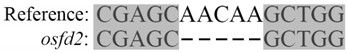Patents
Literature
56 results about "Complementation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In genetics, complementation occurs when two strains of an organism with different homozygous recessive mutations that produce the same mutant phenotype (for example, a change in wing structure in flies) produce offspring with the wild-type phenotype when mated or crossed. Complementation will occur only if the mutations are in different genes. In this case, each strain's genome supplies the wild-type allele to "complement" the mutated allele of the other strain's genome. Since the mutations are recessive, the offspring will display the wild-type phenotype. A complementation test (sometimes called a "cis-trans" test) can be used to test whether the mutations in two strains are in different genes. Complementation will not occur if the mutations are in the same gene. The convenience and essence of this test is that the mutations that produce a phenotype can be assigned to different genes without the exact knowledge of what the gene product is doing on a molecular level. The complementation test was developed by American geneticist Edward B. Lewis.
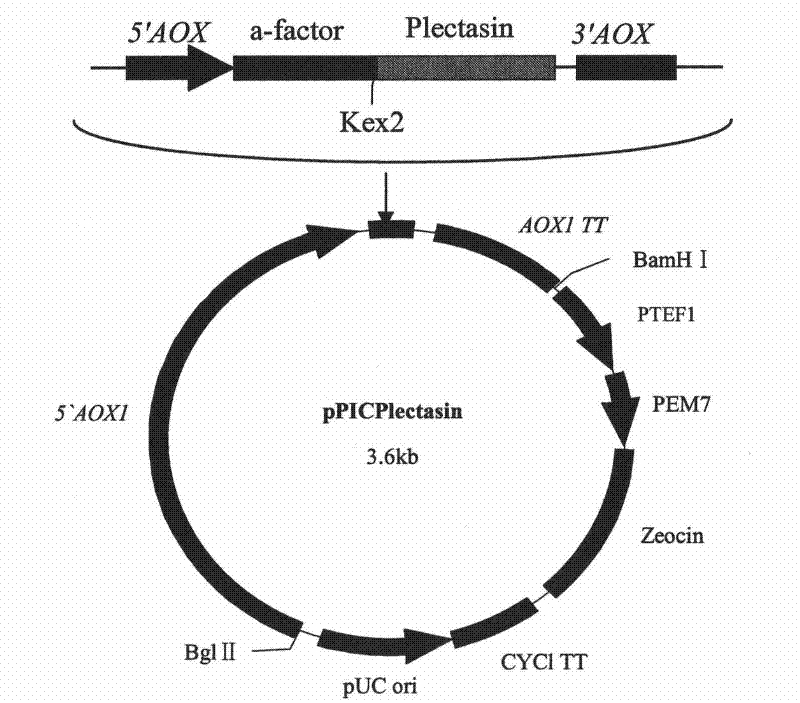
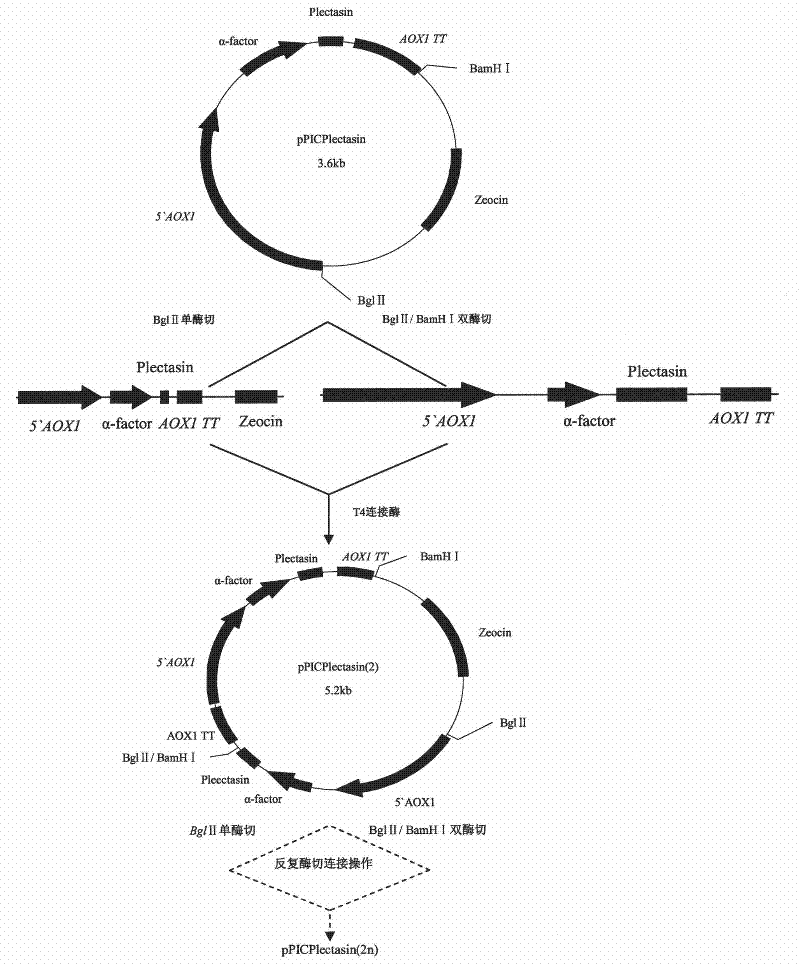
Multi-copy high expressed recombined plectasin by pichia pastoris
ActiveCN102409003AIncrease expression abundanceFungiAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPichia pastorisPlectasin
The invention discloses a preparation method of multi-copy high expressed recombined plectasin by pichia pastoris. The method comprises the following steps: a plectasin expressing gene sequence is designed according to preference performance to codon translated by pichia pastoris; the optimized plectasin gene is fused on an alpha-factor signal peptide C terminus of an expression vector pPICZalphaA to construct a single-copy expression vector, the vector comprises a plectasin expression cassette containing a start signal element alcohol oxygen dehydrogenase strong promoter (AOX), alpha-factor signal peptide gene and a plectasin gene fused in C terminus, a stop signal element AOX (TT) and the like. A complementation principle of restriction endonuclease Bg1II and BamHI cohesive end is used to obtain plectasin gene-containing recombinant plasmid of different copy cascade expression cassettes, pichia pastoris is electrotransformed and secreted and expressed plectasin with high efficiency under the methanol induction. The expression level and plectasin gene copy number exist a linear relation. The constructed multi-copy high expressed yeast cells can be used for raising the output and reducing the cost, and is adapted to large scale production of plectasin.
Owner:FEED RESEARCH INSTITUTE CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Rice leaf color control gene heme oxygenase2 (HO2) and application thereof
InactiveCN103114076AAppropriate leaf colorIncrease productionBacteriaOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyChloroplast
The invention discloses a rice leaf color control gene heme oxygenase2 (HO2) and an application thereof. A gene which is cloned from a rice leaf control mutant ho2 and is proved to have the effect of controlling the color of a rice leaf is named after HO2. A transgene functional complementation assay proves that the HO2 is the gene which controls the color of the rice leaf. Comparative analysis on amino acid sequences shows that HO2 protein belongs to a hemeoxygenase protein family. Phenotype observation and biophysical analysis prove that the cloned gene has the effects of regulating and controlling the development of chloroplasts and then controlling the color of the leaf. The invention also discloses an application of the rice leaf color control gene HO2 in fine seed breeding and cross breeding by taking a green yellow leaf character as a marker character by using genetic engineering. The rice leaf color control gene HO2 is obtained by using a map-based cloning technology, and the effects of the gene is tested through the transgene functional complementation test. Therefore, the rice leaf color control gene HO2 has the effect of ensuring rice to keep an appropriate leaf color, so that the photosynthetic efficiency of the rice is improved, and finally the rice yield can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
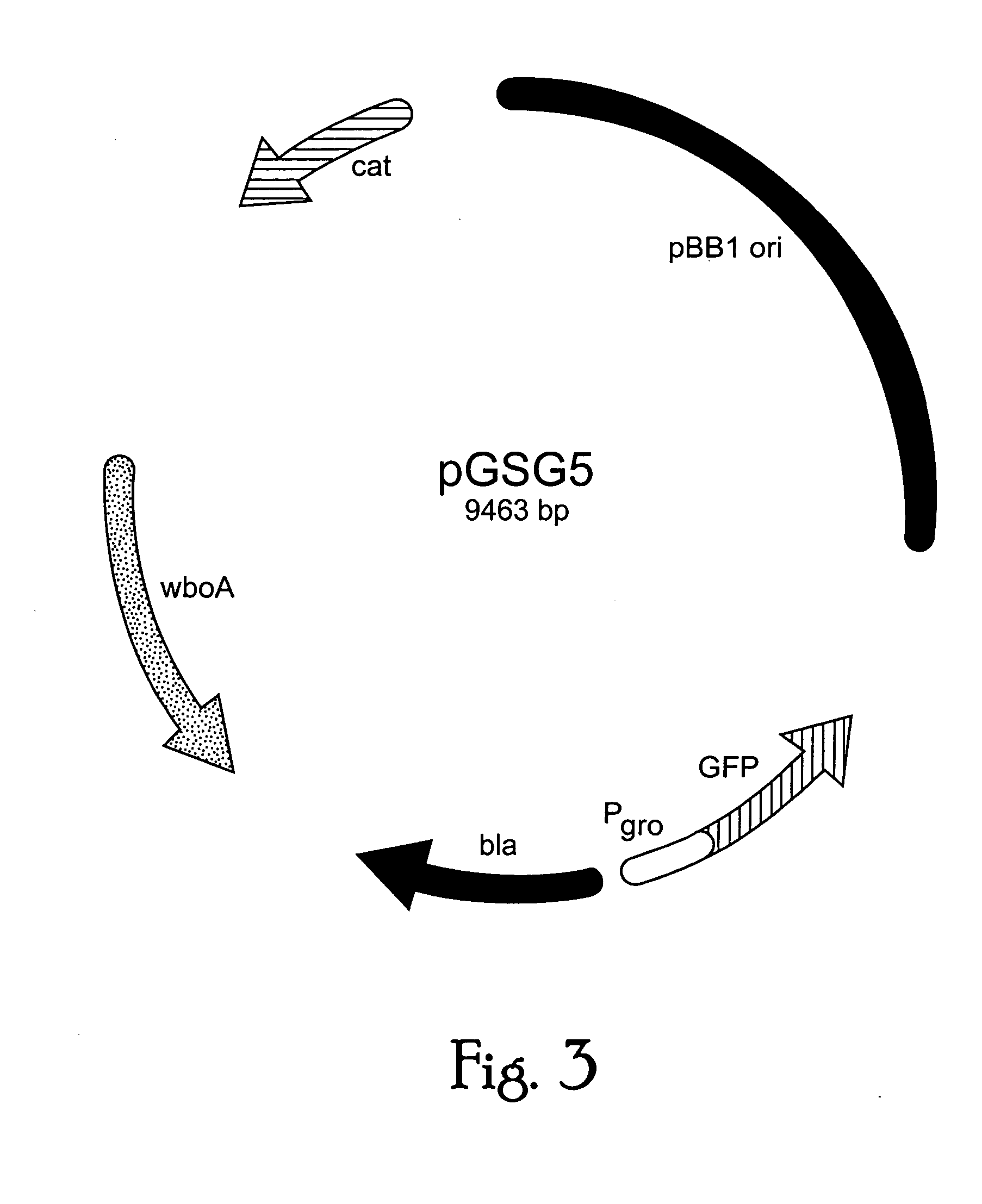
Immunogenic compositions including rough phenotype Brucella host strains and complementation DNA fragments
InactiveUS20050142151A1Sufficient attenuationEasy to operateBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsHeterologousHeterologous Antigens
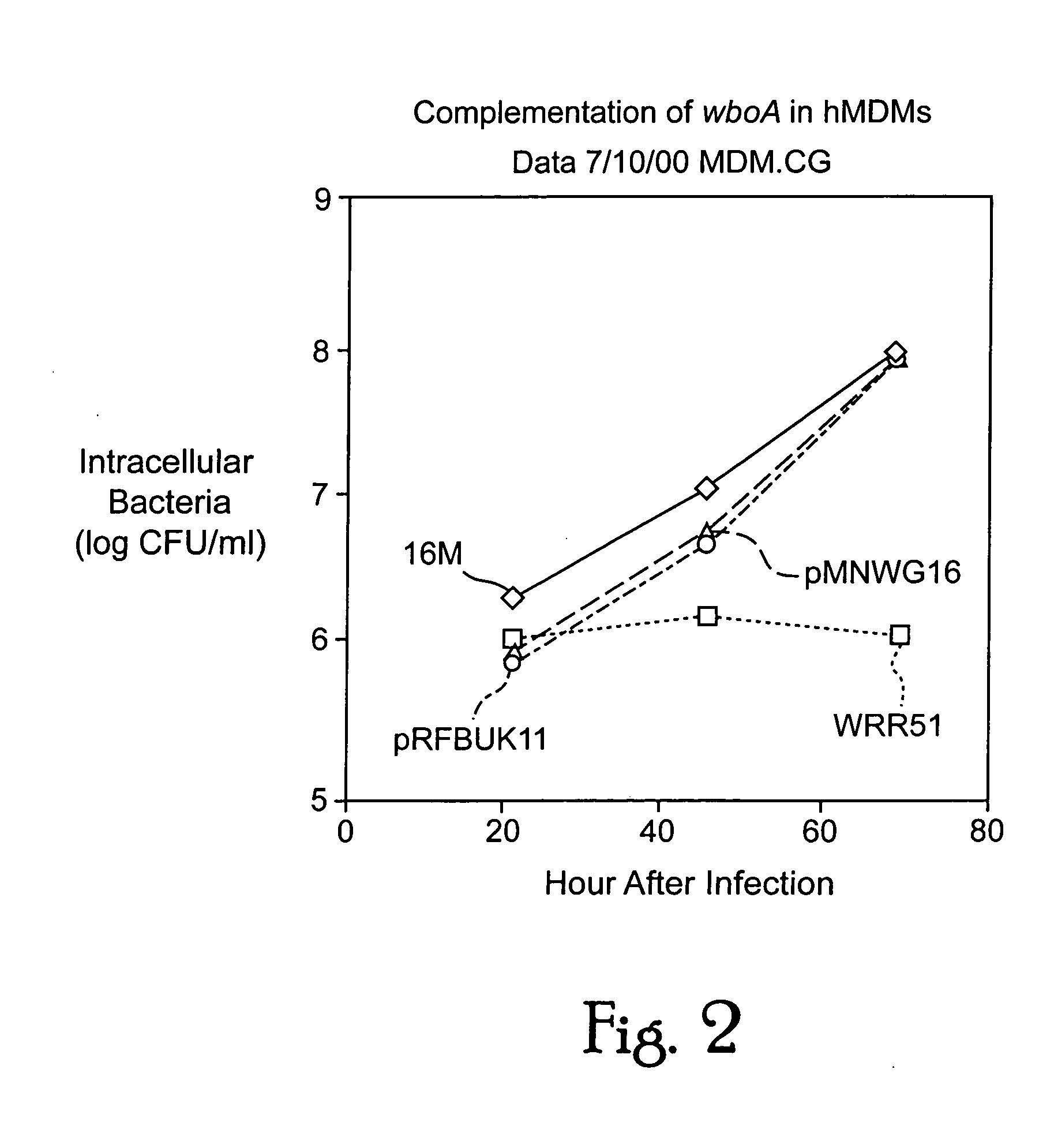
Live attenuated vaccines against brucellosis and infection by other diseases are described. It has been discovered that trans complementation of the Brucella wboA gene can be used to maintain an expression vector in an attenuated Brucella host cell in a vaccinee. Further, heterologous antigens can be expressed using this Brucella platform, thus effecting a multivalent vaccine against Brucella and the disease corresponding to the heterologous antigen.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
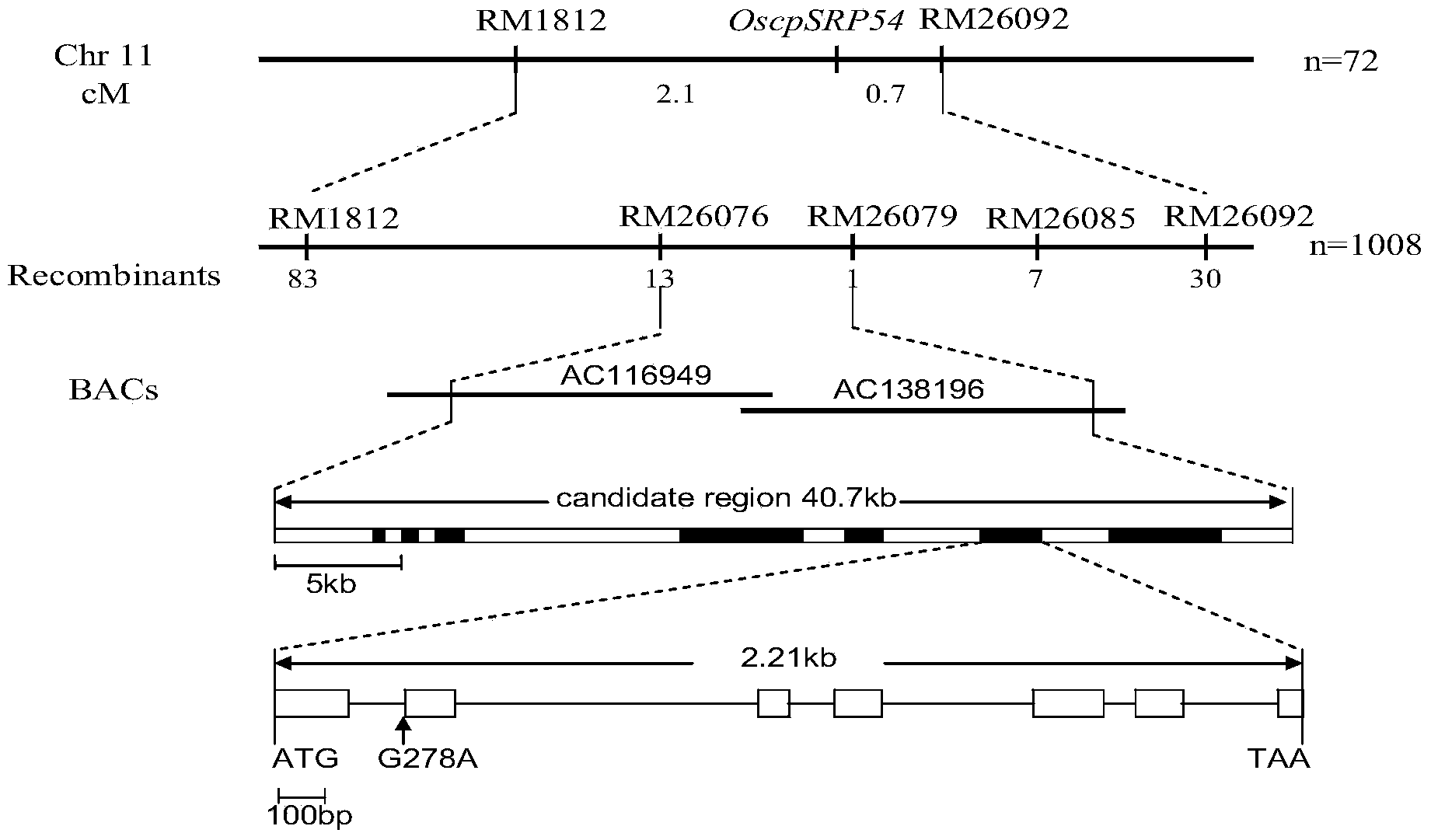
Paddy rice leaf color control gene OscpSRP54 and protein encoded by same
InactiveCN103613649AIncrease productionImprove photosynthesis efficiencyBacteriaPlant peptidesBiotechnologyChloroplast
