Patents
Literature
6474results about "Unicellular algae" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Product and process for transformation of Thraustochytriales microorganisms
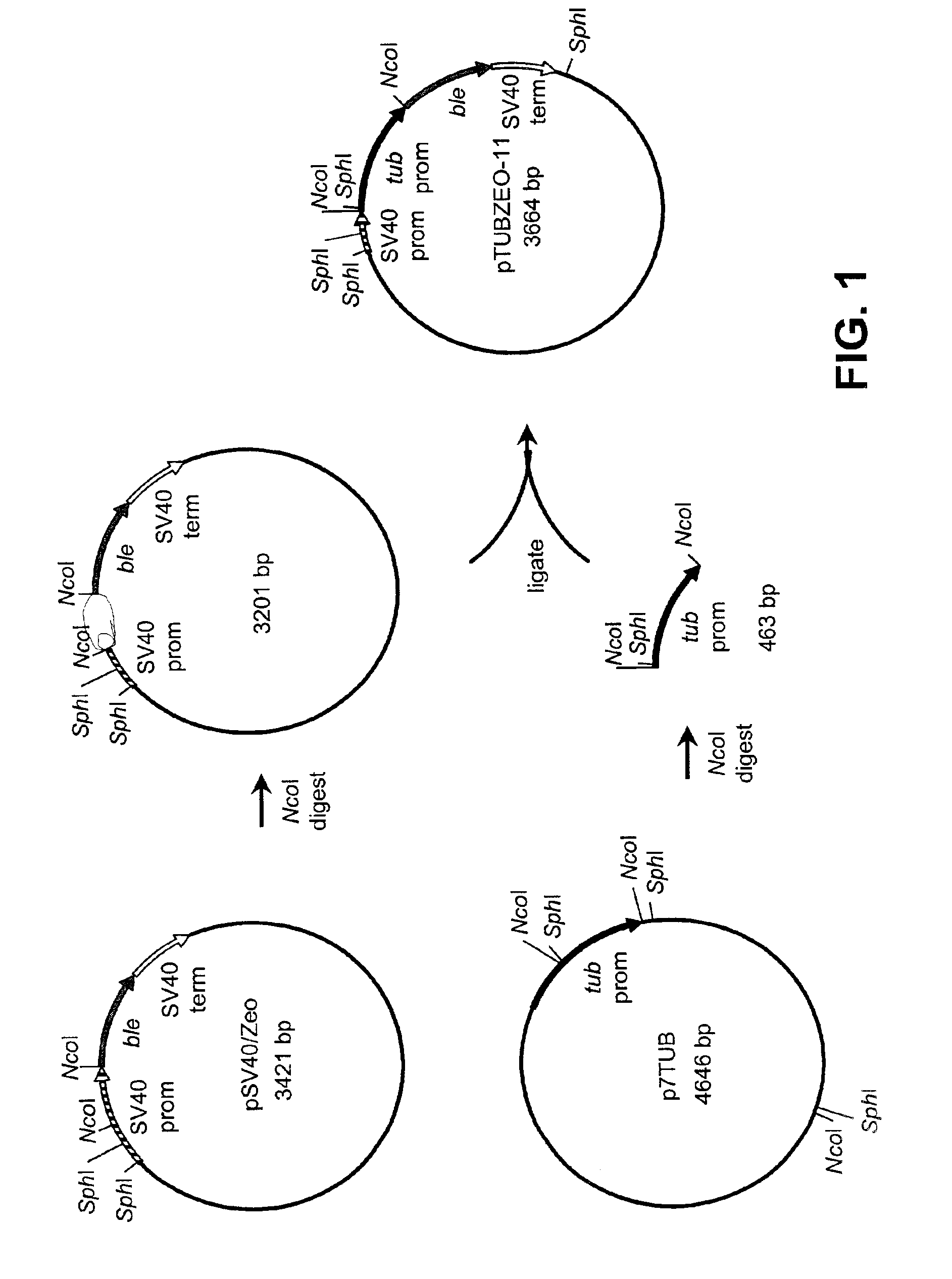
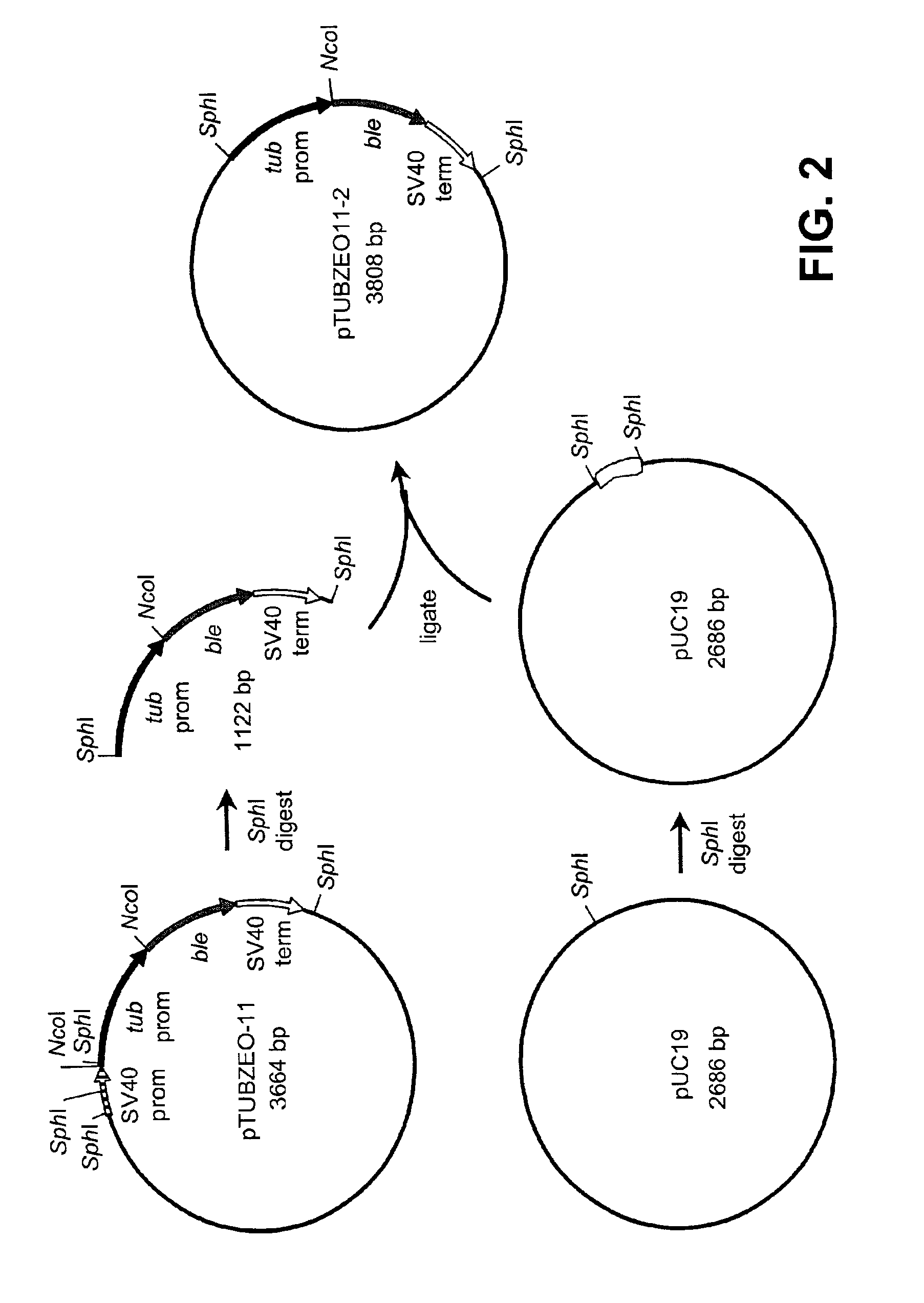
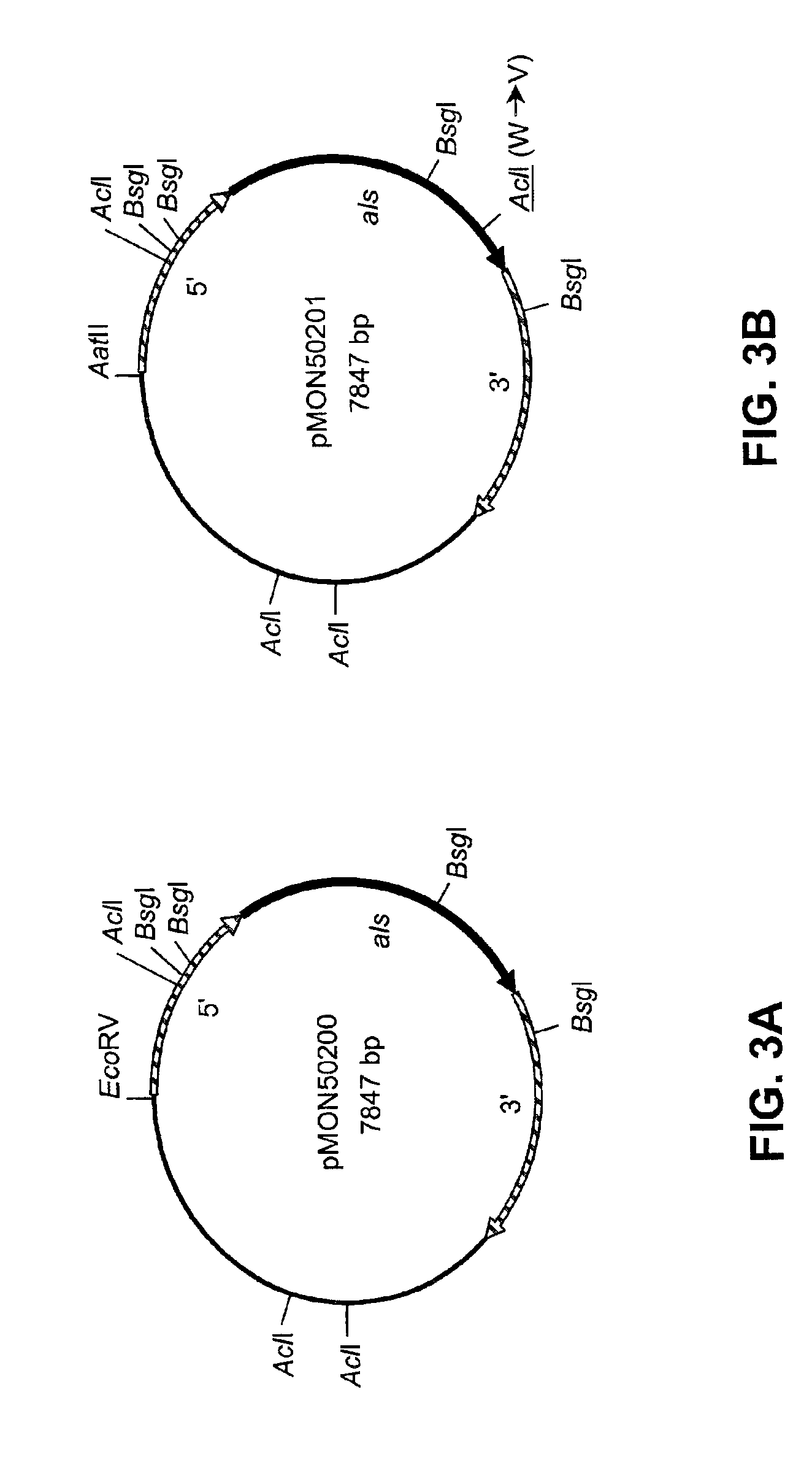
Disclosed are nucleic acid and amino acid sequences for acetolactate synthase, acetolactate synthase regulatory regions, α-tubulin promoter, a promoter from a Thraustochytriales polyketide synthase (PKS) system, and fatty acid desaturase promoter, each from a Thraustochytriales microorganism. Also disclosed are recombinant vectors useful for transformation of Thraustochytriales microorganisms, as well as a method of transformation of Thraustochytriales microorganisms. The recombinant nucleic acid molecules of the present invention can be used for the expression of foreign nucleic acids in a Thraustochytriales microorganism as well as for the deletion, mutation, or inactivation of genes in Thraustochytriales microorganisms.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
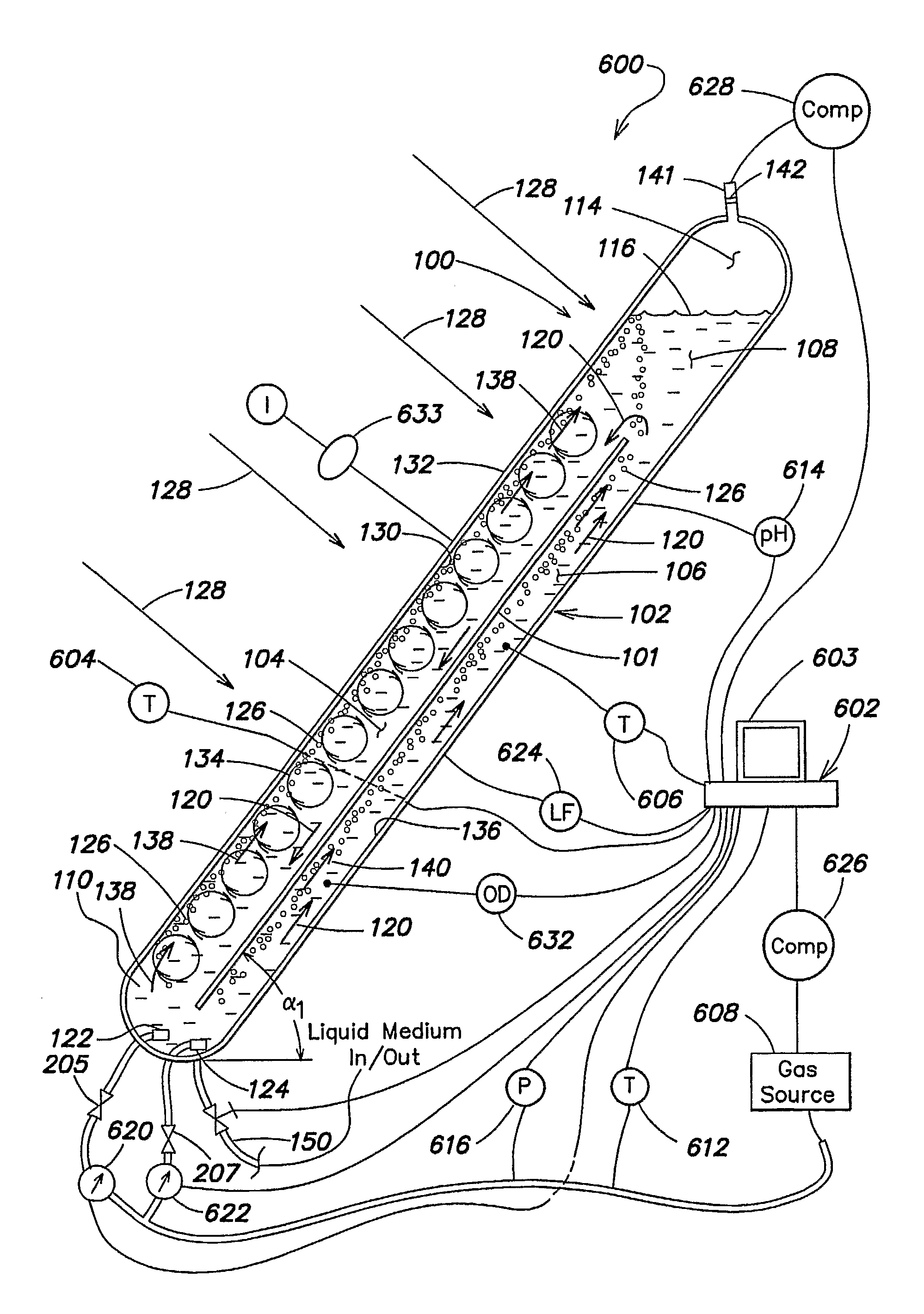
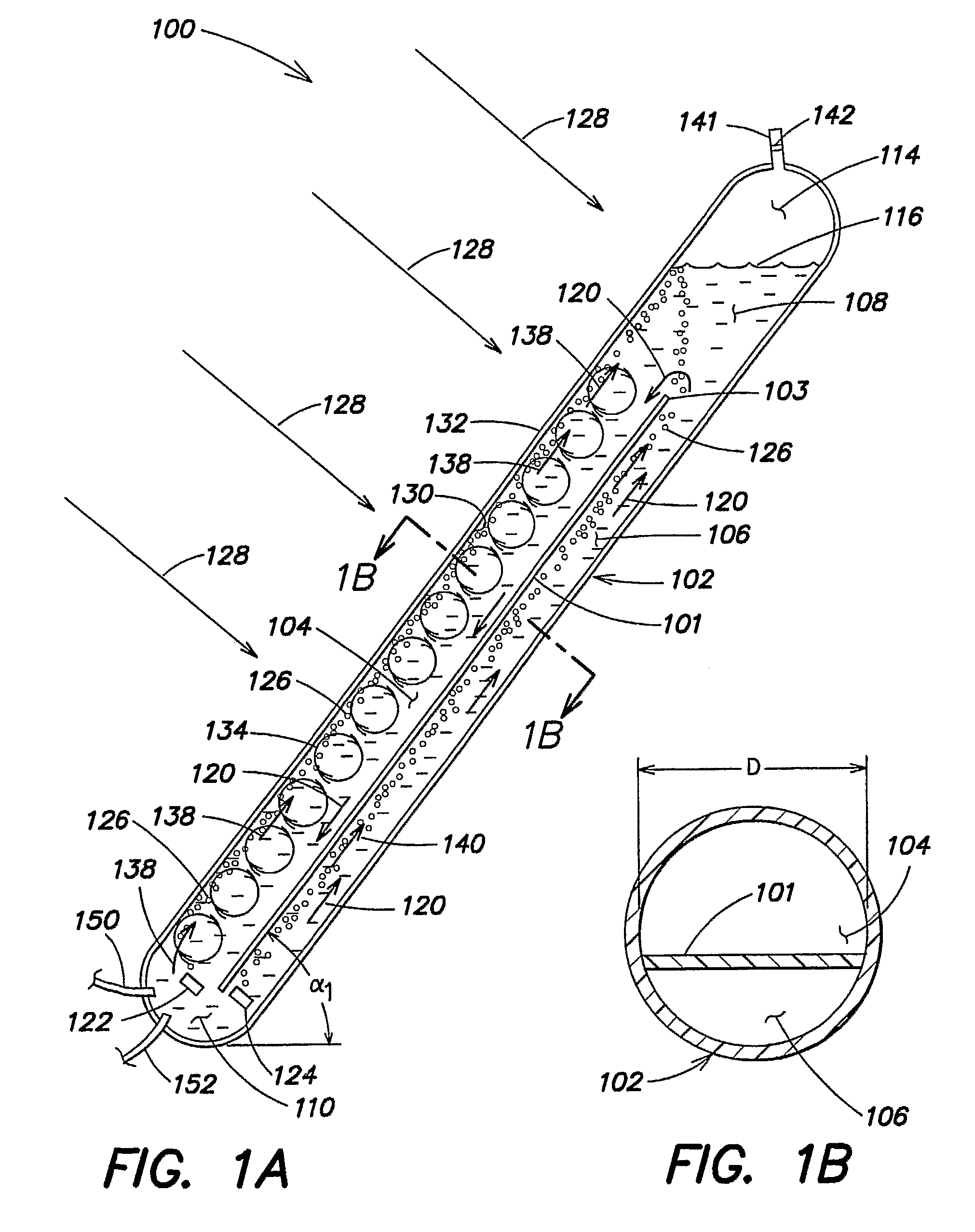
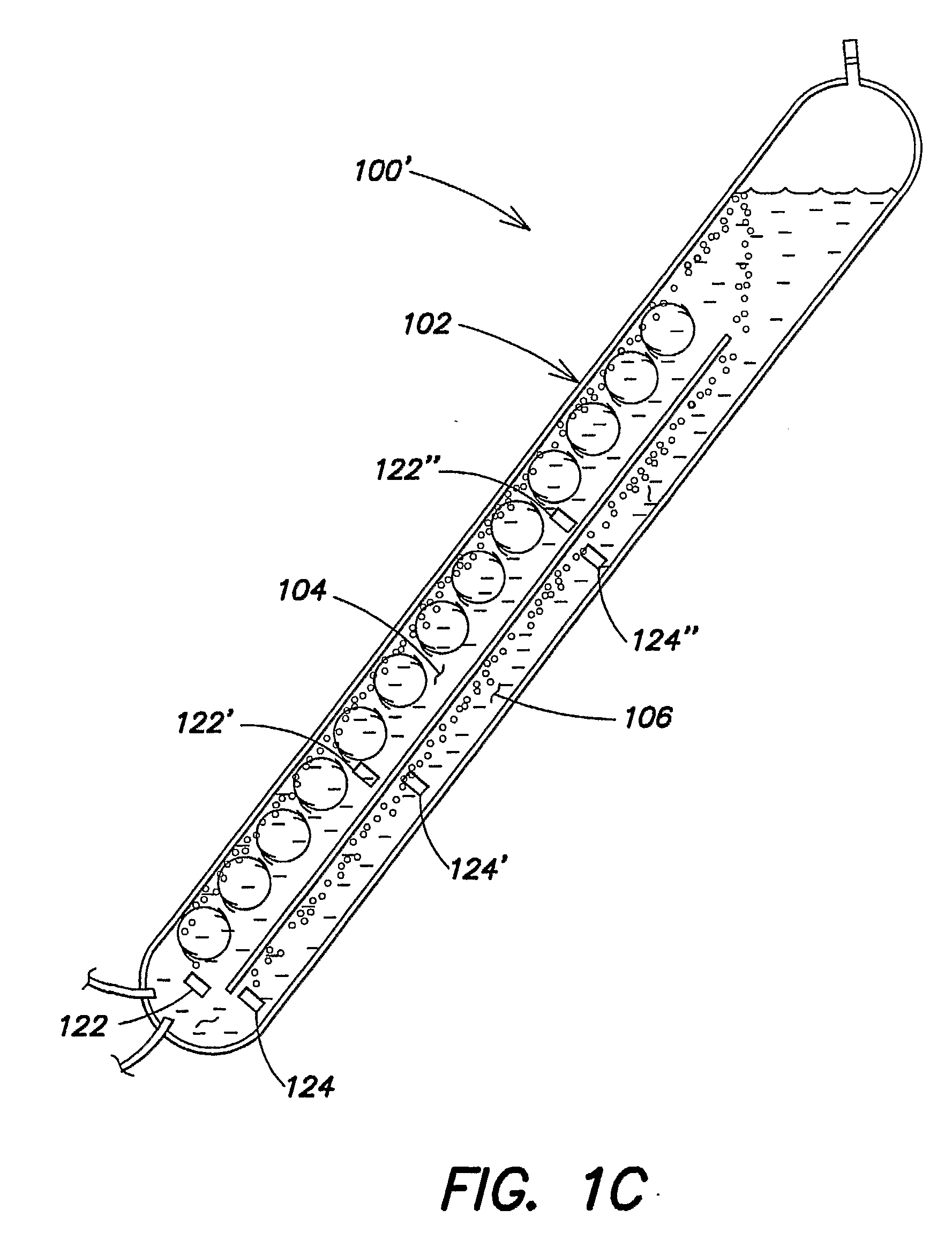
Synthetic and biologically-derived products produced using biomass produced by photobioreactors configured for mitigation of pollutants in flue gases
InactiveUS20050239182A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiodieselLiquid medium
Certain embodiments and aspects of the present invention relate to photobioreactor apparatus designed to contain a liquid medium comprising at least one species of photosynthetic organisms therein, and to methods of using the photobioreactor apparatus as part of a production process for forming an organic molecule-containing product, such as a polymeric material and / or fuel-grade oil (e.g. biodiesel), from biomass produced in the photobioreactor apparatus. In certain embodiments, the disclosed organic molecule / polymer production systems and methods, photobioreactor apparatus, methods of using such apparatus, and / or gas treatment systems and methods provided herein can be utilized as part of an integrated combustion and polymer and / or fuel-grade oil (e.g. biodiesel) production method and system, wherein photosynthetic organisms utilized within the photobioreactor are used to at least partially remove certain pollutant compounds contained within combustion gases, e.g. CO2 and / or NOx, and are subsequently harvested from the photobioreactor, processed, and utilized as a source for generating polymers and / or organic molecule-containing products (e.g. fuel-grade oil (e.g. biodiesel)) and / or as a fuel source for a combustion device (e.g. an electric power plant generator and / or incinerator).
