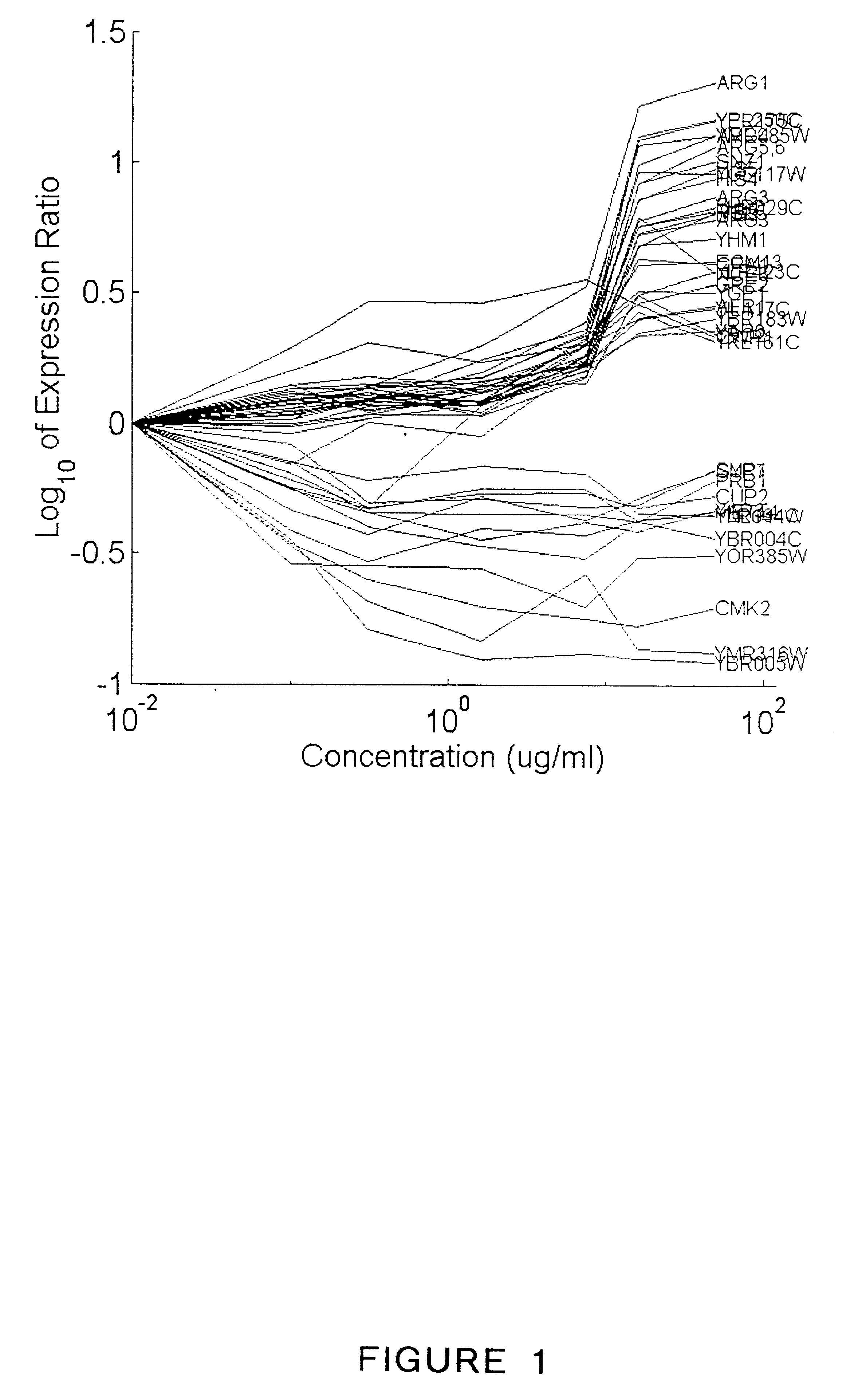
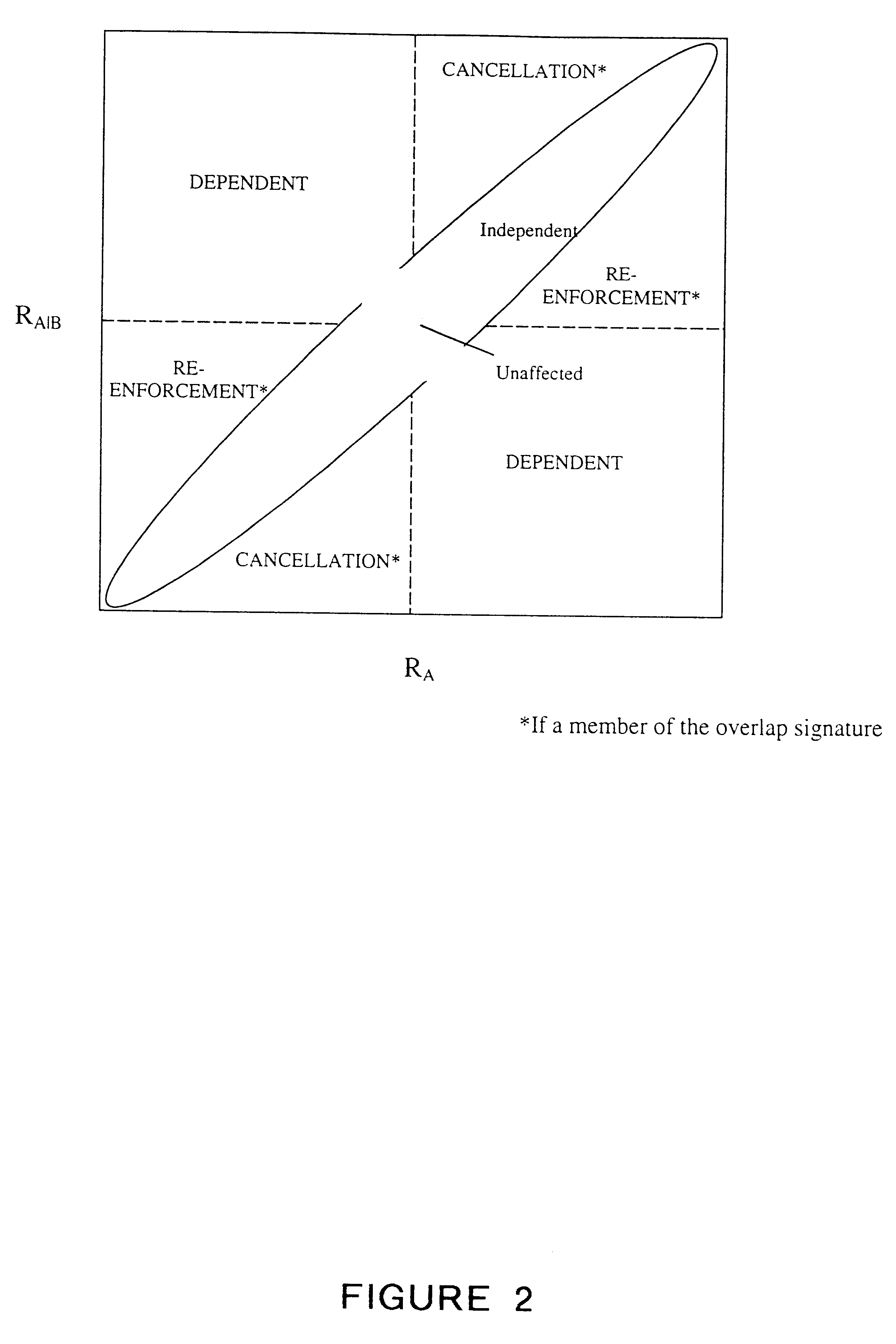
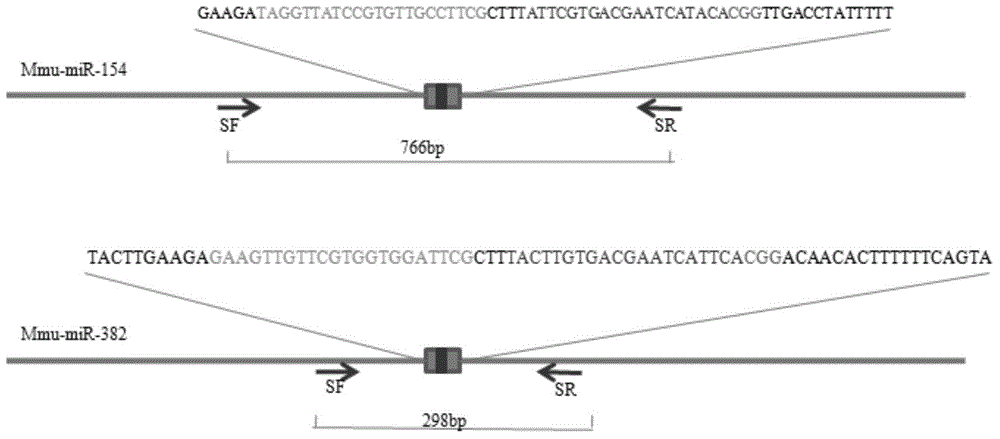
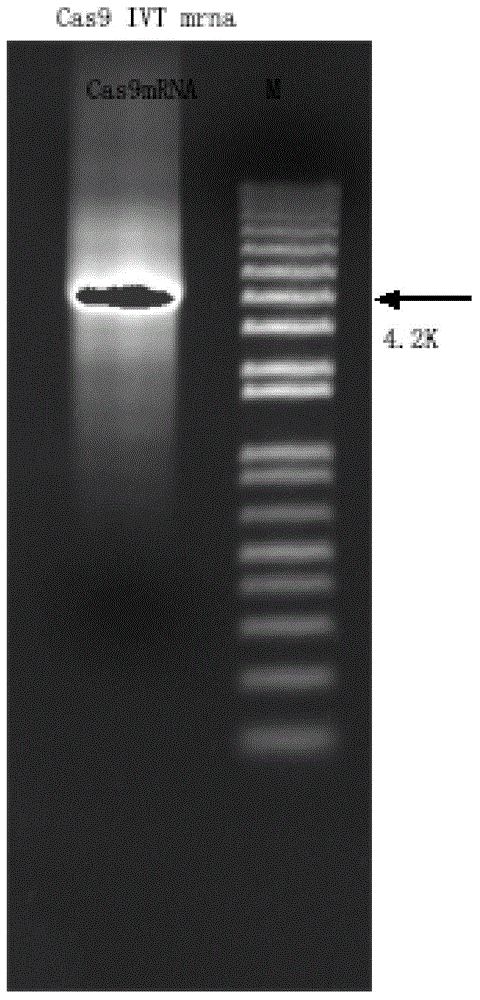
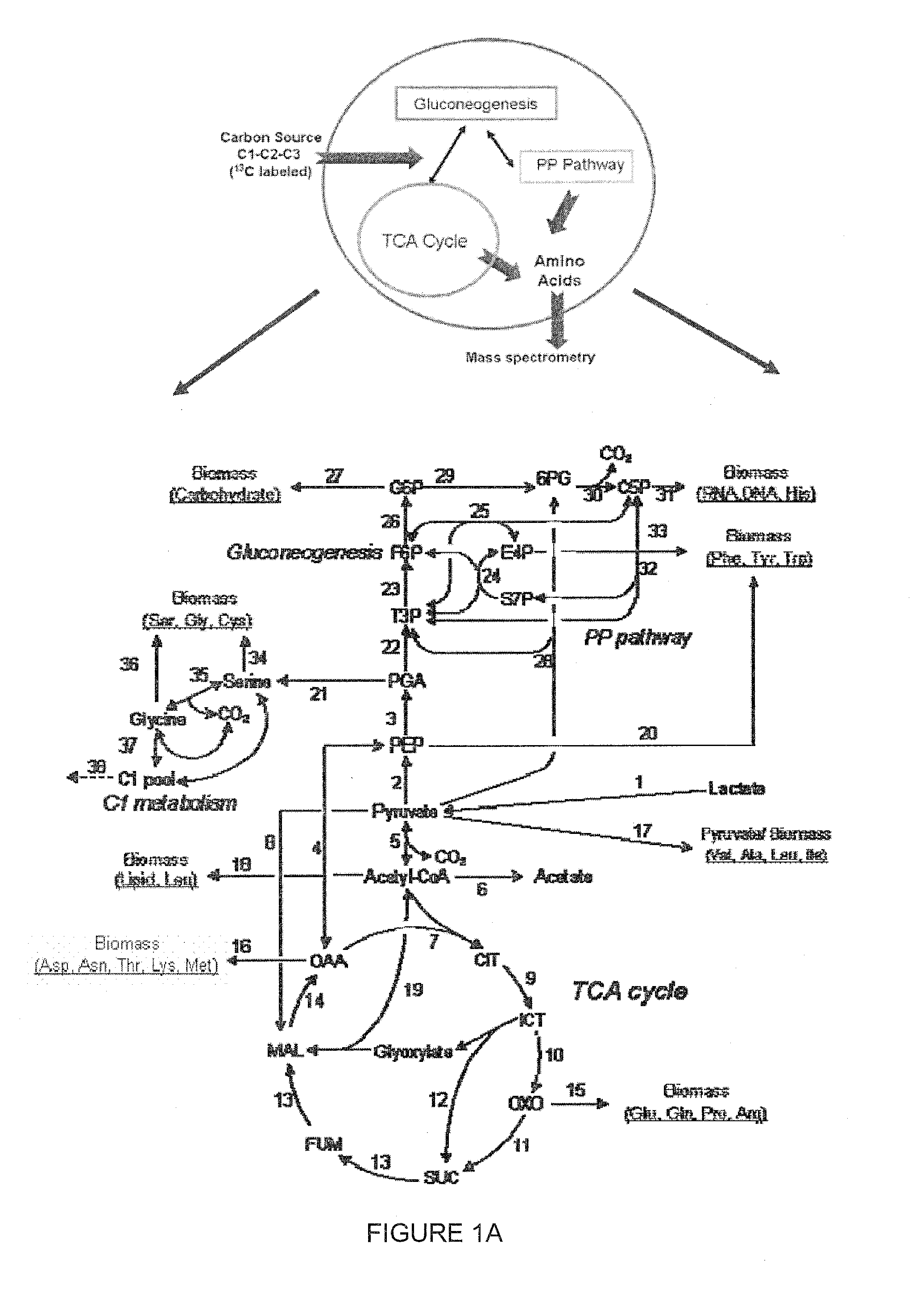
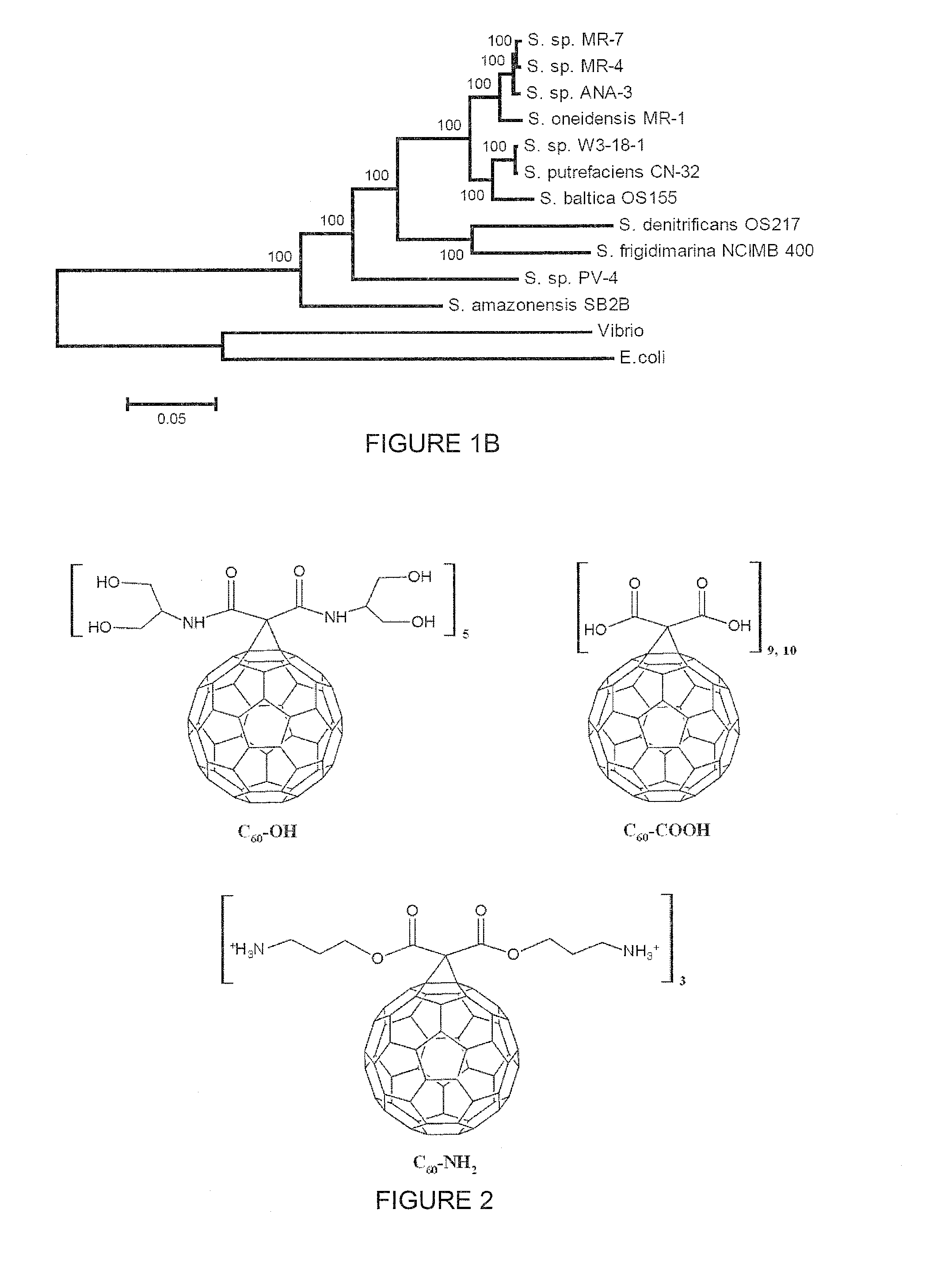
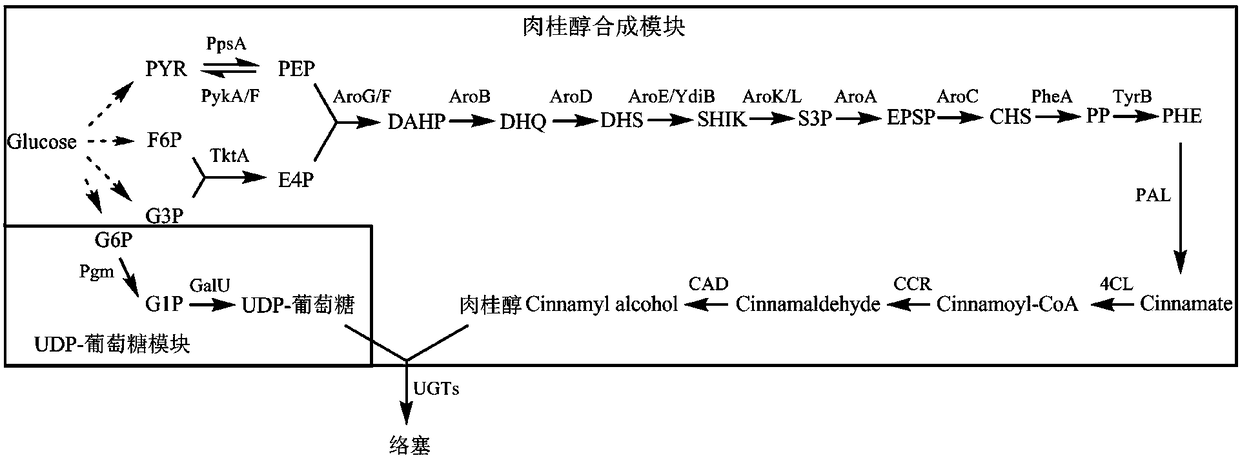
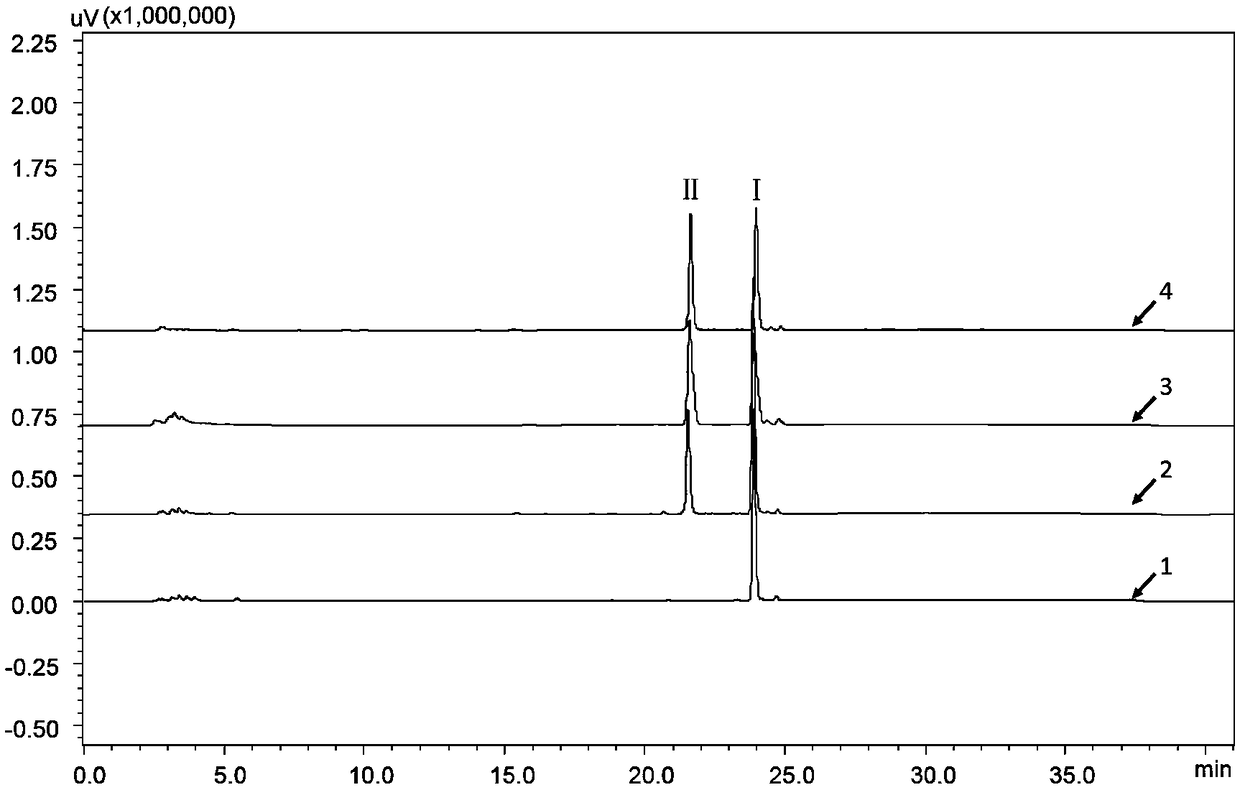
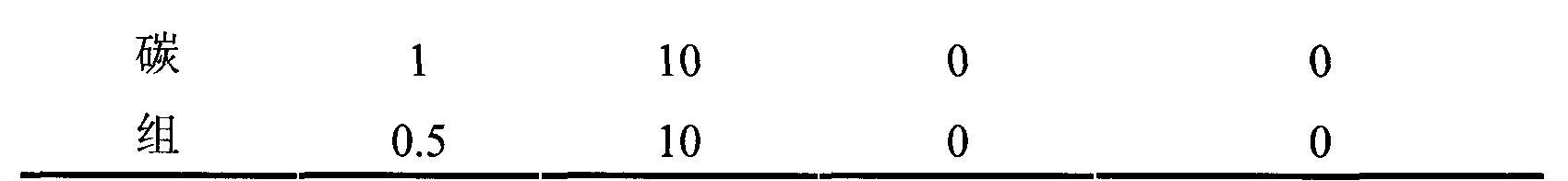Patents
Literature
178 results about "Model organism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A model organism is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are widely used to research human disease when human experimentation would be unfeasible or unethical. This strategy is made possible by the common descent of all living organisms, and the conservation of metabolic and developmental pathways and genetic material over the course of evolution.
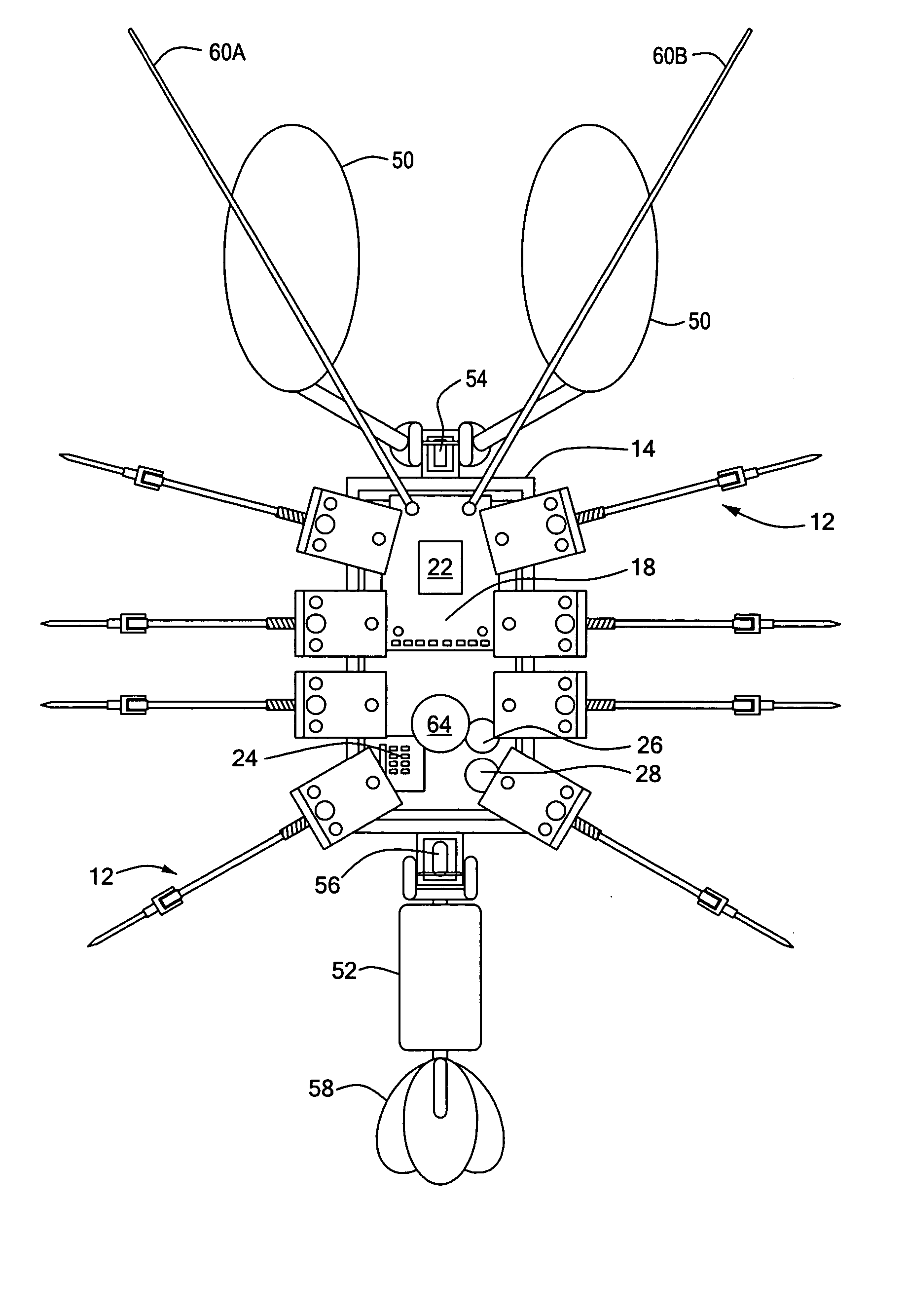
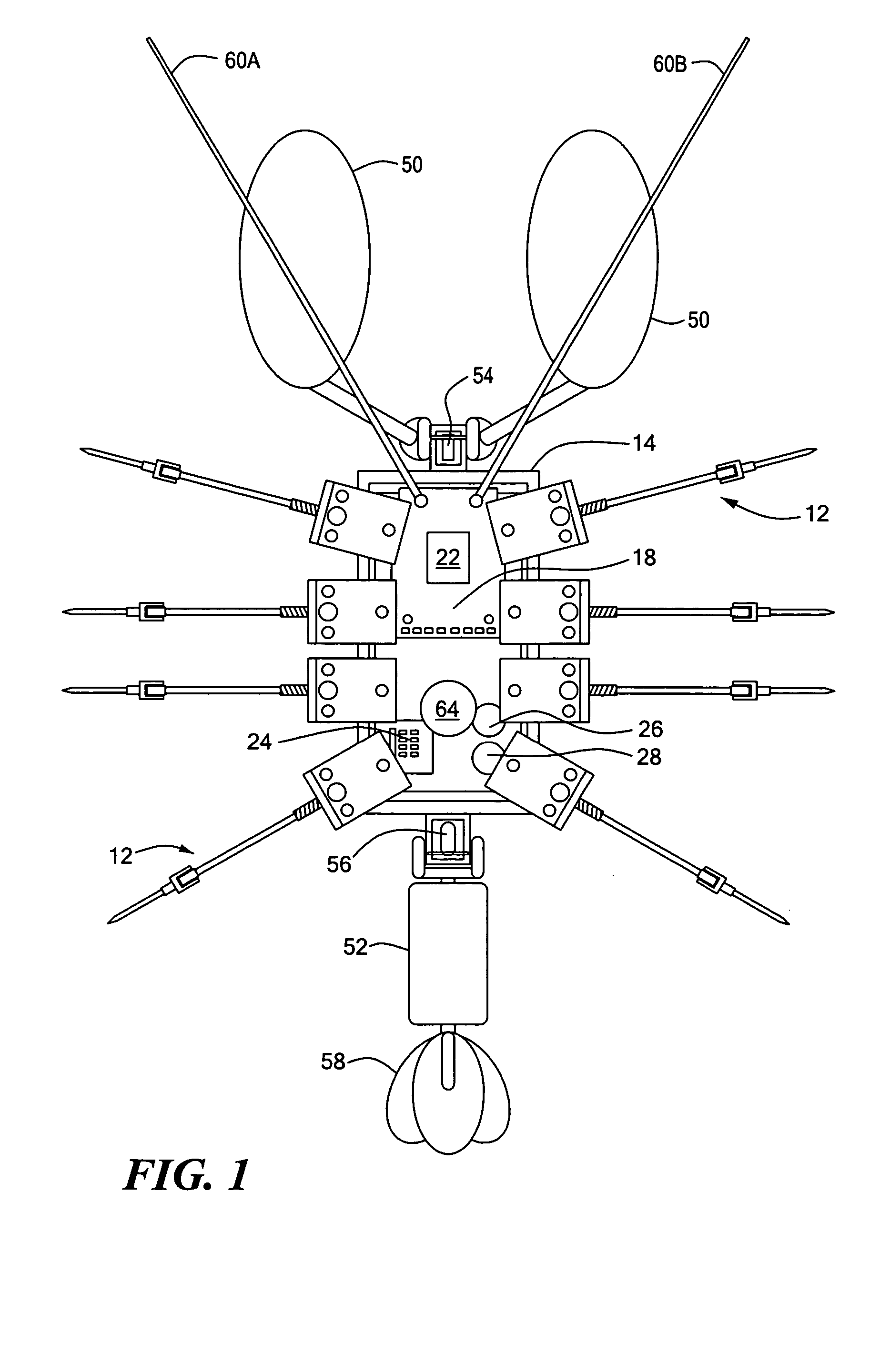
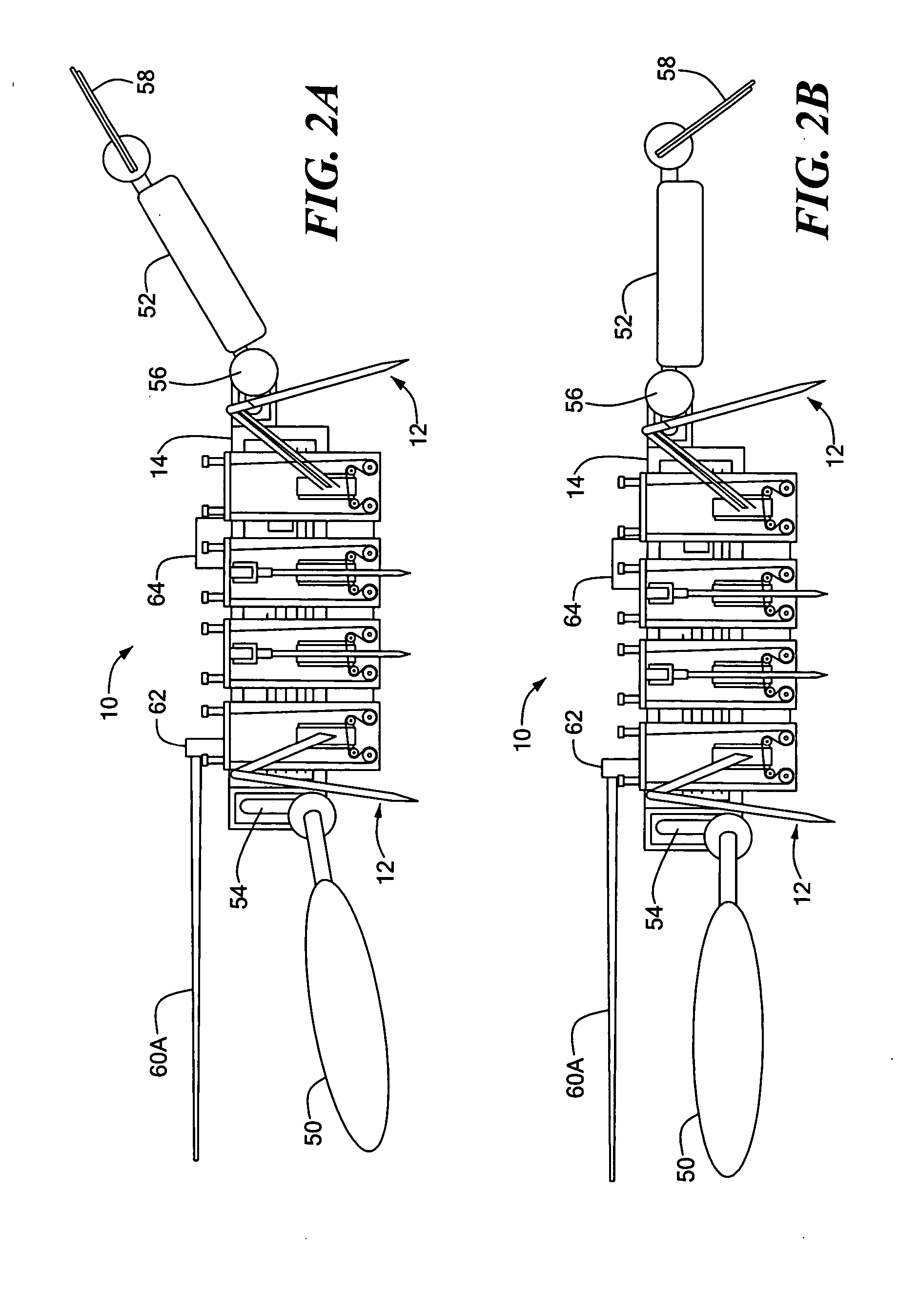
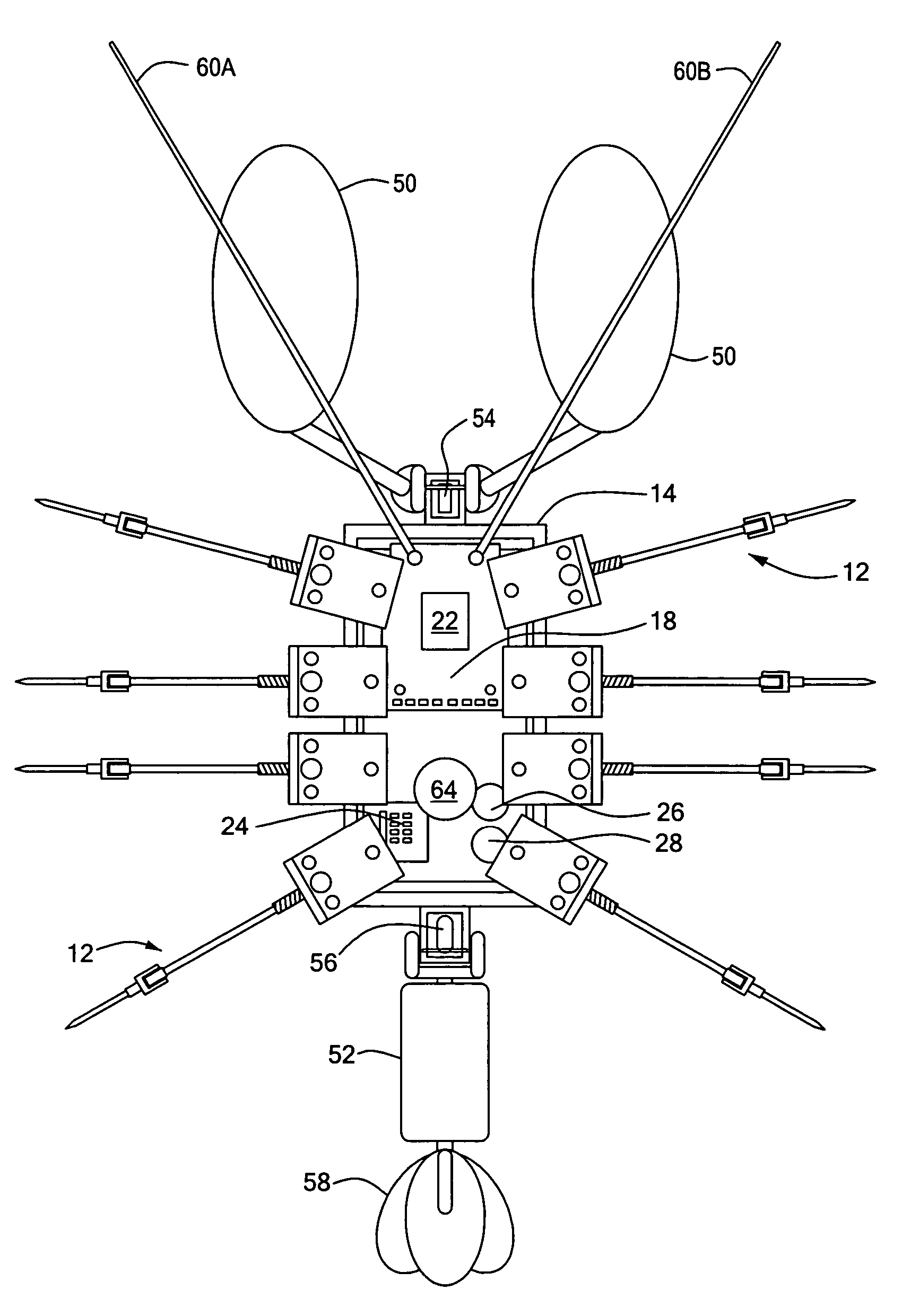
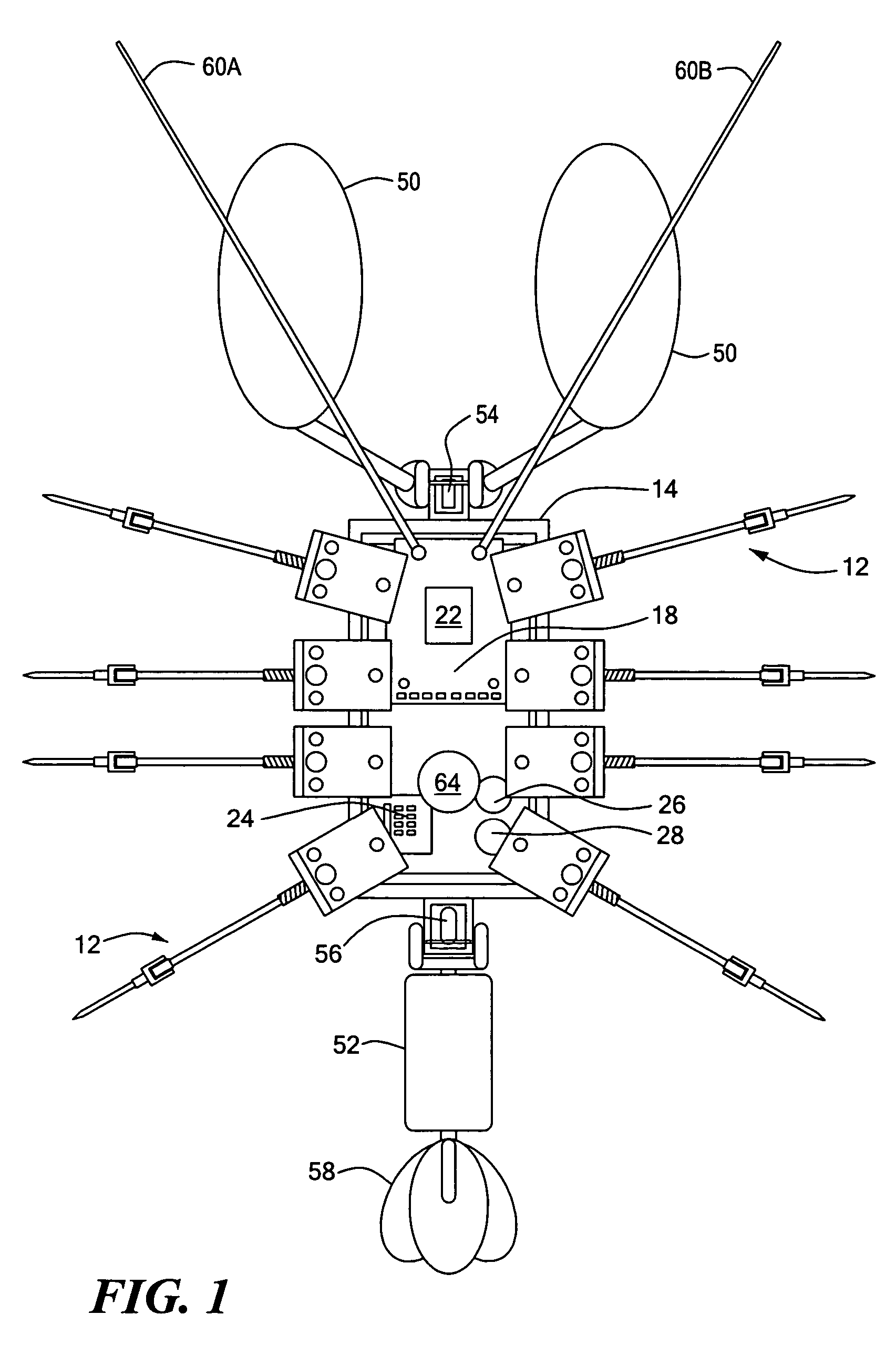
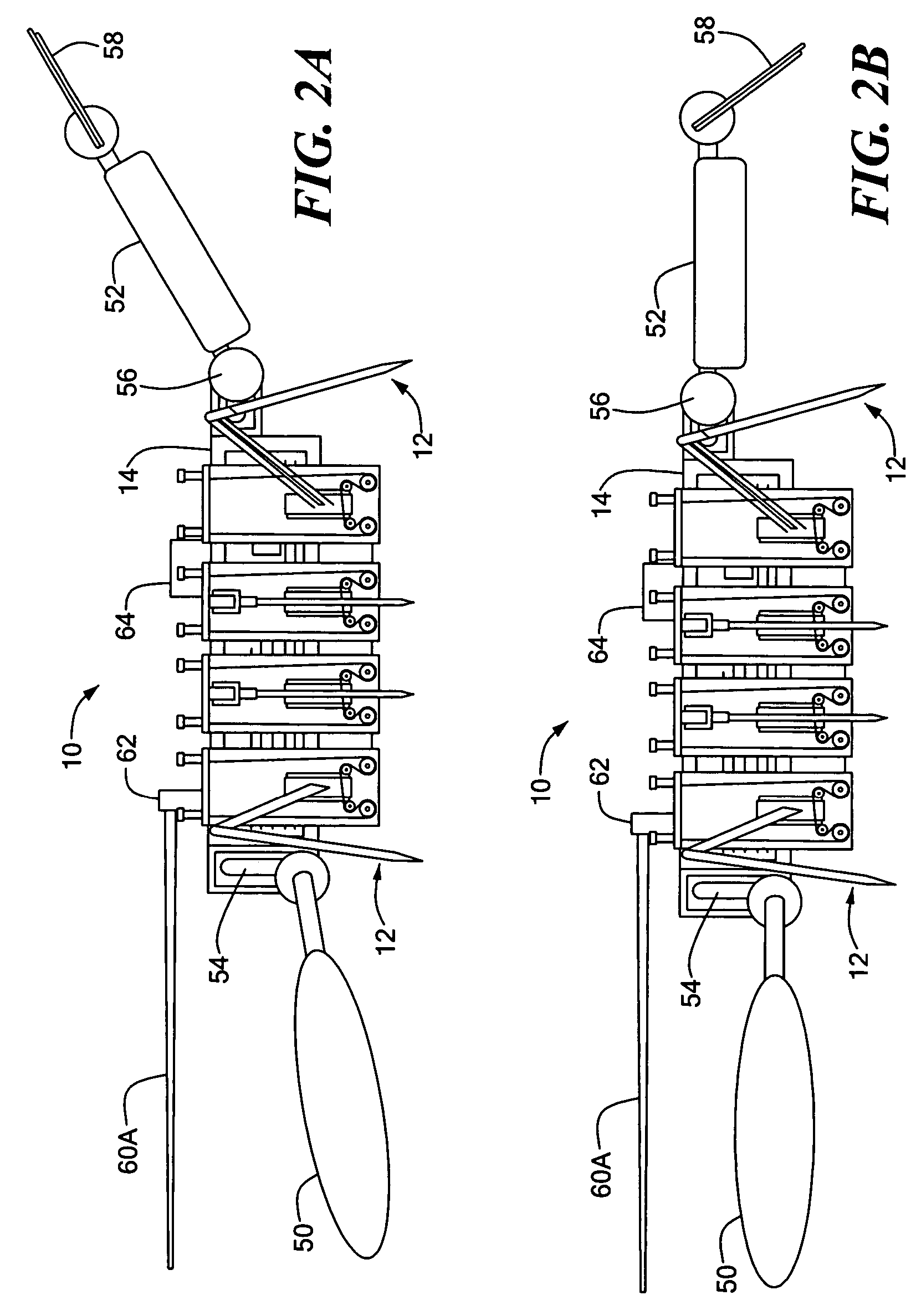
Process and architecture of robotic system to mimic animal behavior in the natural environment
ActiveUS20050065651A1Programme-controlled manipulatorArtificial lifeBiomechanicsFinite-state machine
A robotic architecture for capturing the autonomous performance advantages the animal models enjoy in the natural environment is disclosed. A biomimesis process is employed to allow selective utilization of basic physical components and adaptation of a common control paradigm for each of different vehicle types. The biomimetic architecture involves five functional elements: a basic biomorphic plant for capturing the biomechanical advantages of the model organism; a neural circuit-based controller consisting of a finite state machine; myomorphic actuators producing linear graded force in response to trains of current pulses for mediating movements; labeled line code output by neuromorphic sensors; and a reactive behavioral sequencer executing command sequences defined within a behavioral library.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Methods for drug interaction prediction using biological response profiles
This invention provides methods for detecting and predicting drug interaction. In one embodiment of the invention, a plurality of cellular constituents in a biological sample is monitored as the sample is subject to various drug treatments. The response of the cellular constituents are analyzed to detect interactions. This method is particularly useful for predicting drug interaction using a model organism. It is also useful for analyzing interaction between any perturbations to a biological system.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for establishing fragile X-syndrome non-human primate model on basis of CRISPR gene knockout technology
