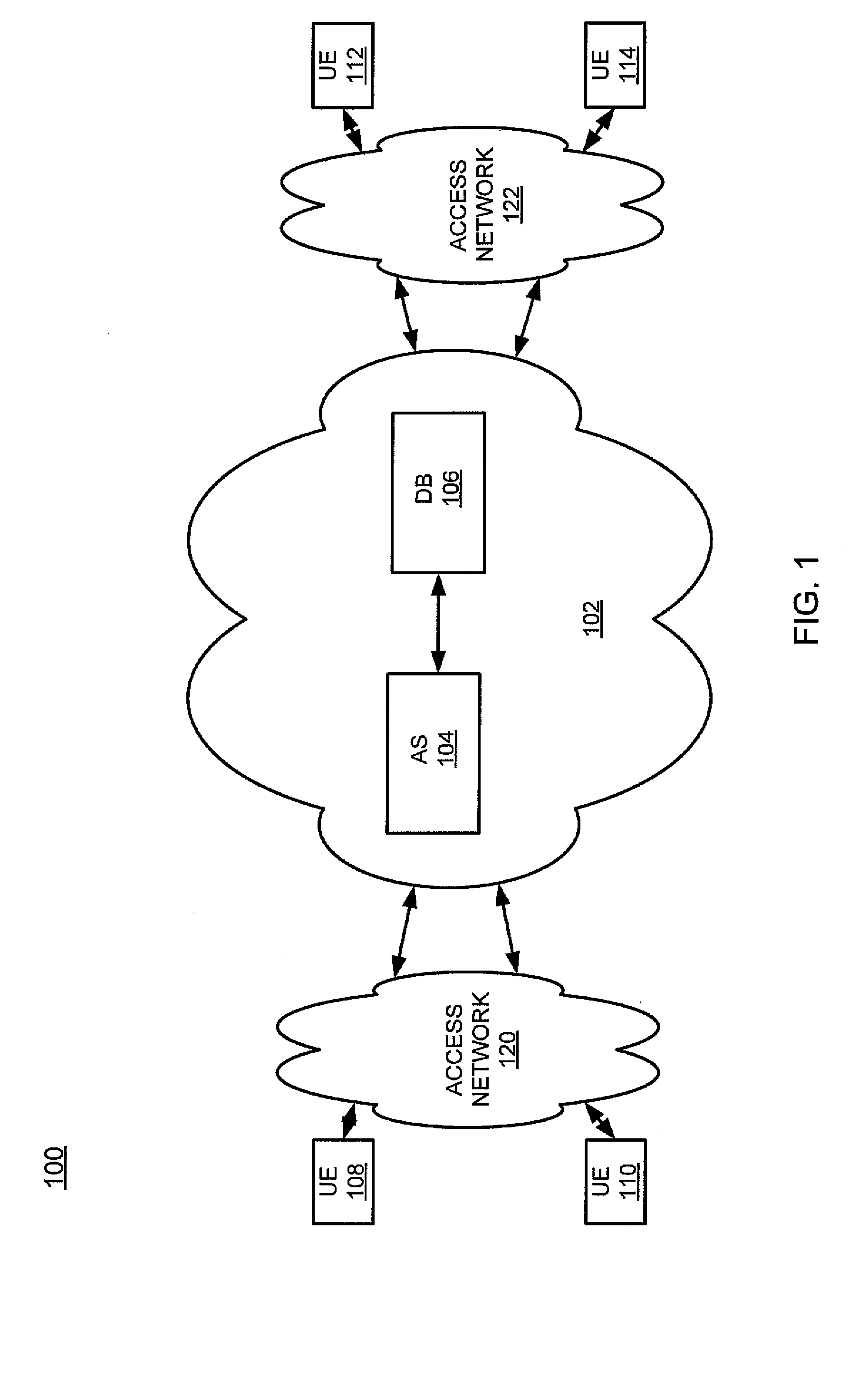
Patents
Literature
596 results about "Cut score" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
CUT SCORE Definition. CUT SCORE is a point on a score scale in which scores at or above the point are in a different category or classification than scores below the point (e.g. pass versus fail).
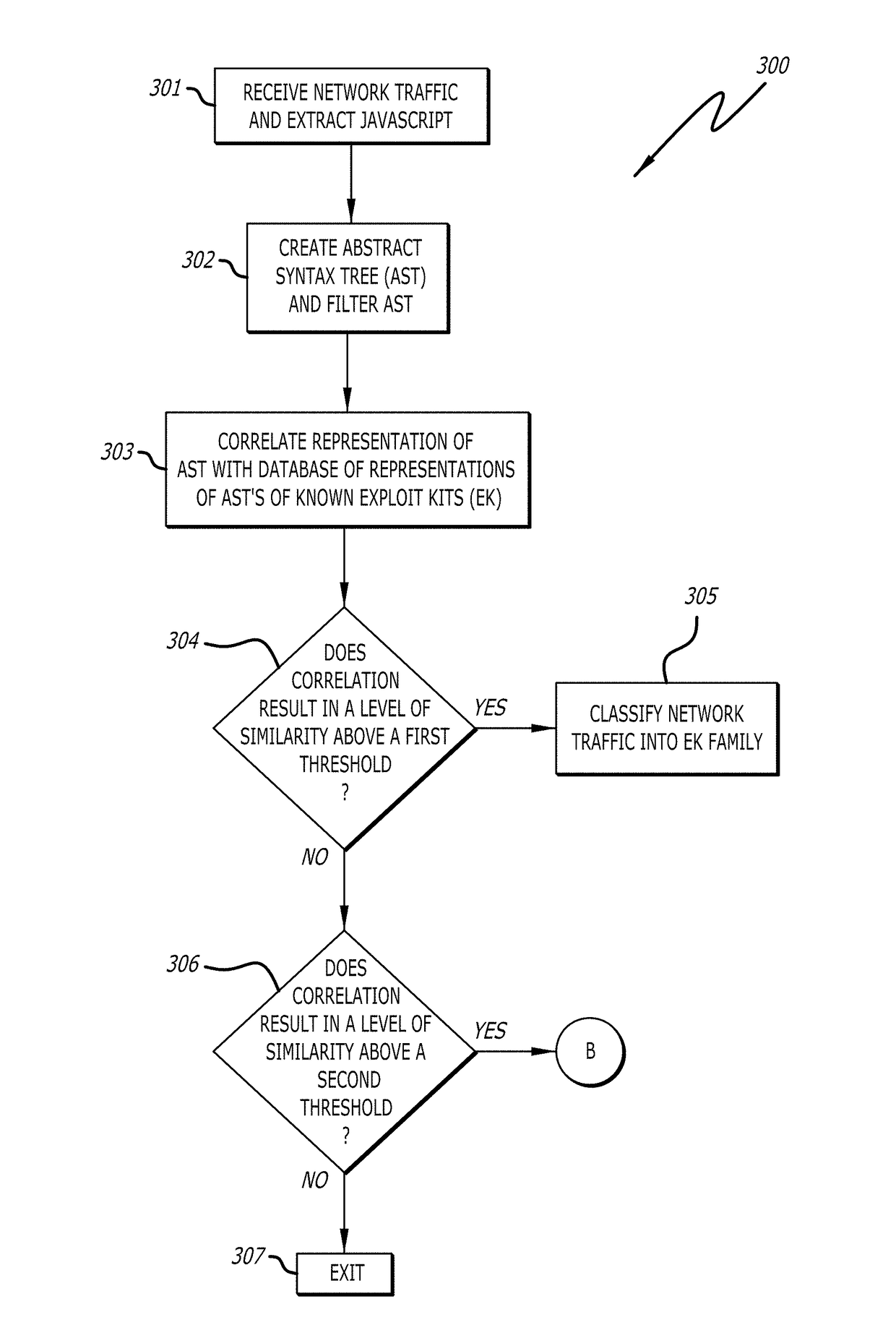
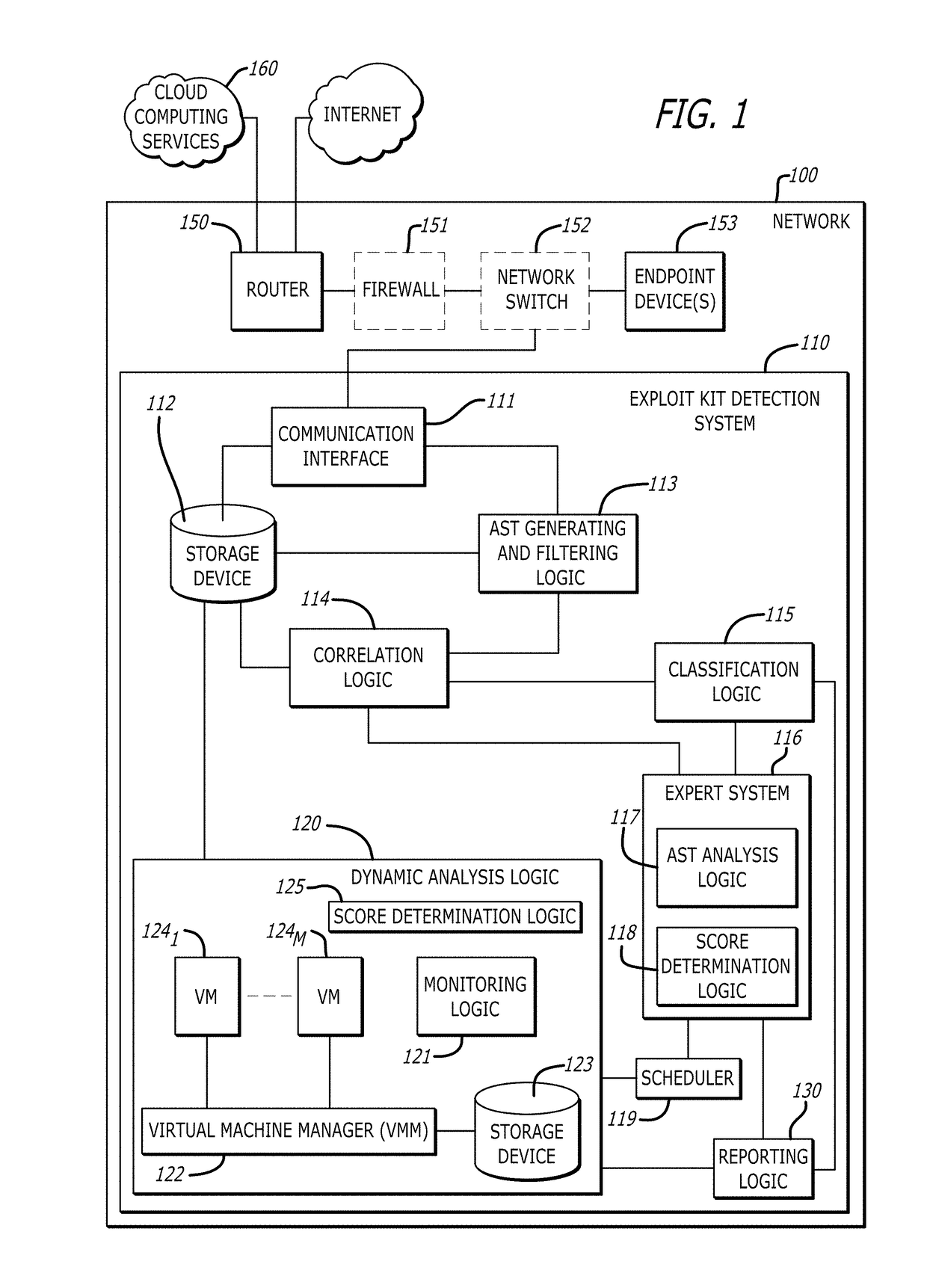
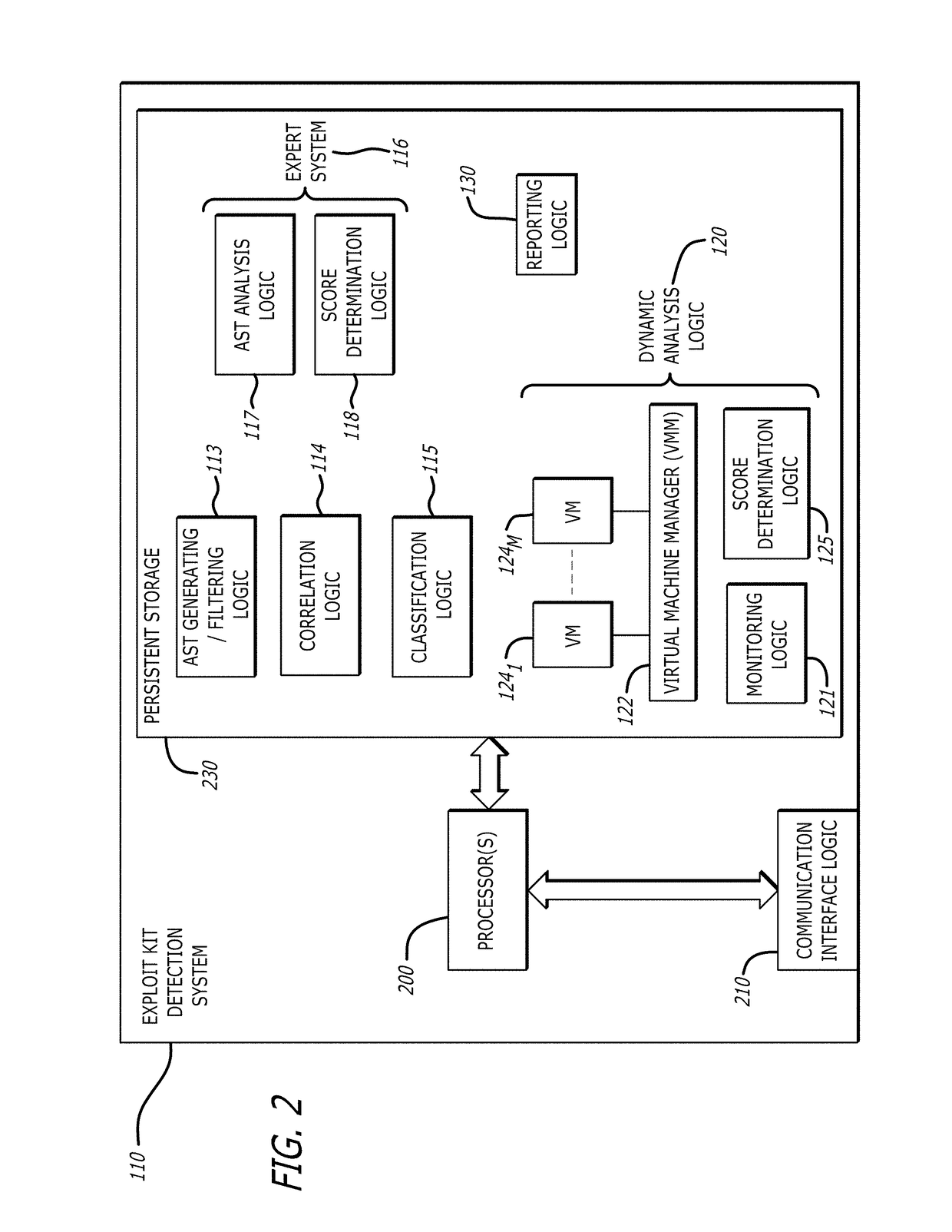
Detection and classification of exploit kits
ActiveUS9825976B1Computer security arrangementsProbabilistic networksExploit kitTheoretical computer science
A non-transitory computer readable storage medium having stored thereon instructions executable by a processor to perform operations including: responsive to determining that a correlation between a representation of the first portion of network traffic and a representation of a known exploit kit results in a score above a first prescribed score value, classifying the representation of the first portion of the received network traffic into an exploit kit family corresponding to the representation the known exploit kit; and responsive to determining that the score is below the first prescribed score value and above a second prescribed score value, (i) analyzing the representation of the first portion of the received network traffic, and (ii) processing, within a virtual machine, a second portion of the received network traffic to determine whether processing of the received network traffic results in behavior indicative of an exploit kit is shown.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
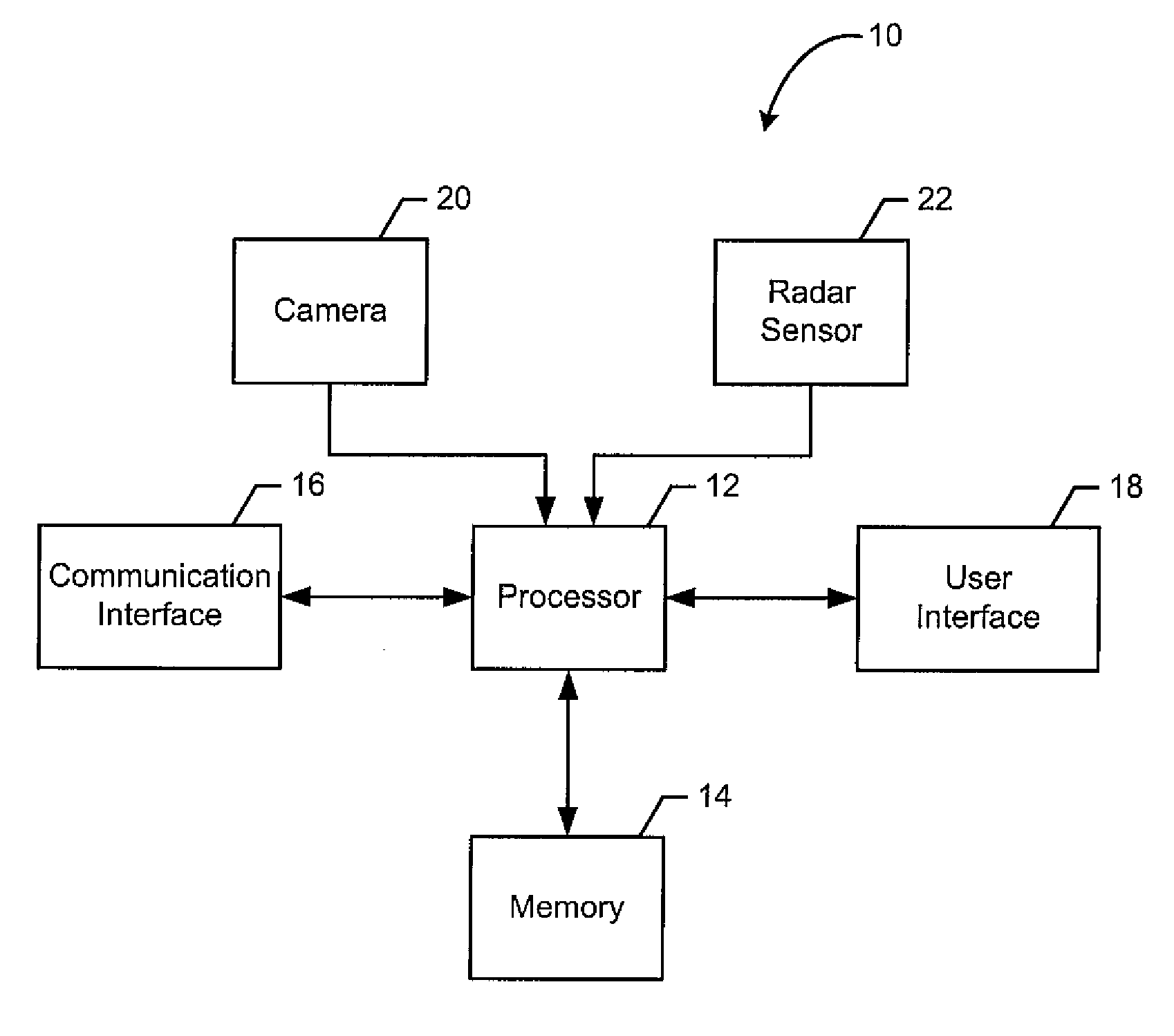
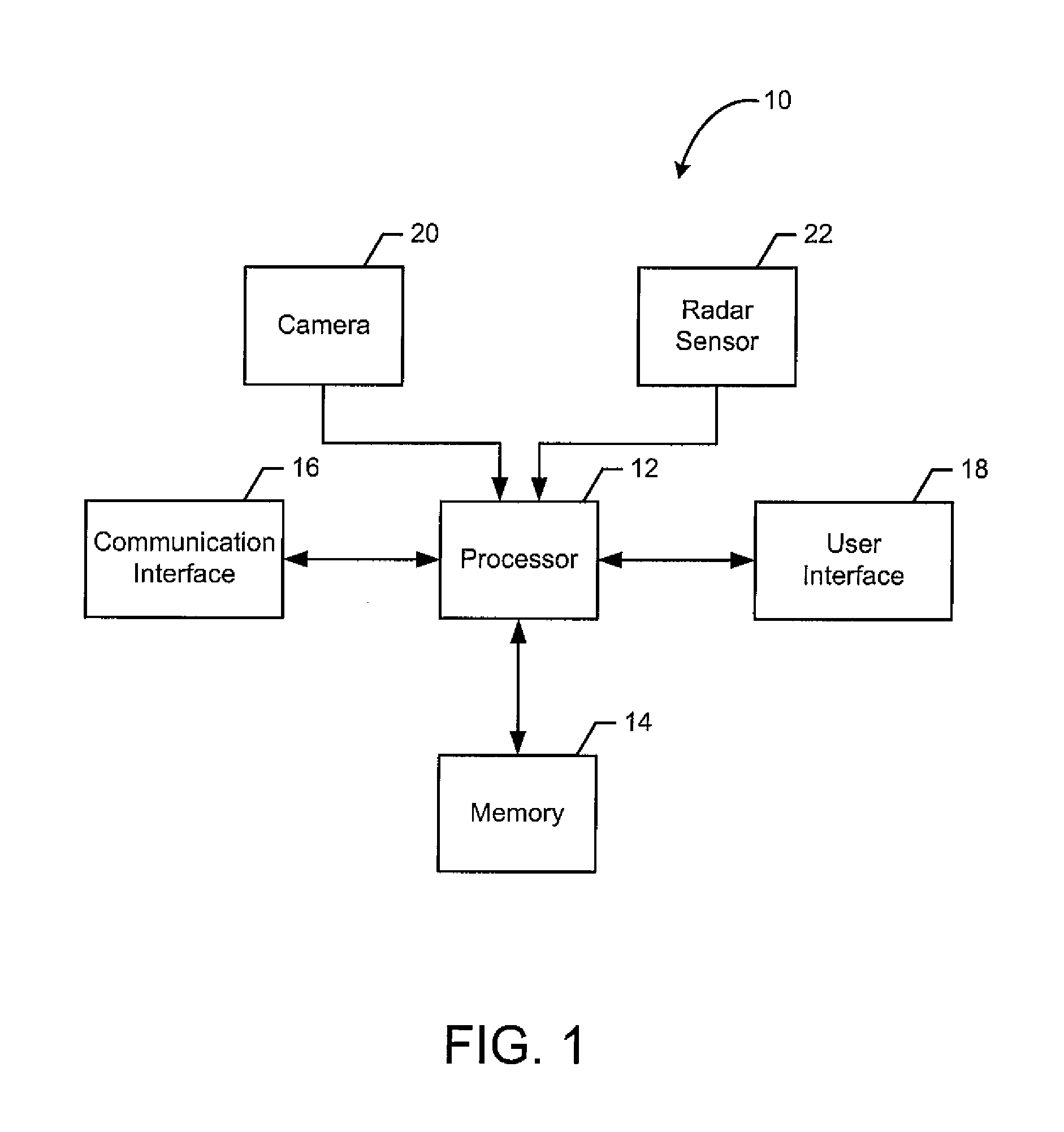
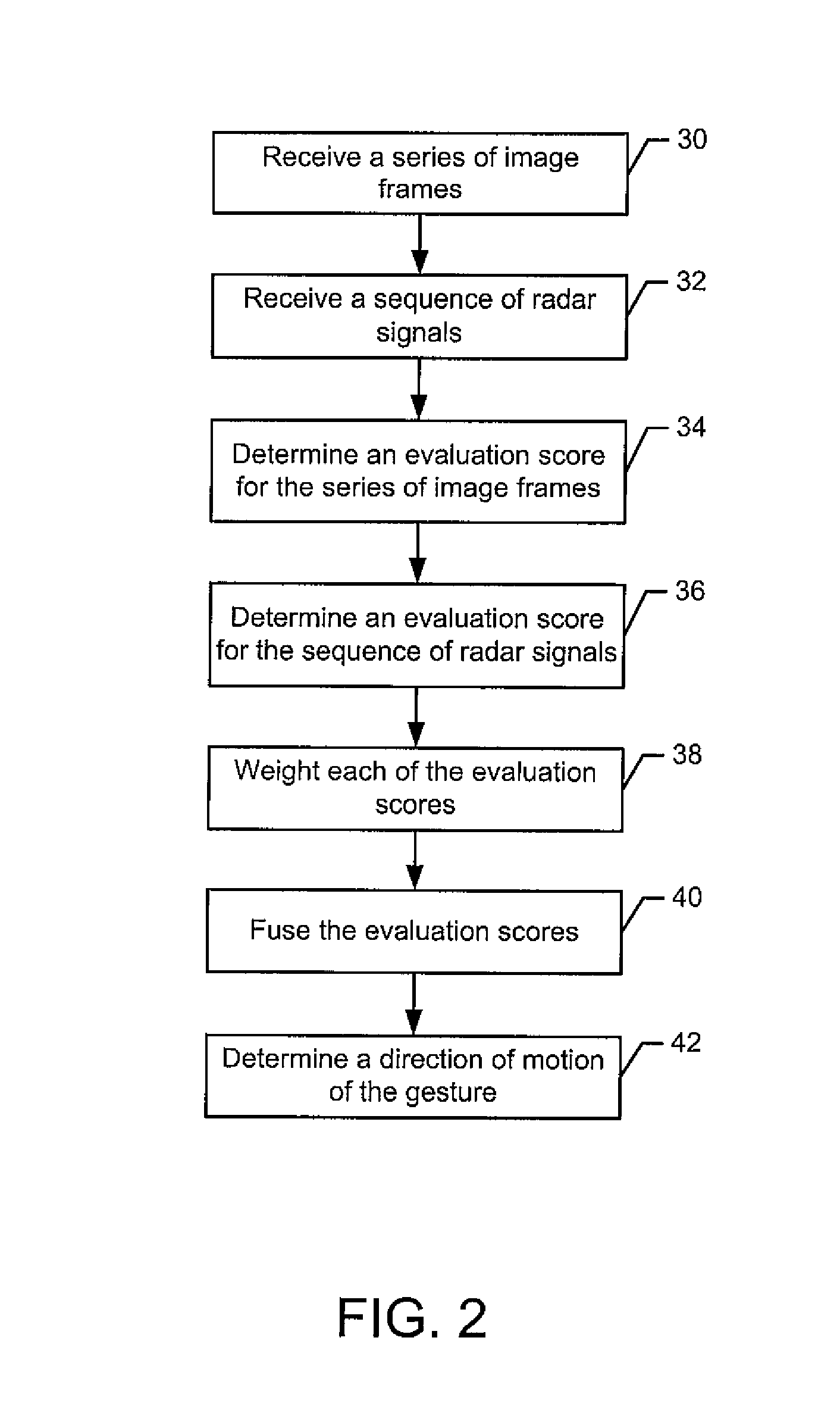
Method and Apparatus for Identifying a Gesture Based Upon Fusion of Multiple Sensor Signals
InactiveUS20140324888A1Improved gesture recognitionReliably recognizeInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsPattern recognitionMultiple sensor
A method, apparatus and computer program product are provided to permit improve gesture recognition based on fusion of different types of sensor signals. In the context of a method, a series of image frames and a sequence of radar signals are received. The method determines an evaluation score for the series of image frames that is indicative of a gesture. This determination of the evaluation score may be based on the motion blocks in an image area and the shift of the motion blocks between image frames. The method also determines an evaluation score for the sequence of radar signals that is indicative of the gesture. This determination of the evaluation score may be based upon the sign distribution in the sequence and the intensity distribution in the sequence. The method weighs each of the evaluation scores and fuses the evaluation scores, following the weighting, to identify the gesture.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
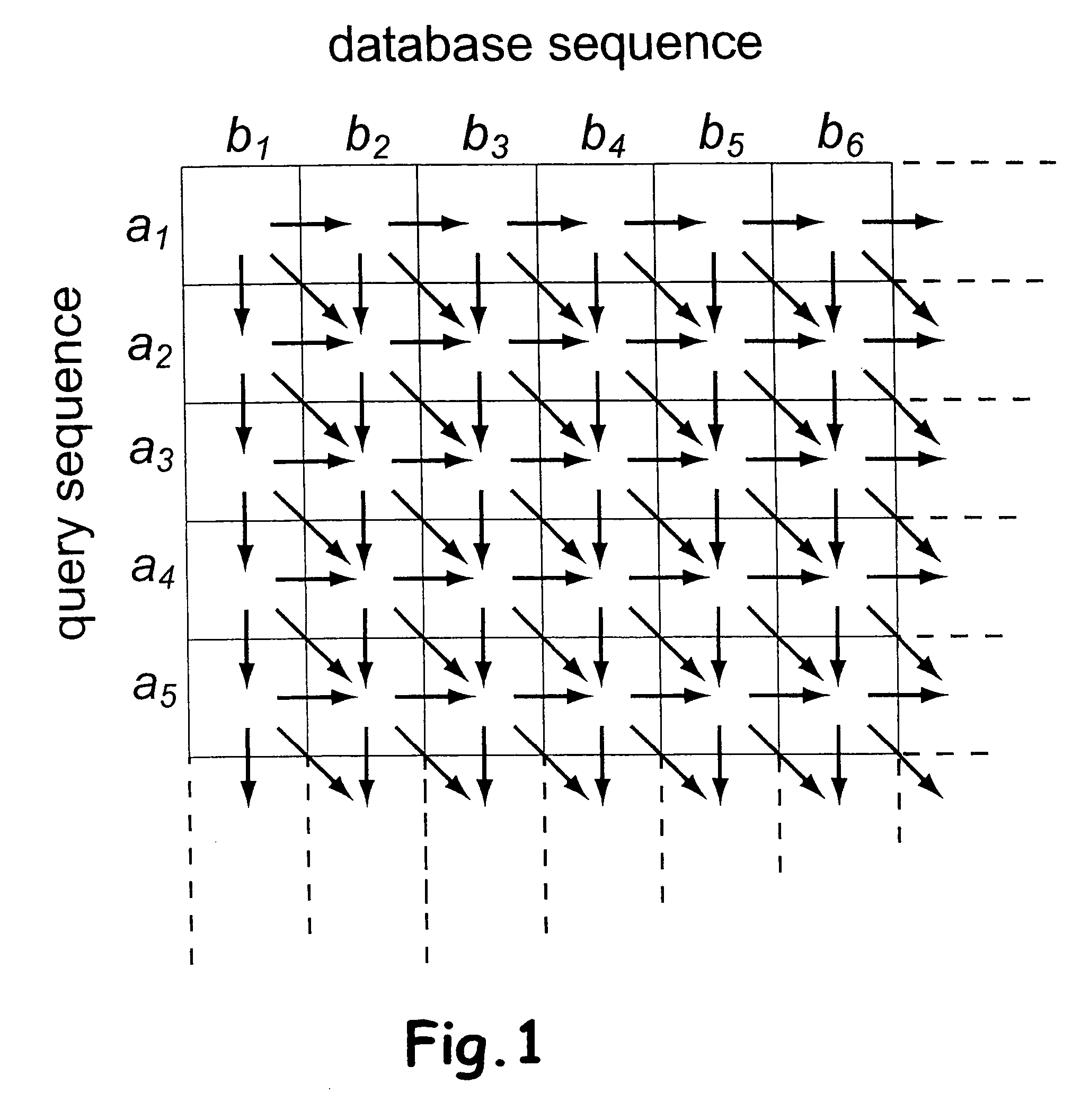
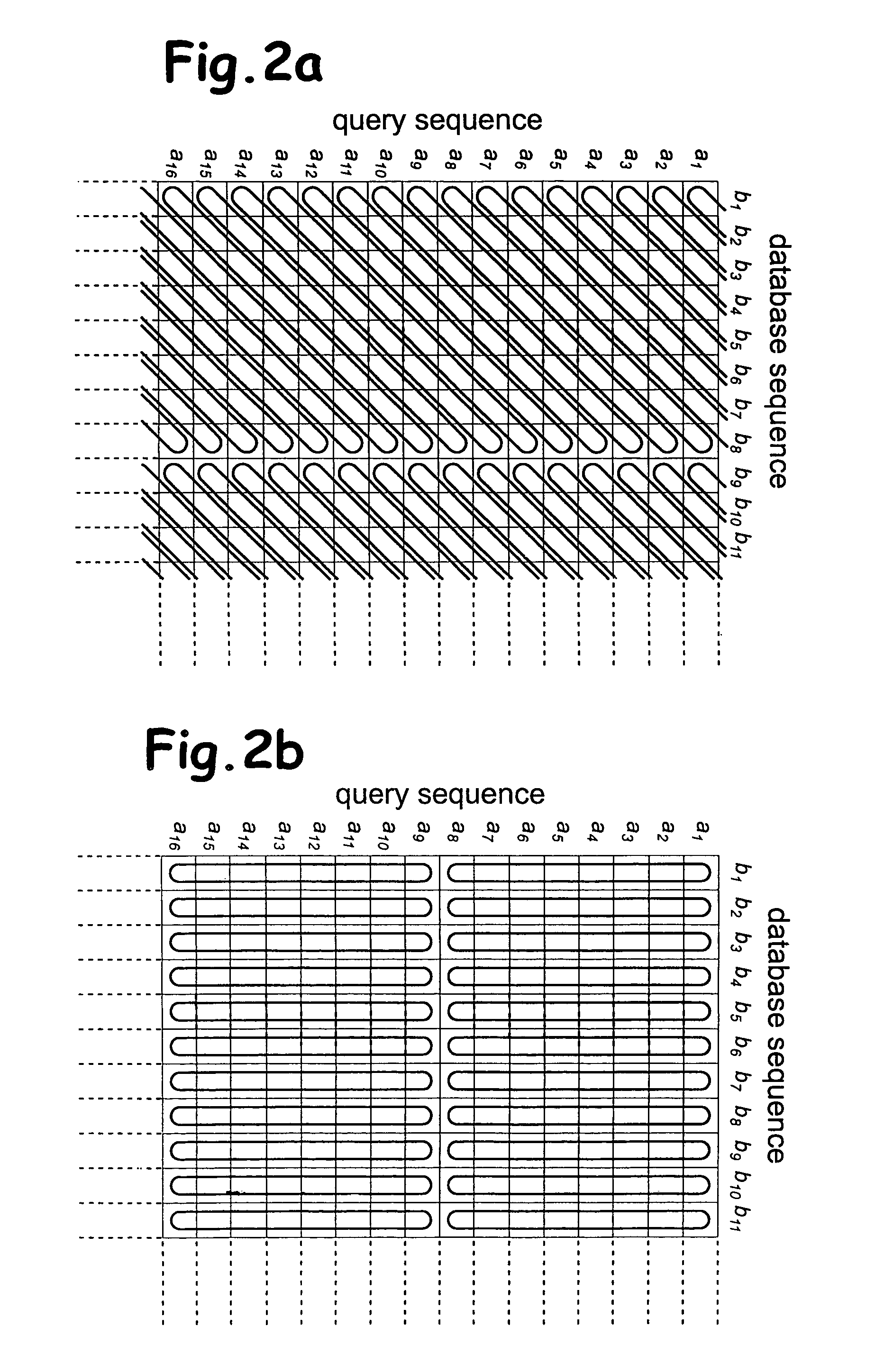
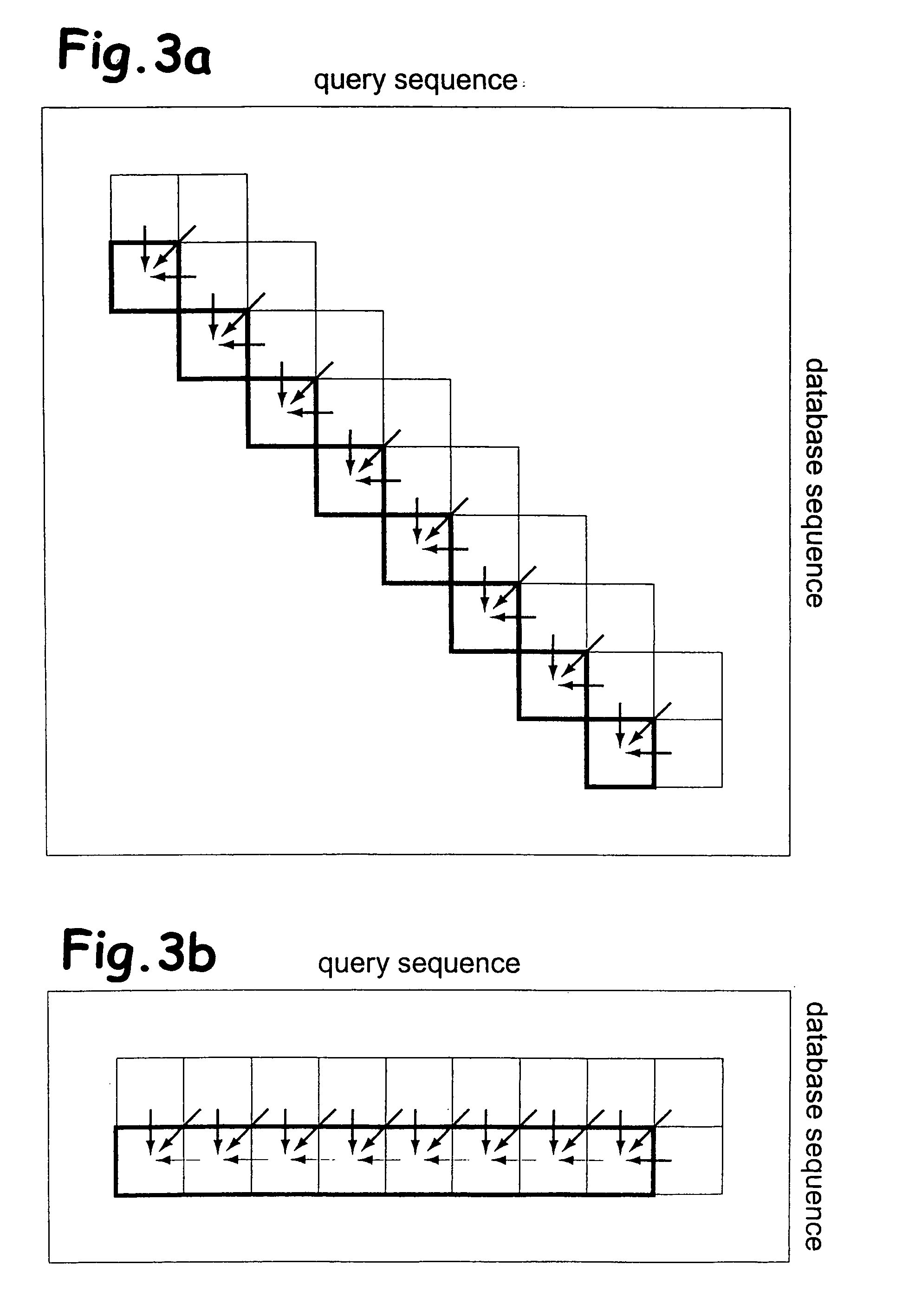
Determination of optimal local sequence alignment similarity score
InactiveUS7917302B2Low costShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyLocal sequence alignmentProtein function prediction
Sequence alignment and sequence database similarity searching are among the most important and challenging task in bio informatics, and are used for several purposes, including protein function prediction. An efficient parallelisation of the Smith-Waterman sequence alignment algorithm using parallel processing in the form of SIMD (Single-Instruction, Multiple-Data) technology is presented. The method has been implementation using the MMX (MultiMedia eXtensions) and SSE (Streaming SIMD Extensions) technology that is embedded in Intel's latest microprocessors, but the method can also be implemented using similar technology existing in other modern microprocessors. Near eight-fold speed-up relative to the fastest previously an optimised eight-way parallel processing approach achieved know non-parallel Smith-Waterman implementation on the same hardware. A speed of about 200 million cell updates per second has been obtained on a single Intel Pentium III 500 MHz microprocessor.