Owner:GREENFUEL TECHNOLOGIES CORPORATION
Process for preparing materials for extraction
InactiveUS20060122410A1Improve extraction efficiencyQuality improvementFungiUnicellular algaeArachidonic acid supplementationFermentation
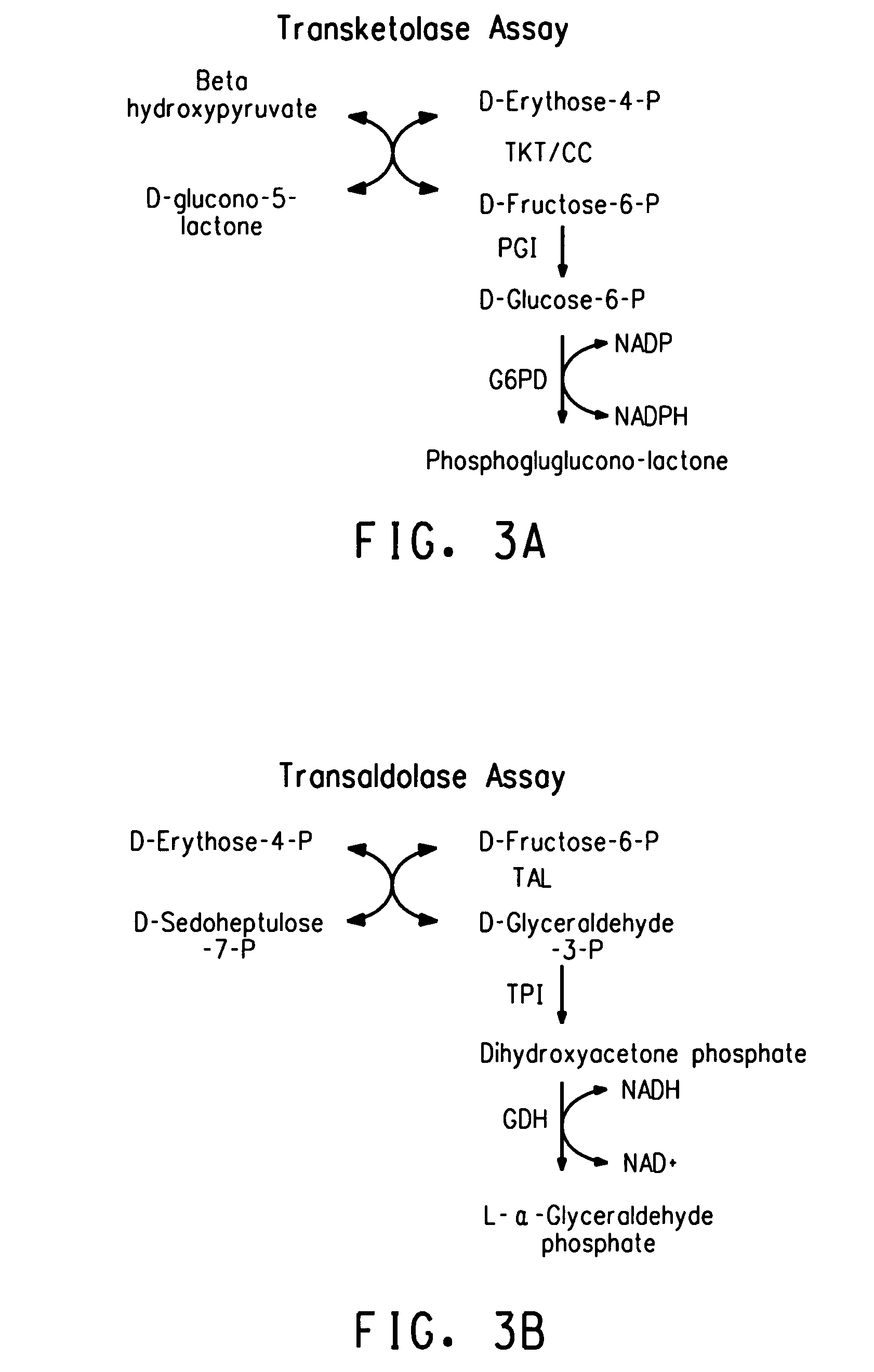
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a biomass, such as from a microbial fermentation, for an extraction process to separate desired chemicals, nutritional products, bioactive components, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids, from the biomass. Particularly preferred substances to extract include docosahexaenoic acid, docosapentaenoic acid, and arachidonic acid. The present invention also includes extracting the prepared biomass. Biomasses to be treated in accordance with the methods of the invention include plant, animal, and microbial biomass, particularly a microorganism such as Crypthecodinium cohnii and a fungus such as Mortierella alpina.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
Use of Cellulosic Materials for Cultivation of Microorganisms
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
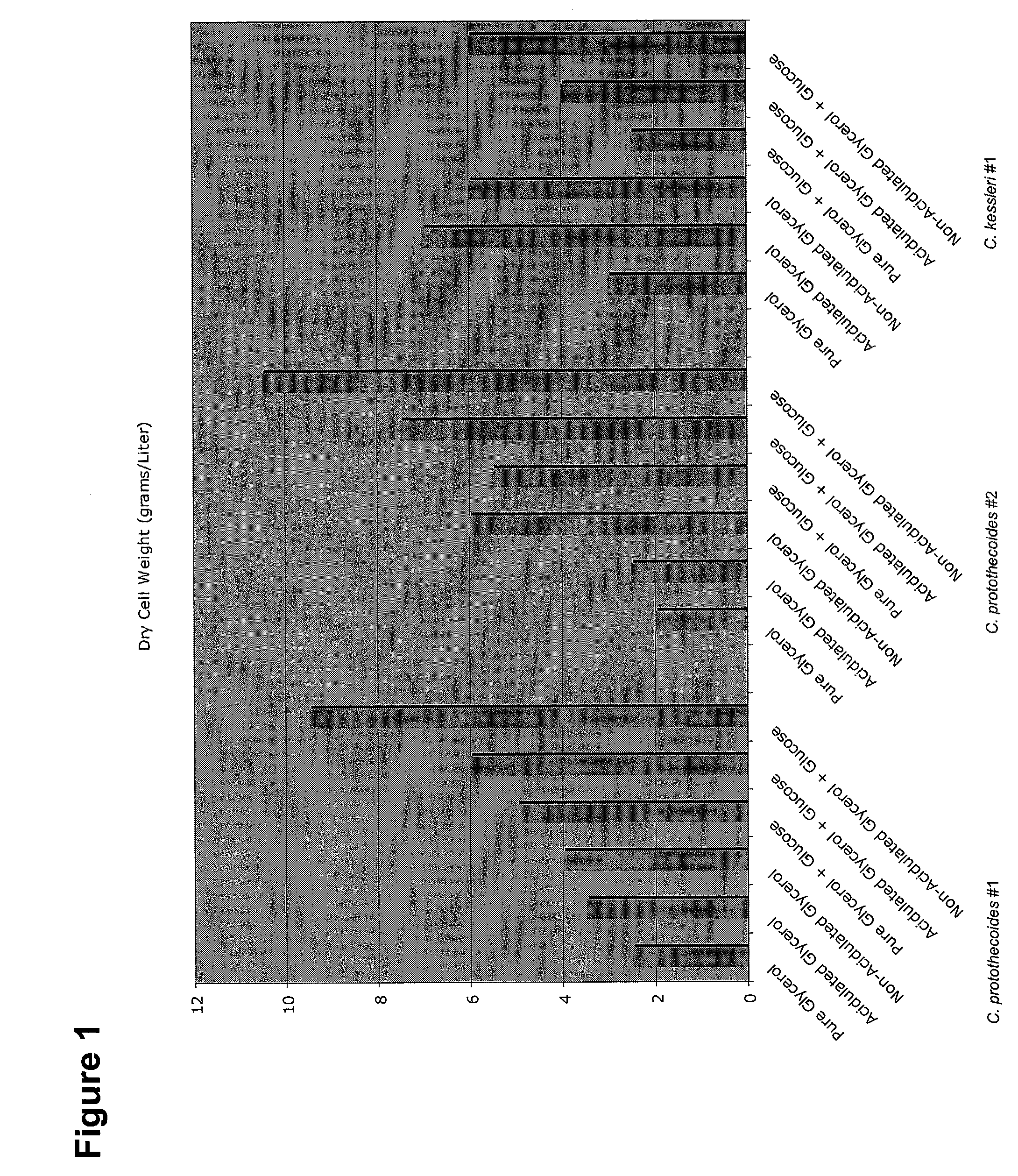
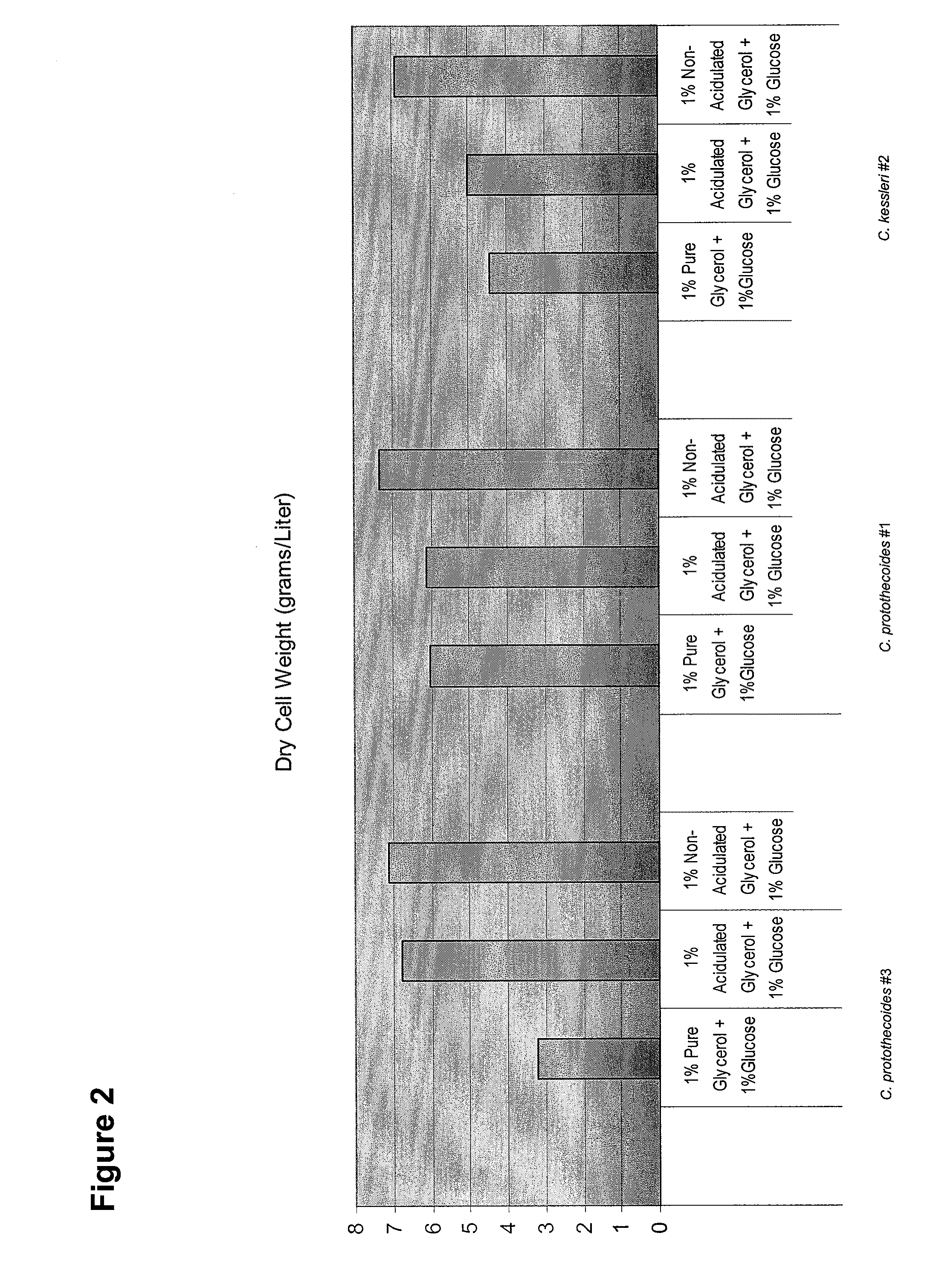
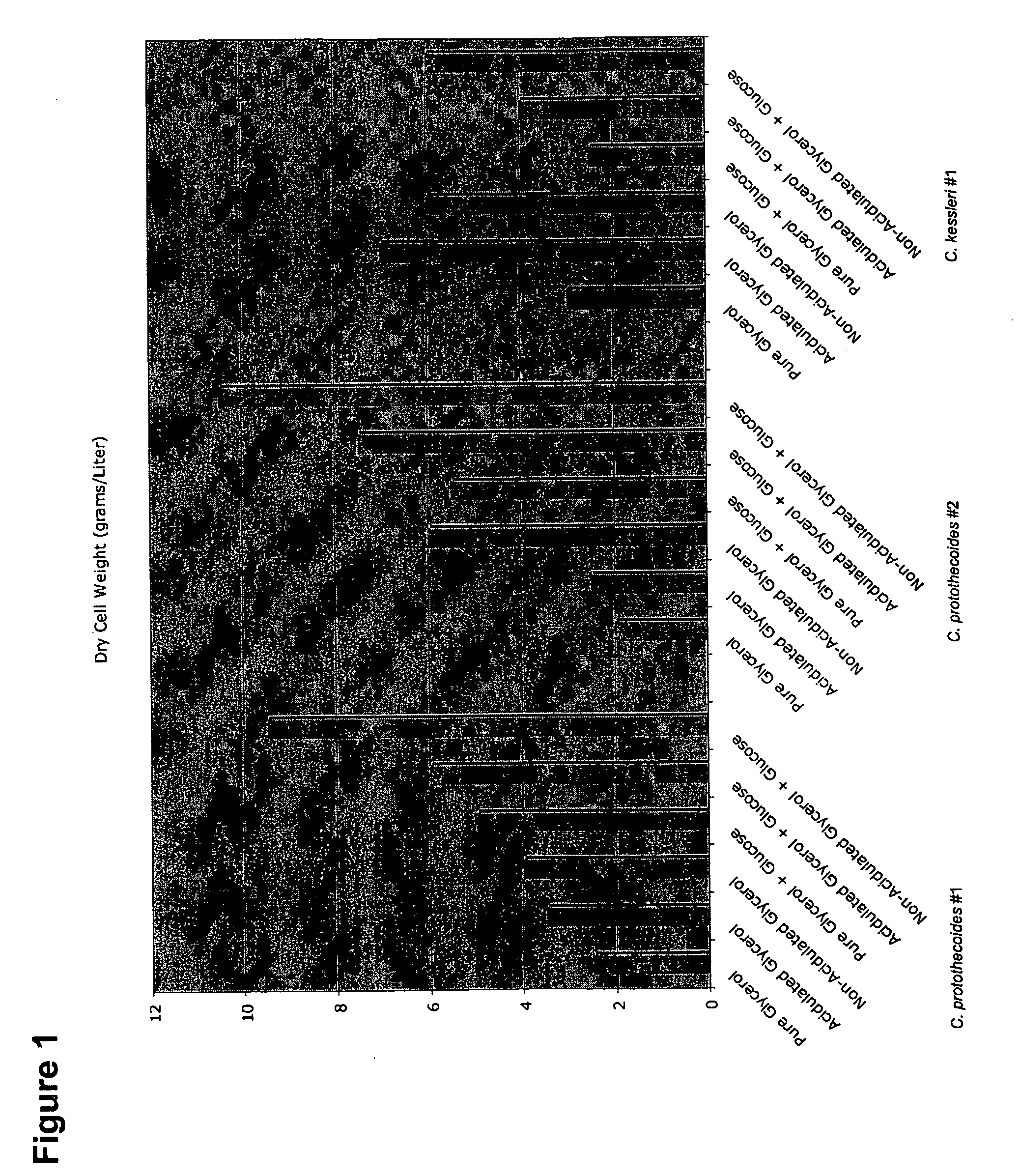
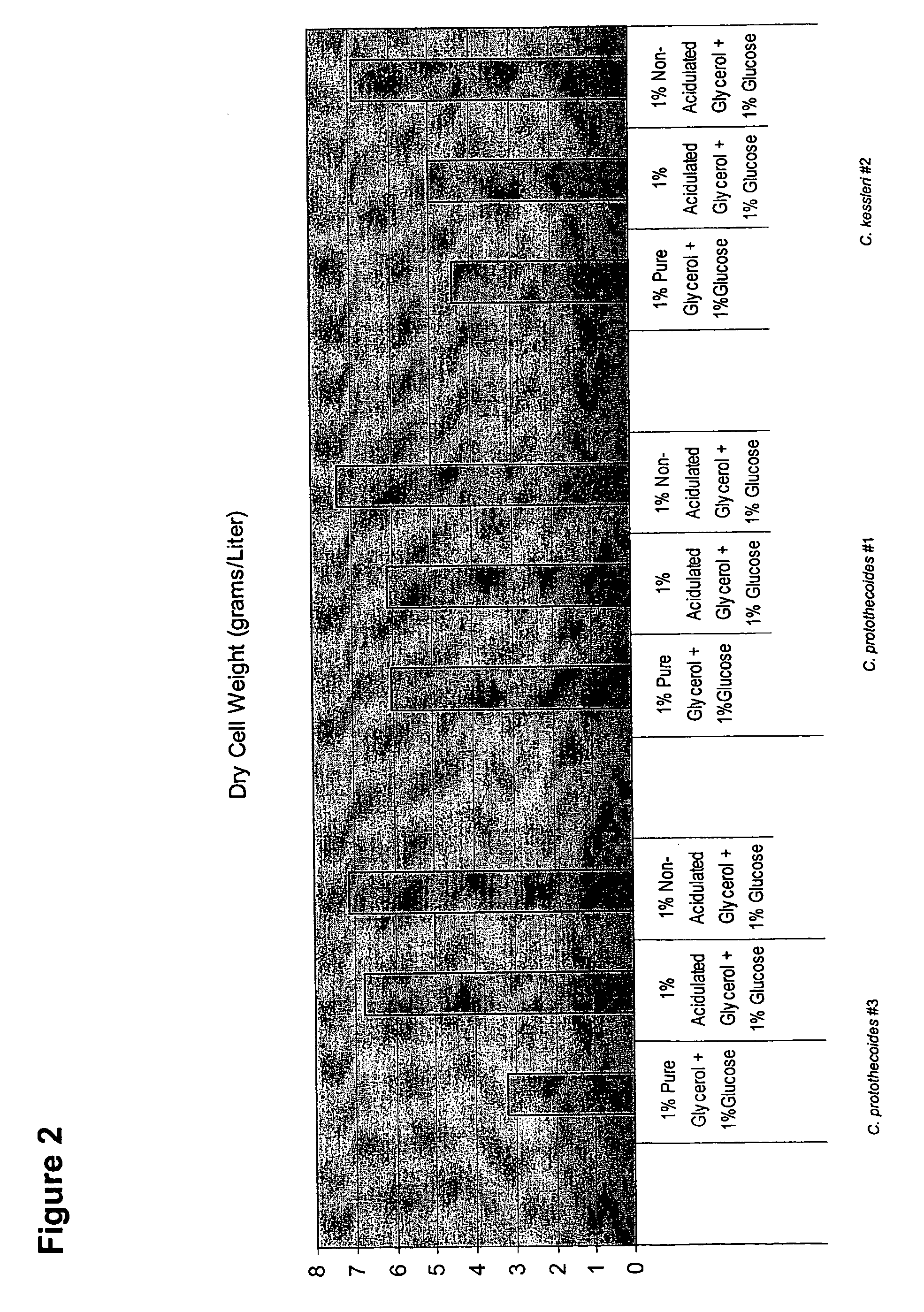
Glycerol Feedstock Utilization for Oil-Based Fuel Manufacturing
InactiveUS20090004715A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsFatty acid chemical modificationMicroorganismTransesterification
The invention provides methods of manufacturing biodiesel and other oil-based compounds using glycerol and combinations of glycerol and other feedstocks as an energy source in fermentation of oil-bearing microorganisms. Methods disclosed herein include processes for manufacturing high nutrition edible oils from non-food feedstock materials such as waste products from industrial waste transesterification processes. Also included are methods of increasing oil yields by temporally separating glycerol and other feedstocks during cultivation processes. Also provided herein are oil-bearing microbes containing exogenous oil production genes and methods of cultivating such microbes on glycerol and other feedstocks.
