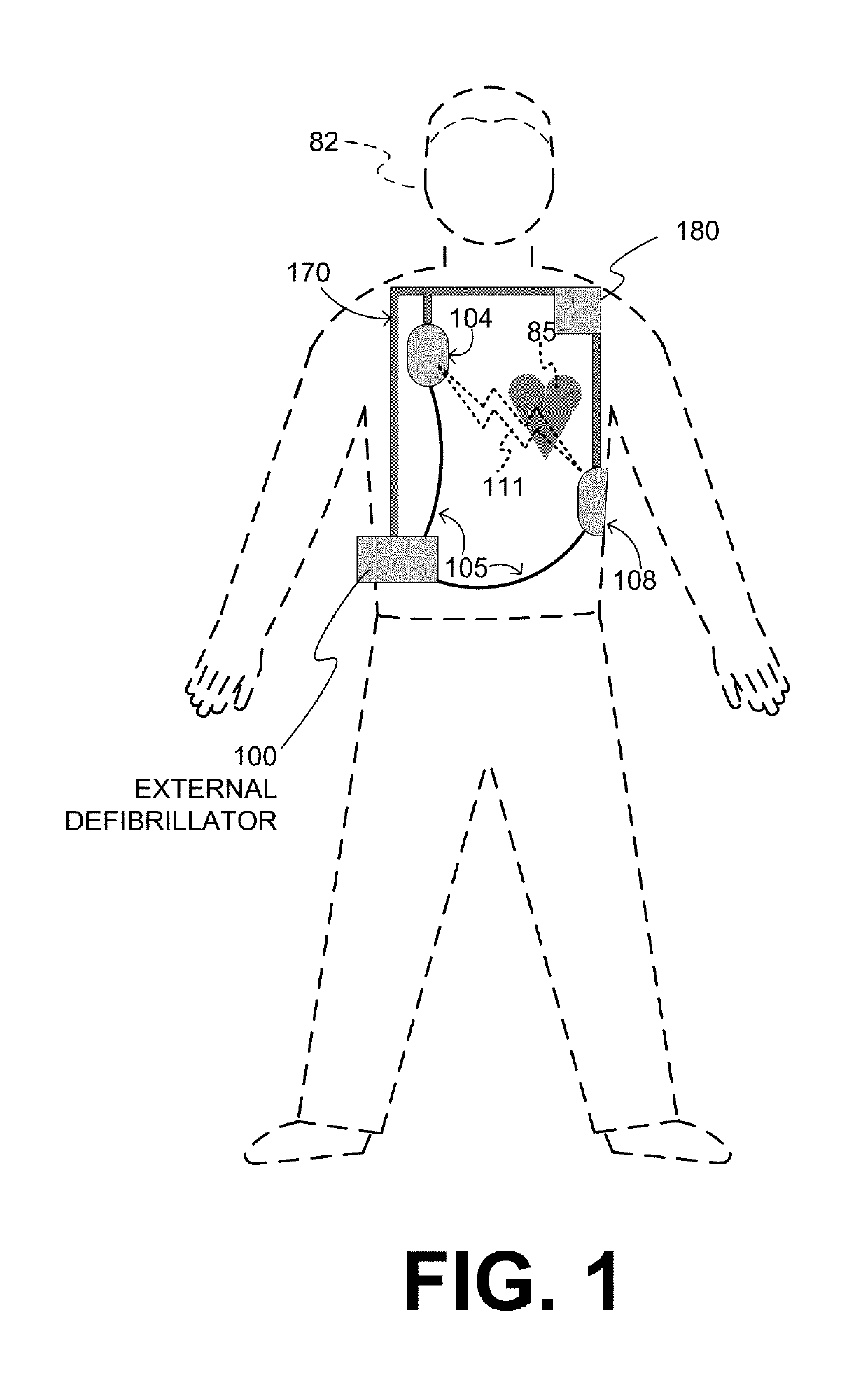
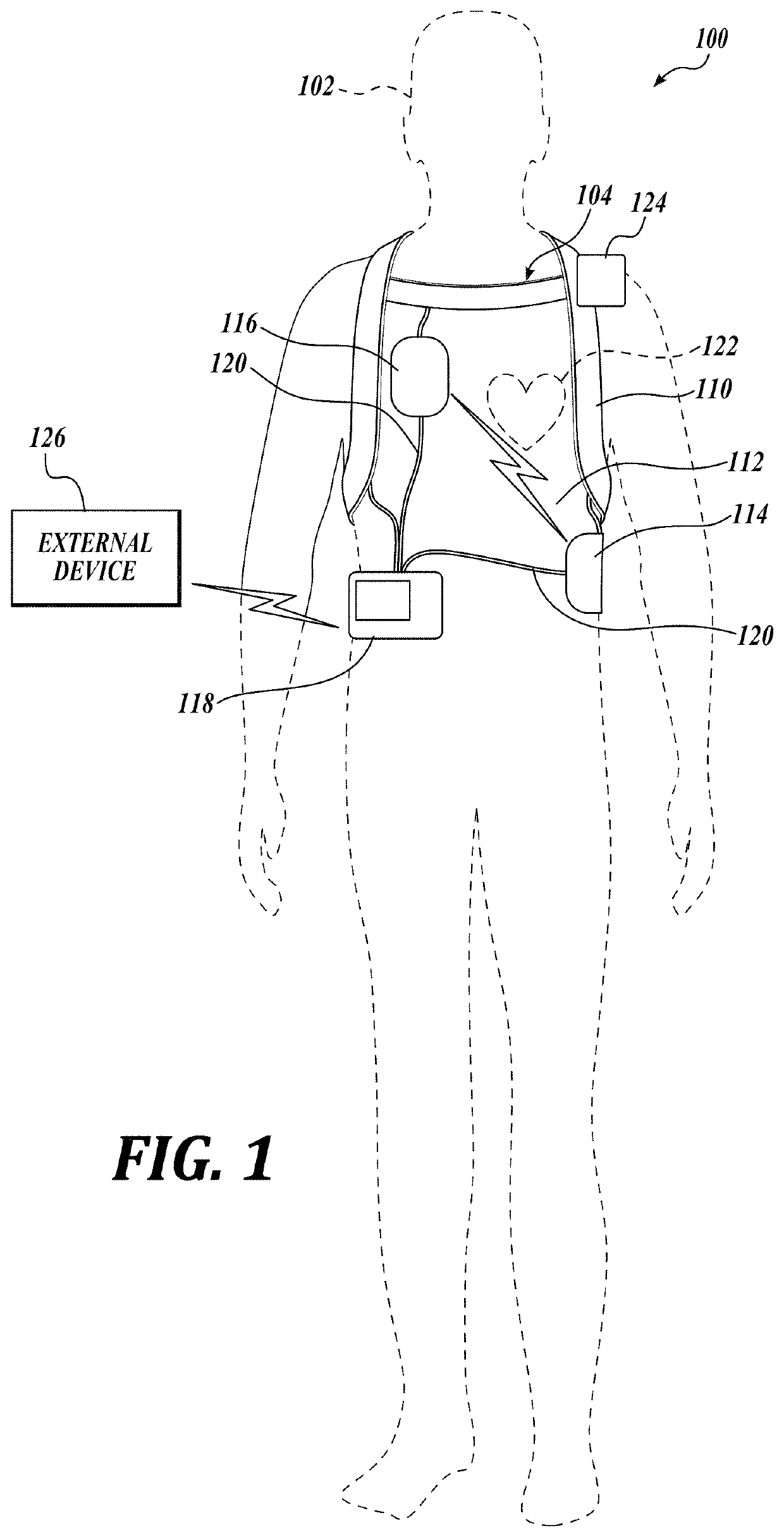
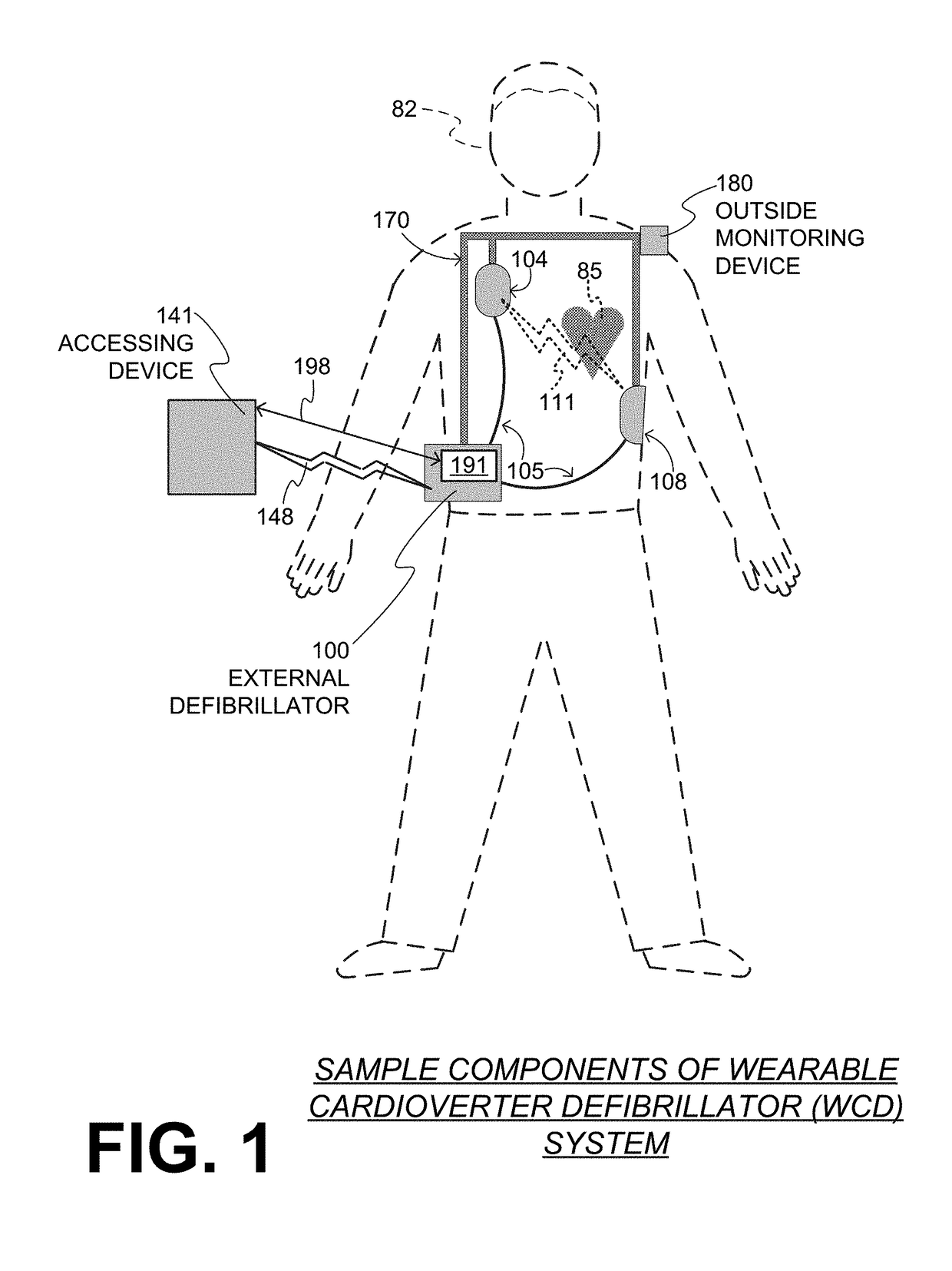
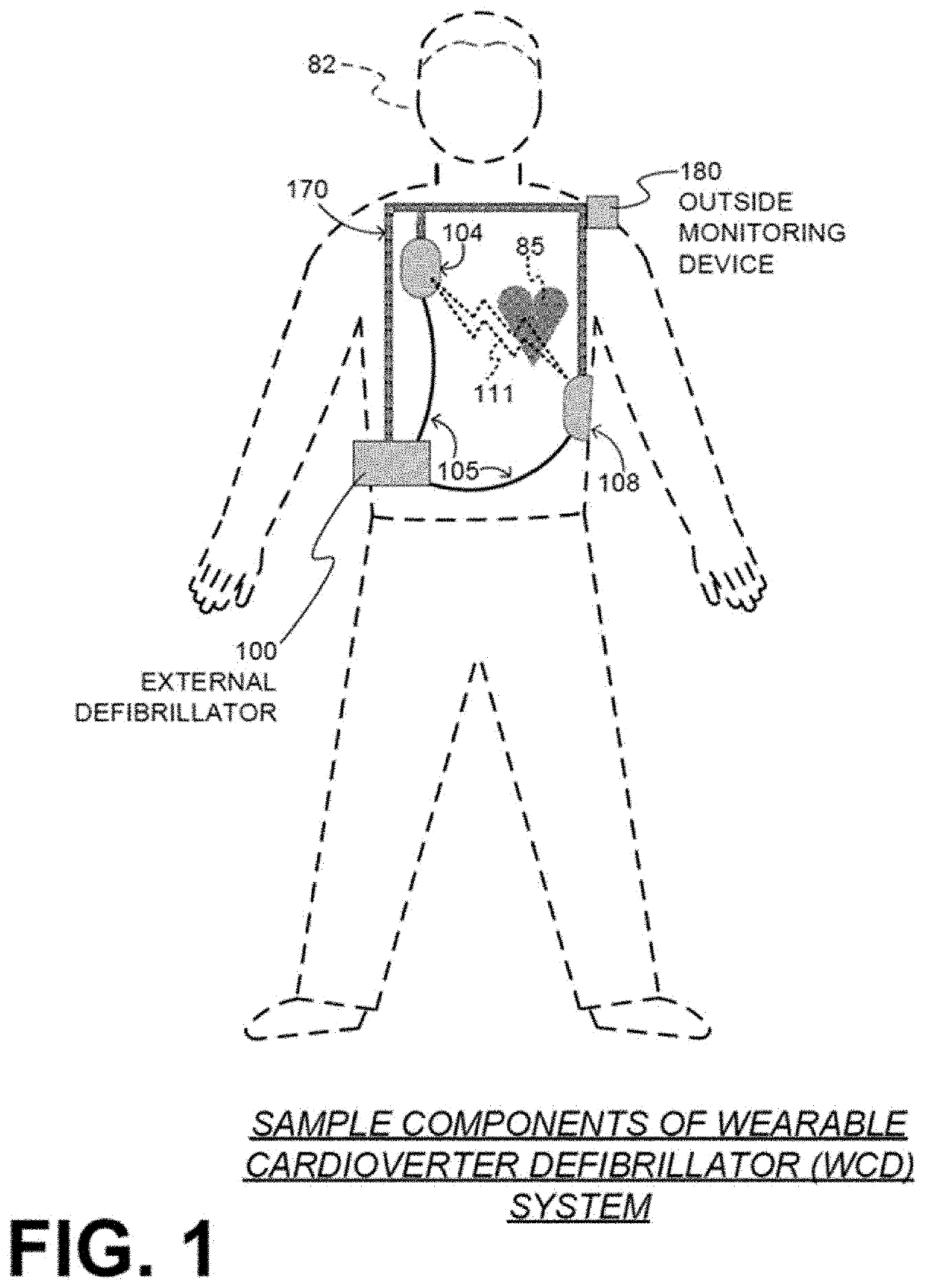
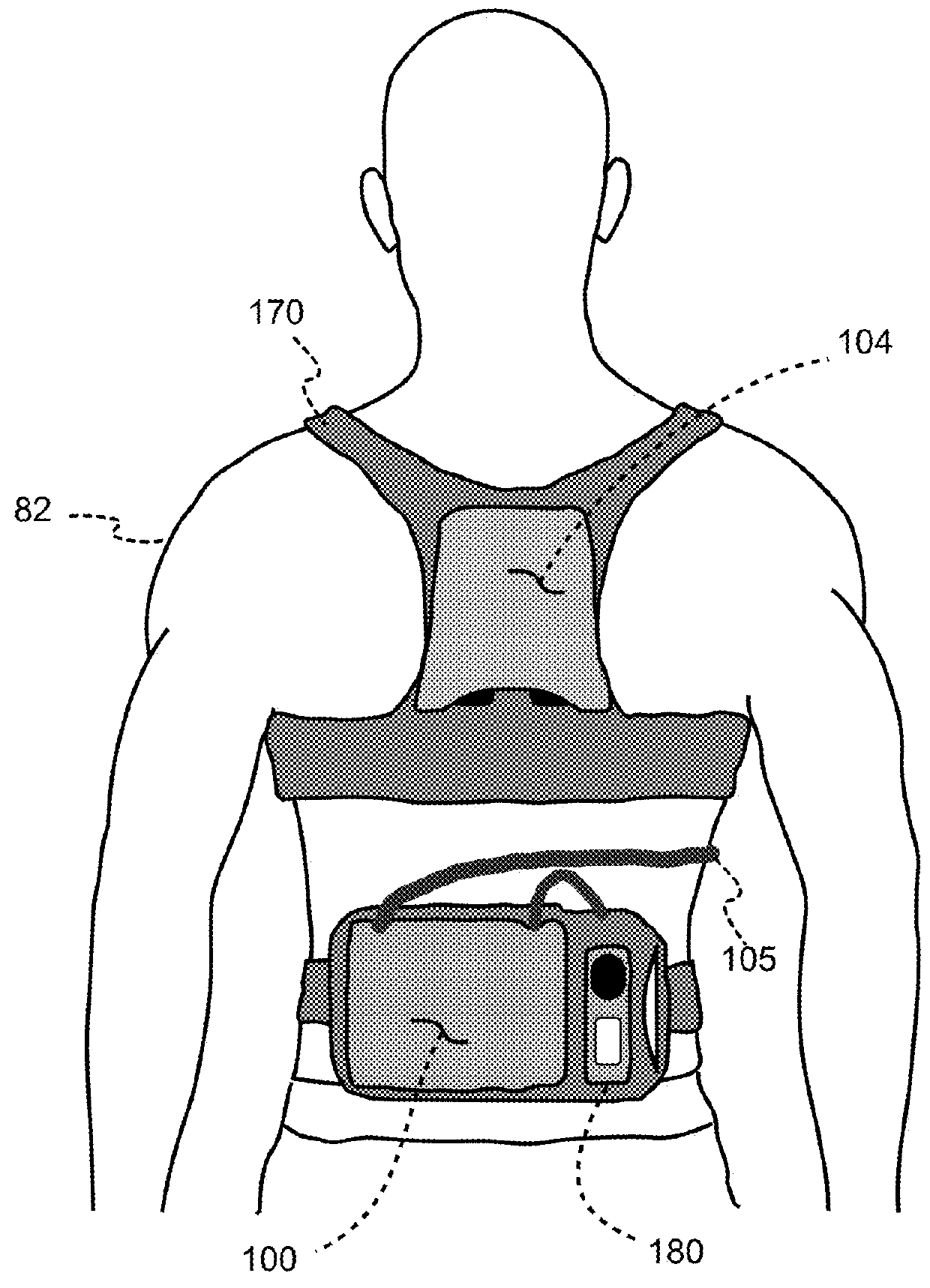
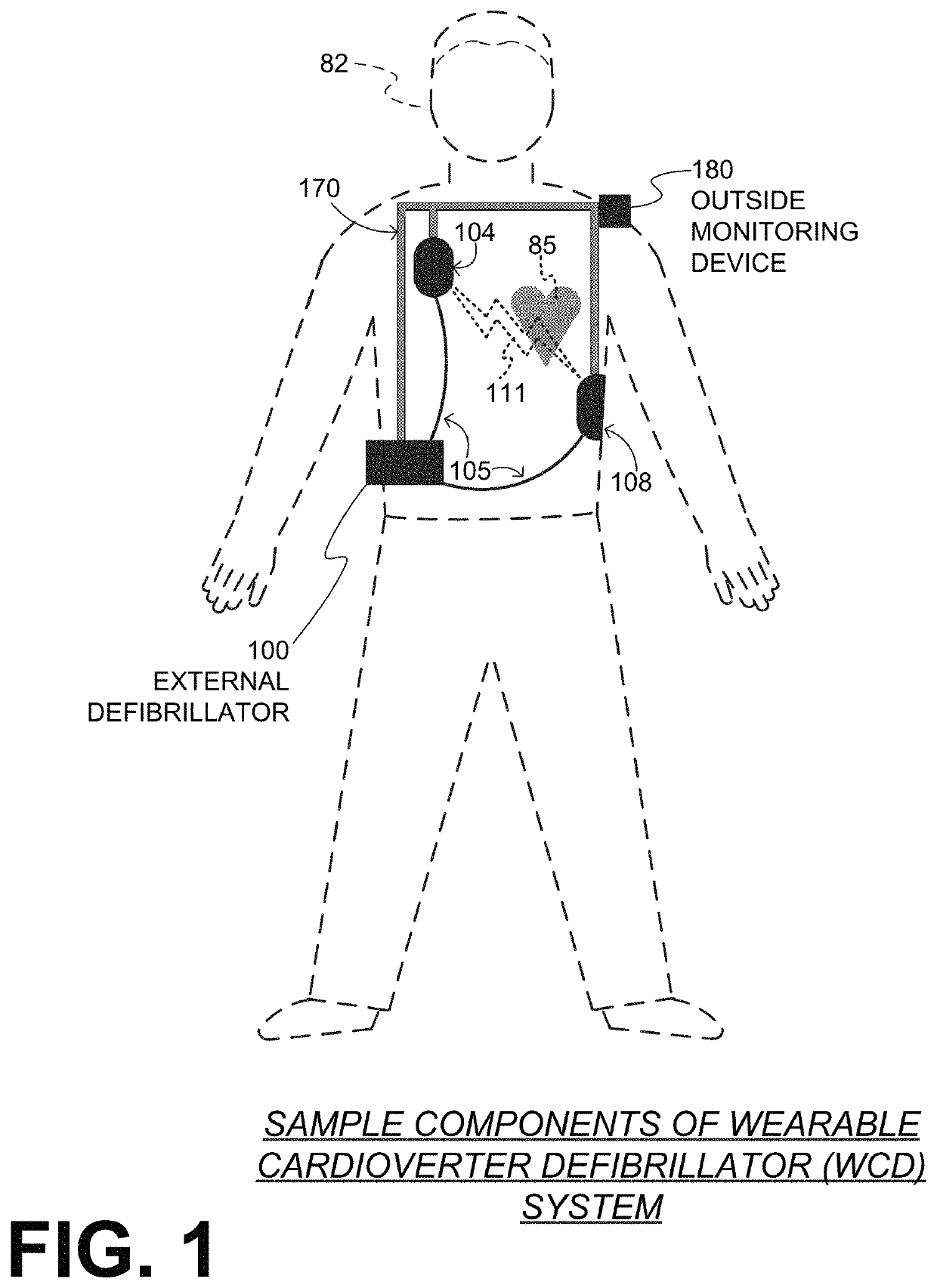
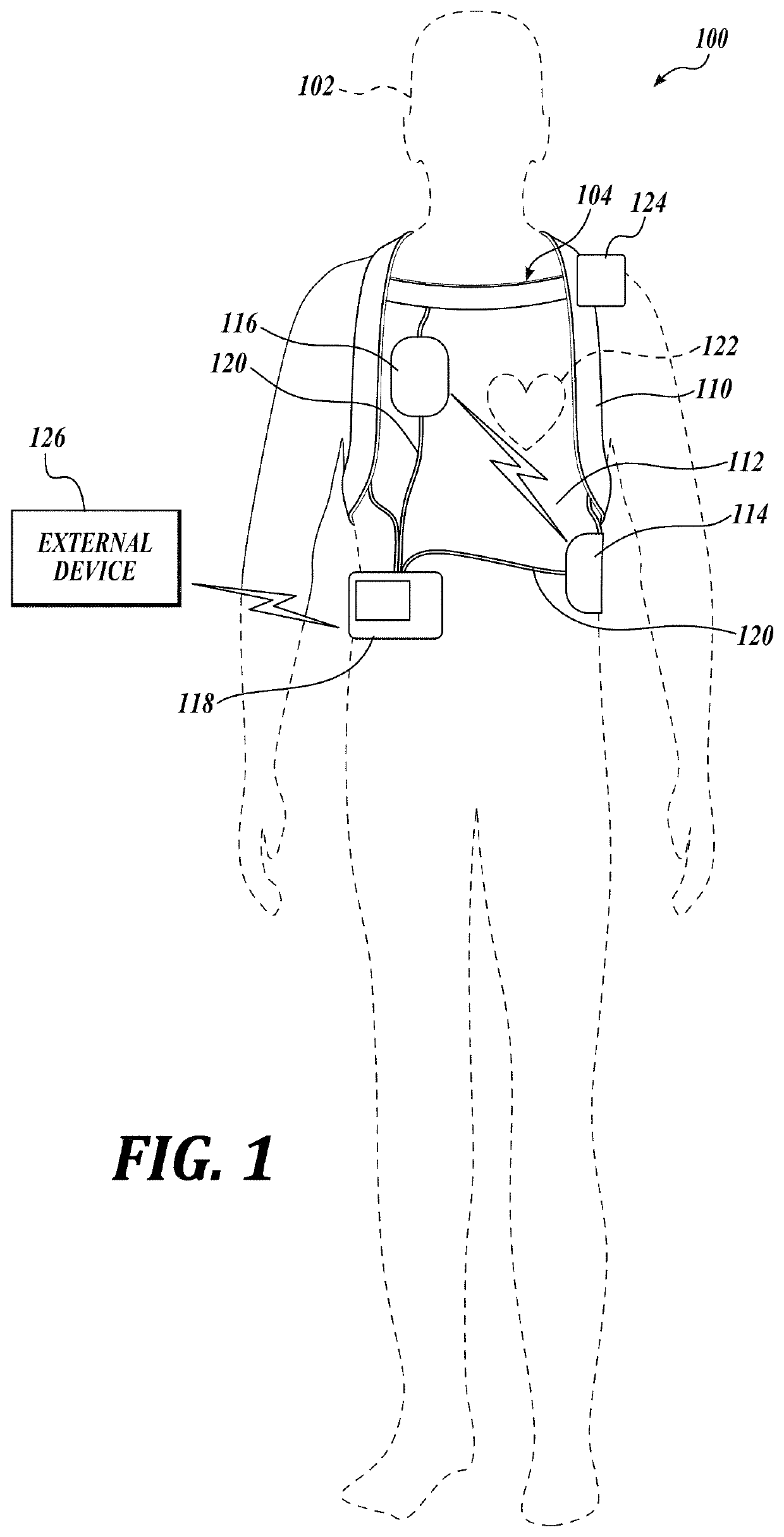
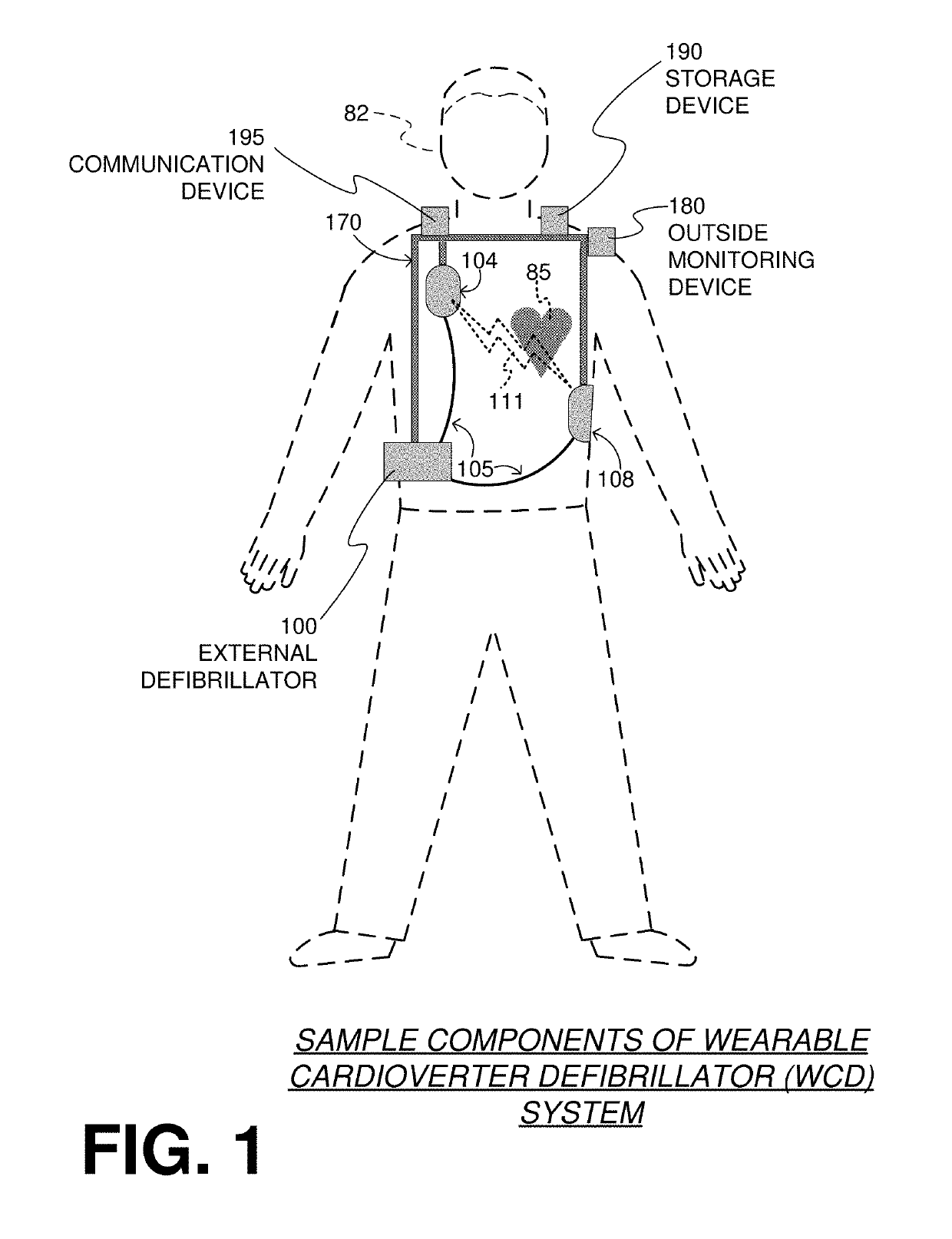
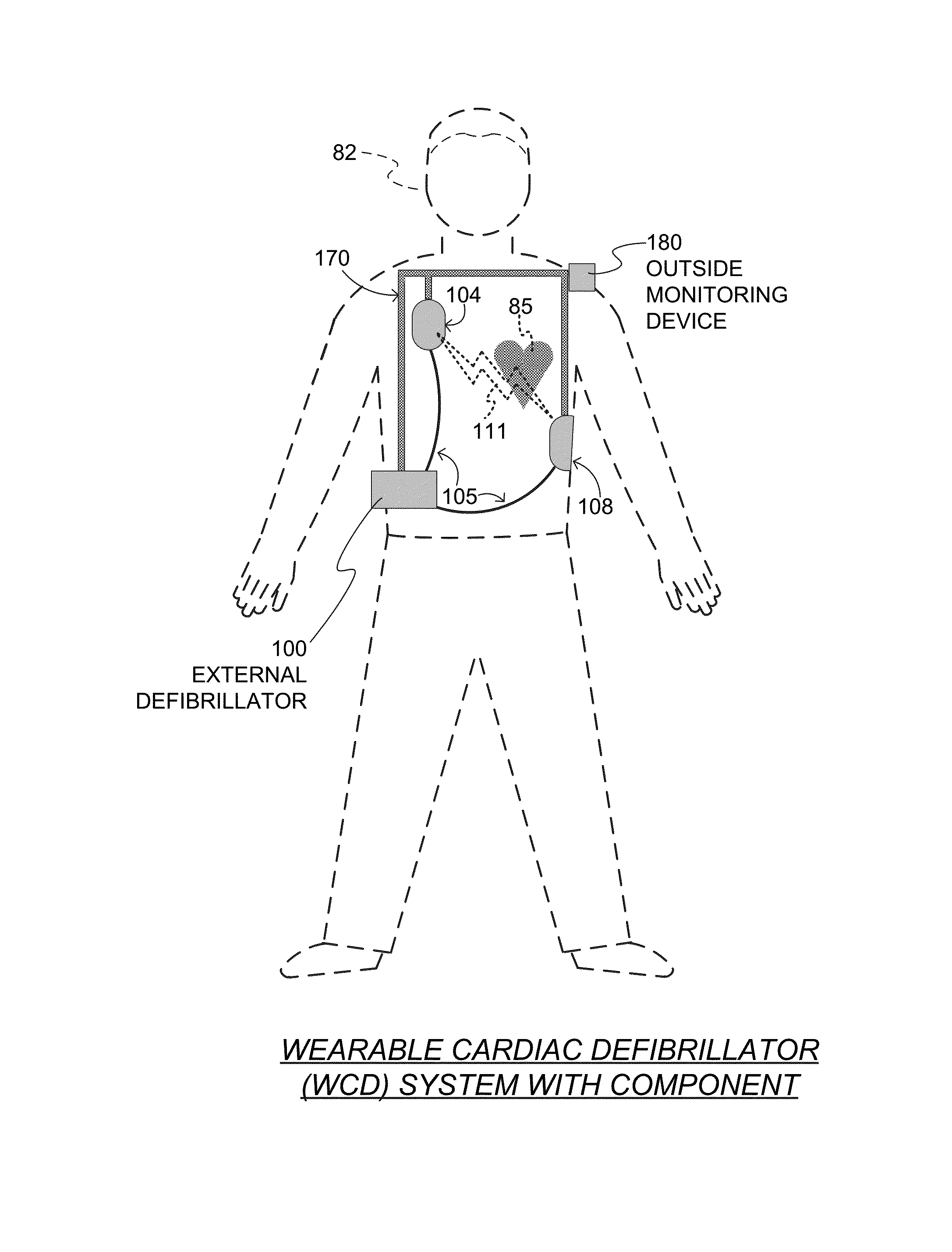
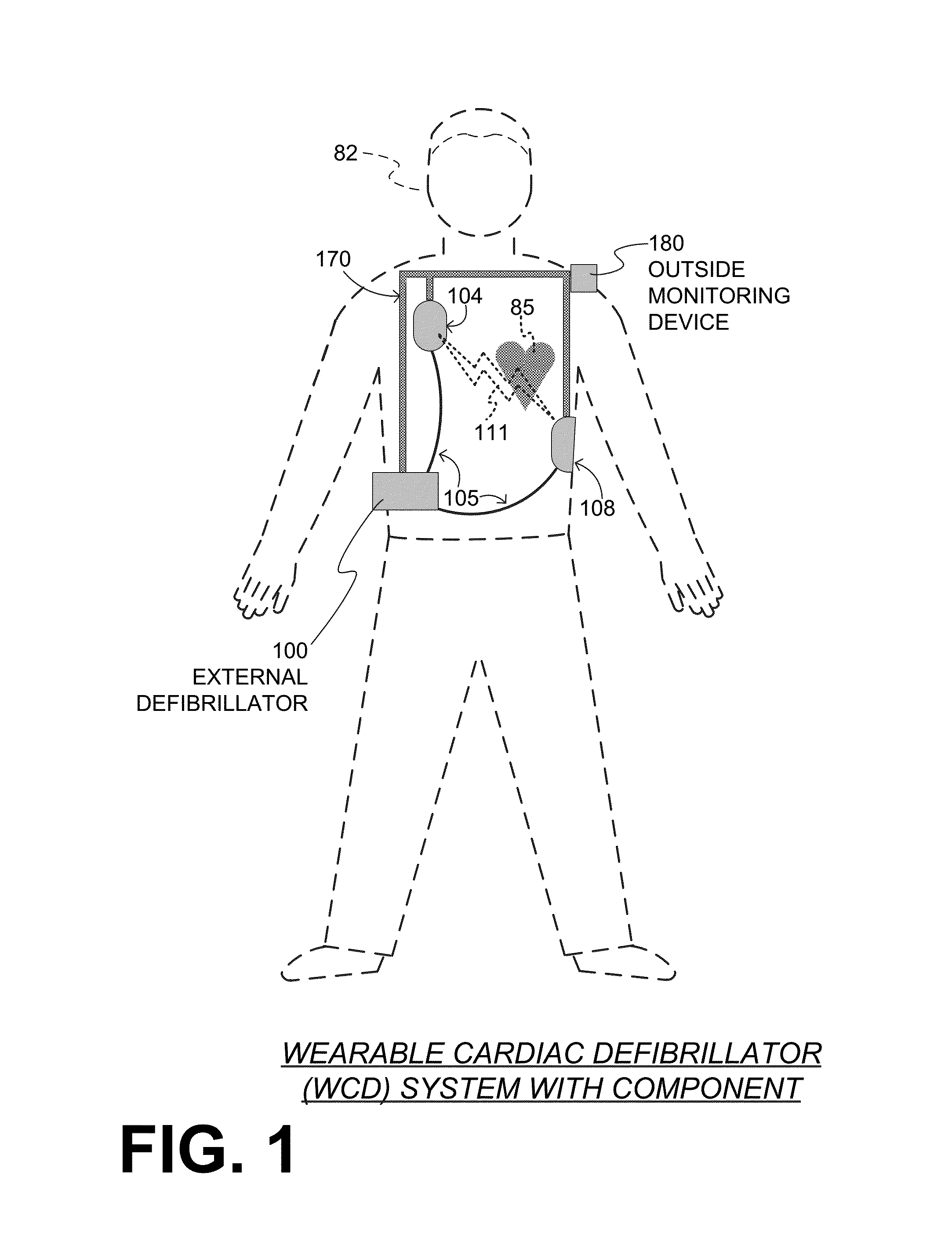
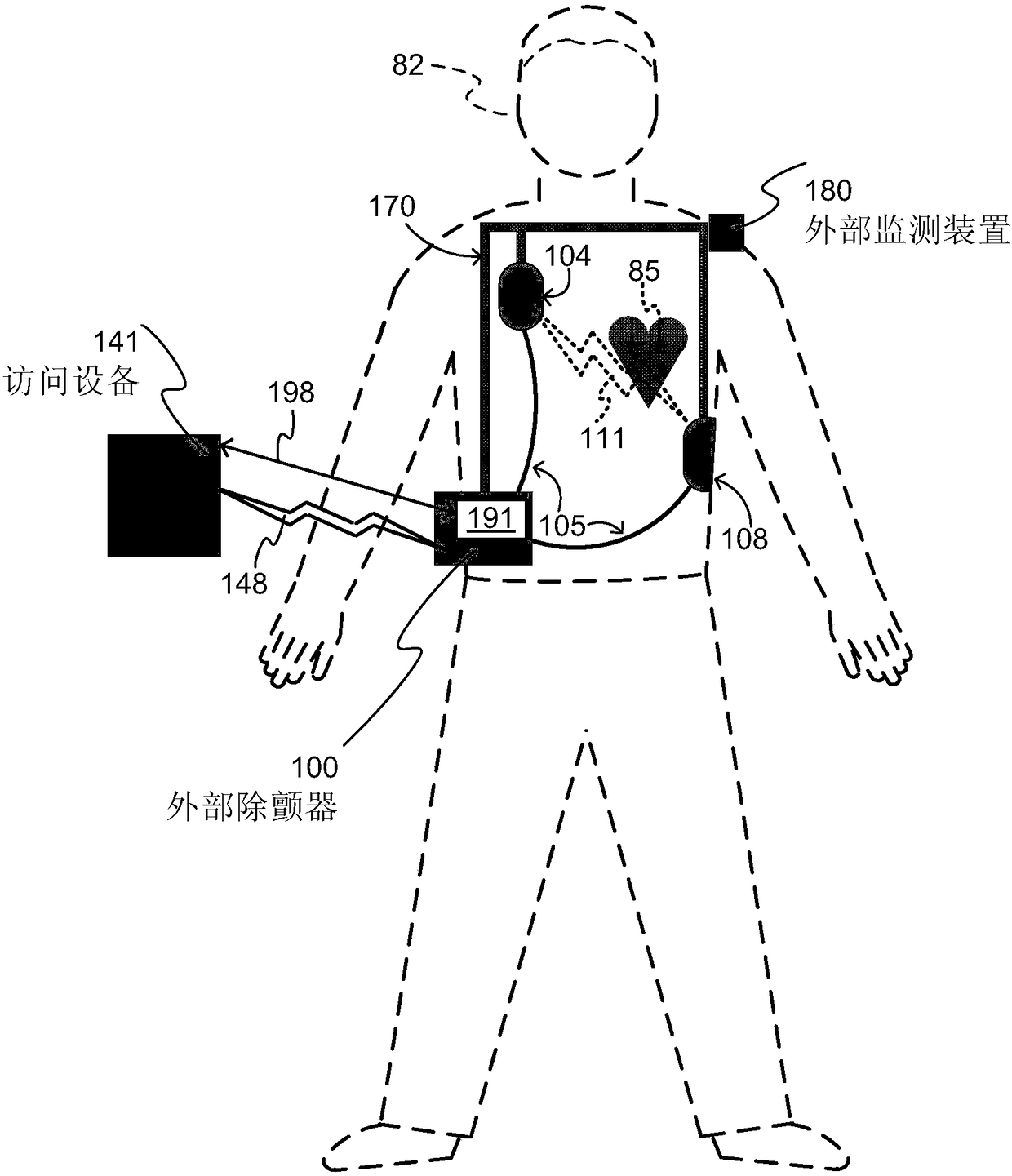
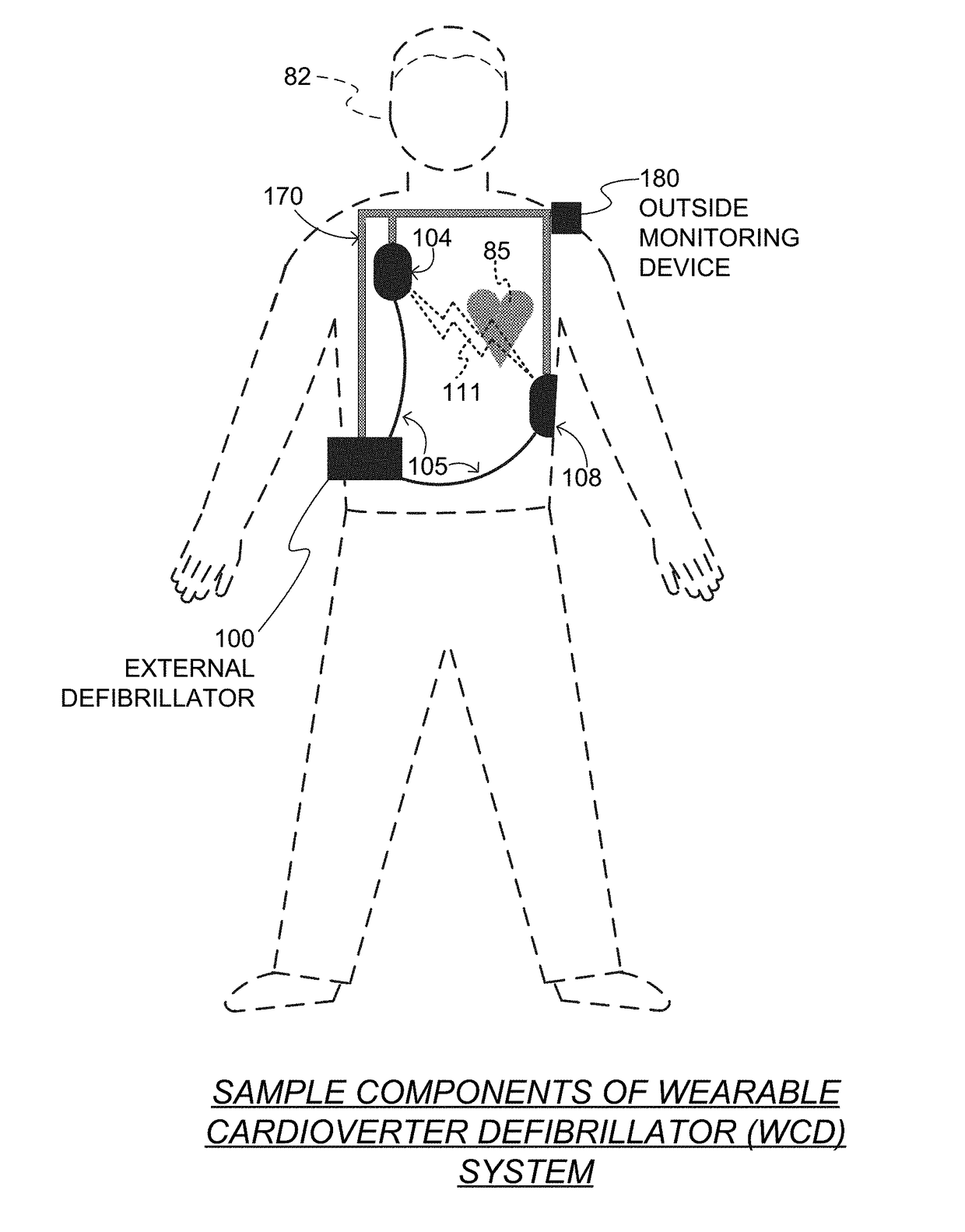
A wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) is a device worn by patients who are at risk for sudden cardiac arrest (SCA). A WCD allows physicians time to assess for their patient's arrhythmic risk and make appropriate plans.
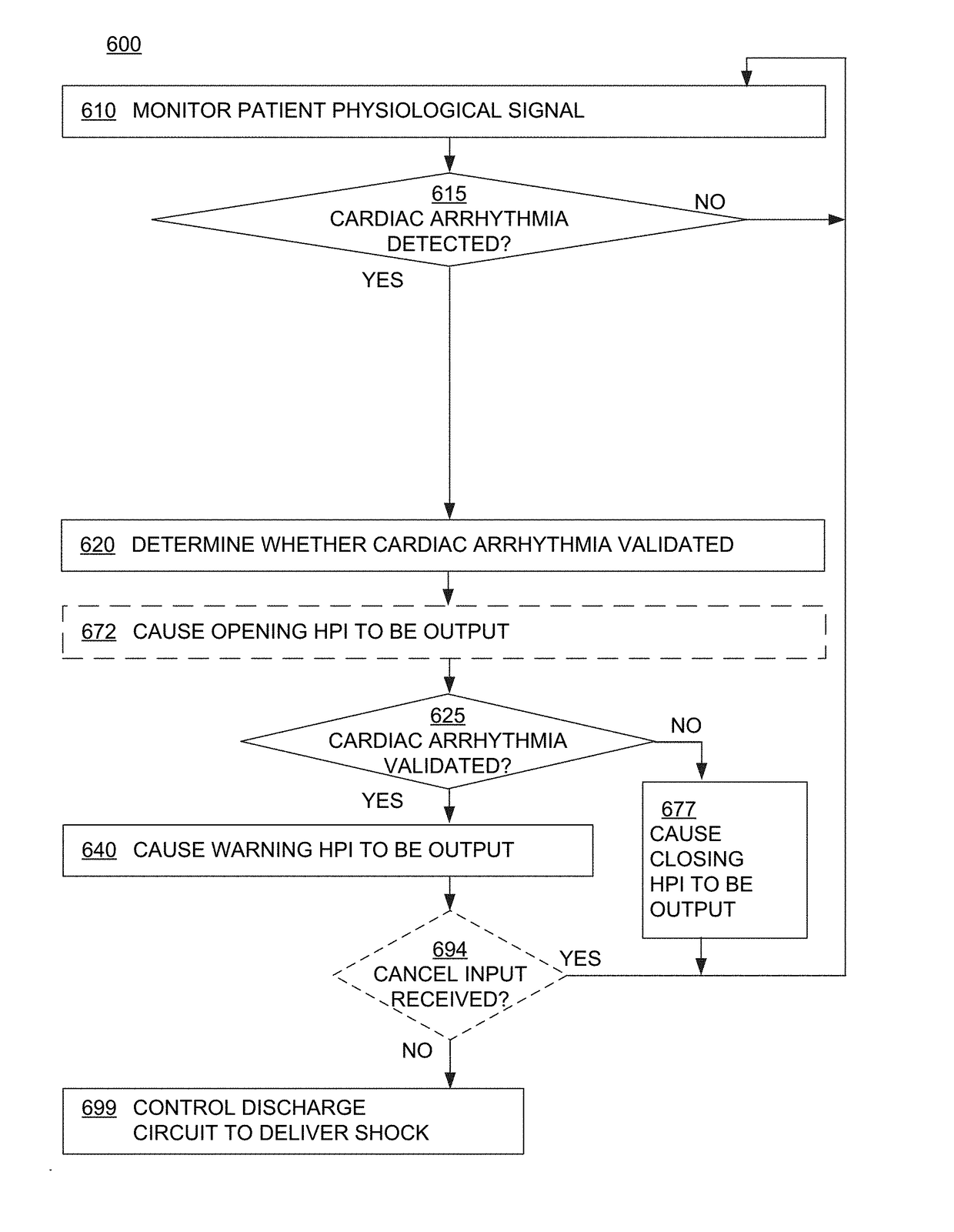
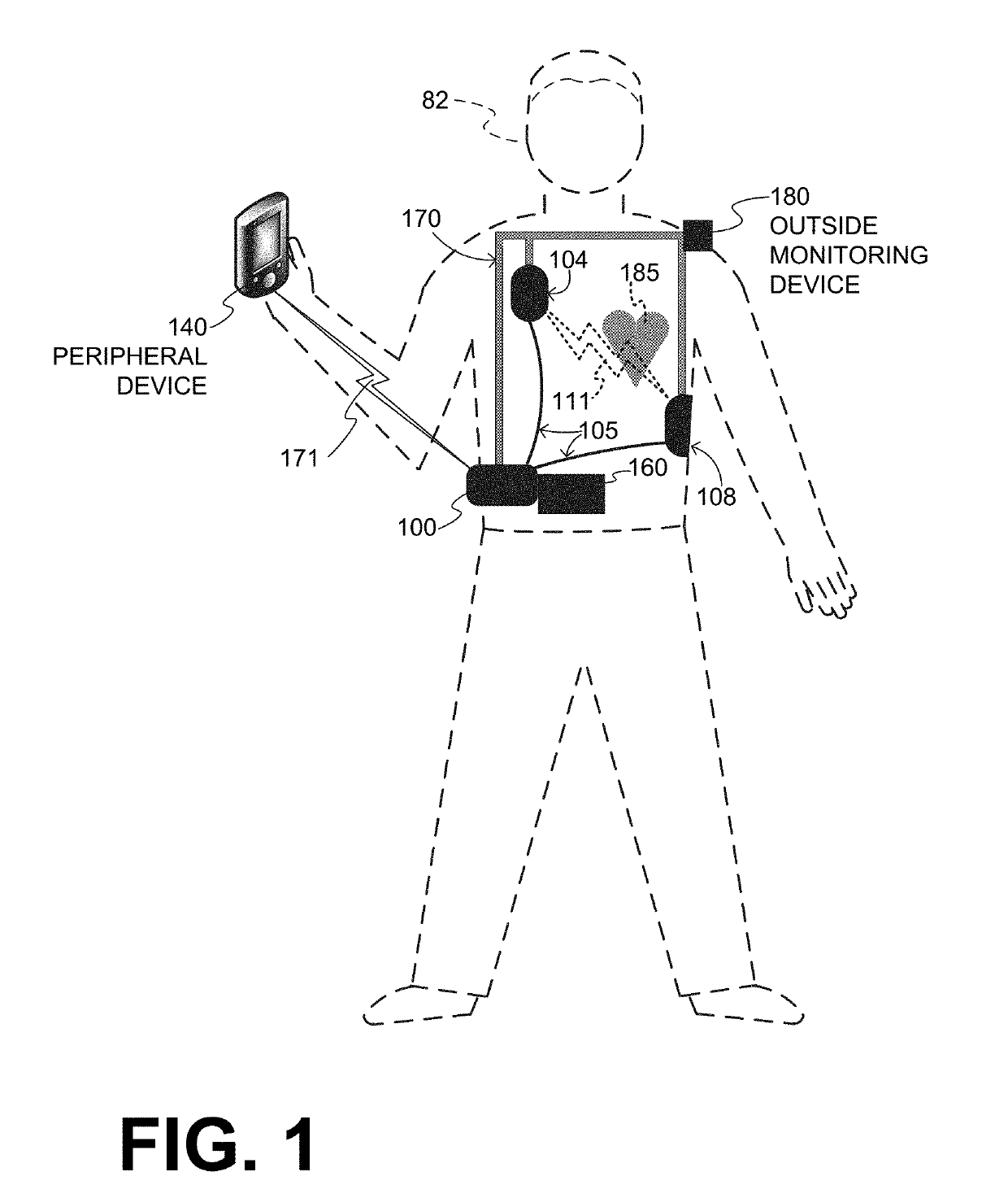
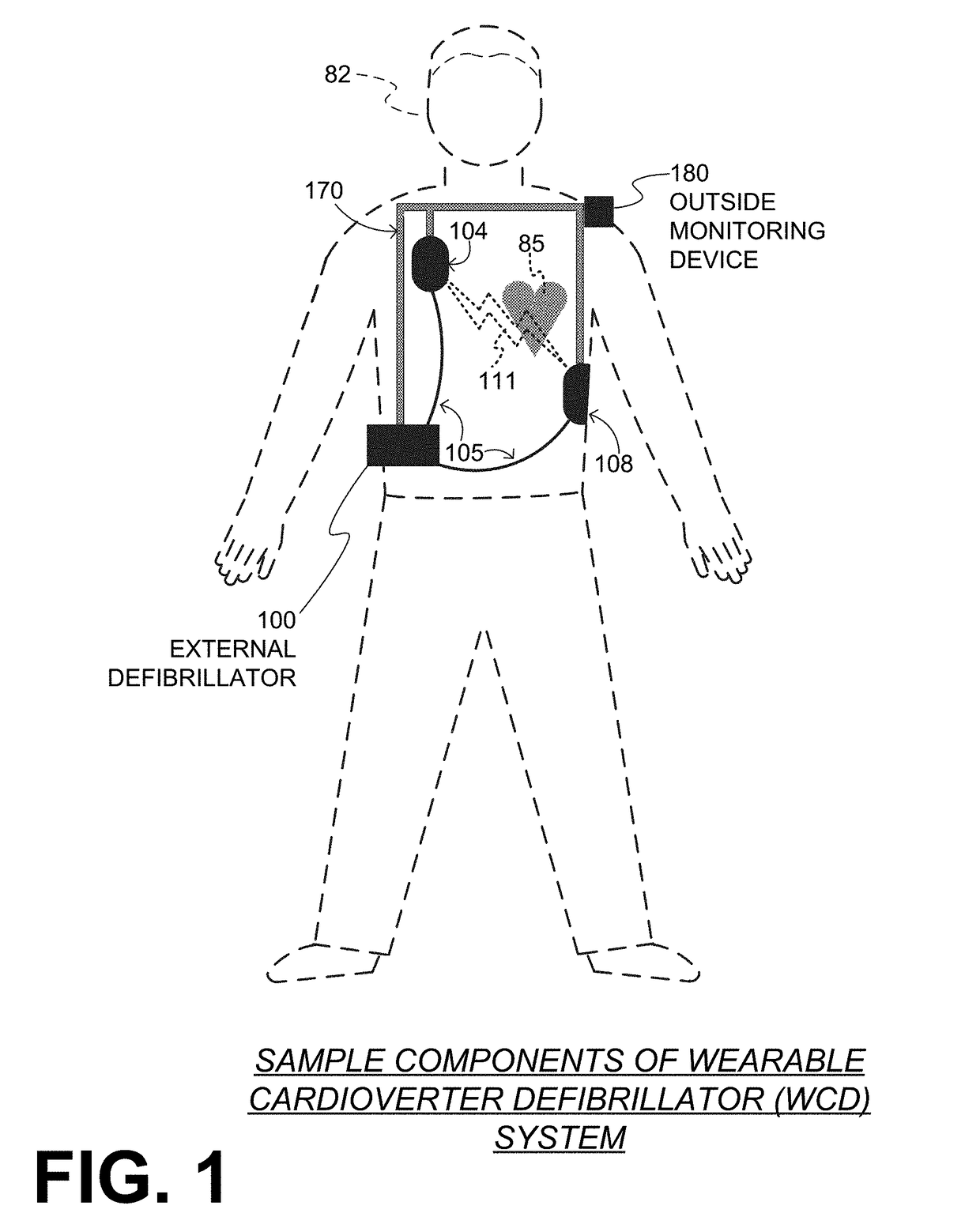
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system informing patient that it is validating just-detected cardiac arrhythmia
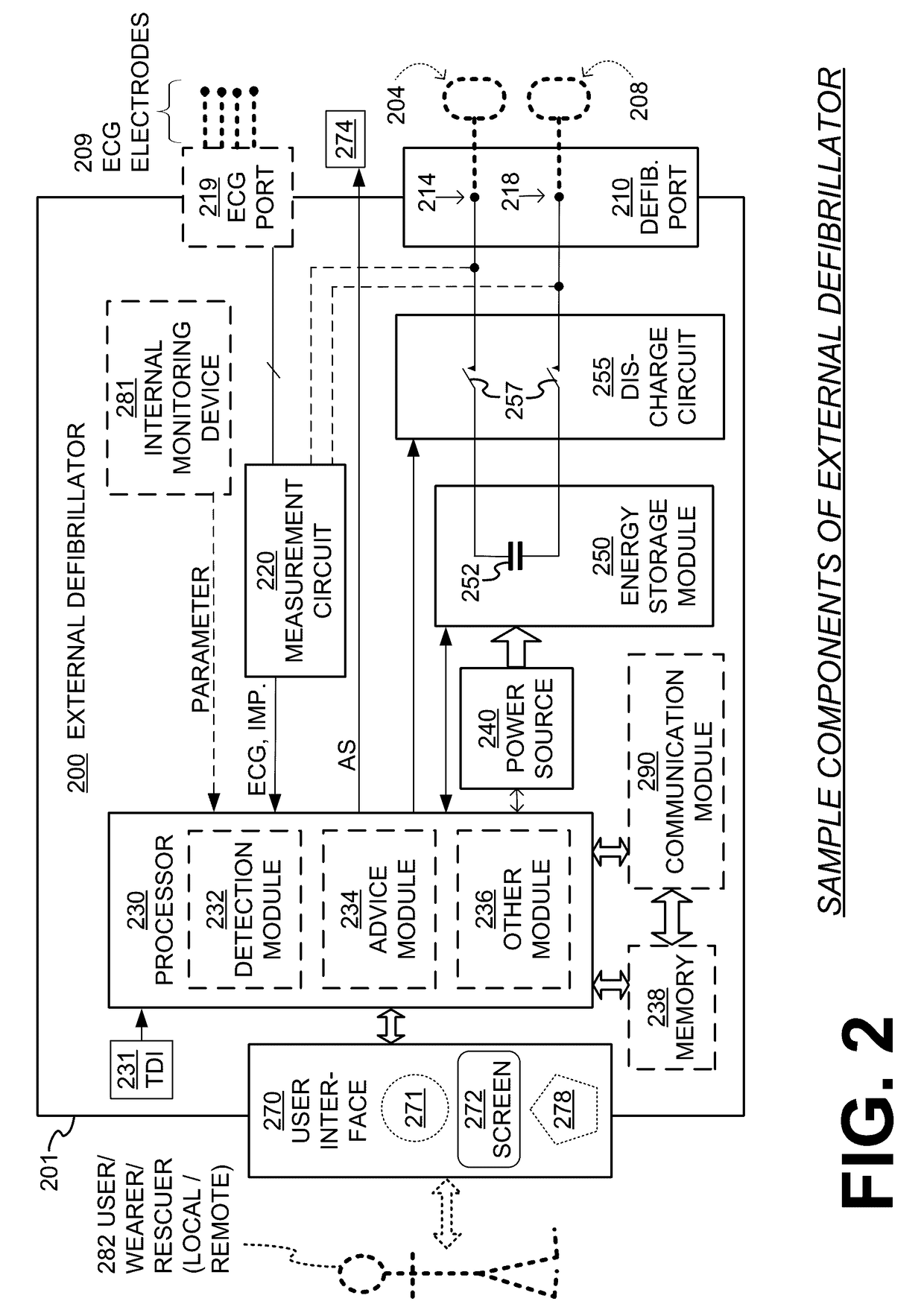
ActiveUS20160082277A1Reduce morbidityHeart defibrillatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringVentricular tachycardiaWearable cardioverter defibrillator
In some embodiments, a wearable cardioverter defibrillator (“WCD”) system may output an opening human-perceptible indication, after detecting a shockable cardiac arrhythmia but before validating it. This may succeed in informing the patient that the WCD system is working, and in particular analyzing a just-detected cardiac arrhythmia. The information may give comfort and confidence to the patient who may be conscious, and be experiencing only ventricular tachycardia but not ventricular fibrillation.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
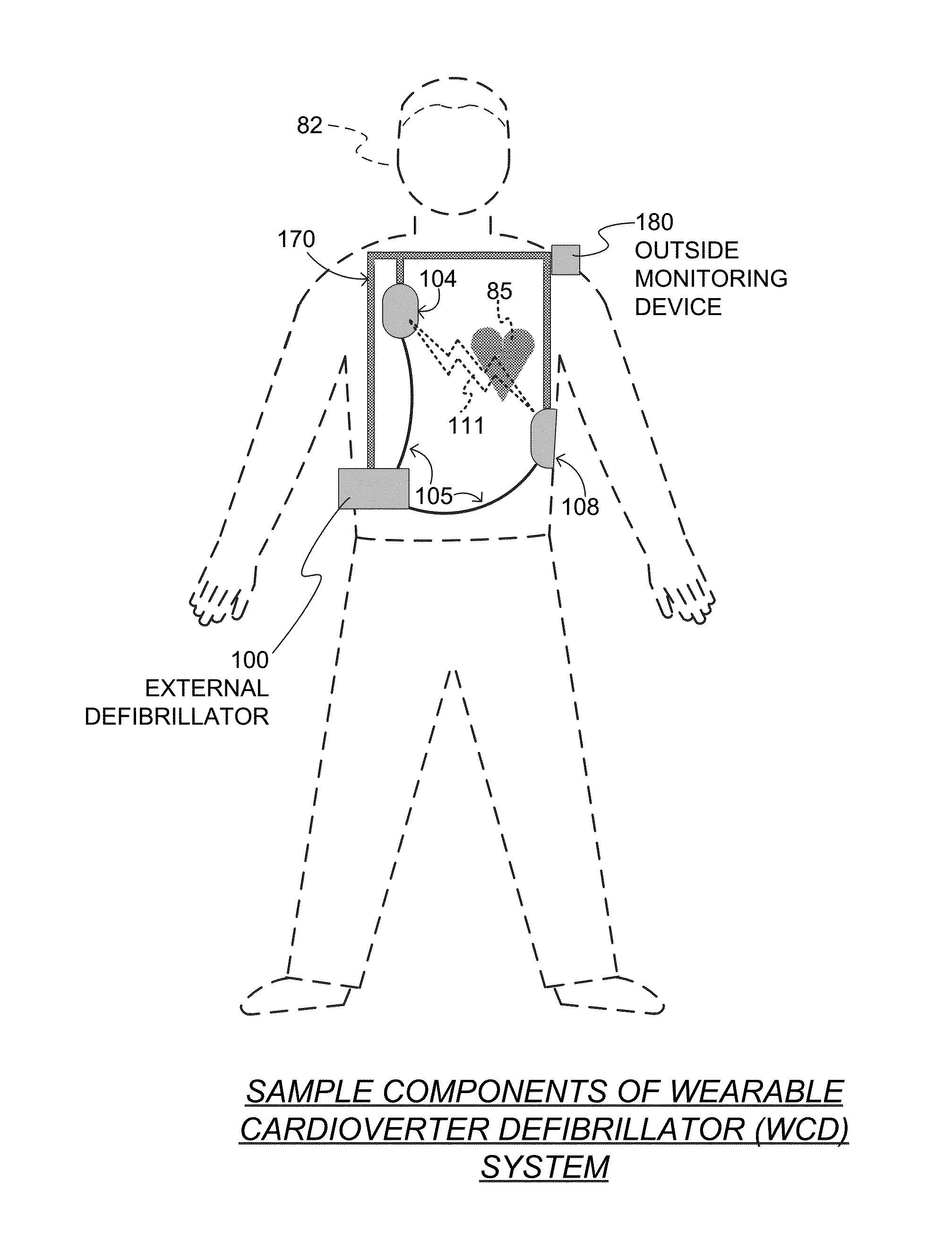
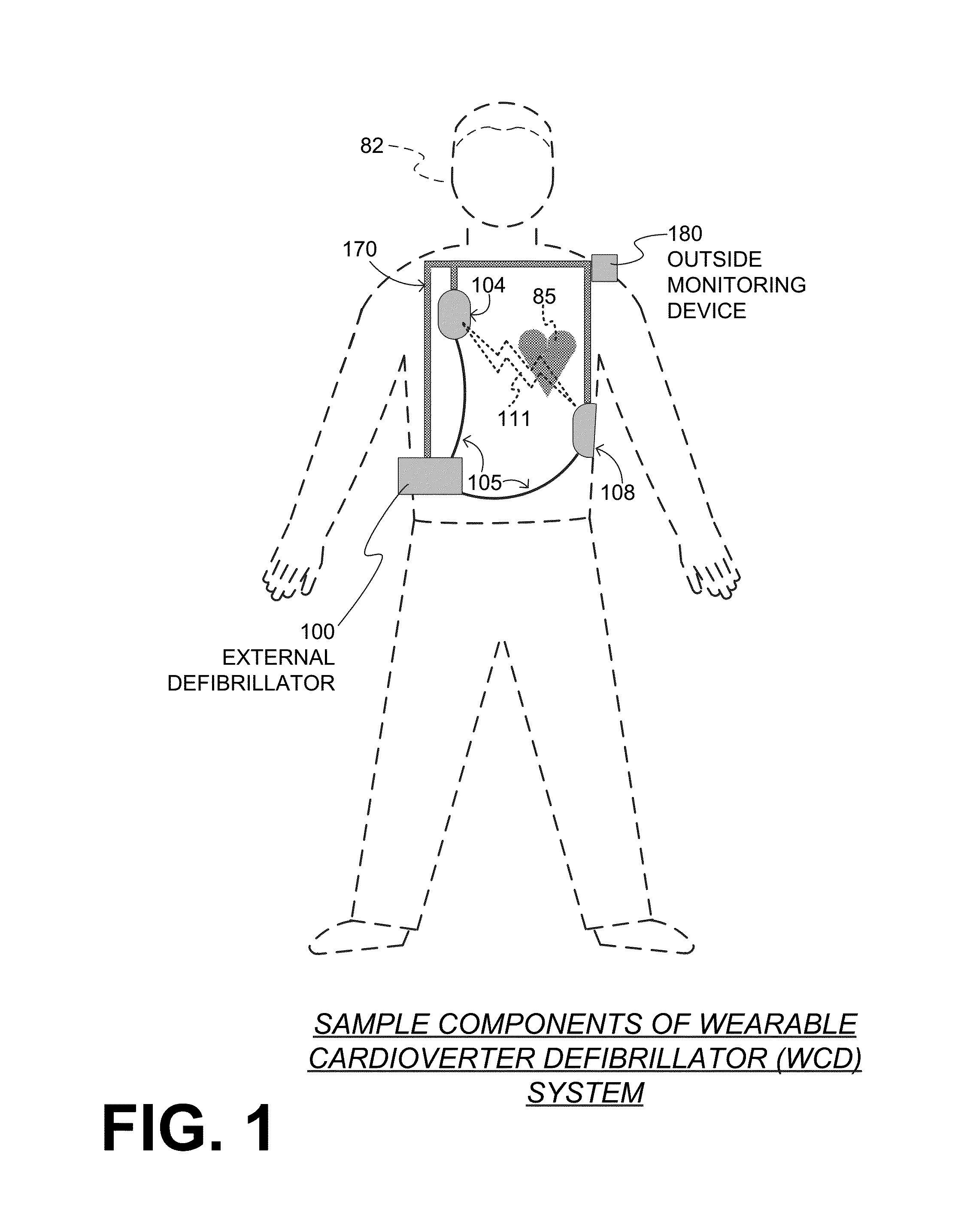
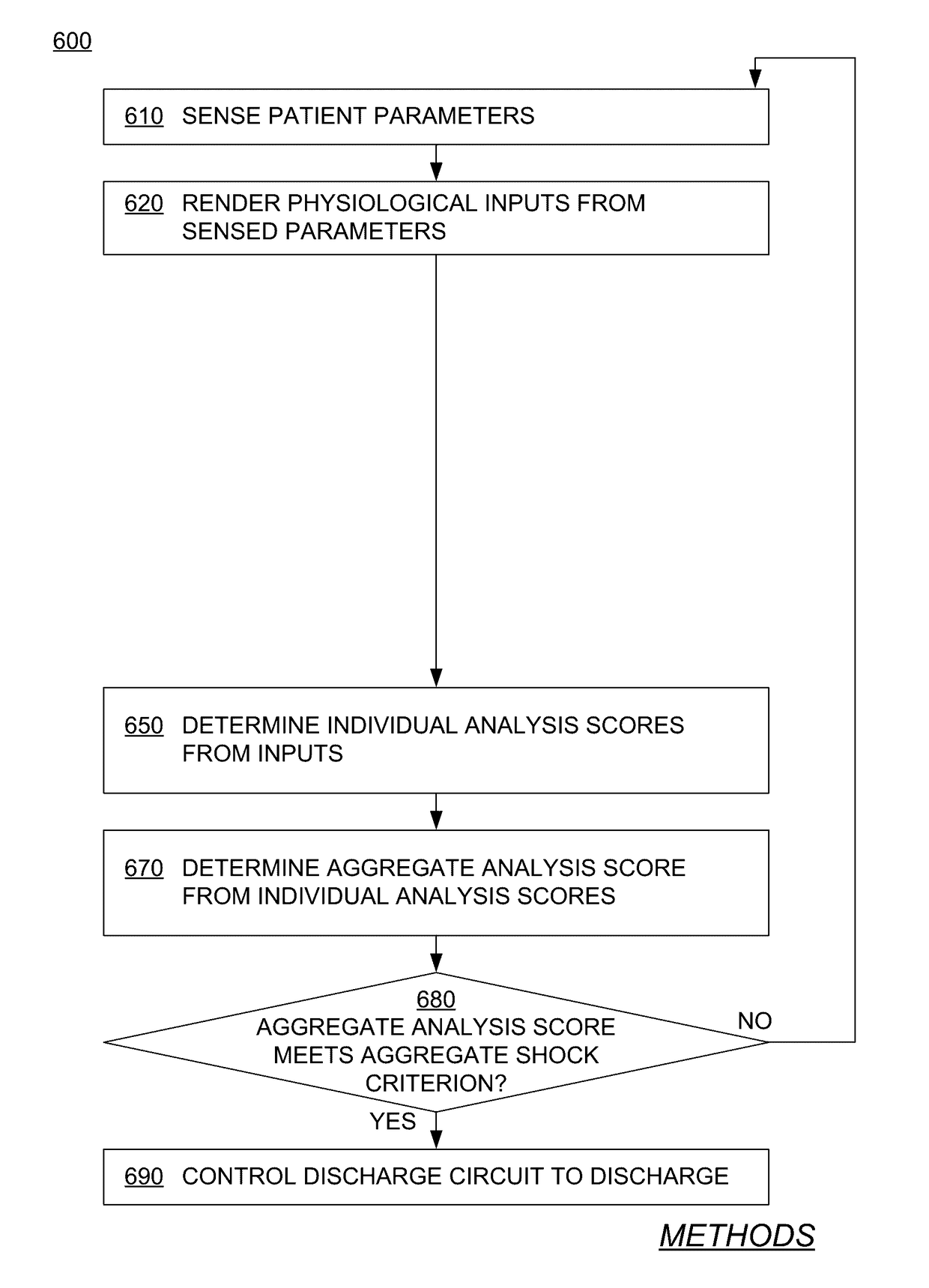
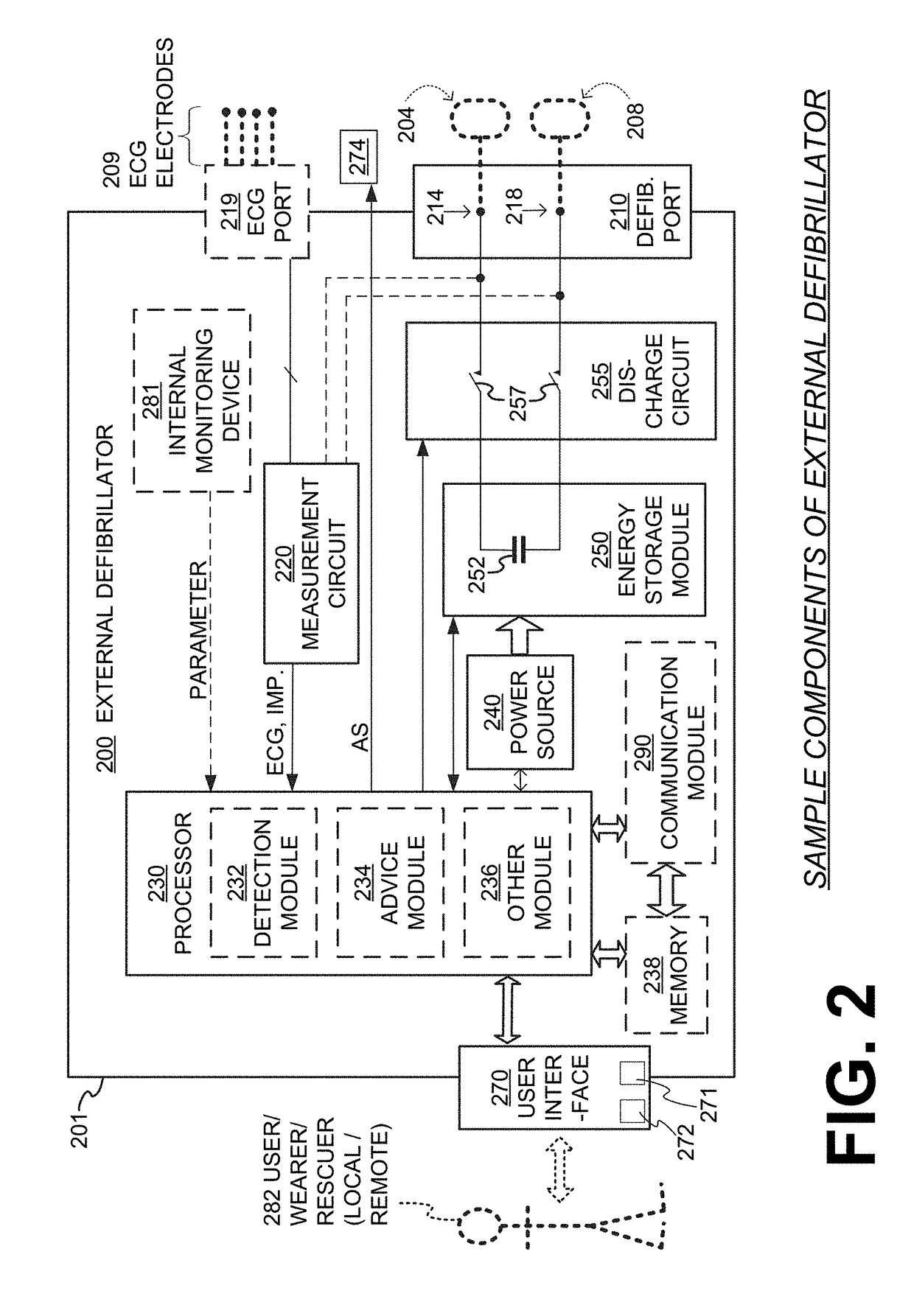
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system making shock/no shock determinations from multiple patient parameters
