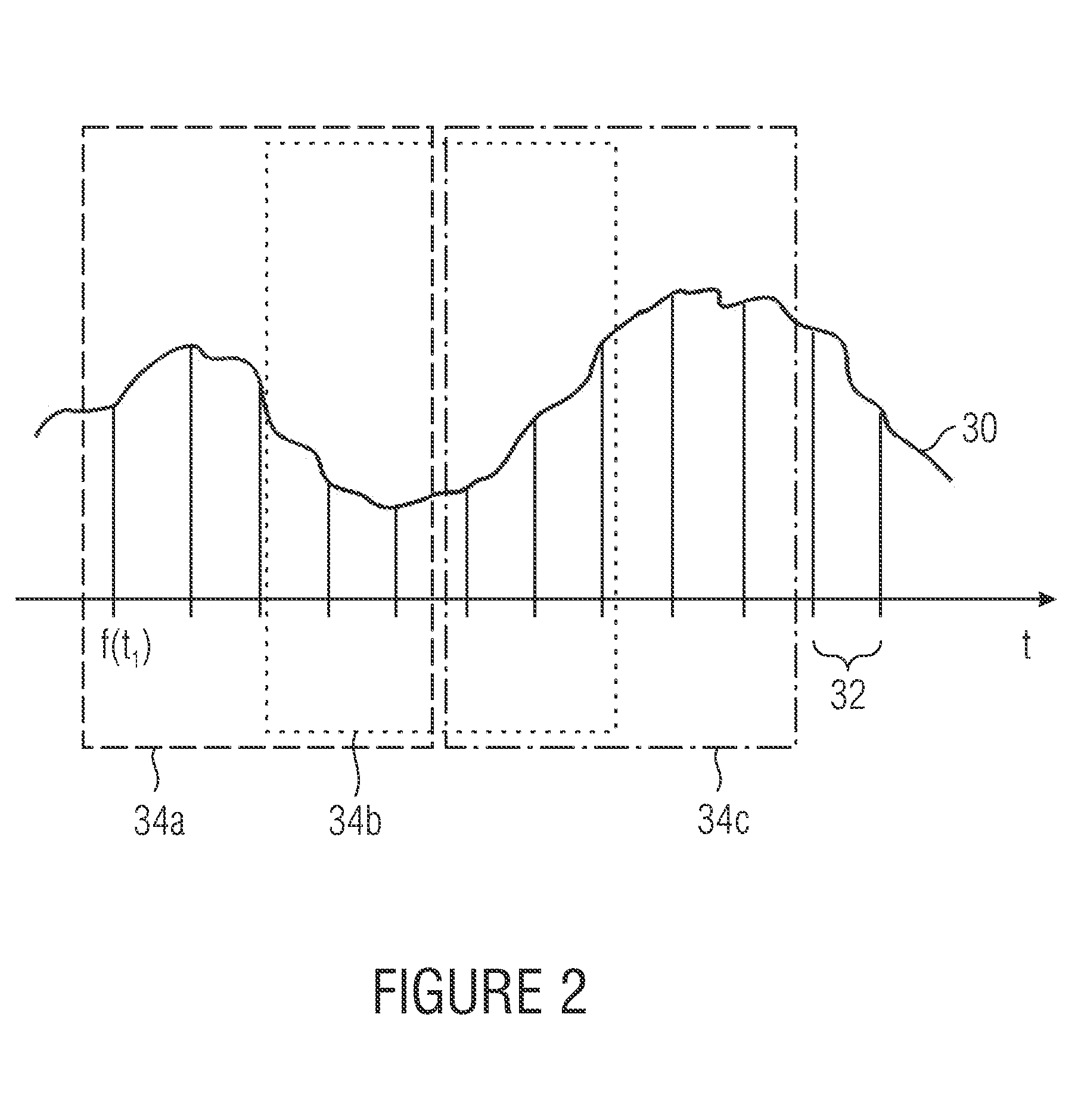
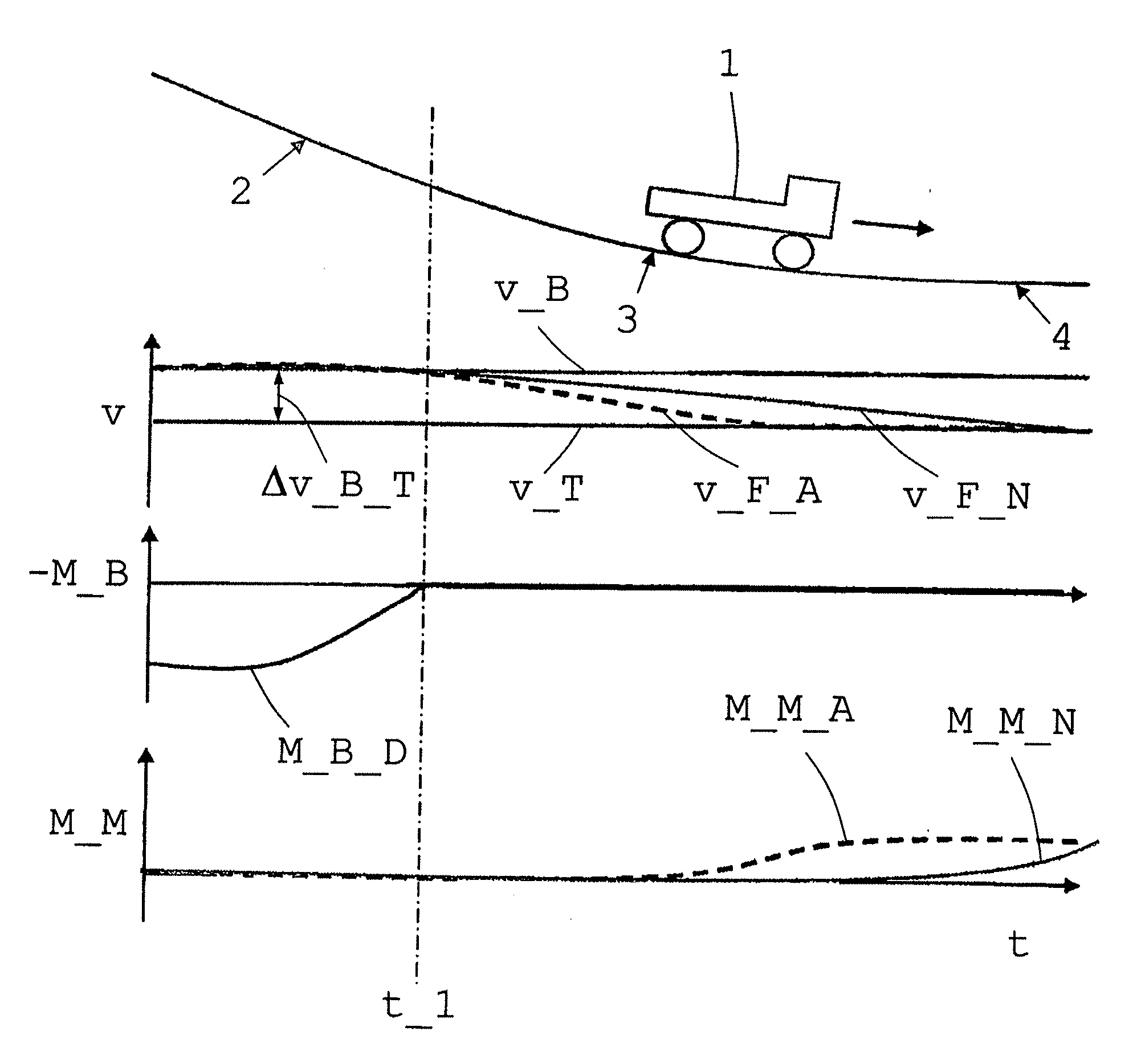
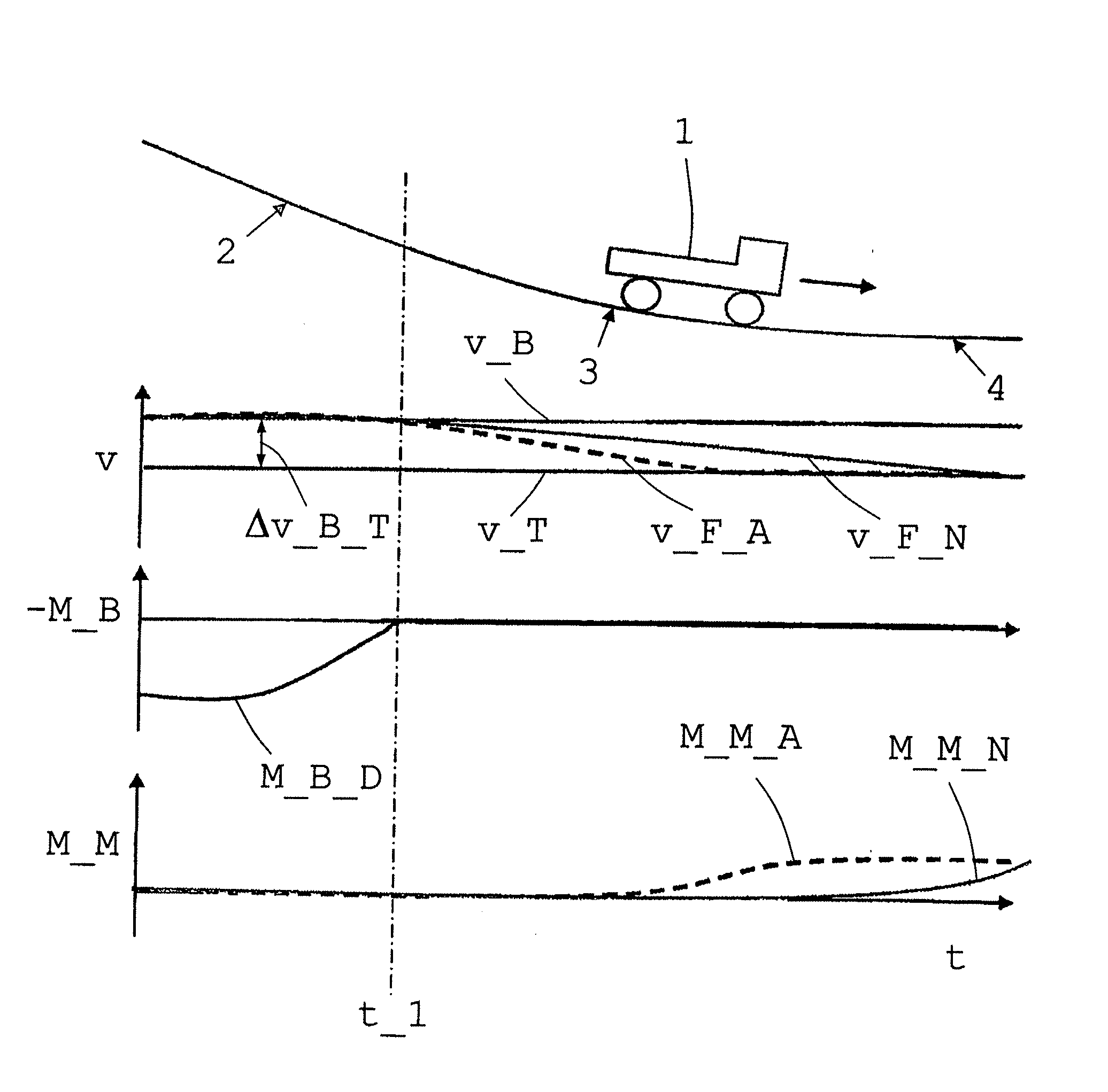
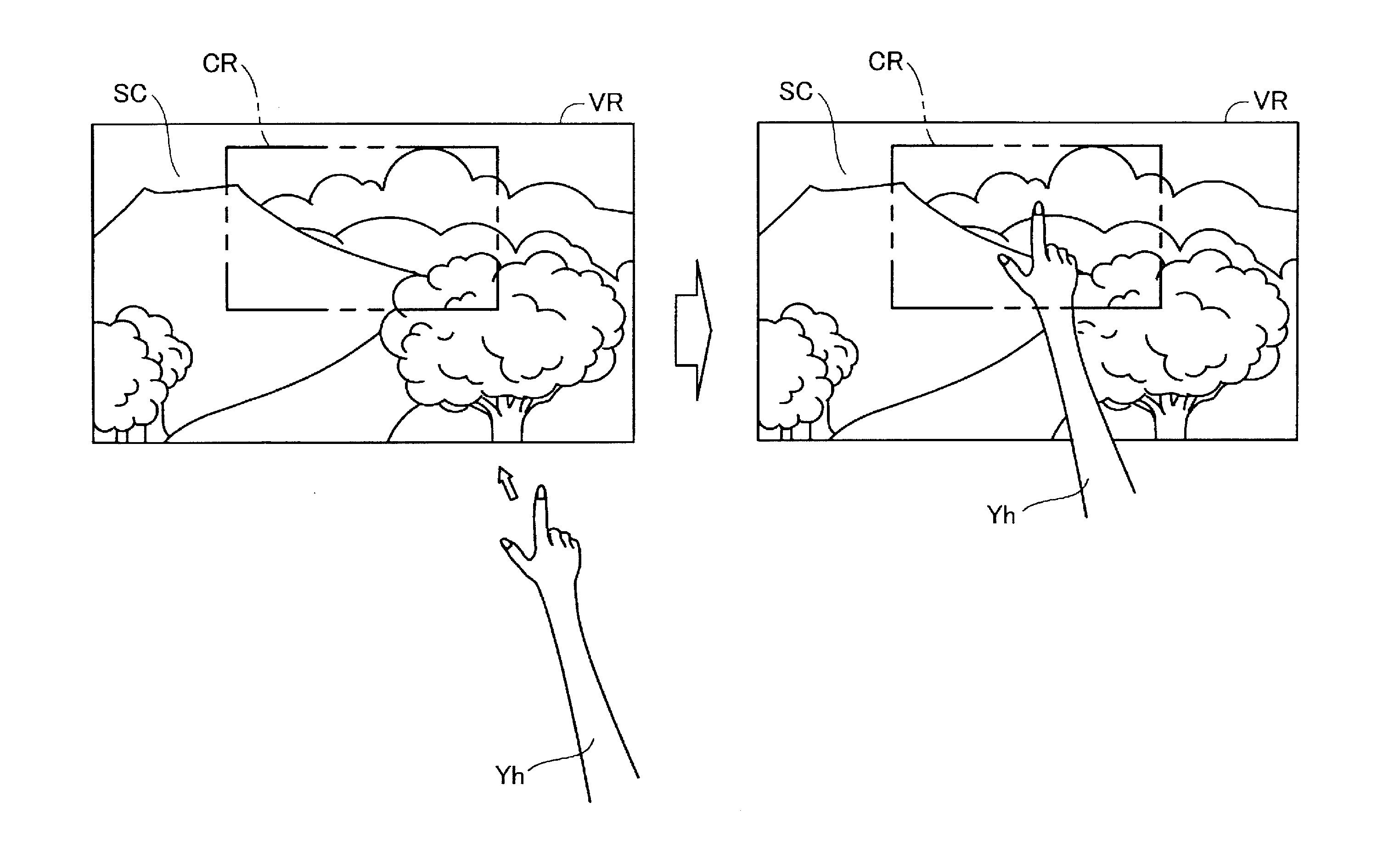
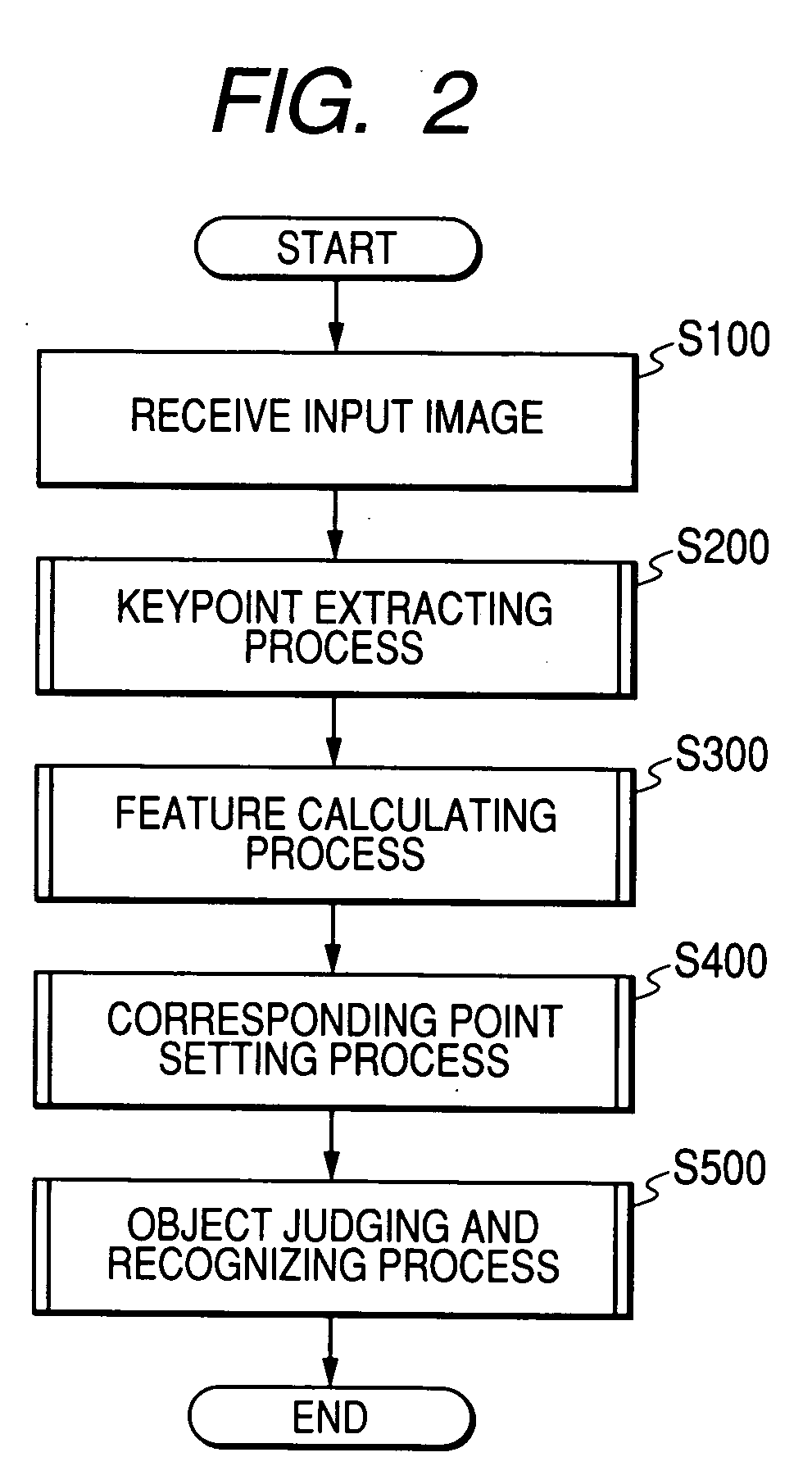
Patents
Literature
229results about How to "Reliably recognize" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
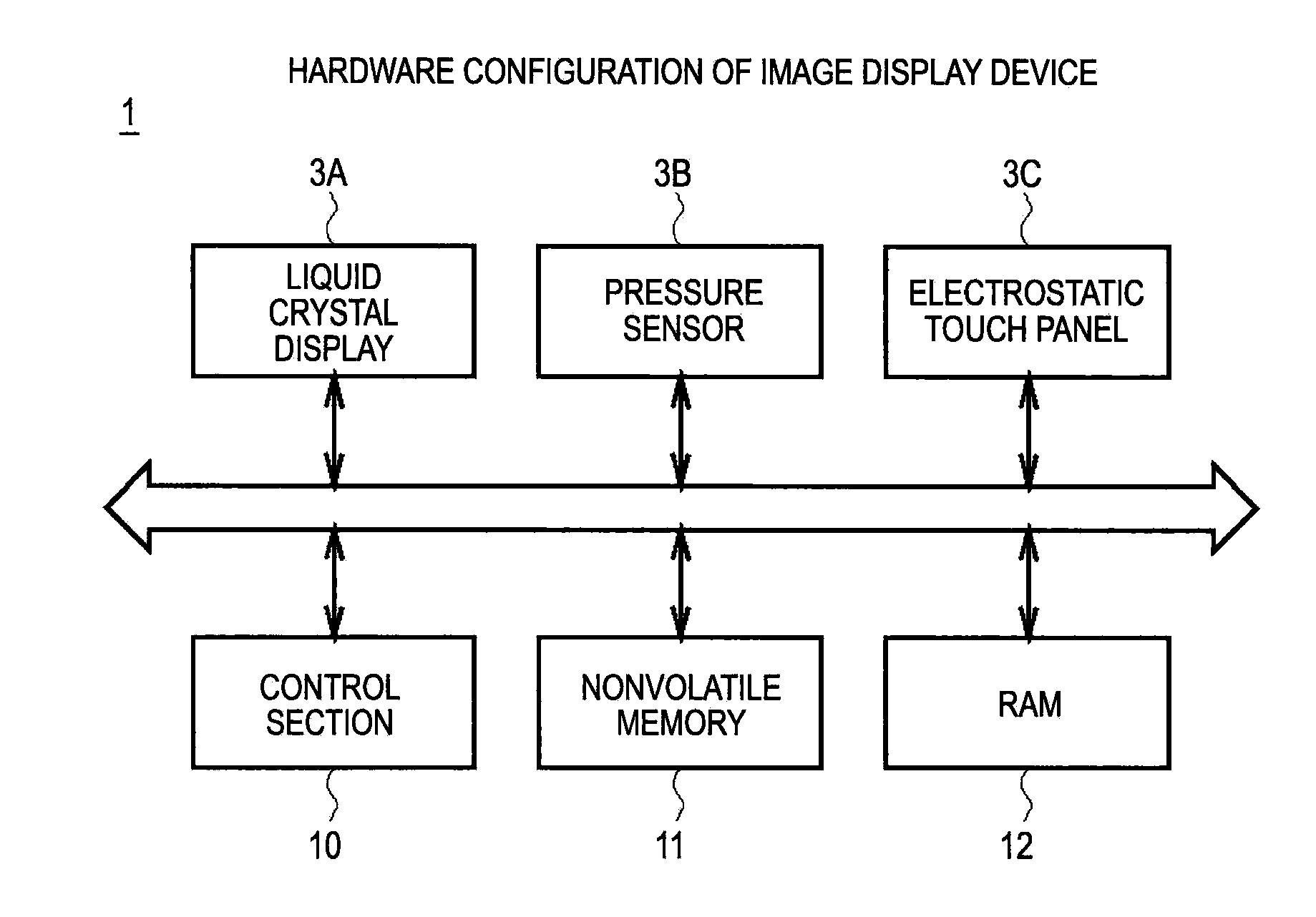
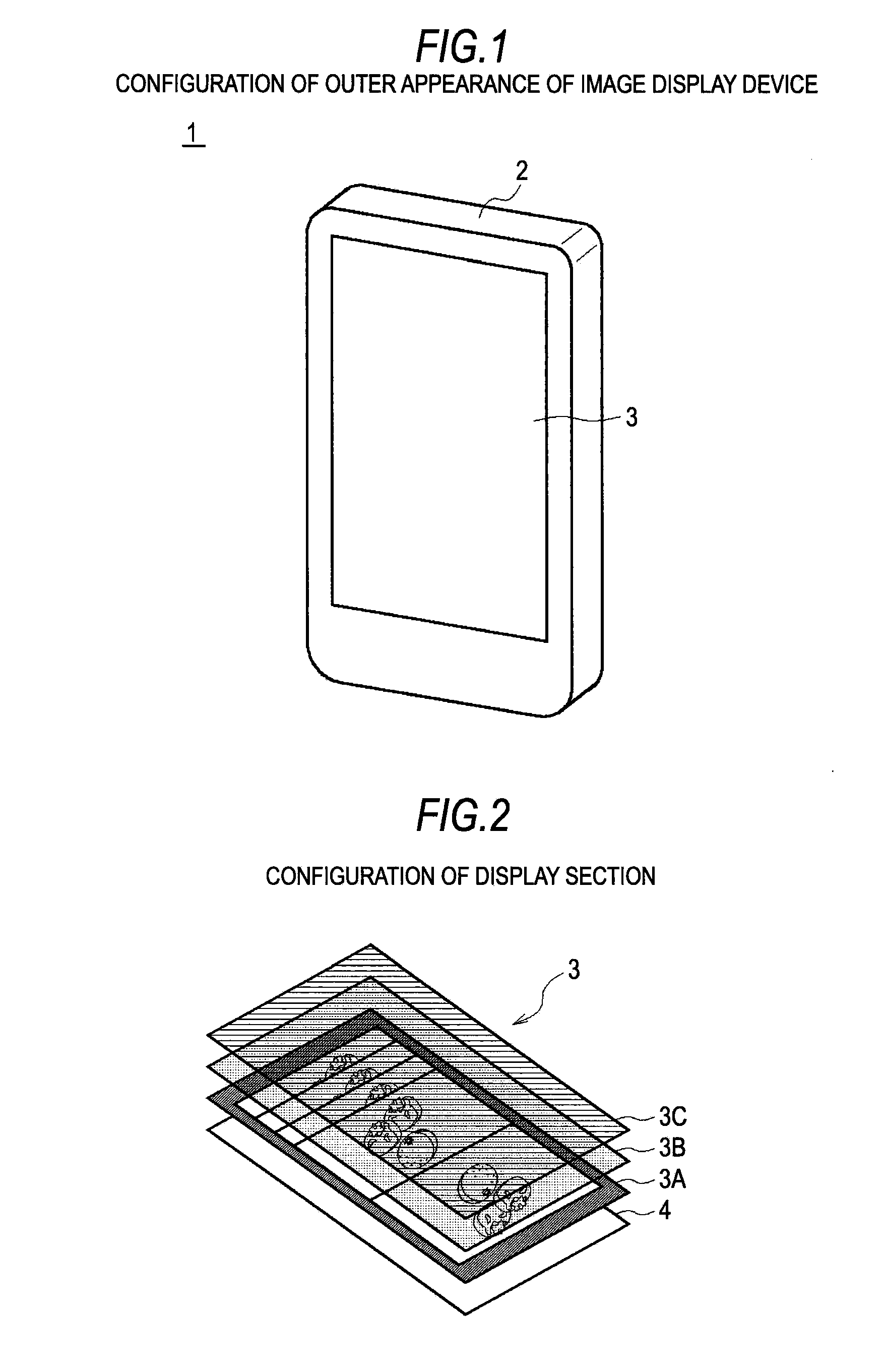
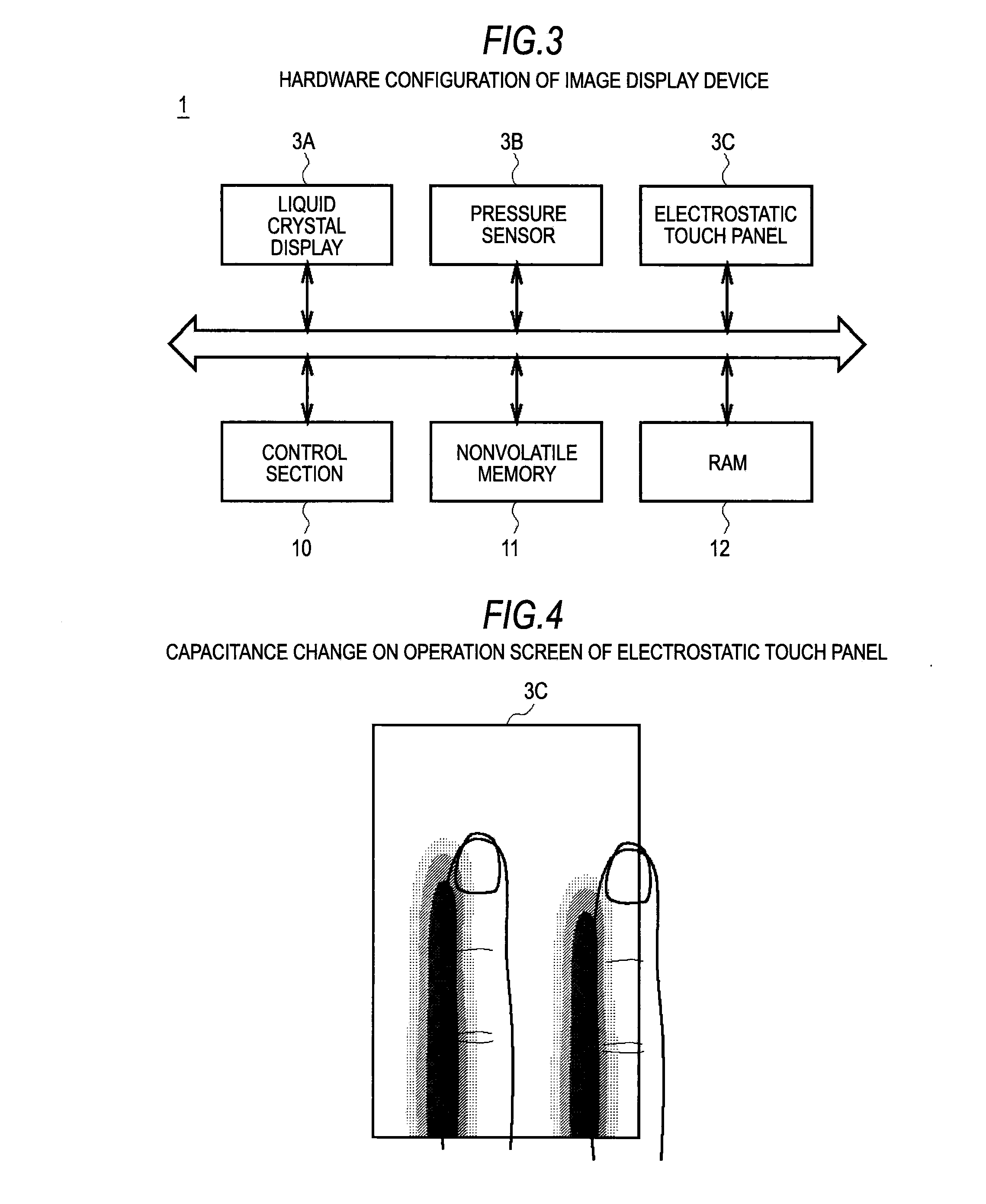
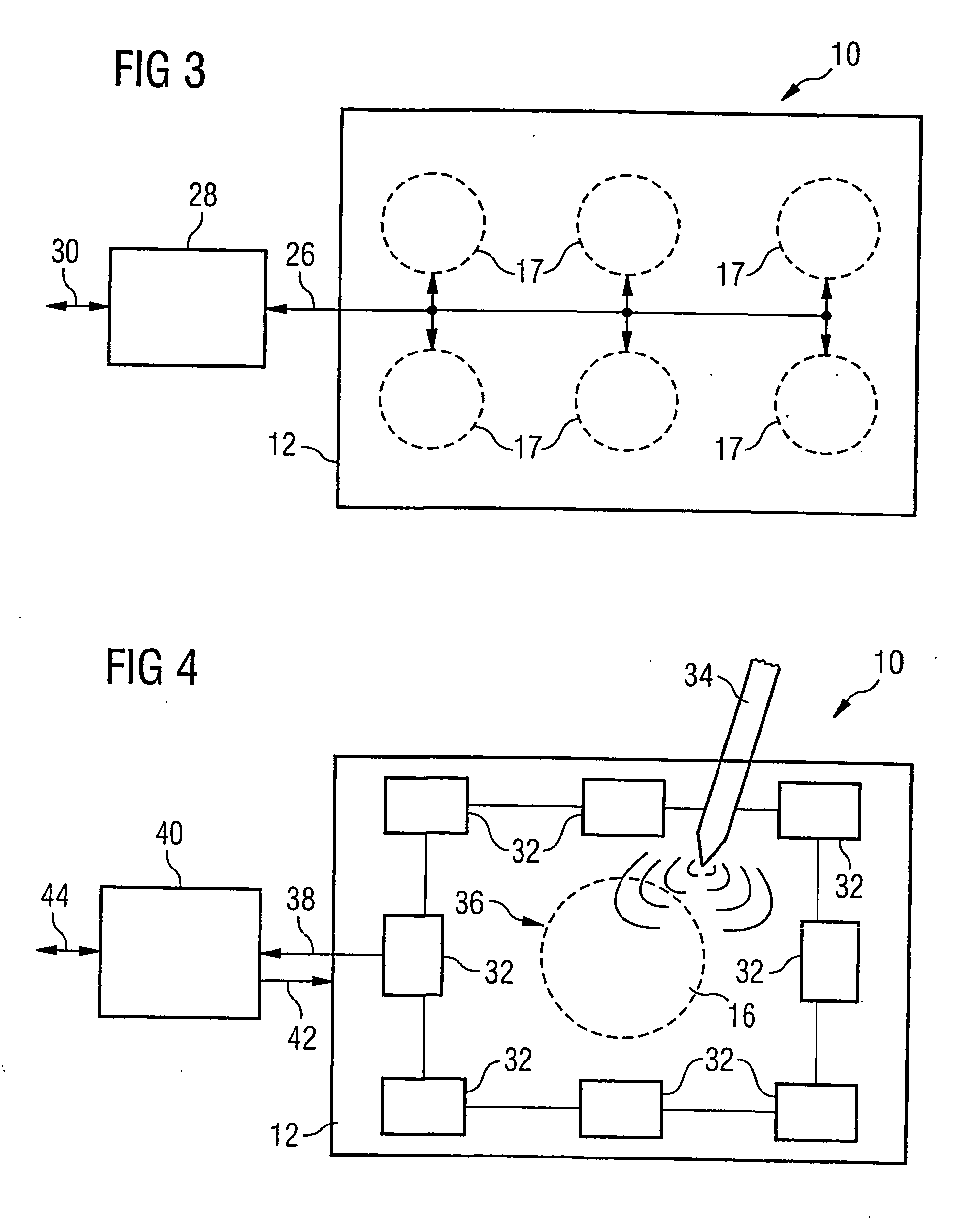
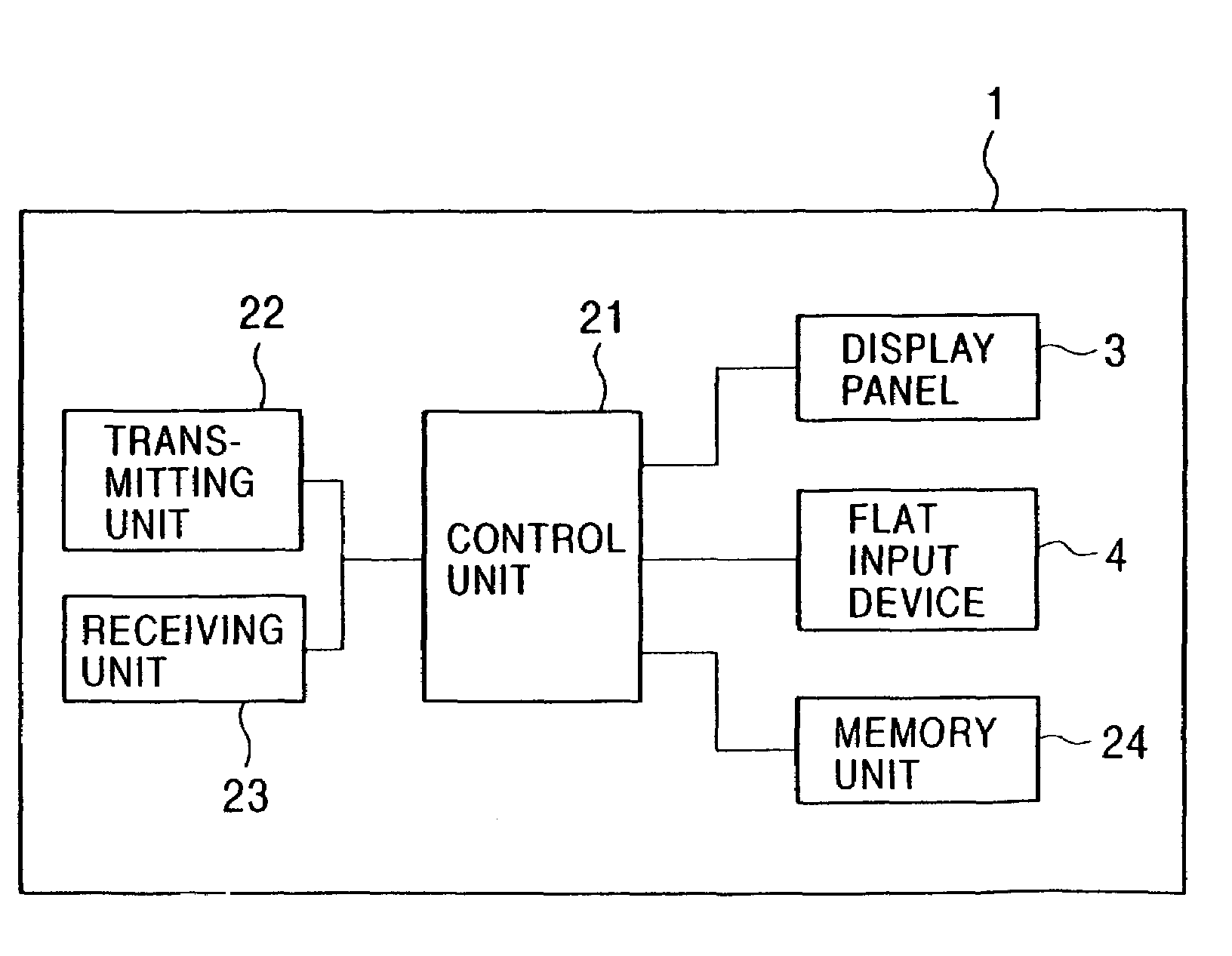
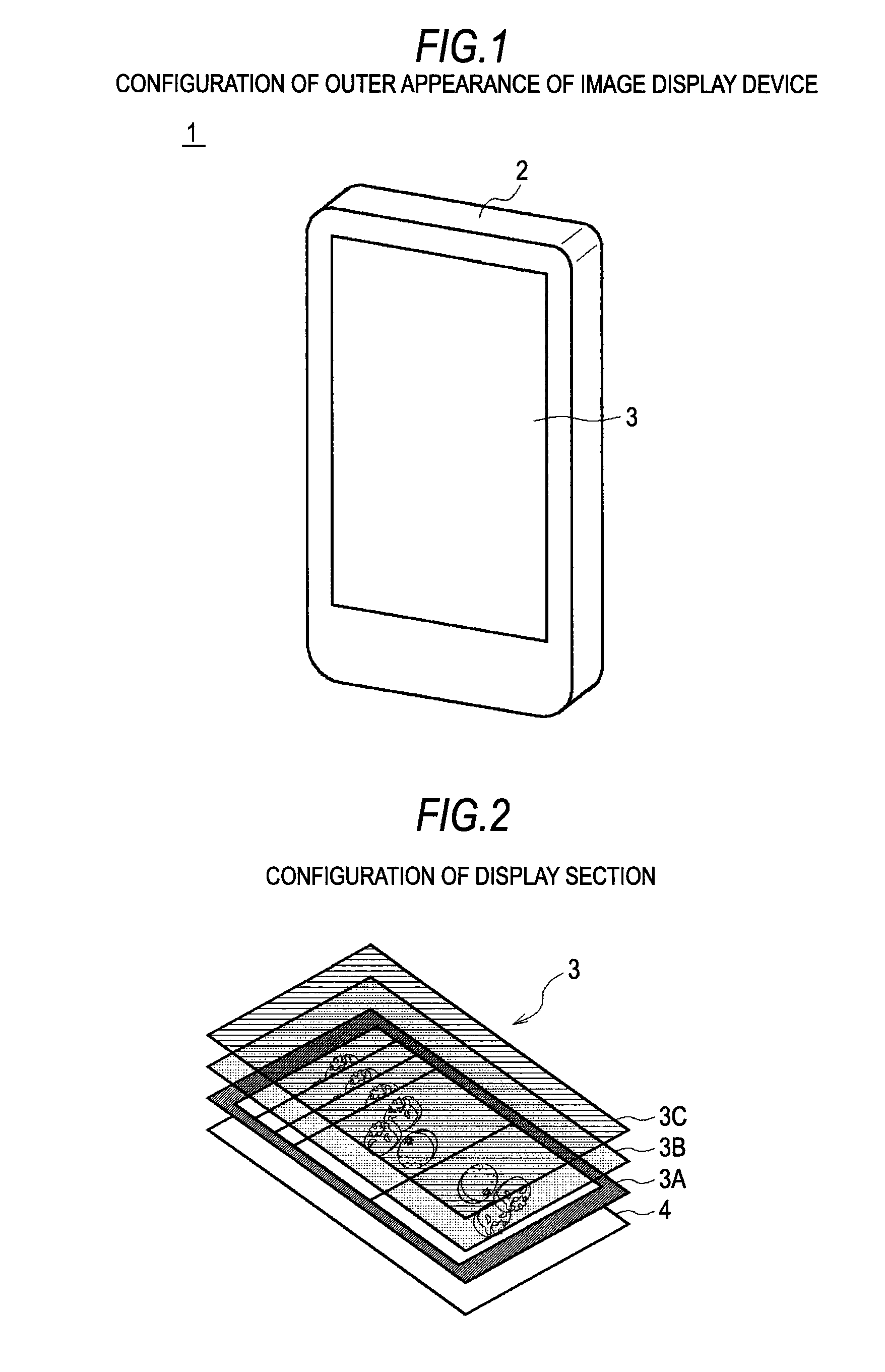
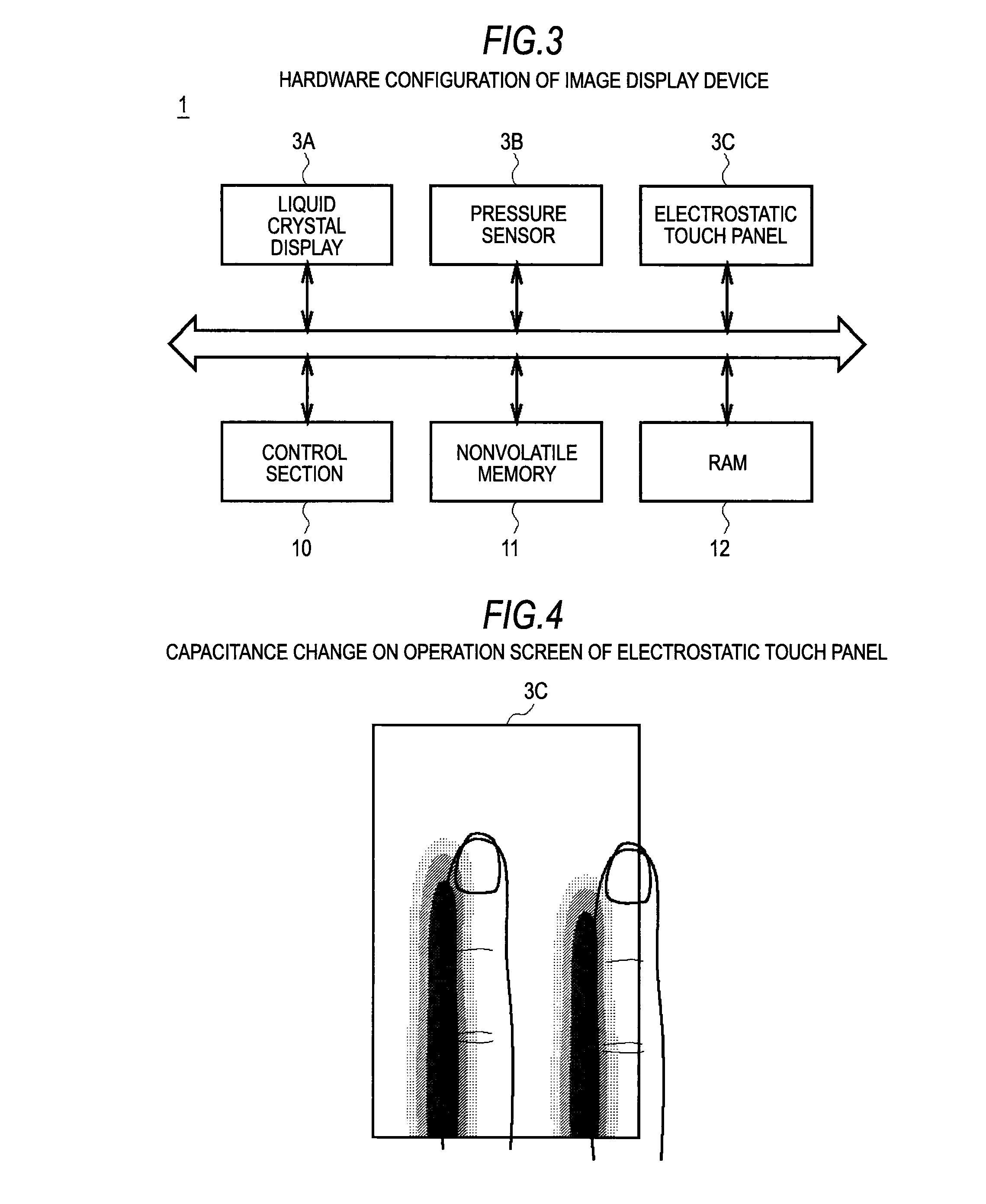
Information processing apparatus, threshold value setting method, and threshold value setting program
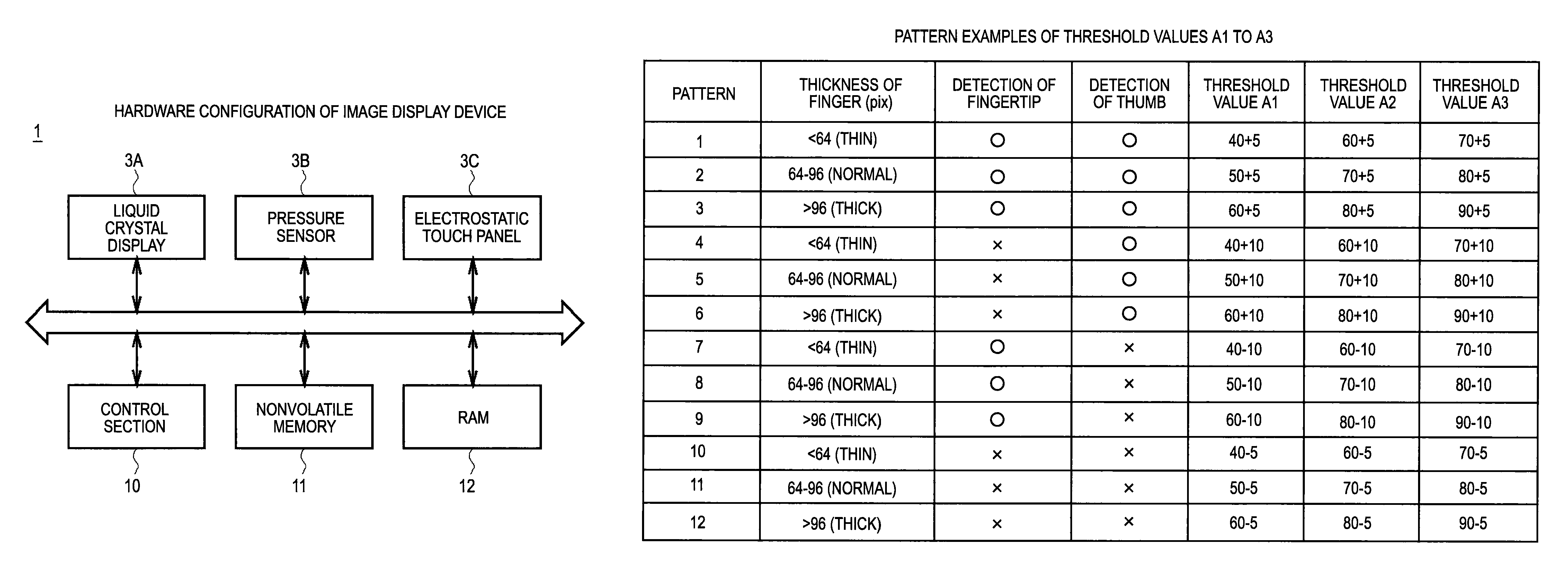
ActiveUS20100225604A1Threshold value can be loweredReliably recognizeInput/output processes for data processingInformation processingValue set
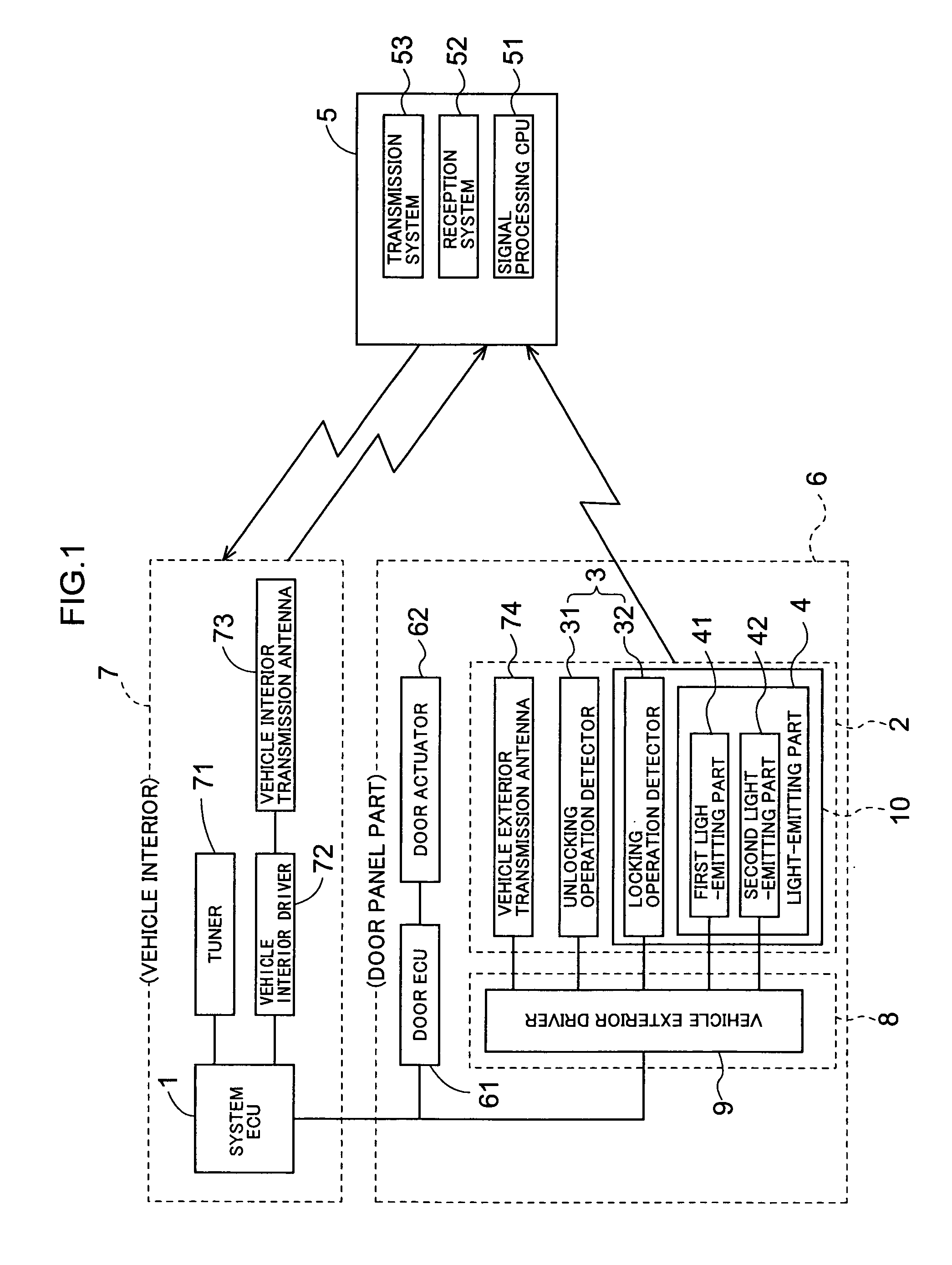
An information processing apparatus includes: a recognition section which recognizes the shape of an object being in contact with an operation screen of an operating section; a pressure detecting section which detects the pressure of the object on the operation screen; a threshold value setting section which sets a threshold value of the pressure, which is a value for determining a pressure operation on the operation screen, on the basis of the shape of the object recognized by the recognition section; and a determination section which determines whether or not a pressure operation has been performed on the operation screen on the basis of the pressure detected by the pressure detecting section and the threshold value set by the threshold value setting section.
Owner:SONY CORP
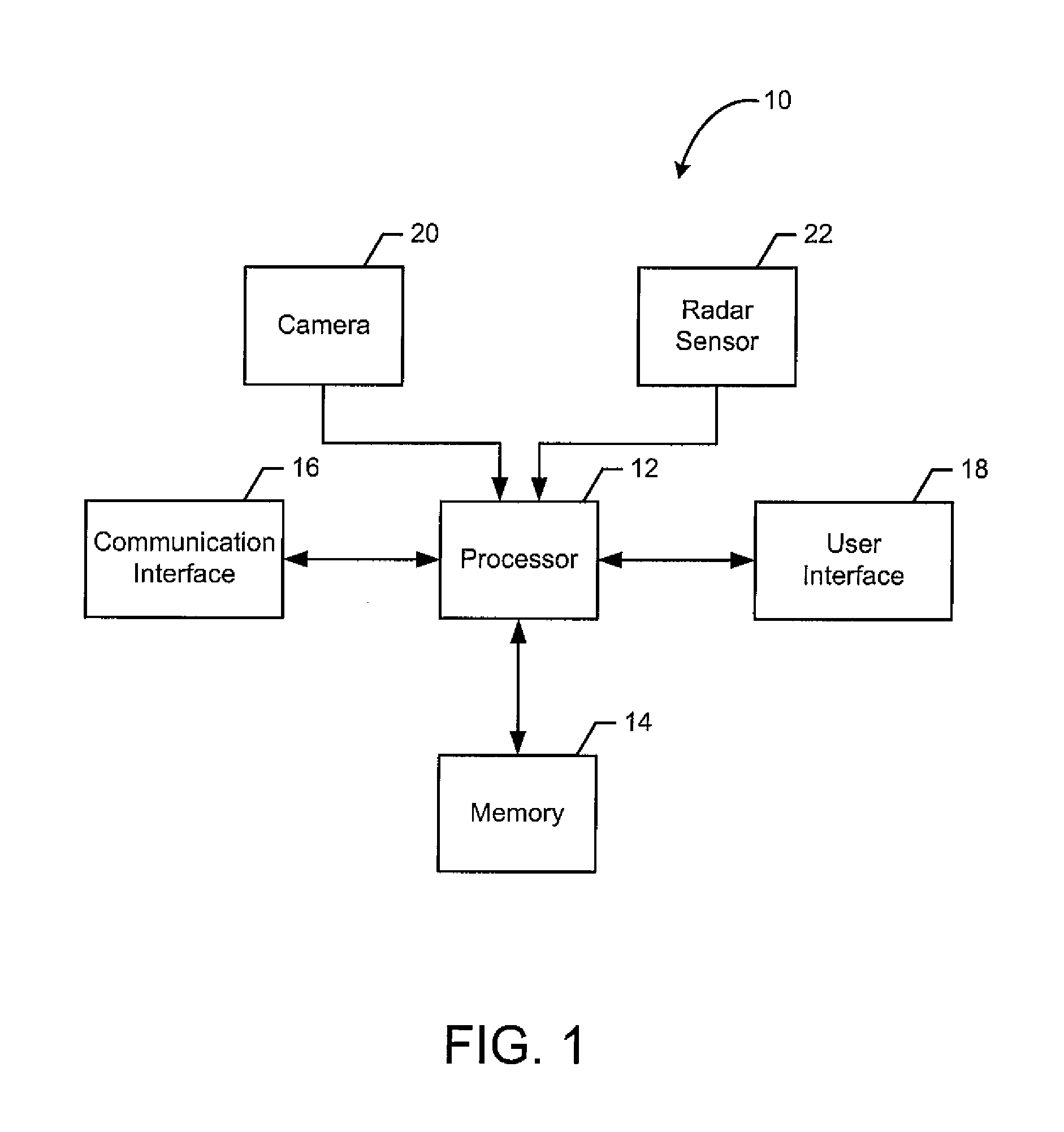
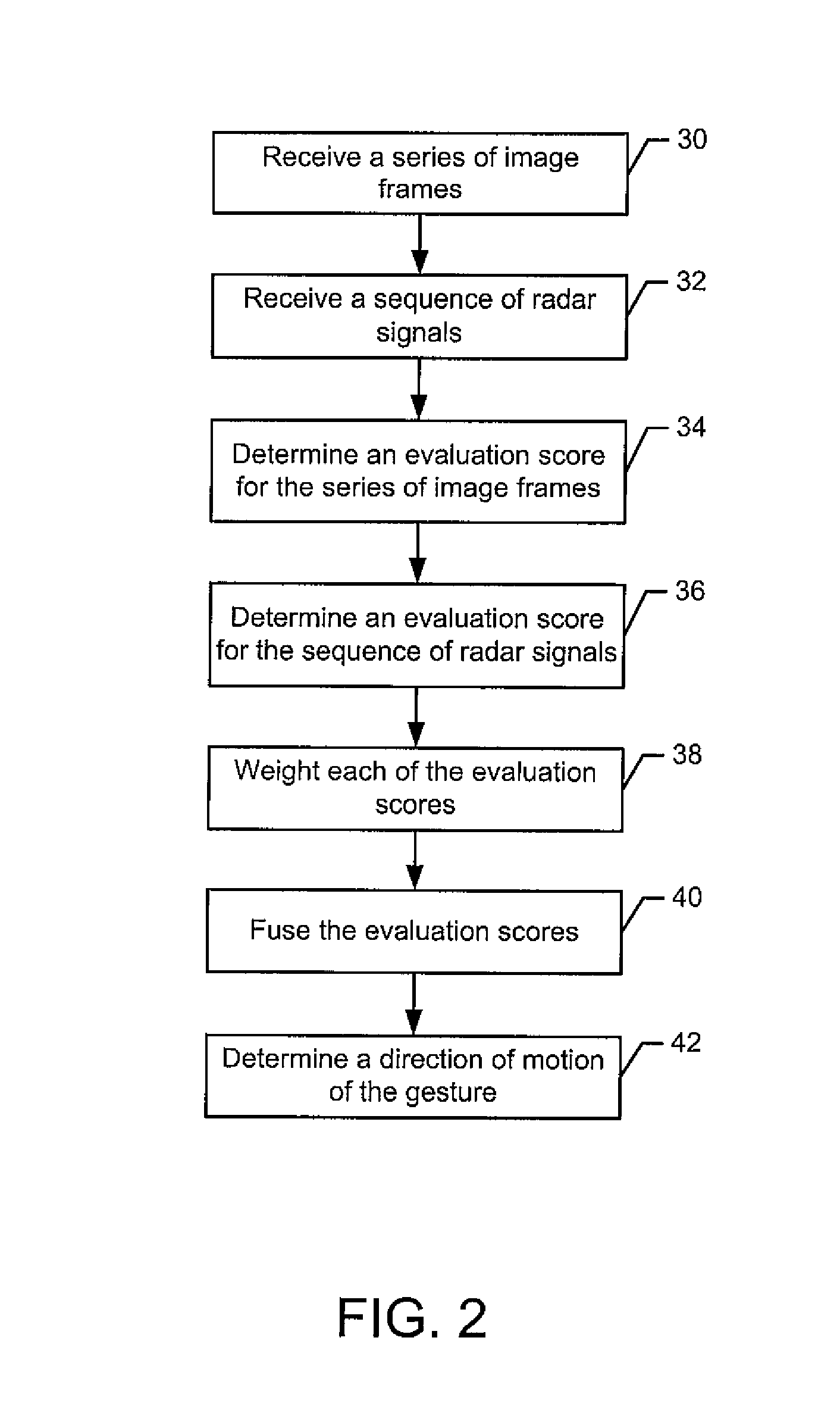
Method and Apparatus for Identifying a Gesture Based Upon Fusion of Multiple Sensor Signals
InactiveUS20140324888A1Improved gesture recognitionReliably recognizeInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsPattern recognitionMultiple sensor
A method, apparatus and computer program product are provided to permit improve gesture recognition based on fusion of different types of sensor signals. In the context of a method, a series of image frames and a sequence of radar signals are received. The method determines an evaluation score for the series of image frames that is indicative of a gesture. This determination of the evaluation score may be based on the motion blocks in an image area and the shift of the motion blocks between image frames. The method also determines an evaluation score for the sequence of radar signals that is indicative of the gesture. This determination of the evaluation score may be based upon the sign distribution in the sequence and the intensity distribution in the sequence. The method weighs each of the evaluation scores and fuses the evaluation scores, following the weighting, to identify the gesture.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Display comprising and integrated loudspeaker and method for recognizing the touching of the display
