Patents
Literature
312 results about "Rotifer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The rotifers (from Latin rota “wheel” and -fer “bearing”), commonly called wheel animals or wheel animalcules, make up a phylum (Rotifera) of microscopic and near-microscopic pseudocoelomate animals. They were first described by Rev. John Harris in 1696, and other forms were described by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1703. Most rotifers are around 0.1–0.5 mm long (although their size can range from 50 μm to over 2 mm), and are common in freshwater environments throughout the world with a few saltwater species.
Mirco algal food nutrient intensifying agent prescription and its preparing process
InactiveCN1653938ABalanced nutritionReasonable ratioAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsShrimpAdditive ingredient
The present invention is one kind of nutrient reinforcing agent for artificial fry raising of marine animal, and relates to the recipe and preparation process of micro algae bait nutrient reinforcing agent. The microalgae bait nutrient reinforcing agent consists of several kinds of micro algae containing different nutritious components and has grain size of 5-20 microns. It contains great amount of DHA, ARA and natural astaxanthin, and can raise the immunity and survival rate of raised marine animal. It can meet the requirement of hatched fries of fishes, shrimps and shells in feed. For example, when the microalgae bait nutrient reinforcing agent is used in raising turbot, it can raise the survival rate and lower the albinism rate greatly.
Owner:QINGDAO SAMUELS INDAL & COMML
Cultivation of dha-rich prey organisms for aquatic species
InactiveUS6789502B2Increase successClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffAquatic speciesOrganism
A method is provided for producing prey organisms such as Artermia and rotifers, for feeding aquacultural organisms in particular at the larval stage. The method comprises cultivating the prey organisms during at least part of their life cycle in an aqueous medium comprising at least one lipid component having a DHA content of at least 30 wt %. The enriched prey organisms preferably have a DHA content of at least 12 wt % of their total lipid content. The prey organisms are suitable feed for larvae of fish including halibut, turbot, bass, and flounder, and crustaceans and molluscs.
Owner:EPAX NORWAY
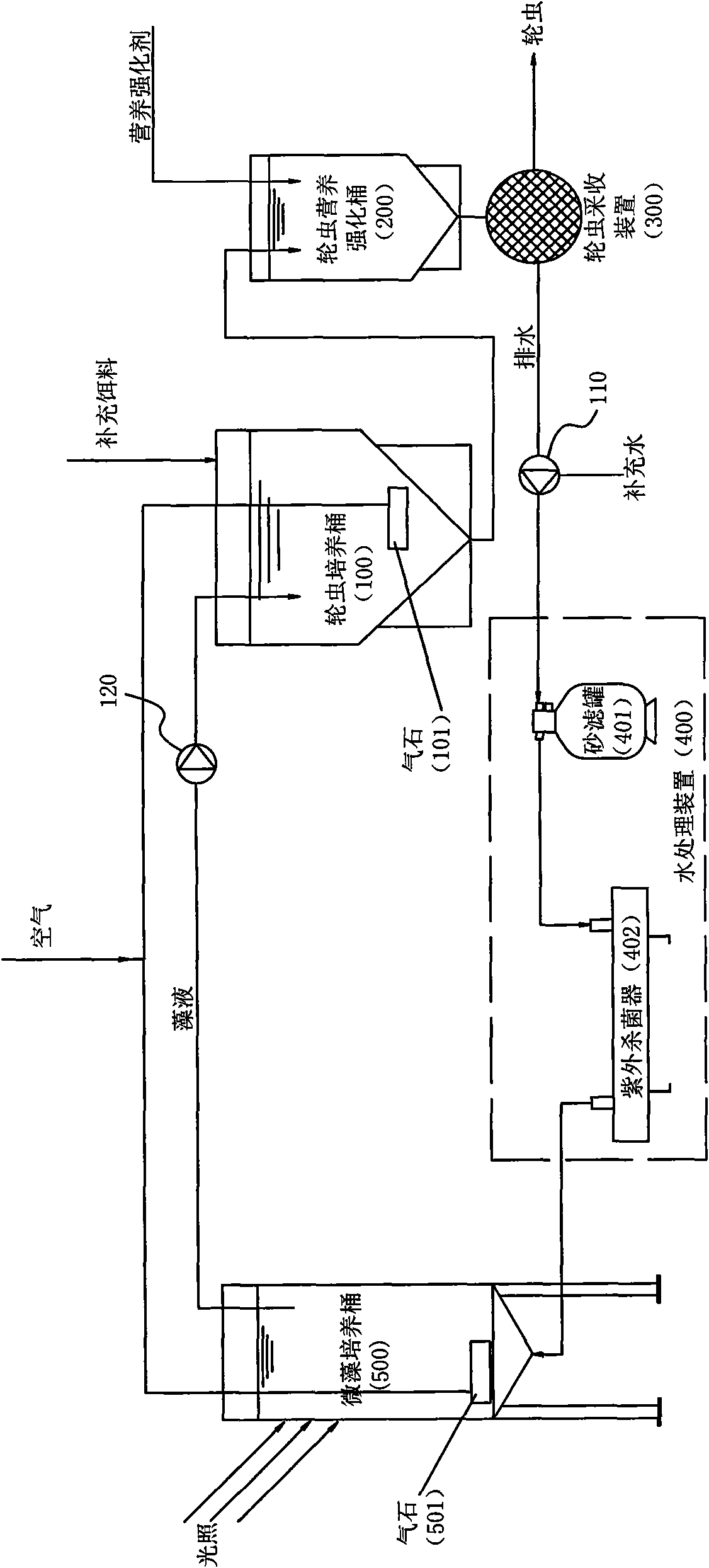
Closed circulating rotifer continuous culturing system
InactiveCN101653106AEfficient and stable productionImprove and enhance nutritional qualityUnicellular algaeAnimal husbandryWater resourcesNutrition quality
The invention provides a closed circulating rotifer continuous culturing system which comprises at least one group of rotifer culturing barrels, at least one group of rotifer culturing reinforcement barrels, a rotifer harvesting device, a water treatment device and at least one group of microalgae culturing barrels, wherein the output ends of the rotifer barrels are connected with the rotifer culturing reinforcement barrels, the output ends of the rotifer culturing reinforcement barrels are connected with the rotifer harvesting device, the rotifer harvesting device is connected with the watertreatment device, the output end of the water treatment device is connected with the microalgae culturing barrel, and the microalgae culturing barrel is communicated with the rotifer culturing barrels. The invention adopts a special microalgae culture control technology, a water treatment technology and a chemostat theory, realizes the recycle of rotifer culture water the continuous production ofrotifers, saves water resources and reduces emission of harmful substances under the condition of ensuring that the rotifers can be efficiently and stably produced; meanwhile, the invention performs nutrition reinforcement to the cultured rotifers, improves and strengthens the nutrition quality of the rotifers, and achieves the purpose of the invention.
Owner:FISHERY MACHINERY & INSTR RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERY SCI
Comprehensive processing method of aquiculture sewerage
InactiveCN101327997ARecycling with purposeOrderly recyclingMultistage water/sewage treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentEcological environmentRotifer
The invention relates to a comprehensive treatment method of aquiculture sewage comprising the following steps: providing a ecological treatment pool, discharging the aquaculture sewage into the ecological treatment pool, then inoculating photosynthetic bacteria and chlorella to reach a first ecological environment; inoculating rotifer and moina macrocopa to reach a second ecological environment; drying the rotifer and daphnias at a low temperature after collecting the same to obtain the solid products; discharging the filtrate after ozone treatment; supplementing new aquiculture sewage into the ecological treatment pool and repeating the above treatment. The method of the invention constructs an integration technology system about physicochemical, biology, ecological combinative technology and provides feasible technical support for the sustainable development of the intensive breeding industry and the establishment of the circular economy mode.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for treating aquaculture wastewater
InactiveCN101885554AReduce nitrogen and phosphorus contentSolve the problem of not being able to remove dissolved pollutants in water bodiesMultistage water/sewage treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentAquatic animalSelf purification
The invention discloses a method for treating aquaculture wastewater. The method comprises the following steps of: performing modular processing on wastewater by using microalgae and beneficial bacteria; and throwing snails, filter-feeding fishes and other aquatic animals into a water body to realize self-purification of an aquaculture water environment after the modular processing. Dominant and beneficial microalgae such as diatom, green algae and the like capable of absorbing nitrogen and phosphor in the aquaculture water body are screened out, inoculated, rapidly cultured and put into the aquaculture water body; the water color is regulated and the alga concentration is controlled by the methods of rational fertilization and rotifer inoculation; the beneficial bacteria are bacillus and photosynthetic bacteria capable of degrading organic matters and ammonia nitrogen in the water body; the beneficial bacteria and feed are proportionally mixed before the feed is put into the water body; after the feed is put into the water body, an underwater biomembrane taking the feed as a matrix is formed; the nitrogen, the phosphor and other harmful pollutants in the aquaculture water body can be effectively removed by jointly using the microalgae and the beneficial bacteria; simultaneously, the utilization efficiency of the feed can be improved by mixing the beneficial bacteria and the feed; and the water body is processed by using the microalgae and the beneficial bacteria, and then the snails and the filter-feeding fishes are put into the water body to prevent excessive multiplication of phycomycete, so that the self-purification of the aquaculture water environment can be realized.
