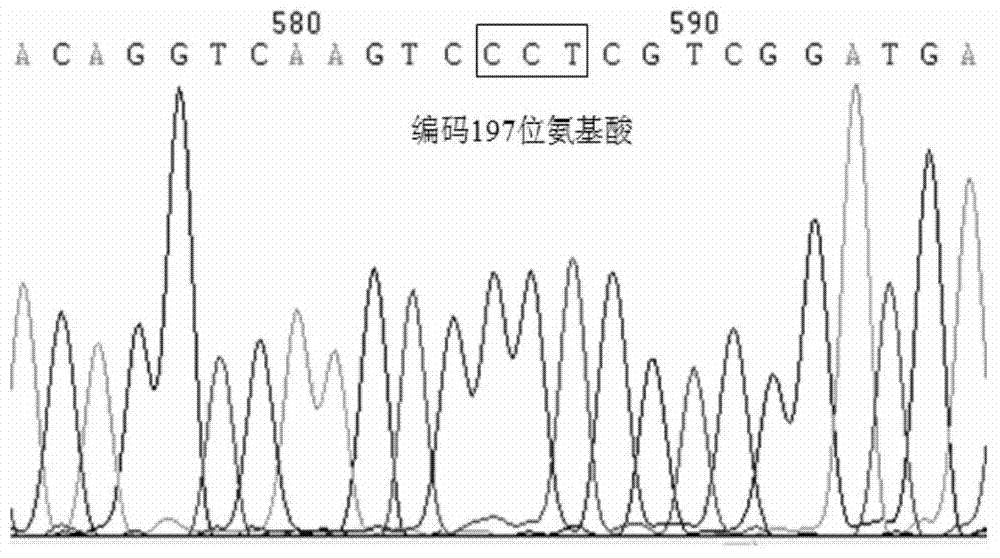
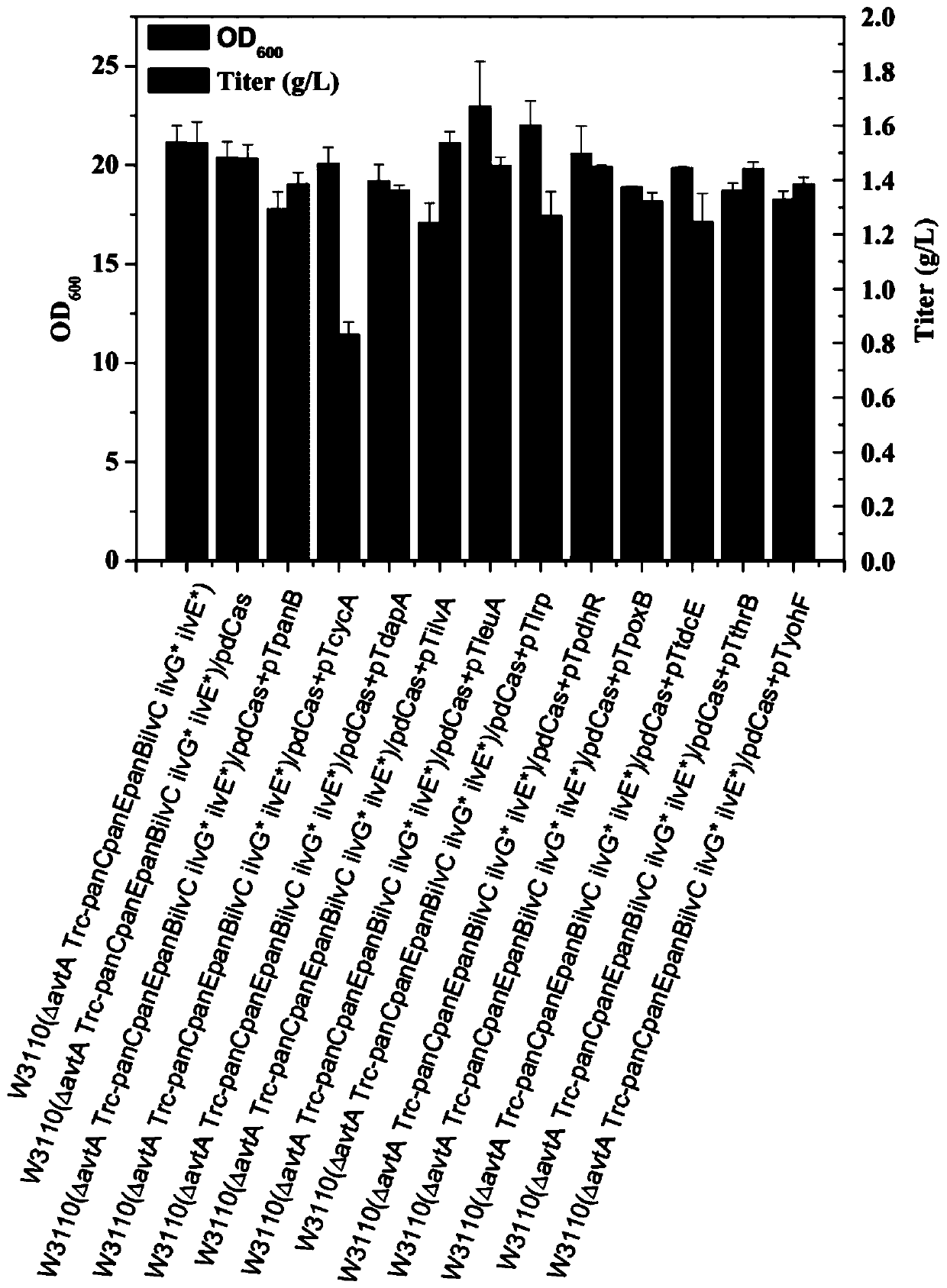
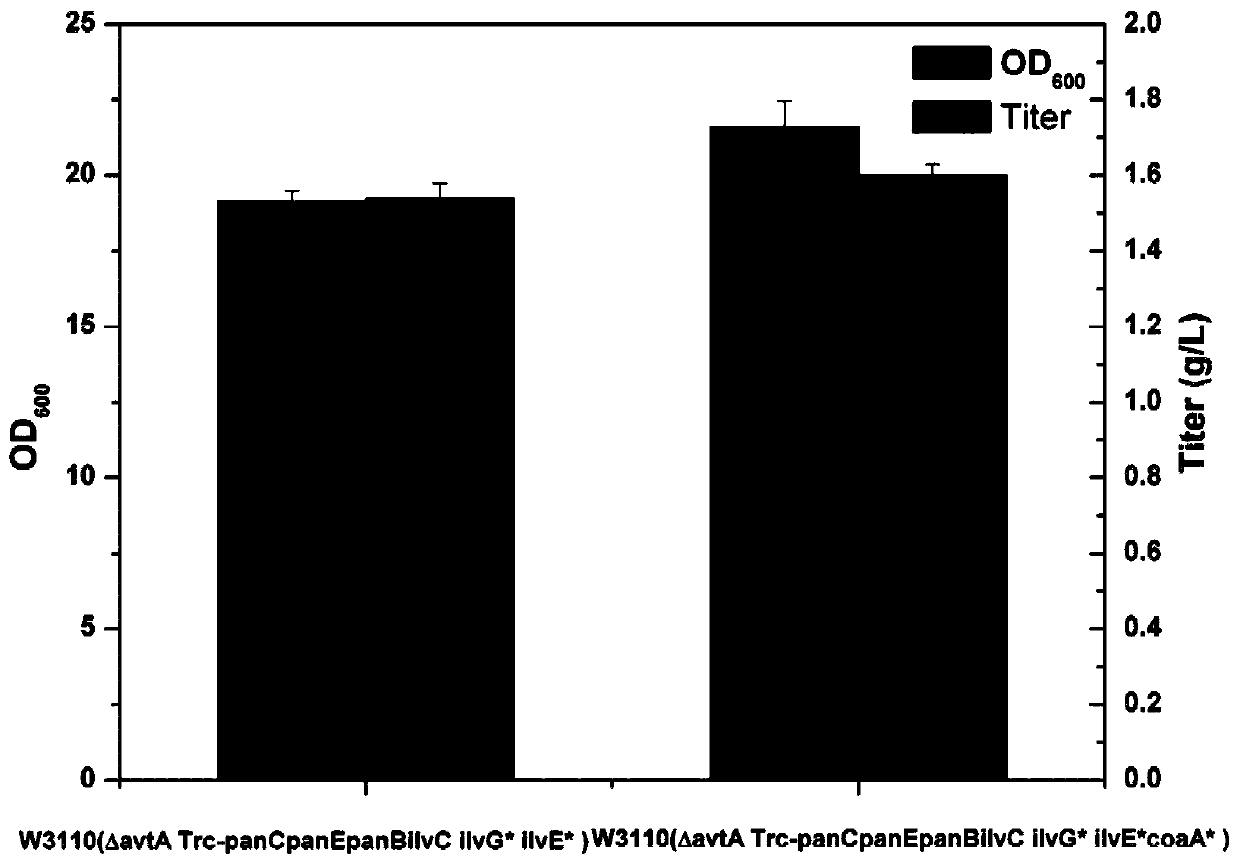
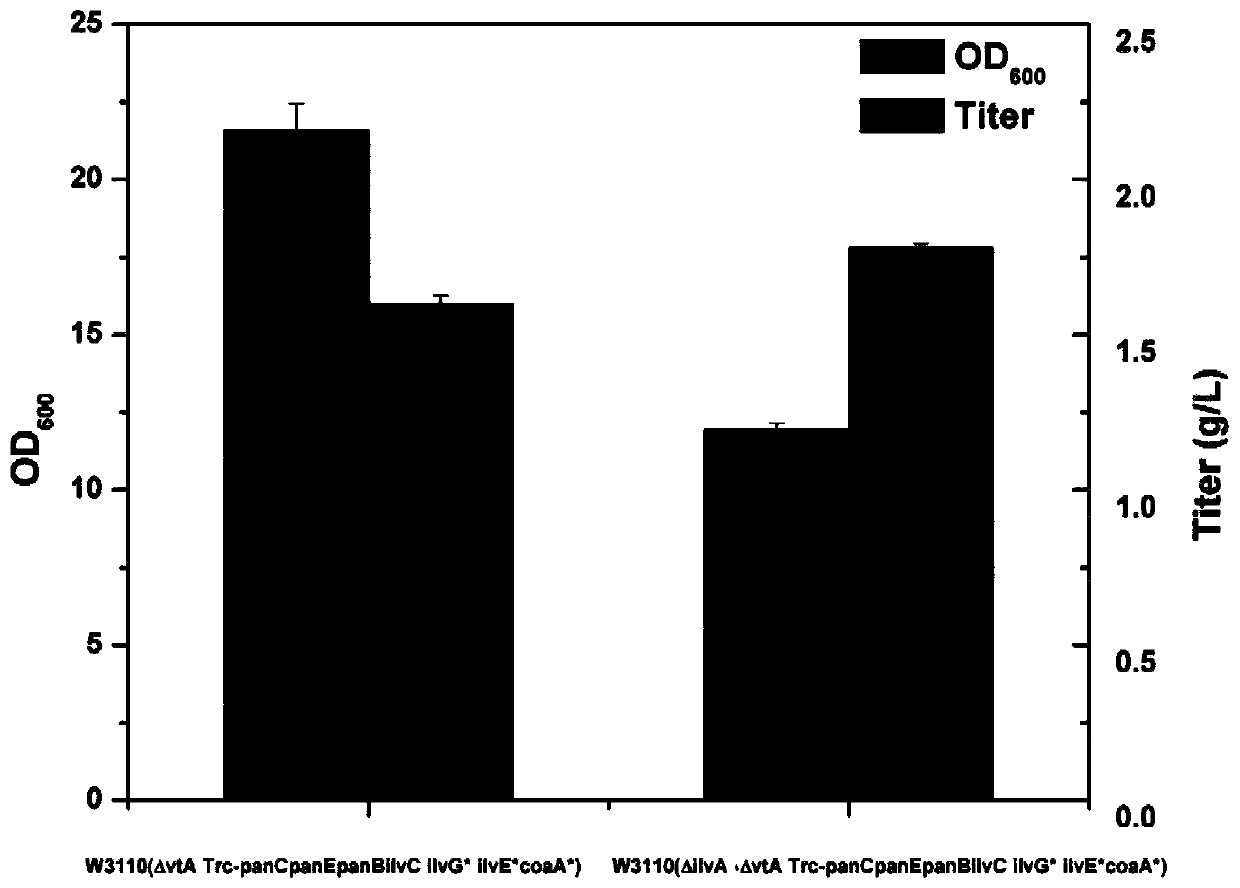
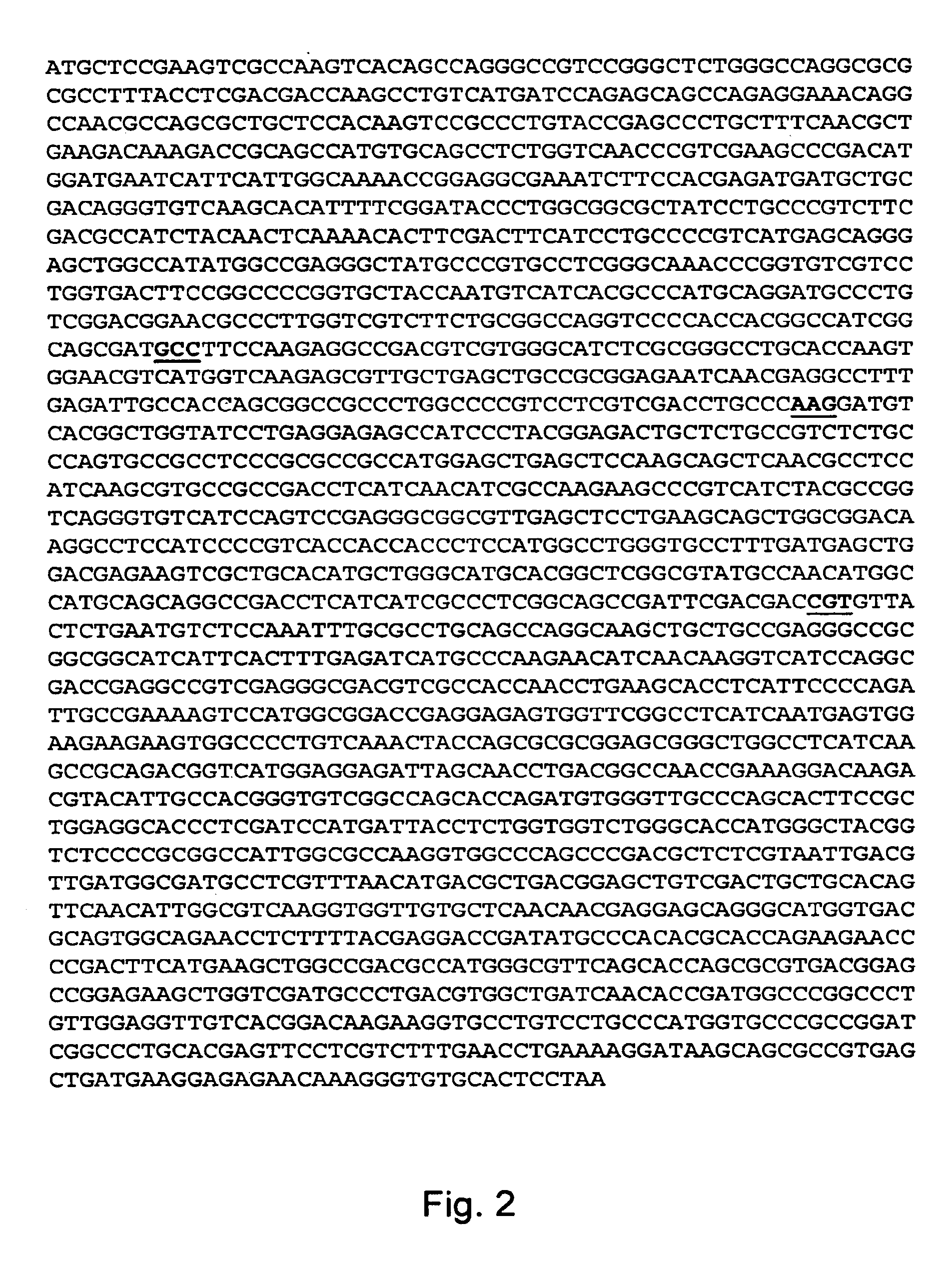Patents
Literature
110 results about "Acetolactate synthase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
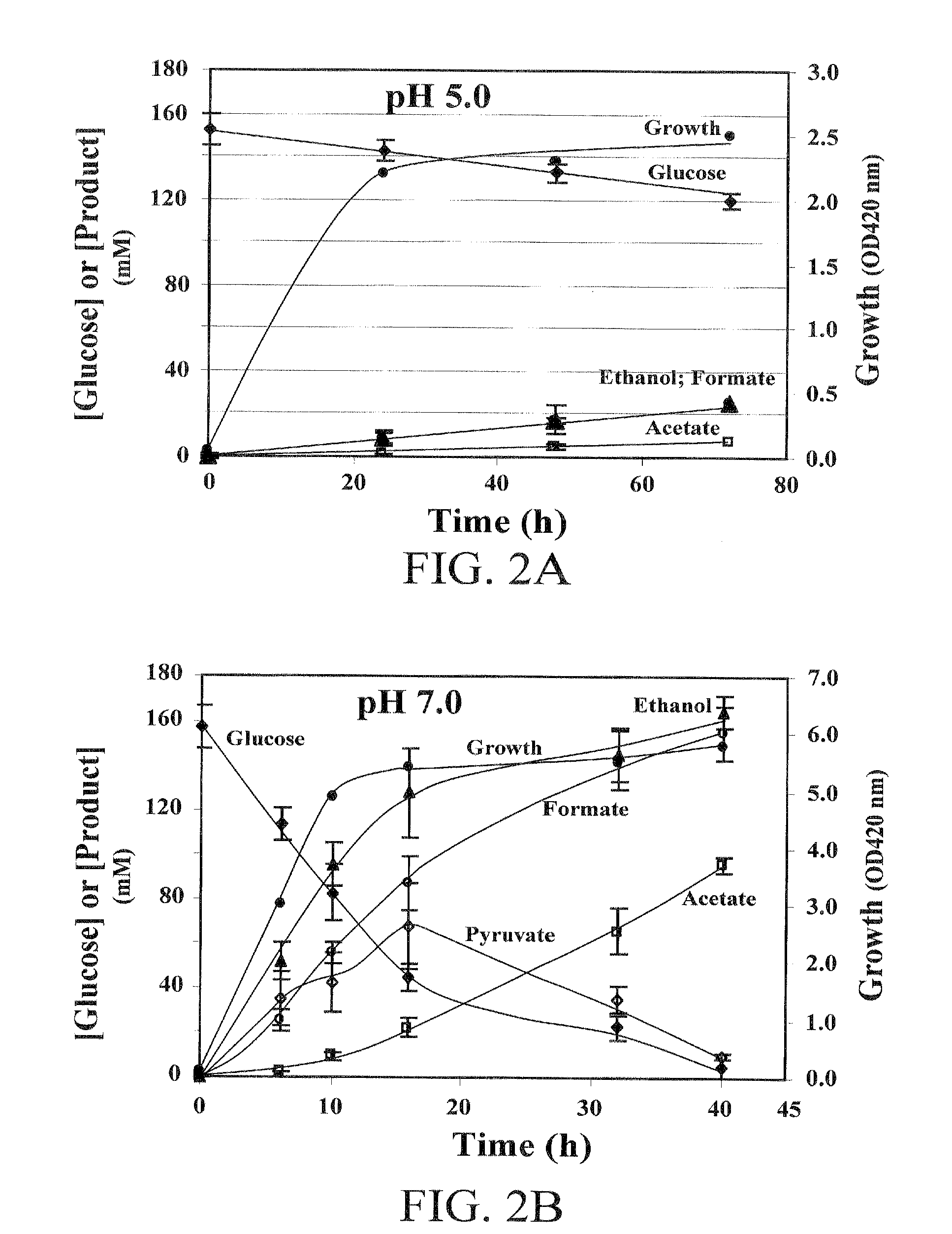
The acetolactate synthase (ALS) enzyme (also known as acetohydroxy acid synthase, or AHAS) is a protein found in plants and micro-organisms. ALS catalyzes the first step in the synthesis of the branched-chain amino acids (valine, leucine, and isoleucine).