InactiveUS20050226455A1Reliably recognizeLimited in purposePlane diaphragmsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsDisplay deviceEngineering
A combination is provided which consists of a loudspeaker and a display in which at least a portion of a sound-emitting surface of the loudspeaker forms the display that is touch-sensitive, and at least one recognition part is provided for recognizing the touching of the display.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
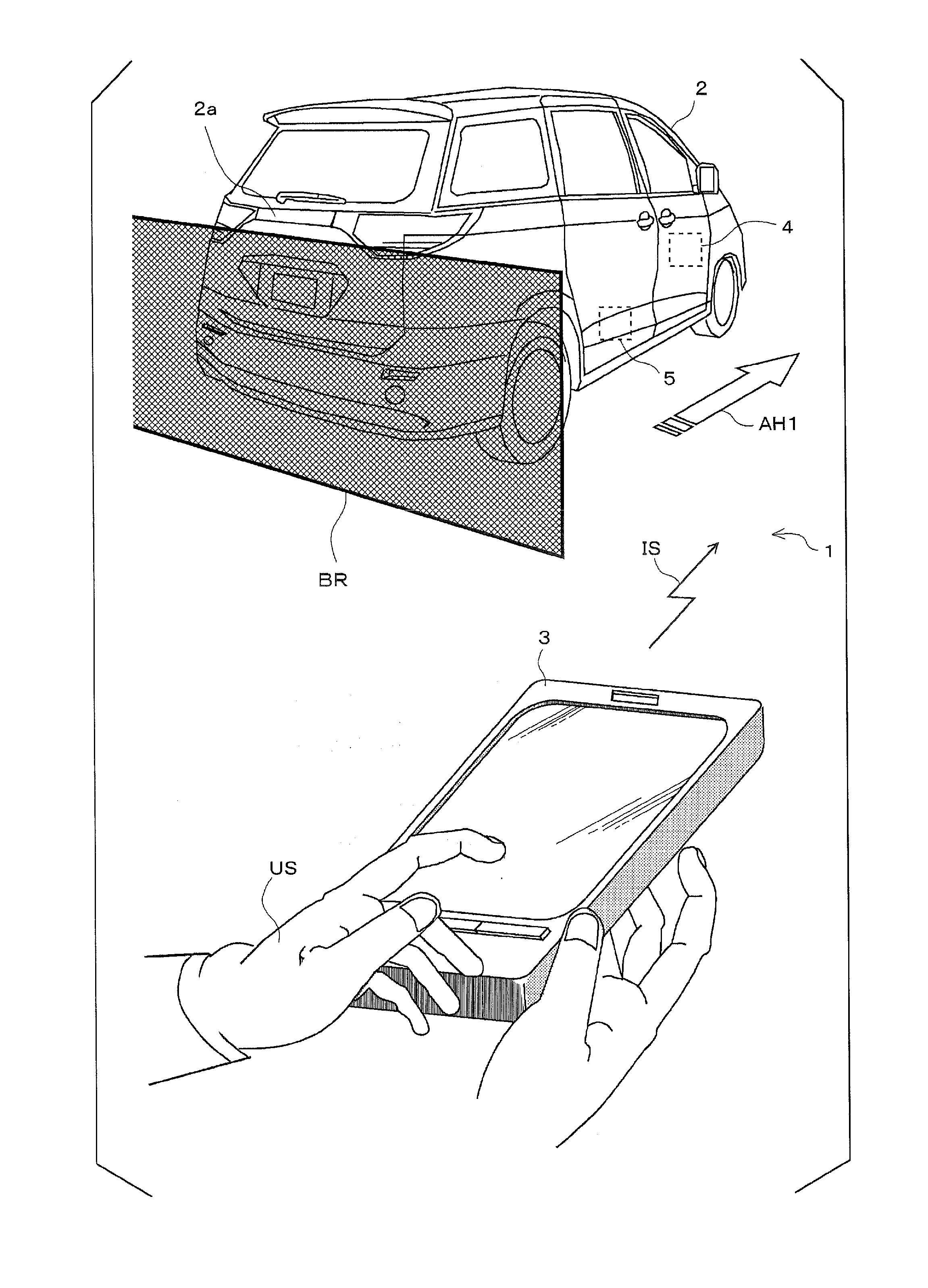
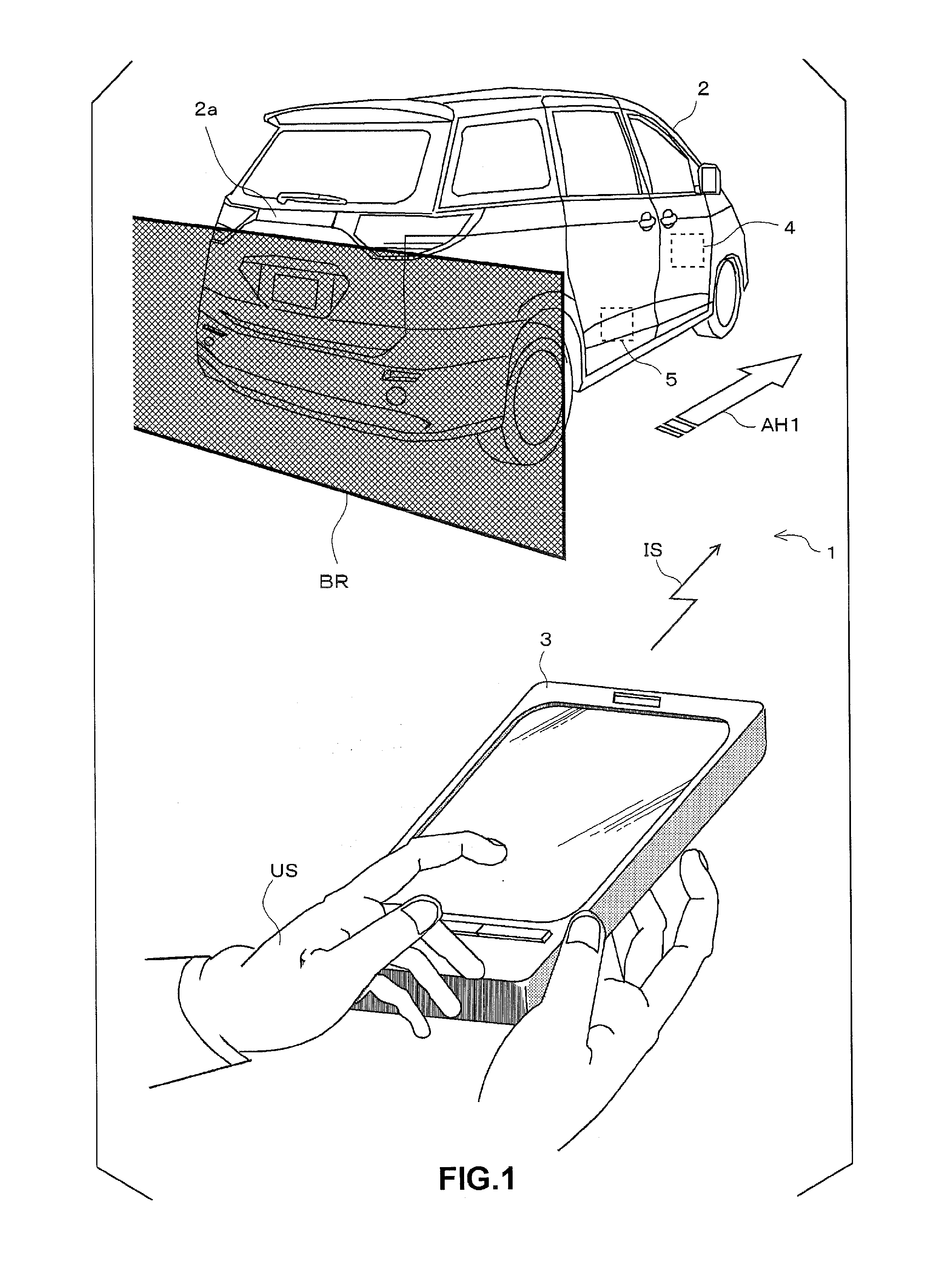
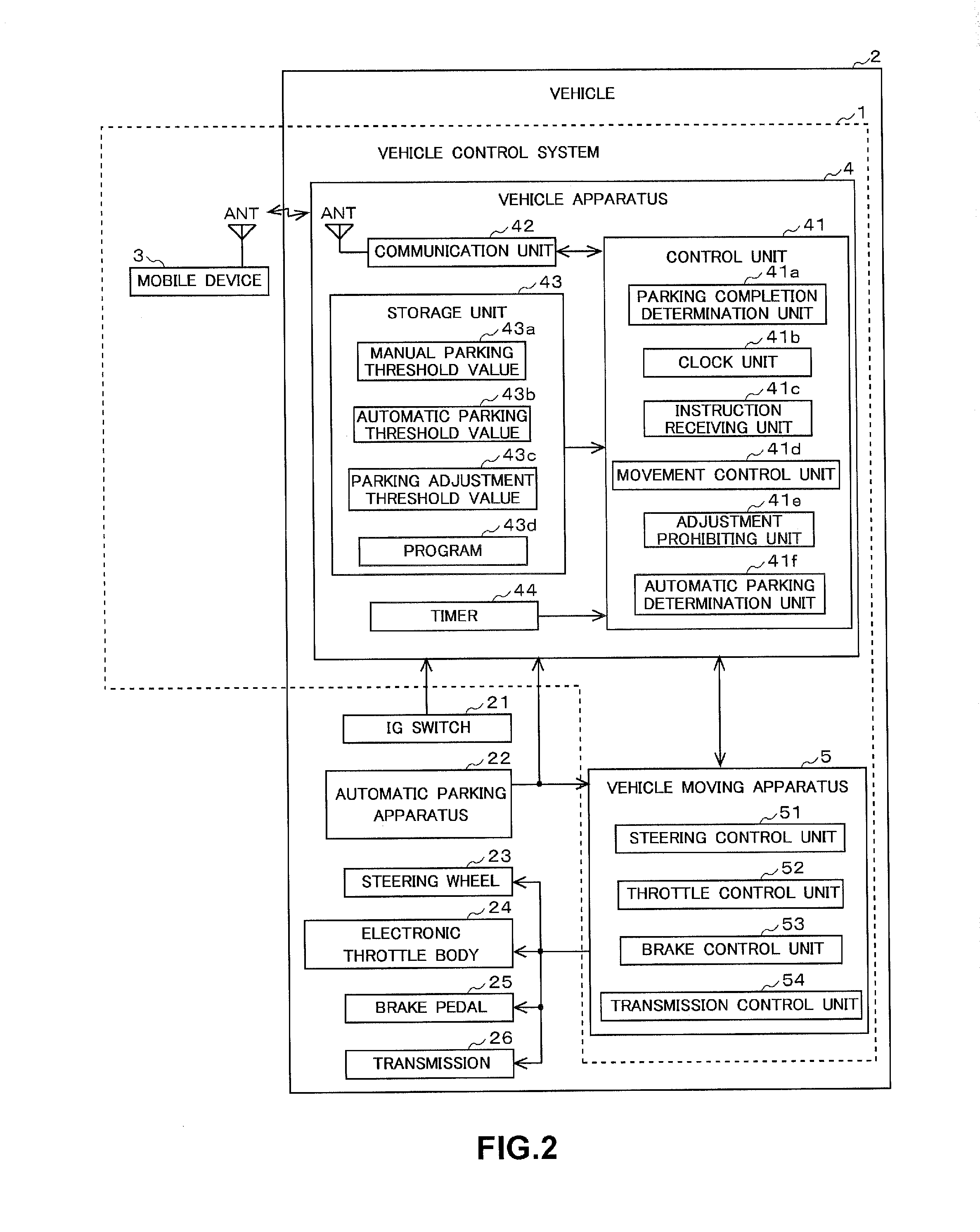
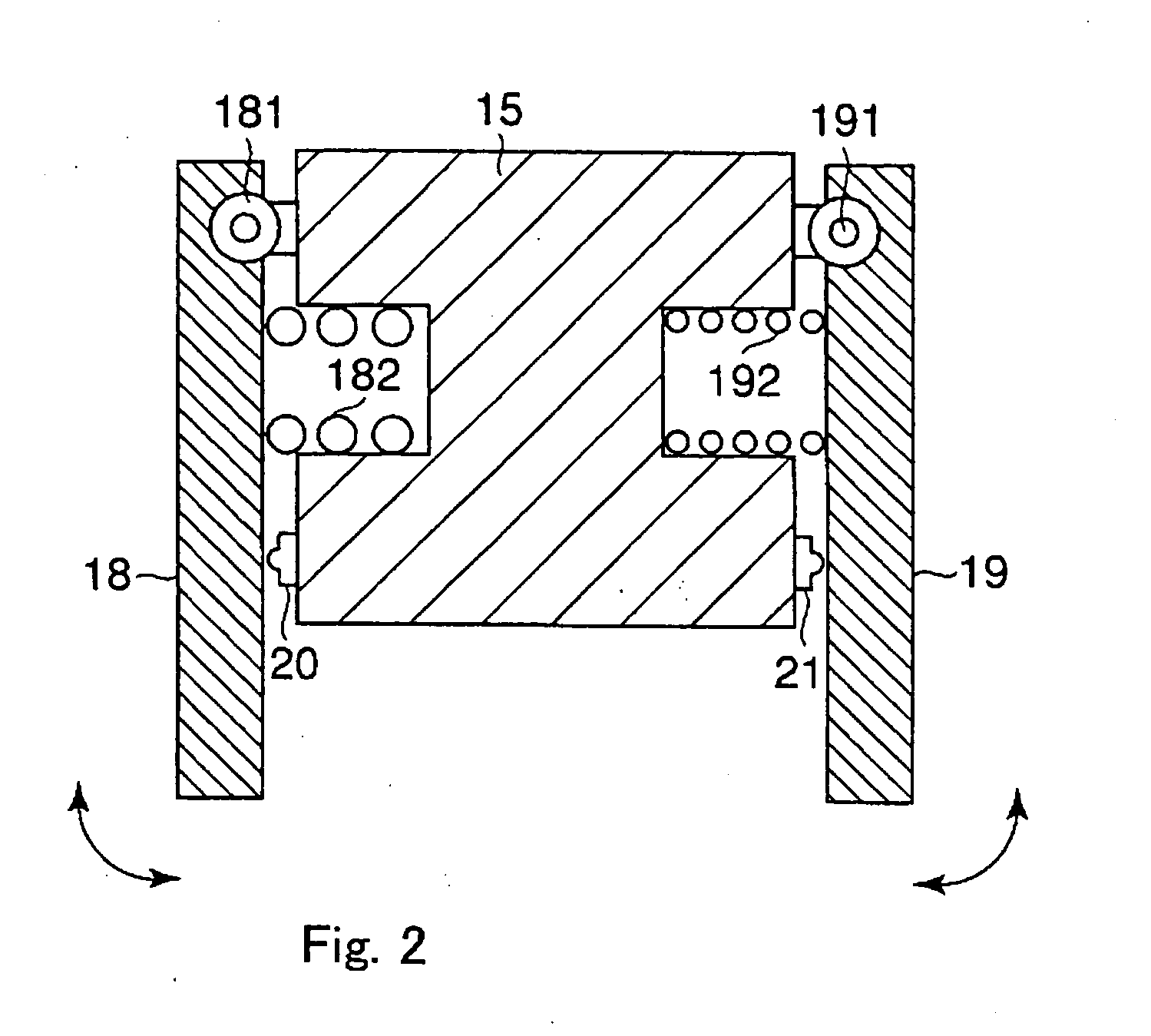
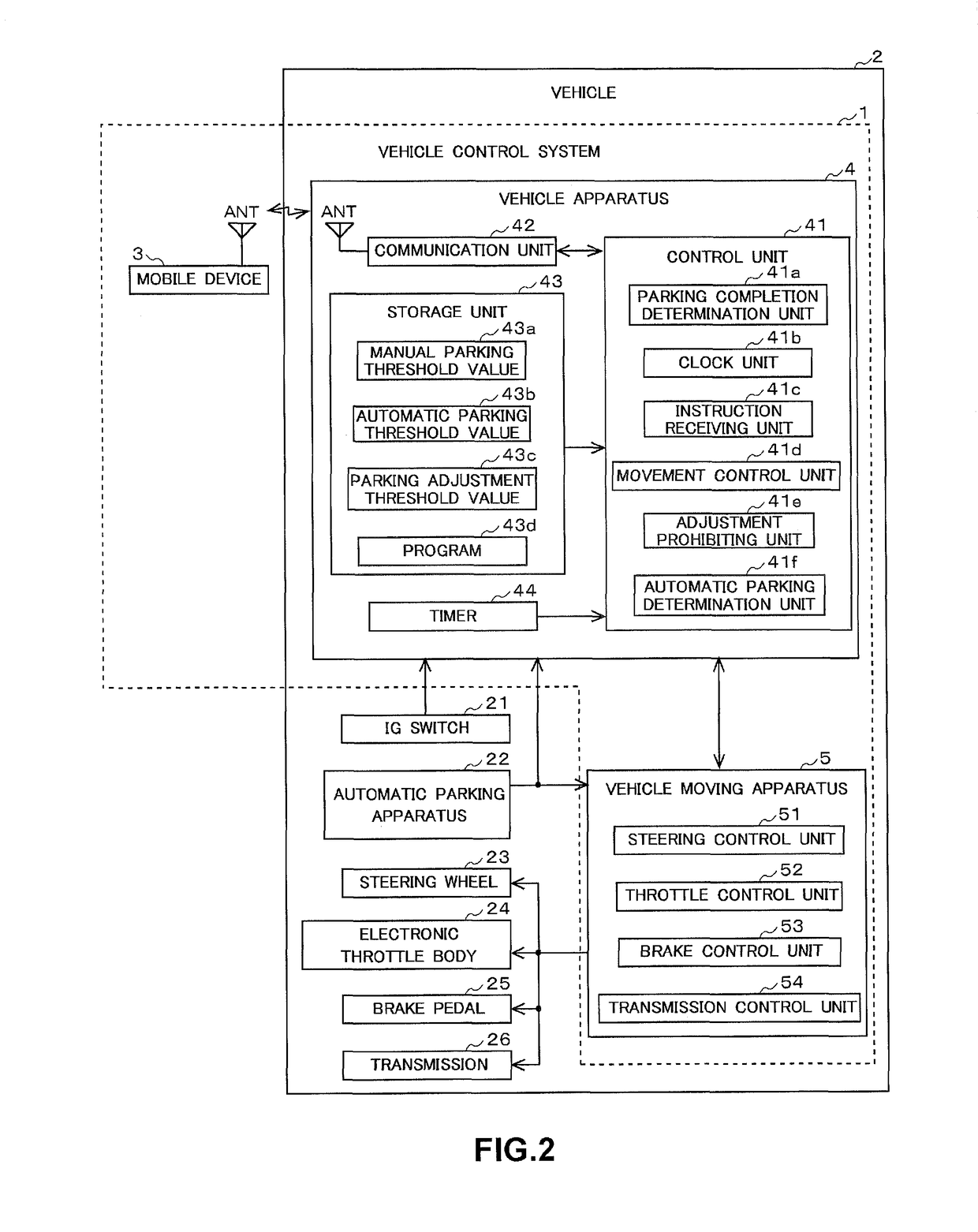
Vehicle apparatus
ActiveUS20150375741A1Improve securityProhibit some movementImage enhancementTelevision system detailsEngineeringMoving parts
A vehicle apparatus used in a vehicle measures a first elapsed time after completion of a parking operation by which the vehicle is parked in a parking region, and prohibits movement of the vehicle to adjust the parking position when the first elapsed time reaches a first predetermined time before receipt of a instruction signal by the receiver Accordingly, it is possible to improve safety by preventing the vehicle from moving out of a parking position even if the moving part is erroneously operated when the predetermined time elapses after the completion of parking operation.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
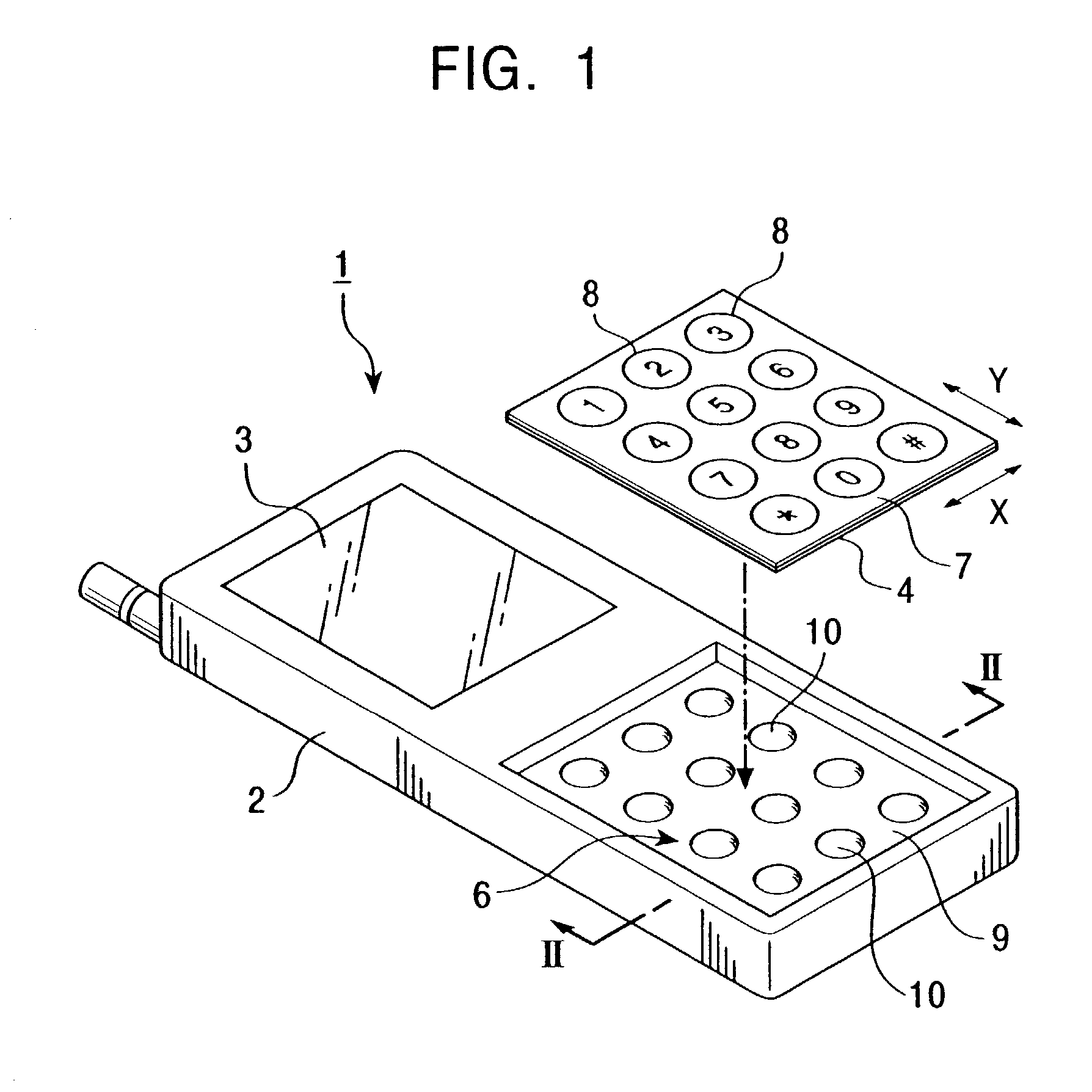
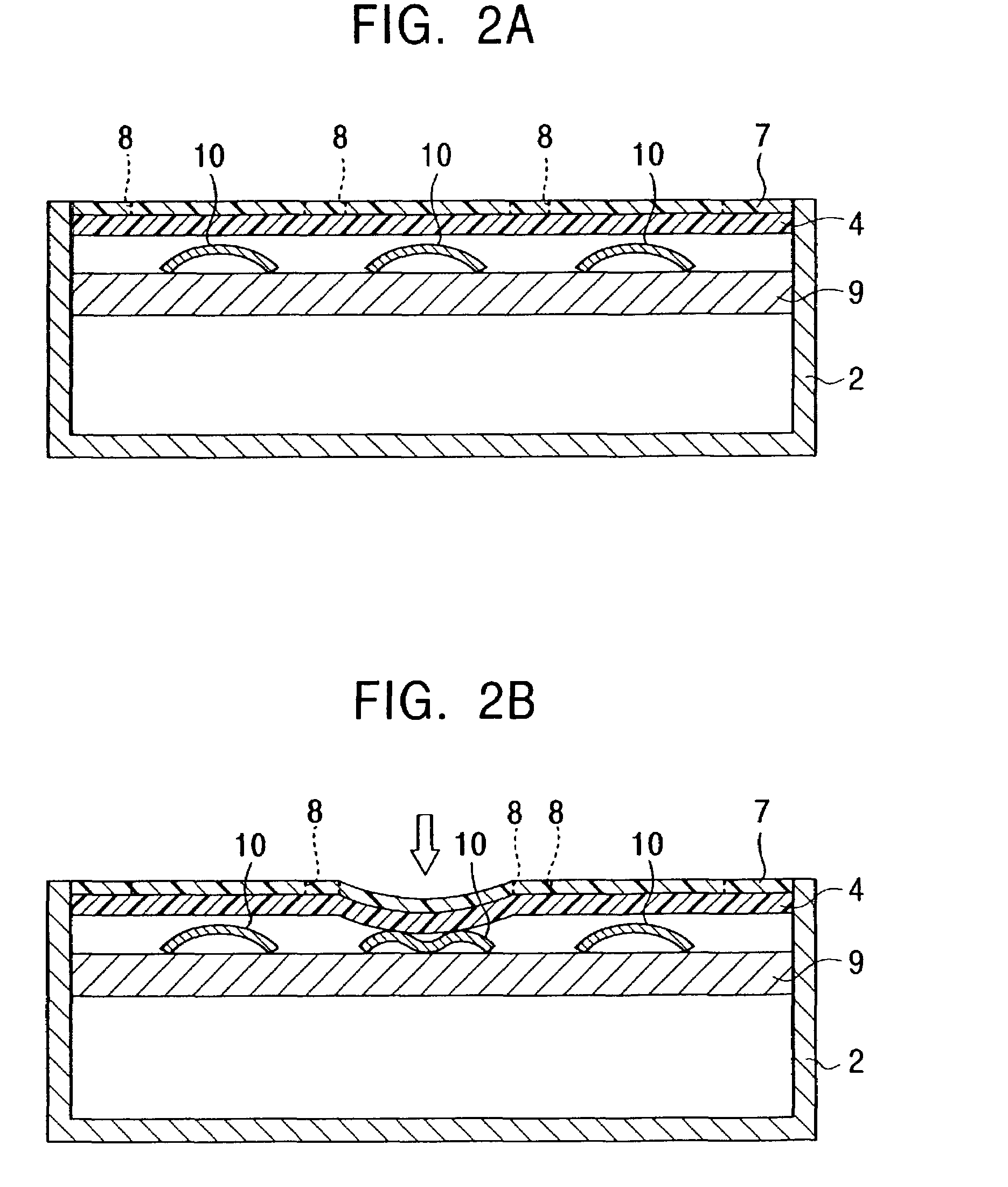
Input apparatus for performing input operation corresponding to indication marks and coordinate input operation on the same operational plane
InactiveUS7312790B2Input operation can be quicklyReduce stepsInput/output for user-computer interactionTransmission systemsData signalEngineering
An input apparatus includes a flat input device of a pressure-sensitive type or a capacitive type, and an indicator sheet on which indication marks are formed is fixed on the surface of the flat input device. A tactile-feel-generating unit is provided behind the flat input device. The tactile-feel-generating unit includes dome-shaped inversion plates which are disposed at positions corresponding to the indication marks. When one of the indication marks is pressed setting an input mode, an operation signal is generated in accordance with an item represented by the indication mark, and a tactile feel is generated by a reaction force of the corresponding inversion plate. When an indication mark is touched, while in an input mode, the control unit recognizes the resulting signal to be a coordinate data signal.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Free space monitoring system for motor vehicles
InactiveUS7136754B2Reliably recognizeEasy to adaptInstruments for road network navigationAnti-collision systemsMobile vehicleDriver/operator