InactiveCN103642836APredictive effectReduce the risk of research and developmentVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryDiseaseFragile X chromosome
The invention discloses a method for establishing a fragile X-syndrome non-human primate model on the basis of a CRISPR gene knockout technology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a FMR1 gene knockout machin model; (2) carrying out identification and related functional analysis on the machin model; (3) carrying out tests on the nerve characteristics and learning and memorizing ability of the machin model. The method utilizes a CRISPR gene knockout technology to establish a fragile X-syndrome non-human primate model. The model fills the blank of non-human primate model, can effectively stimulate the pathological process of human diseases, can be used as an optimum animal model for researching human diseases, can effectively predict the effect of novel vaccine, novel drug or novel diagnostic reagent in clinical applications, and thus greatly reduces the risk of novel drug development.
Owner:SUZHOU TONGSHAN BIO TECH
Method for knocking out microRNA gene family by utilizing CRISPR-Cas9 specificity
InactiveCN104651398AShort cycleReduce investmentVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryF1 generationMicroRNA Gene
The invention discloses a method for knocking out a microRNA gene family by utilizing CRISPR-Cas9 specificity, wherein a target gene is knocked out by mainly adopting a CRISPR / Cas9 system. The microRNA family is knocked out by utilizing the specificity of the CRISPR / Cas9 system for the first time; the disadvantage that only one gene can be knocked out for one time in traditional transgenosis can be overcome by utilizing the novel method; the time for establishing a model organism is reduced to three weeks; furthermore, the construction step is simple; an expensive molecular reagent is also reduced; the period for constructing a genetically modified mouse is greatly shortened to four months; multiple genes constructed for one time can be knocked out simultaneously; the fund investment is obviously reduced; F1 generations of mice can be obtained only in need of 50000 Yuan; the gene modification efficiency can be above 90%; the unreliability of the traditional technology is reduced; the operation technology is simple; and a series of complex steps including constructing a targeting vector, screening ES (Embryonic Stem) cells, selectively breeding chimeric mice and the like are unnecessary.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Enhanced multi-protocol analysis via intelligent supervised embedding (empravise) for multimodal data fusion