Owner:上海楚水水产科技有限公司
Method for small-scale and simple culturing of freshwater rotifers
ActiveCN104082248ASolve the difficult problem of harsh cultivation conditionsReasonable designAnimal husbandryFisheryZoology
The invention discloses a method for small-scale and simple culturing of freshwater rotifers. The method is characterized by including the following steps of 1), freshwater rotifer protospecies collection; 2), screening of the freshwater rotifers; 3), biological culturing of bait of the freshwater rotifers; 4), inoculating and culturing enlargement of the freshwater rotifers; 5), collection of the freshwater rotifers; 6), prevention and control of enemy organisms in the process of culturing of the freshwater rotifers. The method is reasonable in design and high in operability; by performing hybrid culturing on the freshwater rotifers and the bait of the freshwater rotifers respectively, the problem of harshness in requirements on culturing conditions when the freshwater rotifers are cultured independently can be solved effectively, and culturing of the freshwater rotifers in fingerling production seasons can be realized without specific equipment as long as plastic barrels and inflating facilities exist indoors or outdoors. The method is free of limitation of equipment and site and has the advantages of low cost and simplicity and convenience in operation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG INST OF FRESH WATER FISHERIES
Composite nutrition enhancer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101810246AImprove survival rateImprove disease resistanceAnimal feeding stuffOrder copepodaPhaffia rhodozyma
The invention relates to a composite nutrition enhancer and a preparation method thereof, relating to a feed additive. The invention provides the composite nutrition enhancer, which not only contains large amount of DHA, ARA and natural yeast astaxanthin, but also contains multiple Omega 3 unsaturated fatty acids, multiple amino acids and trace elements. The composite nutrition enhancer is formedby composition of fission chytrid microalgae and phaffia rhodozyma with the weight ratio of 50 percent to 80 percent and 20 percent to 50 percent. All the components are weighed and mixed according to matching ratio after being crushed, mixed evenly, powder-sieved till the particle size is 8-25mum, inspected, weighed and packaged. The invention is especially applicable to feeding of live eels fryand shrimp postlarvae, artificial seawater seedling enhanced artemia salina sinnaeus, rotifer and cladocera (micrura), copepods and the like and various egg-laying poultries.
Owner:XIAMEN HUISON BIOTECH
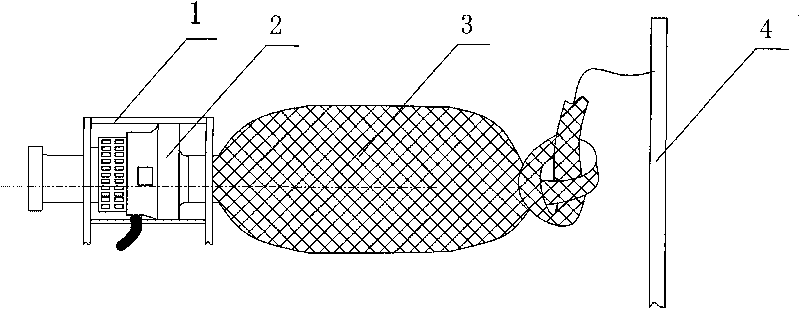
Method for collecting rotifers, Cladocera and copepods zooplankton