In embodiments, a WCD system includes one or more transducers that may sense patient parameters from different parts of the patient's body, and thus render physiological inputs from those parameters. Individual analysis scores may be determined from the physiological inputs, and an aggregate analysis score may be determined from the individual analysis scores. A shock / no shock determination may be made depending on whether or not the aggregate analysis score meets an aggregate shock criterion. Accordingly, multiple inputs are considered in making the shock / no shock determination.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
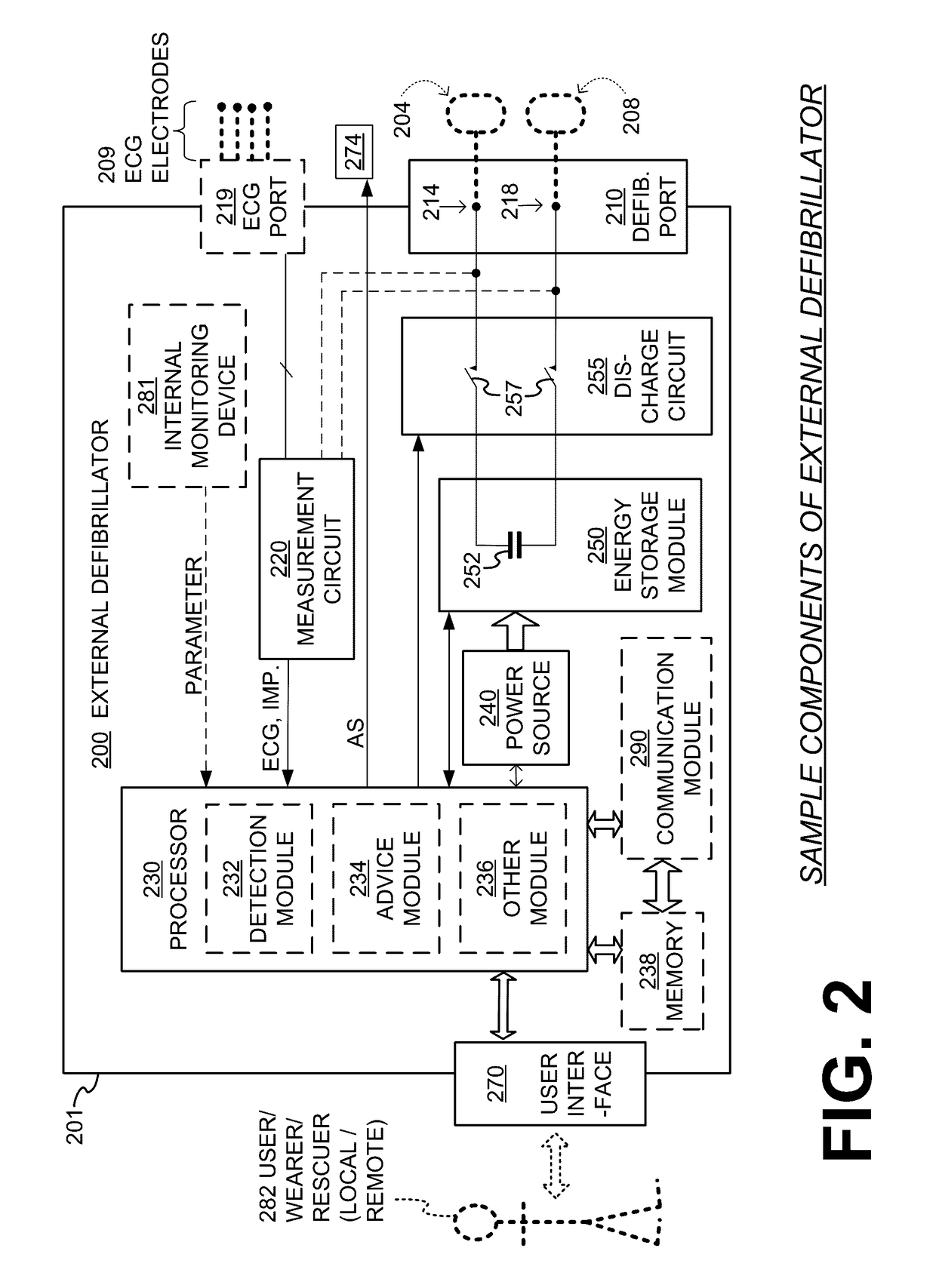
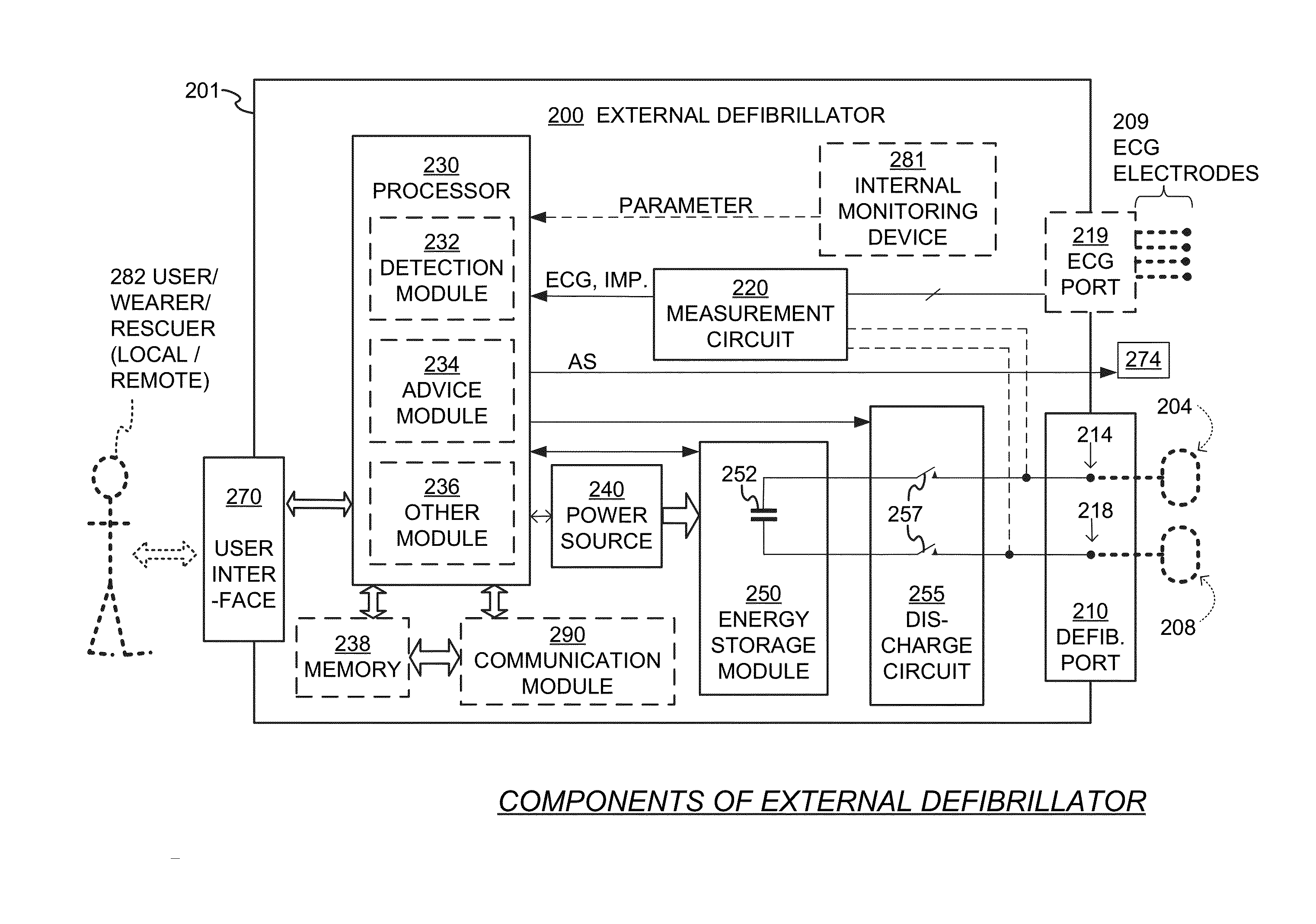
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator components discarding ECG signals prior to making shock/no shock determination
InactiveUS20150328472A1Good chanceHeart defibrillatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalWearable cardioverter defibrillator
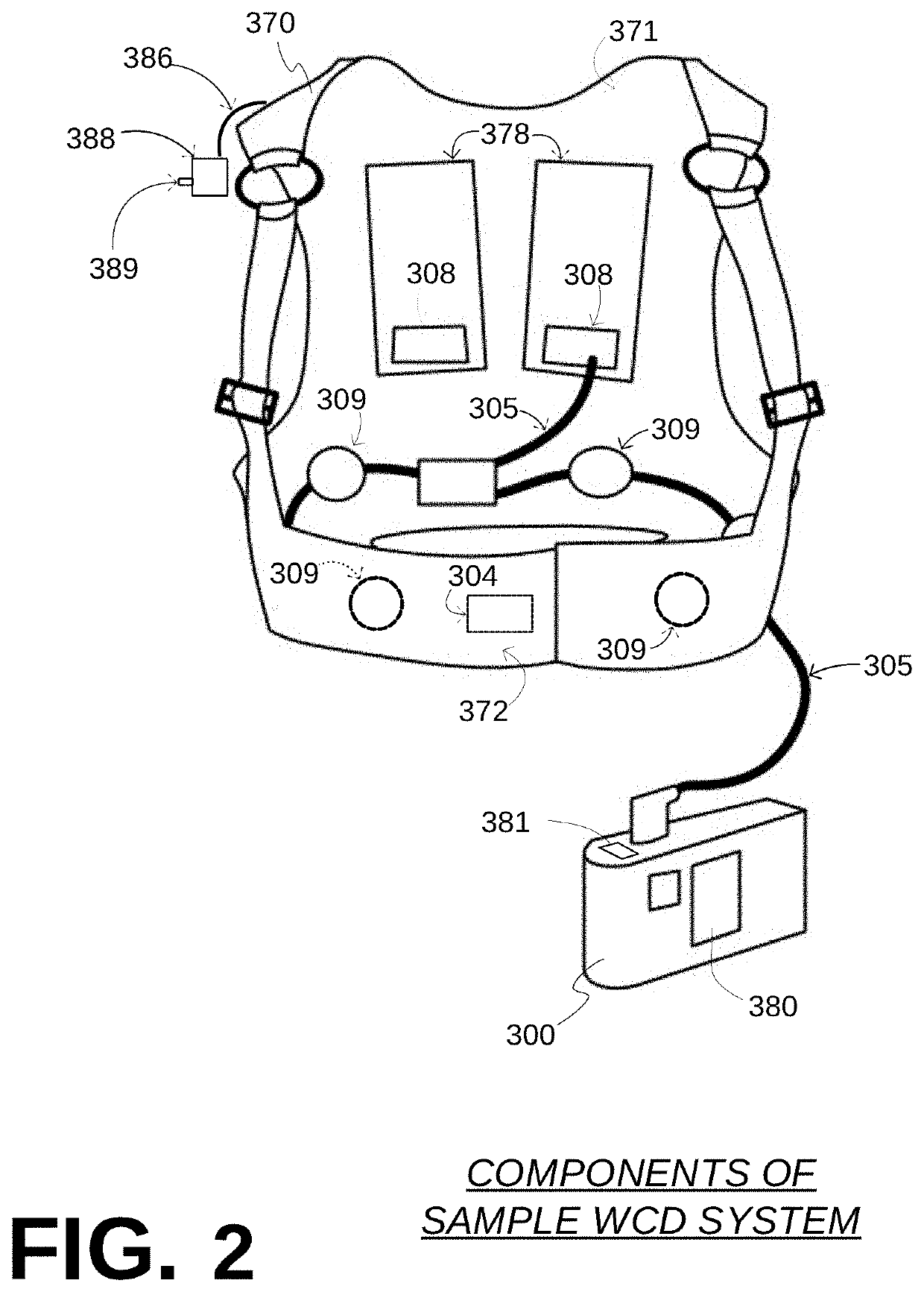
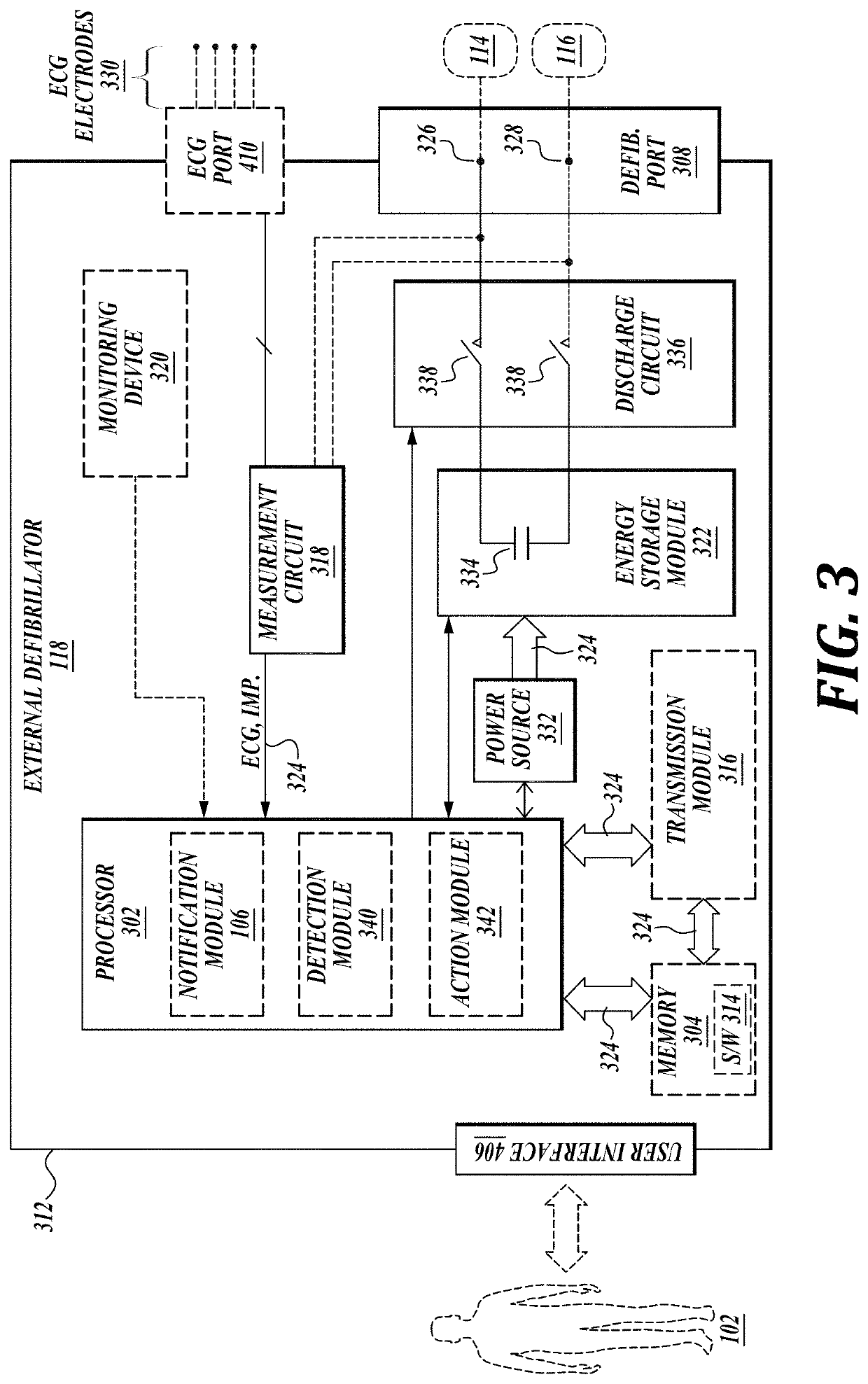
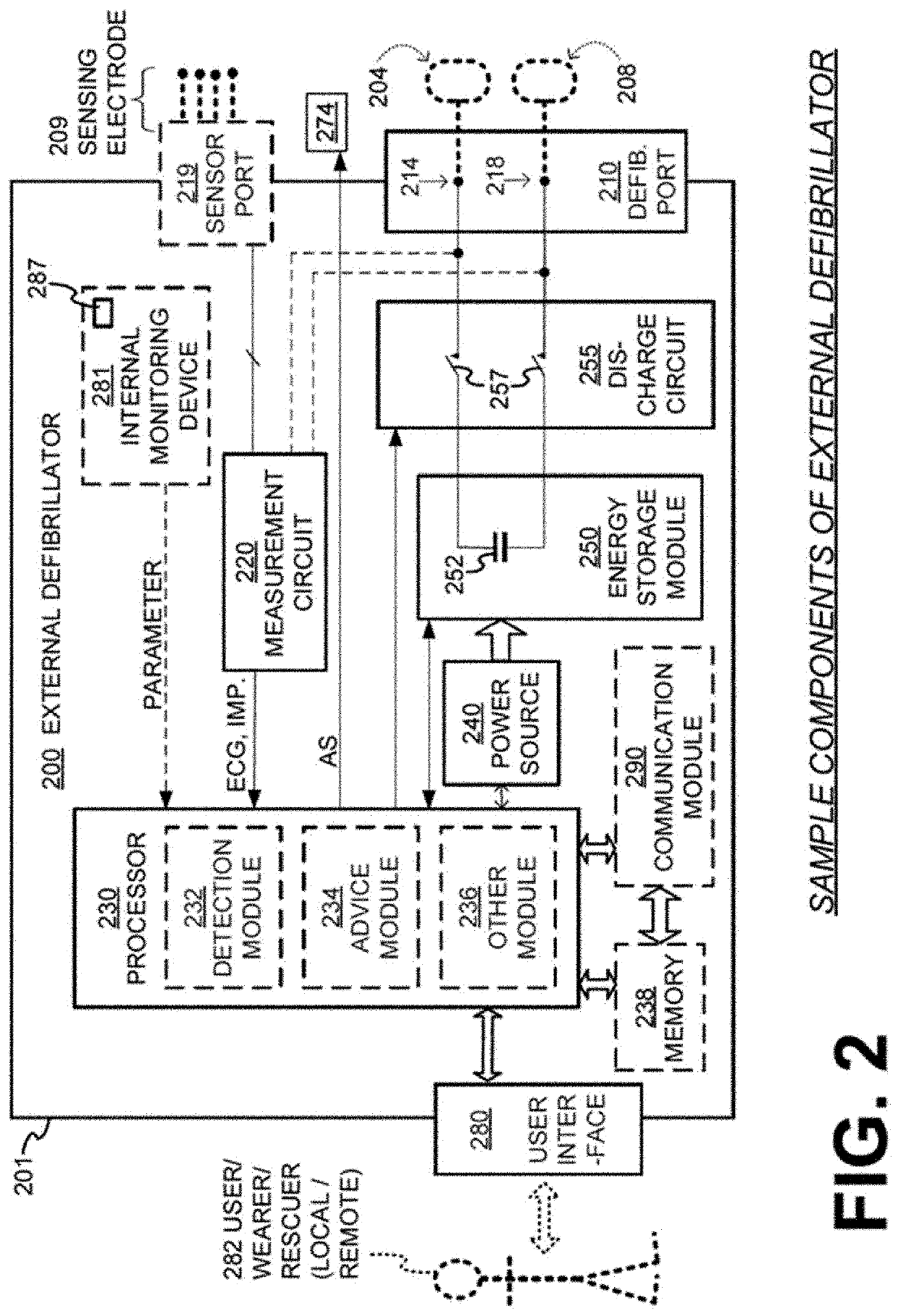
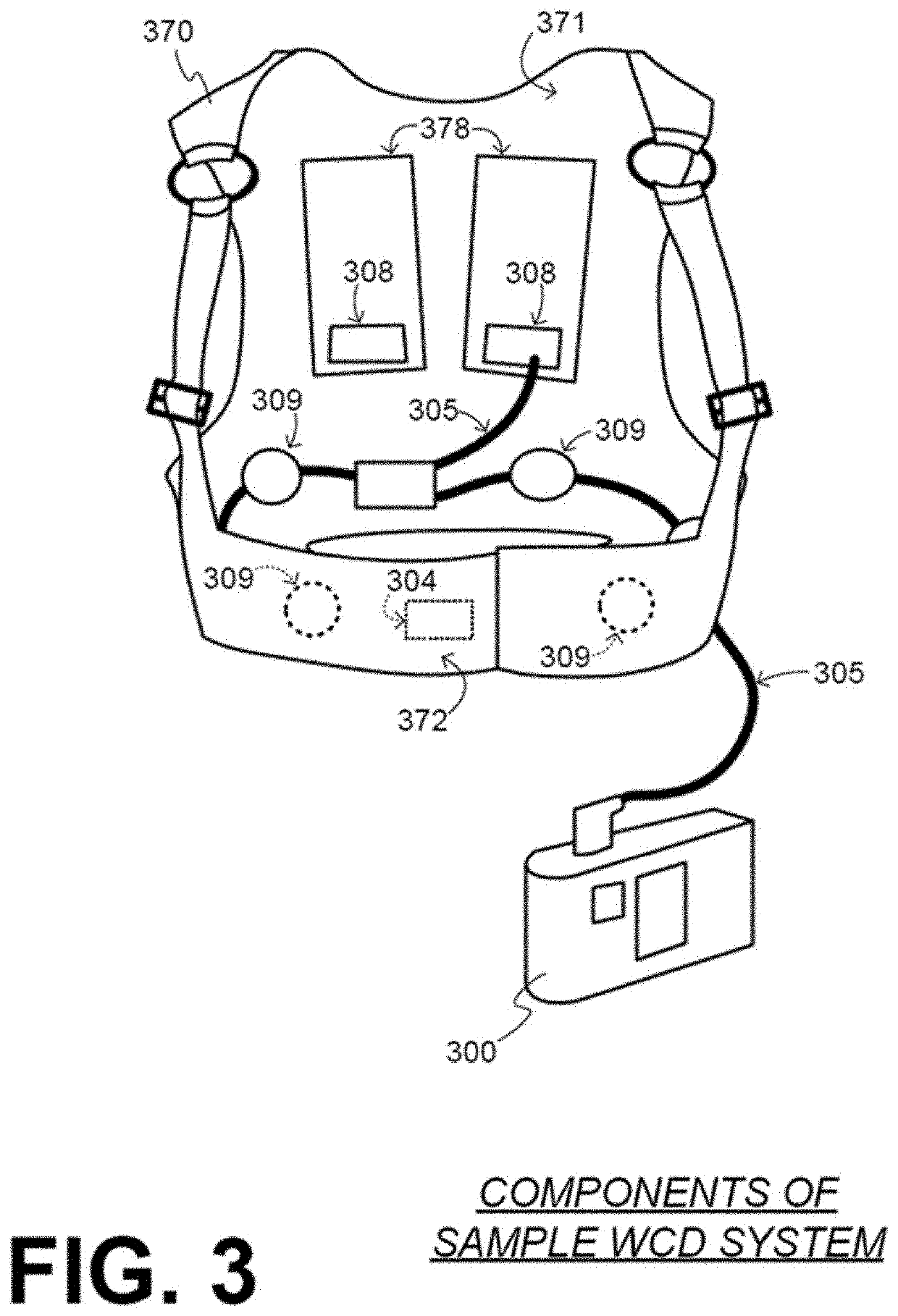
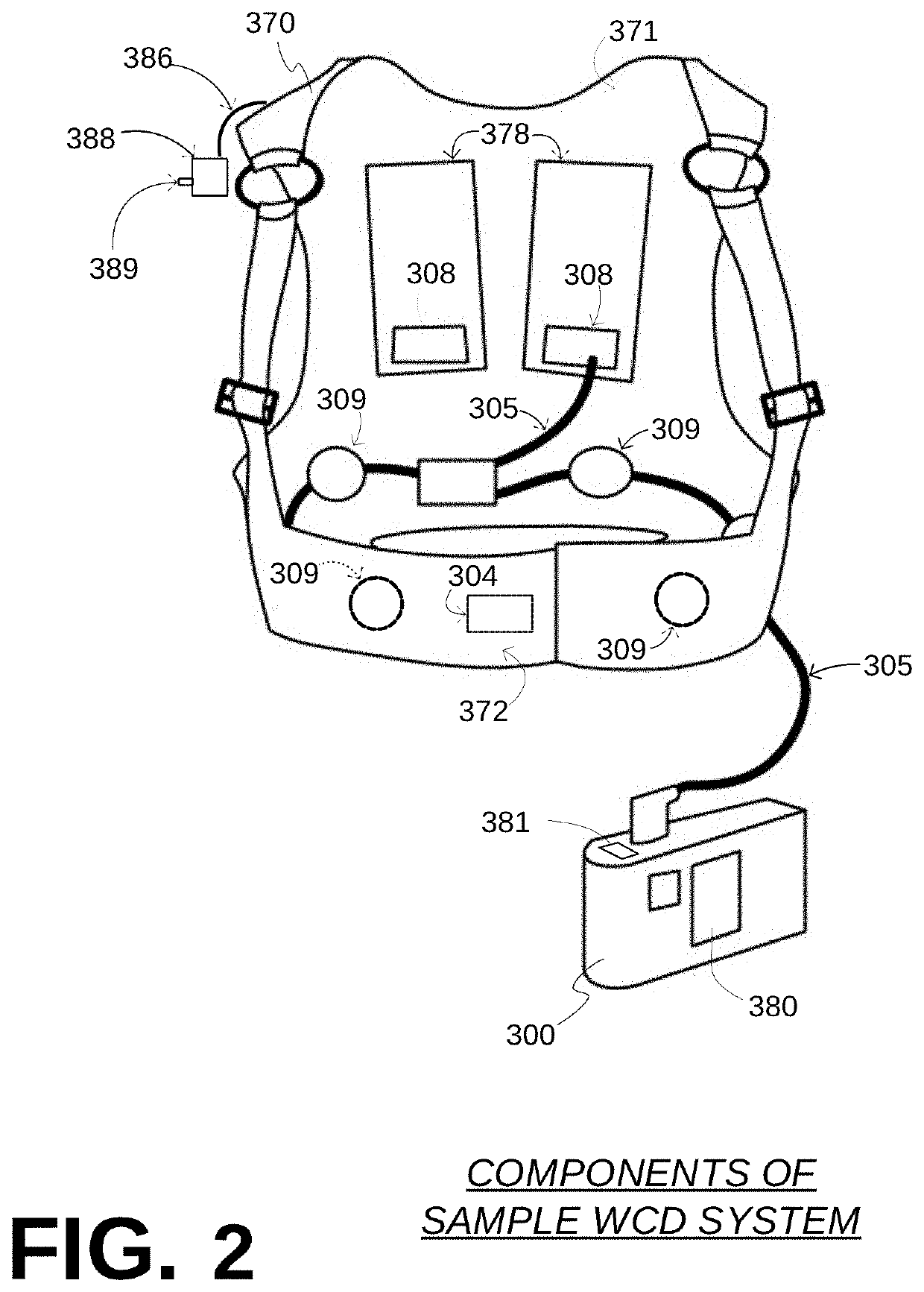
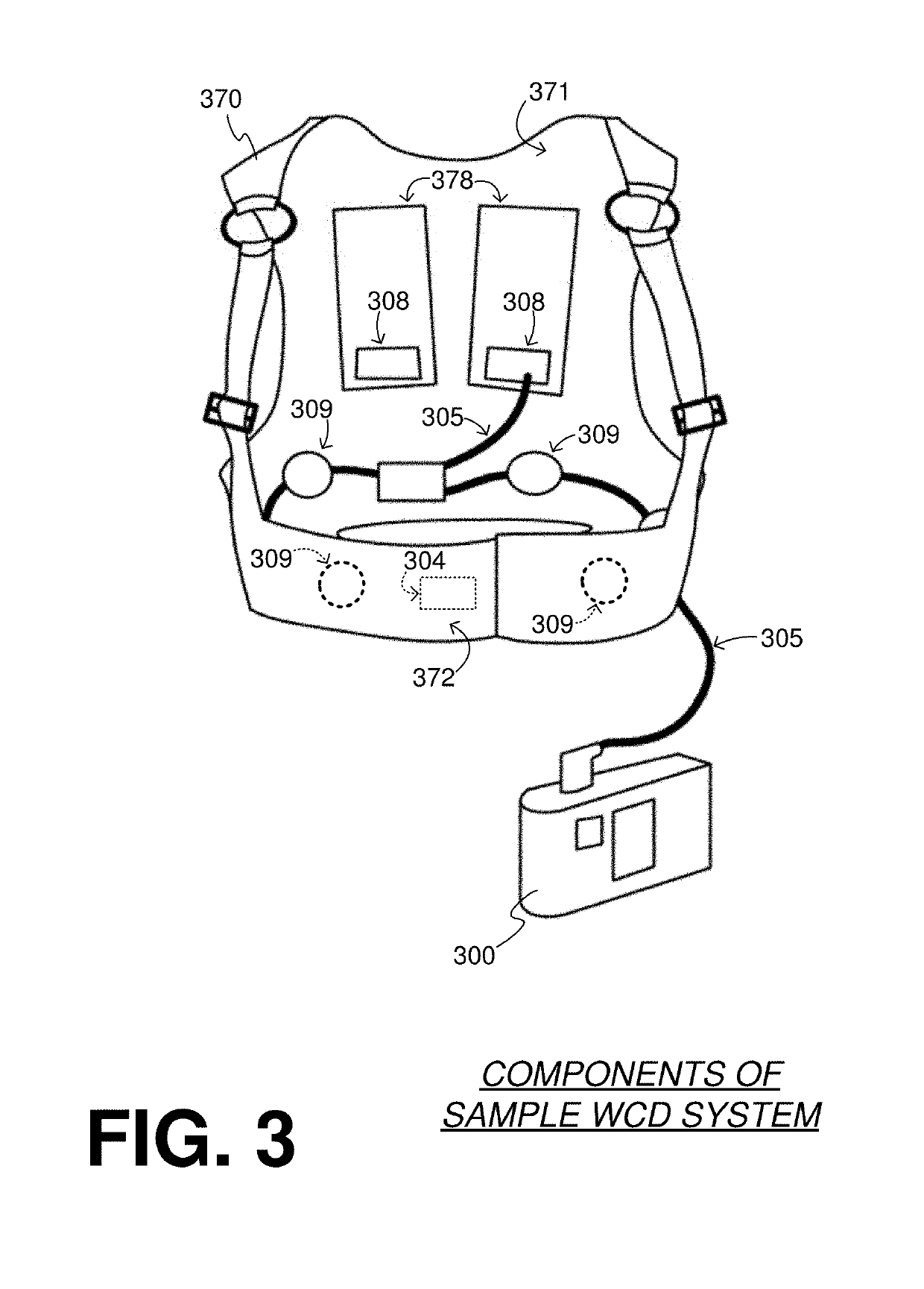
Components of wearable cardiac defibrillator (WCD) systems, software, and methods are provided. A WCD system includes a support structure that a patient can wear and electrodes that can capture at least two of the patient's ECG signals. A component includes an energy storage module that can store an electrical charge, a discharge circuit, and a processor that can make a shock / no shock determination, and cause the discharge circuit to discharge the stored charge, if the determination is to shock. In some embodiments, the processor discards at least one of the ECG signals prior to making the shock / no shock determination. The determination can be made from the remaining one or more ECG signals. In some embodiments, the processor makes an aggregate shock / no shock determination from two or more of the ECG signals.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system reacting to high-amplitude ECG noise
ActiveUS20190030352A1Reduce noiseMore compliantElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsEcg signalWearable cardioverter defibrillator
