Patents
Literature
475 results about "Acquired characteristic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An acquired characteristic is a non-heritable change in a function or structure of a living biotic material caused after birth by disease, injury, accident, deliberate modification, variation, repeated use, disuse, or misuse, or other environmental influences. Acquired traits, which is synonymous with acquired characteristics, are not passed on to offspring through reproduction alone.
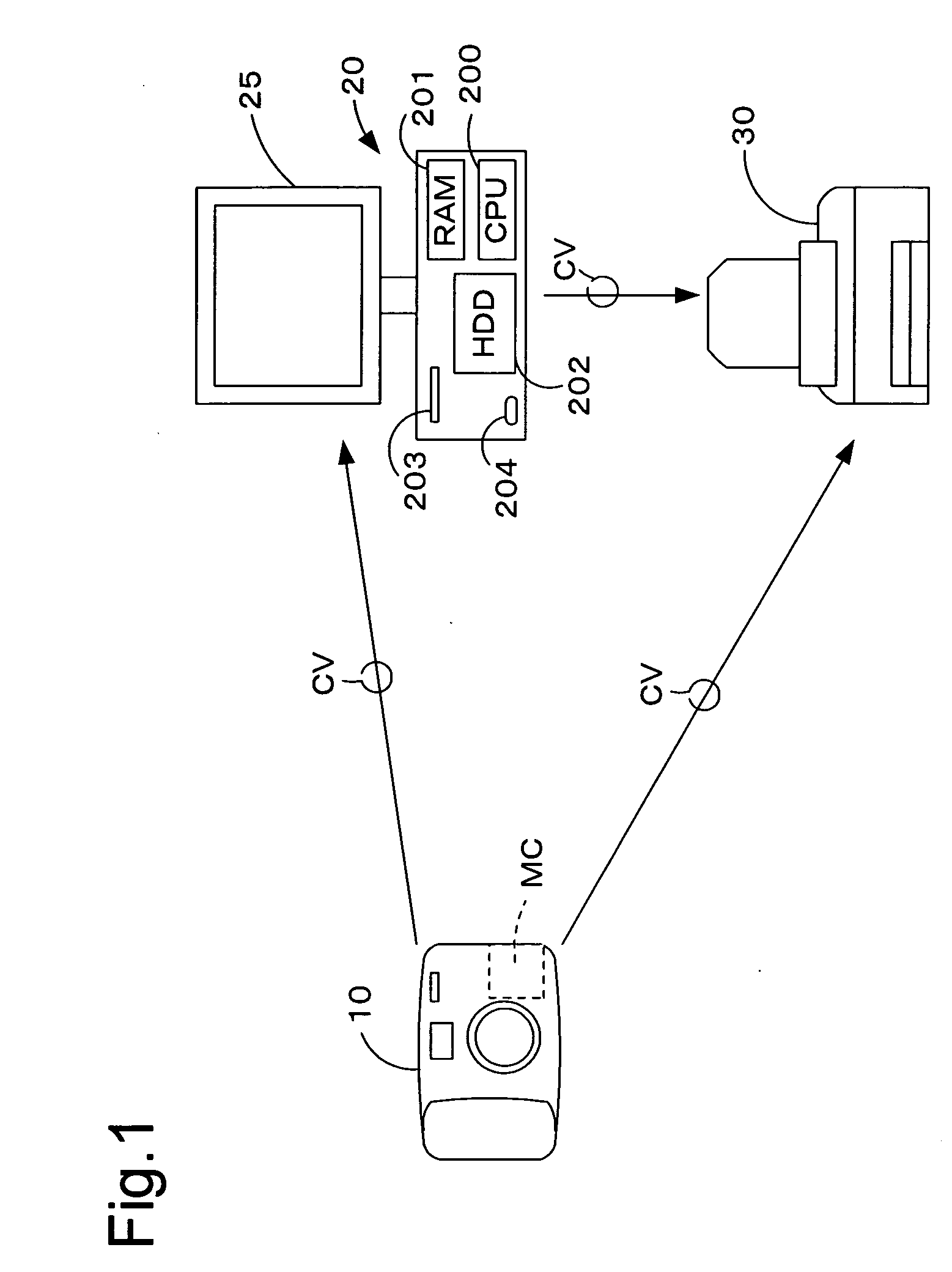
Device for diagnosing physiological state and device for controlling the same
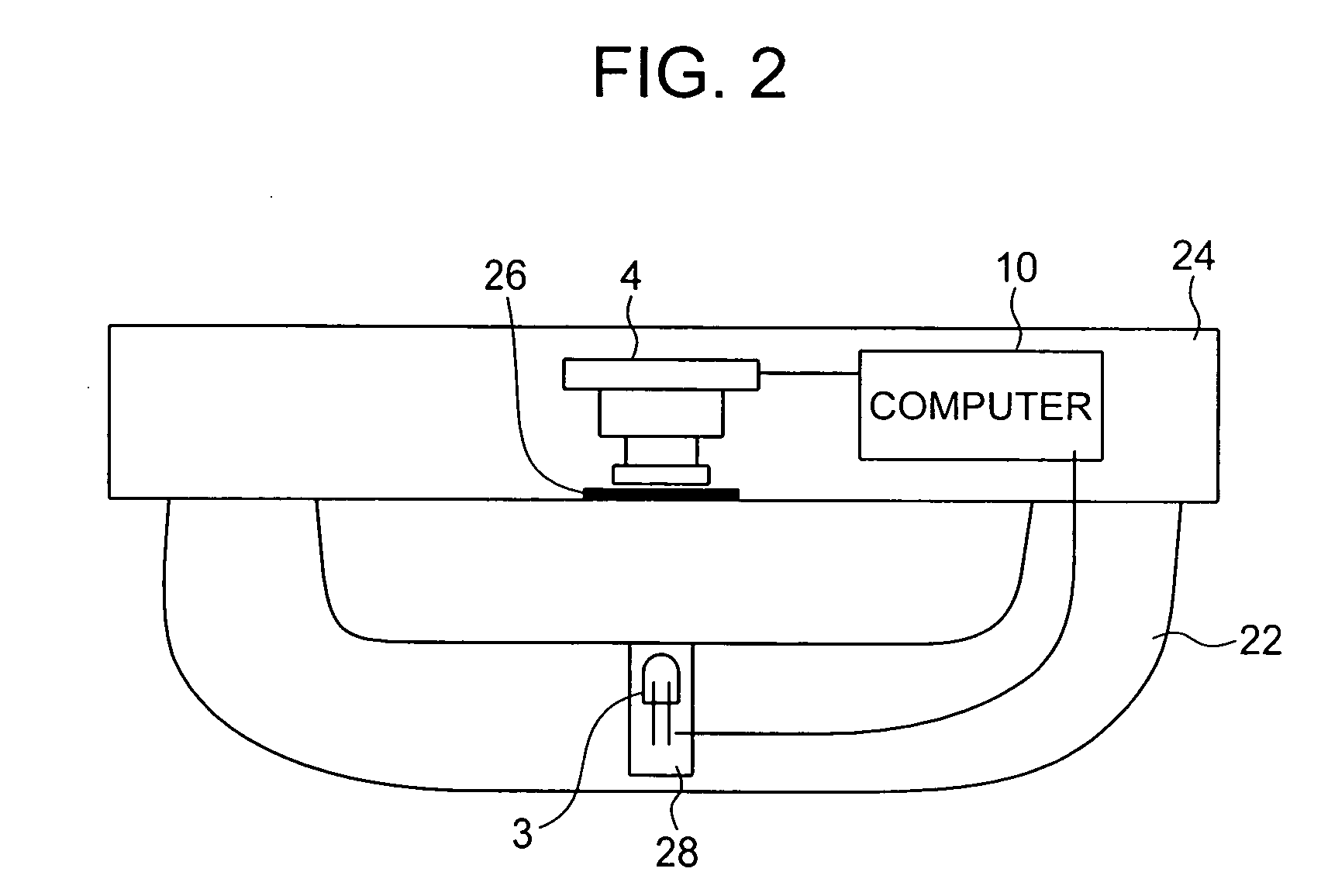
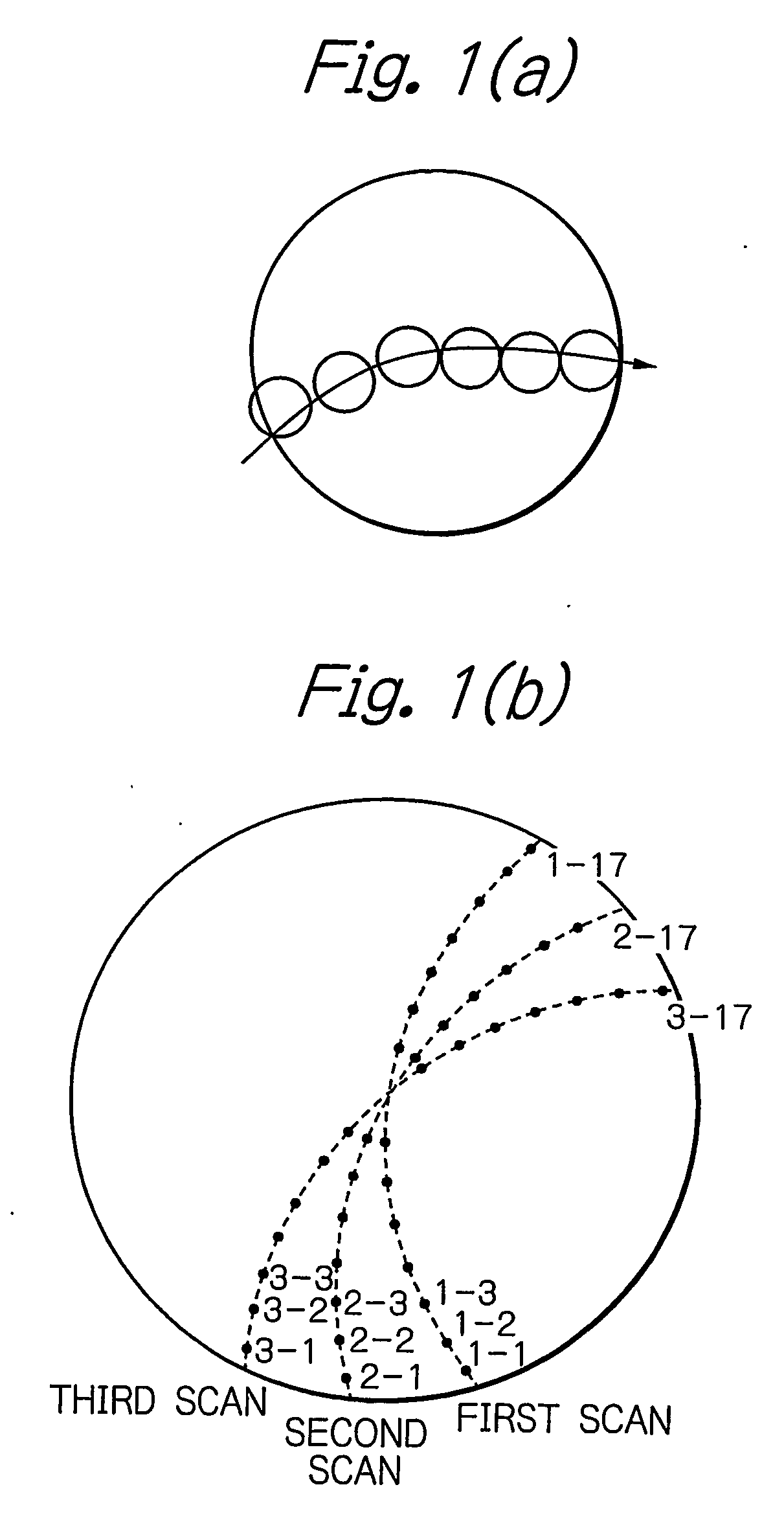
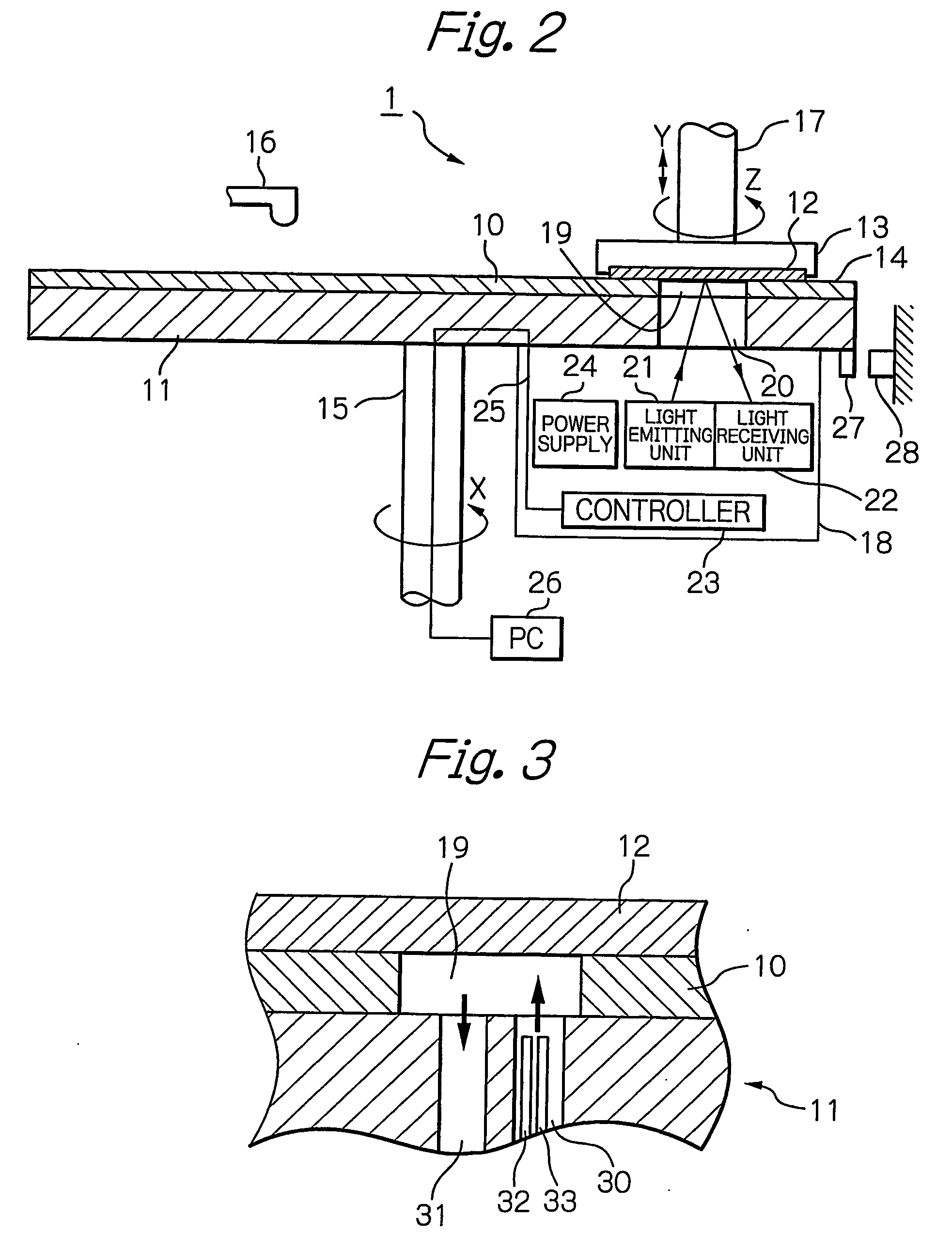
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 01254 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 2, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 2, 1997 PCT Filed May 13, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 35368 PCT Pub. Date Nov. 14, 1996The present invention relates to a device for diagnosing physiological state based on blood pulse waves detected in the body. It is the objective of the present invention to provide a device which correctly diagnoses the current physiological state based on changes in physiological state measured over a specified period of time in the past while taking into consideration the cyclical variation exhibited in physiological state. In order to realize this objective, the device according to the present invention has as its main components: blood pulse wave detector 381 and stroke-volume-per-beat measurer 382 which respectively detect blood pulse wave and stroke volume in the body; blood pulse wave extraction memory 386 which extracts characteristic information from the detected blood pulse wave; memory 383 in which the physiological state calculated from the stroke volume and this characteristic information is stored; output portion 385 which outputs an alarm; and microcomputer 387 which controls each part inside the device. The microcomputer calculates the circulatory parameters based on characteristic information obtained from the waveform extraction memory, and stores the parameters in memory at specified time intervals. At these times, microcomputer 387 calculates the circulatory parameters from the stroke volume per beat and the characteristic information of the blood pulse wave at specified time intervals, and stores the parameters in memory 383. Further, microcomputer 387 reads out from memory 383 the circulatory parameters from a specified time interval in the past, and calculates the average value and standard deviation. Microcomputer 387 then determines whether or not the current circulatory parameters are within a specified range determined by their average value and standard deviation. When the circulatory parameters are determined to be outside this range, microcomputer 387 controls output portion 385 to sound an alarm.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
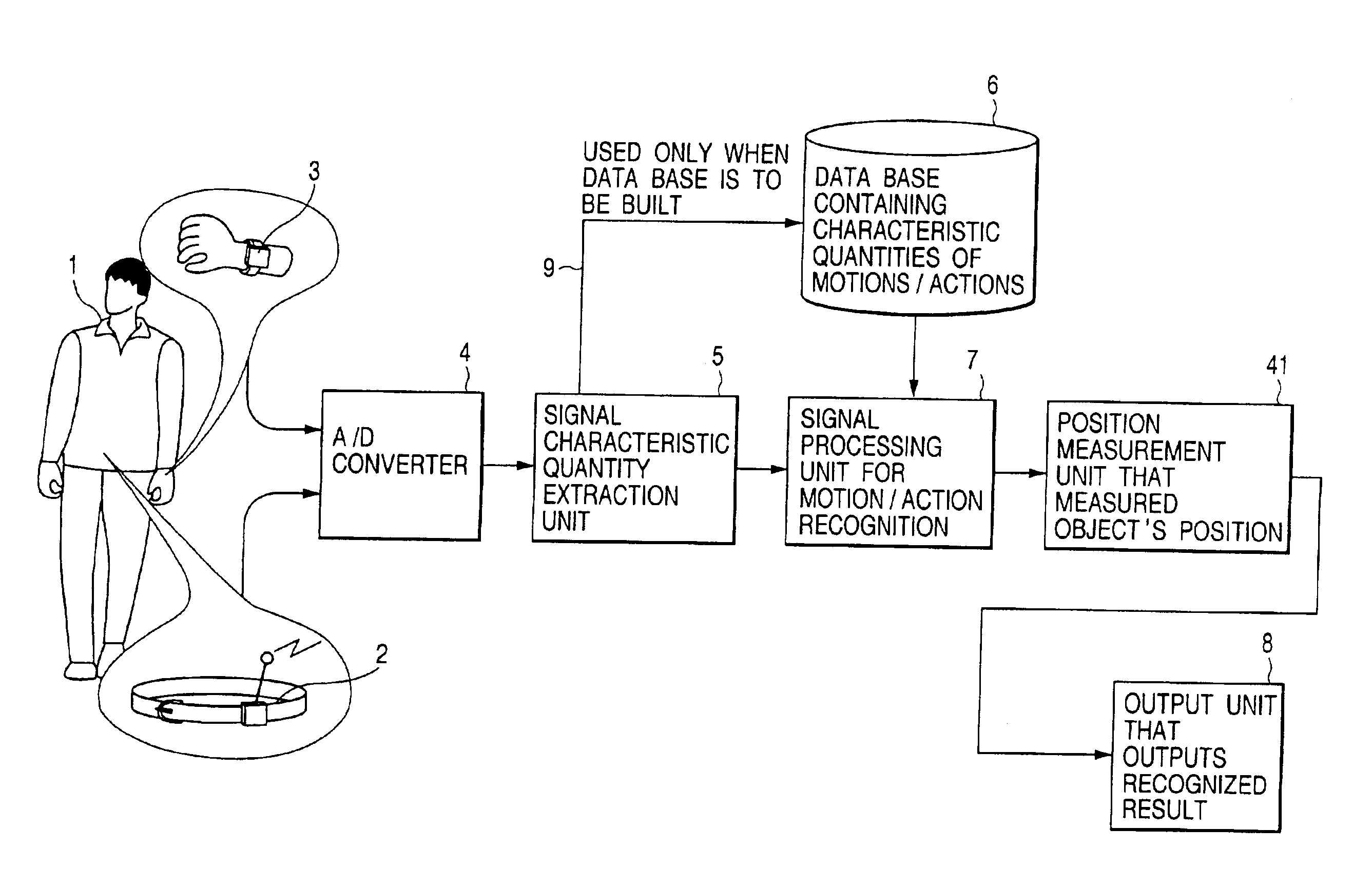
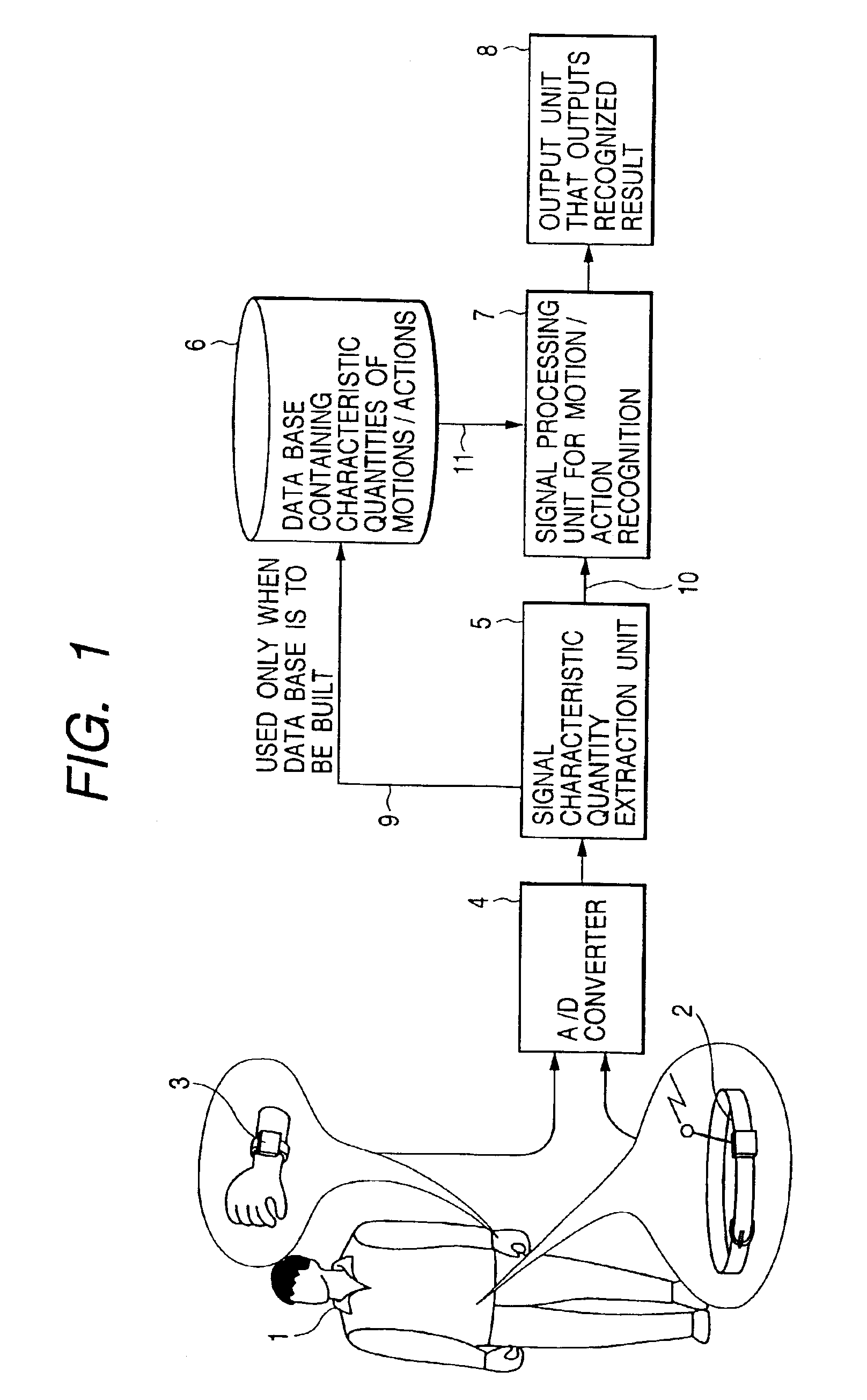
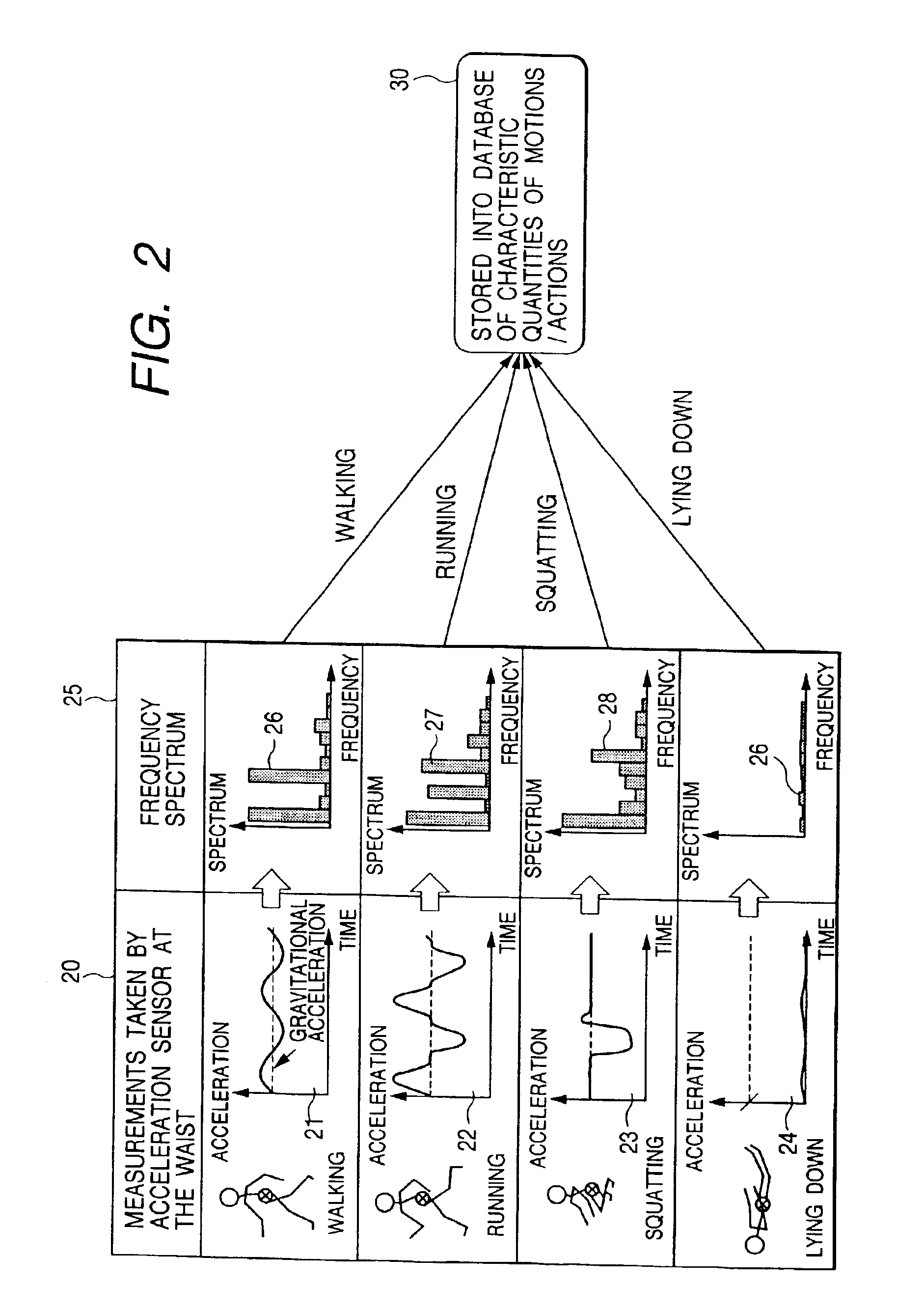
Method, apparatus and system for recognizing actions
InactiveUS6941239B2More precisionFreedom of movementInput/output for user-computer interactionGymnastic exercisingPhysical medicine and rehabilitationState variation
An object of the present invention is to provide a method, an apparatus and a system for automatically recognizing motions and actions of moving objects such as humans, animals and machines.Measuring instruments are attached to an object under observation. The instruments measure a status change entailing the object's motion or action and to issue a signal denoting the measurements. A characteristic quantity extraction unit extracts a characteristic quantity from the measurement signal received which represents the motion or action currently performed by the object under observation. A signal processing unit for motion / action recognition correlates the extracted characteristic quantity with reference data in a database containing previously acquired characteristic quantities of motions and actions. The motion or action represented by the characteristic quantity with the highest degree of correlation is recognized and output.