In complex vehicle maneuvers it is often difficult for the driver of the motor vehicle to estimate along which tract the vehicle will move and how much free space is necessary in order to avoid collision. A process is provided for monitoring the environment space in the direction of travel of the own vehicle, in which image data of the environment around the vehicle in the direction of travel of the vehicle is recorded using a camera system the three-dimensional free space required for unimpeded travel is calculated in advance in a signal processing unit and the vehicle operator is informed regarding whether or not a sufficient free space is available to him for unimpeded travel.
Owner:BAYERISCHE MOTOREN WERKE AG
Wirless network
InactiveUS6901104B1Reduces pulse amplitudeReliably recognizePower managementAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsStart timeWireless network
A wireless network is disclosed including at least one base station and a plurality of assigned terminals for exchanging user data and control data. The base station is arranged for transmitting the start time of at least one signaling sequence of at least terminal. For evaluating the signaling sequences transmitted by the terminals, the base station includes a device for correlating a received signaling sequence and for detecting the pulse evolving from a received and correlated signaling sequence. A terminal generates a signaling sequence by folding two code sequences.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV +1
Speaker Recognition in a Speech Recognition System
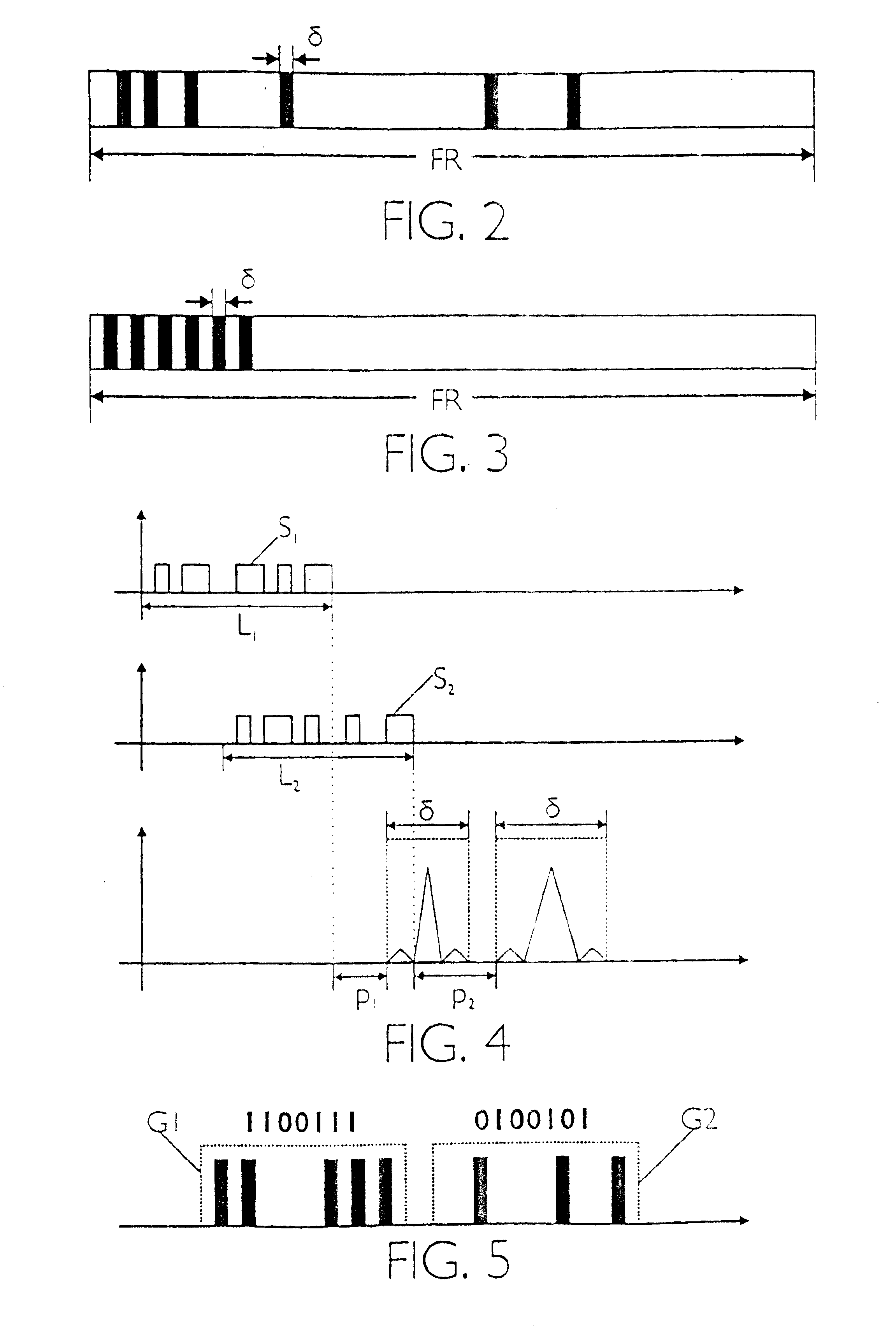
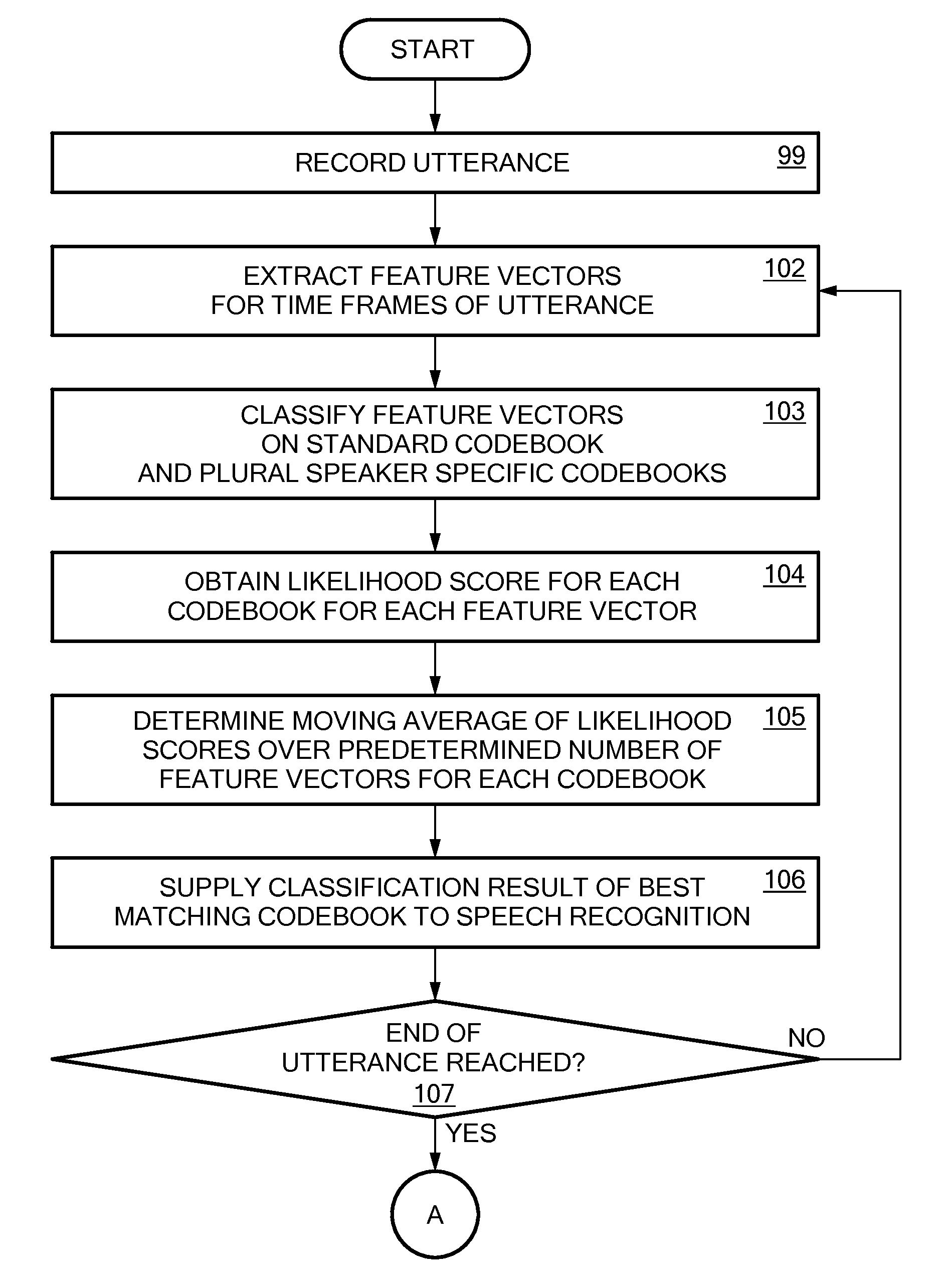
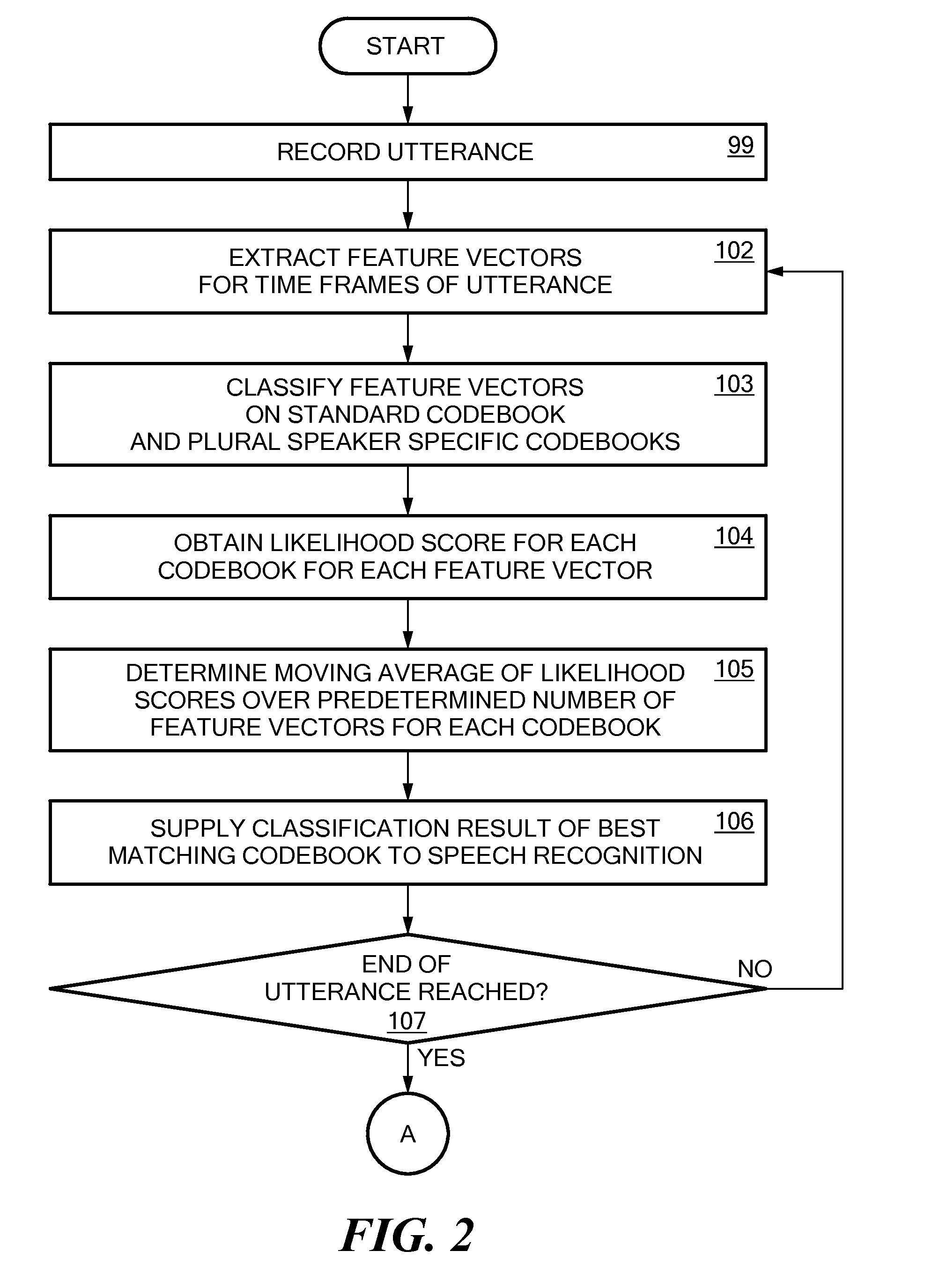
InactiveUS20100198598A1Recognized more reliablyReliably recognizeSpeech recognitionSpeech identificationSpeech sound
A method for recognizing a speaker of an utterance in a speech recognition system is disclosed. A likelihood score for each of a plurality of speaker models for different speakers is determined. The likelihood score indicating how well the speaker model corresponds to the utterance. For each of the plurality of speaker models, a probability that the utterance originates from that speaker is determined. The probability is determined based on the likelihood score for the speaker model and requires the estimation of a distribution of likelihood scores expected based at least in part on the training state of the speaker.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
Method for processing values from a measurement
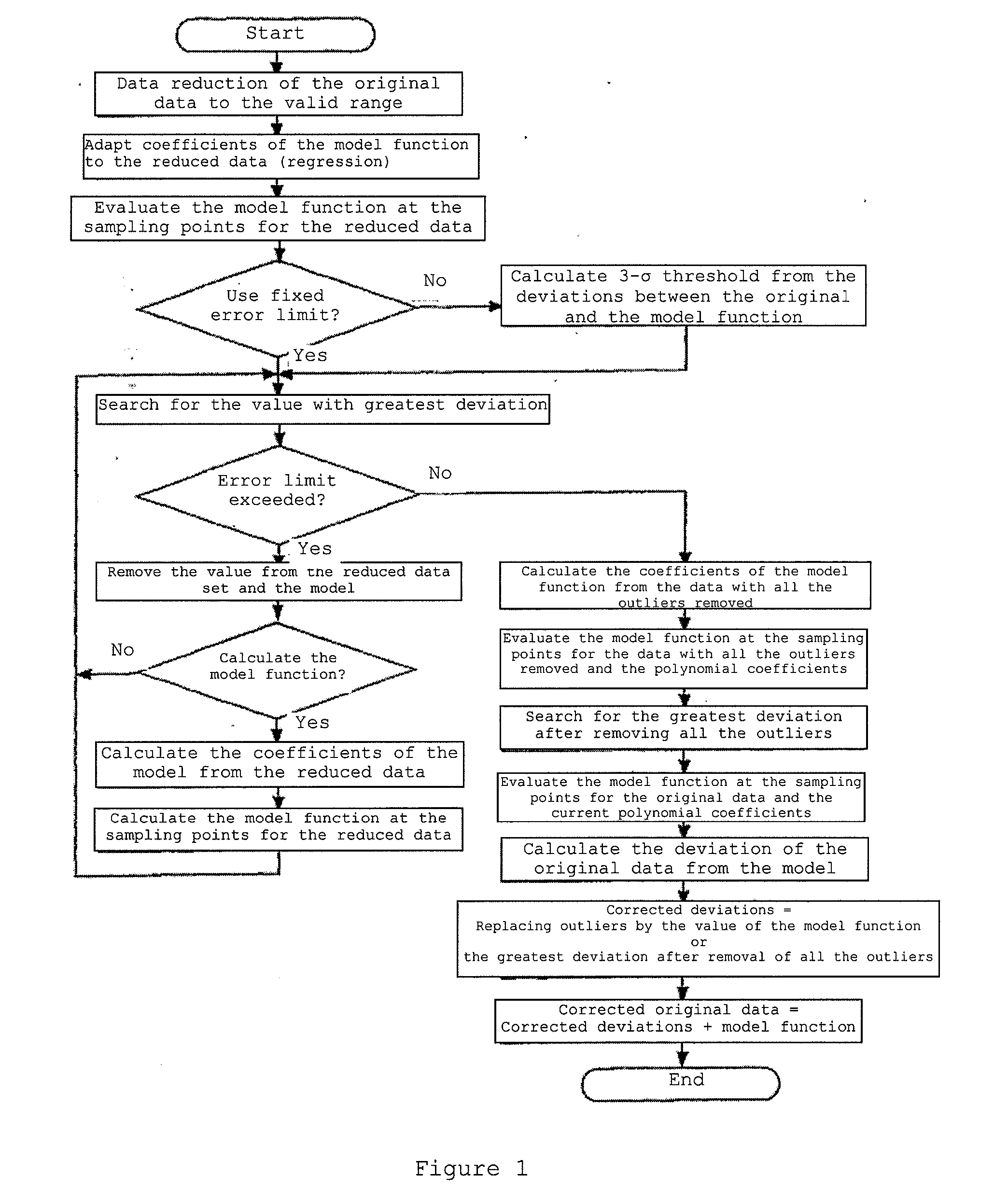
InactiveUS20070105238A1High degree of realityImprove approximationBiological testingComplex mathematical operationsData setComputer science
A method for processing values from a measurement in a data set, such that there is recognition of corrupted values from the measurement. The method of the present invention is structured in such a manner that the values from a measurement are compared by means of a suitable measure of difference from a predefinable or determinable or model function and are evaluated via a predefinable or determinable error bound for that measure of difference.