ActiveUS20140037172A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmDimensionality reduction
The present invention provides a system and method for analysis of multimodal imaging and non-imaging biomedical data, using a multi-parametric data representation and integration framework. The present invention makes use of (1) dimensionality reduction to account for differing dimensionalities and scale in multimodal biomedical data, and (2) a supervised ensemble of embeddings to accurately capture maximum available class information from the data.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Cellular arrays and methods of detecting and using genetic disorder markers
InactiveUS20050244880A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAbnormal tissue growthMalignancy
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
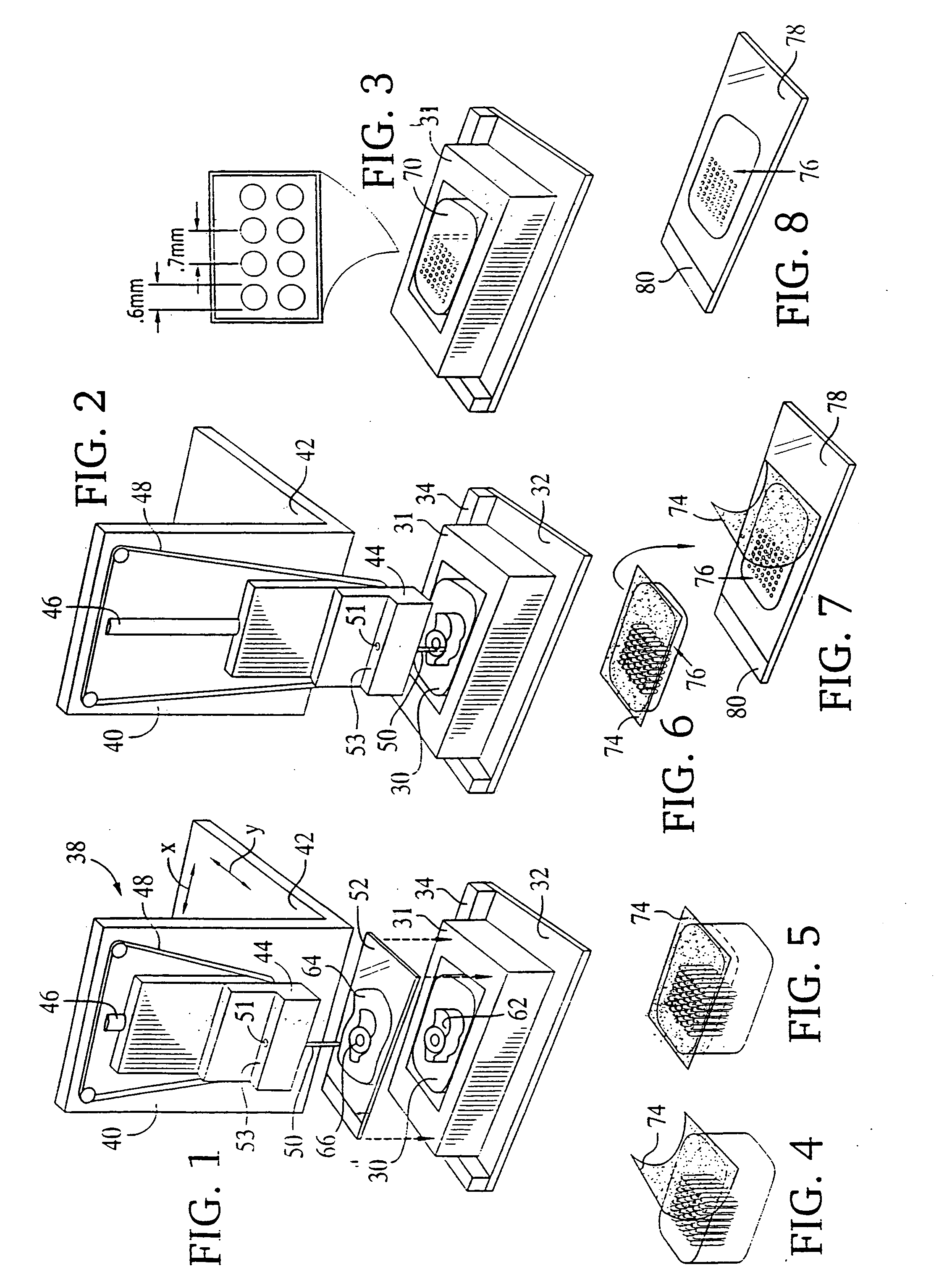
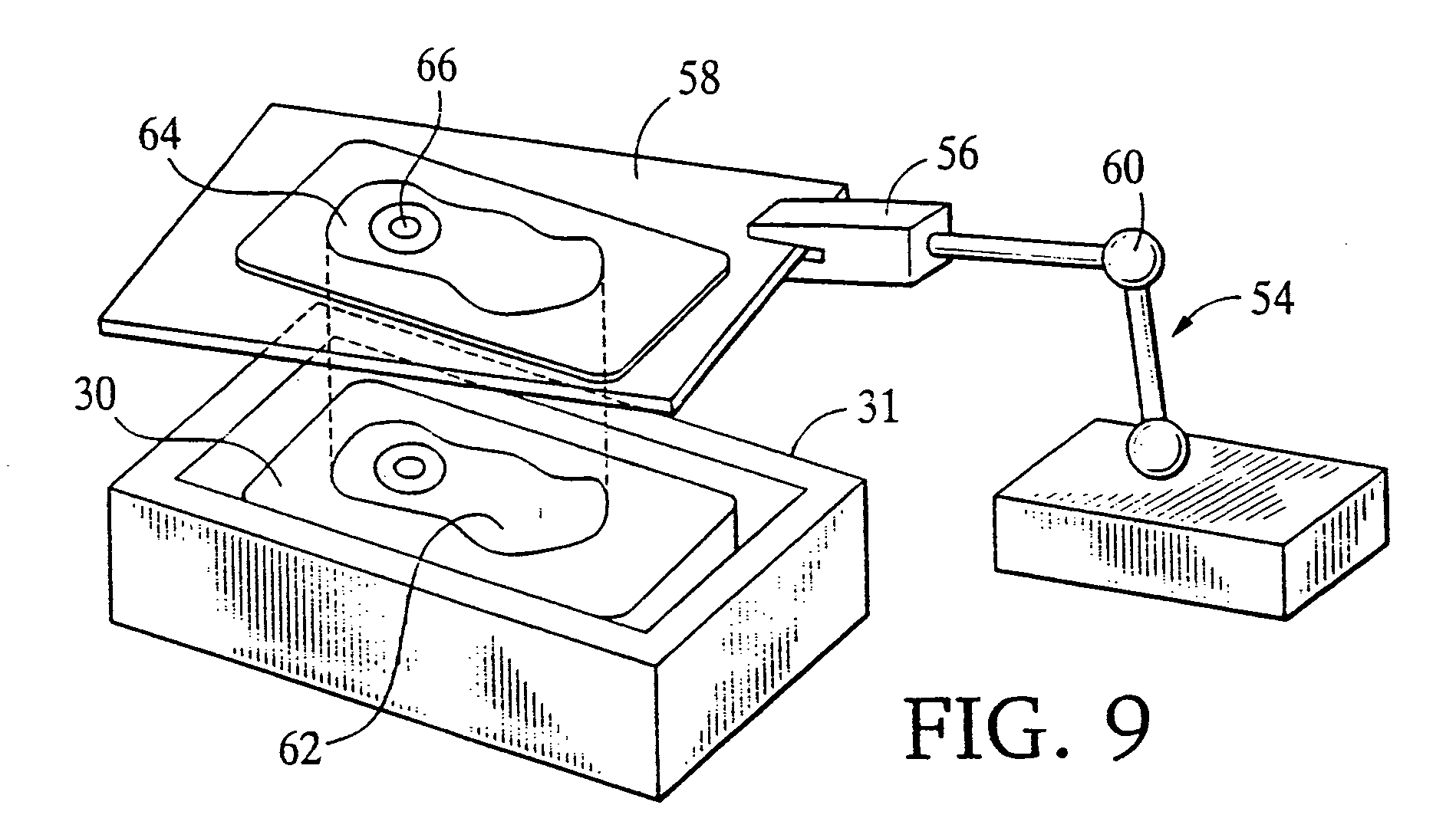
Methods for site-specific genetic modification in stem cells using xanthomonas tal nucleases (XTN) for the creation of model organisms
InactiveUS20140201858A1FermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousXanthomonas campestris
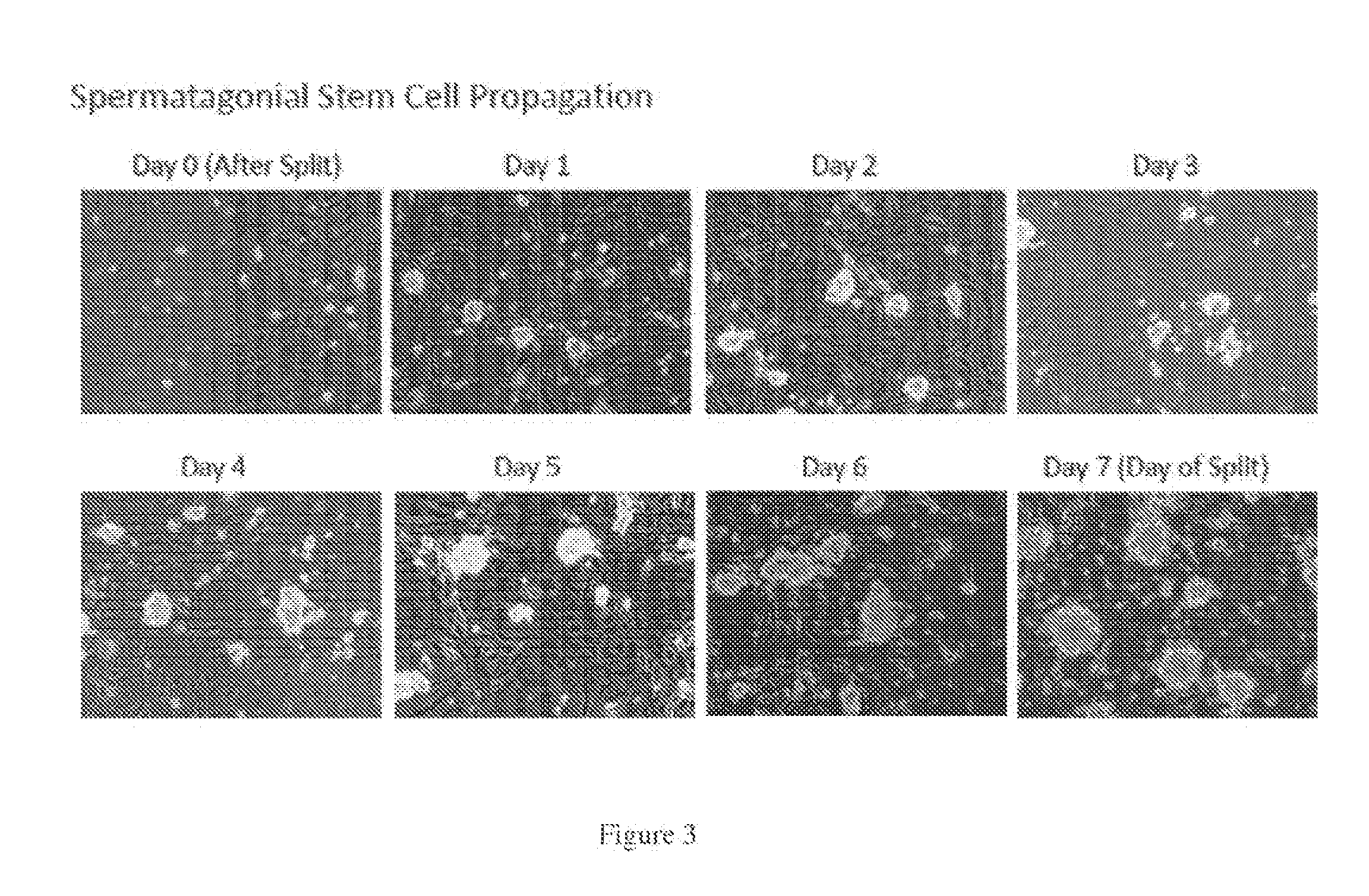
The invention relates to organisms and compositions comprising one or more stem cells or one or more embryos, wherein the one or more stem cells or one or more embryos comprise one or more of the following mutations: (i) a deletion mutation; (ii) a knockout mutation; and / or (iii) an addition of a heterologous nucleic acid sequence; wherein the one or more mutations of (i), (ii), and / or (iii) are site-specific mutations caused by a Xanthomonas TAL nuclease (XTN). The invention also relates to method of mutating an embryo, iPS cell, stem cell, or more particularly a spermatogonial stem cell by exposing the nucleic acid sequence contained within such embryos or cell with a Xanthomonas TAL nuclease.
Owner:TRANSPOSAGEN BIOPHARM +1
Cellular arrays and methods of detecting and using genetic disorder markers
InactiveUS6905823B2Rapidly and accurately detectHigh resolutionImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTissue sampleTissue specimen
A method is disclosed for rapid molecular profiling of tissue or other cellular specimens by placing a donor specimen in an assigned location in a recipient array, providing copies of the array, and performing a different biological analysis of each copy. The results of the different biological analyses are compared to determine if there are correlations between the results of the different biological analyses at each assigned location. In some embodiments, the specimens may be tissue specimens from different tumors, which are