In embodiments a WCD system is worn and / or carried by an ambulatory patient. The WCD system analyzes an ECG signal of the patient, to determine whether or not the patient should be given an electric shock to restart their heart. If so, then the WCD system first gives a preliminary alarm to the patient, asking them to prove they are alive if they are. The WCD system further determines whether the ECG signal contains too much High Amplitude (H-A) noise, which can distort the analysis of the ECG signal. If too much H-A noise is detected for a long time, the WCD system may eventually alert the patient about their activity, so that the ECG noise may be abated. The WCD system may even pause the analysis of the ECG signal, so that there will be no preliminary alarms that could be false until the ECG noise is abated.
Owner:STRYKER CORP +1
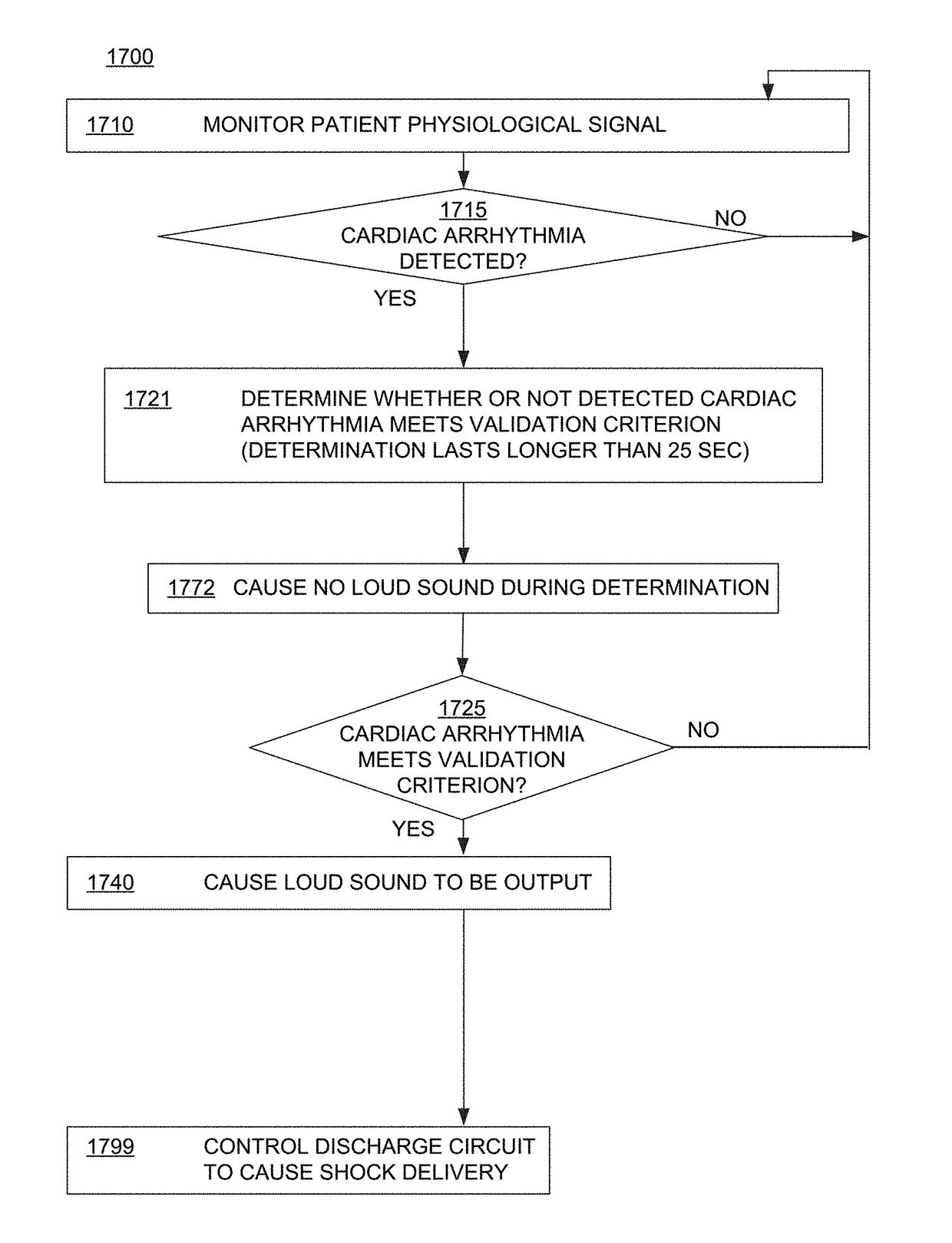
Wcd system validating detected cardiac arrhythmias thoroughly so as to not sound loudly due to some quickly self-terminating cardiac arrhythmias
ActiveUS20170319862A1Heart defibrillatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringWearable cardioverter defibrillatorCardiac arrhythmia
A wearable cardioverter defibrillator (“WCD”) system may output a loud sound after detecting and validating a shockable cardiac arrhythmia. In such embodiments, however, the WCD system might not sound a loud alarm before validating the arrhythmia thoroughly, i.e. for a longer time, thus giving the arrhythmia a further chance to self-terminate. The WCD system may thus detect more robustly the cardiac arrhythmias that do not self-terminate quickly. Such arrhythmias that self-terminate quickly may occur from likely harmless events occurring multiple times in the daily life of the patient, such as the patient becoming “winded” from climbing stairs. In embodiments the WCD system may notify the patient only discreetly, or even not at all. The lack of sounding such a loud alarm responsive to such events reduces the overall number of times in which the patient experiences unwanted attention by others, embarrassment, loss of privacy and dignity, and so on.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
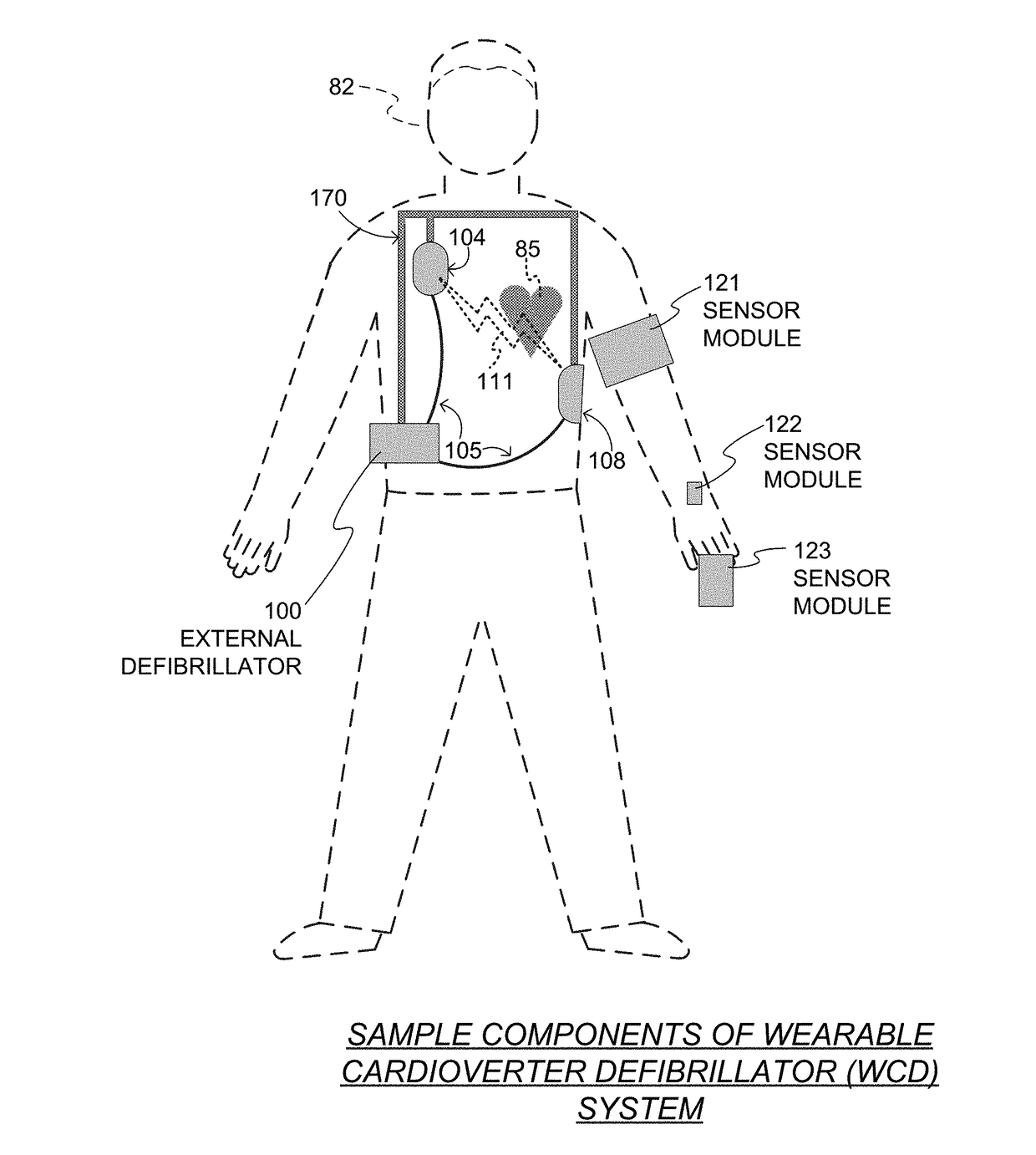