Owner:MICRO EPSILON MESSTECHNIK GMBH & CO KG
Process for checking a laser weld seam
When laser beam welding one or more work pieces faults may occur, which lead to unacceptable losses in quality. For quality assurance, both subjective visual inspections as well as automated checks of the seam are the norm. In the automated processes the work site is conventionally monitored during welding using point or surface detectors (cameras). This type of process can not detect faults which do not occur until after the actual interaction of laser beam and work piece, in particular, solidification phenomena. Beyond this, certain irregularities relevant to quality are not recognized, since relevant process signals are overridden by stronger signals of the process illumination with no information value. It is the task of the present invention to provide a check process, which reliably recognizes seam faults. This task is solved in a process for checking of the seam which is introduced into one or more workpieces by means of laser beam welding, wherein characteristic signals are detected from the region of the seam using a sensor and compared with an index value or set value, and wherein only signals are taken into consideration which are detected in a characteristic time interval following the laser beam welding, which begins, at the earliest, following the solidification of the seam.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Apparatus for Opening and Closing Vehicle Door
InactiveUS20080290668A1Prevent water seepageIncreased durabilityWing handlesAnti-theft devicesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
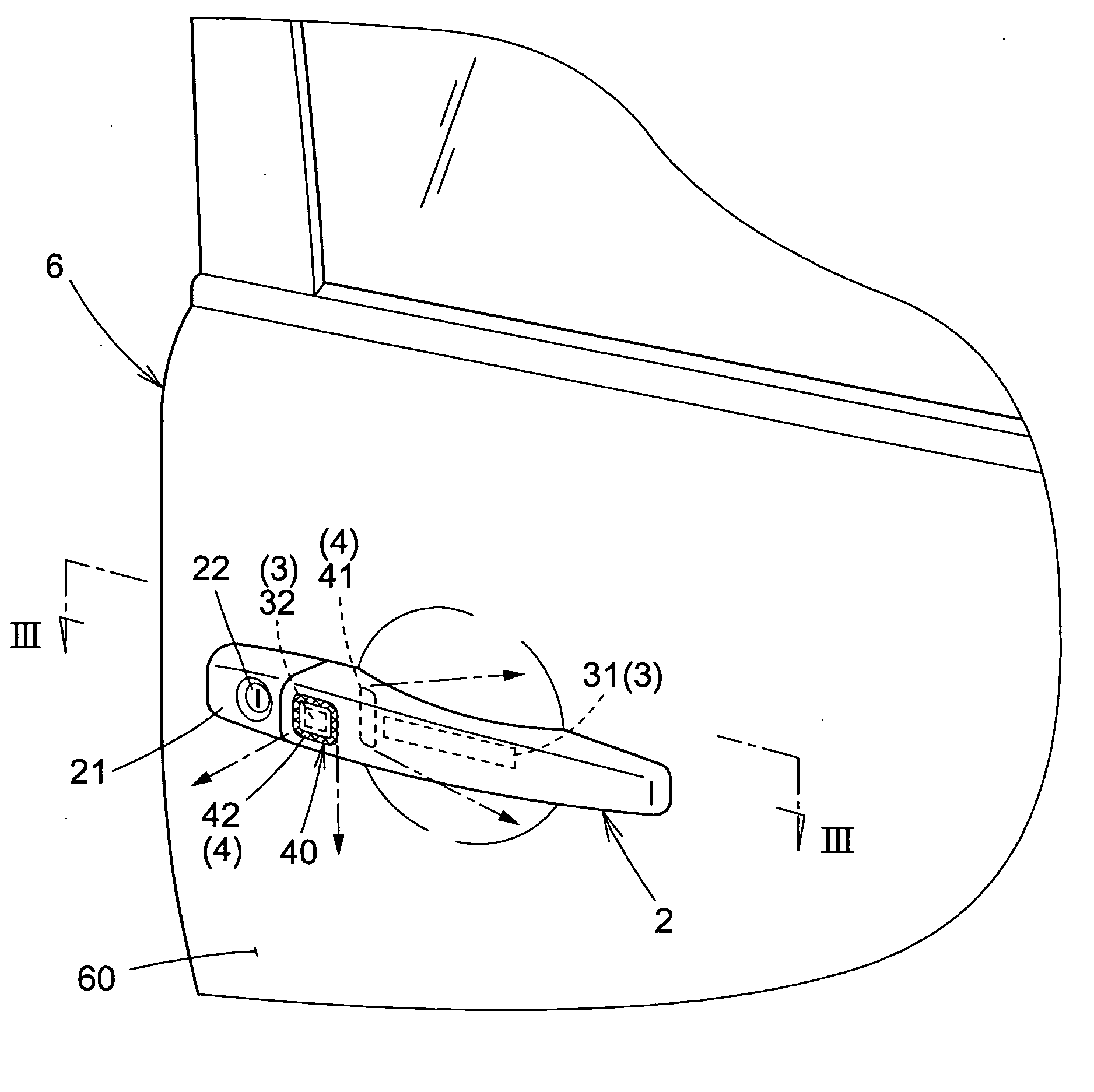
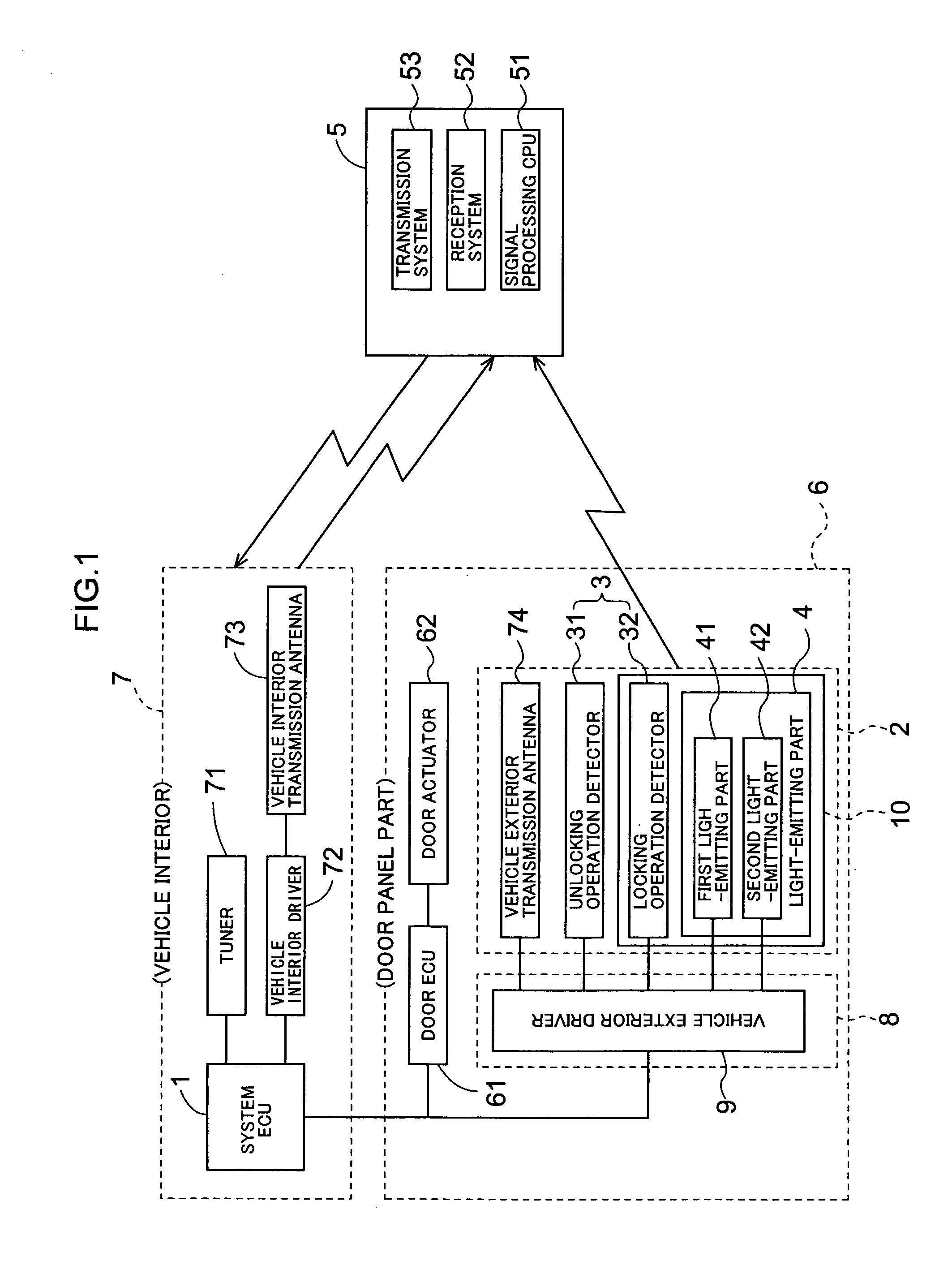
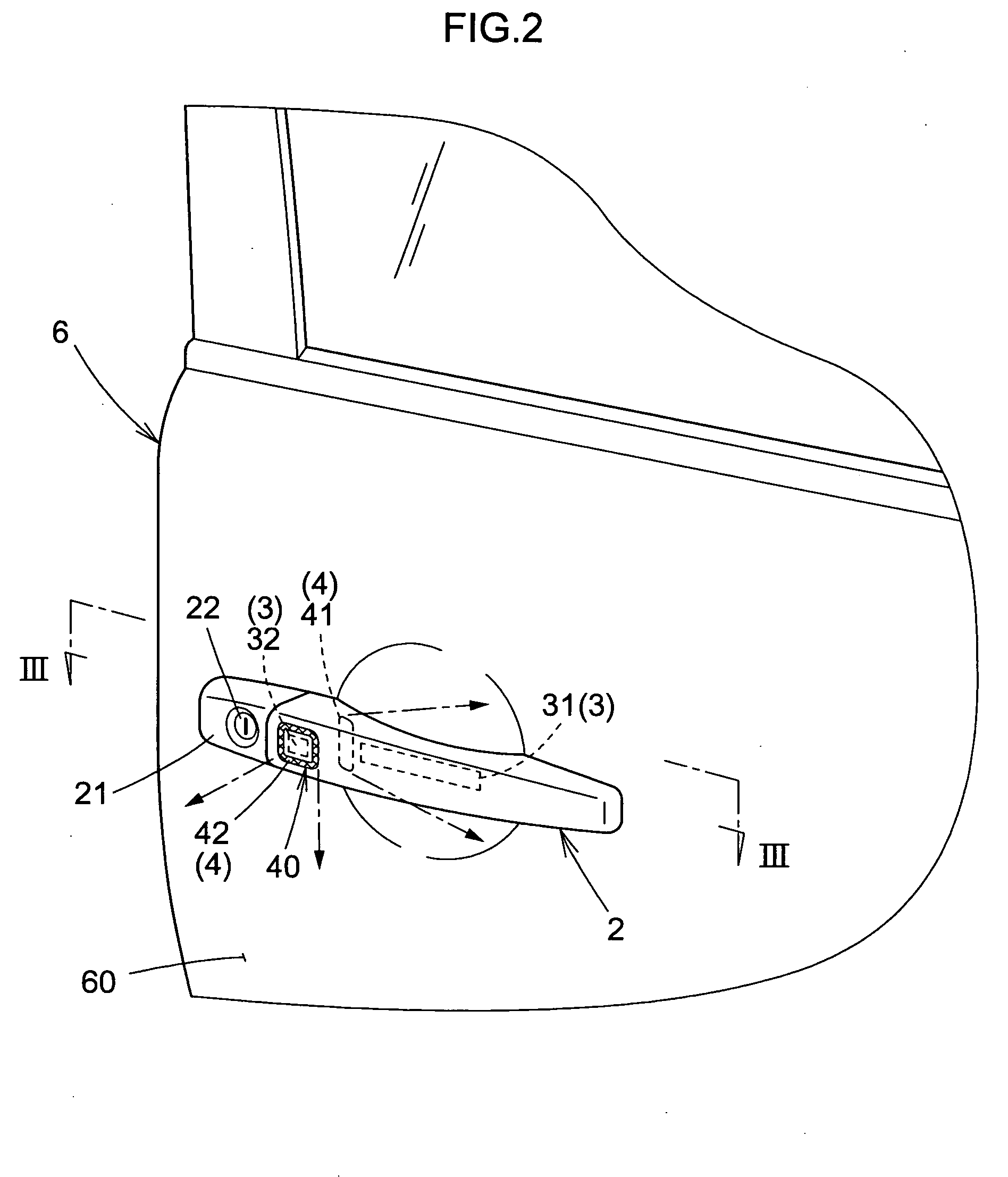
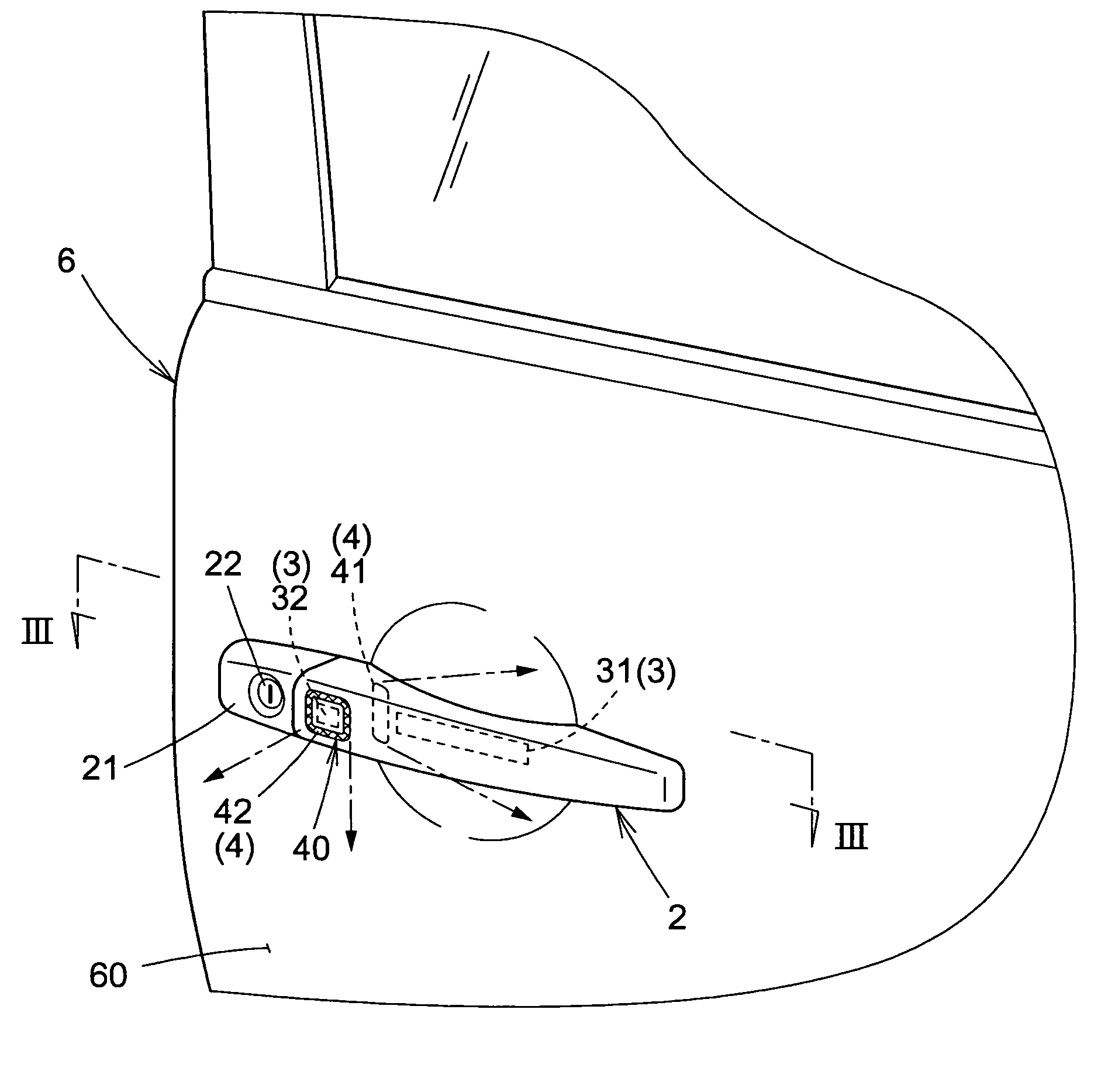
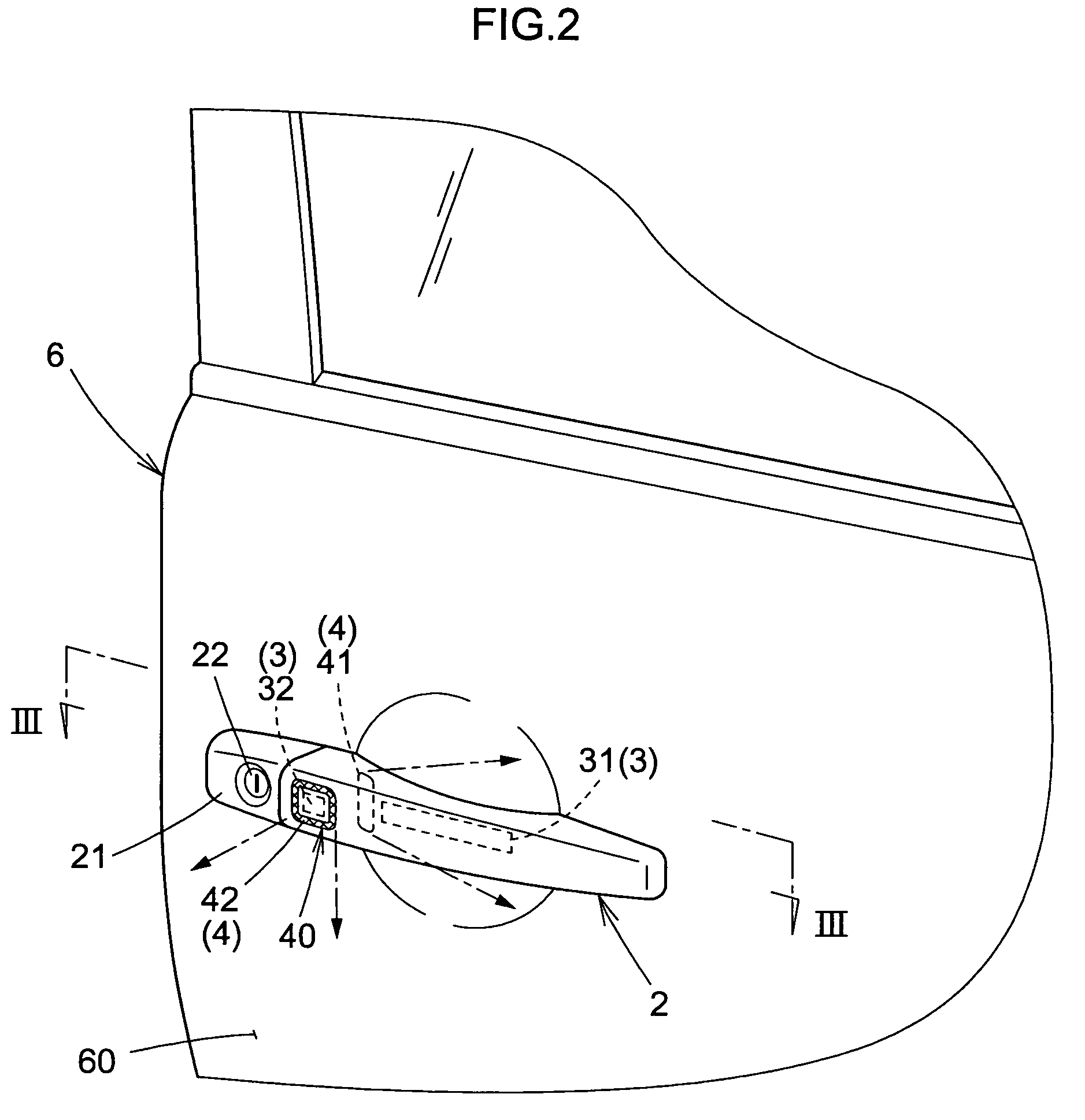
There is provided an apparatus for opening and closing a vehicle door that is exceptionally durable and performs indications so that a person can reliably recognize a locked or unlocked state of a vehicle door.The apparatus for opening and closing a vehicle door comprises control means for recognizing the intention of a person to lock or unlock a vehicle door 6 and controlling the locking or unlocking of the vehicle door 6. The apparatus is characterized in comprising a door handle 2 with which the vehicle door 6 is opened or closed; an operation detector 3 provided to the door handle 2 in order to detect a state of the door handle 2 as operated by the person; an ornamental light part 40 that is provided so as to enclose a periphery of the operation detector 3, and is visible from the exterior of the door handle 2 during actuation of the operation sensor 3 by the person; and a light-emitting part 4 for illuminating the ornamental light part 40. The light-emitting part 4 is energized by the control means according to a controlled state in which the vehicle door 6 is locked or unlocked.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
System and method for modifying media content playback based on limited input
ActiveUS20070291404A1Reduce complexityLimited processing powerRecording carrier detailsDisposition/mounting of recording headsTelecommunicationsMediaFLO
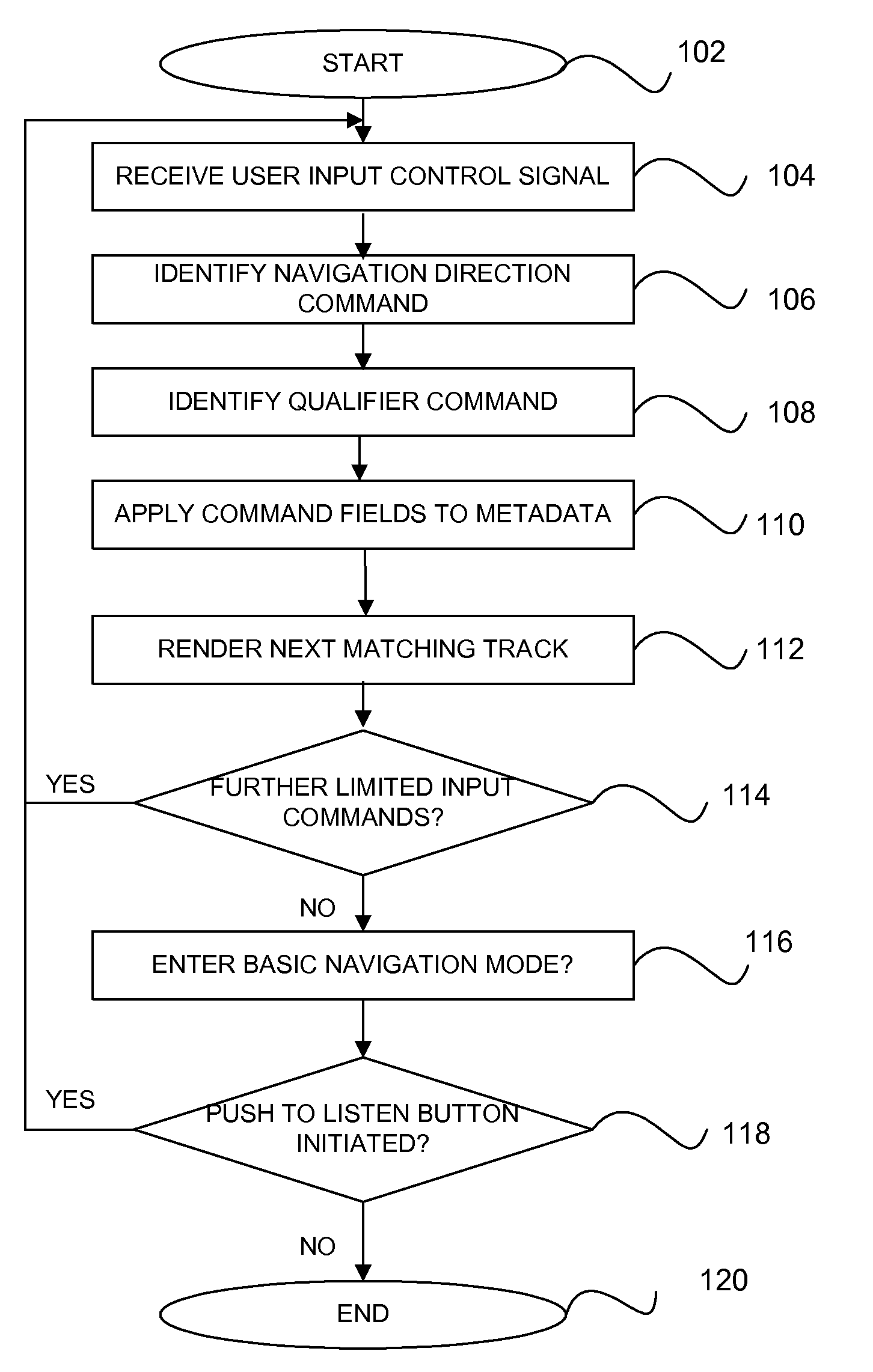
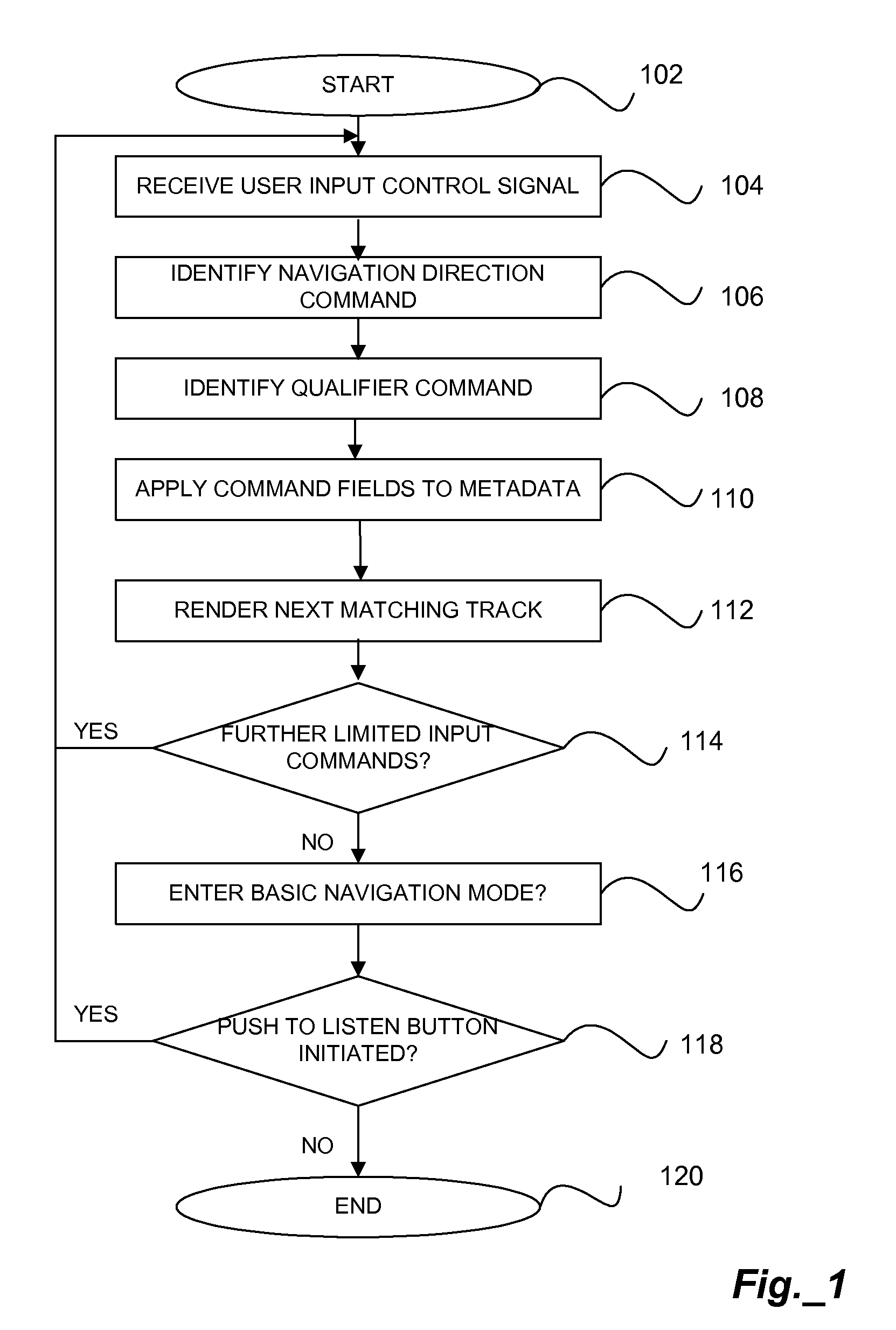
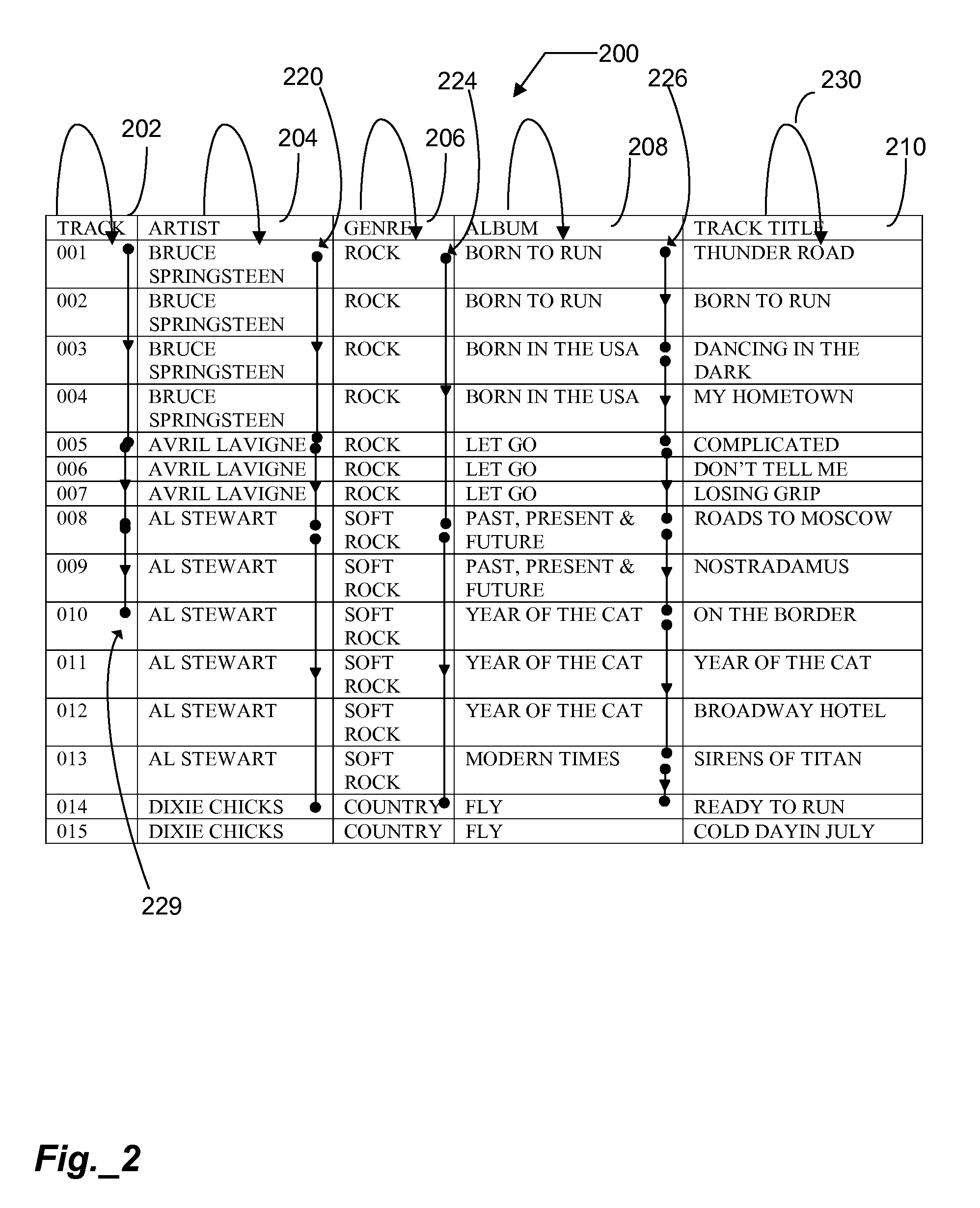
A method for navigating among tracks uses limited input commands. A plurality of tracks is associated with a currently playing queue. One of the tracks in the queue is identified for a current focus. A voice command is received that includes a directional aspect and a metadata filtering aspect. In response, the focus moves to a second track having a different value for the selected metadata filtering category.