The invention relates to a method for collecting rotifers, Cladocera and copepods zooplankton, belonging to the technical field of fish culture. The method comprises the following steps of selecting collecting water areas of river channels, ditches or ponds and the like the zooplankton density of which is higher than 10 / ml in water bodies; fixing a collecting device and starting a submersible pump to ensure that the water inlet of the submersible pump is 30-50cm away from water surface, and collecting the zooplankton once every 1-2 hours after the pump is started; and separating the collected zooplankton according to different application with different mesh bolting silk and cleaning for 1-3 times with clean pond water. The device employed by the invention has simple structure, easy material obtainment and convenient use; the natural zooplankton resources naturally breeding and easily regenerating in various fresh water bodies can be sufficiently utilized, thereby greatly reducing the labor intensity and being suitable for use in standing water, slow flow water areas and water bodies with different sizes. The method has the characteristics of high efficiency, economy, practicality and the like.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI +1
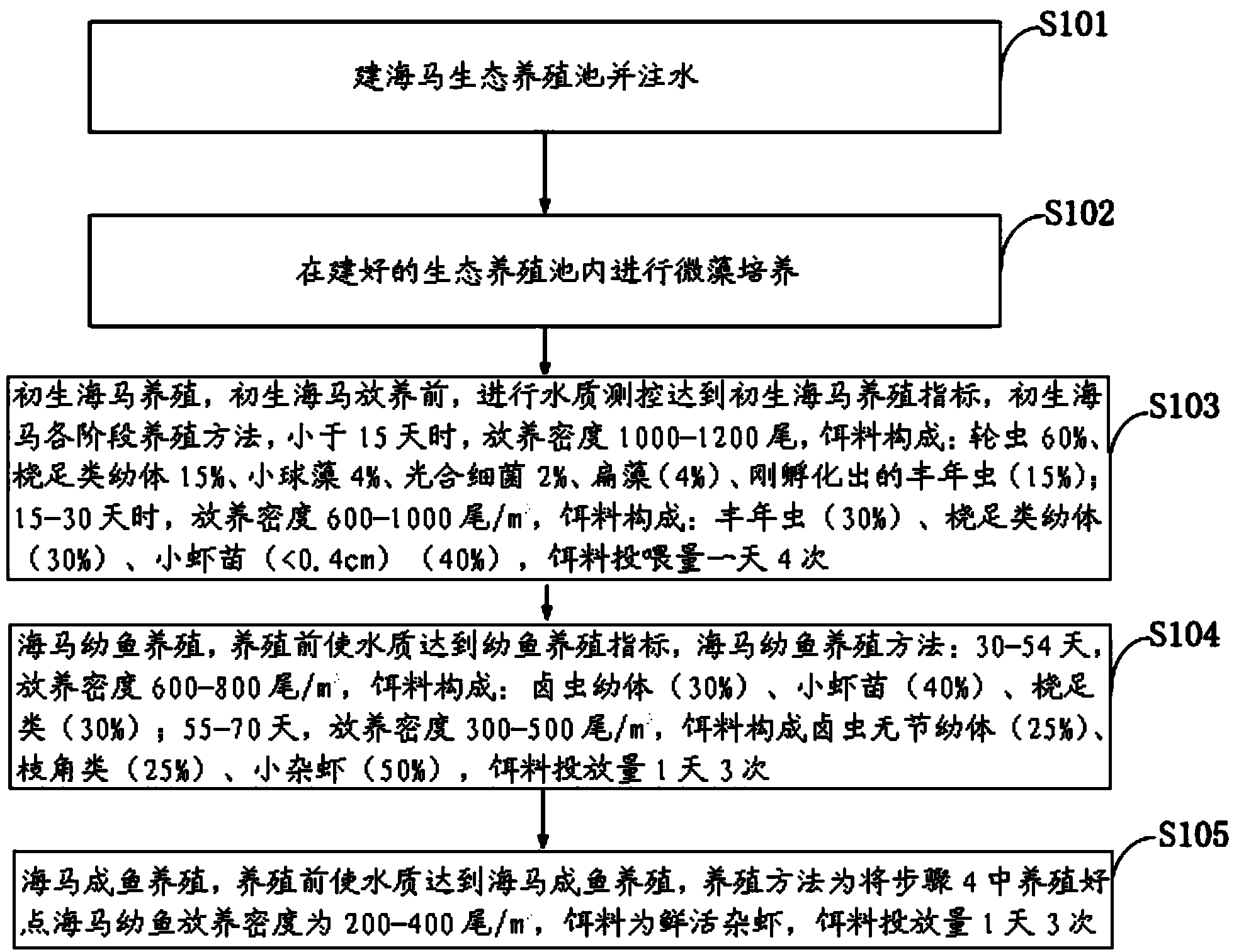
Hippocampus kelloggi ecological breeding method
ActiveCN103548722AImprove survival rateIncrease growth rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaShrimpJuvenile fish
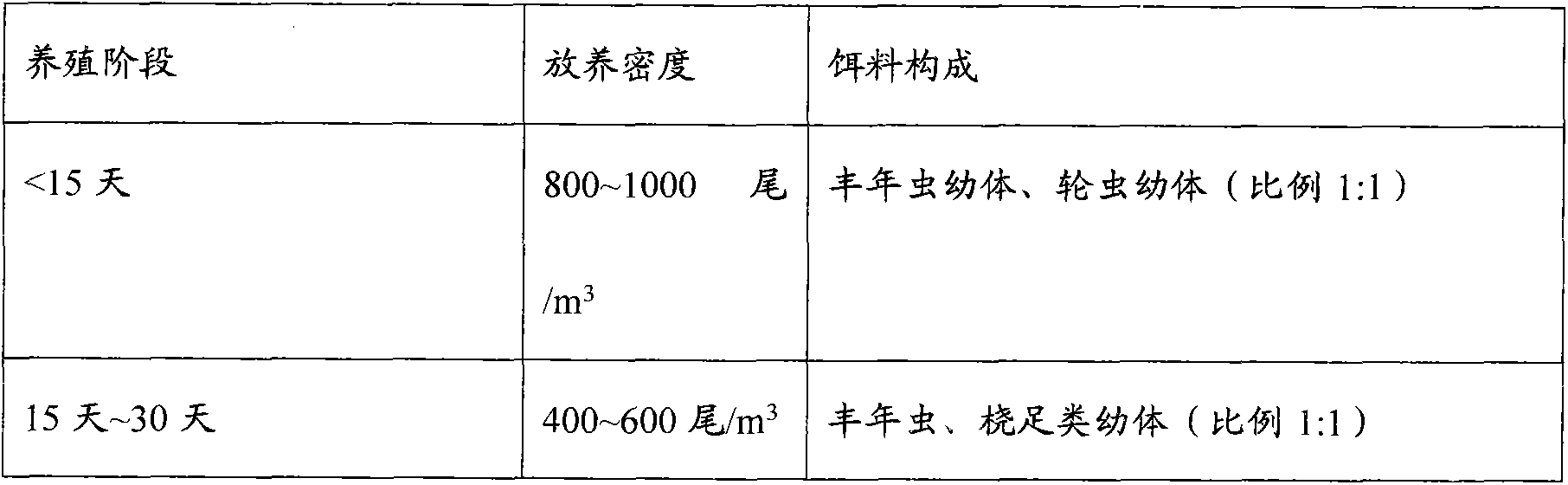
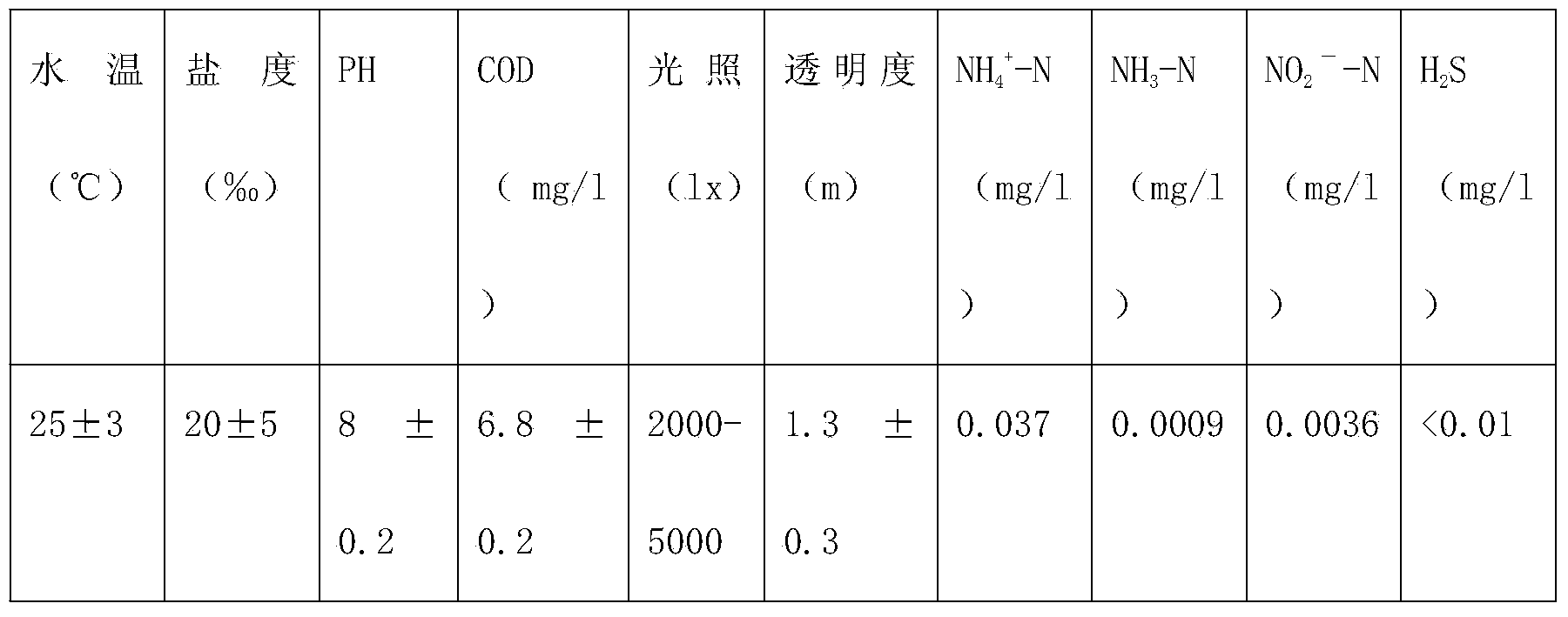
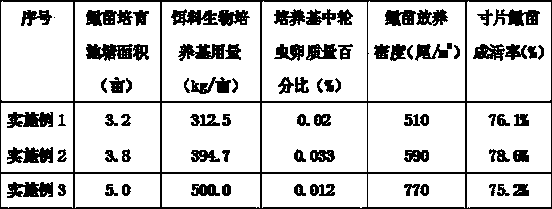
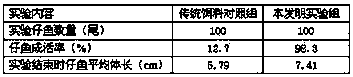
The invention discloses a Hippocampus kelloggi ecological breeding method. The Hippocampus kelloggi ecological breeding method comprises the steps of previous preparation, ecological breeding model establishment, newborn Hippocampus kelloggi breeding, Hippocampus kelloggi juvenile fish breeding and Hippocampus kelloggi adult fish breeding. The previous preparation includes reconstructing a shrimp seed breeding pond into a Hippocampus kelloggi breeding pond, and filling the pond with water after the pond is completely cleaned; ecological breeding model establishment includes in a microalgae cultivation stage, cultivating microalgae in water 3-5 days before Hippocampus kelloggi breeding, utilizing the microalgae as feedstuff of rotifers, artemia and fairy shrimps and improving water quality through photosynthetic bacteria; the newborn Hippocampus kelloggi breeding includes firstly measuring and controlling water quality, namely, detecting various indicators before stocking, then dividing the breeding stages into a breeding stage less than 15 days and a breeding stage between 15-30 days according to the duration of breeding days, and properly controlling the stocking density and feedstuff components of every breeding stage. The Hippocampus kelloggi ecological breeding method and artificial breeding method provide technical support and theoretical foundations for large-scale commercialized Hippocampus kelloggi breeding. By means of the Hippocampus kelloggi ecological breeding method, the breeding cost is reduced by 50%-60%, the quality of the breeding quality can be easily controlled by detecting various indicators before stocking, and high survival rate and growth rate of Hippocampus kelloggi can be guaranteed.