Product and process for transformation of Thraustochytriales microorganisms
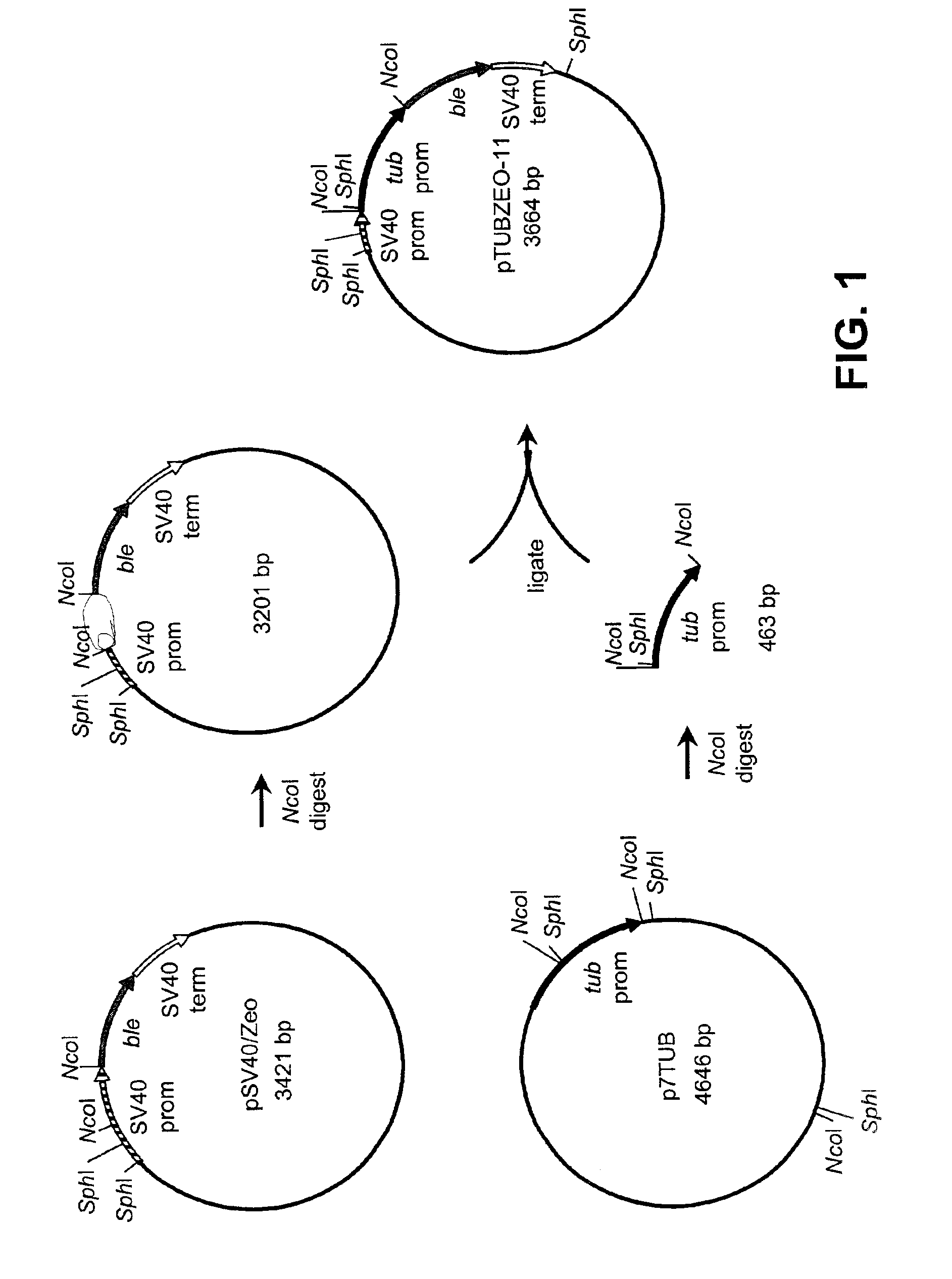
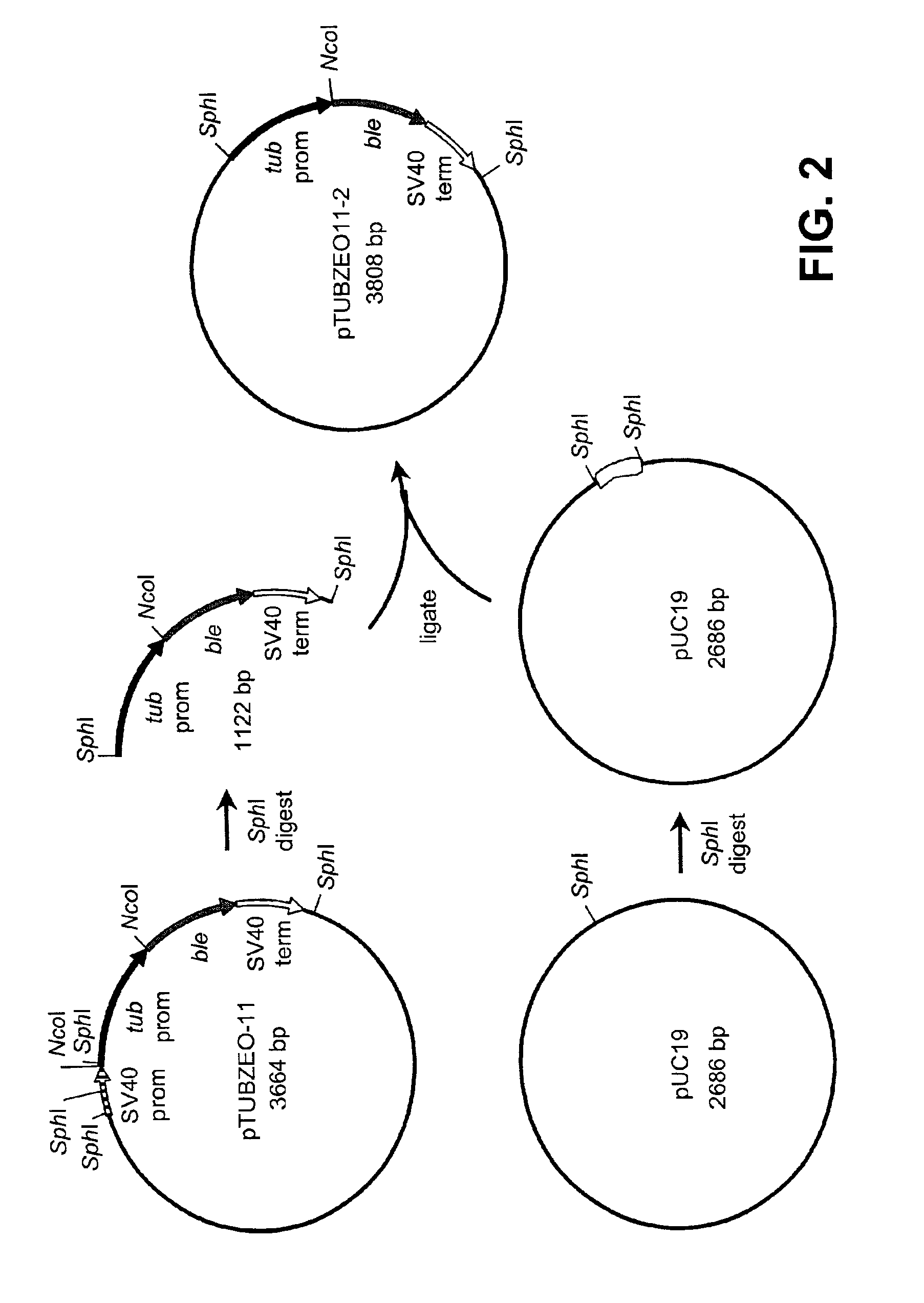
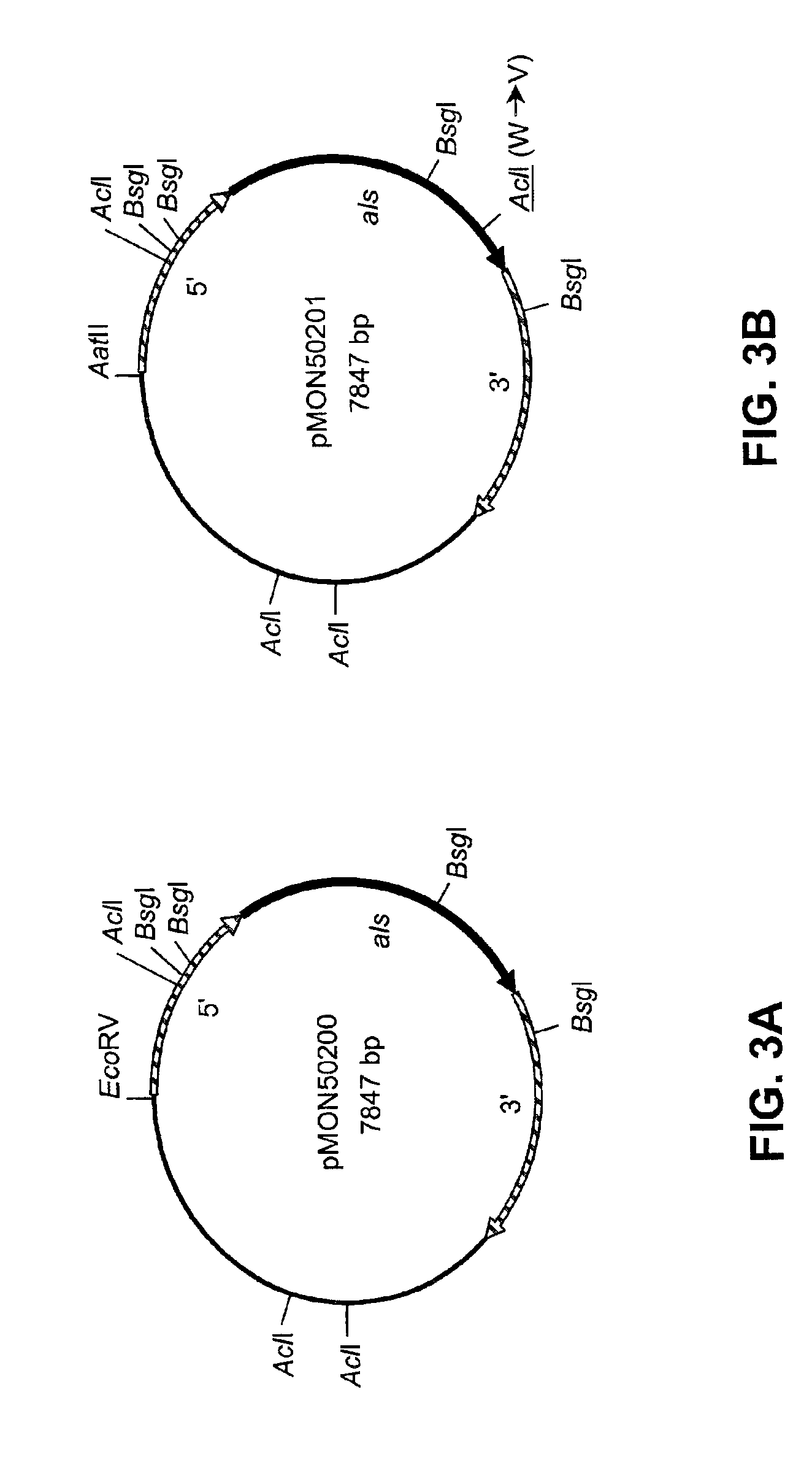
Disclosed are nucleic acid and amino acid sequences for acetolactate synthase, acetolactate synthase regulatory regions, α-tubulin promoter, a promoter from a Thraustochytriales polyketide synthase (PKS) system, and fatty acid desaturase promoter, each from a Thraustochytriales microorganism. Also disclosed are recombinant vectors useful for transformation of Thraustochytriales microorganisms, as well as a method of transformation of Thraustochytriales microorganisms. The recombinant nucleic acid molecules of the present invention can be used for the expression of foreign nucleic acids in a Thraustochytriales microorganism as well as for the deletion, mutation, or inactivation of genes in Thraustochytriales microorganisms.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
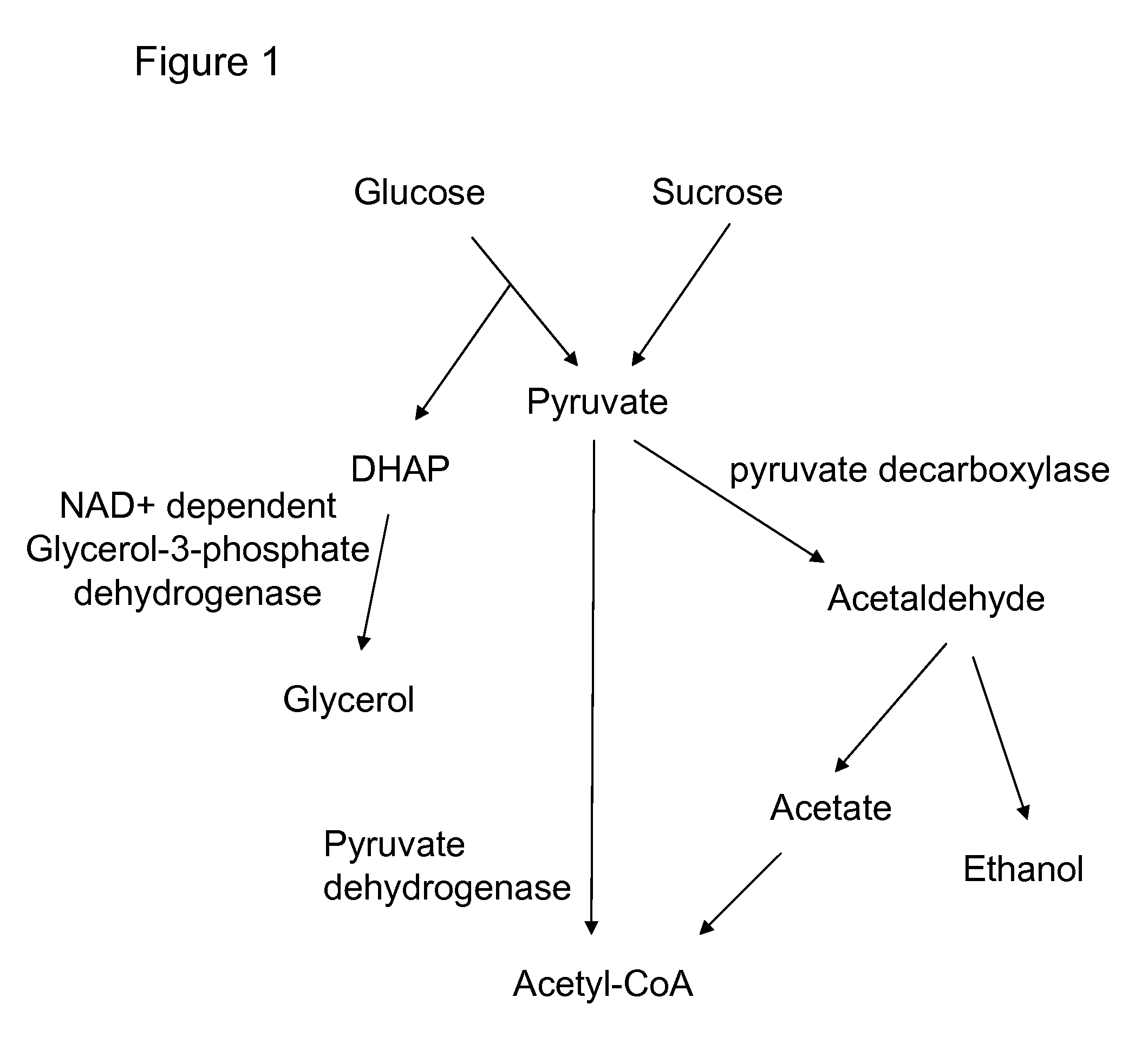
Enhanced pyruvate to acetolactate conversion in yeast
ActiveUS20090305363A1Improve throughputReduction of pyruvate decarboxylase activityFungiTransferasesYeastCytosol
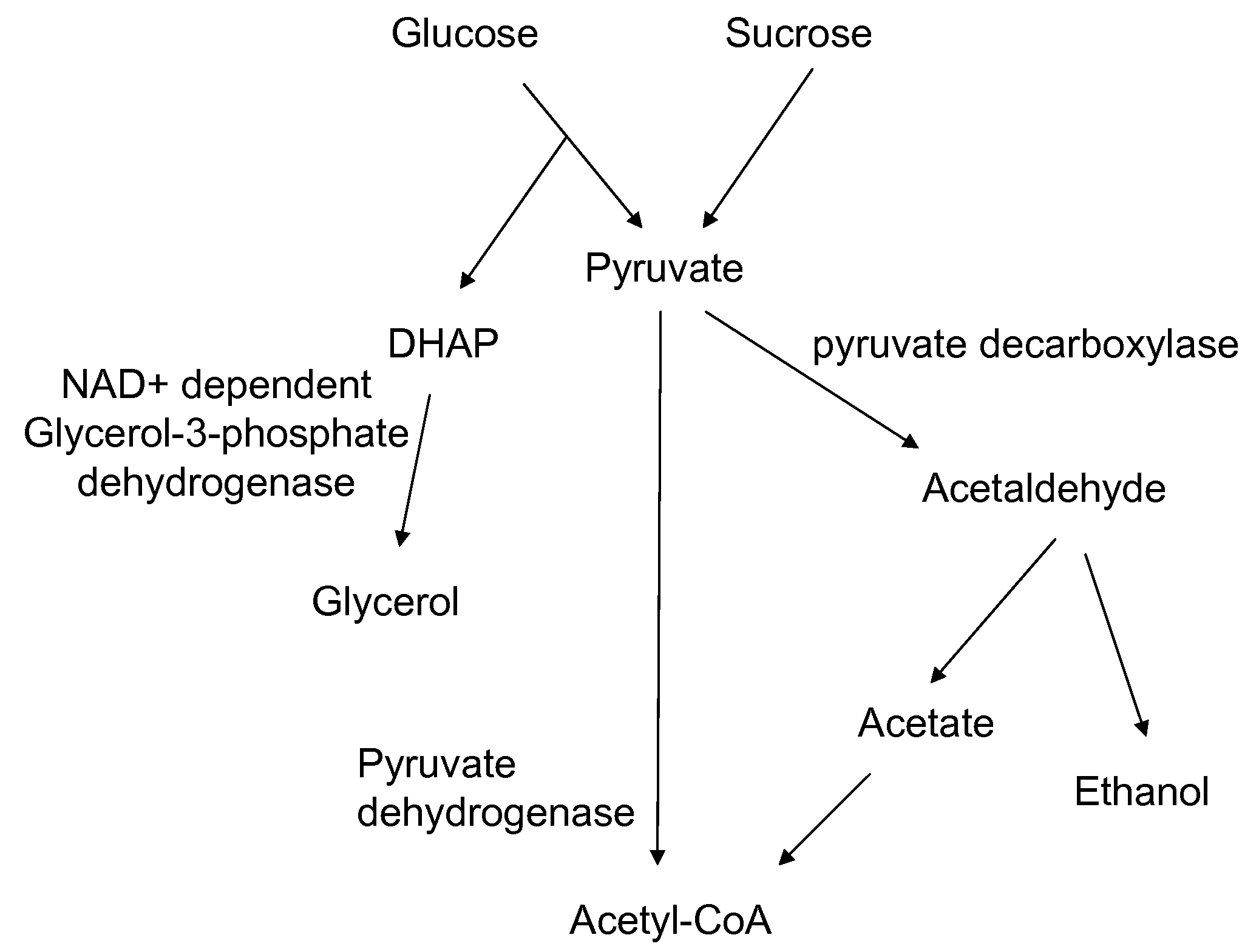
A high flux in conversion of pyruvate to acetolactate was achieved in yeast through expression of acetolactate synthase in the cytosol in conjunction with reduction in pyruvate decarboxylase activity. Additional manipulations to improve flux to acetolactate are reduced pyruvate dehydrogenase activity and reduced glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity. Production of compounds having acetolactate as an upstream intermediate benefit from the increased conversion of pruvate to acetolactate in the described strains.
Owner:GEVO INC
Product and process for transformation of thraustochytriales microorganisms
InactiveUS20050112719A1Reduce sensitivityReduce compoundingAlgae productsSugar derivativesAcetolactate synthaseΑ tubulin