Owner:APPLE INC
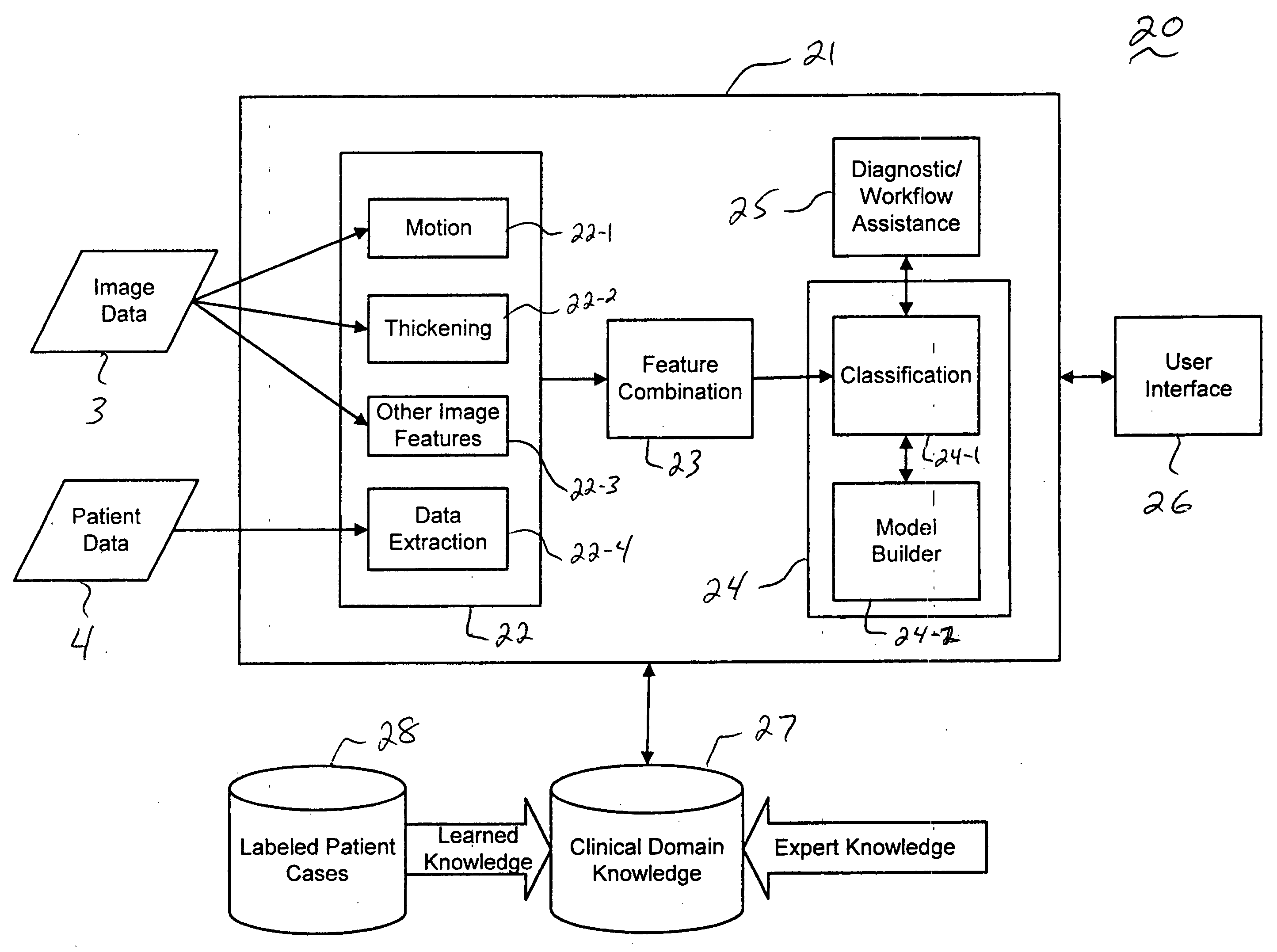
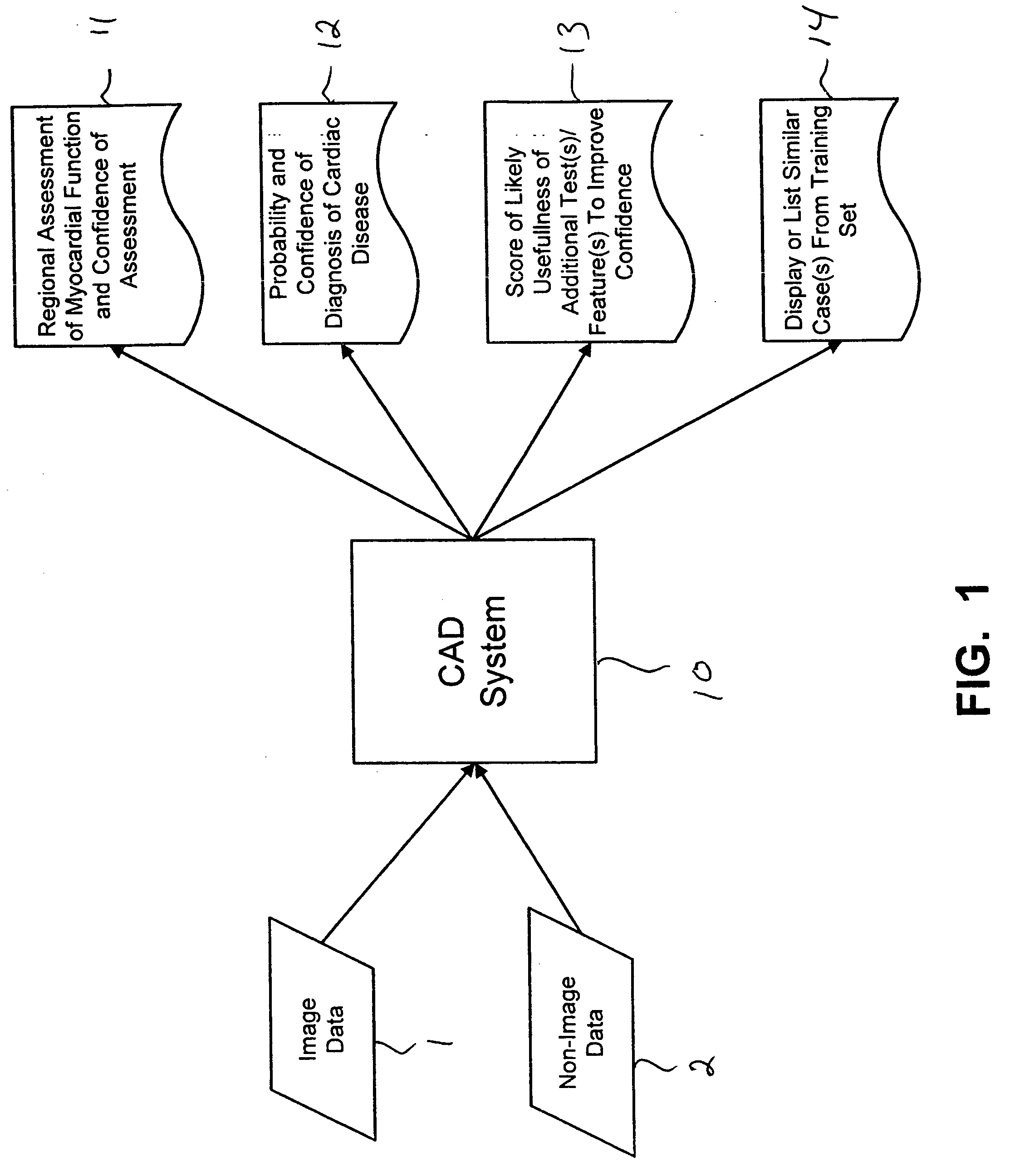
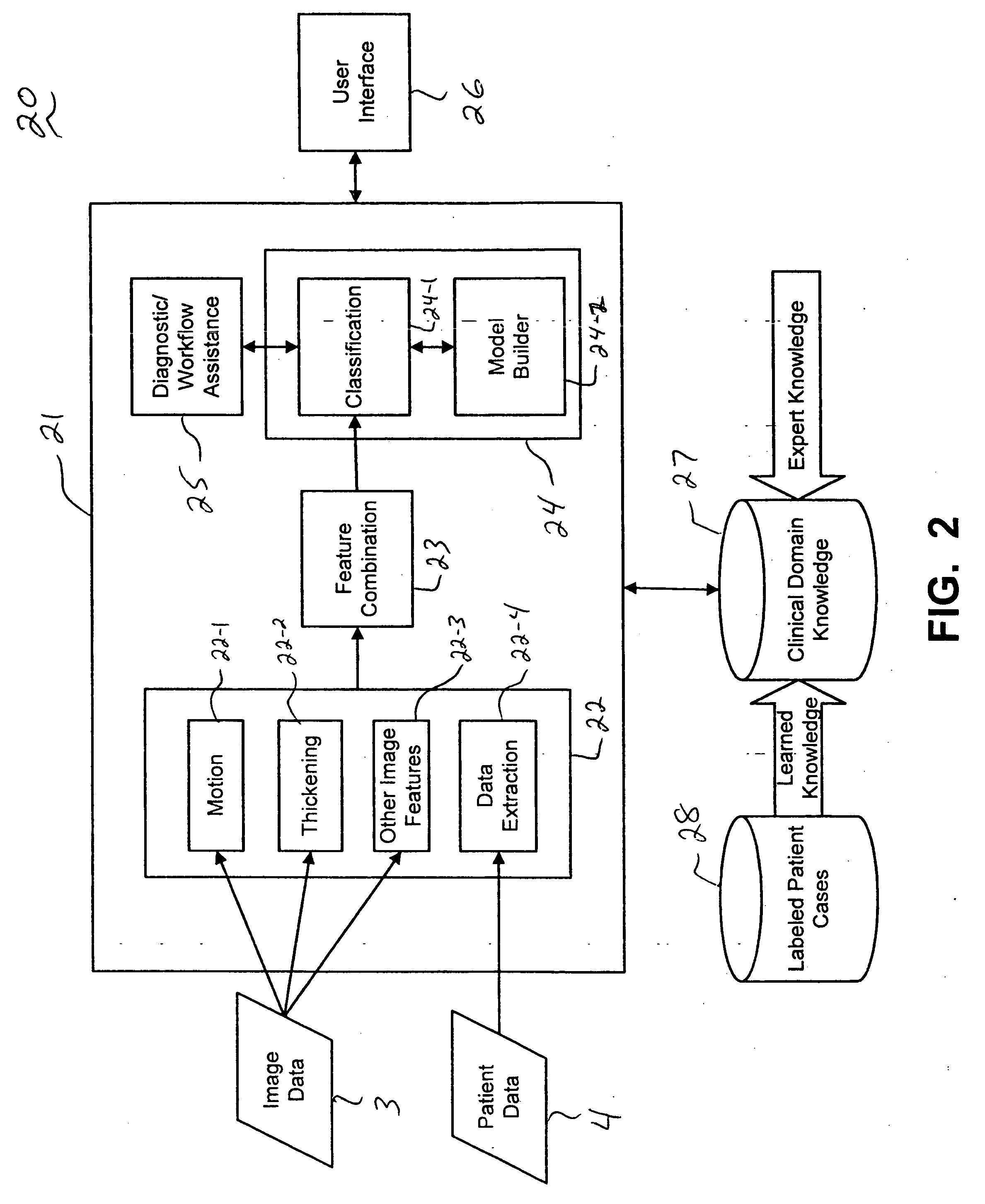
Systems and methods for providing automated regional myocardial assessment for cardiac imaging
ActiveUS20050059876A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementMedical recordAcquired characteristic
Systems and methods are provided for automated assessment of regional myocardial function using wall motion analysis methods that analyze various features / parameters of patient information (image data and non-image data) obtained from medical records of a patient. For example, a method for providing automatic diagnostic support for cardiac imaging generally comprises obtaining image data of a heart of a patient, obtaining features from the image data of the heart, which are related to motion of the myocardium of the heart, and automatically assessing regional myocardial function of one or more regions of a myocardial wall using the obtained features.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
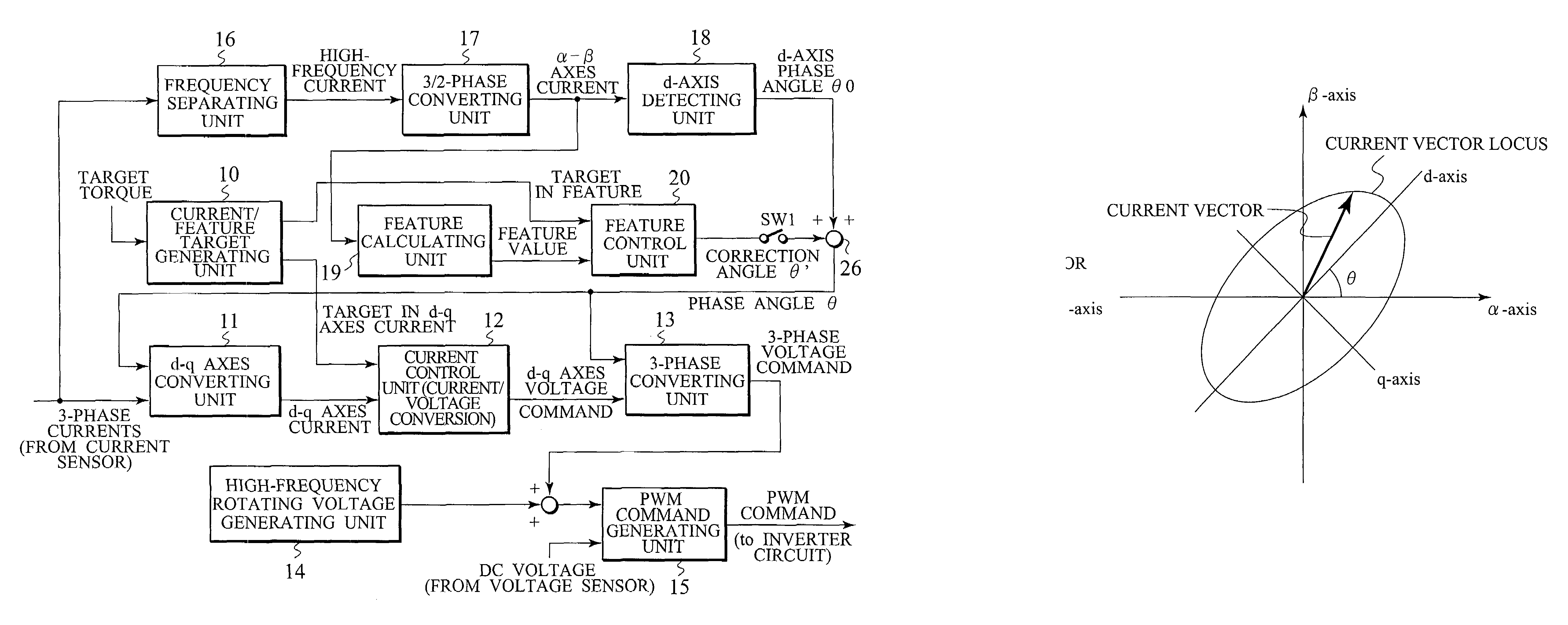
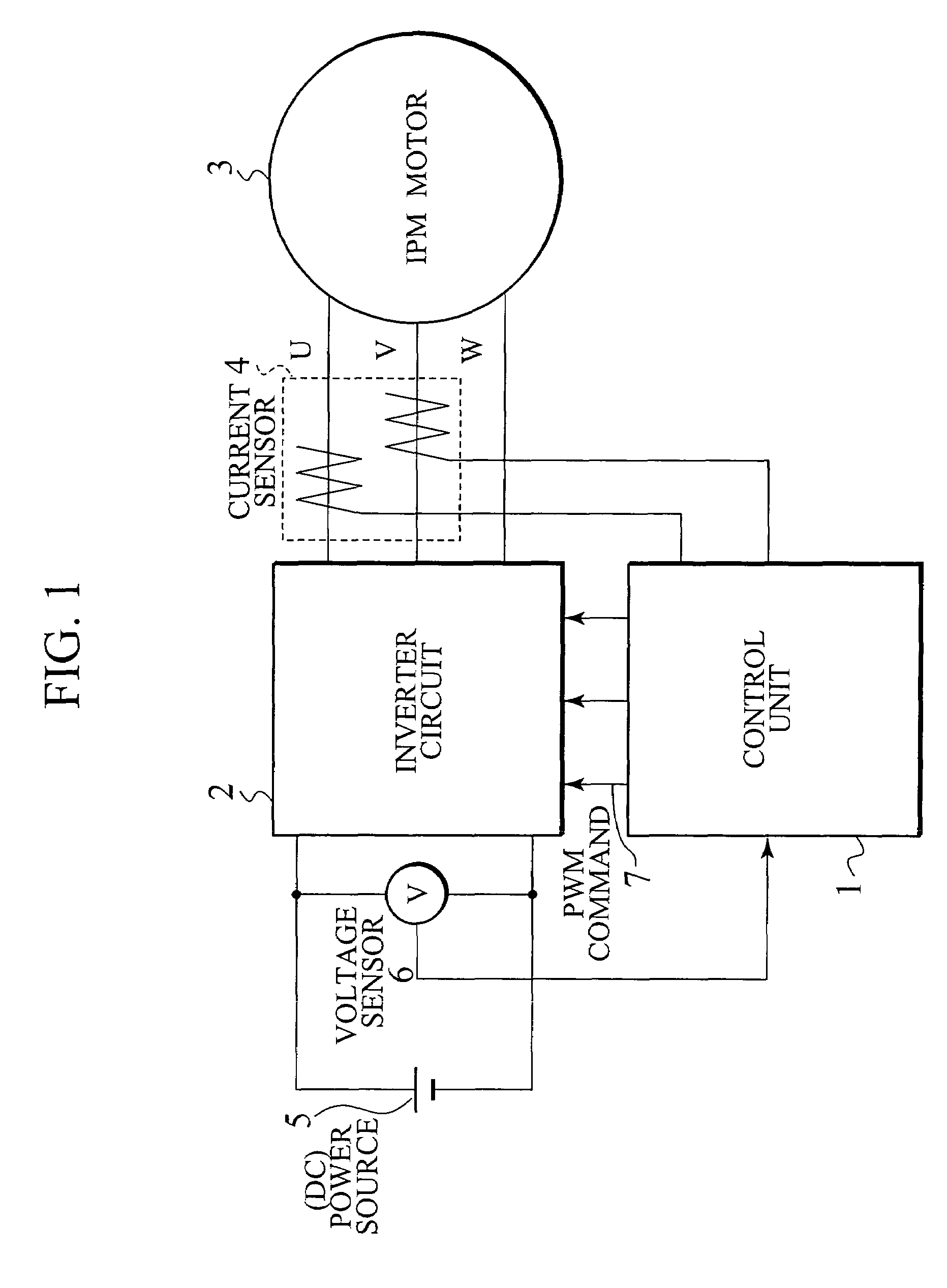
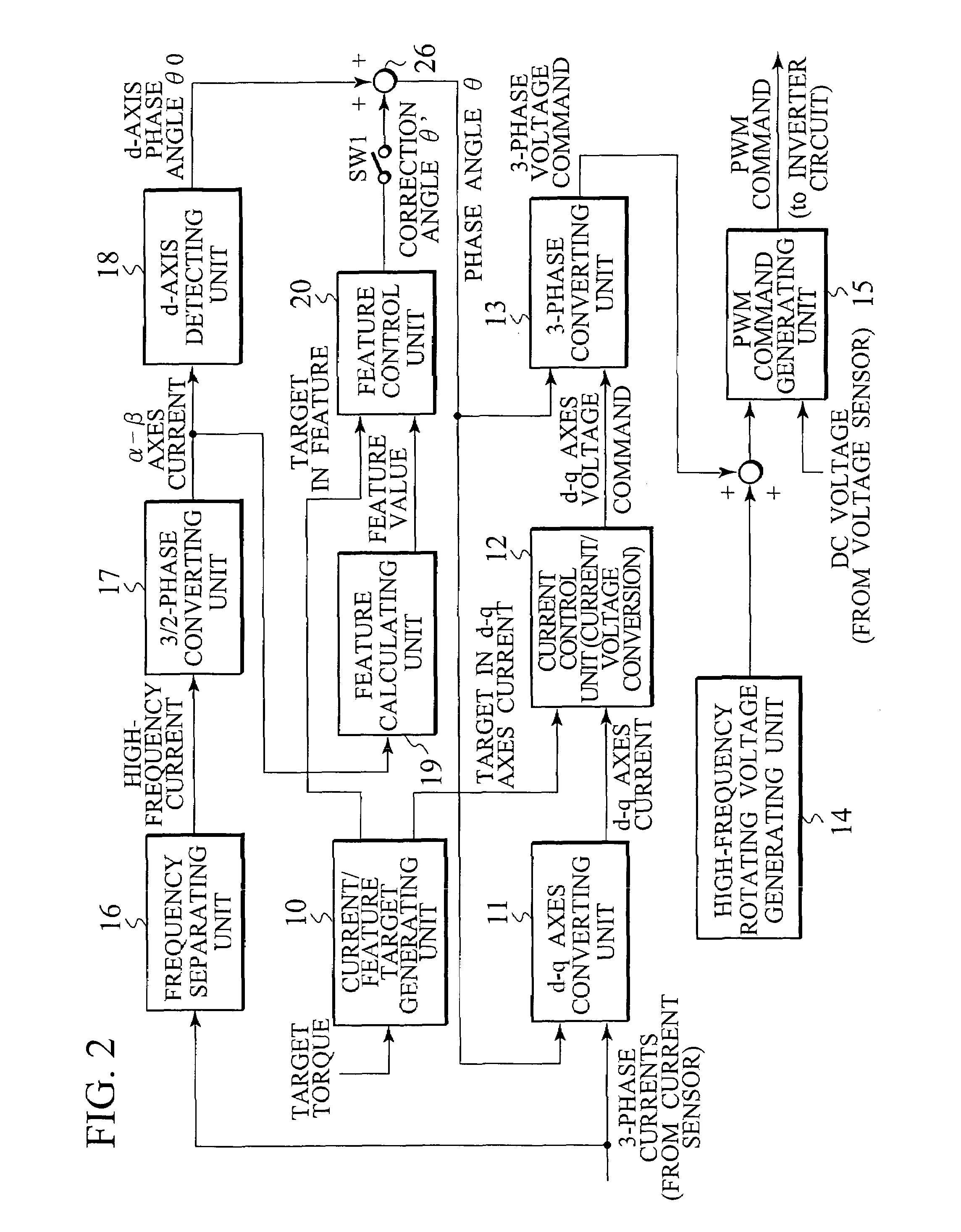
Control device for electric motor
ActiveUS7005828B2Improve artSingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlDriving currentAcquired characteristic
Corresponding to a target torque, the control device calculates a target value of a feature based on at least one of the length of a long axis of a current vector locus and the length of the short axis and further superimposes a superimposed current on a drive current for the motor, the superimposed current having a frequency different from the frequency of the drive current. Further, the control device detects an actual value of the feature based on at least one of the length of a long axis of a current vector locus of the superimposed current and the length of the short axis of the same and finally detects a phase angle of the motor based on the target value and the actual value for the feature. The manipulation of a detecting phase is performed by feedback of a feature obtained by the magnitude of the superimposed current. That is, when the actual feature is more than the target value, the detecting phase is advanced. Conversely, when the actual feature is less than the target value, the detecting phase is delayed.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
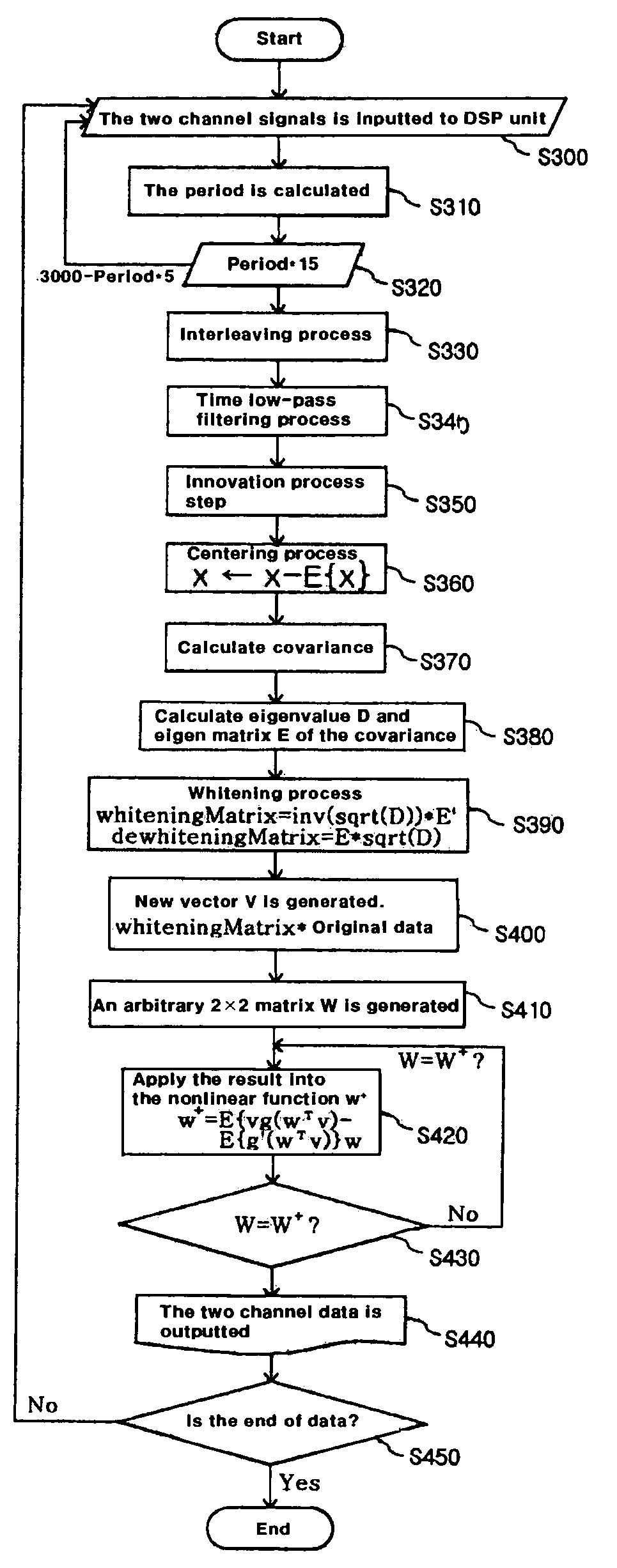
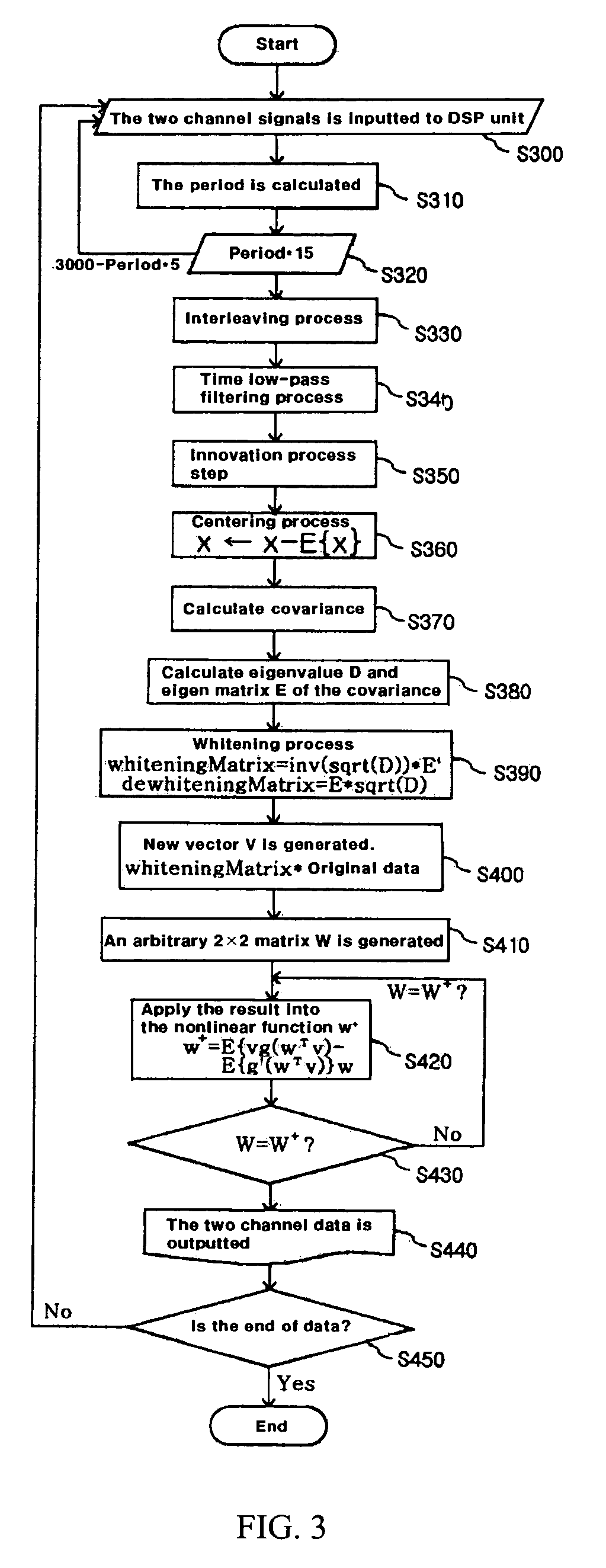
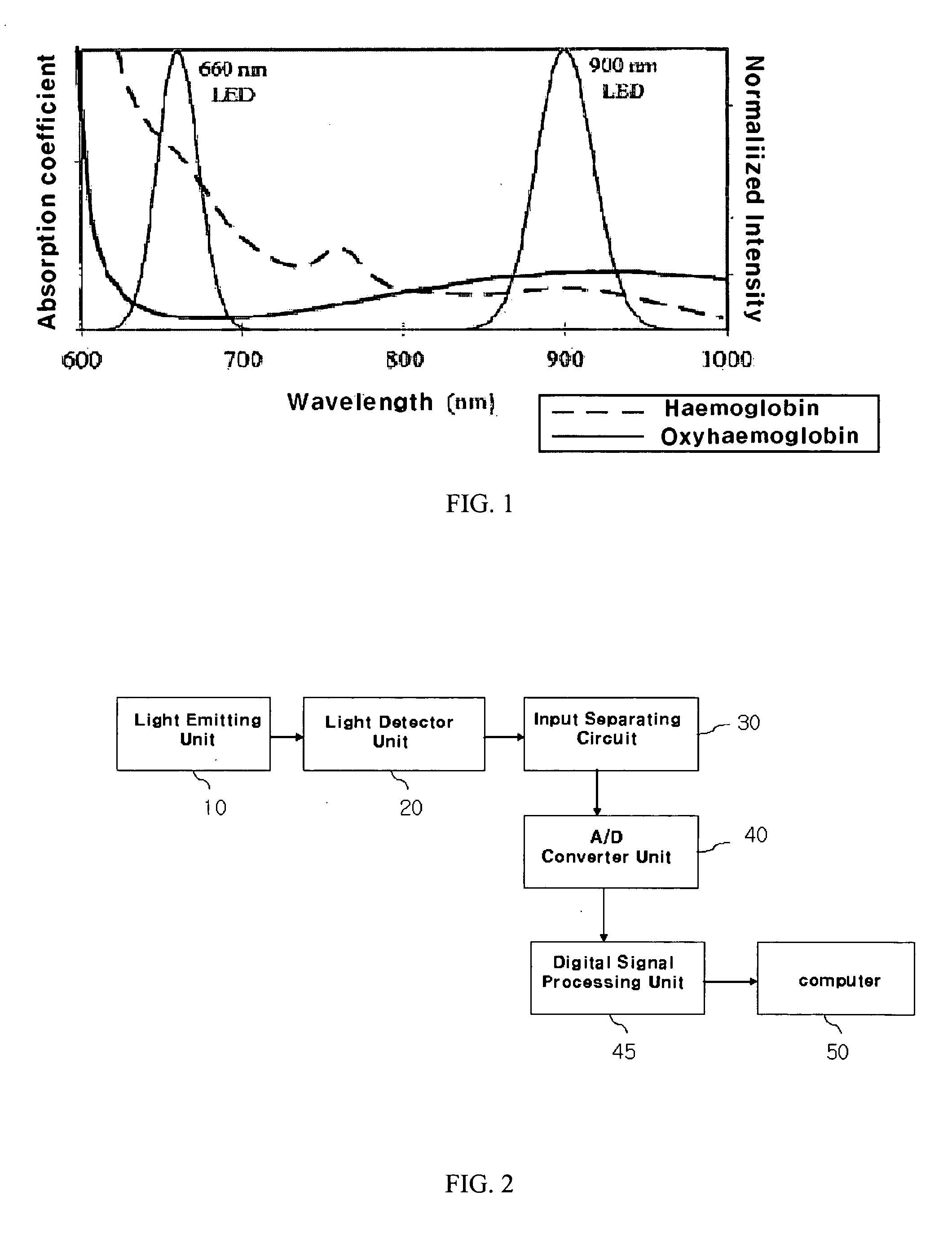
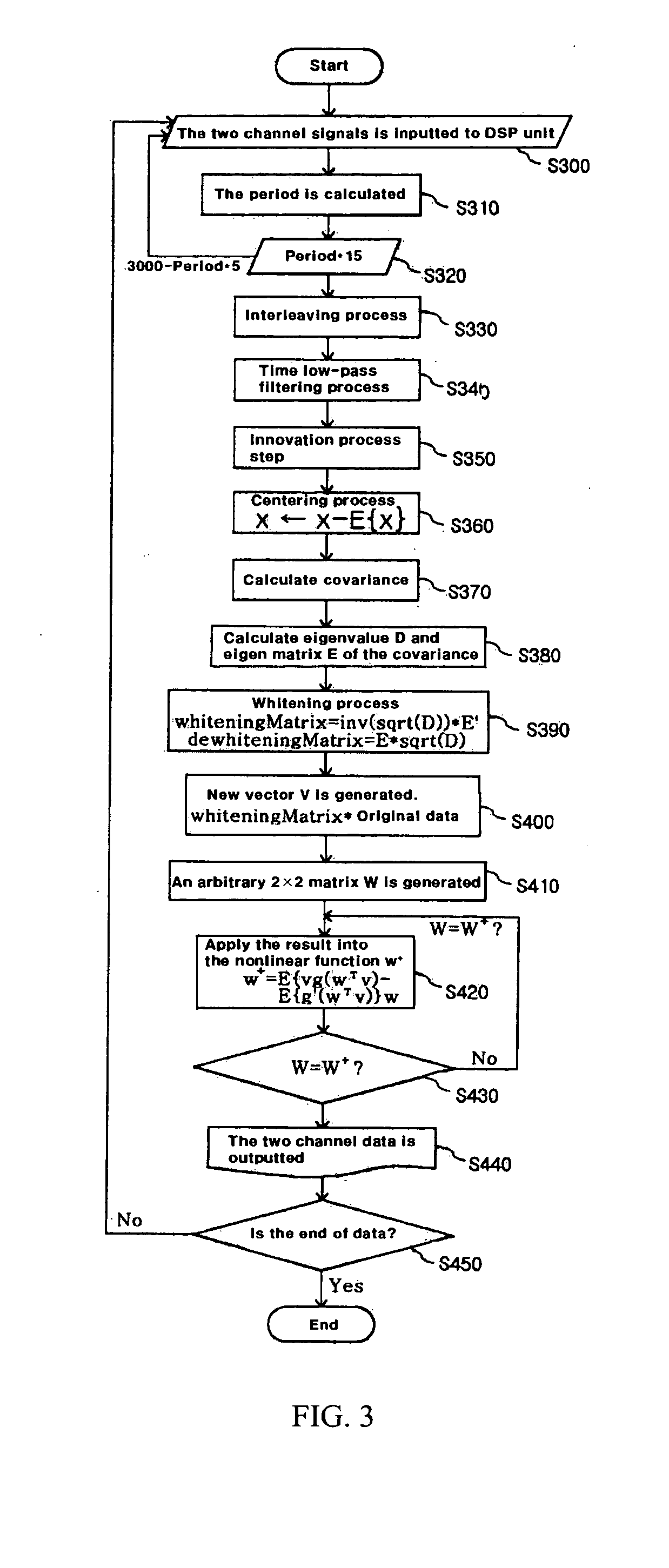
Photoplethysmography (PPG) device and the method thereof
ActiveUS7336982B2Improve performanceReduce Motion ArtifactsCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAcquired characteristicCovariance
A method of measuring Photoplethysmography (PPG) signals may comprise detecting dual wavelength illumination from a light detector so as to provide detected signals, converting the detected signals into digital signals so as to provide digital signals, reducing noises from the digital signals and increasing independency between the digital signals so as to provide preprocessed signals, subtracting the average value from the preprocessed signals so as to provide adjusted signals, obtaining whitening matrix based on covariance, eigen value, and eigen matrix obtained from the adjusted signals, and restoring data using the whitening matrix.