Owner:惠安港德海洋生物科技有限公司
A kind of co-cultivation method of freshwater rotifers and chlorella
ActiveCN102273431AGuaranteed normal reproductionAvoid breedingUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesFresh water organismSafety control
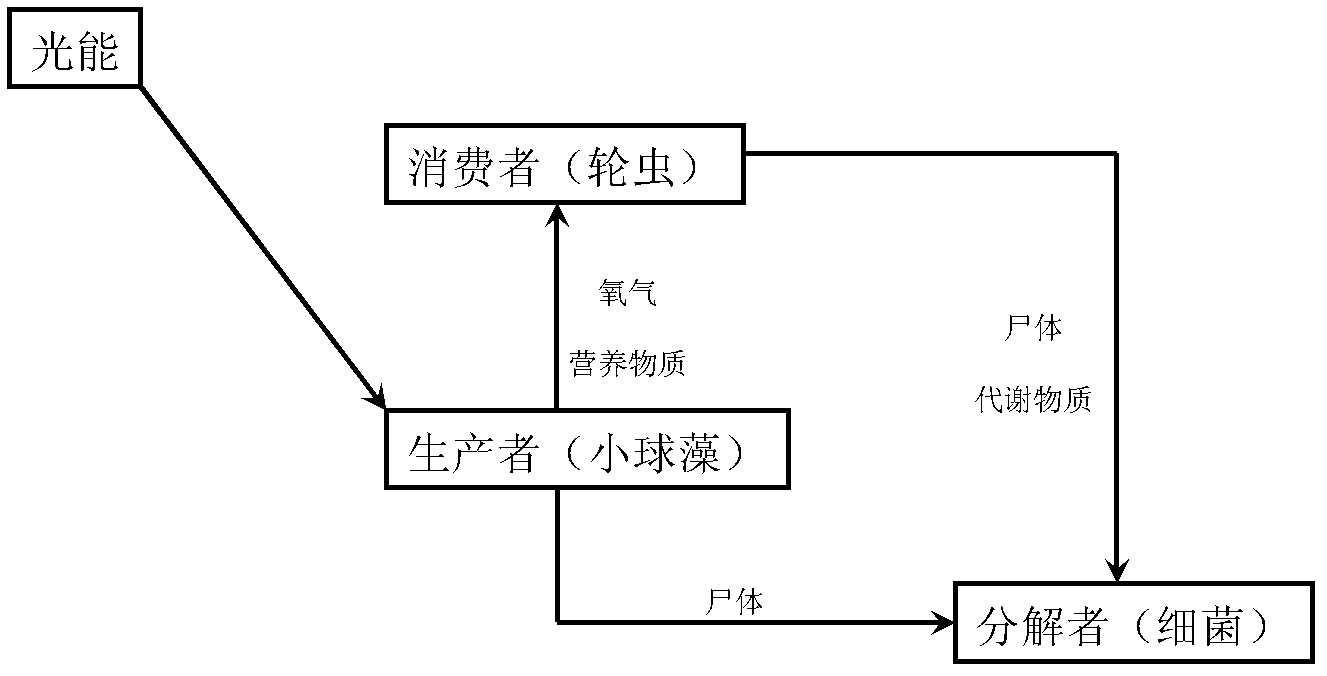
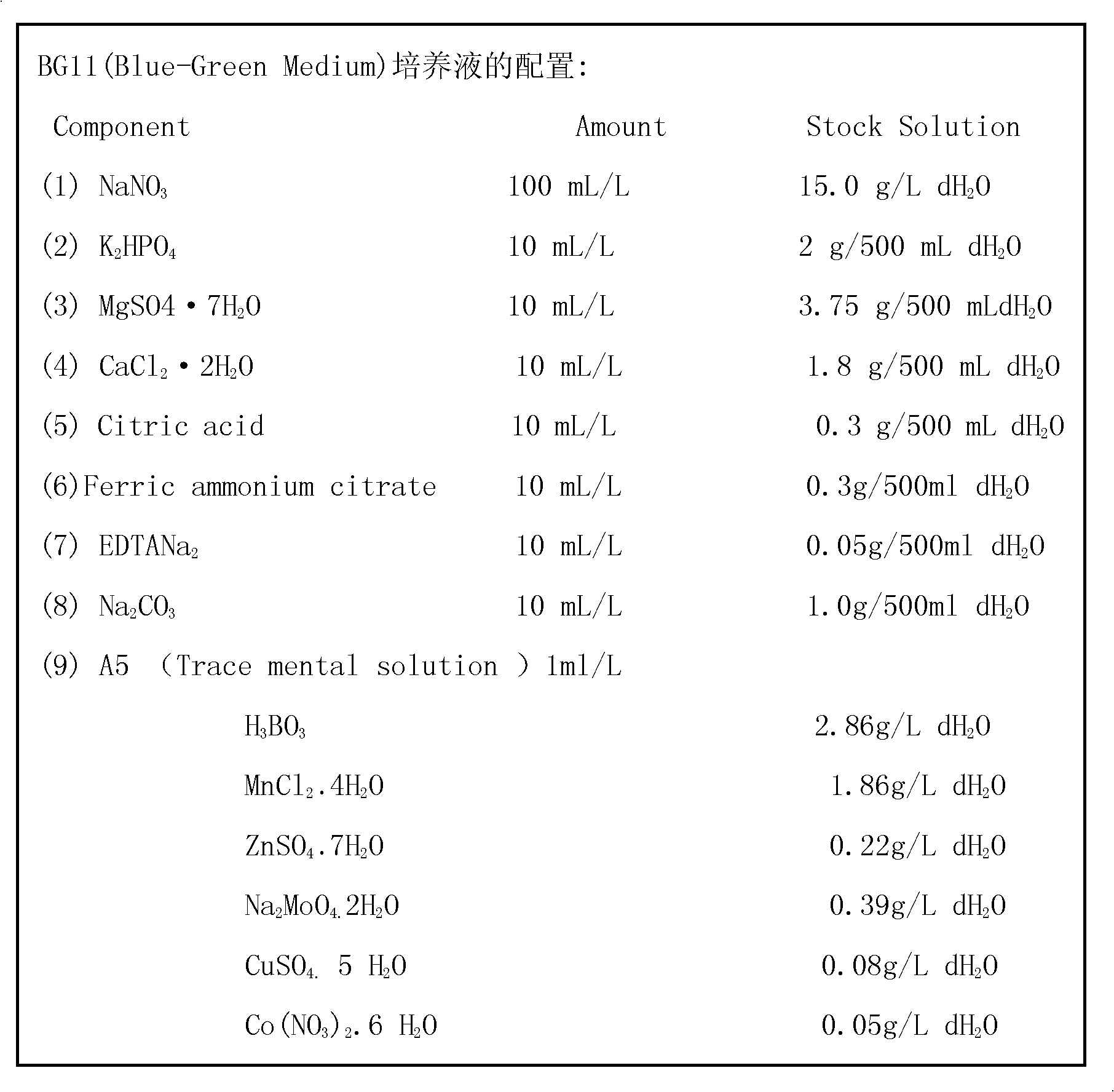
The invention discloses a method for separating dominant rotifers and co-culturing the dominant rotifer and chlorella vulgaris in an O3 / BAC (biological activated carbon) advanced treatment process, which comprises the following steps of: a. determining the rotifers in the O3 / BAC advanced treatment process: researching population structures of planktonic animals in various process flows of waterplant ozone activated carbon advanced wastewater treatment, sampling and respectively quantitatively and qualitatively analyzing; b. separating the dominant rotifers in the O3 / BAC advanced treatment process: acclimating in dark at room temperature over night, picking up health and lively adults by using a dropper for further culturing; c. culturing the chlorella vulgaris: grafting purified single chlorella vulgaris in a Blue-Green Medium culture solution; d. carrying out adaptability on the rotifers: directly grafting the rotifers with the initial grafting density of 10-30 / L in the cultured chlorella vulgaris solution; e. co-culturing: co-culturing according to the initial grafting density of the rotifers; and f. subcultring: if the rotifers in a culturing system is dead, transiting the rotifers for subcultring. Co-culturing the dominant rotifers indoors for a longer time in the O3 / BAC advanced treatment process is realized, and the density of the rotifers is maintained at 400-600 ind / ml. Particularly, experimental material is provided for safety control and risk assessment research of the rotifers in life drinking water.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Coilia ectenes step type breeding method
ActiveCN104472412ASolve the shortageSolve the labor-intensiveClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaYolkFresh water organism
A coilia ectenes step type breeding method comprises the nine steps of reserved parent pool simulated ecological cultivation, parent pool intensive culture, parent selection for induced spawning, parent induced spawning, natural insemination, germ cell collection, germ cell incubation, indoor intensive fry rearing in a cement pool and large-scale fry culture in an outdoor pool. The method is characterized in that filial-generation coilia ectenes adult fishes which are more than 2 years old and cultured by manpower are used as reserved parents for artificial propagation, and a natural ecology cultivation mode is simulated; the selected parents are transported and placed in an induced spawning pool, after parent induced spawning is conducted, the germ cells are collected, counted and transferred to an incubation pool, after the germ cells are collected, the germ cells are placed in the incubation pool with water, fries open the mouths 5-6 days after membrane rupture is conducted, yolks and freshwater rotifers which are filtered through a 80-mesh silk net are fed to the fries, after the fries are cultivated for 15 days, the fries are divided to different pools, and when the fries are as long as 20-30 mm, the fries are placed to outdoor pools to be cultivated.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
Loach water breaker opening bait put into pond and culture method thereof
InactiveCN101647420ANutritional diversityDelicious and easy to getClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDecompositionWater quality
The invention discloses loach water breaker opening bait put into a pond and a culture method thereof, relating to loach bait. The method selects a rotifer as the optimal loach water breaker opening bait put into the pond and the culture method comprises the following steps: (1) before water breaker is put into the pond, cleaning silt of the pond, thoroughly disinfecting the pond and killing harmful bacteria and viruses; (2) putting a proper amount of biological bacterial manure into water; and (3) putting loach water breaker after generating proper density of rotifers. The bait cultured by the method is biological bait and has all-round nutrition; the rotifers favored by the loaches are cultured by bacteria, palatable and easily obtained; biological bacterial manure can carry out photosynthesis to increase dissolved oxygen in water and keep the water quality fresh; and the bacteria can accelerate the decomposition of organic matters in water, reduce water body pollution and oxygen dissolved consumption, fully utilize inorganic matters decomposed in water body to synthesize organic matters and promote the circulation of matters in the water body.