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
Apparatus for opening and closing vehicle door
InactiveUS7819442B2Reliably recognizePrevent water seepageWing handlesAnti-theft devicesElectrical and Electronics engineeringCar door
There is provided an apparatus for opening and closing a vehicle door that is exceptionally durable and performs indications so that a person can reliably recognize a locked or unlocked state of a vehicle door.The apparatus for opening and closing a vehicle door comprises control means for recognizing the intention of a person to lock or unlock a vehicle door 6 and controlling the locking or unlocking of the vehicle door 6. The apparatus is characterized in comprising a door handle 2 with which the vehicle door 6 is opened or closed; an operation detector 3 provided to the door handle 2 in order to detect a state of the door handle 2 as operated by the person; an ornamental light part 40 that is provided so as to enclose a periphery of the operation detector 3, and is visible from the exterior of the door handle 2 during actuation of the operation sensor 3 by the person; and a light-emitting part 4 for illuminating the ornamental light part 40. The light-emitting part 4 is energized by the control means according to a controlled state in which the vehicle door 6 is locked or unlocked.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
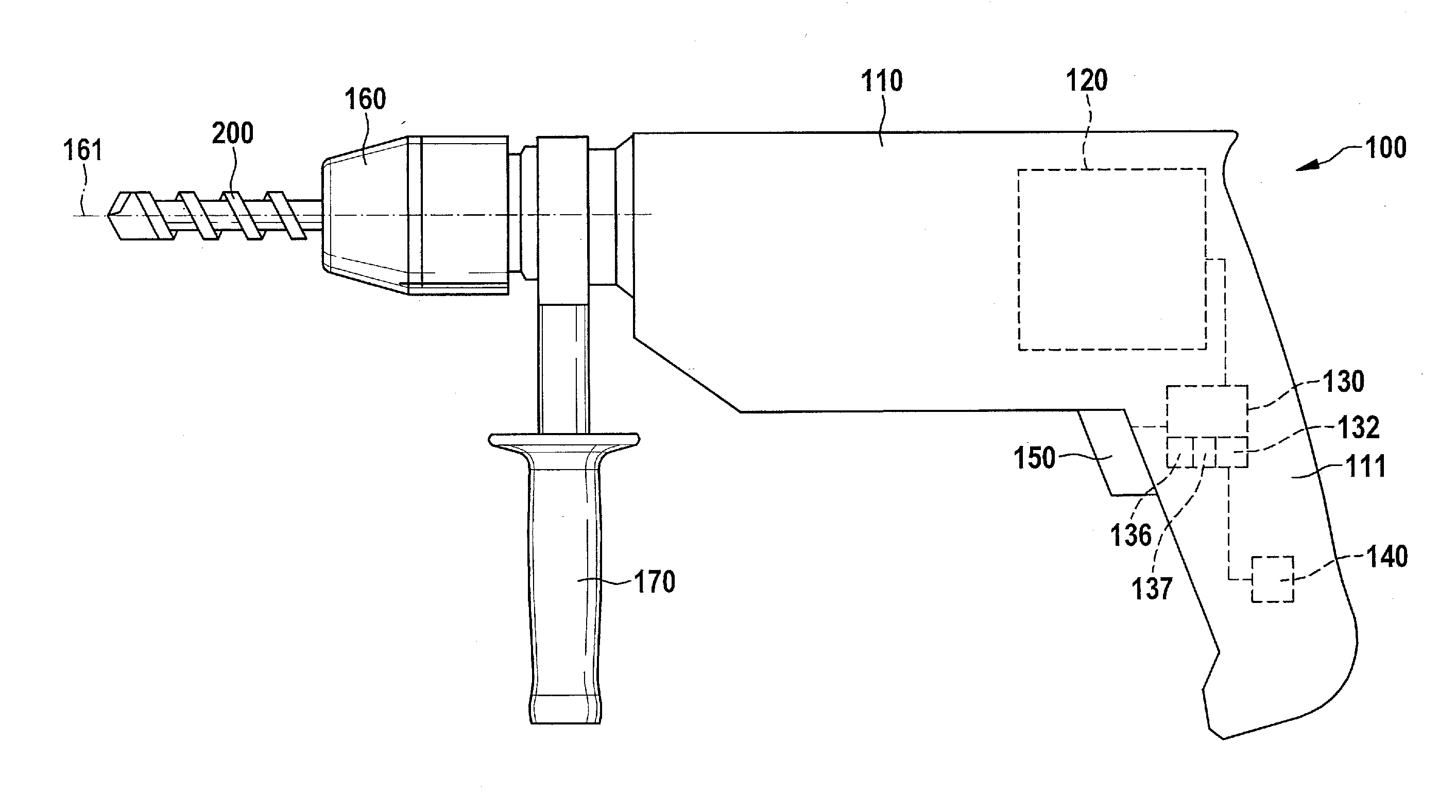
Hand-held power tool and method for operating the hand-held power tool
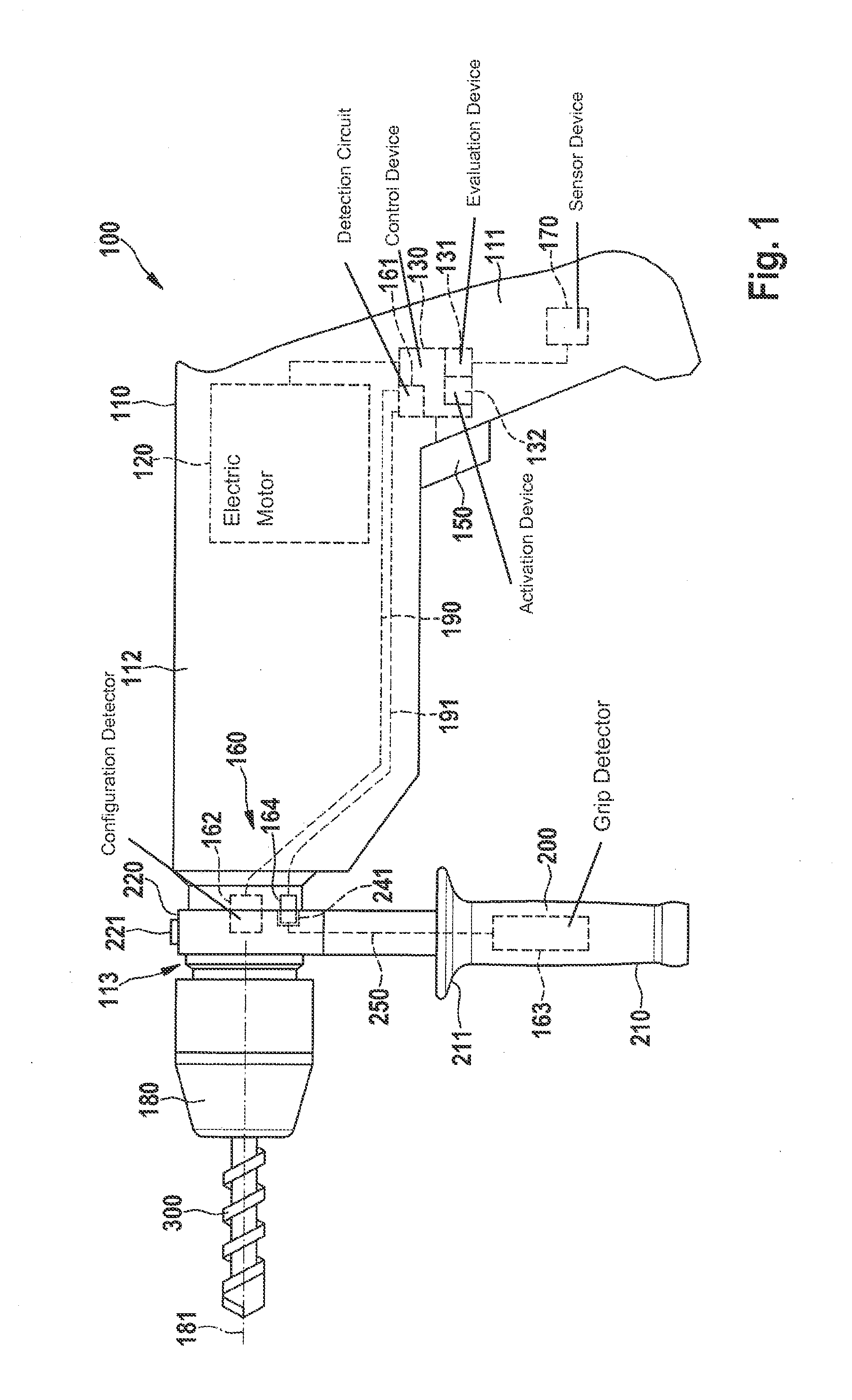
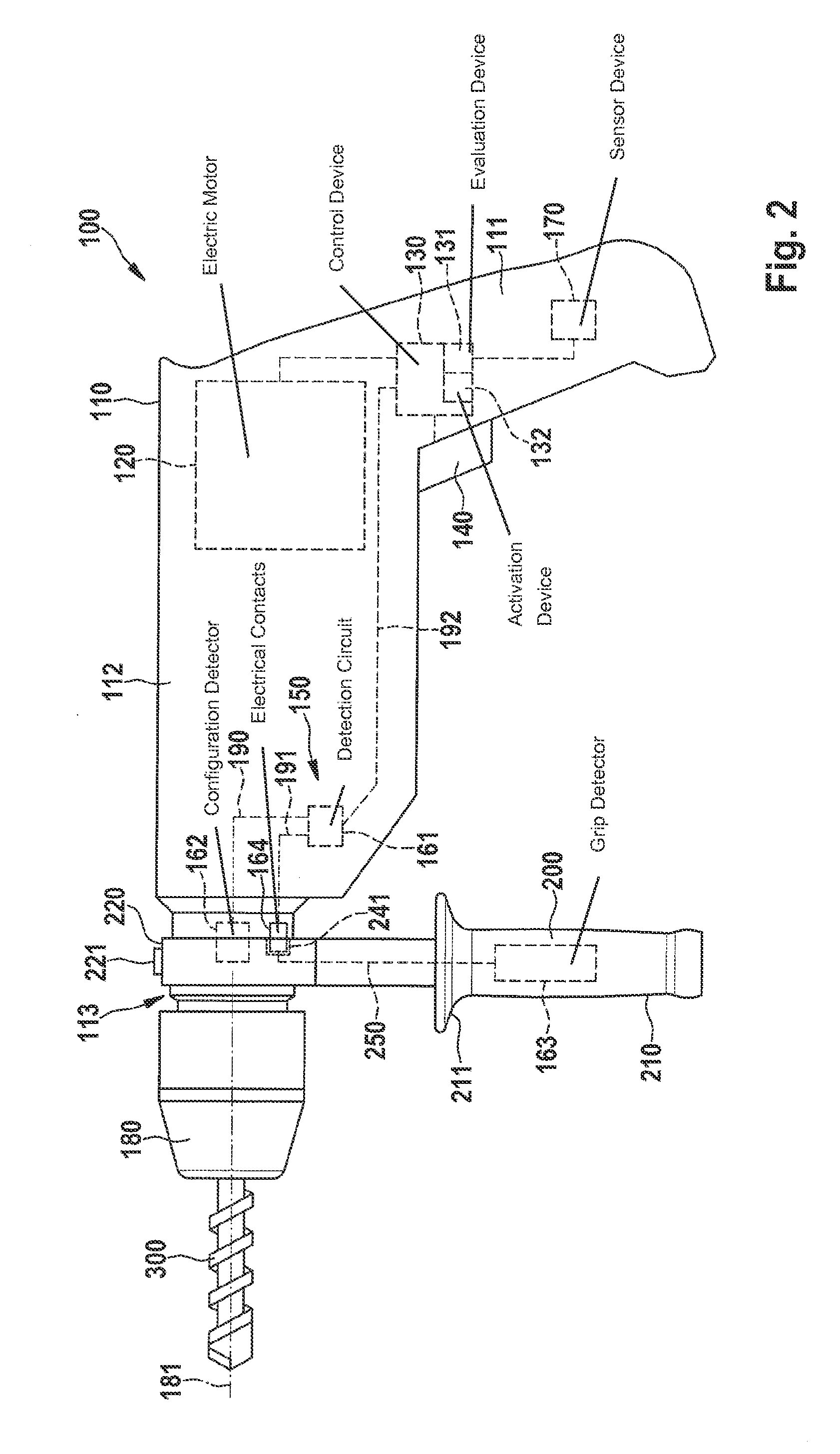
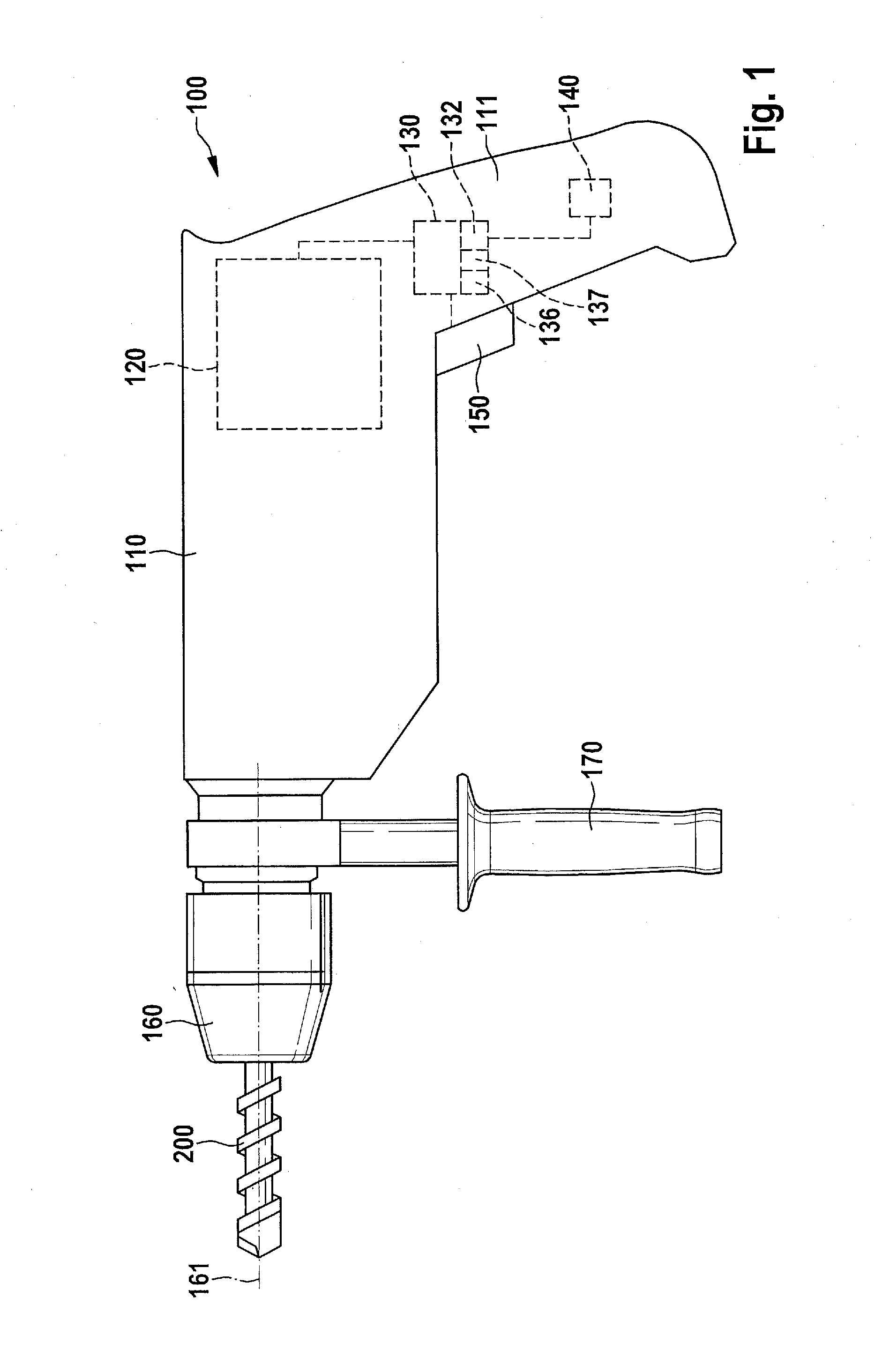
InactiveUS20140231113A1Operational safety is enhancedSimple adaptationDerricks/mastsPortable power-driven toolsHand heldEngineering
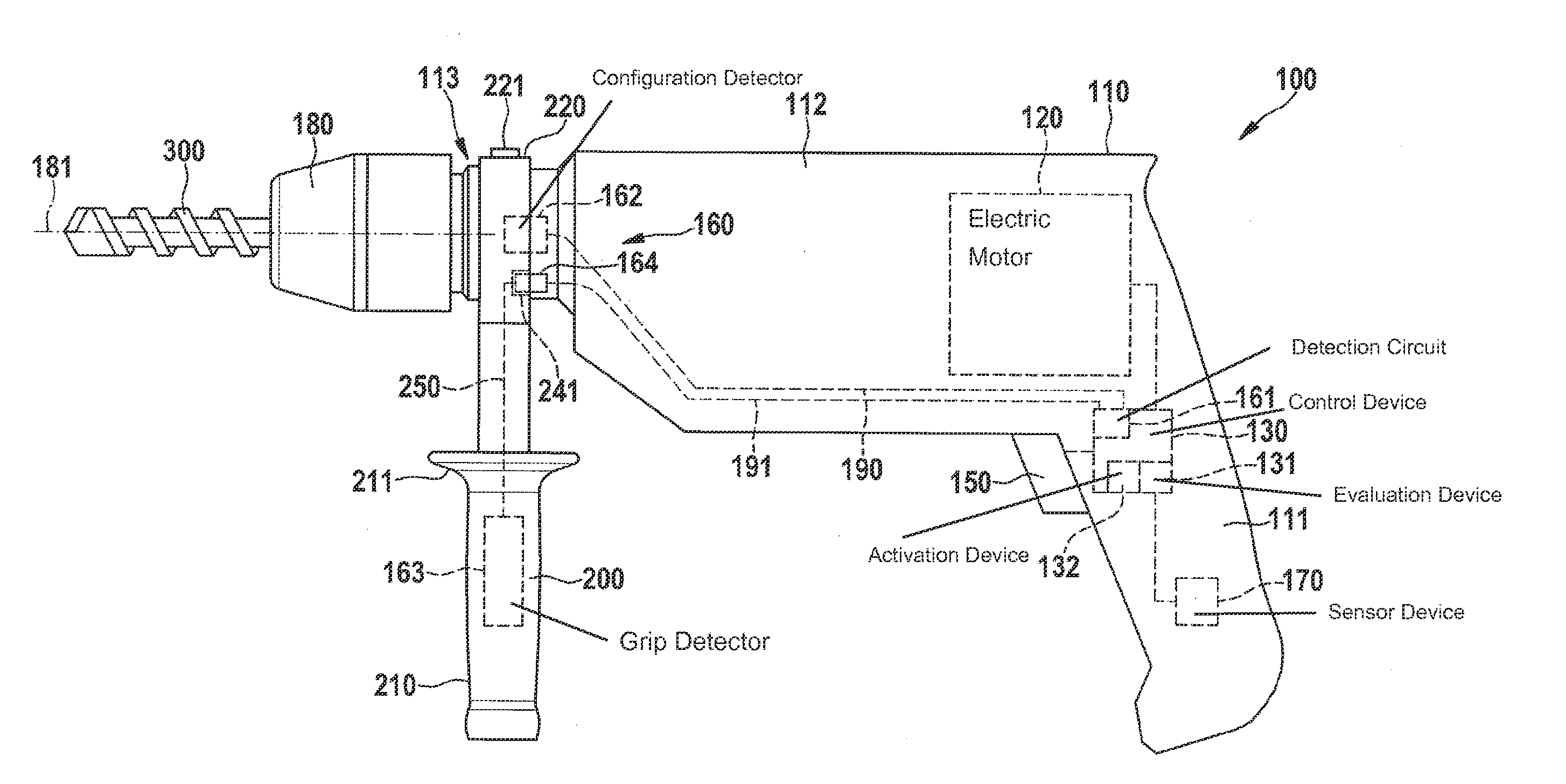
A method is provided for controlling an electric hand-held power tool having a device housing and a coupling device on the device housing side for securing an auxiliary handle to the device housing. It is detected whether the auxiliary handle is secured to the device housing and / or whether the auxiliary handle is gripped by a user. In addition, the instantaneous operating state is ascertained and evaluated. A protective function is activated when the occurrence of a critical operating case is recognized during the evaluation of the instantaneous operating state. It is provided that the evaluation of the instantaneous operating state and / or the activation of the protective function is / are carried out as a function of whether the auxiliary handle is secured to the device housing and / or whether the auxiliary handle is gripped by the user.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Medical device supporting apparatus
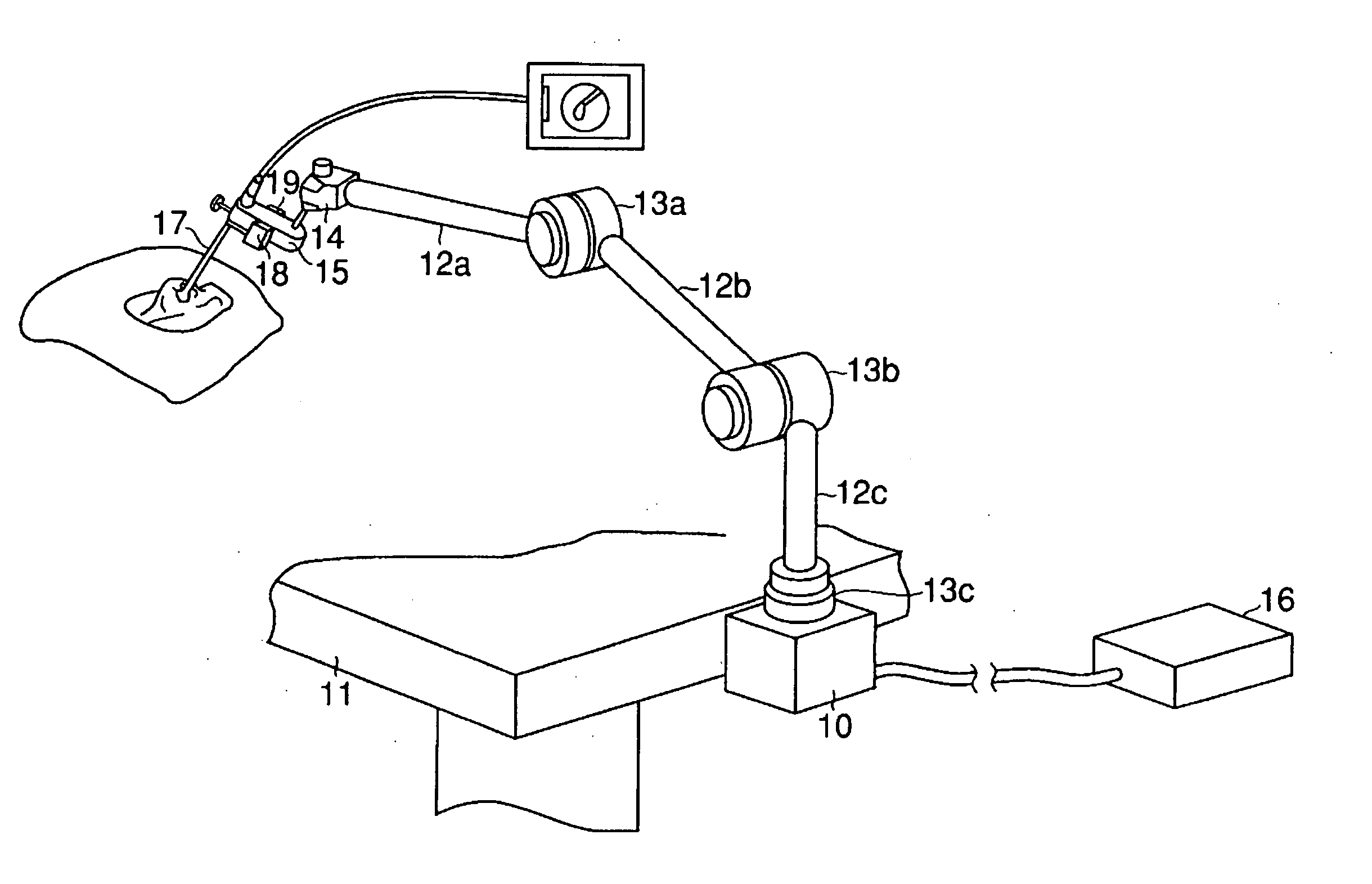
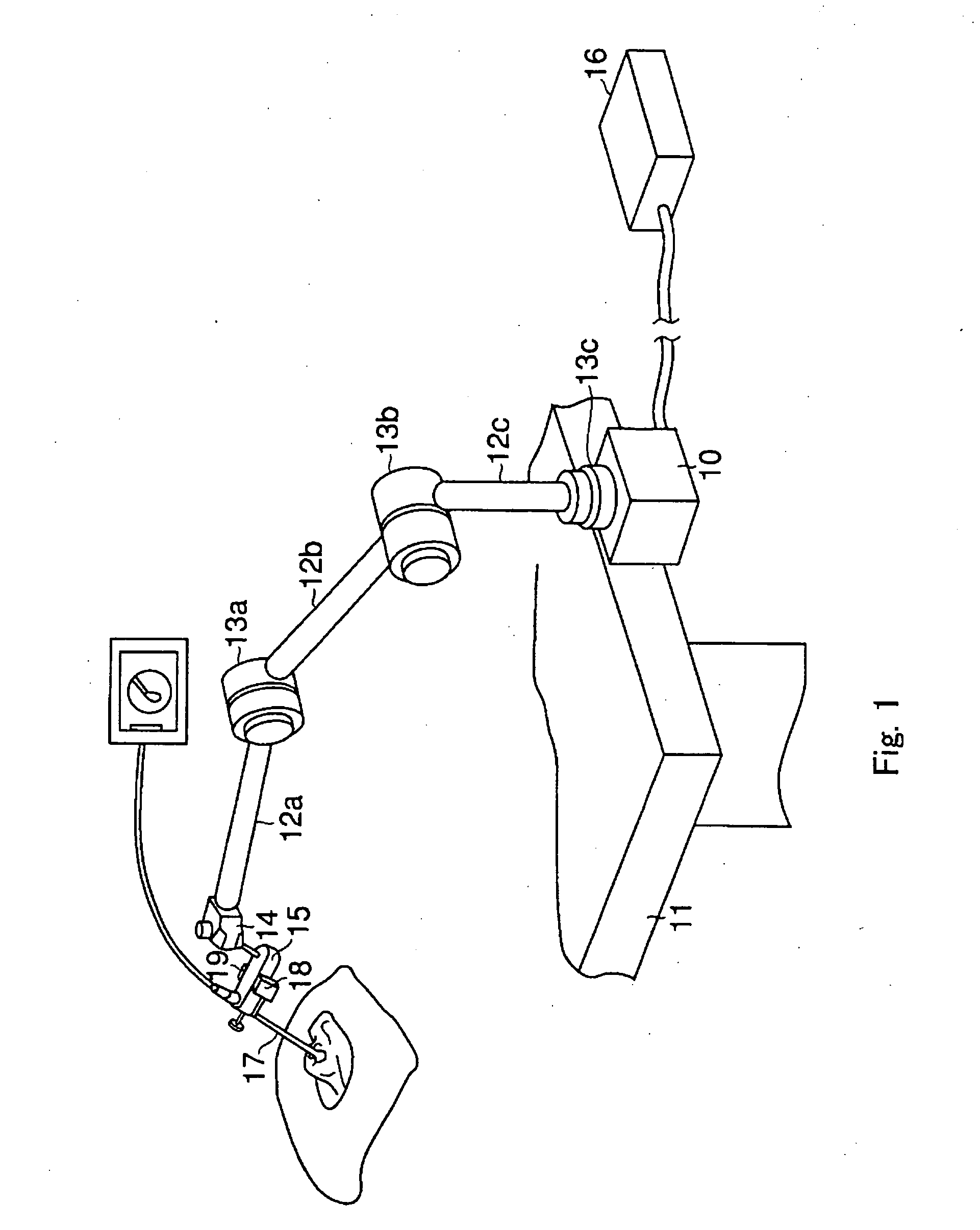
InactiveUS20050075536A1High degree of reliabilityHigh degree of accuracyEndoscopesSurgical instrument detailsThree-dimensional spaceEngineering
A medical device supporting apparatus for supporting a medical device in a three-dimensional space, in which a holding device for holding the medical device is supported by a supporting mechanism three-dimensionally, and the state of the supporting unit is switched between the movable state and the locked state by operating a plurality of final control elements. Operation is stabilized by differentiating the amount of operating force of the plurality of final control elements.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Vehicle apparatus
ActiveUS9731714B2Improve securityProhibit some movementImage enhancementImage analysisEngineeringMoving parts