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system using sensor modules with reassurance code for confirmation before shock
ActiveUS9901741B2High detection specificityHeart defibrillatorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateWearable cardioverter defibrillatorComputer module
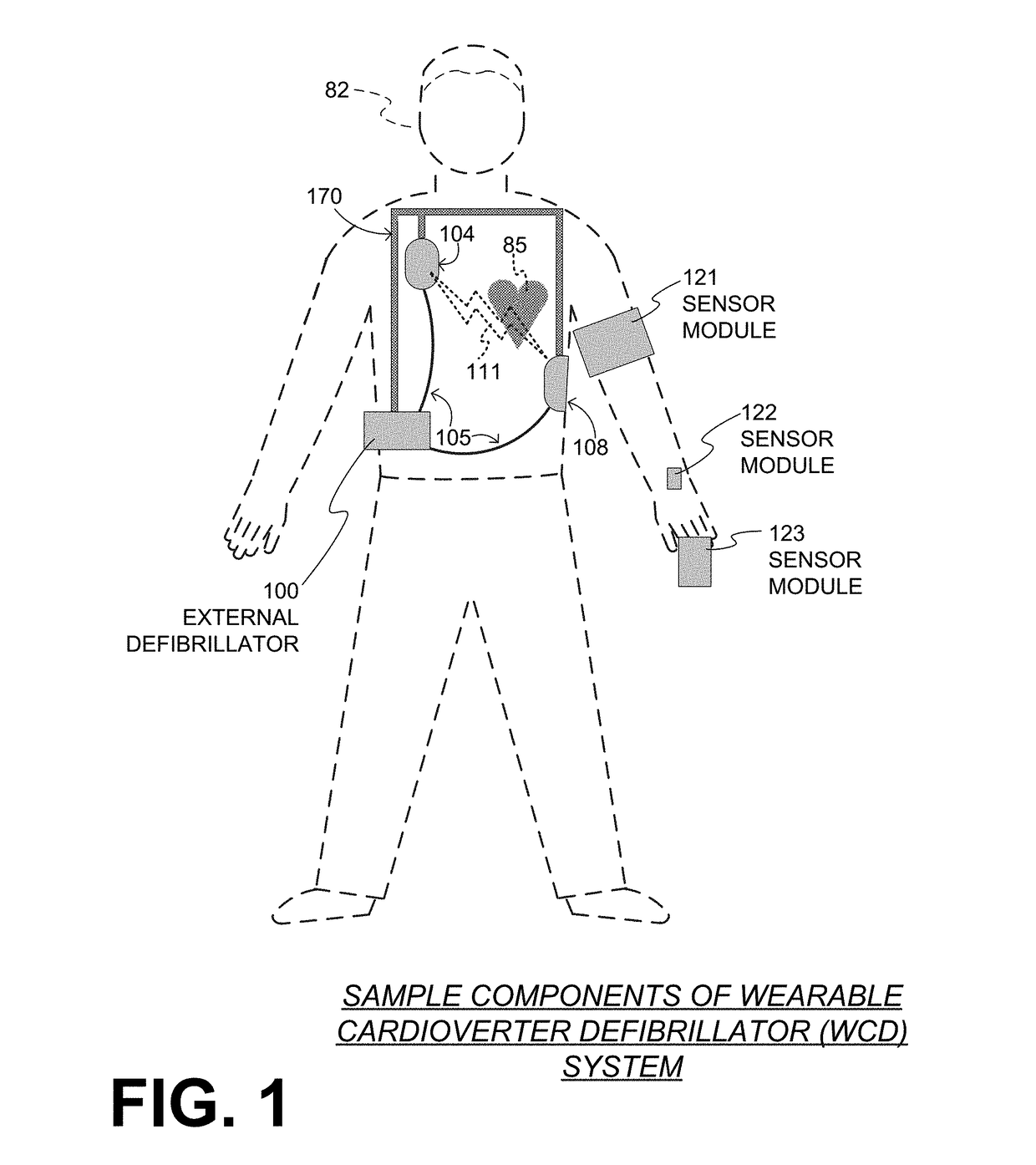
A wearable cardioverter defibrillator (“WCD”) system includes a support structure that can be worn by a patient, and a defibrillator coupled to the support structure. An ECG input, rendered from an ECG of the patient, may meet a primary shock criterion. One or more sensor modules are further provided, which are worn by the patient at different times. The sensor modules may monitor different physiological parameters of the patient, and transmit signals about them. The WCD system further has a multi-sensor interface to receive the transmitted signals, and a processor to determine from them whether a secondary shock criterion is met. If both the primary and the secondary shock criteria are met, the decision is to shock. The signals increase specificity of the detection, while the patient can wear different modules depending on context.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
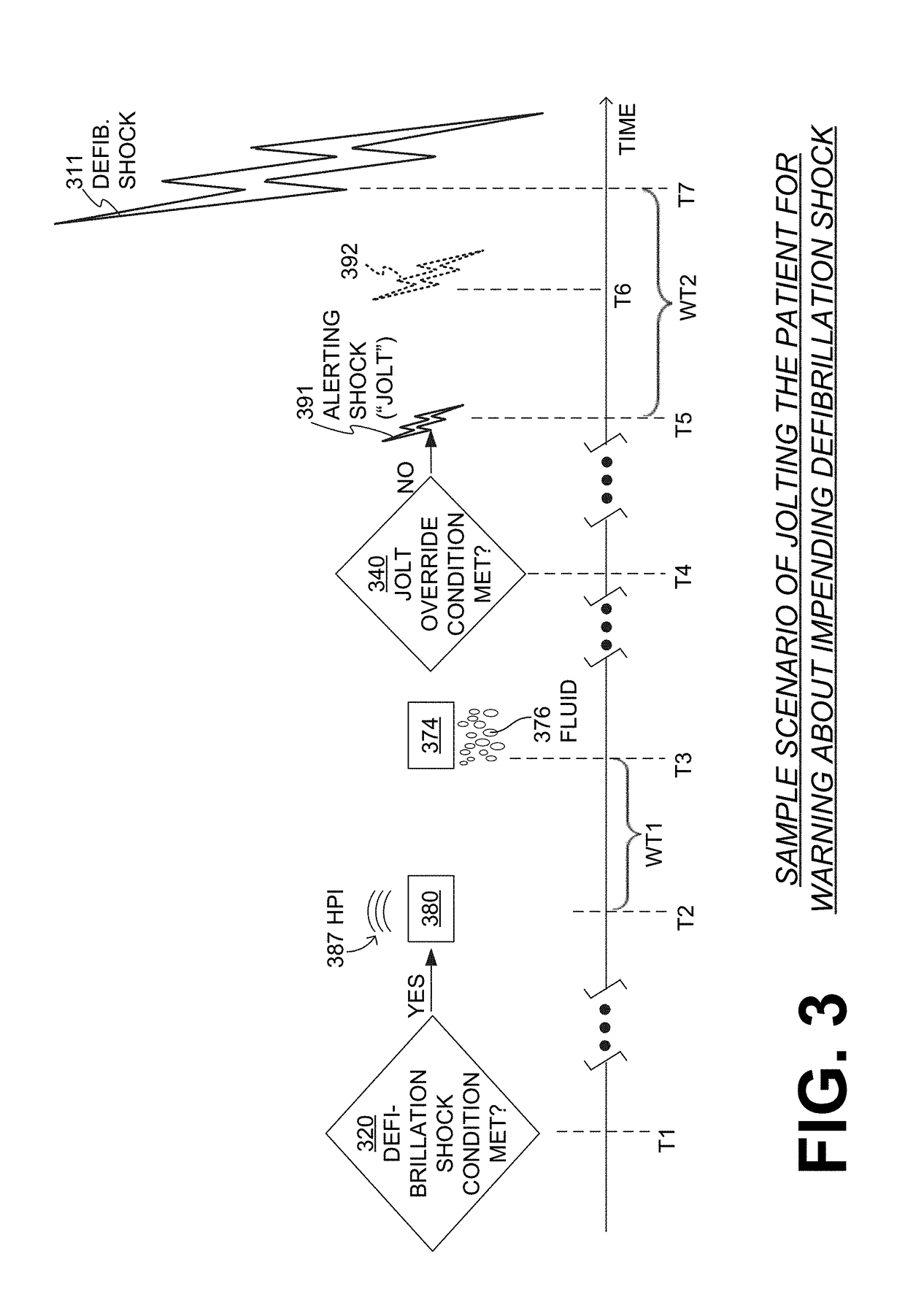
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system warning ambulatory patient by weak alerting shock
ActiveUS20190076666A1Increase opportunitiesHeart defibrillatorsWearable cardioverter defibrillatorEmergency medicine
In embodiments, a wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system is configured to be worn by an ambulatory patient. In the event that the WCD system determines that defibrillation is needed, it delivers a defibrillation shock. To diminish the possibility that the patient will be shocked due to a false positive detection, the WCD system alerts a patient that a defibrillation shock is imminent, and invites them to react to avert it. Alerting may be by a very weak shock, or jolt. Alerting by a jolt can be a last resort warning. An advantage can be that the patient has a higher chance of being alerted by the jolt, especially in the event that the patient is not reacting to other human-perceptible alerts, such as when the patient is riding a motorcycle.