Owner:SEEBERG ERLING CHRISTEN +1
System and method for automatically classifying text
InactiveUS7028250B2Digital data information retrievalNatural language analysisText categorizationDegree of association
A method is provided for automatically classifying text into categories. In operation, a plurality of tokens or features are manually or automatically associated with each category. A weight is then coupled to each feature, wherein the weight indicates a degree of association between the feature and the category. Next, a document is parsed into a plurality of unique tokens with associated counts, wherein the counts are indicative of the number of times the feature appears in the document. A category score representative of a sum of products of each feature count in the document times the corresponding feature weight in the category for each document is then computed. Next, the category scores are sorted by perspective, and a document is classified into a particular category, provided the category score exceeds a predetermined threshold.
Owner:AVOLIN LLC
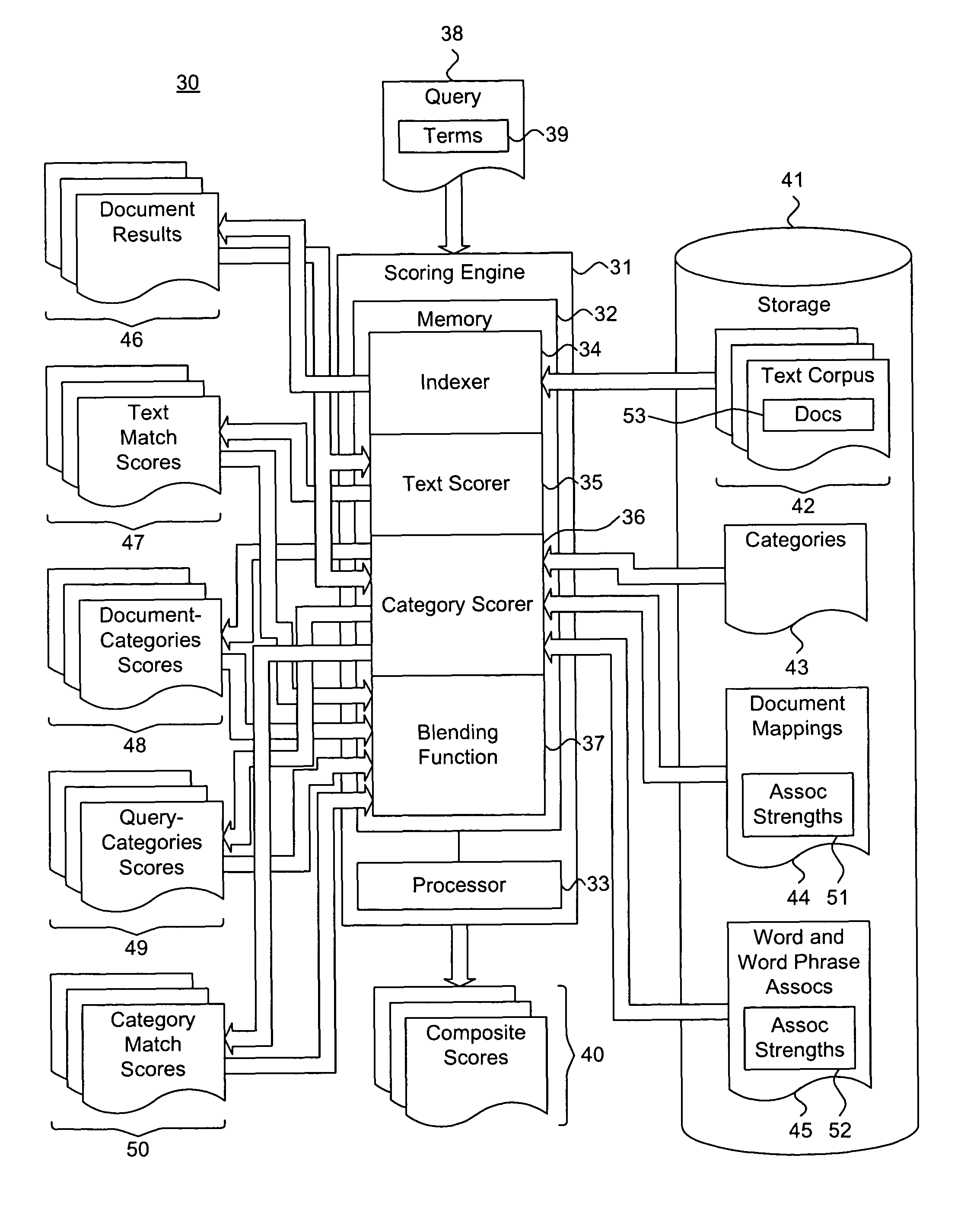
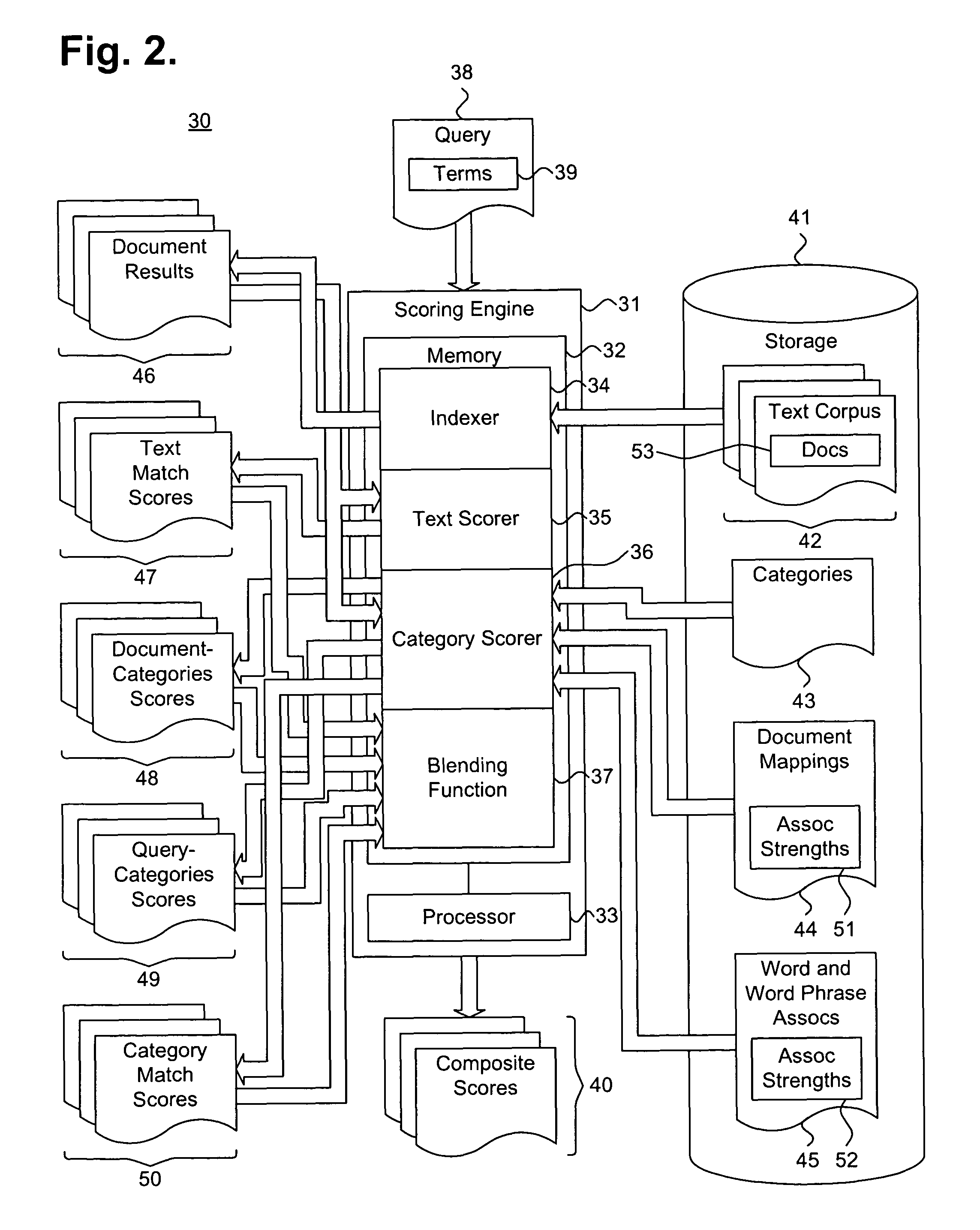
System and method for determining a composite score for categorized search results
ActiveUS7814085B1Web data indexingDigital data processing detailsMultiple categoryDocument preparation
A system and method for scoring documents is described. One or more documents are identified responsive to a search criteria. A text match score indicating a quality of match of the identified documents is determined. A category match score is determined over categories. A document-categories score is determined indicating a quality of match between an identified document and a plurality of categories. A search criteria-categories score is determined indicating a quality of match between the search criteria and the categories. An overall score is determined based on the text match score and the category match score.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
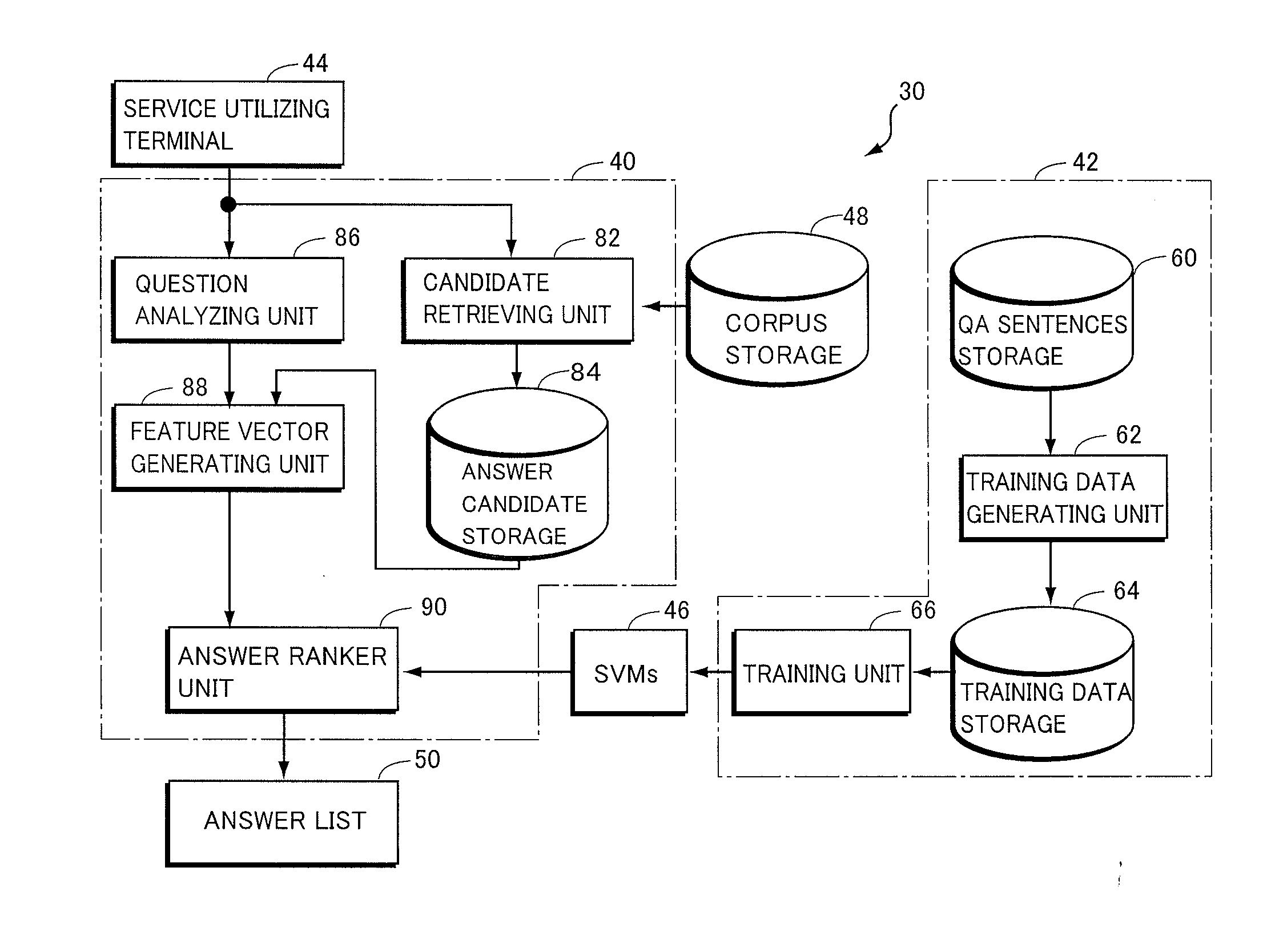
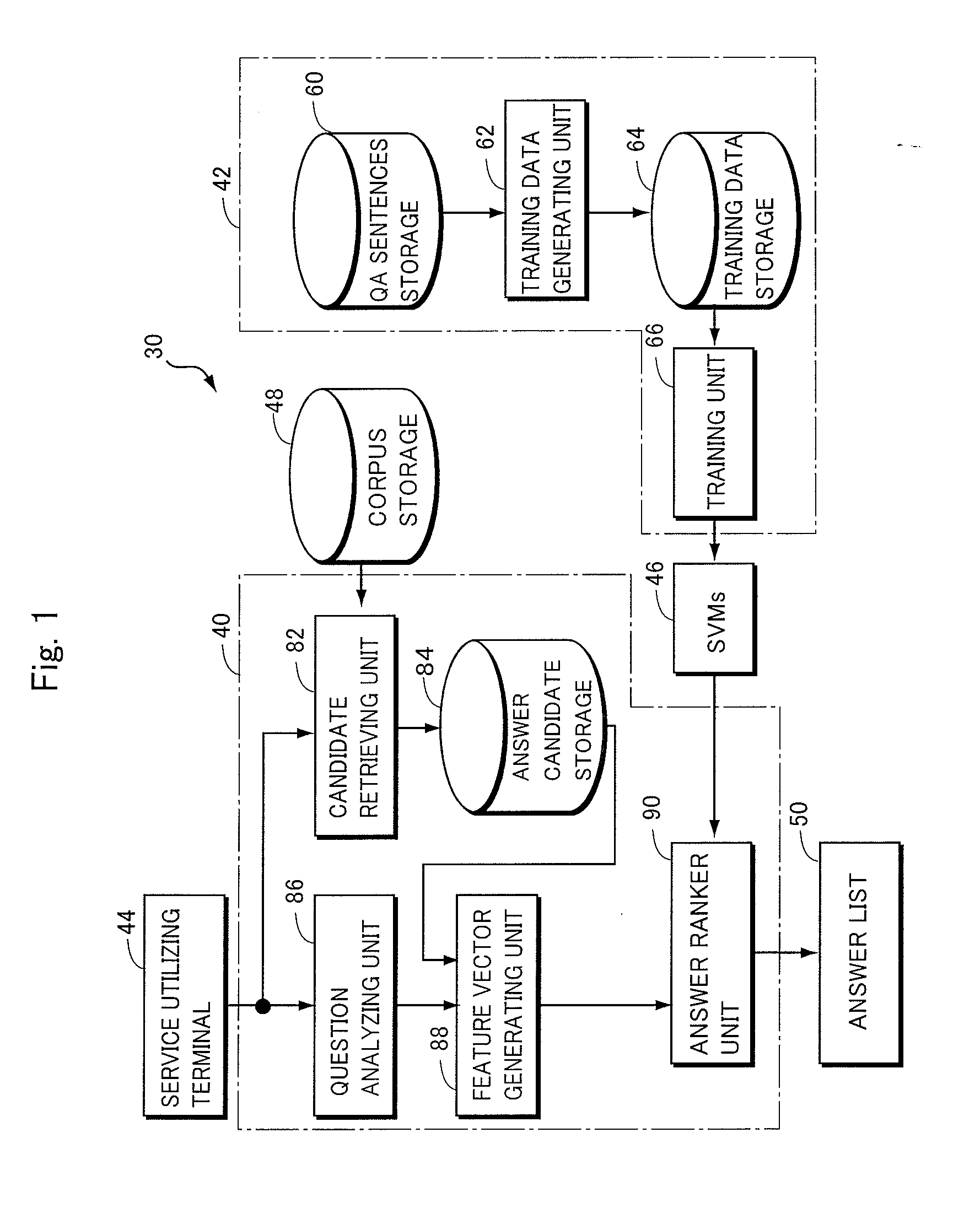
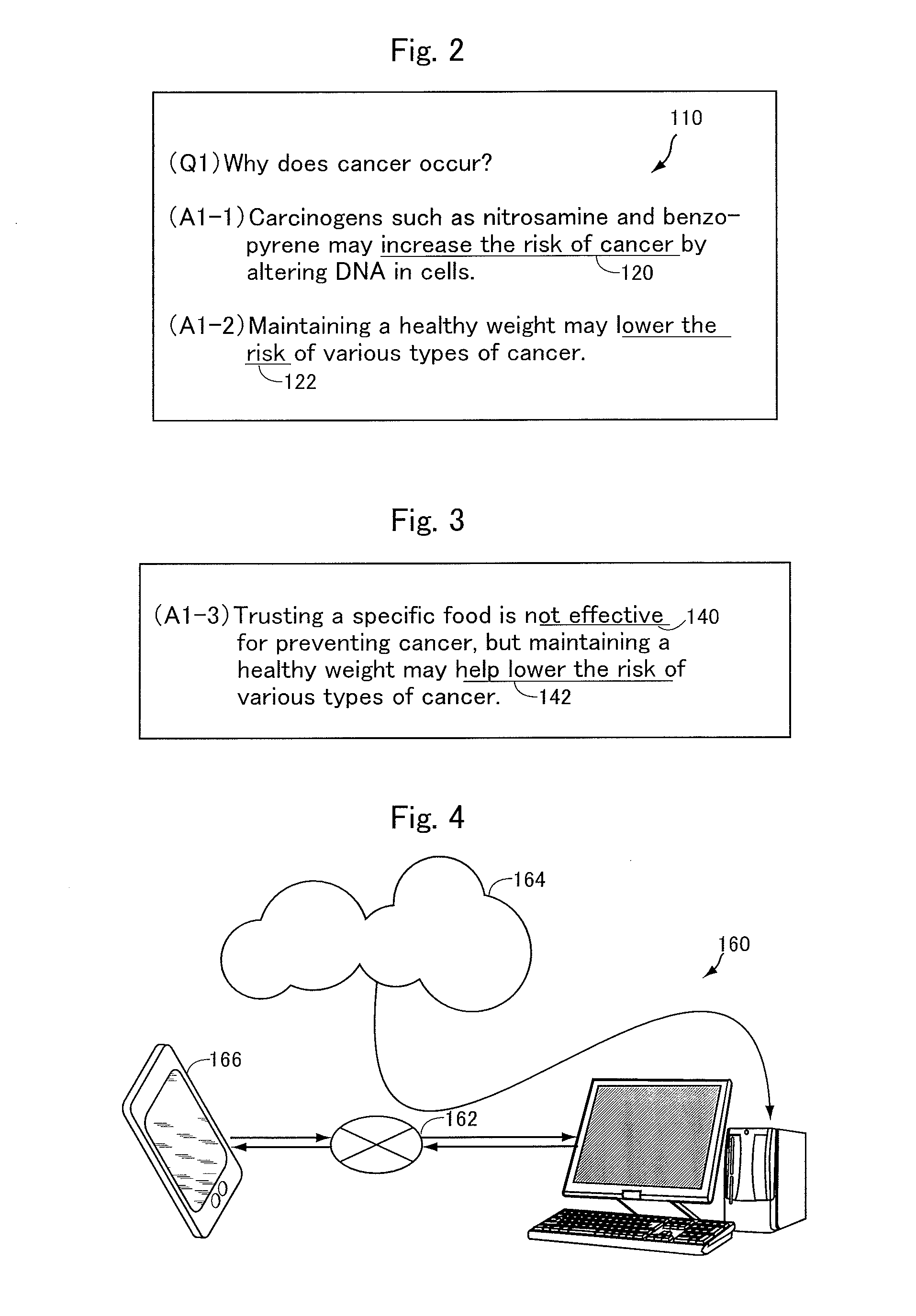
Non-factoid question-answering system and computer program
In order to provide a non-factoid question answering system with improved precision, the question answering system (160) includes: a candidate retrieving unit (222), responsive to a question, extracting answer candidates from a corpus storage (178); a feature vector generating unit (232) for generating features from combinations of a question with each of the answer candidates; SVMs (176) trained to calculate a score of how correct a combination of the question with an answer candidate is, upon receiving the feature vector therefor; and an answer ranker unit (234) outputting the answer candidate with the highest calculated score as the answer. The features are generated on the basis of the results of morphological analysis and parsing of the question, a phrase in the question evaluated as being positive or negative as well as its polarity, and the semantic classes of nouns in the features.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Human workflow aware recommendation engine
Recommendation systems and processes for generating recommendations within the context of a socially-enabled human workflow system are provided. The processes may include accessing workflow data, such as social graphs, organization graphs, collaboration graphs, content data, utilization data, ratings data, and the like, associated with a user requesting a recommendation. The process may further include determining one or more of a user similarity score, task similarity score, goal similarity score, and content similarity score. The process may further include generating one or more recommendations based at least in part on one or more of the user similarity score, task similarity score, goal similarity score, and content similarity score.