The invention discloses a cDNA sequence represented by the SEQ ID No.1 of a paddy rice leaf color control gene OscpSRP54 coding area and an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID No.2 of a protein encoded by the gene. The gene OscpSRP54 which controls the paddy rice leaf color is cloned from a paddy rice light green leaf mutant HM14 through a map-based cloning technology, and the gene OscpSRP54 is proved to be the gene that control the paddy rice leaf color through a functional complementation experiment. Through observation of chloroplast by using a transmission electron microscope, the fact that the OscpSRP54 gene has the function of modulating chloroplast growth and then further controlling the leaf color is proved. The OscpSRP54 gene can be used to modulate paddy rice chloroplast growth so as to improve the photosynthesis efficiency and increase the paddy rice output. The leaf color control gene provided by the invention can also be used as a tracing marker in a genetic transferred plant progeny or an indicating marker for distinguishing pure species from hybrid species in a hybrid seed production process, and can be applied to the fields of good species breeding and hybrid breeding.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
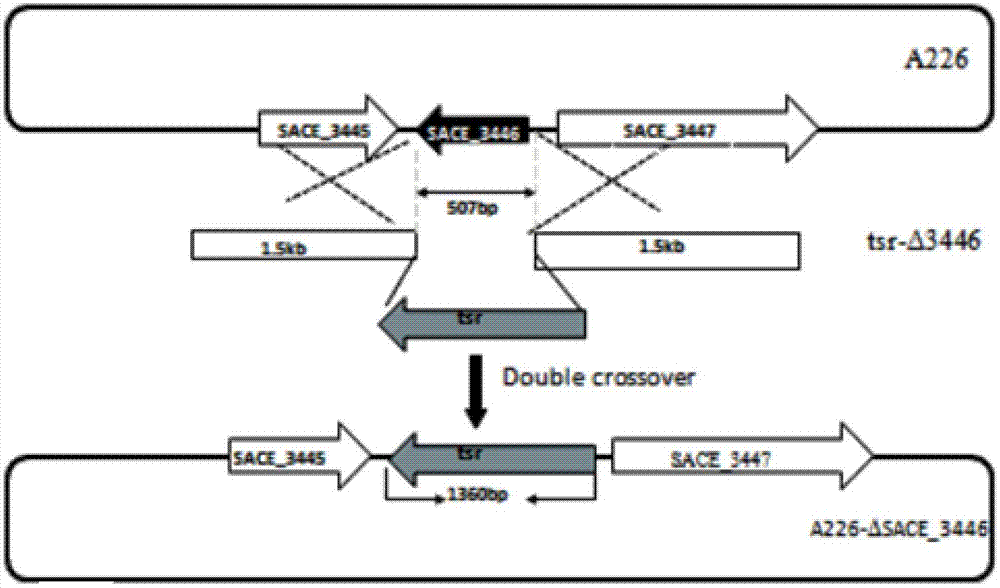
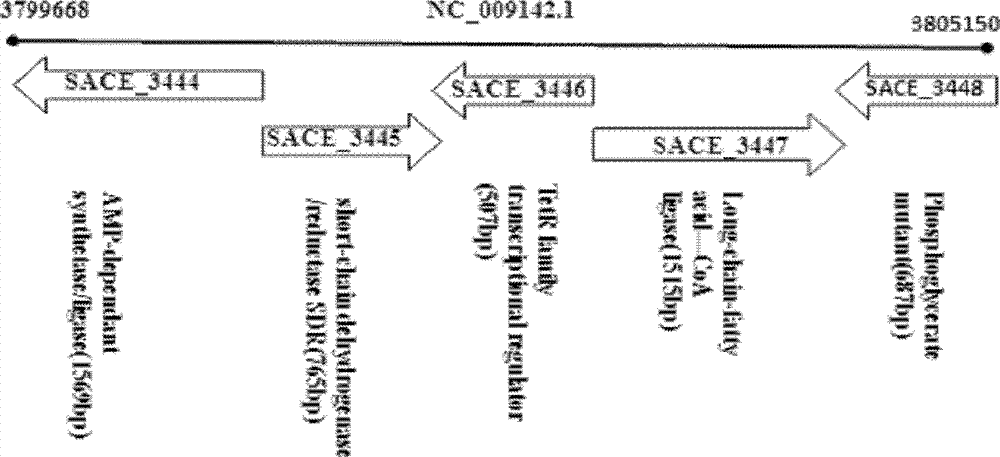
Method for improving erythrocin yield through inactivation saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_3446 gene
The invention discloses a method for improving erythrocin yield through a negative control gene SACE_3446 on an inactivation saccharopolyspora erythraea chromosome. Saccharopolyspora erythraea is used for producing erythrocin. The erythrocin and derived drugs of the erythrocin such as clarithromycin, azithromycin and telithromycin are used widely in clinic. Erythrocin high-producing strain screening is very important in industrial production. The erythromycin biosynthesis negative control gene SACE_3446 is screened from a saccharopolyspora erythraea TetR family. Compared with erythrocin yield of an original strain, deletion mutants of the saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_3446 is improved remarkably, the erythrocin is returned to low yield after gene complementation of the SACE_3446, and therefore the SACE_3446 gene is a erythromycin biosynthesis negative control gene. The inactivation saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_3446 gene can improve the erythrocin yield through a genetic engineering way. Due to the fact that erythromycin biosynthesis gene control is a network system, upstream and downstream control factors acted by SACE_3446 control factors can be found by using the SACE_3446 as an object. The erythrocin yield can also be improved by changing upstream or downstream control factor genes of the saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_3446 control factors.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Rice hybrid pollen fertility gene and uses thereof
InactiveCN101492682AEquivalent or enhanced expressive effectEasy to breedMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyPlant genetic engineering
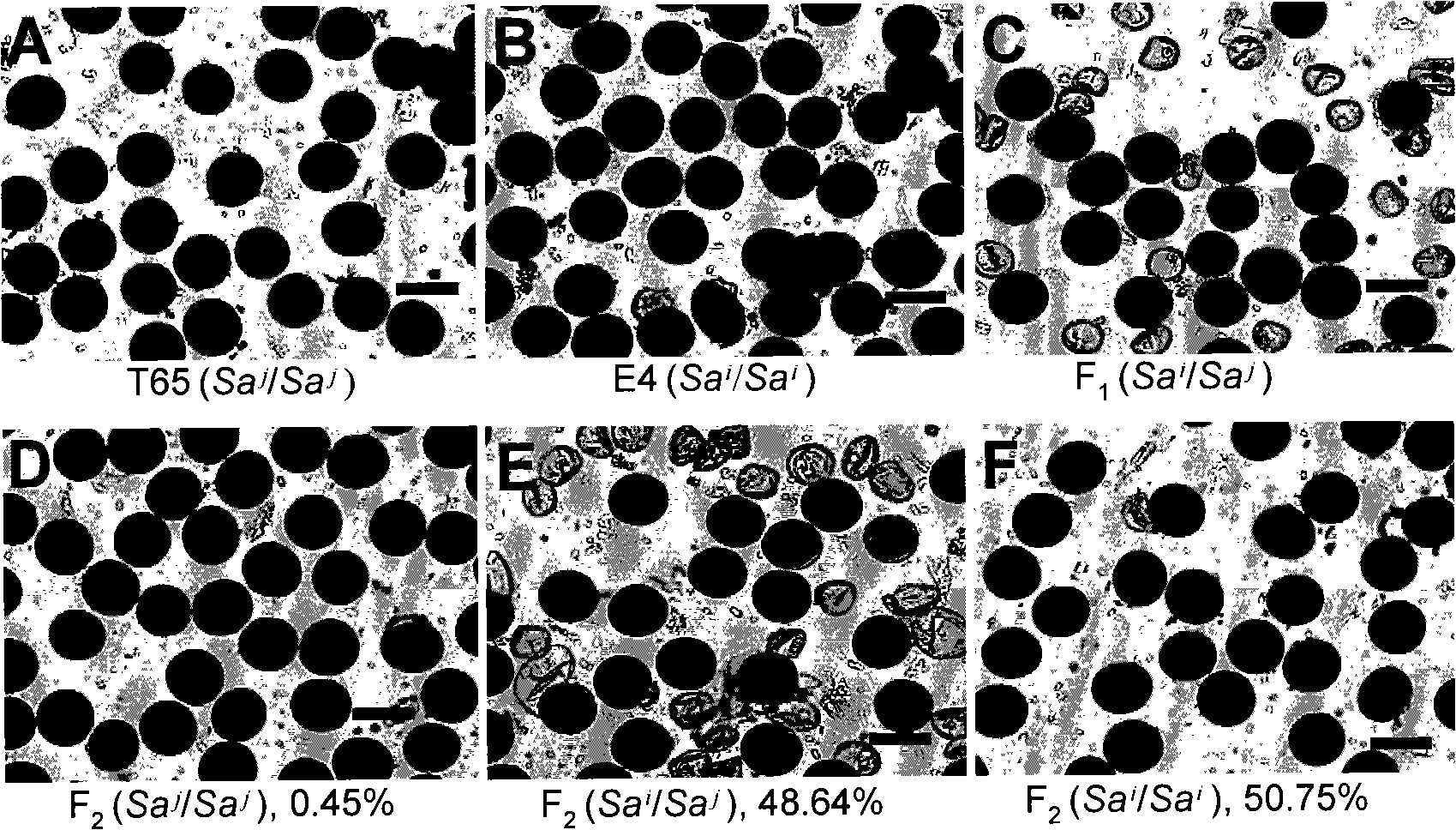
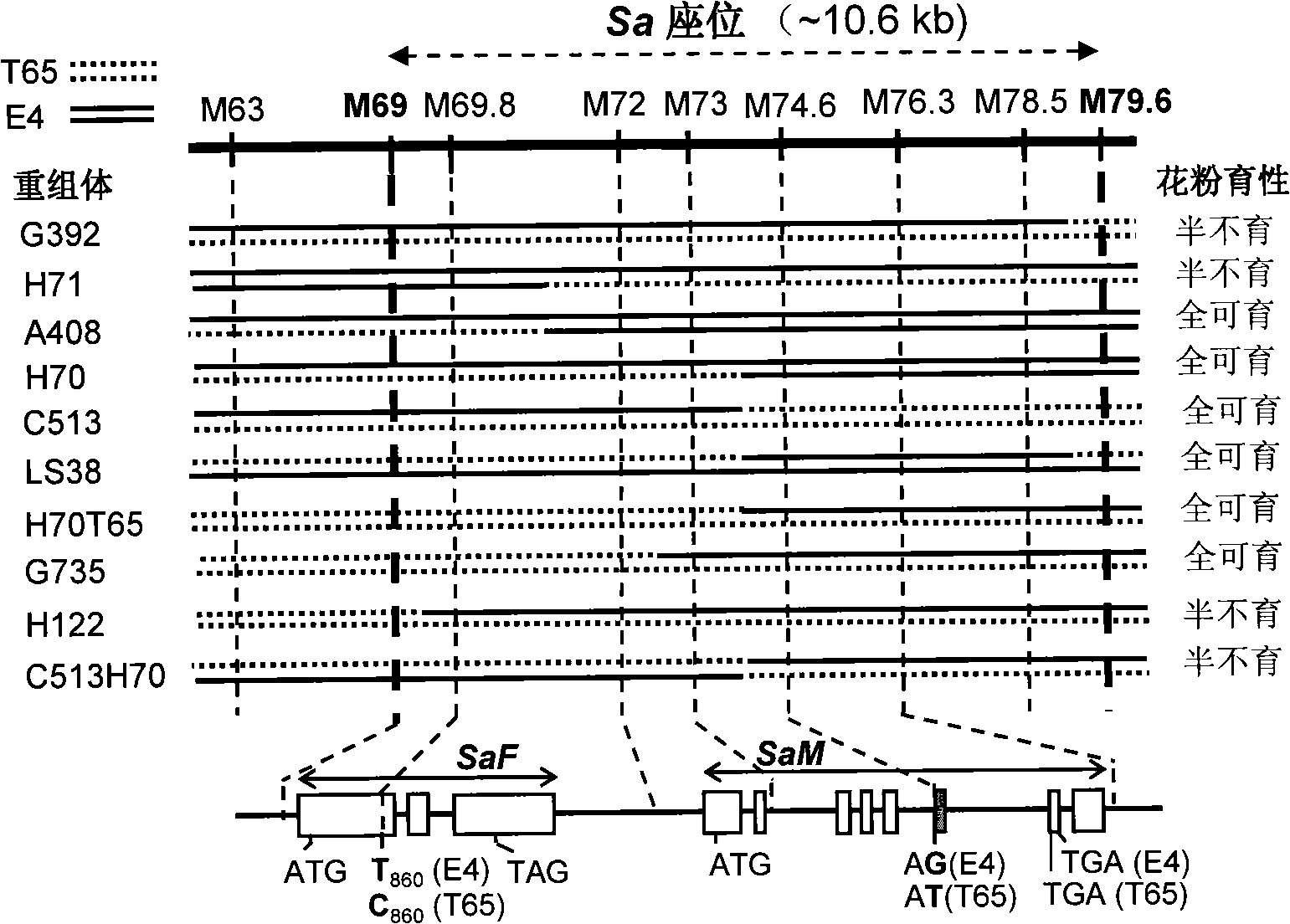
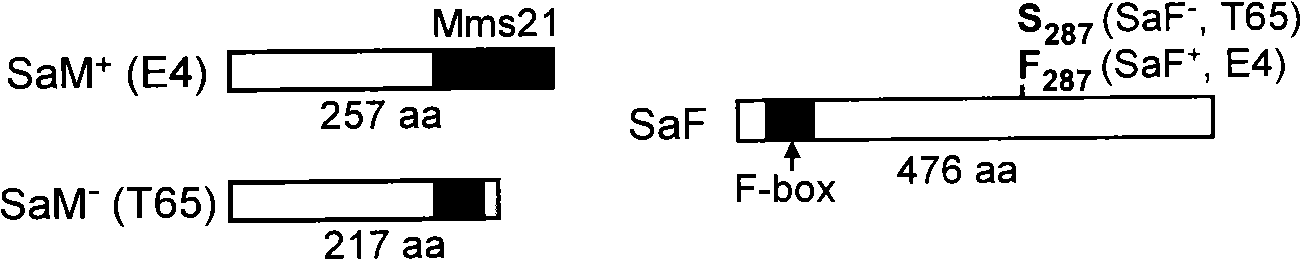
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, in particular to separation, cloning and an application of two genes named SaM and SaF of a rice hybrid pollen fertility gene locus Sa. The bacterial two-hybrid experiments indicate that proteins coded by specific allele of the SaM and SaF of indica and japonica are subjected to specific interaction. In addition, genetic analyses and transgene functional complementation experiments indicate that the SaM heterozygous in a hybrid and the SaF originated from the indica, namely 3 alleles, interact to lead to infertility of hybrid pollen, while lack of any one of the three or inhibition of expression thereof results in hybrid compatibility, namely pollen fertility. The invention also relates to a method for adopting the genes to nurture rice hybrid fertility compatible line and an application thereof and a molecule marker for appraising rice hybrid fertility gene type and the application thereof.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
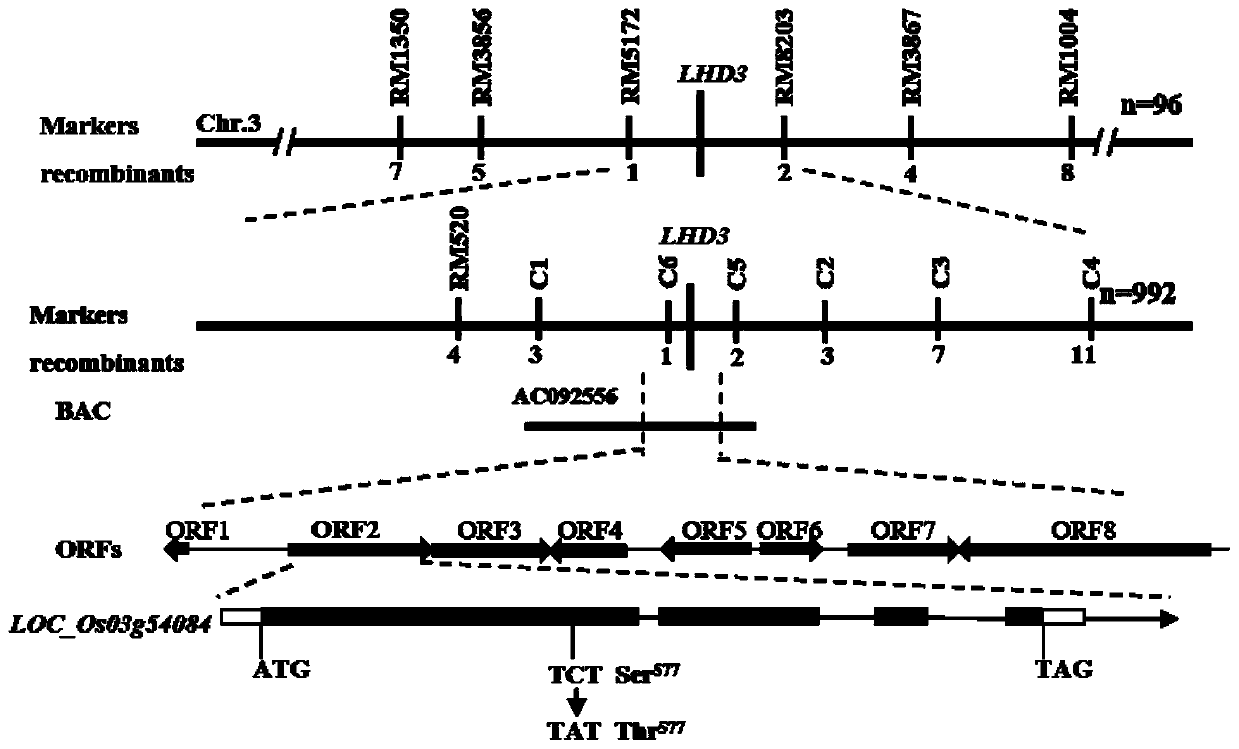
Rice flowering related protein and coding gene LHD3 thereof and application thereof
The present invention discloses a rice flowering related protein and a coding gene LHD3 thereof and an application thereof in rice breeding. The provided rice flowering related protein has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The present invention also provides the gene LHD3 encoding the above-mentioned protein and a nucleotide sequence of the gene LHD3 is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The gene LHD3 is applied in improving rice heading stage and rice photomorphogenesis. The rice flowering gene LHD3 is isolated, cloned and identified, and besides, gene functions are verified according to a complementation experiment. Results of map-based cloning indicate that the gene encodes rice phytochrome C. The rice flowering related protein and the coding gene LHD3 thereof provide germplasm resourcesand theoretical support for breeding new rice varieties with early heading and good photomorphogenesis, and have broad application prospects.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Rice blast bacterium nontoxic gene Avr-Pib and application
InactiveCN101240282AAvoid infectionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceNon toxicity
A rice blast bacterium innocuity gene Avr-Pib is obtained by separation and appraising in T-DNA insertion mutation. The out-knocking mutant of the gene can cause susceptibility of rice breed variety containing Pib disease-resistant gene. The out-knocking mutant and field susceptibility individual plant can recover non-toxicity by function complementation experiment and the breed variety is disease-resistant. The gene can be used as molecule target of newly pesticides and paddy rice disease-resistant genetic engineering.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
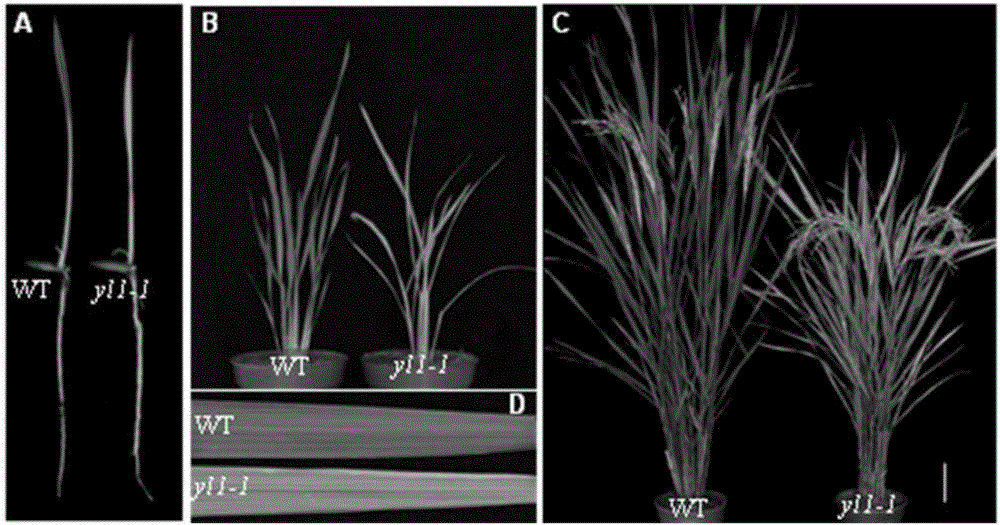
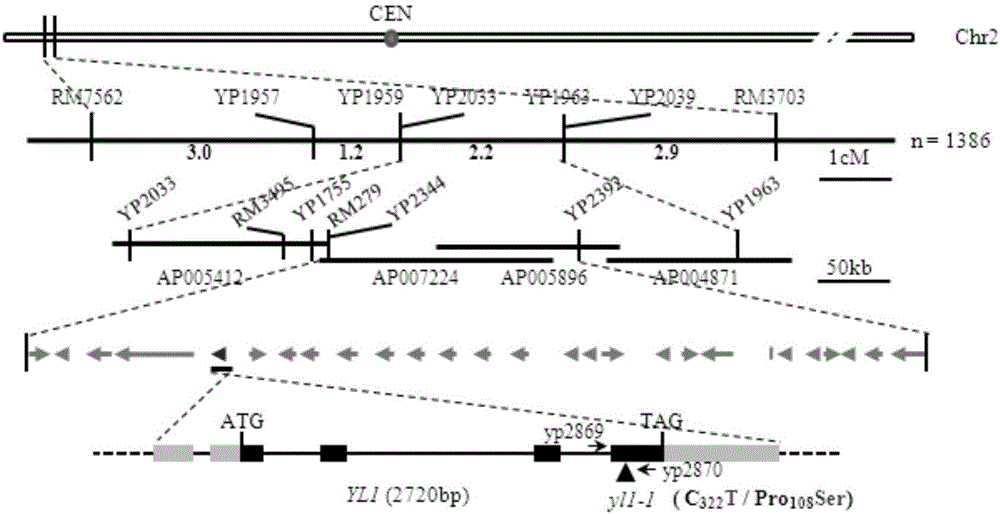
Paddy rice leaf color regulation and control gene YL1 and use thereof