Owner:湖北省水产科学研究所
Compound medicinal composition for destroying and expelling rotifers and protozoa and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101711528AQuick and effective exterminationGood control effectBiocideArthropodicidesDiseaseProtozoa
The invention relates to a compound medicinal composition for destroying and expelling rotifers and protozoa and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the field of veterinary medicament. The compound medicinal composition comprises rhizome zingiberis, stone-like omphalia, areca-nut, common carpesium fruit, male fern rhizome, the tuber of stemona, kuh-seng and anhydrous cupric sulfate. Thecompound medicinal composition of the invention can effectively control fulminant rotifers and protozoa diseases in culture ponds of fishes, shrimps and crabs, and particularly can avoid the shrimps and the crabs hypoxia caused by the fulminant rotifers and protozoa diseases in the culture ponds of the shrimps and the crabs; and at the same time, the compound medicinal composition can kill the protozoa such as chilodonella, the rotifers and the like and the resting eggs of the rotifers. The compound medicinal composition is green, safe and environmentally-friendly, and has no toxic or side effect on the shrimps and the crabs; the compound medicinal composition does not generate medicament residue harm to human health and medicament resistance, and does not pollute the environment; and in the compound medicinal composition, 95 percent of medicament grain has the diameter of 50 microns, the effective component of the medicament can be released quickly, the medicament dosage can be reduced, the medicament resource is saved, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING DABEINONG ANIMAL HEALTH TECH +1
Method for cultivating epinephelus septemfasciatus offspring seeds
InactiveCN102100190AMake sureRegulate water qualityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaShrimpSalinity
The invention discloses a method for cultivating epinephelus septemfasciatus offspring seeds, which comprises the steps of: culturing the offspring seeds under the conditions that the salinity is 28+ / -2, the water temperature is 19+ / -2 DEG C, the pH value is 8+ / -0.3 and the dissolved oxygen is more than 6mg / l, controlling the seedling distributing density to be 8000-15000 / M<3>; before newly hatched larvae enter a pool, putting a composite bacterium (photosynthetic bacterium and nitrobacterium) according to the concentration of 2ppm, adding 0.5ppm of composite bacterium and 1ppm of shrimp feedevery day after 5 days, adding 1ppm of composite bacterium and 1ppm of shrimp feed every day after 25 days, and stopping adding the composite bacterium and the shrimp feed after 50 days; illuminatingthe newly hatched larvae at 2000-4000lx until the newly hatched larvae grow to the 10th day, illuminating the epinephelus septemfasciatus growing from the 11th day to the 30th day at 1000-3000lx and illuminating the epinephelus septemfasciatus growing from the 31st day to the 60th day at 500-1000lx; after the newly hatched larvae enter the pool, sucking and removing pollutants at the bottom of the pool at the beginning of the 30th day; feeding the newly hatched larvae growing from the 4th day to the 7th day SS (Som Somatostatin) type wheel animalcule and hardly developing before the wheel animalcule is fed to the larvae, wherein larva feed comprises the SS small wheel animalcule and common wheel animalcule; and feeding the common wheel animalcule in the newly hatched larvae growing from the 6th day to the 20th day, and developing newly hatched larvae through chlorella pyrenoidosa. The invention has the advantages of reasonable operation process and stable result, and is suitable for culturing cold temperate epinephelus septemfasciatus seeds.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for cultivating fries of coilia ectenes in soil pond
InactiveCN103404462AAchieve reuseImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDiseaseMeroplankton
The invention discloses a method for cultivating fries of coilia ectenes in a soil pond, comprising the steps of selection of an outdoor soil pond fry cultivation pond, secondary intensified cultivation of parent fishes, separation of the parent fishes and the fries, and early-stage cultivation of the fries of the coilia ectenes by cultivating food organisms including rotifer, cladocera and the like. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and convenient to operate, economical and practical, realizes repeated use of the parent fishes, and is low in fry cultivation cost, high in fry survival rate, and strong in disease resistance. By adopting the principle of natural selection, weak and sick fries are eliminated, so that the purpose of improving the fry quality is achieved. In addition, pelagic organisms are cultivated by utilizing glucose, amino acid and other nutrient solutions, so as to provide sufficient baits for the fries, and thus the quick growth of the fries is guaranteed.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Fry culture cultivating method for schizothorax prenanti
ActiveCN105075955AGrow fastReduce the chance of dyingClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffYolkPlankton
The invention discloses a fry culture cultivating method for schizothorax prenanti. After a fish pond is disinfected, fish fry disinfected with a povidone-iodine solution are put in the pond, micro-flow water is adopted for cultivation, cooked egg yolk is thrown and fed to the fry for several days, plankton bait is thrown and fed to the fry after 5-7 days, cut water earthworms and broken juvenile schizothorax prenanti materials are thrown and fed to the fry after 20 days, and juvenile schizothorax prenanti feed is thrown and fed to the fry till the fry reach the specification of larva fish. The schizothorax prenanti fish fry cultivated through the method are low in cost, high in survival rate and quick in growth, the cooked egg yolk, the rotifer and cladocera plankton bait, and the water earthworms and the juvenile schizothorax prenanti feed are thrown and fed to the fry in a staged mode, and therefore the high growth rate can be kept at each stage.
Owner:TONGWEI
Indoor artificial propagation method of rhodeus
ActiveCN103636542ASolution typeAddress stocking densityClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffBroodstockFresh water
An indoor artificial propagation method of rhodeus comprises the steps of intensive breeding of parent rhodeus, mating of the parent rhodeus, collection of offspring seeds and breeding of the offspring seeds. The method is characterized in that for the intensive breeding of the parent rhodeus, an adult rhodeus population cultured in a pond for one year is taken as a parent rhodeus population, female parent rhodeus individuals with clear ovary outlines and fallopian tubes extending to be tubular as well as male parent rhodeus individuals which can flow milky semen from abdomens when being slightly pressed at abdomens are selected at a ratio of 1:1, clams are released in a parent rhodeus culture pond, the offspring seeds are collected through drawing nets after one month and distributed in offspring seed culture ponds for breeding, opening baits for offspring seed breeding are small fresh-water rotifers filtered by a bolting-silk net with the fineness of 80 meshes, later, rotifers and moina filtered by a bolting-silk net with the fineness of 60 meshes are gradually supplemented, fries are fed with rotifers and copepoda filtered by a bolting-silk net with the fineness of 40 meshes when growing to 15 mm in total length, and the fries can be placed in ponds for conventional culture when being cultured to 30 mm in total length.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
Breeding process of polyodon spathula
InactiveCN101019517AReduce loss and wasteImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffSpathulaAnimal science
The breeding process of polyodon spathula belongs to the field of aquatic raising technology. The breeding process includes throwing rotifer and euglena as feed with the cultivation density of 2000-6000 / cu m for fry polyodon spathula and 400-1100 / cu m for small polyodon spathula. The breeding process has high survival rate, high utilization of feed and low cultivation cost.