Owner:SILICON MITUS
Display apparatus and drive control method for the same
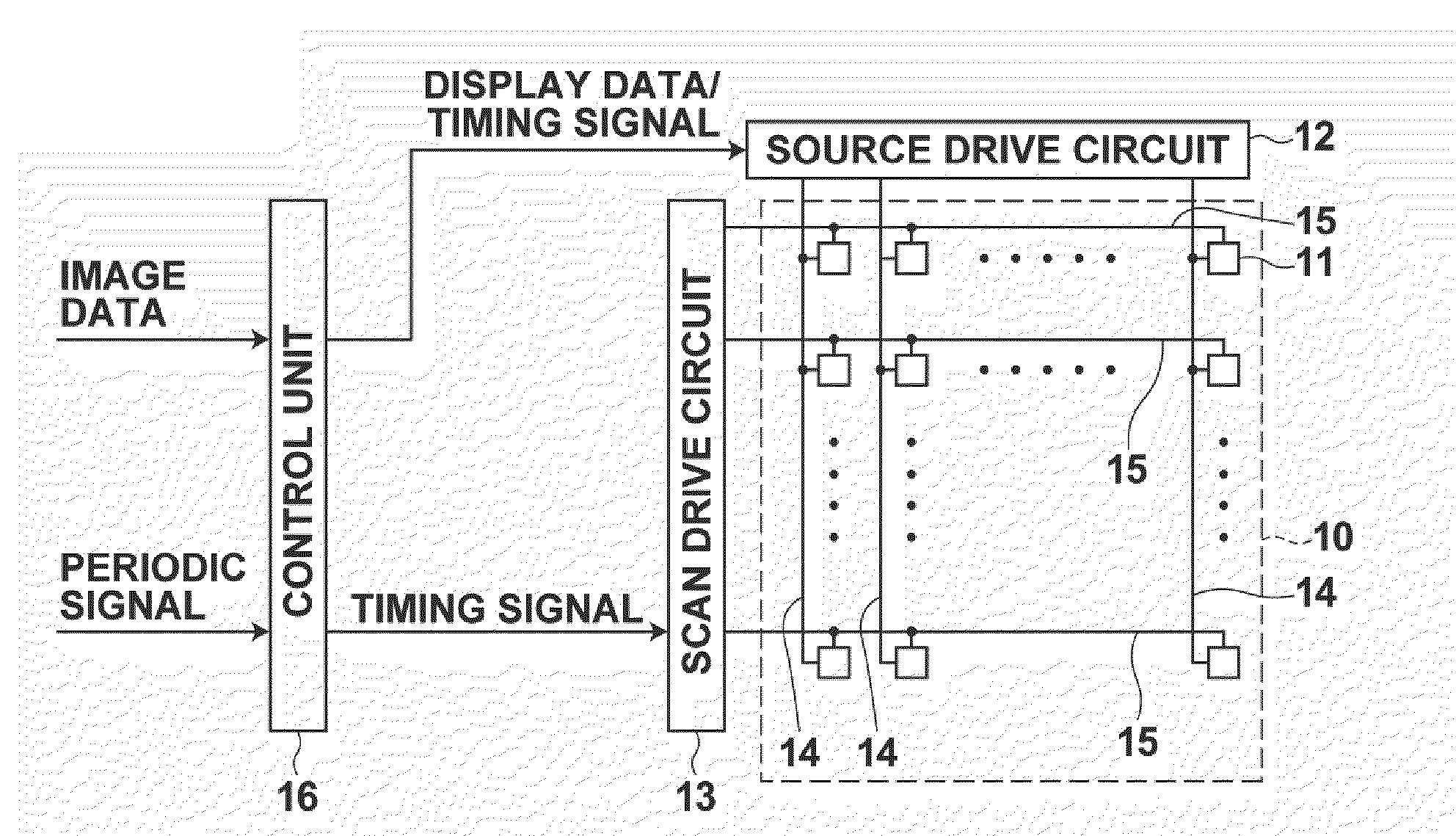
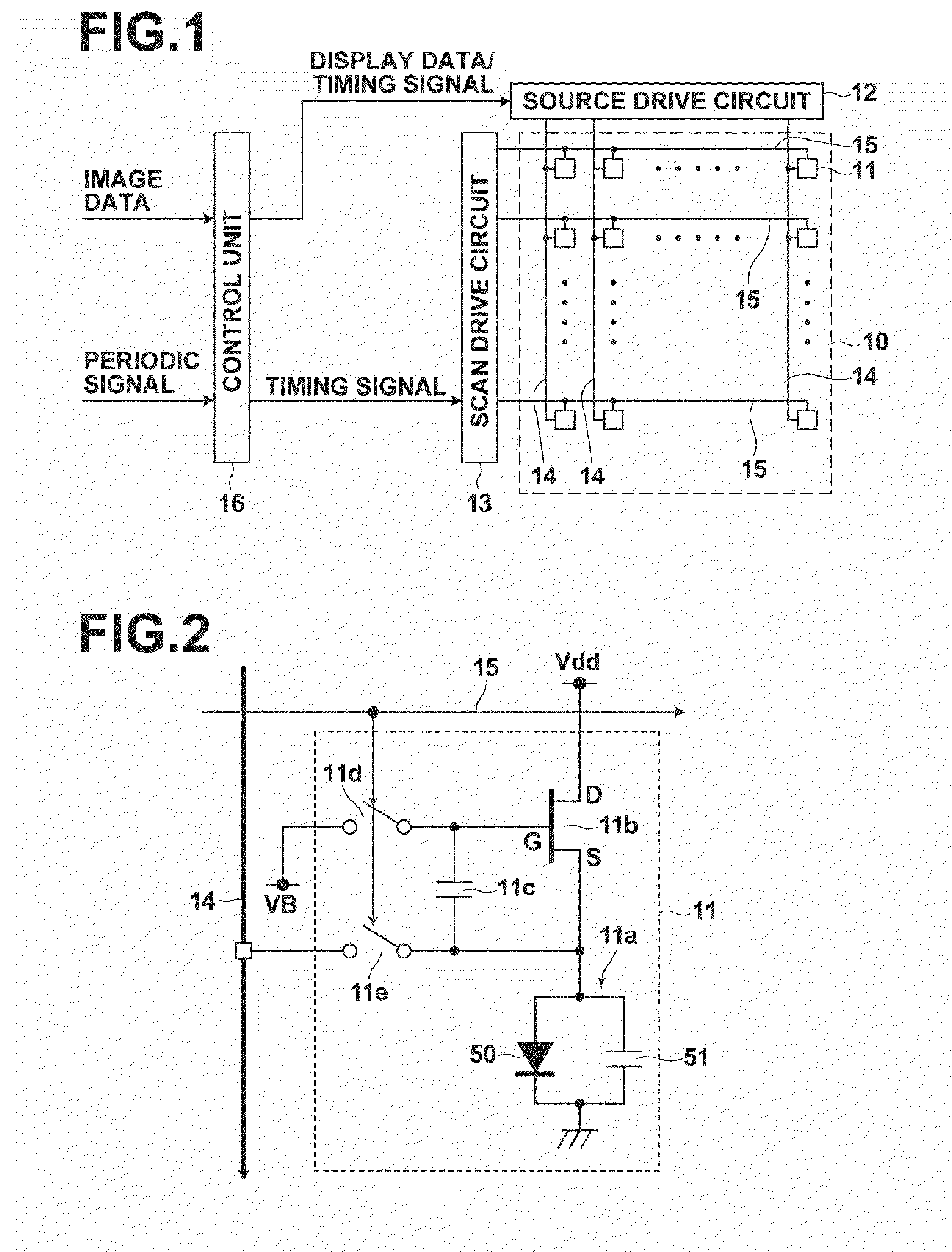
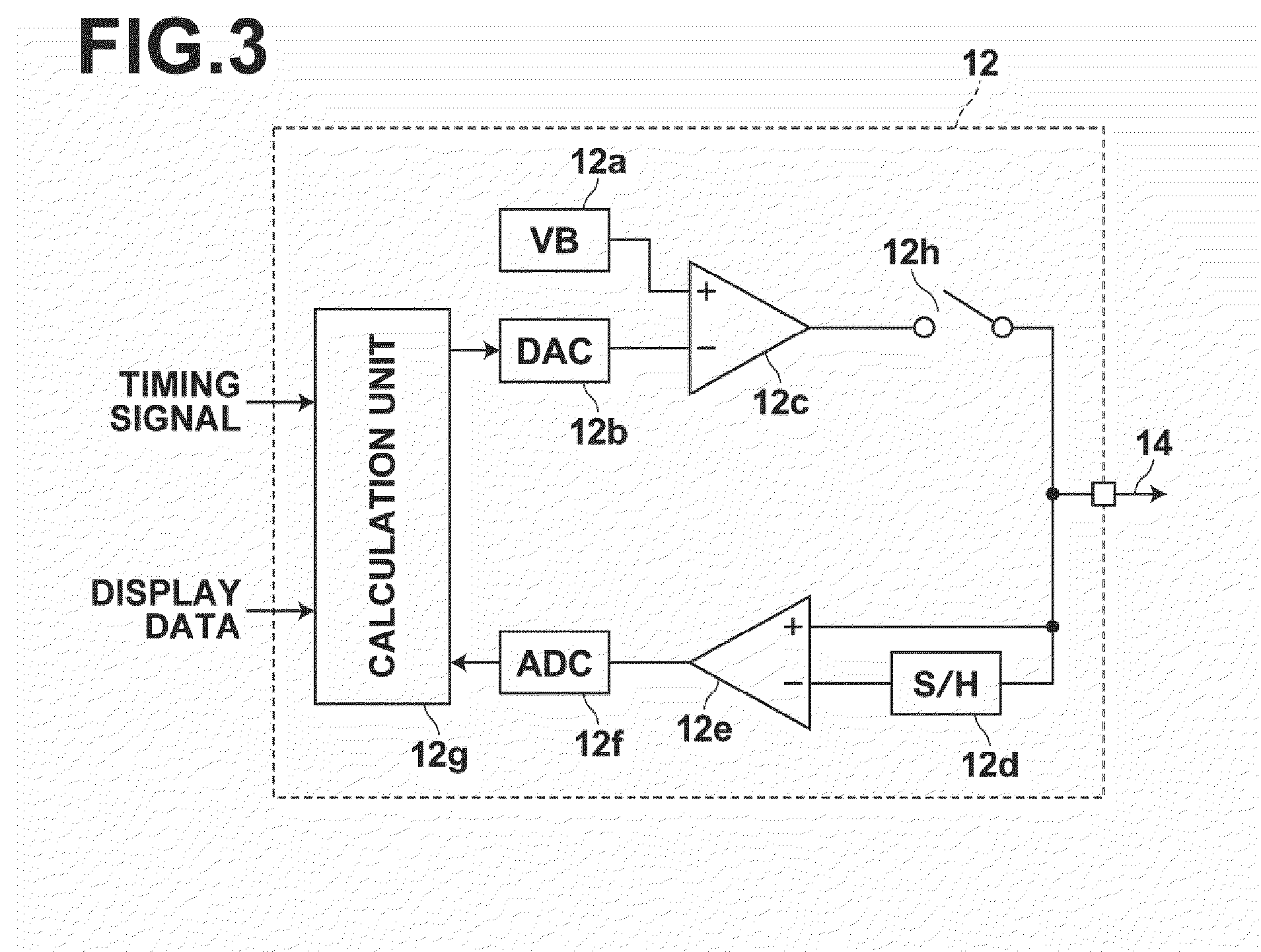
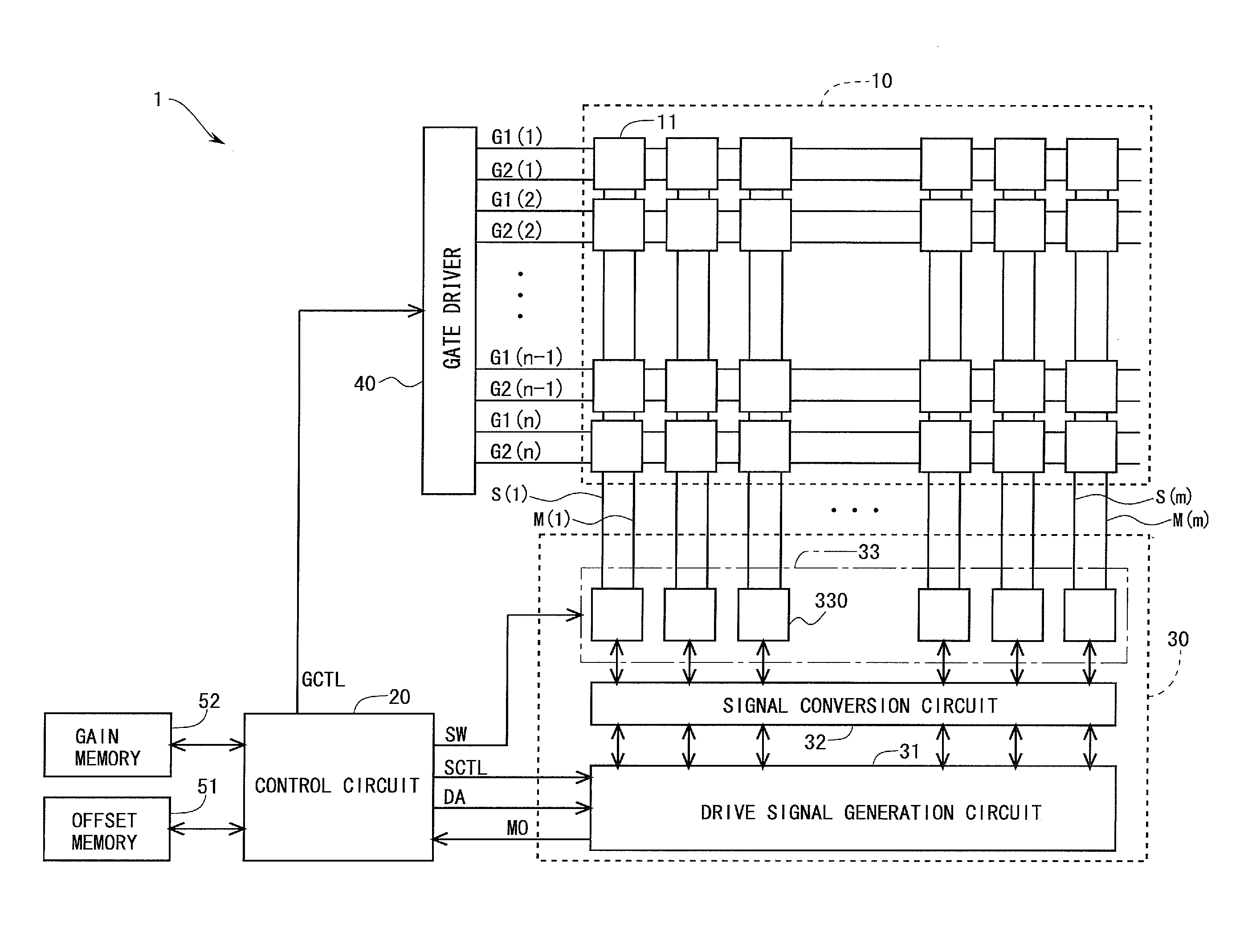
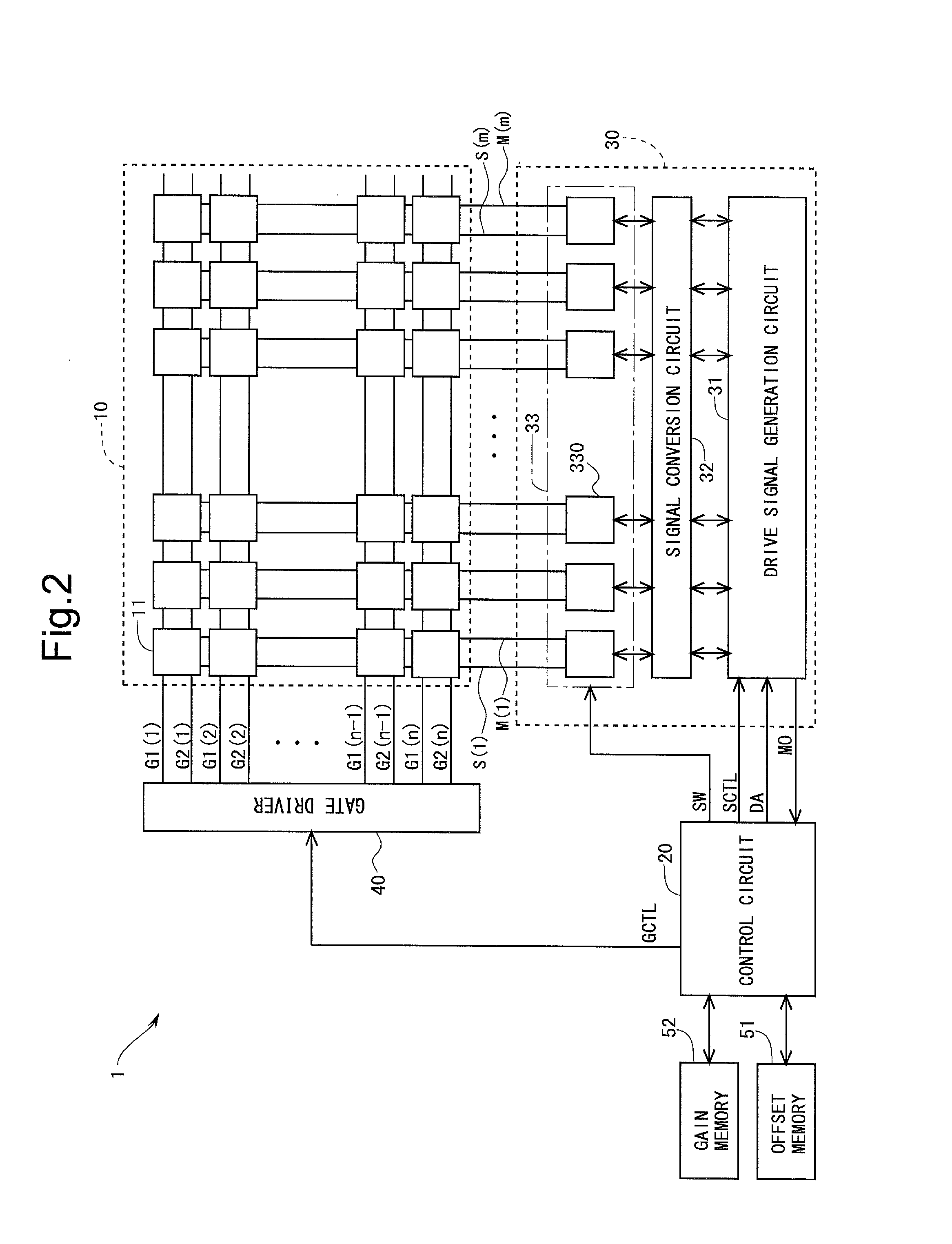
ActiveUS20100039422A1Avoid Threshold Voltage DriftInexpensive and simple circuit structureCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDriving currentAcquired characteristic
Supplying first and second measuring voltages to a source terminal of a drive transistor to obtain first and second voltage variations at the source terminal of the drive transistor when a parasitic capacitance of a light emitting element is charged by currents flowed through the drive transistor by the supply of the voltages, obtaining first and second current values of the drive current of the drive transistor based on the first and second voltage variations, obtaining characteristic values of the drive transistor based on the first and second measuring voltages and the first and second current values, and outputting a data signal based on the obtained characteristic values and a drive voltage of the drive transistor corresponding to the amount of emission of the light emitting element to the source terminal of the drive transistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Photoplethysmography (PPG) device and the method thereof
ActiveUS20050058456A1Improve performanceReduce Motion ArtifactsCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAcquired characteristicCovariance
A method of measuring Photoplethysmography (PPG) signals may comprise detecting dual wavelength illumination from a light detector so as to provide detected signals, converting the detected signals into digital signals so as to provide digital signals, reducing noises from the digital signals and increasing independency between the digital signals so as to provide preprocessed signals, subtracting the average value from the preprocessed signals so as to provide adjusted signals, obtaining whitening matrix based on covariance, eigen value, and eigen matrix obtained from the adjusted signals, and restoring data using the whitening matrix.
Owner:SILICON MITUS
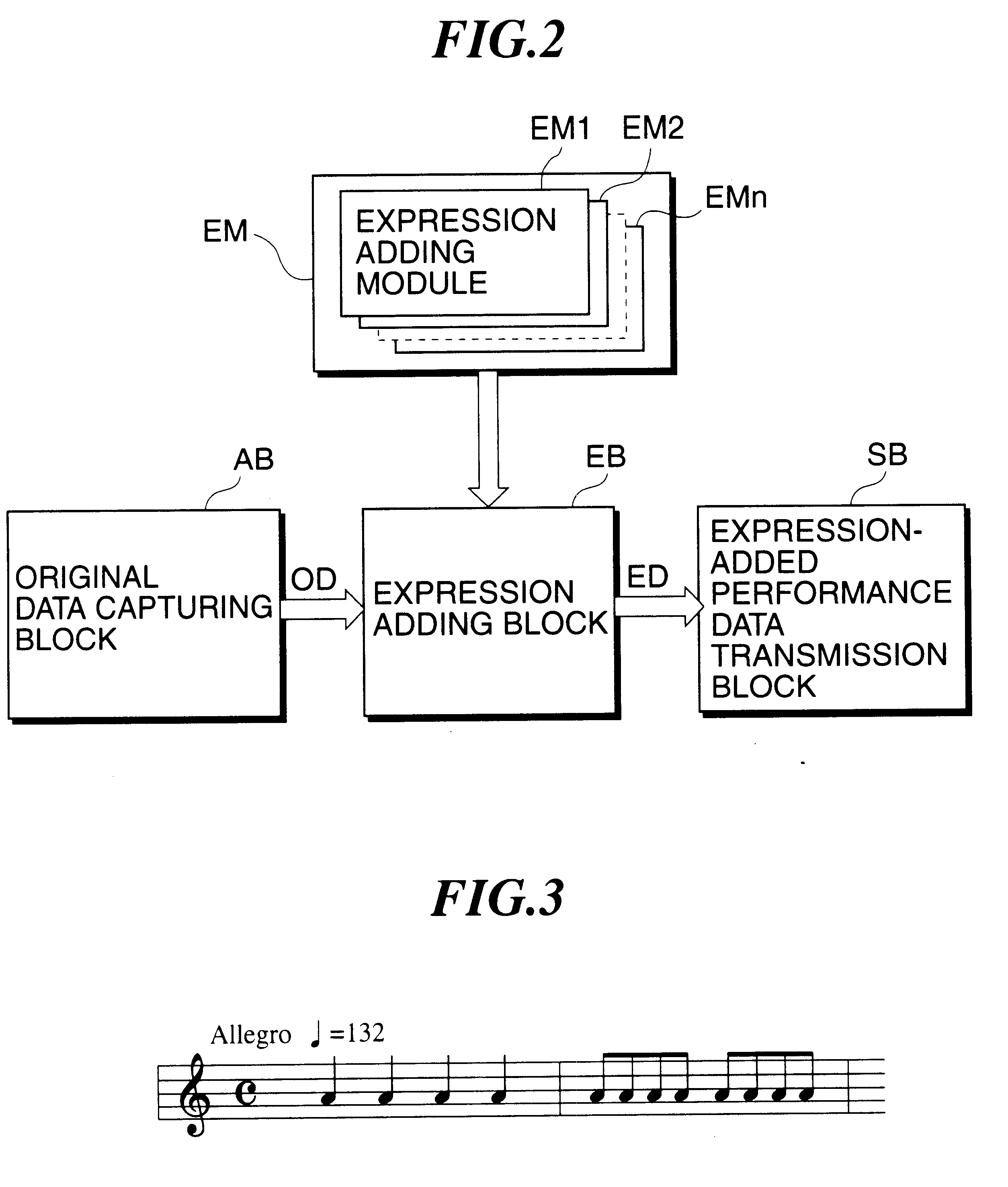
Performance data generating apparatus and method and storage medium
There are provided a performance data generating apparatus and method which is capable of automatically converting original performance data providing an expressionless performance into performance data that enable a variety of musically excellent performances, by means of a novel expression adding converter using various modularized rules and procedures to add expressions based on temporal changes such as tempo and timing, as well as a storage medium that stores a program for executing the method. Performance data are supplied, characteristic information is obtained from the supplied performance data, generating method information is stored which corresponds to predetermined characteristic information and representative of at least one method of generating musical tone control information, generating method information corresponding to the obtained characteristic information is obtained from the stored generating method information, the musical tone control information from the obtained characteristic information and generating method information corresponding to the obtained characteristic information is obtained, and the generated musical tone control information is added to the supplied performance data.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
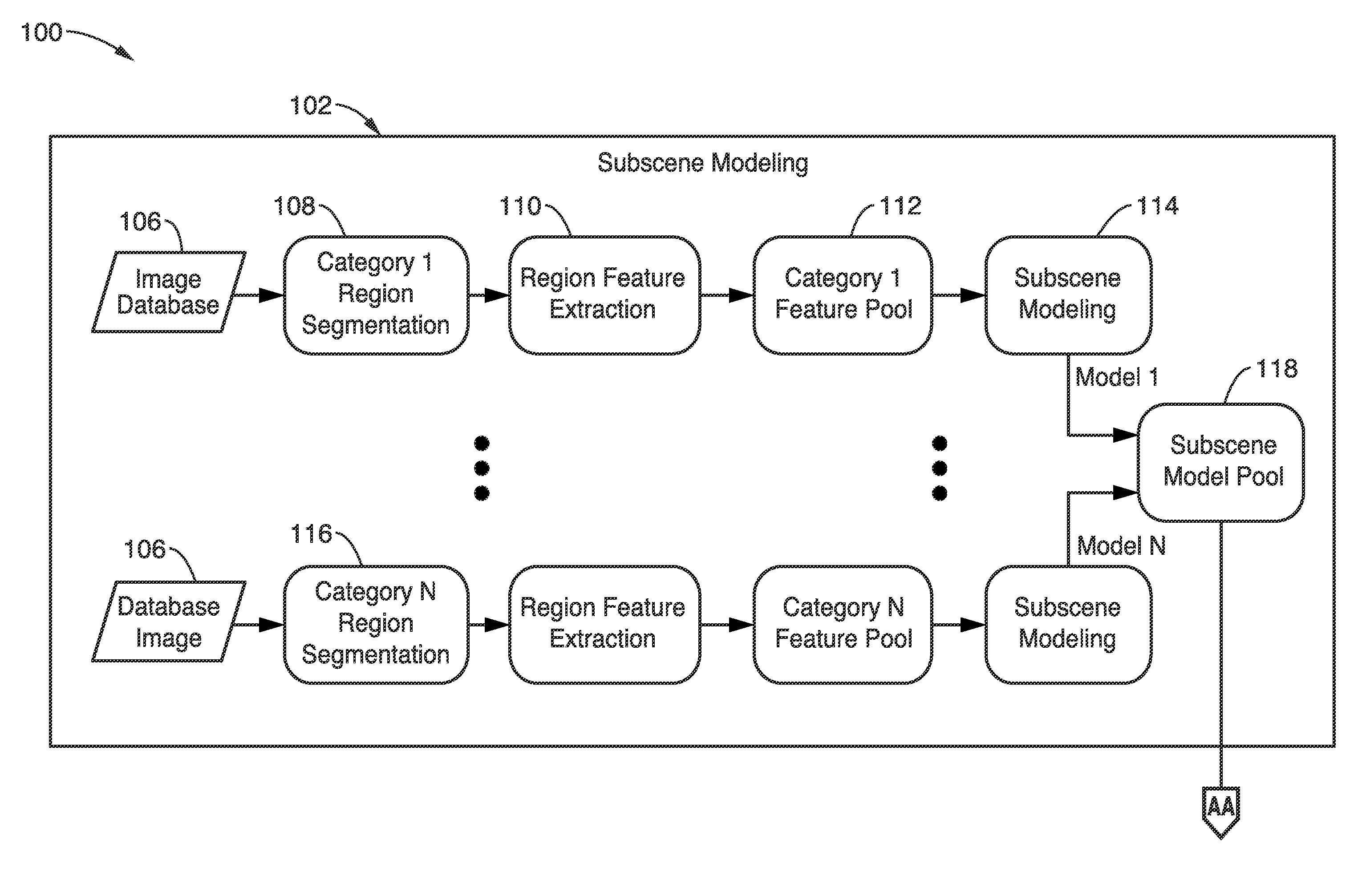
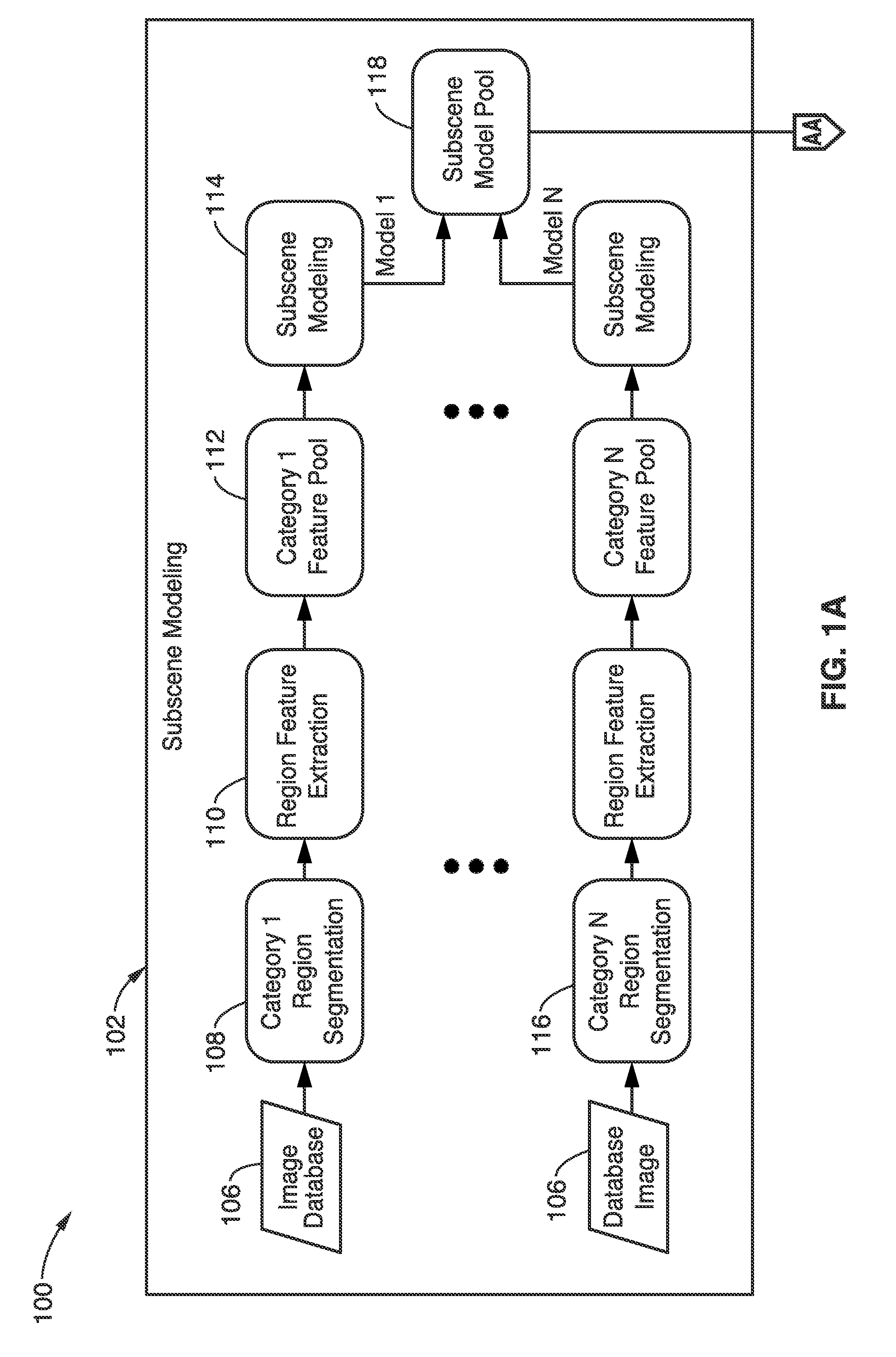
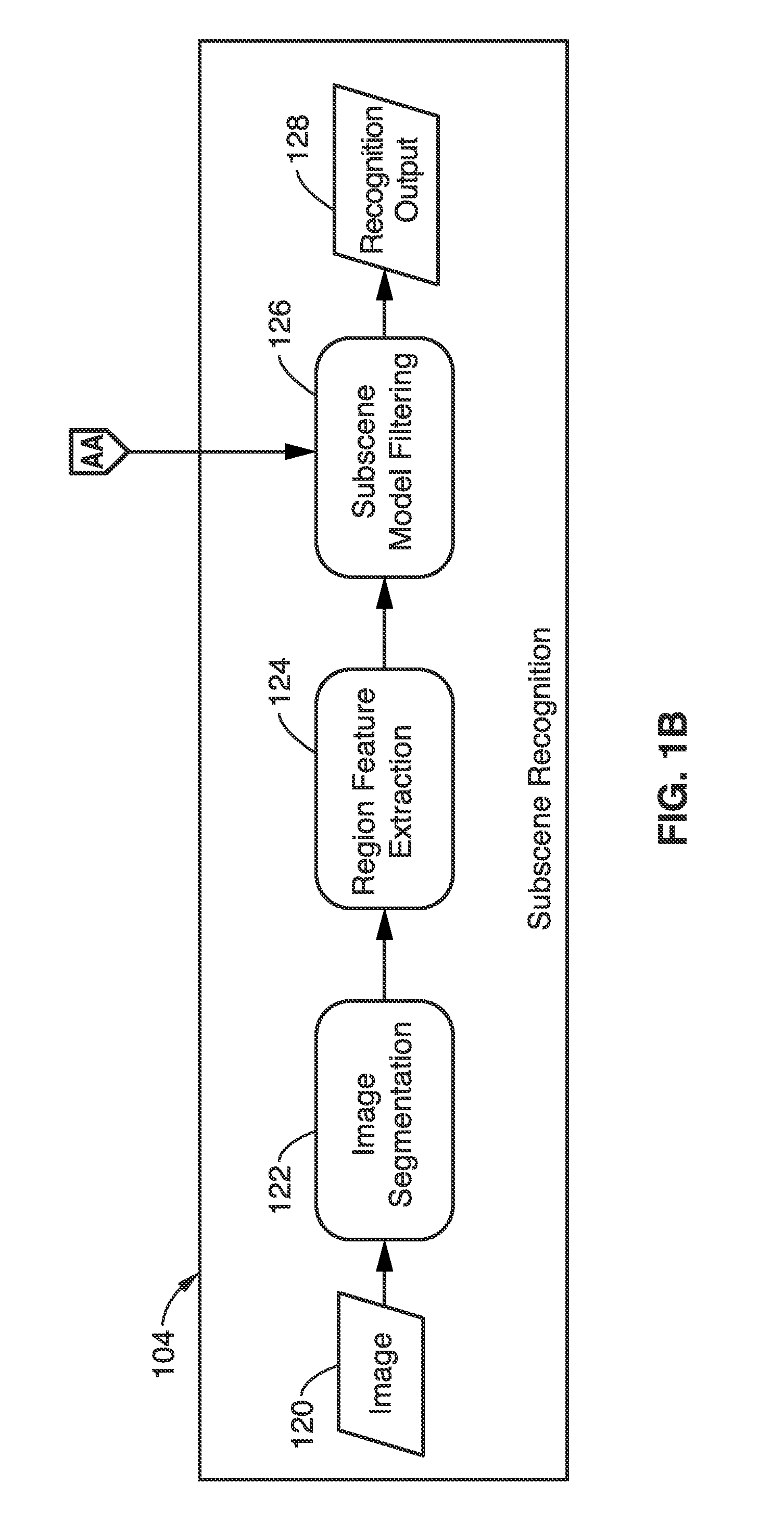
Region description and modeling for image subscene recognition
A method and apparatus is described here that categorizes images by extracting regions and describing the regions with a 16-dimensional subscene feature vector, which is a concatenation of color, texture, and spatial feature vectors. By comparing the spatial feature vectors in images with similarly-obtained feature vectors in a Gaussian mixture based model pool (obtained in a subscene modeling phase), the images may be categorized (in a subscene recognition phase) with probabilities relating to each region or subscene. Higher probabilities are likelier correlations. The device may be a single or multiple core CPU, or parallelized vector processor for characterizing many images. The images may be photographs, videos, or video stills, without restriction. When used real-time, the method may be used for visual searching or sorting.