The invention discloses a paddy rice leaf color regulation and control gene YL1 and a use thereof. The paddy rice leaf color regulation and control gene YL1 has a gene nucleotide sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO. 1. A coded protein sequence is shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO. 2. Through a map-based cloning technology, the novel paddy rice leaf color regulation and control gene YL1 is obtained. Through a transgenosis function complementation experiment, functions of the gene are verified. The YL1 and a chloroplast ATPase protein complex subunit AtpB produce synergism and YL1 gene mutation causes chloroplast ATPase activity reduction so that a photosynthesis-associated protein expression level is reduced, chloroplast development is influenced, chlorophyll content is reduced and a yellow leaf phenotype is produced. The protein and coding gene can further elucidate a paddy rice leaf color regulation and control molecule mechanism, can be used for crop genetic improvement and has an important meaning for high photosynthetic efficiency breeding.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Rice tillering associated protein, encoding gene and use thereof
InactiveCN101585869APromote germinationPromote absorptionMicroorganismsPlant peptidesNatural ecosystemParasitic Weeds
The present invention discloses a rice tillering associated protein, the encoding gene and the use thereof. The protein is selected from the following proteins (a) and (b): (a) a protein which is composed of the amino acid sequence represented by the sequence 4 in the sequence table; (b) a protein which is associated with the plant tillering and is derivate from the protein (a) through substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or a plurality of amino-acid residues to the amino acid sequence represented by the sequence 4 in the sequence table. The transgene complementation test proves that the protein D27 coded by the gene participates in the synthesizing of the strigolactone and regulates the plant tillering or the branch stem developing. Therefore, the genetic engineering technology can be used for regulating the tillering trait of the rice, regulating the nutrition using efficiency of the plant and effectively controlling the destructive parasitic weed. The D27 gene has important application value in the aspect of researching the beneficial fungus association and the destructive parasitic weed in the agriculture and natural ecosystem.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
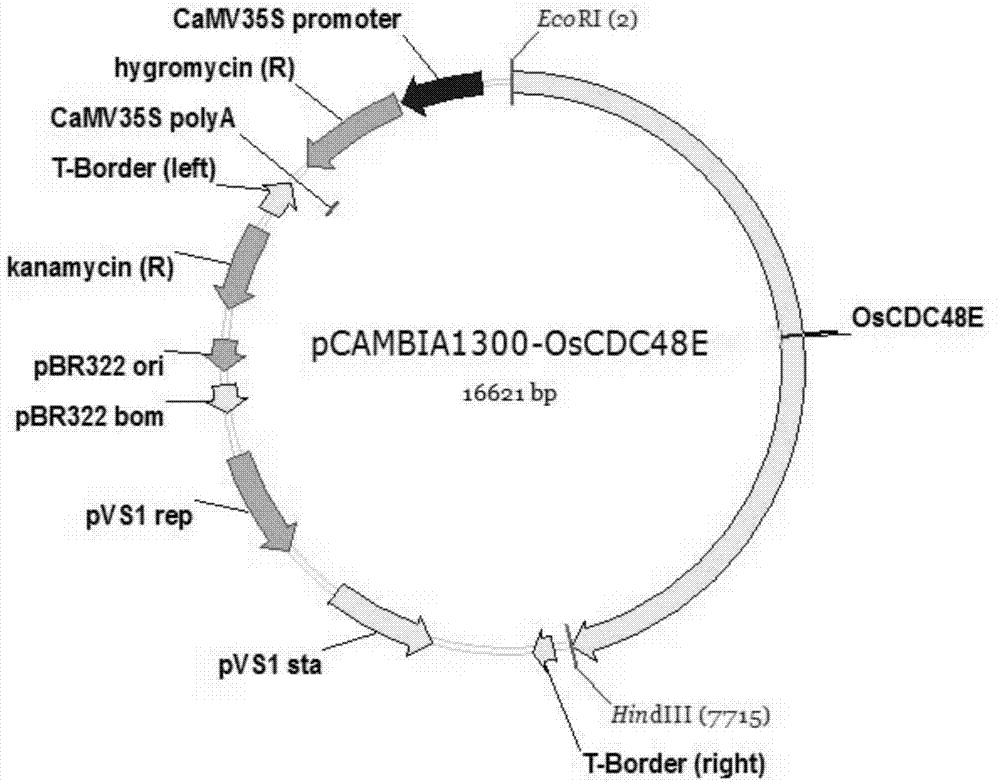
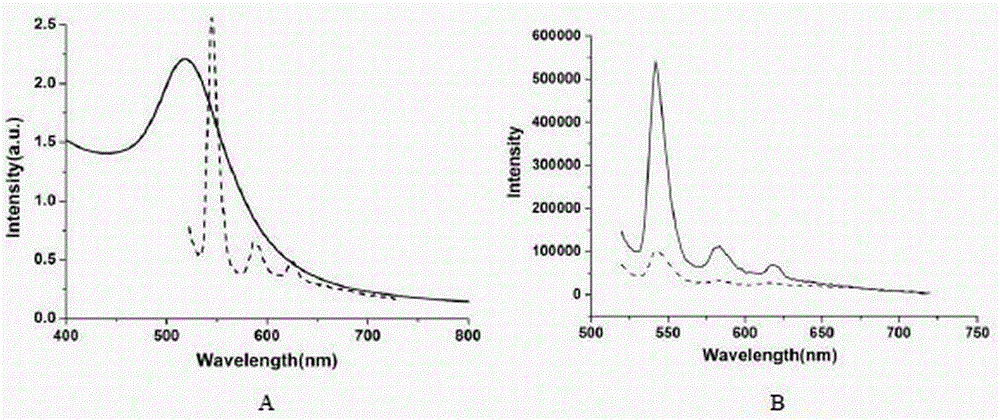
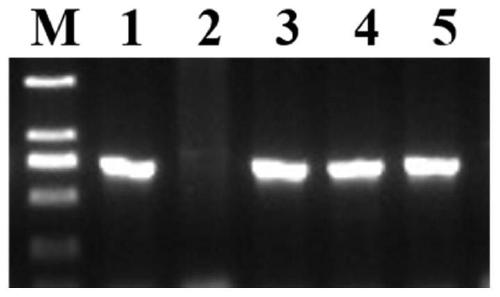
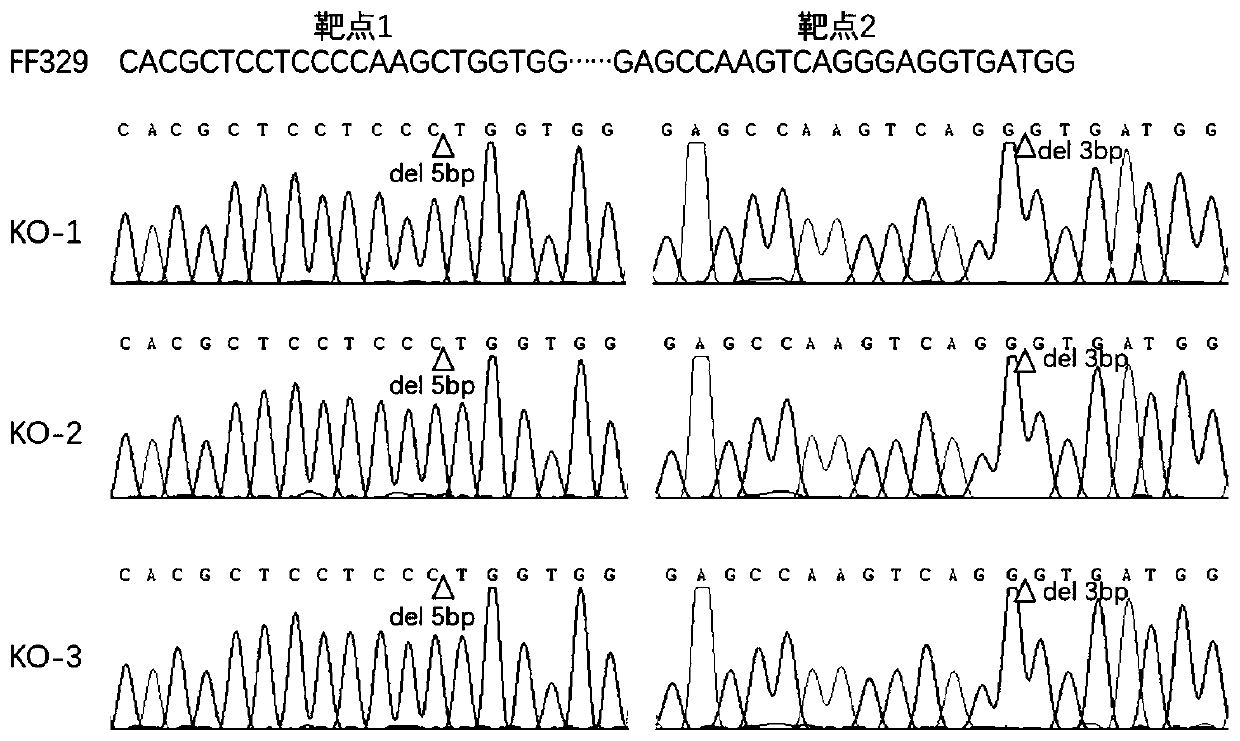
Rice ageing control gene OsCDC48E and coded protein thereof
InactiveCN103788189AEasy to adjustRice Variety ImprovementBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPremature aging
The invention discloses a rice ageing-relevant control gene OsCDC48E sequence and a coded translated protein and an amino acid sequence thereof. Through a map-based cloning technology, a gene OsCDC48E for controlling rice leaf ageing is obtained from a rice premature senile mutant W95 through cloning, and functional complementation experiments prove that the OsCDC48E is a gene which controls the rice growth and development and is relevant to leaf ageing. Observation of a transmission electron microscope, and analysis of a photosynthetic rate and a photoreaction and dark reaction detection technology prove that a premature senile gene cloned from the OsCDC48E has a remarkable adjusting function of growth and development of rice, integrity of thylakoids in chloroplast, structures of organelle of endoplasmic reticulum, and the like. By using a genetic engineering technology, multiple specific marker characters of the ageing gene can be applied to rice variety improvement, yield increase and cultivation of super rice.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
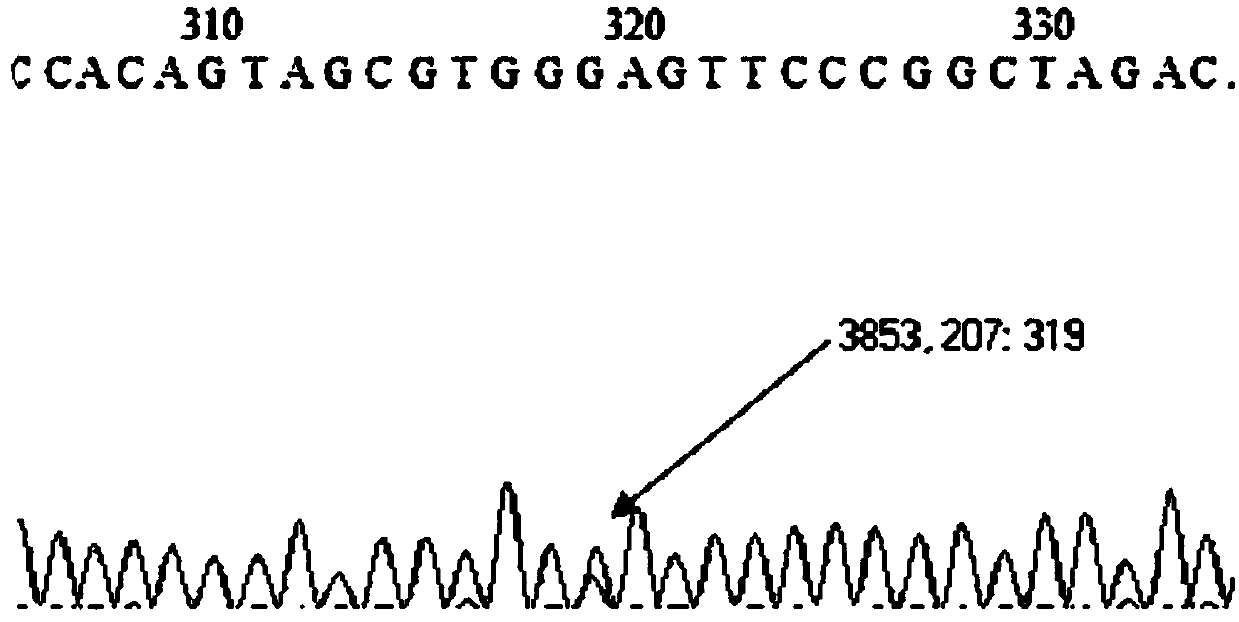
Kit for detecting inheritance gene restoring capability
The invention discloses an agent box for detecting idiogenetics gene repair capacity. The agent box comprises specificity primer pair and specificity fluorescent detecting probe pair for detecting synchronously number rs1136410 SNP site on multi-poly ADP ribose transferase gene (PARP1), number rs1799782 and rs25487 SNP site on human beings X ray intervein complementation repair gene (XRCC1), number rs1799793 and rs13181 on cutting repair complexes gene (ERCC2), general component for detecting fluorescent definite quantity PCR etc.. The agent box of the invention assesses idiogenetics gene repair capacity by detecting synchronously mononucleotide polymorphism site gene type correlative closely to idiogenetics gene repair capacity.
Owner:XINBAXIANG SHANGHAI MOLECULAR MEDICAL TECH SHANGHAI
Method for detecting trace amount of bisphenol A based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer
InactiveCN105319189ARealize detectionEfficient detectionFluorescence/phosphorescenceAptamerChemical physics
Disclosed is a method for detecting a trace amount of bisphenol A based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer. According to the method, a bisphenol A aptamer and a short chain DNA complementing to the bisphenol A aptamer are connected to a fluorescent nanometer material and nanometer gold. Through complementation and pairing of basic groups of two single chains DNA, the fluorescent nanometer material is combined with nanometer gold, and a fluorescence resonance energy transfer effect is produced, wherein fluorescence of the nanometer material is quenched by the nanometer gold. When added into a system, bisphenol A competes with a complementary DNA chain to combine with the bisphenol A aptamer, which results in different combining weights of the two nanometer materials, so that the fluorescence intensity of the system is affected. Bisphenol A is detected through measuring a linear relation between the concentration of bisphenol A and the fluorescence intensity of the system. Under an optimal experiment condition, according to the method, a preferable linear relation is shown when the concentration of bisphenol A is in a range of 0.5-100 ng / mL; the regression equation is Y=430.0X+75095 (R<2>=0.993); and the detection limit is 0.16 ng / mL. It is proved by a labeling and recycling experiment that the method can be used for detecting a real sample.