Disclosed are nucleic acid and amino acid sequences for acetolactate synthase, acetolactate synthase regulatory regions, α-tubulin promoter, a promoter from a Thraustochytriales polyketide synthase (PKS) system, and fatty acid desaturase promoter, each from a Thraustochytriales microorganism. Also disclosed are recombinant vectors useful for transformation of Thraustochytriales microorganisms, as well as a method of transformation of Thraustochytriales microorganisms. The recombinant nucleic acid molecules of the present invention can be used for the expression of foreign nucleic acids in a Thraustochytriales microorganism as well as for the deletion, mutation, or inactivation of genes in Thraustochytriales microorganisms.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Gene encoding resistance to acetolactate synthase-inhibiting herbicides
InactiveUS20060130172A1Inhibit growthInhibition of reproductionTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesAcetolactate synthaseSulfonylurea
A mutant acetolactate synthase (ALS) enzyme that confers cross-resistance to all sulfonylurea, imidazolinone, pyrimidinyloxybenzoate, triazolopyrimidine and sulfonylamino-carbonyl-triazolinone herbicides is provided. The mutant enzyme contains an aspartic acid to glutamic acid substitution mutation at a newly identified conserved region of the ALS enzyme. A gene encoding the enzyme is also provided, as are transgenic plants that have been genetically engineered to contain and express the gene. The transgenic plants are cross-resistant to sulfonylurea, imidazolinone, pyrimidinyloxybenzoate, triazolopyrimidine and sulfonylamino-carbonyl-triazolinone herbicides.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Rice herbicide resistant protein and application thereof in plant bleeding
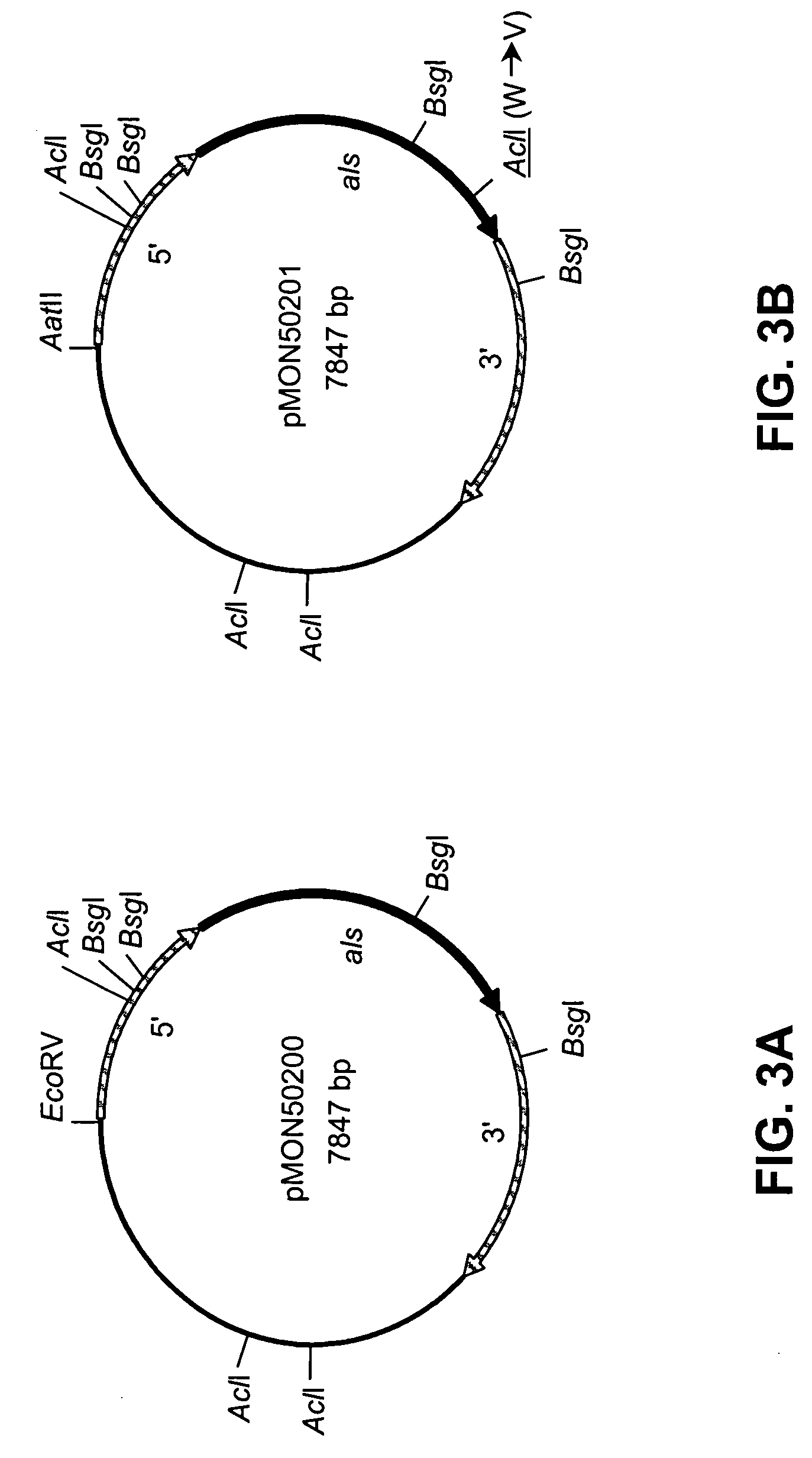
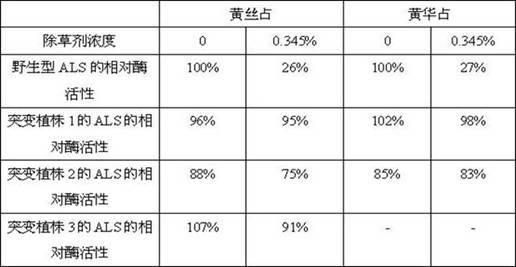
The invention discloses rice herbicide resistant protein and application thereof in plant bleeding. The ALS (acetolactate synthase) protein provided by the invention realizes that a plant has the herbicide resistance, and is derived from rice varieties Huangsizhan and Huanghuazhan, and carries Trp548, Ala96 or Ser627mutation. Furthermore, the invention also provides corresponding nucleic acid, expression cassettes, carriers, cells, plants, and method for obtaining the plants with herbicide resistance and application of the plants, as well as a method for identifying the plants in the invention.