Owner:SONY CORP
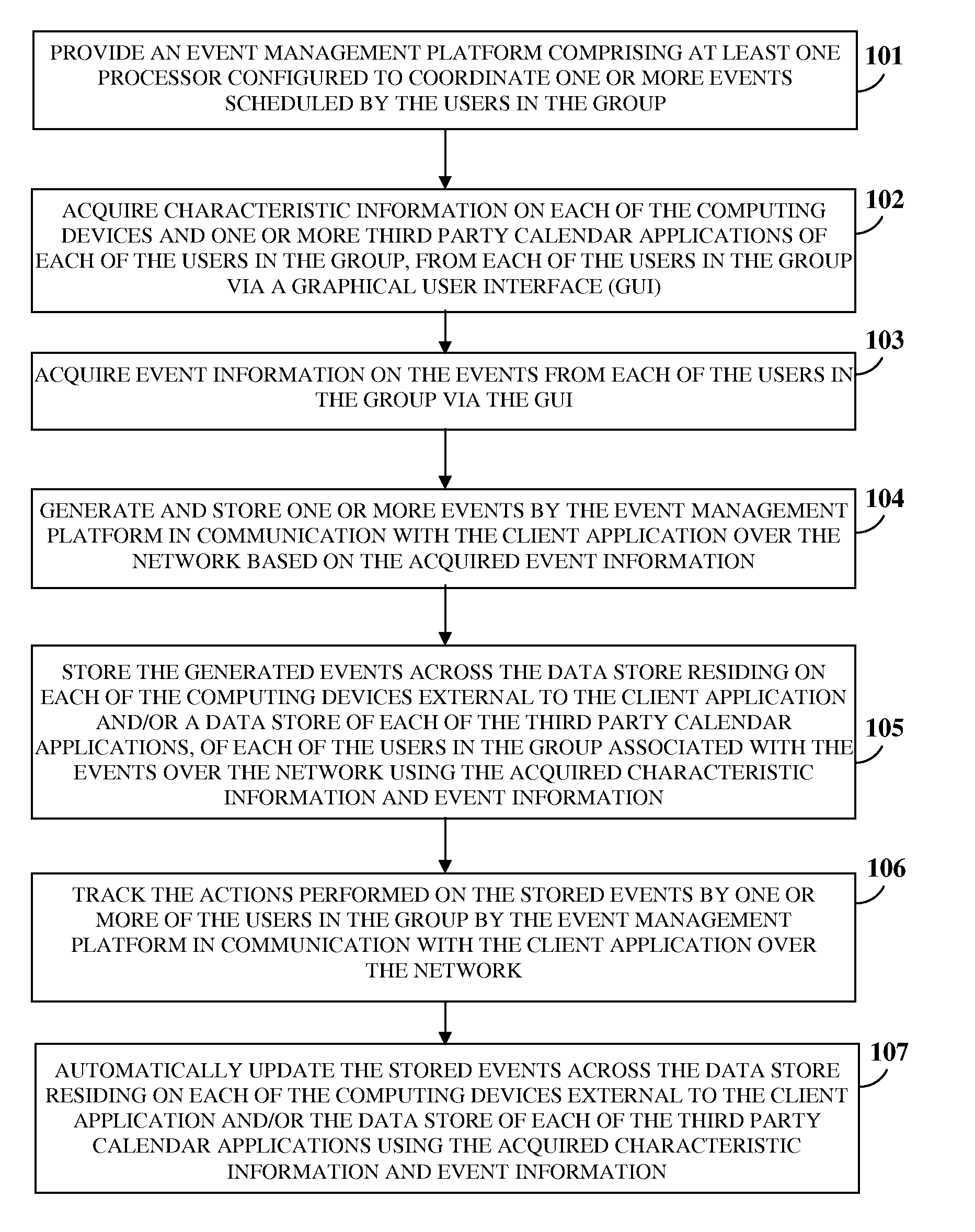
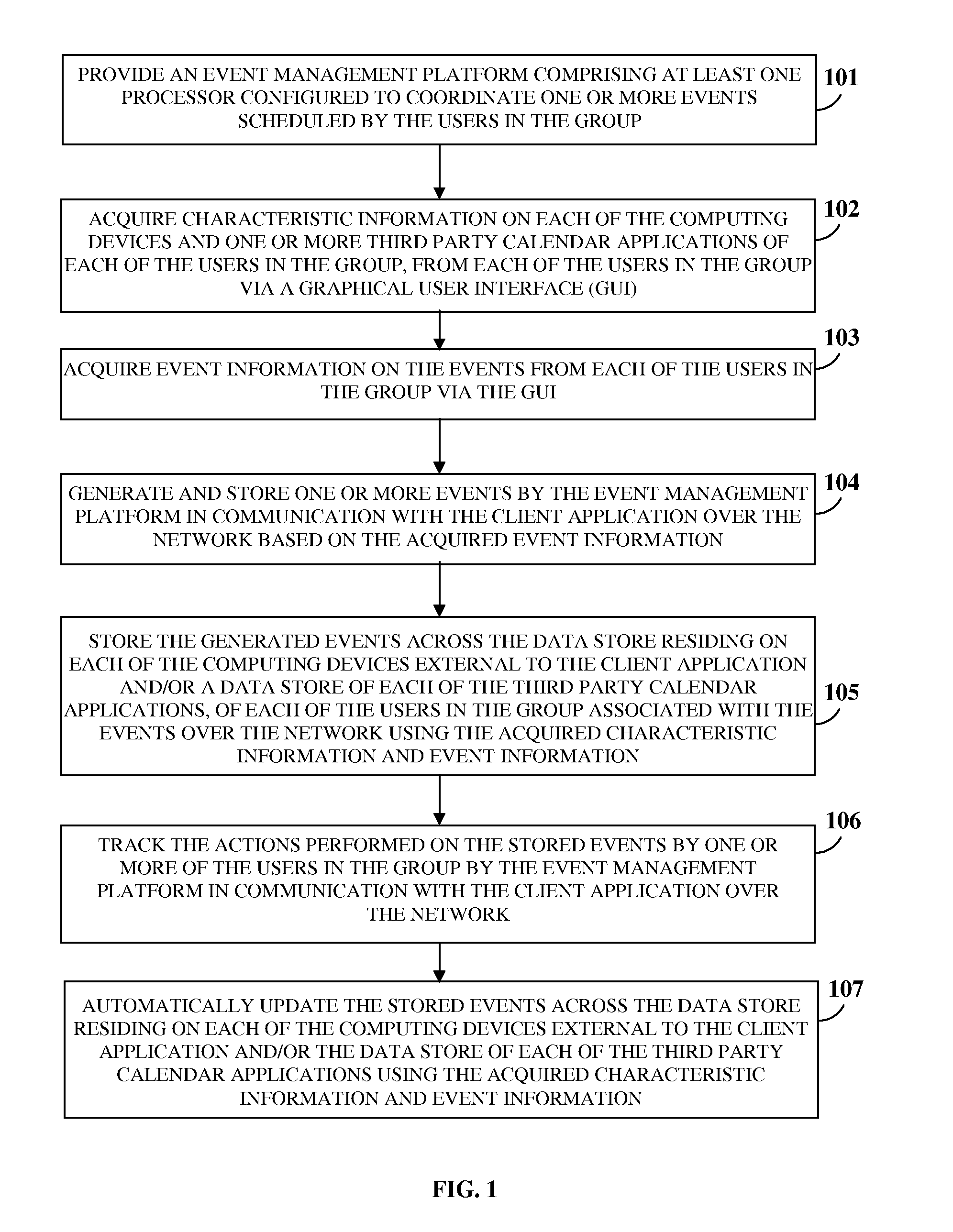
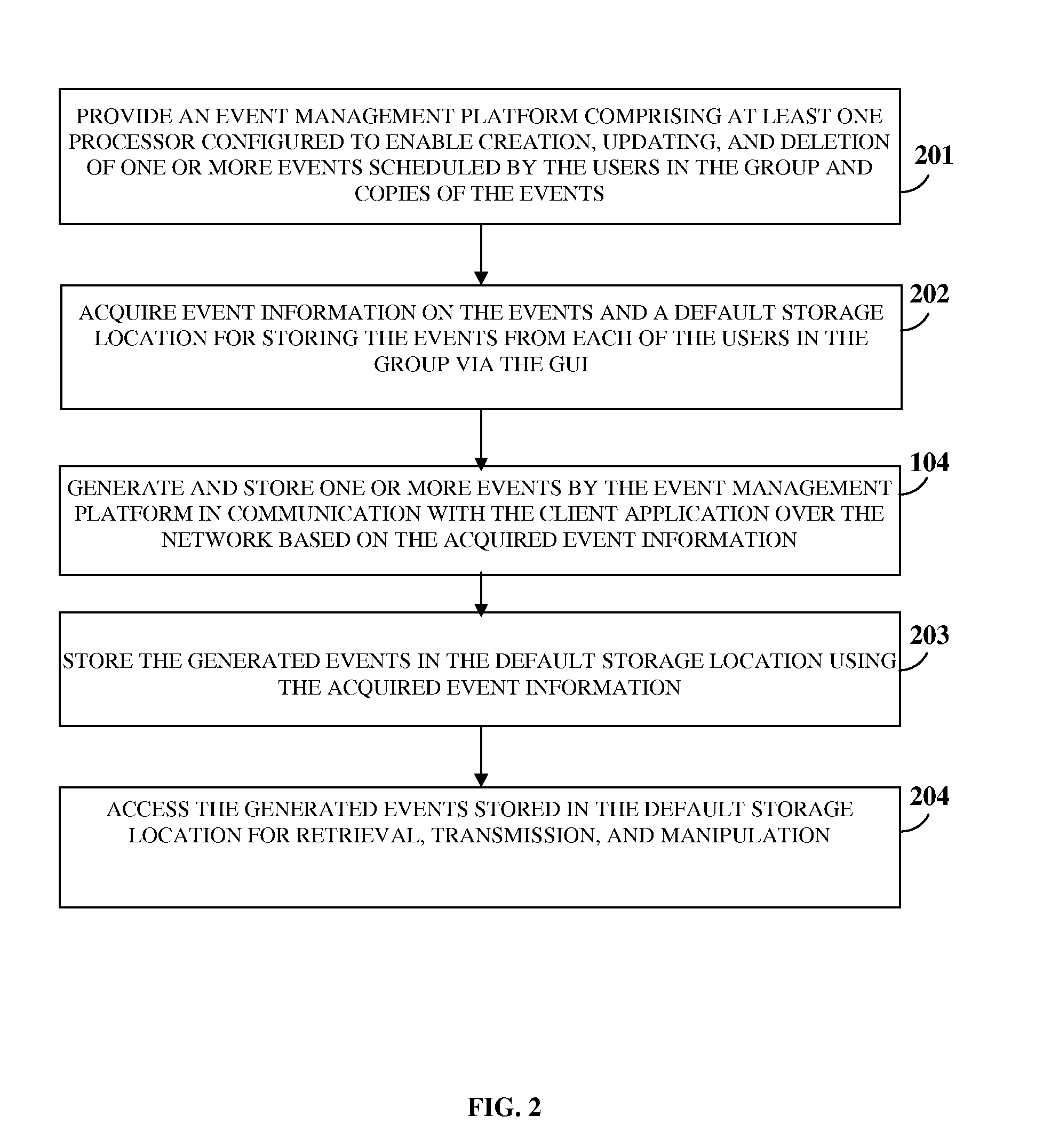
Unified Virtual Group Calendar System
InactiveUS20120284637A1Reliable assessmentIncrease capacityInput/output processes for data processingThird partyAcquired characteristic
A computer implemented method and system for managing events scheduled by multiple users in a group, provides an event management platform (EMP) in communication with a client application on each user's computing device via a network. The EMP acquires characteristic information on each computing device and each user's third party calendar applications (TPCAs), and event information on the events. The EMP, in communication with the client application, generates and stores the events based on the event information. The EMP stores the events across a data store residing on each computing device external to the client application and / or the data stores of the TPCAs, using the acquired characteristic information and event information. The stored events are accessible to each user associated with the events for performing one or more actions that are tracked and automatically updated by the EMP. The EMP also notifies the availability of the users in the group.
Owner:BOYER JOHN EDWARD +1
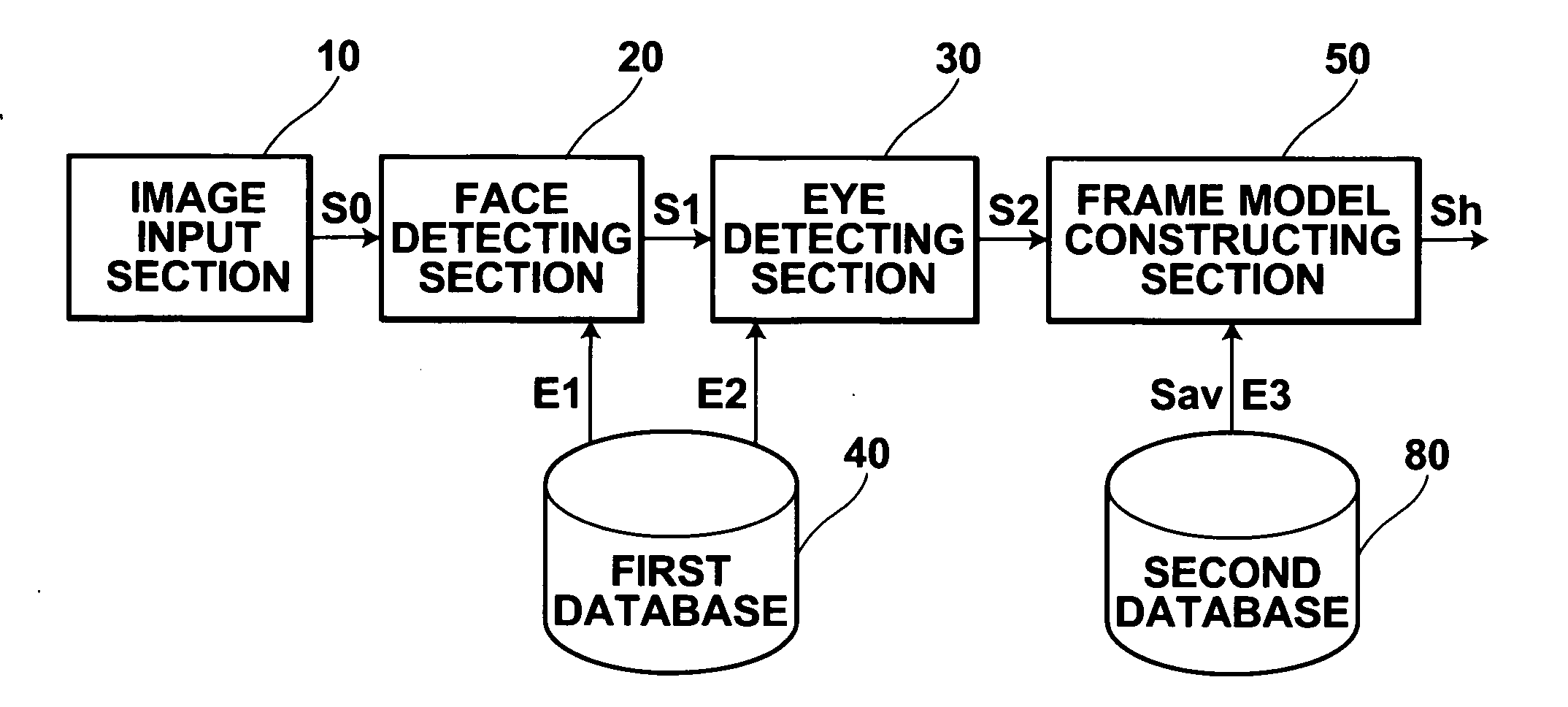
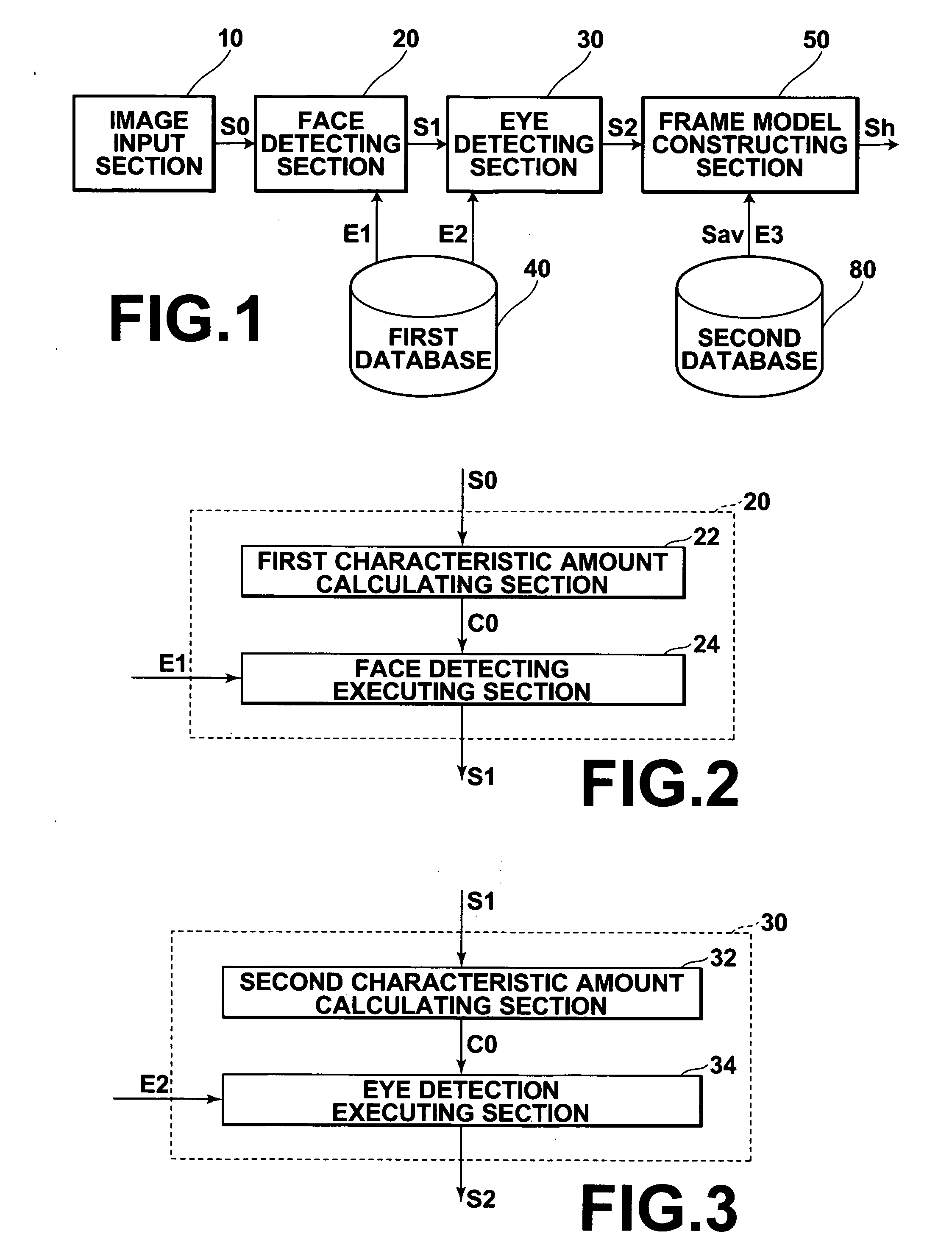
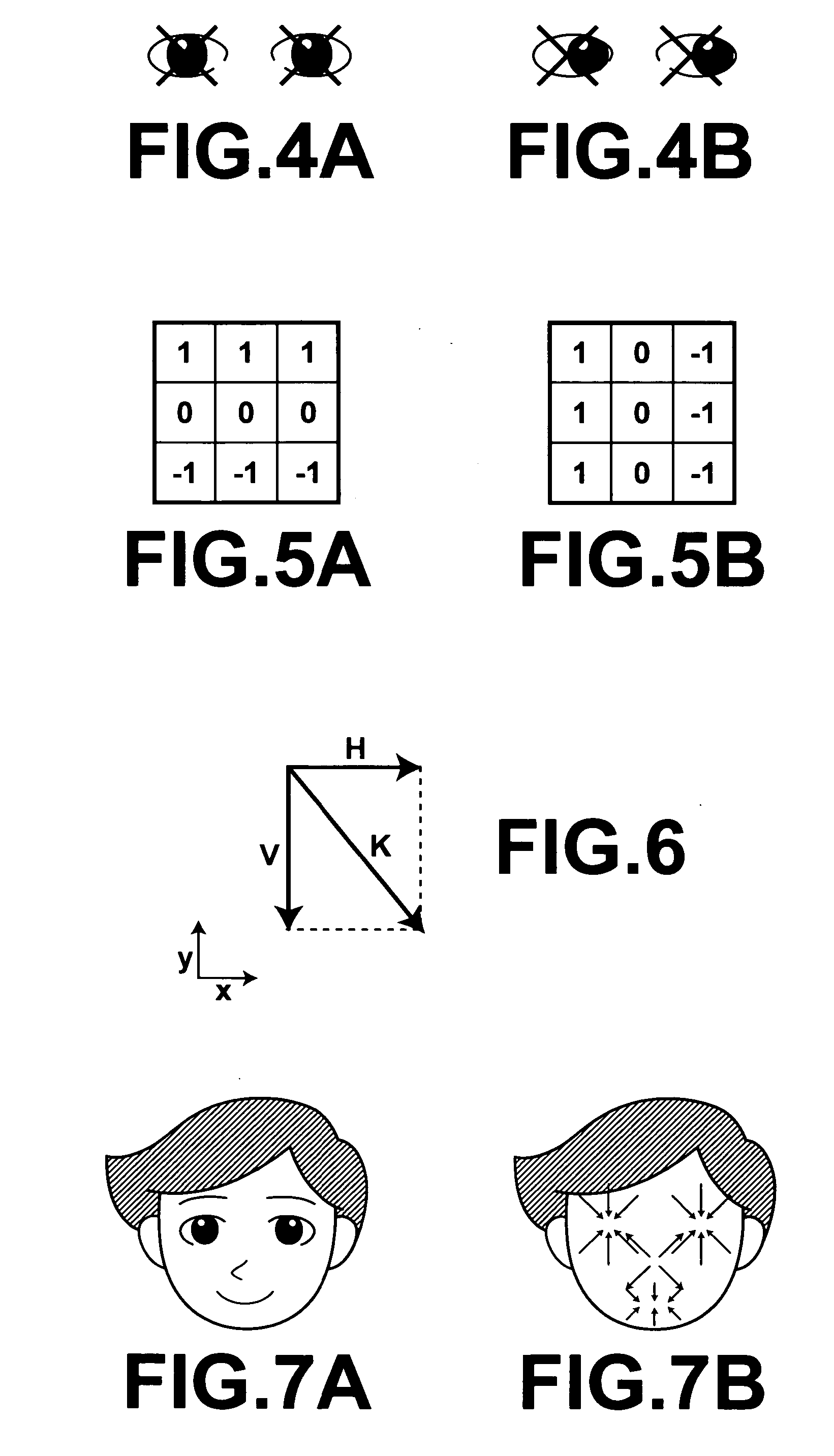
Image processing method, image processing apparatus, and computer readable medium, in which an image processing program is recorded
InactiveUS20060133672A1Improve accuracyImprove robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingAcquired characteristic
A plurality of landmarks, which are employed in statistical models, such as an ASM, that is, a plurality of landmarks that represent the shape and the like of a predetermined subject, such as a face, within an image, are detected. Discrimination regarding whether each pixel within the image is a point that represents a landmark is performed based on discrimination conditions. The discrimination conditions correspond to characteristic amounts, which are obtained by learning characteristic amounts of positions, which are known to be landmarks, and characteristic amounts of positions, which are known to not be landmarks, within a plurality of sample images of the subject, by a machine learning technique.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Automatic storage system of industrial robot
InactiveCN105292892AFree laborReasonable assemblyStorage devicesAcquired characteristicIdentification device
The invention discloses an automatic storage system of an industrial robot. The automatic storage system comprises a robot sorting area, a speed-fold chain, an AGV trolley, an intelligent three-dimensional warehouse and a central controller. The robot sorting area comprises a flat belt conveyor, a robot and a vision identification device. The flat belt conveyor receives a signal sent by the central controller and controls trays to move in the conveying direction of the flat belt conveyor. The vision identification device is installed on any side of the flat belt conveyor and located above the trays. A camera of the vision identification device is used for photographing the tray area below the camera, and the photographing area of the camera at least includes one tray. The vision identification device detects and identifies photos photographed by the camera, sends feature data obtained through identification to the central controller and sends a signal to the robot, and the robot receives the signal to transfer and put specified articles on the storage trays of the speed-fold chain to achieve sorting. According to the automatic storage system of the industrial robot, labor force of workers is liberated, and product detecting, sorting and storing efficiency is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU HUIBO ROBOTICS TECH CO LTD +1
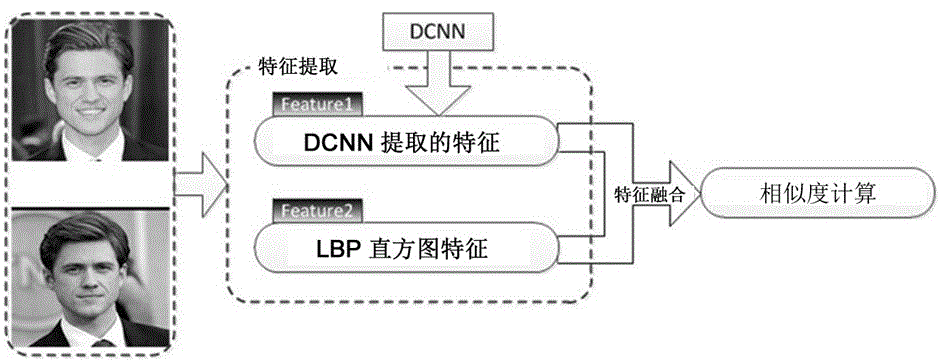
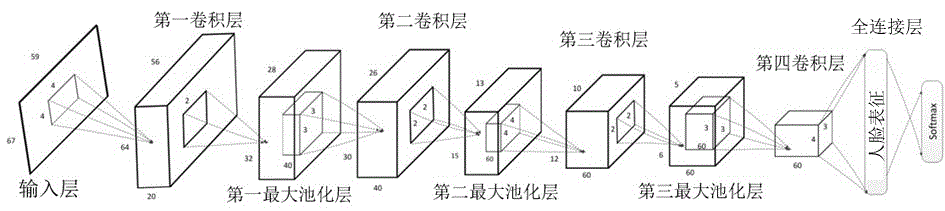
Cross-age face verify method based on characteristic learning
ActiveCN104866829AReduce complexityImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionAcquired characteristicNerve network
The invention discloses a cross-age face verify method based on characteristic learning; the method comprises the following steps: 1, obtaining to-be compared two face images; 2, using a face characteristic point positioning method to carry out align operation for the two face images; 3, respectively carrying out feature extraction for each image, wherein the extraction method includes the following steps: a, automatically extracting high-level meaning characteristics through a depth convolution nerve network; b, calculating LBP histogram characteristics of the image; c, fusing the characteristics obtained in the a and b steps, and expressing characteristic vectors; 4, using a cosine similarity method to calculate a distance between the characteristic vectors obtained by the step3, and determining whether the two images are from a same person or not. The method firstly uses the depth network to cross-age face verify, and creatively combines the handwork design LBP histogram characteristics with depth network autonomous learning characteristics, thus realizing complementation between high-rise meaning characteristic and lower characteristics, and providing better accuracy.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
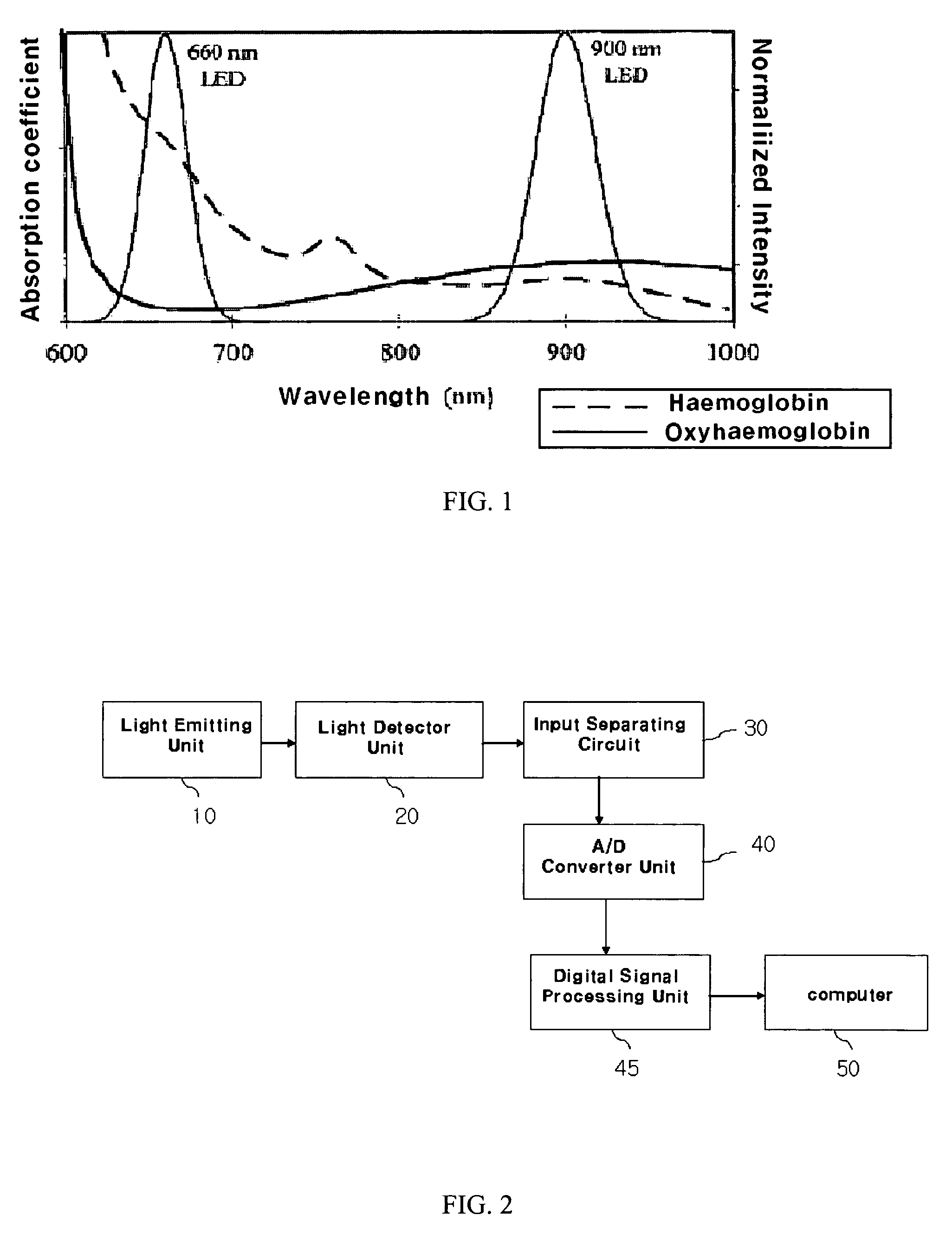
Fetal oximetry system and sensor
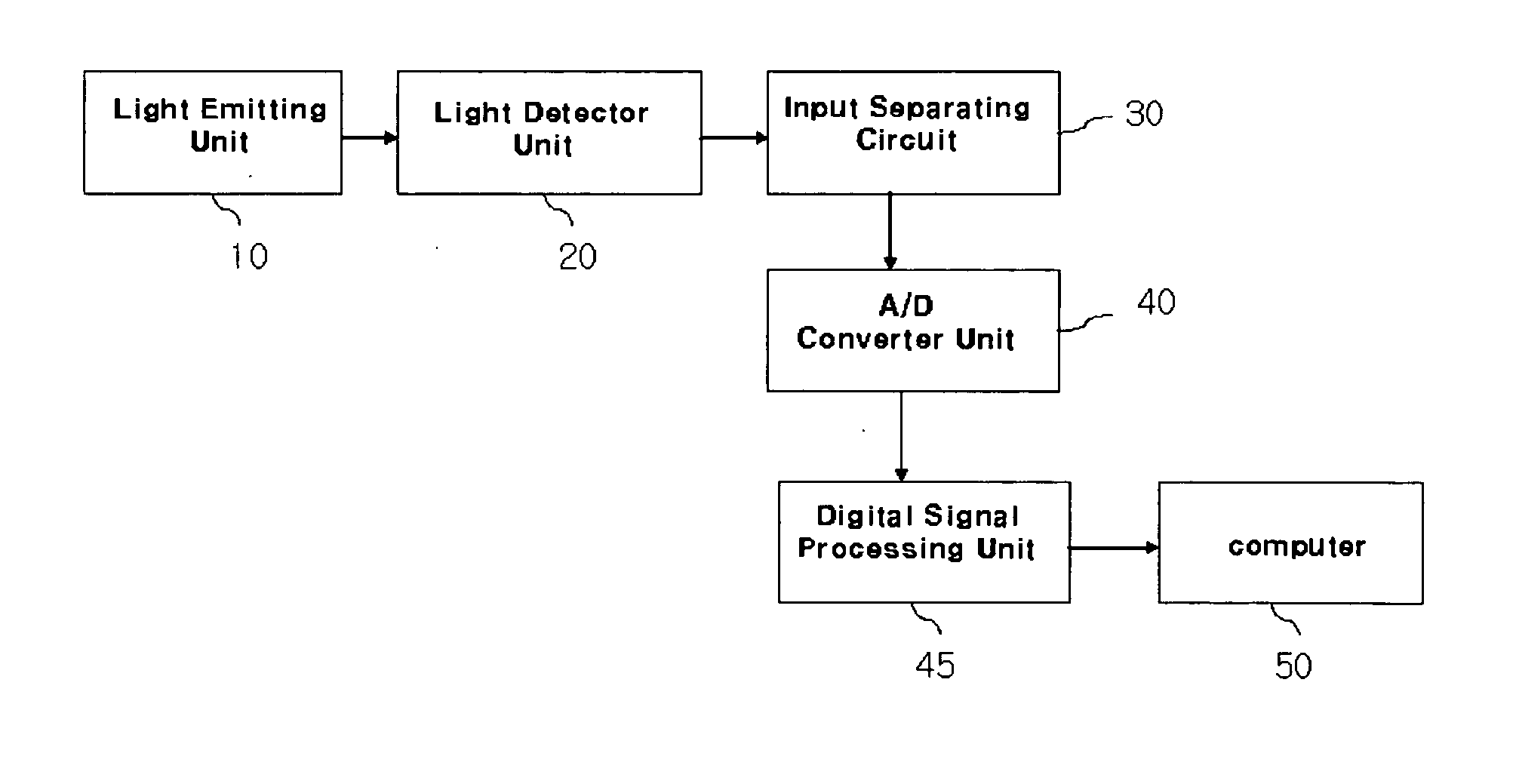
InactiveUS7469158B2Improve accuracyUsable signal timeSensorsBlood characterising devicesAcquired characteristicFetal monitoring