Owner:HARBIN CITY ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Artificial breeding method for parapenaeopsis hardwickii
Disclosed is an artificial breeding method for parapenaeopsis hardwickii. A breeding pond is a circular or square cement pond, the area of the breeding pond is 12-20m<2>, the depth of the breeding pond is 0.7-1.0m, fine water circulation and pollution discharge functions are required, water is transparent, clear and free from harmful heavy metal ions, water with the depth of 70cm-100cm enters the parapenaeopsis hardwickii pond for the first time, the water is disinfected with 0.3mg / L of dibromohydantoin, individuals with plump gonads, strong bodies, no diseases and tawny or breen ovaries are selected as parent shrimps, after the sea parent shrimps are transported for a long distance, shrimp baskets are immediately immerged into the parent shrimp breeding pond, baits for opossum shrimps at a larva stage are yolks, compound feed (prawn crackers, Cheyuan and BP) and rotifers, the rotifers are generally fed twice a day, and the breeding water is filtered by a 100-mesh dilly bag.
Owner:苏州市阳澄湖现代农业发展有限公司
Two-stage cultivation method for loach offspring seeds
InactiveCN104542407AImprove survival rateFeed less oftenClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWeatherfishFodder
The invention discloses a two-stage cultivation method for loach offspring seeds. The two-stage cultivation method includes a primary cultivation stage and a secondary cultivation stage. The primary cultivation stage includes putting newly hatched loach offsprings in a net cage for cultivation and providing palatable feed; the secondary cultivation stage includes putting the loach offsprings subjected to primary cultivation in a pond in the peak season of rotifer, providing the palatable feed, reducing feeding quantity of the feed during the conversion period from branchial respiration to intestinal respiration of the loach offsprings, preventing parasites timely in the later period of cultivation, maintaining sufficient oxygen content of water, and completing the cultivation process of the loach offspring seeds until the length of the loach offsprings reaches 4-5cm. Compared with the prior art, the two-stage cultivation method has the advantages that survival rate of the loach offsprings is increased to more than 40% from present less than 10% in average, and the method is applicable to cultivation of the loach offspring seeds and has a broad application prospect.
Owner:FISHERIES RES INST ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Ecological Japanese sea horse breeding method
InactiveCN103960185ASuitable for artificial breedingClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaShrimpJuvenile fish
The invention discloses an ecological Japanese sea horse breeding method. The ecological Japanese sea horse breeding method comprises the steps of building an ecological sea horse breeding pond one week before breeding, cultivating microalgae in the built ecological breeding pond, and measuring and controlling water quality to reach newborn sea horse breeding indexes before newborn sea horses are bred. When the newborn sea horses is younger than 15 days, the released density is 1000-1200 tail / m<3>, and baits are composed of rotifer, copepods larvae, chlorella, photosynthetic bacteria, tetraselmis and fairy shrimps which are just incubated. During 15-30 days, the released density is 600-1000 tail / m<3>, baits are composed of fairy shrimps, copepods larvae and shrimp seeds, and the baits are fed into the breeding pond four times per day. A sea horse juvenile fish breeding stage comprises the step of enabling the water quality to reach juvenile fish breeding indexes before breeding. During 30-40 days, the released density is 600-800 tail / m<3>, and the baits are fed into the breeding pond three times per day. A sea horse adult fish breeding stage comprises the step of enabling the water quality to reach sea horse adult fish breeding indexes. The released density of sea horse adult fish is 200-400 tail / m<3>, baits are fresh and alive shrimps, and the baits are fed into the breeding pond three times per day. The ecological Japanese sea horse breeding method has the advantages of reducing production cost.
Owner:惠安港德海洋生物科技有限公司
Method for ecologically breeding litopenaeus vannamei by replacing part of feeds with living baits
ActiveCN110973027AHigh nutritional valueGood energyClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffEcological environmentZoology
The invention belongs to the technical field of aquatic product ecological breeding, and particularly relates to a method for ecologically breeding litopenaeus vannamei by replacing part of feeds withliving baits. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of (1) applying fermented dung to the bottom of a pond as a base fertilizer, wherein water intake depth is 60-80cm before litopenaeusvannamei fries are put, and performing disinfection treatment; (2) putting litopenaeus vannamei fries: applying composite microorganism preparations, putting the litopenaeus vannamei fires at the peak period of rotifers, and after 15 days of putting the litopenaeus vannamei fries, putting grass carps; (3) after 30-90 days after putting the litopenaeus vannamei fries, maintaining biomass in the pond to be sufficient, and maintaining bred animals, zooplankton and phytoplankton balanced; and (4) collecting litopenaeus vannamei: continuing breeding the litopenaeus vannamei for 30 days, mainly feeding compound feeds, enabling the shred litopenaeus vannamei to eat biological baits as assistance, after the length of litopenaeus vannamei bodies is 15cm or above, inducing the litopenaeus vannameiwith feeds, and harvesting the litopenaeus vannamei. The method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that more energy in ecological circulation can flow into bred products, ecologicalenvironment circulation is promoted, environmental pollution is reduced, feed feeding is reduced, and the cost can be reduced.
Owner:天津开发区坤禾生物技术有限公司
Method for improving survival rate of pomfret fry
InactiveCN101658147AFast growthImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffFish oilRotifer
The invention discloses a method for improving survival rate of pomfret fry, relates to breeding of pomfret fry, and needs to provide a method for improving survival rate and growth speed of pomfret fry. The method comprises the following steps: measuring a DHA / EPA / ARA proportion in pomfret parent fish tissues and body fatty acid compositions of the pomfret fry, wherein the step is characterized by mixing cuttlefish liver oil, refined fish oil, doxicon and peanut oil to form emulsified oil of which DHA / EPA / ARA proportion is 2.5 / 1.0 / 0.2; adding 0.25 gram, 0.35 gram and 0.45 gram of the emulsified oil into the breeding water in terms of each liter of rotifers to reinforce the rotifers respectively; and feeding the pomfret fry with the rotifers reinforced by adopting the best DHA / EPA / ARA allocation proportion reinforcing baits from the 4th day to the 12th day under the illumination condition of 1,000 to 50,001x at the water temperature of between 20 and 24 DEG C in the water with pomfretfry breeding density of 15,000 to 20,000 fishes per cube. The method is used for breeding the pomfret fry.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for culturing loach fries by using loach initial feed biological culture media
ActiveCN103766290ANo pollution in the processEasy to makeClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaForeign matterAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a method for culturing loach fries by using loach initial feed biological culture media, and relates to an aquaculture technique. The method adopts the following culture medium ingredients in mass percentage: 0.01 to 0.05 percent of rotifer spawns, 20 to 40 percent of bean pulp, 2 to 6 percent of meat and bone meal, 40 to 60 percent of pulverized fermented straws, 10 to 20 percent of fermented chicken manure and 1 to 1.5 percent of composite mineral salts. According to a preparation method, the raw materials are uniformly mixed and pulverized to powder or granular mixtures to be used. According to requirements, no peculiar smell, no foreign taste, no mildew and no foreign matters are generated, and the water content is lower than 17 percent. The method has the advantages that the feed biological culture media are green, safe and pollution-free, the preparation is simple, and the use is convenient; rotifer cultured by the feed biological culture media is palatable for the loach fries, and the biomass is great, and the peak period duration of the rotifer is long; the feed biological culture media are used, the survival rate of the loach fries is obviously improved, the fry cost is reduced, and the scale production requirement of loaches is met.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Ecological method for breeding young shrimps of litopenaeus vannamei in outdoor water
ActiveCN104585105ASuitable for productionAdvanced conceptClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAcanthosomaNitrite
The invention provides an ecological method for breeding young shrimps of litopenaeus vannamei in outdoor water. The method is characterized in that an indoor cement floor is changed into an outdoor cement floor, wherein the inoculation density of algae is controlled to be 5000-8000cell / ml; the inoculation time is controlled to the time before nauplii begin to be changed into zoea under the inoculation density; the synchronization between growth and propagation of the algae and requirements of an ecological system on the density of the algae is ensured; an inoculation density of rotifers is 5-10 / ml, and the inoculation time is the time before the nauplii begin to be changed into the zoea, thereby ensuring that the growth and propagation of the rotifers are e synchronous with the requirements of the young shrimps; the inoculation time of artemia is acanthosoma; the water transparency is retained at 80-120cm; the artemia has the effect of purifying the water; the content of ammonia nitrogen in the overall water is smaller than 0.2, and the content of nitrite is smaller than 0.02; the food intake of the young shrimps and the rotifers are not affected. Through the balance control on a young shrimp rearing water ecological system in the whole production process, the young shrimps take endogenous high-quality natural baits as the major food all the time; the cultured young shrimps of the litopenaeus vannamei are excellent in nutrition, healthy and high in quality.