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
Method for treatment of disorders of the gastrointestinal system
There are provided novel synthetic stool preparations comprising bacteria isolated from a fecal sample from a healthy donor. The synthetic stool preparations are used for treating disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, including dysbiosis, Clostridium difficile infection and recurrent Clostridium difficile infection, prevention of recurrence of Clostridium difficile infection, treatment of Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, and diverticular disease, and treatment of food poisoning such as salmonella. Methods of preparation and methods of use of the synthetic stool preparations are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH +2
Method of forming polysaccharide sponges for cell culture and transplantation
A polysaccharide sponge characterized by having: (i) an average pore size in the range between about 10 mum to about 300 mum; (ii) an average distance between the pores being the wall thickness of the pores in the range between about 5 mum to about 270 mum; and (iii) an E-modulus of elasticity being a measure of the rigidity of the sponge in the range of about 50 kPa to about 500 kPa.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
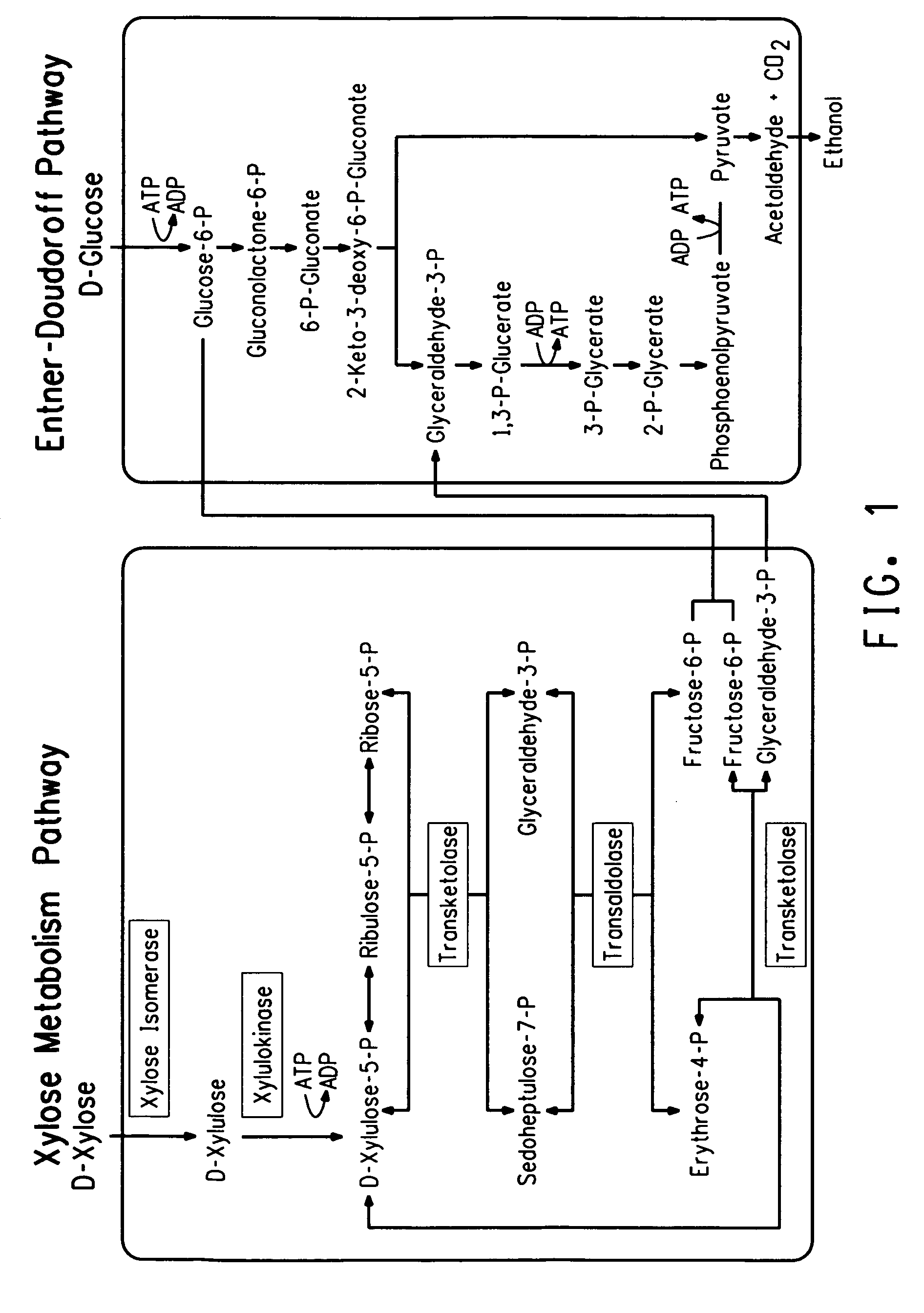
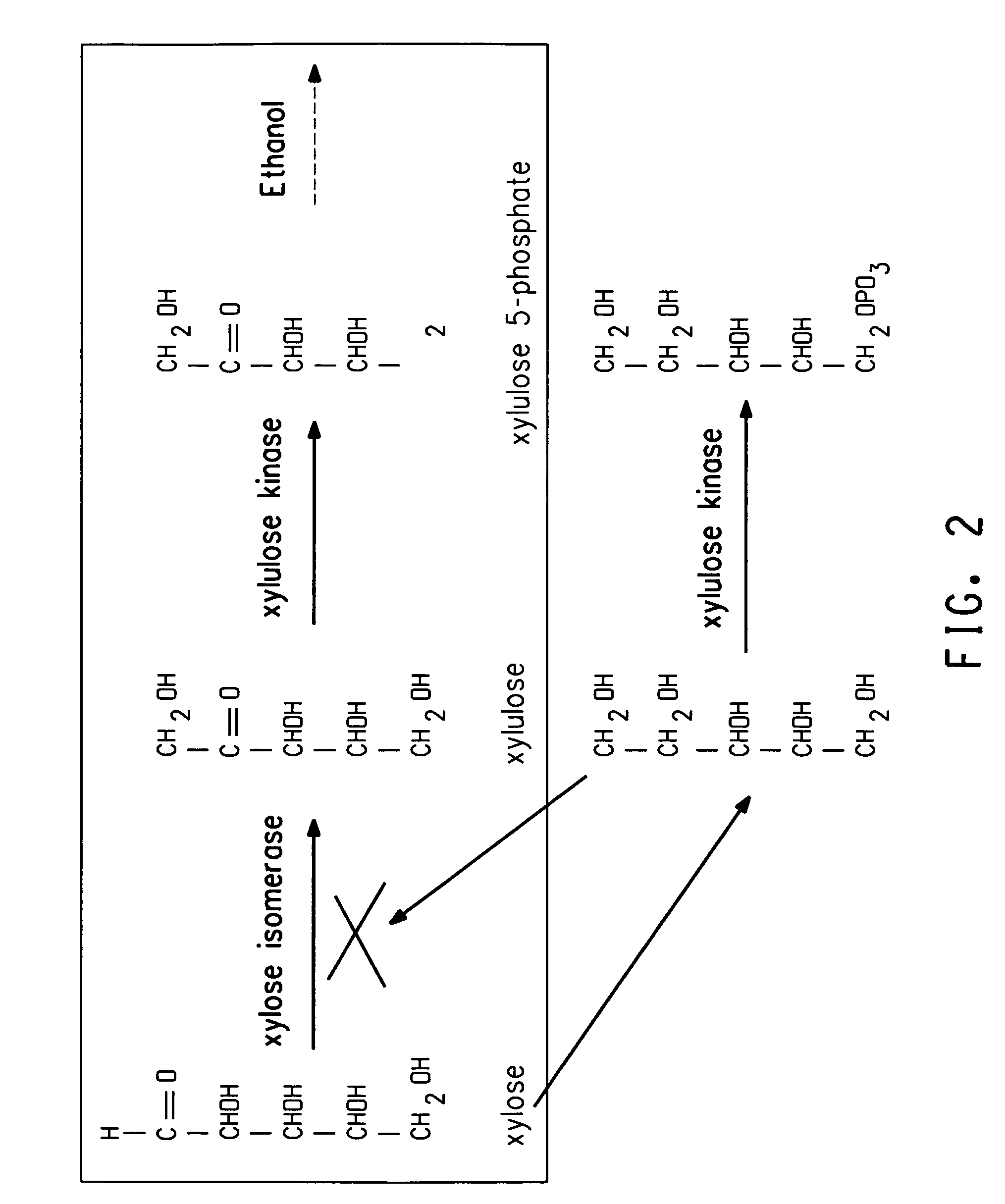
Xylitol synthesis mutant of xylose-utilizing zymomonas for ethanol production
InactiveUS7741119B2Reduce productionIncreased ethanol productionBacteriaUnicellular algaeFructoseOxidoreductase Gene
A strain of xylose-utilizing Zymomonas was engineered with a genetic modification to the glucose-fructose oxidoreductase gene resulting in reduced expression of GFOR enzyme activity. The engineered strain exhibits reduced production of xylitol, a detrimental by-product of xylose metabolism. It also consumes more xylose and produces more ethanol during mixed sugar fermentation under process-relevant conditions.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP +1
Isolation and characterization of novel clostridial species
InactiveUS7704723B2High yieldReadily availableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSyngasAcetic acid
A novel clostridia bacterial species (Clostridium ragsdalei, ATCC BAA-622, “P11”) is provided. P11 is capable of synthesizing, from waste gases, products which are useful as biofuel. In particular, P11 can convert CO to ethanol. Thus, this novel bacterium transforms waste gases (e.g. syngas and refinery wastes) into useful products. P11 also catalyzes the production of acetate.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Process for preparing materials for extraction
InactiveUS7678931B2Improve extraction efficiencyQuality improvementFungiUnicellular algaeArachidonic acid supplementationFermentation
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a biomass, such as from a microbial fermentation, for an extraction process to separate desired chemicals, nutritional products, bioactive components, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids, from the biomass. Particularly preferred substances to extract include docosahexaenoic acid, docosapentaenoic acid, and arachidonic acid. The present invention also includes extracting the prepared biomass. Biomasses to be treated in accordance with the methods of the invention include plant, animal, and microbial biomass, particularly a microorganism such as Crypthecodinium cohnii and a fungus such as Mortierella alpina.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
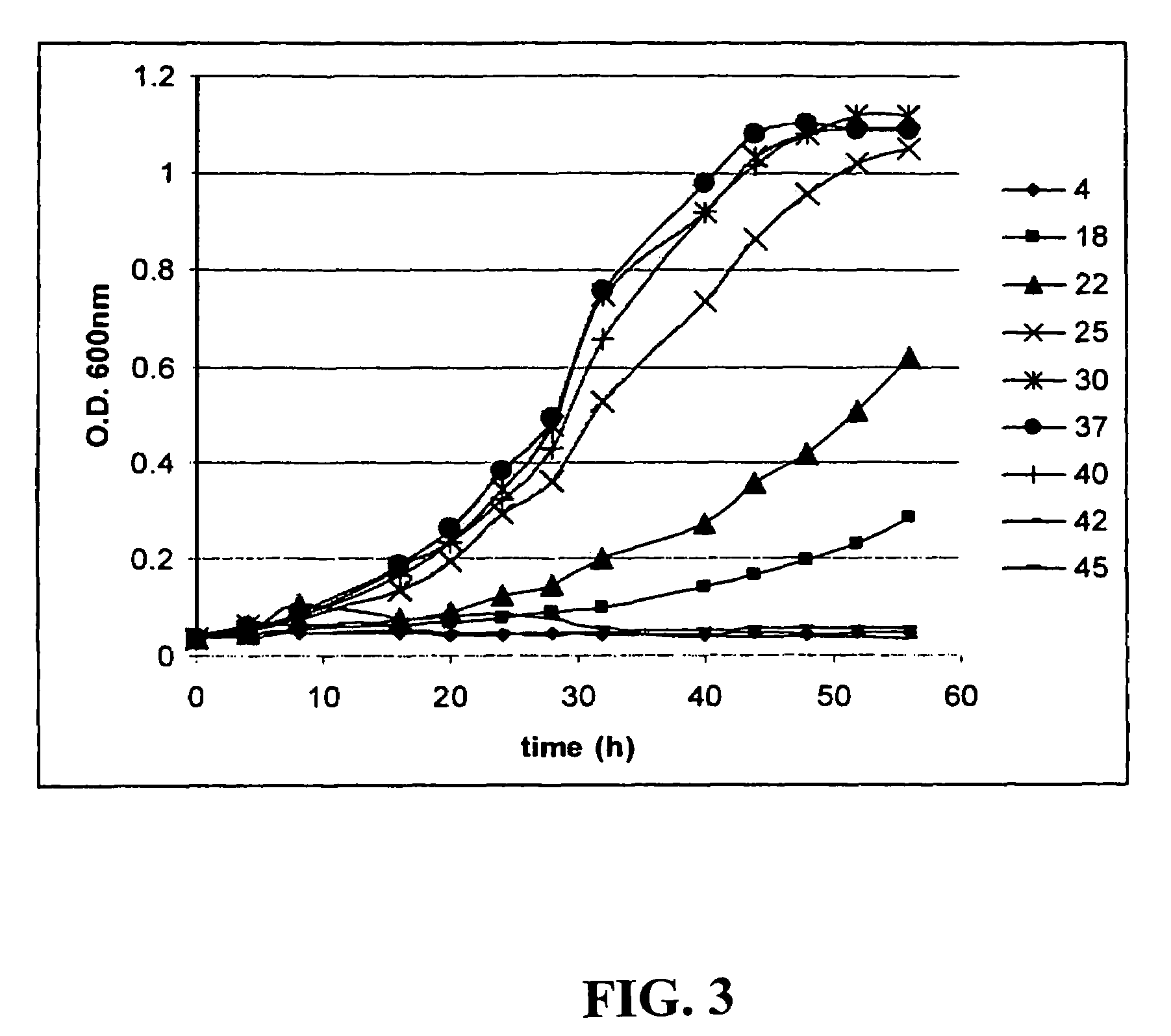
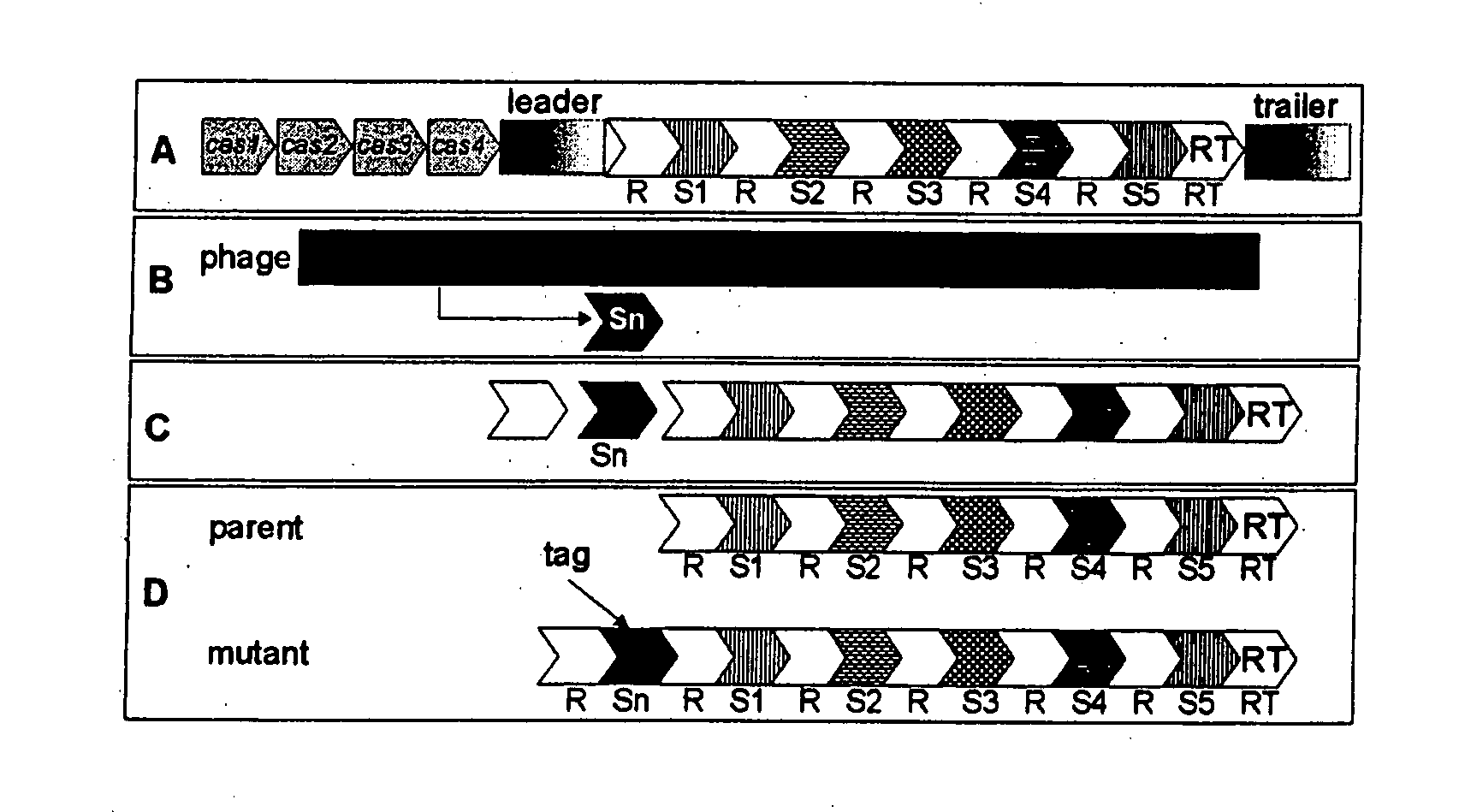
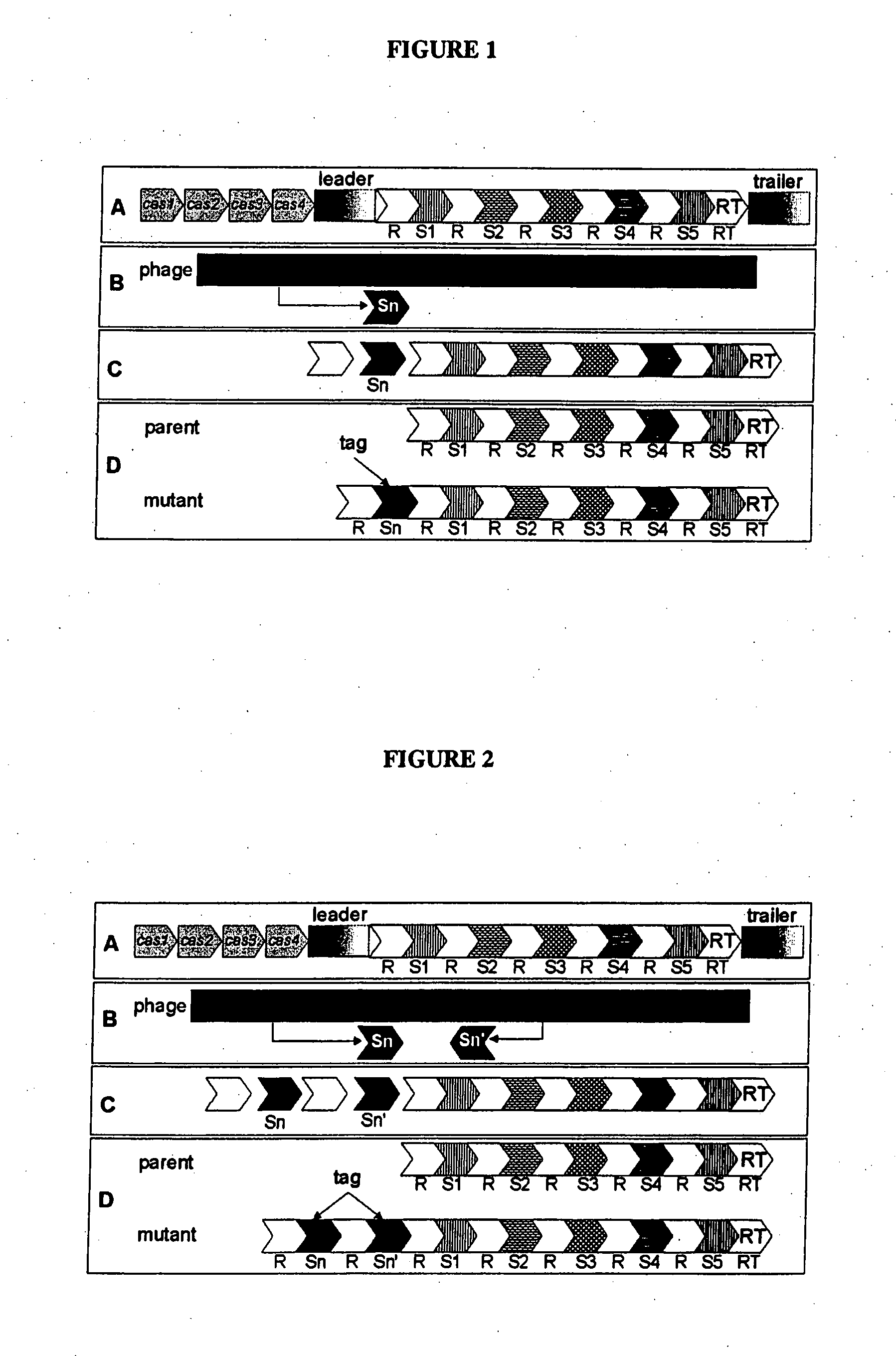
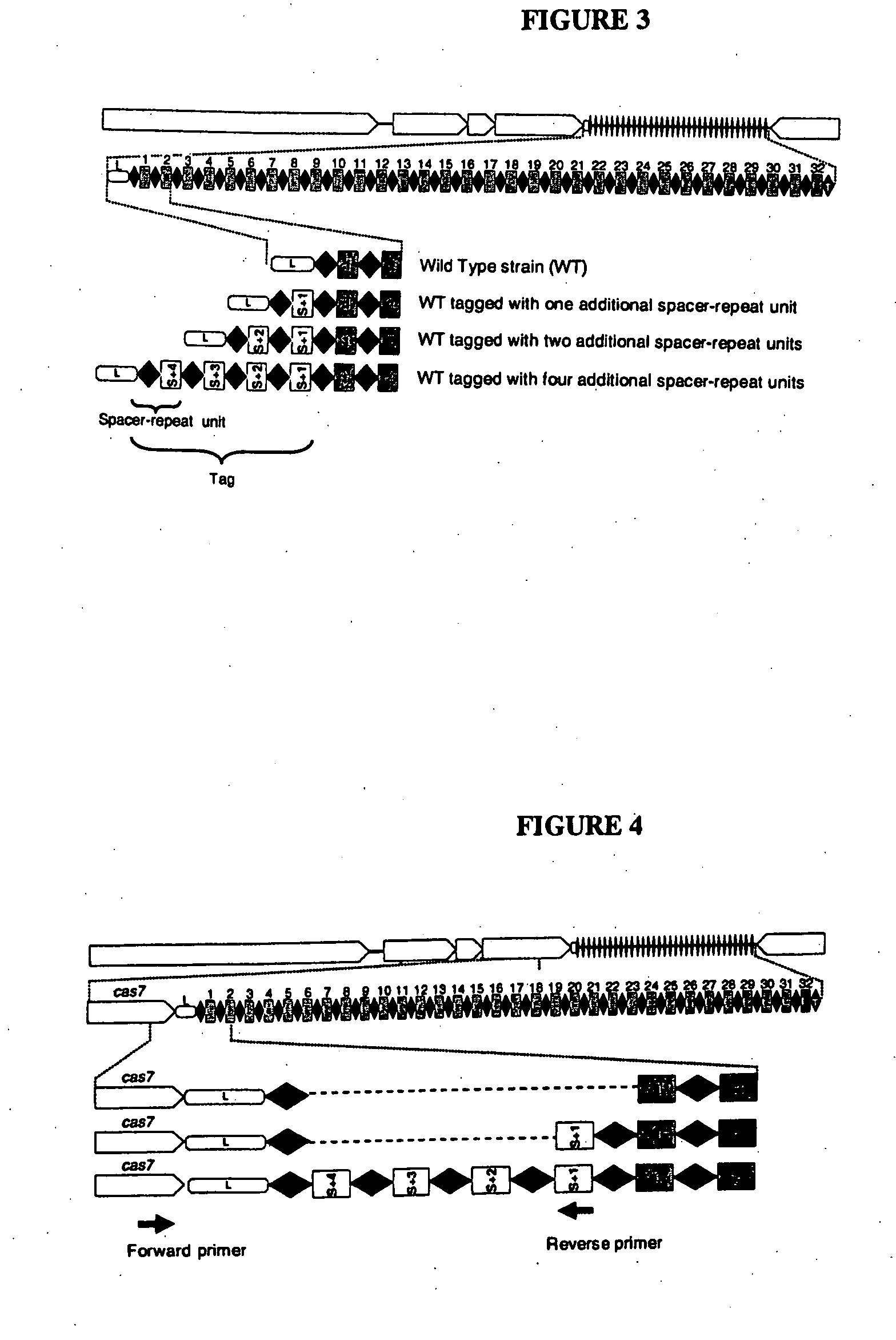
Tagged microorganisms and methods of tagging
The present invention provides methods for tagging and / or identifying microorganisms. In some preferred embodiments, the microorganisms are bacteria. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the bacteria are members of the genus Streptococcus, while in other embodiments, the bacteria are members of other genera. The present invention also provides microorganisms tagged using the methods set forth herein. In some preferred embodiments, the tagged microorganisms are bacteria. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the tagged bacteria are members of the genus Streptococcus, while in other embodiments, the tagged bacteria are members of other genera.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Photobioreactor Cell Culture Systems, Methods for Preconditioning Photosynthetic Organisms, and Cultures of Photosynthetic Organisms Produced Thereby
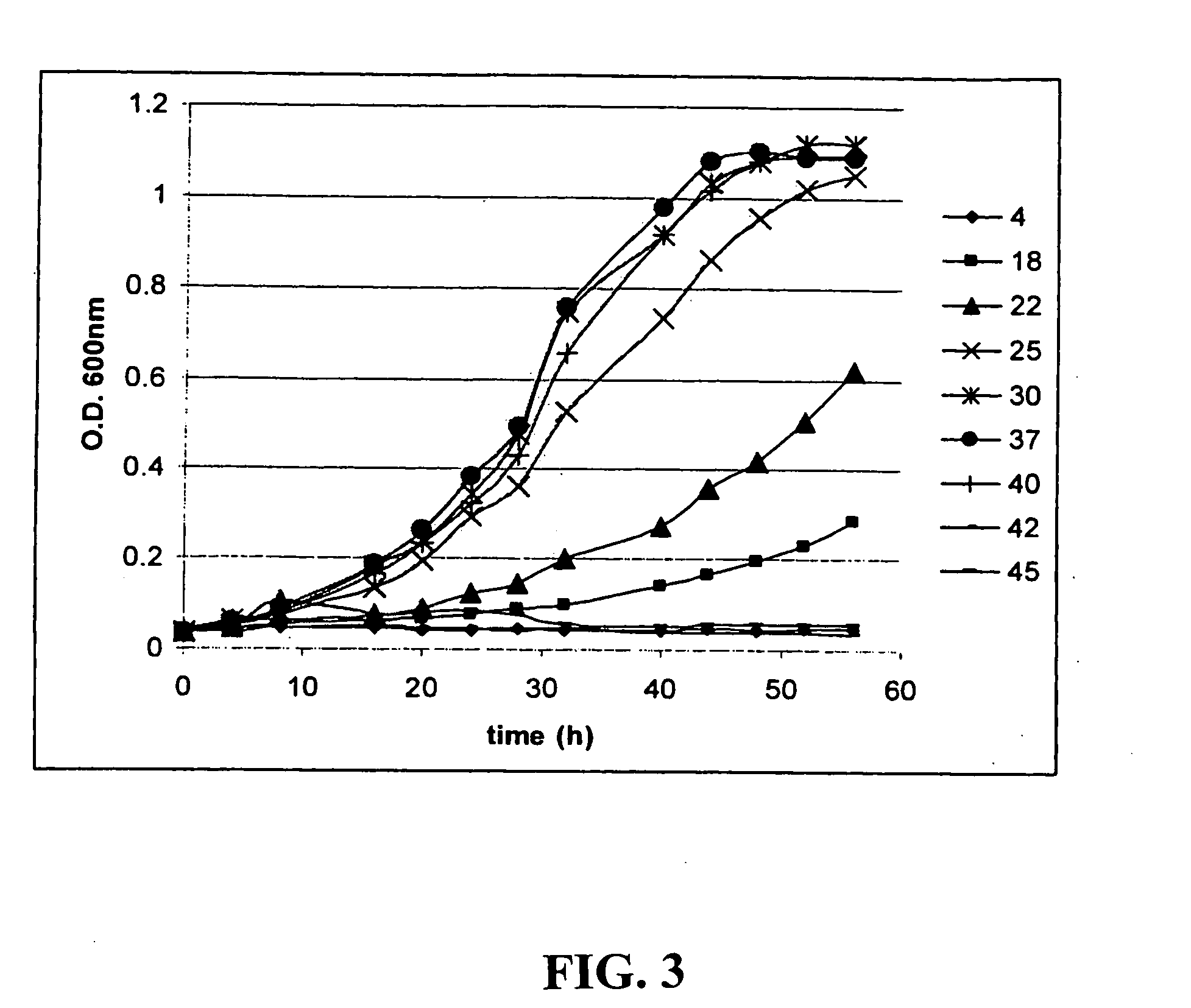
InactiveUS20090011492A1Reduced growth rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPretreatment methodPhotobioreactor
Certain embodiments of the invention involve methods and systems for preselecting, adapting, and preconditioning one or more species of photosynthetic organisms, such as algae, to specific environmental and / or operating conditions to which the photosynthetic organisms will subsequently be exposed during utilization in a photobioreactor apparatus of a gas treatment system. Also disclosed are new algal strains and cultures that can be produced by practicing the preselection, adaption, and preconditioning methods.