An optical measuring device having multiple optical paths between one or more light emitters and one or more light detectors and / or providing at least two sets of wavelength of light along at least one path, with a final measurement being produced as a combination of measurements of the sets of wavelengths of light taken along one or more of the optical paths. Features that contribute to increased safety and ease of use include providing (1) a receiving cavity in a proximal end of an insertion rod that holds a free end of a circuit connector to keep it from becoming tangled or snagged, (2) a mechanism to keep the sensor within an introducer tube during storage and insertion and to expose a portion of the sensor only when the sensor is applied to the unborn baby, (3) a tab on the insertion rod to prevent the circuit connector from becoming tangled or snagged within the introducer tube, (4) a rotating feature whereby if a torque applied on the sensor exceeds a first predetermined amount, the sensor rotates, and a disengaging feature whereby the sensor detaches from insertion rod if a pull-off force exceeds a second predetermined amount, the rotating and disengaging features being independent of one another, (5) a circuit connector that includes at least one of the following features: (a) a stiffening member provided at the proximal end to minimize bending, (b) a shielding layer, and (c) at least one slit to increase the flexibility of the circuit connector, and (6) an interface that includes an identification element that is detected by an external circuit only if the circuit connector is connected to the interface. The present invention also pertains to a method of manufacturing a needle that is used in an invasive sensor, and preferably for fetal monitoring, that provides features not heretofore available in conventional sensors.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
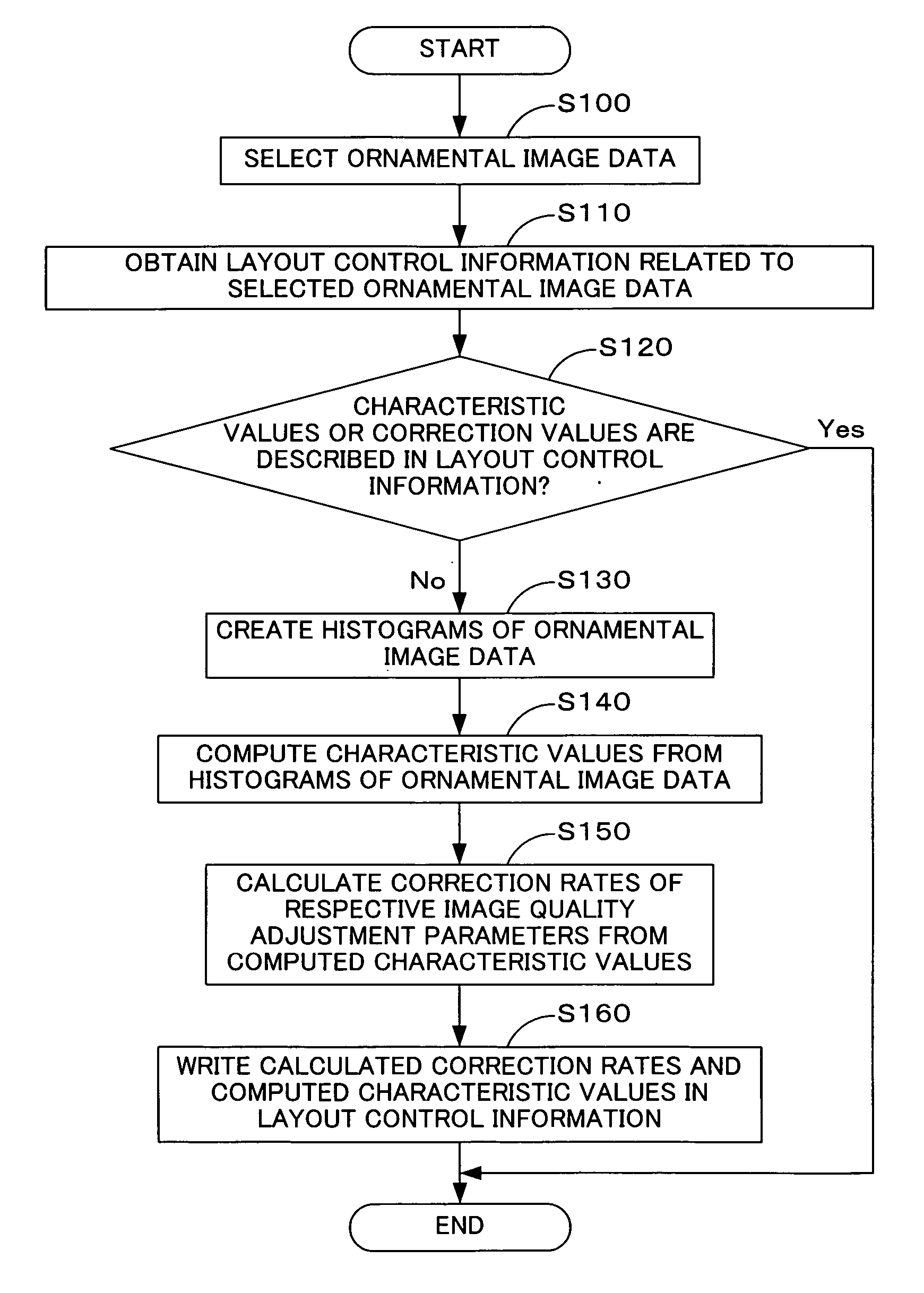
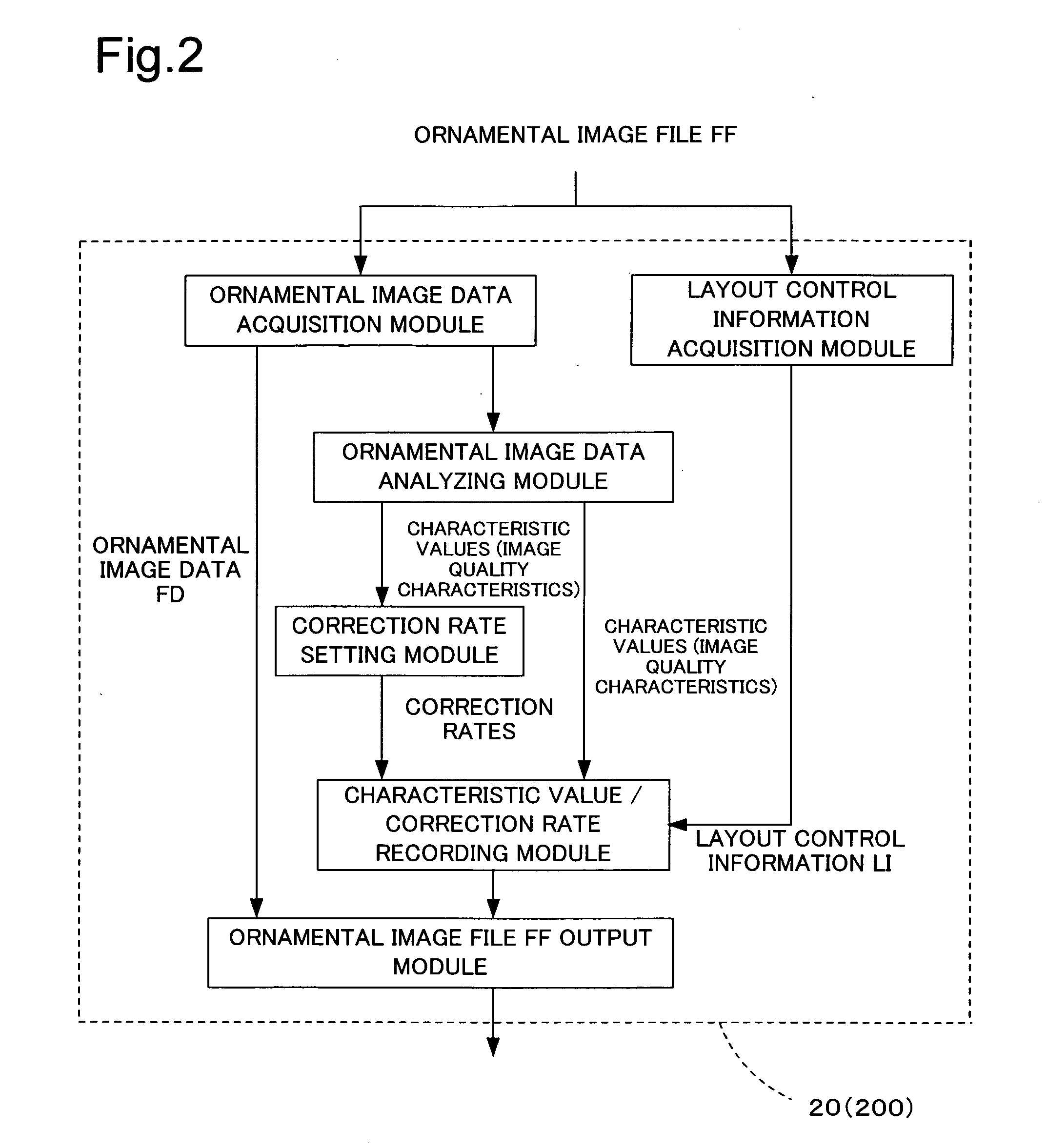
Generation of image quality adjustment information & image quality adjustment with image quality adjustment information
InactiveUS20050141777A1Good image quality balanceEasy and prompt image quality adjustmentImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionAcquired characteristic
A CPU 200 extracts ornamental image data and layout control information from an ornamental image file FF. When the layout control information does not include characteristic values, the CPU 200 analyzes the ornamental image data to acquire characteristic values representing a tendency of image quality of the ornamental image data. The CPU 200 may additionally compute correction rates for correcting values of image quality-relating parameters of objective image data from the acquired characteristic values of the ornamental image data. The CPU 200 writes either the acquired characteristic values or the computed correction rates into the layout control information. The layout control information including the acquired characteristic values or the computed correction rates is output together with the ornamental image data in the form of the ornamental image file FF.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Personal identification and method
InactiveUS20070058841A1Smoothly graspPerson identificationElectrical locking circuitsVeinAcquired characteristic
Personal identification is implemented by picking up finger vein patterns when the user naturally grasps a grip such as doorknob. The device for personal identification has a light source provided to irradiate light on the finger from the palm side, a camera to pick up the vessel image of the finger, and a processor to extract features of the vessel from the image and compare the obtained features with the registered ones. The camera picks up the light that exits from the backside of the finger after penetrating it.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and system for voiceprint recognition based on vector quantization based
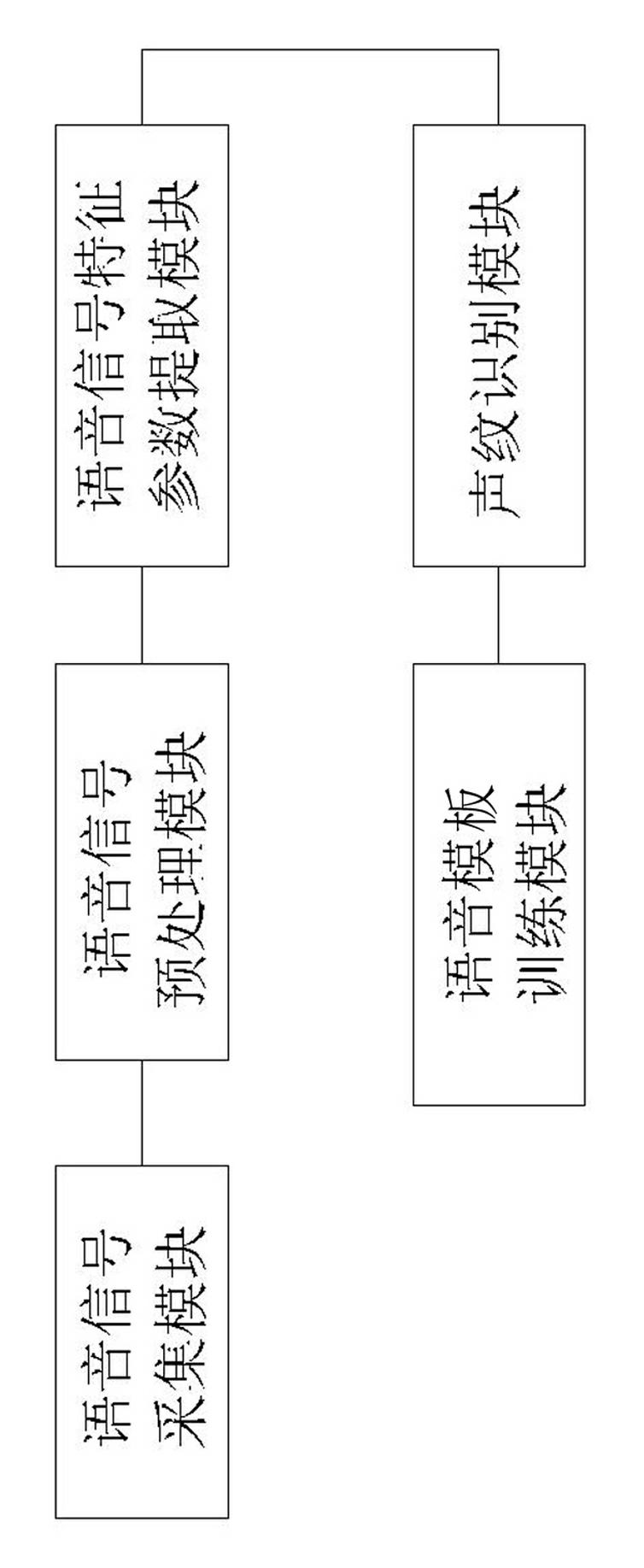
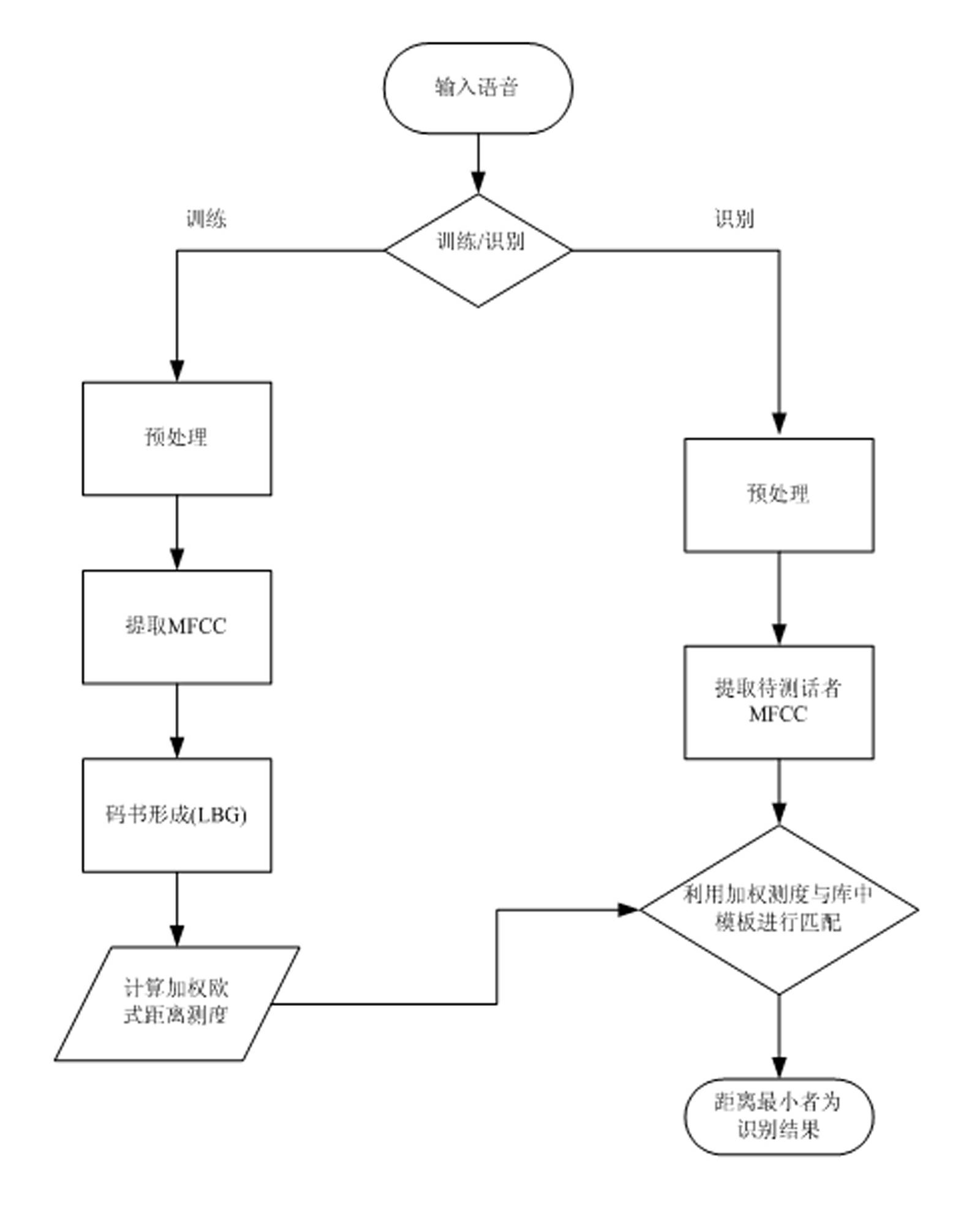
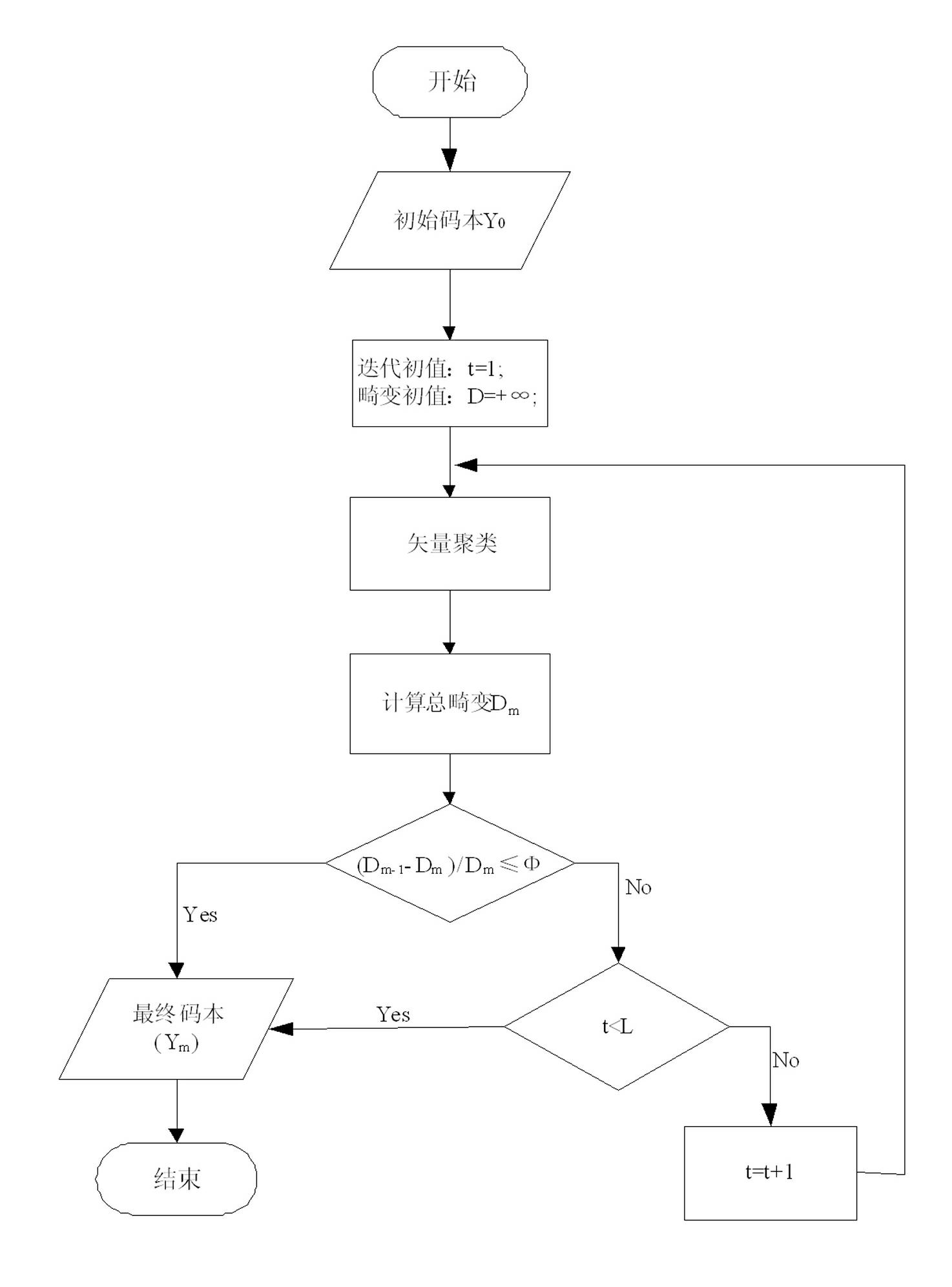
InactiveCN102509547ARealize simulationEasy to identifySpeech recognitionMel-frequency cepstrumCluster algorithm
The invention discloses a method and a system for voiceprint recognition based on vector quantization, which have high recognition performance and noise immunity, are effective in recognition, require few modeling data, and are quick in judgment speed and low in complexity. The method includes steps: acquiring audio signals; preprocessing the audio signals; extracting audio signal characteristic parameters by using MFCC (mel-frequency cepstrum coefficient) parameters, wherein the order of the MFCC ranges from 12 to 16; template training, namely using the LBG (linde, buzo and gray) clustering algorithm to set up a codebook for each speaker and store the codebooks in an audio data base to be used as the audio templates of the speakers; voiceprint recognizing, namely comparing acquired characteristic parameters of the audio signals to be recognized with the speaker audio templates set up in the audio data base and judging according to weighting Euclidean distance measure, and if the corresponding speaker template enables the audio characteristic vector X of a speaker to be recognized to have the minimum average distance measure, the speaker is supposed to be recognized.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
System and method for onboard detection of ballistic threats to aircraft
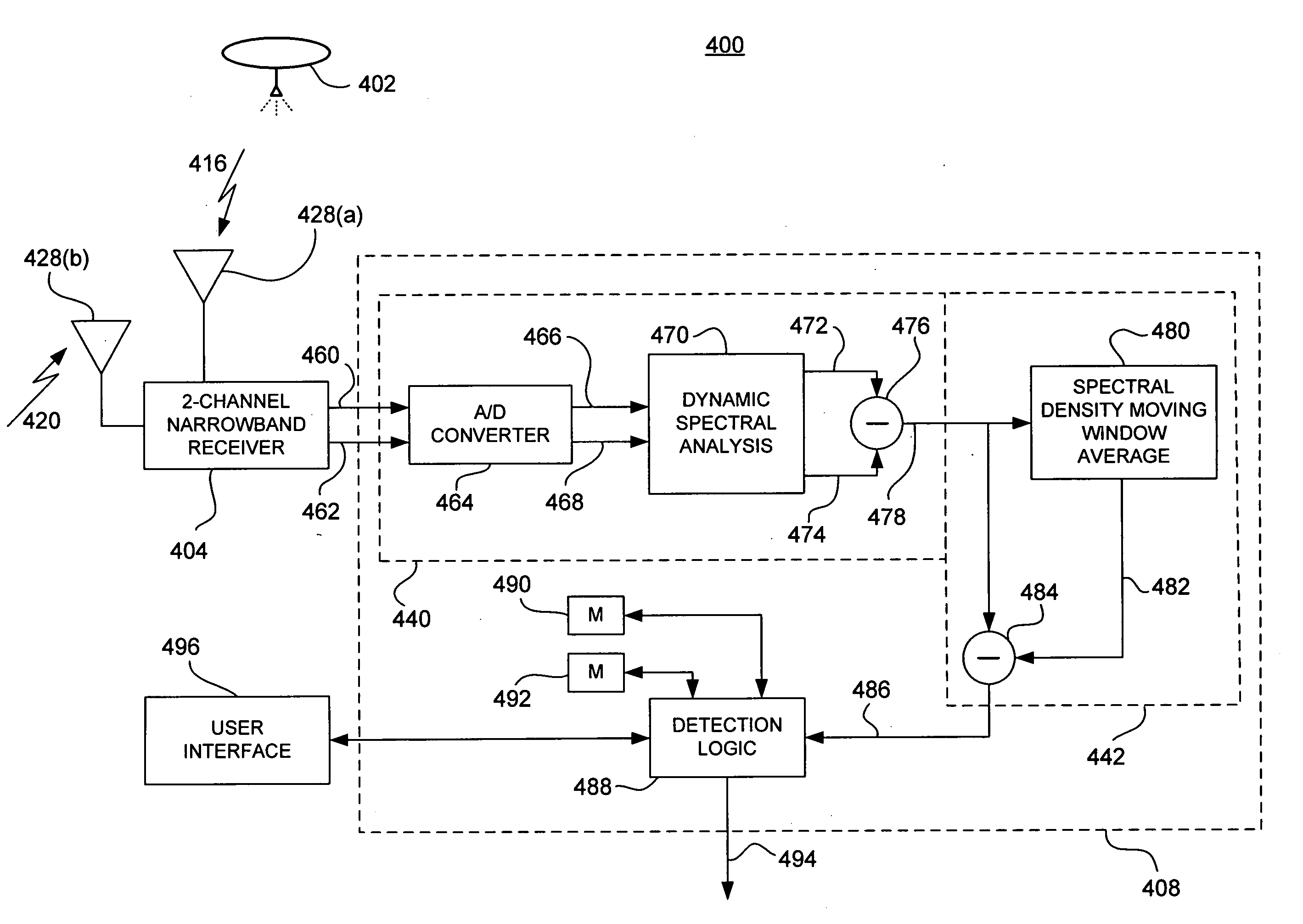
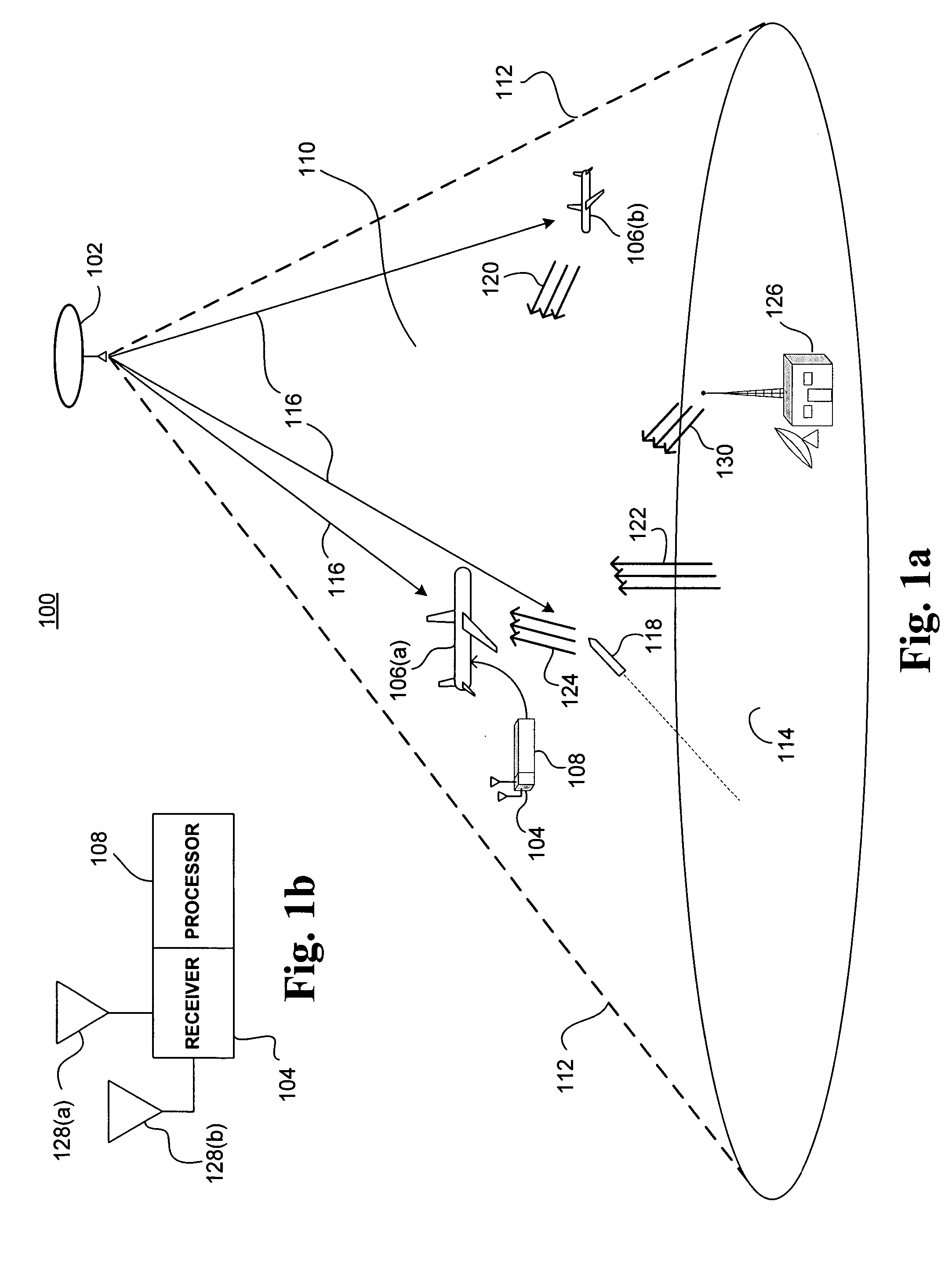
InactiveUS20050275582A1Low costMinimize per-aircraft costCommunication jammingAntennasCountermeasureAcquired characteristic
A bi-static continuous wave radar system and related methods for detecting incoming threats from ballistic projectiles includes a remote source of RF illumination, and a local receiver installed in one or more target aircraft. A first receiving channel acquires direct path illumination from the source and provides a reference signal, and a second receiving channel acquires a scatter signal reflected by a projectile. A processor coupled to each receiver corrects scatter signal Doppler offset induced by relative source motion, isolates narrowband Doppler signals to derive signatures characteristic of the projectile, and by executing appropriate algorithms, compares the derived signatures to modeled signatures stored in memory. If the comparison yields a substantial similarity, the processor outputs a warning signal sufficient to initiate defensive countermeasures.