Owner:HAINAN HAIYI AQUATIC PROD SEED CO LTD
Loach fry cultivation method
ActiveCN103828750AMeet nutritional needsPromote growthClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffYolkPrawn
The invention discloses a loach fry cultivation method. In April in spring, when a natural water body is higher than 18 DEG C in temperature, mature loaches which are regular in body form, strong in physique, much in mucus, healthy and scot-free are used as parents; LRH-A2 and DOM are used for hastening parturition; incubating is carried out at the water temperature which is 25 DEG C after oviposition, and loach fry cultivation is carried out after yolk sacs of most fries are basically disappeared after loach fry incubation; the loach fries are transferred to a pond to conduct cultivation according to a conventional summer fingerling cultivation technology after cultivation is carried out for seven days. According to the loach fry cultivation method, mixed feeding is carried out with yolk liquid and juvenile prawn mixed feed, the nutritional requirement of the mouth-opening periods of the loach fries is met, the loach fries rapidly grow, the complex process of rotifer cultivation is eliminated, the whole cultivation process is easy to operate, the labor amount is greatly reduced, meanwhile, the loach fry pond entering cultivation specification is increased, and the fry cultivation survival rate is improved.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
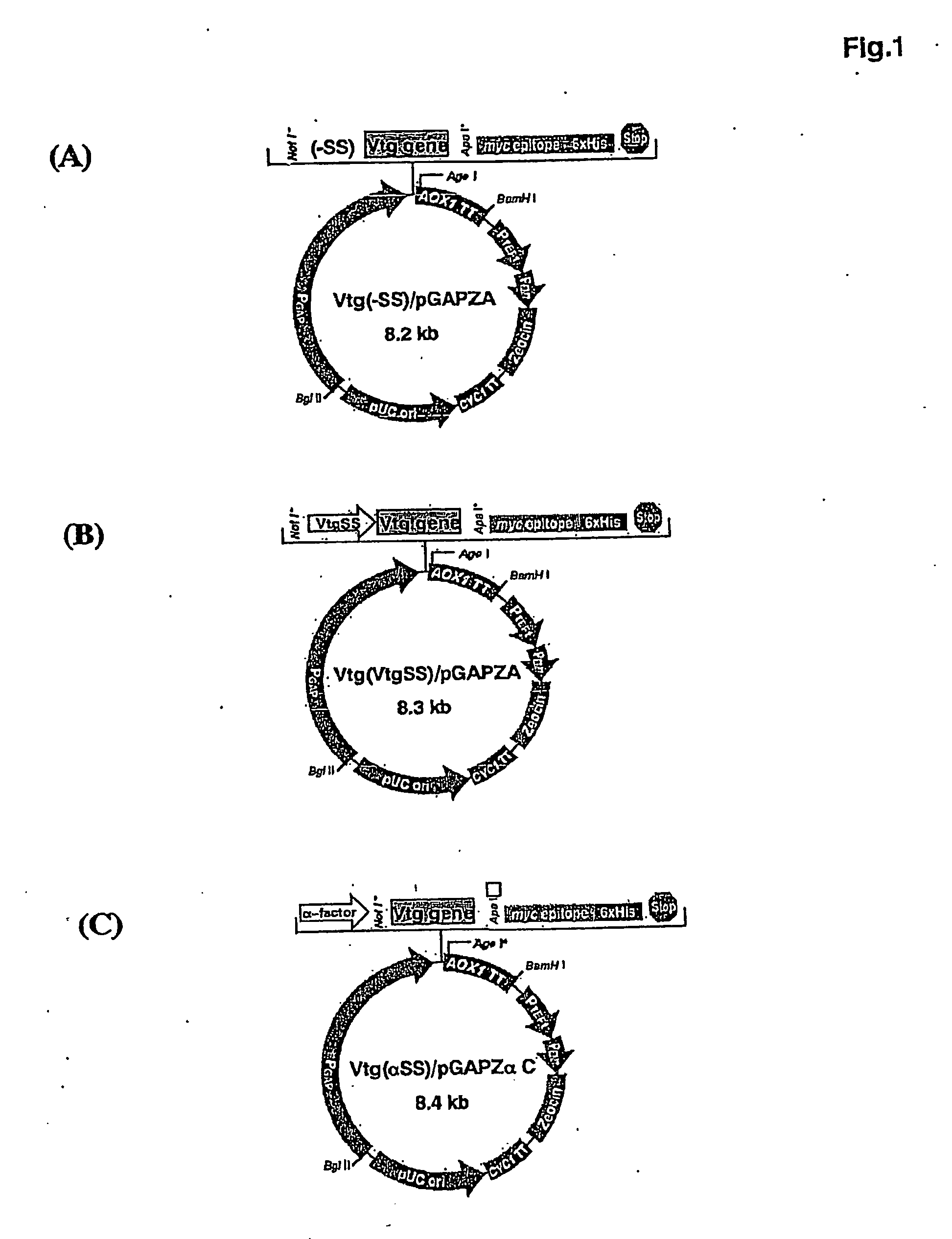
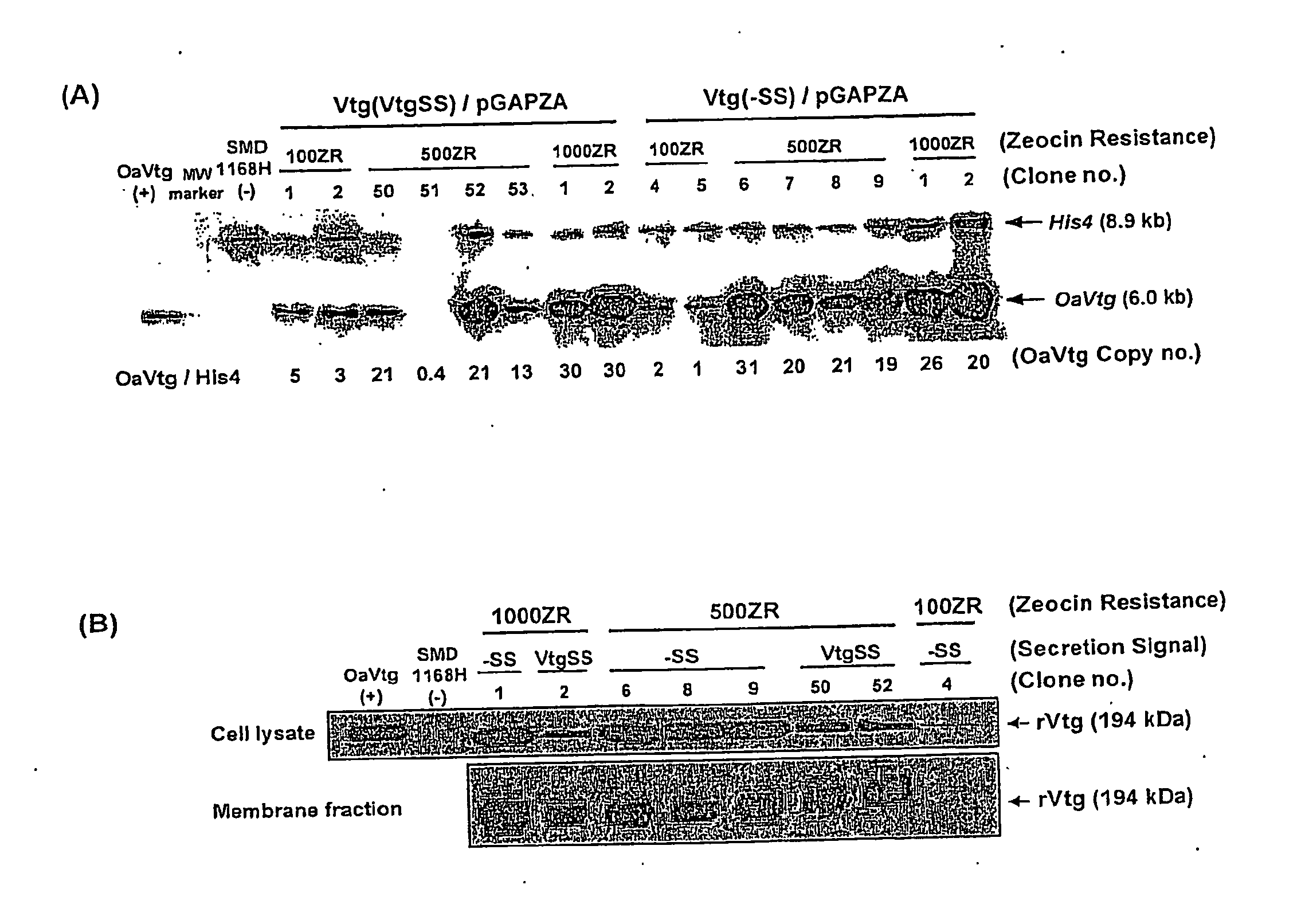
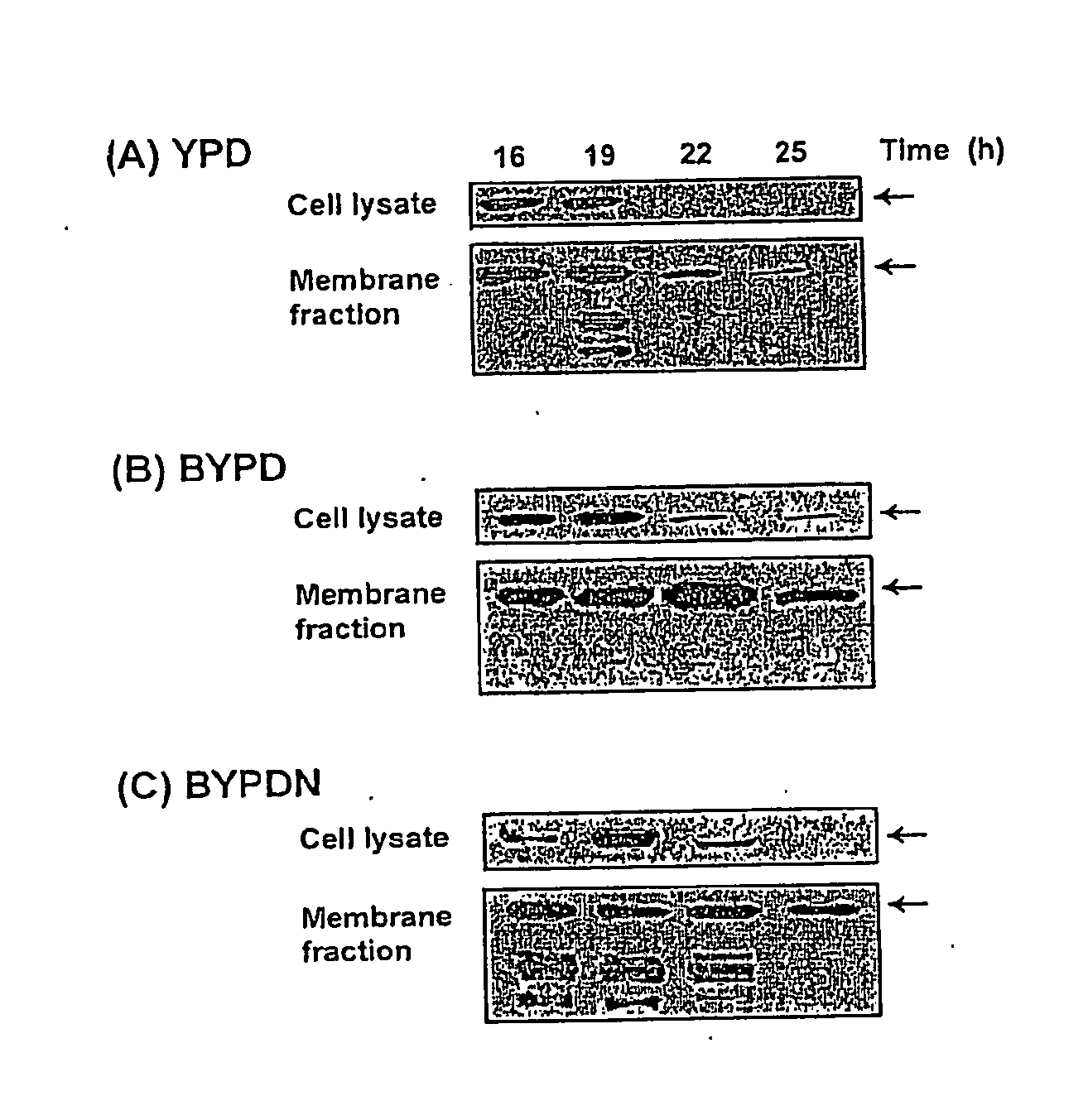
Recombinant vitellogenin enriched feed
The invention provides an expression vector for expression of recombinant vitellogenin in an eukaryotic host. An eukaryotic host, including yeast comprising the expression vector according to the invention may be used as a feed or feed additive for both oviparous and non-oviparous animals, including domesticated animals. A transgenic yeast according to the invention contain increased levels of essential amino acids and fatty acids and may be used as a direct feed or fed to an intermediate live feed such as rotifers or artemias to increase the survival rates of oviparous animal or broodstock.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Freshwater rotifer common nutrient solution and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101595856AReasonable formulaImprove the quality of trainingAnimal husbandryFresh water organismVitamin B12
The invention relates to an organism nutrient solution, in particular to a freshwater rotifer common nutrient solution; the preparation method is that potassium nitrate, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, calcium nitrate hexahydrate, dipotassium phosphate, vitamin B12 and vitamin H are added into phosphate buffer with pH of 7.0-7.5. The invention with different proportions is added to distilled water to prepare the rotifer nutrient solution which is applicable to the common types of freshwater rotifers, and the nutrient solution has high stability, simple preparation, no poison and no harm and wide applicable scope, provides conditions for the indoor culture of the model organism rotifer studied in experimental ecology, improves the indoor culture quality of the freshwater rotifer and reduces the risk of rotifer cultivation.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