A vehicle apparatus used in a vehicle measures a first elapsed time after completion of a parking operation by which the vehicle is parked in a parking region, and prohibits movement of the vehicle to adjust the parking position when the first elapsed time reaches a first predetermined time before receipt of a instruction signal by the receiver Accordingly, it is possible to improve safety by preventing the vehicle from moving out of a parking position even if the moving part is erroneously operated when the predetermined time elapses after the completion of parking operation.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
Vibration control with operating state measurement
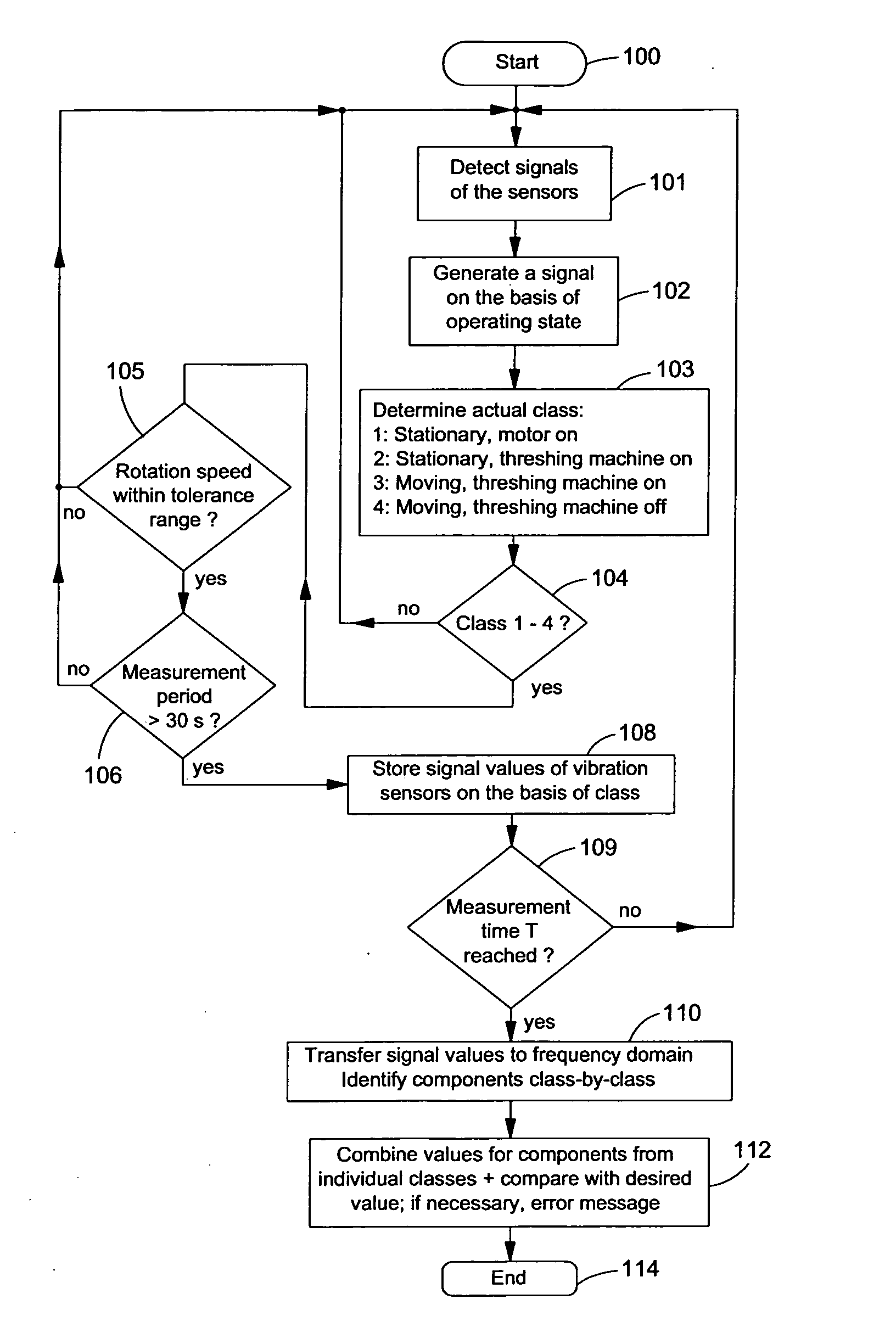
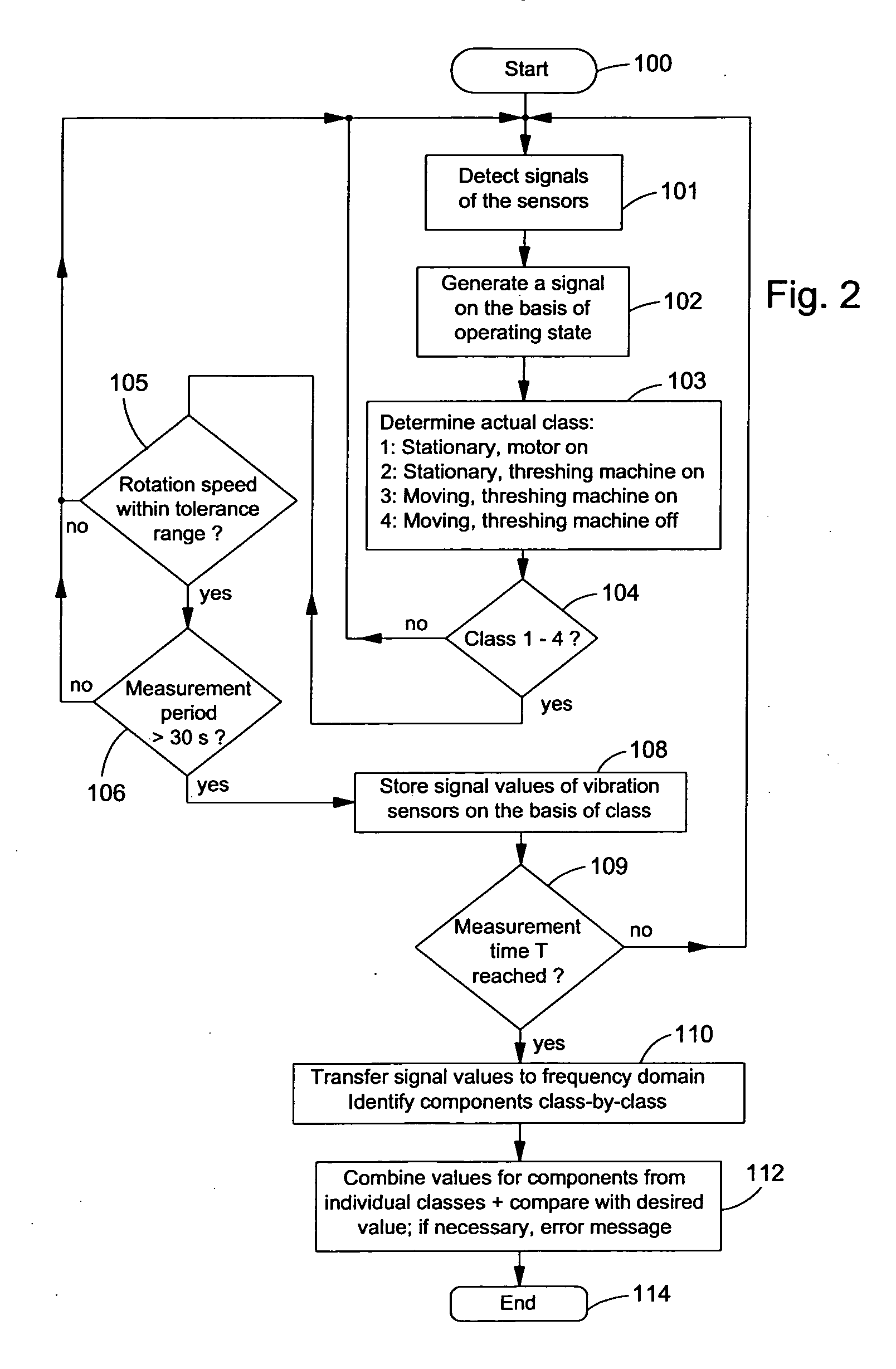
ActiveUS20060276949A1Reliably recognizeLower requirementVehicle testingAnalogue computers for trafficVibration controlMoving parts
The invention relates to a monitoring device and to a method for monitoring the function of the components of an agricultural implement, with a vibration sensor for providing signal values containing information on mechanical vibrations generated by moving components of the implement, an operating state detecting device for providing a signal containing information on the operating state of components of the implement, and a calculating device for generating state information on the basis of the state of the components of the implement. The calculating device can be operated to divide the signal values of the vibration sensor on the basis of the corresponding signals of the operating state detecting device into different classes, which correspond to different combinations of the operating states of the components in the detection of the signal values, and to compare the signal values divided into classes or data derived from these signal values with comparison values for generating state information.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Information processing apparatus, threshold value setting method, and threshold value setting program
ActiveUS8648816B2Operation moreReliably recognizeElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisInformation processingValue set
An information processing apparatus includes: a recognition section which recognizes the shape of an object being in contact with an operation screen of an operating section; a pressure detecting section which detects the pressure of the object on the operation screen; a threshold value setting section which sets a threshold value of the pressure, which is a value for determining a pressure operation on the operation screen, on the basis of the shape of the object recognized by the recognition section; and a determination section which determines whether or not a pressure operation has been performed on the operation screen on the basis of the pressure detected by the pressure detecting section and the threshold value set by the threshold value setting section.
Owner:SONY CORP
Detection of the beginning of an apnea
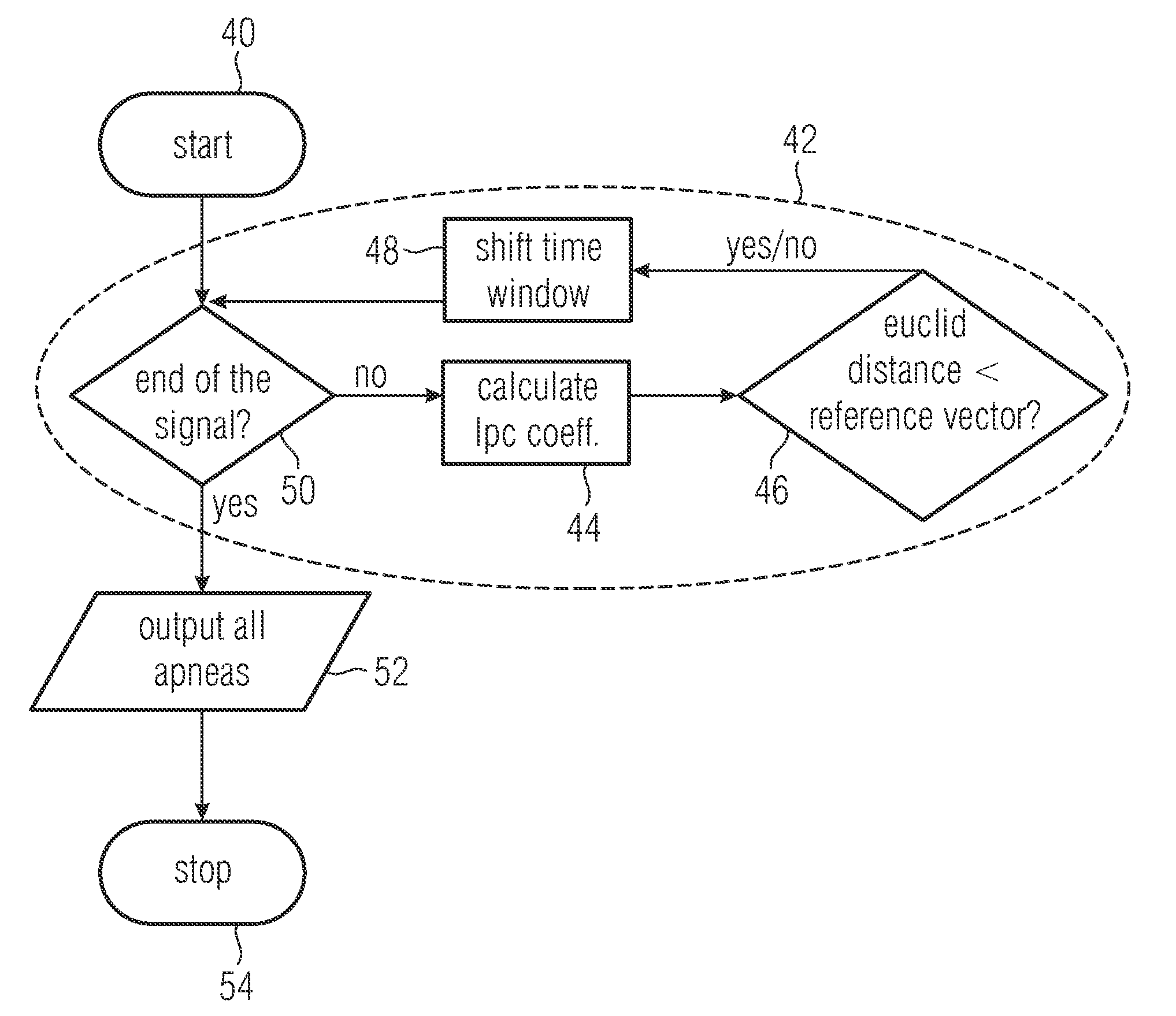
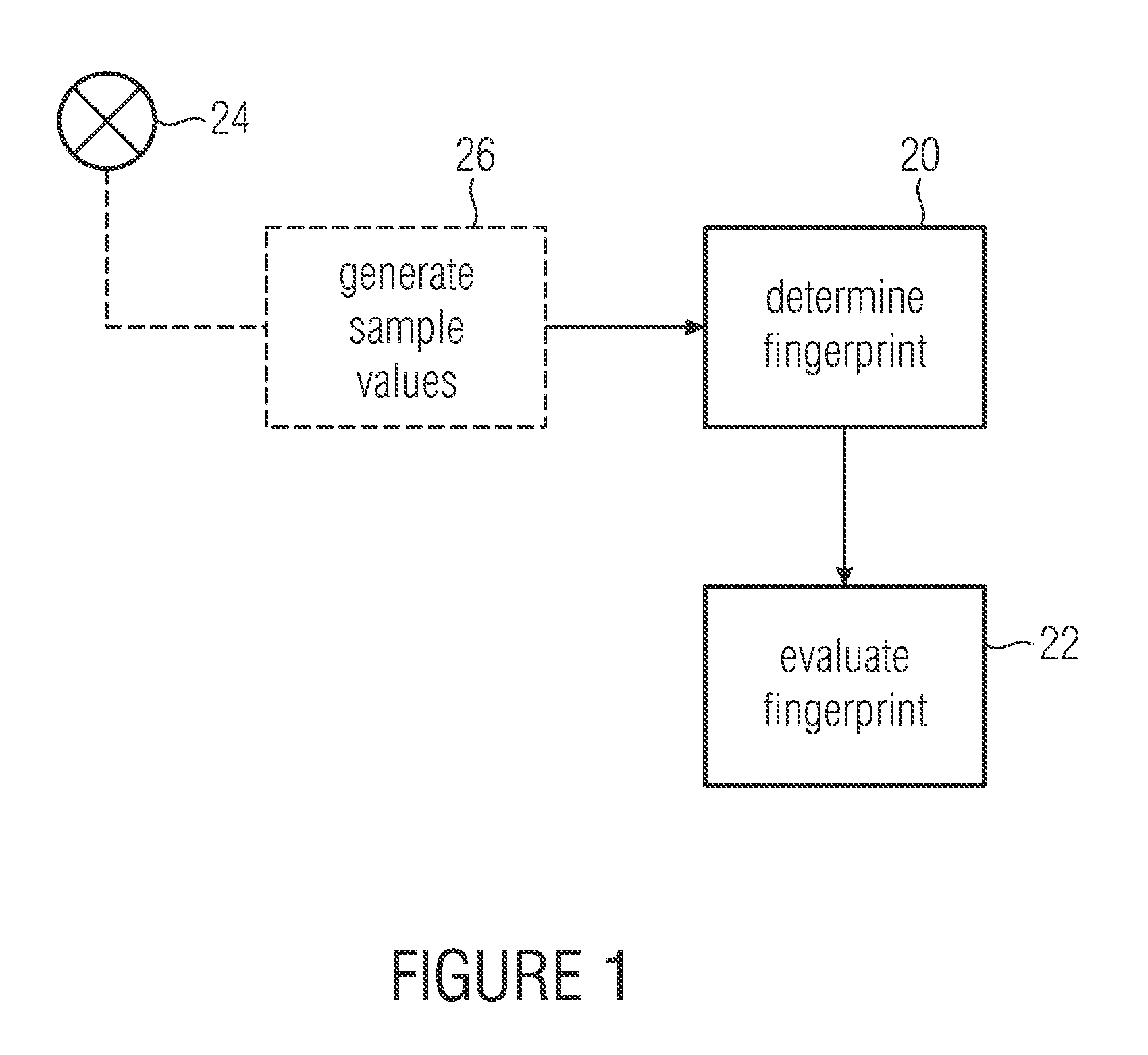
InactiveUS20090062675A1Small amount of calculationMake fastSpeech analysisAuscultation instrumentsComputer scienceApnea
The beginning of an apnea can be recognized reliably if a series of sample values describing the breathing noise of a patient are processed in block-wise manner, and if a fingerprint with a predetermined number of fingerprint coefficients describing a waveform of the sample values within a block is determined for a number of sample values within the block. Since the number of fingerprint coefficients is smaller than the number of sample values within the block, comparison of the fingerprint coefficients with reference fingerprint coefficients characteristic for the waveform at the beginning of an apnea can be performed efficiently and reliably, in order to detect the beginning of the apnea.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method for controlling a rolling or coasting function of a vehicle