Owner:THE TRON GRP +1
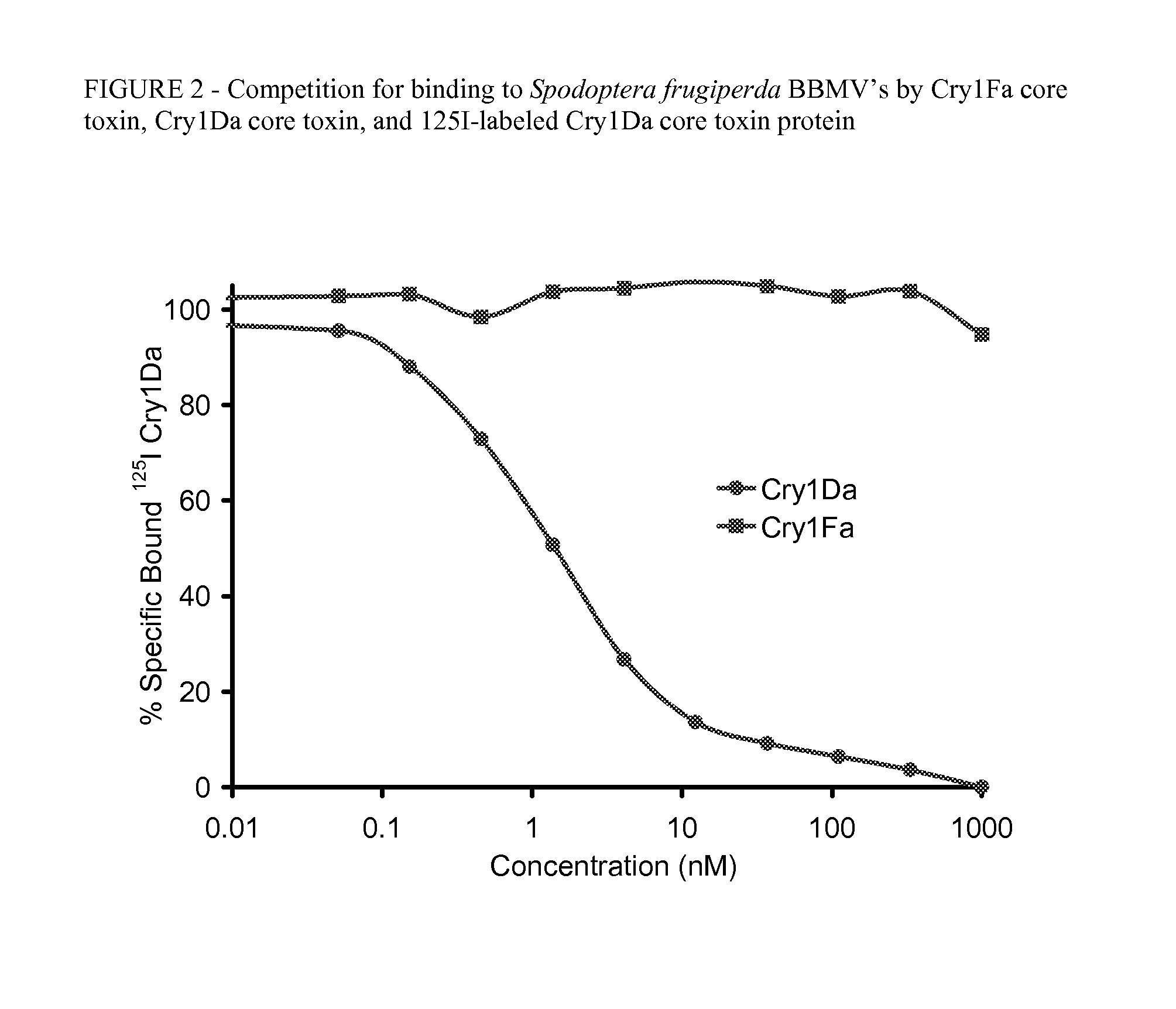
COMBINED USE OF CRY1Da AND CRY1Fa PROTEINS FOR INSECT RESISTANCE MANAGEMENT
InactiveUS20120331589A1Reduce and eliminate requirementReduce selection pressureBiocideFungiCombined useToxin
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
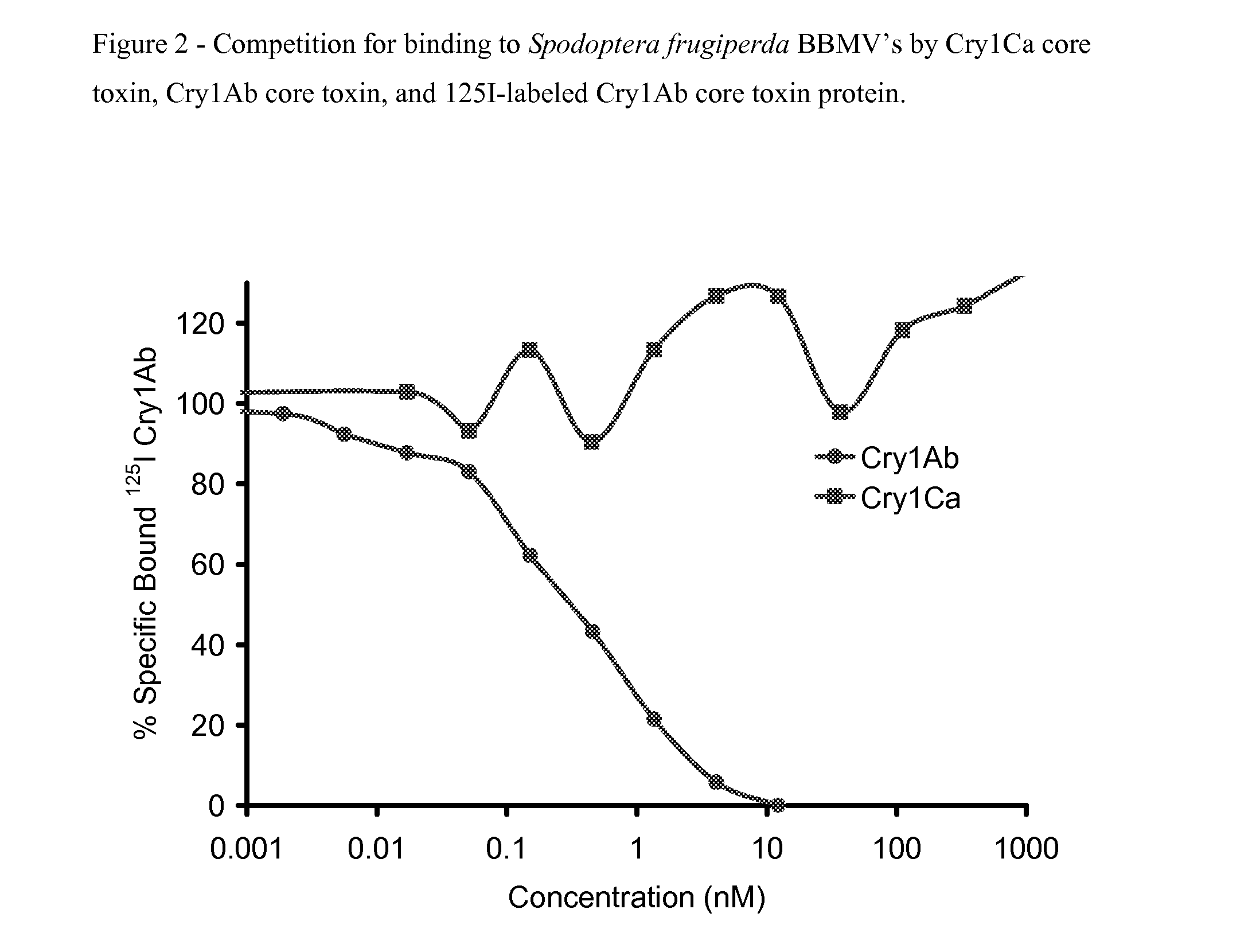
COMBINED USE OF CRY1Ca AND CRY1Fa PROTEINS FOR INSECT RESISTANCE MANAGEMENT
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
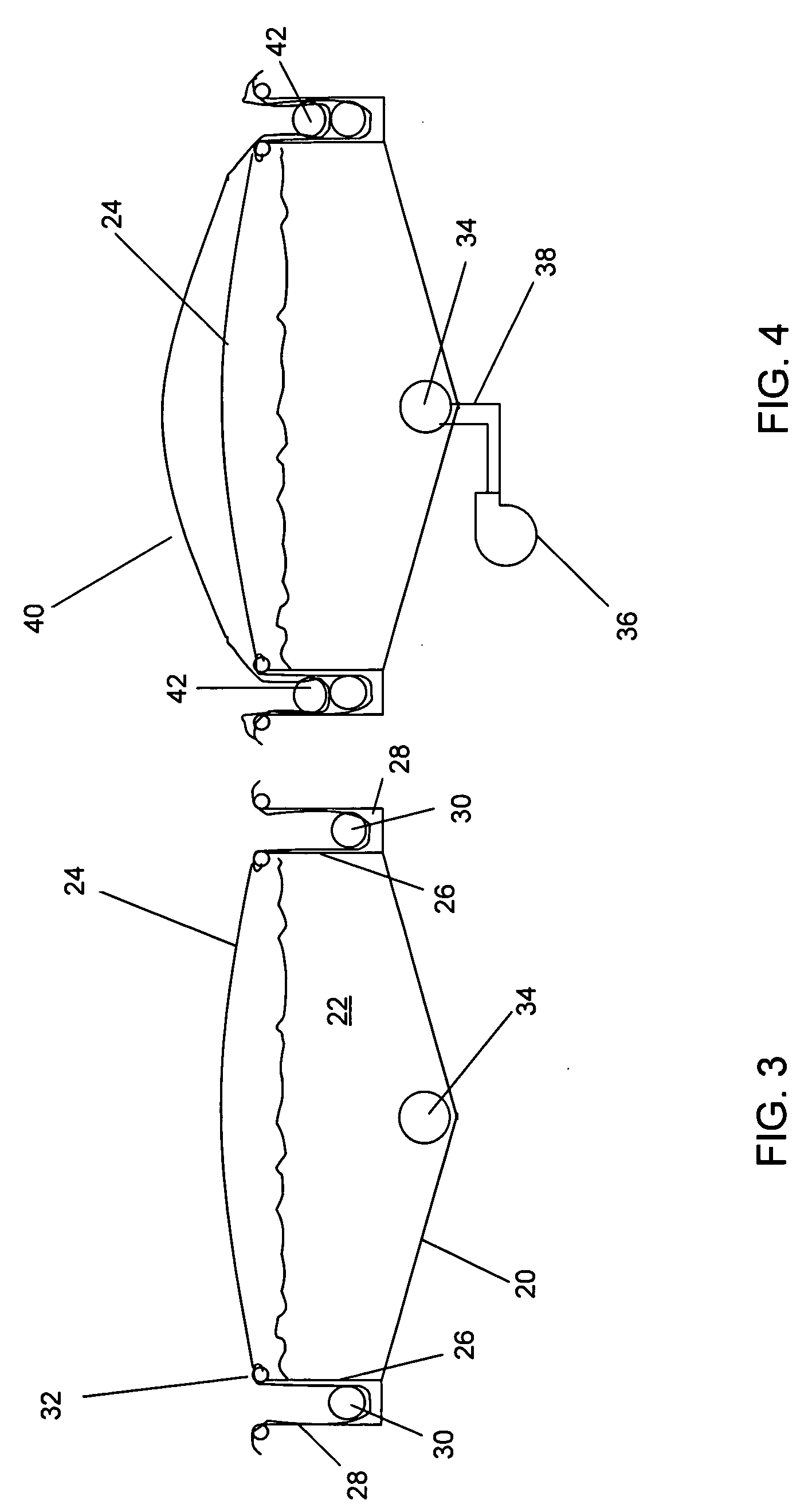
Controlled growth environments for algae cultivation
A method for cultivating algae can include providing a body of water in a substantially enclosed system. The enclosed system can have a length of channel and a cover. The method can optionally include circulating the body of water through the enclosed system under positive pressure conditions. The positive pressure should prevent ingress of any external atmosphere or material. Further, the method can include cultivating the algae in the body of water at conditions which promote growth. Likewise, a system for cultivating algae can include a channel with a cover, water in the channel, and a pump to introduce positive pressure into the system.
Owner:GENIFUEL CORP
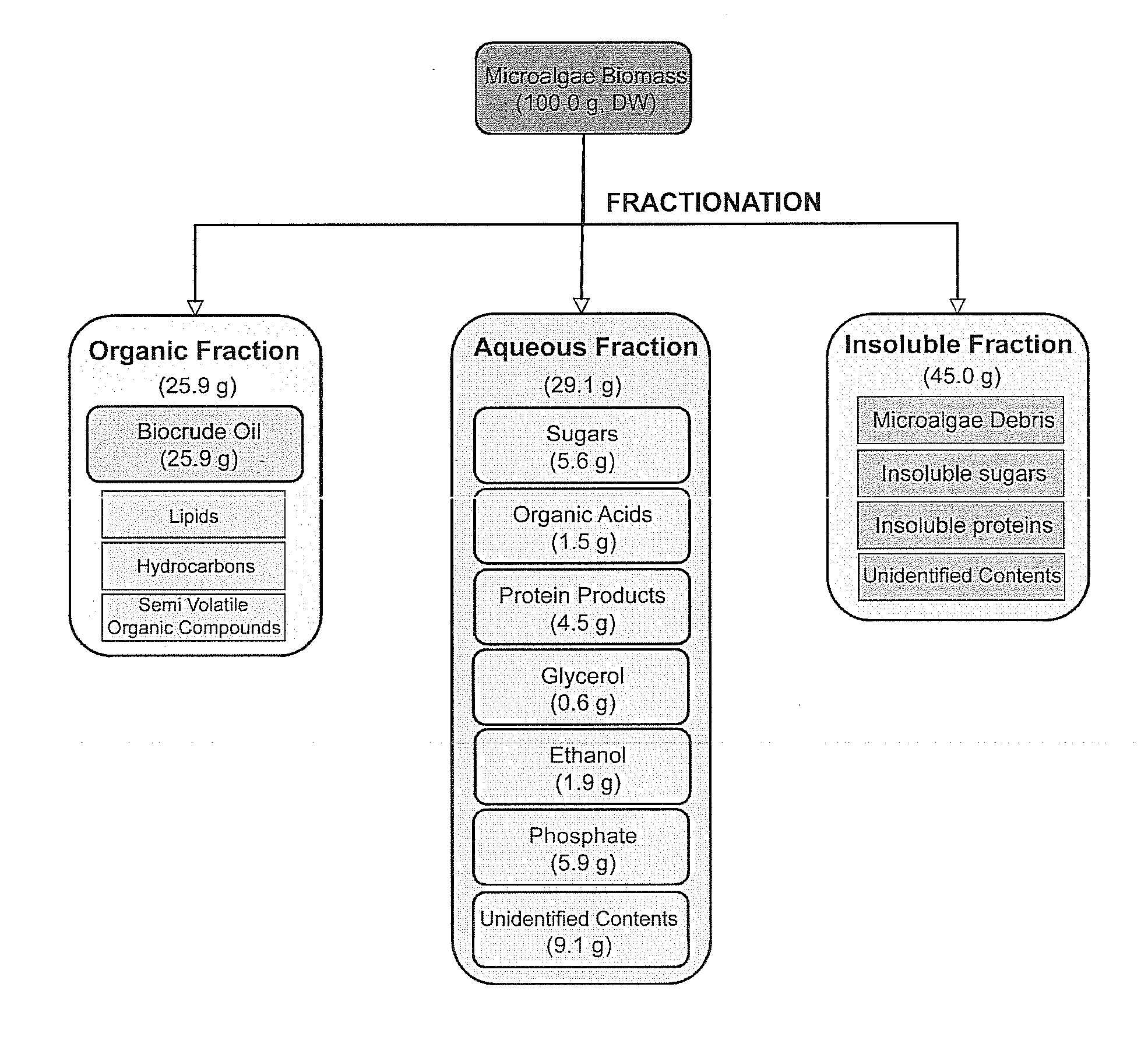
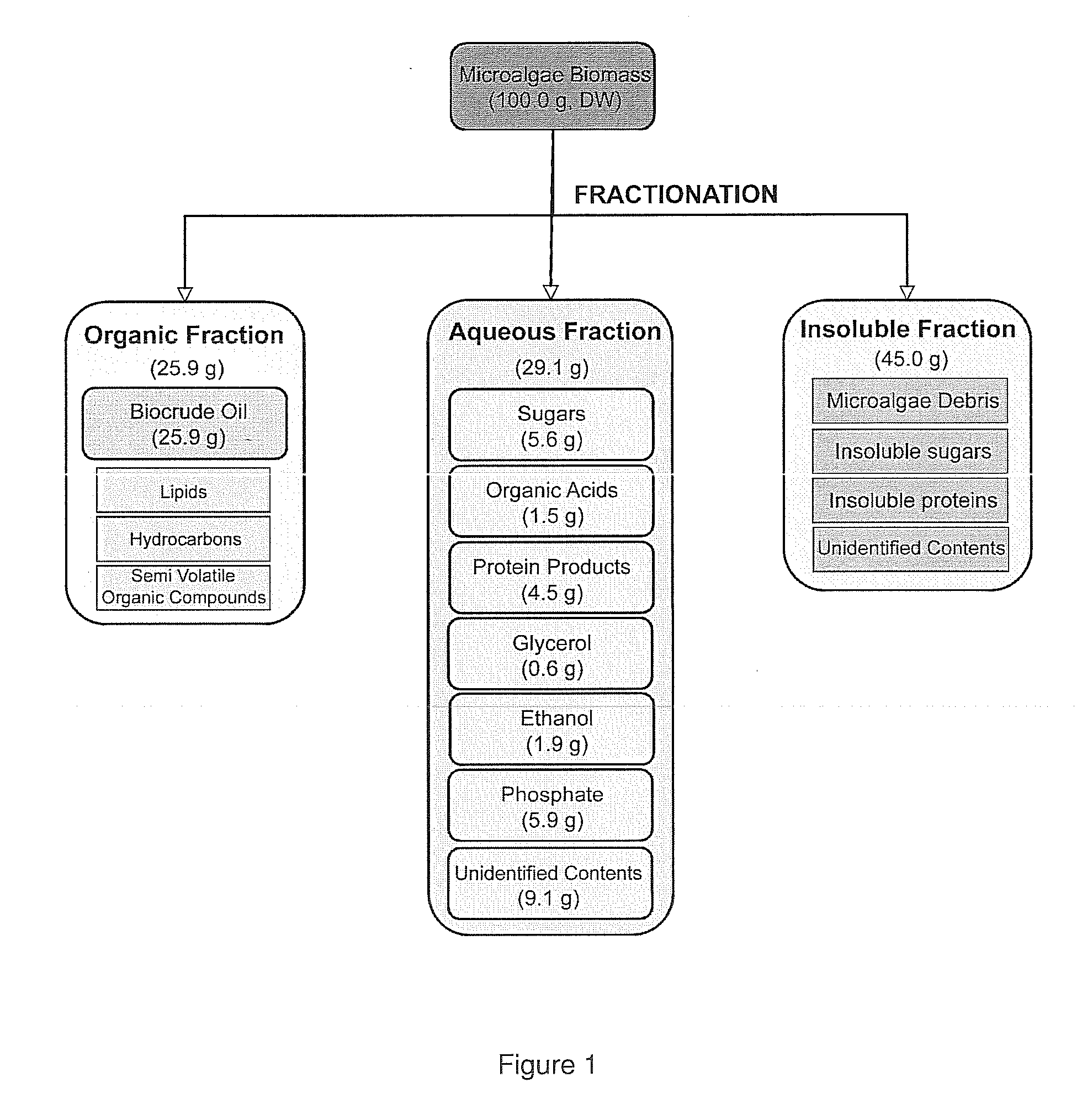
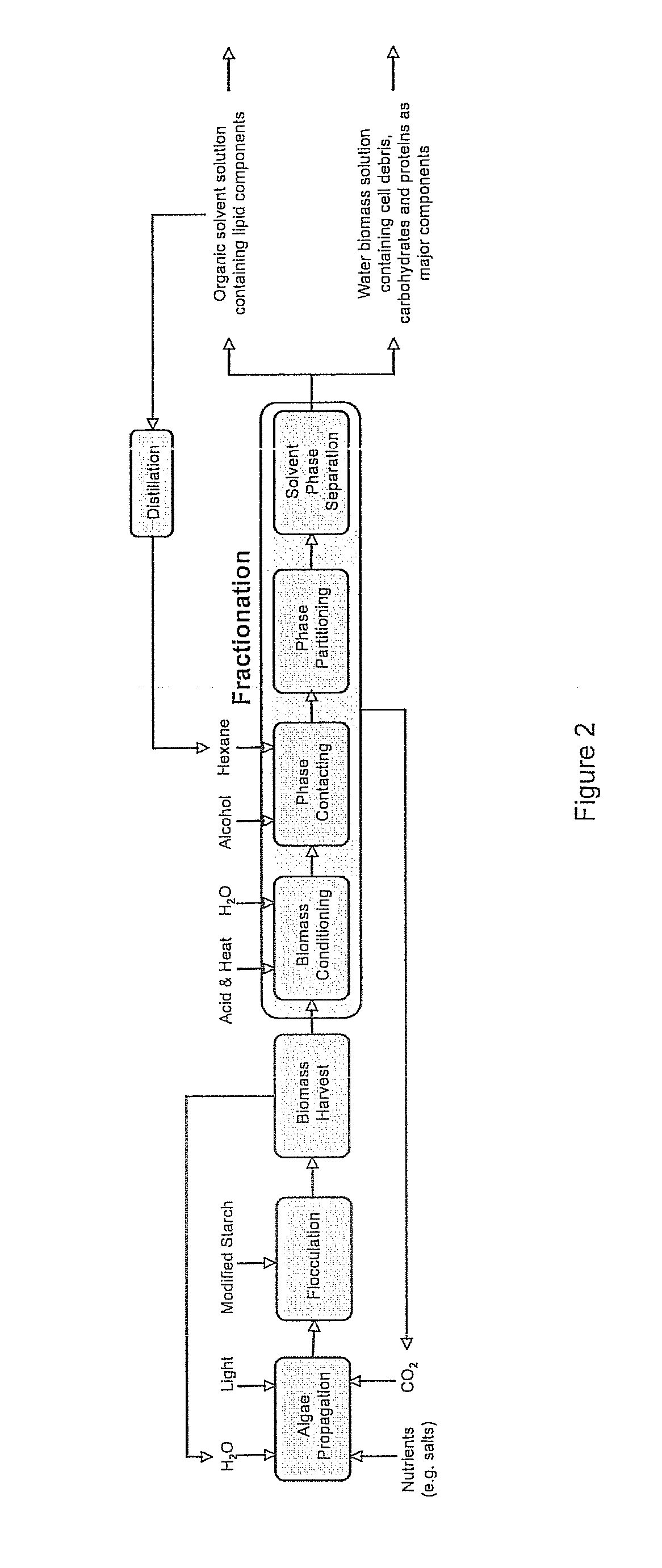
Algae biomass fractionation
A method of fractionating biomass, by permeability conditioning biomass suspended in a pH adjusted solution of at least one water-based polar solvent to form a conditioned biomass, intimately contacting the pH adjusted solution with at least one non-polar solvent, partitioning to obtain an non-polar solvent solution and a polar biomass solution, and recovering cell and cell derived products from the non-polar solvent solution and polar biomass solution. Products recovered from the above method. A method of operating a renewable and sustainable plant for growing and processing algae.