subjected to multiple parallel molecular (including genetic and immunological) analyses. The results of the parallel analyses are then used to detect common molecular characteristics of the genetic disorder type, which can subsequently be used in the diagnosis or treatment of the disease. The biological characteristics of the tissue can be correlated with clinical or other information, to detect characteristics associated with the tissue, such as susceptibility or resistance to particular types of drug treatment. Other examples of suitable tissues which can be placed in the matrix include tissue from transgenic or model organisms, or cellular suspensions (such as cytological preparations or specimens of liquid malignancies or cell lines).
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
New method for screening anti-liver injury medicament by using model organism zebra fish
InactiveCN101810866AHigh modeling success rateImprove work efficiencyInorganic active ingredientsDigestive systemLiver tissueOperability
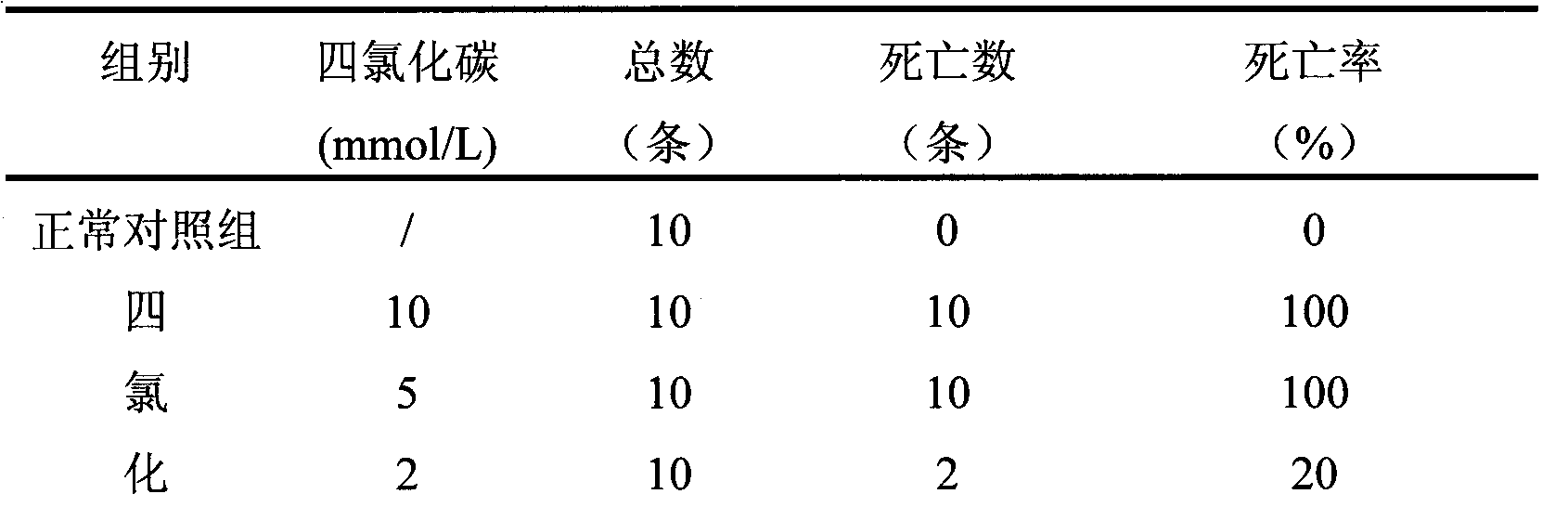
The invention discloses a new method for screening an anti-liver injury medicament by using a model organism zebra fish. The method comprises the following steps: continuously molding the zebra fish serving as a molding object for 3 days by using preferred carbon tetrachloride at the concentration of 1mmol / L to obtain the zebra fish of a liver injury model, and then evaluating the anti-liver injury activity of different receptor medicaments by using ALT and AST levels in the liver tissue of the zebra fish and the pathological change condition of the liver tissue of the zebra fish. Experimental results show that the new method for screening the anti-liver injury medicament by using the model organism zebra fish has high molding success rate, can simulate an in vivo environment to perform quick screening, and has the advantages of strong operability, accurate experimental results, little amount of required reacceptance medicament, strong repeatability, low cost, wide application range, capability of performing batch screening experiments and high work efficiency.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE INST OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
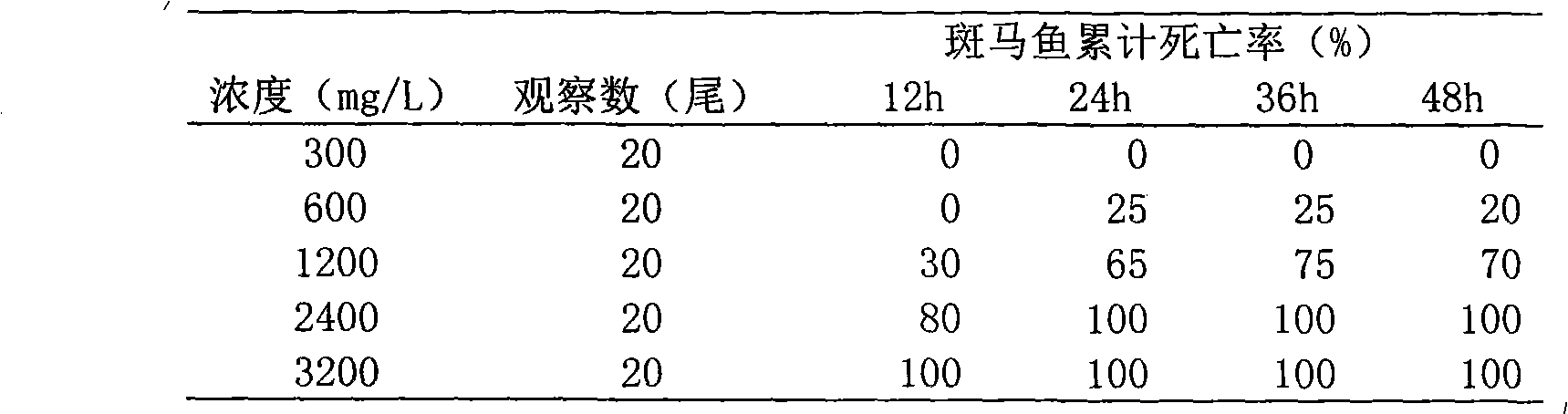
Mode creature method for medicament toxicity research