Owner:SHENZHEN XINGWANG BIOLOGICAL SEED IND +1
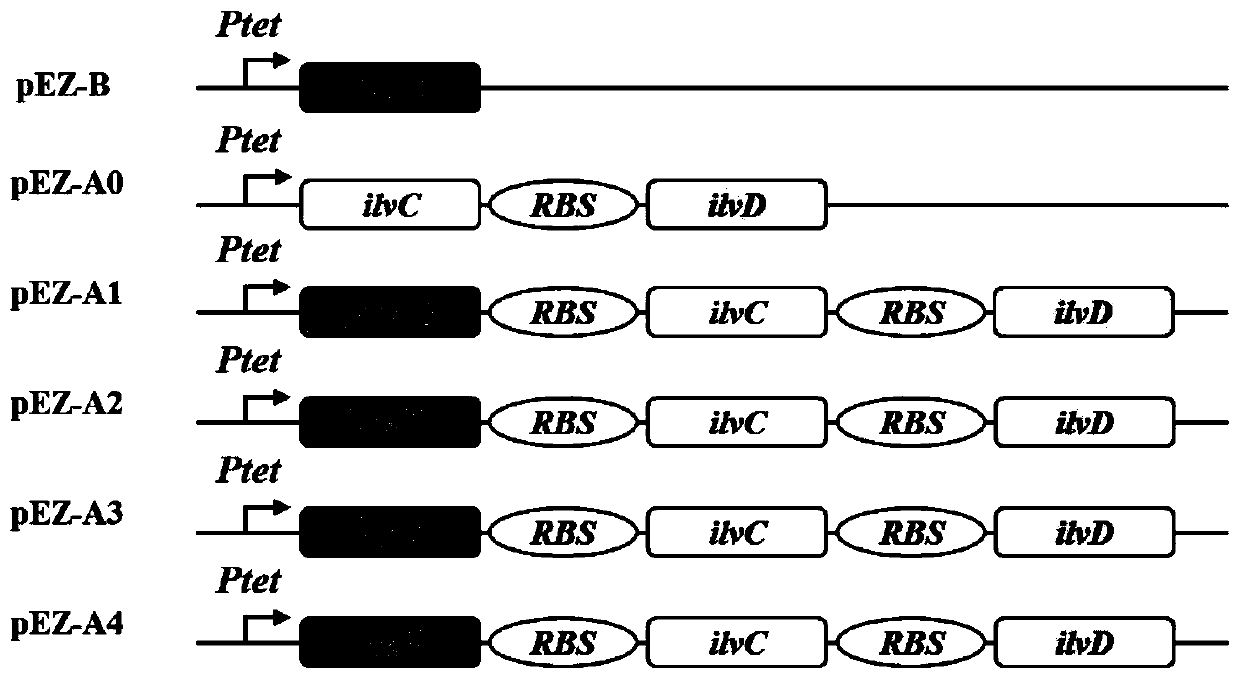
Genetically engineered bacterium for high-yielding L-valine and method for producing L-valine by fermentation
ActiveCN110607268AEasy to synthesizeReduce synthesisBacteriaHydrolasesLactate dehydrogenaseSaccharic acid
The invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium for high-yielding L-valine. A construction method of the genetically engineered bacterium comprises the steps that starting from an escherichia coli W3110, an acetolactate synthase gene alsS of a bacillus subtilis is integrated on a genome of the escherichia coli W3110 and subjected to high expression; an escherichia coli ppGpp 3'-pyrophosphoric acid hydrolytic enzyme mutant R290E / K292D gene spoT is integrated on the genome of the escherichia coli W3110 and subjected to high expression; genes of frdA, frdB, frdC and frdD of four subunits of a lactic dehydrogenase gene ldhA, a pyruvate formate lyase I gene pflB and fumaric reductase on the genome of the escherichia coli W3110 are knocked out; a branched chain amino acid transaminasegene ilvE of the escherichia coli is replaced with leucine dehydrogenase gene bcd of the bacillus subtilis; and an acetyl-hydroxyl acid isomerized reductase gene ilvC of the escherichia coli is replaced with an encoding gene of a mutant L67E / R68F / K75E. According to the genetically engineered bacterium for the high-yielding L-valine, an L-valine fermentation method is further modified. Double-phasedissolved oxygen control is adopted, and the L-valine yield and the saccharic acid conversion rate are improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Engineering of thermotolerant bacillus coagulans for production of d(-)-lactic acid
Genetically modified microorganisms having the ability to produce D(−)-lactic acid at temperatures between 30° C. and 55° C. are provided. In various embodiments, the microorganisms may have the chromosomal lactate dehydrogenase (ldh) gene and / or the chromosomal acetolactate synthase (alsS) gene inactivated. Exemplary microorganisms for use in the disclosed methods are Bacillus spp., such as Bacillus coagulans.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
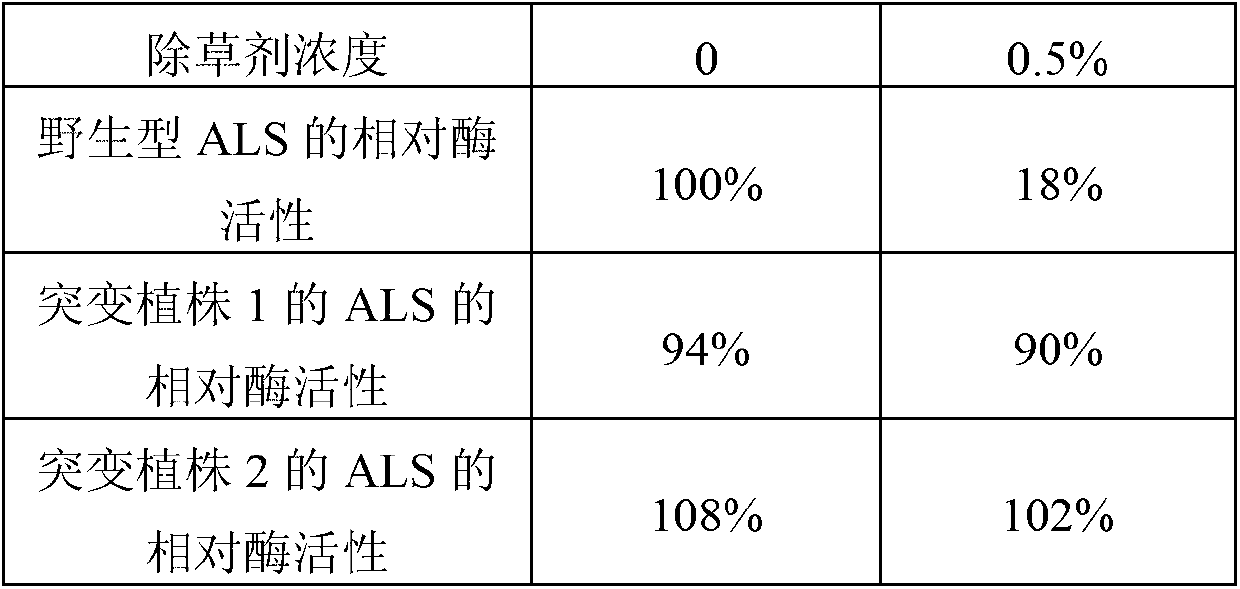
Acetolactate synthase mutant protein with herbicide resistance and application thereof
ActiveCN107245480AImprove toleranceMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesWeedAcetolactate synthase
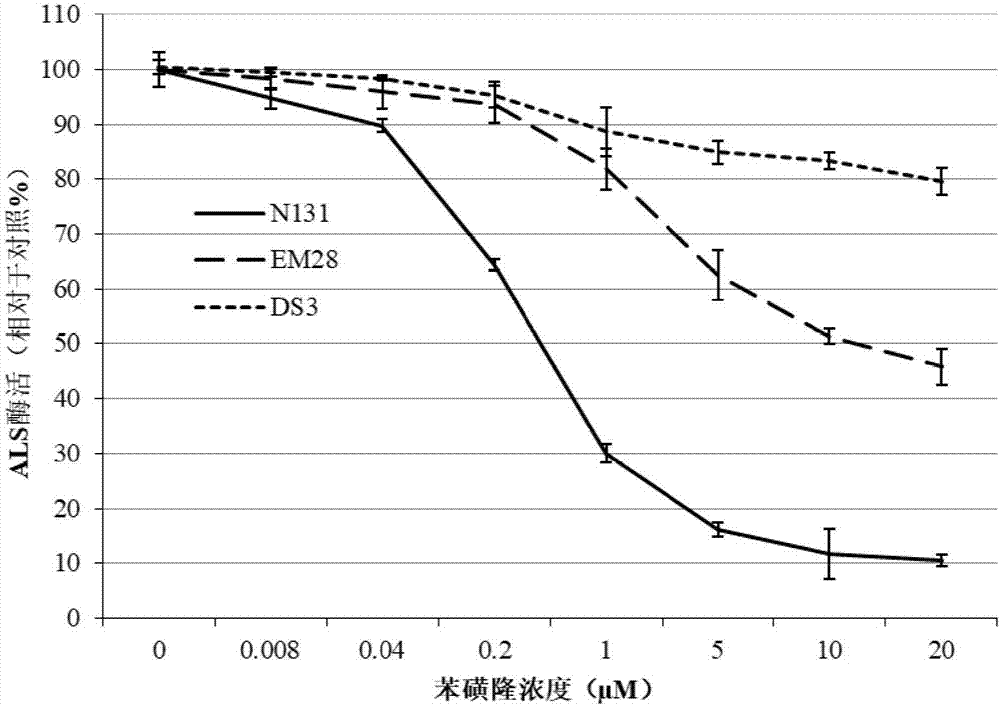
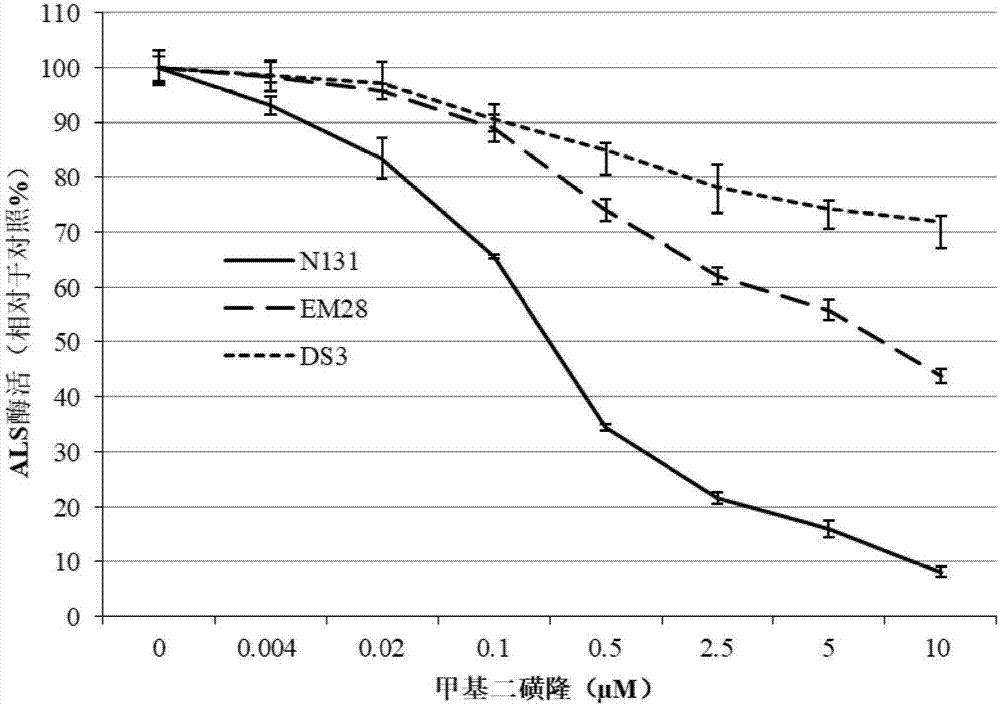
The invention discloses ALS (Acetolactate Synthase) mutant protein. An amino acid sequence of ALS1 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2 and an amino acid sequence of ALS3 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 4. The invention further discloses nucleic acid for coding the mutant protein, an expression box containing the nucleic acid and a recombinant vector or cell. The invention further discloses application of the mutant protein, the nucleic acid, the expression box and the recombinant vector or cell to the aspect of herbicide resistance of plants. The invention further discloses a method for obtaining plants with the herbicide resistance and a resistant plant identification method. The ALS mutant protein disclosed by the invention is a dual-gene and dual-mutation-site ALS inhibitor type herbicide acetolactate synthase mutant which is found from rape for the first time in China; a result of an experiment of applying ALS inhibitor type herbicide tribenuron and mesosulfuron-methyl in the field shows that after the herbicide with 16 times of weed prevention and control recommended utilization concentration is applied to the rape DS3 containing the ALS mutant protein provided by the invention during a 3-leaf to 4-leaf period, the plants still grow and develop, and bear fruits normally.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Applications of ALS (acetolactate synthase) mutant type protein based on gene editing technology and ALS mutant type protein gene in plant breeding
ActiveCN109097346ANo significant change in basic agronomic traitsImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesAgricultural scienceAcetolactate synthase
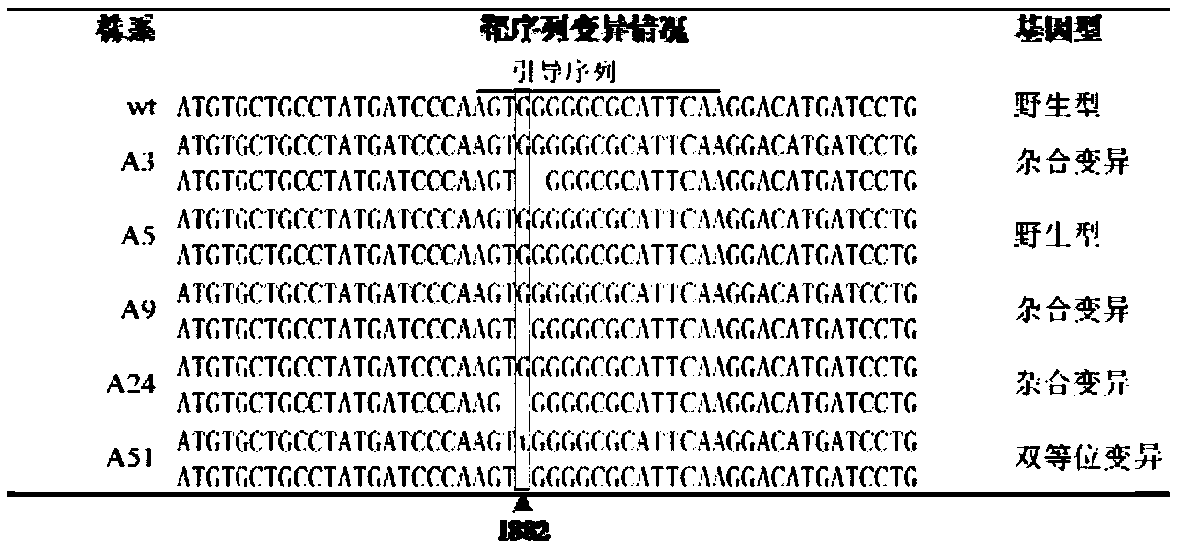
The invention discloses a rice ALS (acetolactate synthase) mutant type protein, a mutant type gene and applications of the rice ALS mutant type protein and the mutant type gene. The amino acid sequence of the ALS mutant type protein has following mutation: the 628-poisiton amino acid corresponding to the amino acid sequence of rice ALS has the mutation. The invention further discloses a breeding method of creating herbicide-resistant rice by gene editing. The CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology is used for editing the ALS gene for the first time, a T-DNA-knockout new material with the stably inherited herbicide resistant characteristic can be obtained in the T2 generation through offspring screening, and basic agronomic traits of the new material have no obvious change. Compared with breeding based on chemical mutagenesis, hybrid transform breeding and the like, the orderly improved molecular breeding technology based on gene editing has the advantages of being rapid, accurate, efficient and the like, and by means of combination with gene function marked genotype selection, breeding efficiency can be greatly increased and breeding progress is substantially accelerated.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
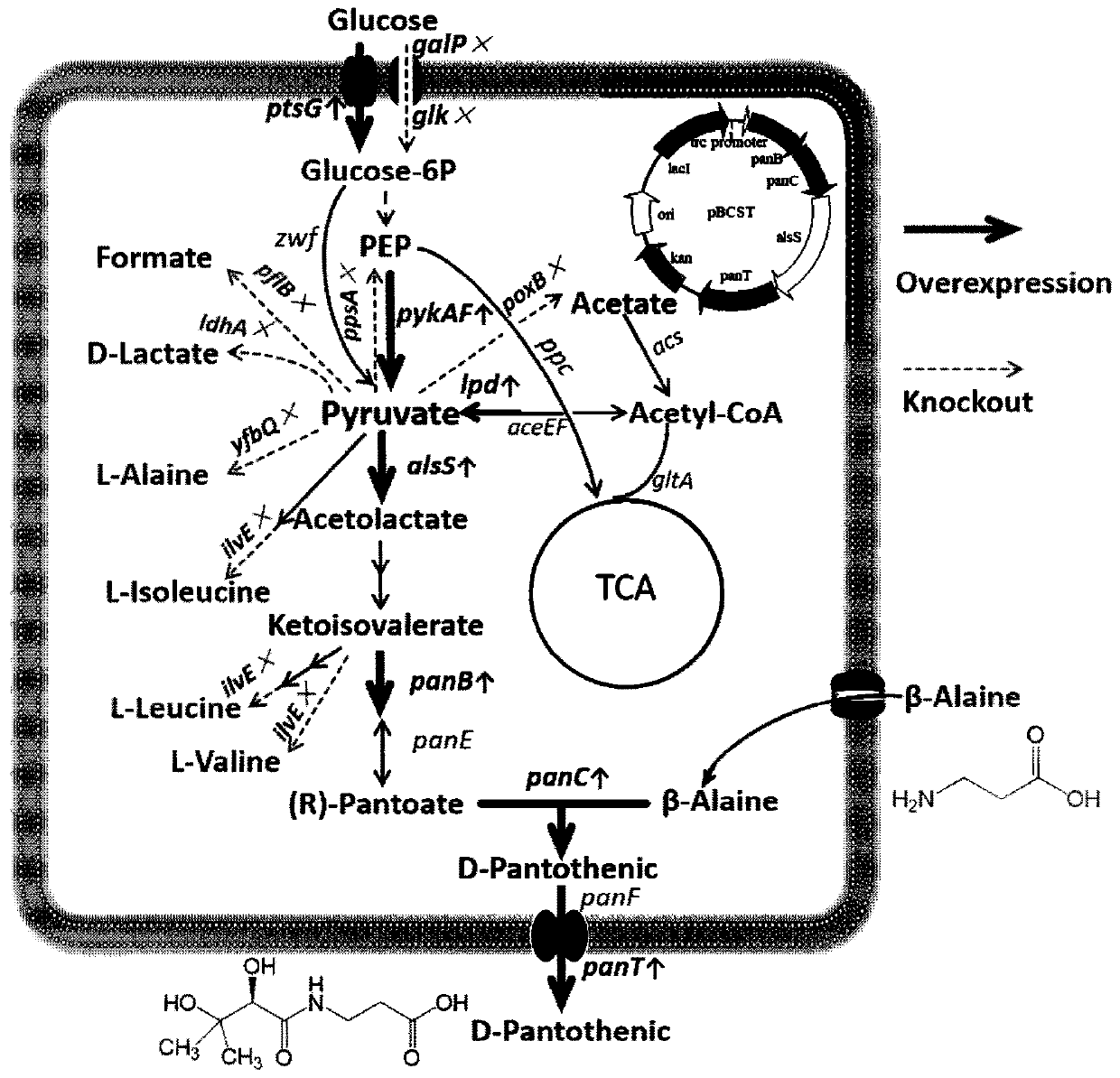
Construction method of high-yield pantothenic-acid genetically engineered bacterium and bacterium strain
ActiveCN111100834APromote accumulationGuaranteed supplyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHeterologous
The present invention relates to a construction method of high-yield pantothenic-acid genetically engineered bacterium and the bacterium strain, and an application of the genetically engineered bacterium in preparation of D-pantothenic acid by microbial fermentation. The construction method is as follows: (1) enhancing expression of lpd gene; (2) knocking out glk and galP, destroying a glucose non-PTS transport system, enhancing expression of ptsG gene and enhancing a glucose PTS transport system; (3) knocking out yfbQ and ppsA genes; (4) knocking out poxB, pflB and ldhA genes; (4) knocking out ilvE gene; (5) introducing heterologous acetolactate synthase gene alsS; and (6) introducing heterologous pantothenic-acid transporter panT into plasmids and finally obtaining the optimal D-pantothenic acid high-yield escherichia coli genetically engineered bacterium strain. D-pantothenic acid potency increases from 2.76 g / L to 6.33 g / L.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-valine with high yield and establishment method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN110468092AEnhanced intracellular contentReduce synthesisBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliAcetolactate synthase
The invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-valine with high yield, which is established by changing the metabolic pathway of escherichia coli. Starting from escherichiacoli W3110, an encoding gene alsS of acetolactate synthase of bacillus subtilis is integrated on a genome of the escherichia coli W3110 and is intensively expressed; in addition, an encoding gene spoTof an escherichia coli ppGpp 3'-pyrophosphoric acid hydrolase mutant [R290E, K292D] is integrated on the genome of the escherichia coli W3110 and is intensively expressed; and furthermore, an encoding gene thiE of thiamine phosphate synthase is knocked off, and thus the genetically engineered bacterium is established. By adopting the genetically engineered bacterium, the problem that L-valine islow in yield as L-valine is weak in synthesis metabolic flux and a key precursor pyruvic acid is insufficient in supply can be solved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Herbicide-resistant rape directive breeding method based on acetolactate synthase (ALS) target esterase
InactiveCN103070068AImprove breeding efficiencyReduce chanceSeed and root treatmentPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyEthylmethane Sulfonate
The invention provides a herbicide-resistant rape directive breeding method based on acetolactate synthase (ALS) target esterase, which belongs to a plant trait breeding method. The method comprises the following steps of selecting materials needed by production of rape or breeding of the rape, processing seeds with ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS), mutagenizing the seeds to be isolated and propagated to a M2 generation, and directionally screening herbicide-resistant mutant characters in a large group under the selection pressure of the herbicide adopting the ALS as the target esterase. In order to increase the probability for acquiring the mutant characters, the directive screening can be continuously conducted in multiple years, or conducted in multiple places in the same year or conducted in multiple places in multiple years until the needed mutant material is screened out.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Heterocyclic asymmetric aromatic dithioether compound and synthesis method and application thereof
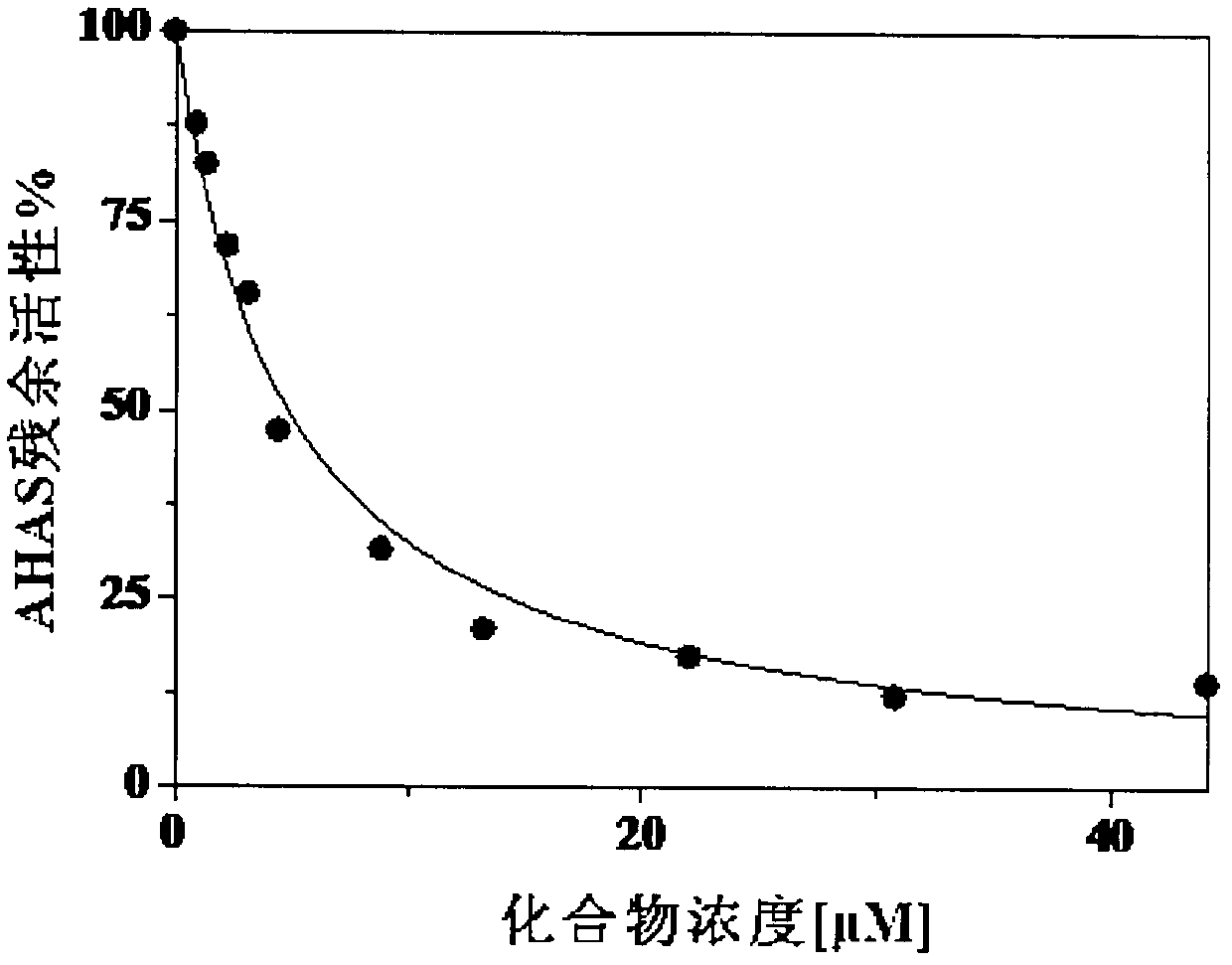
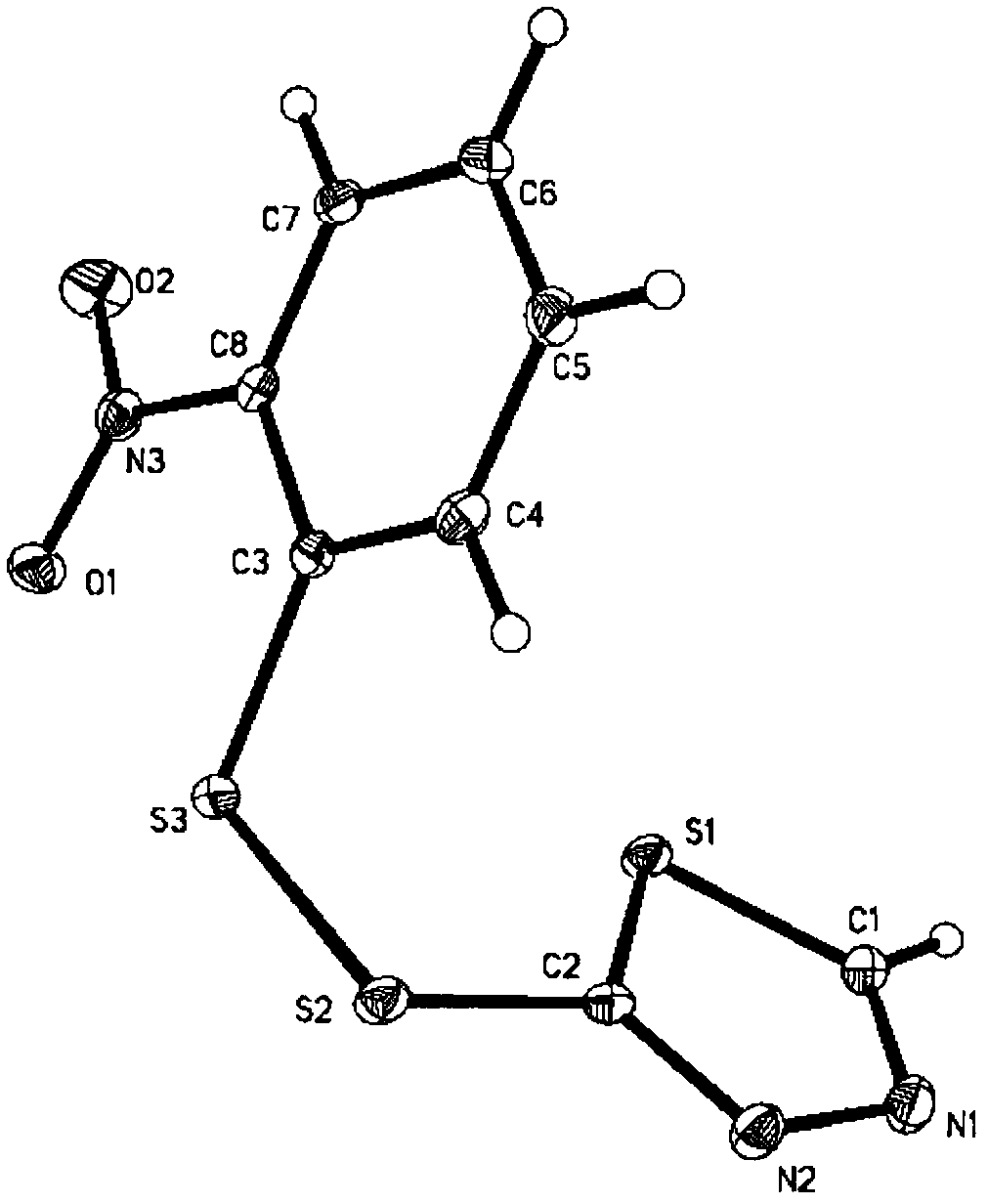
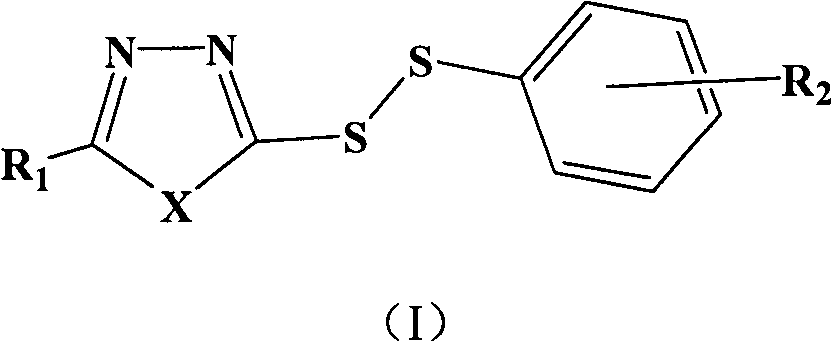
InactiveCN102702130AEnhanced inhibitory effectGood inhibitory effectBiocideOrganic chemistryHalogenSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a heterocyclic asymmetric aromatic dithioether compound and application thereof in herbicide preparation. As shown as in the formula (I), the compound has inhabitation effect to arabidopsis thaliana acetolactate synthase (AHAS) in vitro, has inhabitation effect to rape root length in vivo, has weeding effect for rape and redroot amaranth in potted plant tests, and can be used for preparing novel herbicides containing targeted AHAS. In the formula (I), when X represents S, R1 represents H, C1-C3 alkyl, C1-C3 acylamino, phenyl, hydroxylphenyl phenyl and ortho-C1-C3 alkoxy phenyl, R2 represents H, ortho-nitryl or para-nitryl, ortho-halogen or para-halogen, ortho-C1-C3 alkyl or para-C1-C3 alkyl, ortho-C1-C3 carbalkoxy, para-C1-C3 alkoxy and 3,4-benzo; and when X represents O, R1 represents H, phenyl, hydroxylphenyl phenyl, ortho-C1-C3 alkoxy phenyl, 4-pyridyl and 3-pyridyl, and R2 represents H, ortho-nitryl, para-C1-C3 alkyl and ortho-C1-C3 carbalkoxy.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
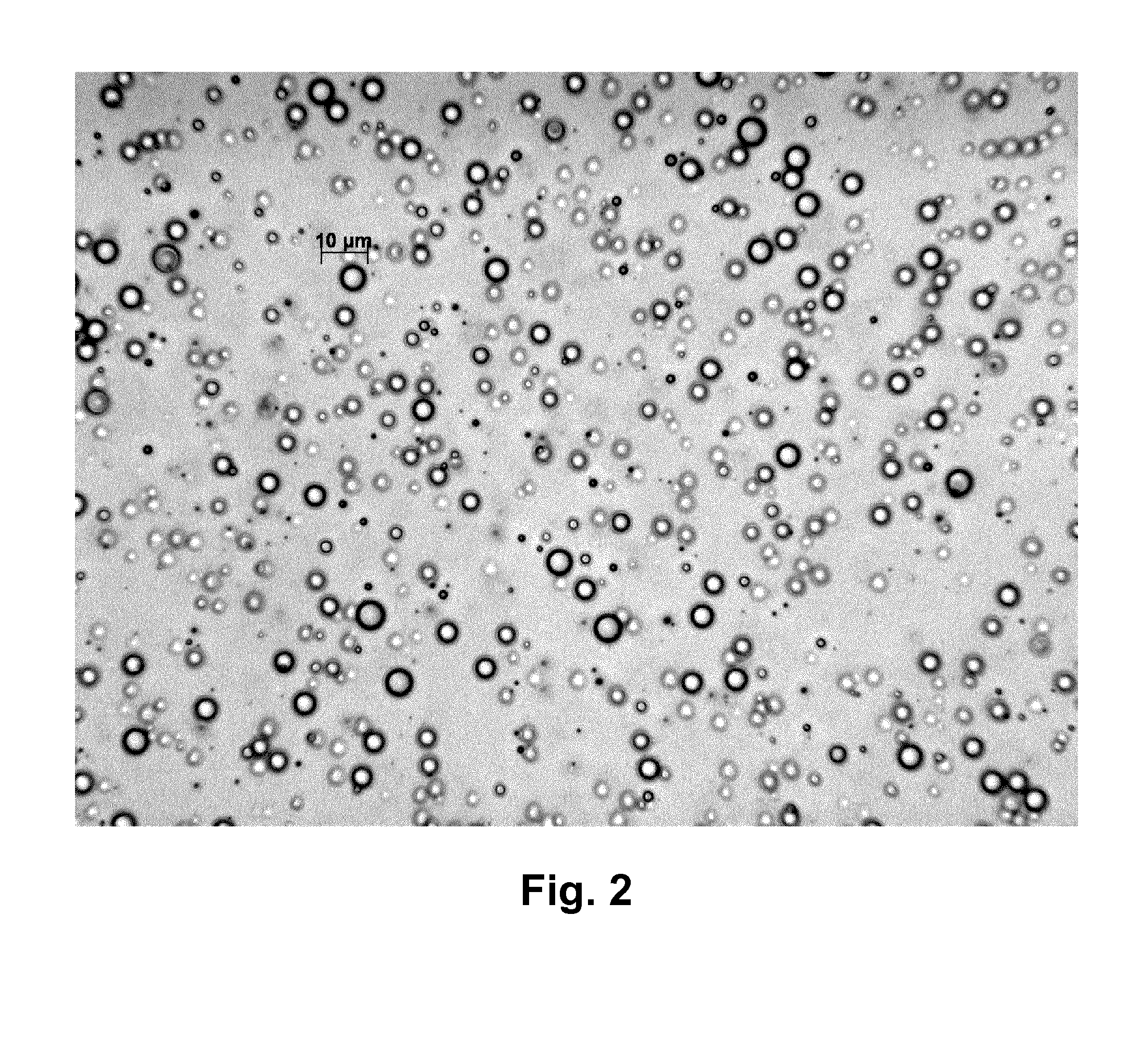
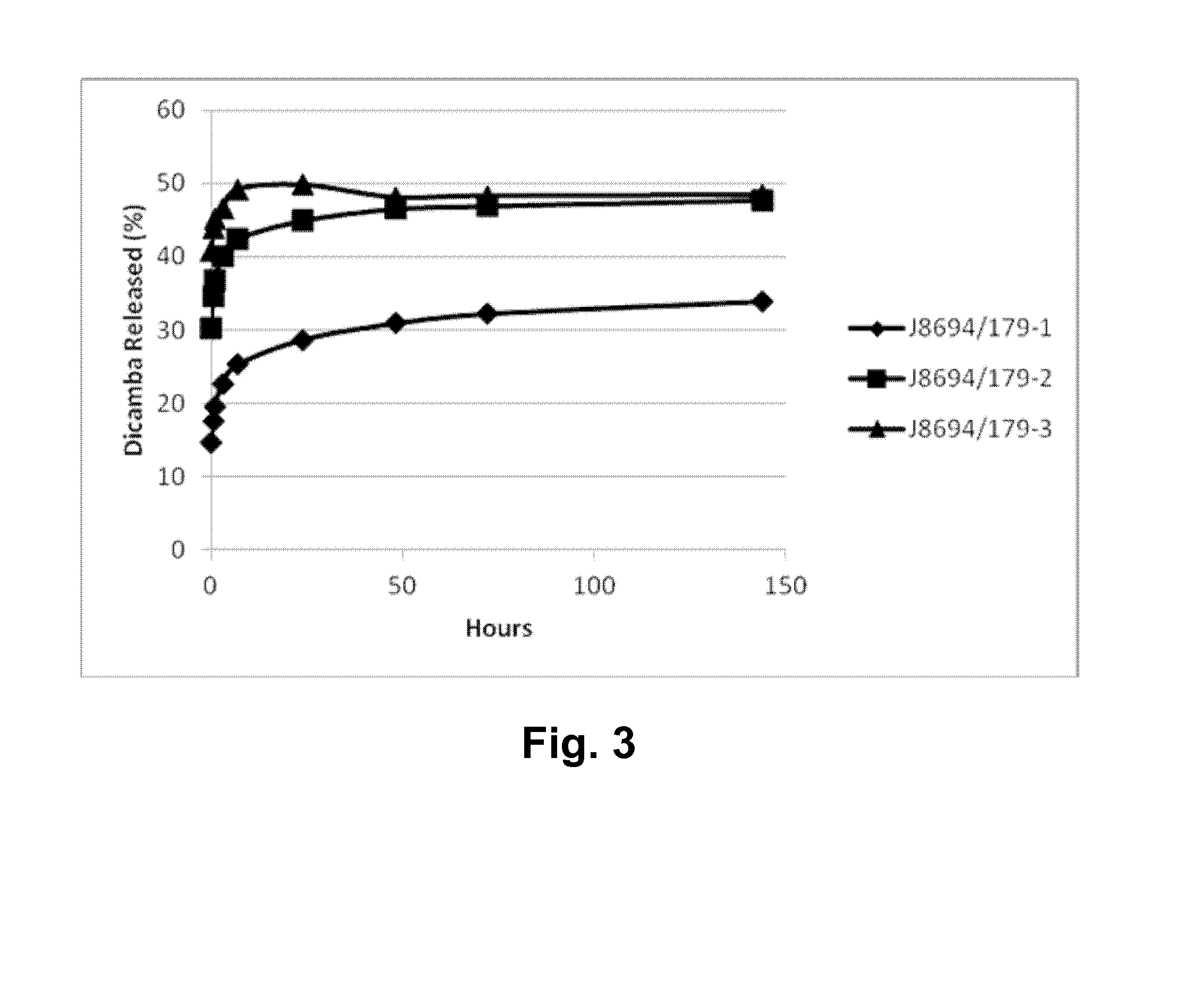
Herbicidal composition comprising polymeric microparticles containing a herbicide
The invention provides a herbicidal composition comprising a mixture of: (a) polymeric microparticles containing a first herbicide, wherein the first herbicide is a synthetic auxin herbicide (e.g. dicamba, MCPA or 2,4-D) or an acetolactate synthase (ALS) inhibitor herbicide (e.g. triasulfuron, tribenuron-methyl, iodosulfuron-methyl, mesosulfuron-methyl, sulfosulfuron, flupyrsulfuron-methyl, or pyroxsulam); wherein the first herbicide, when in a salt-free form and when not contained within polymeric microparticles, antagonises the herbicidal activity of pinoxaden; and (b) pinoxaden; wherein the polymeric microparticles are controlled-release matrices, within which is the first herbicide, and which function in such a way as to control and / or slow down the release of the first herbicide from the polymeric microparticles into a liquid (e.g. aqueous) medium when the polymeric microparticles are placed (e.g. dispersed) in and in contact with the liquid medium. The containing of the first herbicide within the controlled-release polymeric microparticles is thought to mitigate the antagonism of the grass-weed-herbicidal activity of pinoxaden which might otherwise be caused by the first herbicide depending on the circumstances. The invention also provides a method of reducing the antagonistic effect on the control of monocotyledonous weeds in non-oat cereals which is shown by a herbicidal mixture of either a synthetic auxin herbicide with pinoxadenor an ALS inhibitor herbicide with pinoxaden, which comprises applying a herbicidal composition according to the invention. The invention also provides a herbicidal composition comprising (a) polymeric microparticles (e.g. controlled-release matrices), containing a first herbicide as defined above, and either (x) a nonionic surfactant or (y) a surface-modified clay, as defined herein.