InactiveUS20120220422A1Reliably recognizePrevent unnecessary shifting into neutralRoad transportGearing controlAutomatic transmissionDrive motor
A method of controlling a rolling or coasting function of a vehicle with a drive train having a drive motor, an automatic or automated transmission, a controllable shifting means, a brake device and a drive speed control device. The vehicle speed is regulated by the drive speed control device and the braking device is activated, as needed, when driving on a downhill gradient section. To effectively and reliably use the rolling or coasting function in suitable driving situations, taking into account the influence of the driving speed control device, a rolling or a coasting condition for a downhill gradient taper is checked, when driving on the downhill gradient section, and, when the rolling or coasting condition is satisfied, the transmission controls interrupt the flow of power in the drive train before the vehicle entering a flat area, and / or before the driving speed control device generates an engine torque request.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
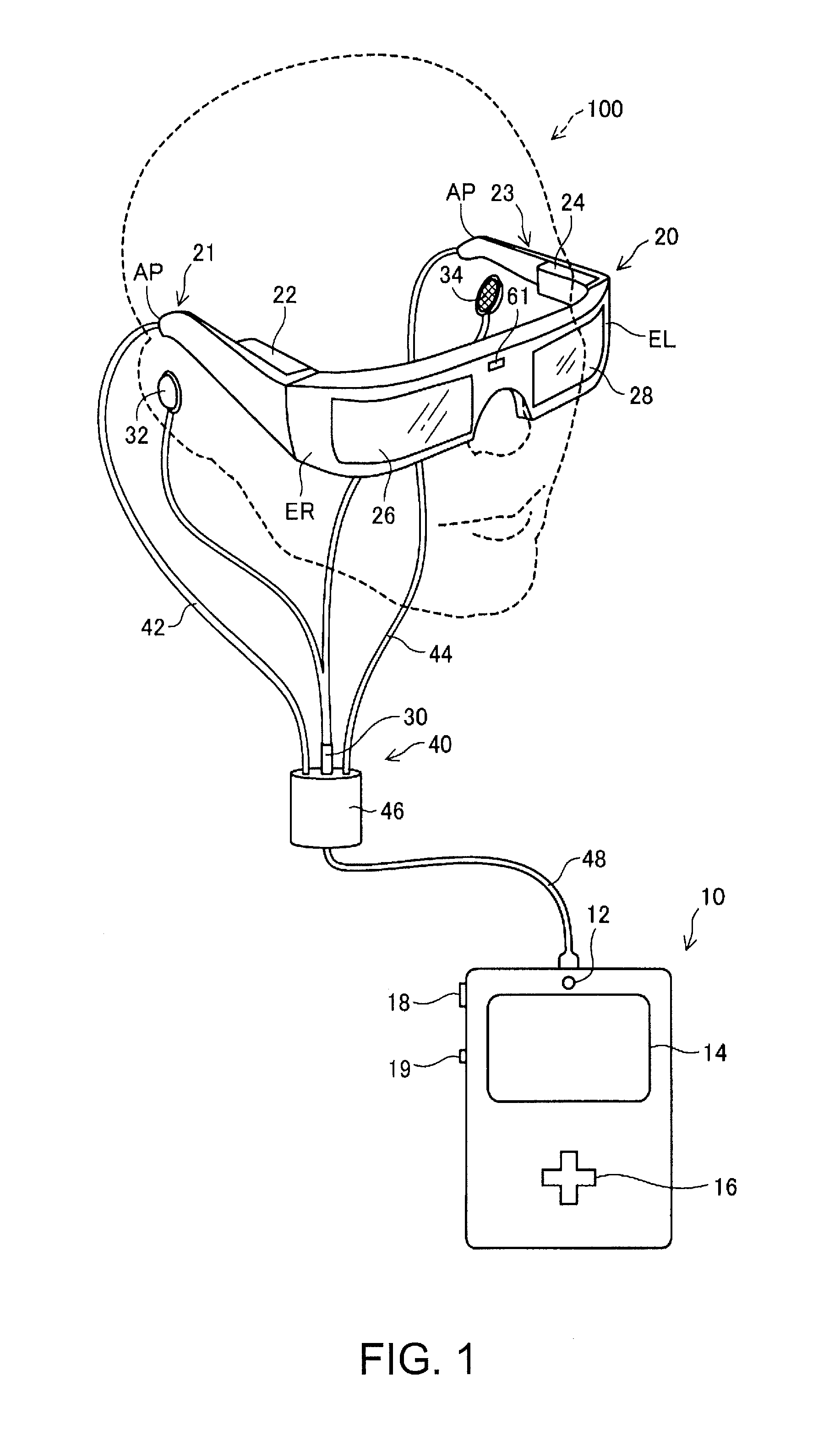
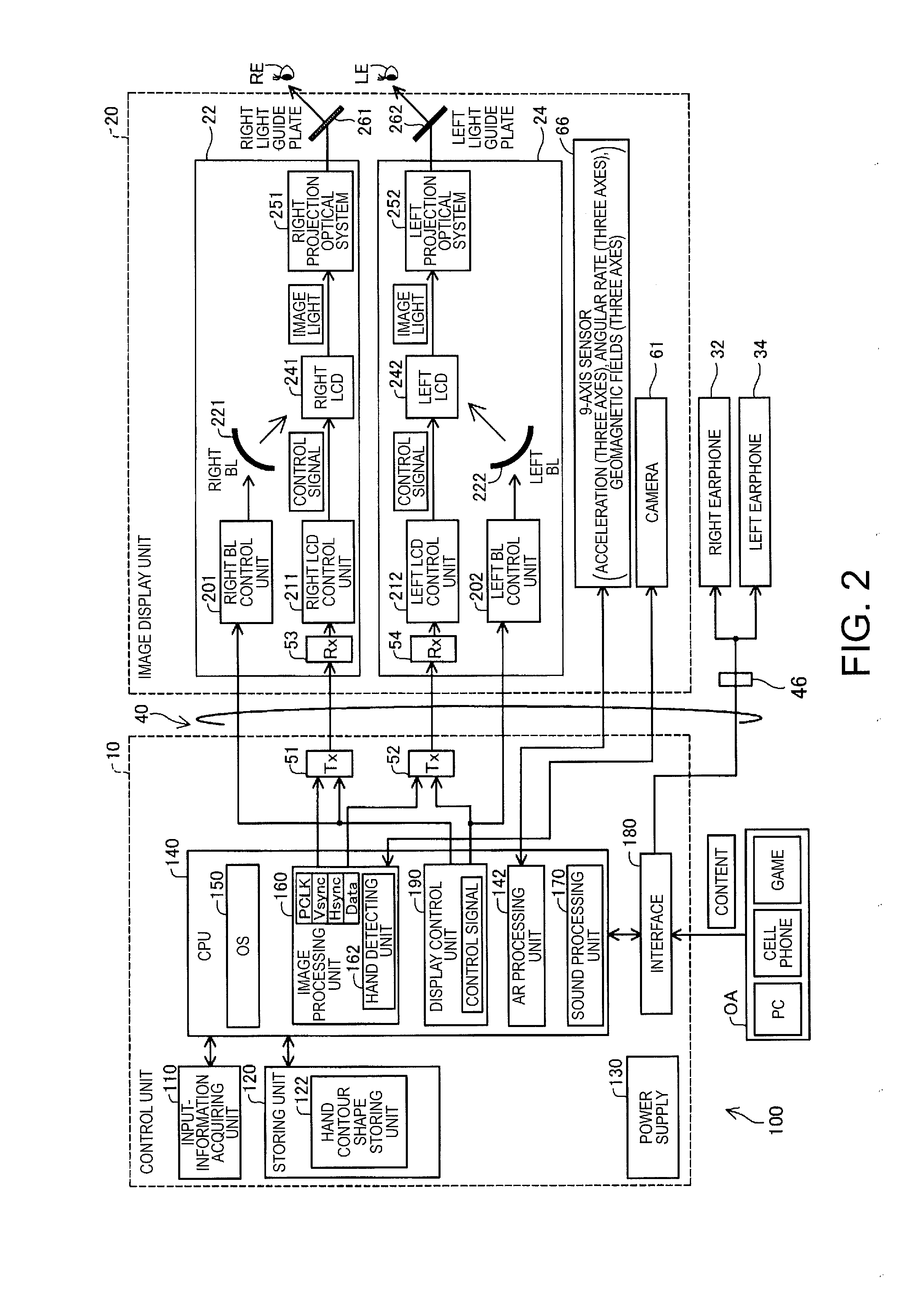
Head mounted display apparatus
ActiveUS20150062000A1Improve detection accuracyImprove convenienceInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceComputer vision
When a hand of the user is recognized in an image pickup region of a camera, a head mounted display monitors behavior of the hand in the image pickup region. When the hand of the user in the image pickup region reaches an outer peripheral region forming an outer periphery of the image pickup region, a notification is give to the user.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
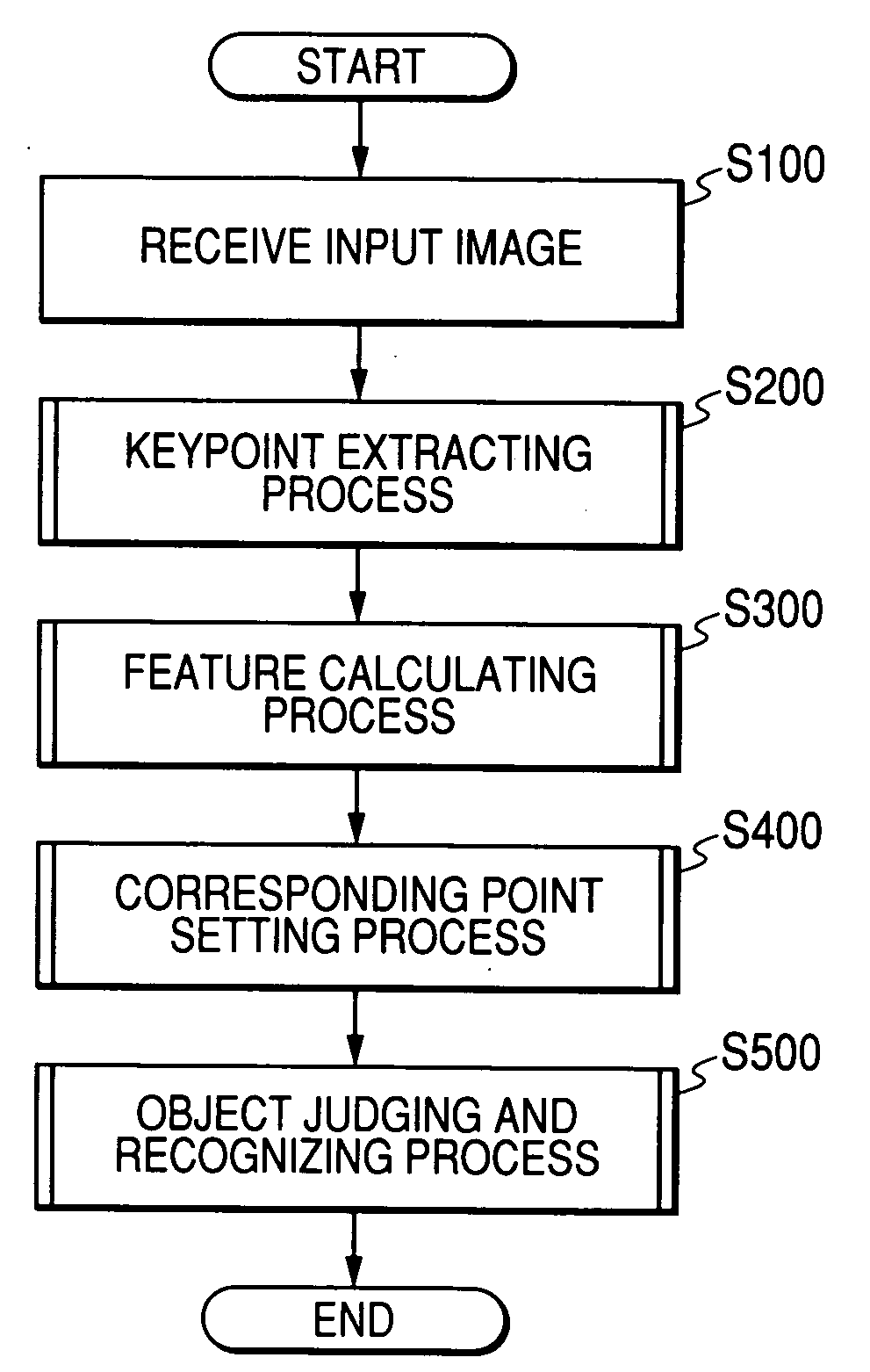
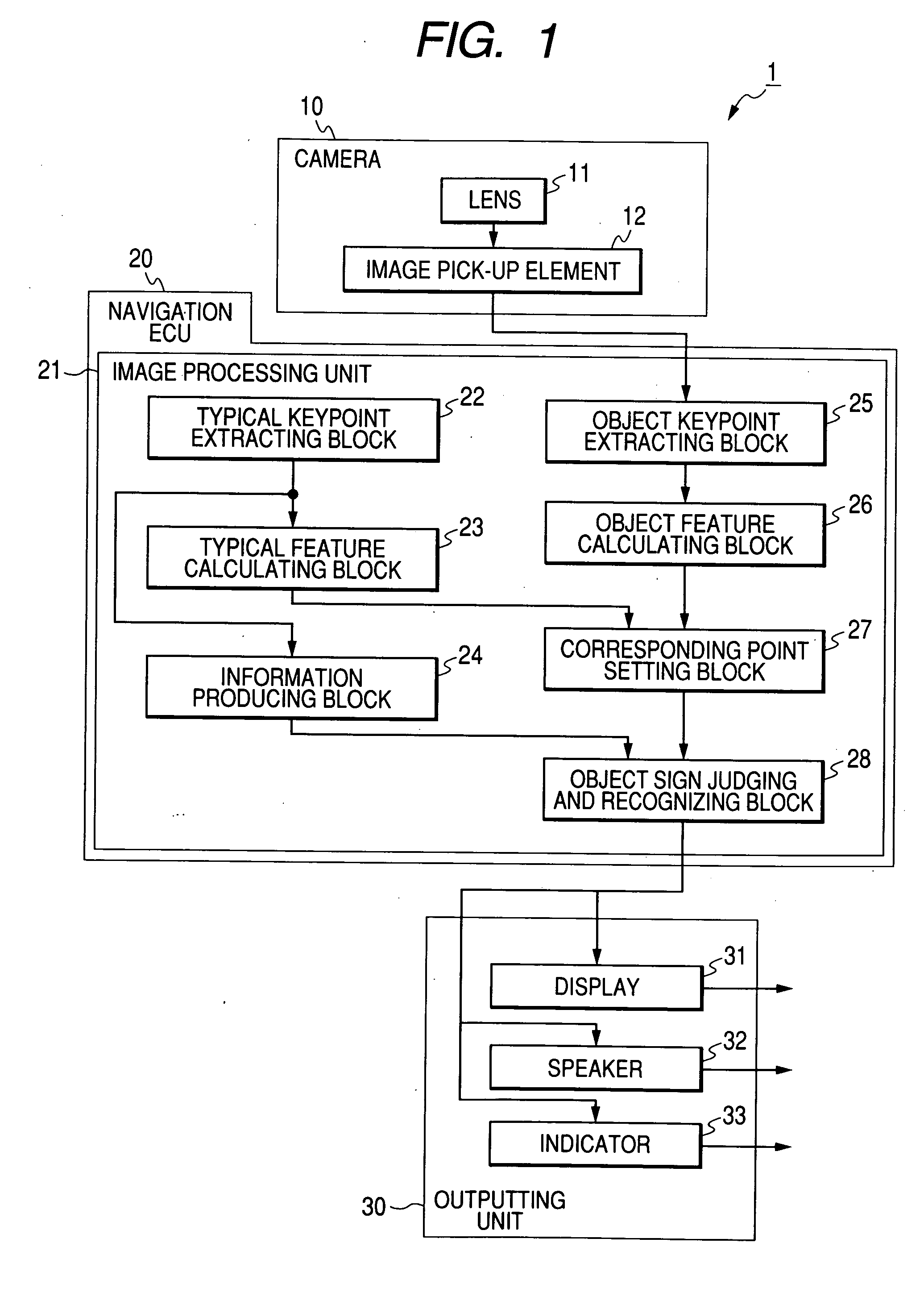
Apparatus for recognizing object in image
ActiveUS20080247651A1Reliably recognizeReliable matchCharacter and pattern recognitionImage extractionIdentification device
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
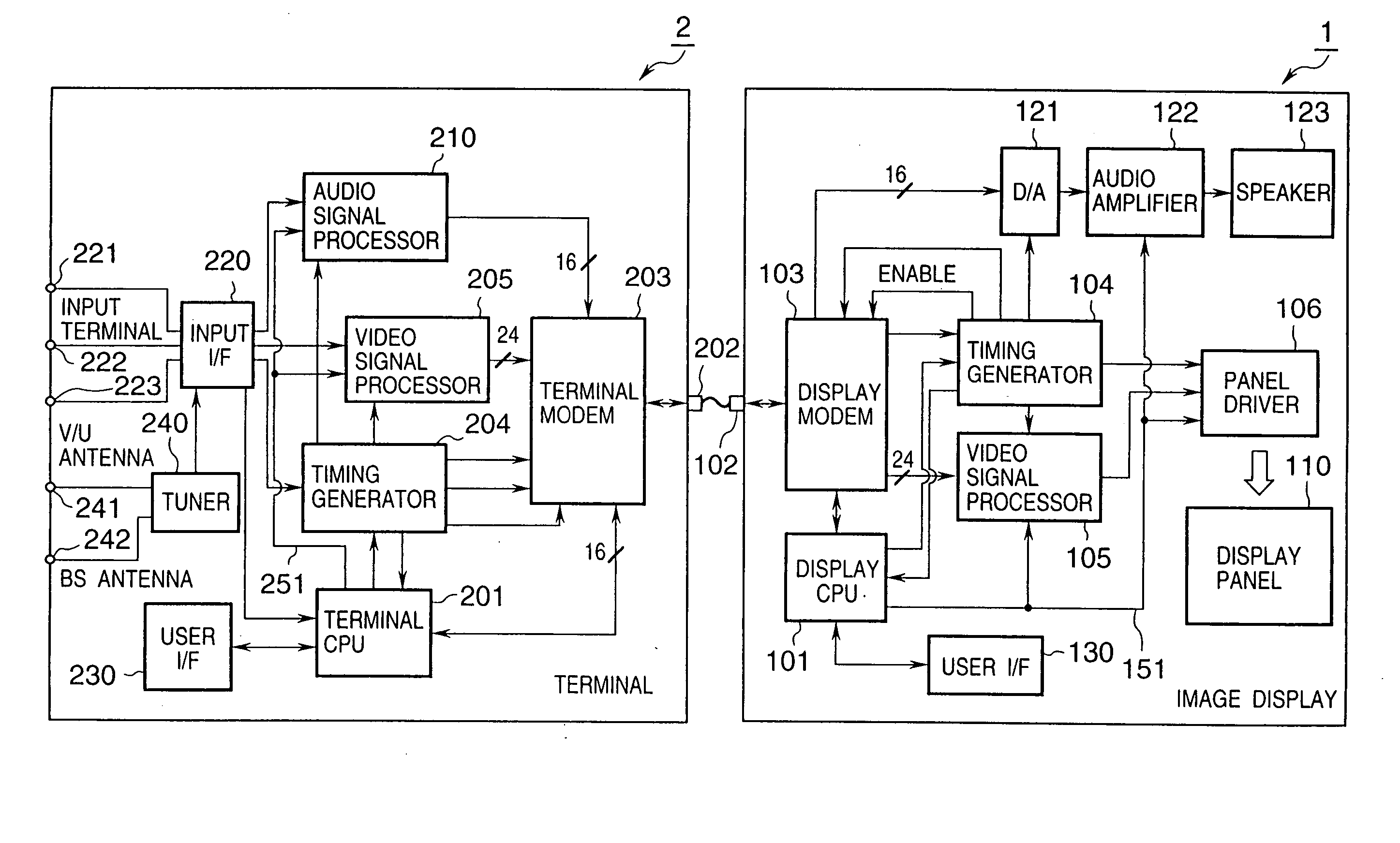
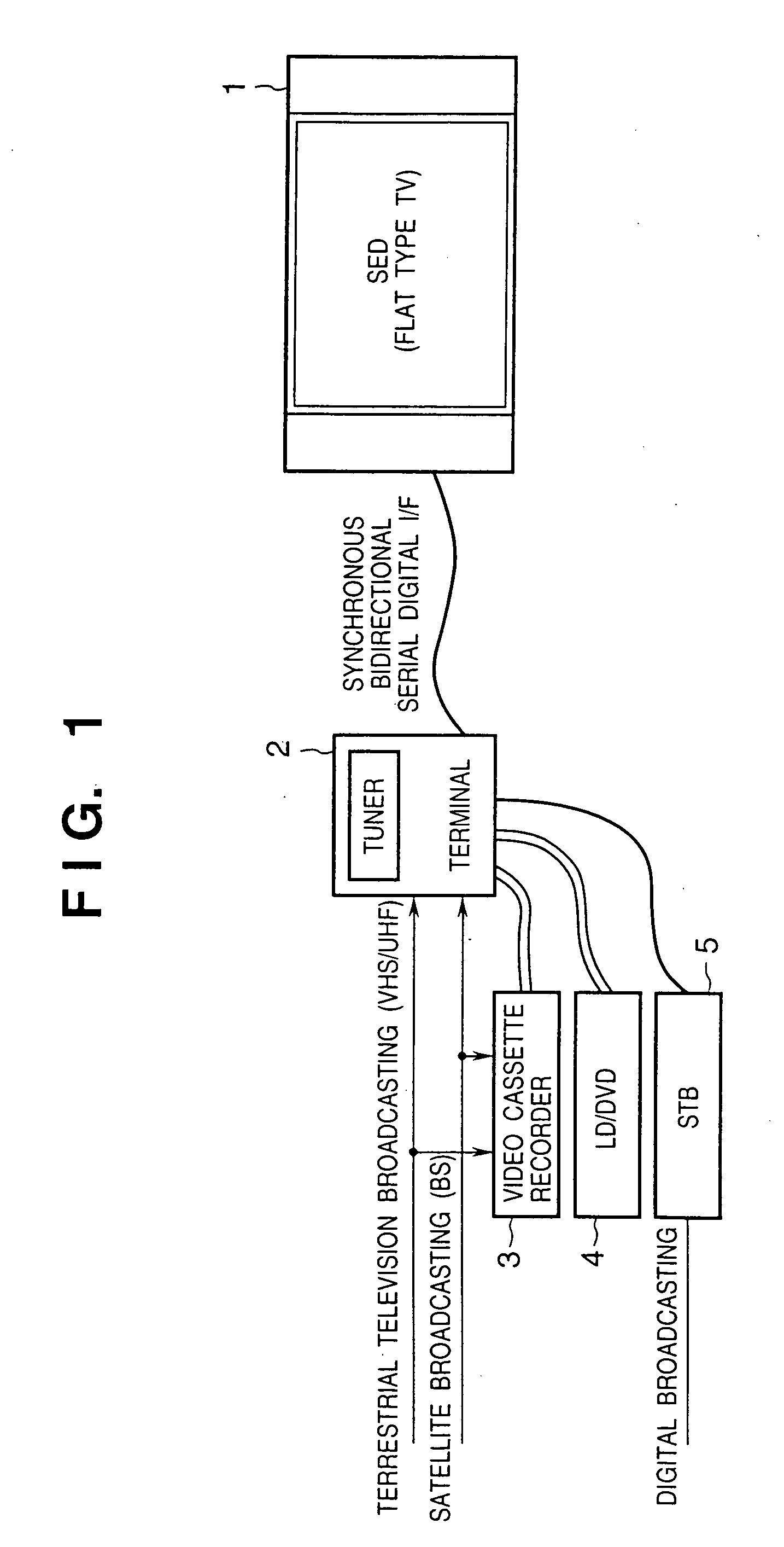
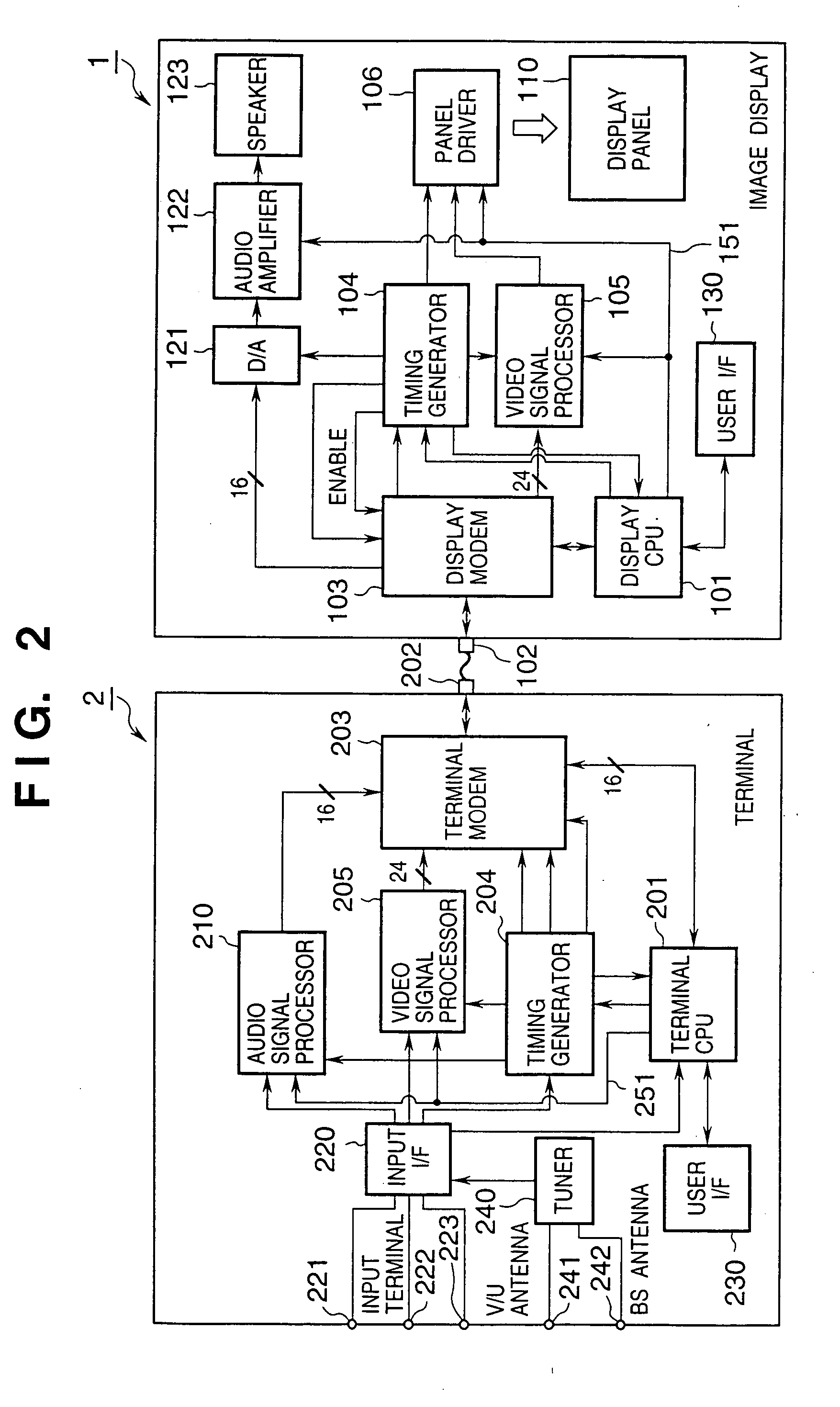
Image display control system and image display system control method
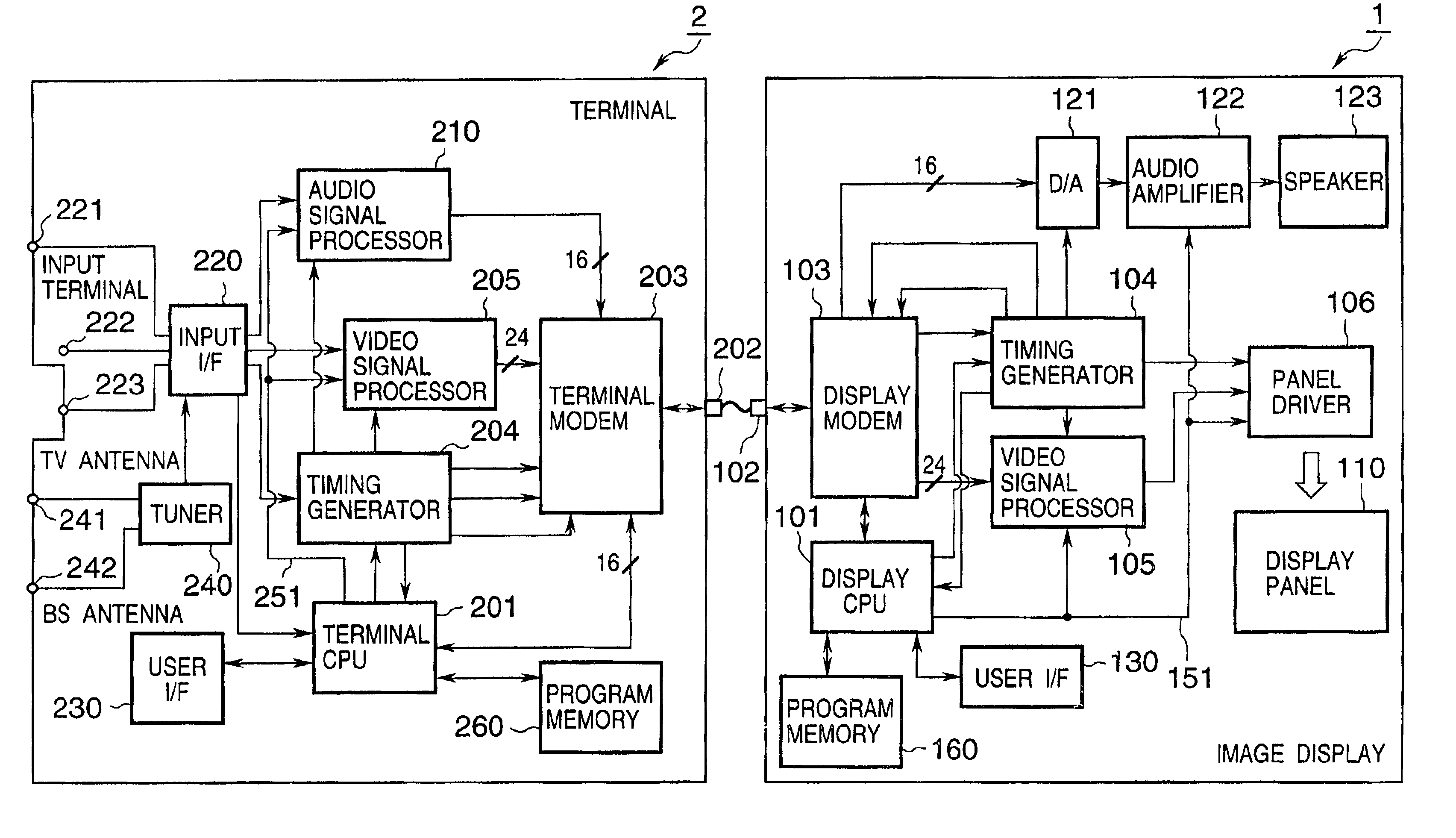
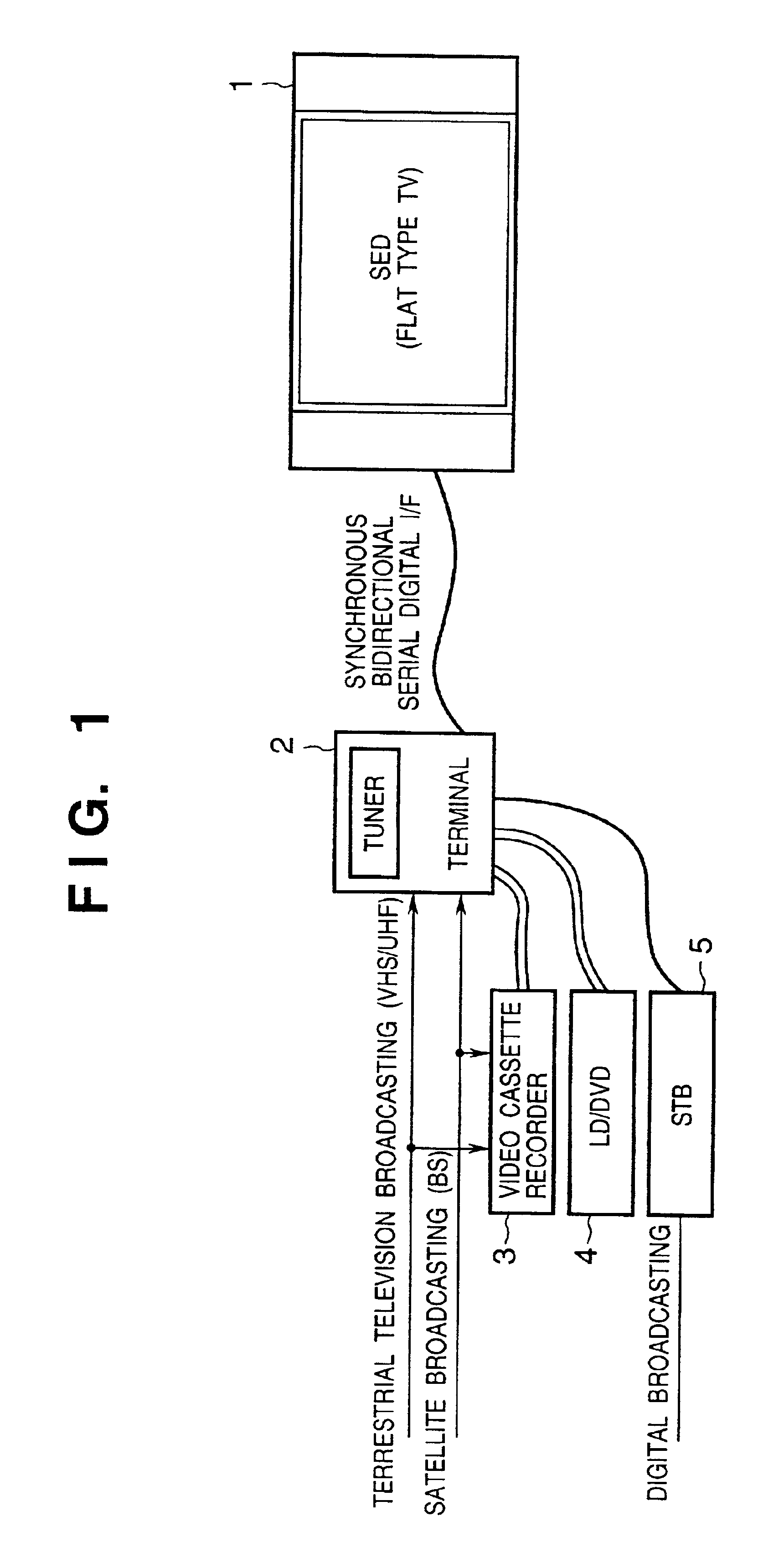
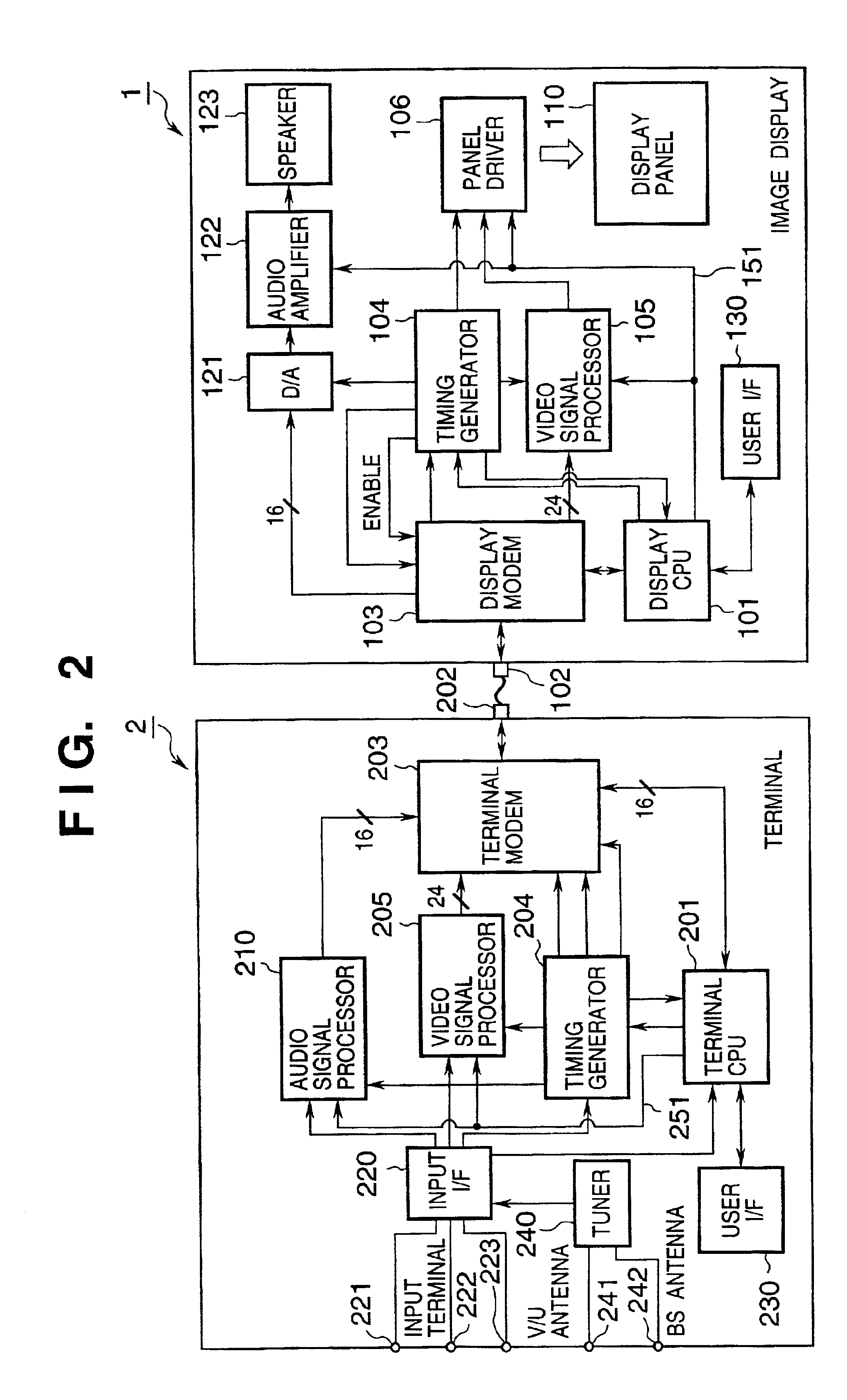
InactiveUS20050156869A1Easily transmit video signalReliably recognizeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAcquired characteristicComputer graphics (images)
This invention discloses an arrangement allowing connection of various kinds of image displays to one supply source in an image display control system having a supply source for transmitting a signal including at least a video signal, and an image display for receiving the signal and displaying a corresponding image. The supply source acquires characteristic data of the image display when it is powered on, determines a signal communication specification with the image display based on the acquired characteristic data, and communicates a signal including the video signal with the determined communication specification. The image display transmits characteristic data for specifying the characteristics of the image display to the supply source, and communicates the signal including the video signal in accordance with the determined communication specification. This invention also discloses an arrangement permitting changing the specifications and version of the control program of the image display.