A method for studying toxicity of drugs by using model organism zebra fish comprises the following steps of: selecting 100 to 200 adult zebra fishes, respectively disposing in bottles containing a solution of 30 to 50 mL, keeping the temperature in the bottles substantially constant at 22 to 25 DEG C, randomly grouping, each group containing 10 to 20 fishes, wherein the solution in one of the groups is pure water (blank), the solutions in other groups are medicinal solutions with different concentrations, and 0.5% to 2% dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) can be added to assist dissolving a drug that has poor water solubility, when an additional solvent comparison group prepared by adding 0.5% to 2% DMSO into the pure water is needed; recording the death number of zebra fishes in the medicinal solutions of different concentrations within 24 h, and calculating the death rate (%); calculating median lethal dose-LD50 by Bliss method according to the experiment result; and representing the acute toxicity by the value of LD50. According to the method, the LD50s of zebra fish of triptolide, matrine and emodin are respectively 5.39*10<-3>, 112.3 and 1.08*10<3> mug / mL. The method can objectively reflect the toxicity of drugs.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
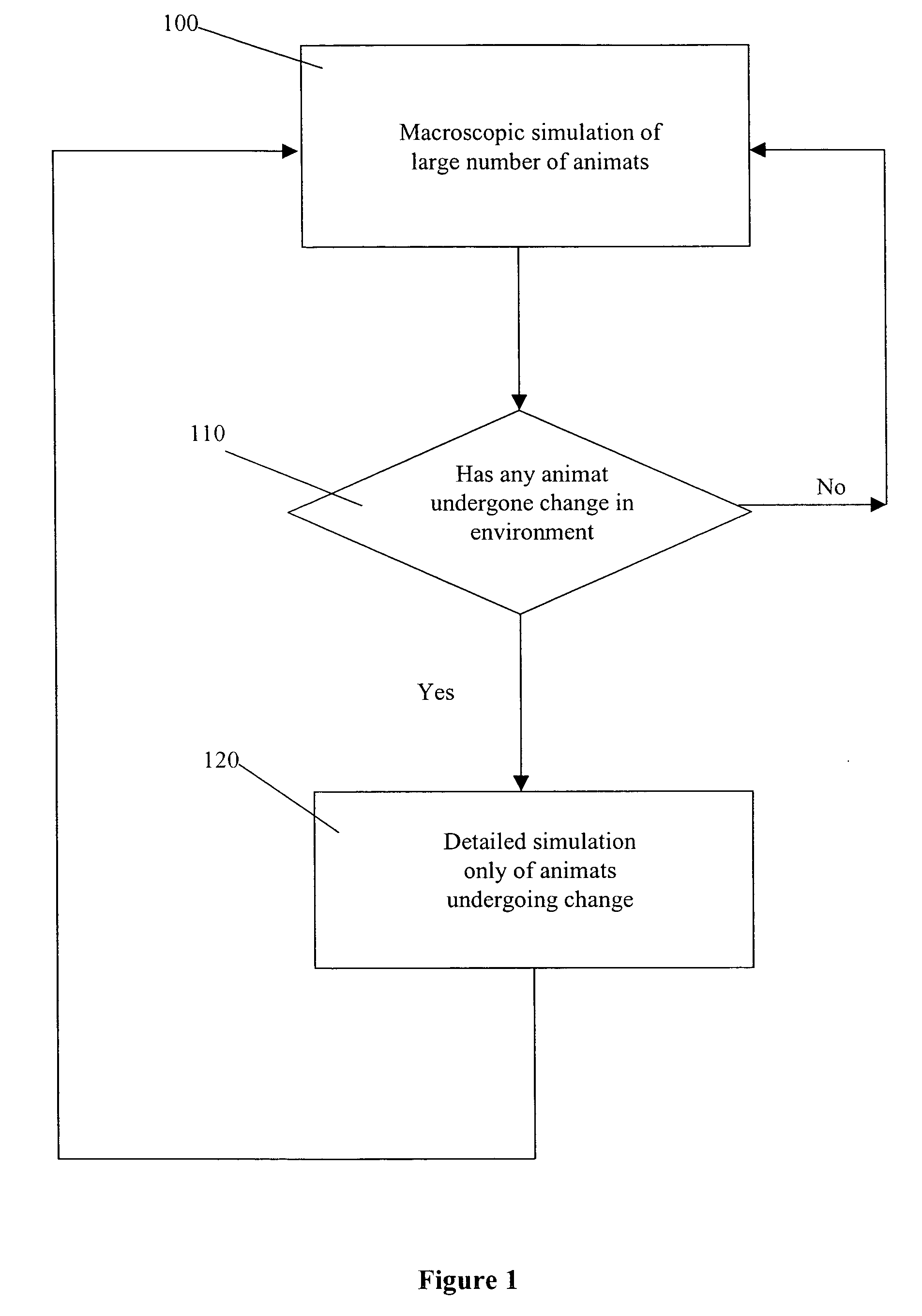
Two mode creature simulation
A technique for simulating the activities of a large number of creatures is described. The technique utilises two modes of simulation. The first mode of simulation is arranged to simulate the activities of all of the creatures. The second mode of simulation is arranged to simulate the activities of a few of the creatures, at a more detailed level than the first mode. The second mode is utilised by the first mode to determine new parameters of individual creatures when the creatures undergo a change in environment.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
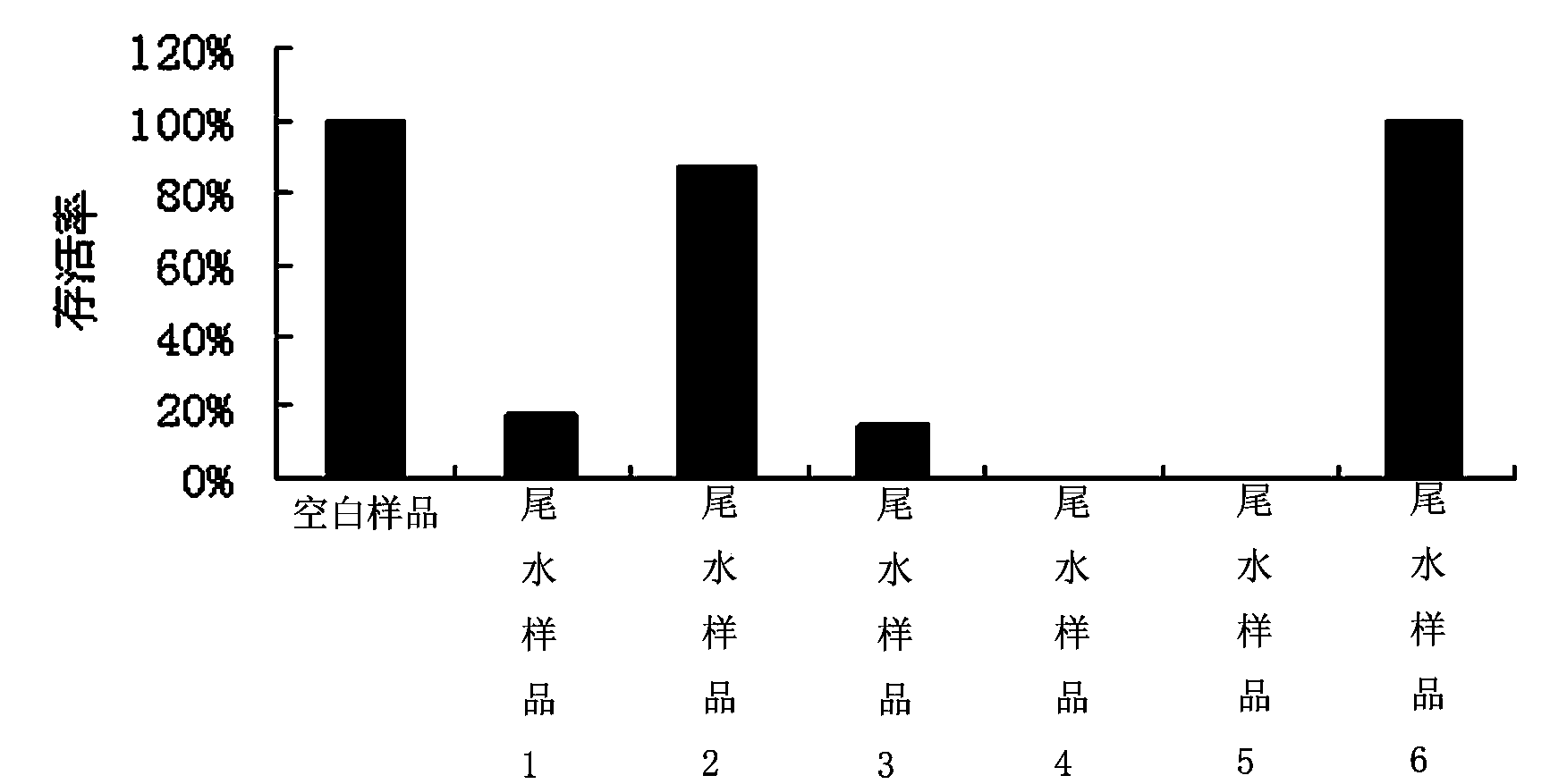
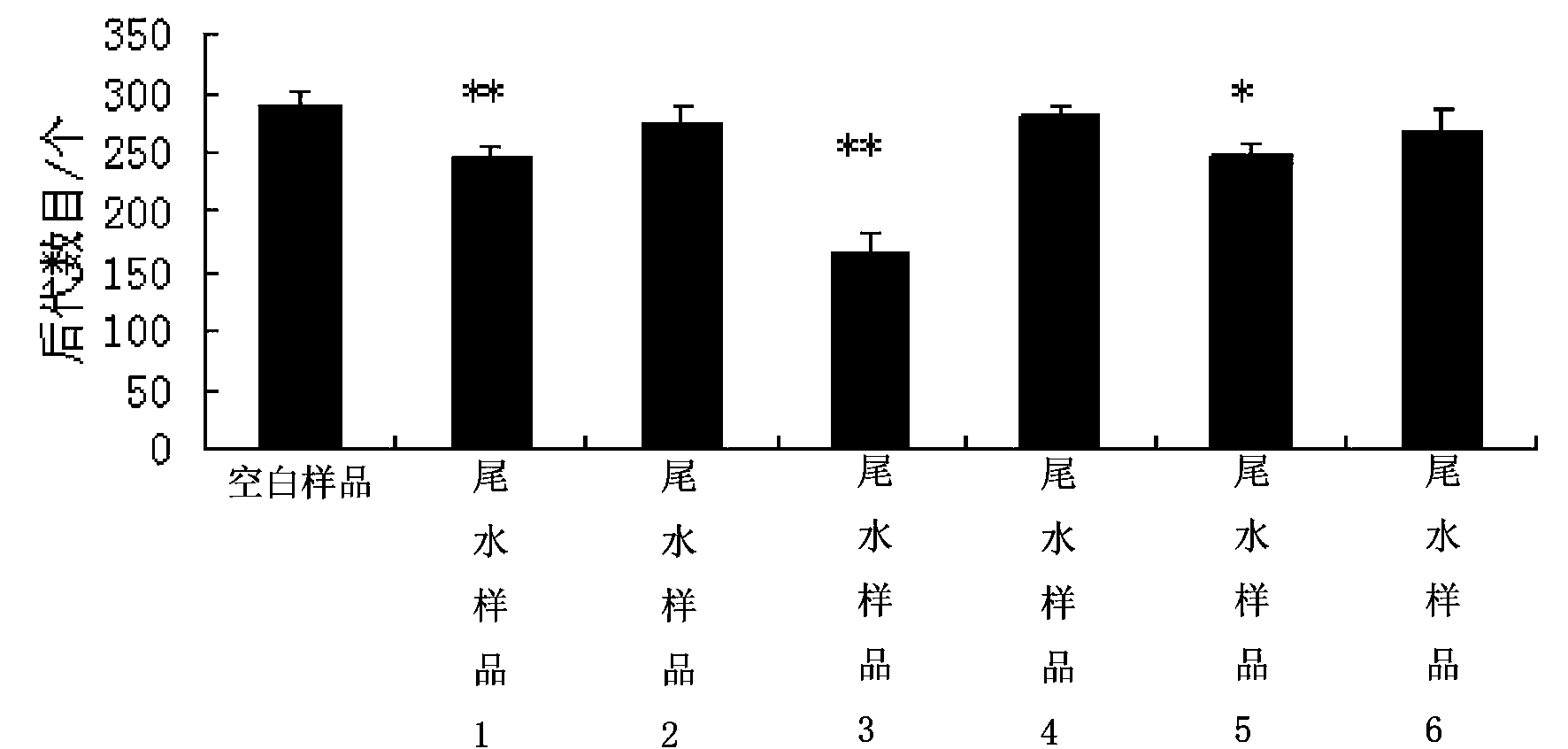
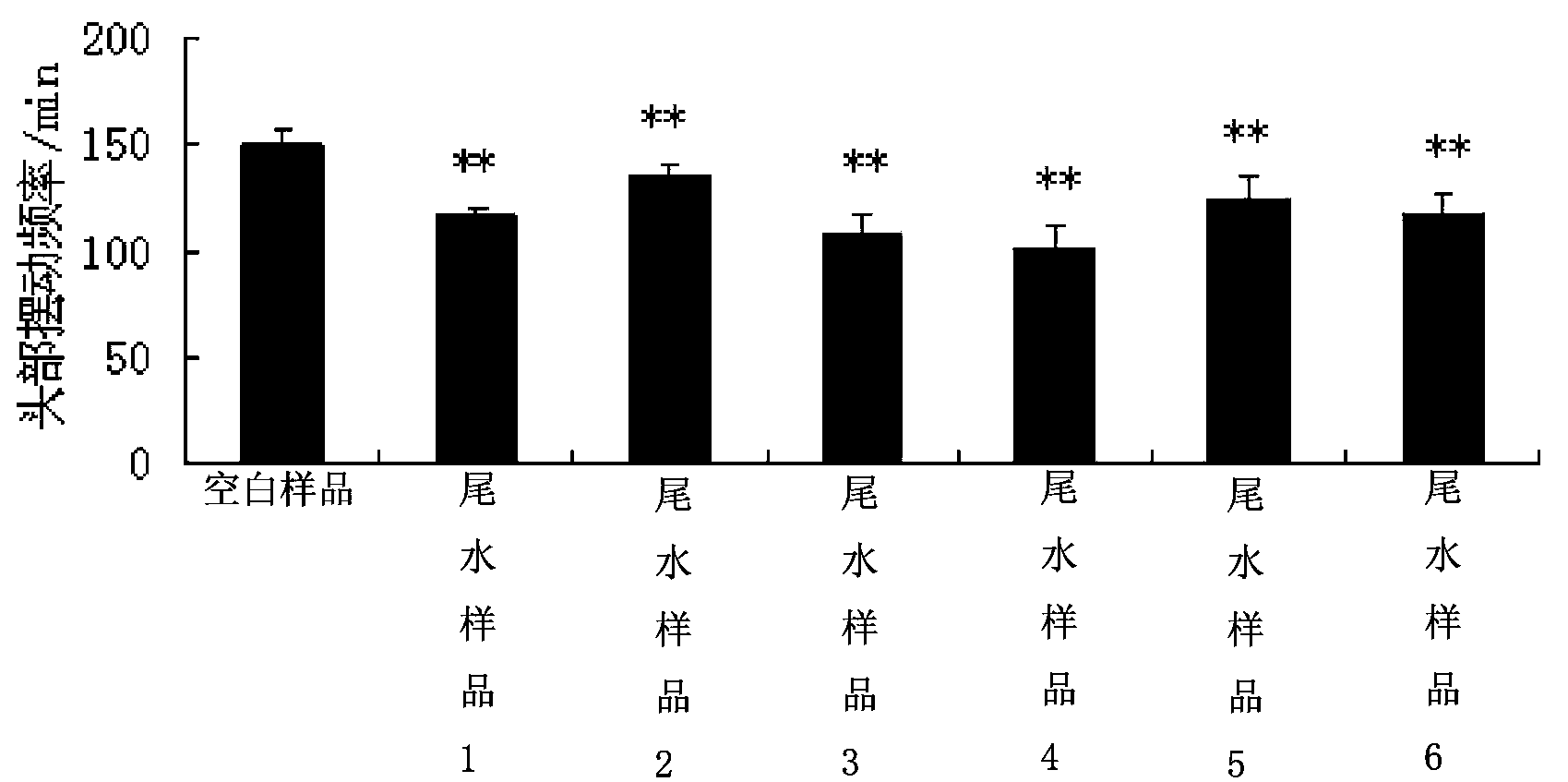
Method for carrying out toxicity analysis on tail water of sewage treatment plant by using caenorhabditis elegans
The invention discloses a method for carrying out toxicity analysis on tail water of a sewage treatment plant by using caenorhabditis elegans. The method comprises the following steps of (1) cultivation of the caenorhabditis elegans; (2) cultivation of escherichia coli OP 50; (3) anabiosis of the caenorhabditis elegans; (4) passage of caenorhabditis elegans; (5) synchronization of the caenorhabditis elegans; and (6) testing the comprehensive toxicity of a to-be-detected tail water sample by using the caenorhabditis elegans. The method provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that model organism-caenorhabditis elegans is utilized to carry out toxicity analysis on the tail water of the sewage treatment plant, and the size of the comprehensive toxicity of the waste water is judged by contrasting the difference of fatality rate, reproduction rate, motor behavior and generation cycle of nematodes and exposing nematodes of a blank control group.