Owner:KESTRA MEDICAL TECH INC +1
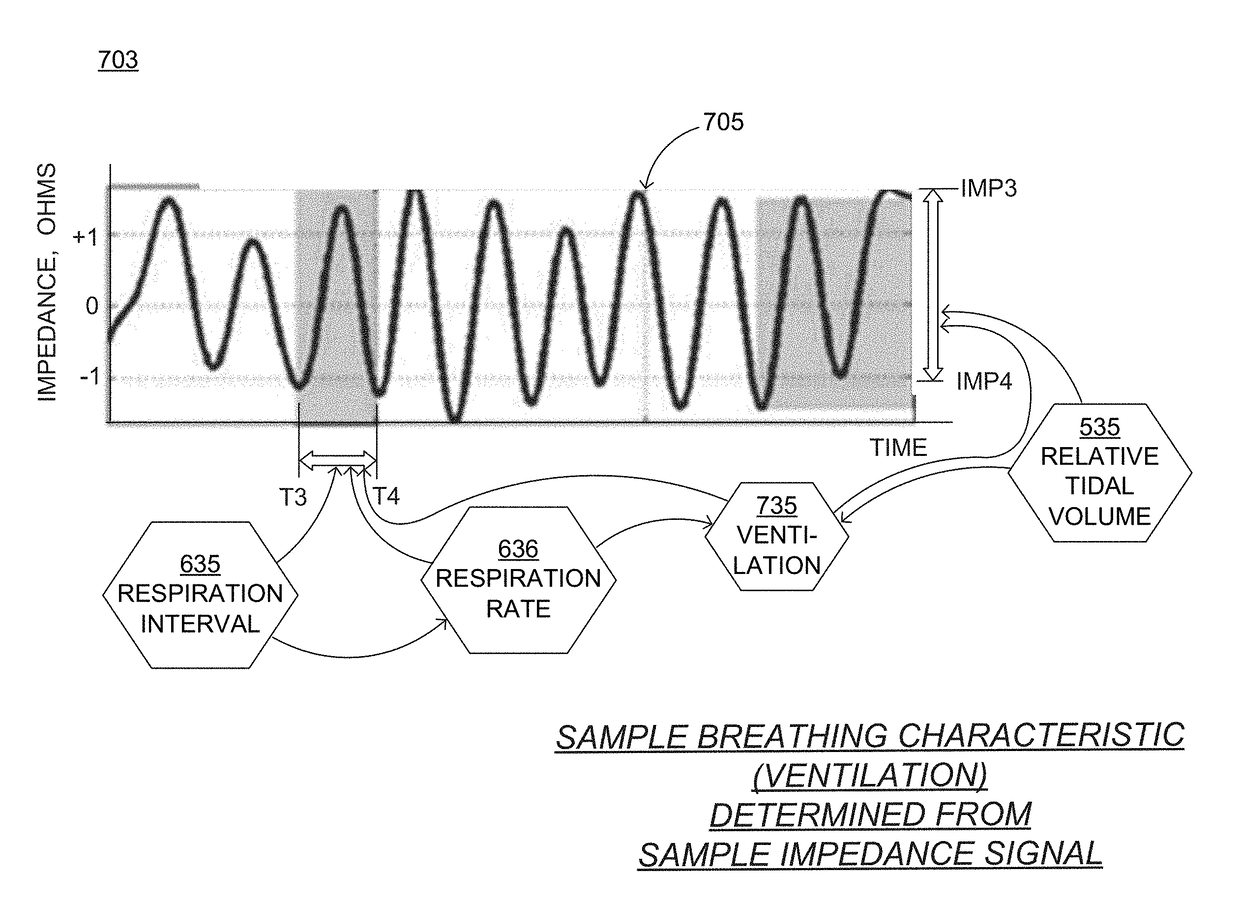
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system measuring patient's respiration
A wearable cardioverter defibrillator (“WCD”) system may include an impedance detector configured to render an impedance signal of the patient. The WCD system may determine, from the impedance signal, a characteristic of breathing by the patient that can be used as a vital sign. The WCD system may determine, from at least the breathing characteristic, whether or not a shock criterion is met. If the shock criterion is met, the WCD system may control a discharge circuit to discharge a stored electrical charge through the patient. An advantage can be that the breathing characteristic may be used to determine whether or not a patient is experiencing a condition that requires defibrillation therapy, such as sudden cardiac arrest. Even more advantages can be had in discerning the state of the patient when the breathing characteristic is combined with other data, such as from a motion detector.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system informing patient that it is validating just-detected cardiac arrhythmia
ActiveUS9757579B2Reduce morbidityElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsVentricular tachycardiaWearable cardioverter defibrillator
In some embodiments, a wearable cardioverter defibrillator (“WCD”) system may output an opening human-perceptible indication, after detecting a shockable cardiac arrhythmia but before validating it. This may succeed in informing the patient that the WCD system is working, and in particular analyzing a just-detected cardiac arrhythmia. The information may give comfort and confidence to the patient who may be conscious, and be experiencing only ventricular tachycardia but not ventricular fibrillation.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system making shock/no shock determinations from multiple patient parameters
In embodiments, a WCD system includes one or more transducers that may sense patient parameters from different parts of the patient's body, and thus render physiological inputs from those parameters. Individual analysis scores may be determined from the physiological inputs, and an aggregate analysis score may be determined from the individual analysis scores. A shock / no shock determination may be made depending on whether or not the aggregate analysis score meets an aggregate shock criterion. Accordingly, multiple inputs are considered in making the shock / no shock determination.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) causing patient's qrs width to be plotted against the heart rate
ActiveUS20170128735A1Detailed analysisHeart defibrillatorsSensorsRR intervalWearable cardioverter defibrillator
A wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system includes a support structure that the patient may wear, and one or more sensors that may acquire patient physiological signals, such as ECG and others. A processor of the WCD system may determine diagnostics from the patient physiological signals. These diagnostics include a six-second ECG portion, heart rates as histograms, heart rates against QRS width, heart rate trends, clinical event counters, diagnostics relating to heart rate variability and about the atrial arrhythmia burden of the patient. In some embodiments, the WCD system includes a user interface with a screen that displays these diagnostics. In some embodiments, the WCD system exports these diagnostics for viewing by a different screen. When viewed, these diagnostics permit more detailed analysis of the state of the patient.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system reacting to high-frequency ECG noise