Owner:陶建臣
Short-chain dehydrogenase and mutant thereof, and preparation and applications of gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to short-chain dehydrogenase and a mutant thereof, and preparation and applications of a gene, specifically to a wild type C=C double bond reductase OYE1 derived from Saccharomyces pastoris, and a mutant thereof, short-chain dehydrogenases LfSDR1, BmSDR5 and BsSDR8 respectively derived from Lactobacillus fermentum, Bacillus megaterium and Bacillus subtilis, mutants thereof, C=C double bond reductase and C=O double bond reductase with stereoselectivity complementation, genes of C=C double bond reductase and C=O double bond reductase, construction and preparation of a recombinant expression vector containing the gene, expression of recombinase, an enzyme catalytic two-step asymmetric reduction reaction of carvone, the conditions of the reaction, and a detection method of the product dihydrocarveol. Compared with the existing chemical method, the method of the invention has the advantages of being easy to operate, mild in reaction condition, environmentally friendly and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Rice OsNBARC1 protein and application of coding gene of rice OsNBARC1 protein in regulation and control of resistance of rice to bacterial leaf blight
ActiveCN111233991AIncrease resistanceDecreased lesion lengthPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyWild type
The invention relates to rice OsNBARC1 protein and application of a coding gene of the rice OsNBARC1 protein in regulation and control of resistance of rice to bacterial leaf blight. An amino acid sequence of the rice OsNBARC1 protein, a sequence of the coding gene of the rice OsNBARC1 protein, and a sequence of a coding region of the coding gene of the rice OsNBARC1 protein are disclosed, and functional verification is conducted by means of gene complementation and gene editing technologies. Experimental results prove that the resistance of OsNBARC1-complementary transgenic plants to bacterial leaf blight is significantly improved, the lesion length is reduced by about 61.9% compared with those of wild-type plants, the resistance of plants with OsNBARC1 genes knocked out to bacterial leafblight is significantly reduced, and the lesion length is improved by about 2.8 times compared with those of the wild-type plants. The experimental results show that the rice OsNBARC1 protein has a function of positively regulating and controlling the disease resistance of rice, can be used for improving the resistance of rice to bacterial leaf blight, and has important significance for cultivation of a novel rice variety with resistance to bacterial leaf blight.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Rice bacterial leaf blight resistant protein, and coding gene and application thereof
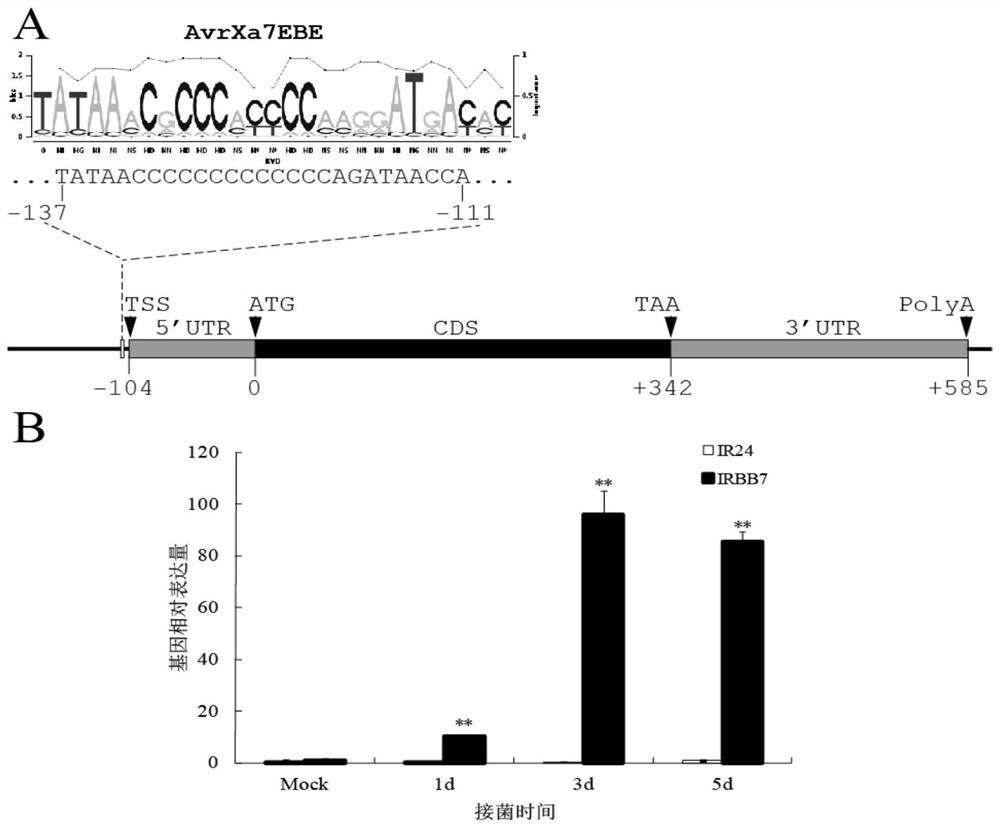
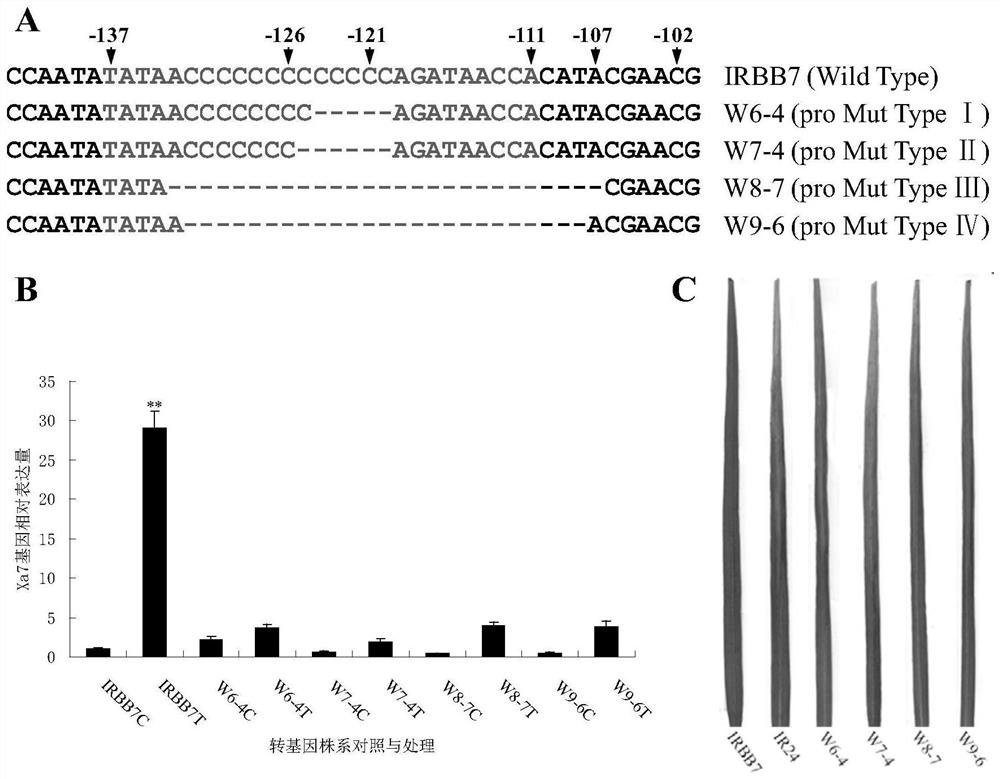
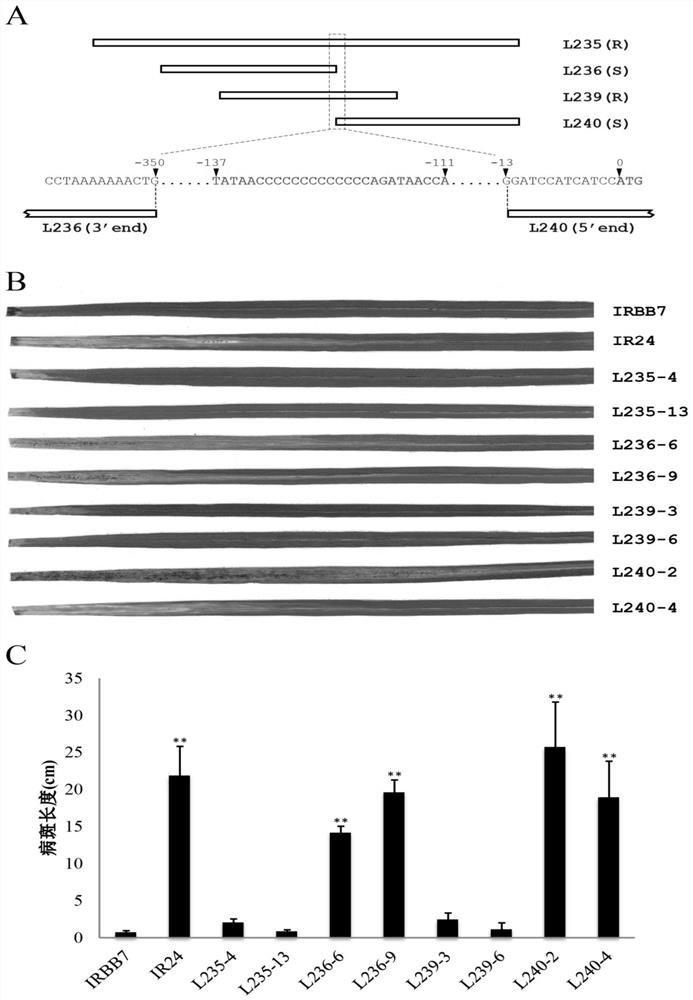
The invention discloses a rice bacterial leaf blight resistant protein, and a coding gene and application thereof. The name of the rice bacterial leaf blight resistant protein is Xa7 protein; the amino acid sequence of the rice bacterial leaf blight resistant protein is shown as SEQ ID NO.1; and the nucleotide sequence of the gene for coding the rice bacterial leaf blight resistant protein is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The cloning of the Xa7 functional gene is finally completed by constructing a genome BAC library of a rice variety IRBB7, screening the library, sequencing candidate insertion fragments, predicting an AvrXa7 recognition site by a target insertion fragment sequence, and carrying out a series of transgenic function complementation tests and gene knockout tests. The invention provides the sequence of the Xa7 functional gene for the first time; and the Xa7 functional gene can be used for researching a rice bacterial leaf blight resistance mechanism, cultivating a rice variety having disease resistance to rice bacterial leaf blight or other disease-resistant crops, or breeding a rice variety having disease resistance to rice bacterial leaf blight.
Owner:PLANT PROTECTION RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
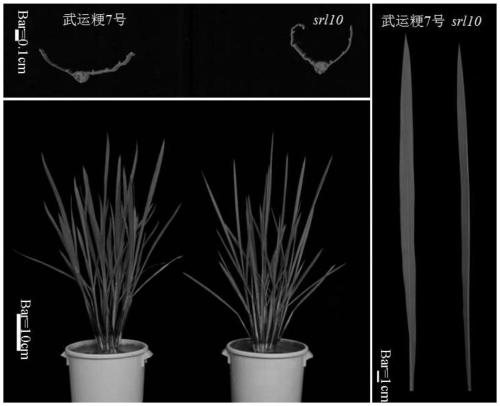
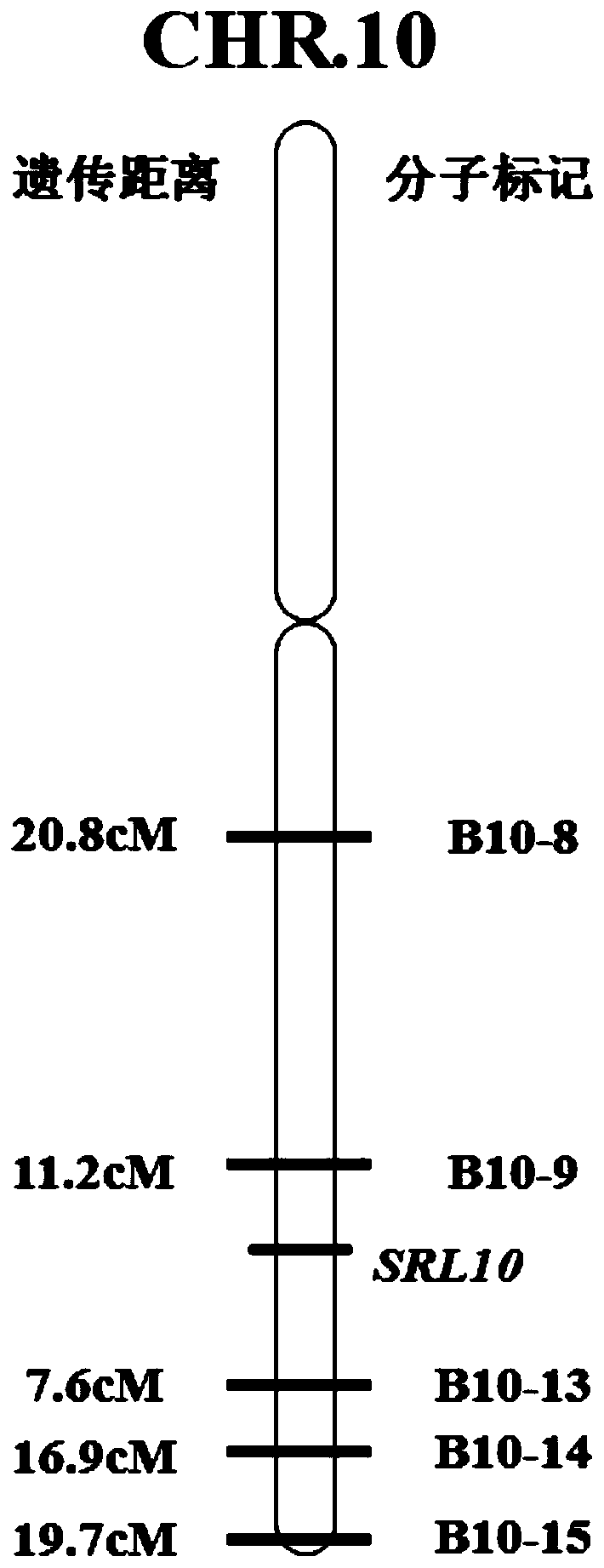
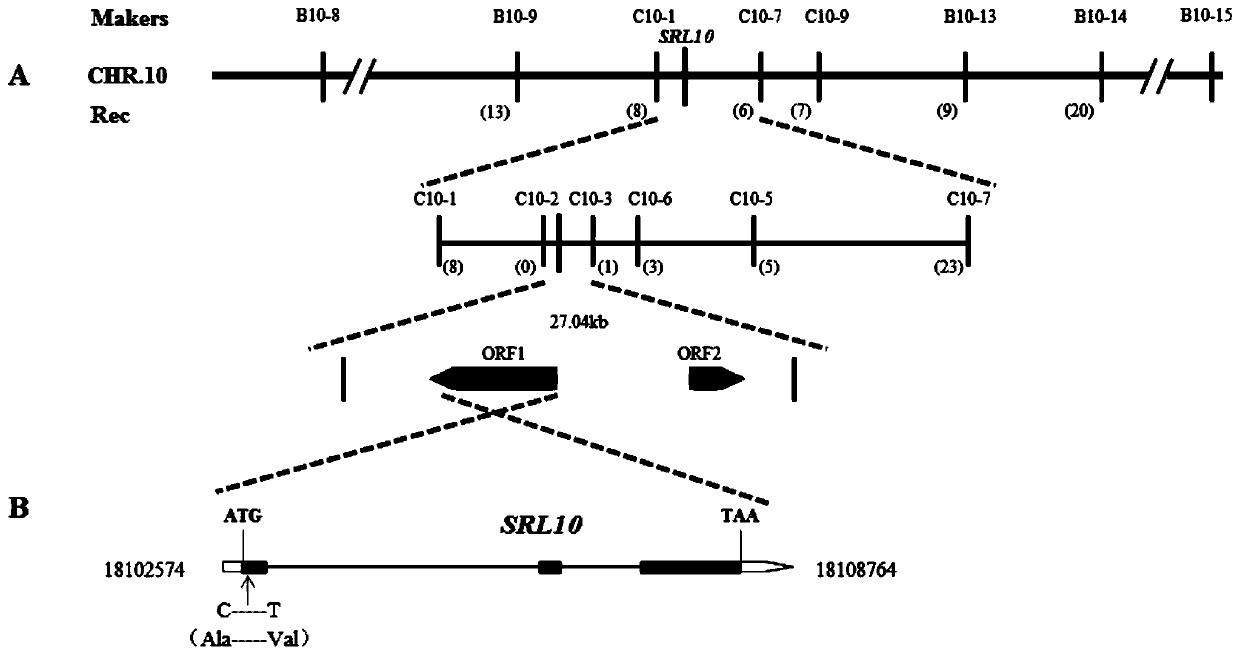
Rice half-leaf-curl gene SRL10 and application thereof
ActiveCN110343158AIncrease curlIncrease productionPlant peptidesFermentationNucleotidePlant genetic engineering
The invention belongs to the field of plant gene engineering, particularly relates to a rice half-leaf-curl gene SRL10 cloned through a map-based cloning technology and determining of the gene function through a transgenic complementation experiment, and meanwhile further relates to gene editing of the gene. The leaf morphology of a plant is improved, the ideal plant type of the rice can be formed, and the yield of crops is improved. The invention discloses a protein for encoding the rice leaf form control gene SRL10. The protein has the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No:2. The inventionfurther meanwhile discloses a gene for encoding the protein. The gene has the nucleotide sequence shown in the SEQ ID No:1.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
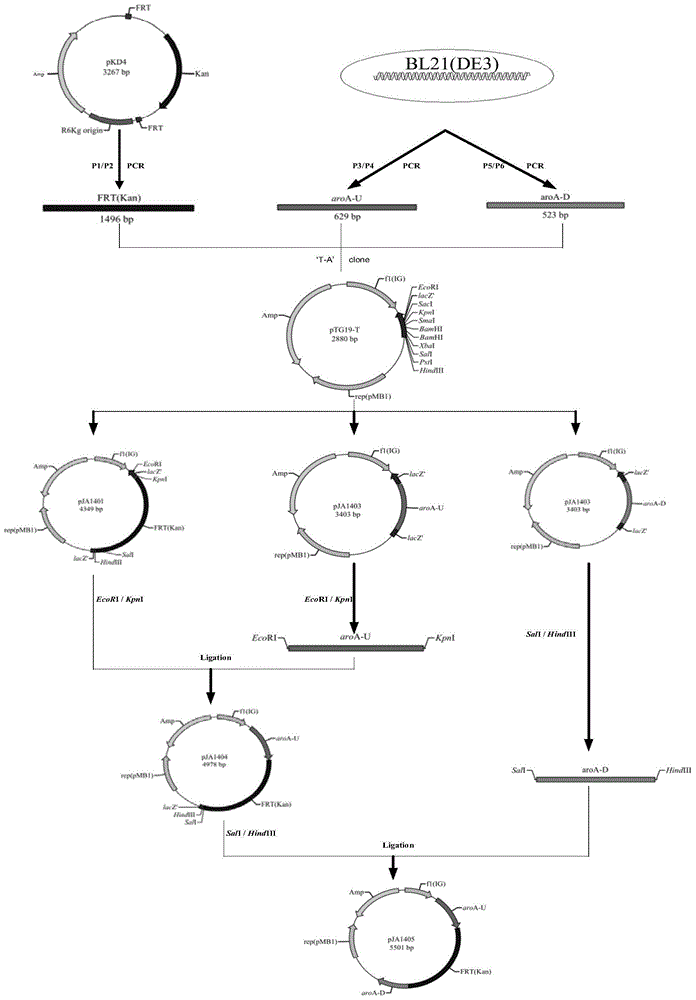
Construction method and application of BL21(DE3)delta aroA strain
ActiveCN104099363AAchieve the effect of killing two birds with one stoneBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlasmidBiotechnology
The invention relates to the field of biological carriers, in particular to a construction method and an application of a BL21(DE3)delta aroA strain. The construction method comprises the following steps: an aroA gene knockout targeting segment is constructed; pKD46 plasmid is transformed into a BL21(DE3) strain, and a BL21(DE3) / pKD46 strain is obtained; and the aroA gene knockout targeting segment is transformed into the strain, and the BL21(DE3)delta aroA strain is obtained. According to the provided construction method of the BL21(DE3)delta aroA strain, homologous flanking sequences larger than 500 bp are adopted, and a Red homologous recombination technology is used for knocking out the aroA gene of the BL21(DE3) strain successfully; the strain can be used for EPSPS functional complementation verification and further achieves strong expression of recombinant foreign protein of a pET system, and dual purposes are achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
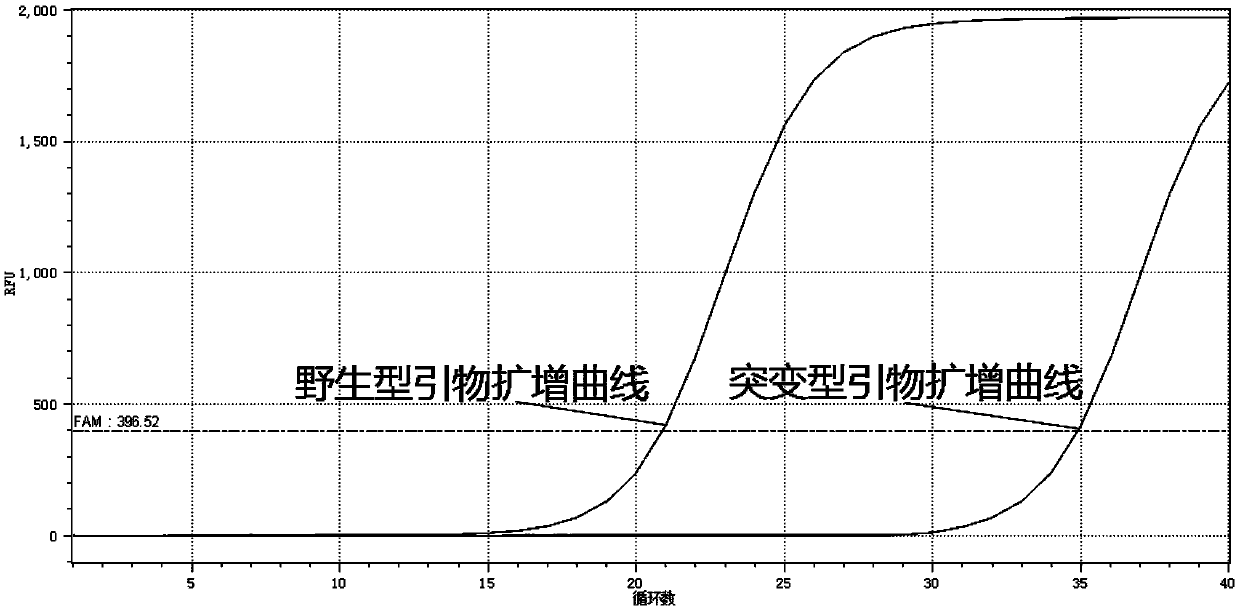
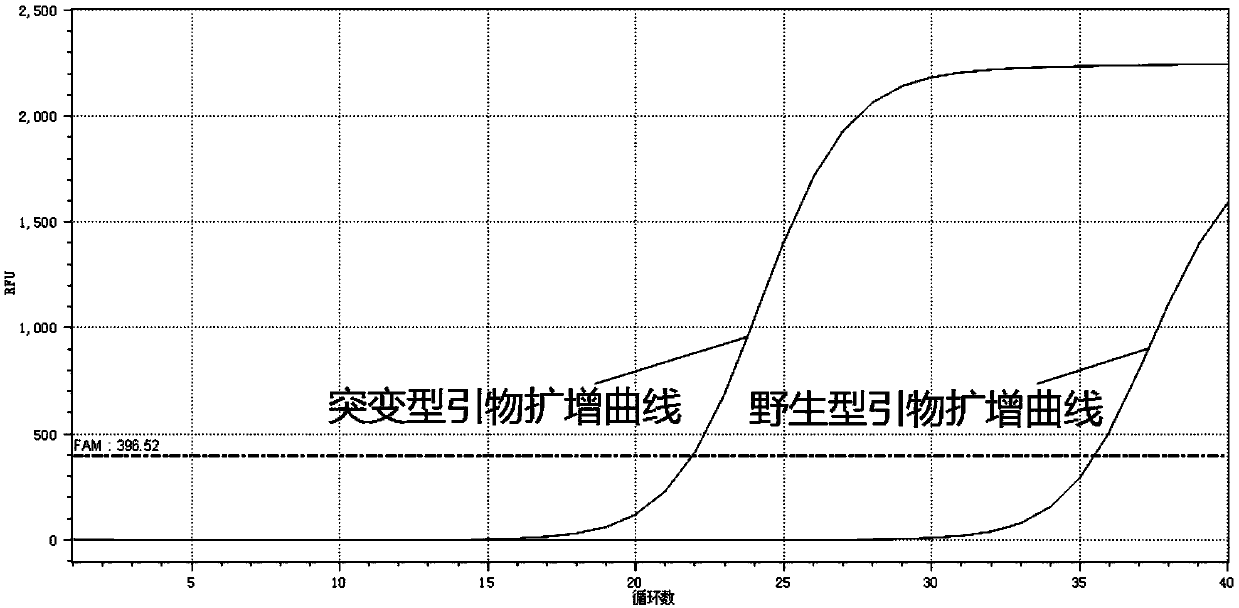
Primers and method for detecting related gene SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) sites of metformin-individualized medications
InactiveCN110699440AStrong specificityHigh priceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBase JMedicine
The present invention relates to primers and a method for detecting related gene SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) sites of metformin-individualized medications. The primers can detect a rs2289669SNP site of a SLC47A1 gene. The primer sequences comprise a wild-type upstream primer, a mutant-type upstream primer and a shared downstream primer. Improvement is made on the basis of ARMS-PCR, a specific primer and the shared downstream primer are designed for SNP sequences, mismatched bases are introduced at a second position of a 3' end of the specific primerto widen a gap between amplification efficiency of complementation and non-complementation of the bases of the 3' end of the specific primer and SNP site bases on a DNA template, thereby greatly improving specificity and accuracy of detection. A real-time PCR technology is introduced, identification can be made according to a [delta]Ct value, that is, the [delta]Ct value is equal to mutant Ct-wild Ct. In general, when [delta]Ct islarger than 7, the SNP site is a wild type, when [delta]Ct is less than -7, the SNP site is a mutant type, and when the [delta]Ct is larger than -2 and less than 2, the SNP site is a heterozygous type. Advantages are that the method is fast, simple, economical, accurate and reliable identification of results, and high in specificity.