Owner:CHANGZHOU TEXTILE GARMENT INST
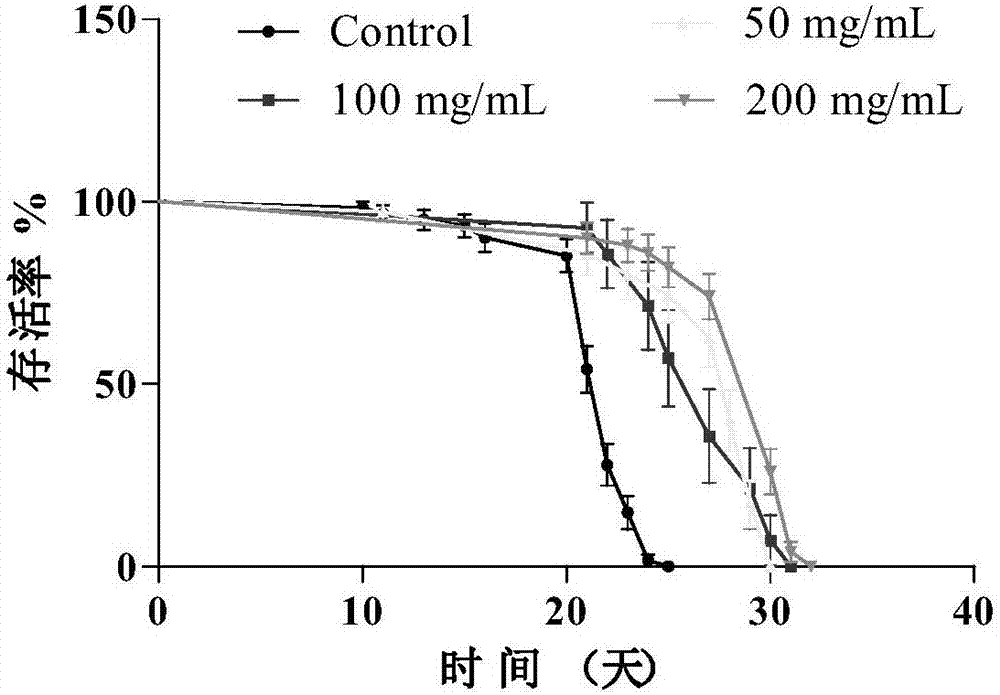
Anti-aging evaluation method based on model organism caenorhabditis elegans and application of the method
InactiveCN107875403AShort life cycleShort experiment cycleCompounds screening/testingPhytochemicalOrganism
The invention discloses an anti-aging evaluation method based on a model organism caenorhabditis elegans and an application of the method and relates to performance evaluation methods for phytochemicals, anti-aging medicines, healthcare products and the like. In the invention, under non-toxic concentration, the anti-aging effect of the to-be-tested substances is evaluated. With the evaluation method, existence of the anti-aging effect of the to-be-tested substances can be evaluated in a short period, wherein the evaluation is completed mainly through detection on life, heat stress capability,anti-ultraviolet irradiation capability, anti-oxidizing damage capability, reproductive capability, body length and lipofuscin content of the caenorhabditis elegans. The method is advantaged in that the model organism, caenorhabditis elegans, is short in growth period, so that the anti-aging effect can be observed rapidly in several weeks. The method has short experimental period and is convenientto carry out.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
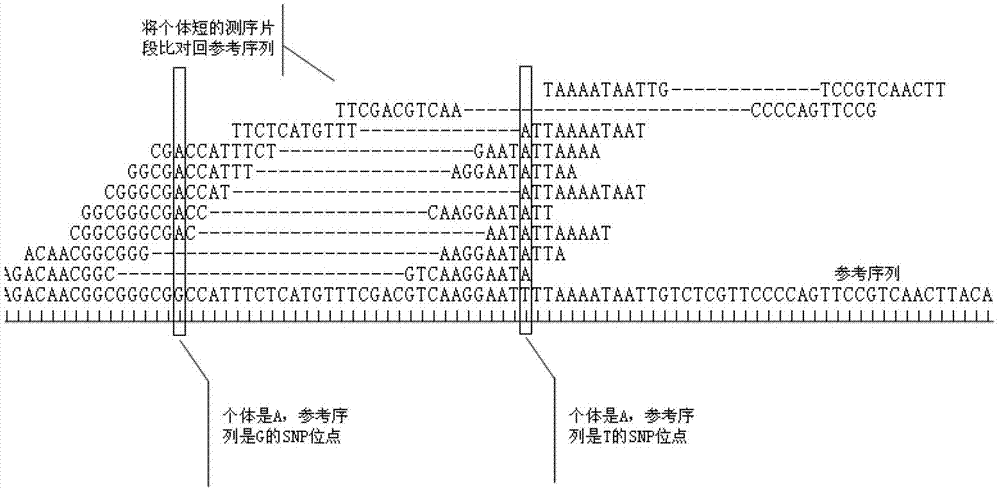
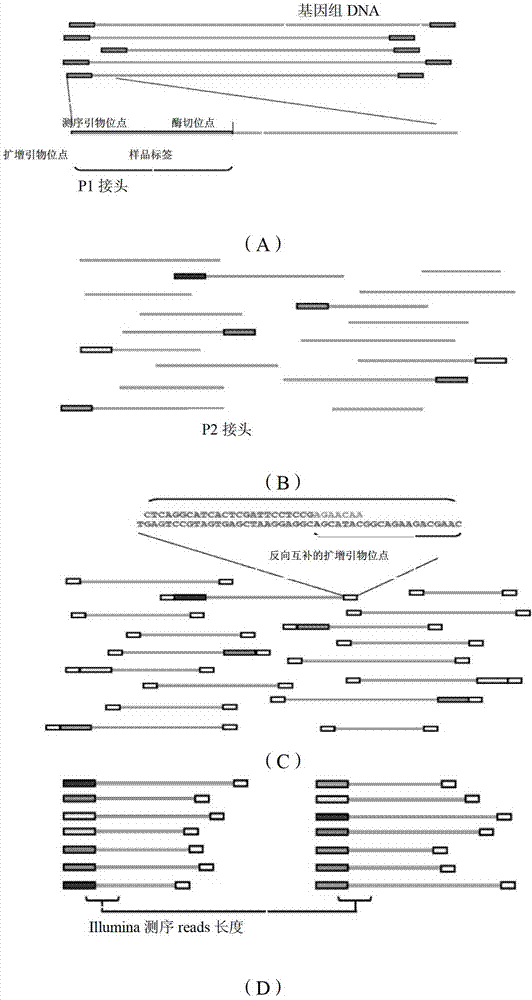
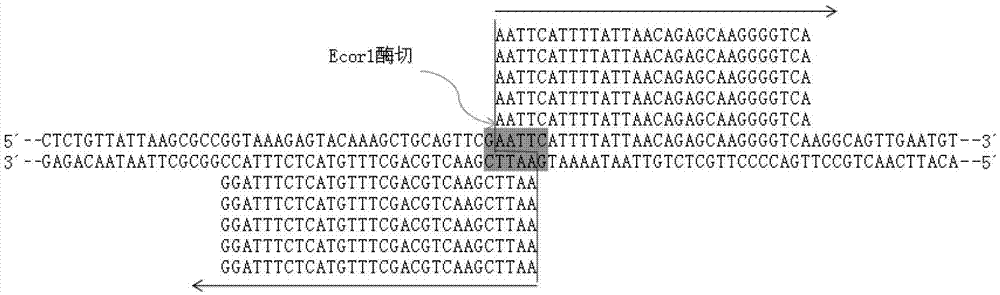
Single nucleotide polymorphism site identification method based on digestion library-establishing and sequencing and bayesian statistics
ActiveCN103114150ALow costThe result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementNon model organismRestriction site
The invention discloses a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) site identification method based on digestion library-establishing and sequencing and bayesian statistics. The method is used for processing RAD (restriction site associated deoxyribonucleic acid) sequencing data, searching candidate SNP on an RAD sequencing fragment, and identifying the SNP reliability by employing a bioinformatics analysis method based on bayesian statistics. The method can be used for model and non-model organisms to eliminate the limitation that lots of species are lack of reference sequences and reduce the sequencing cost, and can be used for solving the bottleneck that a reliable statistical method is absent in the process of performing SNP identification by utilizing the RAD data at present, so that the obtained SNP site accuracy is greatly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAJORBIO BIO PHARM TECH
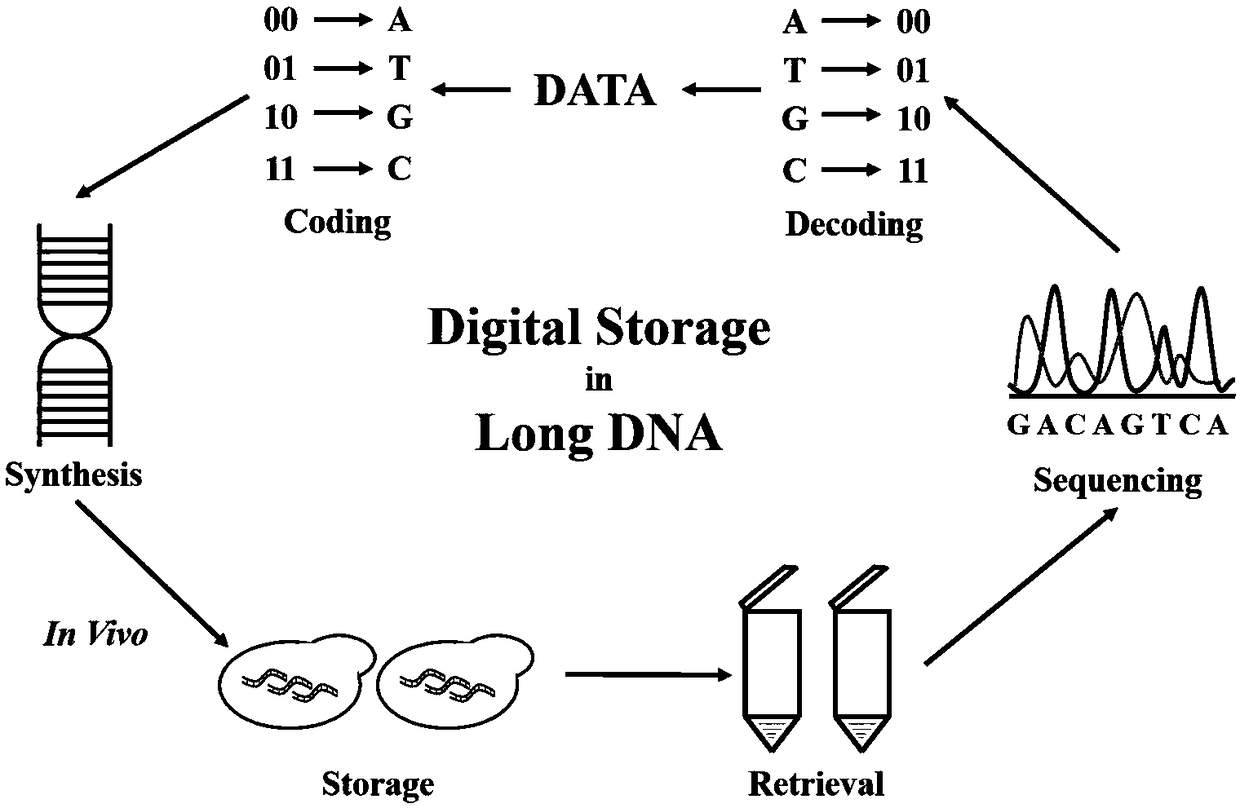
DNA-based Information Storage Method
ActiveCN109460822AIncrease load rateFast copyRedundant data error correctionDNA computersEscherichia coliA-DNA
The invention relates to the technical field of information storage, in particular to a DNA-based information storage method. A long sequence in vivo DNA information storage technique is provide. Themain goal is to construct a coding system with strong error correction mechanism based on LDPC and BCH codes, which can reduce the redundancy of primers and indexes by long sequence coding, and achieve a high actual carrying capacity (above 97%). The main goal is to construct a medium-length DNA sequence (above 1Kbp). Saccharomyces cerevisiae in vivo assembly system is used to assemble and store long sequences and preserve information, and the information can be replicated at low cost, high fidelity and high speed by model organisms such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Escherichia coli or Bacillus. At the same time, because of the existence of strong error correction system, the data in the bacterial cell can be reduced perfectly with low coverage (1-5 X) in the second generation and third generation sequencing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
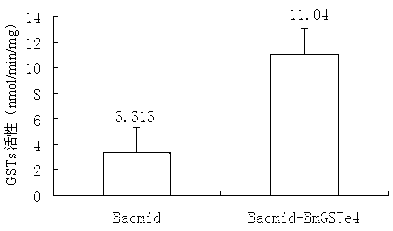
Bombyx mori glutathione-S-transferase BmGSTe4 gene
InactiveCN103160524AHas GSTs activityInhibit apoptosisTransferasesMicroorganism based processesOrder LepidopteraNucleotide
The invention discloses a bombyx mori glutathione-S-transferase BmGSTe4 gene with a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQIDNo.1, and the expression product thereof has glutathione-S-transferase (GSTs) activity, because GSTs plays an important role in the formation of pesticide resistance and oxidation resistance of insects, and bombyx mori is a lepidopterous insect-model organism, a biological control pesticide which can specifically kill lepidoptera pests and is harmless to other beneficial insects is expected to be designed through taking BmGSTe4 genes as targets. In addition, in the invention, a situation that BmGSTe4 genes have a function of inhibiting cell apoptosis is found, therefore, the BmGSTe4 genes can be used as potential targets of anti-cancer drug screening.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
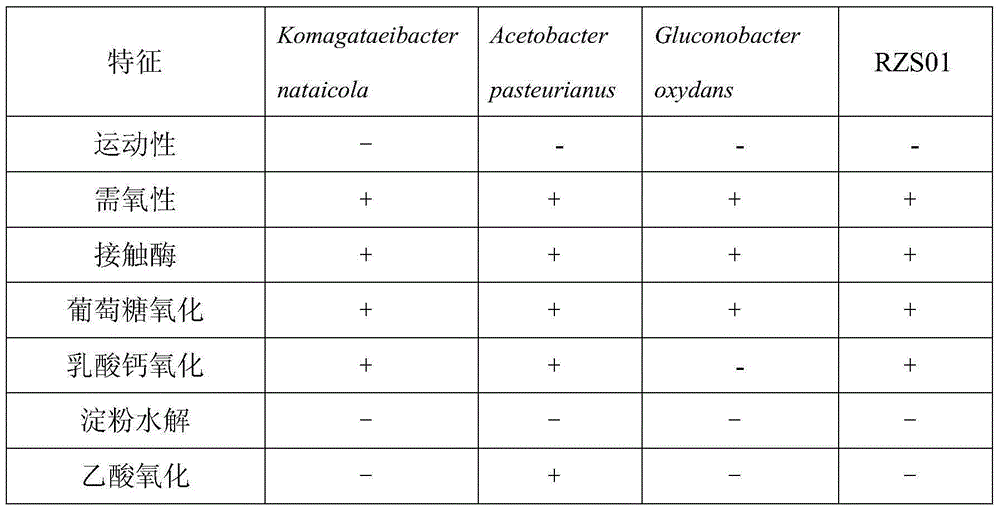
Komagataeibacter nataicola and application thereof
InactiveCN105132331AImprove performanceSeparation and screening methods are simple and easy to obtainBacteriaMicroorganism based processesKomagataeibacter nataicolaGram
The invention discloses a komagataeibacter nataicola RZS01 strain which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with a preservation numberof CGMCC No.10961. The bacterial strain is separated from defective fruits, and the separating and screening method is simple and convenient, so that the bacterial strain is easy to obtain. The bacterial strain is Gram-negative and short-bar-shaped aerobic bacteria, and is stable in performance. The komagataeibacter nataicola RZS01 is the bacterial cellulose producing bacteria, and can be used for producing bacterial cellulose through flask shaking fermentation, static state fermentation, fermentation tank large-scale fermentation or the combination of any two or three of the flask shaking fermentation, the static state fermentation and fermentation tank large-scale fermentation, the cellulose yield is high, large-scale industrial production is facilitated, and remarkable economic benefits are brought. The komagataeibacter nataicola RZS01 is nontoxic, free of pathogenicity, safe to people and livestock, and friendly to environment, serves as model organism for bacterial cellulose production, and has potential application prospects.
Owner:南京荣之盛生物科技有限公司
Beta-amyloid plaque recognition and measurement method based on image processing
ActiveCN107561264AAutomatic measurement quantityAutomatic size measurementImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionStatistical analysis
The invention provides a beta-amyloid plaque recognition and measurement method based on image processing, and belongs to the technical field of biological image processing. The method comprises the following concrete steps that a model organism brain slice is subjected to immunostaining by a beta-amyloid protein monoclonal antibody; after the immune dying, the extracellular beta-amyloid plaque ofthe model organism brain slice shows bright plaque in a fluorescence microscope; a fluorescence microscope is used for shooting a picture of the fluorescence microscope subjected to immunostaining; the picture is processed to recognize the located bright plaque region of the beta-amyloid plaque; through the image processing, the beta-amyloid plaque indicated by the bright plaque is subjected to automatic quantity statistics and feature calculation to obtain the statistics data; the statistics data is matched with feature information of the model organism for statistics analysis. The deposition condition of the beta-amyloid plaque is quantificationally reflected by a method of recognizing and measuring the bright plaque in the pictures shot by the fluorescence microscope.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
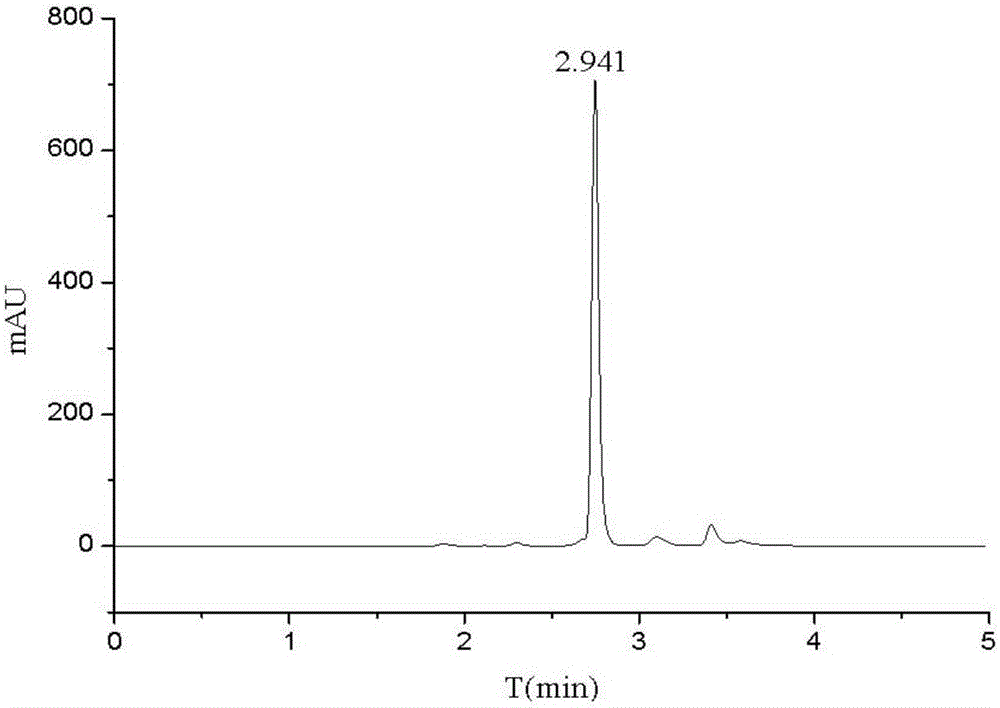
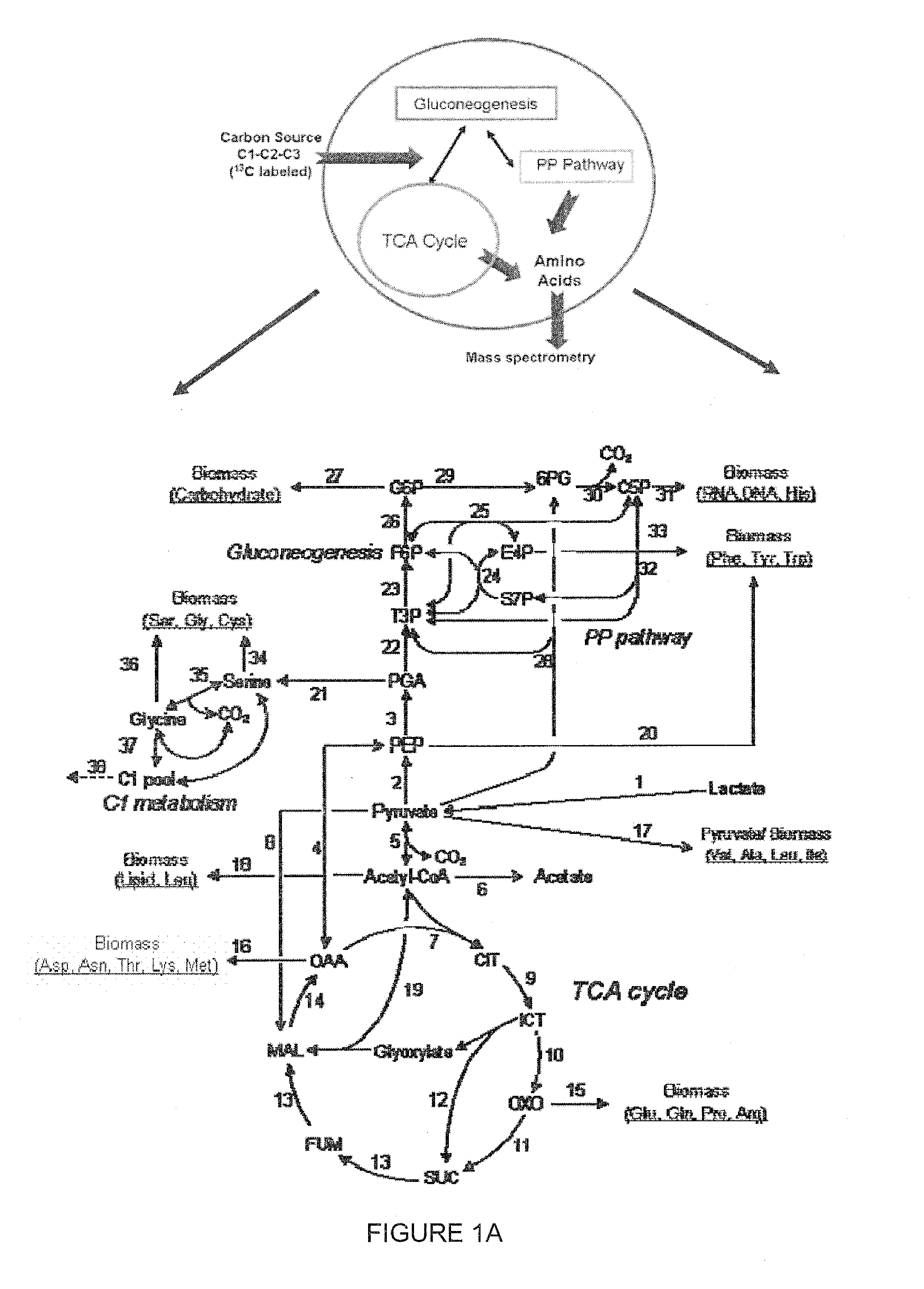