ActiveUS20190030351A1Reduce morbidityMore compliantElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsEcg signalWearable cardioverter defibrillator
In embodiments a wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system is worn by an ambulatory patient. The WCD system analyzes an ECG signal of the patient, to determine whether or not the patient should be given an electric shock to restart their heart. If the WCD system determines that such a shock should be given, then it also determines whether or not a High Frequency (H-F) noise criterion is met by the ECG signal. If that H-F noise criterion is not met, the patient can be shocked. If, however, that H-F noise criterion is met, then the WCD system can confirm before shocking, by sensing another portion of the ECG signal, analyzing again, and so on. Thanks to the confirmation before shocking, the possibility is diminished that the ECG signal will indicate that a shock is needed falsely, due to H-F noise. This can further reduce false patient alarms, and so on.
Owner:STRYKER CORP +1
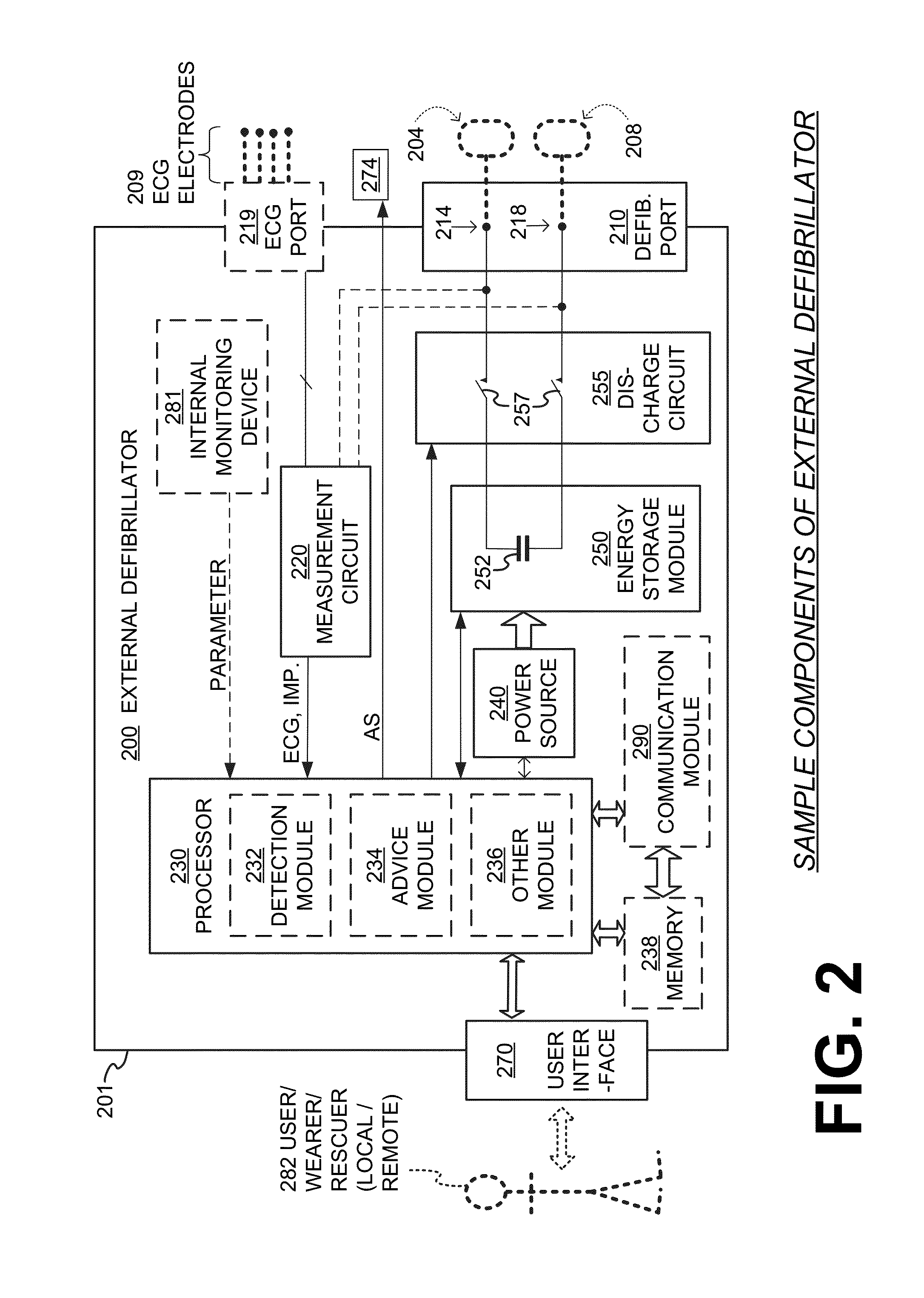
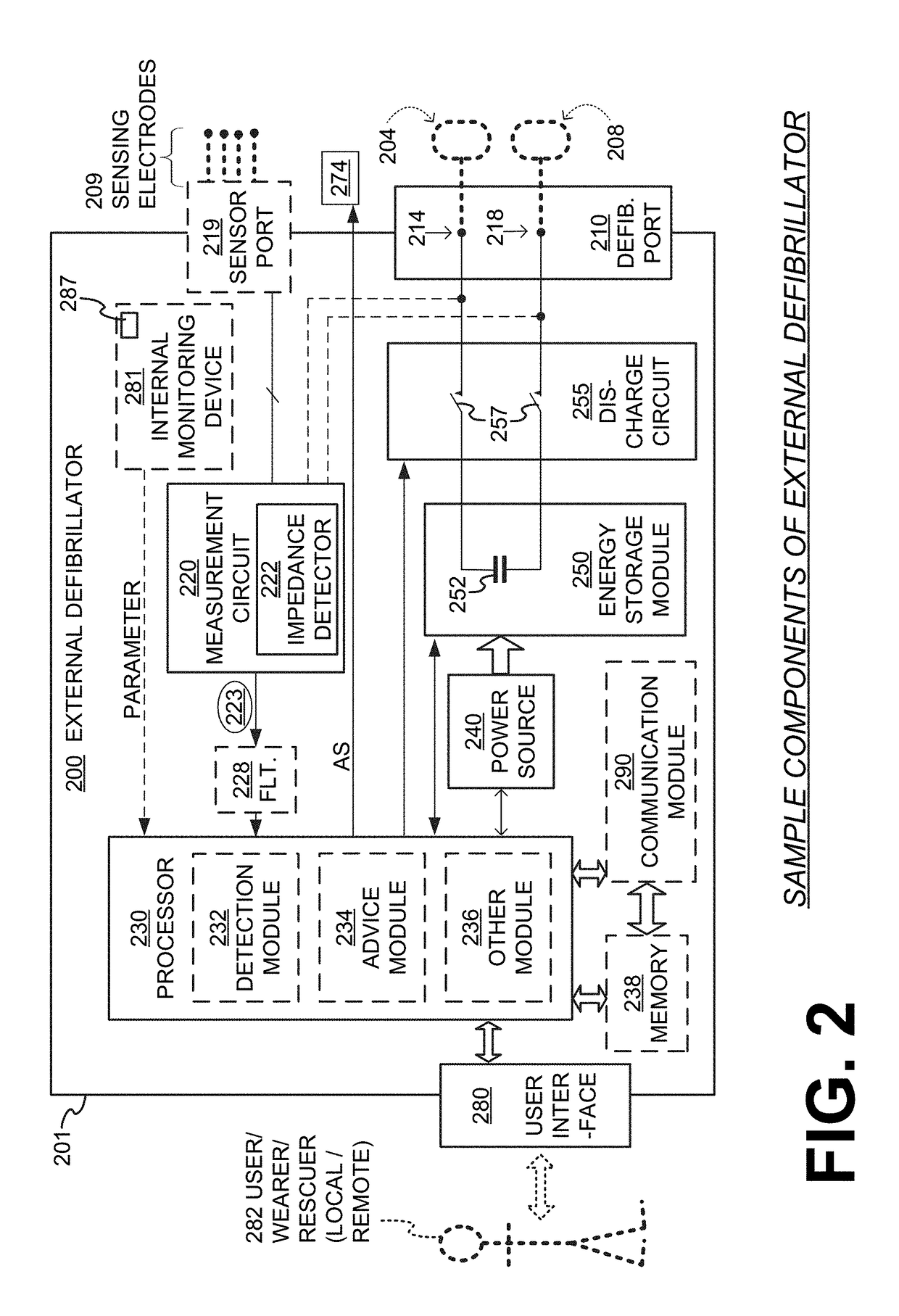
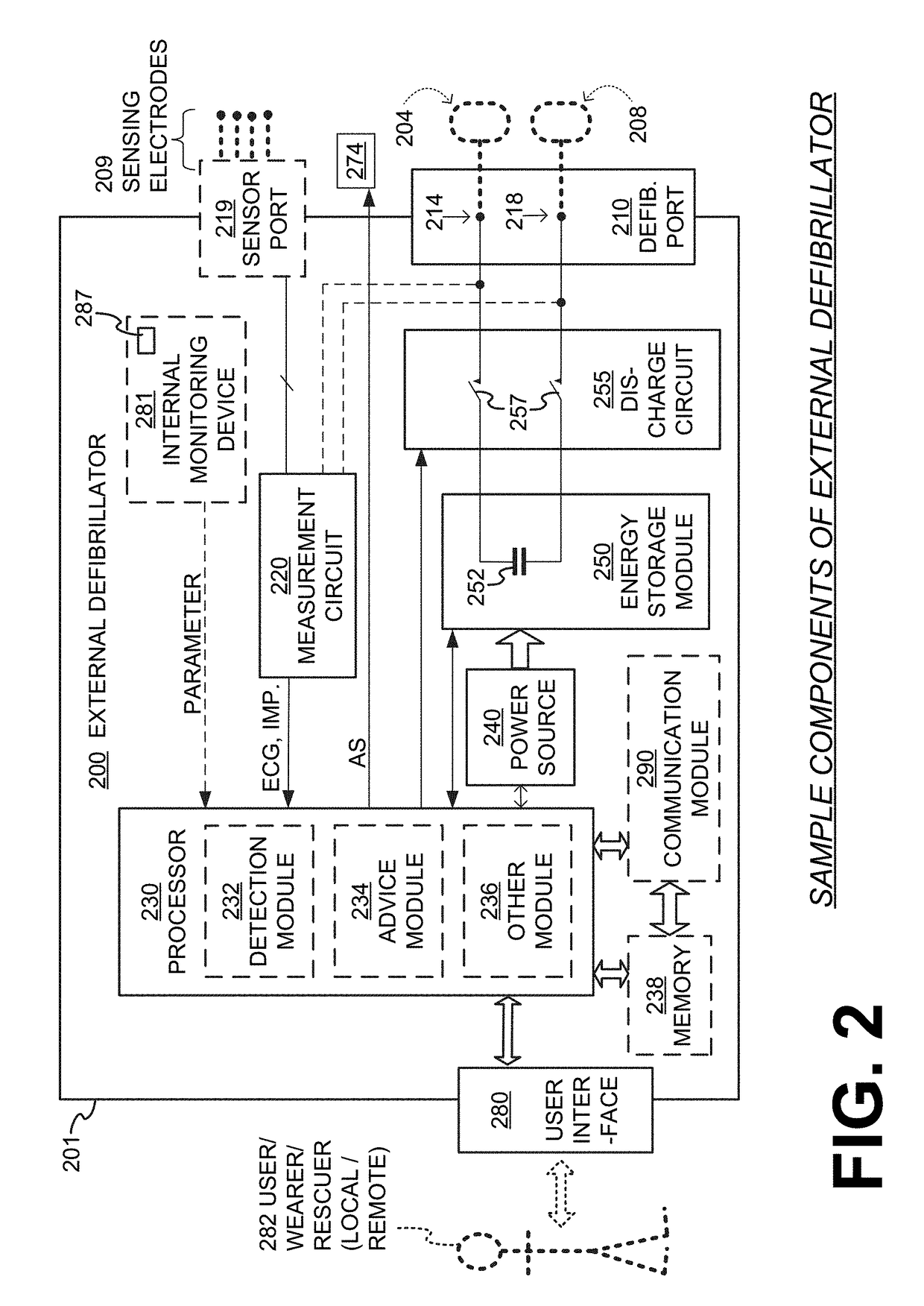
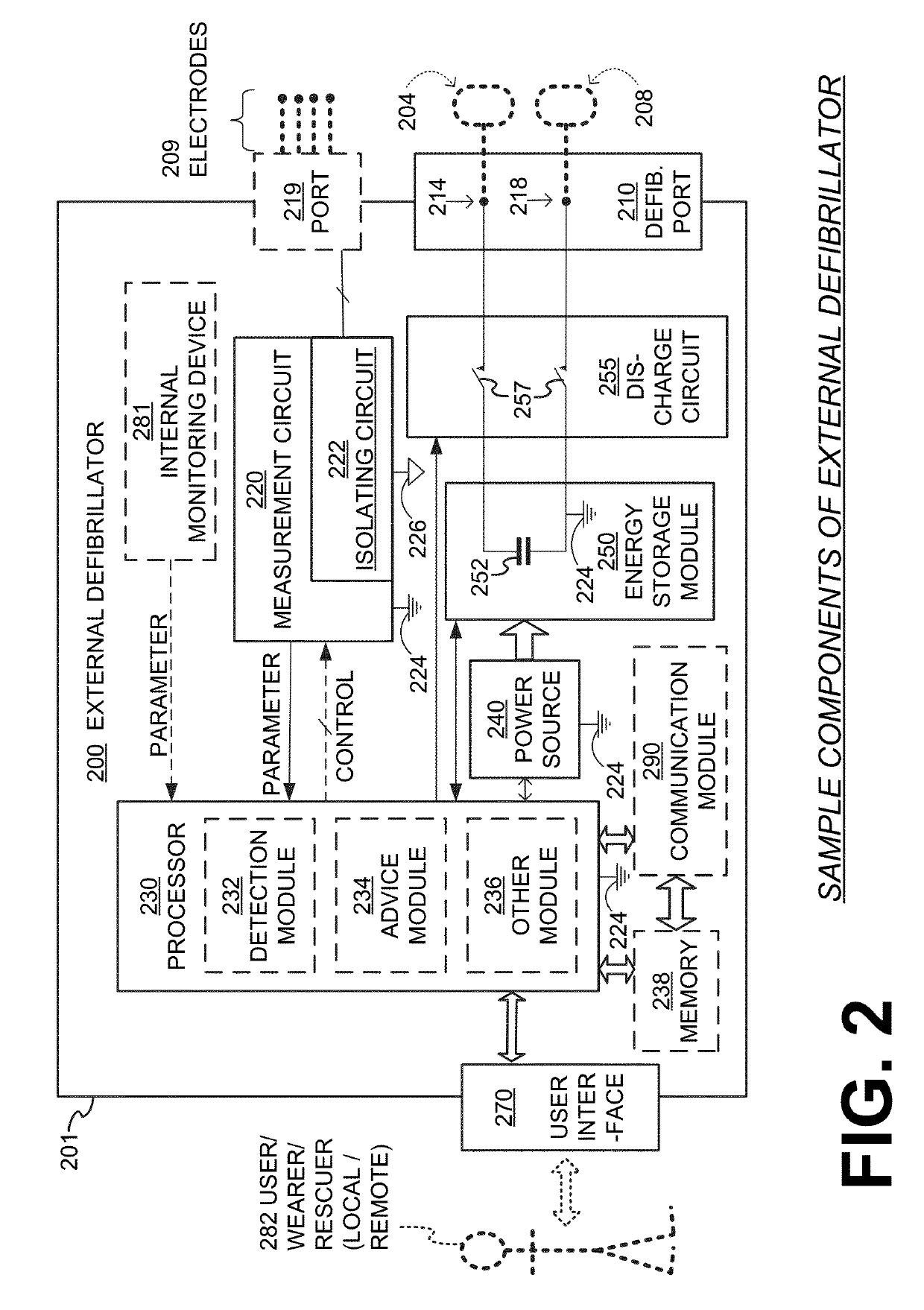
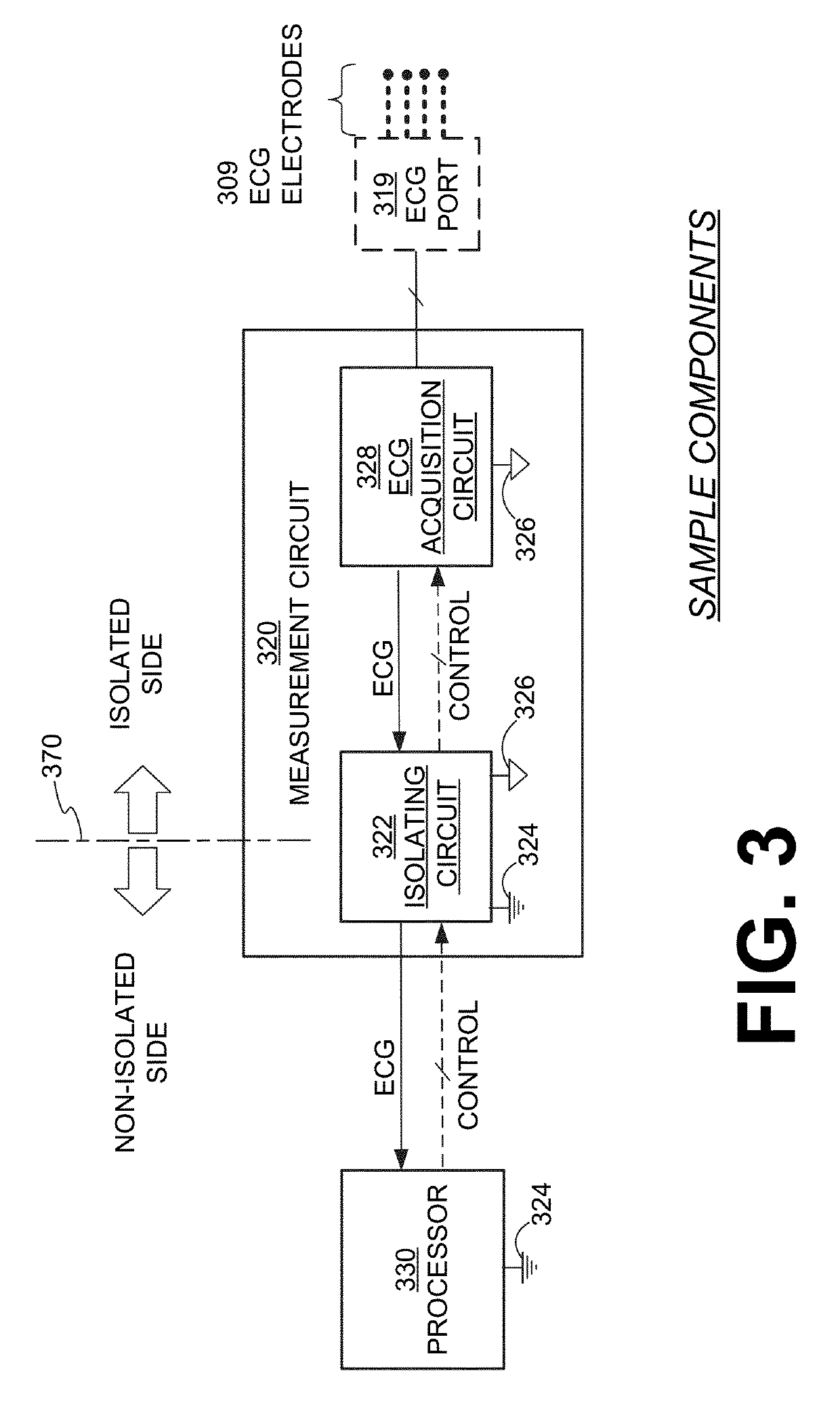
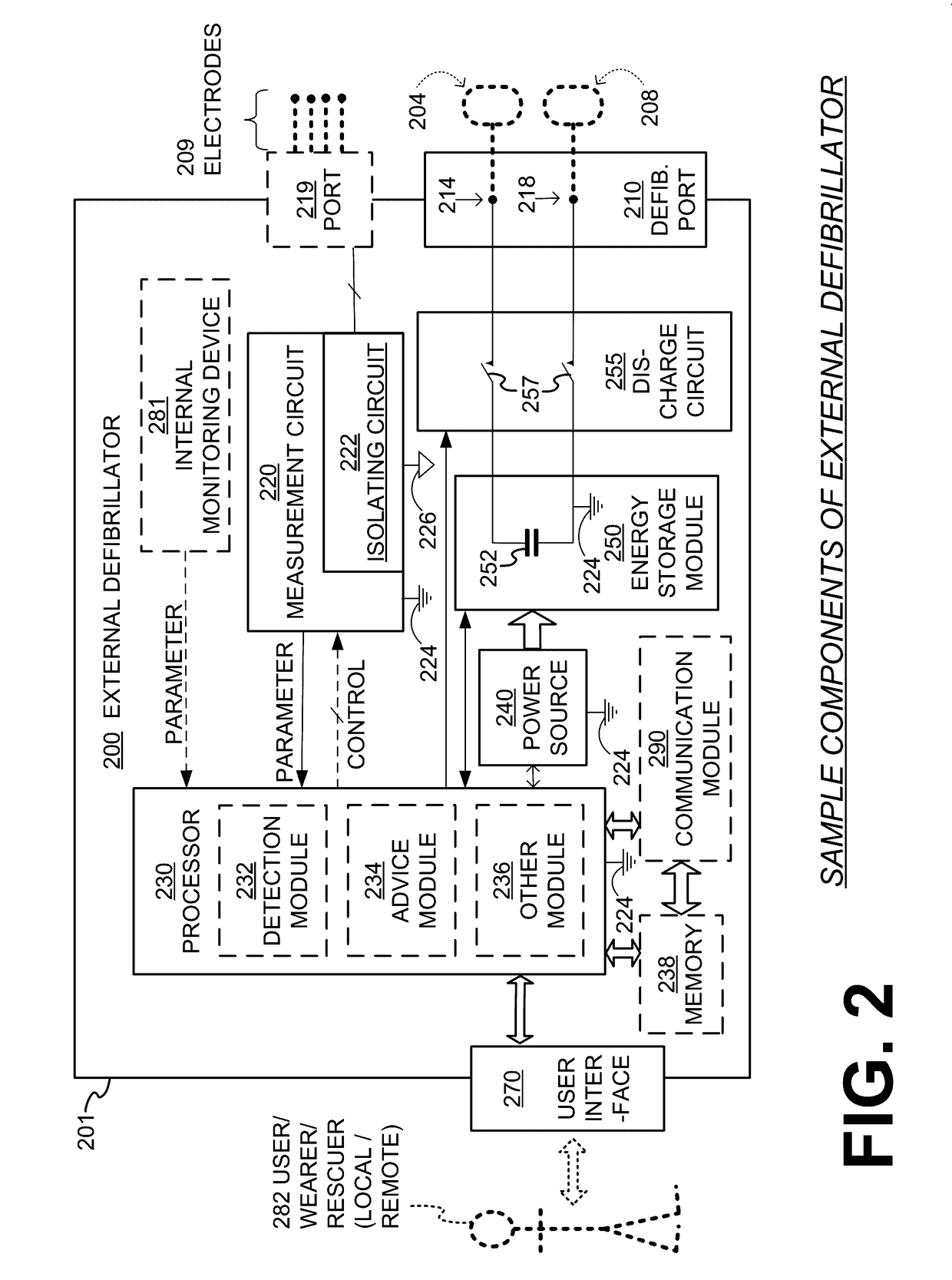
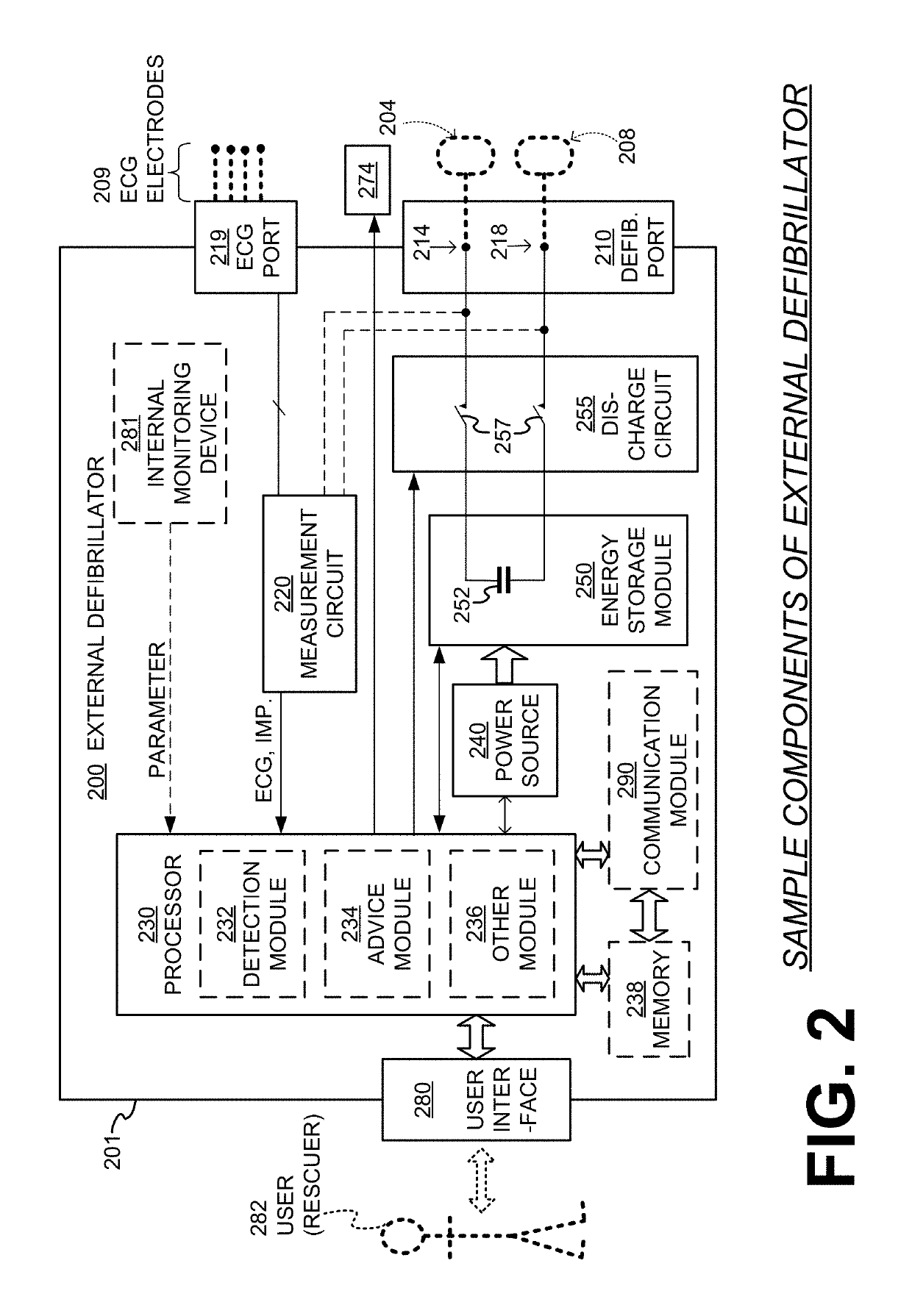
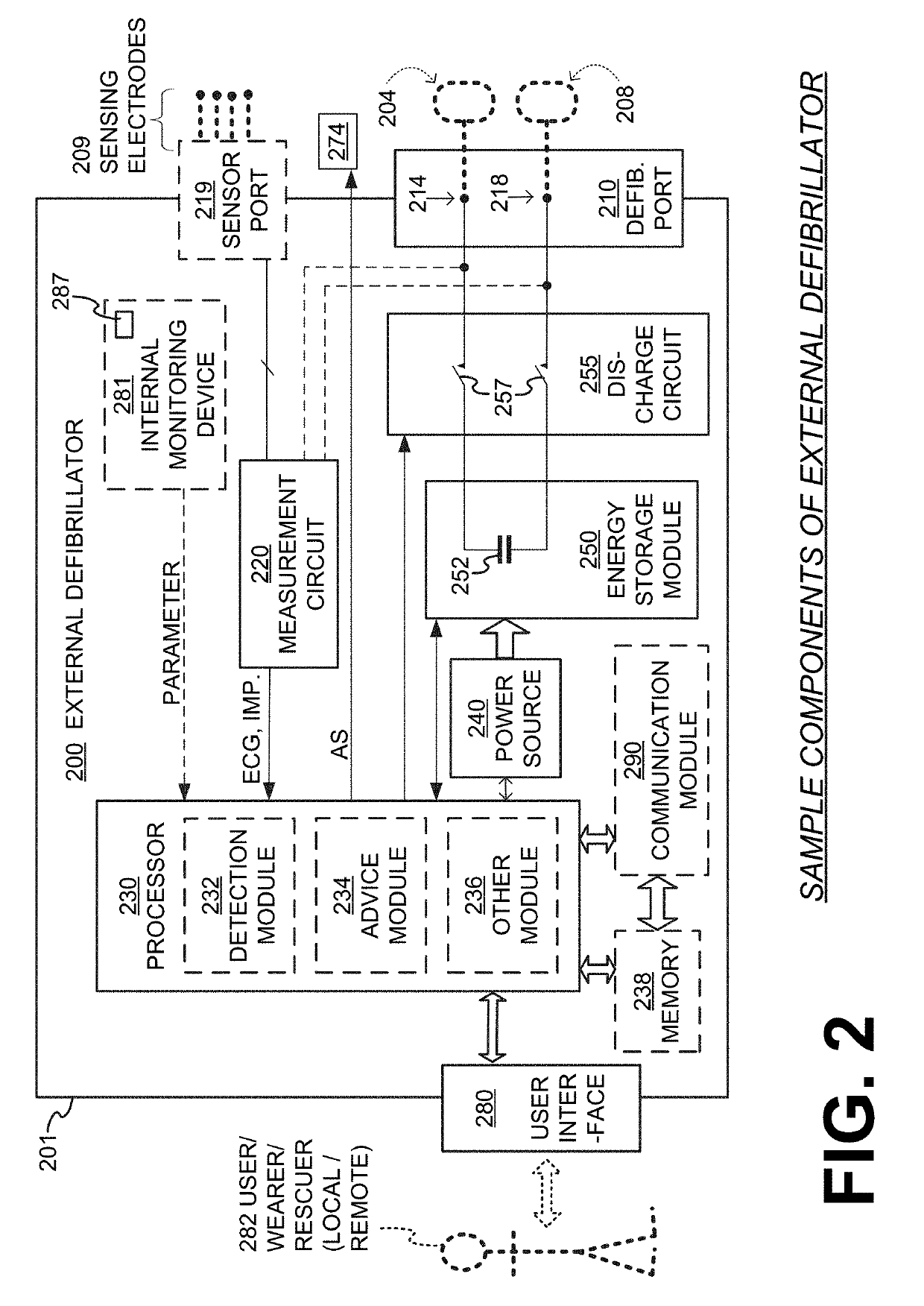
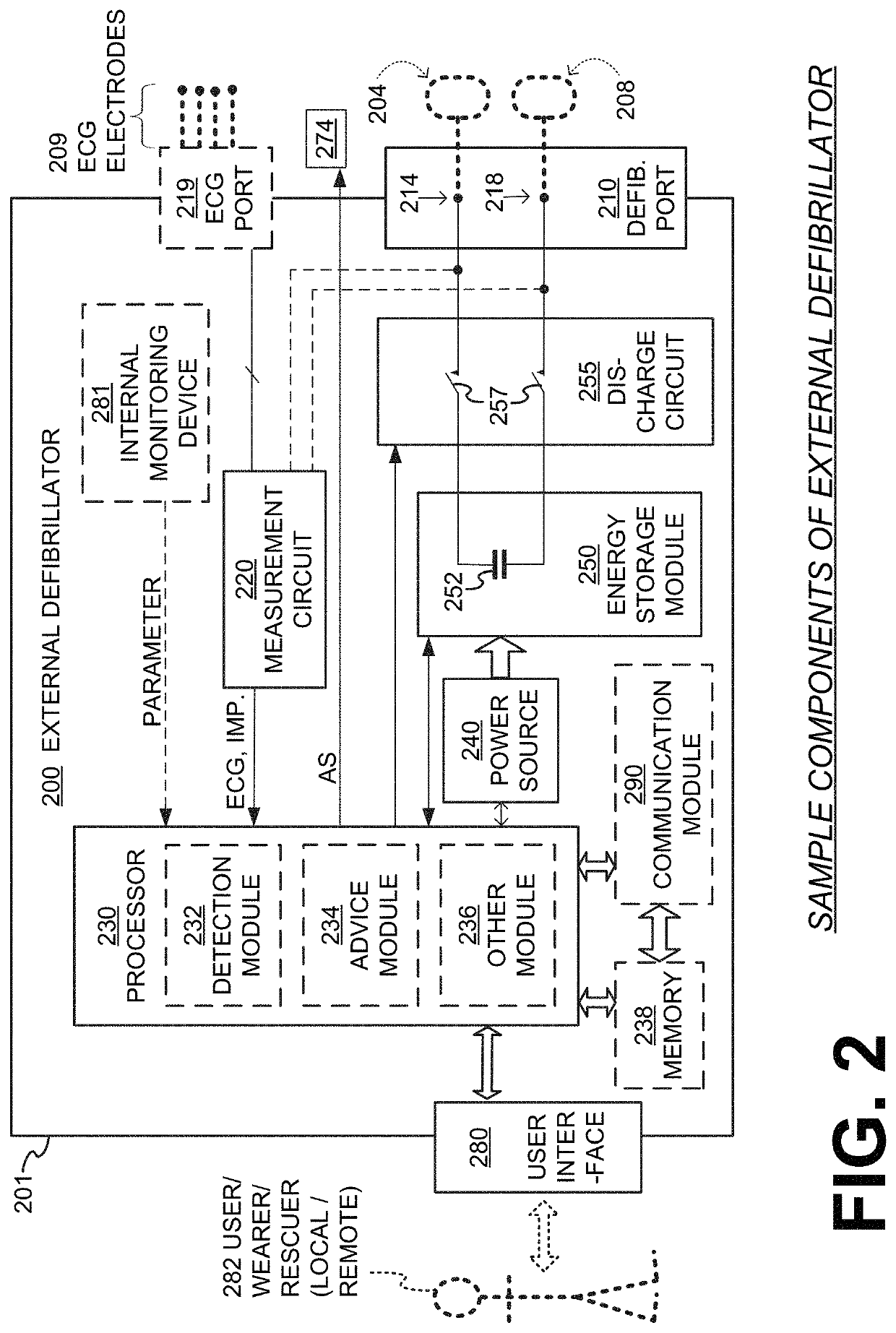
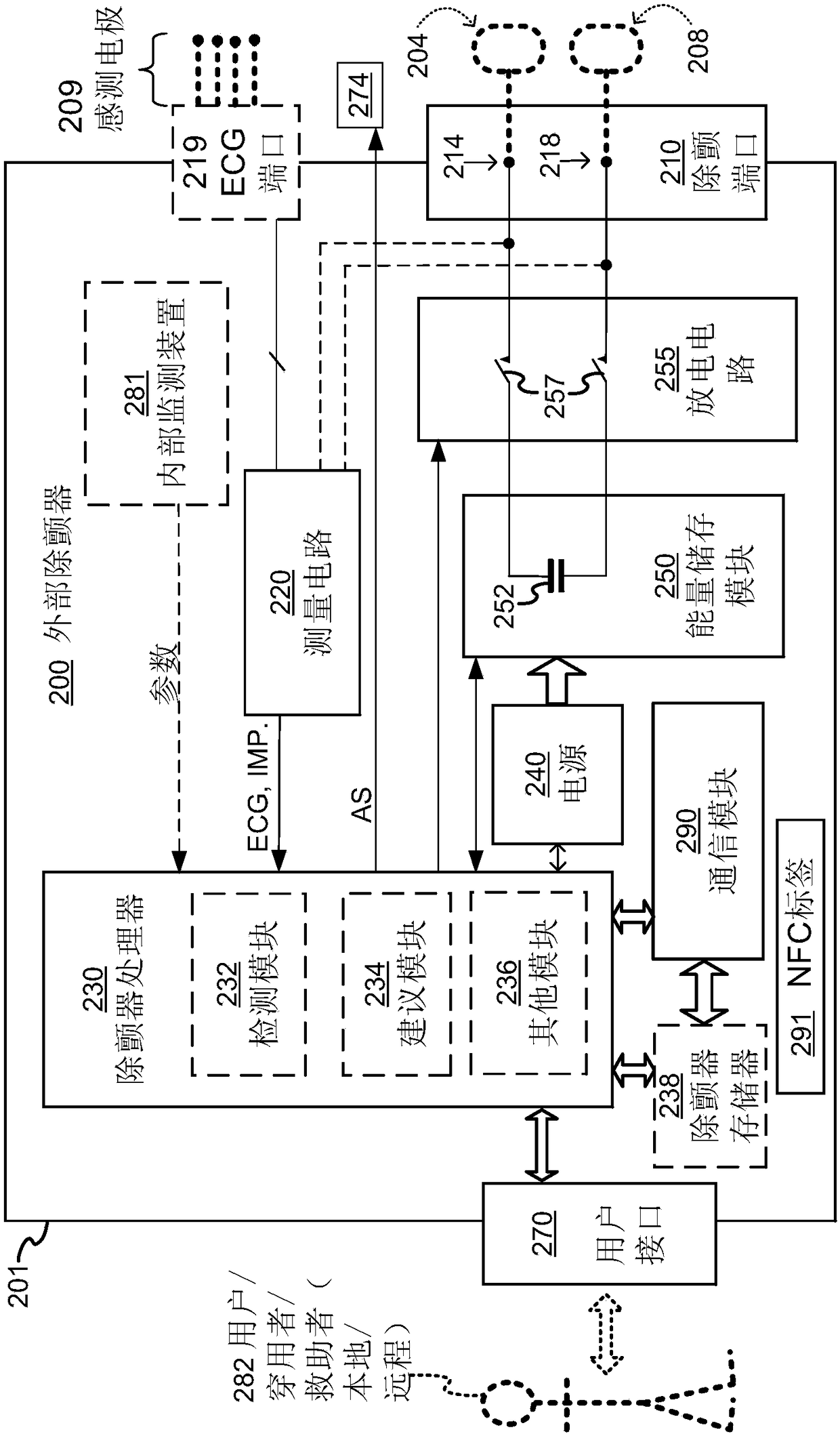
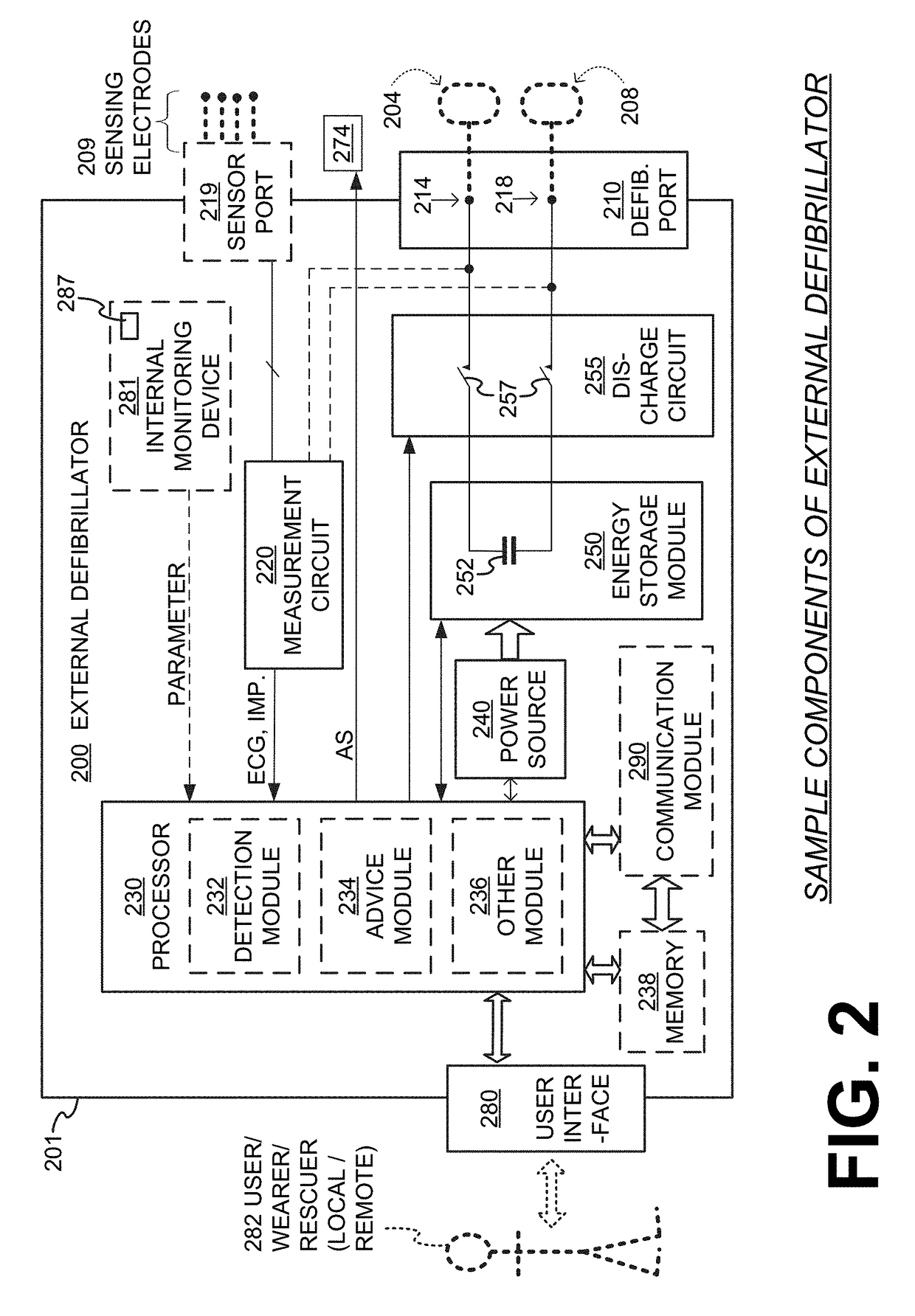
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system with isolated patient parameter component
ActiveUS10322291B2Few erroneous readingImprove overall senseHeart defibrillatorsExternal electrodesElectricityWearable cardioverter defibrillator
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system with isolated patient parameter component
ActiveUS20170157416A1Few erroneous readingFew false alarmHeart defibrillatorsExternal electrodesElectricityWearable cardioverter defibrillator
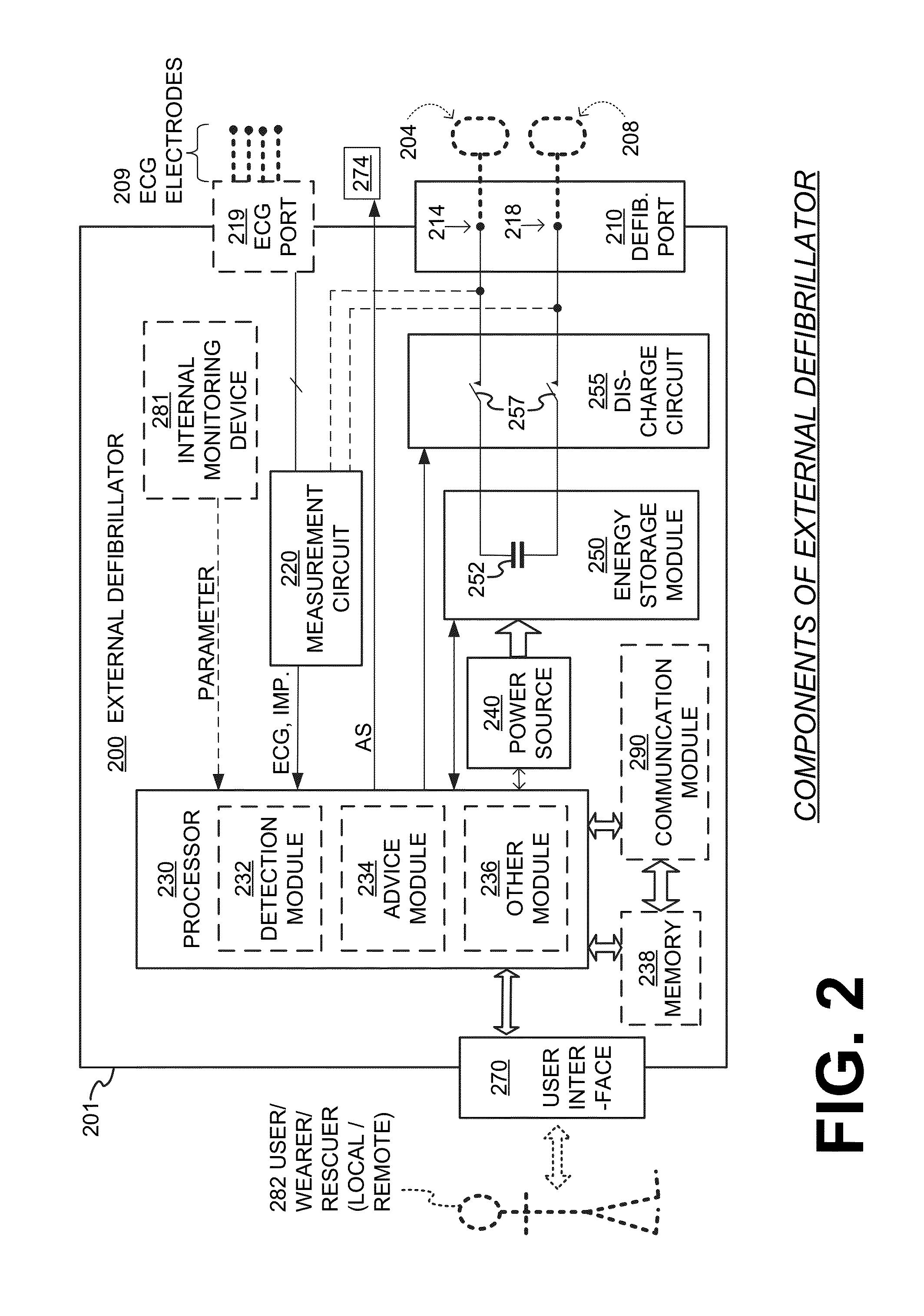
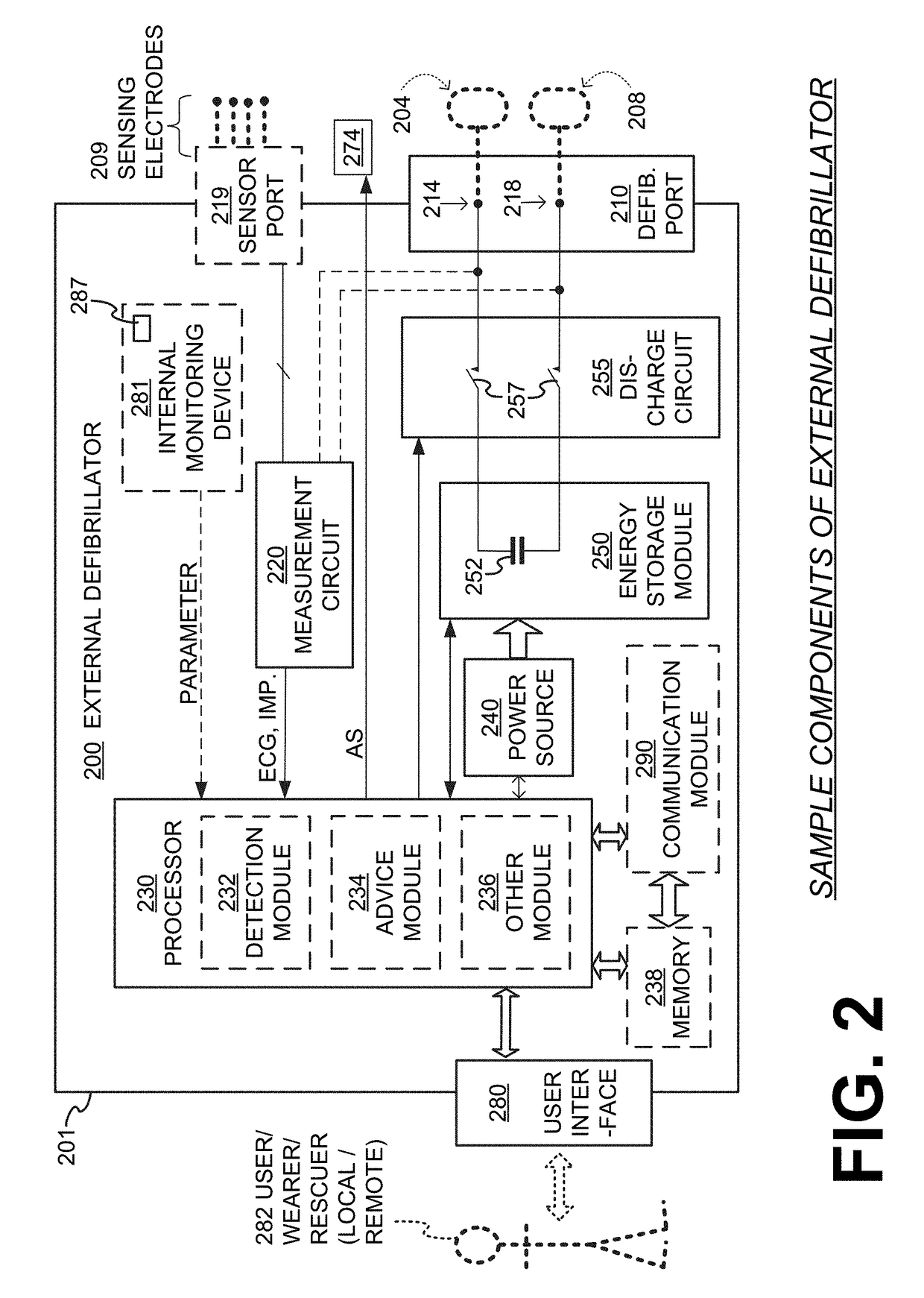
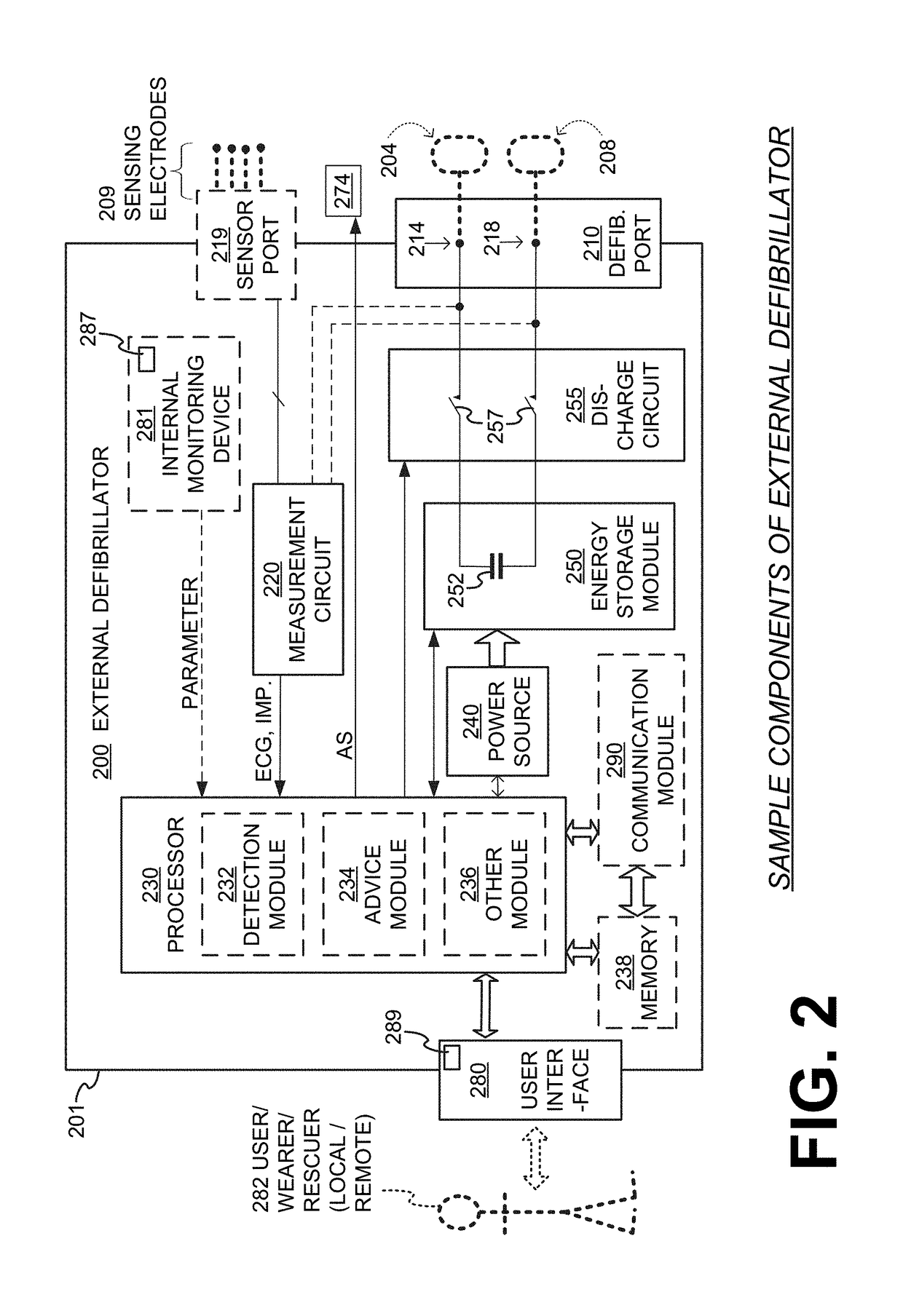
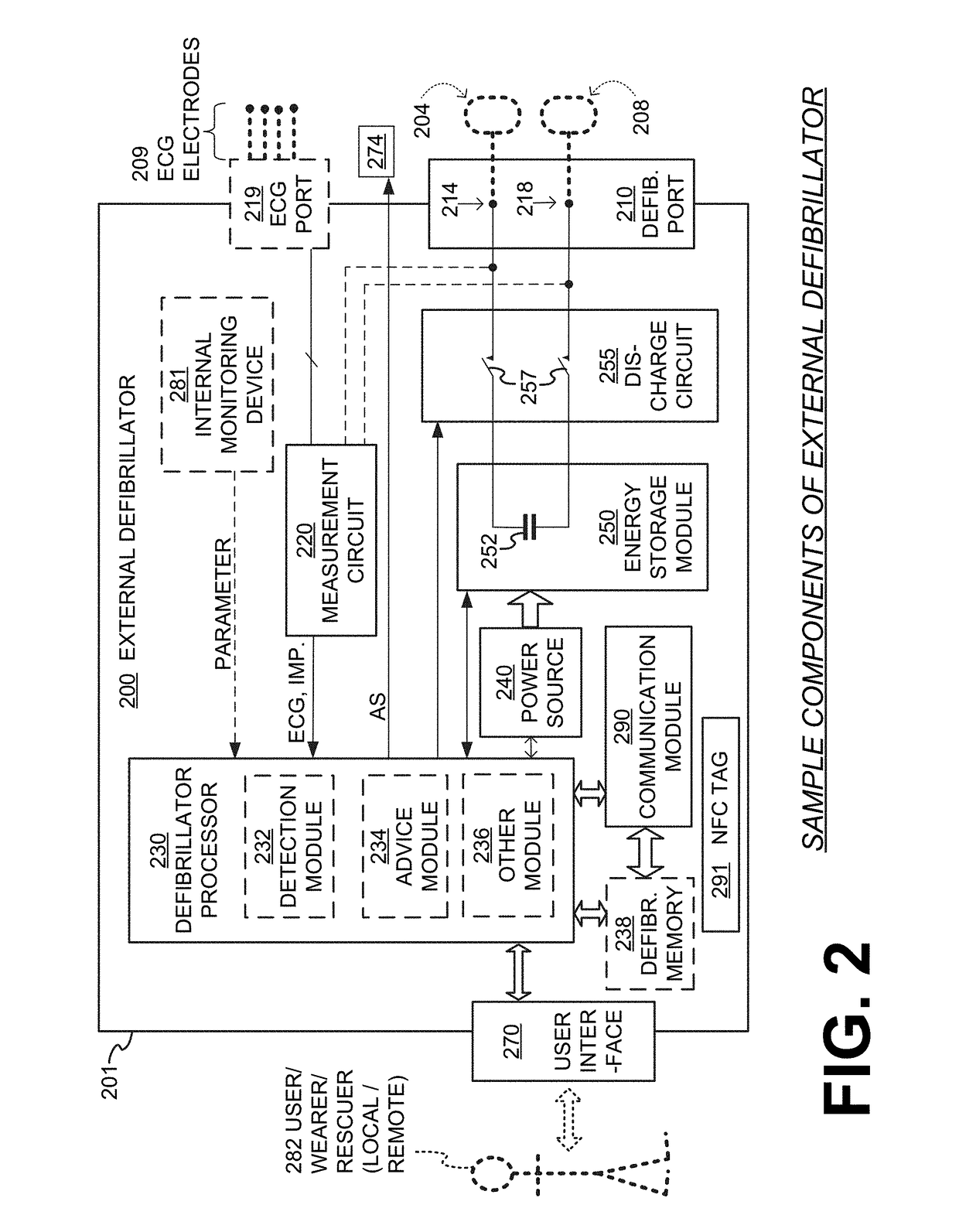
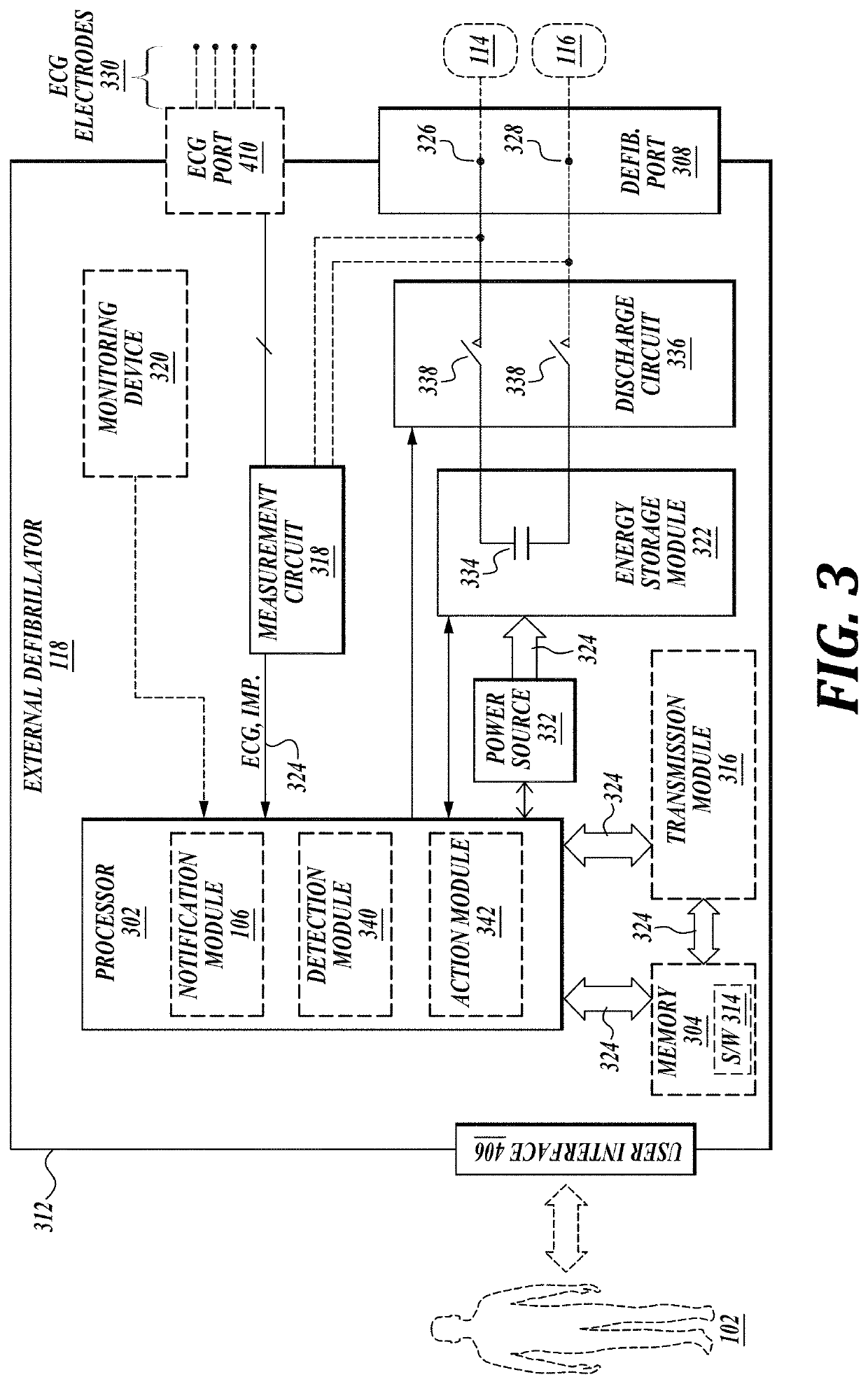
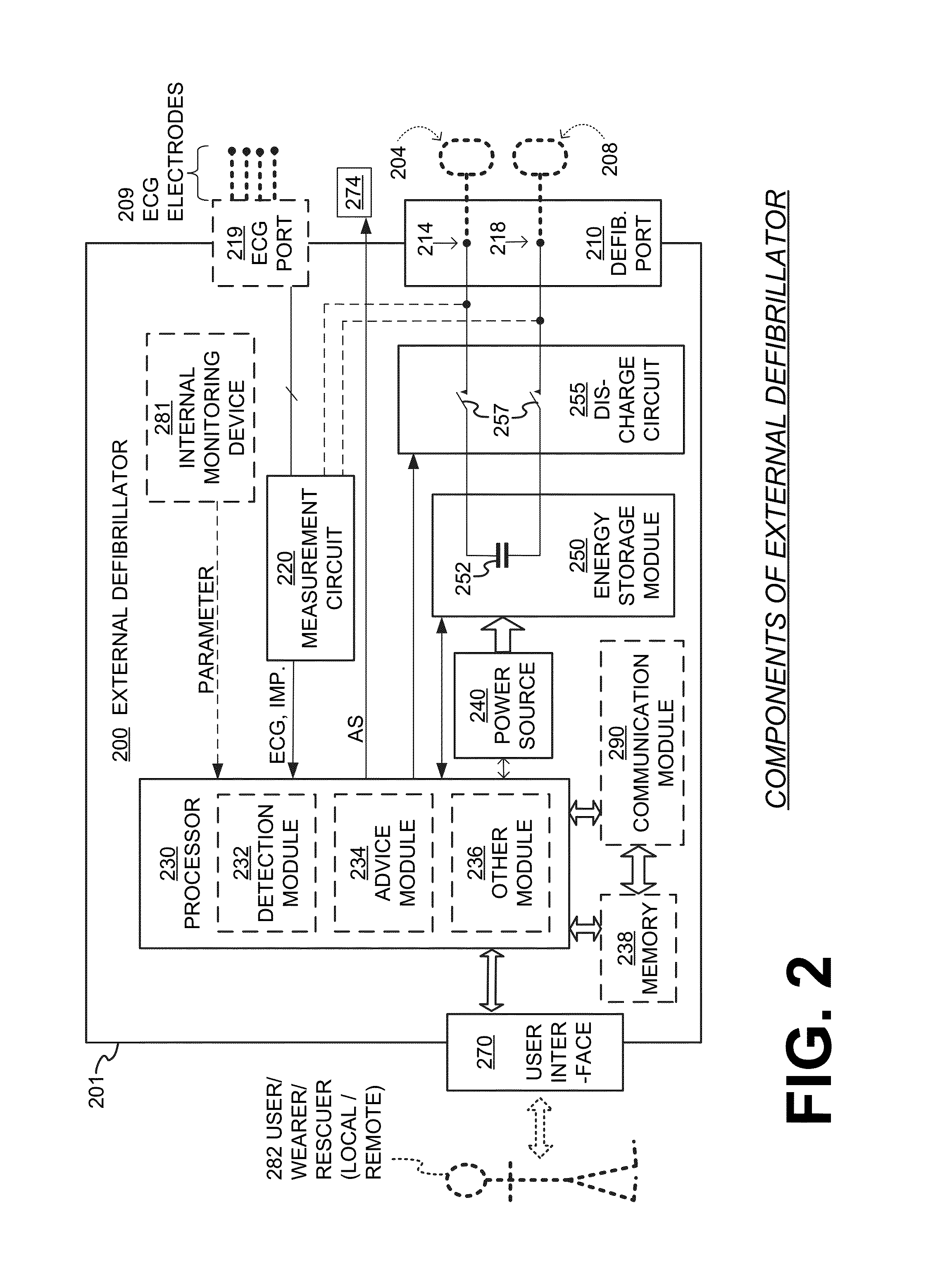
Embodiments are directed to wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) systems that include patient parameter electrodes, such as ECG electrodes, that are at least substantially electrically isolated from other circuits of the WCD system. In embodiments, the WCD system includes a power source, an energy storage module, and a processor each connected to a first circuit ground. A patient parameter sense port, such as an ECG port, is coupled to the patient. A measurement circuit may render a physiological input from the sensed patient parameter received at the patient parameter sense port, and the measurement circuit includes an isolating circuit that electrically isolates the patient parameter sense port from the first circuit ground. The sensing of physiological inputs of the patient can be improved, resulting in fewer erroneous readings and false alarms.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator with improved ECG electrodes