Owner:MAGNET SYST
Multiple contest scoring with flexible prediction
InactiveUS20120244947A1High scorePoint becomes highForecastingVideo gamesComputer scienceComputing systems
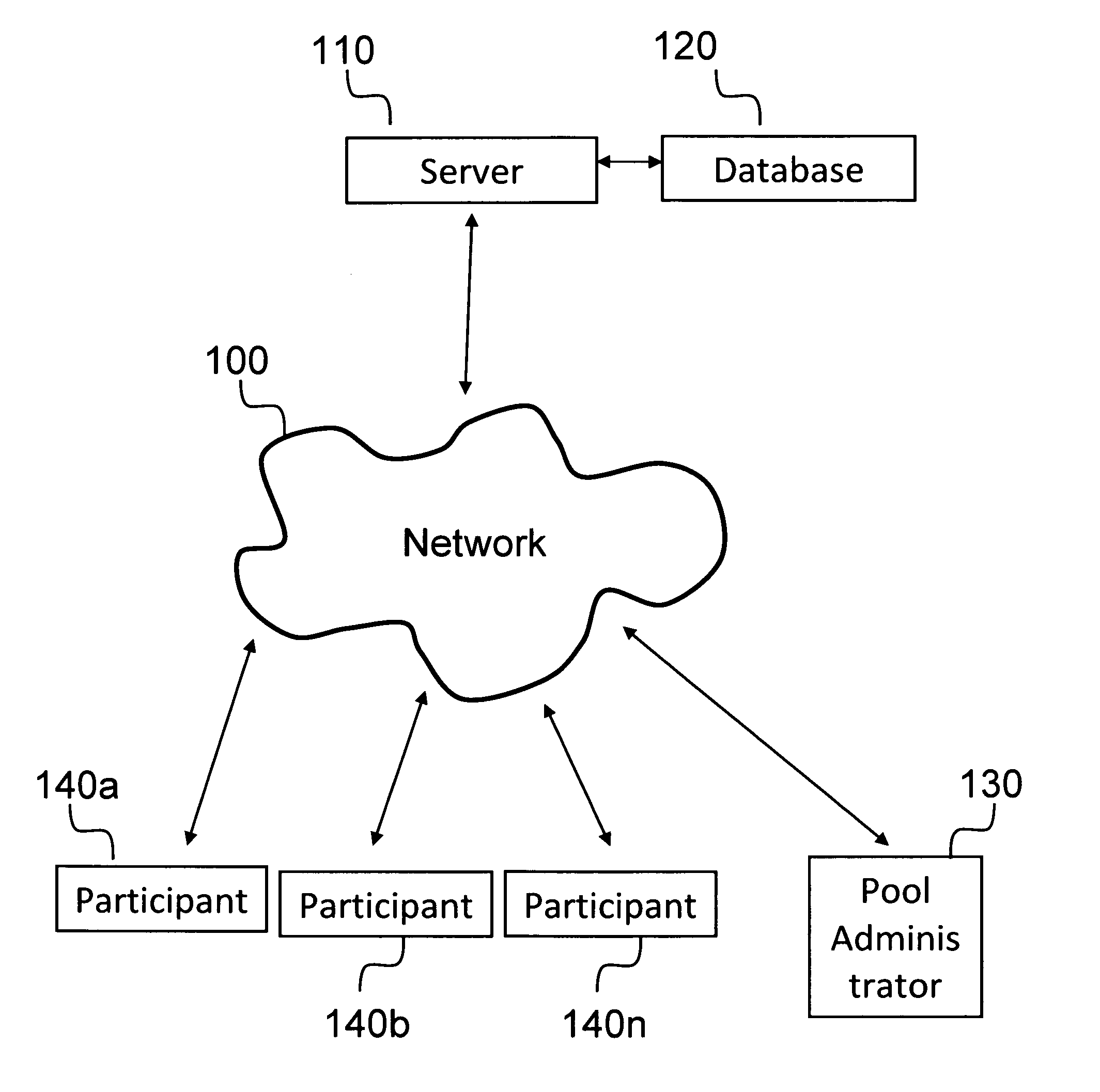
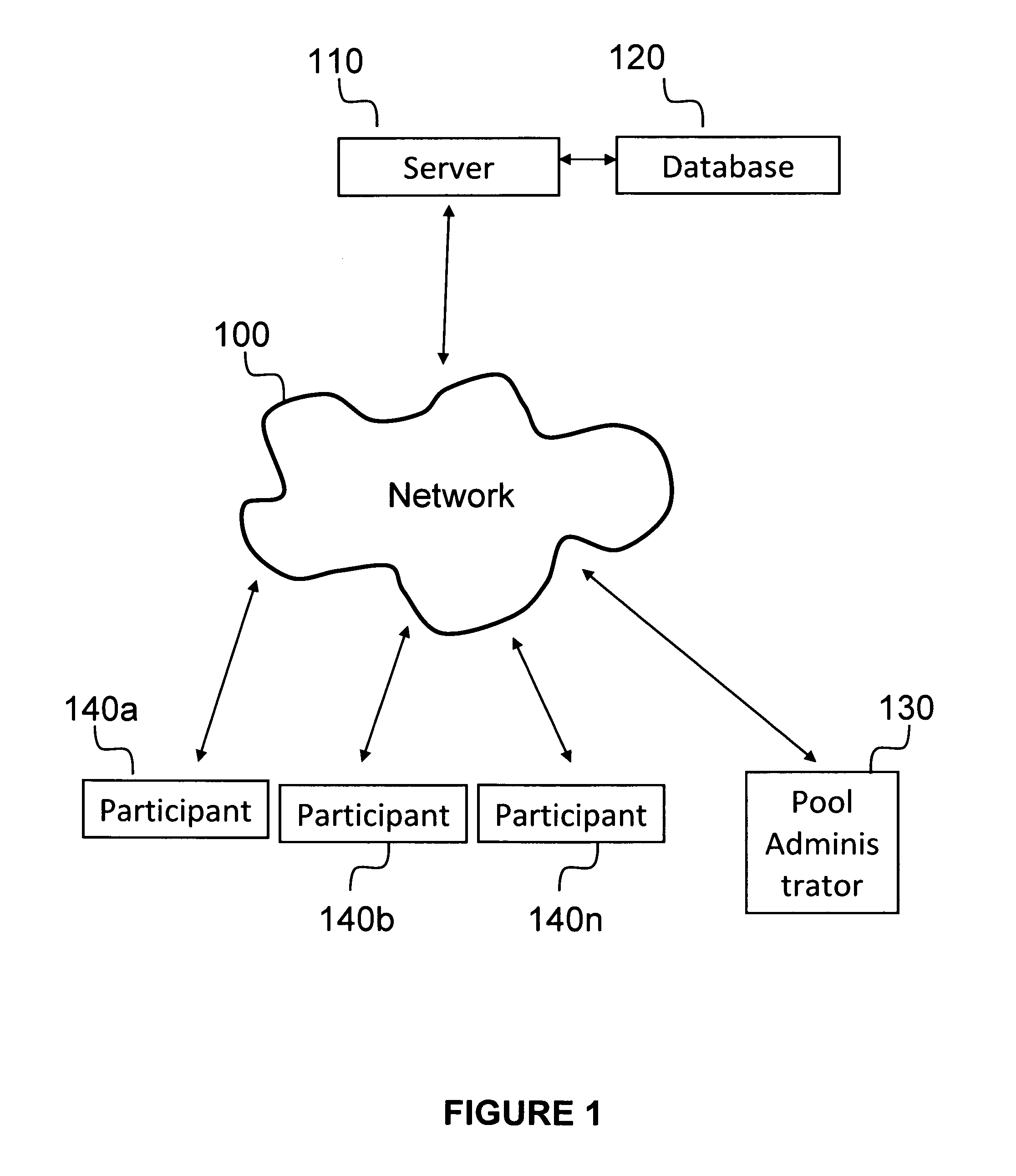
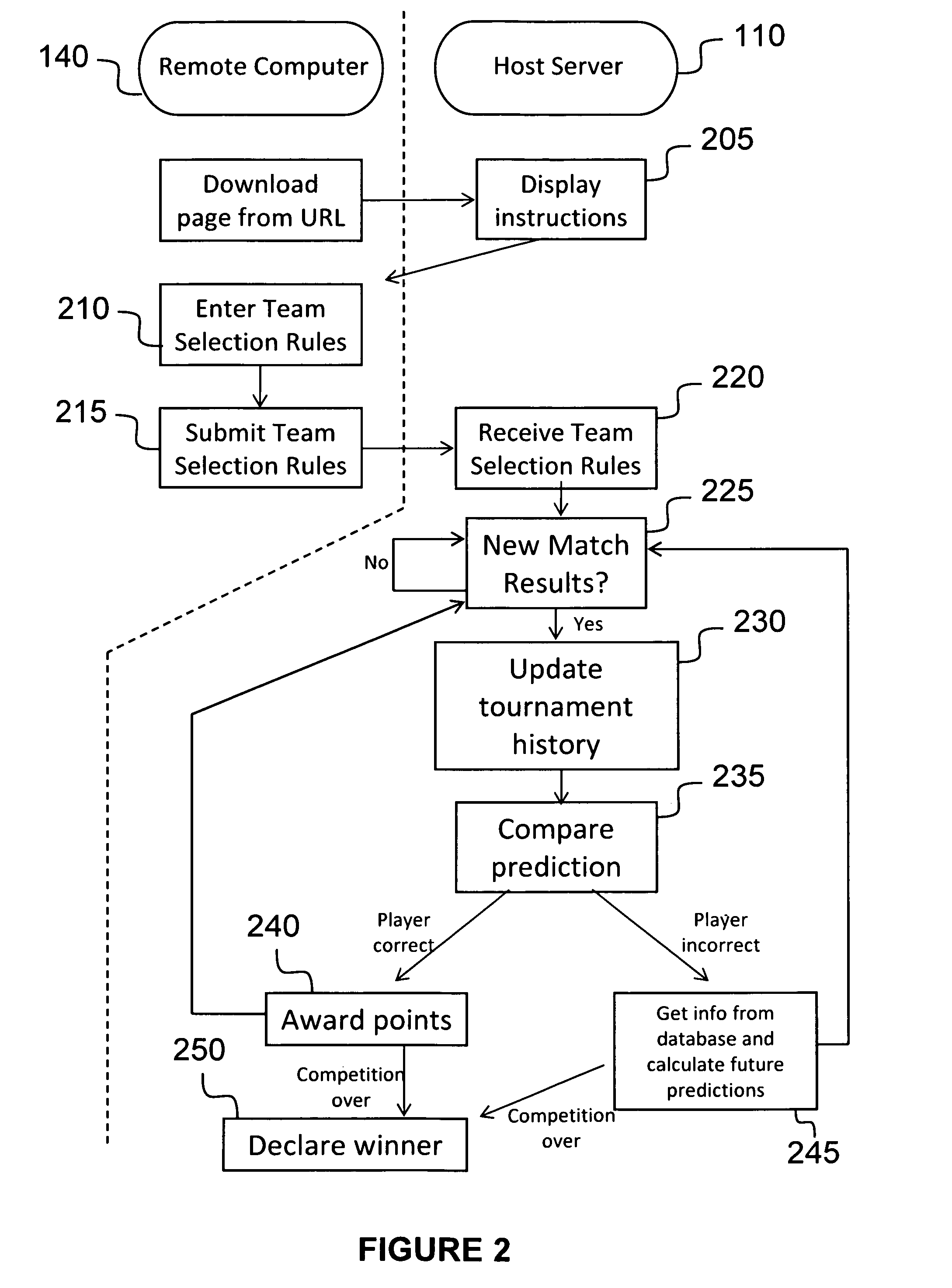
Embodiments of the invention relate to hosting a competition on a computing device, wherein the competition allows participants to select a first set of predicted winners for a predetermined series of matches in a tournament and a second set of predictions for winners if one or more of the first set of predicted winners are eliminated earlier than predicted. The competition may be implemented in any suitable computing system environment, including, but not limited to, a web-based competition hosted on a remote server, a private or company-based competition hosted on a private or company computer.
Owner:BETTEROFFICEPOOL CORP
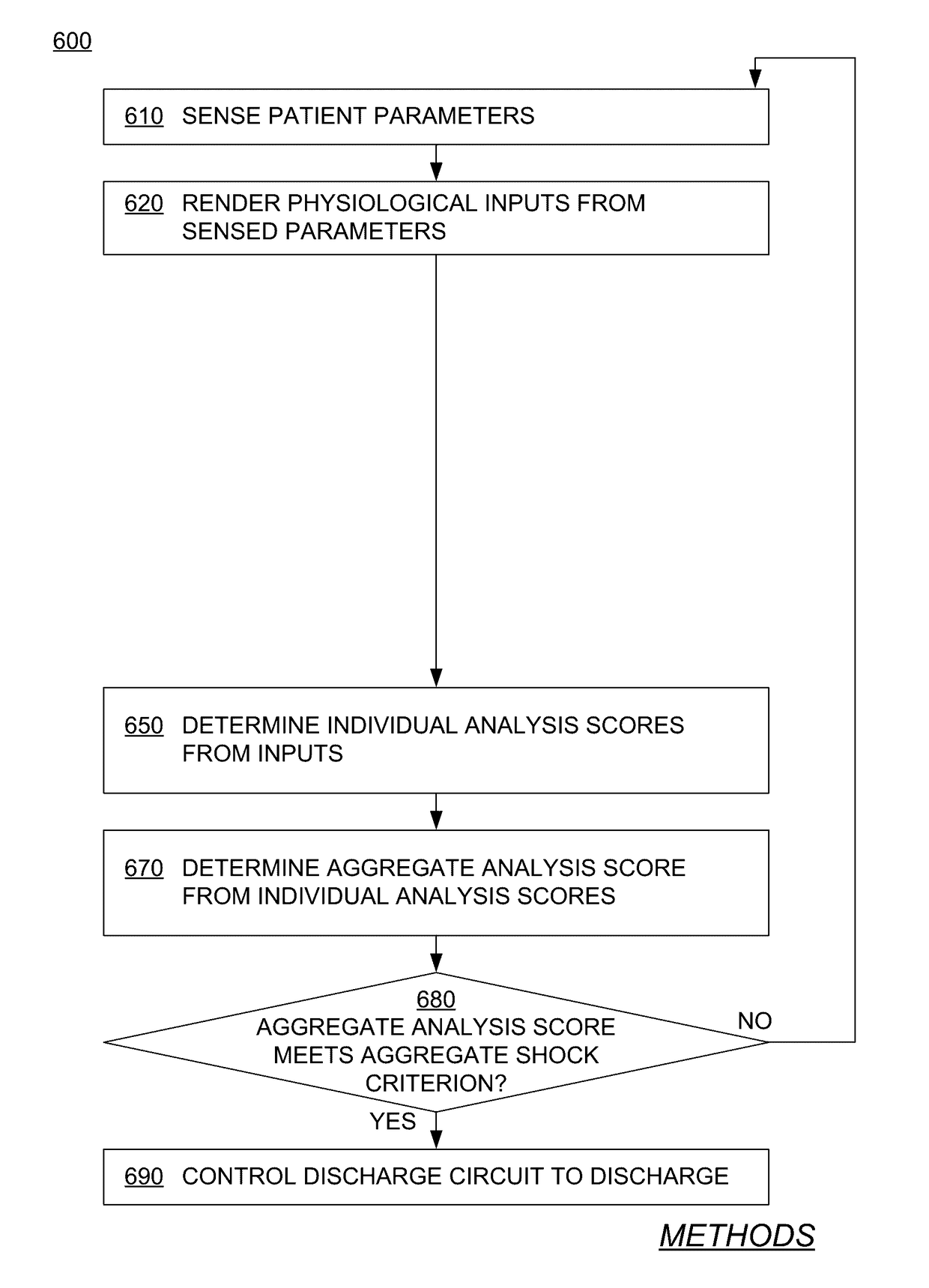
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system making shock/no shock determinations from multiple patient parameters
In embodiments, a WCD system includes one or more transducers that may sense patient parameters from different parts of the patient's body, and thus render physiological inputs from those parameters. Individual analysis scores may be determined from the physiological inputs, and an aggregate analysis score may be determined from the individual analysis scores. A shock / no shock determination may be made depending on whether or not the aggregate analysis score meets an aggregate shock criterion. Accordingly, multiple inputs are considered in making the shock / no shock determination.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
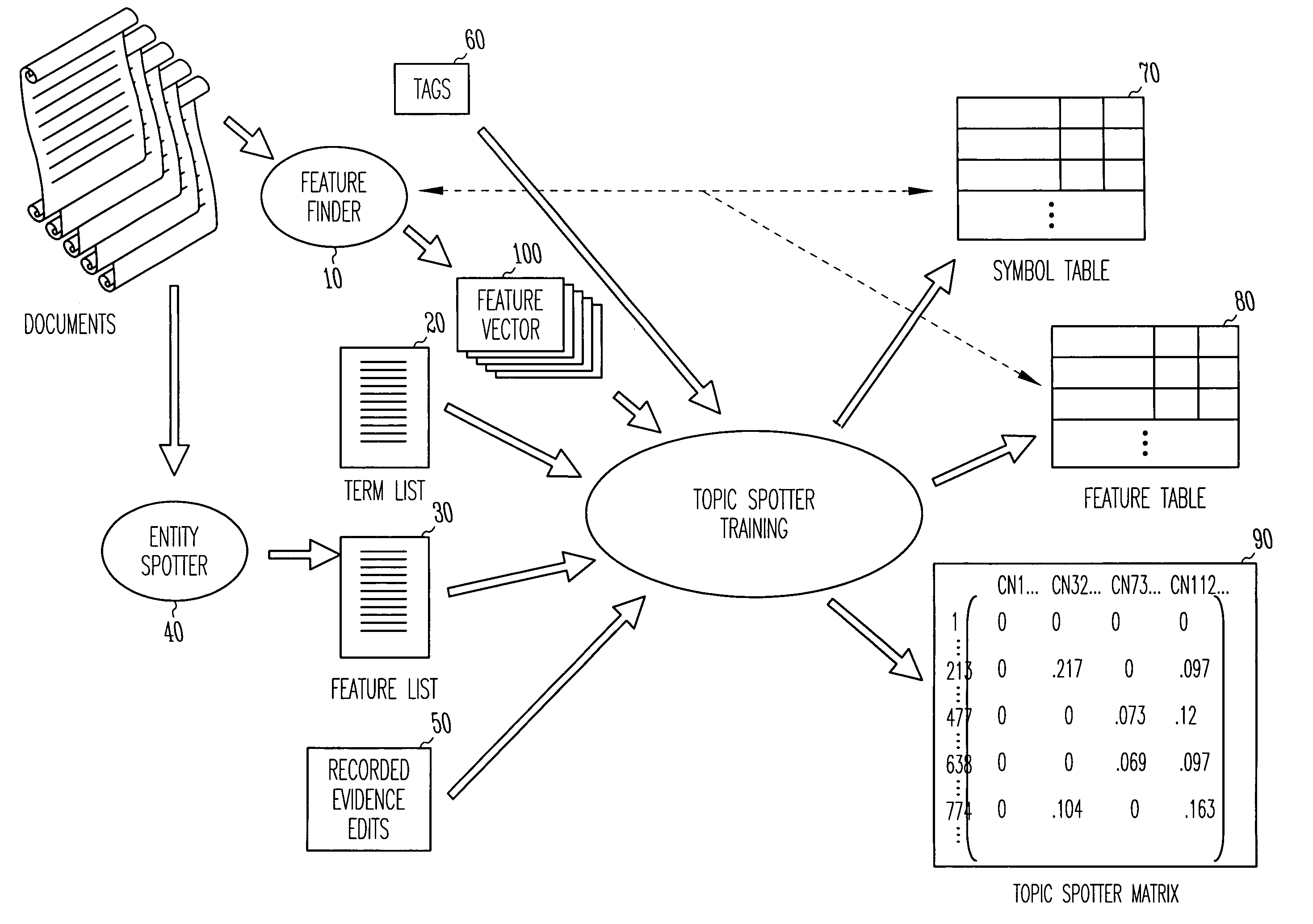
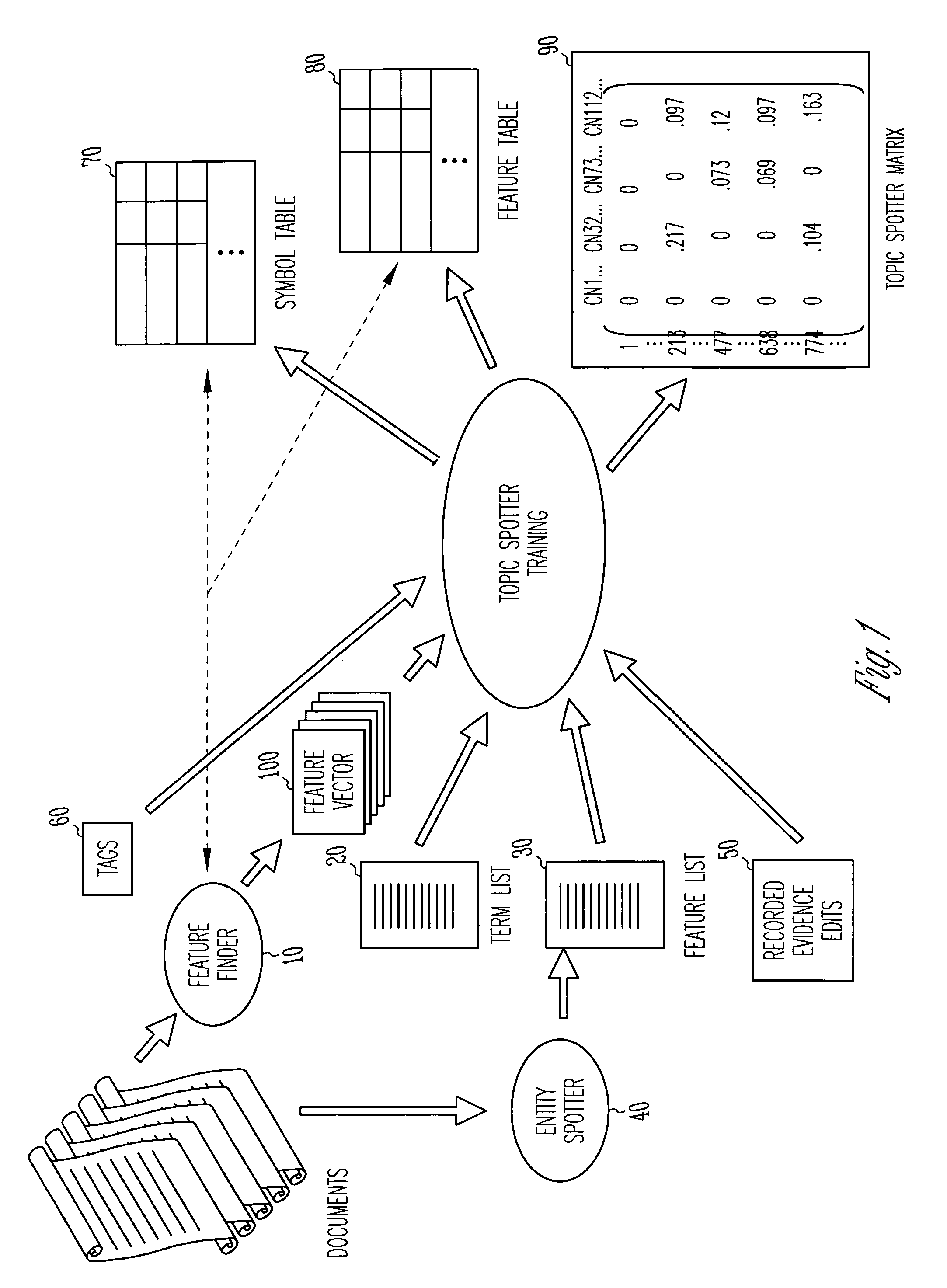
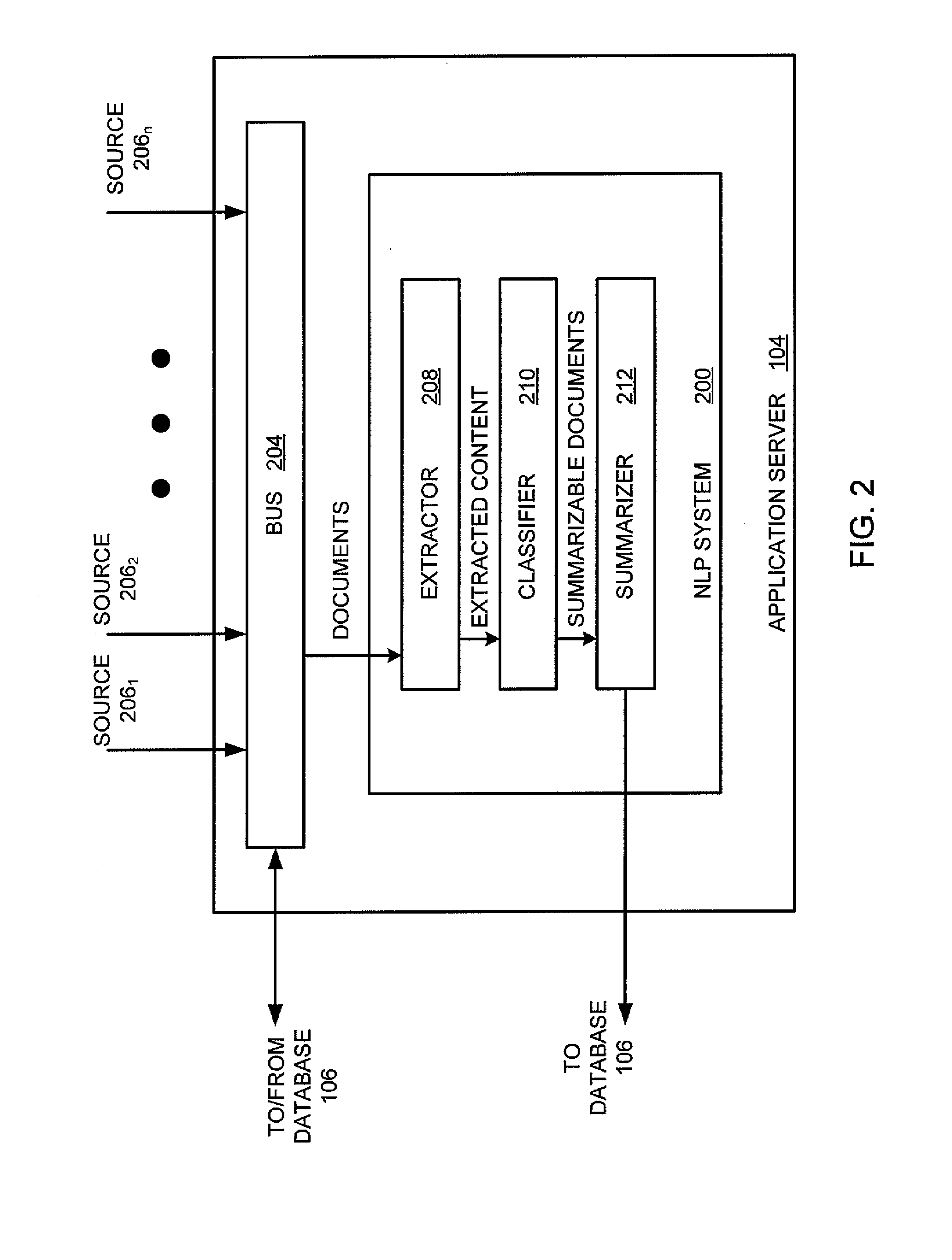
Method and apparatus for automatically summarizing the contents of electronic documents
One embodiment of a method for summarizing an electronic document includes splitting the electronic document into a plurality of terms, wherein each of the plurality of terms is associated with a respective length, a respective informativeness score, and a respective coherence score, automatically selecting a subset of the plurality of terms, such that an aggregate informativeness score of the subset is maximized while an aggregate length of the subset is less than or equal to a maximum length, and arranging the subset as a summary of the electronic document.