Owner:SYNGENTA LTD
Method for preservation of pure state of hybrid plants by chemical emasculation
InactiveCN101595836AFor the purpose of weedingBiocideAnimal repellantsF1 generationAcetolactate Synthetase
The invention discloses a method for preservation of pure state of hybrid plants by chemical emasculation. In the method, a breed sensitive to acetolactate synthase inhibitory type herbicide is selected as female parent and a breed resistant to acetolactate synthase inhibitory type herbicide is selected as male parent, acetolactate synthase inhibitory type herbicide with activity of chemical hybridizing agent is used for processing the female parent to obtain male sterility, the male parent pollinates the female parent, the seeds of the female parent line are harvested to be cross breeds, the obtained F1 generation cross breed has herbicide resistance, after the F1 generation cross breed is planted, and acetolactate synthase inhibitory type herbicide seedling stage processing is used for removing uncrossed female parent seedling, so as to remain real cross breed. The method utilizes herbicide for preservation of pure state while realizing weeding. The invention has more advantages than common breed in the aspect of adapted breed simplified culture requirement.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Paddy rice herbicide resistant protein and gene as well as application of protein and gene
ActiveCN106867977ADoes not affect growthKeep aliveTransferasesFermentationAcetolactate synthaseProteinogenic amino acid
The invention discloses a paddy rice herbicide resistant protein and gene as well as application of the protein and the gene. The herbicide resistant protein is obtained by mutating Ala179 and / or Gly628 in a paddy rice acetolactate synthase protein amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, or is obtained by mutating Ser627 and Va1643 in the paddy rice acetolactate synthase protein amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the gene for encoding the herbicide resistant protein and the application of the herbicide resistant protein and / or the gene for encoding the herbicide resistant protein in preparation of herbicide resistant plants are provided. According to the herbicide resistant protein, the gene and the application disclosed by the invention, acetolactate synthase inhibiting herbicides can be used in a process of planting gramineous plant crops, so that the requirements on direct seeding, mixed seeding, transplantation, mechanical production and the like of gramineous plants can be met, and a good application prospect is achieved.
Owner:HUNAN HYBRID RICE RES CENT
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method and kit of ALS (acetolactate synthetase) inhibitor herbicide-resistant descurainia sophia
ActiveCN103923996AImprove featuresIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAcetolactate synthaseNucleotide
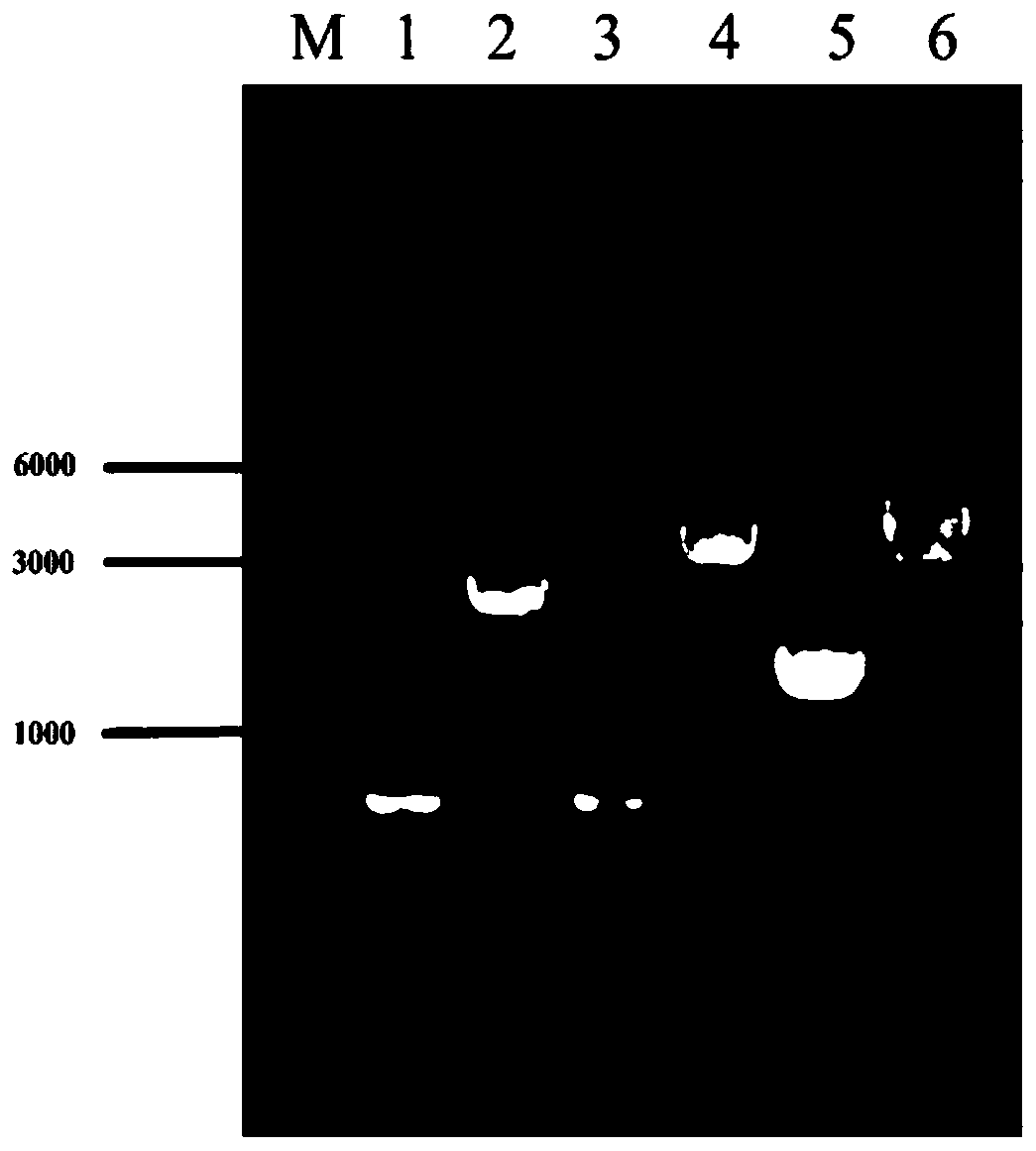
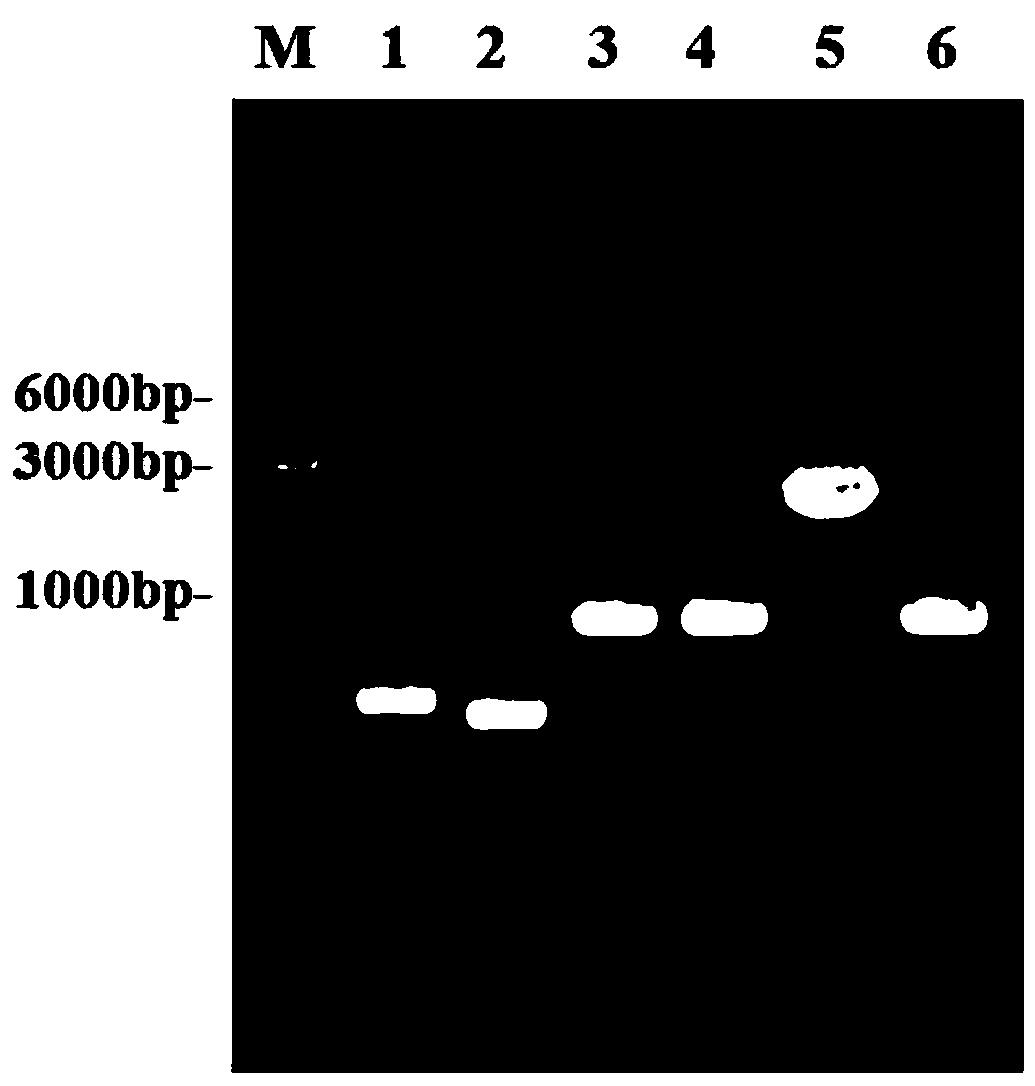
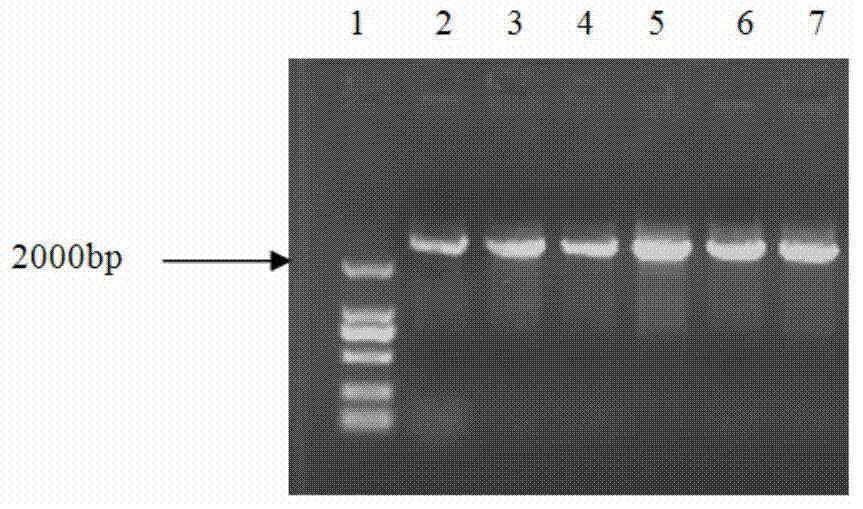
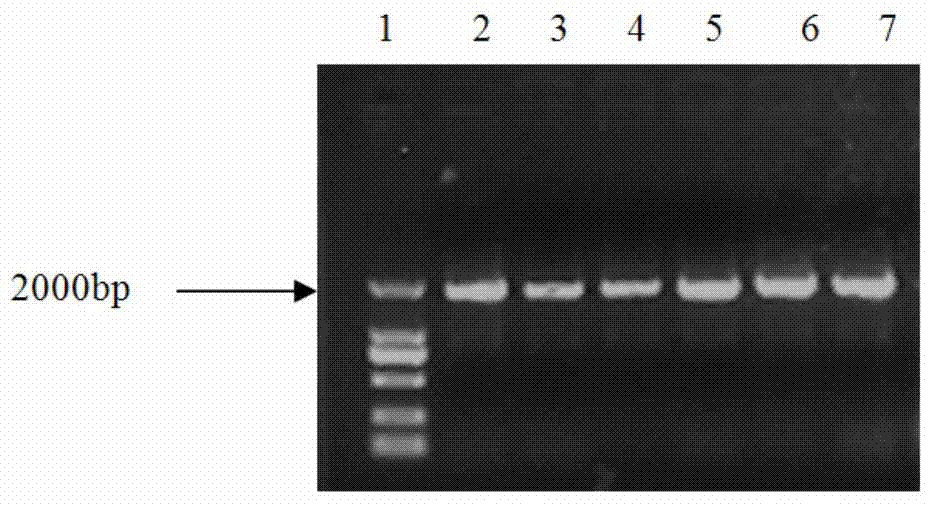
The invention provides a specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer pair for detecting ALS (acetolactate synthetase) inhibitor herbicide-resistant descurainia sophia. The primer pair comprises a primer pair (Seq ID No.1-2) for specific amplification of a B-ALS-1 gene of the descurainia sophia and a primer pair (Seq ID No.3-4) for specific amplification of a B-ALS-2 gene of the descurainia sophia. A PCR detection method adopting the primer pair is excellent in specificity and sensitivity, and a specificity test proves that the two ALS genes of the descurainia sophia can be amplified (figures 1 and 2). As the PCR method is simple, convenient and quick to operate, the sampling detection can be carried out in season based on nucleotide detection, and only 2-4 days are required for a process from sampling to results. The sensitivity and specificity of the method can realize quick identification of suspended ALS inhibitor herbicide-resistant descurainia sophia in the field and confirmation of mutation sites, thus the scientific control of resistant weeds in production practice is guided.