ActiveUS20190159696A1Improve complianceLess attentionElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsEcg signalSkin contact
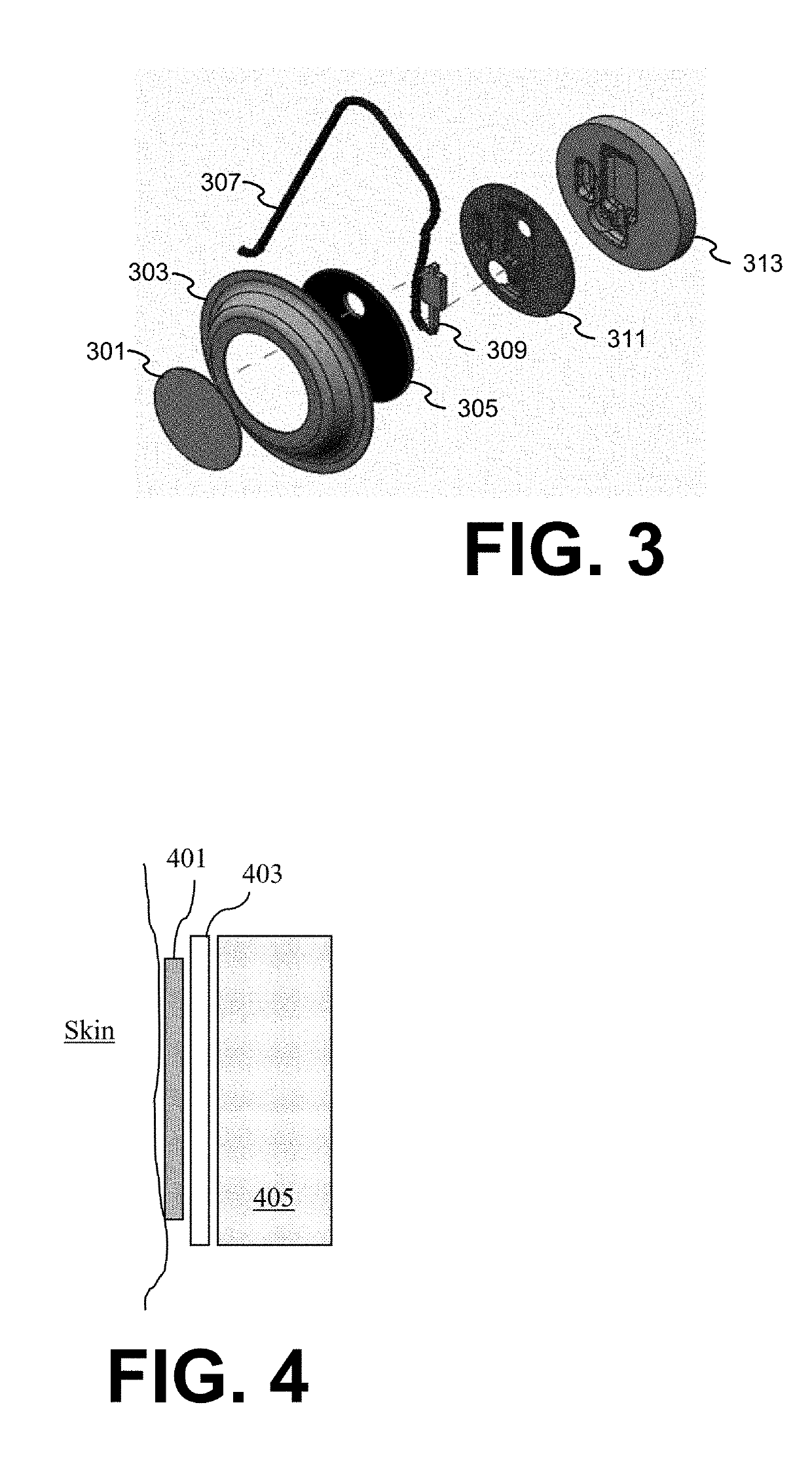
A Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillator (WCD) system comprises an electrode assembly with a permeable ECG electrode and a moisture barrier. In some embodiments, the moisture barrier is configured to reduce drying out of the permeable ECG electrode to improve performance of the WCD system. In a further enhancement, some embodiments of the electrode assembly also include a pillow structure positioned on a non-skin-contacting surface of the electrode assembly to comfortably reduce movement artifact or noise in the received ECG signal.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
Wcd system prioritization of alerts based on severity and/or required timeliness of user response
ActiveUS20200230428A1Physical therapies and activitiesHeart defibrillatorsWearable cardioverter defibrillatorDevice status
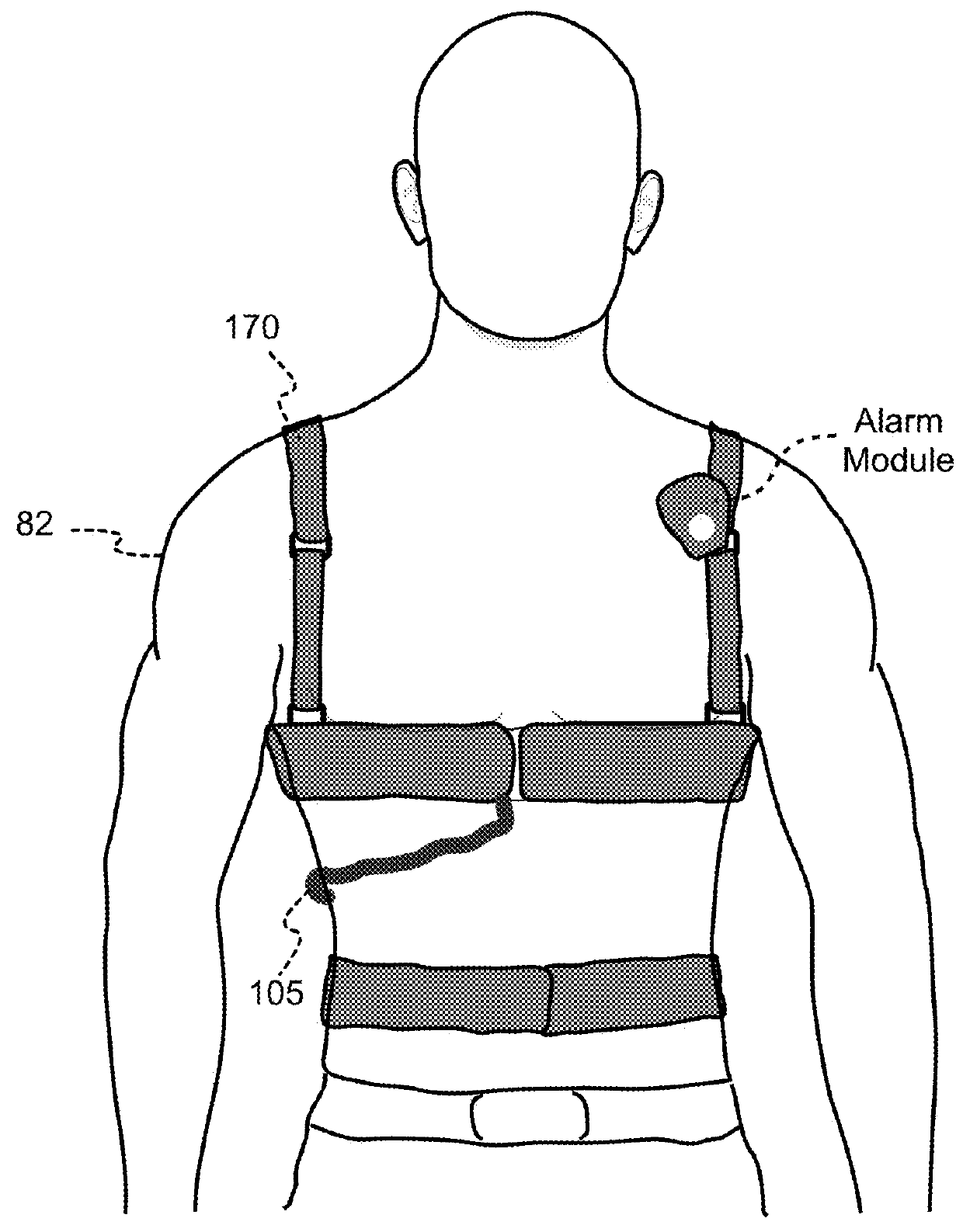
Embodiments of this disclosure are directed to a wearable cardioverter defibrillator (“WCD”) system design in which a WCD implements an alert prioritization scheme to provide the patient with feedback in an order that is less likely to cause confusion. Different conditions (e.g., device status, equipment condition, or physiologic condition) are prioritized based on an analysis of severity of the condition and timeliness of user action needed. The prioritization scheme defines what alert, if any, is presented to the user by the WCD system as a result of various conditions. Generally stated, an alert for the highest priority condition currently detected is presented to the user and maintained until that condition either changes or becomes surpassed in the prioritization scheme.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
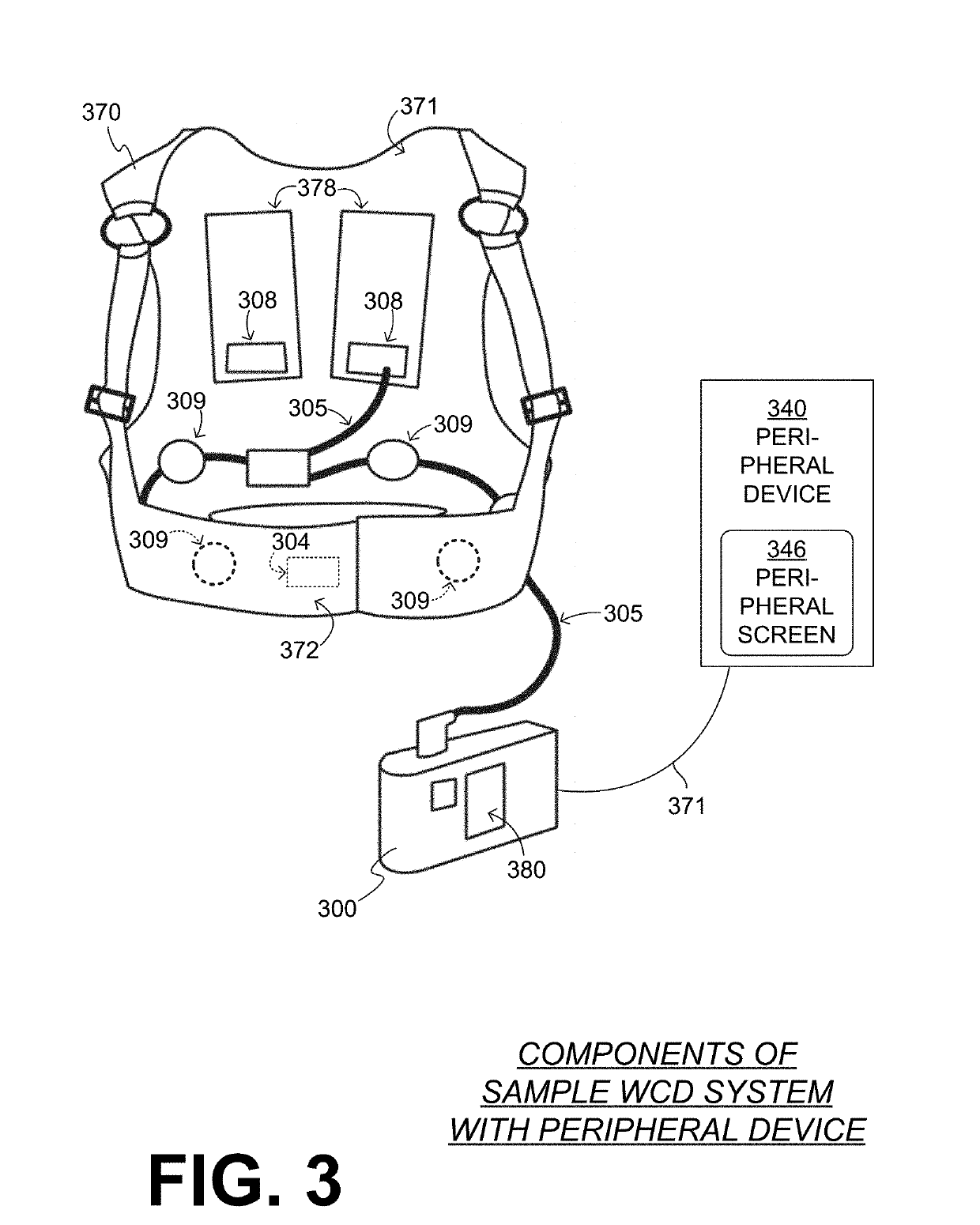
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system having main ui that conveys message and peripheral device that amplifies the message
ActiveUS20190269930A1Improve perceptionHeart defibrillatorsStethoscopeWearable cardioverter defibrillatorOutput device
In embodiments, a Wearable Cardiac Defibrillator (WCD) system is configured to be worn by an ambulatory patient. The WCD system includes a main user interface (UI) output device that can output an image, sound or vibration as a main message about a condition of the patient or the WCD system. The patient may further carry a peripheral device that can also output an image, sound or vibration as a peripheral message about the condition. The peripheral message may mirror the main message at least in part, amplify it, and so on. The availability of the peripheral message provides the patient with the opportunity to better perceive the main message, and the flexibility to receive and react to it discreetly, learn more about the condition, and so on.