Owner:YAHOO ASSETS LLC
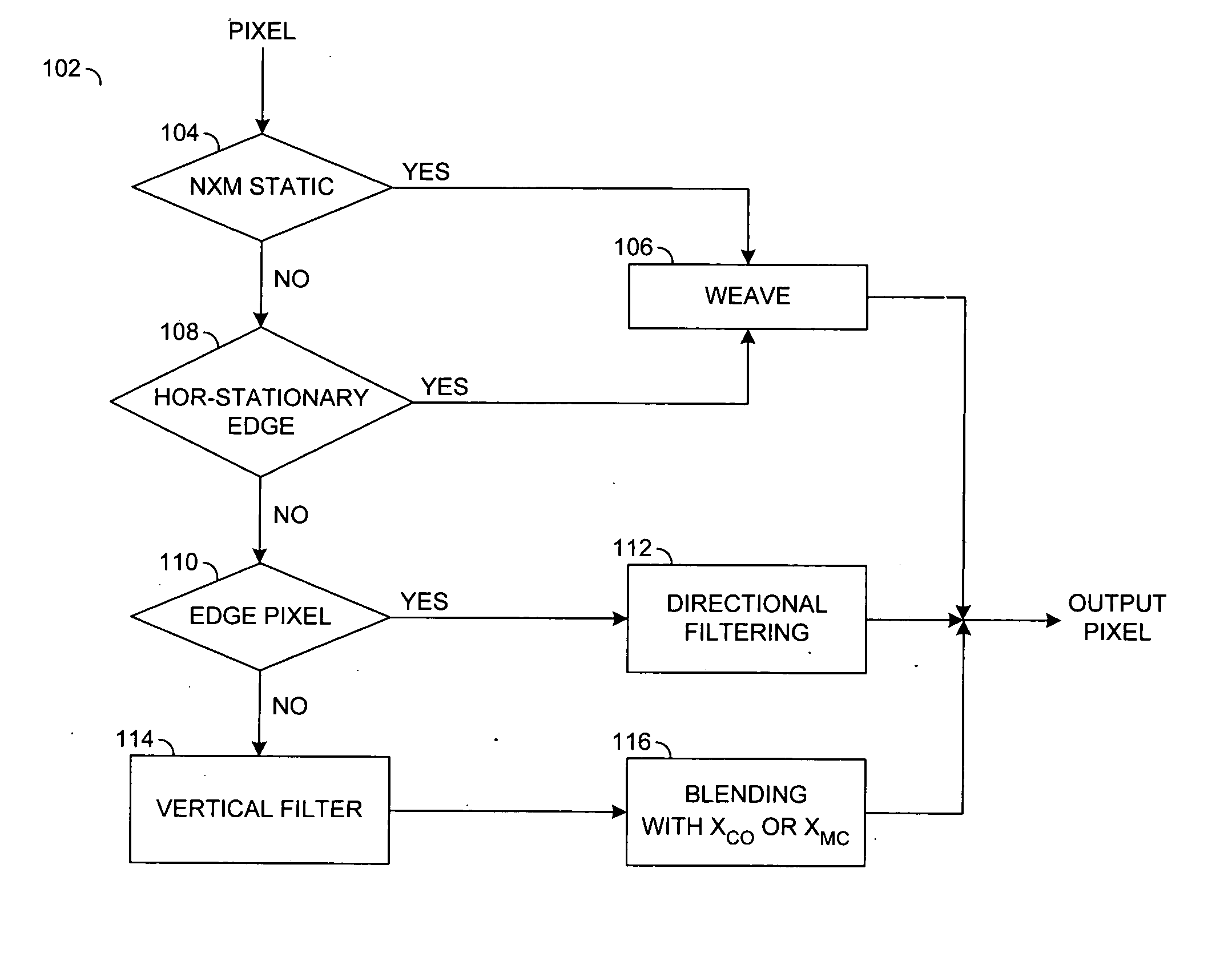
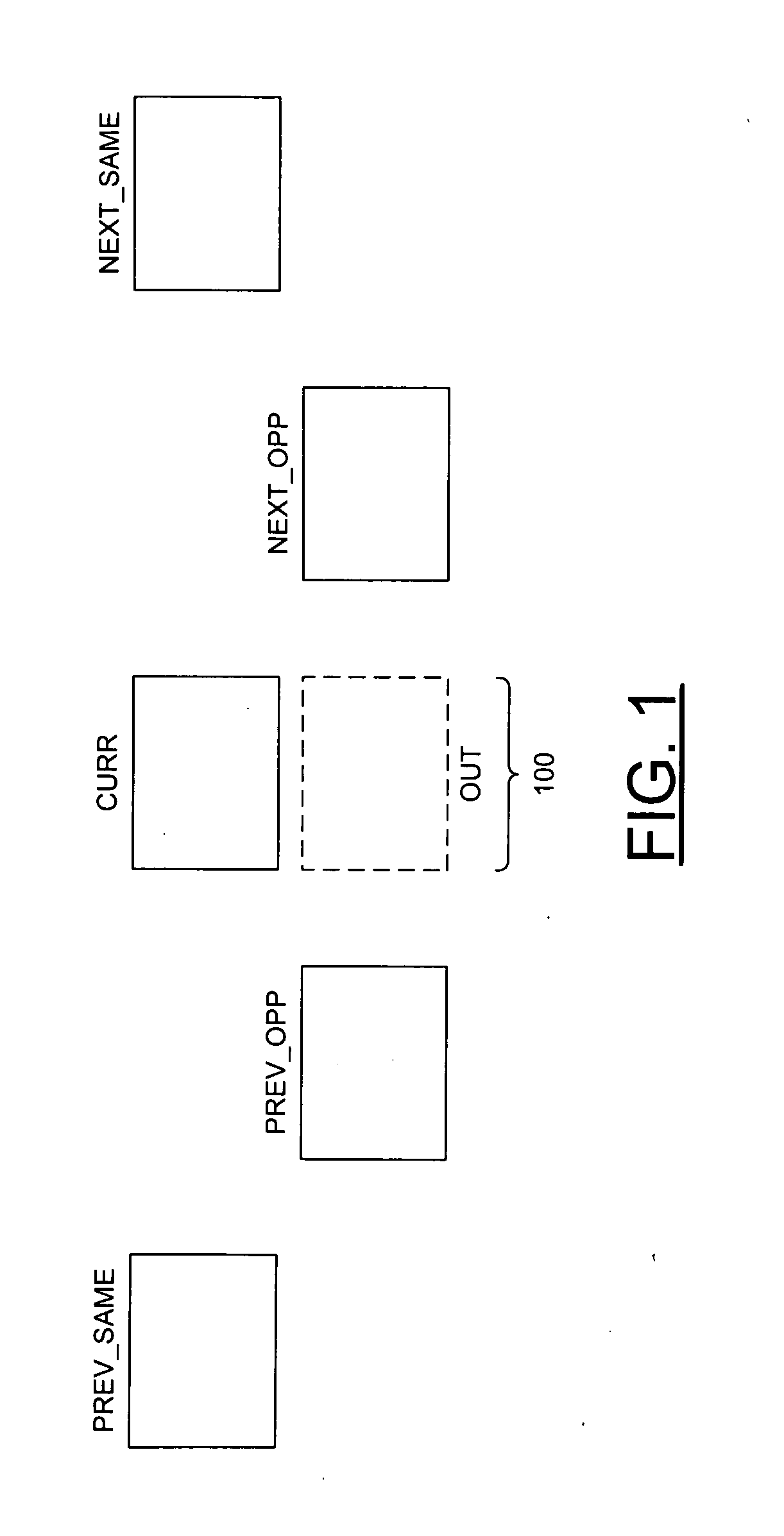
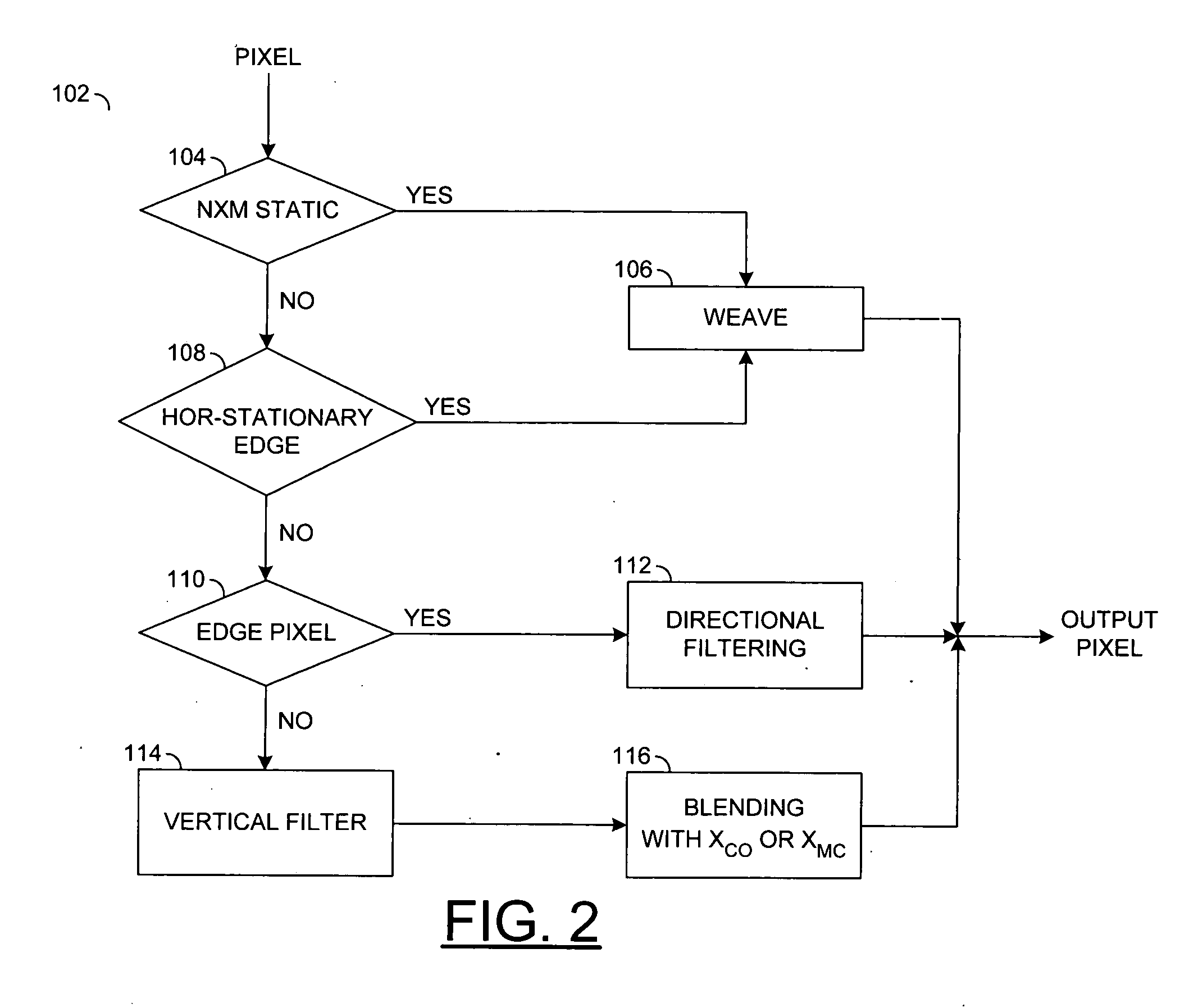
Method and apparatus for video deinterlacing and format conversion
InactiveUS20050134602A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesInterlaced videoComputer science
A method for deinterlacing a picture is disclosed. The method generally includes the steps of (A) generating a plurality of primary scores by searching along a plurality of primary angles for an edge in the picture proximate a location interlaced with a field of the picture, (B) generating a plurality of neighbor scores by searching for the edge along a plurality of neighbor angles proximate a particular angle of the primary angles corresponding to a particular score of the primary scores having a best value and (C) identifying a best score from a group of scores consisting of the particular score and the neighbor scores to generate an interpolated sample at the location.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
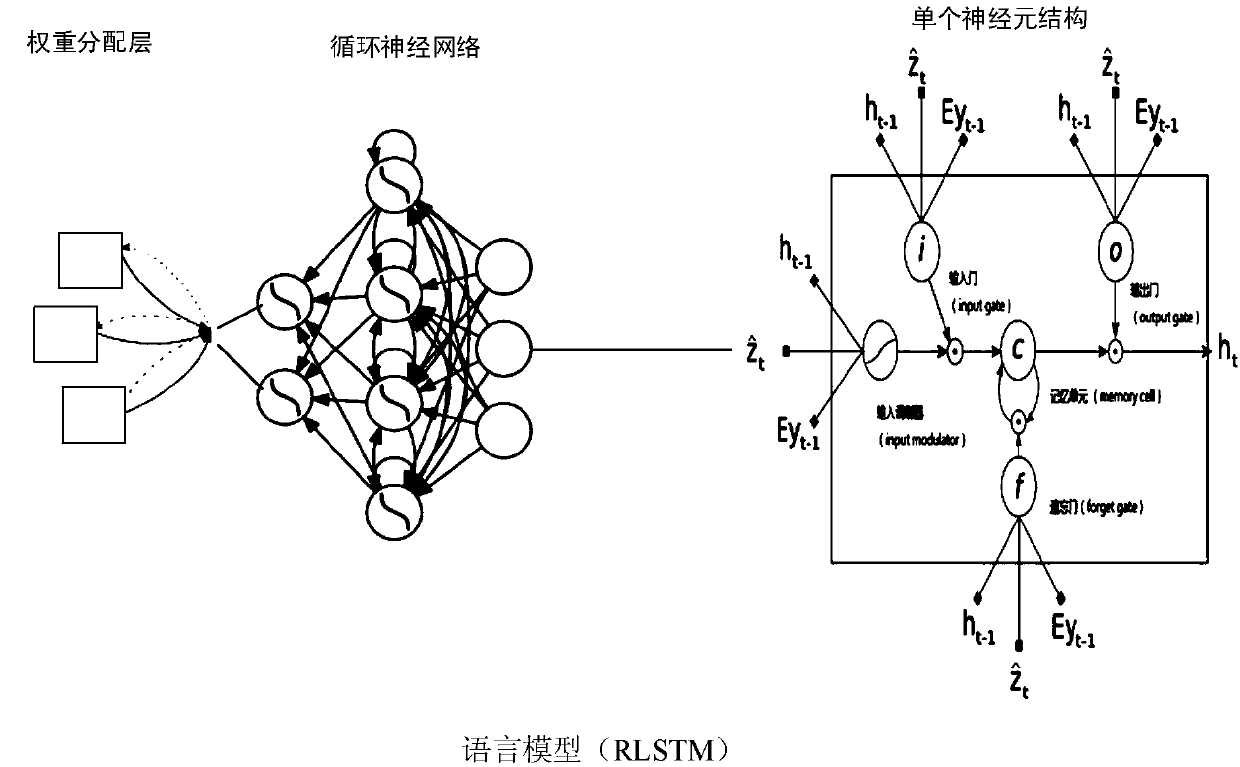
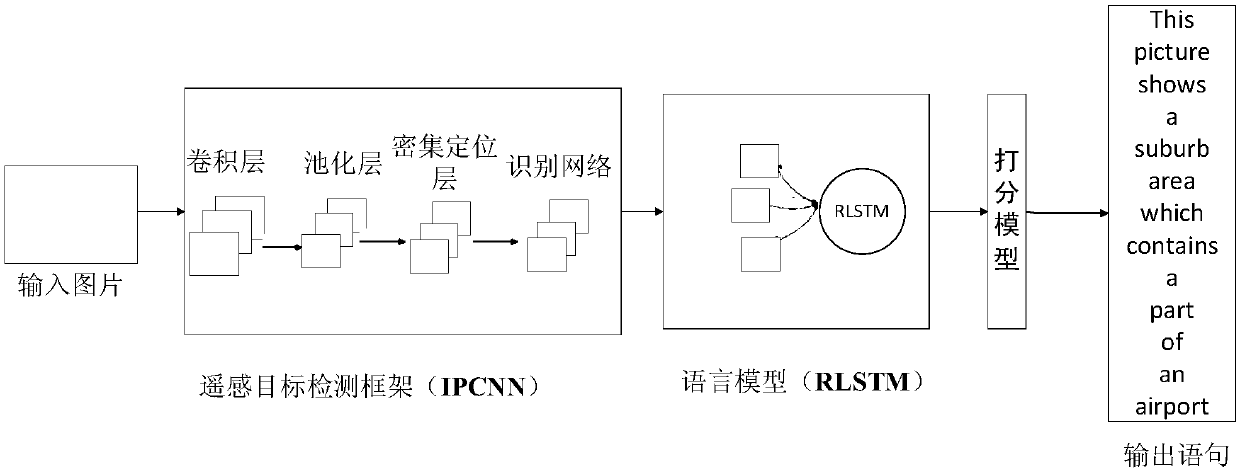
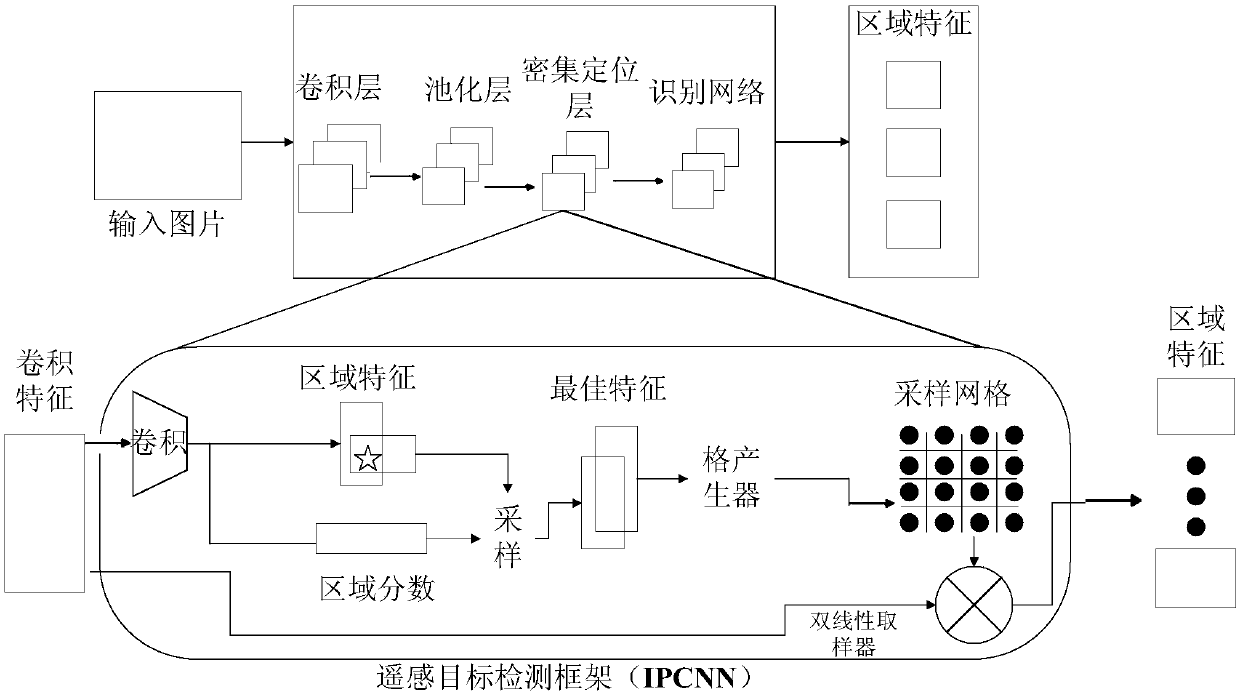
Remote sensing image natural language generation method based on attention mechanism and deep learning
InactiveCN107766894AReduce overfittingHigh outputScene recognitionNeural architecturesShort-term memoryComputer science
The invention relates to a remote sensing image natural language generation method based on an attention mechanism and deep learning. The method comprises the steps of first, preprocessing a remote sensing image and corresponding natural language description; second, inputting the denoised remote sensing image into an intensive positioning convolution neural network (IPCNN); third, inputting region blocks obtained in the second step into a reassignment long-short term memory (RLSTM) network, getting into a weight assignment layer of the RLSTM network, respectively solving the weight of each region by using a multilayer network function, and finally realizing overall output of the natural language description through a deep output layer of the RLSTM network; fourth, inputting the natural language description generated in the third step into a remote sensing image language description scoring model to obtain a score of each sentence; and fifth, inputting a target position, a category label and a natural language description score into a database to wait for calling.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
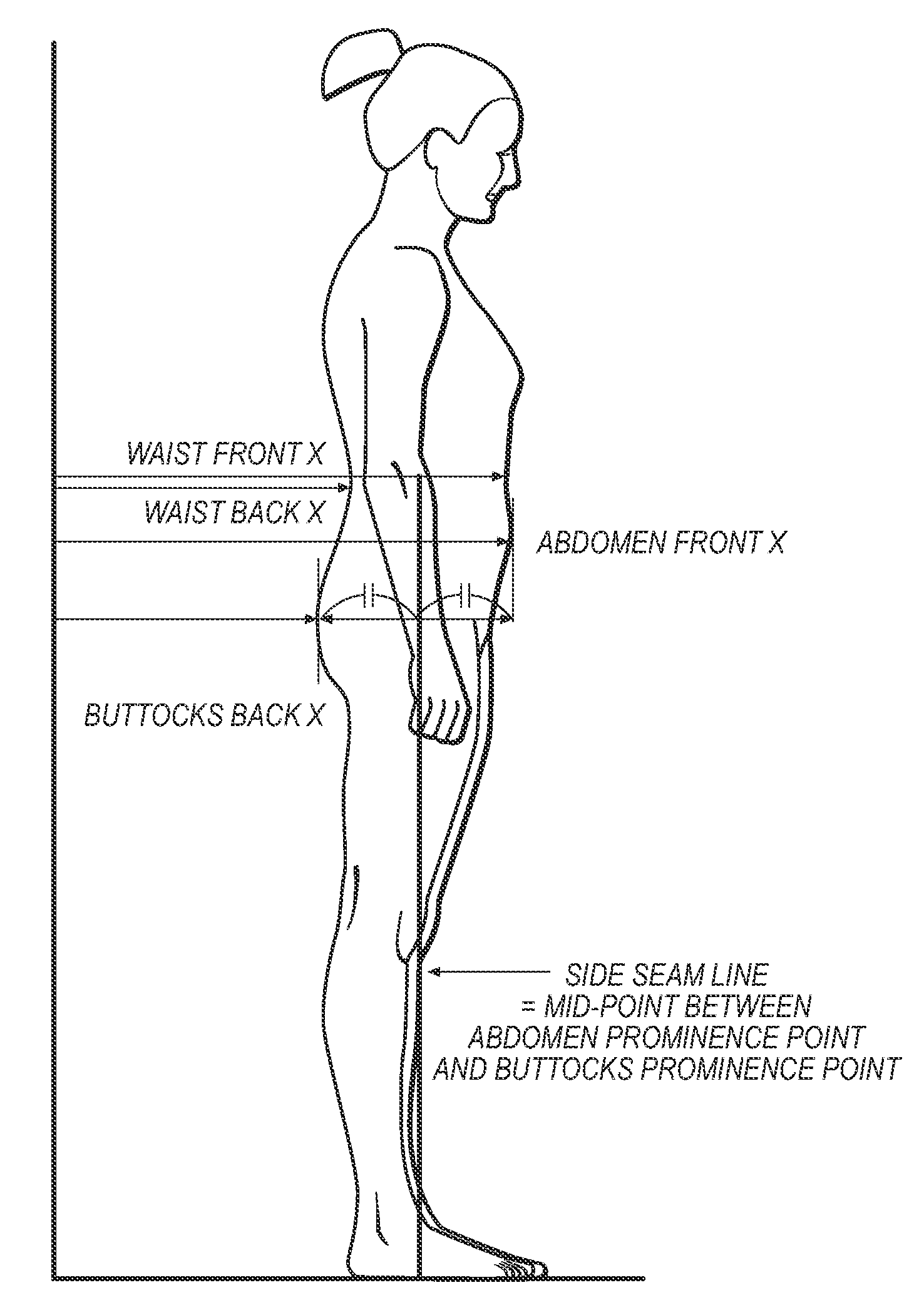
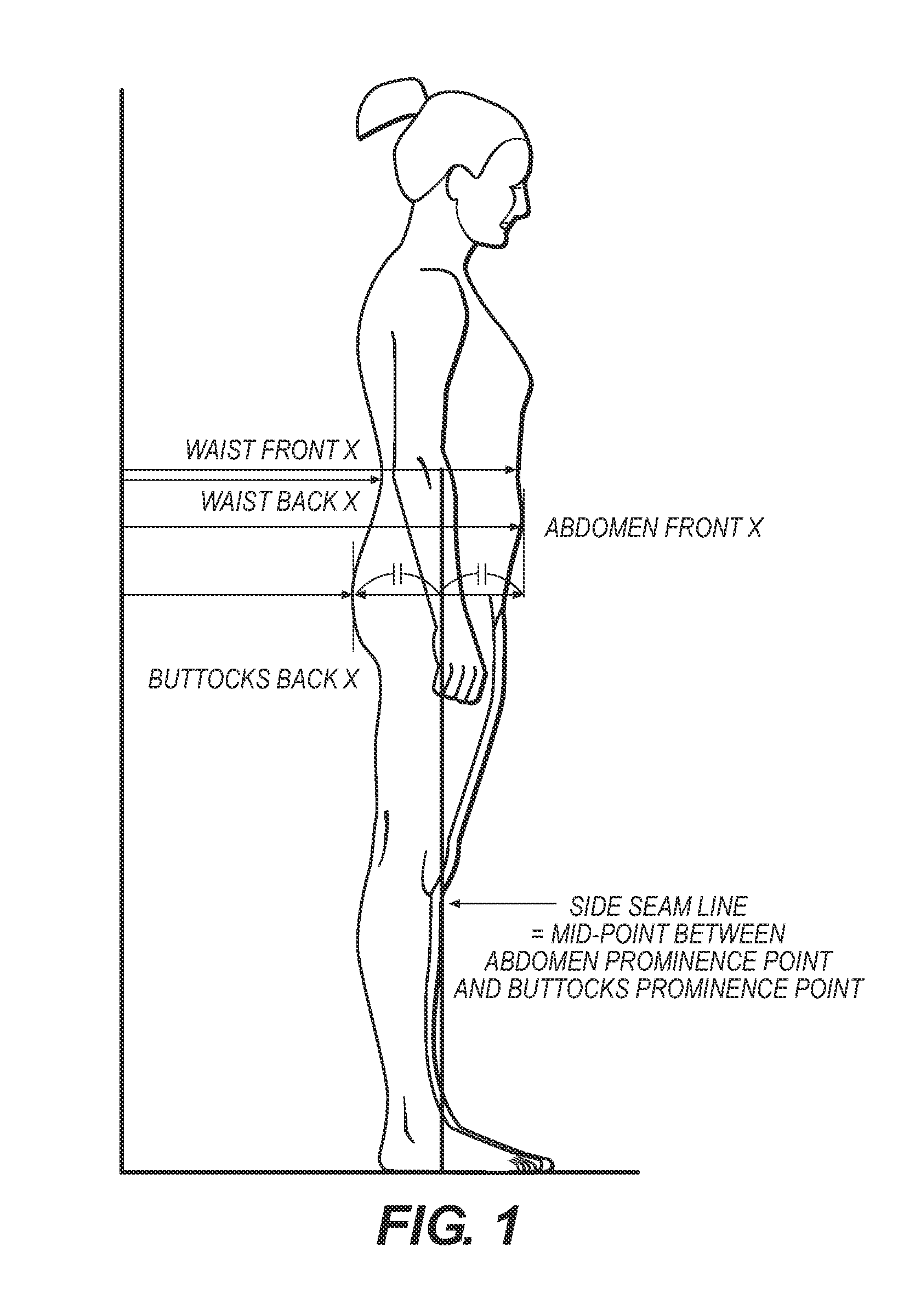
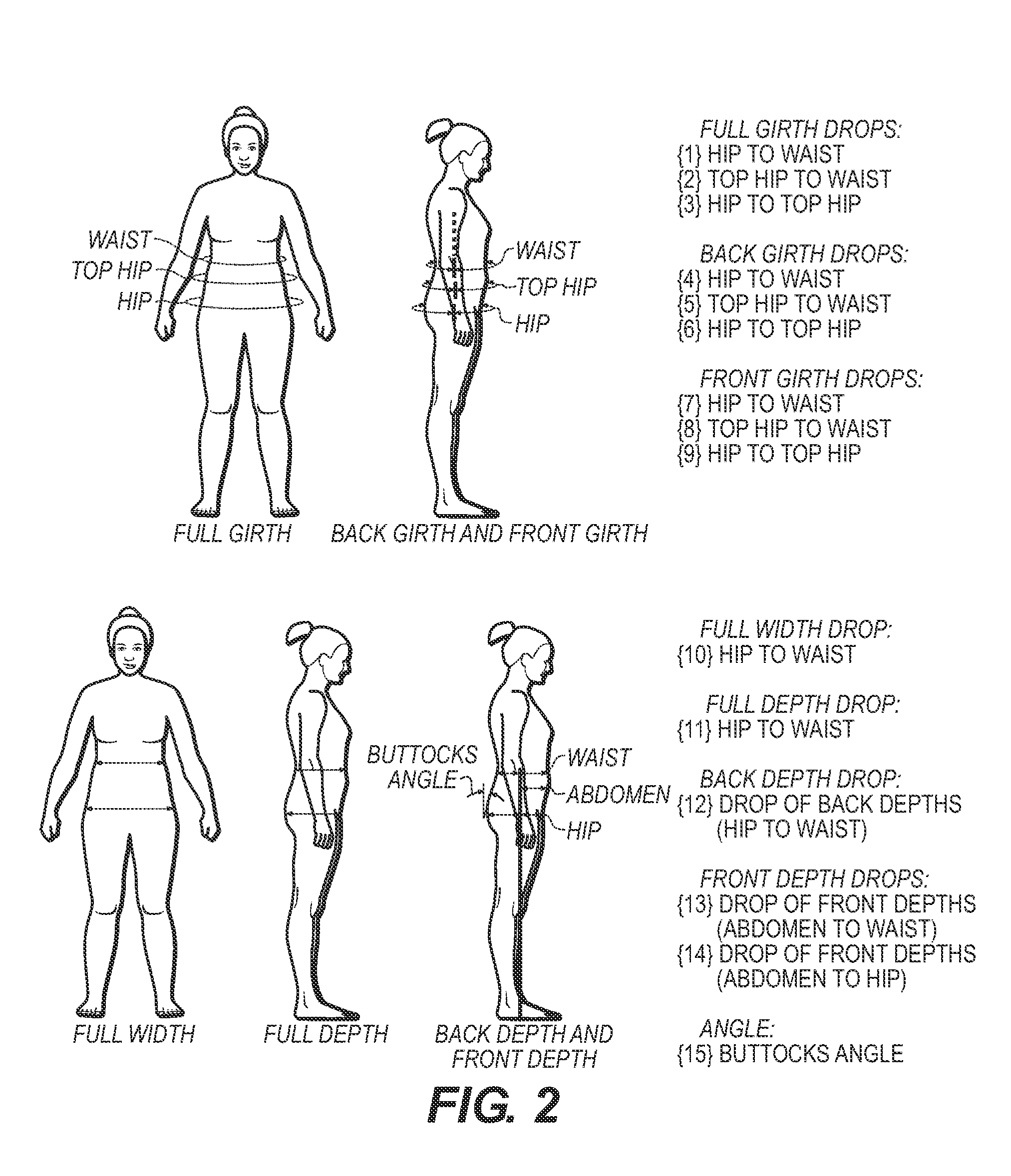
Body shape analysis method and system
A method for categorizing body shape is provided comprising the steps of providing a data set of body shape-defining measurements of a portion of the body of interest from a plurality of subjects' bodies, wherein the measurements define a silhouette and profile (front and side) perspectives of the portion of the body of interest; conducting a principal component (PC) analysis of the data set of measurements to calculate and generate PC scores; conducting cluster analysis using the PC scores as independent variables to produce cluster analysis results; and establishing one or more body shape categories from the cluster analysis results, thereby categorizing body shapes of the plurality of subjects. A shape prototyping system is also provided for designing a custom fit garment for an individual subject, the system being based on the method for categorizing body shape.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Refining inference rules with temporal event clustering
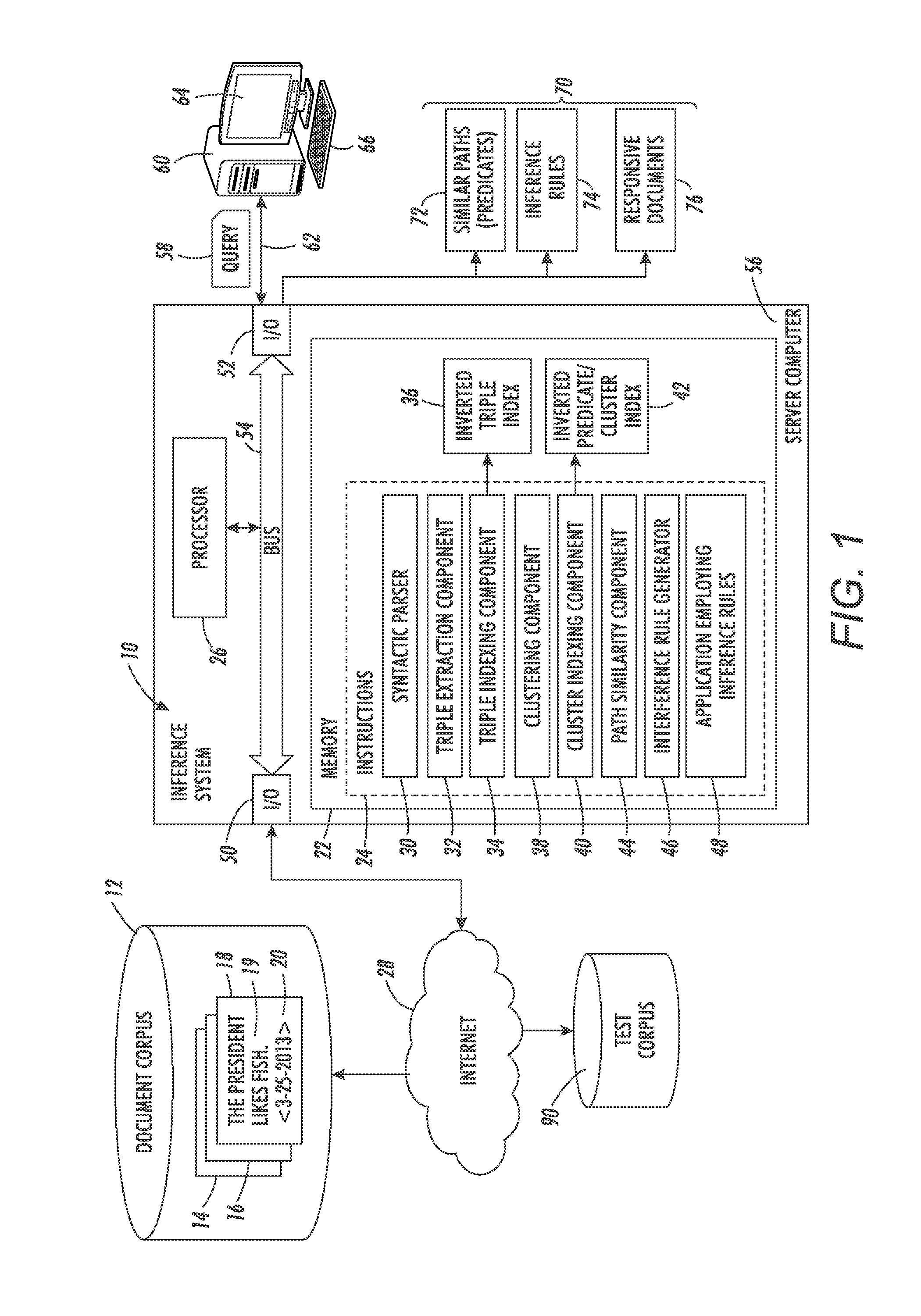
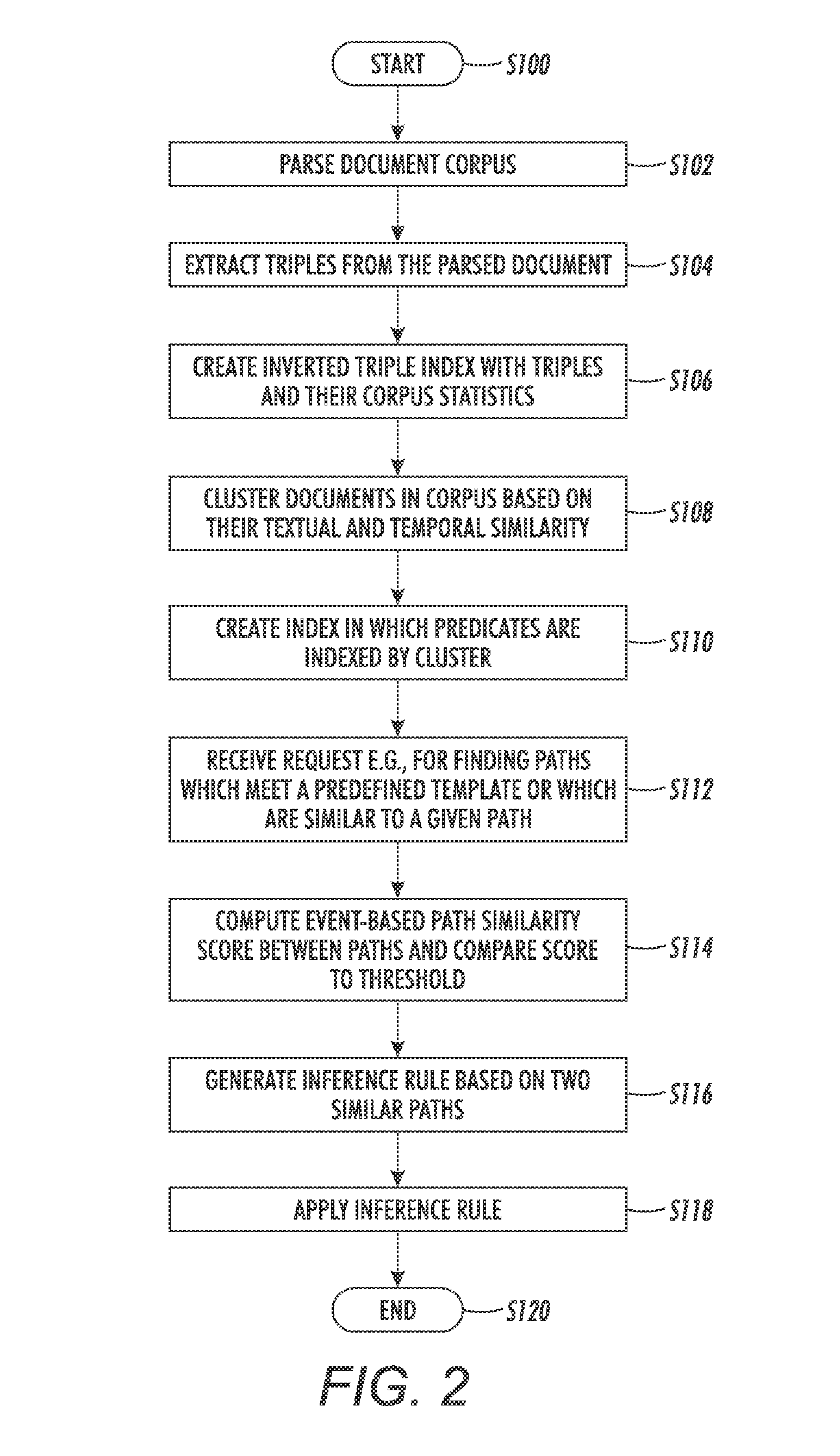
InactiveUS20150127323A1Semantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsTemporal similarityCluster based
A method for computing similarity between paths includes extracting corpus statistics for triples from a corpus of text documents, each triple comprising a predicate and respective first and second arguments of the predicate. Documents in the corpus are clustered to form a set of clusters based on textual similarity and temporal similarity. An event-based path similarity is computed between first and second paths, the first path comprising a first predicate and first and second argument slots, the second path comprising a second predicate and first and second argument slots, the event-based path similarity being computed as a function of a corpus statistics-based similarity score which is a function of the corpus statistics for the extracted triples which are instances of the first and second paths, and a cluster-based similarity score which is a function of occurrences of the first and second predicates in the clusters.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Apparatus system and method for validating users based on fuzzy logic
InactiveUS20090089876A1Valid conversionDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionPasswordTheoretical computer science
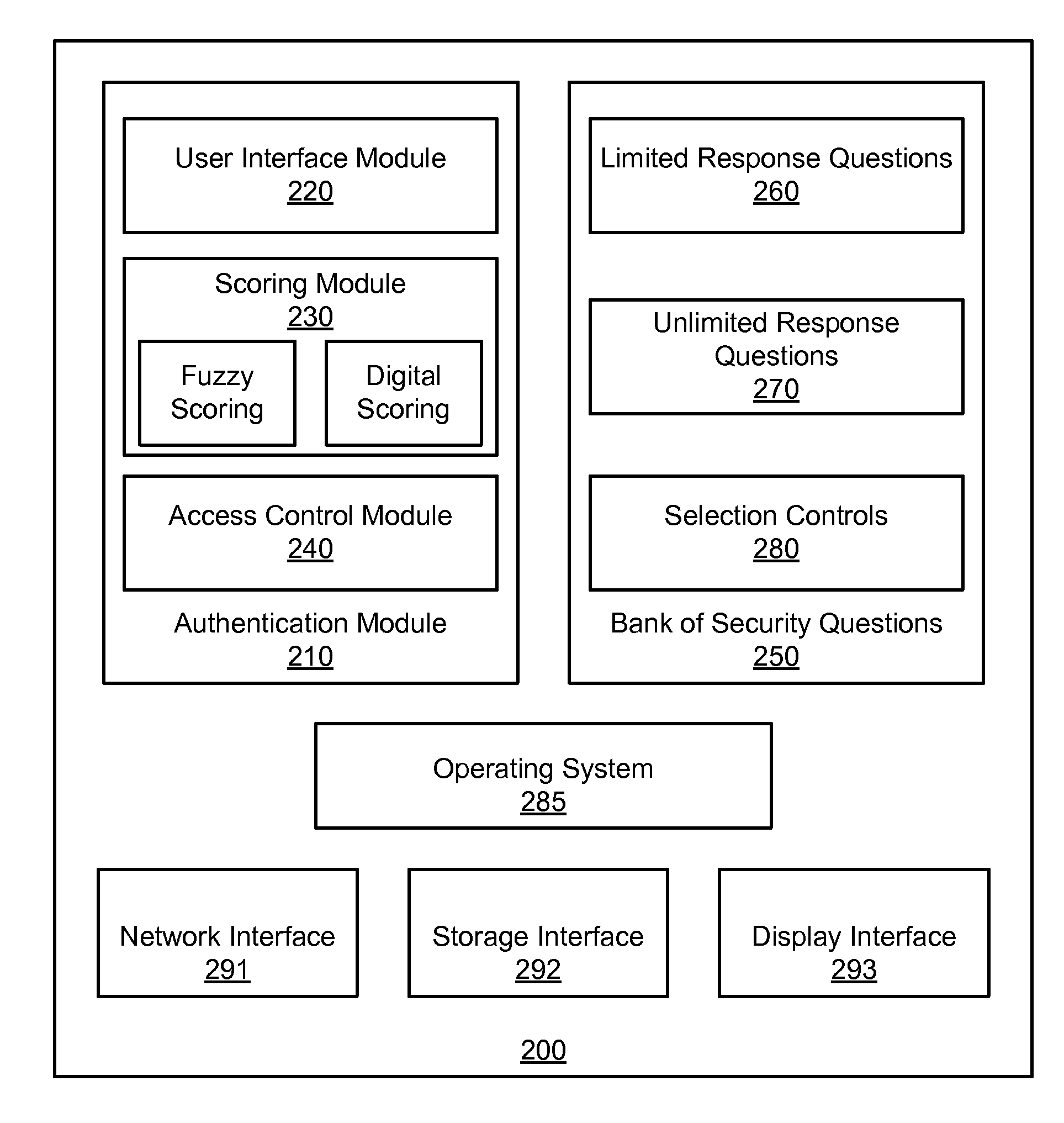
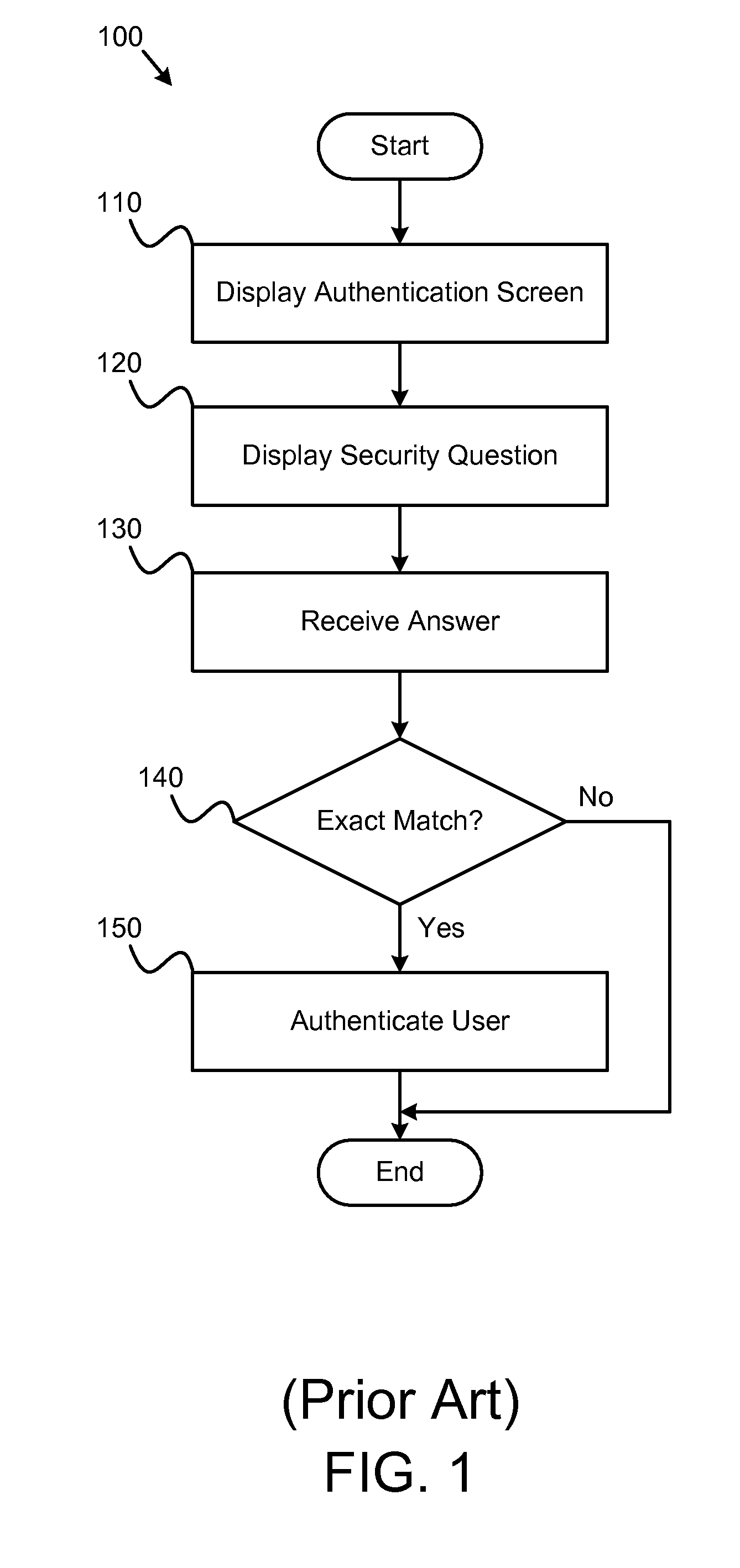
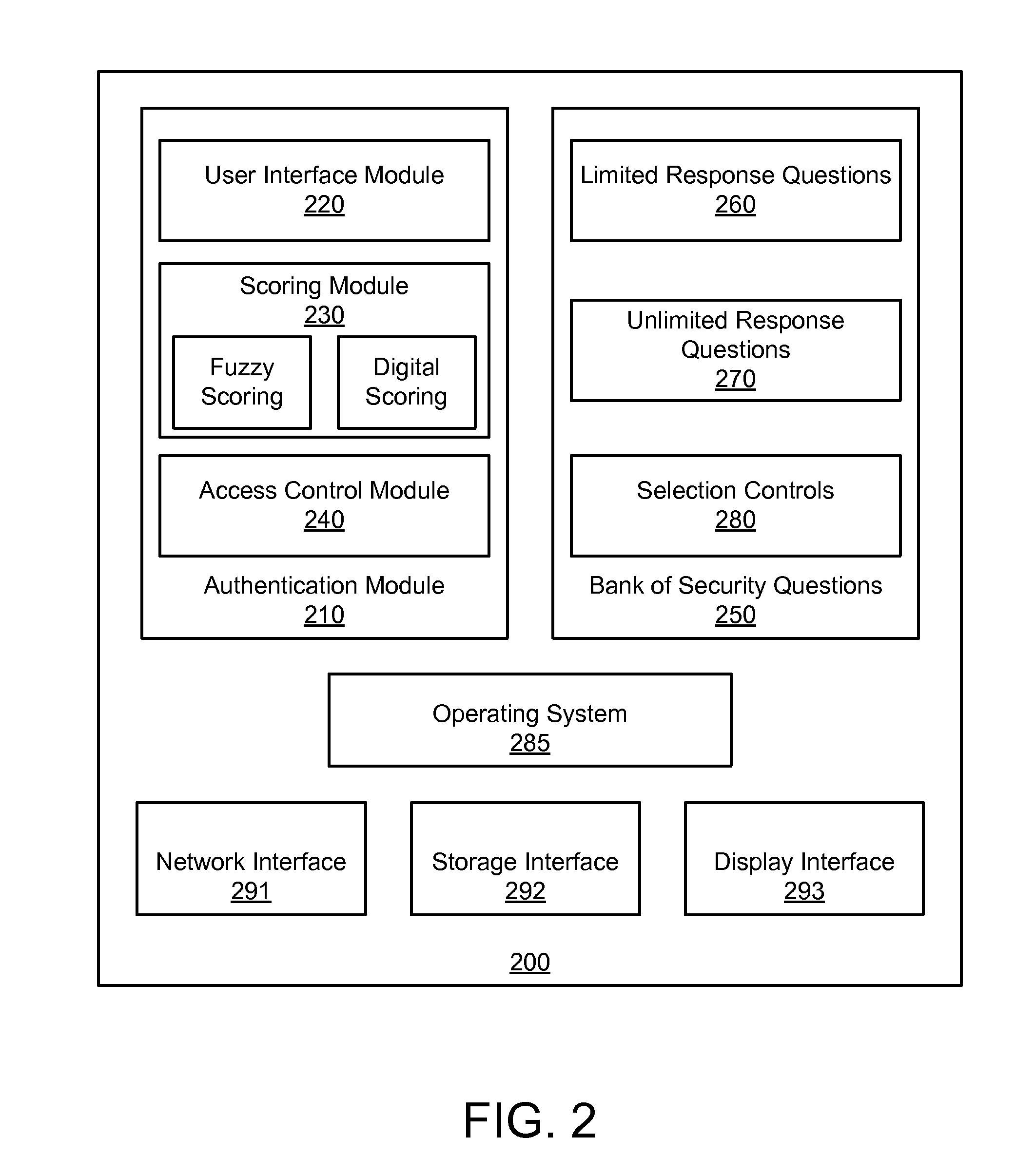