Owner:西安医臻生物医药科技有限公司
Protein related to plant tillering number and coding gene and application thereof
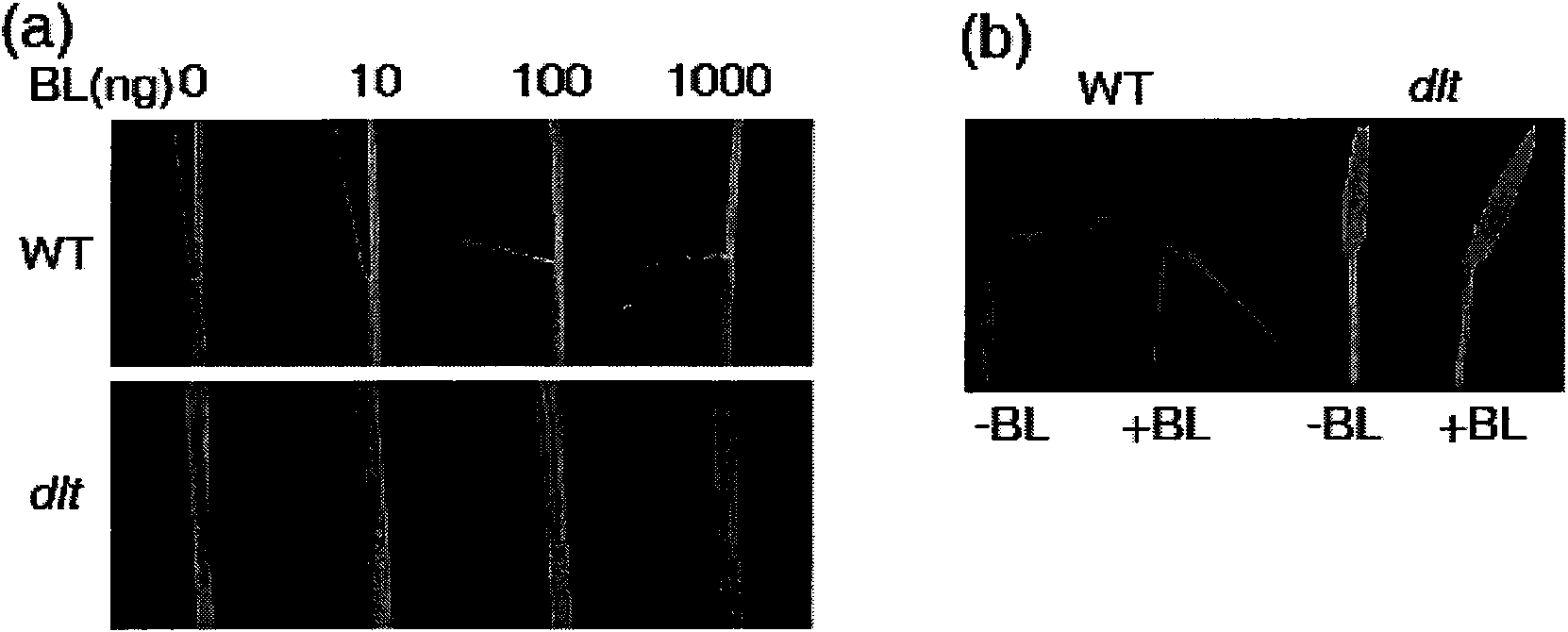
The invention discloses protein relevant to brassinolide signal conduction and a coding gene and the application thereof; the protein is the protein in the 1) or 2); 1) the protein is formed according to an amino acid sequence shown by a sequence 2 in a sequence table; 2) the amino acid residue sequence of the sequence 2 in a sequence table is substituted and / or lost and / or added by one or a plurality of the amino acid residues and is derived by 1) relevant to the plant tillering number. In the invention, DLT gene is cloned by utilizing a rice half-stuntedness little-tillering mutant, and molecule complementation verification is carried out; the result shows that DLT participates in the brassinolide signal conduction process to control the height, tillering and other phenotypes of the rice; after the DLT gene is transferred to the rice, the fact that the tillering number of the transgenosis rice with high DLT gene expression level is obviously increased; the invention has high potential application value on molecular breeding and improving crop production by utilizing genetic engineering measures to regulate plant hormone level.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
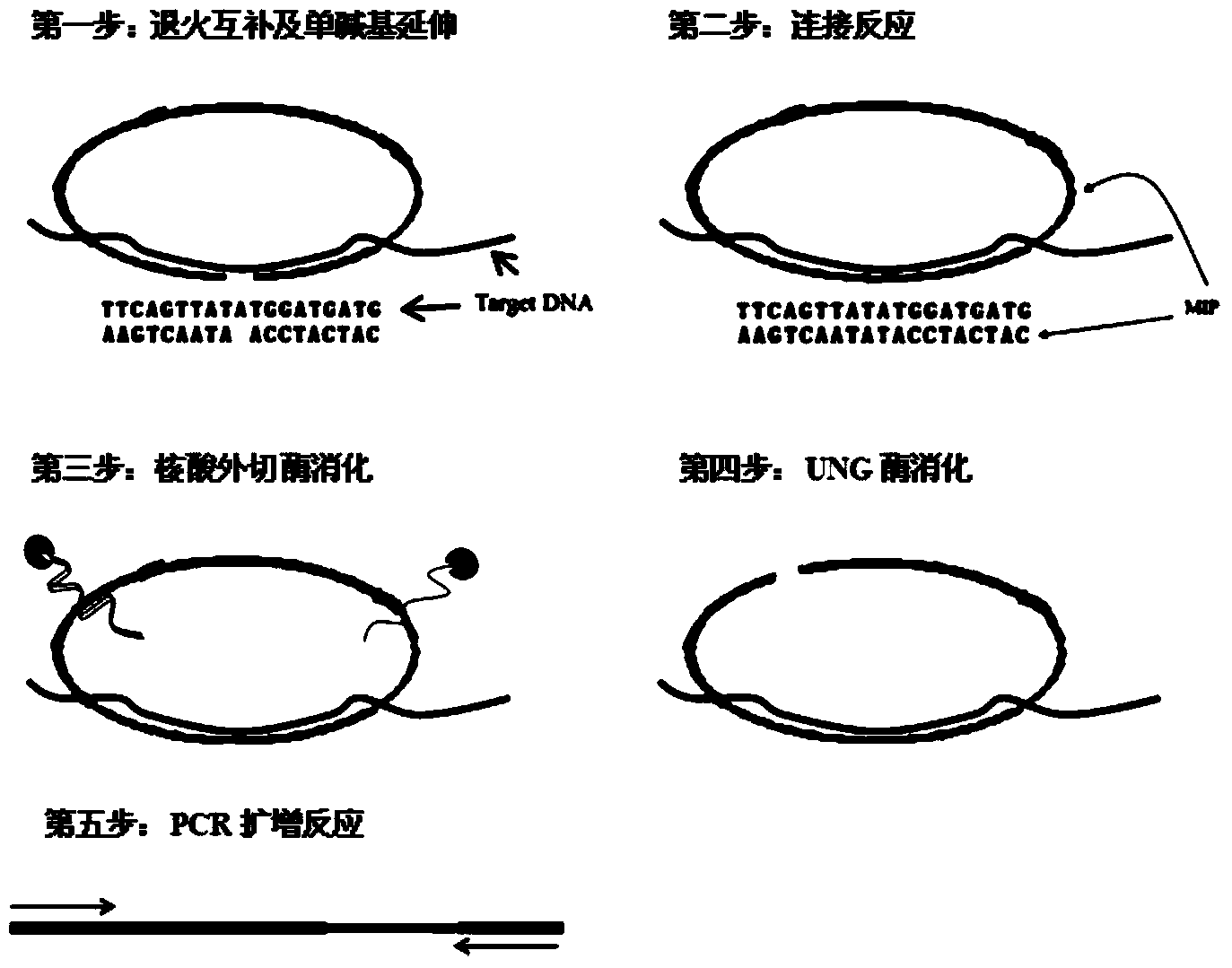
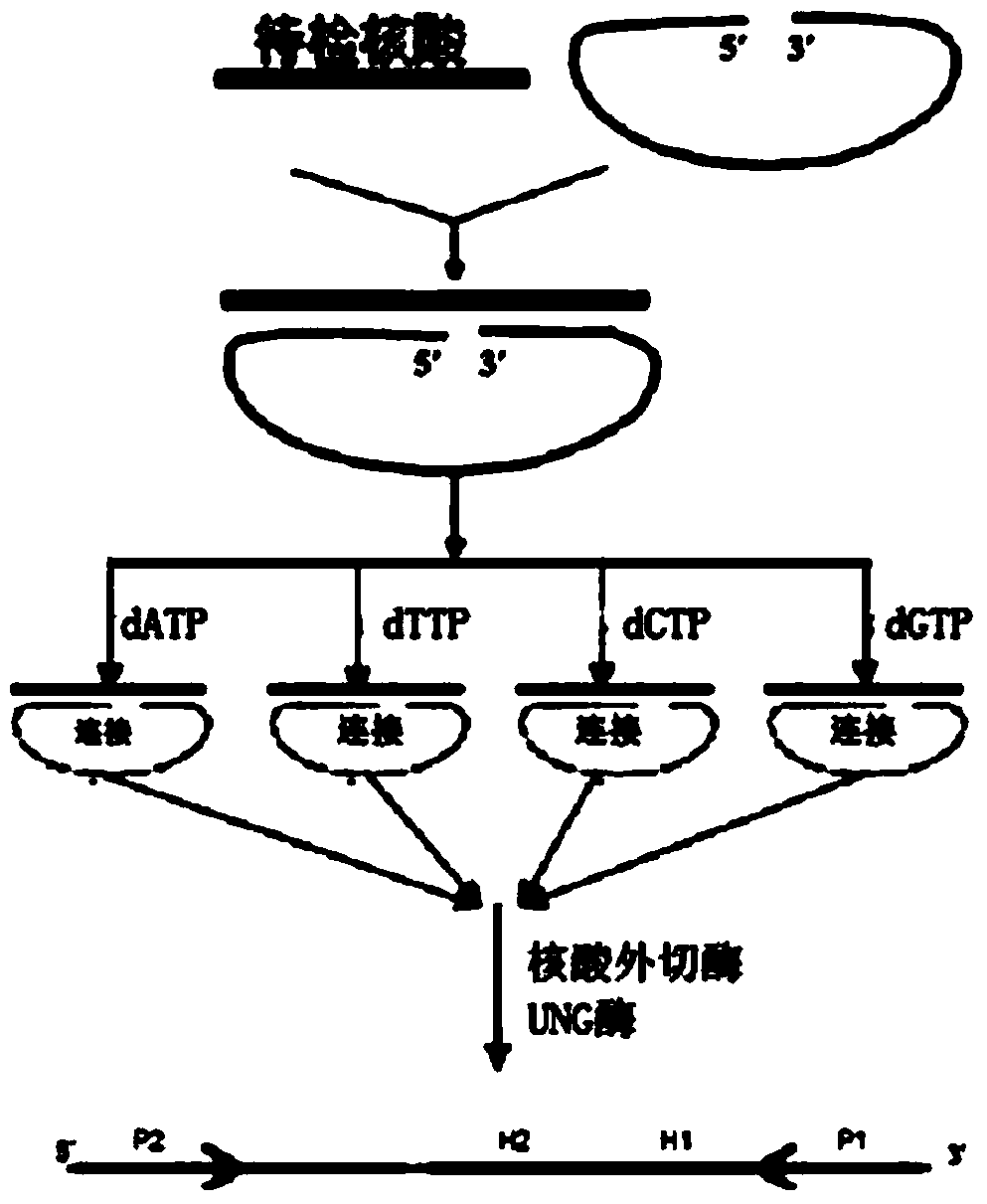
Molecular inversion probe for detecting YVDD drug-resistant mutation of hepatitis B virus and application of molecular inversion probe
InactiveCN103642944AReduced responseReduce dimerizationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEnzyme digestionNucleotide
The invention belongs to the nucleic acid molecule detection field and relates to a molecular inversion probe technology for detecting YVDD drug-resistant mutation of hepatitis B virus, wherein a nucleotide sequence of the molecular inversion probe is expressed as SEQ ID NO: 8; an application method of the molecular inversion probe comprises the steps of designing a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification primer and establishing a single-base extension system of the molecular inversion probe which is applicable to annealing complementation and single-base extension between the molecular inversion probe and a target sequence; establishing a connection system of the molecular inversion probe which is applicable to a connection reaction of the molecular inversion probe; establishing a circumscribed enzyme digestion system for digesting the molecular inversion probe which is not cyclized; establishing a UNG (uracil-N-glycosylase) digestion system for digesting a cyclized molecular inversion probe as a single strand; establishing a PCR amplification reaction system which is applicable to a PCR amplification reaction taking the single stranded molecular inversion probe as a template; and detecting an amplification product. The method is high in sensitivity, specificity and degree of accuracy, simple to operate and applicable to clinical promotion in the absence of expensive detecting instrument.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
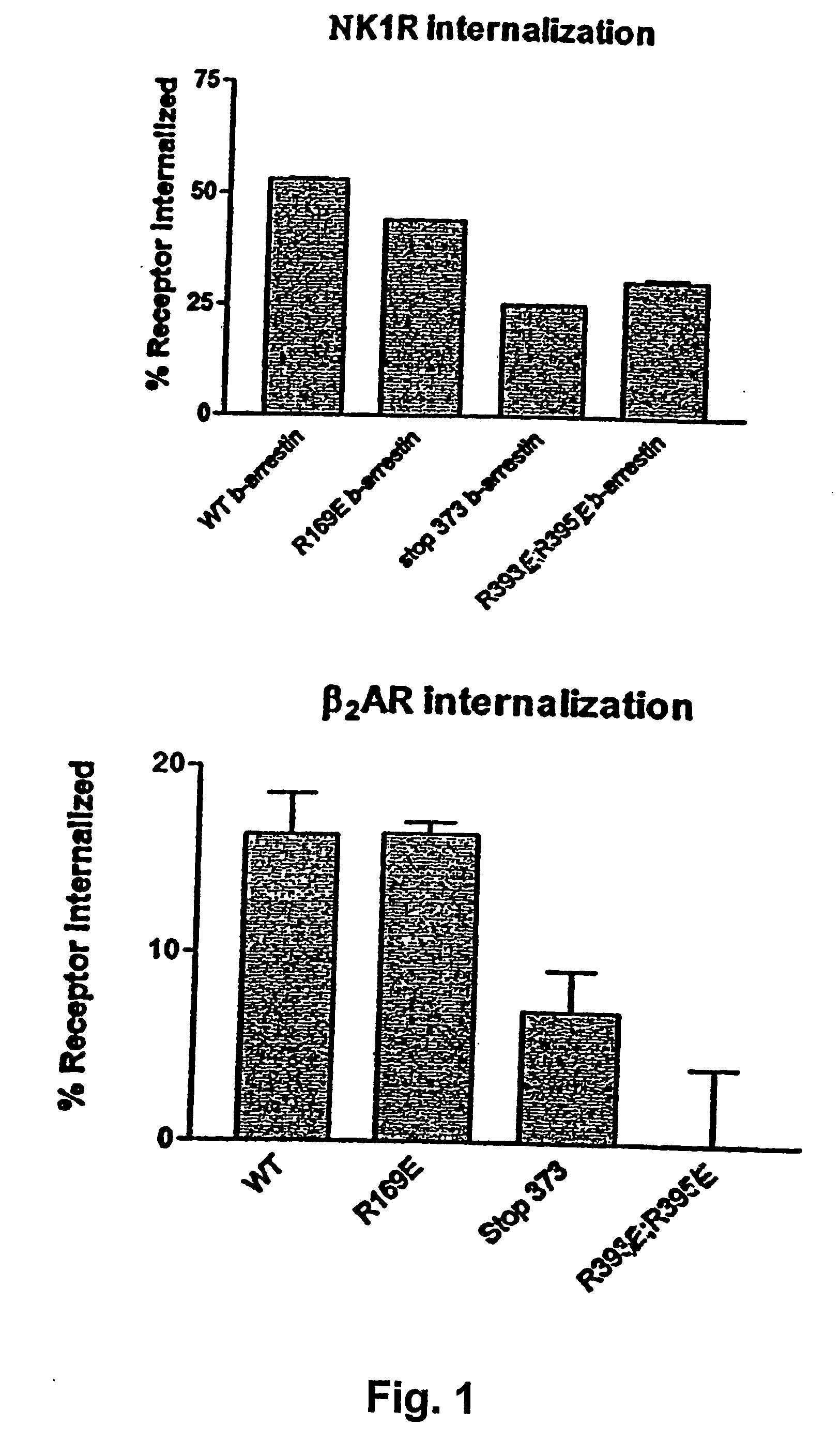
Beta-arrestin based screening assays
InactiveUS20060246507A1Increased and prolonged translocationSignal is enhanced and prolongedMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisActive proteinWild type
Use of mutated β-arrestin for an improved enzyme complementation assay or translocation assay, the improved enzyme complementation assay comprising: i) adding a substrate to a cell comprising a GPCR-EA fusion protein and a β-arrestin-EB fusion protein, wherein the β-arrestin is mutated, ii) adding a ligand to obtain, if possible, a GPCR-EA / β-arrestin-EB complex, and iii) measuring a signal arising from association of EA and EB to create an enzymatically active protein catalyzing conversion of the substrate which leads to a detectable signal, wherein the improvement leads to an increased signal compared with the signal obtained by use of the same process employing a β-arrestin-EB fusion protein, wherein the β-arrestin is wild type β-arrestin, and the improved β-arrestin translocation assay comprising i) providing a cell expressing a GPCR and comprising a β-arrestin associated with an optically detectable molecule, ODM, wherein the β-arrestin is mutated, ii) adding a ligand to obtain, if possible, a GPCR / β-arrestin complex, and iii) detecting a translocation of the optically detectable molecule, wherein the improvement leads to a increased and prolonged translocation of the β-arrestin associated with an optically detectable molecule as compared with the signal obtained by use of the same assay employing a β-arrestin associated with an optically detectable molecule, wherein the β-arrestin is wild type β-arrestin.