Owner:MDA INFORMATION SYST
Method and apparatus for measuring a polishing condition
ActiveUS20060274326A1Easy to confirmEasy to detectPolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesAcquired characteristicEngineering
Owner:EBARA CORP
Method and system relating to monitoring and characterizing heart condition
ActiveUS20060106322A1Enhance heart-condition monitoringImprove assessmentElectrocardiographyCatheterElectricityAcquired characteristic
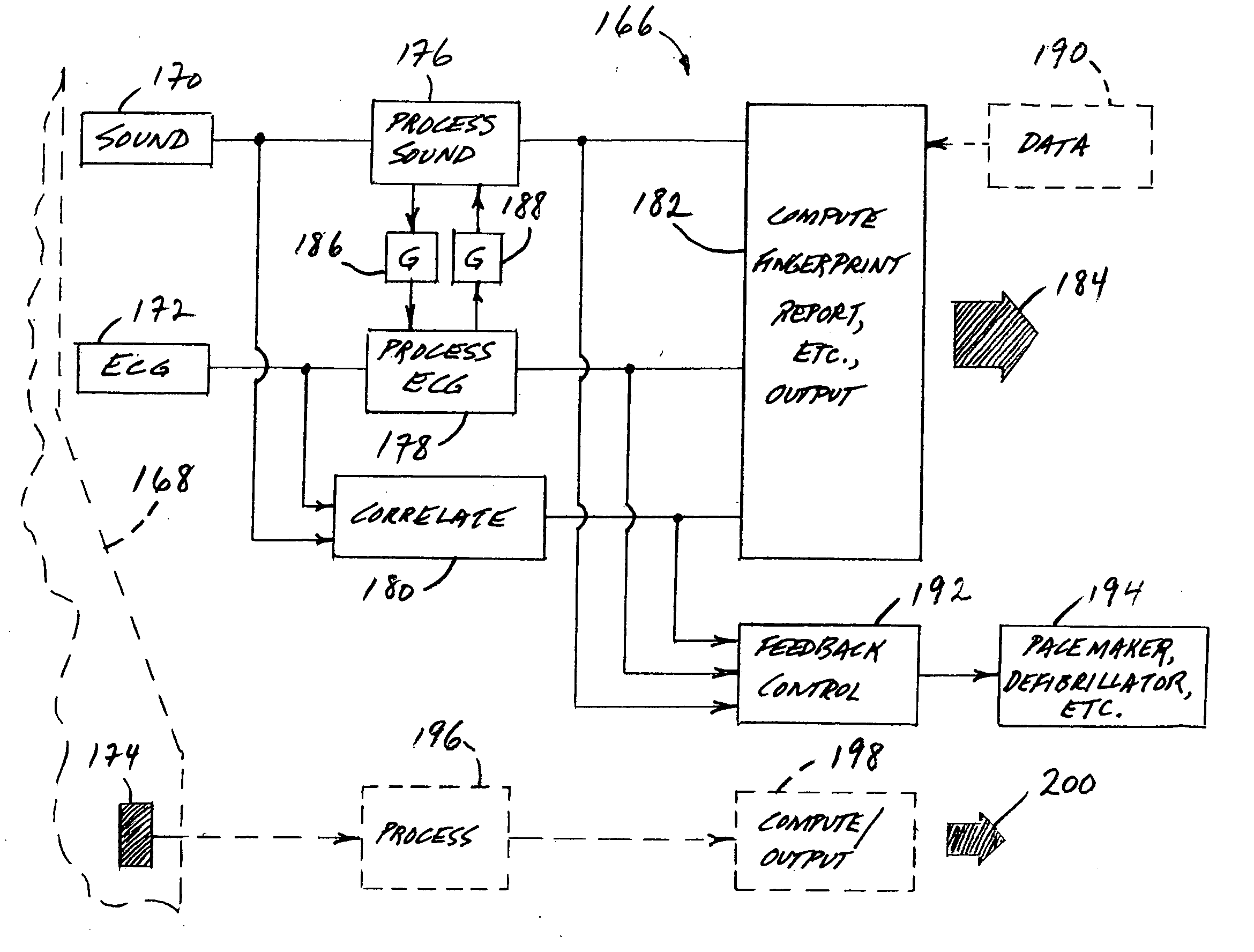
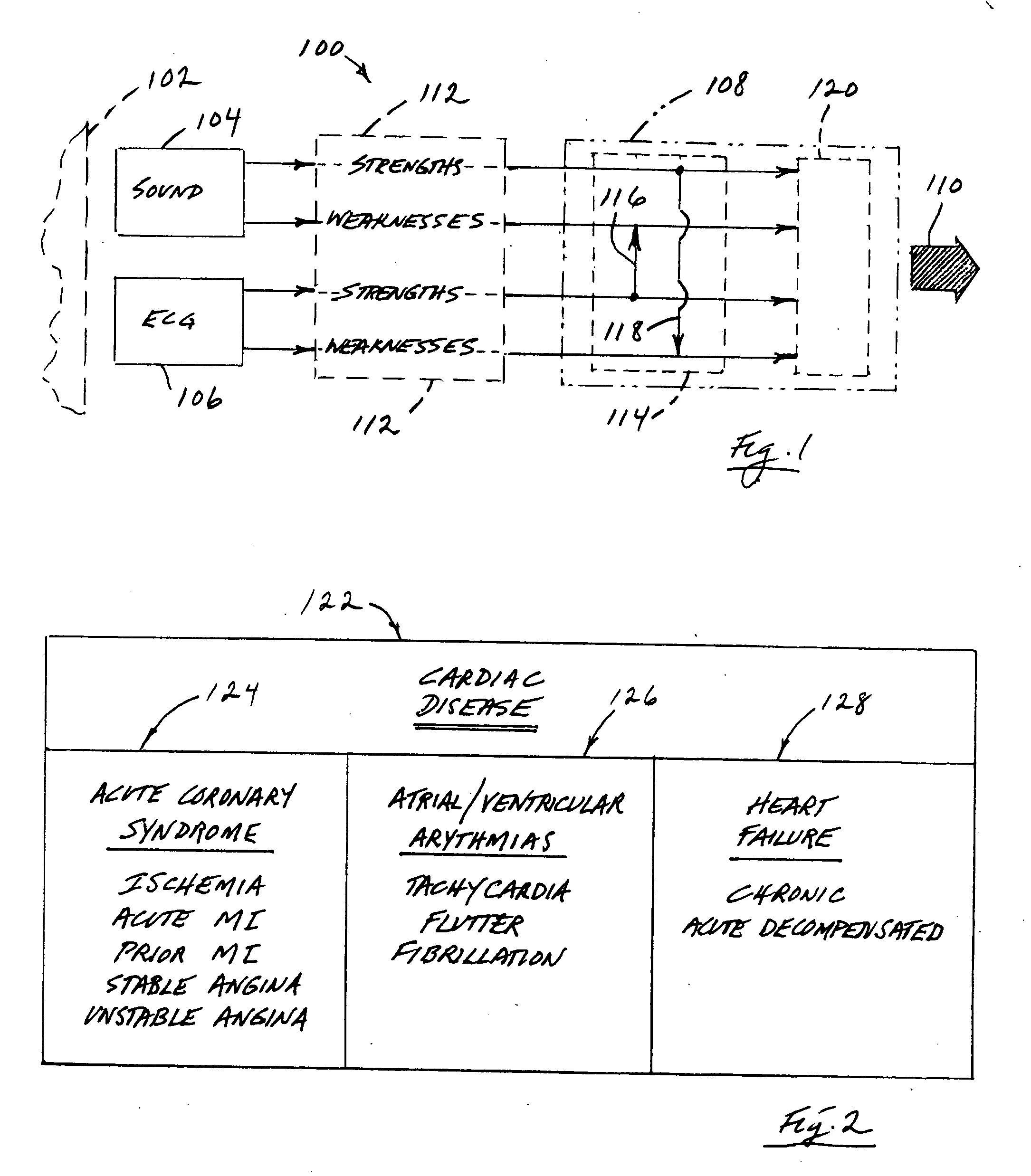
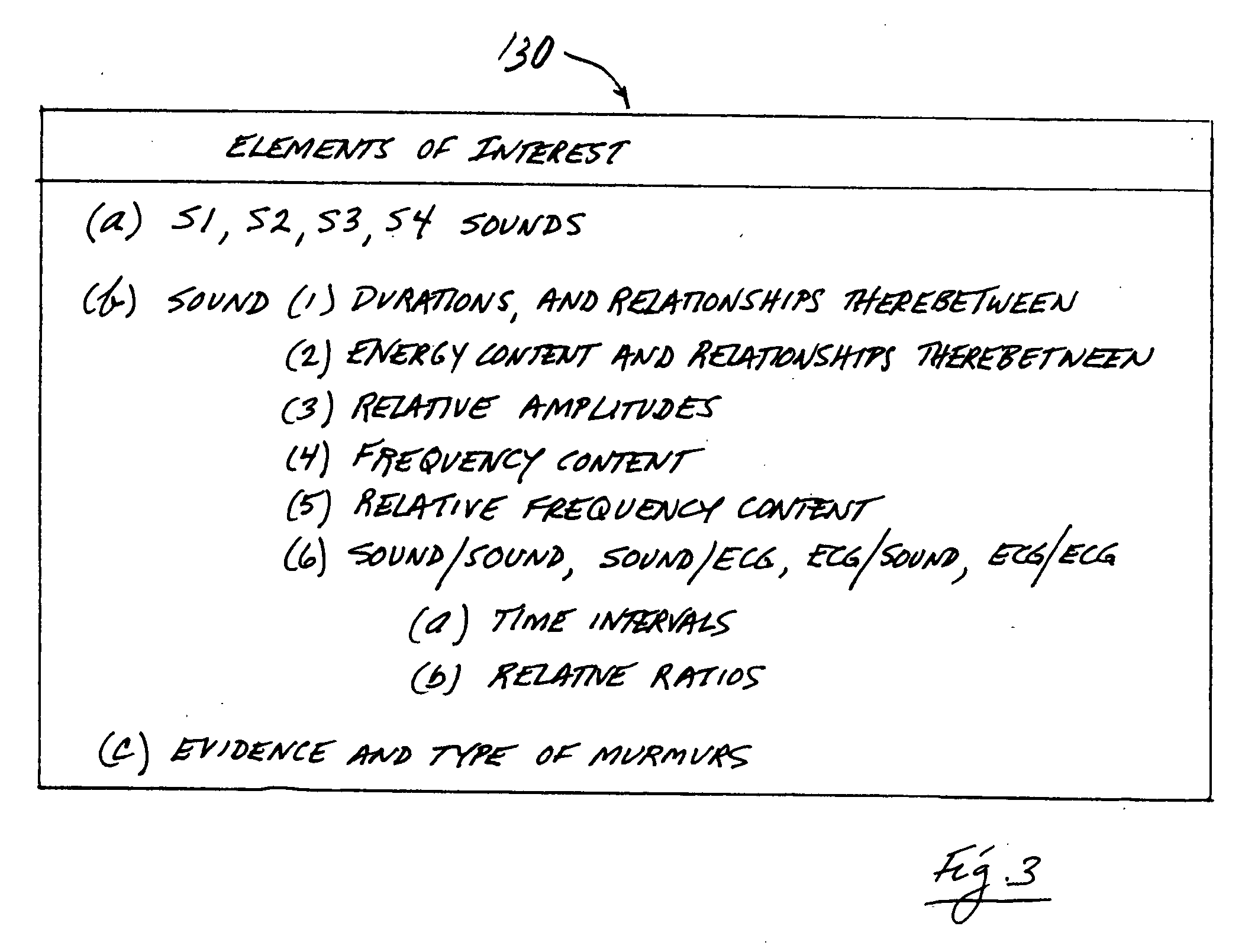
A method and a system for monitoring and characterizing a person's heart condition for various medically related purposes. The method includes the steps of (a) acquiring a selected person's acoustic heart signature, (b) acquiring, substantially simultaneously, that same person's electrical heart signature, (c) choosing elements of determined interest from these two acquired signatures and selectively processing and inter- and / or cross-relating such elements, and (d) employing the results of the relating step to create a heart-condition fingerprint useful in the characterization of that person's heart condition. From a systemic point of view, that system includes (a) acoustic and electrical data-gathering devices employable to collect acoustic and electrical data from a person, and (b) processing structure operatively connected to these devices, operable to process and inter- and / or cross-relate data gathered by the devices for the purpose of generating a reportable heart-condition fingerprint of a person from whom such data has been collected.
Owner:INOVISE MEDICAL
Compressed chewing gum tablet
InactiveUS20060147580A1Cosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAcquired characteristicAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to 1 a chewing gum tablet (10, 20, 30, 40, 50) comprising at least two separate cohered chewing gum modules (11, 12; 21, 22, 23; 31, 32; 41, 42; 51, 52) at least one of said chewing gum modules comprising compressed gum base containing chewing gum granules, wherein the chewing gum tablet comprises a gum base content of at least 5% by weight of the tablel According to the invention, a compressed chewing gum tablet has been obtained featuring extremely impressing abilities of incorporating well-defined amounts of chewing gum ingredients combined with acceptable rheological properties of the complete tablet.
Owner:FERTIN PHARMA AS
Display device and method for driving same
ActiveUS20150379940A1Keep for a long timeAvoid insufficient lengthSolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsAcquired characteristicSignal correction
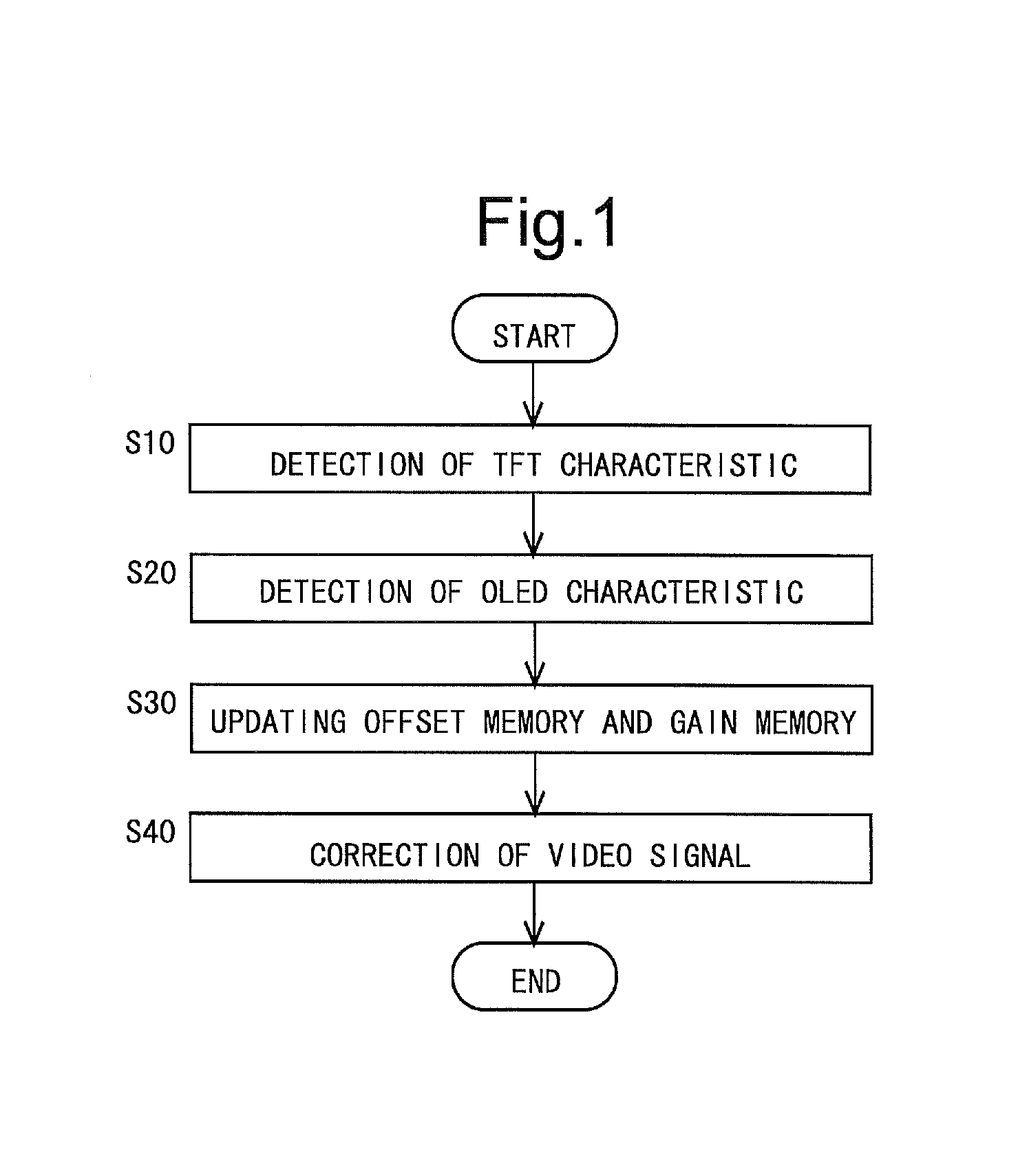
Provided is a driving method whereby it is possible to simultaneously compensate for both degradation of a drive transistor and degradation of a light-emitting element without causing special light emission at the time of detecting characteristics in a display device. In a display device which includes a pixel circuit including an electro-optic element and a drive transistor, a driving method includes: a first characteristic detection step for detecting a characteristic of the drive transistor; a second characteristic detection step for detecting a characteristic of the electro-optic element; a correction data storage step for storing characteristic data obtained based on detection results in the first and second characteristic detection steps as correction data; and a video signal correction step for correcting the video signal based on the correction data. The second characteristic detection step is performed in a light emission period.