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for validating users based on fuzzy logic. An interface with security questions is presented to a user who requires authentication. A typical scenario is authentication for password recovery. The interface comprises security questions for the user to answer. The security questions may be limited or unlimited response questions. The answers to the security questions are either scored using fuzzy logic, which may attribute a value between “1” and “0” based on similarity with the original, correct answer; or scored using digital logic. When fuzzy logic scoring is used, a similarity score is computed for each answer. The similarity score is compared against a similarity score threshold to either grant or deny access. An average similarity score is also computed for all answers and compared against an average similarity score threshold to either grant or deny access.
Owner:LENOVO (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
Method and system for multispectral palmprint verification
InactiveUS20120194662A1Character and pattern recognitionColor television detailsPattern recognitionSpectral bands
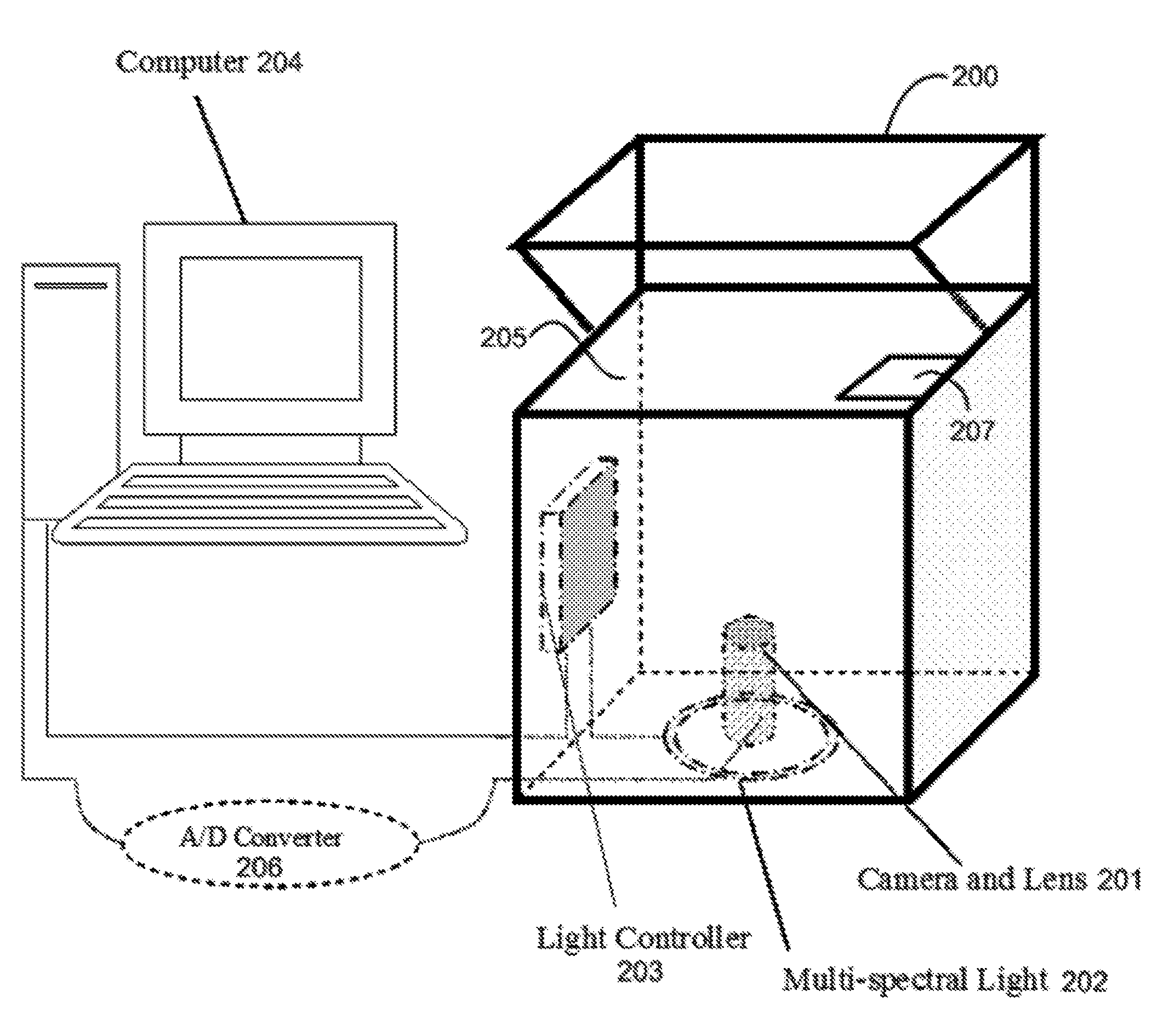
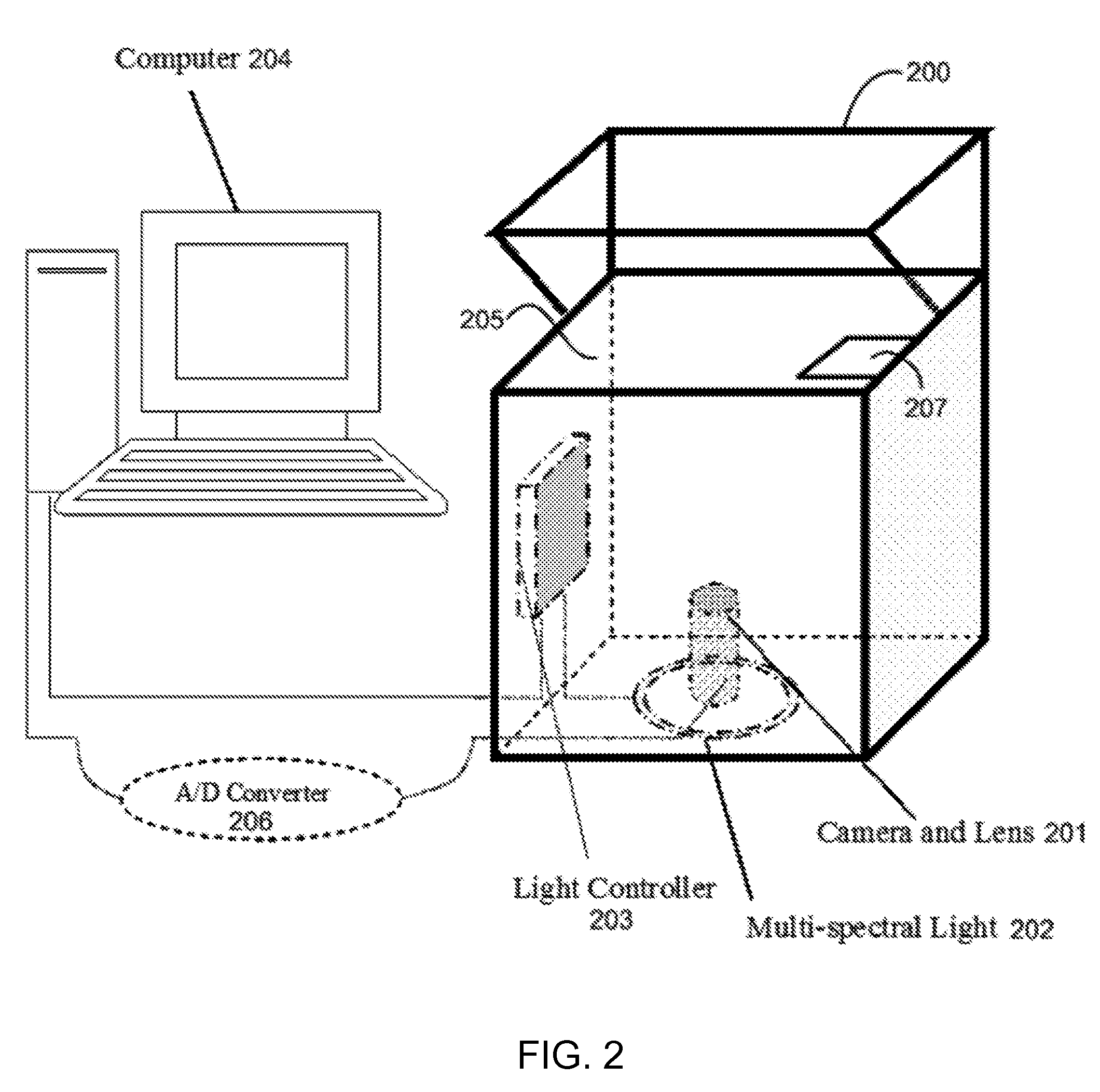
A method for palmprint verification of an individual that includes illuminating a palm of an individual with a plurality of spectral bands, collecting a plurality of palmprint images that are illuminated under the different spectral bands, locating a sub-image from each of the plurality of palmprint images, extracting palmprint feature maps from the sub-images, determining a palmprint matching score for each of the spectral bands based on the palmprint feature maps, computing a fused score by combining at least two of the palmprint matching scores under different spectral bands, without double-counting overlapping regions, and comparing the fused score with a threshold score from a database.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
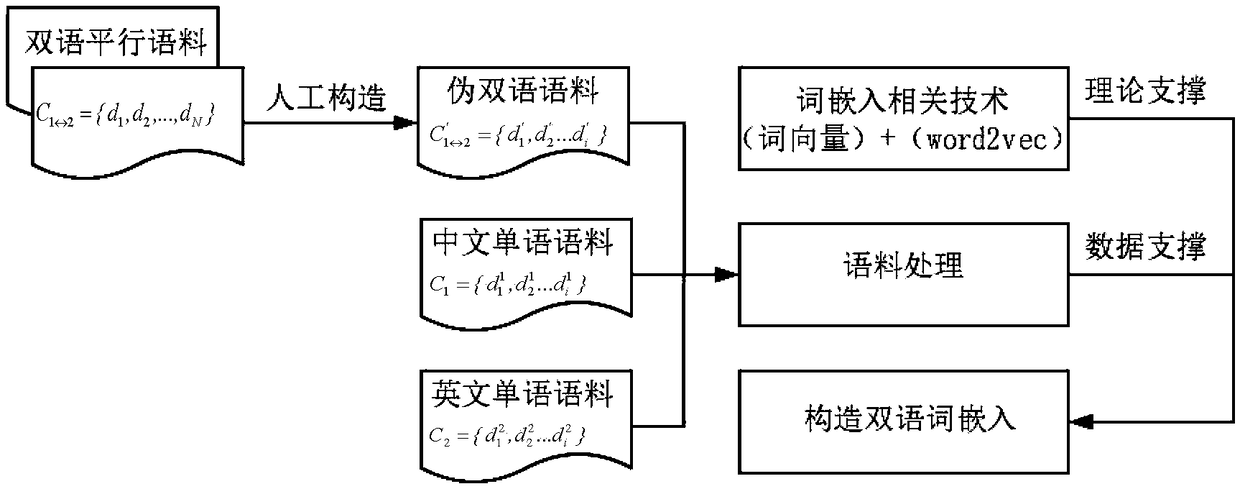
A bilingual word embedding-based cross-language text similarity assessment technique
The invention belongs to the field of language processing, in particular to a cross-language text similarity evaluation technology based on bilingual word embedding. The technical route and workflow of cross-language text similarity evaluation technology based on bilingual word embedding can be divided into three stages: the construction of bilingual word embedding model, the construction of textsimilarity calculation framework based on multi-neural network, and the cross-language similarity calculation. Through this model, a bilingual shared word embedding representation can be generated, which is based on the word vector correlation theory and Skip-Gram model is used to train word vectors on artificially constructed pseudo-bilingual corpus. Secondly, in order to make the generated wordembedding space as complete as possible, monolingual corpus is used as a supplement to learn additional word embedding knowledge. The similarity score of sentences is obtained by combining several neural network structures to learn the semantic representation of sentences. By dividing short text into paragraphs and treating paragraphs as long sentences as sequence input, the similarity iteration on a larger scale can be realized.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
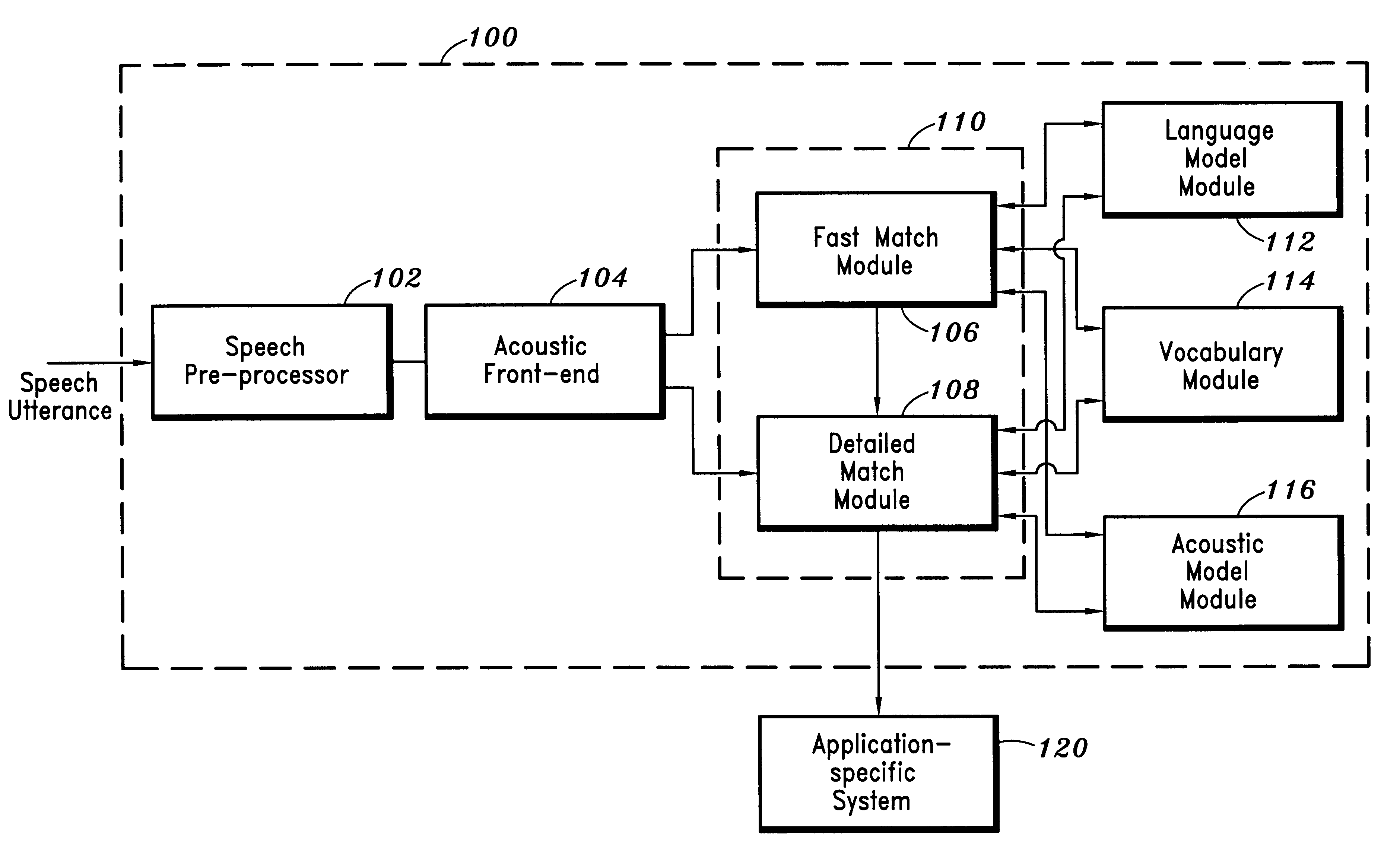
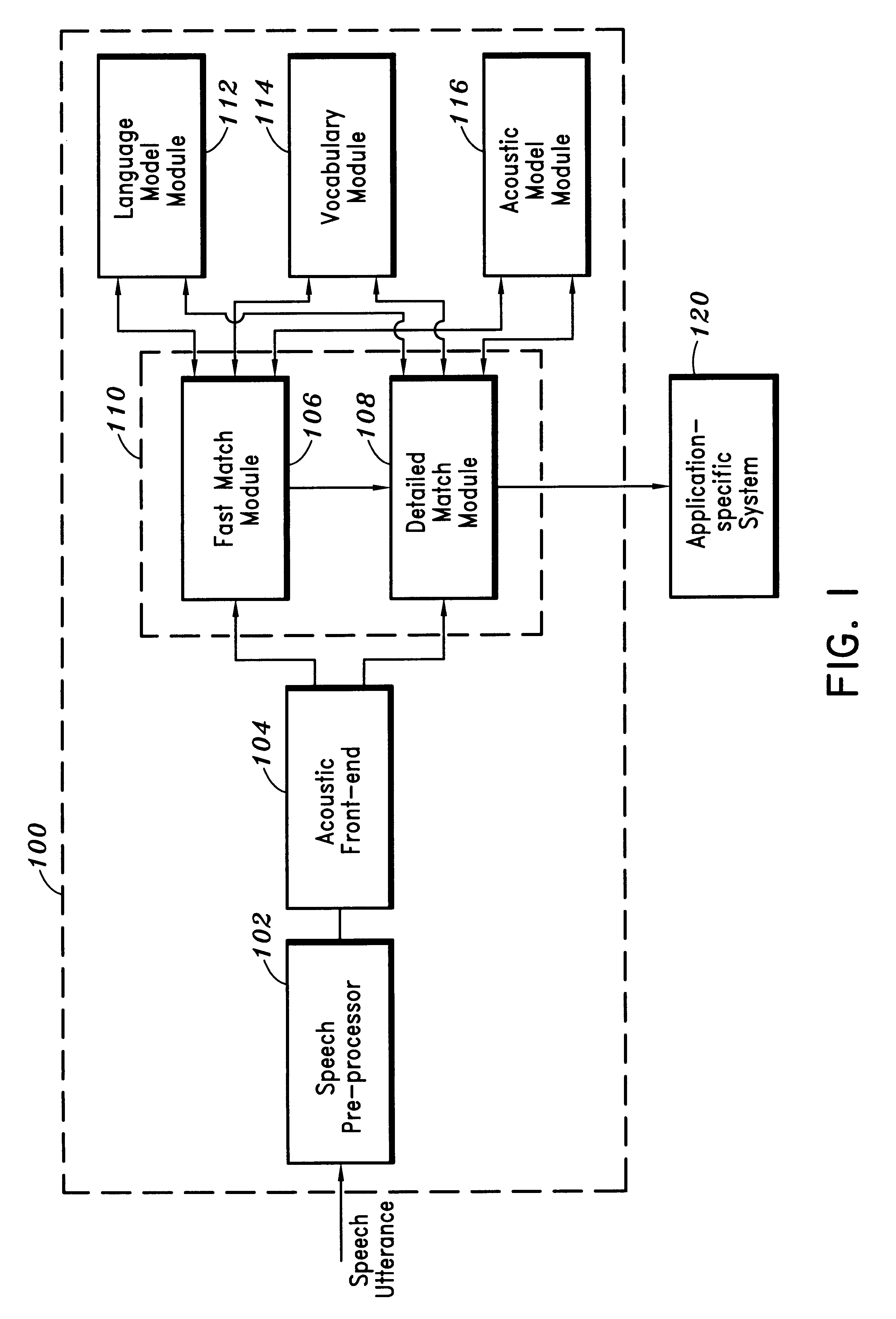
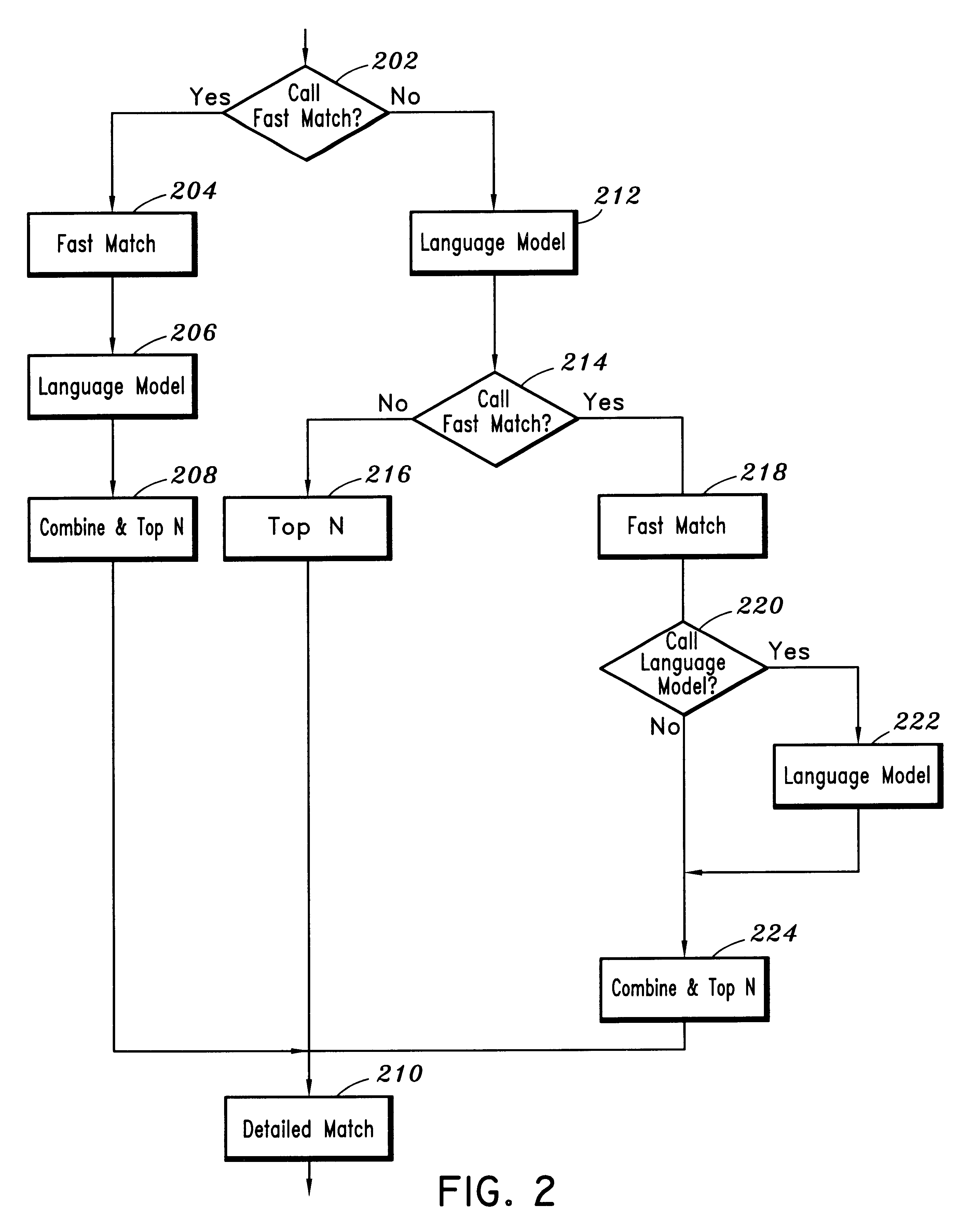
Method for reducing search complexity in a speech recognition system
InactiveUS6178401B1Improve decoding speedReduce in quantitySpeech recognitionSpeech identificationSpeech sound
A method is provided for reducing search complexity in a speech recognition system having a fast match, a detailed match, and a language model. Based on at least one predetermined variable, the fast match is optionally employed to generate candidate words and acoustic scores corresponding to the candidate words. The language model is employed to generate language model scores. The acoustic scores are combined with the language model scores and the combined scores are ranked to determine top ranking candidate words to be later processed by the detailed match, when the fast match is employed. The detailed match is employed to generate detailed match scores for the top ranking candidate words.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
Method for reducing north ad impact in search advertising
A method for reducing ad impact on users in a search results page includes receiving a request to deliver ads in response to a search query for display on a search results page; receiving relevance scores for a plurality of ranked web results that are to be served to the search results page; ranking a plurality of ads identified as relevant to the search query according to a position-normalized, click-through-rate metric and bid values, wherein a predetermined number of the top-ranked ads are placeable in a plurality of North ad slots; incrementally and additively placing the placeable ads sequentially according to rank (k) in their respective North ad slots until a utility score generated by a utility function for a current iteration of ads fails to exceed a threshold value; and delivering to the search results page the ads placed in the North ad slots.