High-efficient method for cultivating fry of turbot family
InactiveCN101473801AImprove germination rateFast growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBroodstockFish larvae
An efficient cultivation method of a turbot family offspring comprises the following steps: parent fish selection, parent fish cultivation, artificial directional mating, hatching, offspring cultivation and getting of commercial offsprings. The parent fish is selected from germplasm parent fish of different batches from different countries; artificial fertilization is performed among different germplasm parent fish, and the same batch of the parent fish are not allowed to mate with each other; offspring cultivation is as follows: at the early period, the adopted facility is a 3m glass reinforced plastics barrel, and bait comprises chlorella, rotifer and artemia; at the middle period, the adopted facility is a 10m cement pond, and the bait is micro pellet bait; at the later period, the adopted facility is a 20-30m cement pond, and the bait is fish larvae pellet bait; and specification of the commercial offsprings is 5-6cm. The method is characterized by adopting the parent fish with different germplasm resources for the artificial directional mating, and seriously controlling inbreeding; and adopting different culturing facilities to cultivate the offspring by three stages, which causes the offspring emergence rate of the commercial offspring to reach 46.8%, and improves growth rate thereof by 36%, and lowers of etiolation rate thereof below 5%. The method can efficiently produce high-quality turbot offsprings, and is applicable to large-scale production.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Breeding method for amphiprion ocellarises
InactiveCN104170777AUniversalPromote spawningClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaSmall animalJuvenile fish
The invention provides a breeding method for amphiprion ocellarises. The breeding method comprises the following three steps: a. breeding parent fishes; b. incubating oosperms; c. breeding young juvenile fish. Fry is bred for 60 d after being incubated, the overall length of the juvenile fish is up to 2 cm to 3 cm, and the breeding process is ended up; during the breeding process, the minced-meat-shaped fresh bait made of rotifer intensified by seawater chlorella for 24 h, artemia and copepods intensified by DHA and the chlorella for 12 h, and marine small animals of which phospholipid content is more than 25% in succession and compound feed are fed as the bait in an individual manner or a superimposed manner; furthermore, water is changed and the amphiprion ocellarises are divided and put in fish tanks in proper time. The breeding method for the amphiprion ocellaris, provided by the invention, provides a way which can be operated in an industrialized and large-scale manner; compared with the prior art, as the breeding method provided by the invention is of popularity to a higher degree, a foundation is provided for large-scale breeding of the amphiprion ocellaris.
Owner:浙江华兴水产科技有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com