Owner:TRUCENT INC
Biomass hydrolysate and uses and production thereof
The present invention includes a palatable, stable composition comprising a biomass hydrolysate emulsion for incorporation, into, or used as, nutritional products, cosmetic products or pharmaceutical products. Preferred sources for biomass are microbial sources, plant sources and animal sources. The present invention also provides methods for making such compositions, specifically, a method for producing a product comprising a nutrient, particularly a long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid, comprising hydrolyzing a biomass comprising the nutrient and emulsifying the hydrolyzed biomass. Such compositions and methods are useful, for example, for increasing intake of nutrients such as omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids having 18 or more carbons.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
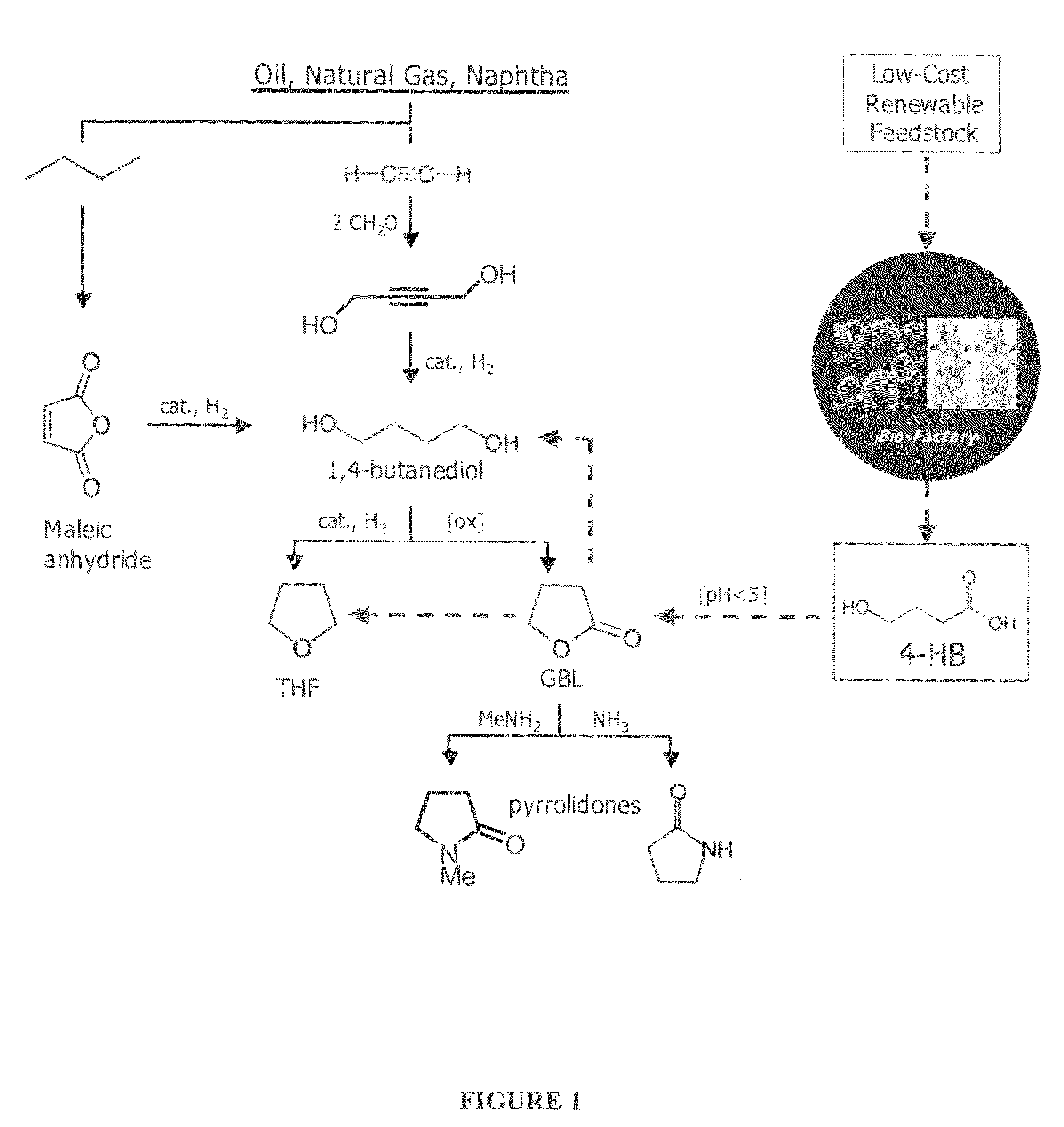
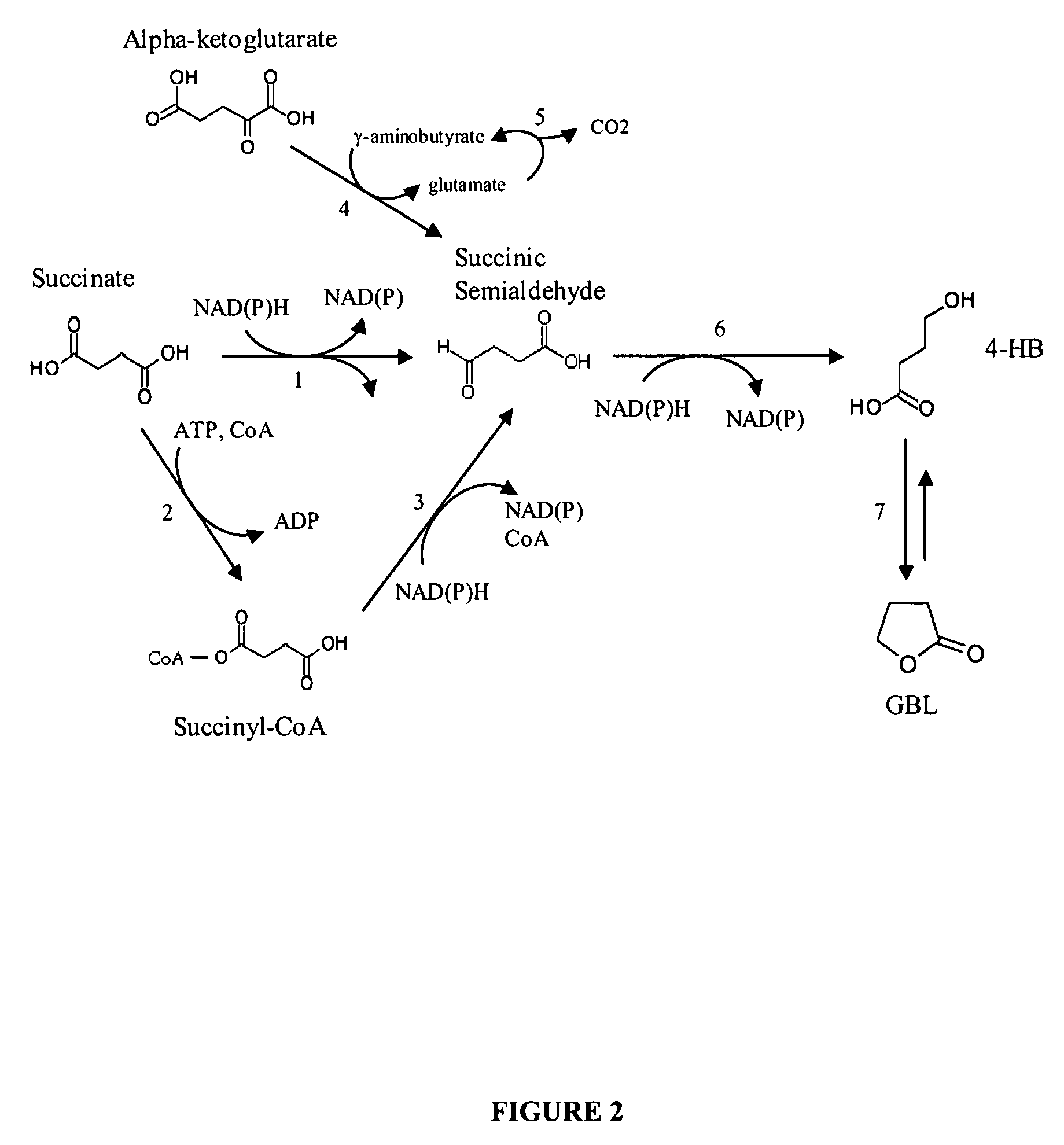
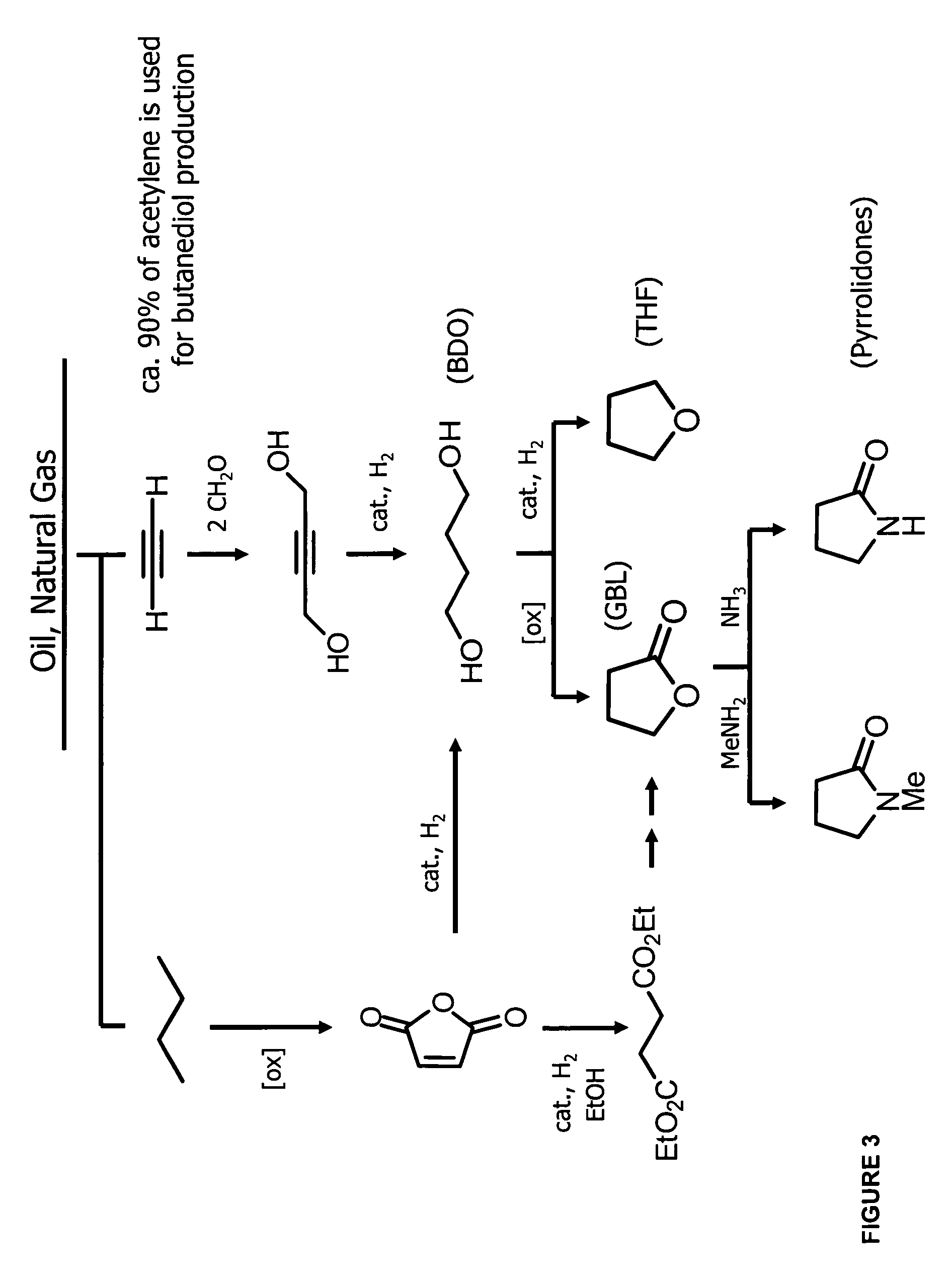
Methods and organisms for the growth-coupled production of 1,4-butanediol
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microorganism comprising one or more gene disruptions, the one or more gene disruptions occurring in genes encoding an enzyme obligatory to coupling 1,4-butanediol production to growth of the microorganism when the gene disruption reduces an activity of the enzyme, whereby the one or more gene disruptions confers stable growth-coupled production of 1,4-butanediol onto the non-naturally occurring microorganism. The microorganism can further comprise a gene encoding an enzyme in a 1,4-butanediol (BDO) biosynthetic pathway. The invention additionally relates to methods of using microorganisms to produce BDO.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
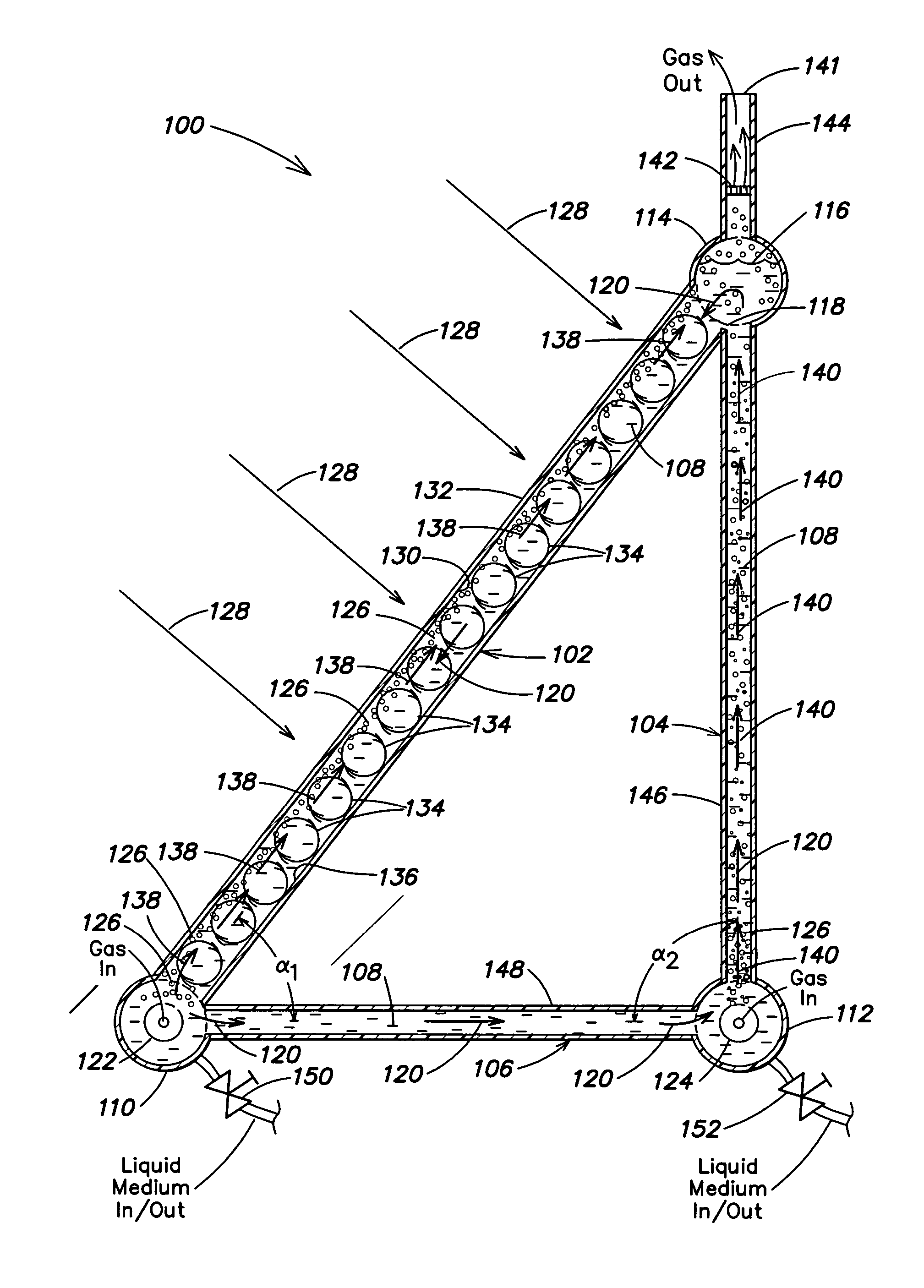
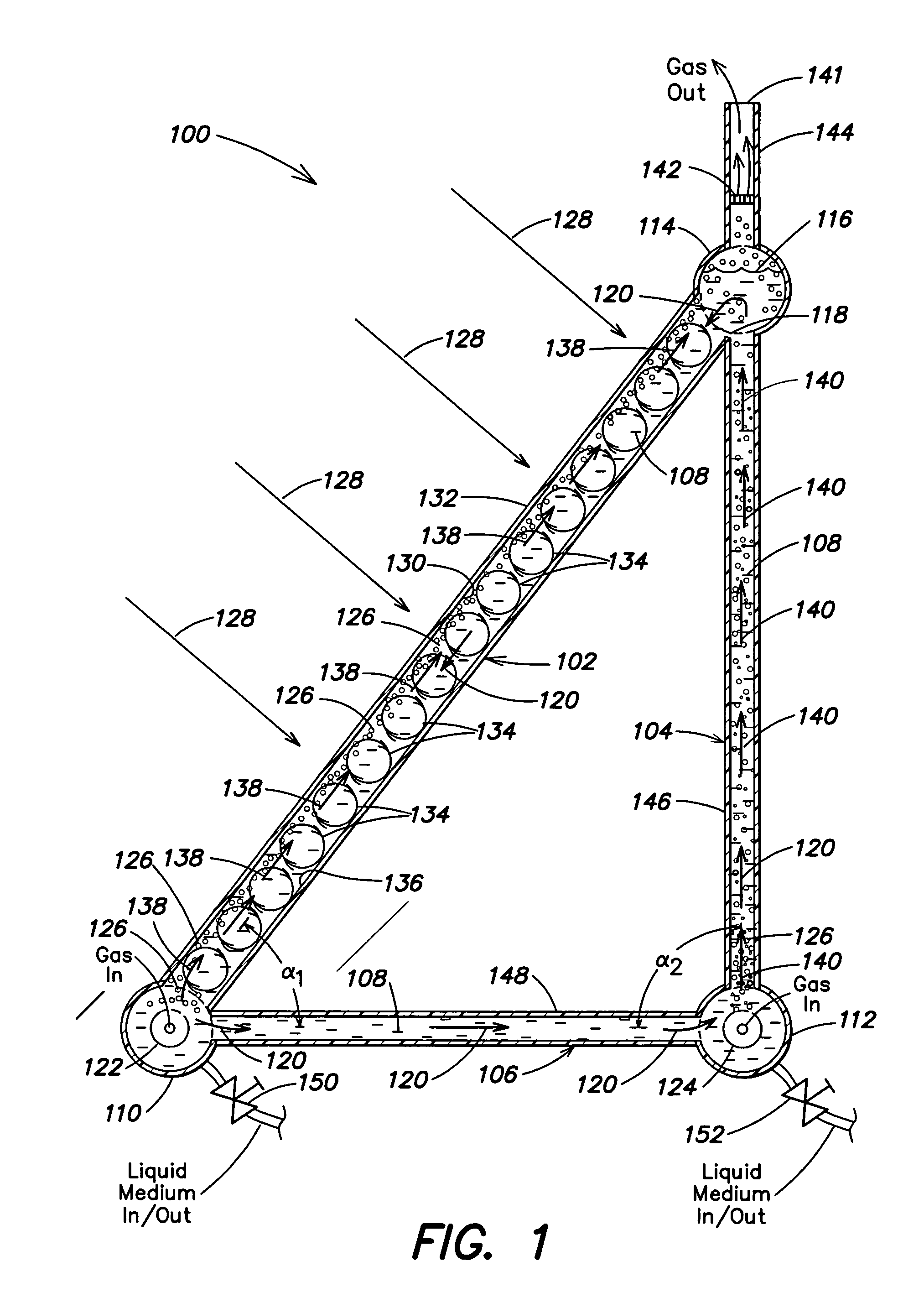
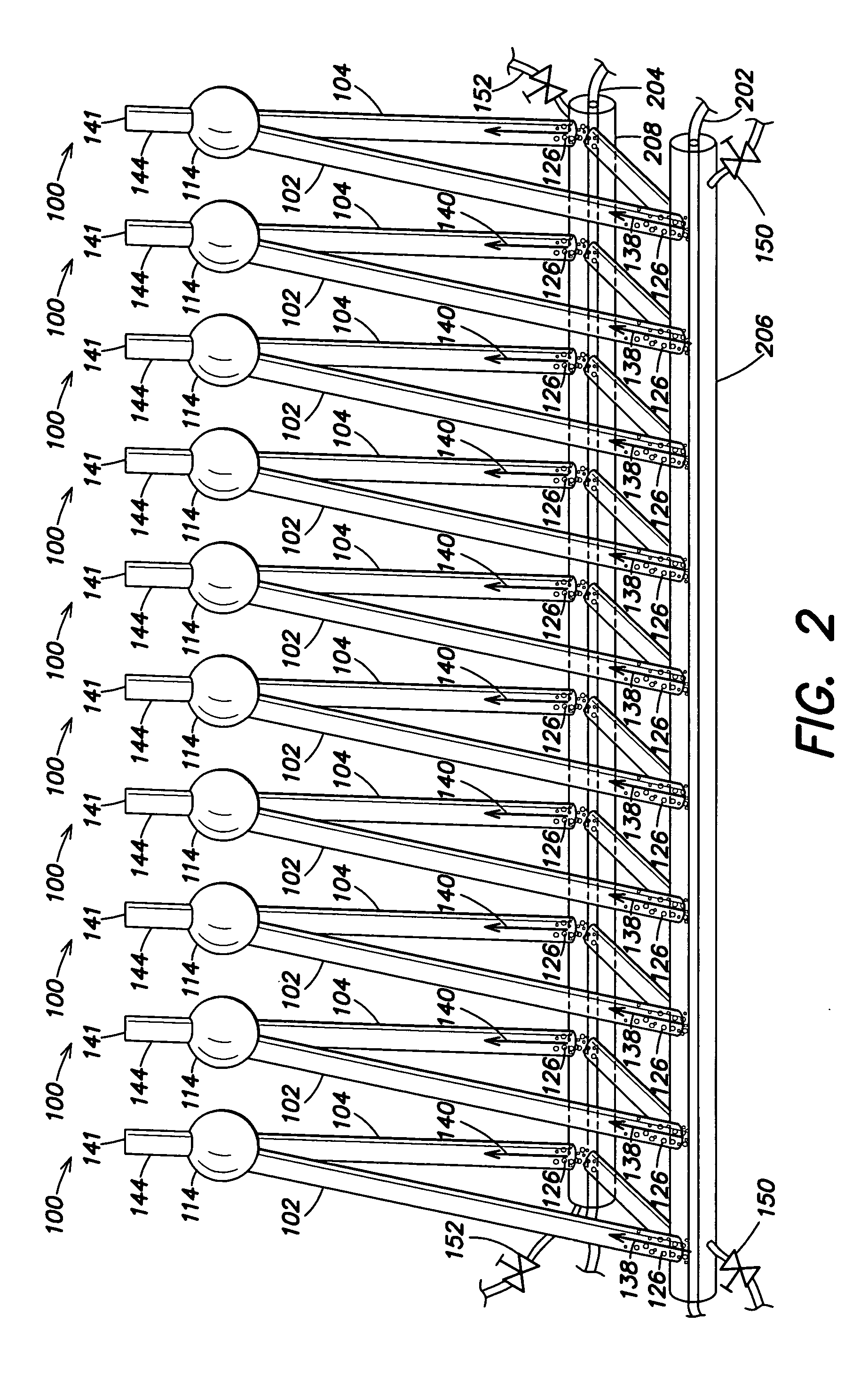
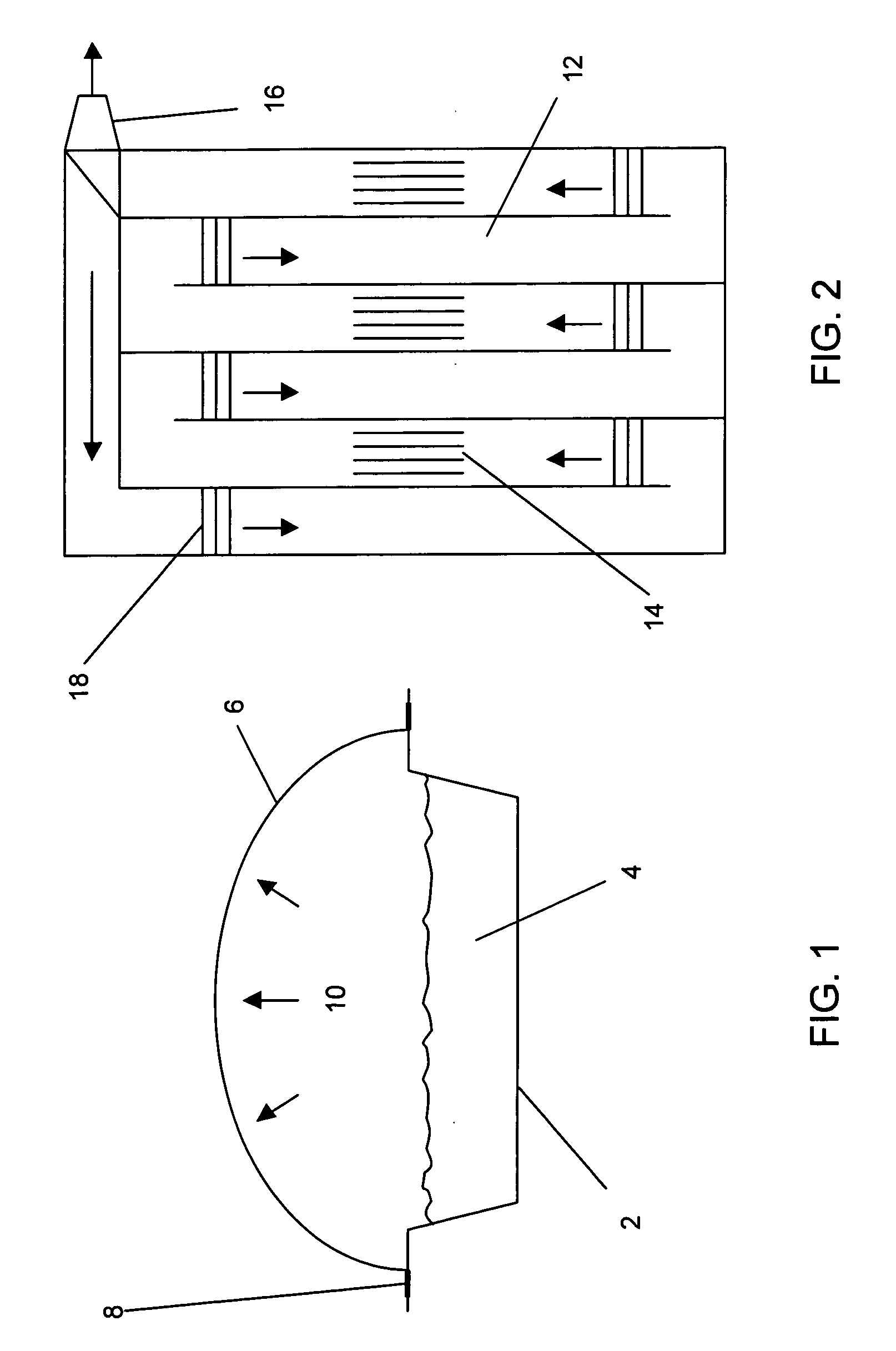
Photobioreactor systems and methods for treating CO2-enriched gas and producing biomass
InactiveUS20080178739A1Facilitate evaporative coolingSupport growthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiquid mediumStream flow
Certain embodiments and aspects of the present invention relate to a photobioreactor including covered photobioreactor units through which a liquid medium stream and a gas stream flow. The liquid medium comprises at least one species of phototrophic organism therein. Certain methods of using the photobioreactor system as part of fuel generation system and / or a gas-treatment process or system at least partially remove certain undesirable pollutants from a gas stream. In certain embodiments, a portion of the liquid medium is diverted from a photobioreactor unit and reintroduced upstream of the diversion position. In certain embodiments, the disclosed photobioreactor system, methods of using such systems, and / or gas treatment apparatus and methods provided herein can be used as part of an integrated combustion method and system, wherein photosynthetic organisms used within the photobioreactor are harvested from the photobioreactor, processed, and used as a fuel source for a combustion system such as an electric power plant.