Owner:OATH INC
Personal identification method, personal identification apparatus, and recording medium
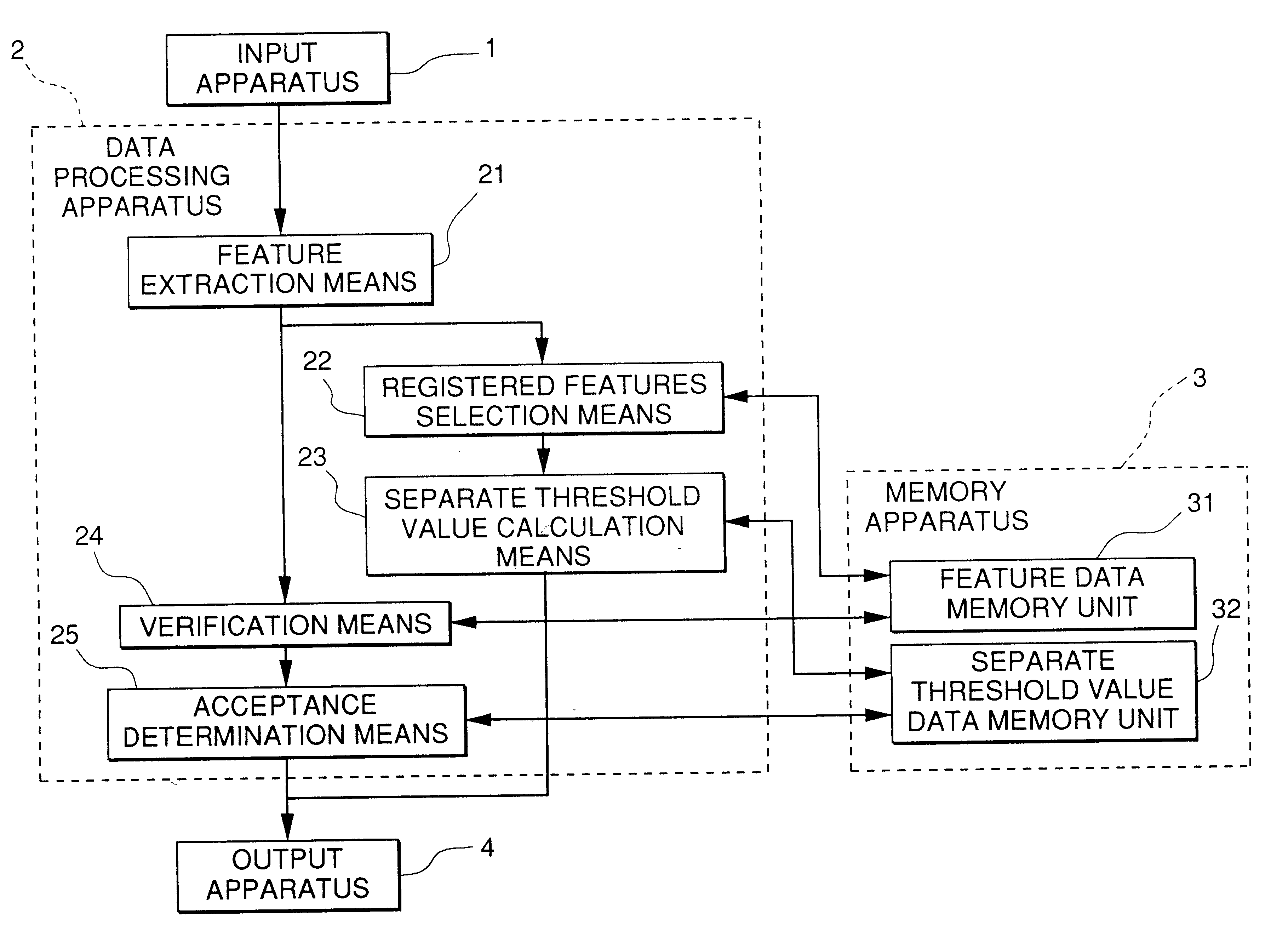
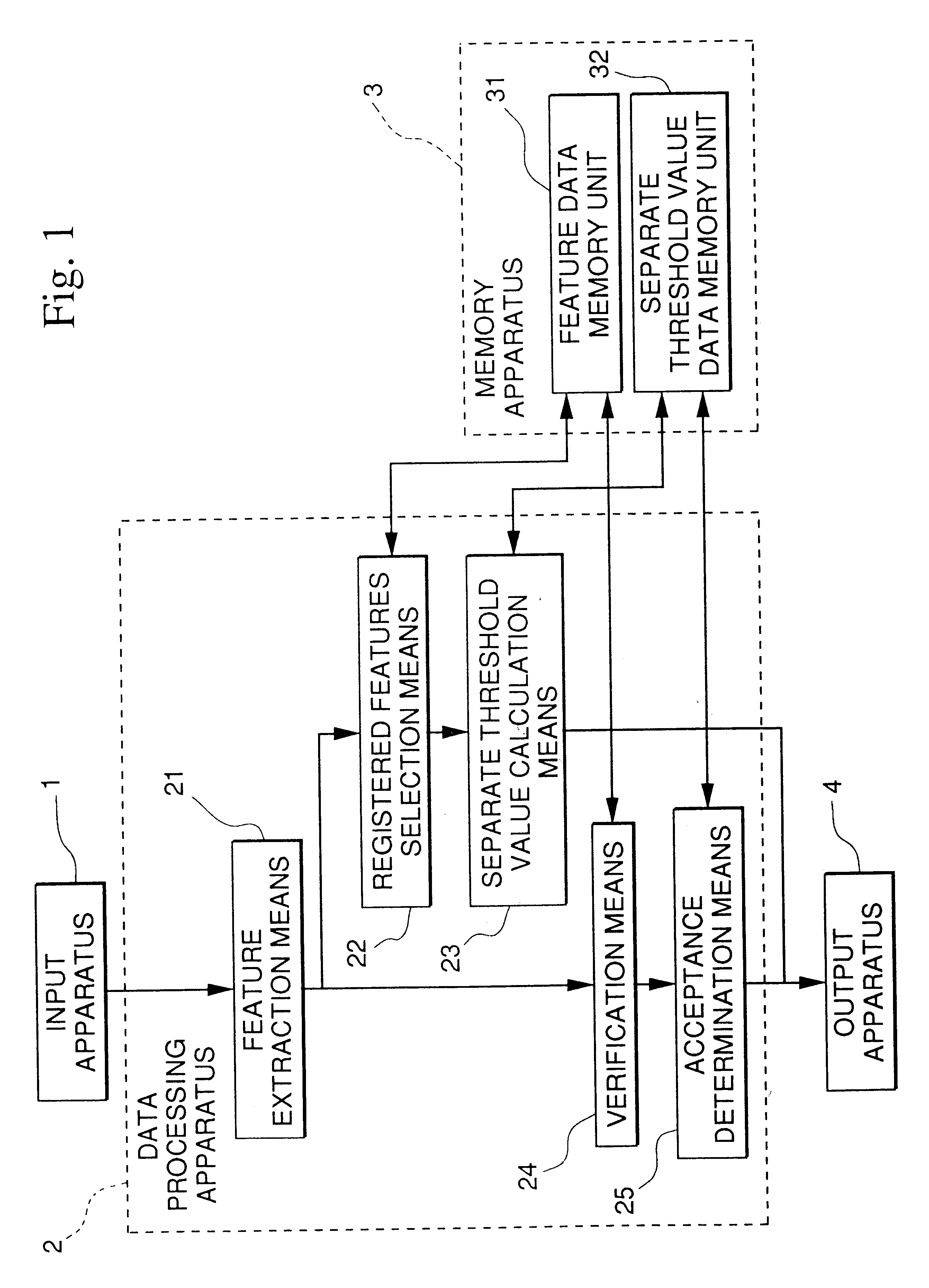
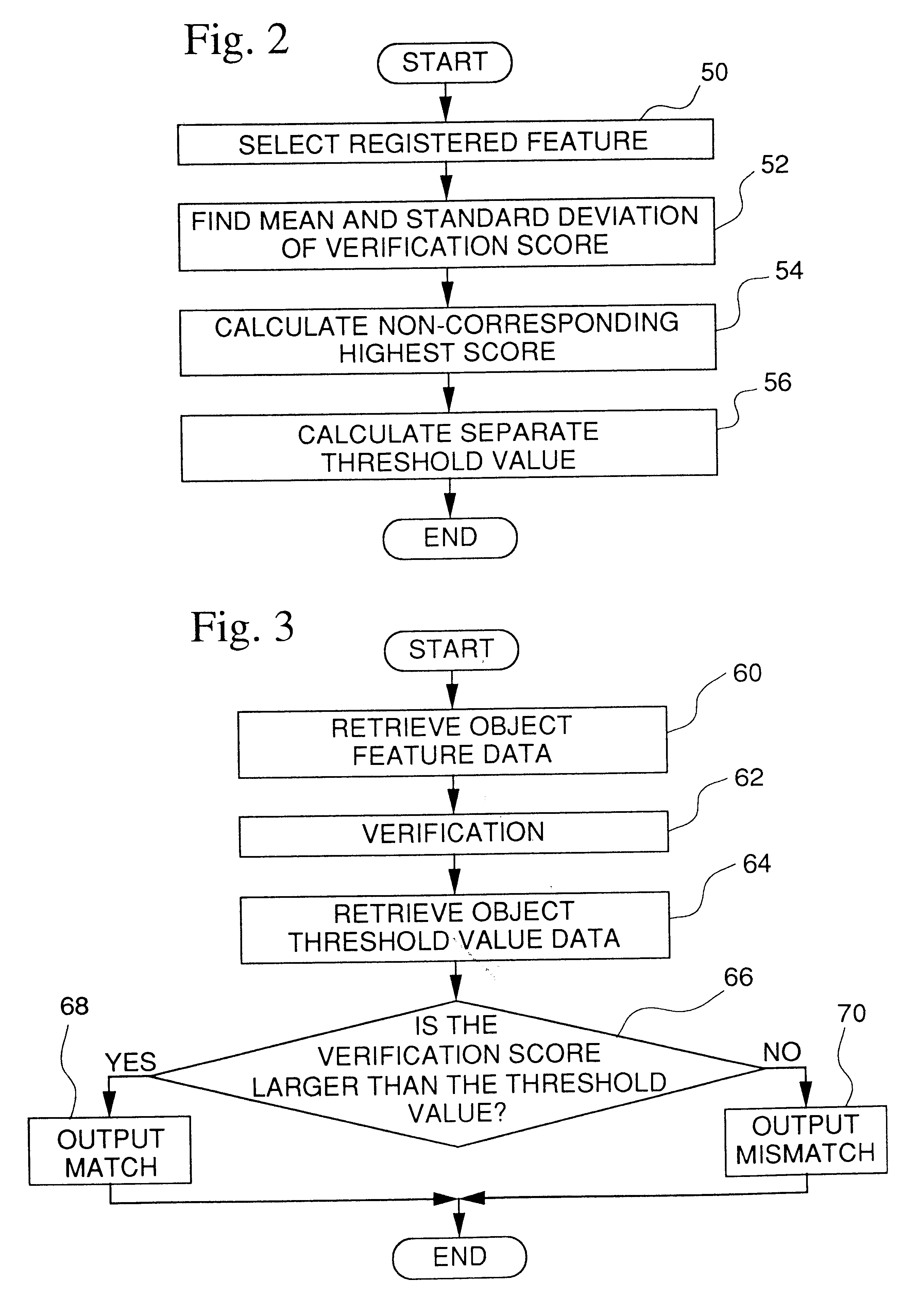
The present invention relates to improving the identification rate for a person without lowering the rate of excluding another person probabilistically. The invention is a personal identification system that finds the verification results of feature data extracted form data showing the physical features of the individual who is the verification source against the pre-registered feature data of the verification object, and identifies the individual by whether or not the degree of similarity obtained by the verification results exceeds a separate threshold value set according to pre-registered feature data, and wherein a separate threshold value calculation device 23 is provided that calculates the separate threshold value based on the verification score distribution of feature data extracted from data showing the physical features of the individual who is the verification source and the corresponding feature data, and the verification score distribution of the feature data extracted from data showing the physical features of the individual who is the verification source and non-corresponding feature data.
Owner:NEC CORP
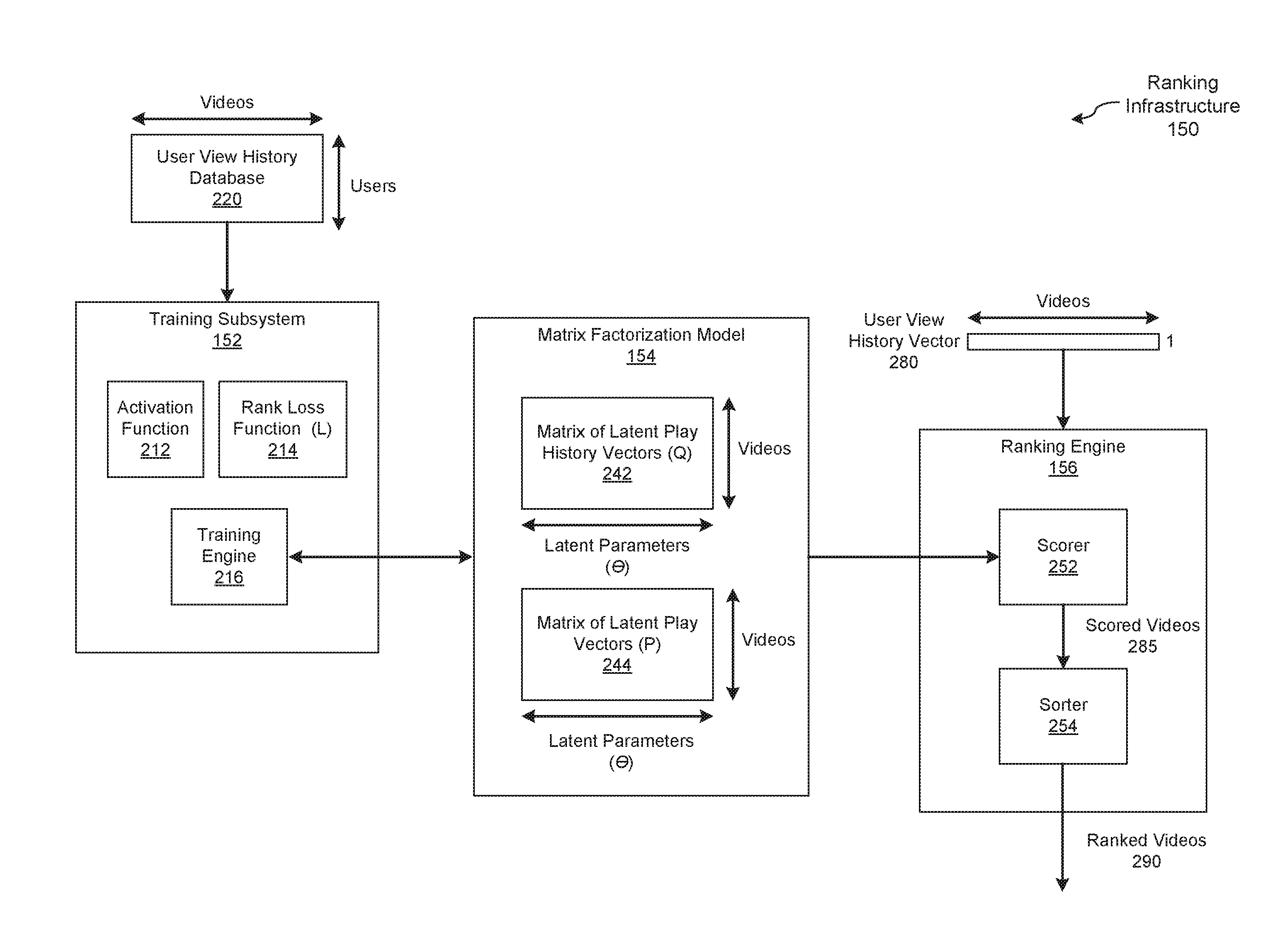
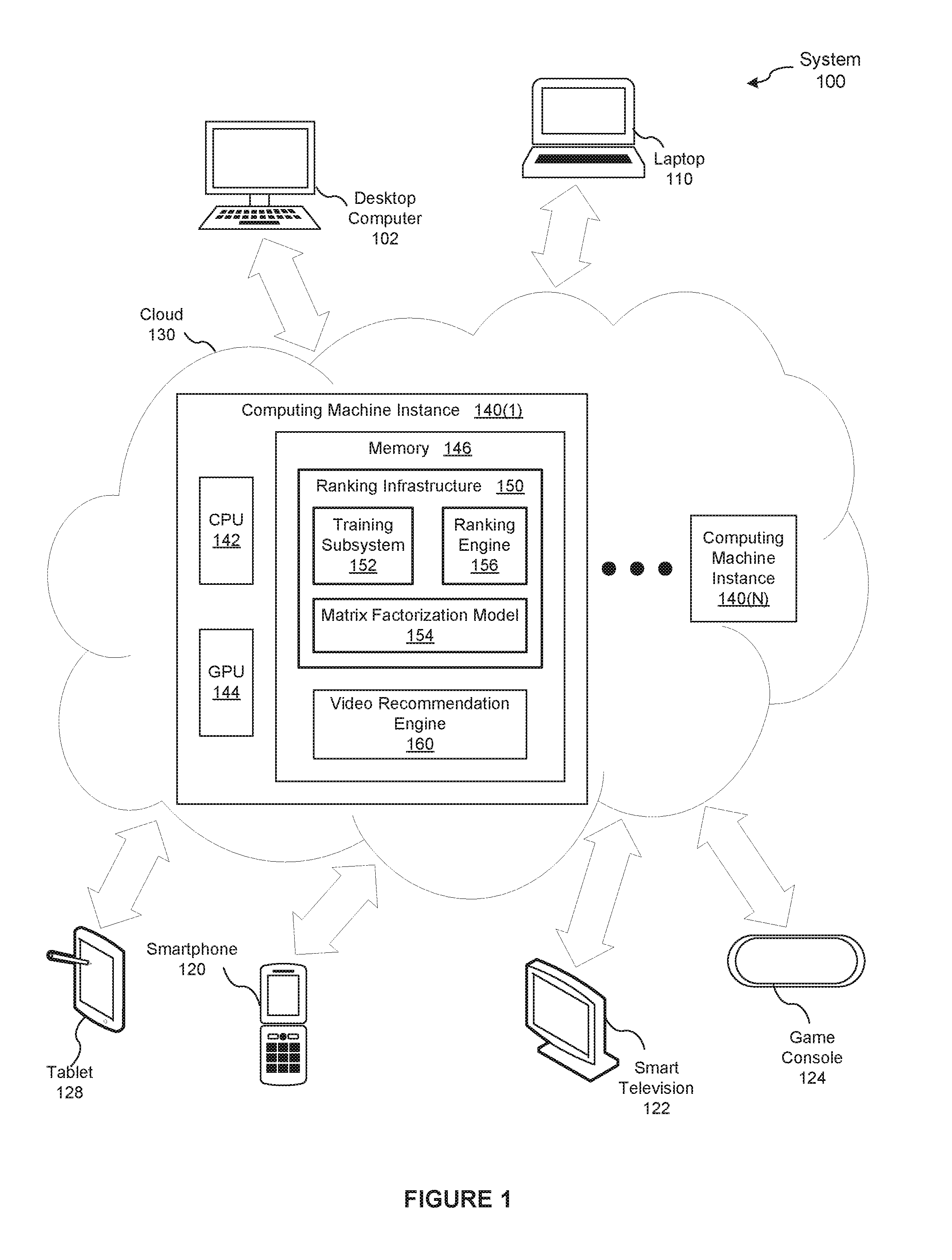
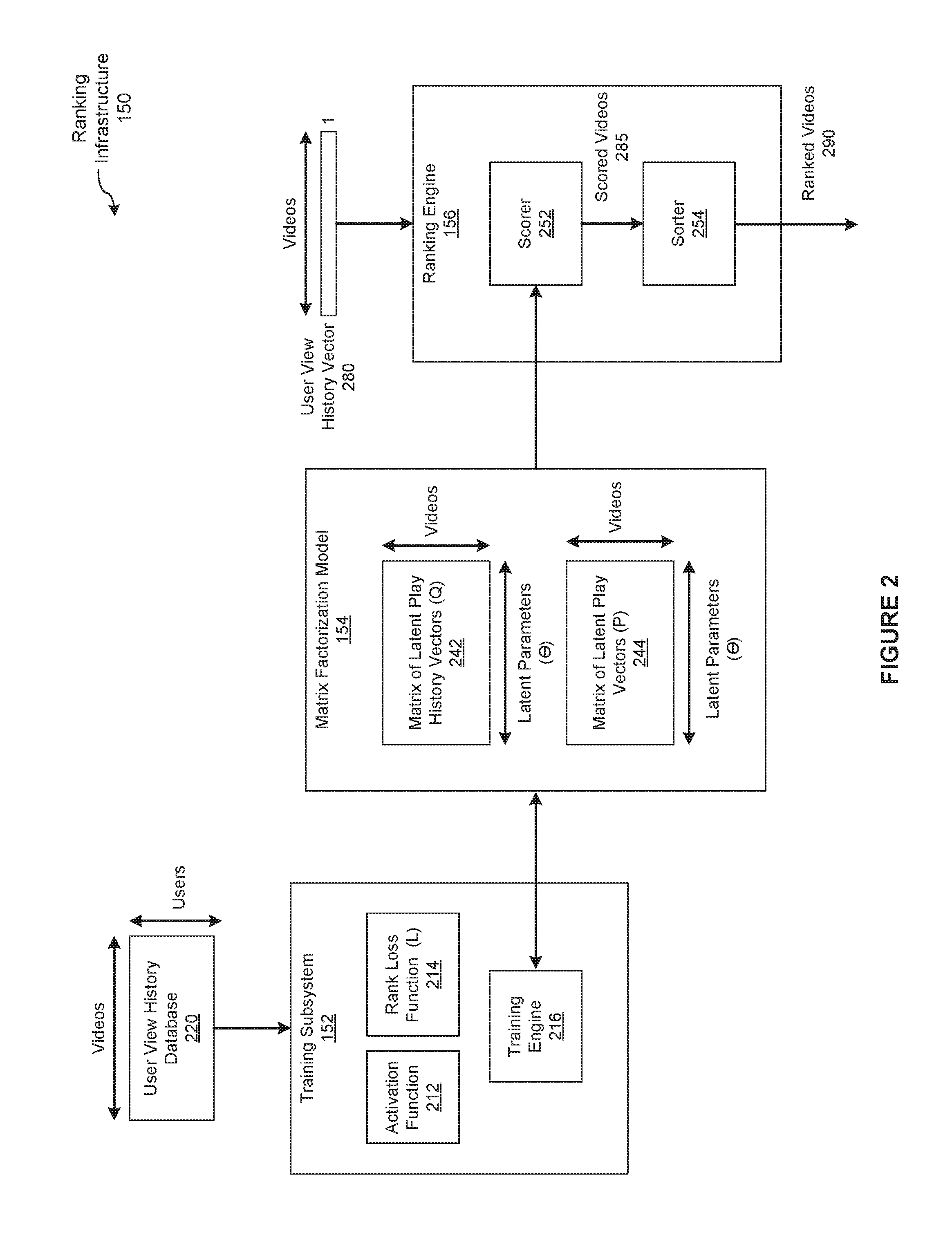
Gaussian ranking using matrix factorization
ActiveUS20170024391A1Efficiently and accurately trainMathematical modelsDigital data information retrievalMatrix decompositionActivation function
In one embodiment of the present invention, a training engine teaches a matrix factorization model to rank items for users based on implicit feedback data and a rank loss function. In operation, the training engine approximates a distribution of scores to corresponding ranks as an approximately Gaussian distribution. Based on this distribution, the training engine selects an activation function that smoothly maps between scores and ranks. To train the matrix factorization model, the training engine directly optimizes the rank loss function based on the activation function and implicit feedback data. By contrast, conventional training engines that optimize approximations of the rank loss function are typically less efficient and produce less accurate ranking models.