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Genetic engineering bacteria capable of producing pantothenic acid at high yield without addition of beta-alanine, construction and application of genetic engineering bacteria
ActiveCN109913398AImprove utilizationReduce feedback inhibitionBacteriaStable introduction of DNACell phenotypeEscherichia coli
The invention relates to genetic engineering bacteria capable of producing pantothenic acid at high yield without addition of beta-alanine, a construction method of the genetic engineering bacteria, and application of the genetic engineering bacteria in preparation of D-pantothenic acid by microbial fermentation. According to the invention, (1), the final step of an escherichia coli D-pantothenicacid synthesis pathway is enhanced, and the utilizing ability of escherichia coli to extracellular beta-alanine, (2), a pantoic acid synthesis pathway is enhanced, (3), ilvG gene is repaired, and thefeedback inhibition effect of by-products on a pantoic acid synthesis pathway is weakened, (4), according to the change in cell phenotype, flux of a valine synthesis pathway is weakened, (5), a CRISPRi technique is used to screen metabolic modification sites of TCA cycle, a PPP pathway and a by-product metabolic pathway, according to the result, an isoleucine synthesis pathway is blocked, and thecompetition of 2-butanoic acid for reaction of acetolactate synthesized from pyruvic acid under catalysis of acetolactate synthase is relieved, and (6), aspartate decarboxylase from other strains is subjected to heterologous expression to obtain a genetical engineering strain capable of producing the pantothenic acid at high yield without addition of the beta-alanine. By combined expression of panB and panC which are derived from corynebacterium glutamicum and panD derived from bacillus subtilis together on pTrc99A plasmids, 1.2g / L of D- pantothenic acid is obtained without adding the beta-alanine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Resistance to Acetolactate Synthase-Inhibiting Herbicides
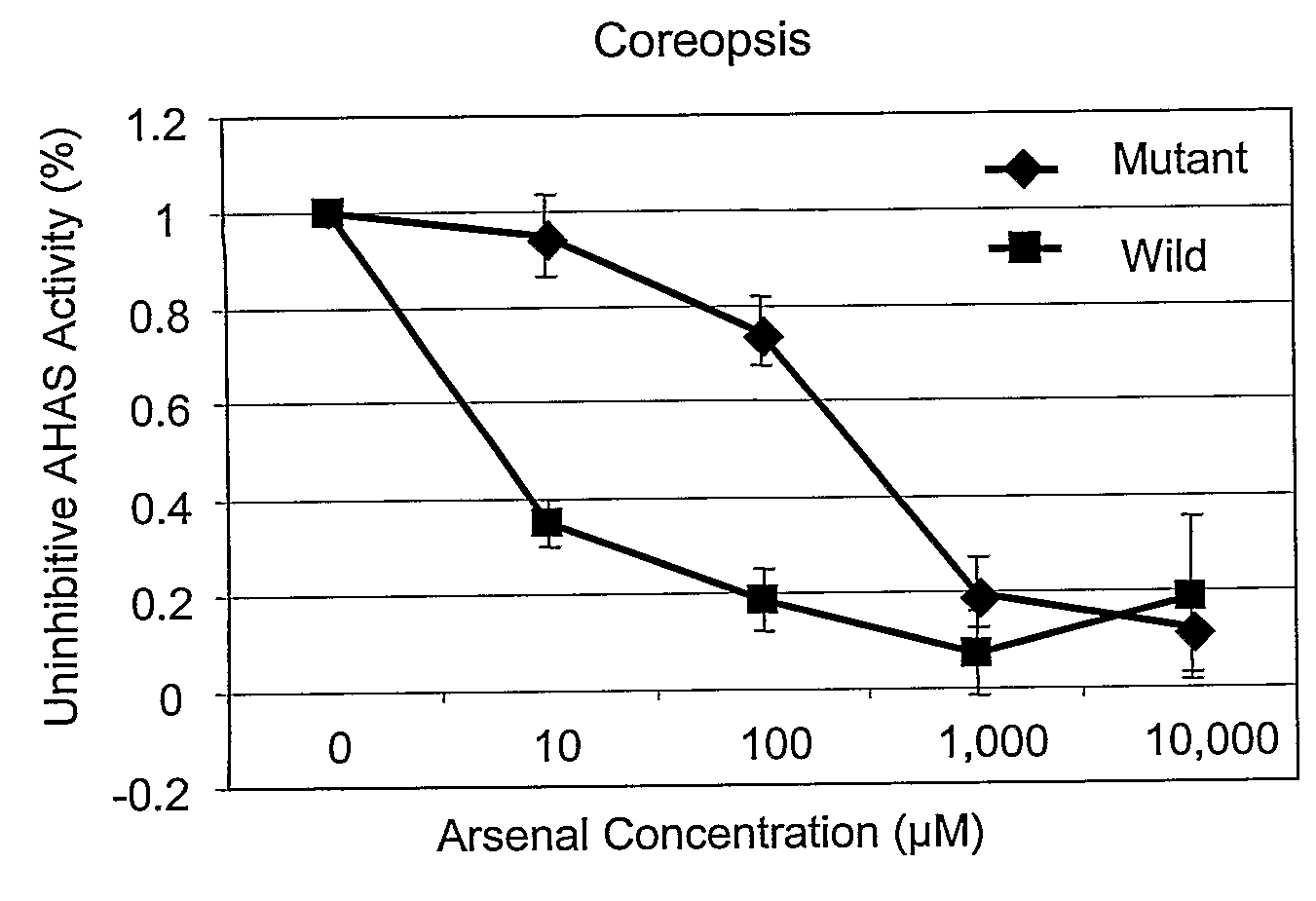
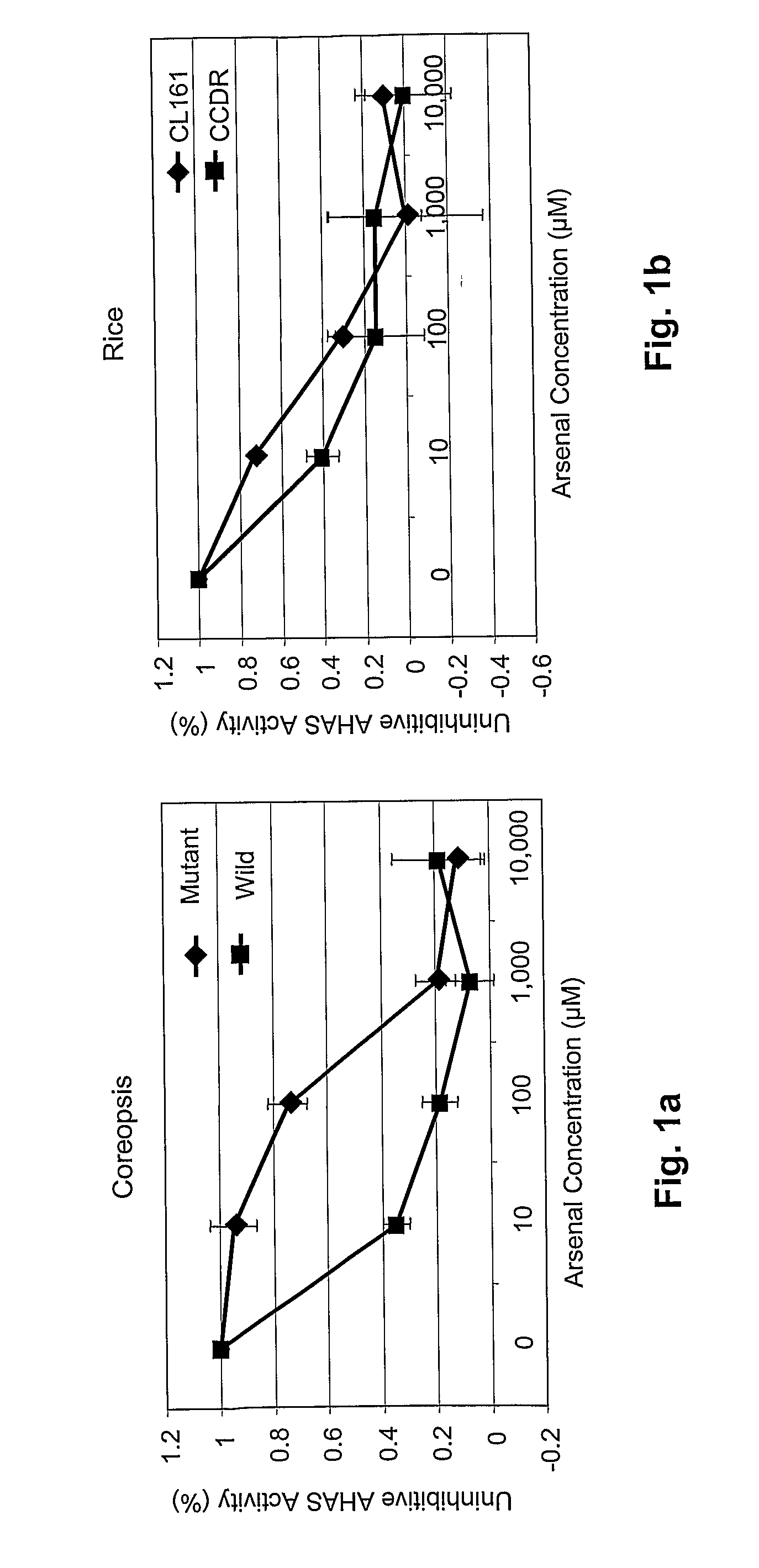
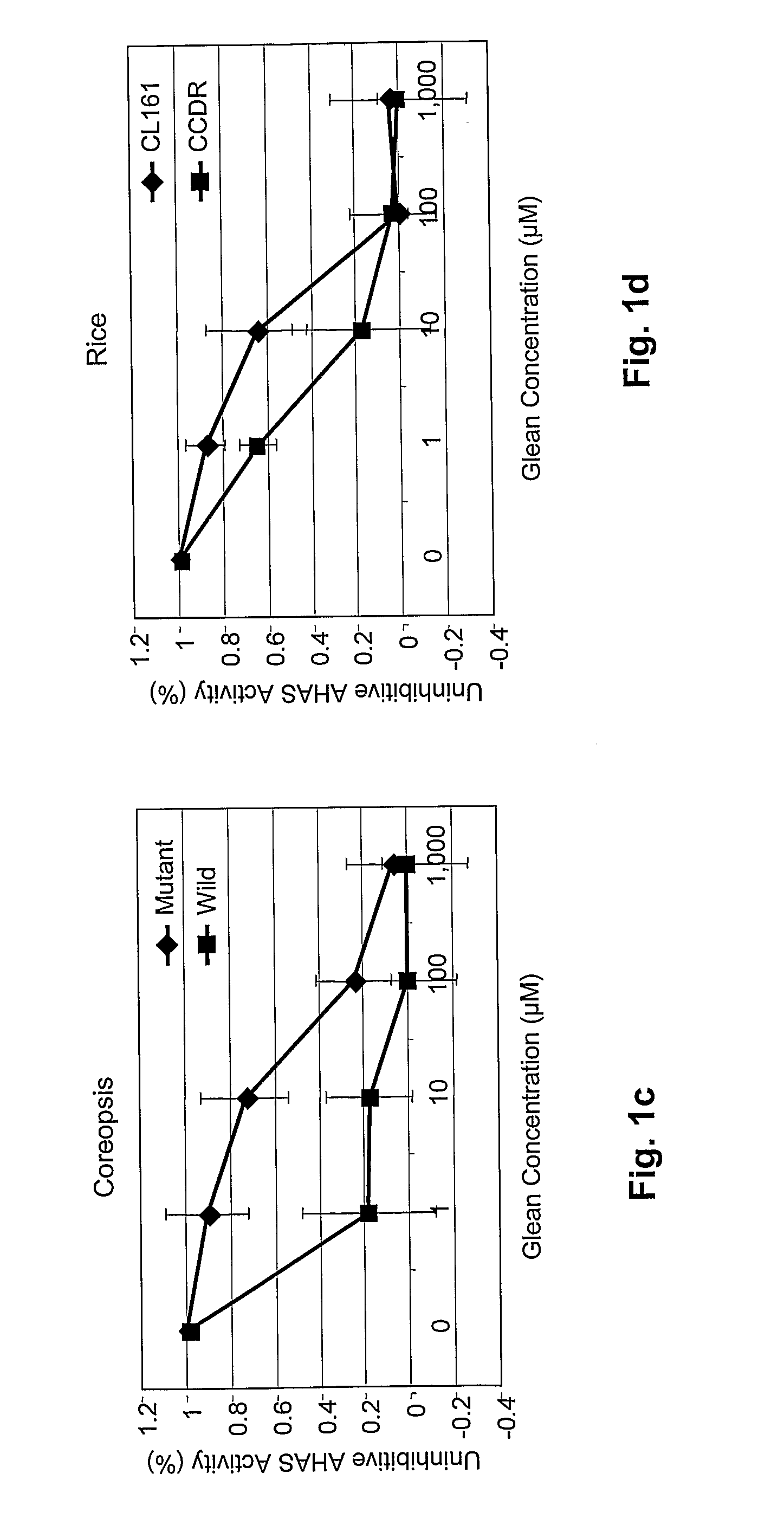
Nucleotide sequences are disclosed that may be used to impart herbicide resistance to green plants. The sources of novel herbicide resistance were originally isolated in mutant Coreopsis plants. Green plants transformed with these sequences are resistant to herbicides that normally inhibit acetolactate synthase (ALS), particularly imidazolinone and sulfonylurea herbicides.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Cabbage type rape herbicide resistance protein and application thereof to plant breeding
The invention discloses an ALS (acetolactate synthase) protection sequence for enabling plants to have herbicide resistance and an application of the sequence. The sequence is derived from a mutant strain of double No.9 of a cabbage type rape variety and the amino acid sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 or 12. In addition, the invention further provides a corresponding nucleic acid, an expression box, a carrier, a cell, a plant, an application and a method for obtaining the plants with the herbicide resistance, and a method for identifying the plants obtained by the invention.