Owner:THE TRON GRP
Storage stable compositions of biological materials
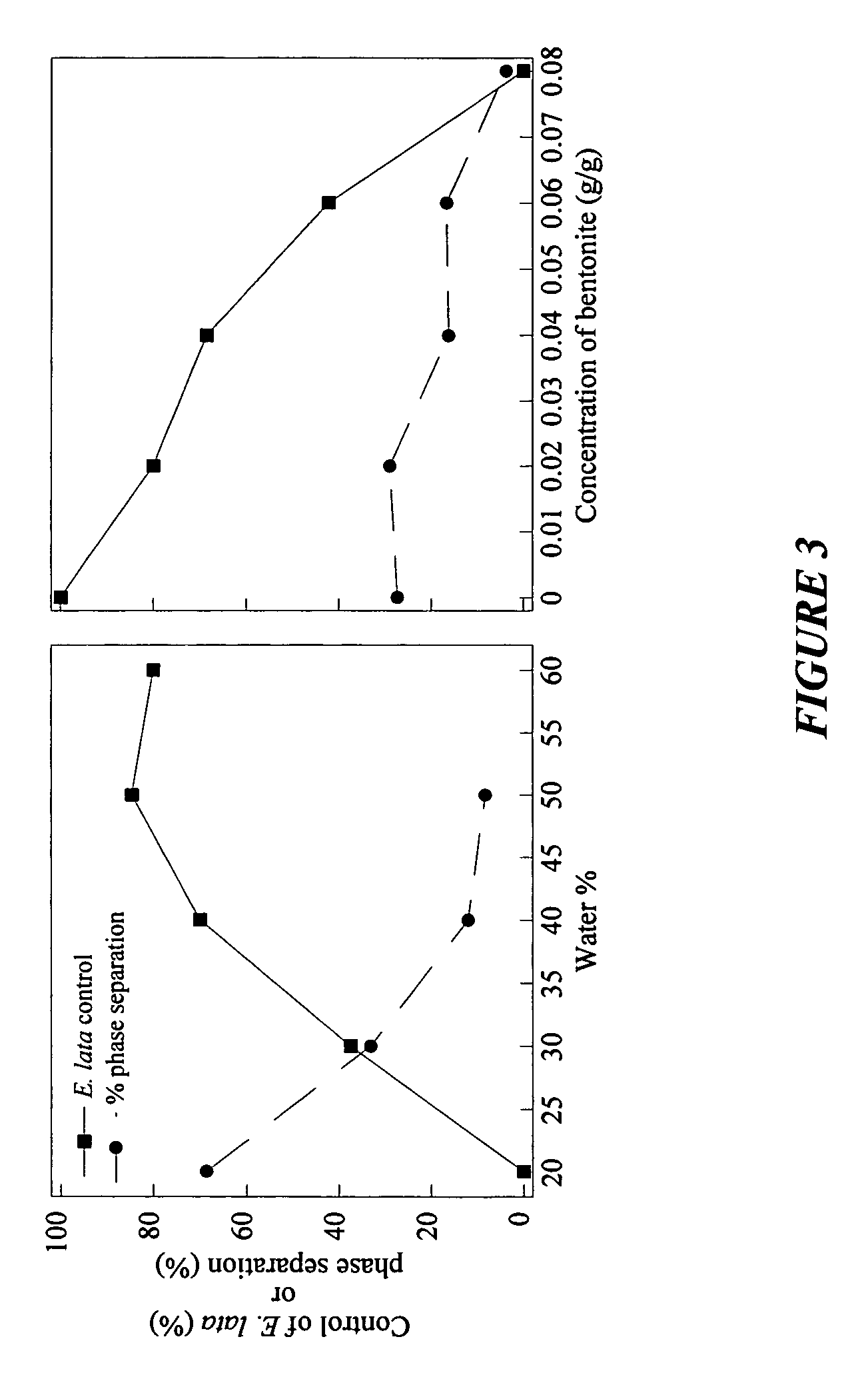
Storage stable compositions of biological materials, including bioactive biological materials are provided in the form of a water-in-oil emulsion, comprising:(a) cellular material selected from living and / or dormant prokaryotic and / or eukaryotic cells and tissues, the cellular material being compatible with water-in-oil emulsions;(b) one or more oils selected from vegetable oils and fish oils;(c) an oil-soluble nonionic polymeric surfactant having a molecular weight of from about 2500 to about 15000; and(d) water.The compositions may also contain a thickener such as a hydrophobic fumed silica or bentonite.Compositions may be used for various purposes, depending on the contained biological material. Specific examples include compositions containing Fusarium lateritium control of Eutypa lata in plant wounds made by cutting or pruning, and compositions containing Lagenidium giganteum for control of mosquitoes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Isolation and characterization of novel clostridial species
InactiveUS20080057554A1High yieldReadily availableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBacteroidesAcetic acid
A novel clostridia bacterial species (Clostridium ragsdalei, ATCC BAA-622, “P11”) is provided. P11 is capable of synthesizing, from waste gases, products which are useful as biofuel. In particular, P11 can convert CO to ethanol. Thus, this novel bacterium transforms waste gases (e.g. syngas and refinery wastes) into useful products. P11 also catalyzes the production of acetate.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Use of a composition made of mineral nutrients and optionally acetogenic and/or butyrogenic bacteria in order to avoid or reduce the formation of gas in the large intestine of a mammal and the resulting abdominal problems
InactiveUS20100247489A1Raise countSufficient supplyHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideAcetic acidMammal
The present invention relates to a composition comprising one or more minerals selected from the group consisting of selenium, molybdenum or tungsten, which is carried out galenically or chemically in a way that the mineral or minerals are released completely or in part, just before, during or shortly after arrival at the large intestine, and their use in the manufacture of a medicament for administering to a mammal for the prevention or reduction of gas formation in the colon thus conditioned abdominal complaints, particularly bloatings, meteorism or abdominal cramps. Furthermore, the invention relates to a procedure for the isolation of acetogenic and butyrogenic bacterial strains that are suitable for therapeutic purposes outlined above.
Owner:SAUR BROSCH ROLAND
Systems, devices, and methods for biomass production
InactiveUS20090047722A1Increased biomass productionDecreasing biomass production costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCellular componentCisterna
Systems, devices, and methods for releasing one or more cell components from a photosynthetic organism. A bioreactor system is operable for growing photosynthetic organisms. Some of the methods include contacting the photosynthetic organism with an energy-activatable sensitizer, and activating the energy-activatable sensitizer, thereby releasing a cellular component from at least one of, for example, a membrane structure, tubule, vesicle, cisterna, organelle, cell compartment, plastid, or mitochondrion, associated with the photosynthetic organisms.
Owner:BIONAVITAS
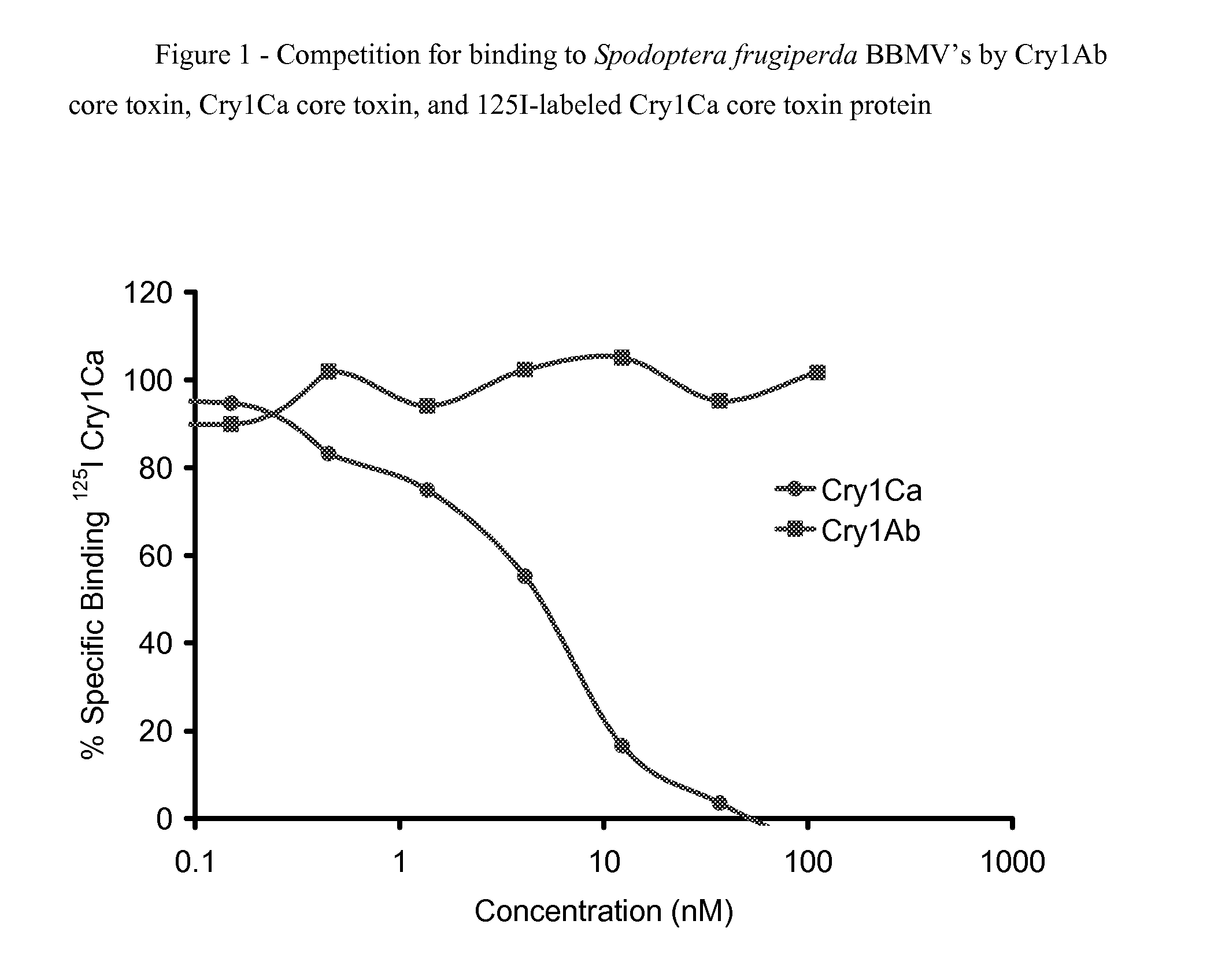
Combined use of cry1ca and cry1ab proteins for insect resistance management
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Combined use of vip3ab and cry1fa for management of resistant insects
InactiveUS20120317682A1Reduce and eliminate requirementNon-cross-resistantBiocideFungiCombined useDrug resistance
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Photobioreactor systems positioned on bodies of water
InactiveUS20090130706A1Maintain depthConstant thicknessBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiquid mediumStream flow
Certain embodiments and aspects of the present invention relate to a photobioreactor including photobioreactor units through which a liquid medium stream and a gas stream flow. The photobioreactor units are floated on a body of water such as a pond or a lake. The liquid medium comprises at least one species of phototrophic organism therein. Certain methods of using the photobioreactor system as part of fuel generation system and / or a gas-treatment process or system at least partially remove certain undesirable pollutants from a gas stream. In certain embodiments, the photobioreactor units are formed of flexible, deformable material and are configured to provide a substantially constant thickness of liquid medium. In certain embodiments, a barrier between the photobioreactor unit and the body of water upon which the unit is floated facilitates thermal communication between the liquid medium and the body of water.
Owner:THE TRON GRP
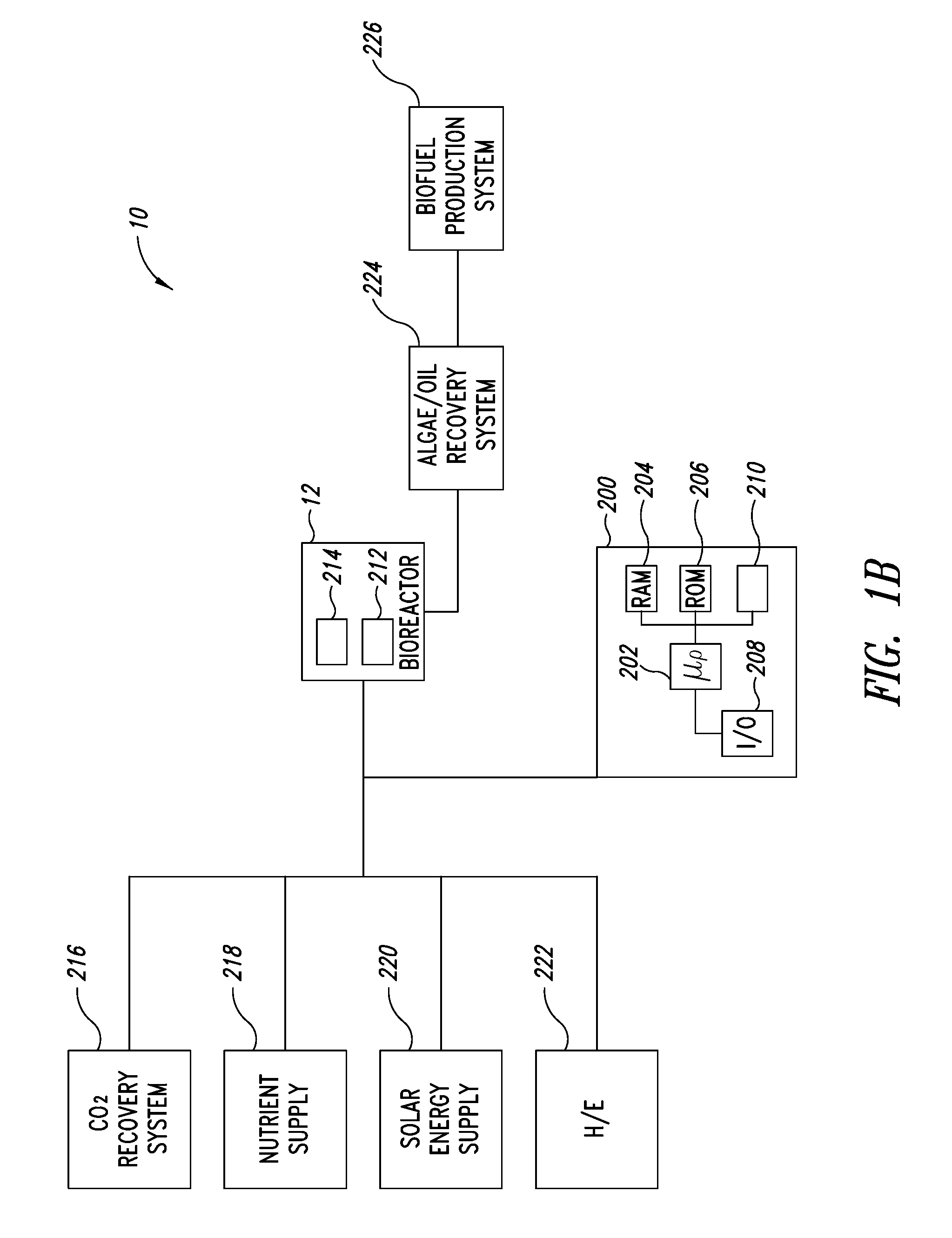
Continuous-Batch Hybrid Process for Production of Oil and Other Useful Products from Photosynthetic Microbes
InactiveUS20080118964A1Lower potentialIncreased complexityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismCarrying capacity
A process for cultivating photosynthetic microbes comprising Closed Systems for continuous cultivation and Open Systems for batch cultivation, in which (a) the Closed System Area occupies no more than 20% of the Total Land Area of the cultivation facility; (b) batch cultures in the Open Systems are initiated with an inoculum from the Closed Systems containing a cell biomass of no less than 5% of the carrying capacity of said Open System; (c) the doubling rate of said photosynthetic microbe is no less than once every 16 hours; and (d) the residence time of the batch culture in said Open System is no more than a period of 5 days.