Owner:NETFLIX
Methods and arrangements for identifying objects
ActiveUS20190188435A1Improve accuracyIncrease speedStatic indicating devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionHypothesisBarcode reader
A variety of technologies having practical application in retail stores are detailed. One is an improved method of identifying items selected by customers. This method includes receiving sensor data from plural sensors, including (a) ceiling-mounted cameras that monitor tracks of customers through aisles of the store, and (b) inventory sensors that are positioned to monitor removal of stock from store shelves. This received sensor data is employed in evaluating plural alternate item identification hypotheses. These hypotheses include a first hypothesis that a customer selected an item having a first identity, and a second hypothesis that the customer selected an item having a second identity. A confidence score is associated with each of the first and second item selection hypotheses. These confidence scores are refined as sensor data is received, e.g., increasing a confidence score of one hypothesis, and reducing a confidence score of another. Such refining continues until one of the hypotheses becomes a winner, due to an associated confidence score fulfilling a predetermined criterion (e.g., reaching a threshold value), at which time the item can be added to a tally for that individual. The winning item identification hypothesis may identify a barcoded item, without that item's barcode ever having been read by a barcode reader. A great number of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Method and system for response time optimization of data query rankings and retrieval
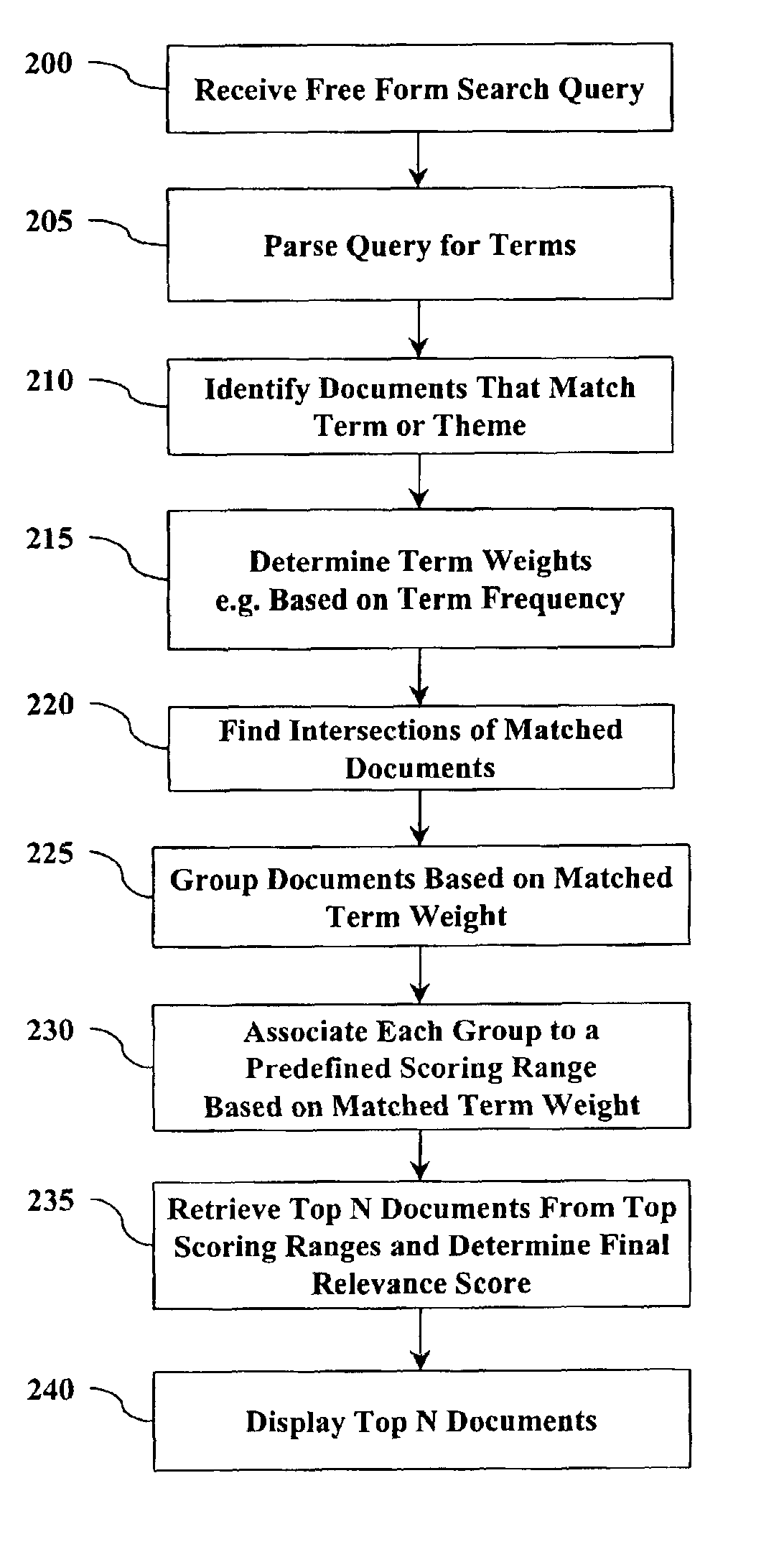
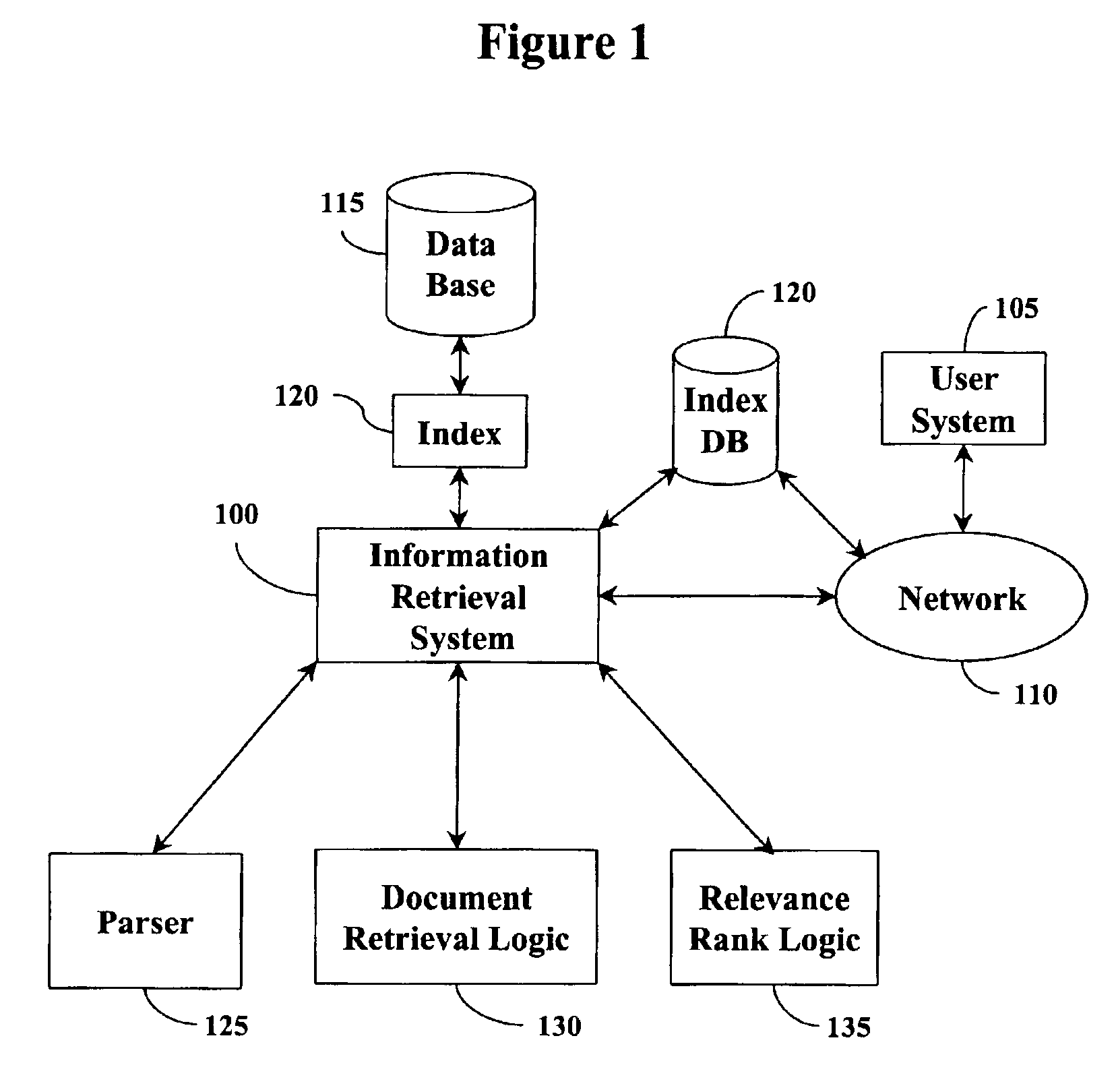
InactiveUS6947920B2Short response timeReduce in quantityData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalRankingDocument preparation
A method and system for optimizing response time for data query rankings and retrieval is provided. In response to a received search query that contains one or more terms, an information retrieval system identifies a candidate set of documents that match any of the terms. Terms are assigned a term weight making them more or less relevant in relation to other terms. A ranking logic defines score bins from a total score range based on possible matched term weights. A relationship is established that classifies a document into a score bin based on a sum of term weights from matched terms. Documents that match more term weights have higher total relevance scores than documents that match less term weights. The most relevant documents are retrievable without having to retrieve the entire set of candidate documents and without having to compute total relevance scores for all the candidate documents.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and system for sorting media items in a playlist on a media device
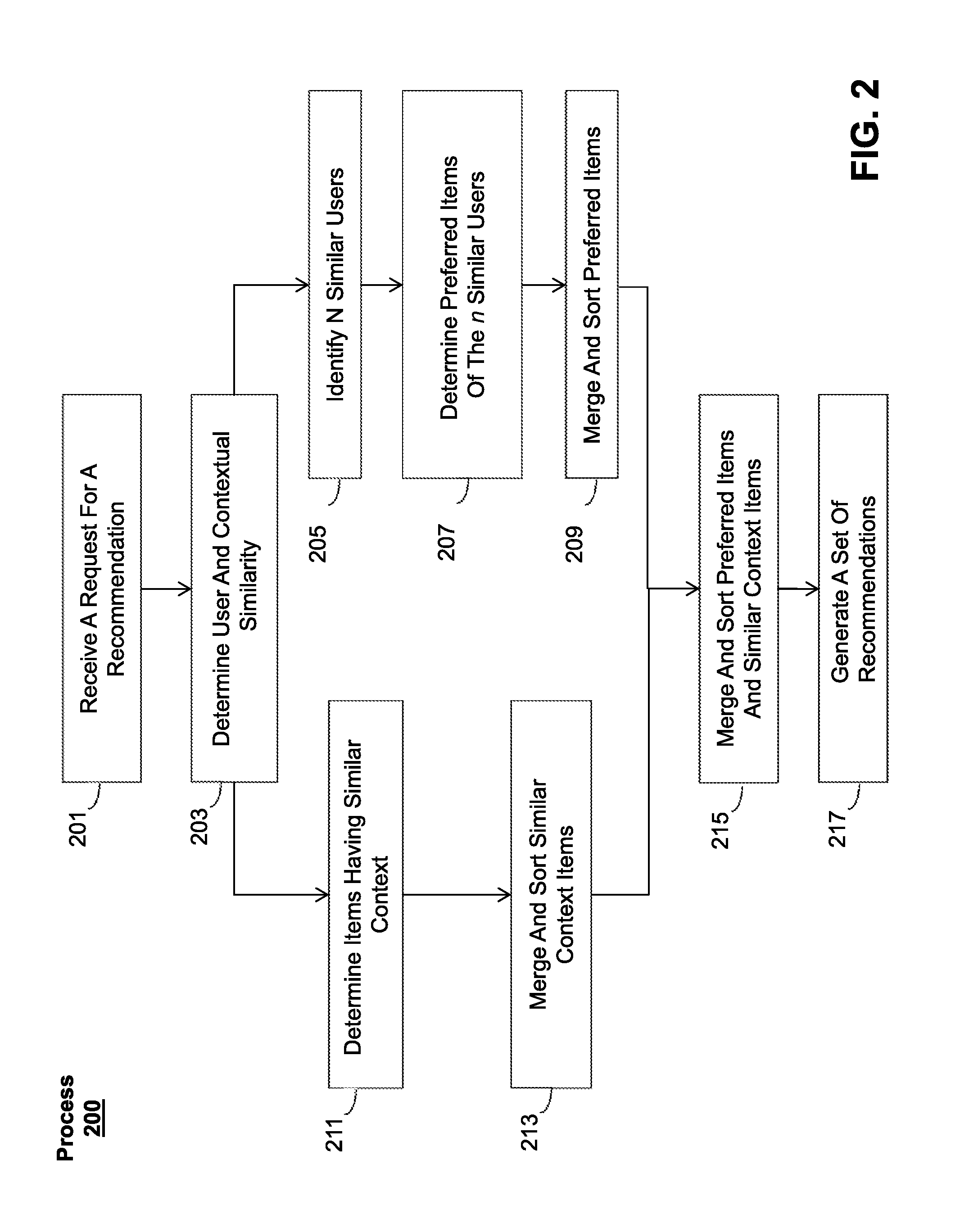
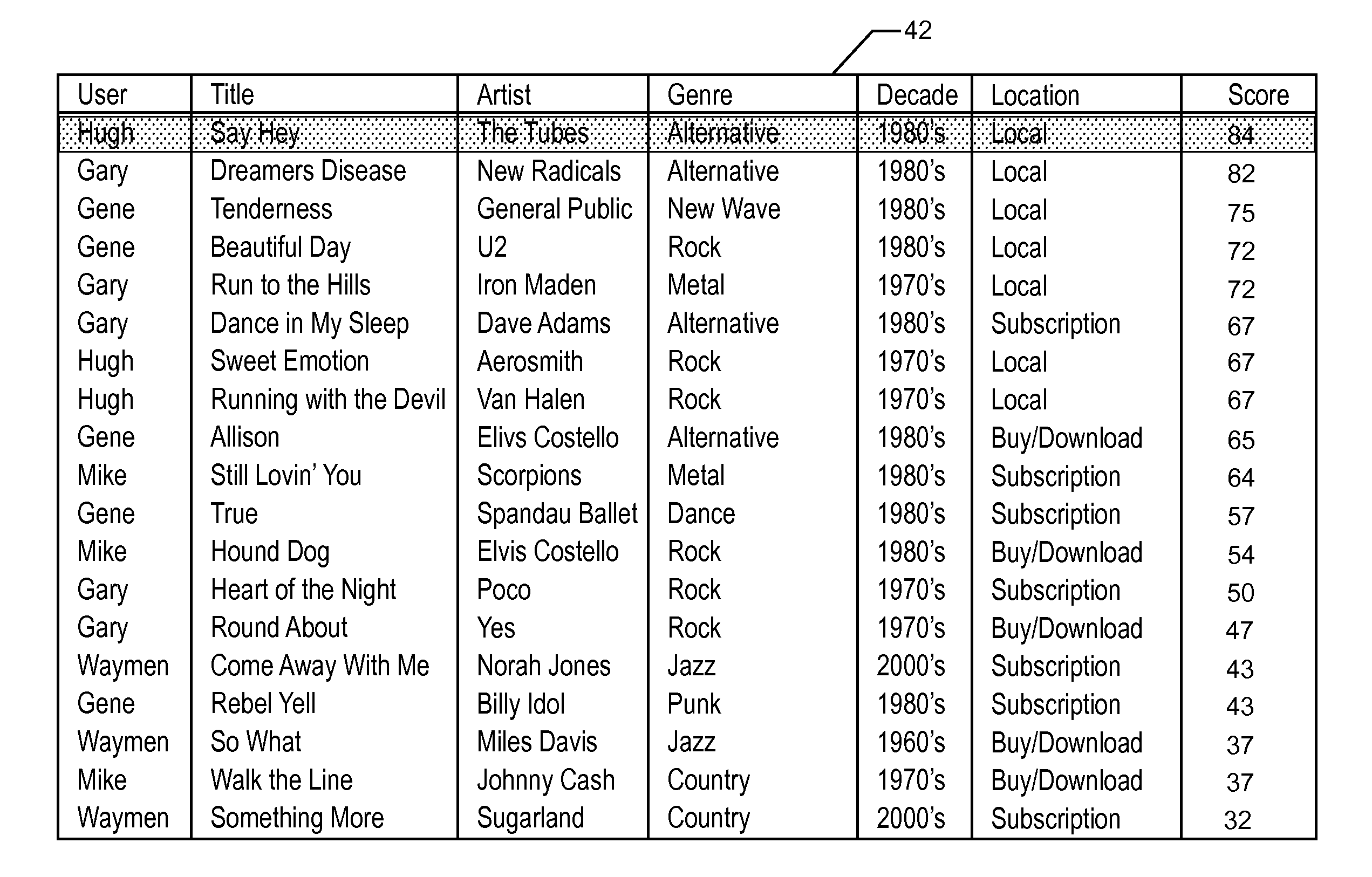
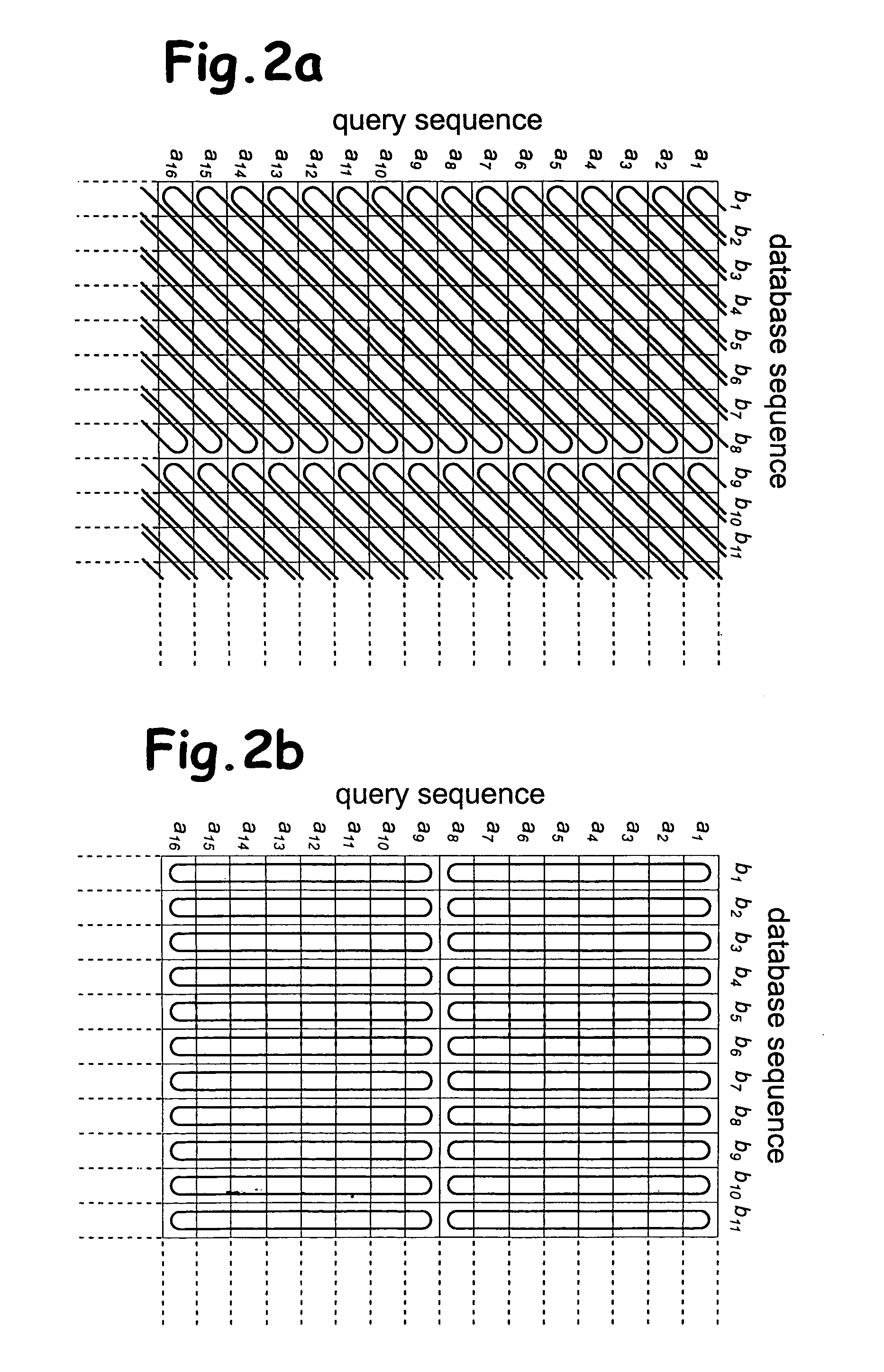
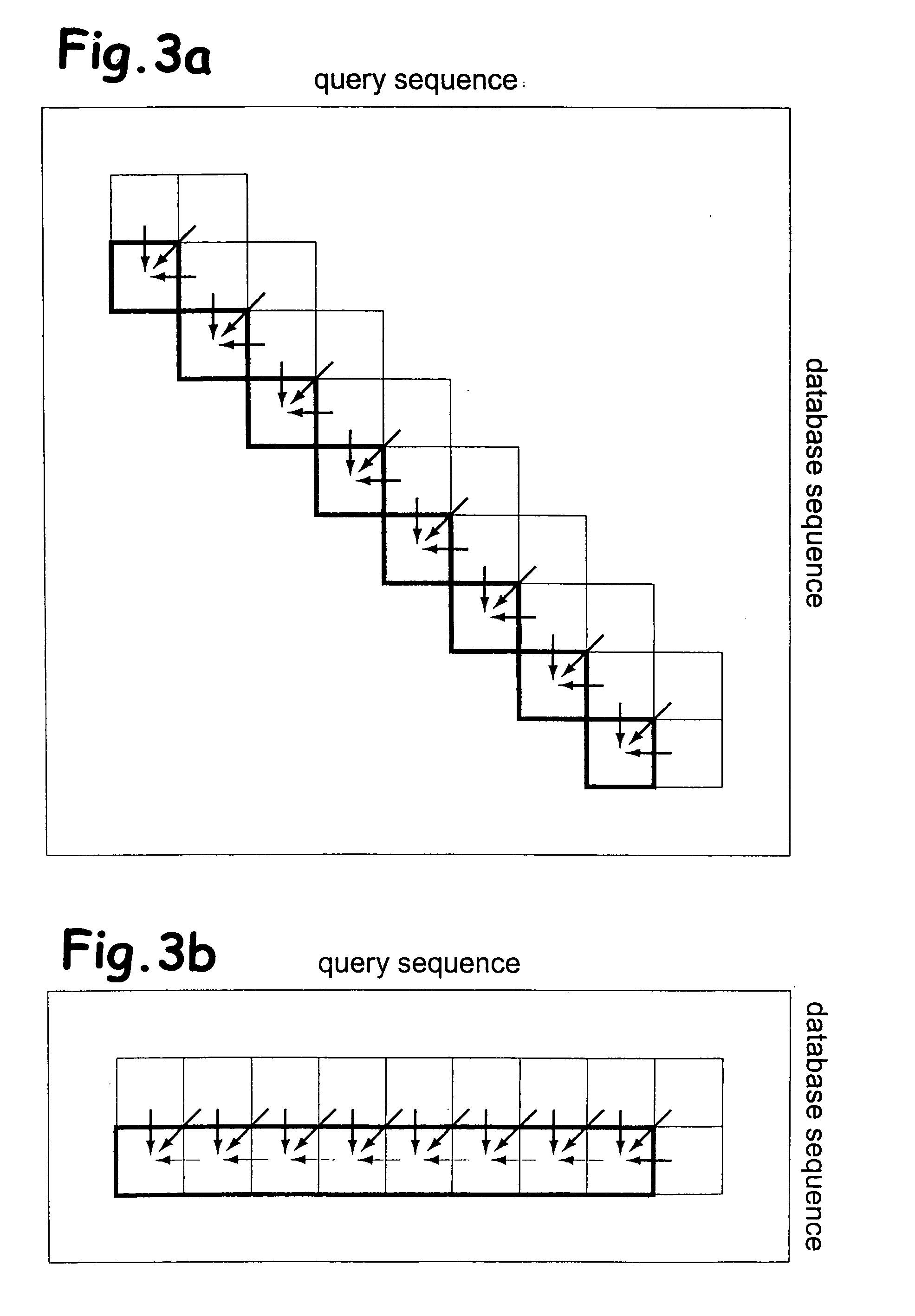
InactiveUS20120042245A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsWorld Wide WebCut score
A computer-implemented method and system are provided for sorting media items in a playlist on a media device that are ranked by score. One embodiment includes changing a user preference associated with a sort criteria selected by the user, wherein each of the media items includes a profile score that is calculated based on user preferences, and a replay score that affects replay of the corresponding media item; recalculating the profile score and the replay score of each of the media items; sorting the media items by the replay scores; and sorting the media items by the sort criteria indicated by a user.
Owner:CONCERT TECH
Method and system for performing searches and returning results based on weighted criteria
InactiveUS20060241901A1Efficiently researchingDigital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsData miningComputer science
A method and system are provided for comparing a focal product with several comparison products. First, selecting a focal product and several attributes relating to the focal product and the comparison products, standardizing and weighting the attributes, and determining for each weighted attribute an attribute score. Next, based on the attribute score, calculating a total score for each comparison product, and based on the total score, presenting to a user or purchaser the comparison products most relevant to the user's criteria.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
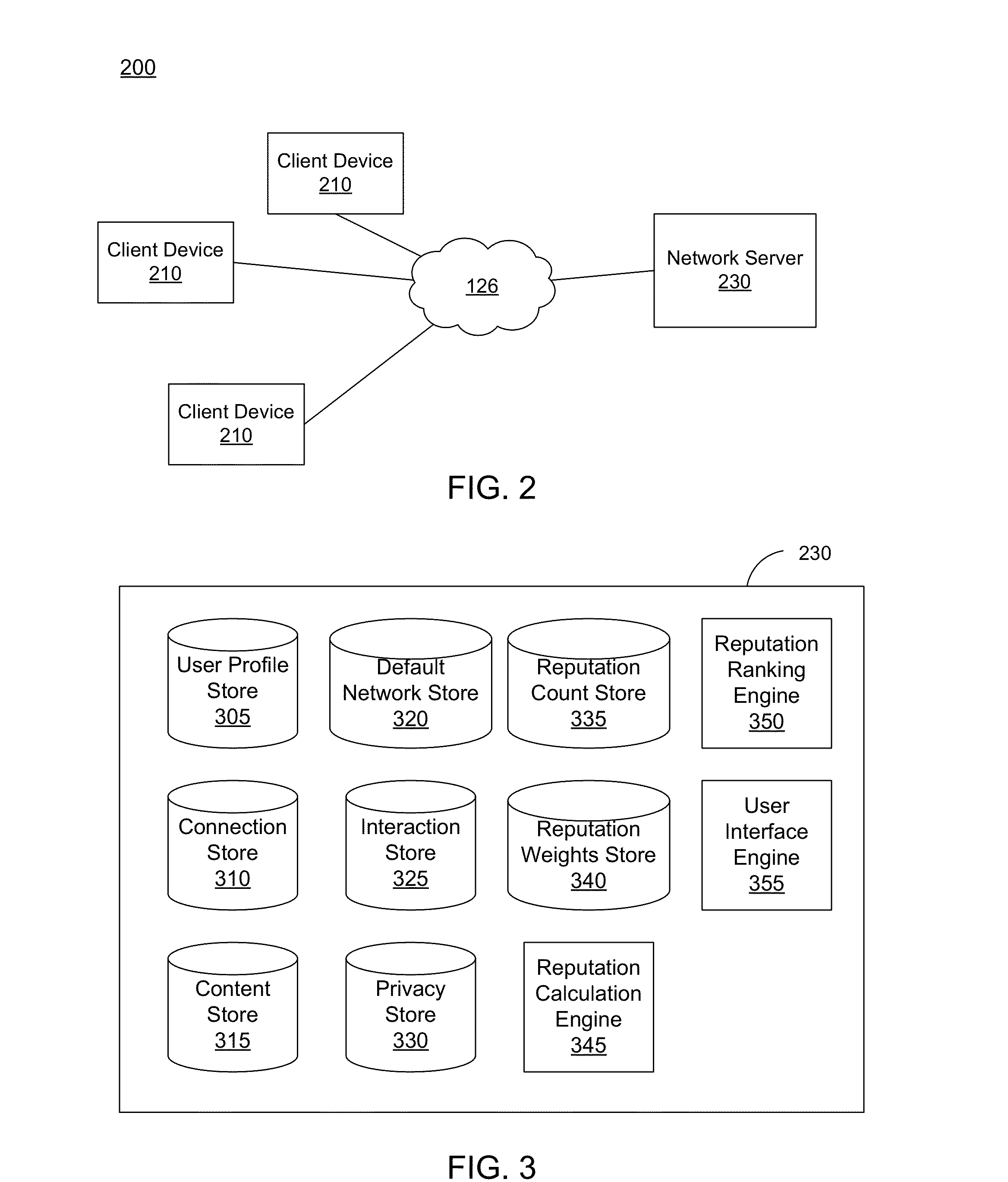
Reputation System in a Default Network
A system and a method are disclosed for computing a reputation score for user profiles of a social network according to actions taken by user profiles of the social network. The reputation score may be based on interactions of a user profile with a content item or based on interactions of user profiles with other user profiles. Actions may be weighted differently in calculating a reputation score as a sum of products of action counts and actions weights. Reputation scores calculated may be used to rank user profiles and to determine reputation levels for user profiles based on exceeding a threshold in reputation score or reputation ranking.