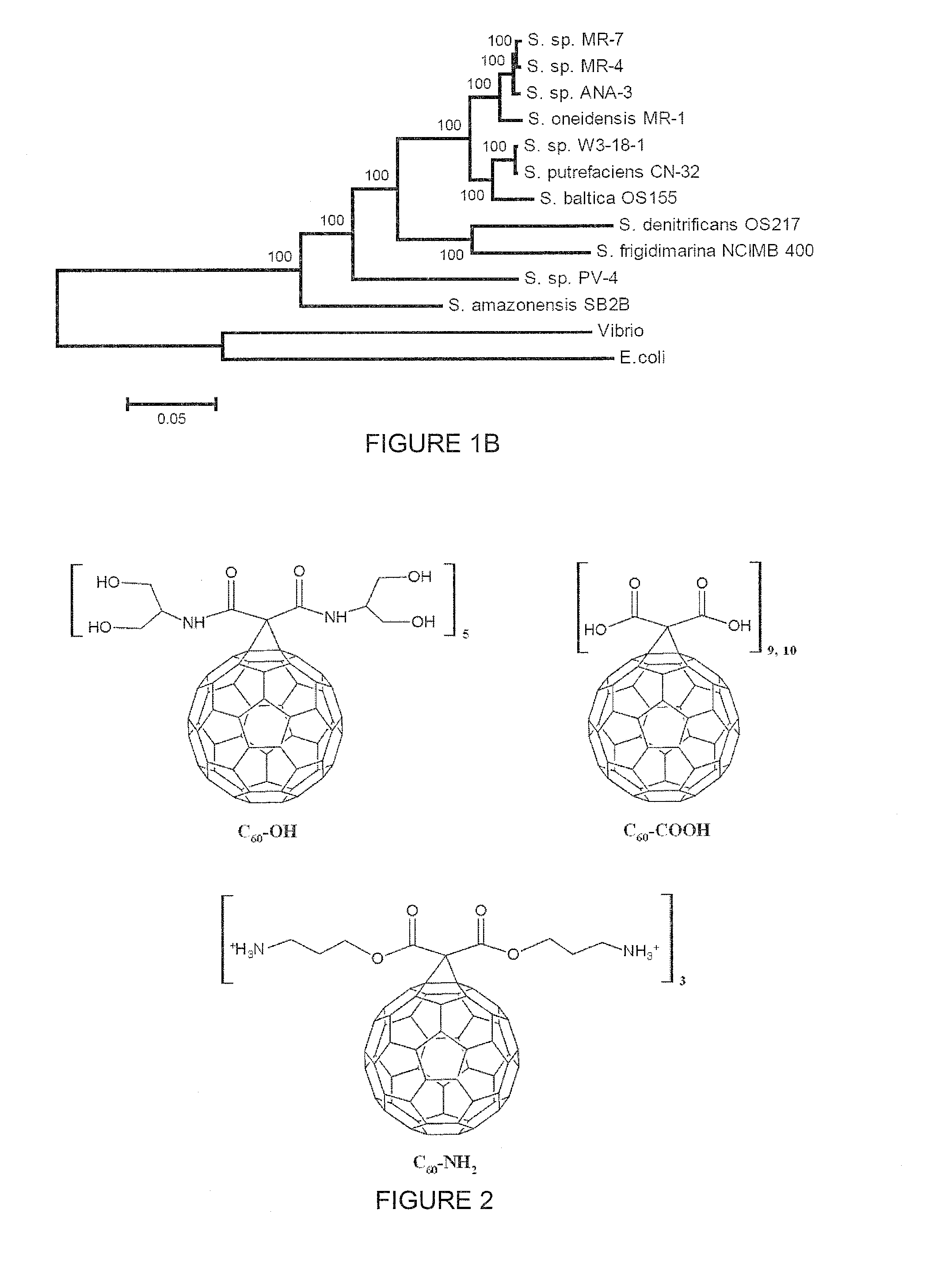
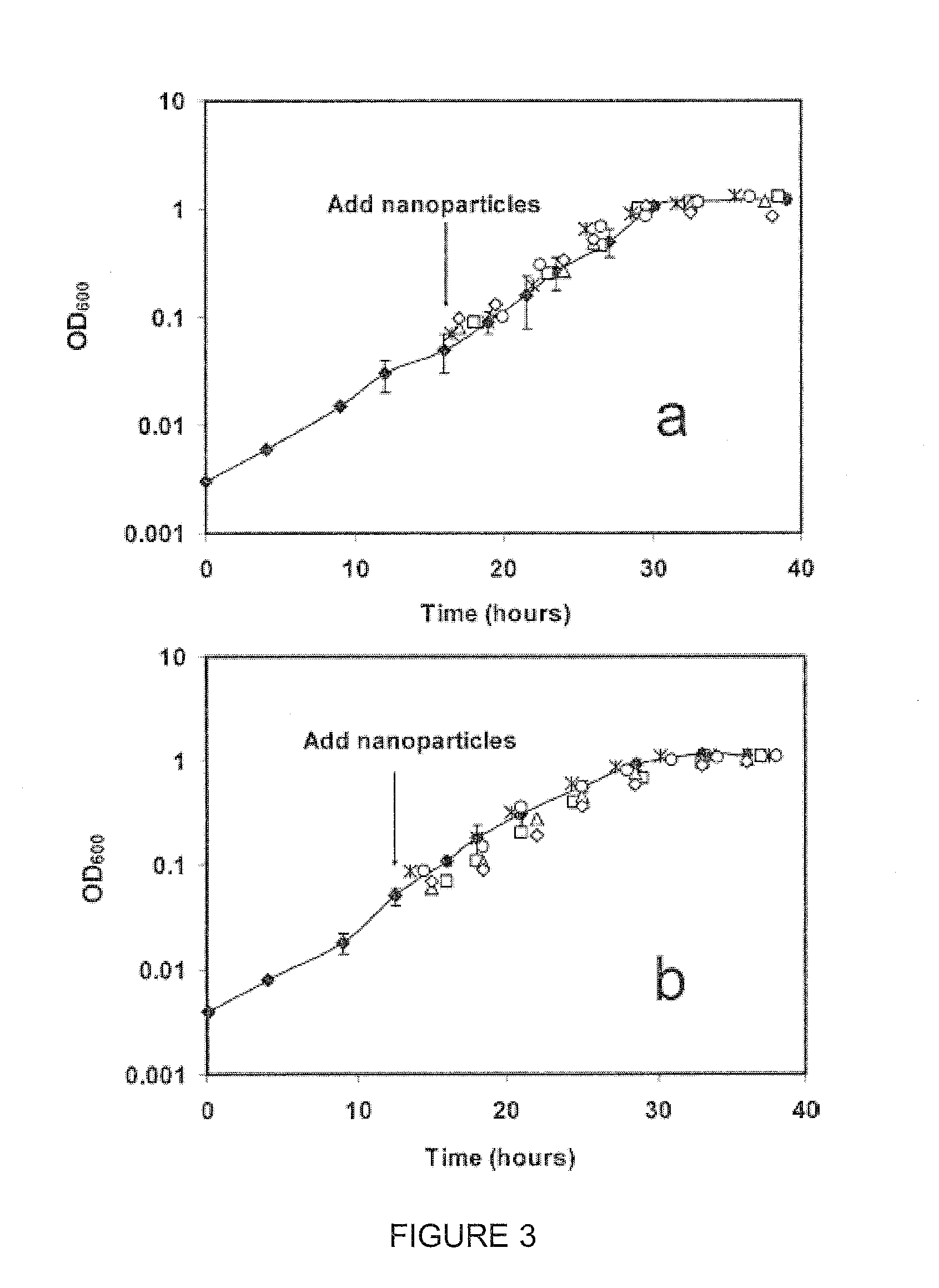
Bioremediation of Nanomaterials
The present invention provides a method comprising the use of microorganisms for nanotoxicity study and bioremediation. In some embodiment, the microorganisms are bacterial organisms such as Gram negative bacteria, which are used as model organisms to study the nanotoxicity of the fullerene compounds: E. coli W3110, a human related enterobacterium and Shewanella oneidensis MR-1, an environmentally important bacterium with versatile metabolism.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Recombinant escherichia coli capable of producing cinnamic alcohol and rosin, and construction method and applications thereof
ActiveCN108203713AClear backgroundGrow fastCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaEscherichia coliUdp glucosyltransferase
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli capable of producing cinnamic alcohol and rosin, and a construction method and applications thereof. The construction method comprises followingsteps: phenylalnine ammonialyase PAL, p-hydroxycinnamic acid coenzyme A ligase 4CL, and cinnamamide coenzyme A reductase CCR are introduced into Escherichia coli so as to obtain the recombinant escherichia coli capable of producing cinnamic alcohol. In the construction method, Escherichia coli is taken as a model organism, the background is clear, growth speed is high, large scale fermentation culture is convenient to realize, and cost is low. The recombinant escherichia coli capable of producing cinnamic alcohol and rosin is obtained via construction of a cinnamic alcohol synthesis pathway, the cinnamic alcohol yield is 300mg / L; UDP glucosyltransferase is introduced into Escherichia coli further, so that organic combination of biological synthesis pathways of rosin and cinnamic alcohol isrealized, the highest rosin yield is 280mg / L. The construction method is capable of providing large scale industrialized production of cinnamic alcohol and / or rosin with foundation.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
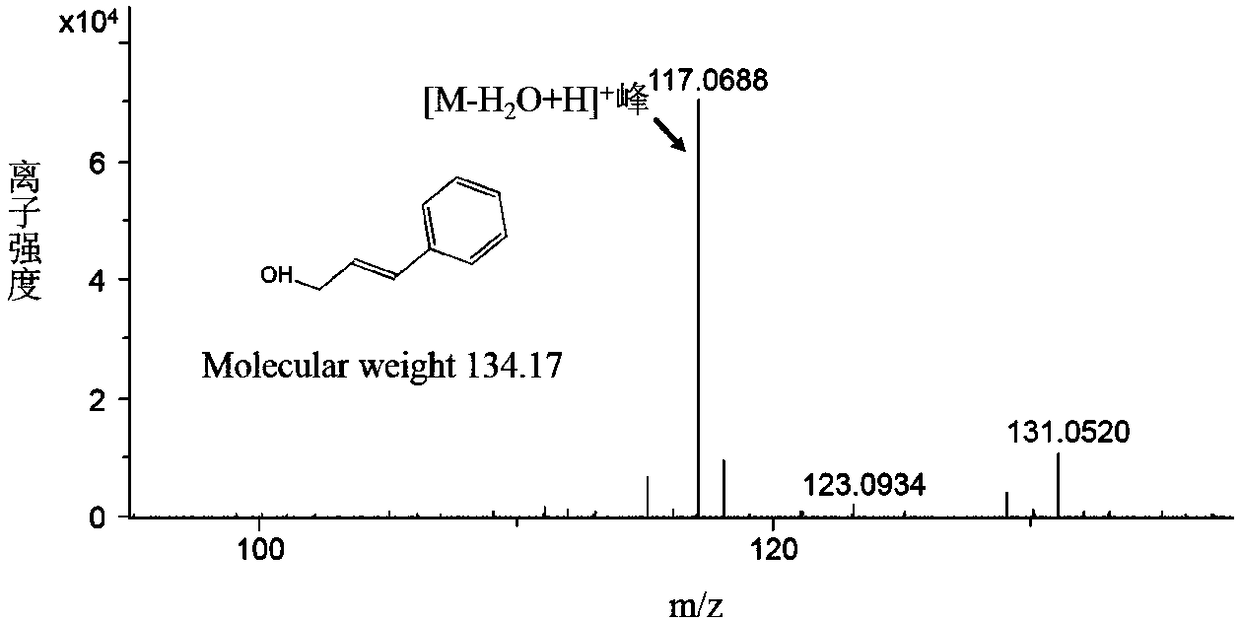
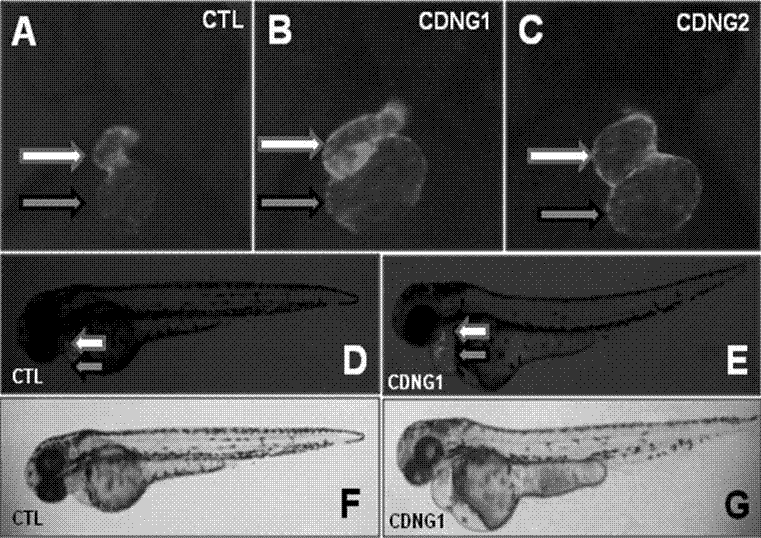
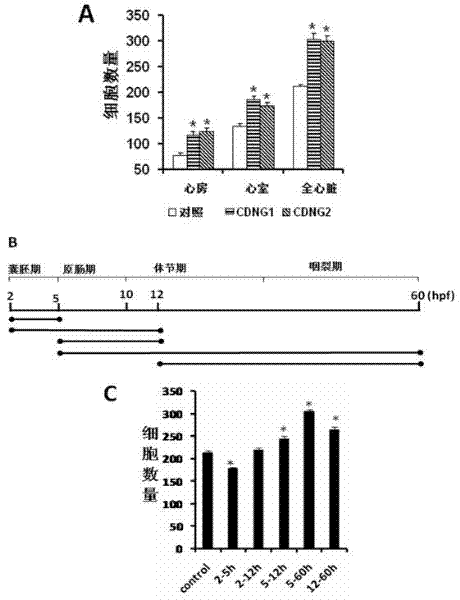
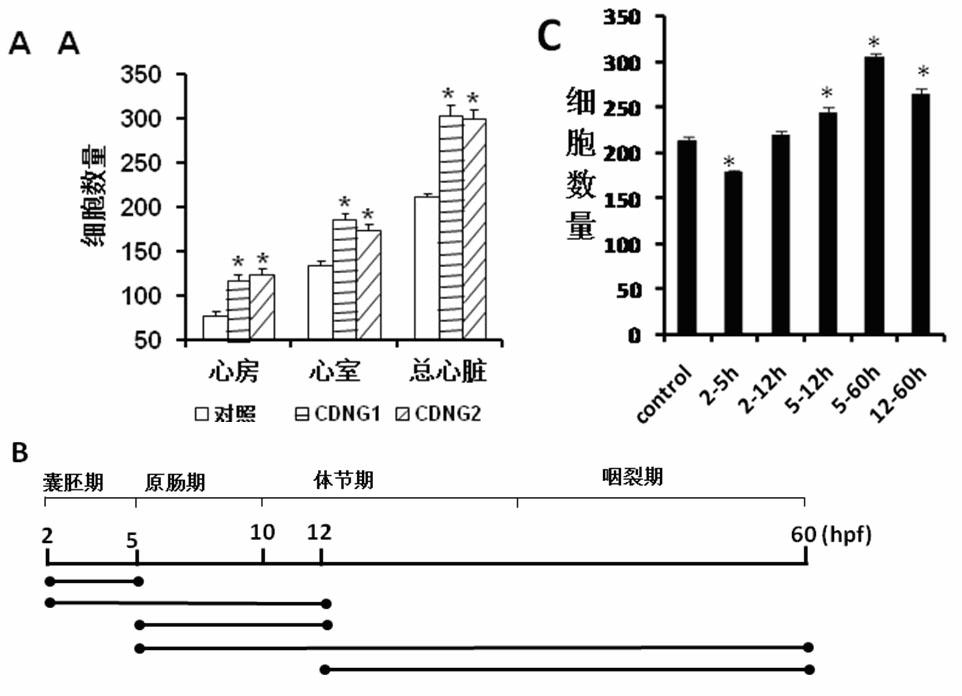
Myocardial small molecular compound for idiosyncratically promoting proliferation of myocardial cells and application thereof
InactiveCN102382127AConservativeRescue abnormal cardiac phenotypesOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseHeart disease
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and particularly relates to a myocardial small molecular compound for idiosyncratically promoting proliferation of myocardial cells and application thereof. The myocardial small molecular compound total comprises a type A, a type B and a type C which have a common core structure, namely (3 (1, 2, 4) triazole (3, 4-b) (1, 3, 4) bismuththiol). The myocardial small molecular compound is obtained from a small molecular compound library by means of model organism zebra fish screening, so as to be capable of idiosyncratically promoting proliferation of myocardial cells inside zebra fish bodies. Importantly, the myocardial small molecular compound is capable of inducing embryonic stem cells of a small mouse to differentiate and proliferate towards the myocardial cells. As proved, the myocardial small molecular compounds are antagonists to inhibit wnt signaling pathways. The myocardial small molecular compound can be used as pilot drugs for treating heart diseases and further is used for optimizing and evaluating candidate drug targets thereof.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for analyzing structure of transcriptome gene sequence of non-model organism
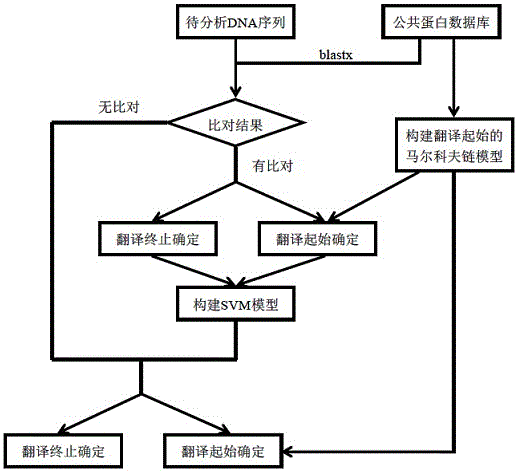
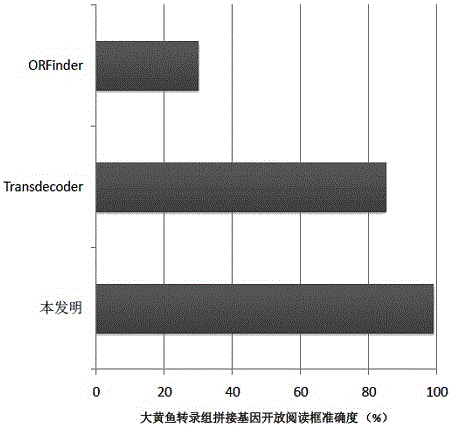
ActiveCN106202998AEnrich the connotation of annotationsDefine biological functionBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsStructural analysisNucleic acid sequence
The invention discloses a method for analyzing a structure of a transcriptome gene sequence of a non-model organism. The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining an optimal comparison result; (2) determining a protein coding mode and determining a translation termination position; (3) determining a coding starting position of the gene sequence; (4) classifying by utilizing a gene mode; (5) determining a nucleic acid sequence of a coding manner by utilizing a transcriptome sequence and training a nucleic acid sequence mode of a coding protein by utilizing a Markov chain; (6) determining a coding manner of a protein coding sequence of a gene which is not compared. The method disclosed by the invention is used for carrying out high-throughput structural analysis on a lot of gene sequences obtained by transcriptome sequencing of any non-model organism and function annotation of the transcriptome sequence is automatically finished in an analysis process; a Markov model and a support vector machine model are constructed by utilizing a compared high-reliability protein coding nucleic acid sequence, and a gene sequence which is not compared is analyzed, so that the credibility of the structural analysis of the sequence is higher.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
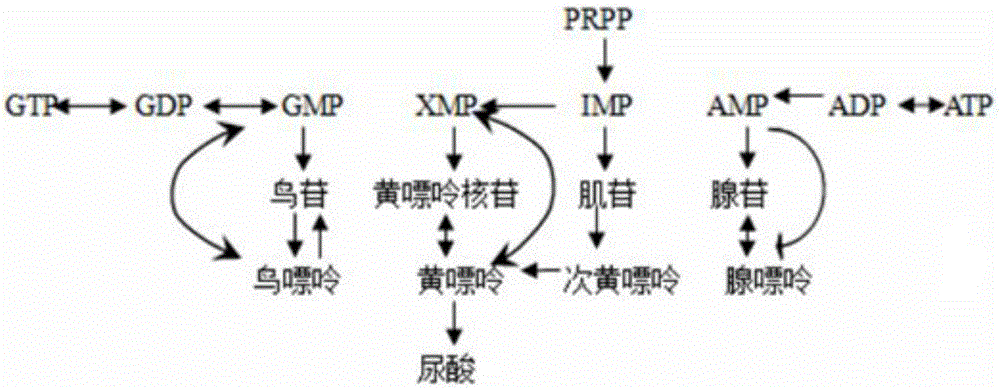
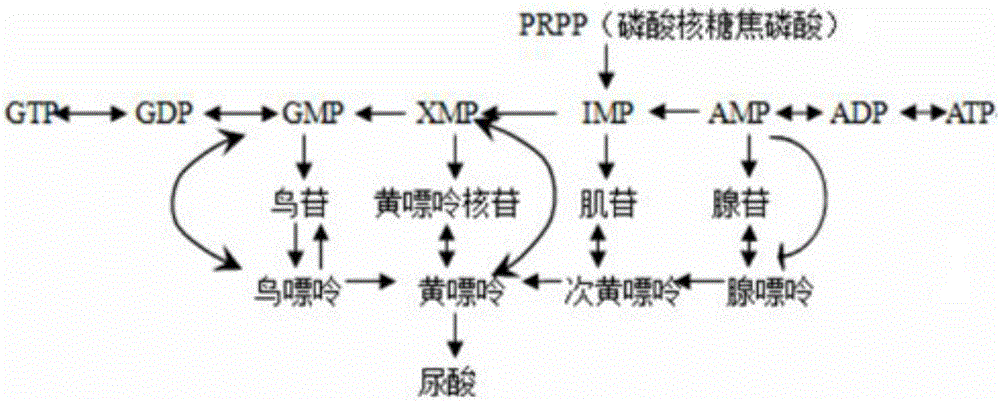
Construction method and application of caenorhabditis elegans hyperuricemia model and screening method of construction method
InactiveCN105833295AHigh similarityTypical pathological featuresCompounds screening/testingHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsMedicineMetabolic pathway
The invention relates to a construction method of a caenorhabditis elegans hyperuricemia model. The method comprises the following steps that 1, the uric acid content in caenorhabditis elegans is measured through a high performance liquid chromatography method; 2, an optimal drug delivery and culture mode is determined; 3, an optical drug delivery substance and drug delivery dosage are determined; 4, the optimal drug delivery time of xanthine is determined; 5, series experiment evaluation is conducted on the caenorhabditis elegans hyperuricemia model obtained through the construction method, and the caenorhabditis elegans hyperuricemia model which is low in damage, efficient, stable and reliable is obtained. According to the construction method, the hyperuricemia animal model is constructed by means of the model organism caenorhabditis elegans which has the high conservative property to human genes and has the similar uric acid metabolic pathway with human beings, the model has typical pathological characterization and is stable and reliable, various quantity indexes have the statistical significance, and a powerful tool is provided for large-scale and high-throughput drug screening of gout and the hyperuricemia symptom.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Freshwater rotifer common nutrient solution and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101595856AReasonable formulaImprove the quality of trainingAnimal husbandryFresh water organismVitamin B12
The invention relates to an organism nutrient solution, in particular to a freshwater rotifer common nutrient solution; the preparation method is that potassium nitrate, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, calcium nitrate hexahydrate, dipotassium phosphate, vitamin B12 and vitamin H are added into phosphate buffer with pH of 7.0-7.5. The invention with different proportions is added to distilled water to prepare the rotifer nutrient solution which is applicable to the common types of freshwater rotifers, and the nutrient solution has high stability, simple preparation, no poison and no harm and wide applicable scope, provides conditions for the indoor culture of the model organism rotifer studied in experimental ecology, improves the indoor culture quality of the freshwater rotifer and reduces the risk of rotifer cultivation.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