Owner:7TM PHARM AS
Rice gene OsFd2 and applications of rice gene OsFd2 in rice resistance to rice blast
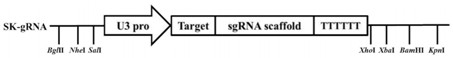
ActiveCN112779271AImprove rice blast resistanceRegulatable endogenous gene targetsPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyRice plants
The invention provides a rice gene OsFd2 and applications of the rice gene OsFd2 in rice resistance to rice blast. A CRISPR / Cas9 method is adopted to knock out the rice gene OsFd2, and the phenotypic complementation of mutant plants can be performed through an overexpression vector genetic transformation method. Magnaporthe oryzae inoculation experiments are respectively carried out on wild type, knocked-out mutant and overexpression complemented plants. Results show that the knocked-out OsFd2 significantly enhances the resistance of rice plants to magnaporthe oryzae, but lethal phenotype at seedling stages is generated; and compared with mutants, the OsFd2 overexpression complemented plants is normal in growth and recovery and more susceptible to rice blast then wild types. Thus, the above results show that the OsFd2 is the gene that negatively regulates rice immunity against the rice blast and the key gene required by the normal growth of rice. The content of the invention is to provide an endogenous gene target for enhancing rice resistance through an induced silencing method when field rice blast occurs.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
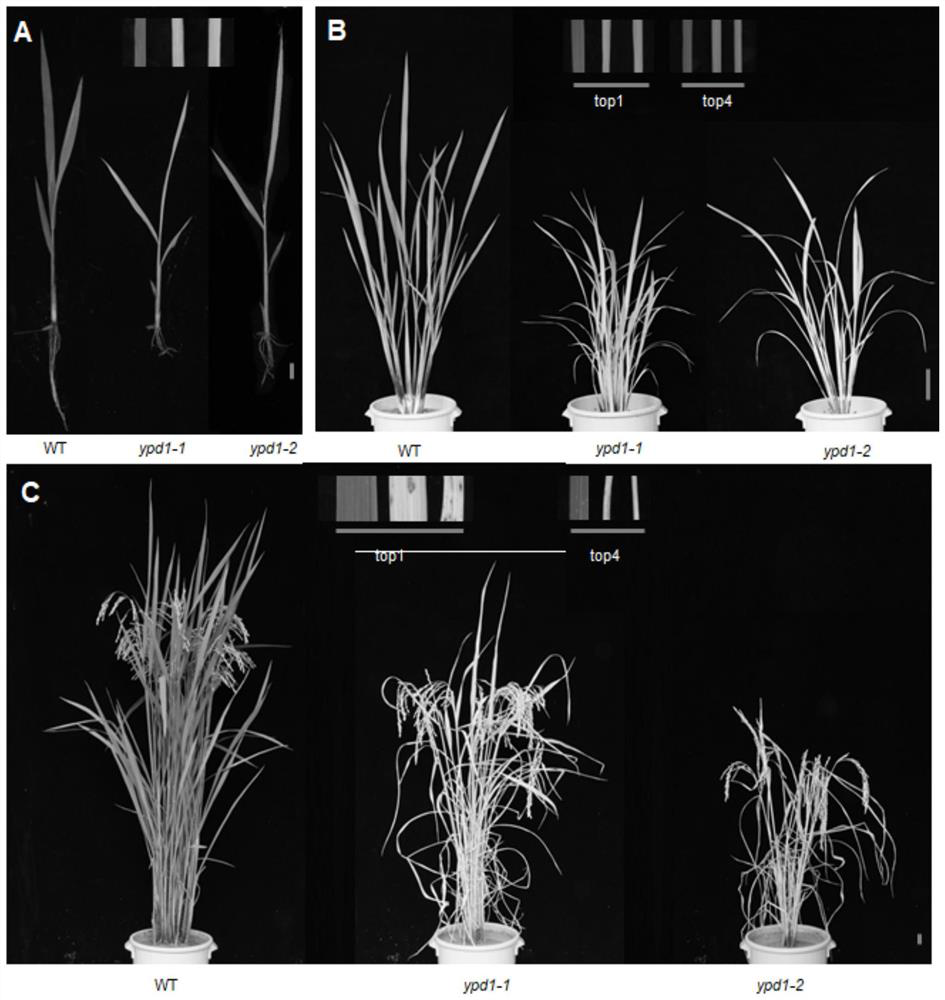
Gene related to rice leaf color variation, premature senility and stress tolerance, protein coded by gene and application of protein
ActiveCN111893122AElucidate the molecular mechanismAffect stress tolerancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyPremature aging
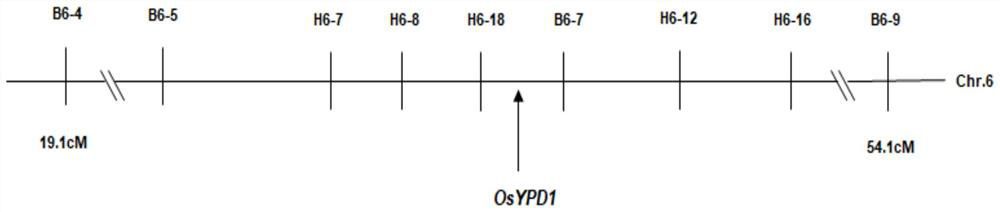
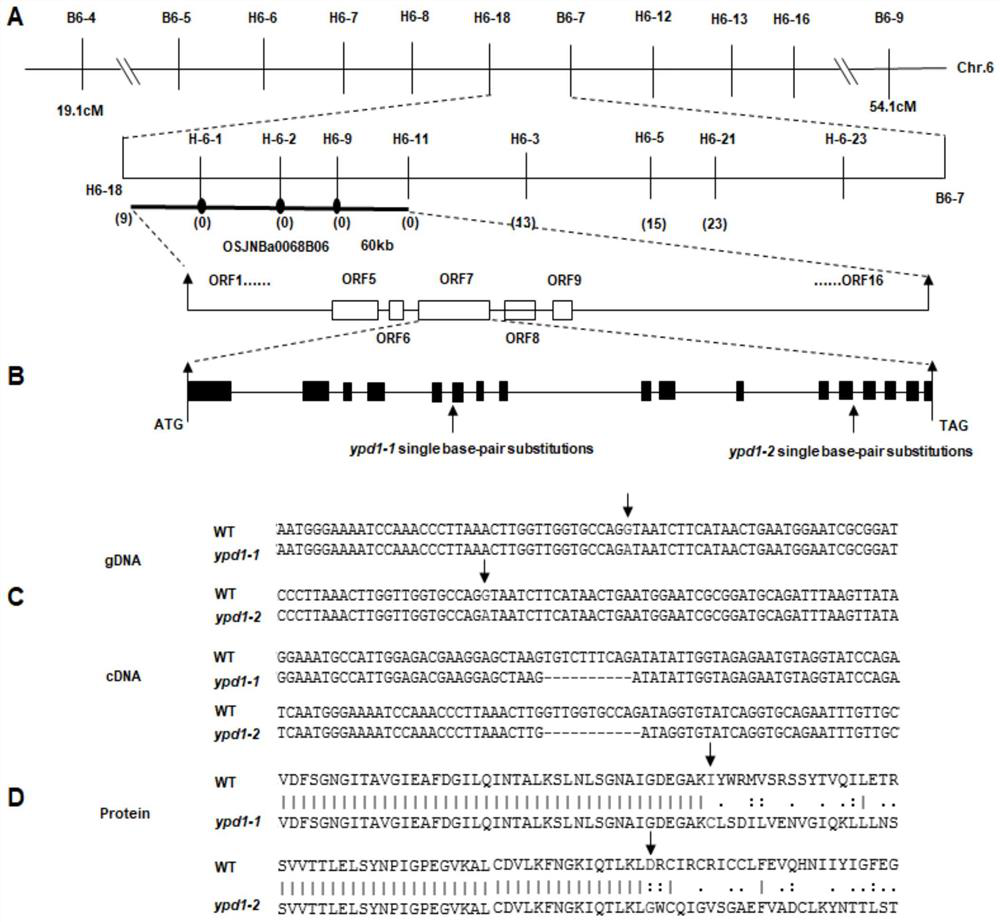
The invention relates to plant genetic engineering, and discloses a gene related to rice leaf color variation, premature senility and stress tolerance, a protein coded by the gene and application of the protein. Nucleotide sequences of the gene are shown as SEQ ID No: 1 and SEQ ID No: 2. The rice OsYPD1 gene is cloned by utilizing a map-based cloning technology, and the function of the gene is identified by utilizing a transgenic complementation experiment; and meanwhile, the influence on rice aging and stress tolerance is studied by utilizing a gene coding product, and the product can be usedfor improving the stress tolerance of rice.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Gene DvCRP2 with Cd2+ resistant and Cu2+ resistant functions, encoding protein and application thereof
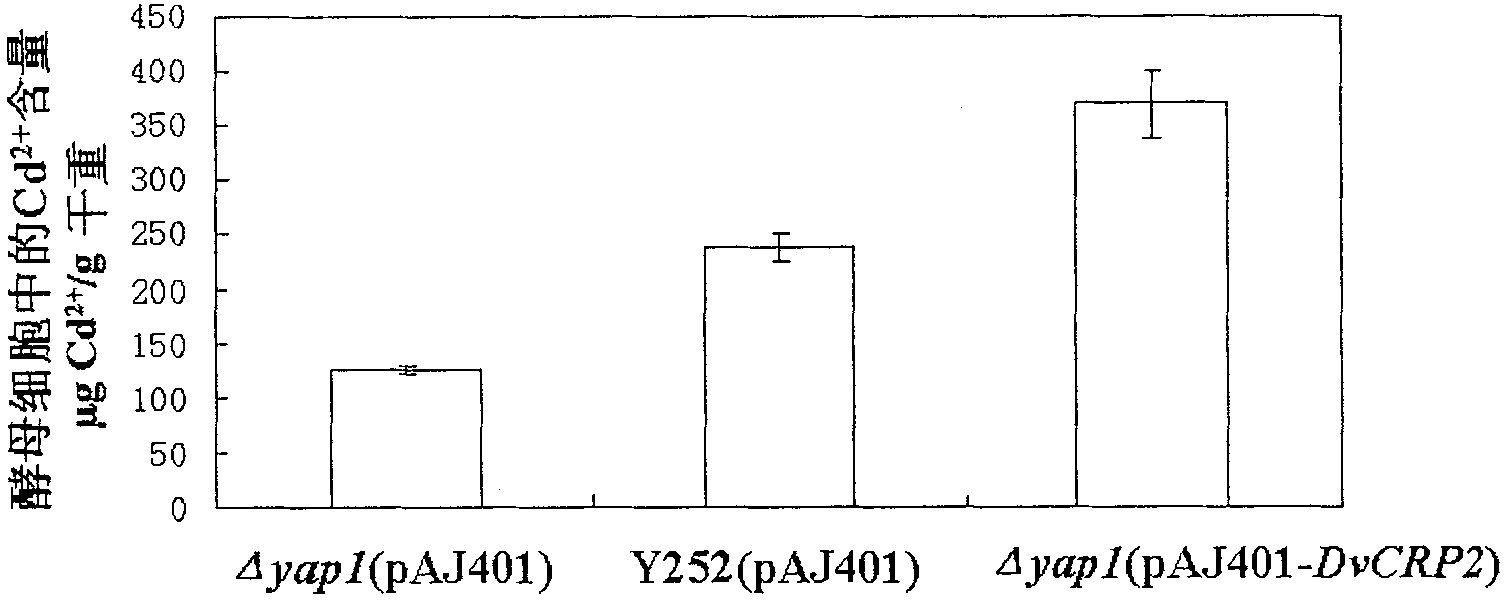
InactiveCN101921779AApplication of Genetic Engineering to Increase AccumulationFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyBiological body
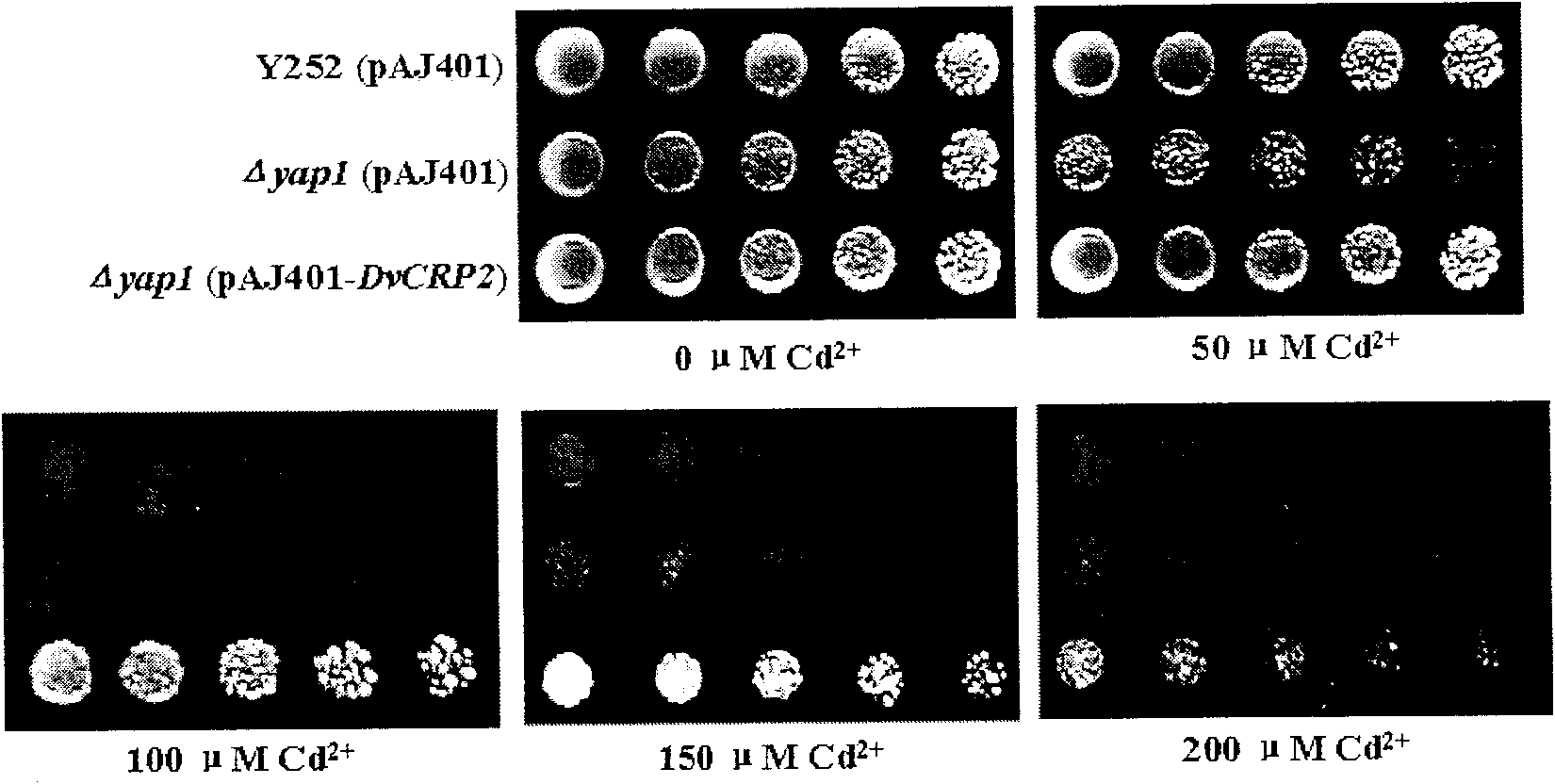
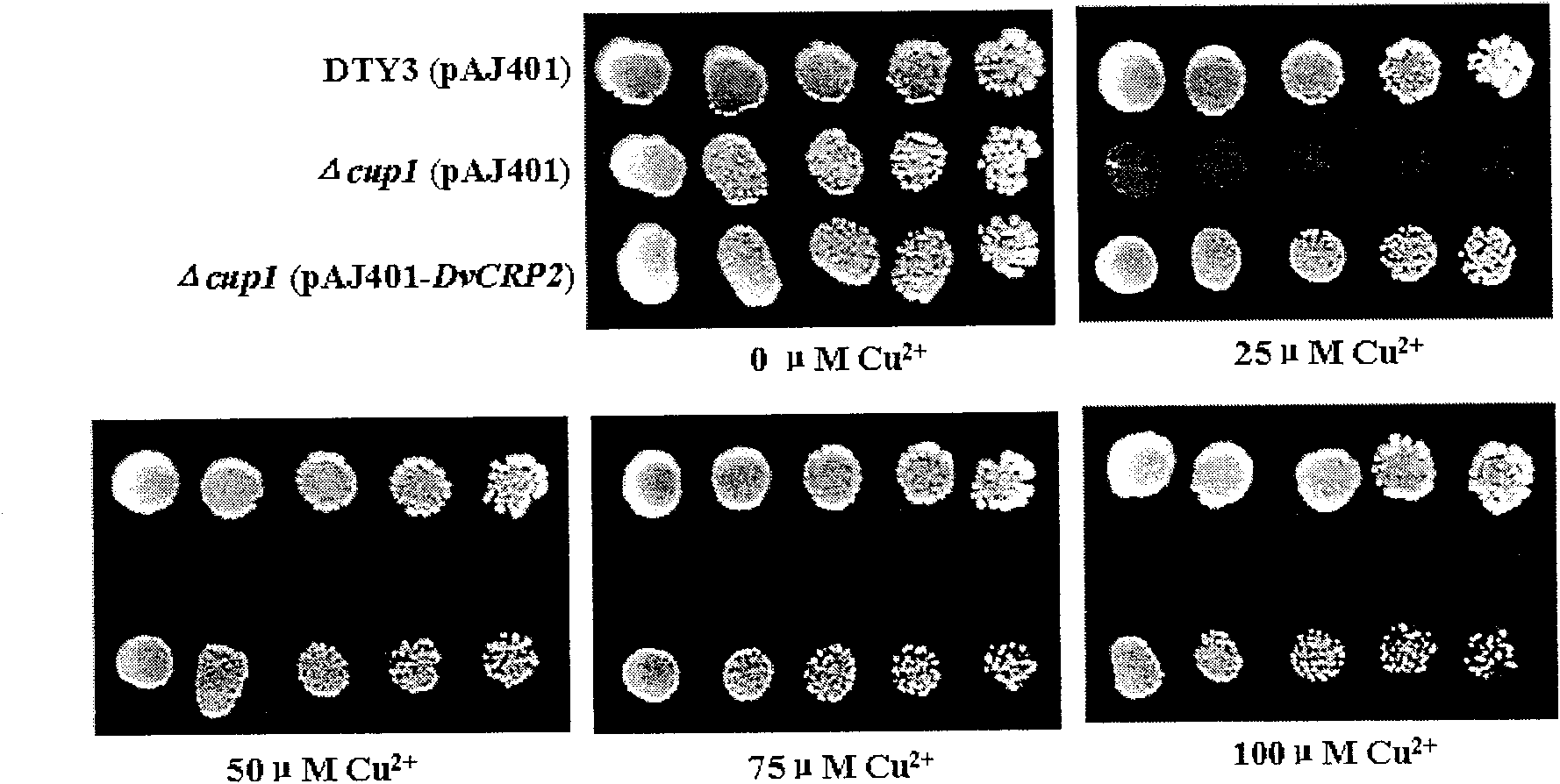
The invention discloses a cDNA sequence of a Dunaliella viridis Cd2+ resistant and Cu2+ resistant gene DvCRP2 and an amino acid sequence for encoding protein, and relates to function and application of the gene. The invention adopts a yeast functional complementation system to screen to obtain the DvCRP2 gene, applies a RACE technology to obtain the overall-length cDNA sequence, and proves that the gene can greatly improve the Cd2+ resistant and Cu2+ resistant capabilities of model organism yeast and significantly increase the accumulation amount of cadmium in yeast cells. The disclosed overall-length gene and the amino acid sequence are first discovered, which are Cd2+ resistant and Cu2+ resistant genes peculiar to Dunaliella viridis. The overall-length gene has application value in improving Cd2+ resistant and Cu2+ resistant capabilities of an organism, increasing accumulation amount of cadmium and copper in the organism in gene engineering aspects.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