Owner:SHARP KK
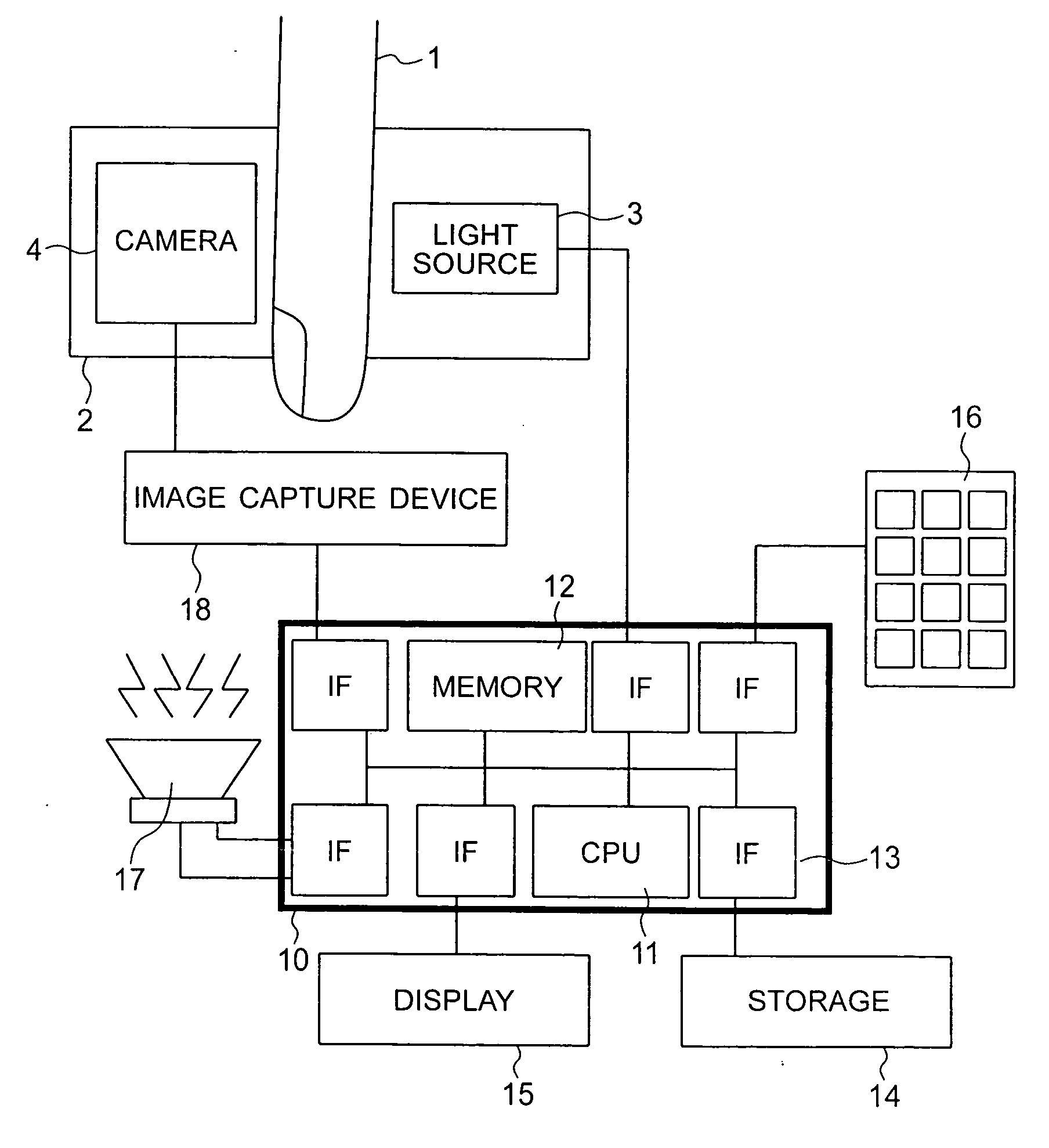
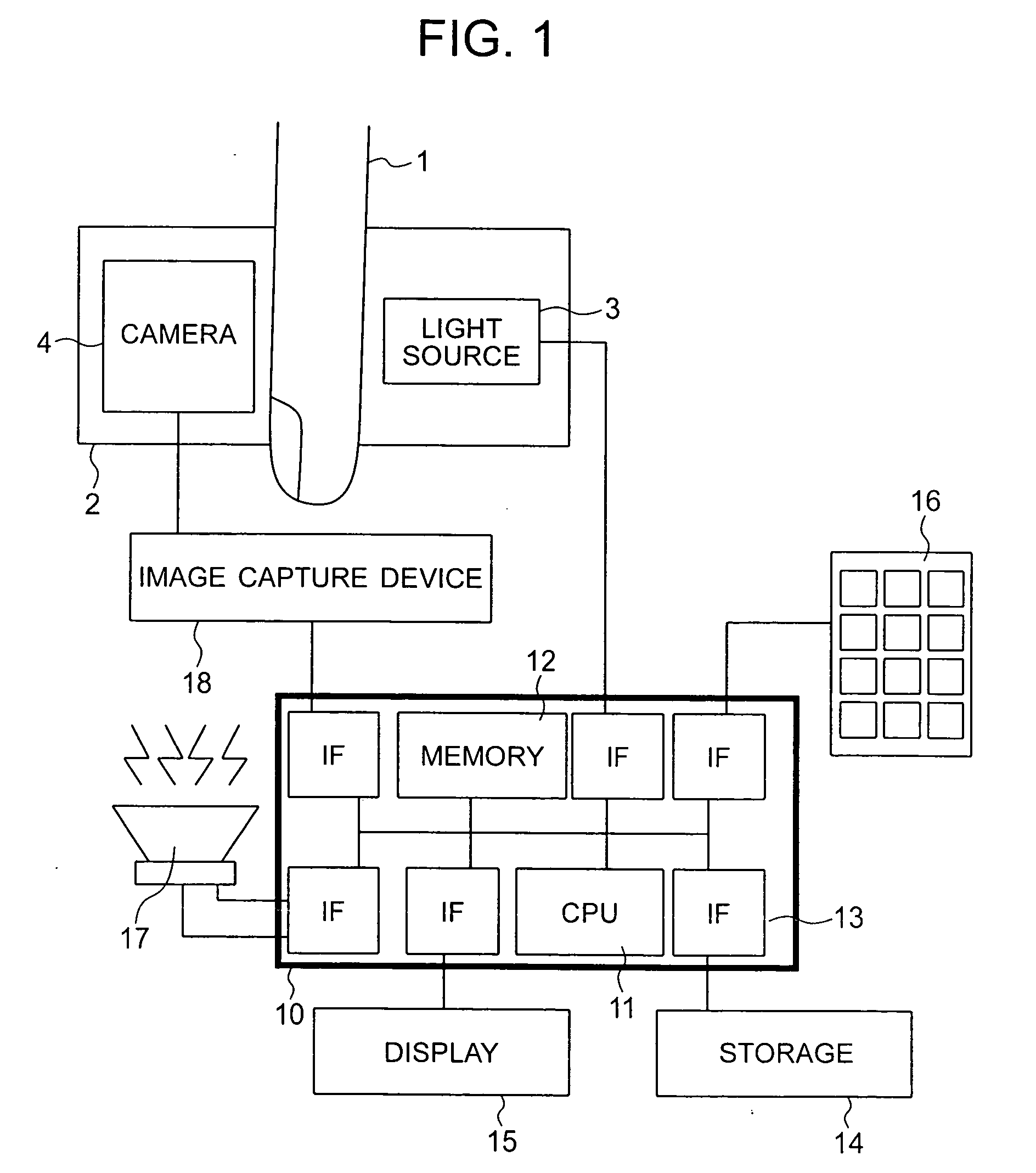
Endoscope apparatus
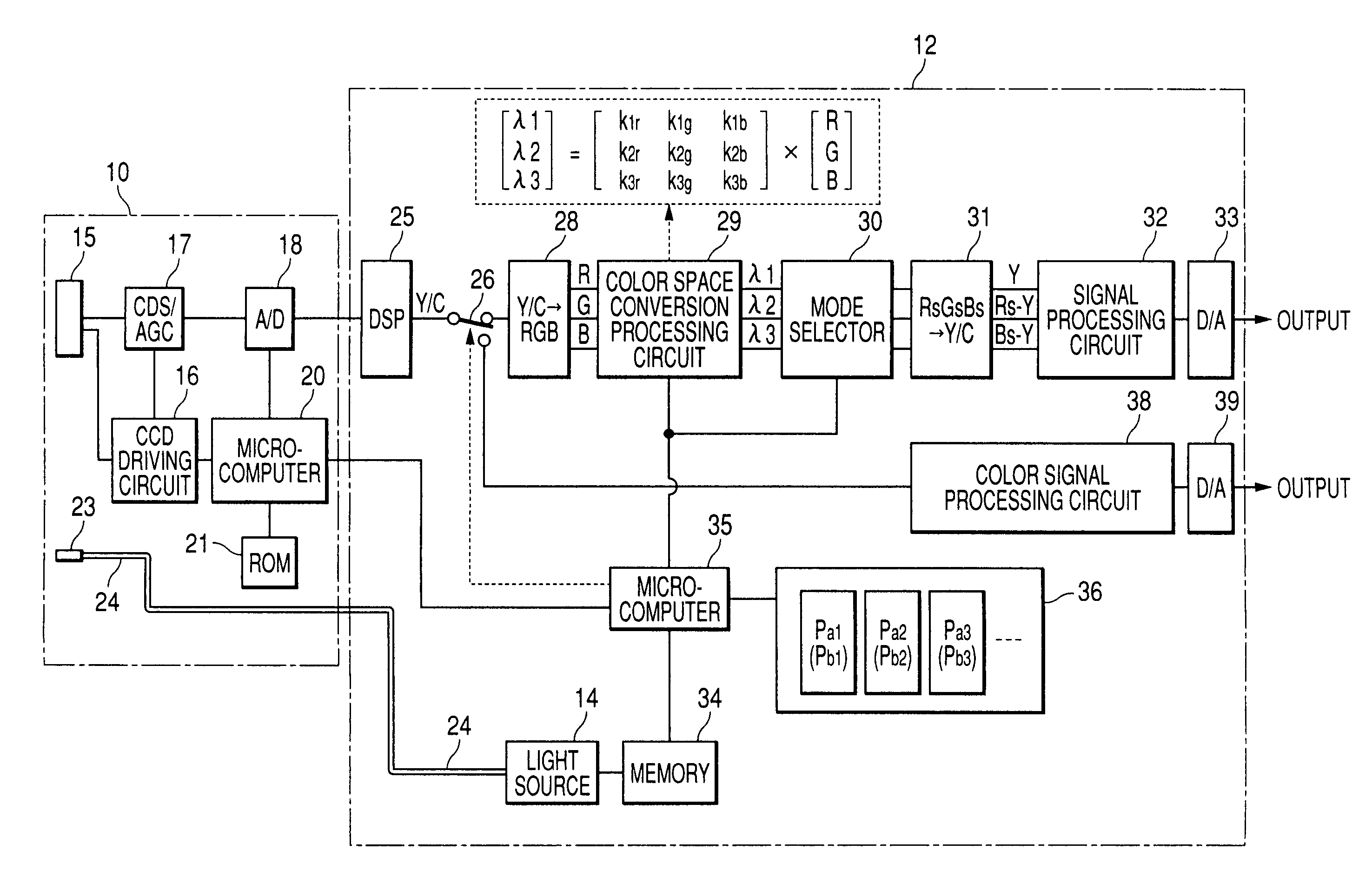
InactiveUS7995093B2Good reproducibilityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAcquired characteristicComputer science
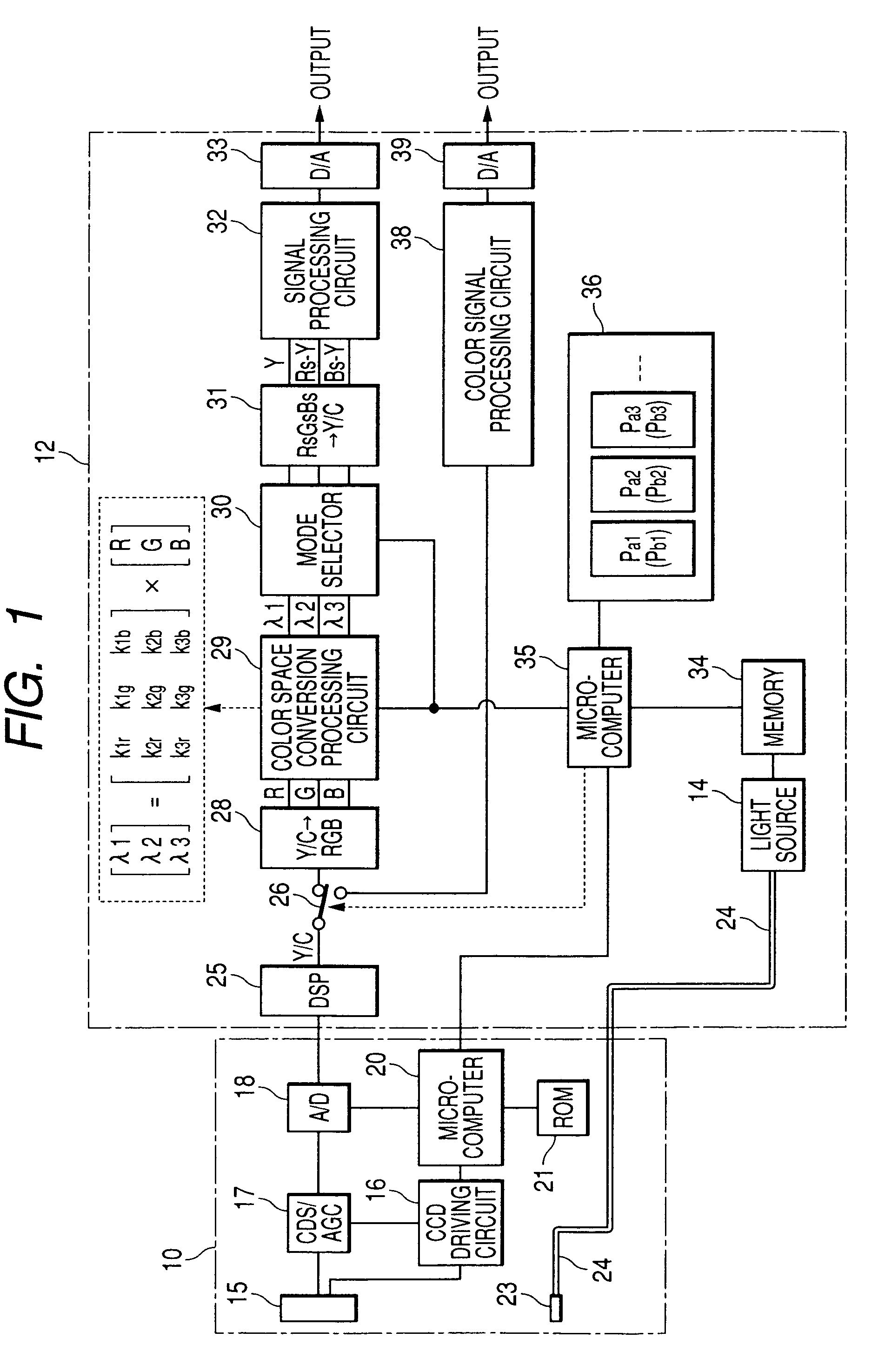
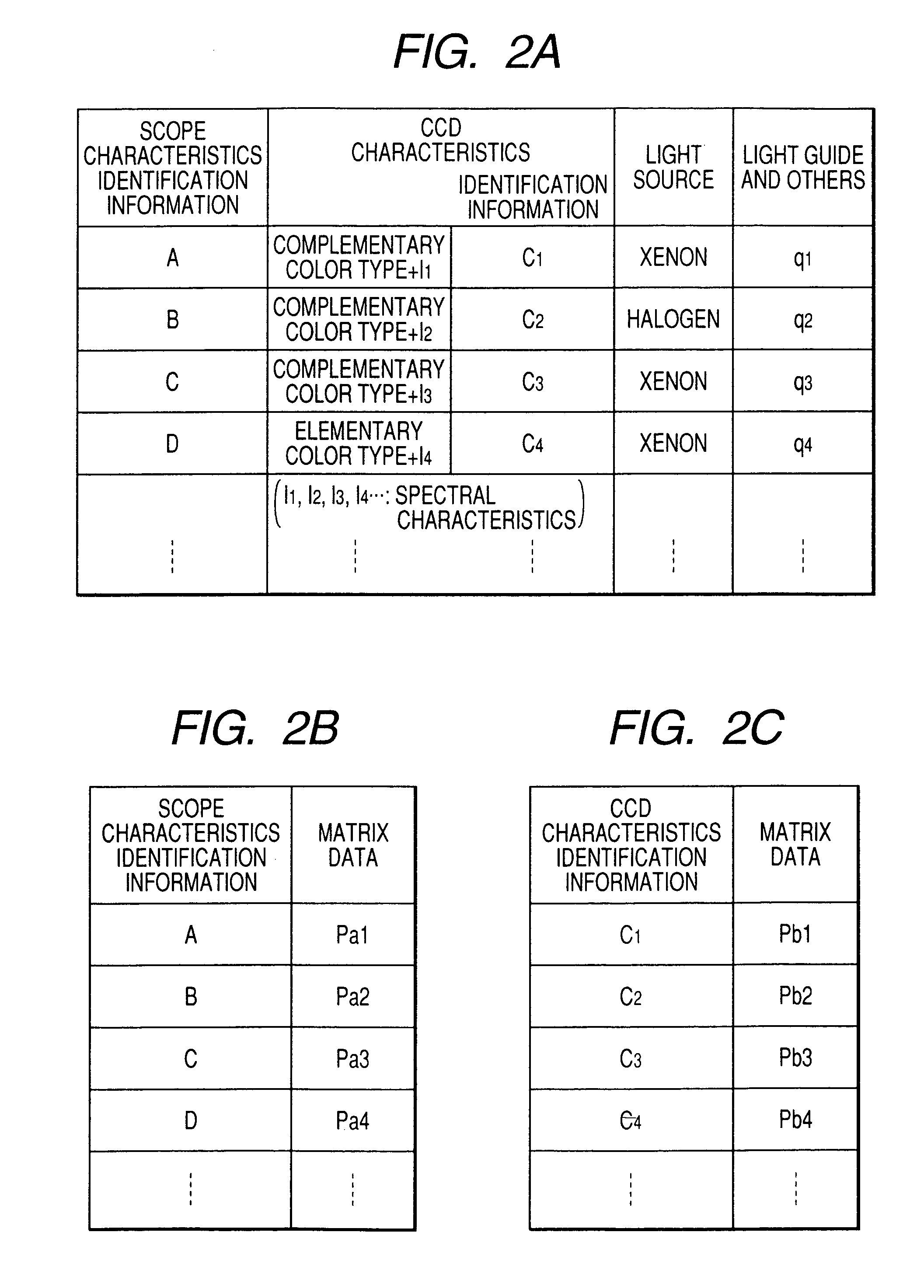
In an endoscope apparatus in which a scope is connected to a processor unit in a freely attachable and detachable way, the endoscope apparatus wherein matrix calculation is conducted for RGB signals formed by using CCD, a color space conversion processing circuit is provided for forming spectral images of the arbitrarily selected wavelength range. CCD characteristics identification information including types of color filters of the CCD and spectral characteristics or scope characteristics information is stored in the ROM of the scope, a plurality of matrix data corresponding to characteristics identification information is stored in the memory of the processor unit, and matrix data corresponding to the obtained characteristics information is read from the memory, thereby forming an excellent spectral image by using data suitable for characteristics of the CCD or the scope.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Biometrics based methods and systems for user authentication
InactiveUS20130343616A1Improve authentication methodStrengthen the systemDigital data authenticationBiometric pattern recognitionFeature vectorAcquired characteristic
Disclosed are computer-implemented methods and systems for authentication of users through capturing and analyzing biometrics data such as keystroke dynamics. Once the keystroke dynamics is acquired, a corresponding feature vector related is calculated by calculating multiple sub-feature values using various algorithms such as normalization, relations between keystroke dynamics events, relations of sums of various sub-feature values, and so forth. The feature vector is then selectively compared to a group of reference feature vectors associated with the user. If it is determined that the newly obtained feature vector is similar to the selected group reference feature vectors, the user is authenticated. The process of determining similarity involves decomposition of feature vectors and reference feature vectors onto multiple sub-vectors and calculation similarity therebetween.
Owner:NEUROLOGIX SECURITY
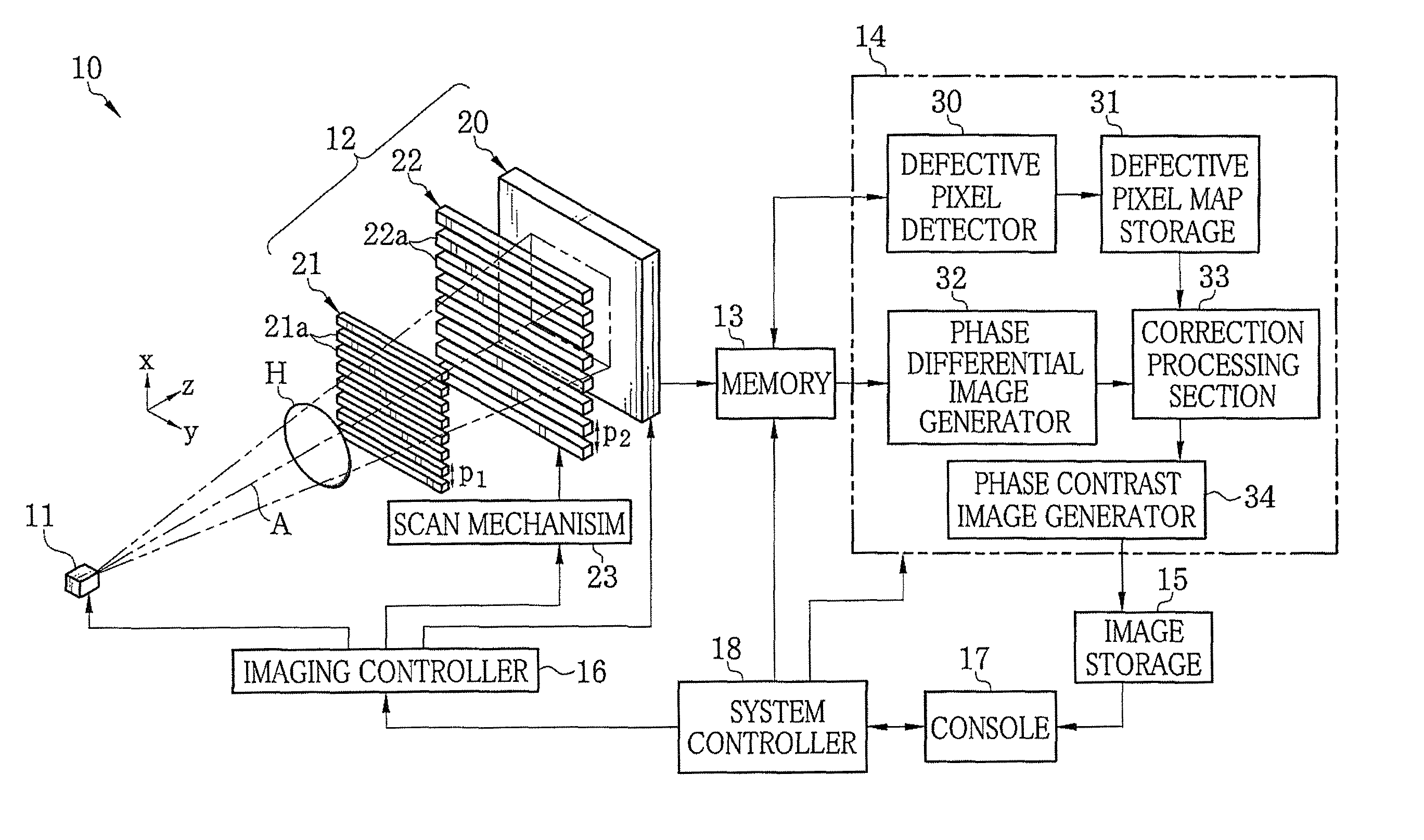
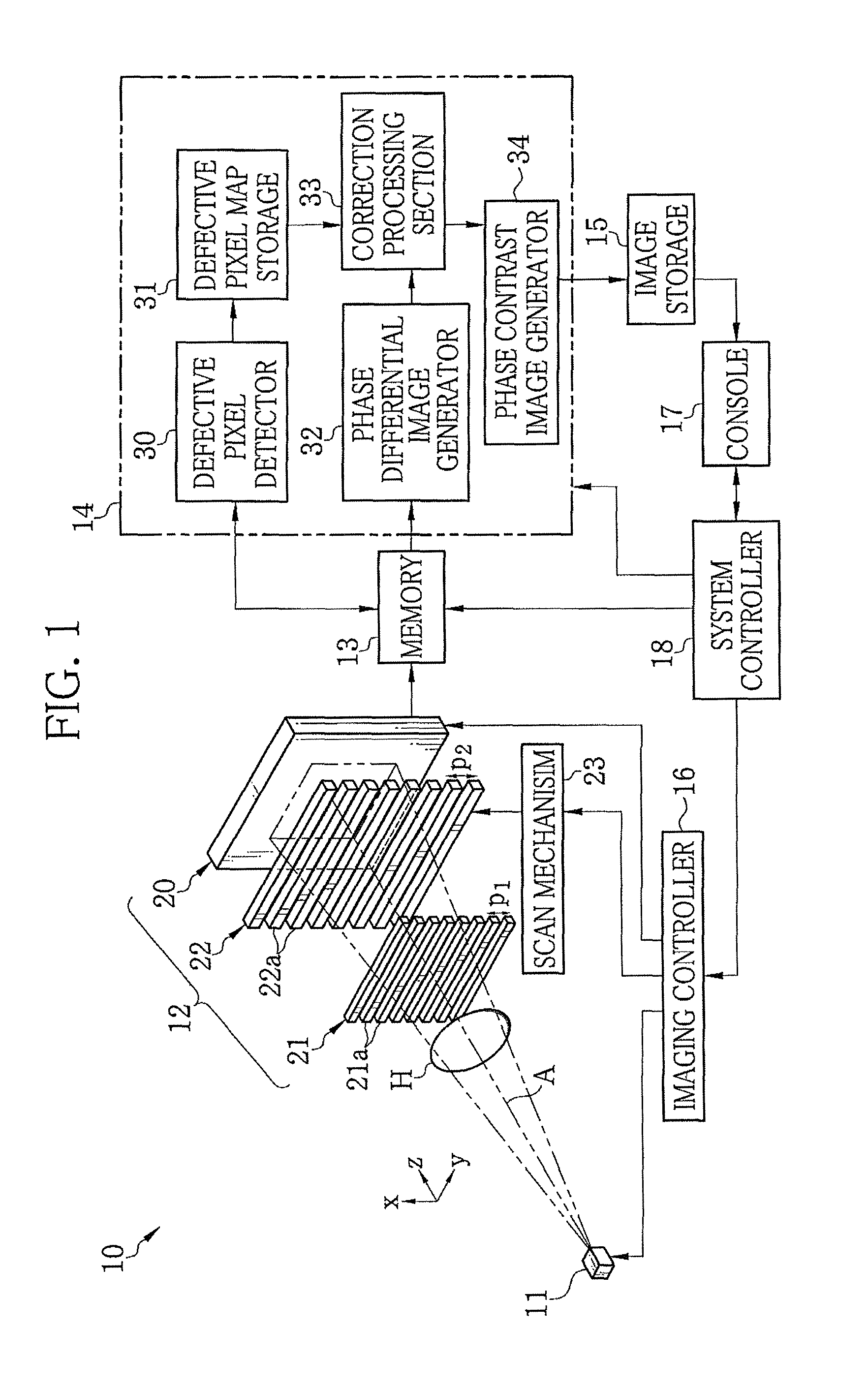
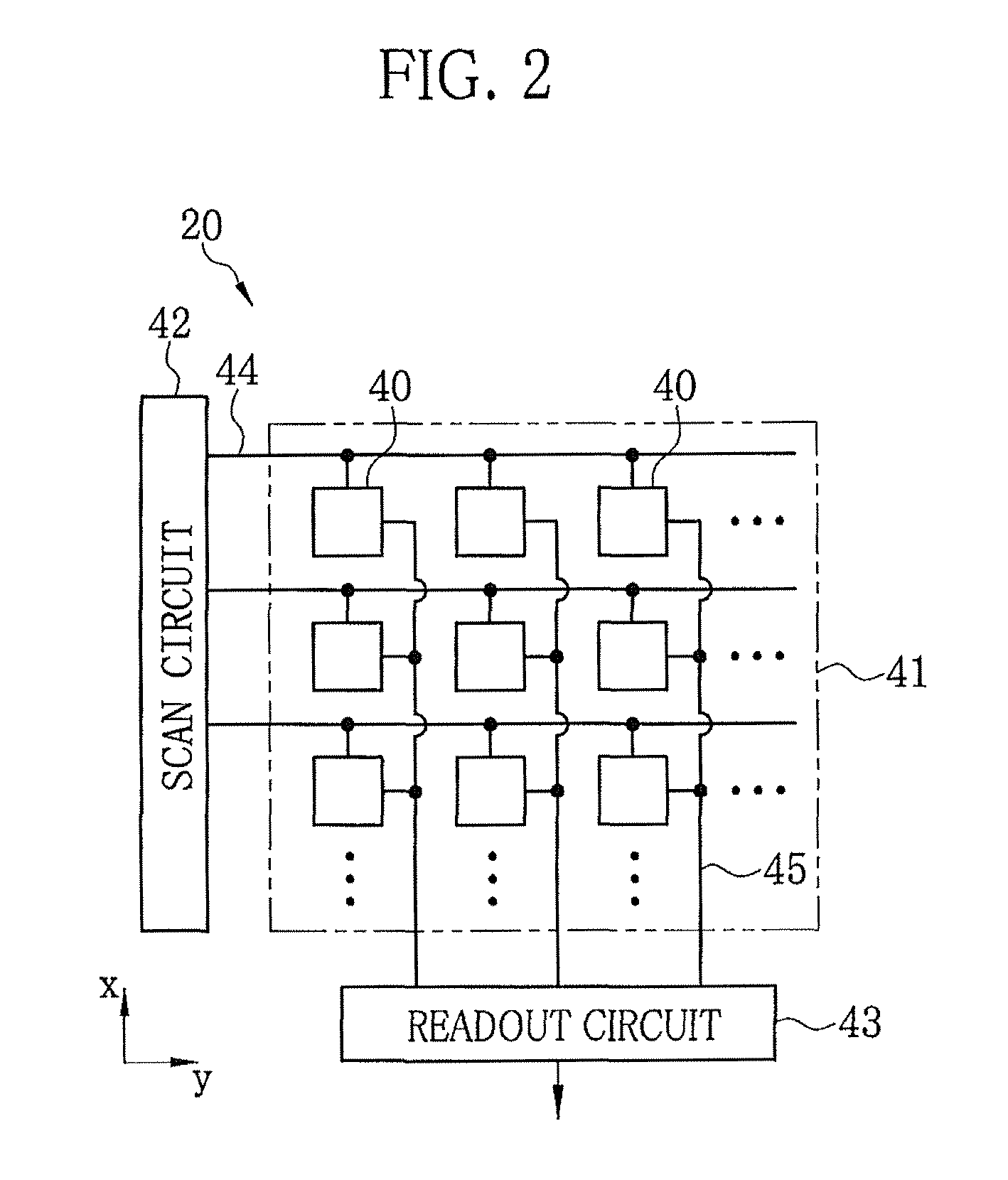
Radiation imaging system and apparatus and method for detecting defective pixel
InactiveUS8591108B2Improve accuracyX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationAcquired characteristicGrating
An X-ray imaging system includes an X-ray source, first and second absorption gratings, and an FPD. The first absorption grating passes X-ray emitted from the X-ray source to form a G1 image. The second absorption grating modulates intensity of the G1 image at each of relative positions to form two or more fringe images. The relative positions differ in phase with respect to a period pattern of the G1 image. The FPD detects two or more frames of image data of the fringe images. A defective pixel detector reads two or more frames of image data stored in a memory and obtains a characteristic value of an intensity modulated signal on a pixel-by-pixel basis based on the read image data. The defective pixel detector detects a defective pixel based on the characteristic value obtained.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
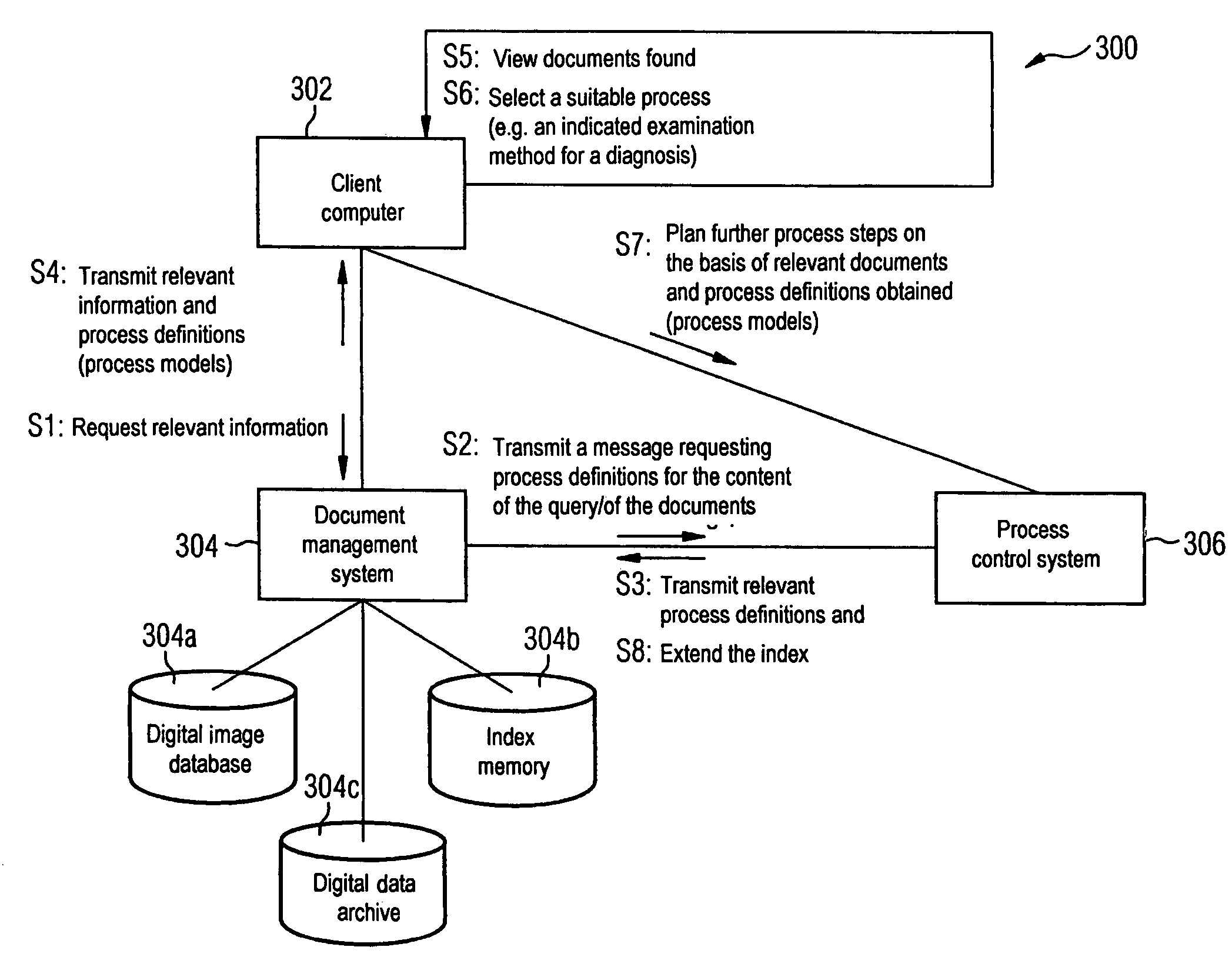
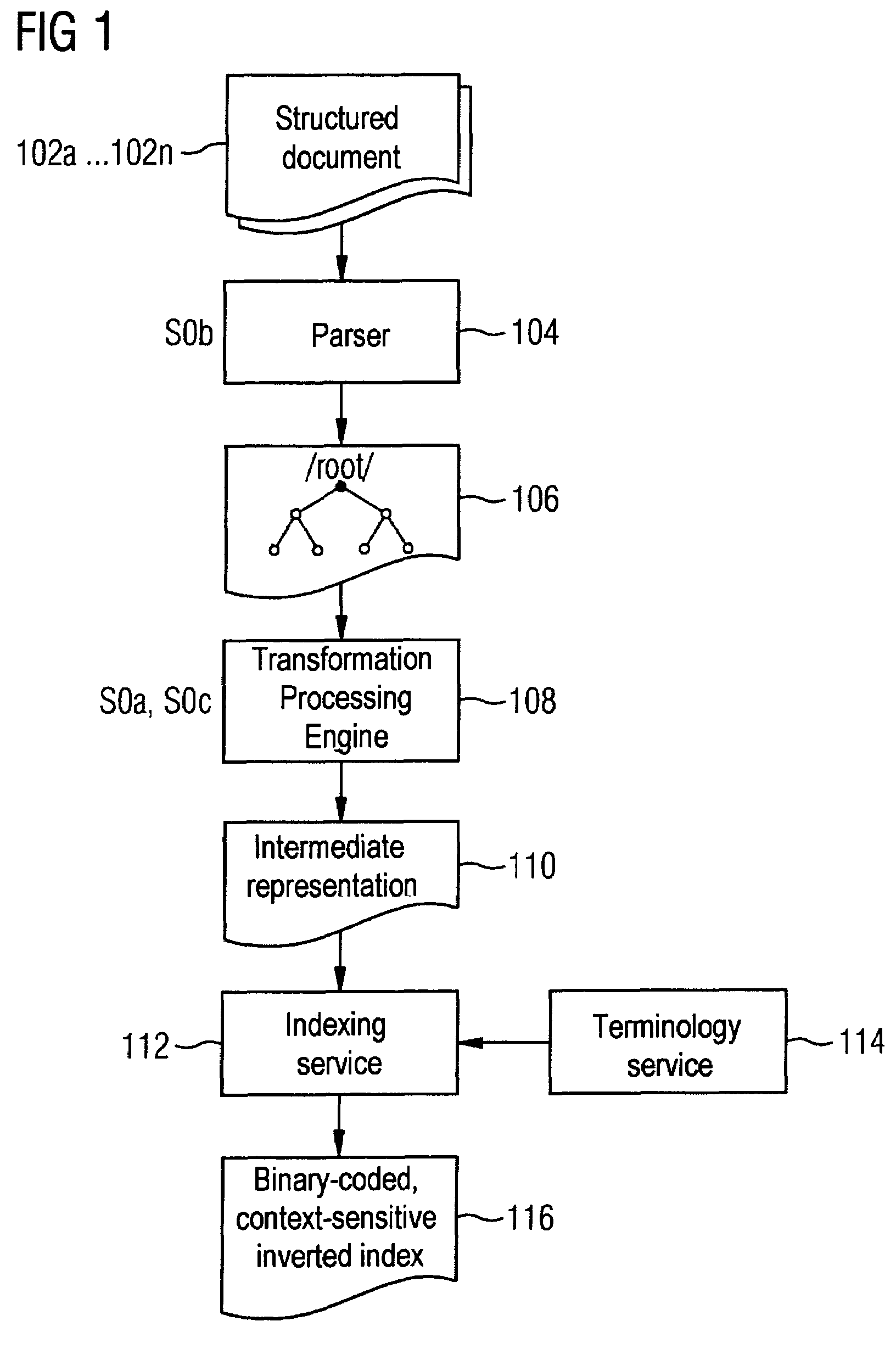
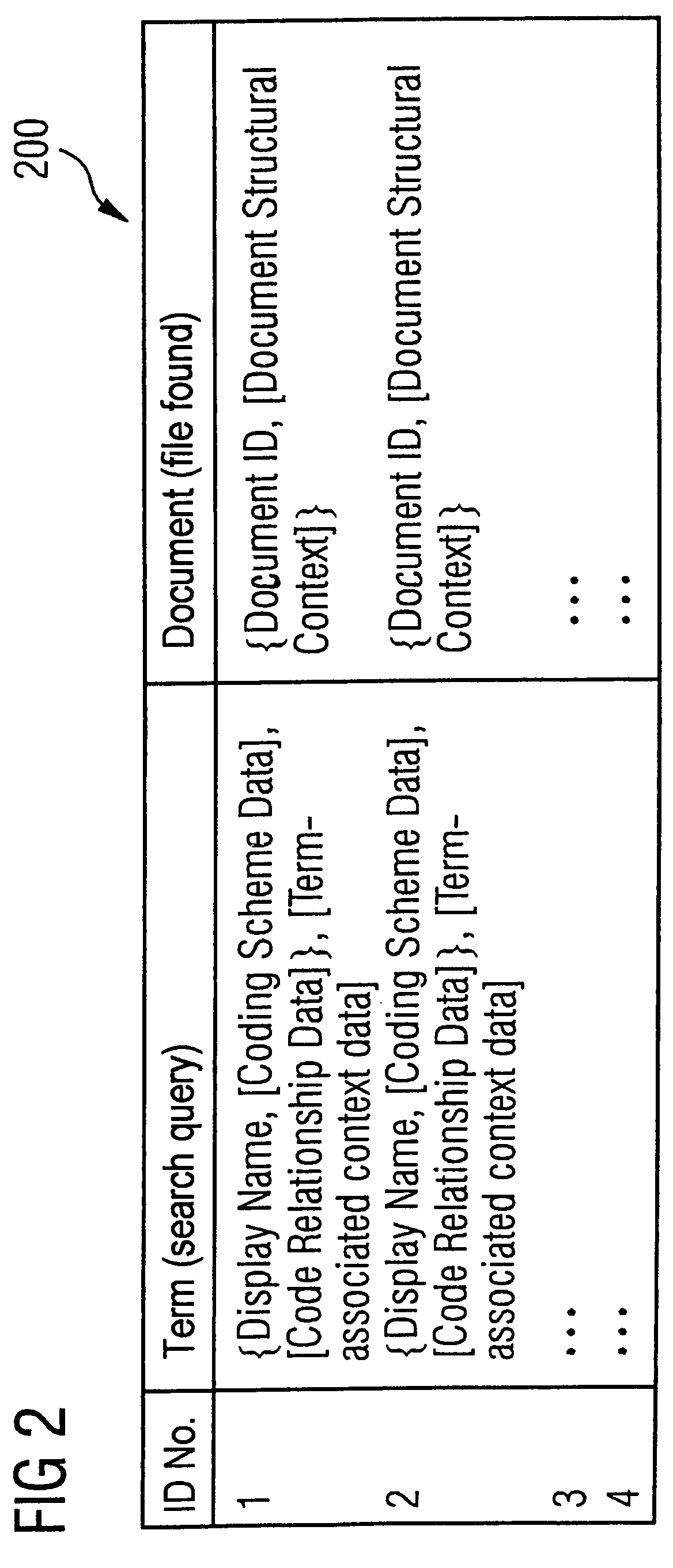
Automatic indexing of digital image archives for content-based, context-sensitive searching
InactiveUS7689544B2Decision supportHigh precisionPicture changing apparatusData processing applicationsAcquired characteristicFeature extraction algorithm
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Vehicle driver fatigue monitoring and early warning system and method
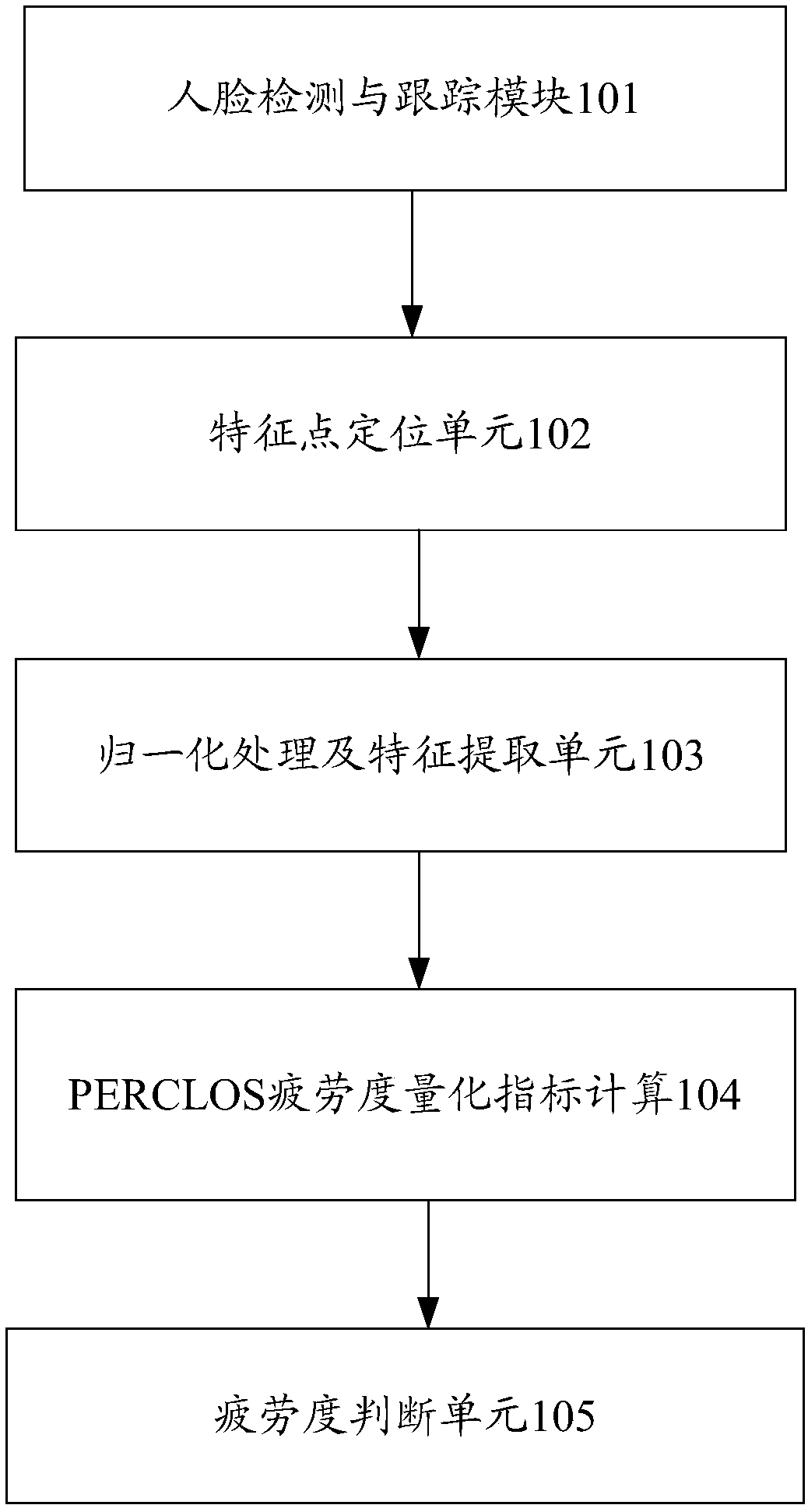
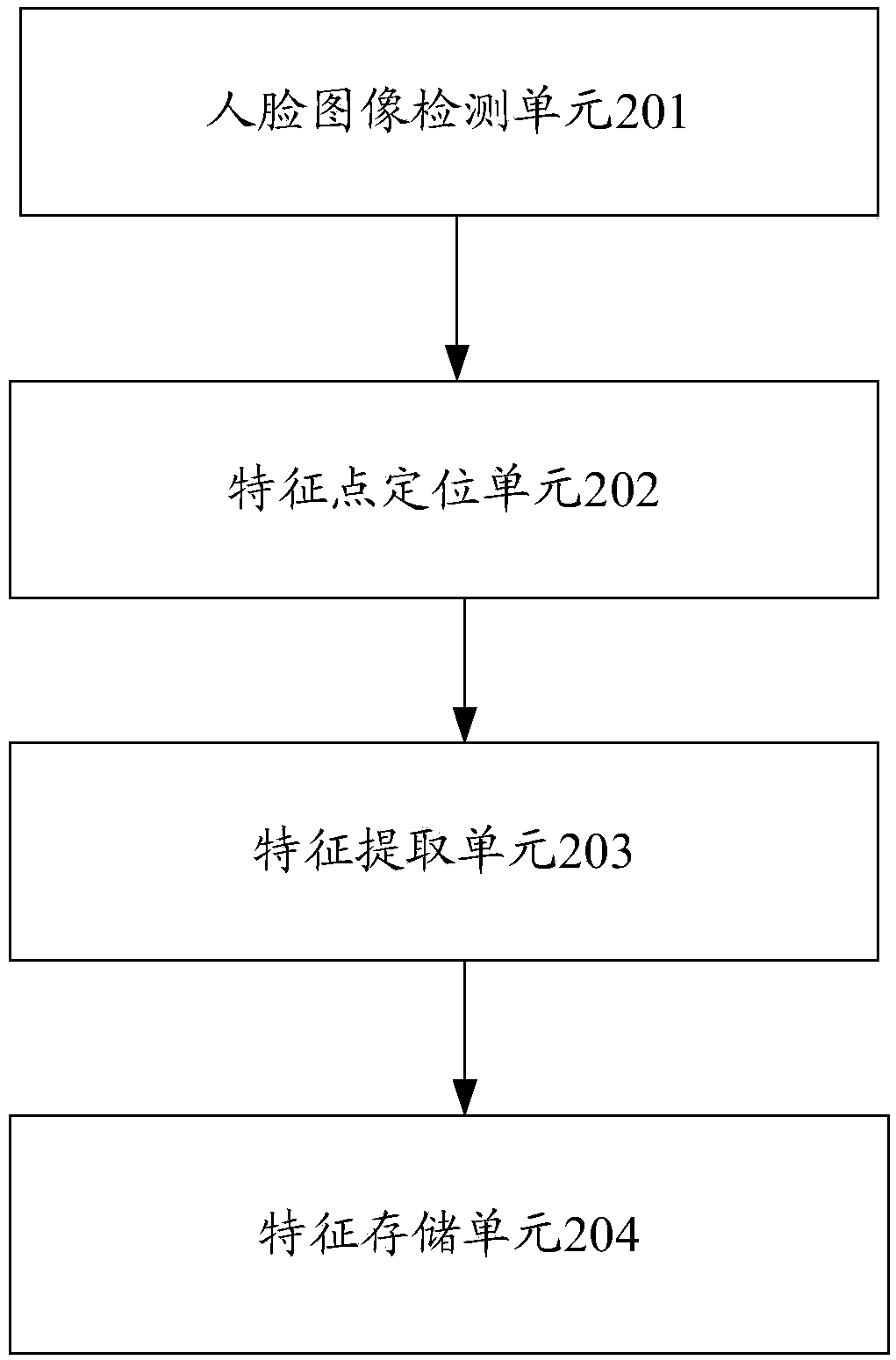
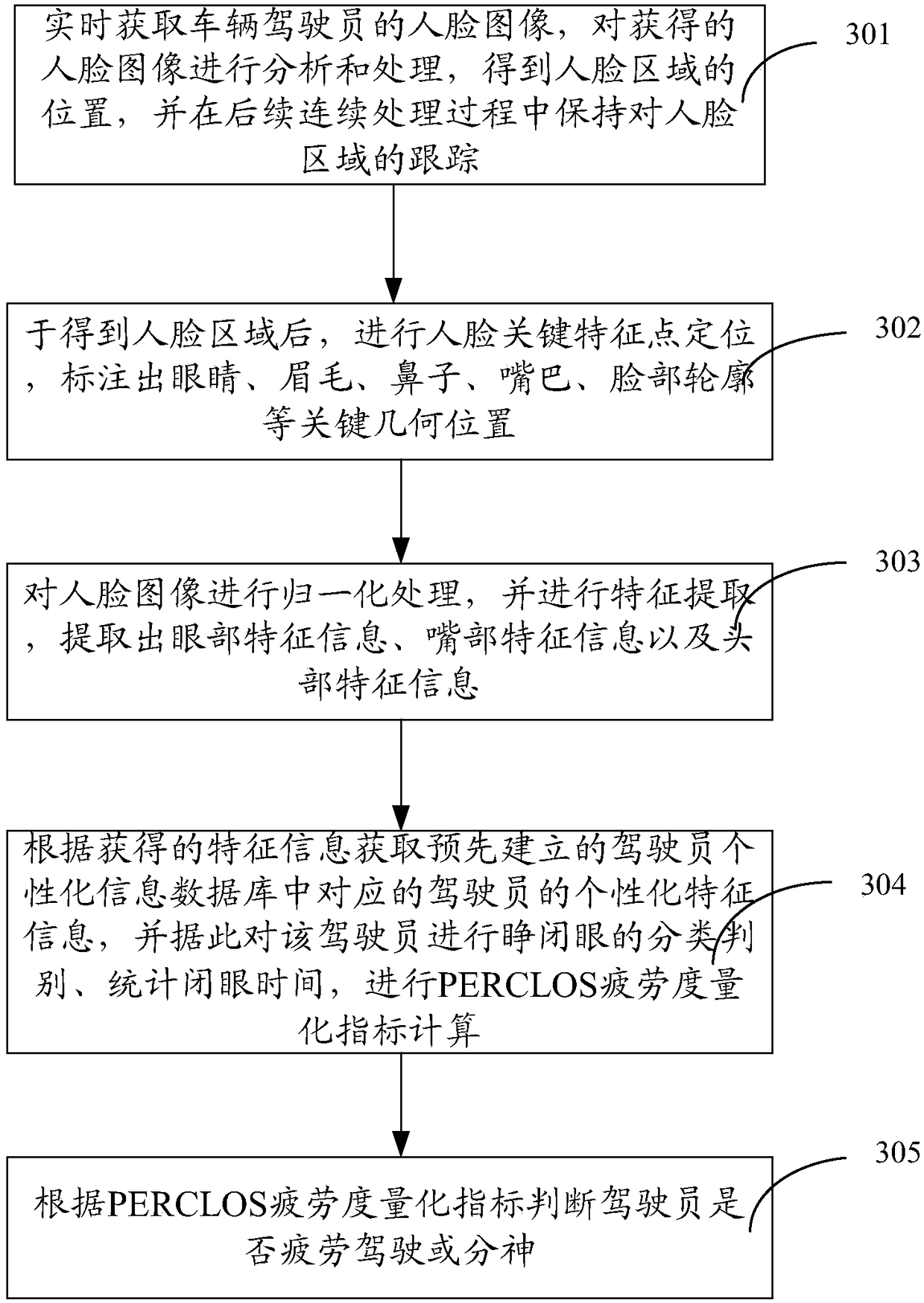
InactiveCN108446600AImprove adaptabilityReduce the incidence of traffic accidentsCharacter and pattern recognitionAlarmsFace detectionEarly warning system
The invention discloses a vehicle driver fatigue monitoring and early warning system and a vehicle driver fatigue monitoring and early warning method. The system comprises a face detecting and tracking module used for acquiring a face image, analyzing and processing the obtained face image to obtain the position of a face region; a feature point positioning unit used for carrying out face key feature point positioning; a normalization processing and feature extraction unit used for carrying out normalization treatment on the face image, carrying out feature extraction, extracting the eye feature information, the mouth feature information and the head feature information; a PERCLOS fatigue degree quantization index calculation unit used for acquiring the personalized feature information corresponding to a driver in a pre-established driver personalized information database according to the obtained feature information, classifying and judging the eye opening and closing states of the driver and counting the eye closing time, and performing the calculation of a PERCLOS fatigue degree quantitative index; and a fatigue degree judging unit used for judging whether the driver is in the fatigue driving state or not according to the PERCLOS fatigue degree quantitative index.