Bioremediation of nanomaterials
The present invention provides a method comprising the use of microorganisms for nanotoxicity study and bioremediation. In some embodiment, the microorganisms are bacterial organisms such as Gram negative bacteria, which are used as model organisms to study the nanotoxicity of the fullerene compounds: E. coli W3110, a human related enterobacterium and Shewanella oneidensis MR-1, an environmentally important bacterium with versatile metabolism.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
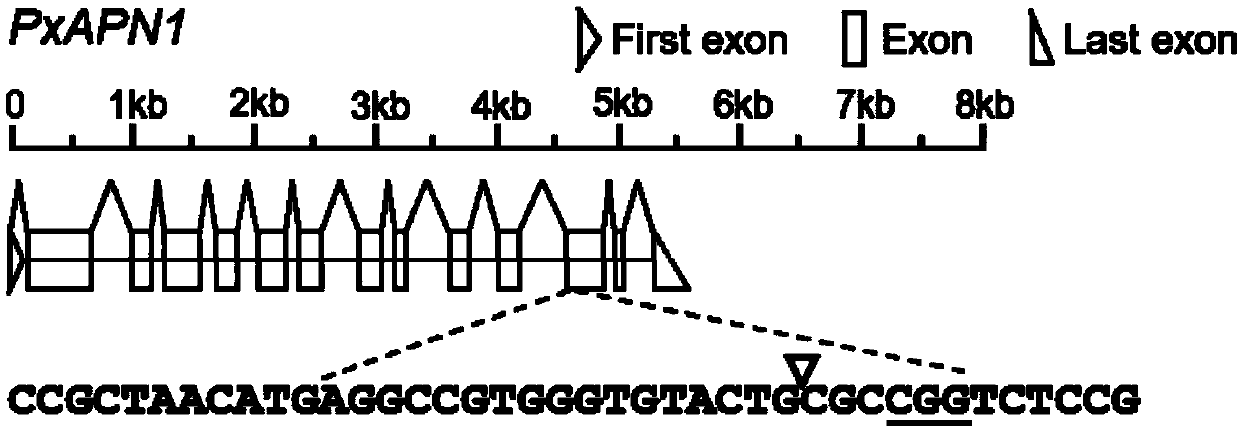
Method for knocking out plutella xylostella APN1 gene with CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing system and application of method
InactiveCN109593762AGood reference valueIncrease resistanceStable introduction of DNAPeptidasesHigh resistancePlutella
The invention discloses a method for knocking out a non-model organism plutella xylostella APN1 gene with CRISPR / Cas9 and an application of the method in molecular research on Bt Cry1Ac insecticidal protein resistance mechanisms. According to the method, a specific sgRNA target sequence of the plutella xylostella APN1 gene is designed and synthesized, sgRNA and Cas9 protein are mixed, the mixtureis microscopically injected into the posterior pole part of early embryonic disc stage eggs of plutella xylostella, plutella xylostella APN1 gene homozygous mutant populations with stable heredity arescreened out by a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system and applied to toxicity bioassay of Bt Cry1Ac insecticidal protein, which proves that plutella xylostella APN1 gene mutation can cause high resistance to Bt Cry1Ac insecticidal protein. The method is simple and efficient, time and labor are saved, technical support is provided for deep research on functional genes in non-model organisms, and a foundation is laid for exploring new pest control strategies.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A method for screening toxicity of traditional Chinese medicine by model organism zebra fish
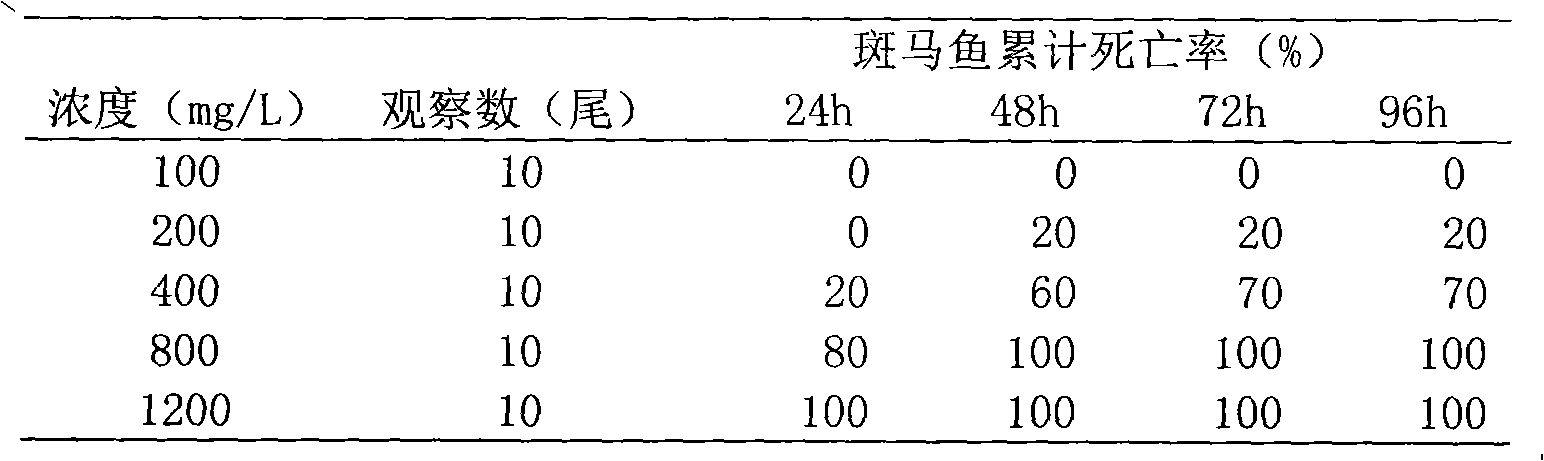
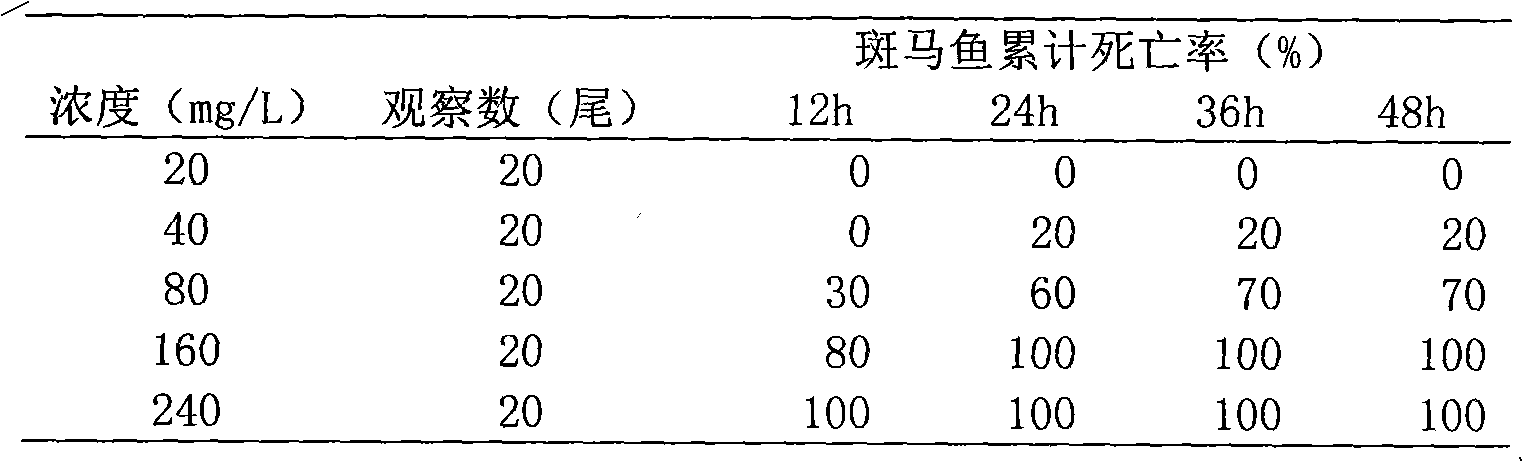
InactiveCN102716501AHigh speedSimple and fast operationIn-vivo testing preparationsMedicineConfidence interval
The purpose of the invention is to provide a method with easy operation and high accuracy for screening toxicity of traditional Chinese medicine by model organism zebra fish. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving a crushed or extracted traditional Chinese medicine material or a patented Chinese herbal prescription into water, preparing test solutions with different concentrations, selecting healthy and active zebra fish with similar sizes, and putting the zebra fish randomly into clean glass jars with an experimental temperature of (20+ / -2) DEG C, continuously observing for 4 hours after the experiment begins, simultaneously carrying out untime observation within 120 hours at a frequency of at least one time observation in every 6 hours, picking out dead fish timely, when the fish fries are poisoned to stop breathing, clamping the fishtail petioles with a pincette, determining that the fish fry is dead when no response is observed in 10 min], calculating and recording accumulated mortality of the zebra fish of each group, and calculating LC 50 and 95% confidence interval by utilizing a karbers method. The method is characterized by a simple operation method and a strong practicality; the method can preliminarily determine the toxicity of the traditional Chinese medicine with a fast speed and a high accuracy.
Owner:SHANGHAI BAINIAN SHIDANDE INSPECTION TECH
Novel method for evaluation of osteoporosis prevention treatment drug effect
InactiveCN102980981AGuaranteed accuracySimple conditionsMaterial analysis by optical meansTesting medicinal preparationsMicroscopic observationDrug administration
The present invention discloses a novel method for model organism zebrafish evaluation of osteoporosis prevention treatment drug effects. The method includes selecting zebrafish as a model animal, grouping and designing experiments by an optimized experimental grouping method, administering by using a preferable drug administration method, using a preferable method to dye zebrafish bones with alizarin red, capturing images by intuitive microscopic observation, and analyzing bone dyed areas to reflect the amount of bone mineralization by using a preferable image analysis software. The entire experimental method is high in operability, can objectively reflect the effects of the drug in zebrafish in vivo on bone mass generation, and can quickly and accurately evaluate the effects of compounds and complex ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. The method can overcome the shortcomings that ordinary in-vitro cell experiments are rigor in experimental conditions and difficult to reflect body effect comprehensive results; and overcomes shortcomings that mammal in-vivo experiments are time-consuming, large amount of drug are tested, and labor intensity is high. The method is high in accuracy of experimental results, the experimental method is high in repeatability, the required drug to be tested is relatively less, the cost is low, labor intensity is low, application range is wide, the experimental studies can be conducted in batch, and the working efficiency is high.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE INST OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Process and architecture of robotic system to mimic animal behavior in the natural environment
A robotic architecture for capturing the autonomous performance advantages the animal models enjoy in the natural environment is disclosed. A biomimesis process is employed to allow selective utilization of basic physical components and adaptation of a common control paradigm for each of different vehicle types. The biomimetic architecture involves five functional elements: a basic biomorphic plant for capturing the biomechanical advantages of the model organism; a neural circuit-based controller consisting of a finite state machine; myomorphic actuators producing linear graded force in response to trains of current pulses for mediating movements; labeled line code output by neuromorphic sensors; and a reactive behavioral sequencer executing command sequences defined within a behavioral library.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Screening method of medicines for inducing formation of myocardial cells by using model organism zebrafish
InactiveCN102520130AIncrease success rateDirect observation of side effectsMicrobiological testing/measurementTesting medicinal preparationsSide effectScreening method
The invention, belonging to the technical field of medicament, particularly relates to a screening method of medicines for inducing the formation of myocardial cells by using a model organism zebrafish, comprising the following steps: first, letting 25-30 pairs of Tg (cmlc2: EGFP) transgenic zebrafish homozygotes mate to obtain embryons, then transferring the embryons into a culture plate, adding a proper amount of zebrafish embryons at the stage of 50% epiboly in every pore, using an embryon culture solution containing 1-30 mu M small molecular compounds in an incubator for culture; then carefully checking the embryon heart size, heart shape and the number of myocardial cells; in addition, checking the whole shape (such as dorsal-ventral body axis, anterior-posterior body axis, etc.) and whether the formation of other organs of the embryons is influenced; and finally preliminarily judging whether the small molecular compounds promote the formation of the myocardial cells without influencing the growth of the other organs according to the experiment results. The new medicines which are screened out by the method has strong specificity and low toxic and side effect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com