Owner:CELLANA
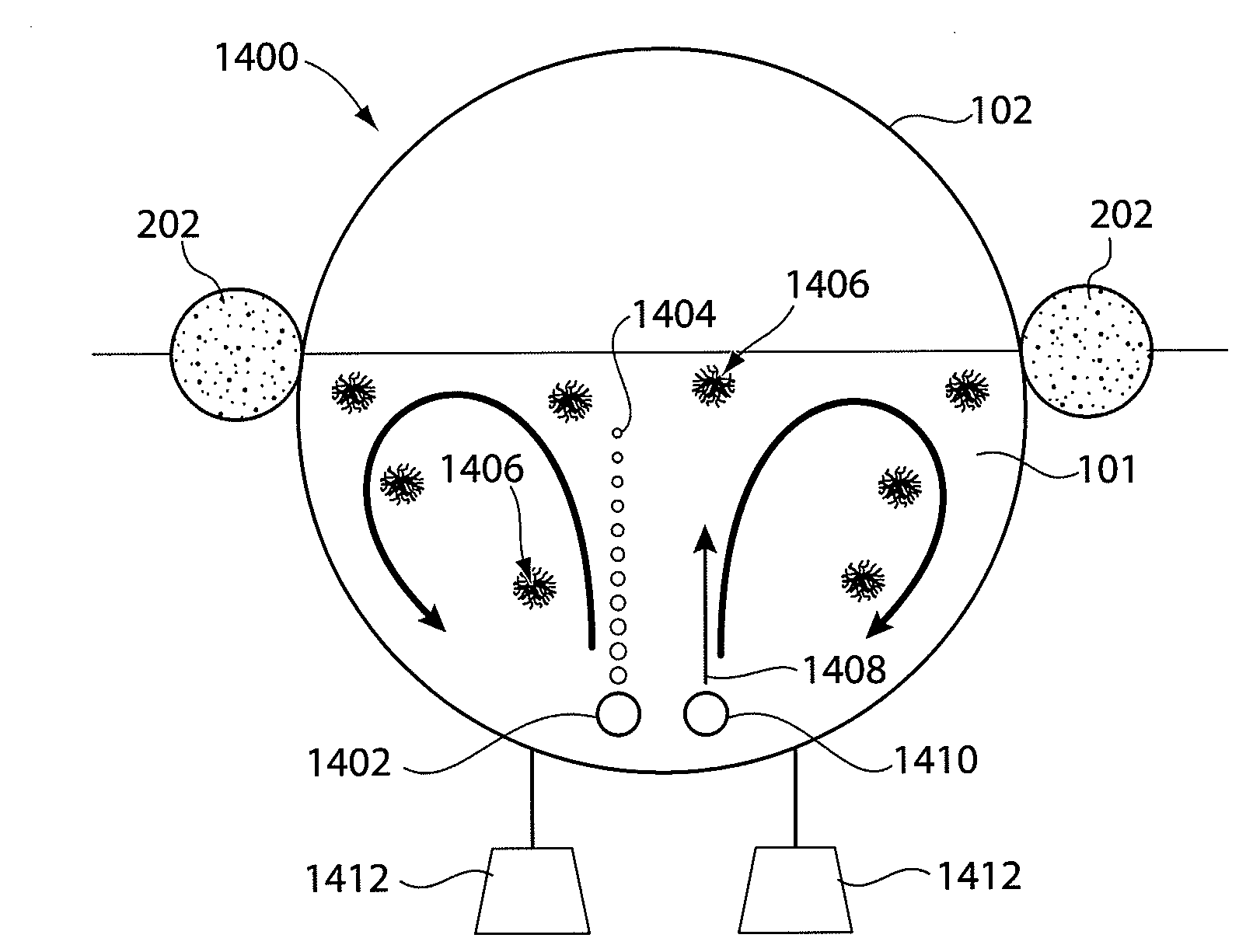
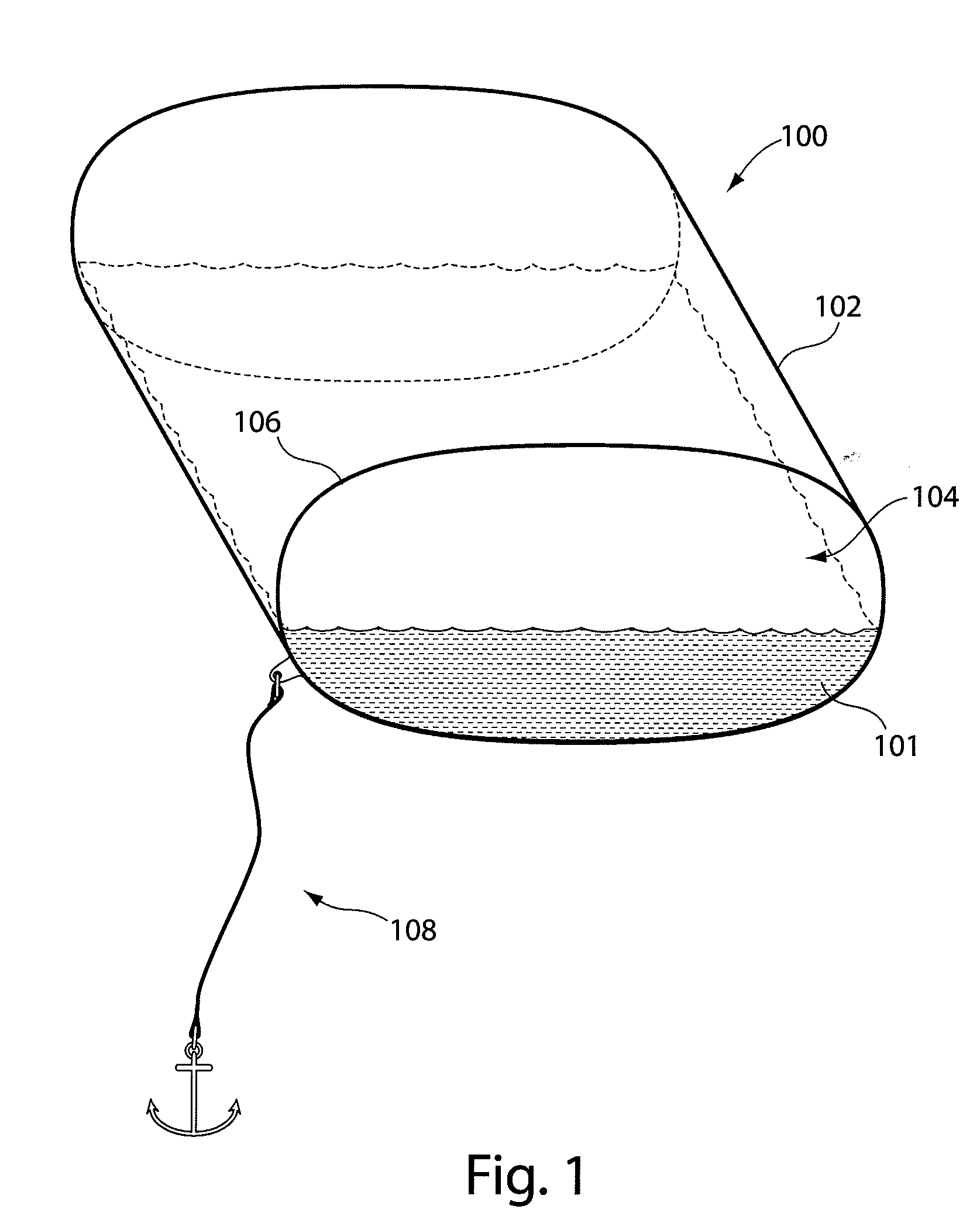
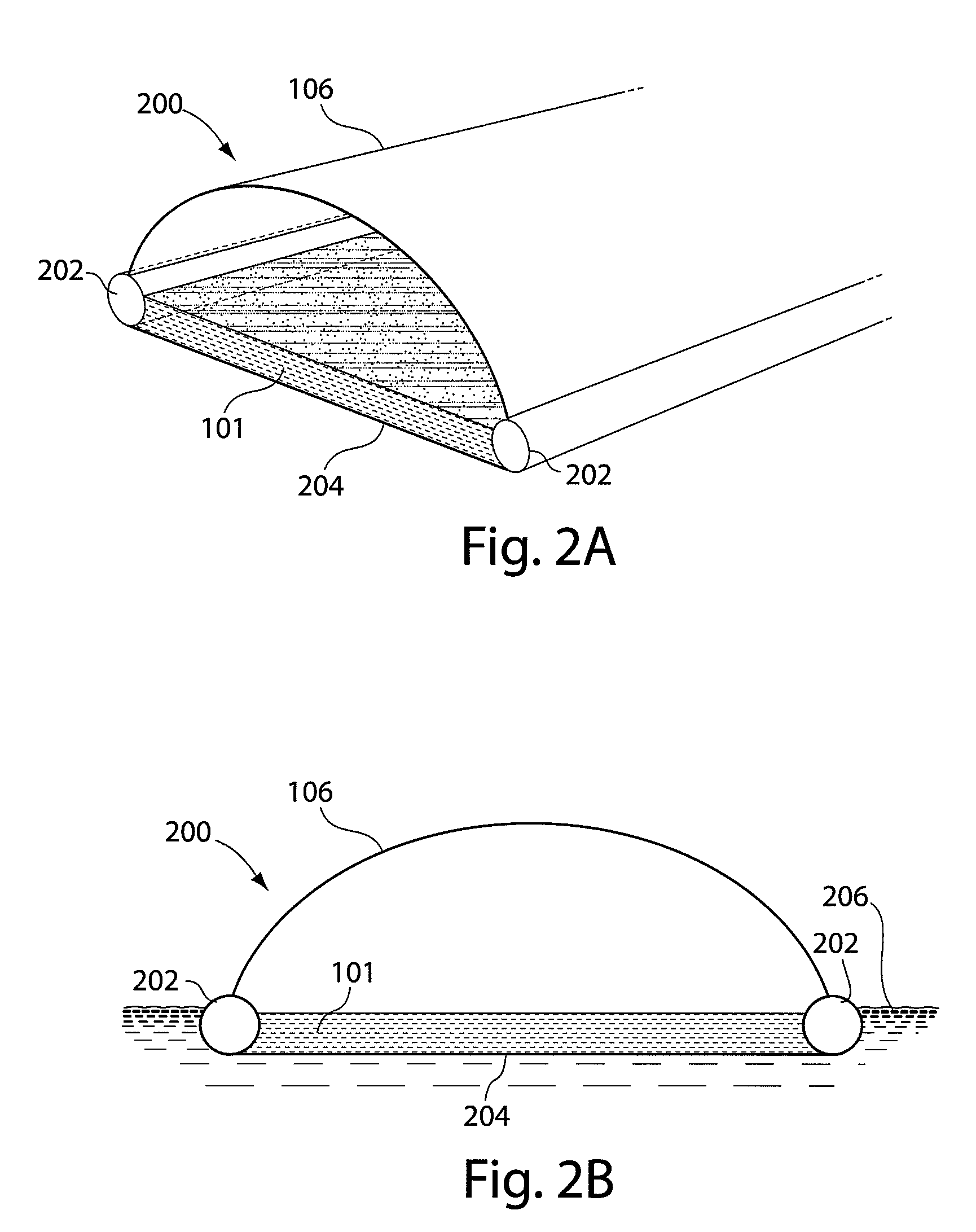
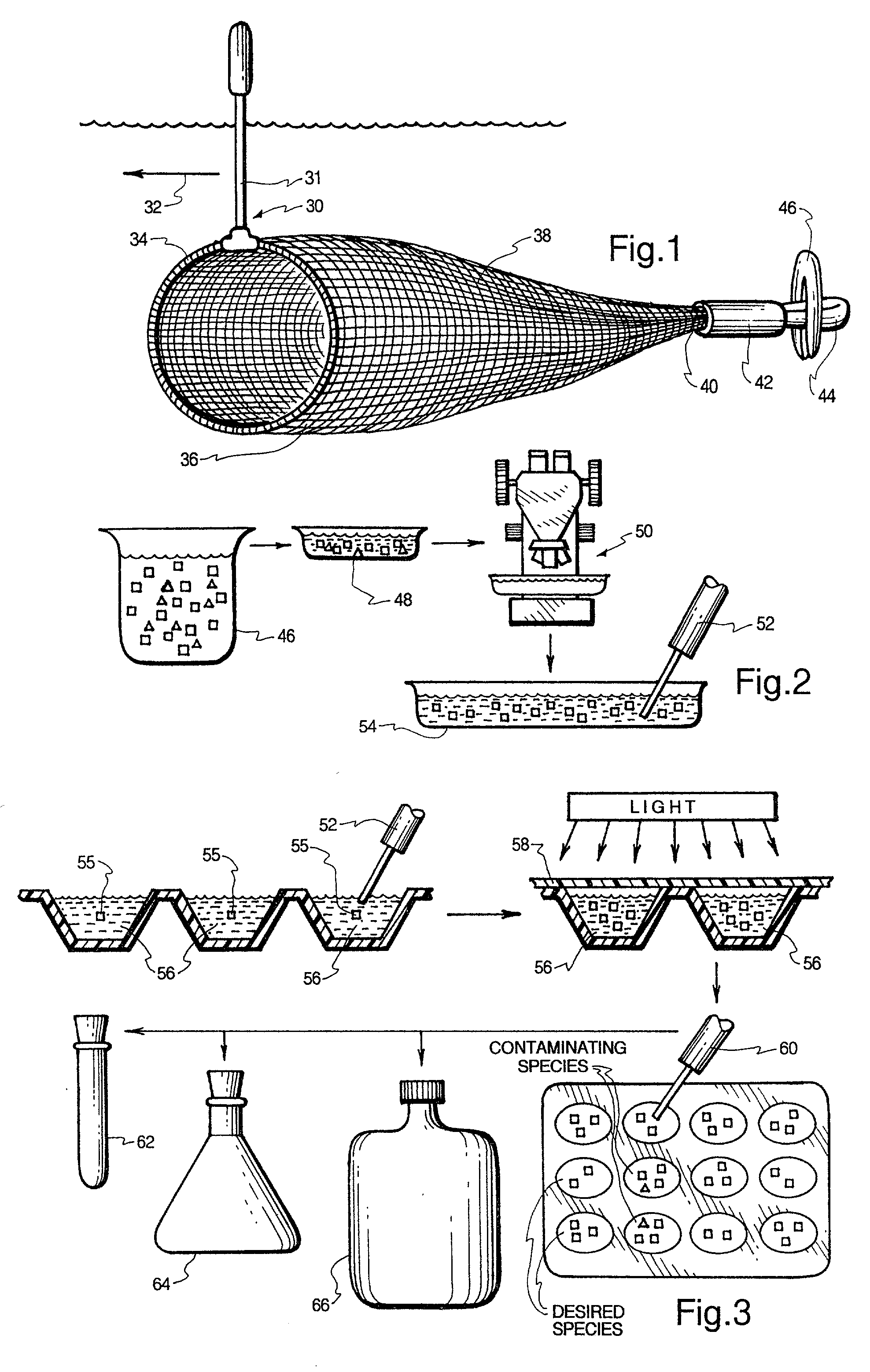
Process and apparatus for isolating and continuosly cultivating, harvesting, and processing of a substantially pure form of a desired species of algae
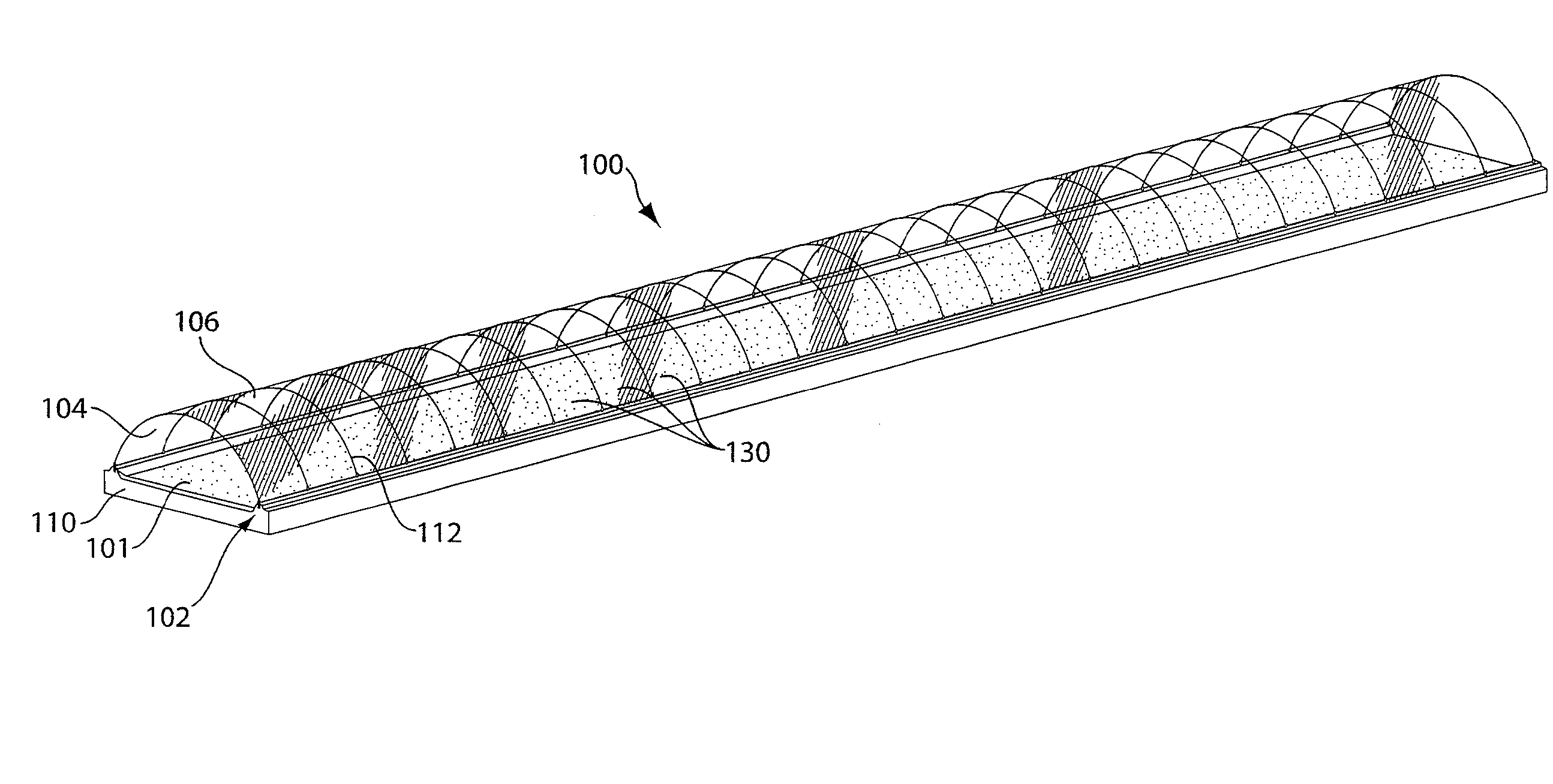
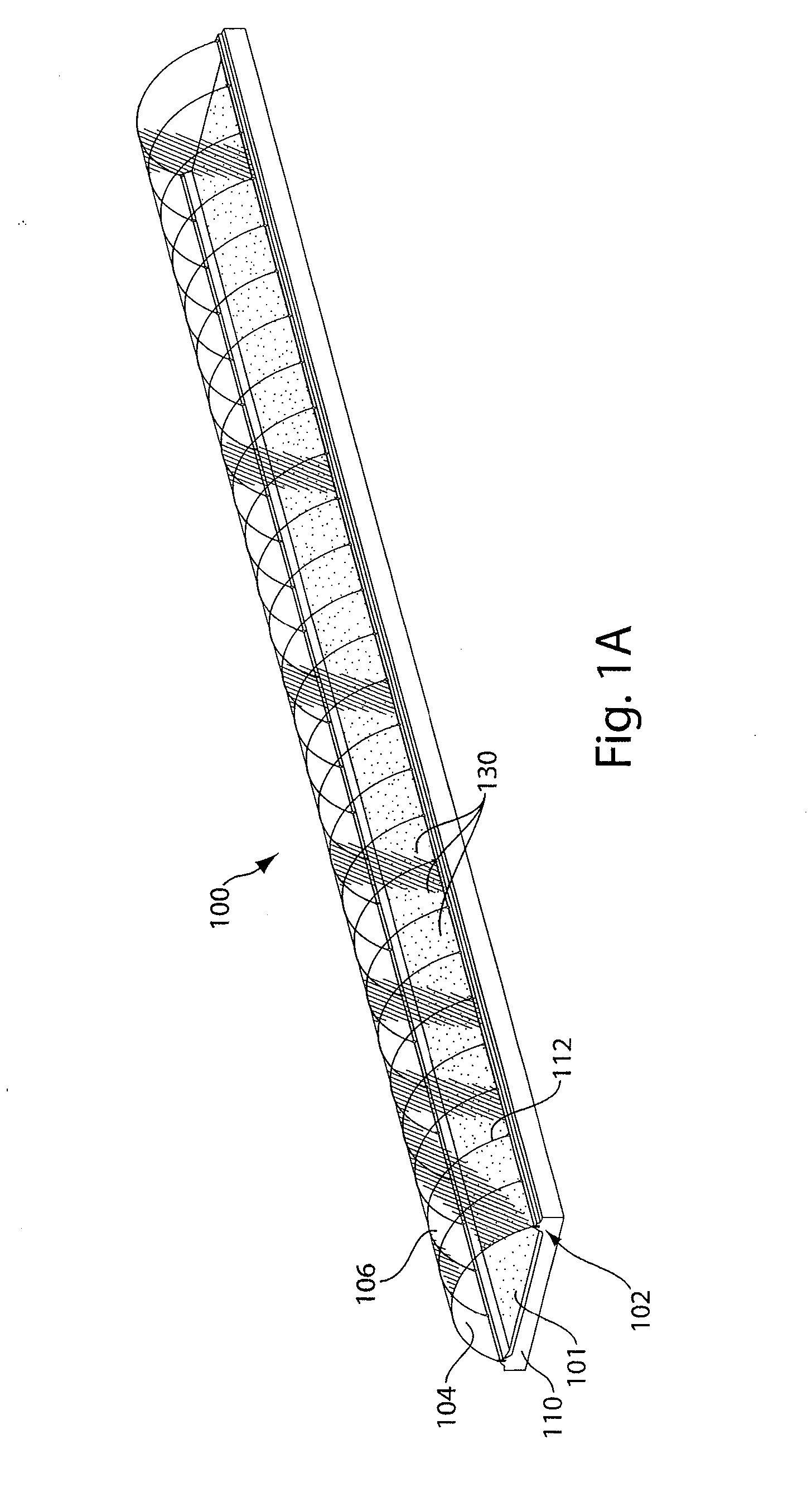
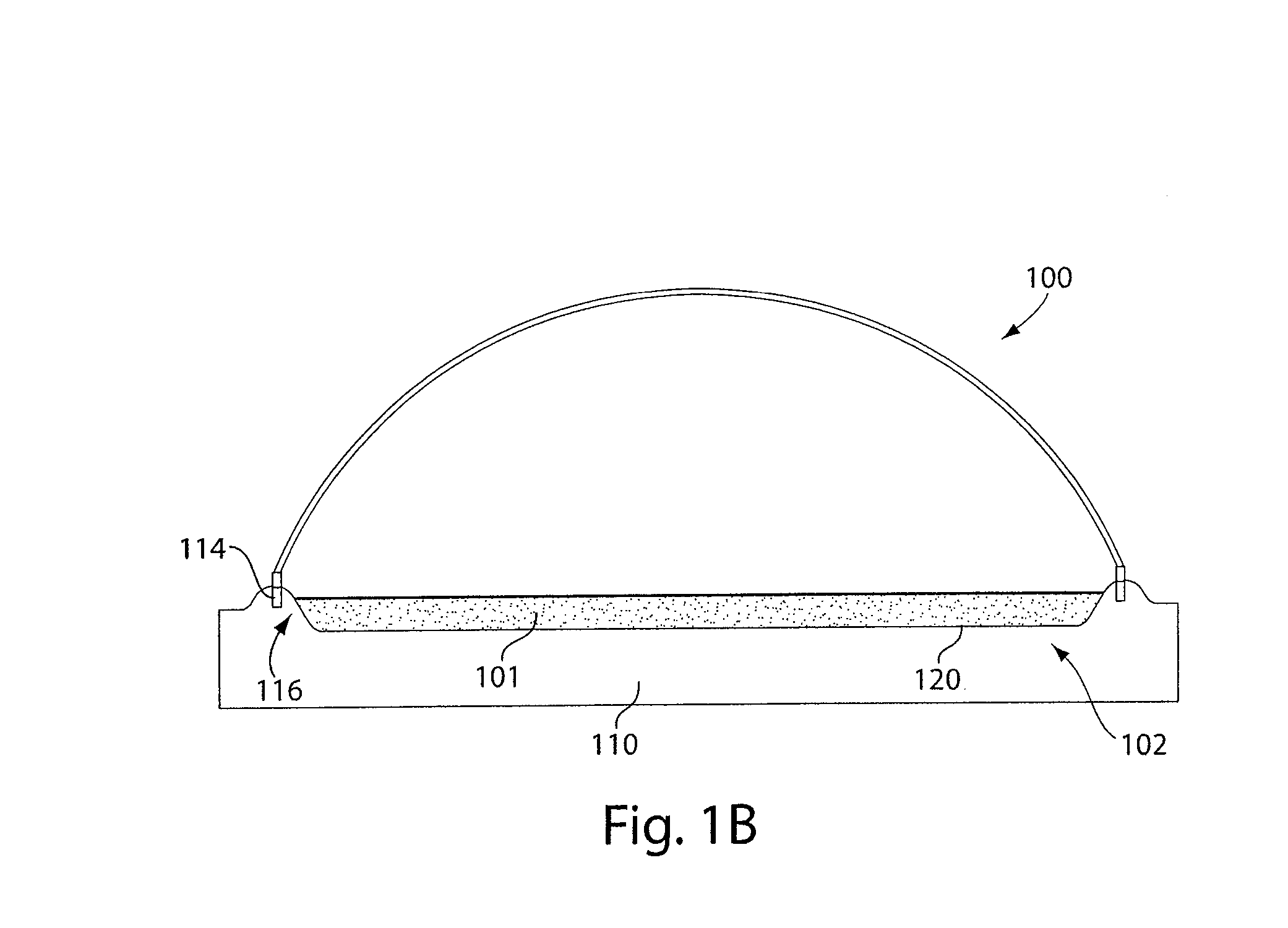
InactiveUS20020034817A1Better and more efficientUnicellular algaeBiochemistry cleaning apparatusAlgaeBiology
Novel closed system methods and apparatus for the production and utilization of algae are disclosed. A substantially pure form of a desired strain of alga is obtained and cultivated (or isolated and grown). The desired species of alga is isolated from the contaminants and other algae and placed in the controlled environment where its growth is cultivated without contaminants. At desired points in time, a portion of the cultivated alga is removed, with the remainder serving as progenitor stock for growing more of the desired alga. The removed alga is processed and placed in product form.