Owner:SAIC MOTOR +1
System and method for off-line multi-view video compression
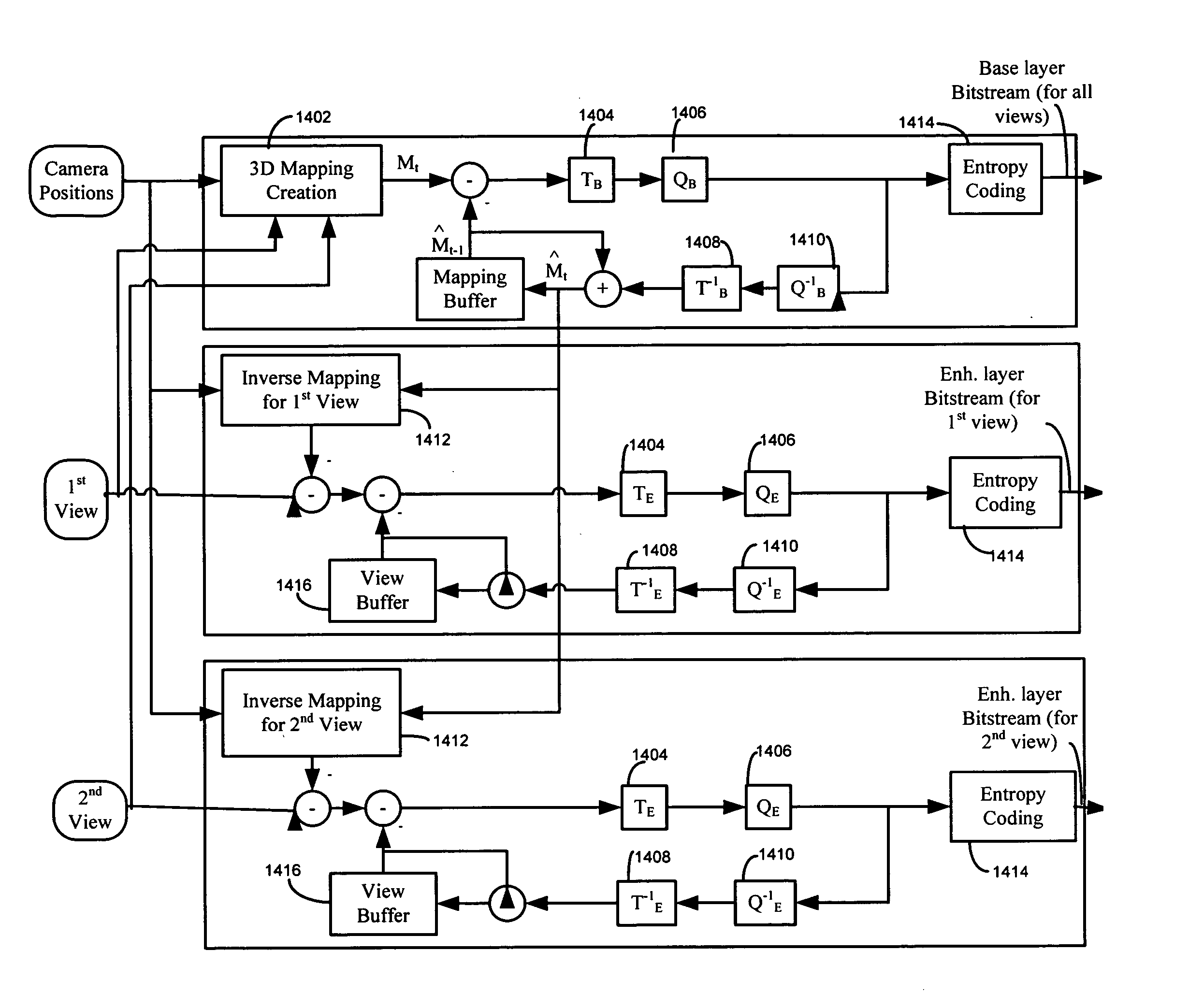
InactiveUS20060023782A1Computer processing power becomes strongSolve narrow bandwidthColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAcquired characteristic3d mapping
Interactive multi-view video presents new types of video capture systems, video formats, video compression algorithms, and services. Many video cameras are allocated to capture an event from various related locations and directions. The captured videos are compressed and are sent to a server in real-time. The compressed video can also be transcoded through an off-line compression approach to further reduce the data amount. A key idea of off-line compression is to decompose all views into a 3D mapping, which consists of a group of feature points in the 3D environment. Each feature point is represented by its 3D coordinates (x, y, z) and the corresponding color components (Y, U, V). The created mapping is the minimum set of feature points that can reconstruct all of the pixels in each view. After the 3D mapping creation, the obtained feature points are predicted and transformed to further decompose the correlations among them. The transformed results are quantized and encoded as a ‘base layer’ bit stream. The dequantized feature points are mapped back onto each view to form a predicted view image. The predicted image is close to the original one; however, there are still some differences between them. The difference is encoded independently as an ‘enhancement layer’ of each view image.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Synchronous display method and device of images
ActiveCN105491414AImprove review efficiencyRealize intelligent judgmentData processing applicationsDigital video signal modificationAcquired characteristicComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides a synchronous display method and device of images. Compression treatment is carried out through periodically capturing screen contents; the transmission capability can be realized at any time; the transmission effect is improved; and the transmission time can be shortened. The captured image contents can be quickly compared according to the feature values analyzed in the image compression process; the images are judged intelligently synchronously; the images are transmitted automatically synchronously without manual operation; the screen contents are prevented from being transmitted repeatedly; the storage pressure of a student user terminal is relieved; comprehensiveness of the contents is ensured; the screen image contents are marked and judged, the review efficiency of a student is improved, when the student reviews, the student can directly view the last few pages of blackboard-writings.
Owner:SHENZHEN EAGLESOUL TECH CO LTD
Speech recognition method, program and apparatus using multiple acoustic models
InactiveUS7065487B2Improve recognition accuracySpeech recognitionFeature vectorAcquired characteristic
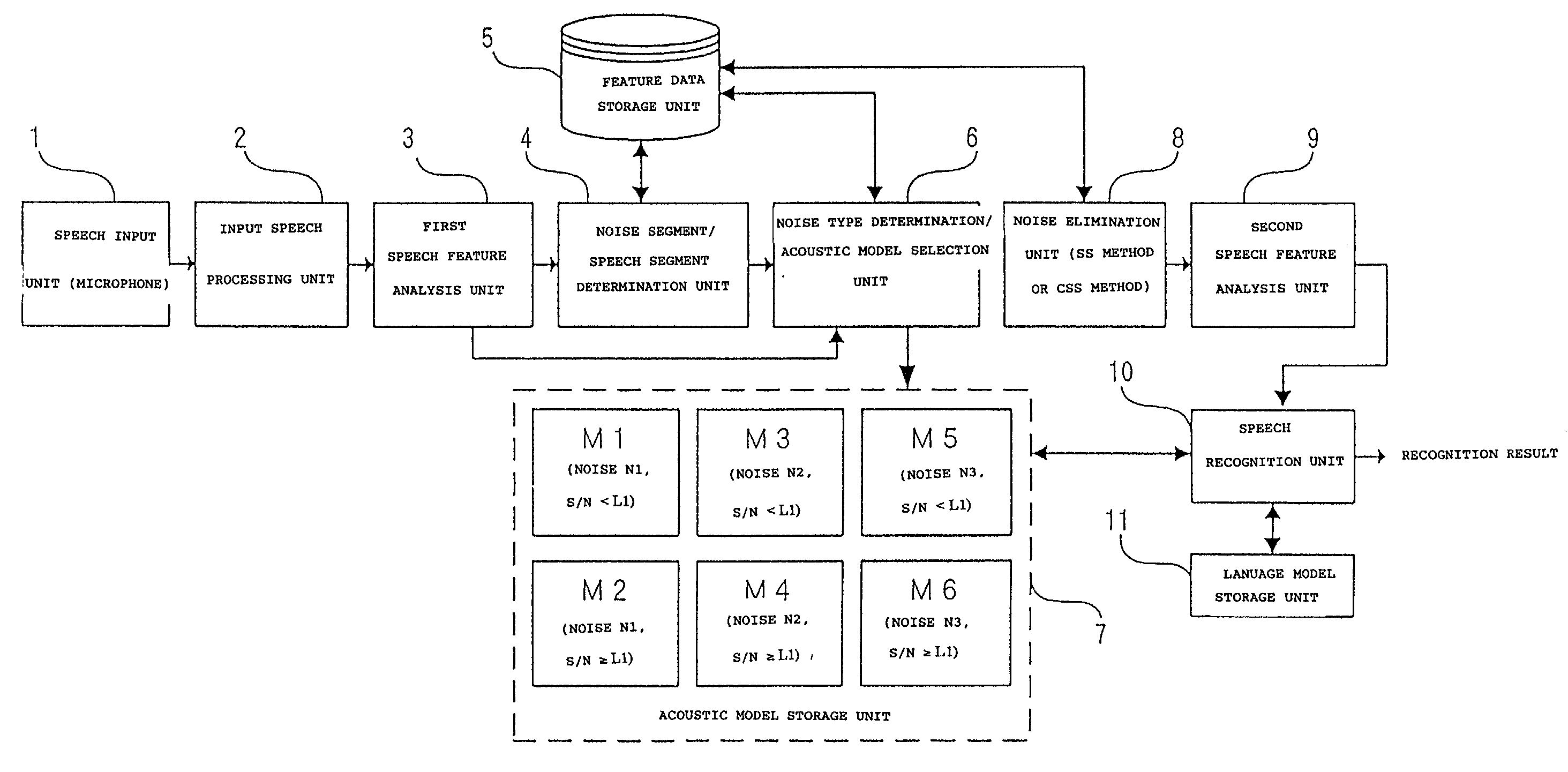
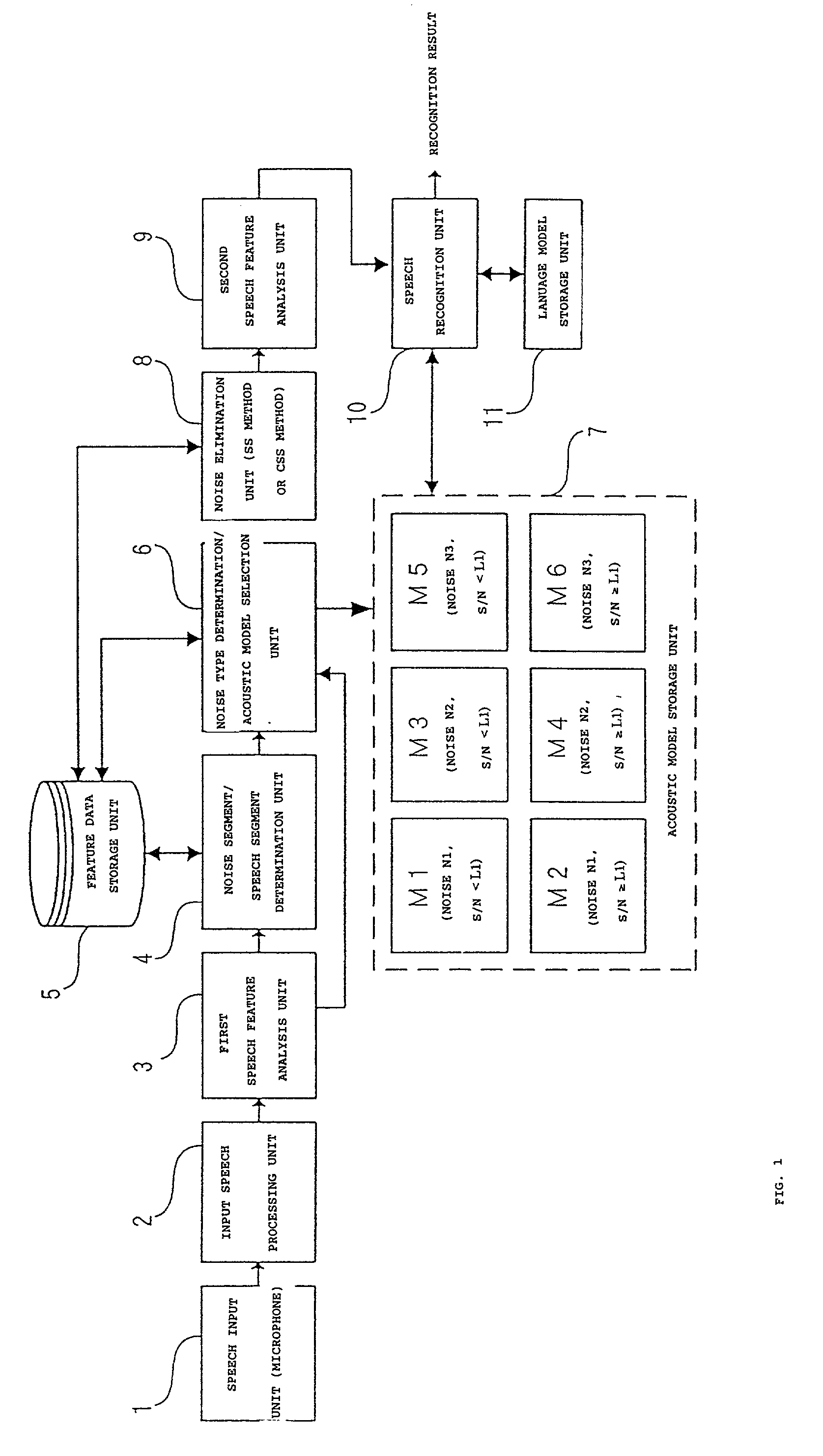
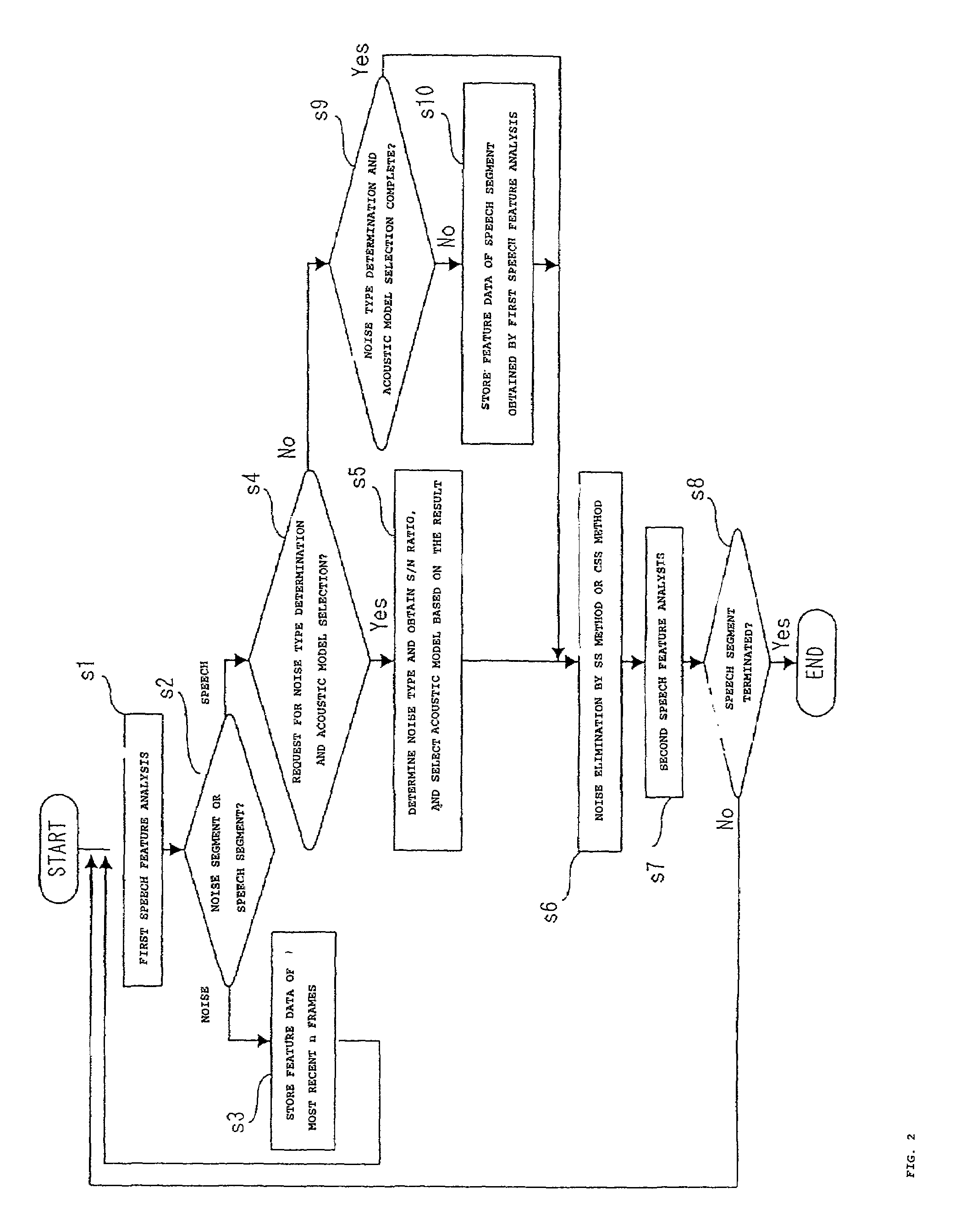
The present invention provides a speech recognition method for achieving a high recognition rate even under an environment where plural types of noise exist. Noise is eliminated by the spectral subtraction noise elimination method from each of speech data on which different types of noise are superposed, and acoustic models corresponding to each of the noise types are created based on the feature vectors obtained by analyzing the features of each of the speech data which have undergone the noise elimination. When a speech recognition is performed, a first speech feature analysis is performed on speech data to be recognized, and it is determined whether the speech data is a noise segment or a speech segment. When a noise segment is detected, the feature data thereof is stored, and when a speech segment is detected, the type of the noise is determined based on the feature data which has been stored, and a corresponding acoustic model is selected based on the result thereof. The noise is eliminated by the spectral subtraction noise elimination method from the speech data to be recognized, and a second feature analysis is performed on the speech data which has undergone the noise elimination to obtain a feature vector to be used in speech recognition.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com