Owner:TACT AI TECHNOLOGIES INC +3
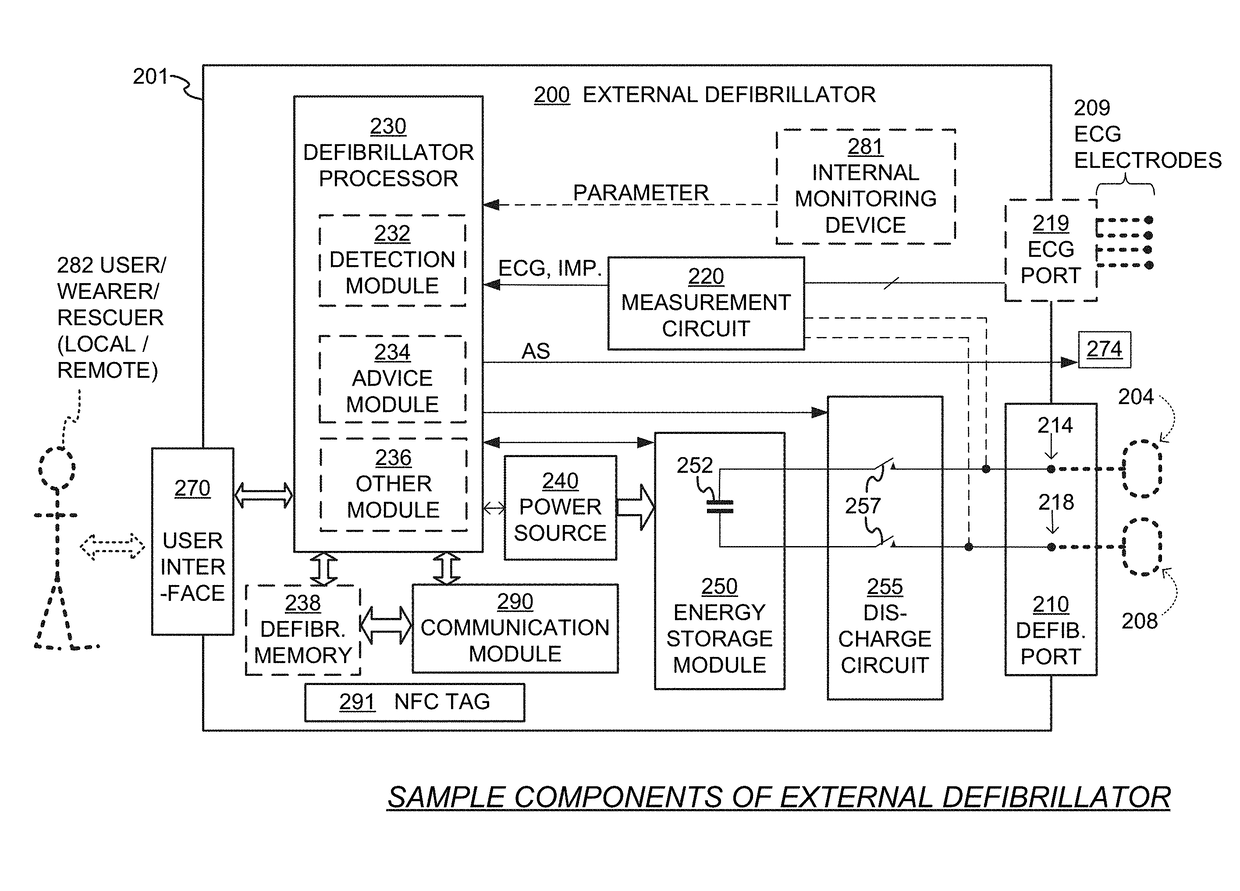
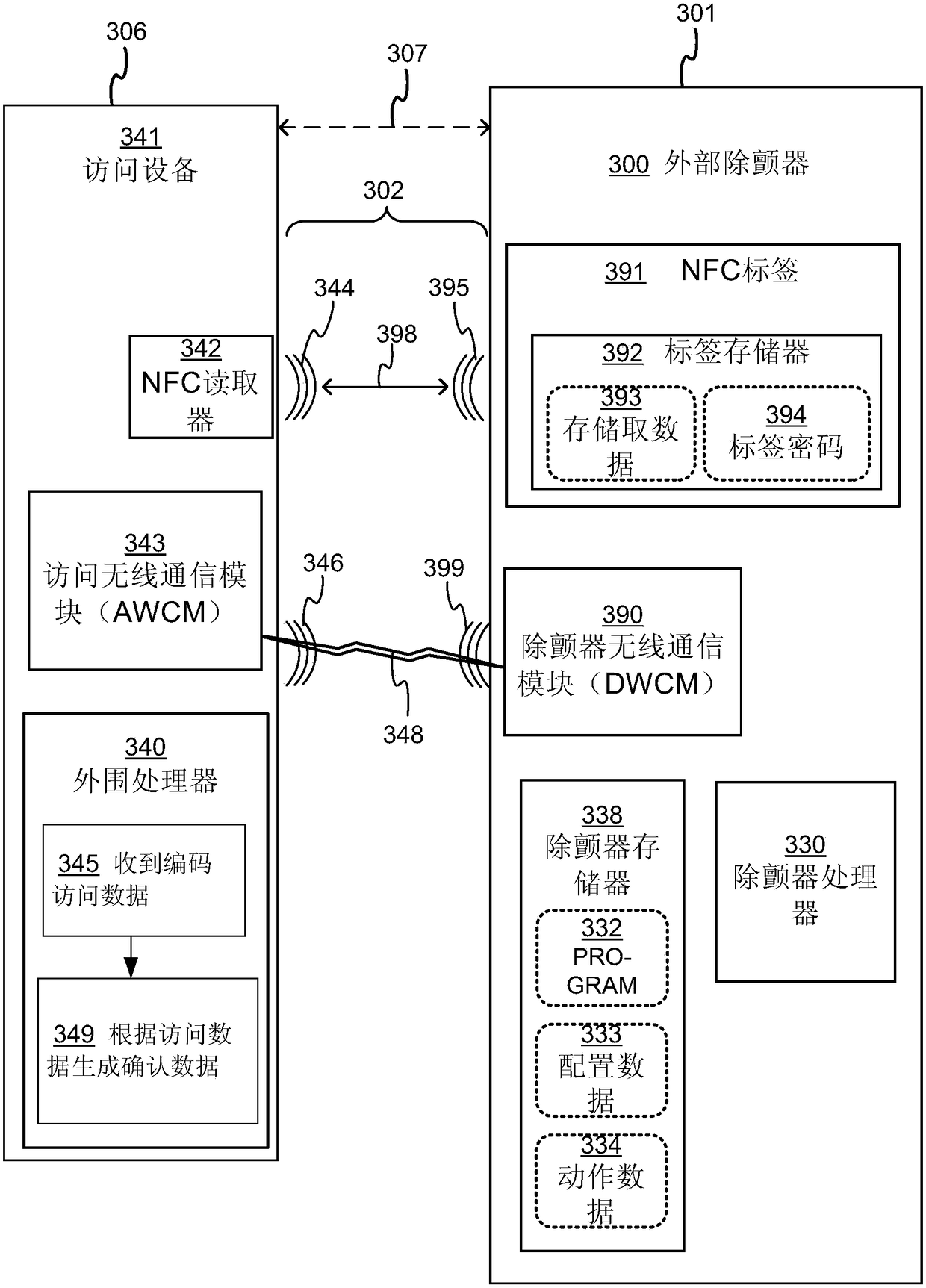
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system using security NFC tag for uploading configuration data
ActiveUS20170182330A1Physical therapies and activitiesMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesComputer hardwareSoftware update
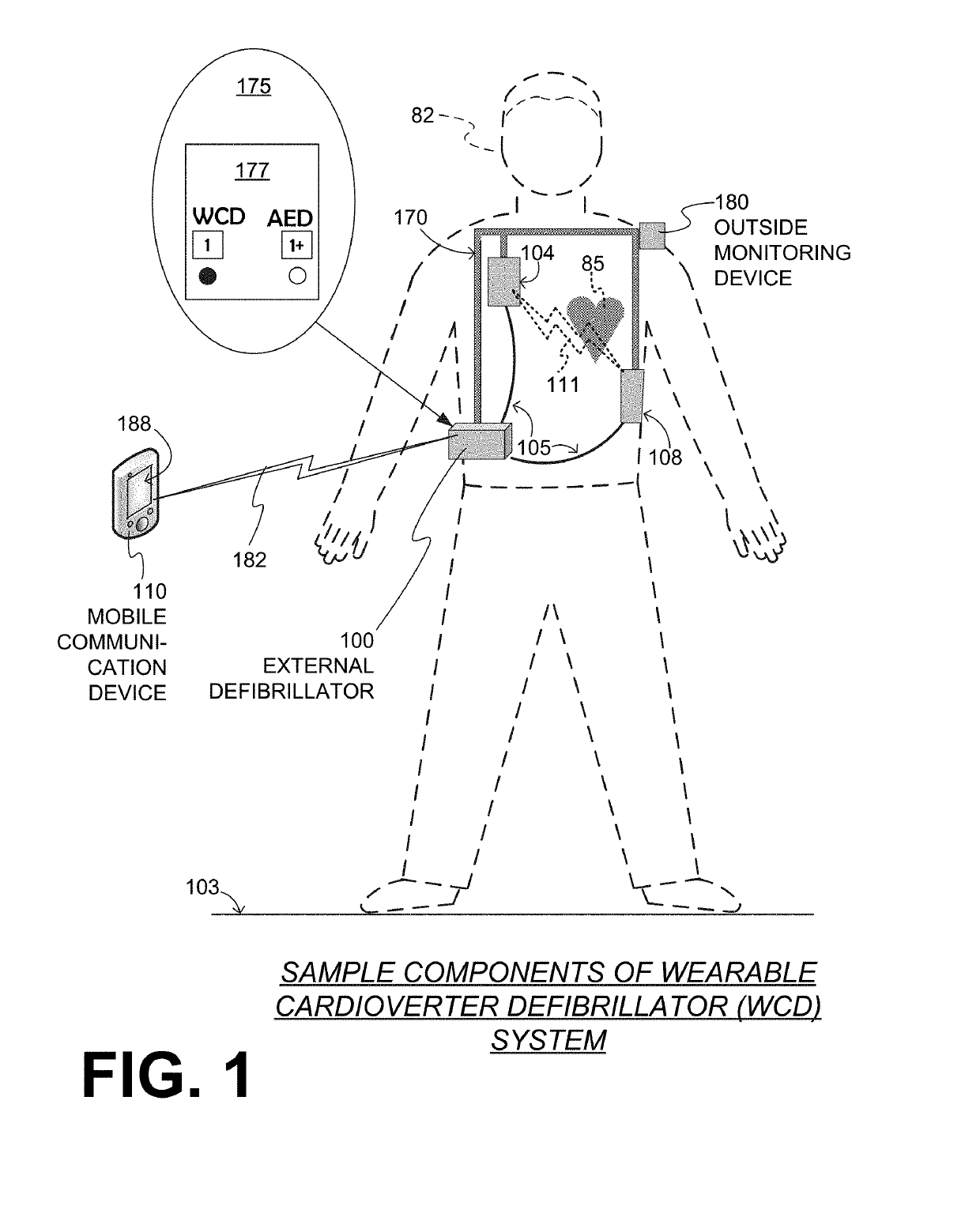
A wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system includes a processor, a memory, a wireless communication module (DWCM), and an NFC tag that stores information for how an accessing device may access the DWCM wirelessly. An accessing device such as a defibrillator configurator with an NFC reader may read the NFC tag of the WCD system, if it has adequate permission to do so. Upon so reading, the accessing device will know how to address the DWCM wirelessly, and thus install or update configuration data, software updates, or request memory downloads from operations. The use of the NFC tag requires close proximity, which hampers both inadvertently programming the wrong WCD system, plus a WCD system being attacked maliciously.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system having wcd mode and also aed mode
ActiveUS20190143131A1Significant amount of timeKeep for a long timeHeart defibrillatorsExternal electrodesPatient needWearable cardioverter defibrillator
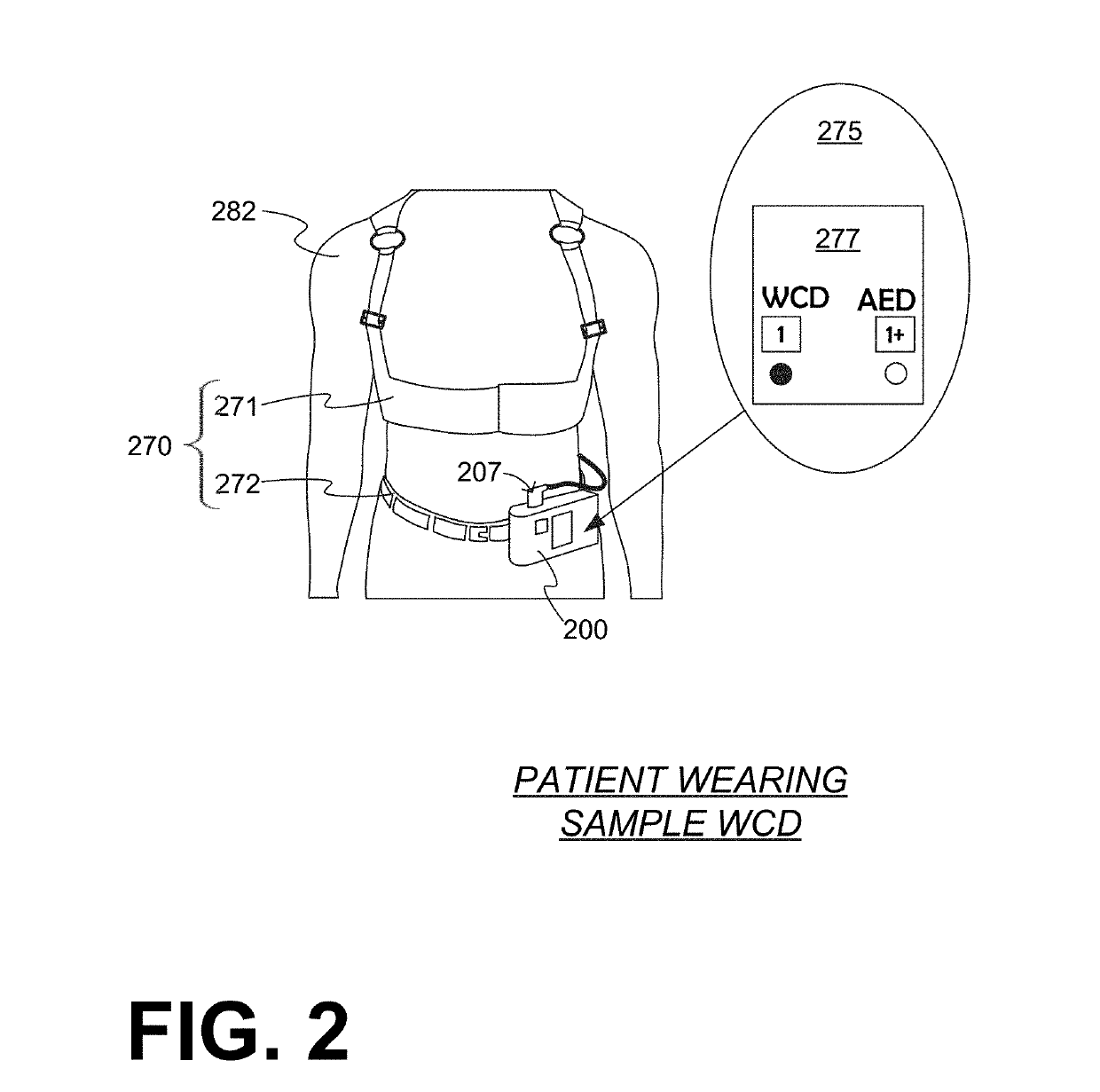
In embodiments, a Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillator (WCD) system includes a support structure for the patient to wear, and components that the support structure maintains on the patient's body. The components include a defibrillator, associated electrodes, and so on. The defibrillator can operate in a WCD mode while the patient wears the support structure. The defibrillator can further operate in a different, AED mode, during which time the patient need not wear a portion of the support structure, or even the entire support structure. Sometimes the AED mode is a type of a fully automatic AED mode. Other times the AED mode is a type of a semi-automated AED mode, where an attendant is present to administer the shock; at such times, the patient may not even need to have electrodes attached. This way the patient is more comfortable for a longer time.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL DEV CO LLC +2
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system using sensor modules for confirmation before shock
ActiveUS20160331987A1High detection specificityStrong specificityHeart defibrillatorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateWearable cardioverter defibrillatorComputer module
A wearable cardioverter defibrillator (“WCD”) system includes a support structure that can be worn by a patient, and a defibrillator coupled to the support structure. An ECG input, rendered from an ECG of the patient, may meet a primary shock criterion. One or more sensor modules are further provided, which are worn by the patient at different times. The sensor modules may monitor different physiological parameters of the patient, and transmit signals about them. The WCD system further has a multi-sensor interface to receive the transmitted signals, and a processor to determine from them whether a secondary shock criterion is met. If both the primary and the secondary shock criteria are met, the decision is to shock. The signals increase specificity of the detection, while the patient can wear different modules depending on context.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator with ai-based features
ActiveUS20200398065A1Patient compliance is goodHeart defibrillatorsAdaptive controlMedical equipmentPatient compliance
“Artificial Intelligence” or “AI” technology can be applied to Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillators (“WCDs”) and other wearable medical equipment in various ways, including:garment fitting and adjustment;analyzing electrocardiogram (“ECG”), other sensor data and / or other patient data (e.g., age, gender, previous medical conditions, etc.) in real time to detect / assess the patient's present condition and / or need for treatment for cardiac and other conditions (e.g., stroke, coughing, apnea, etc.);detect imminent failure of the wearable medical device componentscapturing and reporting data collected from the patient for presenting to cliniciansadjusting thresholds for alarms and notifications based on patient's responses;improving patient compliance based on the patient's past non-compliant behavior and actions that resulted in the patient becoming compliant;providing tests to the patient (e.g., grip test, dexterity tests, balance tests, etc.) and learning the patient's responses to detect / assess the patient's present condition and / or need for treatment;learning the patient's voice, activity, posture, time of day, etc. for implementing intelligent voice recognition / activation of the medical device.
Owner:STRYKER CORP +1
Wcd with separable ECG acquisition features
InactiveUS20180272145A1ElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsAudio power amplifierWearable cardioverter defibrillator
A superior wearable cardioverter defibrillator is disclosed. Embodiments provide one or more remote sensors (e.g., ECG electrodes) that are separable from the rest of the WCD system, which holds the defibrillation electrodes on the body and may also hold a preamplifier for the electrodes. This feature enablesECG electrodes (or other physiological sensors) to be more securely affixed to the patient's body without adversely affecting the patient's desire to don the rest of the WCD.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG
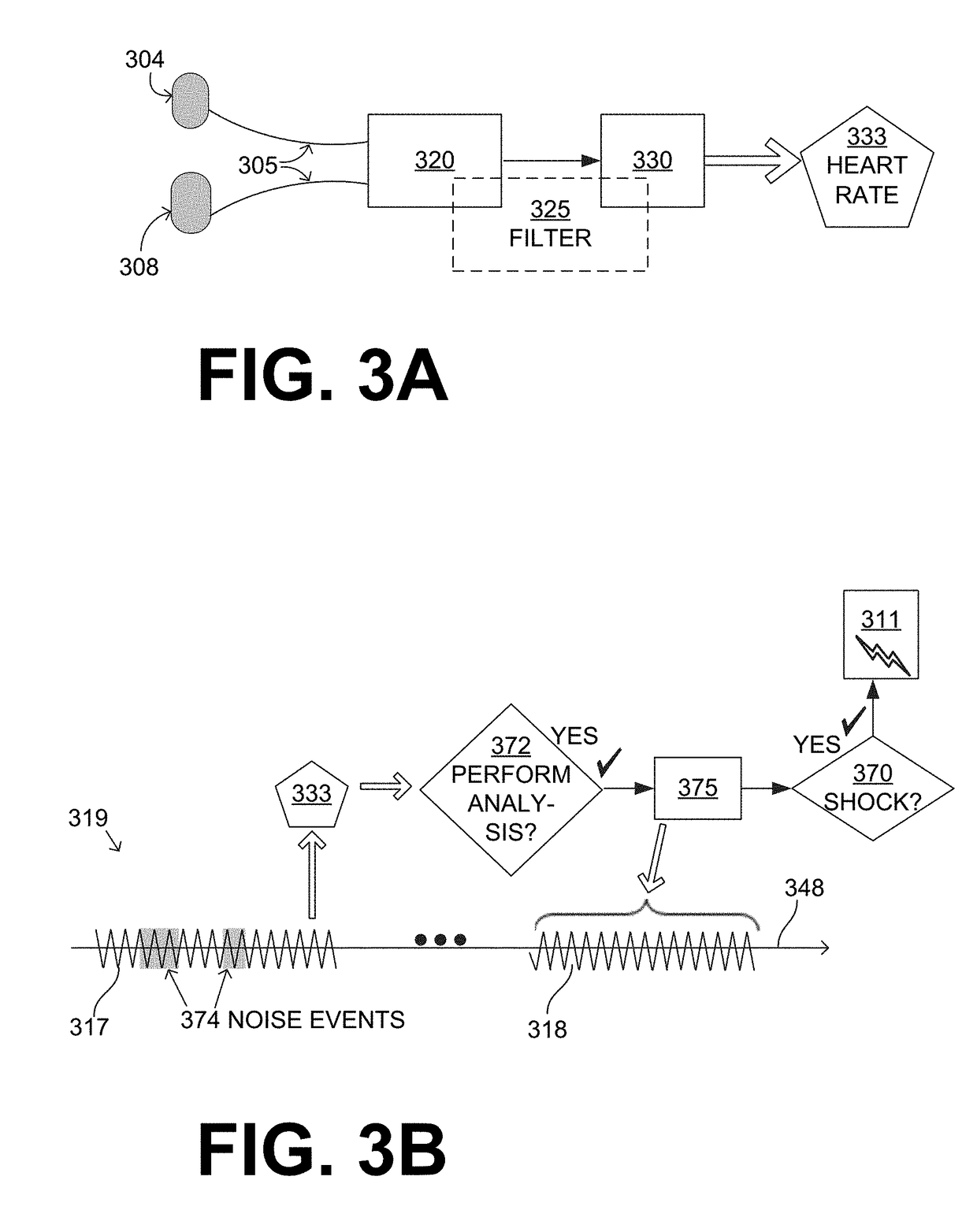
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system detecting QRS complexes in ECG signal by matched difference filter
ActiveUS11077310B1Easy to detectImproved noise suppressionHeart defibrillatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalWearable cardioverter defibrillator
In embodiments, a wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system includes electrodes that render an ECG signal of the patient, and a processor that receives ECG data are derived from the rendered ECG signal. The processor may filter the received ECG data with a matched difference filter to detect QRS complexes, and compute a heart rate from the detected QRS complexes. The matched difference filter itself can have coefficient values associated with a baseline QRS complex, which improves detection.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) causing patient's QRS width to be plotted against the heart rate
ActiveUS10105547B2Detailed analysisElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsRR intervalWearable cardioverter defibrillator
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
WCD system prioritization of alerts based on severity and/or required timeliness of user response
ActiveUS11334826B2Physical therapies and activitiesHeart defibrillatorsWearable cardioverter defibrillatorDevice status
Embodiments of this disclosure are directed to a wearable cardioverter defibrillator (“WCD”) system design in which a WCD implements an alert prioritization scheme to provide the patient with feedback in an order that is less likely to cause confusion. Different conditions (e.g., device status, equipment condition, or physiologic condition) are prioritized based on an analysis of severity of the condition and timeliness of user action needed. The prioritization scheme defines what alert, if any, is presented to the user by the WCD system as a result of various conditions. Generally stated, an alert for the highest priority condition currently detected is presented to the user and maintained until that condition either changes or becomes surpassed in the prioritization scheme.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
Wcd system outputting human-visible indication and proximate programming device with screen reproducing the human-visible indication in real time
ActiveUS20190030350A1Improve protectionConfidenceMedical communicationElectrocardiographyEcg signalTelecommunications link
In embodiments, a wearable medical system (WMS) for an ambulatory patient, which can be a wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system, analyzes the patient's ECG signal to generate a detection outcome. The WMS also has an ambulatory user interface that outputs a human-visible indication. A programming device, such as a PC, a tablet, etc., establishes a communication link with the WMS during an in-person session with the patient. The programming device may include a programming screen that reproduces the human-visible indication in real time. An advantage can be that the person programming the WMS need not strain to look also at the ambulatory user interface at the time they are looking at the programming device. Another advantage can be that the patient will recognize that he or she is better protected, and have their confidence in the WMS increased, and therefore better comply with wearing the WMS as required.
Owner:KESTRA MEDICAL TECH INC +2
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system logging events and broadcasting state changes and system status information to external clients
ActiveUS20190329055A1Quick fixElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsWearable cardioverter defibrillatorEvent data
Methods, apparatus, and systems relating to a Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillator (WCD) system capable of logging event data and / or broadcasting state changes and / or system status information to external clients are described. In an embodiment, a processor stores data corresponding to one or more event markers in memory in response to occurrence of an event. Occurrence of the event is detected based at least in part on detection of one or more parameters by one or more sensors or a signal to be generated by one or more of electrodes of the WCD system. A communication device transmits at least a portion of the stored data to a remote device. A patient condition or a WCD system condition can then be detected based at least in part on analysis of the stored data and / or the transmitted portion of the stored data. Other embodiments are also disclosed and / or claimed.
Owner:STRYKER CORP +1
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator components discarding ECG signals prior to making shock/no shock determination
InactiveUS20160220832A1ElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsEcg signalWearable cardioverter defibrillator
Components of wearable cardiac defibrillator (WCD) systems, software, and methods are provided. A WCD system includes a support structure that a patient can wear and electrodes that can capture at least two of the patient's ECG signals. A component includes an energy storage module that can store an electrical charge, a discharge circuit, and a processor that can make a shock / no shock determination, and cause the discharge circuit to discharge the stored charge, if the determination is to shock. In some embodiments, the processor discards at least one of the ECG signals prior to making the shock / no shock determination. The determination can be made from the remaining one or more ECG signals. In some embodiments, the processor makes an aggregate shock / no shock determination from two or more of the ECG signals.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system uploading configuration data via safety label
A WCD system is configured to exchange data with access equipment different from the WCD system wirelessly, and the access equipment includes a near field communication (NFC) reader, a peripheral processor and an access wireless communication module (AWCM).
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system computing patient heart rate by multiplying ECG signals from different channels
ActiveUS20180289974A1ElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsEcg signalWearable cardioverter defibrillator
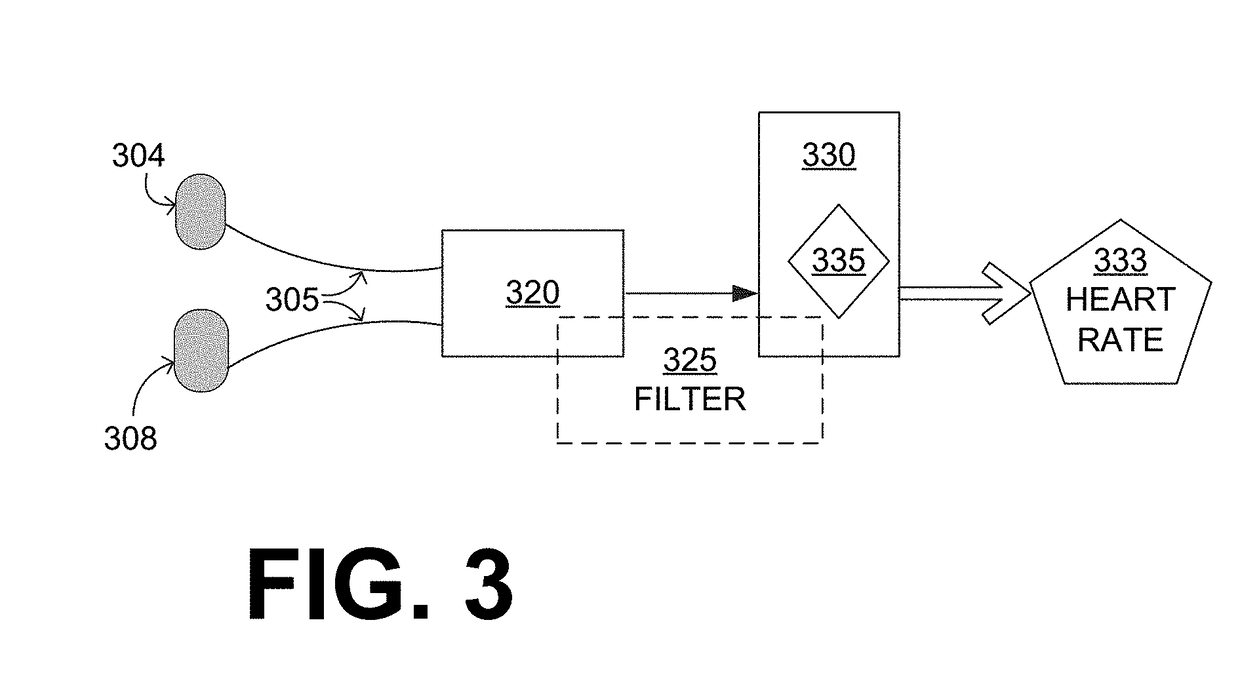
A wearable cardioverter defibrillator system includes a support structure that is configured to be worn by a patient. When thus worn, the support structure may attach electrodes at different locations of the patient's body, so as to define different vectors. A measurement circuit may sense ECG signals from the different vectors substantially concurrently. A processor may multiply together these substantially concurrent ECG signals to derive a product waveform. The processor may then detect peaks in the product waveform, measure durations of time intervals between successive peaks, and determine the patient's heart rate from these durations. An advantage can be that the heart rate may be computed notwithstanding noise in the individual ECG signals.
Owner:STRYKER CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com