Owner:FOXWORDY
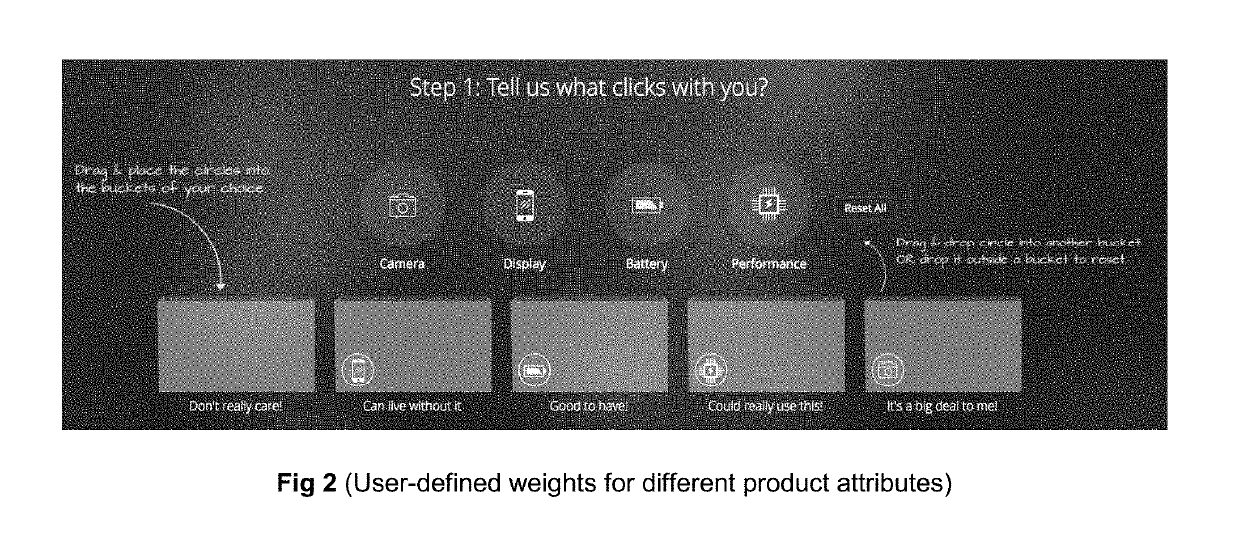
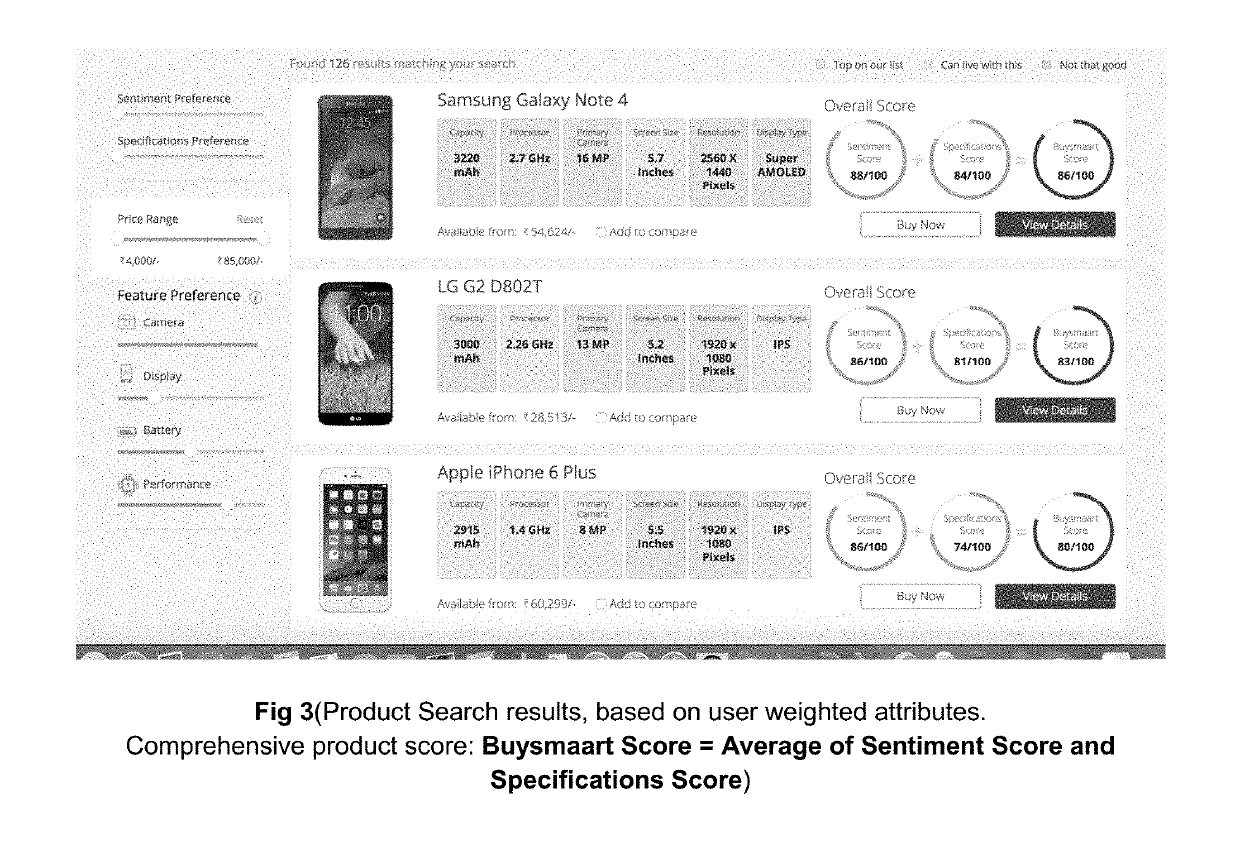
Method for product search using the user-weighted, attribute-based, sort-ordering and system thereof
InactiveUS20190318407A1Digital data information retrievalBuying/selling/leasing transactionsSentiment scoreData mining
A computer-implemented method for product search using the User-Weighted, Attribute-Based, Sort-Ordering comprising the steps of: computing of specification score for product attribute; computing of sentiment score for product attribute; characterized by steps of: —extracting reviews for each product from multiple sources; detecting the attributes described in each product review; detecting the polarity (positive / negative) of the user review with respect to each attribute converting the said attributes into a numerical score for each attribute which captures all the information about that attribute from user-ratings; computing an overall product score using the specifications score and sentiment score for individual product attributes; and displaying the search results sorted according to the overall product score.
Owner:GIRIDHARI DEVANATHAN
Determination of optimal local sequence alignment similarity score
InactiveUS20040024536A1Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyLocal sequence alignmentProtein function prediction
Sequence alignment and sequence database similarity searching are among the most important and challenging task in bio informatics, and are used for several purposes, including protein function prediction. An efficient parallelisation of the Smith-Waterman sequence alignment algorithm using parallel processing in the form of SIMD (Single-Instruction, Multiple-Data) technology is presented. The method has been implementation using the MMX (MultiMedia eXtensions) and SSE (Streaming SIMD Extensions) technology that is embedded in Intel's latest microprocessors, but the method can also be implemented using similar technology existing in other modern microprocessors. Near eight-fold speed-up relative to the fastest previously an optimised eight-way parallel processing approach achieved know non-parallel Smith-Waterman implementation on the same hardware. A speed of about 200 million cell updates per second has been obtained on a single Intel Pentium III 500 MHz microprocessor.
Owner:SEEBERG ERLING CHRISTEN +1
Systems and methods for generating video summary image layouts
InactiveUS20040187078A1Digital data information retrievalModifying/creating image using manual inputComputer graphics (images)Lower score
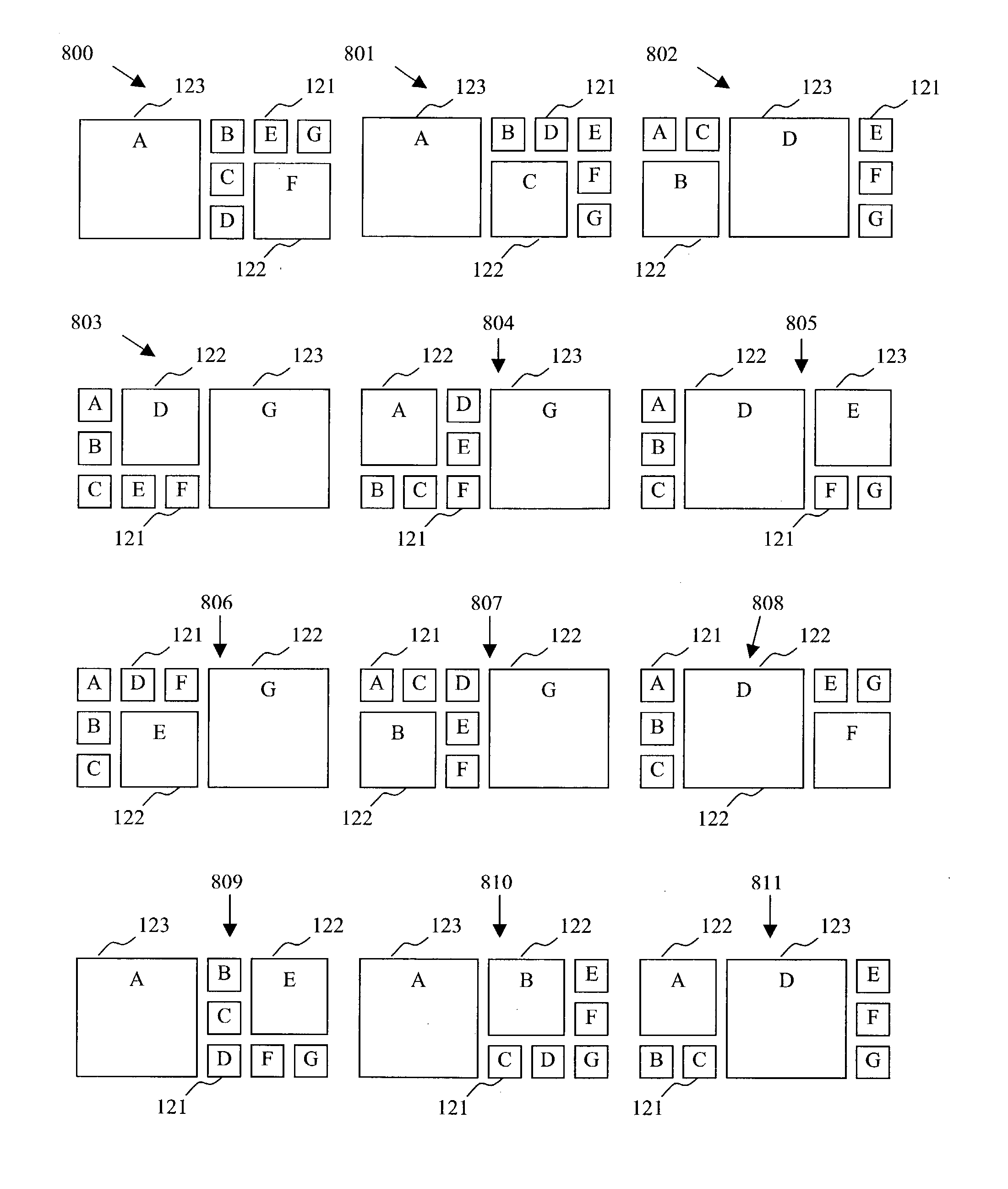
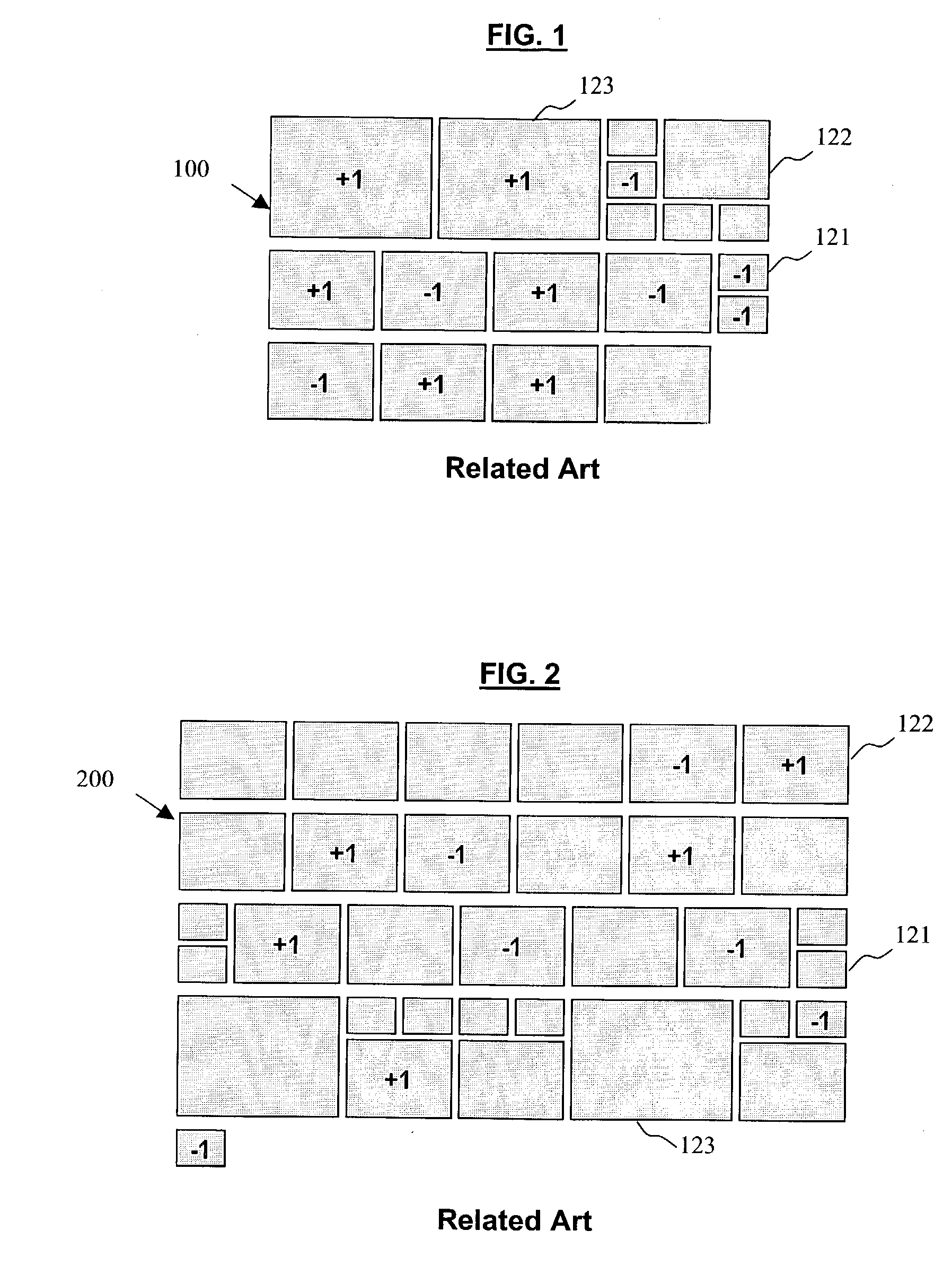
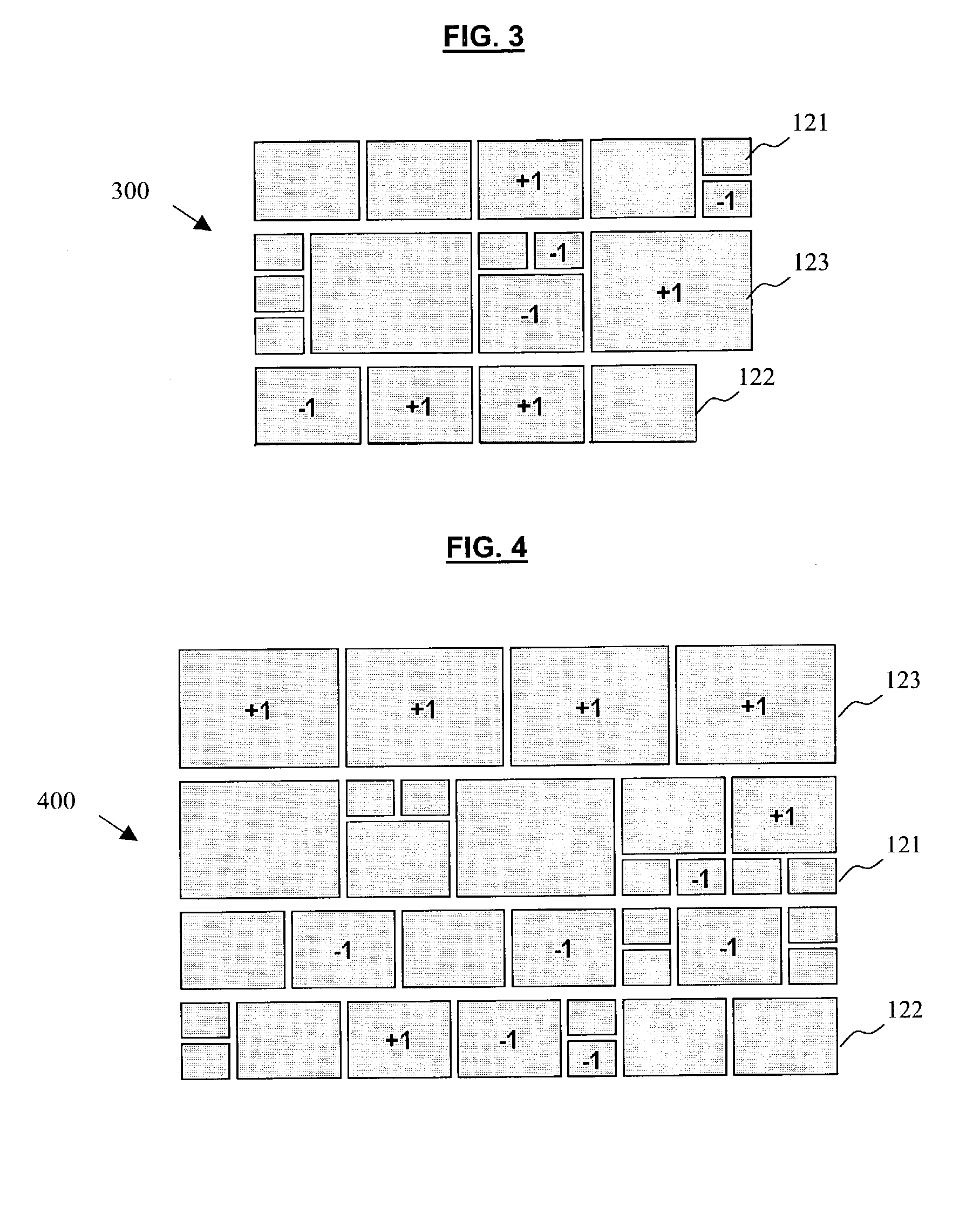
Systems and methods for creating aesthetically pleasing visual image summaries from a collection of input images. The systems and methods determine a visual image summary by creating candidate partial layouts, assigning penalty scores to the candidate partial layouts based on a number of evaluation criteria, evaluating the penalty scores for the candidate partial layouts, and building upon the candidate partial layouts, beginning with the lowest scoring candidate partial layout first, to form complete layouts. The resultant visual image summary fits within a user defined area, maintains the order of the input images, and contains a relative small amount of aesthetically undesirable qualities.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Method for detecting object
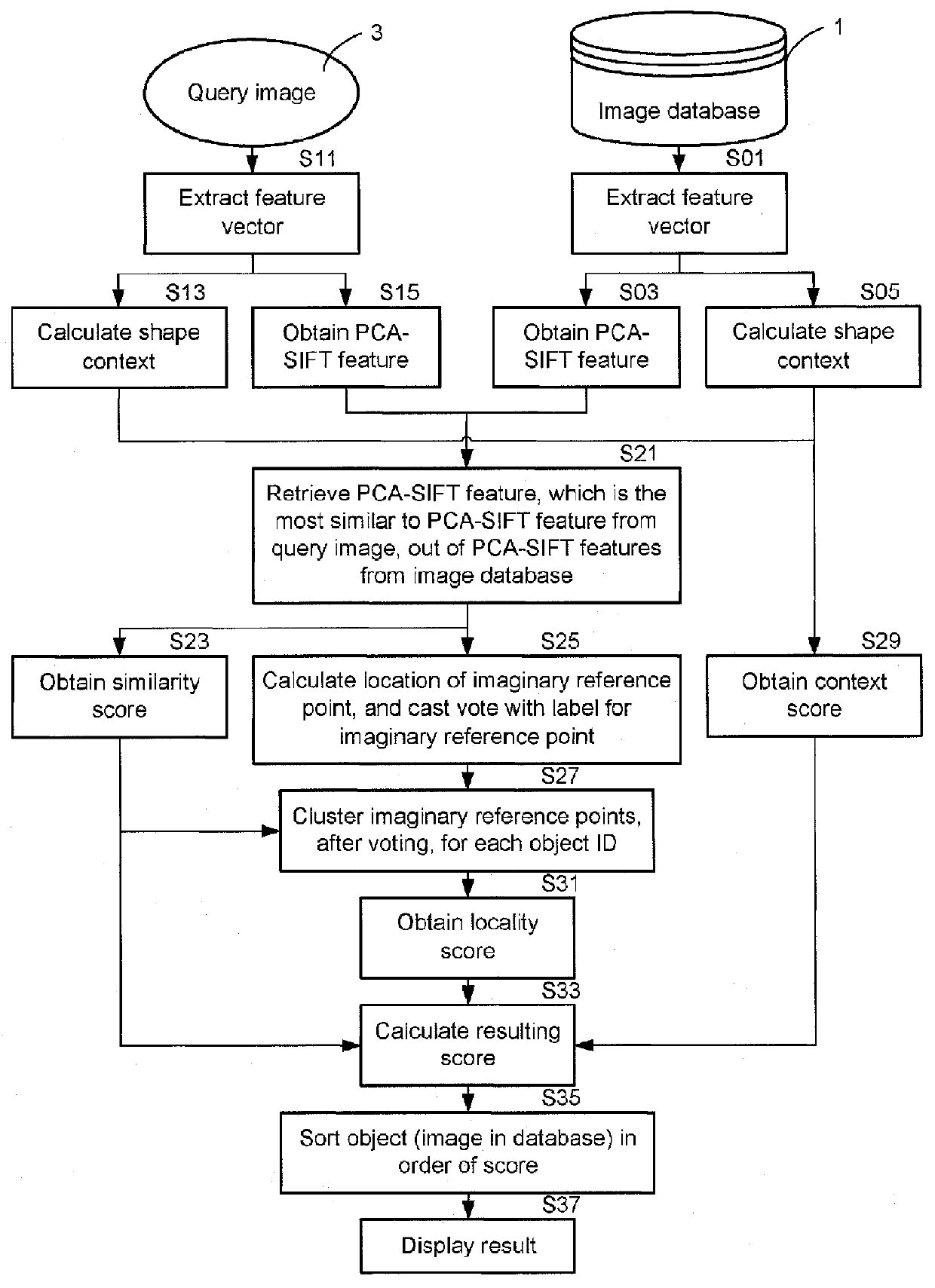
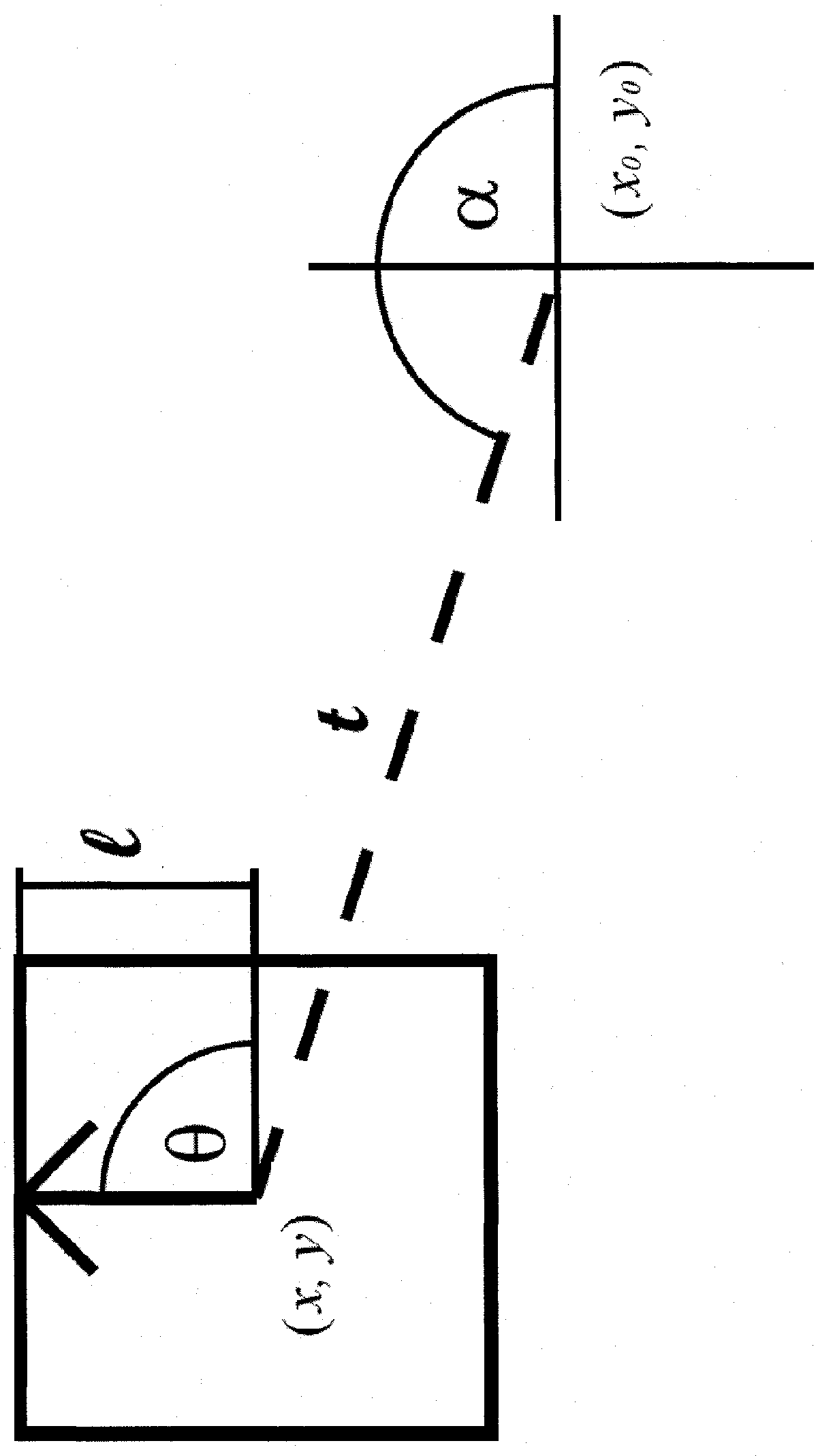
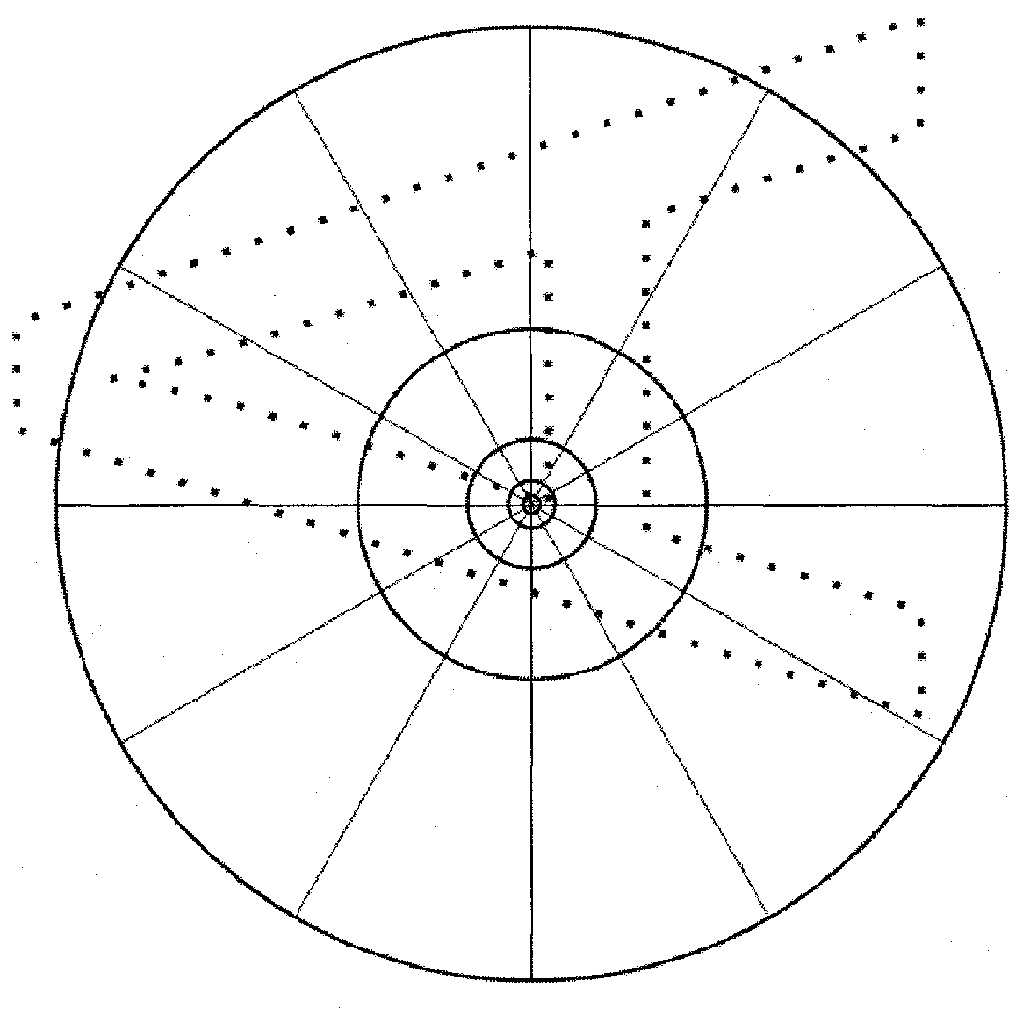
InactiveUS20120143856A1Reduce the impactIncrease valueDigital data processing detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorEuclidean vector
An object detection method that is provided with a step for extracting a plurality of reference feature vectors related to a local area from an image representing an object, and extracting a plurality of query feature vectors related to the local area from a search query image; a step for matching each query feature vector against each reference feature vector, and calculating a similarity score having a value that is higher the closer the distance between both vectors, the larger the local area for which the query feature vector has been extracted, and the larger the local area for which a matching reference feature vector has been extracted; a step for determining a reference feature vector for which a similarity score is highest as the similar vector for each query feature vector; and a step for acquiring a final score by object associated with the similar vectors, and setting the object returning the highest score as the detection result; and wherein the score is calculated by dividing a sum of the similarity score for each similar vector by the number of feature vectors that have matched the object.
Owner:PUBLIC UNIVERSITY CORPORATION OSAKA CITY UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com