Owner:CANON KK
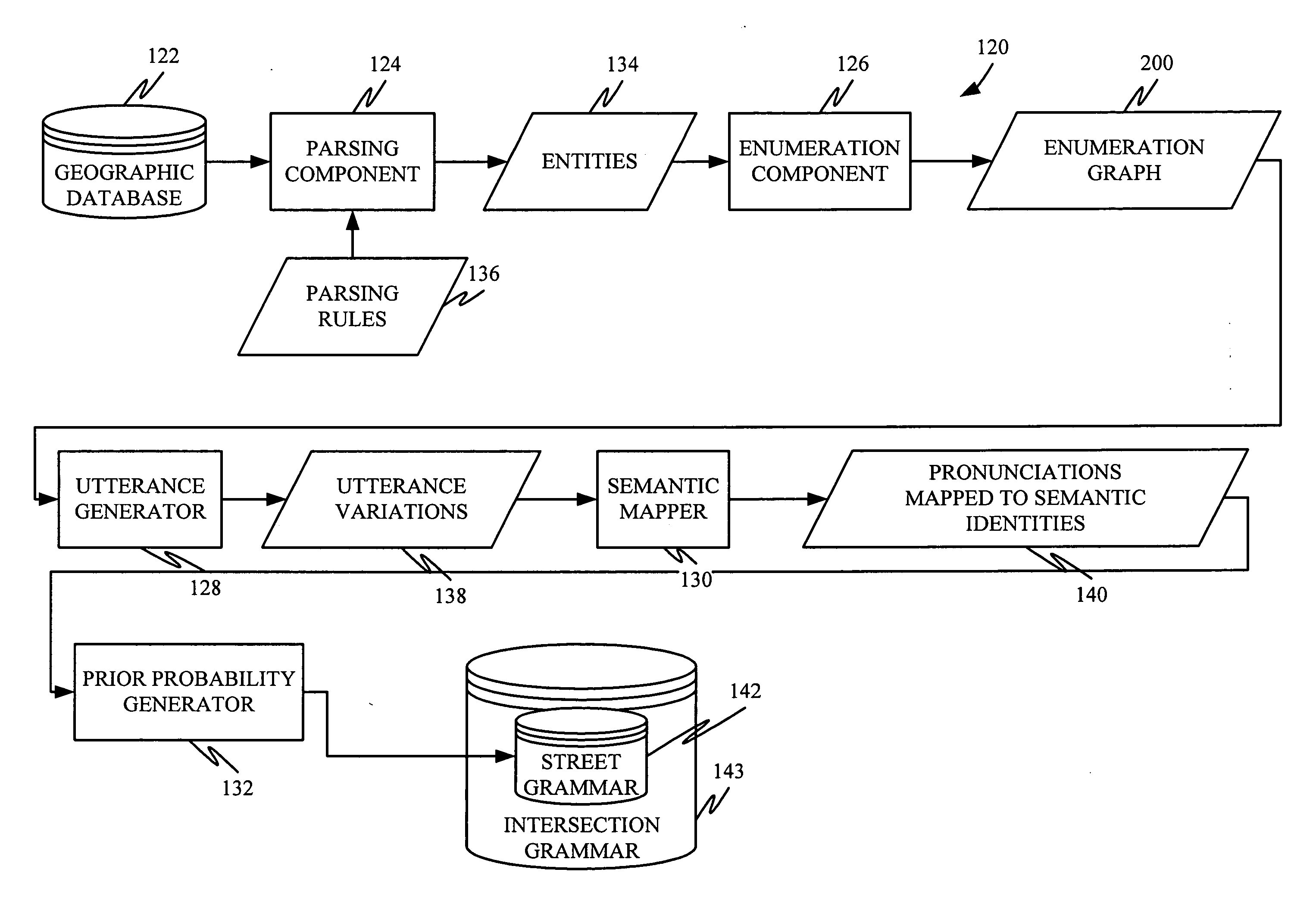
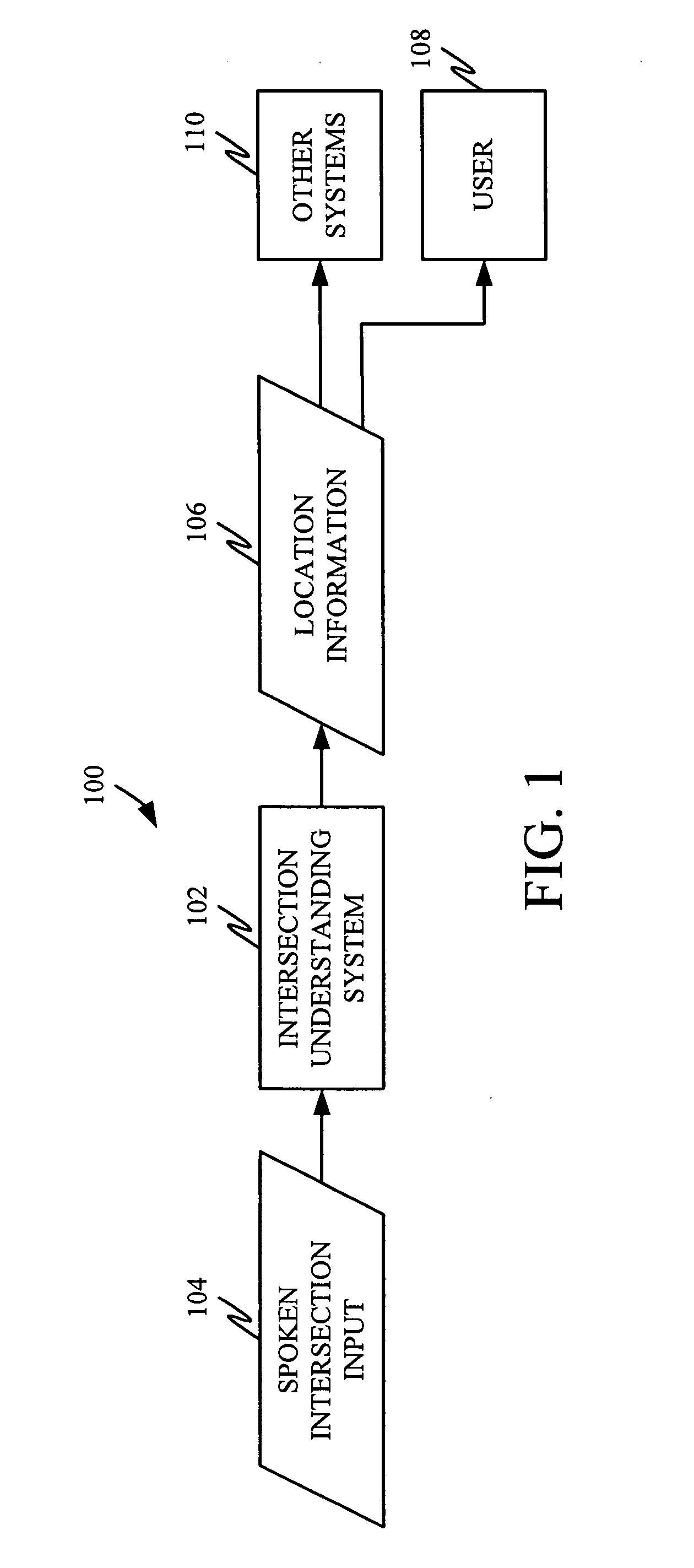
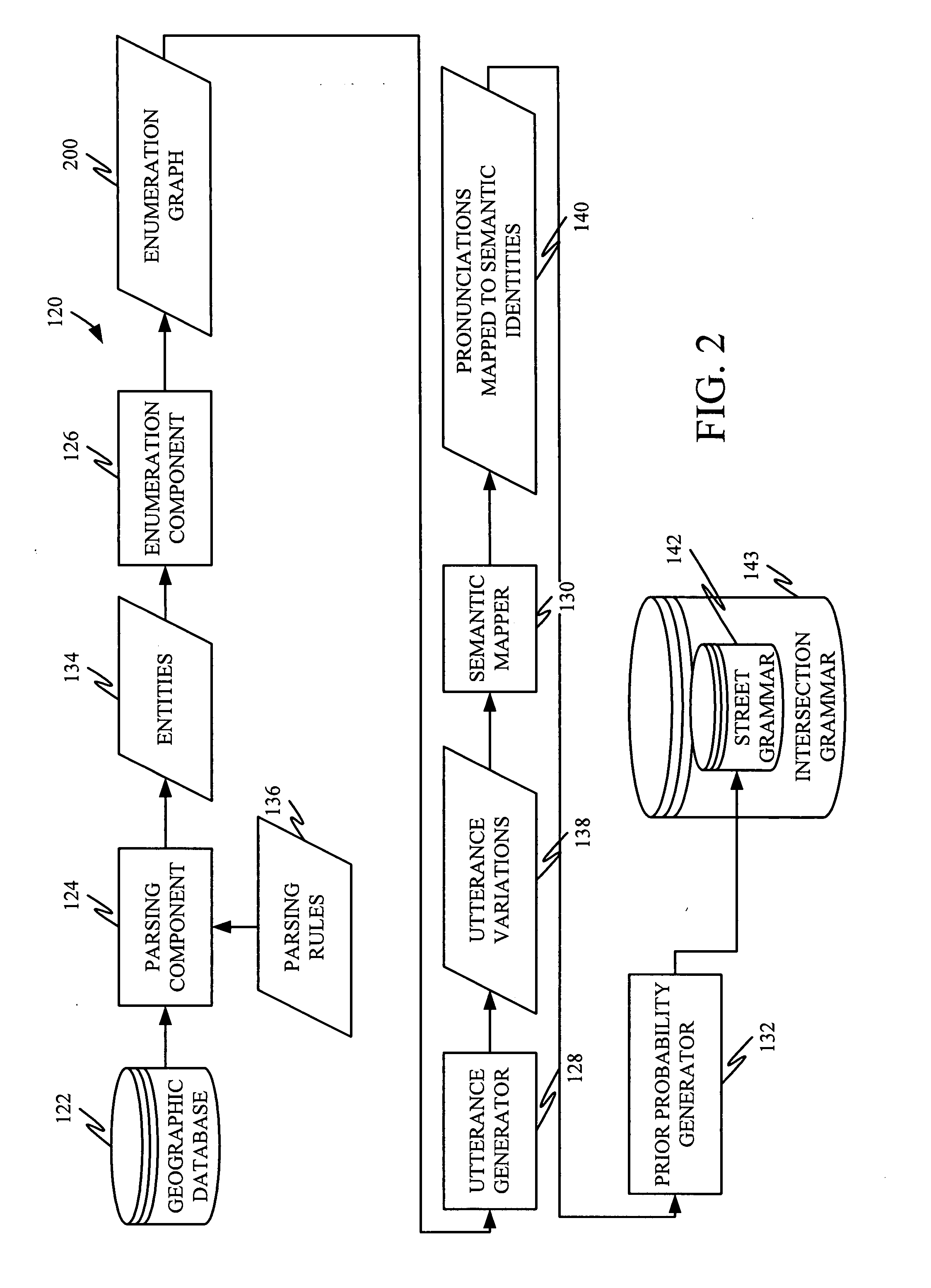
Understanding spoken location information based on intersections
ActiveUS20090037174A1Easy for userDisambiguation potentially much simplerSpeech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsPosition dependentSpeech input
In one embodiment, the present system recognizes a user's speech input using an automatically generated probabilistic context free grammar for street names that maps all pronunciation variations of a street name to a single canonical representation during recognition. A tokenizer expands the representation using position-dependent phonetic tokens and an intersection classifier classifies an intersection, despite the presence of recognition errors and incomplete street names.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Electric machine tool and method for controlling the electric machine tool
ActiveUS20140216773A1Easy to operateImprove securityDerricks/mastsPortable power-driven toolsElectric machineControl engineering
In a method for controlling an electric machine tool having an electric motor for driving a rotating insertion tool, the electric machine tool is operated in one of multiple operating modes, and at least one parameter of the machine tool is detected. The instantaneous operating state of the electric machine tool is ascertained and evaluated based on the detected parameter. A protective function is activated when the presence of a critical operating situation is recognized during the evaluation of the instantaneous operating state. The instantaneous operating mode of the electric machine tool is detected, and the evaluation of the instantaneous operating state is adapted in each case to the instantaneous operating mode.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Fire detector
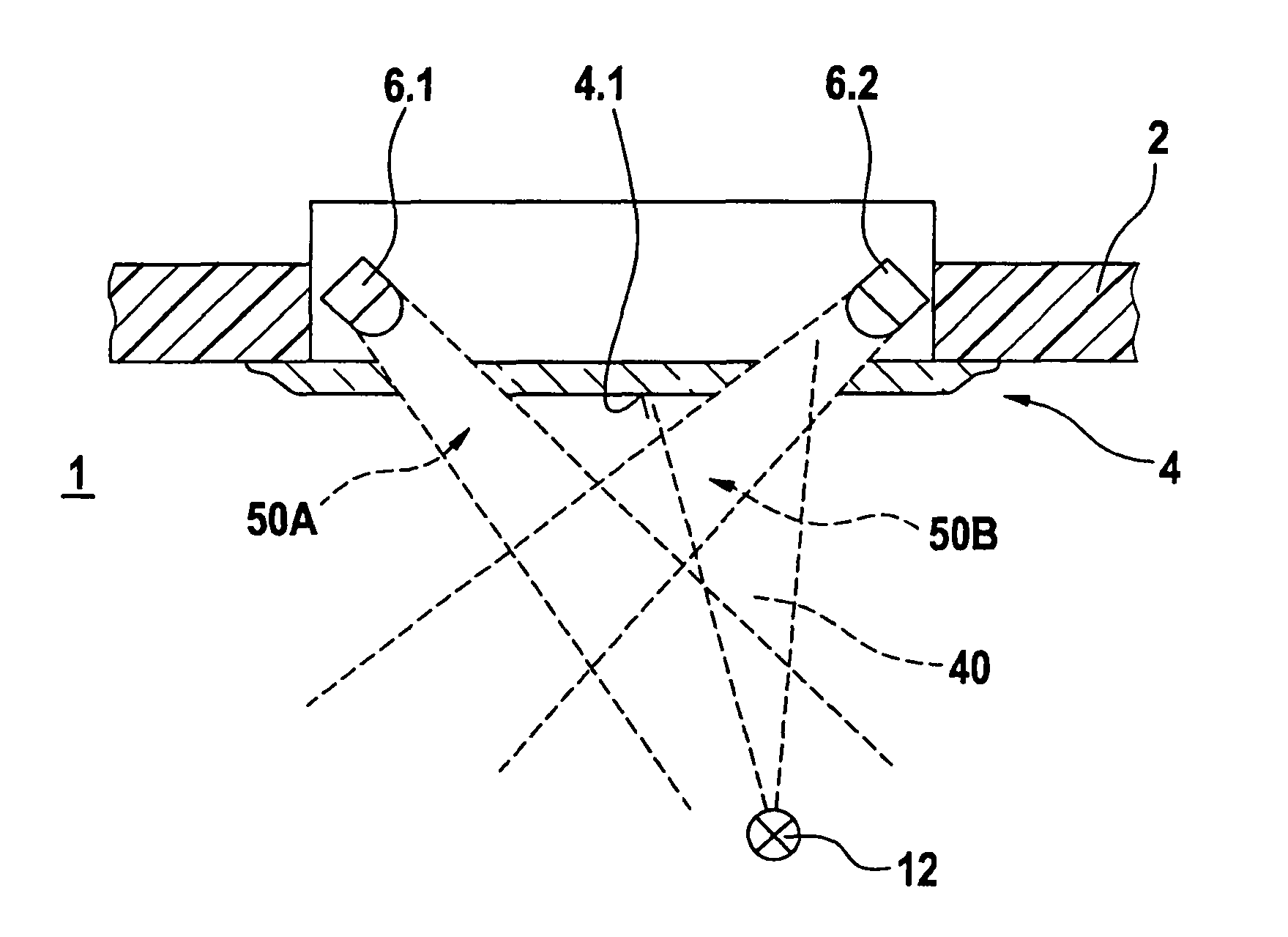
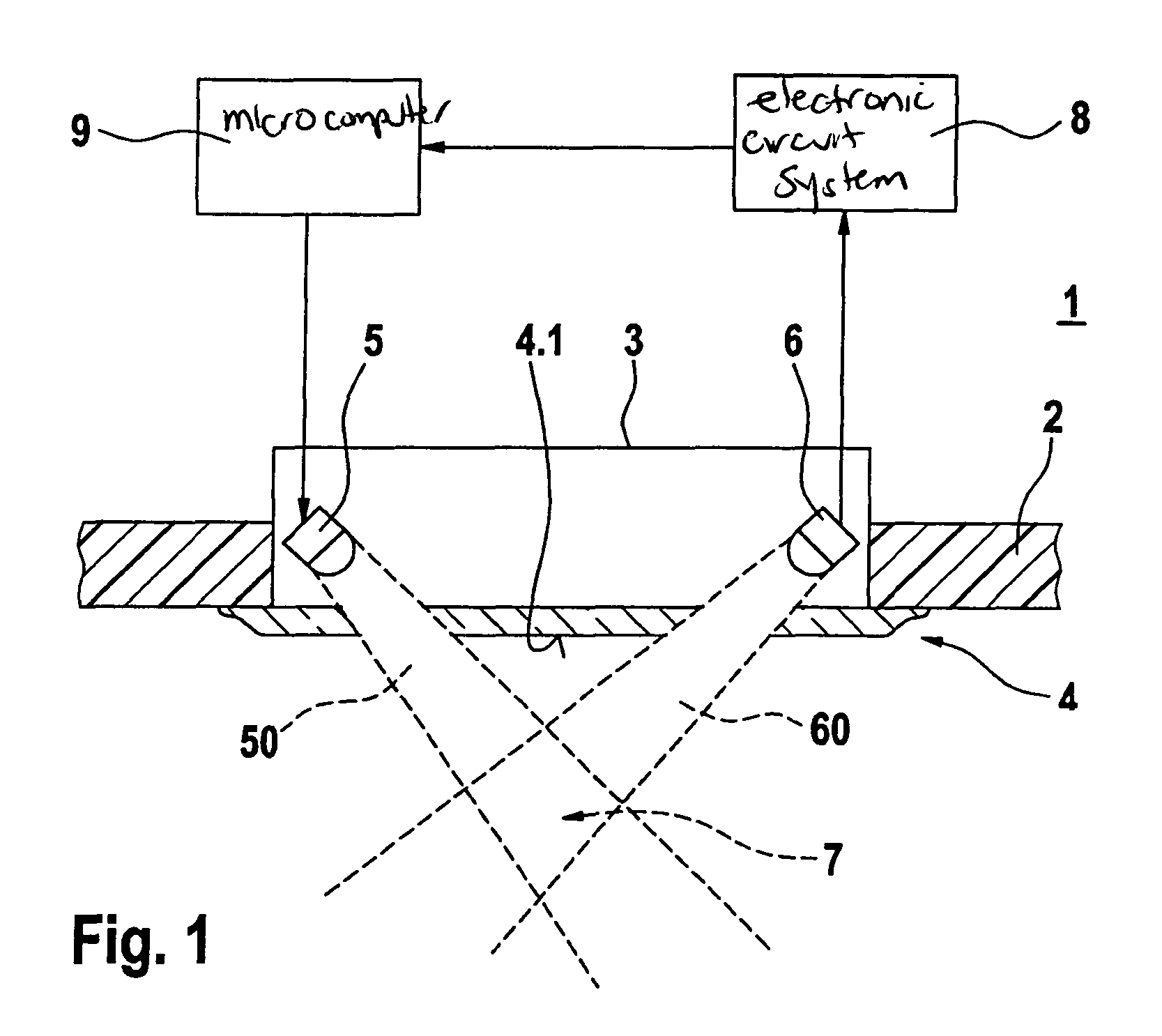
InactiveUS7978087B2Operating reliability can be highReduce sensitivityInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsScattering properties measurementsFire detectorLight beam
A fire detector operating by the scattered radiation principle is described, having at least one radiation transmitter and at least one radiation receiver, whose beam paths form a scattering volume. The fire detector includes, in addition to at least one first radiation transmitter and one first radiation receiver, at least one second radiation transmitter and one second radiation receiver, whose beam paths form at least two spatially separated scattering volumes.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Onboard unit controlling apparatus
InactiveUS20100324779A1Improve convenienceReliably recognizeDashboard fitting arrangementsDigital data processing detailsIn vehicleEngineering
When an occupant's sight line detected by sight line detector is directed to any one of multiple onboard units (a side mirror, a rear view mirror, a navigation system, an in-vehicle phone, an air blowout port, and a meter panel), a controller allows the onboard unit, to which the sight line is directed, to be operable. Thus, the occupant can select the onboard unit, which the occupant wishes to operate, by the sight line without using the hand and further can operate the onboard unit by use of a common steering switch, thereby enhancing the convenience of operation. In addition, a corresponding one of pilot lamps notifies the occupant that the corresponding one of the onboard units, to which the sight line is directed, is operable. Accordingly, the occupant can avoid operating a wrong onboard unit while reliably recognizing the operable onboard unit even if the multiple onboard units are arranged close to one another.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Image display control system and method allowing connection of various kinds of image displays to one supply source
InactiveUS7057667B1Easy to adjustEasy to changeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAcquired characteristicControl system
Owner:CANON KK
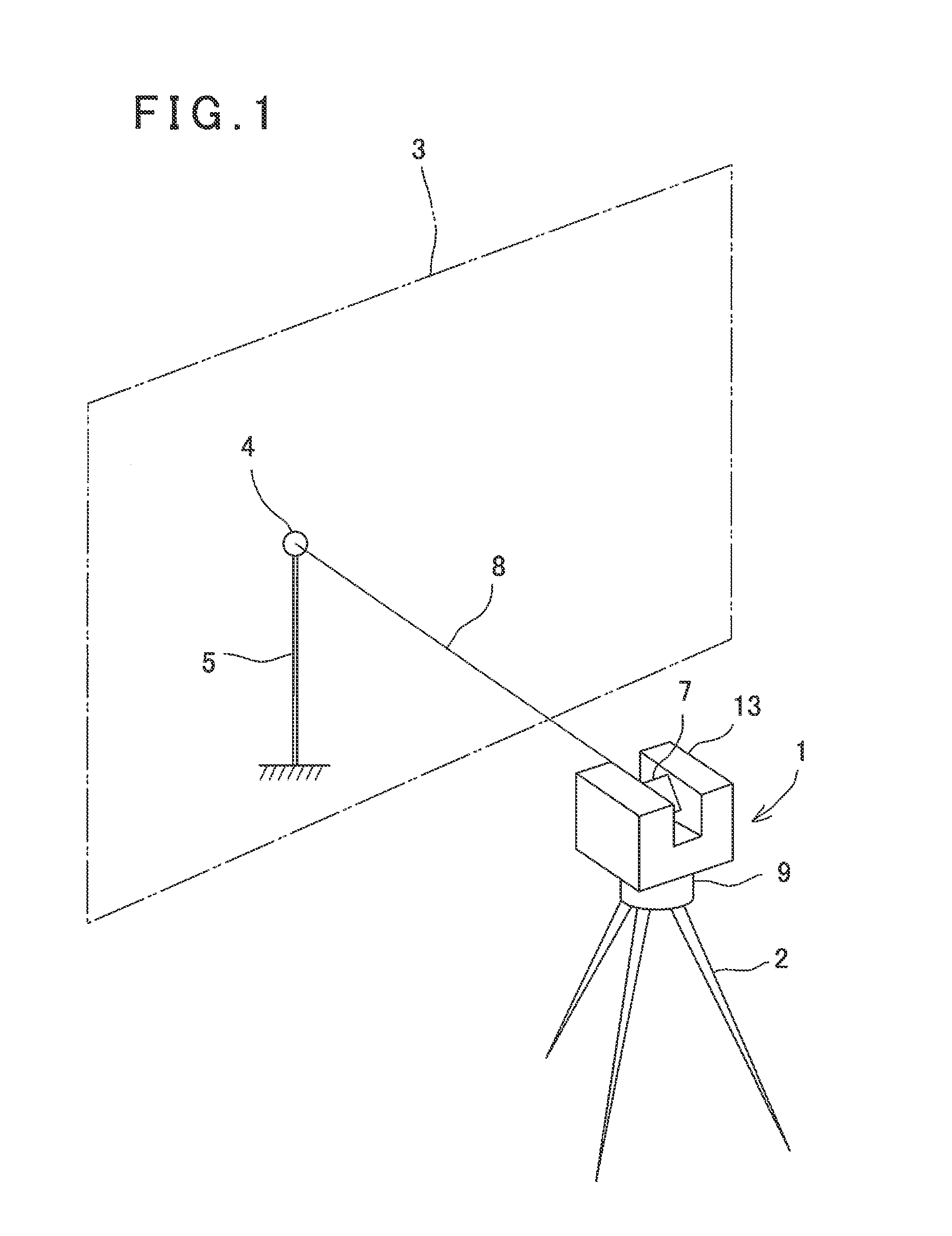
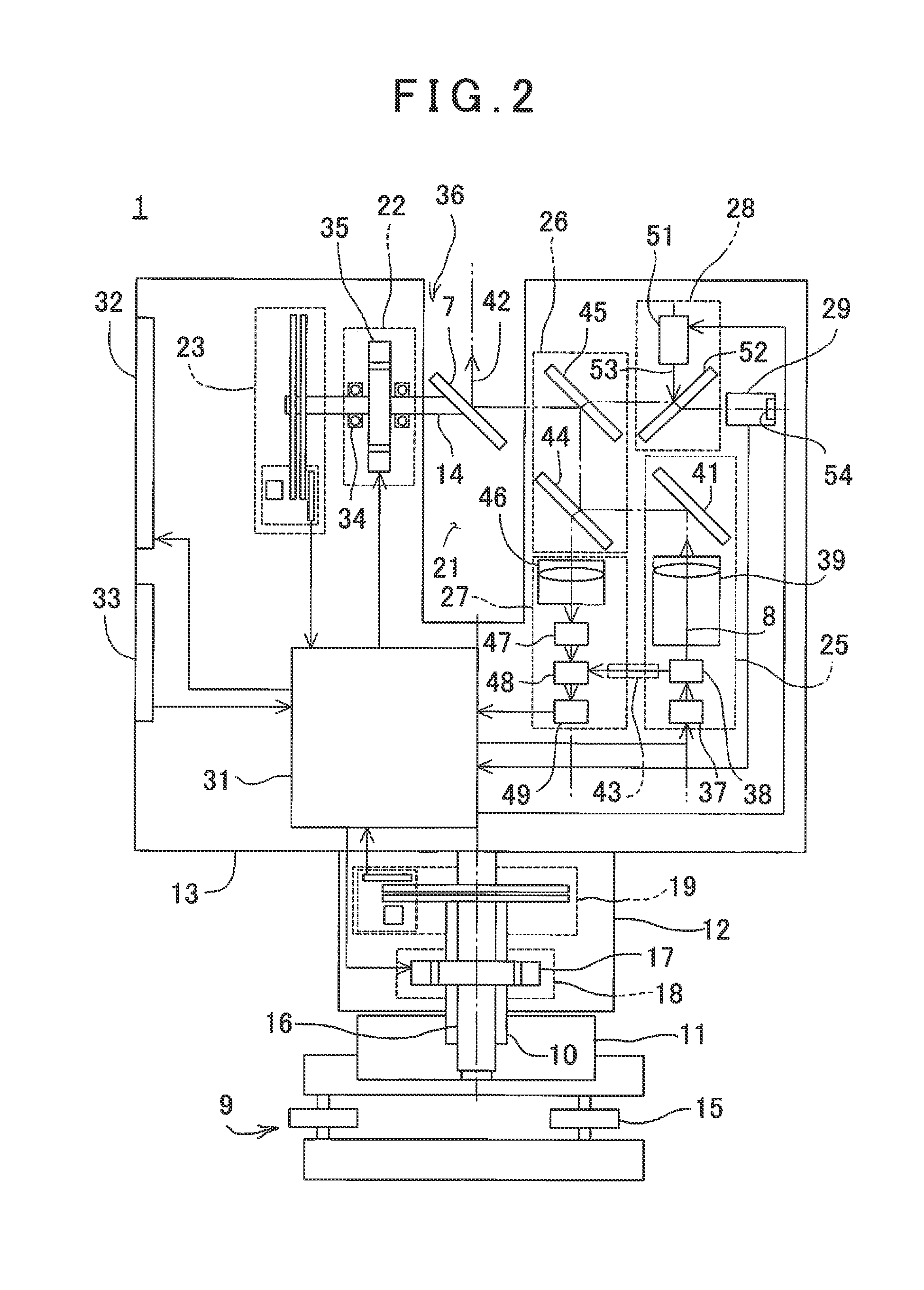
Three-Dimensional Measuring Device and Three-Dimensional Measuring System
ActiveUS20140111618A1Easy to detectImprove detection accuracyActive open surveying meansUsing optical meansThree dimensional measurementImage based
A three-dimensional measuring device includes a light source unit, a light projecting optical unit, a light receiving optical unit, a light receiving element, a scanning unit, an angle detector, an illumination light source unit, an image pickup unit and a control arithmetic unit. The control arithmetic unit comprises a distance data processing unit for controlling the scanning unit, for calculating a distance to the object to be measured based on a received light signal, and for calculating a three-dimensional data of the object based on a calculated distance and a detection signal from the angle detector, and an image data processing unit for acquiring an illuminated image and an unilluminated image, for acquiring a difference image based on both images, for detecting a retroreflective target based on the difference image and a detected intensity of a reflected light from the difference image, and for calculating a position of the target.
Owner:KK TOPCON
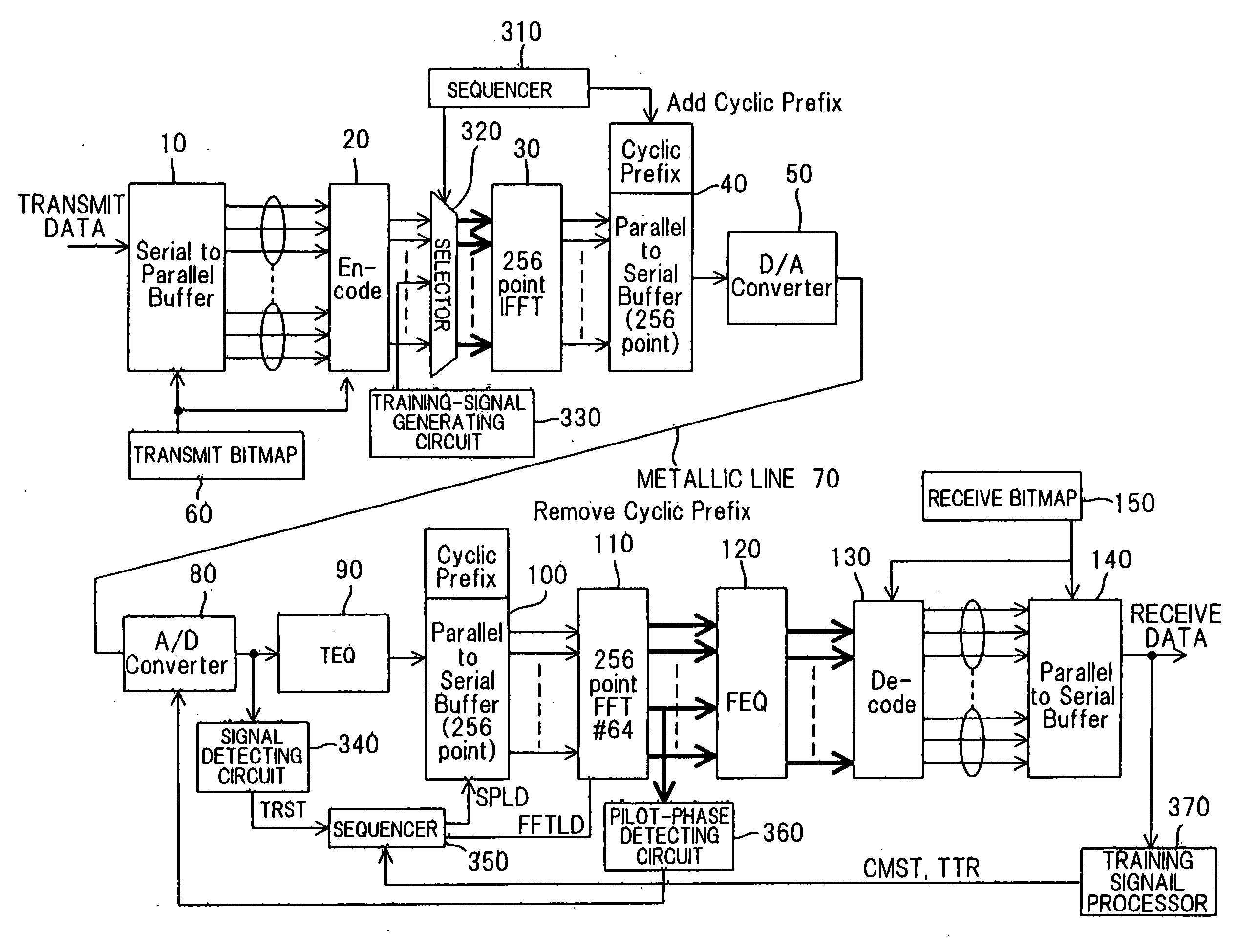
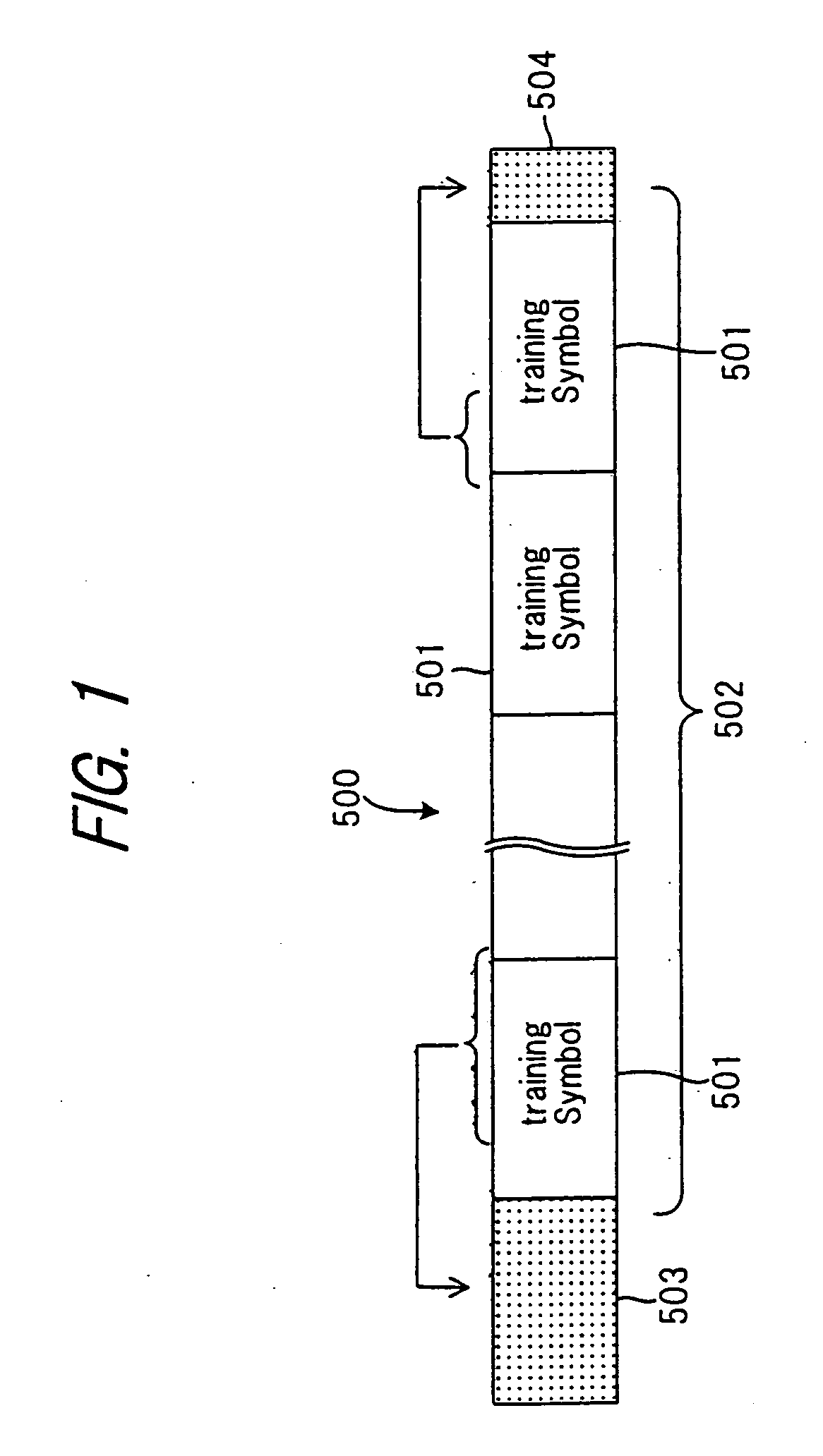
Digital subscriber line transmission method, apparatus and system
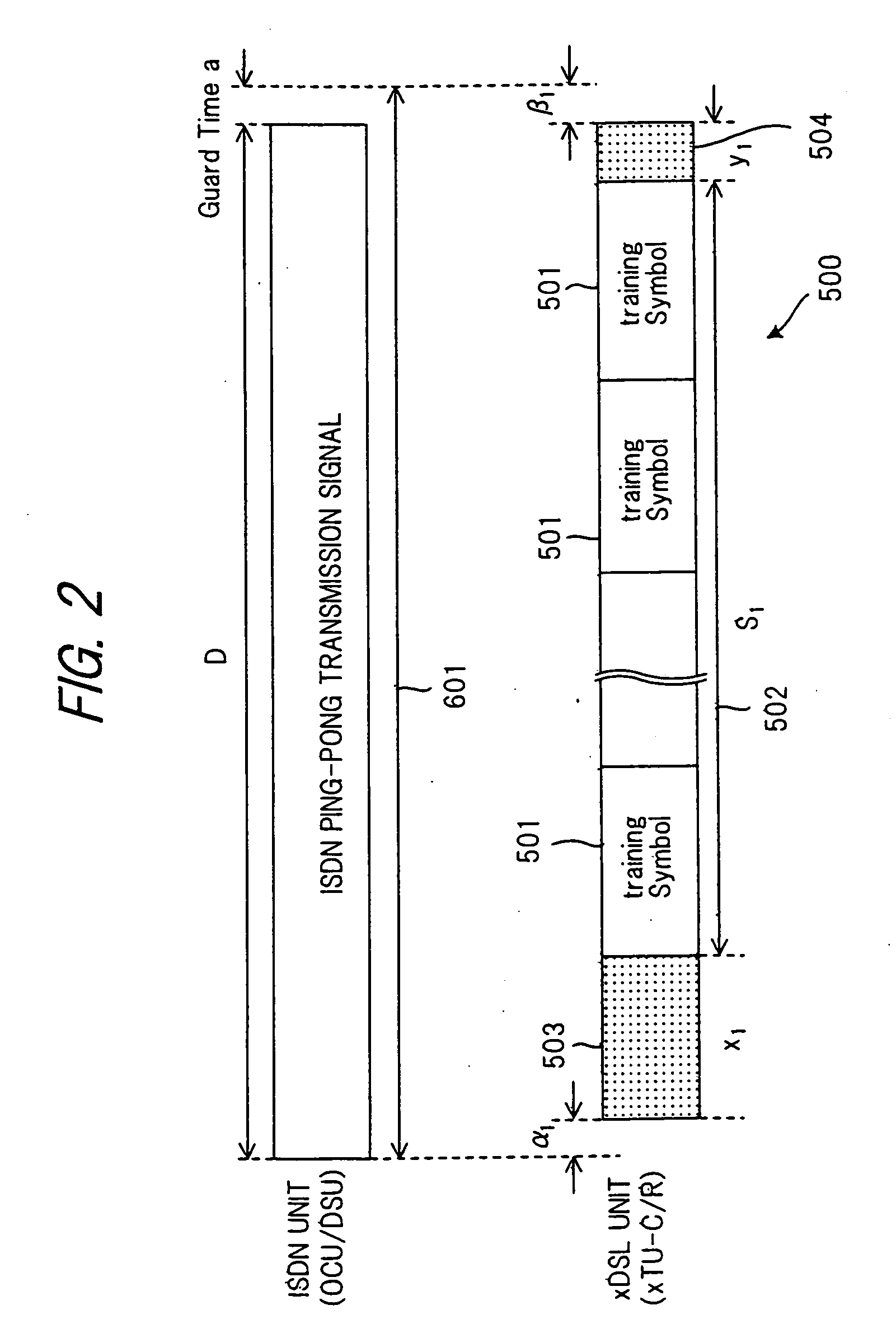
InactiveUS20050237954A1Reduce training timeReliably recognizeTransmission control/equlisationFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime informationDigital subscriber line
When training carried out prior to data communication is performed in digital subscriber line transmission (xDSL), the side which transmits training symbols adds some data that is contained in a training symbol sequence onto at least one of the beginning and end of this symbol sequence and then transmits the training symbol sequence. The receiving side removes the data that has been added onto the training symbol sequence and executes training processing. The length of the training symbol sequence and of a transmit symbol sequence at time of normal communication is set in such a manner that the symbol sequence will not fall within an interval in which effects of near-end crosstalk from a neighboring line are received. Further, at the time of training prior to data communication, timing information, which specifies an interval in which effects of crosstalk from a neighboring line are received, is inserted into a training symbol sequence and the training symbol sequence is transmitted from a device on the office side to a device on the subscriber side.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com