Owner:HENRY ERIC C +3
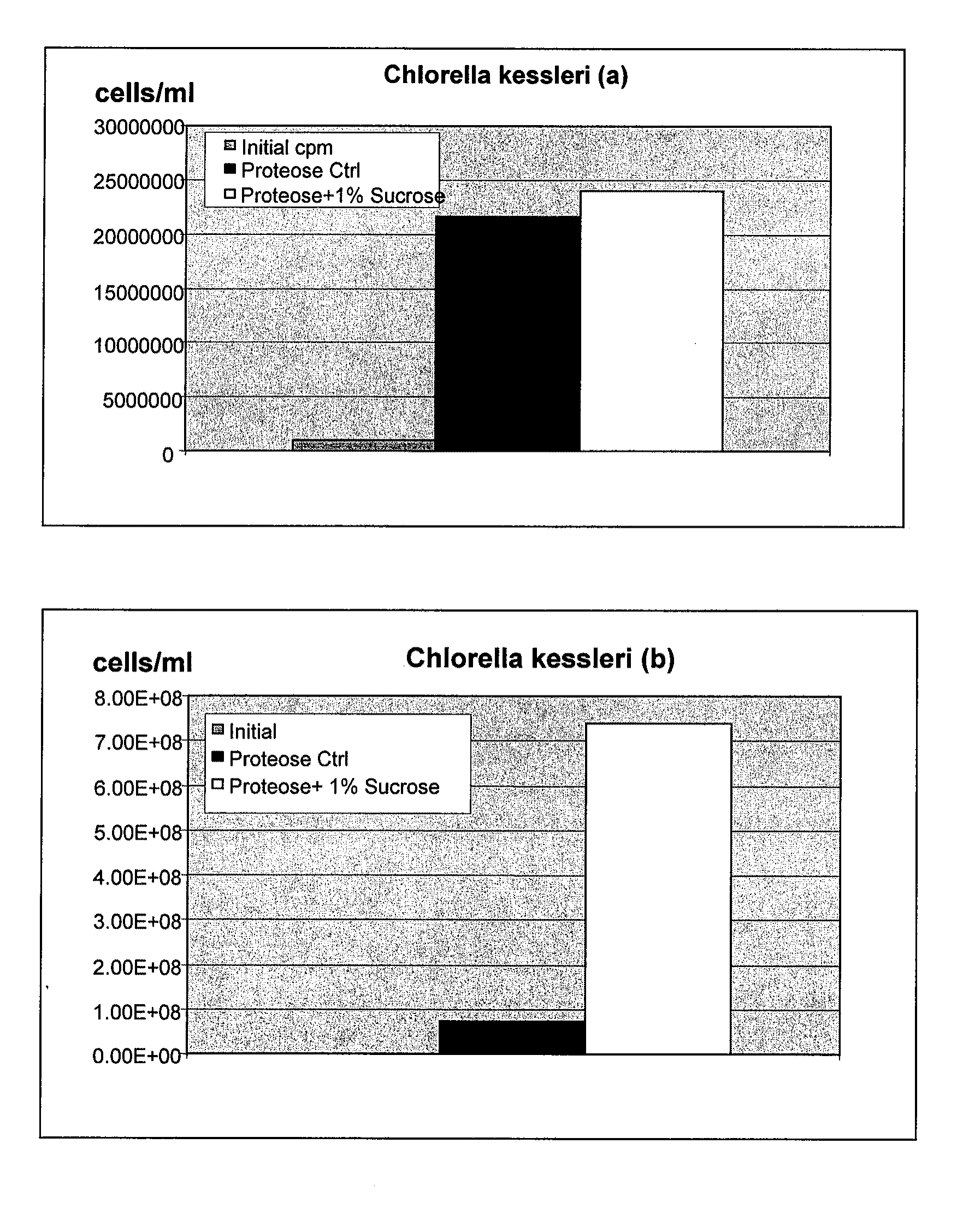
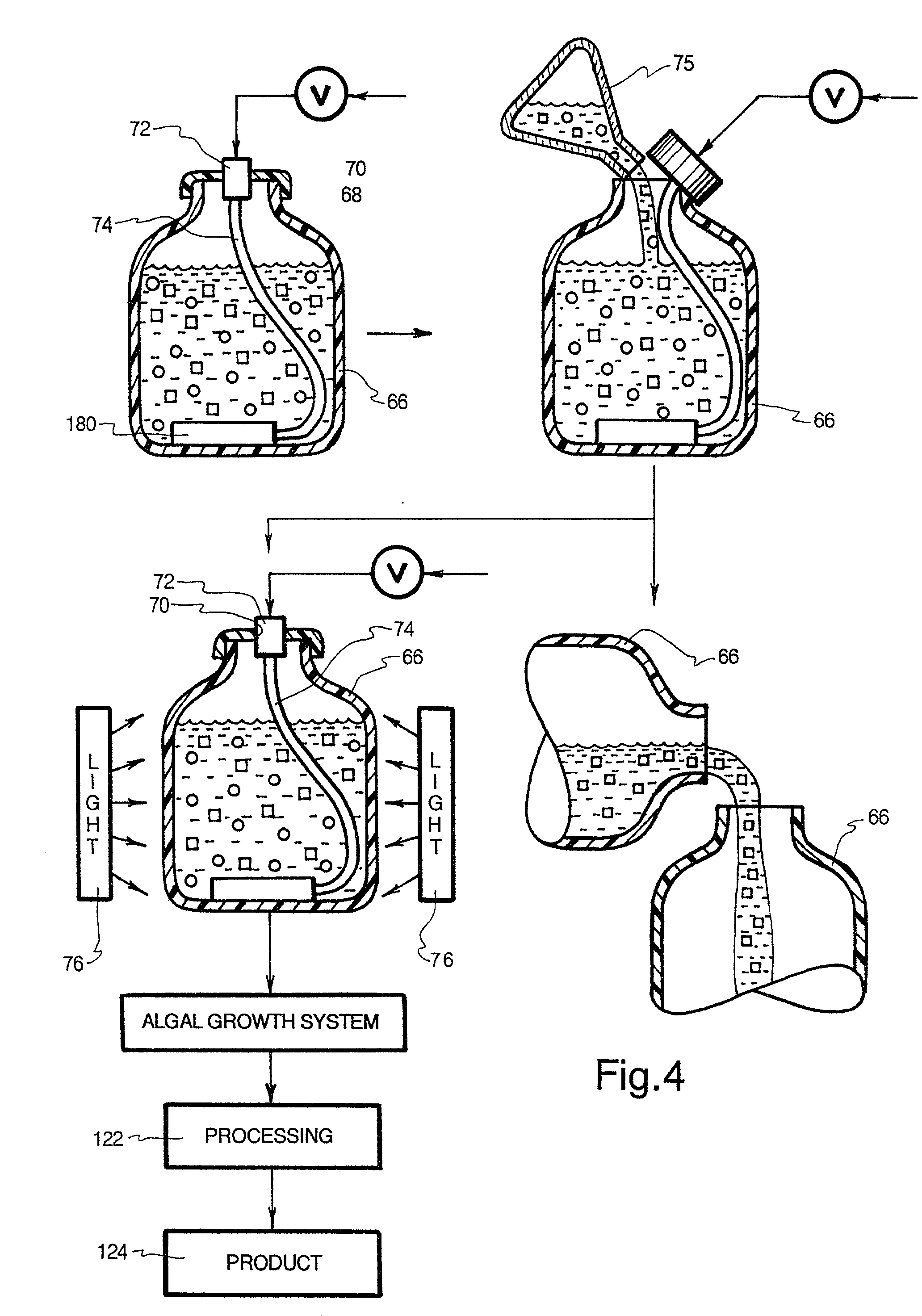
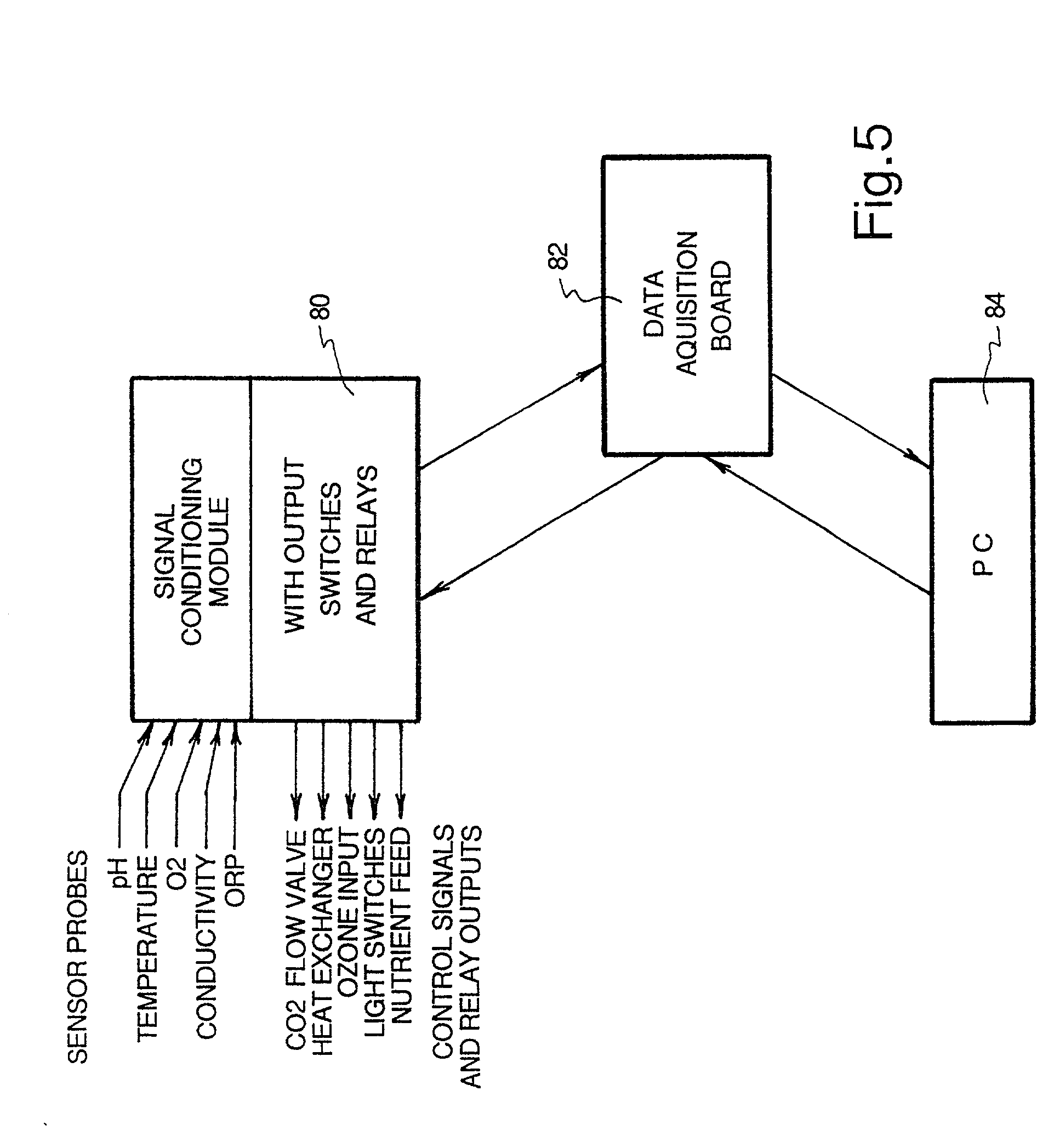
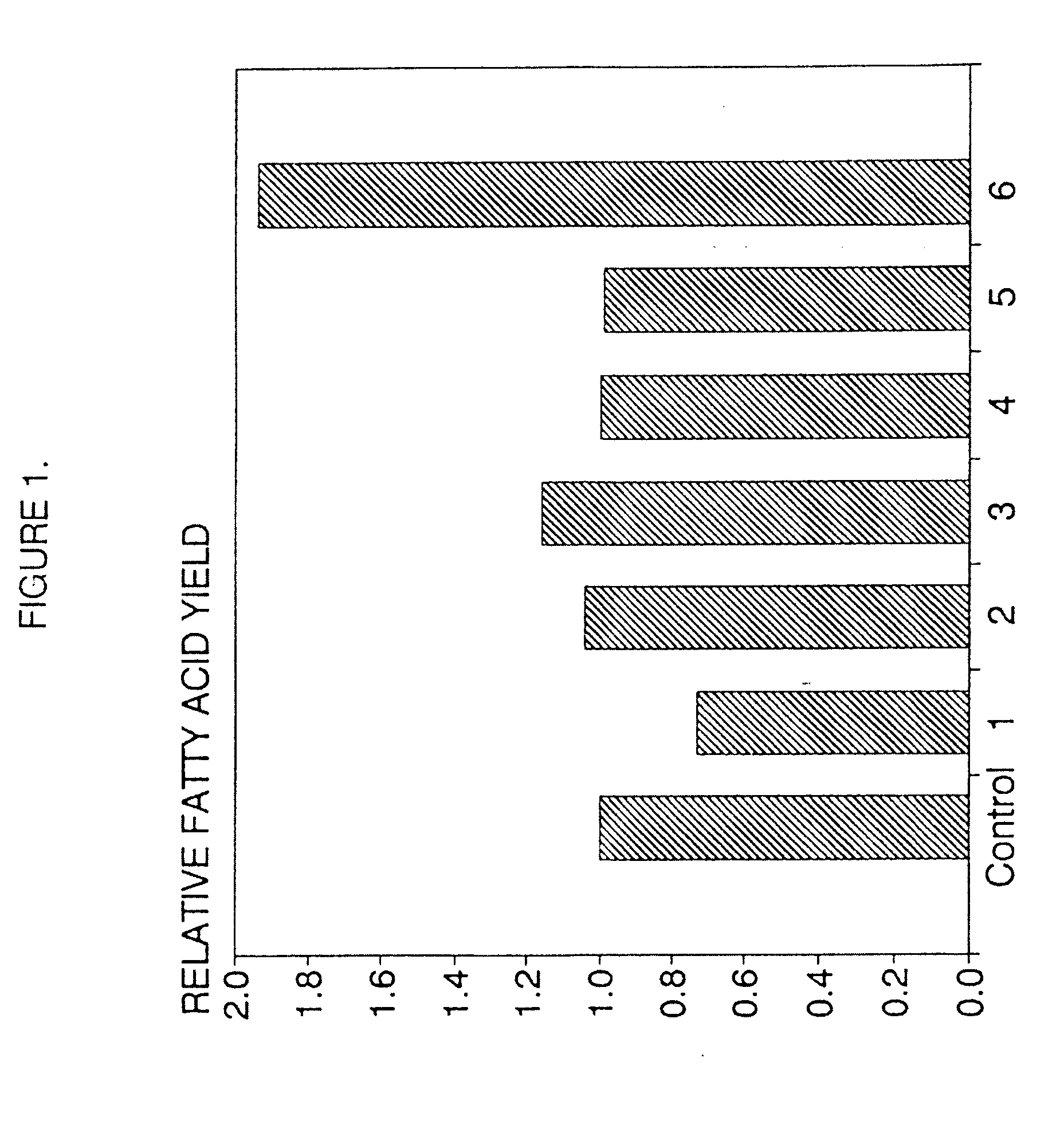
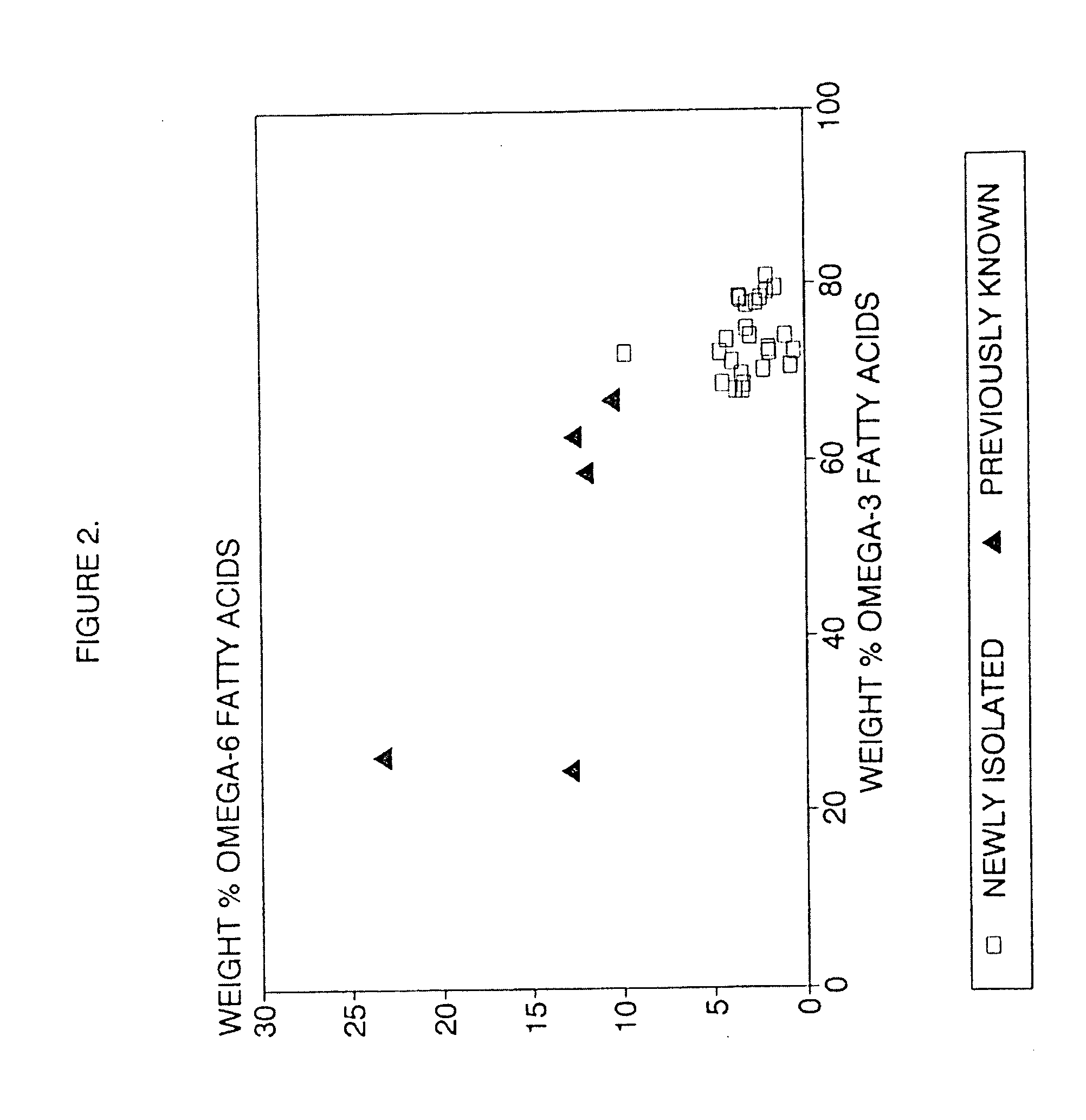
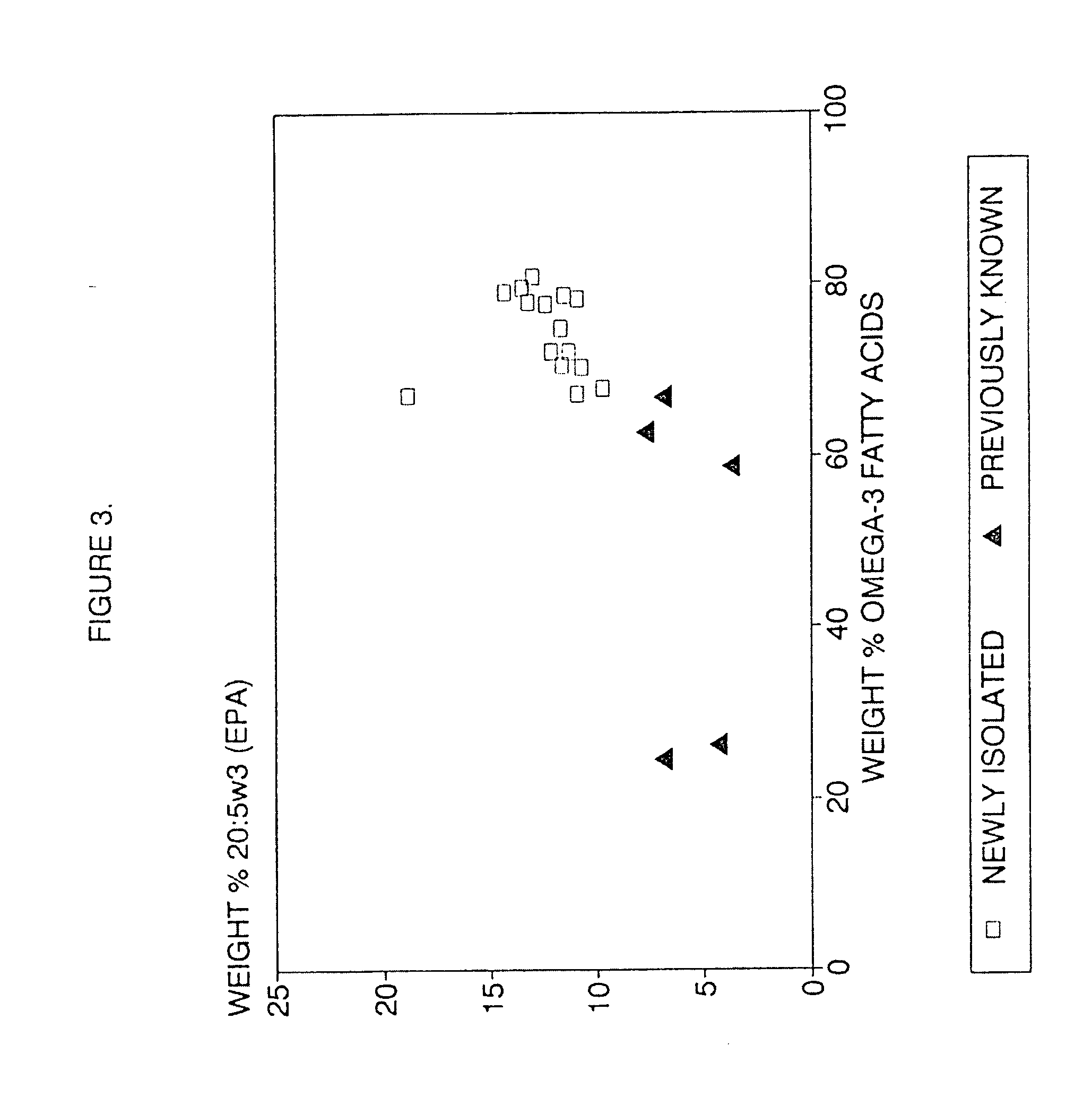
Process for the heterotrophic production of microbial products with high concentrations of omega-3 highly unsaturated fatty acids
InactiveUS20060094089A1Prevent degradationIncrease concentrationUnicellular algaeFermentationLipid formationHigh concentration
A process for the heterotrophic or predominantly heterotrophic production of whole-celled or extracted microbial products with a high concentration of omega-3 highly unsaturated fatty acids, producible in an aerobic culture under controlled conditions using biologically pure cultures of heterotrophic single-celled fungi microorganisms of the order Thraustochytriales. The harvested whole-cell microbial product can be added to processed foods as a nutritional supplement, or to fish and animal feeds to enhance the omega-3 highly unsaturated fatty acid content of products produced from these animals. The lipids containing these fatty acids can also be extracted and used in nutritional, pharmaceutical and industrial applications.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
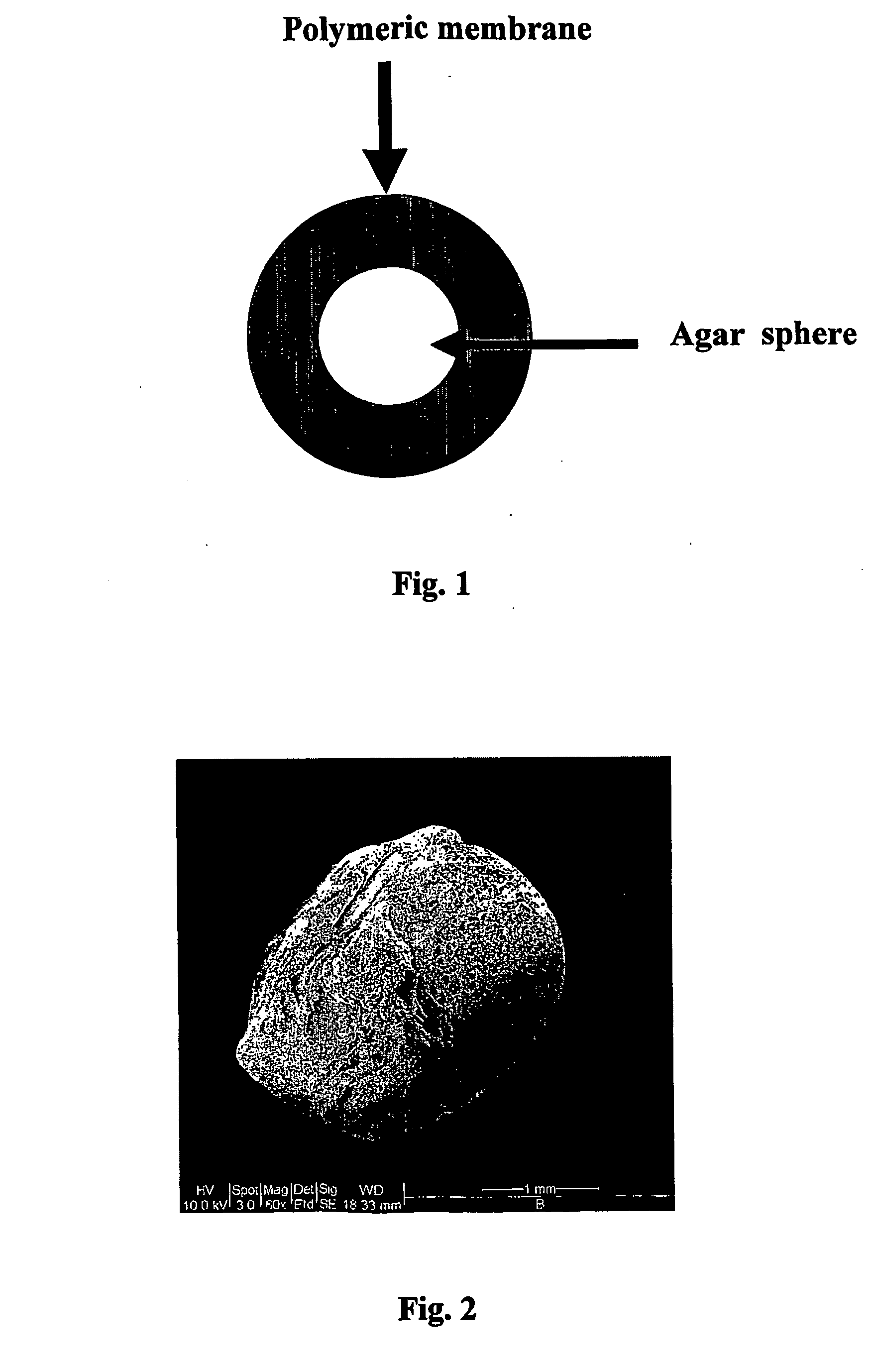
Method for isolating and culturing unculturable microorganisms
The invention provides a method for isolating and culturing a previously unculturable microorganism, which comprises: (i) collecting a sample from an environmental source; (ii) counting / estimating the number of microorganisms in the sample; (iii) diluting the sample in an appropriate medium; (iv) adding a gelating agent such as to entrap one or more microorganisms within a sphere of the gelating agent; (v) coating the spheres containing the entrapped microorganism(s) with a natural or synthetic polymer to form a polymeric membrane; (vi) incubating the coated spheres in the original environment for an appropriate time; (vii) cutting the spheres and scanning for microorganisms colonies; and (viii) isolating the microorganisms, and repeating steps (iii) to (vii) until a pure clone of said previously unculturable microorganism is obtained.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com