Owner:SHENZHEN XINGWANG BIOLOGICAL SEED IND +2
Paddy rice ALS (Acetolactate Synthase) mutant protein for endowing plants with resistance to herbicides, gene and application thereof
PendingCN107090447AHigh ALS activityMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringMutated proteinAcetolactate synthase
The invention discloses a paddy rice ALS (Acetolactate Synthase) mutant protein for endowing plants with resistance to herbicides. The invention further discloses a nucleic acid for coding the protein. The protein comes from a paddy rice mutant plant resisting ALS inhibitor type herbicides, and in comparison with the ALS sequence in the genome of wild paddy rice, the protein sequence of the protein is simultaneously mutated at sites Ser 627 and Gly 628 or only mutated at the site Gly 628. Plants which express the protein sequence can resist (tolerate) acetolactate synthase inhibitor type herbicides, particularly imidazolinone herbicides. The herbicide-resistant effect of the mutant mutated simultaneously at the sides Ser 627 and Gly 628 disclosed by the invention is about 30 percent higher than the herbicide-resistant capability of the mutant plant only contains mutation at the site Ser 627 or Gly 628.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for transformation using mutant acetolactate synthase gene
ActiveUS8017400B2Valid choiceStrong specificityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAcetolactate synthaseWild type
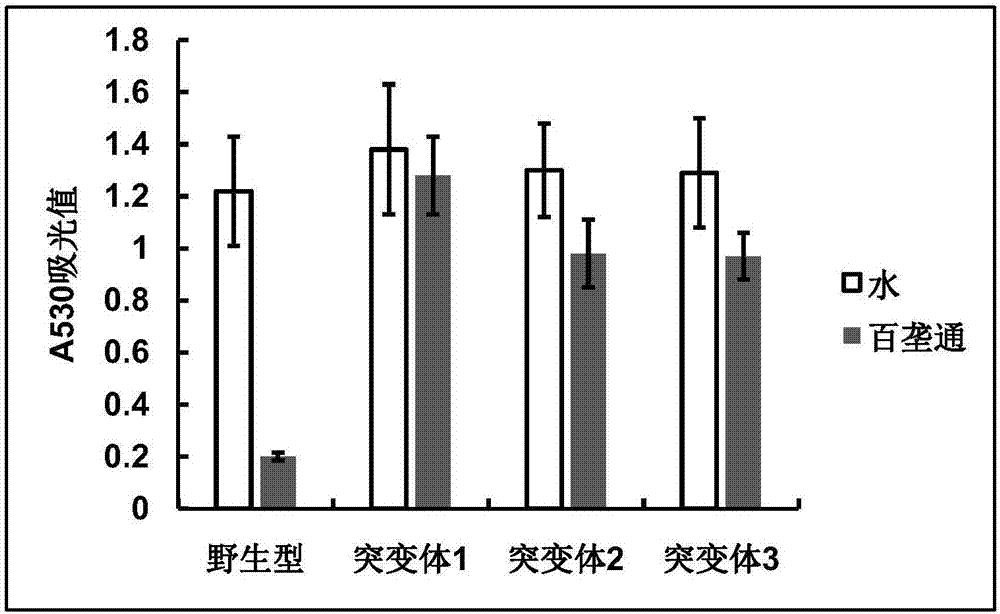
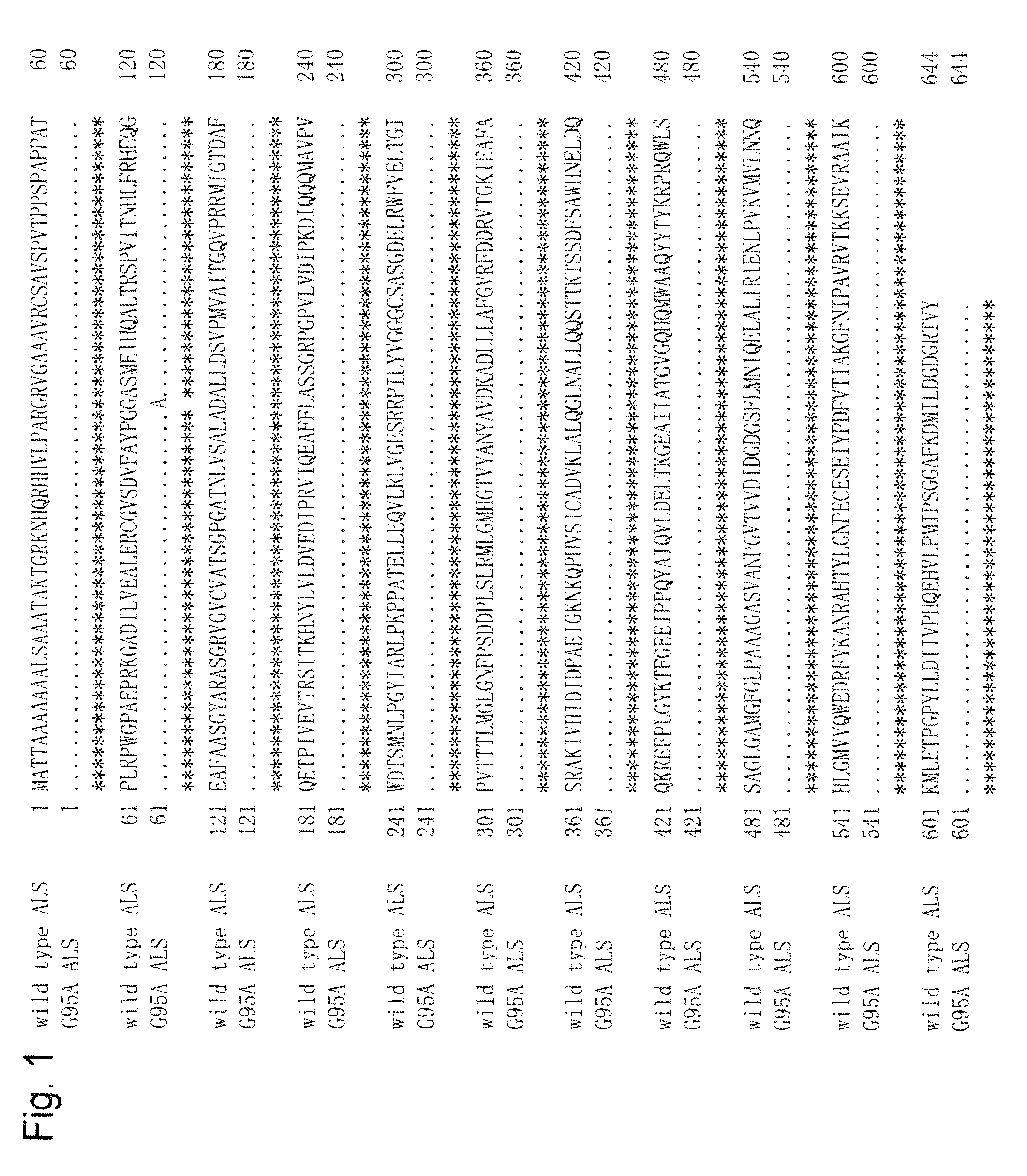
Transformed cells are efficiently selected using a mutant ALS gene having high specificity to PC herbicides. The transformation method comprises the steps of: transforming a host cell with a recombination vector containing a gene of interest and a gene coding for a mutant acetolactate synthase having mutation of glycine corresponds to position 95 of the amino acid sequence of a wild-type acetolactate synthase derived from rice to alanine; culturing the transformed cell obtained in the former step in the presence of a pyrimidinyl carboxy herbicide; and wherein the gene coding for the mutant acetolactate synthase is used as a selection marker.
Owner:KUMIAI CHEM IND CO LTD +1
Engineering of thermotolerant bacillus coagulans for production of D(-)-lactic acid
InactiveCN103547671ABacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetolactate synthaseGenetically engineered
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
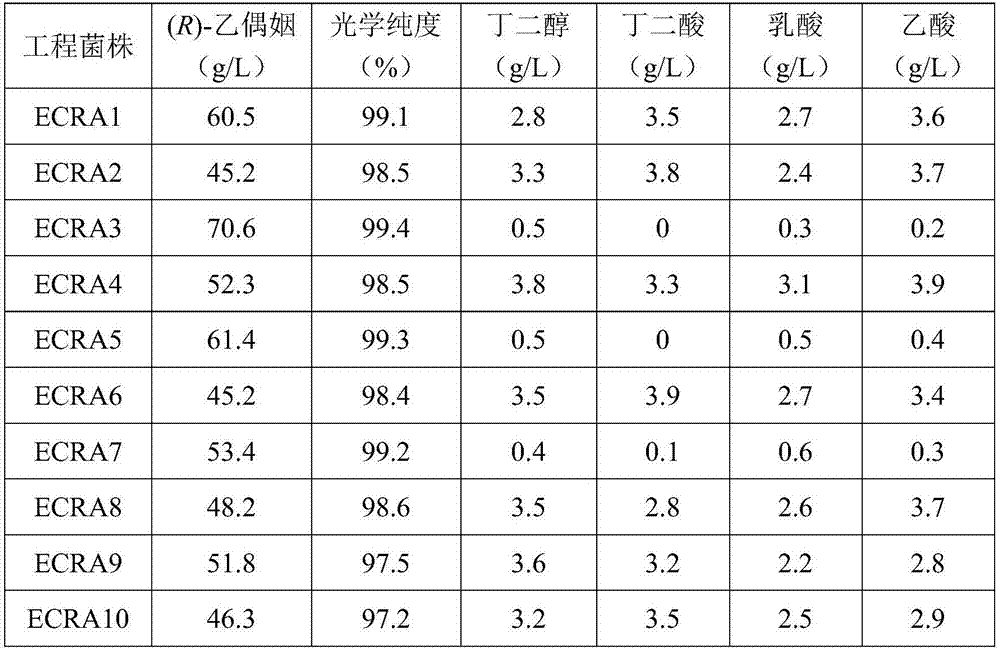
Method for constructing genetic engineering strains for producing (R)-acetoin and application of genetic engineering strains
ActiveCN107129959AReduce pathogenicityNon-pathogenicBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyAcetolactate synthase
The invention discloses a method for constructing genetic engineering strains for producing (R)-acetoin and application of the genetic engineering strains. The method includes optimizing codons of nucleotide sequences of alpha-acetolactate synthase genes, alpha-acetolactate decarboxylase genes and NADH (reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) oxidase genes and acquiring each gene cluster with three genes by the aid of artificial synthesis processes; inserting the gene clusters into expression vectors to obtain polycistron recombinant plasmids; introducing the polycistron recombinant plasmids into host bacteria E. coli and knocking out key genes of main byproduct synthesis paths to obtain the genetic engineering strains for producing the (R)-acetoin. The method and the application have the advantages that raw materials for the genetic engineering strains can come from wide sources and are low in cost, the strains are free of pathogenicity, oxidized form coenzymes NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide+) can be effectively regenerated, the strains are high in (R)-acetoin yield and production efficiency, the maximum yield can reach 72.1 g / L, and the optical purity can reach 99% at least; the (R)-acetoin is produced by the aid of non-grain cassava flour and inexpensive nitrogen sources which are used as fermentation raw materials, and accordingly the production cost can be reduced.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Acetolactate Synthase Herbicide Resistant Sorghum
ActiveUS20080216187A1Confer resistanceBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyPlant tissue
The present invention provides for compositions and methods for producing sorghum crop plants that are resistant to herbicides. In particular, the present invention provides for sorghum plants, plant tissues and plant seeds that contain altered acetolactate synthase (ALS) genes and proteins that are resistant to inhibition by herbicides that normally inhibit the activity of the ALS protein.
Owner:KANSAS STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Slow-release agrochemicals dispenser and method of use
InactiveUS20050181952A1Less herbicideLess pollutionBiocideDead animal preservationCellulosePolymer modified
Acetolactate synthase inhibitors, such as imazapyr and pyrithiobac and mixtures thereof, prepared as slow-release formulations are useful for the preparation of seed dressing, seed priming, seed or particle-substrate coating herbicidal compositions for control of parasitic weeds such as Orobanche spp., Striga spp. and Alectra spp. The use of agrochemicals can be rendered more efficient when coated or bound as a slow release formulation. Particles used as the substrateto be coated may be plant seeds or particles made of a strong or weak ionic resin or a biodegradable carbohydrate natural polymer, a modified polymer, or artificially lignified cellulose. The herbicidal formulation may be covalently linked or adsorbed to the surface of the particle. The same slow release formulations are invaluable for preventing rapid herbicide leaching in agricultural as well as non-agricultural weed control situations.
Owner:HI CAP FORMULATIONS
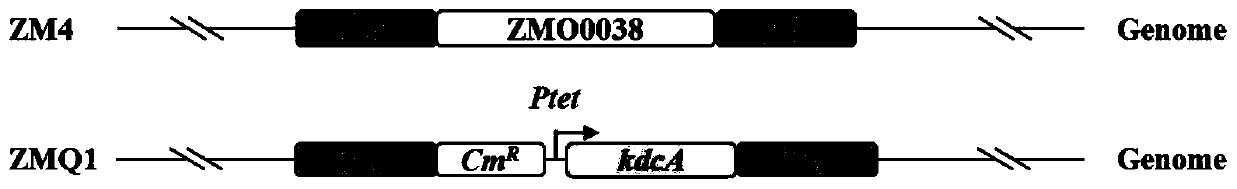
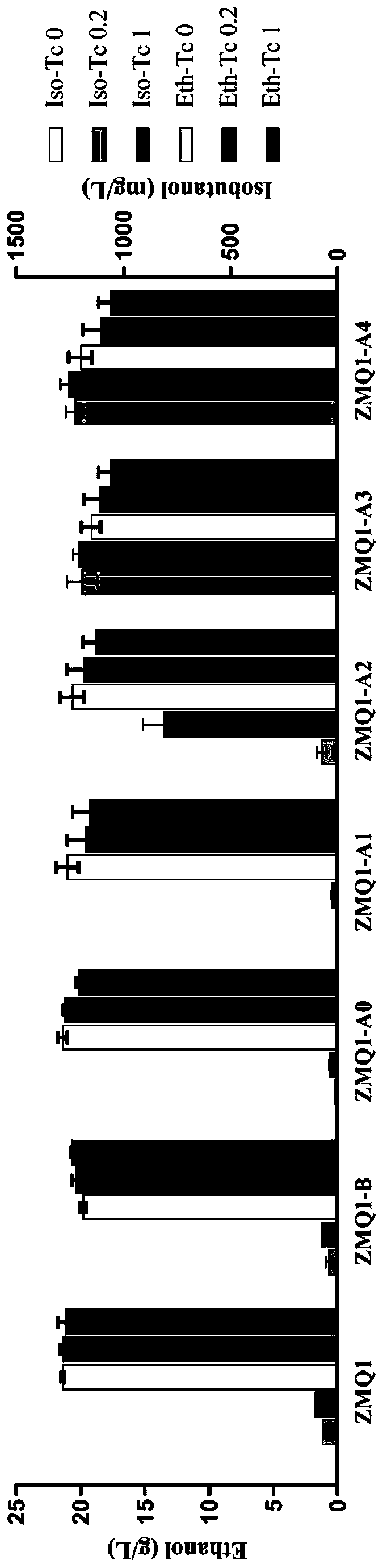
Zymomonas mobilis recombination strain producing isobutanol, construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN110358720ATo achieve the purpose of increasing productionPowerful Restriction Modification SystemBacteriaBiofuelsIsobutanolAcetolactate synthase
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a zymomonas mobilis recombination strain producing isobutanol, a construction method and application thereof. Zymomonas mobilis ZM4 serves as a model strain, firstly, the strain is transformed by means of genetic engineering, a metabolic intermediate in the synthesis pathway of valine of zymomonas mobilis is utilized for introducing a KDCA gene, 2-ketoisovalerate in the valine pathway is converted into a precursor isobutyraldehyde of isobutanol, and then isobutanol is generated under thehelp of alcohol dehydrogenase; secondly, the purpose of increasing the yield is achieved by overexpressing genes in the L-valine synthesis pathway and screening acetolactate synthase in the metabolicpathway;finally, by adjusting the expression quantity of different genes in the metabolic pathway, the purpose of high yield is finally achieved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Herbicide-resistant corn protein and application thereof in plant breeding
The invention provides an ALS (Acetolactate Synthase) protein capable of endowing plants with herbicide resistance. The amino acid sequence of the herbicide-resistant corn protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 or 4. Furthermore, the invention further provides corresponding nucleic acid, expression cassettes, vectors, cells, the plants, application and a method for obtaining the plants with herbicide resistance, and a method for identifying the plants in the invention.
Owner:深圳洁田模式生物科技有限公司
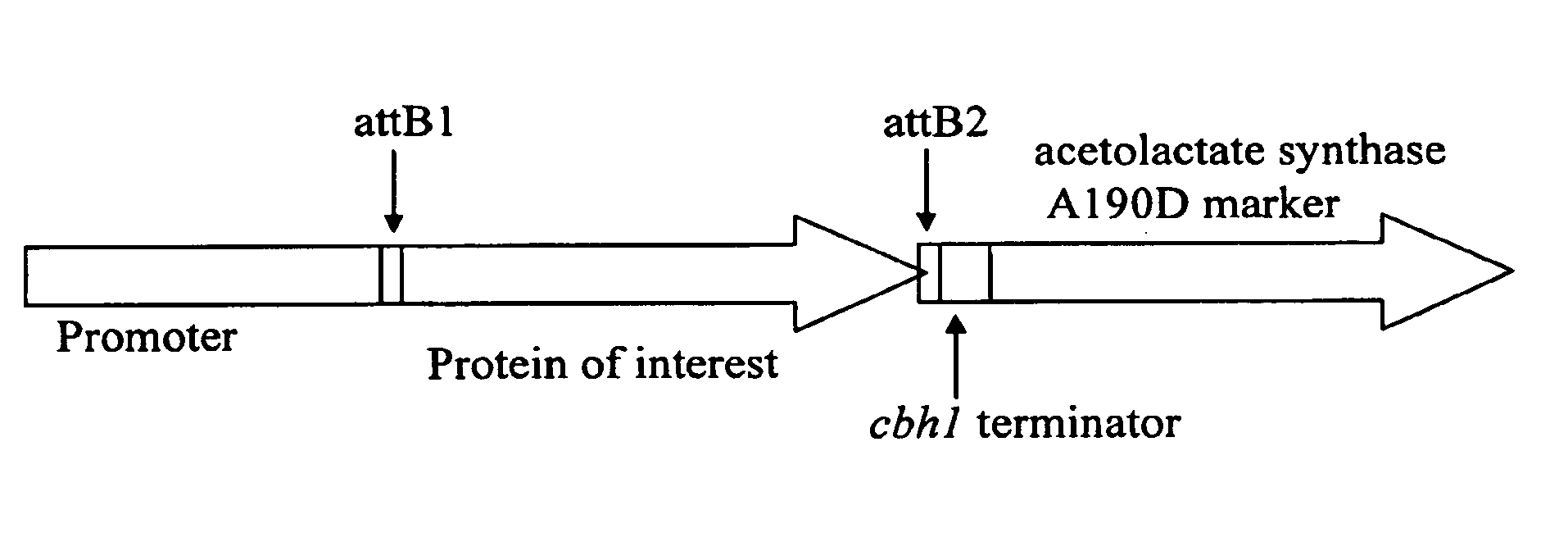
Acetolactate synthase (ALS) selectable marker from Trichoderma reesei
A nucleic acid encoding an acetolactate synthase (ALS) protein that provides resistance to ALS inhibitors, e.g., sulphonylurea and imidazolinone compounds, is provided. The nucleic acid may be used as a selectable marker for expression of a protein of interest in host cells.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Wheat ALS mutation gene and application of protein thereof in aspect of herbicide resistance
ActiveCN106755019AGood growthBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyAcetolactate synthase
The invention discloses a wheat ALS mutation gene. The 331th nucleotide of an ALS gene sequence of 6BL chromosome of a wheat B genome is changed into nucleotide A from G. The invention further discloses wheat ALS mutation protein encoded by the wheat ALS mutation gene and application of the wheat ALS mutation protein. The protein is from a wheat mutant plant of an anti-ALS inhibitor herbicide. Compared with a wheat mild ALS sequence, the protein sequence mutates at a Val111 site. A green plant expresses that the mutation protein sequence can be resistant and tolerant to an acetolactate synthase inhibitor herbicide, especially an imidazolone herbicide. After 3mL of imazameth / L water (9-fold recommended concentration) is applied to a wheat seedling with one leaf and one core of the wheat ALS mutation protein, the plant can still normally grow, develop and fruit.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com