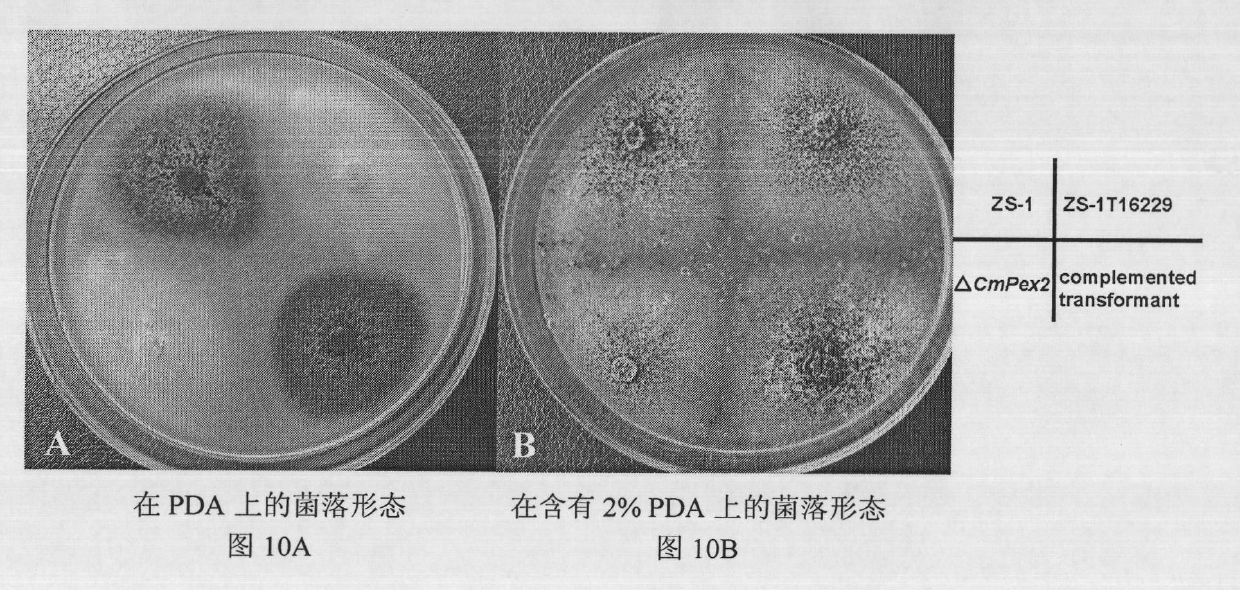
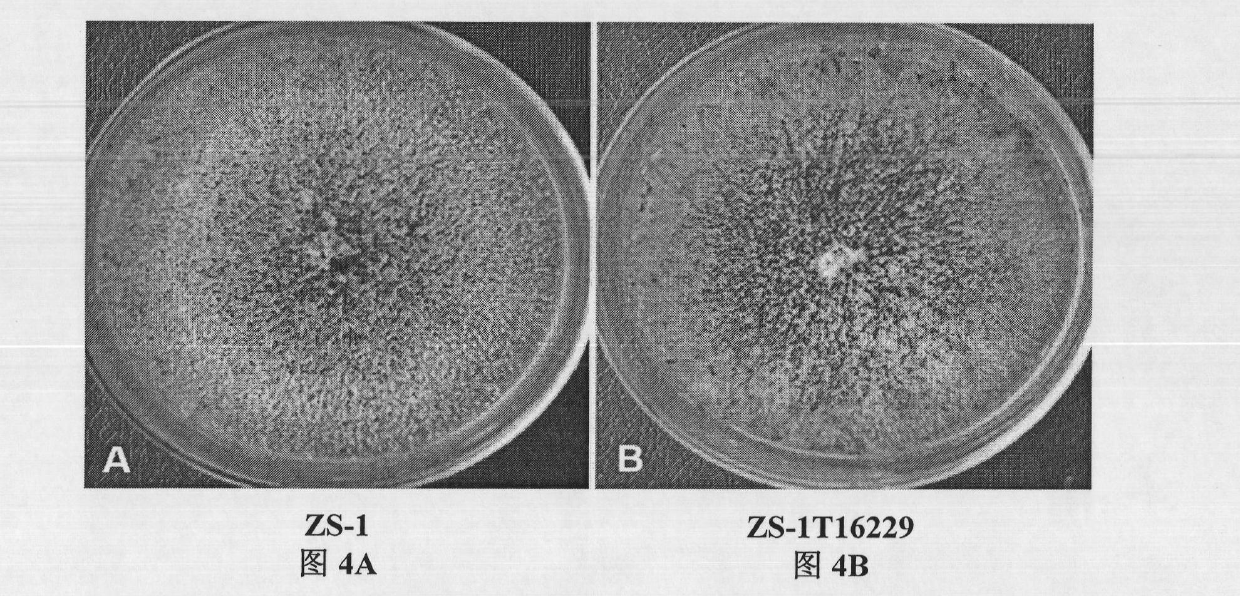
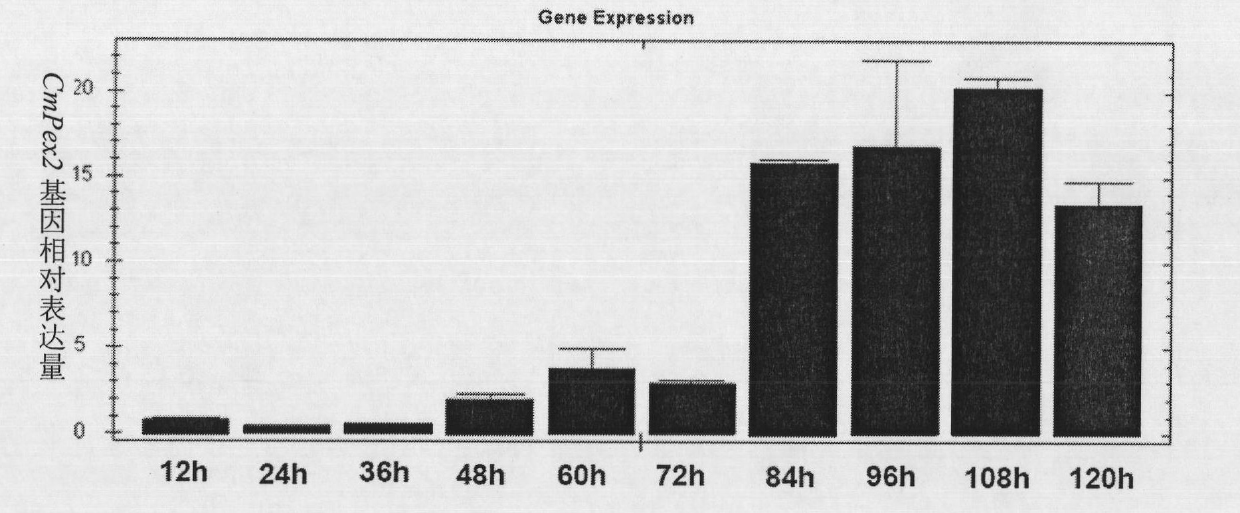
Biocontrol fungus coniothyrium minitans sporulation-related gene CmPex2 and application thereof
The invention relates to a sporulation-related gene clone in biocontrol fungus coniothyrium minitans and application thereof. The invention provides a gene sequence of peroxisome synthesis related gene CmPex2 in the coniothyrium minitans and an encoded protein sequence thereof. The invention also provides application of the peroxisome related gene CmPex2 in the coniothyrium minitans. The expression analysis of the peroxisome related gene CmPex2 in the coniothyrium minitans indicates that the expression level of the gene remarkably increases at the conidium generation stage, and a gene targeting knockout and gene complementation test indicates that the gene is closely related to the conidium generation of the biocontrol fungus coniothyrium minitans. The gene can be taken as a candidate gene for controlling the conidium output of the coniothyrium minitans and is used for increasing the conidium output of the coniothyrium minitans and reducing the scale production cost of the coniothyrium minitans.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
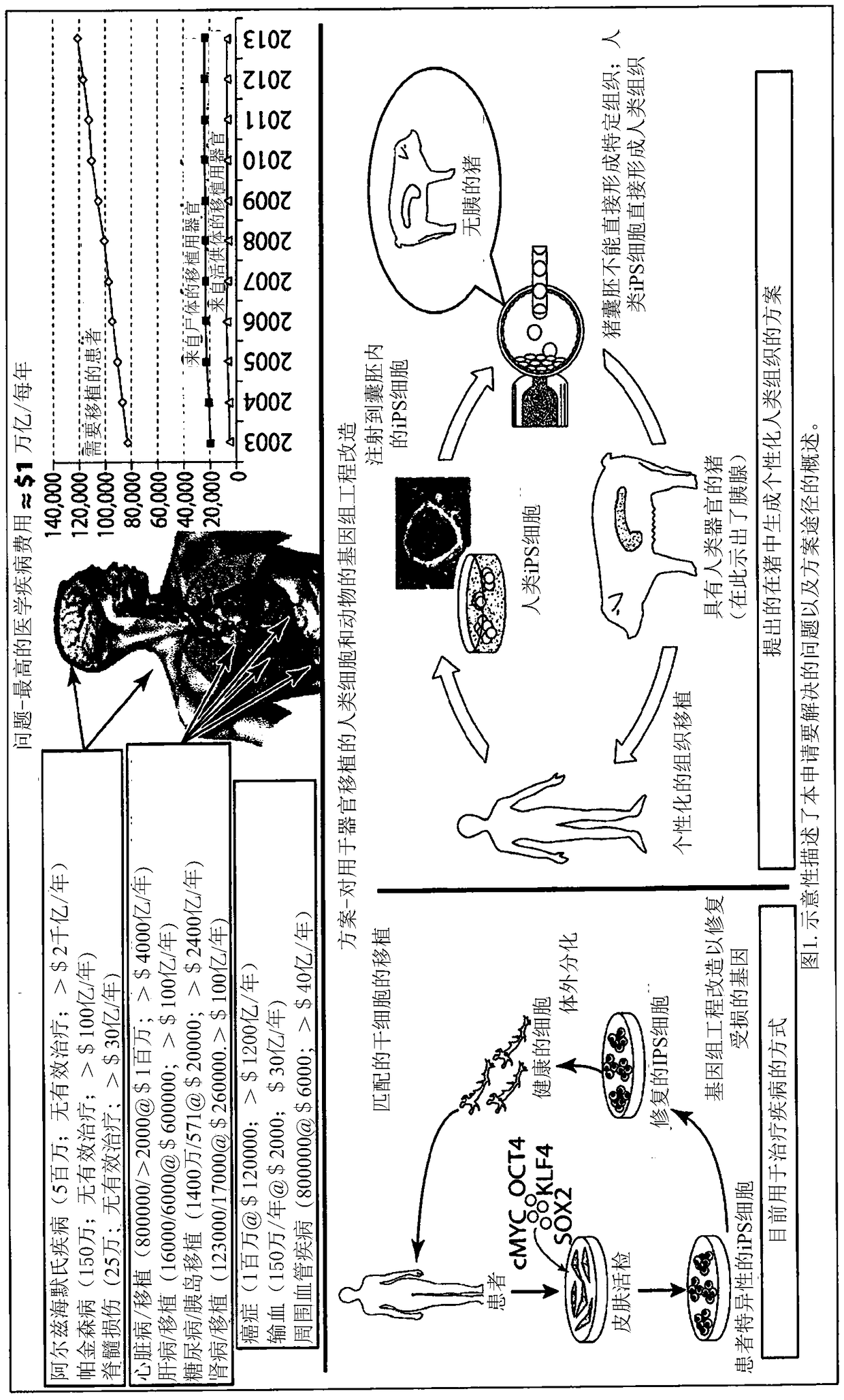
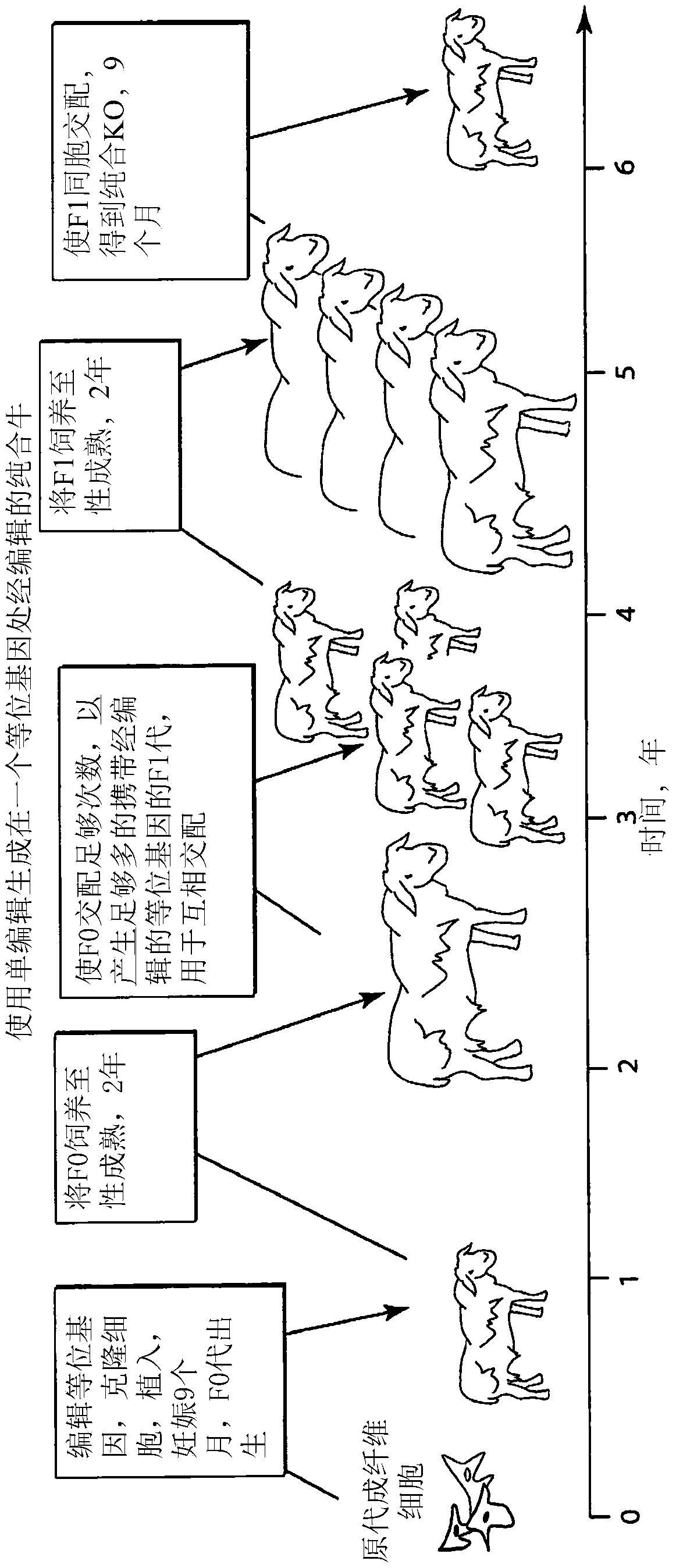
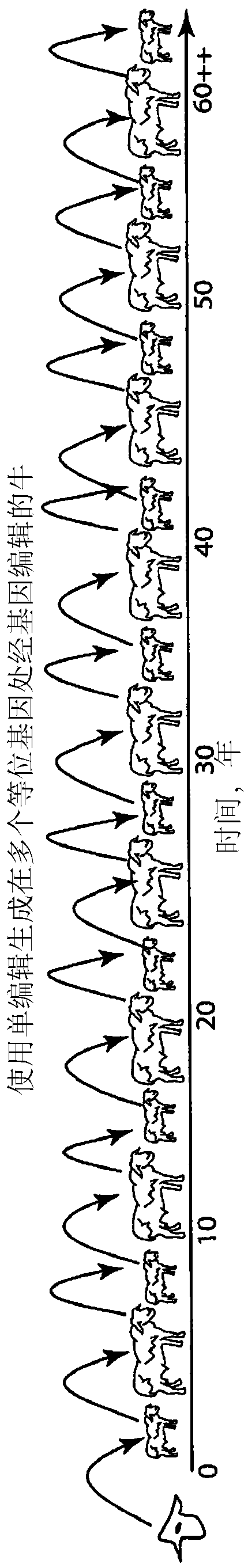
Engineering of humanized by geneti complementation
Provided here are methods for editing of a host genome to knock out or debilitate genes responsible for the growth and / or differentiation of a target organ and injecting that animal at an embryo stagewith donor stem cells to complement the missing genetic information for the growth and development of the organ. The result is a chimeric animal in which the complemented tissue (human / humanized organ) matches the genotype and phenotype of the donor. Such organs may be made in a single generation and the stem cell may be taken or generated from the patient's own body. As disclosed herein, it is possible to do so by simultaneously editing multiple genes in a cell or embryo creating a 'niche"' for the complemented tissue. Multiple genes can be targeted for editing using targeted nucleases and homology directed repair (HDR) templates in vertebrate cells or embryos.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +2
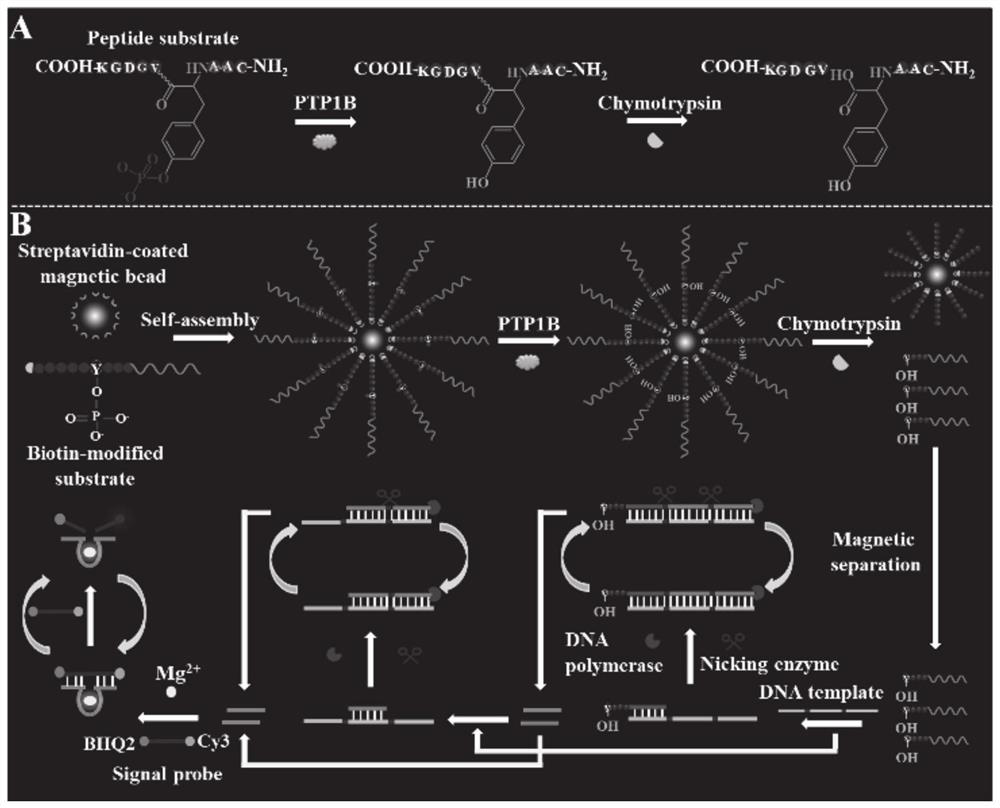
Tyrosine phosphatase biosensor as well as detection method and application thereof
ActiveCN111979295AImprove efficiencyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPhosphorylationNucleotide
The invention discloses a tyrosine phosphatase biosensor as well as a detection method and application thereof. The tyrosine phosphatase biosensor comprises magnetic beads, a peptide-DNA conjugate, aDNA template and a signal probe, wherein one end of a peptide chain in the peptide-DNA conjugate is linked to a 5' end of a first DNA sequence, the peptide chain contains phosphorylated tyrosine, theother end of the peptide chain is used for linking the magnetic beads; the DNA template consists of two second DNA sequences and a third DNA sequence from a 5' end to a 3' end, the third DNA sequencecan be complemented with a first DNA sequence, the DNA template is hybridized and polymerized with the first DNA sequence so as to form double-chain DNA with two nickase recognition sites, and complementary chains of the second DNA sequences are dnazyme; and the signal probe is a nucleotide sequence, fluorophores and quenchers are respectively linked to two ends of the nucleotide sequence, and thenucleotide sequence can be complemented with the dnazyme; and the dnazyme is an RNA sequence capable of realizing cracking and complementation in dependent reaction of divalent cations
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
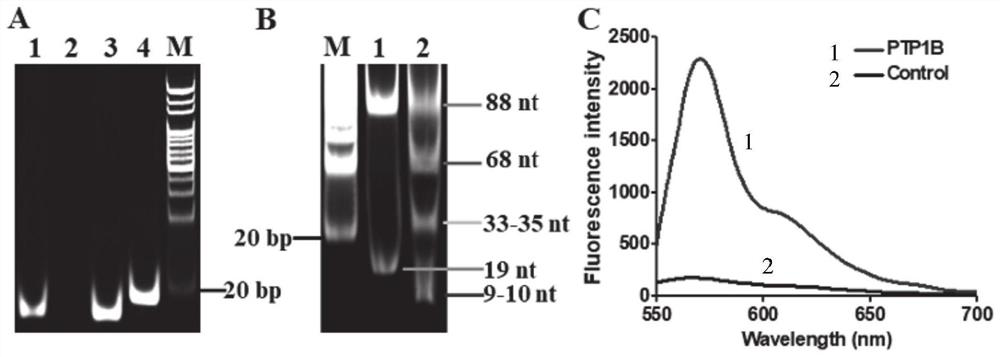
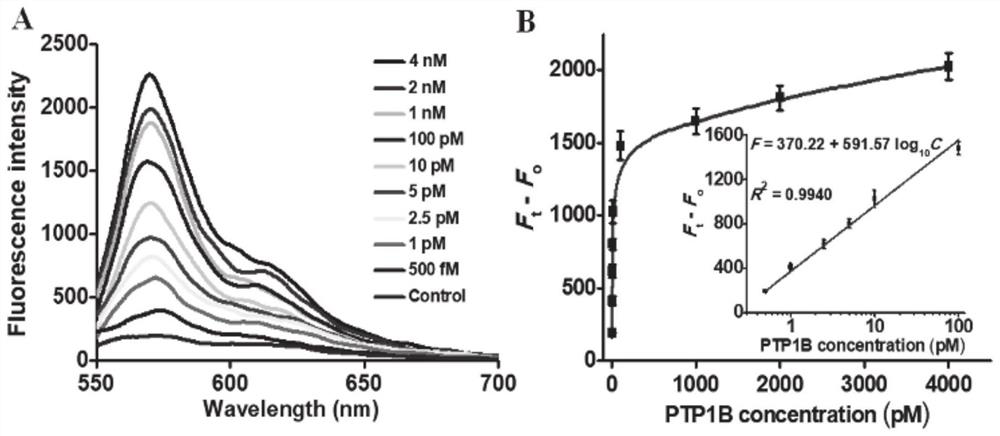
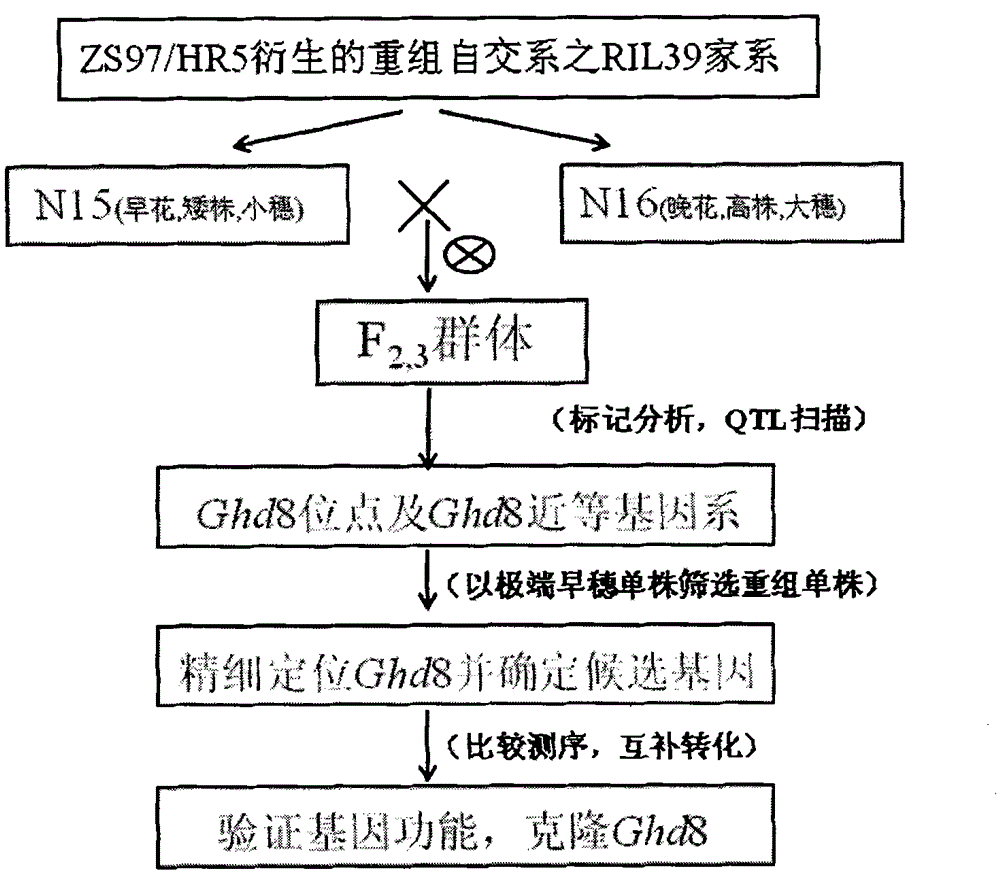
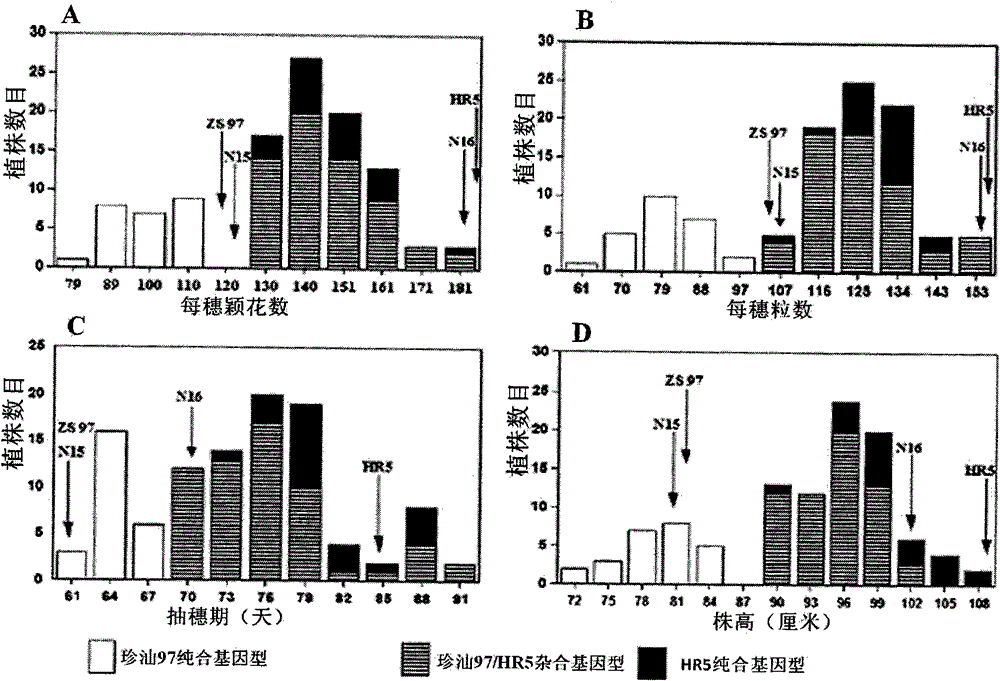
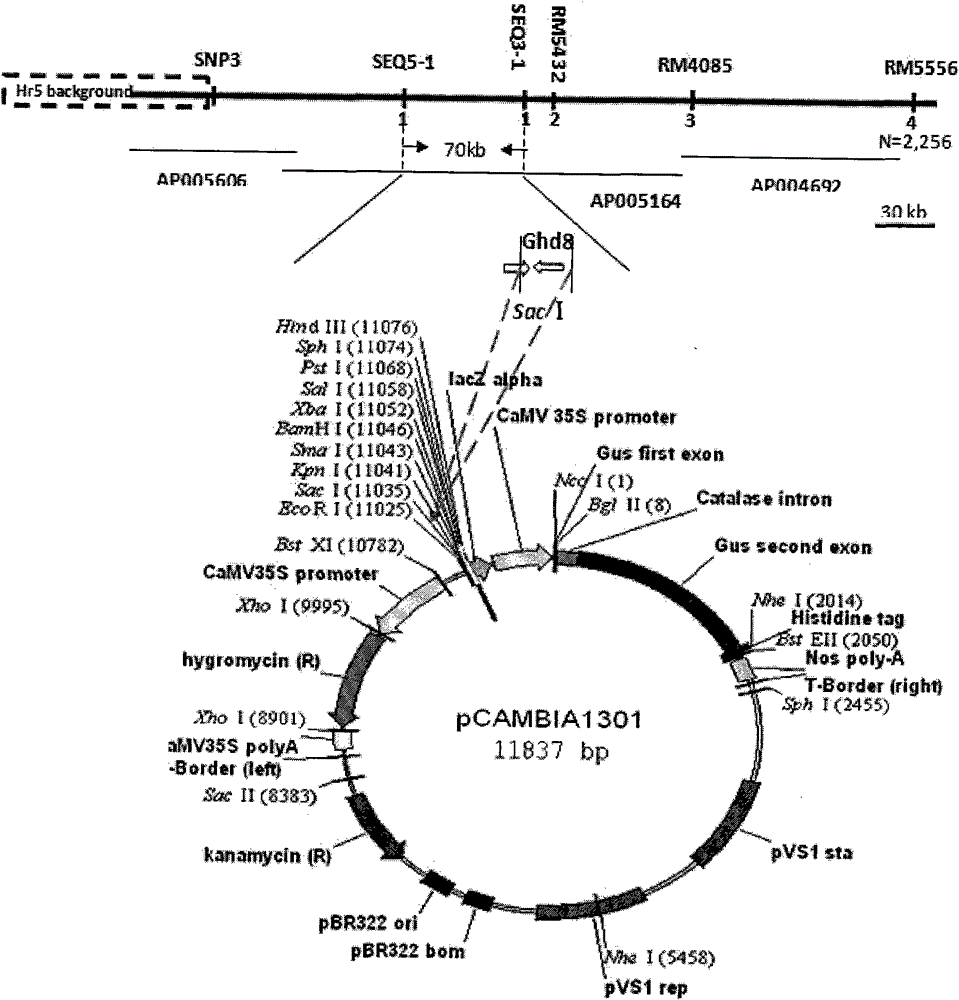
Clone and application of pleiotropic gene Ghd8 for controlling yield, florescence and plant height of rice grain
InactiveCN101892246BAvoid time-consuming disadvantagesSimple methodPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyPlant genetic engineering
The invention relates to the plant genetic engineering field, in particular to clone of a pleiotropic gene Ghd8 which affects yield, florescence and plant height of rice grain. In the invention, the gene Ghd8 is separated and cloned by experiments such as establishment of a near-isogenic line of a target gene, preliminary location, comparative sequencing, genetic transformation and complementation and the like, wherein the sequence of the gene Ghd8 is shown as SEQ ID NO:2. Compared with a recessive allelic single plant, the yield of a dominant allelic single plant is increased by 58%, the plant height thereof is increased by 25.6%, but the heading stage thereof is only increased by 9 days. By means of results of Ghd8 main mutation site and trait correlation analysis and haploid cluster analysis of protein sequences of different varieties, the near-isogenic lines of different allelic types are established to obtain four favorable Ghd8 allelic types, wherein, the Ghd8-9311 and Ghd8-ruf allelic types can increase yield of the rice grain but not delay blossoming, thus being applicable to breeding the rice grain in areas with good light and temperature conditions; and Ghd8-MH63 and Ghd8-Nip allelic types are not photosensitive, thus being applicable to increasing yield and breeding the rice grain in areas under a short-day condition.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
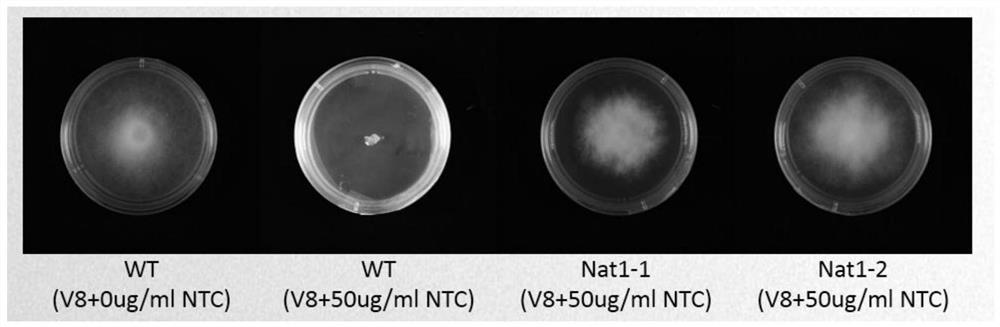
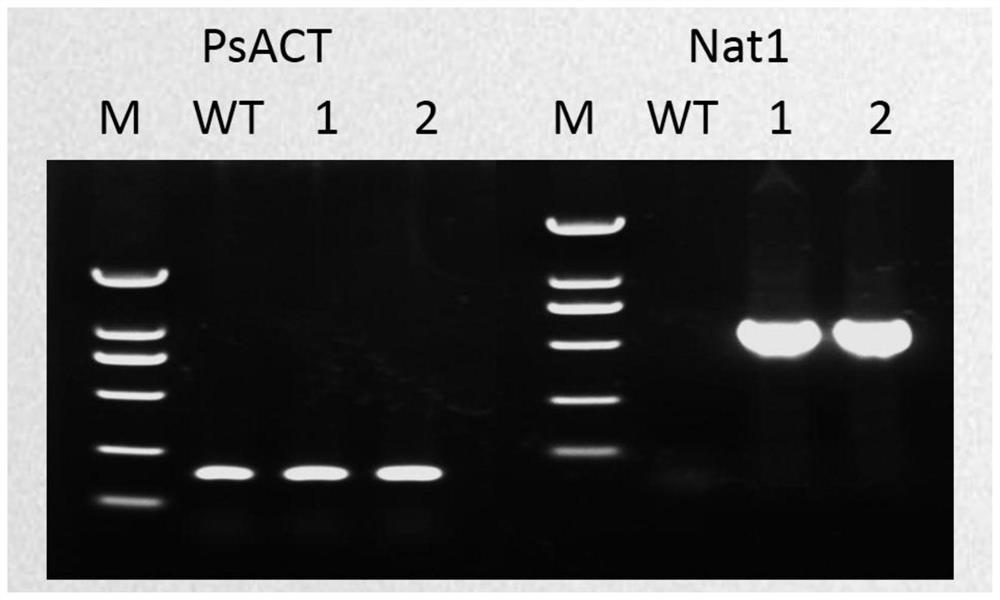
Application of Nat1 gene as selection marker in genetic transformation of oomycetes
PendingCN112813091AMake up for the lack of selectable marker genesReduce workloadFungiMicroorganism based processesPhytophthora sojaeAntibiotic drug
The invention discloses an application of a Nat1 gene as a selection marker in genetic transformation of oomycetes. The invention discloses an antibiotic, namely nourseothricin as a selection marker in transformation of oomycetes. According to the invention, a coding gene Nat1 capable of causing the resistance of oomycetes to nourseothricin is used as a selection marker for screening transformants during phytophthora sojae transformation. Development of the selection marker solves the problem of single selection marker during transformation of oomycetes, and provides powerful guarantee for gene complementation, gene knockout, etc., during transformation of oomycetes.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com